Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was commissioned and funded by the HTA Programme on behalf of NICE as project number 07/05/01. The protocol was agreed in August 2007. The assessment report began editorial review in November 2007 and was accepted for publication in June 2008. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the referees for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
None.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© 2009 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO. This monograph may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NCCHTA, Alpha House, Enterprise Road, Southampton Science Park, Chilworth, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2009 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Background
This report updates the assessment of routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis (RAADP) undertaken on behalf of the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) by Chilcott and colleagues in 2001. 1 However, for ease of use it is intended to be a stand-alone document.
Description of health problem
Human blood is classified according to two main systems: the ABO system and the Rhesus (Rh) system. The Rh system consists of several related proteins, the most important of which is called the Rhesus D (RhD) antigen. People who have this antigen on their red blood cells are said to be RhD positive, whereas those who do not are said to be RhD negative. Both ABO and Rh blood types are inherited characteristics and therefore a fetus may inherit a blood type from its father which differs from that of its mother.
Haemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) is a haemolytic anaemia that affects the fetus or neonate. It results from the transplacental passage of antibodies created by the mother and directed against fetal red cell antigens inherited from the father. Over 90% of all cases of clinically significant HDN affect RhD-positive infants born to RhD-negative mothers.
Aetiology, pathology and prognosis of haemolytic disease of the newborn
Aetiology
Modern laboratory methods have shown that fetal cells are present in the maternal circulation in all pregnancies from a very early stage. However, in some cases a quantity of fetal blood large enough to be detected by less sensitive methods such as the Kleihauer test enters the mother’s circulation. Such a transfer of fetal blood is termed a fetomaternal haemorrhage (FMH) and is not uncommon. FMH occurs most frequently at delivery. However, it may also occur during events such as miscarriage or abortion, invasive tests and procedures during pregnancy, or abdominal trauma; it also sometimes occurs in the absence of any observable risk. During the first trimester approximately 3% of women have enough fetal blood cells in their circulation to be detectable. This figure rises to 12% in the second trimester and 45% in the third trimester, until at delivery up to 50% of women delivering an ABO-compatible infant have detectable circulating fetal red cells. 2
Fetomaternal haemorrhage does not normally cause any adverse effects. However, if the mother is RhD negative and the fetus RhD positive, the mother may react to the fetal blood cells in her circulation by developing a template for producing anti-D antibodies,3 a process known as RhD sensitisation or primary immunisation. Such women are said to be ‘sensitised’ and the event leading to sensitisation is known as the ‘sensitising event’. The amount of blood required is small: most women who become sensitised do so as a result of an FMH of less than 0.1 ml. 4 Although some RhD-positive women produce anti-D following a sensitising event in pregnancy, this is extremely rare. 5
Primary immunisation may lead to the production of antibodies, which are detectable after 4 weeks. Alternatively, it may lead to sensitisation without visible antibodies. However, once such ‘silent’ sensitisation has occurred, secondary sensitisation may be produced by a much smaller FMH than that which caused the initial sensitisation,6 stimulating the production within 1–2 weeks of anti-D antibodies. These maternal antibodies cross the placenta into the fetal circulation and ‘coat’ or sensitise the infant’s red cells, provoking their premature clearance from the circulation and resulting in anaemia and jaundice. In utero, fetal bilirubin crosses the placenta and is cleared by the maternal circulation, but after delivery its clearance is dependent on the immature neonatal liver, which allows unconjugated bilirubin to accumulate.
Not all RhD-negative pregnant women who are exposed to RhD-positive blood cells become sensitised. The risk of sensitisation is affected by a number of factors including the blood type of the fetus, the volume of fetal blood entering the mother’s circulation, and the mother’s immune response. 7 It has been shown that, when RhD-negative volunteers are given repeated injections of RhD-positive cells, some are sensitised quickly and develop high levels of anti-D antibodies, whereas others produce only moderate amounts of antibody; around 20% appear to be completely non-responsive. Similarly, in pregnancy, some women respond quickly, often in their first RhD-positive pregnancy; if they have a second RhD-positive pregnancy their antibody level rises rapidly and the infant may be severely affected. 8 Such women may be sensitised after a relatively small transplacental haemorrhage (TPH) or an abortion (spontaneous or therapeutic). 9 Mothers who develop antibodies in their third, fourth or later pregnancy have a much lower chance of losing the child. Thus, sensitisation is most likely in the earlier pregnancies, and women who reach their third or later RhD-positive pregnancy without developing antibodies appear to be less sensitive to the RhD antigen. 8 The risk of sensitisation is increased when the mother and fetus have the same ABO blood group. 10 In the absence of antenatal and postpartum anti-D prophylaxis, the risk of sensitisation following a single ABO-compatible RhD pregnancy is about 16%,9 but it is only 2% if the mother and fetus are ABO incompatible. 11 As approximately 80% of pregnancies are ABO compatible,12 the overall risk of sensitisation, without prophylaxis, is approximately 13% of at-risk pregnancies.
In the absence of any programme of prophylaxis, most RhD-negative women who become sensitised do so following a small FMH at delivery of their first RhD-positive infant. Without RAADP, the majority of those primigravidae who are sensitised before delivery in the absence of an identifiable sensitising event appear to be sensitised in the third trimester. A New Zealand study13 found that 87% (14/16) of primigravidae who developed antibodies did so in the third trimester, compared with only 27% of multigravidae (7/26); these data suggest that many women who develop antibodies early in their second pregnancy have actually been sensitised late in the first pregnancy. Consequently, anti-D antibodies are not usually produced during the first RhD-positive pregnancy; the first RhD-positive infant will generally be affected by maternal antibodies only in the minority of cases in which the mother has already been sensitised as a result of a previous transfusion of RhD-positive red cells, a miscarriage or abortion, or a sensitising event earlier in the pregnancy, and then only following a subsequent FMH during the course of that pregnancy. However, once the mother has been sensitised, her immune response will worsen with each successive RhD-positive pregnancy, and consequently each successive RhD-positive infant will be progressively more severely affected by HDN.
Before the introduction of prophylaxis, anti-D was found immediately after a first pregnancy in approximately 1% of untransfused RhD-negative women who delivered an ABO-compatible RhD-positive infant; in about half of these cases it was detectable between 34 and 40 weeks’ gestation. At 6 months post-delivery, 4–9% of such women had detectable anti-D,10 as did 1–2% of RhD-negative women who had borne a RhD-positive ABO-incompatible infant. 14 However, the ‘true’ rate of sensitisation is greater than that identified by the presence of anti-D at, or 6 months after, delivery, as a proportion of women who have been sensitised do not have detectable anti-D after their first RhD-positive pregnancy, but will give a secondary immune response when stimulated by a second sensitising event, usually during a later pregnancy. Thus, the appearance of anti-D before 28 weeks’ gestation in a subsequent pregnancy is a strong indication of sensitisation in an earlier pregnancy. 15 Before the introduction of routine antenatal and postpartum anti-D prophylaxis, approximately 17% of RhD-negative women were found to have detectable anti-D after their second RhD-positive ABO-compatible pregnancy; in most of these women, the initial sensitisation would have occurred during the first pregnancy. 10
Passive immunisation with anti-D immunoglobulin can prevent sensitisation, although the precise mechanism by which it does so is not known. 10 However, once a woman has developed anti-D antibodies she cannot be desensitised.
Pathology and prognosis
Survival and short-term outcomes
The severity of HDN varies according to certain properties of the antibody, its level in the maternal blood and the duration of exposure of the infant to that level of antibody. In its mildest form the infant has sensitised red cells that are detectable only in laboratory tests. More commonly, the infant has a mild degree of jaundice, which responds to phototherapy. More severe disease involves significant anaemia and progressive hyperbilirubinaemia. Certain neonatal brain structures, such as the thalamus and corpus striatum, are particularly sensitive to damage by unconjugated bilirubin. If severe jaundice is not treated by exchange transfusion the resulting clinical condition, kernicterus, results in permanent brain damage and eventually death in 70% of affected infants. In the most severe form of HDN the in utero anaemia causes hydrops and intrauterine death. 10
Although the chances of survival are related to the severity of the HDN, the management of potentially severely affected infants was eased by the introduction in the early 1980s of intrauterine fetal blood sampling, enabling the identification of fetal RhD type and haemoglobin level, not least because this facilitated direct intravascular intrauterine blood transfusion (IUT). Treatment thus became possible at a much earlier gestational age, and this reduced the incidence of death in utero from severe anaemia. 16 Although overall survival in fetuses undergoing IUT is around 86–90%,17,18 it is lower in those with hydrops, which is indicative of severe haemolytic disease; survival in fetuses with severe hydrops who receive IUT may be as low as 55%, whereas in those with mild hydrops it may be as high as 98%. 17
The most comprehensive recent data on the outcomes of pregnancies in RhD-sensitised women derive from a study of all such pregnancies in Northern Ireland from September 1994 to February 1997. 19 The authors report that there were 124 pregnancies resulting in a total of 130 fetuses. Although there were 11 deaths (8.5%) from various causes, over 90% of infants survived the neonatal period (Table 1).
| Outcome | Number (%) |
|---|---|
| Termination for fetal abnormality | 2 (2) |
| Miscarriage | 5 (4) |
| Stillbirth of unknown cause | 1 (1) |
| Stillbirth following IUT | 2 (2) |
| Live-born affected babies (includes one neonatal death from severe hydrops) | 76 (58) |
| Live-born unaffected babies | 44 (34) (includes 17 RhD-negative pregnancies) |
| Total | 130 (100) |
More recently, a study on the outcome of pregnancy in women with Rh sensitisation treated in a tertiary referral centre in Zagreb, Croatia, between January 1997 and January 2003 included two women with anti-Kell immunisation, six with combined RhD and C immunisation, and 15 with RhD immunisation. 20 In total, 20 of the 23 fetuses (87%) were live-born. Four (17%) had hydrops; three of these were stillborn (two died before it was possible to perform IUT, whereas in the third death was not related to IUT) and the fourth survived.
Longer-term outcomes
Infants who survive HDN may suffer long-term neurodevelopmental problems caused either directly by the condition or indirectly by the prematurity associated with it. Several studies have reported on such problems. The most recent of these is the Northern Ireland study19 noted above. This found that, at 2 years of age, five of the 78 babies affected by HDN (6%) had minor developmental problems (e.g. myopia, squint or delay in language and fine motor skills) and two (3%) had major permanent neurodevelopmental problems. 19
The only studies that have reported long-term outcomes in fetuses who required IUT for HDN (primarily associated with RhD incompatibility) relate to children treated in the 1980s and 1990s (Table 2). These studies indicate that, at this time, about 15% of fetuses receiving IUT died in utero; neonatal deaths reduced total survival to about 80%. Survival was higher in the less severely affected fetuses; in the German study21 only 7/11 (64%) of those who had developed hydrops before the first transfusion survived, compared with 28/32 (88%) of those without hydrops. Because early delivery was felt to pose fewer risks than additional transfusions, some of the recorded sensorineural disabilities may be associated with prematurity rather than specifically with IUT. 22 By comparison, a more recent study23 included 254 fetuses treated with 740 intravascular IUTs at a single centre in the Netherlands between 1988 and 2001; in 85% of the pregnancies (217/254) fetal anaemia was due to maternal RhD alloimmunisation. Overall survival was higher at 89% (225/254); there were 19 fetal deaths (7%) and 10 neonatal deaths (4%). Seven of the fetal deaths and five of the neonatal deaths were considered to be related to IUT, a rate of 1.6% per procedure. Longer-term outcomes were not reported.
| Doyle et al. 199322 | Harper et al. 200624 | Grab et al. 199921 | Hudon et al. 199825 | Janssens et al. 199726 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date of IUT | 1984–90 | 1985–95 | 1986–91 | 1986–92 | 1987–93 |
| Location | Australia | USA | Germany | USA | Netherlands |
| Number of fetuses receiving IUT | 52 | 18 | 43 | 49 | 92 |
| Reason for IUT | Severe erythroblastosis (number associated with anti-D antibodies not stated) | Hydrops (in most cases associated with anti-D either alone or in combination with other antibodies) | Severe erythroblastosis [40/43 (93%) associated with anti-D antibodies] | HDN [41/49 (84%) associated with anti-D antibodies] | Severe erythroblastosis (number associated with anti-D antibodies not stated) |
| Mean number of transfusions per fetus | Not stated. Median 4 per survivor (range 1–8) | Median 4.5 (range 1–7) | 3.2 | 3.3 | 3.2 |
| Intrauterine death | No data | 2 (11%) | 5 (12%) (4/5 before 28 weeks) | 9 (18%) (mean gestational age 23.1 weeks) | 15 (16%) |
| Number live-born | No data | 16 (89%) | 38 (88%) | 40 (82%) | 77 (84%) |
| Neonatal deaths | No data | 0 | 3 (7%) (all preterm) | None reported | 4 (4%) |
| Number surviving | 38 (73%) | 16 (89%) | 35 (81%) | Apparently 40 (82%) | 73 (79%) |
| Hospital stay (days), median (range) | No data | No data | No data | 11 (3–101) | No data |
| Number of survivors followed up | 38 (100% of survivors) at 2 years of age (corrected for prematurity) | 16 (89%) for a mean of 10 years (range 4.5–12.9 years) | 30 (86% of survivors) for up to 6 years | 22 (55% of survivors) for a mean of 14.4 months; 11 (28% of survivors) for 36–62 months | 69 (95% of survivors for 0.5–6 years) |
| Number with moderate or severe neurological impairment (other than hearing impairment) at follow-up | 2/38 (5%)a | 2/16 (13%)b | 0 | 1/22 (5%)c | 3/69 (4%)d |
| Number with mild neurological impairment (other than hearing impairment) at follow-up | 1/38 (3%)e | 5/16 (31%)f | 2/30 (7%)g | 0 | 2/69 (3%)h |
| Number with motor delay requiring physiotherapy | No data | No data | No data | No data | 17% |
| Number with speech delay requiring speech therapy | No data | No data | No data | No data | 13% |
| Number with hearing tested | 38 | 16 | No data | 21 (53% of survivors) tested before initial hospital discharge | 58 (84%) screened at 9 months |
| Number of those tested with permanently impaired hearing | 0 | 2/16 (13%)i | No data | 2/21 (10%)j | 3/58 (5%) |
The studies followed up survivors for different lengths of time and subjected them to different tests; follow-up ranged from 95% to 100% (see Table 2). Three studies screened for hearing disability: the Dutch study26 screened 58 infants (84% of survivors) at 9 months and found non-transient hearing loss in three (5%); one US study screened 16 children (100% of survivors) at a mean age of 10 years and found that two (13%) had hearing loss (one had bilateral profound sensorineural hearing loss and the other unilateral mild conductive hearing loss);24 the other US study screened 21 infants (53% of survivors) before initial hospital discharge and found that two (10%) had a permanent hearing deficit (in one case severe bilateral deafness), a rate that was noted to be probably five to ten times higher than that among infants not affected by HDN. 25
The studies also found that a number of IUT survivors suffered moderate or severe neurological impairment other than hearing loss – primarily cerebral palsy of varying degrees of severity. The Dutch study26 compared outcomes in IUT survivors with those in both a high-risk group of very premature and/or very-low-birthweight infants and a healthy control group. In the high-risk group, 18% of children who survived to the age of 2 years had major or minor disabilities at that age, compared with 6% in the healthy control group and 10% (7/69) in the IUT survivors group. However, because of the very small numbers of IUT survivors there was no statistically significant difference between the proportion of affected children in that group and the proportion of affected children in either the high-risk group or the healthy control group. A small US study24 used a battery of tests to compare IUT survivors with their unaffected siblings and found them to be within normal limits, compared with published norms and sibling controls, in terms of all physical, neurological and cognitive outcomes except for visual attention, for which the IUT survivors had significantly lower scores. However, because of the small sample size the investigators recognised the possibility of a type II error (failing to observe a difference when in fact there is one). In the other US study,25 overall follow-up was very incomplete, making it difficult to know how to interpret the information that the mean developmental scores of those who were assessed were within normal limits; the investigators admit that the children who did not return for evaluation may have been those at increased risk of severe neurodevelopmental compromise, although they felt that they were more likely to have been lost to follow-up as a result of geographical distances.
Thus, the introduction of ultrasonographically-guided IUT has improved the ability to treat severely anaemic fetuses earlier in gestation, but has thereby increased the chances of survival of more severely affected fetuses with the potential for poor neurodevelopmental outcomes. 25 Around 10–12% of fetuses affected by HDN will require IUT,27 and a relatively high proportion of IUT survivors may suffer neurodevelopmental problems such as cerebral palsy, deafness and motor and speech delay that will require specialist input and, in some cases, special education; others will suffer some degree of developmental delay requiring physiotherapy or speech therapy.
Epidemiology – demographic factors (age, sex, ethnicity, income, regional variation)
Ethnic groups vary in terms of the proportion of the population that is RhD negative and thus at risk of sensitisation. Approximately 16% of the white UK population is RhD negative compared with about 5% of West African people, whereas virtually no Chinese people are RhD negative. 10 No data have been identified relating specifically to people of Asian subcontinent origin living in Britain, but data from various parts of that subcontinent suggest that the proportion of this population that is RhD negative is smaller than the proportion of the white UK population that is RhD negative; for example 5.5% of blood donors in Vellore, south India, have been found to be RhD negative,28 as have 9% of young men reporting for army recruitment in Pakistan (ranging from 7.7% of Pathans to 10.9% of those of Kashmiri origin). 29
The incidence of HDN is clearly influenced by the prevalence of RhD-negative people in the population. Thus, if the prevalence of RhD negativity within a given ethnic group is low, there will be fewer women at risk of sensitisation. However, assuming that women draw their partners from their own ethnic group, each RhD-negative woman in an ethnic group with a low prevalence of RhD negativity has a higher risk of having an RhD-positive partner than does an RhD-negative woman in an ethnic group with a higher prevalence of RhD negativity (Table 3).
| Prevalence of RhD negativity within population | Probability of RhD-negative woman having RhD-positive partner by chance |
|---|---|
| 1% | 99% |
| 5% | 95% |
| 9% | 91% |
| 16% | 84% |
The incidence of HDN is not influenced by parental age or socioeconomic status, except inasmuch as these factors affect family size; as noted above, once a RhD-negative woman has been sensitised, her successive RhD-positive pregnancies will be more severely affected, and therefore the impact of HDN will be greater in families in which the mothers undergo more pregnancies.
No data have been identified regarding regional variation in the distribution of HDN in England and Wales, but any such variation is likely to be due primarily to the distribution of people of different ethnic origins.
Incidence of haemolytic disease of the newborn
Before the introduction of anti-D prophylaxis, HDN due to RhD incompatibility affected about one in 20 children born to RhD-negative women in Caucasian populations30 – approximately 1% of all neonates in England and Wales. Only a very small minority of cases of HDN occurred in first pregnancies, but 1 in 100 second pregnancies, and a higher proportion of subsequent pregnancies, were affected.
Currently, only about 500 fetuses a year in England and Wales develop HDN,31 approximately 1 in every 1298 live and stillbirths, less than one-tenth of the earlier figure. Although this change is largely due to the introduction of anti-D prophylaxis, it also reflects changes in family size. It has been estimated that 69% (95% CI 61–76%) of the observed reduction in maternal sensitisation rates in Manitoba (from 9.6 per 1000 total births in 1963 to 2.6 per 1000 total births in 1988) was due to the introduction of anti-D prophylaxis and 24% (95% CI 1–42%) to changes in family structure: in 1988, 40% of all births were first births, compared with only 25% in 1963. 32 Over the same period, advances in neonatal care were such that perinatal survival in infants with RhD HDN rose from 86.2% in 1963 to 97.4% in 1988. 32
In the UK, standard postpartum anti-D prophylaxis was introduced in 1969. Prophylaxis was extended in 1976 to include abortions and spontaneous miscarriages, and in 1981 to include a number of potential sensitising events. 33 Following the introduction of postpartum anti-D prophylaxis the proportion of RhD-negative women found by routine antenatal testing to have demonstrable anti-D within 6 months of the delivery of their first RhD-positive ABO-compatible pregnancy fell from 4–9% to 0.1–0.5%, and the proportion with demonstrable anti-D by the end of their second RhD-positive ABO-compatible pregnancy fell from 17% to around 1.5%. 10 However, as these figures will not include women sensitised during their final pregnancy, the true figures will be higher. 34 Nearly half of the 1.5% known to have been sensitised (0.7% overall) seem to have been sensitised as a result of FMH during the first pregnancy, a similar number have been sensitised as a result of FMH during the second pregnancy, and the remainder (approximately 0.2% overall) have been sensitised as a result of failure to provide sufficient postpartum anti-D to cover a large FMH at the first delivery. 10
In 1953, 310 deaths in England and Wales were attributed to RhD HDN – 1 in every 2180 births. 10 An audit found that registered deaths and stillbirths attributed to RhD HDN in England and Wales between 1977 and 1987 fell by more than 70% over that period, from 106 (18.4 per 100,000 births) in 1977 to 27 (3.9 per 100,000 births) in 1987. This fall occurred mainly between 1977 and 1983 and was due to a large reduction in the number of cases in which the mother was believed to have been sensitised by a pregnancy following which she was not given anti-D prophylaxis; there was no change in the number of deaths following sensitisation of the mother during the first pregnancy or after having been given anti-D following one or more previous pregnancies (i.e. failure of prophylaxis). 35 By 1989 the number of registered deaths and stillbirths had fallen to 10 (1.5 per 100,000 live births)36 – 1 in approximately 66,500 live births or one-thirtieth of the 1950s figure. However, although these official figures clearly demonstrate the reduction in HDN mortality, they underestimate the true impact of the disease because they do not include fetal loss before 28 weeks. A retrospective review of births between 1987 and 1991 to mothers resident in Scotland found that five times as many deaths from RhD HDN were uncertified as were certified through the General Register Office. Of the 20 deaths identified, 11 occurred before 28 weeks’ gestation, but only four before 20 weeks’ gestation. The major cause of under-reporting was the exclusion from the certification data of both therapeutic and spontaneous abortions. 37,38 Thus, although HDN was reported as the main or subsidiary cause of five stillbirths and one neonatal death (or 1 in approximately 108,200 total births) in England and Wales in 2005,39 the Scottish data suggest that the true number of fetal and perinatal deaths in that year was likely to have been around 30 (1 in approximately 21,640 total births). In 2001 the Trent Confidential Enquiry into Stillbirths and Deaths in Infancy (CESDI) reported that in 1999 there were three deaths at between 20 weeks of pregnancy and 1 year of life as a result of RhD alloimmunisation in a population of approximately 5 million; this is consistent with an overall figure of around 30 for England and Wales (S Wood, 2001, personal communication).
CESDI notifications for England, Wales and Northern Ireland indicate that, for the period 1994–9, an average of 18 fetal and infant deaths a year in England, Wales and Northern Ireland were due to RhD incompatibility (M Macintosh, 2001, personal communication). To these must be added any fetal losses that occur before 20 weeks’ gestation. The Scottish data suggest that 20% (4/20) of all fetal and infant deaths due to RhD incompatibility occur before 20 weeks. This represents an additional 25% (4/16) in relation to the number of deaths that occurred from 20 weeks’ gestation onwards. Consequently, on the basis of the CESDI figures for England, Wales and Northern Ireland, an average of five additional deaths a year can be estimated to occur before 20 weeks, leading to an average total of 23 deaths a year. As noted above, the CESDI figures are likely to under-report the incidence of deaths due to RhD incompatibility, and therefore this figure is compatible with the figure of 30 estimated earlier. The data summarised in Table 4 indicate that the majority of deaths due to HDN occur after 24 weeks’ gestation and thus are stillbirths and neonatal and postneonatal deaths.
| Gestational age | Scotland 1987–91,37 n (%) | UK excluding Scotland 1994–9 (CESDI data), n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Under 20 weeks | 4 (20) | No data |
| 20–24 weeks | 3 (15) | 19 (17) |
| Stillbirth | 7 (35) | 51 (48) |
| Neonatal death | 5 (25) | 36 (33) |
| Postneonatal death | 1 (5) | 3 (3) |
| Total | 20 (100) | 109 (100) |
Although a programme of RAADP cannot prevent every case of fetal loss, stillbirth, neonatal death or postnatal death attributable to RhD incompatibility, it can be expected to prevent a substantial majority of such cases.
Impact of health problem
Significance for patients in terms of ill-health (burden of disease)
Any discussion of the impact of maternal sensitisation is complex, as the major burden of the condition relates to the direct impact on the health and well-being of children affected by HDN and the indirect impact which that has on their parents and any siblings. However, there are also some direct implications for maternal health and well-being. This section discusses, first, the direct impact of sensitisation on maternal health and well-being; second, the direct impact of HDN on the health of the infant; and, third, the indirect impact of HDN on the well-being of the family.
Health and well-being of the mother
RhD sensitisation has a direct impact on maternal well-being as a result of the anxiety caused by the continuous monitoring of pregnancies in sensitised women, even if these pregnancies result in healthy babies.
There is a further implication for those sensitised women whose fetuses require IUT. More than 25% of these women develop additional antibodies apart from anti-D. As a consequence, should they require blood transfusions in future, it would be very difficult to find compatible blood for them (Professor M Contreras, 2007, personal communication).
Health of the affected child
HDN has both short- and long-term implications for affected infants. In the short term they may undergo a number of therapeutic procedures including IUT, exchange transfusion and phototherapy. These interventions are short-lived and their full impact on the infant’s health and health-related quality of life is difficult to estimate. However, it should be noted that IUT is associated with an estimated death rate of approximately 2% per procedure. 23,40
In the longer term, with appropriate management, the majority of children affected by HDN achieve normal neurodevelopmental outcomes. However, those most severely affected do not achieve normal outcomes. The studies by Hudon et al. 25 and Janssens et al. 26 indicate that the most common permanent disabilities in this group are cerebral palsy and deafness; minor developmental problems include speech and motor delay, requiring physiotherapy and speech therapy.
Cerebral palsy has substantial implications for both health (including reduced life expectancy) and quality of life (Table 5 provides a summary of quality of life in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy). The impact of cerebral palsy on quality of life in children is difficult to quantify because of the shortage of validated instruments for measuring quality of life in children, especially those with disabilities,41 the presence of communication barriers, and the wide range of impairments found in people with cerebral palsy. 42 However, it is important when possible to obtain the perspective of the children and adolescents with cerebral palsy themselves because those who are capable of self-reporting consistently rate their quality of physical and psychosocial health more highly than do their parents. 43 Even so, in a recent study of Californian children and adolescents with cerebral palsy (age 5–18 years), Varni et al. 43 found that those who were able to self-report using the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory version 4.0 [PedsQL 4.0; 69/148 (47%)] reported considerably lower health-related quality of life than healthy children in terms of both physical and psychosocial well-being. Parental proxy reports attributed significantly higher physical and school functioning to children who were capable of self-report than to those who were not, but indicated no significant difference between the two groups in terms of emotional and social functioning. Self- and proxy reports indicated significantly lower physical and psychosocial functioning in children with quadriplegia than in those with hemiplegia and diplegia. 43
| Study | Country | Population | Tool | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dickinson et al. 200745 | Europe | Children with CP (aged 8–12 years) capable of self-report | KIDSCREEN | Self-reported quality of life was similar to that of children of the same age in the general population surveyed 2 years previously in all domains except for the school environment (which was better in children with CP) and physical well-being (which was not comparable as a modified version of the questionnaire was used with children with CP) |
| Pirpiris et al. 200644 | USA | Children with mild to moderate CP (mean age 10 years), mostly considered too young to self-report | PedsQL 4.0, PODCI | Parentally and self-reported functional and psychosocial well-being were lower than in non-affected peers |
| Varni et al. 200543 | USA | Children and adolescents with CP (mean age 10 years) capable of self-report | PedsQL 4.0 | Self-reported physical and psychosocial well-being were considerably lower than in healthy children |
A US study by Pirpiris et al. 44 also found that both functional and psychosocial well-being in children with mild to moderate cerebral palsy were lower than in non-affected peers; however, there was no correlation between physical function and psychosocial well-being, and children with mild cerebral palsy had lower self- and parentally reported psychosocial well-being than would be predicted by their functional disability. By contrast, a European study45 of 8- to 12-year-old children with cerebral palsy found that the quality of life of the 61% (500/818) who were able to self-report, as measured using the KIDSCREEN questionnaire, was similar to that of children of the same age in the general population who had been surveyed 2 years previously in all domains except for the school environment (where the quality of life of those with cerebral palsy was better) and physical well-being (which could not be formally compared because a slightly modified version of this domain of the questionnaire had been used with the children with cerebral palsy). However, 54% of the children with cerebral palsy reported pain during the previous week and this was significantly associated with poorer quality of life in relation to physical well-being, moods and emotions, autonomy, relationships with parents, self-perception and school environment. No information was presented regarding the quality of life of those children who were not able to self-report.
It is possible that the difference in results between the European and Californian studies may be due at least in part to the different age ranges involved: the Californian study included adolescents, who may have been less optimistic than younger children. Thus, in a Canadian study,46 young adults (aged 19–23) with cerebral palsy who were capable of responding to a survey anticipated less success in future relationships, post-secondary education, employment and independent living than did matched control subjects, although adolescents (aged 13–15) with cerebral palsy did not differ from control subjects in their future expectations.
A US study47 evaluated parentally reported pain frequency in 198 children (mean age 10 years 7 months) with moderate to severe cerebral palsy. In total, 11% reported pain very often/almost every day. Pain was more prevalent with more severe impairment and was associated with missed school days and days in bed.
Many of the physical problems associated with cerebral palsy are exacerbated in adult life. Mobility may become more limited and this is often accompanied by an increase in spasticity and pain. 48 In a US study49 of adults with cerebral palsy with no more than mild cognitive impairment, 67% reported pain of more than 3 months’ duration, which was generally experienced on a daily basis. Similarly, a Norwegian survey50 found that 28% of people with cerebral palsy without intellectual disability reported daily pain for 1 year or more, compared with 15% of the general population. An Italian study51 found that, although 29/70 (41%) adults with cerebral palsy had walked independently (i.e. without sticks or other aids) before the age of 18, only 16 (22%) currently did so; the majority of those who had lost the ability to do so found this very frustrating.
Despite advances in education, technology, home support and environmental access for people with disability,52 recent studies indicate that many people with cerebral palsy are unable to achieve the same degree of independence as their peers. Thus, in 1996, although 75% of a Dutch cohort of young adults with cerebral palsy were mainly independent with respect to the activities of daily living, 24% required sheltered or institutional accommodation; 30% lived with their parents, compared with 20% of the general Dutch population of the same age; and only 12.5% lived with a partner, compared with 60% of the general Dutch population of the same age. 48 Only 16% had paid employment other than sheltered labour; 41% attended a day activity centre for the disabled. 48 In a US study52 of non-institutionalised adults with cerebral palsy aged from 19 to 74 years, most of whom had moderate to severe disabilities, 67% lived independently of parents or relatives, but almost half of these had an attendant. Approximately 25% had been married at some point in their lives. In total, 53% were competitively employed (57% of those with moderate and 35% of those with severe physical disability); 7% were in semicompetitive employment; 18% were in sheltered employment; and only 16% had never been involved in an organised work situation. However, 50% had speech deficits that severely compromised verbal communication, and by the age of 25 approximately 75% had stopped walking by choice because of the fatigue and inefficiency involved. 52 Neither of these studies may be fully representative of people with cerebral palsy: the Dutch study obtained responses from only 46% (80/173) of young adults who met the study inclusion criteria,48 whereas the US study population was limited to non-institutionalised adults and was self-selected through contacts with the local United Cerebral Palsy Affiliate. 52
Deafness also has substantial implications for quality of life. Even if they are provided with hearing aids and appropriate tuition and speech therapy at a young age, over 90% of prelingually deaf children are unlikely ever to develop good speech and good speech-reception skills. 53 They will therefore be excluded from many aspects of a largely hearing society and may suffer delayed social development and isolation. In an Australian cohort study54 the parentally-reported psychosocial well-being of 7- to 8-year-old children with significant congenital hearing loss was significantly poorer than that of their hearing peers. Such problems persist in later life. In Belgium, a national health survey of people aged 15 years and older55 found that those with a hearing disability of any kind reported poorer physical and mental health than those with normal hearing.
Parental and sibling well-being: psychological effects of fetal loss, stillbirth, neonatal death or postnatal death
Research has shown that the experience of losing a child is by far the most painful grief experience. 56 Contributory factors are likely to be the fact that such loss appears to go against the natural order and that, as both parents are equally affected, they are less able to support each other than they would be in the loss of a parent or sibling. Such factors are also likely to be relevant in relation to stillbirth and fetal loss. Although several studies have considered the impact on parents of stillbirth and neonatal death, none has been found that specifically studies the impact of fetal loss as a result of HDN.
Following perinatal death, mothers naturally experience sadness, anxiety, guilt and depressive symptoms. Although these feelings diminish in severity over the first year, it is normal for them to continue for up to 2 years. Fathers experience similar levels of grief, anxiety and depression, although they generally display less active grief than mothers. Some parents suffer prolonged symptoms that require psychological treatment, and 20% of both mothers and fathers suffer post-traumatic stress disorder in the pregnancy following a stillbirth. Increases in parental discord and relationship break-up have also been identified following perinatal death. Older siblings may also suffer a severe sense of loss. 57–59
Some studies, including two prospective studies,60–62 have suggested that grief following stillbirth or fetal loss is related to length of gestation. However, other studies indicate that length of gestation is not necessarily a factor in the case of wanted pregnancies. A US study63 found that, at 2 months post-termination, women who had terminated wanted pregnancies for fetal anomalies experienced grief as intense as those who had suffered spontaneous perinatal loss. Although the terminated pregnancies were of a younger gestational age (under 20 weeks) than the spontaneous losses, the grief responses were similar, being determined by the ‘wantedness’ of the pregnancy and not by gestational age. 63 A second US study64 also found that the termination of a wanted pregnancy because of fetal anomalies was experienced as a perinatal death rather than as an elective abortion. The grief was independent of gestational age and it was felt that, in a wanted pregnancy, bonding started before conception. 64 Once parents perceive both the pregnancy and the baby as real, and begin to attach to their baby as their child, with a pet name and a personality, the grief that follows a loss is intense and will last for months to years. For some parents this attachment happens very early in the pregnancy. 58
No work has been undertaken on the valuation of parental grief following miscarriage, stillbirth or neonatal death, and it is considered that, for ethical reasons, such work would be impossible to undertake (M Jones-Lee, 2001, personal communication).
Parental and sibling well-being: ability to achieve intended family size
To its parents, any infant or fetus who dies is an irreplaceable individual. However, most parents affected by miscarriage, stillbirth, neonatal death or postneonatal death can hope to achieve their intended family size by a subsequent pregnancy. This may be considerably less easy when the infant or fetus has died as a result of RhD sensitisation, as that will affect all subsequent RhD-positive pregnancies in that mother. If the father is homozygous RhD positive (i.e. has two RhD-positive genes) then all future pregnancies will be affected and will require intensive monitoring and intervention, with the possibility of an unsuccessful outcome. If the father is heterozygous (i.e. has one RhD-positive gene and one RhD-negative gene) there is still a 50% probability that a given pregnancy will be affected. 65 As the severity with which the fetus is affected increases with each RhD-positive pregnancy, a successful outcome becomes less likely with each successive pregnancy.
Although we are not aware of any published work in this field it seems likely that failure to achieve intended family size may be the cause of long-term psychiatric morbidity in the parents. It is theoretically possible for couples to complete their family using donor insemination with RhD-negative sperm, but it is not known how many affected couples in the UK are offered, or accept, this option. Moreover, donor insemination in itself may not be devoid of long-term psychological consequences. A review found that, although donor insemination parents generally appeared to be comparable to, or better than, natural parents in their interaction and emotional involvement with their children, some studies had identified an increase in emotional/behavioural problems in children conceived by donor insemination. 66 One study of 60 couples who had children conceived both naturally and by donor insemination found that the men were significantly closer to their children by donor insemination than to their ‘other’ children. 67 However, another study found that parents who used donor insemination because of infertility feared that, when they disclosed their status to the child, he/she would reject them and search for his/her genetic father; in addition, the majority of men in this study felt jealous of the donor. 68 Clearly, the psychological issues for fathers would differ if donor insemination were used because of RhD incompatibility rather than because of male infertility; we are not aware of any studies of its use specifically because of RhD incompatibility.
Parental and sibling well-being: effects of living with a disabled child
Living with a disabled child may affect parental and sibling well-being. In a German study69 parents in families with children with mental and/or physical disabilities assessed the quality of life of all family members as significantly lower than did parents in families with children without disabilities. This conflicts with the findings of a Canadian study46 in which adolescents and young adults with cerebral palsy and their mothers, fathers and siblings were broadly similar to control groups in their mean scores for family functioning, life satisfaction and perceived social support. However, the Canadian investigators note that their results may be affected by self-selection bias, in that families in which care of the family member with cerebral palsy was particularly stressful and time-consuming may have chosen not to participate in the study; they also note that the control families were identified by the families of a person with cerebral palsy, who may have selected families with levels of functioning similar to their own. Fathers and siblings seemed to be more affected than mothers by the presence of a family member with cerebral palsy. Parental future expectations were lower for adolescents and young adults with cerebral palsy than for those without. 46
An Australian study70 identified that the parents of children with mild to severe cerebral palsy experienced significantly more emotional worry/concern and limitations in time available for their personal needs as a result of their child’s physical or psychosocial health than did the parents of unaffected children; moreover, their child’s health had a significantly greater impact on family activities. As might be expected, the limitations in time, and the impact on family activities, were greater in parents of children with severe rather than mild cerebral palsy but the emotional impact was the same regardless of whether the child had mild or severe cerebral palsy. 70 A US study71 also found that parents of children with mild to severe cerebral palsy suffered greater emotional worry/concern and limitations in time available for their personal needs than a normative sample. A Canadian study72 found that the primary caregivers of children with cerebral palsy (in 95% of cases a parent, primarily the mother) reported significantly more physical and psychological ill-health than the general population of caregivers; they also had lower incomes, despite the absence of any important differences in education between the two samples. 72 A Turkish study73 found that quality of life in mothers who looked after children with cerebral palsy at home was significantly lower than that of mothers of children with minor health problems (fever, cough or diarrhoea) in all dimensions except physical functioning. Quality of life was significantly lower among the mothers of children with the least independent motor function compared with the mothers of less badly affected children. 73 More generally, an Australian study74 found that the majority of mothers of children with a physical disability, intellectual disability or autism had significantly poorer mental health than local population norms.
Families with children with intellectual disabilities are significantly more disadvantaged on all indicators of socioeconomic position than families with children without such disabilities. 75 A British study76 suggests that differences in socioeconomic position, household composition and maternal characteristics (age, marital status and general health) between mothers of children with intellectual disabilities and mothers of ‘typically developing’ children account for the lower levels of happiness seen in the mothers of the disabled children. The economic impact on the family of the presence of a disabled child extends beyond childhood: in the US, the prospective Wisconsin study77 found that, by the age of 53, the parents of adult children with developmental disabilities had significantly lower incomes and savings than comparison parents.
The presence of a child with prelingual deafness in a hearing family also has an impact on family members; however, some parents express marked anxiety about a child’s deafness, others little or none. The impact on siblings varies depending on characteristics such as age, gender and birth order, family characteristics such as size and ethnicity, and parenting strategies; older hearing sisters are adversely affected because they frequently provide too much care for the deaf sibling, whereas older hearing brothers are less affected in this respect; all siblings are potentially equally affected by differential parental treatment of their deaf and hearing children. Sibling relationships are more difficult when the deaf child is younger than the hearing sibling(s),78 as would be the case with deafness caused by HDN.
Significance for the NHS
In 2005, the most recent year for which figures are available, there were 645,835 live births and 3483 stillbirths in England and Wales. 39 As around 10% of all births in the UK are of RhD-positive infants delivered of RhD-negative women, each year in England and Wales approximately 65,000 live births and stillbirths will fall into this category. In the absence of RAADP around 1% of RhD-negative women who deliver a RhD-positive infant will become sensitised antenatally – approximately 650 women a year in England and Wales. Around 550 of these women are likely to have a subsequent pregnancy that will require close monitoring; approximately 415 of the fetuses are likely to develop RhD HND and 31 of these are likely to suffer fetal death, stillbirth, neonatal death or postneonatal death. Some of the 550 sensitised women who undergo second pregnancies will go on to have further pregnancies and again a proportion of these will be affected. It seems likely that, when third and subsequent pregnancies in sensitised women are taken into account, there will be approximately 520 pregnancies a year in sensitised women in England and Wales.
Affected pregnancies must be monitored closely because the timing of IUT is a major part of optimal management; it should be delivered only in moderate to severe anaemia but before moderate to severe hydrops develops. 79 The obstetric input required to manage these cases is considerable, including:
-
monitoring of the maternal serum antibody level at least monthly until 28 weeks’ gestation and every 2 weeks thereafter80
-
consultant review, with Doppler scans, at a frequency determined by the level of risk: in many women this will be weekly, especially after 30 weeks (C Dhillon, 2008, personal communication)
-
possible delivery at 34–36 weeks, with subsequent special care costs.
In utero transfusion may be required every 2–4 weeks and in severe cases the mother may also require infusions of immunoglobulin (N Davies, 2001, personal communication). The level of monitoring varies from case to case but the cost is clearly substantial.
In total, 10–12% of fetuses affected by HDN require IUT to correct anaemia,27,81 and its provision has led to a major reduction in the need for elective premature delivery (e.g. at 28 weeks). However, the benefit of avoiding elective premature delivery, and the resulting risks, has to be balanced against an estimated fetal loss from IUT of approximately 1–3%. 40 IUT requires a highly specialised unit with skilled personnel, equipment (particularly ultrasound) and access to specialised blood products.
Some neonates with HDN require postnatal exchange transfusions for rapidly rising serum concentrations of bilirubin that are not responsive to intensive phototherapy. 31 Such infants present less frequently than in the past because neonatal jaundice and immediate anaemia are not major problems in newborns treated until near term with a successful IUT programme. However, because babies who have undergone IUT commonly develop anaemia between 2 and 6 weeks of age, they require monitoring and, if necessary, treatment with erythropoietin or top-up transfusions. 2,82
Two UK studies have identified outcomes (including resource use) in pregnancies in women with RhD antibodies. One study83 collected data relating to all such women in the seven maternity units served by the Mersey and North Wales Blood Centre, Liverpool, between December 1993 and November 1994, and the other study19 collected data relating to all such women in Northern Ireland between September 1994 and February 1997. A third, substantially smaller study20 collected similar data in a tertiary care centre in Zagreb, Croatia. A very high proportion of infants in the Croatian study required IUT, intensive treatment unit (ITU) admission, exchange transfusions and/or phototherapy, presumably because the study included only severely affected pregnancies transferred to the tertiary care centre, whereas the two British studies presented data relating to all pregnancies in women with RhD antibodies. However, it is difficult to know how to interpret the noticeable difference between the two British studies in both the proportion of affected babies and the resource implications associated with their care (Table 6).
| Mersey and North Wales, December 1993–November 1994,83 n (%) | Northern Ireland, September 1994–February 1997,19 n (%) | Zagreb, Croatia, January 1997–January 2003,20 n (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of pregnancies | 100 | 124 (130 fetuses) | 23 |
| Termination for fetal abnormality | None reported | 2 (2) | 0 |
| Miscarriage | 4 (4) | 5 (4) | 0 |
| Intrauterine death | 2 (one following IUT) | 0 | 3 (13) |
| Stillbirth of unknown cause | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Stillbirth due to cardiac abnormality | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 |
| Stillbirth following IUT | None reported | 2 (2) | 0 |
| Live-born affected babies | 34 (34) | 76 (58) (includes one neonatal death from severe hydrops) | At least 17 (≥ 74) |
| Live-born unaffected babies | 60 (60) (includes 38 RhD-negative pregnancies) | 44 (34) (includes 17 RhD-negative pregnancies) | No more than 3 (≤ 13) (includes one RhD-negative pregnancy) |
| Total fetuses requiring IUT | 4 (4)a (includes one intrauterine death) | Not reported | 9 (39) (median number of transfusions 3, range 1–5) |
| Babies requiring admission to neonatal ITU | Not reported | 59 (45) (mean length of stay 21.4 days) | 6 (26) (median length of stay 6 days, range 3–8 days) |
| Babies requiring exchange or top-up transfusions | 6 (6) | 29 (22) (mean number of transfusions per baby 2.1) | 14 (61) (median number of transfusions per baby 2, range 1–6) |
| Babies requiring phototherapy | 8 (8) | 55 (42) (mean length 5.1 days) | 17 (74) |
Resource utilisation data are also available from an audit of 70 pregnancies referred to the Liverpool Women’s Hospital for the management of RhD disease and 15 more pregnancies managed in consultation with colleagues in district general hospitals, over the 3.5 years before the introduction of RAADP. Between them these 85 pregnancies required:
-
292 visits to consultant specialists (mean of 3.4 per pregnancy)
-
102 scans (mean of 1.2 per pregnancy)
-
118 amniocenteses (mean of 1.4 per pregnancy)
-
86 intrauterine transfusions (mean of one per pregnancy)
-
three emergency Caesarean sections for cord complications during the procedures in the third trimester.
One perinatal death and two deaths under 22 weeks were related to the procedures. 84
Clinical experts suggest that practice has changed in recent years such that there are fewer invasive procedures such as amniocentesis but substantially more Doppler ultrasound scans per affected pregnancy. This has resulted in an increase in the number of antenatal outpatient visits but a marked reduction in the number of invasive procedures and the incidence of sensitisation and fetal loss associated with them.
If, as suggested earlier in this section, in the absence of RAADP there would be approximately 520 pregnancies a year in sensitised women in England and Wales then the implication of the study carried out in Northern Ireland19 is that, in addition to around 37 fetal or neonatal deaths, these pregnancies would result in approximately 21 children with minor developmental problems and eight with major permanent developmental problems. These children would require significant NHS and other resources. Although cerebral palsy varies widely in severity, treatment may be complex and long term, including therapy, special education, medication, orthopaedic surgery and the provision of appliances; in adulthood, special accommodation and employment may also be needed. 70,71 Profound deafness is also associated with substantial costs. In the US the expected lifetime cost to society of a child with profound deafness of prelingual onset was estimated in the late 1990s to exceed US$1 million because of the need for special education and because of reduced work productivity. 85 In the UK the mean societal cost of a year of life at 7–9 years of age at 2003 prices was estimated to be £14,093 for children with congenital bilateral permanent hearing impairment and £4207 for normally hearing children. 86
Current service provision
It is current national guidance that RAADP be offered to all non-sensitised pregnant women who are RhD negative. The clinician responsible for the prenatal care of a non-sensitised RhD-negative woman should enable her to make an informed choice about treatment taking into account circumstances under which such prophylaxis would not be necessary (for instance, if the woman has opted to be sterilised after the birth of her baby or is otherwise certain that she will not have another child after her current pregnancy, or if she is in a stable relationship with the father of the child and he is known or found to be RhD negative). Use of RAADP should not be affected by use of prophylactic anti-D for a potential sensitising event earlier in the same pregnancy. 87
It is also current standard practice in the UK to give 500 IU of intramuscular anti-D immunoglobulin within 72 hours of delivery to all RhD-negative pregnant women who deliver RhD-positive infants and who are not already sensitised. 88 This dose will cover a TPH of at least 4 ml of fetal red cells (i.e. 99% of all TPHs). 10 The size of any FMH is routinely estimated and further anti-D given if indicated. Any event during pregnancy with the potential to cause sensitisation should also prompt assessment of FMH and administration of anti-D within 72 hours. Such events include chorion villus sampling, (late) miscarriage, termination of pregnancy, amniocentesis, abdominal trauma, antepartum haemorrhage and external cephalic version.
There is some uncertainty about the current uptake of RAADP in England and Wales. It has not been universally adopted: in their submission,89 the Royal College of Physicians and Royal College of Pathologists state that, in 2005, a survey of 328 UK maternity units found that only 75% were offering RAADP; of these, 81% were using the two-dose regimen. They also refer to a recent postal survey of 233 hospital transfusion laboratories which found that, of the 173 laboratories (75%) which responded, only 155 (90%) had fully implemented RAADP. There are no data on the level of uptake in terms of the number of RhD-negative pregnant women in those centres that have implemented RAADP who actually receive RAADP. 90
The Royal Colleges of Physicians and Pathologists also refer to anecdotal evidence that many centres are changing from a two-dose to a single-dose regimen, presumably for logistic reasons and perhaps also in the hope of increasing compliance. 89 The Bio Products Laboratory (BPL) submission91 indicates that 55% of hospitals that have implemented RAADP are currently using D-Gam 500 IU in a two-dose regimen, whereas Behring92 state that 71 centres in England and Wales are currently using a single 1500-IU dose of Rhophylac.
Description of technology under assessment
The technology under assessment is RAADP for non-sensitised pregnant women who are RhD negative. Prophylactic anti-D, whether antenatal or postpartum, can only suppress primary RhD immunisation; it has no effect in women who have already developed anti-D, however weak,10 and therefore should not be given to such women.
The half-life of prophylactic anti-D is approximately 3 weeks; it can be detected by serological tests for several weeks, by the indirect antiglobulin test (IAT) for around 8 weeks, and by more sensitive techniques for up to 12 weeks (exceptionally, for several months). 80
RAADP may take the form of either two doses of at least 500 IU of anti-D immunoglobulin, the first at 28 weeks’ and the second at 34 weeks’ gestation, or a single dose of at least 1500 IU at 28 weeks (1500 IU of Rhophylac is sufficient anti-D to neutralise the sensitising potential of approximately 15 ml of RhD-positive red blood cells93). In theory, if prophylactic anti-D has a half-life of up to 12 weeks, a two-dose regimen will provide greater protection in late pregnancy. The British Committee for Standards in Haematology supports the use of the two-dose regimen recommended in the previous NICE guidance and notes that more evidence is required to establish the comparative efficacy of a single dose of 1500 IU at 28 weeks. 94
RAADP is additional to any antenatal anti-D prophylaxis (AADP) offered in response to a potential sensitising event, and postpartum anti-D prophylaxis is still required within 72 hours of delivery if the infant is RhD positive.
When the original assessment of RAADP was undertaken on behalf of NICE by Chilcott et al. in 2001,1 only two products were licensed for use in the UK. These products, manufactured by BPL and Baxter Healthcare, were both two-dose regimens. Since then two additional products have been licensed for UK use; these products, manufactured by CSL Behring and Baxter BioScience, are both single-dose regimens (for details see Summary of product characteristics). This updated assessment has been prompted by the availability of these single-dose products, as well as by the wish to reflect potential changes in the management of sensitised pregnancies, rather than by any significant change in the evidence base relating to the efficacy of RAAPD.
As noted above, it is current national guidance that RAADP be offered to all non-sensitised pregnant women who are RhD negative. Prenatal identification of the fetus’s RhD blood group would enable RAADP to be targeted only to those non-sensitised RhD-negative women pregnant with RhD-positive infants. This approach has not previously been possible because identification of the blood group of the fetus used to require a sample of fetal cells, obtained using invasive procedures (amniocentesis or chorion villus biopsy), which themselves carry the risk of FMH and consequent sensitisation or, in women who have already undergone silent sensitisation, boosting of the maternal immune response,95 in addition to an 0.5–1.0% risk of spontaneous abortion. 96 However, recent technological developments have made it possible to predict the fetal RhD genotype non-invasively by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using fetal DNA present in the mother’s plasma. 95 In principle, this technology permits the screening of all non-sensitised RhD-negative pregnant women to enable antenatal prophylaxis to be targeted only to those carrying RhD-positive fetuses. However, to be feasible in practice the test results must yield no false negatives (i.e. cases in which the fetus appears to be RhD negative but is actually RhD positive), and this level of accuracy does not yet appear to have been achieved. 96 (The existence of false positives is less important, as it simply means that, as in current practice, a RhD-negative woman carrying a RhD-negative fetus will be given unnecessary prophylaxis. 96) Moreover, targeted antenatal prophylaxis would only be possible if it was demonstrated that the test was reliable when undertaken before 28 weeks’ gestation. This has yet to be achieved. However, in their submission,89 the Royal College of Physicians and Royal College of Pathologists anticipate that a test which has 99% accuracy at 15+ weeks’ gestation will become routinely available within 12–24 months, that the costs of implementation will not be prohibitive, and that the advantages in terms of the reduced use of anti-D (for potential sensitising events as well as for RAADP) will be significant. However, were such a test to be routinely used it would still be necessary to use anti-D in compliance with the current guidelines either in the absence of test results or if the results were equivocal, as well as in cases in which the fetus is confirmed to be RhD positive. 91
In most cases it is likely that RAADP is administered by midwives based in the community and/or antenatal clinic. Side effects (short-term discomfort at the injection site and, very rarely, anaphylaxis) are rare and do not necessitate monitoring of recipients other than by extending the clinical audit process to include RAADP. However, as with other blood products, scrupulous record keeping is essential to be able to link individual women with specific batches of anti-D. This is important both because of the risk of infection transmission and because of the importance of traceability for the interpretation of blood tests if a blood transfusion is needed at a later date. 89
Summary of intervention
Anti-D immunoglobulin is a blood product extracted from human plasma obtained from blood donors with high-titre circulating anti-D antibodies. 97 Originally these donors were RhD-negative women sensitised through pregnancy, and men and women immunised through transfusion; their antibody titres were then regularly boosted by the injection of RhD-positive red blood cells. However, as the demand for anti-D rose following the introduction of antenatal prophylaxis it became necessary in both the USA and Australia to deliberately immunise RhD-negative donors specifically for the purpose of obtaining anti-D immunoglobulin,98,99 and we understand that this is now universal practice (Professor M Contreras, 2007, personal communication).
Historically, most RhD immunoglobulin products have been prepared using the Cohn cold ethanol fractionation method. 100 The yield of anti-D immunoglobulin G (IgG) obtained using this method is low – only 50–60% of the anti-D present in the original plasma. Anti-D prepared by this method contains proteins that may cause adverse reactions if given intravenously and so it can only be given intramuscularly, unless it has been specifically treated to remove these proteins. It also contains small but significant amounts of other plasma proteins, especially immunoglobulin A (IgA) and immunoglobulin M (IgM), which may cause localised itching, swelling and discomfort and, very rarely, anaphylactic reactions. 101
Anti-D can also be prepared using ion-exchange chromatography. This method retains over 90% of the anti-D present in the original plasma. Anti-D prepared in this way contains no demonstrable non-IgG protein and may therefore be given either intramuscularly or intravenously; if given intravenously it is more effective weight for weight than anti-D produced by the Cohn method given intramuscularly. However, care is needed when administering large quantities (in response to a massive TPH or an inadvertent RhD-incompatible blood transfusion) as intravenous delivery of the amount recommended for intramuscular use under such circumstances (6000 IU every 12 hours until the total required dose is given) may cause an unpleasant, and possibly hazardous, transfusion reaction. Anti-D prepared using the original ion-exchange chromatography methods is unstable in solution and must be prepared before injection; it is therefore less convenient for health-care personnel to use. 101 More recently, however, a multistep chromatographic fractionation method has been developed that yields a liquid-stable anti-D (Rhophylac). 100
There are two main concerns relating specifically to the safety of antenatal anti-D: the risk of enhanced anti-D immunisation of the mother (‘augmentation’) and the effect of passive anti-D on the fetus. 15 In addition, there are theoretical concerns relating to the possibility of transmission of viral or prion diseases; these apply equally to postnatal administration of anti-D, although of course antenatal administration exposes the fetus as well as the mother to any such risk. These concerns are discussed in turn in the following sections.
Concerns relating to exposure of the pregnant woman to passive anti-D
In theory, the presence of low levels of passive anti-D in the maternal circulation following RAADP could result in the enhancement of a primary immune response to RhD-positive red blood cells following FMH. However, this has not been observed in clinical trials. 15
There is also the possibility of short-term adverse events such as allergic or anaphylactic responses. Such adverse events are rare. None of the studies reviewed here reported occurrences of such short-term adverse events, and the manufacturers’ submissions report very few. BPL state that, between October 1999 and March 2005, they issued over 700,000 vials of anti-D and received 15 reports of related adverse events, five of which were classed as serious. These included one probable and one possible anaphylactic reaction and one case with tongue swelling. 91 Baxter reported in 2001 that anti-D was well tolerated – over 2.9 million doses of its product were given worldwide between January 1990 and July 2000 and only 11 reports of adverse reactions were received by Baxter. Two of these were classified as serious but both occurred long after the administration of anti-D and so were thought not to be related. Only two of the adverse reactions were thought to be possibly related to treatment – one of a visual field defect and palpitations, the other of hot flushes. 102 Baxter do not present more recent data but state that their product’s safety profile is unchanged. 103 Behring note that, between its initial launch in 1996 and the end of 2006, 2.07 million doses of Rhophylac were distributed worldwide and only 30 suspected adverse drug reactions relevant to its safety were reported, one per 69,000 doses. 92
Concerns relating to exposure of the fetus to passive anti-D
Concerns have been expressed regarding the potential risks of RAADP to the fetus, who will not benefit directly from the intervention, which is intended to protect his or her future siblings. 104 It is theoretically possible that the transfer of passive anti-D from the mother could cause fetal anaemia. However, there is no evidence that anti-D given to the mother during pregnancy is harmful to the infant, and the dosage used appears to be insufficient to cause observable haemolysis or anaemia in the fetus, even when repeated large doses are given. Although a minority (< 10%) of infants will be found to have laboratory evidence of red cell sensitisation, this is subclinical and does not result in anaemia, jaundice or the need for phototherapy. 15,105
There is some uncertainty about the possibility of longer-term adverse effects arising from exposure to anti-D. Concern has been expressed that exposing babies to anti-D in utero may have an effect on the immune system and may potentially also cause problems for RhD-negative baby girls in their later reproductive lives. 104 However, many babies who were exposed to anti-D in utero have now grown to adulthood and no evidence has been published to suggest any cause for concern.
Concerns relating to the possible transfer of viral or prion infection
Because the only source of therapeutic IgG is human plasma there are safety concerns related to the possible transfer of viral or prion infection. These vary according to the different manufacturing methods used.
Overall, immunoglobulins prepared by the Cohn cold ethanol fractionation method have an excellent safety record, which predates the introduction of specific virology testing of donors and viral inactivation of the end product. 106 This method has been shown to produce non-infective immunoglobulin from plasma contaminated with hepatitis virus. 107
By contrast, contaminated anti-D prepared by ion-exchange chromatography and used for intravenous postpartum prophylaxis was responsible for outbreaks of hepatitis C in the late 1970s in Germany107,108 and Ireland. 109 These outbreaks predated the identification of hepatitis C in 1989 and the introduction of screening of donations in 1991. 110 In Ireland, subsequent screening of all women exposed to anti-D manufactured by the Irish Blood Transfusion Service Board between 1970 and 1994 found that, although infection with hepatitis C was primarily associated with exposure to anti-D in 1977, it was also associated, although to a much lesser extent, with exposure between 1991 and 1994; again, the anti-D was an intravenous preparation manufactured by column chromatography. The investigators noted that this second, small-scale outbreak would probably not have been identified had investigations into the much larger 1977 outbreak not been undertaken in 1991 and 1994. 110 Anti-D prepared by ion-exchange chromatography currently undergoes several processes to minimise the risk of virus transmission; these include virus inactivation by solvent–detergent treatment and nanofiltration. 92 However, these measures may be of limited value against non-enveloped viruses such as hepatitis A and parvovirus B19. 111
As with other human-derived blood products, the risk of new variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (vCJD) transmission is unquantifiable. 112 Both the extent of vCJD infection in the population and its transmissibility by blood products are unknown. 9 The four cases of probable transfusion-associated vCJD identified in the UK in the last 4 years all involved donations of non-leucodepleted red blood cells transfused between 1996 and 1999, and no cases of vCJD have been associated with fractionated plasma products. 113 Nonetheless, because of the long incubation period it is not possible to conclude that there is no risk of vCJD infection. 114 Steps currently taken to inactivate viruses are unlikely to affect prion infectivity (although the manufacturer claims that the nanofiltration processes used in the production of Rhophylac contribute to the removal of abnormal prion protein92). Moreover, as plasma is pooled to produce batches of immunoglobulin, many recipients will be exposed to plasma from an individual donor: in the routine manufacture of Rhophylac the pool size is 300 l. 93 Therefore, as a precautionary measure, to minimise the theoretical risk of transmission of vCJD from blood products, all anti-D used in the UK is manufactured from US plasma, as bovine spongiform encephalopathy and vCJD have not been reported in the US.
Despite these measures, because anti-D is a human plasma-based product there is, naturally, public concern over its safety, and all staff should both receive, and give potential recipients, suitable evidence-based information about the product. Around one-third of RhD-negative women who have children are likely only ever to have RhD-negative children. Therefore, if the introduction of targeted RAADP became possible as a result of advances in non-invasive fetal genotyping, the proportion of childbearing RhD-negative women with a lifetime exposure to anti-D IgG could in theory be reduced from 100% (assuming 100% compliance with blanket RAADP) to 75%. However, in reality the reduction would be slightly less than 25% as some women would require ad hoc prophylaxis for potential sensitising events that occurred before the fetal genotype was known.
Summary of product characteristics
The product characteristics are briefly summarised in Table 7. Fuller details are presented in the following sections. It should be noted that the previous study1 reviewed the clinical effectiveness of any regimen of RAADP and the cost-effectiveness of RAADP using products manufactured by BPL and Baxter Healthcare; these are similar, but not necessarily identical, to D-Gam and Partobulin SDF respectively. The manufacturers have submitted updated data in relation to these products. The cost-effectiveness of Rhophylac and WinRho was not assessed in the previous review.
| D-Gam | Partobulin SDF | Rhophylac | WinRho SDF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Bio Products Laboratory | Baxter BioScience | CSL Behring | Baxter BioScience |
| Method of production | Fractionation | Modified fractionation | Chromatographic adsorption | Anion-exchange column chromatography |
| Administration route | Intramuscular | Intramuscular | Intramuscular or intravenous | Intramuscular or intravenous |
| Licensed RAADP regimen | 2 × 500 IU | 2 × 1000–1650 IU | 1 × 1500 | 1 × 1500 |
| List price of RAADP | £54 | £70 | £46.50 | £313.50 |
| Current NHS price of RAADP | £39 | £38–42 | Not known | Not known |
D-Gam
D-Gam is produced by BPL, a not-for-profit, government-owned plasma fractionation unit. 91 It is available in vials containing 250, 500, 1500 and 2500 IU of human anti-D immunoglobulin in the form of a solution ready for injection. 115 The 500-IU dose is licensed for RAADP in non-sensitised RhD-negative women at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation, for routine postpartum prophylaxis following delivery of a RhD-positive baby, and for potentially sensitising events during the second half of pregnancy. The 250-IU dose is licensed to treat potentially sensitising events up to 20 weeks’ gestation, and the 1500- and 2500-IU doses are licensed to provide larger doses to treat a large FMH. 91
D-Gam is produced by fractionation. It is therefore suitable for intramuscular use only. Because of the possible risk of vCJD transmission, since 1999 only US plasma has been used in its manufacture. In July 2001 a solvent–detergent step was incorporated into the fractionation process as a safeguard against the transmission of lipid-enveloped viruses. The BPL’s submission emphasises that there have been no previous substantiated reports of virus transmission involving BPL anti-D and that, internationally, there is no evidence of virus transmission with intramuscularly administered immunoglobulins. 91
The price listed in the British National Formulary116 (BNF) for 500 IU of non-proprietary anti-D is £27.00 per vial. However, the current NHS price for 500 IU of D-Gam is said to be £19.50 per vial. 91
Partobulin SDF
Partobulin SDF is produced by Baxter BioScience. It is licensed for the prevention of RhD immunisation in RhD-negative women in pregnancy or at delivery of a RhD-positive baby; in abortion/threatened abortion, ectopic pregnancy or hydatidiform mole; or when undergoing TPH resulting from antepartum haemorrhage, amniocentesis, chorionic biopsy, obstetric manipulative procedure or abdominal trauma. It is also licensed for the treatment of RhD-negative people following incompatible transfusions of RhD-positive blood or erythrocyte concentrate. 117
Partobulin SDF is produced from US plasma using a modified Cohn–Oncley fractionation process. 102 To reduce the risk of disease transmission the manufacturing process includes solvent–detergent treatment to ensure the inactivation of lipid-enveloped viruses such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C and HIV, and nanofiltration to minimise the risk from non-enveloped viruses such as hepatitis A and parvovirus B19. 103 In addition, donors are selected by medical interview and individual donations and plasma pools are screened for hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg) and antibodies to HIV and hepatitis C virus and plasma pools are tested for genomic material of hepatitis C virus. 117
Because it is produced by fractionation, Partobulin SDF is suitable for intramuscular use only. The recommended dose for routine antenatal prophylaxis is two doses of 1000–1650 IU, given slowly by deep intramuscular injection, at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation. If hypersensitivity reactions occur during administration the injection should be stopped immediately. Patients should be observed for at least 20 minutes after administration. 117 True hypersensitivity reactions are said to be rare, but patients may suffer allergic-type responses such as hives, generalised urticaria, tightness of the chest, wheezing, hypotension and other allergic or anaphylactic reactions. Patients may also experience local pain or tenderness at the injection site. 117 In addition, as Partobulin SDF contains a small quantity of IgA it may cause hypersensitivity reactions in IgA-deficient individuals. 117
Partobulin SDF is supplied in prefilled syringes containing 1250 IU of anti-D at a list price of £35;116 however, the contract prices are said to be between £19 and £21 per syringe, depending on the volumes contracted for. 103
Rhophylac
Rhophylac is produced by CSL Behring Ltd. It is licensed for the prevention of RhD immunisation in RhD-negative women in pregnancy or at delivery of a RhD-positive baby; in abortion/threatened abortion, ectopic pregnancy or hydatidiform mole; or when undergoing transplacental haemorrhage resulting from antepartum haemorrhage, amniocentesis, chorionic biopsy, obstetric manipulative procedure or abdominal trauma. It is also licensed for the treatment of RhD-negative people following incompatible transfusions of RhD-positive blood or other products containing red blood cells. 111
Rhophylac is manufactured from pooled human plasma obtained from hyperimmunised donors, using a combination of different chromatographic adsorption stages. The risk of transmitting viral infections is minimised by careful donor selection, screening of individual donations and plasma pools for specific markers of infection, and virus inactivation or elimination by the chromatographic purification process and by solvent–detergent treatment and nanofiltration. 92 The measures taken are considered effective for HIV and hepatitis B and C viruses but may be of limited value against non-enveloped viruses such as hepatitis A and parvovirus B19. 111 Although nanofiltration has been shown to contribute to the removal of abnormal prion protein92 the test prion was scrapie and not vCJD. Thus, the possibility of transmitting infective agents, including unknown or emerging viruses and other pathogens, cannot be totally excluded. 111
The safety and tolerability of Rhophylac has been evaluated in six clinical studies. In these studies 931 doses of Rhophylac were administered to 628 individuals, 447 (71%) of whom were pregnant women. Drug-related adverse events were rare and mild; they included pain or itching at the injection site and headaches. No anaphylactic or severe allergic reactions were reported. As noted earlier, 2.07 million doses of Rhophylac have been distributed worldwide between its first launch in Switzerland in 1996 and the end of 2006, and only 30 adverse drug reactions relevant to its safety have been reported, one per 69,000 doses. 92 Although no details are provided, these adverse drug reactions, together with the evidence from clinical studies, presumably underlie the product leaflet statement that patients may suffer fever, malaise, headache, cutaneous reactions and chills, and that there have been rare reports of nausea, vomiting, hypotension, tachycardia and allergic or anaphylactic reactions. 111 As Rhophylac may contain traces of IgA it may cause hypersensitivity reactions in IgA-deficient individuals. 111
The dose of Rhophylac recommended for routine antenatal prophylaxis is one dose of 1500 IU given by intravenous or intramuscular injection at, according to the manufacturer, 28–30 weeks’ gestation. If symptoms of allergic or anaphylactic-type reactions occur during administration the injection should be stopped immediately. Patients should be observed for at least 20 minutes after administration. 111
Rhophylac is supplied in prefilled syringes containing 1500 IU of anti-D immunoglobulin for intravenous or intramuscular injection111 at a list price of £46.50 per syringe. 116
WinRho SDF
WinRho SDF is produced by Baxter BioScience. Although it is licensed for routine antenatal prophylaxis, in the UK it is marketed and used solely for the treatment of immune thrombocytopenic purpura. The manufacturer therefore notes that it is priced specifically for this market and should not be routinely used for RAADP, although it could be so used if there were supply problems. 103
WinRho SDF is prepared from pooled human plasma using an anion-exchange column chromatography method. The risk of transmission of viruses, including HIV and hepatitis B and C viruses, is reduced by the use of filtration to remove lipid-enveloped and non-enveloped viruses, and solvent–detergent treatment to inactivate lipid-enveloped viruses. However, the possibility of disease transmission, including the transmission of unknown infectious agents, cannot be wholly excluded. 118
In a small number of cases, administration of WinRho SDF has been accompanied by discomfort and swelling at the site of injection and a slight elevation in temperature. As with all plasma derivatives there is a very small chance of an idiosyncratic or anaphylactic reaction to WinRho SDF in individuals who are hypersensitive to blood products. 119
When used for routine antenatal prophylaxis the recommended dose of WinRho SDF is one dose of 1500 IU given intramuscularly or intravenously at 28 weeks’ gestation. In the UK, WinRho is supplied as a powder for reconstitution; the list price of a 1500-IU vial with diluent is £313.50. 116
Identification of important subgroups
As noted earlier, important subgroups in relation to RAADP include women who will be sterilised after the birth, women who are certain that they will have no more children and women who are in a stable relationship with the genetic father of their children, with the father known or found to be RhD negative – current guidance87 notes that RAADP is not necessary under these circumstances. Although it is desirable to avoid unnecessary blood product administration it should be noted that all three groups are problematic. Some women who are sterilised after childbirth later become pregnant through in vitro fertilisation. Some women who are certain that they will have no more children do nonetheless go on to have more. In relation to the third group, the British Committee for Standards in Haematology (BCSH) guideline for blood grouping and antibody testing in pregnancy79 draws attention to the complexities of paternal testing and the potential for misidentification of the father; the Canadian guidelines caution that a partner’s RhD status should not be tested unless the pregnant woman both volunteers and confirms in private that he is the biological father. 120
Current usage in the NHS
Implementation of the policy of RAADP appears to be fairly widespread. As noted in the previous section on current service provision, in 2005 a survey of 328 UK maternity units found that 75% were offering RAADP. 89 In total, 173/233 (75%) UK hospital transfusion laboratories responded to a recent postal survey carried out on behalf of the Royal College of Pathologists; of these, 155/173 (90%) had fully implemented RAADP. 89
Although the precise RAADP regimen used by the different centres varies, the single-dose regimen appears to be gaining popularity. In 2005, 81% of the UK maternity units that offered RAADP used the two-dose regimen. 89 BPL claims that 55% of hospitals that have implemented RAADP currently use D-Gam 500 at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation. 91 However, the more recent survey of hospital transfusion laboratories found that 53/173 (31%) were using the single 1500-IU dose at 28 weeks. 89 Although the survey did not collect data on compliance, a recent audit in two UK hospitals found 86.5% compliance with the two-dose regimen. 121
MacKenzie et al. 122 found that the proportion of women refusing at least one antenatal prophylaxis injection increased from 0.8% in the period 1992–6 to 3.5% by 1997–2003. They attribute this to concerns about the possible transmission of infection by blood products and suggest that these concerns may have been exacerbated when the preparation originally used for RhD prophylaxis was withdrawn because of concerns relating to vCJD transmission. 122 A retrospective audit carried out in two UK hospitals in 2004121 found much higher refusal rates: 10.6% of eligible women (22/207) refused the first 28-week dose of a two-dose RAADP regimen and 13.5% (28/207) refused the second dose; none of the women who declined the first dose at 28 weeks’ gestation received the second dose at 34 weeks. However, very few women were documented as declining RAADP because of concerns about infection transmission (Table 8). Moreover, the first two reasons given in Table 8 relate to circumstances in which RAADP is not indicated. Although higher compliance may perhaps be achieved with a single-dose than with a two-dose regimen it should be noted that the majority of women who declined the two-dose regimen declined at the first dose and it therefore seems unlikely that they would have consented to a single-dose regimen.
| Reason for declining | Number of women declining | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| First dose | Second dose | Overall | |
| Partner RhD negative | 6 | 8 | 8 |
| Last planned pregnancy | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| Fear of infection | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| No reason documented | 12 | 14 | 14 |
| Total | 22 | 28 | 28 |
Anticipated costs associated with intervention
The anticipated costs associated with RAADP are the cost of anti-D itself plus the cost of administration. The list prices of the different types of anti-D are:
-
D-Gam: £27.00 per vial = £54.00
-
Partobulin SDF: £35.00 per vial = £70.00
-
Rhophylac: £46.50 per vial = £46.50
-
WinRho SDF: £313.50 per vial = £313.50.
RAADP administration costs are minimal if anti-D can be provided during routine antenatal appointments. Resource implications for the management of adverse events associated with anti-D are extremely small.
Chapter 2 Definition of the decision problem
This review seeks to identify any evidence for advances in practice in RAADP since the 2002 appraisal conducted by NICE. 87 It assesses the current clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of RAADP for RhD-negative women.
Decision problem
The decision problem has been specified as follows.
Intervention
RAADP given by injection in any of the licensed regimens, in line with current NICE guidance, which recommends that RAADP be offered to all non-sensitised pregnant women who are RhD negative regardless of whether they have already been offered prophylactic anti-D following a sensitising event earlier in the pregnancy:
-
two doses of at least 500 IU at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation (D-Gam)
-
two doses of 1000–1650 IU at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation (Partobulin)
-
one dose of 1500 IU at 28 weeks’ gestation (Rhophylac)
-
one dose of 1500 IU at 28 weeks’ gestation (WinRho).
Population (including subgroups)
The population includes all non-sensitised primigravidae and multigravidae pregnant women who are RhD negative. Ethnic minorities within England and Wales are considered within a subgroup analysis.
It should be noted that, because of the feasibility and ethical considerations of determining the genotype of the father, and the lack of certainty associated with whether a woman will have more children, an evaluation of these subgroups has not been carried out as stated in the assessment protocol. For example, the Royal College of Nursing123 states that the current guidance ‘presents some practical difficulties for midwives’ in that ‘in addition to the sensitivities of discussing paternity, there are difficulties associated with an institution assuming that the father is indeed RhD-negative as reported without having this confirmed by internal testing. Routine testing of the partners of RhD-negative women would have logistical, administrative and financial implications.’
Relevant comparators
RAADP delivered using different dosing regimens and different methods and no RAADP.
Outcomes
-
Reduction in the incidence of sensitisation (alloimmunisation) in RhD-negative women delivered of RhD-positive infants (the at-risk population).
-
Reduction in incidence of HDN.
-
Survival of the child.
-
Disability of the child.
-
Health-related quality of life.
-
Adverse effects of treatment.
Study types
-
Systematic reviews.
-
Randomised controlled trials (RCTs).
-
Non-randomised controlled studies.
Overall aims and objectives of assessment
The review has the following aims:
-
to evaluate the clinical effectiveness of anti-D for RhD-negative pregnant women, in any licensed regimen, in terms of a reduction in the incidence of sensitisation (alloimmunisation) in RhD-negative women delivered of RhD-positive infants, a reduction in the incidence of HDN, survival of the child, disability of the child, and health-related quality of life of the child and parents (if relevant evidence is available)
-
to evaluate the adverse effect profile
-
to estimate the incremental cost-effectiveness of different dosing regimens and different methods of administration of anti-D prophylaxis
-
to identify key areas for primary research
-
to estimate the possible overall cost in England and Wales.
Chapter 3 Assessment of clinical effectiveness
Methods for reviewing effectiveness
Identification of studies
The aim of the search strategy was to provide as comprehensive a retrieval as possible of trials relating to antenatal anti-D prophylaxis (AADP) for RhD-negative women.
Sources searched
Keyword and thesauri searches were undertaken in MEDLINE, CINAHL, EMBASE, BIOSIS, Science Citation Index, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, NHS Health Technology Assessment database and NHS Economic Evaluations Database from inception to July 2007. Websites containing registers of trials and ongoing research were also searched. These included the National Research Register and the MetaRegister of the Current Controlled Trials websites. In addition, the bibliographies of retrieved papers (including the previous review1) were scrutinised. No specific searches were carried out to identify conference abstracts, other than those identified by the searches detailed above.
Keyword strategies
Sensitive keyword strategies using free text and, when available, thesaurus terms were developed to search the electronic databases. Synonyms relating to the intervention (e.g. Rh-Hr Blood-Group System, Rho(D) Immune Globulin, Rh Isoimmunisation and anti-D prophylaxis) were combined with synonyms relating to the patient population (e.g. pregnancy, pregnancy complications, pregnancy trimesters, prenatal care, postnatal care).
Search restrictions
A methodological filter aimed at identifying controlled clinical trials (including before and after studies) was used in the searches of MEDLINE, EMBASE and CINAHL. Further filters were used to identify papers relating to cost/s and systematic reviews. Language restrictions were not used on any database, and no date restrictions were applied. All searches were undertaken between May and August 2007.
A copy of the general search strategy can be found in Appendix 1.
Specific systematic searches for adverse event data were not undertaken, and the clinical review therefore includes only adverse event data reported by the included studies.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria were as follows:
-
Population: pregnant women who are RhD negative.
-
Intervention: RAADP using either two doses of at least 500 IU at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation or a single dose of at least 1500 IU at 28 weeks’ gestation, in either case followed by a further dose of anti-D given at, or within 72 hours of, delivery if the infant is RhD positive.
-
Comparator: RAADP using different dosing regimens and/or methods of administration and no RAADP.
-
Outcomes: sensitisation (alloimmunisation) rates among RhD-negative women delivered of RhD-positive infants (the at-risk population); incidence of HDN; survival of the child; disability of the child; health-related quality of life; adverse effects of treatment.
-
Study design: any of systematic reviews, randomised controlled trials, non-randomised controlled trials.
The exclusion criterion was studies considered methodologically unsound or not reporting results in the necessary detail.
Study selection was undertaken by one researcher. Any studies that gave rise to uncertainty were reviewed by a second researcher and any disagreements resolved by discussion. Publication bias was not investigated.
Data abstraction strategy
Data were abstracted by one researcher using a standardised data extraction form. Any studies that gave rise to uncertainty were reviewed by a second researcher and any disagreements resolved by discussion. Missing data were sought from authors when possible.
Critical appraisal strategy
Published papers were assessed according to the accepted hierarchy of evidence, whereby meta-analyses of RCTs are taken to be the most authoritative forms of evidence, with uncontrolled observational studies the least authoritative. Because of the paucity of RCTs in this area, data from non-randomised studies were also used. The quality of randomised studies was assessed using quality criteria based on those proposed by the NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD)124 (see Appendix 2). However, the CRD quality criteria for observational studies were of very limited relevance to the specific non-randomised studies included in this review, and their quality was therefore judged primarily on the basis of two key factors: the comparability of the intervention and control groups, and the use of intention to treat analysis.
Methods of data synthesis
The prespecified outcomes outlined in the section on inclusion and exclusion criteria have been tabulated and discussed within a descriptive synthesis. Where appropriate, meta-analysis has been used to synthesise data. The meta-analyses were conducted using binary logistic regression with a fixed-effects model, using Minitab statistical software. The study and treatment groups were used as the variables for the model. The outcome of the regression analysis was an odds ratio for the treatment arm versus the control arm. Because of the low event probability the odds ratio was assumed to be a good approximation to the relative risk of sensitisation in the cohort who received RAADP, compared with the relative risk of sensitisation in patients who received conventional management. The Minitab software was also used to calculate a p-value for statistical heterogeneity. No subgroup analyses were undertaken.
Results
Quantity and quality of research available
Quantity of research available
The original systematic review carried out on behalf of NICE1 was not limited to specific licensed anti-D dosage regimens. It identified 11 studies comparing an intervention group receiving RAADP with a control group (see Table 9 for details). However, only eight of these studies met the inclusion criteria for the current review by stating that they used one of the currently licensed regimens. These were:
-
the studies by Huchet et al. ,125 MacKenzie et al. ,126 Mayne et al. 127 and Tovey et al. ,128 which used two doses of 500 IU at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation
-
the study by Bowman et al. ,129 which used two doses of 1500 IU at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation
-
the 1978130 and 1987131 studies by Bowman and Pollock and the study by Trolle,132 which used a single dose of 1500 IU at 28 weeks’ gestation.
| Study | Study type | Date and location of intervention | Date and location of control | Patient selectiona | Specific product (production method) and route of administration | Dosage and administration schedule |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bBowman et al. 1978129 | Prospective study, historical/geographical controls | December 1968–August 1976, Winnipeg, Canada | March 1967–December 1974, Manitoba, Canada | Primigravidae | Rho(D) immune globulin (Cohn method), Connaught Laboratories, Toronto; i.m.131 | 2 × 1500 IU, 28 and 34 weeks |
| bBowman and Pollock 1978130 | Prospective study, historical controls | March 1976–June 1977, Manitoba, Canada | March 1967–December 1974, Manitoba, Canada | Primigravidae and unsensitised multigravidae | Rho(D) immune globulin (Cohn method), Connaught Laboratories, Toronto; i.m. | 1500 IU, 28 weeks |
| bBowman and Pollock 1987131 | Retrospective study, historical controls | June 1977–February 1986, Manitoba, Canada | March 1967–December 1974, Manitoba, Canada | Primigravidae and unsensitised multigravidae | RhIG-IV (WinRho) (ion exchange), Winnipeg Rh Institute; usually i.m. but could be i.v. | 1500 IU, 28 weeks |
| Hermann et al. 1984134 | Prospective study, historical controls | Not stated, Växjö, Sweden | 1968–77, Växjö, Sweden | Primigravidae and unsensitised multigravidae | Rhesonativ, KabiVitrum AB, Sweden; i.m. | 1250 IU, 32–34 weeks |
| bHuchet et al. 1987125 | Quasi-RCT | January 1983–June 1984, Paris | January 1983–June 1984, Paris | Primigravidae | Product not specified; i.m. | 2 × 500 IU, 28 and 34 weeks |
| Lee and Rawlinson 1995135 | RCT | Not stated, UK | Not stated, UK | Primigravidae | Not specified | 2 × 250 IU, 28 and 34 weeks |
| bMacKenzie et al. 1999126 | Community intervention trial (controlled before-and-after study) | 1990–6, Oxfordshire | 1990–6, Northants | Primiparae | Not specified | 2 × 500 IU, 28 and 34 weeks |
| bMayne et al. 1997127 | Retrospective before-and-after study | 1993–5, southern Derbyshire | 1988–90, southern Derbyshire | Primiparae | Not specified | 2 × 500 IU, 28 and 34 weeks |
| Parsons et al. 1998136 | Retrospective survey, geographical controls | 1988–95, Nova Scotia | 1988–95, Scotland | Not stated | Not specified | One dose, 28 weeks |
| bTovey et al. 1983128 | Prospective study, historical controls | 1980–1, Yorkshire | 1978–9, Yorkshire | Primigravidae | Not specified | 2 × 500 IU, 28 and 34 weeks |
| bTrolle 1989132 | Prospective study, historical controls | 1980–5, Kolding, Denmark | 1972–7, Kolding, Denmark | Primigravidae and unsensitised multigravidae | Not specified | 1500 IU, 28 weeks |
An article by Thornton et al. 133 was also included as it presented follow-up data relating to the study by Tovey et al. ,128 studying the safety and efficacy of antenatal prophylaxis by examining obstetric data relating to women in that trial in their first and subsequent pregnancies. There was agreement between the first and second reviewers in relation to study selection and validity.
The updated searches identified four additional papers that related to relevant studies of clinical effectiveness (see Table 10 for summary). Only one of these related to a study that was not included in our previous review. This was the relatively recent RCT by MacKenzie et al. 100 comparing intravenous with intramuscular Rhophylac. A conference abstract by MacKenzie et al. 137 related to the 1999 community intervention study by MacKenzie et al. ;126 it did not present any additional data. A further two papers by Bowman14,101 related to a clinical trial of WinRho whose results were combined with those of the subsequent service programme of RAADP with WinRho in Bowman and Pollock’s 1987 analysis of failures of intravenous anti-D. 131 As the clinical trial effectively takes the form of a case series compared with the control group reported in the 1978 study of Bowman et al. 129 there seems no reason to differentiate between the trial and the service programme components of the 1987 study, and therefore the results reported by Bowman et al. in 198014 and by Bowman in 1982101 have been considered as interim results in relation to the 1987 study.
| Paper | Status |
|---|---|
| MacKenzie et al. 2004100 | Included as a new independent study |
| MacKenzie et al. 1998137 | Included as relating to a previously included study (MacKenzie et al. 1999125) |
| Bowman et al. 198014 | Included as relating to a previously included study (Bowman and Pollock 1987131) |
| Bowman 1982101 | Included as relating to a previously included study (Bowman and Pollock 1987131) |
It was not possible to read an additional, potentially relevant study by Eklund and Nevanlinna,138 as it was published in Finnish and had no English abstract. However, as it was published in 1971 it seems highly likely that it dealt with postpartum rather than antenatal prophylaxis. Similarly, it was not possible to obtain a potentially relevant paper by Potron et al. ,139 but because this was published in 1973 it seems likely that it too would have dealt with postpartum rather than antenatal prophylaxis. Finally, we were unable to find any further information regarding a proposed multicentre trial of monoclonal anti-D,140 and understand that the principal investigator is now deceased.
A population study by Koelewijn141 of the effect of the introduction of RAADP in the Netherlands did not meet our inclusion criteria as it used a single dose of only 1000 IU of anti-D at 30 weeks’ gestation.
Thus, the electronic literature searches identified 670 potentially relevant references, 12 of which referred to eight relevant studies of clinical effectiveness. Only one reference related to a study that had not been included in our earlier review (Figure 1). For details of excluded studies, including those included in the previous review, see Appendix 3.
FIGURE 1.
Assessment of clinical effectiveness: summary of study selection and exclusion.
The updated searches did not identify the 1978 study of Bowman and Pollock,130 which was identified by the searches for our earlier review;1 this brought the total number of included studies to nine. A summary of the 1977 McMaster Conference on the prevention of RhD immunisation142 was identified from a citation. This included brief summaries of the results of three unpublished studies of RAADP. Two of these studies, the Australian and Hamilton studies, did not meet our inclusion criteria because, although both were said to use a two-dose regimen, the actual dose was not specified. These studies do not appear to have been published elsewhere and attempts to obtain fuller reports from the investigators have been unsuccessful. The third, Swedish study was excluded because it used a single unspecified dose at 34 weeks’ gestation; it appears to represent an interim analysis of the study published in 1984 by Hermann et al. ,134 included in our previous review,1 which used a dose of 1250 IU. A study of alloimmunisation following RAADP in north-east Scotland143 was subsequently drawn to our attention; this could not be included because it identified sensitised women as a proportion of all RhD-negative women who had received RAADP and was therefore not comparable with the included studies, which identified them as a proportion of only those RhD-negative women who had subsequently been delivered of RhD-positive infants.
An additional study, described by Baxter Healthcare as pivotal, appeared to have been completed by 1993 but was still unpublished in 2005. 119 This used intravenous anti-D (WinRho SD) according to three regimens, only one of which (2 × 1200 IU) is currently licensed:
-
1 × 600 IU (at 28 weeks)
-
1 × 1200 IU (at 28 weeks)
-
2 × 1200 IU (at 28 and 34 weeks).
There appears to have been no untreated control group, although reference is made to the expected level of sensitisation. Follow-up was very poor: of 806 RhD-negative women delivered of an RhD-positive infant, only 325 (40%) were tested 6 months after delivery for evidence of sensitisation. For these reasons this study was not felt to meet our inclusion criteria.
In summary, we identified only one relevant study that was not included in our earlier review. This was the RCT by MacKenzie et al. 100
Quality of included research
Overall, the quality of included research was not high. We identified only one true RCT, that by MacKenzie et al. 100 This used a computer-generated randomisation schedule but did not state how treatment allocation was concealed. The randomised comparison was between the same dose of Rhophylac (1 × 1500 IU) given intravenously and intramuscularly. However, the study was not powered to demonstrate a difference in efficacy between these two administration routes as the sample size had been calculated to test the null hypothesis that Rhophylac was inferior to currently marketed anti-D products in terms of the number of sensitisations. In other words, the sample size had been calculated not to compare one of the two randomised groups with the other but to compare the pooled results of the two randomised groups with the pooled results of the earlier studies, whose populations differed from the study population chronologically and in most cases also geographically.
A quasi-RCT by Huchet et al. 125 used year of birth to allocate participants to treatment groups (those born in odd years forming the intervention group and those in even years the control group); it compared two 500-IU doses of anti-D with no treatment.
Because of the shortage of RCTs comparing a currently licensed dose of anti-D with no treatment, all relevant non-randomised studies were retained for further consideration. They are:
-
a community intervention trial (controlled before-and-after study) by MacKenzie et al. 126
-
a retrospective before-and-after study by Mayne et al. 127
-
five non-randomised studies with historical or geographical controls. 128–132
Many of these studies were poorly designed. The greatest concerns relate to the comparability of the intervention and control groups: although the larger non-randomised studies are probably large enough to ensure comparability in terms of potential confounding factors such as ABO blood group distribution and maternal age, the use in a number of studies of non-contemporary or geographically distant controls raises the issue of possible differences in clinical care other than the use of RAADP (see further below). The use of intention to treat analysis is also important in assessing the impact of a programme of RAADP. The lack of blinding is less problematic given the objective nature of the main outcome measure (the presence/absence of anti-D). Table 11 contains a summary of study quality based on the comparability of the control groups and the use of intention to treat analysis; more detailed comments on study quality are presented in Appendix 4.
| Study | Study type | Study quality | ITT analysis | Date and location of intervention | Date and location of control | Patient selectiona | Number of RhD– women in intervention group delivered of RhD+ infant | Specific product (production method) and route of administration | Dosage and administration schedule | Source of funding |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bowman et al. 1978129 | Prospective study, historical/geographical controls | Poor | No | December 1968–August 1976, Winnipeg, Canada | March 1967–December 1974, Manitoba, Canada | Primigravidae | 1357 | Rho(D) immune globulin (Cohn method), Connaught Laboratories, Toronto; i.m.131 | 2 × 1500 IU, 28 and 34 weeks | National Health and Medical Research Council of Canada |
| Bowman and Pollock 1978130 | Prospective study, historical controls | Fair | No | March 1976–June 1977, Manitoba, Canada | March 1967–December 1974, Manitoba, Canada | Primigravidae and unsensitised multigravidae | 1804 | Rho(D) immune globulin (Cohn method), Connaught Laboratories, Toronto; i.m. | 1500 IU, 28 weeks | Not stated |
| Bowman and Pollock 1987131 | Retrospective study, historical controls | Poor | No | June 1977–February 1986, Manitoba, Canada | March 1967–December 1974, Manitoba, Canada | Primigravidae and unsensitised multigravidae | 9303 | RhIG-IV (WinRho) (ion exchange), Winnipeg Rh Institute; usually i.m. but could be i.v. | 1500 IU, 28 weeks | Not stated |
| Huchet et al. 1987125 | Quasi-RCT | Good | Yes | January 1983–June 1984, Paris | January 1983–June 1984, Paris | Primiparae (not all of whom were primigravidae) | 599 | Product not specified; i.m. | 2 × 500 IU, 28 and 34 weeks | Not stated |
| MacKenzie et al. 1999126 | Community intervention trial (controlled before-and-after study) | Good | Yes | 1990–6, Oxfordshire | 1990–6, Northants | Primiparae | 3320 | Product and route of administration not specified | 2 × 500 IU, 28 and 34 weeks | Bio Products Laboratories |
| MacKenzie et al. 2004100 | Open-label RCT; results presented as uncontrolled study | Poor | No | Date not specified, UK and US | i.m. controls contemporary with i.v. intervention; no untreated controls, UK and US | Unselected (primigravidae 28.5%) | 270 (figure includes those receiving i.v. and i.m. Rhophylac) | Rhophylac i.v. vs i.m. | 1 × 1500 IU, 28 weeks | Chiltern International |
| Mayne et al. 1997127 | Retrospective before-and-after study | Fair | Yes | 1993–5, southern Derbyshire | 1988–90, southern Derbyshire | Primiparae | 1425 | Product and route of administration not specified | 2 × 500 IU, 28 and 34 weeks | Bio Products Laboratories |
| Tovey et al. 1983128 | Prospective study, historical controls | Fair | Yes | 1980–1, Yorkshire | 1978–9, Yorkshire | Primigravidae | 1238 | Product and route of administration not specified | 2 × 500 IU, 28 and 34 weeks | Not stated |
| Trolle 1989132 | Prospective study, historical controls | Poor | No | 1980–5, Kolding, Denmark | 1972–7, Kolding, Denmark | Primigravidae and unsensitised multigravidae | 346 | Product and route of administration not specified | 1500 IU, 28 weeks | Not stated |
The studies vary in terms of their patient selection criteria and dosage regimens. Five studies125–129 recruited their intervention group from primigravidae. Four of these studies126–129 recorded data relating to these women in subsequent pregnancies. Bowman et al. ,129 MacKenzie et al. 126 and Mayne et al. 127 did this to assess the prevalence of sensitisation arising from the first pregnancy; only the study by Tovey et al. 128,133 also provided data relating to the incidence of sensitisation resulting from subsequent RhD-positive pregnancies in which RAADP was not provided.
The studies by Bowman and Pollock,130,131 MacKenzie et al. 100 and Trolle132 recruited both primigravidae and unsensitised multigravidae. In MacKenzie et al. 100 almost three-quarters (71.5%) of the participants had been pregnant before and, of these, 81.9% had received anti-D in a previous pregnancy; as noted in the later section on critical review and synthesis of information, this may offer some degree of protection in subsequent pregnancies and may therefore have affected the study results.
As noted above, the 2004 study by MacKenzie et al. 100 compared RAADP using the same anti-D preparation (Rhophylac) administered intravenously and intramuscularly. The remaining studies compared RAADP with no RAADP; none used placebo. Four studies125–128 used 500 IU at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation, one129 used 1500 IU at 28 and 24 weeks, and four100,130–132 used a single dose of 1500 IU at 28 weeks.
It was originally stated that studies would be included in the review only if they used the specific licensed interventions, as follows:
-
D-Gam 500 IU or Partobulin SDF 1000–1650 IU given intramuscularly at weeks 28 and 34 of pregnancy
-
Rhophylac 1500 IU given as a single dose intramuscularly or intravenously at week 28 of pregnancy
-
WinRho SDF 1500 IU given as a single dose intramuscularly or intravenously at week 28 of pregnancy.
However, only two studies met this criterion: the 1987 study by Bowman and Pollock,131 which used WinRho, and the 2004 study by MacKenzie et al. ,100 which used Rhophylac. In their 1978 studies, Bowman et al. 129 and Bowman and Pollock130 used anti-D prepared by the Connaught laboratories using the Cohn method. The remaining studies did not specify what product was used, and some did not even state the route of administration (see Table 11). Consequently, the review has not been limited to studies which stated that they used one of the specific varieties of anti-D listed above.
All of the included studies with the exception of that by Bowman and Pollock in 1978130 stated that women in both the intervention and control groups who were delivered of RhD-positive infants received postpartum anti-D. It seems highly likely that this was also the case in that study.
Only three of the included studies had contemporary controls: the RCT by MacKenzie et al. ,100 the quasi-RCT by Huchet et al. 125 and the community intervention trial by MacKenzie et al. 126 The 1978 study by Bowman et al. 129 purported to be a community intervention trial with contemporary controls. However, it in fact combined the results for a contemporary control group with the results for a geographically contiguous group of women during an overlapping but not identical time period (JM Bowman, 2001, personal communication). As preintervention data were not provided for the two groups it is not clear to what extent they were actually comparable. Because the intervention group was a city population and the control group was derived in the main from a largely rural population, they may have differed in relation to key variables such as rates of Caesarean section and other invasive procedures. They certainly differed in that the intervention group included only women who for all of their pregnancies were treated in accordance with the trial protocol, whereas the reported control group included women who had had previous pregnancies. Although these pregnancies appeared not to have resulted in alloimmunisation, they may in some cases have resulted in silent sensitisation, thus potentially elevating the alloimmunisation rate in the control group and exaggerating the effectiveness of RAADP.
It has been suggested that, because the antiglobulin tests formerly used to identify maternal anti-D are less sensitive than more recent assays, studies using controls that antedate the intervention group by several years are likely to underestimate the true incidence of alloimmunisation in the control group and therefore the degree of protection provided by AADP. 15 However, the community intervention trial by MacKenzie et al. 126 used a retrospective analysis of prospectively collected data to demonstrate the baseline comparability of the two communities compared in the prospective study in terms of rates of alloimmunisation. It also demonstrated that the rate of sensitisation in the control group fell substantially over time, although the reduction was not as great as in the intervention group. This change over time in the control group is presumably due to changes in obstetric practice, possibly including a more comprehensive use of anti-D following potential sensitising events; it suggests that studies which use historical controls may overestimate, rather than underestimate, the degree of protection provided by RAADP when compared with current good practice.
Although most TPHs large enough to cause sensitisation occur in the last trimester, some women become sensitised before the 28th week. However, Trolle132 excluded women who were sensitised between the first antibody screen test in the first trimester and the 28th week from the intervention group but apparently not from the control group. Moreover, in this study, 38.8% of women in the control group had received more than 1 µl of fetal blood, compared with only 7.9% in the intervention group (p < 0.001). The study results are therefore likely to be biased in favour of the intervention.
The studies also vary in terms of the time at which they collected data on sensitisation. The true rate of sensitisation is greater than that identified by the presence of anti-D at, or 6 months following, delivery (see Chapter 1, Aetiology, pathology and prognosis). However, only two of the included studies – the 1999 study by MacKenzie et al. 126 and the study by Mayne et al. 127 – provided data on the number of women found to be sensitised during a subsequent pregnancy. Moreover, these data also underestimate the true rate of sensitisation because, although they include women in whom silent sensitisation did not become identifiable until a subsequent pregnancy, they exclude those women who did not undergo a subsequent pregnancy.
Assessment of effectiveness
Critical review and synthesis of information
As noted earlier (see Quality of included research), the studies reviewed here vary in terms of the administration schedule and doses of anti-D, and the primary outcome measures used, as well as in their choice of study design and use of intention to treat analysis. The clinically important outcome measure in relation to RAADP is the number of RhD-negative women delivered of a RhD-positive baby who are found to be sensitised during a subsequent RhD-positive pregnancy, although this will underestimate the total number of sensitised women as it will not take into account those who do not go on to become pregnant again. Only two studies, those by MacKenzie et al. 126 and Mayne et al. ,127 took this as their primary end point; both were community-based studies and therefore their results included women who in fact did not receive RAADP in their first pregnancy. However, two studies that did not take it as their primary end point, the studies by Bowman et al. 129 and Tovey et al. ,128 also included information on the number of RhD-negative women delivered of RhD-positive infants in either the intervention or the control group who were found to be sensitised during a subsequent RhD-positive pregnancy (Table 12).
| Study | Study design | Dosage | Anti-D prophylaxis group | Control group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | r | % Sensitised (95% CI) | n | r | % Sensitised (95% CI) | |||
| Bowman et al. 1978129 | Prospective study, historical/geographical controls | 2 × 1500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) (initially at 34 weeks only) | 343 | 0 | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | No data | ||
| MacKenzie et al. 1999126 | Community intervention trial | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | 3320 | 12 | 0.4 (0.2–0.6) | 3146 | 26 | 0.8 (0.5–1.1) |
| Mayne et al. 1997127 | Before-and-after study | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | 1425 | 4 | 0.3 (0.0–0.6) | 1426 | 16 | 1.1 (0.6–1.7) |
| Tovey et al. 1983128 | Prospective study, historical controls | 2 × 500 IU(28 and 34 weeks) | 325 | 2 | 0.6 (–0.2 to 1.5) | 582 | 11a | 1.9 (0.8–3.0) |
As noted in the previous section on quantity and quality of research available, MacKenzie et al. 126 found a fall over time in the number of women in the control group who were found to be sensitised during a subsequent RhD-positive pregnancy. This change, which was not statistically significant, may have been due to the growth of good practice in the delivery of anti-D, both postpartum and antenatally, in response to potential sensitising events, and this may also have affected the intervention group; it was stated that it was not due to the use of antenatal prophylaxis in some women in the control group. Thus, Mayne et al. 127 noted that the introduction of a programme of RAADP was associated with an increase in requests for anti-D following vaginal bleeding or antepartum haemorrhage: they conjectured that this was due to heightened awareness of anti-D among midwives and community doctors, and that it may therefore have contributed to reducing the overall sensitisation rate in women receiving RAADP.
Other outcome measures used in the studies are sensitisation during pregnancy or within 3 days of delivery, and sensitisation at postnatal follow-up. Data relating to sensitisation at these different dates are tabulated in Appendix 5. As these figures differ, an attempt is made in Table 13 to estimate the total number of sensitised women in each study. As none of the included studies presents the total number of women found to be sensitised at either delivery or 6-month follow-up, with the exception of the studies by MacKenzie et al. 126 and Mayne et al. ,127 which present sensitisation rates during the subsequent pregnancy, the figures in Table 13 are likely to underestimate the true prevalence of sensitisation at 6 months because the extent of overlap between women with demonstrable antibodies at delivery and at follow-up is not clear. Moreover, all of the studies are likely to underestimate the numbers of women who would be found to be sensitised were they to become pregnant again, either because they did not measure that outcome and thus did not take into account the phenomenon of silent sensitisation or because, in the case of the studies by MacKenzie and Mayne, they could not identify those women who were sensitised but did not become pregnant again.
| Study | Study design | Dosage | Patient Selection | Anti-D prophylaxis group | Control group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | r | % Sensitised, including silent sensitisation (95% CI) | n | r | % Sensitised, including silent sensitisation (95% CI) | ||||
| Bowman et al. 1978129 | Prospective study, historical/geographical controls | 2 × 1500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) (initially at 34 weeks only) | Primigravidae | 1357a | 1 | 0.1 (–0.1 to 0.3) | 2768 | 45 | 1.6 (1.2–2.1) |
| Bowman and Pollock 1978130 | Prospective study, historical controls | 1 × 1500 IU (28 weeks) | Unselected | 1804 | 5 | 0.3 (0.0–0.5) | 3533 | 62 | 1.8 (1.3–2.2) |
| Bowman and Pollock 1987131 | Retrospective study, historical controls | 1 × 1500 IU (28 weeks) | Unselected | 9303 | 25 | 0.3 (0.2–0.4) | 3533 | 62 | 1.8 (1.3–2.2) |
| Trolle 1989132 | Prospective study, historical controls | 1 × 1500 IU (28 weeks) | Unselected | 346 | 0 | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 354 | 6 | 1.7 (0.4–3.0) |
| MacKenzie et al. 2004100 | Open-label RCT; results presented as uncontrolled study | 1 × 1500 IU (28 weeks) | Unselected | 248 (per protocol population) | 0 | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | – | – | – |
| Huchet et al. 1987125 | Quasi-RCT | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | Primiparae | 461 | 0 | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 454 | 4 | 0.9 (0.0–1.7) |
| Multiparae | 138 | 1 | 0.7 (–0.7 to 2.1) | 136 | 3 | 2.2 (–0.3 to 4.7) | |||
| Unselected | 599 | 1 | 0.2 (–0.2 to 0.5) | 590 | 7 | 1.2 (0.3–2.1) | |||
| MacKenzie et al. 1999126 | Community intervention trial | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | Primiparae | 3320 | 12 | 0.4 (0.2–0.6) | 3146 | 26 | 0.8 (0.5–1.1) |
| Mayne et al. 1997127 | Before-and-after study | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | Primiparae | 1425 | 4 | 0.3 (0.0–0.6) | 1426 | 16 | 1.1 (0.6–1.7) |
| Tovey et al. 1983128 | Prospective study, historical controls | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | First pregnancy | 1238 | 4b | 0.3 (0.0–0.6) | 2000 | 19b | 1.0 (0.5–1.4) |
| Second pregnancy | 604b | 1b | 0.2 (–0.2 to 0.5) | 582 | 9b | 1.5 (0.5–2.5) | |||
| Third pregnancies | 2037b | 6b | 0.3 (0.1–0.5) | 2721b | 32b | 1.2 (0.8–1.6) | |||
Comparability of results
The studies vary in the results that they present. Six studies – the study by Bowman et al. ,129 the two studies by Bowman and Pollock130,131 and the studies by Huchet et al. ,125 Tovey et al. 128 and Trolle132 – report in effect the aggregated results of treating individual women. Although Bowman and Pollock130 set out to describe the results of providing RAADP on a Canadian province-wide basis, they in fact only present the results for those women who actually received RAADP (stated to be only 89% of those at risk). In addition, as noted above, Trolle132 screened women for antibodies before inclusion and gave no indication of the numbers who were excluded from the study on this basis.
Studies that only include data relating to women known both to have received the intervention and to have received it before sensitisation will provide an indication of the clinical effectiveness of RAADP but will overestimate its efficacy in non-trial conditions. Efficacy can only be indicated by community studies that demonstrate the likely reduction in sensitisation rates achievable in practice by offering the intervention in a geographical area and including all women in that area in an intention to-treat analysis. Only two studies were of this nature, those by MacKenzie et al. 126 and Mayne et al. 127 MacKenzie et al. 126 gave prophylaxis to all non-sensitised pregnant RhD-negative nulliparae, and reported the results in terms of the number of those women found to be sensitised in their second continuing pregnancy. Mayne et al. 127 gave prophylaxis to primigravidae and women with no living children, but presented the results for all women ‘at risk’ (i.e. all RhD-negative women delivered of RhD-positive babies having a subsequent pregnancy), thus indicating the overall efficacy of the programme, which in its second and subsequent years was said to reach most RhD-negative primiparae in the area.
It would therefore not be surprising if the results obtained by before-and-after studies differed from those of the other studies, as only the before-and-after studies included a number of untreated women in the intervention group. Moreover, as noted above, they report the effect of a policy of RAADP in primigravidae on sensitisation in subsequent pregnancies, and the number of women found to be sensitised at this point could theoretically also include women sensitised early in their second rather than in their first pregnancy.
Finally, there were some discrepancies between the studies in terms of the inclusion or exclusion from the reported results of cases of apparent sensitisation in women who received RAADP. For comparability with the before-and-after studies, Table 14 displays the overall numbers of sensitised women including, where possible, any stated to have been excluded from the authors’ analyses. Table 15 provides details of the numbers of women excluded from the authors’ analyses, and the reasons for this, together with further information relating to the women sensitised despite being in the intervention groups, i.e. potential failures of protection.
| Study | Study design | Dosage | Patient selection | Anti-D prophylaxis group | Control group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | r | % Sensitised, including silent sensitisation (95% CI) | n | r | % sensitised, including silent sensitisation (95% CI) | ||||
| Bowman et al. 1978129 | Prospective study, historical/geographical controls | 2 × 1500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) (initially at 34 weeks only) | Primigravidae | 1357b | 1 | 0.1 (–0.1 to 0.3) | 2768 | 45 | 1.6 (1.2–2.1) |
| Bowman and Pollock 1978130 | Prospective study, historical controls | 1 × 1500 IU (28 weeks) | Unselected | 1806 | 11 | 0.6 (0.3–1.0) | 3533 | 62 | 1.8 (1.3–2.2) |
| Bowman and Pollock 1987131 | Retrospective study, historical controls | 1 × 1500 IU (28 weeks) | Unselected | 9295 | 30 | 0.3 (0.2–0.4) | 3533 | 62 | 1.8 (1.3–2.2) |
| Trolle 1989132 | Prospective study, historical controls | 1 × 1500 IU (28 weeks) | Unselected | 346 | 0 | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 354 | 6 | 1.7 (0.4–3.0) |
| Huchet et al. 1987125 | Quasi-RCT | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | Primiparae | 461 | 0 | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 454 | 4 | 0.9 (0.0–1.7) |
| Multiparae | 138 | 1 | 0.7 (–0.7 to 2.1) | 136 | 3 | 2.2 (–0.3–4.7) | |||
| Unselected | 599 | 1 | 0.2 (–0.2 to 0.5) | 590 | 7 | 1.2 (0.3–2.1) | |||
| MacKenzie et al. 1999126 | Community intervention trial | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | Primiparae | 3320 | 12 | 0.4 (0.2–0.6) | 3146 | 26 | 0.8 (0.5–1.1) |
| Mayne et al. 1997127 | Before-and-after study | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | Primiparae | 1425 | 4 | 0.3 (0.0–0.6) | 1426 | 16 | 1.1 (0.6–1.7) |
| Tovey et al. 1983128 | Prospective study, historical controls | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | First pregnancy | 1238 | 4c | 0.3 (0.0–0.6) | 2000 | 19c | 1.0 (0.5–1.4) |
| Second pregnancy | 604c | 1c | 0.2 (–0.2 to 0.5) | 582 | 9c | 1.5 (0.5–2.5) | |||
| All pregnancies | 2037c | 6c | 0.3 (0.1–0.5) | 2721c | 32c | 1.2 (0.8–1.6) | |||
| Study | Number of sensitised women in intervention groupa | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Bowman et al. 1978129 | 1, unspecified number | Considered by the investigators probably to be a case of passive RhD antibody persisting at 6 months after delivery; as the woman was lost to follow-up at 9 months it was not possible to establish whether it still existed at that point. In the first 6 months of the study an unspecified number of women were sensitised before 34 weeks; these were not included in the analysis |
| Bowman and Pollock 1978130 | 5, 6 | Two women were sensitised before 28 weeks; one multigravida may have undergone silent sensitisation as a result of an earlier abortion when no anti-D was given or may have been sensitised before receiving prophylaxis at 29 weeks in the current pregnancy; and two more multigravidae may either have undergone silent sensitisation in a previous pregnancy or may represent failures of prophylaxis. In addition, two primigravidae appeared to have been sensitised before what they stated was their first pregnancy; three multigravidae appeared to have undergone silent sensitisation by an earlier pregnancy; and one had received an RhD-positive blood transfusion: these were all excluded from the analysis |
| Bowman and Pollock 1987131 | 25, 5 | 13 failures of prophylaxis; four women in whom sensitisation could be due either to failure of prophylaxis or to failure to treat following a previous abortion or delivery; five women sensitised by 28 weeks in current pregnancy; and three women sensitised by 28 weeks who possibly underwent silent sensitisation in an earlier pregnancy. In addition, five women who appeared to have undergone silent sensitisation in a previous pregnancy were excluded from the analysis |
| Huchet et al. 1987125 | 1 | Apparently a failure of prophylaxis – the woman in question had received anti-D during a previous pregnancy, which was terminated for therapeutic reasons |
| MacKenzie et al. 1999126 | 12 | Six women were delivered of their first pregnancy outside Oxfordshire: four certainly and two possibly did not receive antenatal prophylaxis during that first pregnancy; one woman had undergone a potential sensitising event at 18 weeks for which anti-D may not have been given; one woman, who delivered at 37 weeks, had undergone a large fetomaternal haemorrhage, probably at 35 weeks (routine prophylaxis had been given at 29 and 35 weeks); and four women had received prophylaxis at 28 and 34 weeks and did not appear to have suffered an incident likely to provoke a fetomaternal haemorrhage |
| Mayne et al. 1997127 | 4 | Three women had previously delivered in places where routine antenatal prophylaxis was unlikely; one had not received prophylaxis during her first pregnancy despite the existence of a programme of RAADP |
| Tovey et al. 1983128 | 5 | All seem due to failures of prophylaxis, although two women sensitised during their first pregnancy had low but persisting levels of antibodies, which might possibly be rare ‘naturally occurring’ anti-D |
| Trolle 1989132 | 0, unspecified number | An unspecified number of women who had been sensitised by 28 weeks were excluded from the study |
The 2004 study by MacKenzie et al. 100 found no difference in efficacy or safety between Rhophylac administered intravenously and Rhophylac administered intramuscularly. However, this does not prove that there was no difference, as the study was not powered to identify such a difference, even though this was the randomised comparison.
The studies were broadly comparable in terms of the percentage of women in the control groups who were sensitised: this ranged from 1.2–1.8% in unselected groups, 0.8–1.6% in primiparae and 1.4–2.2% in multiparae (see Table 14). MacKenzie et al. 126 found an unexpected, and statistically non-significant, reduction in the number of cases observed in the control arm between the two study periods, from 1.3% in 1980–6 to 0.8% in 1990–6.
In all studies the proportion of women who were sensitised was lower in the intervention arm than in the control arm. However, the difference between sensitisation rates in the intervention and control arms varied between studies. As might be expected, this difference was particularly small, at 0.4–0.7%, in the before-and-after studies by MacKenzie et al. 126 and Mayne et al. 127 as their intention to treat analyses will have included women who had not received RAADP.
Meta-analysis of clinical effectiveness
In our earlier review we conducted meta-analysis on three groups of studies using the overall results presented in Table 14, which include, where possible, women excluded from the authors’ analyses:
-
Group 1: the four studies that used a dosage regimen of 500 IU at 28 weeks and 34 weeks and reported results for primigravidae – Huchet et al. ,125 MacKenzie et al. ,126 Mayne et al. 127 and Tovey et al. 128
-
Group 2: the three studies that used a dosage regimen of 1500 IU at 28 weeks – the two studies by Bowman and Pollock130,131 and that by Trolle. 132 These studies included both primigravidae and multigravidae.
-
Group 3: the two community-based UK studies that used a dosage regimen of 500 IU at 28 weeks and 34 weeks and reported results for primigravidae – MacKenzie et al. 126 and Mayne et al. 127
As the current systematic review identified no additional studies comparing RAADP with no treatment, we present the results of these meta-analyses again here. On the basis of face validity, visual examination of the absolute trial results, individual odds ratios within trials and results of the meta-analyses (Table 16), the trials show a remarkable consistency in results, even between dosage regimens. Consequently, the results of the meta-analysis of group 3 trials are deemed to give a representative reflection of the actual effectiveness of RAADP and these figures are used in the economic evaluation.
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test for heterogeneity (p-value) | 0.812 | 0.940 | 0.976 |
| Odds ratio of sensitisation with antenatal prophylaxis (95% CI) | 0.33 (0.20–0.55) | 0.20 (0.13–0.29) | 0.37 (0.21–0.65) |
| Sensitisation rate of control group (95% CI) | 0.89% (0.21–1.56%) | 1.60% (0.37–2.83%) | 0.95% (0.18%–1.71%) |
| Sensitisation rate of antenatal prophylaxis group using meta-analysis (95% CI) | 0.30% (0.22–0.38%) | 0.34% (0.28–0.40%) | 0.35% (0.29–0.40%) |
Sensitisation rates for the conventional management groups were calculated by applying to each study the average of the sensitisation event probabilities estimated in the logistic regression model. Within group 2, the 1987 study by Bowman and Pollock131 used the same control arm results as the 1978 study by the same authors. 130 To prevent double counting, which would have a significant effect on the overall results because of the size of the studies, the two studies were combined into a three-arm study within the meta-analysis, consisting of two treatment arms and one control arm.
The results of the meta-analyses are shown in Table 16 and Figures 2–4.
FIGURE 2.
Group 1: 2 × 500 IU in RhD-negative primigravidae. Note: number of women in intervention group in brackets.
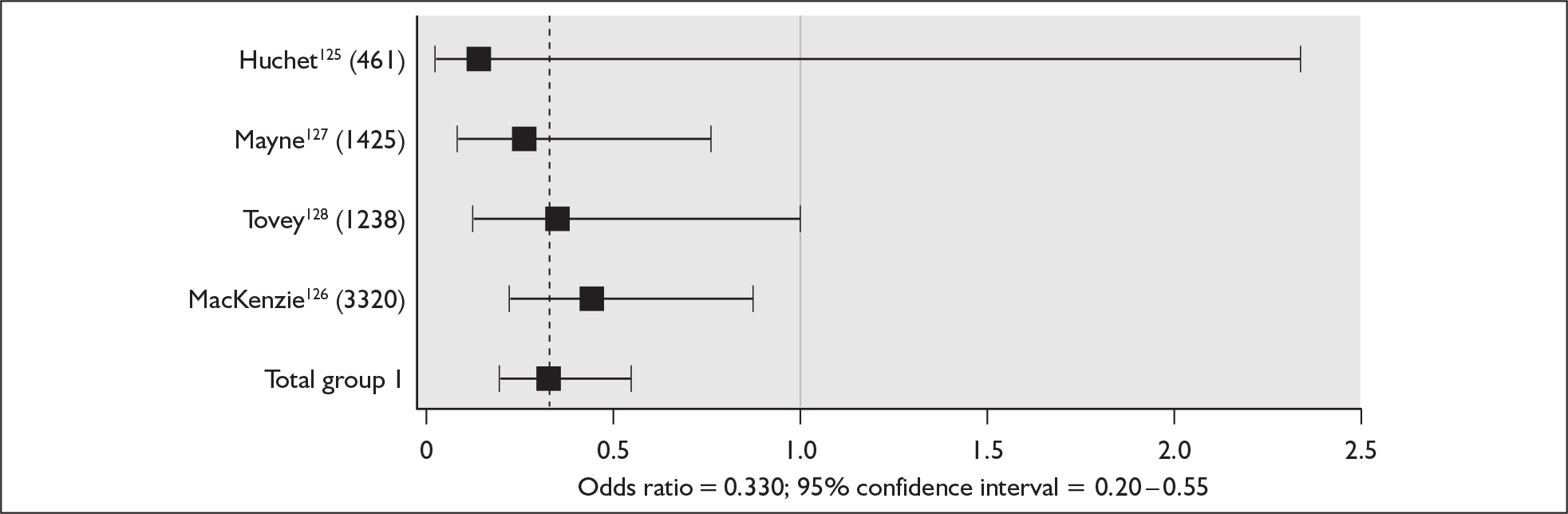
FIGURE 3.
Group 2: 1 × 1500 IU in unselected RhD-negative women. Note: number of women in intervention group in brackets.
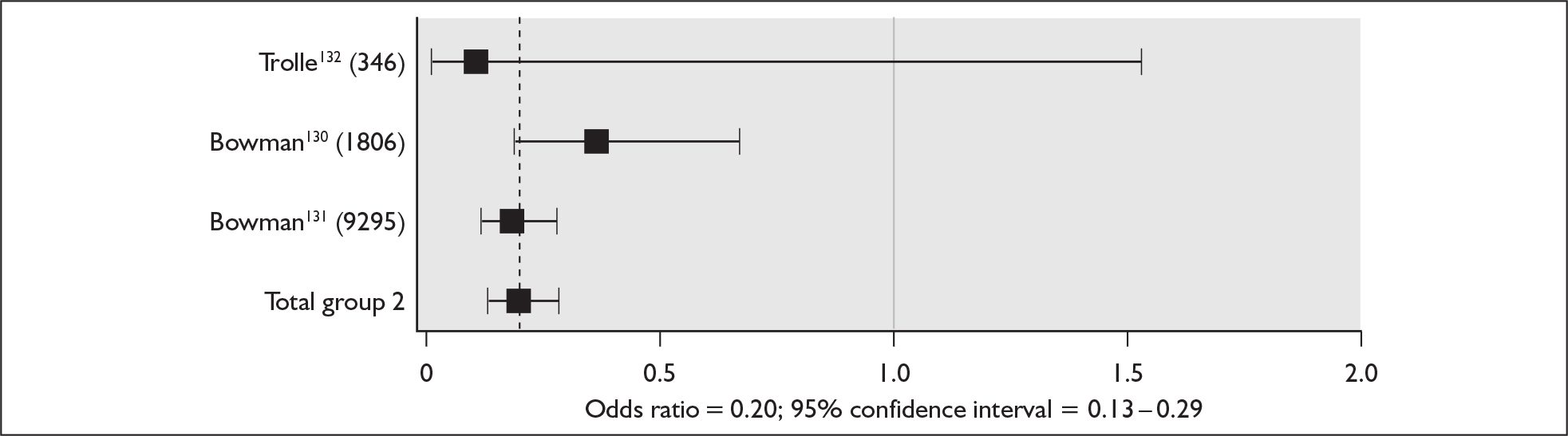
FIGURE 4.
Group 3: 2 × 500 IU in RhD-negative primigravidae. Note: number of women in intervention group in brackets.
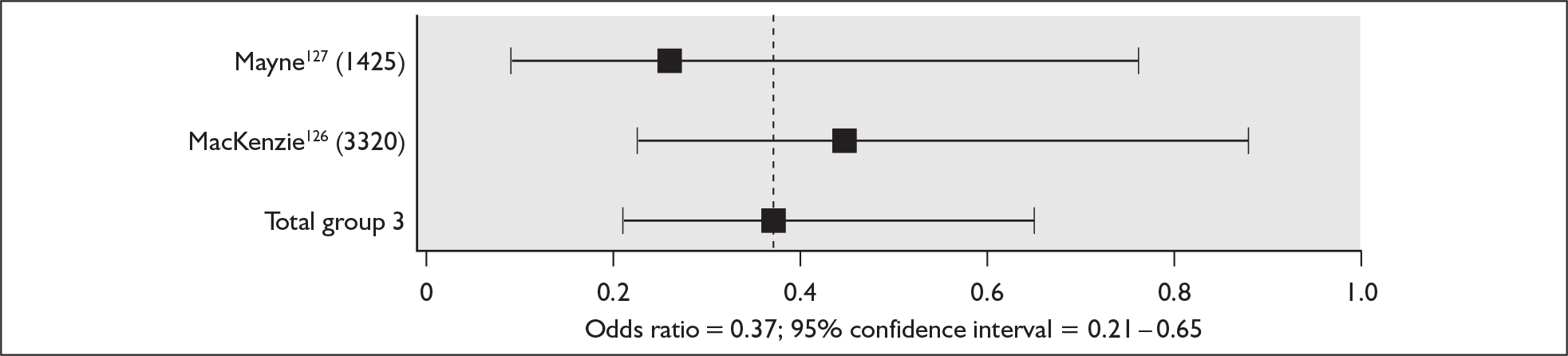
Comparison of dosage regimens
Pooling the data from those studies that used one dose of 1500 IU at 28 weeks (group 2) produced a point estimate for sensitisation in the RAADP group of 0.34%. In comparison, the study by Bowman et al. ,129 which used two doses of 1500 IU at 28 and 34 weeks, reported a rate of 0.1%. Although this suggests that, as one might expect, two doses of 1500 IU are more effective than one, there are no trials that directly compare these two regimens.
In theory, two doses of 500 IU at 28 and 34 weeks should also be more effective than a single dose of 1500 IU at 28 weeks, as they would result in a slightly higher residual anti-D at term. 15 Pooling the data from those studies that used two doses of 500 IU at 28 and 34 weeks yields a point estimate for sensitisation in the RAADP group of 0.30%, marginally lower than that for a single dose of 1500 IU (0.34%). However, because the sensitisation rate in the control groups was lower in the studies using two doses of 500 IU than in all of the other studies, the point estimate of the odds ratio for one dose of 1500 IU at 28 weeks is lower (0.20; i.e. more effective) than that for two doses of 500 IU (0.33). For both the odds ratios and the point estimates of the sensitisation rates the 95% confidence intervals of the estimates overlap, implying that the differences are not statistically significant.
Compliance
Only one of the included studies, the 1999 study by MacKenzie et al. ,126 examined the extent to which comprehensive prophylaxis was achieved. This study found that, of a sample of eligible women delivered in the John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, during 1992–6, only 89% received the first dose of a two-dose regimen, only 76% received both doses and only 29% received both doses at the correct gestation. This audit was later extended to include the years 1997–2003. 122 During the latter period 90% of women received the first dose and 79% both doses. Although these modest improvements were not statistically significant, in the later period the timing of both injections had improved significantly. Despite this improvement in compliance there was estimated to be no reduction in the sensitisation rate among women who had delivered their first baby in the Oxford district and who would have been eligible for RAADP during that pregnancy.
Longer-term outcomes
Bowman et al. 129 provided information on the clinical outcomes of 17 subsequent RhD-positive pregnancies in the 62 sensitised women in the study’s control group. Seven of the 17 infants (41%) required treatment related to HDN (Table 17).
| Outcome | Number of pregnancies (%) |
|---|---|
| Fetal and exchange transfusion required | 2 (12%) |
| Exchange transfusion and early delivery required | 3 (18%) |
| Phototherapy required | 2 (12%) |
| Direct Coombs’ test positivea – treatment not required | 5 (29%) |
| Direct Coombs’ test negative – unaffected | 5 (29%) |
In the study by Tovey et al. 128 anti-D antibodies were identified during their first pregnancy in 18 women in the control group: 14 of their infants (78%) were mildly affected, two (11%) were moderately affected, requiring exchange transfusion, one died for reasons other than RhD HDN and one was RhD negative. Between them these 18 women, and one other woman in the control group in whom the antibody had been detected before her first pregnancy, went on to have 11 further pregnancies: five (45%) of these infants were mildly affected, two (18%) were moderately affected and one was severely affected (requiring six exchange transfusions).
Thornton et al. 133 studied the effect of RAADP given only in the first pregnancy on sensitisation rates in subsequent pregnancies. This was a follow-up to the study by Tovey et al. 128 and reports on the same cohorts of women. Thornton et al. 133 found that only one woman who had received RAADP in her first pregnancy produced anti-D antibodies in her second pregnancy, none produced anti-D antibodies in the third pregnancy and only one produced anti-D antibodies in the fourth pregnancy (Table 18). Overall, sensitisation occurred in six women in the treatment group and in 32 women in the control group. No explanation was proposed as to why prophylaxis provided in the first pregnancy should appear to confer benefits in subsequent pregnancies.
| First pregnancy | Second pregnancy | Third pregnancy | Fourth pregnancy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment group (n = 1234) | Control group (n = 1881) | Treatment group (n = 604) | Control group (n = 582) | Treatment group (n = 167) | Control group (n = 121) | Treatment group (n = 32) | Control group (n = 18) |
| 4 (0.32%) | 19 (1%) | 1 (0.17%) | 9 (1.5%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (2.5%) | 1 (3.1%) | 1 (5.5%) |
More recently, a retrospective longitudinal observational study carried out by MacKenzie et al. 144 compared the rate of RhD sensitisation following the implementation of a policy of restricted prophylaxis, in which RAADP was offered to all non-sensitised RhD-negative pregnant women with no living children booked for confinement in the Oxford Health District, with that predicted by mathematical modelling following a policy of universal prophylaxis, in which RAADP would be offered to all RhD-negative pregnant women irrespective of parity. This study also found that the policy of restricted prophylaxis provided continuing protection in subsequent pregnancies.
Thornton et al. 133 provided data relating to preterm deliveries, birth weights and perinatal deaths in both the first and second pregnancy, and abortions in the second pregnancy, in RhD-negative women who, following RAADP in their first pregnancy, had delivered a RhD-positive baby in that first pregnancy. These data were compared with those relating to untreated RhD-negative women who gave birth to RhD-positive babies in their first pregnancy and to RhD-positive mothers who were comparable except for the RhD status. No significant differences were observed either in terms of these outcomes or in terms of maternal hypertension and proteinuria in the first, second and third pregnancies. 133
ABO compatibility
As noted in Chapter 1 (see Aetiology, pathology and prognosis), in approximately 20% of pregnancies in RhD-negative women the mother and fetus have different ABO blood groups. Sensitisation is less common when mother and baby are ABO incompatible. This is demonstrated by information from the control group of the study by Bowman et al. 129 (Table 19).
| ABO compatibility | n | r | % Sensitised (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primigravidae | 2768 | 45 | 1.6 (1.2–2.1) |
| Compatible | 2257 | 44 | 1.9 (1.4–2.5) |
| Incompatible | 511 | 1 | 0.2 (–0.2 to 0.6) |
| Multigravidae | 765 | 17 | 2.2 (1.2–3.3) |
| Compatible | 602 | 14 | 2.3 (1.4–3.5) |
| Incompatible | 163 | 3 | 1.8 (–0.2 to 3.9) |
Summary of clinical effectiveness
In the eight studies that compared RAADP with no prophylaxis, RAADP was given to, or available for, RhD-negative women undergoing a total of around 19,719 pregnancies that resulted in RhD-positive babies. Of these pregnancies, 65 (0.33%) resulted in sensitisation. The control groups for these studies (six groups in all, as all three studies by Bowman used the same control population) included a total of 11,049 pregnancies in women at risk of RhD sensitisation that resulted in RhD-positive babies: 136 of these pregnancies (1.2%) resulted in sensitisation.
The largest study, by Bowman and Pollock,131 accounts for nearly half of the total number of pregnancies in which RAADP was given or available. However, its design is relatively weak, comparing women who received RAADP between 1977 and 1986 with controls from the same geographical area during the period 1967–74.
Overall, it would appear that of the 65 pregnancies in the intervention groups that were reported to have resulted in sensitisation (including silent sensitisation):
-
29 represented possible or probable failures of treatment (i.e. cases in which sensitisation occurred despite appropriate administration of anti-D)
-
at least 19 represented probable or possible logistic failures (i.e. instances in which, in the absence of any recognised sensitising event, sensitisation preceded the administration of prophylaxis or in which prophylaxis was not administered despite the existence of a policy of antenatal prophylaxis)
-
12 were sensitised as a result of a previous delivery in a place where routine antenatal prophylaxis was either certainly or probably not provided.
Overall, therefore, the number of eligible pregnancies that resulted in sensitisation despite antenatal prophylaxis would appear to be as low as 29/19,719 (0.15%; 95% CI 0.1–0.2%). This figure would rise to a maximum of 48/19,719 (0.24%; 95% CI 0.2–1.3%) with the inclusion of logistic failures of prophylaxis – women sensitised either before the date at which the first dose of antenatal prophylaxis would have been administered or following failure to administer either routine prophylaxis or prophylaxis following a potential sensitising event.
The best indication of the likely efficacy of a programme of routine AADP in England and Wales comes from the two non-randomised community-based studies by MacKenzie et al. 126 and Mayne et al. 127 The pooled results of these two studies suggest that, compared with no RAADP, such a programme may reduce the sensitisation rate from 0.95% to 0.35%. This gives an odds ratio for the risk of sensitisation of 0.37, and an absolute reduction in risk of sensitisation in RhD-negative mothers at risk (i.e. carrying a RhD-positive child) of 0.6%. The number of such women needed to treat (NNT) to avoid one case of sensitisation is 1/0.006, which is 166. However, in the absence of a programme of non-invasive fetal genotyping a RhD-negative woman will not know if she is carrying a RhD-positive child; in fact, only 60% of them will be, making the overall NNT = 10/6 × 166 = 278.
Further, a woman will only benefit clinically if she has an RhD-positive infant and she would have been sensitised and she goes on to have a further infant who is also RhD positive. It is the avoidance of HDN in that infant which constitutes the clinical benefit.
In Chapter 1 (see Significance for the NHS) we estimated that currently, were there no programme of RAADP, approximately 650 RhD-negative women a year would be sensitised antenatally and that subsequent pregnancies in these women would lead to around 31 fetal or neonatal losses per year. Avoidance of sensitisation can be expected to avoid fetal loss in 4.8% of cases (this takes into account the fact that women who become immunised during a first pregnancy may be ‘high responders’ who produce a vigorous response to a small FMH). An estimate of the overall NNT to avoid a fetal or neonatal loss in a subsequent pregnancy is therefore 278/0.048 = 5790.
Adverse events
No serious adverse events related to the administration of RAADP were reported by any of the studies included in the review of clinical effectiveness. MacKenzie et al. 100 reported a few cases of mild pain, soreness or itching at the injection site following administration of Rhophylac. Bowman et al. 100 reported mild adverse reactions (marked flushing and mild chest discomfort that disappeared within 30 seconds without the use of medication) in two out of 3733 women given WinRho either antenatally or postpartum; they both received WinRho from a lot containing unacceptable levels of moisture and aggregated IgG.
The study by MacKenzie et al. 100 was unique in screening for blood group alloantibodies and viral markers both before RAADP and 6 months after the last administration of anti-D. Anti-C was identified in the sera of three women who had received intravenous Rhophylac. In terms of viral markers two women seroconverted for hepatitis A virus antibodies, three for cytomegalovirus and one for anti-HBc (hepatitis B core antigen); for these women the route of Rhophylac administration was not specified but the investigators considered it unlikely that any of the observed seroconversions were related to Rhophylac; one of the seroconversions for hepatitis A virus followed immunisation for international travel. Moreover, as the investigators acknowledge, the note for guidance from the Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products145 on the clinical investigation of human anti-D immunoglobulin for intravenous and/or intramuscular use states that, because of the effectiveness of procedures to control potential viral contamination, ‘it is no longer considered appropriate to use clinical trials to investigate viral safety with regard to enveloped viruses’, and that, although these procedures may be of limited value against non-enveloped viruses such as hepatitis A and parvovirus B19, ‘the safety of the products with respect to non-enveloped viruses cannot currently be adequately evaluated in clinical studies’.
In 2006, 77 adverse events relating to the administration of anti-D for all indications were reported to the SHOT (Serious Hazards of Transfusion) Committee. All involved lack of communication and poor documentation. The nature of the majority of these incidents is not specified. However, it was stated that 13 women with immune anti-D received treatment with anti-D immunoglobulin, although not necessarily as part of RAADP. 89 This is a particular cause for concern because it implies a failure to identify a pregnant woman as sensitised, which can in turn lead to failure to monitor immune antibodies during pregnancy, with the risk of adverse outcomes if the fetus is affected by HDN.
Discussion
All of the evidence indicates that RAADP reduces the incidence of sensitisation. In assessing the impact of a programme of RAADP the most relevant studies are those by MacKenzie et al. 126 and Mayne et al. 127 These are community-based studies with high external validity as they demonstrate the effectiveness of RAADP in real life in the UK rather than under trial conditions and as measured by the most clinically relevant outcome measure, the number of women found to be sensitised in a subsequent pregnancy. Meta-analysis of the data from these studies indicates that the introduction of such a programme is associated with a fall of 0.6% (from 0.95% to 0.35%) in the number of women found in a subsequent pregnancy to be sensitised, an odds ratio of 0.37 (95% CI 0.21–0.65).
However, although the implementation of a programme of RAADP should lead to a significant fall in the residual numbers of women becoming sensitised, some women continue to become sensitised. There are five possible reasons for continuing cases of sensitisation:
-
failure to recognise potential sensitising events in pregnancy as such and to treat them appropriately
-
failure to assess the extent of FMH adequately
-
failure to comply with postpartum prophylaxis guidelines
-
refusal of RAADP by the mother
-
failure to implement RAADP by some trusts and incomplete adherence to advice (i.e. poor compliance with the second dose).
Before the introduction of RAADP there was not universal adherence to UK guidelines, particularly with respect to administration of anti-D following potentially sensitising events in pregnancy. An audit of anti-D sensitisation carried out in Yorkshire between 1988 and 1991146 found that the guidelines were followed fully in only 52% (30/58) of possible sensitising events for which full data were available. In Scotland an audit found that, in 1992, anti-D was given in only 70% (195/280) of recorded antenatal events which should have resulted in its administration. 147 A questionnaire survey published in 1994 found that many A&E departments in England and Wales were not adequately prepared for treating with anti-D women bleeding in early pregnancy and were not following the guidelines so to do. 148 A retrospective study of 922 RhD-negative women delivered in Merseyside in 1994 found that, in 39% (158/396) of potentially sensitising events, the guideline recommendations were not recorded as having been followed. 149 In an audit of singleton pregnancies delivered in nine hospitals within a hundred-mile radius of Manchester between 1 August 1994 and 31 July 1995, anti-D was recorded as being administered after 79% (478/602) of potentially sensitising events overall, but administration rates in the individual hospitals ranged from 58% to 96%. 150 In 1998 an audit of 3274 RhD-negative women in Northern Ireland found that anti-D was given after only 44% (117/264) of potentially sensitising events that occurred before, and 58% (184/319) of those that occurred after, 20 weeks’ gestation. However, in some cases this was because the women themselves had not sought advice from maternity care staff within 72 hours of the event. 151
The evidence suggests closer adherence to the guidelines for postpartum administration. Appropriate postnatal prophylaxis was given in 95% of cases (497/520) in Merseyside in 1994149 and in 98% of cases (1820/1852) in Northern Ireland in 1998. 151
It should be noted that the above studies were all carried out in the 1990s. Although more recent evidence has not been found it is possible that compliance with guidance relating to the administration of anti-D following potentially sensitising events in pregnancy may have improved following the introduction of RAADP and the consequent raising of awareness of the importance of antenatal prophylaxis. Probably only a minority of the current cases of sensitisation are attributable to failure to comply with current established UK guidelines relating to either postpartum prophylaxis or prophylaxis in response to potential sensitising events. Nevertheless, these observations inevitably raise the question of whether sensitisation rates cannot be further reduced by stricter adherence to these guidelines rather than by offering RAADP to all RhD-negative pregnant women who are not already sensitised.
There is no evidence to suggest that RAADP is associated with adverse effects of any consequence for either mother or child other than the possibility of transmission of bloodborne infections; this is minimised by the safeguards built into the modern manufacturing process.
One-dose versus two-dose regimens
No head-to-head studies have been undertaken that compare a one-dose with a two-dose regimen of RAADP, and the studies reviewed above do not provide any evidence to suggest that two 500-IU doses of anti-D at 28 and 34 weeks are more or less effective than a single dose of 1500 IU at 28 weeks. However, the Royal College of Nursing has expressed concern that a single dose given at 30 weeks (as is possible under the licensed indication for Rhophylac) may not provide protection against an FMH occurring at 28 or 39 weeks. 123 Although it is obvious that anti-D given at 30 weeks cannot provide protection against an FMH at 28 weeks, the argument that it may also be insufficient to provide protection at 39 weeks relates to the half-life of prophylactic anti-D, as discussed in Chapter 1 (see Description of technology under assessment). There is some support for the suggestion that a single dose may be inadequate, at least if given at 28 rather than 30 weeks. Bowman4 observed that, in some failures of RAADP, the interval between a single dose at 28 weeks and delivery was over 13 weeks and 5 days and therefore recommended a second dose 12 weeks after the first for women who had not delivered by that date. Moreover, neither regimen would provide adequate protection against an undetected FMH of > 10 ml occurring between approximately 34 and 40 weeks’ gestation. 3
Turner et al. 152 have carried out a meta-analysis around the clinical effectiveness studies identified within our earlier systematic review. 123 This paper uses Bayesian methods to weight the clinical efficacy studies according to the amount of internal and external bias associated with each of them. The result of this meta-analysis is similar to that described by the meta-analysis carried out earlier in this chapter (see Critical review and synthesis of information) of the two clinical efficacy studies with the least external bias, which helps to validate this result.
This bias modelling paper could also in theory be used to assess the difference in efficacy between the one-dose and two-dose regimens. This would require elicitation of bias using the opinion of clinical experts and unfortunately this is not viable in the time available. However, this work could be carried out in the future as an additional analysis around any differences in efficacy of the two dosing regimens.
Several other arguments in addition to clinical effectiveness have been put forward to support the use of one or other regimen. These arguments, which relate to compliance, cost, and safety, are summarised briefly below.
Compliance
It has been suggested that compliance would be higher with a single-dose regimen. 89 In their 2006 study of compliance with RAADP, MacKenzie et al. 122 found that, in 1997–2003, 13% of women did not receive the second dose of a two-dose regimen, whereas in 23% there was an inappropriately long interval between the two doses; they argue that a single-dose strategy would eliminate these problems. However, a recent study121 has found that the majority of women who declined the two-dose regimen declined at the first dose and it therefore seems unlikely that the use of a single-dose regimen would have a significant impact on maternal consent rates. Moreover, as noted by the Royal College of Nursing, the single-dose regimen only allows one opportunity to offer RAADP, whereas with the two-dose regimen, if the first dose is not administered, there is at least an opportunity to reduce the level of risk somewhat with the 34-week dose. 123
Cost
The single-dose regimen using Rhophylac is cheaper than the two-dose regimen using D-Gam even though it uses more anti-D (1500 versus 1000 IU) (see Chapter 1, Summary of product characteristics). A single-dose regimen would also offering savings in laboratory and midwife administration time. 90
Safety
None of the manufacturers can supply both the 1500-IU dose needed for the single-dose regimen and the 500-IU dose that is suitable for treating most sensitising events. Adoption of the single-dose regimen would therefore mean either exposing women to more than one manufacturer’s product, in conflict with the BCHS guidelines that batch exposure should be limited to limit donor exposure, or using higher doses than necessary to treat potential sensitising events. 89
Intravenous versus intramuscular administration
As noted earlier, the ion-exchange chromatography method produces anti-D that may be given either intramuscularly or intravenously, whereas anti-D produced by the Cohn cold ethanol fractionation method can only be given intramuscularly. There are various arguments for and against the intravenous and intramuscular administration of anti-D. Anti-D prepared using the original ion-exchange chromatography method had the disadvantage of being unstable in solution and therefore needing to be reconstituted before injection,101 but more recently a liquid-stable version (Rhophylac) has been developed. 100 Anti-D produced by ion-exchange chromatography is said to be purer than that produced by the cold ethanol method and is therefore less likely to produce a reaction in the recipient. 100 Moreover, intravenous administration causes less discomfort for the recipient100 but is less convenient for antenatal prophylaxis in the community setting. 100
The ion-exchange chromatography method is also more efficient, retaining over 90% of the anti-D present in the original plasma100 compared with only 50–60% using the Cohn method. 101 Moreover, if given intravenously, anti-D prepared by the ion-exchange chromatography method is more effective weight for weight than anti-D produced by the Cohn method given intramuscularly, making it in theory possible to use a smaller dose,101 although this is not reflected in the licensed doses. However, as noted in Chapter 1 (see Concerns relating to the possible transfer of viral or prion infection), on the only occasions when anti-D is known to have transmitted viral infection it was anti-D prepared by ion-exchange chromatography that was implicated. Although the cold ethanol fractionation process used to produce the intramuscular product has intrinsic virucidal benefits, additional procedures have subsequently been introduced to the chromatography method to protect against future cases of viral transmission. However, these additional procedures may be of limited value against non-enveloped viruses such as hepatitis A virus and parvovirus B19. 111
Availability of donor plasma
Problems have been encountered in the past in relation to the availability of anti-D. If such problems are likely to be encountered in the future then an argument can be made for those strategies that minimise the volume of plasma required. These include:
-
the use of a two-dose 500-IU regimen, as this uses two-thirds of the quantity of anti-D used by the single-dose regimen and there is no evidence that it is not equally effective
-
the use of the ion-exchange chromatography method of preparation, as this retains 30–40% more anti-D than the Cohn method.
Indeed, it can be argued that plasma-sparing strategies should be preferred regardless of any anticipated problems relating to supplies of donor plasma because of ethical concerns relating to the issue of harm to the plasma donors. In most donors an adequate antibody titre is obtained or maintained only by regular injection of RhD-positive red cells, a procedure that is not without risk to the donor. 153
Tovey and Taverner8 have argued that, if the provision of RAADP in every pregnancy is difficult to achieve because of either the cost or the availability of sufficient anti-D, the cheaper alternative of giving RAADP to all RhD-negative primigravidae, and to RhD-negative secundigravidae whose first baby was RhD-negative, would ensure that most RhD-negative mothers receive anti-D during their first RhD-positive pregnancy and should enable all RhD-negative mothers to have at least three live children.
Targeted prophylaxis
As noted in Chapter 1 (see Description of technology under assessment), non-invasive fetal genotyping has not yet been demonstrated to be sufficiently accurate to enable its use to target provision of RAADP to only those non-sensitised RhD-negative women pregnant with RhD-positive infants. However, a test that is sufficiently accurate at an early enough gestational date may become available in the next few years.
Even though non-invasive fetal genotyping cannot currently be used to target RAADP it has other potential benefits. The BCSH guideline for blood grouping and antibody testing in pregnancy80 suggests that its use is clinically relevant when the mother has high antibody levels and/or a history of HDN and the father is heterozygous for RhD, because knowledge of the genotype of the fetus will affect the management of a pregnancy in a sensitised RhD-negative woman: if the fetus is predicted to be RhD positive, invasive procedures, which carry an inherent risk of boosting maternal anti-D levels, may then be avoided until Doppler monitoring indicates that the fetus is anaemic. 95
Results in context of other reviews
Only one systematic review of RAADP was identified other than that updated in this report. This was the Cochrane review by Crowther and Middleton. 154 As Cochrane reviews include only RCTs and quasi-RCTs, this review included only two studies: that by Huchet et al. ,125 which met our inclusion criteria, and that by Lee and Rawlinson,135 which was excluded from the current review because it used an unlicensed regimen (two doses each of 250 IU). Crowther and Middleton154 found that RAADP reduced the incidence of sensitisation compared with no RAADP.
Chapter 4 Assessment of cost-effectiveness
The cost-effectiveness of providing RAADP to RhD-negative women has been evaluated from a UK NHS perspective. The comparators assessed against a base case of no RAADP, for both primigravidae and multigravidae, are:
-
500 IU at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation (D-Gam)
-
1250 IU at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation (Partobulin)
-
1500 IU at 28 weeks’ gestation (Rhophylac)
-
1500 IU at 28 weeks’ gestation (WinRho).
Systematic review of existing cost-effectiveness evidence
A systematic review of economic evaluations was carried out using the search criteria and databases set out within the clinical effectiveness section (see Chapter 3, Identification of studies); the only variation from this was that the study design was defined as economic evaluations. A total of 11 papers (nine different studies) were identified by the systematic searches (Figure 5); eight of these studies were included in the RAADP assessment report for NICE in 2001,155 later published as a NICE Health Technology Assessment report. 1 These were the studies by Adams et al. ,156 Baskett and Parsons,157 Lim et al. ,158 Mackenzie et al. ,126 Selinger,159 Torrance and Zipursky,160 Tovey et al. 128 and Vick et al. 161,162 Two of these studies126,128 were also included as studies of clinical effectiveness. Only one additional economic evaluation was identified by the updated searches. This was the previous RAADP NICE Health Technology Assessment by Chilcott et al. carried out in 2001. 1
FIGURE 5.
Assessment of cost-effectiveness: summary of study selection and exclusion.
Because of the variability between the studies a quality assessment has not formally been carried out. However, the following sections of this report present an overview of the nine included economic evaluations. The description of eight of the studies presented here has been taken from the previous anti-D Health Technology Assessment by Chilcott et al. carried out in 20011 for the NICE appraisal of RAADP. Of the nine studies included in the review, five evaluations used UK costs, but only the studies by Vick et al. 161,162 and Chilcott et al. 1 describe a detailed modelling evaluation that appears to be applicable to the UK NHS. Four of the studies are over 20 years old and an additional three of the studies are over 10 years old; hence, caution should be taken if comparing these results with those of the model presented here. The economic evaluations included in the review cover a range of RAADP regimens, as summarised in Table 20.
| Economic evaluation | Primi- (P) or multigravidae (M) | 2 × 500 IU at 28 and 34 weeks | 2 × 1250 IU at 28 and 34 weeks | 1 × 1500 IU at 28 weeks | 1 × 1250 IU at 28 weeks | Unknown dose at 28 weeks | Unknown dose and timing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lim et al.158 | M | ✓ | |||||
| Tovey et al.163 | P | ✓ | |||||
| Adams et al.156 | P | ✓ | |||||
| Torrance et al.160 | P and M | ✓ | |||||
| Baskett et al.157 | M | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Vick et al.161,162 | P and M | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Selinger et al.159 | P | ✓ | |||||
| Mackenzie et al.126 | P | ✓ | |||||
| Chilcott et al.1,164 | P and M | ✓ | ✓ |
Reduction of RhO(D) sensitisation: a cost-effective analysis
Lim and colleagues158 put forward both a cost-effectiveness and a cost–benefit analysis of RAADP at 28 weeks’ gestation, although the details reported are very limited. The study is the first American study on the incidence of gestational sensitisation, using patient data collected from hospitals in the Los Angeles area between 1976 and 1978. Data from 3995 deliveries are used in the analysis. The actual methods used for calculating cost-effectiveness and cost–benefit are not well detailed. The cost of preventing one sensitisation using anti-D administered at 28 weeks (unspecified amount) was estimated to be US$8450.96. The authors believe that lifesaving benefit will be realised from more liberal usage of anti-D. It should be noted that savings arising from preventing sensitisation and savings in newborn intensive care unit costs, which have been included in other evaluations, are not included in this analysis.
The Yorkshire antenatal anti-D immunoglobulin trial in primigravidae
Tovey and colleagues128 compare a group of primigravidae receiving 500 IU of AADP at 28 and 34 weeks’ pregnancy with historical controls. The main outcome measure is cost per immunisation avoided. The extra cost in anti-D immunoglobulin was approximately £1600 for each woman sensitised. As little economic information is provided, more detail cannot be reported here.
Cost implications of routine antenatal administration of Rh immune globulin
The evaluation put forward by Adams and colleagues156 estimates the benefits, risks and costs using decision analytic modelling of a programme of RAADP administered to RhD-negative primiparae in the US. The comparators within the model are:
-
routine antepartum and postpartum administration of 1500 IU of anti-D IgG for RhD-negative primiparae at 28 weeks’ gestation
-
postpartum administration.
The model enables the number of women experiencing each outcome to be estimated. These outcomes are:
-
the number of births with mild or moderate/severe RhD HDN
-
the number of women without second pregnancies
-
the number of women with unaffected pregnancies.
The model also has the ability to assess the impact of alternative strategies on morbidity, mortality and medical care cost. The primary outcome for the model is cost per case avoided, and the results are presented by ethnic group, as follows:
-
cost per case avoided: white = US$28,571, black = US$22,222, Asian = US$11,429.
The authors claim to present a conservative analysis by overestimating the risks of the antepartum programme and underestimating benefits.
Cost-effectiveness of antepartum prevention of Rh immunisation
The economic evaluation by Torrance and Zipursky160 assesses both the cost-effectiveness and the cost–utility of an RAADP prevention programme in Ontario, Canada. The purpose of the study is to assess whether a programme of RAADP is not only cost-effective but also sufficiently cost-effective to warrant its use.
The key economic results of the study are summarised below:
-
cost-effectiveness: cost per immunisation prevented = US$2700; cost per case of Rh disease prevented = US$3700; cost per life saved = US$29,500, cost per life-year saved = US$1500
-
cost–utility: cost per quality-life adjusted life-year (QALY) gained = US$1500.
The authors conclude that RAADP treatment of all RhD-negative pregnant women is sufficiently cost-effective to warrant its use. Treating primiparae is found to be more favourable than treating multiparae. It is recognised that the results are specific to Ontario only and are therefore not generalisable worldwide.
Prevention of Rh(D) alloimmunisation: a cost–benefit analysis
Baskett and colleagues157 report a cost–benefit analysis of the prevention and treatment of RhD alloimmunisation in Nova Scotia, Canada. This economic evaluation uses patient data collected from the Rh Programme of Nova Scotia between 1982 and 1986. The evaluation weighs the costs of additional medical procedures and hospital days associated with the complications resulting from RhD alloimmunisation against the costs associated with one dose of anti-D IgG at 28 weeks (unspecified amount) and its administration. The effectiveness of the conventional treatment comparator is based upon previously published studies of a historical population from a different country, which brings into question the validity of this study. The study reports the total additional costs associated with subsequent complications. The author suggests that 80.1% of the additional health-care expenses were incurred because of the need for neonatal intensive care. The headline result of the study is that an RhD alloimmunisation prevention programme is cost-effective. Based on 1986 prices the cost per case treated is calculated to be US$3986 while the cost per case prevented is calculated to be US$1495.
Cost-effectiveness of antenatal anti-D prophylaxis
Vick et al. 161,162 describe a model to calculate the incremental cost per RhD alloimmunisation prevented and the incremental cost per RhD HDN fetal loss prevented for six different AADP programmes. The evaluation uses ‘real world’ data obtained from blood transfusion centres, hospitals and haematology laboratories in Scotland to assess the incremental cost-effectiveness. The results calculated from the model are presented in Table 21.
| Dose regimen | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 × 1250 IU | 2 × 500 IU | 2 × 1250 IU | |
| Incremental cost per RhD alloimmunisation prevented | |||
| Primigravidae vs no routine AADP | –£1172 | –£197 | £1464 |
| All women vs primigravidae | £2915 | £4908 | £8272 |
| Incremental cost per Rh HDN loss prevented | |||
| Primigravidae vs no routine AADP | –£17,136 | –£2,845 | –£21,268 |
| All women vs primigravidae | £42,346 | £71,308 | £120,174 |
This is the only model for which extensive detail of the methods and sensitivity analysis are provided. The economic outcomes are robust although there is some concern about the inclusion of cost savings arising in the current (i.e. treated) pregnancy, the clinical justification for which is unclear. A cost per QALY outcome is not assessed because of the difficulties involved in assigning quality of life gains appropriately. A policy of RAADP for RhD-negative primigravidae has a better cost-effectiveness ratio than a policy of RAADP for all RhD-negative pregnant women. When comparing dose protocols the 1 × 1250 IU dosage regimen is more effective and less costly than the 2 × 1250 IU programme. It should be noted that, although in this analysis cost savings are estimated to arise in the current pregnancy, this is not in fact the case. The net costs of the programme may therefore be underestimated.
Building on success: antenatal prophylaxis. The pharmacoeconomics of antenatal prophylaxis
Selinger159 reports a cost–benefit evaluation of two doses of 500 IU of antenatal prophylaxis at 28 and 34 weeks of pregnancy versus perinatal care for the treatment of RhD disease. Resource and effectiveness data relate to the Oxford Regional Health Authority, and evaluation takes the form of annual costs. Selinger calculates that, within this setting, the antenatal prophylaxis programme would have a cost advantage of £48,700 (37%) per year over perinatal care (£132,000–£83,300). However, he suggests that this may be an overestimate and that, as a result of other resource and cost factors that have not been captured within the evaluation, the true cost advantage of antenatal prophylaxis may be approximately 30%. This, however, assumes that all RhD HND is eradicated. The author suggests the need for further high-quality trials.
Routine antenatal Rhesus D immunoglobulin prophylaxis: the results of a prospective 10-year study
MacKenzie et al. 126 assess the clinical and financial impact of 500 IU of RAADP for RhD-negative nulliparae at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation. The evaluation uses empirical resource and cost data to evaluate the cost savings associated with implementing antenatal prophylaxis. The study reports the reductions in resource requirements that might be achieved as a consequence of implementing the programme across England and Wales. It is estimated that the savings from reduced antenatal and postnatal management as a result of such a programme would be £3,431,000. It is suggested that this may be a conservative estimate as 16% of the study population had previous pregnancies outside the study district and probably had not received RAADP. The uptake of the programme of routine antenatal prophylaxis appears to be promising. However, the costs of the programme are estimated at £2,135,000 for nulliparae only, and double that – i.e. more than the estimated savings – for all RhD-negative pregnant women.
A review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine anti-D prophylaxis for pregnant women who are Rhesus negative
This assessment report, produced by Chilcott et al. 1 for NICE in 2001 for the 2002 RAADP appraisal,87 evaluates the use of two regimens of RAADP against no routine anti-D:
-
two doses of 500 IU at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation
-
two doses of 1250 IU at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation.
The evaluation suggested that there was insufficient evidence to indicate a difference in efficacy between the dosing regimens and hence the difference between economic outcomes is dependent only on price differences between the indications.
The model evaluates the cost-effectiveness of RAADP for primigravidae and multigravidae in terms of the following outcomes:
-
cost per fetal loss, stillbirth, neonatal death or postneonatal death avoided
-
cost per life-year gained (LYG)
-
number of disabilities avoided
-
cost per QALY gained as a result of disabilities avoided.
The cost per LYG and cost per QALY gained for primigravidae versus no RAADP were estimated to be around £5000 and £11,000–£13,000, respectively, whereas the incremental LYG and incremental QALY gained for primigravidae and multigravidae versus primigravidae were estimated at around £15,000 and £46,000–£52,000 respectively. Because of the limited evidence concerning the impact of fetal loss and parental grief in terms of health-related quality of life, a threshold analysis was undertaken around this parameter. The threshold analysis suggested that, to obtain a cost-effectiveness ratio below £30,000 per QALY for anti-D given to primigravidae and multigravidae, the lost child, associated parental grief and subsequent high intervention pregnancy would need to be valued at more than nine QALYs.
Independent economic assessment
There were no new health economic models provided within the manufacturers’ submissions for this assessment report. The independent economic model that was developed in 2001 for the NICE RAADP appraisal87 has been modified to incorporate recent additional evidence identified for this review. This review reassesses the use of 500 IU and 1250 IU of anti-D at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation and, in addition, evaluates the use of a single dose of 1500 IU of anti-D at 28 weeks’ gestation. Although coverage of RAADP is currently approximately 90%,89 these regimens are evaluated against no RAADP to enable the assessment of all interventions against the same comparator and to enable a reassessment of the cost-effectiveness of RAADP against no RAADP. Within this assessment, in an attempt to improve upon the cost per QALY analysis, we have also revisited the assumptions around valuation of fetal loss and quality of life of those who suffer from developmental problems. Population parameters, costs and current statistics such as average life expectancy and the probability associated with having subsequent children have also been updated within this assessment.
Methods
Modelling methodology and scope
The model simulates the experience of a hypothetical cohort of women to whom national fertility rates are assumed to apply. The experience of this cohort over time is assumed to match the experience of a mixed population of primigravidae and multigravidae during any one year. The model follows a NHS perspective and all costs and utilities are discounted at a rate of 3.5% each year.
The interventions for both primigravidae and multigravidae are:
-
500 IU at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation (D-Gam)
-
1250 IU at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation (Partobulin)
-
1500 IU at 28 weeks’ gestation (Rhophylac)
-
1500 IU at 28 weeks’ gestation (WinRho).
It should be noted that, although WinRho is licensed for use as RAADP, the manufacturers state that it is marketed and used solely for the clotting disorder immune thrombocytopenic purpura and hence is priced specifically for that market. 103 Interventions are compared against each other and against a policy of no RAADP.
The outcomes of interest within the model are:
-
cost per sensitisation avoided
-
cost per affected pregnancy avoided
-
cost per fetal loss avoided (where fetal loss includes stillbirths and neonatal and postnatal deaths)
-
cost per LYG
-
cost per QALY gained.
Efficacy of RAADP
The systematic review of clinical effectiveness presented in Chapter 3 did not identify any evidence to suggest a difference in efficacy between the different regimens of RAADP. On the basis of face validity, visual examination of the absolute trial results, individual odds ratios within trials and results of the meta-analyses (shown in Table 16), the trials show a remarkable consistency in results, even between dosage regimens. Consequently, the results of the meta-analysis of group 3 trials (see Chapter 3, Critical review and synthesis of information) are deemed to give a representative reflection of the actual effectiveness of RAADP, and these figures are used in the economic evaluation. Therefore, within the economic model the base-case sensitisation rate is assumed to be 0.95% and the odds ratio for each of the regimens of RAADP is assumed to be 0.37. Thus, any differences in the economic results between the different RAADP regimens are dependent on price only. However, an economic model is required to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of RAADP given to RhD-negative women in comparison with no RAADP and to compare the cost-effectiveness of RAADP for all RhD-negative women versus RhD-negative primigravidae.
A cohort of 104,000 women is modelled to represent the number of RhD-negative women in England and Wales based on a birth rate of 12.1 per 1000 women per year165 and assuming that 16% of the population is RhD negative. 10 Of these women, 45,041 are RhD-negative primigravidae, based on the probability of having a second, third and fourth pregnancy (conditional on having the previous pregnancy) being 85%, 40% and 35% respectively. 165 Of the primigravidae, 61% will have a RhD-positive baby and, therefore, their pregnancy will be at risk. This proportion is based on the zygosity of the father, and its derivation is described in the next section. This results in 27,430 pregnancies at risk. In the case described the mothers are given RAADP for all pregnancies and, therefore, 0.35% will become sensitised based on the meta-analysis described in Chapter 3 (see Critical review and synthesis of information). This results in an estimated 97 sensitisations. Of these women, 85% are expected to go on to have a second pregnancy,165 and around 70% of these second pregnancies will be RhD positive and with an affected fetus. The increase in the proportion of RhD-positive fetuses during the second pregnancy is based upon the fact that, once a couple have had one RhD-positive baby, they are more likely to have another one (see the next section for method of calculation). This results in 58 cases of HDN in the next pregnancy.
This cycle is then repeated. The number of non-sensitised RhD-negative women entering a second pregnancy is the original number of non-sensitised women minus the prevalent number of women sensitised during earlier pregnancies multiplied by 85%, the percentage of women having a second pregnancy. This results in 38,285 non-sensitised RhD-negative women entering a second pregnancy. Of these, 70% (25,392 pregnancies) will have a RhD-positive baby and, therefore, their pregnancy will be at risk. As RAADP is given, 0.35% of these will become sensitised for the first time (90 sensitisations). The number entering a third pregnancy equals the number sensitised for the first time in the second pregnancy plus the number sensitised in the first pregnancy who continued on to a second pregnancy multiplied by 40%, the percentage of women having a third pregnancy given that they have had a second pregnancy. Of these fetuses, 70% will be RhD positive and, therefore, will be affected. This results in 48 cases of HDN in the next pregnancy.
This process is then repeated again, with the percentage of women entering a fourth pregnancy given that they have had a third pregnancy reduced to 35%.
This method of calculation has been used for all scenarios, and so in the case in which AADP is not administered, the sensitisation rate is 0.95% instead of 0.35%. When prophylaxis is given only to primigravidae, only the first 45,041 pregnancies are given antenatal prophylaxis and, therefore, the risk of sensitisation in second and subsequent pregnancies returns to 0.95%. Based on the above assumptions and parameter values the clinical outcomes for the base-case population of England and Wales for no RAADP, RAADP for RhD-negative primigravidae and RAADP for all RhD-negative women are as shown in Table 22.
| Pregnancy number | Number of RhD-negative pregnancies | Number having RhD-positive baby who have not been sensitised previously | Number sensitised in current pregnancy | Number sensitised from previous pregnancy who go on to have another baby | Prevalent number of sensitised women during each pregnancy | Number of affected (RhD-positive) fetuses following sensitisation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No RAADP | First | 45,041 | 27,430 | 261 | 0 | 261 | 0 |
| Second | 38,285 | 25,295 | 240 | 221 | 462 | 155 | |
| Third | 15,314 | 10,123 | 96 | 185 | 281 | 129 | |
| Subsequent | 5360 | 3520 | 33 | 98 | 132 | 69 | |
| Total | 104,000 | 66,368 | 630 | 505 | 1135 | 353 | |
| RAADP given to RhD-negative primigravidae | First | 45,041 | 27,430 | 97 | 0 | 97 | 0 |
| Second | 38,285 | 25,392 | 241 | 82 | 324 | 58 | |
| Third | 15,314 | 10,165 | 97 | 129 | 226 | 91 | |
| Subsequent | 5360 | 3534 | 34 | 79 | 113 | 55 | |
| Total | 104,000 | 66,522 | 468 | 291 | 759 | 204 | |
| RAADP given to all RhD-negative women | First | 45,041 | 27,430 | 97 | 0 | 97 | 0 |
| Second | 38,285 | 25,392 | 90 | 82 | 172 | 58 | |
| Third | 15,314 | 10,208 | 36 | 69 | 105 | 48 | |
| Subsequent | 5360 | 3566 | 13 | 37 | 49 | 26 | |
| Total | 104,000 | 66,596 | 235 | 188 | 424 | 132 |
Proportion of RhD-positive babies born to RhD-negative women
The proportion of RhD-positive babies born to RhD-negative women is dependent upon the zygosity of the father. If the father is homozygous (i.e. he has two RhD-positive genes) all of his children will be RhD positive, but if he is heterozygous (i.e. he has one RhD-positive gene and one RhD-negative gene) his children will have a 50% chance of being RhD negative. 65 Therefore the model assumes:
Assuming that the probability of a father in the general population being RhD positive is 84%,10 based on the above, the probability of a RhD-negative woman having a RhD-positive baby is 61%. This closely matches published estimates. 156,162 However, following one RhD-positive baby, a woman may be more likely to have another RhD-positive baby because of the genetic make-up of the father. This probability is dependent upon the baby having the same father in consecutive pregnancies and is therefore highly uncertain. It is calculated as shown in Table 23.
| Parameter | Mean value | SEa | Source/calculation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Births within marriage | 369,997 | – | Office for National Statistics166 |
| Percentage of births of same father within marriage | 100% | – | Assumption |
| Births outside of marriage | 269,724 | – | Office for National Statistics166 |
| Percentage of births of same father outside marriage | 50% | 15% | Assumption |
| Percentage of babies with same father in next pregnancy | 79% | 5% | Calculated from rows above: (a/a + c) × b + (c/a + c) × d |
| Probability that baby will be RhD positive in first pregnancy/in subsequent pregnancies given different father | 61% | 4% | Calculated as described above |
| Probability that baby will be RhD positive given same father | 73% | 4% | Calculated using formula above |
| Probability that baby will be RhD positive in second, third and fourth pregnancies | 70% | 4% | Calculated based on weighted probability of the fetus being RhD positive given the same or different father |
These calculations are based on the assumption that there is the same probability of a baby having the same father as for the previous pregnancy, independent of size of family. As shown in Table 23 the probability that the baby will be RhD positive in subsequent pregnancies is reasonably robust to changes in the proportion of babies with the same father in that pregnancy, with a standard error of 4%.
HDN outcomes
To assess the implications of HDN, a literature search was undertaken to identify the possible outcomes associated with HDN and their impacts upon costs and health-related quality of life. The largest study identified around the outcomes associated with HDN is a study by Craig et al. 19 based on all pregnant women in Northern Ireland from September 1994 to February 1997. This study is described in further detail in Chapter 1 (see Aetiology, pathology and prognosis). Because of the small proportion of babies affected by HDN, large studies of RhD-negative women have very few occurrences of the disease. Therefore, although this study was based on all pregnant women in Northern Ireland over a 3-year period, there were three fetal losses and two babies born with major developmental problems and five born with minor developmental problems as a result of HDN. Thus, based on this study, for an at-risk fetus the probability of fetal loss is around 4%, the probability of minor developmental problems (including myopia, squint, delays in language development) is around 6%, and the probability of major developmental problems (including severe permanent neurodevelopmental delay such as cerebral palsy) is around 3%. However, given the small number of HDN-related events, these estimates are subject to considerable uncertainty.
Within the model a fetal loss is associated with a loss of 79 life-years and 70 QALYs. This is based on the theory that a fetus that has not been affected by HDN is likely to have lived to average life expectancy and hence this has been modelled in the same way as for other diseases that would end life prematurely. After discounting, this equates to 28 life-years and 24 QALYs lost. A separate parameter has not been included for any reduction in the quality of life of the parent(s). However, a threshold analysis has been carried out to assess the impact of different views on the QALY loss associated with a fetal loss. This parameter includes both the life-years lost by the fetus and the QALYs lost by the parent(s). These have not been assessed distinctly because of the different weightings people would place upon the value of each.
Within the model the quality of life of a child with minor developmental problems is based on a study that assessed the health utility of low-birthweight babies,166 given the limited data around children with myopia, squint and language delay. The control group of this study has been used to represent the health utility of babies who are not affected by HDN. Therefore health utility scores of 0.85 and 0.88 were used to represent children with minor developmental problems and children and adults with no developmental problems respectively. Children with myopia and squint are typically provided with glasses to correct the problem; the cost of an eye test is around £16167 and the cost of glasses is around £84168 (average of published prices), meaning that the annual cost is estimated to be around £100 per patient. Teachers and carers of children with language delay are likely to require education by language and speech therapists as to how they may help such children to progress with their language development more rapidly; however, the annual societal cost for these children is extremely variable. Moreover, the proportion of children affected by each of myopia, squint and language delay associated with HDN is highly uncertain. Therefore, the model assumes that the annual cost for children with minor developmental problems is £100 based on the myopia/squint estimates. At age 16 these costs are no longer paid by the NHS and the quality of life implications of the minor developmental problems are assumed to become negligible.
To value the health-related quality of life and costs associated with major developmental problems the model uses data from cerebral palsy studies, as this is likely to be one of the major developmental problems associated with HDN. The health utility score associated with major developmental problems is assumed to be 0.42 based on a study of young adults with a range in severity of cerebral palsy who self-assessed their own quality of life. 169 The cost associated with this group is based on a study by Beecham et al. 170 This study calculates the additional cost of a person with cerebral palsy in comparison with a non-disabled child in the UK. The costs incurred to the NHS and Personal Social Services (PSS) taken from this study include inpatient hospital stays, outpatient appointments, A&E attendances, community health services (including chiropody, orthotist, occupational therapy, physiotherapy, speech therapy, psychiatry, psychology, counselling and contact with doctors and surgeons) and primary care services (including general practitioner, opticians and dentist). The annual cost is therefore assumed to be £458 on average, although the confidence intervals associated with this cost are wide and skewed because of the large variation in severity of major developmental problems and the treatment costs associated with them. The life expectancy of people with major developmental problems is assumed to be between 40 and 79, based on an extrapolation of data from a paper by Hemming et al. ,171 which presents an assessment of the life expectancy of people with cerebral palsy in the UK. The upper bound is such that the life expectancy of a person with a major developmental problem will not be greater than the life expectancy of a person without a developmental problem within the model.
It should be noted that the parameters associated with the outcomes of HDN are subject to considerable uncertainty because of limitations in the evidence base. The impact of this uncertainty on the cost-effectiveness of RAADP has been explored within the sensitivity analysis.
Cost of routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis
The cost of anti-D was taken from the BNF. 116 At current prices the cost is between £27 and £313.50 per vial depending upon manufacturer and dosage; however, the cost paid by hospitals may be lower than these listed prices. The cost of 500 IU of D-Gam is reported by the manufacturer of this product to be £19.50 per vial. 91 Similarly, the NHS price quoted for Partobulin by the manufacturer is between £19 and £21. Therefore, the cost of anti-D and its administration has been tested within a threshold analysis. It should be noted that, because the current market price in the anti-D field varies with supply and demand and could easily change, the formulation that is more expensive in terms of list price may in some cases be less expensive because of local price negotiations. Therefore, comparisons between the cost-effectiveness of the anti-D regimens should be interpreted with caution.
Cost of management of sensitisation
The cost of the management of sensitisations is taken from a range of sources including Selinger,159 Craig et al. ,159 Kumar and Regan,31 Greenough et al. 172 and expert opinion (Dr D Peebles, 2007, personal communication). NHS reference costs from 2005–6173 are applied to the interventions required as shown in Table 24. The total average cost per person is estimated to be £2885. However, this is a complex condition and hence many factors including differences in severity will affect the cost of treatment. Further, some may require repeat Doppler scans or transfusions given inconclusive results and some additional costs not included here may be incurred for mothers ‘rooming in’ (i.e. staying at the hospital but without requiring treatment). Because of the uncertainty associated with this parameter a wide standard error of £700 has been applied, which ensures that all estimates are greater than £0.
| Intervention | Percentage of sensitised mothers/babies requiring intervention | Average number required per person | Average days per treatment | Unit cost of intervention | Total cost | Listed NHS reference costs used for the unit costs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood tests, bilirubin, monitoring, etc. | 100% | 6 | 1 | £93 | £558 | Antenatal outpatients – other high-risk expectant mother follow-up visit |
| Doppler scanning | 90% | 4 | 1 | £83 | £299 | Doppler ultrasound |
| In utero transfusion | 5% | 3 | 1 | £93 | £14 | Antenatal outpatients – other high-risk expectant mother follow-up visit |
| Phototherapy | 71% | 1 | 3 | £724 | £1542 | Neonates with one minor diagnosis – non-elective |
| Exchange transfusion | 5% | 2 | 1 | £724 | £72 | Neonates with one minor diagnosis – non-elective |
| Neonatal follow-up visits | 10% | 2 | 1 | £724 | £145 | Neonates with one minor diagnosis – elective |
| Neonatal intensive care unit | 5% | 1 | 5 | £1020 | £255 | Neonatal intensive care unit – level 1 |
| Total | £2885 |
Model parameters and assumptions
The parameters used within the model as described above are outlined in Table 25. Costs refer to 2007 prices.
| Parameter | Mean value | SEa | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discount rate for utilities | 3.5% | – | Recommended by NICE |
| Discount rate for costs | 3.5% | – | Recommended by NICE |
| Number of women requiring treatment | 104,000 | – | Office for National Statistics165 |
| Average woman’s life expectancy (years) | 79 | – | Office for National Statistics165 |
| Crude birth rate: all births per 1000 population | 12.1 | – | Office for National Statistics165 |
| Sensitisation rate without RAADP | 0.95% | 0.39% | Based on meta-analysis (see Chapter 3, Assessment of effectiveness) |
| Relative risk of sensitisation with RAADP (all regimens) | 0.37 | Log norm (–1.23 to 0.69) | Based on meta-analysis (see Chapter 3, Assessment of effectiveness) |
| Cost of RAADP per vial | |||
| 500 IU at 28 and 34 weeks (D-Gam) | £27.00 | – | British National Formulary 116 |
| 1250 IU at 28 and 34 weeks (Partobulin) | £35.00 | – | |
| 1500 IU at 28 weeks (Rhophylac) | £46.50 | – | |
| 1500 IU at 28 weeks (WinRho) | £313.50 | – | |
| Percentage of RhD-negative people | 16%b | – | Romen and Pernoll 200365 |
| Percentage of fathers who are heterozygous | 55% | 10% | Romen and Pernoll 200365 |
| Percentage of RhD+ babies in RhD– women (first baby) | 61% | 4% | Assumption based on Romen and Pernoll 200365 (see Table 23 for details). |
| Percentage of RhD+ babies in RhD– women (second, third and fourth babies) | 70% | 4% | |
| Percentage of first pregnancies proceeding to next pregnancy | 85% | – | Office for National Statistics165 |
| Percentage of second pregnancies proceeding to next pregnancy | 40% | – | Office for National Statistics165 |
| Percentage of third pregnancies proceeding to next pregnancy | 35% | – | Office for National Statistics165 |
| Fetal loss rate per woman at risk | 4% | 1% | Craig et al. 200019 |
| Percentage of babies affected by HDN with minor developmental problems | 6% | 2% | Craig et al. 200019 |
| Duration of minor developmental problems (years) | 16 | 5 | Based on the fact that the NHS stops paying for children’s treatment at age 16 |
| Percentage of babies affected by HDN with major permanent developmental problems | 3% | 1% | Craig et al. 200019 |
| Life expectancy of person with major developmental problems | 60 | Uniform (40–79) | Assumption based on Hemming et al. 2005171 |
| QoL for person with no developmental problems | 0.88 | 0.02 | Saigal et al. 2006166 |
| QoL for minor developmental problems | 0.85 | 0.02 | Saigal et al. 2006166 |
| QoL for major developmental problems | 0.42 | 0.03 | Rosenbaumet al. 2007169 |
| Cost of anti-D administration per dose | £5 | £2 | Submission to NICE from the Association of Radical Midwives, 2001 |
| Cost of management of a sensitised woman | £2885 | £700 | Based on Selinger 1997,159 Kumar and Regan31 and Greenough et al.172 and NHS reference costs 2005–6173 |
| Cost of minor developmental problems per year | £100 | £35 | Assumption based on treatment of myopia/squint167,168 |
| Cost of major developmental problems per year | £458 | Gamma (5.84, 0.76) | Beecham et al. 2001170 (uplifted to 2006 prices) |
Within the model the following assumptions have also been made:
-
there will be approximately the same proportion of primigravidae and multigravidae every year
-
sensitisations do not affect the first RhD-positive child
-
anti-D used within one pregnancy has no effect in reducing sensitisations during the next pregnancy
-
the proportion of RhD-negative people is based on the Caucasian population given that this group makes up over 90% of the population of England and Wales;165 the cost-effectiveness of RAADP for ethnic minorities is tested in a subgroup analysis
-
the proportion of homozygous males is the same regardless of ethnic minority
-
fetal loss of the newborn results in 79 life-years lost (average life expectancy) and 70 QALYs lost, which equates to 28 discounted life-years lost and 24 discounted QALYs lost.
Subgroup analysis
Because the proportion of RhD-negative people varies with ethnic race, a subgroup analysis has been carried out to assess the implications for cost-effectiveness of using RAADP amongst some of the ethnic minorities in England and Wales. The parameters used within this analysis are taken from Contreras10 and Ali et al. 29 and are shown in Table 26.
| Ethnicity | Proportion RhD negative | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Caucasian | 16% | Contreras10 |
| Asian | 9% | Ali et al.29 |
| West African | 5% | Contreras10 |
| Chinese | 1% | Contreras10 |
This subgroup analysis assumes that 55% of fathers are heterozygous irrespective of ethnicity.
Sensitivity analysis
One-way sensitivity analysis has been undertaken to identify key determinants of cost-effectiveness. Probabilistic sensitivity analysis has been undertaken to explore the impact of joint uncertainty in all model parameters upon the cost-effectiveness results. The confidence intervals used to describe the uncertainty in the parameters within the probabilistic sensitivity analysis are the same as those used within the one-way sensitivity analysis. The uncertainty around the parameters is described using the normal distribution unless otherwise stated. The parameters assessed within the one-way sensitivity analysis are as follows:
-
Odds ratio for sensitisation rate of anti-D – The efficacy of RAADP is assumed to vary between 0.21 and 0.65 based on the meta-analysis of the clinical studies (see Chapter 3, Assessment of effectiveness).
-
Base-case sensitisation rate – The base-case sensitisation rate is assumed to vary between 0.18% and 1.71% based on the meta-analysis of the clinical studies (see Chapter 3, Assessment of effectiveness).
-
Proportion of heterozygous males – This parameter will affect the proportion of RhD-positive babies born to RhD-negative mothers and hence it is important to assess whether it is a key determinant of cost-effectiveness. Evidence identified suggests that this parameter lies between 55% and 60%; however, a wider confidence interval of 35% and 75% has been used because of the limited evidence available in this area.
-
Fetal loss rate per woman at risk – The fetal loss rate is varied using a normal distribution with confidence intervals of 2% and 6%. This range ensures that all estimates are greater than 0%.
-
Yearly cost of major developmental problems; life expectancy for people with major developmental problems, quality of life of people with major developmental problems – There is limited evidence around the outcomes of HDN and their costs and consequences. Therefore, the major parameters impacting upon these outcomes are assessed within the one-way sensitivity analysis using the standard errors presented within the studies used for each of these parameters.
-
Cost of management of sensitisation – The mid-estimate for this parameter is £2885 per sensitisation; however, previous estimates have been lower and it is anticipated that this cost will vary considerably in practice. Therefore, a sensitivity analysis has been carried out using a wide standard error of £700, which ensures that all estimates fall above £0.
-
Percentage of births outside marriage with the same father – This parameter affects the proportion of RhD-positive babies in second, third and fourth pregnancies. There is no evidence around the proportion of babies having the same father (and mother) as the previous baby; therefore, a mid-estimate of 50% is assumed to be reasonable. This parameter requires a large standard error to account for the large amount of uncertainty associated with it; therefore, upper and lower confidence intervals are assumed to be 26% and 74% based on a standard error of 12%. This standard error allows all estimates to fall between 0% and 100%.
The parameters associated with minor developmental problems have not been assessed within the one-way sensitivity analysis as they are expected to have a similar but smaller impact on the results as the parameters associated with major developmental problems. As discussed earlier in this chapter a threshold analysis around the valuation of a fetal loss and around the cost of anti-D has also been carried out (see HND outcomes and Cost of RAADP respectively).
Results
Results of the deterministic analysis
The incremental cost-effectiveness outcomes associated with RAADP for RhD-negative primigravidae and for all RhD-negative women are shown in Tables 27 and 28 respectively.
| Anti-D dose | Total additional cost | Number of sensitisations avoided | Number of affected pregnancies avoided | Number of fetal losses avoided | LYG | QALYs gained | Cost per sensitisation avoided | Cost per affected pregnancy avoided | Cost per fetal loss avoided | Cost per LYG | Cost per QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline valuea | £1,796,546 | 630 | 353 | 14 | 2,878,648 | 2,533,240 | |||||
| 2 × 500 IU (D-Gam) | £2,360,604 | 162 | 150 | 6 | 250 | 207 | £14,561 | £15,783 | £394,580 | £9457 | £11,384 |
| 2 × 1250 IU (Partobulin) | £3,081,262 | 162 | 150 | 6 | 250 | 207 | £19,006 | £20,602 | £515,040 | £12,344 | £14,859 |
| 1 × 1500 IU (Rhophylac) | £1,797,590 | 162 | 150 | 6 | 250 | 207 | £11,088 | £12,019 | £300,471 | £7201 | £8669 |
| 1 × 1500 IU (WinRho) | £13,823,575 | 162 | 150 | 6 | 250 | 207 | £85,267 | £92,426 | £2,310,641 | £55,378 | £66,661 |
| Anti-D dose | Total cost | Number of sensitisations avoided | Number of affected pregnancies avoided | Number of fetal losses avoided | LYG | QALYs gained | Cost per sensitisation avoided | Cost per affected pregnancy avoided | Cost per fetal loss avoided | Cost per LYG | Cost per QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 × 500 IU (D-Gam) | £2,645,120 | 233 | 72 | 3 | 120 | 100 | £11,358 | £36,679 | £916,982 | £21,977 | £26,455 |
| 2 × 1250 IU (Partobulin) | £3,457,346 | 233 | 72 | 3 | 120 | 100 | £14,846 | £47,942 | £1,198,556 | £28,725 | £34,578 |
| 1 × 1500 IU (Rhophylac) | £2,010,568 | 233 | 72 | 3 | 120 | 100 | £8634 | £27,880 | £697,002 | £16,705 | £20,108 |
| 1 × 1500 IU (WinRho) | £15,564,594 | 233 | 72 | 3 | 120 | 100 | £66,836 | £215,831 | £5,395,767 | £129,317 | £155,666 |
The model results show that WinRho RAADP would not be considered cost-effective in comparison with the other regimens of RAADP. Excluding WinRho, for all other regimens of RAADP given to RhD-negative primigravidae versus no RAADP, the cost per sensitisation avoided and the cost per affected pregnancy avoided are estimated to be between £11,000 and £21,000. The cost per fetal loss avoided is estimated to be between £300,000 and £515,000. These high estimates are due to the low proportion of fetal losses occurring as a result of HDN within a group of pregnant RhD-negative women.
RAADP given to all RhD-negative women is expected to decrease the number of sensitisations, the number of affected pregnancies and the number of fetal losses, but it is also expected to increase costs. Therefore, giving RAADP to RhD-negative primigravidae and multigravidae compared with giving RAADP to RhD-negative primigravidae only results in a cost per sensitisation avoided of between £8000 and £15,000 and a cost per affected pregnancy avoided of between £28,000 and £48,000 for all regimens of RAADP excluding WinRho. The cost per fetal loss avoided is estimated to be between £697,000 and £1.2 million.
Giving RAADP to RhD-negative primigravidae compared with no RAADP results in a cost per LYG of between £7000 and £12,000 for all RAADP regimens excluding WinRho. For RAADP given to RhD-negative primigravidae and multigravidae versus RhD-negative primigravidae only, the cost per LYG is estimated to be between £17,000 and £29,000. The cost per QALY gained as a result of RAADP given to RhD-negative primigravidae versus no RAADP is between £9000 and £15,000 for all RAADP regimens apart from the one-dose regimen of 1500 IU of WinRho, which has a cost per QALY gained of around £67,000. For RhD-negative primigravidae and multigravidae compared with primigravidae only, the cost per QALY gained as a result of RAADP is between £20,000 and £35,000 for all anti-D products, again with the exception of 1500 IU of WinRho, which has a cost per QALY gained of around £156,000. As described previously, any comparisons between the different regimens of RAADP should be considered with caution given the variability in actual prices paid by hospitals for anti-D.
Results of the subgroup analysis
Ethnic minorities in England and Wales are less likely to be RhD negative and hence the absolute number of women requiring routine anti-D is expected to be smaller for these subgroups; however, the impact per person is expected to increase if we assume that the father is of the same ethnicity. For example, considering Asian, West African and Chinese people, the model predicts that, although the proportionate number of sensitisations, affected pregnancies and fetal losses will be lower in these ethnic minorities than in the Caucasian population, the cost per sensitisation, cost per affected pregnancy and cost per fetal loss will also be lower. Consequently, the cost-effectiveness ratio is estimated to be slightly better for ethnic minorities. Because the efficacy of each of the RAADP regimens is assumed to be the same within the model, the impact of changes in the proportion of people who are RhD negative is expected to have the same relative impact across the different regimens. Therefore, these results are presented in terms of a 500-IU dose of anti-D (D-Gam) at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation (Table 29).
| Ethnicity (% RhD negative)a | Total additional cost | Number of sensitisations avoided | Number of affected pregnancies avoided | Number of fetal losses avoided | LYG | QALYs gained | Cost per sensitisation avoided | Cost per affected pregnancy avoided | Cost per fetal loss avoided | Cost per LYG | Cost per QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Caucasian (16%) | £1,796,546 | 630 | 353 | 14.1 | 2,878,648 | 2,533,240 | |||||
| RhD-negative Caucasian primigravidae | £2,360,604 | 162 | 150 | 6 | 250 | 207 | £14,561 | £15,783 | £394,580 | £9457 | £11,384 |
| All RhD-negative Caucasian women | £2,645,120 | 233 | 72 | 3 | 120 | 100 | £11,358 | £36,679 | £916,982 | £21,977 | £26,455 |
| Baseline Asian (9%) | £1,073,357 | 375 | 216 | 8.64 | 1,619,211 | 1,424,923 | |||||
| RhD-negative Asian primigravidae | £1,302,875 | 99 | 93 | 4 | 154 | 128 | £13,188 | £14,080 | £352,012 | £8436 | £10,155 |
| All RhD-negative Asian women | £1,473,105 | 136 | 43 | 2 | 72 | 60 | £10,797 | £34,316 | £857,902 | £20,561 | £24,750 |
| Baseline West African (5%) | £615,566 | 215 | 125 | 5.0 | 899,553 | 791,617 | |||||
| RhD-negative West African primigravidae | £715,875 | 57 | 54 | 2 | 90 | 75 | £12,494 | £13,226 | £330,651 | £7925 | £9539 |
| All RhD-negative West African women | £814,149 | 77 | 25 | 1 | 41 | 34 | £10,525 | £33,158 | £828,949 | £19,867 | £23,915 |
| Baseline Chinese (1%) | £126,868 | 44 | 26 | 1.0 | 179,909 | 158,322 | |||||
| RhD-negative Chinese primigravidae | £141,583 | 12 | 11 | 0 | 19 | 16 | £11,856 | £12,445 | £311,116 | £7456 | £8976 |
| All RhD-negative Chinese women | £162,045 | 16 | 5 | 0 | 8 | 7 | £10,284 | £32,119 | £802,986 | £19,245 | £23,166 |
Results of the one-way sensitivity analysis
Several key uncertain parameters within the model (see Sensitivity analysis) have been explored within a one-way sensitivity analysis to assess the robustness of the model. Because the only difference modelled between the RAADP regimens is the price of the drug, each of the model parameters would be expected to have a similar impact upon the cost-effectiveness ratio independent of the RAADP regimen of anti-D. Therefore, these results are presented in Table 30 in terms of a 500-IU dose of anti-D (D-Gam) at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation to avoid unnecessary repetition.
| Parameter | Parameter value | Cost per QALY gained | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primigravidae | Multigravidae | |||
| Base case | £11,384 | £26,455 | ||
| Odds ratio for sensitisation rate of RAADP | Base case | 0.37 | ||
| LB | 0.21 | £8551 | £19,836 | |
| UB | 0.65 | £22,571 | £52,596 | |
| Base-case sensitisation rate | Base case | 0.95% | ||
| LB | 0.18% | £70,452 | £164,801 | |
| UB | 1.71% | £5255 | £12,090 | |
| Proportion of heterozygous males | Base case | 55% | ||
| LB | 35% | £8497 | £19,463 | |
| UB | 75% | £15,817 | £37,279 | |
| Fetal loss rate per woman at risk | Base case | 4% | ||
| LB | 2% | £17,378 | £40,396 | |
| UB | 6% | £8466 | £19,669 | |
| Cost of anti-D administration per dose | Base case | £5 | ||
| LB | £1 | £9646 | £22,393 | |
| UB | £9 | £13,121 | £30,516 | |
| Cost of management of sensitisation | Base case | £2885 | ||
| LB | £1513 | £12,458 | £29,215 | |
| UB | £4257 | £10,310 | £23,694 | |
| Rate of major developmental problems | Base case | 3% | ||
| LB | 1% | £14,180 | £32,705 | |
| UB | 5% | £9469 | £22,176 | |
| Yearly cost of major developmental problems | Base case | £458 | ||
| LB | £78 | £11,559 | £26,614 | |
| UB | £1532 | £10,886 | £26,005 | |
| Life expectancy for people with major developmental problems | Base case | 60 | ||
| LB | 40 | £11,077 | £25,704 | |
| UB | 79 | £11,556 | £26,879 | |
| QoL of people with major developmental problems | Base case | 0.42 | ||
| LB | 0.36 | £11,029 | £25,630 | |
| UB | 0.48 | £11,762 | £27,334 | |
| Percentage of births outside marriage with same father | Base case | 50% | ||
| LB | 26% | £11,193 | £25,662 | |
| UB | 74% | £11,581 | £27,281 | |
The one-way sensitivity analysis suggests that changing many of the model assumptions has only a small impact upon the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER). The parameters that have the greatest impact upon the ICER are the base-case sensitisation rate and the odds ratio for the sensitisation rate associated with RAADP. If the base-case sensitisation rate was lower than predicted, anti-D would have a lower absolute effect and hence the cost per QALY gained would increase. At a base-case sensitisation rate of 0.18% (the lower 95% confidence interval), the cost per QALY gained for providing RAADP to all RhD-negative pregnant women is estimated to be around £162,000. At a base-case sensitisation rate of 0.95%, increasing the odds ratio for the sensitisation of RAADP in comparison with no RAADP to its upper 95% confidence interval of 0.65 gives a cost per QALY gained of around £50,000 for RAADP given to all RhD-negative women.
Decreasing the fetal loss rate as a result of HDN from 4% to 2% would increase the cost per QALY gained by around £8000 to £34,000. Decreasing the impact of HDN in any way will increase the ICER to some extent as RAADP will then have less of an impact in terms of efficacy. However, different assumptions around the quality of life and cost of people with major developmental problems do not affect the ICER substantially, increasing it by around £1000 and £3000 respectively. Similarly, different assumptions around the costs of anti-D administration and the management of sensitisation do not have a big impact upon the ICER.
Threshold analysis of the valuation of a fetal loss
Because the valuation of a fetal loss is subjective, according to how the individual may value the QALYs lost associated with the fetus and the QALYs lost by the parent(s), a threshold analysis has been carried out to investigate the impact of different valuations associated with fetal loss. The results are presented in Table 31.
| Threshold | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £20K | £25K | £30K | £35K | £40K | £45K | £50K | ||
| RAADP given to RhD-negative primigravidae versus no RAADP | D-Gam | 17 | 13 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 4 |
| Partobulin | 24 | 18 | 14 | 12 | 9 | 8 | 7 | |
| Rhophylac | 12 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 2 | |
| RAADP given to all RhD-negative women versus primigravidae | D-Gam | 36 | 26 | 20 | 16 | 13 | 10 | 8 |
| Partobulin | 50 | 38 | 30 | 24 | 20 | 16 | 14 | |
| Rhophylac | 25 | 18 | 13 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 4 | |
These results show that RAADP given to RhD-negative primigravidae compared with no RAADP would be considered cost-effective at a threshold of £30,000 per QALY gained if a fetal loss is assumed to be worth 10, 14 and 6 QALYs lost for D-Gam, Partobulin and Rhophylac respectively. Similarly, RAADP given to all RhD-negative women compared with RhD-negative primigravidae only would be considered cost-effective at a threshold of £30,000 per QALY gained if a fetal loss is assumed to be worth 20, 30 and 13 QALYs lost for D-Gam, Partobulin and Rhophylac respectively. These QALY losses are a combination of both the parental QALYs lost and those QALYs lost as a result of the death of the fetus itself. As a lifetime lost with a life expectancy of 79 years is equal to 24 QALYs after discounting, Partobulin would be considered cost-effective for all RhD-negative women compared with RhD-negative primigravidae at a threshold of £30,000 per QALY gained if the loss of a fetus was assumed to be equal to the loss of a life with average lifetime expectancy and six QALYs lost by the parent(s).
Threshold analysis of the cost of anti-D
Because the listed price of anti-D in the BNF116 may be different from the actual cost of the drug, a threshold analysis has been carried out. This analysis evaluates the estimated price of anti-D in order for it to be cost-effective at a range of thresholds. The results are presented in Figure 6 below.
FIGURE 6.
Cost per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained based on cost of anti-D and its administration per person.
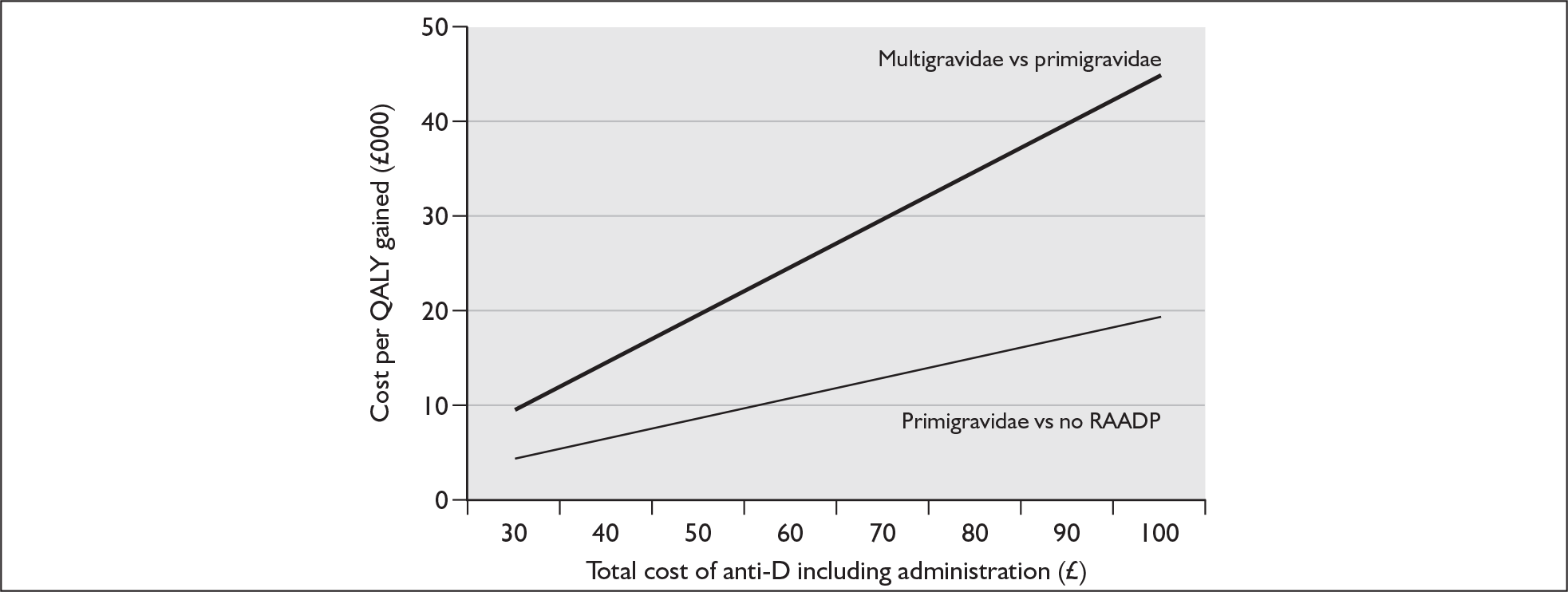
This shows that, at a cost per QALY gained of £30,000, RAADP given to all RhD-negative women compared with RAADP given to primigravidae only would be considered cost-effective at a cost of £76. However, because the results presented here include an administration cost of £5 per dose, a two-dose regimen of RAADP would be considered cost-effective at a cost of £33 per dose [(£33 × 2) + £10 = £76] whereas, at this threshold, a one-dose regimen would be considered cost-effective at a cost of £71 per dose (£71 + £5 = £76).
Results of the probabilistic sensitivity analysis
The results of the probabilistic sensitivity analysis for RAADP given to primigravidae versus no RAADP and RAADP given to primigravidae and multigravidae versus primigravidae only in terms of LYG and QALYs gained are shown in Tables 32 and 33 respectively.
| Anti-D regimen | Total additional cost | LYG | QALYs gained | Cost per LYG | Cost per QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base case: no RAADPa | £1,788,704 | 2,878,650 | 2,532,262 | ||
| D-Gam: 2 × 500 IU | £2,361,850 | 250 | 208 | £9434 | £11,347 |
| Partobulin: 2 × 1250 IU | £3,082,766 | 251 | 208 | £12,305 | £14,821 |
| Rhophylac: 1 × 1500 IU | £1,798,655 | 250 | 208 | £7184 | £8634 |
| WinRho: 1 × 1500 IU | £13,825,342 | 250 | 208 | £55,281 | £66,446 |
| Anti-D regimen | Total additional cost | LYG | QALYs gained | Cost per LYG | Cost per QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D-Gam: 2 × 500 IU | £2,645,112 | 121 | 101 | £21,871 | £26,306 |
| Partobulin: 2 × 1250 IU | £3,457,481 | 121 | 100 | £28,633 | £34,409 |
| Rhophylac: 1 × 1500 IU | £2,010,281 | 121 | 101 | £16,610 | £19,977 |
| WinRho: 1 × 1500 IU | £15,564,912 | 121 | 101 | £128,746 | £154,758 |
The results of the probabilistic sensitivity analysis closely match those of the deterministic analysis. Any slight difference in the efficacy of each of the RAADP regimens is due to the stochastic nature of the analysis. After taking into account the uncertainty associated with the model parameters, each of the RAADP regimens with the exception of WinRho has an ICER that is between £9000 and £15,000 per QALY gained for RAADP given to RhD-negative primigravidae versus no RAADP, and between £20,000 and £34,000 per QALY gained for RAADP given to primigravidae and multigravidae compared with primigravidae only. WinRho has a cost per QALY gained of around £66,000 for RAADP given to primigravidae versus no RAADP and around £155,000 for RAADP given to all RhD-negative women versus RhD-negative primigravidae only.
Figure 7 presents cost-effectiveness acceptability curves for each of the regimens of RAADP versus no RAADP and each other. These curves describe the probability that each of the regimens of RAADP and no RAADP have a cost per QALY ratio that is better than a given willingness to pay threshold (λ).
FIGURE 7.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves (CEACs).
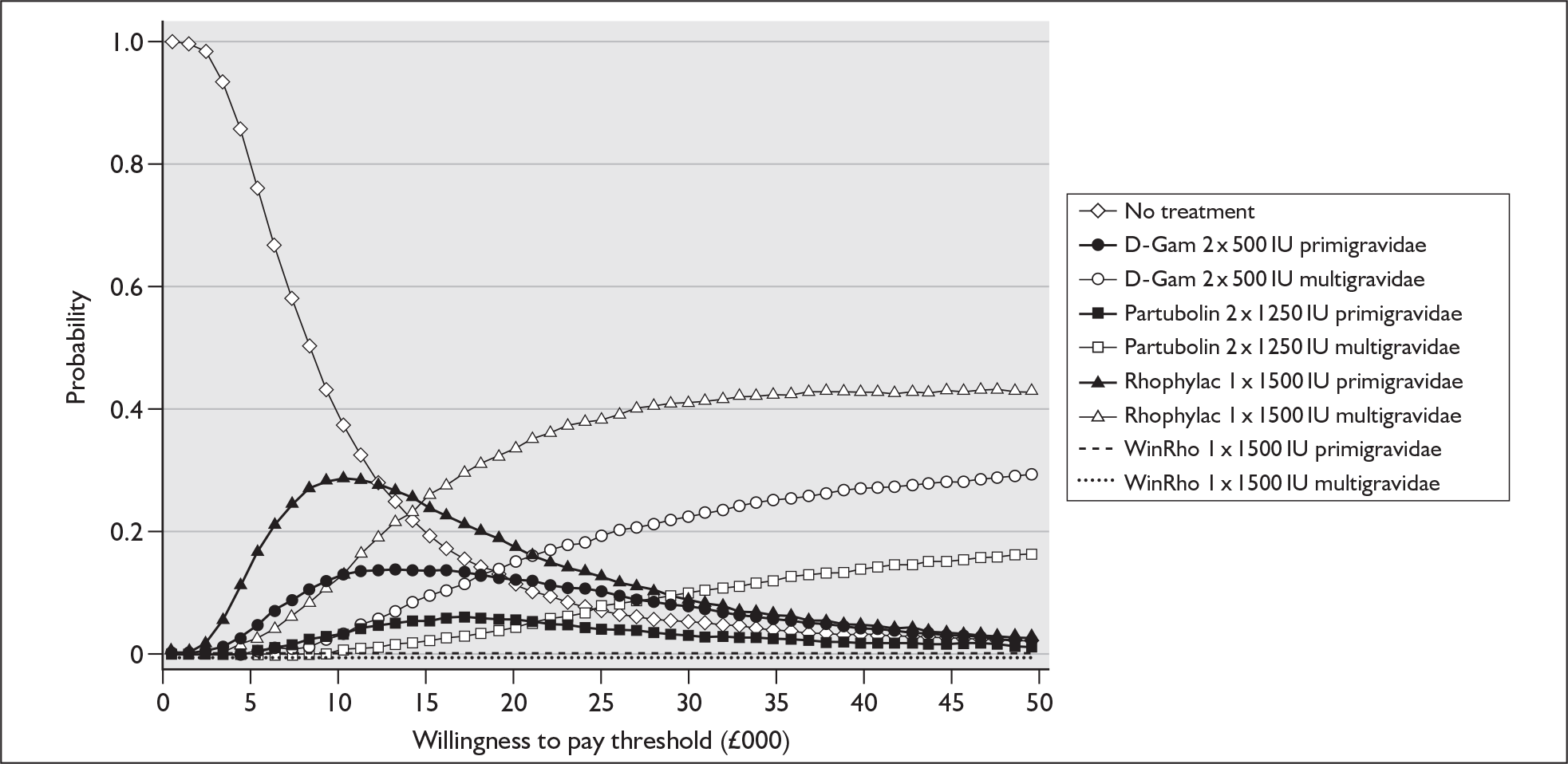
Figure 7 suggests that, at a threshold of £30,000 per QALY gained, it is more likely to be cost-effective to give RAADP to all RhD-negative pregnant women than to not provide RAADP or to provide RAADP to primigravidae only. Because the model assumes that the efficacy of the different anti-D regimens is the same, the cheaper regimens of anti-D are estimated to be more cost-effective. Therefore, based on the BNF drug prices,116 one dose of 1500 IU of Rhophylac at 28 weeks’ gestation is most likely to be cost-effective (around 40% probability) followed by two doses of 500 IU of D-Gam (around 25% probability) and two doses of 1250 IU of Partobulin (around 10% probability) at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation. The comparison of cost-effectiveness between these three RAADP regimens should be interpreted with caution because of the variability in actual prices paid by hospitals for anti-D. The probability that any of the regimens of RAADP (excluding WinRho) given to all RhD-negative pregnant women is cost-effective at a threshold of £30,000 compared with RAADP given to RhD-negative primigravidae or providing no RAADP is around 70%. One dose of 1500 IU of WinRho is not likely to be considered cost-effective at any threshold because it is substantially more expensive and because of the availability of its comparators.
Discussion
Generalisability of the results
Assuming that there are approximately the same number of primigravidae and multigravidae births each year the results may be considered representative of Caucasian people within England and Wales. For ethnic minorities within England and Wales, RAADP is expected to be more cost-effective although required less often because of the lower proportion of RhD-negative genotypes in these subgroups. This impact can be seen within the subgroup analysis presented earlier in this chapter (see Results of the deterministic analysis).
The economic model is fairly robust to changes in parameter values. The three key parameters affecting the ICER are:
-
the base-case sensitisation rate
-
the odds ratio associated with the sensitisation rate with RAADP
-
the assumption around the valuation of a fetal loss.
The ICER does not increase by more than £15,000 per QALY for all other parameters assessed within the one-way sensitivity analysis.
The base-case results presented suggest a lower cost per QALY gained as a result of a programme of RAADP than was suggested within the previous RAADP NICE Health Technology Assessment report. 1 Within this assessment report a greater degree of benefit is assumed as a result of the avoidance of sensitisations, as the number of life-years lost associated with a fetal loss is assumed to be equal to average life expectancy. Also, the parameters around developmental problems and the cost of management of sensitisations have been substantially revised. The cost of RAADP itself has increased in comparison with the original assessment and additional comparators of one dose of 1500 IU of anti-D were also considered within this assessment. Finally, population parameters have been revised and average life expectancy has increased by 5 years.
It is important to note that the cost per QALY comparing the different regimens of RAADP presented is driven by the costs of the drugs, as efficacy is assumed to be the same for all dosing regimens of anti-D. There is an argument to suggest that the two-dose regimen could be more effective than the one-dose regimen because of the half-life of anti-D; however, there is no published evidence around this. The cost of anti-D is based on BNF drug prices,116 but as actual prices paid by hospitals vary according to supply and demand, the cost-effectiveness in practice may be better than that presented here. Furthermore, the actual price paid for the different regimens of RAADP may vary, and the formulation that is more expensive in terms of list price may in some cases be the cheaper drug because advantageous prices have been negotiated locally. It should be noted that, although WinRho is licensed for use as RAADP, the manufacturers state that it is marketed and used solely for the clotting disorder immune thrombocytopenic purpura, and hence is priced specifically for that indication. 103 The manufacturers suggest that WinRho should not routinely be considered for RhD-negative pregnant women but that, if there were disruptions to the supply of the other three available products, WinRho SDF could provide an alternative to supplement anti-D supplies. 103
The assessment of RAADP given to all RhD-negative women versus RhD-negative primigravidae is dependent on the assumption that anti-D given in the first pregnancy will not have an impact upon the sensitisation rate of the subsequent pregnancies. There is some evidence to suggest that anti-D given in the first pregnancy may decrease the probability of a sensitisation occurring within subsequent pregnancies133 and hence providing RAADP to RhD-negative primigravidae would be more cost-effective than predicted here. Further research is required in this area.
Finally, there is a small probability that sensitisations may occur in the first pregnancy and hence the first RhD-positive baby may be affected by HDN. Because anti-D should be given to women who have potential sensitising events, we have assumed that this would not be the case. If sensitisations were to occur within the first pregnancy, the absolute number of sensitisations would increase from those estimated within the model, but the relative impact on the cost-effectiveness of anti-D would remain approximately the same.
Quality of life of the parents
The model does not explicitly take into account the quality of life of the parents as a result of the loss of a child, or of being responsible for a disabled child, because of difficulties in the empirical measurement of these quantities. Research suggests that, although quality of life is likely to decrease substantially in the year after the loss of a child, in subsequent years the parents’ quality of life is likely to increase to a similar level as before the loss. 174 In general, published evidence suggests that the quality of life of parents of disabled children is lower than that of parents of non-disabled children, but this is also difficult to quantify and is likely to vary considerably. There is also likely to be anxiety caused by continuous monitoring of those pregnancies in which the mother is sensitised, which is likely to temporarily reduce the mother’s quality of life. The implications of a reduction in parental quality of life following sensitisation or HDN is that the cost per QALY gained would be slightly lower than currently predicted.
Compliance and one versus two doses
Within the model it has been assumed that compliance with RAADP for the one-dose or the two-dose regimen would be 100%. Current evidence suggests that only around 90% of women eligible for RAADP receive the drug,89 potentially leading to more sensitisations than estimated by the model. If there was a difference in compliance between the one-dose and two-dose regimens this could affect the cost-effectiveness ratio. Compliance may be greater with the one-dose regimen than with the two-dose regimen for logistical reasons; conversely, the one-dose regimen offers only one opportunity to provide RAADP. 123 There are currently no published studies comparing compliance between the two regimens but if it was substantially better for one of the routine anti-D regimens then it would improve the overall efficacy of that regimen and hence provide better outcomes.
The analysis also assumes that RAADP can be provided within routine antenatal appointments. Some patients may require additional appointments for the administration of RAADP and some hospitals may have separate clinics for anti-D administration, which will lead to greater costs. If anti-D is not offered during routine appointments this may also have an impact on compliance and hence an effect upon the effectiveness of the drug.
Fetal genotyping
It is now possible to test the genotype of the fetus using non-invasive methods. It should be noted that fetal genotyping would affect not only RAADP but also anti-D given for other indications and hence it is beyond the scope of this assessment. However, a brief exploratory analysis of the new technology is presented here.
Because just under two-thirds of babies born to RhD-negative mothers are RhD positive, fetal genotyping could save around one-third of RhD-negative women having to be given anti-D. However, if the sensitivity of the fetal genotyping test is not 100% (i.e. each fetus who is RhD positive is detected) then the number of sensitisations is likely to increase. The sensitivity of the fetal genotyping test is currently estimated to be around 99%175 and hence would need to improve if the proportion of sensitisations is to remain the same.
Fetal genotyping may be associated with an improvement in efficacy in terms of the reduction in the mother’s anxiety about the anti-D administrations and the reduction in exposure to different blood products. However, as discussed in Chapter 1 (see Summary of intervention), adverse effects associated with this exposure are extremely rare. Therefore, the efficacy of RAADP using fetal genotyping is unlikely to improve, meaning that for it to be considered cost-effective the cost would need to be less than that of current treatment.
Based on our model, the cost of fetal genotyping compared with the cost of anti-D can be denoted by the formula:
This simplifies to:
The cost of RAADP and its administration lies between £51.50 and £319.50 (assuming a £5 administration cost for each dose of anti-D). Therefore, for fetal genotyping to reduce costs associated with RAADP it would need to be priced below that shown in Table 34, including administration.
| Anti-D | Cost of anti-D | Cost of fetal genotyping |
|---|---|---|
| D-Gam | £64 | £24.96 |
| Partobulin | £80 | £31.20 |
| Rhophylac | £51.50 | £20.09 |
| WinRho | £319.50 | £124.22 |
Current estimates suggest that fetal genotyping is likely to cost around £40 per person. 175 This suggests that fetal screening is likely to be more costly than providing all RhD-negative pregnant women with routine anti-D, except in the case of WinRho. It should be noted that this analysis does not allow for price reductions in anti-D and hence the cost of fetal genotyping may need to be lower than that estimated here. Furthermore, if the test was not 100% specific the cost of the test would need to be lower still to allow for the additional anti-D given to those women who were carrying an RhD-negative fetus. Therefore, research into fetal genotyping should aim to improve sensitivity and reduce the cost of the test.
Chapter 5 Assessment of factors relevant to the NHS and other parties
Routine anti-D is currently estimated to be used in around 90% of hospitals89 and hence the implications for current service provision of recommending RAADP are small. Anti-D can usually be provided during routine antenatal appointments and hence the burden on services not currently providing anti-D is expected to be minimal. The costs associated with providing no RAADP (management of sensitisations, lifetime costs of developmental problems) are estimated to be around £1.8 million throughout England and Wales. The additional costs of supplying RAADP to RhD-negative primigravidae and to all RhD-negative women in England and Wales each year are shown in Tables 35 and 36 respectively.
| Anti-D regimen | Cost of anti-D | Cost of administration | Cost savings associated with HDNa | Total cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 × 500 IU (D-Gam) | £2,432,222 | £450,411 | £522,029 | £2,360,604 |
| 2 × 1250 IU (Partobulin) | £3,152,880 | £450,411 | £522,029 | £3,081,262 |
| 1 × 1500 IU (Rhophylac) | £2,094,413 | £225,206 | £522,029 | £1,797,590 |
| 1 × 1500 IU (WinRho) | £14,120,398 | £225,206 | £522,029 | £13,823,575 |
| Anti-D regimen | Cost of anti-D | Cost of administration | Cost savings associated with HDNa | Total cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 × 500 IU (D-Gam) | £2,741,264 | £507,641 | £603,785 | £2,645,120 |
| 2 × 1250 IU (Partobulin) | £3,553,490 | £507,641 | £603,785 | £3,457,346 |
| 1 × 1500 IU (Rhophylac) | £2,360,533 | £253,821 | £603,785 | £2,010,568 |
| 1 × 1500 IU (WinRho) | £15,914,558 | £253,821 | £603,785 | £15,564,594 |
The use of RAADP for RhD-negative primigravidae is estimated in total to cost the NHS an additional £1.8–£3.1 million per year (excluding WinRho) compared with no RAADP according to the RAADP regimen. Giving RAADP to RhD-negative multigravidae in addition to RhD-negative primigravidae increases the costs by a further £2–£3.5 million per year (excluding WinRho).
Chapter 6 Discussion
Statement of principal findings
All of the evidence indicates that RAADP reduces the incidence of sensitisation. In assessing the impact of the introduction of a programme of RAADP the most relevant studies are those by MacKenzie et al. 126 and Mayne et al. 127 Meta-analysis of the data from these studies indicates that the introduction of such a programme is associated with a fall of 0.6% (from 0.95% to 0.35%) in the number of women found in a subsequent pregnancy to be sensitised, an odds ratio of 0.37 (95% CI 0.21–0.65). These are community-based studies with high external validity as they demonstrate the effectiveness of RAADP in real life in the UK rather than under trial conditions and as measured by the most clinically relevant outcome measure, the number of women found to be sensitised in a subsequent pregnancy.
Although some instances of sensitisation are inevitable, others can be avoided (namely those attributable to failure to provide prophylaxis when appropriate despite the existence of a policy of RAADP). However, the avoidance of such cases will require careful adherence to guidelines. Further, a woman will only benefit clinically if she has an RhD-positive infant and she would have been sensitised and she goes on to have a further infant who is also RhD positive. It is the avoidance of HDN in that infant which constitutes the clinical benefit of RAADP.
No head-to-head studies have been undertaken that compare a one-dose with a two-dose regimen of RAADP, and the studies reviewed above do not provide any evidence to suggest that two 500-IU or 1250-IU doses of anti-D at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation are more or less effective than a single dose of 1500 IU of anti-D at 28–30 weeks’ gestation. However, the Royal College of Nursing has expressed concern that a single dose given at 30 weeks (as is possible under the licensed indication for Rhophylac) will clearly not provide protection against an FMH at 28 weeks and may be insufficient to provide protection against an FMH at 39 weeks. 123 Several other arguments in addition to clinical effectiveness have been put forward to support the use of one or other regimen; these relate to compliance and safety. However, there is no published evidence that demonstrates any such differences. It could also be argued that the regimen that uses least anti-D, and places least demand on plasma donors, has an advantage.
There is no evidence to suggest that RAADP is associated with adverse effects of any consequence for either mother or child other than the possibility of transmission of bloodborne infections; this risk is minimised by the safeguards built into the modern manufacturing process.
The economic analysis of RAADP is based on the model developed for the 2002 NICE RAADP appraisal. 88 However, as well as considering the cost-effectiveness of the two-dose regimens, D-Gam and Partobulin, this assessment also evaluates the use of the one-dose regimens, Rhophylac and WinRho. Of the nine studies identified within the cost-effectiveness review, only those by Vick et al. 161,162 and Chilcott et al. 1,164 describe a detailed modelling study that appears to be applicable to the UK NHS. Furthermore, no new mathematical models were provided within the manufacturers’ submissions for the appraisal. The health economic model developed by the assessment group suggests that the cost per QALY gained of RAADP given to RhD-negative primigravidae versus no RAADP is between £9000 and £15,000, and of RAADP given to all RhD-negative women rather than RhD-negative primigravidae only is between £20,000 and £35,000, depending on the RAADP regimen (excluding WinRho). However, as the actual prices paid by hospitals vary, the cost-effectiveness in practice may be better than that presented here. The one-dose regimen of 1500 IU of WinRho is estimated to have a cost per QALY gained above £60,000. The cost-effectiveness of RAADP improves slightly for ethnic minorities in England and Wales.
Strengths and limitations of the assessment
This assessment report reviews the work carried out for the NICE RAADP appraisal from 2002;87 despite further research being recommended within the original report, no additional evidence was identified to be used within the analysis in terms of either clinical effectiveness or cost-effectiveness. Therefore, both the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness are based largely on data taken from the 1990s. However, the clinical effectiveness of anti-D is based on two large community-based UK studies with high external validity. There is no comparative evidence available regarding the efficacy of different RAADP regimens, and therefore the economic comparison of the different regimens is dependent on price only. However, the model of cost-effectiveness is reasonably robust to changes in the parameter values and, hence, at a threshold of £35,000 it is likely that D-Gam, Partobulin and Rhophylac RAADP given to all RhD-negative pregnant women will be cost-effective.
Uncertainties
The key uncertainties associated with the assessment of RAADP are:
-
the efficacy of different dosing regimens of RAADP
-
the quality of life of children suffering from HDN and of their parents (including parents of stillborn children)
-
the incidence rate of outcomes as a result of HDN
-
the costs associated with HDN in terms of the management of sensitisation and the management of people with developmental problems over their lifetime.
Other relevant factors
Problems have been encountered in the past in relation to the availability of anti-D. If such problems are likely to be encountered in the future then an argument can be made for those strategies that minimise the volume of plasma required. These include:
-
the use of a two-dose 500-IU D-Gam regimen, as this uses two-thirds of the quantity of anti-D used by the single-dose regimen
-
the use of the ion-exchange chromatography method of preparation, as this retains 30–40% more anti-D than the Cohn method.
Since the NICE guidance was issued in 2002, rates of compliance with RAADP seem to have increased. 89 However, although the implementation of a programme of RAADP should lead to a significant fall in the residual numbers of women affected, some women continue to become sensitised despite the existence of such a programme. There are five possible reasons for continuing cases of sensitisation:
-
the failure to recognise potential sensitising events in pregnancy as such and to treat them appropriately
-
the failure to assess the extent of FMH adequately
-
the failure to comply with postpartum prophylaxis guidelines
-
the refusal of RAADP by the mother
-
the failure to implement RAADP by some trusts and incomplete adherence to advice (i.e. poor compliance with the second dose).
Consideration of these issues is required.
The Royal College of Nursing123 suggests that Section 1.2 of the NICE Technology Appraisal No. 4187 presents some practical difficulties for midwives as ‘in addition to the sensitivities of discussing paternity, there are difficulties associated with an institution assuming that the father is indeed RhD-negative as reported without having this confirmed by internal testing’. Other practical concerns have been raised with regards to the certainty with which a woman may know that she is not going to have another child. These issues were not considered in a subgroup analysis as planned because of their feasibility in practice.
Finally, non-invasive fetal genotyping has not yet been demonstrated to be sufficiently accurate to enable its use to target provision of RAADP only to those non-sensitised RhD-negative women pregnant with RhD-positive infants. However, a test that is sufficiently accurate at an early enough gestational date may become available in the next few years.
Chapter 7 Conclusions
All of the evidence indicates that RAADP reduces the incidence of sensitisation and hence HDN. Furthermore, anti-D is associated with minimal adverse events. The economic model suggests that, at a threshold of £35,000 per QALY gained, RAADP given to all RhD-negative pregnant women is likely to be considered cost-effective compared with RAADP given to RhD-negative primigravidae or not offering RAADP. The total cost of providing RAADP to RhD-negative primigravidae in England and Wales is estimated to be around £1.8–£3.1 million per year depending upon the regimen of RAADP used (excluding WinRho). This takes into account the cost of RAADP and its administration, the cost of the management of sensitisation and the cost savings associated with avoiding HDN. The additional cost of providing RAADP to all RhD-negative pregnant women in England and Wales is estimated to be around £2–£3.5 million.
Further research is required to:
-
compare the efficacy of the different RAADP regimens; issues relating to compliance and safety may also influence the efficacy of the different regimens of RAADP and hence further research would also be useful in these areas
-
confirm or disprove the preliminary findings that protection against sensitisation provided by RAADP in primigravidae extends beyond the first pregnancy
-
aim to improve non-invasive genotyping of the fetus.
It is recognised that it would be unrealistic to seek to compare the efficacy of the different RAADP regimens by means of an RCT as each regimen is considered to be equally effective in practice and therefore the size of any trial powered to demonstrate a difference would be wholly unfeasible. However, the relative efficacy of the different regimens, and the impact of the potentially varying levels of compliance with them, could be assessed using large-scale audits of residual sensitisations.
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to the following clinical experts: Ms Julie Wray, Lecturer in Midwifery; Dr Hora Soltani, Senior Lecturer in Midwifery; and Dr Therese Callaghan, Consultant Haematologist. We would also like to thank the following advisors: Professor Dame Marcela Contreras, Professor of Transfusion Medicine; Professor Stan Urbaniak, Professor of Transfusion Medicine; and Rumona Dickson, Claire McLeod and Angela Boland from the Liverpool Reviews and Implementation Group. Thanks also to Andrea Shippam, Project Administrator, ScHARR, for her help in the retrieval of papers and in preparing and formatting the report. Finally, thanks to Jim Chilcott for providing advice around the original NICE Health Technology Assessment of routine antenatal anti-D.Jim Chilcott and Eva Kaltenthaler are guarantors.
About ScHARR
The School of Health and Related Research (ScHARR) is one of the four Schools that comprise the Faculty of Medicine at the University of Sheffield. ScHARR brings together a wide range of medical- and health-related disciplines including public health, general practice, mental health, epidemiology, health economics, management sciences, medical statistics, operational research and information science. It includes the Sheffield unit of the Trent RDSU, which is funded by NIHR to facilitate high-quality health services research and capacity development.
The ScHARR Technology Assessment Group (ScHARR-TAG) synthesises research on the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of health-care interventions for the NIHR HTA Programme on behalf of a range of policy-makers, including the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. ScHARR-TAG is part of a wider collaboration of six units from other regions. The other units are Southampton Health Technology Assessment Centre (SHTAC), University of Southampton; Aberdeen Health Technology Assessment Group (Aberdeen HTA Group), University of Aberdeen; Liverpool Reviews and Implementation Group (LRiG), University of Liverpool; Peninsula Technology Assessment Group (PenTAG), University of Exeter; NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York; and West Midlands Health Technology Assessment Collaboration (WMHTAC), University of Birmingham.
Contribution of authors
H Pilgrim was the review lead and undertook the cost-effectiveness review. M Lloyd-Jones undertook the clinical effectiveness review. A Rees conducted the literature searches.
Disclaimers
The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the HTA Programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Chilcott J, Lloyd-Jones M, Wight J, Forman K, Wray J, Beverley C, et al. A review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine anti-D prophylaxis for pregnant women who are rhesus (RhD) negative. Health Technol Assess 2003;7:1-72.
- Stockman JA, de Alarcon PA. Overview of the state of the art of Rh disease: history, current clinical management, and recent progress. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2001;23:385-93.
- MacKenzie I. Antenatal anti-D prophylaxis: one dose or two?. Br J Midwifery 2004;12:13-9.
- Bowman JM. The prevention of Rh immunization. Transfusion Med Rev 1988;2:129-50.
- Filbey D, Berseus O, Carlberg M. Occurrence of anti-D in RhD-positive mothers and the outcome of the newborns. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1996;75:585-7.
- Selinger M. Immunoprophylaxis for rhesus disease – expensive but worth it?. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1991;98:509-12.
- Harrod KS, Hanson L, VandeVusse L, Heywood P. Rh negative status and isoimmunization update. A case-based approach to care. J Perinat Neonat Nurs 2003;17:166-78.
- Tovey LA, Taverner JM. A case for the antenatal administration of anti-D immunoglobulin to primigravidae. Lancet 1981;1:878-81.
- Urbaniak SJ, Greiss MA. RhD haemolytic disease of the fetus and the newborn. Blood Rev 2000;14:44-61.
- Contreras M. The prevention of RH haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn – general background. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105:7-10.
- Bowman J. Rh-immunoglobulin: Rh prophylaxis. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2006;19:27-34.
- Bowman JM. Fetomaternal ABO incompatibility and erythroblastosis fetalis. Vox Sang 1986;50:104-6.
- Tuohy JF, Sangalli M, Kim L. Red blood cell iso-immunisation in the Wellington area of New Zealand: the case for antenatal prophylaxis. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2004;44:458-9.
- Bowman JM, Friesen AD, Pollock JM, Taylor WE. WinRho: Rh immune globulin prepared by ion exchange for intravenous use. Can Med Assoc J 1980;123:1121-7.
- Urbaniak SJ. The scientific basis of antenatal prophylaxis. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105:11-8.
- Stewart G, Day RE, Del Priore C, Whittle MJ, Turner TL, Holland BM. Developmental outcome after intravascular intrauterine transfusion for rhesus haemolytic disease. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonat Ed 1994;70:F52-53.
- van Kamp IL, Klumper FJ, Bakkum RSLA, Oepkes D, Meerman RH, Scherjon SA, et al. The severity of immune fetal hydrops is predictive of fetal outcome after intrauterine treatment. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185:668-73.
- Farina A, Calderoni P, Carinci P, Rizzo N. Survival analysis of transfused fetuses affected by Rh-alloimmunization. Prenat Diagn 2000;20:881-5.
- Craig S, Morris K, Tubman T, McClure B. The fetal and neonatal outcomes of rhesus D antibody affected pregnancies in Northern Ireland. Ir Med J 2000;93:17-8.
- Matijevic R, Grgic O, Klobucar A, Miskovic B. Diagnosis and management of Rh alloimmunization. Fetal Diagn Ther 2005;20:393-401.
- Grab D, Paulus WE, Bommer A, Buck G, Terinde R. Treatment of fetal erythroblastosis by intravascular transfusions: outcome at 6 years. Obstet Gynecol 1999;93:165-8.
- Doyle LW, Kelly EA, Rickards AL, Ford GW, Callanan C. Sensorineural outcome at 2 years for survivors of erythroblastosis treated with fetal intravascular transfusions. Obstet Gynecol 1993;81:931-5.
- van Kamp IL, Klumper FJCM, Oepkes D, Meerman RH, Scherjon SA, Vandenbussche FPHA, et al. Complications of intrauterine intravascular transfusion for fetal anemia due to maternal red-cell alloimmunization. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;192:171-7.
- Harper DC, Swingle HM, Wiener CP, Bonthius DJ, Aylward GP, Widness JA. Long-term neurodevelopmental outcome and brain volume after treatment for hydrops fetalis by in utero intravascular transfusion. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;195:192-200.
- Hudon L, Moise KJ, Hegemier SE, Hill RM, Moise AA, Smith EO, et al. Long-term neurodevelopmental outcome after intrauterine transfusion for the treatment of fetal hemolytic disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:858-63.
- Janssens HM, de Haan MJ, van Kamp I, Brand R, Kanhai HH, Veen S. Outcome for children treated with fetal intravascular transfusions because of severe blood group antagonism. J Pediatr 1997;131:373-80.
- Ouwehand WH, Goodyear E, Camilleri-Ferrante C, Burgess C, Rankin A. Epidemiology of RhD haemolytic disease of the newborn in East Anglia. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105:23-4.
- Das PK, Nair SC, Harris VK, Rose D, Mammen JJ, Bose YN, et al. Distribution of ABO and Rh-D blood groups among blood donors in a tertiary care centre in South India. Trop Doct 2001;31:47-8.
- Ali N, Anwar M, Bhatti FA, Nadeem M, Nadeem A, Ali M. Frequency of ABO and Rh blood groups in major ethnic groups and casts of Pakistan. Pakistan J Med Sci 2005;21:26-9.
- Editorial . Prevention of haemolytic diseases of the newborn due to anti-D. Br Med J Clin Res Ed 1981;282:676-7.
- Kumar S, Regan F. Management of pregnancies with RhD alloimmunisation. Br Med J 2005;330:1255-8.
- Joseph KS, Kramer MS. The decline in Rh hemolytic disease: should Rh prophylaxis get all the credit?. Am J Public Health 1998;88:209-15.
- Robson SC, Lee D, Urbaniak S. Anti-D immunoglobulin in RhD prophylaxis. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105:129-34.
- Duguid JKM, Bromilow IM. What is the true rate of RhD isoimmunisation in the UK?. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105.
- Clarke CA. Preventing rhesus babies: the Liverpool research and follow up. Arch Dis Child 1989;64:1734-40.
- Hussey RM, Clarke CA. Deaths from Rh haemolytic disease in England and Wales in 1988 and 1989. Br Med J 1991;303:445-6.
- Whitfield CR, Raafat A, Urbaniak SJ. Underreporting of mortality from RhD haemolytic disease in Scotland and its implications: retrospective review. Br Med J 1997;315:1504-5.
- Murphy KW, Whitfield CR. Rhesus disease in this decade. Contemp Rev Obstet Gynaecol 1994;6:61-7.
- Editorial . Mortality Statistics: Childhood, Infant and Perinatal. Review of the Registrar General on Deaths in England and Wales, 2005 2007.
- Schumacher B, Moise KJ. Fetal transfusion for red blood cell alloimmunization in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 1996;88:137-50.
- Bjornson KF, McLaughlin JF. The measurement of health-related quality of life (HRQL) in children with cerebral palsy. Eur J Neurol 2001;8:183-93.
- Livingston MH, Rosendbuam PL, Russell DJ, Palisano RJ. Quality of life among adolescents with cerebral palsy: what does the literature tell us?. Dev Med Child Neurol 2007;49:225-31.
- Varni JW, Burwinkle TM, Sherman SA, Hanna K, Berrin SJ, Malcarne VL, et al. Health-related quality of life in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy: hearing the voices of the children. Dev Med Child Neurol 2005;47:592-7.
- Pirpiris M, Gates PE, McCarthy JJ, D’Astous J, Tylkowksi C, Sanders JO, et al. Function and well-being in ambulatory children with cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop 2006;26:119-24.
- Dickinson HO, Parkinson KN, Ravens-Sieberer U, Schirripa G, Thyen U, Arnaud C, et al. Self-reported quality of life of 8–12-year-old children with cerebral palsy: a cross-sectional European study. Lancet 2007;369:2171-8.
- Magill-Evans J, Darrah J, Pain K, Adkins R, Kratchovil M. Are families with adolescents and young adults with cerebral palsy the same as other families?. Dev Med Child Neurol 2001;43:466-72.
- Houlihan CM, O’Donnell M, Conaway M, Stevenson RD. Bodily pain and health-related quality of life in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 2004;46:305-10.
- van der Dussen L, Nieuwstraten W, Roebroeck M, Stam HJ. Functional level of young adults with cerebral palsy. Clin Rehabil 2001;15:84-91.
- Schwartz L, Engel JM, Jensen MP. Pain in persons with cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1999;80:1243-6.
- Jahnsen R, Villien L, Aamodt G, Stanghelle JK, Holm I. Musculoskeletal pain in adults with cerebral palsy compared with the general population. J Rehabil Med 2004;36:78-84.
- Bottos M, Feliciangeli A, Sciuto L, Gericke C, Vianello A. Functional status of adults with cerebral palsy and implications for treatment of children. Dev Med Child Neurol 2001;43:516-28.
- Murphy KP, Molnar GE, Lankasky K. Employment and social issues in adults with cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2000;81:807-11.
- Margolis AC. Implications of prelingual deafness. Lancet 2001;358.
- Wake M, Hughes EK, Collins CM, Poulakis Z. Parent-reported health-related quality of life in children with congenital hearing loss: a population study. Ambul Pediatr 2004;4:411-17.
- Van Oyen H, Tafforeau J, Demarest S. The impact of hearing disability on well-being and health. Sozial- Und Praventivmedizin 2001;46:335-43.
- Jacob SR, Scandrett-Hibdon S. Mothers grieving the death of a child. Case reports of maternal grief. Nurse Pract 1994;19:60-5.
- Badenhorst W, Hughes P. Psychological aspects of perinatal loss. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2007;21:249-59.
- Hutti MH. Social and professional support needs of families after perinatal loss. J Obstet Gynecol Neonat Nurs 2004;34:630-8.
- Callister LC. Perinatal loss. A family perspective. J Perinat Neonat Nurs 2006;20:227-34.
- Vance JC, Foster WJ, Najman JM, Embelton G, Thearle MJ, Hodgen FM. Early parental responses to sudden infant death, stillbirth or neonatal death. Med J Aust 1991;155:292-7.
- Vance JC, Najman JM, Thearle MJ, Embelton G, Foster WJ, Boyle FM. Psychological changes in parents eight months after the loss of an infant from stillbirth, neonatal death, or sudden infant death syndrome – a longitudinal study. Pediatrics 1995;96.
- Janssen HJEM, Cuisinier MCJ, de Graauw KPHM, Hoogduin KAL. A prospective study of risk factors predicting grief intensity following pregnancy loss. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1997;54:56-61.
- Zeanah CH, Dailey JV, Rosenblatt MJ, Saller DN. Do women grieve after terminating pregnancies because of fetal anomalies? A controlled investigation. Obstet Gynecol 1993;82:270-5.
- Kolker A, Burke BM. Grieving the wanted child: ramifications of abortion after prenatal diagnosis of abnormality. Health Care Women Int 1993;14:513-26.
- Roman A, Pernell M, Decherney AH, Nathan L. Current obstetric and gynecologic diagnosis and treatment. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional; 2002.
- Brewaeys A. Review: parent–child relationships and child development in donor insemination families. Hum Reprod Update 2001;7:38-46.
- Durna EM, Bebe J, Leader LR, Steigrad SJ, Garrett DG. Donor insemination: effects on parents. Med J Aust 1995;163:248-51.
- Baron L, Blanco L, Valzacchi GR, Pasqualini S. Oocyte donation (OD) and donor insemination (DI): a comparative psychological study of parents and children. Fertil Steril 1998;70.
- Bode H, Weidner K, Storck M. Quality of life in families of children with disabilities. Dev Med Child Neurol 2000;42.
- Wake M, Salmon L, Reddihough D. Health status of Australian children with mild to severe cerebral palsy: cross-sectional survey using the Child Health Questionnaire. Dev Med Child Neurol 2003;45:194-9.
- Vargus-Adams J. Health-related quality of life in childhood cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2005;86:940-5.
- Brehaut JC, Kohen DE, Raina P, Walter SD, Russell DJ, Swinton M, et al. The health of primary caregivers of children with cerebral palsy: how does it compare with that of other Canadian caregivers?. Pediatrics 2004;114:e182-91.
- Eker L, Tuzun EH. An evaluation of quality of life of mothers of children with cerebral palsy. Disabil Rehabil 2004;26:1354-9.
- McConnell D, Llewellyn G. Health of mothers of school-age children with disabilities. Aust N Z J Public Health 2006;30:572-4.
- Emerson E. Mothers of children and adolescents with intellectual disability: social and economic situation, mental health status, and the self-assessed social and psychological impact of the child’s difficulties. J Intellect Disabil Res 2003;47:385-99.
- Emerson E, Hatton C, Llewellyn G, Blacker J, Graham H. Socio-economic position, household composition, health status and indicators of the well-being of mothers of children with and without intellectual disabilities. J Intellect Disabil Res 2006;50:862-73.
- Parish SL, Seltzer MM, Greenberg JS, Floyd F. Economic implications of caregiving at midlife: comparing parents with and without children who have developmental disabilities. Ment Retard 2004;42:413-26.
- Bat-Chava Y, Martin D. Sibling relationships of deaf children: the impact of child and family characteristics. Rehabil Psychol 2002;47:73-91.
- Oepkes D, van Scheltema PA. Intrauterine fetal transfusions in the management of fetal anemia and fetal thrombocytopenia. Semin Fetal Neonat Med 2007;12:432-8.
- British Committee for Standards in Haematology . Guideline for Blood Grouping and Antibody Testing in Pregnancy 2006. www.bcshguidelines.com/pdf/pregnancy_070606.pdf.
- Ulm B, Svolba G, Ulm MR, Bernaschek G, Panzer S. Male fetuses are particularly affected by maternal alloimmunization to D. Transfusion 1999;39:169-73.
- Murray NA, Roberts IAG. Haemolytic disease of the newborn. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonat 2007;92:F83-8.
- Howard H, Martlew V, McFadyen I, Clarke C, Duguid J, Bromilow I, et al. Consequences for fetus and neonate of maternal red cell allo-immunisation. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonat Ed 1998;78:F62-6.
- Walkinshaw S. Antenatal prophylaxis – proposing. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105.
- Mohr PE, Feldman JJ, Dunbar JL, McConkey-Robbins A, Niparko JK, Rittenhouse RK, et al. The societal costs of severe to profound hearing loss in the United States. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 2000;16:1120-35.
- Schroeder L, Petrou S, Kennedy C, McCann D, Law C, Watkin PM, et al. The economic costs of congenital bilateral permanent childhood hearing impairment. Pediatrics 2006;117:1101-12.
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence . Guidance on the Use of Routine Antenatal Anti-D Prophylaxis for RhD-Negative Women 2002.
- Lee D, Contreras M, Entwistle CC, Forman KM, Fraser ID, Gascoigne EW, et al. Recommendations for the use of anti-D immunoglobulin. Prescribers’ J 1991;31.
- Royal College of Physicians and Royal College of Pathologists . National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Review of Technology Appraisal Guidance – No. 41: Guidance on the Use of Routine Antenatal Anti-D Prophylaxis for RhD-Negative Women 2007.
- Nottingham City Primary Care Trust . Health Technology Appraisal: Pregnancy – Routine Anti-D Prophylaxis for Rhesus Negative Women (review of TA41) 2007.
- Dash CH. Submission to NICE on the use of anti-D as routine antenatal prophylaxis (RANP) to aid updating technology appraisal guidance. Elstree: Bio Products Laboratory (BPL); 2007.
- CSL Behring UK . Rhophylac® manufacturer’s Submission. Routine Antenatal Anti-D Prophylaxis for Rh D-Negative Women 2007.
- CSL Behring UK . Initial Comments on the Technical Content of the Assessment Report 2008.
- British Committee for Standards in Haematology . Guidelines for the Use of Prophylactic Anti-D Immunoglobulin 2006.
- Finning KM. Prediction of fetal D status from maternal plasma: introduction of a new noninvasive fetal RHD genotyping service. Transfusion 2002;42:1079-85.
- Daniels G, Finning K, Martin P, Soothill P. Fetal blood group genotyping from DNA from maternal plasma: an important advance in the management and prevention of haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. Vox Sang 2004;87:225-32.
- ACOG practice bulletin . Prevention of Rh D alloimmunization. Number 4, May 1999 (replaces educational bulletin Number 147, October 1990). Clinical management guidelines for obstetrician-gynecologists. American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1999;66:63-70.
- Smith JA. Issues in anti-D plasma procurement. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105.
- Schiff P, Kelle AJ, Wylie B. Meeting the demand for anti-D in Australia. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105.
- MacKenzie IZ, Bichler J, Mason GC, Lunan CB, Stewart P, Al-Azzawi F, et al. Efficacy and safety of a new, chromatographically purified rhesus (D) immunoglobulin. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2004;117:154-61.
- Bowman JM. The advantages of intravenous Rh-immune globulin. Clin Obstet Gynecol 1982;25:341-7.
- Baxter Healthcare . The Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness of Anti-D Prophylaxis for Rhesus Negative Women in Pregnancy 2007.
- Harrop S. Letter from Baxter Healthcare to NICE 2007.
- Wickham S. Routine Antenatal Anti-D – a Review of the Evidence 2001. www.bcshguidelines.com/pdf/pregnancy_070606.pdf.
- Maayan-Metzger A, Schwartz T, Sulkes J, Merlob P. Maternal anti-D prophylaxis during pregnancy does not cause neonatal haemolysis. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonat Ed 2001;84:F60-2.
- Tabor E. The epidemiology of virus transmission by plasma derivatives: clinical studies verifying the lack of transmission of hepatitis B and C viruses and HIV type 1. Transfusion 1999;39:1160-8.
- Foster PR, McIntosh RV, Welch AG. Hepatitis C infection from anti-D immunoglobulin. Lancet 1995;346.
- Meisel H, Reip A, Faltus B, Lu M, Porst H, Wiese M, et al. Transmission of hepatitis C virus to children and husbands by women infected with contaminated anti-D immunoglobulin. Lancet 1995;345:1209-11.
- Power JP, Lawlor E, Davidson F, Yap PL, Kenny-Walsh E, Whelton MJ, et al. Hepatitis C viraemia in recipients of Irish intravenous anti-D immunoglobulin. Lancet 1994;344:1166-7.
- Smith DB, Lawlor E, Power J, O’Riordan J, McAllister J, Lycett C, et al. A second outbreak of hepatitis C virus infection from anti-D immunoglobulin in Ireland. Vox Sang 1999;76:175-80.
- CSL Behring UK . Rhophylac 300 (1500 IU) 2006. http://emc.medicines.org.uk/emc/assets/c/html/DisplayDoc.asp?DocumentID=12087.
- Turner ML, Ironside JW. New-variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: the risk of transmission by blood transfusion. Blood Rev 1998;12:255-68.
- Editorial team . Fourth case of transfusion-associated vCJD infection in the United Kingdom. Eurosurveillance 2007;12.
- Burnouf T, Padilla A. Current strategies to prevent transmission of prions by human plasma derivatives. Transfusion Clin Biol 2006;13:320-8.
- BPL (Bio Products Laboratory) . D-GAM(R), Human Anti-D Immunoglobulin 2004. www.sahha.gov.mt/showdoc.aspx?id=771%26filesource=4%26file=dh50_07_Anti-d_spc.pdf.
- British Medical Association and Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain . British National Formulary (BNF) 2007.
- Baxter Healthcare Ltd . Summary of Product Characteristics 2003. www.ecomm.baxter.com/ecatalog/loadResource.do?bid=13716.
- WinRho(R) SDF Product Monograph 2007. www.cangene.com/pdf/2006/Healthcare%20info%20for%20website%20070109.pdf.
- Baxter Healthcare Corporation . Rho(D) Immune Globulin Intravenous (human). WinRho(R) SDF 2005. www.fda.gov/medwatch/SAFETY/2006/WinRho_PI_%2021-DEC-2005.pdf.
- Fung Kee Fung K, Eason E, Crane J, Armson A, De La Ronde S, Farine D, et al. Maternal–Fetal Medicine Committee, Genetics Committee. Prevention of Rh alloimmunization. J Obstet Gynaecol Canada 2003;25:765-73.
- Chaffe B, Ford J, Bills V. Routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis and patient compliance with the two-dose regimen. Transfusion Med 2007;17:399-403.
- MacKenzie IZ, Findlay J, Thompson K, Roseman F. Compliance with routine antenatal rhesus D prophylaxis and the impact on sensitisations: observations over 14 years. Int J Obstet Gynaecol 2006;113:839-43.
- Royal College of Nursing National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence . Health Technology Appraisal: Pregnancy – Routine Anti-D Prophylaxis for Rhesus Negative Women (review of TA41) 2007.
- NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination . Undertaking Systematic Reviews of Research on Effectiveness: CRD’s Guidance for Those Carrying Out or Commissioning Reviews 2001.
- Huchet J, Dallemagne S, Huchet C, Brossard Y, Larsen M, Parnet-Mathieu F. Application anté-partum du traitement préventif d’immunisation rhésus D chez les femmes rhésus négatif. Evaluation parallèle des passages transplacentaires d’hématies foetales. Résultats d’une étude multicentrique menée en région parisienne [Ante-partum administration of preventive treatment of Rh-D immunization in rhesus-negative women. Parallel evaluation of transplacental passage of fetal blood cells. Results of a multicenter study carried out in the Paris region]. Journal De Gynecologie, Obstetrique Et Biologie De La Reproduction 1987;16:101-11.
- MacKenzie IZ, Bowell P, Gregory H, Pratt G, Guest C, Entwistle CC. Routine antenatal Rhesus D immunoglobulin prophylaxis: the results of a prospective 10 year study. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1999;106:492-7.
- Mayne S, Parker JH, Harden TA, Dodds SD, Beale JA. Rate of RhD sensitisation before and after implementation of a community based antenatal prophylaxis programme. Br Med J 1997;315.
- Tovey LA, Townley A, Stevenson BJ, Taverner J. The Yorkshire antenatal anti-D immunoglobulin trial in primigravidae. Lancet 1983;2:244-6.
- Bowman JM, Chown B, Lewis M, Pollock JM. Rh isoimmunization during pregnancy: antenatal prophylaxis. Can Med Assoc J 1978;118:623-7.
- Bowman JM, Pollock JM. Antenatal prophylaxis of Rh isoimmunization: 28-weeks’-gestation service program. Can Med Assoc J 1978;118:627-30.
- Bowman JM, Pollock JM. Failures of intravenous Rh immune globulin prophylaxis: an analysis of the reasons for such failures. Transfusion Med Rev 1987;1:101-12.
- Trolle B. Prenatal Rh-immune prophylaxis with 300 micrograms immune globulin anti-D in the 28th week of pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1989;68:45-7.
- Thornton JG, Page C, Foote G, Arthur GR, Tovey LA, Scott JS. Efficacy and long term effects of antenatal prophylaxis with anti-D immunoglobulin. Br Med J 1989;298:1671-3.
- Hermann M, Kjellman H, Ljunggren C. Antenatal prophylaxis of Rh immunization with 250 mcg anti-D immunoglobulin. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1984;63:4-14.
- Lee D, Rawlinson VI. Multicentre trial of antepartum low-dose anti-D immunoglobulin. Transfusion Med 1995;5:15-9.
- Parsons ML, Van den Hoj MC, Armson BA, Coffey J, Liston RM, Peddle LJ, et al. A comparison of the rate of RhD alloimmunisation between Nova Scotia and Scotland. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105.
- MacKenzie IZ, Bowell PJ, Pratt G, Gregory H, Guest C, Entwistle CC. Routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis: results of a prospective 10-year study. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105.
- Eklund J, Nevanlinna HR. Prevention of Rh immunization in Finland. Results obtained in a two-year national anti-D programme. Duodecim 1971;87:861-6.
- Potron G, Quereux C, Freal C. Prevention of Rh disease by anti-D plasma. A 2-year study. Revue Francaise De Transfusion 1973;16:11-3.
- Weaver J. A multicentre study to examine the potential effect of monolocal anti-D IgG on prevention of haemolytic disease of the new-born when given routinely to RhD negative pregnant women both antenatally and at delivery. National Research Register; 2000.
- Koelewijn JM. Effect of a single gift of antenatal anti-D-prophylaxis with 1000 IU in week 30 on the incidence of rhesus-D-immunization in the first trimester of next pregnancy. Vox Sang 2003;91.
- Davey MG, Zipursky A. McMaster Conference on prevention of Rh immunization. Vox Sang 1979;36:50-64.
- Urbaniak J, Greiss A, Promwong C, Witterick R, Burnett J. Alloimmunisation in D negative women following routine antenatal anti-D immunoglobulin prophylaxis (RAADP) in the north east of Scotland: a five-year retrospective study. Vox Sang 2006;91:136-7.
- MacKenzie IZ, Roseman F, Findlay J, Thompson K, McPherson K. Clinical validation of routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis questions the modelling predictions adopted by NICE for rhesus D sensitisation rates: results of a longitudinal study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2007;139:38-42.
- Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products (CPMP) . Note for Guidance on the Clinical Investigation of Human Anti-D Immunoglobulin for Intravenous and Or Intramuscular Use 2000. www.emea.europa.eu/pdfs/human/bpwg/057599en.pdf.
- McSweeney E, Kirkham J, Vinall P, Flanagan P. An audit of anti-D sensitisation in Yorkshire. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105:1091-4.
- Ghosh S, Murphy WG. Implementation of the rhesus prevention programme: a prospective study. Scott Med J 1994;39:147-9.
- Gilling-Smith C, Toozs-Hobson P, Potts DJ, Touquet R, Beard RW. Management of bleeding in early pregnancy in accident and emergency departments. Br Med J 1994;309:574-5.
- Howard H, Martlew VJ, McFadyen IR, Clarke CA. Preventing Rhesus D haemolytic disease of the newborn by giving anti-D immunoglobulin: are the guidelines being adequately followed?. J Obstet Gynaecol 1997;104:37-41.
- Vause S, Maresh M. Indicators of quality of antenatal care: a pilot study. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1999;106:197-205.
- Vause S, Wray J, Bailie C. Management of women who are Rhesus D negative in Northern Ireland. J Obstet Gynaecol 2000;20:374-7.
- Turner RM, Spiegelhalter DJ, Smith GCS, Thompson SG. Bias Modelling in Evidence Synthesis 2007. www.mrc-bsu.cam.ac.uk/BSUsite/Publications/Preprints/biasmodelling.pdf.
- Tovey GH. Should anti-D immunoglobulin be given antenatally?. Lancet 1980;2:466-8.
- Crowther CA, Middleton P. Anti-D administration in pregnancy for preventing Rhesus alloimmunisation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1999;1.
- Chilcott J, Lloyd Jones M, Wight J, Forman K, Wray J, Beverley C. Assessment Report of the Clinical Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness of Routine Anti-D Prophylaxis for Pregnant Women Who Are RhD-Negative 2002. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/index.jsp?action=download%26o=32364.
- Adams MM, Marks JS, Koplan JP. Cost implications of routine antenatal administration of Rh immune globulin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1984;149:633-8.
- Baskett TF, Parsons ML. Prevention of Rh(D) alloimmunization: a cost-benefit analysis. Can Med Assoc J 1990;142:337-9.
- Lim OW, Fleisher AA, Ziel HK. Reduction of Rh0(D) sensitization: a cost-effective analysis. Obstet Gynecol 1982;59:477-80.
- Selinger M. Building on success: antenatal prophylaxis. London: Bio Products Laboratory; 1997.
- Torrance GW, Zipursky A. Cost-effectiveness of antepartum prevention of Rh immunization. Clin Perinatol 1984;11:267-81.
- Vick S, Cairns J, Urbaniak S, Whitfield C, Rafaat A. An economic evaluation of antenatal anti-D prophylaxis in Scotland. Aberdeen: Aberdeen University, Health Economics Research Unit; 1995.
- Vick S, Cairns J, Urbaniak S, Whitfield C, Raafat A. Cost-effectiveness of antenatal anti-D prophylaxis. Health Econ 1996;5:319-28.
- Tovey LAD. Antenatal anti-D immunoglobulin. Lancet 1983;2.
- Chilcott J, Tappenden P, Lloyd Jones M, Wight J, Forman K, Wray J, et al. The economics of routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis for pregnant women who are rhesus negative. Int J Obstet Gynaecol 2004;111:903-7.
- Office for National Statistics . Birth Statistics. Review of the Registrar General on Births and Patterns of Family Building in England and Wales 2005 2007.
- Saigal S, Stoskopf B, Pinelli J, Streiner D, Hoult L, Paneth N, et al. Self-perceived health-related quality of life of former extremely low birth weight infants at young adulthood. Pediatrics 2006;118:1140-8.
- Curtis L, Netten A. Unit costs of health and social care. Canterbury: PPSRU, University of Kent; 2006.
- Department of Health . HC12: Charges and Optical Voucher Values 2007. www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/PublicationsPolicyAndGuidance/DH_4131675.
- Rosenbaum PL, Livingston MH, Palisano RJ, Galuppi BE, Russell DJ. Quality of life and health-related quality of life of adolescents with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 2007;49:516-21.
- Beecham J, O’Neill T, Goodman R. Supporting young adults with hemiplegia: services and costs. Health Soc Care Community 2001;9:51-9.
- Hemming K, Hutton J, Colver A, Platt MJ. Regional variation in survival of people with cerebral palsy in the United Kingdom. Pediatrics 2005;116.
- Greenough A, Hartnoll G, Hambley H, Richards J. Treatment requirement of infants with rhesus isoimmunisation within a geographically defined area. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonat Ed 2002;87:F202-3.
- Department of Health . NHS Reference Costs 2005–06 2006. www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/PublicationsPolicyAndGuidance/DH_062884.
- Oswald A, Powdthavee N. Death and the Calculation of Hedonic Damages 2007. www.shef.ac.uk/content/1/c6/07/54/59/oswald.pdf.
- Ospienko L. RhD NIPD in the UK. Kenilworth, UK: Safe Network; 2007.
- Bichler J, Schondorfer G, Pabst G, Andresen I. Pharmacokinetics of anti-D IgG in pregnant RhD-negative women. Int J Obstet Gynaecol 2003;110:39-45.
- Kennedy MS, McNanie J, Waheed A. Detection of anti-D following antepartum injections of Rh immune globulin. Immunohematology 1998;14:138-40.
- Witter FR, Shirey RS, Nicol SL, Ness PM. Postinjection kinetics of antepartum Rh immune globulin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;163.
Appendix 1 Literature search strategies
General search strategy for anti-D/pregnancy
-
Rh-Hr Blood-Group System/
-
“Rho(D) Immune Globulin”/
-
Rh Isoimmunisation/
-
anti-d prophylaxis.tw.
-
or/1–4
-
exp pregnancy/
-
exp pregnancy complications/
-
exp pregnancy trimesters/
-
pregnan$.tw.
-
prenatal care/
-
postnatal care/
-
or/6–11
-
5 and 12
Appendix 2 Quality assessment
Quality assessment criteria for experimental studies (based on the criteria proposed by the NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination124)
| Was the method used to assign participants to the treatment groups really random? (Adequate methods: computer-generated random numbers, random number tables; inadequate methods: alternation, case record numbers, birth dates, days of the week) | |
| What method of assignment was used? | |
| Was the treatment allocation adequately concealed? (Adequate methods: centralised or pharmacy-controlled randomisation, serially numbered identical containers, on-site computer-based system with randomisation sequence that is not readable until allocation, other robust methods to prevent foreknowledge by clinicians or patients; inadequate methods: alternation, case record numbers, birth dates, days of the week, open random number lists, serially numbered envelopes, even if opaque) | |
| What method was used to conceal treatment allocation? | |
| Was the number of participants who were randomised stated? | |
| Were details of baseline comparability presented? | |
| Was baseline comparability achieved? | |
| Were the eligibility criteria for study entry specified? | |
| Were any co-interventions identified that may influence the outcomes for each group? | |
| Were the outcome assessors blinded to the treatment allocation? | |
| Were the care providers blinded to the treatment allocation? | |
| Were the participants who received the intervention blinded to the treatment allocation? | |
| Was the success of the blinding procedure assessed? | |
| Were at least 80% of the participants originally included in the randomised process followed up in the final analysis? | |
| Were the reasons for withdrawal stated? | |
| Was an intention to treat analysis included? |
Appendix 3 Table of excluded studies with rationale
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Australian study142 | Anti-D dose not specified |
| Eklund and Nevanlinna 1971138 | In Finnish, no English abstract; from publication date seems highly likely that it dealt with postpartum rather than antenatal prophylaxis |
| Hamilton study142 | Anti-D dose not specified |
| Hermann et al. 1984134 | Wrong anti-D regimen (single dose of 1250 IU at 32–34 weeks) |
| Koelewijn 2003141 | Wrong anti-D regimen (single dose of 1000 IU at 30 weeks) |
| Lee and Rawlinson 1995135 | Wrong anti-D regimen (two doses of 250 IU at 28 and 34 weeks) |
| Parsons et al. 1998136 | Anti-D dose not specified |
| Potron et al. 1973139 | Could not be obtained by library; from publication date seems highly likely that it dealt with postpartum rather than antenatal prophylaxis |
| Swedish study142 | Wrong anti-D regimen (unspecified dose at 34 weeks); appears to be the same study as that by Hermann et al.134 above |
| Unpublished study cited by Baxter Healthcare119 | Only one of three arms received a licensed anti-D regimen; there appeared to be no untreated control group; follow-up was very poor |
| Urbaniak et al. 2006143 | Identified sensitised women only as a proportion of all RhD-negative women who had received RAADP, not specifically those who had subsequently been delivered of RhD-positive infants; its results were therefore not comparable with those of the other included studies |
| Manufacturer/study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Baxter BioScience | |
| Hermann et al. 1984134 | Unlicensed dose (1 × 1250 IU) |
| Lee and Rawlinson 1995135 | Unlicensed dose (2 × 250 IU) |
| Thornton et al. 1989133 | Included in this report as a follow-up to the study by Tovey et al. 1983128 and not as a separate study, as inappropriately carried out by Baxter BioScience |
| BPL | |
| None | |
| CSL Behring | |
| Bichler et al. 2003176 | Pharmacokinetic study; no relevant outcomes |
| Kennedy et al. 1998177 | Pharmacokinetic study; no relevant outcomes |
| Witter et al. 1990178 | Pharmacokinetic study; no relevant outcomes |
Appendix 4 Characteristics of included studies
Bowman et al. 1978129
Method: As described, this was a community intervention trial in which, between December 1968 and August 1976, antenatal anti-D was given to all RhD-negative primigravidae delivered in two Winnipeg hospitals but not to those delivered at the other three hospitals in the city; by January 1972 enough untreated women had been accumulated to act as control subjects and antenatal prophylaxis was offered to all RhD-negative women whose delivery was to take place in Winnipeg hospitals. However, data from the trial control arm of primigravidae delivered in the three Winnipeg hospitals were combined with data related to RhD-negative primigravidae with no history of blood transfusion or abortion, and multigravidae with no previous evidence of RhD alloimmunisation who had been given immunoglobulin after all previous RhD-positive abortions and deliveries, in Manitoba between 1 March 1967 and 15 December 1974; these appear to have been all such women who gave birth to RhD-positive babies in Manitoba during this period (clarification from Bowman, personal communication).
Participants: RhD-negative primigravidae to be delivered in Winnipeg hospitals. Women who entered the trial as primigravidae re-entered the trial in all subsequent pregnancies.
Interventions: Approximately 1500 IU of intramuscular anti-D at 34 weeks; from May 1969 a second dose was added at 28 weeks. Women in both the intervention and control groups delivered of RhD-positive babies received 1500 IU of anti-D postpartum.
Outcomes: Incidence of immunisation during pregnancy and within 3 days of delivery; incidence of immunisation at 6–9 months following delivery.
Notes: The groups for which data are provided are dissimilar at baseline in that the intervention group included only women who, for all of their pregnancies, were treated in accordance with the trial protocol, whereas the ‘control’ group included women who had had previous pregnancies. Although these had not resulted in identifiable sensitisation, it is possible that multigravidae in the control group developed RhD alloimmunisation because of ‘sensibilisation’ resulting from inadequate treatment related to previous pregnancies. Only 74% of the intervention group were screened at 6–9 months after delivery; it is not clear whether, in the reported control group, only those women who had been found to be immunised during pregnancy or within 3 days of delivery were screened at 6–9 months.
The authors state that in May 1969 a dose of anti-D was introduced at 28 weeks because of evidence that some women were becoming alloimmunised before 34 weeks. No information is given regarding these women, who presumably belonged to the intervention group.
Quality: Poor.
Bowman and Pollock 1978130
Method: Comparison with historical controls (those RhD-negative primigravidae with no history of blood transfusion or abortion, and multigravidae with no previous evidence of RhD alloimmunisation who had been given immunoglobulin after all previous RhD-positive abortions and deliveries, in Manitoba between 1 March 1967 and 15 December 1974, whose data were reported in Bowman et al. 129)
Participants: All pregnant RhD-negative women in Manitoba with RhD-positive husbands and without evidence of RhD alloimmunisation in their current pregnancy. These fell into two categories:
-
group 1: primigravidae, plus multigravidae who had received RhD immunoglobulin antenatally and postnatally in all previous RhD-positive pregnancies and after all previous abortions
-
group 2: multigravidae who had received RhD immunoglobulin only postnatally or not at all after previous RhD-positive pregnancies and abortions.
Only 89% of those women at risk received antenatal prophylaxis and had their results included in the analysis. In addition, two women who had become alloimmunised before what they stated was their first pregnancy were excluded from the analysis as they could not be considered failures of antenatal prophylaxis.
Interventions: 1500 IU of intramuscular anti-D as close to 28 weeks’ gestation as possible.
Outcomes: Incidence of immunisation during pregnancy and within 3 days of delivery; incidence of immunisation at 6–9 months following delivery.
Notes: Only 45% of the intervention group were screened at 6–9 months after delivery; it is not clear whether, in the reported control group, only those women who had been found to be immunised during pregnancy or within 3 days of delivery were screened at 6–9 months. It is possible that multigravidae in both the intervention and control groups developed RhD alloimmunisation not because of a failure of antenatal prophylaxis but because of ‘sensibilisation’ resulting from inadequate treatment after previous pregnancies.
Quality: Fair.
Bowman and Pollock 1987131
Method: Retrospective comparison with historical controls (those RhD-negative primigravidae with no history of blood transfusion or abortion, and multigravidae with no previous evidence of RhD alloimmunisation who had been given immunoglobulin after all previous RhD-positive abortions and deliveries, in Manitoba between 1 March 1967 and 15 December 1974, whose data were reported in Bowman et al. 129). Although Urbaniak15 claims that this study includes all of the cases reported in Bowman’s earlier trials, this does not seem possible given the reported dates of the experiences recorded in this study.
This study is said to combine the results of a clinical trial of WinRho, reported briefly elsewhere,14,101 with the results of the subsequent service programme. In this trial pregnant women were initially given 120 µg (600 IU) of WinRho intravenously at 28 weeks but, after it was realised that RhD antibody could seldom be demonstrated for more than 6 weeks after that injection, the protocol was soon modified by the addition of a second 120-µg dose at 34 weeks. 14 By 30 September 1980, 2792 women had received AADP with WinRho as part of this clinical trial. By that date, 1992 women had delivered RhD-positive babies; none of the 870 who were only tested at delivery showed signs of sensitisation and only one of the 1122 who were tested both at delivery and 4–6 months later showed evidence of sensitisation. 14 Because of the success of the trial, WinRho was licensed for clinical use in Canada in June 1980 and was used thereafter in the Manitoba programme of RAADP. 101 However, as the clinical trial is effectively a case series, which makes reference to control group data from the 1978 study of Bowman et al. ,129 there seems no reason to differentiate between the trial and the service programme components of the study.
Participants: RhD-negative women delivered of RhD-positive babies in Manitoba between June 1977 and February 1986.
Interventions: 1500 IU of intramuscular anti-D at 28 weeks’ gestation. Women in both the intervention and control groups delivered of RhD-positive babies received postnatal anti-D.
Outcomes: Incidence of immunisation during pregnancy and within 3 days of delivery.
Notes: The authors’ comparison is with the primigravidae only in the ‘control’ group reported in Bowman et al. 129 It is not clear why their comparison was not with the unselected group. The 6-week and 6-month post-delivery blood samples were not universally available and so it was not possible to determine directly the total number of women RhD immunised by 6 months after delivery.
Quality: Poor.
Huchet et al. 1987125
Method: Quasi-randomised trial; intention to treat analysis.
Participants: RhD-negative primiparae without anti-D antibodies attending antenatal clinics at 23 maternity units in the Paris region.
Interventions: 500 IU of intramuscular anti-D at 28 and 34 weeks (in practice this was administered between weeks 26 and 29 and weeks 32 and 36). All RhD-negative women in the intervention and control groups delivered of RhD-positive babies received 500 IU of intravenous postpartum anti-D.
Outcomes: Incidence of immunisation during pregnancy; incidence of immunisation at delivery; incidence of immunisation at 2–12 months following delivery; number of infants with serious HDN or requiring exchange transfusion; passage of fetal red blood cells during pregnancy; cost-effectiveness of treatment.
Notes: Allocation to treatment groups was by year of birth (those born in even years formed the control group and those born in odd years the intervention group). Results from the postnatal check-up were available for only 79% of the mothers in either the control group or the intervention group who were delivered of an RhD-positive baby.
Quality: Good.
MacKenzie et al. 1999126
Method: Community intervention trial with historical and contemporary controls:
-
a retrospective analysis of the rate of alloimmunisation in RhD-negative women delivered of their first child between 1 January 1980 and 31 December 1986 in Oxfordshire or Northants who underwent a second continuing pregnancy; data on sensitised women were derived from a prospectively maintained serology laboratory register and verified from individual case records, and the at-risk population was calculated using hospital statistics for total annual births to nulliparae and women delivering their second baby and assuming a 16% prevalence of RhD negativity
-
a prospective study of the rates of alloimmunisation in RhD-negative women undergoing a second continuing pregnancy with an expected date of delivery between 1 January 1990 and 31 December 1996 in two similar populations; in one of these populations (Oxfordshire) routine antenatal prophylaxis had been offered since April 1986 to all RhD-negative women with no living children booked for confinement in the county, whereas in the other population (Northants) it had not.
An intention to treat analysis was used.
The update of RAADP in Oxfordshire was assessed by an audit of the clinical records of every fifth RhD-negative women who had delivered her first baby in the John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, from 1987 to 1996.
Participants: Non-sensitised RhD-negative pregnant nulliparae.
Interventions: 500 IU of routine anti-D offered at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation to RhD-negative nulliparae booked for confinement in Oxfordshire but not to those booked for confinement in Northants. In Oxfordshire, standard prophylaxis was offered to all RhD-negative women postpartum, but in Northants it was offered only to those delivered of a RhD-positive baby.
Outcomes: Prevalence of sensitisation during the second continuing pregnancy; success in providing prophylaxis to eligible women; changes in serology laboratory activity; cost of, and potential savings from, the prophylaxis programme.
Notes: The sensitisation rate for 1980–6 was compared with that for 1990–6 because the mean national interval between first and second delivery was 2.4 years and, therefore, women who delivered their first baby in 1987, the first full year of the study, would on average deliver their next baby during 1990.
This study illustrates the dangers inherent in the use of historical controls. A noticeable reduction in the incidence of sensitisation observed in Northants between the two study periods, although not statistically significant, was unexpected and unexplained. It could not be attributed to the use of antenatal prophylaxis. However, the study used the historical data to demonstrate that the two geographically contiguous populations were comparable in their rates of alloimmunisation before the introduction of the anti-D programme.
Quality: Good.
MacKenzie et al. 2004100
Method: Allegedly an RCT (multicentre, open-label, using a computer-generated randomisation scheme) it is in fact a one-arm study in relation to its primary efficacy outcome and is underpowered in relation to its secondary efficacy outcome (which is a randomised comparison).
Participants: RhD-negative women aged ≥ 18 years with no evidence of Rh(D) sensitisation and with known Rh(D)-positive partners, within 14 days before the 28th week of gestation, who had not previously received anti-D during the current pregnancy and who had not received blood or any other bloodborne products during the 6 months before enrolment. In total, 71.5% of participants had been pregnant before and 81.9% had received anti-D in a previous pregnancy.
Interventions: 1500 IU of Rhophylac (a new chromatographically produced Rh immunoglobulin) at 28 weeks’ gestation, with another dose within 72 hours of delivery of a RhD-positive child and additional doses as required to treat potential sensitising events or excessive FMHs. One group received all doses of Rhophylac intravenously and the other received all doses intramuscularly; there was no control group receiving a standard anti-D preparation. Women in either group who delivered within 21 days of RAADP did not receive a postpartum dose unless there was evidence of an excessive FMH. Treatment with anti-D other than Rhophylac constituted a protocol violation.
Outcomes: Incidence of RhD immunisation, assessed 6–11.5 months after delivery and, if positive, retested 3 months later, in mothers who had delivered a RhD-positive baby; relative incidence of RhD immunisations in those receiving intramuscular and intravenous anti-D; routine laboratory safety parameters at 1 week after administration of RAADP (compared with blood taken at the screening visit); viral markers, etc., approximately 6 months after the last administration of anti-D (compared with blood taken shortly before the antenatal injection).
Notes: All safety evaluations were conducted on the intention to treat population (i.e. all women who received at least one dose of Rhophylac); efficacy evaluations were conducted on the per protocol population (i.e. all women from the intention to treat population who had delivered an RhD-positive child and who complied with the study’s inclusion/exclusion criteria). In total, 95% of the per protocol population were available for follow-up.
The primary efficacy outcome in this study is the incidence of RhD immunisation in women in the combined intramuscular and intravenous groups delivered of an RhD-positive child. The sample size was calculated to test the null hypothesis that Rhophylac was inferior to currently marketed anti-D products in immunisation frequency. Although this raises the expectation that participants will be randomised to one of the current anti-D products as well as to Rhophylac, in fact reference is made to a rate of seroconversion in women treated ante- and postnatally reported in earlier studies of approximately 0.1–0.3%. Thus, for the primary efficacy outcome, the comparison is made not with contemporary randomised control subjects but with populations who are separated from the study population in time and, in many of the reported studies, also in geographical location. In relation to this primary outcome, therefore, this is a one-armed study with no randomised comparator group; this is recognised by the investigators who claim that it is acceptable given the existence of other scientific data.
The investigators note that the Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products’ most recent note for guidance on the clinical investigation of human anti-D immunoglobulin145 states that clinical trials are not a suitable method for investigating safety in relation to the transmission of either enveloped or non-enveloped viruses.
Quality: Poor.
Mayne et al. 1997127
Method: Retrospective before-and-after study, comparing data from years when the antenatal anti-D programme was fully operational with data from before its introduction; intention to treat analysis.
Participants: All pregnant RhD-negative primiparae in southern Derbyshire.
Interventions: 500 IU of anti-D given intramuscularly at 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation, plus postpartum anti-D for all women (in the intervention and control groups) delivered of RhD-positive babies.
Outcomes: Number of women sensitised in each group; requests for anti-D after bleeding from the vagina or antepartum haemorrhage.
Notes: The number of requests for anti-D following bleeding increased following the introduction of the anti-D programme. This may have been due to heightened awareness among midwives and community doctors, and may have contributed to reducing the overall sensitisation rate in the intervention group.
Quality: Fair.
Tovey et al. 1983,128 Thornton et al. 1989133
Method: Prospective study with historical controls; intention to treat analysis.
Participants: Non-sensitised RhD-negative primigravidae in Yorkshire who gave birth to RhD-positive infants in 1980–1; controls were 2000 non-sensitised RhD-negative primigravidae in Yorkshire who gave birth to RhD-positive infants in 1978–9.
Interventions: 500 IU of anti-D at 28 and 34 weeks, plus 500 IU of postpartum anti-D for all women (in both the intervention and control groups) delivered of RhD-positive babies.
Outcomes: Incidence of immunisation at delivery; incidence of immunisation at 9–12 months following delivery; prevalence of immunisation in a subsequent pregnancy; pre-eclampsia and proteinuria; gestation at delivery; birthweight; fetal survival at 1 month.
Notes: In total, 85% of the intervention group were screened 6 months after their first delivery. No information is given regarding the proportion receiving such screening after subsequent deliveries or the proportion of women in the control group who were screened. Although historical controls were used they were close in time to the intervention group.
Only 69% of women in the intervention group and 71% in the control group who had had at least one further pregnancy were followed up clinically; however, these were considered to be representative of the full groups.
Quality: Fair.
Trolle 1989132
Method: Prospective study with historical controls; intention to treat analysis.
Participants: All pregnant RhD-negative women in Kolding who did not show any sign of immunisation at the first antibody screen test, performed in the first trimester, and again at 28 weeks (control subjects were all RhD-negative women having RhD-positive babies in Kolding in the years 1972–7).
Interventions: 1500 IU of anti-D at 28 weeks’ gestation; women in both the intervention and control groups who were delivered of RhD-positive babies were given 1000 IU of anti-D the day after delivery if the fetomaternal transfusion was estimated to be less than 15 nl of blood.
Outcomes: Incidence of immunisation 10 months after delivery or in next pregnancy; amount of fetal blood in maternal circulation after delivery.
Notes: The control group was said to be comparable to the study group in all respects with regard to the number of first pregnancies and factors known to provoke fetomaternal transfusion (e.g. instrument-assisted deliveries, Caesarean section and stimulation of labour). However, 38.8% of women in the control group had received more than 1 µl of fetal blood, compared with only 7.9% in the intervention group (p < 0.001). Moreover, only the intervention group underwent antenatal antibody screening in the 28th week, as a result of which, although the control group may include women who were alloimmunised before the 28th week, the intervention group does not. In total, 91% of the control group but only 84% of the intervention group were screened for antibodies. Moreover, although the reporting is unclear, it appears that women in the control group were screened either at 10 months or in the next pregnancy, whereas all women in the intervention group were screened at 10 months, although some women may have undergone silent sensitisation that would only become apparent during a subsequent RhD-positive pregnancy. For all of these reasons, alloimmunisation is more likely to be found in the control group.
Quality: Poor.
Appendix 5 Data abstraction tables
| Study | Study design | Dosage | Patient selection | Anti-D prophylaxis group | Control group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | r | % Sensitised (95% CI) | n | r | % Sensitised | ||||
| Bowman et al. 1978129 | Prospective study, historical/geographical controls | 2 × 1500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) (initially at 34 weeks only) | Primigravidae | 1357 | 1 | 0.1 (–0.1 to 0.3) | 2768 | 45 | 1.6 (1.2–2.1) |
| Bowman and Pollock 1978130 | Prospective study, historical controls | 1 × 1500 IU (28 weeks) | Unselected | 1804 | 5 | 0.3 (0.0–0.5) | 3533 | 62 | 1.8 (1.3–2.2) |
| Bowman and Pollock 1987131 | Retrospective study, historical controls | 1 × 1500 IU (28 weeks) | Unselected | 9303 | 18 | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) | 3533 | 62 | 1.8 (1.3–2.2) |
| Trolle 1989132 | Prospective study, historical controls | 1 × 1500 IU (28 weeks) | Unselected | 346 | No data | 354 | No data | ||
| Huchet et al. 1987125 | Quasi-RCT | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | Primigravidae | 461 | 0 | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 454 | 4 | 0.9 (0.0–1.7) |
| Multigravidae | 138 | 1 | 0.7 (–0.7 to 2.0) | 136 | 2 | 1.5 (–0.6 to 3.5) | |||
| Unselected | 599 | 1 | 0.2 (–0.2 to 0.5) | 590 | 6 | 1.0 (0.2–1.8) | |||
| MacKenzie et al. 1999126 | Community intervention trial | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | Primiparae | 3320 | No data | 3146 | No data | ||
| Mayne et al. 1997127 | Before-and-after study | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | Primiparae | 1425 | No data | 1426 | No data | ||
| Tovey et al. 1983128 | Prospective study, historical controls | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | Primigravidae | 1238 | 2 | 0.2 (–0.1 to 0.4) | 2000 | 18 | 0.9 (0.5–1.3) |
| Multigravidae | 325 | 2 | 0.6 (–0.2 to 1.5) | 582 | 11a | 1.9 (0.8–3.1) | |||
| Unselected | 1563 | 4 | 0.3 (0.0–0.6) | 2582 | 29 | 1.1 (0.7–1.5) | |||
| Study | Study design | Dosage | Patient selection | Anti-D prophylaxis group | Control group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | r | % Sensitised (95% CI) | n | r | % Sensitised (95% CI) | ||||
| Bowman et al. 1978129 | Prospective study, historical/geographical controls | 2 × 1500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) (initially at 34 weeks only) | Primigravidae | 1004 | 1 | 0.1 (–0.1 to 0.3) | 2768a | 45 | 1.6 (1.2–2.1) |
| Bowman and Pollock 1978130 | Prospective study, historical controls | 1 × 1500 IU (28 weeks) | Unselected | 807 | No data | 3533a | 50 | 1.4 (1.0–1.8) | |
| Bowman and Pollock 1987131 | Retrospective study, historical controls | 1 × 1500 IU (28 weeks) | Unselected | 9303a | 25 | 0.3 (0.2–0.4) | 3533a | 50 | 1.4 (1.0–1.8) |
| Trolle 1989132 | Prospective study, historical controls | 1 × 1500 IU (28 weeks) | Unselected | 291 | 0 | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 322b | 6 | 1.9 (0.4–3.3) |
| MacKenzie et al. 2004100 | Open-label RCT; results presented as uncontrolled study | 1 × 1500 IU (28 weeks) | Unselected | 248 (per protocol population) | 0 | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | – | – | – |
| Huchet et al. 1987125 | Quasi-RCT | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | Primigravidae | 362 | 0 | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 360 | 4 | 1.1 (0.0–2.2) |
| Multigravidae | 110 | 1 | 0.9 (–0.9 to 2.7) | 108 | 3 | 2.8 (–0.3 to 5.9) | |||
| Unselected | 472 | 1 | 0.2 (–0.2 to 0.6) | 468 | 7 | 1.5 (0.4–2.6) | |||
| MacKenzie et al. 1999126 | Community intervention trial | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | Primiparae | 3320 | No data | 3146 | No data | ||
| Mayne et al. 1997127 | Before-and-after study | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | Primiparae | 1425 | No data | 1426 | No data | ||
| Tovey et al. 1983128 | Prospective study, historical controls | 2 × 500 IU (28 and 34 weeks) | Primigravidae | 1059 | 2 | 0.2 (–0.1 to 0.5) | No data | No data | |
| Multigravidae | No data | No data | |||||||
| Unselected | No data | No data | |||||||
Glossary
- Alloimmunisation
- Generally, production by an individual of antibodies against constituents of the tissues of another individual of the same species (for instance, following transfusion with blood from a member of a different blood group); in this case, production in a RhD-negative pregnant woman of antibodies against fetal RhD-positive red blood cells.
- Ascites
- Accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity.
- Diplegia
- Cerebral palsy affecting corresponding parts on both sides of the body.
- Erythroblastosis
- Another name for haemolytic disease of the newborn.
- Haemolytic anaemia
- Anaemia caused by destruction of the red blood cells.
- Hemiplegia
- Cerebral palsy affecting one side of the body.
- Hydrops fetalis
- A complex syndrome involving profound anaemia with ascites, generalised oedema, gross enlargement of the liver and spleen, and heart failure. Hydrops forms the most severe manifestation of haemolytic disease of the newborn.
- Hyperbilirubinaemia
- Abnormally high levels of the bile pigment bilirubin in the blood.
- Kernicterus
- A form of brain damage caused by the deposition of bilirubin in brain tissues.
- Miscarriage
- Spontaneous loss of a pregnancy before 24 weeks’ gestation.
- Multigravida
- Pregnant woman who has had one or more previous pregnancies.
- Neonatal death
- Death of a live neonate in the first 28 days after birth.
- Neonate
- Infant in the first 4 weeks of life.
- Nullipara
- Woman who has never given birth to a child.
- Oedema
- Swelling of any organ or tissue because of the accumulation of excess lymph fluid.
- Oesophoria
- A muscle condition in which, when both eyes are open, each eye points accurately at the target but, if one eye is covered, it turns inwards.
- Pathan
- Ethnic group living in southern Afghanistan and northern Pakistan.
- Perinatal death
- Miscarriage, stillbirth or neonatal death.
- Plasma
- The liquid part of the blood (about 60% by volume) in which the red and white blood cells and platelets float.
- Prelingual deafness
- Deafness that is either congenital (as in haemolytic disease of the newborn) or otherwise acquired before the child has acquired speech and language.
- Primigravida
- Woman who is pregnant for the first time.
- Primipara
- Woman who has given birth to only one child.
- Quadriplegia
- Cerebral palsy severely affecting all four limbs.
- Secondary sensitisation (secondary immunisation)
- Stimulation of the production of detectable anti-D antibodies in a sensitised woman in response to a second sensitising event.
- Secundigravida
- Woman who is pregnant for the second time.
- Sensitisation (primary immunisation)
- Development in the mother of a template for producing antibodies against fetal RhD-positive red blood cells; in some cases, primary sensitisation also leads to the production of detectable anti-D antibodies.
- Sensitising event
- Event causing a fetomaternal haemorrhage which leads to primary or secondary sensitisation.
- Silent sensitisation
- Sensitisation that does not result in the production of detectable anti-D antibodies.
- Stillbirth
- Fetus born dead after 20 weeks’ gestation.
List of abbreviations
- AADP
- antenatal anti-D prophylaxis
- BNF
- British National Formulary
- FMH
- fetomaternal haemorrhage
- HDN
- haemolytic disease of the newborn
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- IU
- international unit
- IUT
- intrauterine blood transfusion
- LYG
- life-year gained
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
- NNT
- number needed to treat
- PedsQL 4.0
- Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory version 4.0
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- RAADP
- routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- RhD
- Rhesus D
- TPH
- transplacental haemorrhage
- vCJD
- new variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease
All abbreviations that have been used in this report are listed here unless the abbreviation is well known (e.g. NHS), or it has been used only once, or it is a non-standard abbreviation used only in figures/tables/appendices, in which case the abbreviation is defined in the figure legend or in the notes at the end of the table.
Notes
Health Technology Assessment reports published to date
-
Home parenteral nutrition: a systematic review.
By Richards DM, Deeks JJ, Sheldon TA, Shaffer JL.
-
Diagnosis, management and screening of early localised prostate cancer.
A review by Selley S, Donovan J, Faulkner A, Coast J, Gillatt D.
-
The diagnosis, management, treatment and costs of prostate cancer in England and Wales.
A review by Chamberlain J, Melia J, Moss S, Brown J.
-
Screening for fragile X syndrome.
A review by Murray J, Cuckle H, Taylor G, Hewison J.
-
A review of near patient testing in primary care.
By Hobbs FDR, Delaney BC, Fitzmaurice DA, Wilson S, Hyde CJ, Thorpe GH, et al.
-
Systematic review of outpatient services for chronic pain control.
By McQuay HJ, Moore RA, Eccleston C, Morley S, de C Williams AC.
-
Neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism: cost, yield and outcome.
A review by Pollitt RJ, Green A, McCabe CJ, Booth A, Cooper NJ, Leonard JV, et al.
-
Preschool vision screening.
A review by Snowdon SK, Stewart-Brown SL.
-
Implications of socio-cultural contexts for the ethics of clinical trials.
A review by Ashcroft RE, Chadwick DW, Clark SRL, Edwards RHT, Frith L, Hutton JL.
-
A critical review of the role of neonatal hearing screening in the detection of congenital hearing impairment.
By Davis A, Bamford J, Wilson I, Ramkalawan T, Forshaw M, Wright S.
-
Newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism: a systematic review.
By Seymour CA, Thomason MJ, Chalmers RA, Addison GM, Bain MD, Cockburn F, et al.
-
Routine preoperative testing: a systematic review of the evidence.
By Munro J, Booth A, Nicholl J.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness of laxatives in the elderly.
By Petticrew M, Watt I, Sheldon T.
-
When and how to assess fast-changing technologies: a comparative study of medical applications of four generic technologies.
A review by Mowatt G, Bower DJ, Brebner JA, Cairns JA, Grant AM, McKee L.
-
Antenatal screening for Down’s syndrome.
A review by Wald NJ, Kennard A, Hackshaw A, McGuire A.
-
Screening for ovarian cancer: a systematic review.
By Bell R, Petticrew M, Luengo S, Sheldon TA.
-
Consensus development methods, and their use in clinical guideline development.
A review by Murphy MK, Black NA, Lamping DL, McKee CM, Sanderson CFB, Askham J, et al.
-
A cost–utility analysis of interferon beta for multiple sclerosis.
By Parkin D, McNamee P, Jacoby A, Miller P, Thomas S, Bates D.
-
Effectiveness and efficiency of methods of dialysis therapy for end-stage renal disease: systematic reviews.
By MacLeod A, Grant A, Donaldson C, Khan I, Campbell M, Daly C, et al.
-
Effectiveness of hip prostheses in primary total hip replacement: a critical review of evidence and an economic model.
By Faulkner A, Kennedy LG, Baxter K, Donovan J, Wilkinson M, Bevan G.
-
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in colorectal surgery: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials.
By Song F, Glenny AM.
-
Bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for malignancy.
A review by Johnson PWM, Simnett SJ, Sweetenham JW, Morgan GJ, Stewart LA.
-
Screening for speech and language delay: a systematic review of the literature.
By Law J, Boyle J, Harris F, Harkness A, Nye C.
-
Resource allocation for chronic stable angina: a systematic review of effectiveness, costs and cost-effectiveness of alternative interventions.
By Sculpher MJ, Petticrew M, Kelland JL, Elliott RA, Holdright DR, Buxton MJ.
-
Detection, adherence and control of hypertension for the prevention of stroke: a systematic review.
By Ebrahim S.
-
Postoperative analgesia and vomiting, with special reference to day-case surgery: a systematic review.
By McQuay HJ, Moore RA.
-
Choosing between randomised and nonrandomised studies: a systematic review.
By Britton A, McKee M, Black N, McPherson K, Sanderson C, Bain C.
-
Evaluating patient-based outcome measures for use in clinical trials.
A review by Fitzpatrick R, Davey C, Buxton MJ, Jones DR.
-
Ethical issues in the design and conduct of randomised controlled trials.
A review by Edwards SJL, Lilford RJ, Braunholtz DA, Jackson JC, Hewison J, Thornton J.
-
Qualitative research methods in health technology assessment: a review of the literature.
By Murphy E, Dingwall R, Greatbatch D, Parker S, Watson P.
-
The costs and benefits of paramedic skills in pre-hospital trauma care.
By Nicholl J, Hughes S, Dixon S, Turner J, Yates D.
-
Systematic review of endoscopic ultrasound in gastro-oesophageal cancer.
By Harris KM, Kelly S, Berry E, Hutton J, Roderick P, Cullingworth J, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of trials and other studies.
By Sutton AJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR, Sheldon TA, Song F.
-
Primary total hip replacement surgery: a systematic review of outcomes and modelling of cost-effectiveness associated with different prostheses.
A review by Fitzpatrick R, Shortall E, Sculpher M, Murray D, Morris R, Lodge M, et al.
-
Informed decision making: an annotated bibliography and systematic review.
By Bekker H, Thornton JG, Airey CM, Connelly JB, Hewison J, Robinson MB, et al.
-
Handling uncertainty when performing economic evaluation of healthcare interventions.
A review by Briggs AH, Gray AM.
-
The role of expectancies in the placebo effect and their use in the delivery of health care: a systematic review.
By Crow R, Gage H, Hampson S, Hart J, Kimber A, Thomas H.
-
A randomised controlled trial of different approaches to universal antenatal HIV testing: uptake and acceptability. Annex: Antenatal HIV testing – assessment of a routine voluntary approach.
By Simpson WM, Johnstone FD, Boyd FM, Goldberg DJ, Hart GJ, Gormley SM, et al.
-
Methods for evaluating area-wide and organisation-based interventions in health and health care: a systematic review.
By Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ.
-
Assessing the costs of healthcare technologies in clinical trials.
A review by Johnston K, Buxton MJ, Jones DR, Fitzpatrick R.
-
Cooperatives and their primary care emergency centres: organisation and impact.
By Hallam L, Henthorne K.
-
Screening for cystic fibrosis.
A review by Murray J, Cuckle H, Taylor G, Littlewood J, Hewison J.
-
A review of the use of health status measures in economic evaluation.
By Brazier J, Deverill M, Green C, Harper R, Booth A.
-
Methods for the analysis of quality-of-life and survival data in health technology assessment.
A review by Billingham LJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR.
-
Antenatal and neonatal haemoglobinopathy screening in the UK: review and economic analysis.
By Zeuner D, Ades AE, Karnon J, Brown J, Dezateux C, Anionwu EN.
-
Assessing the quality of reports of randomised trials: implications for the conduct of meta-analyses.
A review by Moher D, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Tugwell P, Moher M, Jones A, et al.
-
‘Early warning systems’ for identifying new healthcare technologies.
By Robert G, Stevens A, Gabbay J.
-
A systematic review of the role of human papillomavirus testing within a cervical screening programme.
By Cuzick J, Sasieni P, Davies P, Adams J, Normand C, Frater A, et al.
-
Near patient testing in diabetes clinics: appraising the costs and outcomes.
By Grieve R, Beech R, Vincent J, Mazurkiewicz J.
-
Positron emission tomography: establishing priorities for health technology assessment.
A review by Robert G, Milne R.
-
The debridement of chronic wounds: a systematic review.
By Bradley M, Cullum N, Sheldon T.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (2) Dressings and topical agents used in the healing of chronic wounds.
By Bradley M, Cullum N, Nelson EA, Petticrew M, Sheldon T, Torgerson D.
-
A systematic literature review of spiral and electron beam computed tomography: with particular reference to clinical applications in hepatic lesions, pulmonary embolus and coronary artery disease.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Hutton J, Harris KM, Roderick P, Boyce JC, et al.
-
What role for statins? A review and economic model.
By Ebrahim S, Davey Smith G, McCabe C, Payne N, Pickin M, Sheldon TA, et al.
-
Factors that limit the quality, number and progress of randomised controlled trials.
A review by Prescott RJ, Counsell CE, Gillespie WJ, Grant AM, Russell IT, Kiauka S, et al.
-
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in total hip replacement: a systematic review.
By Glenny AM, Song F.
-
Health promoting schools and health promotion in schools: two systematic reviews.
By Lister-Sharp D, Chapman S, Stewart-Brown S, Sowden A.
-
Economic evaluation of a primary care-based education programme for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee.
A review by Lord J, Victor C, Littlejohns P, Ross FM, Axford JS.
-
The estimation of marginal time preference in a UK-wide sample (TEMPUS) project.
A review by Cairns JA, van der Pol MM.
-
Geriatric rehabilitation following fractures in older people: a systematic review.
By Cameron I, Crotty M, Currie C, Finnegan T, Gillespie L, Gillespie W, et al.
-
Screening for sickle cell disease and thalassaemia: a systematic review with supplementary research.
By Davies SC, Cronin E, Gill M, Greengross P, Hickman M, Normand C.
-
Community provision of hearing aids and related audiology services.
A review by Reeves DJ, Alborz A, Hickson FS, Bamford JM.
-
False-negative results in screening programmes: systematic review of impact and implications.
By Petticrew MP, Sowden AJ, Lister-Sharp D, Wright K.
-
Costs and benefits of community postnatal support workers: a randomised controlled trial.
By Morrell CJ, Spiby H, Stewart P, Walters S, Morgan A.
-
Implantable contraceptives (subdermal implants and hormonally impregnated intrauterine systems) versus other forms of reversible contraceptives: two systematic reviews to assess relative effectiveness, acceptability, tolerability and cost-effectiveness.
By French RS, Cowan FM, Mansour DJA, Morris S, Procter T, Hughes D, et al.
-
An introduction to statistical methods for health technology assessment.
A review by White SJ, Ashby D, Brown PJ.
-
Disease-modifying drugs for multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By Clegg A, Bryant J, Milne R.
-
Publication and related biases.
A review by Song F, Eastwood AJ, Gilbody S, Duley L, Sutton AJ.
-
Cost and outcome implications of the organisation of vascular services.
By Michaels J, Brazier J, Palfreyman S, Shackley P, Slack R.
-
Monitoring blood glucose control in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review.
By Coster S, Gulliford MC, Seed PT, Powrie JK, Swaminathan R.
-
The effectiveness of domiciliary health visiting: a systematic review of international studies and a selective review of the British literature.
By Elkan R, Kendrick D, Hewitt M, Robinson JJA, Tolley K, Blair M, et al.
-
The determinants of screening uptake and interventions for increasing uptake: a systematic review.
By Jepson R, Clegg A, Forbes C, Lewis R, Sowden A, Kleijnen J.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of prophylactic removal of wisdom teeth.
A rapid review by Song F, O’Meara S, Wilson P, Golder S, Kleijnen J.
-
Ultrasound screening in pregnancy: a systematic review of the clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and women’s views.
By Bricker L, Garcia J, Henderson J, Mugford M, Neilson J, Roberts T, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the taxanes used in the treatment of advanced breast and ovarian cancer.
By Lister-Sharp D, McDonagh MS, Khan KS, Kleijnen J.
-
Liquid-based cytology in cervical screening: a rapid and systematic review.
By Payne N, Chilcott J, McGoogan E.
-
Randomised controlled trial of non-directive counselling, cognitive–behaviour therapy and usual general practitioner care in the management of depression as well as mixed anxiety and depression in primary care.
By King M, Sibbald B, Ward E, Bower P, Lloyd M, Gabbay M, et al.
-
Routine referral for radiography of patients presenting with low back pain: is patients’ outcome influenced by GPs’ referral for plain radiography?
By Kerry S, Hilton S, Patel S, Dundas D, Rink E, Lord J.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (3) antimicrobial agents for chronic wounds; (4) diabetic foot ulceration.
By O’Meara S, Cullum N, Majid M, Sheldon T.
-
Using routine data to complement and enhance the results of randomised controlled trials.
By Lewsey JD, Leyland AH, Murray GD, Boddy FA.
-
Coronary artery stents in the treatment of ischaemic heart disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Meads C, Cummins C, Jolly K, Stevens A, Burls A, Hyde C.
-
Outcome measures for adult critical care: a systematic review.
By Hayes JA, Black NA, Jenkinson C, Young JD, Rowan KM, Daly K, et al.
-
A systematic review to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions to promote the initiation of breastfeeding.
By Fairbank L, O’Meara S, Renfrew MJ, Woolridge M, Sowden AJ, Lister-Sharp D.
-
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators: arrhythmias. A rapid and systematic review.
By Parkes J, Bryant J, Milne R.
-
Treatments for fatigue in multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By Brañas P, Jordan R, Fry-Smith A, Burls A, Hyde C.
-
Early asthma prophylaxis, natural history, skeletal development and economy (EASE): a pilot randomised controlled trial.
By Baxter-Jones ADG, Helms PJ, Russell G, Grant A, Ross S, Cairns JA, et al.
-
Screening for hypercholesterolaemia versus case finding for familial hypercholesterolaemia: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Marks D, Wonderling D, Thorogood M, Lambert H, Humphries SE, Neil HAW.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists in the medical management of unstable angina.
By McDonagh MS, Bachmann LM, Golder S, Kleijnen J, ter Riet G.
-
A randomised controlled trial of prehospital intravenous fluid replacement therapy in serious trauma.
By Turner J, Nicholl J, Webber L, Cox H, Dixon S, Yates D.
-
Intrathecal pumps for giving opioids in chronic pain: a systematic review.
By Williams JE, Louw G, Towlerton G.
-
Combination therapy (interferon alfa and ribavirin) in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a rapid and systematic review.
By Shepherd J, Waugh N, Hewitson P.
-
A systematic review of comparisons of effect sizes derived from randomised and non-randomised studies.
By MacLehose RR, Reeves BC, Harvey IM, Sheldon TA, Russell IT, Black AMS.
-
Intravascular ultrasound-guided interventions in coronary artery disease: a systematic literature review, with decision-analytic modelling, of outcomes and cost-effectiveness.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Hutton J, Lindsay HSJ, Blaxill JM, Evans JA, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to evaluate the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of counselling patients with chronic depression.
By Simpson S, Corney R, Fitzgerald P, Beecham J.
-
Systematic review of treatments for atopic eczema.
By Hoare C, Li Wan Po A, Williams H.
-
Bayesian methods in health technology assessment: a review.
By Spiegelhalter DJ, Myles JP, Jones DR, Abrams KR.
-
The management of dyspepsia: a systematic review.
By Delaney B, Moayyedi P, Deeks J, Innes M, Soo S, Barton P, et al.
-
A systematic review of treatments for severe psoriasis.
By Griffiths CEM, Clark CM, Chalmers RJG, Li Wan Po A, Williams HC.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine for Alzheimer’s disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Clegg A, Bryant J, Nicholson T, McIntyre L, De Broe S, Gerard K, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of riluzole for motor neurone disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Stewart A, Sandercock J, Bryan S, Hyde C, Barton PM, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Equity and the economic evaluation of healthcare.
By Sassi F, Archard L, Le Grand J.
-
Quality-of-life measures in chronic diseases of childhood.
By Eiser C, Morse R.
-
Eliciting public preferences for healthcare: a systematic review of techniques.
By Ryan M, Scott DA, Reeves C, Bate A, van Teijlingen ER, Russell EM, et al.
-
General health status measures for people with cognitive impairment: learning disability and acquired brain injury.
By Riemsma RP, Forbes CA, Glanville JM, Eastwood AJ, Kleijnen J.
-
An assessment of screening strategies for fragile X syndrome in the UK.
By Pembrey ME, Barnicoat AJ, Carmichael B, Bobrow M, Turner G.
-
Issues in methodological research: perspectives from researchers and commissioners.
By Lilford RJ, Richardson A, Stevens A, Fitzpatrick R, Edwards S, Rock F, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (5) beds; (6) compression; (7) laser therapy, therapeutic ultrasound, electrotherapy and electromagnetic therapy.
By Cullum N, Nelson EA, Flemming K, Sheldon T.
-
Effects of educational and psychosocial interventions for adolescents with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review.
By Hampson SE, Skinner TC, Hart J, Storey L, Gage H, Foxcroft D, et al.
-
Effectiveness of autologous chondrocyte transplantation for hyaline cartilage defects in knees: a rapid and systematic review.
By Jobanputra P, Parry D, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
Statistical assessment of the learning curves of health technologies.
By Ramsay CR, Grant AM, Wallace SA, Garthwaite PH, Monk AF, Russell IT.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of temozolomide for the treatment of recurrent malignant glioma: a rapid and systematic review.
By Dinnes J, Cave C, Huang S, Major K, Milne R.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of debriding agents in treating surgical wounds healing by secondary intention.
By Lewis R, Whiting P, ter Riet G, O’Meara S, Glanville J.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.
By Burns T, Knapp M, Catty J, Healey A, Henderson J, Watt H, et al.
-
How to develop cost-conscious guidelines.
By Eccles M, Mason J.
-
The role of specialist nurses in multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By De Broe S, Christopher F, Waugh N.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of orlistat in the management of obesity.
By O’Meara S, Riemsma R, Shirran L, Mather L, ter Riet G.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pioglitazone for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a rapid and systematic review.
By Chilcott J, Wight J, Lloyd Jones M, Tappenden P.
-
Extended scope of nursing practice: a multicentre randomised controlled trial of appropriately trained nurses and preregistration house officers in preoperative assessment in elective general surgery.
By Kinley H, Czoski-Murray C, George S, McCabe C, Primrose J, Reilly C, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of the effectiveness of day care for people with severe mental disorders: (1) Acute day hospital versus admission; (2) Vocational rehabilitation; (3) Day hospital versus outpatient care.
By Marshall M, Crowther R, Almaraz- Serrano A, Creed F, Sledge W, Kluiter H, et al.
-
The measurement and monitoring of surgical adverse events.
By Bruce J, Russell EM, Mollison J, Krukowski ZH.
-
Action research: a systematic review and guidance for assessment.
By Waterman H, Tillen D, Dickson R, de Koning K.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of gemcitabine for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
By Ward S, Morris E, Bansback N, Calvert N, Crellin A, Forman D, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the evidence for the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer.
By Lloyd Jones M, Hummel S, Bansback N, Orr B, Seymour M.
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.
By Brocklebank D, Ram F, Wright J, Barry P, Cates C, Davies L, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging for investigation of the knee joint.
By Bryan S, Weatherburn G, Bungay H, Hatrick C, Salas C, Parry D, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.
By Forbes C, Shirran L, Bagnall A-M, Duffy S, ter Riet G.
-
Superseded by a report published in a later volume.
-
The role of radiography in primary care patients with low back pain of at least 6 weeks duration: a randomised (unblinded) controlled trial.
By Kendrick D, Fielding K, Bentley E, Miller P, Kerslake R, Pringle M.
-
Design and use of questionnaires: a review of best practice applicable to surveys of health service staff and patients.
By McColl E, Jacoby A, Thomas L, Soutter J, Bamford C, Steen N, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.
By Clegg A, Scott DA, Sidhu M, Hewitson P, Waugh N.
-
Subgroup analyses in randomised controlled trials: quantifying the risks of false-positives and false-negatives.
By Brookes ST, Whitley E, Peters TJ, Mulheran PA, Egger M, Davey Smith G.
-
Depot antipsychotic medication in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia: (1) Meta-review; (2) Patient and nurse attitudes.
By David AS, Adams C.
-
A systematic review of controlled trials of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of brief psychological treatments for depression.
By Churchill R, Hunot V, Corney R, Knapp M, McGuire H, Tylee A, et al.
-
Cost analysis of child health surveillance.
By Sanderson D, Wright D, Acton C, Duree D.
-
A study of the methods used to select review criteria for clinical audit.
By Hearnshaw H, Harker R, Cheater F, Baker R, Grimshaw G.
-
Fludarabine as second-line therapy for B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a technology assessment.
By Hyde C, Wake B, Bryan S, Barton P, Fry-Smith A, Davenport C, et al.
-
Rituximab as third-line treatment for refractory or recurrent Stage III or IV follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wake B, Hyde C, Bryan S, Barton P, Song F, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
A systematic review of discharge arrangements for older people.
By Parker SG, Peet SM, McPherson A, Cannaby AM, Baker R, Wilson A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of inhaler devices used in the routine management of chronic asthma in older children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Peters J, Stevenson M, Beverley C, Lim J, Smith S.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of sibutramine in the management of obesity: a technology assessment.
By O’Meara S, Riemsma R, Shirran L, Mather L, ter Riet G.
-
The cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance angiography for carotid artery stenosis and peripheral vascular disease: a systematic review.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Westwood ME, Davies LM, Gough MJ, Bamford JM, et al.
-
Promoting physical activity in South Asian Muslim women through ‘exercise on prescription’.
By Carroll B, Ali N, Azam N.
-
Zanamivir for the treatment of influenza in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burls A, Clark W, Stewart T, Preston C, Bryan S, Jefferson T, et al.
-
A review of the natural history and epidemiology of multiple sclerosis: implications for resource allocation and health economic models.
By Richards RG, Sampson FC, Beard SM, Tappenden P.
-
Screening for gestational diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Scott DA, Loveman E, McIntyre L, Waugh N.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of surgery for people with morbid obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clegg AJ, Colquitt J, Sidhu MK, Royle P, Loveman E, Walker A.
-
The clinical effectiveness of trastuzumab for breast cancer: a systematic review.
By Lewis R, Bagnall A-M, Forbes C, Shirran E, Duffy S, Kleijnen J, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of vinorelbine for breast cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Lewis R, Bagnall A-M, King S, Woolacott N, Forbes C, Shirran L, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty for treatment of hip disease.
By Vale L, Wyness L, McCormack K, McKenzie L, Brazzelli M, Stearns SC.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bupropion and nicotine replacement therapy for smoking cessation: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Woolacott NF, Jones L, Forbes CA, Mather LC, Sowden AJ, Song FJ, et al.
-
A systematic review of effectiveness and economic evaluation of new drug treatments for juvenile idiopathic arthritis: etanercept.
By Cummins C, Connock M, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of growth hormone in children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Cave C, Mihaylova B, Chase D, McIntyre L, Gerard K, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of growth hormone in adults in relation to impact on quality of life: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Loveman E, Chase D, Mihaylova B, Cave C, Gerard K, et al.
-
Clinical medication review by a pharmacist of patients on repeat prescriptions in general practice: a randomised controlled trial.
By Zermansky AG, Petty DR, Raynor DK, Lowe CJ, Freementle N, Vail A.
-
The effectiveness of infliximab and etanercept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Burls A.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of computerised cognitive behaviour therapy for depression and anxiety.
By Kaltenthaler E, Shackley P, Stevens K, Beverley C, Parry G, Chilcott J.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride for ovarian cancer.
By Forbes C, Wilby J, Richardson G, Sculpher M, Mather L, Reimsma R.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of interventions based on a stages-of-change approach to promote individual behaviour change.
By Riemsma RP, Pattenden J, Bridle C, Sowden AJ, Mather L, Watt IS, et al.
-
A systematic review update of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists.
By Robinson M, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Jones L, Riemsma R, Palmer S, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and barriers to implementation of thrombolytic and neuroprotective therapy for acute ischaemic stroke in the NHS.
By Sandercock P, Berge E, Dennis M, Forbes J, Hand P, Kwan J, et al.
-
A randomised controlled crossover trial of nurse practitioner versus doctor-led outpatient care in a bronchiectasis clinic.
By Caine N, Sharples LD, Hollingworth W, French J, Keogan M, Exley A, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost – consequences of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of sex offenders.
By Adi Y, Ashcroft D, Browne K, Beech A, Fry-Smith A, Hyde C.
-
Treatment of established osteoporosis: a systematic review and cost–utility analysis.
By Kanis JA, Brazier JE, Stevenson M, Calvert NW, Lloyd Jones M.
-
Which anaesthetic agents are cost-effective in day surgery? Literature review, national survey of practice and randomised controlled trial.
By Elliott RA Payne K, Moore JK, Davies LM, Harper NJN, St Leger AS, et al.
-
Screening for hepatitis C among injecting drug users and in genitourinary medicine clinics: systematic reviews of effectiveness, modelling study and national survey of current practice.
By Stein K, Dalziel K, Walker A, McIntyre L, Jenkins B, Horne J, et al.
-
The measurement of satisfaction with healthcare: implications for practice from a systematic review of the literature.
By Crow R, Gage H, Hampson S, Hart J, Kimber A, Storey L, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of imatinib in chronic myeloid leukaemia: a systematic review.
By Garside R, Round A, Dalziel K, Stein K, Royle R.
-
A comparative study of hypertonic saline, daily and alternate-day rhDNase in children with cystic fibrosis.
By Suri R, Wallis C, Bush A, Thompson S, Normand C, Flather M, et al.
-
A systematic review of the costs and effectiveness of different models of paediatric home care.
By Parker G, Bhakta P, Lovett CA, Paisley S, Olsen R, Turner D, et al.
-
How important are comprehensive literature searches and the assessment of trial quality in systematic reviews? Empirical study.
By Egger M, Jüni P, Bartlett C, Holenstein F, Sterne J.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and economic evaluation, of home versus hospital or satellite unit haemodialysis for people with end-stage renal failure.
By Mowatt G, Vale L, Perez J, Wyness L, Fraser C, MacLeod A, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of the effectiveness of infliximab for the treatment of Crohn’s disease.
By Clark W, Raftery J, Barton P, Song F, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
A review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine anti-D prophylaxis for pregnant women who are rhesus negative.
By Chilcott J, Lloyd Jones M, Wight J, Forman K, Wray J, Beverley C, et al.
-
Systematic review and evaluation of the use of tumour markers in paediatric oncology: Ewing’s sarcoma and neuroblastoma.
By Riley RD, Burchill SA, Abrams KR, Heney D, Lambert PC, Jones DR, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of screening for Helicobacter pylori to reduce mortality and morbidity from gastric cancer and peptic ulcer disease: a discrete-event simulation model.
By Roderick P, Davies R, Raftery J, Crabbe D, Pearce R, Bhandari P, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine dental checks: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Davenport C, Elley K, Salas C, Taylor-Weetman CL, Fry-Smith A, Bryan S, et al.
-
A multicentre randomised controlled trial assessing the costs and benefits of using structured information and analysis of women’s preferences in the management of menorrhagia.
By Kennedy ADM, Sculpher MJ, Coulter A, Dwyer N, Rees M, Horsley S, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost–utility of photodynamic therapy for wet age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Meads C, Salas C, Roberts T, Moore D, Fry-Smith A, Hyde C.
-
Evaluation of molecular tests for prenatal diagnosis of chromosome abnormalities.
By Grimshaw GM, Szczepura A, Hultén M, MacDonald F, Nevin NC, Sutton F, et al.
-
First and second trimester antenatal screening for Down’s syndrome: the results of the Serum, Urine and Ultrasound Screening Study (SURUSS).
By Wald NJ, Rodeck C, Hackshaw AK, Walters J, Chitty L, Mackinson AM.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of ultrasound locating devices for central venous access: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Calvert N, Hind D, McWilliams RG, Thomas SM, Beverley C, Davidson A.
-
A systematic review of atypical antipsychotics in schizophrenia.
By Bagnall A-M, Jones L, Lewis R, Ginnelly L, Glanville J, Torgerson D, et al.
-
Prostate Testing for Cancer and Treatment (ProtecT) feasibility study.
By Donovan J, Hamdy F, Neal D, Peters T, Oliver S, Brindle L, et al.
-
Early thrombolysis for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Boland A, Dundar Y, Bagust A, Haycox A, Hill R, Mujica Mota R, et al.
-
Screening for fragile X syndrome: a literature review and modelling.
By Song FJ, Barton P, Sleightholme V, Yao GL, Fry-Smith A.
-
Systematic review of endoscopic sinus surgery for nasal polyps.
By Dalziel K, Stein K, Round A, Garside R, Royle P.
-
Towards efficient guidelines: how to monitor guideline use in primary care.
By Hutchinson A, McIntosh A, Cox S, Gilbert C.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of acute hospital-based spinal cord injuries services: systematic review.
By Bagnall A-M, Jones L, Richardson G, Duffy S, Riemsma R.
-
Prioritisation of health technology assessment. The PATHS model: methods and case studies.
By Townsend J, Buxton M, Harper G.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of tension-free vaginal tape for treatment of urinary stress incontinence.
By Cody J, Wyness L, Wallace S, Glazener C, Kilonzo M, Stearns S, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of patient education models for diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Loveman E, Cave C, Green C, Royle P, Dunn N, Waugh N.
-
The role of modelling in prioritising and planning clinical trials.
By Chilcott J, Brennan A, Booth A, Karnon J, Tappenden P.
-
Cost–benefit evaluation of routine influenza immunisation in people 65–74 years of age.
By Allsup S, Gosney M, Haycox A, Regan M.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of pulsatile machine perfusion versus cold storage of kidneys for transplantation retrieved from heart-beating and non-heart-beating donors.
By Wight J, Chilcott J, Holmes M, Brewer N.
-
Can randomised trials rely on existing electronic data? A feasibility study to explore the value of routine data in health technology assessment.
By Williams JG, Cheung WY, Cohen DR, Hutchings HA, Longo MF, Russell IT.
-
Evaluating non-randomised intervention studies.
By Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, D’Amico R, Sowden AJ, Sakarovitch C, Song F, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to assess the impact of a package comprising a patient-orientated, evidence-based self- help guidebook and patient-centred consultations on disease management and satisfaction in inflammatory bowel disease.
By Kennedy A, Nelson E, Reeves D, Richardson G, Roberts C, Robinson A, et al.
-
The effectiveness of diagnostic tests for the assessment of shoulder pain due to soft tissue disorders: a systematic review.
By Dinnes J, Loveman E, McIntyre L, Waugh N.
-
The value of digital imaging in diabetic retinopathy.
By Sharp PF, Olson J, Strachan F, Hipwell J, Ludbrook A, O’Donnell M, et al.
-
Lowering blood pressure to prevent myocardial infarction and stroke: a new preventive strategy.
By Law M, Wald N, Morris J.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of capecitabine and tegafur with uracil for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ward S, Kaltenthaler E, Cowan J, Brewer N.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of new and emerging technologies for early localised prostate cancer: a systematic review.
By Hummel S, Paisley S, Morgan A, Currie E, Brewer N.
-
Literature searching for clinical and cost-effectiveness studies used in health technology assessment reports carried out for the National Institute for Clinical Excellence appraisal system.
By Royle P, Waugh N.
-
Systematic review and economic decision modelling for the prevention and treatment of influenza A and B.
By Turner D, Wailoo A, Nicholson K, Cooper N, Sutton A, Abrams K.
-
A randomised controlled trial to evaluate the clinical and cost-effectiveness of Hickman line insertions in adult cancer patients by nurses.
By Boland A, Haycox A, Bagust A, Fitzsimmons L.
-
Redesigning postnatal care: a randomised controlled trial of protocol-based midwifery-led care focused on individual women’s physical and psychological health needs.
By MacArthur C, Winter HR, Bick DE, Lilford RJ, Lancashire RJ, Knowles H, et al.
-
Estimating implied rates of discount in healthcare decision-making.
By West RR, McNabb R, Thompson AGH, Sheldon TA, Grimley Evans J.
-
Systematic review of isolation policies in the hospital management of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a review of the literature with epidemiological and economic modelling.
By Cooper BS, Stone SP, Kibbler CC, Cookson BD, Roberts JA, Medley GF, et al.
-
Treatments for spasticity and pain in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review.
By Beard S, Hunn A, Wight J.
-
The inclusion of reports of randomised trials published in languages other than English in systematic reviews.
By Moher D, Pham B, Lawson ML, Klassen TP.
-
The impact of screening on future health-promoting behaviours and health beliefs: a systematic review.
By Bankhead CR, Brett J, Bukach C, Webster P, Stewart-Brown S, Munafo M, et al.
-
What is the best imaging strategy for acute stroke?
By Wardlaw JM, Keir SL, Seymour J, Lewis S, Sandercock PAG, Dennis MS, et al.
-
Systematic review and modelling of the investigation of acute and chronic chest pain presenting in primary care.
By Mant J, McManus RJ, Oakes RAL, Delaney BC, Barton PM, Deeks JJ, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of microwave and thermal balloon endometrial ablation for heavy menstrual bleeding: a systematic review and economic modelling.
By Garside R, Stein K, Wyatt K, Round A, Price A.
-
A systematic review of the role of bisphosphonates in metastatic disease.
By Ross JR, Saunders Y, Edmonds PM, Patel S, Wonderling D, Normand C, et al.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of capecitabine (Xeloda®) for locally advanced and/or metastatic breast cancer.
By Jones L, Hawkins N, Westwood M, Wright K, Richardson G, Riemsma R.
-
Effectiveness and efficiency of guideline dissemination and implementation strategies.
By Grimshaw JM, Thomas RE, MacLennan G, Fraser C, Ramsay CR, Vale L, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and costs of the Sugarbaker procedure for the treatment of pseudomyxoma peritonei.
By Bryant J, Clegg AJ, Sidhu MK, Brodin H, Royle P, Davidson P.
-
Psychological treatment for insomnia in the regulation of long-term hypnotic drug use.
By Morgan K, Dixon S, Mathers N, Thompson J, Tomeny M.
-
Improving the evaluation of therapeutic interventions in multiple sclerosis: development of a patient-based measure of outcome.
By Hobart JC, Riazi A, Lamping DL, Fitzpatrick R, Thompson AJ.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography compared with diagnostic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
By Kaltenthaler E, Bravo Vergel Y, Chilcott J, Thomas S, Blakeborough T, Walters SJ, et al.
-
The use of modelling to evaluate new drugs for patients with a chronic condition: the case of antibodies against tumour necrosis factor in rheumatoid arthritis.
By Barton P, Jobanputra P, Wilson J, Bryan S, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism using tandem mass spectrometry: a systematic review.
By Pandor A, Eastham J, Beverley C, Chilcott J, Paisley S.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pioglitazone and rosiglitazone in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Czoski-Murray C, Warren E, Chilcott J, Beverley C, Psyllaki MA, Cowan J.
-
Routine examination of the newborn: the EMREN study. Evaluation of an extension of the midwife role including a randomised controlled trial of appropriately trained midwives and paediatric senior house officers.
By Townsend J, Wolke D, Hayes J, Davé S, Rogers C, Bloomfield L, et al.
-
Involving consumers in research and development agenda setting for the NHS: developing an evidence-based approach.
By Oliver S, Clarke-Jones L, Rees R, Milne R, Buchanan P, Gabbay J, et al.
-
A multi-centre randomised controlled trial of minimally invasive direct coronary bypass grafting versus percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty with stenting for proximal stenosis of the left anterior descending coronary artery.
By Reeves BC, Angelini GD, Bryan AJ, Taylor FC, Cripps T, Spyt TJ, et al.
-
Does early magnetic resonance imaging influence management or improve outcome in patients referred to secondary care with low back pain? A pragmatic randomised controlled trial.
By Gilbert FJ, Grant AM, Gillan MGC, Vale L, Scott NW, Campbell MK, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of anakinra for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Clark W, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Burls A.
-
A rapid and systematic review and economic evaluation of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for treatment of mania associated with bipolar affective disorder.
By Bridle C, Palmer S, Bagnall A-M, Darba J, Duffy S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Liquid-based cytology in cervical screening: an updated rapid and systematic review and economic analysis.
By Karnon J, Peters J, Platt J, Chilcott J, McGoogan E, Brewer N.
-
Systematic review of the long-term effects and economic consequences of treatments for obesity and implications for health improvement.
By Avenell A, Broom J, Brown TJ, Poobalan A, Aucott L, Stearns SC, et al.
-
Autoantibody testing in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus.
By Dretzke J, Cummins C, Sandercock J, Fry-Smith A, Barrett T, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of prehospital intravenous fluids in trauma patients.
By Dretzke J, Sandercock J, Bayliss S, Burls A.
-
Newer hypnotic drugs for the short-term management of insomnia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Dündar Y, Boland A, Strobl J, Dodd S, Haycox A, Bagust A, et al.
-
Development and validation of methods for assessing the quality of diagnostic accuracy studies.
By Whiting P, Rutjes AWS, Dinnes J, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PMM, Kleijnen J.
-
EVALUATE hysterectomy trial: a multicentre randomised trial comparing abdominal, vaginal and laparoscopic methods of hysterectomy.
By Garry R, Fountain J, Brown J, Manca A, Mason S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Methods for expected value of information analysis in complex health economic models: developments on the health economics of interferon-β and glatiramer acetate for multiple sclerosis.
By Tappenden P, Chilcott JB, Eggington S, Oakley J, McCabe C.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of imatinib for first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia in chronic phase: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Dalziel K, Round A, Stein K, Garside R, Price A.
-
VenUS I: a randomised controlled trial of two types of bandage for treating venous leg ulcers.
By Iglesias C, Nelson EA, Cullum NA, Torgerson DJ, on behalf of the VenUS Team.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and economic evaluation, of myocardial perfusion scintigraphy for the diagnosis and management of angina and myocardial infarction.
By Mowatt G, Vale L, Brazzelli M, Hernandez R, Murray A, Scott N, et al.
-
A pilot study on the use of decision theory and value of information analysis as part of the NHS Health Technology Assessment programme.
By Claxton K, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Philips Z, Palmer S.
-
The Social Support and Family Health Study: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of two alternative forms of postnatal support for mothers living in disadvantaged inner-city areas.
By Wiggins M, Oakley A, Roberts I, Turner H, Rajan L, Austerberry H, et al.
-
Psychosocial aspects of genetic screening of pregnant women and newborns: a systematic review.
By Green JM, Hewison J, Bekker HL, Bryant, Cuckle HS.
-
Evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding: comparison of three outpatient procedures within cohorts defined by age and menopausal status.
By Critchley HOD, Warner P, Lee AJ, Brechin S, Guise J, Graham B.
-
Coronary artery stents: a rapid systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hill R, Bagust A, Bakhai A, Dickson R, Dündar Y, Haycox A, et al.
-
Review of guidelines for good practice in decision-analytic modelling in health technology assessment.
By Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Claxton K, Golder S, Riemsma R, et al.
-
Rituximab (MabThera®) for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Knight C, Hind D, Brewer N, Abbott V.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of clopidogrel and modified-release dipyridamole in the secondary prevention of occlusive vascular events: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jones L, Griffin S, Palmer S, Main C, Orton V, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Pegylated interferon α-2a and -2b in combination with ribavirin in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Brodin H, Cave C, Waugh N, Price A, Gabbay J.
-
Clopidogrel used in combination with aspirin compared with aspirin alone in the treatment of non-ST-segment- elevation acute coronary syndromes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Main C, Palmer S, Griffin S, Jones L, Orton V, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Provision, uptake and cost of cardiac rehabilitation programmes: improving services to under-represented groups.
By Beswick AD, Rees K, Griebsch I, Taylor FC, Burke M, West RR, et al.
-
Involving South Asian patients in clinical trials.
By Hussain-Gambles M, Leese B, Atkin K, Brown J, Mason S, Tovey P.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for diabetes.
By Colquitt JL, Green C, Sidhu MK, Hartwell D, Waugh N.
-
Identification and assessment of ongoing trials in health technology assessment reviews.
By Song FJ, Fry-Smith A, Davenport C, Bayliss S, Adi Y, Wilson JS, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of a long-acting insulin analogue, insulin glargine
By Warren E, Weatherley-Jones E, Chilcott J, Beverley C.
-
Supplementation of a home-based exercise programme with a class-based programme for people with osteoarthritis of the knees: a randomised controlled trial and health economic analysis.
By McCarthy CJ, Mills PM, Pullen R, Richardson G, Hawkins N, Roberts CR, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of once-daily versus more frequent use of same potency topical corticosteroids for atopic eczema: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Green C, Colquitt JL, Kirby J, Davidson P, Payne E.
-
Acupuncture of chronic headache disorders in primary care: randomised controlled trial and economic analysis.
By Vickers AJ, Rees RW, Zollman CE, McCarney R, Smith CM, Ellis N, et al.
-
Generalisability in economic evaluation studies in healthcare: a review and case studies.
By Sculpher MJ, Pang FS, Manca A, Drummond MF, Golder S, Urdahl H, et al.
-
Virtual outreach: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of joint teleconferenced medical consultations.
By Wallace P, Barber J, Clayton W, Currell R, Fleming K, Garner P, et al.
-
Randomised controlled multiple treatment comparison to provide a cost-effectiveness rationale for the selection of antimicrobial therapy in acne.
By Ozolins M, Eady EA, Avery A, Cunliffe WJ, O’Neill C, Simpson NB, et al.
-
Do the findings of case series studies vary significantly according to methodological characteristics?
By Dalziel K, Round A, Stein K, Garside R, Castelnuovo E, Payne L.
-
Improving the referral process for familial breast cancer genetic counselling: findings of three randomised controlled trials of two interventions.
By Wilson BJ, Torrance N, Mollison J, Wordsworth S, Gray JR, Haites NE, et al.
-
Randomised evaluation of alternative electrosurgical modalities to treat bladder outflow obstruction in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
By Fowler C, McAllister W, Plail R, Karim O, Yang Q.
-
A pragmatic randomised controlled trial of the cost-effectiveness of palliative therapies for patients with inoperable oesophageal cancer.
By Shenfine J, McNamee P, Steen N, Bond J, Griffin SM.
-
Impact of computer-aided detection prompts on the sensitivity and specificity of screening mammography.
By Taylor P, Champness J, Given- Wilson R, Johnston K, Potts H.
-
Issues in data monitoring and interim analysis of trials.
By Grant AM, Altman DG, Babiker AB, Campbell MK, Clemens FJ, Darbyshire JH, et al.
-
Lay public’s understanding of equipoise and randomisation in randomised controlled trials.
By Robinson EJ, Kerr CEP, Stevens AJ, Lilford RJ, Braunholtz DA, Edwards SJ, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of electroconvulsive therapy for depressive illness, schizophrenia, catatonia and mania: systematic reviews and economic modelling studies.
By Greenhalgh J, Knight C, Hind D, Beverley C, Walters S.
-
Measurement of health-related quality of life for people with dementia: development of a new instrument (DEMQOL) and an evaluation of current methodology.
By Smith SC, Lamping DL, Banerjee S, Harwood R, Foley B, Smith P, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of drotrecogin alfa (activated) (Xigris®) for the treatment of severe sepsis in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Green C, Dinnes J, Takeda A, Shepherd J, Hartwell D, Cave C, et al.
-
A methodological review of how heterogeneity has been examined in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy.
By Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kirby J, Roderick P.
-
Cervical screening programmes: can automation help? Evidence from systematic reviews, an economic analysis and a simulation modelling exercise applied to the UK.
By Willis BH, Barton P, Pearmain P, Bryan S, Hyde C.
-
Laparoscopic surgery for inguinal hernia repair: systematic review of effectiveness and economic evaluation.
By McCormack K, Wake B, Perez J, Fraser C, Cook J, McIntosh E, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness, tolerability and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for epilepsy in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wilby J, Kainth A, Hawkins N, Epstein D, McIntosh H, McDaid C, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to compare the cost-effectiveness of tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and lofepramine.
By Peveler R, Kendrick T, Buxton M, Longworth L, Baldwin D, Moore M, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of immediate angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hartwell D, Colquitt J, Loveman E, Clegg AJ, Brodin H, Waugh N, et al.
-
A randomised controlled comparison of alternative strategies in stroke care.
By Kalra L, Evans A, Perez I, Knapp M, Swift C, Donaldson N.
-
The investigation and analysis of critical incidents and adverse events in healthcare.
By Woloshynowych M, Rogers S, Taylor-Adams S, Vincent C.
-
Potential use of routine databases in health technology assessment.
By Raftery J, Roderick P, Stevens A.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of newer immunosuppressive regimens in renal transplantation: a systematic review and modelling study.
By Woodroffe R, Yao GL, Meads C, Bayliss S, Ready A, Raftery J, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene and teriparatide for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
By Stevenson M, Lloyd Jones M, De Nigris E, Brewer N, Davis S, Oakley J.
-
A systematic review to examine the impact of psycho-educational interventions on health outcomes and costs in adults and children with difficult asthma.
By Smith JR, Mugford M, Holland R, Candy B, Noble MJ, Harrison BDW, et al.
-
An evaluation of the costs, effectiveness and quality of renal replacement therapy provision in renal satellite units in England and Wales.
By Roderick P, Nicholson T, Armitage A, Mehta R, Mullee M, Gerard K, et al.
-
Imatinib for the treatment of patients with unresectable and/or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumours: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wilson J, Connock M, Song F, Yao G, Fry-Smith A, Raftery J, et al.
-
Indirect comparisons of competing interventions.
By Glenny AM, Altman DG, Song F, Sakarovitch C, Deeks JJ, D’Amico R, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of alternative strategies for the initial medical management of non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome: systematic review and decision-analytical modelling.
By Robinson M, Palmer S, Sculpher M, Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Bowens A, et al.
-
Outcomes of electrically stimulated gracilis neosphincter surgery.
By Tillin T, Chambers M, Feldman R.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pimecrolimus and tacrolimus for atopic eczema: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Stein K, Castelnuovo E, Pitt M, Ashcroft D, Dimmock P, et al.
-
Systematic review on urine albumin testing for early detection of diabetic complications.
By Newman DJ, Mattock MB, Dawnay ABS, Kerry S, McGuire A, Yaqoob M, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trial of the cost-effectiveness of water-based therapy for lower limb osteoarthritis.
By Cochrane T, Davey RC, Matthes Edwards SM.
-
Longer term clinical and economic benefits of offering acupuncture care to patients with chronic low back pain.
By Thomas KJ, MacPherson H, Ratcliffe J, Thorpe L, Brazier J, Campbell M, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness and safety of epidural steroids in the management of sciatica.
By Price C, Arden N, Coglan L, Rogers P.
-
The British Rheumatoid Outcome Study Group (BROSG) randomised controlled trial to compare the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of aggressive versus symptomatic therapy in established rheumatoid arthritis.
By Symmons D, Tricker K, Roberts C, Davies L, Dawes P, Scott DL.
-
Conceptual framework and systematic review of the effects of participants’ and professionals’ preferences in randomised controlled trials.
By King M, Nazareth I, Lampe F, Bower P, Chandler M, Morou M, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of implantable cardioverter defibrillators: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Brodin H, Loveman E, Payne E, Clegg A.
-
A trial of problem-solving by community mental health nurses for anxiety, depression and life difficulties among general practice patients. The CPN-GP study.
By Kendrick T, Simons L, Mynors-Wallis L, Gray A, Lathlean J, Pickering R, et al.
-
The causes and effects of socio-demographic exclusions from clinical trials.
By Bartlett C, Doyal L, Ebrahim S, Davey P, Bachmann M, Egger M, et al.
-
Is hydrotherapy cost-effective? A randomised controlled trial of combined hydrotherapy programmes compared with physiotherapy land techniques in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
By Epps H, Ginnelly L, Utley M, Southwood T, Gallivan S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial and cost-effectiveness study of systematic screening (targeted and total population screening) versus routine practice for the detection of atrial fibrillation in people aged 65 and over. The SAFE study.
By Hobbs FDR, Fitzmaurice DA, Mant J, Murray E, Jowett S, Bryan S, et al.
-
Displaced intracapsular hip fractures in fit, older people: a randomised comparison of reduction and fixation, bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty.
By Keating JF, Grant A, Masson M, Scott NW, Forbes JF.
-
Long-term outcome of cognitive behaviour therapy clinical trials in central Scotland.
By Durham RC, Chambers JA, Power KG, Sharp DM, Macdonald RR, Major KA, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of dual-chamber pacemakers compared with single-chamber pacemakers for bradycardia due to atrioventricular block or sick sinus syndrome: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Castelnuovo E, Stein K, Pitt M, Garside R, Payne E.
-
Newborn screening for congenital heart defects: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Knowles R, Griebsch I, Dezateux C, Brown J, Bull C, Wren C.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of left ventricular assist devices for end-stage heart failure: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clegg AJ, Scott DA, Loveman E, Colquitt J, Hutchinson J, Royle P, et al.
-
The effectiveness of the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph and laser diagnostic glaucoma scanning system (GDx) in detecting and monitoring glaucoma.
By Kwartz AJ, Henson DB, Harper RA, Spencer AF, McLeod D.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of autologous chondrocyte implantation for cartilage defects in knee joints: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clar C, Cummins E, McIntyre L, Thomas S, Lamb J, Bain L, et al.
-
Systematic review of effectiveness of different treatments for childhood retinoblastoma.
By McDaid C, Hartley S, Bagnall A-M, Ritchie G, Light K, Riemsma R.
-
Towards evidence-based guidelines for the prevention of venous thromboembolism: systematic reviews of mechanical methods, oral anticoagulation, dextran and regional anaesthesia as thromboprophylaxis.
By Roderick P, Ferris G, Wilson K, Halls H, Jackson D, Collins R, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of parent training/education programmes for the treatment of conduct disorder, including oppositional defiant disorder, in children.
By Dretzke J, Frew E, Davenport C, Barlow J, Stewart-Brown S, Sandercock J, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine and memantine for Alzheimer’s disease.
By Loveman E, Green C, Kirby J, Takeda A, Picot J, Payne E, et al.
-
FOOD: a multicentre randomised trial evaluating feeding policies in patients admitted to hospital with a recent stroke.
By Dennis M, Lewis S, Cranswick G, Forbes J.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computed tomography screening for lung cancer: systematic reviews.
By Black C, Bagust A, Boland A, Walker S, McLeod C, De Verteuil R, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of neuroimaging assessments used to visualise the seizure focus in people with refractory epilepsy being considered for surgery.
By Whiting P, Gupta R, Burch J, Mujica Mota RE, Wright K, Marson A, et al.
-
Comparison of conference abstracts and presentations with full-text articles in the health technology assessments of rapidly evolving technologies.
By Dundar Y, Dodd S, Dickson R, Walley T, Haycox A, Williamson PR.
-
Systematic review and evaluation of methods of assessing urinary incontinence.
By Martin JL, Williams KS, Abrams KR, Turner DA, Sutton AJ, Chapple C, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for children with epilepsy. A systematic review.
By Connock M, Frew E, Evans B-W, Bryan S, Cummins C, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Surveillance of Barrett’s oesophagus: exploring the uncertainty through systematic review, expert workshop and economic modelling.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Somerville M, Stein K, Price A, Gilbert N.
-
Topotecan, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride and paclitaxel for second-line or subsequent treatment of advanced ovarian cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Main C, Bojke L, Griffin S, Norman G, Barbieri M, Mather L, et al.
-
Evaluation of molecular techniques in prediction and diagnosis of cytomegalovirus disease in immunocompromised patients.
By Szczepura A, Westmoreland D, Vinogradova Y, Fox J, Clark M.
-
Screening for thrombophilia in high-risk situations: systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. The Thrombosis: Risk and Economic Assessment of Thrombophilia Screening (TREATS) study.
By Wu O, Robertson L, Twaddle S, Lowe GDO, Clark P, Greaves M, et al.
-
A series of systematic reviews to inform a decision analysis for sampling and treating infected diabetic foot ulcers.
By Nelson EA, O’Meara S, Craig D, Iglesias C, Golder S, Dalton J, et al.
-
Randomised clinical trial, observational study and assessment of cost-effectiveness of the treatment of varicose veins (REACTIV trial).
By Michaels JA, Campbell WB, Brazier JE, MacIntyre JB, Palfreyman SJ, Ratcliffe J, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of screening for oral cancer in primary care.
By Speight PM, Palmer S, Moles DR, Downer MC, Smith DH, Henriksson M, et al.
-
Measurement of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of non-invasive diagnostic testing strategies for deep vein thrombosis.
By Goodacre S, Sampson F, Stevenson M, Wailoo A, Sutton A, Thomas S, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of HealOzone® for the treatment of occlusal pit/fissure caries and root caries.
By Brazzelli M, McKenzie L, Fielding S, Fraser C, Clarkson J, Kilonzo M, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trials of conventional antipsychotic versus new atypical drugs, and new atypical drugs versus clozapine, in people with schizophrenia responding poorly to, or intolerant of, current drug treatment.
By Lewis SW, Davies L, Jones PB, Barnes TRE, Murray RM, Kerwin R, et al.
-
Diagnostic tests and algorithms used in the investigation of haematuria: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.
By Rodgers M, Nixon J, Hempel S, Aho T, Kelly J, Neal D, et al.
-
Cognitive behavioural therapy in addition to antispasmodic therapy for irritable bowel syndrome in primary care: randomised controlled trial.
By Kennedy TM, Chalder T, McCrone P, Darnley S, Knapp M, Jones RH, et al.
-
A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapies for Fabry’s disease and mucopolysaccharidosis type 1.
By Connock M, Juarez-Garcia A, Frew E, Mans A, Dretzke J, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Health benefits of antiviral therapy for mild chronic hepatitis C: randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation.
By Wright M, Grieve R, Roberts J, Main J, Thomas HC, on behalf of the UK Mild Hepatitis C Trial Investigators.
-
Pressure relieving support surfaces: a randomised evaluation.
By Nixon J, Nelson EA, Cranny G, Iglesias CP, Hawkins K, Cullum NA, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of methylphenidate, dexamfetamine and atomoxetine for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents.
By King S, Griffin S, Hodges Z, Weatherly H, Asseburg C, Richardson G, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy for Gaucher’s disease: a systematic review.
By Connock M, Burls A, Frew E, Fry-Smith A, Juarez-Garcia A, McCabe C, et al.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of salicylic acid and cryotherapy for cutaneous warts. An economic decision model.
By Thomas KS, Keogh-Brown MR, Chalmers JR, Fordham RJ, Holland RC, Armstrong SJ, et al.
-
A systematic literature review of the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions to prevent wandering in dementia and evaluation of the ethical implications and acceptability of their use.
By Robinson L, Hutchings D, Corner L, Beyer F, Dickinson H, Vanoli A, et al.
-
A review of the evidence on the effects and costs of implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in different patient groups, and modelling of cost-effectiveness and cost–utility for these groups in a UK context.
By Buxton M, Caine N, Chase D, Connelly D, Grace A, Jackson C, et al.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Takeda A, Davidson P, Price A.
-
An evaluation of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of pulmonary artery catheters in patient management in intensive care: a systematic review and a randomised controlled trial.
By Harvey S, Stevens K, Harrison D, Young D, Brampton W, McCabe C, et al.
-
Accurate, practical and cost-effective assessment of carotid stenosis in the UK.
By Wardlaw JM, Chappell FM, Stevenson M, De Nigris E, Thomas S, Gillard J, et al.
-
Etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Woolacott N, Bravo Vergel Y, Hawkins N, Kainth A, Khadjesari Z, Misso K, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of testing for hepatitis C in former injecting drug users.
By Castelnuovo E, Thompson-Coon J, Pitt M, Cramp M, Siebert U, Price A, et al.
-
Computerised cognitive behaviour therapy for depression and anxiety update: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Kaltenthaler E, Brazier J, De Nigris E, Tumur I, Ferriter M, Beverley C, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.
By Williams C, Brunskill S, Altman D, Briggs A, Campbell H, Clarke M, et al.
-
Psychological therapies including dialectical behaviour therapy for borderline personality disorder: a systematic review and preliminary economic evaluation.
By Brazier J, Tumur I, Holmes M, Ferriter M, Parry G, Dent-Brown K, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of tests for the diagnosis and investigation of urinary tract infection in children: a systematic review and economic model.
By Whiting P, Westwood M, Bojke L, Palmer S, Richardson G, Cooper J, et al.
-
Cognitive behavioural therapy in chronic fatigue syndrome: a randomised controlled trial of an outpatient group programme.
By O’Dowd H, Gladwell P, Rogers CA, Hollinghurst S, Gregory A.
-
A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling.
By Brown TJ, Hooper L, Elliott RA, Payne K, Webb R, Roberts C, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computed tomography screening for coronary artery disease: systematic review.
By Waugh N, Black C, Walker S, McIntyre L, Cummins E, Hillis G.
-
What are the clinical outcome and cost-effectiveness of endoscopy undertaken by nurses when compared with doctors? A Multi-Institution Nurse Endoscopy Trial (MINuET).
By Williams J, Russell I, Durai D, Cheung W-Y, Farrin A, Bloor K, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of oxaliplatin and capecitabine for the adjuvant treatment of colon cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Pandor A, Eggington S, Paisley S, Tappenden P, Sutcliffe P.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness.
By Chen Y-F, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Jowett S, Bryan S, Clark W, et al.
-
Telemedicine in dermatology: a randomised controlled trial.
By Bowns IR, Collins K, Walters SJ, McDonagh AJG.
-
Cost-effectiveness of cell salvage and alternative methods of minimising perioperative allogeneic blood transfusion: a systematic review and economic model.
By Davies L, Brown TJ, Haynes S, Payne K, Elliott RA, McCollum C.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancer: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.
By Murray A, Lourenco T, de Verteuil R, Hernandez R, Fraser C, McKinley A, et al.
-
Etanercept and efalizumab for the treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review.
By Woolacott N, Hawkins N, Mason A, Kainth A, Khadjesari Z, Bravo Vergel Y, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of clinical decision tools for acute abdominal pain.
By Liu JLY, Wyatt JC, Deeks JJ, Clamp S, Keen J, Verde P, et al.
-
Evaluation of the ventricular assist device programme in the UK.
By Sharples L, Buxton M, Caine N, Cafferty F, Demiris N, Dyer M, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of immunosuppressive therapy for renal transplantation in children.
By Yao G, Albon E, Adi Y, Milford D, Bayliss S, Ready A, et al.
-
Amniocentesis results: investigation of anxiety. The ARIA trial.
By Hewison J, Nixon J, Fountain J, Cocks K, Jones C, Mason G, et al.
-
Pemetrexed disodium for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Dundar Y, Bagust A, Dickson R, Dodd S, Green J, Haycox A, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of docetaxel in combination with prednisone or prednisolone for the treatment of hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer.
By Collins R, Fenwick E, Trowman R, Perard R, Norman G, Light K, et al.
-
A systematic review of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of tuberculosis infection.
By Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kunst H, Gibson A, Cummins E, Waugh N, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women.
By Stevenson M, Davis S, Lloyd-Jones M, Beverley C.
-
A systematic review of quantitative and qualitative research on the role and effectiveness of written information available to patients about individual medicines.
By Raynor DK, Blenkinsopp A, Knapp P, Grime J, Nicolson DJ, Pollock K, et al.
-
Oral naltrexone as a treatment for relapse prevention in formerly opioid-dependent drug users: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Adi Y, Juarez-Garcia A, Wang D, Jowett S, Frew E, Day E, et al.
-
Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: a systematic review and cost–utility analysis.
By Kanis JA, Stevenson M, McCloskey EV, Davis S, Lloyd-Jones M.
-
Epidemiological, social, diagnostic and economic evaluation of population screening for genital chlamydial infection.
By Low N, McCarthy A, Macleod J, Salisbury C, Campbell R, Roberts TE, et al.
-
Methadone and buprenorphine for the management of opioid dependence: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Connock M, Juarez-Garcia A, Jowett S, Frew E, Liu Z, Taylor RJ, et al.
-
Exercise Evaluation Randomised Trial (EXERT): a randomised trial comparing GP referral for leisure centre-based exercise, community-based walking and advice only.
By Isaacs AJ, Critchley JA, See Tai S, Buckingham K, Westley D, Harridge SDR, et al.
-
Interferon alfa (pegylated and non-pegylated) and ribavirin for the treatment of mild chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Hartwell D, Davidson P, Price A, Waugh N.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of bevacizumab and cetuximab for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.
By Tappenden P, Jones R, Paisley S, Carroll C.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of epoetin alfa, epoetin beta and darbepoetin alfa in anaemia associated with cancer, especially that attributable to cancer treatment.
By Wilson J, Yao GL, Raftery J, Bohlius J, Brunskill S, Sandercock J, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of statins for the prevention of coronary events.
By Ward S, Lloyd Jones M, Pandor A, Holmes M, Ara R, Ryan A, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of different models of community-based respite care for frail older people and their carers.
By Mason A, Weatherly H, Spilsbury K, Arksey H, Golder S, Adamson J, et al.
-
Additional therapy for young children with spastic cerebral palsy: a randomised controlled trial.
By Weindling AM, Cunningham CC, Glenn SM, Edwards RT, Reeves DJ.
-
Screening for type 2 diabetes: literature review and economic modelling.
By Waugh N, Scotland G, McNamee P, Gillett M, Brennan A, Goyder E, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cinacalcet for secondary hyperparathyroidism in end-stage renal disease patients on dialysis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Anderson R, Mealing S, Roome C, Snaith A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of gemcitabine for metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Takeda AL, Jones J, Loveman E, Tan SC, Clegg AJ.
-
A systematic review of duplex ultrasound, magnetic resonance angiography and computed tomography angiography for the diagnosis and assessment of symptomatic, lower limb peripheral arterial disease.
By Collins R, Cranny G, Burch J, Aguiar-Ibáñez R, Craig D, Wright K, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of treatments for children with idiopathic steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome: a systematic review.
By Colquitt JL, Kirby J, Green C, Cooper K, Trompeter RS.
-
A systematic review of the routine monitoring of growth in children of primary school age to identify growth-related conditions.
By Fayter D, Nixon J, Hartley S, Rithalia A, Butler G, Rudolf M, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness of preventing and treating Staphylococcus aureus carriage in reducing peritoneal catheter-related infections.
By McCormack K, Rabindranath K, Kilonzo M, Vale L, Fraser C, McIntyre L, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation versus electroconvulsive therapy in severe depression: a multicentre pragmatic randomised controlled trial and economic analysis.
By McLoughlin DM, Mogg A, Eranti S, Pluck G, Purvis R, Edwards D, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of direct versus indirect and individual versus group modes of speech and language therapy for children with primary language impairment.
By Boyle J, McCartney E, Forbes J, O’Hare A.
-
Hormonal therapies for early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hind D, Ward S, De Nigris E, Simpson E, Carroll C, Wyld L.
-
Cardioprotection against the toxic effects of anthracyclines given to children with cancer: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Picot J, Levitt G, Sullivan I, Baxter L, Clegg A.
-
Adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By McLeod C, Bagust A, Boland A, Dagenais P, Dickson R, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Prenatal screening and treatment strategies to prevent group B streptococcal and other bacterial infections in early infancy: cost-effectiveness and expected value of information analyses.
By Colbourn T, Asseburg C, Bojke L, Philips Z, Claxton K, Ades AE, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bone morphogenetic proteins in the non-healing of fractures and spinal fusion: a systematic review.
By Garrison KR, Donell S, Ryder J, Shemilt I, Mugford M, Harvey I, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial of postoperative radiotherapy following breast-conserving surgery in a minimum-risk older population. The PRIME trial.
By Prescott RJ, Kunkler IH, Williams LJ, King CC, Jack W, van der Pol M, et al.
-
Current practice, accuracy, effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the school entry hearing screen.
By Bamford J, Fortnum H, Bristow K, Smith J, Vamvakas G, Davies L, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of inhaled insulin in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Black C, Cummins E, Royle P, Philip S, Waugh N.
-
Surveillance of cirrhosis for hepatocellular carcinoma: systematic review and economic analysis.
By Thompson Coon J, Rogers G, Hewson P, Wright D, Anderson R, Cramp M, et al.
-
The Birmingham Rehabilitation Uptake Maximisation Study (BRUM). Homebased compared with hospital-based cardiac rehabilitation in a multi-ethnic population: cost-effectiveness and patient adherence.
By Jolly K, Taylor R, Lip GYH, Greenfield S, Raftery J, Mant J, et al.
-
A systematic review of the clinical, public health and cost-effectiveness of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection and identification of bacterial intestinal pathogens in faeces and food.
By Abubakar I, Irvine L, Aldus CF, Wyatt GM, Fordham R, Schelenz S, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial examining the longer-term outcomes of standard versus new antiepileptic drugs. The SANAD trial.
By Marson AG, Appleton R, Baker GA, Chadwick DW, Doughty J, Eaton B, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of different models of managing long-term oral anti-coagulation therapy: a systematic review and economic modelling.
By Connock M, Stevens C, Fry-Smith A, Jowett S, Fitzmaurice D, Moore D, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of interventions for preventing relapse in people with bipolar disorder.
By Soares-Weiser K, Bravo Vergel Y, Beynon S, Dunn G, Barbieri M, Duffy S, et al.
-
Taxanes for the adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ward S, Simpson E, Davis S, Hind D, Rees A, Wilkinson A.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening for open angle glaucoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burr JM, Mowatt G, Hernández R, Siddiqui MAR, Cook J, Lourenco T, et al.
-
Acceptability, benefit and costs of early screening for hearing disability: a study of potential screening tests and models.
By Davis A, Smith P, Ferguson M, Stephens D, Gianopoulos I.
-
Contamination in trials of educational interventions.
By Keogh-Brown MR, Bachmann MO, Shepstone L, Hewitt C, Howe A, Ramsay CR, et al.
-
Overview of the clinical effectiveness of positron emission tomography imaging in selected cancers.
By Facey K, Bradbury I, Laking G, Payne E.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Anderson R, Rogers G, Dyer M, Mealing S, et al.
-
Drug-eluting stents: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hill RA, Boland A, Dickson R, Dündar Y, Haycox A, McLeod C, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cardiac resynchronisation (biventricular pacing) for heart failure: systematic review and economic model.
By Fox M, Mealing S, Anderson R, Dean J, Stein K, Price A, et al.
-
Recruitment to randomised trials: strategies for trial enrolment and participation study. The STEPS study.
By Campbell MK, Snowdon C, Francis D, Elbourne D, McDonald AM, Knight R, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of functional cardiac testing in the diagnosis and management of coronary artery disease: a randomised controlled trial. The CECaT trial.
By Sharples L, Hughes V, Crean A, Dyer M, Buxton M, Goldsmith K, et al.
-
Evaluation of diagnostic tests when there is no gold standard. A review of methods.
By Rutjes AWS, Reitsma JB, Coomarasamy A, Khan KS, Bossuyt PMM.
-
Systematic reviews of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors in acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
By Leontiadis GI, Sreedharan A, Dorward S, Barton P, Delaney B, Howden CW, et al.
-
A review and critique of modelling in prioritising and designing screening programmes.
By Karnon J, Goyder E, Tappenden P, McPhie S, Towers I, Brazier J, et al.
-
An assessment of the impact of the NHS Health Technology Assessment Programme.
By Hanney S, Buxton M, Green C, Coulson D, Raftery J.
-
A systematic review and economic model of switching from nonglycopeptide to glycopeptide antibiotic prophylaxis for surgery.
By Cranny G, Elliott R, Weatherly H, Chambers D, Hawkins N, Myers L, et al.
-
‘Cut down to quit’ with nicotine replacement therapies in smoking cessation: a systematic review of effectiveness and economic analysis.
By Wang D, Connock M, Barton P, Fry-Smith A, Aveyard P, Moore D.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of strategies for reducing fracture risk in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis with additional data on long-term risk of fracture and cost of disease management.
By Thornton J, Ashcroft D, O’Neill T, Elliott R, Adams J, Roberts C, et al.
-
Does befriending by trained lay workers improve psychological well-being and quality of life for carers of people with dementia, and at what cost? A randomised controlled trial.
By Charlesworth G, Shepstone L, Wilson E, Thalanany M, Mugford M, Poland F.
-
A multi-centre retrospective cohort study comparing the efficacy, safety and cost-effectiveness of hysterectomy and uterine artery embolisation for the treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroids. The HOPEFUL study.
By Hirst A, Dutton S, Wu O, Briggs A, Edwards C, Waldenmaier L, et al.
-
Methods of prediction and prevention of pre-eclampsia: systematic reviews of accuracy and effectiveness literature with economic modelling.
By Meads CA, Cnossen JS, Meher S, Juarez-Garcia A, ter Riet G, Duley L, et al.
-
The use of economic evaluations in NHS decision-making: a review and empirical investigation.
By Williams I, McIver S, Moore D, Bryan S.
-
Stapled haemorrhoidectomy (haemorrhoidopexy) for the treatment of haemorrhoids: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burch J, Epstein D, Baba-Akbari A, Weatherly H, Fox D, Golder S, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness of diabetes education models for Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.
By Loveman E, Frampton GK, Clegg AJ.
-
Payment to healthcare professionals for patient recruitment to trials: systematic review and qualitative study.
By Raftery J, Bryant J, Powell J, Kerr C, Hawker S.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (etodolac, meloxicam, celecoxib, rofecoxib, etoricoxib, valdecoxib and lumiracoxib) for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Chen Y-F, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Fry-Smith A, Harris G, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of central venous catheters treated with anti-infective agents in preventing bloodstream infections: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hockenhull JC, Dwan K, Boland A, Smith G, Bagust A, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Stepped treatment of older adults on laxatives. The STOOL trial.
By Mihaylov S, Stark C, McColl E, Steen N, Vanoli A, Rubin G, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial of cognitive behaviour therapy in adolescents with major depression treated by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. The ADAPT trial.
By Goodyer IM, Dubicka B, Wilkinson P, Kelvin R, Roberts C, Byford S, et al.
-
The use of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hind D, Tappenden P, Tumur I, Eggington E, Sutcliffe P, Ryan A.
-
Ranibizumab and pegaptanib for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Colquitt JL, Jones J, Tan SC, Takeda A, Clegg AJ, Price A.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of 64-slice or higher computed tomography angiography as an alternative to invasive coronary angiography in the investigation of coronary artery disease.
By Mowatt G, Cummins E, Waugh N, Walker S, Cook J, Jia X, et al.
-
Structural neuroimaging in psychosis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Albon E, Tsourapas A, Frew E, Davenport C, Oyebode F, Bayliss S, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children aged 12 years and over.
By Shepherd J, Rogers G, Anderson R, Main C, Thompson-Coon J, Hartwell D, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years.
By Main C, Shepherd J, Anderson R, Rogers G, Thompson-Coon J, Liu Z, et al.
-
Ezetimibe for the treatment of hypercholesterolaemia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ara R, Tumur I, Pandor A, Duenas A, Williams R, Wilkinson A, et al.
-
Topical or oral ibuprofen for chronic knee pain in older people. The TOIB study.
By Underwood M, Ashby D, Carnes D, Castelnuovo E, Cross P, Harding G, et al.
-
A prospective randomised comparison of minor surgery in primary and secondary care. The MiSTIC trial.
By George S, Pockney P, Primrose J, Smith H, Little P, Kinley H, et al.
-
A review and critical appraisal of measures of therapist–patient interactions in mental health settings.
By Cahill J, Barkham M, Hardy G, Gilbody S, Richards D, Bower P, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening programmes for amblyopia and strabismus in children up to the age of 4–5 years: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Carlton J, Karnon J, Czoski-Murray C, Smith KJ, Marr J.
-
A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness and economic modelling of minimal incision total hip replacement approaches in the management of arthritic disease of the hip.
By de Verteuil R, Imamura M, Zhu S, Glazener C, Fraser C, Munro N, et al.
-
A preliminary model-based assessment of the cost–utility of a screening programme for early age-related macular degeneration.
By Karnon J, Czoski-Murray C, Smith K, Brand C, Chakravarthy U, Davis S, et al.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Frampton GK, Tanajewski L, Turner D, Price A.
-
Absorbent products for urinary/faecal incontinence: a comparative evaluation of key product categories.
By Fader M, Cottenden A, Getliffe K, Gage H, Clarke-O’Neill S, Jamieson K, et al.
-
A systematic review of repetitive functional task practice with modelling of resource use, costs and effectiveness.
By French B, Leathley M, Sutton C, McAdam J, Thomas L, Forster A, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectivness of minimal access surgery amongst people with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease – a UK collaborative study. The reflux trial.
By Grant A, Wileman S, Ramsay C, Bojke L, Epstein D, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Time to full publication of studies of anti-cancer medicines for breast cancer and the potential for publication bias: a short systematic review.
By Takeda A, Loveman E, Harris P, Hartwell D, Welch K.
-
Performance of screening tests for child physical abuse in accident and emergency departments.
By Woodman J, Pitt M, Wentz R, Taylor B, Hodes D, Gilbert RE.
-
Curative catheter ablation in atrial fibrillation and typical atrial flutter: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Rodgers M, McKenna C, Palmer S, Chambers D, Van Hout S, Golder S, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic modelling of effectiveness and cost utility of surgical treatments for men with benign prostatic enlargement.
By Lourenco T, Armstrong N, N’Dow J, Nabi G, Deverill M, Pickard R, et al.
-
Immunoprophylaxis against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) with palivizumab in children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wang D, Cummins C, Bayliss S, Sandercock J, Burls A.
-
Deferasirox for the treatment of iron overload associated with regular blood transfusions (transfusional haemosiderosis) in patients suffering with chronic anaemia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By McLeod C, Fleeman N, Kirkham J, Bagust A, Boland A, Chu P, et al.
-
Thrombophilia testing in people with venous thromboembolism: systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Simpson EL, Stevenson MD, Rawdin A, Papaioannou D.
-
Surgical procedures and non-surgical devices for the management of non-apnoeic snoring: a systematic review of clinical effects and associated treatment costs.
By Main C, Liu Z, Welch K, Weiner G, Quentin Jones S, Stein K.
-
Continuous positive airway pressure devices for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea–hypopnoea syndrome: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By McDaid C, Griffin S, Weatherly H, Durée K, van der Burgt M, van Hout S, Akers J, et al.
-
Use of classical and novel biomarkers as prognostic risk factors for localised prostate cancer: a systematic review.
By Sutcliffe P, Hummel S, Simpson E, Young T, Rees A, Wilkinson A, et al.
-
The harmful health effects of recreational ecstasy: a systematic review of observational evidence.
By Rogers G, Elston J, Garside R, Roome C, Taylor R, Younger P, et al.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of oesophageal Doppler monitoring in critically ill and high-risk surgical patients.
By Mowatt G, Houston G, Hernández R, de Verteuil R, Fraser C, Cuthbertson B, et al.
-
The use of surrogate outcomes in model-based cost-effectiveness analyses: a survey of UK Health Technology Assessment reports.
By Taylor RS, Elston J.
-
Controlling Hypertension and Hypotension Immediately Post Stroke (CHHIPS) – a randomised controlled trial.
By Potter J, Mistri A, Brodie F, Chernova J, Wilson E, Jagger C, et al.
Health Technology Assessment Programme
-
Director, NIHR HTA Programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
Prioritisation Strategy Group
-
Director, NIHR HTA Programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
-
Dr Bob Coates, Consultant Advisor, NCCHTA
-
Dr Andrew Cook, Consultant Advisor, NCCHTA
-
Dr Peter Davidson, Director of Science Support, NCCHTA
-
Professor Robin E Ferner, Consultant Physician and Director, West Midlands Centre for Adverse Drug Reactions, City Hospital NHS Trust, Birmingham
-
Professor Paul Glasziou, Professor of Evidence-Based Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Dr Nick Hicks, Director of NHS Support, NCCHTA
-
Dr Edmund Jessop, Medical Adviser, National Specialist, National Commissioning Group (NCG), Department of Health, London
-
Ms Lynn Kerridge, Chief Executive Officer, NETSCC and NCCHTA
-
Dr Ruairidh Milne, Director of Strategy and Development, NETSCC
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Ms Pamela Young, Specialist Programme Manager, NCCHTA
HTA Commissioning Board
-
Director, NIHR HTA Programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
-
Senior Lecturer in General Practice, Department of Primary Health Care, University of Oxford
-
Professor Ann Ashburn, Professor of Rehabilitation and Head of Research, Southampton General Hospital
-
Professor Deborah Ashby, Professor of Medical Statistics, Queen Mary, University of London
-
Professor John Cairns, Professor of Health Economics, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Peter Croft, Director of Primary Care Sciences Research Centre, Keele University
-
Professor Nicky Cullum, Director of Centre for Evidence-Based Nursing, University of York
-
Professor Jenny Donovan, Professor of Social Medicine, University of Bristol
-
Professor Steve Halligan, Professor of Gastrointestinal Radiology, University College Hospital, London
-
Professor Freddie Hamdy, Professor of Urology, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Allan House, Professor of Liaison Psychiatry, University of Leeds
-
Dr Martin J Landray, Reader in Epidemiology, Honorary Consultant Physician, Clinical Trial Service Unit, University of Oxford?
-
Professor Stuart Logan, Director of Health & Social Care Research, The Peninsula Medical School, Universities of Exeter and Plymouth
-
Dr Rafael Perera, Lecturer in Medical Statisitics, Department of Primary Health Care, Univeristy of Oxford
-
Professor Ian Roberts, Professor of Epidemiology & Public Health, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Mark Sculpher, Professor of Health Economics, University of York
-
Professor Helen Smith, Professor of Primary Care, University of Brighton
-
Professor Kate Thomas, Professor of Complementary & Alternative Medicine Research, University of Leeds
-
Professor David John Torgerson, Director of York Trials Unit, University of York
-
Professor Hywel Williams, Professor of Dermato-Epidemiology, University of Nottingham
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programmes, Research and Development Directorate, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Medical Research Council
Diagnostic Technologies & Screening Panel
-
Professor of Evidence-Based Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Consultant Paediatrician and Honorary Senior Lecturer, Great Ormond Street Hospital, London
-
Professor Judith E Adams, Consultant Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Central Manchester & Manchester Children’s University Hospitals NHS Trust, and Professor of Diagnostic Radiology, Imaging Science and Biomedical Engineering, Cancer & Imaging Sciences, University of Manchester
-
Ms Jane Bates, Consultant Ultrasound Practitioner, Ultrasound Department, Leeds Teaching Hospital NHS Trust
-
Dr Stephanie Dancer, Consultant Microbiologist, Hairmyres Hospital, East Kilbride
-
Professor Glyn Elwyn, Primary Medical Care Research Group, Swansea Clinical School, University of Wales
-
Dr Ron Gray, Consultant Clinical Epidemiologist, Department of Public Health, University of Oxford
-
Professor Paul D Griffiths, Professor of Radiology, University of Sheffield
-
Dr Jennifer J Kurinczuk, Consultant Clinical Epidemiologist, National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, Oxford
-
Dr Susanne M Ludgate, Medical Director, Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency, London
-
Dr Anne Mackie, Director of Programmes, UK National Screening Committee
-
Dr Michael Millar, Consultant Senior Lecturer in Microbiology, Barts and The London NHS Trust, Royal London Hospital
-
Mr Stephen Pilling, Director, Centre for Outcomes, Research & Effectiveness, Joint Director, National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health, University College London
-
Mrs Una Rennard, Service User Representative
-
Dr Phil Shackley, Senior Lecturer in Health Economics, School of Population and Health Sciences, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Dr W Stuart A Smellie, Consultant in Chemical Pathology, Bishop Auckland General Hospital
-
Dr Nicholas Summerton, Consultant Clinical and Public Health Advisor, NICE
-
Ms Dawn Talbot, Service User Representative
-
Dr Graham Taylor, Scientific Advisor, Regional DNA Laboratory, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Professor Lindsay Wilson Turnbull, Scientific Director of the Centre for Magnetic Resonance Investigations and YCR Professor of Radiology, Hull Royal Infirmary
-
Dr Tim Elliott, Team Leader, Cancer Screening, Department of Health
-
Dr Catherine Moody, Programme Manager, Neuroscience and Mental Health Board
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Pharmaceuticals Panel
-
Consultant Physician and Director, West Midlands Centre for Adverse Drug Reactions, City Hospital NHS Trust, Birmingham
-
Professor in Child Health, University of Nottingham
-
Mrs Nicola Carey, Senior Research Fellow, School of Health and Social Care, The University of Reading
-
Mr John Chapman, Service User Representative
-
Dr Peter Elton, Director of Public Health, Bury Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Ben Goldacre, Research Fellow, Division of Psychological Medicine and Psychiatry, King’s College London
-
Mrs Barbara Greggains, Service User Representative
-
Dr Bill Gutteridge, Medical Adviser, London Strategic Health Authority
-
Dr Dyfrig Hughes, Reader in Pharmacoeconomics and Deputy Director, Centre for Economics and Policy in Health, IMSCaR, Bangor University
-
Professor Jonathan Ledermann, Professor of Medical Oncology and Director of the Cancer Research UK and University College London Cancer Trials Centre
-
Dr Yoon K Loke, Senior Lecturer in Clinical Pharmacology, University of East Anglia
-
Professor Femi Oyebode, Consultant Psychiatrist and Head of Department, University of Birmingham
-
Dr Andrew Prentice, Senior Lecturer and Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, The Rosie Hospital, University of Cambridge
-
Dr Martin Shelly, General Practitioner, Leeds, and Associate Director, NHS Clinical Governance Support Team, Leicester
-
Dr Gillian Shepherd, Director, Health and Clinical Excellence, Merck Serono Ltd
-
Mrs Katrina Simister, Assistant Director New Medicines, National Prescribing Centre, Liverpool
-
Mr David Symes, Service User Representative
-
Dr Lesley Wise, Unit Manager, Pharmacoepidemiology Research Unit, VRMM, Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Mr Simon Reeve, Head of Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness, Medicines, Pharmacy and Industry Group, Department of Health
-
Dr Heike Weber, Programme Manager, Medical Research Council
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Therapeutic Procedures Panel
-
Consultant Physician, North Bristol NHS Trust
-
Professor of Psychiatry, Division of Health in the Community, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Professor Jane Barlow, Professor of Public Health in the Early Years, Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, Coventry
-
Ms Maree Barnett, Acting Branch Head of Vascular Programme, Department of Health
-
Mrs Val Carlill, Service User Representative
-
Mrs Anthea De Barton-Watson, Service User Representative
-
Mr Mark Emberton, Senior Lecturer in Oncological Urology, Institute of Urology, University College Hospital, London
-
Professor Steve Goodacre, Professor of Emergency Medicine, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Christopher Griffiths, Professor of Primary Care, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Mr Paul Hilton, Consultant Gynaecologist and Urogynaecologist, Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Nicholas James, Professor of Clinical Oncology, University of Birmingham, and Consultant in Clinical Oncology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital
-
Dr Peter Martin, Consultant Neurologist, Addenbrooke’s Hospital, Cambridge
-
Dr Kate Radford, Senior Lecturer (Research), Clinical Practice Research Unit, University of Central Lancashire, Preston
-
Mr Jim Reece Service User Representative
-
Dr Karen Roberts, Nurse Consultant, Dunston Hill Hospital Cottages
-
Dr Phillip Leech, Principal Medical Officer for Primary Care, Department of Health
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Medical Research Council
-
Professor Tom Walley, Director, NIHR HTA Programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Disease Prevention Panel
-
Medical Adviser, National Specialist, National Commissioning Group (NCG), London
-
Director, NHS Sustainable Development Unit, Cambridge
-
Dr Elizabeth Fellow-Smith, Medical Director, West London Mental Health Trust, Middlesex
-
Dr John Jackson, General Practitioner, Parkway Medical Centre, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Mike Kelly, Director, Centre for Public Health Excellence, NICE, London
-
Dr Chris McCall, General Practitioner, The Hadleigh Practice, Corfe Mullen, Dorset
-
Ms Jeanett Martin, Director of Nursing, BarnDoc Limited, Lewisham Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Julie Mytton, Locum Consultant in Public Health Medicine, Bristol Primary Care Trust
-
Miss Nicky Mullany, Service User Representative
-
Professor Ian Roberts, Professor of Epidemiology and Public Health, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Ken Stein, Senior Clinical Lecturer in Public Health, University of Exeter
-
Dr Kieran Sweeney, Honorary Clinical Senior Lecturer, Peninsula College of Medicine and Dentistry, Universities of Exeter and Plymouth
-
Professor Carol Tannahill, Glasgow Centre for Population Health
-
Professor Margaret Thorogood, Professor of Epidemiology, University of Warwick Medical School, Coventry
-
Ms Christine McGuire, Research & Development, Department of Health
-
Dr Caroline Stone, Programme Manager, Medical Research Council
Expert Advisory Network
-
Professor Douglas Altman, Professor of Statistics in Medicine, Centre for Statistics in Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Professor John Bond, Professor of Social Gerontology & Health Services Research, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Andrew Bradbury, Professor of Vascular Surgery, Solihull Hospital, Birmingham
-
Mr Shaun Brogan, Chief Executive, Ridgeway Primary Care Group, Aylesbury
-
Mrs Stella Burnside OBE, Chief Executive, Regulation and Improvement Authority, Belfast
-
Ms Tracy Bury, Project Manager, World Confederation for Physical Therapy, London
-
Professor Iain T Cameron, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology and Head of the School of Medicine, University of Southampton
-
Dr Christine Clark, Medical Writer and Consultant Pharmacist, Rossendale
-
Professor Collette Clifford, Professor of Nursing and Head of Research, The Medical School, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Barry Cookson, Director, Laboratory of Hospital Infection, Public Health Laboratory Service, London
-
Dr Carl Counsell, Clinical Senior Lecturer in Neurology, University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Howard Cuckle, Professor of Reproductive Epidemiology, Department of Paediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynaecology, University of Leeds
-
Dr Katherine Darton, Information Unit, MIND – The Mental Health Charity, London
-
Professor Carol Dezateux, Professor of Paediatric Epidemiology, Institute of Child Health, London
-
Mr John Dunning, Consultant Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Papworth Hospital NHS Trust, Cambridge
-
Mr Jonothan Earnshaw, Consultant Vascular Surgeon, Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Gloucester
-
Professor Martin Eccles, Professor of Clinical Effectiveness, Centre for Health Services Research, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Pam Enderby, Dean of Faculty of Medicine, Institute of General Practice and Primary Care, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Gene Feder, Professor of Primary Care Research & Development, Centre for Health Sciences, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Mr Leonard R Fenwick, Chief Executive, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Mrs Gillian Fletcher, Antenatal Teacher and Tutor and President, National Childbirth Trust, Henfield
-
Professor Jayne Franklyn, Professor of Medicine, University of Birmingham
-
Mr Tam Fry, Honorary Chairman, Child Growth Foundation, London
-
Professor Fiona Gilbert, Consultant Radiologist and NCRN Member, University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Paul Gregg, Professor of Orthopaedic Surgical Science, South Tees Hospital NHS Trust
-
Bec Hanley, Co-director, TwoCan Associates, West Sussex
-
Dr Maryann L Hardy, Senior Lecturer, University of Bradford
-
Mrs Sharon Hart, Healthcare Management Consultant, Reading
-
Professor Robert E Hawkins, CRC Professor and Director of Medical Oncology, Christie CRC Research Centre, Christie Hospital NHS Trust, Manchester
-
Professor Richard Hobbs, Head of Department of Primary Care & General Practice, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Alan Horwich, Dean and Section Chairman, The Institute of Cancer Research, London
-
Professor Allen Hutchinson, Director of Public Health and Deputy Dean of ScHARR, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Peter Jones, Professor of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge
-
Professor Stan Kaye, Cancer Research UK Professor of Medical Oncology, Royal Marsden Hospital and Institute of Cancer Research, Surrey
-
Dr Duncan Keeley, General Practitioner (Dr Burch & Ptnrs), The Health Centre, Thame
-
Dr Donna Lamping, Research Degrees Programme Director and Reader in Psychology, Health Services Research Unit, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London
-
Mr George Levvy, Chief Executive, Motor Neurone Disease Association, Northampton
-
Professor James Lindesay, Professor of Psychiatry for the Elderly, University of Leicester
-
Professor Julian Little, Professor of Human Genome Epidemiology, University of Ottawa
-
Professor Alistaire McGuire, Professor of Health Economics, London School of Economics
-
Professor Rajan Madhok, Medical Director and Director of Public Health, Directorate of Clinical Strategy & Public Health, North & East Yorkshire & Northern Lincolnshire Health Authority, York
-
Professor Alexander Markham, Director, Molecular Medicine Unit, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Dr Peter Moore, Freelance Science Writer, Ashtead
-
Dr Andrew Mortimore, Public Health Director, Southampton City Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Sue Moss, Associate Director, Cancer Screening Evaluation Unit, Institute of Cancer Research, Sutton
-
Professor Miranda Mugford, Professor of Health Economics and Group Co-ordinator, University of East Anglia
-
Professor Jim Neilson, Head of School of Reproductive & Developmental Medicine and Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, University of Liverpool
-
Mrs Julietta Patnick, National Co-ordinator, NHS Cancer Screening Programmes, Sheffield
-
Professor Robert Peveler, Professor of Liaison Psychiatry, Royal South Hants Hospital, Southampton
-
Professor Chris Price, Director of Clinical Research, Bayer Diagnostics Europe, Stoke Poges
-
Professor William Rosenberg, Professor of Hepatology and Consultant Physician, University of Southampton
-
Professor Peter Sandercock, Professor of Medical Neurology, Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Edinburgh
-
Dr Susan Schonfield, Consultant in Public Health, Hillingdon Primary Care Trust, Middlesex
-
Dr Eamonn Sheridan, Consultant in Clinical Genetics, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Dr Margaret Somerville, Director of Public Health Learning, Peninsula Medical School, University of Plymouth
-
Professor Sarah Stewart-Brown, Professor of Public Health, Division of Health in the Community, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Professor Ala Szczepura, Professor of Health Service Research, Centre for Health Services Studies, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Mrs Joan Webster, Consumer Member, Southern Derbyshire Community Health Council
-
Professor Martin Whittle, Clinical Co-director, National Co-ordinating Centre for Women’s and Children’s Health, Lymington