Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the EME programme as project number 14/200/20. The contractual start date was in August 2016. The final report began editorial review in February 2020 and was accepted for publication in December 2020. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The EME editors and production house have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the final report document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2021. This work was produced by Walsh et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2021 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Introduction
Parts of this report are based on Walsh et al. 1 © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license.
One in two women and one in five men aged > 50 years will have a fragility fracture. Fractures lead to pain, disability, loss of independence and increased mortality. This is a huge health burden for affected individuals, the NHS and social care, and it is increasing as the population ages.
About 30% of women aged > 65 years are osteopenic (i.e. they have below-average bone density) and are at risk of developing osteoporosis and fractures. More than 50% of all fractures in postmenopausal women occur in those with osteopenia. These women are generally not given osteoporosis treatment at present because of the individual risk–benefit ratio. Previously, these women could have been offered hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for bone protection, but adverse effects of HRT have limited its use. Bisphosphonates are the mainstay of osteoporosis treatment for women at higher risk, but use of these medications has declined because of physician and patient wariness of adverse events. 2 More costly treatments, such as teriparatide and denosumab, are restricted to patients with more severe osteoporosis who do not respond to bisphosphonate treatment. Calcium and vitamin D supplements are generally recommended for osteopenic adults, but effects on bone density are small and may not outweigh the risk of adverse effects. 3
Therefore, there is a need for an effective, safe, well-tolerated, inexpensive and widely applicable preventative option for osteopenic women.
Selenium is a chemical element present in several human proteins. Twenty-five human selenoproteins have been identified. 4 Known functions of selenoproteins include thyroid hormone synthesis (iodothyronine deiodinases) and anti-oxidants (thioredoxin reductases and glutathione peroxidases). 5,6 Selenoproteins are anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant; they reduce levels of interleukin 6 (IL-6) and reactive oxygen species, both of which are potent stimuli for bone resorption. 7–10
Selenium is obtained from diet, particularly seafood, meat and cereals. The main determinant of food selenium content is soil selenium content. The recommended adequate intake for adults aged > 50 years in the UK is 75 µg/day for men and 60 µg/day for women,11 but in the UK the mean intake is only 40 µg/day. 12 Selenium intakes have been declining in the UK in the past few decades and are generally low in Europe compared with the USA. The main reason for the decreasing intake in the UK is a change in the source of flour for bread-making from North America (which contains higher selenium) to Europe. More recently, the levels of selenium in UK soils have declined because of changes in fertiliser practice (e.g. replacing single superphosphate with triple superphosphate) and reduced industrial emissions. 13
Studies of all-cause mortality suggest that the optimum range of serum selenium for human health is between about 120 and 150 µg/l. Most adults in the UK have serum selenium between 80 and 100 µg/l. 12
We previously reported that, in 1144 older women from the UK, France and Germany, higher serum selenium or selenoprotein P (SePP) was associated with higher bone mineral density of the lumbar spine and total hip, and lower biochemical markers of bone turnover. 14 High bone turnover is the principal mechanism of osteoporotic bone loss. We also noted associations of selenium levels with balance and grip strength. Selenium status was inversely related to thyroid hormone status (selenium is required for thyroid hormone synthesis), but the associations of selenium with bone measures were independent of thyroid hormones.
It is plausible that selenium could affect bone metabolism. Selenoproteins are expressed in osteoblasts and osteoclasts, and are found in the bone microenvironment. 7,15 Selenoproteins are anti-inflammatory and reduce IL-6, a potent stimulus for bone resorption. 8 Selenoproteins are anti-oxidant and reduce reactive oxygen species; these also stimulate bone resorption via increased RANK-L signalling. 15 Oxidative stress markers are associated with high bone resorption markers and lower bone mineral density (BMD). 16,17 An increase in reactive oxygen species has been proposed as a key mechanism by which sex hormone deficiency causes age-related bone loss through the same RANK pathway. 18 Therefore, it is possible that selenium could directly antagonise the cellular mechanism of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
There is experimental animal evidence to support the hypothesis that selenium has a role in bone biology and reduces bone turnover. Selenium-deficient mice have poorer bone microarchitecture, higher bone resorption markers and higher inflammatory markers than selenium supplemented mice. 19 Selenium-deficient rats have poor bone microarchitecture and abnormal skeletal growth. 20,21
Selenium status has also been associated with BMD in men in the Netherlands,22 and higher selenium intake was associated with lower hip fracture risk in older adults in the USA,23 but there was no association with BMD in postmenopausal Turkish women. 24 In a US study of hip fracture risk in women aged ≥ 65 years, the counties that had the highest rates were those situated in a belt across the south of the USA, and the lowest rates were in the north. 25 By contrast, a current map of soil selenium content in the USA shows that the highest level of selenium content is in the north of the USA and the lowest level is in a belt across the south of the USA (http://mrdata.usgs.gov/geochem/doc/averages/se/usa.html; accessed 5 February 2021).
Endemic selenium deficiency in humans has been associated with the osteoarthropathy Kashin–Beck disease. 26
Several other age-related disorders are linked to inadequate selenium status, including poor cognitive function and reduced muscle strength. 27 Selenium may be an independent predictor of mortality among older community-dwelling adults. 28 Selenium supplementation with coenzyme Q10 reduced cardiovascular mortality and markers of inflammation, increased IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1) and altered microRNA expression in older Swedish adults. 29–31 In the Nutritional Prevention of Cancer trial, selenium supplementation reduced all-cancer risk in people with lower baseline serum selenium,32 and meta-analyses generally find a beneficial effect of selenium on cancer risk. 12
The possible adverse effects of selenium supplementation are thyroid dysfunction (because some selenoproteins are involved in thyroid hormone synthesis) and increased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus. 33
We hypothesised that, in a relatively selenium-deficient population such as the UK, selenium supplementation would decrease bone turnover by reducing the action of reactive oxygen species on osteoclast activity and may improve muscle function. In the longer term, both of these actions could have benefits with regard to reducing fracture risk.
The aim of the study was to determine if selenium supplementation is beneficial for bone health and muscle function in postmenopausal women.
The objectives of the study were to determine if selenium supplementation in postmenopausal women with osteopenia:
-
decreases bone turnover
-
improves physical function score and grip strength
-
is safe (particularly for thyroid function and diabetes)
-
decreases markers of oxidative stress and inflammation.
Chapter 2 Methods
Study design
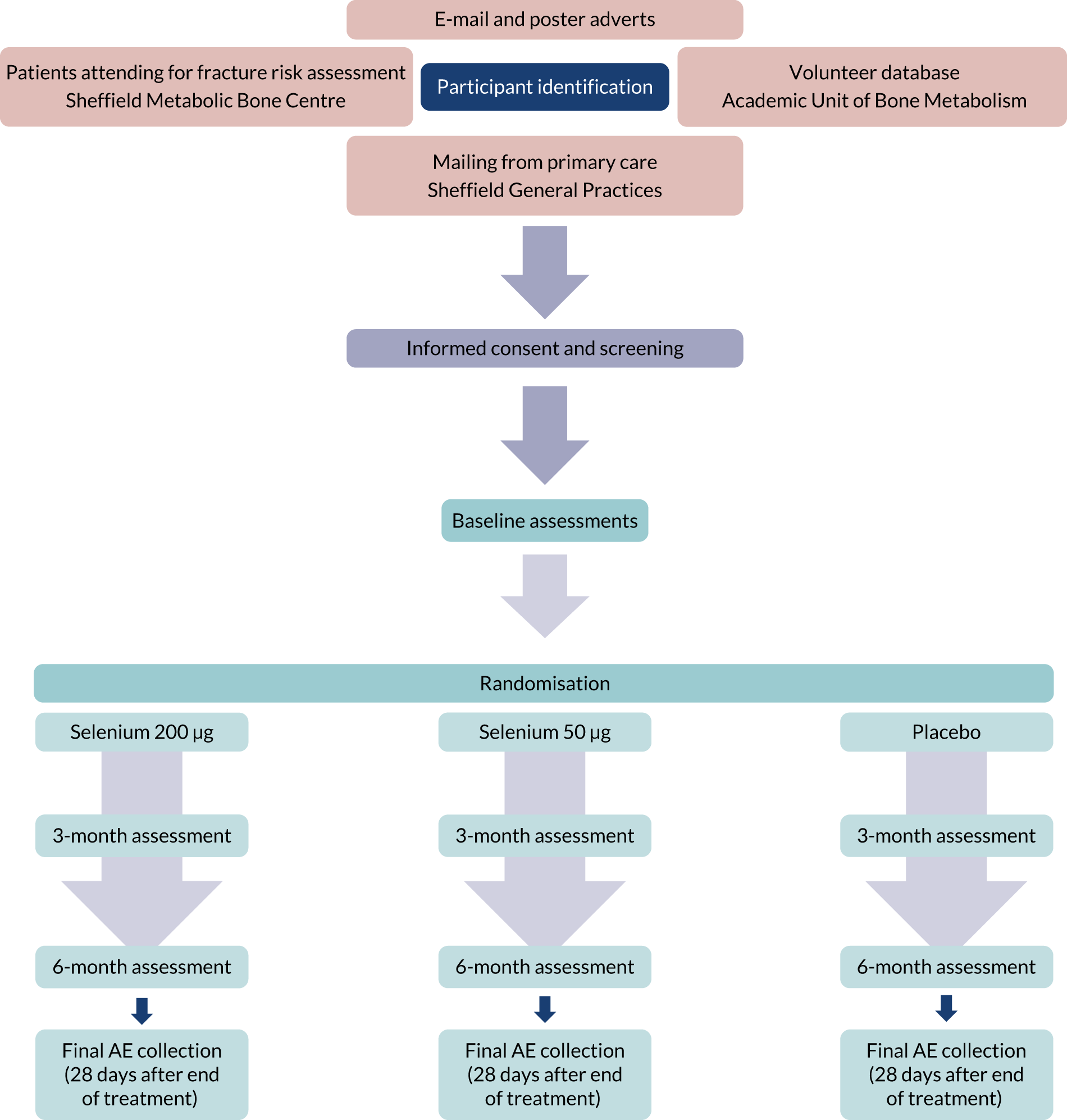
We conducted a 6-month randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of selenium supplementation in 120 postmenopausal women with osteopenia and osteoporosis (see Appendix 1).
The interventions were sodium selenite tablets Selenase 50 µg and 200 µg (biosyn, Germany) and placebo. The tablets were overencapsulated and a matching placebo was manufactured to maintain the blind (Sharp Clinical Services, UK). We chose a dose of 200 µg because this dose has previously been shown to be effective in the Nutritional Prevention of Cancer trial and in treatment of Graves’ ophthalmopathy. We estimated that this dose would increase serum selenium by about 60 µg/l.
The 50 µg dose was included to assess dose response; if 50 µg and 200 µg had similar effects, we could recommend the 50 µg dose for clinical use, at a lower cost and with a lower risk of adverse effects.
The primary end point was a between-group difference in urine N–terminal cross-linking telopeptide of type I collagen (NTX)/Cr at 26 weeks.
Bone turnover markers change much more rapidly than BMD, so we can determine quickly and cost-effectively if an intervention is likely to work. We chose NTX because the relationship between change in NTX and change in fracture risk is well described with bisphosphonates:34 a 30% decrease in NTX is associated with a 40% reduction in spine fracture, and 66% of the vertebral fracture risk reduction at 3 years is explained by change in NTX. In addition, NTX was the marker mostly strongly related to selenium status in our observational study. 14
The secondary end points were as follows:
-
Change in serum selenium, SePP: systematic review identified blood selenium and SePP as robust biomarkers of selenium status, over the range of deficiency to repletion. 35
-
Change in other bone turnover markers: procollagen type I N propeptide (PINP), osteocalcin (OC) and C–terminal cross-linking telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX).
-
Change in BMD: lumbar spine and total hip by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA).
-
Change in muscle function: short physical performance battery (SPPB) and hand grip strength. SPPB score is a measure of lower limb strength and balance. It predicts falls, loss of function in activities of daily living, nursing home admission and mortality. 36–38
-
Change in anti-oxidant activity: glutathione peroxidase activity (a selenium-containing anti-oxidant that is increased in postmenopausal women with osteopenia). 17
-
Change in inflammatory markers: the pro-resorptive inflammatory cytokine IL-6 and highly sensitive C-reactive protein (hsCRP).
The study was approved by Yorkshire and the Humber Research Ethics Committee (REC reference 16/YH/0393). All participants gave written informed consent, and the study was conducted in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki. Potential participants were identified from a database of previous study volunteers, patients attending the Sheffield Metabolic Bone Centre for fracture risk assessment, and through poster and e-mail publicity. The trial was supervised by a Trial Steering Committee (TSC) and a Data Monitoring Committee (DMC). The committees had independent membership, each including bone and diabetes specialist physicians and a statistician. They approved the protocol and statistical analysis plan (SAP) and met every 6 months during the trial. The DMC had access to serious adverse event (SAE) information and unblinded data, and reported to the TSC. Committee reports were uploaded to the NIHR monitoring team.
This was a single-centre trial in Sheffield, UK. Participants were recruited between January 2017 and April 2018 from a database of volunteers, poster and e-mail advertising, and patients attending the metabolic bone centre for bone densitometry.
The inclusion criteria were women:
-
aged > 55 years, and at least 5 years since last menstrual period
-
with osteopenia or osteoporosis (DXA BMD lowest T-score between –1.0 and –3.0 at lumbar spine or total hip), who did not require pharmacological treatment for fracture prevention
-
willing and able to give informed consent.
The exclusion criteria were:
-
diabetes mellitus
-
thyroid dysfunction [history of hyper- or hypothyroidism, or thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) outside the local reference range]
-
any conditions known to affect bone metabolism, such as inflammatory disease, parathyroid disease, malabsorption, high alcohol intake (> 21 units per week) and prolonged immobility
-
fracture or orthopaedic surgery in the past year
-
osteoporosis treatment or drugs known to affect bone metabolism in the past year
-
selenium supplements in the past 60 days
-
previous adverse reaction to selenium or any of the Investigational Medical Product (IMP) or placebo excipients.
Women taking calcium and vitamin D supplements were not excluded as long as they had been taking the calcium and vitamin D for at least 60 days and planned to continue throughout the trial. All participants were given a single oral dose of 100,000 IU colecalciferol at screening to ensure that they were vitamin D sufficient at the start of trial treatment.
We did not set inclusion/exclusion criteria based on serum selenium status because it was important that the results of this study were generalisable into practice. However, we specified that only women with baseline serum selenium < 120 µg/l would be included in the primary analysis.
The study had 90% power to detect a 20% between-group difference at the 2.5% (two-sided) level [approximately 10 nmol bone collagen equivalents (BCE)/mmolCr] in NTX/Cr.
We determined 20% as a plausible effect size, based on estimated change in serum selenium and the regression co-efficient of serum selenium and NTX/Cr in our previous study. We did not expect as large a change in bone turnover as in a potent anti-resorptive drug such as a bisphosphonate, but it might be similar to a weaker anti-resorptive such as a selective oestrogen receptor modulator (SERM). In a study of 6 months of treatment with the SERM lasofoxifene in 51 postmenopausal women,39 NTX/Cr decreased by 29%. We also used this study to estimate the standard deviation (SD) (12.5 nmol BCE/mmolCr) and the correlation between NTX/Cr at baseline and 6 months (0.7).
A 20% decrease in NTX is clinically significant; a 20% decrease in NTX (about 1 SD decrease) with bisphosphonate treatment is associated with a 30% decrease in incident vertebral fracture. 40
The sample size was calculated using the pwr library41 in R (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
Assuming a SD of 12.5, and a significant difference of 10 nmol BCE/mmolCr, to achieve 90% power to detect this difference at the 0.025% (two-sided) level would require 41 patients per group. The primary analysis was an analysis of covariance, and, having assumed that the correlation between NTX/Cr at baseline and 26 weeks was 0.7, 21 patients per group were required. 42 To allow for dropout, group imbalance, estimated number of participants with serum selenium > 120 µg/l and the secondary end-point analyses, we recruited 40 patients per group.
Participants were block randomised equally to the three intervention arms. The randomisation list was generated by Sharp Clinical, and the IMP packs were delivered to the study site labelled by randomisation number. Participants were given the IMP pack labelled with their randomisation number.
We included an interim analysis of baseline serum selenium after the first 40 participants were recruited, with a plan to increase the sample size if many women had serum selenium > 120 µg/l. The only data reviewed were blinded baseline serum selenium. The final minimum sample size was determined as follows: (100/number of participants with baseline serum < 120 µg/l) × 40. The outcome of the interim analysis was planned as follows:
-
If the minimum sample size is < 120, a target sample size of 120 will be maintained.
-
If the minimum sample size is 121–165, the target sample size will be increased accordingly. If the number of participants with baseline serum selenium > 120 µg/l could be high enough to suggest significant group imbalance in the final primary end-point analysis, the DMC will consider whether stratification for baseline serum selenium should be introduced for subsequent randomisation.
-
If the minimum sample size is > 165, the DMC will consider whether or not the trial should continue and make a recommendation to the TSC.
All of the first 40 participants had baseline serum selenium < 120 µg/l, so we maintained the original recruitment target of 120 participants. We conducted a secondary analysis of all participants to determine whether or not baseline serum selenium was a determinant of bone turnover response.
Statistics
A detailed SAP was developed and approved by the TSC prior to locking the trial database. We conducted an intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis (all randomised participants) and per-protocol analysis. The per-protocol analysis included completing participants who took at least 75% of IMP, which was assessed by reported missed doses and returned tablet count.
Baseline data were assessed for comparability between the treatment groups. The normality of either the raw data or the residuals from the model using a density plot or histogram was assessed.
Primary end point: urine NTX/Cr at 26 weeks
An analysis of covariance was used with 26-week NTX/Cr measurement as the dependent outcome variable, and treatment group and baseline NTX/Cr measurement as the independent variable. The residuals from the model were not normally distributed, so NTX/Cr was log-transformed and the treatment group differences were back-transformed so that they could be presented as a ratio.
The statistical analysis plan prespecified a Hochberg testing procedure that allows an investigation into the three treatment arms to take place while maintaining the overall type I error rate at 5%. This stated that significance would be declared for a comparison between placebo and selenium if and only if both selenium doses were significant at the 5% level or if either dose was significant at the 2.5% level. If and only if significance was declared for both selenium doses, a comparison would be made between the doses. A comparison between 200 µg selenium and 50 µg selenium would be made at the 5% level of significance.
We examined the impact of baseline selenium levels on the NTX response to selenium supplementation by fitting a linear model with NTX at follow-up as the dependent variable and baseline selenium, baseline NTX and dose as independent variables.
The statistical analysis plan prespecified a multiple imputation strategy with 20 imputations utilising baseline and week 13 measurements of NTX/Cr, age of patient and treatment allocation. It also specified that additional variables associated with missing data would also be included in the multiple imputation model to make the missing-at-random assumption as plausible as possible. The nature of missingness and other baseline variables was explored in relation to missing data on the primary end point using univariable logistic regression models. The only baseline variable predictive of missingness was body mass index (BMI). The final multiple imputation model therefore utilised baseline and week 13 measurements of NTX/Cr, age of patient, BMI of patient at baseline and treatment allocation. The results using the imputation model did not differ from those for the ITT population.
Secondary end points
Urine NTX at 13 weeks and BMD by DXA at 26 weeks were analysed, as described for the primary end point.
All other secondary end-point measurements at 13 and 26 weeks were compared between treatment groups using linear mixed models with a random intercept to allow multiple measurements on individuals.
The models included fixed factors for treatment group and post-randomisation time, and a covariate for the baseline measurement of the outcome. To determine if the effect of treatment changed with time, an interaction between treatment group and time was tested. If this interaction was not statistically significant, then it was removed from the model and the overall treatment difference was reported. If there was a significant difference between treatment groups, the pairwise comparisons were made between each treatment group and the placebo group and the two doses were compared.
Efficacy measurements
Blood samples for biochemical measurements were taken fasted in the morning. Serum samples were obtained in serum-separating tubes, allowed to clot for 30 minutes and then centrifuged at 2500 r.p.m. for 10 minutes and separated into aliquots.
Urine samples were obtained as triplicate samples from fasted second morning voids on each of the 3 days before the study visit, or on the 2 days before and the day of the study visit. Equal volume aliquots from the urine samples were pooled into a single sample by the study team, then the pooled sample was separated into aliquots.
Samples were frozen at –80 °C and analysed in batches at the end of the study.
Urine NTX was measured by automated immunoassay (Vitros ECiQ, Ortho Clincal Diagnostics, High Wycombe, UK) at PathLab London [interassay coefficient of variation (CV) 6%]. NTX was expressed as a ratio to urinary creatinine concentration measured by the dry slide method (Vitros 250, Ortho Clinical Diagnostics, interassay CV 3%).
Serum selenium was measured by X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy,43 SePP was measured by immunoassay,44 and glutathione peroxidase was measured by an enzyme analysis by Professor Lutz Schomburg, Institute for Experimental Endocrinology, Charité – University Medical School Berlin.
CTX, OC, PINP and 25OHD (25-hydroxyvitamin D) were measured by automated immunoassay (IDS-iSYS, Immunodiagnostic Systems, Boldon, UK) by the University of Sheffield Academic Unit of Bone Metabolism. The interassay CVs are 6.5, 5.0, 7.2 and 6.7%, respectively.
IL-6 and hsCRP were measured by automated immunoassay by the Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Clinical Immunology Laboratory.
Height and weight were measured with an electric scale and stadiometer to the nearest 0.1 cm and 0.1 kg. Pulse and blood pressure were measured with an automated sphygmomanometer (Dinamap™, GE Healthcare, Chalfont St Giles, UK).
Grip strength was assessed using a digital hand dynamometer (Saehan Corporation, Masan, Republic of Korea). Three measurements were taken for each hand, and the best value was used for analysis.
The SPPB score was calculated from a chair stand and narrow walk test. 36
BMD was assessed using DXA of the spine and hip (Hologic DIscovery, Hologic Inc., Marlborough, MA, USA) at baseline and at 6 months, in accordance with standard scanning protocols, by specialist DXA scan technicians in the Sheffield Clinical Research Facility.
Dietary selenium and other nutrient intakes were assessed with 7-day diet diaries. The purpose of the food diaries was to describe participants’ habitual dietary intake of selenium and nutrients that influence bone turnover. The diaries were analysed using DIETQ (Tinuviel Software, Warrington, UK) by a nutritionist with experience in clinical research.
Safety measurements
Safety assessments for diabetes and thyroid function were made at screening (non-fasted), baseline, 13 weeks and 26 weeks. The measurements were made in real time by Sheffield Teaching Hospitals pathology laboratories. Participants with parameters outside the reference range were withdrawn from treatment and followed up as ITT.
Adverse events (including questioning for possible symptoms of selenium toxicity) were collected from the time of consent, at study visits and by monthly telephone contact throughout the treatment period and 4 weeks after the end of treatment.
Timing of assessments
See Appendix 2.
Deviations from protocol
We intended to measure hydroperoxidases as a marker of reactive oxygen species, but the commercially available assay was withdrawn before completion of the study.
Chapter 3 Results
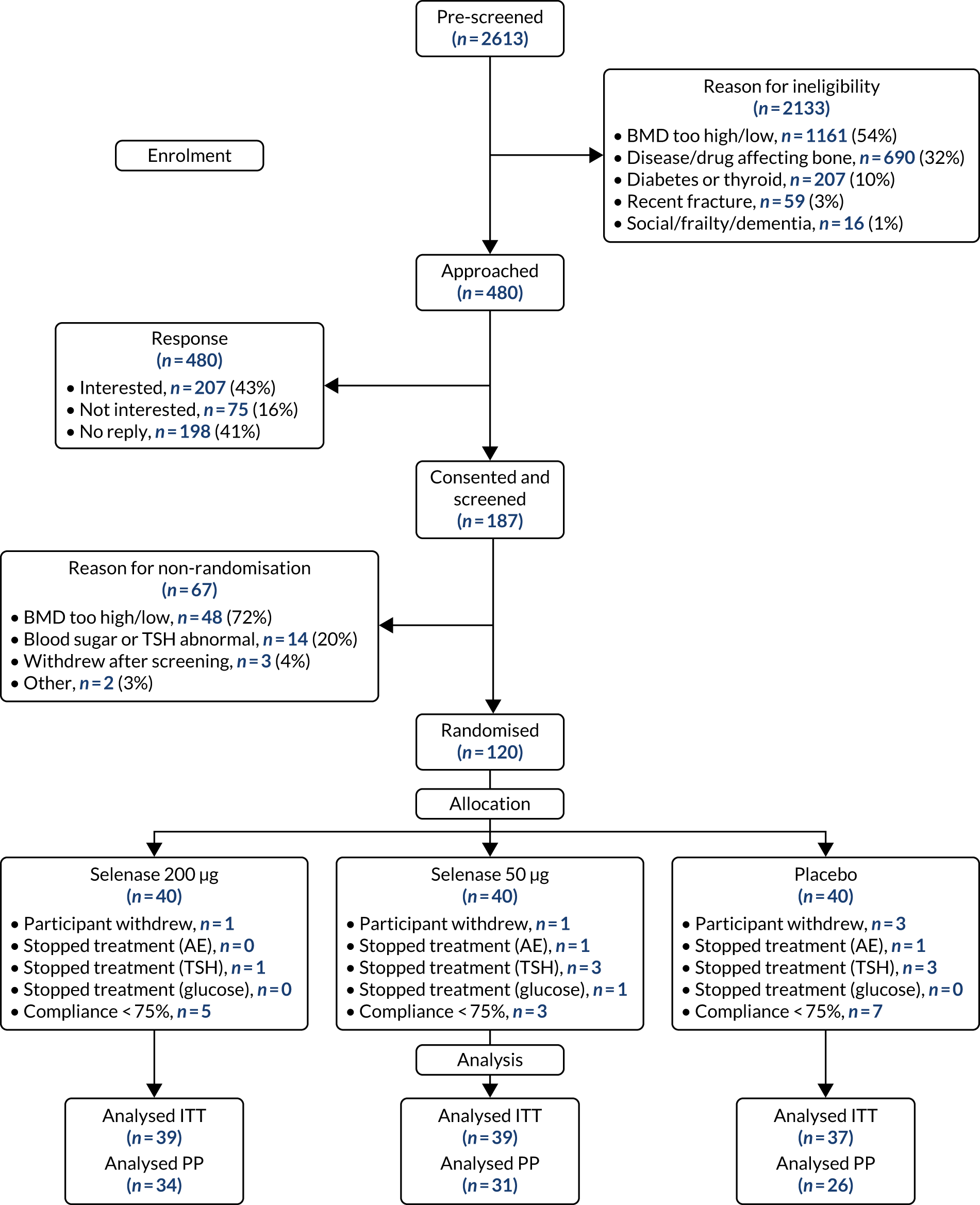
We recruited 120 women between January 2017 and April 2018. One hundred and fifteen women completed follow-up and were included in the ITT analysis (Figure 1).
The participants’ baseline characteristics are shown in Tables 1–3. The groups were generally well balanced, and the mean baseline serum selenium was 79.4 µg/l. All participants had baseline serum selenium < 120 µg/l and so were included in the primary analysis.
FIGURE 1.
The CONSORT (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) flow diagram. PP, per protocol.
| Variable | Summary statistic | Selenase 50 µg (n = 39) | Selenase 200 µg (n = 39) | Placebo (n = 37) | All (N = 115) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | Mean (SD) | 66.7 (6.1) | 64.5 (6.1) | 66.6 (6.0) | 65.9 (6.1) |
| Range | 56.0 to 79.0 | 55.0 to 77.0 | 56.0 to 83.0 | 55.0 to 83.0 | |
| Height (cm) | Mean (SD) | 162.0 (6.4) | 161.5 (7.9) | 160.6 (5.7) | 161.4 (6.7) |
| Range | 147.1 to 174.3 | 147.4 to 176.9 | 144.0 to 170.2 | 144.0 to 176.9 | |
| Weight (kg) | Mean (SD) | 65.5 (9.2) | 66.9 (10.8) | 65.7 (11.2) | 66.0 (10.4) |
| Range | 45.3 to 85.5 | 47.3 to 96.8 | 47.2 to 85.7 | 45.3 to 96.8 | |
| SPPB (score/12) | Median (IQR) | 11.0 (10.0 to 11.5) | 10.0 (9.0 to 11.0) | 11.0 (9.0 to 11.0) | 11.0 (9.0 to 11.0) |
| Range | 5.0 to 12.0 | 6.0 to 12.0 | 7.0 to 12.0 | 5.0 to 12.0 | |
| Hand grip strength dominant (kg) | Median (IQR) | 19.9 (16.2 to 22.7) | 19.2 (17.2 to 21.8) | 19.1 (15.9 to 21.1) | 19.2 (16.2 to 21.5) |
| Range | 12.7 to 31.0 | 7.4 to 34.9 | 10.4 to 27.9 | 7.4 to 34.9 | |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | Mean (SD) | 132 (18) | 132 (18) | 131 (22) | 132 (19) |
| Range | 104 to 169 | 108 to 176 | 97 to 186 | 97 to 186 | |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | Mean (SD) | 68 (8) | 71 (10) | 72 (12) | 70 (10) |
| Range | 56 to 89 | 54 to 94 | 51 to 97 | 51 to 97 | |
| Glucose (mmol/l) | Mean (SD) | 5.2 (1.0) | 5.1 (0.6) | 5.0 (0.6) | 5.1 (0.8) |
| Range | 3.5 to 8.3 | 3.7 to 7.2 | 3.9 to 6.7 | 3.5 to 8.3 | |
| Insulin (pmol/l) | Median (IQR) | 49.8 (32.9 to 70.4) | 48.7 (33.8 to 68.5) | 44.7 (29.3 to 74.1) | 47.0 (32.2 to 70.3) |
| Range | 21.3 to 276.6 | 17.8 to 283.6 | 14.4 to 137.4 | 14.4 to 283.6 | |
| TSH (mIU/l) | Mean (SD) | 2.01 (0.94) | 1.95 (0.89) | 1.90 (0.87) | 1.96 (0.89) |
| Range | 0.70 to 4.20 | 0.64 to 3.60 | 0.87 to 4.20 | 0.64 to 4.20 | |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | Mean (SD) | 36.0 (2.5) | 36.2 (2.4) | 35.6 (2.3) | 35.9 (2.4) |
| Range | 30.0 to 42.0 | 31.0 to 43.0 | 32.0 to 41.0 | 30.0 to 43.0 | |
| 25OHD (ng/ml) | Mean (SD) | 39.5 (12.1) | 37.7 (12.7) | 37.8 (10.8) | 38.3 (11.8) |
| Range | 16.9 to 70.0 | 19.1 to 68.6 | 17.7 to 62.8 | 16.9 to 70.0 |
| Variable | Summary statistic | Selenase 50 µg | Selenase 200 µg | Placebo | All |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum selenium (µg/l) | Mean (SD) | 79.3 (15.6) | 78.8 (16.5) | 80.2 (14.2) | 79.4 (15.3) |
| Range | 43.2 to 108.9 | 35.1 to 110.6 | 49.4 to 116.5 | 35.1 to 116.5 | |
| SePP (mg/l) | Mean (SD) | 5.21 (1.47) | 5.15 (1.37) | 5.22 (1.45) | 5.19 (1.42) |
| Range | 1.59 to 7.69 | 1.96 to 8.49 | 2.53 to 8.24 | 1.59 to 8.49 | |
| Glutathione peroxidase activity (IU/l) | Median (IQR) | 178.4 (120.9 to 272.0) | 192.8 (105.0 to 245.1) | 171.8 (106.7 to 249.6) | 183.4 (107.2 to 251.8) |
| Range | 20.2 to 435.0 | 21.8 to 334.3 | 12.7 to 387.5 | 12.7 to 435.0 | |
| hsCRP (mg/) | Median (IQR) | 0.75 (0.41 to 1.29) | 0.94 (0.41 to 1.75) | 1.29 (0.47 to 2.40) | 0.95 (0.45 to 1.85) |
| Range | 0.15 to 24.70 | 0.15 to 40.10 | 0.15 to 7.14 | 0.15 to 40.10 | |
| IL-6 (ng/l) | Median (IQR) | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.7) | 1.0 (1.0 to 2.2) | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.7) | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.8) |
| Range | 1.0 to 14.8 | 1.0 to 23.2 | 1.0 to 6.8 | 1.0 to 23.2 |
| Variable | Summary statistic | Selenase 50 µg (n = 39) | Selenase 200 µg (n = 39) | Placebo (n = 37) | All (n = 115) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lumbar spine BMD (T-score) | Mean (SD) | –1.8 (1.0) | –1.8 (0.6) | –1.7 (0.9) | –1.8 (0.8) |
| Range | –2.9 to 0.7 | –3.0 to –0.2 | –3.1 to 2.0 | –3.1 to 2.0 | |
| Total hip BMD (T-score) | Mean (SD) | –1.2 (0.7) | –0.9 (0.6) | –1.3 (0.7) | –1.1 (0.7) |
| Range | –2.3 to 1.3 | –2.4 to 0.6 | –2.7 to 0.5 | –2.7 to 1.3 | |
| NTX/Cr (nmolBCE/mmol) | Median (IQR) | 38.2 (33.7 to 49.7) | 42.0 (35.0 to 49.5) | 37.5 (29.7 to 49.1) | 38.2 (31.4 to 49.7) |
| Range | 19.4 to 70.8 | 20.2 to 103.4 | 16.3 to 124.1 | 16.3 to 124.1 | |
| PINP (µg/l) | Median (IQR) | 50.1 (37.5 to 68.6) | 49.6 (39.9 to 62.3) | 49.8 (38.7 to 60.0) | 49.8 (38.9 to 62.3) |
| Range | 23.1 to 96.1 | 23.3 to 98.6 | 27.5 to 105.7 | 23.1 to 105.7 |
Nine participants had missing data for baseline or week 26 NTX/Cr, so 106 were included in the primary end-point analysis. Baseline characteristics for participants with and participants without complete primary end-point data were similar.
The sample size calculation assumed a correlation between baseline and week 26 NTX/Cr measurement of 0.7. In the ITT population, the Pearson correlation between baseline and week 26 NTX/Cr was 0.62 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.49 to 0.73]. The residuals from the model were not normally distributed, so NTX/Cr was log-transformed and the treatment group differences were back-transformed so that they could be presented as a ratio.
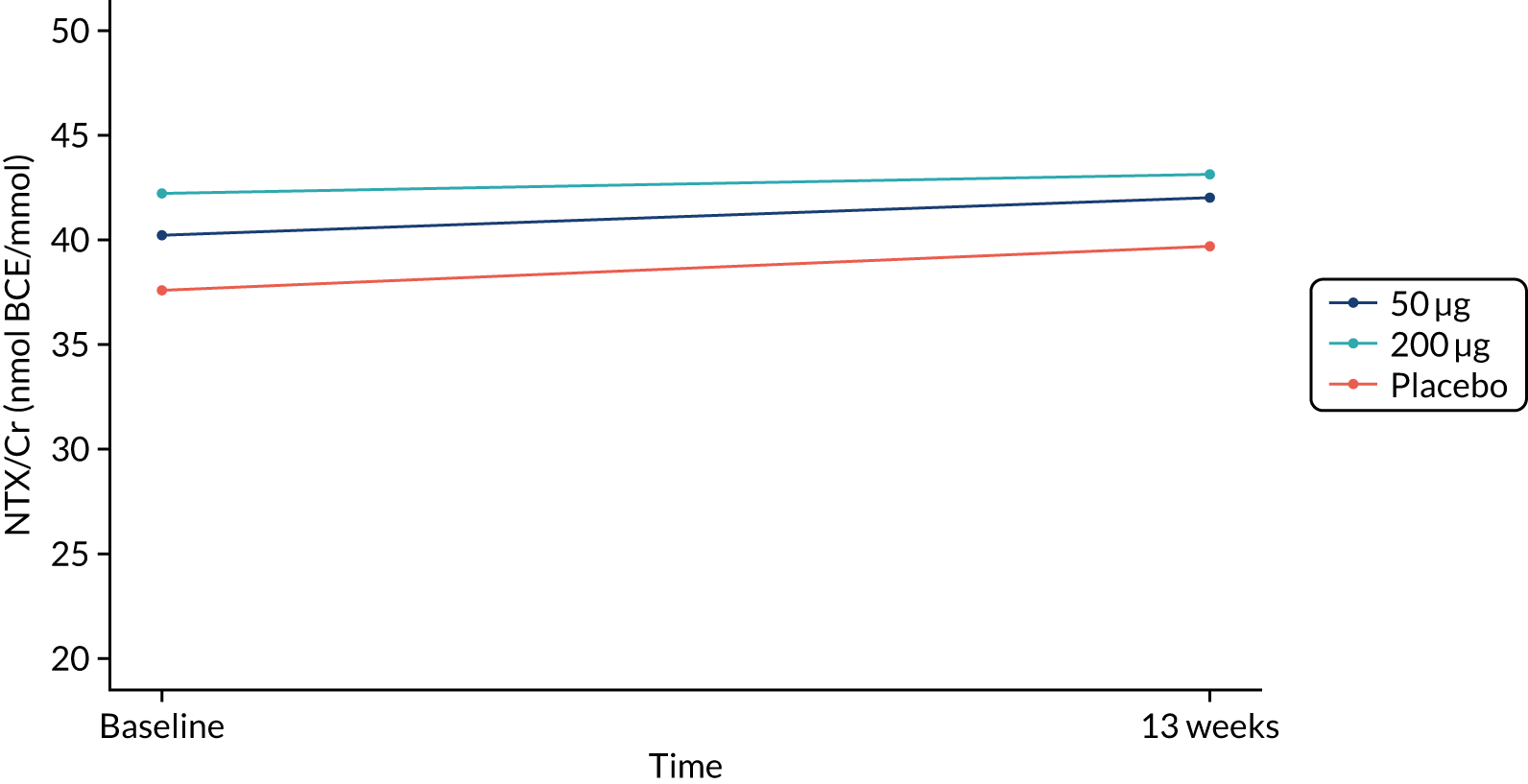
The primary end point (urine NTX/Cr) did not differ between treatment groups after 26 weeks or 13 weeks (Figures 2 and 3 and Table 4). Eighty-six participants were included in the per-protocol analysis, and NTX/Cr did not differ between treatment groups after 26 weeks or 13 weeks (Table 5).
FIGURE 2.
NTX/Cr 26 weeks: ITT analysis.
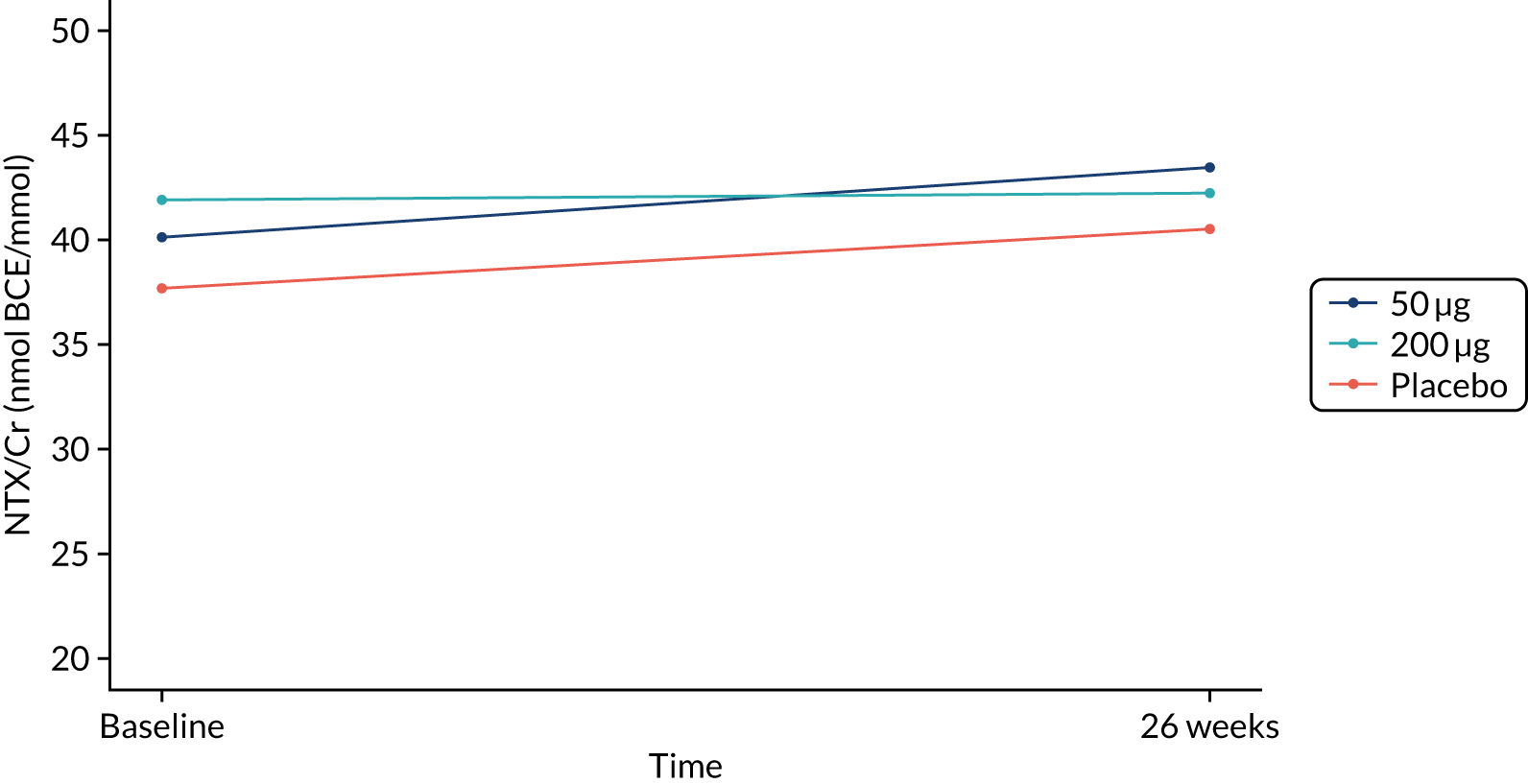
FIGURE 3.
NTX/Cr 13 weeks: ITT analysis.
| Time point | Placebo | Selenase (50 µg) | Selenase (200 µg) | 50 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with 50 µg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | |
| NTX/Cr (nmolBCE/mmol) (primary outcome) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 34 | 37.7 (32.5 to 43.6) | 35 | 40.1 (35.9 to 44.8) | 37 | 41.9 (37.0 to 47.4) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 34 | 40.5 (34.9 to 47.0) | 35 | 43.4 (37.4 to 50.5) | 37 | 42.2 (37.5 to 47.6) | 1.03 (0.88 to 1.19) | 0.737 | 0.97 (0.83 to 1.12) | 0.658 | 0.94 (0.81 to 1.09) | 0.429 |
| NTX/Cr (nmolBCE/mmol) (secondary outcome) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 35 | 37.6 (32.6 to 43.3) | 36 | 40.2 (36.1 to 44.7) | 39 | 42.2 (37.5 to 47.6) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 35 | 39.7 (34.4 to 45.8) | 36 | 42.0 (37.3 to 47.3) | 39 | 43.1 (39.0 to 47.7) | 1.01 (0.90 to 1.13) | 0.881 | 1.00 (0.89 to 1.12) | 0.988 | 0.99 (0.89 to 1.11) | 0.890 |
| Time point | Placebo | Selenase (50 µg) | Selenase (200 µg) | 50 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with 50 µg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | |
| NTX/Cr (nmolBCE/mmol) (primary outcome) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 25 | 37.4 (31.8 to 44.0) | 29 | 41.0 (36.2 to 46.5) | 32 | 40.9 (36.0 to 46.6) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 25 | 42.4 (35.2 to 51.1) | 29 | 44.3 (37.6 to 52.3) | 32 | 40.6 (35.7 to 46.1) | 0.98 (0.82 to 1.17) | 0.803 | 0.90 (0.76 to 1.06) | 0.210 | 0.92 (0.78 to 1.08) | 0.294 |
| NTX/Cr (nmolBCE/mmol) (secondary outcome) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 25 | 37.4 (31.8 to 44.0) | 28 | 41.7 (36.8 to 47.2) | 33 | 40.8 (36.0 to 46.3) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 25 | 41.2 (35.8 to 47.5) | 28 | 43.4 (37.9 to 49.7) | 33 | 42.3 (38.2 to 46.9) | 0.98 (0.86 to 1.12) | 0.766 | 0.97 (0.86 to 1.10) | 0.619 | 0.99 (0.88 to 1.11) | 0.845 |
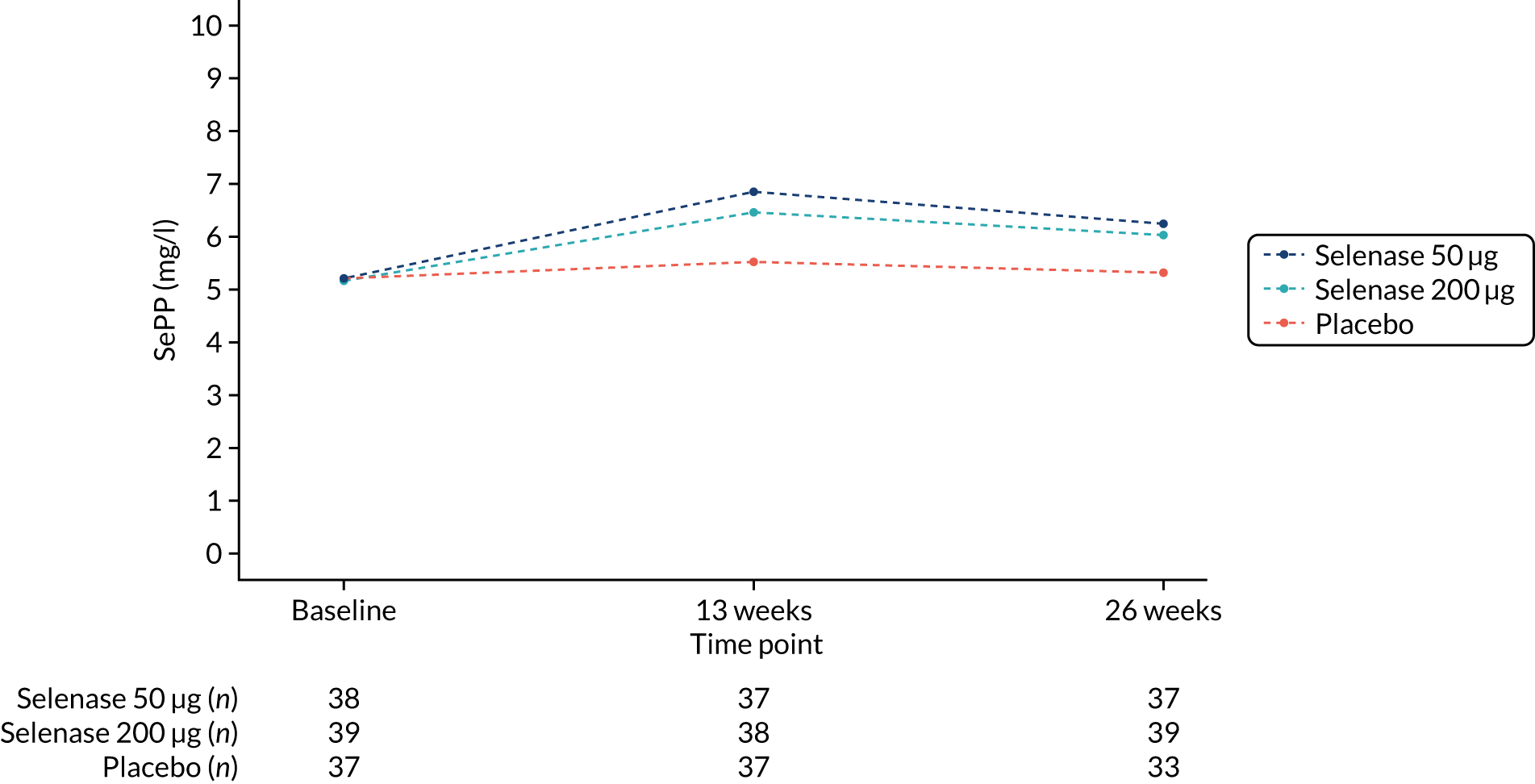
Mean serum selenium increased from baseline to 26 weeks in the treatment groups; 78.8 µg/l (95% CI 73.5 to 84.2 µg/l) to 105.7 µg/l (95%CI 99.5 to 111.9 µg/l) in the 200 µg group, and 79.3 µg/l (95% CI 74.2 to 84.4 µg/l) to 96.2 µg/l (95% CI 90.7 to 101.6 µg/l) in the 50 µg group. There was no change in the placebo group (Table 6 and Figure 4). Mean serum SePP increased from baseline to 26 weeks in the treatment groups; 5.15 mg/l (95% CI 4.71 to 5.60 mg/l) to 6.03 mg/l (95% CI 5.54 to 6.51 mg/l) in the 200 µg group and 5.21 mg/l (95% CI 4.73 to 5.70 mg/l) to 6.25 mg/l (95% CI 5.79 to 6.70 mg/l) in the 50 µg group. There was no change in the placebo group (see Table 6 and Figure 5).
| Time point | Placebo | Selenase (50 µg) | Selenase (200 µg) | 50 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with 50 µg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | Differenceb (95% CI) | p-value | Differenceb (95% CI) | p-value | Differenceb (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Serum selenium (µg/l) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 37 | 80.2 (75.5 to 85.0) | 38 | 79.3 (74.2 to 84.4) | 39 | 78.8 (73.5 to 84.2) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 37 | 81.7 (77.1 to 86.4) | 37 | 104.1 (98.5 to 109.7) | 38 | 107.9 (102.3 to 113.4) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 33 | 77.7 (73.3 to 82.2) | 37 | 96.2 (90.7 to 101.6) | 39 | 105.7 (99.5 to 111.9) | 20.5 (14.5 to 26.5) | < 0.001 | 27.5 (21.6 to 33.4) | < 0.001 | 7.0 (1.1 to 12.8) | 0.020 |
| SePP (mg/l) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 37 | 5.22 (4.73 to 5.70) | 38 | 5.21 (4.73 to 5.70) | 39 | 5.15 (4.71 to 5.60) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 37 | 5.50 (5.11 to 5.91) | 37 | 6.85 (6.24 to 7.46) | 38 | 6.47 (5.89 to 7.04) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 33 | 5.31 (4.75 to 5.87) | 37 | 6.25 (5.79 to 6.70) | 39 | 6.03 (5.54 to 6.51) | 1.17 (0.62 to 1.72) | < 0.001 | 0.88 (0.34 to 1.42) | 0.002 | –0.29 (–0.83 to 0.25) | 0.287 |
FIGURE 4.
Serum selenium by treatment group at 13 weeks and 26 weeks.
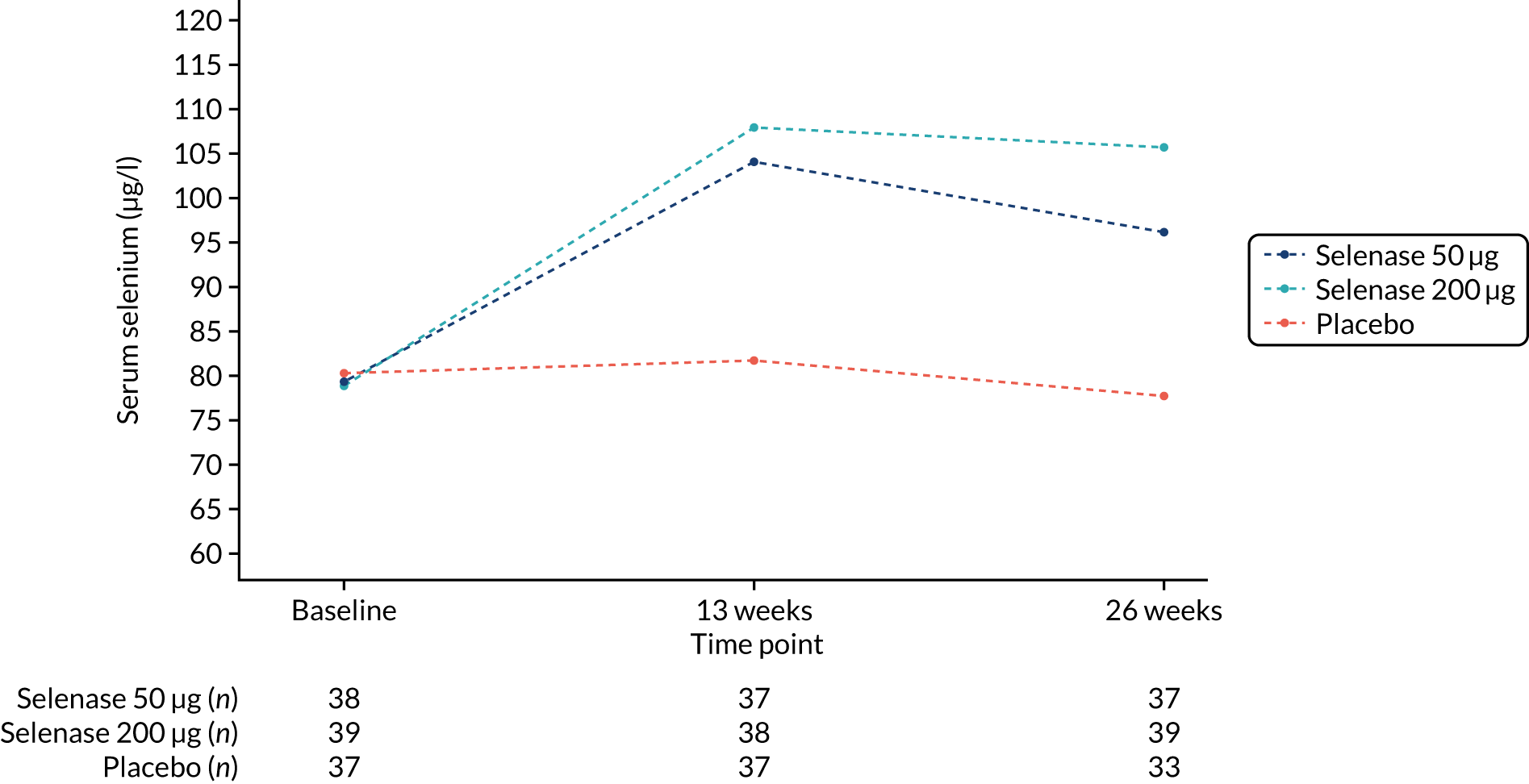
FIGURE 5.
Serum SePP by treatment group at 13 weeks and 26 weeks.
A linear regression model was fitted with log(week 26 NTX/Cr) as the dependent variable and log (baseline NTX/Cr), baseline selenium and treatment group as the independent variables. The interaction between treatment group and baseline selenium was not statistically significant (p = 0.465), suggesting that treatment group did not modify the relationship between baseline selenium and week 26 NTX/Cr.
There were no differences between treatment groups in any of the other biochemical markers of bone turnover (PINP, CTX or OC) at 26 weeks or 13 weeks (Table 7).
| Time point | Placebo | Selenase (50 µg) | Selenase (200 µg) | 50 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with 50 µg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | |
| PINP (µg/l) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 37 | 48.2 (43.3 to 53.6) | 38 | 50.2 (44.6 to 56.5) | 39 | 49.6 (44.5 to 55.4) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 36 | 46.1 (41.5 to 51.3) | 37 | 49.9 (44.0 to 56.7) | 39 | 49.6 (44.0 to 56.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 34 | 47.0 (42.5 to 52.0) | 37 | 46.8 (41.0 to 53.3) | 37 | 47.0 (41.3 to 53.6) | 0.97 (0.91 to 1.04) | 0.381 | 0.99 (0.93 to 1.06) | 0.816 | 1.02 (0.96 to 1.09) | 0.508 |
| OC (µg/l) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 37 | 15.7 (13.4 to 18.4) | 38 | 14.8 (12.7 to 17.2) | 39 | 15.7 (13.8 to 17.9) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 36 | 14.0 (12.2 to 16.1) | 37 | 15.7 (13.8 to 17.9) | 39 | 15.0 (13.3 to 17.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 34 | 14.4 (12.6 to 16.4) | 37 | 14.1 (12.3 to 16.2) | 37 | 13.9 (12.4 to 15.6) | 1.07 (0.95 to 1.21) | 0.343 | 1.01 (0.89 to 1.15) | 0.848 | 0.95 (0.84 to 1.08) | 0.439 |
| CTX (µg/l) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 37 | 0.15 (0.11 to 0.22) | 38 | 0.14 (0.10 to 0.19) | 39 | 0.15 (0.12 to 0.21) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 35 | 0.13 (0.10 to 0.17) | 36 | 0.15 (0.11 to 0.21) | 37 | 0.13 (0.10 to 0.18) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 34 | 0.13 (0.09 to 0.17) | 37 | 0.12 (0.09 to 0.16) | 37 | 0.11 (0.09 to 0.15) | 1.07 (0.80 to 1.45) | 0.656 | 0.97 (0.72 to 1.30) | 0.811 | 0.90 (0.67 to 1.20) | 0.470 |
There was a small statistically significant but not clinically relevant difference in lumbar spine BMD T-score at 26 weeks in the 50 µg group (T-score difference 0.2) compared with the placebo group and the 200 µg group (T-score difference –0.1). Total hip BMD did not differ between treatment groups at 26 weeks (Table 8).
| Time point | Placebo | Selenase (50 µg) | Selenase (200 µg) | 50 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with 50 µg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | Differenceb (95% CI) | p-value | Differenceb (95% CI) | p-value | Differenceb (95% CI) | p-value | |
| DXA T-score total hip | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 34 | –1.3 (–1.5 to –1.0) | 38 | –1.2 (–1.5 to –1.0) | 39 | –0.9 (–1.1 to –0.7) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 34 | –1.2 (–1.5 to –1.0) | 38 | –1.2 (–1.4 to –1.0) | 39 | –0.9 (–1.1 to –0.7) | (–0.1 to 0.1) | 0.954 | 0.0 (–0.1 to 0.1) | 0.958 | 0.0 (–0.1 to 0.1) | 0.911 |
| DXA T-score lumbar spine | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 34 | –1.7 (–2.0 to –1.4) | 37 | –1.9 (–2.2 to –1.6) | 37 | –1.8 (–2.0 to –1.6) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 34 | –1.8 (–2.1 to –1.5) | 37 | –1.8 (–2.1 to –1.5) | 37 | –1.9 (–2.1 to –1.7) | 0.2 (0.0 to 0.3) | 0.013 | 0.2 (–0.1 to 0.1) | 0.802 | –0.1 (–0.3 to 0.0) | 0.021 |
There was a statistically significant but small (0.5/12) unfavourable difference in the SPPB score in the 50 µg group compared with the placebo group at 26 weeks, but there was no difference between the 200 µg group and the placebo group; overall, there was no significant treatment effect (p = 0.08). Grip strength did not differ between treatment groups (Table 9).
| Time point | Placebo | Selenase (50 µg) | Selenase (200 µg) | 50 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with 50 µg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | Differenceb (95% CI) | p-value | Differenceb (95% CI) | p-value | Differenceb (95% CI) | p-value | |
| SPPB (score/12) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 37 | 10.2 (9.7 to 10.7) | 39 | 10.3 (9.7 to 10.9) | 39 | 10.0 (9.6 to 10.5) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 37 | 10.8 (10.5 to 11.3) | 39 | 10.3 (9.8 to 10.8) | 39 | 10.4 (9.7 to 11.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 36 | 10.9 (10.5 to 11.4) | 38 | 10.4 (9.9 to 10.9) | 39 | 10.3 (9.7 to 10.8) | –0.5 (–1.1 to –0.03) | 0.037 | –0.5 (–1.0 to 0.05) | 0.074 | 0.1 (–0.4 to 0.6) | 0.759 |
| Grip strength dominant hand (kg) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 37 | 18.6 (17.3 to 20.0) | 39 | 19.8 (18.3 to 21.3) | 39 | 19.5 (17.9 to 21.1) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 37 | 18.6 (17.3 to 20.0) | 39 | 19.4 (18.0 to 20.8) | 39 | 19.2 (17.9 to 20.5) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 36 | 18.1 (16.6 to 19.5) | 36 | 18.9 (17.4 to 20.4) | 39 | 18.4 (16.9 to 19.8) | –0.3 (–1.2 to 0.6) | 0.490 | –0.3 (–1.2 to 0.6) | 0.497 | 0.01 (–0.9 to 0.9) | 0.987 |
| Grip strength non-dominant hand (kg) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 37 | 16.8 (15.5 to 18.2) | 38 | 18.1 (16.8 to 19.3) | 38 | 17.6 (16.3 to 18.9) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 37 | 17.1 (15.8 to 18.4) | 37 | 17.2 (16.0 to 18.4) | 38 | 17.3 (15.7 to 18.8) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 36 | 16.1 (14.7 to 17.5) | 36 | 17.0 (15.8 to 18.2) | 38 | 16.7 (15.1 to 18.3) | –0.7 (–1.6 to 0.2) | 0.131 | –0.3 (–1.2 to 0.6) | 0.589 | 0.4 (–0.5 to 1.3) | 0.402 |
Measurements of anti-oxidant activity and inflammation did not differ between treatment groups (Table 10). The majority of IL-6 measurements were below the limit of detection of 1.6 ng/l (74/110 at baseline, 71/110 at week 13 and 74/108 at week 26), so no further analysis was conducted on the IL-6 measurements.
| Time point | Placebo | Selenase (50 µg) | Selenase (200 µg) | 50 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with 50 µg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean (95% CI) | n | Mean (95% CI) | n | Mean (95% CI) | Difference (95% CI) | p-value | Difference (95% CI) | p-value | Difference (95% CI) | p-value | |
| GPx activity (IU/l)a,b | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 37 | 183.5 (152.4 to 214.5) | 38 | 192.6 (156.4 to 228.8) | 39 | 180.9 (155.1 to 206.8) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 37 | 184.4 (158.0 to 210.8) | 37 | 204.2 (175.6 to 232.9) | 38 | 180.7 (151.1 to 210.3) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 33 | 175.4 (147.5 to 203.2) | 37 | 176.8 (149.2 to 204.3) | 39 | 160.1 (132.4 to 187.8) | 10.1 (–17.5 to 37.8) | 0.470 | –8.8 (–36.1 to 18.6) | 0.527 | –18.9 (–45.9 to 8.1) | 0.169 |
| hsCRP (mg/l)c,d | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 36 | 1.14 (0.80 to 1.63) | 35 | 0.80 (0.55 to 1.15) | 38 | 1.00 (0.65 to 1.41) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 36 | 1.12 (0.75 to 1.65) | 35 | 0.77 (0.55 to 1.08) | 38 | 1.04 (0.78 to 1.38) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 35 | 1.31 (0.88 to 1.94) | 33 | 0.81 (0.58 to 1.13) | 37 | 1.09 (0.74 to 1.60) | 0.84 (0.63 to 1.15) | 0.282 | 0.99 (0.74 to 1.32) | 0.933 | 1.17 (0.87 to 1.57) | 0.310 |
The safety assessments for diabetes and thyroid function did not differ between treatment groups. There was a small difference in glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) between 200 µg and placebo groups at 26 weeks (–1.0 mmol/mol), but this is not clinically significant (Table 11). Seven participants were withdrawn from treatment at week 13 because of abnormal TSH (200 µg, n = 1; 50 µg, n = 3; placebo, n = 3), and one was withdrawn because of abnormal blood glucose (in the 50 µg group).
| Time point | Placebo | Selenase (50 µg) | Selenase (200 µg) | 50 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with 50 µg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean (95% CI) | n | Mean (95% CI) | n | Mean (95% CI) | Difference (95% CI) | p-value | Difference (95% CI) | p-value | Difference (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Fasting blood glucose (mmol/l)a,b | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 37 | 5.0 (4.8 to 5.2) | 39 | 5.2 (4.9 to 5.5) | 38 | 5.1 (4.9 to 5.3) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 37 | 4.9 (4.6 to 5.1) | 37 | 5.1 (4.9 to 5.3) | 37 | 4.9 (4.7 to 5.1) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 36 | 4.9 (4.7 to 5.1) | 38 | 4.9 (4.9 to 5.1) | 38 | 4.9 (4.8 to 5.1) | 0.2 (–0.1 to 0.4) | 0.150 | 0.04 (–0.2 to 0.3) | 0.709 | –0.1 (–0.4 to 0.1) | 0.280 |
| Insulin (pmol/l)c,d | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 33 | 46.3 (37.4 to 57.4) | 33 | 52.7 (41.8 to 66.6) | 36 | 51.6 (41.8 to 63.7) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 32 | 46.0 (36.5 to 57.9) | 31 | 54.0 (43.2 to 67.6) | 35 | 55.5 (43.3 to 71.2) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 33 | 46.8 (38.3 to 57.2) | 32 | 46.4 (37.7 to 57.1) | 35 | 47.3 (38.8 to 57.6) | 0.99 (0.82 to 1.21) | 0.944 | 1.05 (0.87 to 1.27) | 0.624 | 1.06 (0.87 to 1.28) | 0.575 |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol)a,b | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 37 | 35.6 (34.8 to 36.4) | 39 | 36.0 (35.2 to 36.8) | 39 | 36.2 (35.4 to 36.9) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 36 | 36.9 (34.9 to 38.9) | 37 | 36.6 (35.8 to 37.3) | 38 | 35.7 (34.8 to 36.6) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 36 | 36.3 (35.5 to 37.0) | 38 | 36.6 (35.9 to 37.4) | 37 | 36.1 (35.2 to 37.0) | –0.3 (–1.3 to 0.6) | 0.480 | –1.0 (–2.0 to –0.1) | 0.028 | –0.7 (–1.6 to 0.2) | 0.128 |
| TSH (mIU/l)c,d | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 37 | 1.74 (1.51 to 2.00) | 39 | 1.80 (1.55 to 2.11) | 39 | 1.74 (1.48 to 2.04) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 36 | 2.19 (1.86 to 2.58) | 37 | 2.41 (2.05 to 2.82) | 36 | 2.31 (1.91 to 2.80) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 36 | 2.39 (2.04 to 2.81) | 39 | 2.19 (1.87 to 2.57) | 39 | 2.22 (1.84 to 2.69) | 0.96 (0.84 to 1.10) | 0.568 | 0.97 (0.85 to 1.10) | 0.682 | 1.01 (0.88 to 1.16) | 0.870 |
Analyses were repeated in the per-protocol group for all efficacy and safety end points, and the results did not differ from those for the ITT population.
The study group were generally vitamin D replete. There was a small difference in 25OHD between 200 µg and placebo groups at 26 weeks, but this is not clinically significant (Table 12).
| Time point | Placebo | Selenase (50 µg) | Selenase (200 µg) | 50 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with 50 µg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | |
| 25OHD (ng/ml) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 37 | 36.3 (33.0 to 40.0) | 38 | 37.7 (34.0 to 41.8) | 39 | 35.8 (32.2 to 39.8) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 13 weeks | 37 | 33.1 (30.3 to 36.2) | 37 | 34.6 (30.7 to 39.0) | 39 | 30.9 (27.6 to 34.5) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 36 | 32.5 (29.2 to 36.2) | 37 | 31.9 (27.9 to 36.6) | 39 | 29.4 (25.8 to 33.5) | 0.98 (0.91 to 1.05) | 0.485 | 0.93 (0.87 to 1.00) | 0.041 | 0.96 (0.89 to 1.02) | 0.176 |
The dietary intake of vitamin D, calcium and selenium assessed by a 7-day diet diary were similar in all three treatment groups (Table 13). The dietary selenium intake decreased between baseline and 26 weeks in all three groups.
| Time point | Placebo | Selenase (50 µg) | Selenase (200 µg) | 50 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with placebo | 200 µg compared with 50 µg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | n | Meana (95% CI) | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | Ratiob (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Dietary vitamin D (µg/day) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 34 | 2.1 (1.5 to 2.8) | 35 | 2.5 (2.0 to 3.0) | 39 | 2.2 (1.8 to 2.8) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 34 | 1.9 (1.4 to 2.6) | 35 | 2.2 (1.8 to 2.8) | 39 | 2.0 (1.8 to 2.8) | 1.06 (0.78 to 1.44) | 0.732 | 1.02 (0.75 to 1.37) | 0.923 | 0.96 (0.71 to 1.30) | 0.796 |
| Dietary calcium (mg/day) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 34 | 769.9 (685.2 to 865.0) | 35 | 850.7 (774.7 to 934.1) | 39 | 795.5 (711.3 to 889.6) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 34 | 740.3 (664.6 to 824.7) | 35 | 829.0 (736.9 to 932.5) | 39 | 688.9 (596.3 to 795.9) | 1.03 (0.91 to 1.18) | 0.629 | 0.91 (0.78 to 1.03) | 0.122 | 0.88 (0.78 to 1.00) | 0.041 |
| Dietary selenium (µg/day) | ||||||||||||
| Baseline | 34 | 78.7 (73.8 to 83.9) | 34 | 79.6 (74.5 to 85.0) | 39 | 76.9 (71.2 to 83.0) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 26 weeks | 34 | 40.6 (35.4 to 46.5) | 34 | 39.4 (34.3 to 45.1) | 39 | 35.5 (31.1 to 40.7) | 0.96 (0.81 to 1.16) | 0.682 | 0.89 (0.75 to 1.06) | 0.189 | 0.92 (0.77 to 1.10) | 0.372 |
The number and severity of adverse events and the systems affected by adverse events were similar across treatment groups (Tables 14 and 15).
| System | Placebo (N = 37) | Selenase 50 µg (N = 39) | Selenase 200 µg (N = 39) | All (N = 115) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Events (n) | Participants, n (%) | Events (n) | Participants, n (%) | Events (n) | Participants, n (%) | Events (n) | Participants, n (%) | |
| All | 34 | 23 (62.2) | 34 | 27 (69.2) | 27 | 17 (43.6%) | 95 | 67 (58.3) |
| Infection and infestation | 10 | 9 (24.3) | 8 | 8 (20.5) | 10 | 7 (17.9) | 28 | 24 (20.9) |
| Gastrointestinal | 5 | 5 (13.5) | 5 | 4 (10.3) | 4 | 4 (10.3) | 14 | 13 (11.3) |
| Musculoskeletal and connective | 3 | 3 (8.1) | 6 | 5 (12.8) | 3 | 3 (7.7) | 12 | 11 (9.6) |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | 7 | 6 (16.2) | 1 | 1 (2.6) | 1 | 1 (2.6) | 9 | 8 (7.0) |
| Respiratory | 3 | 2 (5.4) | 2 | 2 (5.1) | 2 | 1 (2.6) | 7 | 5 (4.3) |
| Skin and subcutaneous | 1 | 1 (2.7) | 3 | 3 (7.7) | 2 | 2 (5.1) | 6 | 6 (5.2) |
| Renal and urinary | 1 | 1 (2.7) | 2 | 2 (5.1) | 2 | 2 (5.1) | 5 | 5 (4.3) |
| Neurological | 1 | 1 (2.7) | 2 | 2 (5.1) | 1 | 1 (2.6) | 4 | 4 (3.5) |
| Surgical and medical procedures | 1 | 1 (2.7) | 2 | 2 (5.1) | 0 | 0 (0.0) | 3 | 3 (2.6) |
| Vascular | 0 | 0 (0.0) | 3 | 2 (5.1) | 0 | 0 (0.0) | 3 | 2 (1.7) |
| Eye | 1 | 1 (2.7) | 0 | 0 (0.0) | 0 | 0 (0.0) | 1 | 1 (0.9) |
| General | 0 | 0 (0.0) | 0 | 0 (0.0) | 1 | 1 (2.6) | 1 | 1 (0.9) |
| Neoplasms | 1 | 1 (2.7) | 0 | 0 (0.0) | 1 | 1 (2.7) | 2 | 2 (1.8) |
| Psychiatric | 0 | 0 (0.0) | 0 | 0 (0.0) | 1 | 1 (2.6) | 1 | 1 (0.9) |
| Grade | Placebo (N = 37) | Selenase 50 µg (N = 39) | Selenase 200 µg (N = 39) | All (N = 115) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Events (n) | Participants, n (%) | Events (n) | Participants, n (%) | Events (n) | Participants, n (%) | Events (n) | Participants, n (%) | |
| All | 34 | 23 (62.2) | 34 | 27 (69.2) | 27 | 17 (43.6) | 95 | 67 (58.3) |
| Grade 1 | 22 | 16 (43.2) | 23 | 20 (51.3) | 22 | 15 (38.5) | 67 | 51 (44.3) |
| Grade 2 | 11 | 9 (24.3) | 11 | 9 (23.1) | 5 | 4 (10.3) | 27 | 22 (19.1) |
| Grade 3 | 1 | 1 (2.7) | 0 | 0 (0.0) | 0 | 0 (0.0) | 1 | 1 (0.9) |
There were three serious adverse events: a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction at week 18 (in the 50 µg/day group); a diagnosis of bowel cancer after routine screening at week 2 (in the placebo group); and a pulmonary embolus due to metastatic bowel cancer at week 4 (in the 200 µg/day group). All SAEs were judged by the principal investigator as unrelated to trial medication.
Chapter 4 Discussion
We have conducted a well-powered, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the effects of selenium supplementation on musculoskeletal health in postmenopausal women. We found no effect on biochemical markers of bone turnover, BMD or physical function with Selenase 200 µg or 50 µg daily. None of the end-point results differed between the ITT analysis and the per-protocol analysis. This is an important result because it is from the first randomised controlled trial of selenium supplementation for musculoskeletal health, to our knowledge.
Serum selenium in the 200 µg treatment group increased from 80 µg/l to 105 µg/l. Mortality data suggest that the optimum range for serum selenium is 120–150 µg/l. Although serum selenium did not reach this range, based on the correlation of serum selenium and NTX/Cr in our previous study, an increase of 30% should be enough to demonstrate some change in bone markers if there was any effect. Biochemical markers of bone turnover are dynamic and respond to bone active agents within a few weeks. For example, bone markers decrease by about 20% within 2 weeks of starting calcium supplements. 45 Selenium at 200 µg/day has been shown to be effective in Graves’ eye disease and cancer prevention studies, so there is good evidence that this dose is high enough to be biologically active in humans. It is possible that higher dose supplements would have an effect on bone, but there was no dose–response effect across the two doses we studied. In addition, higher doses may increase the risk of adverse effects. 33
There was a small increase in lumbar spine BMD in the 50 µg group, but, in the absence of any effect on bone turnover or any BMD effect in the 200 µg group, this is likely to be a spurious result.
There were enough promising epidemiological, observational and pre-clinical data to suggest that selenium might have beneficial effects on musculoskeletal health.
Higher selenium status is associated with BMD in men in the Netherlands. 22 Higher dietary selenium intake is associated with lower hip fracture risk in older adults in the USA23 and higher BMD in middle-aged and older adults in China46 and Europe. 14,22 However, there was no association with BMD in postmenopausal Turkish women. 24
Lower serum selenium and dietary selenium are associated with lower muscle mass and poorer muscle function in older adults. 27,47–49
The proposed mechanism of action of selenium to reduce reactive oxygen species, and therefore reduce the pro-resorptive drive to osteoclasts, was plausible. However, we saw no effect at all on markers of bone resorption. It may be that selenium status is a marker for other factors acting on bone health or that a single factor approach is ineffective and selenium is part of a more complex system that is not yet fully characterised.
The population in this study was generally representative of postmenopausal women in the UK, in terms of BMI, BMD, vitamin D status and calcium intake. Their dietary selenium intake at baseline was higher than expected for the UK, but at 26 weeks it was more typical. 50 We do not know if this is a true change in dietary behaviour over the course of the study; we might speculate that participants reduced their dietary selenium intake because they were receiving a supplement. However, selenium is a ubiquitous nutrient, and it would be difficult to reduce it in isolation.
We studied women only, and it is possible that the effects of selenium on bone would be different in men. However, postmenopausal women have higher bone resorption than men, and we hypothesised that selenium could act particularly through one of the resorption pathways activated by oestrogen deficiency. Therefore, in the absence of any effect in women, we do not think that an effect in men is likely.
We conclude that selenium supplementation at these doses is not beneficial for musculoskeletal health in postmenopausal women. Other trials have demonstrated benefit in cancer prevention, so selenium may have benefits for human health. However, it is not likely to be effective for treatment of osteoporosis and reduction in fracture risk.
Chapter 5 Patient and public involvement
The Sheffield Lay Advisory Panel for Bone Research has contributed to this study. The panel was established in 2009 and has made valuable contributions to these aspects of research in the Academic Unit of Bone Metabolism since then. It has received training in research methods, research governance and grant application processes. The panel was consulted about trial design and contributed to the grant application, protocol and recruitment strategy.
The panel received updates on the study’s progress at its monthly meetings; during these meetings, panel members had the opportunity to discuss the study with investigators and other members of the study team.
Now that the study is complete, the Sheffield Lay Advisory Panel for Bone Research will write a lay summary of the results, which will be sent to study participants and publicised through the University of Sheffield, Sheffield Teaching Hospitals and the Royal Osteoporosis Society.
Acknowledgements
We thank Fatma Gossiel for managing the biochemical measurements, Margaret Paggiosi for the bone densitometry, Julie Walker, Angela Green and Jill Thompson for nursing and clerical support, Marian Schini for sub-investigator support, Kim Ryalls for pharmacy management, and Aimee Card for governance support. We would also like to thank the chairpersons and members of the TSC and DMC. The study was conducted in and with the support of the Sheffield NIHR Clinical Research Facility. The study was also supported by the Sheffield School of Health and Related Research, with advice on study implementation from Professor Cindy Cooper.
Contributions of authors
Dr Jennifer S Walsh (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7122-2650) (Senior Clinical Lecturer, Bone Metabolism) developed the protocol, recruited all participants, oversaw the study, contributed to data interpretation and wrote this report.
Dr Richard Jacques (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6710-5403) (Senior Lecturer, Medical Statistics) developed the protocol, recruited all participants, did the statistical analysis and wrote this report.
Professor Lutz Schomburg (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9445-1555) (Professor of Biochemistry) gave technical advice and made the measurements of selenium, SePP and GPx.
Professor Tom Hill (Professor of Nutrition) contributed to protocol development, data interpretation and report writing.
Professor John Mathers (https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3406-3002) (Professor of Nutrition) contributed to protocol development, data interpretation and report writing.
Professor Graham Williams (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8555-8219) (Professor of Endocrinology) contributed to protocol development, data interpretation and report writing.
Professor Richard Eastell (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0323-3366) (Professor of Bone Metabolism) contributed to protocol development, clinical oversight, data interpretation and report writing.
Publication
Walsh JS, Jacques RM, Schomburg L, Hill TR, Mathers JC, Williams GR, Eastell R. Effect of selenium supplementation on musculoskeletal health in older women: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [published online ahead of print March 23 2021]. Lancet Healthy Longevity 2021.
Data-sharing statement
All data requests should be submitted to the corresponding author for consideration. Access to available anonymised data may be granted following review.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research. The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, the MRC, NETSCC, the EME programme or the Department of Health and Social Care. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the EME programme or the Department of Health and Social Care.
References
- Walsh JS, Jacques RM, Schomburg L, Hill TR, Mathers JC, Williams GR, et al. Effect of selenium supplementation on musculoskeletal health in older women: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [published online ahead of print March 23 2021]. Lancet Healthy Longevity 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-7568(21)00051-9.
- Jha S, Wang Z, Laucis N, Bhattacharyya T. Trends in media reports, oral bisphosphonate prescriptions, and hip fractures 1996-2012: an ecological analysis. J Bone Miner Res 2015;30:2179-87. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2565.
- Reid IR, Bolland MJ. Calcium and/or vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of fragility fractures: who needs it?. Nutrients 2020;12. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041011.
- Moghadaszadeh B, Beggs AH. Selenoproteins and their impact on human health through diverse physiological pathways. Physiology 2006;21:307-15. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00021.2006.
- Köhrle J, Jakob F, Contempré B, Dumont JE. Selenium, the thyroid, and the endocrine system. Endocr Rev 2005;26:944-84. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2001-0034.
- Hatfield DL, Tsuji PA, Carlson BA, Gladyshev VN. Selenium and selenocysteine: roles in cancer, health, and development. Trends Biochem Sci 2014;39:112-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2013.12.007.
- Jakob F, Becker K, Paar E, Ebert-Duemig R, Schütze N. Expression and regulation of thioredoxin reductases and other selenoproteins in bone. Methods Enzymol 2002;347:168-79. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(02)47015-2.
- Duntas LH. Selenium and inflammation: underlying anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Horm Metab Res 2009;41:443-7. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1220724.
- Vaananen HK, Zhao H, Mulari M, Halleen JM. The cell biology of osteoclast function. J Cell Sci 2000;113:377-81.
- Battin EE, Brumaghim JL. Antioxidant activity of sulfur and selenium: a review of reactive oxygen species scavenging, glutathione peroxidase, and metal-binding antioxidant mechanisms. Cell Biochem Biophys 2009;55:1-23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-009-9054-7.
- Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition . SACN Position Statement on Selenium and Health 2013. www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/339431/SACN_Selenium_and_Health_2013.pdf (accessed 17 September 2020).
- Rayman MP. Selenium and human health. Lancet 2012;379:1256-68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61452-9.
- Rayman MP. Food-chain selenium and human health: emphasis on intake. Br J Nutr 2008;100:254-68. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114508939830.
- Hoeg A, Gogakos A, Murphy E, Mueller S, Köhrle J, Reid DM, et al. Bone turnover and bone mineral density are independently related to selenium status in healthy euthyroid postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012;97:4061-70. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2012-2121.
- Zhang Z, Zhang J, Xiao J. Selenoproteins and selenium status in bone physiology and pathology. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014;1840:3246-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.08.001.
- Cervellati C, Bonaccorsi G, Cremonini E, Romani A, Fila E, Castaldini MC, et al. Oxidative stress and bone resorption interplay as a possible trigger for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Biomed Res Int 2014;2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/569563.
- Hahn M, Conterato GM, Frizzo CP, Augusti PR, da Silva JC, Unfer TC, et al. Effects of bone disease and calcium supplementation on antioxidant enzymes in postmenopausal women. Clin Biochem 2008;41:69-74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2007.10.010.
- Manolagas SC. From estrogen-centric to aging and oxidative stress: a revised perspective of the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev 2010;31:266-300. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2009-0024.
- Cao JJ, Gregoire BR, Zeng H. Selenium deficiency decreases antioxidative capacity and is detrimental to bone microarchitecture in mice. J Nutr 2012;142:1526-31. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.111.157040.
- Min Z, Zhao W, Zhong N, Guo Y, Sun M, Wang Q, et al. Abnormality of epiphyseal plate induced by selenium deficiency diet in two generation DA rats. APMIS 2015;123:697-705. https://doi.org/10.1111/apm.12404.
- Moreno-Reyes R, Egrise D, Neve J, Pasteels JL, Schoutens A. Selenium deficiency-induced growth retardation is associated with an impaired bone metabolism and osteopenia. J Bone Miner Res 2001;16:1556-63. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.2001.16.8.1556.
- Beukhof CM, Medici M, van den Beld AW, Hollenbach B, Hoeg A, Visser WE, et al. Selenium status is positively associated with bone mineral density in healthy aging European men. PLOS ONE 2016;11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0152748.
- Zhang J, Munger RG, West NA, Cutler DR, Wengreen HJ, Corcoran CD. Antioxidant intake and risk of osteoporotic hip fracture in Utah: an effect modified by smoking status. Am J Epidemiol 2006;163:9-17. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwj005.
- Arikan DC, Coskun A, Ozer A, Kilinc M, Atalay F, Arikan T. Plasma selenium, zinc, copper and lipid levels in postmenopausal Turkish women and their relation with osteoporosis. Biol Trace Elem Res 2011;144:407-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9109-7.
- Jacobsen SJ, Goldberg J, Miles TP, Brody JA, Stiers W, Rimm AA. Regional variation in the incidence of hip fracture. US white women aged 65 years and older. JAMA 1990;264:500-2. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1990.03450040096038.
- Moreno-Reyes R, Suetens C, Mathieu F, Begaux F, Zhu D, Rivera MT, et al. Kashin-Beck osteoarthropathy in rural Tibet in relation to selenium and iodine status. N Engl J Med 1998;339:1112-20. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199810153391604.
- Lauretani F, Semba RD, Bandinelli S, Ray AL, Guralnik JM, Ferrucci L. Association of low plasma selenium concentrations with poor muscle strength in older community-dwelling adults: the InCHIANTI Study. Am J Clin Nutr 2007;86:347-52. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/86.2.347.
- Lauretani F, Semba RD, Bandinelli S, Ray AL, Ruggiero C, Cherubini A, et al. Low plasma selenium concentrations and mortality among older community-dwelling adults: the InCHIANTI Study. Aging Clin Exp Res 2008;20:153-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03324762.
- Alehagen U, Alexander J, Aaseth J. Supplementation with selenium and coenzyme Q10 reduces cardiovascular mortality in elderly with low selenium status. A secondary analysis of a randomised clinical trial. PLOS ONE 2016;11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0157541.
- Alehagen U, Johansson P, Aaseth J, Alexander J, Brismar K. Increase in insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 after supplementation with selenium and coenzyme Q10. A prospective randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial among elderly Swedish citizens. PLOS ONE 2017;12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178614.
- Alehagen U, Johansson P, Aaseth J, Alexander J, Wågsäter D. Significant changes in circulating microRNA by dietary supplementation of selenium and coenzyme Q10 in healthy elderly males. A subgroup analysis of a prospective randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial among elderly Swedish citizens. PLOS ONE 2017;12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174880.
- Duffield-Lillico AJ, Reid ME, Turnbull BW, Combs GF, Slate EH, Fischbach LA, et al. Baseline characteristics and the effect of selenium supplementation on cancer incidence in a randomized clinical trial: a summary report of the Nutritional Prevention of Cancer Trial. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2002;11:630-9.
- Rayman MP, Blundell-Pound G, Pastor-Barriuso R, Guallar E, Steinbrenner H, Stranges S. A randomized trial of selenium supplementation and risk of type-2 diabetes, as assessed by plasma adiponectin. PLOS ONE 2012;7. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045269.
- Eastell R, Hannon RA, Garnero P, Campbell MJ, Delmas PD. Relationship of early changes in bone resorption to the reduction in fracture risk with risedronate: review of statistical analysis. J Bone Miner Res 2007;22:1656-60. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.07090b.
- Hurst R, Collings R, Harvey LJ, King M, Hooper L, Bouwman J, et al. EURRECA-Estimating selenium requirements for deriving dietary reference values. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2013;53:1077-96. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2012.742861.
- Guralnik JM, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L, Glynn RJ, Berkman LF, Blazer DG, et al. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J Gerontol 1994;49:M85-94. https://doi.org/10.1093/geronj/49.2.m85.
- Minneci C, Mello AM, Mossello E, Baldasseroni S, Macchi L, Cipolletti S, et al. Comparative study of four physical performance measures as predictors of death, incident disability, and falls in unselected older persons: the insufficienza Cardiaca negli Anziani Residenti a Dicomano Study. J Am Geriatr Soc 2015;63:136-41. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.13195.
- Veronese N, Bolzetta F, Toffanello ED, Zambon S, De Rui M, Perissinotto E, et al. Association between Short Physical Performance Battery and falls in older people: the Progetto Veneto Anziani Study. Rejuvenation Res 2014;17:276-84. https://doi.org/10.1089/rej.2013.1491.
- Rogers A, Glover SJ, Eastell R. A randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, trial to determine the individual response in bone turnover markers to lasofoxifene therapy. Bone 2009;45:1044-52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2009.07.089.
- Eastell R, Barton I, Hannon RA, Chines A, Garnero P, Delmas PD. Relationship of early changes in bone resorption to the reduction in fracture risk with risedronate. J Bone Miner Res 2003;18:1051-6. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.6.1051.
- Champely S. Pwr: Basic Functions for Power Analysis. R Package Version 1.2-2 n.d. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pwr (accessed 17 September 2020).
- Frison L, Pocock SJ. Repeated measures in clinical trials: analysis using mean summary statistics and its implications for design. Stat Med 1992;11:1685-704. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.4780111304.
- Hoeflich J, Hollenbach B, Behrends T, Hoeg A, Stosnach H, Schomburg L. The choice of biomarkers determines the selenium status in young German vegans and vegetarians. Br J Nutr 2010;104:1601-4. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114510002618.
- Hollenbach B, Morgenthaler NG, Struck J, Alonso C, Bergmann A, Köhrle J, et al. New assay for the measurement of selenoprotein P as a sepsis biomarker from serum. J Trace Elem Med Biol 2008;22:24-32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2007.11.003.
- Naylor KE, Jacques RM, Paggiosi M, Gossiel F, Peel NF, McCloskey EV, et al. Response of bone turnover markers to three oral bisphosphonate therapies in postmenopausal osteoporosis: the TRIO study. Osteoporos Int 2016;27:21-3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-015-3145-7.
- Wang Y, Xie D, Li J, Long H, Wu J, Wu Z, et al. Association between dietary selenium intake and the prevalence of osteoporosis: a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2019;20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-019-2958-5.
- Perri G, Mendonça N, Jagger C, Walsh J, Eastell R, Mathers JC, et al. Dietary selenium intakes and musculoskeletal function in very old adults: analysis of the Newcastle 85+ Study. Nutrients 2020;12. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12072068.
- Chen YL, Yang KC, Chang HH, Lee LT, Lu CW, Huang KC. Low serum selenium level is associated with low muscle mass in the community-dwelling elderly. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2014;15:807-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2014.06.014.
- Beck J, Ferrucci L, Sun K, Walston J, Fried LP, Varadhan R, et al. Low serum selenium concentrations are associated with poor grip strength among older women living in the community. Biofactors 2007;29:37-44. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.5520290104.
- Public Health England . National Diet and Nutrition Survey. Results from Years 7 and 8 (combined) of the Rolling Programme (2014 2015 to 2015 2016) 2018.
Appendix 1 Trial flow chart
Appendix 2 Schedule of procedures
| Procedure | Screening | Baseline | 4 weeks | 8 weeks | 13 weeks | 17 weeks | 21 weeks | 26 weeks | 30 weeks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Informed consent | ✓ | ||||||||
| Medical history for eligibility | ✓ | ||||||||
| DXA BMDa | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Colecalciferol 100,000 units | ✓ | ||||||||
| Practice placebo (optional) | ✓ | ||||||||
| Screening bloodsb | ✓ | ||||||||
| Blood for DNA | ✓ | ||||||||
| Serum selenium | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Height and weight | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Pulse and blood pressure | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Bloods for end-of-study analysisc | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Urine for end-of-study analysisd | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Physical function tests | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Diet diary | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| Concomitant medications | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Randomisation | ✓ | ||||||||
| Dispensing of study drug | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| Safety bloodse | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| Compliance check | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Adverse events | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
List of abbreviations
- 25OHD
- 25-hydroxyvitamin D
- BCE
- bone collagen equivalents
- BMD
- bone mineral density
- BMI
- body mass index
- CI
- confidence interval
- CTX
- C–terminal cross-linking telopeptide of type I collagen
- CV
- coefficient of variation
- DMC
- Data Monitoring Committee
- DXA
- dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
- HbA1c
- glycated haemoglobin
- HRT
- hormone replacement therapy
- hsCRP
- highly sensitive C-reactive protein
- IL-6
- interleukin 6
- IMP
- Investigational Medical Product
- ITT
- intention to treat
- NTX
- N–terminal cross-linking telopeptide of type I collagen
- OC
- osteocalcin
- PINP
- procollagen type I N propeptide
- REC
- Research Ethics Committee
- SAE
- serious adverse event
- SAP
- statistical analysis plan
- SD
- standard deviation
- SePP
- selenoprotein P
- SERM
- selective oestrogen receptor modulator
- SPPB
- short physical performance battery
- TSC
- Trial Steering Committee
- TSH
- thyroid-stimulating hormone
