Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the EME programme as project number 11/116/03. The contractual start date was in September 2013. The final report began editorial review in April 2022 and was accepted for publication in February 2023. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The EME editors and production house have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ manuscript and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the final manuscript document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this manuscript.
Permissions
Copyright statement
Copyright © 2024 Maher et al. This work was produced by Maher et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care. This is an Open Access publication distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution CC BY 4.0 licence, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, reproduction and adaptation in any medium and for any purpose provided that it is properly attributed. See: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. For attribution the title, original author(s), the publication source – NIHR Journals Library, and the DOI of the publication must be cited.
2024 Maher et al.
Chapter 1 Introduction
Parts of this chapter have been reproduced from the published protocol paper by Peter Saunders et al.,1 an Open Access article which is distributed in accordance with Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license, which allows anyone unrestricted use, to distribute, adapt work or build upon the material for any purpose, including commercially, under the condition that appropriate credit is given to the original author(s). See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The text below encompasses minor additions and formatting changes to the original text.
Connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is characterised by inflammation and/or fibrosis that results in thickening and distortion of the alveolar wall with consequent impairment of gas exchange. Affected individuals typically present with progressive breathlessness which frequently causes respiratory failure and death. There are many described causes of ILD, however, one of the commonest is that resulting from lung involvement by systemic autoimmune disease. This group of conditions, the connective tissue diseases (CTDs), are an important cause of disability and death in the working-age population. Over the last 20 years improvements in therapy for the CTDs has seen the prognosis for individuals with these conditions dramatically improve. Despite these improvements in care there has been little change in therapy for ILD occurring as a consequence of CTD. For this reason, for those individuals with CTD, respiratory disease has grown in importance. For many CTD sufferers ILD is now the major cause of disability and exercise limitation while in systemic sclerosis it is now the principal cause of mortality. 2 In scleroderma approximately 60% of sufferers develop ILD,3 in mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) the proportion is similar4 while in idiopathic inflammatory myositis (IIM) the figure is estimated to be as high as 75% depending on auto-antibody subtype. 5
The pathogenesis of CTD-ILD is complex and poorly understood. It is however, generally accepted that underlying immune system dysfunction and immune-mediated pulmonary inflammation are critical to CTD-ILD development and progression. Abnormalities of cellular and humoral immune function have been described in ILD associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc),6–8 idiopathic inflammatory myopathy9 and several other CTDs. 9 The mechanism by which these processes lead to fibrosis remains poorly understood as do the factors that determine which individuals with CTD develop ILD. Nonetheless evidence from treatment trials suggests that modulation of inflammation with immunosuppressant therapies, particularly cyclophosphamide (CP), results in some regression of ILD and prevents the development of further fibrosis.
Different CTDs manifest varying forms of ILD. Individuals with scleroderma and MCTD most commonly develop the histological lesion of non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP). Those with IIM typically have combined organising pneumonia and NSIP (referred to in the literature as fibrosing organising pneumonia). By contrast to these conditions, individuals with rheumatoid disease frequently have fibrosis with the histological pattern of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) and tend to be resistant to therapy with high-dose immunosuppression. For this reason, the current study excluded individuals with rheumatoid-associated ILD.
Evidence for existing connective tissue disease-interstitial lung disease therapies
The field of rheumatology has seen rapid developments over the 20 years with the introduction of a range of monoclonal antibody therapies that have revolutionised the standard of care for this patient group. Despite this, at the time of the planning of this research there had been few, if any, improvements in the management of CTD-associated ILD. The trial evidence existing at the time (and even now) was limited to individuals with scleroderma-associated ILD with treatment approaches being extrapolated to cover individuals with other forms of CTD-ILD.
The long-standing standard of care for severe, progressive CTD-ILD in the UK has been immunosuppression with intravenous CP administered monthly for 6 months, followed by maintenance oral immunosuppression. 10,11 The rationale for this strategy is based on two clinical trials performed in scleroderma-associated ILD. The first of these, Scleroderma Lung Study (SLS),12 was a multicentre study conducted at 13 centres in the USA. The trial recruited 158 subjects with scleroderma ILD who had evidence of a restrictive defect on spirometry, exertional dyspnoea and an inflammatory cell infiltrate on bronchoalveolar lavage. Subjects were administered oral CP at a dose of ≥2 mg/kg of body weight per day or matching placebo for 52 weeks. The primary end point was the baseline adjusted FVC at week 52 expressed as a % of predicted. The mean absolute difference between groups at 52 weeks was 2.53% (0.28–4.79%) favouring CP. A greater number of subjects (20 vs. 13) were discontinued in the CP arm. There were a greater number of adverse events (AEs) in the treatment arm compared to placebo and these included haematuria, neutropenia and lymphopenia. A smaller, 45-patient, UK-based multicentre trial6 assessed the efficacy of 6, once-monthly intravenous infusions of CP combined with low-dose prednisolone and followed by oral azathioprine compared with placebo over 52 weeks in subjects with scleroderma-associated ILD. The study demonstrated a 4.19% difference in 52-week FVC between groups favouring active treatment although this did not achieve statistical significance (p = 0.08). Two subjects withdrew from the active group because of side effects but there were no reported cases of haematuria or cytopenia.
The use of CP is limited by a number of toxicity-related issues. Common side effects with treatment include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, abdominal discomfort, diarrhoea and hair loss. These are especially common with oral dosing of CP. High doses of CP are associated with haemorrhagic cystitis. The drug also causes cumulative toxicity to the epithelial lining of the bladder leading to an appreciable risk of bladder cancer in individuals receiving a lifetime dose of >20 g (a 6-month treatment course of CP is usually between 6 and 8 g). CP use is also associated with irreversible gonad failure in both males and female. For these reasons, CP treatment is usually limited to individuals with severe or life-threatening ILD and even in those for whom treatment is deemed successful, longer term or repeated cycles of therapy are avoided.
Since initiation of RECITAL there have been further treatment developments for individuals with scleroderma-associated ILD. The SLS2 study,13 another US-based multicentre trial, compared mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) at a dose of 1500 mg twice daily for 24 months to oral CP (target dose 2 mg/kg/day) for 12 months followed by placebo for 12 months in 142 subjects with scleroderma ILD. The primary end point of change in FVC over 24 months was not different between groups. The baseline adjusted %predicted FVC improved by 2.19% in the mycophenolate group and by 2.88% in the CP group. Mycophenolate was better tolerated with 20 discontinuations over 24 months compared with 32 in the CP arm. Leucopoenia and thrombocytopaenia occurred more commonly in the CP group. Tocilizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting the inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-6 has recently been approved in the USA and Europe as a treatment for systemic sclerosis-associated ILD. This was on the basis of two trials, both of which were primarily designed to test tocilizumab as a treatment for the skin thickening seen as part of scleroderma. In the first of these trials (the phase 2 faSScinate study),14 subjects with rapidly deteriorating diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis and evidence of active inflammation (defined as the presence of arthritis or an elevated C-reactive protein) were randomised to receive weekly subcutaneous tocilizumab or matched placebo. There was a trend towards improvement in skin thickening in the active treatment group and an exploratory analysis suggested a benefit on change in FVC with tocilizumab; although it should be noted that not all patients in the trial had ILD. A subsequent phase 3 study (focuSSed)15 again recruited individuals with rapidly progressive diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis and evidence of inflammation. The primary end point was also change in skin thickening measured using the modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS) at 48 weeks. Change in FVC was a key secondary end point. The study failed to meet its primary end point. However, subjects in the tocilizumab arm had stabilisation of FVC over 48 weeks while subjects on placebo lost FVC. Presence of ILD was not an inclusion criterion for the study; however, of the 210 subjects who were randomised, 136 (65%) had evidence of ILD on computer tomography (CT) scan performed at enrolment. Post hoc analysis of this subgroup with ILD showed a change of FVC of −0.1% in the treatment arm compared with −6.3% in the placebo group.
Nintedanib, a multityrosine kinase inhibitor, was approved as a therapy for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) in 2014. IPF is the most rapidly progressive of the fibrotic ILDs encountered in routine clinical practice. In paired phase three trials nintedanib was shown to reduce the rate of decline in FVC over 52 weeks by approximately 50%. 16 Consequently, nintedanib was assessed as a potential therapy for scleroderma-associated ILD in the multicentre SENSCIS trial. 17 In this study 576 patients with >10% fibrosis on CT scan in the context of a diagnosis of scleroderma-associated ILD were randomised 1 : 1 to receive nintedanib or matched placebo. Subjects were permitted to be on stable background therapy with either MMF or methotrexate. The primary end point was 52-week change in FVC. Over the course of the study the placebo group lost 93 ml in FVC (less than half the rate of decline seen in IPF) while the treatment group lost 52.4 ml, a difference of 41 ml (2.9 to 79 ml) between groups (p = 0.04). In general, nintedanib was well tolerated with gastrointestinal upset, especially diarrhoea, being the commonest side effect. A pre-planned subgroup analysis suggested that the greatest therapeutic benefit was seen in subjects treated with both nintedanib and MMF in combination. 18 A further study with nintedanib was conducted in patients with progressive fibrotic ILD of any cause (INBUILD trial). 19 Of the 663 subjects in the trial, 170 (26%) had an autoimmune ILD (including scleroderma, MCTD and myositis-associated ILD). Overall, the trial showed a benefit of treatment with nintedanib compared to placebo on the primary end point of 52-week change in FVC. This effect was consistent across subgroups including the autoimmune ILD group. On the strength of SENSCIS and INBUILD nintedanib has been approved as a treatment for scleroderma ILD and for chronic fibrosing ILD with a progressive phenotype.
Current treatment practice
While scleroderma ILD has been a major focus for clinical trials, no randomised controlled trials have been performed for ILD in the context of MCTD or IIM. In both disease groups current best practice is derived by extrapolation from scleroderma trials supported by evidence from retrospective cohort analyses. For both disease groups the most commonly used therapies include corticosteroids, MMF and CP. When it comes to treating scleroderma-associated ILD, there are now two approved therapies in nintedanib and tocilizumab. However, in England, Wales and Northern Ireland, neither of these drugs has received approval from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) and as such neither is routinely used as a treatment for scleroderma ILD (however, nintedanib received approval from NICE in November 2021 for the treatment of progressive pulmonary fibrosis of any cause and is therefore available for a subset of patients). No guidelines currently exist for the treatment of CTD-ILD. However, a recent European-based Delphi exercise provided recommendations for the use of MMF, CP and nintedanib as treatments for progressive or extensive scleroderma-associated ILD. 20
Rituximab
Scleroderma-associated ILD remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality despite the widespread use of CP and MMF. 21 The same is true for MCTD and the idiopathic inflammatory myositidies where the lack of evidence-based therapies further complicates treatment choice. Rituximab (RT), a chimeric (human/mouse) monoclonal antibody with a high affinity for the CD20 surface antigen expressed on pre-B and B-lymphocytes, results in rapid depletion of B cells from the peripheral circulation for 6–9 months. 22,23 Evidence for the efficacy of B cell depletion exists in a number of immune-mediated conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis,24–26 antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis,27,28 immune thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP),29 membranous nephropathy and pemphigus. In these conditions RT tends to be better tolerated than previously used immunosuppressant regimens and, in many cases, was associated with reductions in corticosteroid usage.
Several case series suggest RT may also be effective in ILD occurring in the context of immunological over-activity, with favourable responses reported in antisynthetase (ASS) associated ILD30 and SSc-ILD. 31,32 Our own experience has demonstrated RT to be an effective, potentially life-saving therapeutic intervention in the treatment of very severe, progressive CTD-ILD unresponsive to conventional immunosuppression. 33 In a retrospective analysis34 of 50 subjects with ILD due to a variety of aetiologies all of whom had failed multiple prior therapies we demonstrated that RT therapy was associated with an average improvement in FVC and stabilisation of DLco in the subsequent 6–12 months following treatment. In an open-label prospective study31 of 14 individuals with scleroderma ILD, 8 were randomised to receive two cycles (each cycle being 4, weekly doses of RT at a dose of 375 mg/m2) while the remaining 6 subjects received standard care. At 1 year FVC improved from 68.1 ± 19.7% predicted to 75.6 ± 19.7% predicted in the RT group compared with a drop from 86.0 ± 19.5% predicted to 81.7 ± 20.7% predicted in the standard of care group. Although these data suggest a benefit of RT it should be noted that in addition to being a small open-label study there were clear differences in baseline disease severity between the RT and the standard of care arms. Another recently published open-label trial35 compared RT (two times 1000 mg) to intravenous CP (500 mg/m2) in 60 subjects with scleroderma ILD with the primary outcome being change in FVC at 24 weeks. RT was associated with an improvement in FVC (from 61.3 ± 11.3 to 67.5 ± 13.6% predicted) while the CP arm saw a loss of FVC over 6 months (from 59.3 ± 13.0 to 58.1 ± 11.2% predicted). RT, but not CP, was associated with an improvement in skin score. There were fewer side effects in the RT arm. The major limitations of the study were the open-label design and the exclusion of subjects aged over 60.
Potential risks of rituximab
Rituximab was first approved for clinical use in 1997 for the treatment of relapsed or refractory CD20 positive B-cell low grade or follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. 36 Since then, it has been widely used as a treatment for a broad range of conditions including rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with angiitis, idiopathic thrombocytopaenia purpura, pemphigus vulgaris and myasthenia gravis. The safety profile of RT is therefore well-established. Common side effects include rash, itchiness, hypotension and dyspnoea at, or close to, the time of infusion and are usually associated with hypersensitivity to the drug (this is more likely in those who have had occupational or domestic exposure to mice). RT is also associated with an increased risk of infection. Severe but very rare side effects include reactivation of hepatitis B, progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy (PML) and toxic epidermal necrolysis syndrome. The risk of hepatitis B can be mitigated by pre-treatment testing. The potential adverse effects of RT are comparable, or even less frequent, than those associated with other commonly used treatments for CTD-ILD, especially CP.
Rationale for current study
Despite current best treatment, individuals with extensive ILD due to scleroderma have a median survival of less than 5 years and a similar poor prognosis is observed in individuals with inflammatory myositis and MCTD. 33 This high level of morbidity and mortality associated with CTD-ILD and the absence of clinical trial data in MCTD and the idiopathic inflammatory myositidies speaks to the need for more effective and better-tolerated therapies for this group of diseases. Available data suggest that RT is effective in improving lung function in people with CTD-associated ILD and multiple studies show that it tends to be better tolerated than CP. The current study is the first to assess a broad-based, pragmatic population of patients with CTD-associated ILD. This is important for establishing best care for a group of patients who are normally disenfranchised from clinical trials because of the rarity of their condition.
Drug costs are higher for RT than for CP and this often represents a barrier for use of the drug in the National Health Service (NHS) in the UK. Assuming that RT is associated with fewer AEs and better efficacy then it is to be anticipated that increased drug costs will be offset by reduced healthcare costs overall. To assess whether this is the case the trial includes a Full Economic Costing (FEC) so that the true costs of both RT and CP can be analysed.
The aim of the study was to compare the safety and efficacy of RT against that of CP as first-line therapy in patients with severe, progressive CTD-associated ILD. The study therefore tested the hypothesis that RT is superior to intravenous CP, in terms of both safety and efficacy, as a treatment for extensive and progressive CTD-ILD.
Rationale for primary outcome
The primary outcome for this study was rate of change in FVC over 24 weeks. FVC provides a measure of lung volume. With worsening pulmonary fibrosis FVC tends to diminish. In trials of patients with a range of fibrotic ILDs (including IPF, scleroderma ILD and progressive fibrotic ILD of any cause) change in FVC has been accepted by the Federal Drugs Administration (FDA) in the USA and the European Medicines Agency as a surrogate for survival. 37 As such, FVC has been the regulatory end point of choice for the approval of medications targeting ILD. Additionally, in scleroderma ILD both baseline FVC and change in FVC over time have been linked to longer-term prognosis and survival. 33,38 Twenty-four weeks was chosen for the primary end point as this was felt to be the time-point at which the effect of RT and CP alone could best be measured. Beyond 24 weeks subjects were permitted to receive other immunosuppressants according to the recommendation of their treating clinician (and as tends to happen in routine clinical practice). FVC change at 48 weeks was captured as a secondary end point with the prior recognition that this might also be influenced by treatments received beyond 24 weeks.
Rationale for biomarkers
There are currently no available biomarkers for assessing response to therapy or risk of disease progression in CTD-ILD. By closely studying patients in each treatment arm and undertaking exploratory biomarker analysis it was hoped that we might identify potential disease and therapy-specific biomarkers for future development and use in clinical practice. Serial samples of whole blood [for ribonucleic acid (RNA) and DNA analysis], serum and plasma were collected to explore changes in the levels of a range of candidate biomarkers. The choice of biomarkers was driven by insights derived from other fibrotic and inflammatory ILDs and included measures of extra cellular matrix turnover (collagen neoepitopes, matrix metalloprotease-7),39 epithelial damage [cancer antigen 125 (CA125), cytokeratin 19 fragment, Krebs von den lungen-6]40 and inflammatory cell activation (IL-6, monocyte chemotractant protein-1, Chitinase-3-like protein-1, CC motif chemokine ligand 18). 40 The aim of this part of the study was to identify a candidate biomarker panel for use in future studies and for development as a clinical tool for guiding therapeutic decision making.
Aims and objectives
The primary aim of the study was to compare the safety and efficacy of RT against that of CP as first-line therapy in patients with severe, progressive CTD-ILD. Secondary aims of the study were to compare the full economic cost of both RT and CP and to assess a range of circulating protein and cellular biomarkers for their ability to predict response to therapy and to provide early insights into treatment outcomes.
Primary objective
-
To demonstrate that intravenous RT has superior efficacy compared to current best treatment (intravenous CP) for CTD-ILD as measured by change in FVC at 24 weeks.
Secondary objectives
-
To compare the safety profile of RT to intravenous CP in individuals with CTD-ILD.
-
To assess the health economic benefits of RT compared to current standard of care for CTD-ILD – including measurements of healthcare utilisation, quality of life (QoL) and carer burden.
-
To evaluate a range of exploratory biomarkers for disease severity, prognosis and treatment response in CTD-ILD.
Chapter 2 Research methods/design
Parts of this chapter have been reproduced from the published protocol paper by Peter Saunders et al.,1 an Open Access article which is distributed in accordance with CC BY 4.0 license, which allows anyone unrestricted use, to distribute, adapt work or build upon the material for any purpose, including commercially, under the condition that appropriate credit is given to the original author(s). See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The text below encompasses minor additions and formatting changes to the original text.
The study was a Phase 2b, UK multicentre, prospective, randomised, double-blind, double-dummy trial of intravenous RT compared with intravenous CP in patients with severe, progressive CTD-ILD. Patients were randomised to one of two groups; both groups received placebo to match the opposite regimen. The aim was to recruit 116 subjects (aiming for 52 patients reaching end-of-study in each arm and anticipating a 10% drop out).
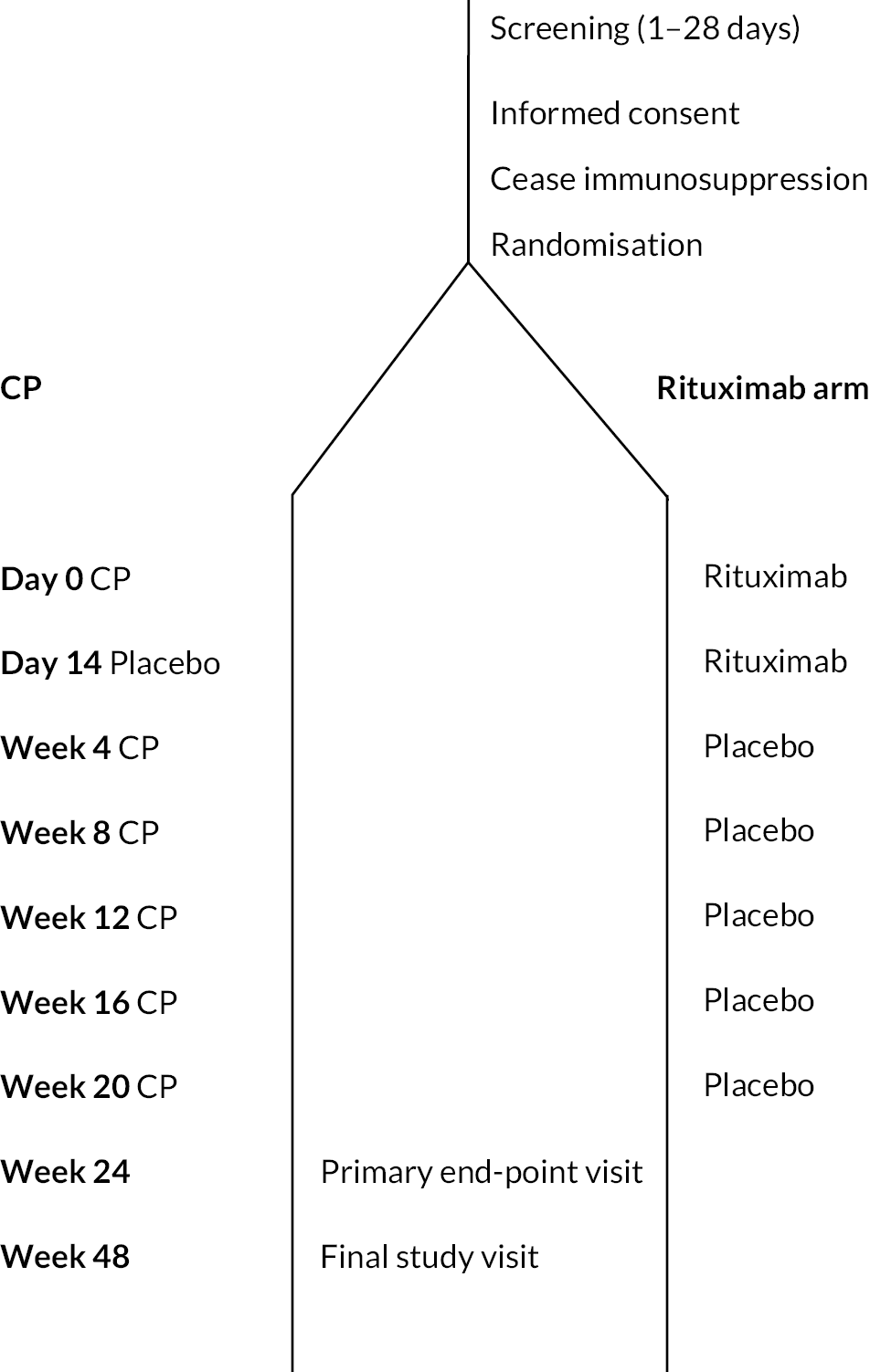
As a consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic, in April 2020, the Data Monitoring Committee (DMC), endorsed by Sponsor, Trial Management Group (TMG) and Trial Steering Committee (TSC) recommended ending the study after the 101st subject completed treatment. There was consensus agreement that recruiting further patients (to achieve the pre-specified plan of 104 subjects completing treatment) would have only a limited impact on the power of the study to show an advantage of RT over CP. Given that the COVID-19 pandemic had major implications for the benefit : risk ratio of starting new immunosuppressant therapy and that it was unclear how long the pandemic would last, early closure of the RECITAL study was strongly recommended. Patients were followed up for 48 weeks. The end of trial, defined as when the last patient randomised had completed their last visit at 48 weeks, was reached in January 2021. The schedule for study visits including the assessments and procedures performed is presented in Table 1. The scheduled study visits occurred at the specified week postrandomisation ±7 days unless otherwise specified. Figure 1 is the flow diagram of the study design schedule.
| Time | Screening visit(s) | Randomise | Treatment visits | Follow-up visit | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–2 | Visit day 0 | Visit week 2 |
Visit week 4 | Visit week 8 |
Visit week 12 |
Visit week 16 |
Visit week 20 |
Visit week 24 | Visit week 48 | ||
| Consent | X | ||||||||||
| Study drug | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| AE checking | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Physical exam | X | ||||||||||
| Vital signs (pulse, BP) |
X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Routine bloods tests | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Spirometry | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Blood sample for lymphocyte subsets/Ig level | X | X | X | ||||||||
| CK (in myositis patients) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Ig levels | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| ECG | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Lung function tests | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| 6 MWT* | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Urinalysis | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Pregnancy test | X | ||||||||||
| QoL questionnaires | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Health economic diary | X | X | |||||||||
| mRSS (scleroderma) | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| Hepatitis B and C serology | X | ||||||||||
| Blood sample biomarker(s) | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| Blood sample genetics | X | ||||||||||
| Concomitant medication | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
FIGURE 1.
Study flow diagram.
The study was conducted in accordance with good clinical practice (GCP). The study protocol received ethical approval from National Research Ethics Service (NRES) Committee London – Westminster on 15 July 2013 (Reference No.: 13/LO/0968). Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) clinical trial authorisation was received on 18 October 2013.
The process for obtaining participant informed consent was in accordance with Research Ethics Committee (REC) guidance, GCP and all other applicable regulatory requirements. All study subjects provided written informed consent, this included consent to inform the participant’s general practitioner (GP) or, when appropriate, the local consultant of involvement in the study. A separate consent was obtained to provide blood for RNA, DNA and biomarker analysis. The study was registered on the International Standard Randomised Controlled Trial Number (ISRCTN) registry on 01 April 2015 under reference number 16474148 and ClinicalTrial.gov on 22 May 2013 under reference number NCT01862926. The first participant was randomised on 2 January 2015 and the last participant was randomised on 24 February 2020.
Methods
Study setting
RECITAL study was conducted at 11 UK sites, all of which were accredited by NHS England as specialist ILD or Rheumatology centres. The investigators were qualified by education, training and experience to assume responsibility for the proper conduct of the trial and provided evidence of such qualifications through up-to-date curriculum vitae and GCP training certificates. The local principal investigator (PI), who could be either a respiratory physician or rheumatologist, was responsible for the proper conduct of the study, for the safety and welfare of study participants and being thoroughly familiar with the appropriate use of the investigational products. They were responsible for ensuring that all persons supporting the trial were appropriately qualified and trained, adequately informed about the protocol, the investigational product(s), and their trial-related duties and functions. Both the Sponsor and local trust legal representatives signed the site agreements. GCP training was required for all staff responsible for trial activities. The frequency of repeat training was dictated by the requirements of their employing institution, or two yearly where the institution had no policy. The PI or delegate was required to document and explain any deviation from the approved protocol and to communicate this to the Sponsor.
Study population
Participant inclusion criteria
-
A diagnosis of CTD, based on internationally accepted criteria, in one of the following categories:41–44
-
systemic sclerosis
-
idiopathic interstitial myopathy (including polymyositis/dermatomyositis)
-
MCTD.
-
-
Severe and/or progressive ILD associated with the underlying CTD.
-
Chest high-resolution computer tomography performed within 12 months of randomisation.
-
Intention of the caring physician to treat the ILD with intravenous CP (with treatment indications including; deteriorating symptoms attributable to ILD, deteriorating lung function tests, worsening gas exchange or extent of ILD at first presentation) and where there is a reasonable expectation that immunosuppressive treatment will stabilise or improve CTD-ILD. In individuals with scleroderma it is anticipated that patients will fulfil the criteria for extensive disease defined by Goh et al. 33
-
Written informed consent.
Participant exclusion criteria
-
Age <18 or >80 years.
-
Previous treatment with RT and/or intravenous CP.
-
Known hypersensitivity to RT or CP or their components.
-
Significant (in the opinion of the investigator) other organ comorbidity including cardiac, hepatic or renal impairment.
-
Coexistent obstructive pulmonary disease (e.g. asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema) with pre-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC < 70%.
-
Patients at significant risk for infectious complications following immunosuppression including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) positive or other immunodeficiency syndromes such as hypogammaglobulinaemia.
-
Suspected or proven untreated tuberculosis.
-
Viral hepatitis.
-
Infection requiring antibiotic treatment in the preceding 4 weeks.
-
Unexplained neurological symptoms [which may be suggestive of progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy (PML)]. Neurological symptoms arising as a consequence of the underlying CTD do not necessitate exclusion.
-
Other investigational therapy (participation in research trial) received within 8 weeks of randomisation.
-
Immunosuppressive or CTD disease-modifying therapy (other than corticosteroids) received within 2 weeks of the first intravenous treatment.
-
Pregnant or breastfeeding women, or women of child-bearing potential, not using a reliable contraceptive method for up to 12 months following investigational medicinal product (IMP).
-
Unexplained haematuria or previous bladder carcinoma.
-
CT scan > 12 months from randomisation.
-
Unable to provide informed written consent.
Recruitment
The study was conducted in rheumatology or ILD units at 11 UK centres. The diagnosis of CTD and associated ILD was confirmed by the local study PI or coinvestigator, where delegated by the local PI in accordance with the study delegation of responsibilities log. Potential patients were assessed for eligibility and approached for written informed consent. All potential patients were given an ethically approved patient information sheet (PIS) and an appointment was made for them with the research nurse or another member of the research team delegated the responsibility to discuss enrolment into the study. The patients were allowed to specify the time they wished to spend deliberating, usually up to 24 hours. Periods shorter or longer than 24 hours were permitted when the patient requested it. The informed consent form (ICF) was signed and dated by the participant before entering the study. The participants received a copy of the signed and dated consent form and the original was retained with the study data. A second copy was filed in the participant’s medical notes.
Patients undertook a screening assessment to ensure they met all the eligibility criteria. Screening and enrolment logs were kept of all patients with CTD-ILD considered for the study.
Intervention
As summarised in Table 2, patients were randomised on a 1 : 1 double-blind basis to receive either:
-
RT 1000 mg given for two doses at day 0 and day 14. Placebo was administered monthly from week 4 to week 20.
-
CP given at a dose of 600 mg/m2 body surface area (BSA) rounded to the nearest 100 mg every 4 weeks from day 0 through to week 20. Placebo was given at day 14.
| RT group | CP group | |
|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | IV active RT 1000 mg | IV 600 mg mg/m2 BSA |
| Day 14 | IV active RT 1000 mg | Placebo |
| Week 4 | Placebo | IV 600 mg mg/m2 BSA |
| Week 8 | Placebo | IV 600 mg mg/m2 BSA |
| Week 12 | Placebo | IV 600 mg mg/m2 BSA |
| Week 16 | Placebo | IV 600 mg mg/m2 BSA |
| Week 20 | Placebo | IV 600 mg mg/m2 BSA |
Cyclophosphamide and RT usually have different infusion regimens. For the first dose, RT is infused at slowly ascending rates to minimise the risk of significant hypersensitivity/anaphylactic reactions. To maintain study blind, the day 0 dose (which could be either RT or CP) was infused according to the ascending rate regimen used for RT.
To ensure an equal representation of CTD subtypes in each treatment arm, randomisation was stratified based upon underlying CTD diagnosis (according to the three diagnostic categories listed in the inclusion criteria).
Non-IMP permitted concomitant medication (NIMPs) administered to both groups at day 0, prior to administration of study IMP were mesna (as a prophylactic treatment against CP-induced haemorrhagic cystitis), hydrocortisone, chlorphenamine and paracetamol (all as prophylaxis against RT-induced allergic reactions); at day 14 hydrocortisone, chlorphenamine and paracetamol; and at visits from week 4 to 20 mesna. Post treatment, subjects were provided a 2-day supply of ondansetron for use if experiencing nausea.
Drug preparation and supply
Bath ASU was responsible for manufacture of the IMPs and matched-placebo to standards compliant with good medical practice (GMP) requirements.
The IMPs used in this study were infusions of either CP, RT or matching placebo. All products were compounded using licensed starting materials as per the relevant summary of product characteristics (SmPC). All active drugs were prepared by the addition of drug solution to a 250 ml NaCl 0.9% Freeflex® infusion bag following the withdrawal of a comparable volume of solution to ensure the final bag volume remained at 250 ml. The matching placebo was a suitability labelled 250 ml NaCl 0.9% Freeflex bag.
Starting materials: RT (Roche EU/1/98/067/001 EU/1/98/067/002).
Cyclophosphamide (Baxter PL 001 16/0388).
Sodium chloride infusion (Fresenius Kabi PL 08828/0084).
Following manufacturing, the fully reconstituted study IMP was transported, in a temperature-monitored environment (by Movianto UK limited) to study sites. Each infusion bag arrived together with the qualified person (QP) batch release certificate. A copy of the QP release was filed in the site pharmacy file along with the shipping paperwork. Temperature monitoring during transit occurred via a temperature monitoring device within the shipment. Any identified temperature excursions during transit to site was reported by pharmacy to the Trial Manager, using the Temperature Excursion Report Form. Site pharmacies documented receipt of IMP using the IMP accountability Log.
Randomisation allocation was performed using an Interactive Web-based Randomisation System (InForm). Randomised patients were given a study specific 24 hours emergency contact immediately following randomisation. The card included: study title, details of the IMPs, patient trial number, chief investigator (CI)/PI’s contact details along with out-of-hours contact details in case of emergency.
A patient was withdrawn if their treatment code was unblinded by the investigator or treating physician. The primary reason for discontinuation (the event or condition which led to the unblinding) was recorded in the electronic case report form.
Dispensing procedure
It was the responsibility of the site pharmacy to dispense IMP in accordance with the study protocol and against a prescription provided by the medical team. The study-specific prescription and accountability logs were used by all sites.
Initial infusion
Site pharmacies documented the dispensing details on the prescription form. Details were also recorded on a subject-specific IMP accountability log (one log used per patient). Entries on the accountability log were signed by the dispenser and checked by a second member of staff. The IMP accountability log was updated with the date of dispensing.
Ongoing infusions
A new prescription was completed for each dose required for each subject recruited. Site pharmacies checked the details on the prescription against the corresponding subject-specific IMP accountability log to ensure the correct patient number and visit number. Site pharmacies completed the next entry on the accountability log for each ongoing prescription received. The IMP accountability log was updated with the date of dispensing.
Blinding
The study was double-blind. Medication was identified by a unique trial identifier (randomisation code). Patients and investigators remained blinded until after database lock and only the DMC had access to unblinded information.
The investigator was encouraged to maintain the blind as far as possible. Investigators were able to unblind individual patient’s treatment via the eCRF in the case of an emergency, when knowledge of the study treatment was essential for the appropriate clinical management or welfare of the patient. The PI was asked to provide a reason for unblinding and was required to enter their password as confirmation. The PI was then shown which treatment arm the patient was allocated to. The investigator referred to the unblinding instructions stored securely in the investigator site file (ISF). An email notification stating that a patient was unblinded was sent out to local investigator, pharmacy and the Trial Manager.
A decision to unblind was made in three cases prior to week 24 where information of the treatment allocation was deemed essential (to allow the treatment of disease progression for two patients and because of a SAE in one case). There were five other instances where patients were unblinded; this occurred after they had received all doses of IMP, either during the follow-up period or following study completion and was performed to enable appropriate choice of therapy for ongoing disease worsening. All details of the eight instances of unblinding were recorded in the eCRF, the ISF/trial master file (TMF) (or pharmacy file when manual unblinding was used).
Backup manual unblinding
When the investigator needed to unblind the treatment for the patient in case of electronic failure of the database (InForm), a manual backup system was also provided. A randomisation list was provided to the Sponsor pharmacy department. During normal hours the investigator was able to contact the Sponsor pharmacy department via switchboard on 020 7352 8121. Outside of normal hours, the Sponsor pharmacy on-call pharmacist could be contacted via the same number.
Storage and administration
The investigational products were stored securely in a temperature-controlled unit between 2 and 8°C within a pharmacy department. Temperature logs were kept and made available for monitoring and audit purposes. Specific instructions for storage and administration were provided in a study-specific IMP handling manual which was provided in the ISF and pharmacy file.
Accountability procedures for the investigational medicinal product(s)
The site hospital pharmacy department was responsible for maintaining and updating the study pharmacy IMP Accountability Log, filed in the hospital pharmacy file. A study prescription form documented the dispensing of IMP to the research nurse or doctor; this was retained in the pharmacy file. The research nurse or doctor was responsible for completing an IMP Administration Record Form at the point of administration; the completed form was filed in the ISF.
Any IMP dispensed to the research nurse or doctor that was not administered, for example due to cancellation, was returned to pharmacy for destruction. All unused IMP, including unused returns, were destroyed by the site pharmacy in accordance with local pharmacy practice, once agreed by the local PI and Sponsor. Destruction of unused IMP was documented on the IMP Destruction Form and filed in the hospital pharmacy file.
All used or partially used IMP was discarded in accordance with local cytotoxic waste disposal procedures; no used IMP was returned to pharmacy. A record of discarded used IMP was made on the IMP Administration Form and filed in the ISF.
Prohibited concomitant medication
-
Pre-existing immunosuppression (including azathioprine, MMF, methotrexate, and ciclosporin) was stopped, following signed informed consent and during the screening period, at least 14 days prior to the first intravenous treatment. Hydroxychloroquine was on the list of prohibited medications until the last amendment of the study protocol. Following identification of a number of protocol deviations, due to administration of hydroxychloroquine, the CI confirmed that inclusion of hydroxychloroquine on the proscribed list was an oversight by the protocol design team. The topic was discussed by the DMC who agreed that hydroxychloroquine posed no risks to patients enrolled in the study and receiving IMP. Consequently, hydroxychloroquine was removed from the list of withheld concomitant medications with study amendment 13, approved in April 2018.
-
Between weeks 0 and 24, patients were not permitted to receive additional immunosuppression (including oral agents, intravenous immunoglobulins or other monoclonal antibody therapies) other than corticosteroids.
Missing data
Every effort was made to minimise missing baseline and outcome data during the trial. Reasons for non-entry were collected using the InForm database comment facilities.
Outcomes
Primary outcome
The primary outcome for the study was change in FVC measured in ml over 24 weeks. Spirometry was measured at baseline and at every subsequent visit (weeks 2, 4, 8, 12, 16, 20 and 24) according to the standards outlined in the guidelines from the American Thoracic Society (ATS) and European Respiratory Society. 45 Sites were encouraged to undertake spirometry at the same time (plus or minus 1 hour) at each visit to minimise the effects of diurnal variation on FVC measurements. The Global Lung Function Initiative (GLI) predictive equations were used to calculate the predicted normal and percentage predicted values for FVC. 46
Twenty-four weeks was chosen as the time point for the primary outcome measure on the basis that this was the point in time at which the effect of the investigational drugs alone could best be determined. After 24 weeks, subjects were permitted to start other immunosuppressant agents and thus interpretation of later time points is confounded by this variable use of immunosuppressants other than CP or RT.
Secondary outcomes
A range of physiological, QoL and biomarker measures were assessed as secondary end points for the study.
Questionnaires
Short Form 36
The Short Form 36 (SF36) questionnaire is a validated 36-item tool describing health-related QoL. It measures each of the following eight health domains: physical functioning, role-physical, bodily pain, general health, vitality, social functioning, emotional and mental health. From these eight subscales two component scores are derived: a physical health component score and a mental health component score. It also includes a single item that assesses perceived change in health status over the past year. The higher the scoring, the better health and functioning. Short Form questionnaire – 36 items (SF-36) was measured at baseline, 24 and 48 weeks.
EuroQol-5 Dimensions, 5-level version
EuroQol-5 Dimensions is a well-established and validated instrument which evaluates five dimensions of QoL which include mobility, self-care, usual activities (e.g. work, study, housework, family or leisure activities), pain/discomfort and anxiety/depression. Each dimension is answered on a five-level scale. The questionnaire encompasses a visual analogue scale (VAS) numbered 0 (worst imaginable health) to 100 (best imaginable health) by which respondents can report their perceived health status. EQ-5D was measured at baseline, 24 and 48 weeks.
St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire
St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) is a respiratory disease-specific instrument designed to measure impact of respiratory symptoms on overall health, daily life and perceived well-being. It was initially developed for individuals with chronic obstructive airways disease, but it has subsequently been validated in other respiratory conditions including ILD. 47 It includes 50 items and scores range from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating more limitation. SGRQ was measured at baseline, 24 and 48 weeks.
King’s brief interstitial lung disease
King’s Brief Interstitial Lung Disease (K-BILD) is a 15-item self-completed validated questionnaire describing health status during the past 2 weeks in responders with (ILD). 48 It covers three domains (psychological, breathlessness and activities and chest symptoms) and the score ranges from 0 to 100, with higher scores denoting best health status. K-BILD was measured at baseline, 24 and 48 weeks.
Scleroderma Health Assessment Questionnaire
Scleroderma Health Assessment Questionnaire (SHAQ) is a disease-specific tool measuring disease status and changes in disease status over time and it is composed of the standard Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) and additional VAS scales to measure symptoms specific to scleroderma and overall disease severity. SHAQ was measured in individuals with scleroderma at baseline, 24 and 48 weeks.
Physiological measures
Lung function
In addition to the measurement of FVC as described for the primary outcome, FVC was also measured at 36 and 48 weeks. Gas transfer was measured at baseline, 24 and 48 weeks according to the standards outlined in the guidelines from the ATS and European Respiratory Society (ATS guidelines). The diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLco) was obtained and the percentage predicted values were obtained using the predictive equations provided by GLI. 49
Forced vital capacity and DLco are both assessed in the routine clinical management of individuals with ILD. Both measurements are used as determinants of treatment response and/or disease progression.
6-minute walk test
The 6-minute walk test is performed by asking subjects to walk as far as possible, using a 30 m track, in 6 minutes. During the test, distance walked, oxygen saturations and subjective breathlessness are all recorded. The test was conducted on room air, according to AST guidelines. 50 In subjects with ILD both 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) and evidence of oxygen desaturation have been shown to be prognostically important.
Death
For patients who died during the course of the trial sites were asked to provide information regarding date and cause of death. Prior to unblinding deaths were adjudicated to determine whether the cause of death was related to the underlying CTD or associated ILD. All-cause and disease-related deaths were analysed separately.
Disease progression and treatment failure
Disease progression was determined to be the time of first occurrence of either; (1) >10% decline in FVC from baseline (day 0), (2) lung transplant, (3) death or (4) treatment failure (as defined by the need for open-label rescue therapy with either RT or CP at any point during the 48 weeks of the study). Time to disease progression and time to treatment failure were analysed separately.
Skin thickening
In the subgroup of subjects with systemic sclerosis skin thickening was measured using the mRSS at baseline and then weeks 12, 24, 26 and 48. mRSS was assessed using the method described by Rodnan et al. as further clarified by Khanna et al. 51 Skin thickness was estimated by palpation in 17 defined body areas on a 0–3 scale giving a total score of between 0 and 51. Wherever possible, the protocol required that the same investigator made the assessment of mRSS at each study visit.
Corticosteroid usage
Prior studies comparing RT to CP in other disease settings have suggested that the requirement for rescue corticosteroids differs between treatment regimens. To assess corticosteroid use, detailed information, including formulation, dose and duration of treatment, with any corticosteroid medication was captured at each study visit. To enable comparison of different corticosteroid regimens all doses were converted to the equivalent dose of hydrocortisone prior to the final analysis.
Physician global assessment of disease activity
At each visit, the PI was asked to provide a gestalt assessment of overall disease activity on a 10 cm visual analogue scale.
Healthcare utilisation and cost-effectiveness analysis
To assess the costs to the NHS associated with RT and CP, a prospective healthcare utilisation and cost-effectiveness analysis was undertaken. Subjects were asked to keep diaries to record all healthcare interactions including primary care services, hospitalisation and outpatient attendance. Participants were asked to provide information on both the frequency and duration of healthcare interactions. Costs were also calculated for grade 3 and 4 AEs.
Biomarkers
Lymphocyte subsets were analysed, according to standard clinical practice, at baseline and 6 months. Plasma, serum, whole blood (for DNA) and PAXgene tubes (for RNA analysis) were collected at each blood draw to enable assessment of experimental anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic biomarkers such as CA125, C3M, pro C6, CCL18 and YKL40.
Safety
Vital signs (temperature, weight, pulse, blood pressure, oxygen saturations, oxygen status, respiratory rate) and the findings from physical examination were recorded at each study visit. Blood samples for laboratory tests (full blood count, urea, electrolytes, liver function tests) and urine for urinalysis were collected at every infusion visit (baseline and weeks 2, 4, 8, 12, 16 and 20)
Pharmacovigilance
The Sponsor provided all sites with the Sponsor’s pharmacovigilance standard operating procedure (SOP) for recording and reporting of AEs; this complies with UK Regulations and patient version guideline reporting requirements, applicable to all Clinical Trials of Investigational Medicinal Products (CTIMPs). The study complied with Health Research Authority safety reporting procedures (URL: www.hra.nhs.uk/approvals-amendments/managing-your-approval/safety-reporting/; accessed 3 September 2021).
Pharmacovigilance definitions were adapted from the European Commission guidance (2011/C 172/01) titled, ‘Detailed guidance on the collection, verification and presentation of adverse reaction reports arising from clinical trials on medicinal products for human use’. AEs were defined as any untoward medical occurrence in a clinical trial participant who is administered an IMP and which does not necessarily have a causal relationship with this treatment [i.e. any unfavourable or unintended change in the structure (signs), function (symptoms) or chemistry (lab data) in a patient to whom an IMP has been administered, including occurrences unrelated to that product]. All study subjects were reviewed by the PI or designee and asked about AEs at each study visit (day 0, weeks 2, 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24 and 48). Following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic some of the safety assessments were undertaken by telephone or video call in the context of COVID-19 pandemic. All AEs were assessed by the local PI or delegate as to whether they met the criteria for a serious adverse event (SAE) as defined in the protocol and Sponsor’s SOP. SAE definitions included any AEs which:
-
resulted in death or:
-
were life-threatening (placed the patient, in the view of the investigator, at immediate risk of death)
-
required hospitalisation or prolongation of existing hospitalisation (hospitalisation is defined as an inpatient admission, regardless of length of stay; even if it is a precautionary measure for observation; including hospitalisation for an elective procedure, for a pre-existing condition)
-
resulted in persistent or significant disability or incapacity (substantial disruption of one’s ability to conduct normal life functions)
-
consisted of a congenital anomaly or birth defect (in offspring of patients or their parents taking the IMP regardless of time of diagnosis).
All SAEs/serious adverse reactions (SARs) (including those which were expected) had to be reported in the eCRF by the investigator/or designee within 24 hours of their becoming aware of the event. The eCRF sent a notification of each SAE report to the Sponsor who reviewed the report within two working days of receipt. All SAEs, whether related or unrelated to the treatment were recorded in the hospital notes and eCRF. The Sponsor had access to SAEs via the eCRF.
All SAEs were assessed by the local PI for their severity (mild, moderate or severe) and relatedness (Definitely, Probably, Possibly, Unlikely and Not related). SAEs deemed to be definitely, probably or possibly related to the trial IMP were categorised as SARs. The Sponsor prepared the Development Safety Update Report (DSUR) in collaboration with the CI in accordance with regulatory requirements. The CI reviewed all SAEs reported in the database and confirmed the assessment of relatedness and expectedness. The Sponsor and CI also assessed all SARs for expectedness against section 4.8 of the SmPC (MHRA-approved reference safety information). No suspected unexpected serious adverse reactions (SUSAR) were reported in this trial.
Monitoring
The trial was monitored according to a monitoring plan developed in accordance with Sponsor SOPs and based on the trial risk assessment. Monitoring was conducted to ensure that the RECITAL study was conducted, recorded and reported in accordance with the protocol, SOPs, GCP and the applicable regulatory requirements. Monitoring included but was not limited to, checks on consent forms, source data verification (SDV), investigator site file and pharmacy file, local procedures, delegation logs, IMP storage and accountability and IMP destruction.
Quality control procedures at clinical sites included formal in-person site initiation training, electronic case report form (CRF) review and the periodic checking of essential documents, ISFs and pharmacy site files (PSFs).
In addition to reviewing the CRF data, the monitor/manager:
-
monitored SAE/R narratives against patient source data
-
discussed study progress with the investigator and other site staff
-
reviewed the ISF for completeness
-
tracked protocol deviations/violations
-
tracked patient progress in the study
-
reviewed any changes in site staff or facilities
-
reviewed the drug accountability records in pharmacy and checked drug supplies.
Following monitoring, a report was written and shared with the investigator team to ensure that the team understood the findings of the report and actions recommended by the Sponsor. The Regulatory Compliance Manager was responsible for all monitoring undertaken by the study monitor and study manager. The findings were presented to the Clinical Research Oversight Committee (Clin-ROC) to inform the committee of all quality assurance/quality control activities undertaken by the research and compliance team.
On-site monitoring was performed at all 11 recruiting sites between 2015 and 2020. The on-site monitoring visits, in addition to activities performed remotely, involved SDV of a sample of patients at the site, checks to ensure documentation were performed according to GCP, a review of the clinic notes to check for unreported notable or serious events, a pharmacy monitoring visit and investigator site file and PSF review.
In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, the close-out visits were undertaken by sending all sites a ‘Self-Monitoring Form’ to enable Sponsor to monitor study activities remotely.
The trial statistician performed risk-based central statistical monitoring and produced a study report prior to all DMC meetings and guided the committee through the report. Usually, the Chair of the DMC reported its recommendations in writing to the TSC within 2 weeks of the meeting.
Statistical analysis
A statistical analysis plan (SAP) was produced and agreed with the TSC and DMC prior to analysis (see the project webpage www.fundingawards.nihr.ac.uk/award/11/116/03). Deviations from the SAP were recorded in the SAP deviation document. A summary of the planned analysis strategy for the primary and secondary outcomes can be found below.
Primary efficacy analysis
-
Analysis of the primary outcome was by modified intention to treat. In other words, data were included in respect of all subjects who met all the entry criteria for the trial and had been randomised and received at least one dose of study drug. The data was analysed according to the initial randomisation groups with no changes made in respect of subsequent withdrawals or crossovers.
-
The hypothesis to be tested was that RT is superior to CP. The study was to be considered positive if statistical significance at the level of 0.05 (two-tailed) was achieved.
-
To test the hypothesis above and estimate the difference in FVC at week 24 (together with 95% confidence interval), a three-level hierarchical (mixed/multilevel) model with unstructured correlation matrix and adjusted for baseline FVC and CTD type (stratification factor) treating the primary outcome as an interaction term between treatment and visits, including at week 24 was used.
Representing FVC in mL as FVCiv (in ml) for patient I at visit v with treatment (RT or CP) t(i), the FVCiv is modelled as the sum of four components:
-
baseline FVC: represents the estimated FVC at baseline. This term comprised an individual level random effect which was drawn from a distribution parameterised using the associated centre-level random effect. Hence unexplained variations in the FVC measures were split into three components corresponding to the three levels of the model, that is the variation attributable to the centre (between centre variation) and the individual (between individual variation), as well as the residual variation (within individual variation).
-
CTD diagnosis stratum (categorical) used for randomisation was added as a covariate.
-
visit: represents the visit number as a categorical variable.
-
treatment: a binary variable representing treatment arm.
-
Interaction term: this represents a coefficient that captures the changes in FVC at each visit between the arms. The magnitude of change at 24 weeks and its 95% confidence interval will be calculated to answer the research question.
-
No other baseline covariates were added as no substantial imbalances were revealed between the arms.
The Stata code used for the primary outcome was:
mixed changeFVC i.CTD i.week i.Arm#i.week || SITENAME: || SUBJECTNUMBERSTR:
Secondary efficacy analysis
-
Analysis of secondary efficacy outcomes was also performed by modified intention to treat.
-
Change in continuous physiological variables between baseline and 48 weeks were assessed by similar multilevel model as described for the primary outcome.
-
Categorical change in physiological variables was measured using chi-squared tests under the null hypothesis of no difference between the treatment groups.
Mortality, treatment failure and progression-free survival were measured using Kaplan–Meier estimates. A log-rank test was used to compare treatment groups and a Cox proportional hazards model was used to determine hazard ratios (HRs) for survival analyses.
Sample size
Previous studies of intravenous CP in SSc demonstrated a 1% decline in FVC at 12 months, with a coefficient of variation of 7.8%. Our observational data and a previous non-randomised study of RT (used as rescue therapy in those failing treatment with CP) suggested improvements in FVC at 6–12 months of between 9.5% and 20% compared to baseline. Using 1 : 1 randomisation, a sample size of 52 patients in each group gives a 90% power to detect a 5% difference (approximately 140 ml) between groups at 24 weeks in the change in FVC (as measured in ml) with a significance level (alpha) of 0.05 (two-tailed). Anticipating a dropout rate of 10% our target recruitment was 58 patients in each arm of the study. On the basis of data derived in other interstitial lung diseases 5% change in FVC is associated with change in long-term prognosis and can therefore be considered a clinically meaningful difference between the two groups. Given the number of individuals treated with CP at units participating in the study, this number was considered feasible to deliver within the planned trial timelines.
Primary efficacy variable
-
Change in FVC (expressed in ml) at week 24.
Secondary efficacy variables
-
Change in DLco at 24 weeks.
-
Change in health-related QoL scores (SGRQ, SF-36, K-BILD).
-
Change in Global Disease Activity Score (GDAS).
-
Change in 6MWD over 48 weeks.
-
Change in FVC and DLco at 48 weeks.
-
Absolute categorical change of %FVC at 24 and 48 weeks (decrease by >5%, increase by >5% and change within <5%).
-
Absolute categorical change of %FVC at 24 and 48 weeks (decrease by >10%, increase by >10% and change within <10%).
-
48-week change in FVC.
-
Disease-related mortality (adjudicated by steering committee at close of study).
-
Overall survival.
-
Progression-free survival [i.e. avoiding any of the following: mortality, transplant, treatment failure (see below) or decline in FVC > 10% compared to baseline].
-
Treatment failure (as determined by need for transplant or rescue therapy with either open-label CP or RT at any point until 48 weeks).
-
Total corticosteroid requirement over 48 weeks.
-
Change from baseline in SpO2 at 24 and 48 weeks.
-
Healthcare utilisation during study period (visits to primary care, unscheduled hospital visits, emergency admissions).
-
Scleroderma-specific end points (change in scleroderma HAQ, mRSS).
Safety variables
-
Vital signs (temperature, weight, pulse, blood pressure, oxygen saturations, oxygen status, respiratory rate).
-
Physical examination (skin, lungs, cardiovascular, abdomen).
-
Laboratory tests (blood counts, urea, electrolytes, liver function tests, urinalysis).
-
Adverse and SAEs.
-
Discontinuation of RT or CP due to intolerance or side effects.
Exploratory variables
-
Change in lymphocyte subsets in relation to efficacy outcomes.
-
Change in plasma protein levels following therapy and in relation to markers of disease activity (FVC, DLco, QoL, global disease scores).
-
Outcome in relation to underlying CTD.
Cost-effectiveness analysis
A cost-effectiveness analysis was conducted to estimate the costs and outcomes associated with using RT versus CP to treat patients with CTD-ILD in the RECITAL study. Data on health resources used, such as primary care service, hospitalisation, outpatient, oxygen, their frequencies and durations were collected from patient diaries as reported during the RECITAL clinical trial. The average frequencies of resources used were calculated by dividing the number of visits by the number of patients who used the service, as reported in the RECITAL diary. The proportion of patients who used a specific healthcare service was calculated in an intention-to-treat analysis, dividing the number of patients who used a particular healthcare service by the total number of patients randomised for each treatment arm.
We calculated the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) to compare the costs and effectiveness of RT versus CP. This was calculated by the difference in costs divided by the difference in effects of both technologies. A willingness to pay (WTP) threshold of £30,000 per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained was assumed in this analysis (based on the commonly accepted thresholds used by the UK NICE). A discount rate on the cost and effects was not applied due to the temporal framework as our analysis did not exceed 1 year. The uncertainties around the input parameters were assessed by carrying out probabilistic sensitivity analysis (PSA), incremental net monetary benefit (INMB) and cost-effectiveness acceptability curve (CEAC).
Model input parameters
Resources use
The probabilities of requiring a healthcare service among the patients with CTD-ILD were derived from clinical trials whenever feasible (see Table 3).
| Resource used | Parameters | % patients using the resource | Frequency (mean) | Duration mean (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclophosphamide – CP | ||||
| Primary care services | Community and social services visits | 10 | 2.6 | 60 |
| Dentist | 4 | 2 | 30 | |
| GP | 54 | 2.56 | 15.54 | |
| Nurse | 34 | 4.53 | 13.38 | |
| Occupational therapy | 2 | 1 | 20 | |
| Optician | 2 | 1 | 45 | |
| Phlebotomist | 4 | 2 | 7.5 | |
| Physiotherapist | 10 | 1.4 | 36.43 | |
| A&E | Hospital A&E | 34 | 2.35 | - |
| Hospital outpatient | Hospital outpatient | 72 | 7.83 | - |
| Hospital inpatient | Hospital inpatient | 2 | 1 | - |
| Telephone calls | GP | 16 | 1.88 | - |
| Nurse | 12 | 2 | - | |
| Ambulatory oxygen | Ambulatory oxygen | 36 | - | - |
| AEs | Chest infection | 6 | - | - |
| Febrile illness | 2 | - | - | |
| Lung infection | 10 | - | - | |
| Pulmonary oedema | 2 | - | - | |
| Flu (Influenza A) | 2 | - | - | |
| Non-cardiac chest pain | 2 | - | - | |
| Rituximab – RT | ||||
| Primary care service | Community and social services visits | 2 | 12 | 60 |
| Dentist | 2 | 1 | 30 | |
| GP | 51 | 2.5 | 15.24 | |
| Nurse | 20 | 6.3 | 23.98 | |
| Occupational therapy | 2 | 6 | 55 | |
| Phlebotomist | 2 | 4 | 5 | |
| Physiotherapist | 6 | 4.67 | 48.93 | |
| Urgent care | 2 | 1 | 15 | |
| Palliative care | 2 | 2 | 45 | |
| A&E | Hospital A&E | 25 | 1.62 | - |
| Hospital outpatient | Hospital outpatient | 59 | 5.2 | - |
| Telephone calls | GP | 20 | 1.4 | 12.75 |
| Nurse | 10 | 2 | 7.22 | |
| Ambulatory oxygen | Ambulatory oxygen | 20 | - | - |
| AEs | Lung infection | 11.8 | - | - |
| Community-acquired pneumonia | 2 | - | - | |
| Dyspnoea | 2 | - | - | |
| Sepsis | 2 | - | - | |
| Urinary tract infection | 3.9 | - | - | |
| Worsening ILD and consolidation infection | 2 | - | - | |
Costs and utility values
All costs were estimated using the NHS perspective, therefore, only direct medical costs were accounted for and expressed in Great British pounds (£). QALYs were derived from the utility values [EuroQol-5 Dimensions, five-level version (EQ-5D-5L)] extracted from RECITAL Clinical Trial and collected at 24 and 48 weeks. The primary outcome was cost-effectiveness, as defined by Great British pound costs, QALYs (or effectiveness), ICER and INMB. A strategy was considered cost-effective if it was: (1) more effective and less expensive (dominant strategy); (2) more effective and more expensive with an ICER < £30,000.
Model assumptions
In the formulation of the key assumptions, we made conservative estimates to avoid favouring intervention. Key assumptions of the model were: we assumed only grade 3 and 4 AEs (moderate and severe) and all hospitalisation required to treat AEs were non-elective short stay (day-case) to account for the total cost of the AE; we included the main treatment options reported in the RECITAL diary as alternatives to treat the reported AEs; we assumed that AEs occurred once; CP dosage was calculated assuming an idealised patient with a weight of 70 kg; one-way sensitivity analysis was carried out assuming either a 10% increase or decrease in input parameters. We examined the main assumptions in a sensitivity analysis.
Sensitivity analysis
The robustness of the outcome was assessed by sensitivity analyses. One-way sensitivity analyses were performed based on the parameters with the highest level of uncertainty (including all costs and utility values). These analyses consisted of varying each key parameter, assuming either a 10% increase or decrease in input parameters. Besides that, the impact of the uncertainties around the key parameters on the ICER was assessed through 1000 PSA using Monte Carlo simulation. PSA was carried out with all parameters being simultaneously varied in pre-specified ranges using pre-set distributions (gamma for cost and beta for utility values) (see Table 4).
| Resource used | Parameters | Unit cost (£) | Cost (£) per item | Total cost per category | Distribution | Source | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Costs | |||||||
| Drug | CP, 600 mg (CP) | 15.22 | 5062.29 | 5062.29 | Gamma | British National Formulary (BNF) (NICE), 2021 | Every 4 weeks for a total of six doses |
| Primary care services | CP – Community and social services visits | 51/hour | 663.00 | 6569.38 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 138 | Social worker (adult services): 45 (£51) per hour (costs including qualifications given in brackets). Assume 1-hour session |
| CP – Dentist | 133/hour | 266.00 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 130 | NHS dentist (performer-only): £105 per hour; £133 per hour of patient contact | ||
| CP – GP | 255/hour | 4557.11 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 126 | GP – with qualification cost: £255 per hour of patient contact (including direct care staff costs) | ||
| CP – Nurse | 42/hour | 721.18 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 124 | Nurse (GP practice): £38 (£42) per hour (costs including qualifications given in brackets) | ||
| CP – Occupational therapy | 49/hour | 16.33 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 141 | Community occupational therapist (local authority): £45 (£49) per hour (costs including qualifications given in brackets) | ||
| CP – Optician | 255/hour | 191.25 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 126 | We assume the same salary as the GP to estimate the unit cost for an optician | ||
| CP – Phlebotomist | 20/hour | 10.00 | Gamma | PSSRU (2015) p. 173 | Clinical support worker nursing (community): £20 per hour | ||
| CP – Physiotherapist | 34/hour | 144.51 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 151 | Physiotherapists/oTs (Band 4) | ||
| A&E | CP – Hospital A&E | 212/episode | 8480 | 8480 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 106 | A&E: £212 total cost per user |
| Hospital outpatient | CP – Hospital outpatient | 135/episode | 38,070 | 38,070 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 87 | Outpatient attendances: £135 weighted average of all outpatient attendances. We assumed the weighted average of all outpatient attendance costs because there are several reasons for outpatient reported in the diary |
| Hospital inpatient | CP – Hospital inpatient | 3366/episode | 3366 | 3366 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 87 | Non-elective inpatient stays (long stays): £3366 |
| Telephone calls | CP – GP | 8.41/e-consultation | 126.15 | 149.07 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 128 | GP telephone calls: £8.41 average cost per e-consultation |
| CP – Nurse | 1.91/e-consultation | 22.92 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 128 | Nurse face-to-face contacts: £1.91 average cost per e-consultation | ||
| Ambulatory oxygen | CP – Ambulatory oxygen | 91.02/2 weeks | 1638.36 | 1638.36 | Gamma | Whitty et al. (2020) | The average cost for ambulatory oxygen for 2 weeks was estimated to be £ 91.02 (95% CI £ 77.83–104.21) per participant |
| Adverse events | CP – AEs | - | 31,003.03 | 31,003.03 | Gamma | Calculated | AE cost was calculated by accounting the AE treatment cost + hospitalisation (day-case) |
| Drug | RT, 1 g | 349.25 | 35,623.50 | 35,623.50 | Gamma | BNF (NICE), 2021 | At baseline and repeated at 14 days |
| Primary care services | RT – Community and social services visits | 51/hour | 612.00 | 6946.91 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 138 | Social worker (adult services): 45 (£51) per hour (costs including qualifications given in brackets). Assume 1-hour session |
| RT – Dentist | 133/hour | 66.50 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 130 | NHS dentist (performer-only): £105 per hour; £133 per hour of patient contact | ||
| RT – GP | 255/hour | 4210.05 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 126 | GP – with qualification cost: £255 per hour of patient contact (including direct care staff costs) | ||
| RT – Nurse | 42/hour | 1052.52 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 124 | Nurse (GP practice): £38 (£42) per hour (costs including qualifications given in brackets) | ||
| RT – Occupational therapy | 49/hour | 269.50 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 141 | Community occupational therapist (local authority): £45 (£49) per hour (costs including qualifications given in brackets) | ||
| RT – Phlebotomist | 20/hour | 6.67 | Gamma | PSSRU (2015) p. 173 | Clinical support worker nursing (community): £20 per hour | ||
| RT – Physiotherapist | 34/hour | 388.18 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 151 | Physiotherapists/oTs (Band 4) | ||
| A&E | RT – Hospital A&E | 212/episode | 8480 | 8480 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 106 | A&E: £212 total cost per user |
| Hospital outpatient | RT – Hospital outpatient | 135/episode | 21,060.00 | 21,060.00 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 87 | Outpatient attendances: £135 weighted average of all outpatient attendances. We assumed the weighted average of all outpatient attendance costs because there are several reasons for outpatient reported in the diary |
| Telephone calls | RT – GP | 8.41/e-consultation | 117.74 | 136.84 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 128 | GP telephone calls: £8.41 average cost per e-consultation |
| RT – Nurse | 1.91/e-consultation | 19.10 | Gamma | PSSRU (2020) p. 128 | Nurse face-to-face contacts: £1.91 average cost per e-consultation | ||
| Ambulatory oxygen | RT – Ambulatory oxygen | 91.02/2 weeks | 910.20 | 910.20 | Gamma | Whitty et al. (2020) | The average cost for ambulatory oxygen for 2 weeks was estimated to be £ 91.02 (95% CI £ 77.83 to 104.21) per participant |
| AEs | RT – AEs | - | 24,097.69 | 24,097.69 | Gamma | Calculated | AE cost was calculated by accounting the AE treatment cost + hospitalisation (day-case) |
| Utility | |||||||
| Parameters | Value | Distribution | Source | ||||
| CP – EQ-5D at week 24 | 0.308 | Beta | RECITAL Clinical Trial | ||||
| RT – EQ-5D at week 24 | 0.330 | Beta | RECITAL Clinical Trial | ||||
| CP – EQ-5D at week 48 | 0.633 | Beta | RECITAL Clinical Trial | ||||
| RT – EQ-5D at week 48 | 0.637 | Beta | RECITAL Clinical Trial | ||||
Trial oversight committees
An independent DMC undertook interim review of the trial’s progress including updated figures on recruitment, data quality and main outcomes and safety data. More specifically the DMC:
-
assessed data quality, including completeness (and by doing so encouraged collection of high-quality data)
-
monitored recruitment figures and losses to follow-up
-
monitored compliance with the protocol by participants and investigators
-
monitored evidence for treatment differences in the main efficacy outcome measures
-
monitored evidence for treatment harm (e.g. toxicity data, SAEs, deaths)
-
decided whether to recommend that the trial continues to recruit participants or whether recruitment should be terminated either for everyone or for some treatment groups
-
suggested additional data analyses for the monitoring purposes of DMC
-
advised on protocol modifications suggested by investigators or the Sponsor (e.g. to inclusion criteria, trial end points or sample size)
-
monitored compliance with previous DMC recommendations
-
considered the ethical implications of any recommendations made by the DMC
-
assessed the impact and relevance of external evidence.
The committee met by teleconference every 6 months or at least annually for the duration of the study and comprised:
-
Dr Andrew Wilson – Chair – University of East Anglia
-
Dr Clive Kelly – Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead (to May 2019 – retired)
-
Dr Harsha Gunawardena – North Bristol NHS Trust, Southmead
-
Dr Ashley Jones – Centre for Medical Statistics and Health Evaluation, University of Liverpool.
The TSC provided overall supervision for the trial and considered reports from the TMG, the trial team and the DMC. The roles and responsibilities were set out in the TSC Charter.
Independent members
-
Dr Tim Harrison – Chair, University of Nottingham.
-
Dr Bridget Griffiths – Freeman Hospital, Newcastle.
-
Dr Nik Hirani – University of Edinburgh.
-
Mrs Kim Fliglestone – Consumer representative.
-
Mrs Alexandra Marler – Consumer representative.
Non-independent members
-
Mrs Ira Jakupovic – Royal Brompton and Harefield NHS Foundation Trust.
-
Mrs Vicky Taylor – Efficacy and Mechanism Evaluation (EME) (until 15 September 2015).
-
Ms Maggie Shergill – EME (15 September 2015–07 September 2018).
-
Anna Williams – EME (7 March 2018 until the end of the study).
-
Dr Rachel Hoyles – Oxford Radcliffe Hospitals NHS Trust.
-
Dr Helen Parfrey – Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
-
Prof Deborah Ashby – Imperial College London.
All TSC and DMC members were required to complete the TSC/DMC Charter and declare any potential competing interests.
There were four substantial and one non-substantial protocol amendments, which are summarised in Table 5.
| Protocol version | Date | Summary of changes |
|---|---|---|
| 4.0 | 23 September 2013 | As part of the MHRA review process we were required to amend protocol regarding unblinding and to provide clarification on the constitution and labelling of the placebo. |
| 5.0 | 31 January 2014 | New safety information became available recommending screening for hepatitis B serology before commencing patients on RT. We amended the protocol and PIS to reflect this. |
| 6.0 | 15 October 2014 | Updated the schedule of study events to clarify requirements for immunoglobulin levels, CK measurement, myositis testing, lymphocyte subsets and exploratory research samples. Details on IMP(s) destruction specifications were clarified. |
| 6.1 | 15 December 2014 | Protocol V6.1 – submitted as non-substantial changes to the study protocol in relation to mesna dosing. |
| 7.0 | 7 February 2018 | Changes to the protocol to clarify wash-out period prior to IMP dosing, blood glucose measurement, unblinding procedure and use of corticosteroids during the study. |
Breaches and protocol deviations
There were no serious breaches reported in this trial. Protocol deviations were recorded on the electronic Protocol deviation log in the database and were included in TMG, DMC and TSC reports.
A cumulative summary of all the protocol deviations recorded in the database is given in Report Supplementary Material 1, Table S1. The protocol deviations were included and discussed in DMC reports.
Chapter 3 Results
Screening and recruitment
Screening for participants started in December 2014 and ended February 2020. The last visit of the last patient was in January 2021. A total of 11 sites as seen in Table 6 screened participants and Royal Brompton Hospital was the largest recruitment site. A graph of recruitment against projected recruitment is given in Figure 2. The graph demonstrates that the study had a slower than anticipated recruitment rate and this was determined mainly by issues related to excess treatment costs for RT (these proved to be a major problem with respect to initiating centres and delivering the study on time and target). Another factor that increasingly affected the recruitment rate towards the end of the study was the availability of a generic alternative to RT, which cost significantly less and meant that some eligible patients received treatment with RT outside the setting of the trial thus reducing the pool of patients available to be recruited.
| Site number | Site | Number signing consent form | Number randomised | Date open to recruitment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Royal Brompton Hospital | 66 | 65 | 3 November 2014 |
| 2 | Southampton | 2 | 2 | 15 March 2016 |
| 3 | Royal Devon and Exeter | 5 | 5 | 17 June 2016 |
| 4 | Royal Free | 5 | 4 | 4 October 2016 |
| 5 | Birmingham | 4 | 4 | 14 November 2016 |
| 6 | Oxford | 3 | 3 | 8 November 2017 |
| 7 | Sheffield | 6 | 6 | 26 April 2017 |
| 8 | Aintree | 4 | 3 | 5 May 2017 |
| 9 | Cambridge | 5 | 5 | 12 July 2017 |
| 10 | Manchester | 2 | 2 | 21 November 2017 |
| 11 | Coventry | 2 | 2 | 1 November 2018 |
| Total | 104 | 101 |
FIGURE 2.
Graph of projected and actual recruitment to RECITAL.
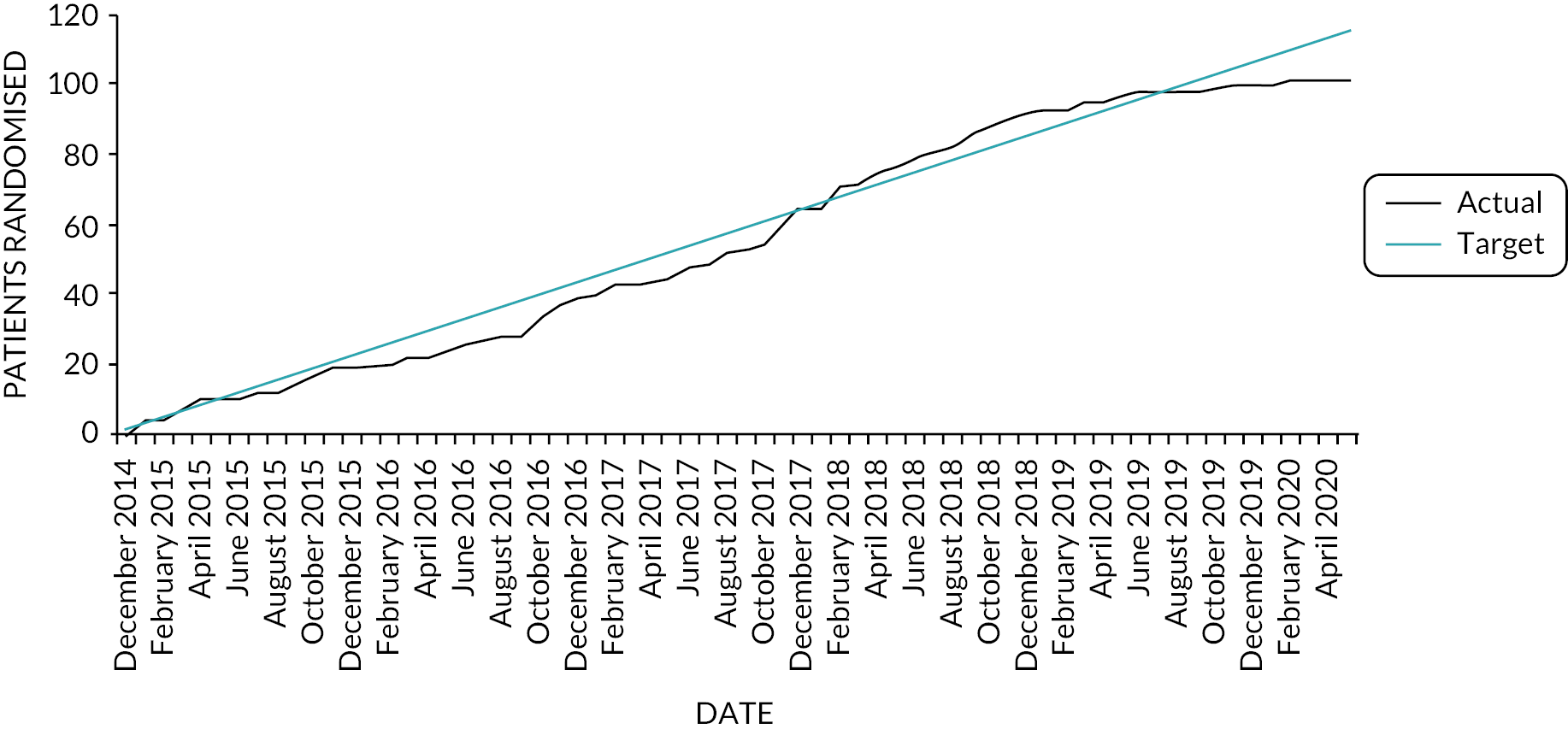
In response to COVID-19 pandemic the trial was kept open, however, patients active in the trial at the time were reluctant to attend study or follow-up visits. Some of these visits were conducted over telephone or video calls. Given these factors, and especially the unprecedented impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on trial recruitment and conduct, it was decided that any further recruitment would be almost impossible and would unacceptably extend trial timelines. Recruitment was therefore halted in April 2020 (with the agreement of the Sponsor, Data safety monitoring committee, TSC and funder), however, the study continued until the final patient completed their week 48 visit.
Participant flow
The Consolidated Standard of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) flow chart for RECITAL is detailed in Figure 3. In summary, a total of 145 patients were assessed for eligibility. Of these 104 were recruited and 101 randomised. Of the 101 randomised patients, 50 were randomised to CP and 51 were randomised to RT. Of these, four did not receive at least one treatment for the reasons given in the withdrawals table and Consort diagram. The number of patients who therefore received at least one treatment and were part of the modified intention to treat statistical analysis was 48 in the CP arm and 49 in the RT arm.
FIGURE 3.
The CONSORT flow chart.
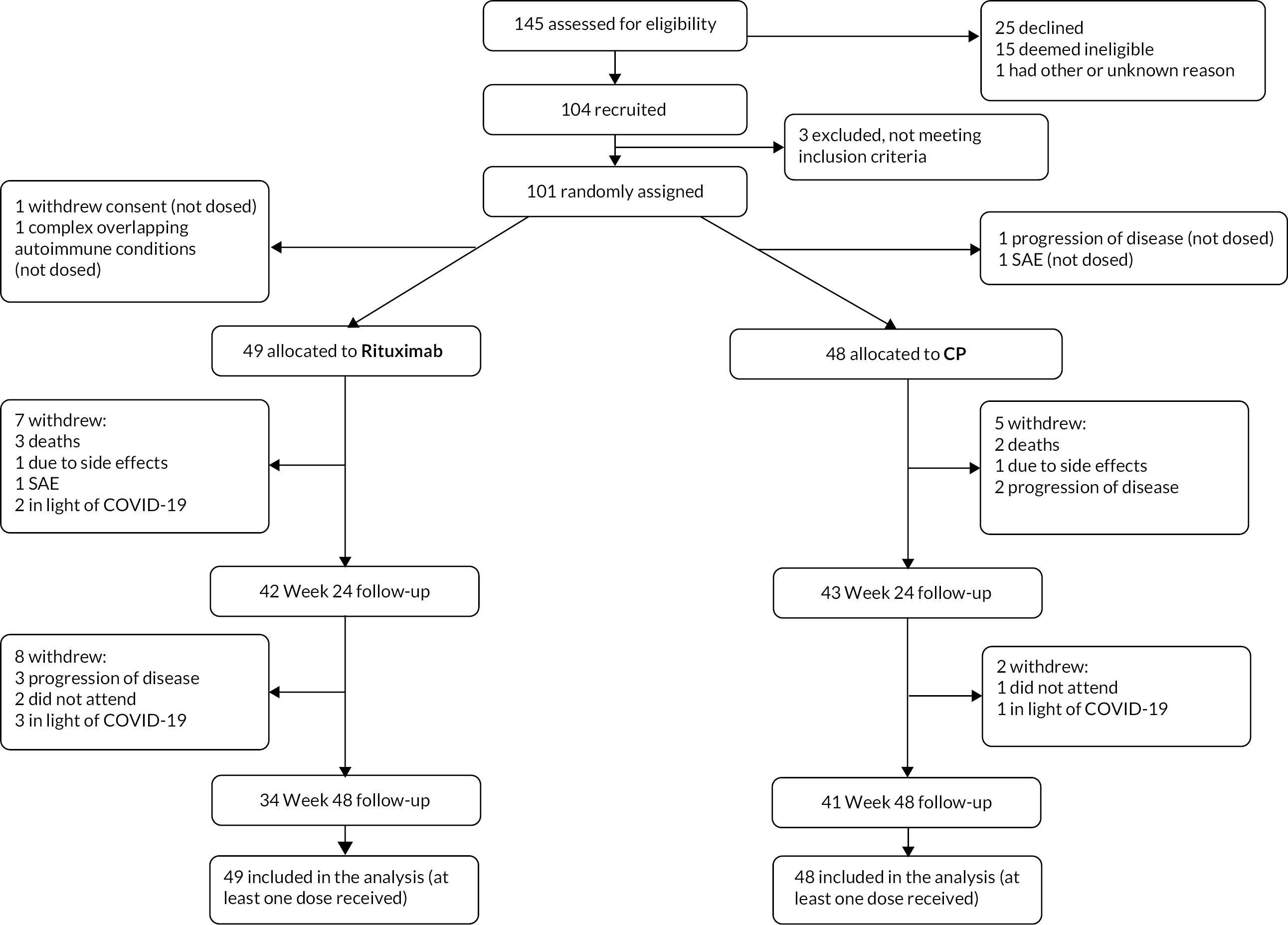
Patient withdrawal
The study drug was discontinued when in the opinion of the local investigator/caring physician, an individual participant’s disease progressed despite receiving study therapy. Individuals with progressive disease were unblinded from the study when it was felt appropriate by their caring physician and offered the alternative treatment regimen on an open-label basis (i.e. patients receiving RT were offered CP and those receiving CP were considered for RT). Such treatment was given outside of the study.
Subjects discontinuing the study drug were invited to continue with planned monitoring and end-of-study visits. The protocol requested that data were collected for all individuals who were randomised into the study whether or not they received their assigned treatment or discontinued the study prematurely. Subjects discontinuing study treatment were asked to return for the primary end point (week 24) and final (week 48) follow-up visits. Permanent discontinuation from the study occurred when consent was withdrawn.
Temporary discontinuation or omission of IMP was possible when there were contraindications to treatment being given at a specific visit for example due to an episode of significant infection or if hospitalisation was required.
Patients were free to withdraw consent to trial procedures and visits at any time; although doing so resulted in incomplete patient follow-up. In these cases, permission was sought to retain study data collected up until the time of withdrawal. Local investigators were asked to ascertain the reasons for the withdrawal, including discontinuation of study drug, withdrawal from study investigations and/or follow up, withdrawal due to AEs, failure to attend, non-compliance, withdrawal of consent or for other reasons. The RECITAL Trial Manager was notified of withdrawals within five working days, unless withdrawal was due to an SAE, in which case the investigator followed SAE reporting procedures.
A total of 23 randomised patients dropped out of the study (the detailed reasons for these dropouts are given in Appendix 1, Table 34).
Baseline characteristics
As shown in Table 7, the subjects enrolled in the trial were predominantly female (n = 66, 68.0%) and had a mean age of 56.6 ± 11.5 years. This is in keeping with the known demographics of CTD-ILD. Forty-four subjects (45.4%) had an IIM-associated ILD, 37 (38.1%) had scleroderma ILD and 16 (16.5%) had MCTD-associated ILD. Following randomisation, baseline characteristics were balanced between the two treatment groups as shown in Table 8. The mean age was 56.7 ± 11.6 years in the CP arm and 56.6 ± 11.4 years in the RT arm. There were more females in the CP arm (72.9%) compared to the RT arm (63.3%), however, the groups were well balanced by ethnicity, underlying disease and baseline disease severity. Subjects in both groups had significant physiological impairment with a mean FVC % predicted 71 ± 20% and 68 ± 17% in the CP and RT arms, respectively.
| Baseline characteristics | N = 97 |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 56.6 (11.5) |
| Sex | |
| Female | 66 (68.0%) |
| Male | 31 (32.0%) |
| Ethnicity | |
| Any other ethnic group | 2 (2.1%) |
| Asian | 16 (16.5%) |
| Black | 12 (12.4%) |
| Mixed | 1 (1.0%) |
| White | 66 (68.0%) |
| CTD type | |
| IIM | 44 (45.4%) |
| MCTD | 16 (16.5%) |
| Systemic sclerosis | 37 (38.1%) |
| Time since onset of CTD (years) | 4.7 (6.9) |
| Treatment group | ||
|---|---|---|
| CP | RT | |
| N = 48 | N = 49 | |
| Age (years) | 56.7 (11.6) | 56.6 (11.4) |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 35 (72.9%) | 31 (63.3%) |
| Male | 13 (27.1%) | 18 (36.7%) |
| Ethnicity | ||
| Any other ethnic group | 1 (2.1%) | 1 (2.0%) |
| Asian | 7 (14.6%) | 9 (18.4%) |
| Black | 5 (10.4%) | 7 (14.3%) |
| Mixed | 1 (2.1%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| White | 34 (70.8%) | 32 (65.3%) |
| CTD type | ||
| IIM | 22 (45.8%) | 22 (44.9%) |
| MCTD | 7 (14.6) | 9 (18.4%) |
| Systemic sclerosis | 19 (39.6%) | 18 (36.7%) |
| Time since onset of CTD (years) | 4.8 (6.2) | 4.5 (7.6) |
| FVC (L) | 2.23 (0.85) n = 48 | 2.25 (0.77) n = 49 |
| FVC %predicted | 71 (20) n = 48 | 68 (17) n = 49 |
| DLco (CO/min/mmHg) | 3.35 (1.0) n = 46 | 3.46 (1.0) n = 45 |
| DLco % predicted | 40 (14) n = 46 | 40 (14) n = 45 |
| SpO2 | 96 (2) n = 48 | 97 (2) n = 49 |
| 6MWD (m) | 363 (111) n = 48 | 356 (126) n = 48 |
| EQ-5D | 55 (20) | 58 (22) |
| mRSS | 7.2 (8.6) n = 24 | 9.2 (8.2) n = 17 |
| GDAS | 5.03 (1.76) n = 40 | 4.58 (1.97) n = 38 |
| SGRQ | 55.8 (20.0) n = 47 | 52.1 (17.6) n = 45 |
| K-BILD | 46.1 (20.3) n = 49 | 51 (21.2) n = 48 |
As shown in Table 9, when considered by underlying CTD, there were some demographic differences between the individual diagnostic groups. Individuals with IIM consisted of a greater proportion of men (45.5%) compared to other groups; MCTD 25.0% and scleroderma 18.9%. Subjects with IIM also had a much shorter time from diagnosis (2.2 ± 3.0 years) when compared to MCTD (6.5 ± 10.5 years) and scleroderma (6.9 ± 7.6 years). There were fewer white patients (37.5%) in the MCTD group compared with IIM (77.3%) and scleroderma (70.3%). Subjects with MCTD (FVC 66 ± 14 % predicted and a DLco 37 ± 13% predicted) and scleroderma (FVC 69 ± 20% predicted and DLco 34 ± 10% predicted) had greater physiological impairment than the subjects with IIM (FVC 71 ± 19% predicted and DLco 34 ± 10% predicted).
| CTD type | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IIM | MCTD | Systemic sclerosis | |
| N = 44 | N = 16 | N = 37 | |
| Unblinded drug details | |||
| CP | 22 (50.0%) | 7 (43.8%) | 19 (51.4%) |
| RT | 22 (50.0%) | 9 (56.3%) | 18 (48.6%) |
| Age (years) | 56.5 (9.9) | 59.1 (9.5) | 55.7 (13.9) |
| Sex | |||
| Female | 24 (54.5%) | 12 (75.0%) | 30 (81.1%) |
| Male | 20 (45.5%) | 4 (25.0%) | 7 (18.9%) |
| Ethnicity | |||
| Any other ethnic group | 1 (2.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.7%) |
| Asian | 4 (9.1%) | 5 (31.3%) | 7 (18.9%) |
| Black | 4 (9.1%) | 5 (31.3%) | 3 (8.1%) |
| Mixed | 1 (2.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| White | 34 (77.3%) | 6 (37.5%) | 26 (70.3%) |
| Time since onset of CTD (years) | 2.2 (3.0) | 6.5 (10.5) | 6.9 (7.6) |
| FVC (L) | 2.46 (0.89) n = 44 | 2.00 (0.85) n = 17 | 2.06 (0.61) n = 37 |
| FVC (% pred) | 71 (19) n = 44 | 66 (14) n = 17 | 69 (20) n = 37 |
| DLco (% predicted) | 47 (14) n = 42 | 37 (13) n = 13 | 34 (10) n = 36 |
| SpO2 | 96 (2) n= 44 | 96 (3) n = 17 | 97 (2) n = 37 |
| 6MWD (m) | 394 (108) n = 43 | 333 (117) n = 16 | 331 (122) n = 37 |
| EQ-5D | 56 (23) | 68 (19) | 52 (18) |
| mRSS | - | - | 7.9 (7.6) n = 34 |
| GDAS | 5.1 (2.0) n = 36 | 4.4 (1.6) n = 13 | 4.7 (1.9) n = 29 |
| SGRQ | 52.2 (19.0) n = 42 | 56.9 (17.9) n = 14 | 55.4 (19.3) n = 36 |
| K-BILD | 49.0 (20.5) n = 44 | 51.7 (22.9) n = 17 | 46.3 (20.2) n = 36 |
Primary outcome
Of the 101 randomised subjects, 49 in the RT and 48 in the CP arm received at least one dose of therapy and were included in the modified intention-to-treat analysis. At 24 weeks, both RT and CP resulted in an improvement in FVC from baseline (97 ± 234 ml and 99 ± 329 ml, respectively) (see Table 10 and Figure 4). In the primary end-point analysis, applying an adjusted mixed-effects model corrected for diagnosis and baseline FVC the difference in FVC between RT and CP at week 24 was −40 ml (95% CI −153 to 74 ml) p = 0.493. Table 11 and Figure 5 show the adjusted difference between groups at each time point.
| Week | Arm | N | FVC difference (L) | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 0 | CP | 49 | 0.000 | - |
| Week 2 | CP | 47 | −0.038 | 0.171 |
| Week 4 | CP | 44 | −0.002 | 0.560 |
| Week 8 | CP | 44 | −0.090 | 0.233 |
| Week 12 | CP | 43 | 0.040 | 0.191 |
| Week 16 | CP | 43 | −0.009 | 0.220 |
| Week 20 | CP | 43 | 0.024 | 0.252 |
| Week 24 | CP | 45 | 0.099 | 0.329 |
| Week 48 | CP | 42 | 0.138 | 0.440 |
| Week 0 | RT | 49 | 0.000 | - |
| Week 2 | RT | 48 | −0.013 | 0.374 |
| Week 4 | RT | 46 | −0.065 | 0.281 |
| Week 8 | RT | 46 | 0.027 | 0.377 |
| Week 12 | RT | 46 | −0.001 | 0.206 |
| Week 16 | RT | 45 | 0.002 | 0.291 |
| Week 20 | RT | 42 | 0.018 | 0.295 |
| Week 24 | RT | 43 | 0.097 | 0.234 |
| Week 48 | RT | 35 | 0.112 | 0.249 |
FIGURE 4.
Observed change in FVC from baseline over time. Bars represent the standard deviation.
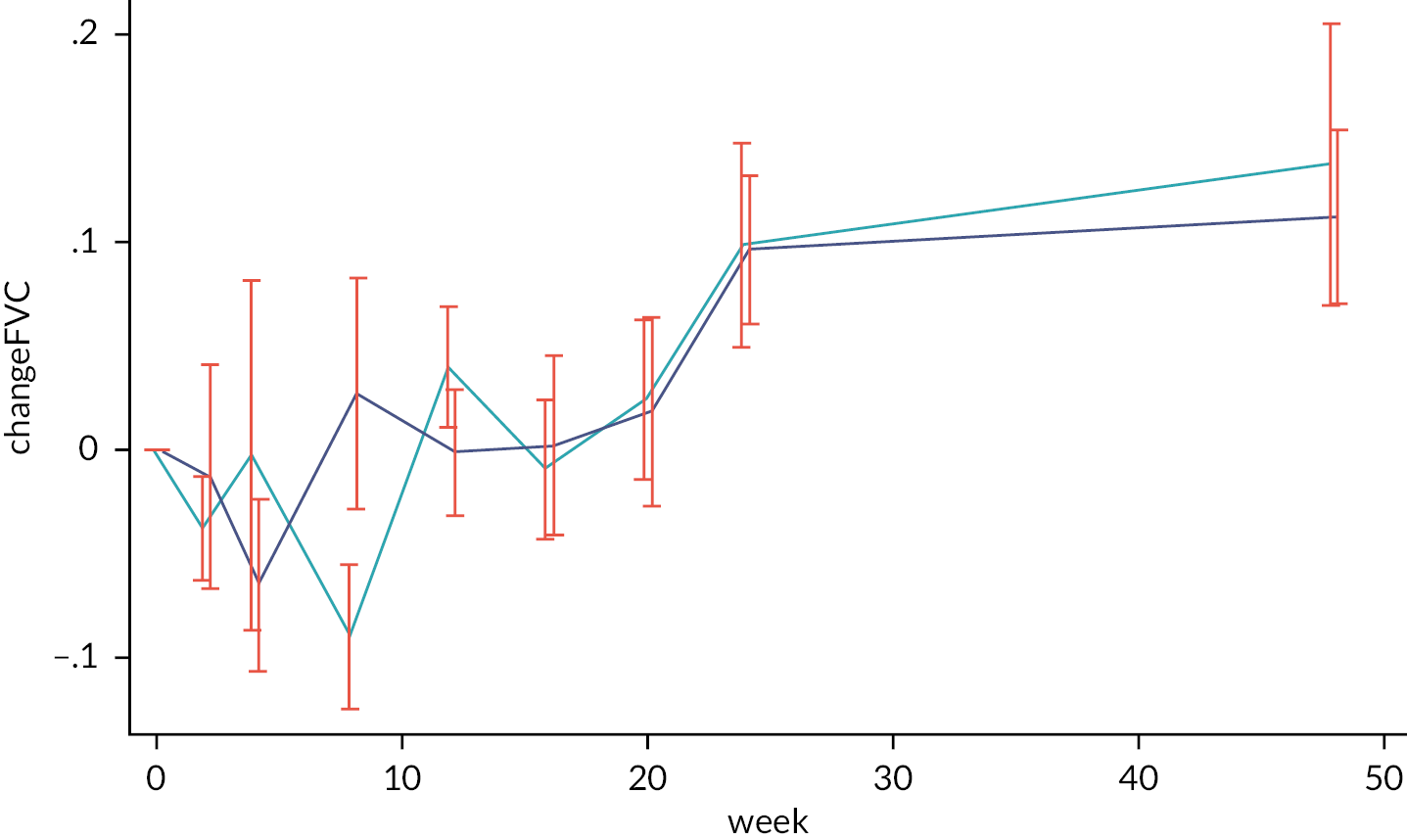
| Coefficient | p-value | [95% CI] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseFVC | 0.981 | <0.001 | 0.940 | 1.021 |
| CTD | ||||
| MCTD | −0.053 | 0.270 | −0.147 | 0.041 |
| Systemic sclerosis | −0.151 | <0.001 | −0.225 | −0.078 |
| week | ||||
| Week 2 | −0.039 | 0.420 | −0.133 | 0.056 |
| Week 4 | 0.011 | 0.828 | −0.086 | 0.107 |
| Week 8 | −0.065 | 0.190 | −0.161 | 0.032 |
| Week 12 | 0.056 | 0.255 | −0.041 | 0.153 |
| Week 16 | 0.005 | 0.925 | −0.092 | 0.102 |
| Week 20 | 0.038 | 0.441 | −0.059 | 0.135 |
| Week 24 | 0.112 | 0.021 | 0.017 | 0.208 |
| Week 48 | 0.153 | 0.002 | 0.055 | 0.251 |
| Arm#week | ||||
| RT#Week 0 | −0.017 | 0.755 | −0.125 | 0.091 |
| RT#Week 2 | 0.009 | 0.867 | −0.100 | 0.119 |
| RT#Week 4 | −0.085 | 0.135 | −0.197 | 0.027 |
| RT#Week 8 | 0.071 | 0.214 | −0.041 | 0.184 |
| RT#Week 12 | −0.076 | 0.185 | −0.189 | 0.036 |
| RT#Week 16 | −0.023 | 0.693 | −0.136 | 0.091 |
| RT#Week 20 | −0.041 | 0.482 | −0.156 | 0.074 |
| RT#Week 24 | −0.040 | 0.493 | −0.153 | 0.074 |
| RT#Week 48 | −0.058 | 0.345 | −0.178 | 0.062 |
| _cons | 0.172 | 0.029 | 0.018 | 0.326 |
FIGURE 5.
Adjusted model of change in FVC (and 95% CI) at each visit.
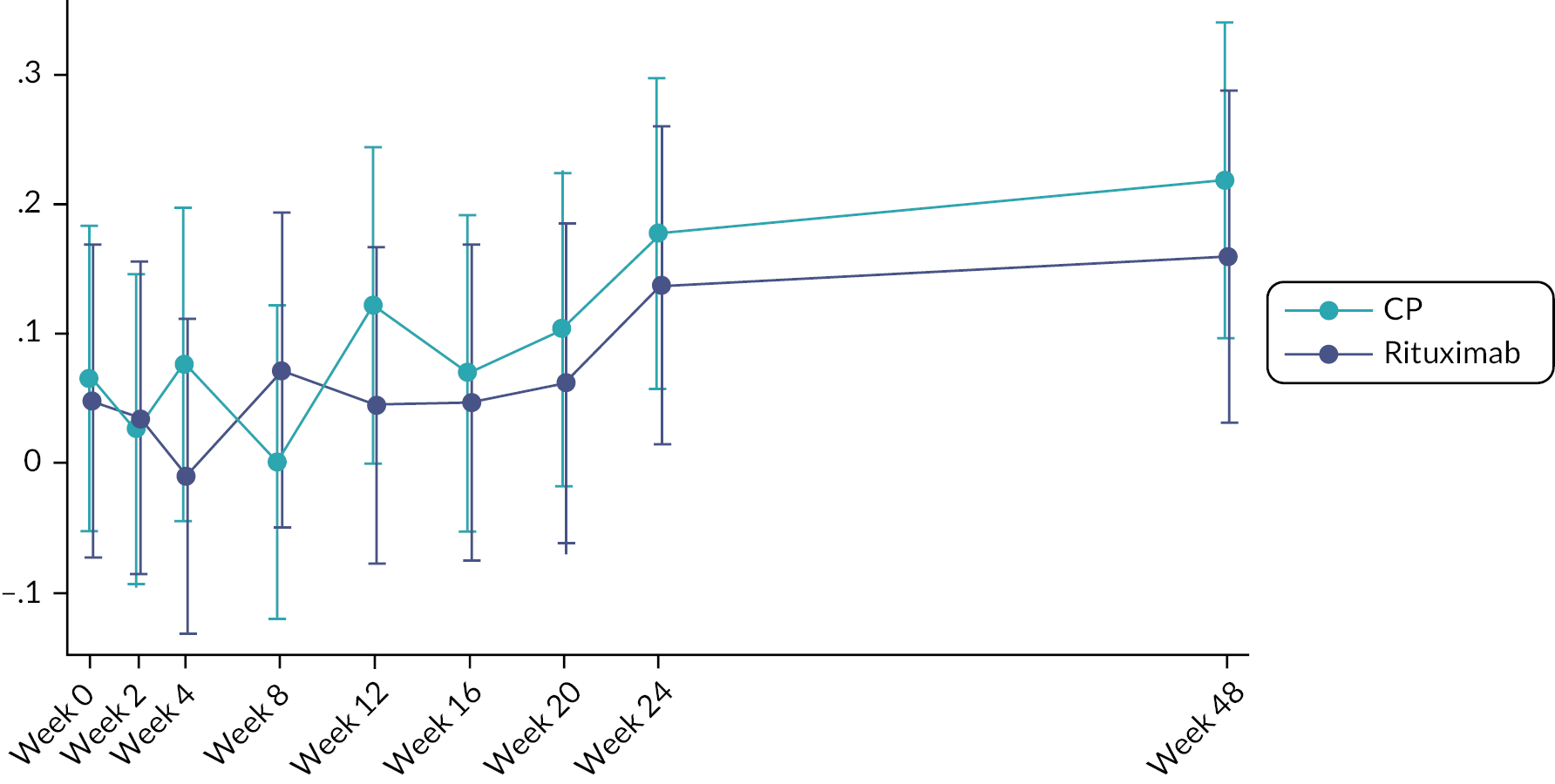
The difference between groups persisted in an unadjusted model and in adjusted and unadjusted fixed-effects models (see Report Supplementary Material 1, Tables S2, S3 and S4). Visual inspection of the FVC data disclosed one extreme outlying FVC value for a single subject (who received CP) at week 4 (see Report Supplementary Material 1, Figure S1). A sensitivity analysis was performed to confirm that this value was not impacting interpretation of the primary end point (see Report Supplementary Material 1, Table S5).
Primary outcome by connective tissue disease subtype
Randomisation between treatment arms was stratified by underlying CTD diagnosis. In a pre-planned analysis response to treatment was assessed in each of the three CTD subgroups. The effect of both CP and RT was consistent across all three groups with the largest magnitude of benefit being seen in subjects with IIM and the least benefit being seen in the scleroderma subgroup (see Figure 6).
FIGURE 6.
Change in FVC (and 95% CI) by CTD subgroup at each visit.
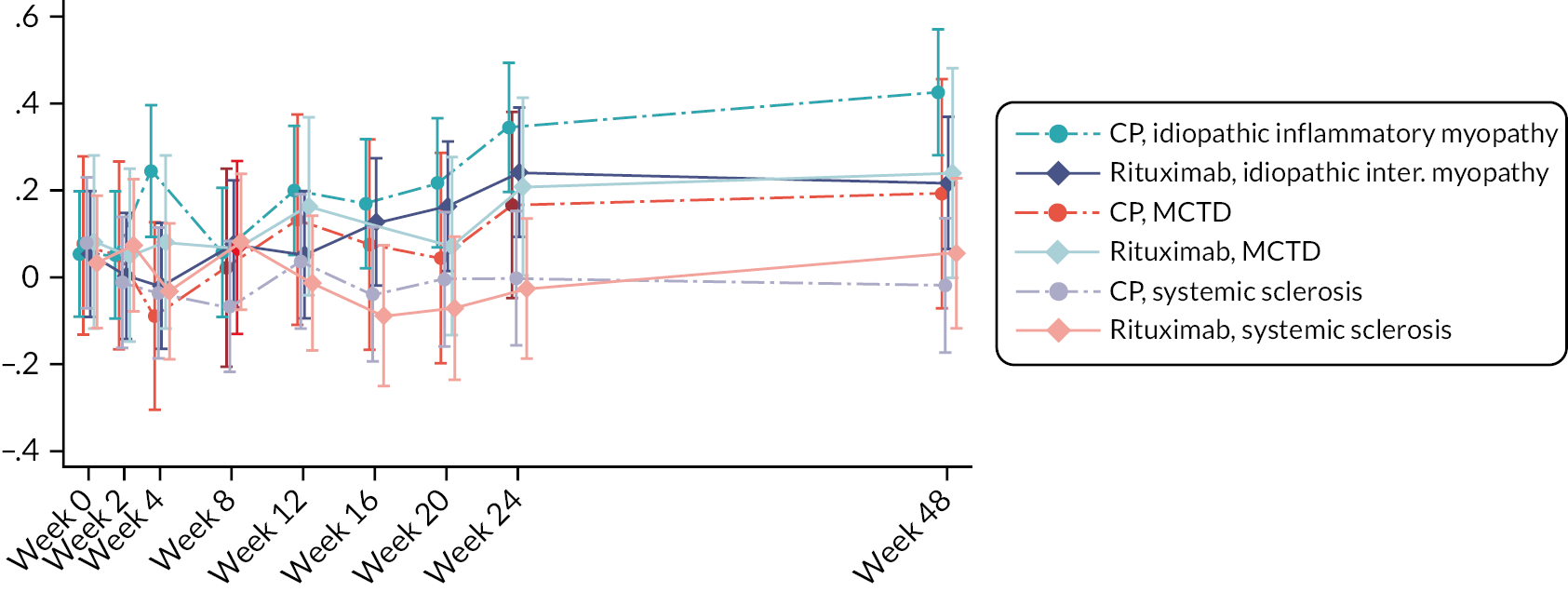
Secondary outcomes
Week 48 change in FVC
The improvement seen in FVC at 24 weeks in both treatment arms persisted out to week 48. The CP arm saw a 138 ± 440 ml improvement in FVC while in the RT arm the improvement at week 48 was 112 ± 249 ml (see Table 10 and Figure 4). In the adjusted mixed-effects model the difference between RT and CP at week 48 was −58 ml (95% CI −178 to 62 ml), p = 0.345 Table 11 and Figure 5). As with the week-24 FVC, the treatment effect at week 48 was consistent across disease subgroups (see Figure 6).
Change in DLco at weeks 24 and 48
DLco improved in both treatment arms at both week 24 and 48. In the CP arm DLco increased by 1.43 ± 23.05% at week 24 and 3.00 ± 31.35% at week 48. In the RT arm the improvements were 6.98 ± 17.19% at week 24 and 7.43 ± 16.08% at week 48 (see Table 12). The differences between arms in the adjusted mixed-effects model were 0.186 (95%CI −0.054 to 0.425) ml/min/mmHg at week 24 and 0.117 (−0.137 to 0.372) ml/min/mmHg at week 48 in favour of RT (see Table 13). The differences between groups remained consistent in an unadjusted mixed-effects model and in adjusted and unadjusted fixed-effects models (see Report Supplementary Material 1, Tables S6 and S7).
| Arm | N | DLco % change | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 0 | CP | 46 | 0.00 | - |
| Week 12 | CP | 39 | 0.38 | 18.741 |
| Week 24 | CP | 44 | 1.43 | 23.052 |
| Week 48 | CP | 38 | 3.00 | 31.345 |
| Week 0 | RT | 45 | 0.00 | - |
| Week 12 | RT | 41 | 1.73 | 14.878 |
| Week 24 | RT | 38 | 6.98 | 17.190 |
| Week 48 | RT | 32 | 7.43 | 16.082 |
| Coefficient | p-value | [95% CI] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline DLco | 0.960 | <0.001 | 0.887 | 1.033 |
| CTD | ||||
| MCTD | −0.239 | 0.087 | −0.512 | 0.034 |
| Systemic sclerosis | −0.385 | <0.001 | −0.599 | −0.171 |
| order | ||||
| Week 12 | −0.036 | 0.710 | −0.224 | 0.152 |
| Week 24 | 0.058 | 0.532 | −0.123 | 0.239 |
| Week 48 | 0.133 | 0.170 | −0.057 | 0.322 |
| Arm#order | ||||
| RT#Week 0 | 0.003 | 0.977 | −0.225 | 0.232 |
| RT#Week 12 | 0.119 | 0.334 | −0.122 | 0.360 |
| RT#Week 24 | 0.186 | 0.128 | −0.054 | 0.425 |
| RT#Week 48 | 0.117 | 0.367 | −0.137 | 0.372 |
| _cons | 0.320 | 0.073 | −0.029 | 0.670 |
6-minute walk distance
In both groups 6MWD was well preserved at baseline. Nonetheless, there was a small improvement in walk distance in both groups at week 24 (see Table 14). For the CP arm 6MWD improved by 10.4 ± 78.6 m compared to an improvement of 10.9 ± 74.2 m in the RT arm. The adjusted mixed-effects model demonstrated little difference between groups at 24 weeks [−0.72 m (95% CI −24.76 to 23.32 m, p = 0.953)] (see Table 15). At week 48 the CP arm showed an improvement of 15.1 ± 82.8 m compared to −6.8 ± 69.8 m in the RT arm (see Table 14). The adjusted difference between groups was −22.46 m (95% CI −48.43 to 3.51 m, p = 0.090) (see Table 15).
| Arm | N | 6MWD change (m) | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 0 | CP | 48 | 00.0 | - |
| Week 12 | CP | 40 | 12.9 | 56.7 |
| Week 24 | CP | 46 | 10.4 | 78.6 |
| Week 48 | CP | 39 | 15.1 | 82.8 |
| Week 0 | RT | 48 | 00.0 | - |
| Week 12 | RT | 46 | 02.0 | 66.1 |
| Week 24 | RT | 40 | 10.9 | 74.2 |
| Week 48 | RT | 32 | -6.8 | 69.8 |
| Coefficient | p-value | [95% CI] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline 6MWD | 0.86 | <0.001 | 0.78 | 0.93 |
| CTD | ||||
| MCTD | −5.47 | 0.674 | −30.94 | 20.00 |
| Systemic sclerosis | −11.36 | 0.256 | −30.96 | 8.24 |
| Order | ||||
| Week 12 | 13.74 | 0.155 | −5.21 | 32.69 |
| Week 24 | 10.39 | 0.261 | −7.71 | 28.49 |
| Week 48 | 14.64 | 0.133 | −4.47 | 33.76 |
| Arm#order | ||||
| RT#Week 0 | −0.95 | 0.935 | −23.89 | 21.99 |
| RT#Week 12 | −12.44 | 0.311 | −36.49 | 11.61 |
| RT#Week 24 | −0.72 | 0.953 | −24.76 | 23.32 |
| RT#Week 48 | −22.46 | 0.090 | −48.43 | 3.51 |
| _cons | 57.39 | 0.002 | 21.40 | 93.39 |
Quality of life outcomes
EQ-5D
Global QoL measured using the EQ-5D improved at 24 weeks in both treatment arms with an increase of 3.5 ± 20.5 units in the CP arm and 6.2 ± 17 units in the RT arms. At week 48 the change was –1.2 ± 23.5 units for CP and 3.9 ± 15.8 units for RT (see Table 16). The difference between RT and CP groups at week 24 was 3.06 units (95% CI −3.05 to 9.18 units. p = 0.326) and at week 48 4.77 units (95% CI −1.73 to 11.27 units, p = 0.150) (see Table 17). These differences persisted in unadjusted and fixed-effects models (see Report Supplementary Material 1, Tables S8 and S9).
| Arm | N | EQ-5D difference | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 0 | CP | 49 | 00.0 | - |
| Week 24 | CP | 43 | 03.5 | 20.5 |
| Week 48 | CP | 40 | −1.2 | 23.5 |
| Week 0 | RT | 49 | 00.0 | - |
| Week 24 | RT | 41 | 06.2 | 17.7 |
| Week 48 | RT | 35 | 03.9 | 15.8 |
| EQ-5D_score | Coefficient | p-value | [95% CI] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseline_EQ-5D | 0.74 | <0.001 | 0.64 | 0.84 |
| CTD | ||||
| MCTD | −3.25 | 0.248 | −8.77 | 2.27 |
| Systemic sclerosis | −6.06 | 0.003 | −10.07 | −2.06 |
| Order | ||||
| Week 24 | 4.12 | 0.159 | −1.61 | 9.84 |
| Week 48 | −0.55 | 0.853 | −6.41 | 5.30 |
| Arm#order | ||||
| RT#Week 0 | 0.43 | 0.882 | −5.24 | 6.10 |
| RT#Week 24 | 3.06 | 0.326 | −3.05 | 9.18 |
| RT#Week 48 | 4.77 | 0.150 | −1.73 | 11.27 |
| _cons | 17.65 | 0.000 | 10.53 | 24.76 |
Global Disease Activity Score
The physician attributed GDAS decreased (improved) following both CP and RT at both week 24 (−2.9 ± 2.5 units and −2.8 ± 1.8 units for CP and RT, respectively) and week 48 (−2.9 ± 2.5 units and −1.7 ± 2.3 units for CP and RT, respectively (see Table 18). In the adjusted mixed-effects model the difference between the two arms was −0.14 (95% CI −0.85 to 0.57 units, p = 0.700) at 24 weeks and 0.9 (95% CI 0.11 to 1.68, p = 0.025) at week 48 (see Table 19). Unadjusted and fixed-effects models gave comparable results (see Report Supplementary Material 1, Tables S10 and S11).
| Arm | N | GDAS difference | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 0 | CP | 40 | 00.0 | - |
| Week 24 | CP | 37 | −2.9 | 02.1 |
| Week 48 | CP | 33 | −2.9 | 02.5 |
| Week 0 | RT | 38 | 00.0 | - |
| Week 24 | RT | 35 | −2.8 | 01.8 |
| Week 48 | RT | 26 | −1.7 | 02.3 |
| Coefficient | p-value | [95% CI] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline GDAS | 0.62 | <0.001 | 0.50 | 0.74 |
| CTD | ||||
| MCTD | 0.54 | 0.090 | −0.09 | 1.17 |
| Systemic sclerosis | 0.42 | 0.082 | −0.05 | 0.89 |
| Order | ||||
| Week 24 | –2.88 | 0.000 | −3.55 | −2.22 |
| Week 48 | –2.76 | 0.000 | −3.45 | −2.08 |
| Arm#order | ||||
| RT#Week 0 | −0.19 | 0.591 | −0.86 | 0.49 |
| RT#Week 24 | −0.14 | 0.700 | −0.85 | 0.57 |
| RT#Week 48 | 0.90 | 0.025 | 0.11 | 1.68 |
| _cons | 1.67 | 0.000 | 0.86 | 2.48 |
King’s Brief Interstitial Lung Disease Questionnaire
Quality of life as measured by K-BILD improved in both the CP and RT arms at both week 24 (9.4 ± 20.8 units and 8.8 ± 17.0 units for CP and RT, respectively) and 48 weeks (5.6 ± 25.6 units and 6.4 ± 16.2 units for CP and RT, respectively) (see Table 20). In the adjusted mixed-effects model the difference between the two arms was 0.4 units (95% CI −5.73 to 6.52 units, p = 0.899) at 24 weeks and 1.15 units (95% CI −5.34 to 7.64 units, p = 0.728) at 48 weeks (see Table 21). Unadjusted and fixed-effects models gave comparable results (see Report Supplementary Material 1, Tables S12 and S13).
| Arm | N | K-BILD difference | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 0 | CP | 49 | 0.0 | - |
| Week 24 | CP | 45 | 9.4 | 20.8 |
| Week 48 | CP | 43 | 5.6 | 25.6 |
| Week 0 | RT | 48 | 0.0 | - |
| Week 24 | RT | 42 | 8.8 | 17.0 |
| Week 48 | RT | 35 | 6.4 | 16.2 |
| Coefficient | p-value | [95% CI] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline K-BILD | 0.74 | <0.001 | 0.64 | 0.83 |
| CTD | ||||
| MCTD | −7.70 | 0.008 | −13.37 | −2.02 |
| Systemic sclerosis | −8.11 | <0.001 | −12.46 | −3.75 |
| Order | ||||
| Week 24 | 9.48 | 0.001 | 4.00 | 14.97 |
| Week 48 | 5.62 | 0.048 | 0.05 | 11.18 |
| Arm#order | ||||
| RT#Week 0 | 1.26 | 0.672 | −4.56 | 7.07 |
| RT#Week 24 | 0.40 | 0.899 | −5.73 | 6.52 |
| RT#Week 48 | 1.15 | 0.728 | −5.34 | 7.64 |
| _cons | 16.49 | 0.000 | 10.04 | 22.95 |
St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire
Quality of life as measured by SGRQ improved (improvement with SGRQ results in a reduction in score) in both the CP and RT arms at both week 24 (−4.8 ± 19.6 units and −3.4 ± 15.4 units for CP and RT, respectively) and 48 weeks (−6.4 ± 24.3 units and −3.2 ± 16.6 units for CP and RT, respectively) (see Table 22). In the adjusted mixed-effects model the difference between the two arms was 0.63 units (95% CI −5.64 to 6.91 units, p = 0.843) at 24 weeks and 2.82 units (95% CI −3.69 to 9.34 units, p = 0.396) at 48 weeks (see Table 23). Unadjusted and fixed-effects models gave comparable results (see Report Supplementary Material 1, Tables S14 and S15).
| Arm | N | SGRQ difference | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 0 | CP | 47 | 0.0 | - |
| Week 24 | CP | 42 | −4.8 | 19.6 |
| Week 48 | CP | 40 | −6.4 | 24.3 |
| Week 0 | RT | 45 | 0.0 | - |
| Week 24 | RT | 39 | −3.4 | 15.4 |
| Week 48 | RT | 35 | −3.2 | 16.6 |
| Coefficient | p-value | [95% CI] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline SGRQ | 0.83 | <0.001 | 0.71 | 0.95 |
| CTD | ||||
| MCTD | 2.50 | 0.454 | −4.04 | 9.04 |
| Systemic sclerosis | 7.32 | 0.002 | 2.60 | 12.05 |
| Order | ||||
| Week 24 | −4.87 | 0.068 | −10.09 | 0.35 |
| Week 48 | −6.66 | 0.014 | −11.97 | −1.36 |
| Arm#order | ||||
| RT#Week 0 | −0.52 | 0.862 | −6.44 | 5.39 |
| RT#Week 24 | 0.63 | 0.843 | −5.64 | 6.91 |
| RT#Week 48 | 2.82 | 0.396 | −3.69 | 9.34 |
| _cons | 6.22 | 0.124 | −1.71 | 14.15 |
Skin thickness (modified Rodnan skin score)
Skin thickness was assessed in the subset of subjects with systemic sclerosis using the mRSS. There was a slight deterioration in mRSS in the CP arm at 24 weeks (1.6 ± 5.7 units) with a return to baseline at week 48 (−0.1 ± 3.8 units). In the RT arm there was a numerical improvement in mRSS at both week 24 (−3.4 ± 8.1 units) and week 48 (−2.1 ± 4.8 units) (see Table 24). In the adjusted mixed-effects model the difference between the two arms was −4.47 units (95% CI −7.99 to −0.95 units, p = 0.013) at 24 weeks and –2.55 units (95% CI −6.37 to 1.28 units, p = 0.192) at 48 weeks in favour of RT (see Table 25). Unadjusted and fixed-effects models gave comparable results (see Report Supplementary Material 1, Tables S16 and S17).
| Arm | N | mRSS change | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 0 | CP | 18 | 0.0 | - |
| Week 12 | CP | 16 | 3.4 | 6.4 |
| Week 24 | CP | 16 | 1.6 | 5.7 |
| Week 48 | CP | 16 | −0.1 | 3.8 |
| Week 0 | RT | 16 | 0.0 | - |
| Week 12 | RT | 15 | −1.1 | 6.3 |
| Week 24 | RT | 13 | −3.4 | 8.1 |
| Week 48 | RT | 9 | −2.1 | 4.8 |
| Coefficient | p-value | [95% CI] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline mRSS | 0.86 | <0.001 | 0.70 | 1.03 |
| Order | ||||
| Week 12 | 3.40 | 0.011 | 0.77 | 6.02 |
| Week 24 | 1.65 | 0.219 | −0.98 | 4.27 |
| Week 48 | −0.04 | 0.976 | −2.67 | 2.59 |
| Arm#order | ||||
| RT#Week 0 | 0.38 | 0.820 | −2.89 | 3.65 |
| RT#Week 12 | −4.06 | 0.019 | −7.46 | −0.66 |
| RT#Week 24 | −4.47 | 0.013 | −7.99 | −0.95 |
| RT#Week 48 | −2.55 | 0.192 | −6.37 | 1.28 |
| _cons | 0.90 | 0.473 | −1.57 | 3.37 |
Corticosteroid exposure
The hydrocortisone equivalent of each steroid therapy administered to subjects (whether oral, intravenous, inhaled or topical) during the trial was calculated on blinded data by the study team and confirmed by the study CI. When the steroid treatment started before the trial only the portion of therapy taken after day 0 (start of study medication) was included in the calculations. The daily dosage per day per patient was calculated for each day for the whole study group and for individual CTD subtypes (see Figures 7–10). For the calculation the denominator was not the number of patients randomised but the number of patients currently followed (subjects were censored at death or following withdrawal from the trial). The mean follow-up was 311.7 (±94.7) days from day 0. The mean per-subject total steroid exposure during the study was 13,291 (±14,657) mg/hydrocortisone in the CP and 11,469 (±10,041) mg/hydrocortisone in the RT group. The daily mean dose per patient was 42.89 (±47.30) mg/hydrocortisone/day in the CP and 37.61 (± 32.93) mg/hydrocortisone/day in the RT group.
FIGURE 7.
Daily steroid exposure across whole study group.
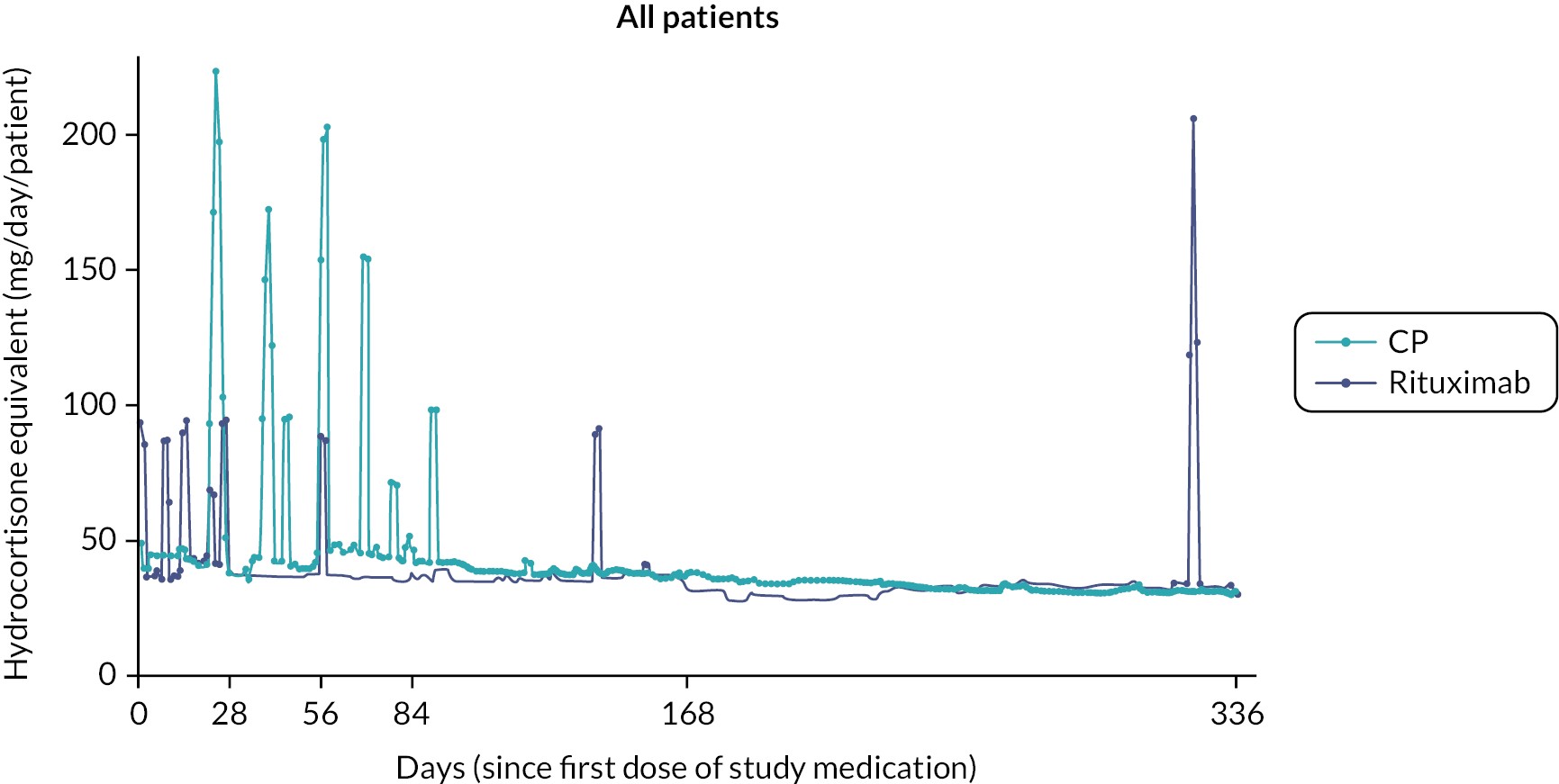
FIGURE 8.
Daily steroid exposure in the idiopathic inflammatory myopathy subgroup.
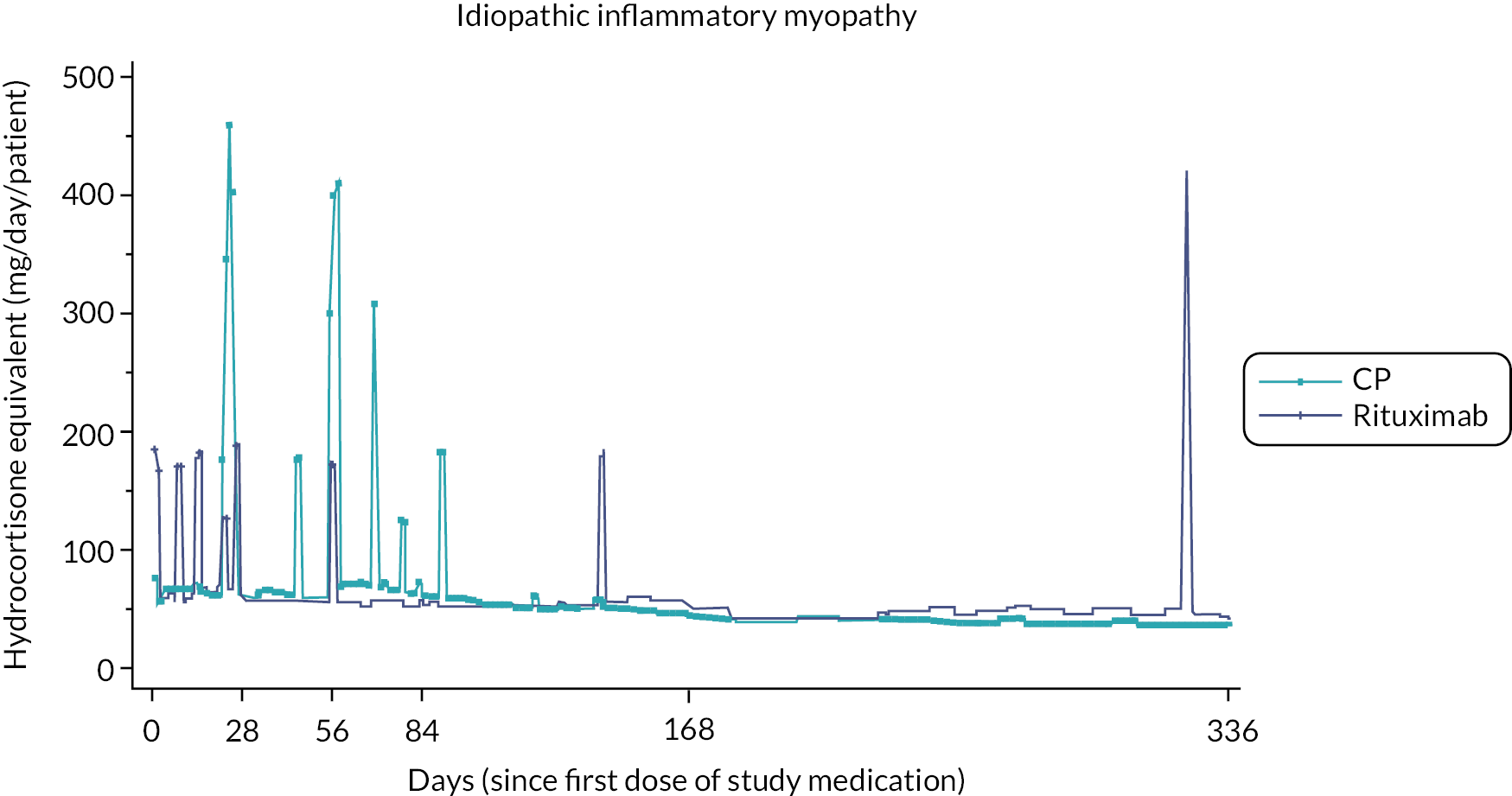
FIGURE 9.
Daily steroid exposure in the systemic sclerosis subgroup.
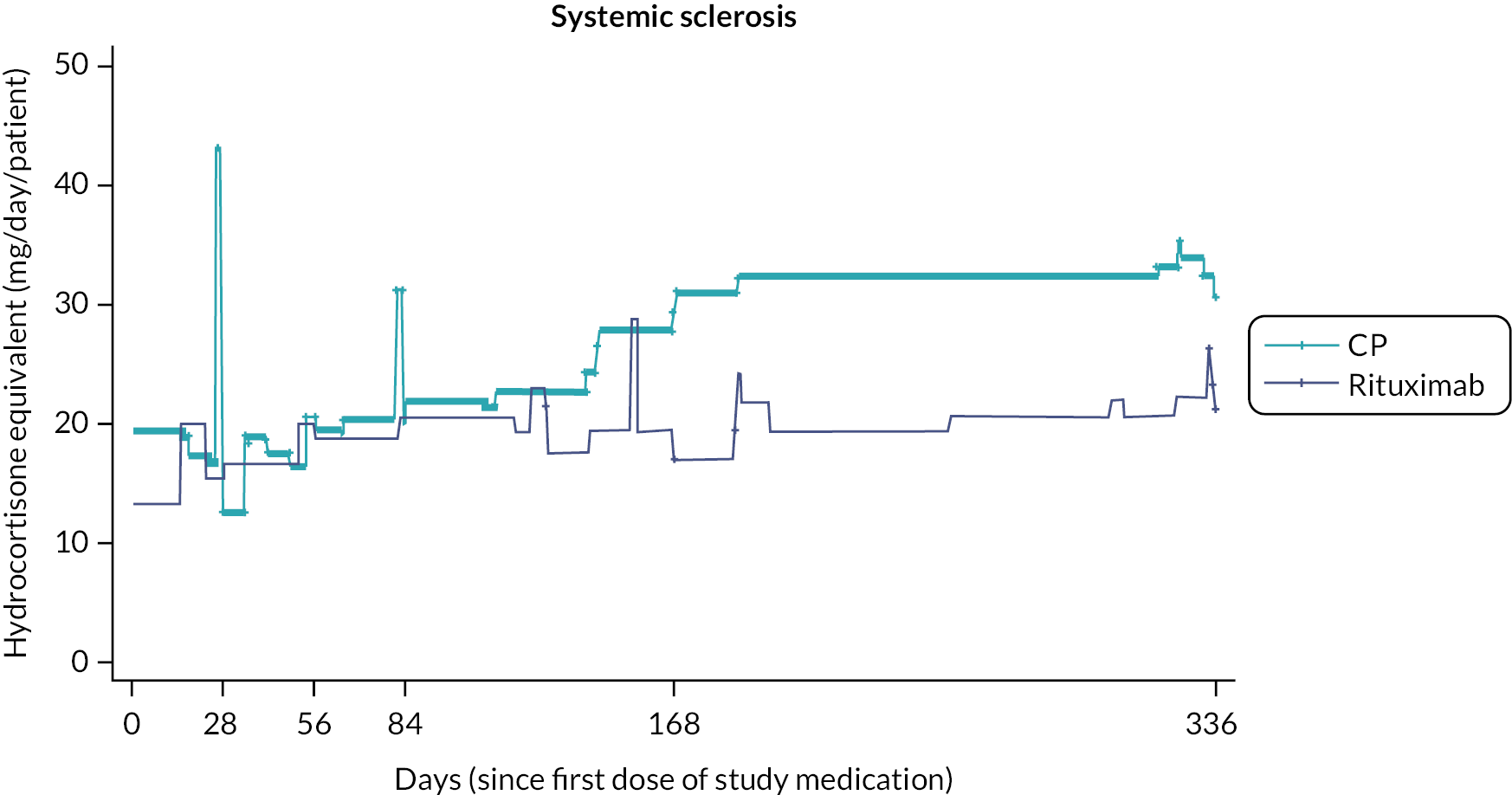
FIGURE 10.
Daily steroid exposure in the MCTD subgroup.
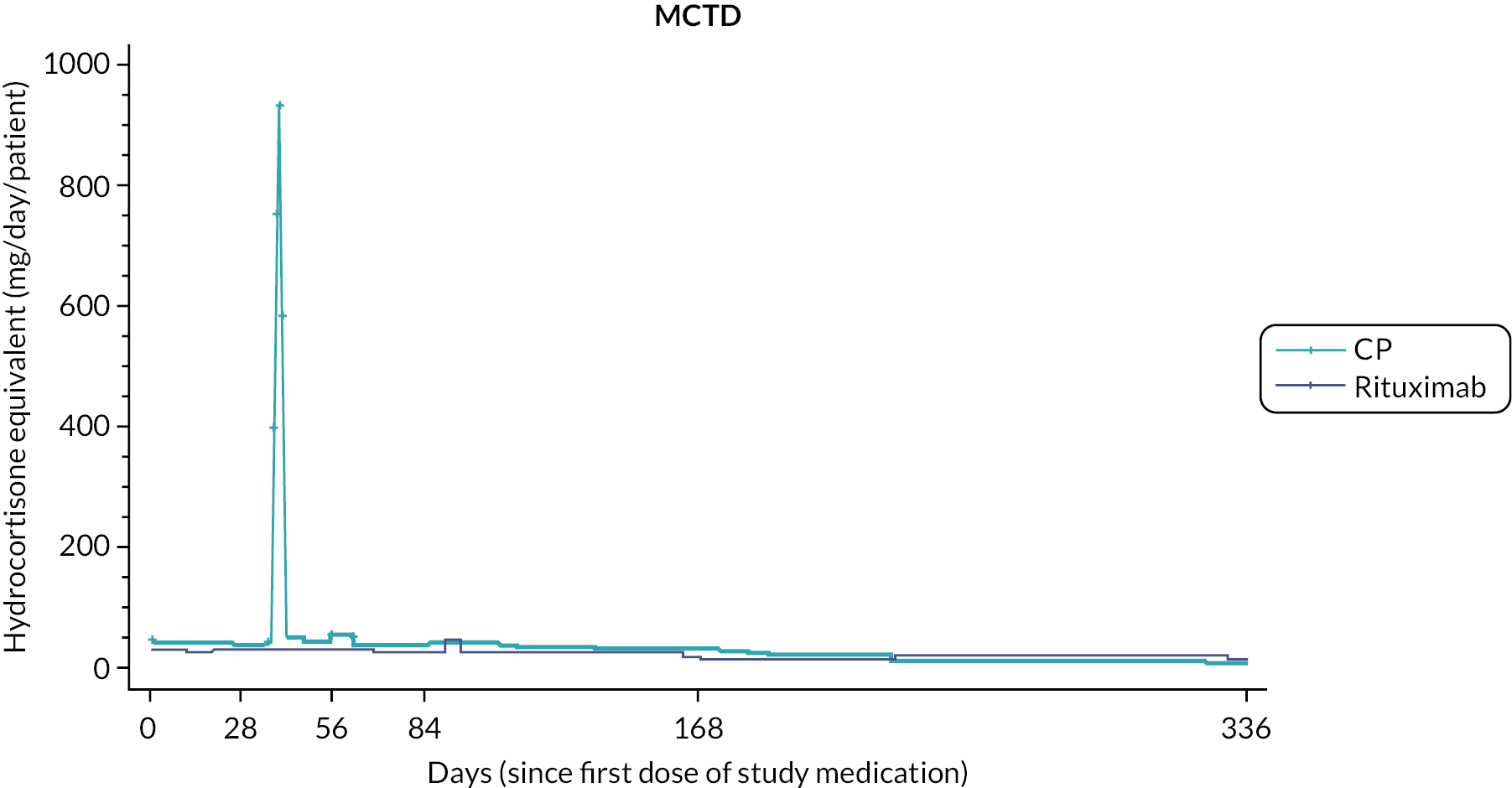
Survival analyses
During the course of the study there were five deaths with a sixth death occurring shortly after a week 48 visit and therefore being captured within the trial database (see Appendix 1, Table 34 for details). All were deemed to be due to complications of either CTD or interstitial lung disease. Three (plus the additional late death) occurred in subjects receiving RT and two in subjects receiving CP. There was no difference between groups in time to death as assessed by an adjusted Cox proportional hazards model [HR 1.72 (95% CI 0.311 to –9.56, p = 0.534)] (see Figure 11 and Table 26). The rates of progression-free survival (see Figure 12 and Table 27) [HR 1.11 (95% CI 0.625 to 1.99, p = 0.715)], and time to treatment failure (see Figure 13 and Table 28), [HR 1.25 (95% CI 0.34 to 4.65, p = 0.742)] did not differ between treatment arms.
FIGURE 11.
Overall survival.
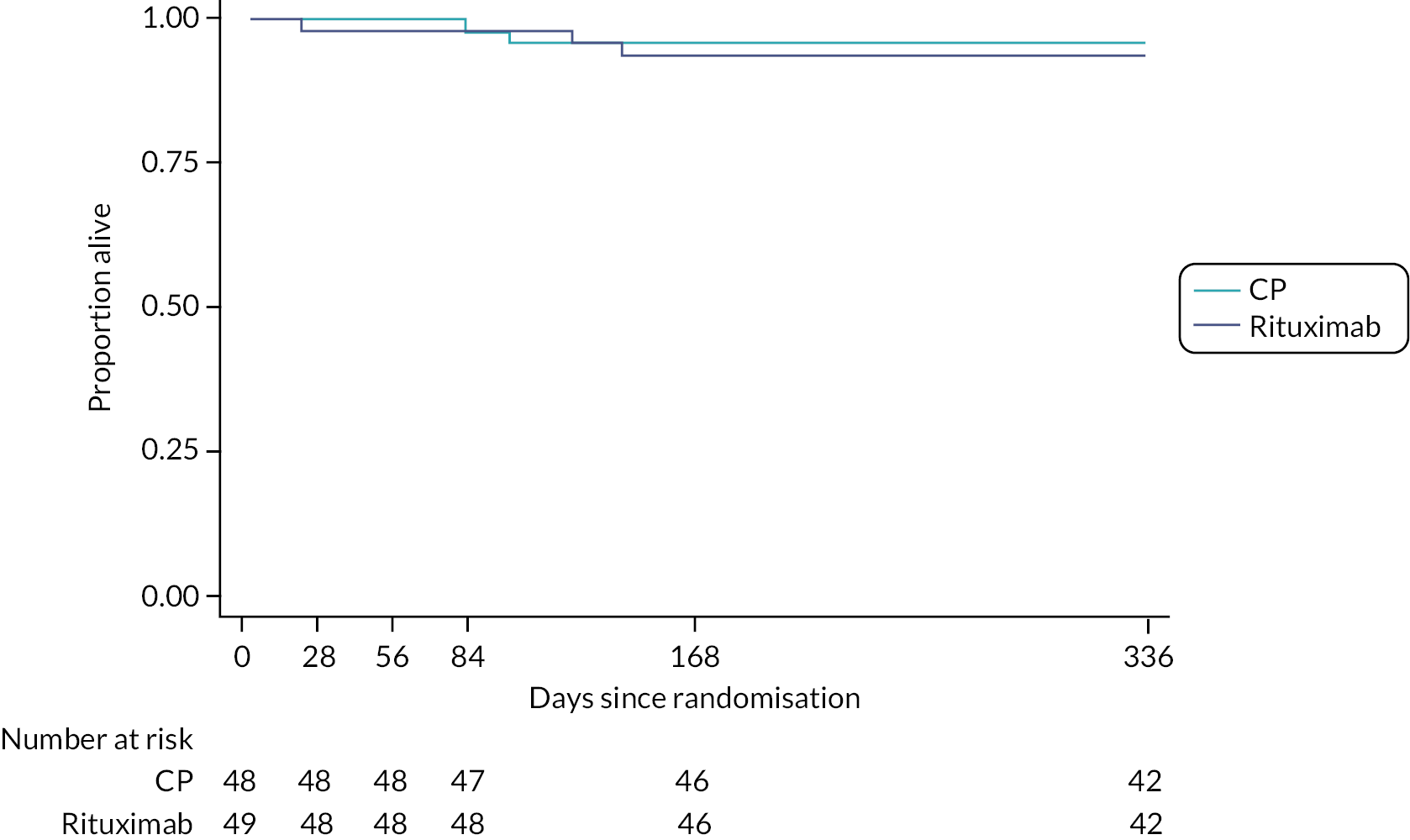
| Haz. ratio | Std. err. | z | p-value | [95% CI] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall survival | 1.723 | 1.507 | 0.622 | 0.534 | 0.311 | 9.563 |
FIGURE 12.
Progression-free survival.
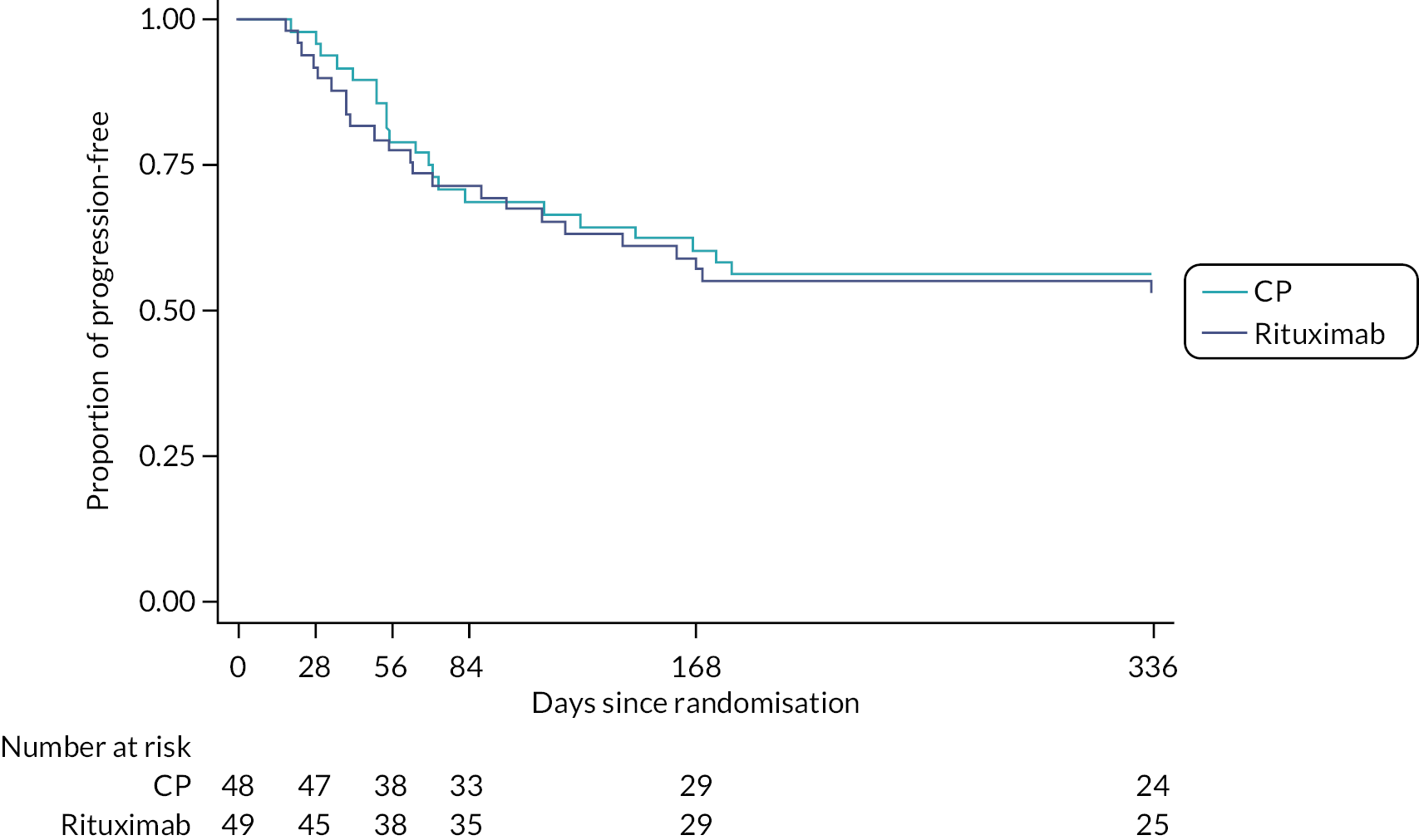
| Haz. ratio | Std. err. | z | p-value | [95% CI] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Progression-free survival | 1.114 | 0.329 | 0.365 | 0.715 | 0.625 | 1.987 |
FIGURE 13.
Time to treatment failure.
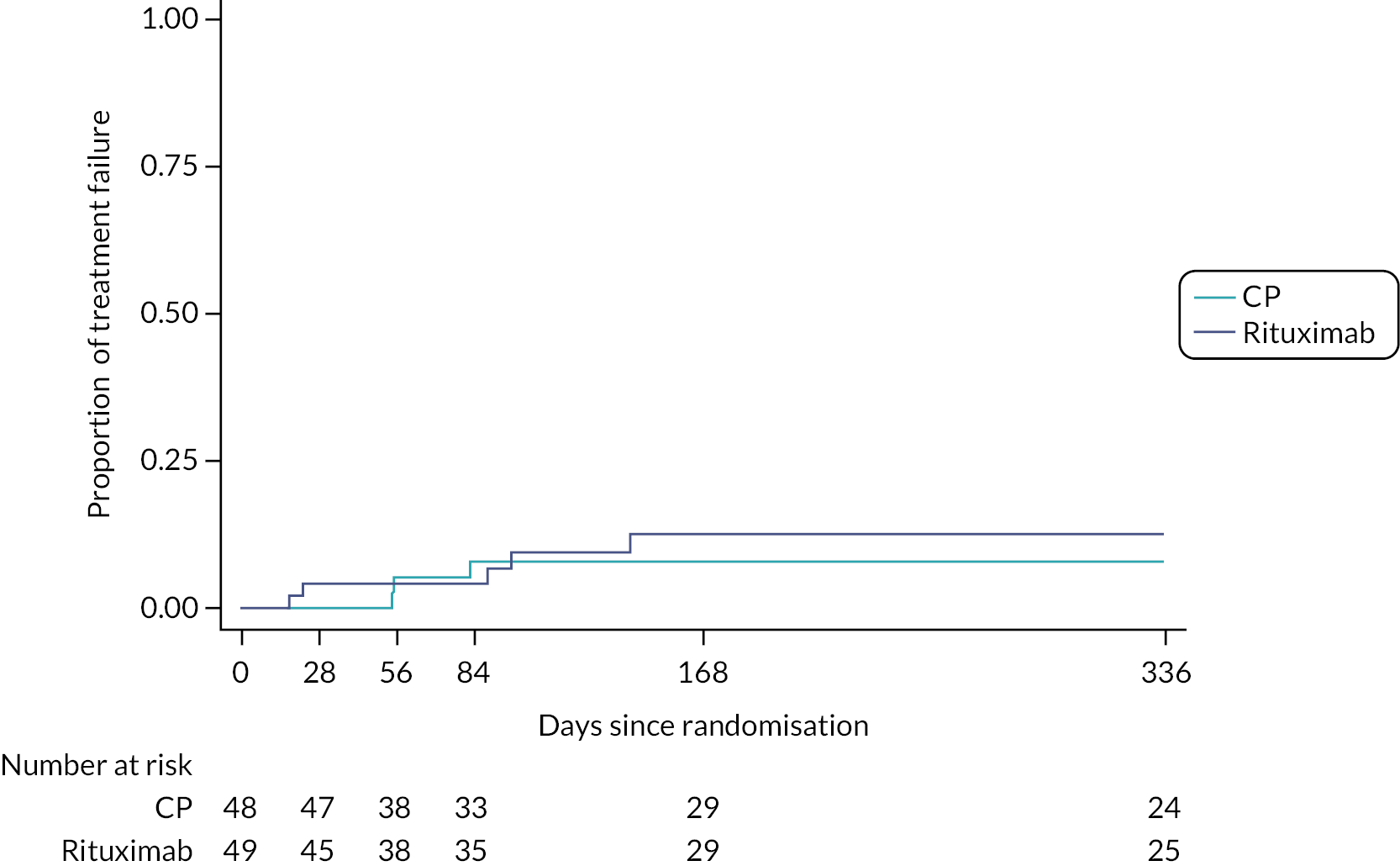
| Haz. ratio | Std. err. | z | p-value | [95% CI] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time to treatment failure | 1.247 | 0.837 | 0.329 | 0.742 | 0.335 | 4.645 |
Cost-effectiveness analysis
At the end of 12 months, RT (cost: £93,227.14; QALYs: 0.330) was a dominant strategy over CP (cost: £94,338.13; QALYs: 0.308) for treating patients with CTD-ILD, generating a cost savings of £1110.99; and an increase in QoL of 0.022 QALYs per patient (see Table 29). RT treatment provides an incremental monetary benefit compared to CP.
| Incremental | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategy | Cost | QALYs | Cost | QALYs | INMB | ICER |
| RT | £93,227.14 | 0.330 | −£1110.99 | 0.022 | £1821.35 | Dominant |
| CP | £94,338.13 | 0.308 | ||||
Probabilistic sensitivity analysis
Using 1000 Monte Carlo simulations, PSA revealed that at a WTP of £30,000, RT treatment is dominant over CP to treat patients with CDT-ILD. Although the scatter plot shows some uncertainty around the outcomes, most of ICERs of RT versus CP are within quadrant 2. Therefore, they are less costly and more effective, showing themselves to be dominant (see Figure 14). The CEAC (see Figure 15) indicates the probability of the intervention being cost-effective when compared to the alternatives, according to the different thresholds or values per QALYs. RT proved to be cost-effective in 81.4% of the simulations and the CP in 18.6% of the simulations, assuming a £30,000 WTP limit. Thus, there is a strong probability of RT being the cost-effective therapy.
FIGURE 14.
Scatter plot of ICER of RT vs. CP.
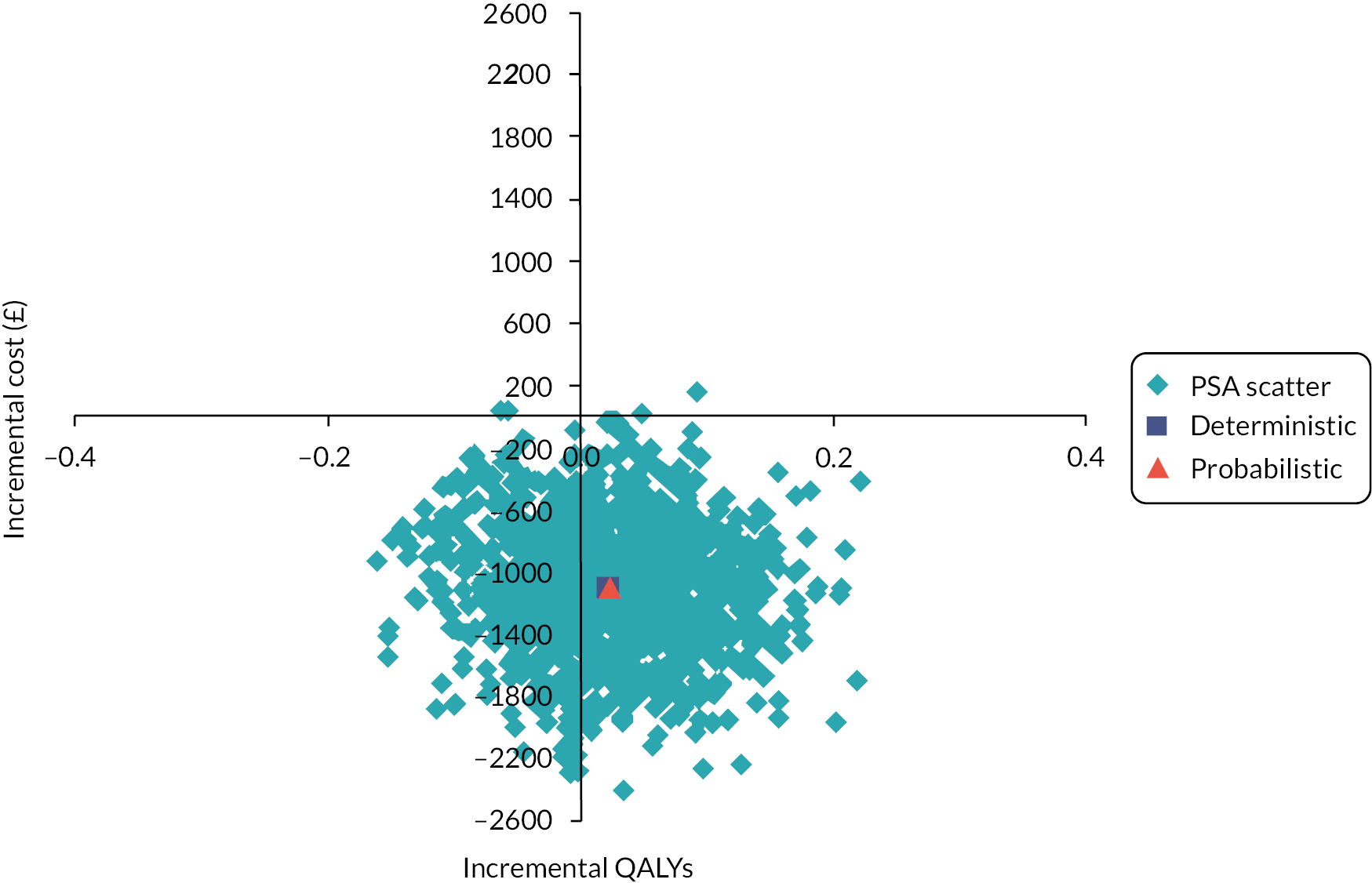
FIGURE 15.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve of RT vs. CP.
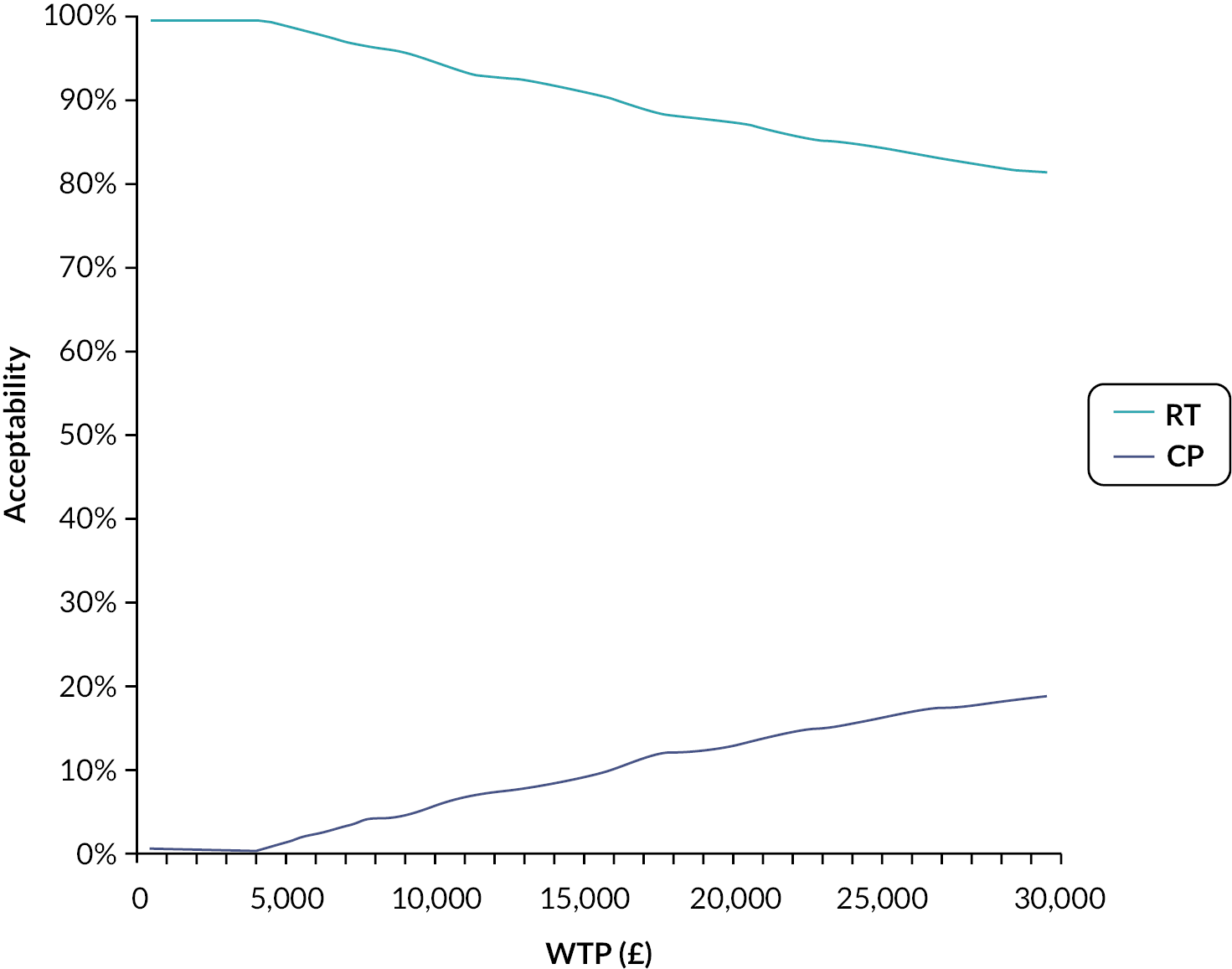
One-way sensitivity analysis
The one-way sensitivity analysis showed that the three main parameters that most influence the ICER values are the outpatient costs and the treatment of AEs in the CP group, alongside the RT cost. RT only becomes not cost-effective relative to CP if the price increases by over 5%, to £366.71 (see Figure 16).
FIGURE 16.
One-way sensitivity analyses of significant parameters that impact cost-effectiveness – Tornado diagram (ICER).
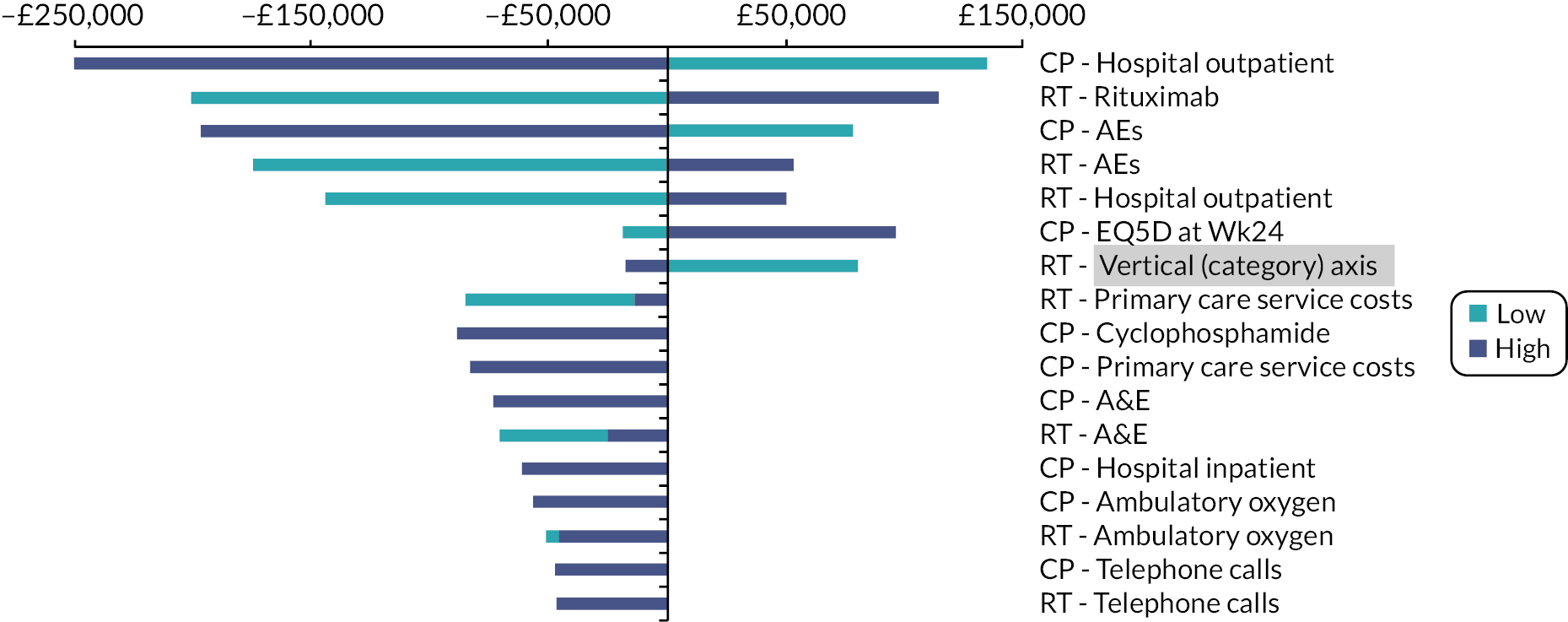
Safety
Adverse events and serious adverse events
A total of 1091 AEs occurred during the study period, 646 in the CP treatment arm and 445 in the RT arm. There were 62 SAEs of which 33 occurred in the CP arm and 29 in the RT arm. The relationship of AEs and SAEs to treatment phase and assignment of causality are shown in Table 30. The vast majority (>95%) of patients had more than one AE (see Table 31). The classification of AEs by system-organ-class is shown in Table 32. The categories in which there was a clear numerical difference between groups included gastrointestinal disorders, general disorders and administration site conditions and nervous system disorders (all of which occurred more frequently in the CP arm) and vascular disorders (which occurred more frequently in the RT arm).
| Trial phase | AE severity | Relatedness | CP | RT | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Screening | Not serious | Unrelated | 23 | 13 | 36 |
| Screening | Not serious | Unlikely | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Screening | Not serious | Possible | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Screening | Serious | Unrelated | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Treatment emergent | Not serious | Unrelated | 134 | 126 | 260 |
| Treatment emergent | Not serious | Unlikely | 51 | 50 | 101 |
| Treatment emergent | Not serious | Possible | 96 | 65 | 161 |
| Treatment emergent | Not serious | Probable | 164 | 72 | 236 |
| Treatment emergent | Not serious | Definite | 18 | 9 | 27 |
| Treatment emergent | Serious | Unrelated | 7 | 5 | 12 |
| Treatment emergent | Serious | Unlikely | 2 | 5 | 7 |
| Treatment emergent | Serious | Possible | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Treatment emergent | Serious | Probable | 6 | 3 | 9 |
| Treatment emergent | Serious | Definite | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Post-treatment | Not serious | Unrelated | 65 | 33 | 98 |
| Post-treatment | Not serious | Unlikely | 9 | 14 | 23 |
| Post-treatment | Not serious | Possible | 23 | 16 | 39 |
| Post-treatment | Not serious | Probable | 26 | 13 | 39 |
| Post-treatment | Not serious | Definite | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Post-treatment | Serious | Unrelated | 8 | 2 | 10 |
| Post-treatment | Serious | Unlikely | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| Post-treatment | Serious | Possible | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Post-treatment | Serious | Probable | 3 | 5 | 8 |
| Post-treatment | Serious | Definite | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Did not receive study drug | Not serious | Unrelated | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Did not receive study drug | Serious | Unrelated | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Factor | Number of subjects (% of total) | |
|---|---|---|
| CP (%) | RT (%) | |
| Number of AEs | ||
| 1 | 3 (6) | 2 (4) |
| 2 | 1 (2) | 5 (10) |
| 3 | 0 (0) | 3 (6) |
| 4 | 2 (4) | 4 (8) |
| 5 | 2 (4) | 4 (8) |
| 6 | 3 (6) | 1 (2) |
| 7 | 0 (0) | 7 (14) |
| 8 | 2 (4) | 2 (4) |
| 9 | 1 (2) | 1 (2) |
| 10 | 2 (4) | 3 (6) |
| 11 | 4 (8) | 2 (4) |
| 12 | 3 (6) | 2 (4) |
| 13 | 4 (8) | 2 (4) |
| 14 | 7 (14) | 1 (2) |
| 15 | 5 (10) | 4 (8) |
| 16 | 1 (2) | 0 (0) |
| 17 | 0 (0) | 2 (4) |
| 18 | 1 (2) | 0 (0) |
| 20 | 2 (4) | 0 (0) |
| 21 | 2 (4) | 1 (2) |
| 22 | 0 (0) | 2 (4) |
| 27 | 1 (2) | 0 (0) |
| 28 | 1 (2) | 0 (0) |
| 31 | 0 (0) | 1 (2) |
| 41 | 1 (2) | 0 (0) |
| 42 | 1 (2) | 0 (0) |
| Factor | CP (%) | RT (%) |
|---|---|---|
| N | 646 | 445 |
| System organ class | ||
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | 3 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) |
| Cardiac disorders | 10 (1.6) | 6 (1.4) |
| Ear and labyrinth disorders | 2 (0.3) | 1 (0.2) |
| Eye disorders | 16 (2.5) | 9 (2.0) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | 170 (26.4) | 71 (16.0) |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | 91 (14.1) | 52 (11.7) |
| Hepatobiliary disorders | 1 (0.2) | 1 (0.2) |
| Immune system disorders | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.5) |
| Infections and infestations | 50 (7.8) | 46 (10.4) |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | 8 (1.2) | 5 (1.1) |
| Investigations | 11 (1.7) | 8 (1.8) |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | 5 (0.8) | 3 (0.7) |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | 44 (6.8) | 40 (9.0) |
| Nervous system disorders | 72 (11.2) | 35 (7.9) |
| Psychiatric disorders | 9 (1.4) | 10 (2.3) |
| Renal and urinary disorders | 8 (1.2) | 1 (0.2) |
| Reproductive system and breast disorders | 5 (0.8) | 4 (0.9) |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | 94 (14.6) | 101 (22.8) |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | 38 (5.9) | 32 (7.2) |
| Surgical and medical procedures | 1 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) |
| Vascular disorders | 7 (1.1) | 16 (3.6) |
Laboratory safety results
Laboratory blood results were flagged up if they fell outside pre-specified values (see Table 33). For listings of patients with measurements outside cut-off values (see Report Supplementary Material 1, Tables S18, S19, S20, S21, S22 and S23). A new, transient leucopoenia was seen in only one patient receiving CP at week 24 and this subsequently resolved. All other documented episodes of leucopoenia predated the initiation of therapy. Similarly, the only documented episode of neutropenia was present at baseline in a single individual receiving RT. Similarly, there were no sustained elevations of either creatinine or liver enzymes in either treatment arm and no changes in blood parameters which were deemed clinically significant.
| Description | Cut-off value |
|---|---|
| White cell count | <4 × 109/L |
| Neutrophils | 1.5 × 109/L |
| Creatinine | >ULN or 1.5× baseline value |
| ALT | >2× ULN |
| ALP | >2× ULN |
| Bilirubin | >2× ULN |
Chapter 4 Discussion
Main results
This trial compared RT to intravenous CP in a basket trial design comprising ILD in the context of three different CTDs. Although the study failed to show superiority of RT to CP in the primary efficacy end point of 24-week change in FVC, an improvement in lung function (both FVC and DLco) and respiratory- and disease-related QoL was observed in both treatment arms. RT was associated with fewer AEs than CP and lower corticosteroid exposure over the full 48 weeks of the study. There were no differences between treatments in terms of overall survival, progression-free survival or time to treatment failure. A health economic comparison suggests that overall, when accounting for numbers of hospital visits, contact with healthcare professionals and AEs, RT is cheaper for the National Health Service than CP.
Comparison with other studies
Rituximab
To our knowledge there have not been any previous randomised controlled trials of RT in patients specifically with CTD-ILD. The majority of prior evidence has been generated in retrospective cohorts and open-label studies. In a retrospective analysis of 50 individuals (33 of whom had CTD-ILD) treated with RT as rescue therapy following failure of other treatments including CP, Keir et al. 34 reported a median improvement in FVC between 6 and 12 months of 6.7% from pre-treatment baseline and stabilisation (0% change) in DLco. This contrasted with median declines in FVC and DLco of 14.3% and 18.8%, respectively in the 6–12 months prior to treatment. On average, these patients had much more severe disease than the subjects enrolled in RECITAL with a mean baseline FVC of 44% predicted and DLco 24.5% predicted.
In a 14-patient open-label proof-of-concept study Daoussis et al. 31 assessed the role of RT in patients with SSc-ILD. The authors randomly assigned patients (based on year of birth, with those born in an even year assigned to RT) to receive either two cycles of RT (consisting 375 mg of RT per week for 4 weeks) at baseline and again at 6 months with (undefined) standard of care. Eight of the 14 subjects were assigned to RT. There was a marked imbalance between groups in disease severity. In the RT group baseline FVC was 68.1 ± 19.7% predicted and DLco 52.3 ± 20.7% predicted compared with FVC 86 ± 19.6% predicted and DLco 65.3 ± 21.4% predicted in the standard of care group. At 1 year after study enrolment the RT-treated subjects saw an absolute improvement in FVC of over 7% with mean FVC rising to 75.6 ± 19.7%. In the standard of care group there was an absolute drop in FVC of over 4% down to 81.7 ± 20.7%. RT treatment was also associated with improvements in DLco and skin thickening over 12 months.
In a retrospective study conducted across six Portuguese rheumatology units the effect of RT was assessed in 49 patients with a range of autoimmune and CTD-associated ILDs (with the commonest ILD, accounting for almost two-thirds of cases, being rheumatoid-associated ILD). 52 The authors divided patients based on whether their imaging was most consistent with UIP or NSIP. In both groups there was an improvement in FVC within the first year (4.3% in the NSIP group and 4.2% in the UIP group).
A recent randomised open-label controlled trial35 of 60 subjects with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis and lung involvement compared RT (1000 mg at baseline and 2 weeks) to CP (500 mg/m2 BSA every month for 6 months). At 6 months the authors saw an improvement in FVC in the RT group from 61.3% ± 11.3% predicted to 67.5 ± 13.6% predicted (an absolute change of 140 ml) while in the CP arm it declined from 59.3 ± 13.0 to 58.1 ± 11.2%. The mRSS improved in the RT but not the CP arm and there were fewer AEs associated with RT.
The DESIRES study53 was a randomised placebo-controlled study of 56 individuals with a mRSS score > 10 which compared RT (375 mg/m2 per week for 4 weeks) to placebo. The primary end point of the study was change in mRSS at 24 weeks. The study met its primary end point. Just under 90% of patients in each arm had interstitial lung disease although average lung function was well preserved at entry into the study; FVC was 87.9 ± 15.8% predicted in the RT arm and 89.4 ± 17.9% predicted in the placebo arm. DLco was 84.1 ± 19.3% predicted and 80.6 ± 16.6% predicted in the RT and placebo arms, respectively. At 6 months there was a small improvement in FVC compared with baseline in the RT group of 0.09% compared to a decline of 2.87% in the placebo group; a difference of 2.96% (95% CI 0.08 to 5.84%, p = 0.044). The data generated by this trial have led to the approval of RT as a treatment for systemic sclerosis in Japan.
Overall, the results of RECITAL are comparable to these prior studies. The effect of RT was bigger in retrospective and open-label studies but this is in keeping with the general observation that non-blinded and especially retrospective cohort analyses tend to overestimate treatment efficacy. 54 This issue notwithstanding we observed positive effects of RT on all measures of lung physiology, QoL and, in the scleroderma subset, skin thickening which were comparable in magnitude to these prior observations. The effect of RT in the systemic sclerosis ILD subset of RECITAL mirror the effects of RT reported in the DESIRES study.
Cyclophosphamide
The role of CP has been studied in three randomised controlled trials (RCTs). The first two of these, SLS-112 and -213 were, as the names of the trials suggest, only conducted in individuals with scleroderma-associated ILD. In both studies, CP was administered orally on a daily basis for 12 months (dosing CP beyond 12 months is precluded by the drug’s cumulative toxicity). SLS1, conducted in 158 subjects, provided a comparison of CP with placebo. SLS2, which randomised 142 subjects, compared CP to MMF. In SLS-1, CP resulted in 2.53% (95% CI 0.28 to 4.79%) improvement in FVC compared to baseline with a mean adjusted difference compared with placebo at 12 months of 2.97% (95% CI 0.75 to 5.19%). There was no significant difference between groups in DLco at 12 months. There was a clinically meaningful improvement in dyspnoea score (measured using the transitional dyspnoea index) of 1.4 ± 0.23 in the CP group compared to a worsening of −1.5 ± 0.45 in the placebo group. The beneficial effect on FVC of CP was lost by 24 months with no difference between groups in this outcome at this timepoint. Side effects were more common in the CP arm; those most frequently reported included haematuria, leukopenia, neutropenia and anaemia.
In SLS-2 treatment with 12 months of oral CP was associated with a 2.88% (95% CI 1.19 to 4.58) improvement in FVC at 24 months compared with baseline. Mycophenolate mofetil, administered at a dose of 1500 mg twice daily for 2 years was associated with a similar magnitude of benefit at 24 months with an improvement of 2.19% (95% CI 1.53 to 3.84%) compared to baseline. DLco remained stable in the mycophenolate arm and decreased slightly in the CP arm. Again, the commonest side effects were leukopenia and anaemia which occurred in 30 subjects on CP and 4 on mycophenolate. Overall, by the end of the trial, a higher proportion of subjects remained on treatment with mycophenolate.
In a small, 45-patient trial of monthly intravenous CP for 6 months followed by oral azathioprine compared with placebo in individuals with scleroderma-associated ILD, Hoyles et al. observed a 1.4% improvement in FVC compared to baseline in the treatment group; this compared with a 3% loss of FVC in the placebo arm. Because of recruitment challenges the study was underpowered and the differences between arms failed to reach statistical significance. AEs resulting in withdrawal only occurred in two subjects on CP (these were intractable nausea and abnormal liver function tests). The commonest side effects in the active treatment arm were nausea, mood disturbance, mouth ulceration, rash, diarrhoea and altered liver function tests.
Overall, both the efficacy and tolerability of CP seen in RECITAL were in keeping with that observed in these previous trials (with intravenous CP being better tolerated than orally dosed CP). The lack of a bone marrow effect in RECITAL compared with SLS-1 and SLS-2 likely relates to the differences in administration route and the lower cumulative exposure achieved by intravenous dosing. The bigger treatment effect observed with CP in the RECITAL study likely reflects the inclusion of a sizable proportion of individuals with myositis. As shown in subgroup analysis of RECITAL the largest treatment effect appeared to occur in individuals with myositis while the effect in the scleroderma ILD subgroup was more in keeping with that seen in SLS-1 and SLS-2.
Mycophenolate
Mycophenolate mofetil, an immunosuppressant medication originally developed to prevent organ rejection following transplant, is widely used in the treatment of CTD-ILD despite only limited evidence to support its use. In a retrospective study of 125 individuals with a diverse range of CTD-ILDs treated at a single centre, Fischer et al. reported a one-year improvement in FVC of 4.9% ± 1.9% compared with FVC prior to treatment initiation. 55 The improvement was most striking in the individuals with a non-UIP pattern on CT scan. As mentioned above, MMF at a dose of 1.5 g twice daily for 2 years was compared to 12 months of oral CP in the SLS-2 study. MMF failed to show a benefit compared with CP but as noted, both drugs resulted in improved FVC compared with baseline. 13
In the SENSCIS trial,17 which compared nintedanib to placebo in individuals with SSc-ILD, subjects were permitted to be on mycophenolate as long as they had been on a stable dose for at least 6 months prior to study enrolment. Approximately half of subjects in the study were taking MMF at baseline. In a post hoc analysis the greatest rate of annual decline in FVC was observed in patients who were neither receiving nintedanib nor MMF. 18 Mycophenolate approximately halved the rate of decline while the group of patients with the greatest preservation of lung function were those taking both nintedanib and mycophenolate.
Nintedanib
Nintedanib is a multityrosine kinase inhibitor which was first developed as an antifibrotic therapy for patients with IPF. In trials performed in individuals with IPF nintedanib approximately halves the loss of FVC over 52 weeks. 16,56 In the SENSCIS trial nintedanib was compared with placebo in 580 individuals with SSc-ILD and a minimum of 10% disease extent on CT. 18 Over 52 weeks patients receiving nintedanib lost 52.4 ml of FVC compared with a loss of 93.3 ml in the placebo group; a difference of 41 ml (95% CI 2.9 to 79.0 ml). There was no difference in change of QoL over 12 months between treatment groups. On the back of this study nintedanib was approved in Europe and the USA as a treatment for SSc-ILD.
In the INBUILD trial, nintedanib was compared to placebo in a basket trial incorporating patients with any form of progressive fibrotic lung disease (variously referred to as progressive pulmonary fibrosis, progressive fibrosing-ILD or chronic fibrotic ILD with a progressive phenotype). 57 To be included in the trial patients had to have evidence of pulmonary fibrosis with >10% disease extent on CT scan and evidence of disease progression in the prior 2 years as characterised by either: (1) >10% loss of FVC, (2) >5% but <10% loss of FVC combined with worsening symptoms, (3) >5% but <10% loss of FVC combined with evidence of worsening fibrosis on serial CT scans or, (4) worsening symptoms combined with evidence of worsening fibrosis on serial CT scans. The study enrolled 663 subjects of whom 170 had various forms of autoimmune-related ILD; of these 39 had SSc-ILD and 19 had MCTD-ILD. Overall the effect of nintedanib was similar to that seen in IPF trials with an approximate halving in the rate of FVC decline over 52 weeks [a difference between nintedanib and placebo arms of 107 ml (95% CI 65.4 to 148.5 ml)]. The effect of nintedanib was consistent across disease subgroups including in those patients with CTD-ILD.
Tocilizumab
Tocilizumab is a humanised monoclonal antibody targeted against the IL-6 receptor. It has recently been approved as a treatment for SSc-ILD following two clinical trials which were designed to test the drug’s efficacy in treating the skin thickening associated with scleroderma. Both trials recruited individuals with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis which had been rapidly deteriorating in the prior year. Furthermore, patients had to have evidence of active inflammation characterised by one of arthritis, a raised C reactive protein level or a raised platelet count. It was not necessary for subjects to have ILD to be enrolled in the studies and overall only about two-thirds of participants in either trial had evidence on CT of ILD. The first study, the faSScinate trial, enrolled 87 patients and showed a trend towards improved skin thickening. 14 An unexpected finding in the study was the rapid rate of FVC decline in the placebo group and the striking attenuation of this decline in the active treatment arm. This study was followed by a 210-patient phase 3 study (the focuSSed trial) that used the same inclusion and exclusion criteria. 15 Again, the primary end point for the study was change in skin score measured using mRSS and again this showed a trend towards (but not a statistically significant) benefit with active treatment. As with the faSScinate trial, the placebo group lost >200 ml of FVC in 1 year and this loss was attenuated by treatment with tocilizumab. In general, tocilizumab was safe and well tolerated in both trials.
Interpreting RECITAL in the context of previous trials
Rituximab is frequently used as rescue therapy for individuals with treatment-refractory ILD in the context of a range of different CTDs. Although no specific guidelines exist to guide the treatment of CTD-ILD, a recent Delphi consensus statement on the identification and management of scleroderma-associated ILD recommended the use of RT in individuals whose disease progresses despite treatment with MMF, CP or nintedanib. 20 This use of RT has been supported by observations derived from retrospective cohorts and open-label studies but has not been tested in randomised placebo-controlled trials. An absence of randomised controlled trials in patients with either myositis or MCTD-associated ILD has resulted in an absence of guidance for the treatment of either condition. In clinical practice treatment decisions for these two groups of patients are most often extrapolated from observations made in SSc-ILD. RECITAL is the first basket trial to assess the treatment of these distinct but related disorders.
The magnitude of treatment effect observed with both RT and CP is in keeping with that seen previously in trials conducted in SSc-ILD. Subgroup analysis of the change in FVC at 24 and 48 weeks suggests that the pattern of treatment responsiveness was similar across all three forms of CTD-ILD albeit the magnitude of treatment response (for both CP and RT) was greatest in the subgroup of patients with myositis-associated ILD. The improvements in QoL, which exceeded the minimal clinically important differences of the tools used,58–61 mirrored findings observed in SLS-1 and SLS-2 with CP. 13,62 The improvement seen with RT in skin score seen in the SSc-ILD subgroup also mirrored that reported in the DESIRES study and suggests that RT may have an advantage over CP in systemic sclerosis in that treatment benefits extended beyond the lung.
The SLS-1 and SLS-2 trials, which provide the bulk of the evidence for the use of CP in CTD-ILD, both studied oral dosing of CP. It is recognised that many of the side effects of CP (especially bladder malignancy and gonad failure) are driven by cumulative exposure. In this regard, intravenous dosing of CP, as was performed in RECITAL, tends to be associated with a lower side effect burden and better tolerability. This notwithstanding, RT resulted in fewer side effects and was overall much better tolerated than CP. As shown by our health economic analysis this reduced side effect burden has important financial benefits for the National Health Service.
Choice of regimen
Given the widespread acceptance of the need for active immunosuppressant therapy in patients with extensive or progressive CTD-ILD it was not possible to contemplate a placebo comparator arm. We recognised at the time of designing the study that the need for an active comparator would make it challenging to show a statistically significant difference between treatment arms. Comparing RT to CP also introduced further design challenges; to maintain study blinding we had to introduce a double-dummy design and had to ensure matching of infusion regimens at the first dose (including coadministration of concomitant therapies typically coadministered with both drugs). Furthermore, we had to adapt the measurement of the primary end point to suit both regimens; in other CP trials FVC has typically been measured at 52 weeks. However, the effect of RT tends to wain at 6 months and in clinical practice RT dosing is frequently repeated at 6-monthly intervals. Additionally, we felt it important to allow participants access to other therapies after 24 weeks accepting that this might modify the therapeutic responses seen beyond this time point. For these reasons, we settled on a week 24 primary end point with a secondary FVC end point at 48 weeks. Ultimately, the results of RECITAL suggest that the choice of timing for the measurement of the primary end point had little impact on the outcome of the trial. Both RT and CP led to similar improvements in FVC at both 24 and 48 weeks.
When used in the treatment of vasculitis and rheumatoid arthritis RT tends to be given repeatedly every 6 months. 63 It is therefore possible that further dosing of RT at 6 months might have had an additive benefit to that seen at 24 weeks. However, this was felt to be beyond the scope of the current trial. In the clinical experience of the authors, myositis-associated ILD is the CTD-ILD which most frequently relapses and requires repeated treatment. 64 Although the subgroup analyses should be considered hypothesis-generating at best, the different FVC responses seen between 24 and 48 weeks in the two treatment arms suggest that the myositis group, in particular, might have benefited from repeat RT dosing at 6 months. This should be considered as a question to be addressed in a future clinical trial.
In clinical practice RT is frequently coadministered with a second immunosuppressant agent such as MMF to maximise therapeutic effect. 65 Such an approach is avoided with CP because of concerns regarding over-immunosuppression. Although mycophenolate has not been compared to placebo in an RCT, the available evidence, as discussed above, suggests that the drug has a beneficial effect in CTD-ILD. It is therefore possible that upfront combination therapy with both RT and MMF would have been more effective than treatment with either drug alone, but this remains to be tested in future trials.
Cost-effectiveness
In the UK, RT is not routinely commissioned by the NHS, in part because of a lack of evidence to support efficacy and in part because of perceived cost. Drug costs for RT are substantially higher than the drug costs for CP. However, the economic analysis performed as part of the RECITAL study indicates that when considering the patterns of healthcare interaction undertaken by participants in the trial, suggests that RT represents the dominant strategy (i.e. it can be delivered at lower costs with improved quality-of-life outcomes) compared to CP. Even under less favourable assumptions, where the parameters with the highest level of uncertainty were varied, RT continued to be a cost-effective alternative, assuming a £30,000 WTP threshold. Furthermore, since the RECITAL trial was initiated, RT has gone off patent and a number of cheaper biosimilar drugs are now available. The reduced costs of these alternatives further enhance the cost of RT compared to CP as a treatment for CTD-ILD. Our cost-effectiveness analysis therefore suggests that RT in patients with CTD-ILD is potentially cost-saving compared to CP. Further prospective studies are needed to elucidate the uncertainties in our analyses and to improve the strength of evidence.
Strengths of RECITAL
Previous studies in CTD-ILD have tended to be confined to individuals with scleroderma-associated ILD; consequently, there are a lack of evidence-based therapies for non-scleroderma CTD-ILDs. While in an ideal situation one might wish to conduct separate trials in each of the specific CTD-ILDs the rarity of each individual disorder makes this unfeasible. With the design of this trial we aimed to overcome this challenge by using a basket approach to enrol subjects with a range of distinct underlying CTDs. In choosing this approach we selected a cohort of patients with an underlying autoimmune disorder for which there was some evidence that RT might be effective. We chose to exclude disorders such as rheumatoid disease and Sjögren syndrome for which we anticipated, based on anecdotal clinical experience, RT would likely be less effective. Our results provide the first RCT evidence for the efficacy of either RT or CP as treatments for myositis and MCTD-associated ILD.
In addition to the basket design, we maintained a pragmatic approach to identifying suitable patients with the goal of enrolling patients for whom clinicians would realistically consider RT (or by corollary) CP therapy in a real-world setting. As such, inclusion and exclusion criteria were kept to a minimum and screen failures were minimised. In support of this approach being effective, the trial demographics are reflective of the general population of patients with CTD-ILD and show an appropriate balance of gender and ethnicity for the diseases studied. Consequently, the results of this study can be broadly applied to individuals encountered in routine clinical practice with the studied spectrum of CTD-ILDs.
Limitations
A major limitation of the trial is the failure to meet the primary end point of RT superiority over CP in 24-week FVC change. As such, the ability to draw conclusions from secondary end points and the health economics analysis are limited. Other limitations of the trial include the mixed study population. It is possible that by combining disease groups a clear benefit of RT treatment was overlooked in a specific CTD-associated ILD. The lack of a placebo arm, although ethically unavoidable, renders it impossible to determine whether RT has a true treatment effect in CTD-ILD. Nonetheless, given the natural history of CTD-ILD and the high-associated mortality, it seems unlikely that the improvements in lung physiology and QoL that we observed were driven by spontaneous improvement in ILD.
Trial recruitment was terminated slightly early because of the COVID-19 pandemic resulting in 97 patients being included in the modified intention-to-treat analysis rather than the planned 104. Based on the actual trial data, this did not have an appreciable effect on the final power of the study. Another effect of the COVID-19 pandemic has been to raise concerns regarding the effect of specific immunosuppressants, especially RT, on the risk of developing severe complications from viral infection. 66 Although this is an important consideration, this risk needs to be balanced against the considerable risk of ILD progression and death in individuals with extensive or progressive CTD-ILD. The results of RECITAL should better inform necessary risk/benefit discussions with patients when discussing the role of RT in the treatment of CTD-ILD.
A disproportionate number of patients were recruited into the trial from a single centre (Royal Brompton). This in part reflects the Brompton’s role as the UK’s largest referral centre for complex ILD. However, it is important to note that a number of centres around London identified subjects for participation in RECITAL and referred them to Royal Brompton specifically for participation in the trial. Furthermore, all of the 11 UK centres who participated in RECITAL recruited at least 1 patient into the study and there was a good spread of recruitment across the country.
Generalisability
The study has good external validity as it recruited from multiple centres throughout the UK. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were kept to a minimum and there were very few screen failures; suggesting that the recruited patients are representative of those requiring treatment in routine clinical practice.
Although patients had to discontinue immunosuppressants other than corticosteroids to participate in the trial this was in keeping with standard clinical practice for administration of CP. Importantly, after week 24 (i.e. 4 weeks after the final dose of CP) subjects were permitted to receive any immunosuppressant treatment deemed appropriate by their local treating physician.
The basket design of the trial has ensured that we have generated evidence across a range of rarer disorders which could not have been meaningfully studied in isolation.
Reporting equality, diversity and inclusion
Connective tissue disease most frequently occurs in women. This was reflected by recruitment to RECITAL, with almost 70% or participants being female. CTD-associated ILD is reported to occur across all ethnic groups; however, there are no good data to suggest that CTD-ILD is any more, or less, common in specific racial groups. Nonetheless, recruitment to RECITAL showed excellent ethnic diversity with over 10% of participants self-reporting as black and a further 15% self-reporting as Asian. No specific steps were taken to recruit minority groups; the final composition of the trial suggests that the protocol and geographic spread of chosen centres favoured inclusive enrolment.
Public and patient involvement
We involved patients in the design and delivery of the study to ensure that the trial addressed questions relevant to patients, was deliverable and that the results are ultimately disseminated to all stakeholder groups. In all of these respects, patient and public involvement in the trial were effective. Patient involvement ensured that the trial design was sympathetic to the needs of patients with multisystem disease and that unnecessary visits and testing were avoided. The trial received important support from the largest patient charity in the UK in this disease area; Scleroderma and Raynaud’s UK (SRUK). The charity provided signposting to RECITAL on their website and worked to encourage patient engagement with clinical trials.
Two consumer representatives were independent members of the TSC, representing the wider patient community by participating in annual or bi-annual meetings. Their support included oversight of the conduct of the trial, advice on recruitment and retention and valuable feedback was given on the patient documentation and the recruitment poster prior to these being submitted to the Ethics Committee. The consumer representatives were given the opportunity to attend the meetings where the results were discussed, and dissemination of the findings was decided.
Involvement was also sought through the patient public involvement committee of the Royal Brompton Biological Research Unit (BRU) and the research findings were fed back to participants through bi-annual research newsletters and public patient participants days held in the Royal Brompton Education Centre.
Conclusion
The results of this trial show that both RT and CP improve FVC and QoL in individuals with CTD-ILD. Treatment with RT was associated with numerically fewer AEs and a trend towards reduction in corticosteroid exposure. In a cost-effectiveness analysis RT was found to offer cost savings compared with CP. RT should be considered as a treatment option in individuals with severe or rapidly progressive CTD-associated ILD especially in individuals at risk of CP-specific toxicity (e.g. gonad failure or bladder malignancy).
Implications for clinical practice
The results of RECITAL support the use of RT as an alternative first-line therapy for progressive or severe ILD in the context of scleroderma, IIM or MCTD. RT has clinically meaningful effects on FVC and measures of QoL. Furthermore, RT was better tolerated than CP and reduced corticosteroid exposure (something which should reduce the long-term side effect burden associated with corticosteroids). Our cost-effectiveness analysis suggests that adopting the use of RT over CP will reduce the cost burden of CTD-ILD to the NHS. In the scleroderma subgroup it appeared that RT had the added benefit of improving skin thickening; a finding which accords with prior studies in this disease group.
Recommendations for research
As is almost always the case, the results of RECITAL raise numerous questions which merit addressing in future clinical trials and studies. Our recommendations for future research include:
-
Assessment of the role of repeated (every 6 months) dosing of RT in the treatment of CTD-ILD with a particular focus on myositis-associated ILD.
-
RT is often used in combination with mycophenolate. A study of upfront combination with RT and mycophenolate compared to either drug alone would provide important guidance to clinicians when deciding on optimal initial therapy for CTD-ILD.
-
The basket design of our study makes it hard to draw firm conclusions regarding the role of RT or CP in specific subgroups of patients. Nonetheless, future research to address the characteristics of individuals responding to specific therapies will be important for driving a personalised approach to the treatment of CTD-ILD.
Acknowledgements
Contributions of authors
Toby M Maher (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7192-9149) (Professor of Interstitial Lung Disease and Consultant Respiratory Physician) led the design and management of the trial, was involved in applying for funding, running of the trial and in identifying and recruiting study subjects, developed the statistical analysis plan and led the drafting of the report.
Veronica A Tudor (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2021-2866) (Trial Manager) oversaw and co-ordinated the running of the trial, trial monitoring, amendments to the protocol, and the collection, cleaning and provision of the trial data and drafting the report.
Peter Saunders (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9299-0299) (Research Fellow, Consultant Respiratory Medicine and Interstitial Lung Disease) was involved in the running of the trial and in identifying and recruiting study subjects and critical revision of the report.
Fernando Zanghelini (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4913-9498) (Research Associate in Health Economics) contributed to the health economic analysis and critical revision of the report.
Carlota Grossi Sampedro (https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3722-5425) (Research Scientist, Health Economics) contributed to the health economic analysis and critical revision of the report.
Georgios Xydopoulos (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2597-2784) (Senior Research Associate, Health Economics) contributed to the health economic analysis and critical revision of the report.
Michael A Gibbons (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2668-1954) (Honorary Associate Clinical Professor, Consultant Respiratory Medicine) was involved in the running of the trial and in identifying and recruiting study subjects, contributed to the management of the trial and critical revision of the report.
Sophie V Fletcher (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9239-9829) (Consultant Respiratory Medicine) was involved in the running of the trial and in identifying and recruiting study subjects, contributed to the management of the trial and critical revision of the report.
Christopher P Denton (https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3975-8938) (Professor of Experimental Rheumatology) contributed to the design of the trial, was involved in applying for funding, running of the trial and in identifying and recruiting study subjects, and critical revision of the report.
Maria Kokosi (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6427-1681) (Honorary Consultant in Interstitial Lung Disease) was involved in the running of the trial and in identifying and recruiting study subjects and critical revision of the report.
Rachel K Hoyles (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2740-8415) (Consultant Respiratory Physician) contributed to the design of the trial, was involved in applying for funding, running of the trial and in identifying and recruiting study subjects, and critical revision of the report.
Helen Parfrey (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4515-5634) (Consultant Respiratory Physician) contributed to the design of the trial, was involved in applying for funding, running of the trial and in identifying and recruiting study subjects, and critical revision of the report.
Elisabetta A Renzoni (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1118-797X) (Consultant Respiratory Physician) contributed to the design of the trial, was involved in applying for funding and critical revision of the report.
Athol U Wells (https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2108-6248) (Consultant Respiratory Physician) contributed to the design of the trial, was involved in applying for funding and critical revision of the report.
Deborah Ashby (https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3146-7466) (Professor of Medical Statistics and Clinical Trials) contributed to the design of the trial, was involved in applying for funding, developed the statistical analysis plan and critical revision of the report.
Richard J Fordham (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5520-6255) (Professor in Public Health Economics) contributed to the health economic analysis and critical revision of the report.
Matyas Szigeti (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7250-7888) ((Biostatistician) led the statistical analysis and contributed to the writing and critical revision of the report.
Philip L Molyneaux (https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1301-8800) (Consultant Respiratory Physician) contributed to the design of the trial, involved in applying for funding, running of the trial and in identifying and recruiting study subjects, and critical revision of the report.
Other members of the trial team
In addition to the authors, the RECITAL trial team included other colleagues whom we would like to thank and acknowledge for their contribution to the trial setup and management: Mrs Ira Jakupovic, Dr Vicky Tsipouri and Mr Matthew Gill.
Patient and public involvement
The authors would like to thank Mrs Kim Fliglestone and Mrs Alexandra Marler who acted as consumer representatives.
Recruitment sites
| Site | PI | Research nurse or trial practitioner |
|---|---|---|
| Royal Brompton Hospital, Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust | Toby Maher | Natalie Dwyer |
| University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust | Sophie Fletcher | James Cullinane |
| Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust | Michael Gibbons | Jessica Mandizha |
| Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust | Christopher Denton | Ivy Wanjiku |
| Sandwell and West Birmingham NHS Hospitals Trust | Arvind Rajasekaran | Irene Echavez-Naguicnic |
| Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust | Rachel Hoyles | Debby Nicoll |
| Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust | Mohammed Akil | Elvina Lee |
| Aintree University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust | Lisa Spencer | Jo Brown |
| Cambridge University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust | Helen Parfrey changed to Frances Hall | Lissamma Titti |
| University Hospital of South Manchester NHS Foundation Trust | Nazia Chaudhuri | Sukoluhle Moyo |
| University Hospital Coventry and Warwickshire NHS Foundation Trust | Shirish Dubey changed to Dhananjay Desai | Susan Dale |
Other study investigators: Daphne Babalis, Nazia Chaudhuri, Felix Chua, Arnab Data, Marcus Flather, Gregory Keir, Bipen Patel, Henry Penn and Zhe Wu.
Participants
Finally, and most importantly, we would like to thank all patients who took part in the trial, without whom this study would not have been possible.
Data-sharing statement
All data requests should be submitted to the corresponding author for consideration. Access to anonymised data may be granted following review.
Patient data
This work uses data provided by patients and collected by the NHS as part of their care and support. Using patient data is vital to improve health and care for everyone. There is huge potential to make better use of information from people’s patient records, to understand more about disease, develop new treatments, monitor safety and plan NHS services. Patient data should be kept safe and secure, to protect everyone’s privacy, and it’s important that there are safeguards to make sure that it is stored and used responsibly. Everyone should be able to find out about how patient data are used. #datasaveslives You can find out more about the background to this citation here: https://understandingpatientdata.org.uk/data-citation.
Disclaimers
This manuscript presents independent research. The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, the MRC, the EME programme or the Department of Health and Social Care. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, the EME programme or the Department of Health and Social Care.
References
- Saunders P, Tsipouri V, Keir GJ, Ashby D, Flather MD, Parfrey H, et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for the treatment of connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease (RECITAL): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2017;18:1-11.
- Tyndall AJ, Bannert B, Vonk M, Airò P, Cozzi F, Carreira PE, et al. Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: a study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:1809-15.
- Hoffmann-Vold A-M, Fretheim H, Halse A-K, Seip M, Bitter H, Wallenius M, et al. Tracking impact of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis in a complete nationwide cohort. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 2019;200:1258-66.
- Reiseter S, Gunnarsson R, Mogens Aaløkken T, Lund MB, Mynarek G, Corander J, et al. Progression and mortality of interstitial lung disease in mixed connective tissue disease: a long-term observational nationwide cohort study. Rheumatology 2018;57:255-62.
- Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2021.
- Luzina IG, Atamas SP, Wise R, Wigley FM, Xiao HQ, White B. Gene expression in bronchoalveolar lavage cells from scleroderma patients. Am J Resp Cell Mol Biol 2002;26:549-57.
- Lafyatis R, O’Hara C, Feghali‐Bostwick CA, Matteson E. B cell infiltration in systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheum 2007;56:3167-8.
- Bosello S, De Santis M, Lama G, Spanò C, Angelucci C, Tolusso B, et al. B cell depletion in diffuse progressive systemic sclerosis: safety, skin score modification and IL-6 modulation in an up to thirty-six months follow-up open-label trial. Arthritis Res Therap 2010;12:1-10.
- Hoyles RK, Ellis RW, Wellsbury J, Lees B, Newlands P, Goh NS, et al. A multicenter, prospective, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of corticosteroids and intravenous cyclophosphamide followed by oral azathioprine for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:3962-70.
- Tashkin DP, Elashoff R, Clements PJ, Goldin J, Roth MD, Furst DE, et al. Cyclophosphamide versus placebo in scleroderma lung disease. N Engl J Med 2006;354:2655-66.
- Perosa F, Prete M, Racanelli V, Dammacco F. CD20-depleting therapy in autoimmune diseases: from basic research to the clinic. J Intern Med 2010;267:260-77.
- Clements PJ, Roth MD, Elashoff R, Tashkin DP, Goldin J, Silver RM, et al. Scleroderma lung study (SLS): differences in the presentation and course of patients with limited versus diffuse systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 2007;66:1641-7.
- Tashkin DP, Roth MD, Clements PJ, Furst DE, Khanna D, Kleerup EC, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil versus oral cyclophosphamide in scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease (SLS II): a randomised controlled, double-blind, parallel group trial. Lancet Resp Med 2016;4:708-19.
- Khanna D, Denton CP, Jahreis A, van Laar JM, Frech TM, Anderson ME, et al. Safety and efficacy of subcutaneous tocilizumab in adults with systemic sclerosis (faSScinate): a phase 2, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2016;387:2630-40.
- Khanna D, Lin CJ, Furst DE, Goldin J, Kim G, Kuwana M, et al. Tocilizumab in systemic sclerosis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Resp Med 2020;8:963-74.
- Richeldi L, Du Bois RM, Raghu G, Azuma A, Brown KK, Costabel U, et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med 2014;370:2071-82.
- Distler O, Highland KB, Gahlemann M, Azuma A, Fischer A, Mayes MD, et al. Nintedanib for systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease. N Engl J Med 2019;380:2518-28.
- Highland KB, Distler O, Kuwana M, Allanore Y, Assassi S, Azuma A, et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease treated with mycophenolate: a subgroup analysis of the SENSCIS trial. Lancet Resp Med 2021;9:96-106.
- Wells AU, Flaherty KR, Brown KK, Inoue Y, Devaraj A, Richeldi L, et al. Nintedanib in patients with progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases: subgroup analyses by interstitial lung disease diagnosis in the INBUILD trial: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Lancet Resp Med 2020;8:453-60.
- Hoffmann-Vold A-M, Maher TM, Philpot EE, Ashrafzadeh A, Barake R, Barsotti S, et al. The identification and management of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: evidence-based European consensus statements. Lancet Rheumatol 2020;2:e71-83.
- Volkmann ER, Tashkin DP, Sim M, Li N, Goldmuntz E, Keyes-Elstein L, et al. Short-term progression of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis predicts long-term survival in two independent clinical trial cohorts. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;78:122-30.
- Leandro MJ, Cambridge G, Ehrenstein MR, Edwards JC. Reconstitution of peripheral blood B cells after depletion with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:613-20.
- Edwards J, Leandro M, Cambridge G. B lymphocyte depletion therapy with rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin 2004;30:393-40.
- Emery P, Fleischmann R, Filipowicz‐Sosnowska A, Schechtman J, Szczepanski L, Kavanaugh A, et al. The efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment: results of a phase IIB randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:1390-400.
- Cohen SB, Emery P, Greenwald MW, Dougados M, Furie RA, Genovese MC, et al. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:2793-806.
- Jones RB, Cohen Tervaert JW, Hauser T, Luqmani R, Morgan MD, Peh CA, et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. N Engl J Med 2010;363:211-20.
- Stone JH, Merkel PA, Spiera R, Seo P, Langford CA, Hoffman GS, et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N Engl J Med 2010;363:221-32.
- Arnold DM, Dentali F, Crowther MA, Meyer RM, Cook RJ, Sigouin C, et al. Systematic review: efficacy and safety of rituximab for adults with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Ann Intern Med 2007;146:25-33.
- Sem M, Molberg Ø, Lund MB, Gran JT. Rituximab treatment of the anti-synthetase syndrome – a retrospective case series. Rheumatology 2009;48:968-71.
- Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2010.
- Daoussis D, Liossis S-NC, Tsamandas AC, Kalogeropoulou C, Kazantzi A, Sirinian C, et al. Experience with rituximab in scleroderma: results from a 1-year, proof-of-principle study. Rheumatology 2010;49:271-80.
- Keir GJ, Maher TM, Hansell DM, Denton CP, Ong VH, Singh S, et al. Severe interstitial lung disease in connective tissue disease: rituximab as rescue therapy. Eur Resp J 2012;40:641-8.
- Goh NS, Desai SR, Veeraraghavan S, Hansell DM, Copley SJ, Maher TM, et al. Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: a simple staging system. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 2008;177:1248-54.
- Keir GJ, Maher TM, Ming D, Abdullah R, de Lauretis A, Wickremasinghe M, et al. Rituximab in severe, treatment-refractory interstitial lung disease. Respirology 2014;19:353-9.
- Sircar G, Goswami RP, Sircar D, Ghosh A, Ghosh P. Intravenous cyclophosphamide vs. rituximab for the treatment of early diffuse scleroderma lung disease: open label, randomized, controlled trial. Rheumatology 2018;57:2106-13.
- Pierpont TM, Limper CB, Richards KL. Past, present, and future of rituximab: the world’s first oncology monoclonal antibody therapy. Front Oncol 2018;8.
- Karimi-Shah BA, Chowdhury BA. Forced vital capacity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: FDA review of pirfenidone and nintedanib. N Engl J Med 2015;372:1189-91.
- Goh NS, Hoyles RK, Denton CP, Hansell DM, Renzoni EA, Maher TM, et al. Short‐term pulmonary function trends are predictive of mortality in interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2017;69:1670-8.
- Jenkins RG, Simpson JK, Saini G, Bentley JH, Russell A-M, Braybrooke R, et al. Longitudinal change in collagen degradation biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an analysis from the prospective, multicentre PROFILE study. Lancet Resp Med 2015;3:462-72.
- Maher TM, Oballa E, Simpson JK, Porte J, Habgood A, Fahy WA, et al. An epithelial biomarker signature for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an analysis from the multicentre PROFILE cohort study. Lancet Resp Med 2017;5:946-55.
- Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med 1975;292:403-7.
- Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis: (first of two parts). N Engl J Med 1975;292:344-7.
- Alarcon-Segovia D, Cardiel M. Comparison between 3 diagnostic criteria for mixed connective tissue disease. Study of 593 patients. J Rheumatol 1989;16:328-34.
- Zappala C, Latsi P, Nicholson A, Colby T, Cramer D, Renzoni E, et al. Marginal decline in forced vital capacity is associated with a poor outcome in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Resp J 2010;35:830-6.
- Graham BL, Steenbruggen I, Miller MR, Barjaktarevic IZ, Cooper BG, Hall GL, et al. Standardization of spirometry 2019 update: an official American thoracic society and European respiratory society technical statement. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 2019;200:e70-88.
- Quanjer PH, Stanojevic S, Cole TJ, Baur X, Hall GL, Culver BH, et al. Multi-ethnic reference values for spirometry for the 3–95-yr age range: the global lung function 2012 equations. Eur Resp Soc 2012;40:1324-43.
- Yorke J, Jones PW, Swigris JJ. Development and validity testing of an IPF-specific version of the St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire. Thorax 2010;65:921-6.
- Patel AS, Siegert RJ, Brignall K, Gordon P, Steer S, Desai SR, et al. The development and validation of the King’s Brief Interstitial Lung Disease (K-BILD) health status questionnaire. Thorax 2012;67:804-10.
- Stanojevic S, Graham BL, Cooper BG, Thompson BR, Carter KW, Francis RW, et al. Official ERS technical standards: Global Lung Function Initiative reference values for the carbon monoxide transfer factor for Caucasians. Eur Resp J 2017;50.
- Brooks D, Solway S. ATS statement on six-minute walk test. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 2003;167.
- Khanna D, Furst DE, Clements PJ, Allanore Y, Baron M, Czirjak L, et al. Standardization of the modified Rodnan skin score for use in clinical trials of systemic sclerosis. J Scleroderma Relat Disord 2017;2:11-8.
- Duarte AC, Cordeiro A, Fernandes BM, Bernardes M, Martins P, Cordeiro I, et al. Rituximab in connective tissue disease–associated interstitial lung disease. Clin Rheumatol 2019;38:2001-9.
- Clarke J. Rituximab shows promise for skin disease in SSc. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2021;17.
- Concato J, Shah N, Horwitz RI. Randomized, controlled trials, observational studies, and the hierarchy of research designs. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1887-92.
- Fischer A, Brown KK, Du Bois RM, Frankel SK, Cosgrove GP, Fernandez-Perez ER, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil improves lung function in connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease. J Rheumatol 2013;40:640-6.
- Maher TM, Stowasser S, Nishioka Y, White ES, Cottin V, Noth I, et al. Biomarkers of extracellular matrix turnover in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis given nintedanib (INMARK study): a randomised, placebo-controlled study. Lancet Resp Med 2019;7:771-9.
- Flaherty KR, Wells AU, Cottin V, Devaraj A, Walsh SL, Inoue Y, et al. Nintedanib in progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. N Engl J Med 2019;381:1718-27.
- Nolan CM, Birring SS, Maddocks M, Maher TM, Patel S, Barker RE, et al. King’s Brief Interstitial Lung Disease questionnaire: responsiveness and minimum clinically important difference. Eur Resp J 2019;54.
- Sinha A, Patel AS, Siegert RJ, Bajwah S, Maher TM, Renzoni EA, et al. The King’s Brief Interstitial Lung Disease (KBILD) questionnaire: an updated minimal clinically important difference. BMJ Open Resp Res 2019;6.
- Kim JW, Clark A, Birring SS, Atkins C, Whyte M, Wilson AM. Psychometric properties of patient reported outcome measures in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chron Resp Dis 2021;18.
- Volkmann ER, Tashkin DP, LeClair H, Roth MD, Kim G, Goldin J, et al. Treatment with mycophenolate and cyclophosphamide leads to clinically meaningful improvements in patient-reported outcomes in scleroderma lung disease: results of scleroderma lung study II. ACR Open Rheumatol 2020;2:362-70.
- Khanna D, Yan X, Tashkin DP, Furst DE, Elashoff R, Roth MD, et al. Impact of oral cyclophosphamide on health-related quality of life in patients with active scleroderma lung disease: results from the scleroderma lung study. Arthritis Rheum 2007;56:1676-84.
- Garcia-Montoya L, Villota-Eraso C, Yusof MYM, Vital EM, Emery P. Lessons for rituximab therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet Rheumatol 2020;2:e497-509.
- Morisset J, Johnson C, Rich E, Collard HR, Lee JS. Management of myositis-related interstitial lung disease. Chest 2016;150:1118-28.
- Fraticelli P, Fischetti C, Salaffi F, Carotti M, Mattioli M, Pomponio G, et al. Combination therapy with rituximab and mycophenolate mofetil in systemic sclerosis. A single-centre case series study. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2018;36:142-5.
- Strangfeld A, Schäfer M, Gianfrancesco MA, Lawson-Tovey S, Liew JW, Ljung L, et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death in people with rheumatic diseases: results from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician-reported registry. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80:930-42.
Appendix 1 Description of reasons for study drug discontinuation and withdrawals
| Study number and reason given | Treatment group | Suggested grouping |
|---|---|---|
| 002 Patient withdrew consent due to not being able to tolerate the side effects. Patient did not consent for/withdrawn from trial procedures/follow-up visits | Cyclophosphamide | Perceived side effects |
| 003 Progression of disease but agreed to attend follow-up visits. Patient was unblinded. Patient did not consent for/withdrawn from trial procedures/follow-up visits | Cyclophosphamide | Disease progression |
| 004 Patient did not attend week 16 and week 20 visits due to side effects. Withdrawn from treatment but to attend for follow-up visits. Patient did not consent for/withdrawn from trial procedures/follow-up visits | Rituximab | Perceived side effects |
| 015 Progression of disease and patient withdrawn from trial procedures/follow-up visit | Rituximab | Disease progression |
| 016 Patient did not attend her week 48 appointment and is uncontactable | Rituximab | Unwilling to continue |
| 021 Death – admitted to ICU with disease progression and patient unblinded | Rituximab | Death – Disease progression |
| 026 Death – a post-mortem was conducted and this lists as the cause of her death (1a.) Pneumonia, (1b.) Myositis and scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease on immunosuppressive therapy | Rituximab | Death – Disease progression |
| 034 Did not attend week 8 due to SAE. Withdrawn from treatment but to attend for follow-up visits | Rituximab | Disease progression |
| 048 Patient withdrew due to disease progression. Patient did not consent for/withdrawn from trial procedures/follow-up visits | Cyclophosphamide | Disease progression |
| 059 Patient randomised but withdrew consent from trial procedures and follow-up visits | Rituximab | Unwilling to continue |
| 061 Progression of disease, patient was randomised, but not dosed at day 0. Patient was removed from the study. | Cyclophosphamide | Disease progression |
| 062 SAE Pneumonia. Patient withdrew consent from trial procedures and follow-up visits | Cyclophosphamide | Unwilling to continue |
| 068 Patient randomised, but withdrawn due to complex overlapping autoimmune conditions | Rituximab | Disease progression |
| 073 PI decision to treat patient with alternative therapy, post week 24 visit. Patient attended week 48 follow-up | Rituximab | Disease progression |
| 084 Death due to pulmonary hypertension | Cyclophosphamide | Death |
| 086 Death, presumed progression of underlying disease | Rituximab | Death |
| 089 Death due to respiratory failure | Cyclophosphamide | Death |
| 092 Death – SAE – congestive heart failure | Rituximab | Death |
| 093 This subject did not attend week 48 follow-up visit | Cyclophosphamide | Unwilling to continue |
| 094 This subject did not attend week 48 follow-up visit | Rituximab | Unwilling to continue |
| 096 Withdrawn by site – appointment unable to go ahead due to coronavirus pandemic | Rituximab | COVID-19 pandemic |
| 100 Withdrawn by site – appointment unable to go ahead due to coronavirus pandemic | Cyclophosphamide | COVID-19 pandemic |
| 102 Withdrawn by site – appointment unable to go ahead due to coronavirus pandemic | Rituximab | COVID-19 pandemic |
| 103 24.3.2020 – a telephone consultation took place with the PI. Due to the COVID-19 epidemic and patient’s anxiety about attending the hospital to finish, PI agreed to withdraw the patient | Rituximab | COVID-19 pandemic |
| 104 Withdrawn by site – appointment unable to go ahead due to coronavirus pandemic | Rituximab | COVID-19 pandemic |
| 105 Patient concerned about risks related to COVID-19 pandemic and visiting the hospital | Rituximab | COVID-19 pandemic |
List of abbreviations
- 6MWD
- 6-minute walk distance
- AE
- adverse event
- ALP
- alkaline phosphatase
- ALT
- alanine aminotransferase
- ANCA
- antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody
- ATS
- American Thoracic Society
- BSA
- body surface area
- CA125
- cancer antigen 125
- CC BY 4.0
- Creative Commons Attribution
- CEAC
- cost-effectiveness acceptability curve
- CI
- chief investigator
- CONSORT
- Consolidated Standard of Reporting Trials
- CP
- cyclophosphamide
- CRF
- case report form
- CT
- computer tomography
- CTD
- connective tissue disease
- DLCO
- diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide
- DMC
- Data Monitoring Committee
- DNA
- deoxyribonucleic acid
- ECG
- electrocardiogram
- EME
- efficacy and mechanism evaluation
- EQ-5D
- EuroQol-5 Dimensions
- EQ-5D-5L
- Euroqol-5 Dimensions, five-level version
- FEV1
- forced expiratory volume in 1 second
- FVC
- forced vital capacity
- GCP
- good clinical practice
- GP
- general practitioner
- HAQ
- health assessment questionnaire
- HIV
- human immunodeficiency virus
- HR
- hazard ratio
- IIM
- idiopathic inflammatory myositis
- IL
- interleukin
- ILD
- interstitial lung disease
- IMP
- investigational medicinal product
- INMB
- incremental net monetary benefit
- IPF
- idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- ISF
- investigator site file
- ISRCTN
- International Standard Randomised Controlled Trial Number
- K-BILD
- King’s Brief Interstitial Lung Disease
- MCTD
- mixed connective tissue disease
- MHRA
- Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency
- MMF
- mycophenolate mofetil
- mRSS
- modified Rodnan skin score
- NHS
- National Health Service
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- PI
- principal investigator
- PIS
- patient information sheet
- PML
- progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy
- PSA
- probabilistic sensitivity analysis
- PSF
- pharmacy site file
- QoL
- quality of life
- QP
- qualified person
- RCT
- randomised controlled trials
- RNA
- ribonucleic acid
- SAE
- serious adverse event
- SAP
- statistical analysis plan
- SAR
- serious adverse reaction
- SD
- standard deviation
- SDV
- source data verification
- SF36
- the Short Form 36 questionnaire
- SGRQ
- St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire
- SHA
- scleroderma health assessment
- SLS
- Scleroderma Lung Study
- SmPC
- summary of product characteristics
- SOPs
- standard operating procedure
- SpO2
- saturation of oxygen
- SSc
- systemic sclerosis
- TMG
- Trial Management Group
- TSC
- Trial Steering Committee
- TTP
- thrombocytopenic purpura
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- WTP
- willingness to pay threshold
- UIP
- usual interstitial pneumonia
- VAS
- visual analogue scale
Notes
Supplementary material can be found on the NIHR Journals Library report page (https://doi.org/10.3310/LYWQ8541).
Supplementary material has been provided by the authors to support the report and any files provided at submission will have been seen by peer reviewers, but not extensively reviewed. Any supplementary material provided at a later stage in the process may not have been peer reviewed.
