Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the EME programme as project number 09/100/25. The contractual start date was in November 2010. The final report began editorial review in April 2018 and was accepted for publication in October 2018. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The EME editors and production house have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the final report document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Mark A Hull has received an unrestricted scientific grant for another project and also conference travel funding from SLA Pharma AG (Liestal, Switzerland). He has provided paid consultancy for Bayer AG (Leverkusen, Germany) and Thetis Pharmaceuticals LLC (Branford, CT, USA), and his institution received fees for his consultancy work for Thetis Pharma, which owns the rights to omega-3 fatty acid derivative molecules. Furthermore, he was a National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Efficacy and Mechanism Evaluation Board member (2014–18). Colin J Rees has had research funded by Arc Medical Inc. (Tucker, GA, USA), Norgine (Amsterdam, the Netherlands) and Olympus Corporation (Tokyo, Japan), and has received paid honoraria and travel grants from Norgine, Boston Scientific (Marlborough, MA, USA) and Olympus. He has been a paid expert witness for Arc Medical. None of these bear any relation to the Systematic Evaluation of Aspirin and Fish Oil (seAFOod) trial. Alan A Montgomery is a member of the NIHR Health Technology Assessment Clinical Evaluation and Trials Board. Trish Hepburn has ownership of shares in AstraZeneca plc (Cambridge, UK).
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2019. This work was produced by Hull et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2019 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Introduction
Parts of this chapter have been reproduced from Hull et al. 1 © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Background
The health burden of colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC) continues to represent a huge health burden in the UK. There were approximately 41,300 new cases of CRC (also known as bowel cancer) in the UK in 2014, making it the fourth most common cancer. 2 In the UK, 1 in 14 men and 1 in 19 women will be diagnosed with CRC during their lifetime. CRC is the second most common cause of cancer death in the UK, causing 16,000 deaths in 2014. Worldwide, it has been estimated that nearly 1.4 million cases were diagnosed in 2012. 2 Despite significant advances in the diagnosis and treatment of CRC, overall 5-year survival is currently only 59% (survival figure is for England and Wales for 2010 and 2011). 2
Prevention of colorectal cancer
One strategy to reduce CRC incidence and mortality is prevention. The scientific and clinical rationale for prevention of CRC is well established and is based on the following:
-
Knowledge of several environmental and behavioural factors that increase CRC risk, including dietary factors (e.g. red and processed meat intake), excess body weight (i.e. obesity), lack of physical activity, tobacco smoking and excess alcohol consumption. The World Cancer Research Fund has estimated that approximately 45% of CRCs are preventable based on modification of these lifestyle factors. 3
-
The long natural history of colorectal carcinogenesis, during which a benign, precursor lesion termed a colorectal adenoma (or polyp) develops and transforms into a malignant neoplasm over a period of years (estimated to be approximately 5–10 years). 4,5
-
Improved outcomes for CRC treatment after diagnosis at earlier stages of CRC (98% 1-year overall survival for stage I CRC compared with 40% for stage IV disease; 95% 5-year survival for stage I compared with 7% for stage IV disease). 6,7
Colorectal cancer prevention strategies that are currently used, or are under evaluation, include:
-
population screening –
-
early CRC diagnosis by a guaiac faecal occult blood test (FOBt) or a faecal immunochemical test (FIT), conferring secondary benefit from colorectal adenoma identification and removal at colonoscopy
-
detection and removal (by polypectomy) of colorectal adenomas by primary screening endoscopy [colonoscopy or flexible sigmoidoscopy (FS)]
-
-
endoscopic surveillance of high-risk groups, for example individuals with long-standing colitis or previous colorectal adenoma(s)
-
chemoprevention (a term first coined in 1976 to describe the use of drugs, vitamins or other nutritional agents to try to reduce the risk of, or delay the development or recurrence of, cancer)
-
health education, leading to beneficial lifestyle modification and screening uptake
-
promotion of awareness and earlier diagnosis of CRC by education aimed at the public and health-care professionals.
Chemoprevention of colorectal cancer
Despite the undoubted clinical effectiveness of endoscopic polypectomy,8,9 CRC remains a significant problem in screened populations and high-risk surveillance cohorts because of a combination of factors that include suboptimal screening uptake, poor acceptability of endoscopic procedures and ‘interval’ CRC (i.e. those cancers that are diagnosed despite FOBt/FIT and/or endoscopy). 10–13 In a Dutch biennial FIT-based CRC screening programme,14 23% of individuals developed a FIT-interval CRC. The corresponding interval CRC rate for guaiac FOBt programmes is approximately 50%. 15 Moreover, 18 years’ follow-up of the Minnesota guaiac FOBt trial (in which the colonoscopy rate was nearly 40%) found only a 20% reduction in CRC incidence. 13 The UK once-only FS trial10 demonstrated only a 23% reduction in CRC incidence in the intervention group compared with the control group at 10 years. It is also clear that CRC occurs even in patients under close colonoscopic surveillance (1.7 CRCs per 1000 person-years),16 with an estimated post-colonoscopy CRC (PCCRC) rate of between 2% and 9%. 17 Overall, only 10% of CRCs in the UK in 2013 were diagnosed within the UK screening programmes. 18 Therefore, there is still an unmet clinical need for safe and effective primary CRC chemoprevention in combination with existing screening and surveillance programmes.
The natural history and molecular pathogenesis of colorectal carcinogenesis
The molecular pathogenesis of CRC (histopathological term: colorectal adenocarcinoma) has been the subject of several recent reviews. 4,19 In recent years, the original multistage model of cumulative genetic mutations, proceeding through a benign adenoma stage (the so-called adenoma–carcinoma sequence), based on loss of function of the ‘gatekeeper’ tumour suppressor gene adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), which was proposed by Fearon and Vogelstein,20 has been superseded by widespread acceptance that ‘sporadic’ (i.e. not occurring on a background of a distinct genetic predisposition syndrome or inflammatory bowel disease) CRC is not ‘one disease’, but occurs via several pathogenic pathways, which are not mutually exclusive. 21,22
The chromosomal instability (CIN) pathway is characterised by chromosomal abnormalities, including aneuploidy, usually associated with loss-of-function APC mutation and later-stage gain-of-function KRAS mutation. 23 It is exemplified by the rare genetic predisposition syndrome familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), an autosomal dominant condition that occurs in carriers of a heterozygous germline APC mutation. 24 The microsatellite instability (MSI) pathway is driven by defective deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) mismatch repair (MMR), leading to accumulation of further somatic mutations (termed MSI-high) including BRAF. 23 It is exemplified by Lynch syndrome, in which carriers of mutations in MMR genes (most commonly MLH1 and PMS2) exhibit increased cancer (including colorectal) risk. 25 Furthermore, a CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP) pathway is recognised in colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas, by which epigenetic changes in DNA methylation lead to altered gene function, in particular silencing of the MMR gene MLH1 leading to defective MMR, which is associated strongly with BRAF mutation. 23 Epigenetic silencing of MLH1 explains the substantial overlap between MSI and CIMP pathways. 4
There are limited data on how early during colorectal carcinogenesis the above phenotypes manifest themselves. 4 There are some data to suggest that CIN features are present in adenomas. 4,26 The CIMP pathway is linked strongly to benign serrated lesions (see below).
Colorectal adenoma
The importance of the benign precursor lesion, which exhibits epithelial cell dysplasia but not invasion of the epithelial basement membrane (termed the adenoma, or adenomatous polyp), as a risk stratification biomarker of future CRC risk but also as a clinically significant lesion (the removal of which is associated with reduced CRC incidence and mortality), has been reviewed in detail. 5
In parallel with more nuanced understanding of the diverse molecular pathogenesis of CRC, the histopathological classification and terminology of the colorectal adenoma has been revised. 5 In particular, hyperplastic-serrated pathway lesions are now acknowledged as separate entities from the more common (conventional) dysplastic adenoma (which can be tubular, villous or mixed tubulo-villous in morphology). Serrated lesions are recognised to have malignant potential per se and may account for 20–30% of CRCs. 27 The World Health Organization’s (WHO’s) WHO Classification of Tumours of the Digestive System28 in 2010 included the term sessile (a term used to recognise that the vast majority of these lesions are ‘flat’ and not polypoid when viewed endoscopically) serrated adenoma. However, the term sessile serrated polyp is now preferred on the basis that the majority of sessile serrated lesions do not display any dysplasia, which is a prerequisite for pathological classification as an adenoma. 5 The traditional serrated adenoma is a separate, rare, fully dysplastic lesion with classical serrated appearances. 27 For the purposes of this report, the term serrated adenoma will continue to be used as the terminology employed continuously throughout the Systematic Evaluation of Aspirin and Fish Oil (seAFOod) trial from 2009 onwards.
Sessile serrated adenomas are more prevalent in the proximal (also known as right) colon (most commonly defined as proximal to the splenic flexure) than the distal (also known as left) colon. 4 Conventional tubular/tubulo-villous adenomas are more uniformly distributed throughout the right and left colon. 4 Molecular features also distinguish between conventional adenomas and serrated adenomas, with a high prevalence of CIN features in conventional adenomas and serrated adenomas commonly displaying a CIMP-high, BRAF mutation-positive, MSI-high phenotype. 4,21,27 Results from a study29 of CRCs suggest that, in reality, there is likely to be a continuous positive gradient of CIMP-high, MSI-high and BRAF mutation frequency in tumours along the distal to proximal colon, rather than an anatomical dichotomy in the distal transverse colon. There is conflicting evidence that a given tumour genotype/phenotype predicts that of synchronous/metachronous lesions, but the majority of data pertain to CRC, not to colorectal adenomas. 4
As direct precursor lesions of CRC, the removal of which is unequivocally associated with decreased future CRC risk,8,9 the colorectal adenoma is a clinically important lesion in its own right. 5 It has been estimated (based on cohort prevalence studies) that approximately 1 in 10–20 colorectal adenomas may eventually acquire a malignant phenotype. 5 The features associated with malignant progression are size, grade of dysplasia and ‘villousness’, namely the degree of villous histological architecture in an individual lesion. 5 On the other hand, the colorectal adenoma can also be considered a biomarker of future CRC risk, regardless of its individual malignant potential. 5 Both colorectal adenoma number and colorectal adenoma size are widely used as the basis for future CRC risk stratification for surveillance after colonoscopy in the UK and elsewhere in the world. 30–33 A common feature of guidelines is the definition of the ‘advanced’ colorectal adenoma based on size (≥ 10 mm), with or without additional histological (e.g. grade of dysplasia, ‘villousness’) features. 30,31,33
Colorectal adenoma measures
Based on widespread acceptance of the number and size of colorectal adenomas as a CRC risk biomarker, the colorectal adenoma has been used as a surrogate colonoscopic end point of reduced CRC risk in chemoprevention trials following polyp clearance at an index procedure (the ‘polyp-prevention trial’). Historically, the presence or absence of any colorectal adenoma [the so-called adenoma detection rate (ADRa)] has been employed as the primary end point in chemoprevention trials, with reliance on this binary end point reflecting the varying quality of colonoscopy between different endoscopists and susceptibility of colorectal adenoma detection to observer variation. 5,34–36 However, this percentage value does not take into account any change in colorectal adenoma number (or size), unlike pre-clinical rodent studies and proof-of-concept clinical studies in FAP patients, in which lesion number and size are routinely measured. 37 More recently, driven by the dramatic improvement in colonoscopy quality and quality assurance (QA) reporting,38 colorectal adenoma number has begun to be reported as a primary outcome in ‘sporadic’ polyp-prevention trials as the mean adenomas per participant (MAP). 39 Population-based studies have consistently demonstrated that colorectal adenoma multiplicity predicts future CRC incidence and mortality. 40–42
Candidate colorectal cancer chemoprevention agents
The existing literature on several potential CRC chemoprevention agents, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), hormone replacement therapy and micronutrients (e.g. folic acid, vitamin D), is well summarised in published reviews. 34,36 The largest body of evidence supports the use of the NSAID aspirin for CRC chemoprevention. 43,44
Aspirin
Observational and randomised controlled trial (RCT) data44,45 suggest primary prevention efficacy of low-dose (usually defined as < 325 mg daily) aspirin; these data are summarised in comprehensive reviews. In brief, observational follow-up studies of historical RCTs of aspirin (variable dose: 75–1000 mg daily) for antithrombotic indications have reported that aspirin reduces the risk of CRC incidence [hazard ratio (HR) 0.75, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.56 to 0.97] and mortality, with a lag period of approximately 8 years, compatible with the long natural history of ‘sporadic’ colorectal carcinogenesis. 46,47 A similar phenomenon was also observed in the Women’s Health Study,48 which is the only placebo-controlled RCT of aspirin (i.e. 100 mg of aspirin taken on alternate days) with a primary CRC prevention end point. Original 10-year follow-up did not reveal any effect on CRC incidence, but reduced CRC incidence (HR 0.80, 95% CI 0.67 to 0.97) emerged after longer follow-up. 48 A consistent finding from these RCTs has been the differential effect of aspirin on proximal, as opposed to distal, CRC, with the risk reduction associated with aspirin being primarily for proximal CRC. 47,48
Consistent with its role as an established biomarker of CRC risk, a random-effects meta-analysis49 of four previous polyp-prevention RCTs of aspirin (using daily doses varying from 81 mg to 325 mg), using ADRa as the primary outcome measure, reported a pooled risk ratio for ‘advanced’ colorectal neoplasm or any size of colorectal adenoma in aspirin users of 0.72 (95% CI 0.57 to 0.90) and 0.83 (95% CI 0.72 to 0.96), respectively, an effect that was already apparent at colonoscopy in the first year of follow-up in these studies (risk ratio 0.62, 95% CI 0.48 to 0.81). Three of these aspirin RCTs reported MAP data as a secondary outcome, and all demonstrated a consistent reduction in the MAP value associated with aspirin use. 49
Aspirin (900 mg) has also been shown to reduce CRC (and other cancer) risk in Lynch syndrome. 50 Chemopreventive efficacy of aspirin in Lynch syndrome was not associated with reduced colorectal adenoma risk during routine surveillance colonoscopy follow-up in a non-screening programme setting. 51
However, despite the strength of the evidence that regular, long-term aspirin use prevents CRC, aspirin has not yet been widely adopted for primary or secondary CRC chemoprevention because of continuing uncertainty about the optimal daily dose [different trials have reported efficacy of either high- (> 300 mg) or low-dose (< 100 mg) aspirin49] and the absence of a clearly defined at-risk population in whom benefit would outweigh the small risk of gastrointestinal (GI) and intracerebral bleeding associated with aspirin. 44,52,53 Nevertheless, the US Preventive Services Task Force52 has recommended low-dose aspirin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and CRC in some adults aged 50–59 years who have a 10-year CVD risk of ≥ 10%.
Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors
Consistent with the role of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2-dependent prostaglandin (PG) E2 in the early stages of colorectal carcinogenesis,54 selective COX-2 inhibitors (i.e. celecoxib and rofecoxib) displayed significant chemopreventive efficacy in RCTs in FAP patients (20–30% reduction in polyp number and size)55 and in individuals with previous ‘sporadic’ colorectal adenoma (risk reduction of approximately 20%). 34 However, the unexpected CVD toxicity associated with prolonged selective COX-2 inhibition, which became apparent in the polyp-prevention trials, precludes a role for selective COX-2 inhibitors in primary ‘sporadic’ CRC chemoprevention. 56
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are important components of a normal diet. Two classes of PUFAs, ω-6 and ω-3, are classified as essential in that they cannot be readily synthesised in the human body and so must be obtained from dietary sources. 57 The principal bioactive ω-3 PUFAs are C20:5ω-3 [in CX:Yω-Z, X denotes the number of carbon atoms; Y denotes the number of carbon–carbon double bonds and Z denotes the carbon atom from which the first double bond starts from the ω (methyl) end], eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and C22:6ω-3 docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which are found predominantly in oily, cold-water fish such as mackerel, having entered the food chain following synthesis by plankton and algae. 57 In addition, C18:3ω-3 alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is found in vegetables, but can be converted to EPA and then DHA (by a series of elongases and desaturases58) only very inefficiently (approximately 5%) in humans. 59 In ‘Western’ diets, ω-6 PUFAs dominate, including C20:4ω-6 arachidonic acid (AA), which is the predominant substrate for the COX enzymes in humans. 57
Anticolorectal cancer activity of eicosapentaenoic acid
Eicosapentaenoic acid is an attractive candidate as a ‘natural’ CRC chemoprevention agent based on several strands of evidence. 60 There is strong pre-clinical evidence that ω-3 PUFAs have anti-CRC activity. 61 However, a systematic review of epidemiological studies has not demonstrated unequivocal benefit from dietary ω-3 PUFA intake on CRC risk. 62 This may be related to the methodological difficulties of measuring ω-3 PUFA or fish intake retrospectively. Alternatively, ω-3 PUFA exposure may not be sufficient for consistent anti-CRC activity in individuals consuming moderate amounts of fish (a portion of oily fish two or three times per week provides only the equivalent of approximately 500 mg per day of EPA and DHA combined). Omega-3 PUFA intake can be increased by ‘over-the-counter’ fish oil supplements, which contain a complex mix of ω-3 and ω-6 PUFAs. 63 However, many of these supplements are associated with a range of minor, troublesome side effects [e.g. eructation (burping), halitosis]. In the prospective VITAL (VITamin And Lifestyle) cohort study, which has uniquely collected data on fish oil supplement use, as well as dietary fish intake, fish oil supplement users were shown to have a 49% reduced CRC risk compared with non-users, an effect primarily observed in men. 64
Purified and concentrated EPA is available in several forms and pharmaceutical formulations. 65,66 EPA alone (without DHA) is available as the free fatty acid (FFA), as a triglyceride (TG) conjugate (the predominant natural form of EPA) or as an ethyl ester (EE) conjugate. 65 Dietary EPA-TG is converted to EPA-FFA in the small intestine by the action of pancreatic lipase, which is released in response to (particularly fatty) food intake. It is unclear which form of EPA is absorbed best from the small intestine and has maximal bioavailability, especially during prolonged use. 65,66 Administration of EPA with food maximises absorption of all forms of EPA. 65 A 500-mg gastroresistant capsule formulation of 99% pure EPA as the FFA has been produced (SLA Pharma AG, Liestal, Switzerland). This formulation was used for the administration of 2 g of EPA-FFA daily as four capsules in the RCT in FAP patients described below. 67 Alternative formulations of purified EPA exist, including a 574-mg formulation of 90% EPA-TG (equivalent to 400 mg of EPA-FFA) in a soft gelatin capsule (Igennus Healthcare Nutrition, Cambridge, UK) that can be used to provide the equivalent 2-g daily dose of EPA-FFA in five capsules.
Eicosapentaenoic acid in all three forms (i.e. FFA, TG and EE) has been demonstrated to have chemopreventive activity in several rodent models of colorectal carcinogenesis, including azoxymethane-induced intestinal tumorigenesis and the ApcMin/+ mouse model of FAP. 61,68,69 Preliminary evidence that EPA has chemopreventive efficacy in humans was provided by two separate Phase II studies of 2 g of EPA-FFA daily in patients with previous colorectal adenoma(s), which demonstrated a significant reduction in rectal epithelial cell mitosis frequency (not observed with a 1-g daily dose), which was associated with a fivefold increase in rectal mucosal EPA content. 70,71 These studies led to a Phase III RCT of the effect of 2 g of EPA-FFA daily for 6 months on rectal polyposis in patients with FAP (n = 58). 67 This RCT provided the first definitive evidence of chemopreventive efficacy of EPA in humans, with a net decrease in rectal adenoma number and cumulative rectal adenoma size of 22.4% and 29.8%, respectively, between the EPA and placebo groups. 67 The percentage reduction in adenomatous polyp burden was similar to that observed in FAP patients treated with celecoxib,55 a drug that was subsequently demonstrated to prevent ‘sporadic’ colorectal adenomas. 34 In 2012, high dietary intake of marine-derived ω-3 PUFAs was associated with reduced colorectal adenoma risk. 72 The protocol for a RCT of 2.7 g of EPA daily for prevention of rectal aberrant crypt foci was published in 2012 (UMIN000008172), but the trial has yet to report results. 73
Mechanisms of the antineoplastic activity of eicosapentaenoic acid and aspirin
The precise mechanism(s) by which aspirin and EPA have anti-CRC activity is not fully understood. 43,45,61 However, it is currently accepted that, even though these agents are likely to act via multiple COX-dependent and COX-independent mechanisms, modulation of COX activity plays an important role in their antineoplastic effects. EPA and, particularly, aspirin are both potent inhibitors of COX-1, but they alter COX-2 activity in different ways, leading to the production of different bioactive lipid mediators, including PGE3 (EPA) and 15R-HETE (hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid) (aspirin). 57 There is some evidence that PGE3 (unlike pro-tumorigenic PGE2) has antitumorigenic activity74 and it is known that aspirin-triggered lipoxins derived from 15R-HETE have antiangiogenic properties. 75
Aspirin irreversibly acetylates the COX enzymes. 75 When EPA acts as a substrate for aspirin-acetylated COX-2, it leads to synthesis of 18R-hydroxyeicosapentaenoic acid (18R-HEPE), which can be converted in a 5-lipoxygenase-dependent manner to resolvin (Rv) E1. 75,76 RvE1 has potent anti-inflammatory activity,76 but it is currently not known whether or not RvE1 has direct antineoplastic activity. 77 Specialised pro-resolving (lipid) mediators, such as resolvins and lipoxins, including RvE1, are technically difficult to measure in biological samples and are likely to exert any biological activity at trace concentrations;77 therefore, it remains unclear whether or not sufficient quantities are generated in humans to have meaningful antineoplastic activity. 78
Although RvE1 synthesis provides a hypothesis for a potential interaction between EPA and aspirin, the available clinical evidence suggests that the antiplatelet (COX-1-dependent) effects of EPA and aspirin are simply additive based on the accumulated evidence of extensive use of dual therapy in cardiology patients79 and the effects of the two agents in ex vivo human platelet aggregation studies. 80,81 Colorectal carcinogenesis and atherosclerosis share common pathophysiological mechanisms and clinical risk factors, including obesity. 82 As a consequence, ischaemic heart disease and stroke are common in elderly populations with colorectal neoplasia. 82 Therefore, an attractive feature of CRC chemoprevention using EPA and/or aspirin is the potential for additional vascular benefit in elderly colorectal adenoma ‘formers’ at simultaneous risk of occlusive vascular events. 43,79
A precision-medicine approach to colorectal cancer chemoprevention
A precision or stratified medicine approach to chemoprevention, whereby the need for chemoprevention and the use of a specific agent is determined based on an individual benefit–risk assessment, has yet to be realised.
The preliminary finding of the APACC polyp-prevention trial,83 that the pattern of COX-2 expression in an index colorectal adenoma predicted the preventative efficacy of aspirin, suggests that baseline colorectal adenoma characteristics have potential as predictive biomarkers of individual chemoprevention efficacy.
Red blood cell (RBC) membrane ω-3 PUFA levels (as a validated surrogate biomarker of ω-3 PUFA tissue exposure84,85) have been long established as a biomarker of dietary ω-3 PUFA exposure in cancer epidemiological studies. 86 Between 2014 and 2016, ω-3 PUFA levels were used in RCTs of ω-3 PUFAs as a biomarker of target tissue ω-3 PUFA exposure (termed ‘bioavailability’ here), but also as a possible indicator of compliance and/or placebo group ‘contamination’ by over-the-counter (OTC) ω-3 PUFA use. 67,87,88
In a RCT of EPA-FFA in patients with CRC liver metastasis, tumour EPA content predicted exploratory survival outcomes. 88 However, there was no relationship between the individual rectal mucosal EPA content and the reduction in rectal polyp number in the small RCT of EPA in FAP patients. 67 Therefore, there is a need for further evaluation of RBC and colorectal mucosal ω-3 PUFA levels, as well as novel biomarkers based on the mechanism of action of EPA, as predictors of individual therapeutic response.
There are no validated biomarkers of aspirin anti-CRC activity. However, all the COX-dependent lipid mediators described earlier are measurable by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS)77,89 and may find utility as therapeutic biomarkers. 77
Safety and tolerability of eicosapentaenoic acid and aspirin
Aspirin and ω-3 PUFAs are already used widely in patient populations, that are relevant to ‘sporadic’ CRC prevention, for prophylaxis following myocardial infarction (aspirin and ω-3 PUFAs), hypertriglyceridaemia (ω-3 PUFAs) and stroke (aspirin). 79
The safety and tolerability of aspirin (≤ 325 mg daily) in previous polyp-prevention trials has been excellent. 34,49 Aspirin use is associated with a dose- and age-dependent increased risk of upper GI and intracranial bleeding. 45,90 Cuzick et al. 53 have put forward the case for a favourable benefit–risk profile for aspirin dosing of ≤ 325 mg daily for 10 years for primary CRC (and other adenocarcinoma) prevention in average-risk individuals aged 50–65 years.
There is little doubt about the safety and tolerability of ‘nutraceutical’ forms of EPA, confirmed by vast experience of intake in healthy human populations. 91–93 Gastroresistant EPA-FFA of 2 g daily has been compared with placebo for up to 6 months in four RCTs, in which tolerability has been excellent. 67,70,71,87 In the RCT involving FAP patients, there was no significant excess of adverse events (AEs) in the EPA-FFA group compared with the placebo group, with only one patient withdrawing from the EPA-FFA group as a result of nausea and epigastric pain. 67 In two Phase II studies of colorectal adenoma patients, there was a slight excess of mild to moderate AEs in the EPA-FFA group compared with the no-treatment70 and placebo groups. 71 In the latter study,71 the GI AEs observed in the EPA-FFA 2-g daily group were not apparent in those taking 1 g of EPA-FFA daily. 71 EPA-TG may be associated with fewer GI AEs, particularly diarrhoea, than EPA-FFA. 66 However, a formal comparison of tolerability between different EPA formulations in a RCT has not yet been undertaken.
Although aspirin and ω-3 PUFAs share antiplatelet activity and both agents prolong bleeding time, excess bleeding episodes with their combined use have not been observed in cardiological practice, in which they are widely used together following myocardial infarction. 79,94 However, clinically significant bleeding events associated with treatment with EPA either alone or in combination with aspirin have, to date, not been monitored in a RCT.
The NHS Bowel Cancer Screening Programme
The NHS Bowel Cancer Screening Programme (BCSP) in England began in 2006. It is currently based on a biennial guaiac FOBt targeted at all individuals aged 60–74 years who are covered by NHS registration data in England (the uptake, based on a returned FOBt kit, is approximately 50–60%). 95 Individuals with an abnormal FOBt (≈2%) are invited for colonoscopy via a specialist screening practitioner (SSPr)-run clinic. All colonoscopy is undertaken by screening-accredited colonoscopists working within a continuous QA framework based on multiple measures, including individual caecal intubation rate, withdrawal time and ADRa. 38,95 Recording of endoscopic findings and subsequent histopathological assessment is also directed by BCSP guidelines and a QA reporting system. 96,97 Any abnormality detected is discussed with the patient at a SSPr follow-up clinic. Detection of a CRC (≈10%, but variable dependent on the number of prevalent vs. incident screening investigations) prompts further management by the local multidisciplinary team (MDT) for CRC. Detection of one or more colorectal adenomas prompts surveillance colonoscopy within the BCSP, as per British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines. 30 Individuals classified as being at ‘low risk’ (i.e. those having one or two subcentimetre colorectal adenomas) are not offered colonoscopy, but remain in the biennial guaiac FOBt programme. Those individuals with three or four small colorectal adenomas (i.e. < 10 mm in size) or one colorectal adenoma of ≥ 10 mm in diameter are classified as being at ‘intermediate risk’ and are offered another colonoscopy at 3 years from the index procedure. Individuals with five or more subcentimetre colorectal adenomas, or three colorectal adenomas with at least one colorectal adenoma of ≥ 10 mm in diameter (i.e. 12% of men and 6.2% of women who undergo screening colonoscopy), are recommended to undergo surveillance colonoscopy 12 months from the screening colonoscopy. 98
Since 2013, the bowel scope programme has been rolled out across England, whereby, in addition to the biennial guaiac FOBt invitation, a single FS is offered to all individuals aged 55 years. 99 The presence of a colorectal adenoma of ≥ 10 mm in diameter, three or more small (i.e. < 10 mm) colorectal adenomas or any adenoma with ‘advanced’ features prompts an invitation for full colonoscopic evaluation, with the combined colorectal adenoma findings from the FS and colonoscopy directing the subsequent surveillance strategy within the BCSP, as described above. 95
The seAFOod polyp-prevention trial
Based on strong proof of concept for primary CRC chemoprevention activity of EPA67 and aspirin,49 the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR)/Medical Research Council (MRC) Efficacy and Mechanism Evaluation (EME) programme funded a 2 × 2 factorial RCT of 2 g of EPA-FFA daily and/or 300 mg of aspirin in ‘high-risk’ individuals identified in the English BCSP. The trial was termed the seAFOod polyp-prevention trial. 100
Main research question
Does the ω-3 PUFA EPA prevent colorectal adenomas, either alone or in combination with aspirin?
Objectives
Primary objective
The primary objective was to determine whether or not EPA prevents colorectal adenomas, either alone or in combination with aspirin. This was addressed by testing the following hypotheses:
-
2 g of EPA-FFA daily is more effective than placebo for reduction in colorectal adenoma recurrence.
-
300 mg of aspirin daily is more effective than placebo for reduction in colorectal adenoma recurrence.
Secondary objectives
The secondary objectives were to assess the tolerability and safety of EPA-FFA and EPA-TG alone and in combination with aspirin.
Chapter 2 Methods
Parts of this chapter have been reproduced from Hull et al. 1 © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
The trial protocol has been published in open-access form. 100
Trial design
The seAFOod polyp-prevention trial was a randomised, blinded, placebo-controlled 2 × 2 factorial trial. The trial was designed to integrate fully into the screening and surveillance phases of the BCSP in England so that participation would not alter routine clinical practice.
Participants were randomised to one of four groups to receive EPA-FFA or EPA-TG (both 2 g of FFA equivalent daily) daily with food, or identical placebo, AND 300 mg of enteric-coated aspirin daily taken with food, or identical placebo, until the day before surveillance colonoscopy (at 12 months). The primary outcome was the number of individuals with one or more colorectal adenomas at the surveillance colonoscopy (the ADRa). Secondary outcomes included the total number of colorectal adenomas per participant, subtype (advanced, conventional, serrated, left and right) of adenomas (ADRa and number), the number of participants reclassified as being at intermediate risk for future surveillance, EPA and other PUFA levels in RBCs and rectal mucosa, dietary fish intake and assessment of the tolerability and safety of EPA (both FFA and TG formulations) alone and in combination with aspirin.
Trial setting and participants
NHS Bowel Cancer Screening Programme recruiting sites
The English BCSP is organised into local centres of a variable number (usually 1–3) of individual BCSP sites (hospitals undertaking endoscopy), which receive referrals for screening colonoscopy after guaiac FOBt analysis at five regional hubs. Participants identified as ‘high risk’ at participating sites were randomised and followed to surveillance colonoscopy at 12 months. The trial was integrated into the BCSP to utilise routine clinical pathways in order to collect quality-assured data from screening and surveillance colonoscopies.
During the trial, 61 BCSP sites were opened. The date of the first participant, first visit (FPFV) was 11 November 2011; the last participant in was 10 June 2016; and the last participant, last visit (LPLV) was 8 June 2017. Despite approval from the BCSP Research Advisory Committee, widespread engagement from SSPrs and Clinical Research Network (CRN)-funded research nurses (RNs) and a trial extension in 2014, the trial did not recruit to target, recruiting 709 participants against a revised target of 755. The sample size calculation remained at 853, based on the predicted effect size of the interventions, giving 80% power. However, recruitment figures achieved prior to the 2014 extension, the limited recruitment period mandated by the funder and the limitations set by the expiry date on the capsule (EPA-TG) investigational medicinal product (IMP) suggested that recruitment of 755 individuals would be feasible in the extended intervention period (see Statistical methods).
The original strategy was to open 15 recruiting sites from two BCSP hubs (North-East and Eastern). This was based on data from the national BCSP database that suggested that each BCSP centre could identify approximately 50 high-risk patients per year. Trial screening data supported this assumption; however, the eligibility rate was much lower than expected, primarily because of a higher than expected number of screened high-risk individuals who were excluded because of the need for repeat colonoscopy or FS to check for adenoma excision within a 3-month window. Analysis of up-to-date BCSP data in early 2012 revealed that the number of cases requiring repeat endoscopy as part of routine BCSP care had increased nationally during the grant application and set-up phases of the trial. It was determined that a second colonoscopy or FS did not significantly alter the overall ADRa at the 12-month surveillance colonoscopy (see Changes to the protocol). Therefore, the protocol was amended (version 4.0, dated 24 May 2012)100 to include these patients, without loss of statistical power.
A trial site expansion strategy was also implemented in 2012, increasing the number of recruiting sites across England, from Cornwall to Cumbria, to 60 (representing ≈50–60% of English BCSP centres). In late 2015, a decision was made to add one further site that had expressed a strong interest to be involved in the trial.
Delays were experienced in gaining NHS trust research and innovation (R&I) approvals as a result of a general lack of Good Clinical Practice accreditation and research training for BCSP staff, many of whom had not previously contributed to a Clinical Trial of an Investigational Medicinal Product (CTIMP). Sites were supported by the Nottingham Clinical Trials Unit (NCTU) and local CRNs to access training. The median time to gain R&I approval at trial sites was 11.5 (range 4–19) weeks. In addition to a site initiation visit, supplementary training was provided to sites by the co-ordinating centre for participating local investigators, RNs and SSPrs via an instructional video.
In February 2014, recruitment was disrupted significantly when the manufacturer of the original capsule IMP (EPA-FFA) was no longer able to provide stock for the trial. Until an alternative capsule IMP could be identified, approved, manufactured and distributed, sites continued to recruit until local stock was exhausted, at which point that site temporarily suspended recruitment. To maximise recruitment during this period, the top eight most active sites were prioritised for allocation of remaining central stock of capsule IMP. Stock management also ensured that all participants completed the intervention phase of the trial using the same EPA formulation (FFA or TG). This strategy enabled the trial to continue recruiting between February and October 2014, after which a new capsule IMP became available. Partly because of this delay, a 36-month extension was approved (in October 2014) by the NIHR EME board in order to complete trial recruitment.
Identification of participants
Individuals identified as ‘high risk’ at screening colonoscopy on the basis of colorectal adenoma number and (endoscopic) size, and confirmed later by the histopathology report, were screened for the trial and approached by a member of the site research team to determine whether or not they were interested in trial participation. For those participants who had a bowel scope FS, summated colorectal adenoma findings were used to define individuals as ‘high risk’.
All ‘high-risk’ participants were given written trial information on discharge by a BCSP SSPr or RN. They were provided with a patient information leaflet (PIL), given a verbal explanation of the trial and given the opportunity to ask questions.
Participants were able to discuss the trial with their family, friends and/or health-care professionals before they attended a routine BCSP outpatient follow-up visit 7–14 days after screening colonoscopy. All participants provided written informed consent.
Eligibility criteria
Patients were eligible for inclusion if they were aged 55–73 years and were a BCSP participant identified as ‘high risk’ (i.e. they had five or more small colorectal adenomas or three or more colorectal adenomas with at least one being ≥ 10 mm in diameter) at the first complete screening colonoscopy. This included participants who were identified as ‘high risk’ at colonoscopy after FOBt screening, or who were deemed ‘high risk’ on the basis of the combined findings from a bowel scope FS and subsequent full colonoscopy. If the first screening colonoscopy was defined as complete, the participant was immediately stratified as ‘high risk’. If the first colonoscopy was incomplete, that individual was required to have a second colonoscopy to complete the initial examination, after which both procedures were added together as the screening colonoscopy result for the purposes of BCSP surveillance and trial eligibility.
Patients were excluded from the trial if:
-
They had a requirement for more than one repeat colonoscopy or FS within the BCSP 3-month screening window (see Changes to the protocol).
-
They had a malignant change in a colorectal adenoma requiring management by a CRC MDT.
-
They were regularly (i.e. more than three doses per week) taking prescribed or OTC aspirin or regularly (i.e. more than three doses per week) taking prescribed or OTC non-aspirin NSAIDs. This was not an exclusion criterion if the drug was self-prescribed and not recommended by a doctor and if the individual was willing to stop taking it for the duration of the trial.
-
They had aspirin intolerance or hypersensitivity, including aspirin-sensitive asthma.
-
They had had active peptic ulcer disease within 3 months or previous peptic ulcer (and were not on proton pump inhibitor prophylaxis).
-
They had a fish or seafood allergy.
-
They used or were planning to regularly use (i.e. more than three doses per week) fish oil supplements. This was not an exclusion criterion if the supplements were self-prescribed and not recommended by a doctor and if the individual was willing to stop taking them for the duration of the trial.
-
They had a known clinical diagnosis or were a gene carrier of a hereditary CRC predisposition (e.g. FAP).
-
They had Lynch syndrome, also known as hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer (HNPCC).
-
They had a previous or planned colorectal resection.
-
They had known bleeding diathesis or concomitant warfarin therapy or use of any other anticoagulant or antiplatelet agent.
-
They had severe liver impairment.
-
They had severe renal failure (i.e. creatinine clearance of < 10 ml/minute).
-
They currently used methotrexate at a weekly dose of ≥ 15 mg.
-
They were not able to comply with trial procedures and IMP use.
-
They had a serious medical illness interfering with trial participation.
-
They were taking part in another interventional clinical trial.
-
They failed to give written informed consent.
Responsibilities for checking eligibility and obtaining informed consent could be delegated to the SSPr or RN according to site approvals, but eligibility was confirmed by the local principal investigator (PI) for all participants.
Changes to the protocol
Soon after FPFV on 11 November 2011, it became apparent from screening log activity at individual BCSP sites that the eligibility rate was ≈15–20%, rather than the 60% that had been predicted in the original recruitment projection. A contributing factor was the higher than expected use of other non-aspirin antiplatelet agents, such as clopidogrel, which was later added as an exclusion criterion in January 2012 (protocol version 3.1, dated 12 January 2012). Another major contributing factor was the larger than expected number of ‘high-risk’ individuals (≈25%) who required a repeat endoscopy after randomisation. Repeat endoscopy was originally an exclusion criterion because the primary end point might be confounded by colorectal adenoma detection and removal at an extra endoscopic procedure between the screening (index) and 1-year surveillance colonoscopies. However, subsequent analysis in April 2012 of 1189 ‘high-risk’ patients who underwent 1-year surveillance colonoscopy in 2010 in 26 BCSP centres did not support this notion. The overall ADRa at surveillance colonoscopy [including those who underwent repeat partial colonoscopy or FS (ADRa 54%), repeat full colonoscopy (ADRa 67%) or no repeat procedure (ADRa 63%)] was 62%, which was consistent with the value (60%) used in the original sample size calculation. Therefore, the protocol was amended to allow recruitment of those individuals who required no more than one repeat endoscopic procedure [either colonoscopy (full or partial) or FS] within a 3-month screening episode window (version 4.0, dated 24 May 2012). 100 A number of other changes to details contained within the protocol are documented in the statistical analysis plan (SAP) (version 1.1, dated 24 August 2017). These are listed in Statistical methods.
During trial recruitment, the trial was included as part of a larger MRC-funded programme of research [Systematic Techniques for Assisting Recruitment to Trials (START)] to assess web-based recruitment strategies. A separate protocol was approved for the cluster randomised (by site) substudy of a web-based information tool and the PIL was updated accordingly. Details of this study and the seAFOod trial contribution will be reported separately by the MRC-START study team.
Trial procedures
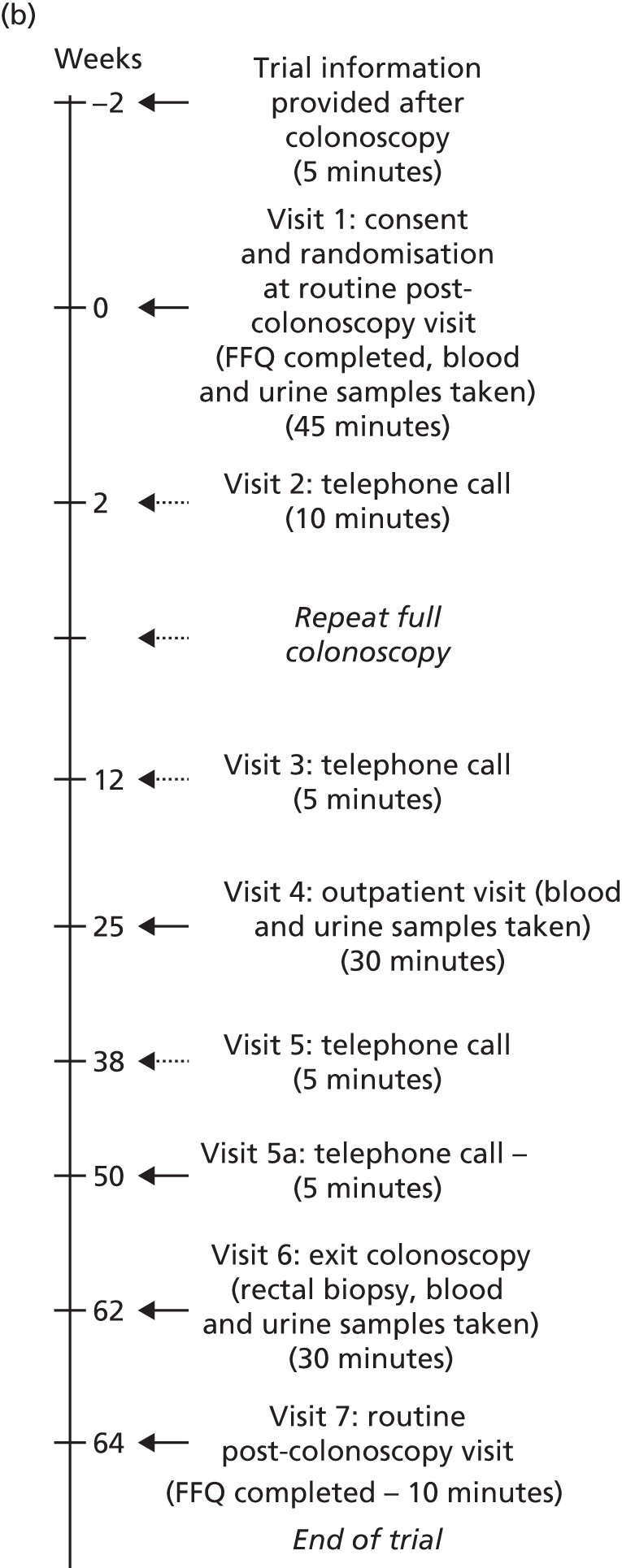
Trial procedures were performed as shown in Figure 1.
FIGURE 1.
The seAFOod trial participant pathway. (a) Participants whose visit 6 date was scheduled from the first complete colonoscopy; and (b) participants whose visit 6 date was scheduled from a repeat full colonoscopy. FFQ, Food Frequency Questionnaire.
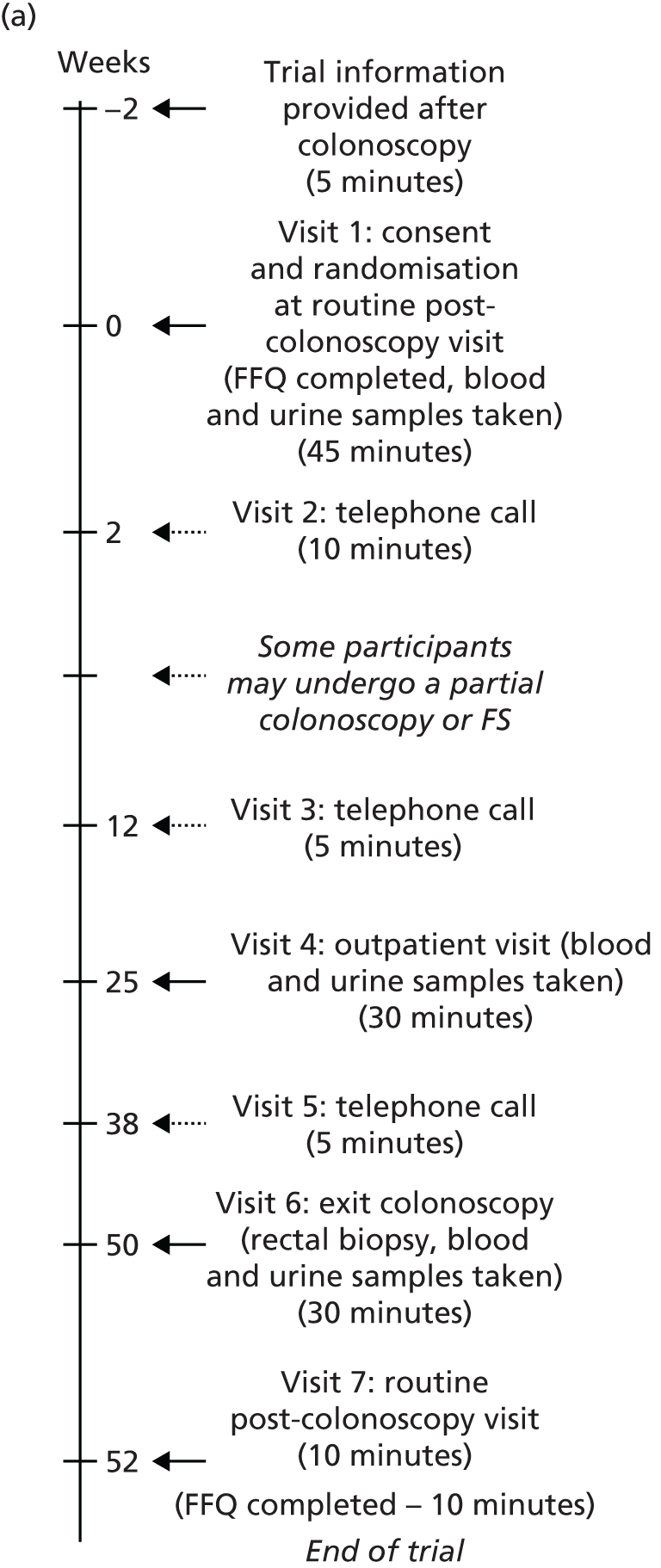
Baseline visit
Individuals attending a routine outpatient follow-up BCSP appointment to obtain results of the screening colonoscopy were approached. Individuals who were eligible and willing to take part in the trial were asked to provide written informed consent. Demographic information and details of participants’ medical histories were collected and participants were randomised. It was preferred that participants were randomised within 4 weeks of the first complete BCSP screening colonoscopy. However, to maximise recruitment, randomisation was allowed outside this time window as long as it was recorded on the protocol deviation log. A prescription was issued for the supply of IMP for 6 months. The local hospital pharmacy dispensed the trial treatment. A second prescription for a further 6 months of IMP was provided at visit 4.
Biological samples were taken, comprising a blood sample [2 × 6-ml K2EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) Vacutainer® tubes; Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD), Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA] and a urine specimen of 5–10 ml. Samples were taken only if the participant provided separate, specific consent for collection of blood and urine.
In addition, participants were asked to complete a pre-treatment Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) so that any change in dietary ω-3 PUFA intake during trial involvement could be determined.
Repeat endoscopy
Participants were informed whether or not a repeat colorectal endoscopic examination was required at the baseline visit. This was one of the following: a second full colonoscopy, a partial colonoscopy (planned incomplete views of the colorectum) or a FS. Participants undergoing one repeat endoscopy within 3 months of the screening colonoscopy remained eligible for the trial. The results of the colonoscopy were collected at visit 3. These participants were in the intervention period of the trial for a maximum of 15 months, rather than 12 months, so an additional 3-month trial prescription was dispensed to cover this period. If a participant who had already undergone a repeat endoscopy had a further repeat procedure scheduled by the local BCSP team, this made him or her ineligible for the trial.
All participants were asked to commence the IMP immediately following consent at the baseline visit (visit 1). Those participants who were due to undergo a repeat endoscopy procedure temporarily stopped IMP 10 days prior to the endoscopic procedure and restarted IMP 4 days after the endoscopy. Participants who underwent a partial colonoscopy or FS had a surveillance colonoscopy 12 months after the first complete screening colonoscopy, as per BCSP guidelines. Participants who underwent a second full colonoscopy had a surveillance colonoscopy date booked as per BCSP team preference, but preferably dated 12 months after the first screening colonoscopy.
Visits 2 and 3: telephone calls at 2 and 12 weeks
Participants were contacted by the SSPr/RN by telephone at 2 and 12 weeks after starting trial treatment. Participants were asked about any symptoms or new medical problems since the last contact and were reminded to take the IMP as directed.
Participants who were due to undergo a repeat colorectal endoscopic procedure between visits 2 and 3 were reminded to discontinue IMP temporarily. Colonoscopic findings at the repeat procedure were collected and recorded in the same way as for the baseline visit.
Visit 4: outpatient visit
At 6 months, participants were invited to attend the BCSP site, at which time mid-treatment blood and urine specimens were collected from those who had provided consent. Participants were asked about any symptoms or new medical problems since the last contact. Any unused trial treatment from the first prescription was collected and counted. Each participant then received a new prescription for trial treatment for a further 6 months.
Visit 5: telephone call
A third telephone contact was conducted with participants at 38 weeks after starting the trial treatment. The SSPr/RN asked about any symptoms or new medical problems since the last contact and reminded the participant to take trial treatment as directed.
Visit 5a: telephone call
An extra telephone contact was conducted for participants who had a repeat full colonoscopy between visits 2 and 3 after starting the trial treatment. The SSPr/RN asked about any symptoms or new medical problems since the last contact and reminded the participant to take his/her trial treatment as directed. The SSPr/RN liaised with the hospital pharmacy about delivery of a third dispensing of IMP to these participants. The relevant participants then received a new prescription for trial treatment for a further 3 months.
Visit 6: surveillance colonoscopy
Participants attended for routine surveillance colonoscopy at 12 months from the date of the screening colonoscopy. Participants took the final dose of trial treatment on the day before surveillance colonoscopy. Blood and urine specimens were obtained, as well as four random biopsies of macroscopically normal rectal mucosa (at least 2 cm from any polyp) at the end of the surveillance colonoscopy.
Colorectal adenoma outcomes at the 12-month surveillance colonoscopy were collected as per usual BCSP practice, including the number, size (maximum dimension in mm from the histopathology report, or the endoscopic size if the adenoma was not retrieved or was removed by hot biopsy), site [proximal to the splenic flexure (right) or at/distal to the splenic flexure (left)], histological type (tubular/tubulo-villous, villous, serrated) and presence of high-grade dysplasia of all colorectal adenomas.
Visit 7: routine post-colonoscopy visit
Participants were seen after surveillance colonoscopy as part of routine BCSP follow-up, during which a second FFQ was completed. Participants had the option to complete the FFQ at visit 6 or over the telephone if they decided to receive colonoscopy results by telephone.
Randomisation
Participants were registered in the trial using a secure web-based randomisation system. Randomisation was based on a computer-generated, internet-based treatment assignment determined by a pseudo-random code using random permuted blocks of randomly varying size, created by NCTU. Participants in the trial were allocated with equal probability to either treatment group. It was planned to stratify by BCSP centre. However, after database lock, it was discovered that BCSP site had been used, rather than BCSP centre. As sites could be associated only with an individual BCSP centre, this still ensured balance between centres.
Participants were randomised to a simple 2 × 2 factorial design (Table 1) to:
-
2 g of EPA-FFA, or an equivalent FFA dose of 90% EPA-TG (2780 mg), daily by mouth, or their identical placebos (capric and capryllic acid medium-chain TGs for both formulations)
in addition to:
-
300 mg of enteric-coated aspirin daily by mouth (as one 300-mg tablet taken with food) or identical placebo.
|
|
|
|
The sequence of treatment allocations was concealed until interventions had all been assigned and recruitment, data collection and all other trial-related assessments were completed. The actual allocation was not divulged to either the staff at the BCSP site or the participant. The trial prescription produced by the randomisation system referenced specific trial treatment containers. The trial drug prescription was signed by the local PI or a co-investigator, as defined by the site delegation log.
Interventions
The IMPs used in this trial were gastroresistant capsules of 99% pure EPA in the FFA form (EPA-FFA), 90% EPA as the TG conjugate (EPA-TG) in soft gelatin capsules, enteric-coated aspirin tablets and their identical placebos.
In February 2014, the supplier of the EPA-FFA IMP (SLA Pharma AG) disclosed that it could no longer provide further capsule IMP to the trial. The Trial Management Group (TMG), NIHR EME programme and the Trial Steering Committee (TSC) made the decision to continue the trial using an alternative EPA formulation and identical (medium-chain TG) placebo. Close consultation with the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) and the Research Ethics Committee (REC) was also undertaken. A substantial amendment (number 14) was approved by the REC on 26 August 2014 and the trial received a Clinical Trials Authorisation (CTA) from the MHRA on 29 August 2014 for a new capsule IMP (EPA-TG). The new formulation maintained FFA equivalence (2000 mg daily) with the previous EPA-FFA formulation by using 5 × 574-mg 90% EPA-TG capsules per day (a total of 2870 mg), taking into account the percentage weight per weight (w/w) content of EPA and the presence of the glycerol backbone in the re-esterified TG.
The CTA required a specific simplified IMP dossier for the 90% EPA-TG, detailing its multistep manufacture, and also a cover document for the existing investigator brochure, which compared the chemical structure, GI absorption, bioavailability and tolerability profiles of the FFA and TG forms of EPA.
Although the 90% EPA-TG capsules that were proposed as a new IMP were publicly available for purchase as a nutritional supplement (from Igennus Healthcare Nutrition), the MHRA requested a programme of stability testing to meet manufacturing QA requirements for a CTIMP (see Appendix 1). A programme of accelerated (30 °C, 65% relative humidity) and standard (25 °C, 60% relative humidity) stability testing of capsules began in July 2014 (performed by ALS Food & Pharmaceutical, Carlisle, UK) and was performed once every 3 months. The core data set comprised the peroxide value (POV), para-anisidine value (pAV) and derived total oxidation (TOTOX) value, as well as a full PUFA analysis, to determine the EPA content. Data from initial accelerated testing at 3 months gave a minimum 12-month shelf life under standard conditions for the trial to continue with the new capsule IMP. Rolling stability testing provided a continuous extension of shelf life until 12 June 2016, when capsule IMP use ceased, as per the maximum approved shelf life (3 years) of the capsule IMP approved by MHRA.
The commercially available 90% EPA-TG capsule was also encapsulated with a differently coloured soft gelatin coat (olive green) to be able to produce an identical placebo because of the difference in appearance of EPA and medium-chain TG oils.
Participants took only one formulation of the EPA, which was either FFA or TG, or its matching placebo. Stocks of the IMP were managed during the transition period from the FFA formulation to the TG formulation to ensure that sites had sufficient stock of EPA-FFA and placebo capsules to manage existing and new participants throughout each individual intervention period.
The trial treatment was taken daily from the date of randomisation to the day before the 12-month surveillance colonoscopy.
Suppliers
SLA Pharma AG supplied EPA-FFA capsules and an identical placebo free of charge. Igennus Healthcare Nutrition supplied the 90% EPA-TG capsules and an identical placebo at cost price. Aspirin and its identical placebo were supplied by Bayer AG (Leverkusen, Germany) free of charge.
Eicosapentaenoic acid-free fatty acid dose
Participants took two 500-mg gastroresistant capsules of 99% pure EPA-FFA (or placebo) twice daily with food, giving a total daily dose of 2 g of EPA-FFA. Previous experience suggested that 2 g of EPA-FFA daily is well tolerated; principal side effects are diarrhoea, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, which are generally mild in severity and minimised or avoided by dosing with food or dose reduction to 1 g daily. A dose-reduction algorithm was used for participants experiencing side effects and managed by the local RN or SSPr.
Eicosapentaenoic acid-triglyceride dose
Alternatively, five soft gelatin 574-mg capsules of 90% EPA-TG (or placebo), equivalent to 2780 mg, were taken orally with food each day. It was preferred that three of the EPA-TG capsules were taken with the largest meal of the day and two capsules were taken with a smaller meal. Each capsule contained approximately 516 mg of EPA-TG, which is equivalent to 398 mg of EPA-FFA. Other PUFAs in the formulation included 3.9% (w/w) AA. The 90% EPA-TG did not have pharmaceutical marketing approval [see the project web page: www.journalslibrary.nihr.ac.uk/programmes/eme/0910025/#/ (accessed 25 April 2019)]. Clinical studies have indicated that EPA-TG (usually in a fish oil mixture with other PUFAs) is well tolerated at doses exceeding 2 g per day over periods of up to 6 months. The principal known side effects are the same as indicated for EPA-FFA. 101–105
Aspirin
Participants were randomised to one 300-mg enteric-coated aspirin tablet (or placebo), taken orally once a day with food. Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) was supplied as 300-mg enteric-coated tablets in accordance with the Summary of Product Characteristics for aspirin (see Appendix 2). These tablets had marketing approval in the European Union.
Placebos
The EPA-FFA and EPA-TG placebos consisted of identical capsules of capric and capryllic acid medium-chain TGs that had previously been used in placebo-controlled trials of EPA. 67
The placebo for aspirin consisted of the same excipients as the active formulation of the drug minus the active ingredient.
Discontinuation of treatment
In the event of an adverse drug reaction (ADR), either serious or non-serious, the local PI or attending physician was to take direct and appropriate action to provide care for the participant and to decide whether or not the trial treatment should be discontinued. However, unless there was a clear contraindication, trial treatment was continued, or stopped temporarily.
In all cases, the reasons for discontinuation of trial treatment were recorded in the clinical record file and if the investigator had recorded more than one reason, he or she was to indicate the main reason.
Treatment was discontinued permanently if the participant needed treatment with a contraindicated drug: ≥ 15 mg of methotrexate weekly, any dose of warfarin or any other anticoagulant therapy, any other antiplatelet agent such as clopidogrel, or prescription of aspirin for any other indication. These participants were still followed up for the remainder of the trial.
Prescriptions and accountability
The local PI or delegated pharmacy trial staff member was responsible for ensuring trial treatment accountability, including reconciliation of trial treatment and maintenance of trial treatment records, throughout the course of the trial, in accordance with UK regulatory requirements. On receipt of a delivery of trial treatment, details were checked for accuracy and receipt was acknowledged by signing and dating the documentation provided. In addition, receipt was acknowledged in the web-based system by the local pharmacy team, which had access to the web-based stock control system. Stock did not become available for allocation until it was accepted in the stock control system.
The local hospital pharmacy completed the dispensing process by addition of a participant’s name, subject number, date of dispensing and visit number to each allocated container. This process was repeated again at visits 4 and 5a if required.
Blinding
Participants, SSPr/RNs, local investigators and those assessing the outcomes were all blinded to treatment allocation. The statistical analysis for the trial was also blinded until data were locked, except for independent Data Monitoring Committee (DMC) reports.
Trial treatment
The trial treatment was packaged and labelled in accordance with UK regulatory requirements. The containers were clearly marked and had a unique identification number.
Bulk supplies of EPA-FFA, EPA-TG, aspirin and placebo capsules and tablets were delivered to Stockport Pharmaceuticals (Stockport, UK) for packaging and labelling to allow preparation of blinded supplies.
Blinded supplies were then stored at Stockport Pharmaceuticals for distribution to participating sites under a web-based stock control system reviewed regularly by the NCTU pharmacist.
Unblinding
Access to the sequence of treatment allocations was confined to the NCTU data manager and a central pharmacy, in case of out-of-hours unblinding. In the event of the need to break the code, the date and reason were recorded on the web-based unblinding system. The local hospital pharmacy had access to the web-based unblinding system in normal office hours and out-of-hours access was provided via the sponsor at St James’s University Hospital. The requirement for unblinding was considered low. All participants were given a trial identification card, containing details of the IMPs, which participants were encouraged to show when seeking advice or management from any health professional. Unblinding did not occur during the trial.
End of the trial
Participants left the trial when they completed their routine post-surveillance colonoscopy visit (visit 7).
Cases of failure to receive allocated treatment and withdrawal from follow-up were reported, and the reason(s) for withdrawal (if given) were documented. If a participant did not receive allocated treatment but agreed to remain in the trial, outcome data collection continued in accordance with the protocol. Participants were informed at the start of the trial that data collected up to the point of withdrawal would be retained and used in the final analysis.
Trial withdrawal
Participants could withdraw from the intervention or the trial at any time without giving a reason and without compromising future management. Data collected up to the point of withdrawal were retained for the purposes of the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis. Participants could withdraw from the intervention only but continue in the trial, thereby completing outcome measures. To maximise primary outcome data collection, BCSP surveillance colonoscopy data were also collected from participants who withdrew from the trial, as per the informed consent.
Outcome measures
Primary outcome
The primary outcome was the number of participants with one or more colorectal adenomas detected at the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy 12 months after the screening examination (ADRa).
Secondary outcomes
The secondary outcomes were as follows:
-
Total number of colorectal adenomas per participant at BCSP surveillance colonoscopy (total MAP).
-
Detection of one or more ‘advanced’ (i.e. ≥ 10 mm in diameter, high-grade dysplasia or villous histology) colorectal adenomas at the 12-month BCSP surveillance colonoscopy (advanced ADRa).
-
Number of ‘advanced’ colorectal adenomas per participant at the 12-month BCSP surveillance colonoscopy (advanced MAP).
-
Detection of one or more conventional adenomas (conventional adenoma end points were defined after database lock) at the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy (conventional ADRa).
-
Number of conventional adenomas (conventional adenoma end points were defined after database lock) per participant at the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy (conventional MAP).
-
Detection of one or more serrated adenomas at the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy (serrated ADRa).
-
Number of serrated adenomas per participant at the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy (serrated MAP).
-
The region of the colorectum (right colon: any part of the colon proximal to the splenic flexure; left colon: the rectum and the colon at/distal to the splenic flexure) in which adenomas are detected at the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy.
-
Reclassification from ‘high risk’ to ‘intermediate risk’ after the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy (BCSP risk stratification at the first surveillance colonoscopy states that any individual who does not continue to fulfil ‘high-risk’ criteria is classified as ‘intermediate risk’ for further colonoscopic surveillance at 3 years).
-
Detection of CRC prior to, or at, the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy.
-
Dietary fish and other seafood intake at baseline and at the end of the trial.
-
Red blood cell EPA and rectal EPA levels at baseline, 6 months (RBC only) and 12 months from randomisation.
-
Absolute RBC fatty acid (i.e. DHA, AA, EPA-to-AA ratio) levels and difference from baseline at 6 months and 12 months.
-
Rectal mucosal fatty acid (i.e. DHA, AA, EPA-to-AA ratio) levels at surveillance colonoscopy.
-
Adverse events, including clinically significant bleeding episodes (i.e. haemorrhagic stroke or GI bleeding requiring hospital admission or investigation).
Exploratory outcomes
-
Colorectal adenoma size.
-
Association between change of RBC EPA level at 12 months and individual number of total colorectal adenomas.
-
Association between rectal and RBC EPA levels at 12 months.
Research governance
The trial was conducted in accordance with (1) the recommendations adopted by the 18th World Medical Assembly, Helsinki 1964, amended at the 48th General Assembly, Somerset West, Republic of South Africa, October 1996 (www.wma.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/DoH-Oct1996.pdf); (2) the principles of the International Conference of Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use – Good Clinical Practice (ICH-GCP) guidelines (https://ichgcp.net); and (3) the Medicines for Human Use (Clinical Trials) Regulations 2004106 (UK Statutory Instrument 2004/1031) and any subsequent amendments of the Clinical Trial Regulations.
The National Research Ethics Service (NRES) Trent – Trent REC (reference number 10/H0405/90) gave ethics approval for the trial for NHS participants. First, MHRA CTA approval was obtained on 16 March 2011. The trial was approved by the BCSP Research Committee on 13 October 2009.
This project was funded by the EME programme, a MRC and NIHR partnership (project number 09/100/25). The trial was registered (as ISRCTN05926847) in a publicly available database prior to FPFV.
The final, approved protocol was version 6.0, approved on 11 August 2014. There were a number of administrative and procedural changes made to the protocol during the trial, which are outlined in Appendix 3.
Protocol deviations
The protocol defined a protocol violation as:
-
> 50% of trial medication returned in total
-
inadvertent use of OTC medication containing aspirin, NSAIDs or fish oil for > 2 weeks in total
-
surveillance colonoscopy occurring outside the allowed time windows (48–52 weeks after the last complete screening BCSP colonoscopy, or 60–64 weeks for participants undergoing a repeat full colonoscopy within 3 months of initial screening).
The protocol deviation log collected the above violations and any additional protocol deviations (i.e. any deviation from the protocol that occurred during a participant’s time in the trial, whether deliberate or non-deliberate).
Trial oversight
Oversight committees were assembled to ensure the proper management and conduct of the trial, and to uphold the safety and well-being of participants. The general purpose, responsibilities and structures of the committees were described in the protocol.
Trial Management Group
The TMG comprised the chief investigator, members of the NCTU and other visiting members of the wider trial team, including the University of Bradford biobank and lipid analysis team and an expert in human nutrition, as required. This group met regularly, with supplementary meetings as required, to oversee the day-to-day operational aspects of the trial, reviewing progress and resolving issues that arose.
Trial Steering Committee
The TSC was led by an independent chairperson and consisted of members with professional expertise in delivering RCTs, CRC diagnosis and management, primary care gastroenterology and the BCSP. The TSC also had a patient and public involvement (PPI) representative (an individual who had undergone BCSP colonoscopy) during the course of the trial. The TSC monitored, reviewed and supervised the progress of the trial, particularly advising on recruitment and retention, as well as ensuring adherence to the trial protocol. It also monitored blinded data to consider safety and effectiveness indications. The TSC considered reports from the DMC when making recommendations. The chief investigator, trial manager and at least one co-investigator were also in attendance as non-independent members to provide information to the committee. The trial sponsor (University of Leeds) and IMP providers were invited to attend as observers.
The TSC met independently prior to the start of the trial and agreed terms of reference in a charter. The committee met approximately every 6 months thereafter, convening supplementary meetings as required (e.g. related to the capsule IMP switch).
Data Monitoring Committee
An independent DMC, which met approximately every 6–12 months, was established with access to unblinded data to provide independent review and recommendations in the light of potential treatment effect and harm, as well as to assist and advise the TSC and the TMG. The DMC consisted of a chairperson and members with expertise in colorectal surgery and prevention, early detection and treatment of CRC, and statistics. The DMC met prior to the start of the trial and agreed terms of reference in a charter. Only the DMC had access to unblinded data until the final end-point assessment was completed.
Risk assessment and safety monitoring
A risk assessment was conducted as part of protocol development and was monitored regularly throughout the trial for new risks. The main risks to the trial were reliance on the BCSP to recruit to a large multicentre RCT, as the BCSP had not previously hosted CTIMP research and staff were not experienced in recruiting participants. Compliance with trial medication and drug accountability was reliant on participants returning medication and patient reports, as well as staff maintaining detailed records of medication logs.
Recruitment sites were supported by the NCTU, which initially provided training through a site initiation visit, as well as supplementary training, as required. Investigators had access to a research area of the trial website (www.seafood-trial.co.uk) and access to the NCTU trial team for day-to-day queries. To obtain high-quality data, regular central monitoring checks were performed according to the monitoring plan, including review of recruitment, retention and data collection rates by the TMG, TSC and DMC.
Data on AEs and serious adverse events (SAEs) were collected. As agreed by the sponsor, REC, DMC and TSC, the DMC was provided with a listing of all AEs and SAEs, including any deaths (if applicable), at each DMC meeting.
As part of the switch from the EPA-FFA formulation to the EPA-TG formulation, a review was undertaken of the Reference Safety Information (RSI) for the trial. Evidence was provided in a supplement, including MHRA-stipulated RSI for the EPA formulations, version 2.0, dated 22 August 2016 (approved by the MHRA on 3 October 2016) to the investigator brochure version 6, dated 10 January 2014, that the FFA and TG formulations were likely to have a similar pharmacological and risk/AE profile, as well as similar anti-CRC efficacy, in the seAFOod trial population [see the project web page: www.journalslibrary.nihr.ac.uk/programmes/eme/0910025/#/ (accessed 25 April 2019)].
Monitoring
Following an internal assessment of the trial by the quality assurance manager at the NCTU, the trial was assessed as a medium-risk trial requiring low-intensity monitoring. Based on this risk category and the specific risks identified, the monitoring strategy consisted of on-site routine and triggered monitoring visits, central monitoring and review of regular reports by trial oversight committees, as well as assessment and oversight of third-party vendors. On-site visits were conducted by either the trial manager or a trial monitor. Central monitoring was conducted by the NCTU and reviewed regularly by the TMG, the TSC and the DMC. On-site and central monitoring revealed no major common concerns during the trial. Sites that received an on-site monitoring visit at some point during the trial accounted for 68% of randomised participants.
Patient and public involvement
There was PPI throughout the trial. One PPI member was integral to trial design, grant application and production of participant-facing trial materials. He then took no further part in the trial. Subsequent PPI input on the TSC was provided by a different PPI member. Both PPI representatives brought personal experience of the BCSP pathway to their roles. Two PPI representatives from Independent Cancer Patients’ Voice contributed to the production of site and participant results summaries and to the development of the dissemination plan for the trial findings.
Payments to participants
Participants were not paid to participate in the trial. Visits 1, 6 and 7 were planned to co-ordinate with routine BCSP appointments. However, an additional visit at 6 months (visit 4) was required; therefore, participants were offered a reimbursement of travel expenses up to a maximum of £10.
The seAFOod polyp-prevention trial biobank
Blood, urine and rectal mucosa sample collection in the seAFOod polyp-prevention trial is described in detail in an appendix of the trial protocol, which has been published. 100
In brief, a blood sample and a urine specimen were obtained at visits 1, 4 and 6. Blood was immediately separated into plasma, leucocytes and RBCs. Rectal biopsies were obtained only at the surveillance colonoscopy at visit 6.
Sample cryovials were stored in either a Liebherr Underbench –20 °C freezer (Liebherr Group, Bulle, Switzerland) supplied by the seAFOod trial or the existing trust freezer facility at –20 °C or colder, in PathoSeal bags (DGP Intelsius Ltd, York, UK). Storage temperature was monitored using a Hanna HI-141 CH Datalogger (Hanna Instruments Ltd, Leighton Buzzard, UK), or a similar system provided by the trust site, and recorded on sample worksheets.
University of Bradford staff, in close collaboration with the NCTU, organised the collection of samples from each BCSP site approximately every 6 months by a specialist courier (CitySprint Health, London, UK). The original proposal was to transfer samples to the central biobank facility every 3 months. However, the expansion of participating trial sites in 2012–13 meant that the collection strategy was revised. BCSP sites were grouped into 10 individual routes by CitySprint Health so that collection from these sites could be scheduled for the same day. Sites were asked to confirm whether or not they required a collection, and the number of PathoSeal bags at that site, to allow CitySprint Health to supply the correct thermal box size. If sites were unable to accommodate a collection on their scheduled route day, individual collections were arranged. The day before collection, CitySprint Health arranged for pre-addressed thermal boxes, which contained dry ice, to be sent to appropriate BCSP sites. The lid of the thermal box was removed only when necessary for adding samples. All sealed PathoSeal bags collected since the last courier sample collection were placed in the thermal box and dry ice was spread around the bags to ensure that they were completely covered. The thermal boxes were delivered to the University of Bradford on the same day or, in the case of routes involving longer distances, the following morning. No units were received with low dry ice levels and all samples were received frozen.
Each BSCP site completed a shipment form that documented the samples being transported. A carbon copy of the shipment form was kept in the site file with the carbon copy of the completed sample worksheets. The original shipment form and the original completed sample worksheets were sent with the samples.
On receipt of each shipment of transportation units at Bradford, a sample tracking form was completed. Contents were then checked against the sample worksheet. Cryovials were transferred into sample boxes (10 × 10 cell cryoboxes, manufactured by Sarstedt, Nümbrecht, Germany) specific to each sample type, and cryoboxes were kept on ice at all times when removed from the freezer. All details were entered onto a separate sample tracking form for each thermal box. Samples were stored in type-specific cryoboxes and racks, minimising disruption when samples were removed for analysis.
All samples were stored in a dedicated –80 °C freezer (New Brunswick™ U570 –80 °C; Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany), which was connected to the emergency power supply at the Institute of Cancer Therapeutics, University of Bradford, and supported with a CO2 back-up system (New Brunswick) and Centroller AD11+ (Centroller, Staines, UK) telephone alarm system. Freezer temperature was monitored daily.
The details from the sample tracking form and the sample worksheets were entered into the seAFOod trial biobank sample database. The database allocated a unique Clinical Trials Pharmacology Laboratory (CTPL) tracking identification (ID) to each participant-specific set of samples in a PathoSeal bag (i.e. if a participant had samples taken on three visits, they received three CTPL IDs). The CTPL ID was marked on the sample worksheet and the sample tracking form. The database was stored on the University of Bradford server, in the ‘Secure’ section, accessible only by nominated CTPL staff, and backed up regularly, as described in the University of Bradford’s computer policy. The database was the primary source for sample tracking; however, paper documents were available as a secondary source if necessary, stored in participant and shipment folders in the secure Human Tissue Act-approved laboratory. 107
Samples were obtained at BSCP sites between FPFV (i.e. 11 November 2011) and LPLV (i.e. 8 June 2017). The first samples received at Bradford were delivered on 18 July 2012 and the last sample shipment took place on 27 July 2017. In the intervening time, 332 collections were made from BCSP sites, with 1775 individual PathoSeal bags received.
Samples were stored at BSCP sites for between 1 and 696 days (mean 124 ± 92 days, median 115 days). There were 1378 (78%) sample sets stored at BSCP sites for < 6 months. Thirty (2%) sample sets were stored at BSCP sites for > 12 months.
The majority of sample sets (n = 1021; 58%) were stored in BCSP sites at –20 °C (range –16 to –24 °C), with 230 (13%) sample sets stored at –40 °C (range –25 to –69 °C) and 524 (30%) sets stored at or below –70 °C.
One or more biological samples were received from 677 of 709 (95%) randomised seAFOod trial participants. Of the 709 participants, 73% (519) of participants provided full sample sets of blood, urine and rectal mucosa from all three visits. There were 76 participants who provided samples at two visits (visits 1 and 4, n = 49; visits 4 and 6, n = 15; visits 1 and 6, n = 12). Eighty-two participants provided samples at only a single visit (visit 1, n = 75; visit 4, n = 2; visit 6, n = 5).
Overall, a total of 7322 biological samples were received (16,258 sample aliquots):
-
1715 plasma samples (6746 aliquots)
-
1714 leucocyte samples (1714 aliquots)
-
1707 RBC samples (3421 aliquots)
-
1664 urine samples (3309 aliquots)
-
522 rectal biopsies (1068 aliquots).
Compliance with biological sample collection [defined as the proportion of sample sets expected (n = 2127) that were received with at least one sample aliquot] was 80% (blood), 78% (urine) and 74% (rectal mucosa).
Laboratory protocol deviations were monitored carefully by sample worksheets:
-
80% of blood samples were obtained per protocol (centrifugation within 30 minutes and transfer to the freezer within 60 minutes).
-
2% of sample sets were received without worksheets.
-
1% of samples sets were received with insufficient data to assess timing.
-
8% of blood was separated after 30 minutes, but frozen within 1 hour of collection.
-
9% of blood samples took > 1 hour to separate (often related to split hospital sites for endoscopy and sample handling).
A small number of other protocol deviations were noted, including:
-
1% of sample sets that suffered a temperature deviation (but no thaw).
-
1% of sample sets that defrosted at some point.
-
0.5% of sample sets suffered ‘other’ deviations (including wrong anticoagulant blood tube used and biopsies placed in formalin).
Fatty acid measurement and analysis
The methods used are described in detail by Volpato et al. 89 In brief, fatty acids were extracted from washed RBC membranes, or rectal mucosal homogenates, using an isopropanol/chloroform method with acid hydrolysis, in order to measure the total membrane/tissue fatty acid pool. 89 Liquid chromatography, in combination with electrospray ionisation triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry (ESI-MS), was performed with a Waters Alliance™ 2695 High Pressure LC module (Waters, Milford, MA, USA) in combination with a Waters Micromass™ Quattro Ultima triple quadrupole mass spectrometer on derivatised samples, in the presence of internal standard (deuterated ALA), as described by Volpato et al. 89 Data are expressed as the percentage of each fatty acid relative to the total fatty acid peak chromatographic area for the ω-3 PUFAs C18:3 (ALA), C20:5 EPA, C22:5 docosapentaenoic acid (DPA) and C22:6 DHA; the ω-6 PUFAs C18:2 linoleic acid (LA) and C20:4 AA; and the monounsaturated C18:1ω-9 oleic acid and saturated fatty acids C18:0 stearic acid and C16:0 palmitic acid. 89
Measurement of dietary fish intake
Participants were asked to complete a FFQ at baseline (visit 1) and at the end of the intervention (visit 6 or 7). The validated European Prospective Investigation of Cancer (EPIC) short FFQ was used, which is a semiquantitative, paper-based FFQ that includes 130 food items and supplementary questions about use of fat, milk, cooking methods, salt and supplement use. 108 The FFQ measures an individual’s habitual food intake over the preceding 12 months. The primary purpose of the FFQ was to determine if there was any change in dietary marine ω-3 PUFA intake during trial participation. As fish is the primary source of bioactive ω-3 PUFAs EPA and DHA, the reported consumption of fish was analysed before and after intervention with IMP.
Total fish consumption and consumption of oily fish were considered separately. Six FFQ food item variables were used for the analysis of total fish (i.e. fried fish, fish fingers, white fish, oily fish, shellfish, roe). Consumption of oily fish was based on a single food item variable (oily fish). Participants indicated the frequency of food consumption, ranging from ‘never or less than once per month’ to ‘six times per day’. This was recoded into frequency per day (Table 2). The consumption of total fish per day was calculated by summing the reported fish consumption for each of the six fish variables.
| FFQ category | Frequency per day |
|---|---|
| Never or less than once per month | 0 |
| 1–3 times per month | 0.07 |
| Once per week | 0.14 |
| 2–4 times per week | 0.43 |
| 5 or 6 times per week | 0.79 |
| Once per day | 1 |
| 2 or 3 times per day | 2.5 |
| 4 or 5 times per day | 4.5 |
| ≥ 6 times per day | 6 |
The data were used to recode participants into four categories (i.e. never, low, middle or high), based on their weekly consumption of total fish and oily fish (Table 3). Categorisation of weekly fish consumption was based on the Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition recommendation to consume two portions of fish per week, one of which should be oily. 109
| Category | Reported frequency of consumption |
|---|---|
| Total fish | |
| Never | 0 |
| Low | < 1 portion per week (0.01–0.13 per day) |
| Middle | 1–2.99 portions per week (0.14–0.429 per day) |
| High | ≥ 3 portions per week (0.43–highest per day) |
| Oily fish | |
| Never | 0 |
| Low | < 1 portion per week (0.07 per day) |
| Middle | 1–2.99 portion per week (0.14 per day) |
| High | ≥ 3 portions per week (0.43–highest per day) |
Further analysis of the dietary PUFA intake data is planned and will include full nutrient and food group analysis using FETA (FFQ EPIC Tool for Analysis) software (www.srl.cam.ac.uk/epic/epicffq/; accessed April 2018).
Planned laboratory studies
The nested laboratory studies originally planned for the EME-funded seAFOod trial project are described in the trial protocol version 6.0, dated 11 August 2014 [see the project web page: www.journalslibrary.nihr.ac.uk/programmes/eme/0910025/#/ (accessed 25 April 2019)]. The switch in capsule IMP that occurred in 2014 required a more detailed PUFA analysis than was originally planned to test equivalence of the bioavailability of FFA and TG formulations measured by RBC and rectal mucosal EPA content. Therefore, funding for much of the planned biomarker work was diverted to a more extensive PUFA analysis.
Statistical methods
Changes from the protocol to the statistical analysis plan
A number of changes to details contained within the protocol are documented in the SAP (version 1.1, dated 24 August 2017) [see the project web page: www.journalslibrary.nihr.ac.uk/programmes/eme/0910025/#/ (accessed 25 April 2019)]. These are listed in Table 4.
| Protocol | SAP | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| The protocol does not include a comparison between the two formulations of EPA used in the trial, EPA-FFA and EPA-TG, as a secondary end point | The SAP includes the prespecified secondary end point ‘Red Blood Cell (RBC) EPA and rectal EPA levels at baseline, 6 months (RBC only) and 12 months from randomisation’ in section 2.9.2 (Secondary end points). The corresponding statistical analysis is specified in section 6.3 (Secondary analyses) | The formulation of EPA changed during the trial (details in section 2.4). The daily doses of FFA and TG formulations were calculated to be FFA dose equivalent, but there are no available data to determine bioavailability equivalence during clinical use over 6–12 months. Although it is assumed that the two formulations would be approximately bioequivalent, it was deemed important to summarise the EPA levels in participants receiving both formulations. Formal equivalence methods and set margins for non-inferiority are not being used, as the trial was not designed, nor powered, to examine this |
| The protocol does not include information on the secondary end points being derived from the FFQ | The SAP includes the prespecified secondary end point ‘Dietary fish and other seafood intake at baseline and at the end of the study’ in section 2.9.2 (Secondary end points). The corresponding statistical analysis is specified in section 6.3 (Secondary analyses) | It will be important to determine whether there is an imbalance between groups in the intake of dietary fish and seafood or any change in such intake during trial participation. This variable will also be used as a covariate in a sensitivity analysis of the primary end point |
| The protocol does not include the MAP as an end point. The protocol states ‘the total number of adenomas per participant at BCSP surveillance colonoscopy’ | The mean adenoma number per person has been included in the secondary end points for adenomas, advanced adenomas and serrated adenomas in section 2.9.2 (Secondary end points). This has also been added to the statistical analyses in section 6.3 (Secondary analyses) | The MAP is now established as a colonoscopic end point, in addition to the ADRa |
|
The protocol states that ‘If fewer than 5% of participants have missing data for the primary end point then complete-case analysis will be performed’ The protocol states that ‘Losses to follow-up and protocol violations will be treated as missing data for the ITT population’ |
Section 3 of the SAP (General analysis considerations) provides information about the participant populations being used in the trial and procedures for the investigation and use of missing data. In summary, the primary end point will be analysed for all participants in the ITT population. The proportion of participants who have missing data will be reported, and the interpretation of the primary analysis will take into account this proportion. A per-protocol analysis will be performed as a sensitivity analysis, which will exclude participants with major protocol violations (which will be defined prior to release of treatment allocation) | The primary analyses should be based on the ITT population. In accordance with the ITT principle, all participants should be included in the ITT population (i.e. the data for participants who have violated the protocol should be included) |
| The per-protocol population criteria were stated as ‘More than 50% of trial medication returned in total; inadvertent use of OTC medication containing aspirin, NSAIDs or fish oil for more than 2 weeks in total; surveillance colonoscopy occurs outside the allowed time windows (48–52 weeks after the last complete screening BCSP colonoscopy, or 60–64 weeks for participants undergoing a repeat full colonoscopy within 3 months of trial screening)’ | Section 3.1 in the SAP (Analysis populations) includes suggestions about what major protocol violations may result in exclusion from the per-protocol population. It also states that specific criteria will be determined in a meeting prior to treatment codes being revealed | Data review prior to treatment unblinding will provide information about what protocol violations and deviations occurred during the trial and will allow judgements about the criteria for exclusion from the per-protocol population to be made |
| Serrated adenomas | There was no specific end point or analysis relating to serrated adenomas detailed in the protocol. The SAP prespecifies end points of ‘The number of participants with a recurrence of serrated adenoma at the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy’ and ‘The number of serrated adenomas per participant at the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy’ in section 2.9.2 (Secondary end points). The corresponding statistical analysis is specified in section 6.3 (Secondary analyses) | The serrated adenoma is now established as a marker of malignant potential arising from a molecular pathway distinct from the traditional adenoma–carcinoma sequence. Therefore, the serrated adenoma should be analysed separately from the conventional adenoma |
In addition, the changes documented in Table 5 were made after database lock and release of the treatment codes.
| Change from SAP | Justification |
|---|---|
|
Change to planned analysis: recruiting site rather than BCSP centre was used as a covariate in the primary analysis An additional sensitivity analysis was performed that treated BSCP centre and site as random effects in a multilevel model |
After database lock and release of the treatment codes, it was discovered that the randomisation had stratified by site rather than by BCSP centre. As site was nested in BCSP centre, the balance across treatment groups through stratification was maintained for BCSP centre |
| Additional secondary end point and analyses: the number of participants with at least one conventional colorectal adenoma and the number of conventional colorectal adenomas per participant were analysed in the same way as for serrated adenomas | Because the number of participants with at least one serrated adenoma and the number of serrated adenomas per participant had been analysed, as well as the ADRa and MAP for total colorectal adenomas, it was felt that similar data for conventional colorectal adenomas should be reported |
| Additional sensitivity analyses: the sensitivity analyses for the primary outcome were analysed without adjustment for repeat colonoscopy, as supportive analyses. Similarly, the secondary outcomes were analysed without adjustment as supportive analyses | Data on whether or not participants had had a repeat colonoscopy were not collected from the start of the trial. Therefore, there were no data for the first 61 participants. This meant that the data from these participants were not included in the analysis. It was felt important to investigate the robustness of these results by including the additional participants, although the potential confounding effect of different endoscopic procedures (full colonoscopy, partial colonoscopy or FS) could not be taken into account |
| Additional sensitivity analyses: two further sensitivity analyses were performed. One adjusted for the baseline EPA level and the other adjusted for oily fish intake | It was felt that both of these variables could have an impact on the primary outcome. It was therefore deemed appropriate to perform analyses including these variables in the model |
| Unplanned exploratory end points and analyses: colorectal adenoma size analysed with adjustment for histology type, taking into account multiple adenomas per participant | FAP RCTs have consistently measured and analysed colorectal adenoma number and size. Given the secondary outcome data on colorectal adenoma number, colorectal adenoma size was felt to represent an important exploratory analysis |
| Modification of the definition of advanced adenoma: the definition in the protocol and SAP was changed from ‘≥ 10 mm diameter, high-grade dysplasia or tubulo-villous/villous histology’ to ‘≥ 10 mm diameter, high-grade dysplasia or villous histology’ | Data collected on colorectal adenoma characteristics at surveillance colonoscopy did not allow tubulo-villous adenomas to be distinguished from tubular adenomas so that the ‘advanced’ definition was based on villous histology alone, not tubulo-villous histology |
| Modification of the definition of the ITT population: the definition of the ITT population included all participants who had been randomised. However, the population analysed excluded two participants who were withdrawn immediately after randomisation | Two participants were randomised and then immediately withdrawn from the trial. They had no trial data (including baseline data collected), and therefore could not contribute to the trial. They were excluded from the ITT population |
| Analysis of safety data: the summaries detailed in the SAP were amended. AEs and ADRs were not summarised by preferred term. GI AEs and ADRs were summarised by preferred term and formulation. In addition, GI ADRs were summarised according to severity and preferred term | GI AEs and ADRs were the most commonly reported. It was therefore judged to be useful to summarise these AEs and ADRs by preferred term. AEs and ADRs for all other system organ classes were not summarised by preferred term, given their low frequency and severity |
Sample size
The original sample size estimate of 904 participants (to ensure 768 evaluable patients and assuming a 15% loss to follow-up) in trial protocol versions 1–3 was based on a RCT of the same dose and preparation of EPA-FFA in FAP patients,67 a meta-analysis of aspirin RCTs49 and detailed 2007–8 audit data from the South of Tyne and Tees BCSP centres.
For the protocol revision in May 2012 (related to inclusion of patients who required a repeat endoscopic procedure during the 3-month screening window), the sample size was re-estimated using audit data on surveillance colonoscopy in 1189 patients classified as ‘high risk’ in 2010, from the North-East BCSP hub (nine BCSP centres) and the Southern BCSP hub (17 BCSP centres). A total of 930 (78%) patients went straight to surveillance after a single screening colonoscopy. Colorectal ADRa data at surveillance colonoscopy were available for 738 patients and, of these, one or more colorectal adenomas were detected in 465 (63%) patients. Corresponding figures for ‘high-risk’ patients having a repeat partial colonoscopy or FS within 3 months of an initial screening colonoscopy showed that one or more adenomas were detected at first surveillance colonoscopy in 59 out of 110 (54%) patients, and for patients having a repeat full colonoscopy, one or more adenomas were detected in 56 out of 83 (67%). The overall ADRa at first surveillance colonoscopy was 62%, which was consistent with the original estimate of 60%; therefore, the sample size remained unchanged.
To detect a minimum 18% relative reduction in adenoma risk in each two-group comparison [less than the 22% reduction in polyp number compared with placebo in the FAP trial67 and below the absolute reduction in polyp number at 1 year (38%) in aspirin RCTs49] from a 60% adenoma recurrence rate at surveillance colonoscopy to 49%, 678 evaluable ‘high-risk’ individuals were required to be randomised equally to the four treatment groups, with 80% power at a 5% two-sided significance level.
Standard practice for 2 × 2 factorial designs, in the absence of an interaction, bases the sample size estimate on the two-group comparison of treatment versus placebo (and divides the total equally between the four groups). With the sample size of 678 based on this method, there is, in fact, a slight reduction in power (to 75%), which arises if both treatments work, because then the overall comparison for treatment A is not 0.49 versus 0.6, but is 0.445 versus 0.545 (averaging over the placebo and treatment B groups). To keep power at 80% for the above figures, a simulation using Stata® version 10 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA) and employing the proposed analysis method indicated that 192 individuals were required per group (a total of 768 evaluable ‘high-risk’ individuals).
In trial protocol versions 1–3, a 15% drop-out rate was assumed. However, feedback from BCSP sites and experience from the first few months of the trial suggested that the drop-out rate of ‘high-risk’ BCSP patients was < 15%. Allowing for a 10% drop-out rate, the proposed sample size increased to 768/0.9 = 853 individuals.
For the purposes of the trial extension granted by the EME board in 2014, we proposed a revised realistic recruitment target of 755, which provided 71% power to detect the same effect size as above, still assuming a 10% drop-out rate.
Analysis plan
A SAP was finalised prior to database lock and release of treatment codes to the statistician. All summaries and statistical analyses were conducted using Stata version 15.0.
Analysis populations
-
Intention-to-treat population: all randomised participants with post-randomisation data. Analysis was according to the treatment group to which they were randomised.
-
Safety population: all randomised participants who had at least one dose of trial medication. Analysis was according to the treatment they actually received.
-
Per-protocol population: all randomised participants not deemed to have a major protocol violation. Major protocol violations that resulted in exclusion from the per-protocol population were –
-
had not taken sufficient medication (participants who had taken ≤ 75% of their expected EPA and/or ≤ 50% of their expected aspirin)
-
found to be ineligible post-randomisation
-
any use of OTC medication containing aspirin, NSAIDs or fish oil for > 2 weeks during the treatment period.
-
The final composition of the per-protocol population was determined by final data review prior to the treatment codes being revealed.
Analysis of the primary end point was based on the ITT population. The analysis was repeated based on the per-protocol population. This was considered supportive to the primary analysis.
Analyses of all secondary end points, with the exception of AEs, were based on the ITT population.
Summaries of the AEs were based on the safety population.
Missing data
Sensitivity analyses were performed to support the primary analyses. All secondary analyses assumed that the data were missing at random and no imputation was performed.
Primary outcome
The primary outcome was the number of participants with one or more colorectal adenomas detected at the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy 12 months after the screening examination (the ADRa).
The primary outcome was analysed by an ‘at-the-margins’ approach,110 after first examining whether or not there was any evidence of an interaction between EPA and aspirin. An ‘at-the-margins’ approach analyses all participants randomised to EPA (i.e. EPA + aspirin plus EPA + placebo aspirin, combined) versus all participants not randomised to EPA (i.e. placebo EPA + aspirin plus placebo EPA + placebo aspirin, combined), and all participants randomised to aspirin versus all participants not randomised to aspirin. Given that there was no evidence of an interaction, the log relative risk was estimated using a mixed-effects log-binomial regression model, with BCSP site included as a random effect, and the risk differences and ratios presented. Both interventions were fitted simultaneously and the analysis was adjusted for ‘repeat colorectal endoscopic procedure within 3 months required’ and BCSP site. This was a change to the analyses defined in the SAP, which stated that BCSP centre would be included as a random effect.
Sensitivity analyses for the primary outcome
The following sensitivity analyses were performed on the primary end point:
-
Analysis using the per-protocol population.
-
Analysis as a multilevel model. Some BCSP centres comprise multiple hospital sites; therefore, a sensitivity analysis was conducted in which both BCSP centre and site were treated as random effects in a multilevel model.
-
Multiple imputation of missing primary end-point data.
-
Further adjustment of baseline variables with any marked imbalance, if appropriate.
-
Investigation of the effect of treatment adherence using complier-average causal effect (CACE) estimation methods. 111,112 ITT analysis does not represent the treatment effect of non-compliance with treatment; therefore, CACE analysis was deemed to be important if any treatment effect was directly affected by the level of compliance. The percentage of the required total dose taken by participant from randomisation to first surveillance colonoscopy (both in binary and continuous form) was included in the model as an instrumental variable to estimate such an effect.
-
Further adjustment for EPA capsule formulation, that is EPA-FFA (or placebo) or EPA-TG (or placebo).
-
Further adjustment for oily fish intake.
-
Further adjustment for baseline RBC EPA levels.
Secondary outcomes
-
The total number of colorectal adenomas per participant at the 12-month BCSP surveillance colonoscopy was analysed using a Poisson regression model. The incidence rate ratio (IRR) and 95% CIs were presented.
-
The number of participants with an ‘advanced’ colorectal adenoma (≥ 10 mm maximum dimension, high-grade dysplasia or villous histology) at the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy (advanced ADRa) was analysed using a log-binomial regression model. The risk difference and 95% CIs were presented.
-
The number of ‘advanced’ colorectal adenomas per participant at the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy (advanced MAP) was analysed using a Poisson regression model. The IRR and 95% CIs were presented.
-
The number of participants with one or more conventional colorectal adenomas at surveillance colonoscopy (conventional ADRa) was derived from the total and serrated adenoma data and was analysed using a log-binomial regression model. Risk difference and 95% CIs were presented.
-
The number of conventional colorectal adenomas per participant at surveillance colonoscopy (conventional MAP) was derived from the total and serrated adenoma data and was analysed using a Poisson regression model. The IRR and 95% CIs were presented.
-
The number of participants with one or more serrated adenomas at surveillance colonoscopy (serrated ADRa) was analysed using a log-binomial regression model. The risk difference and 95% CIs were presented.
-
The number of serrated adenomas per participant at surveillance colonoscopy (serrated MAP) was analysed using a Poisson regression model. The IRR and 95% CIs were presented.
-
The region of the colorectum (right colon: any part of the colon proximal to the splenic flexure; left colon: the rectum and the colon at/distal to the splenic flexure) that colorectal adenomas were detected at the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy was explored, using a Poisson random-effects model with bivariate response (corresponding to adenoma counts in the left and right colon), in which treatment and a baseline adenoma count were independent variables together with random intercepts corresponding to participant and BCSP site. The IRR and 95% CIs were presented.
-
The number of ‘high-risk’ participants reclassified as ‘intermediate risk’ after the first BCSP surveillance colonoscopy was analysed using a log-binomial regression model. The risk difference and 95% CIs were presented.
-
The number of participants with CRC detected prior to, or at, the first BCSP surveillance were to be summarised descriptively; however, there were no participants with CRC.
-
The levels of RBC EPA and rectal mucosal EPA were summarised at baseline (RBC only) and at visits 4 (RBC only) and 6 for those receiving EPA-FFA and those receiving EPA-TG. In addition, the change from baseline to visits 4 and 6 were summarised.
-
The levels of DHA, AA and the EPA-to-AA ratio were summarised at baseline (RBC only) and at visits 4 (RBC only) and 6 (RBC and rectal mucosal) for those receiving EPA-FFA and those receiving EPA-TG. In addition, the change from baseline to visits 4 and 6 were summarised for RBC samples.
-
Dietary fish and other seafood intake (oily fish and total) at baseline (visit 1) and at the end of the trial (visit 6 or 7) were summarised by treatment group.
Safety analyses
Adverse events were summarised for the safety population, that is all participants who received at least one dose of trial medication. Summaries were based on the IMP that the participant received, irrespective of randomisation.
Both AEs and treatment-emergent ADRs were summarised by system organ class. GI AEs were also summarised by preferred term and by formulation. ADRs were summarised by severity using the preferred term. The worst case (i.e. severe and/or related to trial treatment) was assumed if severity or causality were missing, unless otherwise stated.
Clinically significant bleeding episodes (i.e. haemorrhagic stroke or acute GI bleeding requiring hospital admission or investigation) were identified by the chief investigator using a manual search of the full list of AEs and SAEs.
Common GI AEs associated with ω-3 PUFA and/or aspirin use were presented separately as clinically meaningful symptom categories, which were defined by the chief investigator.
Serious adverse reactions and ADRs that led to trial discontinuation were summarised by treatment group and preferred term.
All treatment-emergent ADRs were listed.
Exploratory analyses
-
Colorectal adenoma size was estimated using a multilevel model, adjusting for colorectal adenoma histology type and number of colorectal adenomas per individual.
-
Rectal and RBC EPA levels were plotted against the individual number of total, conventional, serrated and left- and right-sided colorectal adenomas by treatment group.
-
A correlation between rectal mucosal and RBC EPA levels at 12 months was investigated by graph and the correlation coefficient was calculated.
Chapter 3 Results
Parts of this chapter have been reproduced from Hull et al. 1 © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Recruitment and follow-up
Between November 2011 and June 2016, 3911 ‘high-risk’ individuals were screened for eligibility, of whom 3202 (82%) were not randomised (Table 6 and Figures 2–4). The mean duration from receipt of local research and development (R&D) approval to FPFV for the 53 sites that randomised patients was 6.3 months. Conversion from screening to randomisation of patients did not appear to be influenced by the size of the site or the number of patients undergoing screening colonoscopy. Sites did report that the time taken to undertake trial screening and recruitment (as well as limited availability of, and changes to, research staff) were reasons for low recruitment.
| Site number | R&D approval date | Date of FPFV | Time from R&D approval to FPFV (months) | Patients | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Screened (n) | Recruited (n) | Randomised (%) | ||||
| 1 | 18 August 2011 | 7 February 2012 | 6 | 121 | 19 | 16 |
| 2 | 23 September 2011 | 24 November 2011 | 2 | 123 | 14 | 11 |
| 3 | 17 April 2012 | 22 May 2012 | 1 | 92 | 18 | 20 |
| 4 | 31 August 2012 | 29 November 2012 | 3 | 114 | 20 | 18 |
| 5 | 20 September 2011 | 23 April 2012 | 7 | 151 | 37 | 25 |
| 6 | 19 August 2011 | 20 February 2012 | 6 | 77 | 20 | 26 |
| 7 | 5 May 2011 | 31 May 2012 | 13 | 56 | 9 | 16 |
| 8 | 20 July 2011 | 23 March 2012 | 8 | 100 | 30 | 30 |
| 9 | 14 June 2011 | 21 June 2012 | 12 | 147 | 12 | 8 |
| 10 | 25 August 2011 | 10 October 2012 | 14 | 73 | 6 | 8 |
| 11 | 30 June 2011 | 18 January 2012 | 7 | 120 | 23 | 19 |
| 12 | 27 June 2011 | 21 March 2012 | 9 | 53 | 9 | 17 |
| 13 | 8 February 2012 | N/A | N/A | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| 14 | 5 July 2011 | 12 April 2012 | 9 | 107 | 27 | 25 |
| 15 | 13 January 2012 | 15 March 2012 | 2 | 89 | 25 | 28 |
| 16 | 11 April 2011 | 30 January 2012 | 10 | 64 | 11 | 17 |
| 17 | 2 June 2011 | 12 January 2012 | 7 | 66 | 6 | 9 |
| 18 | 24 April 2012 | 27 June 2013 | 14 | 45 | 6 | 13 |
| 20 | 17 February 2012 | 25 April 2012 | 2 | 53 | 21 | 40 |
| 22 | 6 July 2012 | 18 December 2012 | 5 | 26 | 8 | 31 |
| 24 | 29 August 2012 | 9 January 2013 | 4 | 8 | 1 | 13 |
| 25 | 10 April 2012 | 29 May 2012 | 2 | 103 | 12 | 12 |
| 26 | 7 November 2012 | 10 February 2015 | 27 | 22 | 5 | 23 |
| 27 | 5 May 2011 | 11 November 2011 | 6 | 93 | 24 | 26 |
| 28 | 7 December 2011 | 2 February 2012 | 2 | 177 | 35 | 20 |
| 29 | 27 July 2011 | 9 February 2012 | 6 | 14 | 1 | 7 |
| 30 | 5 July 2012 | N/A | N/A | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| 31 | 18 August 2011 | 23 May 2012 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| 32 | 23 August 2011 | 30 August 2012 | 12 | 92 | 11 | 12 |
| 33 | 11 April 2012 | 25 June 2013 | 14 | 51 | 12 | 24 |
| 34 | 22 March 2012 | 29 October 2012 | 7 | 44 | 9 | 20 |
| 35 | 30 March 2012 | 10 July 2012 | 3 | 44 | 12 | 27 |
| 36 | 14 September 2012 | 15 March 2013 | 6 | 95 | 9 | 9 |
| 37 | 8 March 2013 | 22 August 2013 | 6 | 85 | 10 | 12 |
| 38 | 18 September 2012 | 11 January 2013 | 4 | 133 | 10 | 8 |
| 39 | 10 October 2012 | 12 November 2012 | 1 | 28 | 4 | 14 |
| 40 | 5 October 2012 | 26 October 2012 | 1 | 97 | 22 | 23 |
| 41 | 13 September 2012 | 11 March 2013 | 6 | 76 | 12 | 16 |
| 42 | 10 September 2012 | 9 January 2013 | 4 | 30 | 6 | 20 |
| 43 | 23 January 2013 | N/A | N/A | 12 | 0 | 0 |
| 44 | 6 November 2012 | 14 February 2013 | 3 | 89 | 15 | 17 |
| 45 | 12 October 2012 | 17 January 2013 | 3 | 62 | 12 | 19 |
| 47 | 23 January 2013 | N/A | N/A | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| 49 | 6 September 2012 | 20 November 2012 | 2 | 52 | 15 | 29 |
| 50 and 51 | 9 November 2012 | 16 January 2013 | 4 | 231 | 47 | 16 |
| 52 | 16 August 2012 | 11 October 2013 | 14 | 141 | 9 | 6 |
| 53 | 17 August 2012 | 23 January 2013 | 5 | 124 | 29 | 23 |
| 54 | 20 August 2012 | 21 September 2012 | 1 | 48 | 16 | 33 |
| 55 | 3 October 2012 | 4 January 2013 | 3 | 16 | 4 | 25 |
| 56 | 28 August 2012 | 18 September 2013 | 13 | 59 | 8 | 14 |
| 57 | 23 October 2012 | 11 April 2013 | 6 | 59 | 10 | 17 |
| 58 | 19 July 2012 | 11 October 2012 | 3 | 33 | 5 | 15 |
| 60 | 12 November 2012 | 17 June 2013 | 7 | 35 | 6 | 17 |
| 61 | 1 February 2013 | 17 April 2013 | 2 | 19 | 6 | 32 |
| 62 | 5 September 2012 | 10 October 2012 | 1 | 24 | 8 | 33 |
| 63 | 7 September 2015 | 21 April 2016 | 7 | 11 | 2 | 18 |
| Total | 3911 | 709 | ||||
FIGURE 2.
Flow of participants through the trial. a, AE was an option to discontinue from the trial in an earlier version of the CRF; however, this option was removed in later versions. HNPCC, hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer.
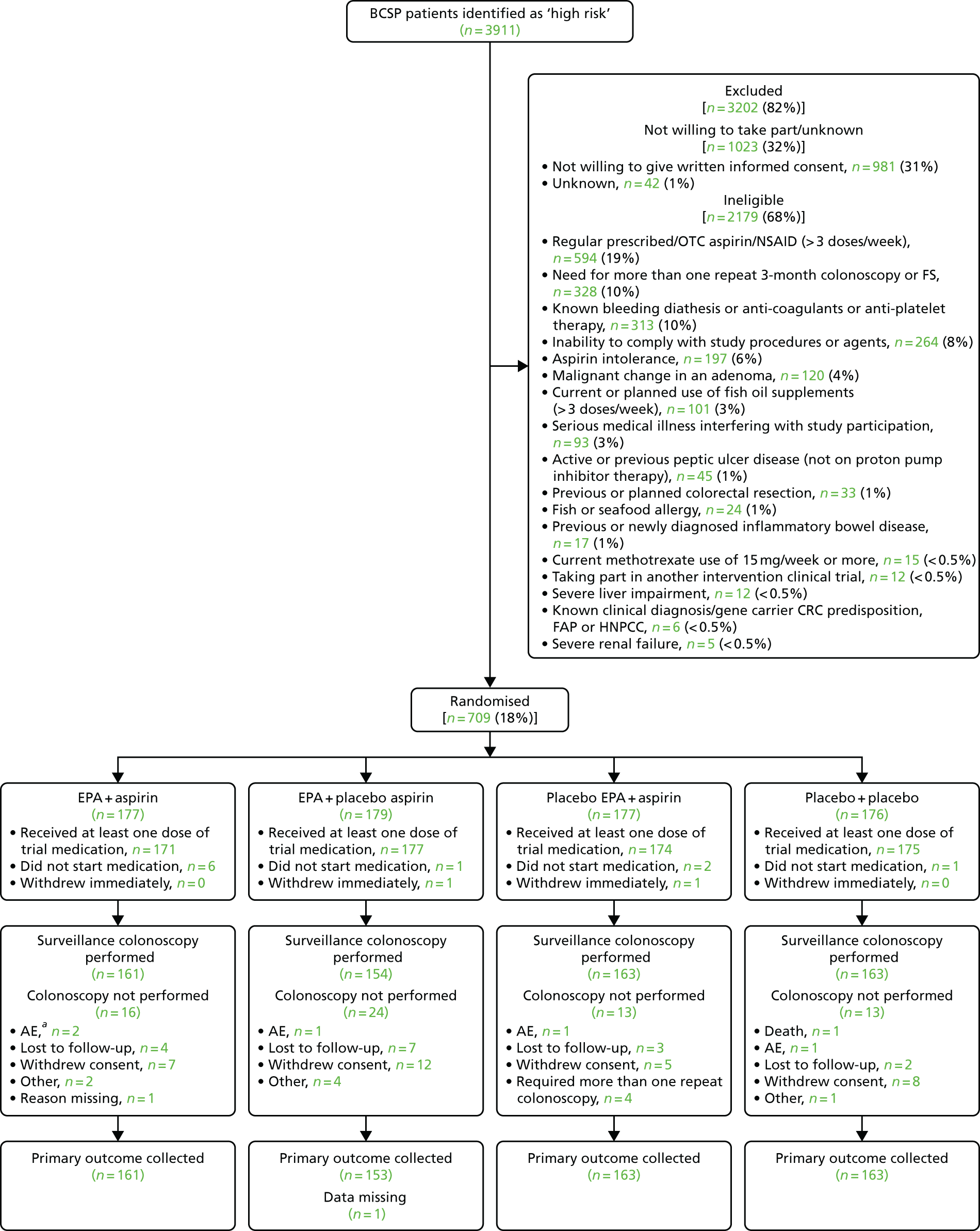
FIGURE 3.
Cumulative trial recruitment by month.
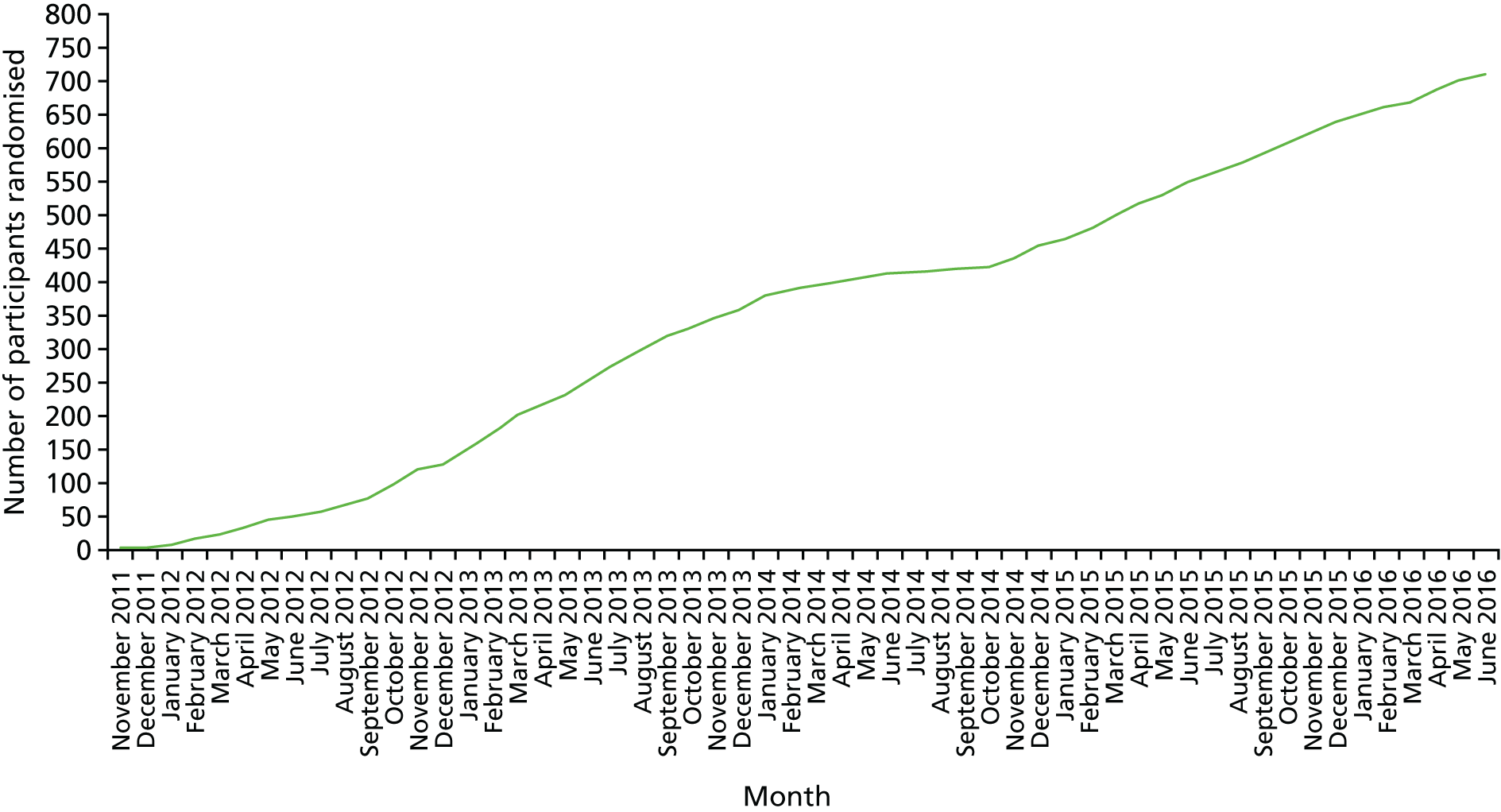
FIGURE 4.
Actual monthly trial recruitment.
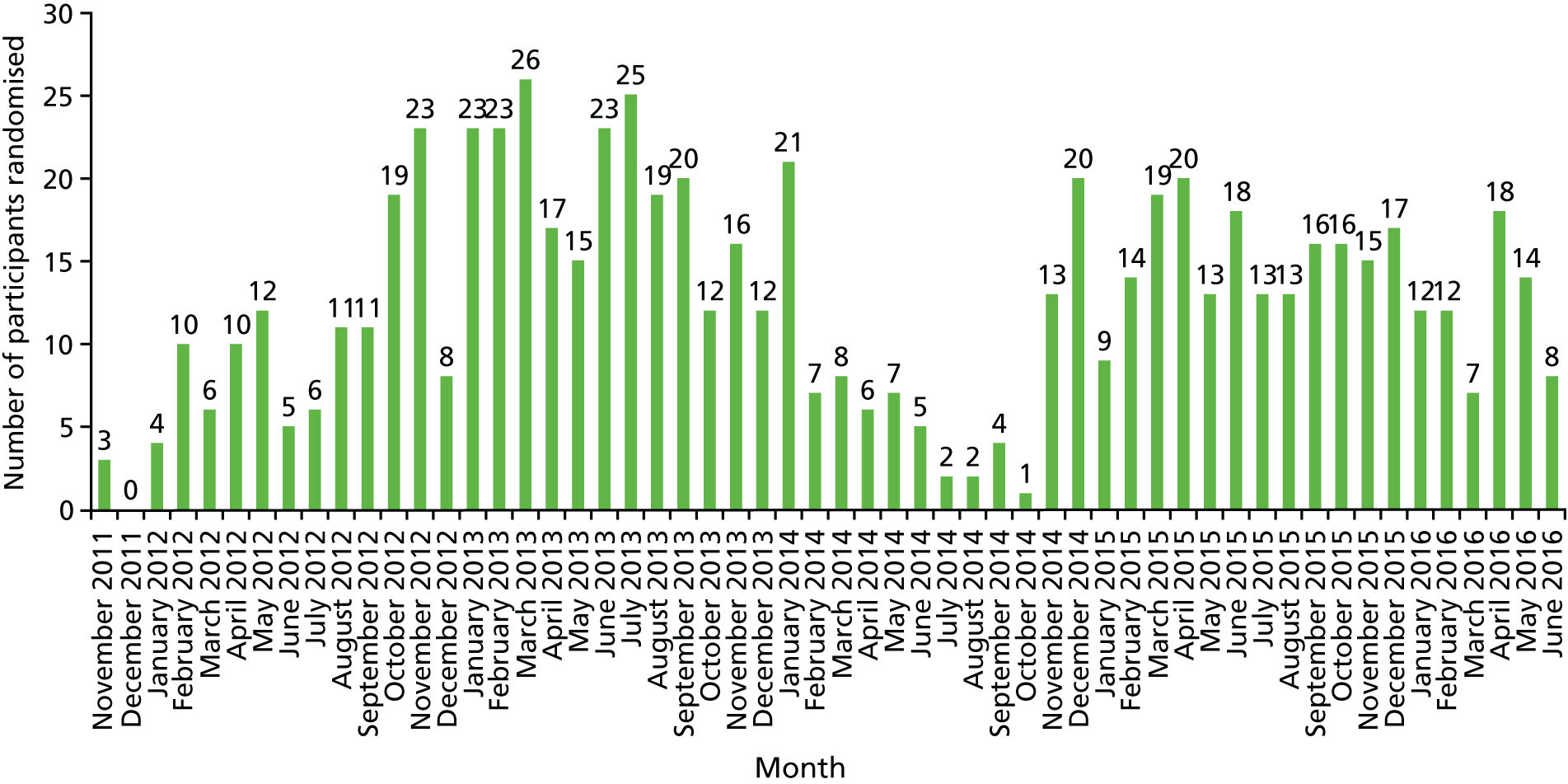
Overall, 2179 (56%) patients met one or more of the exclusion criteria (see Figure 4). The other 1023 individuals either did not wish to take part in the trial or were not randomised for unknown reasons. The most frequent reasons for no randomisation were not being willing to give written consent [n = 981 (25%)], taking more than three doses per week of a prescribed/OTC aspirin/NSAID [n = 594 (15%)], the need for more than one repeat colonoscopy or FS [n = 328 (8%)] and known bleeding diathesis or anticoagulant use or antiplatelet therapy [n = 313 (8%)]. Overall, only 18% (n = 709) of screened ‘high-risk’ individuals were randomised (see Figure 2).
By 12 June 2016 (the date stipulated by the MHRA as the end date for randomisation related to the approved shelf life of the second capsule IMP (90% EPA-TG), 709 patients had been randomised, which was 83% of the target (n = 853). Reduced recruitment between February and October 2014 (see Table 6 and Figures 3 and 4) was related to diminishing stocks of active and placebo EPA-FFA at sites, prior to the introduction of 90% EPA-TG IMP in November 2014. The mean number of randomisations per month during the whole recruitment phase of the trial was 13. Excluding the run-in period of 12 months, during which sites opened at a variable rate, and the period when capsule IMP stocks were diminishing (February to October 2014), the mean number of randomisations per month was 16 (range 7–26 per month).
Of the 709 participants randomised, 177 participants were randomised to receive EPA + aspirin, 179 were randomised to receive EPA + placebo aspirin, 177 were randomised to receive placebo EPA + aspirin and 176 were randomised to receive placebo EPA + placebo aspirin (see Figure 2). Two participants withdrew immediately after randomisation; one was randomised to EPA + placebo aspirin and one was randomised to placebo EPA + aspirin (see Figure 2).
A total of 422 (60%) participants were randomised to active or placebo EPA-FFA and 287 (40%) participants were randomised to active or placebo 90% EPA-TG. Participants took only one form of capsule IMP (EPA-FFA or EPA-TG) in all cases.
A total of 641 participants (90% of those randomised) underwent surveillance colonoscopy, with endoscopic data being available for 640 of these participants (see Figure 2). The main reasons for not performing surveillance colonoscopy were withdrawal of consent and loss to follow-up (Table 7 and see Figure 2). The ‘other’ reasons for discontinuation in the trial were the participant was withdrawn because of being randomised in error (n = 3), the histology report confirmed a malignant polyp and the participant was referred to MDT for review, failure to comply with trial treatment as a result of ongoing medical problems, the participant being prescribed aspirin and development of cancer (all n = 1).
| Reason | Trial group, n (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 177) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 178) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 176) | Placebo + placebo (N = 176) | |
| Total discontinued in trial | 16 (9) | 24 (13) | 13 (7) | 13 (7) |
| Death | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1) |
| AE | 2 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) |
| Lost to follow-up | 4 (2) | 7 (4) | 3 (2) | 2 (1) |
| Withdrew consent | 7 (4) | 12 (7) | 5 (3) | 8 (5) |
| Required more than one repeat colonoscopy | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4 (2) | 0 (0) |
| Other | 2 (1) | 4 (2) | 0 (0) | 1 (1) |
| Missing | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Baseline characteristics
Baseline characteristics were well balanced across all four treatment groups with respect to demographic data, medical history and baseline colorectal adenoma details (Table 8).
| Characteristic | Trial group | Total (N = 707) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 177) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 178) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 176) | Placebo + placebo (N = 176) | ||
| Age at enrolment (years) | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 65.6 (4.7) | 65.2 (4.5) | 65.3 (4.5) | 65.2 (4.6) | 65.3 (4.6) |
| Median (IQR) | 66.4 (62.3–68.6) | 64.9 (62.2–68.5) | 64.8 (62.2–68.5) | 64.8 (62.3–68.6) | 65.3 (62.2–68.6) |
| Sex, n (%) | |||||
| Male | 146 (82) | 138 (78) | 140 (80) | 139 (79) | 563 (80) |
| Female | 31 (18) | 40 (22) | 36 (20) | 37 (21) | 144 (20) |
| Body mass index (kg/m2), n (%) | |||||
| Underweight (< 18.5) | 0 (< 0.5) | 2 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 (< 0.5) | 3 (< 0.5) |
| Normal (18.5–24.9) | 39 (22) | 29 (16) | 23 (13) | 32 (18) | 123 (17) |
| Overweight (25.0–29.9) | 77 (44) | 77 (43) | 81 (46) | 76 (43) | 311 (44) |
| Obese (≥ 30) | 61 (34) | 70 (39) | 71 (40) | 68 (39) | 270 (38) |
| Diabetes | |||||
| Ever diagnosed? | |||||
| n (%) | 15 (8) | 24 (13) | 18 (10) | 24 (14) | 81 (11) |
| Years since first diagnosis | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 8.0 (5.3) | 8.5 (5.8) | 9.3 (5.3) | 10.8 (5.5) | 9.3 (5.5) |
| Median (IQR) | 5.0 (5.0–12.0) | 7.0 (5.0–10.5) | 8.5 (5.0–12.0) | 10.0 (6.5–14.0) | 8.0 (5.0–12.0) |
| Cigarette smoking, n (%) | |||||
| Current smoker | 32 (18) | 13 (7) | 27 (15) | 34 (19) | 106 (15) |
| Ex-smoker | 80 (45) | 96 (54) | 89 (51) | 82 (47) | 347 (49) |
| Never smoked | 65 (37) | 69 (39) | 60 (34) | 60 (34) | 254 (36) |
| Cigarettes smoked per day (current smoker) | |||||
| None | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| 1–10 | 11 (6) | 6 (3) | 12 (7) | 16 (9) | 45 (6) |
| 11–20 | 17 (10) | 6 (3) | 12 (7) | 12 (7) | 47 (7) |
| ≥ 21 | 3 (2) | 1 (1) | 3 (2) | 6 (3) | 13 (2) |
| Missing | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (< 0.5) |
| Units of alcohol per week, n (%) | |||||
| None | 27 (15) | 28 (16) | 26 (15) | 29 (16) | 110 (16) |
| 1–7 | 51 (29) | 68 (38) | 64 (36) | 51 (29) | 234 (33) |
| 8–21 | 60 (34) | 41 (23) | 58 (33) | 55 (31) | 214 (30) |
| ≥ 22 | 38 (21) | 39 (22) | 28 (16) | 41 (23) | 146 (21) |
| Missing | 1 (1) | 2 (1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (< 0.5) |
| Medical history,a n (%) | |||||
| Abdominal pain/dyspepsia | 41 (23) | 40 (22) | 41 (23) | 36 (20) | 158 (22) |
| Diarrhoea | 9 (5) | 19 (11) | 15 (9) | 19 (11) | 62 (9) |
| Halitosis | 5 (3) | 5 (3) | 5 (3) | 5 (3) | 20 (3) |
| Bleeding | 14 (8) | 20 (11) | 18 (10) | 20 (11) | 72 (10) |
| Stroke | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 3 (< 0.5) |
| Colorectal adenoma characteristics | |||||
| Total number of adenomas | 856 | 892 | 927 | 856 | 3531 |
| Adenomas per participant | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 4.8 (2.3) | 5.0 (2.2) | 5.3 (2.7) | 4.9 (2.6) | 5.0 (2.5) |
| Median (IQR) | 4 (3–6) | 5 (3–6) | 5 (3–6) | 4 (3–5) | 4 (3–6) |
| ‘Advanced’b adenomas per participant | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 1.1 (0.9) | 1.3 (1.0) | 1.2 (0.9) | 1.2 (0.9) | 1.2 (0.9) |
| Median (IQR) | 1 (1–1) | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) |
| Size of largest adenoma (mm) per participant | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 14.3 (7.3) | 14.8 (6.9) | 14.3 (6.9) | 13.7 (5.6) | 14.3 (6.7) |
| Median (IQR) | 13 (10–17) | 13.5 (11–18) | 13 (10–18) | 12.5 (10–16) | 13 (10–17) |
| At least one adenoma proximal to splenic flexure, n (%) | 144 (81) | 146 (82) | 153 (87) | 141 (80) | 584 (83) |
| Histology type,c n (%) | |||||
| Conventional | 809 (95) | 844 (95) | 895 (97) | 812 (95) | 3360 (95) |
| Tubular/tubulo-villous | 803 (94) | 834 (93) | 885 (95) | 807 (94) | 3329 (94) |
| Villous | 6 (< 1) | 10 (1) | 10 (1) | 5 (1) | 31 (1) |
| Serrated | 21 (2) | 30 (3) | 18 (2) | 22 (3) | 91 (3) |
| Not sent to histopathology | 21 (2) | 16 (2) | 13 (2) | 18 (2) | 68 (2) |
| Missing | 5 (1) | 2 (< 1) | 1 (< 1) | 4 (< 1) | 12 (< 1) |
| High-grade dysplasia,c n (%) | |||||
| No | 811 (95) | 841 (94) | 874 (94) | 796 (93) | 3322 (94) |
| Yes | 21 (2) | 33 (4) | 40 (4) | 41 (5) | 135 (4) |
| Missing | 24 (3) | 18 (2) | 13 (1) | 19 (2) | 74 (2) |
| Participants with any regular prescribed medication prior to trial entry | |||||
| n (%) | 92 (52) | 93 (52) | 88 (50) | 81 (46) | 354 (50) |
| Participants who had any of the following regular prescribed medications,a n (%) | |||||
| Statin | 55 (31) | 54 (30) | 51 (29) | 50 (28) | 210 (30) |
| Calcium | 0 (0) | 3 (2) | 3 (2) | 1 (< 1) | 7 (1) |
| Calcium + vitamin D | 4 (2) | 1 (< 1) | 4 (2) | 2 (1) | 11 (2) |
| Metformin | 9 (5) | 12 (7) | 11 (6) | 14 (8) | 46 (7) |
| Glitazone | 0 (0) | 1 (< 1) | 1 (< 1) | 1 (< 1) | 3 (< 1) |
| Proton pump inhibitor | 20 (11) | 27 (15) | 24 (14) | 19 (11) | 90 (13) |
| Aspirin | 1 (< 1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (< 1) |
| Fish oil | 2 (1) | 4 (2) | 2 (1) | 1 (< 1) | 9 (1) |
| Non-aspirin NSAID | 5 (3) | 4 (2) | 1 (< 1) | 1 (< 1) | 11 (2) |
| Other | 48 (27) | 34 (19) | 37 (21) | 34 (19) | 153 (22) |
| Participants who required repeat endoscopy at trial entry, n (%) | |||||
| No | 133 (75) | 128 (72) | 133 (76) | 136 (77) | 530 (75) |
| Yes | 34 (19) | 33 (19) | 24 (14) | 25 (14) | 116 (16) |
| Missing | 10 (6) | 17 (10) | 19 (11) | 15 (9) | 61 (9) |
The mean age of participants was 65 years. A male-to-female ratio of approximately 4 : 1 was observed, which reflects the sex distribution of ‘high-risk’ patients in the English BCSP. 95,99 A total of 581 (82%) participants were overweight; of these, 270 (38%) were obese. Despite the high prevalence of excess body weight, the prevalence of known type 2 diabetes was low, and only approximately half of the participants were on regular prescribed drugs at trial entry; the drug was usually a statin, proton pump inhibitor or metformin. Baseline drug use was balanced across the treatment groups.
There was a slight imbalance across groups with respect to smoking status, with fewer current smokers in the EPA + placebo aspirin group.
Overall, 158 (22%) participants had a medical history of abdominal pain or dyspepsia, which is consistent with the high prevalence of these symptoms in the general population. 113 Ten per cent of participants recorded a prior episode of bleeding and 20 (3%) reported halitosis at baseline. A medical history of symptoms and clinical events at baseline relevant to EPA and/or aspirin therapy was balanced across the treatment groups. Fewer participants reported diarrhoea at trial entry in the EPA + aspirin group than in the other three groups.
‘High-risk’ participants had a mean of five colorectal adenomas and one advanced colorectal adenoma at entry screening colonoscopy. Of 3531 evaluable colorectal adenomas at baseline, 3360 (97%) were conventional (tubular/tubulo-villous and villous) and 91 (3%) were serrated adenomas. Overall, 584 (83%) ‘high-risk’ participants had at least one colorectal adenoma proximal to the splenic flexure at screening colonoscopy. Screening colonoscopy findings were balanced across the treatment groups (see Table 8).
Compliance with the allocated intervention
Compliance with both capsule and tablet IMPs was excellent, with mean percentage compliance levels, calculated by capsule/tablet counting, of between 94% and 97%. A total of 10 participants never took any dose of either capsules or tablets and a further seven participants took only one of the treatments (EPA/placebo EPA or aspirin/placebo aspirin) (Table 9).
| Adherence | Trial group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 177) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 178) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 176) | Placebo + placebo (N = 176) | |
| Participants who never started taking either of capsules or tablets, n (%) | 7 (4) | 2 (1) | 4 (2) | 4 (2) |
| Never started either, n (%) | 6 (3) | 1 (1) | 2 (1) | 1 (1) |
| Never started capsules but started tablets, n (%) | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) |
| Never started tablets but started capsules, n (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 2 (1) |
| Capsules taken as percentagea of total expected | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 96 (15) | 94 (13) | 95 (12) | 95 (14) |
| Median (IQR) | 100 (97–100) | 99 (96–100) | 100 (97–100) | 100 (97–100) |
| Minimum, maximum | 10, 197 | 27, 101 | 40, 123 | 20, 100 |
| Tablets taken as percentagea of total expected | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 97 (8) | 97 (9) | 97 (6) | 97 (9) |
| Median (IQR) | 100 (98–100) | 99 (97–100) | 100 (98–100) | 100 (98–100) |
| Minimum, maximum | 10, 100 | 27, 101 | 55, 100 | 71, 196 |
Concomitant medication during the trial
During the trial intervention phase, approximately one-quarter of participants started regular prescribed medication, in addition to existing drugs, which included a statin, calcium + vitamin D supplement, metformin, proton pump inhibitors, aspirin, fish oil and a non-aspirin NSAID. Slightly more participants started regular, concomitant medication in the placebo + placebo group (Table 10).
| Concomitant medication | Trial group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 177) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 178) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 176) | Placebo + placebo (N = 176) | |
| Participants starting regular prescribed medication during the trial, n (%) | 42 (24) | 43 (24) | 42 (24) | 55 (31) |
| Number of participants who started the following regular prescribed medicationsa | ||||
| Statins | 6 | 12 | 6 | 9 |
| Calcium + vitamin D | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Metformin | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Proton pump inhibitors | 5 | 13 | 8 | 12 |
| Aspirin | 3 | 6 | 1 | 5 |
| Fish oil | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Non-aspirin NSAIDs | 13 | 9 | 16 | 23 |
| Other | 25 | 17 | 17 | 23 |
Dietary fish intake before trial participation
Most participants completed a FFQ at baseline; there were similar percentages across dietary fish intake categories in each of the treatment groups. The total fish and oily fish intake at baseline was similar across the four treatment groups (Table 11).
| Dietary fish intake | Trial group, n (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 177) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 178) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 176) | Placebo + placebo (N = 176) | |
| Participants who completed FFQ at baseline | 177 (100) | 176 (99) | 173 (98) | 174 (99) |
| Total fish intake at baseline | ||||
| Never | 4 (2) | 7 (4) | 4 (2) | 11 (6) |
| Low | 12 (7) | 13 (7) | 9 (5) | 10 (6) |
| Medium | 97 (55) | 92 (52) | 109 (63) | 97 (56) |
| High | 51 (29) | 52 (30) | 44 (25) | 44 (25) |
| Missinga | 13 (7) | 12 (7) | 7 (4) | 12 (7) |
| Oily fish intake at baseline | ||||
| Never | 48 (27) | 52 (30) | 43 (25) | 42 (24) |
| Low | 54 (31) | 52 (30) | 53 (31) | 69 (40) |
| Medium | 41 (23) | 46 (26) | 52 (31) | 42 (24) |
| High | 32 (18) | 23 (13) | 22 (13) | 20 (11) |
| Missinga | 2 (1) | 3 (2) | 3 (2) | 1 (1) |
Polyunsaturated fatty acid levels in trial participants
Given the importance of the comparison of EPA levels in individuals randomised to either FFA or TG formulations of EPA, to determine if it was appropriate to pool the primary and secondary outcome data for these groups, PUFA data are presented below before the analyses for the primary and other secondary outcomes.
The RBC EPA level was measured as an accepted biomarker of tissue EPA exposure, as well as the rectal mucosal EPA level measured at the end of the intervention period.
Red blood cell EPA and rectal mucosal EPA levels were compared between each treatment group, at each time point and between users of EPA-FFA and EPA-TG formulations. As expected, active EPA groups had higher RBC levels of EPA than placebo EPA users after the intervention began (Figures 5–7). RBC EPA levels were similar between participants, who received either active FFA or TG formulations of EPA, at baseline, mid-treatment and at the end of the intervention period (see Figures 5–7). Moreover, the increase in RBC EPA level from baseline to the 6-month and 12-month time points for all participants was similar across the two EPA formulations and for rectal mucosal EPA levels at 12 months (Table 12) (see Figures 5–7). There was also no clear difference in RBC or rectal mucosal DHA content between EPA-FFA and EPA-TG users (Table 13; see also Table 12).
FIGURE 5.
The RBC EPA levels by formulation and by trial group at baseline.
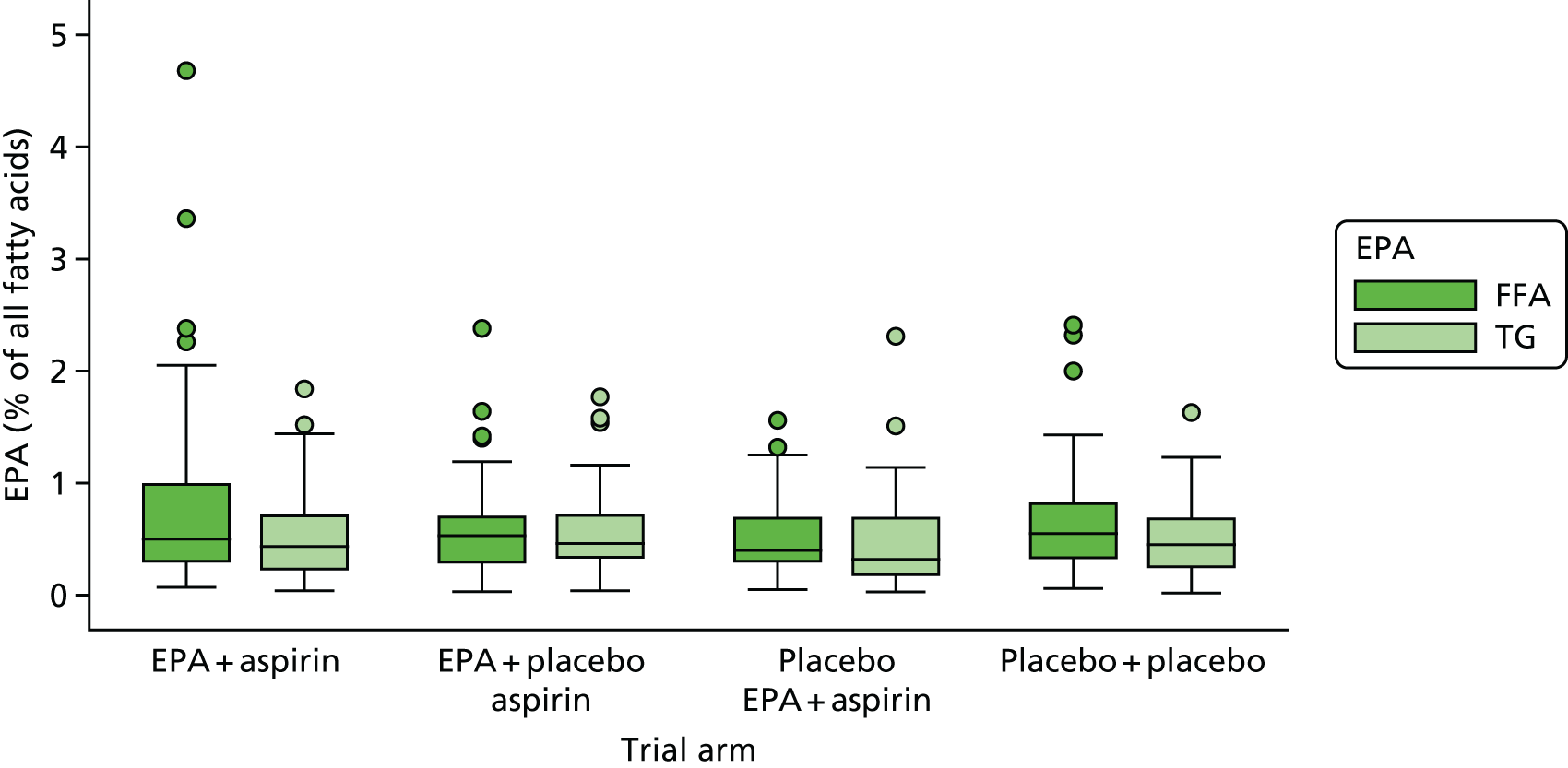
FIGURE 6.
The RBC EPA levels by formulation and by trial group at 6 months.
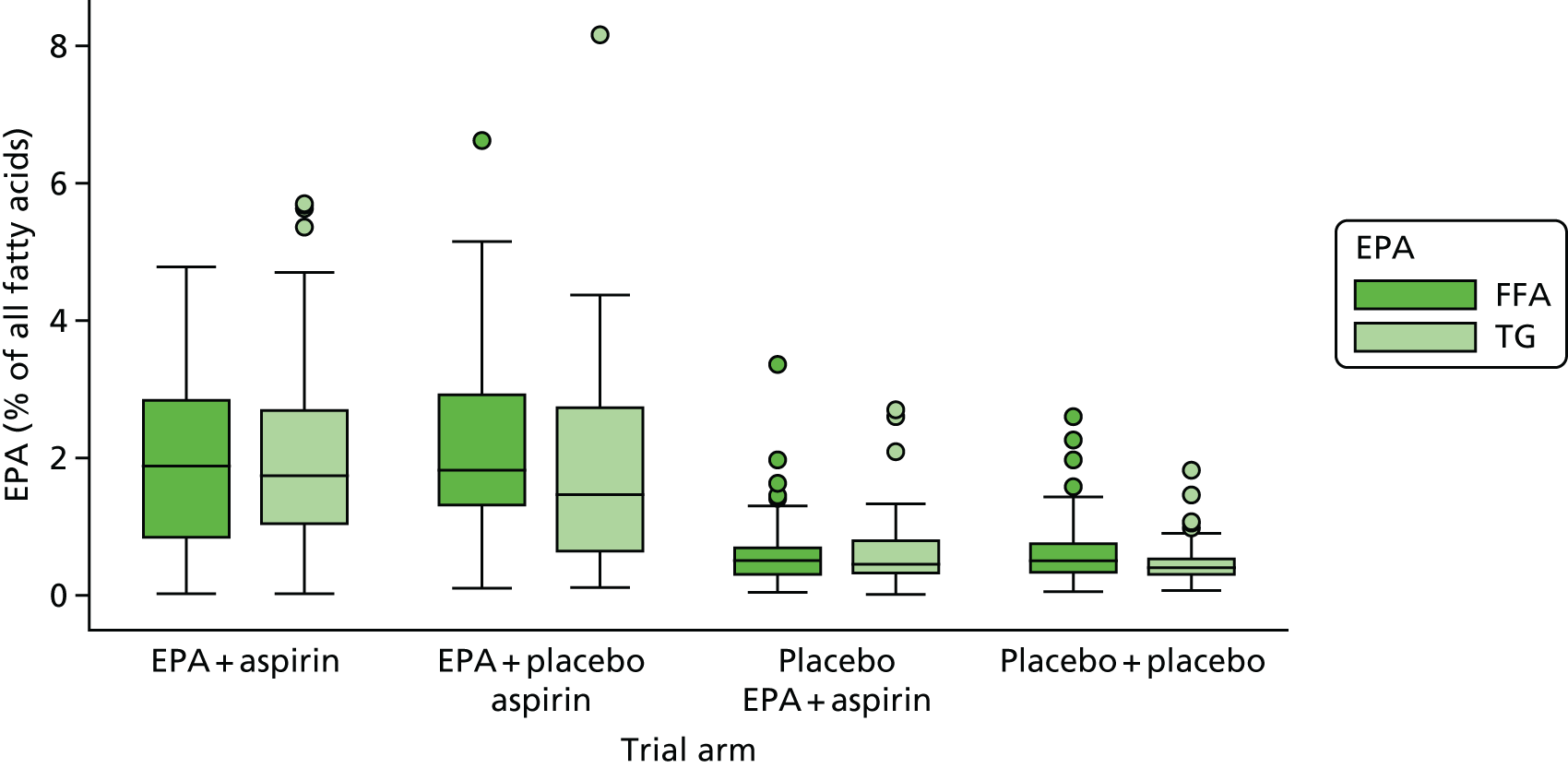
FIGURE 7.
The RBC EPA levels by formulation and by trial group at 12 months.
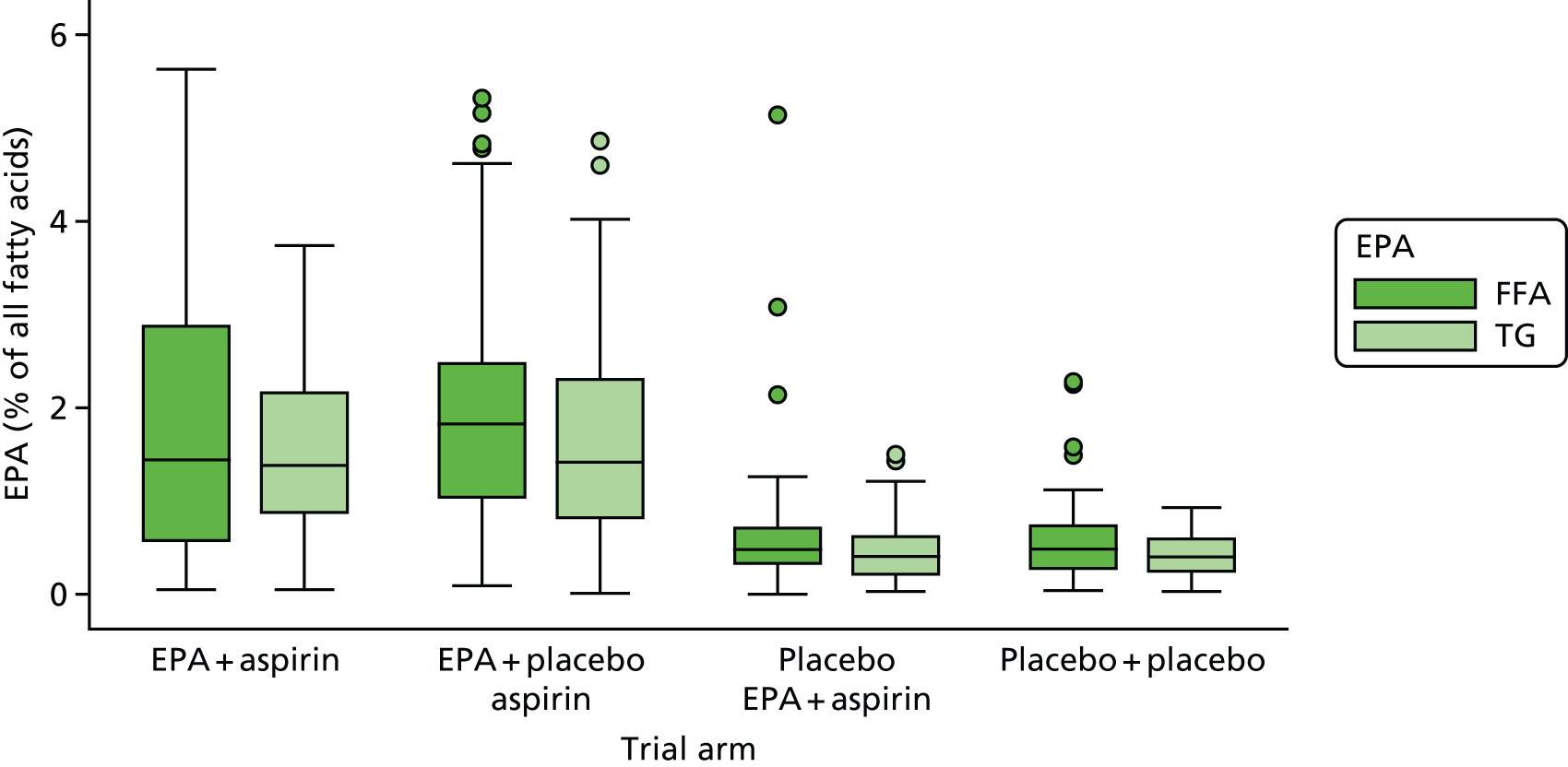
| RBC and rectal mucosal EPA levelsa | EPA | Total (N = 355) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFA (N = 212) | TG (N = 143) | ||
| RBC EPA levela | |||
| Baseline | |||
| Mean (SD) | 0.6 (0.6) | 0.5 (0.4) | 0.6 (0.5) |
| Median (IQR) | 0.5 (0.3–0.8) | 0.4 (0.3–0.7) | 0.5 (0.3–0.8) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.0, 4.7 | 0.0, 1.8 | 0.0, 4.7 |
| n | 181 | 128 | 309 |
| 6 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | 2.0 (1.3) | 1.9 (1.4) | 1.9 (1.3) |
| Median (IQR) | 1.9 (0.9–2.9) | 1.6 (0.9–2.7) | 1.8 (0.9–2.8) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.0, 6.6 | 0.0, 8.2 | 0.0, 8.2 |
| n | 164 | 108 | 272 |
| 12 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | 1.9 (1.4) | 1.6 (1.0) | 1.8 (1.3) |
| Median (IQR) | 1.7 (0.9–2.8) | 1.4 (0.8–2.2) | 1.6 (0.9–2.4) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.1, 5.6 | 0.0, 4.9 | 0.0, 5.6 |
| n | 157 | 100 | 257 |
| Absolute change in RBC EPA levela from baseline at 6 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | 1.3 (1.4) | 1.3 (1.4) | 1.3 (1.4) |
| Median (IQR) | 1.3 (0.3–2.3) | 1.1 (0.4–2.2) | 1.2 (0.3–2.3) |
| Minimum, maximum | –4.5, 6.1 | –1.7, 7.2 | –4.5, 7.2 |
| n | 151 | 103 | 254 |
| Absolute change in RBC EPA levela from baseline at 12 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | 1.2 (1.4) | 1.1 (1.1) | 1.2 (1.2) |
| Median (IQR) | 1.0 (0.1–2) | 0.9 (0.3–1.6) | 1.0 (0.2–1.9) |
| Minimum, maximum | –3.0, 5.2 | –0.8, 4.2 | –3.0, 5.2 |
| n | 143 | 95 | 238 |
| Rectal mucosal EPA levela at 12 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | 1.3 (1.0) | 1.8 (1.1) | 1.5 (1.1) |
| Median (IQR) | 1.1 (0.6–1.7) | 1.6 (1.0–2.3) | 1.3 (0.7–2.0) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.0, 5.2 | 0.4, 5 | 0.0, 5.2 |
| n | 153 | 96 | 249 |
| RBC levelsa | EPA | Total (N = 355) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFA (N = 212) | TG (N = 143) | ||
| RBC DHA levela | |||
| Baseline | |||
| Mean (SD) | 2.1 (1.4) | 2.3 (1.8) | 2.2 (1.5) |
| Median (IQR) | 2.0 (1.0–2.9) | 2.1 (1.0–3.0) | 2.0 (1.0–2.9) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.1, 7.7 | 0.1, 9.7 | 0.1, 9.7 |
| n | 181 | 128 | 309 |
| 6 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | 2.0 (1.2) | 1.6 (1.2) | 1.8 (1.2) |
| Median (IQR) | 2.0 (1.0–2.5) | 1.5 (0.6–2.0) | 1.7 (0.8–2.4) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.0, 7.5 | 0.1, 6.8 | 0.0, 7.5 |
| n | 164 | 108 | 272 |
| 12 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | 2.2 (1.5) | 1.9 (1.1) | 2.1 (1.4) |
| Median (IQR) | 2.2 (1.3–2.8) | 1.9 (1.2–2.3) | 1.9 (1.2–2.7) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.1, 14.4 | 0.0, 6.6 | 0.0, 14.4 |
| n | 157 | 100 | 257 |
| Change from baseline at 6 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | –0.2 (1.4) | –0.5 (1.6) | –0.3 (1.5) |
| Median (IQR) | –0.2 (–0.9 to 4.0) | –0.4 (–1.2 to 3.0) | –0.2 (–1.0 to 3.0) |
| Minimum, maximum | –4.5, 5.4 | –8.6, 3.7 | –8.6, 5.4 |
| n | 151 | 103 | 254 |
| Change from baseline at 12 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | –0.1 (1.4) | –0.3 (1.7) | –0.2 (1.5) |
| Median (IQR) | –0.2 (–0.9 to 8.0) | –0.3 (–1.4 to 7.0) | –0.2 (–1.1 to 7.0) |
| Minimum, maximum | –4.2, 4.3 | –7.7, 2.8 | –7.7, 4.3 |
| n | 143 | 95 | 238 |
| RBC AA levela | |||
| Baseline | |||
| Mean (SD) | 6.3 (3.9) | 7.0 (4.9) | 6.6 (4.4) |
| Median (IQR) | 5.8 (3.7–8.2) | 6.3 (3.9–9.0) | 5.9 (3.7–8.3) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.4, 27.9 | 0.5, 32.1 | 0.4, 32.1 |
| n | 181 | 128 | 309 |
| 6 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | 5.6 (2.9) | 5.5 (3.3) | 5.5 (3.1) |
| Median (IQR) | 5.8 (3.5–7.2) | 4.7 (2.7–7.8) | 5.4 (2.9–7.2) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.1, 18.5 | 0.3, 16.6 | 0.1, 18.5 |
| n | 164 | 108 | 272 |
| 12 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | 6.1 (3.7) | 6.1 (3.1) | 6.1 (3.4) |
| Median (IQR) | 6 (3.8–7.7) | 5.8 (3.8–7.9) | 5.9 (3.8–7.7) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.3, 26.1 | 0.0, 13.3 | 0.0, 26.1 |
| n | 157 | 100 | 257 |
| Change from baseline at 6 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | –0.8 (3.8) | –1.1 (4.8) | –0.9 (4.2) |
| Median (IQR) | –0.9 (–2.6 to 1.0) | –0.9 (–3.2 to 1.9) | –0.9 (–3.0 to 1.3) |
| Minimum, maximum | –14.6, 10.4 | –25.9, 7.3 | –25.9, 10.4 |
| n | 151 | 103 | 254 |
| Change from baseline at 12 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | –0.3 (4.1) | –0.8 (5.1) | –0.5 (4.5) |
| Median (IQR) | –0.6 (–2.8 to 2.1) | –0.6 (–3.9 to 2.3) | –0.6 (–3.0 to 2.2) |
| Minimum, maximum | –11.9, 13.1 | –22.9, 7.9 | –22.9, 13.1 |
| n | 143 | 95 | 238 |
| RBC EPA-to-AA ratio levela | |||
| Baseline | |||
| Mean (SD) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.0) | 0.1 (0.1) |
| Median (IQR) | 0.1 (0.1–1.0) | 0.1 (0.1–1.0) | 0.1 (0.1–1.0) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 0.6 | 0, 0.3 | 0, 0.6 |
| n | 181 | 128 | 309 |
| 6 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | 0.4 (0.2) | 0.3 (0.2) | 0.4 (0.2) |
| Median (IQR) | 0.4 (0.2–5.0) | 0.3 (0.2–4.0) | 0.4 (0.2–5.0) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 0.8 | 0, 0.7 | 0, 0.8 |
| n | 164 | 108 | 272 |
| 12 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | 0.3 (0.2) | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.2) |
| Median (IQR) | 0.3 (0.2–4.0) | 0.2 (0.2–4.0) | 0.3 (0.2–4.0) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 0.8 | 0, 0.7 | 0, 0.8 |
| n | 157 | 100 | 257 |
| Change from baseline at 6 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | 0.3 (0.2) | 0.3 (0.2) | 0.3 (0.2) |
| Median (IQR) | 0.3 (0.1–4.0) | 0.3 (0.1–4.0) | 0.3 (0.1–4.0) |
| Minimum, maximum | –0.5, 0.7 | –0.1, 0.6 | –0.5, 0.7 |
| n | 151 | 103 | 254 |
| Change from baseline at 12 months | |||
| Mean (SD) | 0.2 (0.2) | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.2 (0.2) |
| Median (IQR) | 0.2 (0.1–3.0) | 0.2 (0.1–3.0) | 0.2 (0.1–3.0) |
| Minimum, maximum | –0.3, 0.7 | –0.1, 0.6 | –0.3, 0.7 |
| n | 143 | 95 | 238 |
Rectal mucosal EPA levels at the end of the intervention period were higher in those who received EPA-TG than in those who received EPA-FFA, but with substantial overlap between the two groups (Figure 8). This was not reflected in the rectal mucosal EPA-to-AA ratio at the end of the intervention period, which was similar for both EPA-FFA and EPA-TG users (Table 14).
FIGURE 8.
Rectal mucosal EPA levels by formulation and by trial group at 12 months.
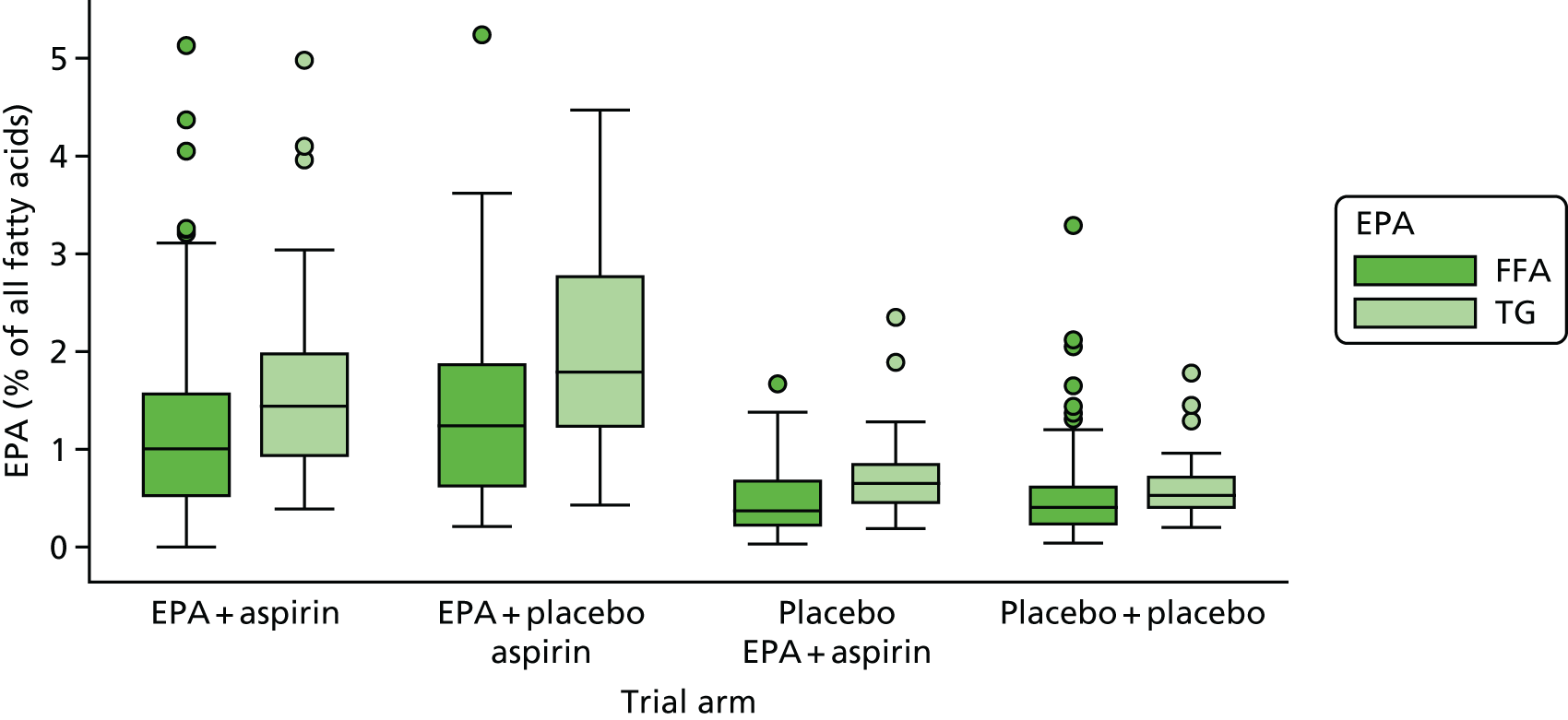
| Rectal mucosal levelsa at 12 months | EPA | Total (N = 355) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFA (N = 212) | TG (N = 143) | ||
| EPA levela | |||
| Mean (SD) | 1.3 (1.0) | 1.8 (1.1) | 1.5 (1.1) |
| Median (IQR) | 1.1 (0.6–1.7) | 1.6 (1.0–2.3) | 1.3 (0.7–2) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.0, 5.2 | 0.4, 5.0 | 0.0, 5.2 |
| n | 153 | 96 | 249 |
| DHA levela | |||
| Mean (SD) | 0.9 (0.6) | 1.2 (0.4) | 1.0 (0.5) |
| Median (IQR) | 0.7 (0.5–1.4) | 1.2 (1.0–1.4) | 1.0 (0.6–1.4) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.1, 4.3 | 0.4, 2.1 | 0.1, 4.3 |
| n | 153 | 96 | 249 |
| AA levela | |||
| Mean (SD) | 4.4 (2.8) | 5.8 (1.6) | 5.0 (2.5) |
| Median (IQR) | 3.5 (2.3–6.3) | 5.5 (4.7–6.5) | 5.0 (2.8–6.4) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.3, 17.7 | 1.9, 11.4 | 0.3, 17.7 |
| n | 153 | 96 | 249 |
| EPA-to-AA ratio levela | |||
| Mean (SD) | 0.3 (0.2) | 0.3 (0.2) | 0.3 (0.2) |
| Median (IQR) | 0.3 (0.2–0.4) | 0.3 (0.2–0.4) | 0.3 (0.2–0.4) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.0, 0.9 | 0.1, 8.0 | 0.0, 0.9 |
| n | 153 | 96 | 249 |
As there was no clear difference in RBC or rectal mucosal EPA incorporation, or EPA-to-AA ratio, between those allocated EPA-FFA and those allocated EPA-TG, it was felt appropriate to combine primary and secondary outcome data from those who received either type of capsule IMP.
Analysis populations
The ITT population was defined as all randomised participants with post-randomisation data (Table 15). Participants in the ITT population were analysed regardless of adherence to their allocated group and without imputation for missing data. Although 709 participants were randomised, two participants withdrew immediately and provided no data. Therefore, 707 participants were included in the ITT population (see Table 15). All baseline summaries and efficacy analyses were based on this population. Data from surveillance colonoscopy at 12 months was available for 640 participants.
| Participants | Trial group (n) | Total (n) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin | EPA + placebo aspirin | Placebo EPA + aspirin | Placebo + placebo | ||
| Randomised | 177 | 179 | 177 | 176 | 709 |
| Excluded from ITT population as a result of withdrawal immediately after randomisation | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Included in ITT population | 177 | 178 | 176 | 176 | 707 |
| Included in per-protocol population | 156 | 172 | 163 | 168 | 659 |
| Included in safety population | 170 | 177 | 174 | 176 | 697 |
The per-protocol population included all participants who had taken sufficient medication (participants who had taken > 75% of expected capsules and/or > 50% of expected tablets), were not found to be ineligible post randomisation and had not used any OTC medication containing aspirin, NSAIDs or fish oil during the treatment period. The population comprised 659 participants and was used for one of the sensitivity analyses to determine the robustness of the primary analysis.
The safety population was defined as all participants who took at least one dose of allocated treatment. It comprised 697 participants. The 10 participants who did not receive active or placebo EPA or aspirin were excluded from this population.
Primary outcome
Colorectal adenoma data from the 12-month surveillance colonoscopy were available for 640 participants: 161 (91%), 153 (86%), 163 (93%) and 163 (93%) (percentage of the total number of participants in each group) in the EPA + aspirin, EPA + placebo aspirin, placebo EPA + aspirin and placebo EPA + placebo aspirin groups, respectively. The median time between randomisation and the 12-month surveillance colonoscopy was between 344 and 348 days in the four treatment groups (Table 16).
| Primary outcome data | Trial group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 177) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 178) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 176) | Placebo + placebo (N = 176) | |
| Participants with colorectal adenoma data at 12 months (n) | 161 | 153 | 163 | 163 |
| Median (IQR) days from randomisation to surveillance colonoscopy | 348 (337–364) | 349 (333–363) | 348 (335–364) | 344 (334–360) |
| Participants with one or more colorectal adenomas at surveillance colonoscopy (ADRa), n (%) | 98 (61) | 97 (63) | 100 (61) | 100 (61) |
| Factorial margins | Active EPA (n = 314) | Placebo EPA (n = 326) | Active aspirin (n = 324) | Placebo aspirin (n = 316) |
| Participants with one or more colorectal adenomas at surveillance colonoscopy, n (%) | 195 (62) | 200 (61) | 198 (61) | 197 (62) |
Of 161 participants in the EPA + aspirin group, 98 (61%) had at least one colorectal adenoma (the ADRa) at the surveillance colonoscopy, whereas 97 out of 153 participants (63%) in the EPA + placebo aspirin group had at least one colorectal adenoma (the ADRa) at the surveillance colonoscopy. The ADRa was 61% (100/163) in the placebo EPA + aspirin group and 61% (100/163) in the placebo EPA + placebo aspirin group.
When summarised according to factorial margins, the ADRa was similar across interventions, with an ADRa of 195 (62%) for those who received active EPA versus an ADRa of 200 (61%) for those who did not receive EPA, and an ADRa of 198 (61%) for individuals who received active aspirin versus an ADRa of 197 (62%) for those who did not receive aspirin (62%) (see Table 16).
Primary outcome analysis
The test of interaction showed that there was no evidence of any interaction between EPA and aspirin for the ADRa (p = 0.85). Therefore, primary and secondary outcomes were analysed according to factorial margins, that is the treatment effects for EPA and aspirin were reported separately.
Table 17 shows adjusted risk differences of the ADRa for the treatment effect of EPA and aspirin. The point estimates and 95% CIs for both EPA and aspirin showed that there was no evidence of a statistically significant difference. These analyses were adjusted for whether or not the participant had a repeat endoscopic procedure (i.e. full colonoscopy, partial colonoscopy or FS) and included BCSP site as a random effect. Supportive analyses that were not adjusted by repeat colonoscopy showed similar results (see Appendix 4, Table 40).
| Risk difference and ratio | EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin |
|---|---|---|
| Adjusted by site as a random effect and by repeat colonoscopy at baseline (n = 588) | ||
| Risk difference (95% CI) (%); p-value | –0.9 (–8.8 to 6.9); 0.813 | –0.6 (–8.5 to 7.2); 0.876 |
| Risk ratio (95% CI) | 0.98 (0.87 to 1.12) | 0.99 (0.87 to 1.12) |
The point estimates for EPA and aspirin were –0.9% and –0.6%, respectively, with 95% CIs that included zero, indicating no statistically significant difference from no treatment for both interventions. The trial was designed to detect an absolute ADRa difference of 10%. Figure 9 and Table 17 show that the lower limit of the 95% CIs did not reach –10% for either EPA or aspirin.
FIGURE 9.
Forest plot of the treatment effect of EPA and aspirin on the ADRa. The blue vertical line represents the prespecified target reduction of ADRa (10%). Adjusted by site as a random effect and by repeat colonoscopy at baseline.
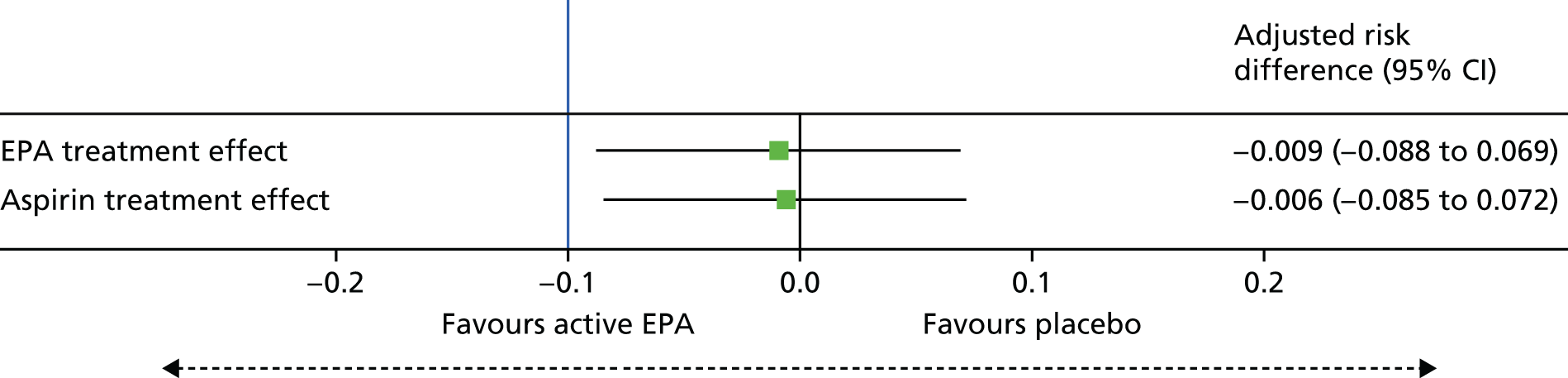
Sensitivity analyses for the primary outcome
Several sensitivity analyses were conducted to investigate the robustness of the primary analysis. Although the point estimates and 95% CIs varied between different analyses, they were supportive of the primary analysis (Table 18 and Figure 10).
| Analysis | Estimate (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |
| Using per-protocol population (risk difference) (%) | –0.6 (–8.7 to 7.4) | –0.6 (–8.7 to 7.4) |
| Multilevel model treating recruiting centre and site as random effects (odds ratio) | 0.96 (0.68 to 1.34) | 0.97 (0.70 to 1.34) |
| Multiple imputation of missing data (risk difference) (%) | 0.1 (–7.3 to 7.6) | –0.7 (–8.3 to 6.8) |
| Adjustment of baseline variables with imbalancea (risk difference) (%) | –0.7 (–8.5 to 7.1) | –0.7 (–8.5 to 7.1) |
| Adjustment of oily fish intake during the trial (risk difference) (%) | –2.5 (–11.1 to 6.0) | –2.4 (–11.0 to 6.1) |
| CACE analysis taking account of treatment adherence | ||
| Binary adherence (risk difference) (%) | –1.0 (–9.9 to 7.9) | –0.7 (–8.5 to 7.1) |
| Continuous adherence (risk difference) (%) | –1.2 (–10.0 to 7.5) | –0.8 (–8.8 to 7.1) |
| Adjustment of EPA formulation (risk difference) (%) | –0.9 (–8.8 to 6.9) | –0.4 (–8.3 to 7.4) |
| Adjustment of baseline RBC EPA (risk difference) (%) | –4.2 (–12.6 to 4.2) | 2.3 (–6.0 to 10.6) |
FIGURE 10.
Forest plots for the sensitivity analyses of the ADRa. (a) EPA vs. placebo; (b) aspirin vs. placebo; and (c) multilevel model. Results using the multilevel model are presented as odds ratios, whereas all other sensitivity analyses are presented using the risk difference. Adjusted by site as a random effect and by repeat colonoscopy at baseline. Some analyses were adjusted by further variables.
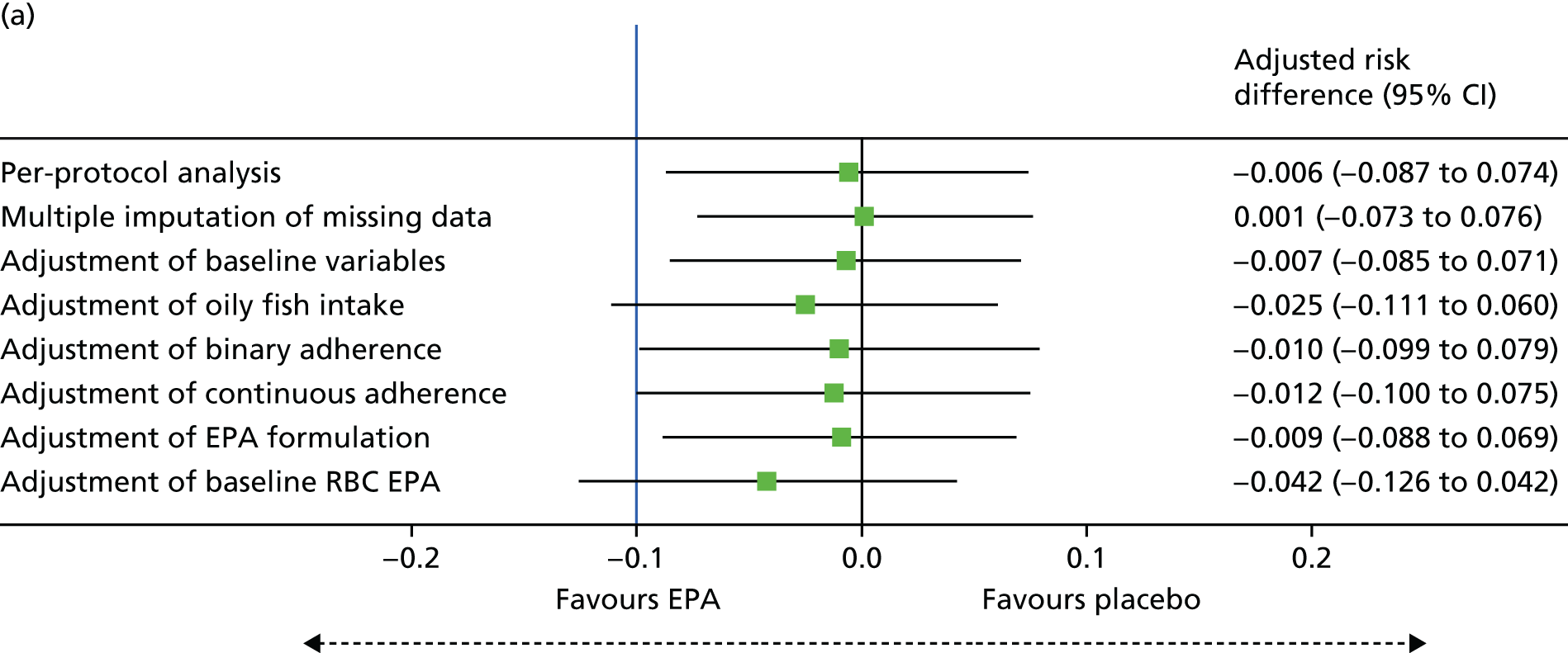
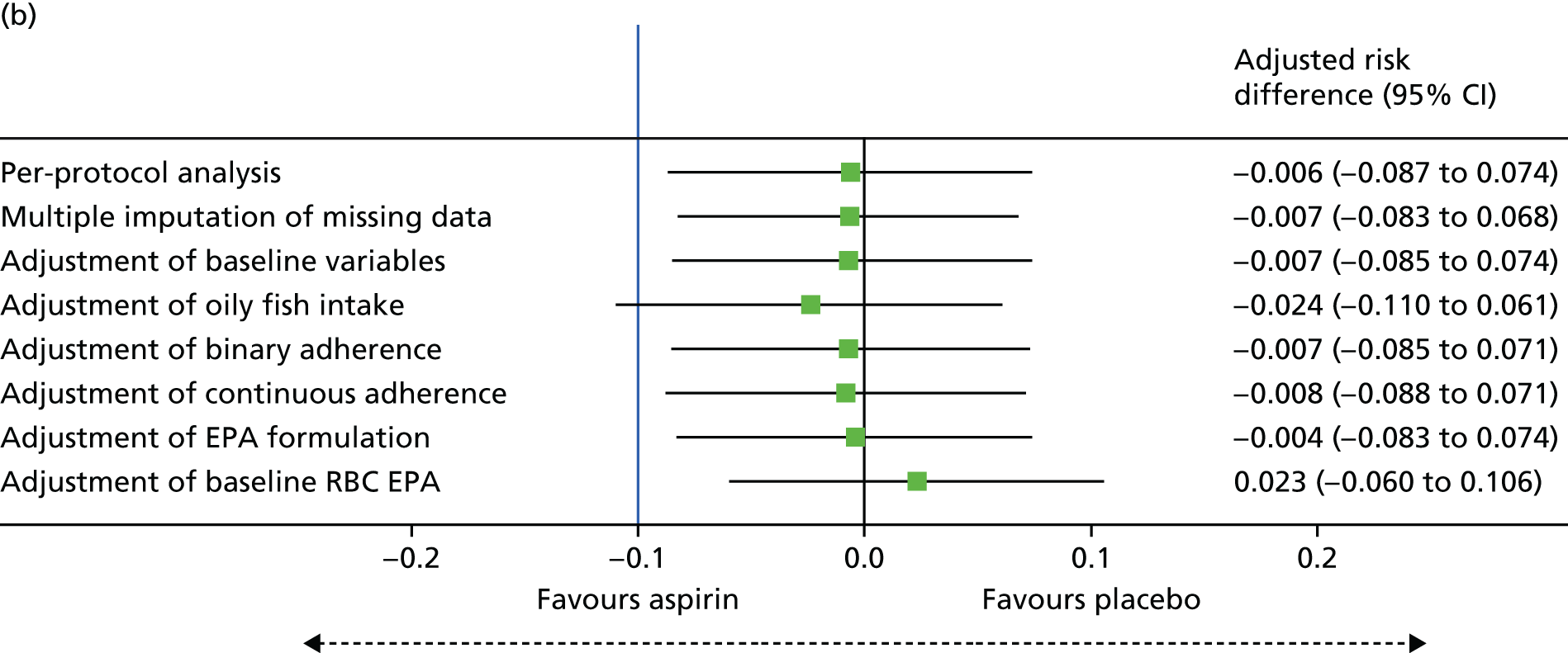
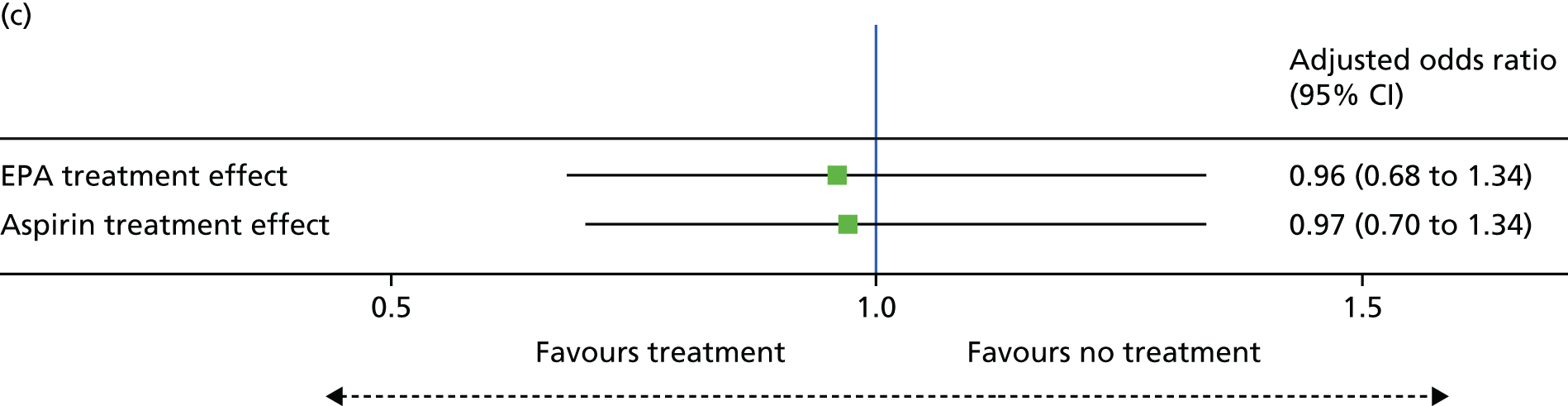
The multilevel model included both BCSP centre and site as random effects to account for sites embedded within the same BCSP (see Figure 10).
Secondary outcomes
Secondary outcomes were analysed in a similar way to the primary outcome. Results were summarised according to the outcome type, that is the risk difference for the binary outcome (ADRa) and the IRR for count outcomes (Tables 19–25 and Figure 17). Point estimates and CIs reported are according to factorial margins, that is EPA compared with no EPA and aspirin compared with no aspirin.
| Secondary colorectal adenoma outcomes | Trial group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 177) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 178) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 176) | Placebo + placebo (N = 176) | |
| Participants with colorectal adenoma data at 12 months (n) | 161 | 153 | 163 | 163 |
| Overall number of colorectal adenomas | 166 | 238 | 209 | 231 |
| Overall number of advanced colorectal adenomas | 9 | 8 | 11 | 12 |
| Histology of colorectal adenomas (n) | ||||
| Conventional | 155 | 205 | 194 | 220 |
| Serrated | 4 | 21 | 10 | 8 |
| Missing | 7 | 12 | 5 | 3 |
| Location of colorectal adenomas (n) | ||||
| Left | 58 | 98 | 101 | 93 |
| Right | 108 | 140 | 107 | 138 |
| Missing | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Trial group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (n = 161) | EPA + placebo aspirin (n = 153) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (n = 163) | Placebo + placebo (n = 163) | |
| Total number of colorectal adenomas per participant | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 1.0 (1.2) | 1.6 (2.1) | 1.3 (1.6) | 1.4 (2.0) |
| Median (IQR) | 1 (0–1) | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–2) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 6 | 0, 10 | 0, 13 | 0, 16 |
| Incidence rate for total number of colorectal adenomas per person per year | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 1.1 (1.3) | 1.6 (2.2) | 1.3 (1.7) | 1.5 (2.1) |
| Median (IQR) | 1 (0–1.2) | 1 (0–2.1) | 1 (0–2.1) | 1.1 (0–2.2) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 6.7 | 0, 10.8 | 0, 13.5 | 0, 16.6 |
| Incidence rate by margins | EPA | No EPA | Aspirin | No aspirin |
| Mean (SD) | 1.3 (1.8) | 1.4 (1.9) | 1.2 (1.5) | 1.6 (2.1) |
| Median (IQR) | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–2.1) | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–2.2) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 10.8 | 0, 16.6 | 0, 13.5 | 0, 16.6 |
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |||
| IRR (95% CI) | 0.91 (0.79 to 1.05) | 0.78 (0.68 to 0.90) | ||
| Trial group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 161) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 153) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 163) | Placebo + placebo (N = 163) | |
| Participant with any advanced colorectal adenoma (advanced ADRa), n (%) | 8 (5) | 8 (5) | 10 (6) | 11 (7) |
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |||
| Risk difference for number of participants with any advanced colorectal adenomas (95% CI) (%) | –0.6 (–4.4 to 3.1) | –0.3 (–4.1 to 3.5) | ||
| Number of advanced colorectal adenomas per participant | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.1 (0.3) | 0.1 (0.2) | 0.1 (0.3) | 0.1 (0.3) |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 2 | 0, 1 | 0, 2 | 0, 2 |
| Incidence rate for number of advanced colorectal adenomas per person per year | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.1 (0.3) | 0.1 (0.2) | 0.1 (0.3) | 0.1 (0.3) |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 2.1 | 0, 1.2 | 0, 2.1 | 0, 2.1 |
| Incidence rate by margins | EPA | No EPA | Aspirin | No aspirin |
| Mean (SD) | 0.1 (0.3) | 0.1 (0.3) | 0.1 (0.3) | 0.1 (0.3) |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 2.1 | 0, 2.1 | 0, 2.1 | 0, 2.1 |
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |||
| IRR (95% CI) | 0.82 (0.43 to 1.56) | 0.99 (0.52 to 1.86) | ||
| Trial group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 161) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 153) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 163) | Placebo + placebo (N = 163) | |
| Participants with any conventionala colorectal adenomas (conventional ADRa), n (%) | 88 (55) | 83 (54) | 91 (56) | 92 (56) |
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |||
| Risk difference for number of participants with any conventionala adenomas (95% CI) (%) | –3.3 (–11.2 to 4.7) | 1.7 (–6.2 to 9.6) | ||
| Number of conventional colorectal adenomas per participant | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 1.0 (1.2) | 1.4 (1.9) | 1.2 (1.6) | 1.4 (2) |
| Median (IQR) | 1 (0–1) | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–2) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 6 | 0, 10 | 0, 13 | 0, 16 |
| Incidence rate for number of conventional colorectal adenomas per person per year | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 1.0 (1.3) | 1.4 (2) | 1.2 (1.7) | 1.4 (2.1) |
| Median (IQR) | 1 (0–1.1) | 1 (0–2.1) | 1 (0–2.1) | 1 (0–2.1) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 6.7 | 0, 10.8 | 0, 13.5 | 0, 16.6 |
| Incidence rate by margins | EPA | No EPA | Aspirin | No aspirin |
| Mean (SD) | 1.2 (1.7) | 1.3 (1.9) | 1.1 (1.5) | 1.4 (2) |
| Median (IQR) | 1.0 (0–1.9) | 1.0 (0–2.1) | 1.0 (0–1.9) | 1.0 (0–2.1) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 10.8 | 0, 16.6 | 0, 13.5 | 0, 16.6 |
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |||
| IRR (95% CI) | 0.86 (0.74 to 0.99) | 0.82 (0.71 to 0.94) | ||
| Trial group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 161) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 153) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 163) | Placebo + placebo (N = 163) | |
| Participants with any serrated colorectal adenomas (serrated ADRa), n (%) | 4 (2) | 11 (7) | 6 (4) | 7 (4) |
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |||
| Risk difference for number of participants with any serrated adenomas (95% CI) (%) | 0 (–3.2 to 3.2) | –2.7 (–6.1 to 0.7) | ||
| Number of serrated colorectal adenomas per participant | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.0 (0.2) | 0.1 (0.7) | 0.1 (0.4) | 0.0 (0.2) |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 1 | 0, 8 | 0, 4 | 0, 2 |
| Incidence rate for number of serrated colorectal adenomas per person per year | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.0 (0.2) | 0.1 (0.8) | 0.1 (0.3) | 0.1 (0.3) |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 1.1 | 0, 8.6 | 0, 3.4 | 0, 2.2 |
| Incidence rate by margins | EPA | No EPA | Aspirin | No aspirin |
| Mean (SD) | 0.1 (0.6) | 0.1 (0.3) | 0.0 (0.3) | 1.0 (0.6) |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 8.6 | 0, 3.4 | 0, 3.4 | 0, 8.6 |
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |||
| IRR (95% CI) | 1.44 (0.79 to 2.60) | 0.46 (0.25 to 0.87) | ||
| Trial group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 161) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 153) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 163) | Placebo + placebo (N = 163) | |
| Participants with any left colorectal adenomas (left ADRa), n (%) | 42 (26) | 58 (38) | 65 (40) | 55 (34) |
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |||
| Risk difference for number of participants with any left colorectal adenomas (95% CI) (%) | –7.8 (–15.5 to –0.2) | –1.8 (–9.4 to 5.8) | ||
| Number of left colorectal adenomas per participant | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.4 (0.7) | 0.6 (10.1) | 0.6 (0.9) | 0.6 (1.0) |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 3 | 0, 5 | 0, 5 | 0, 5 |
| Incidence rate for number of left colorectal adenomas per person per year | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.4 (0.7) | 0.7 (10.1) | 0.6 (0.9) | 0.6 (1.0) |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (0–0.9) | 0 (0–1.1) | 0 (0–1.1) | 0 (0–1) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.0, 3.3 | 0.0, 5.4 | 0.0, 4.4 | 0.0, 5.6 |
| Incidence rate by margins | EPA | No EPA | Aspirin | No aspirin |
| Mean (SD) | 0.5 (0.9) | 0.6 (1.0) | 0.5 (0.8) | 0.6 (10.1) |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1.1) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1.1) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.0, 5.4 | 0.0, 5.6 | 0.0, 4.4 | 0.0, 5.6 |
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |||
| IRR (95% CI) | 0.75 (0.60 to 0.94) | 0.85 (0.69 to 1.06) | ||
| Trial group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 161) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 153) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 163) | Placebo + placebo (N = 163) | |
| Participants with any right colon adenomas (right ADRa), n (%) | 69 (43) | 72 (47) | 63 (39) | 66 (40) |
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |||
| Risk difference for number of participants with any right colon adenomas (95% CI) (%) | 6.0 (–1.9 to 13.9) | –3.1 (–11.0 to 4.7) | ||
| Number of right colon adenomas per participant | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.7 (1.0) | 0.9 (1.5) | 0.7 (1.3) | 0.8 (1.7) |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0, 6 | 0, 9 | 0, 13 | 0, 16 |
| Incidence rate for number of right colon adenomas per person per year | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.7 (1.1) | 1.0 (1.6) | 0.7 (1.4) | 0.9 (1.8) |
| Median (IQR) | 0.0 (0.0–1.1) | 0.0 (0.0–1.1) | 0.0 (0.0–1.1) | 0.0 (0.0–1.1) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.0, 6.7 | 0.0, 10.4 | 0.0, 13.5 | 0.0, 16.6 |
| Incidence rate by margins | EPA | No EPA | Aspirin | No aspirin |
| Mean (SD) | 0.8 (1.4) | 0.8 (1.6) | 0.7 (1.3) | 0.9 (1.7) |
| Median (IQR) | 0.0 (0.0–1.1) | 0.0 (0.0–1.1) | 0.0 (0.0–1.1) | 0.0 (0.0–1.1) |
| Minimum, maximum | 0.0, 10.4 | 0.0, 16.6 | 0.0, 13.5 | 0.0, 16.6 |
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |||
| IRR (95% CI) | 1.02 (0.85 to 1.22) | 0.73 (0.61 to 0.88) | ||
FIGURE 11.
Distribution of the total number of colorectal adenomas per participant at 12 months by trial group. (a) EPA + aspirin; (b) EPA + placebo aspirin; (c) placebo EPA + aspirin; and (d) placebo + placebo.
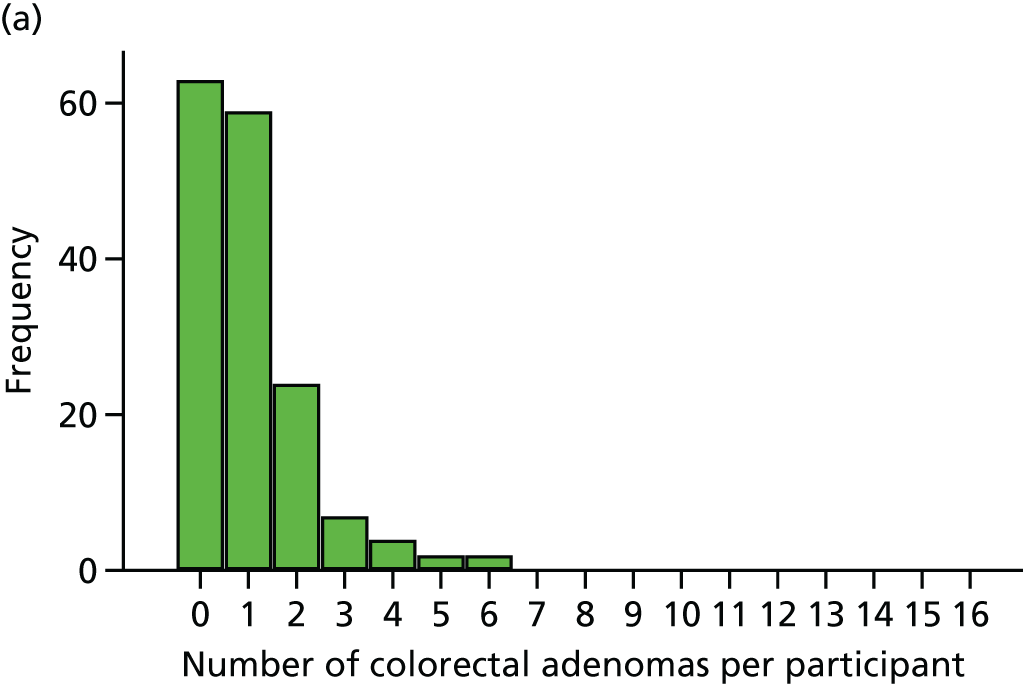
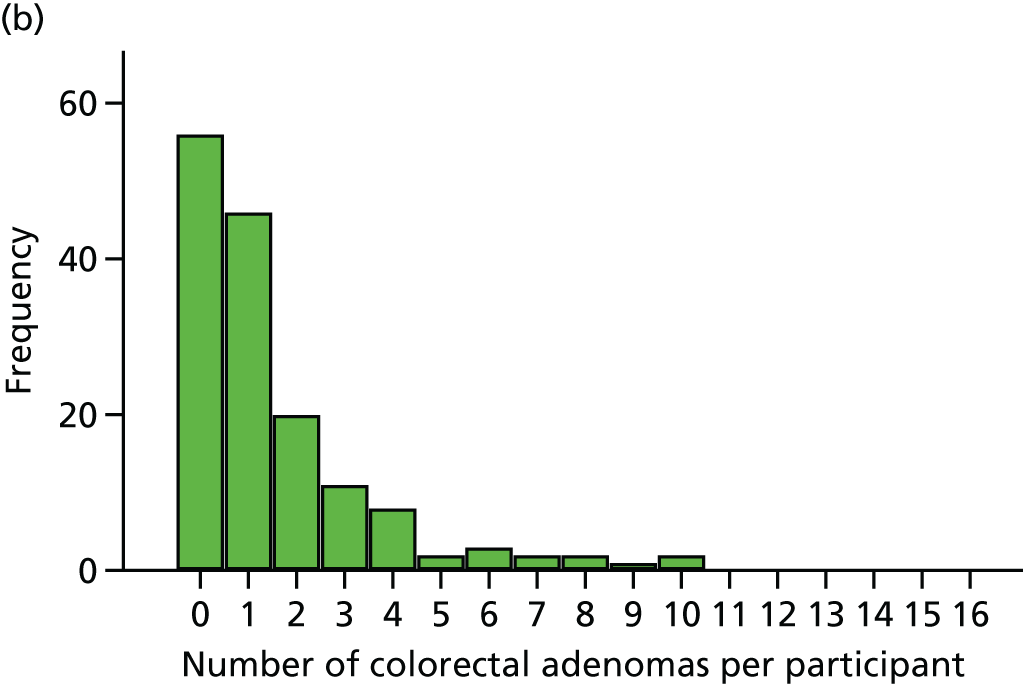
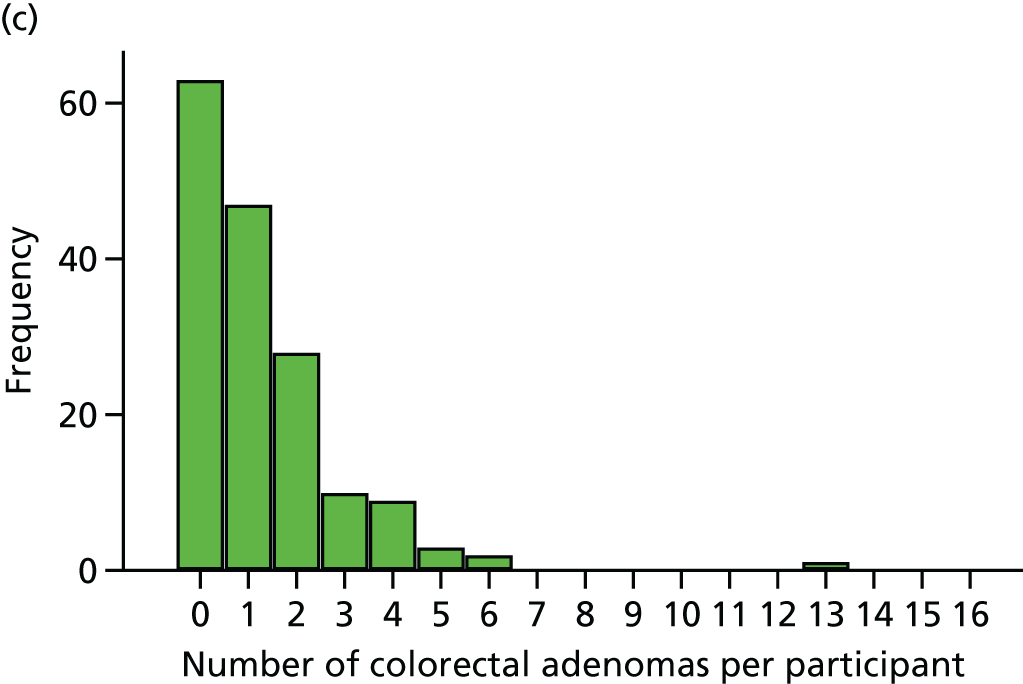
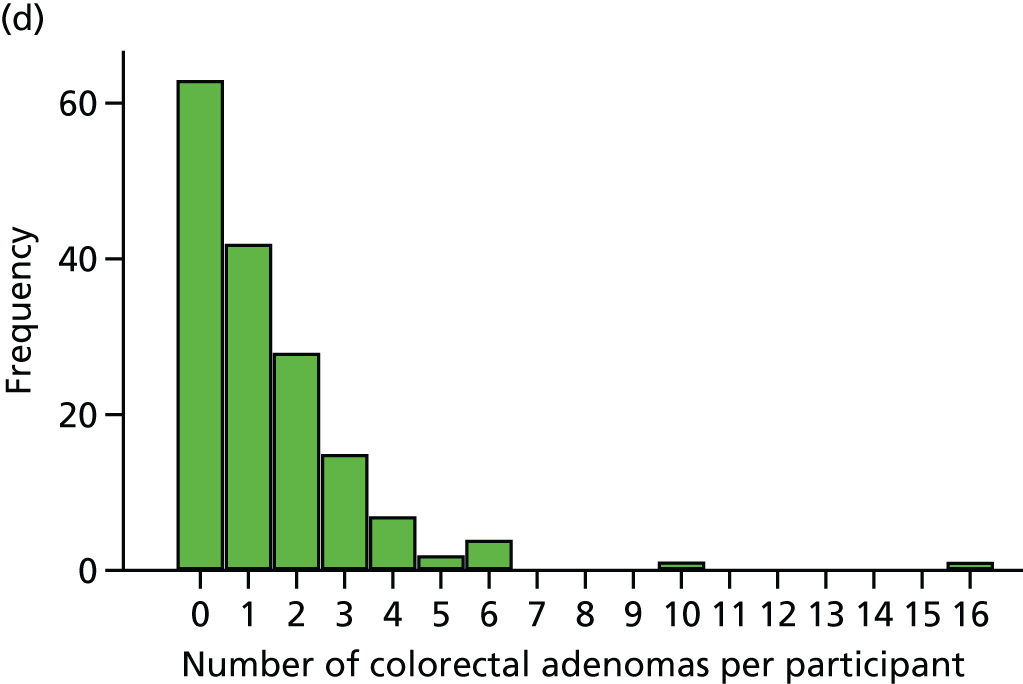
Summary data on colorectal adenomas reported at surveillance colonoscopy are listed in Table 19.
The median number of colorectal adenomas per participant at the 12-month surveillance colonoscopy was 1 for all four trial groups (see Table 20). The median incidence rate was 1 colorectal adenoma per person per year for all four groups. However, fewer colorectal adenomas were detected in the combination EPA + aspirin group (see Table 19), with a reduced total MAP value (see Table 20).
The factorial margin analysis revealed that the IRR for EPA versus no EPA was 0.91 (95% CI 0.79 to 1.05) in favour of EPA (see Table 20). The IRR for aspirin versus no aspirin was 0.78 (95% CI 0.68 to 0.90). The distribution of individual total colorectal adenoma counts was similar across all four groups (see Figure 11).
The advanced ADRa was 8 (5%) in participants who received both EPA and aspirin, as well as EPA + placebo aspirin, but was 10 (6%) and 11 (7%) in participants who received placebo EPA + aspirin and placebo EPA + placebo aspirin, respectively (see Table 21). Risk differences for the advanced ADRa for EPA and aspirin were –0.6% and –0.3%, respectively. The mean incidence rate was 0.1 advanced colorectal adenomas per person per year. Analysis of the advanced MAP ‘at the margins’ revealed IRRs of 0.82 for EPA and 0.99 for aspirin, but with 95% CIs crossing unity. The distribution of individual advanced colorectal adenoma counts was similar across all four groups (Figure 12).
FIGURE 12.
Distribution of the number of advanced colorectal adenomas per participant at 12 months by trial group. (a) EPA + aspirin; (b) EPA + placebo aspirin; (c) placebo EPA + aspirin; and (d) placebo + placebo.
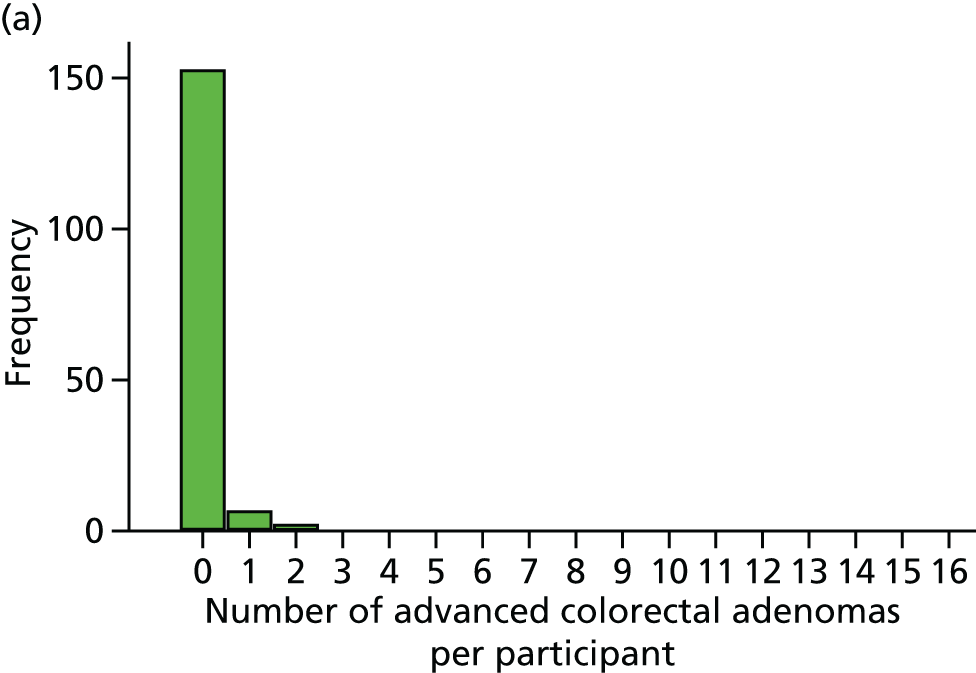
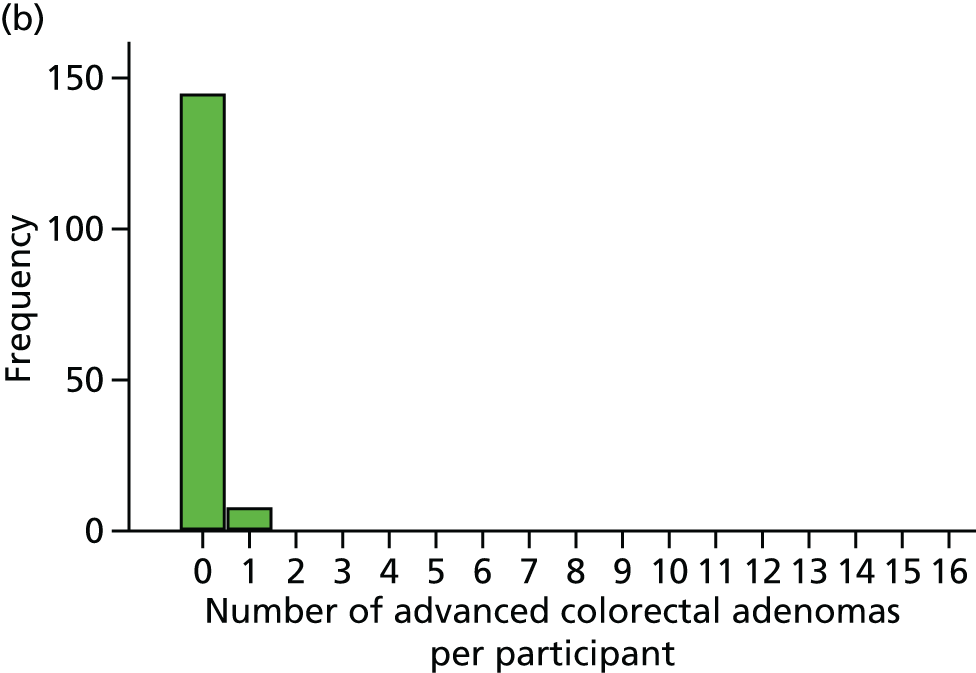
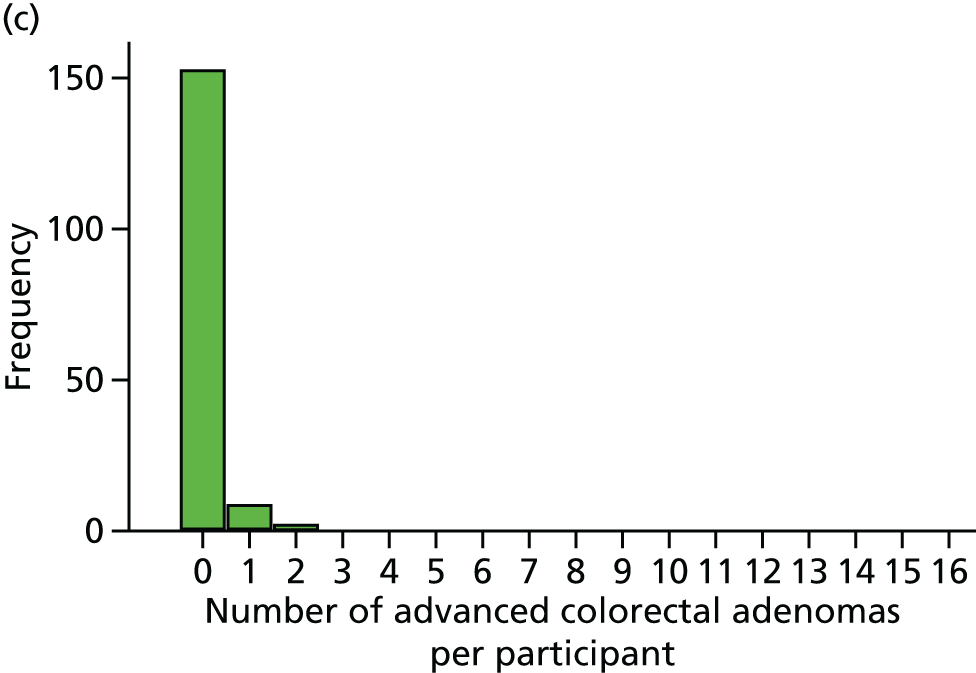
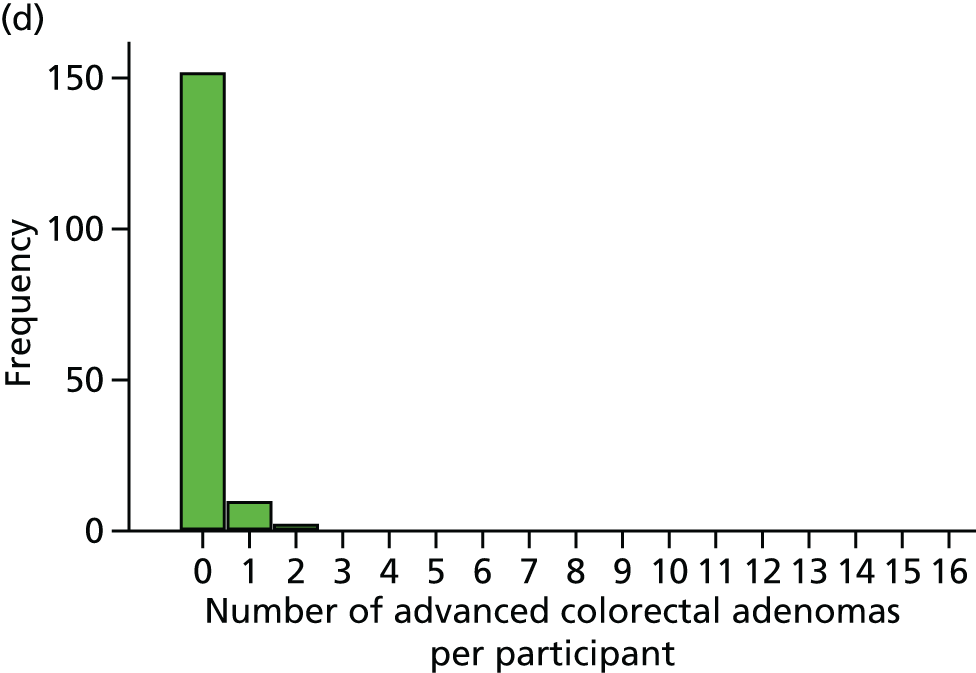
The conventional ADRa was 55% for EPA + aspirin (88/161), 54% for EPA + placebo aspirin (83/153) and 56% for both placebo EPA + aspirin (91/163) and placebo EPA + placebo aspirin (92/163) (see Table 22). Risk differences for EPA and aspirin were –3.3% and 1.7%, respectively. The median incidence rate was 1 conventional adenoma per person per year for all four groups, with a lower mean value for the combined EPA + aspirin group (see Table 22). IRRs for the number of conventional colorectal adenomas were 0.86 (95% CI 0.74 to 0.99) for EPA versus no EPA and 0.82 (95% CI 0.71 to 0.94) for aspirin versus no aspirin (see Table 22). The distribution of individual conventional colorectal adenoma counts was similar across all four groups (Figure 13).
FIGURE 13.
Distribution of the number of conventional colorectal adenomas per participant at 12 months by trial group. (a) EPA + aspirin; (b) EPA + placebo aspirin; (c) placebo EPA + aspirin; and (d) placebo + placebo.
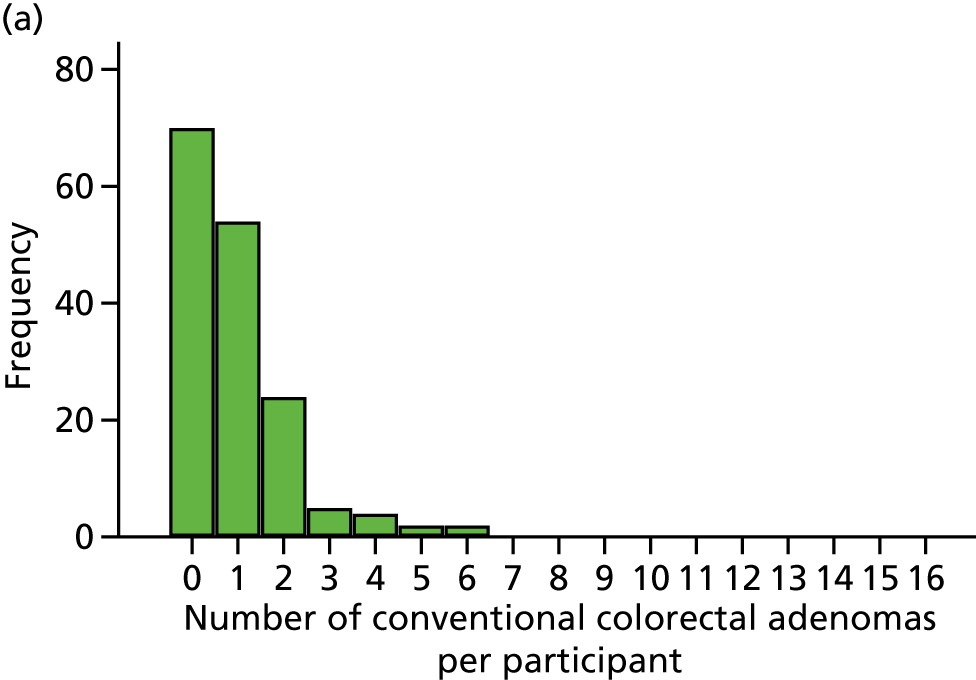
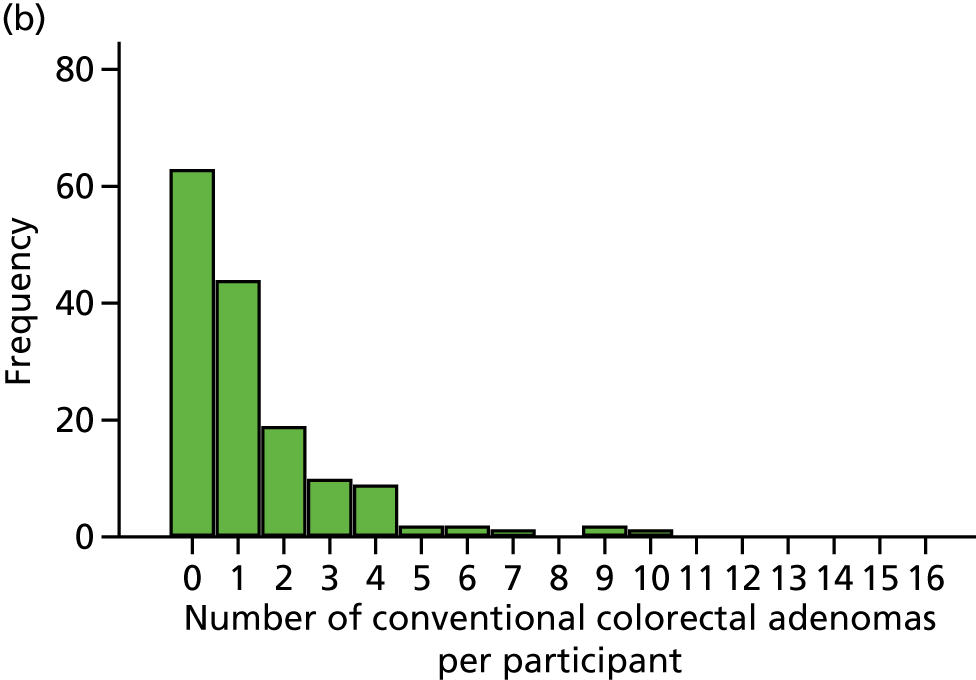
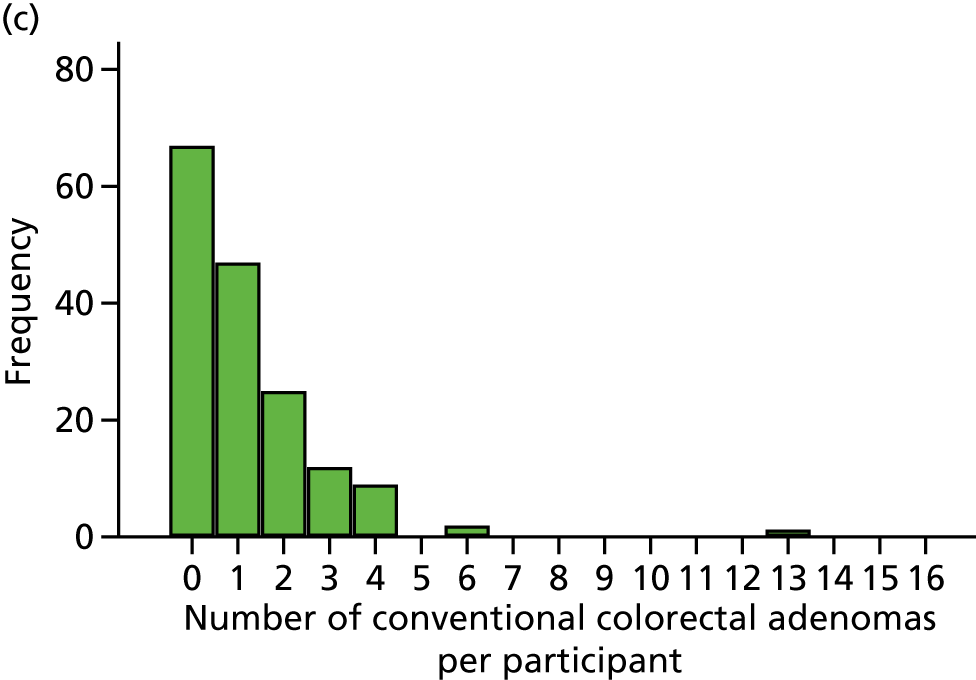
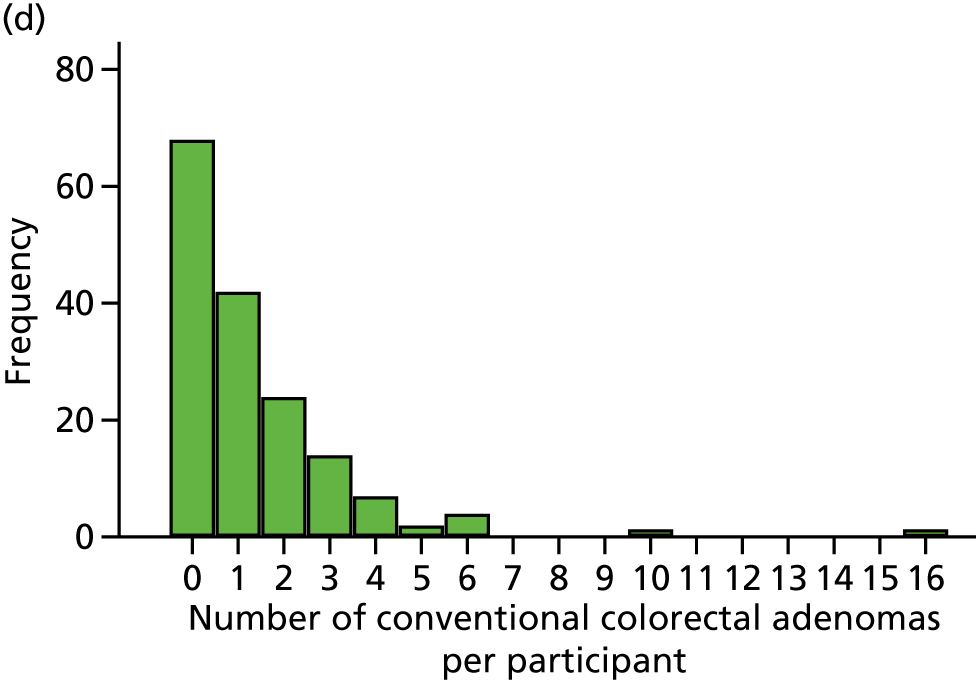
The serrated ADRa values were small for all treatment groups: 4 (2%) for EPA + aspirin, 11 (7%) for EPA + placebo aspirin, 6 (4%) for placebo EPA + aspirin and 7 (4%) for placebo EPA + placebo aspirin (see Table 23). The risk differences for the serrated ADRa were 0% (95% CI –3.2% to 3.2%) for EPA and –2.7% (95% CI –6.1% to 0.7%) for aspirin. The median incidence rate was zero for all four groups and the mean incidence rate was 0.1 serrated adenomas per person per year for all trial groups except the EPA + aspirin group, which was zero. IRRs for the number of serrated adenomas were 1.44 (95% CI 0.79 to 2.60) for EPA versus no EPA and 0.46 (95% CI 0.25 to 0.87) for aspirin versus no aspirin (see Table 23). The distribution of individual serrated colorectal adenoma counts was similar across all four groups (Figure 14).
FIGURE 14.
Distribution of the number of serrated colorectal adenomas per participant at 12 months by trial group. (a) EPA + aspirin; (b) EPA + placebo aspirin; (c) placebo EPA + aspirin; and (d) placebo + placebo.
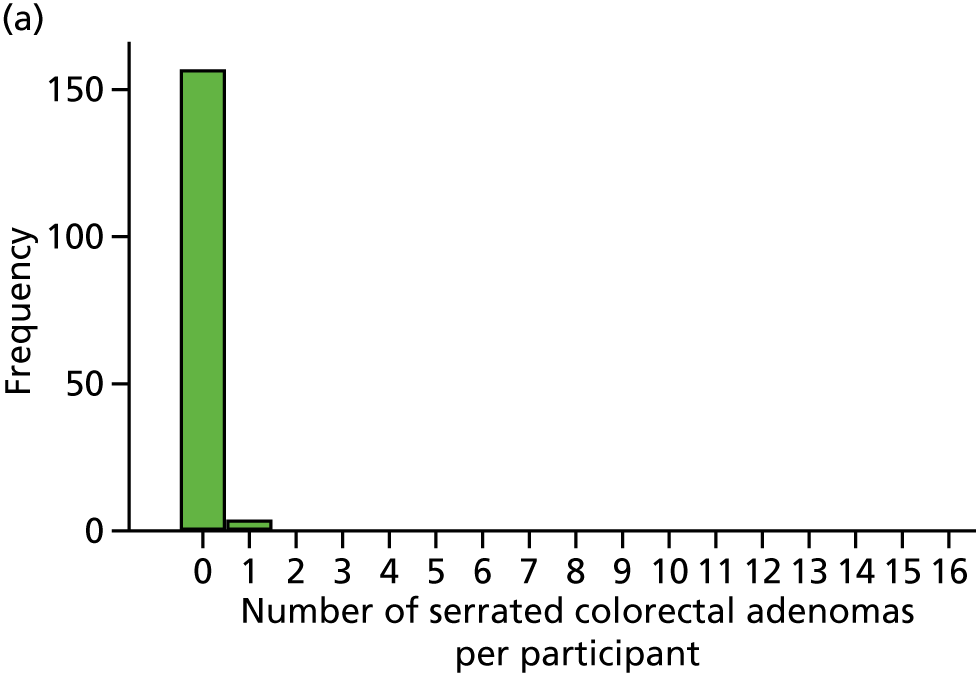
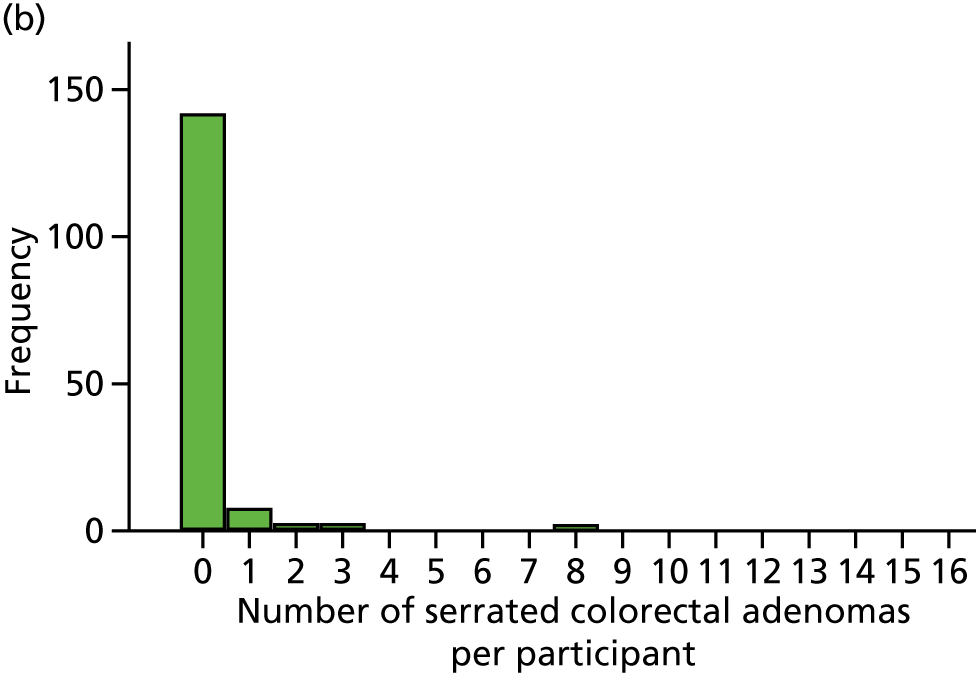
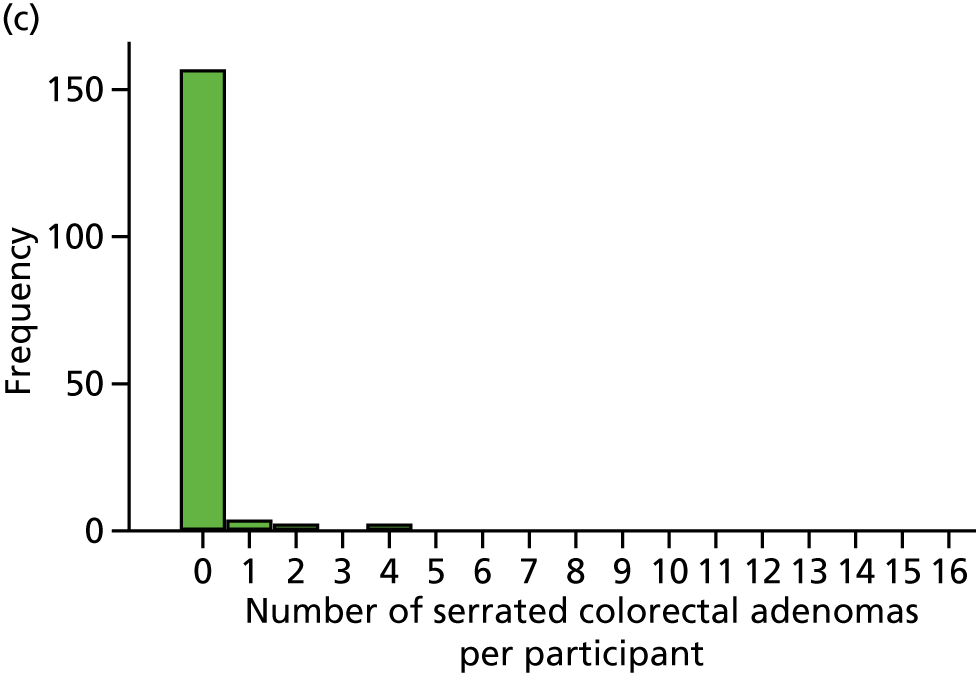
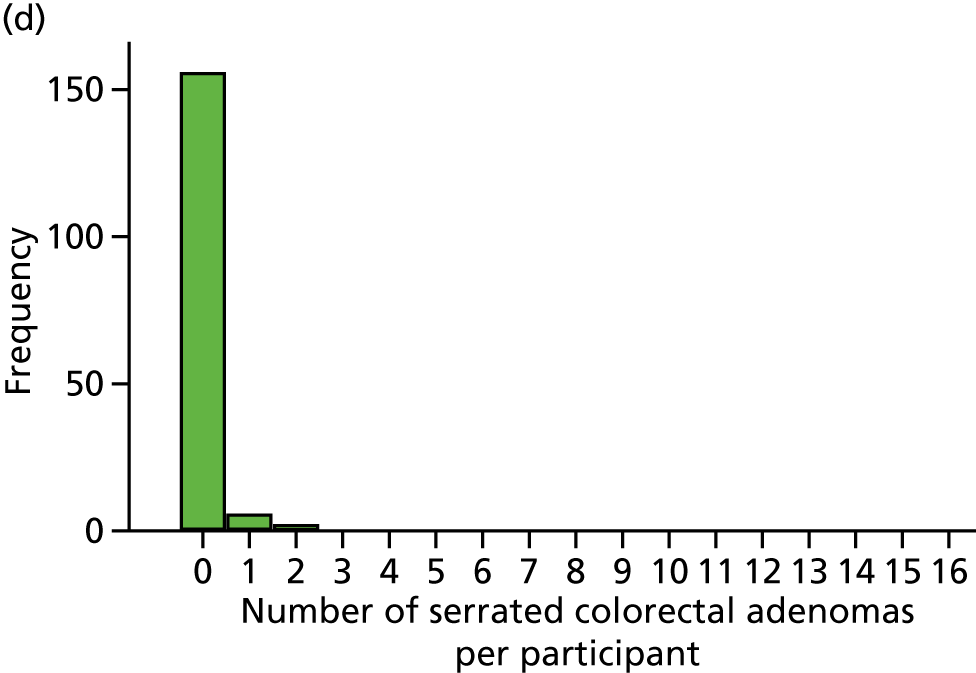
The distribution of individual left-sided colorectal adenoma counts in each treatment group is shown in Figure 15. Risk differences for the number of participants with at least one left colorectal adenoma (left ADRa) were –7.8% for EPA versus no EPA (95% CI –15.5% to –0.2%) and –1.8% for aspirin versus no aspirin (95% CI –9.4% to 5.8%). The mean incidence rate ranged from 0.4 to 0.7 left colorectal adenomas per person per year. IRRs for left MAP were 0.75 (95% CI 0.60 to 0.94) for EPA versus no EPA and 0.85 (95% CI 0.69 to 1.06) for aspirin versus no aspirin (see Table 24).
FIGURE 15.
Distribution of the number of left colorectal adenomas per participant at 12 months by trial group. (a) EPA + aspirin; (b) EPA + placebo aspirin; (c) placebo EPA + aspirin; and (d) placebo + placebo.
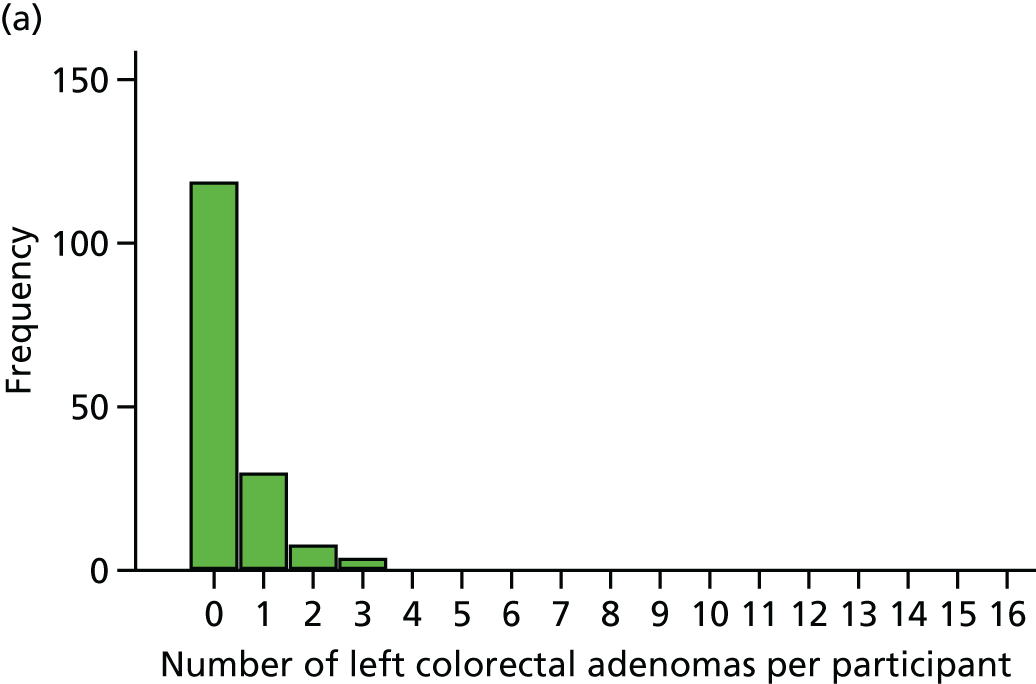
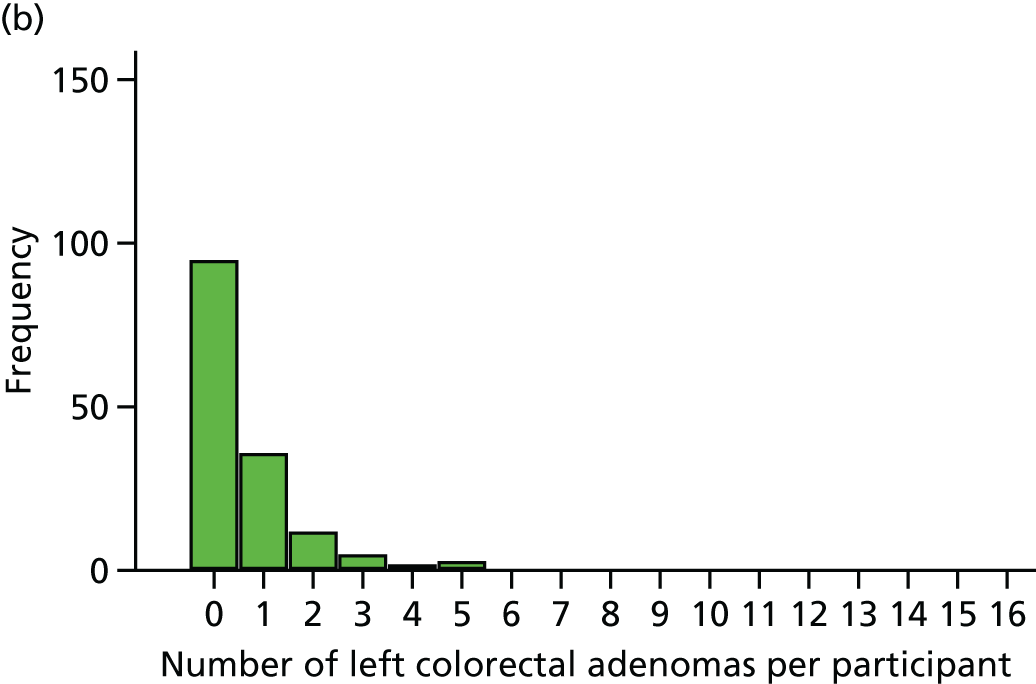
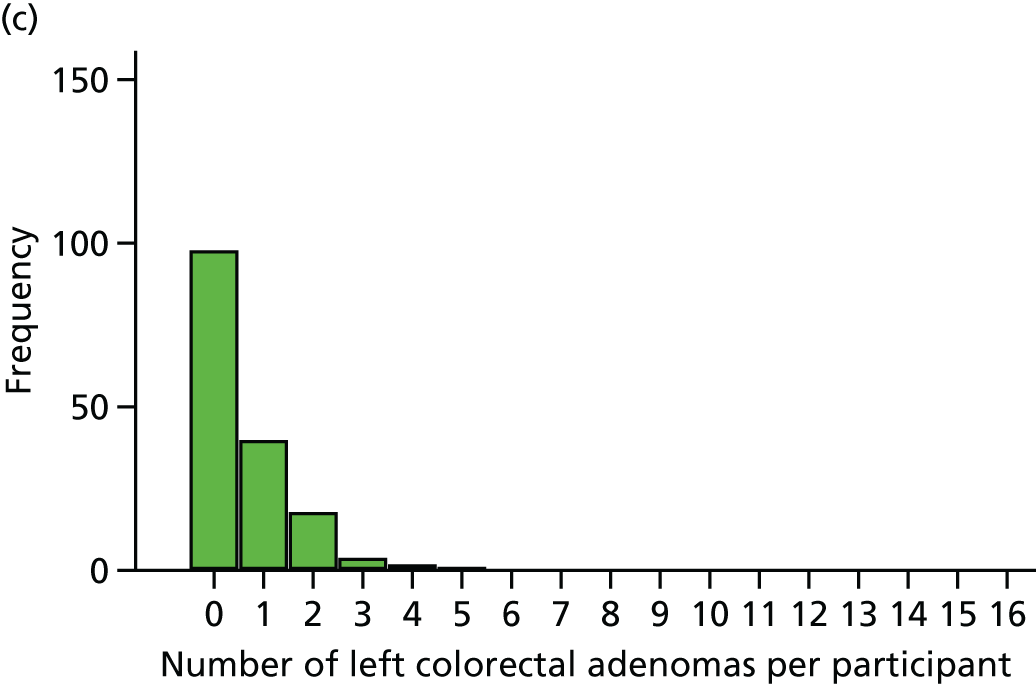
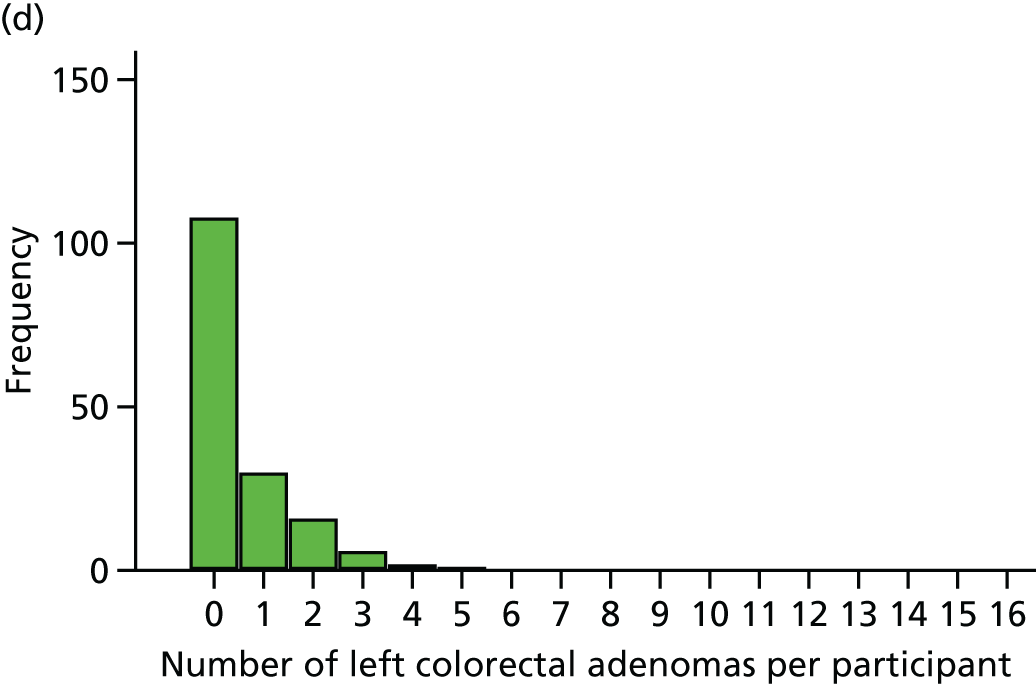
For the number of participants with at least one right-sided colorectal adenoma (right ADRa), the risk differences were 6% (95% CI –1.9% to 13.9%) for EPA versus no EPA and –3.1% (95% CI –11% to 4.7%) for aspirin versus no aspirin. The mean incidence rate ranged from 0.7 to 1.0 right colorectal adenomas per person per year. IRRs were 1.02 (95% CI 0.85 to 1.22) for EPA versus no EPA and 0.73 (95% CI 0.61 to 0.88) for aspirin versus no aspirin (see Table 25). The distribution of individual right-sided colorectal adenoma counts in each treatment group is shown in Figure 16.
FIGURE 16.
Distribution of the number of right colorectal adenomas per participant at 12 months by trial group. (a) EPA + aspirin; (b) EPA + placebo aspirin; (c) placebo EPA + aspirin; and (d) placebo + placebo.
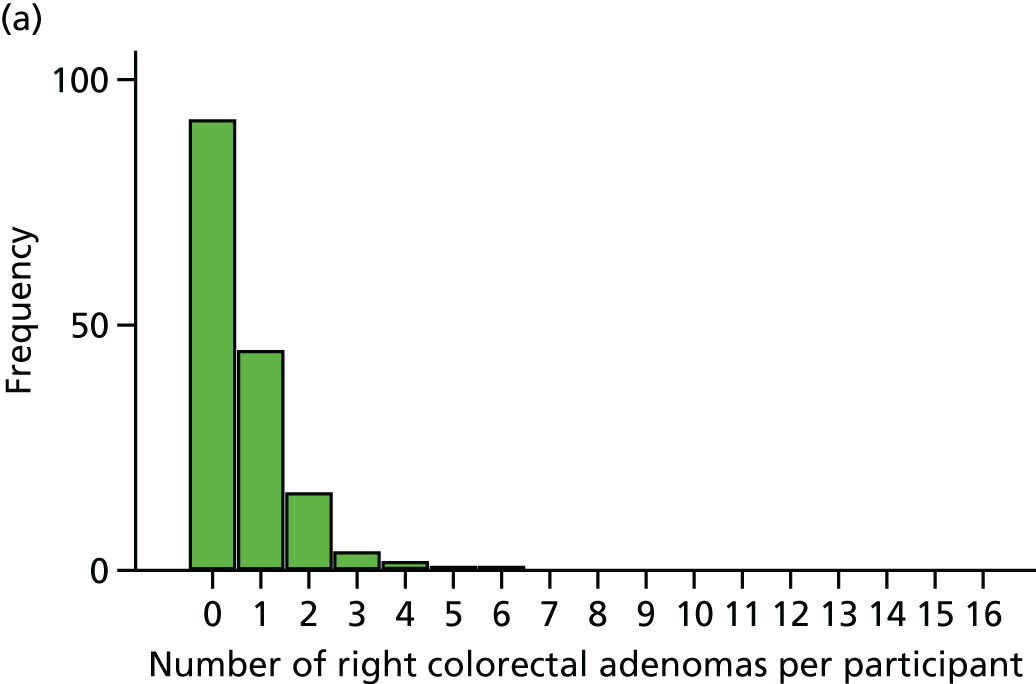
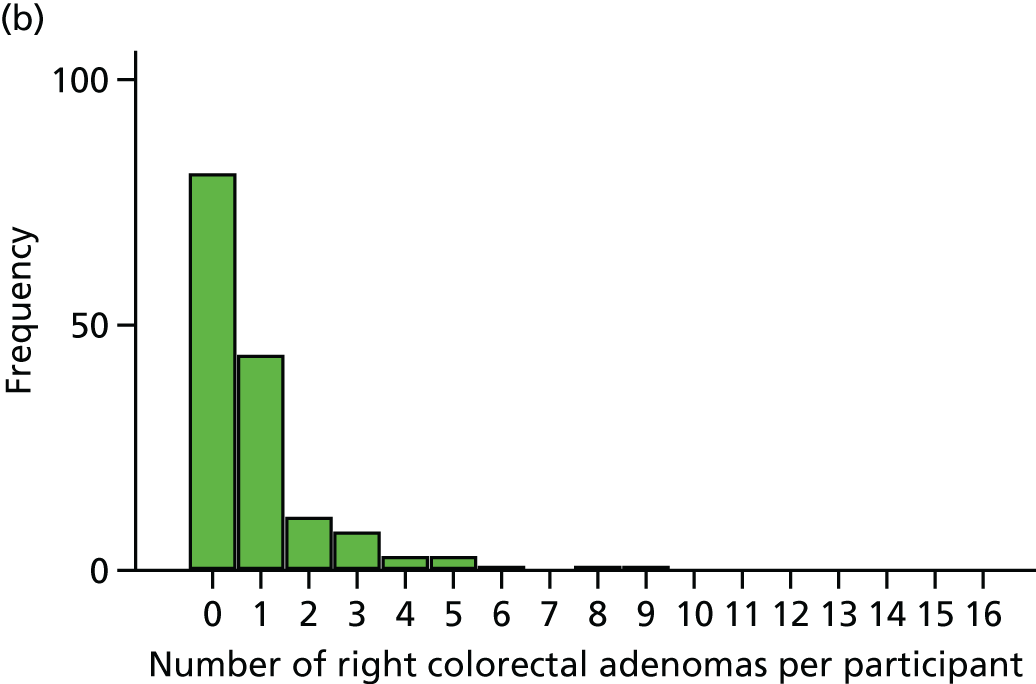
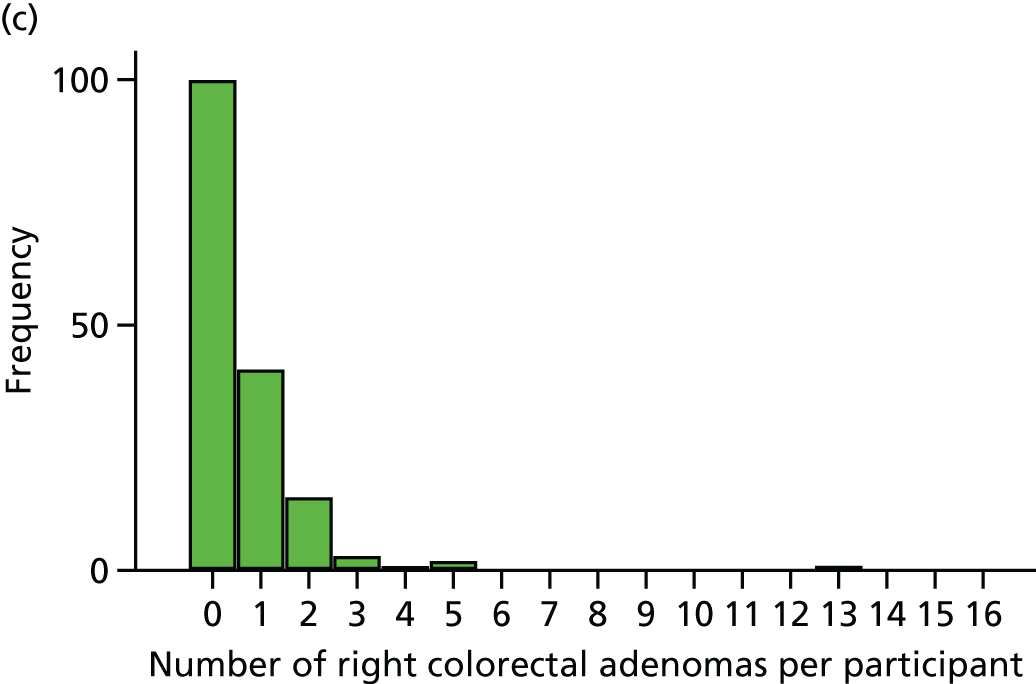
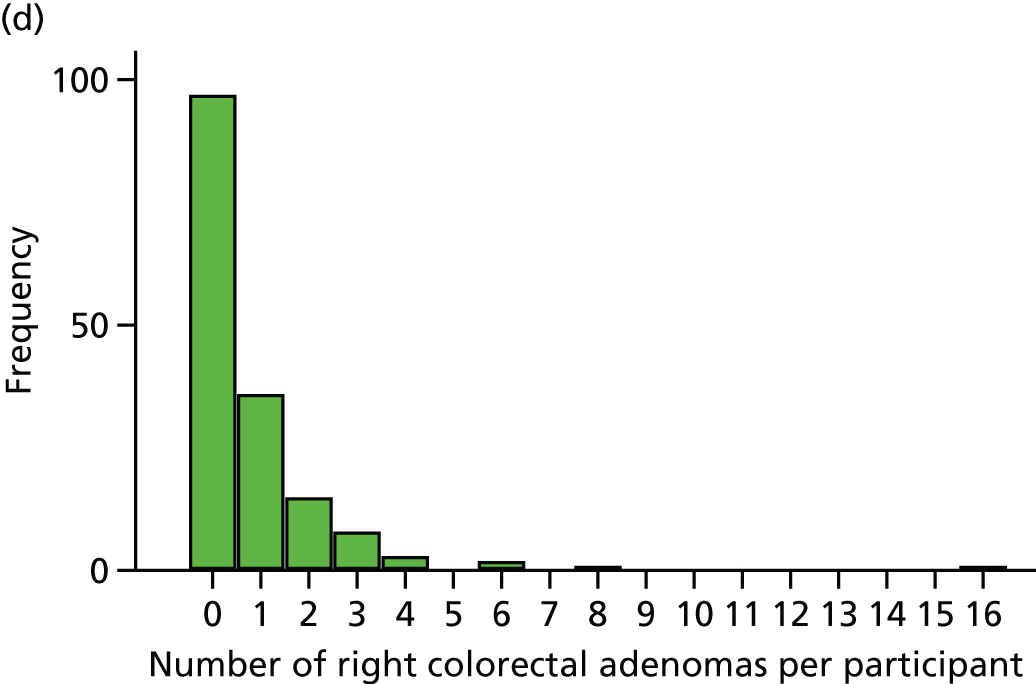
Following the 12-month surveillance colonoscopy, the majority of BCSP patients were reclassified as being at intermediate risk: 146 (91%) participants were reclassified as being at intermediate risk at follow-up in the EPA + aspirin group, compared with 128 (84%) in the EPA + placebo aspirin group, 140 (86%) in the placebo EPA + aspirin group and 147 (90%) in the placebo EPA + placebo aspirin group (Table 26). The risk differences for EPA versus no EPA and aspirin versus no aspirin were small (–0.2% and 0.9%, respectively).
| Trial group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 161) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 153) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 163) | Placebo + placebo (N = 163) | |
| Participants reclassified as being at intermediate risk at follow-up, n (%) | 146 (91) | 128 (84) | 140 (86) | 147 (90) |
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |||
| Risk difference for number of participants reclassified as being at intermediate risk at 12 months (95% CI) (%) | –0.2 (–5.4 to 5.1) | 0.9 (–14.1 to 6.2) | ||
Adjusted IRRs and 95% CIs for the secondary MAP data are summarised in Figure 17. Risk differences and 95% CIs for the secondary ADRa data are summarised in Figure 18.
FIGURE 17.
Forest plots for secondary MAP analysis. (a) EPA vs. placebo; and (b) aspirin vs. placebo. Adjusted by site as a random effect and by repeat colonoscopy at baseline.
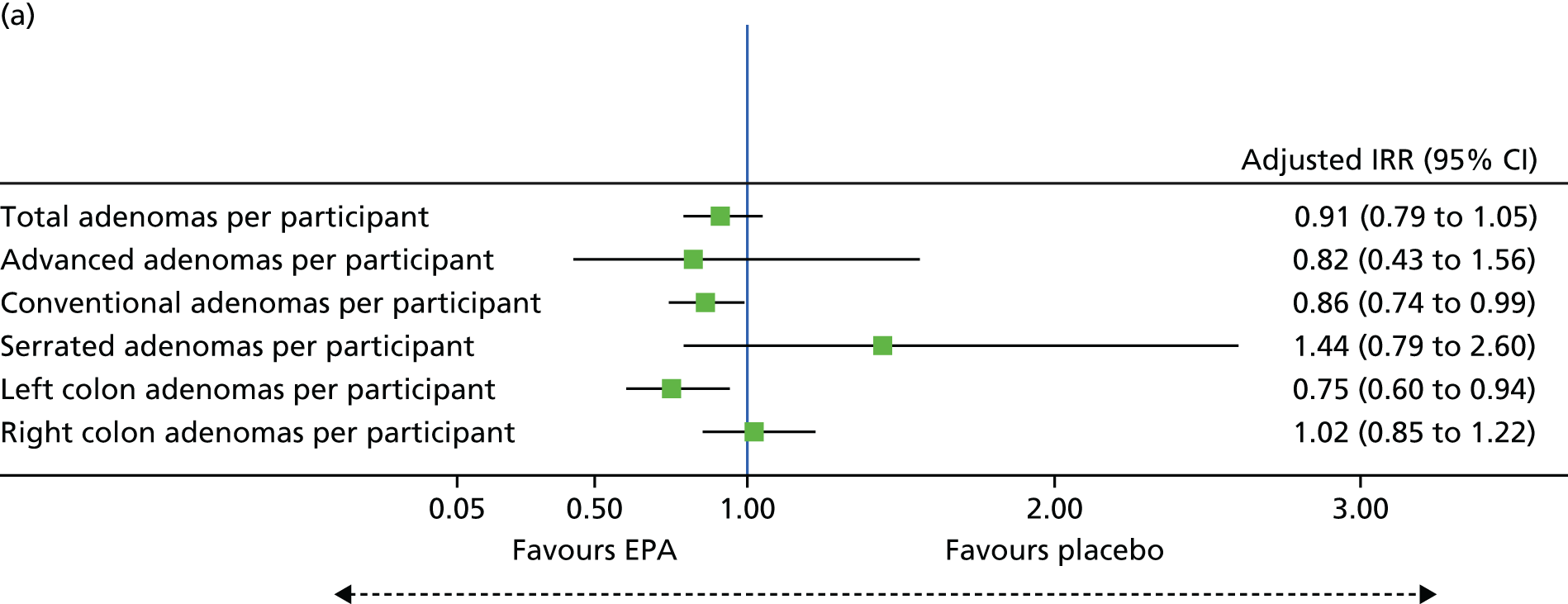
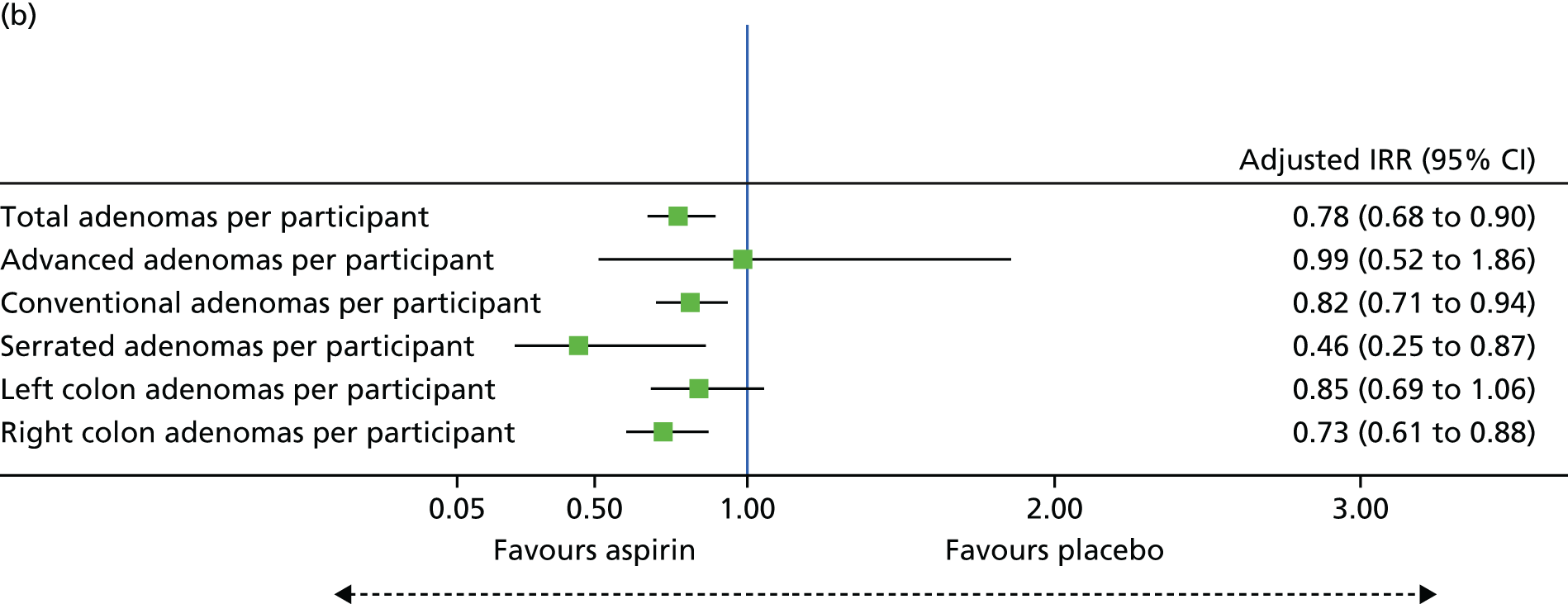
FIGURE 18.
Forest plots for secondary ADRa analysis. (a) EPA vs. placebo; and (b) aspirin vs. placebo. Adjusted by site as a random effect and by repeat colonoscopy at baseline.
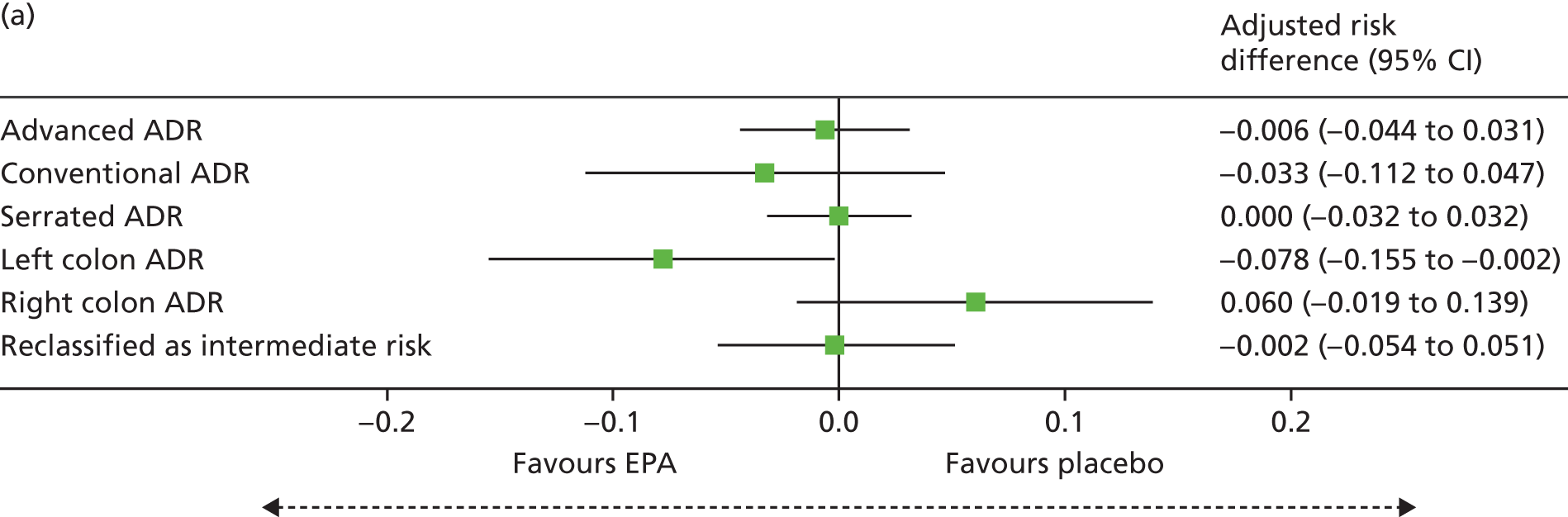
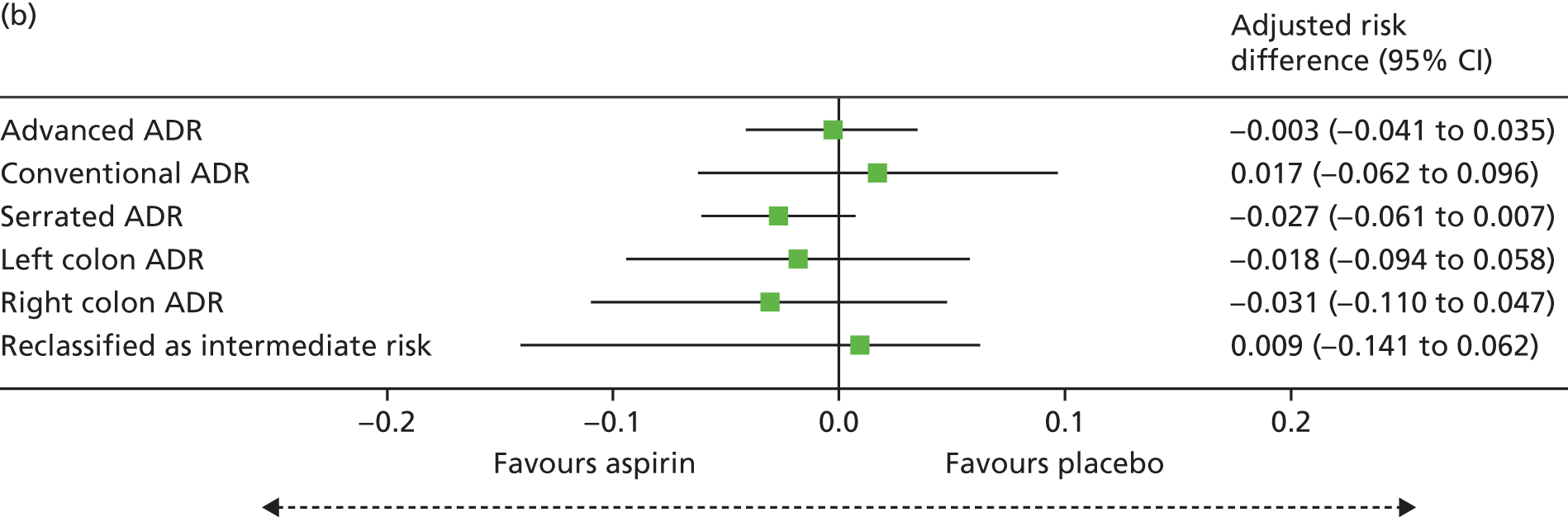
Although potential trends may have been observed in the secondary colorectal adenoma data, consideration needs to be given to the large number of analyses that were undertaken (and, therefore, the potential for spuriously significant results), the small sample numbers for some of the colorectal adenoma subtypes and the potential dependencies between the variables.
Number of participants with colorectal cancer detected prior to or at first surveillance colonoscopy
There was no report of any CRC detected at the 12-month surveillance colonoscopy or during the intervention phase of the trial.
Dietary fish intake during trial participation
Approximately 80% of participants completed a FFQ at 12 months, with similar percentages in each of the four treatment groups (Table 27). The total fish and oily fish intakes at 12 months were similar across the four treatment groups (see Table 27), as was the proportion of individuals changing intake level between baseline and the end of trial participation (Table 28). Approximately 50% of each treatment group remained at the same level of oily fish intake during the trial.
| Dietary fish intake | Trial group, n (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 177) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 178) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 176) | Placebo + placebo (N = 176) | |
| Participants who completed FFQ at 12 months | 138 (78) | 135 (76) | 143 (81) | 146 (89) |
| Total fish intake at 12 months | ||||
| Never | 3 (2) | 3 (2) | 3 (2) | 11 (8) |
| Low | 6 (4) | 7 (5) | 8 (6) | 12 (8) |
| Medium | 77 (56) | 74 (55) | 85 (59) | 82 (56) |
| High | 45 (33) | 41 (30) | 34 (24) | 32 (22) |
| Missinga | 7 (5) | 10 (7) | 13 (9) | 9 (6) |
| Oily fish intake at 12 months | ||||
| Never | 33 (24) | 38 (28) | 36 (25) | 42 (29) |
| Low | 40 (29) | 37 (28) | 40 (28) | 46 (32) |
| Medium | 35 (26) | 39 (29) | 47 (33) | 38 (26) |
| High | 26 (19) | 16 (12) | 15 (10) | 17 (12) |
| Missinga | 4 (3) | 5 (4) | 5 (3) | 3 (2) |
| Change of dietary fish intake | Trial group, n (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 177) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 178) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 176) | Placebo + placebo (N = 176) | |
| Change of fish intake at 12 months compared with baseline | ||||
| Stayed the samea | 80 (45) | 80 (45) | 86 (50) | 84 (48) |
| Reduced intake | 21 (12) | 18 (10) | 22 (13) | 26 (15) |
| Increased intake | 23 (13) | 18 (10) | 18 (10) | 15 (9) |
| Missing | 53 (30) | 62 (35) | 50 (28) | 51 (29) |
| Change of oily fish intake at 12 months compared with baseline | ||||
| Stayed the same | 65 (37) | 66 (38) | 78 (45) | 77 (44) |
| Reduced intake | 33 (19) | 32 (18) | 32 (19) | 32 (18) |
| Increased intake | 36 (20) | 30 (17) | 26 (15) | 31 (18) |
| Missing | 43 (24) | 50 (28) | 40 (23) | 36 (20) |
Safety
The safety population comprised 697 participants who received at least one dose of EPA or aspirin, or their respective placebos (see Table 15).
Overall, there were no safety concerns in participants receiving either EPA or aspirin. There was an excess of AEs and SAEs in participants receiving EPA + placebo aspirin (Table 29). In this group, 13 participants reported five or more (87 in total) AEs, which resulted in this imbalance (see Table 29). A larger proportion of participants receiving EPA + placebo aspirin reported at least one ADR, with 57 (32%) individuals reporting 119 ADRs. This excess was contributed to by five participants who reported five or more ADRs. Fewer SAEs were reported in the EPA + aspirin group. Five (3%) participants reported at least one SAE, compared with 7% who reported at least one SAE in all the other treatment groups. Only nine SAEs were felt to be related to trial medication.
| AEs, ADRs and SAEs | Trial group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 170) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 177) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 174) | Placebo + placebo (N = 176) | |
| Participants who reported any AE, n (%) | 76 (45)a | 82 (46) | 68 (39) | 78 (44) |
| Total number of AEs | 129 | 211 | 154 | 160 |
| Severity of all AEs (n) | ||||
| Mild | 110 | 161 | 122 | 119 |
| Moderate | 18 | 47 | 28 | 33 |
| Severe | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 |
| Missing | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| AEs per participant, n (%) | ||||
| 0 | 94 (55) | 95 (54) | 106 (61) | 98 (56) |
| 1 | 41 (24) | 35 (20) | 31 (18) | 43 (24) |
| 2 | 24 (14) | 18 (10) | 15 (9) | 10 (6) |
| 3 | 6 (4) | 11 (6) | 10 (6) | 16 (9) |
| 4 | 3 (2) | 5 (3) | 6 (3) | 3 (2) |
| 5 | 2 (1) | 7 (4) | 3 (2) | 2 (1) |
| > 5 | 0 (0) | 6 (3) | 3 (2) | 4 (2) |
| Participants who reported any ADRs, n (%) | 43 (25) | 57 (32) | 41 (24) | 38 (22) |
| Total number of ADRs | 63 | 119 | 83 | 63 |
| Severity of ADRs (n) | ||||
| Mild | 50 | 96 | 61 | 44 |
| Moderate | 13 | 22 | 19 | 17 |
| Severe | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Missing | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Number of ADRs per participant, n (%) | ||||
| 0 | 127 (75) | 120 (68) | 133 (76) | 138 (78) |
| 1 | 28 (16) | 28 (16) | 18 (10) | 23 (13) |
| 2 | 11 (6) | 13 (7) | 13 (7) | 9 (5) |
| 3 | 3 (2) | 7 (4) | 5 (3) | 4 (2) |
| 4 | 1 (1) | 4 (2) | 3 (2) | 1 (1) |
| 5 | 0 (0) | 2 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 (0) |
| > 5 | 0 (0) | 3 (2) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) |
| Participants who reported any SAE, n (%) | 5 (3) | 12 (7) | 12 (7) | 13 (7) |
| Total number of SAEs | 6 | 16 | 17 | 16 |
| Number of SAEs per participant, n (%) | ||||
| 0 | 165 (97) | 165 (93) | 162 (93) | 163 (93) |
| 1 | 4 (2) | 9 (5) | 10 (6) | 11 (6) |
| 2 | 1 (1) | 2 (1) | 0 (0) | 1 (1) |
| 3 | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) |
| 4 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | 0 (0) |
| Number of SAEs related to IMP | 1 | 1 | 7 | 0 |
The majority of AEs and ADRs were mild in severity in each of the treatment groups.
Gastrointestinal disorders were the most frequently reported AE (Table 30), with 209 participants reporting at least one GI AE. A larger number of GI AEs were reported in the EPA + placebo aspirin group, contributed by an excess of individuals who reported multiple GI AEs. However, the distribution of GI AEs was similar across the other three groups (Table 31).
| AEs | Trial group (n) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin | EPA + placebo aspirin | Placebo EPA + aspirin | Placebo + placebo | |
| Participants in the safety population | 170 | 177 | 174 | 176 |
| Participants reporting at least one AE | 76 | 82 | 68 | 78 |
| Cardiac disordersa | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Congenital, familial and genetic disorders | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Ear and labyrinth disorders | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Eye disorders | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| GI disorders | 68 | 146 | 86 | 85 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | 4 | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| Hepatobiliary disorders | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Immune system disorders | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Infections and infestations | 14 | 14 | 15 | 12 |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | 7 | 5 | 11 | 6 |
| Investigations | 3 | 3 | 0 | 1 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | 12 | 9 | 10 | 13 |
| Neoplasms: benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | 1 | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| Nervous system disorders | 4 | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| Psychiatric disorders | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Renal and urinary disorders | 4 | 1 | 5 | 2 |
| Reproductive system and breast disorders | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | 3 | 9 | 3 | 3 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | 3 | 4 | 5 | 9 |
| Social circumstances | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Surgical and medical procedures | 3 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Vascular disorders | 1 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| GI AEs | Trial group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin | EPA + placebo aspirin | Placebo EPA + aspirin | Placebo + placebo | |
| Participants in safety population (n) | 170 | 177 | 174 | 176 |
| Number of participants with any GI AE, n (%) | 47 (28) | 67 (38) | 44 (25) | 51 (29) |
| Total number of GI AEs | 68 | 146 | 86 | 85 |
| Number of GI AEs per participant | ||||
| 1 | 30 | 29 | 20 | 32 |
| 2 | 14 | 17 | 13 | 10 |
| 3 | 2 | 9 | 7 | 6 |
| 4 | 1 | 8 | 2 | 1 |
| 5 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| > 5 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
There was an excess of diarrhoea, abdominal pain and nausea in those allocated active EPA (Table 32). The excess of mild to moderate diarrhoea was most prominent in the group receiving EPA alone. There did not appear to be any consistent differences in the reporting of GI AEs between individuals receiving EPA-FFA and those receiving EPA-TG (see Table 32).
| GI AEs | Trial group | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin | EPA + placebo aspirin | Placebo EPA + aspirin | Placebo + placebo | |||||
| FFA | TG | FFA | TG | FFA | TG | FFA | TG | |
| Participants in safety population (n) | 99 | 71 | 107 | 70 | 99 | 75 | 109 | 167 |
| Participants reporting at least one GI AE, n (%) | 25 (25) | 22 (31) | 43 (40) | 24 (34) | 24 (24) | 20 (27) | 38 (35) | 13 (19) |
| GI AE (n) | ||||||||
| Abdominal discomfort | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Abdominal distension | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Abdominal pain | 3 | 2 | 14 | 13 | 6 | 1 | 9 | 3 |
| Abdominal pain lower | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Abdominal pain upper | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Anal haemorrhage | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Anal inflammation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Anal pruritus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Breath odour | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 |
| Change of bowel habit | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Constipation | 6 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 0 |
| Defaecation urgency | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Diarrhoea | 8 | 2 | 23 | 15 | 11 | 9 | 6 | 6 |
| Dyspepsia | 5 | 11 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 14 | 4 |
| Epigastric discomfort | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Eructation | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Faeces discoloured | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Flatulence | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Frequent bowel movements | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Gastric haemorrhage | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Gastritis | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| GI sounds are abnormal | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| Gingival polyp | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Haematochezia | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Haemorrhoidal haemorrhage | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Haemorrhoids | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hiatus hernia | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Melaena | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Mouth haemorrhage | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nausea | 5 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Oesophagitis | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Proctalgia | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Rectal haemorrhage | 4 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Rectal tenesmus | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Retching | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tongue discolouration | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tongue eruption | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tongue haemorrhage | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Post database lock and code release, the chief investigator summarised all GI AEs according to symptoms that are commonly associated with fish oil intake, categorised as diarrhoea, upper GI symptoms, lower abdominal symptoms, eructation/halitosis and other. These were summarised by the treatment group and EPA formulation that the participants received. There were no notable differences between the formulations in each trial treatment group (see Appendix 5).
Similar to the profile of AEs, there were more ADRs reported in the EPA + placebo aspirin group than in the other three groups (Table 33). The most commonly reported ADRs across all treatment groups were GI disorders. The distribution of GI ADRs across the four groups was similar (Table 34) (see Appendix 4, Tables 41 and 43).
| ADRs | Trial group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin | EPA + placebo aspirin | Placebo EPA + aspirin | Placebo + placebo | |
| Participants in the safety population (n) | 170 | 177 | 174 | 176 |
| Participants reporting at least one ADR, n (%) | 43 (25) | 57 (32) | 41 (24) | 38 (22) |
| Total number of ADRs | 63 | 119 | 83 | 63 |
| GI disorders (n) | 46 | 110 | 69 | 58 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions (n) | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Infections and infestations (n) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications (n) | 4 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Investigations (n) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders (n) | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders (n) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Nervous system disorders (n) | 3 | 3 | 4 | 0 |
| Psychiatric disorders (n) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Renal and urinary disorders (n) | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders (n) | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders (n) | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| GI ADRs | Trial group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin | EPA + placebo aspirin | Placebo EPA + aspirin | Placebo + placebo | |
| Total number of GI ADRs | 46 | 110 | 69 | 58 |
| Number of GI ADRs | ||||
| 1 | 20 | 26 | 16 | 22 |
| 2 | 11 | 13 | 10 | 7 |
| 3 | 0 | 7 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| 5 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
There were a small number of SAEs reported (Table 35) (see Appendix 4, Table 42). The most frequently reported SAEs were cardiac and GI disorders. Among the nine cardiac disorders, five were episodes of atrial fibrillation (AF) and all of these were reported in the EPA + placebo aspirin group. Three were reported by one participant and two additional participants reported one each. Three myocardial infarctions were reported by participants: one in the EPA + placebo aspirin group, two in the placebo EPA + aspirin group and one in the placebo + placebo group. One participant in the placebo EPA + aspirin group had an arrhythmia.
| SAEs | Trial group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin | EPA + placebo aspirin | Placebo EPA + aspirin | Placebo + placebo | |
| Participants in the safety population (n) | 170 | 177 | 174 | 176 |
| Participants reporting at least one SAE, n (%) | 5 (3) | 12 (7) | 12 (7) | 13 (7) |
| Total number of SAEs | 6 | 16 | 17 | 16 |
| Cardiac disorders (n) | 0 | 6 | 2 | 1 |
| GI disorders (n) | 0 | 2 | 5 | 2 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions (n) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Hepatobiliary disorders (n) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Infections and infestations (n) | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications (n) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Investigations (n) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Neoplasms: benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) (n) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 4 |
| Nervous system disorders (n) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Psychiatric disorders (n) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders (n) | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Vascular disorders (n) | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 |
Eight ADRs led to trial discontinuation for four participants, one from each of the four trial groups. The eight ADRs came from six preferred term names (Table 36).
| ADRs that led to trial discontinuation | Trial group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 170) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 177) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 174) | Placebo + placebo (N = 176) | |
| Participants who discontinued the trial because of an ADR, n (%) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) |
| ADR by preferred term name (n) | ||||
| Abdominal pain | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Deep-vein thrombosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Lymphoma | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Melaena | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Skin disorder | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Clinically significant acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding episodes
No haemorrhagic strokes were reported during the trial. A manual search of AEs and SAEs revealed six acute upper GI bleeding events that were considered by the chief investigator to be of clinical significance. These were ‘oesophageal haemorrhage’ (in the placebo EPA + aspirin group), ‘gastro-oesophageal reflux disease’ (in the placebo EPA + aspirin group) and ‘alcohol withdrawal syndrome’ (in placebo EPA + placebo aspirin group), which were all reported as SAEs, and ‘gastric haemorrhage’ (in the EPA + placebo aspirin group) and two cases of ‘melaena’ (in the EPA + placebo aspirin and placebo EPA + aspirin groups), which were recorded as AEs. It is possible that one of the cases of melaena (in a participant receiving EPA + placebo aspirin) was a SAE because the participant had been hospitalised, but this event was recorded specifically as an AE by the site. All tables reflect this categorisation.
Deaths
One death was reported during the trial. During contact made to arrange visit 5, site staff were made aware that a participant had died from bladder cancer, which was deemed to be unrelated to the intervention.
Protocol deviations
Protocol deviations were reported for between 64% and 73% of participants in each treatment group. Most deviations were judged to be minor, with the majority being trial visits outside the time window. The number and types of deviations appeared similar between treatment groups.
There were 11 deviations related to randomisation error (Table 37). Ten of these were as a result of participants being ineligible, and one participant was randomised prior to consent. None of these errors occurred in participants who were randomised to the placebo + placebo group. There was no reason to suspect that the deviation was related to the treatment group to which the participant had been randomised.
| Treatment group | Detailsa | Included in per-protocol population? | Outcome collected? |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin | Not eligible | No | Yes |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Patient not eligible for trial as was intermediate risk | No | Yes |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Patient does not meet inclusion criteria; withdrawn from trial | No | No |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Participant did not fulfil inclusion criteria as had only two polyps > 10 mm, but was still considered a high-risk patient by the BCSP | No | Yes |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Patient has three adenomas and all less than the required measurement for patient to be included in the trial | No | No |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Randomised in error. Patient had hyperplastic polyps | No | Yes |
| EPA + aspirin | Randomised in error. Patient had four adenomas; however, none was more than 10 mm | No | Yes |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Patient should not have been included as had had previous BCSP colon – this not first BCSP colon | Yes | Yes |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Patient randomised prior to consent, as patient prescription needed to be signed by PI, and he [was] not available at site on day of consent. Patient did not want to consent then come back for prescription on another day | Yes | Yes |
| EPA + aspirin | Incorrectly recruited due to confusion of the term ‘high risk’ | No | No |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Patient randomised at age 74 in error due to randomisation database allowing the patient in by accident | Yes | No |
Exploratory analyses
Colorectal adenoma size
Given the decrease in total colorectal adenoma number associated with EPA and aspirin treatment, colorectal adenoma size was analysed consistent with size analysis in previous RCTs of chemoprevention agents in FAP patients. 55,67 Colorectal adenoma size was summarised within each participant across each treatment group. Analyses were based on the within-participant mean value (Table 38).
| Adenoma size | Trial group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin (N = 177) | EPA + placebo aspirin (N = 178) | Placebo EPA + aspirin (N = 176) | Placebo + placebo (N = 176) | |
| Participants with colorectal adenoma data at 12 months (n) | 161 | 153 | 163 | 163 |
| Participants with at least one colorectal adenoma (n) | 98 | 97 | 100 | 100 |
| Participants with mean colorectal adenoma size available (n) | 97 | 97 | 100 | 100 |
| Participants with mean colorectal adenoma size missing (n) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Size (mm)a of adenoma at 12 months | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 3.5 (2.3) | 3.3 (2.2) | 4.2 (3.3) | 3.7 (2.4) |
| Median (IQR) | 3.0 (2.0–3.5) | 3.0 (2.0–4.0) | 3.5 (2.3–5.0) | 3.0 (2.0–4.4) |
| Minimum, maximum | 1, 12 | 1, 15 | 1.0, 28.5 | 1, 15 |
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |||
| Adjustedb difference in means (95% CI) | –0.47 (–1.04 to 0.98) | 0.42 (–0.14 to 0.99) | ||
The adjusted mean difference between the EPA and no EPA groups was –0.47 mm (i.e. the mean adenoma size was smaller in those receiving EPA than in those not receiving EPA). The mean adjusted difference between the aspirin and no aspirin groups was 0.42 mm (i.e. the mean adenoma size was bigger in those receiving aspirin than in those not receiving aspirin). There was no statistically significant difference between EPA and placebo users, or between aspirin and placebo users.
Relationship between individual colorectal adenoma number and eicosapentaenoicacid levels
The relationship between the change in RBC EPA levels at 12 months from baseline and secondary outcomes, according to EPA factorial margin, was also investigated descriptively by plotting individual values. There was no evidence of a clear relationship between individual increase in RBC EPA level and total colorectal adenoma number (Figure 19). This was also the case for the rectal EPA level at 12 months. The fact that there were three ‘outlier’ individuals in the placebo EPA group who had a large increase in RBC EPA level during the intervention phase suggests that ‘contamination’ by own-use ω-3 PUFA intake may have occurred in these cases (see Figure 19).
FIGURE 19.
Change in RBC EPA levels at 12 months from baseline against total number of colorectal adenomas per participant by EPA treatment groups. (a) Placebo EPA; and (b) active EPA.
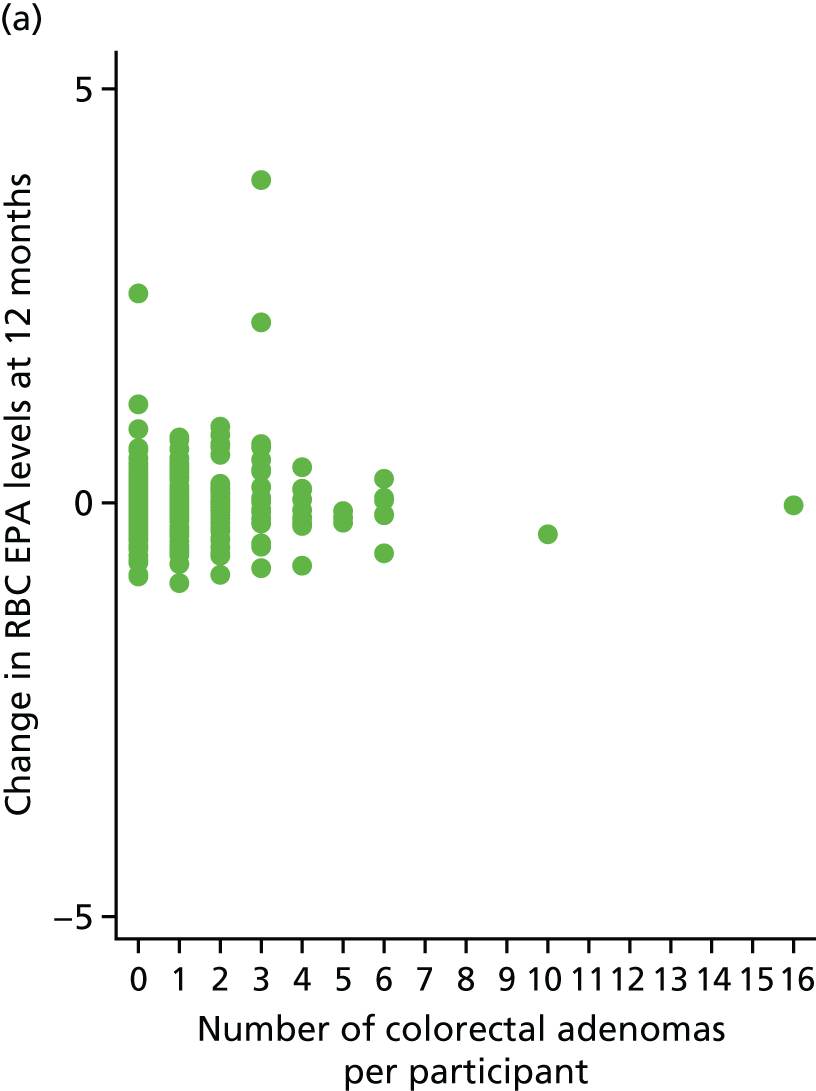
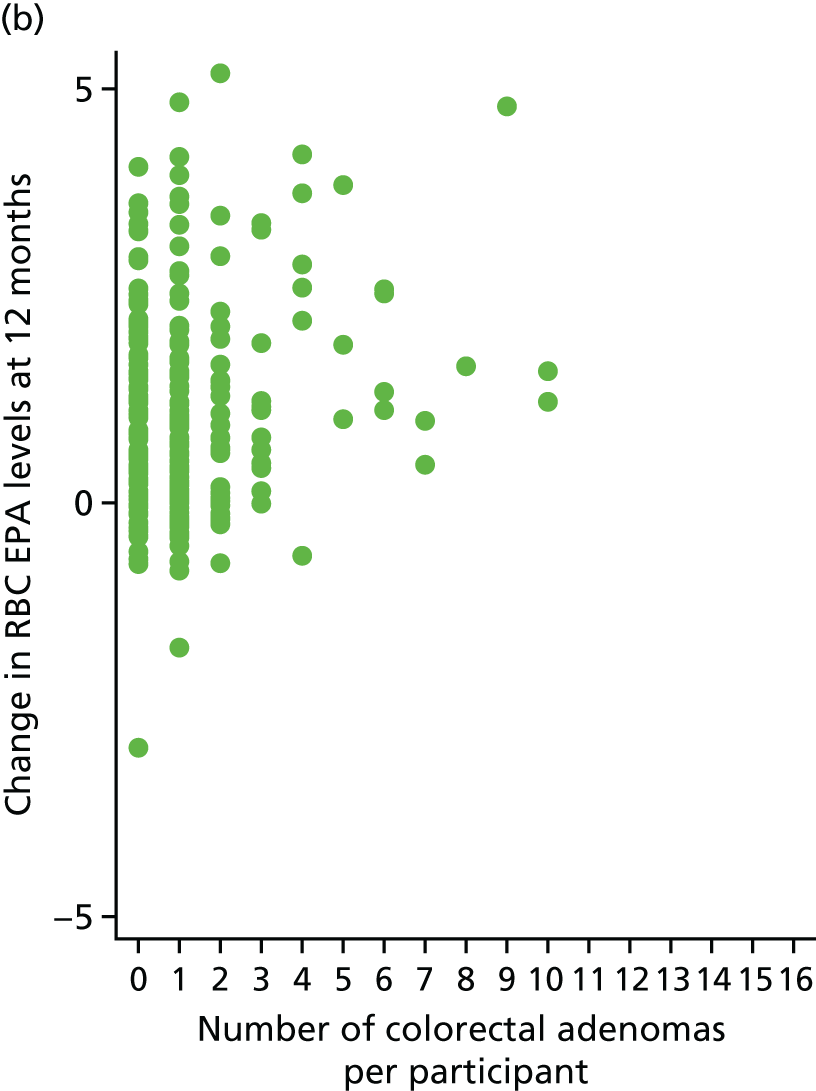
Relationship between red blood cell and rectal mucosal eicosapentaenoic acid levels in participants
The relationship between RBC and rectal mucosal EPA levels at 12 months was of moderate strength, with a correlation coefficient of 0.455 (Figure 20).
FIGURE 20.
Scatterplot of the individual rectal mucosal EPA level against the corresponding RBC EPA level at 12 months.
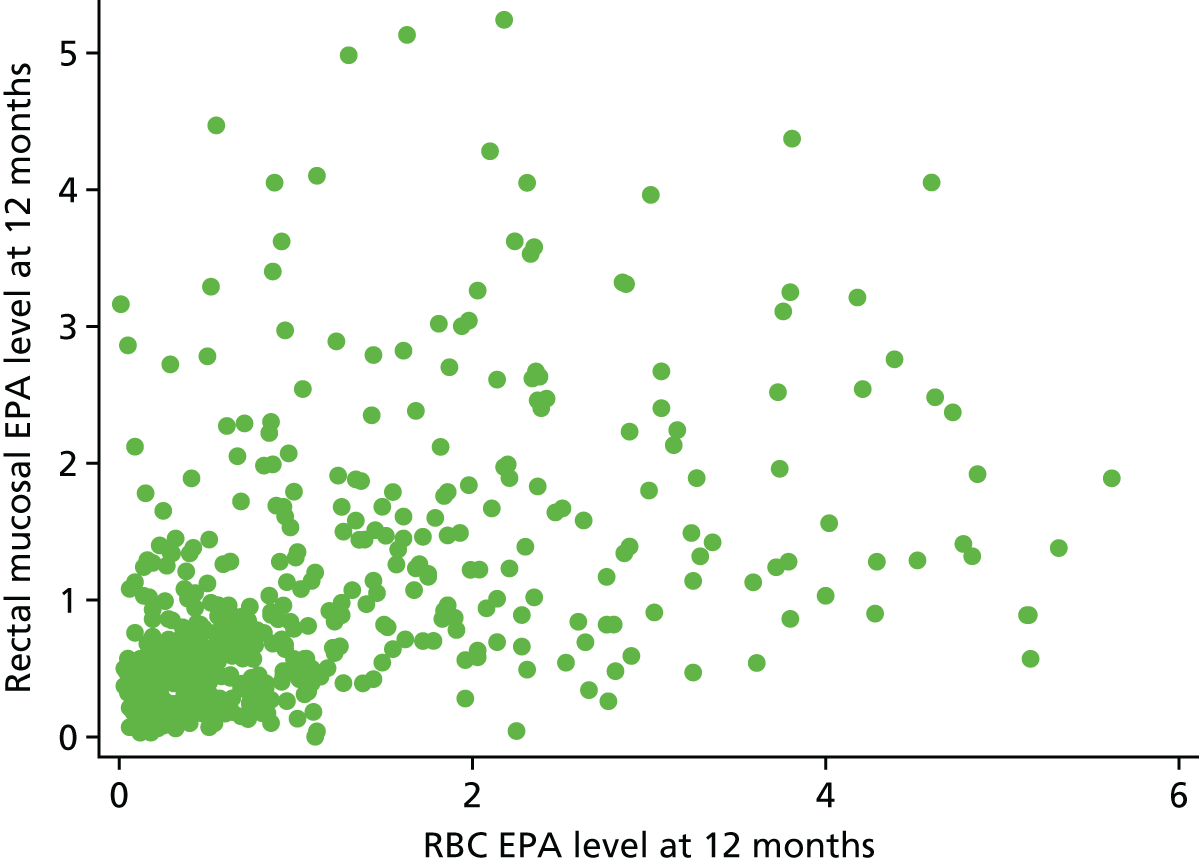
Chapter 4 Discussion
Parts of this chapter have been reproduced from Hull et al. 1 © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Summary of colorectal adenoma findings
The seAFOod polyp-prevention trial found no evidence of an effect of either EPA or aspirin on the primary end point of the proportion of individuals with one or more colorectal adenomas at the 12-month surveillance colonoscopy (the ADRa) in patients deemed ‘high risk’ in the English BCSP. Overall, ≈60% of trial participants had at least one colorectal adenoma at surveillance colonoscopy. The trial was designed to detect an absolute difference between groups of 10 percentage points, or a relative difference of 18%, assuming an ADRa of 60% in the double placebo group. The 95% CIs for the primary analyses excluded a difference of this magnitude on ADRa for both treatments. Moreover, the primary outcome data were robust to sensitivity analyses.
Secondary analyses of the effects of EPA and aspirin on colorectal adenoma number provided evidence of chemopreventive activity of both agents. Aspirin was effective at reducing the total number of colorectal adenomas per participant, but there was no evidence of an effect on total MAP by EPA. Other secondary analyses suggested that there are colorectal adenoma subtype- and site-selective effects of EPA and aspirin. Participants randomised to EPA had a reduced number (MAP) and ADRa for conventional dysplastic colorectal adenomas in the left colon and rectum compared with those randomised to placebo. Participants randomised to aspirin had a reduced number of adenomas in the right colon, particularly for serrated adenomas, and also a reduced risk of conventional colorectal adenomas. An exploratory analysis found no evidence of any effect of either EPA or aspirin on recurrent colorectal adenoma size.
Colorectal adenoma end points
The ADRa was chosen as the primary end point, on historical grounds that previous ‘sporadic’ polyp-prevention trials had all used this binary measure of the presence of any colorectal adenoma at surveillance colonoscopy as the primary measure of colorectal adenoma risk. 49 We expected the high ADRa at the 1-year surveillance colonoscopy of ‘high-risk’ individuals in the English BCSP compared with previous polyp-prevention trials. 98 The high ADRa in the seAFOod trial population of obese, male-predominant ‘polyp formers’ will also have been driven by the uniformly excellent colonoscopy quality in the BCSP, in which the ADRa figures prominently as an individual QA measure. 38,95,97 It is noteworthy that those previous aspirin RCTs with the highest placebo ADRa {47.1% [Aspirin and Folate Polyp-Prevention Study (AFPPS)114] and 53.4% [APACC115]} reported the smallest (statistically insignificant) risk reduction associated with aspirin (risk ratio 0.88 and 0.95, respectively) compared with the other two aspirin RCTs,49 despite the overwhelming evidence for a CRC chemoprevention effect of aspirin. 43–48 Therefore, the use of the ADRa as a biomarker of chemoprevention efficacy in screening cohorts undergoing high-quality colonoscopic assessment with a high ADRa must be questioned.
By contrast, previous chemoprevention RCTs in FAP patients with a large colorectal adenoma burden have reported efficacy based on colorectal adenoma number and size. 55,67,116 Moreover, three of the four previous aspirin ‘sporadic’ polyp-prevention trials have reported colorectal adenoma multiplicity as a secondary outcome. 115,117,118 Therefore, adenoma number was stipulated as a secondary end point in the seAFOod trial. Reduction in colorectal adenoma multiplicity is widely accepted as an indicator of anti-CRC activity in pre-clinical studies. 61 More recently, adenoma number has gained credence as a biomarker in ‘sporadic’ colorectal adenoma prevention RCTs,39 driven by increasing use of MAP as an outcome measure in colonoscopy QA studies. 38 Moreover, colorectal adenoma number predicts future CRC incidence and mortality in population-based observational studies. 40–42 We suggest that subsequent chemoprevention RCTs utilise MAP as the primary measure of chemopreventative efficacy, especially in ‘high-risk’ study populations with a high ADRa, in which the ADRa will be a relatively insensitive measure of colorectal adenoma risk. The recent polyp-prevention RCT of metformin did indeed employ co-primary end points of colorectal adenoma incidence (ADRa) and number (MAP). 39
Site and adenoma subtype specificity of the chemopreventive effects of aspirin and eicosapentaenoic acid
All three aspirin RCTs, which reported colorectal adenoma number as a secondary outcome,115,117,118 demonstrated a significant reduction in total MAP in the aspirin group compared with the placebo group. The APACC trial reported total MAP data at the 12-month colonoscopic follow-up, similar to the seAFOod trial. 115,119 Coupled with the known CRC-preventative properties of aspirin demonstrated during observational follow-up of large-scale aspirin RCTs,46–48 our data (and those from the previous polyp-prevention trials)115,117,118 justify colorectal adenoma number as a clinically relevant biomarker of CRC risk in CRC chemoprevention trials, in addition to the ADRa. The similar magnitude decrease in colorectal adenoma number that we observed for aspirin in the seAFOod trial compared with the previous aspirin RCTs suggests that the reductions in colorectal adenoma number that we have reported are likely to be genuine and be clinically meaningful for CRC risk reduction. However, we do acknowledge that the number of secondary comparisons that have been made increases the possibility that findings could be spurious.
With increased understanding that different colorectal carcinogenesis pathways exist, improved insight into differential effects of chemopreventive agents on distinct colorectal adenoma types is of paramount importance. Chemopreventive activity of EPA against conventional colorectal adenomas (but not serrated lesions), based on both MAP and ADRa outcomes, is consistent with the known efficacy of the same dose of EPA-FFA in FAP patients67 with rectal adenomas, which are conventional, wholly dysplastic lesions occurring on a background of germline mutation of one APC allele and tumour initiation after loss of heterozygosity of the other APC allele. 120 By contrast, we report that EPA has no chemopreventive activity against serrated adenomas. Based on secondary colorectal adenoma number analysis, a possible signal that EPA use may actually increase serrated lesion risk requires careful examination in future studies of ω-3 PUFA supplementation/dietary intake and CRC risk, in which there is stratification based on location and the different molecular subtypes of CRC.
By contrast, the effect of aspirin on proximal colorectal adenoma multiplicity was partly explained by the strong preventative activity against serrated lesions. The seAFOod trial data add to an existing body of evidence that the reduction in CRC incidence and mortality by aspirin is explained by a dominant effect on proximal CRC, with less preventative efficacy against distal CRC. 47,48 Post hoc analysis of data from the AFPPS trial114 has revealed that risk of right-sided (but not left-sided) serrated polyps was lower in those allocated aspirin than in those allocated placebo. 121 Moreover, a meta-analysis of observational studies of lifestyle factors and serrated polyp risk has reported that serrated polyp risk is decreased in aspirin users (relative risk 0.81, 95% CI 0.67 to 0.99). 122
The seAFOod trial data suggest that aspirin also has some antineoplastic activity against conventional adenomas. However, in contrast with EPA, aspirin (100–600 mg daily) has not been demonstrated to have efficacy against rectosigmoid polyps in FAP RCTs,123,124 which is consistent with the dominant ‘right-sidedness’ of aspirin chemopreventative activity. 47,48
Only two previous ‘sporadic’ polyp-prevention trials have reported an a priori analysis of colorectal adenoma risk related to location in the colorectum. 114,125 In the RCT of the selective COX-2 inhibitor rofecoxib, there was no differential effect on ADRa dependent on location in either the right or left colon. 125 In the AFPPS trial, no differential effects of aspirin on right or left ADRa were observed, similar to the seAFOod trial data. 121 There has been no location-dependent analysis of colorectal adenoma number in a polyp-prevention trial prior to the seAFOod trial.
The seAFOod trial data, in combination with greater insight into the molecular pathogenesis of early stages of colorectal carcinogenesis,4 should prompt a paradigm shift in polyp-prevention trials driving data collection on colorectal adenoma subtype (conventional adenoma vs. serrated polyp) and tumour location (proximal/right vs. distal/left), leading to evaluation of stratified chemoprevention. It remains unclear whether or not the biology of the early stages of colorectal carcinogenesis during initiation and growth of a colorectal adenoma differs significantly such that rectal lesions should be classified separately from colonic neoplasia. At the present time, available evidence suggests that the molecular pathologies of colorectal adenomas from the rectum and distal colon do not differ significantly. 126
Dose considerations
The seAFOod trial evaluated 300 mg of aspirin daily based on the random-effects meta-analysis of aspirin polyp-prevention RCTs that demonstrated a significant colorectal adenoma risk reduction at doses of 300–325 mg daily, particularly for advanced lesions (risk ratio 0.71, 95% CI 0.56 to 0.92 for advanced ADRa), albeit in subjects approximating to ‘intermediate-risk’ surveillance populations. 49 Observational data on CRC risk suggest that lower daily doses of aspirin are likely to have ‘right-predominant’ effects on colorectal adenoma multiplicity similar to those reported herein. 48
The FFA-equivalent dose of 2 g of EPA daily was based on the same dose of EPA-FFA that demonstrated efficacy in the proof-of-concept RCT in FAP patients. 67 This is a relatively high daily amount of ω-3 PUFA, which would be difficult to provide using more widely available fish oil or re-esterified TG formulations. 65 Restricted supply of the original EPA-FFA formulation, beyond TMG control, meant that we had to switch the IMP to an EPA-TG formulation and matching placebo during the recruitment phase of the trial. This, however, provided a unique (originally unplanned) opportunity to compare ‘bioavailability’ of two EPA formulations, with the same FFA dose, in the context of prolonged dosing in a RCT. The data suggest that there is no meaningful difference in tissue EPA incorporation, measured by RBC membrane and rectal mucosal EPA levels, between EPA-FFA and EPA-TG. Therefore, colonoscopic outcome data from the two populations receiving either EPA-FFA/placebo or EPA-TG/placebo were combined.
Mechanistic considerations
We have not yet addressed the mechanistic basis for differential chemopreventive activity of EPA along the colorectum. Conventional dysplastic ‘sporadic’ colorectal adenomas are found along the length of the colon and can exhibit molecular features compatible with CIN, MSI and CIMP+ pathways, but with proportionally more CIN+ lesions in the distal colon. 4,23 Therefore, differential activity of EPA against the distinct molecular CRC subtypes should be investigated, particularly in view of the absence of any efficacy signal against serrated lesions that are predominantly CIMP+ and often exhibit features of MSI. 4,21,23
We cannot rule out that differences in mucosal EPA levels explain colorectal site selectivity of the modest chemopreventive activity of EPA. There are no human data describing ω-3 PUFA levels in different regions of the colorectum. However, rodent data suggest that there is no gradient in mucosal EPA exposure along the colon. 127 One clinical study has measured ω-3 PUFA levels in the sigmoid colon (but not the rectum). 128 However, data from this Japanese study cannot be compared with the rectal mucosal PUFA levels measured in the seAFOod trial because of profound differences in baseline characteristics of the two study populations, including dietary ω-3 PUFA intake. 128
We have recently reported that mixed ω-3 PUFA supplementation is associated with an increase in short-chain fatty acid (SCFA)-producing bacterial genera such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria in faecal samples. 129 Although SCFA levels are believed to be higher in the caecum and ascending colon than in the distal colon,130 the SCFA receptor free fatty acid receptor (FFAR) 2, also known as GPR43, is expressed at higher levels in the left colon. 131 Therefore, a valid hypothesis is that differential antineoplastic activity of EPA may relate to increased antineoplastic SCFA-FFAR2 signalling in the distal versus proximal colon. 132
Both EPA and aspirin inhibit the COX enzymes COX-1 and COX-2. 57 Independent reports have described how expression of COX-2, which is believed to play a critical role in intestinal tumorigenesis,54 is higher in distal colonic neoplasms than in the proximal colonic lesions. 133,134 Differential expression and activity of COX-1 in colorectal adenomas in different parts of the colorectum has not been studied. Differences in gene expression in non-neoplastic mucosa and baseline colorectal adenoma characteristics that may predict response to EPA and/or aspirin deserve further investigation.
The mechanism of the CRC-preventative activity of aspirin remains unclear despite intense scrutiny over several years. 44,45 Postulated mechanisms of action include COX-dependent and COX-independent activity, either directly on colorectal epithelial cells or indirectly via the antiplatelet activity of aspirin. 45 More recently, subversion of the host anti-tumour immune response by COX-dependent PGE2 has been reported,135 which is abrogated by aspirin, thus driving more effective host anti-tumour immunosurveillance. This mechanism of action may explain the preferential antineoplastic activity of aspirin against proximal colonic neoplasms, which are more likely to exhibit a higher neo-antigenic load (and hence potential to stimulate a host anti-tumour immune response) as a result of defective DNA MMR in MSI tumours. 136
Combination colorectal cancer chemoprevention
The individual effects of EPA and aspirin on colorectal adenoma number beg the question of the antineoplastic activity of combined treatment, which, given the single agent effects apparent on the ‘at-the-margins’ analysis, one might expect to be apparent for total colorectal adenoma number. The trial was powered to be able to detect only a major interaction between EPA and aspirin with an ‘inside-the-table’ analysis of this 2 × 2 factorial RCT. Comparison between the four treatment groups highlighted that total and left-sided colorectal adenoma multiplicity was lower in the combined EPA and aspirin treatment group, consistent with efficacy of both agents on left-sided, conventional colorectal adenomas. A key objective of future work, in order to translate the seAFOod trial findings into clinical application, will be to apply precision/personalised medicine principles to pose the question regarding which individuals might gain most from chemoprevention with one or both agents, based on baseline colorectal adenoma characteristics and/or other mucosal biomarkers.
Use of the NHS Bowel Cancer Screening Programme for a polyp-prevention trial
The rationale for the study of a ‘high-risk’ population undergoing 1-year surveillance colonoscopy within the English BCSP was based on data from previous aspirin polyp-prevention trials that suggested that colorectal adenoma risk reduction associated with aspirin use was already evident (and exceeded the risk reduction at 3–4 years) at 1 year, combined with the high ADRa. 49 The relatively short follow-up duration raises the question of how far colorectal adenoma outcomes at 12 months simply reflect missed colorectal neoplasia from the screening examination. However, BCSP data98,100 and other reports137,138 have confirmed that the colorectal adenoma yield at 12 months from baseline assessment is significantly higher than the yield from a procedure within 3 months of the index assessment, implying that de novo colorectal adenoma growth contributes significantly to colorectal adenoma ‘recurrence’ rather than solely ‘missed lesions’. In reality, colorectal adenomas detected at a 12-month endoscopic procedure will almost certainly represent a mixed population of ‘new’ and ‘missed’ lesions, even after the highest-quality colonoscopic examination, but this does not negate the role of the colorectal adenoma as a biomarker of chemoprevention efficacy (related to regression of existing colorectal adenomas, as well as inhibition of new growth), as accepted in proof-of-concept FAP RCTs. 37
The low yield of advanced colorectal adenomas in the seAFOod trial is probably explained by the short surveillance interval and high-quality colonoscopic colorectal adenoma clearance achieved in the BCSP, but also the rather stringent ‘advanced’ lesion definition, which required complete (100%) ‘villousness’ of conventional dysplastic adenomas, unlike previous observational and intervention studies that have included lesions with > 25% ‘villousness’ in the definition of ‘advanced’ colorectal adenoma. 32,139
Using the English BCSP as a vehicle for the seAFOod trial provided several advantageous features to the design and performance of the trial, including strict, protocol-driven colonoscopy screening and surveillance procedures, uniform colonoscopy, and histopathology performance and reporting. 95–97 In particular, strict timing of the 12-month surveillance colonoscopy in the seAFOod trial was a major advantage over previous ‘sporadic’ polyp-prevention trials undertaken in non-screening settings49,125,141 and was essential for interpretable PUFA biomarker data at 12 months. The trial population had a strong male predominance, mirroring BCSP practice,95 which limits the generalisability of the data to women. The high prevalence of overweight and obesity in the trial population probably indicates the major contribution of excess body weight to early-stage colorectal carcinogenesis,140 and is highly relevant to general CRC chemoprevention in non-screening populations given the high prevalence of overweight and obesity in many areas of the world. 142
A large number (nearly 4000) of individuals stratified as ‘high risk’ after BCSP screening colonoscopy were identified and screened by participating trial sites, as expected from BCSP data pertaining to the prevalent screening round, which suggested that ‘high-risk’ features were detected in 9.8–10.3% of screening colonoscopies (Public Health England, 2009, personal communication). 95 However, since the seAFOod trial opened for recruitment, subsequent incident screening rounds have detected less colorectal neoplasia and more recent BCSP data demonstrate that ‘high-risk’ features make up only 8.3% of screening colonoscopy outcomes (Public Health England, 2009, personal communication). The reduction in incidence of ‘high-risk’ colorectal neoplasia probably contributed to the slower than expected recruitment during the trial.
Only 18% of ‘high-risk’ individuals were randomised. This is a higher screen success rate than in several previous polyp-prevention trials that reported a trial screening success rate,141,143 but lower than we anticipated. Exclusion criteria included concomitant use of anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents, including existing aspirin use (19%). In addition, a higher than expected proportion of patients (31%) declined to be screened for and participate in the trial, despite the fact that the trial design did not entail an additional colonoscopy and that venepuncture for blood sampling was optional. Trial acceptability was lower than expected from a cohort of patients who had already engaged fully with a multistage screening process and who had been informed that they had ‘high-risk’ colorectal neoplasia necessitating surveillance colonoscopy in 12 months’ time. Formal data pertaining to reasons for declining participation were not collected on the basis that any individual did not need to provide a reason for his or her decision. However, an informal review showed that reasons for declining participation at screening included concern about risk associated with the IMP (particularly aspirin) and unwillingness to start medication when previously not taking any regular drugs, but also, conversely, unwillingness to add further medication to an existing drug regimen.
The screen failure rate varied significantly between the BCSP sites despite the strict, uniform inclusion criteria based on BCSP practice and an identical BCSP screen pathway used at all BCSP sites. Several patient (e.g. differential prevalence of comorbidities requiring antiplatelet/anticoagulant use in different regions of England) and research staff factors (e.g. research time available to PI and SSPrs, as well as CRN-funded RN support) contributed to marked differences in recruitment efficiency. In addition, BCSP screening colonoscopy activity varied widely across individual sites, thereby limiting the identification of ‘high-risk’ individuals at some sites. Recognition of the most-suitable BCSP sites for any similar polyp-prevention trial will be key to improving recruitment efficiency, particularly when ‘high-risk’ individuals remain a relatively fixed proportion (7–9%) of guaiac FOBt-positive patients. A general theme (but with notable exceptions) was that BCSP sites that utilised CRN-funded research staff best had a higher recruitment rate. This may reflect insufficient time that many BCSP staff have available for research and/or some SSPrs having limited understanding of clinical trials research and a protectionist approach towards patients; these need to be addressed prior to a future polyp-prevention trial set in the BCSP.
The switch from guaiac FOBt to FIT in the UK BCSP programmes may alter colorectal neoplasia incidence rates relevant to future trial recruitment projections.
Safety and tolerability of eicosapentaenoic acid and aspirin
Overall, safety and tolerability of both agents was excellent, with no excess of clinically significant bleeding events, even in the combined treatment group. However, we did mandate stopping IMP before and after any planned invasive procedures (including polypectomy at repeat endoscopy) in the unlikely event that the combined antiplatelet activity of EPA and aspirin increased bleeding risk. Excellent tolerability of EPA and aspirin contributed to high compliance levels and trial retention, with limited drop-out.
Eicosapentaenoic acid was associated with an excess of mild to moderate GI AEs, including diarrhoea. Although ω-3 PUFA products have an excellent safety profile and daily doses of up to 4 g are ‘generally recognized as safe’ (GRAS) by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), mild to moderate GI AEs are recognised, commonly diarrhoea, dyspepsia, eructation (burping) and an unpleasant ‘fishy’ taste. 144 These GI symptoms often occur in the general population unrelated to dietary or ‘nutraceutical’ ω-3 PUFA intake. 113 Therefore, we confirmed that the treatment groups were well matched for prevalent GI symptoms at baseline. Dose-related ω-3 PUFA-related GI symptoms can occur. 65,144,145 However, an open clinical question has been whether or not prolonged dosing with the different forms of EPA and mixed ω-3 PUFAs (FFA vs. TG vs. EE) available in ‘nutraceutical’ preparations is associated with differential GI tolerability. 65 The seAFOod trial data do not indicate any major difference in GI tolerability between the same FFA-equivalent dose of the EPA-FFA and EPA-TG formulations in the context of a 12-month intervention trial.
Mild to moderate GI AEs, particularly diarrhoea and abdominal pain, were more common in those allocated to EPA alone, as opposed to EPA plus aspirin. A valid hypothesis is that aspirin co-therapy is causally protective for ω-3 PUFA intolerance. This requires further investigation in the context of subsequent studies of combined antineoplastic activity of both agents.
Five episodes of AF were reported in three participants, all of whom were allocated active EPA alone. Several RCTs have investigated ω-3 PUFA supplementation for primary and secondary prevention of AF that are summarised in recent American Heart Association guidelines on ω-3 PUFA use and prevention of CVD. 146 Overall, there is no supportive evidence for use of ω-3 PUFAs for AF prevention. There has been no signal in any previous RCT of increased AF risk in ω-3 PUFA users. 146
An important component of the trial was dietary ω-3 PUFA analysis to exclude significant change in dietary ω-3 PUFA intake prompted by participant-facing trial information, prior to consent, that suggested possible anti-CRC activity of EPA. Using the established short-form EPIC FFQ,108 we confirmed that there was no evidence of increased fish intake during the intervention phase and that the four treatment groups were well matched on dietary fish intake at baseline and at the end of trial participation.
Biomarkers of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid tissue exposure
The seAFOod trial biobank obtained excellent coverage considering the geographical spread of a large number of trial sites. There was widespread engagement from SSPrs and RNs at sites, with careful sample handling and storage at sites prior to temperature-controlled transport to the biobank in Bradford. The trial protocol outlines the lipid mediator analyses that were originally proposed. 100 At the start of the trial, measurement of RBC PUFA levels was planned in only a small subset of participants. However, the capsule IMP switch necessitated the measurement of PUFA levels in all RBC and rectal mucosal samples to provide the strongest possible evidence that the trial cohorts exposed to EPA-FFA and EPA-TG gained equivalent exposure to EPA and could be combined for primary and secondary outcome analysis. Therefore, many planned measurements were not carried out, but these should be performed in the future if further funding can be obtained for biomarker analysis.
Baseline RBC PUFA values in the seAFOod trial cohort were comparable with previous cross-sectional UK studies and data from other Western countries with relatively low population ω-3 PUFA levels and dietary fish intake. 147 Despite self-reported compliance being excellent by capsule counting, the increase in RBC EPA levels observed in EPA users was highly variable, a phenomenon that has been seen in several previous ω-3 PUFA studies, in which individual RBC fatty acid profiles have been measured. 88,129,148 The explanation for large variations in RBC membrane EPA levels, despite uniform dosing, remains unclear and requires further investigation in the large trial cohort. There was no evidence that COX inhibition by concurrent aspirin use is associated with higher RBC membrane or rectal mucosal EPA content.
To our knowledge, this is the first large-scale RCT evidence that oral administration of EPA results in incorporation of EPA in the rectum. There was a medium-strength correlation between the RBC % EPA value at 12 months and the rectal mucosal % EPA content. The RBC membrane EPA and DHA content is considered to be the best proxy biomarker of tissue ω-3 PUFA exposure. 84,148 Further exploratory analysis of the seAFOod trial data is required to explore the predictive value of the rectal mucosal EPA level for individual EPA efficacy against left-sided colorectal neoplasia. Integration of dietary ω-3 PUFA intake, baseline PUFA levels and ‘nutraceutical’ EPA dosing is needed in a treatment-independent analysis of the relationship between EPA level and colorectal adenoma recurrence risk during surveillance. A similar analysis performed in the context of the WELCOME trial149 of ω-3 PUFA use in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease provided new insights into the role of DHA in treatment of that condition.
There was no evidence of significant conversion of EPA to DHA in either RBC membranes or rectal mucosa, consistent with previous human data from EPA intervention trials. 67,87 Therefore, the trial data do not support the concept of EPA as the ‘universal ω-3 PUFA donor’, which can substitute for mixed EPA-DHA preparations. The question of whether or not equivalent doses of EPA alone, DHA alone or a EPA-DHA mix have different antineoplastic activity in the intestine has been tested only in rodents, in which equivalent anti-CRC effects have been observed. 61 Equivalent bioactivity of EPA and DHA in a CRC chemoprevention context cannot be assumed from the seAFOod trial; this will be a critical public-facing message from the trial to minimise incorrect assumptions about, and use of, mixed ω-3 PUFA preparations in the context of CRC chemoprevention. The majority of prescription and health supplement ω-3 PUFAs are a mix of EPA and DHA with a smaller proportion of other PUFAs. 150 However, separate EPA formulations are licensed for treatment of severe hypertriglyceridaemia and are marketed as health supplements. 144,151 The low cost and excellent safety/tolerability profile of EPA, combined with existing health claims regarding ω-3 PUFAs, means that, even with modest CRC chemopreventative activity, it may be adopted widely in a cancer-prevention setting by the public.
‘Contamination’ of the treatment groups by participant use of OTC formulations is an ever-present risk in placebo-controlled trials of agents that are available for purchase by the public. The seAFOod trial fatty acid analysis allows us to speculate about possible placebo contamination by ‘own’ ω-3 PUFA use by identifying those individuals who were randomised to placebo EPA who had a rise in RBC EPA level. Further analysis of concomitant changes in DHA levels is now required. Individual RBC ω-3 PUFA profiles suggest that placebo contamination, if it did occur, was very rare and did not interfere with the findings pertaining to EPA use.
Aspirin use entails a small, but significant, risk of serious harm from GI and intracranial bleeding. 152 This has hampered translation of the significant body of evidence supporting the CRC chemopreventative properties of aspirin into routine clinical practice. The seAFOod trial data add to this body of evidence and emphasise the chemopreventative activity of aspirin against proximal and serrated neoplasms, which are widely considered to be more ‘missable’ at colonoscopy and contribute significantly to the burden of interval CRC.
Concluding remarks
In summary, the seAFOod polyp-prevention trial has demonstrated that the ω-3 PUFA EPA (2 g of FFA daily) and aspirin (300 mg daily) did not reduce colorectal adenoma risk (measured by the ADRa) at a 1-year surveillance colonoscopy in ‘high-risk’ individuals with colorectal neoplasia in the English BCSP. However, chemopreventative efficacy of both agents was observed, as measured by the reduction in colorectal adenoma number per patient at surveillance colonoscopy. The colorectal adenoma subtype- and location-dependent specificity of EPA and aspirin are consistent with previous observations. Existing data on CRC risk reduction by aspirin suggest that the colorectal adenoma risk reduction observed for both agents is likely to translate into a clinically meaningful decrease in long-term CRC risk. Both agents were safe and well tolerated in patients aged 55–75 years with ‘high-risk’ colorectal neoplasia, although EPA therapy alone was associated with a slight excess of mild to moderate GI AEs. There was no difference in tolerability of the two EPA formulations used in the trial.
Results in context
Despite several decades of research into the efficacy of several drug (e.g. aspirin, selective COX-2 inhibitors) and nutrient (e.g. folic acid, vitamin D, ω-3 PUFAs) interventions for chemoprevention of CRC, meaningful translation into clinical practice has yet to occur. 153 The weight of the evidence that long-term (> 5 years) use of aspirin is associated with a ≈25% decrease in the risk of CRC incidence and mortality, particularly marked for proximal CRC (the predominant interval CRC type during colonoscopy screening and surveillance, as well as the CRC type not afforded protection by FS screening),46–48 makes the lack of ‘effectiveness’ trials driving clinical use of this agent even more surprising.
One reason for this lack has been the dependency on the polyp-prevention trial, using the colorectal adenoma as an accepted surrogate biomarker of CRC risk,49 in the absence of direct data regarding how a decrease in either colorectal adenoma incidence (ADRa) or number (MAP) translate into subsequent CRC risk reduction.
Historically, the ADRa has been favoured as the colorectal adenoma end point of choice in polyp-prevention trials. The ADRa may be considered the most relevant end point related to the use of a CRC chemoprevention agent to reduce the frequency of, or need for, endoscopic surveillance of patients with previous colorectal neoplasia, stratification for which is based largely on colorectal adenoma incidence. 30–33 Whether or not the use of a CRC chemoprevention agent will lead to a significant reduction in the amount of surveillance colonoscopy performed is a question that can be addressed only by ‘effectiveness’ studies in which long-term use of a concurrent chemoprevention agent and surveillance colonoscopy requirement are observed using a ‘big-data’ linkage approach or perhaps a ‘point-of-care’ randomised trial.
Reduction in colorectal adenoma multiplicity (MAP) arguably has more biological meaning as a read-out of reduced colorectal neoplastic risk associated with a potential CRC chemoprevention agent, hence its widespread use in FAP trials and pre-clinical studies. 37,61 This read-out is more suited to consideration of a chemoprevention agent for long-term CRC risk reduction, as opposed to more efficient use of colonoscopic surveillance for benign colorectal neoplasia. Consistent with use of colorectal adenoma number as a biomarker of future CRC risk in chemoprevention trials, observational data suggest that colorectal adenoma multiplicity at baseline endoscopy is associated with increased CRC incidence and mortality compared with the general population. 40–42 Moreover, a pooled analysis of eight prospective colonoscopy surveillance studies reported that initial colorectal adenoma number at colonoscopy predicts subsequent advanced colorectal neoplasia (advanced colorectal adenoma and CRC combined), in a stepwise manner with increasing baseline colorectal adenoma number. 139
The seAFOod trial data on colorectal adenoma number, as well as existing MAP data for aspirin,115,117,118 should focus more attention on the further validation of colorectal adenoma number as a colonoscopic end point, particularly given that colonoscopy performance and reporting has improved significantly, leading to better routine data quality on colorectal adenoma characteristics.
Strengths and limitations
Trial design
A key strength of the seAFOod trial was integration in the English BCSP, which continues colonoscopic surveillance in the BCSP, unlike in Scotland, where ongoing surveillance responsibility is passed to general endoscopy services. This provided several advantages to the trial, including:
-
consistent high-quality colonoscopy performance and reporting above that available in general colonoscopy populations
-
accurate screening colonoscopy data from the BCSP, with which to predict screening colonoscopy outcomes for recruitment projections
-
uniform, protocol-driven care within the BCSP, particularly the small window for the 12-month surveillance colonoscopy in the BCSP, despite high procedural pressure in NHS endoscopy units
-
use of a ‘high-risk’ surveillance cohort and 1-year colonoscopy outcomes, which minimised the intervention period compared with previous polyp-prevention trials,34–36,141,143 with consequent time and cost savings.
Another strength was the comprehensive seAFOod trial biobank with careful QA control. The biobank will be critical for further biomarker-driven, stratified analysis of the trial data. Availability of dietary and tissue biomarker data for the ω-3 PUFA intervention allowed interpretation of the EPA effect on colorectal outcomes, analysis of which could be confounded by dietary and OTC ω-3 PUFA exposure.
The small number of advanced colorectal adenomas found during the seAFOod trial is a limitation and probably relates to the short surveillance interval, as well as the excellent quality of the clearance screening colonoscopy. Previous polyp-prevention trials have reported an advanced ADRa of ≈10% in the placebo group of patient populations, approximating to combined ‘high-risk’ and ‘intermediate-risk’ BCSP patients with more heterogeneous follow-up (1–5 years). 34,36,141,143 Detailed data on advanced ADRa and MAP at surveillance colonoscopy were not available from the BCSP when the seAFOod trial was designed but are now available from the seAFOod trial and other reports98 in order to determine the feasibility of using advanced neoplasia as a primary or main secondary outcome.
As the first chemoprevention CTIMP in the BCSP, the outcome and performance data from the seAFOod trial will be invaluable for any future polyp-prevention trial (see Chapter 5, Recommendations for research). The seAFOod trial has established the BCSP as a realistic vehicle for interventional research during the endoscopy phase of the patient pathway.
Trial performance
Failure to reach the recruitment target
Although the BCSP sites provided a large number of potential ‘high-risk’ trial participants at a constant rate, consistent with well-characterised colonoscopy outcomes after guaiac FOBt screening,95 recruitment of ‘high-risk’ individuals after screening colonoscopy (18%) was significantly lower than projected (60%) owing to several factors, which included:
-
Exclusion because of increasing use of antiplatelet agents, such as clopidogrel, although concurrent aspirin use (19%) occurred almost as predicted from pilot data (20%).
-
Exclusion because of the need for additional endoscopic assessment in the BCSP, which varied significantly across BCSP sites/different BCSP colonoscopists and had not been reported prior to trial design.
-
Unwillingness of patients to take part in the trial. Acceptability of the trial was not tested in a pilot study, nor subjected to broader PPI assessment prior to opening, except for the lay input provided by the PPI representative in the application team (a BCSP colonoscopy patient) and the review inherent in both Research Ethics Service and BCSP Research Advisory Committee assessments. Assumptions about a high acceptability level for the trial were based on the necessary prior engagement of ‘high-risk’ individuals in the BCSP, the recent provision of a diagnosis that stratified potential participants who were at a higher risk of future CRC, and a short intervention period prior to a subsequent routine colonoscopy with no change to normal BCSP practice. Anecdotally, a major reason for unwillingness to join this CTIMP after the screening colonoscopy was patient relief at not having CRC (all patients are informed that there is a 1 in 10 chance of CRC at colonoscopy, prior to the procedure) and a strong desire to ‘forget about my colon for a while’, at least until surveillance colonoscopy.
-
Limited research experience of some BCSP staff, coupled with reluctance to discuss research participation during routine clinical care episodes, may have contributed to a high screen failure rate. There was a lengthy ‘lag time’ at many sites between local R&D approval and FPFV, which contributed significantly to reduced overall recruitment.
Although recruitment reached only 83% (n = 709) of the target (853 randomised participants), we do not believe that the smaller sample size affected the primary results of the trial because the 95% CI for the risk difference in ADRa for both EPA and aspirin did not include –10%. Therefore, assuming no change in the point estimate, a larger sample size would tend only to decrease the width of the CI, thereby moving the lower 95% CI limit further from the hypothesised absolute risk difference of –10%.
Capsule investigational medicinal product switch
The need to switch capsule IMP during the trial was unforeseen, beyond the control of the TMG and very disruptive to recruitment for at least 12 months, especially for BCSP sites that exhausted IMP stock and had to suspend recruitment for several months.
The potential consequences of a switch in one of the IMPs for analysis of the trial results was given very careful consideration. After extensive discussions between the TMG, oversight committees and the funder (which also sought anonymous peer review), it was concluded that the proposed replacement active IMP (90% EPA-TG) was sufficiently similar to the original active IMP (EPA-FFA) in terms of content, FFA-equivalent dose and probable bioavailability to continue the trial, on the basis that colorectal adenoma outcome data from those who received EPA-FFA or EPA-TG could almost certainly be combined. This potential threat to trial integrity has now become a unique aspect of the trial whereby two different (2-g FFA dose equivalent) EPA formulations have been compared in a RCT, demonstrating no clear difference in either tolerability or EPA bioavailability (as measured by RBC and rectal mucosal EPA content) during dosing over several months.
Chapter 5 Conclusions
Parts of this chapter have been reproduced from Hull et al. 1 © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Implications for health care
Although there was no difference in the ADRa across treatment groups in the seAFOod trial, the decrease in total colorectal adenoma number associated with aspirin and its selectivity for proximal colorectal adenomas and serrated polyps adds to a substantial body of evidence that, although aspirin use is associated with overall CRC risk reduction in unselected groups,46–48 there are patient groups for whom, and clinical situations in which, additional benefit from aspirin chemoprevention might be gained. For example, these data are the first randomised trial data to bolster the argument that individuals with the rare, but increasingly recognised (in screening programmes), hyperplastic-serrated polyposis syndrome might benefit from aspirin prophylaxis, as well as those with ‘sporadic’ serrated polyps. 154 Moreover, further evidence that there is proximal colonic selectivity for aspirin CRC chemoprevention highlights potential uses of aspirin in concert with FS screening and for reduction of clinically important PCCRCs, which are more commonly proximal than screen-detected CRCs. 15
In the absence of any effect of 2 g of EPA daily on the total colorectal ADRa in the seAFOod trial and numerically small effects on colorectal number (MAP) and incidence rate (ADRa) in the left/distal colorectum only, no firm guidance about ‘nutraceutical’ EPA use, dietary ω-3 PUFA intake or use of RBC ω-3 PUFA as a predictive risk biomarker, in the context of CRC risk reduction, can be made prior to further exploratory, hypothesis-generating analysis of the seAFOod trial data and biobank samples (see Recommendations for research). However, even small chemoprevention benefit from EPA is likely to be accepted and taken up by a significant proportion of the public, who might consider that ω-3 PUFAs have wider health benefits.
Recommendations for research
The seAFOod trial data available to date will stimulate a debate about how the colorectal adenoma is best used as an ‘efficacy’ RCT end point. The colorectal adenoma can be viewed solely as an endoscopic biomarker of carcinogenic potential, and hence CRC risk, but also as a clinically important lesion, the presence of which prompts endoscopic removal and stratification for future endoscopy, with implications for endoscopy provision. This distinction is key to how CRC chemoprevention is viewed: as a long-term strategy for reduction in CRC risk and/or as adjuvant therapy for those in endoscopic screening/surveillance programmes with a view to decreasing need for colonoscopy. The lack of effect on total ADRa of either EPA or aspirin (and absence of any short-term reduction in colonoscopy frequency with no shift from ‘high’ to ‘intermediate’ risk classification) argues against a role as adjuvant therapy for those in endoscopic screening/surveillance programmes. By contrast, a reduction in MAP suggests chemopreventive activity that may manifest eventually as reduced CRC incidence. It will be important to determine long-term colonoscopy and CRC outcomes in the seAFOod trial participants using routinely collected BCSP data and National Cancer Registration and Analysis Service (NCRAS) data. Trial participants have already provided consent for use of long-term, post-trial data. Although the small sample size of the seAFOod trial cohort is likely to provide insufficient CRC diagnoses to provide a meaningful comparison, analysis of subsequent colonoscopy frequency and colorectal adenoma outcomes should be able to test whether or not short-term treatment provides longer-term chemoprevention of colorectal adenomas (with the weakness that ongoing aspirin or ω-3 PUFA use will not be known). An Office for Data Release request to Public Health England will be made prior to gaining approval from the BCSP Research Advisory Committee for this follow-up study.
Future ‘effectiveness’ evaluation of the two seAFOod trial interventions will be dependent on whether or not colorectal adenoma number (MAP) is used as a CRC risk biomarker. Including the seAFOod trial, there are now four independent RCTs (Table 39) that have reported on colorectal adenoma number associated with aspirin use. 115,117,118 A key piece of work will be to attempt a meta-analysis of the colorectal adenoma number data from these trials to derive an overall colorectal adenoma risk reduction ratio for aspirin use that can be aligned with the observational data on CRC risk reduction, to propose a clinically meaningful MAP reduction value.
| Study | Dose (mg) | Duration | Total MAP (SD) | Statistical test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | Active | ||||
| Sandler et al.118 | 325 | Median 12.8 months | 0.49 (0.99) | 0.30 (0.87) | p = 0.003 |
| Benamouzig et al.115 | 160/300 | 12 months | 0.86 (0.30) | 0.45 (0.15) | p = 0.01 |
| Logan et al.117 | 300 | Mean 3–3.5 years | 0.47 (0.92) | 0.31 (0.70) | p = 0.015 |
| The seAFOod trial | 300 | 12 months | 1.6 (2.1) | 1.2 (1.5) | IRR 0.78 (95% CI 0.68 to 0.90) |
The observation that both EPA and aspirin have selectivity for CRC chemopreventive activity based on colorectal adenoma type and location prompts the question as to whether or not a precision-stratified-medicine approach to CRC chemoprevention can be taken whereby baseline colorectal adenoma features can be used to predict the type and/or location of colorectal adenoma recurrence and, therefore, best ‘personalised’ chemoprevention with a given chemoprevention agent. The detailed trial data set on endoscopic and histological features of baseline colorectal adenomas can be used to investigate the relationship between baseline colorectal adenoma features (location, type, number) and recurrence in the placebo-only group of the seAFOod trial. Other post-polypectomy tissue biomarkers may have utility for prediction of aspirin and EPA efficacy, such as tissue COX-2 expression. 83 A recent study has demonstrated that COX-2 and 15-prostaglandin dehydrogenase (PGDH) expression (combined to provide a surrogate marker of tissue PGE2 content) in baseline colorectal adenomas predicts the chemopreventive efficacy of the selective COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib,155 building on the previous data from the APACC trial. 83 To this end, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) polypectomy specimens from the screening colonoscopy from the seAFOod trial placebo group can be obtained, as detailed in the trial protocol. 100 Other, novel, tissue biomarkers based on the proposed mechanism of action of the type and location specificity of EPA and aspirin can also be tested, for example FFAR2 protein expression in FFPE polypectomy specimens, but also in the non-neoplastic rectal mucosal samples available in the seAFOod trial biobank. Rectal mucosal samples will be invaluable for investigation of any ‘field effect’ mucosal biomarker with predictive value for colorectal adenoma type recurrence.
The intriguing observation that combined EPA and aspirin use in the seAFOod trial was associated with fewest total and left-sided colorectal adenomas, when comparing across the four treatment groups, suggests that the two agents might have an additive relationship for CRC chemoprevention (with the additional, beneficial feature that aspirin co-therapy may improve tolerability of EPA treatment). In the first instance, an exploratory analysis of the predictive value of the baseline/post-intervention RBC and/or post-intervention rectal mucosal EPA level for the reduction in total and left MAP associated with aspirin should be performed in order to strengthen the case for an ‘efficacy’ RCT of combined aspirin–EPA (or mixed ω-3 PUFA) treatment or stratified (by baseline EPA level) aspirin use.
Two large RCTs of mixed ω-3 PUFA treatment are due to report in the near future. The ASCEND (A Study of Cardiovascular Events iN Diabetes) trial (NCT00135226)156 is a 2 × 2 factorial study of long-term (median 7.5 years) ω-3 PUFAs (840 mg of EPA/DHA EEs daily) and aspirin (100 mg daily) treatment for prevention of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in patients with diabetes (n = 15,480). Cancer outcomes are a secondary end point with the ability to continue with post-trial follow-up. VITAL (VITamin D and OmegA 3 TriaL) (NCT01169259) is a 2 × 2 factorial study of the same dose and formulation of ω-3 PUFAs (840 mg of EPA/DHA EEs) and vitamin D3 (2000 IU daily) in 25,871 participants. 157 Colorectal cancer is a specified secondary outcome. It will be very interesting to interpret the results of the ASCEND trial and VITAL in the light of the seAFOod trial data, particularly in relation to CRC location. It should be noted that both trials tested a smaller dose of mixed ω-3 PUFAs than the daily dose of EPA employed in the seAFOod trial.
The data on recruitment performance and placebo group outcomes will be invaluable for any future CRC chemoprevention RCT set in the BCSP. A key lesson is that the ADRa seems to lack discriminatory power, at least in the ‘high-risk’ colorectal adenoma cohort investigated in the seAFOod trial, given that the intervention with known chemopreventive efficacy (aspirin) did not demonstrate an ADRa signal.
As discussed earlier, the comprehensive data set of PUFA levels in RBCs and rectal mucosa at baseline and after ‘nutraceutical’ EPA intervention should prompt an analysis of the predictive value of individual ‘EPA status’ at baseline and after intervention, independent of allocation to active EPA or placebo, for colorectal adenoma reduction. An understanding of whether or not ‘EPA high’ status is associated with reduced colorectal adenoma recurrence, regardless of whether or not EPA supplementation was provided, may have important consequences for dietary ω-3 PUFA guidelines and possible measurement of ω-3 PUFA status for CRC risk stratification.
The seAFOod trial biobank is also a rich resource of pre- and post-treatment plasma and urine samples, with which to extend and strengthen the tissue biomarker analysis. For example, parallel measurement of urinary PGE-M levels (the main metabolite of PGE2) may provide further insight into the use of baseline colorectal adenoma COX-2/15-PGDH/PGE2 status127 and was originally specified in the trial protocol. 100 The possible additive relationship between EPA and aspirin observed for total and left MAP justifies the use of the biobank repository to address the hypothesis that RvE1 is measurable in plasma samples from individuals treated with EPA, with and without aspirin, as described in the trial protocol. 100
The seAFOod trial data should drive several studies aimed at understanding the mechanism(s) of action of both interventions. Differential preventative activity against conventional and serrated pathway lesions by EPA and aspirin has highlighted the relatively poor characterisation of the molecular phenotype of colorectal adenomas compared with CRC,4,154 as well as the continuing lack of understanding of mechanism(s) of action of both agents. Further in vitro studies (using human CRC cells) of aspirin and EPA should use representative cellular models of CIN, MSI-H and CIMP+ phenotypes. 158 The tumour immunology of the colorectal adenoma has been largely ignored, perhaps because of the relative difficulty in collecting sufficient, fresh human colorectal adenoma tissue and absence of a suitable animal model. 159 However, regulation of host immune surveillance as a mechanism of primary CRC chemoprevention activity remains a valid hypothesis for both seAFOod trial interventions. 160 We have recently reported that mixed ω-3 PUFA treatment is associated with an increase in abundance of SCFA-producing bacteria in the colon. 129 The hypothesis that the propensity for EPA benefit in the distal colorectum relates to increased anticarcinogenic SCFA-FFAR2 signalling132 should now be tested by measuring stool SCFA concentrations in human studies, in parallel with FFAR2 expression studies using rectal mucosa from the seAFOod trial biobank.
The seAFOod trial biobank contains a blood leucocyte sample for genomic DNA extraction for nearly all participants, as well as individual participant consent to perform genetic single nucleotide polymorphism studies relevant to CRC risk and both interventions. The results of the ω-3 PUFA biomarker analyses above will generate hypotheses about which genetic polymorphisms that are known to control ω-3 PUFA levels,161 for example fatty acid desaturase (FADS) genes, should be characterised in parallel with the dietary analysis.
Acknowledgements
We thank all those who took part in the trial and clinical staff at the participating sites.
Sponsor
The University of Leeds acted as sponsor for the research and the trial.
The seAFOod Collaborative Group
Trial and data management: Nottingham Clinical Trials Unit
Lelia Duley, Professor of Clinical Trials Research; Alan A Montgomery, Professor of Medical Statistics and Clinical Trials and Deputy Director; Trish Hepburn, Senior Medical Statistician; Wei Tan, Medical Statistician; Dan Simpkins, Senior Data Manager; Anna Sandell, Trial Manager from November 2011 to 2014; Kirsty Sprange, Trial Manager from May 2014 to August 2015 then Senior Trial Manager from 2015; Sarah Fahy, Trial Manager from October 2015 to September 2016; Aisha Shafayat, Trial Manager from December 2016; Eleanor Harrison, Trial Administrator from October 2011 to January 2012; Margarita Carucci, Trial Administrator from February 2012 to July 2014 then Trial Co-ordinator from August 2014 to August 2015; Natalie Hutchings, Trial Administrator from September 2014 to June 2016; Robert Allen, Trial Co-ordinator from August 2016; Gill Bumphrey, Trial Pharmacist from March 2011 to June 2015; Sarah Walker, Data Co-ordinator from February 2013 to August 2017; Matthew Foster, Data Administrator; Chris Rumsey, Information Technology Programmer; Justin Fenty, Statistician from April 2011 to September 2012; and Veronica Moroz, Statistician from May 2009 to December 2010.
Co-applicants
Richard F Logan, Professor of Clinical Epidemiology, University of Nottingham; Colin J Rees, Professor of Gastroenterology and Consultant Gastroenterologist, Newcastle University and South Tyneside NHS Foundation Trust; Gayle Clifford, South of Tyne Bowel Cancer Screening Centre, BCSP, SSPr; Paul M Loadman, Professor of Pharmacokinetics and Drug Metabolism, University of Bradford and Yorkshire Experimental Cancer Medicine Centre; Anna Nicolaou, Professor of Biological Chemistry, University of Bradford; Devon Devonport, Patient and Public Representative (BCSP Patient Representative); Paul Silcocks, Senior Lecturer in Medical Statistics, University of Nottingham; and Hywel Williams, Professor of Dermato-epidemiology, University of Nottingham.
Trial Management Group
Professor Mark A Hull, Professor of Molecular Gastroenterology and Honorary Consultant Gastroenterologist; Diane Whitham, Associate Professor in Clinical Trials; Alan A Montgomery, Professor of Medical Statistics and Clinical Trials and Acting Director; Anna Sandell, Trial Manager; Eleanor Harrison, Trial Administrator; Wei Tan, Medical Statistician; Eleanor Mitchell, Senior Trial Manager; Kirsty Sprange, Trial Manager/Senior Trial Manager; Margherita Carucci, Trial Co-ordinator; Gill Bumphrey, Trial Pharmacist; Sarah Fahy, Trial Manager; Natalie Hutchings, Trial Administrator; Brian Barnes, Data Manager; Matthew Foster, Data Administrator; Aisha Shafayat, Trial Manager; and Robert Allen, Trial Co-ordinator.
Trial Steering Committee (independent members)
Professor Will Steward (Chairperson), Triallist and ex-Chairperson, National Cancer Research Institute CRC Clinical Studies Group, University of Leicester; Professor Greg Rubin, Triallist with primary care gastroenterology expertise, Newcastle University Institute of Health Sciences; Sally Benton, Director, NHS Bowel Cancer Screening Southern Programme Hub (previous Director: Professor Stephen Halloran); Mr Alan Reece, BCSP Patient ‘Service User’ Representative; Dr Elmar Detering, Representative of Bayer Pharma AG (Observer); and Mr Justin Slagel, Representative of SLA Pharma AG, until IMP switch (Observer).
Data Monitoring Committee (independent members)
Professor Bob Steele (Chairperson), Professor of Surgery, University of Dundee; Professor Dion Morton, Consultant, University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust; and Professor John Norrie, Chair of Medical Statistics and Trial Methodology, Director of Edinburgh Clinical Trials Unit, University of Edinburgh.
Institute of Cancer Therapeutics, University of Bradford
Professor Paul M Loadman, Professor of Pharmacokinetics and Drug Metabolism; Ms Amanda Race, Research Assistant; Ms Elizabeth Macken, Research Assistant; and Ms Jade Spencer, Research Assistant.
University of Sheffield
Dr Elizabeth A Williams, Senior Lecturer in Human Nutrition.
Trial sites
-
North Tees and Hartlepool Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust: Matthew Rutter (PI), Debbie Wilson, Anne Eastick, Carol Adams, Susan Kelsey and Tracey Johnston on behalf of the site.
-
Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust: John Mansfield (PI), Heather Dixon, Elaine Stephenson, Maria Price, Mary Doona, Bev Douthwaite, Carrie Parker, Emma Crossland, Julie James, Lesley Dodd, Nicola George, Sasha Skentelbery and Sharron Lee on behalf of the site.
-
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust: Tom Lee (PI), Mark Welfare (PI), Helen Bailey, Heather Dixon, Jane Dickson, Linda Patterson, Julie James, Lesley Dodd, Nicola George and Sasha Skentelbery on behalf of the site.
-
Derby Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust: Andrew Goddard (PI), Maria Hartley, Helen Gibbs, Tracey Ambler, Beverley Powell, Christine Harrison and Keren Kerr on behalf of the site.
-
Chesterfield Royal Hospital NHS Foundation Trust: Keith Dear (PI), Tracey Ambler, Carmel Cooke, Lucinda Wilson, Teri-Ann Sewell, Helen Gibbs and Maria Hartley on behalf of the site.
-
Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust: Ian Beales (PI), Siobhan Parslow-Willams, Carmen Walker, David Tomlinson, Gemma Shearing, Jocelyn Keshet-Price, Jodie Graham, Kerrie Self, Melissa Rosbergen and Rachel Stebbings on behalf of the site.
-
Calderdale and Huddersfield NHS Foundation Trust: Ashwin Verma (PI), Mandy Mellor, Bridget Keegan, Matthew Robinson, Natalie Austin, Philipa Gilbert and Stephanie Rich on behalf of the site.
-
The Mid Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust: Syed Shah (PI), Lynsey Bourner, Annette Jones, Deborah Cooper, Jackie Ward, Patricia Kane, Rebecca Foster, Sarah Buckley, Steph Lupton, Thelma Darian, Toni Rank, Tracey Lowry and Bridget Keegan on behalf of the site.
-
County Durham and Darlington NHS Foundation Trust: Clare Westwood (PI), Peter McCourt, Claire Shaw, Michelle Wood, Anna Archer, Emma Fenby, Gillian Matthews and Lynn Smith on behalf of the site.
-
City Hospitals Sunderland NHS Foundation Trust: John Painter (PI), Pauline Oates, Verity Bennet, Hayley McMillan, Tracey Robson, Amanda King, Angela Hamilton, Dawn Charlton, Gayle Clifford, Mary Ritchie, Nicola Dempsey and Pamela Bowden on behalf of the site.
-
Gateshead Health NHS Foundation Trust: Jitendra Singh (PI), Hayley McMillan, Verity Bennett, Ann Wilson, Sophie Gelder, Amanda King, Angela Hamilton, Dawn Charlton, Gayle Clifford, Mary Ritchie, Nicola Dempsey, Pamela Bowden, Sharon McCourt and Suzanne Nicholson on behalf of the site.
-
South Tyneside NHS Foundation Trust: Colin J Rees (PI), Gayle Clifford, Carly Brown, Philippa Laverick, Hayley McMillan, Mary Ritchie, Nicola Dempsey and Verity Bennett on behalf of the site.
-
Harrogate and District NHS Foundation Trust: Jonathan Harrison (PI), Barbara Heath, James Featherstone, Denise Cullingworth, Joanne Bell, Liz Potrykus and Pam Roth on behalf of the site.
-
Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust: Richard Baker (PI), Ruth Fazakerley, Annette Jones, Doris Quartey, Felicia Onoviran, Claire Burton, Denise Cullingworth, Joanne Bell, Melissa Mellis, Nicola Bell and Pamela Roth on behalf of the site.
-
York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust: James Turvill (PI), Nicola Broadley, Feveresterh Fallah, James Featherstone, Joanne Ingham, Julie Sackville Hamilton, Kay Kell, Paula Strider, Rebecca Coop, Denise Cullingworth and Elizabeth Potryrus on behalf of the site.
-
Bradford Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust: Linda Juby (PI), Sophie Stephenson, Karl Ward, Philippa El Sayed, Rhian Simpson, Wendy Jepson, Hilary Bayton and Natalie Austin on behalf of the site.
-
Airedale NHS Foundation Trust: Philip DaCosta (PI), Diana Wilkinson, Hilary Bayton, Jean Martin, Natalie Austin and Elleanor Waldron on behalf of the site.
-
Northern Lincolnshire and Goole NHS Foundation Trust: Syed Muzaffar Ahmad (PI), Kirstie Smith, Ruth Loveday, Karen Martin, Kathy Dent and Sandra Evans on behalf of the site.
-
North Cumbria University Hospitals NHS Trust: Frank Hinson (PI), Sara Underwood, Beverley Wilkinson, Christine Pearson, Jane Chester and Sue Meyrick on behalf of the site.
-
Hull and East Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust: Graeme Duthie (PI), Bronwen Williams, Martin Lewis, Paula Brown and Sally Wood on behalf of the site.
-
George Elliot Hospital NHS Trust: Edmond Sung (PI), Emiley Archer, Kerry Flahive and Linda Stretton on behalf of the site.
-
Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust: Steve Foley (PI), Julian Williams (PI), Alison Large, Joyce Ntata, Karen Newcombe, Kathryn Moore, Sarah Chadderton, Chris Murfita and Shelley Biddles on behalf of the site.
-
Northampton General Hospital NHS Trust: Udi Shmueli (PI), Ethelwolda Goyena, Andrea Jones, Caroline Duncombe, Elizabeth Tee, Jan Miles, Kathy McGrath, Mariska Pochin and Nancy Hopewell on behalf of the site.
-
Kettering General Hospital NHS Trust: Andrew Dixon (PI), Joanne Walsh, Andrew Chilton, Margaret Turns, Maria Hill, Arrah Ashuarey and Ellen Nkhata on behalf of the site.
-
University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust: John de Caestecker (PI), Alison Moore, Donna Ward, Elizabeth Andrzejewshi and Howard Fairey on behalf of the site.
-
University Hospitals Coventry and Warwickshire NHS Trust: Jayne Eaden (PI), Steven Clay, Denise Gocher, Susan Dawson, Linda Stretton, Carol Wheatley, Kerry Flahive, Emily Archer, Katie James, Jaqueline Farmer and Jaqui Dagush on behalf of the site.
-
South Warwickshire NHS Foundation Trust: Martin Osborne (PI) Kerry Flahive, Emily Archer and Lucy Hughes on behalf of the site.
-
University Hospitals of Morecambe Bay NHS Foundation Trust: Colin Brown (PI), Jill Condor, Carmel Thomas, Carol Summer, Jane Chester, Maggie Coughlan and Susan Meyrick on behalf of the site.
-
Poole Hospital NHS Foundation Trust: Sally Parry (PI), Diane Simpson, Tracey Deacy, Christine Dickson and Sarah Patch on behalf of the site.
-
The Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust: Sean Weaver (PI), Hannah Dewhurst, Emma Gunter, Ian Leadbitter, James Page, Nigel Butter, Nina Barratt, Maggie Bunce and Samntha Newman on behalf of the site.
-
Dorset County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust: James Shutt (PI), Chris Hovell (PI), Abby Oglesby, Karen Hogben, Jackie Gibbins and Vicky Hanson on behalf of the site.
-
Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Trust: John Stebbing (PI), Karen Penry, Avril Adams, Daniel Jennings, Rachel Gallifent, Victoria Bartlett-Hunter, Anne Allen, Heather Swannack and Jessica Buckwell on behalf of the site.
-
Frimley Park Hospital NHS Trust: Henry Tilney (PI), Karen Penry, Carrie Burgess, Jacqueline Brighton, Anne Allen, Heather Swannack, Jessica Buckwell and Rachel Gallifent on behalf of the site.
-
Bolton NHS Foundation Trust: George Lipscomb (PI), Tracey Lawton, Janine Hurst, Jean Cummings, Karen Jewers, Louise Dawson, Shirley Cocks, Caroline Rogers and Gillian Cusack on behalf of the site.
-
King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust: Guy Chung-Faye (PI), Rayhan Ahmed, Stefi Stegner and Mun Lim on behalf of the site.
-
Lewisham and Greenwich NHS Trust: John O’Donohue (PI), Abel Jalloh, Martha Handousa, Hazel Harrop, Katrina Armar, Laletha Agoramoorthy, Priscilla Phiri, Shanna Wilson, Stefania Stegner, Theodora Nago and Tim Soete on behalf of the site.
-
Basildon and Thurrock University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust: Javaid Subhani (PI), Anne Nicholson, Karen Steggles, Marco Bondoc, Anne Case and Sibongile Gorogodo on behalf of the site.
-
University Hospitals Bristol NHS Foundation Trust: Tom Creed (PI), Shiney George, Edel Robbins, Jane Bowles, Jennifer Anstey and Nicola Barrah on behalf of the site.
-
North Bristol NHS Trust: Melanie Lockett (PI), Ann Treasure, Carol Brain, Lisa Lillywhite and Suriya Kirkpatrick on behalf of the site.
-
Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Trust: Rupert Pullan (PI), Sarah Tobin, Natalie Taylor, Kathryn Bird, Kerenza Boulton, Pauline Mercer and Georgina Ayres on behalf of the site.
-
Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust: Chris Hayward (PI), Sue Inniss, Ann-Marie Rowe, Judy Sercombe, Tim Johns and Kathryn Bird on behalf of the site.
-
North West Anglia NHS Foundation Trust (Hinchingbrooke): Phillip Roberts (PI), Julie Maddocks, Lelsey-Anne Exon and Janet Jones on behalf of the site.
-
North West Anglia NHS Foundation Trust (Peterborough): Naveen Kumar (PI), Julie Maddocks, Lelsey Ann Exon and Janet Jones on behalf of the site.
-
Royal Cornwall Hospitals NHS Trust: James Bebb (PI), Keely Lane, Benita Adams, Fiona Hammonds, Heidi Duckworth, Helen Anderson, Lisa Trembath, Christine Taylor, Patricia Petrauske and Rebecca Warren on behalf of the site.
-
Cheltenham General and Gloucestershire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust: Simon Hellier (PI), Linda Hill, Estelle Nabela, Karen Holbrook, Natalie Bynorth, Paula Townshend, Sarah White, Sophie Delacruz and Christian Loveridge on behalf of the site.
-
Royal Wolverhampton Hospitals NHS Trust: Matt Brookes (PI), Marie Green, Jayne Rankin and Jill Brown on behalf of the site.
-
West Hertfordshire Hospitals NHS Trust: Alistair King (PI), Linda Sarginson, Elaine Walker, Olabisi Adeoti and Sarah Cerys on behalf of the site.
-
Taunton and Somerset NHS Foundation Trust: Paul Thomas (PI), Jayne Foot, Leane Foote, Lucy Brotherton, Gillian Shire, Irene Cruickshank, Kelly Brown, Jennifer Williams, Julia Heneker and Karen Triggs on behalf of the site.
-
Yeovil District Hospital NHS Foundation Trust: Steve Gore (PI), Katie Spurdle, Alison Lewis, Donna Haywood, Kate Ronaldson, Sarah Board and Suzette David on behalf of the site.
-
Sherwood Forest Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust: Steve Foley (PI), Terri-Ann Sewell, Cheryl Heeley, Lynne Allsop and Dominic Nash on behalf of the site.
-
Blackpool Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust: Mark Hendrickse (PI), Greta Duyvenvoorde, Rachael Wheeldon, Sue Hesketh, Louise Newton, Carly Hollin, Louise Johnson, Lucy Clarkson, Ruth Connelley, Sarah Strickland and Sylvia Taylor on behalf of the site.
-
Lancashire Teaching Hospital Foundation Trust: Philip Shields (PI), Emma Durant, Ailsa Watt, Alexandra Williams, Janet Mills, Mark Verlander and Louise Newton on behalf of the site.
-
Colchester Hospital University NHS Foundation Trust: Donagh O’Riordan (PI), Aine Turner, Alison Ghosh, Cathleen Chabo, Marianne Morgan, Natalie Wheatley, Nyasha Nago and Orla Thunder on behalf of the site.
-
Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust: Simon Williams (PI), Joanne Bradley, Ginny Rose, John Cuckow, Stephanie Bell and Susan Cuckow on behalf of the site.
-
East and North Hertfordshire NHS Trust: Peter McIntyre (PI), Elizabeth Green, Clare Collins, Nicola McNiff, Poppa de Sousa and Roisin Schimmel on behalf of the site.
-
University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust: Phil Boger (PI), Emma Levell and Janet Jones on behalf of the site.
Contributions of authors
Mark A Hull (Professor of Molecular Gastroenterology and Honorary Consultant Gastroenterologist) was the Chief Investigator and authored the final report.
Kirsty Sprange (Trial Manager and Senior Trial Manager) oversaw trial delivery and contributed to the final report.
Trish Hepburn (Senior Medical Statistician) oversaw the statistical analysis and contributed to the final report.
Wei Tan (Medical Statistician, NCTU) performed the statistical analysis and contributed to the final report.
Aisha Shafayat (Trial Manager, NCTU) oversaw the trial and contributed to the final report.
Colin J Rees (Professor of Gastroenterology and Consultant Gastroenterologist) contributed to the trial design and delivery, and to the final report.
Gayle Clifford (BCSP SSPr) contributed to the trial design and the final report.
Richard F Logan (Professor of Epidemiology) contributed to the trial design and delivery, and to the final report.
Paul M Loadman (Professor of Pharmacokinetics and Drug Metabolism) contributed to the trial delivery, led the trial biobank and contributed to the final report.
Elizabeth A Williams (Senior Lecturer in Human Nutrition) contributed to the FFQ analysis and to the final report.
Diane Whitham (Research Manager) contributed to the trial design and delivery, and to the final report.
Alan A Montgomery (Professor of Medical Statistics and Clinical Trials) oversaw the statistical analysis and contributed to the final report.
Publications
Hull MA, Sandell AC, Montgomery AA, Logan RF, Clifford GM, Rees CJ, et al. A randomized controlled trial of eicosapentaenoic acid and/or aspirin for colorectal adenoma prevention during colonoscopic surveillance in the NHS Bowel Cancer Screening Programme (the seAFOod Polyp Prevention Trial): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2013;14:237.
Hull MA, Sprange K, Hepburn T, Tan W, Shafayat A, Rees CJ, et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid and aspirin, alone and in combination, for the prevention of colorectal adenomas (seAFOod Polyp Prevention trial): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 2 × 2 factorial trial. Lancet 2018;392:2583–94.
Data-sharing statement
All data requests should be submitted to the corresponding author for consideration. Access to anonymised data may be granted following review.
Patient data
This work uses data provided by patients and collected by the NHS as part of their care and support. Using patient data is vital to improve health and care for everyone. There is huge potential to make better use of information from people’s patient records, to understand more about disease, develop new treatments, monitor safety, and plan NHS services. Patient data should be kept safe and secure, to protect everyone’s privacy, and it’s important that there are safeguards to make sure that it is stored and used responsibly. Everyone should be able to find out about how patient data are used. #datasaveslives You can find out more about the background to this citation here: https://understandingpatientdata.org.uk/data-citation.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research. The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, the MRC, NETSCC, the EME programme or the Department of Health and Social Care. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the EME programme or the Department of Health and Social Care.
References
- Hull MA, Sprange K, Hepburn T, Tan W, Shafayat A, Rees CJ, et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid and aspirin, alone and in combination, for the prevention of colorectal adenomas (seAFOod Polyp Prevention trial): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 2 × 2 factorial trial. Lancet 2018;392:2583-94.
- Cancer Statistics for the UK. London: Cancer Research UK; n.d.
- World Cancer Research Fund International . About Our Cancer Prevention Recommendations. What Are They and How Do They Reduce Cancer Risk? n.d. www.wcrf.org/int/cancer-facts-figures/preventability-estimates/cancer-preventability-estimates-diet-nutrition (accessed 2 November 2017).
- Grady WM, Markowitz SD. The molecular pathogenesis of colorectal cancer and its potential application to colorectal cancer screening. Dig Dis Sci 2015;60:762-72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-014-3444-4.
- Strum WB. Colorectal adenomas. N Engl J Med 2016;374:1065-75. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1513581.
- Bowel Cancer Survival Statistics. London: Cancer Research UK; n.d.
- Cancer Survival by Stage at Diagnosis for England (Experimental Statistics): Adults Diagnosed 2012, 2013 and 2014 and Followed Up to 2015. Newport: ONS; 2016.
- Nishihara R, Wu K, Lochhead P, Morikawa T, Liao X, Qian ZR, et al. Long-term colorectal-cancer incidence and mortality after lower endoscopy. N Engl J Med 2013;369:1095-105. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1301969.
- Zauber AG, Winawer SJ, O’Brien MJ, Lansdorp-Vogelaar I, van Ballegooijen M, Hankey BF, et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectal-cancer deaths. N Engl J Med 2012;366:687-96. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1100370.
- Atkin WS, Edwards R, Kralj-Hans I, Wooldrage K, Hart AR, Northover JM, et al. Once-only flexible sigmoidoscopy screening in prevention of colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010;375:1624-33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60551-X.
- Baxter NN, Goldwasser MA, Paszat LF, Saskin R, Urbach DR, Rabeneck L. Association of colonoscopy and death from colorectal cancer. Ann Intern Med 2009;150:1-8. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-150-1-200901060-00306.
- Hoff G, Grotmol T, Skovlund E, Brett Hauer M. Norwegian Colorectal Cancer Prevention Study Group . Risk of colorectal cancer seven years after flexible sigmoidoscopy screening: randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2009;338. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b1846.
- Mandel JS, Church TR, Bond JH, Ederer F, Geisser MS, Mongin SJ, et al. The effect of fecal occult-blood screening on the incidence of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2000;343:1603-7. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200011303432203.
- van der Vlugt M, Grobbee EJ, Bossuyt PMM, Bos A, Bongers E, Spijker W, et al. Interval colorectal cancer incidence among subjects undergoing multiple rounds of fecal immunochemical testing. Gastroenterology 2017;153:439-47.e2. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.004.
- Gill MD, Bramble MG, Rees CJ, Lee TJ, Bradburn DM, Mills SJ. Comparison of screen-detected and interval colorectal cancers in the Bowel Cancer Screening Programme. Br J Cancer 2012;107:417-21. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2012.305.
- Robertson DJ, Greenberg ER, Beach M, Sandler RS, Ahnen D, Haile RW, et al. Colorectal cancer in patients under close colonoscopic surveillance. Gastroenterology 2005;129:34-41. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2005.05.012.
- Corley DA, Jensen CD, Marks AR, Zhao WK, Lee JK, Doubeni CA, et al. Adenoma detection rate and risk of colorectal cancer and death. N Engl J Med 2014;370:1298-306. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1309086.
- Routes to Diagnosis 2015 Update: Colorectal Cancer. London: Public Health England; 2016.
- Dienstmann R, Vermeulen L, Guinney J, Kopetz S, Tejpar S, Tabernero J. Consensus molecular subtypes and the evolution of precision medicine in colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2017;17:79-92. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.126.
- Fearon ER, Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 1990;61:759-67. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-I.
- Colussi D, Brandi G, Bazzoli F, Ricciardiello L. Molecular pathways involved in colorectal cancer: implications for disease behavior and prevention. Int J Mol Sci 2013;14:16365-85. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816365.
- Guinney J, Dienstmann R, Wang X, de Reyniès A, Schlicker A, Soneson C, et al. The consensus molecular subtypes of colorectal cancer. Nat Med 2015;21:1350-6. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3967.
- Lee MS, Menter DG, Kopetz S. Right versus left colon cancer biology: integrating the consensus molecular subtypes. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2017;15:411-19. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2017.0038.
- Galiatsatos P, Foulkes WD. Familial adenomatous polyposis. Am J Gastroenterol 2006;101:385-98. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00375.x.
- Giardiello FM, Allen JI, Axilbund JE, Boland CR, Burke CA, Burt RW, et al. Guidelines on genetic evaluation and management of Lynch syndrome: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2014;147:502-26. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.04.001.
- Roger L, Jones RE, Heppel NH, Williams GT, Sampson JR, Baird DM. Extensive telomere erosion in the initiation of colorectal adenomas and its association with chromosomal instability. J Natl Cancer Inst 2013;105:1202-11. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djt191.
- East JE, Vieth M, Rex DK. Serrated lesions in colorectal cancer screening: detection, resection, pathology and surveillance. Gut 2015;64:991-1000. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2014-309041.
- Bosman FT, Carnerio F, Hruban RH, Theise ND. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Digestive System. Lyon: IARC; 2010.
- Yamauchi M, Morikawa T, Kuchiba A, Imamura Y, Qian ZR, Nishihara R, et al. Assessment of colorectal cancer molecular features along bowel subsites challenges the conception of distinct dichotomy of proximal versus distal colorectum. Gut 2012;61:847-54. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300865.
- Cairns SR, Scholefield JH, Steele RJ, Dunlop MG, Thomas HJ, Evans GD, et al. Guidelines for colorectal cancer screening and surveillance in moderate and high risk groups (update from 2002). Gut 2010;59:666-89. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2009.179804.
- Hassan C, Quintero E, Dumonceau JM, Regula J, Brandão C, Chaussade S, et al. Post-polypectomy colonoscopy surveillance: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) guideline. Endoscopy 2013;45:842-51. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1344548.
- Lieberman DA, Rex DK, Winawer SJ, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Levin TR. Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after screening and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2012;143:844-57. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.001.
- Winawer SJ, Zauber AG, Fletcher RH, Stillman JS, O’Brien MJ, Levin B, et al. Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer and the American Cancer Society. Gastroenterology 2006;130:1872-85. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2006.03.012.
- Arber N, Levin B. Chemoprevention of colorectal neoplasia: the potential for personalized medicine. Gastroenterology 2008;134:1224-37. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2008.02.012.
- Dulai PS, Singh S, Marquez E, Khera R, Prokop LJ, Limburg PJ, et al. Chemoprevention of colorectal cancer in individuals with previous colorectal neoplasia: systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ 2016;355. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i6188.
- Song M, Garrett WS, Chan AT. Nutrients, foods, and colorectal cancer prevention. Gastroenterology 2015;148:1244-60.e16. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.12.035.
- Lynch PM. Chemoprevention of familial adenomatous polyposis. Fam Cancer 2016;15:467-75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10689-016-9901-9.
- Lee TJ, Rutter MD, Blanks RG, Moss SM, Goddard AF, Chilton A, et al. Colonoscopy quality measures: experience from the NHS Bowel Cancer Screening Programme. Gut 2012;61:1050-7. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300651.
- Higurashi T, Hosono K, Takahashi H, Komiya Y, Umezawa S, Sakai E, et al. Metformin for chemoprevention of metachronous colorectal adenoma or polyps in post-polypectomy patients without diabetes: a multicentre double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2016;17:475-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00565-3.
- Atkin WS, Morson BC, Cuzick J. Long-term risk of colorectal cancer after excision of rectosigmoid adenomas. N Engl J Med 1992;326:658-62. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199203053261002.
- Cottet V, Jooste V, Fournel I, Bouvier AM, Faivre J, Bonithon-Kopp C. Long-term risk of colorectal cancer after adenoma removal: a population-based cohort study. Gut 2012;61:1180-6. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300295.
- Løberg M, Kalager M, Holme Ø, Hoff G, Adami HO, Brett Hauer M. Long-term colorectal-cancer mortality after adenoma removal. N Engl J Med 2014;371:799-807. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1315870.
- Cuzick J, Otto F, Baron JA, Brown PH, Burn J, Greenwald P, et al. Aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for cancer prevention: an international consensus statement. Lancet Oncol 2009;10:501-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70035-X.
- Drew DA, Cao Y, Chan AT. Aspirin and colorectal cancer: the promise of precision chemoprevention. Nat Rev Cancer 2016;16:173-86. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.4.
- Patrignani P, Patrono C. Aspirin and cancer. J Am Coll Cardiol 2016;68:967-76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2016.05.083.
- Flossmann E, Rothwell PM. British Doctors Aspirin Trial and the UK-TIA Aspirin Trial . Effect of aspirin on long-term risk of colorectal cancer: consistent evidence from randomised and observational studies. Lancet 2007;369:1603-13. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60747-8.
- Rothwell PM, Wilson M, Elwin CE, Norrving B, Algra A, Warlow CP, et al. Long-term effect of aspirin on colorectal cancer incidence and mortality: 20-year follow-up of five randomised trials. Lancet 2010;376:1741-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61543-7.
- Cook NR, Lee IM, Zhang SM, Moorthy MV, Buring JE. Alternate-day, low-dose aspirin and cancer risk: long-term observational follow-up of a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2013;159:77-85. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-159-2-201307160-00002.
- Cole BF, Logan RF, Halabi S, Benamouzig R, Sandler RS, Grainge MJ, et al. Aspirin for the chemoprevention of colorectal adenomas: meta-analysis of the randomized trials. J Natl Cancer Inst 2009;101:256-66. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djn485.
- Beck SL. Effects of aspirin on colorectal cancer related to Lynch syndrome. J Adv Pract Oncol 2012;3:395-8. https://doi.org/10.6004/jadpro.2012.3.6.6.
- Burn J, Bishop DT, Mecklin JP, Macrae F, Möslein G, Olschwang S, et al. Effect of aspirin or resistant starch on colorectal neoplasia in the Lynch syndrome. N Engl J Med 2008;359:2567-78. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0801297.
- Bibbins-Domingo K. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force . Aspirin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and colorectal cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med 2016;164:836-45. https://doi.org/10.7326/M16-0577.
- Cuzick J, Thorat MA, Bosetti C, Brown PH, Burn J, Cook NR, et al. Estimates of benefits and harms of prophylactic use of aspirin in the general population. Ann Oncol 2015;26:47-5. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu225.
- Wang D, Dubois RN. The role of COX-2 in intestinal inflammation and colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2010;29:781-8. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.421.
- Steinbach G, Lynch PM, Phillips RK, Wallace MH, Hawk E, Gordon GB, et al. The effect of celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, in familial adenomatous polyposis. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1946-52. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200006293422603.
- Funk CD, FitzGerald GA. COX-2 inhibitors and cardiovascular risk. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2007;50:470-9. https://doi.org/10.1097/FJC.0b013e318157f72d.
- Smith WL. Cyclooxygenases, peroxide tone and the allure of fish oil. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2005;17:174-82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2005.02.005.
- Al-Hilal M, Alsaleh A, Maniou Z, Lewis FJ, Hall WL, Sanders TA, et al. MARINA study team . Genetic variation at the FADS1-FADS2 gene locus influences delta-5 desaturase activity and LC-PUFA proportions after fish oil supplement. J Lipid Res 2013;54:542-51. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.P032276.
- Burdge GC, Calder PC. Dietary alpha-linolenic acid and health-related outcomes: a metabolic perspective. Nutr Res Rev 2006;19:26-52. https://doi.org/10.1079/NRR2005113.
- Hull MA. Cyclooxygenase-2: how good is it as a target for cancer chemoprevention?. Eur J Cancer 2005;41:1854-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2005.04.013.
- Cockbain AJ, Toogood GJ, Hull MA. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids for the treatment and prevention of colorectal cancer. Gut 2012;61:135-49. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2010.233718.
- MacLean CH, Newberry SJ, Mojica WA, Khanna P, Issa AM, Suttorp MJ, et al. Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on cancer risk: a systematic review. JAMA 2006;295:403-15. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.295.4.403.
- Qato DM, Wilder J, Schumm LP, Gillet V, Alexander GC. Changes in prescription and over-the-counter medication and dietary supplement use among older adults in the United States, 2005 vs 2011. JAMA Intern Med 2016;176:473-82. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.8581.
- Kantor ED, Lampe JW, Peters U, Vaughan TL, White E. Long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake and risk of colorectal cancer. Nutr Cancer 2014;66:716-27. https://doi.org/10.1080/01635581.2013.804101.
- Schuchardt JP, Hahn A. Bioavailability of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids. Prostaglandins, Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2013;89:1-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plefa.2013.03.010.
- Ghasemifard S, Turchini GM, Sinclair AJ. Omega-3 long chain fatty acid ‘bioavailability’: a review of evidence and methodological considerations. Prog Lipid Res 2014;56:92-108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2014.09.001.
- West NJ, Clark SK, Phillips RK, Hutchinson JM, Leicester RJ, Belluzzi A, et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid reduces rectal polyp number and size in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut 2010;59:918-25. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2009.200642.
- Fini L, Piazzi G, Ceccarelli C, Daoud Y, Belluzzi A, Munarini A, et al. Highly purified eicosapentaenoic acid as free fatty acids strongly suppresses polyps in Apc(Min/+) mice. Clin Cancer Res 2010;16:5703-11. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1990.
- Petrik MB, McEntee MF, Chiu CH, Whelan J. Antagonism of arachidonic acid is linked to the antitumorigenic effect of dietary eicosapentaenoic acid in Apc(Min/+) mice. J Nutr 2000;130:1153-8. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/130.5.1153.
- Courtney ED, Matthews S, Finlayson C, Di Pierro D, Belluzzi A, Roda E, et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) reduces crypt cell proliferation and increases apoptosis in normal colonic mucosa in subjects with a history of colorectal adenomas. Int J Colorectal Dis 2007;22:765-76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-006-0240-4.
- West N, Belluzzi A, Lund E. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), as the free fatty acid, reduces colonic crypt cell proliferation in patients with sporadic colorectal polyps [abstract]. Gut 2009;58.
- Murff HJ, Shrubsole MJ, Cai Q, Smalley WE, Dai Q, Milne GL, et al. Dietary intake of PUFAs and colorectal polyp risk. Am J Clin Nutr 2012;95:703-12. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.111.024000.
- Higurashi T, Hosono K, Endo H, Takahashi H, Iida H, Uchiyama T, et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) efficacy for colorectal aberrant crypt foci (ACF): a double-blind randomized controlled trial. BMC Cancer 2012;12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-12-413.
- Hawcroft G, Loadman PM, Belluzzi A, Hull MA. Effect of eicosapentaenoic acid on E-type prostaglandin synthesis and EP4 receptor signaling in human colorectal cancer cells. Neoplasia 2010;12:618-27. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.10388.
- Serhan CN, Yacoubian S, Yang R. Anti-inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediators. Annu Rev Pathol 2008;3:279-312. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pathmechdis.3.121806.151409.
- Arita M, Bianchini F, Aliberti J, Sher A, Chiang N, Hong S, et al. Stereochemical assignment, antiinflammatory properties, and receptor for the omega-3 lipid mediator resolvin E1. J Exp Med 2005;201:713-22. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20042031.
- Kasuga K, Suga T, Mano N. Bioanalytical insights into mediator lipidomics. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2015;113:151-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2015.02.011.
- Nabavi SF, Bilotto S, Russo GL, Orhan IE, Habtemariam S, Daglia M, et al. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and cancer: lessons learned from clinical trials. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2015;34:359-80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-015-9572-2.
- Lavie CJ, Milani RV, Mehra MR, Ventura HO. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and cardiovascular diseases. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009;54:585-94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2009.02.084.
- Larson MK, Ashmore JH, Harris KA, Vogelaar JL, Pottala JV, Sprehe M, et al. Effects of omega-3 acid ethyl esters and aspirin, alone and in combination, on platelet function in healthy subjects. Thromb Haemost 2008;100:634-41. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH08-02-0084.
- Thorngren M, Gustafson A. Effects of 11-week increases in dietary eicosapentaenoic acid on bleeding time, lipids, and platelet aggregation. Lancet 1981;2:1190-3. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(81)91436-7.
- Chan AO, Jim MH, Lam KF, Morris JS, Siu DC, Tong T, et al. Prevalence of colorectal neoplasm among patients with newly diagnosed coronary artery disease. JAMA 2007;298:1412-19. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.298.12.1412.
- Benamouzig R, Uzzan B, Martin A, Deyra J, Little J, Girard B, et al. APACC Study Group . Cyclooxygenase-2 expression and recurrence of colorectal adenomas: effect of aspirin chemoprevention. Gut 2010;59:622-9. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2008.175406.
- Fekete K, Marosvölgyi T, Jakobik V, Decsi T. Methods of assessment of n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid status in humans: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr 2009;89:2070S-2084S. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2009.27230I.
- Roy S, Brasky TM, Belury MA, Krishnan S, Cole RM, Marian C, et al. Associations of erythrocyte ω-3 fatty acids with biomarkers of ω-3 fatty acids and inflammation in breast tissue. Int J Cancer 2015;137:2934-46. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29675.
- Katan MB, Deslypere JP, van Birgelen AP, Penders M, Zegwaard M. Kinetics of the incorporation of dietary fatty acids into serum cholesteryl esters, erythrocyte membranes, and adipose tissue: an 18-month controlled study. J Lipid Res 1997;38:2012-22.
- Cockbain AJ, Volpato M, Race AD, Munarini A, Fazio C, Belluzzi A, et al. Anticolorectal cancer activity of the omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid. Gut 2014;63:1760-8. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2013-306445.
- Watson H, Cockbain AJ, Spencer J, Race A, Volpato M, Loadman PM, et al. Measurement of red blood cell eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) levels in a randomised trial of EPA in patients with colorectal cancer liver metastases. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2016;115:60-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plefa.2016.10.003.
- Volpato M, Spencer JA, Race AD, Munarini A, Belluzzi A, Cockbain AJ, et al. A liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method to measure fatty acids in biological samples. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2017;1055–6:125-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.04.030.
- Rothwell PM, Price JF, Fowkes FG, Zanchetti A, Roncaglioni MC, Tognoni G, et al. Short-term effects of daily aspirin on cancer incidence, mortality, and non-vascular death: analysis of the time course of risks and benefits in 51 randomised controlled trials. Lancet 2012;379:1602-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61720-0.
- Bailey RL, Denby N, Haycock B, Sherif K, Steinbaum S, von Schacky C. Perceptions of a healthy diet: insights from a 3-country survey. Nutr Today 2015;50:282-7. https://doi.org/10.1097/NT.0000000000000119.
- Cao Y, Lu L, Liang J, Liu M, Li X, Sun R, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids and primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Cell Biochem Biophys 2015;72:77-81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0407-5.
- Makhoul Z, Kristal AR, Gulati R, Luick B, Bersamin A, Boyer B, et al. Associations of very high intakes of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids with biomarkers of chronic disease risk among Yup’ik Eskimos. Am J Clin Nutr 2010;91:777-85. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2009.28820.
- Harris WS. Expert opinion: omega-3 fatty acids and bleeding-cause for concern?. Am J Cardiol 2007;99:44C-46C. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2006.11.021.
- Logan RF, Patnick J, Nickerson C, Coleman L, Rutter MD, von Wagner C. English Bowel Cancer Screening Evaluation Committee . Outcomes of the Bowel Cancer Screening Programme (BCSP) in England after the first 1 million tests. Gut 2012;61:1439-46. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300843.
- Loughrey MB, Shepherd NA. The pathology of bowel cancer screening. Histopathology 2015;66:66-77. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.12530.
- NHS Cancer Screening Programmes . Reporting Lesions in the NHS Bowel Cancer Screening Programme Guidelines from the Bowel Cancer Screening Programme Pathology Group 2007. www.bcsp.nhs.uk/files/NHS%20BCSP%20Publication%201.pdf (accessed 6 June 2019).
- Lee TJ, Nickerson C, Goddard AF, Rees CJ, McNally RJ, Rutter MD. Outcome of 12-month surveillance colonoscopy in high-risk patients in the National Health Service Bowel Cancer Screening Programme. Colorectal Dis 2013;15:e435-42. https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.12278.
- McGregor LM, Bonello B, Kerrison RS, Nickerson C, Baio G, Berkman L, et al. Uptake of bowel scope (flexible sigmoidoscopy) screening in the English national programme: the first 14 months. J Med Screen 2016;23:77-82. https://doi.org/10.1177/0969141315604659.
- Hull MA, Sandell AC, Montgomery AA, Logan RF, Clifford GM, Rees CJ, et al. A randomized controlled trial of eicosapentaenoic acid and/or aspirin for colorectal adenoma prevention during colonoscopic surveillance in the NHS Bowel Cancer Screening Programme (The seAFOod Polyp Prevention Trial): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2013;14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-14-237.
- Dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamin E after myocardial infarction: results of the GISSI-Prevenzione trial. Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio della Sopravvivenza nell’Infarto miocardico. Lancet 1999;354:447-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(99)07072-5.
- Bays H. Clinical overview of Omacor: a concentrated formulation of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Am J Cardiol 2006;98:71i-76i. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.12.029.
- Bays HE. Safety considerations with omega-3 fatty acid therapy. Am J Cardiol 2007;99:35C-43C. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2006.11.020.
- Covington MB. Omega-3 fatty acids. Am Fam Physician 2004;70:133-40.
- Kris-Etherton PM, Harris WS, Appel LJ. American Heart Association . Nutrition Committee. Fish consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2002;106:2747-57. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000038493.65177.94.
- Great Britain . The Medicines for Human Use (Clinical Trials) Regulations 2004 2004.
- Great Britain . Human Tissue Act 2004 2004.
- McKeown NM, Day NE, Welch AA, Runswick SA, Luben RN, Mulligan AA, et al. Use of biological markers to validate self-reported dietary intake in a random sample of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer United Kingdom Norfolk cohort. Am J Clin Nutr 2001;74:188-96. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/74.2.188.
- Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition/Committee on Toxicity . Advice on Fish Consumption: Benefits &Amp; Risks 2004. www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/338801/SACN_Advice_on_Fish_Consumption.pdf (accessed 31 August 2017).
- Montgomery AA, Peters TJ, Little P. Design, analysis and presentation of factorial randomised controlled trials. BMC Med Res Methodol 2003;3. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-3-26.
- Shrier I, Steele RJ, Verhagen E, Herbert R, Riddell CA, Kaufman JS. Beyond intention to treat: what is the right question?. Clin Trials 2014;11:28-37. https://doi.org/10.1177/1740774513504151.
- White IR. Uses and limitations of randomization-based efficacy estimators. Stat Methods Med Res 2005;14:327-47. https://doi.org/10.1191/0962280205sm406oa.
- Heading RC. Prevalence of upper gastrointestinal symptoms in the general population: a systematic review. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl 1999;231:3-8.
- Baron JA, Cole BF, Sandler RS, Haile RW, Ahnen D, Bresalier R, et al. A randomized trial of aspirin to prevent colorectal adenomas. N Engl J Med 2003;348:891-9. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa021735.
- Benamouzig R, Deyra J, Martin A, Girard B, Jullian E, Piednoir B, et al. Daily soluble aspirin and prevention of colorectal adenoma recurrence: one-year results of the APACC trial. Gastroenterology 2003;125:328-36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-5085(03)00887-4.
- Giardiello FM, Hamilton SR, Krush AJ, Piantadosi S, Hylind LM, Celano P, et al. Treatment of colonic and rectal adenomas with sulindac in familial adenomatous polyposis. N Engl J Med 1993;328:1313-16. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199305063281805.
- Logan RF, Grainge MJ, Shepherd VC, Armitage NC, Muir KR. ukCAP Trial Group . Aspirin and folic acid for the prevention of recurrent colorectal adenomas. Gastroenterology 2008;134:29-38. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2007.10.014.
- Sandler RS, Halabi S, Baron JA, Budinger S, Paskett E, Keresztes R, et al. A randomized trial of aspirin to prevent colorectal adenomas in patients with previous colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2003;348:883-90. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa021633.
- Benamouzig R, Uzzan B, Deyra J, Martin A, Girard B, Little J, et al. Association pour la Prévention par l’Aspirine du Cancer Colorectal Study Group (APACC) . Prevention by daily soluble aspirin of colorectal adenoma recurrence: 4-year results of the APACC randomised trial. Gut 2012;61:255-61. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300113.
- Zhang L, Shay JW. Multiple roles of APC and its therapeutic implications in colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2017;109. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djw332.
- Wallace K, Grau MV, Ahnen D, Snover DC, Robertson DJ, Mahnke D, et al. The association of lifestyle and dietary factors with the risk for serrated polyps of the colorectum. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2009;18:2310-7. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.epi-09-0211.
- Bailie L, Loughrey MB, Coleman HG. Lifestyle risk factors for serrated colorectal polyps: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2017;152:92-104. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.09.003.
- Burn J, Bishop DT, Chapman PD, Elliott F, Bertario L, Dunlop MG, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled prevention trial of aspirin and/or resistant starch in young people with familial adenomatous polyposis. Cancer Prev Res 2011;4:655-65. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-11-0106.
- Ishikawa H, Wakabayashi K, Suzuki S, Mutoh M, Hirata K, Nakamura T, et al. Preventive effects of low-dose aspirin on colorectal adenoma growth in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis: double-blind, randomized clinical trial. Cancer Med 2013;2:50-6. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.46.
- Baron JA, Sandler RS, Bresalier RS, Quan H, Riddell R, Lanas A, et al. A randomized trial of rofecoxib for the chemoprevention of colorectal adenomas. Gastroenterology 2006;131:1674-82. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2006.08.079.
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Network . Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012;487. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11252.
- Jiang Y, Djuric Z, Sen A, Ren J, Kuklev D, Waters I, et al. Biomarkers for personalizing omega-3 fatty acid dosing. Cancer Prev Res 2014;7:1011-22. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-14-0134.
- Tokudome S, Kuriki K, Yokoyama Y, Sasaki M, Joh T, Kamiya T, et al. Dietary n-3/long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids for prevention of sporadic colorectal tumors: a randomized controlled trial in polypectomized participants. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2015;94:1-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plefa.2014.09.001.
- Watson H, Mitra S, Croden FC, Taylor M, Wood HM, Perry SL, et al. A randomised trial of the effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplements on the human intestinal microbiota. Gut 2018;67:1974-83. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314968.
- Cummings JH, Pomare EW, Branch WJ, Naylor CP, Macfarlane GT. Short chain fatty acids in human large intestine, portal, hepatic and venous blood. Gut 1987;28:1221-7. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.28.10.1221.
- Kaji I, Karaki S, Tanaka R, Kuwahara A. Density distribution of free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFA2)-expressing and GLP-1-producing enteroendocrine L cells in human and rat lower intestine, and increased cell numbers after ingestion of fructo-oligosaccharide. J Mol Histol 2011;42:27-38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-010-9304-4.
- Pan P, Skaer CW, Wang HT, Oshima K, Huang YW, Yu J, et al. Loss of free fatty acid receptor 2 enhances colonic adenoma development and reduces the chemopreventive effects of black raspberries in ApcMin/+ mice. Carcinogenesis 2017;38:86-93. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgw122.
- Chapple KS, Cartwright EJ, Hawcroft G, Tisbury A, Bonifer C, Scott N, et al. Localization of cyclooxygenase-2 in human sporadic colorectal adenomas. Am J Pathol 2000;156:545-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64759-1.
- Nasir A, Lopez A, Boulware D, Malafa M, Coppola D. Correlation between COX-2 and APC expression in left versus right-sided human colon cancer. Anticancer Res 2011;31:2191-5.
- Zelenay S, van der Veen AG, Böttcher JP, Snelgrove KJ, Rogers N, Acton SE, et al. Cyclooxygenase-dependent tumor growth through evasion of immunity. Cell 2015;162:1257-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.015.
- Roseweir AK, McMillan DC, Horgan PG, Edwards J. Colorectal cancer subtypes: translation to routine clinical pathology. Cancer Treat Rev 2017;57:1-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.04.006.
- Bensen S, Mott LA, Dain B, Rothstein R, Baron J. The colonoscopic miss rate and true one-year recurrence of colorectal neoplastic polyps. Polyp Prevention Study Group. Am J Gastroenterol 1999;94:194-9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.00796.x.
- van Rijn JC, Reitsma JB, Stoker J, Bossuyt PM, van Deventer SJ, Dekker E. Polyp miss rate determined by tandem colonoscopy: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol 2006;101:343-50. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00390.x.
- Martínez ME, Baron JA, Lieberman DA, Schatzkin A, Lanza E, Winawer SJ, et al. A pooled analysis of advanced colorectal neoplasia diagnoses after colonoscopic polypectomy. Gastroenterology 2009;136:832-41. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2008.12.007.
- Keum N, Lee DH, Kim R, Greenwood DC, Giovannucci EL. Visceral adiposity and colorectal adenomas: dose-response meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann Oncol 2015;26:1101-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu563.
- Baron JA, Barry EL, Mott LA, Rees JR, Sandler RS, Snover DC, et al. A trial of calcium and vitamin D for the prevention of colorectal adenomas. N Engl J Med 2015;373:1519-30. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1500409.
- Obesity and Overweight. Fact Sheet. 2017. Geneva: WHO; 2017.
- Schatzkin A, Lanza E, Corle D, Lance P, Iber F, Caan B, et al. Lack of effect of a low-fat, high-fiber diet on the recurrence of colorectal adenomas. Polyp Prevention Trial Study Group. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1149-55. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200004203421601.
- Hilleman D, Smer A. Prescription omega-3 fatty acid products and dietary supplements are not interchangeable. Manag Care 2016;25:46-52.
- Anti M, Armelao F, Marra G, Percesepe A, Bartoli GM, Palozza P, et al. Effects of different doses of fish oil on rectal cell proliferation in patients with sporadic colonic adenomas. Gastroenterology 1994;107:1709-18. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(94)90811-7.
- Siscovick DS, Barringer TA, Fretts AM, Wu JH, Lichtenstein AH, Costello RB, et al. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (fish oil) supplementation and the prevention of clinical cardiovascular disease: a science advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017;135:e867-84. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000482.
- Stark KD, Van Elswyk ME, Higgins MR, Weatherford CA, Salem N. Global survey of the omega-3 fatty acids, docosahexaenoic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid in the blood stream of healthy adults. Prog Lipid Res 2016;63:132-52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2016.05.001.
- Harris WS, Thomas RM. Biological variability of blood omega-3 biomarkers. Clin Biochem 2010;43:338-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2009.08.016.
- Scorletti E, Bhatia L, McCormick KG, Clough GF, Nash K, Hodson L, et al. Effects of purified eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: results from the WELCOME* study. Hepatology 2014;60:1211-21. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27289.
- Kleiner AC, Cladis DP, Santerre CR. A comparison of actual versus stated label amounts of EPA and DHA in commercial omega-3 dietary supplements in the United States. J Sci Food Agric 2015;95:1260-7. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6816.
- Clarke TC, Black LI, Stussman BJ, Barnes PM, Nahin RL. Trends in the Use of Complementary Health Approaches Among Adults: United States, 2002–2012 2015. www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhsr/nhsr079.pdf (accessed 22 December 2017).
- Li L, Geraghty OC, Mehta Z, Rothwell PM. Oxford Vascular Study . Age-specific risks, severity, time course, and outcome of bleeding on long-term antiplatelet treatment after vascular events: a population-based cohort study. Lancet 2017;390:490-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30770-5.
- Potter JD. The failure of cancer chemoprevention. Carcinogenesis 2014;35:974-82. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgu063.
- East JE, Atkin WS, Bateman AC, Clark SK, Dolwani S, Ket SN, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology position statement on serrated polyps in the colon and rectum. Gut 2017;66:1181-96. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314005.
- Wang J, Cho NL, Zauber AG, Hsu M, Dawson D, Srivastava A, et al. Expression of COX-2 and 15-PGDH in adenomas removed during pretreatment colonoscopy to predict chemopreventive efficacy of the selective COX-2 inhibitor, celecoxib. J Clin Oncol 2017;35. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.35.4_suppl.524.
- Bowman L, Mafham M, Stevens W, Haynes R, Aung T, Chen F, et al. ASCEND: A Study of Cardiovascular Events iN Diabetes: characteristics of a randomized trial of aspirin and of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in 15,480 people with diabetes. AM Heart J 2018;198:135-44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2017.12.006.
- Manson JE, Bassuk SS, Lee IM, Cook NR, Albert MA, Gordon D, et al. The VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL (VITAL): rationale and design of a large randomized controlled trial of vitamin D and marine omega-3 fatty acid supplements for the primary prevention of cancer and cardiovascular disease. Contemp Clin Trials 2012;33:159-71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cct.2011.09.009.
- Berg KCG, Eide PW, Eilertsen IA, Johannessen B, Bruun J, Danielsen SA, et al. Multi-omics of 34 colorectal cancer cell lines – a resource for biomedical studies. Mol Cancer 2017;16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0691-y.
- Wang Y, Sedimbi S, Löfbom L, Singh AK, Porcelli SA, Cardell SL. Unique invariant natural killer T cells promote intestinal polyps by suppressing TH1 immunity and promoting regulatory T cells. Mucosal Immunol 2018;11:131-43. https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2017.34.
- Miccadei S, Masella R, Mileo AM, Gessani S. ω3 polyunsaturated fatty acids as immunomodulators in colorectal cancer: new potential role in adjuvant therapies. Front Immunol 2016;7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2016.00486.
- Simopoulos AP. Genetic variants in the metabolism of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids: their role in the determination of nutritional requirements and chronic disease risk. Exp Biol Med 2010;235:785-95. https://doi.org/10.1258/ebm.2010.009298.
Appendix 1 Simplified investigational medicinal product dossier: investigational medicinal product stability testing
Appendix 2 Aspirin Summary of Product Characteristics
Reproduced with permission from Bayer AG.
Reproduced with permission from Bayer AG.
Appendix 3 Summary of protocol amendments
| Amendment reference; date | Amendment details | Previous version number and date | New version number and date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Substantial amendments (SAs) | |||
| SA02; 8 August 2011 | Changes to the protocol and PIL to ensure wording is clearer for trial personnel and participants | seAFOod trial protocol version 1.1, dated 14 April 2011 | seAFOod trial protocol version 2.0, dated 8 August 2011 |
| SA04; 30 November 2011 |
|
seAFOod trial protocol version 2.0, dated 8 August 2011 | seAFOod trial protocol version 3.0, dated 28 November 2011 |
| SA06; 25 May 2012 | Change to exclusion criteria to include patients who need a second repeat screening endoscopy, allowing inclusion of participants who have a second screening procedure | seAFOod trial protocol version 3.0, dated 28 November 2011 | seAFOod trial protocol, version 4.0, dated 4 May 2012 |
| SA10; 19 June 2013 | Change to inclusion criteria to include patients identified through the bowel scope FS screening programme | seAFOod trial protocol version 4.0, dated 4 May 2012 | seAFOod trial protocol version 5.0, dated 17 June 2013 |
| SA14; 14 August 2014 | Changes to the protocol in line with the introduction of the replacement capsule IMP. This includes additional information on the new EPA-TG formulation | seAFOod trial protocol version 5.0, dated 17 June 2013 | seAFOod trial protocol version 6.0, dated 11 August 2014 |
Appendix 4 Additional tables, listings and figures
| Estimate (95% CI) (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| EPA vs. no EPA | Aspirin vs. no aspirin | |
| Primary analysis (risk difference) | 0.7 (–6.8 to 8.3) | –1.2 (–8.7 to 6.3) |
| Using per-protocol population (risk difference) | 1.0 (–6.7 to 8.8) | –1.0 (–8.7 to 6.7) |
| Multilevel model treating recruiting centre and site as random effects (odds ratio) | 1.03 (0.75 to 1.42) | 0.95 (0.69 to 1.31) |
| Multiple imputation of missing data (risk difference) | 0.1 (–7.3 to 7.6) | –0.7 (–8.3 to 6.8) |
| Adjustment of baseline variables with imbalancea (risk difference) | 1.1 (–6.4 to 8.6) | –1.5 (–9.0 to 5.9) |
| Adjustment of oily fish intake during the trial (risk difference) | –1.3 (–9.5 to 6.9) | –2.7 (–10.9 to 5.5) |
| CACE analysis taking account of treatment adherence | ||
| Binary adherence (risk difference) | 0.8 (–7.1 to 8.7) | –1.2 (–8.9 to 6.4) |
| Continuous adherence (risk difference) | 0.4 (–7.3 to 8.1) | –1.3 (–8.6 to 6.4) |
| Adjustment of EPA formulation | 0.8 (–6.7 to 8.3) | –1.1 (–8.3 to 7.4) |
| Further adjustment for baseline RBC EPA (risk difference) | –2.1 (–10.2 to 5.9) | 1.7 (–6.3 to 9.8) |
| Treatment group | Description | System organ class name | Preferred term name | SAE | Severity | Start date | End date | Action taken | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Heartburn | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 7 March 2013 | 15 March 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Moderate | 5 March 2013 | 14 March 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Moderate | 5 March 2013 | 14 March 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Vomiting | GI disorders | Vomiting | No | Mild | 18 February 2014 | 20 February 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Abdominal wind | GI disorders | Flatulence | No | Mild | 2 July 2013 | 20 August 2013 | No action taken | Recovered with sequelae |
| EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 22 April 2014 | 2 May 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Indigestion | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Moderate | 23 August 2015 | 30 August 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Condition improving |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 23 October 2012 | 15 November 2012 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Gastric irritation | GI disorders | Epigastric discomfort | No | Mild | 15 November 2015 | 15 November 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 22 February 2016 | 22 February 2016 | Trial medication already discontinued | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 8 June 2013 | 9 June 2013 | Unknown | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Halitosis | GI disorders | Breath odour | No | Mild | 16 June 2013 | 23 June 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 24 November 2013 | 24 November 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Indigestion | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 3 March 2014 | 10 March 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Indigestion | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 20 April 2014 | 21 June 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Halitosis | GI disorders | Breath odour | No | Mild | 3 March 2014 | 10 March 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 1 November 2013 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Indigestion | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 25 February 2014 | 15 April 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Indigestion | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 30 April 2014 | 27 October 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 1 July 2015 | 4 March 2016 | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Mild | 6 November 2015 | 23 December 2015 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 5 April 2016 | 16 April 2016 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 5 April 2016 | 16 April 2016 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Mild | 5 April 2016 | 16 April 2016 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 24 October 2015 | 1 January 2016 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 28 April 2012 | 4 May 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Mild | 28 April 2012 | 4 May 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Halitosis | GI disorders | Breath odour | No | Mild | 16 August 2012 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| Placebo + placebo | Acid indigestion | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 2 August 2012 | 15 August 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 19 September 2012 | 15 May 2013 | Unknown | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Rash | Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Rash | No | Mild | 16 November 2012 | 8 April 2013 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 18 July 2013 | 20 July 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Gastritis | GI disorders | Gastritis | Yes | Mild | 18 October 2013 | 1 November 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Epigastric pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain upper | No | Mild | 27 November 2013 | 28 November 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 14 September 2013 | N/A | Trial medications reduced | Condition present and unchanged |
| Placebo + placebo | Abdominal discomfort | GI disorders | Abdominal discomfort | No | Mild | 26 January 2014 | 31 March 2014 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Indigestion | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 26 January 2014 | 31 March 2014 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 26 January 2014 | 31 March 2014 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Epigastric pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain upper | No | Mild | 26 January 2014 | 31 March 2014 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 11 May 2014 | N/A | Trial medications reduced | Condition present and unchanged |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 21 May 2012 | 26 May 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Oesophageal bleeding | GI disorders | Oesophageal haemorrhage | Yes | Severe | 23 July 2012 | 30 July 2012 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Epistaxis | Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Epistaxis | No | Mild | 5 June 2012 | 5 June 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Anal bleeding | GI disorders | Anal haemorrhage | No | Mild | 15 November 2012 | 15 November 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 08 December 2012 | 6 January 2013 | No action taken | Condition improving |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Moderate | 27 June 2014 | 26 July 2014 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 25 June 2014 | 26 June 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Medication aftertaste | General disorders and administration site conditions | Product taste abnormal | No | Mild | 26 December 2014 | 29 April 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 30 May 2015 | 31 May 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Head pressure | Nervous system disorders | Head discomfort | No | Mild | 1 April 2015 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 2 June 2015 | 3 June 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Moderate | 14 July 2012 | 14 July 2012 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 7 June 2012 | 15 July 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 7 June 2012 | 15 July 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Bruising | Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | Contusion | No | Mild | 1 September 2016 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 7 October 2013 | 30 October 2013 | Trial medications delayed | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Defaecation urgency | GI disorders | Defaecation urgency | No | Na | 1 May 2016 | N/A | Trial medication period completed | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 30 March 2016 | 25 August 2016 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | Na | Moderate | 1 May 2016 | 6 June 2016 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Mild | 29 June 2012 | 6 July 2012 | Unknown | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 29 June 2012 | 6 July 2012 | Unknown | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 21 March 2013 | 31 March 2013 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered with sequelae |
| EPA + aspirin | Negative thoughts | Psychiatric disorders | Negative thoughts | No | Mild | 19 April 2013 | 19 June 2013 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered with sequelae |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 22 May 2015 | 10 July 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Bruising | Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | Contusion | No | Mild | 26 May 2015 | 11 May 2016 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 2 February 2016 | 1 March 2016 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Halitosis | GI disorders | Breath odour | No | Mild | 15 December 2015 | 30 January 2016 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Moderate | 26 May 2015 | N/A | No action taken | Condition improving |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Headache | Nervous system disorders | Headache | No | Moderate | 20 May 2015 | 22 July 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Urinary frequency | Renal and urinary disorders | Pollakiuria | No | Mild | 20 May 2015 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal discomfort | GI disorders | Abdominal discomfort | No | Mild | 17 January 2013 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Moderate | 10 January 2013 | 17 January 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Moderate | 7 May 2013 | 16 August 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 10 September 2014 | N/A | No action taken | Condition improving |
| Placebo + placebo | Halitosis | GI disorders | Breath odour | No | Mild | 28 March 2013 | 1 June 2013 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Mild | 1 August 2013 | 14 August 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Moderate | 3 July 2015 | 18 September 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Condition present and unchanged |
| Placebo + placebo | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Moderate | 19 May 2015 | 2 June 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered with sequelae |
| Placebo + placebo | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Mild | 6 June 2015 | 26 June 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Moderate | 22 June 2015 | 29 June 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Moderate | 20 May 2015 | 22 June 2015 | Trial medications reduced | Condition deteriorated |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 9 April 2015 | 20 May 2015 | No action taken | Condition deteriorated |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 16 April 2012 | 25 May 2012 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Acid reflux (oesophageal) | GI disorders | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | No | Mild | 15 February 2015 | 14 May 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Acid reflux (oesophageal) | GI disorders | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | No | Moderate | 30 January 2015 | 10 February 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Acid reflux (oesophageal) | GI disorders | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | No | Mild | 25 December 2014 | 30 January 2015 | Trial medications reduced | Condition deteriorated |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Excessive flatulence | GI disorders | Flatulence | No | Mild | 10 May 2015 | 5 June 2015 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Loose motions | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 10 May 2015 | 12 May 2015 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Acid reflux (oesophageal) | GI disorders | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | No | Mild | 10 May 2015 | 2 June 2015 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Acid reflux (oesophageal) | GI disorders | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | No | Mild | 18 May 2015 | 30 May 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Burping | GI disorders | Eructation | No | Mild | 6 August 2015 | 9 August 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Burping | GI disorders | Eructation | No | Mild | 5 August 2015 | 31 July 2016 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Exacerbation of asthma | Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Asthma | No | Moderate | 24 July 2016 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Flatulence | GI disorders | Flatulence | No | Mild | 28 February 2016 | N/A | No action taken | Condition improving |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Flatulence | GI disorders | Flatulence | No | Mild | 27 October 2015 | 11 January 2016 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Loose stools | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Moderate | 27 October 2016 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| Placebo + placebo | Wind | GI disorders | Flatulence | No | Mild | 19 November 2015 | 7 December 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Acid reflux (oesophageal) | GI disorders | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | No | Mild | 1 July 2016 | 27 October 2016 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Bloating | GI disorders | Abdominal distension | No | Mild | 1 June 2016 | 4 July 2016 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 5 July 2012 | 3 August 2012 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 5 July 2012 | 3 August 2012 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Loose stools | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 16 April 2013 | 30 July 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Excessive flatulence | GI disorders | Flatulence | No | Mild | 16 April 2013 | 30 July 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Oesophageal reflux | GI disorders | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | No | Na | 20 February 2013 | N/A | Unknown | Na |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Defaecation urgency | GI disorders | Defaecation urgency | No | Mild | 7 October 2012 | 15 June 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Hyperhidrosis | Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Hyperhidrosis | No | Mild | 14 March 2013 | 15 June 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Loose stools | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 7 October 2012 | 15 June 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 5 November 2012 | 10 December 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Halitosis | GI disorders | Breath odour | No | Mild | 7 October 2012 | 15 June 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Dizziness | Nervous system disorders | Dizziness | No | Mild | 14 March 2013 | 15 June 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Blood in stool | GI disorders | Haematochezia | No | Mild | 20 May 2013 | 21 May 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Blood in stool | GI disorders | Haematochezia | No | Mild | 3 February 2013 | 4 February 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Blood in stool | GI disorders | Haematochezia | No | Mild | 17 June 2013 | 18 June 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 15 July 2013 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Duodenitis | GI disorders | Duodenitis | Yes | Moderate | 7 September 2013 | 13 September 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 1 October 2013 | 20 January 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Blood in stool | GI disorders | Haematochezia | No | Mild | 5 November 2013 | 8 November 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Stool discolored | GI disorders | Faeces discoloured | Yes | Severe | 30 August 2013 | 13 September 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Reflux oesophagitis | GI disorders | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | Yes | Moderate | 7 September 2013 | 13 September 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 12 May 2014 | 9 September 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Blood in stool | GI disorders | Haematochezia | No | Mild | 21 December 2014 | 28 December 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 13 January 2014 | N/A | No action taken | Condition improving |
| EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 10 September 2014 | 27 November 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Borborygmi | GI disorders | Gastrointestinal sounds abnormal | No | Mild | 7 April 2014 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + aspirin | Halitosis | GI disorders | Breath odour | No | Mild | 7 April 2014 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| Placebo + placebo | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 8 June 2014 | N/A | No action taken | Condition improving |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Gastric bleeding | GI disorders | Gastric haemorrhage | No | Mild | 19 September 2014 | N/A | Trial medications permanently stopped | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Defaecation urgency | GI disorders | Defaecation urgency | No | Mild | 31 March 2014 | 12 December 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Oesophagitis | GI disorders | Oesophagitis | No | Mild | 19 September 2014 | N/A | Trial medications permanently stopped | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Flatulence | GI disorders | Flatulence | No | Mild | 31 March 2014 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Gastritis | GI disorders | Gastritis | No | Mild | 19 September 2014 | N/A | Trial medications permanently stopped | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 26 August 2014 | N/A | Trial medications reduced | Condition present and unchanged |
| Placebo + placebo | Stomach ache | GI disorders | Abdominal pain upper | No | Mild | 11 August 2014 | 13 August 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Bruising of leg | Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | Contusion | No | Mild | 12 February 2015 | 28 February 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Bruising of leg | Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | Contusion | No | Mild | 10 September 2014 | 1 October 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 1 October 2015 | 31 December 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Dizzy | Nervous system disorders | Dizziness | No | Mild | 1 July 2016 | 31 July 2016 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 1 July 2016 | 31 July 2016 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 1 July 2016 | 31 July 2016 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Burping | GI disorders | Eructation | No | Mild | 1 September 2012 | 1 December 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 1 September 2012 | 1 December 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Mild | 7 August 2012 | 12 August 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Indigestion | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 7 August 2012 | 12 August 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Stool discoloured | GI disorders | Faeces discoloured | No | Mild | 1 March 2013 | 1 April 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Bruising of hand | Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | Contusion | No | Mild | 20 July 2013 | 27 July 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Loose stools | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 1 September 2014 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 11 April 2015 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Loose stools | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 23 April 2015 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Gastritis | GI disorders | Gastritis | No | Mild | 27 June 2016 | 1 July 2016 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Hiatus hernia | GI disorders | Hiatus hernia | No | Mild | 27 June 2016 | 1 July 2016 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Moderate | 5 March 2016 | 1 July 2016 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Change of bowel habit | GI disorders | Change of bowel habit | No | Mild | 11 November 2015 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Epigastric pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain upper | No | Mild | 14 January 2012 | 28 May 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Belching | GI disorders | Eructation | No | Mild | 14 January 2012 | 28 May 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 1 February 2015 | 30 September 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 1 September 2015 | 30 September 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Mild | 9 April 2013 | 13 April 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Mild | 14 February 2013 | 18 February 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Moderate | 25 December 2012 | 27 December 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Moderate | 4 January 2013 | 6 January 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Mild | 17 March 2013 | 28 March 2013 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Change of bowel habit | GI disorders | Change of bowel habit | No | Moderate | 1 August 2013 | 23 August 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Nauseous | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Moderate | 3 July 2015 | 3 July 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Retching | GI disorders | Retching | No | Moderate | 24 April 2015 | 12 May 2015 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Loose stools | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Moderate | 16 March 2016 | 22 March 2016 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Faeces discoloured | GI disorders | Faeces discoloured | No | Moderate | 16 March 2016 | 22 March 2016 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal cramps | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Moderate | 16 March 2016 | 22 March 2016 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Gout | Metabolism and nutrition disorders | Gout | No | Mild | 8 May 2017 | 18 May 2017 | Study med. Period completed | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Headache | Nervous system disorders | Headache | No | Moderate | 9 August 2012 | 28 August 2012 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Anal mucositis | GI disorders | Anal inflammation | No | Moderate | 12 October 2015 | 30 July 2016 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 19 December 2015 | 19 December 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Angioedema | Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Angioedema | No | Moderate | 22 December 2015 | 23 December 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 28 November 2011 | 5 March 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Moderate | 20 March 2012 | 29 March 2012 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Indigestion | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 27 February 2012 | 9 May 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Moderate | 23 January 2016 | 22 March 2016 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Moderate | 21 August 2015 | 23 August 2015 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Gout | Metabolism and nutrition disorders | Gout | No | Mild | 14 June 2013 | 27 June 2013 | Trial medications delayed | Recovered with sequelae |
| Placebo + placebo | Frequent bowel movements | GI disorders | Frequent bowel movements | No | Moderate | 18 December 2012 | 19 December 2012 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Excessive flatulence | GI disorders | Flatulence | No | Moderate | 18 December 2012 | 19 December 2012 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Excessive flatulence | GI disorders | Flatulence | No | Mild | 1 December 2012 | 19 December 2012 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Condition improving |
| Placebo + placebo | Heartburn | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Moderate | 21 March 2014 | 12 April 2014 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 24 May 2012 | 16 June 2012 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered with sequelae |
| Placebo + placebo | Medication aftertaste | General disorders and administration site conditions | Product taste abnormal | No | Mild | 26 March 2013 | 26 March 2014 | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| Placebo + placebo | Abdominal distension | GI disorders | Abdominal distension | No | Mild | 26 March 2013 | 26 March 2014 | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 2 March 2015 | 10 March 2015 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Vomiting | GI disorders | Vomiting | No | Severe | 2 March 2015 | 5 March 2015 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Indigestion | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Moderate | 16 July 2015 | 20 July 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Belching | GI disorders | Eructation | No | Mild | 15 November 2012 | 21 November 2012 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Mild | 15 November 2012 | 21 November 2012 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Vomiting | GI disorders | Vomiting | No | Mild | 16 May 2013 | 20 July 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 16 May 2013 | 20 July 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Halitosis | GI disorders | Breath odour | No | Mild | 16 May 2013 | 1 July 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 16 April 2013 | 16 May 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Taste abnormality | Nervous system disorders | Dysgeusia | No | Mild | 16 May 2013 | 1 July 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Mild | 16 May 2013 | 20 July 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 12 November 2013 | 13 November 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Stomach pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain upper | No | Mild | 3 September 2014 | 4 September 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Perianal bleeding | GI disorders | Anal haemorrhage | No | Mild | 24 December 2013 | 24 December 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Knee pain | Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Arthralgia | No | Mild | 13 January 2014 | 24 February 2014 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Bleeding postoperatively | Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | Post procedural haemorrhage | No | Mild | 20 December 2012 | 3 January 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Haematuria | Renal and urinary disorders | Haematuria | No | Mild | 13 August 2014 | 19 August 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Haematuria | Renal and urinary disorders | Haematuria | No | Mild | 24 December 2013 | 26 December 2013 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 17 January 2015 | 19 January 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 2 February 2015 | N/A | Trial medications permanently stopped | Na |
| EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 14 November 2014 | 16 November 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Bleeding PR (excluding gut haemorrhage and piles) | GI disorders | Rectal haemorrhage | No | Mild | 20 December 2015 | 22 December 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Bleeding PR (excluding gut haemorrhage and piles) | GI disorders | Rectal haemorrhage | No | Mild | 25 June 2015 | 24 July 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Pustule | Infections and infestations | Rash pustular | No | Mild | 12 December 2013 | 8 January 2014 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Loose motions | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 1 July 2013 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 1 July 2013 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Generalised itching | Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Pruritus generalised | No | Mild | 24 January 2014 | 25 July 2014 | Trial medications delayed | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Acid reflux (oesophageal) | GI disorders | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | No | Moderate | 28 April 2014 | 12 May 2014 | Trial medications delayed | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Mild | 28 November 2012 | 29 November 2012 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Stomach pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain upper | No | Mild | 28 November 2012 | 29 November 2012 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Stomach pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain upper | No | Mild | 17 November 2012 | 28 November 2012 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Mild | 2 November 2012 | 28 November 2012 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Mild | 2 November 2012 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| Placebo + placebo | Lower abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain lower | No | Moderate | 8 January 2013 | 10 January 2013 | Trial medications delayed | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Indigestion | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Moderate | 13 January 2013 | 22 January 2013 | Trial medications delayed | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Indigestion | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Moderate | 25 January 2013 | 10 February 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Moderate | 13 January 2013 | 22 January 2013 | Trial medications delayed | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Moderate | 8 January 2013 | 10 January 2013 | Trial medications delayed | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Moderate | 25 January 2013 | 10 February 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Dizziness | Nervous system disorders | Dizziness | No | Mild | 30 April 2013 | 27 January 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Dizziness | Nervous system disorders | Dizziness | No | Mild | 1 April 2013 | 14 April 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 25 September 2013 | N/A | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Flatulence | GI disorders | Flatulence | No | Mild | 25 September 2013 | N/A | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Moderate | 16 March 2014 | 18 March 2014 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + aspirin | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Moderate | 25 January 2014 | 28 January 2014 | Trial medications delayed | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Severe | 1 May 2014 | 1 July 2014 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Stomach pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain upper | No | Moderate | 1 May 2014 | 1 July 2014 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 31 July 2014 | 14 August 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 24 March 2014 | 3 April 2014 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Abdominal discomfort | GI disorders | Abdominal discomfort | No | Moderate | 3 May 2015 | N/A | Trial medications delayed | Condition improving |
| Placebo + placebo | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 15 May 2013 | 15 May 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Lower abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain lower | No | Mild | 13 October 2013 | 15 October 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Blood in stool | GI disorders | Haematochezia | No | Mild | 7 September 2015 | 11 September 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Stomach discomfort | GI disorders | Abdominal discomfort | No | Mild | 8 August 2015 | 11 September 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 1 August 2015 | 30 May 2016 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Bruising | Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | Contusion | No | Mild | 1 December 2015 | N/A | No action taken | Condition improving |
| EPA + aspirin | Burping | GI disorders | Eructation | No | Mild | 7 July 2015 | 29 May 2016 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Acid reflux (oesophageal) | GI disorders | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | No | Moderate | 20 April 2016 | 2 May 2016 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Medication aftertaste | General disorders and administration site conditions | Product taste abnormal | No | Mild | 7 February 2016 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + aspirin | Flatulence | GI disorders | Flatulence | No | Mild | 10 February 2013 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Lower abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain lower | No | Mild | 1 July 2013 | 1 September 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Lower abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain lower | No | Mild | 24 June 2013 | 27 June 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Tongue eruption | GI disorders | Tongue eruption | No | Mild | 24 June 2013 | 30 August 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Macroscopic haematuria | Renal and urinary disorders | Haematuria | No | Moderate | 1 February 2014 | 20 May 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Vomiting | GI disorders | Vomiting | No | Moderate | 4 December 2013 | 16 December 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Moderate | 4 December 2013 | 16 December 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Heartburn | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 21 November 2013 | 23 November 2013 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered with sequelae |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 21 November 2013 | 23 November 2013 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered with sequelae |
| Placebo + placebo | Black stools | GI disorders | Faeces discoloured | No | Moderate | 12 June 2013 | 12 July 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Acid reflux (oesophageal) | GI disorders | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | No | Mild | 1 May 2013 | 12 June 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 20 April 2013 | 02 May 2013 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 20 April 2013 | 20 June 2013 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Mild | 20 April 2013 | 20 June 2013 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Acid reflux (oesophageal) | GI disorders | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | No | Mild | 29 May 2015 | N/A | Trial medications permanently stopped | Condition improving |
| EPA + aspirin | Acid reflux (oesophageal) | GI disorders | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | No | Moderate | 15 July 2015 | N/A | Trial medications permanently stopped | Condition deteriorated |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Mild | 16 September 2015 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Moderate | 7 March 2016 | 16 March 2016 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 3 July 2015 | 11 August 2015 | No action taken | Condition deteriorated |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Melaena | GI disorders | Melaena | No | Moderate | 3 August 2015 | 11 August 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Mild | 31 May 2016 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Mild | 27 May 2016 | 31 May 2016 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal discomfort | GI disorders | Abdominal discomfort | No | Mild | 1 February 2013 | 25 March 2013 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Frequent bowel movements | GI disorders | Frequent bowel movements | No | Mild | 1 April 2013 | 18 April 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Frequent bowel movements | GI disorders | Frequent bowel movements | No | Mild | 1 July 2013 | 30 July 2013 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 16 December 2013 | 22 December 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 28 August 2013 | 2 September 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Abdominal discomfort | GI disorders | Abdominal discomfort | No | Mild | 31 May 2014 | 4 June 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Increased frequency of bowel movements | GI disorders | Frequent bowel movements | No | Mild | 20 January 2013 | N/A | No action taken | Condition improving |
| EPA + aspirin | Increased frequency of bowel movements | GI disorders | Frequent bowel movements | No | Mild | 6 February 2013 | 2 April 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Indigestion | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 3 April 2014 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| Placebo + placebo | Dry skin | Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Dry skin | No | Mild | 13 January 2014 | N/A | No action taken | Condition improving |
| EPA + aspirin | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Moderate | 21 August 2014 | 29 August 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Itchy skin | Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Pruritus | No | Moderate | 1 July 2015 | 13 October 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Nose bleed | Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Epistaxis | No | Mild | 8 January 2016 | 11 April 2016 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Weight loss | Investigations | Weight decreased | No | Mild | 9 July 2013 | N/A | Trial medications reduced | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Mild | 9 July 2013 | N/A | Trial medications reduced | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + aspirin | Stomach cramps | GI disorders | Abdominal pain upper | No | Mild | 9 July 2013 | N/A | Trial medications reduced | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Mild | 14 August 2013 | 1 May 2014 | Trial medications reduced | Condition improving |
| Placebo + placebo | Loose stools | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 7 January 2015 | 2 April 2015 | Trial medications delayed | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 7 January 2015 | 2 April 2015 | Trial medications delayed | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Mild | 7 January 2015 | 2 April 2015 | Trial medications delayed | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 6 January 2015 | 24 February 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 23 January 2015 | 30 January 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 2 December 2015 | 3 January 2016 | Trial medication period completed | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Mild | 2 December 2015 | 3 January 2016 | Trial medication period completed | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 21 April 2015 | 28 April 2015 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 8 February 2015 | 17 February 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Moderate | 1 September 2015 | 8 October 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Moderate | 1 September 2015 | 8 October 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Moderate | 22 August 2015 | 29 August 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 26 February 2015 | N/A | Trial medications permanently stopped | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Moderate | 22 August 2015 | 29 August 2015 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Constipation | GI disorders | Constipation | No | Mild | 16 October 2015 | N/A | No action taken | Condition improving |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Bruising | Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | Contusion | No | Mild | 16 October 2015 | N/A | No action taken | Condition improving |
| EPA + aspirin | Bloating | GI disorders | Abdominal distension | No | Mild | 1 December 2015 | 7 December 2015 | Trial medication already discontinued | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Feeling unwell | General disorders and administration site conditions | Malaise | No | Mild | 1 December 2015 | 7 December 2015 | Trial medication already discontinued | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 5 June 2013 | 9 June 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Stomach pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain upper | No | Mild | 14 March 2015 | 18 March 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Taste abnormality | Nervous system disorders | Dysgeusia | No | Mild | 22 January 2013 | 5 February 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Epistaxis | Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Epistaxis | No | Moderate | 6 January 2014 | 7 January 2014 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Moderate | 10 October 2013 | 25 November 2013 | No action taken | Recovered with sequelae |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Taste abnormality | Nervous system disorders | Dysgeusia | No | Mild | 14 March 2013 | 20 March 2013 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 25 August 2016 | 27 August 2016 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 28 August 2016 | 30 August 2016 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Moderate | 1 June 2016 | 6 June 2016 | Trial medications reduced | Condition improving |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal discomfort | GI disorders | Abdominal discomfort | No | Mild | 1 November 2016 | N/A | No action taken | Condition present and unchanged |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Mild | 3 March 2015 | N/A | Trial medications reduced | Condition improving |
| EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 15 July 2015 | 30 September 2015 | No action taken | Recovered with sequelae |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Moderate | 7 July 2015 | 8 June 2016 | Trial medications reduced | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Loose stools | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 7 February 2013 | 10 February 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Macroscopic haematuria | Renal and urinary disorders | Haematuria | No | Mild | 12 September 2015 | 15 September 2015 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Bleeding mouth | GI disorders | Mouth haemorrhage | No | Mild | 21 August 2013 | 21 August 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Dyspepsia | GI disorders | Dyspepsia | No | Mild | 23 August 2013 | 25 August 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Moderate | 19 November 2013 | 22 November 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered with sequelae |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Nausea | GI disorders | Nausea | No | Moderate | 19 November 2013 | 22 November 2013 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered with sequelae |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Defaecation urgency | GI disorders | Defaecation urgency | No | Mild | 19 September 2013 | 22 September 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Mild | 19 September 2013 | 22 September 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo + placebo | Abdominal pain | GI disorders | Abdominal pain | No | Moderate | 30 January 2014 | 10 March 2014 | Trial medications permanently stopped | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Chest pain | General disorders and administration site conditions | Chest pain | Yes | Moderate | 29 July 2013 | 31 July 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 12 October 2012 | 14 October 2012 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Diarrhoea | GI disorders | Diarrhoea | No | Mild | 22 November 2012 | 26 November 2012 | No action taken | Condition improving |
| Placebo + placebo | Halitosis | GI disorders | Breath odour | No | Mild | 22 February 2013 | 22 August 2013 | No action taken | Recovered |
| EPA + aspirin | Epistaxis | Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Epistaxis | No | Mild | 4 June 2014 | 12 June 2014 | No action taken | Recovered |
| Treatment group | System organ class name | Preferred term name |
|---|---|---|
| Placebo + placebo | Neoplasms: benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | Renal cancer |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | GI disorders | Gastritis |
| Placebo + placebo | Neoplasms: benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | Lung neoplasm malignant |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | GI disorders | Oesophageal haemorrhage |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Vascular disorders | Thrombosis |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Vascular disorders | Thrombosis |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Infections and infestations | Lower respiratory tract infection |
| EPA + aspirin | Infections and infestations | Pharyngeal abscess |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Investigations | Blood glucose increased |
| Placebo + placebo | Neoplasms: benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | Lung neoplasm malignant |
| Placebo + placebo | GI disorders | Abdominal pain |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | GI disorders | Small intestinal perforation |
| EPA + aspirin | Vascular disorders | Deep-vein thrombosis |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Vascular disorders | Deep-vein thrombosis |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Infections and infestations | Lung infection |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Neoplasms: benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | Oesophageal carcinoma |
| Placebo + placebo | Infections and infestations | Labyrinthitis |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | GI disorders | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | GI disorders | Duodenitis |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | GI disorders | Hiatus hernia |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | GI disorders | Faeces discoloured |
| Placebo + placebo | Vascular disorders | Femoral artery occlusion |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Pulmonary embolism |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Infections and infestations | Post procedural infection |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Hepatobiliary disorders | Liver disorder |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Neoplasms: benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | Lung neoplasm malignant |
| Placebo + placebo | Vascular disorders | Deep-vein thrombosis |
| Placebo + placebo | General disorders and administration site conditions | Chest pain |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Nervous system disorders | Syncope |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Respiratory failure |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Cardiac disorders | AF |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Cardiac disorders | AF |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Cardiac disorders | AF |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Cardiac disorders | AF |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Nervous system disorders | Transient ischaemic attack |
| Placebo + placebo | Infections and infestations | Colonic abscess |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Cardiac disorders | Acute myocardial infarction |
| Placebo + placebo | Cardiac disorders | Acute myocardial infarction |
| Placebo + placebo | Infections and infestations | Lower respiratory tract infection |
| EPA + aspirin | Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Cardiac disorders | Atrial fibrillation |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Infections and infestations | Cellulitis |
| EPA + aspirin | Neoplasms: benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | Prostate cancer |
| EPA + aspirin | Neoplasms: benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | Metastases to bone |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | General disorders and administration site conditions | Chest pain |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | Laceration |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Cardiac disorders | Myocardial infarction |
| Placebo + placebo | Psychiatric disorders | Confusional state |
| Placebo + placebo | Neoplasms: benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | Bladder squamous cell carcinoma stage unspecified |
| EPA + placebo aspirin | Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| Placebo + placebo | Psychiatric disorders | Alcohol withdrawal syndrome |
| Placebo + placebo | Nervous system disorders | Encephalopathy |
| Placebo + placebo | GI disorders | Faeces discoloured |
| EPA + aspirin | General disorders and administration site conditions | Chest pain |
| Placebo EPA + aspirin | Cardiac disorders | Arrhythmia |
| Preferred term name | Severity | Trial group (n) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin | EPA + placebo aspirin | Placebo EPA + aspirin | Placebo + placebo | ||
| Abdominal discomfort | Mild | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Moderate | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Abdominal distension | Mild | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Abdominal pain | Mild | 2 | 16 | 5 | 2 |
| Moderate | 1 | 5 | 2 | 3 | |
| Abdominal pain lower | Mild | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| Moderate | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Abdominal pain upper | Mild | 2 | 4 | 0 | 3 |
| Moderate | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Anal haemorrhage | Mild | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Anal inflammation | Moderate | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Breath odour | Mild | 1 | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| Change of bowel habit | Mild | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Moderate | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Constipation | Mild | 2 | 5 | 3 | 2 |
| Moderate | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Severe | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Defaecation urgency | Mild | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Diarrhoea | Mild | 4 | 18 | 12 | 5 |
| Moderate | 3 | 10 | 1 | 0 | |
| Duodenitis | Moderate | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Dyspepsia | Mild | 11 | 10 | 11 | 9 |
| Moderate | 1 | 0 | 3 | 5 | |
| Epigastric discomfort | Mild | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Eructation | Mild | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| Faeces discoloured | Mild | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Moderate | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Severe | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Flatulence | Mild | 1 | 4 | 2 | 3 |
| Moderate | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Frequent bowel movements | Mild | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Moderate | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Gastric haemorrhage | Mild | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Gastritis | Mild | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| GI sounds abnormal | Mild | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | Mild | 2 | 0 | 3 | 2 |
| Moderate | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Haematochezia | Mild | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 |
| Hiatus hernia | Mild | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Melaena | Moderate | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Mouth haemorrhage | Mild | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Nausea | Mild | 3 | 8 | 1 | 1 |
| Moderate | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| Oesophageal haemorrhage | Severe | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Oesophagitis | Mild | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Rectal haemorrhage | Mild | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Retching | Moderate | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tongue eruption | Mild | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Vomiting | Mild | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Moderate | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Severe | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
Appendix 5 Summary of gastrointestinal adverse events according to the categories defined by the chief investigator
| GI AE | Trial group | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA + aspirin | EPA + placebo aspirin | Placebo EPA + aspirin | Placebo + placebo | |||||
| FFA | TG | FFA | TG | FFA | TG | FFA | TG | |
| Number in safety population | 99 | 71 | 107 | 70 | 99 | 75 | 109 | 167 |
| Participants reporting at least one GI AE, n (%) | 25 (25) | 22 (31) | 43 (40) | 24 (34) | 24 (24) | 20 (27) | 38 (35) | 13 (19) |
| Diarrhoeaa (n) | 9 | 2 | 27 | 15 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 7 |
| Upper GI symptoms (n) | 11 | 18 | 21 | 15 | 11 | 15 | 19 | 9 |
| Lower abdominal symptoms (n) | 4 | 5 | 20 | 17 | 7 | 3 | 18 | 3 |
| Eructation/halitosis (n) | 1 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 |
| Other (n) | 12 | 3 | 19 | 7 | 15 | 14 | 11 | 4 |
List of abbreviations
- AA
- arachidonic acid
- ADR
- adverse drug reaction
- ADRa
- adenoma detection rate
- AE
- adverse event
- AF
- atrial fibrillation
- ALA
- alpha-linolenic acid
- APC
- adenomatous polyposis coli
- BCSP
- NHS Bowel Cancer Screening Programme
- CACE
- complier-average causal effect
- CI
- confidence interval
- CIMP
- CpG island methylator phenotype
- CIN
- chromosomal instability
- COX
- cyclooxygenase
- CRC
- colorectal cancer
- CRN
- Clinical Research Network
- CTA
- Clinical Trials Authorisation
- CTIMP
- Clinical Trial of an Investigational Medicinal Product
- CTPL
- Clinical Trials Pharmacology Laboratory
- CVD
- cardiovascular disease
- DHA
- docosahexaenoic acid
- DMC
- Data Monitoring Committee
- DNA
- deoxyribonucleic acid
- EE
- ethyl ester
- EME
- Efficacy and Mechanism Evaluation
- EPA
- eicosapentaenoic acid
- EPIC
- European Prospective Investigation of Cancer
- FAP
- familial adenomatous polyposis
- FFA
- free fatty acid
- FFAR
- free fatty acid receptor
- FFPE
- formalin fixed paraffin embedded
- FFQ
- Food Frequency Questionnaire
- FIT
- faecal immunochemical test
- FOBt
- faecal occult blood test
- FPFV
- first participant, first visit
- FS
- flexible sigmoidoscopy
- GI
- gastrointestinal
- HR
- hazard ratio
- ID
- identification
- IMP
- investigational medicinal product
- IRR
- incidence rate ratio
- ITT
- intention to treat
- LA
- linoleic acid
- LPLV
- last participant, last visit
- MAP
- mean adenomas per participant
- MDT
- multidisciplinary team
- MHRA
- Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency
- MMR
- mismatch repair
- MRC
- Medical Research Council
- MSI
- microsatellite instability
- NCRI
- National Cancer Research Institute
- NCTU
- Nottingham Clinical Trials Unit
- NIHR
- National Institute for Health Research
- NSAID
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
- OTC
- over the counter
- PCCRC
- post-colonoscopy colorectal cancer
- PG
- prostaglandin
- PGDH
- prostaglandin dehydrogenase
- PI
- principal investigator
- PIL
- patient information leaflet
- PPI
- patient and public involvement
- PUFA
- polyunsaturated fatty acid
- QA
- quality assurance
- RBC
- red blood cell
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- R&D
- research and development
- REC
- Research Ethics Committee
- R&I
- research and innovation
- RN
- research nurse
- RSI
- Reference Safety Information
- Rv
- resolvin
- SAE
- serious adverse event
- SAP
- statistical analysis plan
- SCFA
- short-chain fatty acid
- seAFOod
- Systematic Evaluation of Aspirin and Fish Oil
- SSPr
- specialist screening practitioner
- TG
- triglyceride
- TMG
- Trial Management Group
- TSC
- Trial Steering Committee
- WHO
- World Health Organization
- w/w
- weight per weight
