Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was commissioned by the HTA programme as project number 05/03/01. The contractual start date was in October 2005. The draft report began editorial review in September 2006 and was accepted for publication in March 2008. As the funder, by devising a commissioning brief, the HTA programme specified the research question and study design. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the referees for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
None
Permissions
Copyright statement
© 2009 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO. This monograph may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NETSCC, Health Technology Assessment, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2009 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Background
Definition of preterm birth
Textbooks define preterm birth as any delivery of a viable pregnancy at less than 37 completed weeks of gestation (< 259 days), the lower limit of viability ex utero being generally accepted to be at 23 completed weeks. Births before 23 completed weeks of gestation are classified as either miscarriages or abortions. 1
Aetiology of preterm birth
Preterm birth is a heterogeneous condition; up to 30–40% of all cases of preterm birth are the result of elective delivery for a maternal or a fetal complication where it is judged that the baby is better delivered in the mother’s interest or that of its own, e.g. hypertension, diabetes, intrauterine growth restriction. 2 The remaining 60–70% of preterm births are probably the result of covert or subclinical infective/inflammatory processes, cervical dysfunction, idiopathic (unknown causes), multiple gestations and possible social, nutritional and environmental interactions. 3 This report focuses on this latter group of so-called ‘spontaneous’ preterm births.
Consequences of preterm birth
Preterm delivery, particularly that before 34 weeks’ gestation, accounts for three-quarters of neonatal mortality and one-half of long-term neurological impairment in children. 4–6 Many of the surviving infants also suffer from other serious short-term and long-term morbidity,5,7,8 such as respiratory distress syndrome, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, intraventricular haemorrhage, retrolental fibroplasia and developmental problems. Even those premature infants that are classified as developmentally ‘normal’ or as having ‘mild’ developmental problems, in the longer term have higher rates of multiple problems that affect their lives. 9 Although complications of prematurity are significantly reduced after 32–34 weeks’ gestation, minor morbidities, which often lengthen hospitalisation, remain for neonates born between 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation. 10–14
Clinical burden of preterm birth
Spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation occurs in 7–12% of pregnancies1,15,16 and it occurs in about 4% of pregnancies before 34 weeks’ gestation. 17 Advances in perinatal health care have not reduced the rate of spontaneous preterm birth. 16 Extrapolation from live births data in England and Wales (2004),18 shows that an estimated 76,000 and 26,000 spontaneous preterm births occur before 37 weeks’ and 34 weeks’ gestation, respectively.
Economic burden of preterm birth
Preterm birth has a major and significant direct and indirect cost. There is a direct cost in terms of clinical resource use, e.g. intensive and often prolonged neonatal care as inpatient followed by higher rate of rehospitalisation following discharge,19,20 and emotional, psychological and financial burdens on the parents who are usually the main carers. There are also indirect costs to society where scarce public resources are used for long-term care of the handicapped premature child and one or both parents may have to give up full-time employment to care for their premature child.
Therefore, accurate prediction of the risk of preterm birth among asymptomatic pregnant women and those symptomatic with threatened preterm labour may offer the opportunity to target care at those most likely to benefit. Once information on accuracy and effectiveness become available through systematic reviews, economic modelling will allow the benefit in terms of both human and financial costs to be estimated.
Current service provision
Antenatal care in the UK is a complex care package, within which screening for women at risk of preterm birth is an integral component. Often this is linked to screening for conditions (e.g. pre-eclampsia) that might predispose to the need for elective preterm delivery. Currently there is no routine screening test for spontaneous preterm birth apart from obtaining history of previous pregnancies. Once women are identified as at risk, they may be targeted for more intensive antenatal surveillance and prophylactic measures, either as primary, secondary or tertiary preventions.
Primary prevention is preventing the onset of spontaneous preterm labour in asymptomatic women, e.g. administration of maternal progestational agents by injection or ensuring and maintaining healthy maternal genitourinary tract and periodontal status. Secondary prevention involves steps that can be taken to attenuate, stop or reverse the progress of spontaneous preterm labour in its early stages, well before advanced cervical dilatation, e.g. by administration of tocolytic agents. Tertiary prevention is those measures aimed at preventing neonatal complications associated with prematurity, e.g. maternal administration of antenatal corticosteroids to accelerate fetal lung maturity. This project is focused on primary prevention but it models the effect on outcomes of primary prevention taking into account secondary and tertiary prevention strategies.
Delineation of the problem
Assessment of pregnant women’s risk for preterm birth, based on a combination of patients’ characteristics, symptoms, physical signs and investigations, is important. This is because without an accurate assessment, clinicians are handicapped in the management of women at risk of preterm birth regarding the institution of timely antenatal interventions. Wrong or delayed diagnosis can put mother and baby at risk of an adverse outcome whereas correct prediction of preterm birth will provide an opportunity to institute effective interventions. This Health Technology Assessment report will address these issues using systematic reviews to estimate the accuracy of tests for predicting spontaneous preterm birth and the effectiveness of interventions in preventing or delaying it. The report will incorporate the output of systematic reviews into decision analyses to determine the optimal management strategies.
Two target populations of pregnant women need to be tested for the risk of spontaneous preterm birth (Figure 1). The first is the population of antenatal asymptomatic women carrying a singleton gestation and receiving routine care. In this important, and by far the largest, epidemiological target pregnant population, women are generally in a healthy state, anticipating a normal course of pregnancy. They are usually regarded as ‘low-risk’ unless there are antecedent or current factors and history that might increase the risk of preterm birth. If screening or testing could predict the risk of spontaneous preterm birth among these women, preventative measures may be more appropriately targeted. For example, if ultrasonographic measurement of cervical length in these women identifies shortened cervical length,21 then cervical cerclage may be deployed to prevent progression to spontaneous preterm birth. 22 For these women, the key outcome measure would be prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation.
FIGURE 1.
Target populations and outcomes in the course of pregnancy.
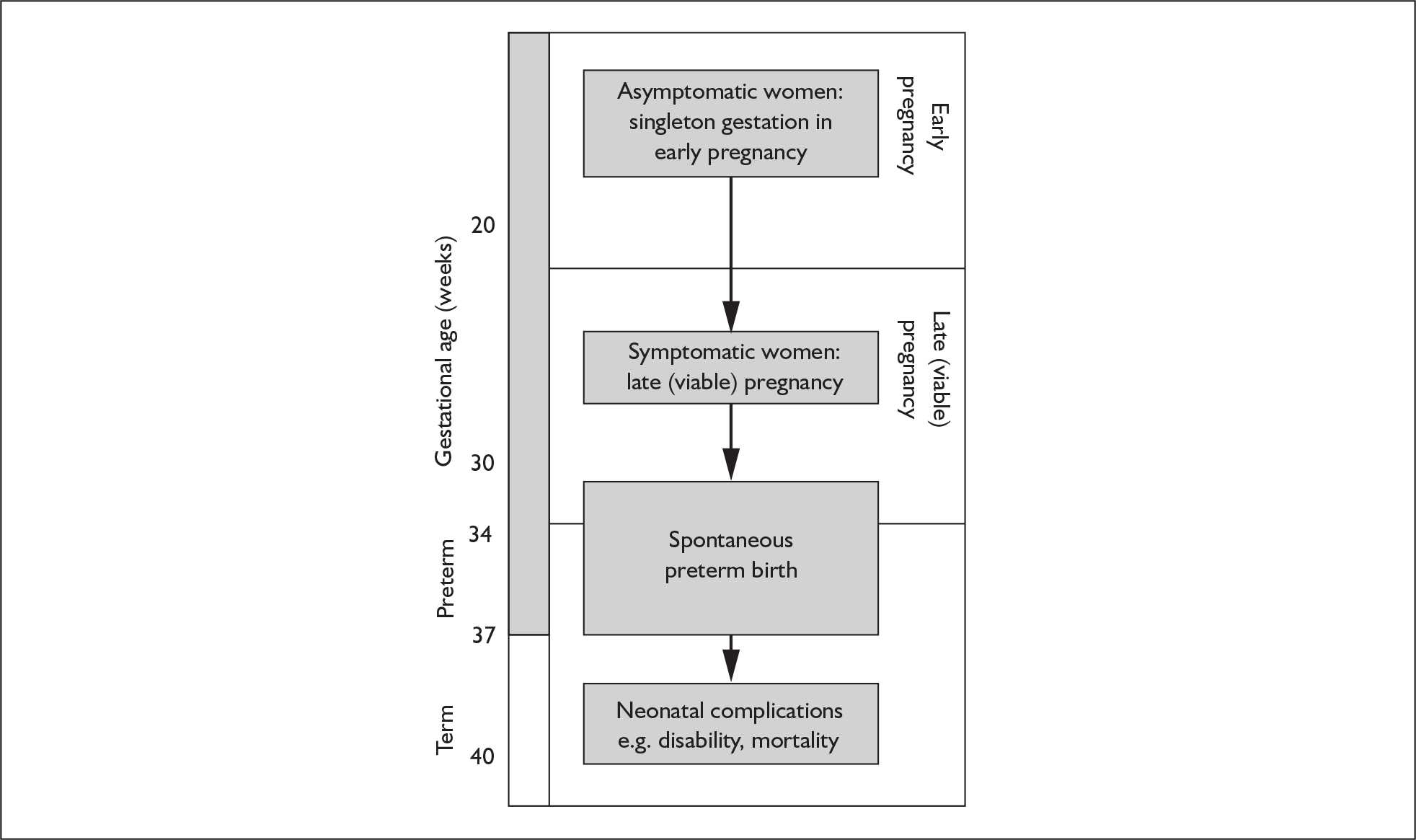
The second population of interest is that of symptomatic women with singleton gestation who present with threatened preterm labour. For these women, there is a need to identify those who will go on to deliver prematurely because the key clinical decisions following testing relate to immediate management and outcome. For example, if cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin testing could predict spontaneous preterm birth among these women before advanced cervical dilatation,23 then antenatal maternal intramuscular corticosteroid injection may be administered to accelerate fetal lung maturity to prevent respiratory distress syndrome. 24 In utero transfer to a tertiary intensive neonatal care unit able to care for the premature neonate may also be considered. 25,26 Such a transfer, which may take some time to arrange (because of logistics, geography or lack of neonatal intensive care cots), would be inappropriate if birth were imminent because it would risk delivery en-route. In such cases, knowledge of a higher likelihood of imminent birth may allow rational use of tocolytic agents, which aim to suppress or diminish contractions allowing time for the administration of antenatal corticosteroids to exert its beneficial effects. 27 Antenatal corticosteroids have maximal effectiveness in preventing neonatal complications of prematurity when delivery is within 2–7 days after administration. 24 Given the duration of time required for corticosteroids to exert beneficial effects and the potential for in utero transfer and tocolytic administration, knowledge of impending birth within 48 hours to 7 days of testing would be a clinically meaningful outcome measure among women symptomatic of threatened preterm labour.
Chapter 2 Aims and objectives
Aim
This Health Technology Assessment (HTA) project was undertaken for the National Screening Committee (NSC) to systematically review evidence on tests that identify women with singleton pregnancy who are at risk of spontaneous preterm birth and interventions that prevent or delay birth to allow the institution of treatments to improve neonatal outcome. The output from these reviews was used in economic modelling to determine the most efficient management strategies.
Objectives
Considering the background and aim, this HTA project was undertaken to meet the following objectives:
-
to determine, among asymptomatic women with singleton gestation in early pregnancy (before 23 completed weeks of gestation):
-
the accuracy of various tests (history, examination and investigations) for predicting the risk of spontaneous preterm birth
-
the effectiveness of various interventions for preventing spontaneous preterm birth.
-
-
to determine, among women with a viable singleton pregnancy (after 23 completed weeks of gestation), symptomatic of threatened preterm labour with intact amniotic membrane and before advance cervical dilatation (less than 2–3 cm dilatation):
-
the accuracy of various tests (history, examination and investigations) for predicting the risk of imminent preterm birth
-
the effectiveness of various antenatal interventions to delay preterm birth to allow the institution of interventions for improving outcome of the premature neonate.
-
-
To determine the cost-effectiveness of testing (in antenatal asymptomatic women and symptomatic women) and of the consequent prevention and treatment strategies in terms of both human and financial costs using decision-analytic modelling.
From this work, this HTA project aims to identify areas where evidence is strong enough to generate recommendations for clinical practice. Additionally, it aims to identify key areas and research questions requiring further primary research.
Chapter 3 Methods
Protocol development
This report is based on systematic reviews, a scientific, replicable method of evidence synthesis explicitly describing the objectives, the search strategy for relevant literature, and the methods for processing information and deriving conclusions. 28 The project followed key steps involved in diagnostic Health Technology Assessment (HTA). 29–31 Systematic reviews of accuracy and effectiveness of tests and interventions were carried out using contemporaneous methodology,32–34 which is in line with the recommendations of the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination,35 and the Cochrane Collaboration including the recommendations of the Cochrane Methods Working Group on Screening and Diagnostic tests. 36
The strategy for undertaking this HTA review was based on a prospective protocol, which included reviews of existing test accuracy and effectiveness reviews, updating those that were out of date, and performing rapid reviews of topics not reviewed in the literature. A literature search was performed first to identify potentially relevant citations. The search strategy can be found in Appendix 1. The systematic reviews of accuracy, effectiveness and economic literature were then executed initially simultaneously, followed by economic modelling and cost-effectiveness analysis integrating the accuracy and effectiveness data.
Once tests and interventions were identified, and clinically relevant tests and treatment combinations were generated; we sought clinical experts’ input for their comments concerning alternative management strategies (see list of experts in the Acknowledgements). We supplied them with a list of tests and interventions and their clinically relevant combinations, and asked whether the list was exhaustive. We also asked them to rank the importance of these tests, interventions and combinations. We provided spaces for comments and opinions if they wished to add these to their replies.
Research question
We addressed the following structured questions.
Populations
Asymptomatic low-risk pregnant women with singleton gestation in early pregnancy and low-risk women symptomatic for threatened preterm labour with a viable singleton pregnancy. We focussed on singleton pregnancies because multiples fall in a high-risk category that represents a different disease spectrum.
Tests
Options available for determining the risk of spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic pregnant women and those available for determining the risk of imminent birth in women symptomatic for threatened preterm labour (Appendix 2).
Interventions
Options available to prevent preterm birth in asymptomatic pregnant women and those available to delay delivery in women symptomatic for threatened preterm labour and to improve neonatal outcome for prematurely born infants (Appendix 3).
Outcomes
Spontaneous preterm birth < 37 weeks’ gestation and < 34 weeks’ gestation in asymptomatic pregnant women, and birth within 24 hours, 48 hours and up to 7–10 days of testing or presentation in women symptomatic for threatened preterm labour. Information on maternal morbidity, neonatal mortality and morbidity, and resource use including admission to neonatal intensive care unit was also sought.
Study designs
-
Test accuracy studies (observational: prospective or retrospective) of defined non-randomised populations in which the results of the test of interest were compared with the outcomes (reference standard) to generate 2 × 2 tables to compute indices of test accuracy.
-
Randomised controlled trials to assess effectiveness of tests (in combination with interventions) or interventions.
-
Economic evaluations providing cost-effectiveness analyses of tests and interventions outlined above.
Systematic reviews of accuracy of tests
We first identified existing reviews, assessed them for their quality and examined their currency. Through this process, gaps were identified where reviews did not exist and where they needed updating. To fill these gaps, we carried out rapid systematic reviews and updated non-current existing reviews where appropriate.
Study identification and selection
We undertook a formal search to identify existing reviews of accuracy of tests for preterm birth. The Cochrane Library, the National Research Register (NRR), the HTA database, the National Guideline Clearinghouse and a range of other guideline and effectiveness collections were searched for systematic reviews, guidelines and ongoing research using Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms and text words. A database of published and unpublished literature was assembled from update searches using an existing search strategy,37 as well as hand searching, contacting manufacturers and consultation with experts in the area. No language restrictions were applied to electronic searches.
The following databases were searched for primary studies: MEDLINE, EMBASE, BIOSIS, MEDION, Pascal, Science Citation Index, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR), Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) and HTA database. In addition, information on studies in progress, unpublished research or research reported in the grey literature was sought by searching a range of relevant databases including Inside Conferences, Systems for Information in Grey Literature (SIGLE), Dissertation Abstracts, ClinicalTrials.gov and the NRR. Citations captured by the search were scrutinised for inclusion in the review in a two-stage process using predefined and explicit criteria regarding populations, index tests, target conditions and study designs. First, a master database of the literature searches was constructed by amalgamation of all the citations from various database sources. The citations were scrutinised by two reviewers. Copies of full manuscripts of all citations that were likely to meet the selection criteria were obtained. Two reviewers then independently selected the studies that met the predefined criteria. These criteria were pilot tested using a sample of papers. Disagreements were resolved by consensus or arbitration involving a third reviewer.
The search revealed a number of test accuracy reviews at various levels of currency (Chapter 4: Identification of accuracy literature). Most of the identified reviews were updated, where the experts surveyed for this project decided the priority on clinical grounds, and a few new rapid reviews were carried out to fill the identified gaps.
To be included in updated systematic reviews, any recent systematic reviews or primary studies had to fulfil the individual criteria as stated in the original reviews, including the following criteria.
-
Population Asymptomatic antenatal women and women symptomatic for threatened preterm labour with singleton gestation to allow interventions that delay delivery and improve neonatal outcome for prematurely born infants.
-
Index tests Tests that purported to predict spontaneous preterm birth as described in Appendix 2.
-
Reference standards and other outcomes Any outcomes as reported in the individual reviews. However, only data relating to the following outcome measures were used in the report: spontaneous preterm birth < 37 weeks’ gestation, < 34 weeks’ gestation or within 2–7 days of testing, and resource use. If relevant outcomes were not reported in the original reviews this is noted.
-
Study design Systematic reviews of test accuracy studies were included; all reviews were of a standard quality accepted by DARE produced by the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD). For primary studies, we looked for observational cohort studies or, if unavailable, ‘case–control’ studies of test accuracy.
Study quality assessment and data extraction
For existing reviews, quality was assessed using existing guidance on conducting test accuracy reviews. 35,36,38 The methodological quality of the selected primary studies was assessed using predefined criteria based on elements of study design, conduct and analysis which are likely to have a direct relationship to bias in a test accuracy study. 39–42 In addition to using study quality as a possible explanation for differences in results (heterogeneity), the extent to which primary research met methodological standards is important per se for assessing the strength of any conclusions that are reached. In the main text of our report, we provide graphical summaries of the five most important quality items while others can be extracted from tables of study characteristics for the individual test (Appendix 5).
Any randomised trials of effectiveness of test–treatment combinations were assessed for validity separate from the diagnostic accuracy studies. Study findings were extracted in duplicate for 10% of randomly selected studies, while the remainder were carried out by one investigator, using predesigned and piloted data extraction forms, which were developed and used in previously published reviews. 21,23,43–45 Previous reviews had assessed studies and extracted data in duplicate. Data extraction was carried out in the context of rapid reviews, where because of the time constraints, missing information was obtained from investigators only if it was crucial to the subsequent analysis and modelling. To avoid introducing bias, unpublished information was coded in the same fashion as the published information.
Data synthesis
A brief narrative review of findings and quality was undertaken for each test considered. We explored causes of variation in results from study to study (heterogeneity), synthesised results from individual studies (meta-analysis) if appropriate and assessed for funnel asymmetry for publication and related biases. Accuracy results were computed separately for different populations, tests and reference standards. Heterogeneity of results between studies was graphically assessed in forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) and distribution of sensitivity and specificity was assessed in summary receiver operating characteristics (ROC) space (for the latter only those ‘more accurate tests’ included in the threshold analysis with the relevant clinical outcomes are shown in this report, the remainder are not shown). The latter show the trade-off between sensitivity and specificity across different studies with explicit or implicit variation in thresholds. A general guide for interpreting summary LRs can be found in Chapter 4, Table 1.
| Category of test accuracy usefulness | Likelihood ratio for a positive test result (LR+) | Likelihood ratio for a negative test result (LR–) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Very useful | > 10 | < 0.1 | Likely to generate large and often conclusive changes from pre-test to post-test probabilities |
| Useful | 5–10 | 0.1–0.2 | Likely to generate moderate shifts in pre-test to post-test probabilities |
| May be useful | 2–5 | 0.2–0.5 | Likely to generate small but sometimes important changes in pre-test to post-test probabilities |
| Not useful | 1–2 | 0.5–1 | May alter pre-test to post-test probabilities to a small (and rarely important) degree |
Subgroup analyses were planned a priori to explore the causes of heterogeneity to check whether variations in populations, index test characteristics, target conditions and study quality affect the estimation of accuracy. Individual factors explaining heterogeneity were also analysed using meta-regression where there were more than ten studies in a review to determine their unique contribution, allowing for other factors. Conclusions regarding the typical estimate of accuracy were interpreted cautiously if there was significant heterogeneity. 46
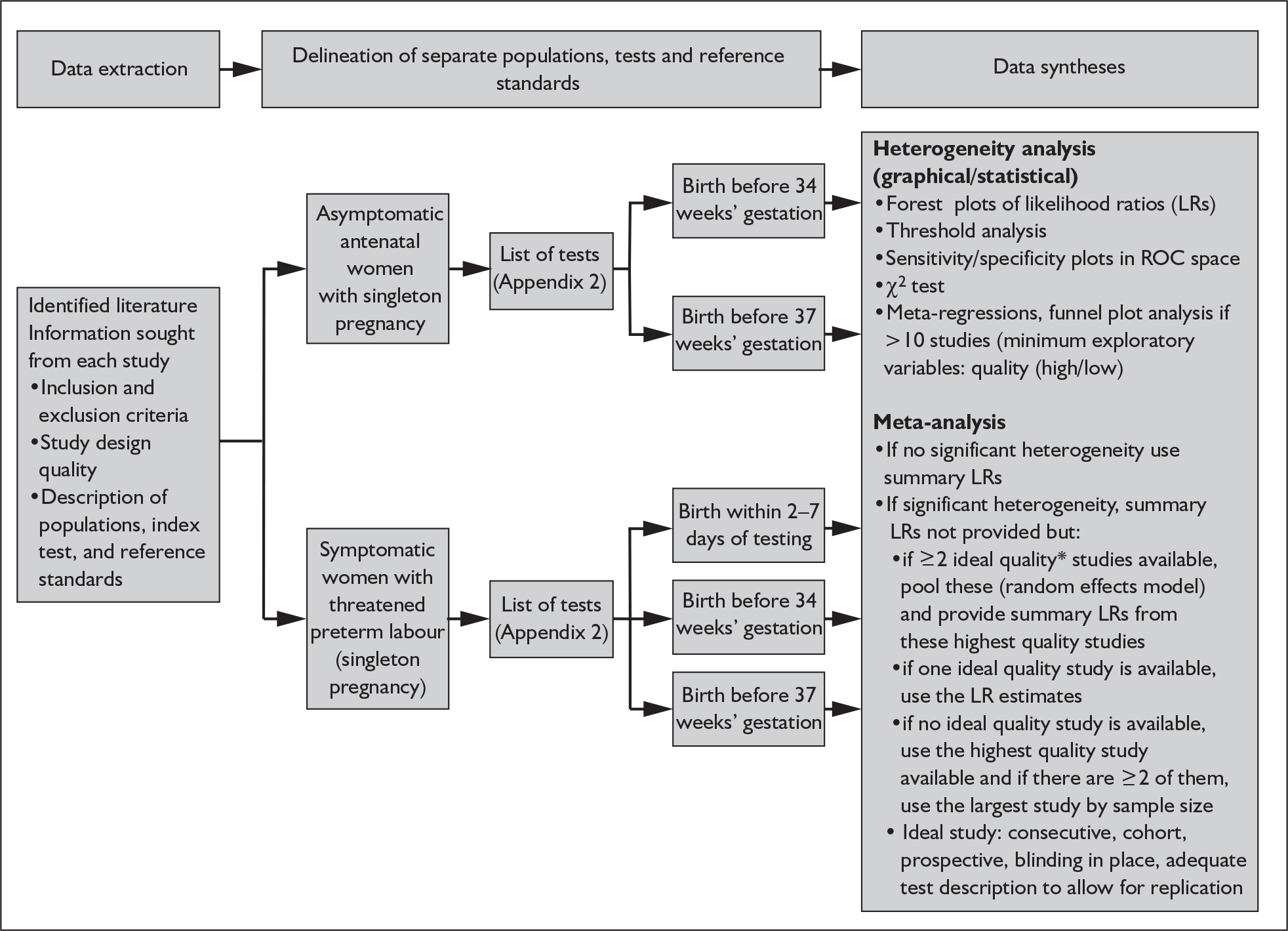
In addition to meta-analyses that generated summary estimates primarily of LRs; we also estimated sensitivity, specificity and summary ROC curves where in our judgement, they would add to the interpretation of the results. 47 LRs are considered more clinically meaningful as measures of test accuracy48–50 and would allow estimation of probabilities for use in the decision-analytic modelling. These post-test probabilities can be used to calculate the absolute effects of interventions according to test results. 51 Publication and related biases were assessed using funnel plots of diagnostic odds ratios against corresponding variances among reviews with more than ten studies. 35 Stata version 8.2 software was used in the statistical analyses. The procedural flow chart for systematic reviews of test accuracy is shown in Figure 2.
FIGURE 2.
Flow chart of procedures for reviews of test accuracy studies. *Ideal study: consecutive cohort, prospective, blinding in place, and adequate test description to allow for replication.
Systematic reviews of effectiveness of interventions
Once accurate tests have been identified, women deemed to be at high risk of developing preterm labour may benefit from interventions that are effective in preventing or delaying progression to preterm birth and associated complications of prematurity. When conducting or updating effectiveness reviews we followed existing guidelines35,52 so that our output would comply with the QUOROM statement. 53
Study identification and selection
As part of the study identification process a detailed search of the relevant literatures was conducted. The Cochrane Library, NRR, the HTA database, the National Guideline Clearinghouse and a range of other guideline and effectiveness collections were searched for systematic reviews, guidelines and ongoing research. This included a MEDLINE search using a systematic review methodological filter for the period 2000–2005. The search strategy used can be found in Appendix 1. Update searches were performed for the DARE and the CDSR in August 2005.
A search was then undertaken to identify potentially relevant trials. This search was restricted by including a methodological search filter to help identify randomised controlled trials The following databases were searched: MEDLINE, EMBASE, BIOSIS, Pascal, Science Citation Index, CDSR, CENTRAL, DARE and HTA database. Information on studies in progress, unpublished research or research reported in the grey literature was sought by searching a range of relevant databases including Inside Conferences, SIGLE, Dissertation Abstracts, the NRR, National Technical Information Service (NTIS) and ClinicalTrials.gov.
The search revealed a number of reviews at various levels of currency. Most of the identified reviews were updated, where experts commissioned for this project decided the priority on clinical grounds, and a small number of new rapid reviews were carried out to fill the identified gaps. Two reviewers independently selected studies for inclusion in the review in a two-stage process using predefined and explicit criteria regarding populations, interventions and outcomes using the procedures outlined below. Disagreements were resolved by consensus or arbitration involving a third reviewer.
To be included in updated systematic reviews, primary studies had to fulfil the individual criteria as stated in the original reviews, including the following criteria:
-
Population Asymptomatic antenatal women and women symptomatic for threatened preterm labour with singleton gestation to allow interventions, which delay delivery and improve neonatal outcome for prematurely born infants.
-
Interventions Interventions and comparators were as described in Appendix 3.
-
Outcomes Any outcomes as reported in the individual reviews. However, only data relating to the following outcome measures were used in the report: spontaneous preterm birth < 37 weeks’ gestation, < 34 weeks’ gestation; within 24 hours, 48 hours, up to 7–10 days of presentation; maternal and neonatal mortality and morbidity (adverse event data); and resource use including admission to neonatal intensive care unit. If relevant outcomes were not reported in the original reviews this was noted.
-
Study design Systematic reviews of randomised controlled trials (RCTs), quasi-RCTs and controlled trials were included; all reviews were of a standard quality accepted by the DARE. When updating systematic reviews the inclusion criteria for the original review were applied to additional trials. Where new rapid reviews were conducted only RCTs were eligible for inclusion.
Study quality assessment and data extraction
Quality of evidence was assessed on two levels: (1) at the level of systematic reviews and (2) at the level of the primary studies included in the reviews. All of the included systematic reviews were of a given standard quality accepted by DARE. The DARE approach to assessing the validity of the individual review considers various factors important to the method of conducting systematic reviews, such as: a well-defined research question, clear inclusion and exclusion criteria, a detailed search strategy, assessment of validity, and provision of sufficient details of the primary studies included in the review. Validity assessment considered factors associated with bias in such trials, e.g. concealment of randomisation, sequence generation, follow-up and blinding. The extent to which primary research met methodological standards is important per se for assessing the strength of any conclusions that are reached.
Two reviewers independently assessed the quality of each study; disagreements were resolved by consensus or arbitration involving a third reviewer. Findings of studies were independently extracted by one reviewer and checked by a second reviewer using predesigned and piloted data extraction forms for effectiveness studies (Appendix 4). The structure for the extraction form for existing systematic reviews was taken from DARE abstract guidelines, and covered the following areas: review details, methodology, including search, inclusion/exclusion criteria, procedures for study selection and data extraction, validity assessment and synthesis, results and conclusions. Summary variables were entered onto Microsoft Word tables. The presentation and content of the extraction table was consistent across intervention topics. The economic extraction form included the following data for input into the economic model: summary estimates [relative risk (RRs)] of effectiveness, variation in outcome (e.g. as the result of specific risk factors), adverse effects and resource use. Procedures for obtaining missing information and resolving disagreements were similar to the ones outlined above.
Data synthesis
A brief narrative of review findings and quality was generated for each intervention considered. For the existing reviews, summary estimates (RRs) of the treatment effects were extracted in relation to the primary outcomes of spontaneous preterm birth, together with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) if these were reported. Data were re-analysed and any anomalies were corrected; where appropriate, subgroups were analysed. If a narrative synthesis had been carried out a concise summary of the main results has been presented. Where additional relevant trials were found, numerical estimates for each identified trial were extracted and the summary estimates of the existing review were recalculated, incorporating the new data. Where singleton and multiple gestations were pooled, data from singletons were extracted separately if possible, or studies were excluded. Heterogeneity of results between studies was statistically assessed where appropriate. Conclusions regarding the typical estimate of an effect of intervention were interpreted cautiously if there was significant heterogeneity. Where no previous reviews exist, numerical estimates from all identified trials were extracted and, if appropriate, summarised by meta-analysis. Revman version 4.1 and Stata version 8.2 software were used in the statistical analyses. The former allows uniformity with Cochrane reviews and the latter allows the data analytic flexibility that was not included in the Revman software.
Economic evaluation
This consisted of a systematic review of existing economic evaluation and a model-based analysis incorporating information extracted from the accuracy and effectiveness reviews. The search strategy was adapted to focus on economic evaluations using terms adapted from the strategies used to identify studies for inclusion in National Health Service Economic Evaluation Database (NHS EED; see http://nhscrd.york.ac.uk/nfaq2.htm). In addition, the two predominant economic evaluation databases were searched: NHS EED and Health Economic Evaluations Database (HEED). Searches for economic working papers were undertaken using the Internet Documents in Economics Access Service (IDEAS) database. Additional searches were undertaken to provide a range of evidence to help populate the decision model. Information to answer these questions was provided by focused searching of appropriate databases, statistical sources and other sources of relevant information. 54
The objective of searching the economic literature was to identify studies reporting costs and consequences associated with preterm birth, which provided estimates for a comparison with a ‘do nothing’ option. Cost information associated with the consequences of preterm birth was identified in the literature. 55–61 The review of economic studies aided the identification of quality of life information that could be used to estimate the proposed secondary outcome of cost per Quality Adjusted Life Year (QALY). Cost data were collected from two principal sources. First from the clinical evidence synthesised into the main strategies of diagnosis and treatment, where relevant studies were examined for their data on costs and resource use. These data were subject to relevant quality criteria. Second, additional cost data were obtained from sources such as the National Schedule for Reference Costs. Primary cost and resource data were collected from Birmingham Women’s Hospital, when there were gaps in the information required for the modelling process, to enable estimations of relative cost-effectiveness of different strategies. Appropriate sensitivity analysis, such as probabilistic sensitivity analysis, was carried out where required. The modelling framework allowed simple decision strategies associated with one screening test and one possible intervention to be evaluated. Where information on the correlation between packages of tests and correlation between packages of treatments was available from the reviews, the framework allowed these more complex strategies to be evaluated, as well as strategies that allow alteration in the form of repeated testing.
The economic evaluation took the form of a cost-effectiveness analysis within a decision-analytic framework based on a primary outcome of cost per case of spontaneous preterm birth avoided. Where possible, and depending on the information available in the reviews, this principal outcome was desegregated into two further outcomes of cost per case of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ and before 37 weeks’ gestation avoided. There is a significant cost and consequence impact associated with births at these different times. 4 Combining the results from the model with additional information from the reviews on neonatal morbidity in cases of spontaneous preterm birth allowed prediction of outcomes in terms of cost per neonatal mortality avoided. The comparator was a policy of no screening/testing and no interventions. If suitable data on neonatal morbidity became available from the reviews then a secondary outcome of cost per QALY associated with each alternative combination of screening/testing and intervention was estimated. The economic evaluation adopts the perspective of the NHS and so private costs to patients associated with the proposed screening and intervention were not included.
The evidence found in the clinical accuracy and effectiveness reviews provided the majority of the parameters required to perform the economic evaluations of alternative tests and interventions. The data were synthesised to construct a decision-analytic model. The model allows comparisons of various strategies of screening tests for risk of spontaneous preterm birth, e.g. bedside cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin testing and interventions to prevent spontaneous preterm birth, e.g. progestational agents, in terms of their relative effectiveness and cost. Alternative combinations of screening or diagnostic tests were paired with appropriate alternative interventions and explored by the decision modelling, to calculate the costs and consequences for each combination. A decision tree was the chosen modelling approach for this evaluation because the time horizons available for both the screening or diagnostic tests and the interventions, being within the duration of the pregnancy, are relatively short.
The number of possible combinations assessed in the modelling framework depended on the results of the reviews. In the event that the reviews reveal a large number of relevant studies on accurate screening tests and effective interventions, the group intended to attempt to prioritise the number of modelling scenarios having sought approval of the National Screening Committee (NSC).
Modifications to the protocol and original grant proposal
Following approval of this HTA project, a systematic review (periodontal assessment in pregnant women) appeared in the literature that impacted on our plans (i.e. it needed to be included in our reviews), having not been considered at bid-proposal stage. Its inclusion was crucial because within the NHS periodontal care is free at the point of delivery to pregnant women, so our assessment may have an impact on the delivery of the service. A review of interventions to promote smoking cessation in pregnant women was also included as a protocol amendment. The clinical experts we consulted suggested reviews that we may consider abandoning either for historical reasons or because of their irrelevance to UK clinical practice. They also suggested additional reviews. However, in view of the deadline imposed by the HTA and the fact that we have included two additional effectiveness reviews (periodontal assessment and smoking cessation), we were unable to fulfil the additional requests. Otherwise, there were no other protocol modifications to the submitted proposal.
Report structure
The results of the three main parts of this project (test accuracy systematic reviews, effectiveness systematic reviews and economic modelling) are reported separately with a discussion section for each. Additional information (results and discussion) for many of the effectiveness reviews is available in the Cochrane Library. The final section of the report considers all of the findings to draw overall conclusions. Recommendations for practice and research appear individually in each section and in the concluding chapter.
Chapter 4 Results of reviews of accuracy of tests
A list of tests reviewed can be found in Appendix 2. We divided the reviews of test accuracy into history, examination and investigations. Figure 3 shows the process of identification of literature reviews for test accuracy studies.
FIGURE 3.
Identification of accuracy literature – systematic review.
Identification of accuracy literature
Previous history of spontaneous preterm birth
Previous medical history of having spontaneous preterm birth is clinically used as a predictor for another spontaneous preterm birth. With the advent of dating scans, this history can be accurately assessed at the antenatal booking consultation.
Study characteristics and quality
There were ten studies evaluating the accuracy of previous history of spontaneous preterm birth among asymptomatic antenatal women in predicting spontaneous preterm birth in the subsequent pregnancy (n = 55,885). 62–71 One study72 was excluded on closer inspection because it used the same population as another included study. 68Appendix 5, Table 68 summarises the salient characteristics of the included studies. There were no studies on symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour. Most of the studies did not differentiate between previous single or multiple episodes of spontaneous preterm birth. Two studies evaluated the accuracy of previous history of two versus one spontaneous preterm birth,65,71 while one study evaluated the accuracy of gestation at which the previous spontaneous preterm birth occurred in predicting spontaneous preterm birth in a subsequent pregnancy. 69
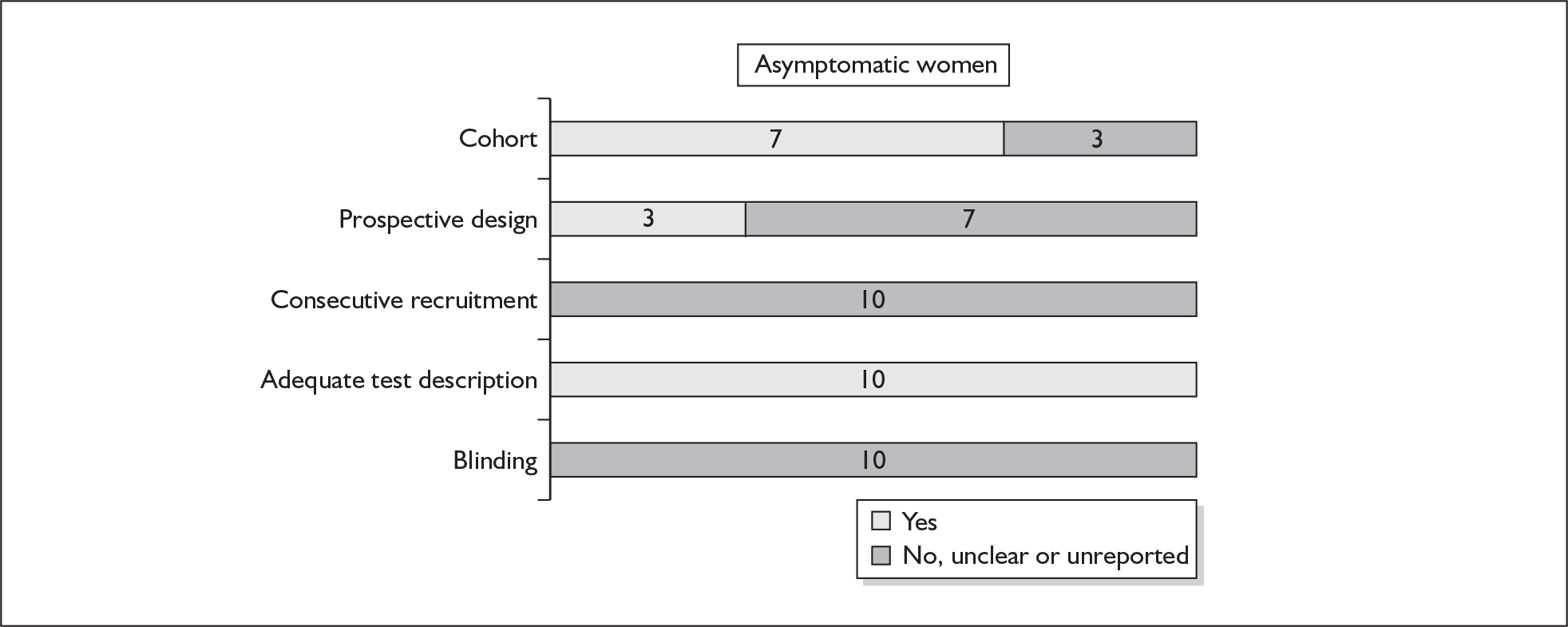
None of the studies fulfilled our criteria for an ideal quality study (consecutive, cohort, prospective, blinding in place, and adequate test description to allow for replication). None of the studies reported blinding and consecutive enrolment. The quality features are summarised in Figure 4. Aside from three studies,64,66,68 the remaining studies reported birth before 37 weeks’ gestation as their outcomes.
FIGURE 4.
Methodological quality of studies of previous history of spontaneous preterm birth in predicting subsequent spontaneous preterm birth included in the systematic review. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
Accuracy of previous history of spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic women
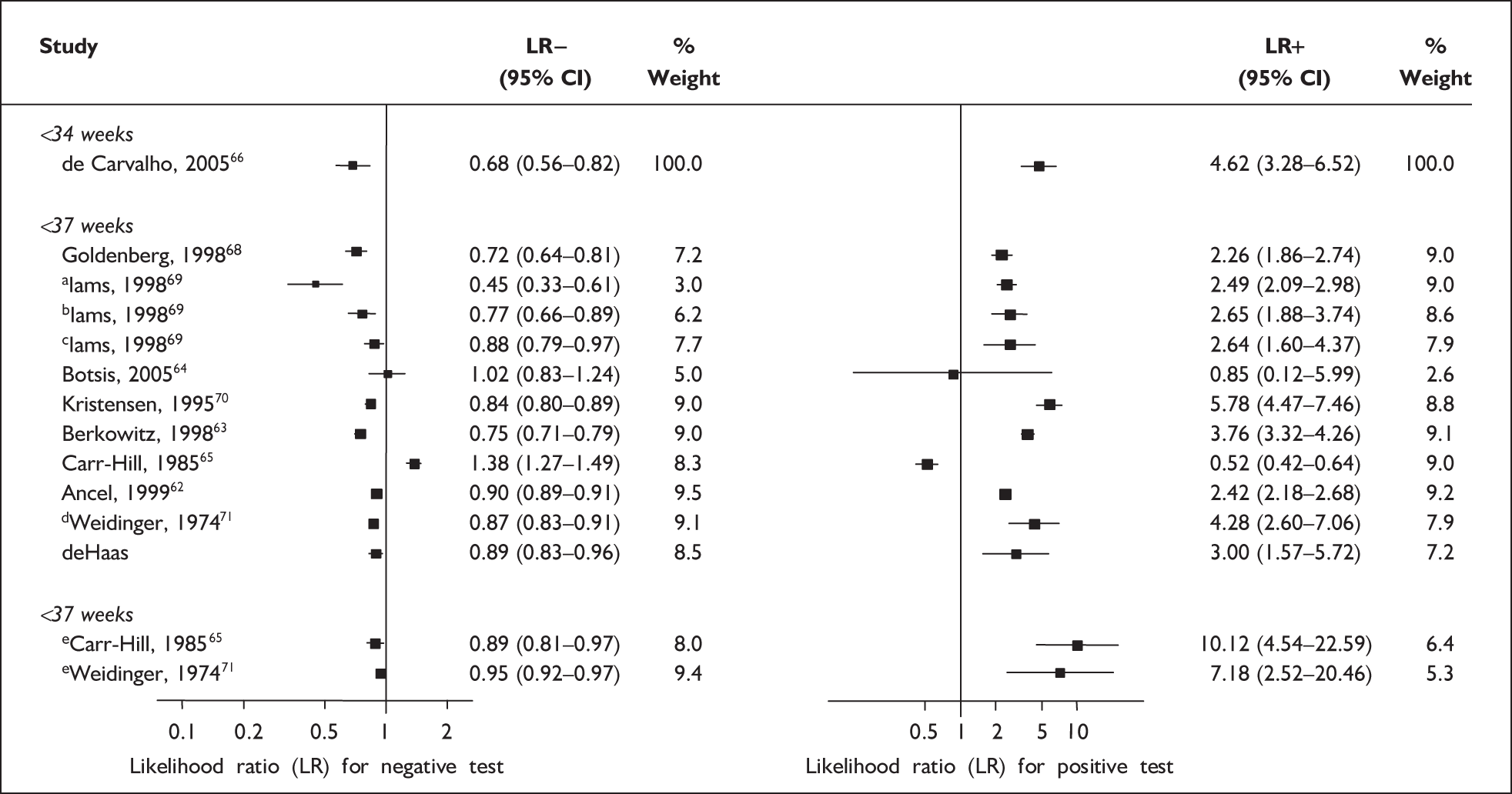
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, previous history of spontaneous preterm birth had a likelihood ratio for a positive test result (LR+) of 4.62 [with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) 3.28–6.52] and a likelihood ratio for a negative test result (LR–) of 0.68 (95% CI 0.56–0.82),66 which was used in the decision-analytic modelling. For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, previous history of spontaneous preterm birth had a range of LR+ from 0.52 (95% CI 0.42–0.64)65 with one previous spontaneous preterm birth to 10.12 (95% CI 4.54–22.59)65 with two previous spontaneous preterm births, and a range of LR– from 0.45 (95% CI 0.33–0.61)69 with previous history of spontaneous preterm birth before 26 weeks’ gestation to LR– of 1.38 (95% CI 1.27–1.49)65 with one previous spontaneous preterm birth. However, LR+ of 2.26 (95% CI 1.86–2.74) and LR– of 0.72 (95% CI 0.64–0.81) from Goldenberg et al. 68 were used in the decision-analytic modelling as it represented the largest higher-quality study. The accuracy of previous history of spontaneous preterm birth in predicting subsequent spontaneous preterm birth is shown in Figure 5 while individual accuracy data are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 69.
FIGURE 5.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of the accuracy of previous history of spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic women for predicting spontaneous preterm birth stratified according to outcome gestation. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.000 for LR+ and LR– of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. Studies are listed in descending order of quality. a, Previous spontaneous preterm birth before 26 weeks’ gestation. b, Previous spontaneous preterm birth before 31 weeks’ gestation. c, Previous spontaneous preterm birth before 36 weeks’ gestation. d, One previous spontaneous preterm birth. e, Two previous spontaneous preterm births.
Digital examination
Physical examination is one of the cornerstones of medicine. Vaginal digital examination to assess the cervix is simple to do but its accuracy in the assessment of either asymptomatic antenatal women or symptomatic pregnant women with threatened preterm labour to predict spontaneous preterm birth has not been evaluated.
Study characteristics and quality
There were ten studies that evaluated the accuracy of cervical digital examination in predicting spontaneous preterm birth, nine in asymptomatic antenatal women (n = 12,325)73–81 and one in symptomatic women (n = 90) with threatened preterm labour. 82 There were variations in testing gestation, frequency of testing and threshold selection among the included studies. Noticeably, for all of the studies, testing gestation commenced after 24 weeks’ gestation, currently accepted as the lower limit of neonatal viability. Aside from three studies, which used birth before 34 and 35 weeks’ gestation76–78 as their outcome measurement, the studies used 37 weeks’ gestation. Individual study characteristics are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 70.
One study fulfilled our criteria for an ideal quality study;77 the remaining studies lacked one or more criteria for an ideal quality study with consecutive enrolment being the most commonly absent feature. Blinding was only reported by four studies in asymptomatic women. The methodological quality of the included studies is summarised in Figure 6.
FIGURE 6.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of digital examination in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
Accuracy of digital examination in asymptomatic women
There was a wide variation in the accuracy of digital examination in asymptomatic antenatal women in predicting spontaneous preterm birth (Figure 7). For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, digital examination showed an LR+ of 9.25 (95% CI 3.91–21.85) and LR– of 0.46 (95% CI 0.19–1.08) in a mixed population of nulliparous/multiparous antenatal asymptomatic women and a threshold of > 2 cm cervical dilatation. 77 These LRs were used in the decision-analytic modelling. For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, LR+ ranged from 0.46 (95% CI 0.03–6.85) in multiparous women with a threshold of > 2–3 cm cervical dilatation80 to 9.17 (95% CI 0.52–160.08) in a mixed population of nulliparous/multiparous antenatal asymptomatic women with a centrally positioned cervix and > 1.5 cm dilatation,75 and LR– ranged from 0.42 (95% CI 0.26–0.68) in nulliparous antenatal women with a soft cervix73 to 2.46 (95% CI 0.11–55.35) in a mixed population of nulliparous/multiparous antenatal asymptomatic women and a threshold of posterior cervix > 1.5 cm dilatation. 75 However, an LR+ of 1.15 (0.86–1.53) and LR– of 0.89 (0.68–1.16) from Parikh et al. ,79 who evaluated digital examination in a mixed population of nulliparous/multiparous women using the threshold of admitting a finger at the cervical internal os, was used in the decision-analytic modelling because it represented a higher-quality methodological study. Individual accuracy results are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 71.
FIGURE 7.
(opposite) Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of digital examination in predicting spontaneous preterm birth as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth. No weights attached because of multiple contributions of subjects within a particular study evaluating different thresholds.
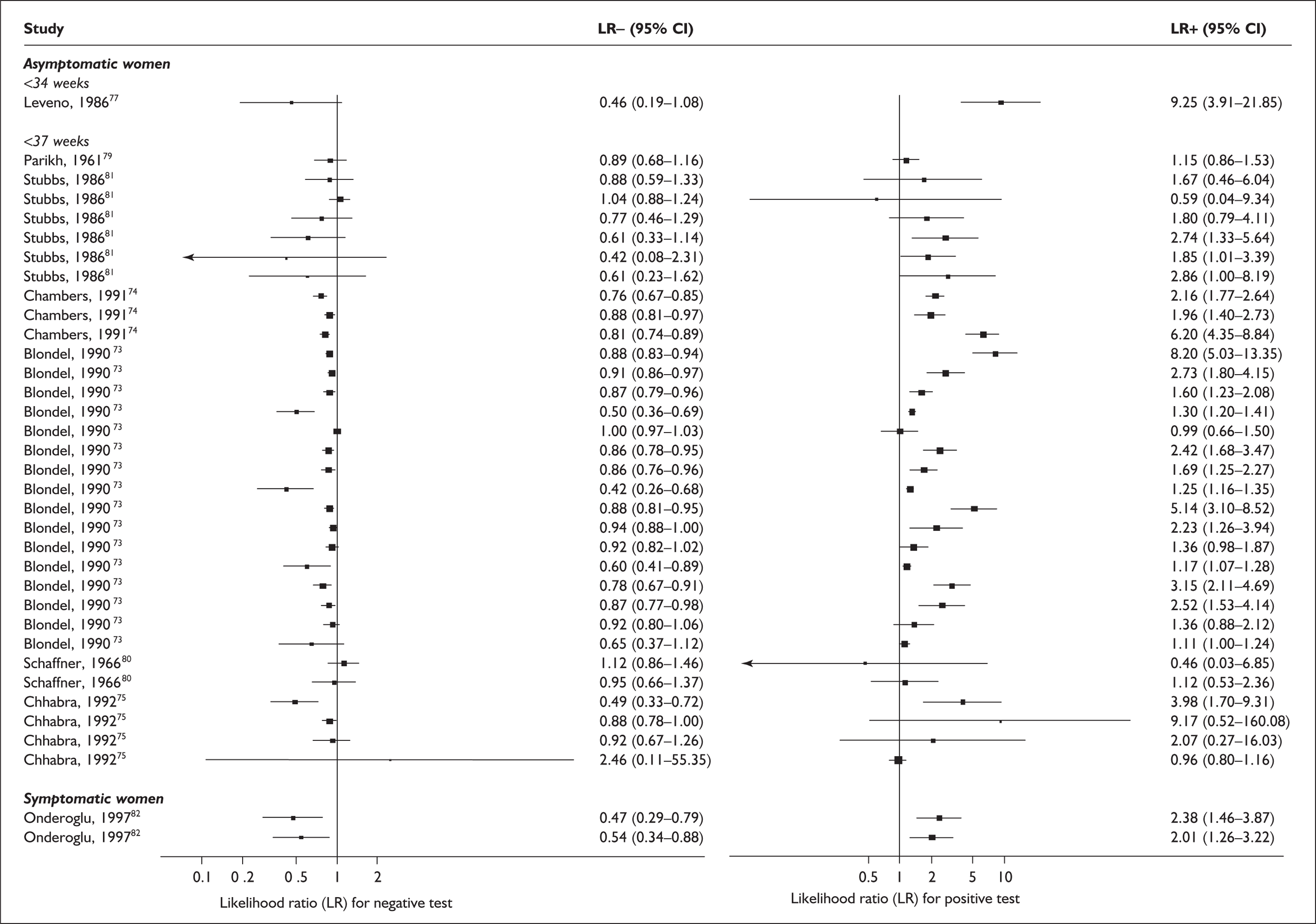
Accuracy of digital examination in symptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, digital examination in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour had a range of LR+ from 2.01 (95% CI 1.26–3.22) to 2.38 (95% CI 1.46–3.87) and LR– from 0.47 (95% CI 0.29–0.79) to 0.54 (95% CI 0.34–0.88) corresponding to a choice of threshold of > 2 cm cervical dilatation or > 40% effacement (the latter threshold corresponded to the less accurate results). 82 These values were used for the decision-analytic modelling. Individual accuracy results are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 71.
Cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin
Cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin (fFN) is a glycoprotein, present in trace quantities, that is usually undetectable in the cervicovaginal secretion. A higher quantity has been purported to be an indication of imminent labour onset. The test is readily available in the form of a commercial rapid test kit. A cotton swab is used to collect samples of cervicovaginal secretions during a speculum examination. The result is either positive (fFN is present), or negative (fFN is not present) obtained within 10–15 minutes of performing the test. These commercial preparations used a positivity threshold of 50 ng/ml.
Study characteristics and quality
There were 58 primary studies (n = 22,905 women) on the accuracy of bedside cervicovaginal fFN testing, comprising 18 studies on asymptomatic antenatal women (n = 18,696) and 40 studies on symptomatic women presenting with threatened preterm labour (n = 4209). Appendix 5, Table 72 summarises each study’s salient features, stratified according to population of women tested, i.e. asymptomatic antenatal women and women with symptoms of threatened preterm labour. The enrolment for the studies ranged from 20 to 6508 women83,84 with a median of 147 women in asymptomatic populations, and from 26 to 725 women85,86 with a median of 86 women for the symptomatic women. All the studies had used cervicovaginal fFN specimens taken from either the posterior fornix or the cervix.
There were three studies in asymptomatic women87–89 and five studies in symptomatic women that fulfilled our definition of high-quality test accuracy studies. 85,90–93 The methodological quality of the included primary studies is summarised in Figure 8. There were 7 and 15 studies that reported the accuracy of the test for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’83,88,94–98 and 37 weeks’ gestation83,84,87,89,94,95,97,99–106 respectively in asymptomatic women. For symptomatic women presenting with threatened preterm labour, 17 studies86,90,92,93,107–119 reported the accuracy of the test in predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7–10 days of testing in addition to eight studies that reported birth before 34 weeks’93,114,120–125 and 31 studies 85,86,90,91,93,103,104,106–109,111,113–115,117,119,122–124,126–136 that reported birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
FIGURE 8.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of bedside test for cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin in predicting spontaneous preterm birth among asymptomatic antenatal women and symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.

Accuracy of fFN in asymptomatic women
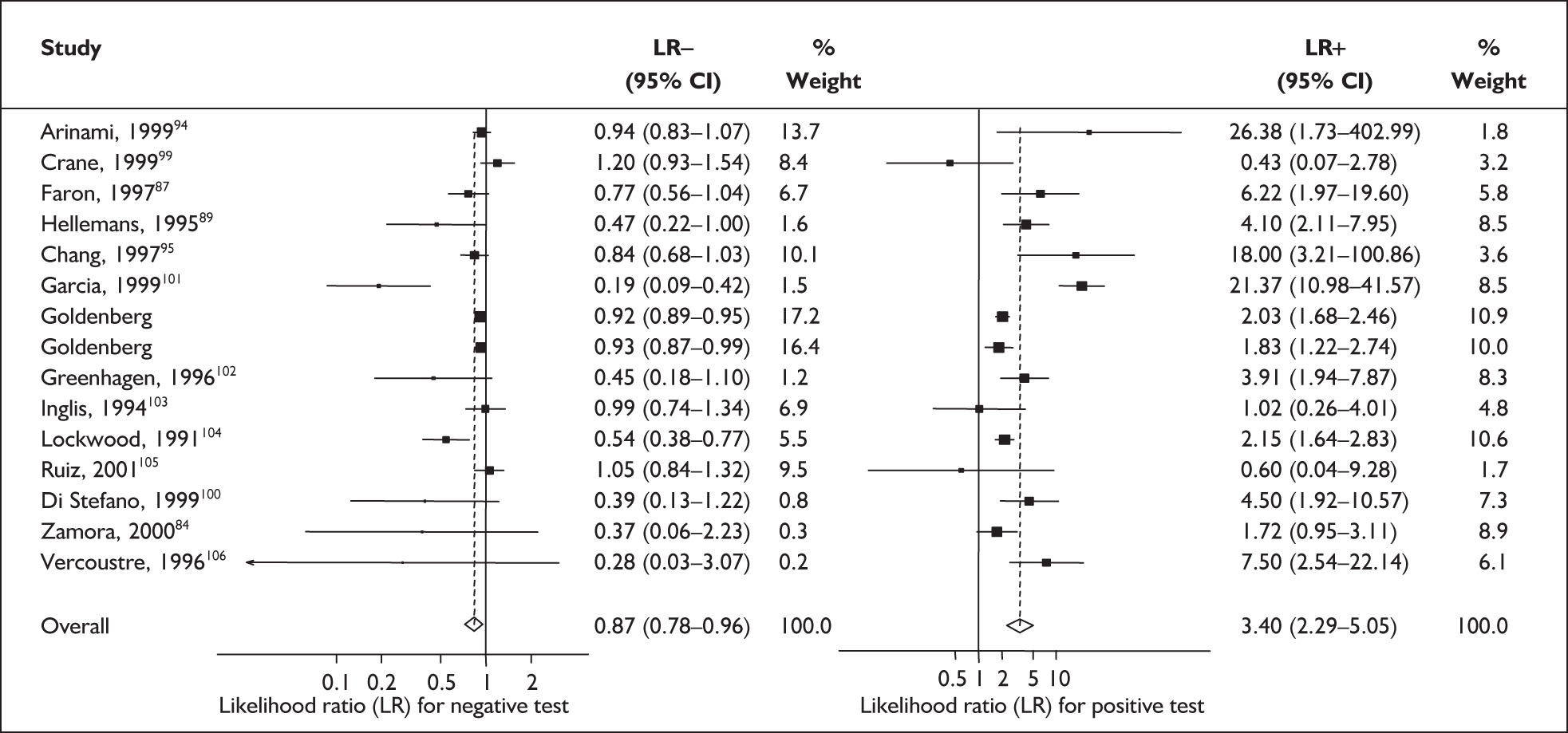
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, the range of LR+ was from 2.57 (95% CI 2.07–3.19) to 86.60 (95% CI 6.26–1198.92) with a summary LR+ of 7.65 (95% CI 3.93–14.86) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00) and the range of LR– was from 0.28 (95% CI 0.05–1.52) to 0.80 (95% CI 0.52–1.24) with a summary LR– of 0.80 (95% CI 0.73–0.88) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.08) (Figure 9). For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, the range of LR+ was from 0.43 (95% 0.07–2.78) to 26.38 (95% 1.73–402.99) with a summary LR+ of 3.17 (95% 2.00–5.02) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00) and the range of LR– was from 0.28 (95% 0.03–3.07) to 1.20 (95% 0.93–1.54) with a summary LR– of 0.87 (95% 0.77–0.97) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00) (Figure 10). Individual test accuracy results from the included studies for asymptomatic women can be found in Appendix 5, Table 74.
FIGURE 9.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) for cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin bedside testing on asymptomatic antenatal women as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00 for LR+ and p = 0.08 for LR–.
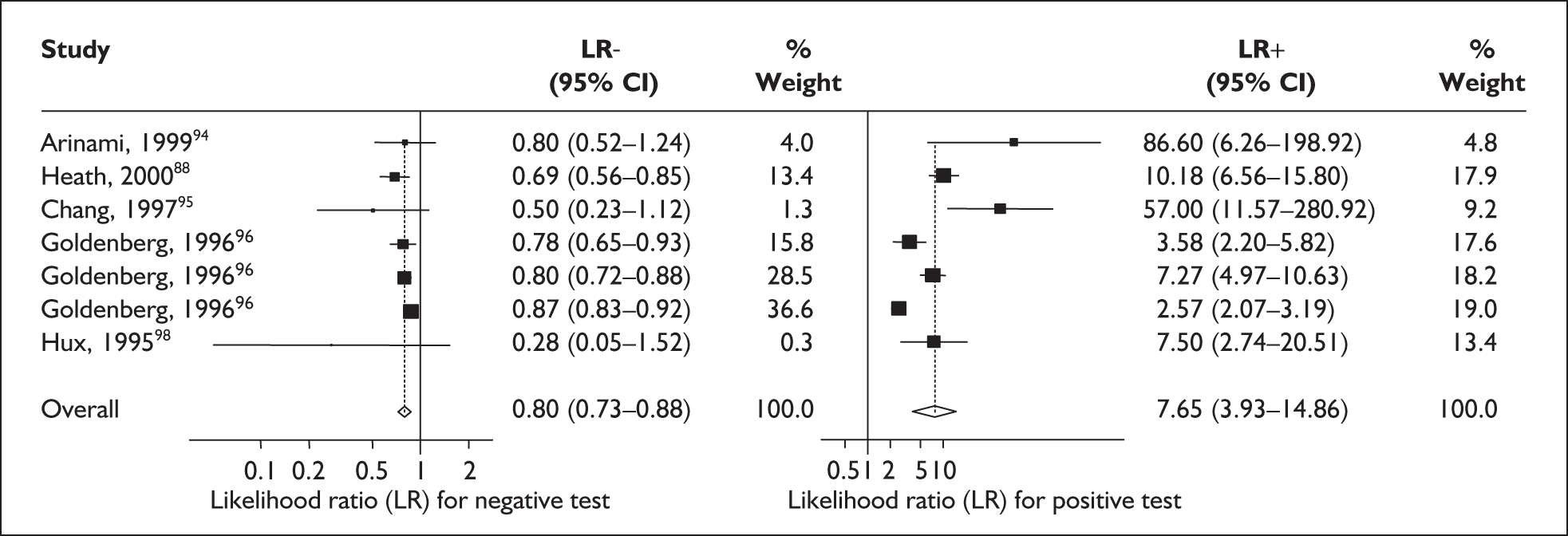
FIGURE 10.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) for cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin bedside testing on asymptomatic antenatal women as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.000 for LR+ and p = 0.000 for LR–.
Accuracy of fFN in symptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7–10 days of testing, the range of LR+ was from 2.12 (95% 1.05–4.28) to 9.29 (95% 5.06–17.06) with a summary LR+ of 4.10 (95% 3.37–4.98) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00) and the range of LR– from 0.09 (95% 0.01–0.58) to 0.59 (95% 0.25–1.39) with a summary LR– of 0.35 (95% 0.27–0.46) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.322) (Figure 11). For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, the range of LR+ was from 1.57 (95% 0.53–4.60) to 5.70 (95% 2.88–11.28) with a summary LR+ of 3.58 (95% 2.56–5.00) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.05), and the range of LR– from 0.12 (95% 0.02–0.79) to 0.91 (95% 0.69–1.20) with summary LR– of 0.34 (95% 0.17–0.68) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00) (Figure 12). For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, the range of LR+ was from 1.00 (95% 0.44–2.30)85 to 14.36 (95% 5.81–35.47)117 with summary LR+ of 3.62 (95% 3.02–4.33) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00), and the range of LR– from 0.08 (95% CI 0.01–0.54)124 to 1.00 (95% 0.44–2.30)85 with a summary LR– of 0.50 (95% 0.43–0.59) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00) (Figure 13). A receiver operating characteristics (ROC) plot of sensitivity versus specificity for cervicovaginal fFN in symptomatic women is shown in Figure 14 and Figure 15. Individual test accuracy results from the included studies for symptomatic women can be found in Appendix 5, Table 73.
FIGURE 11.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) for cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin bedside testing on women presenting with symptoms of threatened preterm labour as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth within 7–10 days of testing. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.002 for LR+ and p = 0.424 for LR–.
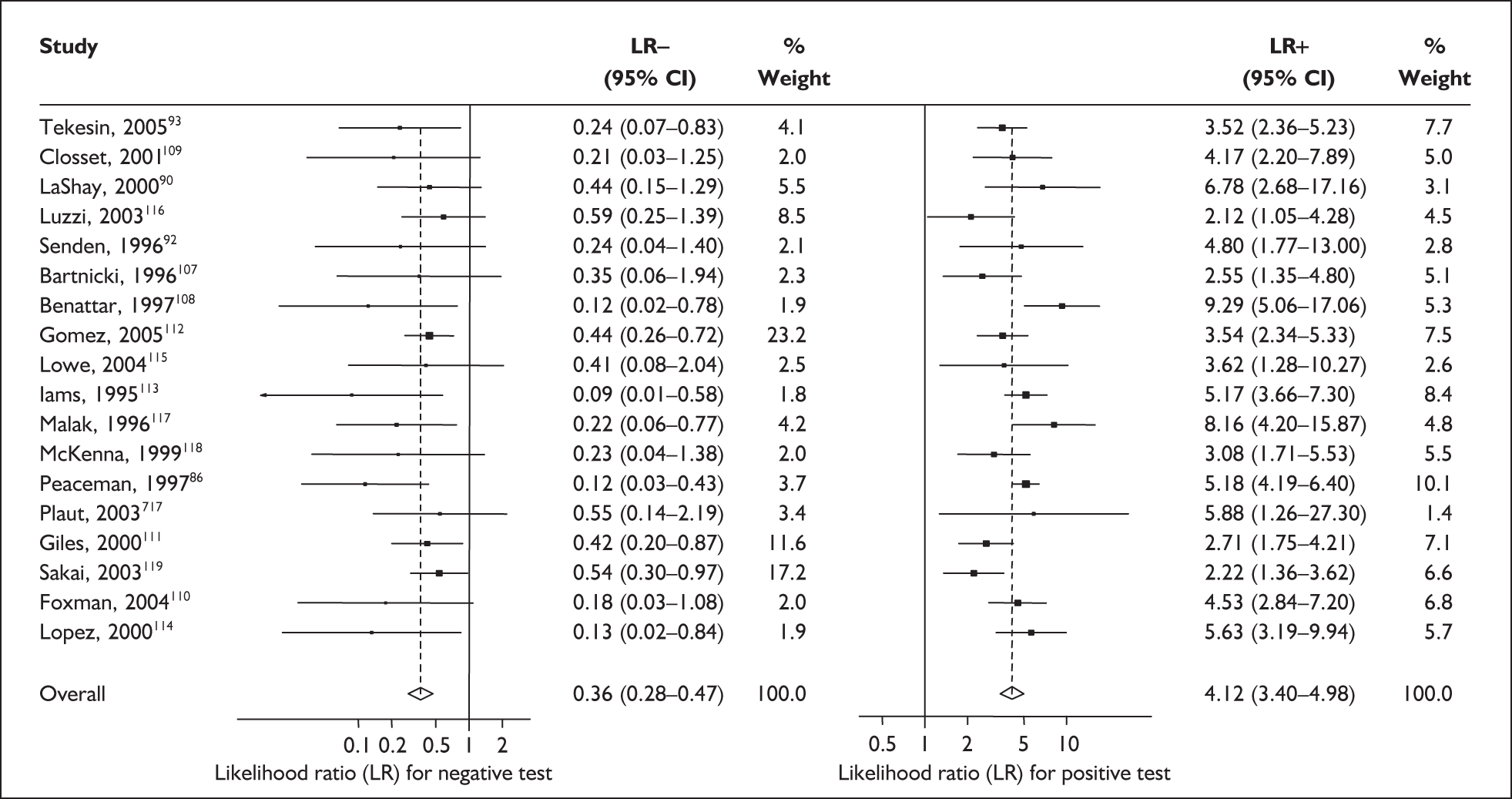
FIGURE 12.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) for cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin bedside testing on women presenting with symptoms of threatened preterm labour as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.052 for LR+ and p = 0.000 for LR–.
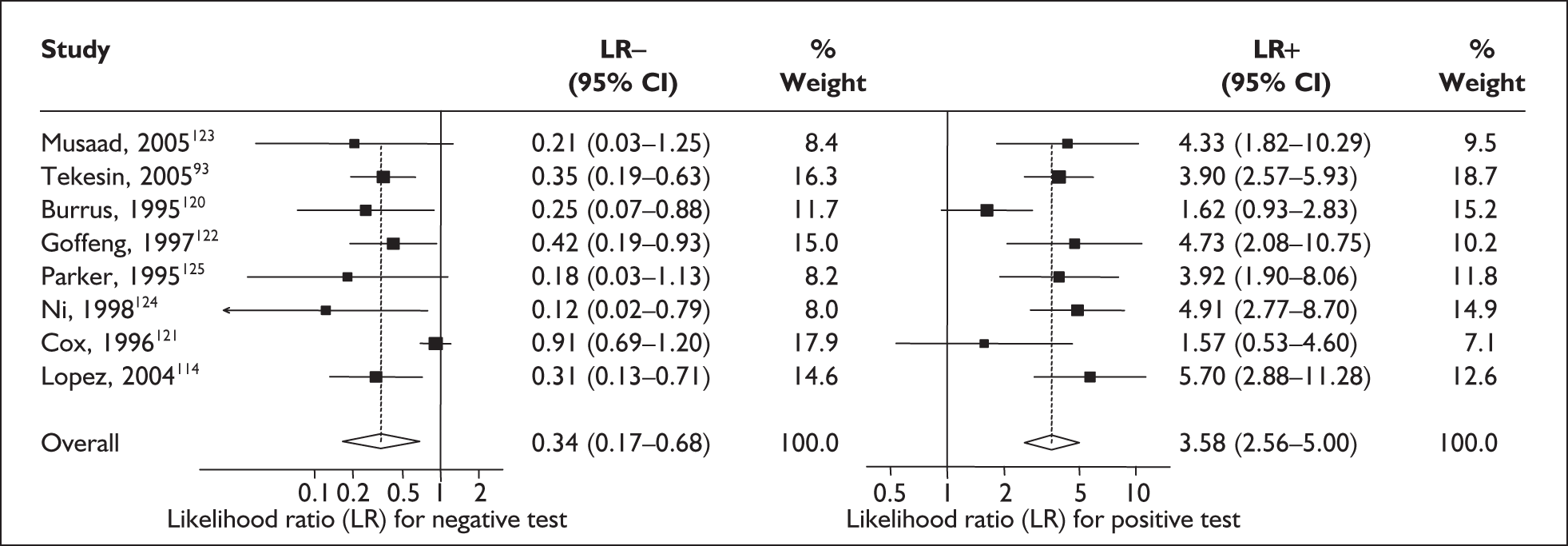
FIGURE 13.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) for cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin bedside testing on women presenting with symptoms of threatened preterm labour as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.000 for LR+ and p = 0.000 for LR–.
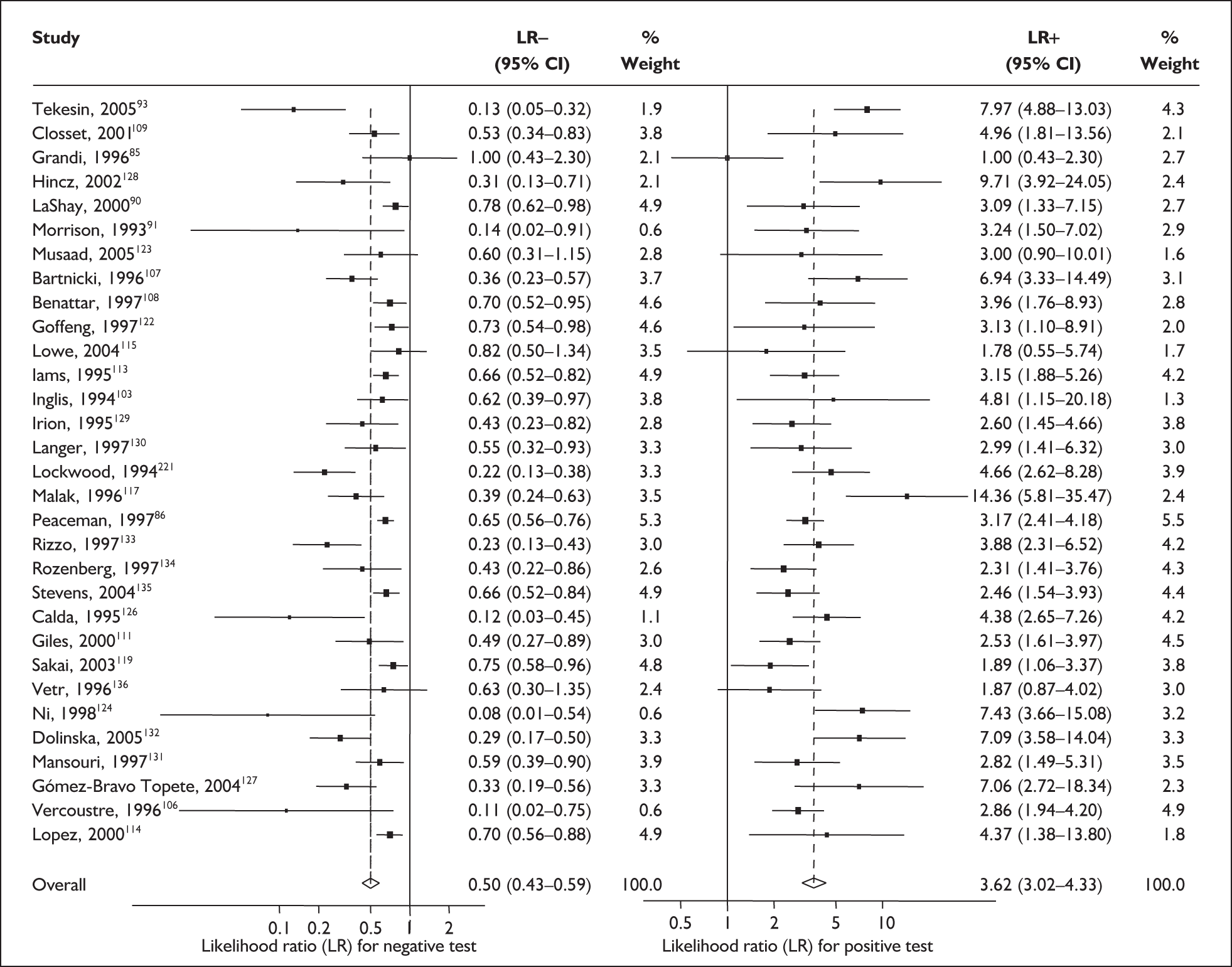
FIGURE 14.
Plot of sensitivity versus 1-specificity in ROC space for cervicovaginal fibronectin studies in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour for predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing.
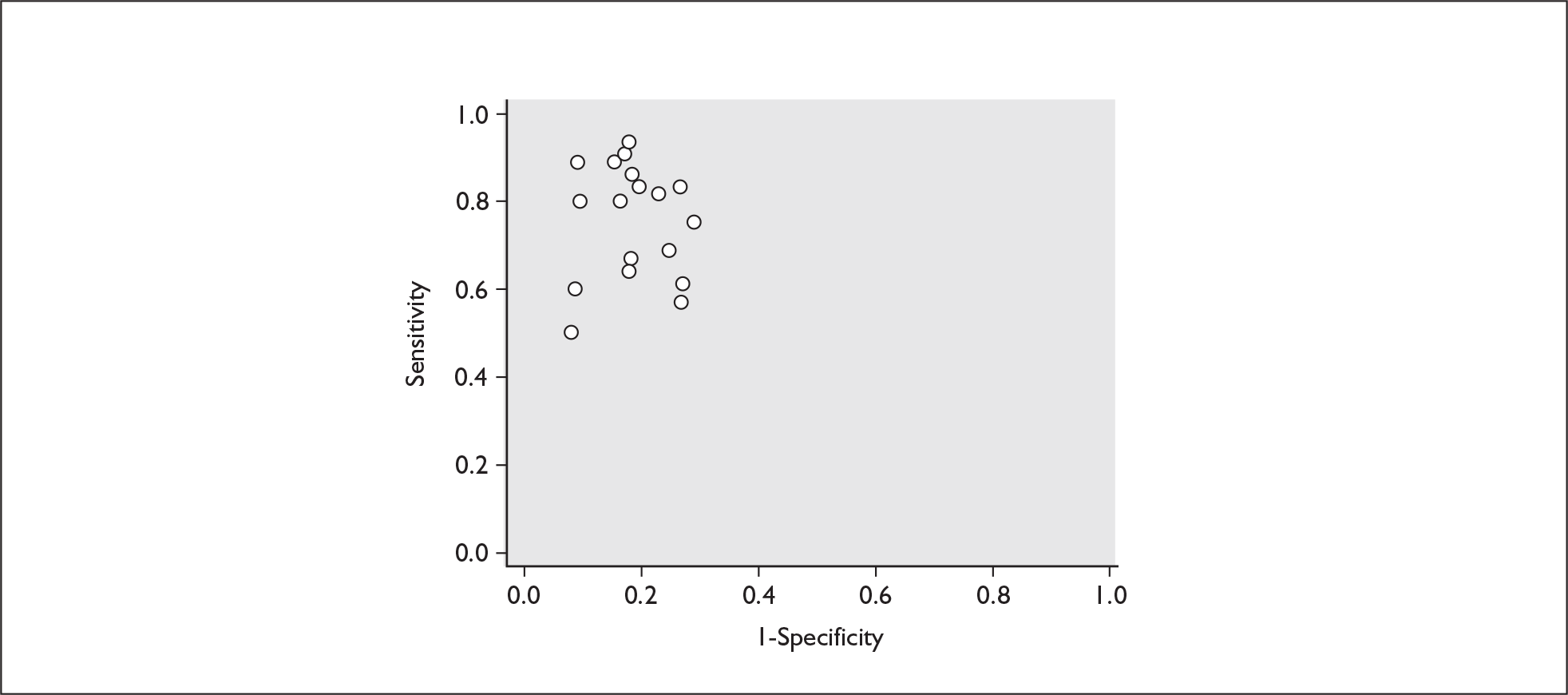
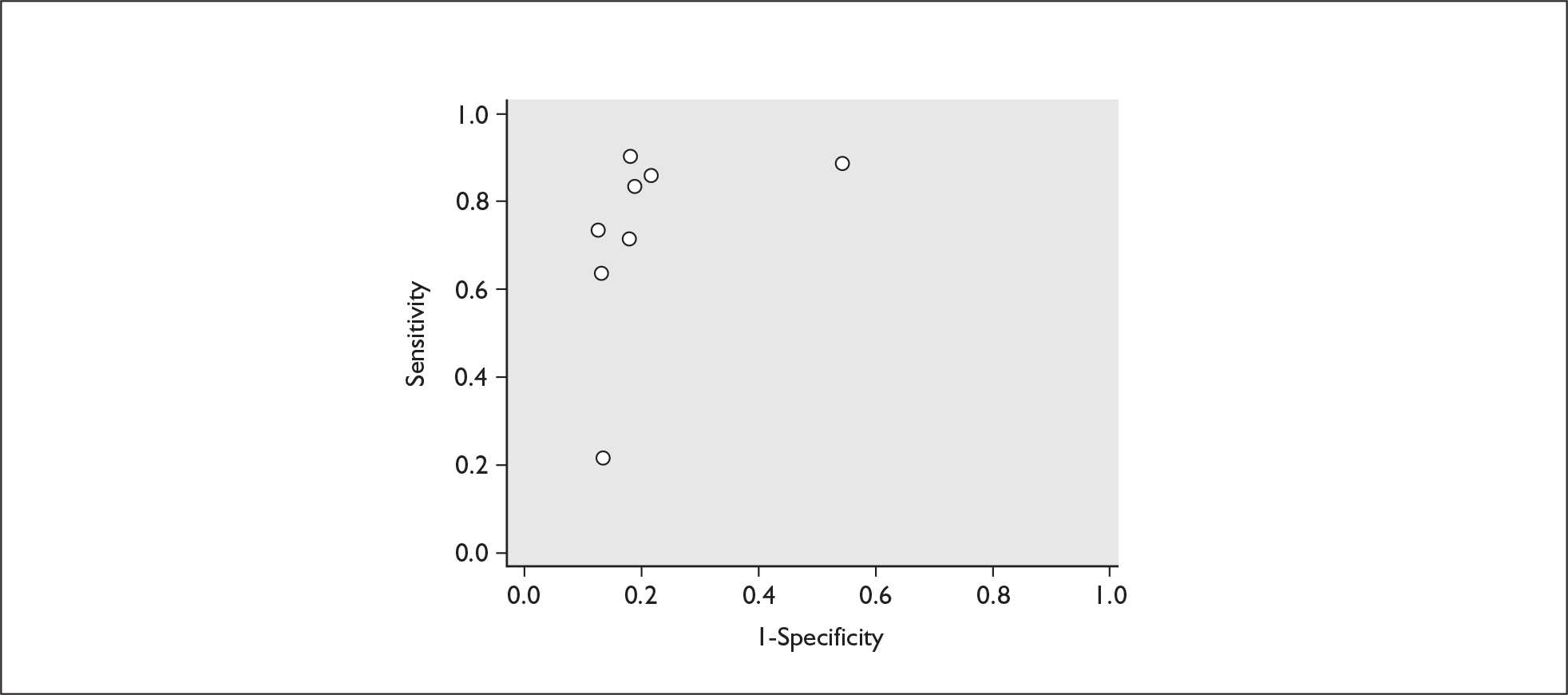
FIGURE 15.
Plot of sensitivity versus 1-specificity in ROC space for cervicovaginal fibronectin studies in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation.
Cervicovaginal prolactin
During pregnancy, prolactin is produced by the decidua (in addition to the maternal adenohypophysis and the fetal pituitary. Disruption of the decidua–membrane matrix during labour, whether preterm or term, may allow the secreted prolactin to leak to the cervix and vagina, where it would be available for detection. It is purported that detection of this cervicovaginal prolactin is a reliable predictor of the onset of spontaneous preterm labour and hence of spontaneous preterm birth. 137 A cotton swab is used to collect samples of cervicovaginal secretions during a speculum examination, which was then sent for laboratory assay.
Study characteristics and quality
There were five primary studies, two evaluating the test in a population of asymptomatic women (n = 80)137,138 and five evaluating the test in symptomatic women (n = 265),137–141 presenting with threatened preterm labour, including two studies that evaluated the test in both populations. 137,138 The study enrolment ranged from 35 women138 to 66 women. 141 In asymptomatic women, the test was performed between 24 and 32 weeks’ gestation. The study enrolment for asymptomatic women ranged from 35 to 66 women138,141 with a median of 40 women. 137 Only two studies, both in symptomatic women, used the same threshold of abnormality of 2.0 ng/ml. 137,140 The remaining studies used 1.5 ng/ml,138 1.8 ng/ml139 and 50 ng/ml thresholds. 141 All the studies evaluated cervicovaginal prolactin test on a single occasion rather than as a serial test.
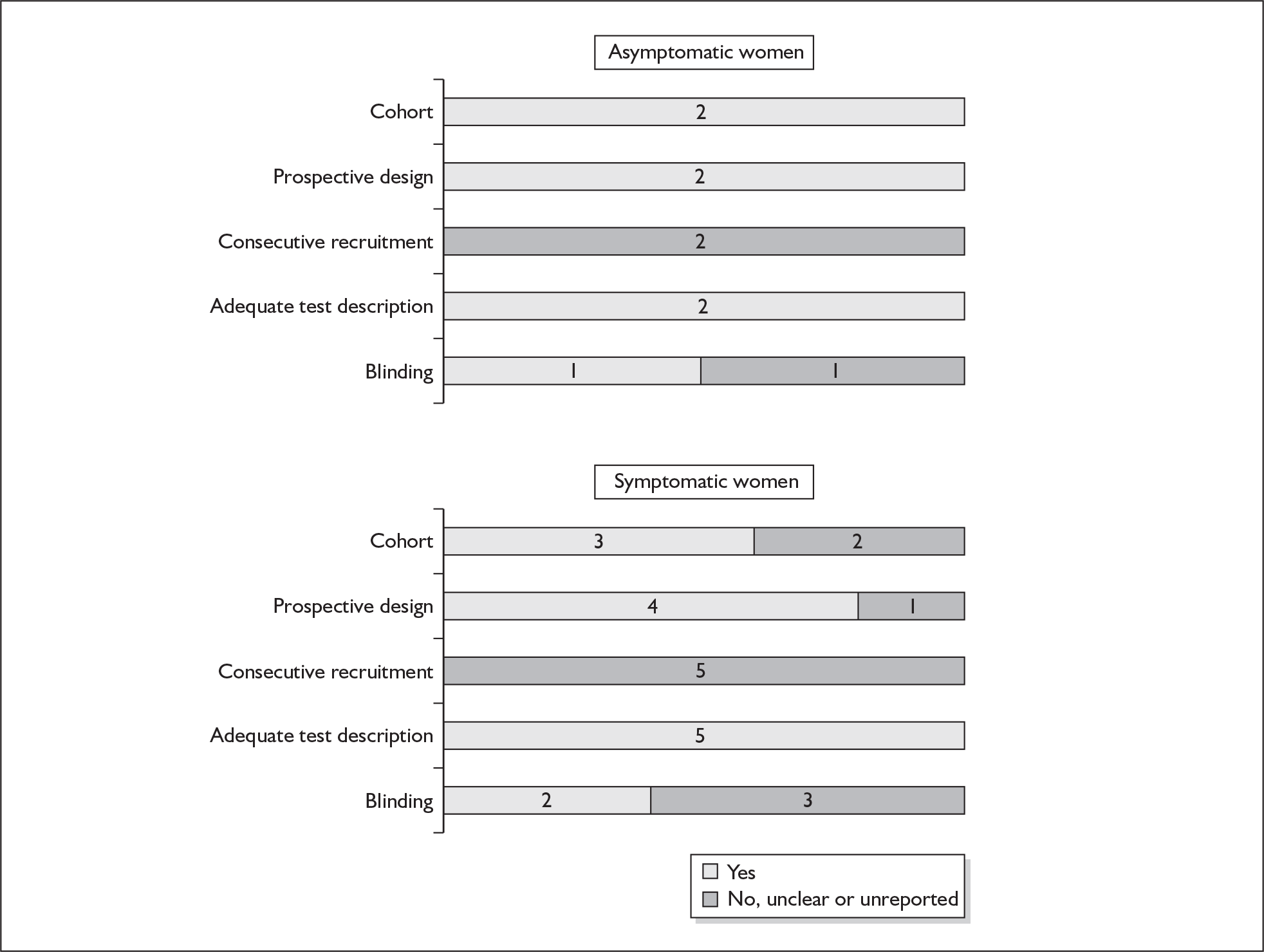
None of the studies reported consecutive enrolment and only three studies, one in the asymptomatic population137 and two in the symptomatic population137,140 reported blinding. The methodological quality of the included primary studies is summarised in Figure 16. None of the studies fulfilled our definition of ideal quality test accuracy study design. One study each reported outcome of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’137 and 37 weeks’ gestation. 138 One study reported outcome within 7 days of testing,137 three studies reported outcome before 34 weeks’ gestation137,138,140 and all studies reported outcome before 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women. 137–141 Information on individual study characteristics can be found in Appendix 5, Table 75, which summarises each study’s salient features, stratified according to the population of women tested, i.e. asymptomatic antenatal women and women with symptoms of threatened preterm labour.
FIGURE 16.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of cervicovaginal prolactin in predicting spontaneous preterm birth among asymptomatic antenatal women and symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
Accuracy of cervicovaginal prolactin in asymptomatic women
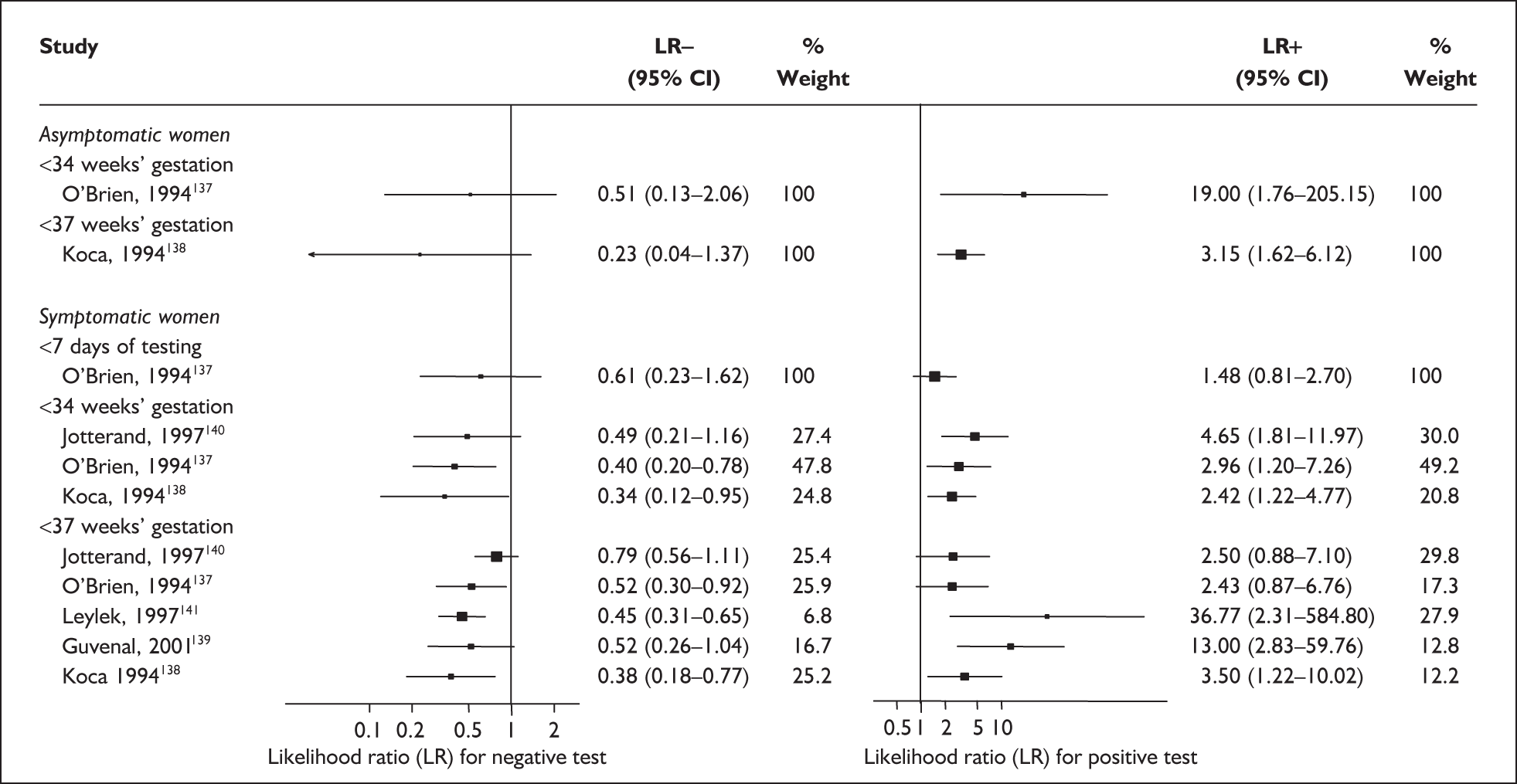
In the single study evaluating the test on asymptomatic women for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, LR+ was 19.00 (95% CI 1.76–205.15) and LR– was 0.51 (95% CI 0.13–2.06),137 while before 37 weeks’ gestation the LR+ was 3.15 (95% CI 1.62–6.12) and LR– was 0.23 (95% CI 0.038–1.37)138 (Figure 17). These LR values were used in the decision-analytic modelling. The accuracy measures of the test in predicting spontaneous preterm births in asymptomatic women are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 76.
FIGURE 17.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of rapid test for cervicovaginal prolactin as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth according to population and outcome gestations. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality. χ2 heterogeneity test for 34 weeks’ gestation p = 0.54 for LR+ and p = 0.86 for LR–; and for 37 weeks’ gestation p = 0.13 for LR+ and p = 0.16 for LR–.
Accuracy of cervicovaginal prolactin in symptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing, LR+ was 1.48 (95% CI 0.81–2.70) and LR– was 0.61 (95% CI 0.23–1.62) (Figure 17). These LRs were used in the decision-analytic modelling. The accuracy for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation ranged from LR+ of 2.42 (95% CI 1.22–4.77) and LR– of 0.34 (95% CI 0.12–0.95)138 to LR+ of 4.65 (95% CI 1.81–11.97) and LR– of 0.49 (95% CI 0.21–1.16). 140 LRs from Jotterand et al. 140 were used in the decision-analytic modelling because this represented the best higher-quality study available. The accuracy for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation ranged from LR+ of 2.43 (95% CI 0.87–6.76) and LR– of 0.52 (95% CI 0.30–0.92)137 to LR+ of 36.77 (95% CI 2.31–584.80) and LR– of 0.45 (95% CI 0.31–0.65)141 (Figure 17). However, only the LR+ of 2.50 (95% CI 0.88–7.10) and LR– of 0.79 (95% CI 0.56–1.11) from Jotterand et al. 140 was used in decision-analytic modelling because it represented the best higher-quality study. Heterogeneity assessment of the LRs did not reveal significant graphical or statistical differences in the accuracy of results except for either positive or negative test results in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women. The accuracy measures of the test in predicting spontaneous preterm births in symptomatic women are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 76.
Cervicovaginal phosphorylated form of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1
The phosphorylated form of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 (phIGFBP-1) is produced by placental decidual cells. It is released and leaks into the cervix during the onset of parturition, whether term or preterm, and so has been put forward as a reliable predictor of the onset of preterm labour and hence of spontaneous preterm birth. The novel test is an immune-chromatographic dipstick test based on monoclonal antibodies that detects the presence of the phosphorylated form of IGFBP-1 release from decidual cells. The test is readily available in the form of a commercial rapid test kit. 142 A cotton swab is used to collect samples of cervicovaginal secretions during a speculum examination. The result is either positive (phIGFBP-1 is present; threshold exceeded 30 μg/l), or negative (phIGFBP-1 less than 30 μg/l) obtained within 10–15 minutes of performing the test.
Study characteristics and quality
There were ten primary studies, involving a total of 568 women. One potentially eligible study for inclusion was excluded because data were unobtainable. 143Appendix 5, Table 77 summarises each study’s salient features, stratified according to the population of women tested, i.e. asymptomatic antenatal women (one study)144 and women with symptoms of threatened preterm labour (nine studies). 142–152 The single study which included an asymptomatic antenatal population had targeted the test, which was performed 3-weekly between 24 and 34 weeks’ gestation, at women who had a previous spontaneous preterm birth. Enrolment in the studies ranged from 32 to 135 women, with a median of 46 women.
Only one study reported consecutive enrolment145 and only two studies reported blinding to test results and/or reference standards. 146,150 Otherwise all studies used cohorts of pregnant women; all except two151,152 reported prospective data collection design and, with one exception,151 had provided adequate test description. The methodological quality of the included primary studies is summarised in Figure 18. The only study on asymptomatic women reported spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation as the reference standard. For studies on symptomatic women, all studies have reported birth before 37 weeks’ gestation as their reference standards. Additionally, three studies also reported birth within 48 hours of testing,145,146,150 four studies reported birth within 7 days of testing,145,146,149,150 and three studies reported birth before 34 weeks’ gestation. 142,149,150
FIGURE 18.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of rapid test for phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1) in cervical secretion in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
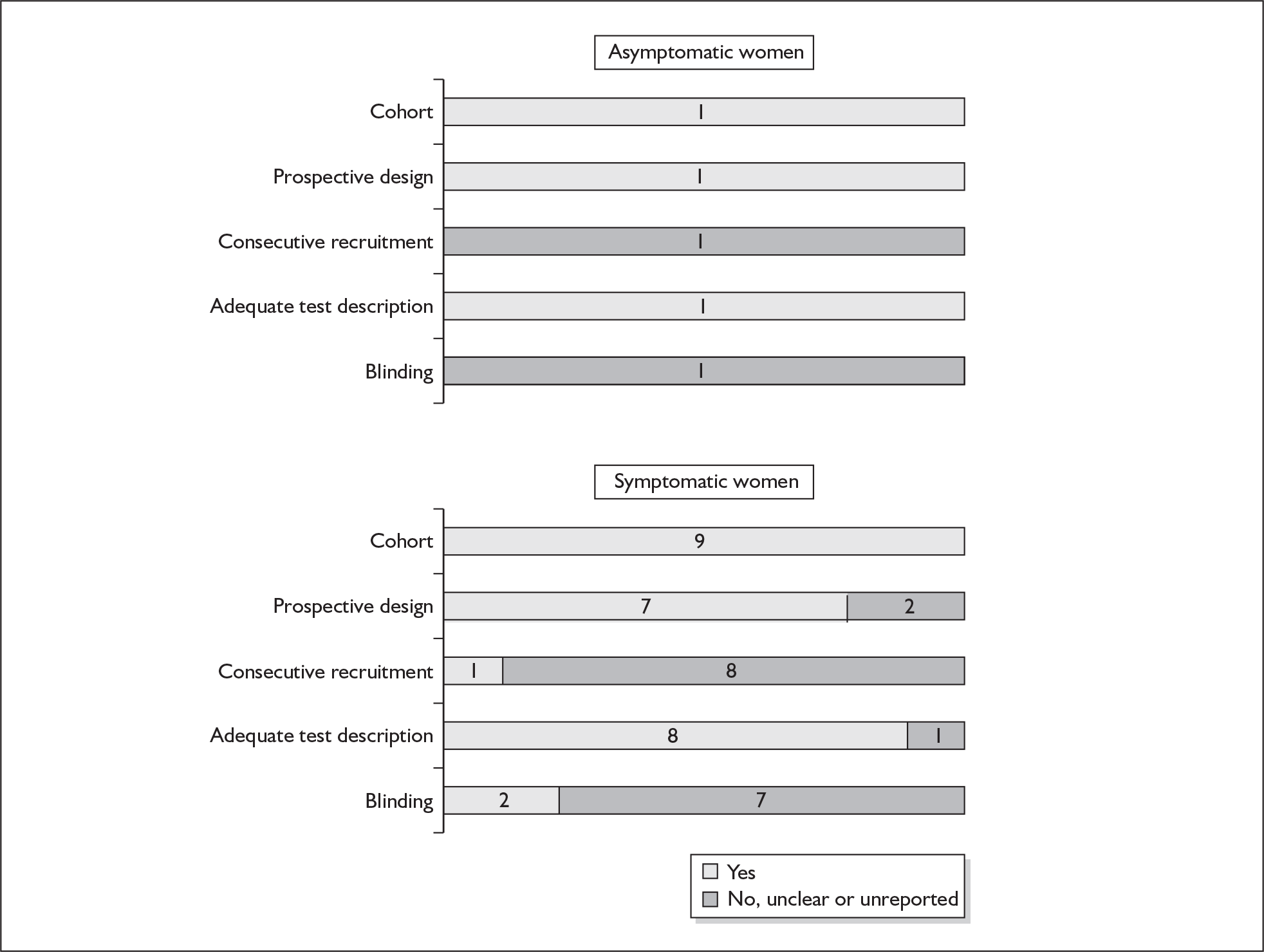
Accuracy of phIGFBP-1 in asymptomatic women
In the single study evaluating the test on asymptomatic women for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, LR+ was 4.17 (95% confidence interval (CI) 2.44–7.13) and LR– was 0.21 (95% CI 0.08–0.51). 144 These values were used in the decision-analytic modelling.
Accuracy of phIGFBP-1 in symptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of testing, summary LR+ was 2.53 (95% CI 1.17–5.48) and summary LR– was 0.32 (95% CI 0.15–0.66) (Figure 19). However, summary LR+ of 1.73 (95% CI 0.92–3.25) and summary LR– of 0.59 (95% CI 0.24–1.45) from two studies of equal size and representing higher-quality studies145,150 were used for the decision-analytic modelling. The accuracy for predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing was shown in Figure 20, where the summary LR+ was 3.29 (95% CI 2.24–4.83) and summary LR– was 0.20 (95% CI 0.10–0.41). Summary LR+ of 2.83 (95% CI 1.57–5.09) and summary LR– of 0.371 (95% CI 0.13–1.04) from the higher-quality studies of equal size145,150 were used in the decision-analytic modelling.The accuracy for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation was shown in Figure 21, where the summary LR+ was 2.96 (95% CI 2.02–4.33) and summary LR– was 0.22 (95% CI 0.08–0.64). However, LR+ of 4.15 (95% CI 1.43–11.99) and LR– of 0.31 (95% CI 0.03–3.38) from the largest higher-quality study150 were used in the decision-analytic modelling. Summary LR+ for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation was 4.26 (95% CI 2.54–7.17) and summary LR– was 0.28 (95% CI 0.20–0.38) (Figure 22). LRs from the largest higher-quality study145 of LR+ of 3.87 (95% CI 1.54–9.72) and LR– of 0.33 (95% CI 0.15–0.71) for this outcome were used for the decision-analytic modelling. Heterogeneity assessment of the LRs did not reveal significant graphical or statistical differences for most of the accuracy results except for positive test results in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in this clinically similar group of women. ROC plots of sensitivity versus specificity for cervicovaginal phIGFBP-1 in symptomatic women predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing as well as before 34 weeks’ gestation are shown in Figure 23 and Figure 24, respectively. The accuracy measures of the test in predicting spontaneous preterm births in symptomatic women are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 78.
FIGURE 19.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of rapid test for phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1) in cervical secretion as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of testing. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.150 for LR+ and p = 0.22 for LR–.
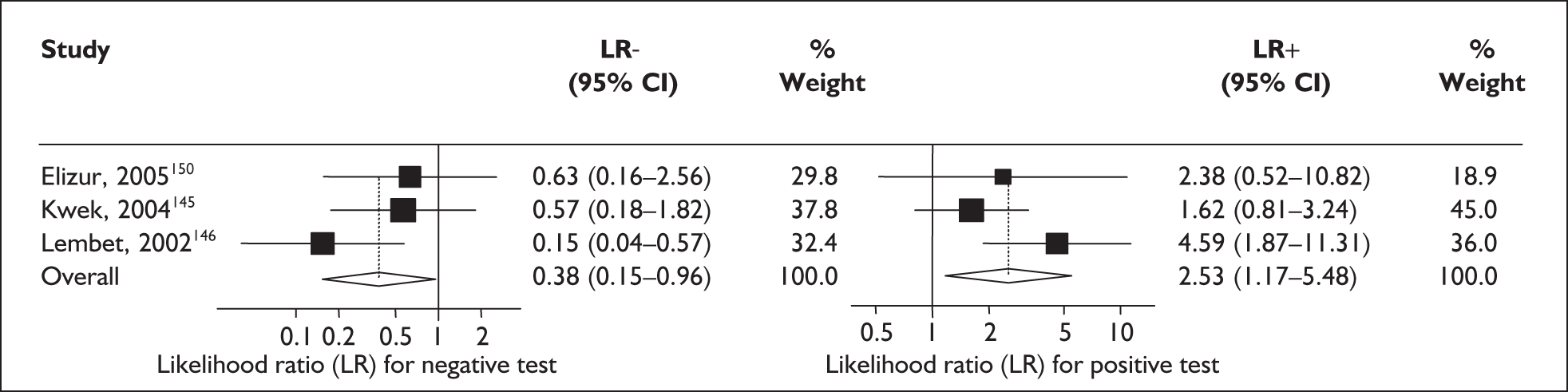
FIGURE 20.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of rapid test for phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1) in cervical secretion as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.57 for LR+ and p = 0.29 for LR–.
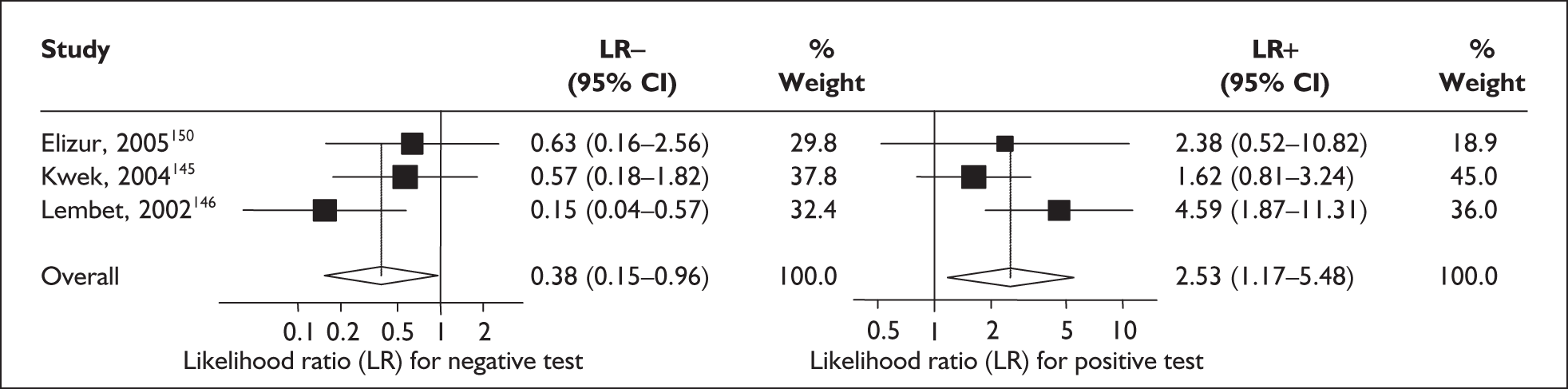
FIGURE 21.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of rapid test for phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1) in cervical secretion as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.76 for LR+ and p = 0.85 for LR–.
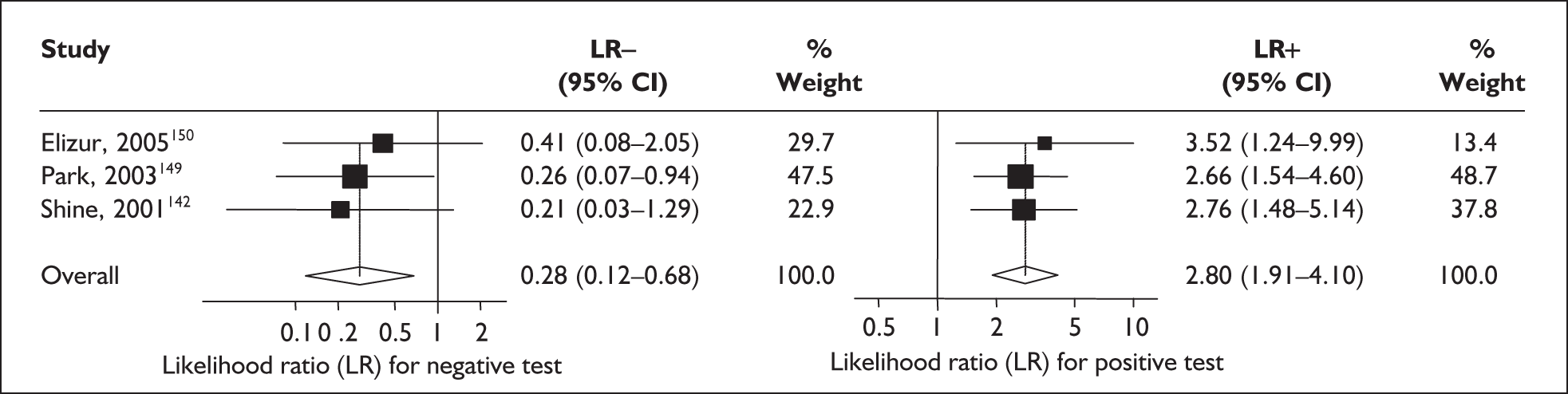
FIGURE 22.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of rapid test for phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1) in cervical secretion as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00 for LR+ and p = 0.79 for LR–.
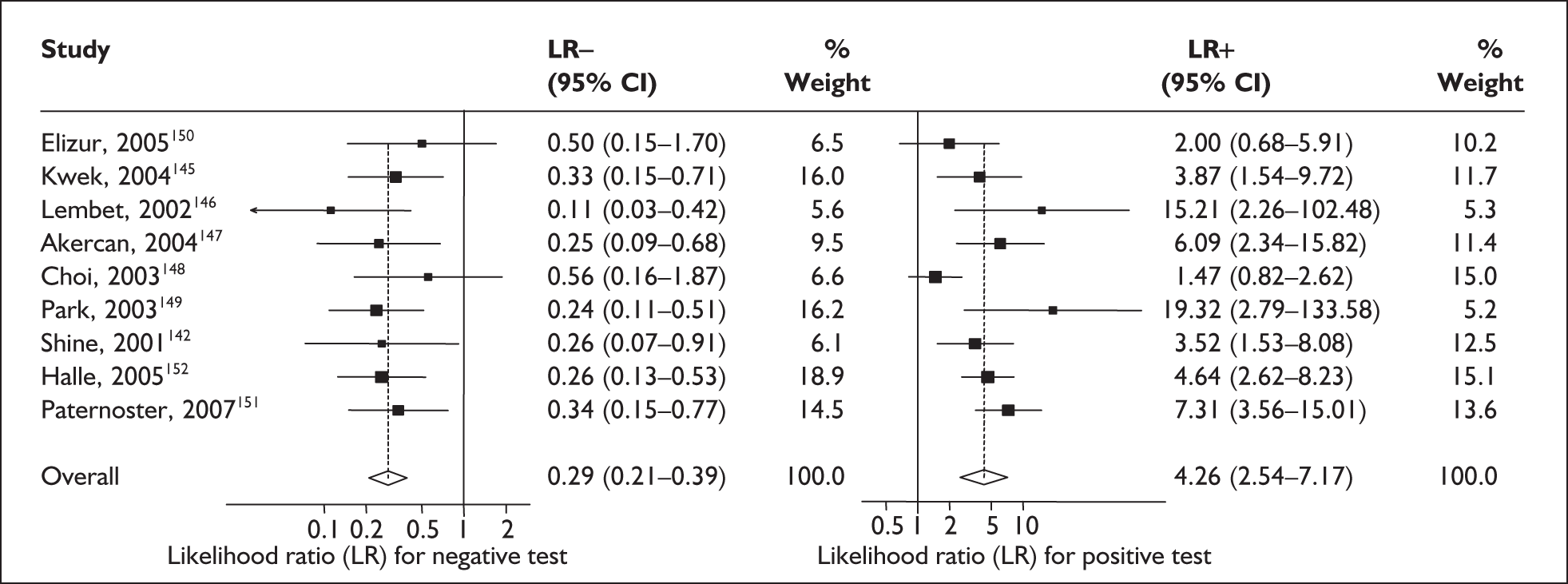
FIGURE 23.
Plot of sensitivity versus 1-specificity in ROC space for cervicovaginal phIGFBP-1 studies in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour for predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing.
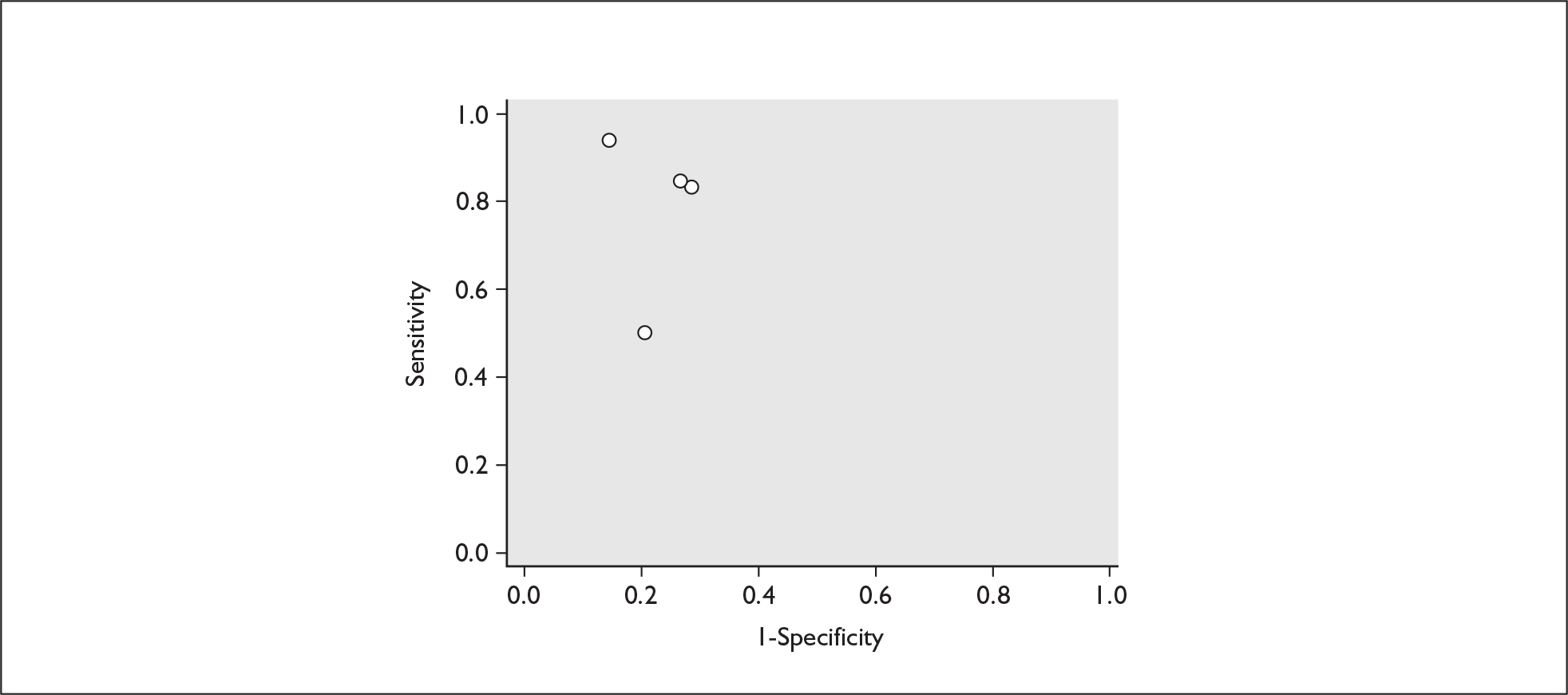
FIGURE 24.
Plot of sensitivity versus 1-specificity in ROC space for cervicovaginal phIGFBP-1 studies in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation.
Serum α-fetoprotein
A high level of maternal serum α-fetoprotein (MSAFP) in the first half of pregnancy has been associated with prematurity for the past three decades. However, its utility as a serum marker for predicting spontaneous preterm birth has never been fully evaluated in a systematic review despite it being commonly used as a screening test for fetal neural tube defects and as an integral part of screening for trisomy 21.
Study characteristics and quality
There were 20 primary accuracy studies that met the selection criteria, all in asymptomatic women. Appendix 5, Table 79 summarises each study’s salient features. 153–171 One citation contributed to two separate studies and results. 156 The most common gestation tested was the mid-trimester (14–28 weeks). The threshold at which studies commonly reported their results were 2.0 and 2.5 multiples of the median (MoMs). The commonest reference standard was spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation with only five studies reporting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation. 154,157,160,168,172 The methodological quality of the included primary studies is summarised in Figure 25 where it is shown that all the included studies were missing one or more ideal quality features.
FIGURE 25.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of maternal serum α-fetoprotein in predicting spontaneous preterm birth among asymptomatic antenatal women. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
Accuracy of MSAFP in asymptomatic women
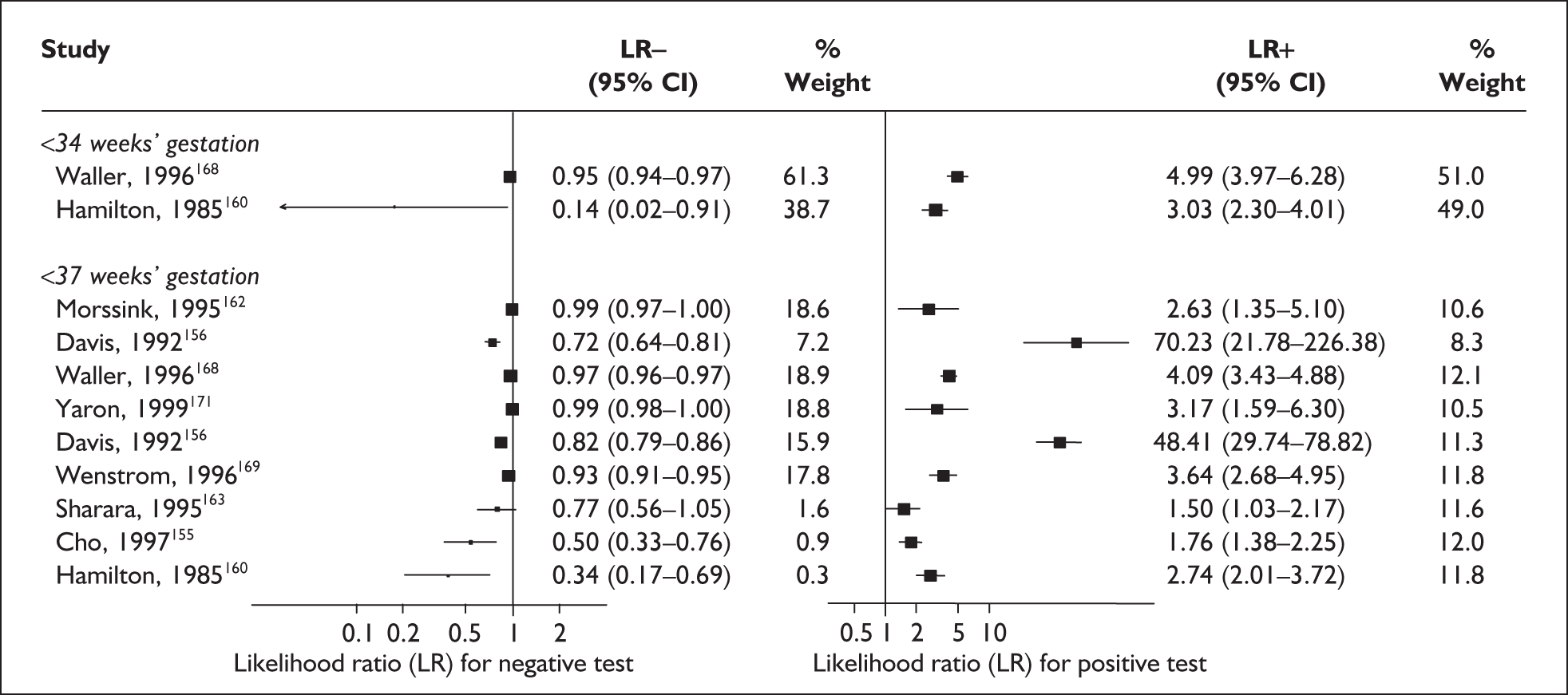
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, MSAFP, with a most commonly used threshold of 2.5 MoM, had a range of LR+ from 3.03 (95% CI 2.30–4.01)160 to 4.99 (95% CI 3.97–6.28)168 and a range of LR– from 0.14 (95% CI 0.02–0.91)160 to 0.95 (95% CI 0.94–0.97). 168 LRs from Waller et al. 168 were used in the decision analyses because it represented the best available higher-quality study.
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation with MSAFP, two thresholds were used more commonly than others: 2.0 MoM and 2.5 MoM. With the threshold of 2.0 MoM, there was a range of LR+ from 0.97 (95% CI 0.51–1.85)164 to 4.21 (95% CI 3.47–5.09)165 and a range of LR– from 0.45 (95% CI 0.20–1.02)153 to 1.01 (95% CI 0.86–1.17). 164 The LR+ of 1.63 (95% CI 0.81–3.27) and LR– of 0.96 (95% CI 0.89–1.03) from Tanaka et al. 166 were used in the decision analyses because this represented the best available higher-quality study. With a threshold of 2.5 MoM, there was a range of LR+ from 1.50 (95% CI 1.03–2.17)163 to 70.23 (95% CI 21.78–226.38) and LR– from 0.34 (95% CI 0.17–0.69)160 to 0.99 (95% CI 0.97–1.00). 162 The LRs from Morssink et al. 162 were used in the decision analyses because it represented the best higher-quality study available. Figure 26 and Figure 27 summarise the accuracy of each threshold in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Individual accuracy results are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 80.
FIGURE 26.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios of maternal serum α-fetoprotein in asymptomatic women (threshold of 2.0 MoM) as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality.
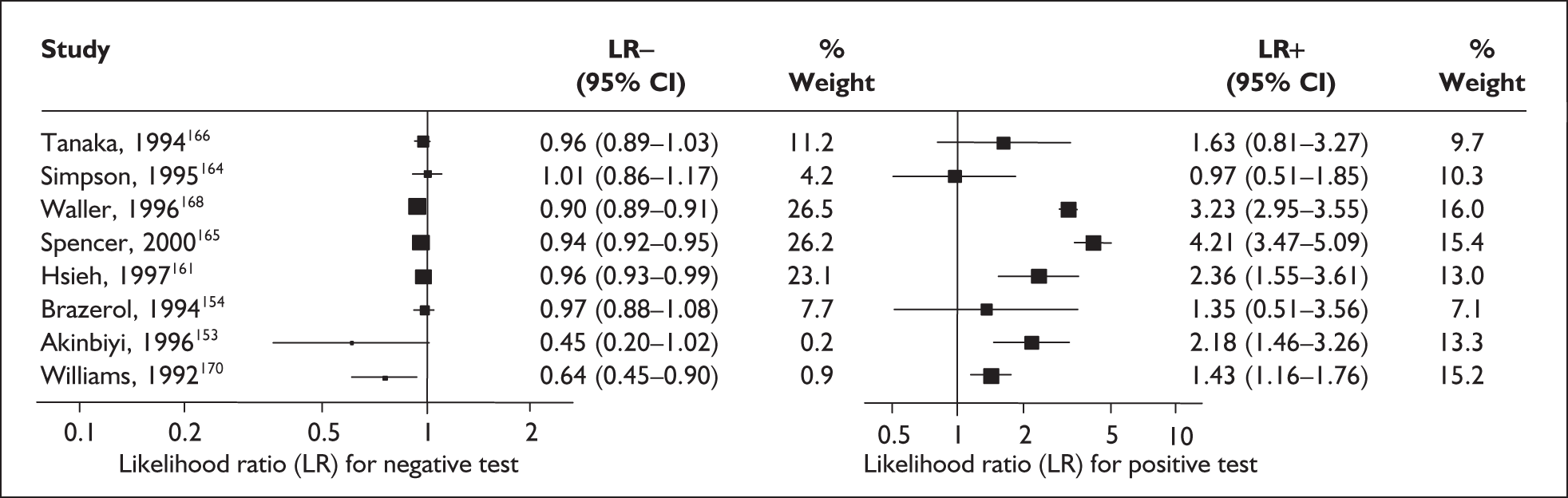
FIGURE 27.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios of maternal serum α-fetoprotein in asymptomatic women (threshold of 2.5 MoM) as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before34 and 37 weeks’ gestation. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality.
Serum relaxin
Relaxin is a peptide hormone produced by the corpus luteum and is known to soften and ripen the human cervix. Hyper-relaxinaemia has been associated with prematurity. 173 Therefore it is purported that measurement of maternal serum relaxin may predict the impending preterm labour that leads to spontaneous preterm birth.
Study characteristics and quality
There were five primary studies on the accuracy of maternal serum relaxin measurements; four were performed on asymptomatic women (n = 3549)173–176 while one involved symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour (n = 34). 177 One study evaluated the test’s serial testing accuracy in predicting spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic women. 173Appendix 5, Table 81 summarises each study’s salient features.
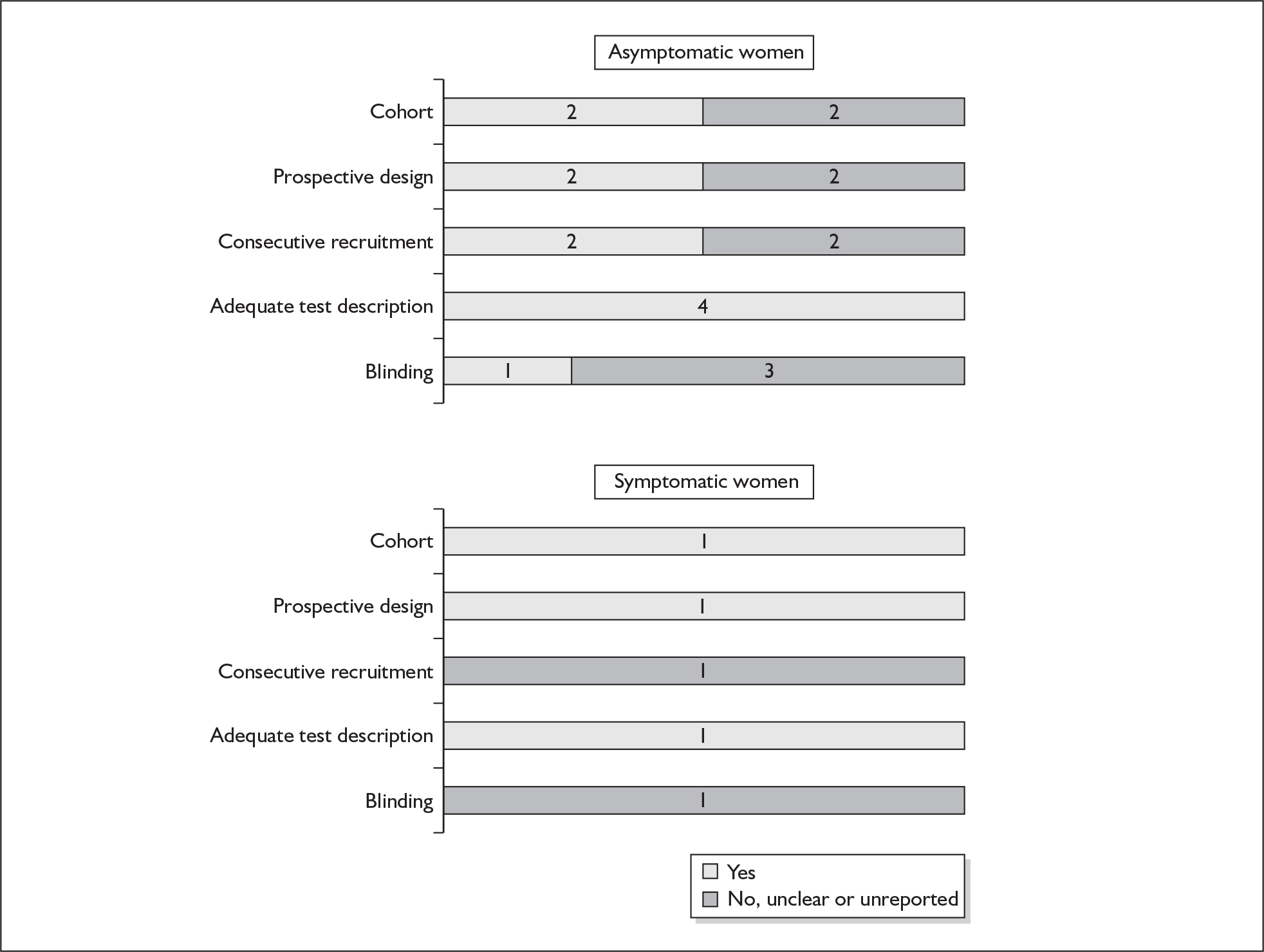
There were no studies included within the systematic review of the accuracy of maternal serum relaxin testing in predicting spontaneous preterm births that fulfil our ideal definition of high-quality test accuracy studies either in asymptomatic or symptomatic women. Blinding was absent in all but one study. 176 However, all studies have an adequate test description report. The methodological quality of the included primary studies is summarised in Figure 28.
FIGURE 28.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of maternal serum relaxin in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
Accuracy of maternal serum relaxin in asymptomatic women
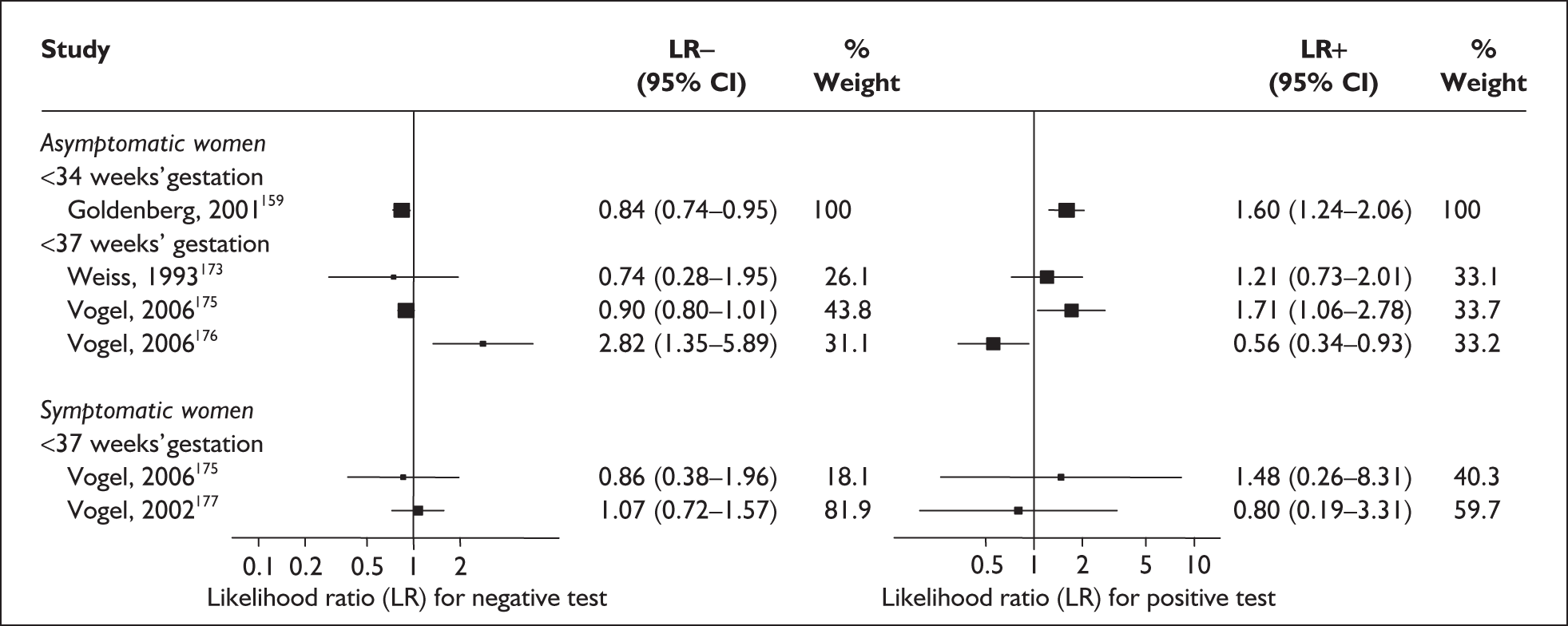
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, serum relaxin had an LR+ of 1.60 (95% CI 1.24–2.06) and LR– of 0.84 (95% CI 0.74–0.95). 174 For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation serum relaxin had an LR+ of 1.21 (95% CI 0.73–2.10) and LR– of 0.74 (95% CI 0.29–1.95). 173 LRs from these studies were used in the decision-analytic modelling because they represented the largest higher-quality studies for the respective outcomes. The accuracy results are summarised in Figure 29. Individual accuracy results are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 82.
FIGURE 29.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of maternal serum relaxin measurement in predicting spontaneous preterm birth stratified according to population and outcomes. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality.
Accuracy of maternal serum relaxin in symptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, maternal serum relaxin had an LR+ of 1.48 (95% CI 0.26–8.31) and LR– of 0.861 (95% CI 0.38–1.96) and before 37 weeks’ gestation it had LR+ of 0.80 (95% CI 0.19–3.31) and LR– of 1.07 (95% CI 0.72–1.57) Figure 29. 177 These LRs were used in decision-analytic modelling because they represented the largest higher-quality study for this reference standard. Individual accuracy results for symptomatic women can be found in Appendix 5, Table 82.
Serum corticotrophin-releasing hormone
Corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH) is a peptide produced by the hypothalamus that in pregnancy is also produced by the placenta. Its role in pregnancy has been postulated as one of the primary endocrine mediators of parturition and possibly also of fetal development. Its rise in the maternal serum has been observed to precede the development of labour and therefore its measurement was purported to predict spontaneous preterm birth.
Study characteristics and quality
There were six primary studies (n = 5034 women) on the accuracy of CRH testing, comprising five studies on asymptomatic antenatal women (n = 4940)174,178–181 and one study on symptomatic women who presented with threatened preterm labour (n = 94). 182Appendix 5, Table 83 summarises each study’s salient features, stratified according to population of women tested, i.e. asymptomatic antenatal women and women with symptoms of threatened preterm labour. One study was not included because it included multiple gestations in its population and iatrogenic preterm birth in its outcome. 183 The studies’ enrolment for asymptomatic women ranged from 181 to 2929 women174,179 with a median of 396 women. 178
There were no studies included within the systematic review of the accuracy of CRH testing in predicting spontaneous preterm births that fulfil our ideal definition of high-quality test accuracy studies either in asymptomatic or symptomatic women. None of the studies in either population reported using consecutive enrolment of women into the study. However, all studies have adequate test description report. Retrospective and case–control study design was used in two studies in asymptomatic women. 174,179 Blinding of carers to the results of CRH tests was absent from two studies on asymptomatic women. 178,180 The methodological quality of the included primary studies is summarised in Figure 30.
FIGURE 30.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of CRH in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
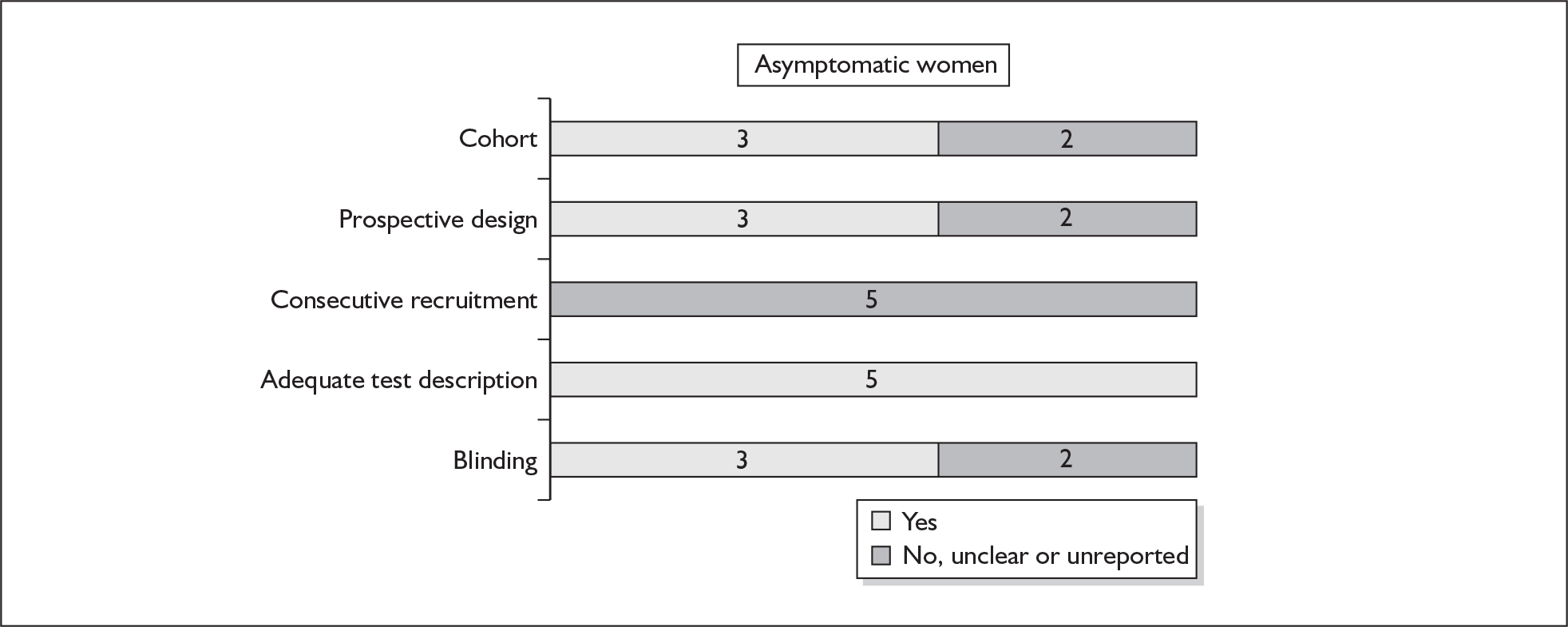
Only two studies used the same threshold of abnormality, one each on asymptomatic and symptomatic women, of greater than 90th percentile value. Four studies, including the lone study on symptomatic women, used CRH as a single test,179–182 while the remainder used it as a serial test. For asymptomatic women, one study used spontaneous preterm birth before 32 weeks’ gestation,174 one 34 weeks’ gestation,181 and two each used 35 weeks’ gestation,174,179 and 37 weeks’ gestation178,180 as the reference standard.
Accuracy of CRH in asymptomatic women
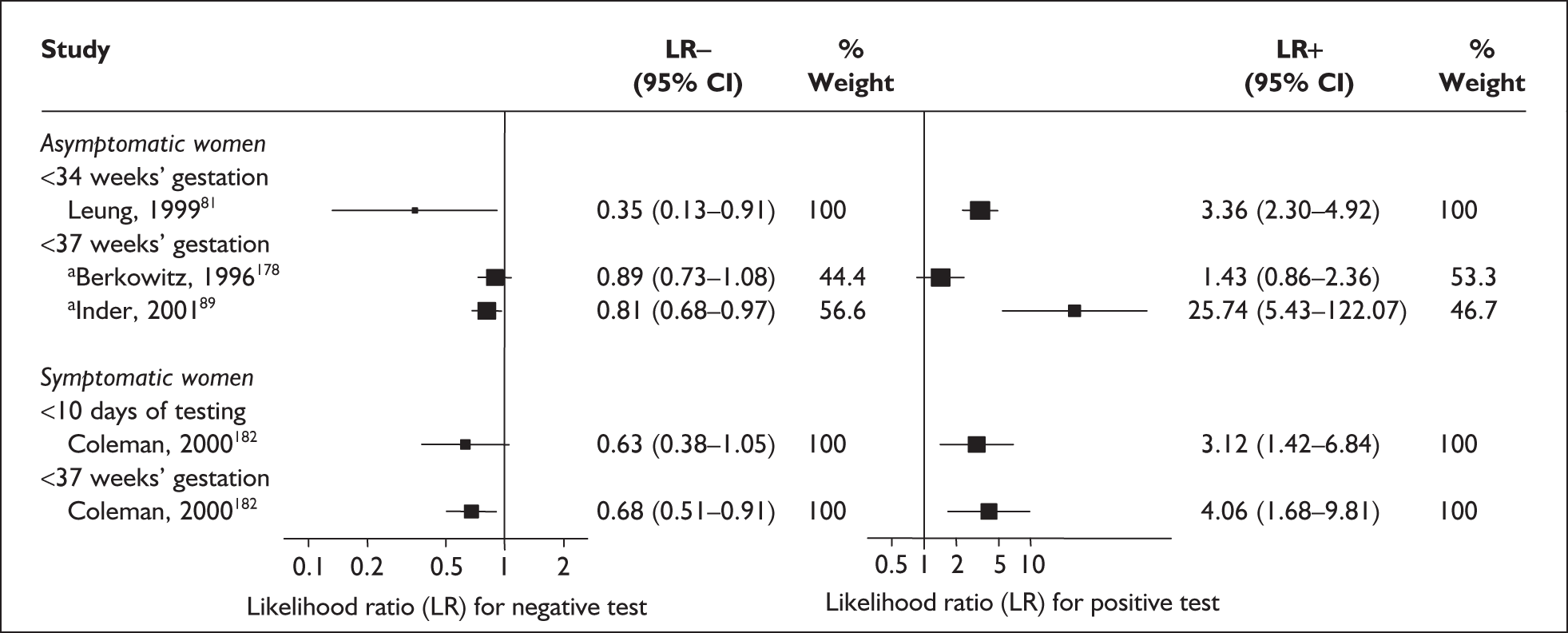
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, a single CRH testing had an LR+ of 3.36 (95% CI 2.30–4.92) and LR– of 0.35 (95% CI 0.13–0.91),181 estimates used in the decision-analytic modelling. For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, CRH had a range of LR+ from 1.43 (95% CI 0.86–2.36) to 25.74 (95% CI 5.428–122.07) and LR– from 0.81 (95% CI 0.68–0.97) to 0.89 (95% CI 0.74–1.08) (Figure 31). 178,180 Estimates from Berkowitz et al. 178 were used in the decision-analytic modelling because it represented the largest higher quality study of the reference standard. Individual accuracy results can be found in Appendix 5, Table 84.
FIGURE 31.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of CRH in predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7–10 days of testing and 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women and before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation strain asymptomatic women. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality. a, Serial testing.
Accuracy of CRH in symptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 10 days of testing, CRH had an LR+ of 3.12 (95% CI 1.42–6.84) and LR– of 0.63 (95% CI 0.38–1.05). For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, it had an LR+ of 3.12 (95% CI 1.42–6.84) and LR– of 0.68 (95% CI 0.51–0.91) (Figure 31). Individual accuracy results can be found in Appendix 5, Table 84.
β-Human chorionic gonadotrophin
The hormone β-human chorionic gonadotrophin (β-hCG) manufactured by the feto-placental unit is known to be present in high concentrations in the amniotic fluid and maternal serum during pregnancy. Disruption of the chorion and the decidua, as occurs when onset of labour is imminent, has been postulated as the rationale for testing for the presence of β-hCG in the cervicovaginal secretions,139 in addition to its presence in the maternal serum. 184 Measurements of β-hCG can be made either by taking a maternal blood serum sample during the asymptomatic antenatal period, usually as part of the ‘triple test’ to screen for Down syndrome, or by taking a cotton-tipped swab of cervicovaginal secretions obtained from speculum examination.
Study characteristics and quality
There were 23 primary articles, of which 19 evaluated the use of mid-trimester maternal serum hCG as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth (n = 177,730 women)157,158,162,165,166,184–197 while one article evaluated it in early first trimester (n = 169),198 and three articles evaluated cervicovaginal hCG as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth in women who presented with symptoms of threatened preterm labour (n = 248). 139,199,200Appendix 5, Table 85 summarises each study’s salient features, stratified according to the population of women tested, i.e. asymptomatic antenatal women and symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
None of the studies fulfilled the ideal quality study design. There were nine case–control studies in asymptomatic women165,185,186,189–193,195 and one in symptomatic women. 139 Four studies in asymptomatic women reported consecutive enrolments,157,166,194,197 while none was reported in symptomatic women. There were 13 retrospective studies in asymptomatic women158,165,184–186,189–193,195,196,198 while all the studies in symptomatic women were prospective. None of the studies on asymptomatic women reported blinding and only one study in symptomatic women reported it. 200 The methodological quality of the included primary studies is summarised in Figure 32.
FIGURE 32.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of human chorionic gonadotrophin in predicting spontaneous preterm birth among asymptomatic antenatal women and symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
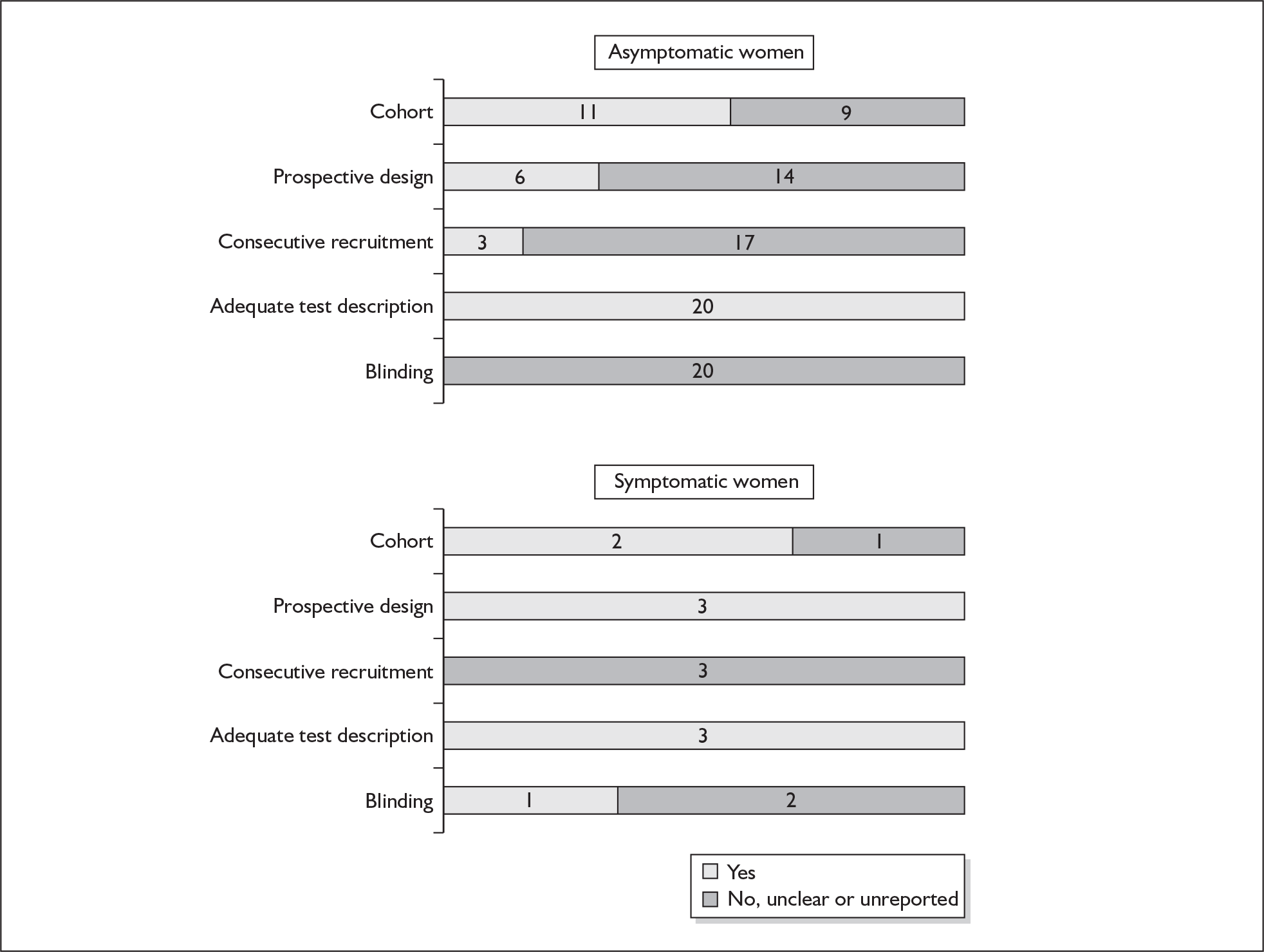
Most of the study in asymptomatic women reported their thresholds in terms of MoM, except for three studies,188,194,198 which used percentiles. The commonest threshold used was 2.0 MoM, values above this were defined as abnormal. The three studies that evaluated cervicovaginal hCG had used 25–27 thinsp;mIU/ml to define their thresholds for an abnormal result. Except for three studies in asymptomatic women, which used birth before 32 weeks’ gestation157,188 and 34 weeks’ gestation,194 the studies used birth before 37 weeks’ gestation as their reference standard. One study reported birth within 7 days of testing in symptomatic women,199 while the remainder reported before 37 weeks’ gestation as their reference standard. There was graphical (Figure 33) and statistical evidence of heterogeneity in the accuracy results (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00 for LR+ and χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00 for LR–) for studies using the commonest clinical characteristics (asymptomatic women, mid-trimester testing gestation, threshold of 2.0 MoM and birth before 37 weeks’ gestation as the reference standard).
FIGURE 33.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of serum β-human chorionic gonadotrophin (β-hCG) testing in asymptomatic pregnant women as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00 for LR+ and χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00 for LR–.
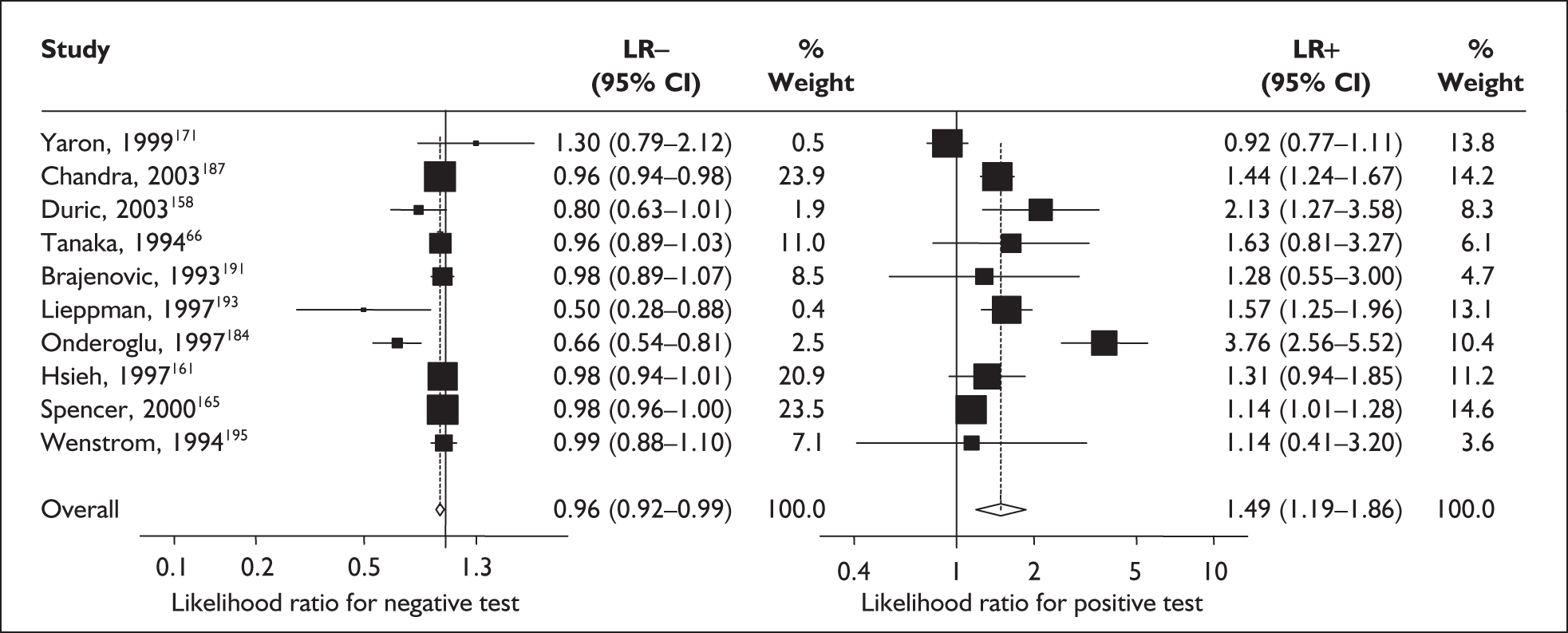
Accuracy of β-hCG in asymptomatic women
Maternal mid-trimester serum β-hCG, which used a threshold of 2.0 MoM, showed variable accuracy in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in asymptomatic women. The LR+ ranged from 0.92 (95% CI 0.77–1.11)197 to 3.76 (95% CI 2.56–5.52)193 and LR– ranged from 0.50 (95% CI 0.28–0.88)191 to 1.30 (95% CI 0.79–2.12)197 (Figure 33). The largest better quality study reported LR+ of 2.77 (95% CI 2.07–3.69) and LR– of 0.984 (95% CI 0.98–0.99) when the first percentile was used as threshold to define abnormality. 188 LRs from Dugoff et al. 188 were used in the decision-analytic modelling because it represents the largest higher-quality study. The accuracy results for asymptomatic women are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 86.
Accuracy of β-hCG in symptomatic women
In a study that reported birth within 7 days of testing, the LR+ was 6.07 (95% CI 3.07–11.99) and LR– was 0.04 (95% CI 0.01–0.16), values which were used for the decision-analytic modelling. 199 Summary LR+ for birth before 37 weeks’ gestation was 2.11(95% CI 1.61–2.77) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.42) and summary LR– was 0.45 (95% CI 0.31–0.66) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.57) (Figure 34). However, LR+ of 2.19 (95% CI 1.35–3.57) and LR– of 0.51 (95% CI 0.30–0.85) from the largest higher-quality study was used in the decision-analytic modelling. 200 The accuracy results for symptomatic women are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 86.
FIGURE 34.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of serum β-human chorionic gonadotrophin (β-hCG) testing in symptomatic pregnant women as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.42 for LR+ and χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.57 for LR–.
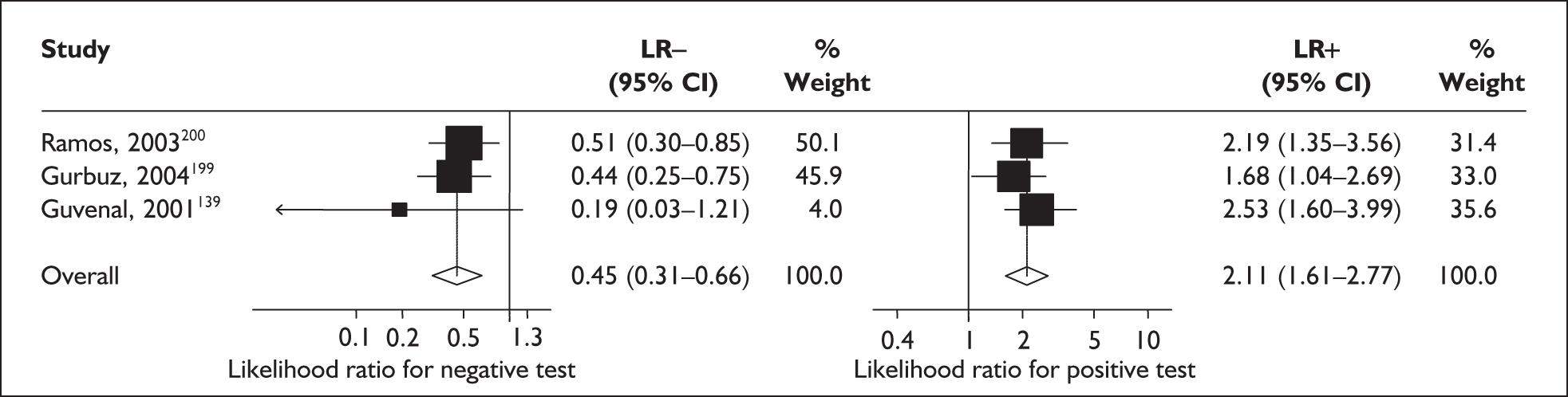
Estriol
Estriol is produced by both mother and fetus during pregnancy. There is a surge in the maternal levels of estriol which occurs several weeks before the onset of spontaneous labour. Measurement of either salivary or serum estriol was therefore purported to be a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth. 201
Study characteristics and quality
There were seven primary studies (n = 60,722 women) on the accuracy of estriol testing as predictor of spontaneous preterm birth, comprising six studies on asymptomatic antenatal women (n = 60,417)157,158,196,202–204 and two studies on symptomatic women presenting with threatened preterm labour (n = 305). 201,202Appendix 5, Table 87 summarises each study’s salient features, stratified according to the population of women tested, i.e. asymptomatic antenatal women and women with symptoms of threatened preterm labour. The studies’ enrolment for asymptomatic women ranged from 399 to 33,145 women157,204 with a median of 601 women,202 while that of symptomatic women ranged from 115 to 190 women. 201,202 Two studies evaluated salivary estriol201,202 while the remainder evaluated maternal serum estriol. 157,158,196,203,204 One study contributed to both asymptomatic and symptomatic populations. 202
There were no studies included within the systematic review of the accuracy of estriol testing in predicting spontaneous preterm births that fulfil our ideal definition of high-quality test accuracy studies either in asymptomatic or symptomatic women. None of the studies in either population reported using consecutive enrolment of women into the study. However, all studies have adequate test description report. Retrospective data collection was used in three studies in asymptomatic women. 158,196,204 Blinding of carers to the results of estriol tests was absent from five studies on asymptomatic women157,158,196,203,204 and one study on symptomatic women. 201 The methodological quality of the included primary studies is summarised in Figure 35.
FIGURE 35.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of estriol in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
Three studies used the same threshold of abnormality of 0.75 MoM in asymptomatic women158,203,204 while the two studies in symptomatic women used 2.1 ng/ml as their threshold. 201,202 Two studies in asymptomatic women used 0.5 MoM as their thresholds157,196 and one study in symptomatic women explored the accuracy of 1.4 ng/ml as the threshold cut-off in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. 202 One study in asymptomatic women evaluated the accuracy of repeat tests in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. 202 For asymptomatic women, one study used spontaneous preterm birth before 32 weeks’ gestation,157 while the remaining studies reported 37 weeks’ gestation as the reference standard. In symptomatic women, one study reported birth within 14 days of testing while another reported 37 weeks’ gestation.
Accuracy of estriol in asymptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, a single salivary estriol testing had an LR+ of 2.55 (95% CI 1.73–3.77) and LR– of 0.56 (95% CI 0.35–0.89) while a repeat test, where one positive result indicated positivity, had an LR+ of 5.46 (95% CI 3.18–9.40) and LR– of 0.61 (95% CI 0.43–0.88) (Figure 36). 202 These estimates were used in the decision-analytic modelling. For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, the serum estriol test had a range of LR+ from 0.76 (95% CI 0.58–1.00) to 2.17 (95% CI 1.33–3.53) and LR– from 0.77 (95% CI 0.60–0.99) to 1.02 (95% CI 1.00–1.04) (Figure 36). 158,196 Estimates from Yaron et al. 196 and Kim et al. 203 [LR+ of 1.19 (95% CI 0.58–2.44) and LR– of 0.98 (95% CI 0.89–1.08)] were used in the decision-analytic modelling because they represented the largest higher-quality studies of the reference standard, with commonly used thresholds of 0.75 MoM and 0.5 MoM respectively. No study reported spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation. Individual accuracy results can be found in Appendix 5, Table 88.
FIGURE 36.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of salivary and serum estriol in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in asymptomatic and symptomatic women. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality. a, Repeat testing within 7 days of the first test.
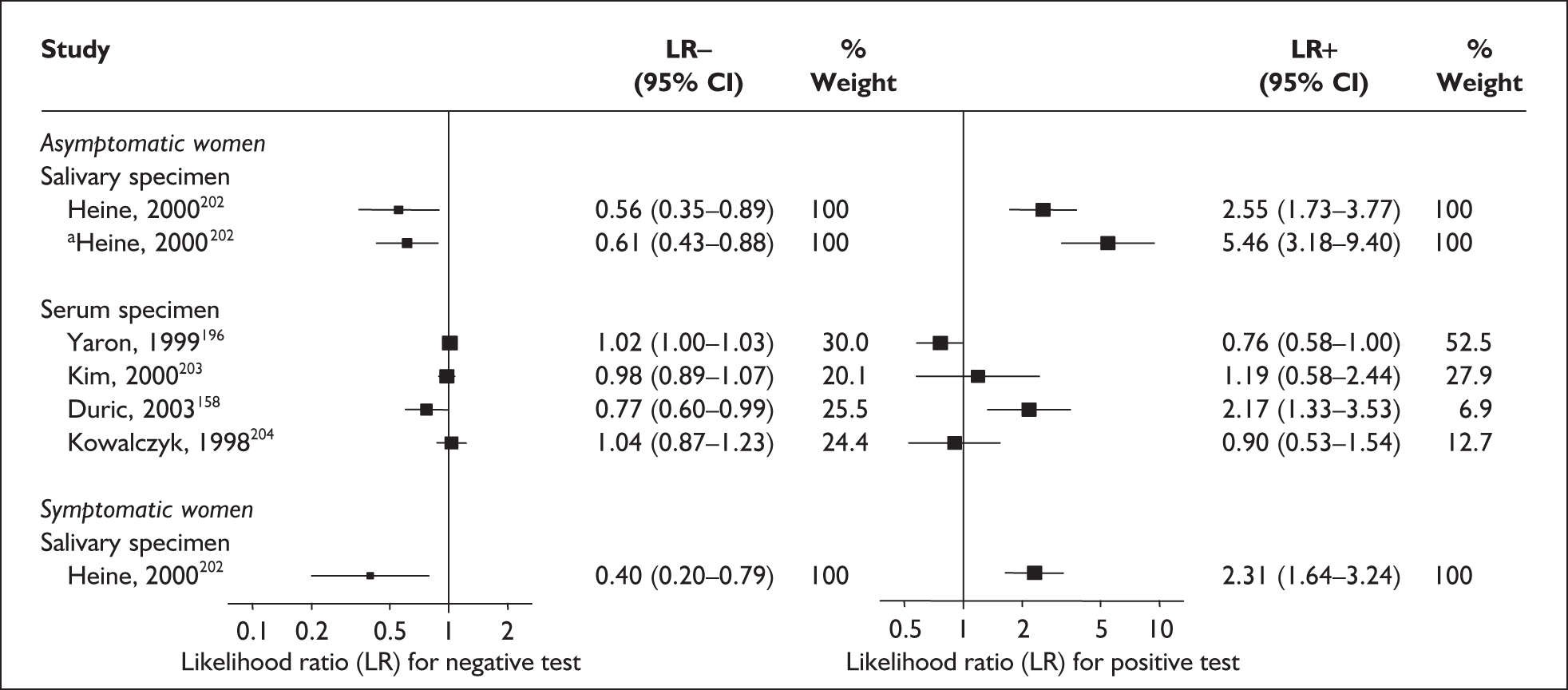
Accuracy of estriol in symptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, salivary estriol had an LR+ of 2.31 (95% CI 1.64–3.24) and LR– of 0.40 (95% CI 0.20–0.79) (Figure 36). 201 No study evaluated serum estriol in predicting spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women. Individual accuracy results can be found in Appendix 5, Table 88.
C-reactive protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an acute-phase reactant associated with the presence of systemic infections and may be, if raised, an indicator of risk for spontaneous preterm birth. It is an easily detectable and reliably measured serological marker obtained from a sample of maternal serum from venepuncture or of amniotic fluid from amniocentesis. It is produced by the hepatocytes in response to the circulating inflammatory cytokines released by the presence of infections. 205
Study characteristics and quality
There were 13 primary articles, involving a total of 2142 women. 205–217 Table 89, Appendix 5, summarises each study’s salient features, stratified according to the population of women tested, i.e. asymptomatic antenatal women and women with symptoms of threatened preterm labour, and the route of testing, i.e. either amniotic sample from an amniocentesis or blood serum from venepuncture. Two studies reported on CRP measurement in amniotic fluid obtained at mid-trimester gestation among asymptomatic women,210,215 while the remaining studies used maternal blood plasma serum levels of CRP obtained either at mid-trimester gestation for asymptomatic women or at presentation for women who presented with symptoms of threatened preterm labour. The study population ranged from 34 to 506 women, with a median of 69 women. Appendix 5, Table 89 summarises the individual study characteristics.
Only one study reported prospective data collection design215 and only seven of the 13 studies included reported consecutive enrolment. 205,206,209,211,214,215,217 Most of the studies had provided adequate test description but blinding was evident in only four studies. 205,206,210,211 The methodological quality of the primary studies included is summarised in Figure 37. There was no uniform test threshold used; they ranged from 1 ng/ml to 110 ng/ml in the included studies. The most commonly used reference standard for asymptomatic women was birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, with one study reporting birth before 34 weeks’ gestation,210 while for symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour, they were birth within 7 days of testing,206,208,211,217 34 weeks’ gestation and 37 weeks’ gestation.
FIGURE 37.
Methodological quality of studies of C-reactive protein in predicting spontaneous preterm birth included in the systematic review. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.

Accuracy of CRP in asymptomatic women
In one study of amniotic fluid CRP level obtained at mid-trimester for predicting preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, the LR+ was 2.63 (95% CI 1.85–3.75) and LR– was 0.29 (95% CI 0.08–0.99). 210 In another study, for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, the LR+ was 4.37 (95% CI 3.03–6.29) and LR– was 0.09 (95% CI 0.01 to 0.60). 215 In three studies of maternal plasma CRP measurements in asymptomatic women at mid-trimester for predicting preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation the range of LR+ was 1.55 (95% CI 1.22–2.13) to 2.06 (95% CI 1.29 to 3.29) and that of LR– was 0.77 (95% CI 0.65–0.91) to 0.86 (95% CI 076–0.98). 212,213,216 Summary LR+ for the accuracy of maternal serum level of CRP measurement in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation was 1.73 (95% CI 1.38–2.16) (heterogeneity test χ2 = 1.06, p = 0.59) and LR– was 0.83 (95% CI 0.76–0.91) (χ2 = 1.20, p = 0.55) (Figure 38). The accuracy of the CRP test in predicting spontaneous preterm births in asymptomatic women is summarised in Appendix 5, Tables 90 and 91.
FIGURE 38.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of the accuracy of mid-trimester maternal serum C-reactive protein level measurement in asymptomatic women for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.59 for LR+ and p = 0.55 for LR–. +Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality.
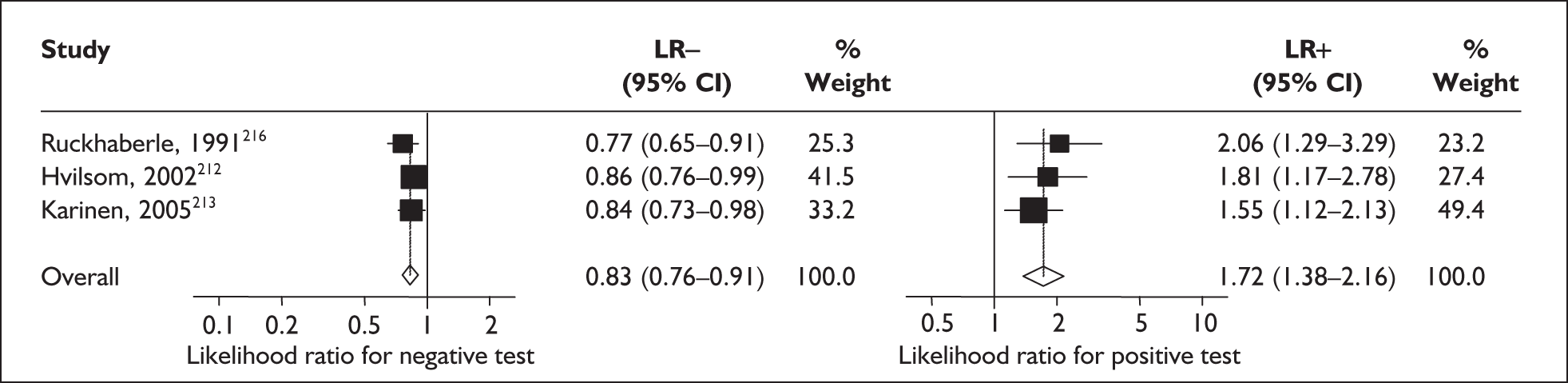
Accuracy of CRP in symptomatic women
In four studies of maternal plasma CRP level measurements in women with threatened preterm labour for predicting preterm birth within 7 days of testing, the range of LR+ was 1.35 (95% CI 0.71–2.55) to 34.36 (95% CI 4.86–243.09) and that of LR– was 0.17 (95% CI 0.05–0.62) to 0.89 (95% CI 0.69–1.15). 206,208,211,217 Summary LR+ for the accuracy of maternal serum level CRP measurement in predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour was 4.538 (95% CI 1.48–13.91) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00) and summary LR– was 0.296 (95% CI 0.08–1.15) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00) (Figure 39). Cammu et al. 206 represented the largest higher-quality study and was therefore used for the decision-analytic modelling. A study on maternal plasma CRP levels in women symptomatic with threatened preterm labour that used 34 weeks’ gestation had an LR+ of 6.75 (95% CI 1.34–34.00) and an LR– of 0.66 (0.38–1.14). 209 This result was used in our decision-analytic modelling. In four studies of maternal plasma CRP measurements in women with threatened preterm labour for predicting preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, the range of LR+ was 1.67 (95% CI 0.76–3.66) to 4.20 (95% CI 1.10–15.98) and that of LR– was 0.47 (95% CI 0.25–0.87) to 0.76 (95% CI 0.48–1.21). 205–207,214 Summary LR+ for spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation was 2.29 (95% CI 1.57–3.35) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.66) and summary LR– was 0.60 (95% CI 0.46–0.79) (χ2 = 2.23, p = 0.53) (Figure 40). The result of Cammu et al. 206 represented the largest higher-quality study and was therefore used for the decision-analytic modelling. A ROC plot of sensitivity versus specificity for serum CRP in symptomatic women predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing is shown in Figure 41. The accuracy of the CRP test in predicting spontaneous preterm births in symptomatic women who presented with threatened preterm labour is summarised in Appendix 5, Table 90 and Table 91.
FIGURE 39.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of the accuracy of maternal serum C-reactive protein level measurement in symptomatic women with threatened labour for predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.001 for LR+ and p = 0.000 for LR–. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality.
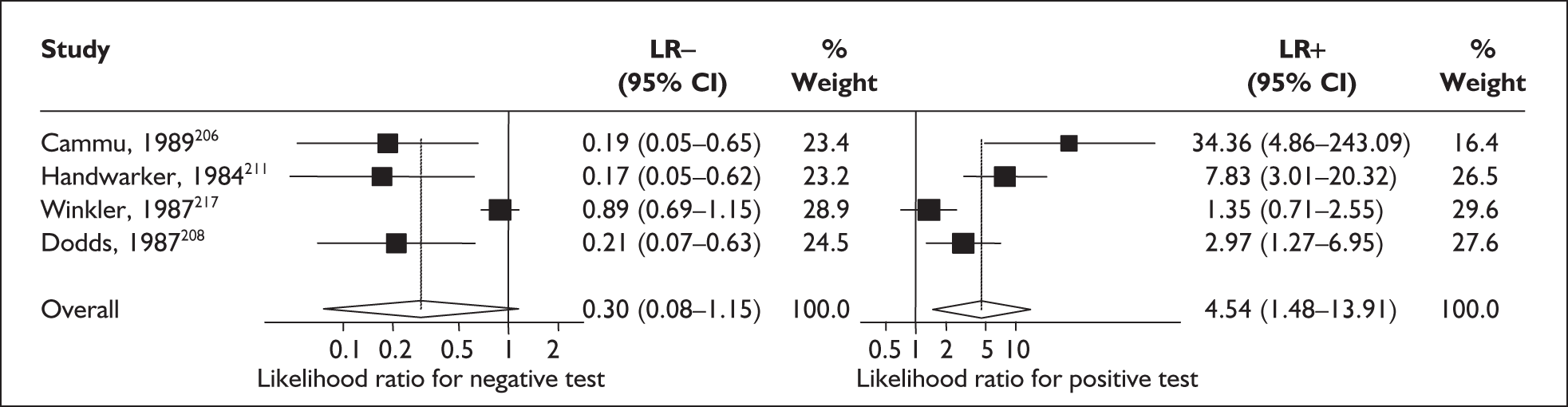
FIGURE 40.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) for maternal serum C-reactive protein level measurement in symptomatic women with threatened labour for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.66 for LR+ and p = 0.53 for LR–. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality.
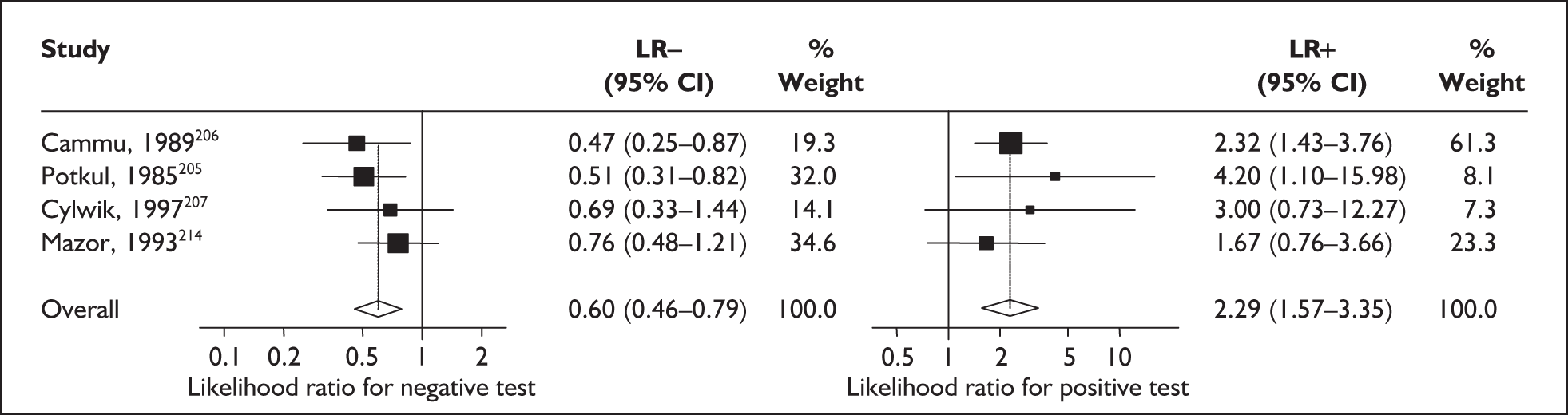
FIGURE 41.
Plot of sensitivity versus 1-specificity in ROC space for maternal serum measurement of C-reactive protein studies in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour for predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing.
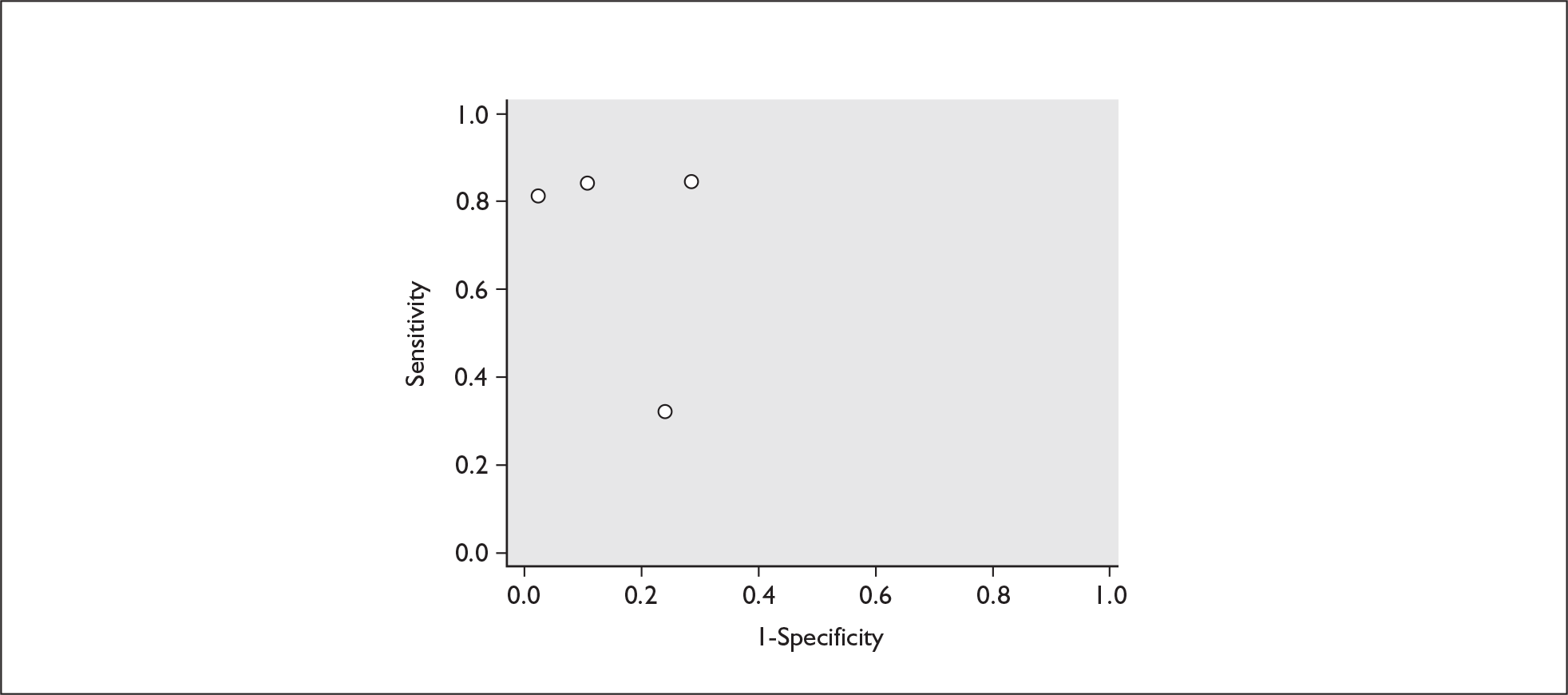
Interleukin-6
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is a protein compound produced in response to the presence of inflammation, usually in response to the presence of an infection. It can be found in amniotic fluid, cervical secretions and in maternal blood serum. Its presence or increasing values have been purported to predict spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women who presented with threatened preterm labour. 218
Study characteristics and quality
There were 26 primary studies (n = 2594 women) on the accuracy of IL-6 testing in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. However, one study,219 which evaluated cervical IL-6 as predictor of spontaneous preterm birth in women who presented with symptoms of threatened preterm labour, was excluded because the author was not able to provide the data within the time constraint of the project. The number of women enrolled ranged from 73103 to 290220 with a median of 161 in asymptomatic women221 and from 18120 to 146218 with a median of 73 in symptomatic women. 103 There were 12 studies evaluating the amniotic level of IL-6, two in asymptomatic women220,222 and ten in symptomatic women,120,218,223–230 as a predictor for spontaneous preterm birth. There were ten studies evaluating cervical IL-6, three in asymptomatic women103,221,231 and seven in symptomatic women90,103,232–236 as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth in women. One study evaluated serial testing of cervical IL-6 in asymptomatic women. 221 There were five studies, all in symptomatic women who presented with threatened preterm labour, which evaluated serum IL-6 as a predictor for spontaneous preterm birth. 235,237–240 Two studies provided information for more than one category of either population103 or type of IL-6 specimen. 235Appendix 5, Table 92 summarises individual study characteristics.
Three studies fulfilled our ideal definition of high-quality test accuracy studies. 103,221,227 All studies in both asymptomatic and symptomatic women provided adequate test description. However, out of 20 studies on symptomatic women, most were lacking in reporting of consecutive enrolment with only three studies reporting consecutive enrolment103,227,233 and blinding of test results, where only eight studies reported it. 90,103,120,224,225,227,237,238 The methodological quality of the primary studies included is summarised in Figure 42. No two studies had reported using the same threshold. Three studies on asymptomatic women reported birth before 37 weeks’ gestation as their reference standard103,220,221 and one each for birth before 34 weeks’222 and 35 weeks’ gestation. 231 For symptomatic women, one study reported spontaneous preterm birth within 24 hours,240 five studies within 48 hours120,223,225,237,239 and four studies reported birth within 5–7 days of testing,226,236,238,241 while the remainder reported birth before 35–37 weeks’ gestation. 90,103,218,224,227–230,233,235
FIGURE 42.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of interleukin-6 in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
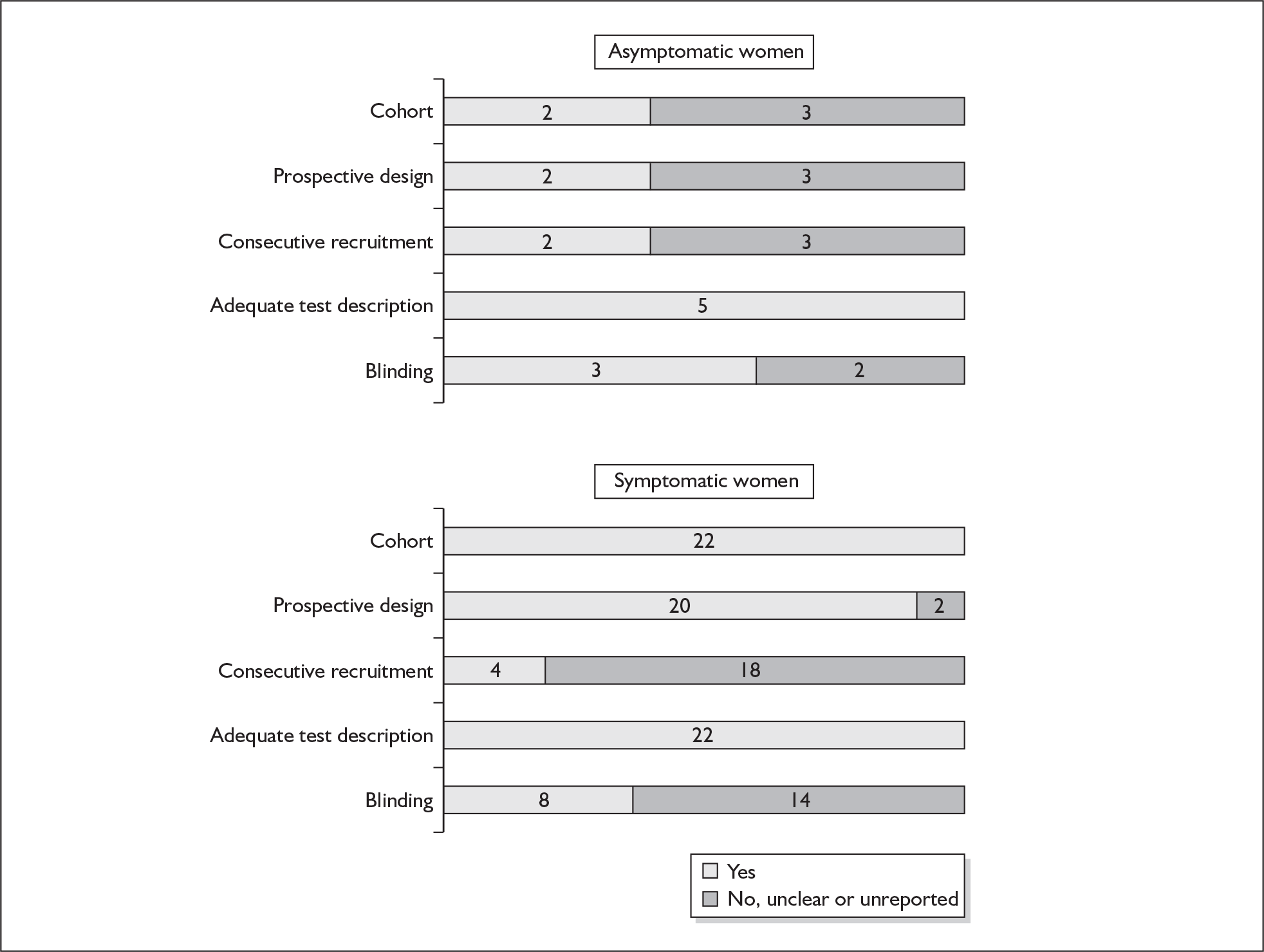
Accuracy of IL-6 in asymptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, a single amniotic fluid IL-6 measurement had a range of LR+ of 2.65 (95% CI 1.37–5.14)220 to 2.95 (95% CI 0.96–9.04)222 (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.87) and LR– of 0.84 (95% CI 0.62–1.13)222 to 0.91 (95% CI 0.84–0.98)220 (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.57) (Figure 43). For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, a single amniotic fluid IL-6 measurement had an LR+ of 1.91 (95% CI 0.99–3.67) and LR– of 0.95 (95% CI 0.90–1.00) (Figure 43). 220 LR estimates from one study were used for decision-analytic modelling because it represented the largest higher-quality study available for amniotic fluid IL-6 in asymptomatic women for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation. 220 Serial testing of cervical IL-6 in asymptomatic women had an LR+ of 3.34 (95% CI 1.96–5.70) and LR– of 0.59 (0.42–0.83) for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. 221 Single testing of cervical IL-6 in asymptomatic women had a range of LR+ from 0.564 (95% CI 0.08–3.97)103 to 2.08 (95% CI 1.10–3.96)231 and a range of LR– from 0.88 (95% CI 0.80–0.98)231 to 1.08 (95% CI 0.87–1.35)103 for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.14 for LR+ and p = 0.003 for LR–). Figure 43 summarises the accuracy results for amniotic fluid IL-6 in predicting spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic women. LR estimates from two studies were used for decision-analytic modelling because they represented the largest higher-quality study available for cervical IL-6 in asymptomatic women for preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation for single and serial testings. 103,221 There is no information on birth before 34 weeks’ gestation using cervical IL-6 testing. Individual accuracy results can be found in Appendix 5, Table 93.
FIGURE 43.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of amniotic fluid interleukin-6 (IL-6)measurement as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality for each type of test. For individual thresholds see Table 92, Appendix 5. a, Amniotic fluid measurement of IL-6. b, Cervicovaginal measurements of IL-6. c, Serial measurement (repeated after a 3- to 4-week interval). d, Threshold 250 pg/ml. e, Threshold 125 pg/ml.
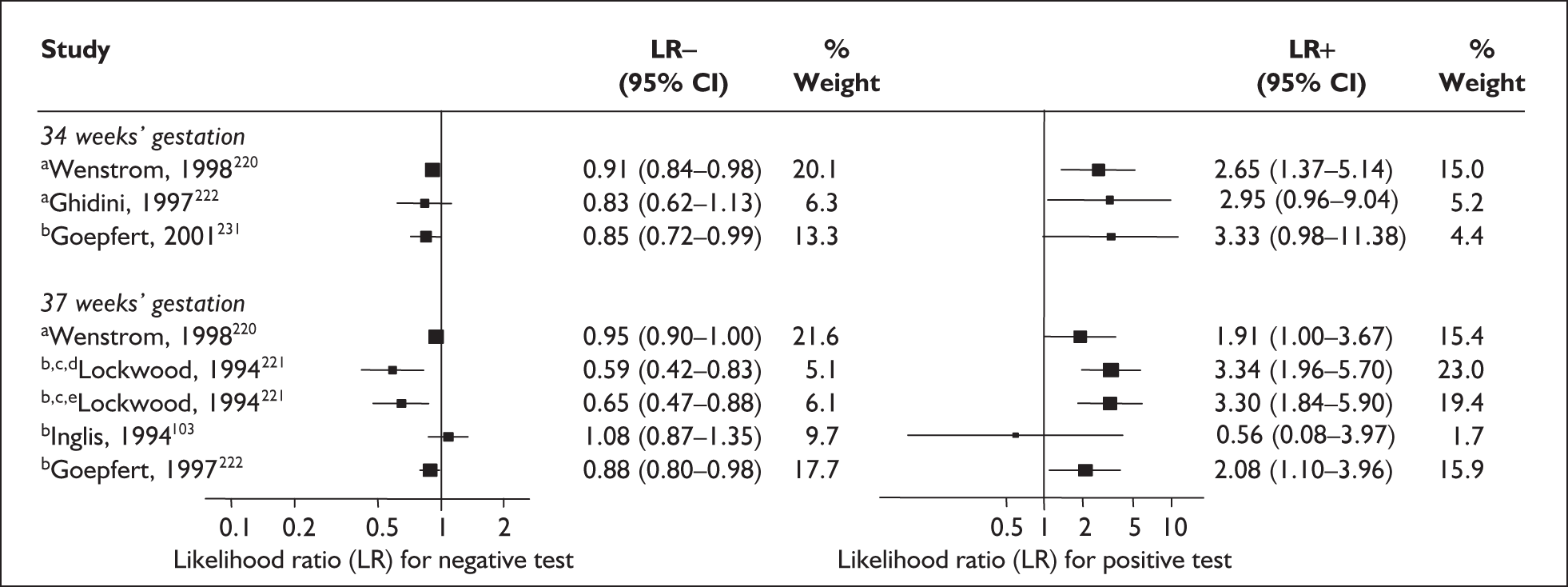
Accuracy of IL-6 in symptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7–10 days of testing, cervical IL-6 had a range of LR+ from 2.40 (95% CI 1.37–4.23)234 to 4.01 (95% CI 2.02–7.96)236 and a range of LR– from 0.12 (95% CI 0.01–1.72)234 to 0.66 (95% CI 0.51–0.85). 236 LR estimates from one study were used for decision-analytic modelling because it represented the largest higher-quality cervical IL-6 study available in symptomatic women for predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7–10 days of testing. 236 Amniotic fluid measurement of IL-6 had a range of LR+ from 2.43 (95% CI 1.36–4.36)226 to 7.01 (95% CI 2.75–17.90)225 and a range of LR– from 0.17 (95% CI 0.06–0.49)225 to 0.24 (0.09–0.61)226 LR estimates from Greci et al.,225 the largest higher-quality study for this reference standard, were used in the decision-analytic modelling. Serum measurement of IL-6 had an LR+ of 3.34 (95% CI 1.48–7.53) and LR– of 0.44 (95% CI 0.30–0.66). 239 The accuracy results for the different types of IL-6 sources are shown in Figure 44.
FIGURE 44.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of interleukin-6 measurement from amniotic fluid and cervical specimen as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth within 7–10 days of testing in symptomatic women. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality for each type of test. a, Amniotic fluid measurement of IL-6. b, Cervicovaginal measurements of IL-6. c, Serum measurement of IL-6.
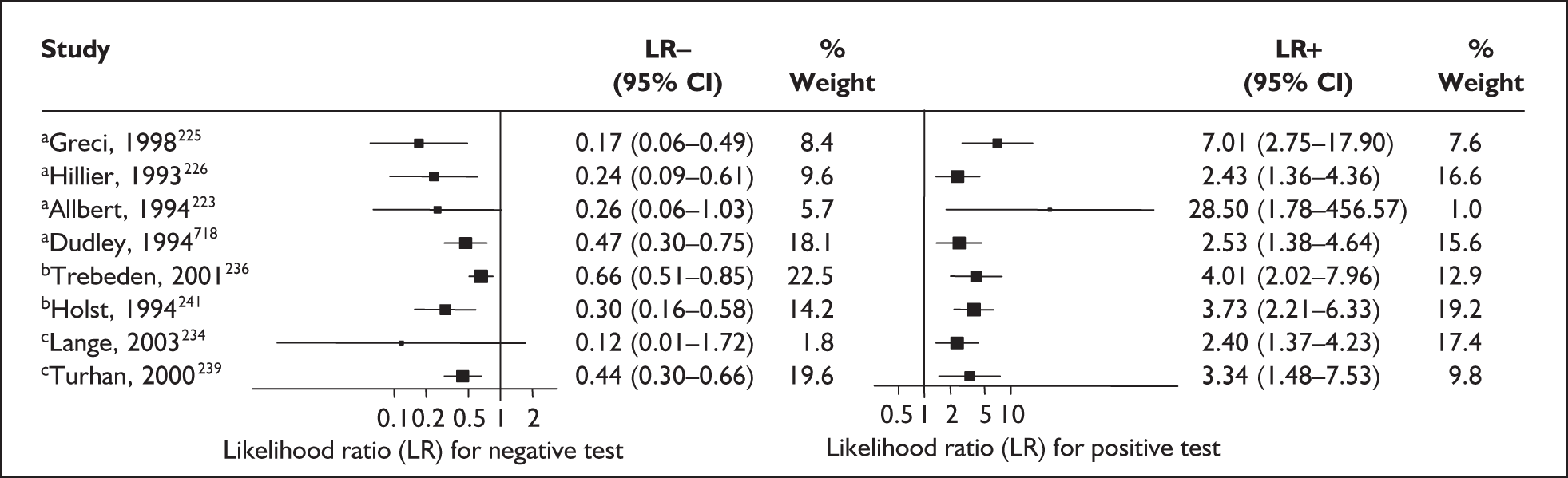
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation (Figure 45), amniotic fluid IL-6 had an LR+ of 7.44 (95% CI 2.01–27.52) and LR– of 0.14 (95% CI 0.06–0.36). 226 For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, cervical IL-6 had a range of LR+ from 2.63 (95% CI 1.44–4.79)234 to 4.92 (95% CI 1.80–13.46)236 and LR– from 0.097 (95% CI 0.01–1.45)234 to 0.74 (95% CI 0.63–0.87);236 the latter estimates were used in the decision-analytic modelling because the study represented the largest higher-quality study of cervical IL-6 in this reference standard. Serum IL-6 had an LR+ of 1.44 (95% CI 0.86–2.41) and LR– of 0.59 (95% CI 0.22–1.58) for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation. 237
FIGURE 45.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of interleukin-6 (IL-6) measurement from amniotic fluid, cervical swab and serum specimen as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality for each type of test. a, Amniotic fluid measurement of IL-6. b, Cervicovaginal measurements of IL-6. c, Serum measurement of IL-6.
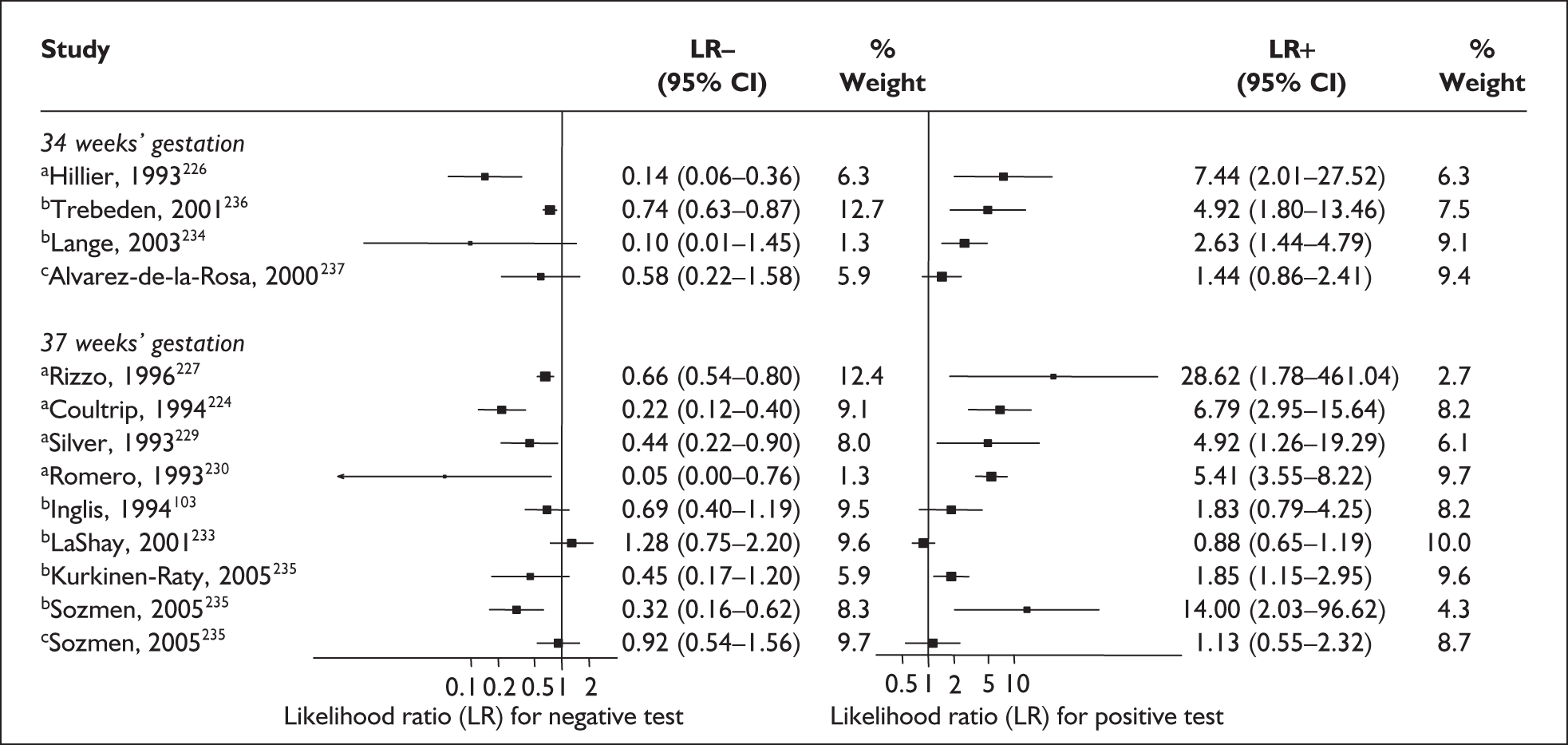
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, amniotic fluid IL-6 had a range of LR+ from 4.92 (95% CI 1.26–19.29)229 to 28.62 (95% CI 1.78–461.04)227 and LR– from 0.05 (95% CI 0.003–0.76)230 to 0.66 (95% CI 0.54–0.80). 227 Estimates from Rizzo et al. 227 were used for the decision-analytic modelling because their study represented the largest higher-quality study for this reference standard. For the same reference standard, cervical IL-6 had a range of LR+ from 1.83 (95% CI 0.79–4.25)103 to 14.0 (95% CI 2.03–96.62)235 and LR– from 0.10 (95% CI 0.01–1.45)234 to 1.29 (95% CI 0.75–2.20) (Figure 45). 90 Estimates from Inglis et al. 103 were used for the decision-analytic modelling because their study represented the sole ideal-quality study within this subgroup of reference standards of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. Serum IL-6 had an LR+ of 1.13 (95% CI 0.55–2.32) and LR– of 0.92 (95% CI 0.54–1.56). 235 A ROC plot of sensitivity versus specificity for amniotic and cervical fluid in symptomatic women is shown in Figure 46. The accuracy of IL-6 in predicting spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic and symptomatic women is summarised in Appendix 5, Table 93.
FIGURE 46.
Plot of sensitivity versus 1-specificity in ROC space for amniotic fluid and cervicovaginal interleukin-6 (IL-6) studies in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour in predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours and 7 days of testing, and before 34 weeks’ gestation.
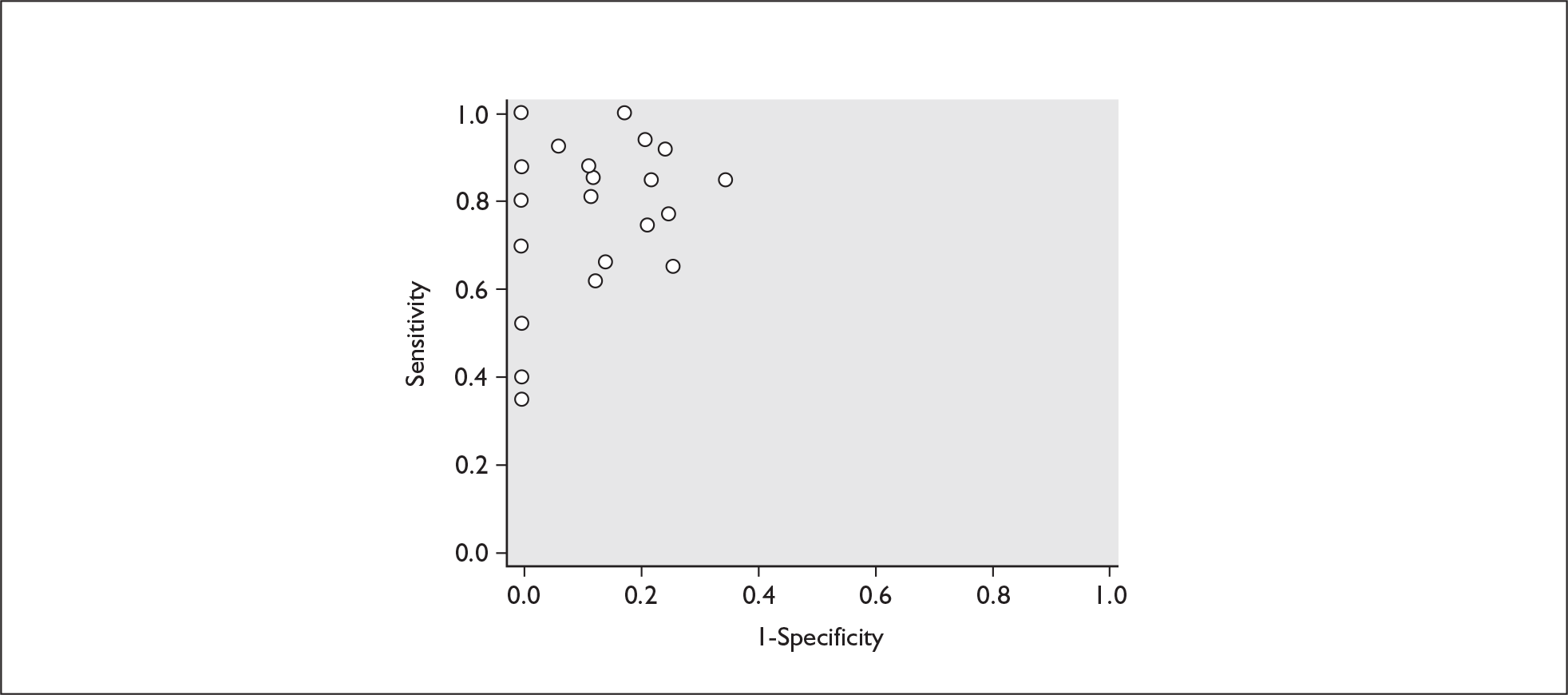
Interleukin-8
Similar to IL-6, interleukin-8 (IL-8) is a protein compound produced in response to the presence of inflammation usually in response to the presence of an infection. It can be found in amniotic fluid, cervical secretions and in maternal blood serum. Its presence in cervicovaginal secretions219 or in increasing values in maternal serum223 have been purported to predict spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women who presented with threatened preterm labour.
Study characteristics and quality
There were five primary studies, involving altogether, a total of 568 women. Three potentially eligible studies for inclusion were excluded because data were unobtainable. 219,240,242Appendix 5, Table 94 summarises each study’s salient features, stratified according to the population of women tested, i.e. asymptomatic antenatal women (two studies)243,244 and women with symptoms of threatened preterm labour (three studies). 223,232,233 One of the included studies, on the asymptomatic antenatal population, had the test performed two-weekly between 24 and 28 weeks’ gestation. 244 Except for one study,223 the studies evaluated IL-8 in cervicovaginal specimens.
None of the studies fulfilled our ideal definition of high-quality test accuracy studies. Blinding and consecutive enrolment were absent from four studies – none of the studies on symptomatic women reported blinding223,232,233 and only one study, in symptomatic women, reported consecutive enrolment. 233 All studies in both asymptomatic and symptomatic women provided adequate test descriptions. The methodological quality of the included primary studies is summarised in Figure 47. No two studies had reported using the same threshold, which varied widely. The two studies on asymptomatic women reported birth before 37 weeks’ gestation as their reference standard but one of them244 additionally reported birth before 32 and 34 weeks’ gestation and had performed their test serially with a two-weekly interval. For symptomatic women, one study reported spontaneous preterm birth within 24 hours,240 five studies within 48 hours120,223,225,237,239 and four studies reported birth within 5–7 days of testing,226,236,238,241 while the remainder reported birth before 35–37 weeks’ gestation. 90,103,218,224,227–230,233,235 There was an insufficient number of studies for statistical heterogeneity analysis to be conducted in the case of IL-8.
FIGURE 47.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of test for interleukin-8 (IL-8) in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
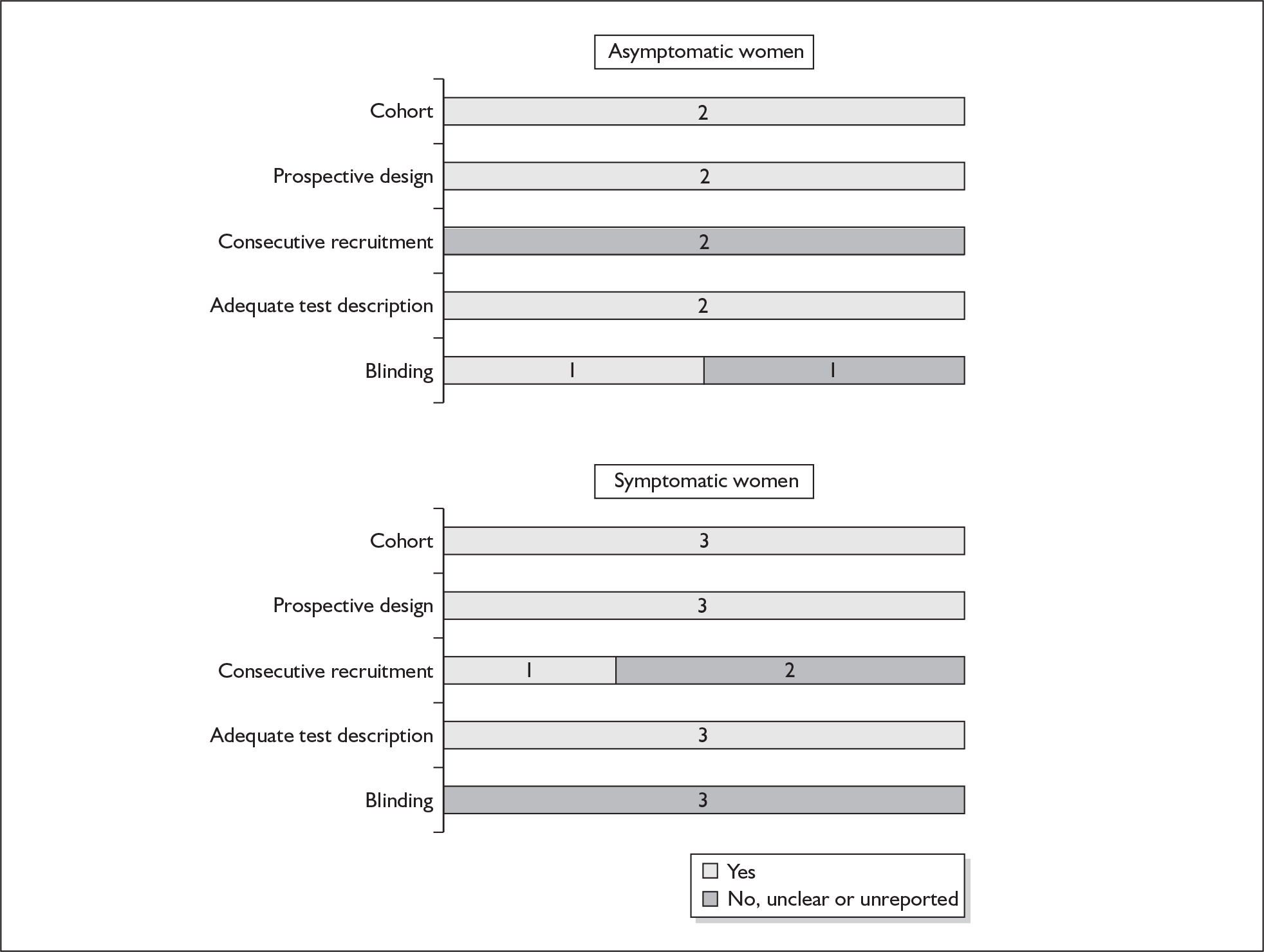
Accuracy of IL-8 in asymptomatic women
In the single study that evaluated the test for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation on asymptomatic women but which involved serial testing of cervical IL-8, LR+ was 2.23 (95% CI 1.46–3.41) and LR– was 0.69 (0.50–0.97). 244 These values were used for the decision-analytic modelling. For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, the LR+ ranged from 1.38 (95% CI 1.04–1.81)244 to LR+ 2.75 (95% CI 1.68–4.52)243 while LR– ranged from 0.68 (95% CI 0.49–0.95)243 to 0.91 (95% CI 0.82–1.01). 244 LRs from Sakai et al. 244 were used in the decision-analytic modelling because it represented the largest higher-quality study available for the population. Figure 48 shows the forest plots of the accuracy of the IL-8 test in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Individual accuracy measures of the test are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 95.
FIGURE 48.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of interleukin-8 (IL-8) measurement from amniotic fluid and cervical specimen as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth stratified according to population and outcome. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality and unless otherwise stated, were single testing, using samples obtained from cervicovaginal swabs. a, Serial testing. b, Amniotic fluid specimens.
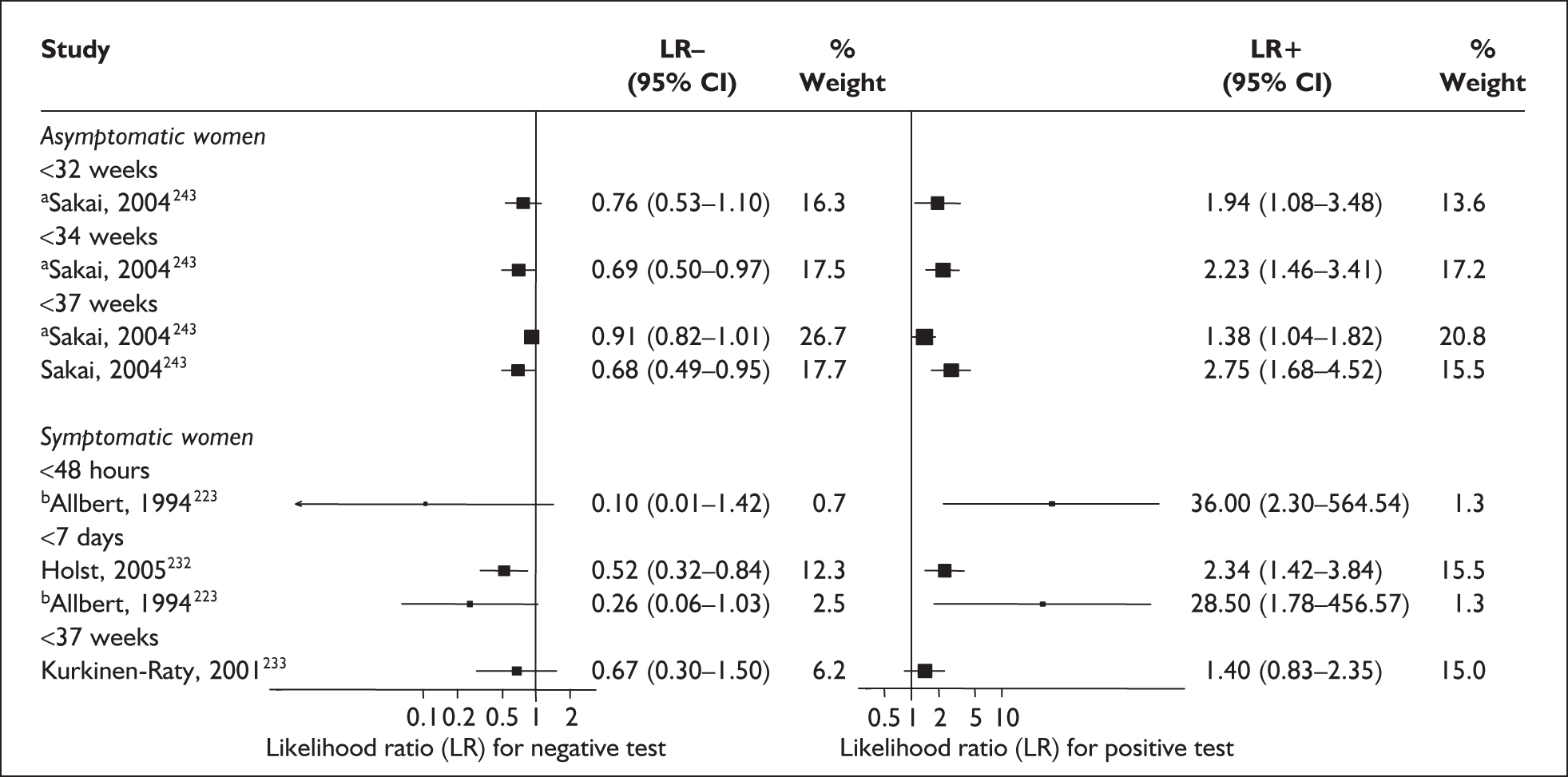
Accuracy of IL-8 in symptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of testing, LR+ was 36.00 (95% CI 2.30–564.54) and LR– was 0.10 (95% CI 0.007–1.42); these LRs were used in the decision-analytic modelling. 223 The accuracy for predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing was shown in Figure 48 where the LR+ ranged from 2.34 (95% CI 1.42–3.84) (cervical IL-8)241 to 28.5 (95% CI 1.78–456.57) (amniotic fluid IL-8)223 and LR– ranged from 0.26 (95% CI 0.06–1.03) (amniotic fluid IL-8)223 to 0.52 (95% CI 0.32–0.84) (cervical IL-8). 241 The LR+ from Holst et al. 241 was used in the decision-analytic modelling because it represented the largest higher quality study. For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks gestation, LR+ was 1.4 (95% CI 0.83–2.35) and LR– was 0.67 (95% CI 0.30–1.50); these LRs were used in the decision-analytic modelling. 233 Figure 48 shows the forest plots of the accuracy of the IL-8 test in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. A ROC plot of sensitivity versus specificity for amniotic fluid IL-8 in symptomatic women is shown in Figure 49. Individual accuracy measures of the test are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 95.
FIGURE 49.
Plot of sensitivity versus 1-specificity in ROC space for amniotic fluid interleukin-8 (IL-8) studies in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour in predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours or 7 days of testing.
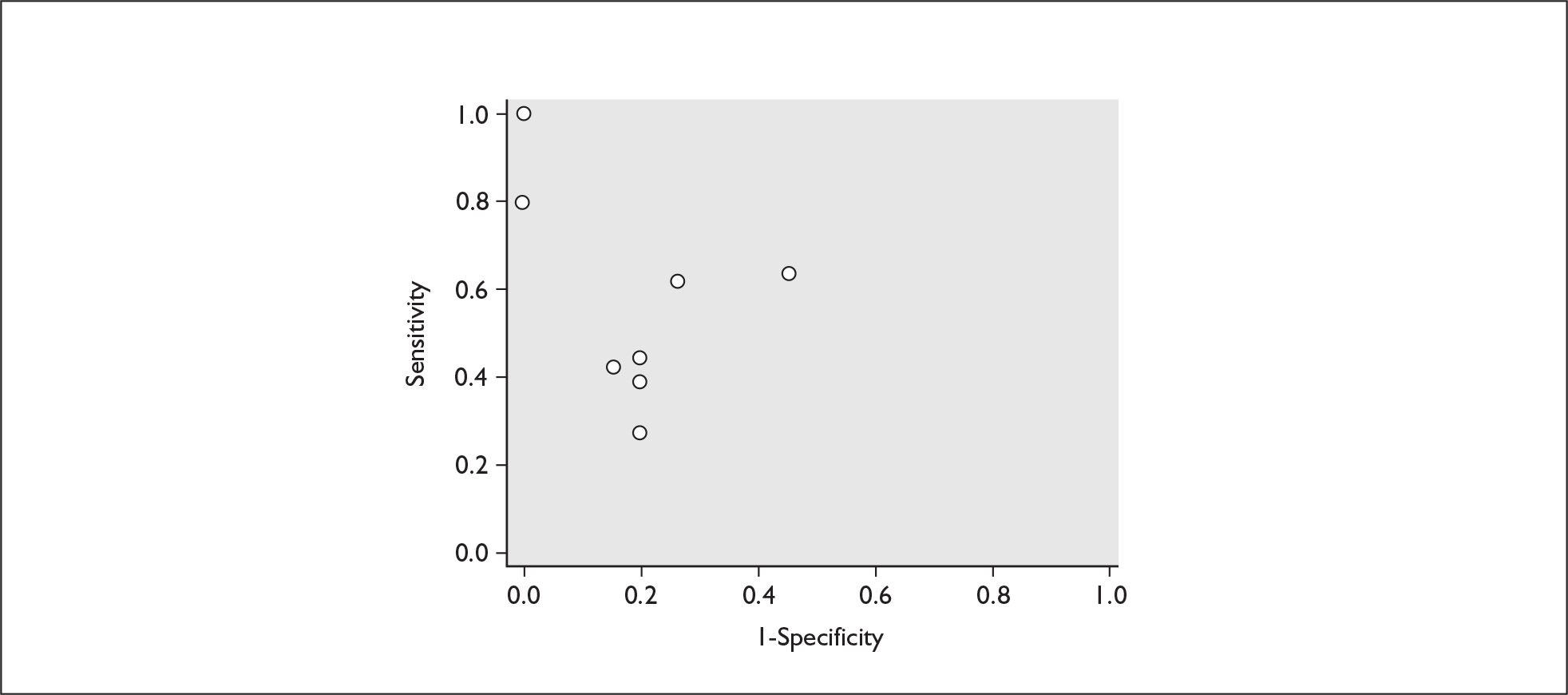
Matrix metalloprotease-9
During pregnancy, matrix metalloprotease-9 (MMP-9) is produced by the decidua, chorion and amnion. Its expression is increased in the choriodecidual membranes during active labour. It is purported that during the process of labour, which involves the disruption of decidua–membrane interface, measurement of MMP-9 may served as a marker for impending preterm labour that leads to spontaneous preterm birth. 245
Study characteristics and quality
There were two primary studies (n = 35) on the accuracy of MMP-9 testing, both were on symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour. One study evaluated MMP-9 in maternal plasma (n = 15)245 while the other (n = 20) evaluated it in maternal plasma and urine specimens. 246 There were no studies on asymptomatic women. Appendix 5, Table 96 summarises each study’s salient features.
There were no studies included within the systematic review of the accuracy of MMP-9 testing in predicting spontaneous preterm births that fulfil our ideal definition of high-quality test accuracy studies either in asymptomatic or symptomatic women. Neither of the studies reported using consecutive enrolment of women into the study or blinding of carers or assessors to test results. However, both studies have an adequate test description report. The methodological quality of the included primary studies is summarised in Figure 50.
FIGURE 50.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of matrix metalloprotease-9 in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
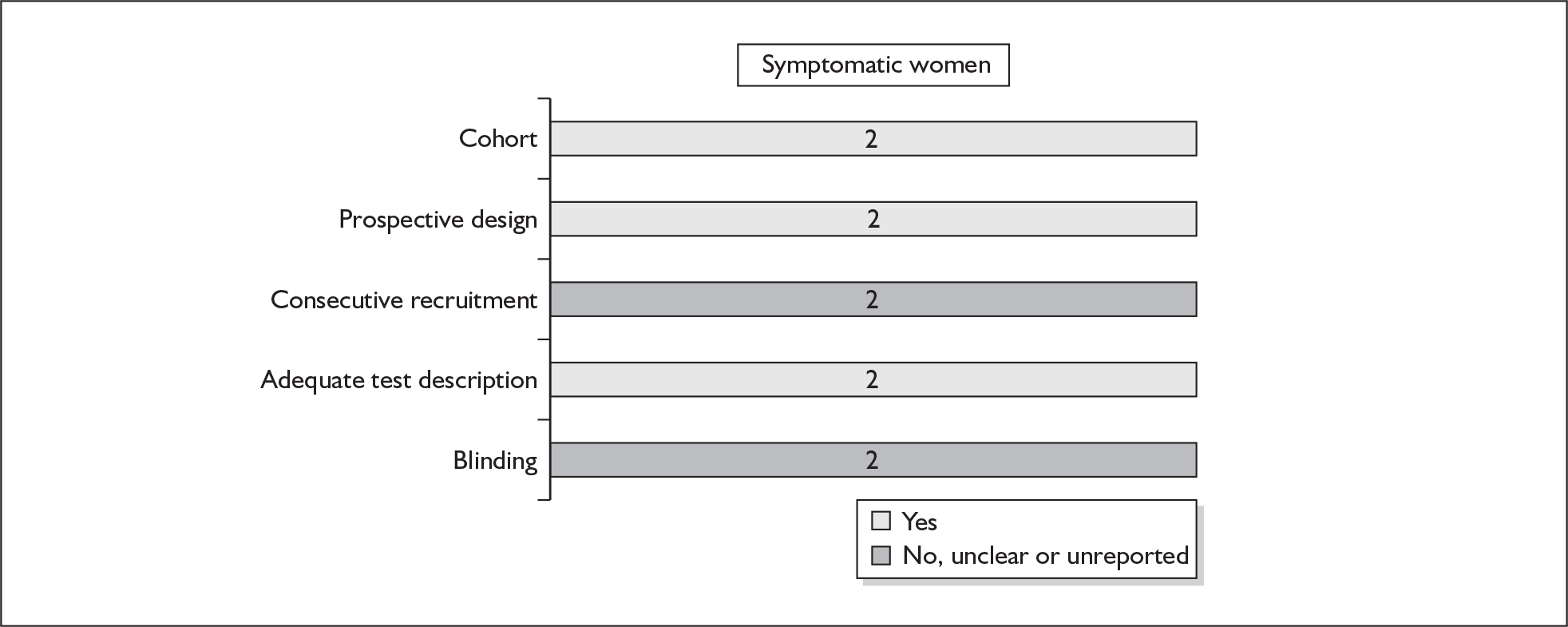
Accuracy of MMP-9 in symptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, maternal plasma MMP-9 had an LR+ of 7.33 (95% CI 1.07–50.27)245 and an LR– of 0.37 (95% CI 0.14–0.94)246 while maternal urinary MMP-9 had a range of LR+ from 6.00 (95% CI 0.87–41.44) to 7.33 (95% CI 1.07–50.27)246 and LR– from 0.37 (95% CI 0.14–0.94)246 to 0.38 (95% CI 0.12–1.19) (Figure 51). 245 Estimates from Makrakis et al. 246 were used in decision-analytic modelling because their study represented the largest higher-quality study for this reference standard. Individual accuracy results for symptomatic women can be found in Appendix 5, Table 97.
FIGURE 51.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios of mmP-9 in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality.
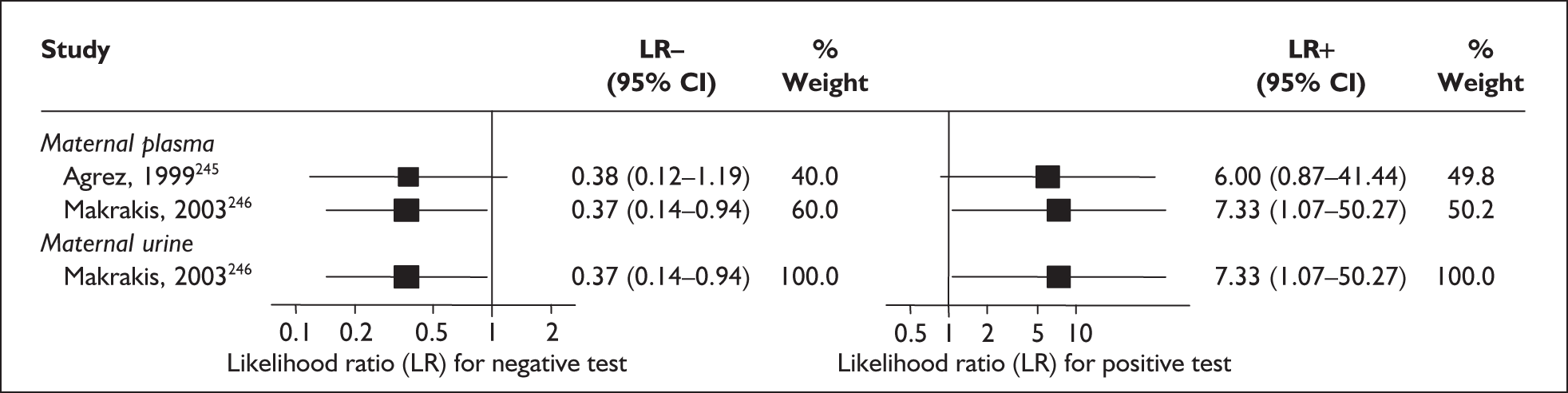
Periodontal assessment
Periodontal health care is provided free at the point of delivery to pregnant women within the UK. It examines the oral cavities for signs of periodontal disease (e.g. periodontitis), which has been purported to predispose to spontaneous preterm birth. 247
Study characteristics and quality
There were 13 primary articles evaluating the accuracy of the state of antenatal periodontal health in asymptomatic women or in the immediate postnatal period as predictor of spontaneous preterm birth (n = 3900 women). 247–259 The number of women enrolled ranged from 36249 to 1313247 with a median of 128. Two studies published their preliminary results (n = 176 women), but their full results were not available at the time of writing. 251,258 The accuracy of one study was not evaluated further because data were not extractable from the publication and the corresponding author was not able to provide it within the time scale of this project. 253 There was no study evaluating the accuracy of periodontal assessment as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth in women who presented with threatened preterm labour. Appendix 5, Table 98 summarises each study’s salient features, stratified according to population of women tested, i.e. asymptomatic antenatal women and symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
None of the studies fulfilled ideal quality study designs. There were ten studies that reported prospective data collection247–251,253,255–257,259 and six that reported case–control design. 248,250,252,254,256,258 Consecutive enrolment was only evident in one study. 247 Blinding was reported in eight studies. 247,248,250,253,255–258 Overall, there were adequate reports of test description from the studies. The methodological quality of the included primary studies is summarised in Figure 52.
FIGURE 52.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of periodontal health assessment in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
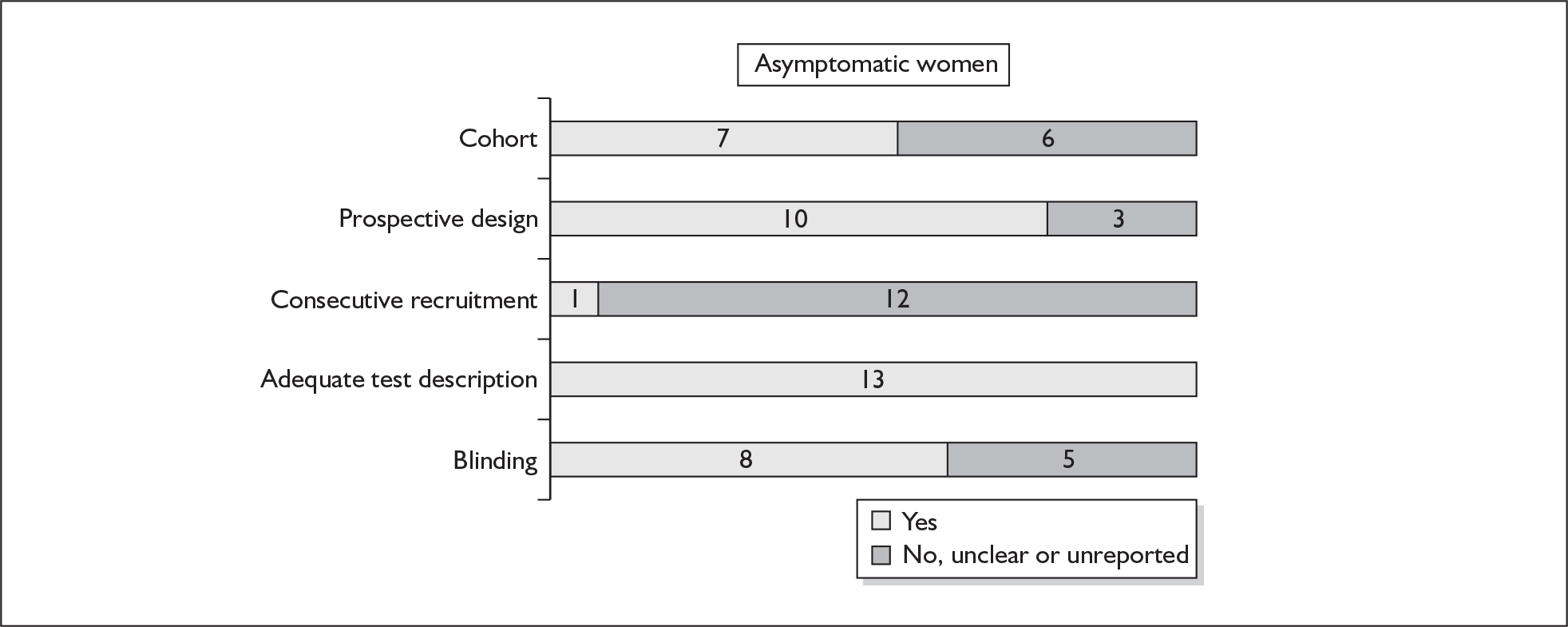
All but one study assessed women’s periodontal status for the presence of periodontitis. The remaining study assessed women’s antibody serology for Porphyromonas gingivalis, the predominant organism implicated in periodontitis in the general population. 248 Seven studies performed their periodontal assessment in the second trimester247–249,251,253,255,259 while six studies performed theirs within 2–5 days of delivery. 250,252,254,256–258 There were as many criteria for determining periodontitis as the number of studies: no two studies had used the same criteria for determining periodontitis. Except for two studies, which used 32 weeks’ gestation,250255 most studies had used 37 weeks’ gestation as their reference standard.
Accuracy of periodontal assessment in asymptomatic women
The presence of periodontal disease showed variable accuracy in predicting spontaneous preterm birth (Figure 53). The LR+ ranged from 0.38 (95% CI 0.04–3.33)256 to 5.00 (95% CI 2.22–11.28)249 and the LR– ranged from 0.22 (95% CI 0.09–0.57)257 to 1.13 (95% CI 0.90–1.42). 251 The largest higher-quality study reported LR+ of 2.26 (95% CI 1.35–3.79) and LR– of 0.79 (95% CI 0.65–0.96). 247 These estimates were used for the decision-analytic modelling. The individual accuracy result of the state of periodontal health in predicting spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic women is summarised in Appendix 5, Table 99. Meta-analysis was not performed because of the clinical heterogeneity in the criteria defining periodontal disease.
FIGURE 53.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios of periodontal health status in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in asymptomatic women. Studies using the same source of IL-6 are arranged in descending order of methodological quality.
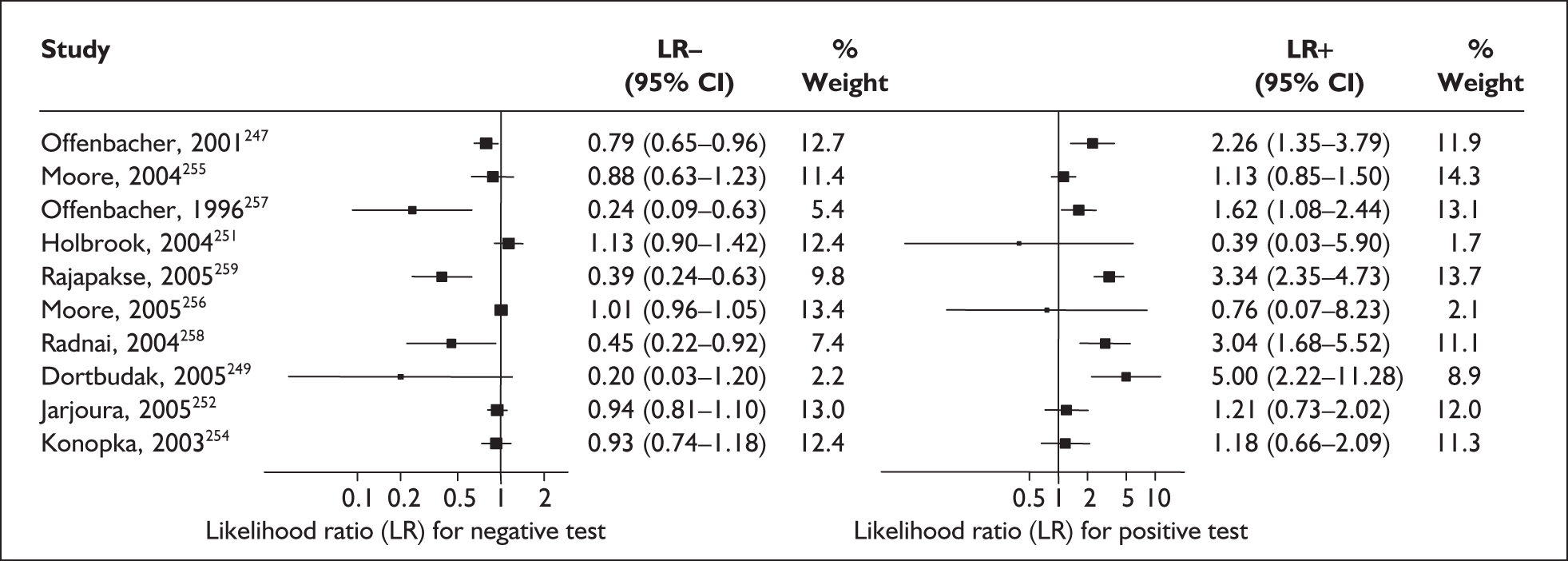
Asymptomatic bacteriuria assessment
Screening for asymptomatic bacteriuria has been a routine component of antenatal care. When present, it has been purported to increase the risk of spontaneous preterm birth. The usual specimen obtained was a mid-stream urine specimen sent for bacterial culture and sensitivity analysis. In light of the recognised contribution of vaginal colonisation to the development of spontaneous preterm labour, there is even a call to re-evaluate the usefulness of screening for asymptomatic bacteriuria. 260 One systematic review had been performed. 261
Study characteristics and quality
There were 26 studies (n = 66,824) evaluating the accuracy of screening for asymptomatic bacteriuria in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. 262–287 Three of the included studies (n = 11,520) evaluated the accuracy of asymptomatic group B streptococcal bacteriuria exclusively. 274,275,286 All the studies used birth before 37 weeks’ gestation as their outcome measurement. Appendix 5, Table 100 summarises the characteristics of the included studies.
None of the studies fulfilled our criteria for an ideal quality study. Specifically, blinding was absent from all the studies. Only six and nine studies used consecutive enrolment271,274,275,278,283,287 and prospective data collection,271,274,275,277,278,283,284,287 respectively. Figure 54 summarises the methodological quality of the included studies.
FIGURE 54.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of asymptomatic bacteriuria assessment in predicting spontaneous preterm birth among asymptomatic antenatal women. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
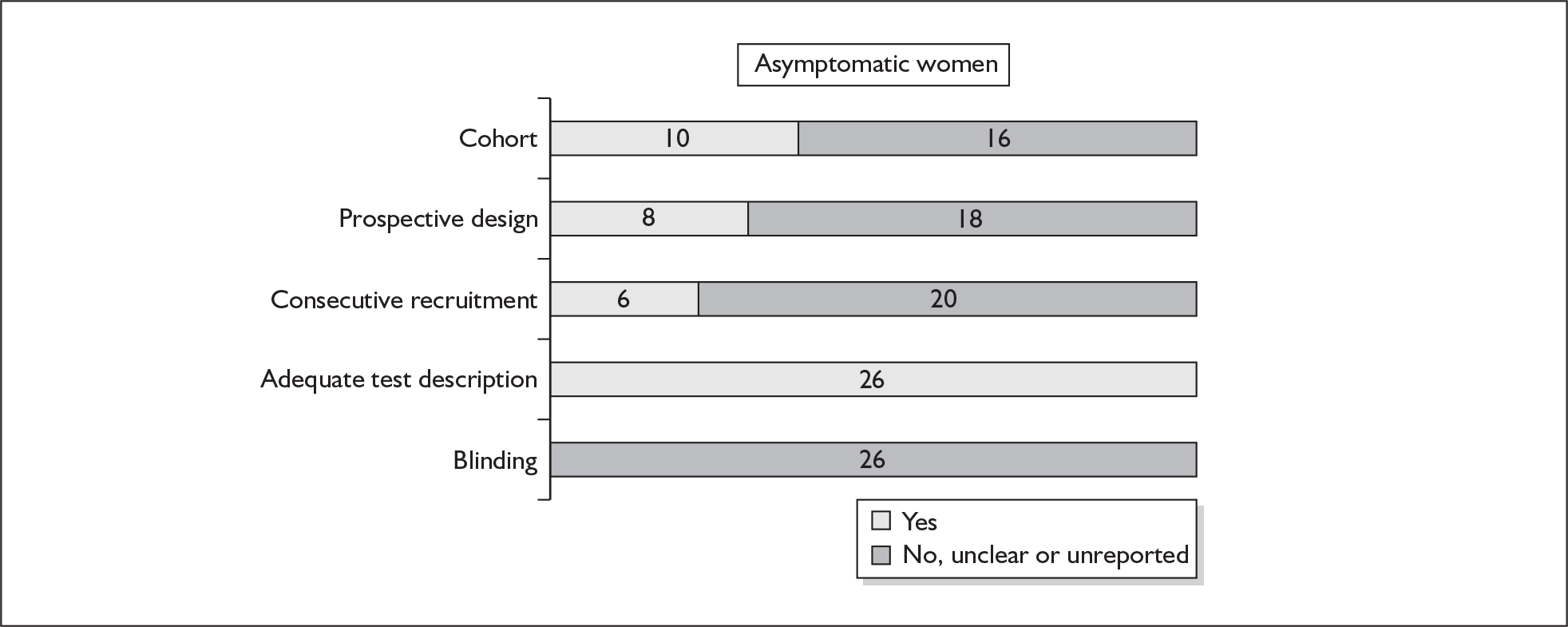
Accuracy of asymptomatic bacteriuria in asymptomatic women
Screening for asymptomatic bacteriuria showed a variable accuracy in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation (Figure 55). LR+ ranged from 0.10 (95% CI 0.01–1.70)265 to 3.83 (95% 2.22–6.59)269 while LR– ranged from 0.43 (95% CI 0.19–0.94) to 1.17 (95% CI 0.64–2.13)263 for asymptomatic bacteriuria. For asymptomatic group B streptococcal bacteriuria, LR+ ranged from 1.52 (95% CI 0.80–2.86)286 to 2.69 (95% CI 1.51–4.76)275 and LR– ranged from 0.96 (95% CI 0.88–1.04)274 to 0.99 (95% CI 0.98–1.01). 286 The LR+ of 2.63 (95% CI 1.54–4.50) and LR– of 0.96 (95% CI 0.92–0.99) from Wren287 was used in the decision-analytic modelling because it represented the best higher-quality study available. Individual accuracy data are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 101.
FIGURE 55.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios of asymptomatic bacteriuria assessment in asymptomatic women as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation stratified according to the type of asymptomatic bacteriuria. Studies are in descending order of quality. a. Caucasian population. b. Bangladeshi population. χ2 heterogeneity test for asymptomatic bacteriuria p = 0.00 for LR+ and p = 0.00 for LR–; for group B streptococcal asymptomatic bacteriuria p = 0.42 for LR+ and p. = 0.16 for LR–.
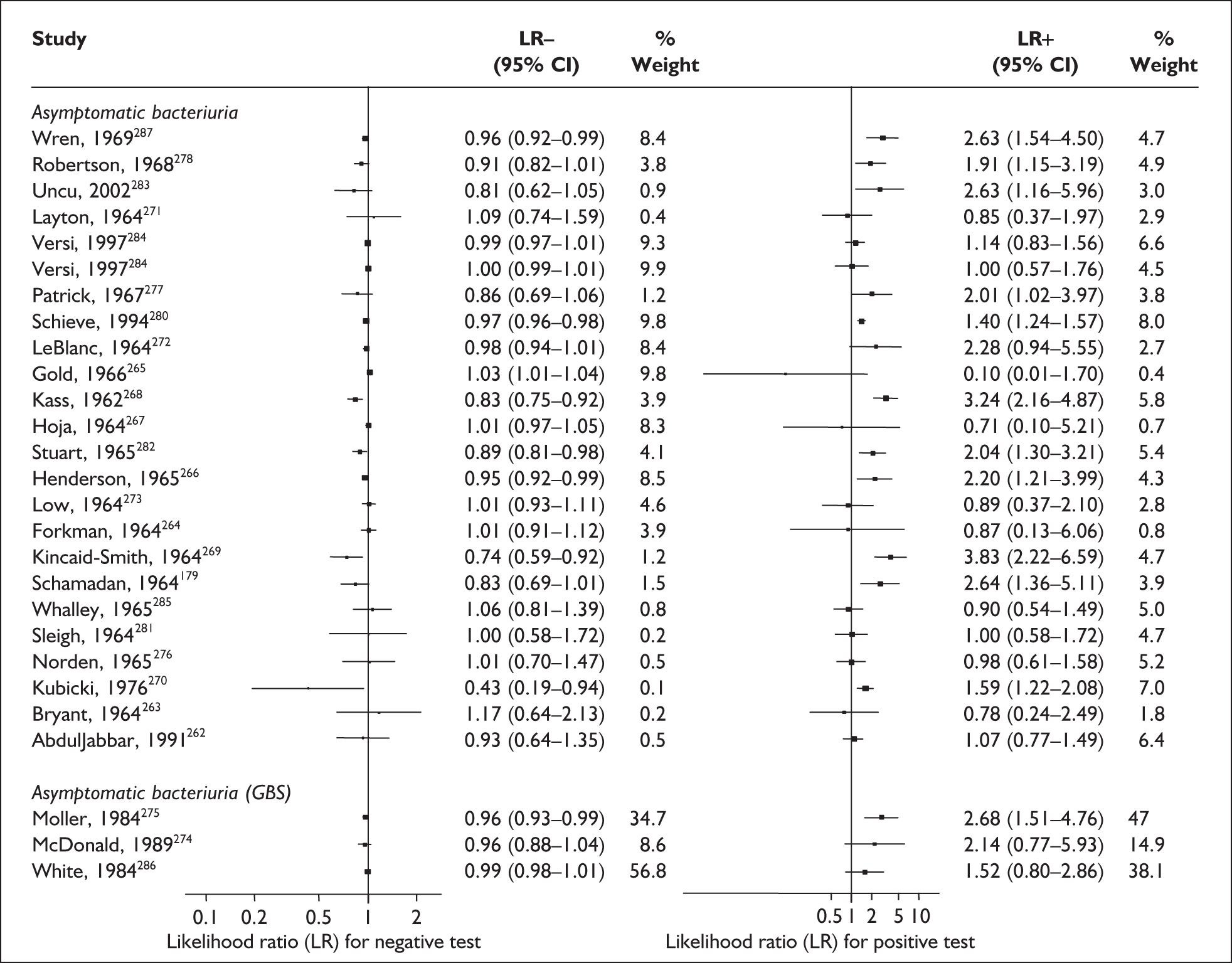
Bacterial vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a condition in women where the normal balance of bacteria in the vagina is disrupted and replaced by an overgrowth of anaerobic bacteria. The condition has been purported to predispose to spontaneous preterm birth. The condition can be tested by taking a high vaginal swab specimen during speculum examination for clinical evaluation (Amsel criteria), Gram staining (Nugent or Spiegel criteria), or standard microbiological culture.
Study characteristics and quality
There were 25 primary studies (n = 35,652 women) on the accuracy of BV testing, comprising 17 studies on asymptomatic antenatal women (n = 33,628) and eight studies on symptomatic women who presented with threatened preterm labour (i = 2024). Appendix 5, Table 102 summarises each study’s salient features, stratified according to the population of women tested, i.e. asymptomatic antenatal women and women with symptoms of threatened preterm labour. The studies’ enrolment ranged from 103 to 12,937 women288,289 with a median of 646 women in the asymptomatic population and from 87 to 753 women241,290 with a median of 211 women for the symptomatic population.
No studies included within the systematic review of the accuracy of BV testing in predicting spontaneous preterm births fulfilled our ideal definition of high-quality test accuracy studies. Blinding of carers to the results of BV tests was often absent from studies on asymptomatic289,291–296 and symptomatic241,290,297–299 women. For symptomatic women, six studies had used a case–control design to assess the accuracy of BV testing in predicting spontaneous preterm births in symptomatic women. 241,290,297,299–301 The methodological quality of the included primary studies is summarised in Figure 56.
FIGURE 56.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of bacterial vaginosis testing in predicting spontaneous preterm birth among asymptomatic antenatal women and symptomatic women who presented with threatened preterm labour. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.

The commonly used criterion to diagnose BV was Gram staining using Nugent’s criteria in the included studies, otherwise the other two methods that were used infrequently were Gram staining using Spiegel’s241,297,301 and bedside diagnosis using Amsel’s clinical criteria. 99,296,299,302 Three studies evaluated the accuracy of serial BV testing in asymptomatic pregnant women for predicting spontaneous preterm births295,303,304 while the remainder evaluated a single BV testing, usually performed at mid-trimester. 99,288,289,291–293,295,303–307
One study in asymptomatic antenatal women collected data for the prediction of spontaneous preterm births at 23–26 weeks’ gestation but was not published. 288 Otherwise, most studies reported births before 37 weeks’ gestation as their reference standards with two exceptions; one study used birth before 32 and 34 weeks’ gestation as its reference standard291 while another study used 35 weeks’ gestation as its reference standard. 294 Similarly, for symptomatic women, the most commonly used reference standard was births before 37 weeks’ gestation, except for three studies that reported births within 7 days of testing and before 33 weeks’ gestation,308 birth before 34 weeks’ gestation241 and births before 35 weeks’ gestation. 298 One study reported birth within 7 days of testing. 308
Accuracy of BV in asymptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, a single BV testing (using Nugent’s criterion) had a range of LR+ from 0.49 (95% CI 0.07–3.16) to 5.31 (95% CI 3.84–7.33) with a summary LR+ of 1.77 (95% CI 1.03 to 3.03) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00) and a range of LR– from 0.32 (95% CI 0.23–0.43) to 1.15 (95% CI 0.90–1.48) with a summary LR– of 0.80 (95% CI 0.69–0.93) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.00) (Figure 57). LR+ of 0.80 (95% CI 0.38–1.72) and LR– of 1.04 (95% CI 0.92–1.17) from the sole ideal quality study were used in the decision-analytic modelling. 293 For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, serial BV testing (using Nugent’s criterion) had a range of LR+ from 1.15 (95% CI 0.67–1.96) to 1.92 (95% 0.63–5.92) with a summary LR+ of 1.38 (95% CI 0.92–2.07) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.56) and a range of LR– from 0.87 (95% 0.49–1.56) to 0.94 (95% 0.85–1.04) with a summary LR– of 0.94 (95% 0.86–1.02) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.96) (Figure 58). LR+ 1.92 (95% CI 0.63–5.92) and LR– 0.93 (95% CI 0.79–1.10) from the largest higher-quality study304 was used in the decision-analytic modelling. For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, a single BV testing (using Amsel’s clinical criterion) had a range of LR+ from 0.87 (95% CI 0.48–1.59)302 to 1.62 (95% CI 0.44–5.91)99 (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.67) and LR– from 0.90 (95% CI 0.63–1.29)99 to 1.02 (95% CI 0.93–1.12) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.79) (Figure 59). 302 Individual accuracy results can be found in Appendix 5, Table 103.
FIGURE 57.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios of a single second trimester bacterial vaginosis (BV) testing using Nugent’s criteria in asymptomatic pregnant women as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. χ2 heterogeneity test for Nugent’s criteria p = 0.00 for LR+ and p. 0.00 for LR–.
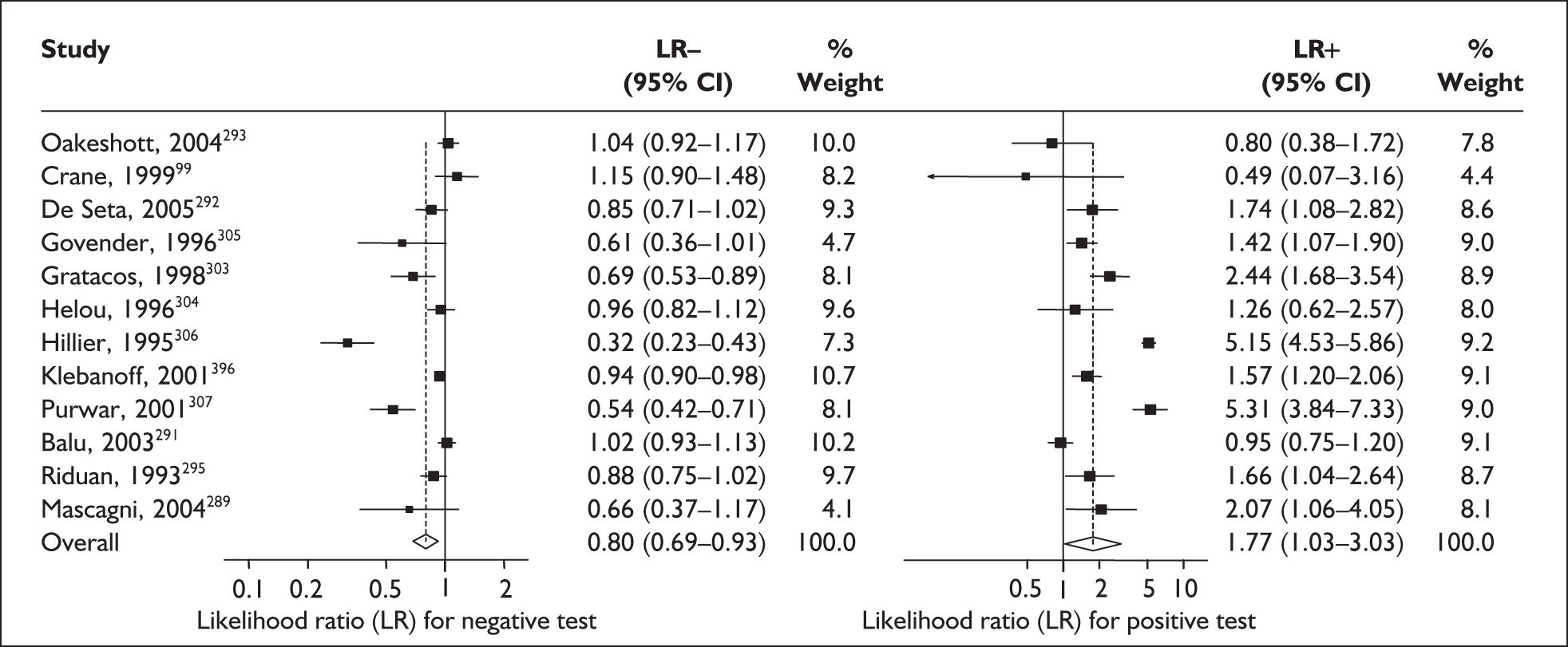
FIGURE 58.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios of serial bacterial vaginosis testing using Nugent’s criteria in asymptomatic pregnant women as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. χ2 heterogeneity test for Nugent’s criteria p = 0.56 for LR+ and p. 0.96 for LR–.
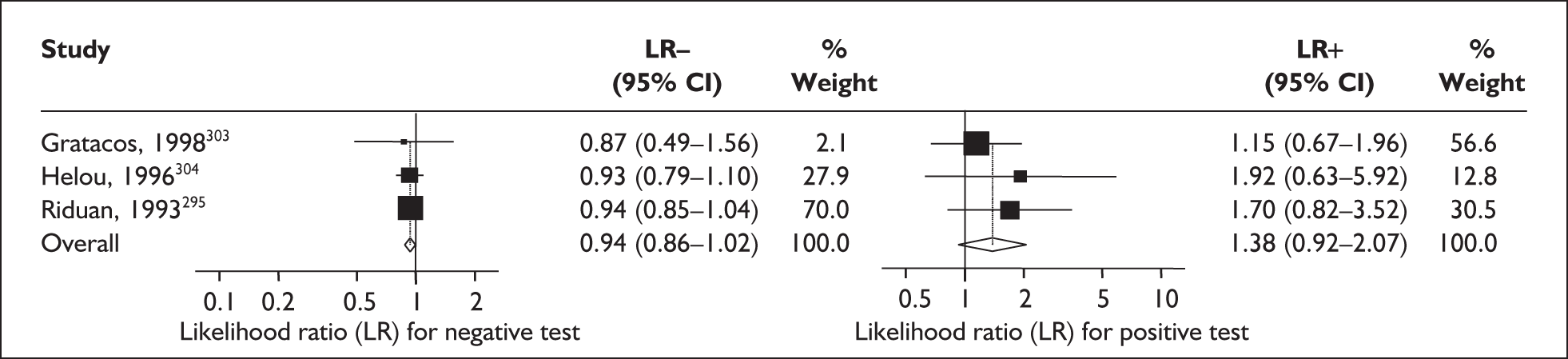
FIGURE 59.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios of a single second-trimester bacterial vaginosis testing using Amsel’s criteria in asymptomatic pregnant women as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. χ2 heterogeneity test for Amsel’s criteria p = 0.67 for LR+ and p. 0.79 for LR–.
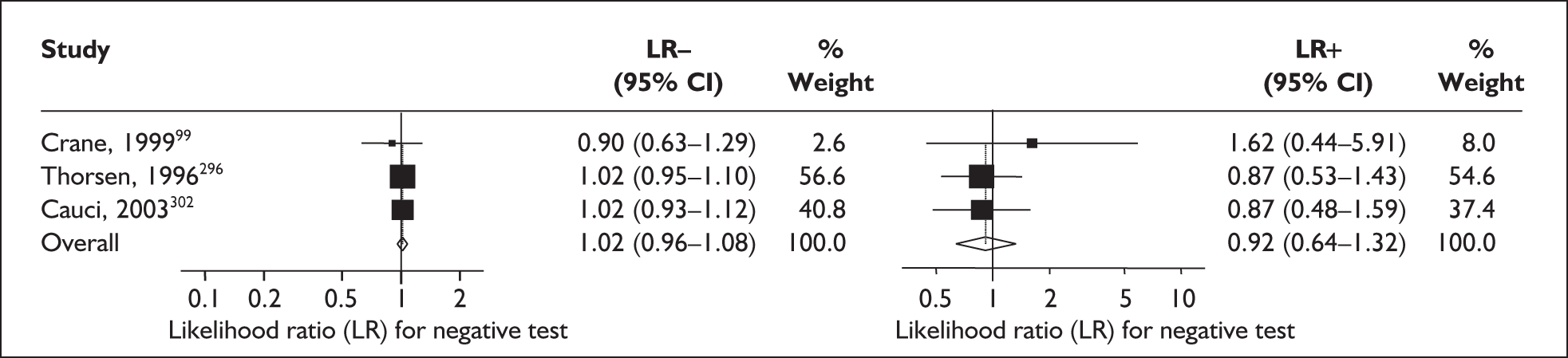
Accuracy of BV in symptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, BV testing (using Nugent’s criteria) had a range of LR+ from 0.91 (95% CI 0.57–1.45) to 1.86 (95% CI 1.31–2.65) with a summary LR+ of 1.28 (95% CI 0.72 to 2.20) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.04) and a range of LR– from 0.89 (95% CI 0.84–0.95) to 1.04 (95% CI 0.87–1.23) with a summary LR– of 0.95 (95% CI 0.86–1.05) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.10) (Figure 60). For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, BV testing (using Spiegel’s criteria) had a range of LR+ from 1.00 (95% 0.76–1.32) to 3.68 (95% CI 1.13–11.97) with a summary LR+ of 1.30 (95% CI 0.95–1.77) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.25) and a range of LR– from 0.66 (95% 0.46–0.96) to 1.00 (95% 0.73 -1.36) with a summary LR– of 0.94 (95% 0.87–1.01) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.04) (Figure 60). Individual accuracy results can be found in Appendix 5, Table 103.
FIGURE 60.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios of bacterial vaginosis testing in symptomatic women as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. χ2 heterogeneity test for Nugent’s criteria p = 0.04 for LR+ and p = 0.010 for LR–; for Spiegel’s criteria p = 0.25 for LR+ and p = 0.04 for LR–;
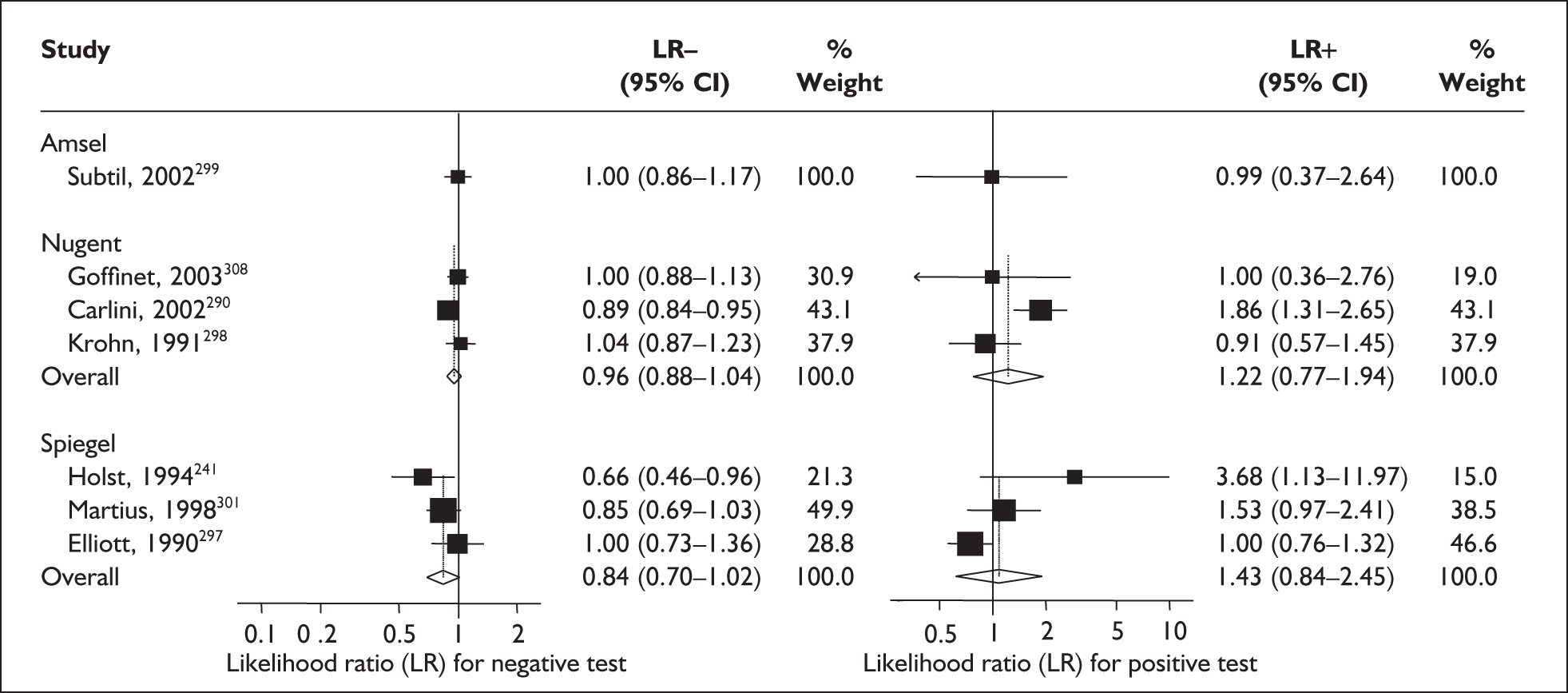
Mammary stimulation test
The antenatal mammary stimulation test is a provocative test of uterine contractility, which purported to identify asymptomatic women at high risk for spontaneous preterm birth. The presence of easily provoked uterine contractility is supposed to be an indication of higher risk of spontaneous preterm birth.
Study characteristics and quality
There were two studies evaluating the mammary stimulation test, both in asymptomatic antenatal women (n = 341)309,310 Both studies enrolled their population during the early third trimester. One study evaluated the accuracy in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation310 while both evaluated the accuracy for prediction before 37 weeks’ gestation. Neither of the studies fulfilled our criteria for an ideal quality study with consecutive enrolment being absent from both studies. Figure 61 summarises the methodological quality of the included study. Both studies used the same test threshold. Individual study characteristics can be found in Appendix 5, Table 104.
FIGURE 61.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of mammary stimulation test in asymptomatic women for predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
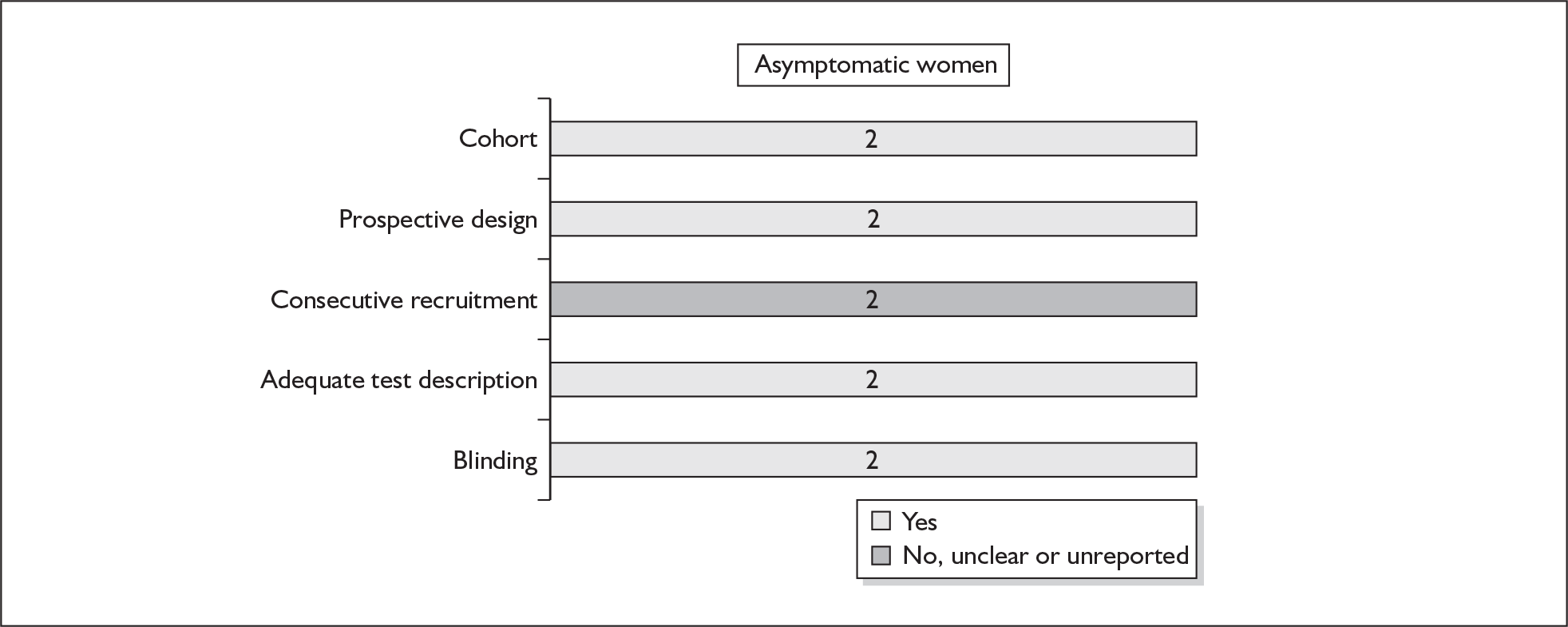
Accuracy of mammary stimulation test in asymptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, the mammary stimulation test had an LR+ of 4.63 (95% CI 2.95–7.25) and LR– of 0.27 (0.08–0.91). 310 For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation the mammary stimulation test had a range of LR+ from 2.04 (95% CI 1.45–2.84)309 to 3.30 (95% CI 1.54–7.08)310 and LR– from 0.23 (0.06–0.85)309 for those with a high Creasy risk score to 0.49 (0.17–1.43) (Figure 62). 310 LRs from Guinn et al. 310 were used in the decision analyses because it represented the largest higher-quality study available. Individual accuracy results can be found in Appendix 5, Table 105.
FIGURE 62.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios of mammary stimulation test as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic women stratified according to outcome. a, High-risk women according to Creasy’s risk scoring system.
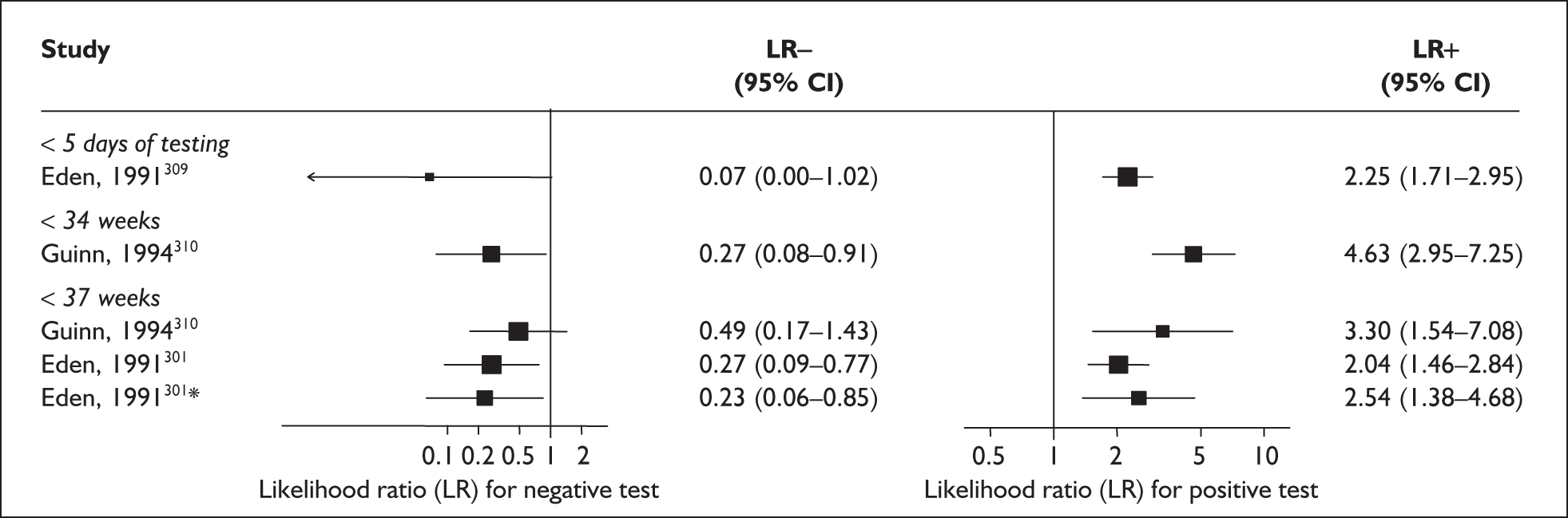
Uterine activity monitoring
The presence of increasingly co-ordinated, frequent and progressively stronger uterine activity often precedes the development of labour. It was thus purported that if uterine activities were monitored then advance warning of impending onset of labour, whether at term or specifically preterm, could be predicted.
Study characteristics and quality
There were four studies evaluating uterine activities, two in asymptomatic antenatal women (n = 370) and two in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour (n = 114). 76,311–313 Three studies used a tocograph while one used emerging technology involving electromyographic recording of uterine activities. 313 There was no consensus on the threshold defining abnormality. Aside from one study, which used birth before 35 weeks’ gestation as its outcome,76 the remaining studies used birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. None of the studies fulfilled our criteria for ideal quality study, consecutive enrolment was absent from any of the studies and blinding was absent from three studies. Figure 63 summarises the methodological quality of the included study. Individual study characteristics are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 106.
FIGURE 63.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of home uterine activity monitoring in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
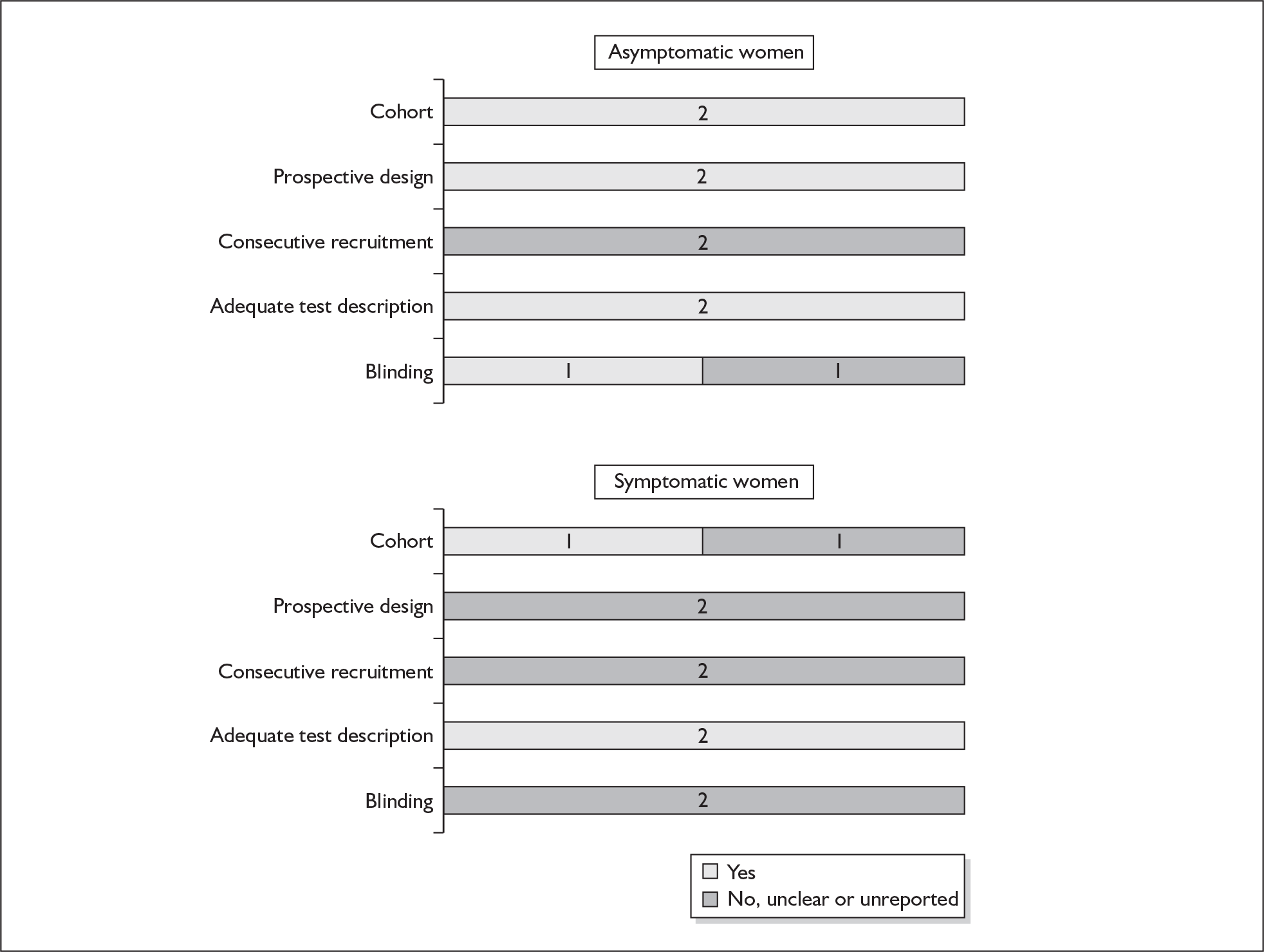
Accuracy of uterine activity monitoring in asymptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth, uterine activity monitoring had a range of LR+ from 0.51 (95% CI 0.03–9.24)76 when the threshold was set for detection of significant uterine activities during the day time, to 4.90 (95% CI 2.99–8.04)312 when four significant contractions were detected within a 1-hour period, and a range of LR– from 0.15 (95% CI 0.04–0.56)312 when four significant contractions were detected within a 1-hour period to 1.01 (95% CI 0.98–1.05)76 for detection of significant uterine activities during the day time. LR+ of 2.41 (95% CI 0.76–7.68) and LR– of 0.95 (95% CI 0.86 –1.04) from Iams et al. 76 were used in the decision-analytic modelling because this study represented the higher-quality study. Figure 64 summarises the accuracy results while Appendix 5, Table 107 shows individual accuracy results for each study.
FIGURE 64.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of uterine activity monitoring as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation* stratified according to populations. a, Uterine activities at night-time. b, Uterine activities in day-time.
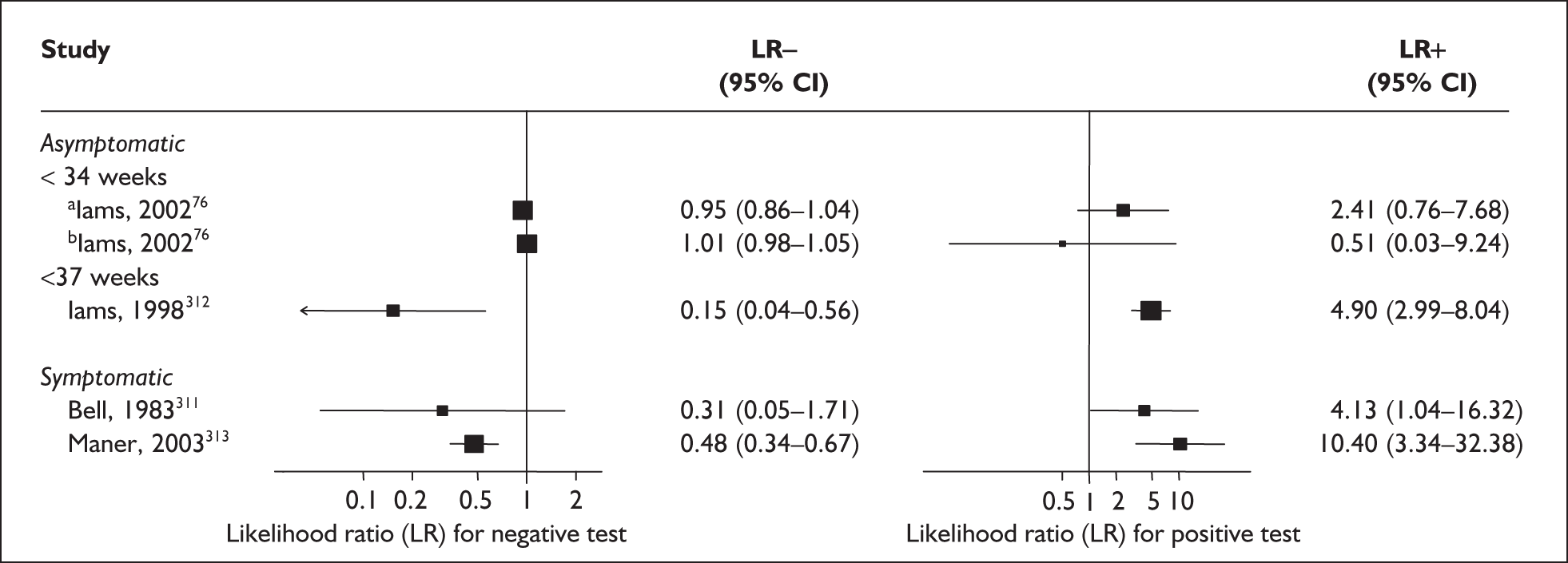
Accuracy of uterine activity monitoring in symptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, uterine activity monitoring had a range of LR+ from 4.13 (95% CI 1.04–16.32)311 to 10.40 (95% CI 3.34–32.38)313 and a range of LR– from 0.31 (95% CI 0.05–1.71)311 to 0.48 (95% CI 0.34–0.67)313 when using tocographic and electromyographic recording, respectively. LRs from Bell311 were used for the decision-analytic modelling because this study represented the best available higher-quality study. Figure 64 summarises the accuracy results while Appendix 5, Table 107 shows individual accuracy results for each study.
Rheobase
Rheobase in the context of a test to predict spontaneous preterm birth involves measurement of the minimal strength of electrical stimulus that is able to cause excitation of a muscle, e.g. tibialis anterior muscle in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour, which would show a higher threshold compared to a quiescent uterus. Mass electrical uterine activities in a genuine spontaneous labour would require greater electrical strength to generate muscular excitation and hence the purported ability of rheobase to predict spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour by detecting these greater electrical signals.
Study characteristics and quality
There was only one study evaluating rheobase in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour (n = 176). 314 Two different thresholds were evaluated (2.8 and 3.4 mA) and outcome of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation was used. The study characteristics can be found Appendix 5, Table 108. Methodological quality is summarised in Figure 65.
FIGURE 65.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of rheobase testing in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
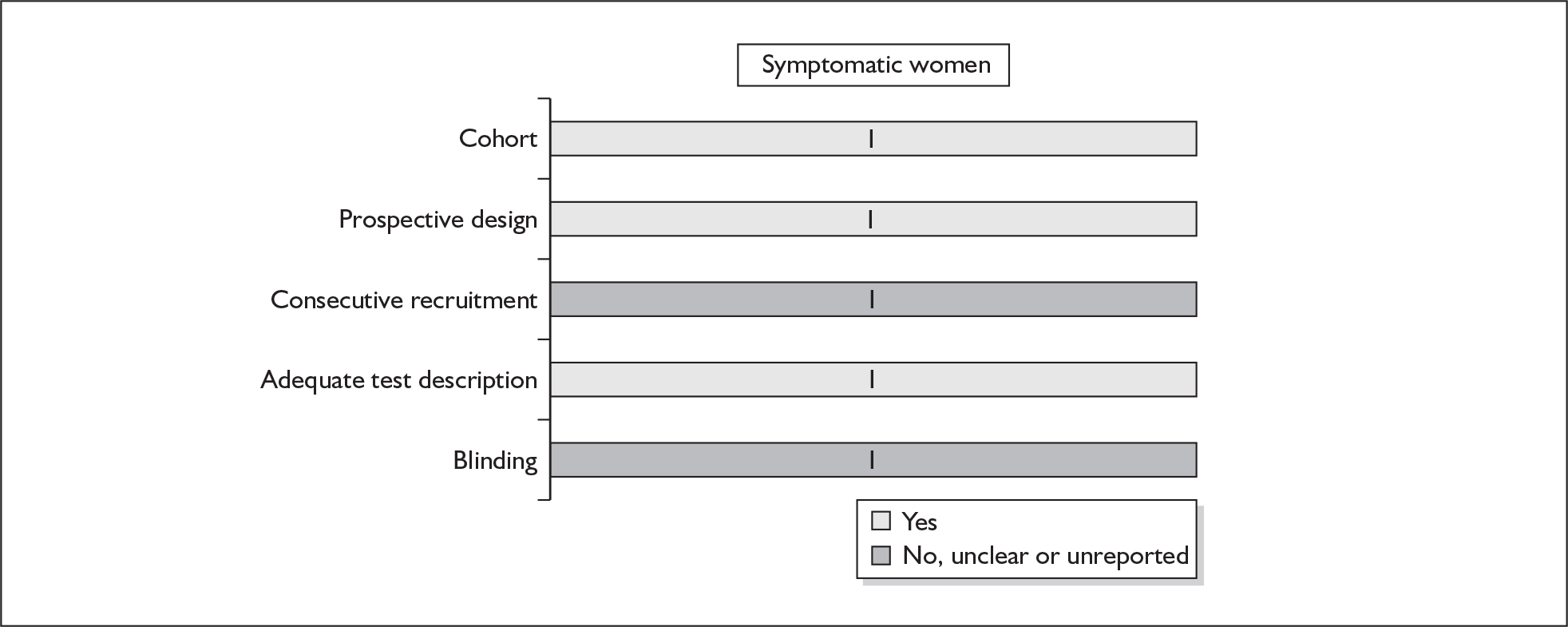
Accuracy of rheobase measurement in symptomatic women
Depending on the thresholds being used, rheobase had an LR+ that ranged from 2.29 (95% CI 1.50–3.52) when 2.8 mA was used to 2.36 (95% CI 1.73–3.20) when 3.4 mA was used, and an LR– that ranged from 0.36 (95% CI 0.19–0.66) when 3.4 mA was used to 0.60 (95% CI 0.41–0.88) when 2.8 mA was used (Figure 66). Individual accuracy results are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 109. Both sets of LRs were used in the decision analyses.
FIGURE 66.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of rheobase measurement as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women stratified according to thresholds.
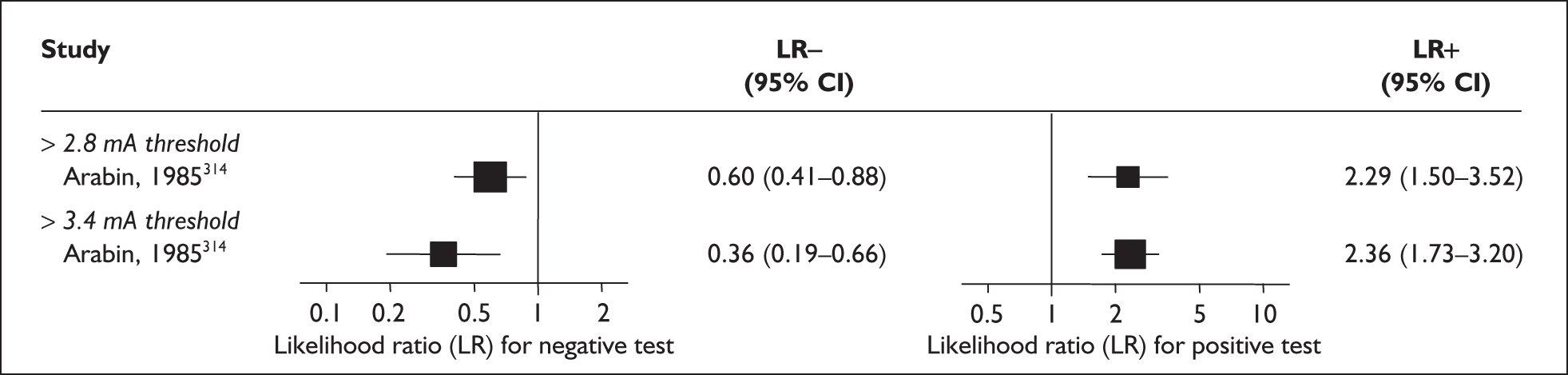
Absence of fetal breathing movements on ultrasound
A decrease in fetal breathing movements observed during a 20-minute observation with real-time ultrasound at the time of admission for threatened preterm labour has been purported to be a predictor of progression to spontaneous preterm birth.
Study characteristics and quality
There were eight primary accuracy articles that met the selection criteria, which included a total of 328 women. 92,315–321 (Appendix 5, Table 110). All of them evaluated fetal breathing movements for a sustained period of 15–20 seconds in a 30- to 45-minute period with real-time ultrasound. The absence of breathing movements, defined as no sustained fetal breathing movements noted during the time-period, indicated a positive result. In all the studies, the test was carried out once, on the delivery suite, at the time of admission. All the studies were of small size, with enrolment ranging from 24317 to 70321 women. One study fulfilled our ideal quality criteria. 92 Methodological quality was summarised in Figure 67.
FIGURE 67.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of the accuracy of fetal breathing movements in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.
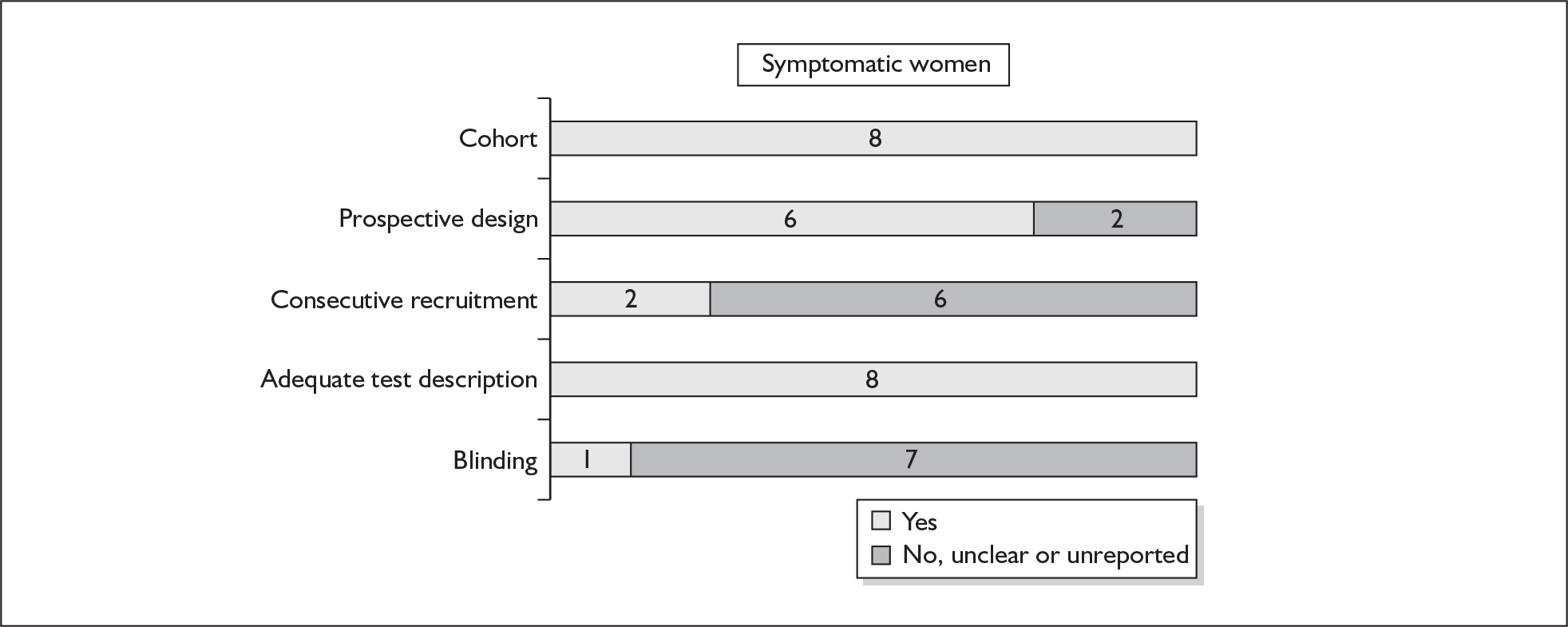
Accuracy of absence of fetal breathing movement in symptomatic women
For predicting preterm birth within 48 hours (Figure 68) and within 7 days of testing (Figure 69), there was a wide variation in the accuracy results. Statistical heterogeneity was not detected in the accuracy results of positive test for birth within 7 days of testing (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.57) and of negative test for birth within 48 hours of testing (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.64). However, within each reference standard subgroup, the studies were of variable methodological quality and heterogeneity was present for the corresponding negative and positive LRs. The ideal quality study,92 which was used in the decision-analytic modelling, showed a LR+ of 4.00 (95% CI 0.73–21.84) for a positive test result and a LR– of 0.67 (95% CI 0.32–1.38) when the test was negative, for predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing (Figure 69). For predicting preterm birth within 48 hours of testing, where the studies were lacking in one or more ideal quality features, the LR+ estimated from a better quality study was 16.08 (95% CI 5.22–49.55) and LR– was 0.16 (95% CI 0.05–0.58)321 (Figure 68). This result was used for the decision-analytic modelling. Individual accuracy results from the included studies are summarised in Appendix 5, Table 111.
FIGURE 68.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) for the absence of fetal breathing movements in predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of testing in women presenting with threatened preterm labour. χ2 heterogeneity test = 17.44, p = 0.00 for LR+ and χ2 = 0.89, p = 0.64 for LR–. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality.
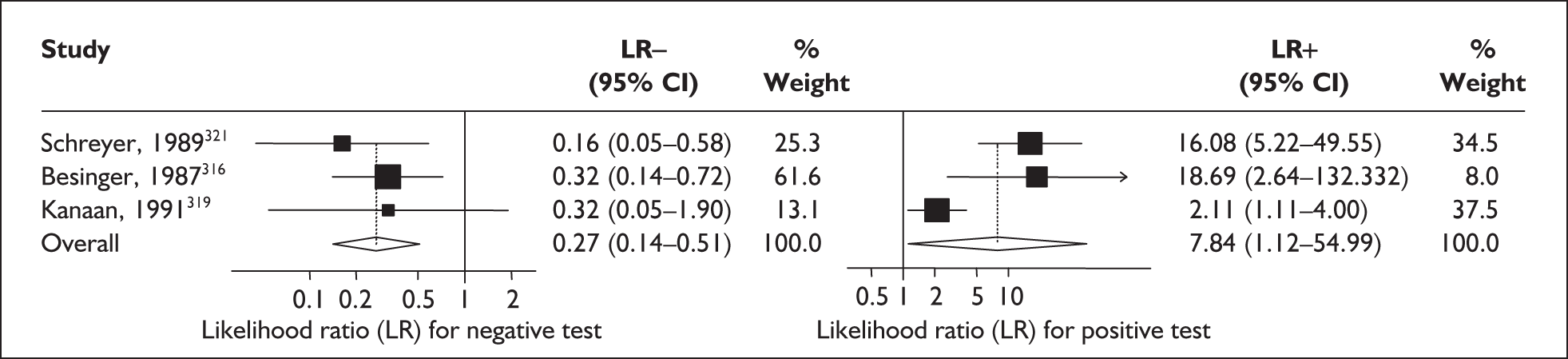
FIGURE 69.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) for the absence of fetal breathing movements in predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing in women presenting with threatened preterm labour. χ2 heterogeneity test = 3.84, p = 0.57 for LR+ and χ2 = 21.10, p = 0.001 for LR–. Studies are arranged in descending order of methodological quality.
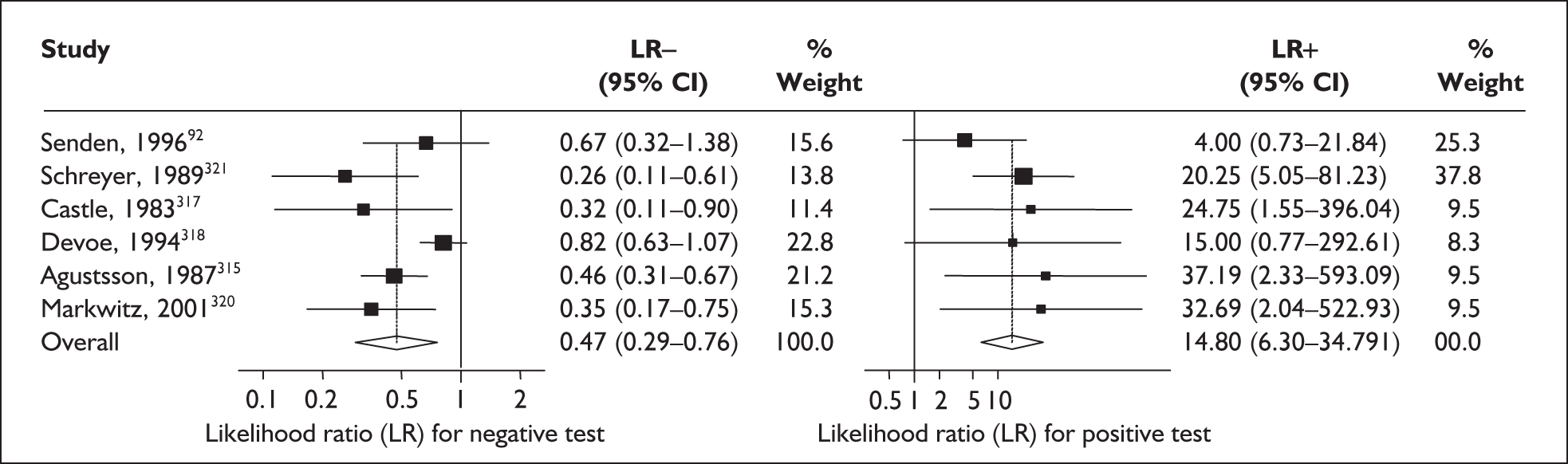
Cervical ultrasound assessment
Antenatal cervical shortening322 and opening of the internal os (funnelling)323 have been purported to increase the risk in asymptomatic women and the likelihood of spontaneous preterm birth in women who presented with threatened spontaneous preterm labour.
Study characteristics and quality
There were a total of 31 studies comprising 13 primary studies on asymptomatic women (n = 21,555 women)66,324–335 and 19 primary studies (n = 2849 women)64,82,112,233,244,336–350 on symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour evaluating the accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound measurement of cervical length in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Appendix 5, Tables 112 and 113 summarise individual study characteristics of the included studies of cervical length measurement in predicting spontaneous preterm birth, evaluating antenatal asymptomatic women and women with threatened preterm labour, respectively.
Additionally, there were 11 studies, comprising six primary studies on asymptomatic women (n = 12,855 women)322,325,329,330,332,334 and five primary studies (n = 509 women)233,323,336,340,343 on the accuracy of symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour evaluating the accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound assessment and measurement of cervical funnelling in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Appendix 5, Table 114 summarises individual study characteristics of the included studies of cervical funnelling assessment in predicting spontaneous preterm birth among asymptomatic antenatal women and symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
There was wide variation in the gestation at which ultrasound cervical length measurement was carried out in asymptomatic antenatal women and the definition for thresholds of abnormality. The most common gestation at which ultrasound measurement of cervical length was carried out was in the late second trimester, between 20 and 24 weeks’ gestation. The most common threshold used in asymptomatic women was 25 mm at this gestation and this was evaluated in two ideal quality studies. 322,325 The outcome frequently used by studies on asymptomatic women was birth before 37 weeks’ gestation but among ideal quality studies, the outcome frequently used was spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation. Among symptomatic women, the most common threshold used was 15 mm and the most common outcome used was spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing using this threshold.
There were five studies on asymptomatic women325,326,329,331,335 and two studies on symptomatic women336,340 on cervical length measurement that fulfilled the ideal definition of a high-quality study and three studies on asymptomatic women322,325,329 and two studies on symptomatic women336,340 evaluating cervical funnelling that fulfilled the ideal definition of a high-quality study. The methodological quality of the included primary studies is summarised in Figure 70.
FIGURE 70.
Methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of cervical length in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies.

Accuracy of cervical length and funnelling in asymptomatic women
When cervical length measurement was performed before 20 weeks’ gestation using a threshold of 25 mm (commonest threshold evaluated at this gestation) for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, it had sLR+ (summary LR+) of 13.38 (95% CI 6.90–25.96) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.07) and sLR– of 0.80 (95% CI 0.71–0.90) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.91). 325,329,331 Figure 71 shows a forest plot of ideal quality studies for cervical length measurement before 20 weeks’ gestation in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation in asymptomatic antenatal women. When performed between 20 and 24 weeks’ gestation, again using a threshold of 25 mm (commonest threshold evaluated at this gestation) it had sLR+ 4.68 (95% CI 3.64–6.03) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.54) and sLR– 0.68 (95% CI 0.60–0.78) (χ2 heterogeneity test p = 0.93). 322,325 Figure 71 shows a forest plot of ideal quality studies for cervical length measurement before 20 weeks’ gestation in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation in asymptomatic antenatal women. Cervical funnelling screening in asymptomatic women had variable LRs depending on the chosen threshold (some studies did not indicate their threshold, merely indicating the presence of the ‘funnelling’ appearance on ultrasound imaging) (Figure 75). LR+ of 4.63 (95% CI 3.31–6.48) and LR– of 0.79 (95% CI 0.71–0.87) from Iams et al. 322 using 5-mm protrusion of the amniotic membrane into the cervical canal as their threshold as a predictor for spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation was used for decision analysis because it represented the higher-quality study available for this threshold and reference standard.
FIGURE 71.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) from ideal quality studies for cervical length measurement before 20 weeks’ gestation (listed in ascending order of thresholds of abnormality) in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation in asymptomatic antenatal women.
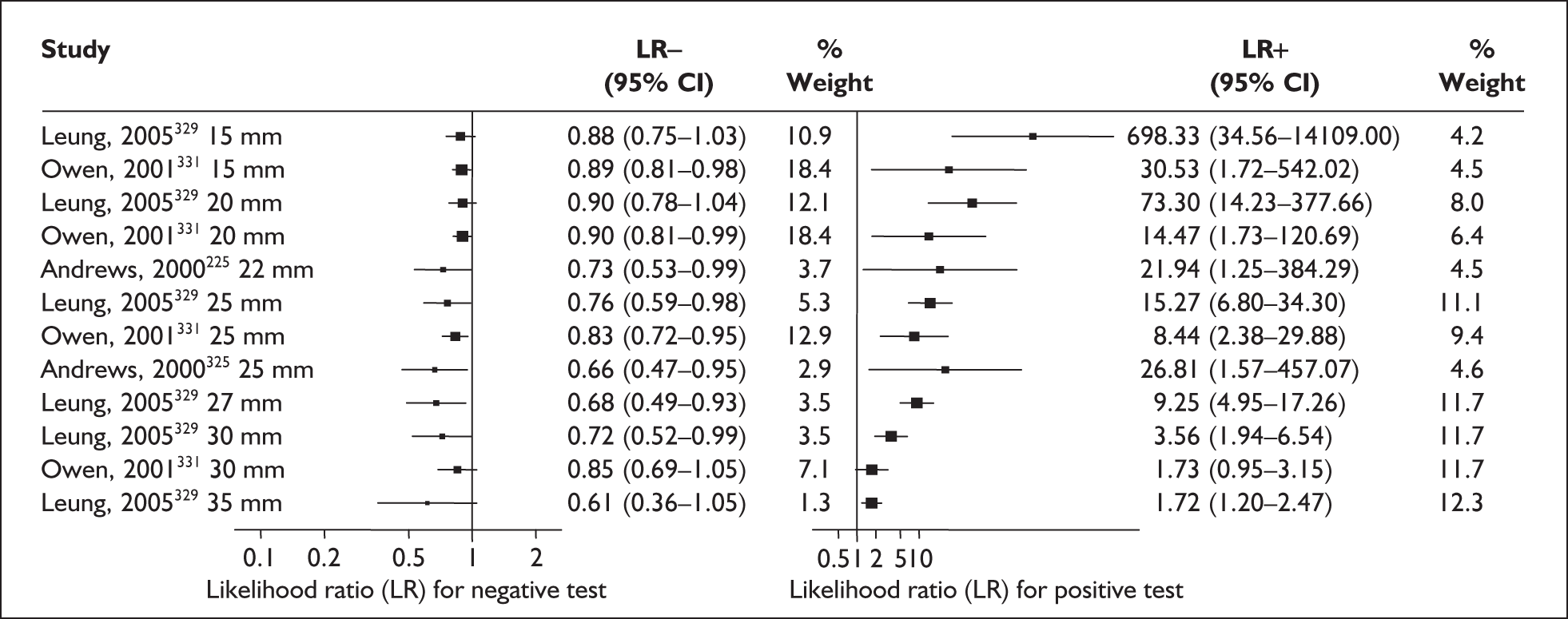
FIGURE 72.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) from ideal quality studies for cervical length measurement between 20 and 24 weeks’ gestation (listed in ascending order of thresholds of abnormality) in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation in asymptomatic antenatal women.
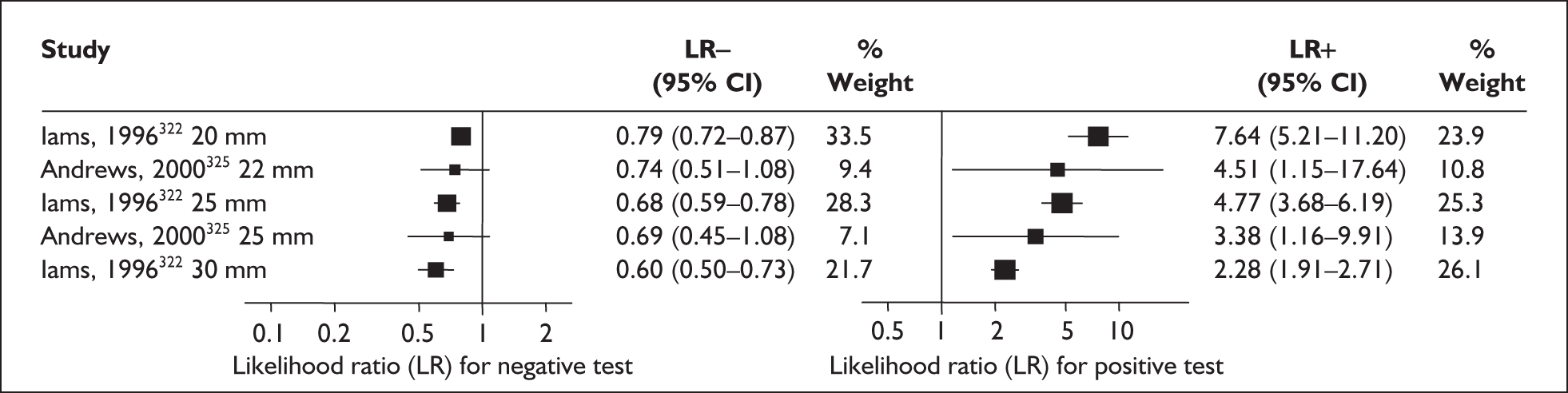
There was no more than a single study of small sample size for any of the evaluated thresholds for cervical measurement performed before 20 weeks’ gestation in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks (Figure 73), therefore this was not considered in the decision analysis. When cervical length was measured between 20 and 24 weeks’ gestation for predicting birth before 37 weeks’ gestation (Figure 74) using a threshold of 32.5 mm, it had an LR+ of 3.99 (95% CI 2.84–5.62) and LR– of 0.33 (95% CI 0.17–0.66). 335 Individual accuracy results are summarised in Appendix 5, Tables 115 and 117.
FIGURE 73.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) from ideal quality studies for cervical length measurement before 20 weeks’ gestation (listed in ascending order of thresholds of abnormality) in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in asymptomatic antenatal women.
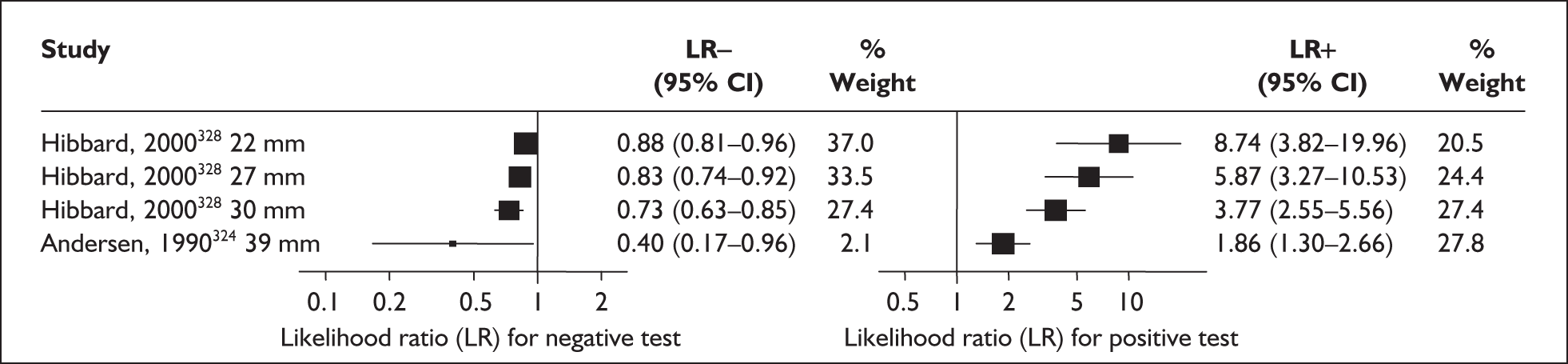
FIGURE 74.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) from ideal quality studies for cervical length measurement between 20 and 24 weeks’ gestation (listed in ascending order of thresholds of abnormality) in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in asymptomatic antenatal women.
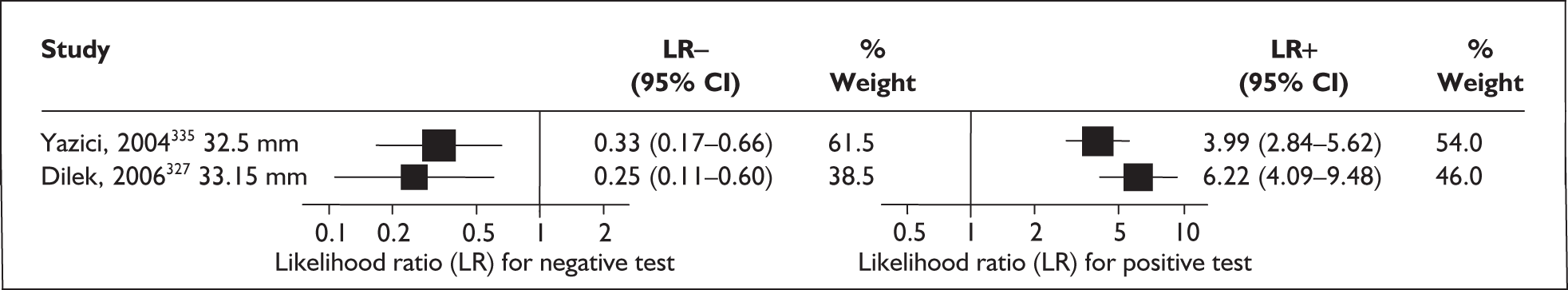
FIGURE 75.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) for cervical funnelling between 20 and 24 weeks’ gestation in predicting spontaneous preterm birth stratified according to reference standards (outcomes) in asymptomatic antenatal women. Studies are arranged in descending order of quality. a, Any definition of funnelling unless otherwise stated.
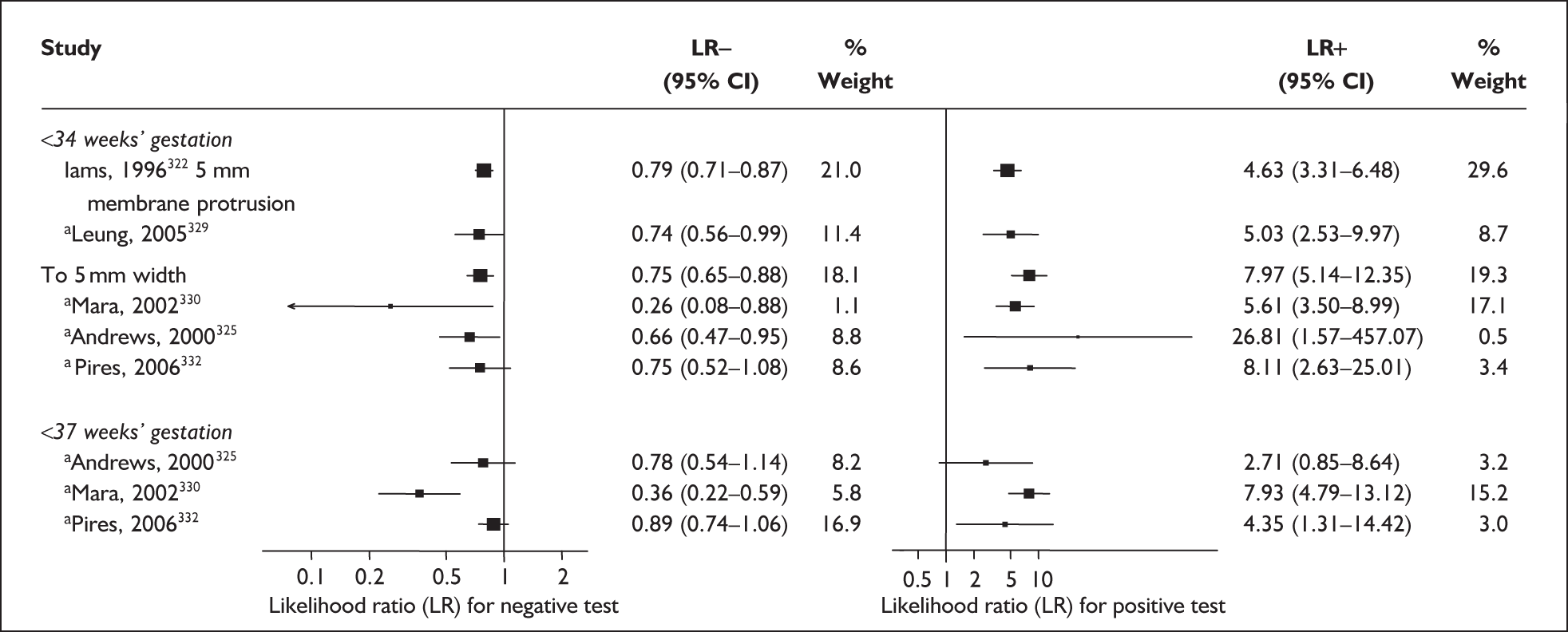
Accuracy of cervical length and funnelling in symptomatic women
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of testing, cervical length measurement in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour had a variable LR depending on the threshold abnormality chosen (Figure 76). LR+ of 6.43 (95% CI 5.17–8.00) and LR– of 0.027 (95% CI 0.0017–0.42) from Tsoi et al. 349 were chosen for decision analysis because their study represented the higher-quality study available for the most common threshold used (15 mm) and reference standard (birth within 48 hours of testing). For predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing, cervical length measurement in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour had a variable LR depending on the threshold abnormality chosen (Appendix 5, Table 116). Figure 77 shows the forest plot of LRs for the most commonly used threshold (< 15 mm) for the reference standard of spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing. LR+ of 8.61 (95% CI 6.65–11.14) and LR– of 0.026 (95% CI 0.0038–0.182) from Tsoi et al. 349 were chosen for decision analysis again because the study was the higher-quality study available for the aforementioned threshold and reference standard.
FIGURE 76.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) from ideal quality studies for cervical length measurement in predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of testing in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
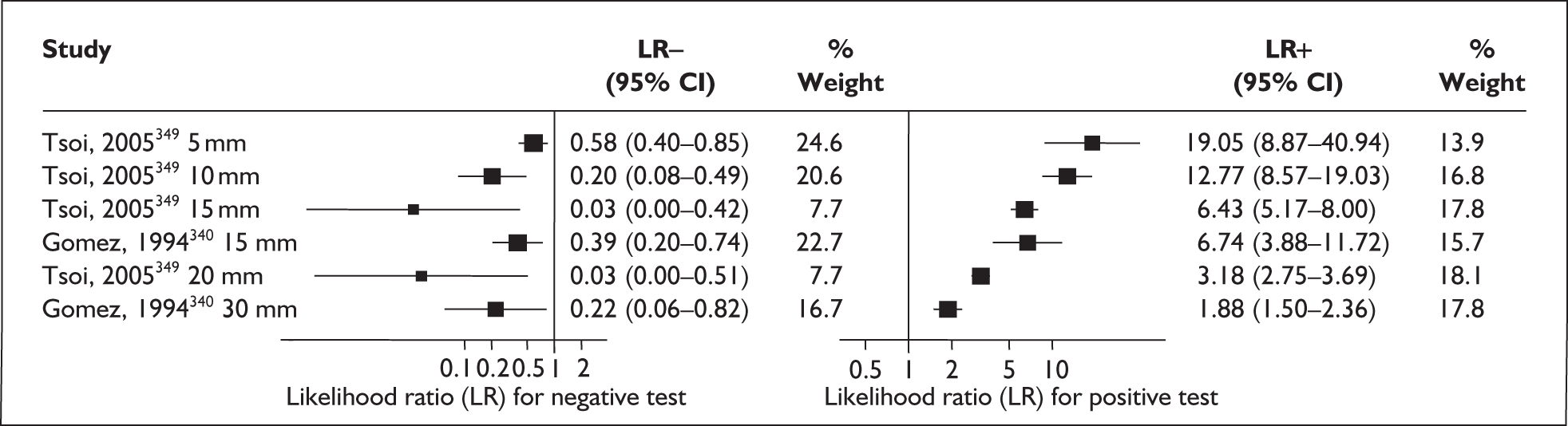
FIGURE 77.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) for cervical length measurement using commonly chosen threshold (15 mm) in predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of testing in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour. Studies are arranged in descending order of quality.
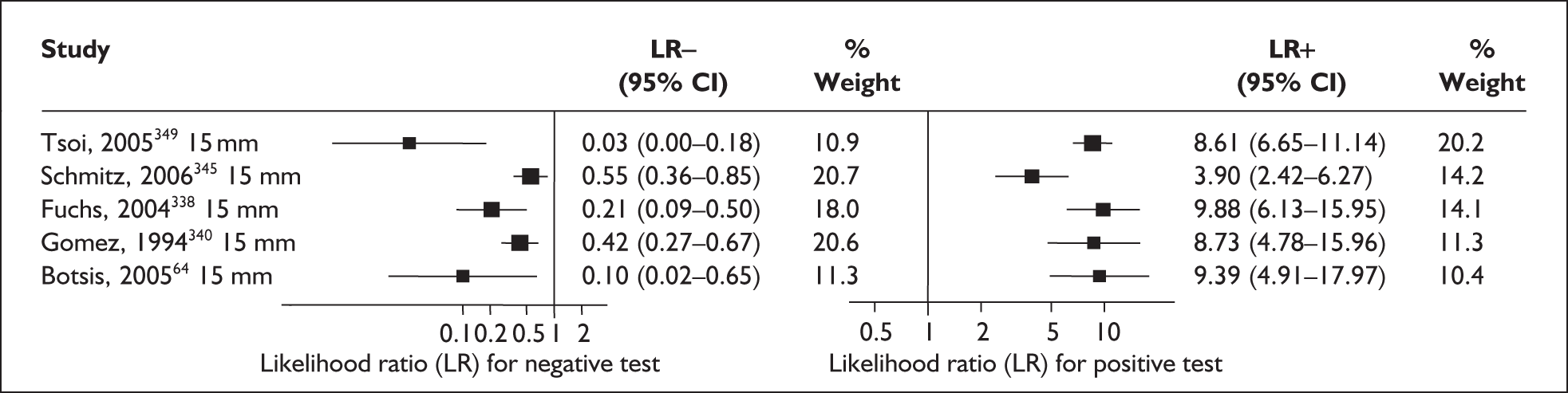
For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, cervical length measurement in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour had a variable LR depending on the threshold abnormality chosen (Appendix 5, Table 116). Figure 78 shows the forest plot of LRs for the most commonly used threshold (< 30 mm) for the reference standard of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation. LR+ of 1.879 (95% CI 1.36–2.59) and LR– of 0.30 (95% CI 0.083–1.07) from Crane et al. 336 were chosen for decision analysis because this study represented an ideal quality study for the aforementioned threshold and reference standard. For predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, cervical length measurement in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour had a variable LR depending on the threshold abnormality chosen (Figure 78). LR+ of 3.36 (95% CI 1.73–6.54) and LR– of 0.35 (95% CI 0.17–0.70) from Gomez et al. 340 using a threshold < 18 mm and LR+ of 2.29 (95% CI 1.68–3.12) and LR– of 0.29 (95% CI 0.15–0.58) from Crane et al. 336 with a threshold < 30 mm were chosen for decision analysis because they represented ideal quality studies available for this reference standard (Figure 79). ROC plots of sensitivity versus specificity for cervical length measurement in symptomatic women predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours and 7 days of testing, and before 34 weeks’ gestation, are shown in Figure 81. Cervical funnelling screening in symptomatic women had variable LRs depending on the chosen threshold (some studies did not indicate their threshold, merely indicating presence of the ‘funnelling’ appearance on ultrasound imaging) (Figure 80). LR+ of 4.70 (95% CI 1.90–11.66) and LR– of 0.61 (95% CI 0.34–1.10) for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation and LR+ of 2.53 (95% CI 1.02–6.25) and LR– of 0.86 (95% CI 0.71–1.03) for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation from Crane et al.,336 using the presence of ‘V-shaped’ ultrasonographic appearance as threshold for funnelling, were used for decision analysis because this study represented an ideal quality study available for this threshold and reference standard. Individual accuracy results for cervical length and funnelling measurement in symptomatic women can be found in Appendix 5, Table 116 and Table 117.
FIGURE 78.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) for cervical length measurement using commonly chosen threshold (30 mm) in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour. Studies are arranged in descending order of quality.
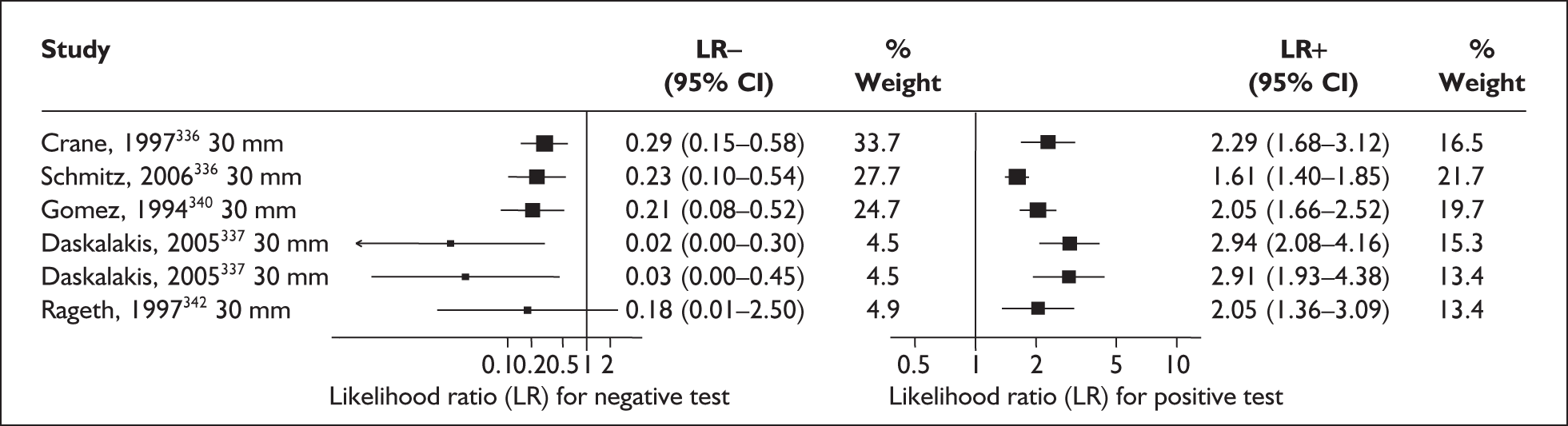
FIGURE 79.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) from ideal quality studies for cervical length measurement in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
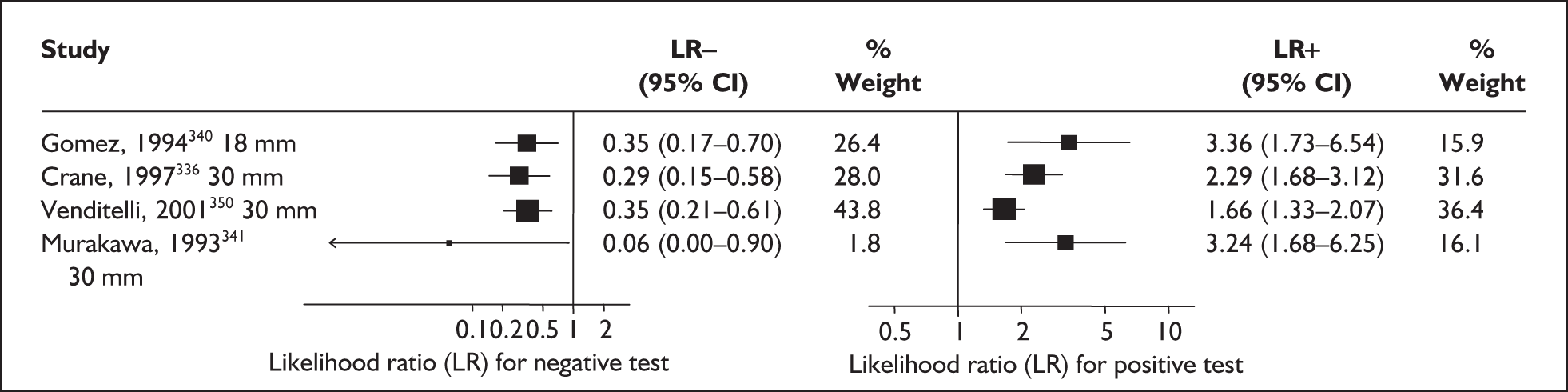
FIGURE 80.
Forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) for cervical funnelling between 24 and 36 weeks’ gestation in predicting spontaneous preterm birth stratified according to reference standards (outcomes) in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour. Studies are arranged in descending order of quality. a, Any definition of funnelling unless otherwise stated.
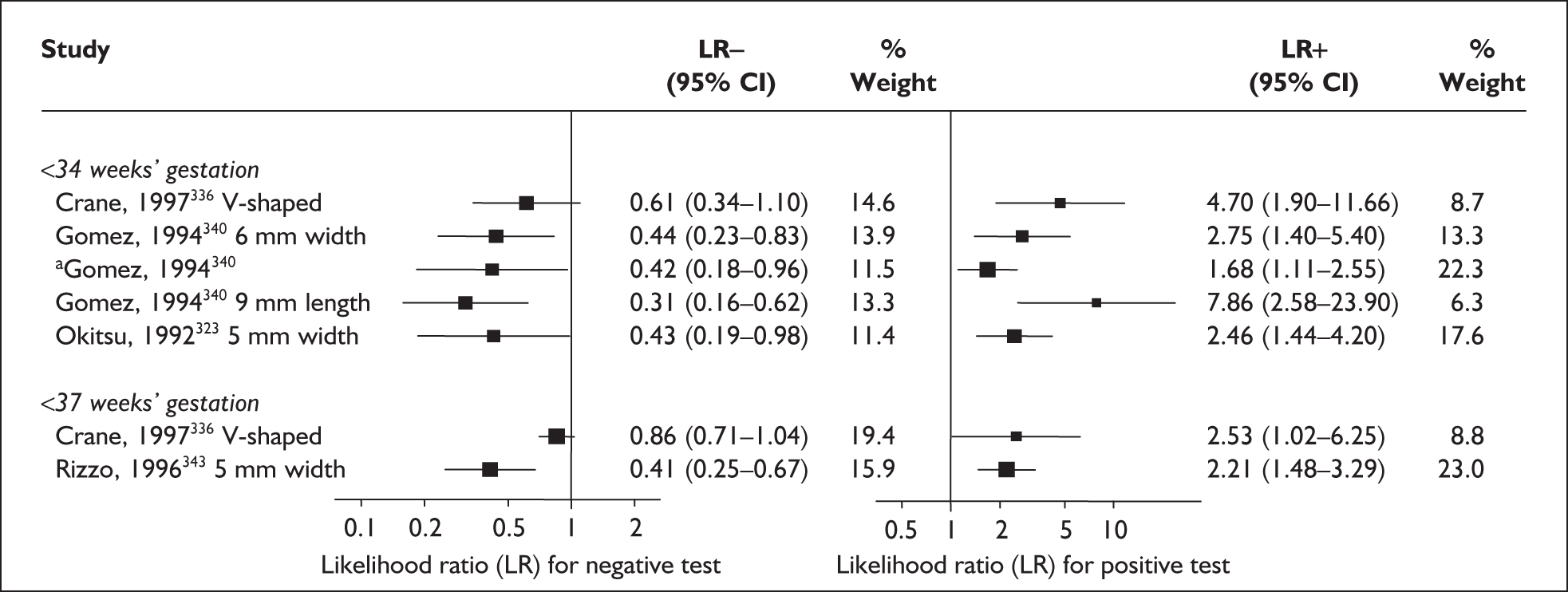
FIGURE 81.
Plot of sensitivity versus 1-specificity in ROC space for cervical length measurement studies in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour in predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours and 7 days of testing (threshold 15 mm), and before 34 weeks’ gestation (threshold 30 mm).
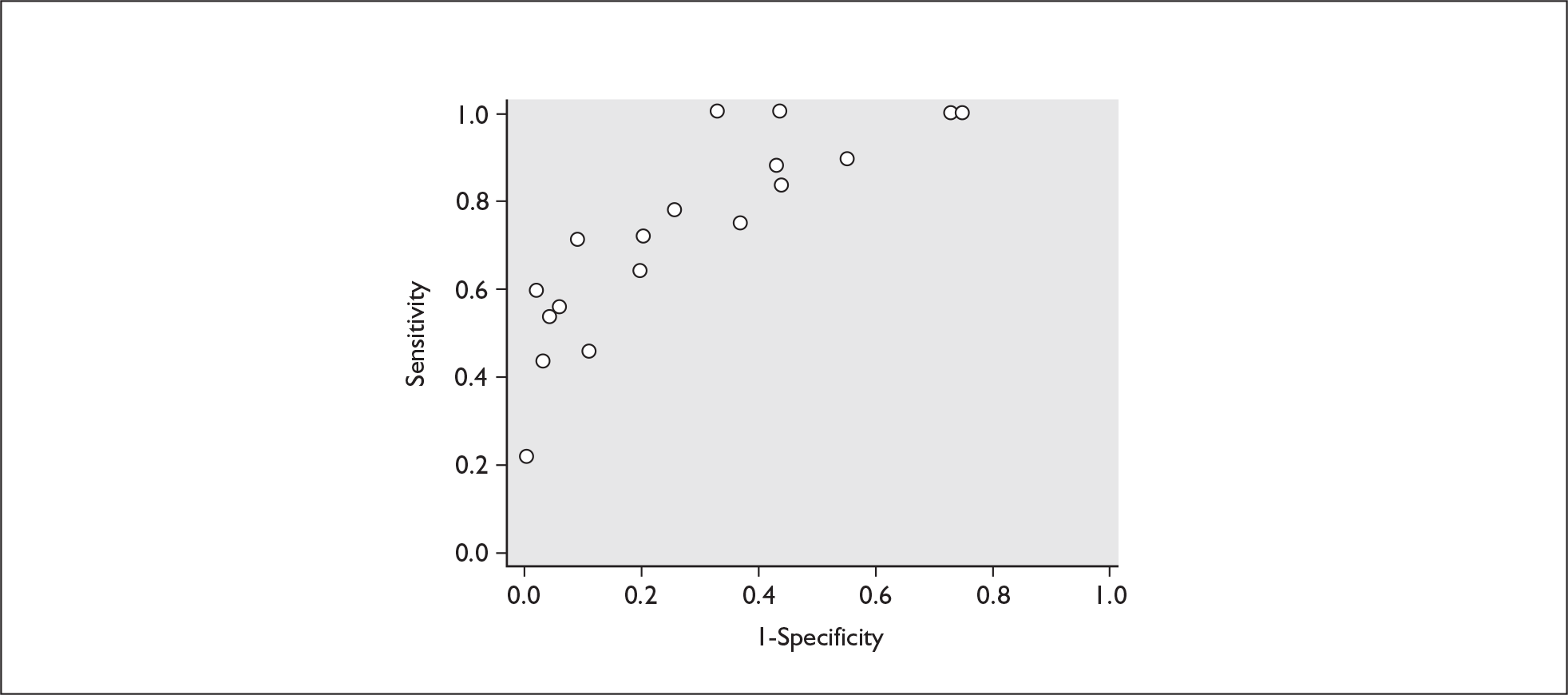
Summary of test accuracy systematic reviews
Summary of test accuracy findings
This review assessed 22 tests aimed at the prediction of spontaneous preterm birth. The numbers of studies per test were small and of poor quality with few exceptions. The median number was 5 (range 0–26) for asymptomatic and 2 (range 0–40) for symptomatic women. We had planned to perform meta-analysis only for the highest-quality studies to improve the validity of our results. This meant that the number of tests suitable for meta-analysis was small (cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin and cervical ultrasound) and the number of studies per meta-analysis was similarly small (median = 3), introducing imprecision in estimation of accuracy.
The overall quality of studies within reviews was variable. There were deficiencies in many areas of methodology (Figure 82) but two quality items, consecutive enrolment and blinding, were more frequently unreported than the other items. No test had universally high quality data, but for some tests, e.g. fibronectin, cervicovaginal phIGFBP-1 and cervical length, a number of high-quality studies were available. Overall, the quality of test accuracy studies in symptomatic women tended to be better than that of studies in asymptomatic women (chi-squared test p ≤ 0.001). The interpretations of the accuracy data on all tests were negatively affected by poor reporting and potential threats to validity identified in assessment of study quality. Although we restricted our reviews to singleton pregnancies, many studies included patients across the clinical risk spectrum, and did not provide separate results for specific parts of the spectrum, such as women without any particular risk factors. For this reason, when assessing the results we often could not be confident about the reported predictive ability of tests.
FIGURE 82.
Summary of methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of accuracy of rheobase testing in predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Data presented as 100% stacked bars. Figures in the stacks represent number of studies. Some studies are reported twice because of their contributions to multiple reviews.
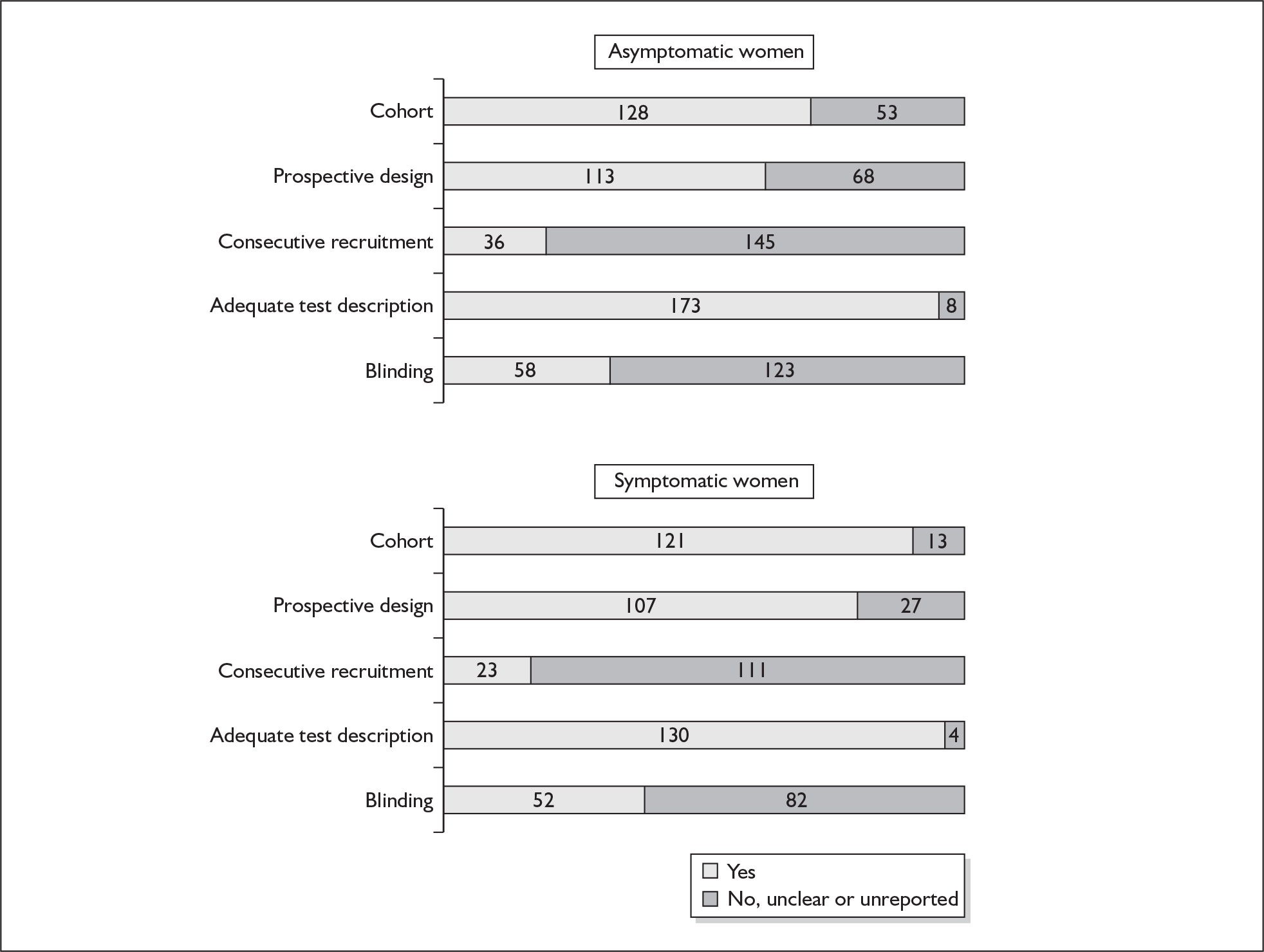
In evaluation of many tests, the limited number of quality studies and the limited number of cases with preterm birth per study seriously constrained the conclusions. As spontaneous preterm birth has prevalence, particularly for important outcomes such as birth before 34 weeks’ gestation or birth within 48 hours of presentation, the small absolute numbers of affected cases introduced imprecision by increasing variance.
The main accuracy results are summarised in Figures 83, 84 and 85 representing prediction of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation in asymptomatic women, within 48 hours and 7 days of testing, and before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women, respectively. For most of the tests evaluated the results were not pooled because of the lack of high-quality studies. Where studies were pooled, we used a random effects model. This method accounts for the statistical heterogeneity that is left unexplained after attempts to identify its sources, where feasible. It produced more conservative estimates of confidence intervals.
FIGURE 83.
Summary forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of the accuracy of various tests as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic women stratified according to reference standards (outcomes of spontaneous birth before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation), tests and selected thresholds. LR values above are those that were considered for decision analyses. These estimates were based on the results of the highest-quality studies. AFP, α-fetoprotein; Cv, cervicovaginal; Cx, cervix; USS, ultrasound.
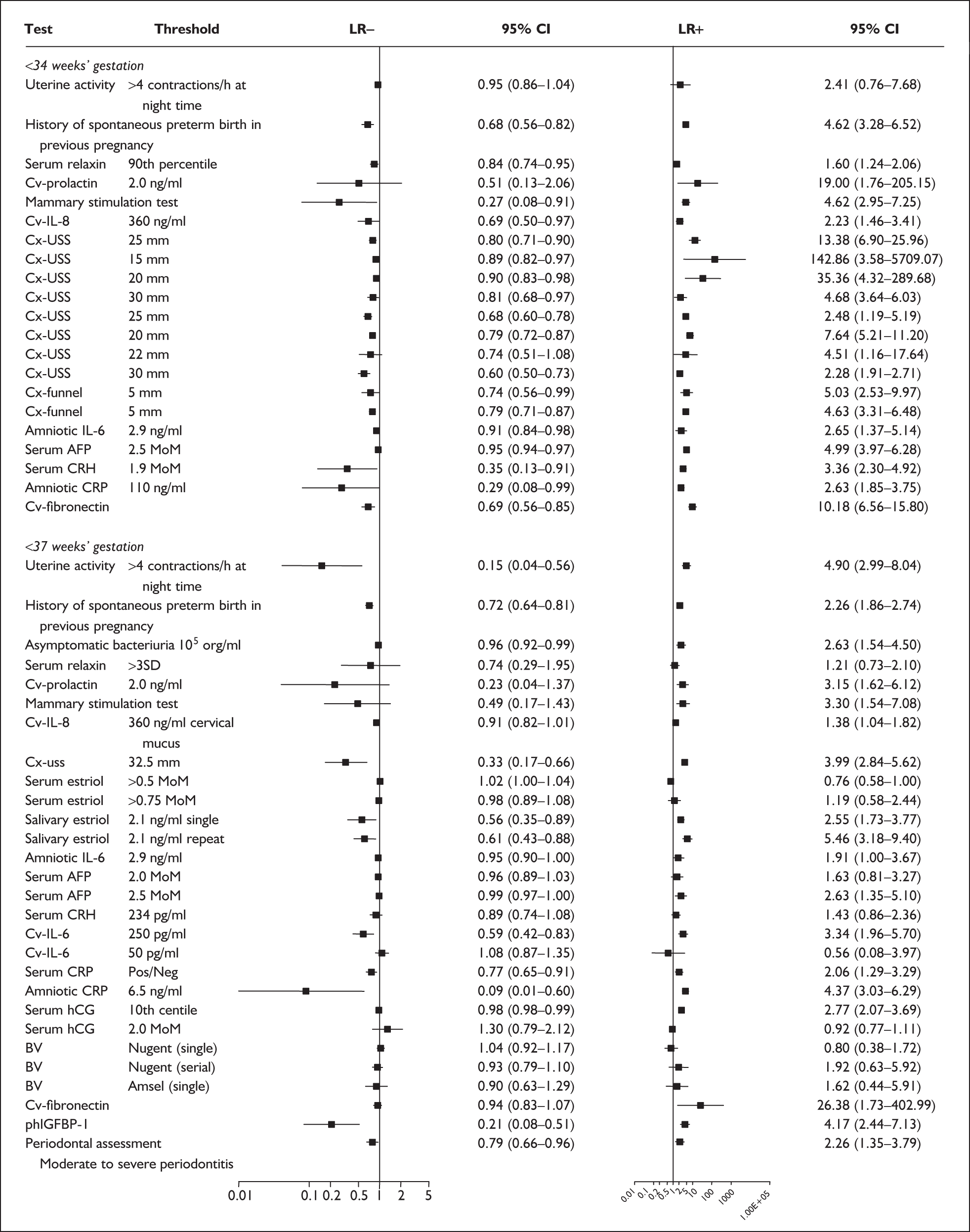
FIGURE 84.
Summary forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of the accuracy of various tests as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women stratified according to reference standards (outcomes of spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours and 7 days of testing), tests and selected thresholds. LR values above are those that were considered for decision analyses. These estimates were based on the results of the highest-quality studies. Cv, cervicovaginal; Cx, cervix.
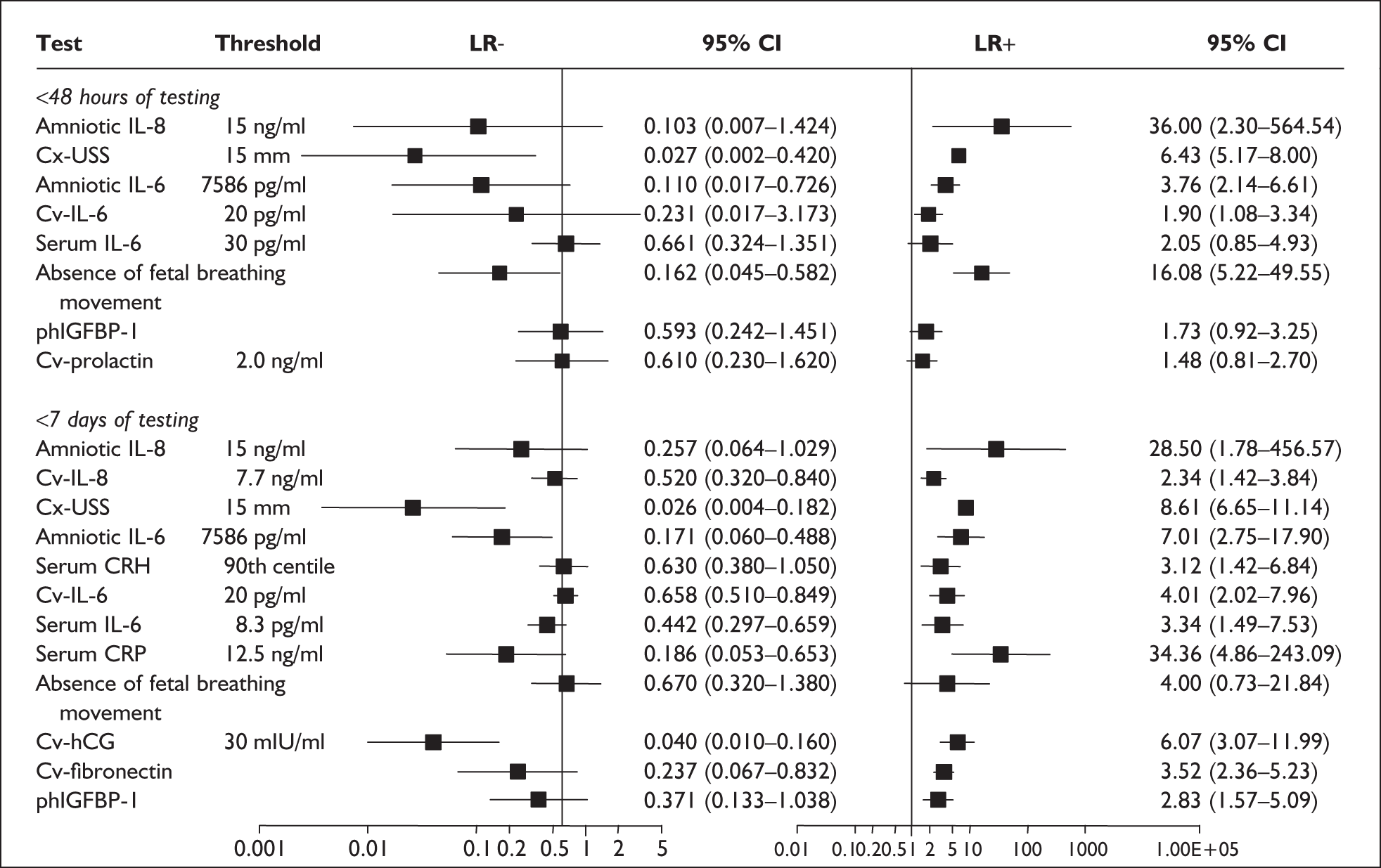
FIGURE 85.
Summary forest plots of likelihood ratios (LRs) of the accuracy of various tests as a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women stratified according to reference standards (outcomes of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation), tests and selected thresholds. LR values above are those that were considered for decision analyses. These estimates were based on the results of the highest-quality studies.
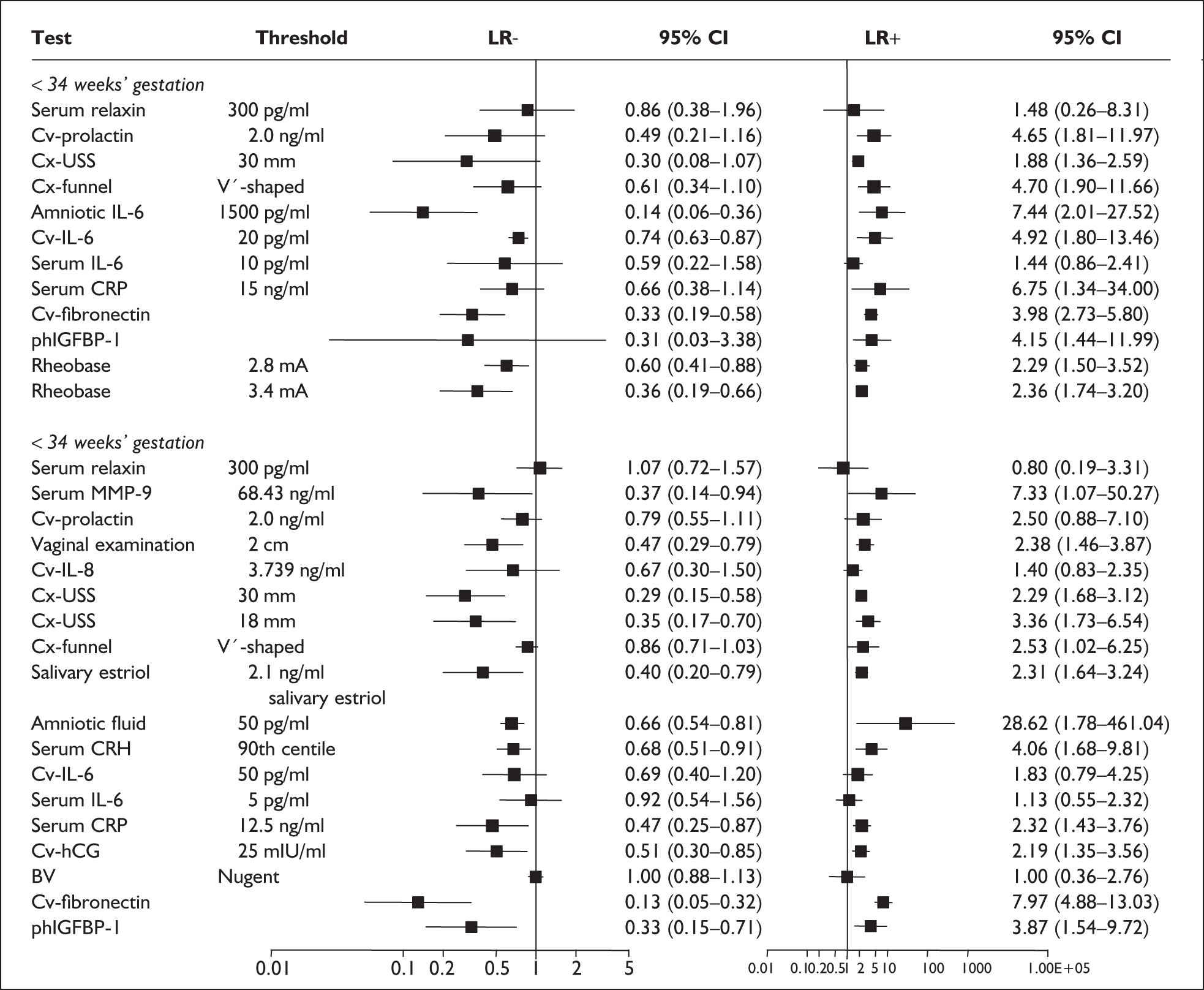
The forest plots shown in Figures 83–85, we believe, summarise suitably the valid information for consideration in clinical decision-making for each of the tests reviewed. These results have been put forward for decision-analytic modelling. The more the LR values depart from 1.0 the greater the change in post-test probability. As proposed by Jaeschke et al. 48 a useful test should have at least an accuracy of LR+ > 5.0 and LR– < 0.2 (Table 1). These estimates require at least moderate disease prevalence for post-test probabilities to show substantial change from pre-test probabilities. In this situation, when a test produces a positive result it will predict with greater likelihood the later development of the condition, i.e. spontaneous preterm birth. When the test result is negative, it would provide reassurance that the condition will probably not develop later. Clinically, however, most tests tend to have a greater usefulness for either LR+ or LR–, not both together. This trade-off was apparent in our accuracy reviews. Considering the point estimates of LRs, screening for spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic antenatal women tended to be more useful for a positive test result compared to a negative test result, i.e. LR+ tended to be further away from 1.0 than LR–. This meant that it was unlikely that the negative test result would rule out the likelihood of spontaneous preterm birth confidently. In symptomatic women, similarly, there was a predominance of more useful LR+ results compared to LR– results.
Screening typically involves the use of a confirmatory test after initial testing, before the institution of therapy. In this project, this is not the case because testing is used to identify a risk group in which preventative interventions (both intensive monitoring and or treatments) will be employed directly after test results become known. In this situation, for a test to serve as a good tool for screening, it should perform well. 48 However, given that there is often a trade-off between LR+ and LR–, the balance between LR+ and LR– that is preferable depends largely on the outcomes of the disease and costs (including potential mortality and morbidity) associated with intervention(s). The consequences of false-positive results include both costs of intensive monitoring and treatment-associated morbidity and costs among otherwise normal women, so it is important that LR+ is suitably high, because erroneously providing interventions to falsely positive cases leads to unwarranted inconvenience, expense and morbidity when the likelihood of spontaneous preterm birth does not change compared to the background risk attributed to low LR+ values. Given the consequences of false-negative results (both costs and morbidity of cases of spontaneous preterm birth as the result of lack of treatment), it is important that LR– is suitably low. This is because erroneously withholding effective interventions from falsely negative results leads to excessive morbidity and expense in the face of spontanenous preterm birth. If available effective interventions are convenient, inexpensive and without adverse effects (to both mother and child), then it is better to have the accuracy trade-offs in favour of LR–, i.e. a test with a low LR– rather than a high LR+.
Figure 83, Figure 84 and Figure 85 demonstrate that considering the point estimates of and imprecision in the LRs, most tests perform either poorly or the level of their performance is uncertain (i.e. has wide confidence intervals). A few tests in asymptomatic antenatal women reached LR+ > 5, putting them in the useful tests category for predicting spontaneous preterm birth. These were ultrasonographic cervical length and funnelling measurement, and cervicovaginal fFN screening. For LR–, only two tests in asymptomatic women had an LR– < 0.2. These were detection of uterine contractions (by home uterine monitoring device) and amniotic fluid CRP measurement. In symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour, there were more tests with LR+ > 5 than in asymptomatic women. These were absence of fetal breathing movements, cervical length and funnelling, amniotic fluid IL-6, serum CRP for predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours or 7 days of testing; and MMP-9, amniotic fluid IL-6, cervicovaginal fFN and cervicovaginal hCG testing for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 or 37 weeks’ gestation. For symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour, measurement of cervicovaginal IL-8, cervicovaginal hCG, cervical length measurement, absence of fetal breathing movement, amniotic fluid IL-6, and serum CRP all showed LR– < 0.2 for predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours or 7 days of testing. Only cervicovaginal fFN and amniotic fluid IL-6 had an LR– < 0.2 in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 or 37 weeks’ gestation. Depending on level of effectiveness of various interventions (Chapter 5) and their associated inconvenience, costs and morbidity, a threshold analysis (Chapter 6) will be required to determine which thresholds of accuracy are required to make testing cost-effective in prevention of spontaneous preterm birth. A summary of the more accurate tests (for clinically important outcomes) considered for the following threshold analysis (Chapter 5) is shown in Table 2.
| LR+ (95% CI) | LR– (95% CI) | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptomatic women | ||||
| Spontaneous preterm birth < 48 hours from testing | ||||
| Measurement of cervical length (15 mm) | 6.43 (5.17–8.00) | 0.027 (0.0017–0.42) | 0.98 (0.84–1.00) | 0.85 (0.81–0.88) |
| Amniotic fluid IL-6 | 3.76 (2.14–6.61) | 0.11 (0.0167–0.726) | 0.92 (0.62–0.99) | 0.76 (0.60–0.88) |
| Amniotic fluid IL-8 (15 ng/ml) | 36.00 (2.30–564.54) | 0.10 (0.0074–1.42) | 0.90 (0.40–1.00) | 0.98 (0.81–1.00) |
| Cervicovaginal IL-6 | 2.90 (1.08–3.34) | 0.23 (0.017–3.17) | 0.88 (0.29–1.00) | 0.54 (0.33–0.74) |
| Absence of fetal breathing movements | 7.84 (1.12–54.99) | 0.27 (0.14–0.51) | 0.76 (0.52–0.89) | 0.90 (0.79–0.99) |
| Spontaneous preterm birth < 7 days from testing | ||||
| Measurement of cervical length (15 mm) | 8.61 (6.65–11.14) | 0.026 (0.0038–0.18) | 0.98 (0.88–1.00) | 0.89 (0.85–0.91) |
| Cervical β-hCG | 6.07 (3.07–11.99) | 0.04 (0.01–0.16) | 0.97 (0.88–1.00) | 0.84 (0.71–0.93) |
| Amniotic fluid IL-6 | 7.01 (2.75–17.90) | 0.17 (0.060–0.49) | 0.85 (0.62–0.97) | 0.88 (0.72–0.97) |
| Serum C-reactive protein | 34.36 (4.86–243.09) | 0.17 (0.05–0.62) | 0.82 (0.48–0.98) | 0.98 (0.87–1.00) |
| Fetal fibronectin | 3.52 (2.36–5.23) | 0.24 (0.067–0.83) | 0.82 (0.48–0.98) | 0.77 (0.69–0.83) |
| Amniotic fluid IL-8 (15 ng/ml) | 28.5 (1.78–456.57) | 0.26 (0.064–1.03) | 0.75 (0.28–0.99) | 0.97 (0.81–1.00) |
| phIGFBP-1 | 3.29 (2.24–4.83) | 0.20 (0.10–0.41) | 0.72 (0.56–0.87) | 0.74 (0.59–0.91) |
| Spontaneous preterm birth < 34 weeks’ gestation | ||||
| Amniotic fluid IL-6 | 7.44 (2.01–27.52) | 0.14 (0.06–0.36) | 0.88 (0.71–0.96) | 0.88 (0.64–0.99) |
| Measurement of cervical length (30 mm) | 2.48 (1.19–5.19) | 0.81 (0.68–0.97) | 0.83 (0.71–0.93) | 0.56 (0.48–0.61) |
| phIGFBP-1 | 2.96 (2.02–4.33) | 0.22 (0.08–0.64) | 0.75 (0.55–0.96) | 0.82 (0.48–0.98) |
| Fetal fibronectin | 3.98 (2.73–5.80) | 0.33 (0.19–0.58) | 0.73 (0.46–0.81) | 0.82 (0.68–0.96) |
| Asymptomatic women | ||||
| Spontaneous preterm birth < 34 weeks’ gestation | ||||
| Mammary stimulation test | 4.62 (2.95–7.25) | 0.27 (0.079–0.91) | 0.78 (0.40–0.90) | 0.83 (0.78–0.88) |
Provisos/limitations arising from problems with primary data
The interpretations of the accuracy data on tests are affected by threats to validity identified in the assessment of study quality (Figure 82). Only a few tests had been evaluated and reported in studies that met our definition of ideal study design as defined in our method section, both in asymptomatic and symptomatic women. The following tests were evaluated in at least one ideal quality study: cervical length and funnelling, IL-6 and cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin in asymptomatic women, with the addition of absence of fetal breathing movement in symptomatic women. The overall quality of studies within reviews was variable with deficiencies in many areas of methodology (Figure 82). Association between design quality components and diagnostic performance has been empirically studied. It cannot be stressed enough that before any measures of test accuracy (whatever their magnitude) count as scientific evidence, it would require adequate reporting of the study’s population (clinical spectrum), design and execution in evaluating the test’s accuracy. We accept, however, that our expectations of the level of detail that should be provided in the literature of the primary studies were perhaps unrealistic given that initiatives to improve test accuracy study design and its subsequent reporting are only recent phenomena.
Studies often did not conform to the standards of reporting for diagnostic studies. In particular, blinding and consecutive enrolment were often either unreported or were not part of the study design. The extent to which these deficiencies have impact on accuracy estimates depends on a number of factors. In both asymptomatic antenatal women and symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour, there is a time interval between (screening) testing and potential outcome of spontaneous preterm birth. In this situation, absence of blinded assessment may lead to alteration(s) of the usual antenatal care that would affect the outcome, i.e. spontaneous preterm birth, which in turn would influence the final accuracy estimates. This is known as ‘treatment paradox’ where test-positive women are given effective treatments leading to prevention of spontaneous preterm birth, which makes an otherwise reasonable test appear inaccurate.
Lack of consecutive enrolment may have resulted in a differing clinical spectrum of women being enrolled in the study, leading to a spectrum bias potentially influencing the final accuracy estimates. Spectrum bias refers to the possibility that a test’s LR+ and/or LR– may vary in groups of patients with differing risks of spontaneous preterm birth. In other words, spectrum bias refers to variation across subgroups, (or, to use the technical term, effect measure modification). We tried to minimise this effect, notwithstanding the inherent study design and reporting inadequacy, by constraining our reviews to singleton and low-risk pregnancies.
Our discussion would not be complete without touching on the issue of interpreting a test’s accuracy in the light of information obtained by any preceding test(s), which has so far been overlooked in diagnostic research. Diagnostic confounding can occur in this situation, which refers to one or more tests having predictive abilities that are related to each other and the outcome so that it is difficult to assess the independent prediction from each of the tests on the diagnosis of the outcome. Our reviews did not assess this issue. There may or may not be increased accuracy when two or more tests are combined in the prediction of spontaneous preterm birth depending on the overlap of information between tests. These issues may only be optimally dealt with by multivariable analysis of the primary studies or Individual Patient Data (IPD) meta-analyses. Such an analysis would generate probabilities of spontaneous preterm birth for patient characteristics and test results to obtain a predictive probability for each profile, e.g. the probability of spontaneous preterm birth from a cervical length measurement in a nulliparous obese woman. If no multivariable analysis is planned, such confounding may be attenuated by selection of patient groups that are as homogeneous as possible with respect to their other characteristics (e.g. patient history and obstetric risk profile in multiparous women). However, such an approach is difficult given the large amount of clinical information that usually exists (e.g. age, parity, and co-morbidities to name a few).
Provisos/limitations arising from review methods
The accuracy review was carried out using a comprehensive search strategy to minimise the risk of missing tests and studies. Nevertheless the research identified for each test was often of variable quality and insufficient in amount to produce precise estimates of accuracy in either or both groups of populations of asymptomatic antenatal women and symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour. For both asymptomatic women and symptomatic women, only three tests had > 20 accuracy studies: asymptomatic bacteriuria (26 studies), serum β-hCG (20 studies) and serum α-fetoprotein for asymptomatic women (20 studies); and cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin (58 studies), cervical length and funnelling (42 studies), and IL-6 (22 studies) for symptomatic women. Where there was a scarcity of primary studies, it was not surprising that the some of the LR estimates were affected by imprecision. Therefore, when assessing their results we could not always be confident about the range of reported predictive ability of tests, especially when there was only a small number of studies with small sample size in each.
Our review has already made explicit the deficiencies in the quality of studies. We would have preferred to base our inferences on high-quality studies, e.g. ideal quality features in asymptomatic antenatal women populations, using a single threshold and outcome (reference standard). To that end, we had planned a priori subgroup analyses according to study quality within our predefined populations and outcomes. However, because of the low number of included studies per test or per specific threshold, often compounded by a lack of reporting clarity, such subgroup analyses were often not possible or had insufficient power. In cases where it was possible, e.g. cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin and cervical length measurement, their subgroup analyses were based on a small number of studies.
Variation in test thresholds for determining abnormality meant that generating summaries of findings was not straightforward. For some tests, e.g. cervical ultrasound measurement of either length or funnelling, the same study may have provided estimates from different thresholds. This precluded valid statistical comparison of these indices because of violation of the principle that the compared study samples should be statistically independent. Recently, this issue was addressed in the literature, but the solution was based on the use of odds ratios, which has other drawbacks. For some other tests, e.g. CRP and interleukins, none of the studies had used the same thresholds, which limited our ability to compare and infer the accuracy estimates obtained. In these situations, we made a systematic attempt (see Methods section) at translating results in a summary ROC space into clinically relevant information. For pooling test results that we were able to pool, we used a random effects approach where unexplained statistical heterogeneity was formally taken into account. We could not explore the reasons for heterogeneity in detail largely because poor reporting and the small number of studies per test would have rendered the use of explorative statistical methods such as meta-regression underpowered. If the pooled results amalgamate heterogeneous individual estimates, these should be interpreted with caution. In situations where we were not able to pool given the absence of high-quality studies, we have arbitrarily chosen accuracy estimates from the largest higher-quality study available for the particular test for our decision-analyses. Given also the uncertain impact of study design issues on the magnitudes of the accuracy estimates, our view is that the summaries we generated provide the best available results for clinical interpretation at the time of completing our work.
Provisos/limitations arising from things not done (omissions)
For some tests we found so few studies [e.g. rheobase (one study), mammary stimulation test (two studies), MMP-9 (two studies)] that besides reporting their individual accuracy estimates no meaningful analyses could be carried out. We had expected, at the inception of our project, to find some studies on the accuracy of abdominal palpation for uterine contractions in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour as a predictor for spontaneous preterm birth. However, within our literature searching no studies were found on this aspect of physical examination, which forms the cornerstone of our clinical practice. For some tests, and this has to be borne in mind, researchers were only just beginning to make headway in evaluating their accuracies where the relevant studies were only just emerging (e.g. periodontal assessment, serum relaxin, phIGFBP-1). Additionally, as our understanding of the aetiology, physiology and pathology of spontaneous preterm birth evolves, more tests would appear that might not be included in our current review.
Where studies were available, absence of primary data in key areas (e.g. description of population, threshold, or outcome) limited our ability to extract and explore the data as completely as we would have liked. As an example, some studies reported mean ± SD for non-Gaussian distributions of index test results and did not provide 2 × 2 tables. Such studies had to be excluded from our review. We tried to minimise this problem by writing to the corresponding author(s) for the required data with variable results. We wrote an initial communiqué followed by another a week later in case of non-response. Generally, we obtained co-operation but for some, our time constraint and their work commitment schedule meant that they were not able to extend co-operation where they would have otherwise liked to. In some circumstances, data were no longer available or accessible, or we have simply had no response. Only after we exhausted this approach did we exclude studies that would otherwise have met our inclusion criteria. Indeed, from the preceding discussion, better quality primary test accuracy studies with better reporting would have improved our assessment of the test accuracy.
Findings in the light of limitations
A confirmatory test usually follows the initial screening, before institution of therapy. In our project, this is not the case. Screening is used to identify a risk group that may benefit from preventative interventions (e.g. intensive monitoring and treatments), which will be employed directly when screening results are known, and without further confirmatory test(s). Screening and tests which offer high LR+ have the potential to minimise unwarranted inconvenience, expense and morbidity associated with false-positive results, which lead to unnecessary interventions; while those which offer low LR– have the potential to minimise unwarranted inconvenience, expense and morbidity associated with false-negative results, which led to spontaneous preterm births. Additionally, tests that detect parameter changes of the final common pathway of spontaneous preterm labour irrespective of the initial stimulus (e.g. be it subclinical infection or a cervical structural abnormality such as cervical shortening/funnelling or vaginal fibronectin) are more likely to be accurate than screening, e.g. for infection. Once these tests become positive it may be less likely that an intervention would be effective.
Given the quality, level and precision of the accuracy evidence, we found that no single test emerged as a front runner in predicting spontaneous preterm births when the test result was positive nor to exclude it when the test result was negative. On a few occasions, this was because of imprecision of the LR estimates, i.e. given a useful LR point estimate, its CIs should not be wide enough to make the LR less useful because of its imprecision. For example, absence of fetal breathing movement had an LR+ of 6.08 (95% CI 5.22–49.55), which would have made it a useful test to predict spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours testing when the result is positive. However, it had an LR– of 0.16 (95% CI 0.05–0.58) where the upper limit of its confidence would have made it a less than useful test when the test result is negative. Had the estimate of the LR– including its CIs been < 0.2, absence of fetal breathing movement would have been a useful test. It may well be that no single screening or testing modality would suffice in the prediction of spontaneous preterm birth and that individual patient data to better delineate the accuracy of test combinations has to be considered in the absence of a novel accurate test.
Recommendations for an economic model
How accuracy results are incorporated into a model includes dealing with challenges relating to the systematic review process (covered above) and patient preferences. One of the key issues concerning screening or predictive tests in this project is that, if available, effective interventions are convenient, inexpensive, and without particular risk of harm or side effects (to both mother and fetus or newborn), it is better to have tests with better LR– than LR+ values. It is worth speculating that in preventing spontaneous preterm birth, it may be difficult from a clinical and patient perspective to distinguish between false-positive and false-negative results and so from this perspective the optimal screening or testing modality will be one which minimises both false-positive (high LR+) and false-negative (low LR–) results. Where screening and/or testing have lower LR– than high LR+, they are unlikely to improve cost-effectiveness when used in combination with cheap, safe and effective treatments. Similarly, where screening and/or testing have higher LR+ it will minimise the unwarranted cost and complications from exposure of women and the fetus to treatments. Depending on the economic threshold analysis, there is a small risk of overlooking potentially accurate screening or testing modalities in the face of cheap, safe and effective interventions to prevent spontaneous preterm birth. We have only put forward data in Figure 83–Figure 85 for decision-analytic modelling because we believe that it provided the most robust estimates, which were derived either from meta-analysis of ideal quality studies or from the largest higher quality study available for the particular test. Ultimately the threshold analysis (Chapter 6) will show what levels of LR+ and LR– will be required to make testing cost-effective in prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
Recommendations for practice
Considering cost-effectiveness, there are no practical recommendations for clinicians for prevention of spontaneous preterm birth with testing performed before preventative treatment.
Recommendations for research
-
New more robustly designed test accuracy studies are required to develop tests that have superior LR– values.
-
Such studies should evaluate the added value of a new test using multivariable analyses.
-
Independent patient data diagnostic meta-analyses are required
Conclusions of test accuracy reviews
The quality of studies and accuracy of tests was generally poor (Figure 82). Some tests were able to achieve high LR+, but at the expense of compromised LR–. Only a few tests reached LR+ > 5 (minimising false positives) or LR– < 0.2 (minimising false negatives) but not both. For LR+ > 5 in asymptomatic antenatal women they are ultrasonographic cervical length measurement and cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin screening, while for LR– < 0.2 in the corresponding population, they are detection of uterine contraction (by home uterine monitoring device) and amniotic fluid CRP measurement. For LR+ > 5 in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour they are absence of fetal breathing movements, cervical length and funnelling, amniotic fluid IL-6, serum CRP (for predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 2–7 days of testing); and MMP-9, amniotic fluid IL-6, cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin and cervicovaginal hCG (for predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 or 37 weeks’ gestation). For symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour, measurement of cervicovaginal IL-8, cervicovaginal hCG, cervical length measurement, absence of fetal breathing movement, amniotic fluid IL-6, and serum CRP all showed LR– < 0.2 for predicting spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours or 7 days of testing. Only cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin and amniotic fluid IL-6 had an LR– < 0.2 in predicting spontaneous preterm birth before 34 or 37 weeks’ gestation.
Chapter 5 Results of reviews of effectiveness of interventions
Identification of literature
We divided the literature into existing reviews and primary studies; the searches identified 257 potentially relevant reviews and 13,363 potentially relevant primary studies. On the basis of reviewing titles and abstracts 348 full text papers were ordered for further assessment (130 reviews and 218 primary studies). Once publications had been collated the total number of included reviews was 36, and the total number of included primary studies was 29 (Figure 86).
FIGURE 86.
Study selection for systematic review of interventions in preventing and delaying, and improving neonatal outcomes consequent on spontaneous preterm birth.
Effectiveness of interventions among asymptomatic women
Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is a persistent bacterial growth in the urinary tract. It occurs in between 5 and 10% of all pregnancies and is associated with an increased risk of spontaneous preterm birth and a low-birthweight infant, although it is unclear whether this link is causal or whether the correlation results from a common underlying factor such as low socioeconomic status. Without treatment, approximately 30% of pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria will develop pyelonephritis, with an associated risk of kidney damage. 351
The review of antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria351 included 14 randomised or quasi-randomised controlled trials (RCTs). Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 118. 265,272,287,352–362 No further trials were found when the searches were updated. Antibiotic therapy was compared with no therapy; and subgroups of continuous therapy and short-course (3–7 days) therapy were examined. The quality of the included studies was generally poor (Figure 87). Data were available on preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. However, many of the studies were published several decades ago, and defined preterm birth as a low-birthweight (< 2500 g) infant, which is a surrogate outcome and may not be useful. Therefore, where preterm birth was defined in this way the study was excluded from the analysis. Six studies used appropriate definitions of preterm birth,265,272,287,355,360,362 and these showed that antibiotic therapy was effective in preventing preterm birth at less than 37 weeks’ gestation, both overall (Figure 88) and where continuous265,272,355,362 (Figure 89) or short-course therapies287,360 (Figure 90) were employed. This was the case whether only trials with a strict definition of preterm birth were included or not. Data on low birthweight from those studies using this as a surrogate for spontaneous preterm birth are shown in Table 3. As can be seen from the table there was no significant difference between the groups in incidence of low birthweight, either overall or for continuous or short-course therapy. As antibiotic therapy was effective in preventing preterm birth, this supports the view that low birthweight is not a useful surrogate outcome for preterm birth. In addition to reducing the risk of preterm birth, antibiotic therapy, either overall or where continuous or short-course therapy was used, was effective in reducing the incidence of pyelonephritis. Summary relative risks (RRs) from the forest plots presented were used in the decision analyses.
FIGURE 87.
Methodological quality of the included trials of antibiotic treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria in preventing spontaneous preterm birth.
FIGURE 88.
Forest plot of the effects of all antibiotic therapy versus no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
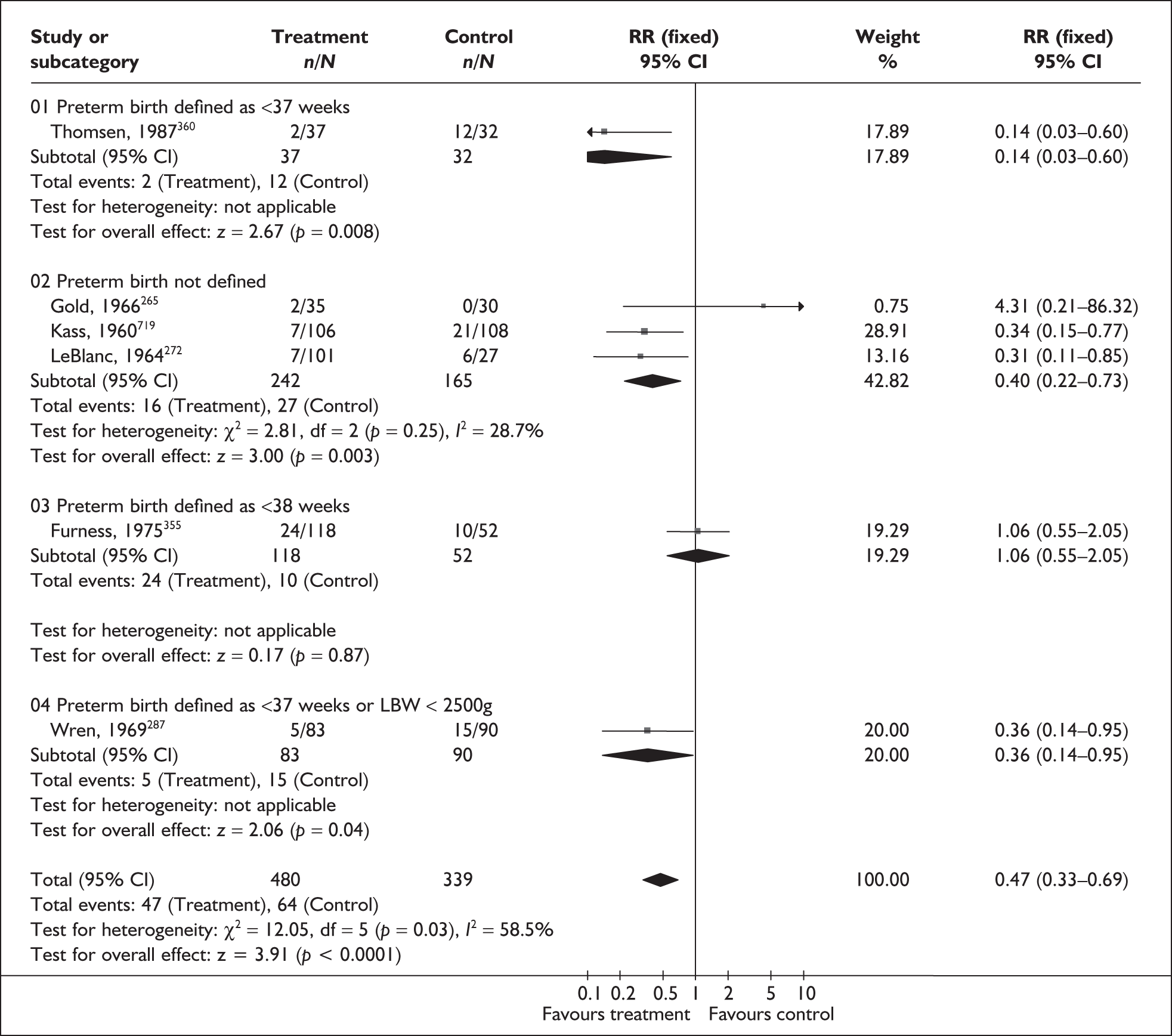
FIGURE 89.
Forest plot of the effects of continuous antibiotic therapy versus no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
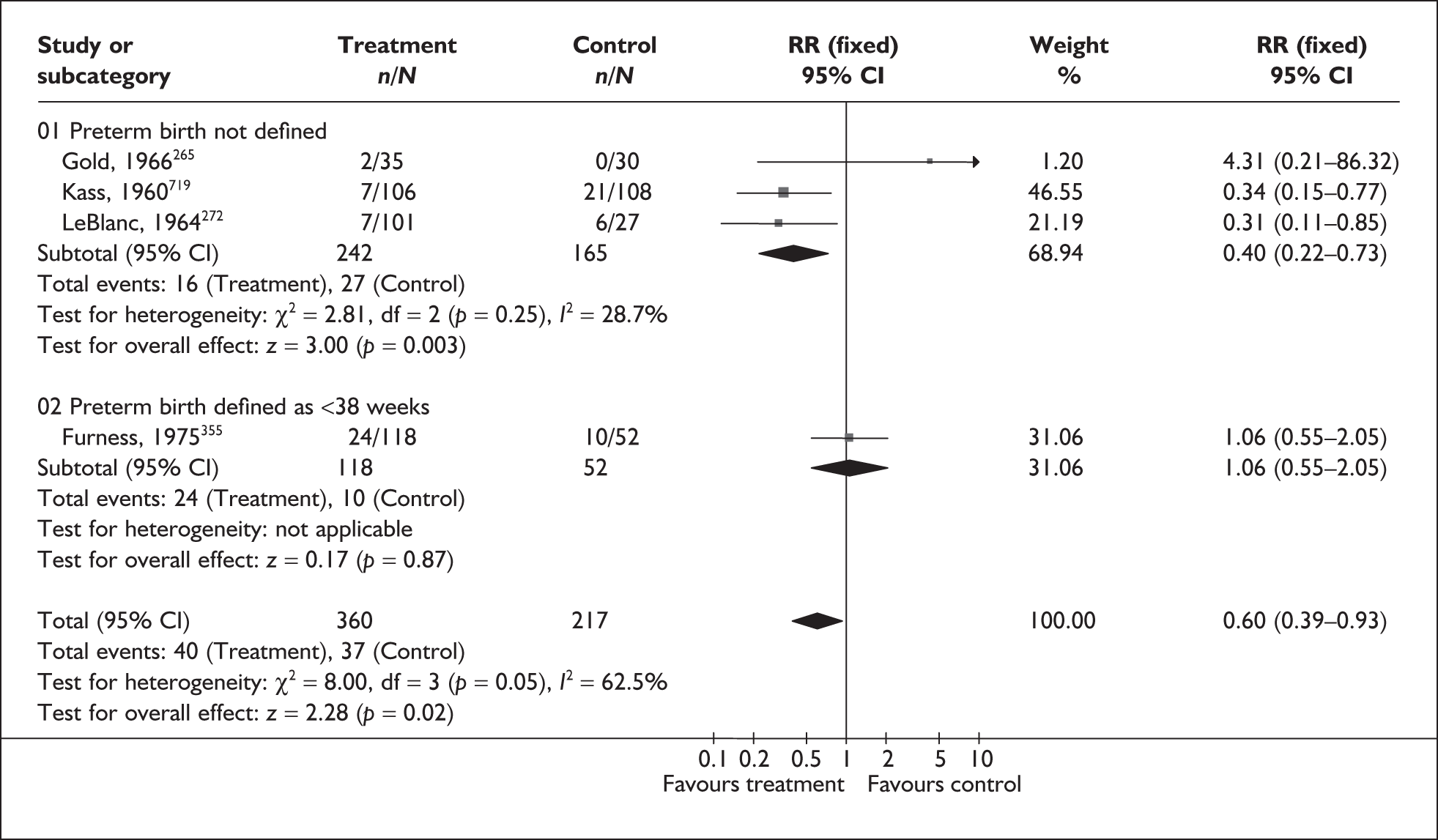
FIGURE 90.
Forest plot of the effects of continuous antibiotic therapy versus no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation.
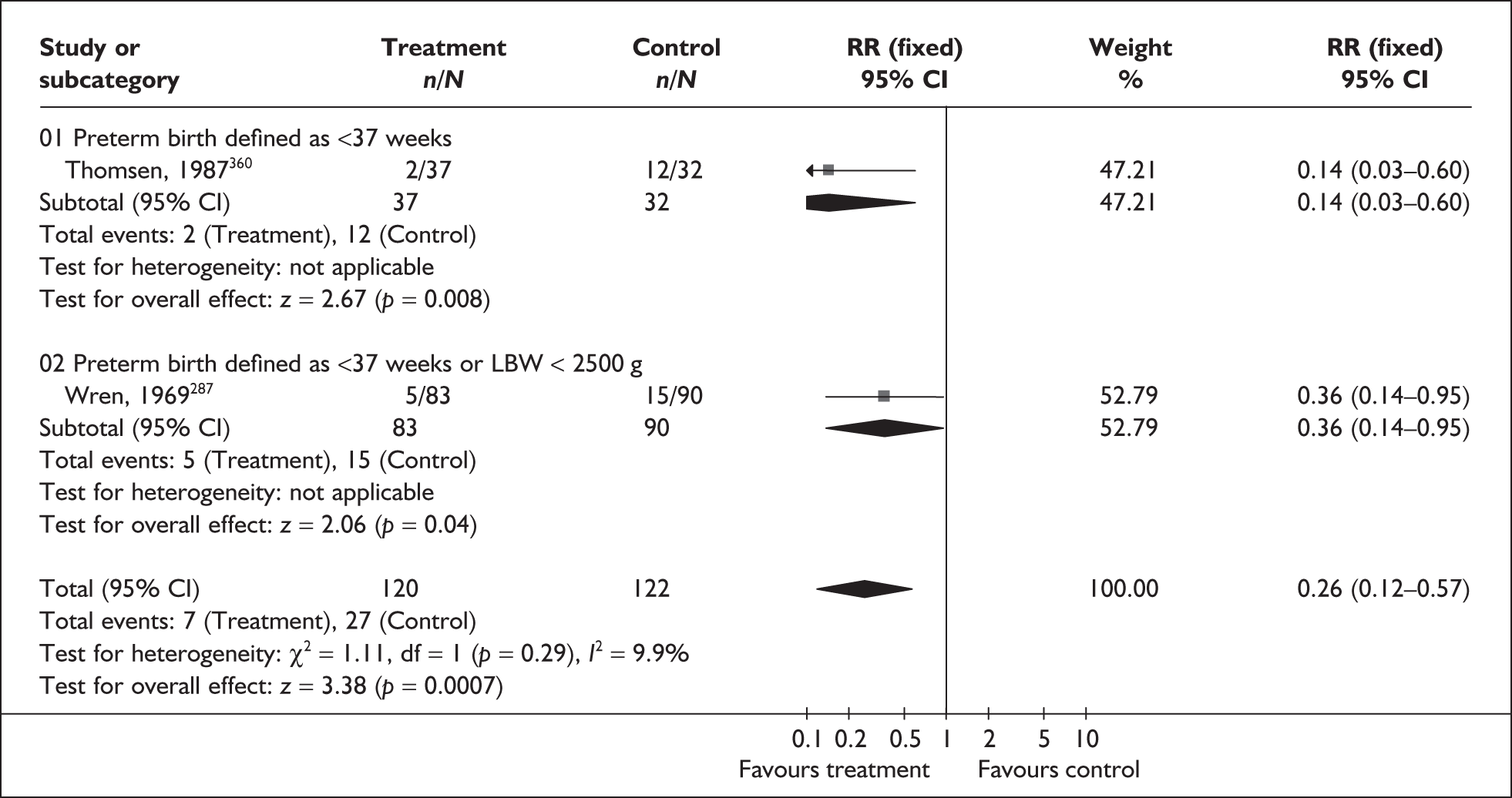
| Outcome (number of RCTs) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low birthweight < 2500 g | |||
| Overall (4 studies, n = 1004) 352,353,356,357 | 0.81 | 0.55–1.19 | 0% (0.57) |
| Continuous (2 studies, n = 400) 356,357 | 0.93 | 0.58–1.49 | |
| Short-course (1 study, n = 281) 352 | 0.62 | 0.32–1.20 | |
| Pyelonephritis | |||
| Overall (13 studies, n = 2189) 265,272,352–355–362 | 0.25 | 0.19–0.33 | 57.7% (0.005) |
| Continuous (6 studies, n = 1005) 265,272,355–357,362 | 0.22 | 0.14–0.33 | |
| Short-course (5 studies, n = 725) 352,354,358,360,361, | 0.38 | 0.23–0.62 | |
Duration of treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is a persistent bacterial growth in the urinary tract. It occurs in between 5 and 10% of all pregnancies and is associated with an increased risk of spontaneous preterm birth and a low-birthweight infant. However, it is unclear whether this link is causal or whether the correlation results from a common underlying factor such as low socioeconomic status. Without treatment approximately 30% of pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria will develop pyelonephritis, with an associated risk of kidney damage.
The review of duration of treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria363 included eight randomised364–371 and two quasi-randomised372,373 controlled trials. No further trials were found when the searches were updated. Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 118. The quality of included studies is shown in Figure 91. Six trials compared different durations of the same antibiotic treatment,364–367,369,372 while four compared different durations of treatment with different antibiotic treatments. 368,370,371,373 Data were available for the outcome of spontaneous preterm birth. There was no significant difference in occurrence of spontaneous preterm birth at less than 37 weeks’ gestation between the groups where RR was 0.81 [95% confidence interval (95% CI) 0.26, 2.57] (n = 101) (Figure 92). 365 Other maternal outcomes are shown in Table 4. There were fewer side effects in the single-dose groups, both overall364–367,369–373 and where different antibiotics were used370,371,373 (Table 4). Overall the quality of the studies was poor, and there was little evidence on which to base an assessment of the effectiveness of different duration of antibiotic treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria. The summary RR from the forest plot presented was not used in the decision analyses.
FIGURE 91.
Quality of the included trials of duration of treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria.
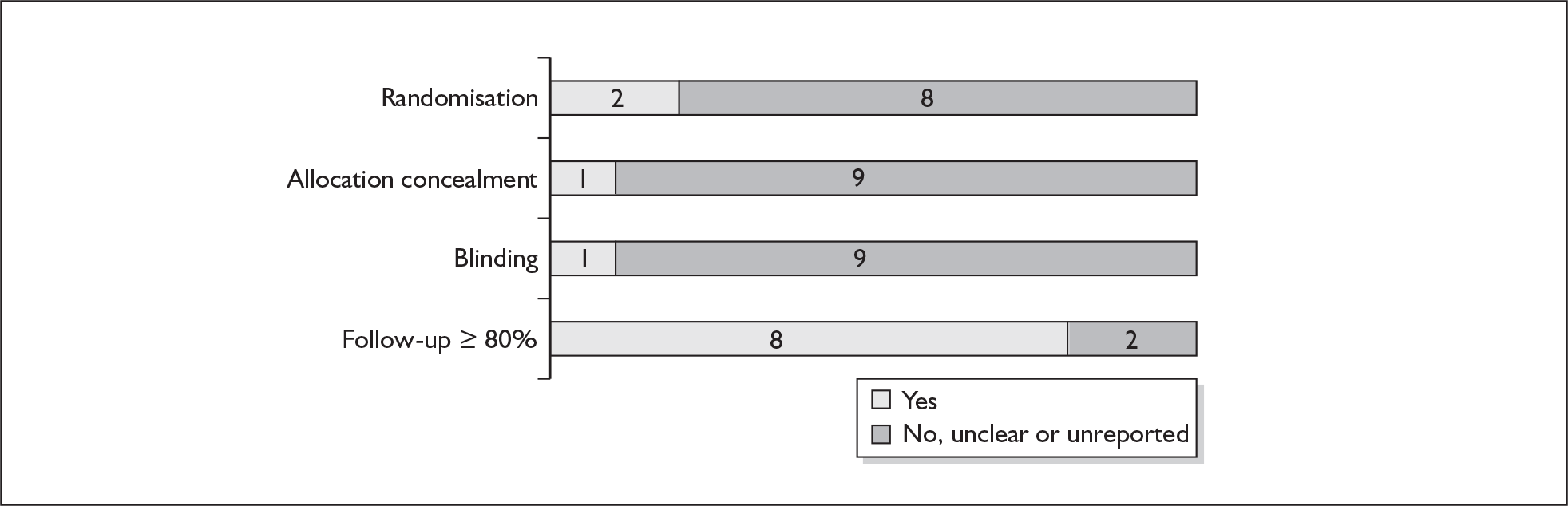
FIGURE 92.
Single-dose versus short-course antibiotics for prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
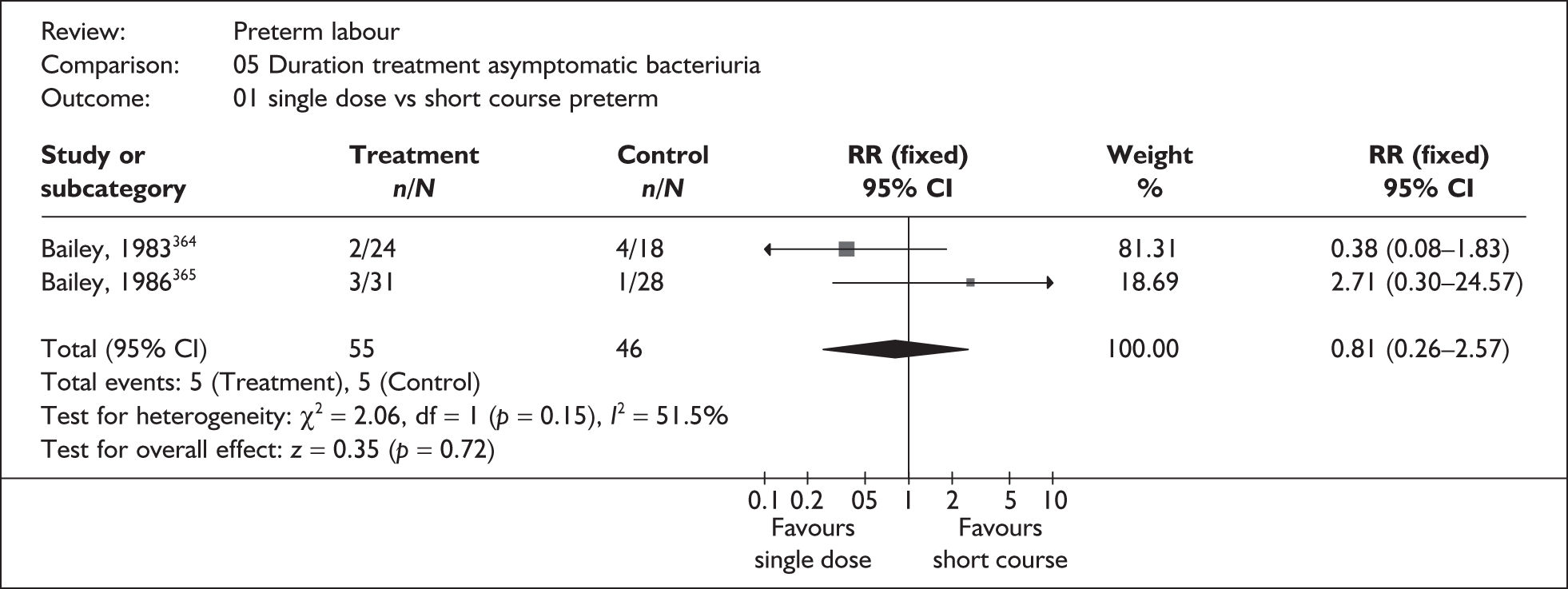
| Outcome (number of RCTs) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pyelonephritis | |||
| (2 studies, n = 102)364,372 | 3.09 | 0.54–17.55 | 0% (0.67) |
| Maternal side effects | |||
| Total (9 studies, n = 507) 364–368,370–373,714 | 0.52 | 0.32–0.85 | 0% (0.81) |
| Same antibiotic (6 studies, n = 353) 364–368,372,714 | 0.65 | 0.32–1.32 | 0% (0.70) |
| Different antibiotics (3 studies, n = 218) 370,371,373 | 0.44 | 0.23–0.84 | 0% (0.81) |
Antibiotics for bacterial vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis is an imbalance of the vaginal flora that results from a reduction in the normal lactobacillary bacterial population, and an increase in anaerobic flora including Gardnerella vaginalis. Usually asymptomatic, bacterial vaginosis is present in up to 35% of pregnancies. 374 Bacterial vaginosis has been linked to an increased risk of poor pregnancy outcome, including premature delivery with its concomitant risks.
The review of antibiotics for bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy375 included 12 RCTs which compared antibiotic therapy with placebo or no treatment,376–387 and one which compared a single daily dose with a double daily dose of a vaginal antibiotic. 388 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 118. No additional RCTs were found when the searches were updated, although one relevant RCT389 was identified after the completion of this review. Both oral and vaginal antibiotics were used. High-risk and low-risk women were included in the review, as were women classified as having intermediate flora as well as bacterial vaginosis. Figure 93 showed that, overall, the quality of the included studies was good with the exception of blinding. Data were available on spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ and 37 weeks’ gestation (Figures 94–103), perinatal mortality (Figures 104–108), and admission to neonatal intensive care (Figure 109). The following subgroups were examined:
-
Any antibiotic versus placebo (Figure 94, Figure 98, Figure 104).
-
Oral antibiotics versus placebo (Figure 95, Figure 99, Figure 105).
-
Vaginal antibiotics versus placebo (Figure 96, Figure 100, Figure 106).
-
Single daily dose versus double daily dose vaginal antibiotic (Figure 102).
-
Previous spontaneous preterm birth: antibiotics versus placebo (Figure 97, Figure 101, Figure 107).
-
Intermediate flora/bacterial vaginosis: antibiotics versus placebo (Figure 103, Figure 108, Figure 109).
FIGURE 93.
Methodological quality of the included trials of antibiotic treatment for bacterial vaginosis.
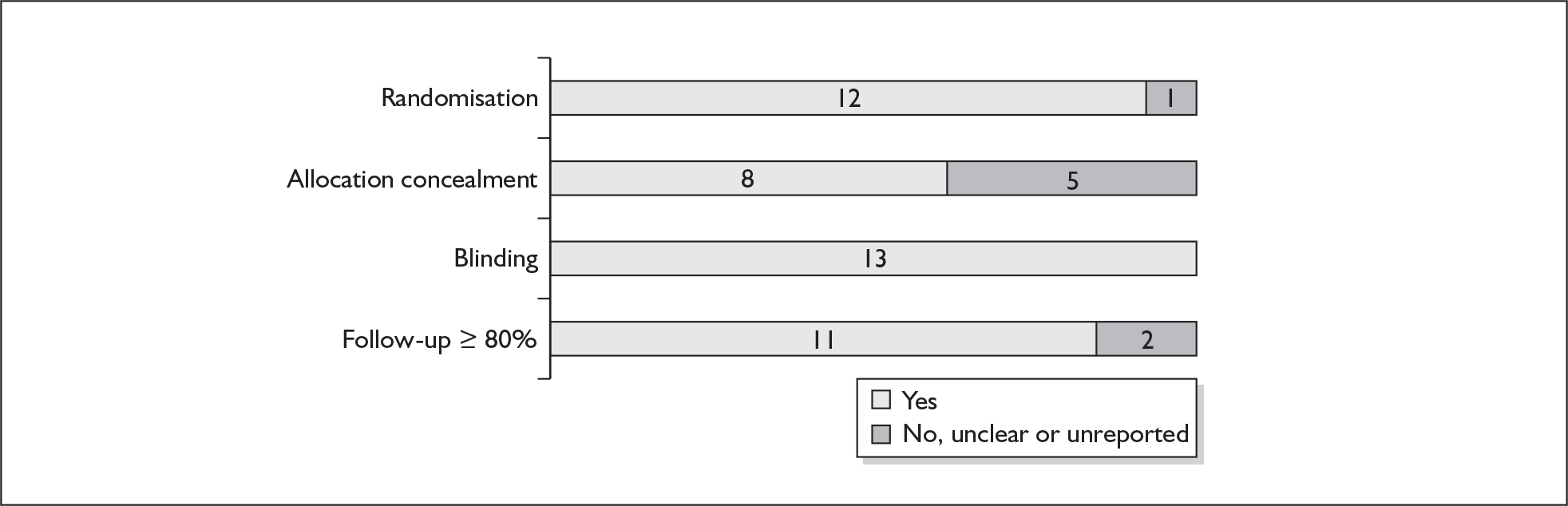
FIGURE 94.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation.
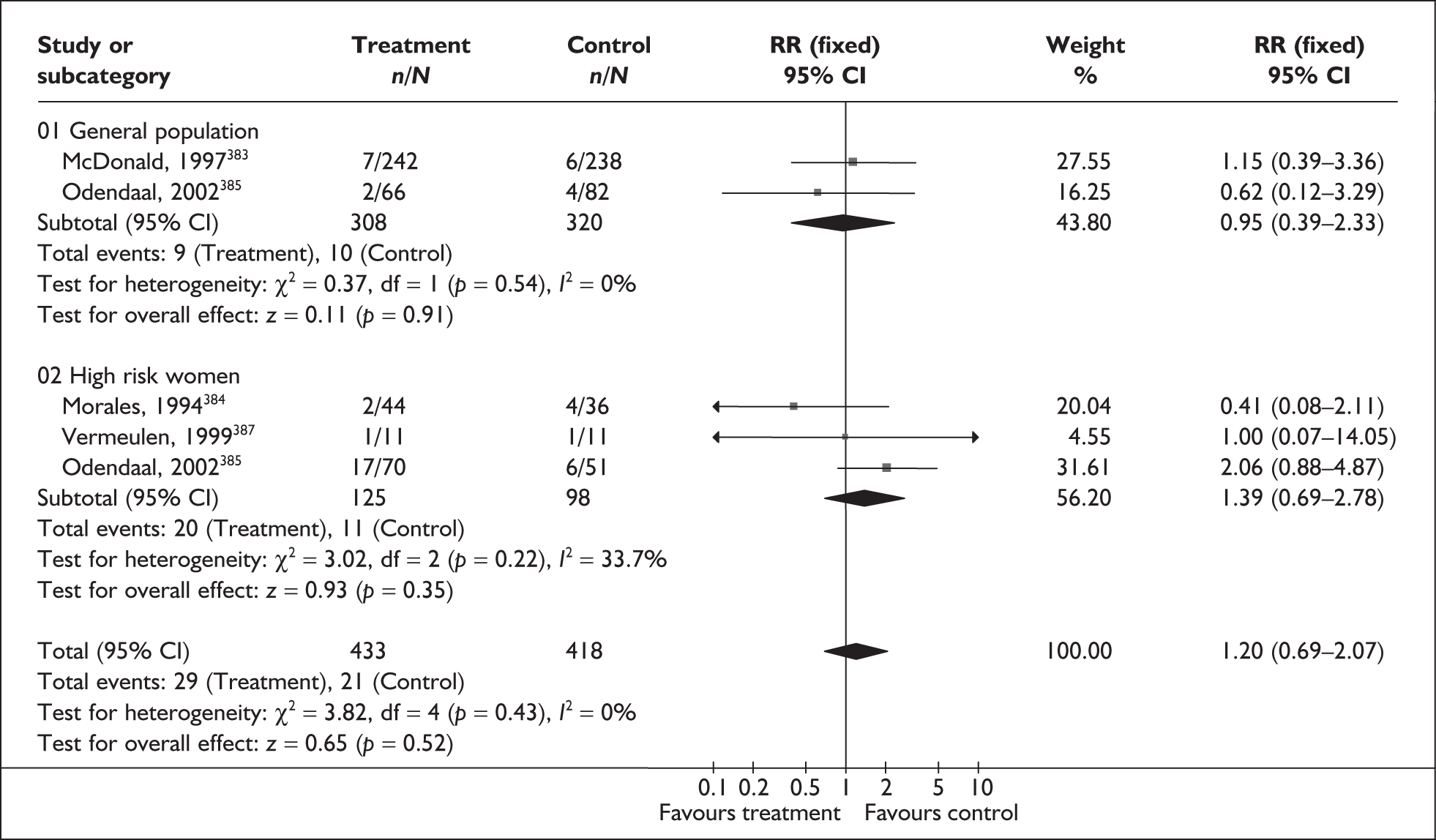
FIGURE 95.
Forest plot of the effects of oral antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation.
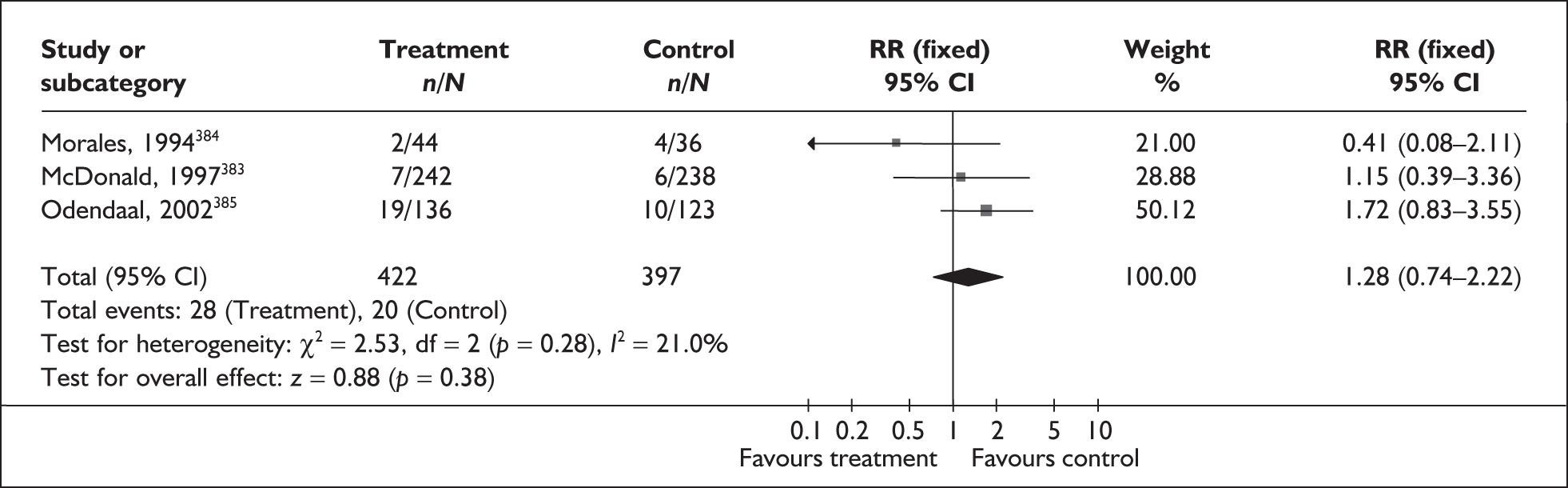
FIGURE 96.
Forest plot of the effects of vaginal antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation.
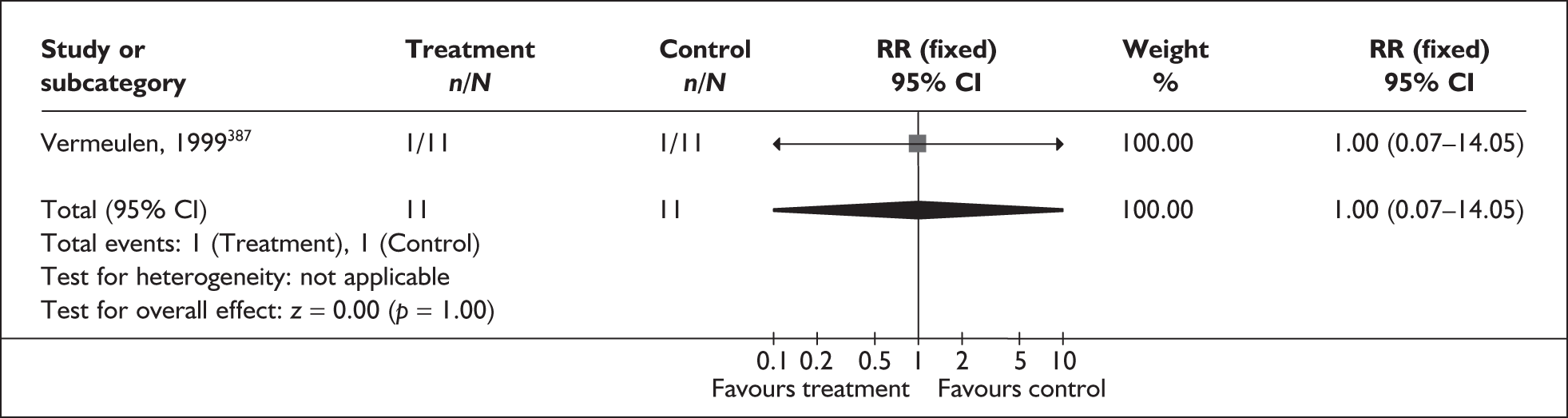
FIGURE 97.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation in women with previous preterm birth.
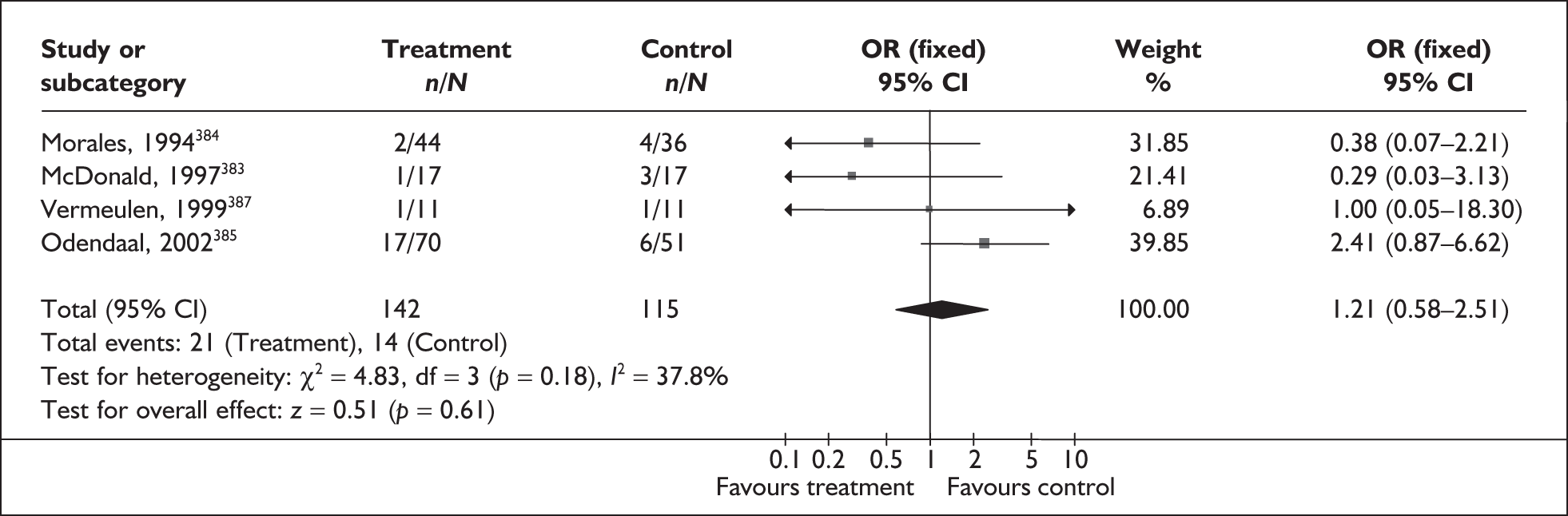
FIGURE 98.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
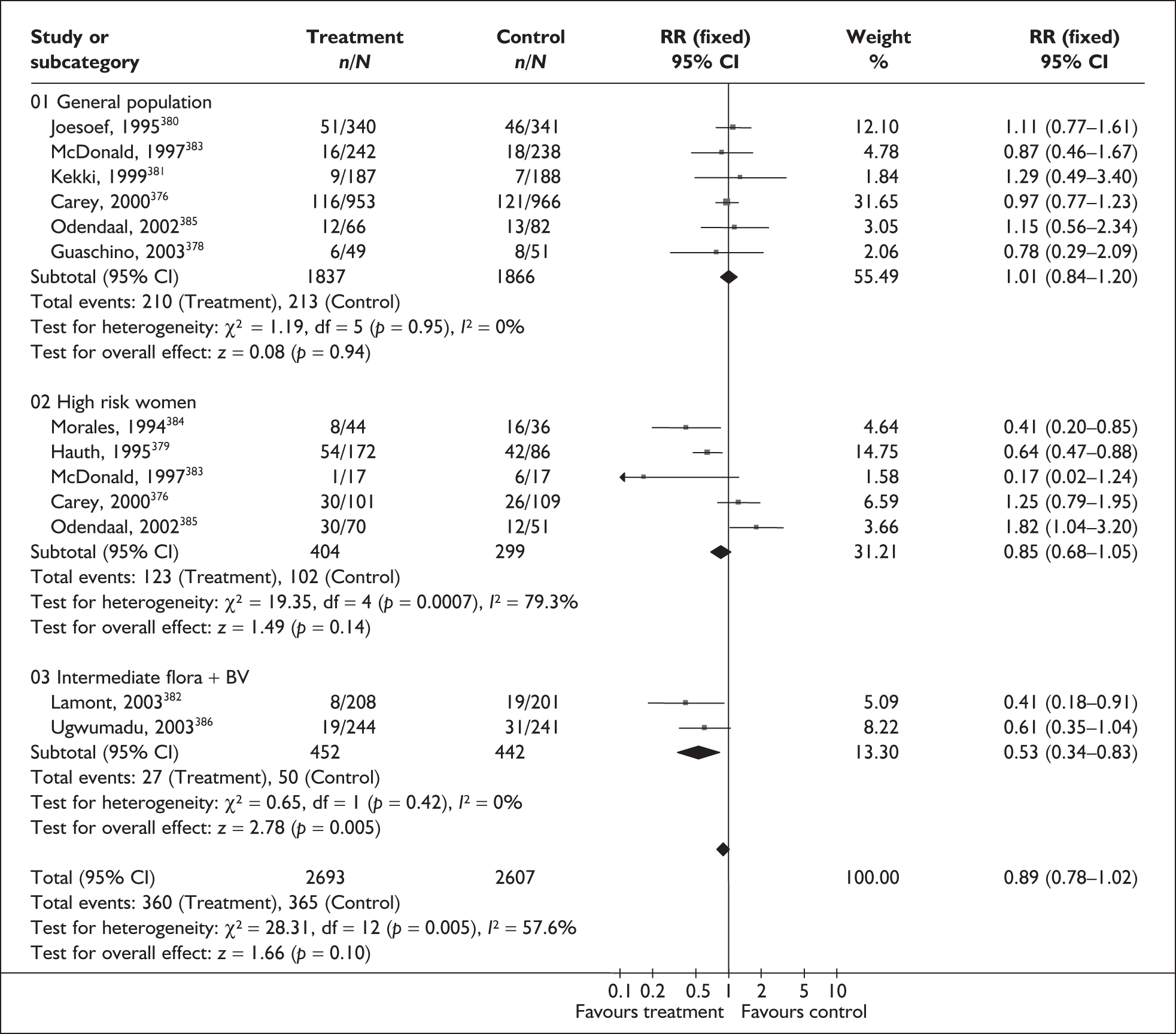
FIGURE 99.
Forest plot of the effects of oral antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
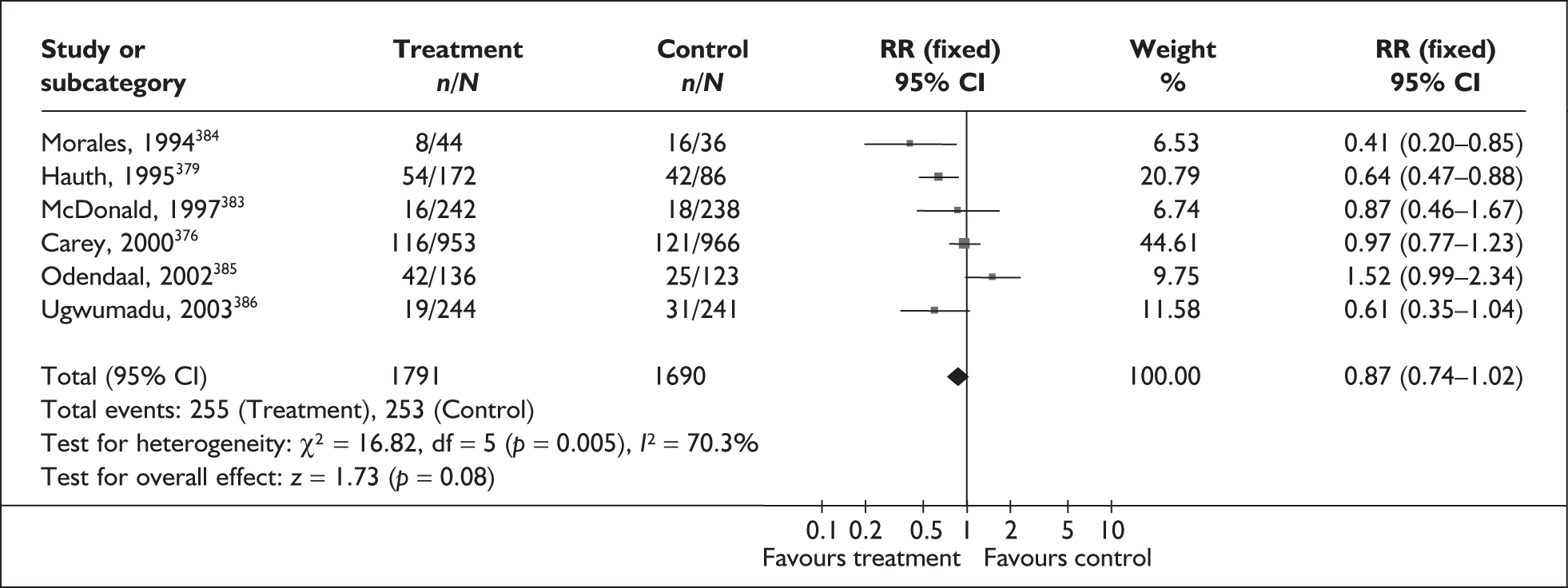
FIGURE 100.
Forest plot of the effects of vaginal antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
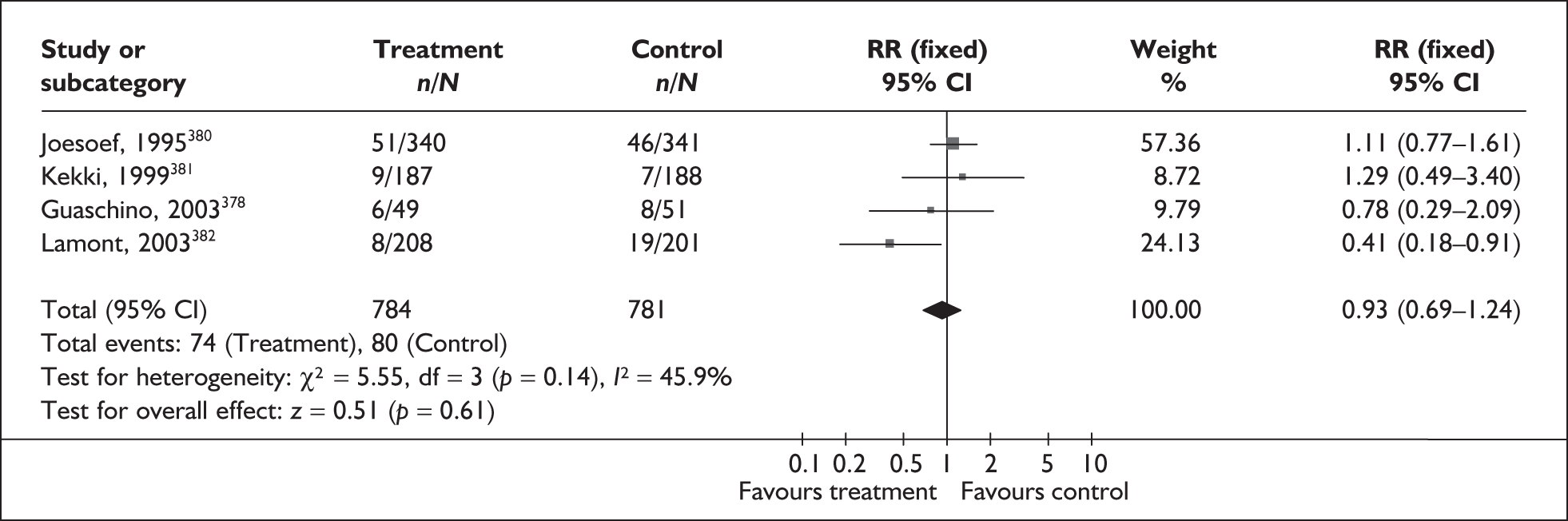
FIGURE 101.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in women with previous preterm birth.
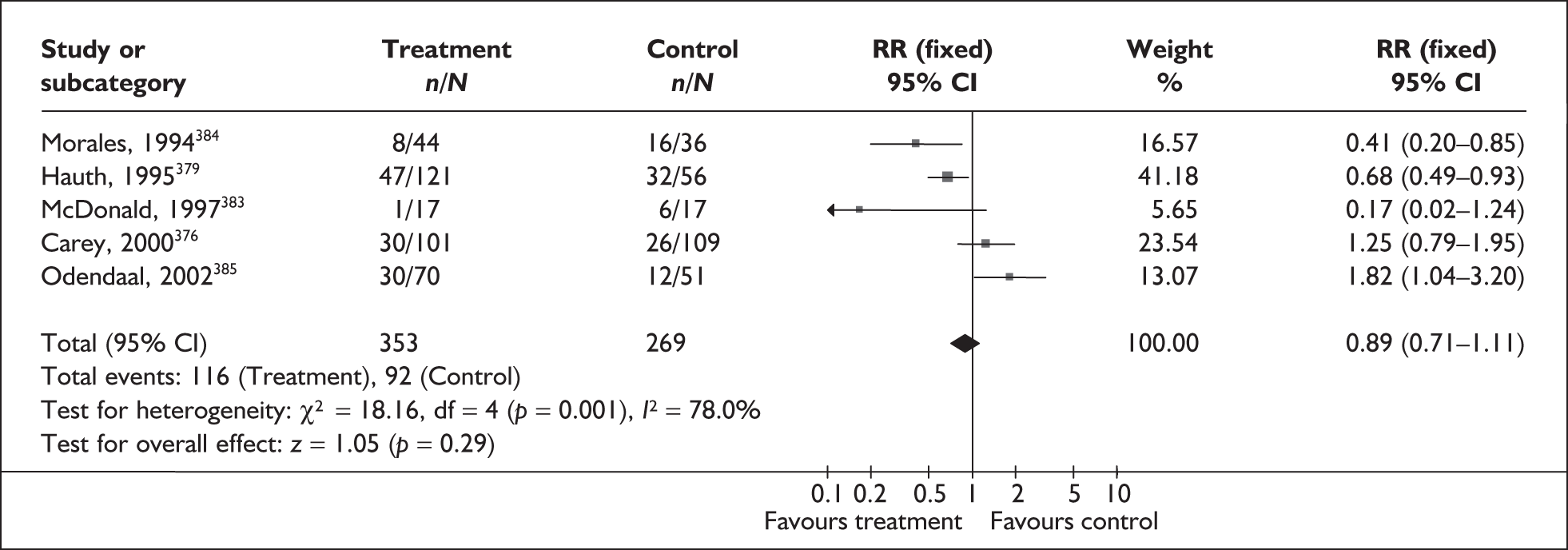
FIGURE 102.
Forest plot of the effects of single daily dose versus double daily dose of vaginal antibiotic for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
FIGURE 103.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in women with intermediate vaginal flora.
FIGURE 104.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of perinatal mortality.
FIGURE 105.
Forest plot of the effects of oral antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of perinatal mortality.
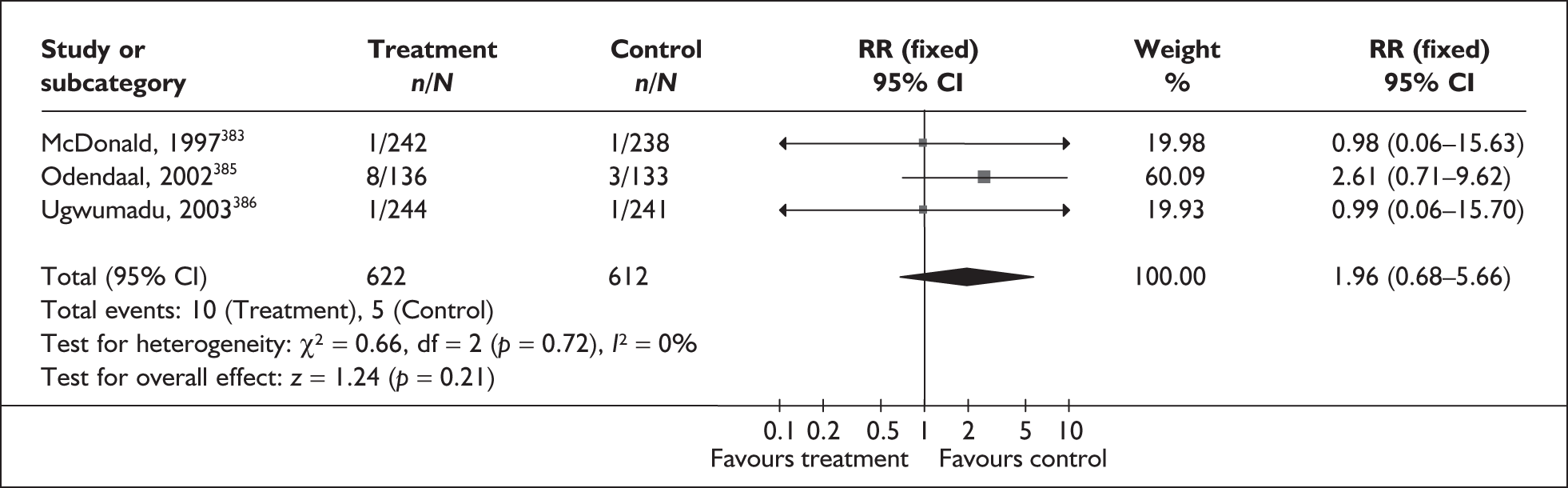
FIGURE 106.
Forest plot of the effects of vaginal antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of perinatal mortality.
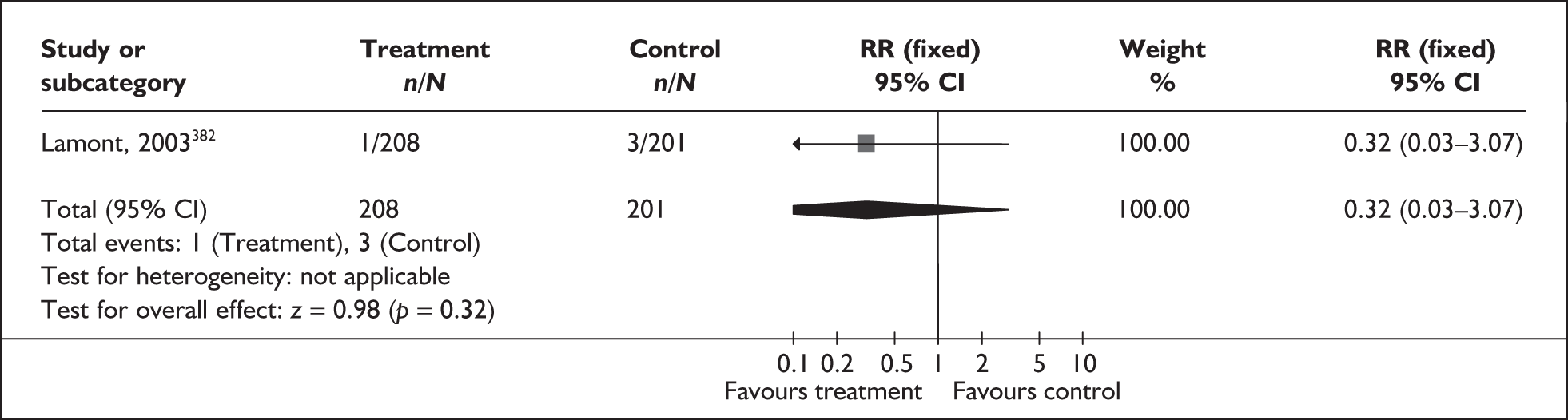
FIGURE 107.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of perinatal mortality in women with previous preterm delivery.
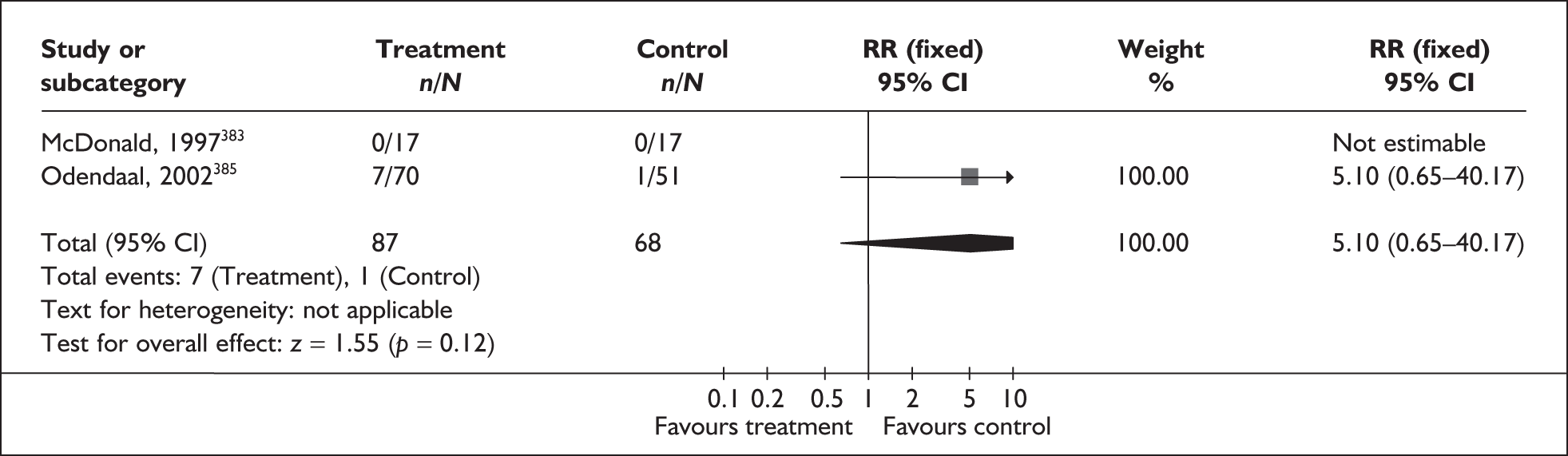
FIGURE 108.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of perinatal mortality in women with intermediate vaginal flora.
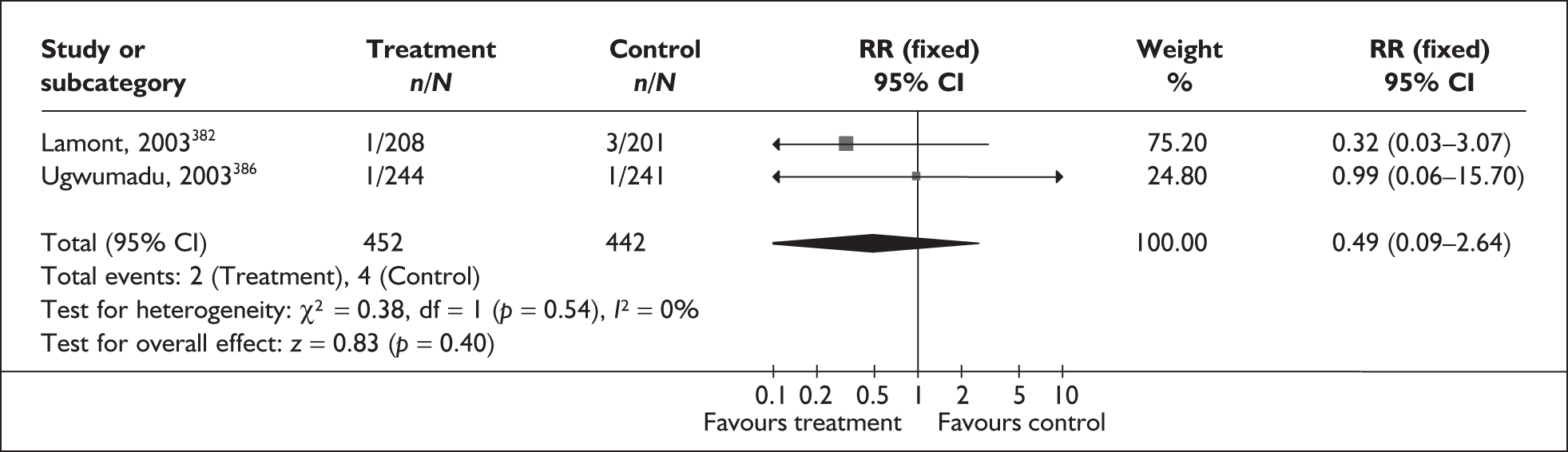
FIGURE 109.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment in women with intermed1110iate vaginal flora for the prevention of admission to neonatal unit.
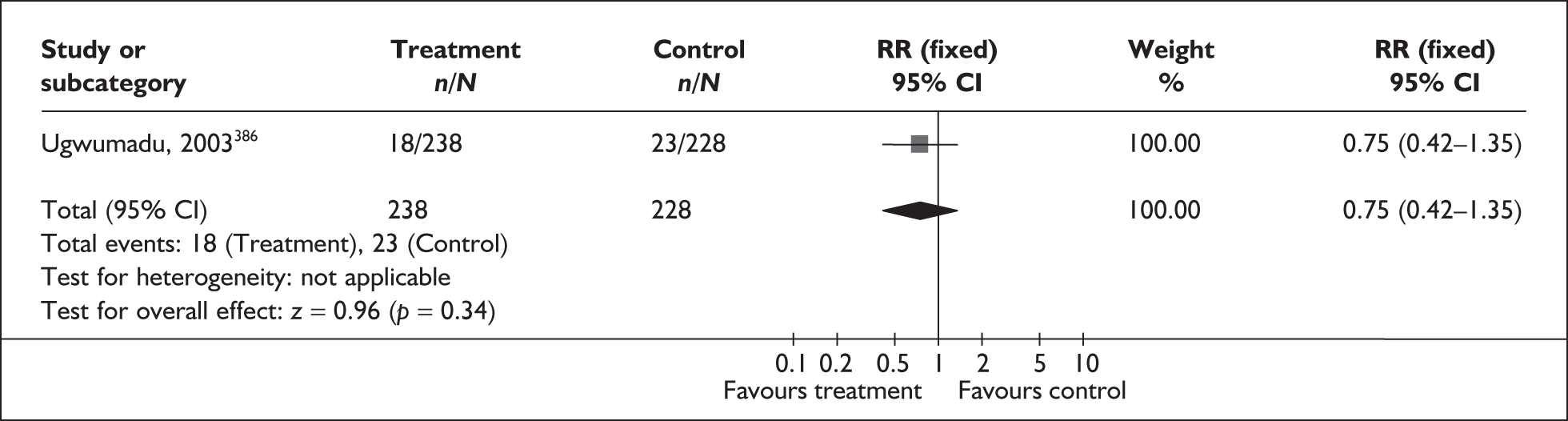
Antibiotic therapy did not significantly affect the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, the incidence of perinatal mortality or the requirement for admission to neonatal intensive care. Spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation was significantly reduced in the subgroup of women with intermediate vaginal flora as well as bacterial vaginosis (Figure 103; RR 0.53, 95% CI 0.34, 0.83, based on two studies with 894 patients). 382,386 One study used oral administration386 and one used vaginal administration of therapy. 382 This reduction in spontaneous preterm birth was not found in other subgroups or in the population as a whole (Figure 98). Other neonatal and maternal outcomes are shown in Tables 5 and 6. Summary RRs from the forest plots presented were used in the decision analyses.
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Premature birth < 32 weeks | |||
| Any antibiotic versus placebo/no treatment | |||
| Total (4 studies, n = 3565) 376,380,383,386 | 1.13 | 0.77–1.68 | 0% (0.48) |
| General population (3 studies, n = 3080) 376,380,383 | 1.08 | 0.71–1.66 | 7.8% (0.34) |
| Women with intermediate flora (1 study, n = 485) 386 | 1.48 | 0.54–4.10 | NA |
| Oral antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (3 studies, n = 2884) 376,383,386 | 0.98 | 0.62–1.54 | 0% (0.65) |
| Vaginal antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 681) 380 | 1.82 | 0.79–4.18 | NA |
| Previous preterm delivery: antibiotics vs placebo (1 study, n = 34) 383 | 0.50 | 0.05–5.01 | NA |
| Intermediate flora/bacterial vaginosis: antibiotics vs placebo (1 study, n = 485) 386 | 1.48 | 0.54–4.10 | NA |
| Late miscarriage | |||
| Intermediate flora/bacterial vaginosis: antibiotics vs placebo (1 study, n = 485) 388 | 0.20 | 0.04–0.89 | NA |
| Low birthweight | |||
| Any antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment | |||
| Total (7 studies, n = 4107) 376,378,380,382–384,386 | 0.95 | 0.79–1.15 | 15.4% (0.31) |
| High-risk women (1 study, n = 80) 383 | 0.41 | 0.17–0.95 | NA |
| General population (4 studies, n = 3151) 376,378,380,383 | 1.00 | 0.80–1.24 | 0% (0.44) |
| Women with intermediate flora (2 studies, n = 876) 382,386 | 0.95 | 0.62–1.47 | 0% (0.44) |
| Oral antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (4 studies, n = 2926) 376,383,384,386 | 0.90 | 0.72–1.11 | 17.3% (0.30) |
| Vaginal antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (3 studies, n = 1181) 378,380,382 | 1.13 | 0.77–1.66 | 14% (0.31) |
| Single daily dose vs double daily dose vaginal antibiotic (1 study, n = 94) 388 | 1.19 | 0.58–2.42 | NA |
| Previous preterm delivery: antibiotics vs placebo (2 studies, n = 114) 383,384 | 0.39 | 0.18–0.82 | 0% (0.81) |
| Intermediate flora/bacterial vaginosis: antibiotics vs placebo (2 studies, n = 876) 382,386 | 0.95 | 0.62–1.47 | 0% (0.44) |
| Neonatal sepsis | |||
| Any antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (2 studies, n = 428) 383,387 | 0.95 | 0.06–15.12 | NA |
| Oral antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 406) 383 | 0.95 | 0.06–15.12 | NA |
| Vaginal antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 22) 387 | Not estimable | Not estimable | NA |
| Previous preterm delivery: antibiotics vs placebo (2 studies, n = 52) 383,387 | Not estimable | Not estimable | NA |
| Incidence of premature pre-labour rupture of membranes | |||
| Any antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (4 studies, n = 2579) 376,378,383,384 | 0.89 | 0.63–1.27 | 71.9% (0.01) |
| Oral antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (3 studies, n = 2479) 376,383,384 | 0.81 | 0.56–1.18 | 76.4% (0.01) |
| Vaginal antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 100) 378 | 2.43 | 0.67–8.86 | NA |
| Previous preterm delivery: antibiotics vs placebo (2 studies, n = 114) 383,384 | 0.14 | 0.04–0.50 | 0% (0.98) |
| Side effects sufficient to stop treatment | |||
| Any antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (3 studies, n = 1450) 377,383,386 | 1.55 | 0.95–2.54 | 0% (0.61) |
| Oral antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (2 studies, n = 965) 377,383 | 1.29 | 0.69–2.40 | 0% (0.73) |
| Intermediate flora/bacterial vaginosis: antibiotics vs placebo (1 study, n = 485) 386 | 2.10 | 0.92–4.77 | NA |
| Side effects not sufficient to stop treatment | |||
| Any antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (3 studies, n = 1340) 377,381,383 | 1.27 | 0.76–2.13 | 29.3% (0.24) |
| Oral antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (2 studies, n = 965) 377,383 | 1.49 | 0.72–3.06 | 58.5% (0.12) |
| Vaginal antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 375) 381 | 1.01 | 0.33–3.06 | NA |
| Postpartum infection | |||
| Any antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (2 studies, n = 618) 381,383 | 0.71 | 0.43–1.15 | 40.6% (0.19) |
| Oral antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 243) 383 | 2.93 | 0.31–27.75 | NA |
| Vaginal antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 375) 381 | 0.64 | 0.38–1.06 | NA |
| Previous preterm delivery: antibiotics vs placebo (1 study, n = 15) 383 | Not estimable | Not estimable | NA |
| Single daily dose vs double daily dose vaginal antibiotic (1 study, n = 94) 388 | 3.27 | 0.35,30.28 | NA |
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low birthweight < 2500 g | |||
| Ceftriaxone i.v. once a day vs cephazolin i.v. every 8 hours. (1 study, n = 172) 405 | 1.12 | 0.42–2.95 | NA |
| Intrauterine growth retardation | |||
| Ceftriaxone i.v. once a day vs cephazolin i.v. every 8 hours. (1 study, n = 178) 405 | 0.78 | 0.22–2.82 | NA |
| Prolonged pyrexia | |||
| Outpatient (ceftriaxone i.m.) vs inpatient (ceftriaxone i.v.) antibiotic treatment. (1 study, n = 120) 402 | 0.13 | 0.01–1.27 | NA |
| Cephazolin i.v. vs ampicillin i.v. + gentamicin (1 study, n = 120) 406 | 0.69 | 0.18–2.59 | NA |
| Ceftriaxone i.m. then cephalexin p.o. vs ampicillin i.v. + gentamicin (1 study, n = 121) 406 | 1.05 | 0.36–3.08 | NA |
| Ceftriaxone i.m. then cephalexin p.o. vs cephazolin i.v. (1 study, n = 117) 406 | 1.47 | 0.44–4.96 | NA |
| Need for change in treatment | |||
| Outpatient (ceftriaxone i.m.) vs inpatient (ceftriaxone i.v.) antibiotic treatment. (1 study, n = 120) 402 | 0.08 | 0.00–1.34 | NA |
| Cephazolin i.v. ampicillin i.v. vs gentamicin. (1 study, n = 118) 406 | 5.17 | 0.25–105.42 | NA |
| Ceftriaxone i.m. then cephalexin p.o. vs ampicillin i.v. + gentamicin. (1 study, n = 121) 406 | 9.45 | 0.52–171.79 | NA |
| Ceftriaxone i.m. then cephalexin p.o. vs cephazolin i.v. (1 study, n = 117) 406 | 1,97 | 0.37–10.32 | NA |
| Ceftriaxone i.v. once a day vs cephazolin i.v. every 8 hours. (1 study, n = 178) 405 | 0.59 | 0.14–2.38 | NA |
| Ampicillin p.o. vs nitrofurantoin p.o. (1 study, n = 86) 404 | 1.44 | 0.22–7.08 | NA |
Antibiotics for gonorrhoea in pregnancy
Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted infection that, if transmitted from mother to child during birth, can result in gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum. As with other genital bacterial infections, maternal gonorrhoea has been linked to increased risk of spontaneous preterm birth. Spontaneous preterm birth associated with such infections is of particular importance in developing countries where the prevalence of infection is high, with rates of gonorrhoeal infection in pregnant women ranging from 1.7 to 20%. 390
The review of antibiotics for gonorrhoea in pregnancy391 included two RCTs (n = 346). 392,393 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 118. Neither of these studies reported outcomes of spontaneous preterm birth, perinatal mortality or other relevant outcomes. The only outcomes reported were microbiological cure and adverse events. There were no significant differences between the antibiotic regimens used (amoxicillin plus probenecid; spectinomycin; ceftriaxone) in either microbiological efficacy or safety, with all treatments being highly effective and with few adverse events. No additional RCTs were found when the searches were updated. As there was no available evidence relating to the outcome of spontaneous preterm birth, it is not possible to form any conclusions about the efficacy of antibiotic treatment for gonorrhoea in the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
Antibiotics for the treatment of syphilis
Syphilis is a serious sexually transmitted disease that can be transmitted by a pregnant woman to her baby, who may be born with serious disability as the result of the congenital form of the disease. Syphilis in pregnancy is also associated with increased risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, spontaneous preterm, perinatal mortality and intrauterine growth restriction. The incidence of syphilis has increased in a number of countries, and this is exacerbated by the spread of human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immune deficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS). Syphilis in pregnancy is usually treated with penicillin.
The review of antibiotic treatment for syphilis394 found no studies that met the inclusion criteria of randomised or quasi-randomised controlled trials of antibiotic treatment for syphilis in pregnant women. No additional RCTs were found when the searches were updated. Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 118. As there was no available evidence it is not possible to form any conclusions about the efficacy of antibiotic treatment for syphilis in the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
Antibiotics for trichomoniasis in pregnancy
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted bacterial infection that causes vaginitis. It is not clear whether trichomonal infection during pregnancy is linked to spontaneous preterm birth, although some studies in the developing world have indicated that this may be the case. Infection with Trichomonas is also associated with acquisition of HIV/AIDS.
The review of interventions for trichomoniasis in pregnancy395 included two studies (n = 842); one RCT396 and one quasi-RCT. 397 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 118. The included RCT was of better quality than the quasi-randomised study. The quality of these studies is summarised in Figure 110. Women receiving treatment with metronidazole were more likely to experience spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation than women in the placebo group. The summary RR from the forest plot presented was not used in the decision analyses (Figure 111).
FIGURE 110.
Methodological quality of the included trials of metronidazole for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
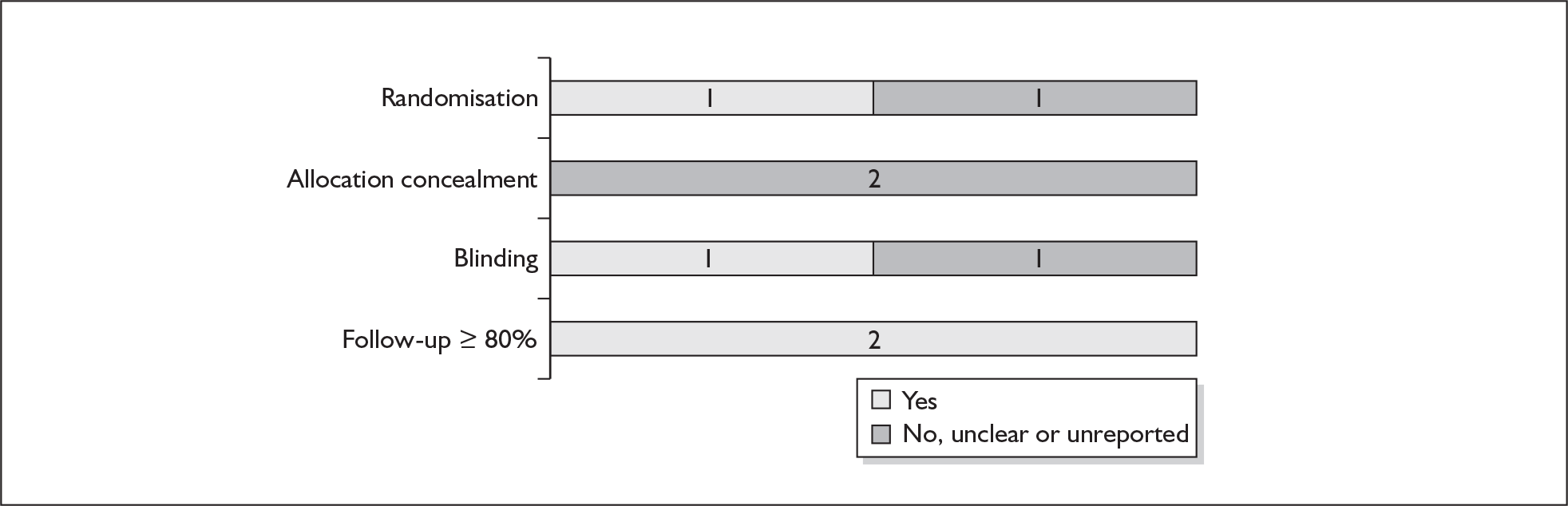
FIGURE 111.
Forest plot of the effects of metronidazole versus no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
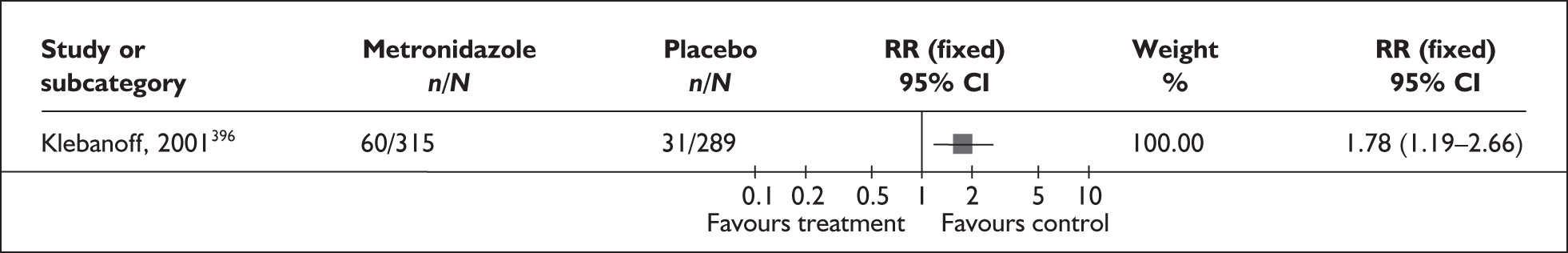
Antibiotics for symptomatic urinary tract infections
Urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis, are common in pregnancy, occurring in up to 8% of pregnancies. Urinary tract infections are associated with an increased risk of spontaneous preterm birth and neonatal infection. A possible mechanism for this association is the bacterial production of arachidonic acid, phospholipases and prostaglandins, which cause cervical softening and an increase in levels of free calcium in the myometrium.
The review of antibiotics for symptomatic urinary tract infection in pregnancy398 included eight RCTs. 399–406 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 118. The quality of the included studies was variable and poor in terms of blinding and allocation concealment (Figure 112). The numbers of participants in the trials were often quite small. No placebo-controlled trials were found; all trials compared one or more regimens of antibiotic treatment. Three studies provided data on spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation and/or neonatal intensive care admissions. 402,405,406 Data for at least one of these outcomes were available on the following comparisons:
-
Outpatient (intramuscular ceftriaxone) versus inpatient (intravenous ceftriaxone) antibiotic treatment.
-
Intravenous ampicillin plus gentamicin versus intravenous cephazolin.
-
Intravenous ampicillin plus gentamicin versus intramuscular ceftriaxone then oral cephalexin.
-
Intramuscular ceftriaxone then oral cephalexin versus intravenous cephazolin
-
Intravenous ceftriaxone once a day plus two doses placebo/day versus intravenous cephazolin every 8 hours.
FIGURE 112.
Methodological quality of the included trials of antibiotic treatment for symptomatic urinary tract infections.
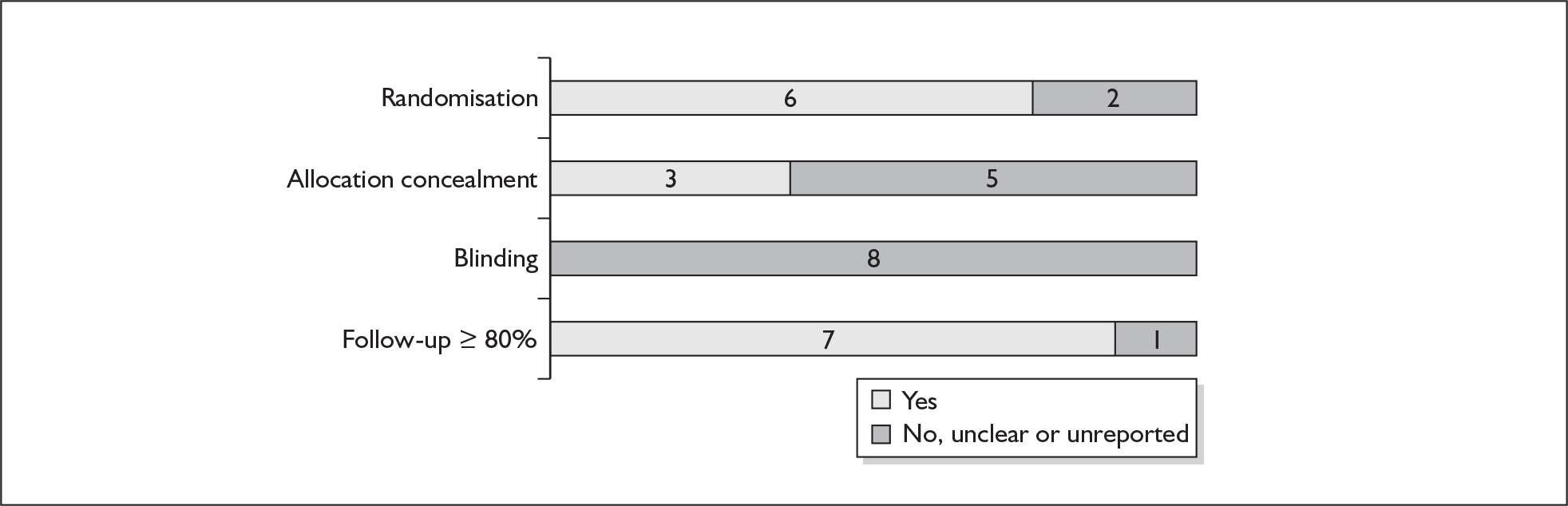
Only one study was found for each comparison, with one study406 contributing to three of the comparisons. There were no significant differences between antibiotic regimens in incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks (Figures 113–117), or in admission to neonatal intensive care units (Figures 118–120), or in other perinatal and maternal outcomes (Table 6). Overall, ampicillin and gentamicin appears to be the most promising treatment combination, as compared with cephazolin or ceftriaxone, but the evidence to support this is limited in terms of both the quantity and quality. Because of the lack of placebo/no treatment comparators, summary RRs were not used in the decision analyses.
FIGURE 113.
Forest plot of the effects of outpatient versus inpatient antibiotics for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
FIGURE 114.
Forest plot of the effects of intravenous cephalozin versus intravenous ampicillin plus gentamicin for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
FIGURE 115.
Forest plot of the effects of intramuscular ceftriaxone versus intravenous ampicillin plus gentamicin for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
FIGURE 116.
Forest plot of the effects of intramuscular ceftriaxone versus intravenous cephazolin for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
FIGURE 117.
Forest plot of the effects of cephalosporins once-a-day versus multiple doses for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
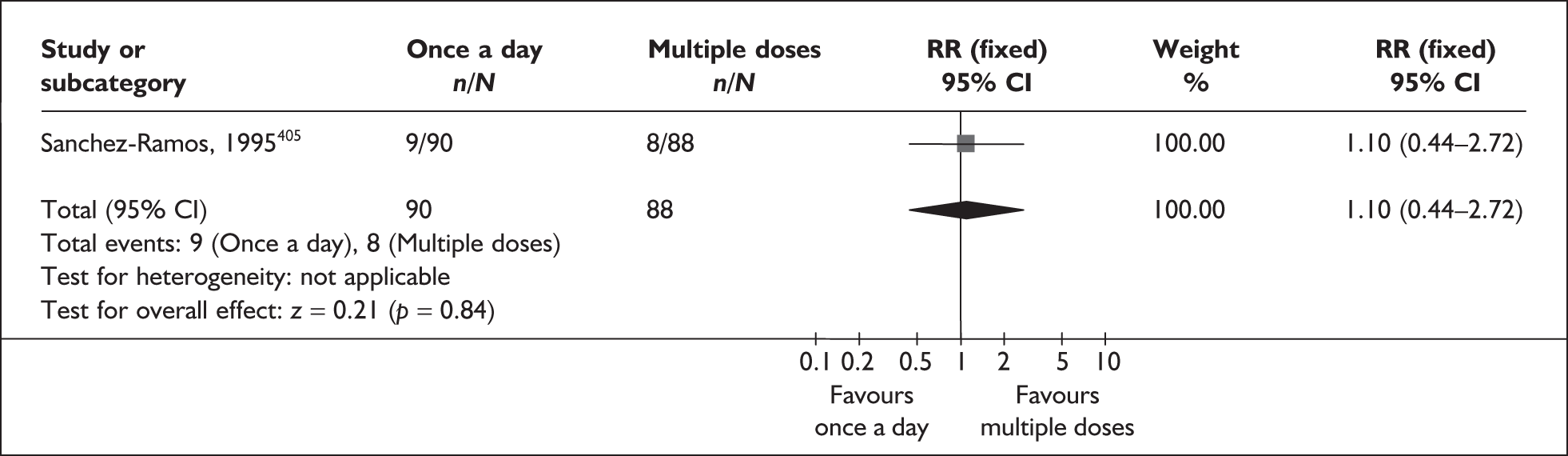
FIGURE 118.
Forest plot of the effects of intravenous cephazolin versus intravenous ampicillin plus gentamicin for the prevention of admission to neonatal intensive care unit.
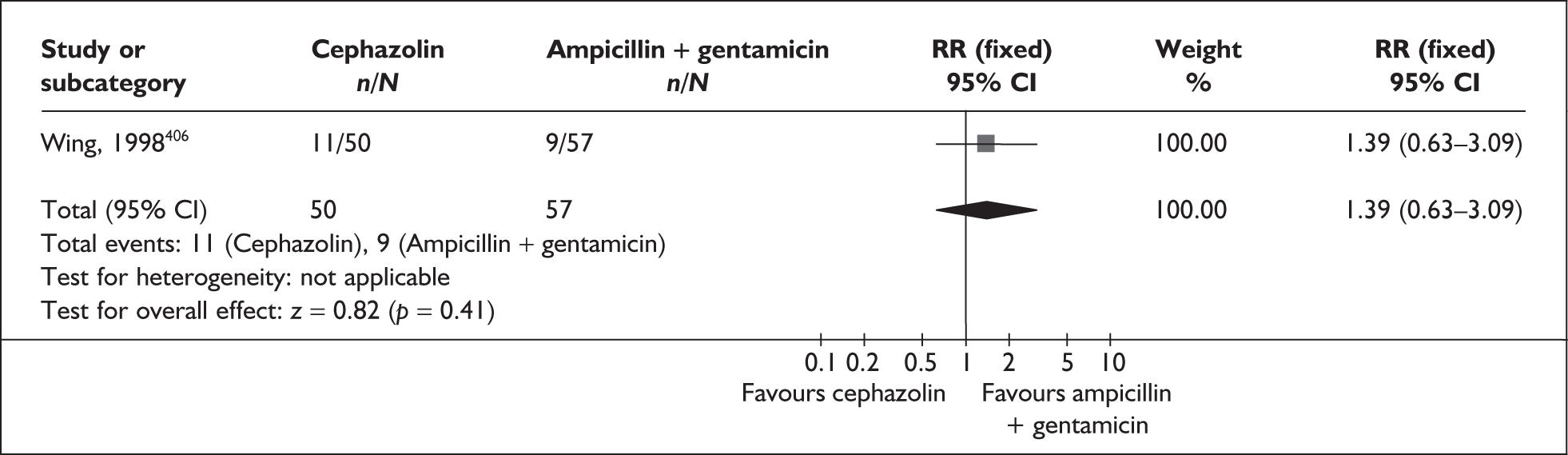
FIGURE 119.
Forest plot of the effects of intramuscular ceftriaxone versus intravenous ampicillin plus gentamicin for the prevention of admission to neonatal intensive care unit.
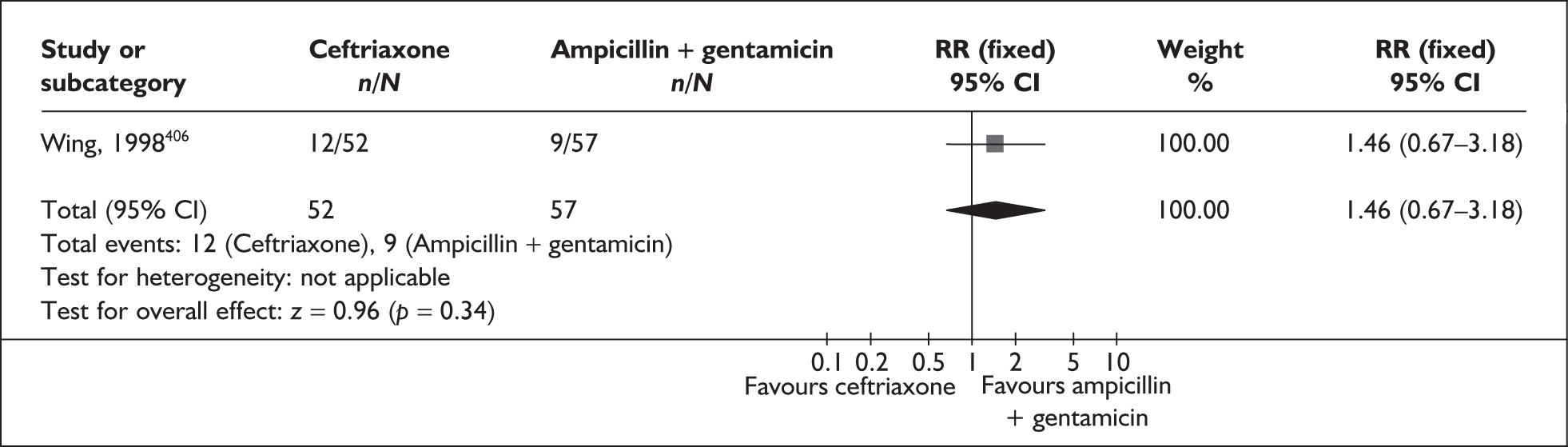
FIGURE 120.
Forest plot of the effects of intramuscular ceftriaxone versus intravenous cephazolin for the prevention of admission to neonatal intensive care unit.
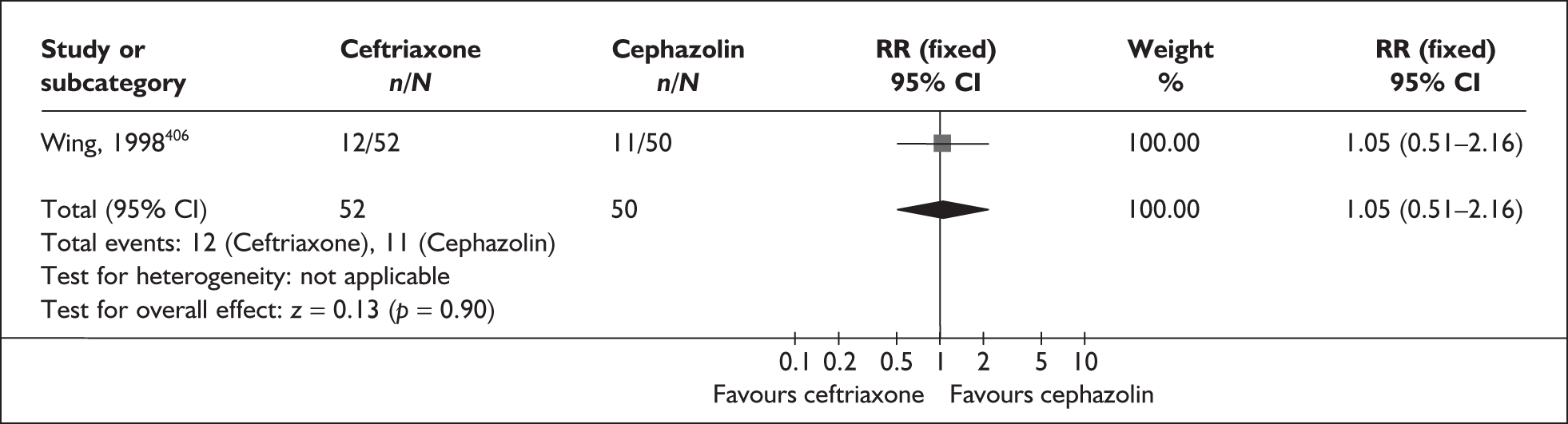
Antibiotics for ureaplasma
Ureaplasma in the vagina is an abnormal bacterial colonisation of the genital tract. Women who present with a high density of such abnormal flora in pregnancy are at increased risk of infections associated with spontaneous preterm birth. This is believed to be the result of an inflammatory cascade, which may lead to pre-labour rupture of membranes. It is unclear whether antibiotic treatment of asymptomatic ureaplasma is effective in preventing such a sequence of events.
The review of antibiotics for ureaplasma in the vagina in pregnancy407 included one RCT (n = 1071). 408 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 118. This study did not report outcomes of spontaneous preterm birth or perinatal mortality. The only outcomes reported were low birthweight, < 2500 g, and adverse events. There were no significant differences between the antibiotic regimens used (erythromycin estolate, erythromycin sterate, clindamycin hydrochloride) and placebo in either incidence of low birthweight (RR 0.70; 95% CI 0.46–1.07) or safety (RR 1.25; 95% CI 0.85–1.85). No additional RCTs were found when the searches were updated. As there was no available evidence relating to the outcome of spontaneous preterm birth, it is not possible to form any conclusions about the efficacy of antibiotic treatment for vaginal ureaplasma in the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth. RRs for this intervention were not included in the decision analysis.
Prophylactic antibiotics for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth
Infections, such as maternal genital tract infection or colonisation by some infectious organisms, have been implicated in the aetiology of preterm birth, and associated with maternal and perinatal mortality and morbidity. A strategy of routine antibiotic prophylaxis has been suggested as an alternative to routine antenatal detection and treatment of infections.
The review of prophylactic antibiotics during the second and third trimester for the prevention of infectious morbidity and mortality409 included five RCTs (n = 1560), which compared antibiotic therapy (oral erythromycin, metronidazole, cefetamet-pivoxil, and parenteralceftriaxone and clindamycin vaginal cream) with placebo or no treatment. 387,410–413 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 118. No additional RCTs were found when the searches were updated; although one trial was removed from the original review because it appeared to include women with a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis before randomisation. High-risk and unspecified or unselected pregnant women with singleton gestations were included in the review. In general, few of the included studies were considered to be of high quality because of deficiencies in allocation concealment and follow-up (Figure 121). No beneficial affect of antibiotic prophylaxis was reported for incidence of spontaneous preterm birth less than 37 weeks’ gestation in high-risk women; results did not change when subgroups for unselected and high-risk women were considered (Figure 122). Prophylactic antibiotic therapy did not reduce the risk of perinatal mortality compared to placebo/no treatment (Figure 123). No data were reported for preterm birth less than 34 weeks’ gestation or requirement of neonatal intensive care. Prophylactic antibiotic therapy was also found to reduce the risk of pre-labour rupture of membranes in unselected women, and infection (puerperal sepsis) and low birthweight in high-risk women (Table 7). Summary RRs were used in the decision analysis for all primary end points. Although this review appears to support the use of prophylactic antibiotics in high-risk women for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth, further research is needed to determine the best type and dose of antibiotic therapy for routine use in pregnant women.
FIGURE 121.
Quality of the included trials of prophylactic antibiotic therapy for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
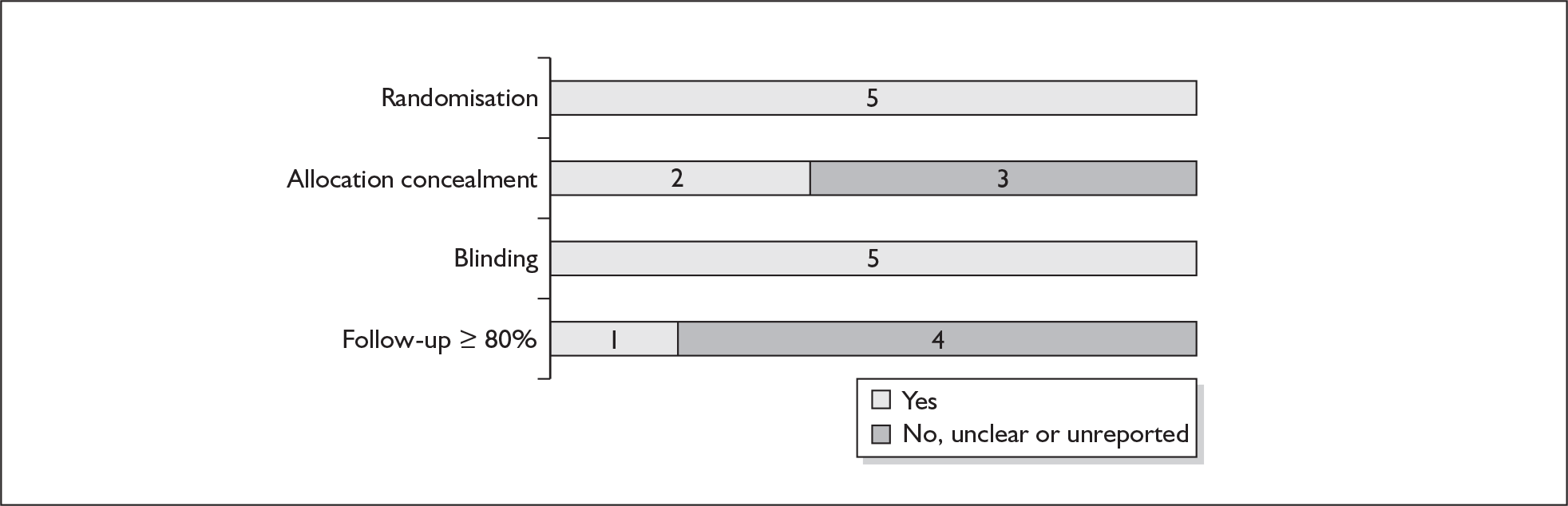
FIGURE 122.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth (birth gestation undefined).
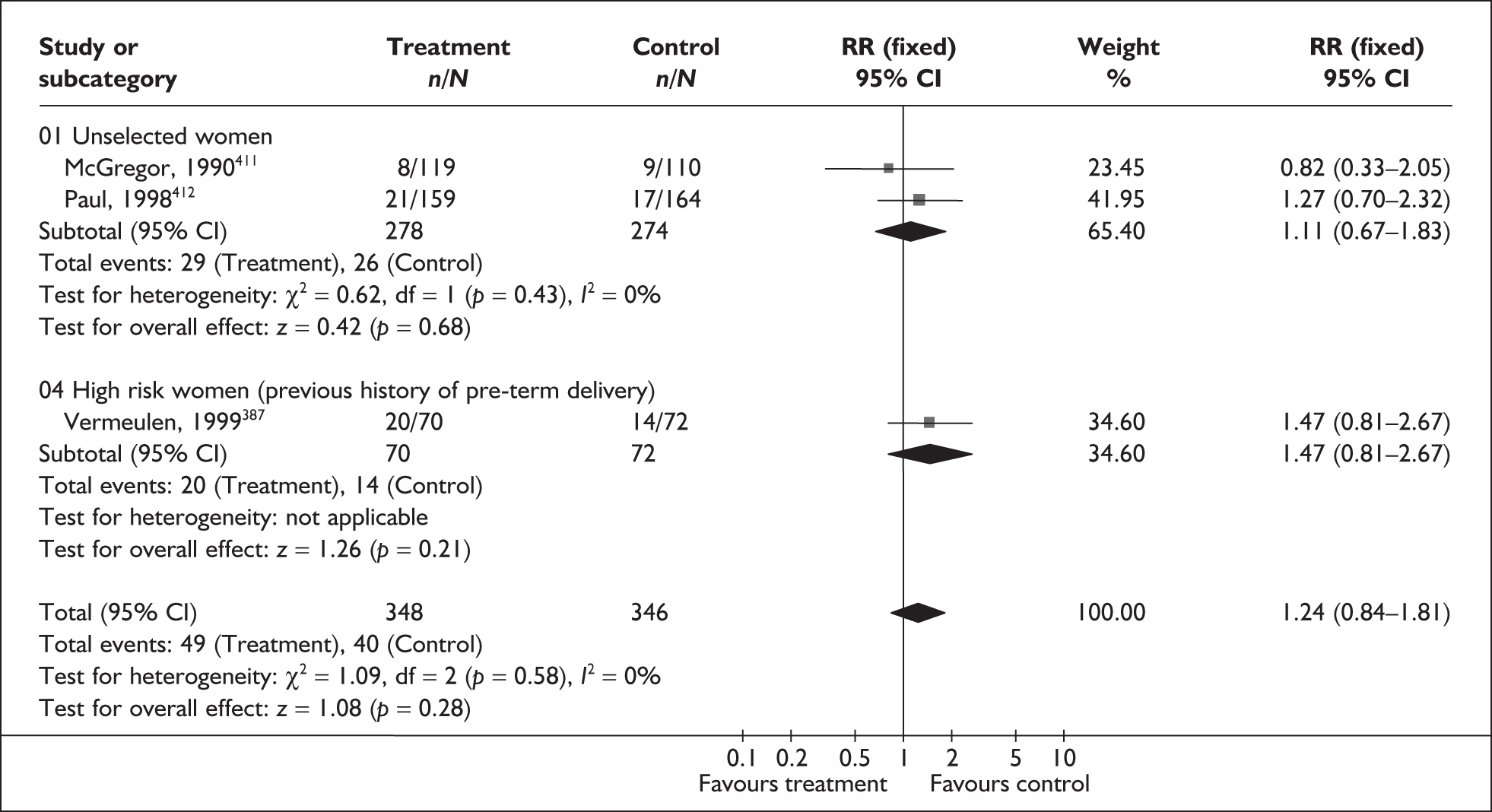
FIGURE 123.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of perinatal mortality.
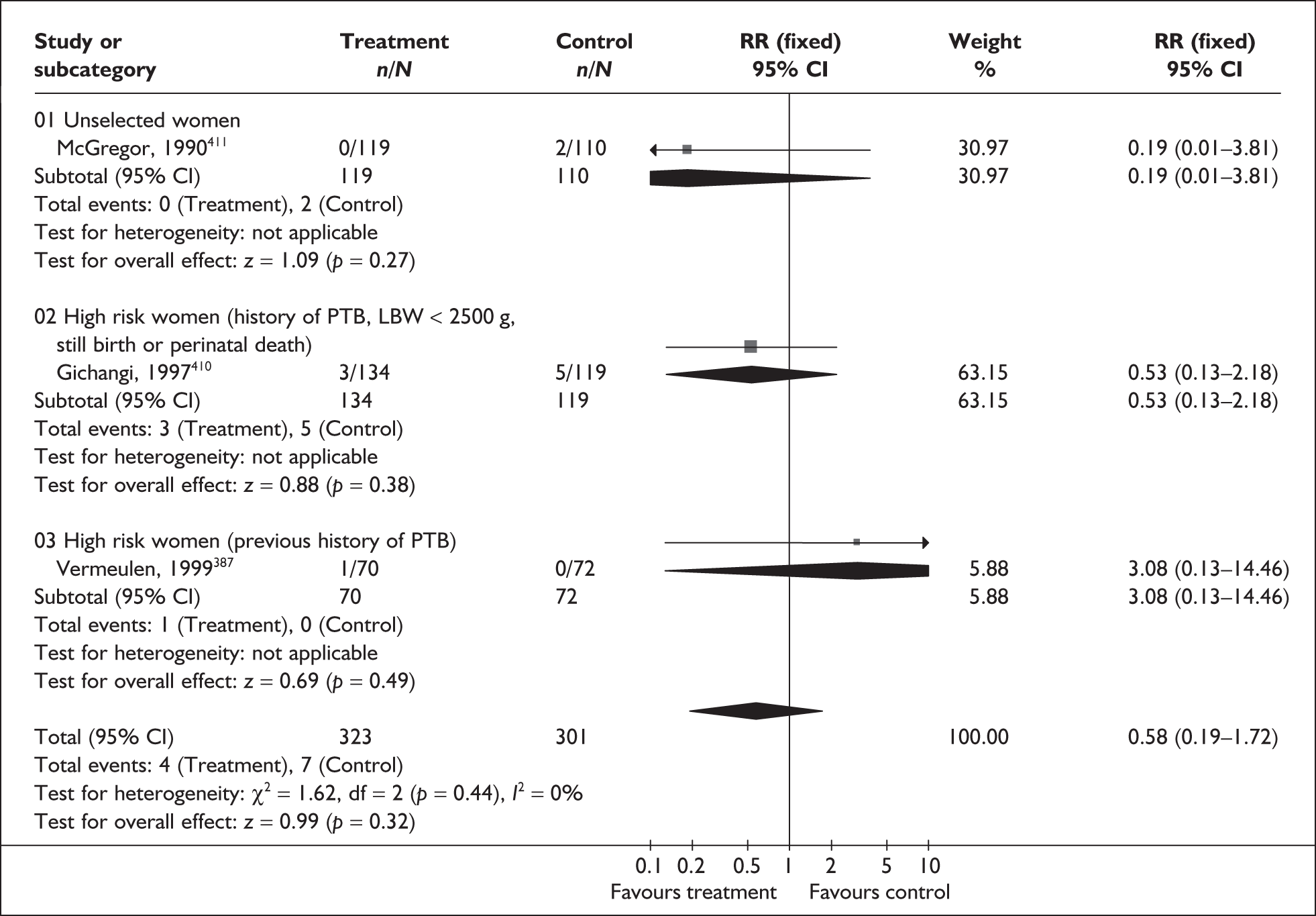
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chorioamnionitis | |||
| Unselected women (1 study, n = 229)411 | 0.62 | 0.10–3.62 | NA |
| Puerperal sepsis/postpartum endometritis | |||
| Unselected women (2 studies, n = 431)411,413 | 0.51 | 0.24–1.08 | 0% (0.40) |
| High-risk women (previous history of preterm delivery, LBW < 2500 g, stillbirth or perinatal death) (1 study, n = 196)410 | 0.55 | 0.33–0.92 | NA |
| Low birthweight | |||
| Unselected women (2 studies, n = 555)412,413 | 1.03 | 0.69–1.55 | 70.8% (0.06) |
| High-risk women (history of preterm delivery, LBW < 2500 g, stillbirth or perinatal death) (1 study, n = 253)460 | 0.57 | 0.37–0.88 | NA |
| Neonatal sepsis | |||
| High-risk women (previous history of preterm delivery) (1 study, n = 142)387 | 11.31 | 0.64–200.79 | NA |
| Congenital abnormality | |||
| Unselected women (2 studies, n = 463)411,413 | 1.49 | 0.20–11.14 | 0% (0.59) |
| Small for gestational age | |||
| Unselected women (1 study, n = 239)411 | 1.29 | 0.42–3.96 | NA |
| PROM | |||
| Unselected women (1 study, n = 229)411 | 0.34 | 0.15–0.78 | NA |
| Gonococcal infection detected postpartum | |||
| High-risk women (1 study, n = 204)410 | 0.35 | 0.13–0.94 | NA |
Antioxidants
The use of antioxidants, such as vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E and zinc, during pregnancy may offer protection against the development of pregnancy complications, including spontaneous preterm birth,414 pre-eclampsia, and pre-labour rupture of fetal membranes. Antioxidants are loosely defined as any substance that when present in low concentrations compared to that of an oxidisable substrate, significantly delays or inhibits oxidation of that substrate. Antioxidants are thought to protect proteins and enzymes from oxidation and destruction by free radicals, and help to maintain cellular membrane integrity. In addition to its antioxidant properties zinc plays an important role in normal growth and development and biological functions such as protein synthesis and nucleic acid metabolism. 415,416 Since these are involved in cell division and growth, zinc is believed to be important for fetal growth and development. 417
The review of antioxidants (vitamins C, E and D, and zinc) included 15 RCTs (n = 4763)418–421 with one RCT422 added to the primary studies identified in these earlier reviews. Further details of these reviews and the RCT can be found in Appendix 6, Table 119. Clinical heterogeneity precluded a quantitative summary of the primary studies relating to zinc supplementation because of variation in dosages, populations and duration of intervention. The quality of the primary studies is shown in Figure 124 where criteria for blinding and follow-up appeared to be met in most of the included trials. Compared to placebo, supplementation with vitamin C, either in combination with vitamin E or alone, or supplementation with zinc did not significantly reduce the risk of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation (Figure 125) or perinatal mortality (Figure 126). No statistically significant between group differences were shown in the incidence of admission to neonatal intensive care (Figure 127). Subgroup analyses based on trial quality or gestation at time of study entry did not alter these results (Table 8).
FIGURE 124.
Methodological quality of RCTs of antioxidants in the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
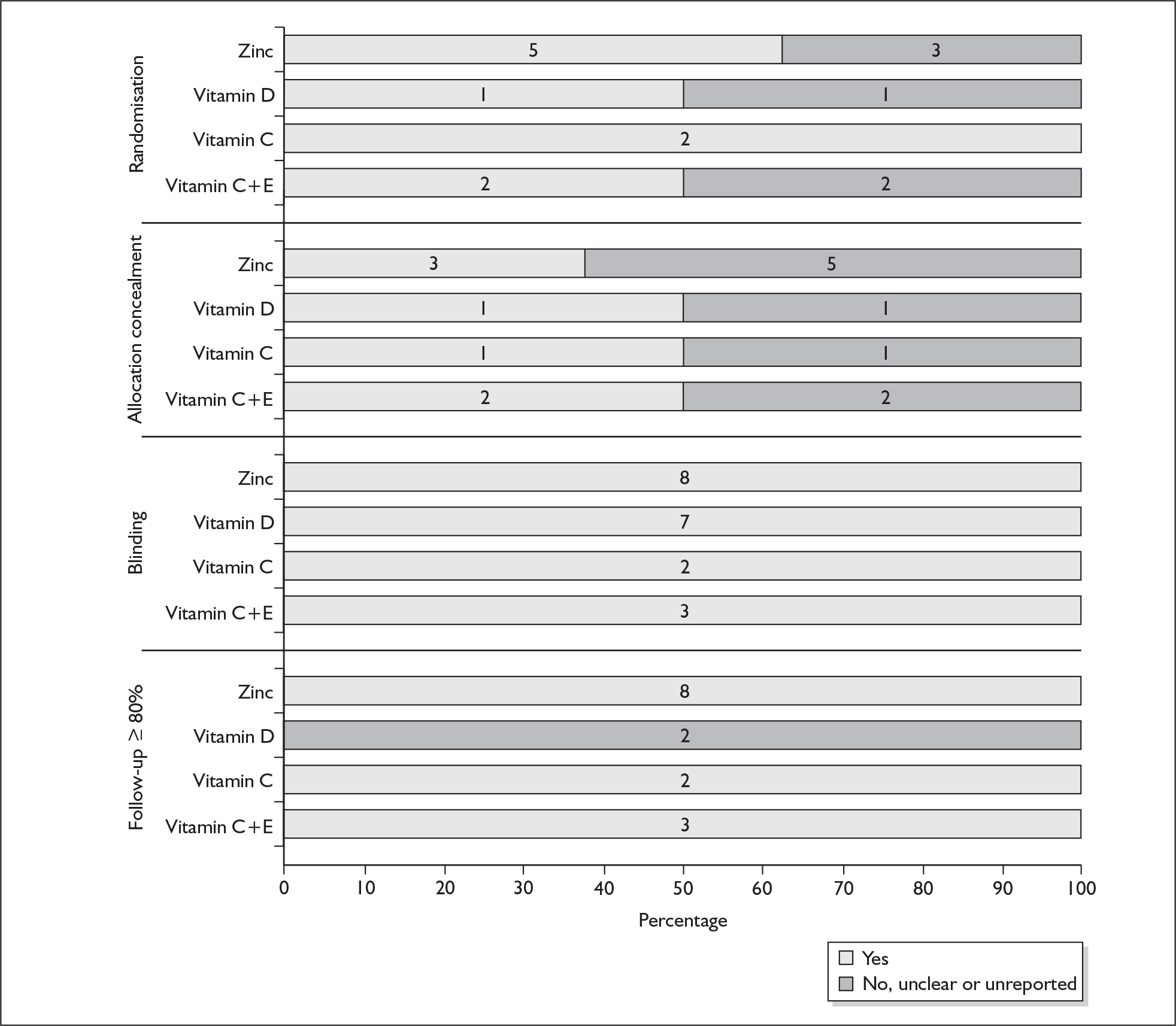
FIGURE 125.
Forest plot of the effects of antioxidants in the prevention of preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
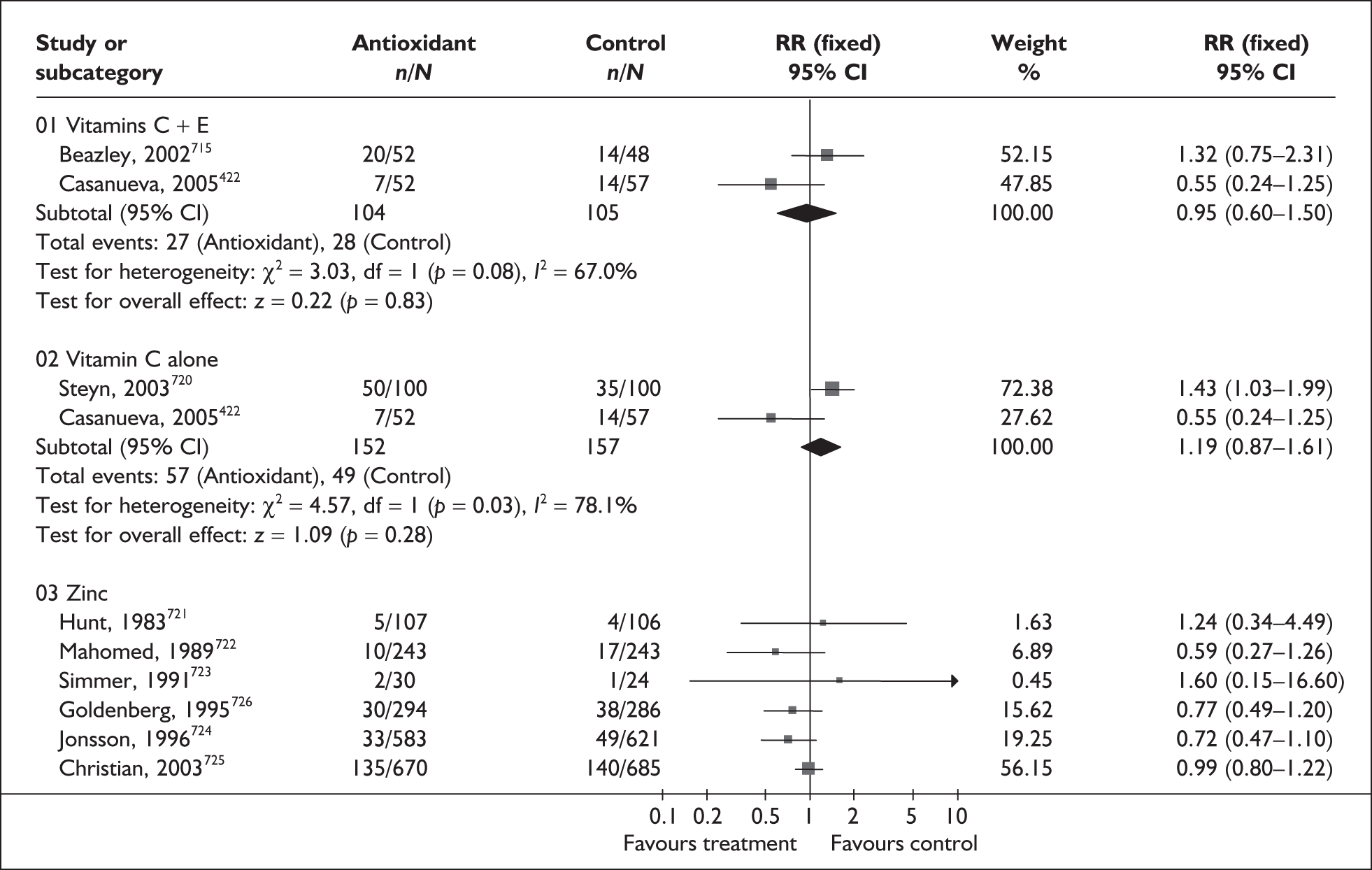
FIGURE 126.
Forest plot of the effects of antioxidants on perinatal mortality.
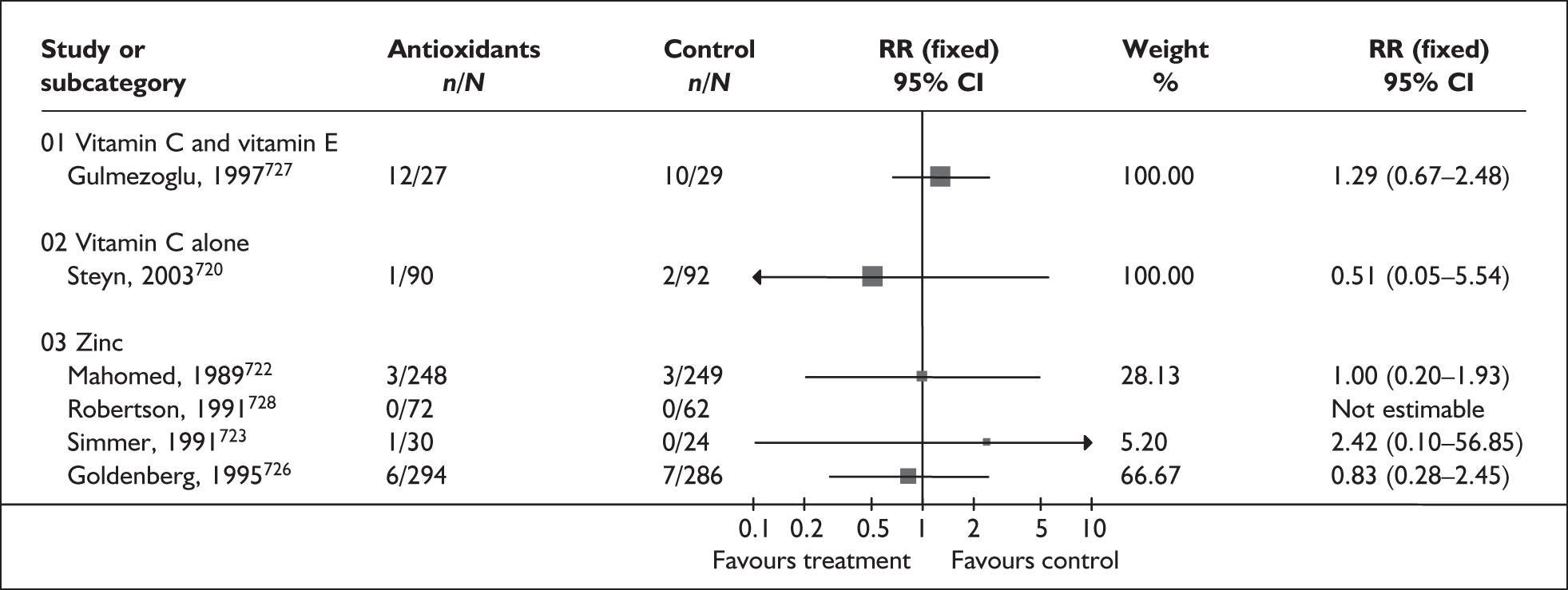
FIGURE 127.
Forest plot of the effects of antioxidants on admission to neonatal intensive care unit.
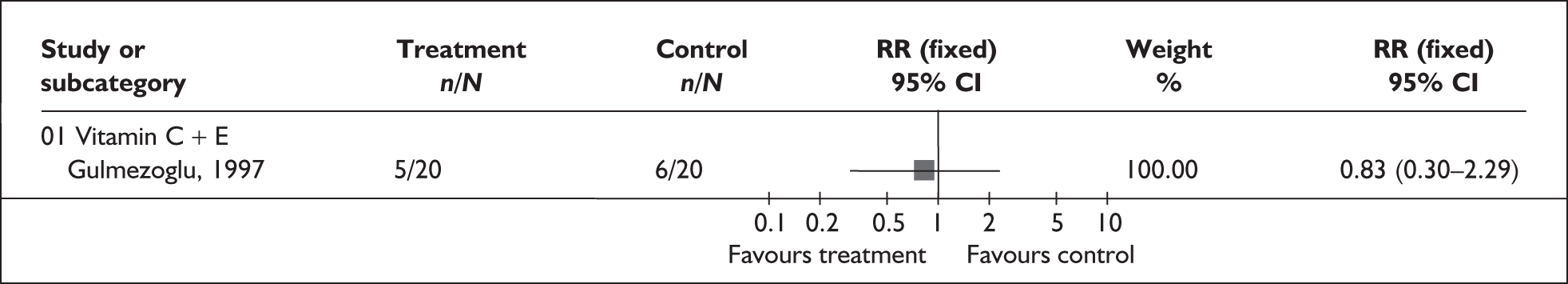
| Subgroup analyses | RR | 95% CI | Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trial quality (high quality)a | |||
| Preterm birth < 37 weeks | |||
| Vitamin C+E (1 study, n = 283)421 | 1.21 | 0.38–3.387 | NA |
| Vitamin C alone (1 study, n = 200)422 | 1.43 | 1.03–1.99 | NA |
| Zinc (1 study, n = 580)418 | 0.77 | 0.49–1.20 | NA |
| Perinatal mortality | |||
| Vitamin C+E (1 study, n = 56)421 | 1.29 | 0.67–2.48 | NA |
| Vitamin C alone (1 study, n = 182)420 | 1.70 | 0.05–5.54 | NA |
| Zinc (1 study, n = 580)418 | 0.83 | 0.28–2.45 | NA |
| Gestation at trial entry [≤ 20 weeks, > 20 weeks, unclassified (< 20 weeks + >20 weeks)] | |||
| Preterm birth < 37 weeks | |||
| Vitamin C+E (unclassified) (1 study, n = 283)421 | 1.21 | 0.38–3.87 | NA |
| (≤ 20 weeks) (1 study, n = 100)715 | 1.32 | 0.75–2.31 | NA |
| Vitamin C alone (unclassified) (1 study, n = 200)422 | 1.43 | 1.03–1.99 | NA |
| (≤ 20 weeks) (1 study, n = 109)422 | 0.55 | 0.24–1.25 | NA |
| Zinc (≤ 20 weeks) (1 study, n = 580)418 | 0.77 | 0.49–1.20 | NA |
| Perinatal mortality | |||
| Vitamin C+E (> 20 weeks) (1 study, n = 56)421 | 1.29 | 0.67–2.48 | NA |
| Vitamin C alone (unclassified) (1 study, n = 200)422 | 0.51 | 0.05–5.54 | NA |
| Zinc (≤ 20 weeks) (1 study, n = 580)418 | 0.83 | 0.28–1.45 | NA |
The effect on other perinatal or maternal outcomes is shown in Table 9. The results do not appear to support the prophylactic use of antioxidants for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth. In addition there is limited evidence about the safety of giving antioxidants to women during pregnancy. When interpreting these results it should be noted that it is unclear whether the primary studies relating to vitamin D and zinc supplementation included women with multiple pregnancies. RRs less than one in the forest plots presented were included in the decision analysis. RRs from the highest-quality study with gestationally defined spontaneous preterm birth outcome were used for the zinc subgroup, and in all other subgroups summary RRs were used.
| Outcome (number of RCTs) | RR | 95% CI | Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stillbirth | |||
| Vitamin C+E (2 studies, n = 339) 420,421 | 0.77 | 0.35–1.71 | 0% (0.69) |
| Vitamin C (1 study, n = 200) 420 | 3.00 | 0.12–72.77 | NA |
| Neonatal death | |||
| Vitamin C+E (1 study, n = 40) 421 | 5.00 | 0.64–39.06 | NA |
| Vitamin C (1 study, n = 181) 422 | 0.69 | 0.12–4.03 | NA |
| Stillbirth + neonatal death | |||
| Zinca (1 study, n = 580)418 | 0.83 | 0.28–2.45 | NA |
| Low birthweight (< 2500 g) | |||
| Vitamin D (1 study, n = 128)419 | 0.55 | 0.24–1.25 | NA |
| Low birthweight (unspecified) | |||
| Zinca (1 study, n = 580)418 | 0.62 | 0.38–1.02 | NA |
| Intrauterine growth restriction | |||
| Vitamin C+E (2 studies, n = 383)420,421 | 0.72 | 0.49–1.04 | 0% (0.59) |
| Bleeding episodes (placental abruption) | |||
| Vitamin C+E (2 studies, n = 339)420,421 | 0.35 | 0.10–1.23 | 0% (0.96) |
| Antepartum haemorrhage + placental abruption | |||
| Vitamin C (1 study, n = 200)420 | 7.00 | 0.88–55.86 | NA |
| Measures of serious maternal morbidity | |||
| Eclampsia: vitamin C+E (1 study, n = 56)421 | 1.07 | 0.07–16.33 | NA |
| Renal failure: vitamin C+E (1 study, n = 56)421 | 0.36 | 0.02–8.41 | NA |
| Disseminated intravascular coagulation: vitamin C+E (1 study, n = 56)421 | 0.36 | 0.02–8.41 | NA |
| Pulmonary oedema: vitamin C+E (1 study, n = 56)421 | 0.54 | 0.05–5.59 | NA |
| 5-min Apgar score < 7 | |||
| Vitamin C+E (1 study, n = 49)421 | 0.63 | 0.21–1.90 | NA |
| Adverse side effects of supplementation | |||
| Acne: vitamin C+E (1 study, n = 56)421 | 3.21 | 0.14–75.68 | NA |
| Transient weakness: vitamin C+E (1 study, n = 56)421 | 5.36 | 0.27–106.78 | NA |
| Skin rash: vitamin C+E (1 study, n = 56)421 | 3.21 | 0.14–75.68 | NA |
| Neonatal hypocalcaemia | |||
| Vitamin D (2 studies, n = 203)419 | 0.13 | 0.02–0.65 | 0% (0.75) |
| Use of mechanical ventilation | |||
| Vitamin C+E (1 study, n = 40)421 | 0.33 | 0.08–1.46 | NA |
| Neonatal sepsis | |||
| Zinc (1 study, n = 580)418 | 0.19 | 0.02–1.66 | NA |
Energy and protein intake
Observational studies have indicated that gestational weight gain and energy intake are positively associated with fetal growth, and may even prevent spontaneous preterm birth. 423,424 Furthermore, higher weight for gestational age has been associated with a reduced risk of morbidity related to type 2 diabetes and heart disease in late adulthood. 425 On the other hand, rapid maternal weight gain during pregnancy has been associated with increased pregnancy complications. 426 A number of strategies designed to optimise energy and protein intake during pregnancy have been developed, but the fetal, infant and maternal health implications are not clear.
The review of energy and protein intake (nutritional advice, energy restriction, isocaloric balanced protein supplementation, high protein supplementation and balanced protein supplementation)427 included 23 studies (n = 5784 women). 428–450 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 123. Overall, the methodological quality of many of the included studies was poor or unclear; results are shown in Figure 128. A small but statistically significant reduction in the risk of spontaneous preterm birth was shown in women receiving dietary advice to increase energy and protein intake compared to women who did not receive nutritional advice (Figure 129). However, it should be noted that this estimate was based on two RCTs, of which one study was very small; results are therefore dominated by a study undertaken in rural Greece in which spontaneous preterm birth was not defined. The risk of spontaneous preterm birth was not shown to statistically differ between groups for the other nutritional strategies assessed.
FIGURE 128.
Methodological quality of trials of energy and protein intake for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
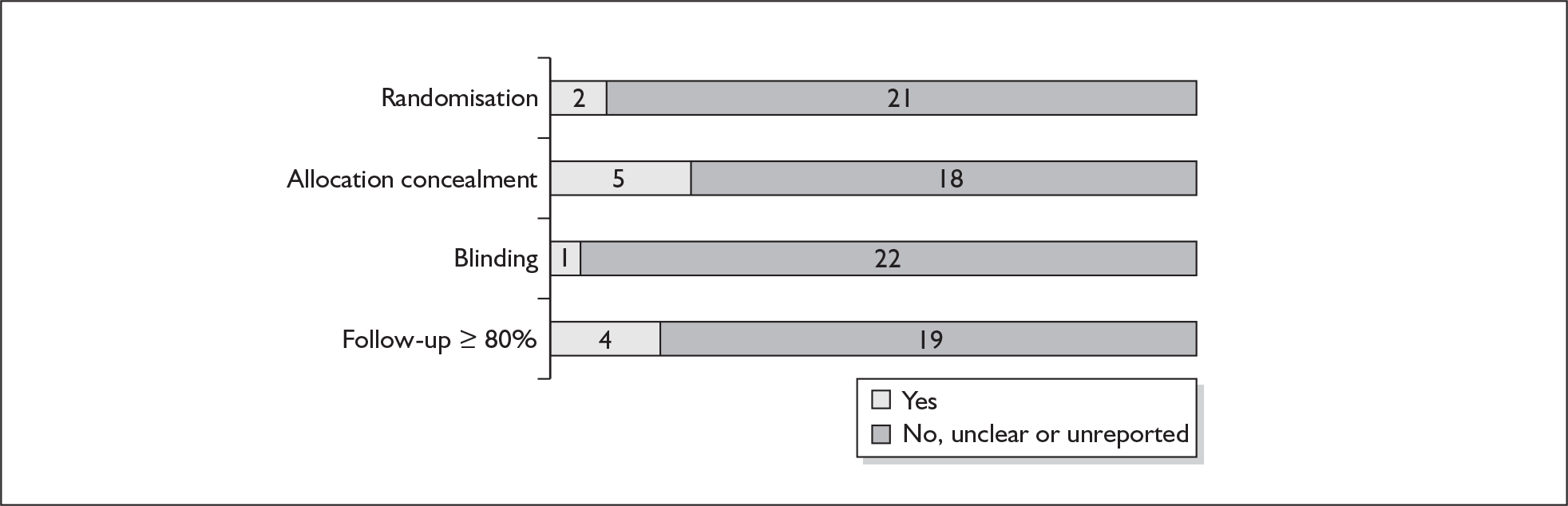
FIGURE 129.
Forest plot of the effect of energy and protein intake interventions for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth (not defined). a, Appropriate randomisation and allocation concealment methods used.
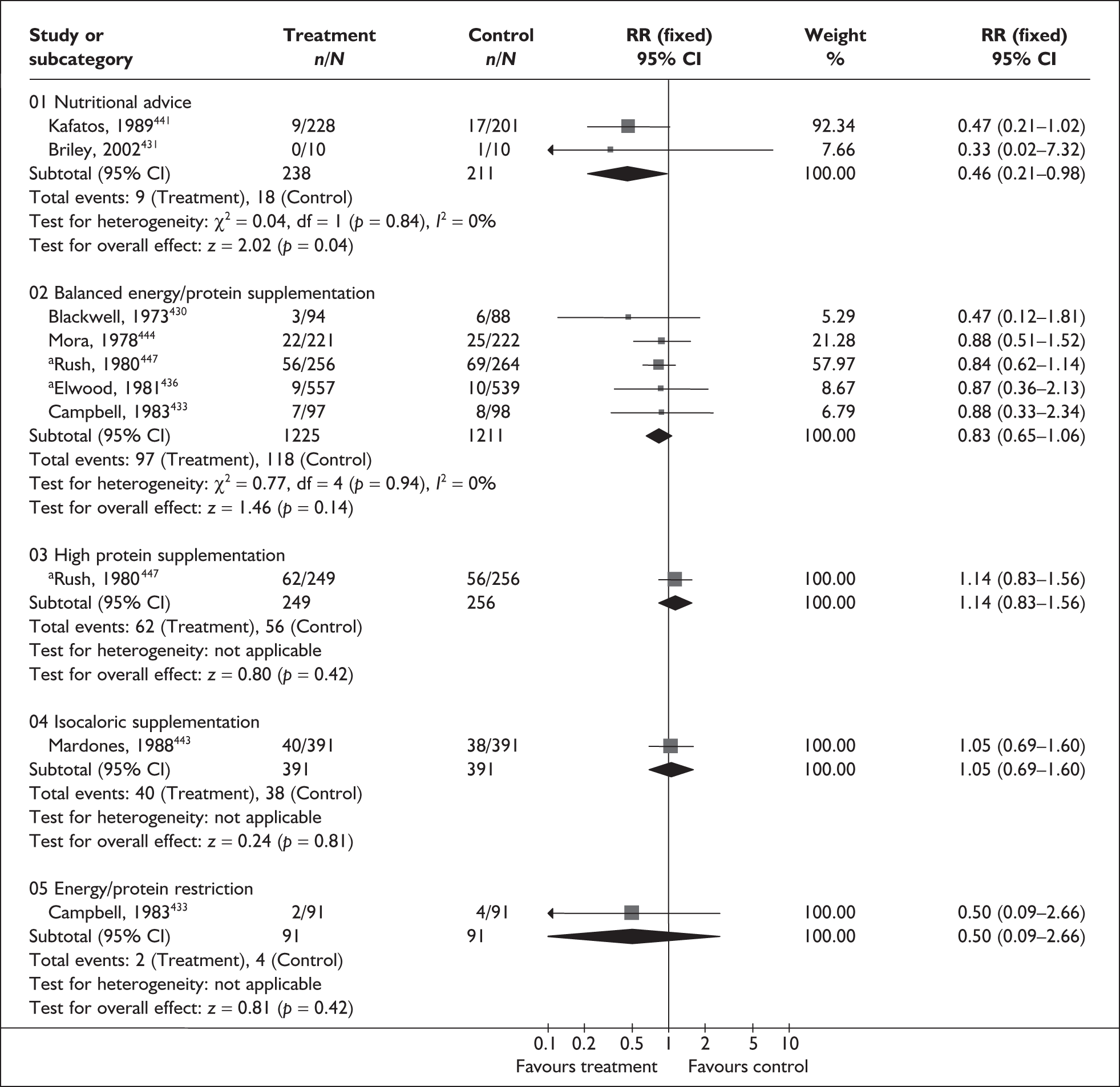
None of the included studies reported incidence of perinatal mortality; however, women receiving a balanced energy/protein supplementation demonstrated a reduction in the risk of stillbirth compared to women receiving mineral/vitamin-only supplementation or no supplementation (Table 10). Women receiving a balanced energy/protein supplementation also demonstrated a small reduction in the risk of giving birth to an infant defined as ‘small-for-gestational-age’, compared to controls (Table 10). Conversely, women receiving a high protein supplementation or an isocaloric supplementation were significantly more likely to give birth to a ‘small-for-gestational-age’ infant compared to women not receiving supplementation; results were based on one trial. No statistically significant between-group differences were shown for any of the nutritional strategies reporting neonatal mortality (Table 10). The effect of energy and protein intake interventions on admission to neonatal intensive care units was not reported. Other perinatal and maternal outcomes are shown in Table 10. Given the methodological uncertainty of the majority of the included studies, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of these energy and protein intake interventions. Summary RRs for perinatal mortality (stillbirth) were used in the decision analyses.
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stillbirth | |||
| Nutritional advice (1 study, n = 431) 441 | 0.37 | 0.07–1.90 | NA |
| Balanced energy/protein supplementation (4 studies, n = 2206) 435,437,444,447 | 0.55 | 0.31–0.97 | 19.6% (0.29) |
| High protein supplementation (1 study, n = 529) 447 | 0.81 | 0.31–2.15 | NA |
| Neonatal mortality | |||
| Nutritional advice (1 study, n = 448) 441 | 1.28 | 0.35–4.72 | NA |
| Balanced energy/protein supplementation (4 studies, n = 2206) 435,437,444,447 | 0.62 | 0.37–1.05 | 0% (0.81) |
| High protein supplementation (1 study, n = 529) 447 | 2.78 | 0.75–10.36 | NA |
| Isocaloric protein supplementation (1 study, n = 782) 443 | 0.50 | 0.05–5.49 | NA |
| Small for gestational age | |||
| Nutritional advice (1 study, n = 404) 441 | 0.97 | 0.45–2.11 | NA |
| Balanced energy/protein supplementation (6 studies, n = 3396)435–437,444,447 | 0.68 | 0.56–0.84 | 0% (0.66) |
| High protein supplementation (1 study, n = 505) 447 | 1.58 | 1.03–2.41 | NA |
| Isocaloric protein supplementation (1 study, n = 782) 443 | 1.35 | 1.12–1.61 | NA |
| Pre-eclampsia | |||
| Nutritional advice (1 study, n = 136) 438 | 0.89 | 0.42–1.88 | NA |
| Balanced energy/protein supplementation (3 studies, n = 516) 437,444,445 | 1.20 | 0.77–1.89 | 47.0% (0.17) |
| Isocaloric protein supplementation (1 study, n = 782) 443 | 1.00 | 0.57–1.75 | NA |
| Energy restriction (2 studies, n = 284) 432,433 | 1.13 | 0.59–2.18 | 53.8% (0.14) |
| Pregnancy-induced hypertension | |||
| Energy restriction (3 studies, n = 384) 429,432,433 | 0.97 | 0.75–1.26 | 0% (0.82) |
Fish oil supplements
Supplementation with marine oils, rich in the long chain n-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, may be useful in prolonging the duration of gestation. Two possible mechanisms have been proposed: fish oil fatty acids could delay delivery by reducing the activity of eicosanoid promoters of the parturition process (particularly prostaglandins F2α and E2), they may also relax the myometrium by increasing the production of prostacyclins PGI2 and PGI3. Some concerns have been raised regarding the safety of fish oil supplementation in pregnancy, particularly with regard to bleeding complications.
The review of marine oil for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth included one multicentre intervention study369 (consisting of a series of six RCTs) and one further RCT451 (n = 1997). Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 124. The quality of the included studies is presented in Figure 130. Overall, the quality of the studies was good. Compared to placebo/no treatment, marine oil supplementation was shown to reduce the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation (Figures 131 and 132); however, this did not reach statistical significance in the docosahexaenoic acid supplement trial. No statistically significant between-group differences were found in the incidence of neonatal mortality or admission to neonatal intensive care units between women receiving marine oil and women receiving placebo or no treatment (Figures 133, 134). Results for other perinatal and maternal variables are shown in Table 11; it should be noted that two twin gestation trials were included in the aggregated trial data presented. Overall, fish oil supplements for women at risk of spontaneous preterm birth appear promising, but results are largely based on one multicentre trial. Further research would be required to confirm these findings. RRs presented for eicosapentaenoic acid plus docosahexaenoic acid were used in the decision analysis.
| Outcome (number of RCTs) | RR | 95% CI | I2, p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spontaneous abortion (aggregated trials: 6 RCTs, n = 1619)369 | 0.58 | 0.17–1.97 | Not reported |
| Stillbirths (aggregated trials: 6 RCTs, n = 2141)369 | 0.87 | 0.45–1.67 | Not reported |
| Intracranial haemorrhage in infant (aggregated trials: 6 RCTs, n = 2226) | 2.36 | 0.61–9.10 | Not reported |
| Admission to neonatal care unit (1 RCT, n = 2138)369 | 0.92 | 0.80–1.07 | Not reported |
| Low birthweight (3 RCTs, n = 559)369 | 1.18 | 0.83–1.67 | 2.7%, 0.36 |
| Duration of hospital stay after delivery (infant) (aggregated trials: 6 RCTs)369 | WMD 0.11 | – 1.40 to 1.62 | Not reported |
| Duration of hospital stay after delivery (mother) (aggregated trials: 6 RCTs)369 | WMD –0.33 | – 2.47 to 1.81 | Not reported |
| Vaginal bleeding (aggregated trials: 6 RCTs, n = 1618)369 | 0.94 | 0.60–1.48 | Not reported |
| Maternal anaemia (aggregated trials: 6 RCTs, n = 846)369 | 1.16 | 0.91–1.48 | Not reported |
FIGURE 130.
Methodological quality of trials of fish oil for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
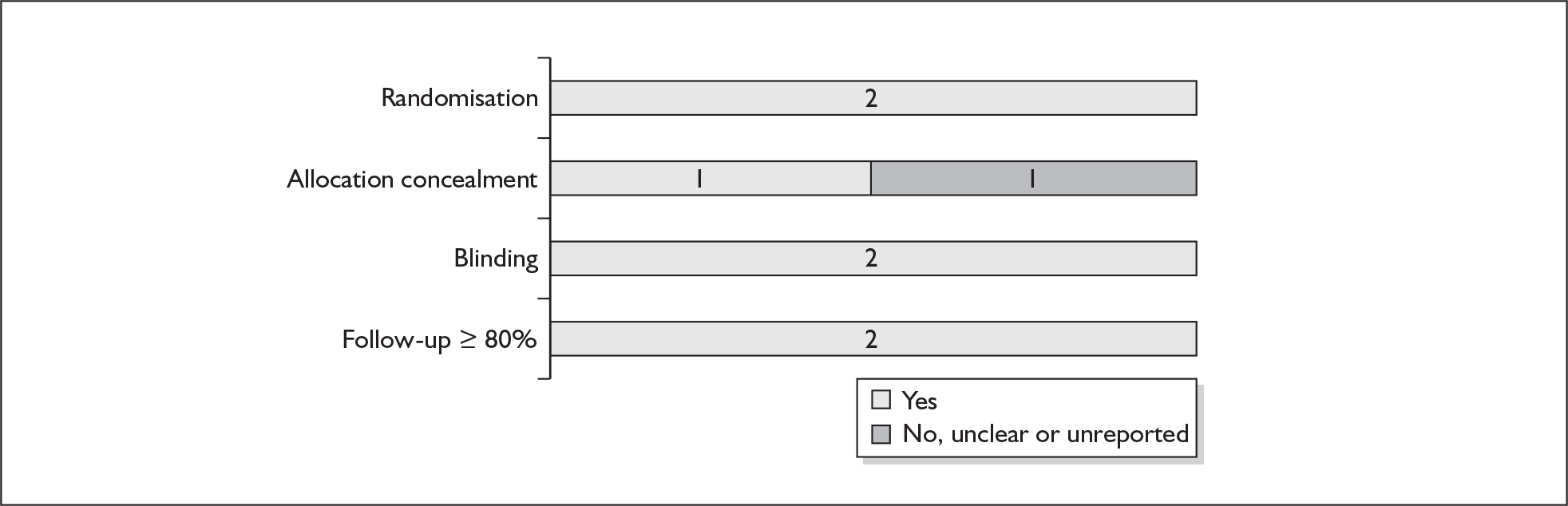
FIGURE 131.
Forest plot of fish oil versus placebo for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in singleton pregnancies before 37 weeks’ gestation.
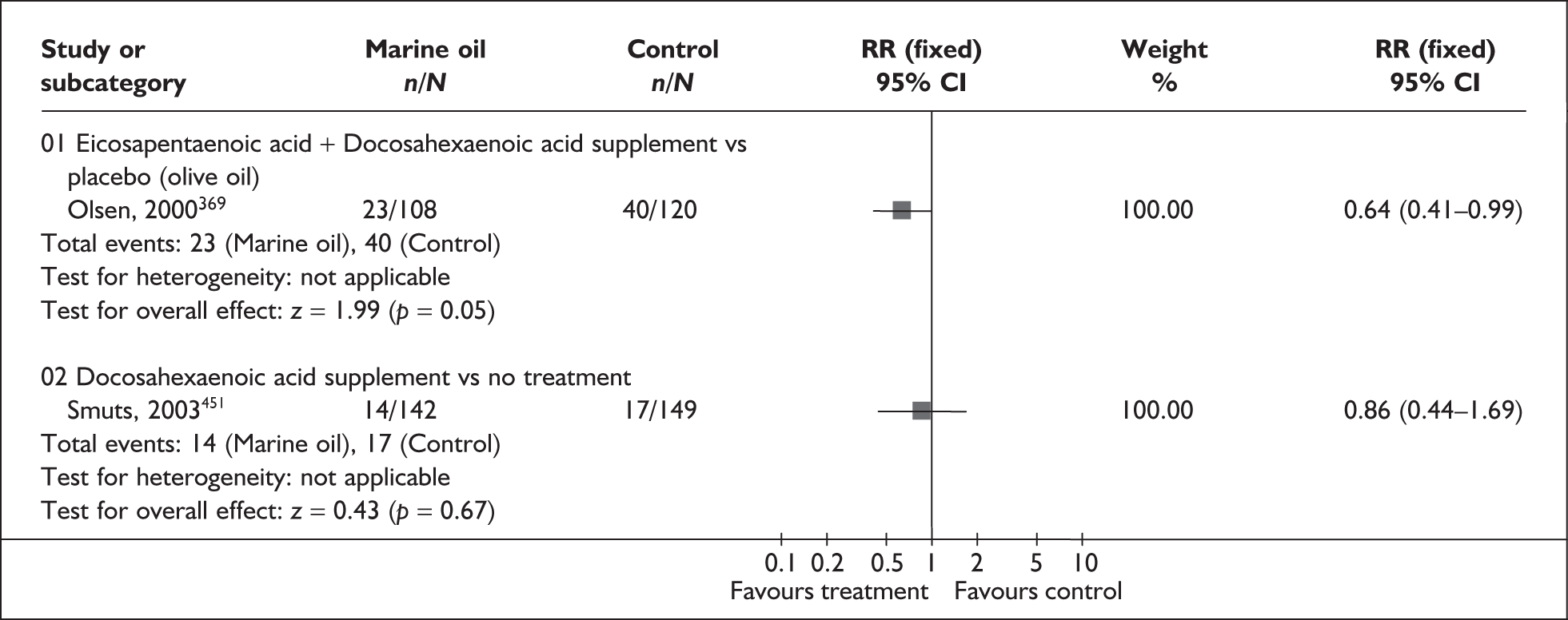
FIGURE 132.
Forest plot of fish oil versus placebo for the inhibition of spontaneous preterm birth in singleton pregnancies before 34 weeks’ gestation.
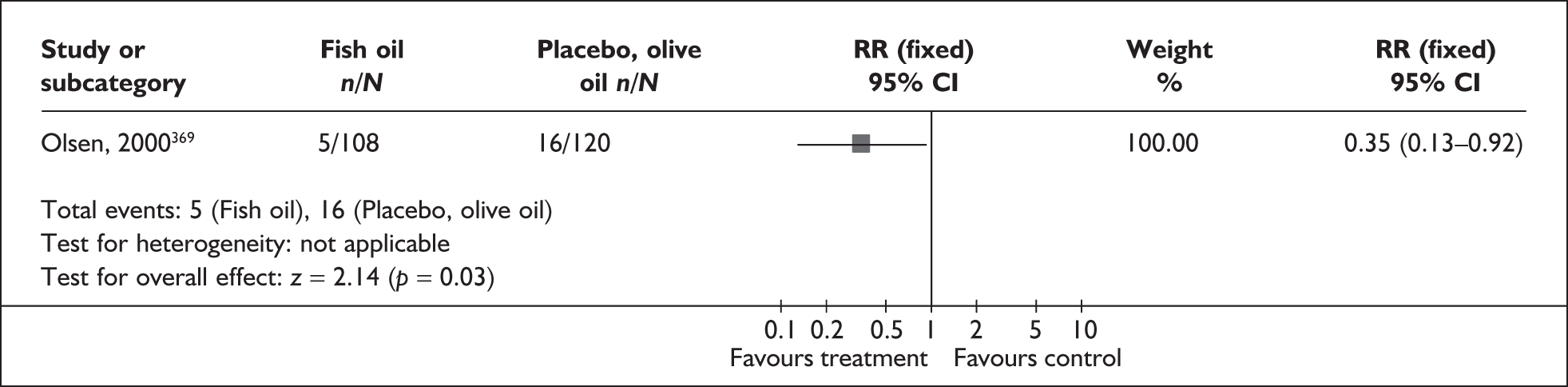
FIGURE 133.
Forest plot of fish oil versus placebo for transfer to intensive neonatal care unit.
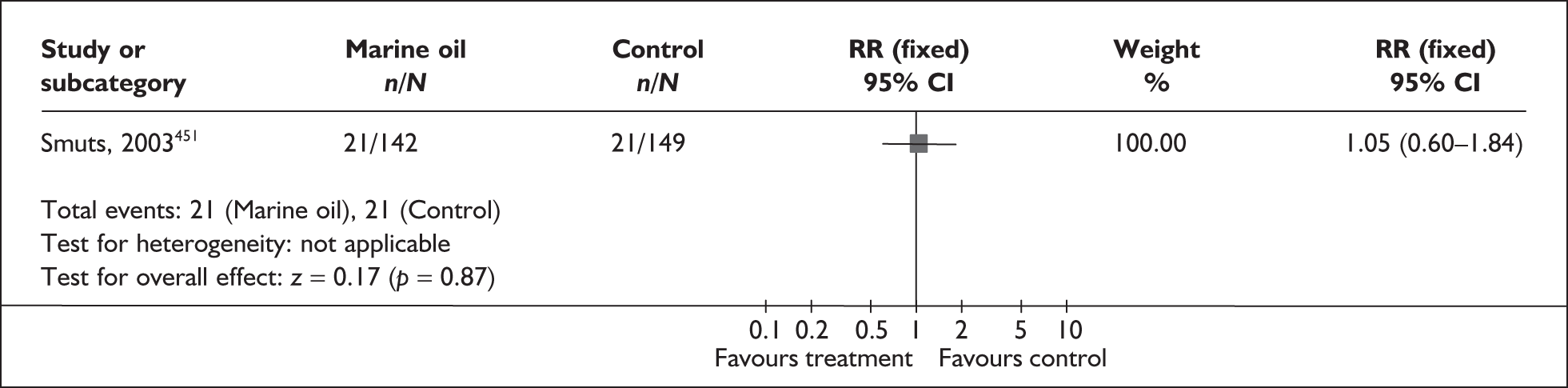
FIGURE 134.
Forest plot of fish oil versus placebo for incidence of early neonatal mortality.
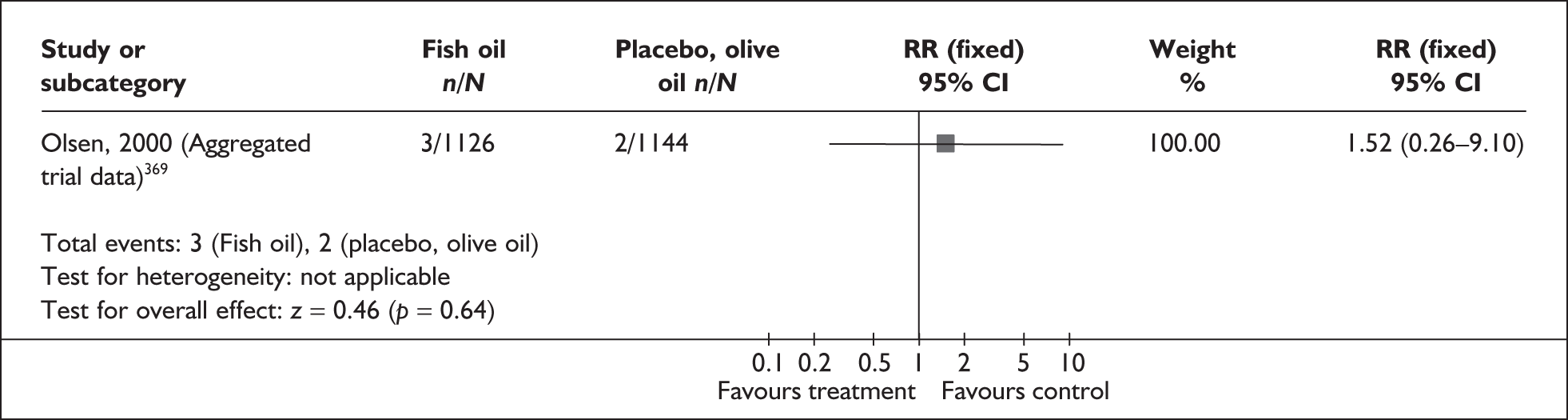
Bed rest
Bed rest in hospital or at home is widely recommended as a first-step treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth. This advice is largely based on observational studies that hard work and hard physical activity during pregnancy could be associated with spontaneous preterm birth,452,453 and that bed rest could reduce uterine activity. 454
The review455 of bed rest (hospital or home) for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth included one quasi-RCT (n = 1266). 456 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 120. Of note, is the fact that high risk of spontaneous preterm birth as defined by the review included previous history of spontaneous preterm birth as well as threatened preterm labour. The quality of the included trial was unclear, as shown in Figure 135. No statistically significant difference was shown between women prescribed bed rest and women who received no treatment for risk of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks (7.9% and 8.5%, respectively) (Figure 136). No other results were available. There is insufficient evidence to support or refute the use of bed rest in hospital or at home for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth. This intervention should be prescribed with caution until effective evidence becomes available. The RR presented in the forest plot below was used in the economic model
FIGURE 135.
Methodological quality of trials of bed rest for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
FIGURE 136.
Forest plot of bed rest versus no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
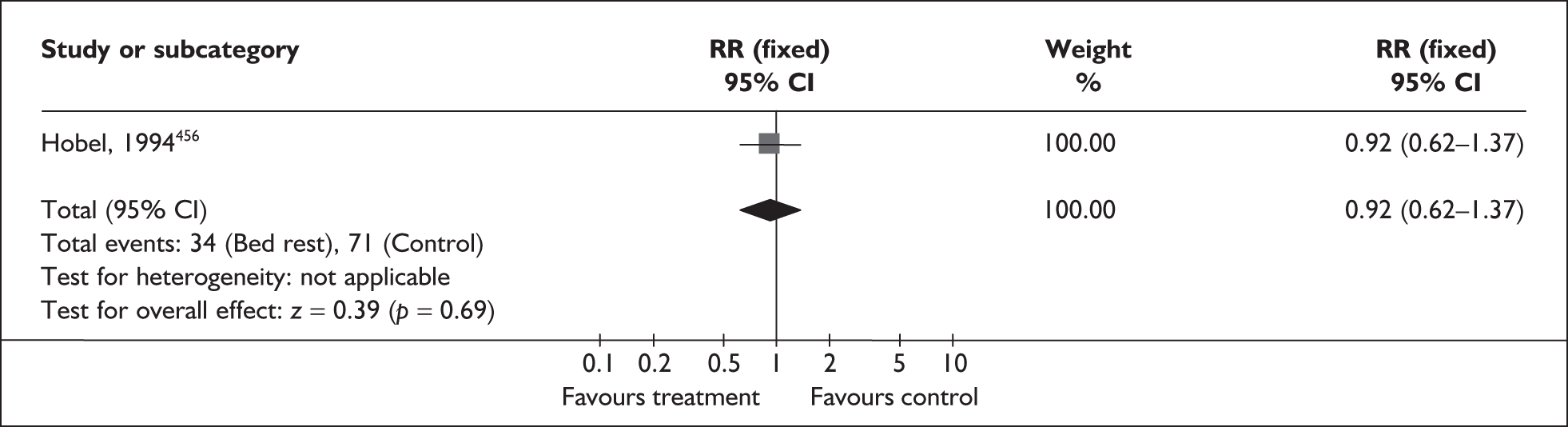
Elective cervical cerclage
Cervical cerclage, or stitch, is a surgical procedure used to keep the cervix closed during pregnancy to prevent delivery in women at risk of spontaneous preterm birth. It is used for the treatment of a weak or incompetent cervix, which may shorten or open without labour too early in a pregnancy. A cervical cerclage is applied after the first trimester to prevent these early changes in a woman’s cervix and subsequent premature labour.
This review of elective cervical cerclage for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth included eight trials (n = 2511); two RCTs457,458 were added to the primary studies identified in an earlier review. 22 Two studies were excluded from the original review; one trial that focused on twin gestations, and one trial that was considered likely to have already been included within another study. Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 121. The quality of all studies is shown in Figure 137. Overall, the quality was good, although there were problems with some of the studies not reporting sufficient detail about how participants were allocated to treatment groups (i.e. randomisation). As cerclage is a surgical procedure, blinding is problematic and only one study fulfilled this criterion.
FIGURE 137.
Methodological quality of included trials of elective cervical cerclage for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
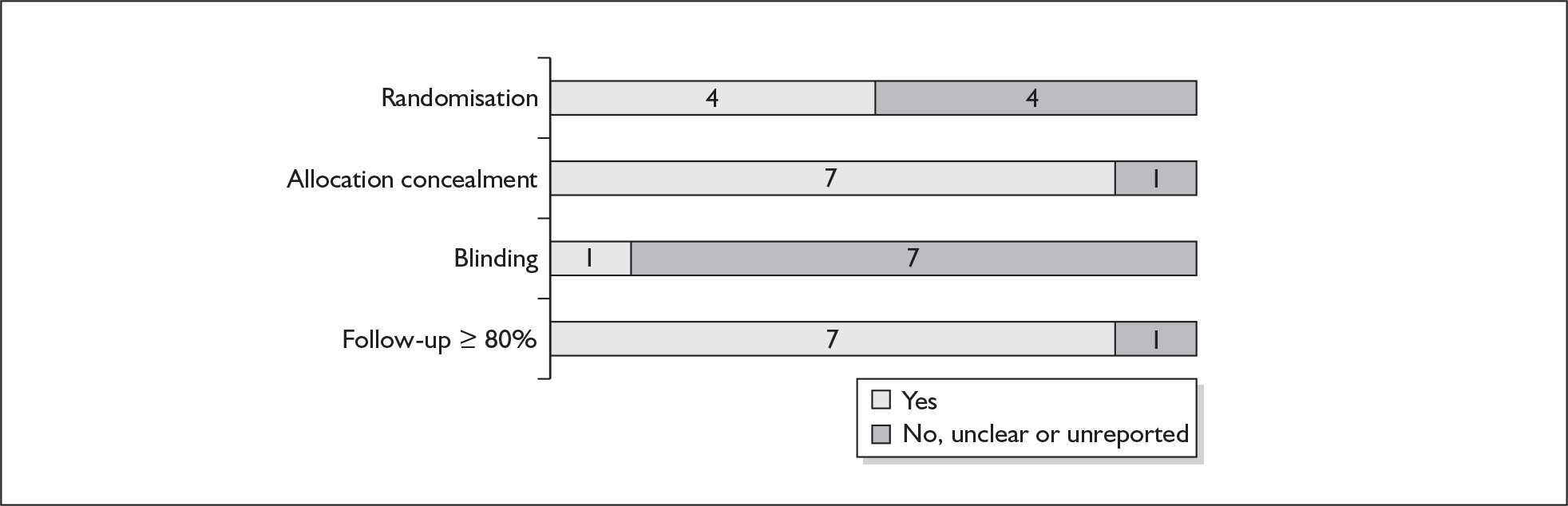
Clinical heterogeneity precluded a quantitative summary because of variation in population and surgical procedure (i.e. type of cerclage used). Two RCTs demonstrated a small but significant reduction in the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation in women receiving cerclage,459,460 compared to standard treatment (Figure 138), although it should be noted that the dataset in one of these trials was extremely small. No statistically significant between-group differences were found in the included trials for incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation (Figure 139), or perinatal mortality (Figure 140). The three trials reporting data on the development of postpartum fever all show a greater incidence of maternal pyrexia in the cerclage group compared to the control group, although the difference was not statistically significant in two of the trials. The effect of cervical cerclage on other perinatal and maternal outcomes is shown in Table 12.
FIGURE 138.
Forest plot of the effects of cervical cerclage versus standard care for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation.
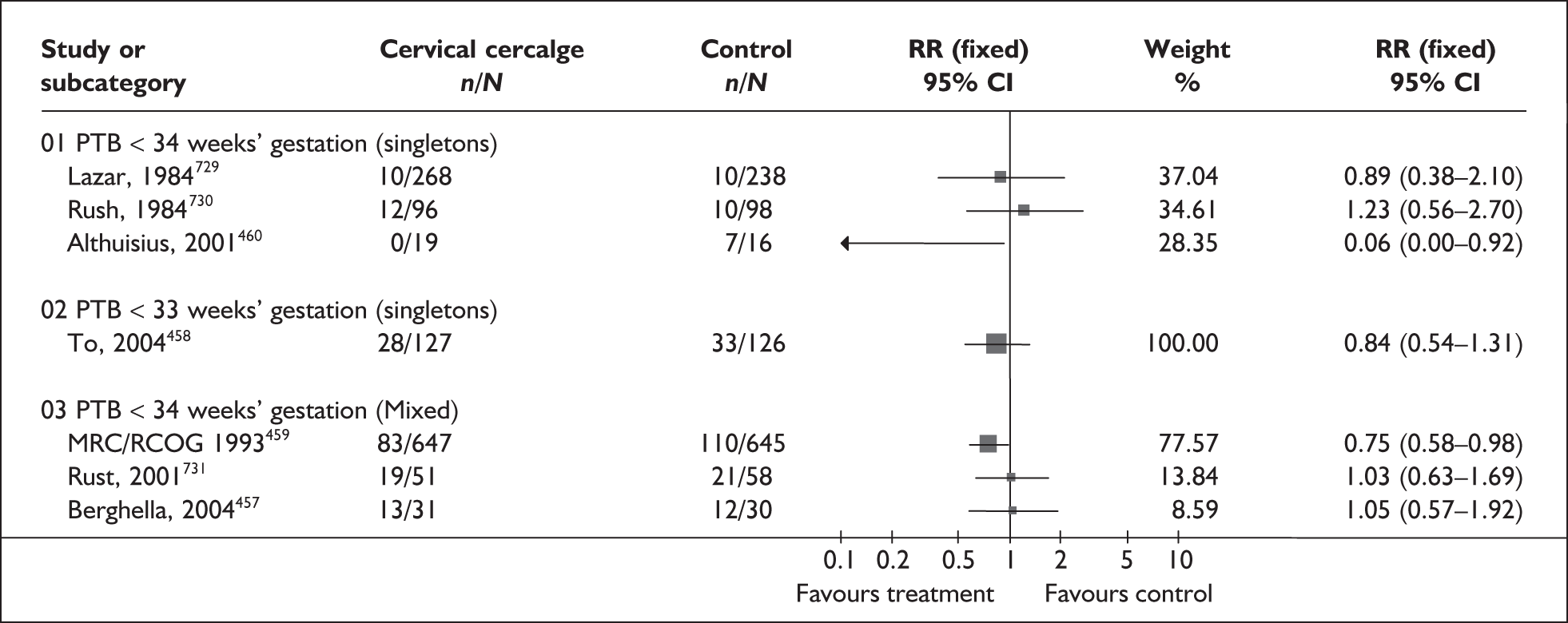
FIGURE 139.
Forest plot of the effects of cervical cerclage versus standard care for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
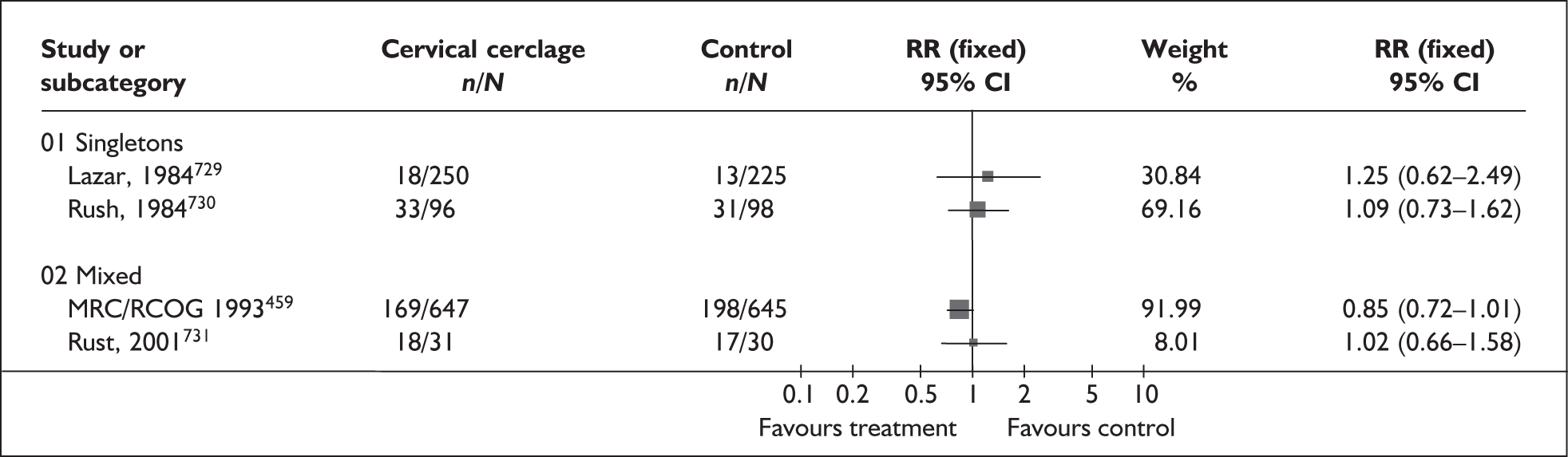
FIGURE 140.
Forest plot of the effects of cervical cerclage versus standard care on perinatal mortality.
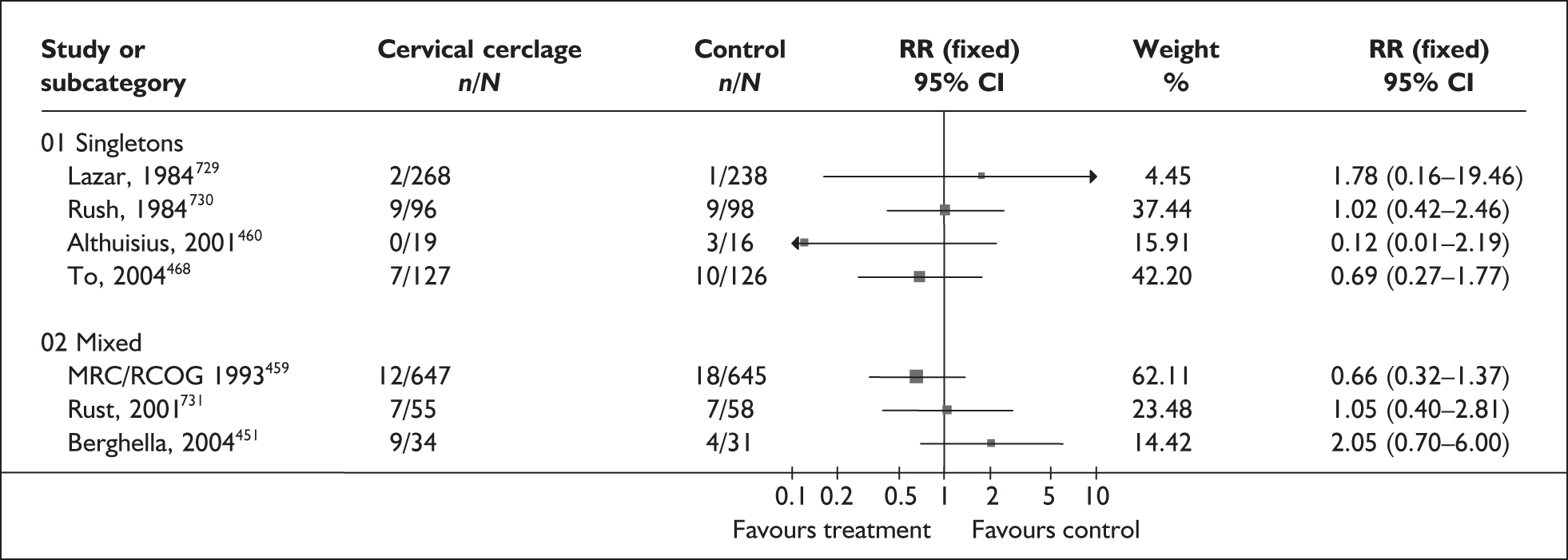
| Outcome (RCT) | Cerclage group % | Control group % | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| PROM | |||
| Rush 1984, n = 19322 | 18 | 12 | 0.50 |
| To 2004, n = 253458 | 18 | 15 | Not reported |
| Chorioamnionitis | |||
| Rust 2001, n = 113 | 20 | 10.3 | 0.20 |
| Postpartum fever | |||
| MRC/COG 1993, n = 1292459 | 5.8 | 2.6 | 0.03 |
| Rush 1984, n = 19322 | 10.4 | 3.1 | 0.06 |
| To 2004, n = 253458 | 3.9 | 0.8 | 0.14 |
| Placental abruption | |||
| Rust 2001, n = 11322 | 10.9 | 13.8 | 0.80 |
Results are dominated by the largest high-quality trial of elective cerclage, which demonstrates a reduction in the risk of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation in women with a mixed population of singleton and multiple pregnancies at risk of spontaneous preterm birth. A trend toward cerclage preventing preterm birth was shown at before 37 weeks’ gestation in the same population. Other infant and maternal outcomes are less well reported and further research is needed regarding the use of cervical cerclage on the incidence of neonatal or maternal complications. Summary RRs for spontaneous preterm birth and perinatal mortality were included in the decision analysis.
Antenatal educational programmes
Educational programmes for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth have been developed to promote early recognition and treatment of spontaneous preterm birth. The programmes focus on increasing the awareness of women and their providers of spontaneous preterm contractions and the importance of early intervention. In some strategies, periodic home uterine monitoring is also included.
The review of educational programmes461 for the prevention of preterm birth included six RCTs462–467 (n = 6445). Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 122. Poor reporting meant that the methodological quality of the included studies was unclear; results are presented in Figure 141. Spontaneous preterm birth prevention educational programmes did not significantly reduce the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth, compared to no intervention (Figure 142); furthermore, no statistically significant difference was found in neonatal mortality between women receiving an educational programme and women who did not (Table 13). The incidence of admission to neonatal care units was not reported. Overall, educational programmes do not appear to beneficially affect the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth in women at risk. It should be noted, however, that two potentially relevant RCTs were not received in time. 468,469 Summary RRs were not included in the decision analyses.
FIGURE 141.
Methodological quality of trials of educational programmes for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
FIGURE 142.
Forest plot of the effect of educational programmes for the inhibition of spontaneous preterm labour (length of gestation not defined).
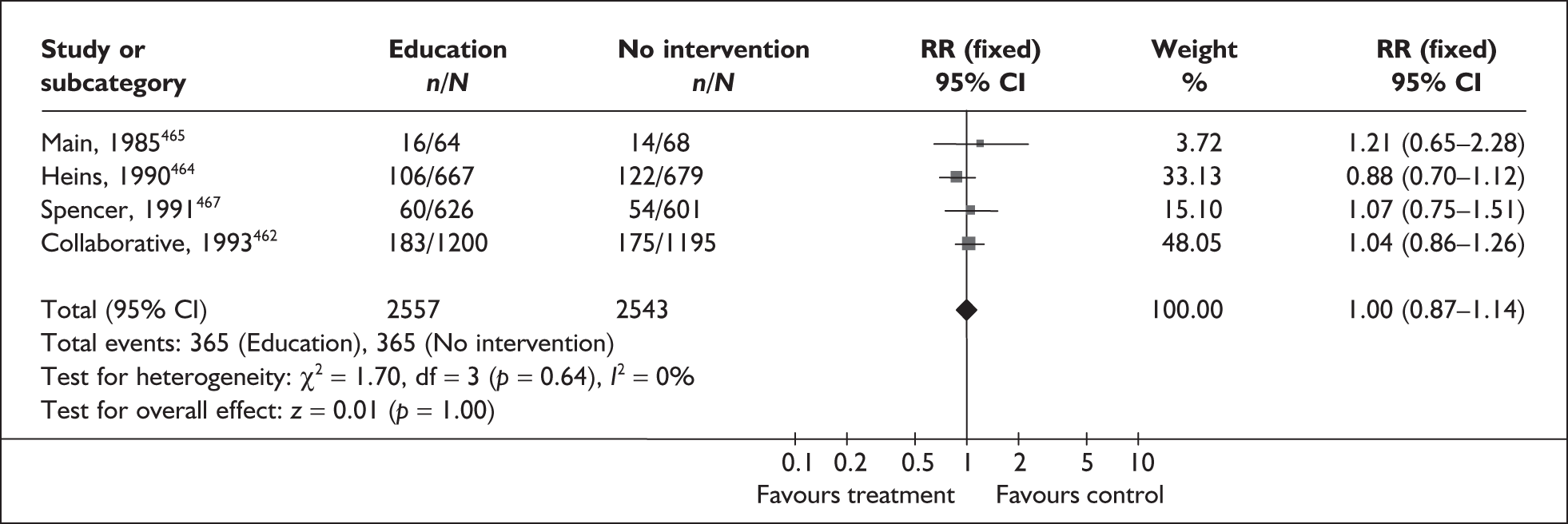
In utero transfer
In utero transfer occurs when a woman at risk of spontaneous preterm birth is transported before delivery to a unit with more specialised facilities for neonates, such as intensive care or care in a particular specialism. In some cases tocolytics are administered to the mother to temporarily delay threatened spontaneous preterm birth, facilitating maternal antenatal corticosteroid administration (to accelerate fetal lung maturity and so prevent respiratory distress syndrome) and the transfer. Some evidence from retrospective cohort studies470,471 suggests that there is an increased risk of neonatal mortality with extrauterine transfer. However, there is no existing systematic review of the efficacy and safety of this intervention, and no randomised trials were retrieved when primary studies were sought. It was therefore not possible to evaluate the impact of in utero transfer on perinatal or maternal outcomes.
Home uterine monitoring
Early detection of threatened preterm labour may increase the proportion of women who receive care while suppression is still a viable option. Clinically the onset of threatened preterm labour is usually preceded by a period of increased uterine activity that can be detected by tocodynamometry (home uterine activity monitoring device). 472
The review of home uterine activity monitoring included three trials (n = 618). 473–475 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 125. The overall quality of these studies, shown in Figure 143, was poor with only one trial considered to be of good quality. Clinical heterogeneity precluded a quantitative summary. No statistically significant difference across trials was shown for the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ or 37 weeks’ gestation in women who received home uterine activity monitoring compared to controls (Figures 144 and 145). Similarly, no statistically significant between-group difference was shown for admission to neonatal intensive care across the primary studies (Figure 146). Other infant and maternal outcomes are less well reported (Table 14) and further research is needed regarding the effect of home uterine activity monitoring on the incidence of neonatal or maternal complications.
FIGURE 143.
Methodological quality of included trials of home uterine activity monitoring for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
FIGURE 144.
Forest plot of the effects of home uterine activity monitoring versus no monitoring for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
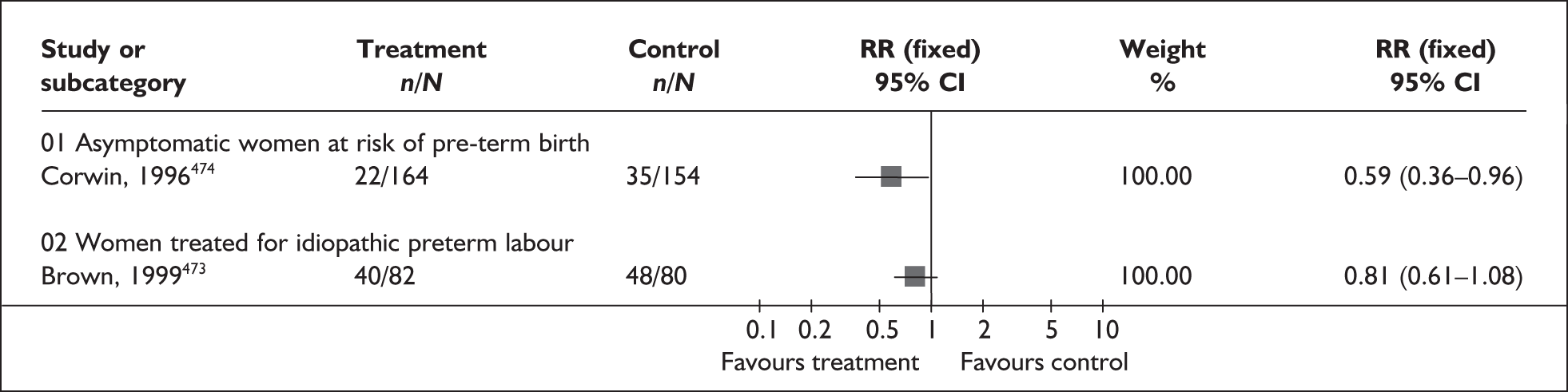
FIGURE 145.
Forest plot of the effects of home uterine activity monitoring versus no monitoring for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation.
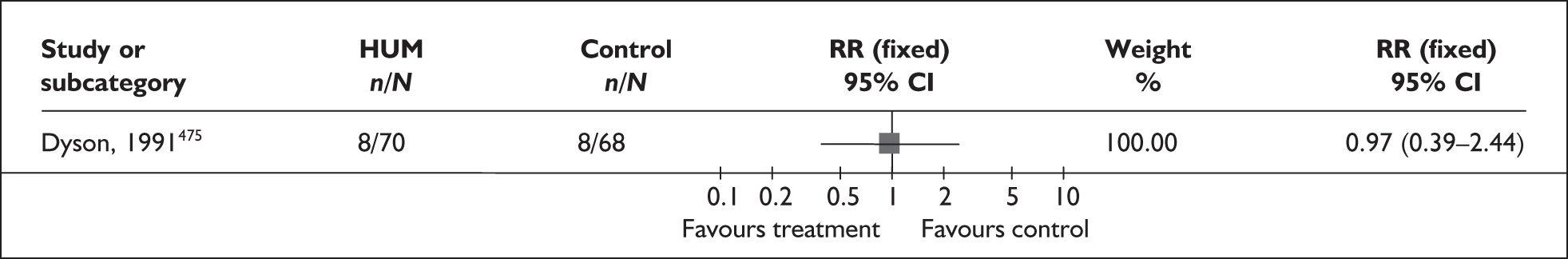
FIGURE 146.
Forest plot of the effects of home uterine activity monitoring versus control on admission to neonatal intensive care unit.
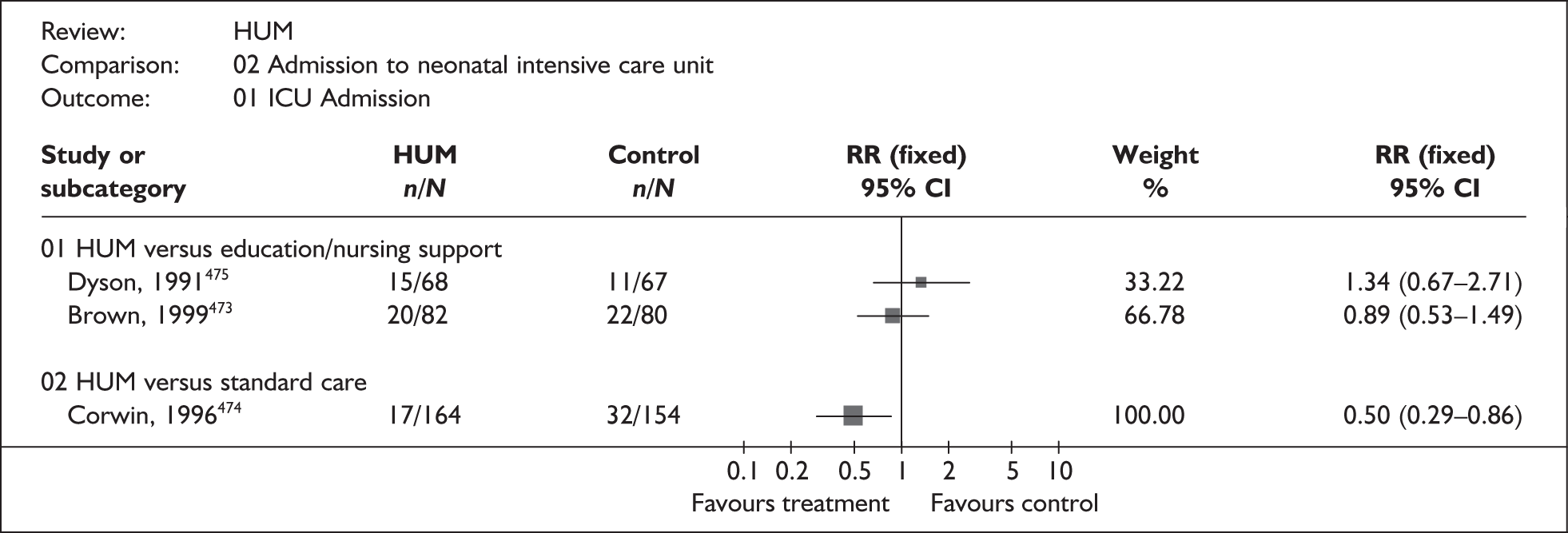
| Outcome (number of RCTs) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Birthweight < 2500 g | |||
| 1 study, n = 133475 | 1.11 | 0.56–2.18 | NA |
| 1 study, n = 279474 | 0.47 | 0.28–0.78 | NA |
| Birthweight < 1500 g | |||
| 1 study, n = 133475 | 0.69 | 0.20–2.33 | NA |
| 1 study, n = 279474 | Not estimable | – | – |
| Neonates receiving mechanical ventilation (1 study, n = 162)473 | 0.65 | 0.11–3.79 | NA |
| Length of hospital stay (1 study, n = 162)473 | WMD 3.60 | 2.92–4.28 | NA |
In the largest, high-quality trial, home uterine monitoring did not show significant reduction in spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in women at risk of spontaneous preterm birth; however, a reduction was shown in the incidence of admission to neonatal intensive care units. 474 It should be noted that this trial compared home uterine monitoring to standard care, whereas the other included trials compared home uterine monitoring to an educational or increased nursing control group. Overall, there was very limited good quality evidence to support the use of home uterine monitoring. RRs for the largest, high-quality study were used in the decision analyses.
Home visits
A number of studies have suggested that pregnancy outcomes may be influenced by women’s psychological well-being during pregnancy and labour, indicating stress and lack of social support as potential risk factors. 476–478 The objective of many home-care programmes is to provide support and care in a familiar environment.
This review of home visits included ten RCTs (n = 9274 women);479–488 two RCTs were added to the primary studies identified in an earlier review. 489 Further details of the review and the two additional RCTs can be found in Appendix 6, Table 126. The quality of these studies was generally poor; results are shown in Figure 147. When compared with women who do not receive a home-visit program, home visits during pregnancy do not significantly reduce the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation or neonatal admission to intensive care (Figures 148 and 149. The effect of home visits on spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation was not reported in the primary studies. The effect of home visits on other perinatal or maternal outcomes is shown in Table 15. The results do not support a beneficial effect of home visits for the inhibition of spontaneous preterm birth. The summary RR for spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation was included in the decision analysis.
FIGURE 147.
Methodological quality of included trials of home visits for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
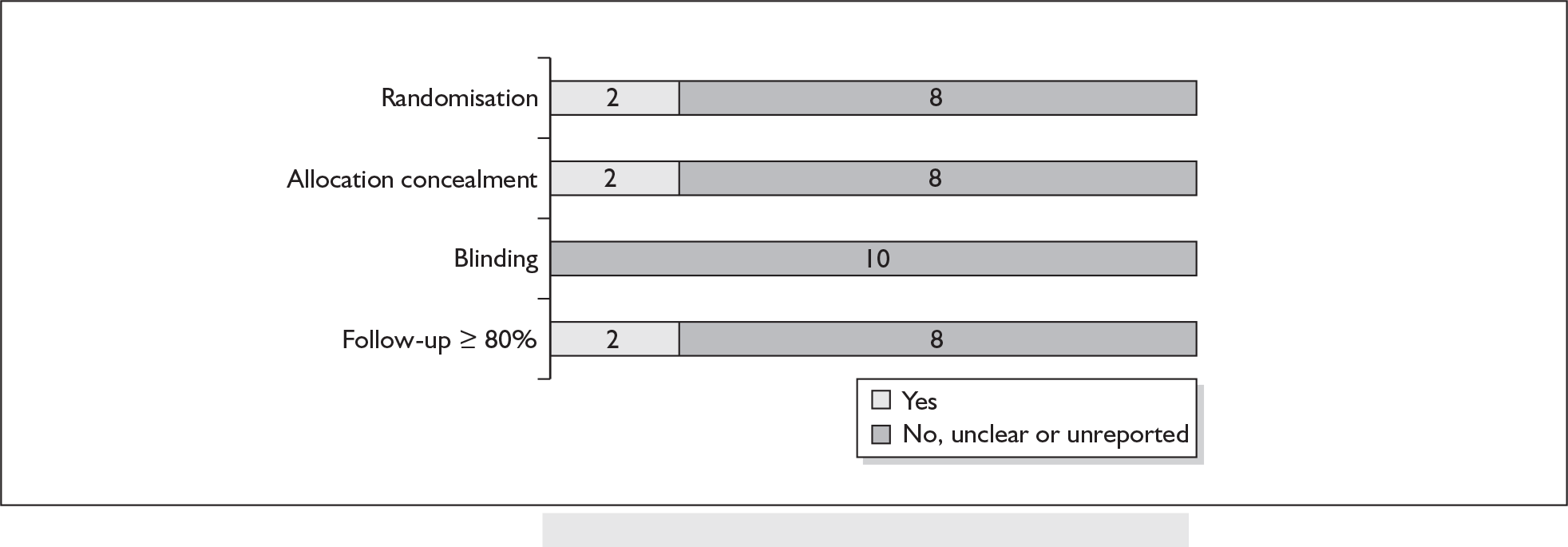
FIGURE 148.
Forest plot of the effects of home visits versus usual care for the inhibition of spontaneous preterm labour before 37 weeks’ gestation.
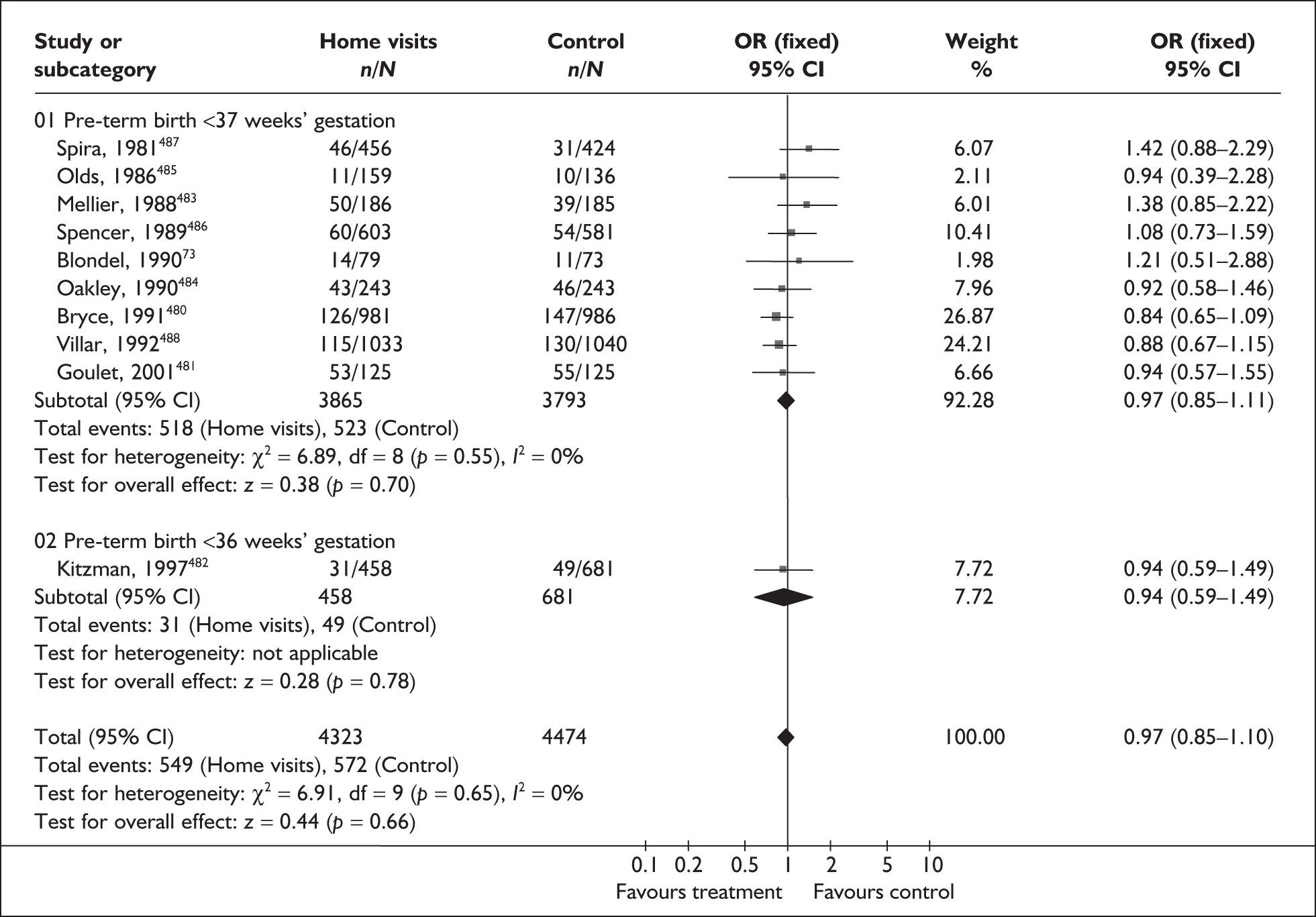
FIGURE 149.
Forest plot of the effects of home visits versus usual care on neonatal admission to intensive care.
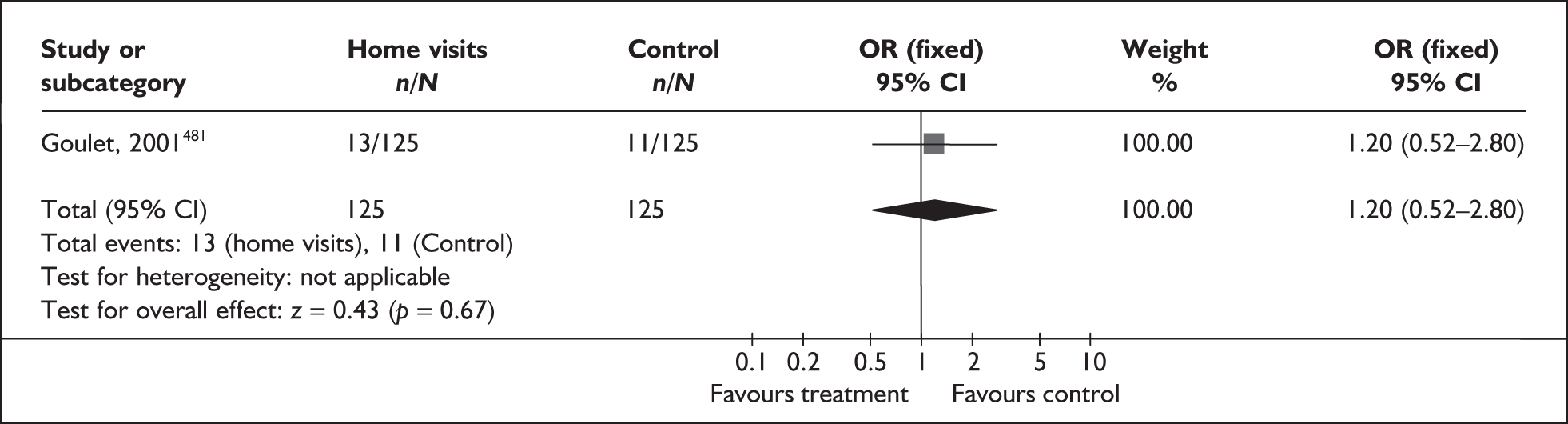
| Outcome (RCTs) | RR | 95% CI | I2, p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital admission during pregnancy | |||
| All home visits (4 studies, n = 1893)478,479,483,487 | 0.88 | 0.77–1.00 | 47.4%, 0.13 |
| Social support (1 study, n = 486)478 | 0.79 | 0.65–0.95 | NA |
| Medical care (3 studies, n = 1407)479,483,487 | 0.94 | 0.75–1.12 | 45.0%, 0.16 |
Hypnosis
Stress may be a factor in triggering spontaneous preterm labour. Hypnosis is a technique that may help to relax the mother and as such has been suggested as a treatment for threatened preterm labour. However, there is no existing systematic review of its use for this indication, and no randomised primary studies where found. It was not therefore possible to evaluate this intervention.
Periodontal care
Evidence indicates that infections can be a major risk factor in spontaneous preterm birth. Case–control, and prospective cohort studies point to an association between periodontal infection and increased rates of spontaneous preterm birth. This rapid review examines whether periodontal therapy reduces the risk of spontaneous preterm birth.
The review of periodontal therapy included one quasi-RCT (n = 400 women). 490 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 127. The quality of the primary study was poor (Figure 150). When compared with no treatment, periodontal therapy reduced the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation (Figure 151). In addition, when compared with no treatment, fewer infants with low birthweight (< 2500 g) were delivered to the periodontal therapy group (Table 16). Incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, perinatal mortality and neonatal admission to intensive care were not reported. Although the results support a beneficial effect of periodontal therapy for prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, the methodological quality of the trial and uncertain accounting of residual confounders warrant caution in the interpretation of these results. Further well-controlled, large trials are needed. The RR from the forest plot presented was used in the decision analyses.
FIGURE 150.
Methodological quality of included trials of periodontal therapy for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
FIGURE 151.
Forest plot of the effects of periodontal therapy versus no treatment for the inhibition of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
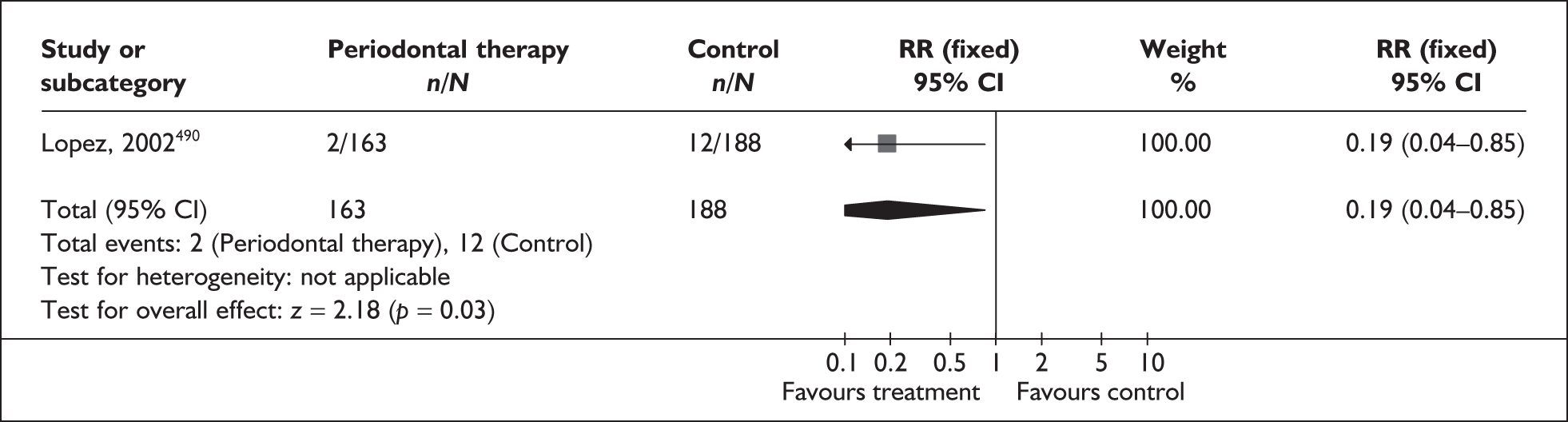
Progestational agents
Progesterone is a hormone that inhibits the uterus from contracting and has been advocated for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth. 491
This review of progesterone included six RCTs (n = 988 women). 492–497 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 128. An additional review of progesterone was identified after the final searches had been completed,498 which included six RCTs and three quasi-RCTs. The quality of the primary studies is shown in Figure 152. Overall, the quality of the studies was reasonable, although poor reporting meant that randomisation and allocation concealment were difficult to assess in some cases. There was a reduction in risk of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation (Figures 153 and 154). No statistically significant between-group difference was found for incidence of perinatal mortality (Figure 155). Delivery within 24 hours, 48 hours or 7 days after treatment initiation was not reported. The effect of progesterone on other perinatal and maternal outcomes is shown in Table 17. Planned subgroup analyses were also performed; the effect of route of administration, timing of treatment initiation, dose and plurality of the pregnancy for risk of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation is shown in Table 18. Overall, the results support the superiority of intramuscular progesterone over placebo in preventing spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. However, further research is needed to evaluate the use of vaginal progesterone in the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth, because although there appeared to be a significant benefit, this was based on only one trial. In addition, there is currently no appropriate intramuscular formulation available in the UK. Further studies are required to confirm the effectiveness of this intervention. Other infant and maternal outcomes are less well reported, with most outcomes taken from a single study. Further research is needed regarding the use of vaginal progesterone in the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth. Summary RRs for spontaneous preterm birth before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation, shown in the forest plots presented, were used in the decision analyses.
FIGURE 152.
Methodological quality of randomised controlled trials of progestogens in the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
FIGURE 153.
Forest plot of the effects of prenatal administration of progesterone for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
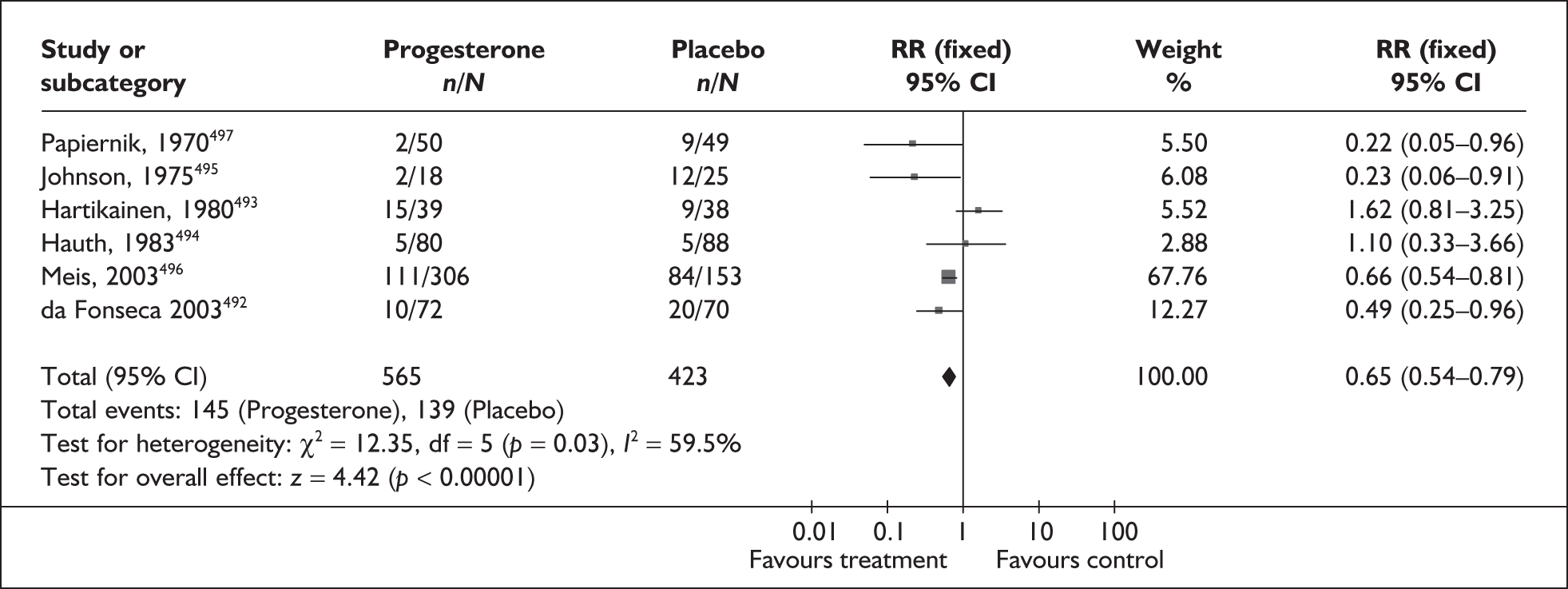
FIGURE 154.
Forest plot of the effects of prenatal administration of progesterone versus placebo for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation.
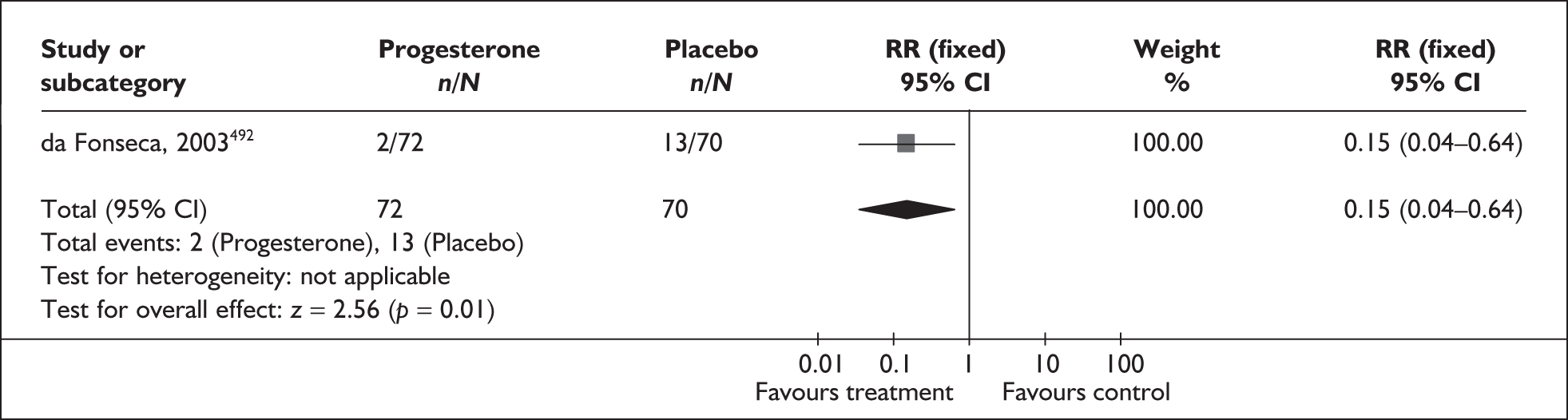
FIGURE 155.
Forest plot of the effects of prenatal administration of progesterone versus placebo on the incidence of perinatal death.
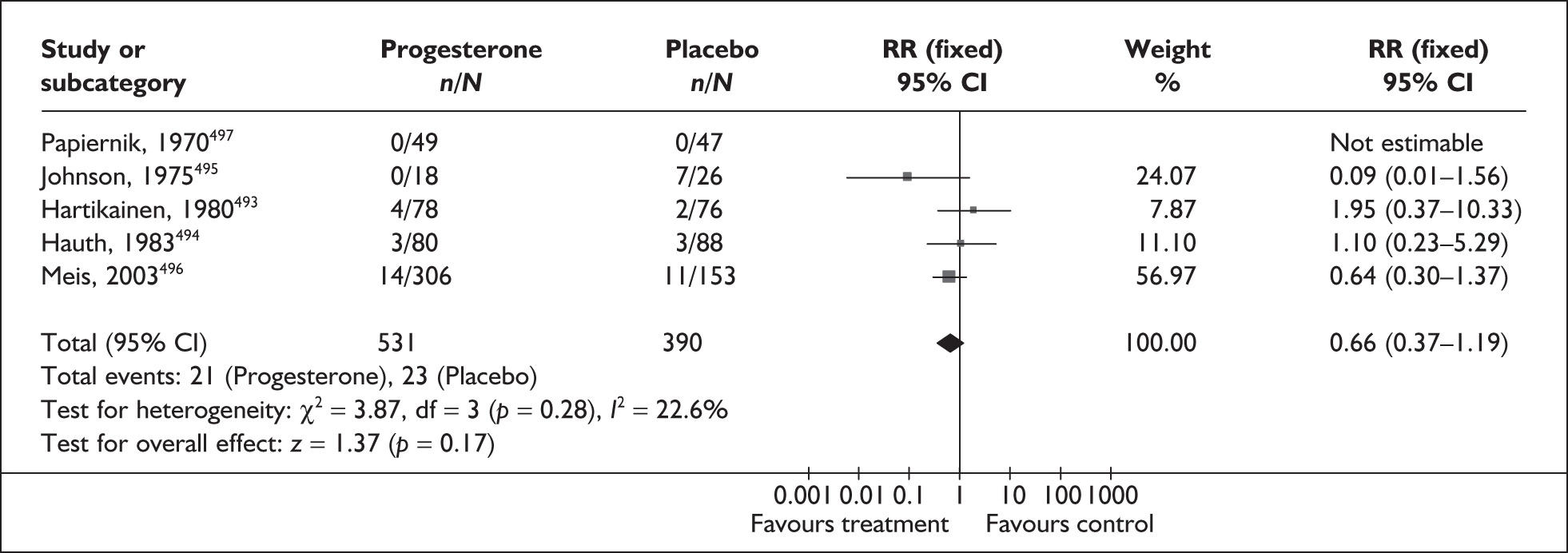
| Outcome (number of RCTs) | RR | 95% CI | I2, p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neonatal death (3 studies, n = 671) 494–496 | 0.59 | 0.27–1.30 | 25.2%, 0.26 |
| Intrauterine death (3 studies, n = 671) 494–496 | 0.56 | 0.19–1.61 | 24.3%, 0.27 |
| Threatened preterm labour (2 studies, n = 601) 492,496 | 0.92 | 0.64–1.33 | 63.6%, 0.10 |
| Use of antenatal corticosteroids (1 study, n = 459) 496 | 0.87 | 0.58–1.30 | NA |
| Use of antenatal tocolytics (2 studies, n = 503) 494,496 | 1.12 | 0.73–1.72 | NA |
| Birthweight < 2500 g (4 studies, n = 763) 492,494–496 | 0.63 | 0.49–0.81 | 0%, 0.56 |
| Infant respiratory distress syndrome (1 study, n = 457) 496 | 0.63 | 0.38–1.05 | NA |
| Mechanical ventilation (1 study, n = 454) 496 | 0.59 | 0.35–1.00 | NA |
| Intraventricular haemorrhage (1 study, n = 458) 496 | 0.25 | 0.08–0.82 | NA |
| Retinopathy of prematurity (1 study, n = 457) 496 | 0.50 | 0.15–1.70 | NA |
| Necrotising enterocolitis (1 study, n = 457) 496 | 0.06 | 0.00–1.03 | NA |
| Neonatal sepsis (1 study, n = 457) 496 | 1.12 | 0.35–3.58 | NA |
| Patent duct arteriosus (1 study, n = 456) 496 | 0.43 | 0.16–1.17 | NA |
| Stratification (number of studies) | RR | 95% CI | I2, p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preterm birth < 37 weeks’ gestation | |||
| Route of administration | |||
| Intramuscular injection (4 studies, n = 771)492xref>,494–496 | 0.61 | 0.50–0.75 | 42.4%, 0.16 |
| Vaginal pessary (1 study, n = 140)498 | 0.49 | 0.25–0.96 | NA |
| Timing of treatment | |||
| < 20 weeks’ gestation (3 studies, n = 672)494,496,492 | 0.64 | 0.52–0.79 | 32.7%, 0.23 |
| > 20 weeks’ gestation (2 studies, n = 239)495,498 | 0.40 | 0.22–0.75 | 0%, 0.33 |
| Cumulative weekly dose | |||
| ≥ 500 mg (3 studies, n = 409)495,496,498 | 0.50 | 0.29–0.86 | 30.3%, 0.24 |
| < 500 mg (2 studies, n = 502)492,494 | 0.63 | 0.51–0.77 | 56.5%, 0.13 |
| Perinatal mortality | |||
| Timing of treatment | |||
| < 20 weeks’ gestation (3 studies, n = 671)492,494,496 | 0.55 | 0.29–1.06 | 16.6%, 0.30 |
| > 20 weeks’ gestation (1 study, n = 96)495 | Not estimable | Not estimable | Not estimable |
| Cumulative weekly dose | |||
| ≥ 500 mg (1 study, n = 168)496 | 1.10 | 0.23–5.29 | NA |
| < 500 mg (2 studies, n = 503)492,494 | 0.48 | 0.23–0.98 | 45.4%, 0.18 |
Smoking cessation programmes in pregnancy
The prevalence of smoking during pregnancy is high with between 20 and 33% of pregnant women engaging in the practice. Smoking is significantly more frequent among women with low socioeconomic status. There is strong evidence linking maternal smoking to an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including spontaneous preterm birth and perinatal death. 499
The review of smoking cessation interventions500 included 64 randomised trials. Fifteen of these trials reported outcomes related to maternal and perinatal health. 501–515 Further details of the review are in Appendix 6, Table 129. No additional studies were found when the searches were updated. The quality of the 15 included studies was generally poor (Figure 156). Data were available for the outcomes of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation (Figure 157) and perinatal death (Figure 158). Smoking cessation programmes in general, and low intensity programmes in particular, significantly reduced the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation (Figure 157) but there were no differences between the groups for perinatal mortality. Women on smoking cessation programmes also had significantly fewer low-birthweight (< 2500 g) infants (Table 19). Data for other perinatal outcomes are also shown in Table 19. Summary RRs from the forest plots presented were used in the decision analyses. Overall, reductions in spontaneous preterm birth and low birthweight suggest that smoking cessation programmes may have beneficial perinatal outcomes, but the quality of the studies is poor and the significance is unclear. Additionally, it is unclear whether changes in smoking behaviour are a consequence of the intervention programmes because there was no direct assessment of smoking cessation. Further good quality research that directly measures the effects of smoking cessation programmes on spontaneous preterm birth is required.
FIGURE 156.
Methodological quality of trials of smoking cessation programmes for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
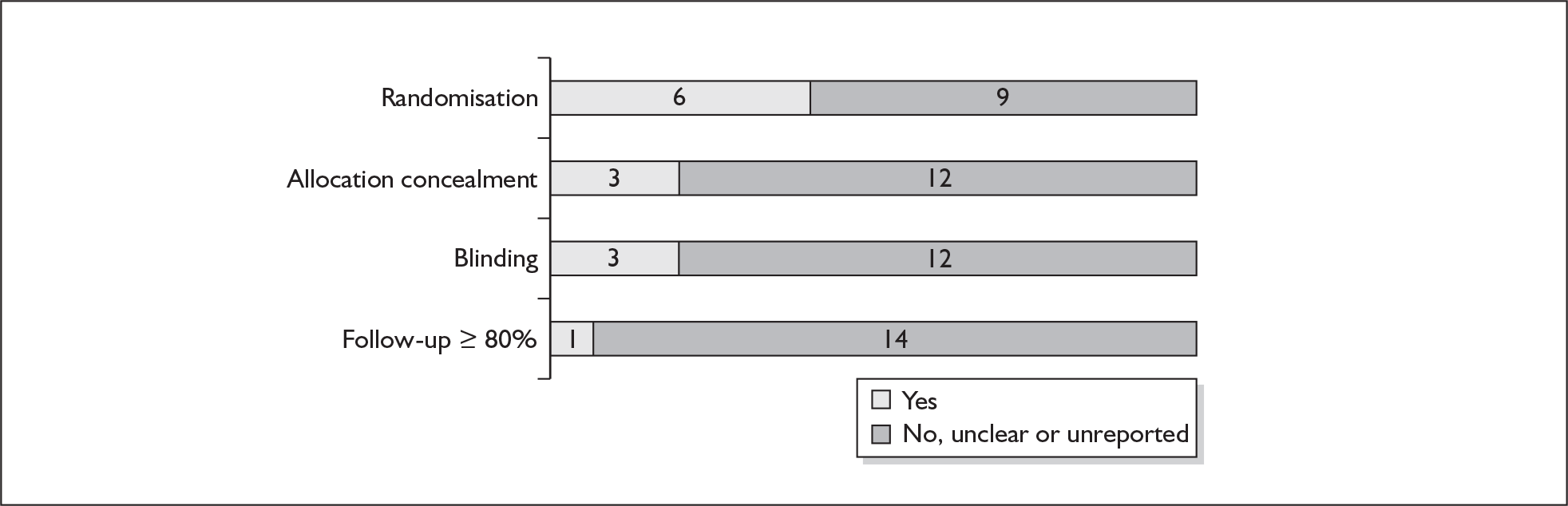
FIGURE 157.
Forest plot of the effects of smoking cessation interventions for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 36 or 37 weeks’ gestation, subgrouped by intensity of intervention.
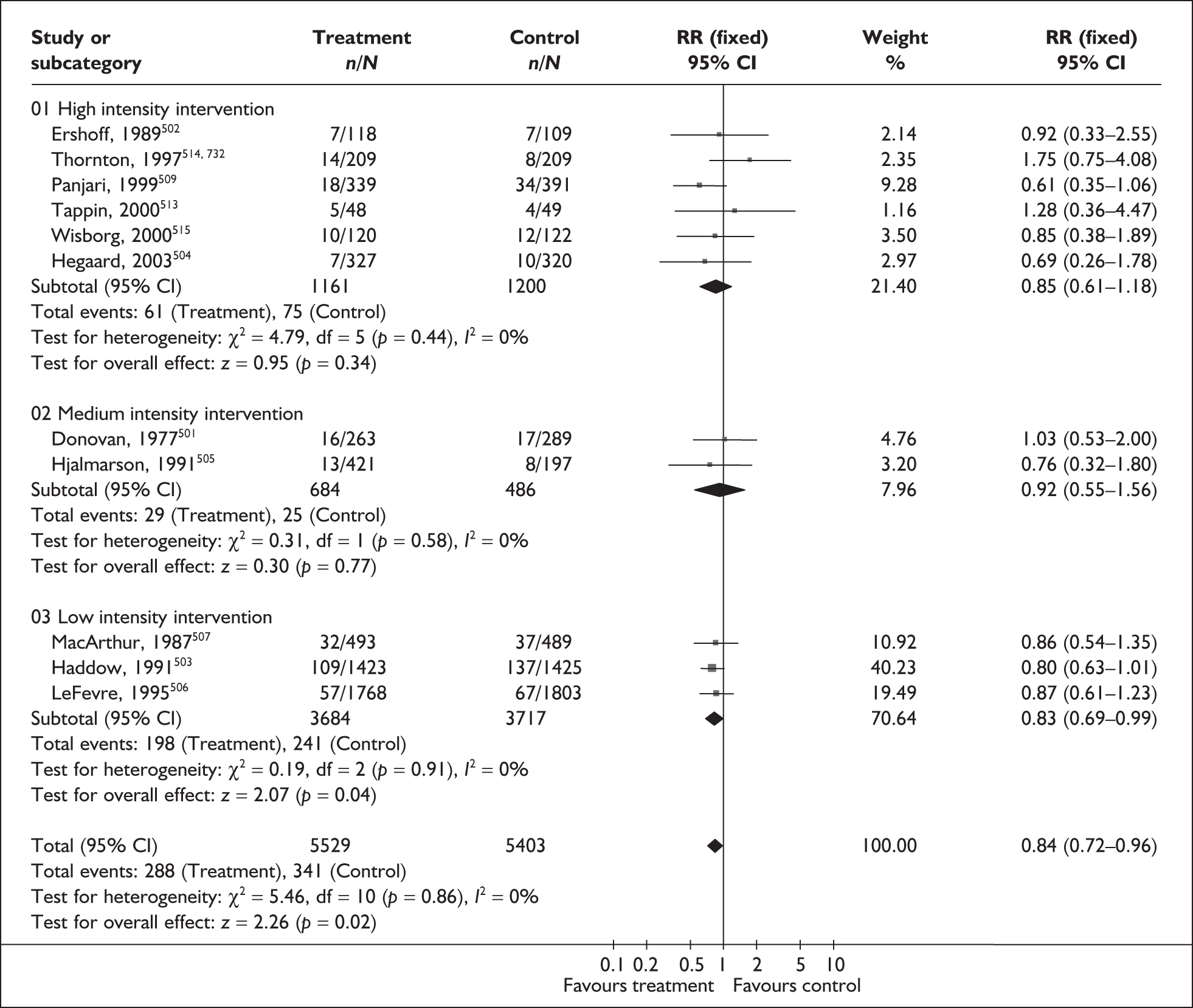
FIGURE 158.
Forest plot of the effects of smoking cessation interventions for the prevention of perinatal mortality.
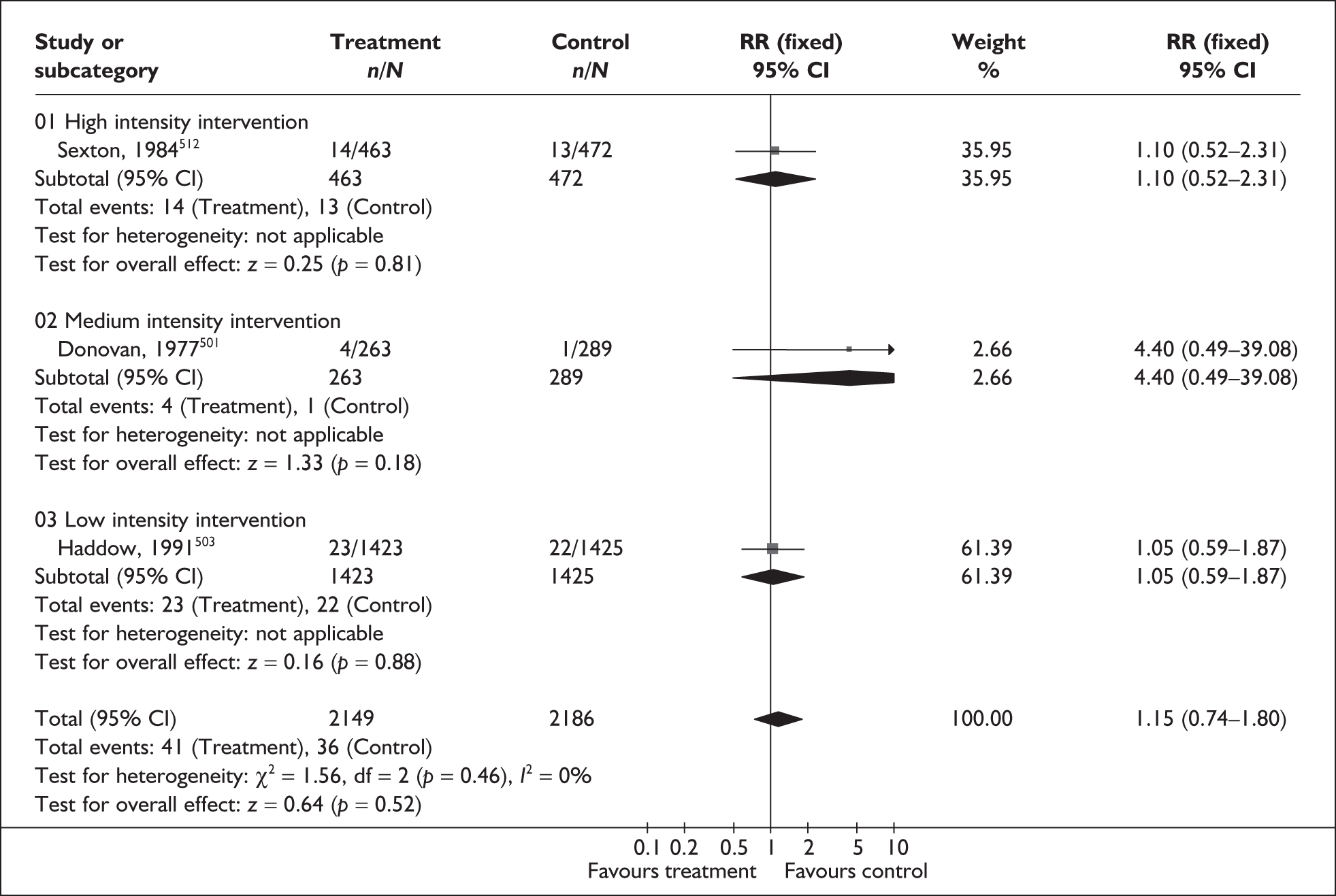
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stillbirth (5 studies, n= 4525)502,503,512–514 | 1.16 | 0.71–1.88 | 0% (0.86) |
| High-intensity intervention (4 studies, n = 1677)502,512–514 | 1.08 | 0.52–2.26 | 0% (0.75) |
| Low-intensity intervention (1 study, n = 2848)503 | 1.24 | 0.66–2.33 | NA |
| Neonatal death (3 studies, n = 4143)503,512,514 | 1.17 | 0.34–4.01 | 25.7% (0.26) |
| High-intensity intervention (2 studies, n = 1333)503,512 | 2.36 | 0.61–9.08 | 0% (0.87) |
| Low-intensity intervention (1 study, n = 2810)514 | 0.40 | 0.08–2.07) | NA |
| Low birthweight < 2500 g (13 studies, n = 8930)501–505,507–512,514,515 | 0.82 | 0.70–0.95 | 0% (0.67) |
| High-intensity intervention (8 studies, n = 3652)501–509 | 0.79 | 0.62–1.00 | 0% (0.43) |
| Medium-intensity intervention (3 studies, n = 1448)510–512 | 0.84 | 0.57–1.23 | 12.1% (0.32) |
| Low-intensity intervention (2 studies, n = 3830)514,515 | 0.83 | 0.67–1.03 | 0% (0.90) |
| Low birthweight < 1500 g (3 studies, n = 4765)505,507.512 | 1.26 | 0.69–2.32 | 0% (0.61) |
| High-intensity intervention (1 study, n = 620)505 | 1.83 | 0.69–2.32 | NA |
| Medium-intensity intervention (1 study, n = 982)507 | 0.89 | 0.34–2.30 | NA |
| Low-intensity intervention (1 study, n = 935)512 | 1.39 | 0.44–4.35 | NA |
Effectiveness of interventions among symptomatic women
Hydration
Hydration has been proposed as a treatment for women presenting with threatened preterm labour contractions. 516 One possible mechanism of action is that volume expansion inhibits contractions by increasing uterine blood flow, so stabilising decidual lysosomes and decreasing prostaglandin production,517 and by decreasing pituitary secretion of antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. 517,518
The review of hydration (intravenous or oral) for the prevention or delay of threatened preterm labour included two randomised controlled trials (n = 228 women). 517,519 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 130. The quality of the included studies is presented in Figure 159. Overall, the methodological quality of the included studies was good, although the trials were small. Compared to bed rest alone, intravenous hydration did not reduce the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 or 37 weeks’ gestation (Figures 160 and 161). Delivery within 48 hours and 7 days of treatment initiation was not estimable; delivery within 24 hours of treatment initiation was not reported. No statistically significant difference was found in admission to neonatal intensive care between women receiving intravenous hydration and women receiving bed rest alone (Figure 162). A separate analysis of women included before 34 weeks’ gestation did not demonstrate any beneficial effect of hydration during the period of evaluation soon after admission; results were based on one study. 517 Overall, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of intravenous hydration for the treatment of women presenting with threatened preterm labour. No eligible studies were found for oral hydration. Summary RRs for spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation and admission to neonatal intensive care were used in the decision analysis.
FIGURE 159.
Methodological quality of trials of hydration for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
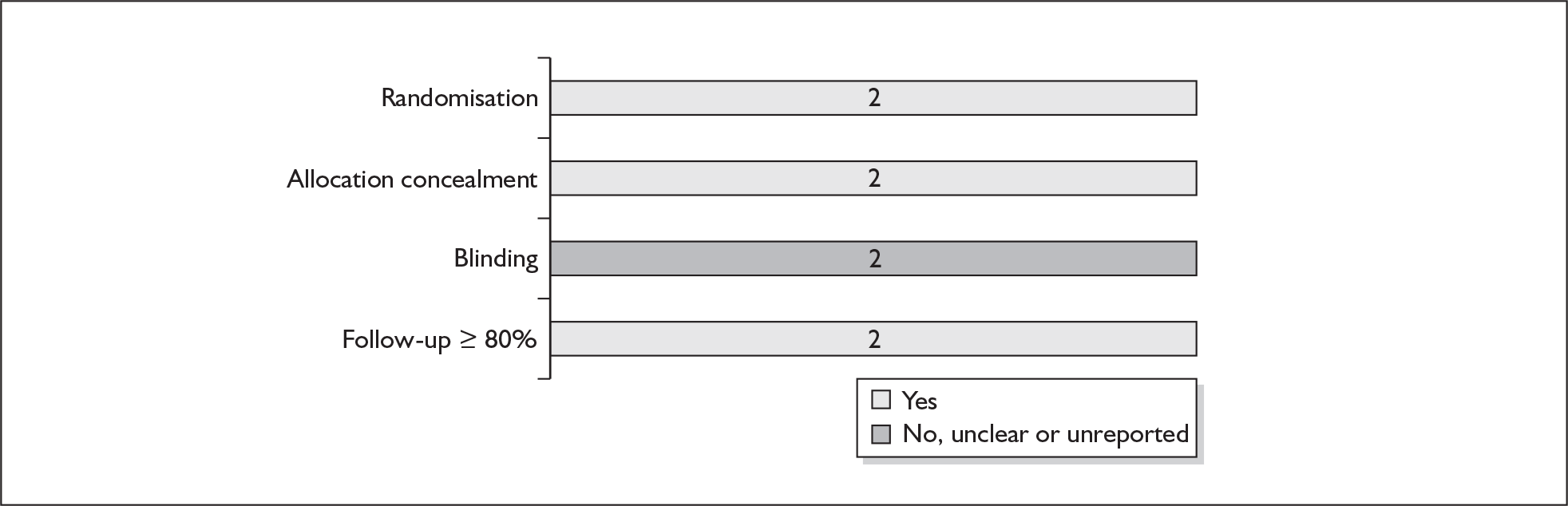
FIGURE 160.
Forest plot of intravenous hydration versus bed rest alone for the inhibition of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
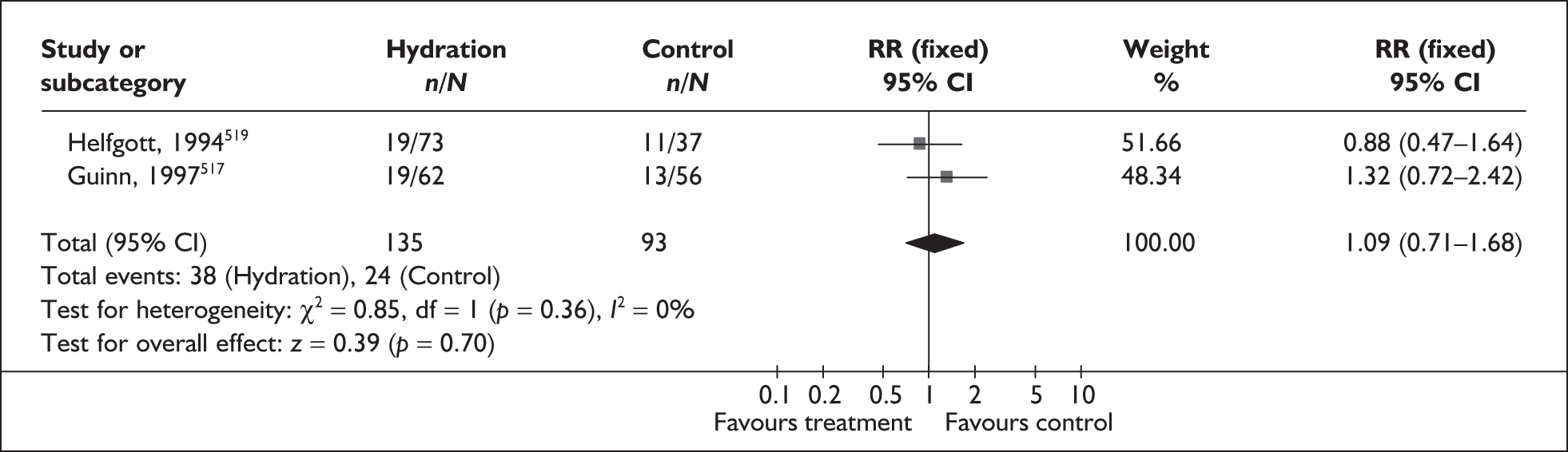
FIGURE 161.
Forest plot of intravenous hydration versus bed rest alone for the inhibition of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
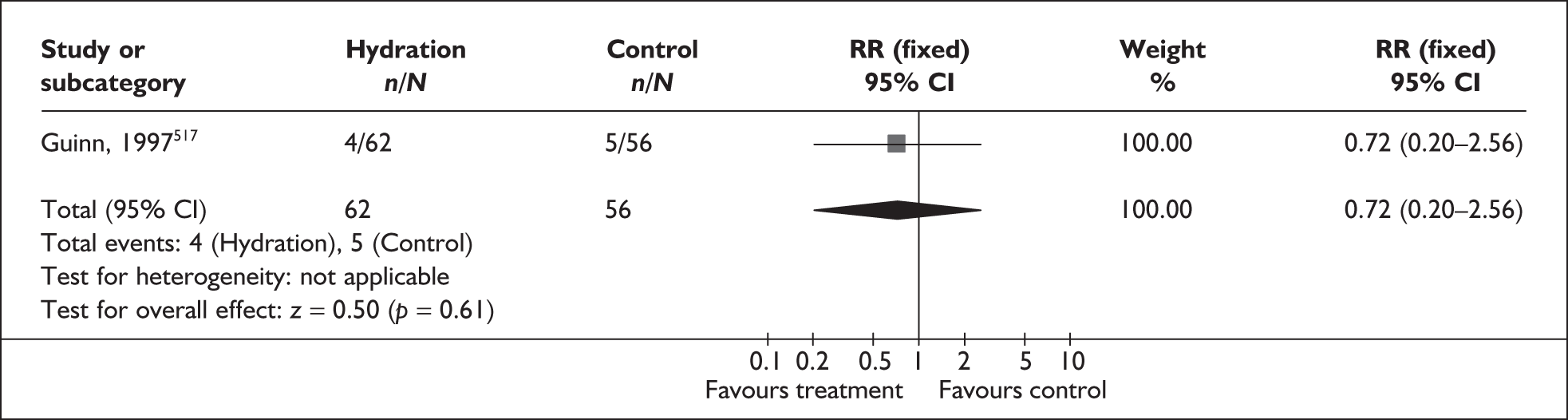
FIGURE 162.
Forest plot of intravenous hydration versus bed rest alone on neonatal admission to intensive care unit.
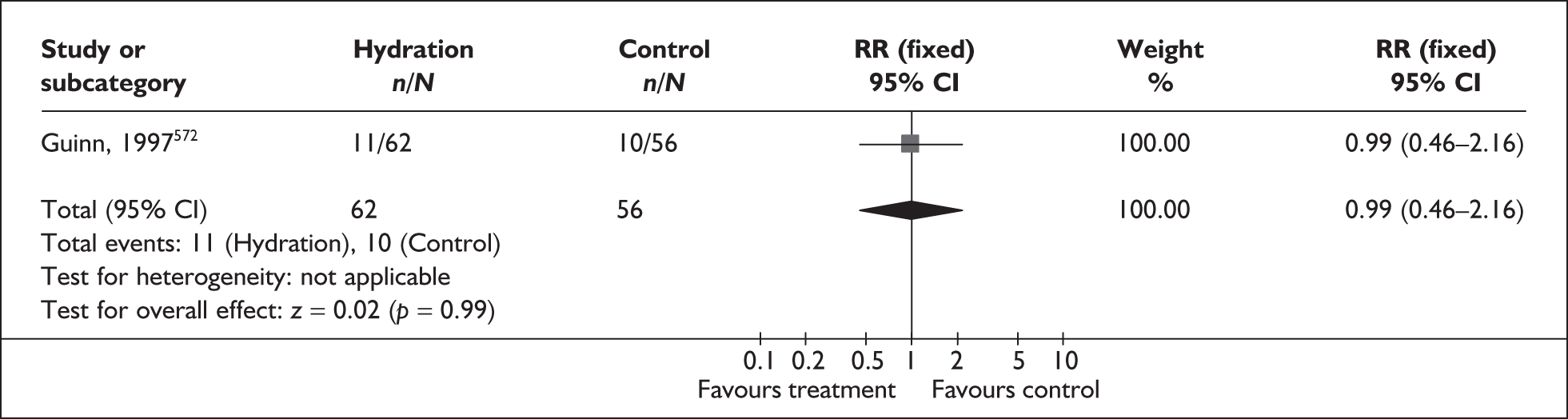
Prophylactic antibiotics in women with intact membranes
Subclinical and clinical infections have been implicated in the aetiology of spontaneous preterm birth, which has led to the suggestion that women with threatened preterm labour should be treated with antibiotics to reduce the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth. As rupture of the membranes can also be a significant factor in threatened preterm labour, it is important to establish if prophylactic antibiotic treatment has an effect before membrane rupture.
The review of prophylactic antibiotics in pregnant women with intact membranes520 included eleven RCTs that compared antibiotic therapy with placebo or no treatment. 521–531 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 131. No additional RCTs were found when the searches were updated. All women included in the trials were experiencing, or thought to be experiencing, symptoms of threatened preterm labour. The original review included trials with multiple pregnancies, which we have subgrouped where possible. The quality of the included studies is shown in Figure 163; overall this was considered good. The following subgroups were examined: any antibiotic versus no antibiotics; betalactam antibiotic alone versus no antibiotics; macrolide alone versus no antibiotics; betalactam and macroclide versus no antibiotics; and antibiotics active against anaerobic bacteria.
FIGURE 163.
Methodological quality of the included trials of prophylactic antibiotic therapy for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
Antibiotic prophylaxis did not significantly affect the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation (Figures 164–168), although a reduced risk of maternal infection was shown for prophylactic antibiotic therapy compared to no antibiotic therapy across all subgroups (Table 20). A trend toward an increase in risk of perinatal mortality (Figures 170 and 171) and neonatal mortality (Table 20) was found for women receiving prophylactic antibiotic therapy, which was demonstrated across all subgroups. Antibiotics active against anaerobic bacteria were shown to significantly affect the incidence of delivery within 7 days of treatment and incidence of admission to neonatal intensive care unit; however, this reduction in risk was not found in other subgroups or the population as a whole (Figures 169, 172 and 173). No studies reported spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation or delivery within 24 hours of treatment.
FIGURE 164.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus no treatment for the prevention of preterm birth before 36 or 37 weeks’ gestation.
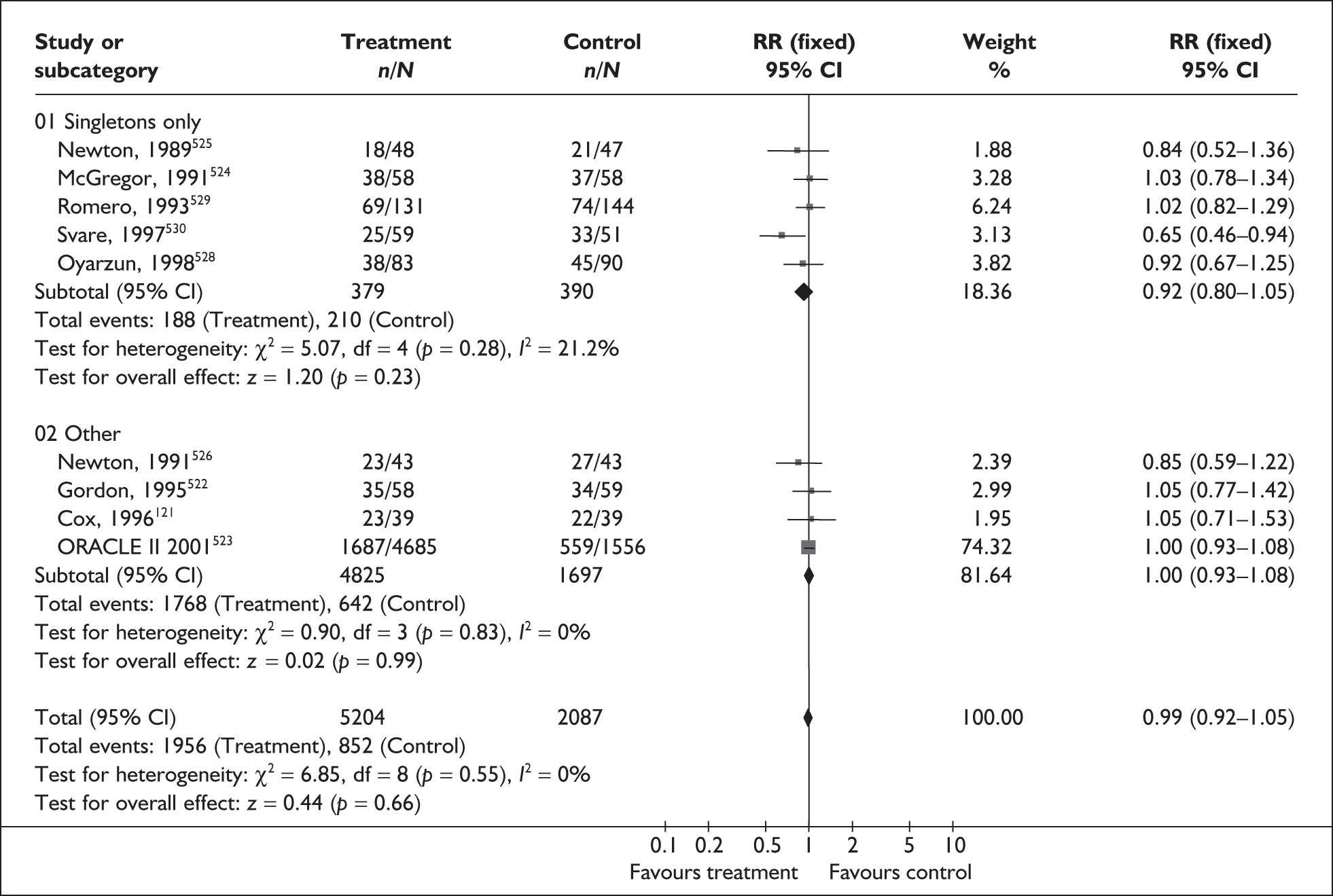
FIGURE 165.
Forest plot of the effects of antibiotic therapy subgrouped by type of antibiotic versus no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 36 or 37 weeks’ gestation. a, Multiple gestations included in trial or not excluded from trial.
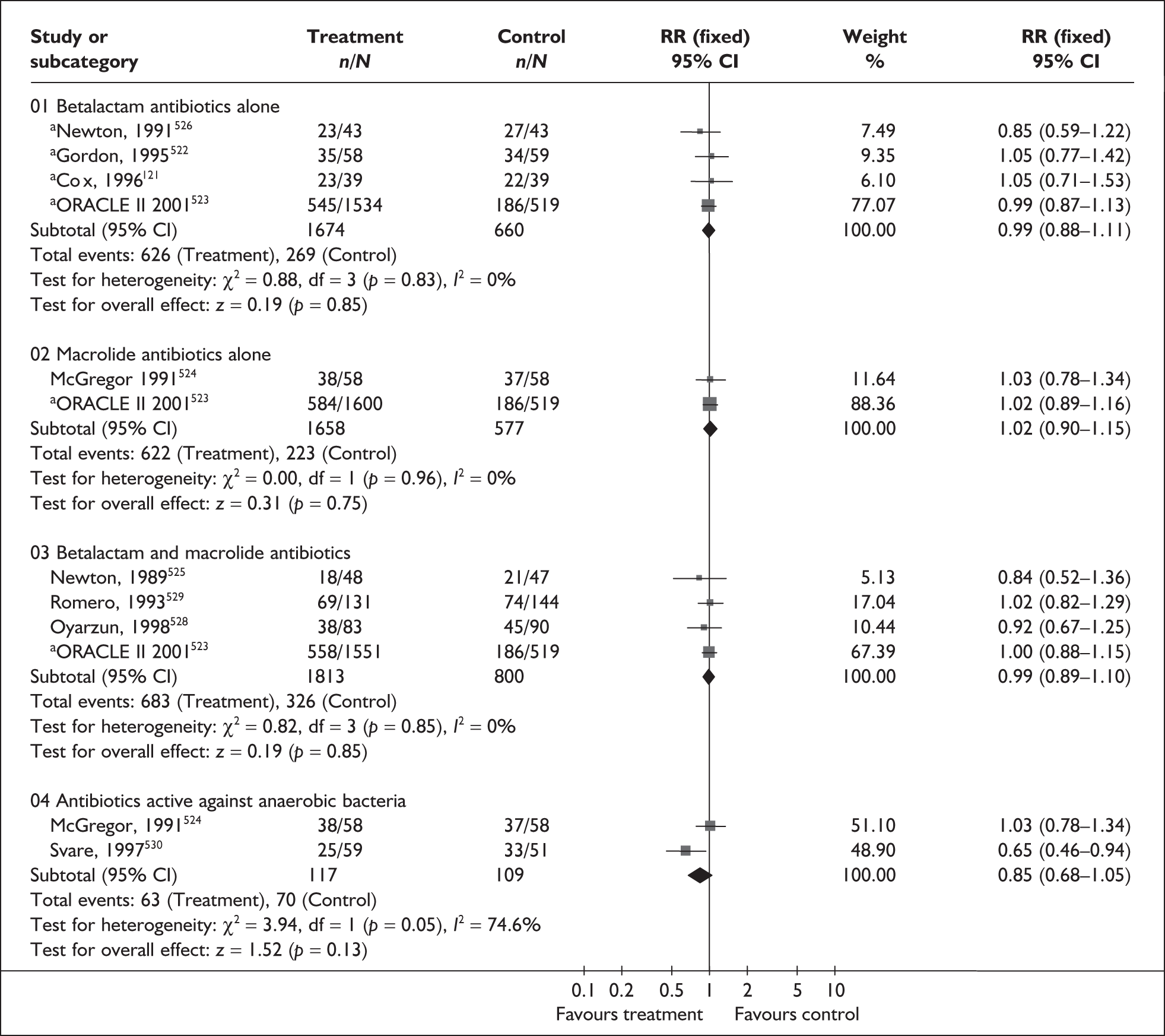
FIGURE 166.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for delivery within 48 hours of treatment.
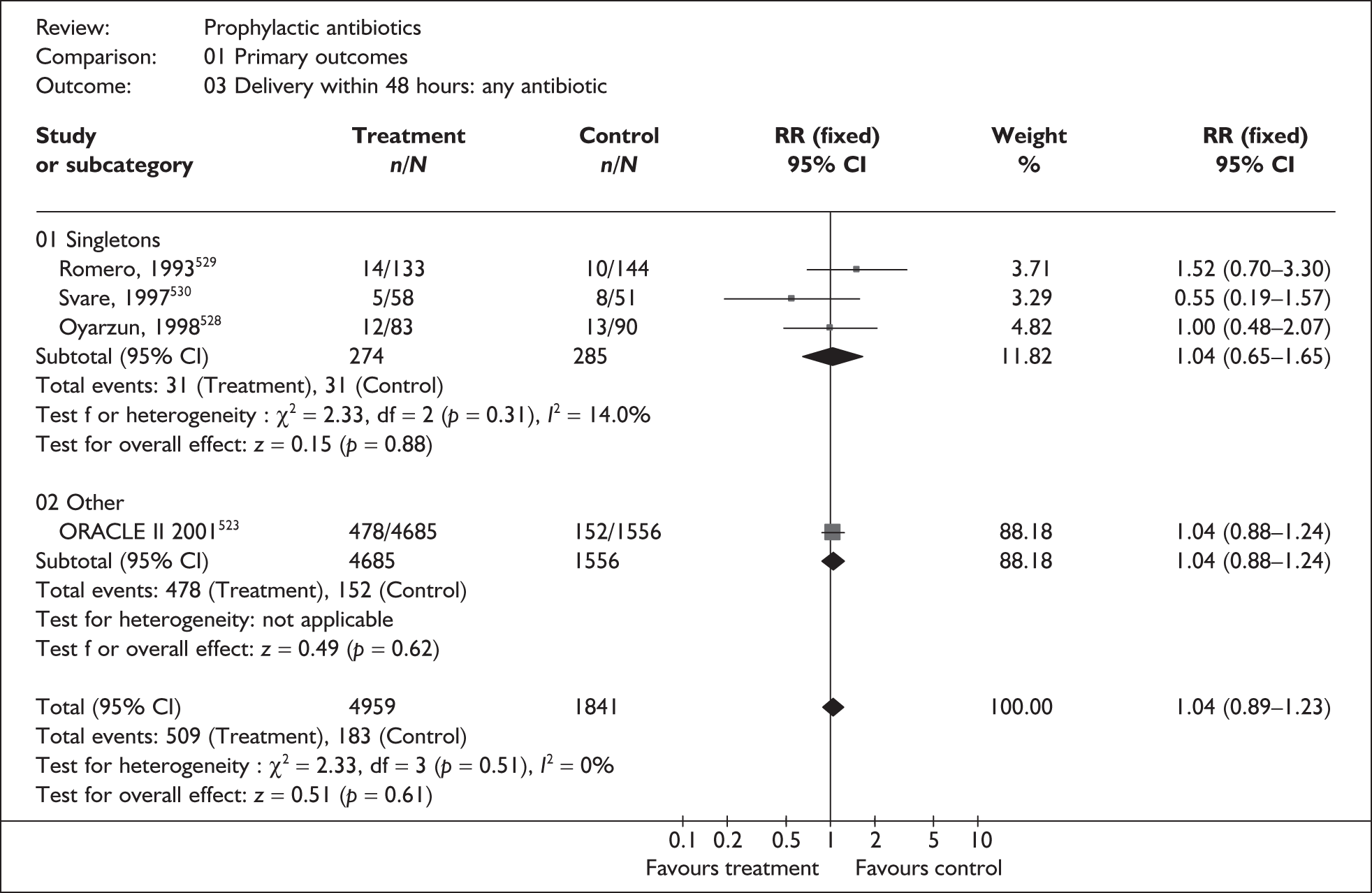
FIGURE 167.
Forest plot of the effects of antibiotic therapy subgrouped by type of antibiotic versus placebo/no treatment for delivery within 48 hours of treatment. Multiple gestations included in trial or not excluded from trial.
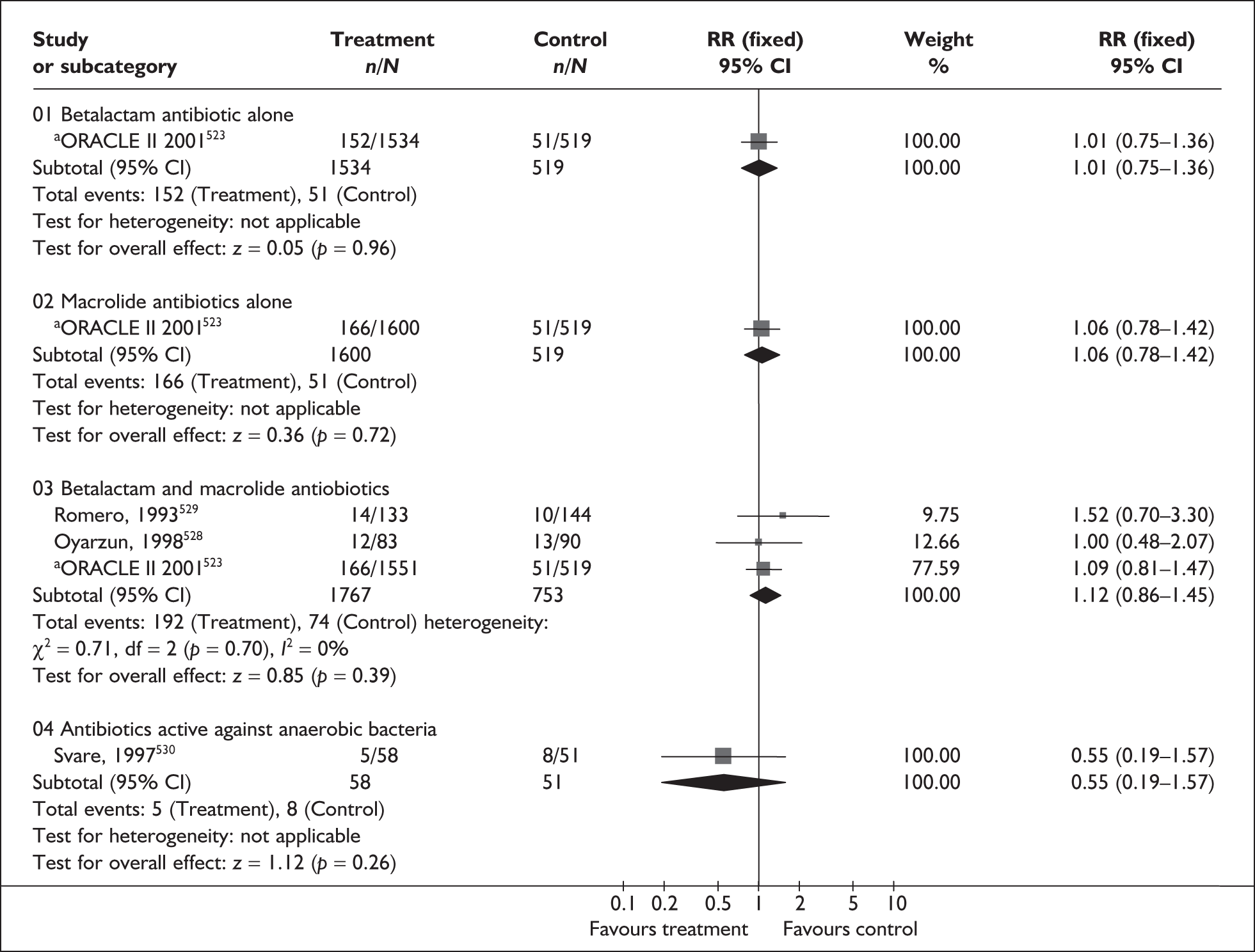
FIGURE 168.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for delivery within 7 days of treatment.
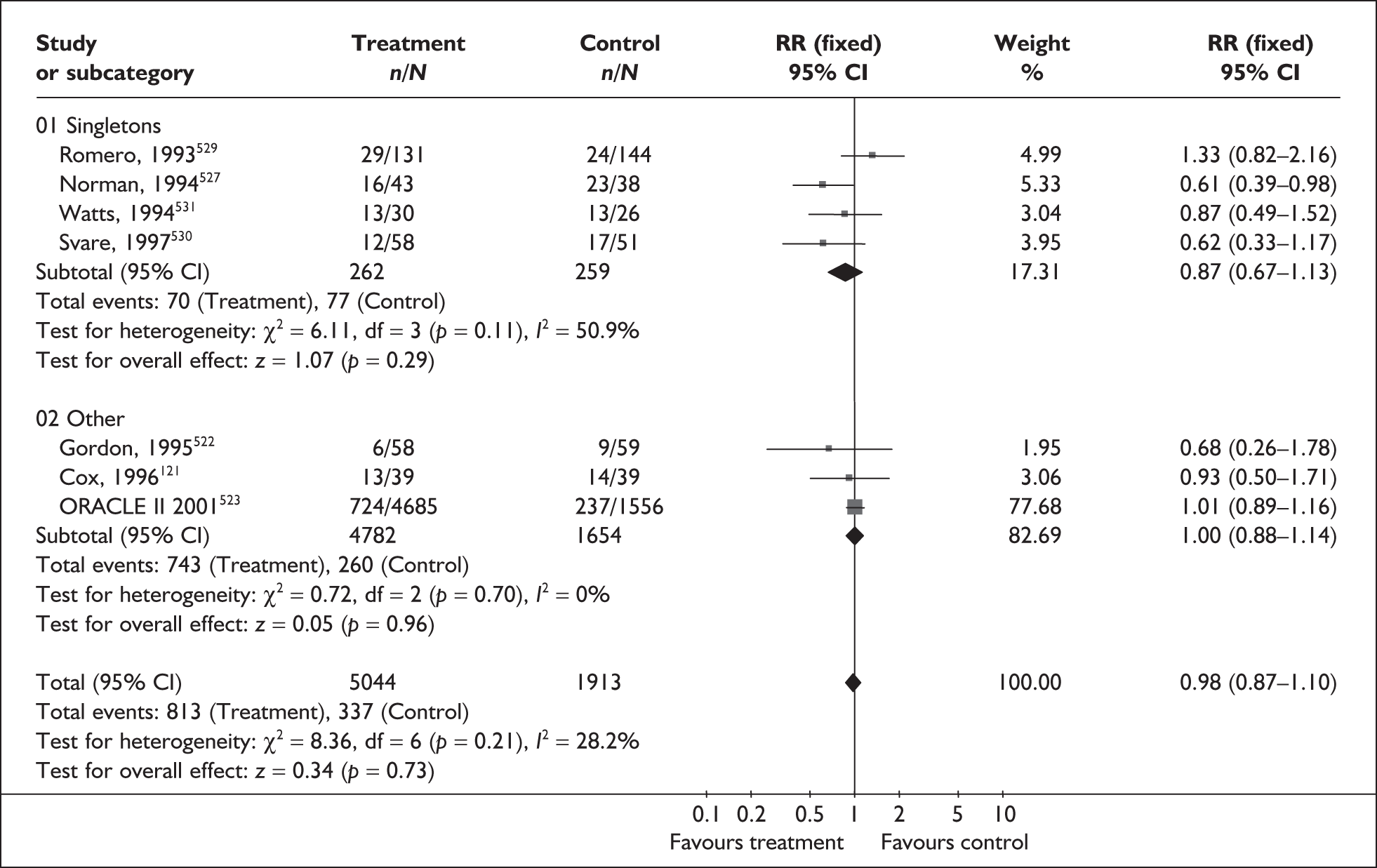
FIGURE 169.
Forest plot of the effects of antibiotic therapy subgrouped by type of antibiotic versus placebo/no treatment for delivery within 7 days of treatment. a, Multiple gestations included in trial or not excluded from trial.
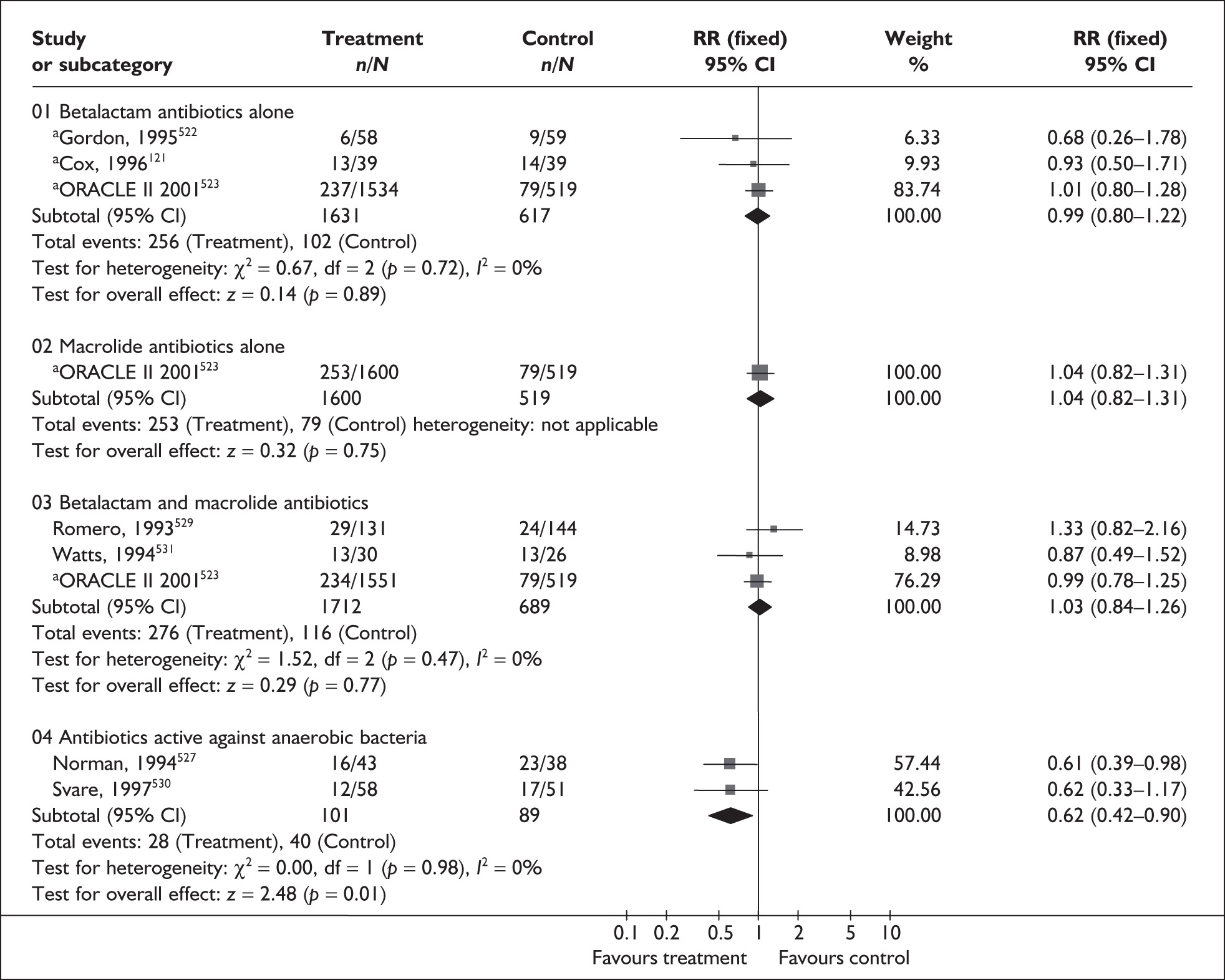
FIGURE 170.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of perinatal mortality.
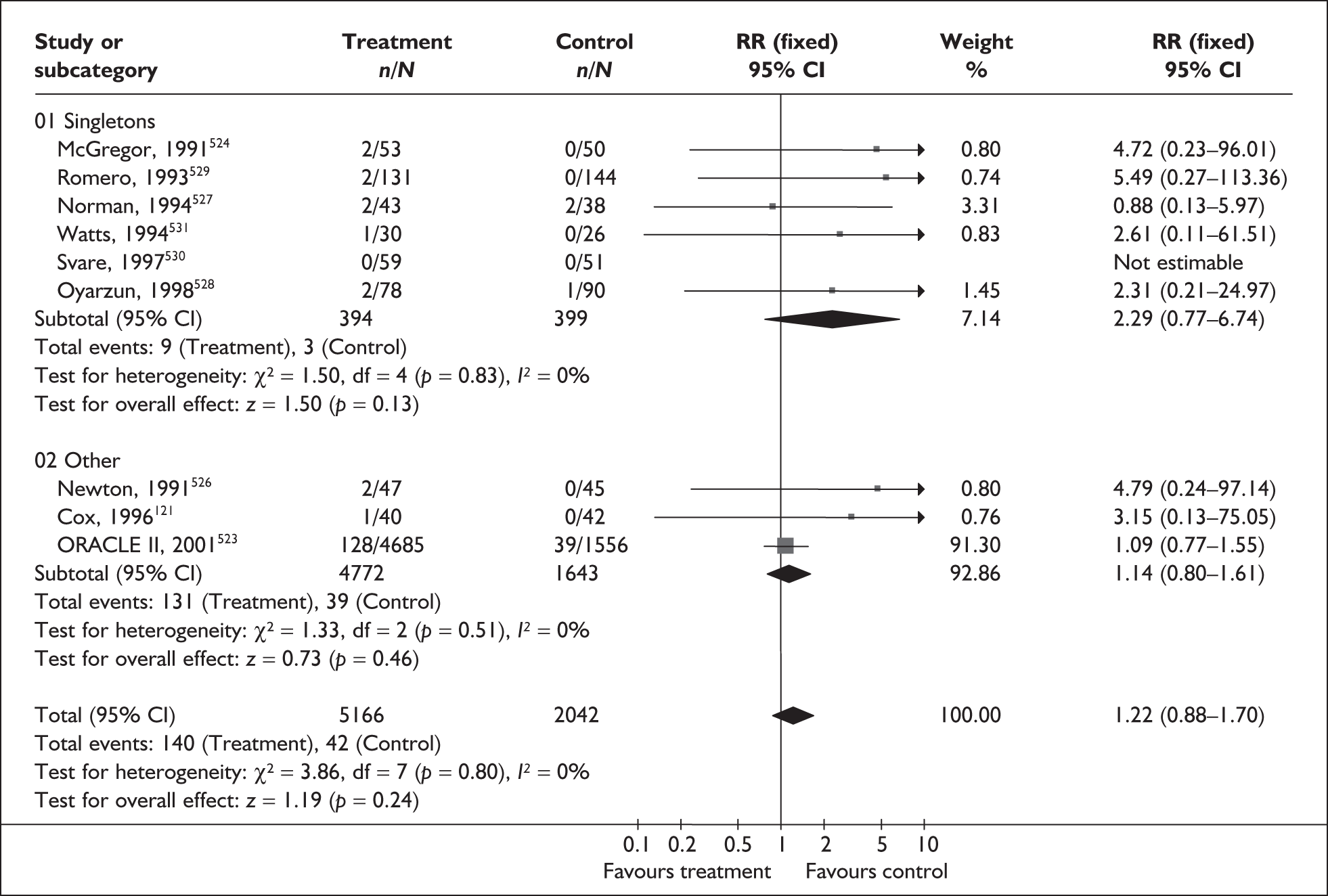
FIGURE 171.
Forest plot of the effects of antibiotic therapy subgrouped by type of antibiotic versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of perinatal mortality. a, Multiple gestations included in trial or not excluded from trial.
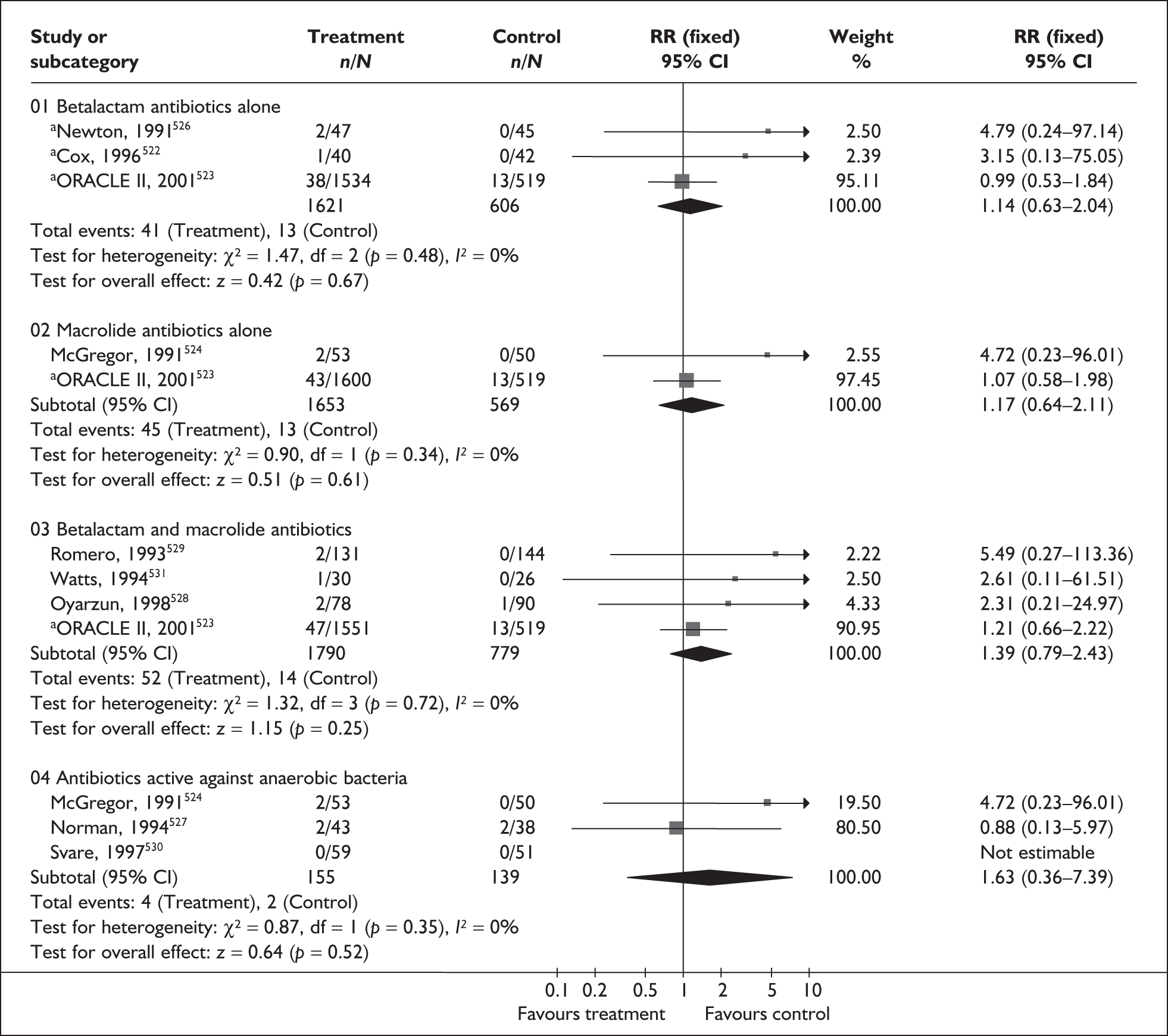
FIGURE 172.
Forest plot of the effects of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of admission to neonatal unit.
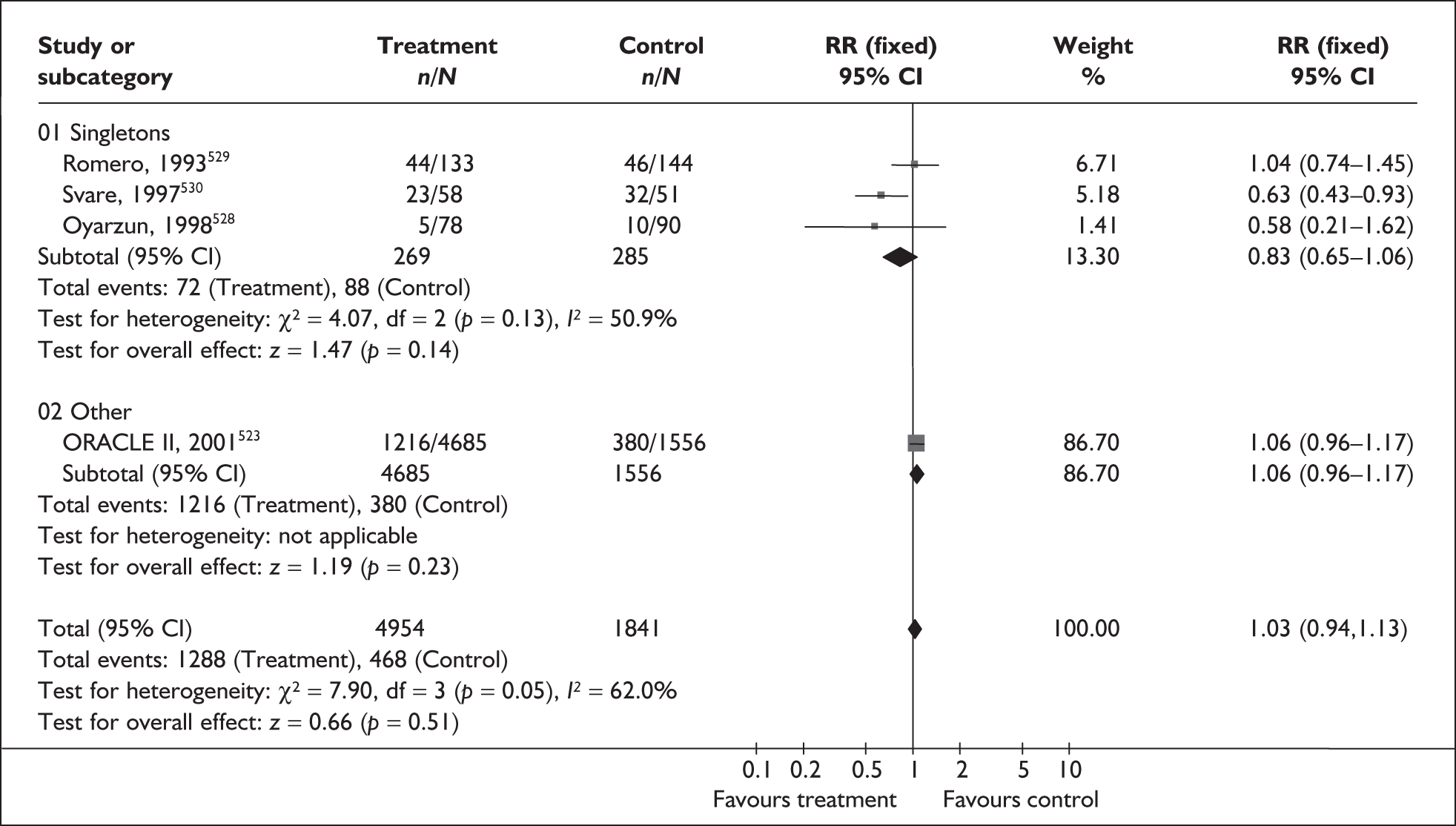
FIGURE 173.
Forest plot of the effects of antibiotic therapy subgrouped by type of antibiotic versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of admission to neonatal unit. a, Multiple gestations included in trial or not excluded from trial.
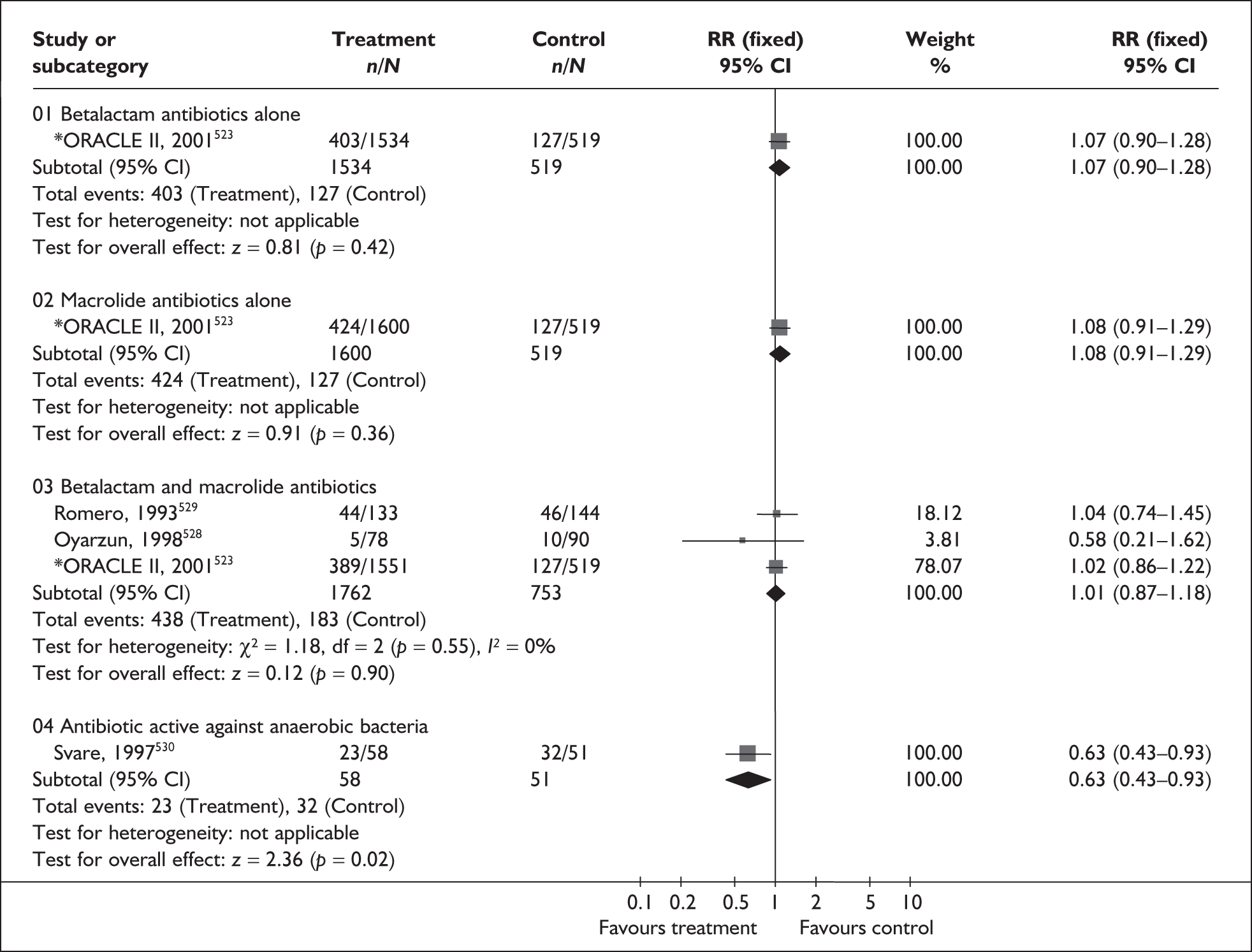
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | Heterogeneity (I2, p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fetal death | |||
| Any antibiotic (mixed): (7 studies, n = 6986)121,523,524,526,527,529,530 | 0.72 | 0.42–1.25 | 0% (0.38) |
| Betalactam antibiotics alone: (3 studies, n = 2227)121,526,523 | 0.90 | 0.37–2.21 | 0% (0.44) |
| Macrolide antibiotics alone: (2 studies, n = 2222)523,524 | 0.54 | 0.20–1.48 | NA, 1 study not estimable |
| Betalactam + macrolide: (2 studies, n = 2347)523,529 | 0.73 | 0.28–1.90 | NA, 1 study not estimable |
| Neonatal death | |||
| Any antibiotic (singletons): (4 studies, n = 462)524,527,528,530 | 1.81 | 0.51–6.45 | 0% (0.62) |
| Any antibiotic (mixed): (3 studies, n = 6415)121,523,526 | 1.49 | 0.94–2.36 | 0% (0.82) |
| Betalactam antibiotics alone: (3 studies, n = 2227)121,523,526 | 1.32 | 0.61–2.86 | 0% (0.74) |
| Macrolide antibiotics alone: (2 studies, n = 2222)523,524 | 1.68 | 0.77–3.64 | 0% (0.48) |
| Betalactam + macrolide: (2 studies, n = 2238)523,528 | 1.68 | 0.78–3.61 | 0% (0.78) |
| Active against anaerobic bacteria: (3 studies, n = 294)524,527,530 | 1.63 | 0.36–7.39 | 0% (0.35) |
| Birthweight < 2500 g | |||
| Any antibiotic (singletons): (2 studies, n = 213)524 | 0.75 | 0.56–1.01 | 0% (0.91) |
| Any antibiotic (mixed): (3 studies, n = 6415)121,523,526 | 1.06 | 0.97–1.16 | 12.7% (0.32) |
| Betalactam antibiotics alone: (3 studies, n = 2227)121,523,526 | 1.08 | 0.94–1.24 | 13.4% (0.32) |
| Macrolide antibiotics alone: (2 studies, n = 2222)523,524 | 1.05 | 0.90–1.22 | 0% (0.13) |
| Betalactam + macrolide: (1 study, n = 2070)523 | 1.02 | 0.87–1.20 | NA |
| Active against anaerobic bacteria: (2 studies, n = 213)524,530 | 0.75 | 0.56–1.01 | 0% (0.91) |
| Respiratory distress syndrome | |||
| Any antibiotic (singletons): (5 studies, n = 689)527–531 | 1.17 | 0.78–1.76 | 0% (0.49) |
| Any antibiotic (mixed): (3 studies, n = 2227)121,523,526 | 0.96 | 0.81–1.14 | 0% (0.95) |
| Betalactam antibiotics alone: (3 studies, n = 2227)121,523,526 | 0.94 | 0.71–1.24 | 0% (0.95) |
| Macrolide antibiotics alone: (1 study, n = 2119)523 | 0.94 | 0.68–1.29 | NA |
| Betalactam + macrolide: (4 studies, n = 2569)523,528,529 | 1.12 | 0.87–1.46 | 0% (0.69) |
| Active against anaerobic bacteria: (2 studies, n = 190)531,527,530 | 0.49 | 0.17–1.40 | 0% (0.80) |
| Mechanical ventilation | |||
| Any antibiotic (mixed): (1 study, n = 6241)523 | 1.02 | 0.84–1.24 | NA |
| Betalactam antibiotics alone: (1 study, n = 2053)523 | 1.01 | 0.71–1.42 | NA |
| Macrolide antibiotics alone: (1 study, n = 2119)523 | 1.02 | 0.73–1.44 | NA |
| Betalactam + macrolide: (1 study, n = 2070)523 | 1.05 | 0.75–1.48 | NA |
| Chronic lung disease | |||
| Any antibiotic (mixed): (1 study, n = 6241)523 | 1.17 | 0.78–1.76 | NA |
| Betalactam antibiotics alone: (1 study, n = 2053)523 | 0.81 | 0.39–1.69 | NA |
| Macrolide antibiotics alone: (1 study, n = 2119)523 | 1.17 | 0.58–2.34 | NA |
| Betalactam + macrolide: (1 study, n = 2070)523 | 1.41 | 0.71–2.78 | NA |
| Neonatal sepsis | |||
| Any antibiotic (singletons): (5 studies, n = 736)524,527–530 | 0.65 | 0.41–1.02 | 11.7% (0.34) |
| Any antibiotic (mixed): (4 studies, n = 2227)121,522,523,526 | 1.05 | 0.71–1.54 | 0% (0.92) |
| Betalactam antibiotics alone: (4 studies, n = 2366)121,522,523,526 | 1.01 | 0.54–1.90 | 0% (0.91) |
| Macrolide antibiotics alone: (2 studies, n = 2222)523,524 | 0.97 | 0.51–1.83 | 0% (0.35) |
| Betalactam + macrolide: (3 studies, n = 2513)523,528,529 | 0.89 | 0.56–1.42 | 45% (0.16) |
| Active against anaerobic bacteria: (3 studies, n = 293)527,529,530 | 0.56 | 0.29–1.11 | 0% (0.74) |
| Necrotising enterocolitis | |||
| Any antibiotic (singletons): (3 studies, n = 465)527,529,530 | 0.33 | 0.11–1.00 | 0% (0.40) |
| Any antibiotic (mixed): (3 studies, n = 2227)121,523,526 | 148 | 0.82–2.67 | 21.7% (0.27) |
| Betalactam antibiotics alone: (3 studies, n = 2227)121,523,526 | 1.31 | 0.52–3.32 | 0% (0.65) |
| Macrolide antibiotics alone: (1 study, n = 2119)523 | 1.30 | 0.44–3.86 | NA |
| Betalactam + macrolide: (2 studies, n = 2345)523,529 | 1.36 | 0.60–3.11 | 29.8% (0.23) |
| Active against anaerobic bacteria: (2 studies, n = 190)527,530 | 0.13 | 0.02–1.01 | 0% (0.55) |
| Neonatal positive blood cultures | |||
| Any antibiotic (singletons): (1 study, n = 168)528 | 0.58 | 0.05–6.24 | NA |
| Any antibiotic (mixed): (2 studies, n = 6358)522,523 | 1.03 | 0.69–1.52 | 0% (0.99) |
| Betalactam antibiotics alone: (2 studies, n = 2170)522,523 | 0.96 | 0.49–1.87 | 0% (0.95) |
| Macrolide antibiotics alone: (1 study, n = 2119)523 | 1.10 | 0.55–2.22 | NA |
| Betalactam + macrolide: (2 studies, n = 2238)523,528 | 1.08 | 0.55–2.10 | 0% (0.59) |
| Intraventricular haemorrhage | |||
| Any antibiotic (singletons): (2 studies, n = 384)523,526 | 0.32 | 0.07–1.49 | 7.2% (0.89) |
| Any antibiotic (mixed): (2 studies, n = 6333)529,530 | 0.84 | 0.52–1.35 | 0% (0.55) |
| Betalactam antibiotics alone: (2 studies, n = 2145)523,527 | 0.84 | 0.38–1.87 | 0% (0.89) |
| Macrolide antibiotics alone: (1 study, n = 2119)523 | 0.83 | 0.35–1.99 | NA |
| Betalactam + macrolide: (2 studies, n = 2345)523,529 | 0.97 | 0.43–2.19 | 0% (0.92) |
| Active against anaerobic bacteria: (1 study, n = 109)530 | 0.18 | 0.02–1.46 | NA |
| Major cerebral abnormality | |||
| Any antibiotic (mixed): (1 study, n = 6241)523 | 1.00 | 0.66–1.51 | NA |
| Betalactam antibiotics alone: (1 study, n = 2053)523 | 0.91 | 0.45–1.87 | NA |
| Macrolide antibiotics alone: (1 study, n = 2119)523 | 0.84 | 0.41–1.74 | NA |
| Betalactam + macrolide: (1 study, n = 2070)523 | 1.14 | 0.57–2.29 | NA |
| Maternal adverse drug reaction | |||
| Any antibiotic (singletons): (4 studies, n = 544)524,529–531 | 1.30 | 0.90–1.87 | 0% (0.43) |
| Any antibiotic (mixed): (1 study, n = 82)121 | 3.15 | 0.13–75.05 | NA |
| Betalactam antibiotics alone: (1 study, n = 82)121 | 3.15 | 0.13–75.05 | NA |
| Macrolide antibiotics alone: (1 study, n = 103)524 | 0.88 | 0.49–1.59 | NA |
| Betalactam + macrolide: (2 studies, n = 331)529,531 | 1.49 | 0.93–2.40 | 0% (0.97) |
| Active against anaerobic bacteria: (2 studies, n = 213)524,530 | 1.04 | 0.59–1.83 | 32.6% (0.22) |
| Maternal infection | |||
| Any antibiotic (singletons): (6 studies, n = 798)524,527–531 | 0.53 | 0.32–0.89 | 0% (0.45) |
| Any antibiotic (mixed): (3 studies, n = 6444)522,523,526 | 0.77 | 0.66–0.91 | 7.7% (0.33) |
| Betalactam antibiotics alone: (3 studies, n = 2227)522,523,526 | 0.74 | 0.56–0.98 | 6.2% (0.34) |
| Macrolide antibiotics alone: (2 studies, n = 2222)523,524 | 0.81 | 0.62–1.07 | 0% (0.40) |
| Betalactam + macrolide: (4 studies, n = 2563)523,528,529,531 | 0.75 | 0.59–0.95 | 0% (0.53) |
| Active against anaerobic bacteria: (3 studies, n = 294)524,527,530 | 0.76 | 0.25–2.34 | 37.8% (0.20) |
Other neonatal and maternal outcomes are shown in Table 20. Summary RRs of any antibiotic therapy versus placebo/no treatment from the forest plots presented were used in the decision analyses. The ORACLE II trial, as the largest included trial, dominates the results of this review, and fails to demonstrate any clear benefit of prophylactic antibiotic therapy for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in women with intact membranes and no evidence of clinical infection. Overall, the review did not find any clear evidence of a beneficial effect of prophylactic antibiotic therapy for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in women with intact membranes.
Betamimetics for tocolysis
Betamimetics were commonly used to arrest threatened premature labour thus delaying spontaneous preterm birth. They act on uterine β2-receptors to induce the relaxation of smooth muscle cells. However stimulation of β-adrenergic receptors may also produce a number of cardiovascular and biochemical disturbances as side effects.
The review of betamimetics (ritodrine, terbutaline, isoxuprine, fenoterol, hexoprenaline) for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth532 included 16 RCTs (n = 21,782);533–548 no additional studies were found when the searches were updated. Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 132. The quality of these studies was mixed as shown in Figure 174; few trials reported adequate allocation concealment. No statistically significant benefit was found on the risk of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation when betamimetics were compared with placebo (Figure 175). When grouped by type of betamimetic, terbutaline was found to significantly reduce risk of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in two small trials, one of unclear methodological quality. The summary RR was put forward for use in the decision analysis. A reduction in the risk of delivery within 48 hours after treatment was shown when ritodrine and terbutaline were compared with placebo (Figure 176). The pooled RR for ritodrine and terbutaline combined was put forward for use in the decision analysis. Compared with ritodrine, terbutaline was found to reduce the incidence of birth within 48 hours of treatment, although this did not reach statistical significance (Figure 177). A reduction in the risk of delivery within 7 days after treatment was shown for ritodrine and terbutaline when compared with placebo (Figure 178).The pooled RR for all betamimetics versus placebo was used in the decision analysis. When compared with ritodrine, terbutaline demonstrated a non-significant reduction in risk of delivery within 7 days (Figure 179). Incidence of admission to neonatal care unit was not reported. Neither placebo nor betamimetic comparisons had a statistically significant relative risk on perinatal mortality (Figures 180 and 181). As can be seen from Table 21 a greater number of cardiovascular changes, and adverse events leading to the discontinuation of therapy were reported in the betamimetics group compared to placebo. There were insufficient data to indicate whether one betamimetic agent was superior to another, with most head-to-head comparisons based on a single trial.
FIGURE 174.
Methodological quality of the included trials of betamimetic therapy for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
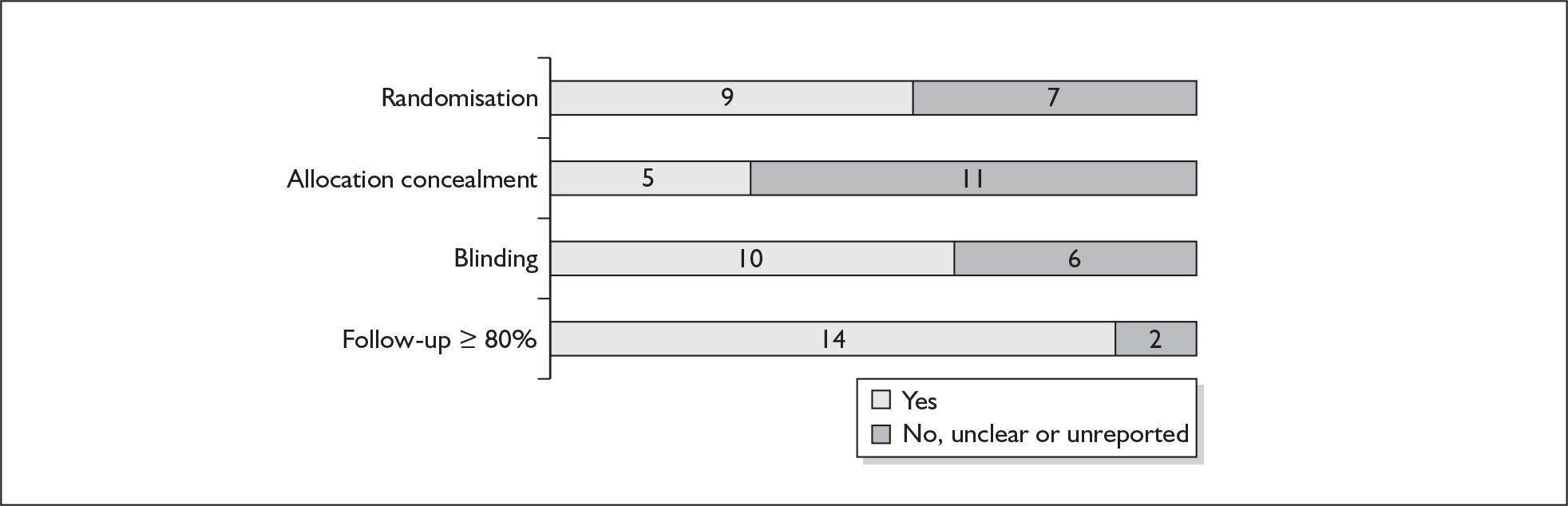
FIGURE 175.
Forest plot of the effects of betamimetics versus placebo for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks gestation.
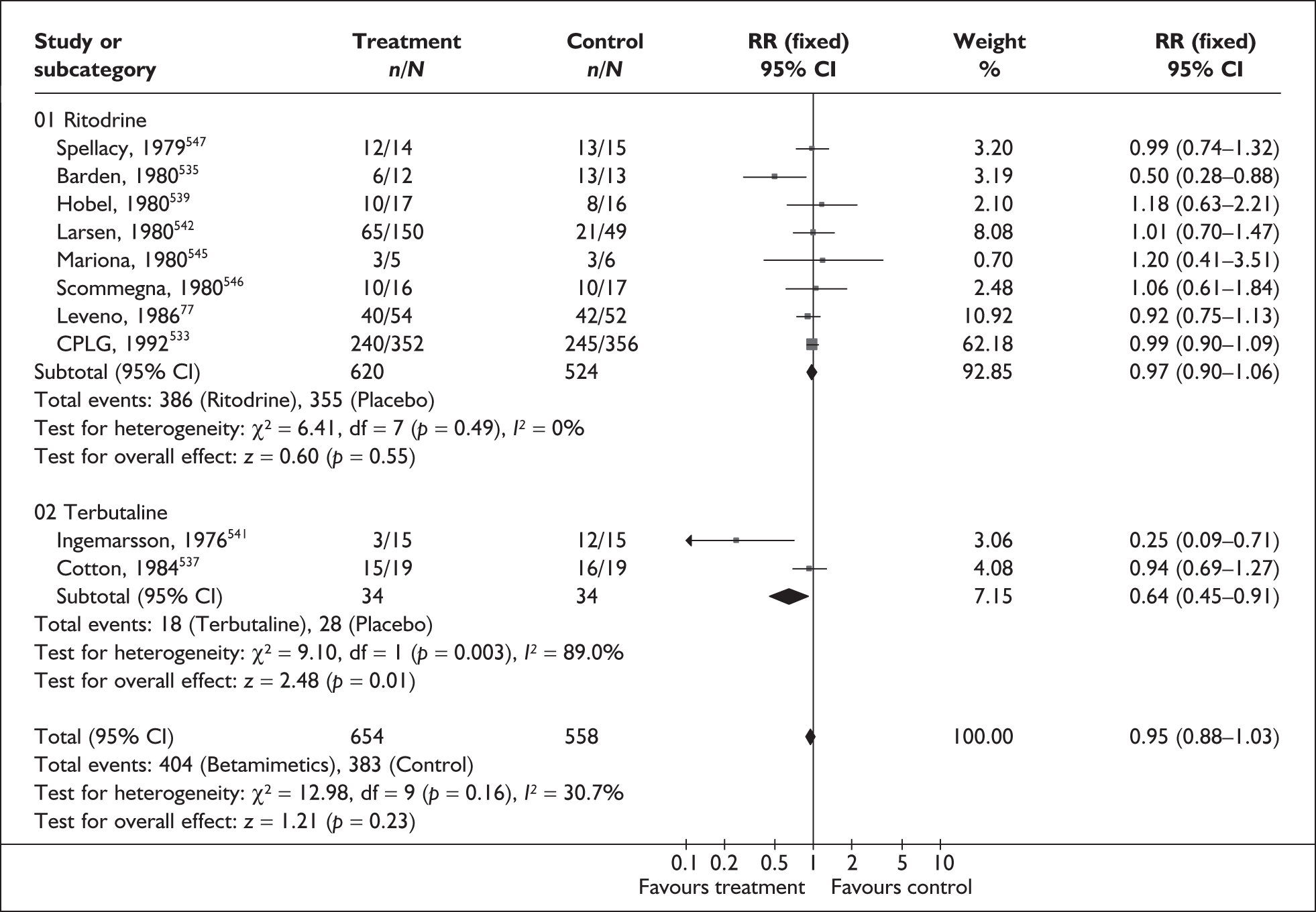
FIGURE 176.
Forest plot of the effects of betamimetics versus placebo or an alternative betamimetic for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of treatment.
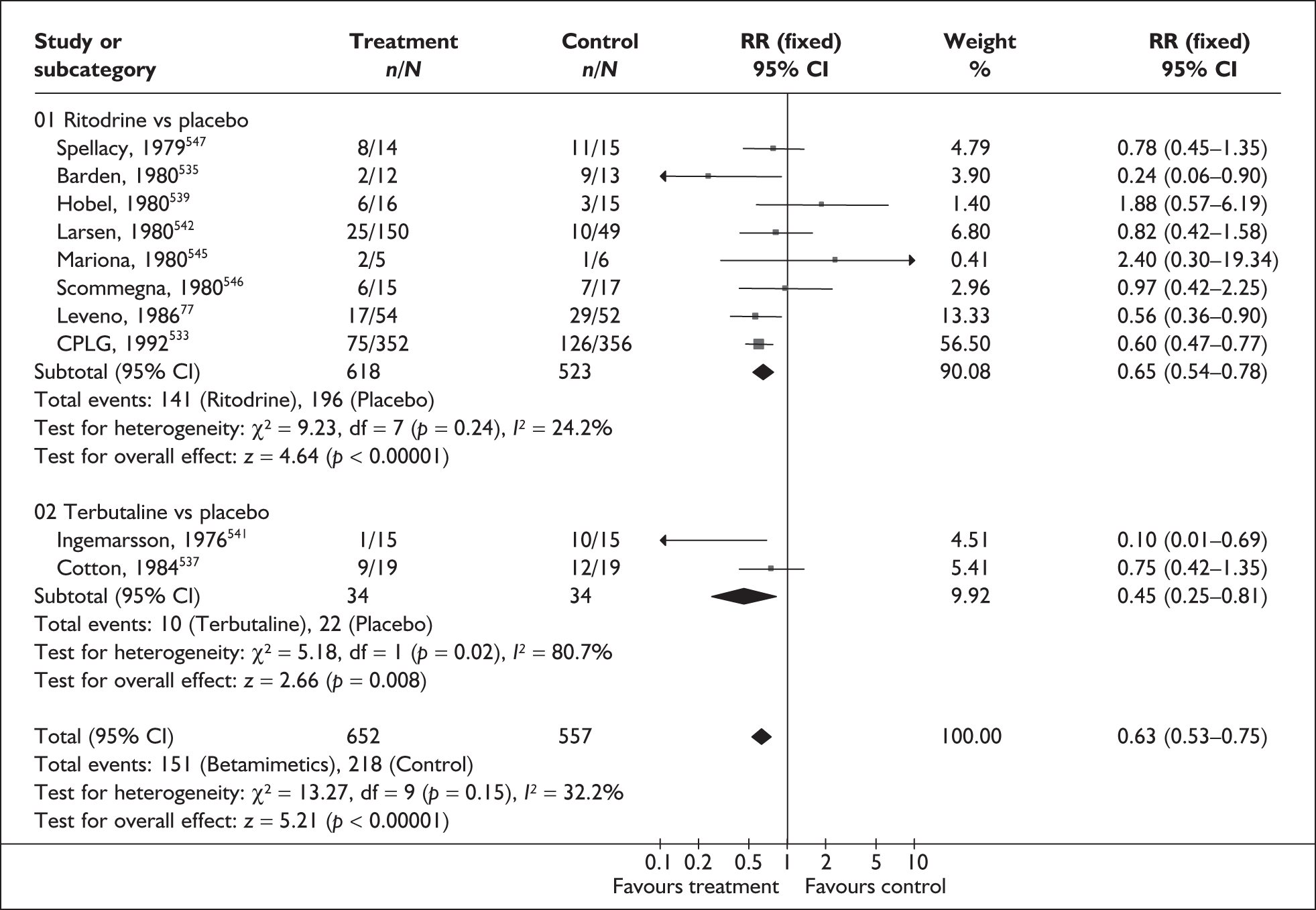
FIGURE 177.
Forest plot of the effects of betamimetics versus an alternative betamimetic for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of treatment.
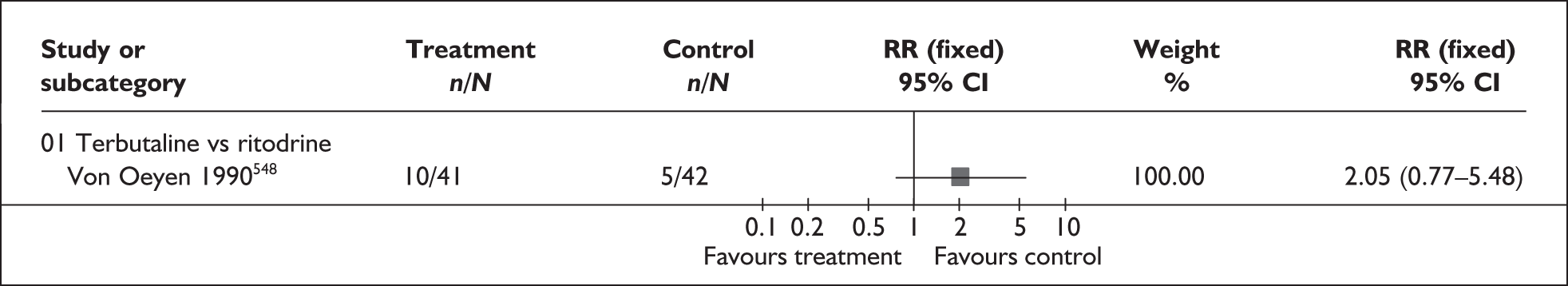
FIGURE 178.
Forest plot of the effects of betamimetics versus placebo or an alternative betamimetic for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of treatment.
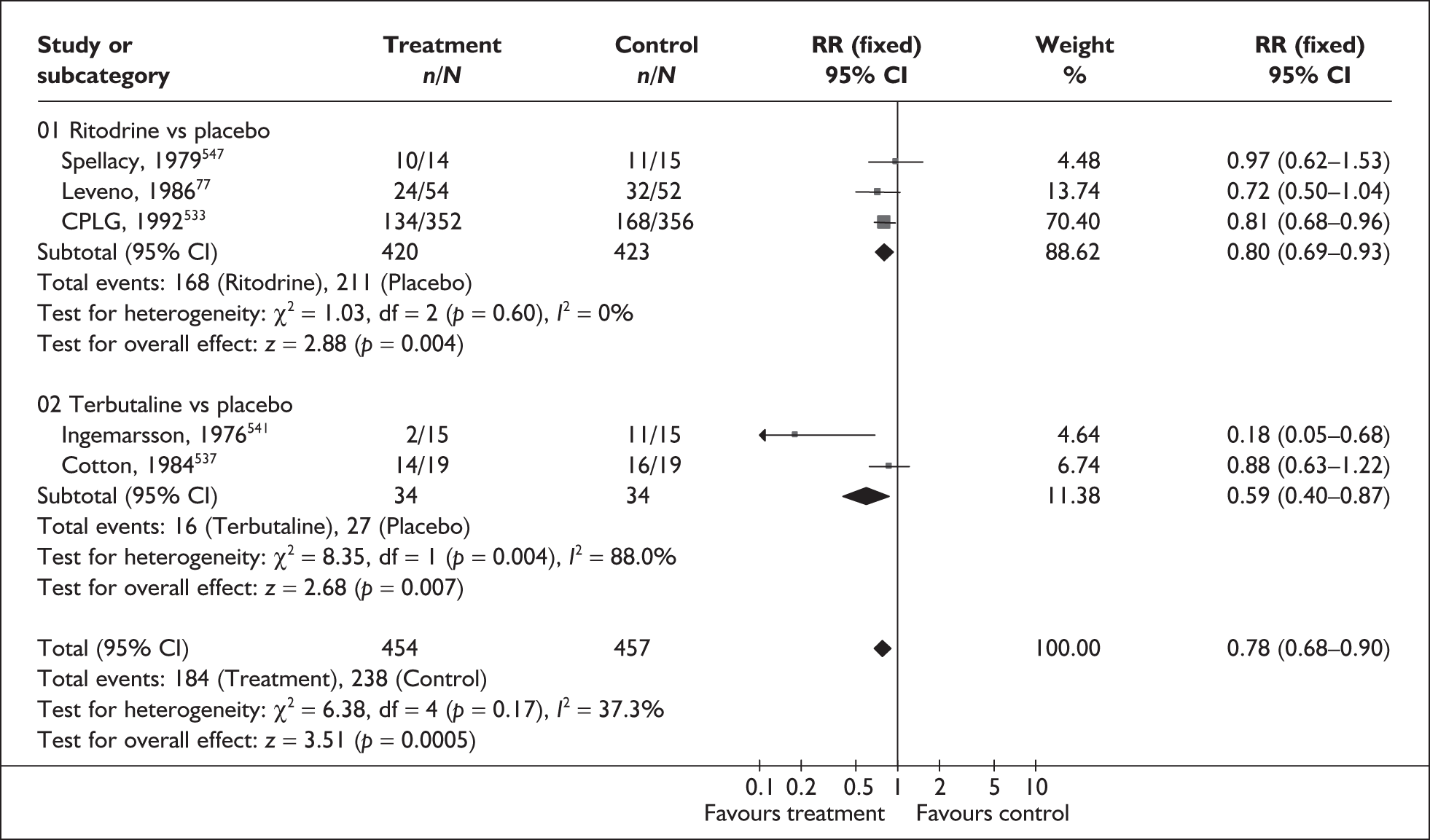
FIGURE 179.
Forest plot of the effects of betamimetics versus an alternative betamimetic for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of treatment.
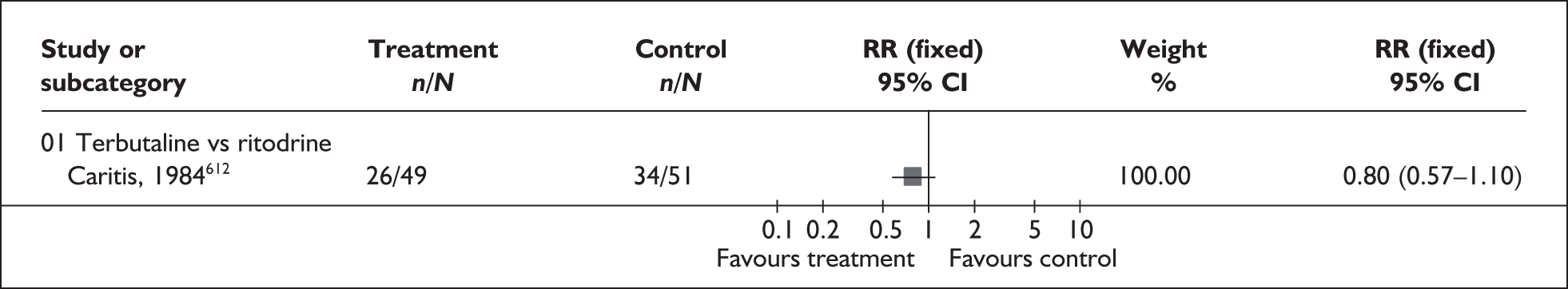
FIGURE 180.
Forest plot of the effects of betamimetics versus placebo on perinatal mortality.
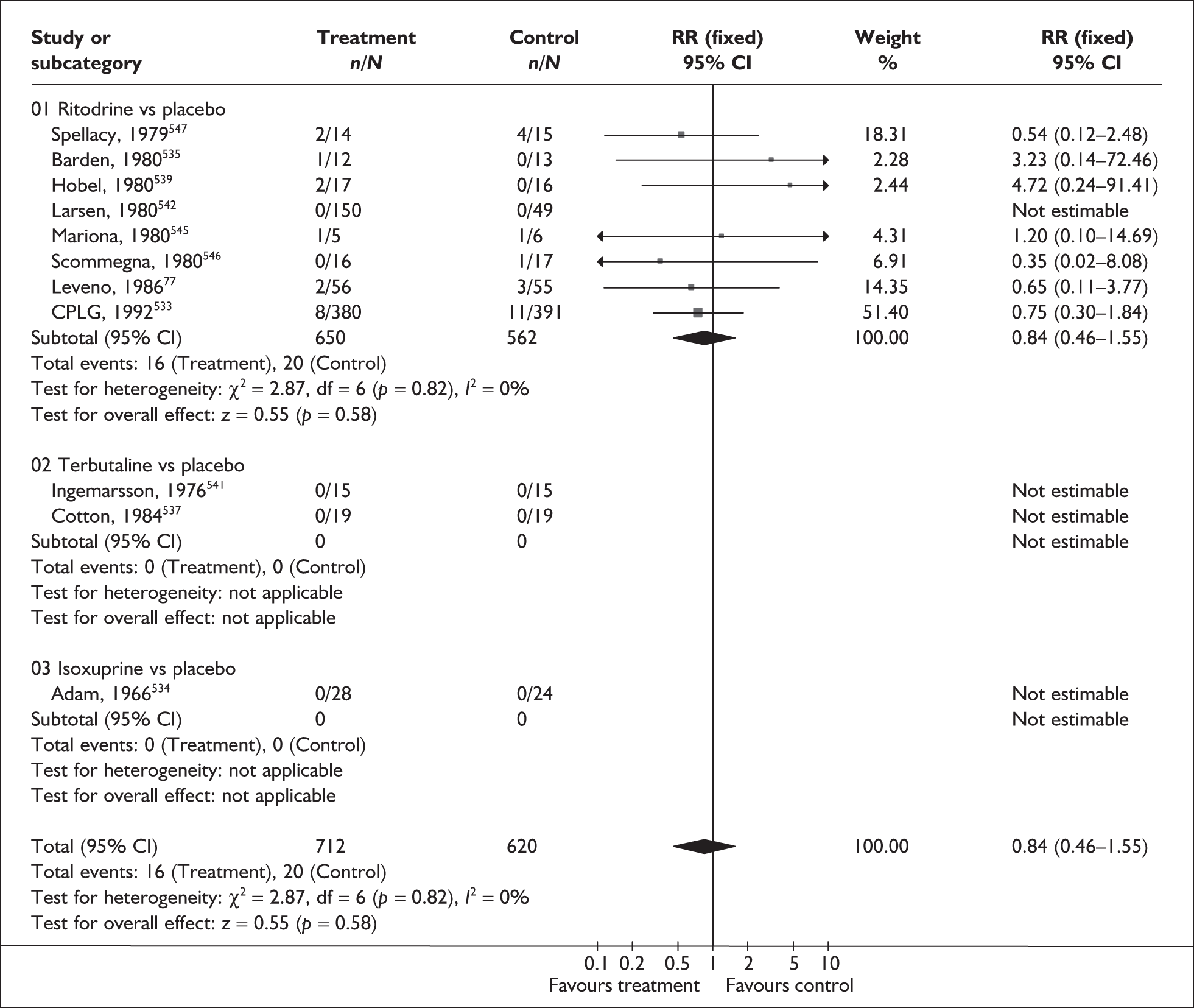
FIGURE 181.
Forest plot of the effects of betamimetics versus an alternative betamimetic on perinatal mortality.
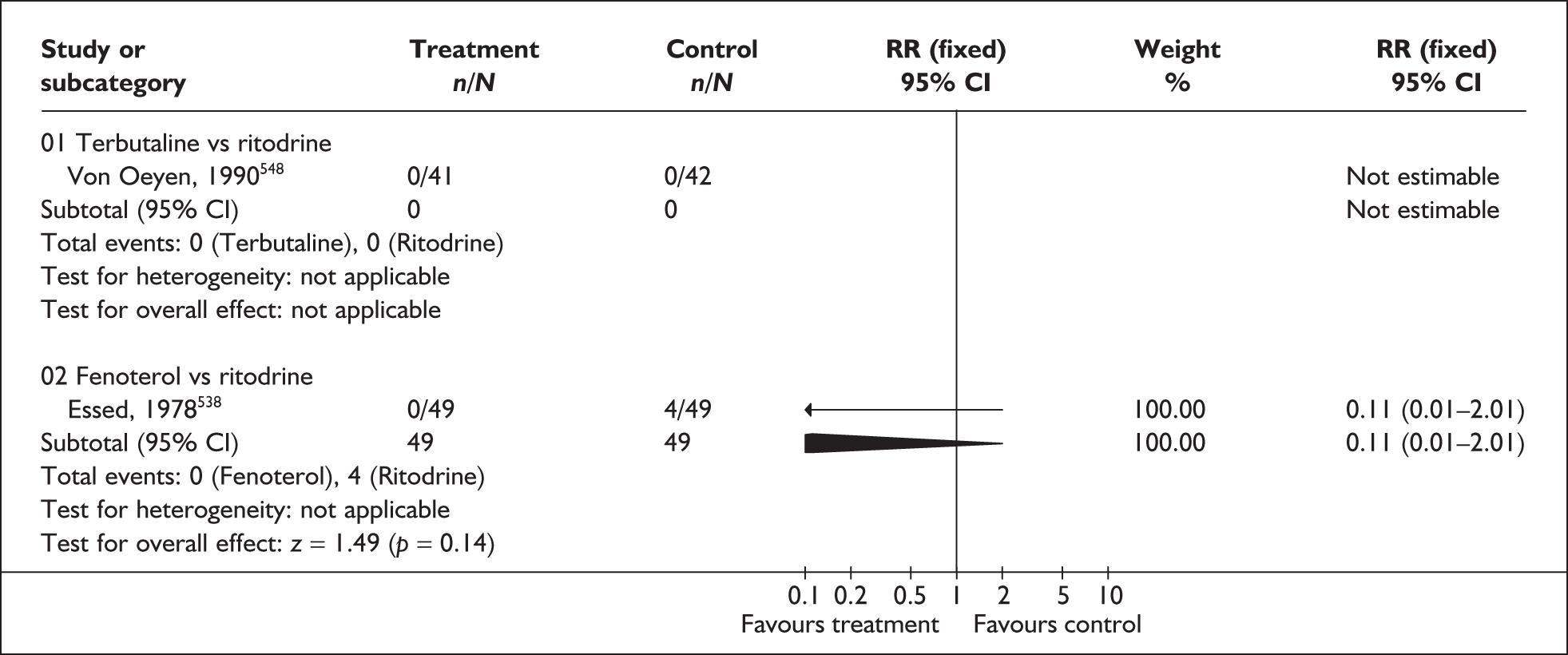
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preterm birth < 28 weeks gestation | |||
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 100)535 | 2.08 | 0.55–7.87 | NA |
| Neonatal death | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (5 studies, n = 1144)532,536,537,541,542 | 1 | 0.48–2.09 | 43.2% (0.13) |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 83)535 | 1.27 | 0.42–3.91 | NA |
| Fenoterol vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 98)533 | 0.13 | 0.02–0.96 | NA |
| Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: (1 study, n = 222)539 | 0.11 | 0.01–2.04 | NA |
| Respiratory distress syndrome | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (8 studies, n = 1239)533,535,537,539,542,543,546,547 | 0.87 | 0.71–1.08 | 22.0% (0.25) |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 101)535 | 1.99 | 0.93–4.27 | NA |
| Fenoterol vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 98)533 | 2 | 0.38–10.42 | NA |
| Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: (1 study, n = 222)539 | 0.71 | 0.35–1.41 | NA |
| Periventricular haemorrhage (grades 3 and 4) | |||
| Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: (1 study, n = 222)539 | 0.14 | 0.01–2.73 | NA |
| >Cerebral palsy | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (1 study, n = 246 537 | 0.19 | 0.02–1.63 | NA |
| Treatment cessation due to side effects | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (4 studies, n = 1051)536,537,541,542 | 11.38 | 5.21–24.86 | 0% (0.48) |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 100)535 | 0.83 | 0.24–2.92 | NA |
| Hexoprenaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 466)543 | 0.28 | 0.08–0.93 | NA |
| Any maternal treatment side effects | |||
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 183)548 | 0.95 | 0.84–1.07 | NA |
| Hexoprenaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 466)543 | 0.83 | 0.76–0.91 | NA |
| Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: (1 study, n = 203)539 | 0.69 | 0.43–1.11 | NA |
| Palpitations | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (4 studies, n = 1042)537,541,542,547 | 10.11 | 6.56–15.58 | 0% (0.99) |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 83)548 | 1.18 | 0.78–1.79 | NA |
| Hexoprenaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 466)543 | 0.75 | 0.60–0.94 | NA |
| Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: (1 study, n = 203)539 | 0.5 | 0.23–1.13 | NA |
| Tachycardia | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (1 study, n = 199)541 | 4.08 | 1.55–10.73 | NA |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 100)535 | 0.66 | 0.43–1.00 | NA |
| Fenoterol vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 96)533 | 0.71 | 0.35–1.45 | NA |
| Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: (1 study, n = 203)539 | 0.88 | 0.33–2.35 | NA |
| Cardiac arrhythmia | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (1 study, n = 708)537 | 3.54 | 0.74–16.92 | NA |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 100)535 | 0.35 | 0.04–3.22 | NA |
| Pulmonary oedema | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (3 studies, n = 852)533,537,543 | 3.03 | 0.12–74.23 | NA |
| Myocardial ischemia | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (1 study, n = 106)542 | 12.53 | 0.72–21.91 | NA |
| Chest pain | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (2 studies, n = 814)537,542 | 11.29 | 3.81–33.46 | 0% (0.52) |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (2 studies, n = 183)535.548 | 1.11 | 0.55–2.25 | 51.9% (0.15) |
| Dyspnoea/Shortness of breath | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (2 studies, n = 814)537,542 | 3.86 | 2.21–6.77 | 0% (0.88) |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (2 studies, n = 183)535,548 | 0.83 | 0.41–1.67 | 0% (0.76) |
| Tremor | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (1 study, n = 708)537 | 10.74 | 6.20–18.59 | NA |
| Hypotension | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (2 studies, n = 136)540,542 | 1.77 | 0.39–8.06 | 49.1% (0.16) |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (2 studies, n = 183)535,548 | 1 | 0.67–1.49 | 74.5% (0.05) |
| Hexoprenaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 466)543 | 0.77 | 0.61–0.96 | NA |
| Hyperglycaemia | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (1 study, n = 708)537 | 2.9 | 2.05–4.09 | NA |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 100)535 | 1.78 | 1.05–3.03 | NA |
| Fenoterol vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 98)533 | 1.33 | 0.31–5.65 | NA |
| Hypokalaemia | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (1 study, n = 708)537 | 6.07 | 4.00–9.20 | NA |
| Nausea/vomiting | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (3 studies, n = 932)537,542,547 | 1.76 | 1.29–2.42 | 0% (0.93) |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 100)535 | 1.5 | 0.71–3.20 | NA |
| Hexoprenaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 466)543 | 0.63 | 0.45–0.89 | NA |
| Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: (1 study, n = 203)539 | 1.21 | 0.38–3.84 | NA |
| Headaches | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (3 studies, n = 936)533,542,547 | 4.07 | 2.60–6.35 | 6.35 |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 83)548 | 0.48 | 0.23–0.99 | NA |
| Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: (1 study, n = 203)539 | 1.01 | 0.06–15.93 | NA |
| Fetal hypoglycaemia | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (3 studies, n = 857)536,537,542 | 1.89 | 0.35–10.04 | NA |
| Fetal tachycardia | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (1 study, n = 30)540 | 2.4 | 1.12–5.13 | NA |
| Sepsis/infection | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (2 studies, n = 809)536,537 | 2.72 | 0.19–39.63 | 73.9% (0.05) |
| Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: (1 study, n = 222)539 | 0.71 | 0.23–2.18 | NA |
| Necrotising enterocolitis | |||
| All betamimetics vs placebo: (2 studies, n = 149)536,542 | 0.42 | 0.06–2.78 | 0% (0.42) |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 101)535 | 0.53 | 0.05–5.67 | NA |
| Increase in fetal heart rate | |||
| Hexoprenaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 466)543 | 0.74 | 0.56–0.98 | NA |
Of the included studies, only one trial does not appear to have used a maintenance regimen as part of its study protocol; however, the dataset for this study is very small. 537 It is therefore not possible to separate the influence of acute treatment with betamimetics from the effect of any maintenance regimen, except for birth within 48 hours of treatment. This should be considered when interpreting these results. In addition, only one trial explicitly states that multiple gestations were excluded. While betamimetics appear to be able to prolong gestation up to 7 days compared to placebo, the risk of adverse effects must also be considered. Indeed, the use of betamimetics as tocolysis is no longer recommended by the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) because of the risk of adverse events.
Oral betamimetics maintenance
Oral tocolytic maintenance therapy can be given after an episode of threatened preterm labour to maintain uterine quiescence. Betamimetics are one of several tocolytic agents that may be offered.
The review of oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy after threatened preterm labour 549 included 11 RCTs (n = 1238);550–560 no additional studies were found when the searches were updated. Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 132. The quality of these studies is shown in Figure 182; few of the included trials were considered to be of high quality. Oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy after acute tocolytic treatment of threatened preterm labour did not significantly affect the risk of spontaneous preterm birth before either 34 or 37 weeks’ gestation (Figure 183 and Figure 184, respectively), delivery within 24 or 48 hours after treatment (Figure 185 and Figure 186, respectively), delivery within 7 days after treatment (Figure 187) or requirement for admission to neonatal intensive care unit (Figure 188) compared to placebo/no treatment. Pooled RRs for betamimetics versus placebo/no treatment presented in the forest plots were used in the decision analyses for all primary outcomes. Although perinatal mortality was reported, it was defined as death before discharge among all live births, as this may include mortality beyond the first week after birth, summary RRs were not used in the decision analysis for perinatal mortality. Compared with placebo/no treatment, an increase in perinatal mortality (defined as death before discharge among live births) was reported, although this was not statistically significant. A greater number of adverse events, and in particular cardiovascular changes, were reported in the betamimetic maintenance group compared with placebo (Table 22). There were insufficient data to indicate whether one betamimetic agent was superior to another, with most head-to-head comparisons based on a single trial for the available information for delaying spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation and within 7 days of treatment with betamimetic maintenance therapy (Figures 189 and 190, respectively). It was unclear in the majority of the primary studies whether trials included both singletons and multiple gestations. Overall, the evidence does not support the use of oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy after threatened preterm labour.
FIGURE 182.
Methodological quality of the included trials of oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth following acute tocolytic therapy in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
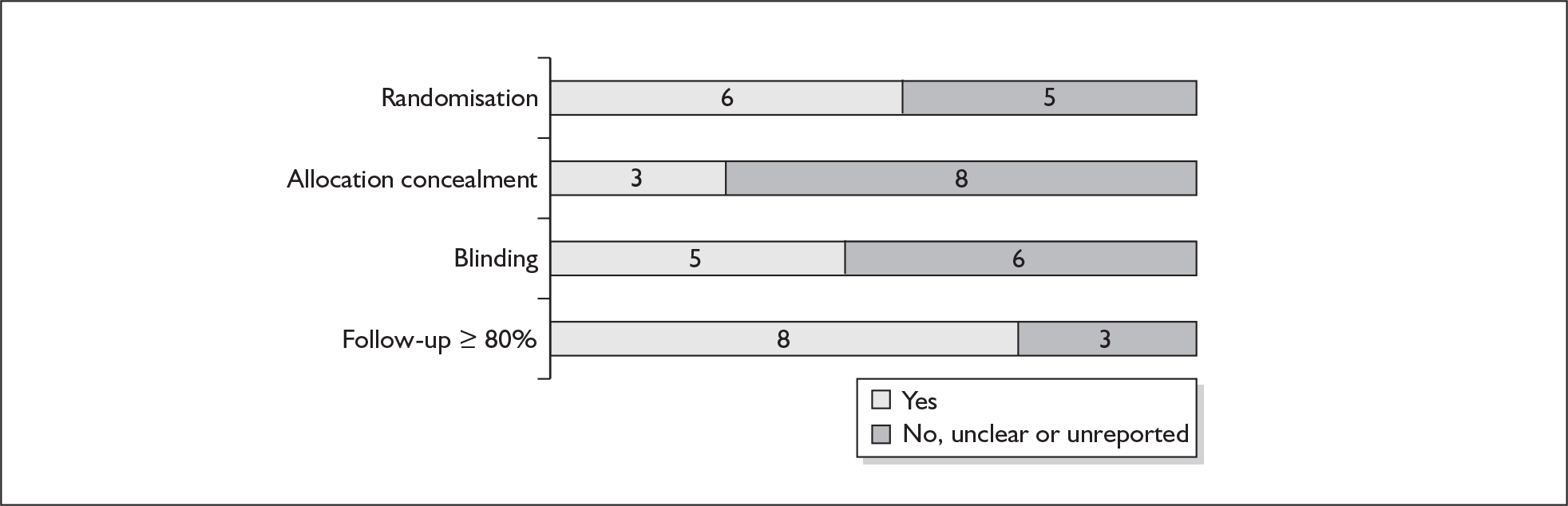
FIGURE 183.
Forest plot of the effects of oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy versus other tocolytic treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation.
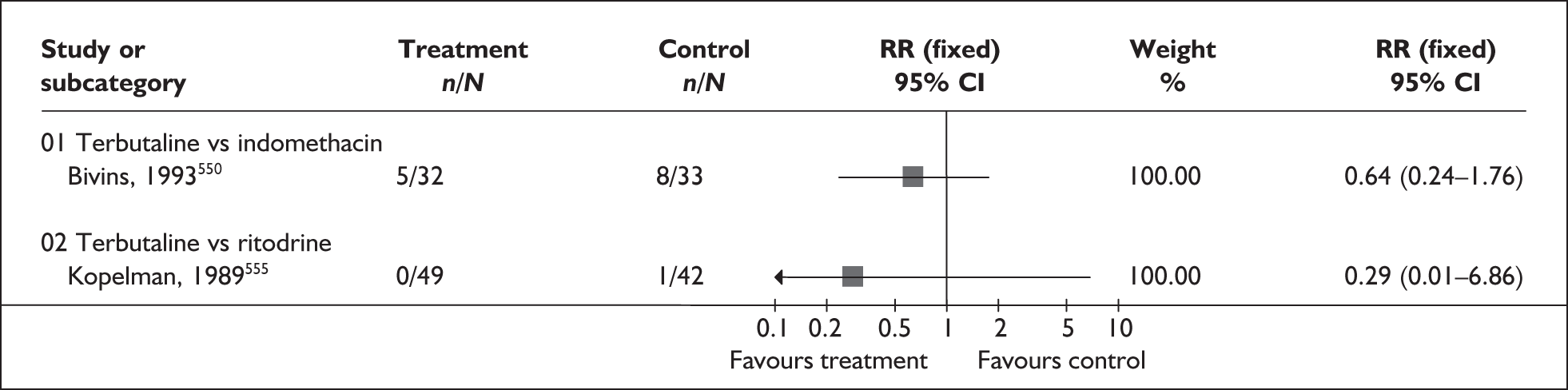
FIGURE 184.
Forest plot of the effects of oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy versus placebo/no treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
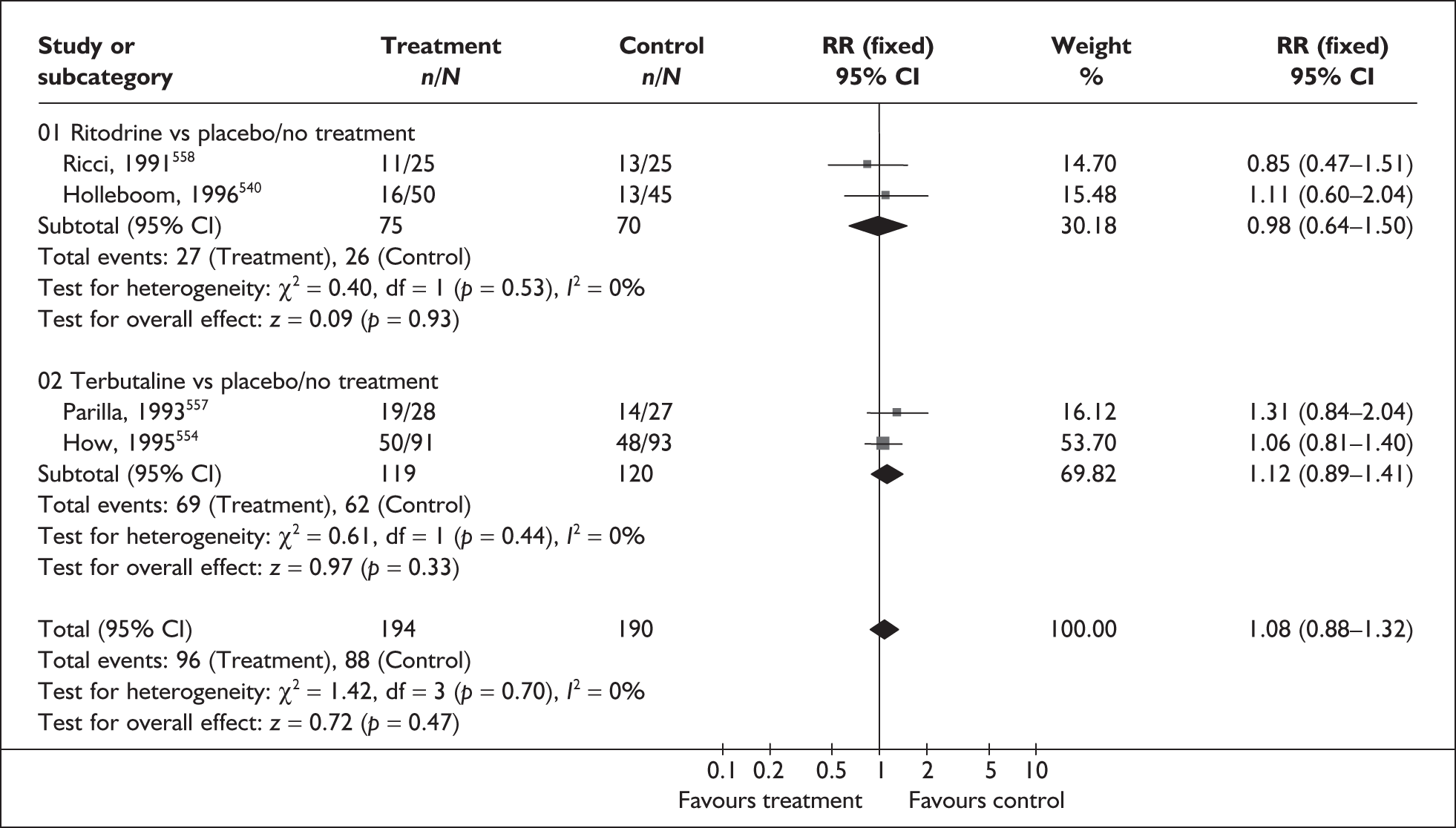
FIGURE 185.
Forest plot of the effects of oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy versus placebo/no treatment on spontaneous preterm birth within 24 hours of treatment.
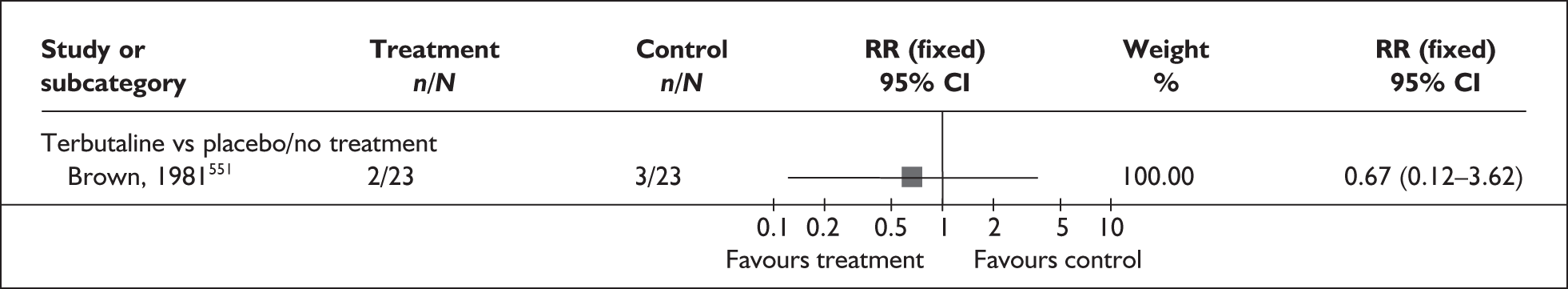
FIGURE 186.
Forest plot of the effects of oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy versus placebo/no treatment on spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of treatment.
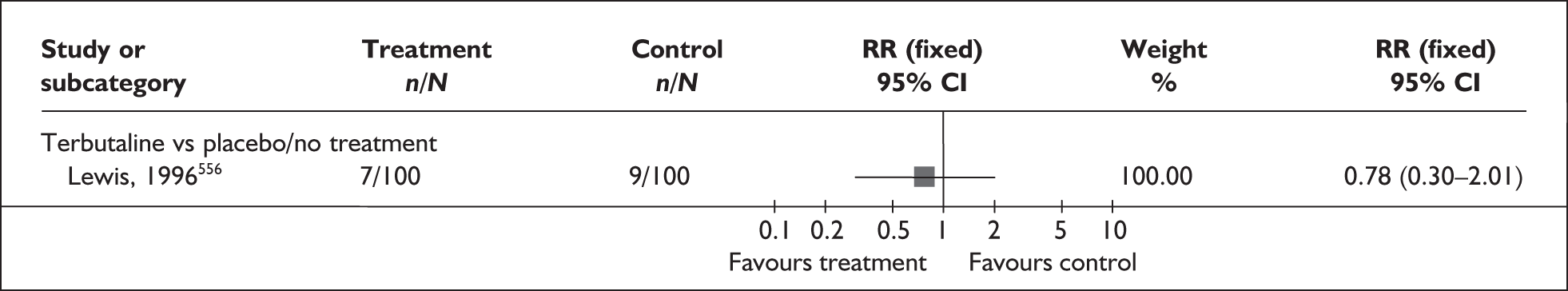
FIGURE 187.
Forest plot of the effects of oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy versus placebo/no treatment on spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of treatment.
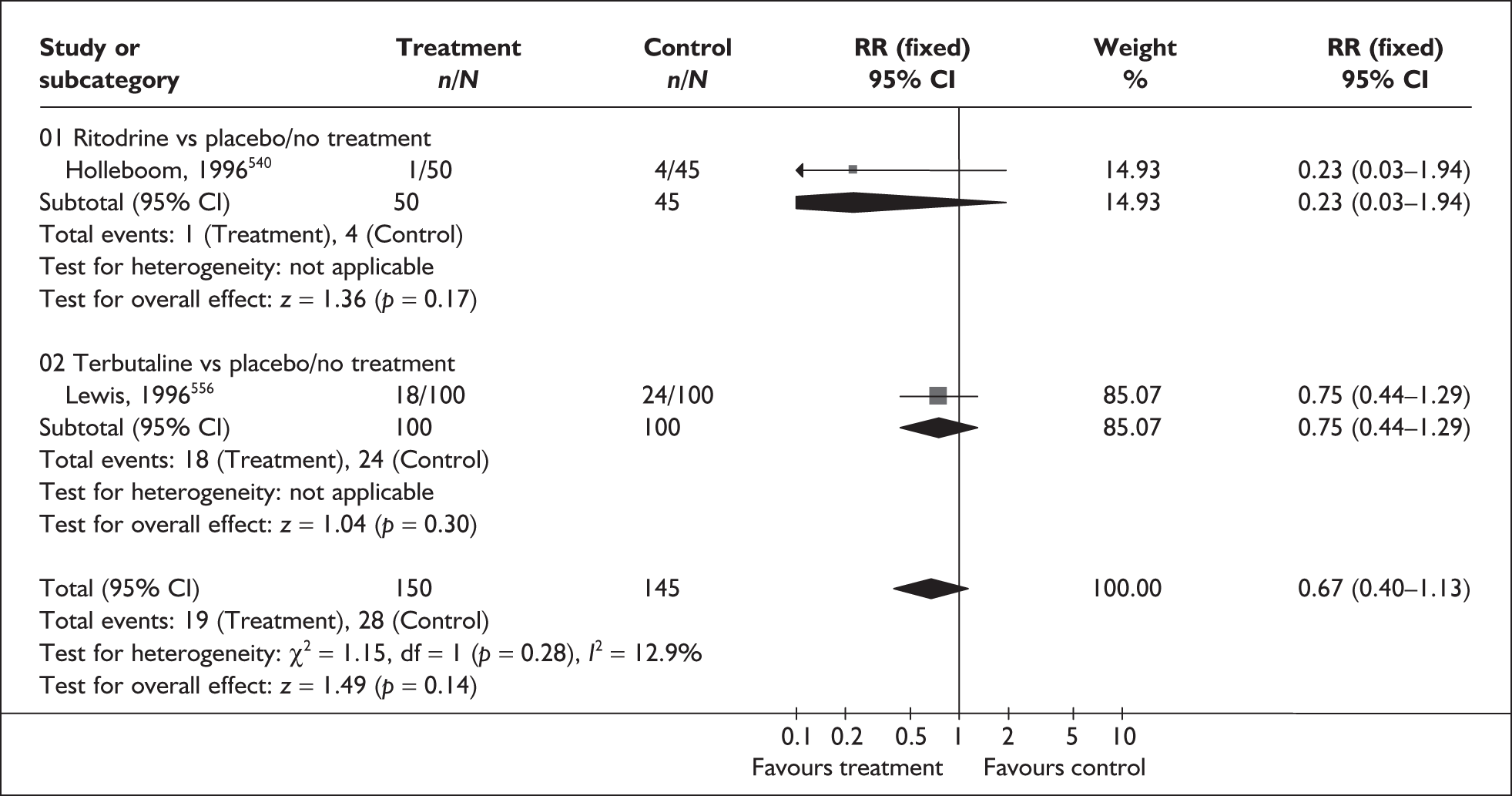
FIGURE 188.
Forest plot of the effects of oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy versus placebo/no treatment or another tocolytic agent on admission to neonatal intensive care unit.
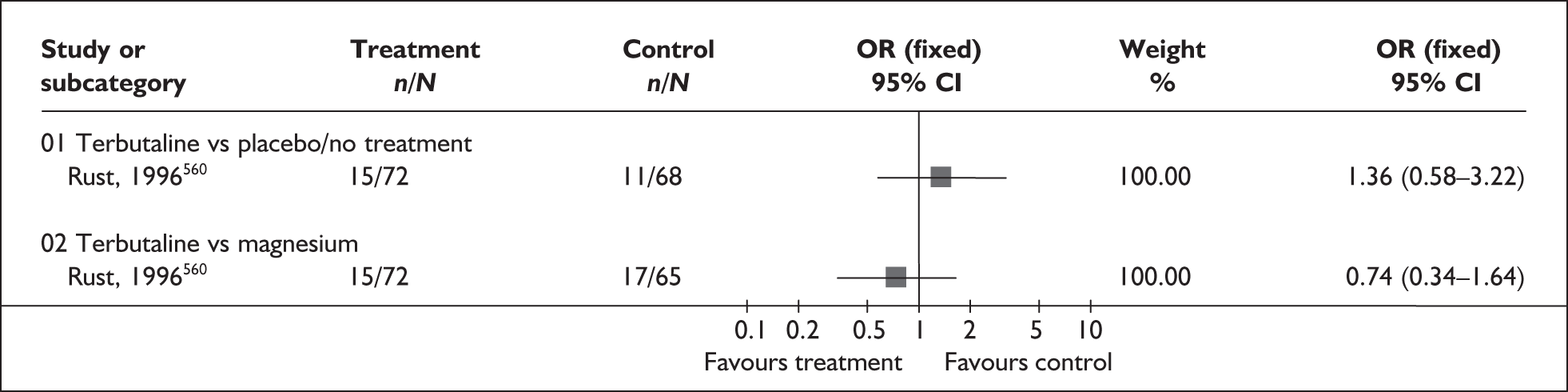
FIGURE 189.
Forest plot of the effects of oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy versus other tocolytic treatment for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
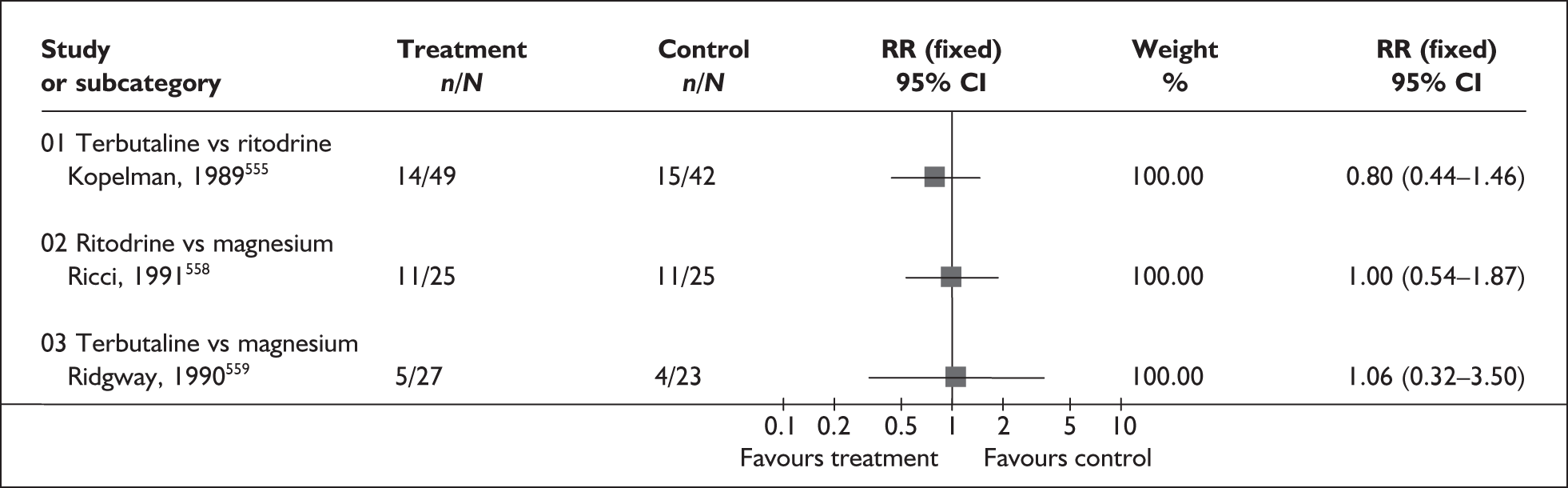
FIGURE 190.
Forest plot of the effects of oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy versus other tocolytic treatment on spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of treatment.
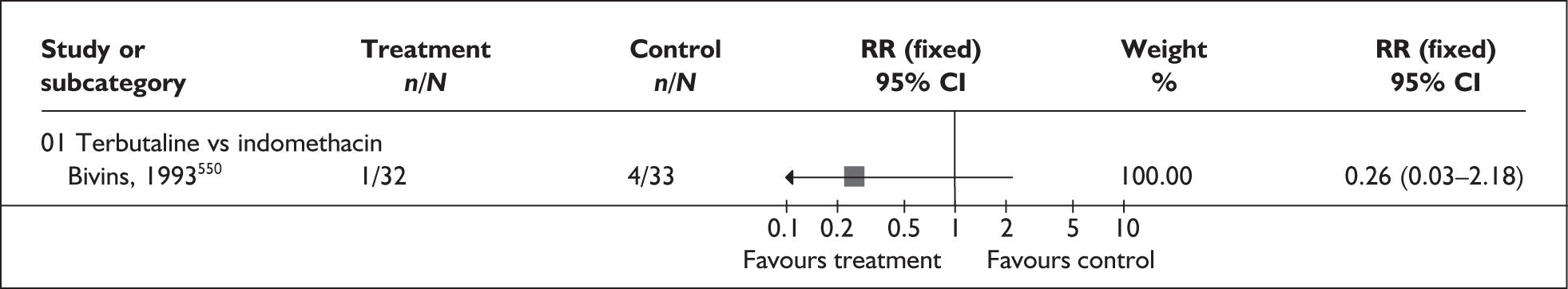
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perinatal mortality (before discharge among live births) | |||
| Betamimetic vs placebo/no treatment: (6 studies, n = 681)551–554,556,558 | 2.41 | 0.86–6.74 | 0% (0.97) |
| Betamimetic vs magnesium: (1 study, n = 50)558 | 0.2 | 0.01–3.97 | NA |
| Respiratory distress syndrome | |||
| Betamimetic vs placebo/no treatment: (5 studies, n = 577) 551,552,554,556,558 | 1.1 | 0.61–1.98 | 17.5% (0.30) |
| Betamimetic vs magnesium: (1 study, n = 50) 558 | 2 | 0.19–20.67 | NA |
| Necrotising enterocolitis | |||
| Betamimetic vs placebo/no treatment: (2 studies, n = 416)554,556 | 0.98 | 0.22–4.28 | 0% (0.44) |
| Intraventricular haemorrhage | |||
| Betamimetic vs placebo/no treatment: (3 studies, n = 466)554,556,558 | 0.97 | 0.27–3.58 | 0% (0.44) |
| Betamimetic vs magnesium: (1 study, n = 50558 | 1 | 0.07–15.12 | NA |
| Neonatal jaundice | |||
| Betamimetic vs placebo/no treatment: (1 study, n = 50 558 | 1.67 | 0.71–3.89 | NA |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 91 555 | 1.45 | 0.84–2.51 | NA |
| Betamimetic vs magnesium: (1 study, n = 50)558 | 0.91 | 0.47–1.75 | NA |
| Mechanical ventilation | |||
| Terbutaline vs indomethacin: (1 study, n = 65)550 | 0.34 | 0.01–8.13 | NA |
| Length of neonatal intensive care stay (days) | |||
| Terbutaline vs indomethacin: (1 study, n = 65)550 | WMD –1.17 | –2.93–0.59 | NA |
| Treatment cessation due to side effects | |||
| Betamimetic vs placebo/no treatment: (1 study, n = 95)553 | 2.71 | 0.11–64.79 | NA |
| Terbutaline vs indomethacin: (1 study, n = 65)550 | 3.09 | 0.13–73.19 | NA |
| Betamimetic vs magnesium: (2 studies, n = 100)558,559 | 0.9 | 0.24–3.46 | 0% (0.52) |
| Palpitations | |||
| Betamimetic vs placebo/no treatment: (1 study, n = 140) 560 | 5.67 | 1.32–24.40 | NA |
| Tachycardia | |||
| Betamimetic vs placebo/no treatment: (2 studies, n = 101)551,552 | 1.55 | 1.02–2.37 | 0% (0.87) |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 91)555 | 0.57 | 0.22–1.47 | NA |
| Betamimetic vs magnesium: (3 studies, n = 237)558,559,560 | 5.61 | 2.41–13.04 | 0% (0.62) |
| Tachypnoea | |||
| Betamimetic vs placebo/no treatment: (1 studies, n = 140) 560 | 2.83 | 0.59–13.56 | NA |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 91)555 | 2.57 | 0.55–12.07 | NA |
| Betamimetic vs magnesium: (1 study, n = 137)560 | 1.35 | 0.40–4.59 | NA |
| Hypotension | |||
| Betamimetic vs placebo/no treatment: (1 study, n = 46) 552 | 1.8 | 1.08–3.01 | NA |
| Nausea | |||
| Betamimetic vs placebo/no treatment: (2 studies, n = 186)552,560 | 0.95 | 0.43–2.13 | 31.5% (0.23) |
| Betamimetic vs magnesium: (3 studies, n = 237 558,559,560 | 1.07 | 0.57–1.98 | 0% (0.75) |
| Vomiting | |||
| Betamimetic vs placebo/no treatment: (2 studies, n = 235)553,560 | 1.28 | 0.44–3.70 | 0% (0.61) |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 91)555 | 0.57 | 0.17–1.89 | NA |
| Betamimetic vs magnesium: (2 studies, n = 187)559,560 | 0.88 | 0.39–1.98 | 4.7% (0.31) |
| Headaches | |||
| Betamimetic vs placebo/no treatment: (1 study, n = 95)554 | 2.71 | 0.11–64.79 | NA |
| Maternal readmission to hospital | |||
| Betamimetic vs placebo/no treatment: (4 studies, n = 335)552,554,557,558 | 1.11 | 0.76–1.62 | 35.8% (0.20) |
| Terbutaline vs indomethacin: (1 study, n = 65)551 | 0.6 | 0.34–1.05 | NA |
| Terbutaline vs ritodrine: (1 study, n = 91)555 | 1.71 | 0.56–5.29 | NA |
| Betamimetic vs magnesium: (1 study, n = 50)558 | 1.09 | 0.60–1.99 | NA |
Terbutaline subcutaneous pump maintenance tocolysis
Women who are undelivered after 48 hours of tocolysis remain at increased risk of spontaneous preterm birth. A number of different drugs have been administered beyond 48 hours in the hope of maintaining uterine quiescence, including terbutaline, which is a relatively selective β2-adrenergic blocker that inhibits uterine muscle contractility. It is administered via a portable subcutaneous pump. Advantages of pump administration include good subcutaneous absorption; steady, lower, more regular doses; and the ability to titrate the infusion rate against contractions.
The review of terbutaline pump maintenance561 for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth included two RCTs (n = 94);562,563 no additional studies were identified. Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 132. The quality of these studies is shown in Figure 191 and is generally good. No statistically significant differences were found between terbutaline pump maintenance and saline pump for prolongation of pregnancy (Figure 192), or admission to neonatal intensive care unit (Figure 193). Similarly, no statistically significant differences were found between terbutaline pump maintenance and saline pump or oral terbutaline therapy in terms of birthweight, risk of respiratory distress syndrome or incidence of early discontinuation (Table 23). Neither of these studies reported outcomes of perinatal mortality. RRs presented in Figures 192 and 193 below were used in the decision analyses. Overall, there is insufficient evidence to demonstrate any benefit from prolonged treatment with subcutaneous administration of terbutaline sulphate, and its safety has not been adequately addressed. Furthermore, one study included multiple births but it was not clear how many. 563
FIGURE 191.
Methodological quality of the included trials of terbutaline pump maintenance therapy for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth following acute tocolytic therapy in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
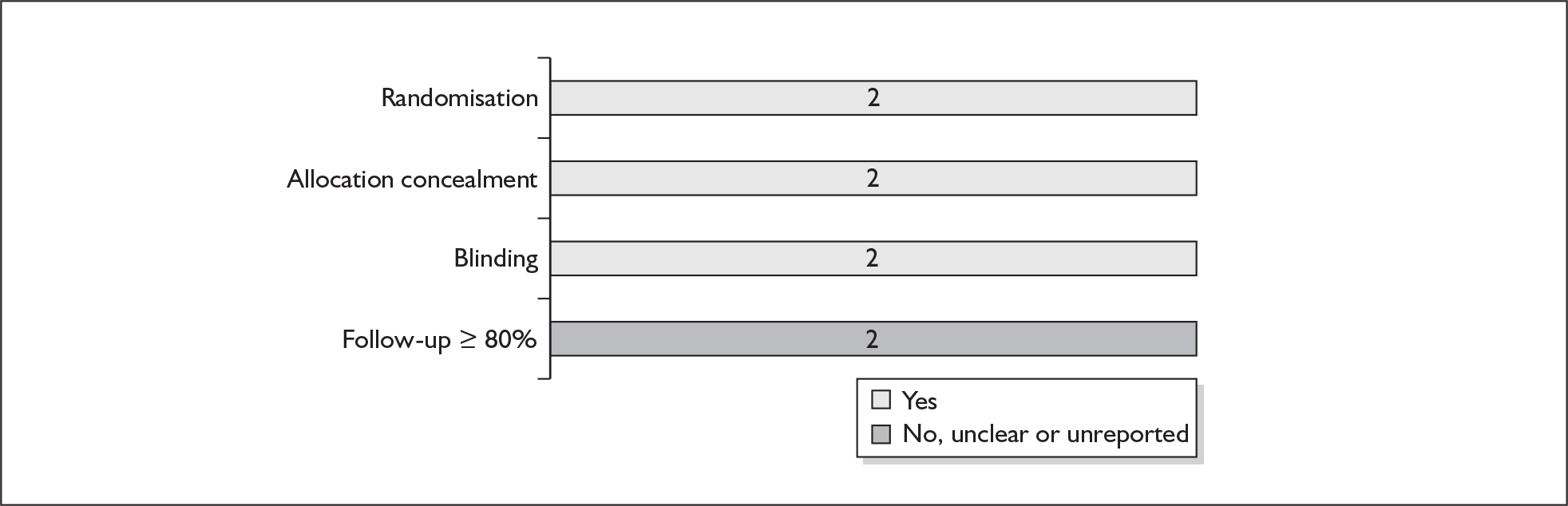
FIGURE 192.
Forest plot of the effects of terbutaline pump maintenance versus saline pump for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation.
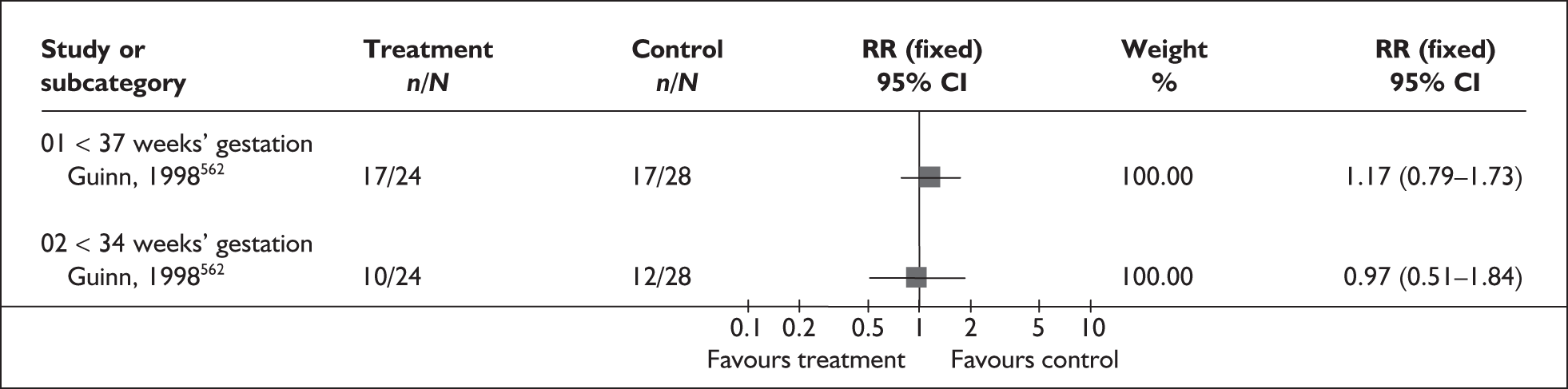
FIGURE 193.
Forest plot of the effects of terbutaline pump maintenance versus saline pump on admission to neonatal intensive care unit.
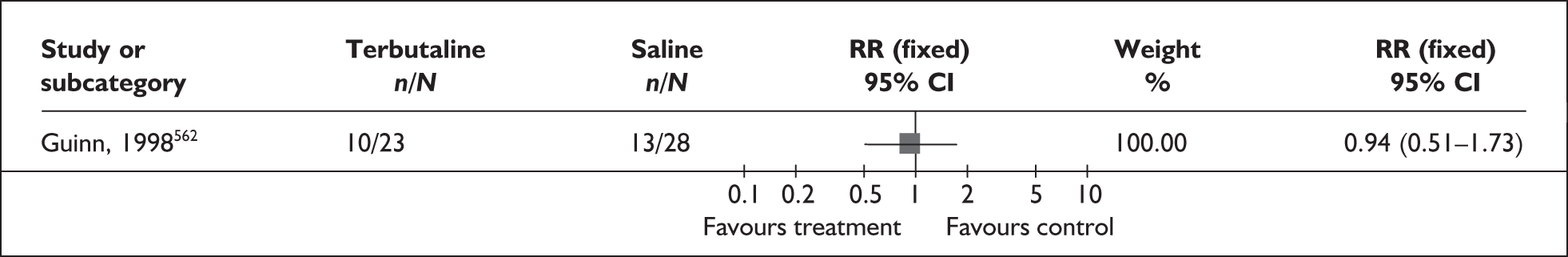
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | Heterogeneity (I2, p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Respiratory distress syndrome | |||
| Terbutaline pump vs saline pump: (2 studies, n = 79)562,563 | 0.85 | 0.23–2.93 | 0% (0.48) |
| Terbutaline pump vs oral terbutaline: (1 study, n = 30)562 | 1 | 0.16–6.20 | NA |
| Early discontinuation of treatment | |||
| Terbutaline pump vs saline pump: (2 studies, n = 79)562,563 | 1.15 | 0.68–1.95 | 8.1% (0.30) |
| Terbutaline pump vs oral terbutaline: (1 study, n = 30)562 | 3 | 0.72–12.55 | NA |
| Birthweight | |||
| Terbutaline pump vs saline pump: (2 studies, n = 79)562,563 | WMD 107.90 | –216.25–432.04 | 0% (0.54) |
| Terbutaline pump vs oral terbutaline: (1 study, n = 30)562 | WMD 484.00 | –25.01–993.01 | NA |
Calcium channel blockers
Dihydropyridines are a class of L-type calcium channel blockers that cause non-specific smooth muscle relaxation by preventing extracellular calcium, required for muscle contractility, from entering muscle cells. Myometrial drugs from this class, including nifedipine and nicardipine, are employed as tocolytics for the treatment of threatened preterm labour. 564
The review of inhibition of threatened preterm labour with calcium channel blockers565 included 12 RCTs. 566–577 Updating the searches retrieved a further five RCTs. 578–582 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 133. The quality of the included studies is generally good (Figure 194). Calcium channel blockers used were nifedipine and nicardipine and comparators were magnesium sulphate,569,574,580,581 a betamimetic (ritodrine, terbutaline, salbutamol),566–568,570–573,575–579 and an oxytocin antagonist (atosiban). 582 No placebo-controlled trials were found. Maintenance therapy was used in 12 of the trials (Table 24). 566–569,571–575,578–580 Twelve studies excluded women with multiple gestations. 566–569,571,574–578,580,581 Studies that included women with multiple gestations are denoted with an asterisk in the forest plots. 570,572,573,579,582 Data were available on the following outcomes: birth within 48 hours of intervention, birth within 7 days of intervention, spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, perinatal mortality and admission to neonatal intensive care. Other maternal and neonatal outcomes are shown in Table 25.
FIGURE 194.
Methodological quality of the included trials of calcium channel antagonists for the treatment of preterm labour to delay spontaneous preterm birth.
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Birth < 37 weeks’ gestation | |||
| Versus betamimetic (6 studies, n = 531)567,568,571,575,577,578 | 0.92 | 0.80–1.05 | 60.9% (0.03) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (5 studies, n = 442)567,568,571,575,578 | 0.84 | 0.73–0.98 | 63.5% (0.03) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 89)577 | 1.14 | 0.80–1.62 | NA |
| Birth < 34 weeks’ gestation | |||
| Versus betamimetic (5 studies, n = 531)571,572,575,577,578 | 0.77 | 0.65–0.91 | 0% (0.79) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (4 studies, n = 442)571,572,575,578 | 0.76 | 0.64–0.91 | 0% (0.64) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 89)577 | 0.81 | 0.45–1.43 | NA |
| Birth within 7 days of intervention | |||
| Versus betamimetic (5 studies, n = 445)572,575,577,578,579 | 0.78 | 0.64–0.94 | 20.8% (0.28) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (4 studies, n = 356)572,575,578,579 | 0.76 | 0.61–0.93 | 36.1% (0.20) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 89) 577 | 0.91 | 0.50–1.66 | NA |
| Birth within 48 h of intervention | |||
| Versus betamimetic (8 studies, n = 620) 567,568,572,573,575–77,579 | 0.81 | 0.63–1.06 | 42.4% (0.10) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (6 studies, n = 491) 567,568,572,573,575,579 | 0.8 | 0.60–1.08 | 31.5% (0.20) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (2 studies, n = 129) 576,578 | 0.85 | 0.49–1.45 | 79.1% (0.03) |
| Birth within 48 h of intervention | |||
| Versus magnesium sulphate: (3 studies, n = 276) 569,574,581 | 0.83 | 0.43–1.57 | 0% (0.94) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (2 studies, n = 202) 569,574 | 0.91 | 0.29–2.88 | 0% (0.79) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 74)581 | 0.78 | 0.36–1.69 | NA |
| Admission to neonatal intensive care unit | |||
| Versus betamimetic (8 studies, n = 640)566,568,571–573,575,577,578 | 0.7 | 0.58–0.84 | 2.5% (0.41) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (7 studies, n = 551)566,568,571–573,575,578 | 0.71 | 0.59–0.86 | 5.5% (0.39) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 89) 578 | 0.24 | 0.03–2.10 | NA |
| Perinatal mortality | |||
| Versus betamimetic (10 studies, n = 732)566–568,570,573,575–579 | 1.23 | 0.55–2.75 | 0% (0.56) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (7 studies, n = 541)566–568,570,573,578,579 | 1.23 | 0.55–2.75 | 0% (0.56) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (3 studies, n = 191)570,576,577 | Not estimable | Not estimable | NA |
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Birth < 35 weeks’ gestation | |||
| Versus betamimetic (maintenance therapy employed) (1 study, n = 61)579 | 0.85 | 0.51–1.41 | NA |
| Perinatal mortality excluding congenital abnormality | |||
| Versus any other tocolytic (10 studies, n = 820)566–570,573–577 | 1.42 | 0.61–3.31 | 0% (0.48) |
| Versus betamimetic (8 studies, n = 618)566–568,570,573,575–577 | 1.2 | 0.49–2.94 | 0% (0.70) |
| Versus magnesium sulphate (maintenance therapy employed) (2 studies, n = 202)569,574 | 5.25 | 0.26–106.01 | NA |
| Fetal death | |||
| Versus any other tocolytic (10 studies, n = 820)566–570,573–578 | 3 | 0.13–71.07 | NA |
| Versus betamimetic (8 studies, n = 618)566–568,570,573,575–577 | 3 | 0.13–71.07 | NA |
| Neonatal death | |||
| Versus any other tocolytic (11 studies, n = 883)566–570,572–577 | 1.58 | 0.74–3.39 | 0% (0.73) |
| Versus betamimetic (9 studies, n = 671)566–568,570,572,573,575–578 | 1.4 | 0.63–3.12 | 0% (0.72) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (6 studies, n = 480)566–568,572,573,575 | 1.4 | 0.63–3.12 | 0% (0.72) |
| Versus magnesium sulphate (maintenance therapy employed) (2 studies, n = 202)569,574 | 5.25 | 0.26–106.01 | NA |
| Neonatal death excluding congenital abnormality | |||
| Versus any other tocolytic (10 studies, n = 820)566–570,573–578 | 1.42 | 0.61–3.31 | 0% (0.48) |
| Versus betamimetic (8 studies, n = 618)566–568,570,573,575–577 | 1.2 | 0.49–2.94 | 0% (0.46) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (5 studies, n = 539)566–568,573,575 | 1.2 | 0.49–2.94 | 0% (0.46) |
| Versus magnesium sulphate (maintenance therapy employed) (2 studies, n = 202)569,574 | 5.25 | 0.26–106.01 | NA |
| Low birthweight < 2500 g | |||
| Versus any other tocolytic (2 studies, n = 143)580,578 | 0.72 | 0.54–0.96 | 45.4% (0.18) |
| Versus betamimetic (maintenance therapy employed) (1 study, n = 53)578 | 0.84 | 0.65–1.10 | NA |
| Versus magnesium sulphate (maintenance therapy employed) (1 study, n = 90)580 | 0.59 | 0.34–1.02 | NA |
| Low birthweight < 1500 g | |||
| Versus any other tocolytic (2 studies, n = 143)580,578 | 0.65 | 0.33–1.29 | 0% (0.42) |
| Versus betamimetic (maintenance therapy employed) (1 study, n = 53)578 | 0.56 | 0.27–1.16 | NA |
| Versus magnesium sulphate (maintenance therapy employed) (1 study, n = 90)578 | 1.2 | 0.21–6.84 | NA |
| Respiratory distress syndrome | |||
| Versus any other tocolytic (12 studies, n = 967)566–568,570,573–575,577–580 | 0.67 | 0.50–0.91 | 0% (0.80) |
| Versus betamimetic (10 studies, n = 755)566–568,570,572,573,575,577,578,579 | 0.66 | 0.47–0.92 | 0% (0.68) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (8 studies, n = 604)566–568,573,575,578,579 | 0.67 | 0.48–0.94 | 0% (0.59) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (2 studies, n = 151)570,577 | 0.49 | 0.09–2.53 | NA |
| Versus magnesium sulphate (maintenance therapy employed) (2 studies, n = 212)574,580 | 0.76 | 0.34–1.68 | 0% (0.58) |
| Neonatal jaundice | |||
| Versus betamimetic (maintenance therapy employed) (2 studies, n = 227) 566,575 | 0.73 | 0.57–0.93 | 47.7% (0.17) |
| Neonatal sepsis | |||
| Versus betamimetic (4 studies, n = 378)566,570,575,577 | 0.73 | 0.46–1.16 | 0% (0.57) |
| Necrotising enterocolitis | |||
| Versus betamimetic (3 studies, n = 323)566,575,577 | 0.21 | 0.05–0.96 | 0% (0.97) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (2 studies, n = 234)566,575 | 0.21 | 0.04–1.25 | 0% (0.82) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 89)577 | 0.2 | 0.01–3.96 | NA |
| Intraventricular haemorrhage: all grades | |||
| Versus betamimetic (4 studies, n = 393)567,575,577,578 | 0.59 | 0.36–0.98 | 0% (0.46) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (3 studies, n = 304)467,575,578 | 0.61 | 0.31–1.01 | 0% (0.49) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 89)577 | 0.2 | 0.01–3.96 | NA |
| Intraventricular haemorrhage: grades 3 and 4 | |||
| Versus betamimetic (3 studies, n = 340)467,575,577 | 0.5 | 0.16–1.55 | 0% (0.48) |
| Transient tachypnoea of newborn | |||
| Versus magnesium sulphate (maintenance therapy employed) (1 study, n = 90)580 | 0.16 | 0.01–3.26 | NA |
| Apgar score < 7 at 5 min | |||
| Versus any other tocolytic (5 studies, n = 568)573–575,577,578 | 0.83 | 0.44,1.54 | 0% (0.65) |
| Versus betamimetic (3 studies, n = 356)575,575,577 | 0.57 | 0.21–1.52 | 0% (0.54) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (2 studies, n = 267)573,575 | 0.57 | 0.21–1.52 | 0% (0.54) |
| Versus magnesium sulphate (maintenance therapy employed) (2 studies, n = 212)574,580 | 1.11 | 0.49–2.52 | 0% (0.59) |
| Maternal adverse drug reaction | |||
| Versus any other tocolytic (12 studies, n = 1022)566–569,571,574–577,579–582 | 0.47 | 0.38–0.58 | 79.0% (< 0.00001) |
| Versus betamimetic (7 studies, n = 576)566,567,571,575–577,579 | 0.36 | 0.28–0.46 | 81.0% (0.0001) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (5 studies, n = 447)566,567,571,575,576 | 0.5 | 0.38–0.65 | 67.8% (0.01) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (2 studies, n = 129)576,577 | 0.07 | 0.03–0.19 | 35.2% (0.21) |
| Versus magnesium sulphate (4 studies, n = 366)569,574,580,581 | 0.62 | 0.37–1.03 | 65.4% (0.03) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (3 studies, n = 292)569,574,580 | 0.4 | 0.21–0.73 | 0% (0.92) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 74)581 | 3.14 | 0.90–10.90 | NA |
| Versus atosiban (No maintenance therapy employed) (1 study, n = 80)582 | 2.29 | 1.06–4.95 | NA |
| Maternal adverse drug reaction requiring cessation of treatment | |||
| Versus any other tocolytic (12 studies, n = 1116)566–570,573–575,577,580,578,581 | 0.16 | 0.07–0.35 | 0% (0.62) |
| Versus betamimetic (9 studies, n = 750)566–568,570,573,575,577,578,579 | 0.09 | 0.03–0.27 | 0% (0.97) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (8 studies, n = 599) 566–568,573,575,578,579 | 0.1 | 0.03–0.31 | 0% (0.94) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (2 studies, n = 151) 570,577 | 0.08 | 0.00–1.30 | NA |
| Versus magnesium sulphate (4 studies, n = 366) 569,574,580,581 | 0.47 | 0.15–1.54 | 16.7% (0.30) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (3 studies, n = 292) 569,574,580 | 0.47 | 0.15–1.54 | 16.7% (0.30) |
Calcium channel antagonists were significantly more effective than betamimetics in studies where maintenance therapy was employed in preventing spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation (Figure 195). There were no other differences in interventions for this outcome. They were significantly more effective than any other tocolytic in preventing spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation (Figure 196), and were more effective than betamimetics both in general and where maintenance therapy was employed (Table 24). Calcium channel antagonists were also more effective in preventing spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of intervention (Figure 197) but not within 48 hours (Figure 198) than any other tocolytic and any betamimetic, both overall and where maintenance therapy was employed (Table 24). This was also the case for admission to neonatal intensive care where there were fewer admissions in the calcium channel antagonist groups than in those given any other tocolytic (Figure 199), any betamimetic and any betamimetic where maintenance therapy was employed (Table 24). There were no significant differences between the groups in incidence of perinatal mortality following the interventions with calcium channel blockers for prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour (Figure 200).
FIGURE 195.
Forest plot of the effects of calcium channel antagonists versus any other tocolytic for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
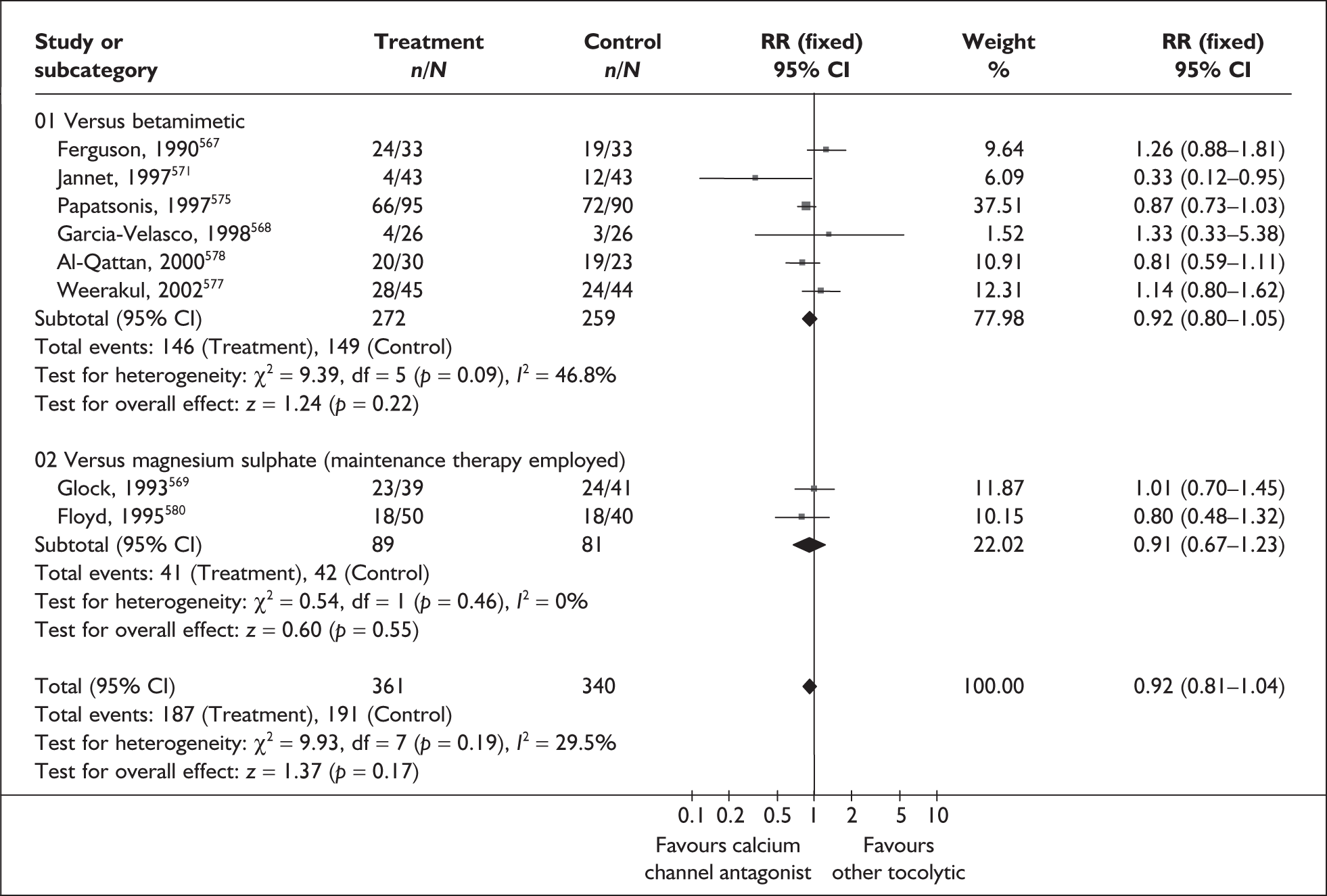
FIGURE 196.
Forest plot of the effects of calcium channel antagonists versus any other tocolytic for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
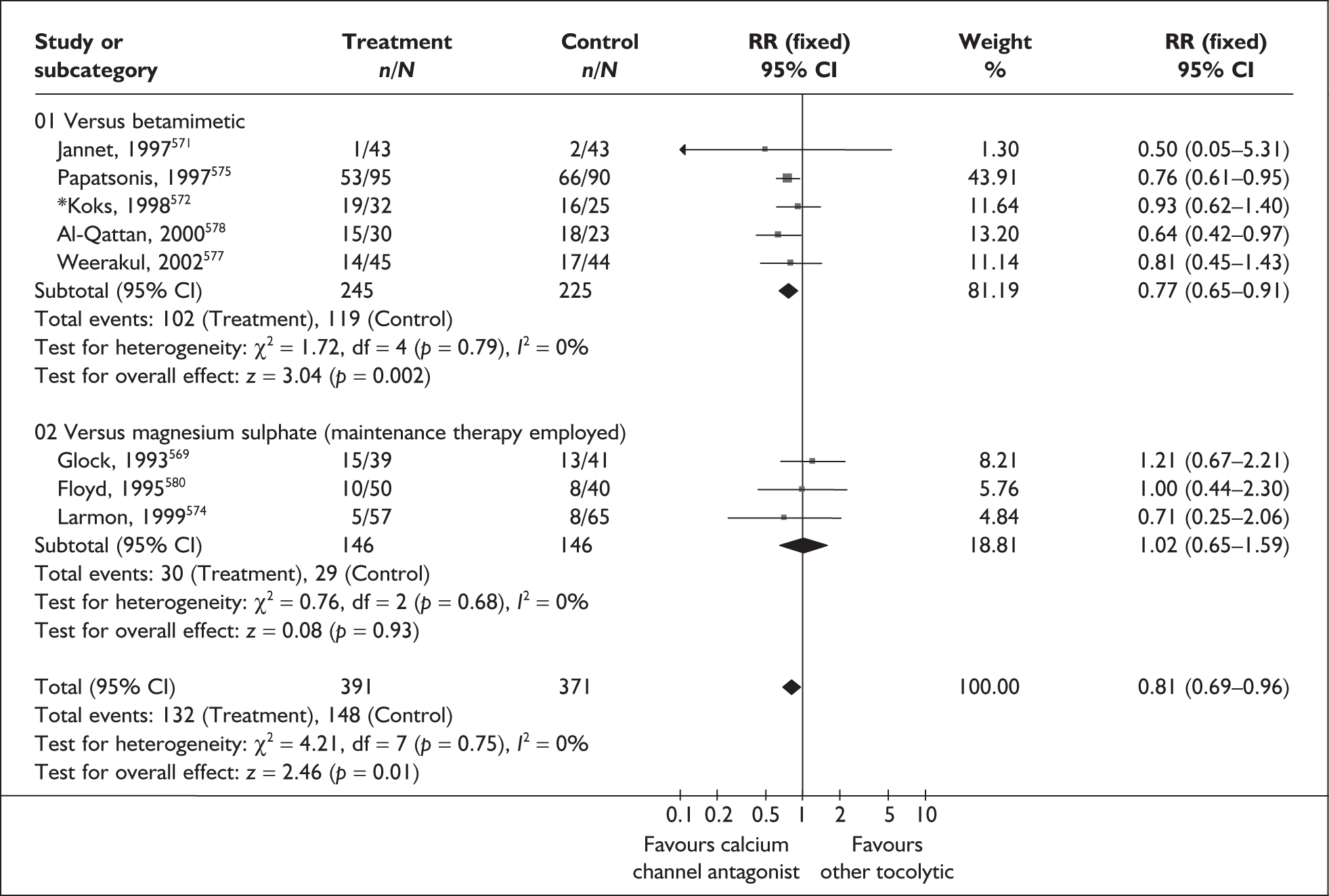
FIGURE 197.
Forest plot of the effects of calcium channel antagonists versus any other tocolytic for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
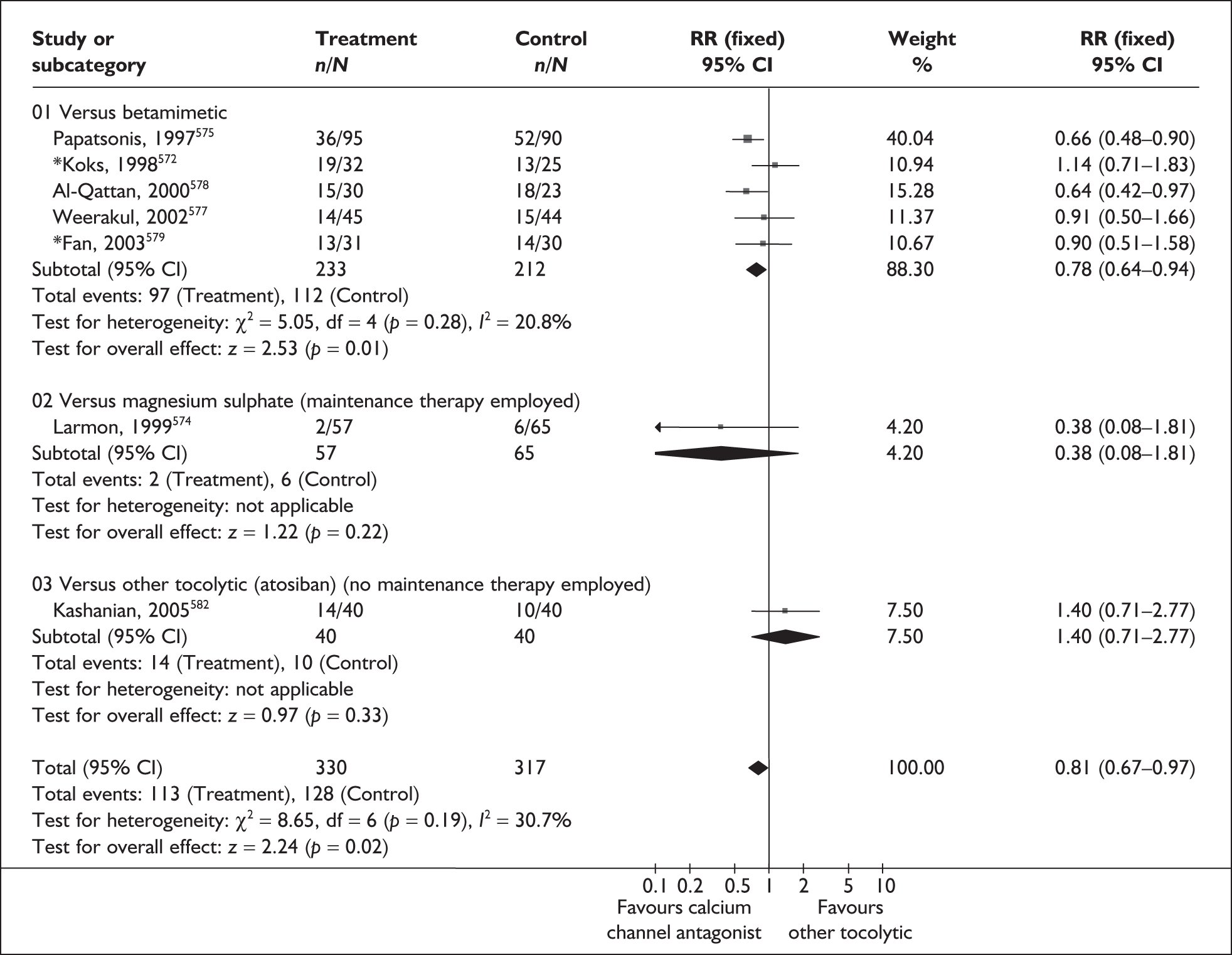
FIGURE 198.
Forest plot of the effects of calcium channel antagonists versus any other tocolytic for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
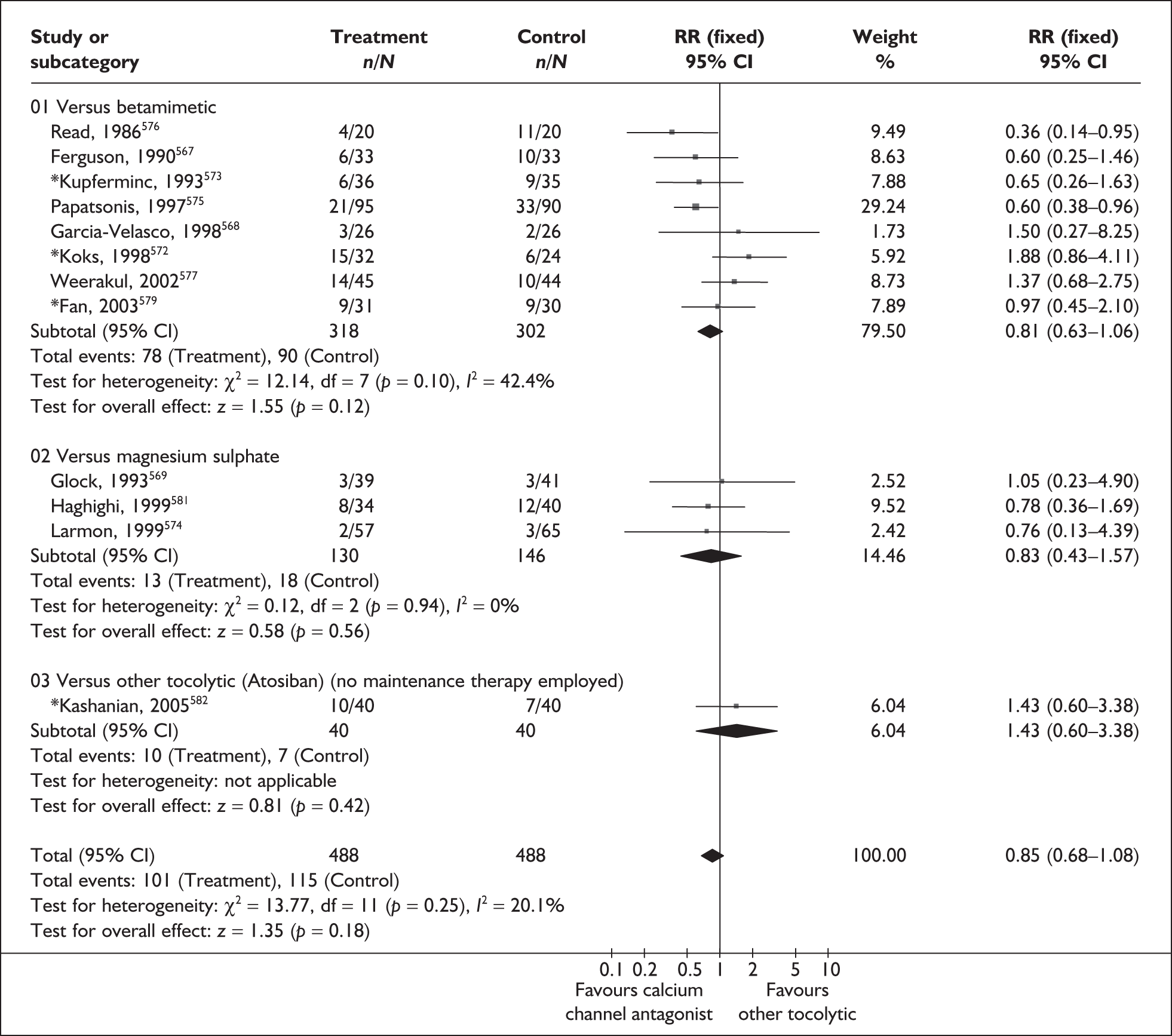
FIGURE 199.
Forest plot of the effects of calcium channel antagonists versus any other tocolytic for the prevention of admission to neonatal intensive care unit.
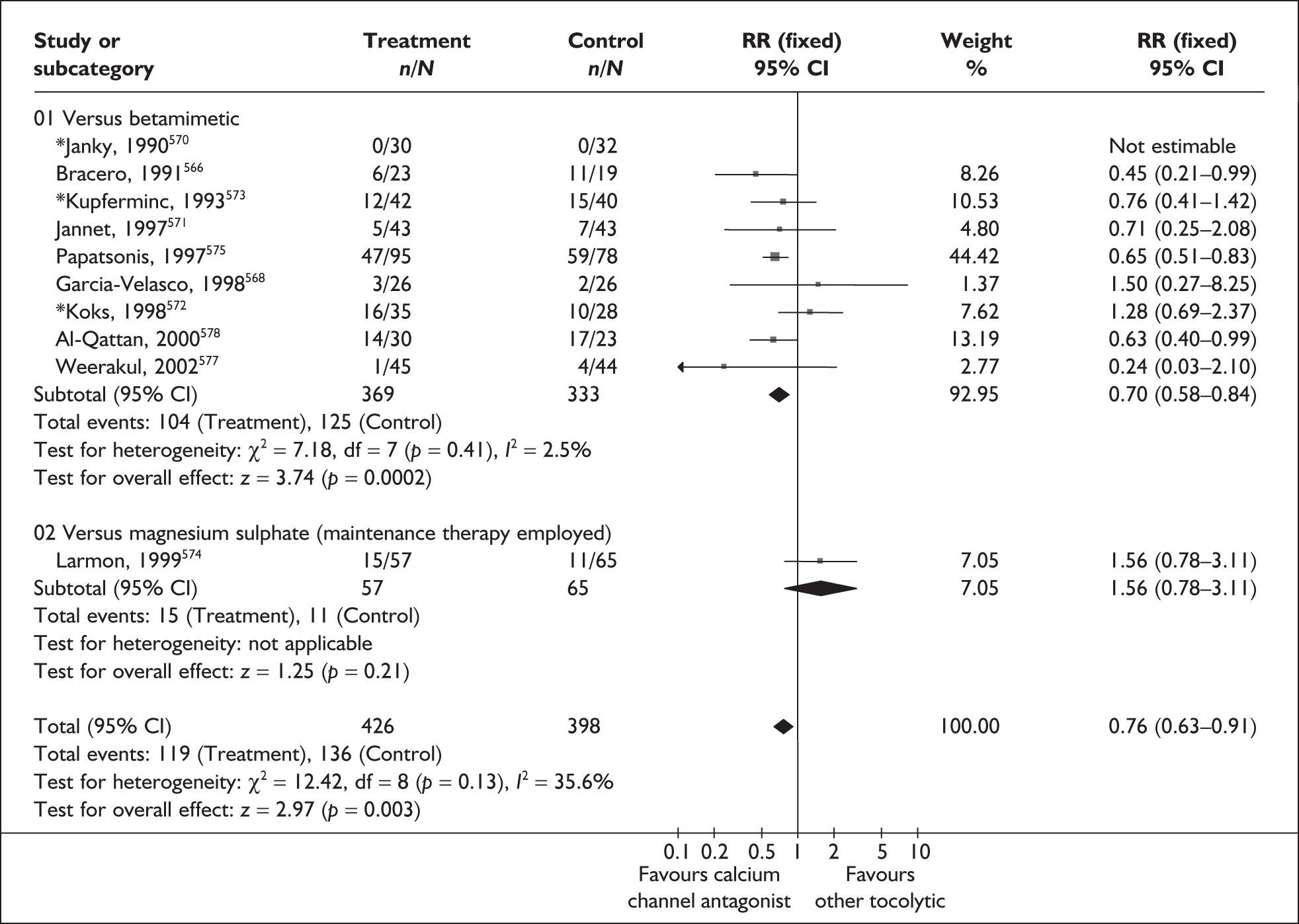
FIGURE 200.
Forest plot of the effects of calcium channel antagonists versus any other tocolytic for the prevention of perinatal mortality.
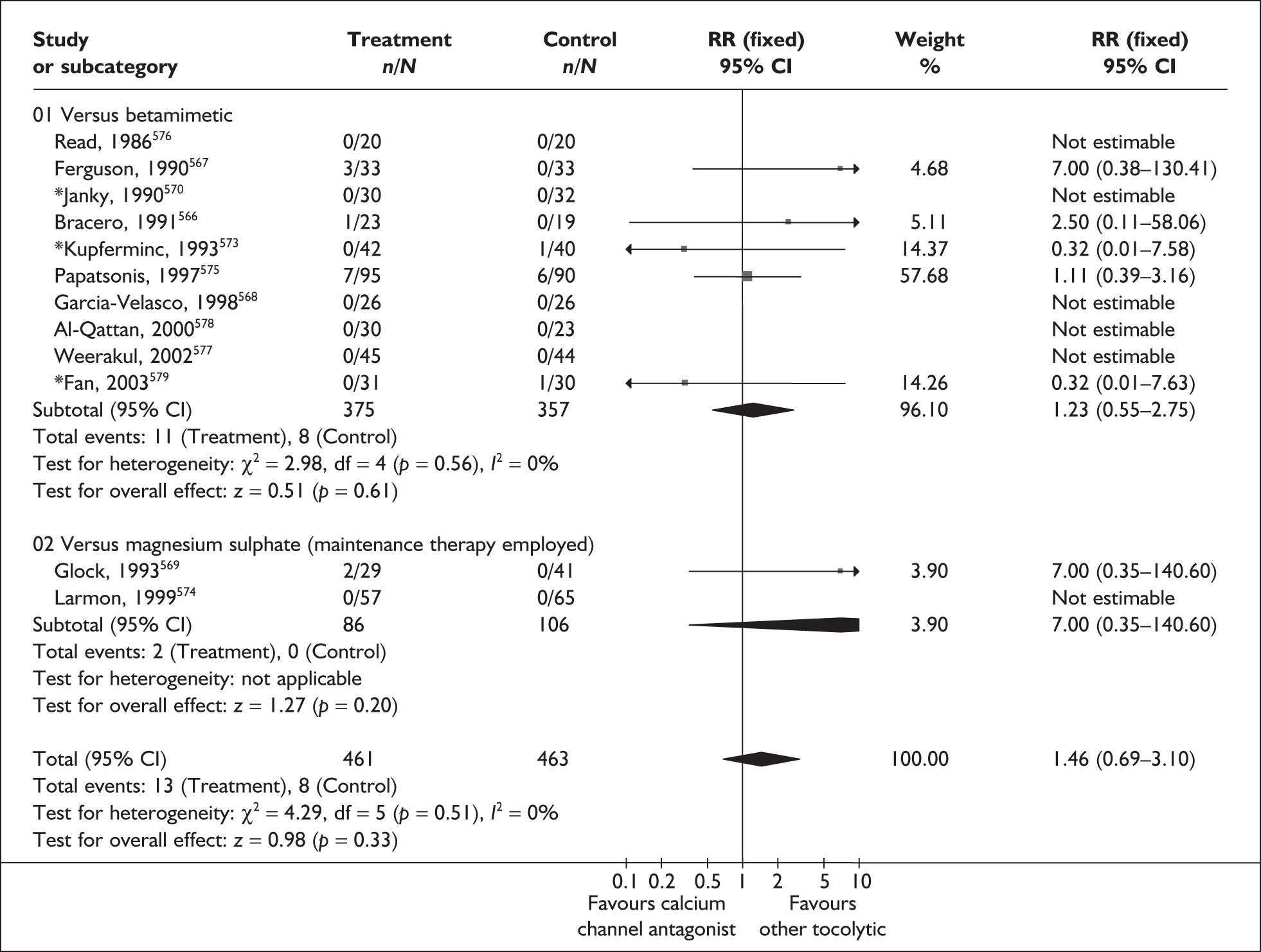
Other maternal and perinatal outcomes are shown in Table 25. There were fewer instances of low-birthweight infants (< 2500 g) in groups given calcium channel antagonists than in groups given other tocolytics. The following outcomes were significantly more favourable in calcium channel antagonist groups than for other tocolytics overall and betamimetics in general: respiratory distress syndrome, neonatal jaundice, neonatal sepsis, necrotising enterocolitis, intraventricular haemorrhage (all grades), maternal adverse drug reaction and maternal adverse drug reaction requiring cessation of treatment. The summary RRs shown were not used in the decision analyses because they did not include a placebo/no treatment comparison. Overall, calcium channel blockers appear to have a reasonable efficacy and safety profile compared to other tocolytics. They appeared to be superior to betamimetics in both respects.
Calcium channel blocker maintenance
Uterine contractions are thought to be initiated by increasing intracellular calcium levels of myometrial cells. Calcium channel blockers are a type of tocolytic agent that counteracts this process and so prevents contractions. Maintenance therapy is used to prevents further contractions after the symptoms of threatened preterm labour have been successfully treated with an initial dose of tocolytic therapy.
The review583 of calcium channel blocker maintenance therapy (nifedipine) for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth included two RCTs (n = 147). 584,585 One trial585 was added to the primary study584 identified in an earlier review. 583 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 133. The quality of the included studies is presented in Figure 201. Only one small study was considered to be of good quality. 585 No reduction in the risk of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 or 37 weeks’ gestation was shown when calcium channel blocker maintenance therapy was compared with no treatment (Figures 202 and 203). There was no difference in admission to neonatal intensive care units with nifedipine versus no treatment (Figure 204). Delivery within 24 hours and 48 hours of treatment initiation was omitted from the review because maintenance therapy was aimed at a longer duration than this. Delivery within 7 days of treatment initiation was not reported. The effect of nifedipine on other outcomes is shown in Table 26. No RCTs were found comparing calcium channel blockers for maintenance therapy with other maintenance tocolytic agents for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth following acute tocolytic therapy for threatened preterm labour. The review does not provide sufficient evidence to assess the use of calcium channel blockers as maintenance therapy for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth following acute tocolytic therapy for threatened preterm labour. Summary RRs presented in the forest plots below were not used in the decision analysis because only RRs that appear to be beneficial were entered into the main model.
FIGURE 201.
Methodological quality of the included trials of nifedipine maintenance therapy for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth following acute tocolytic therapy in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
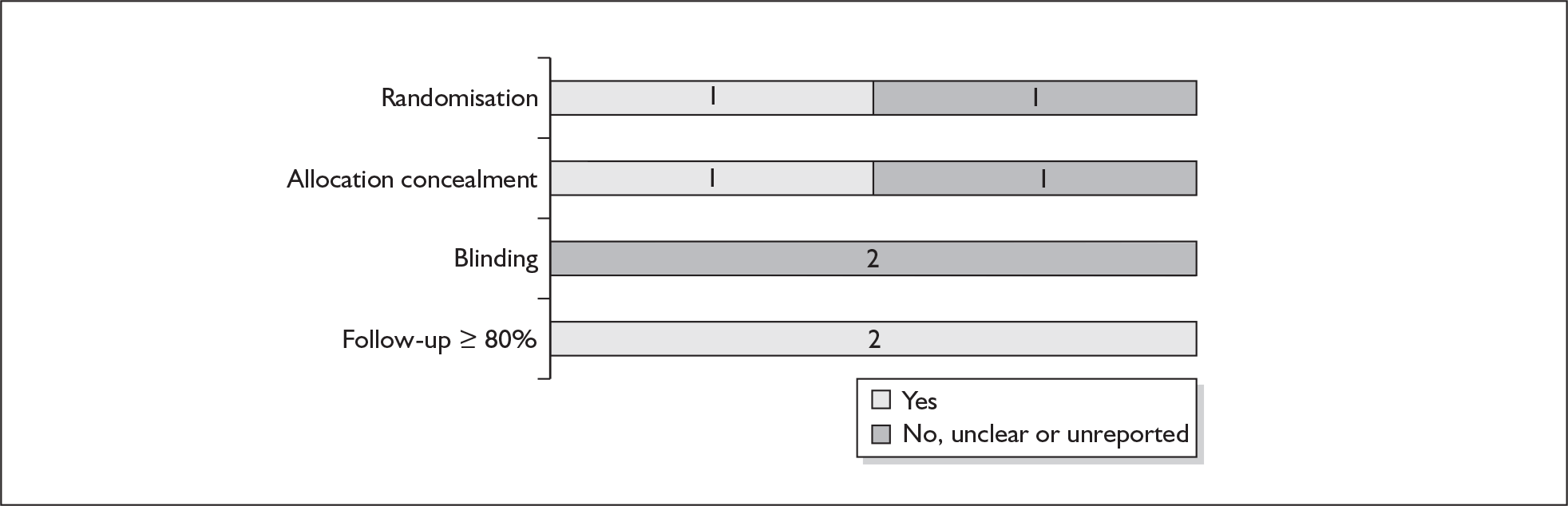
FIGURE 202.
Forest plot of the effects of maintenance nifedipine versus no treatment for the inhibition of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
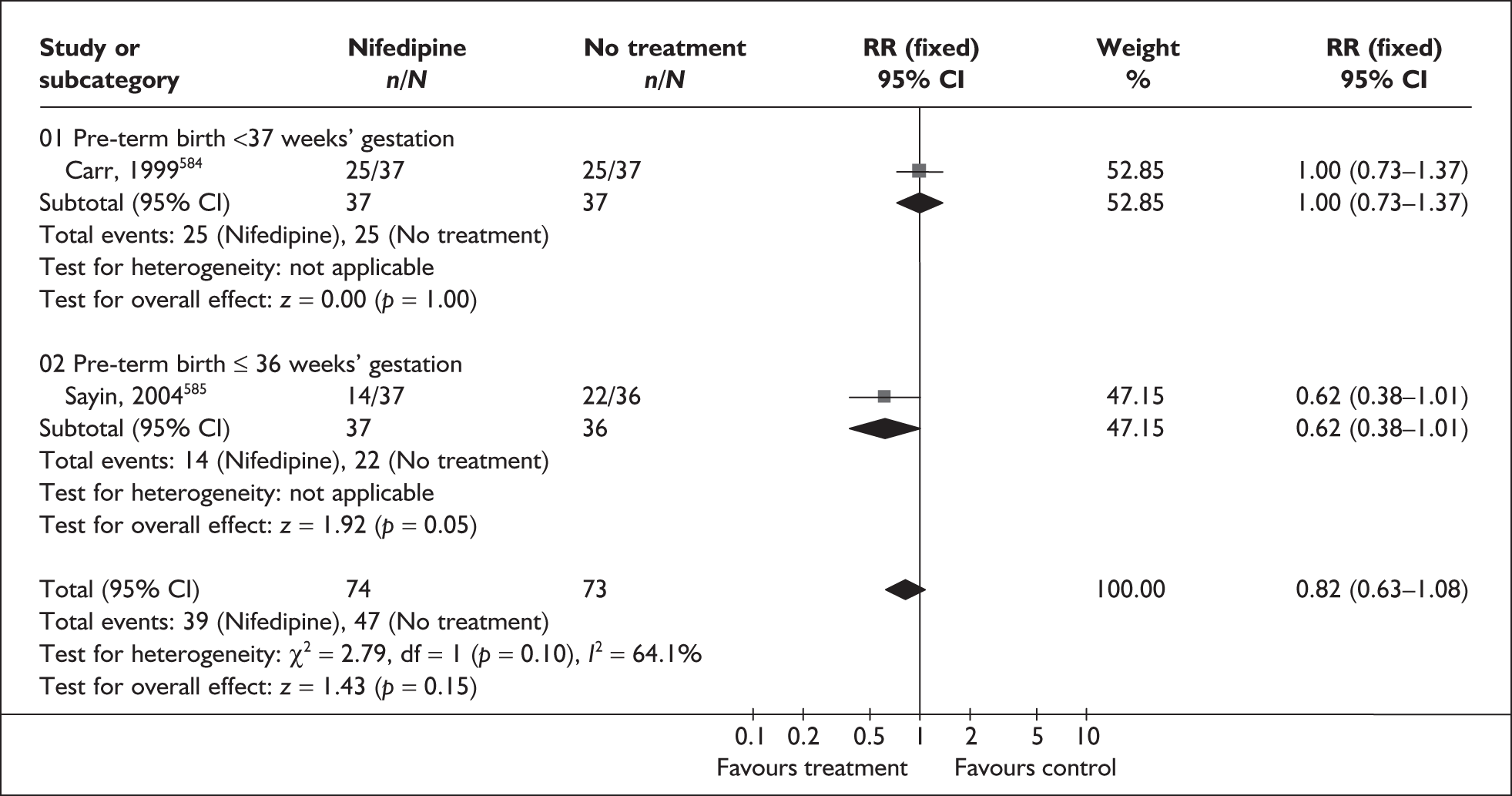
FIGURE 203.
Forest plot of the effects of maintenance nifedipine versus no treatment for the inhibition of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation.
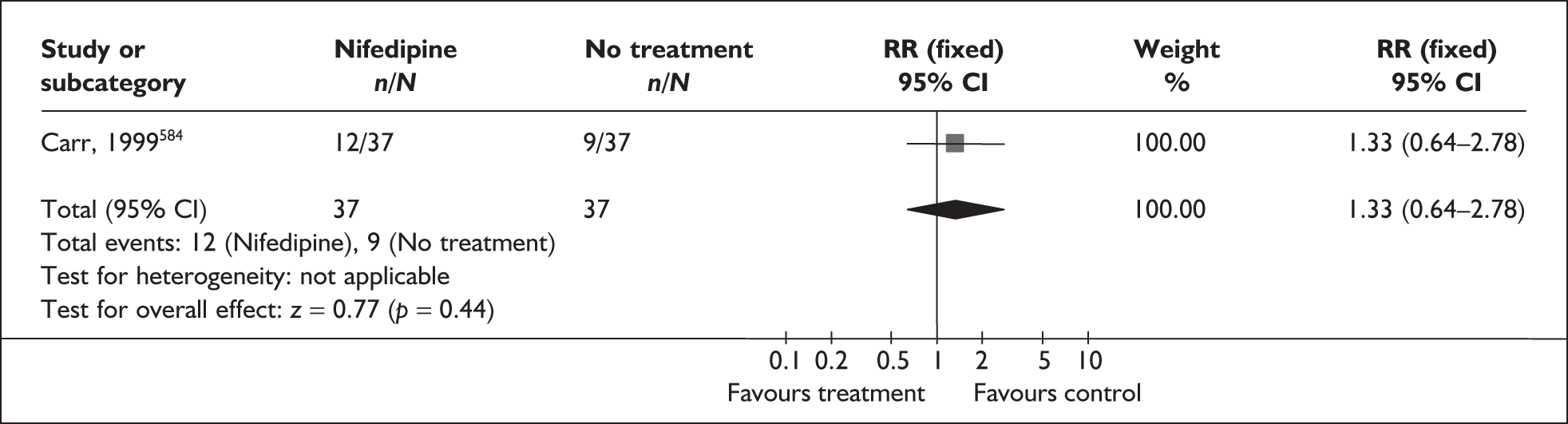
FIGURE 204.
Forest plot of the effects of nifedipine versus no treatment on admission to neonatal intensive care unit.
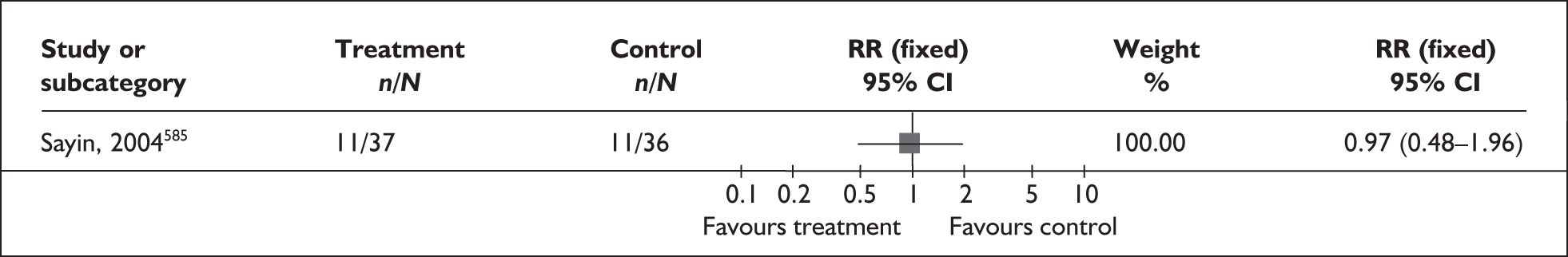
| Outcome (number of RCTs) | RR | 95% CI | I2, p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small for gestational age (1 study, n = 73) 585 | 1.5 | 0.27–8.46 | NA |
| Respiratory distress syndrome (1 study, n = 73)585 | 1 | 0.22–4.64 | NA |
| Mechanical ventilation (1 study, n = 73)585 | 1 | 0.22–4.64 | NA |
| Intraventricular haemorrhage (1 study, n = 73)585 | 1 | 0.06–15.40 | NA |
| Necrotising enterocolitis (1 study, n = 73)585 | 1 | 0.06–15.40 | NA |
| Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (1 study, n = 73)585 | 0.32 | 0.01–7.71 | NA |
| Sepsis/meningitis (1 study, n = 73)585 | 1.95 | 0.18–20.53 | NA |
| Pneumonia (1 study, n = 73)585 | 1.46 | 0.26–8.23 | NA |
| Neonatal mortality (1 study, n = 73)585 | 0.19 | 0.01–3.92 | NA |
| Neonatal jaundice (1 study, n = 73)585 | 0.97 | 0.63–1.51 | NA |
Oxytocin receptor antagonists
Oxytocin receptor antagonists are competitive antagonists of human oxytocin receptors within the uterus and potentially the decidual and fetal membranes. They act to reduce the level of oxytocin, which is believed to initiate uterine contractibility, and as such have been proposed as effective tocolytic agents for women symptomatic of threatened preterm labour to postpone birth. The oxytocin receptor antagonist atosiban is the only treatment currently licensed for the treatment of threatened preterm labour in the UK.
The review586 of oxytocin receptor antagonists (atosiban) included six RCTs (n = 1695). 587–592 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 138. Overall, the quality of included primary studies was good (Figure 205). When compared with placebo, atosiban did not reduce the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, or the incidence of delivery within 48 hours of treatment initiation (Figures 206 and 207, respectively). No statistically significant difference was found in the incidence of neonatal mortality or admission to neonatal intensive care between women receiving atosiban and women receiving placebo (Figures 208 and 209, respectively). When compared to betamimetics, atosiban did not significantly differ in the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation or incidence of delivery within 48 hours, or 7 days, of treatment initiation (Figures 210–212). No statistically significant difference was found in the incidence of neonatal mortality or admission to neonatal intensive care between women receiving atosiban and women receiving betamimetics (Figures 213 and Figure 214, respectively). Delivery within 24 hours of treatment initiation was not reported. The effect of atosiban on other outcomes is shown in Table 27. Summary RRs presented in the forest plots below were not used in the decision analyses. Overall, the results do not support the superiority of atosiban over betamimetics or placebo in terms of tocolytic efficacy or infant outcomes; however, some outcomes were based on only one small trial, so large trials with placebo comparators are recommended. Importantly, rescue tocolysis was employed in all the included trials; because these women received additional treatment the comparison of neonatal outcomes is not appropriate.
FIGURE 205.
Methodological quality of RCTs of oxytocin receptor antagonists for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
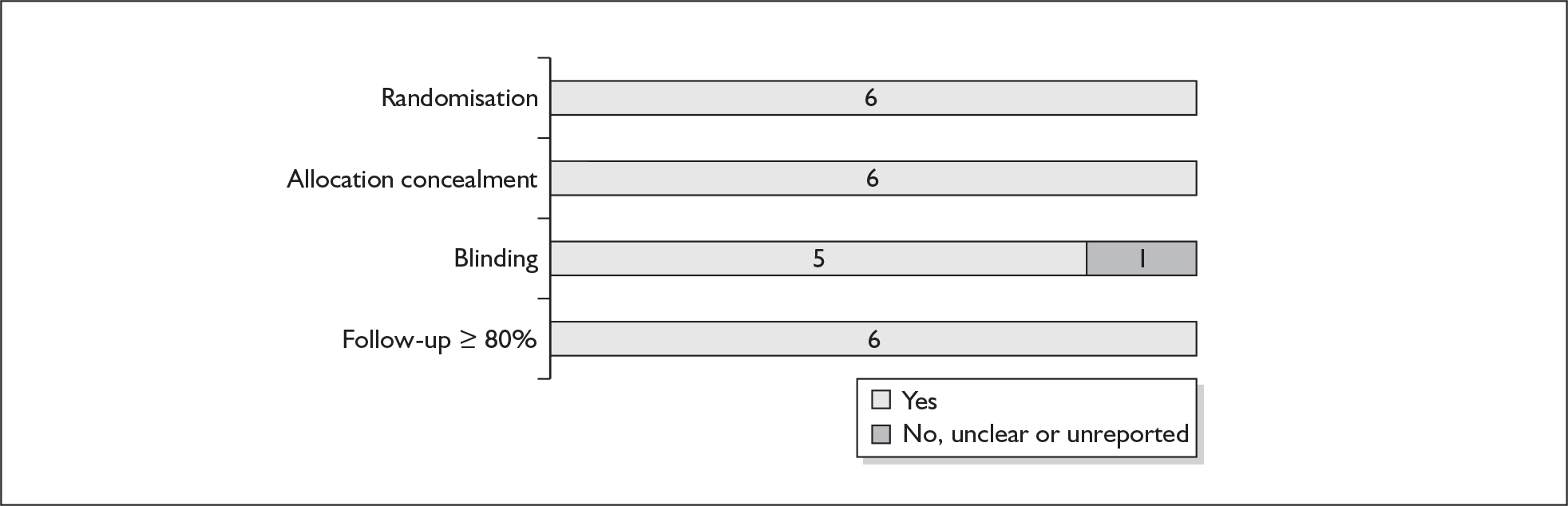
FIGURE 206.
Forest plot of the effects of atosiban versus placebo therapy on prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
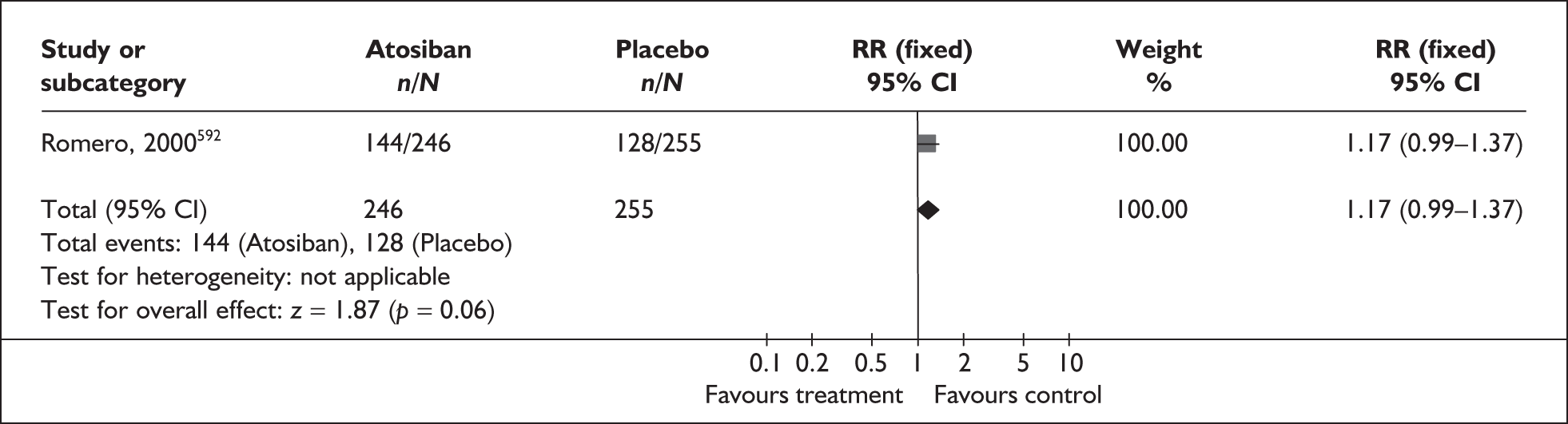
FIGURE 207.
Forest plot of the effects of atosiban versus placebo therapy on prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of initiation of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
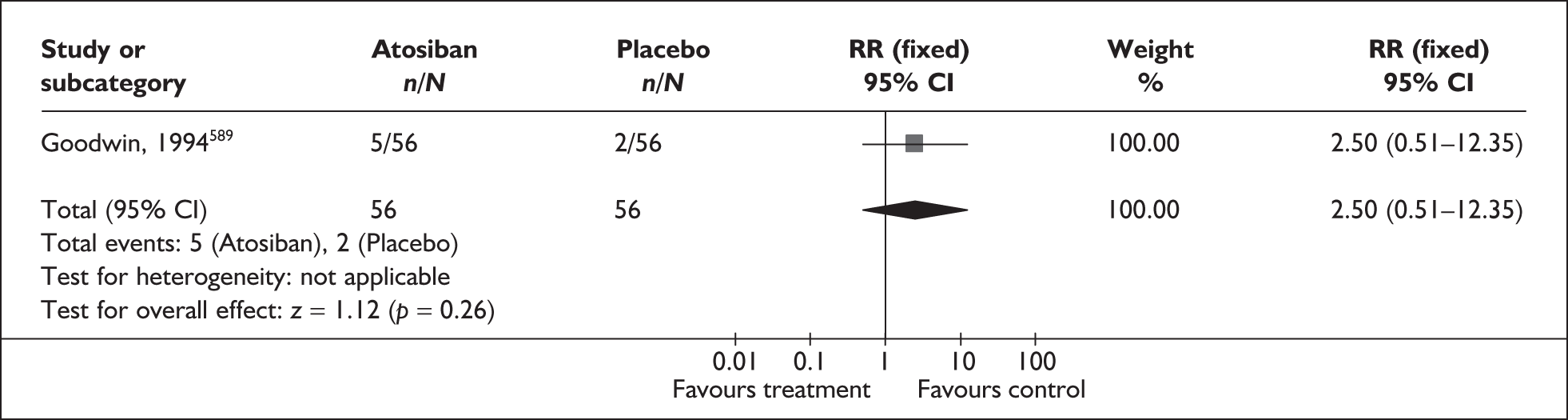
FIGURE 208.
Forest plot of the effects of atosiban versus placebo therapy on perinatal mortality.
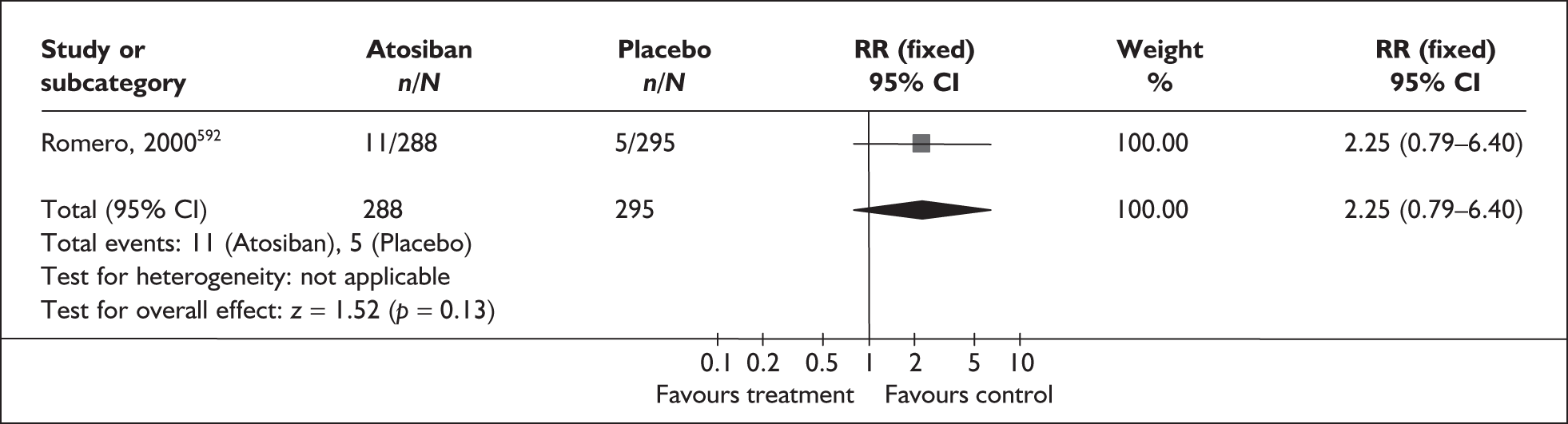
FIGURE 209.
Forest plot of the effects of atosiban versus placebo therapy on neonatal admission to intensive care unit.
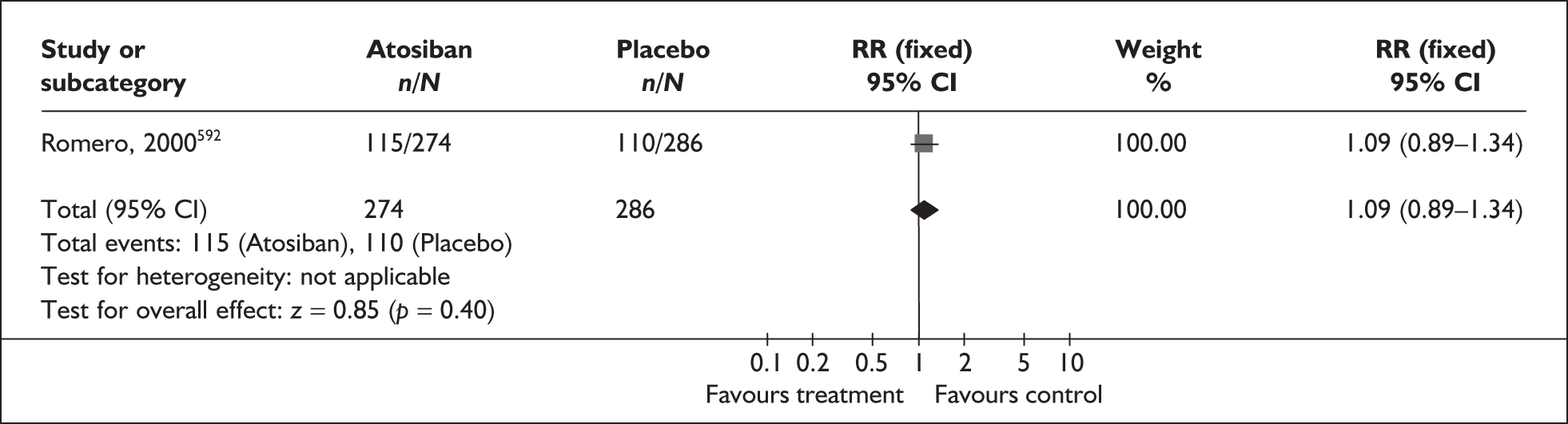
FIGURE 210.
Forest plot of the effects of atosiban versus betamimetic therapy on prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
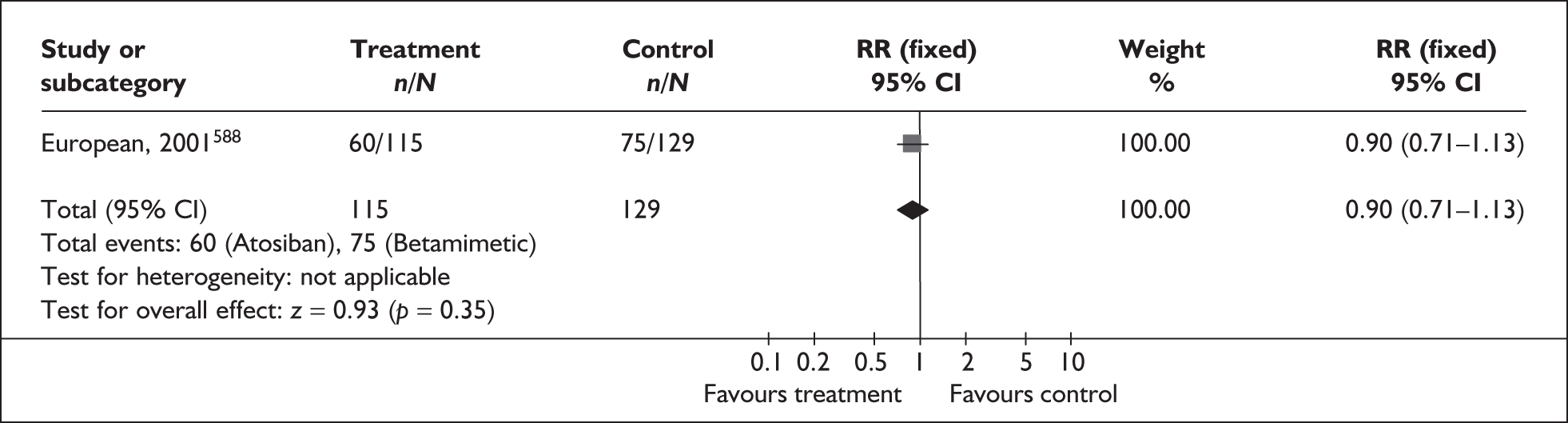
FIGURE 211.
Forest plot of the effects of atosiban versus betamimetic therapy on prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of initiation of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
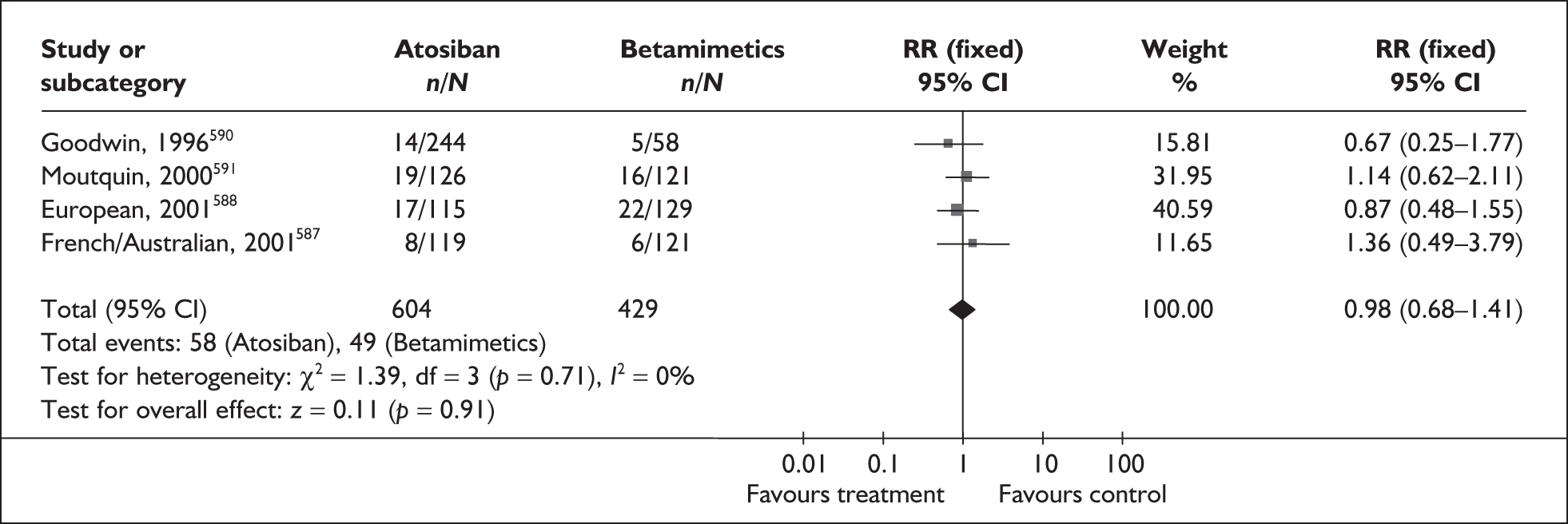
FIGURE 212.
Forest plot of the effects of atosiban versus betamimetic therapy on prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
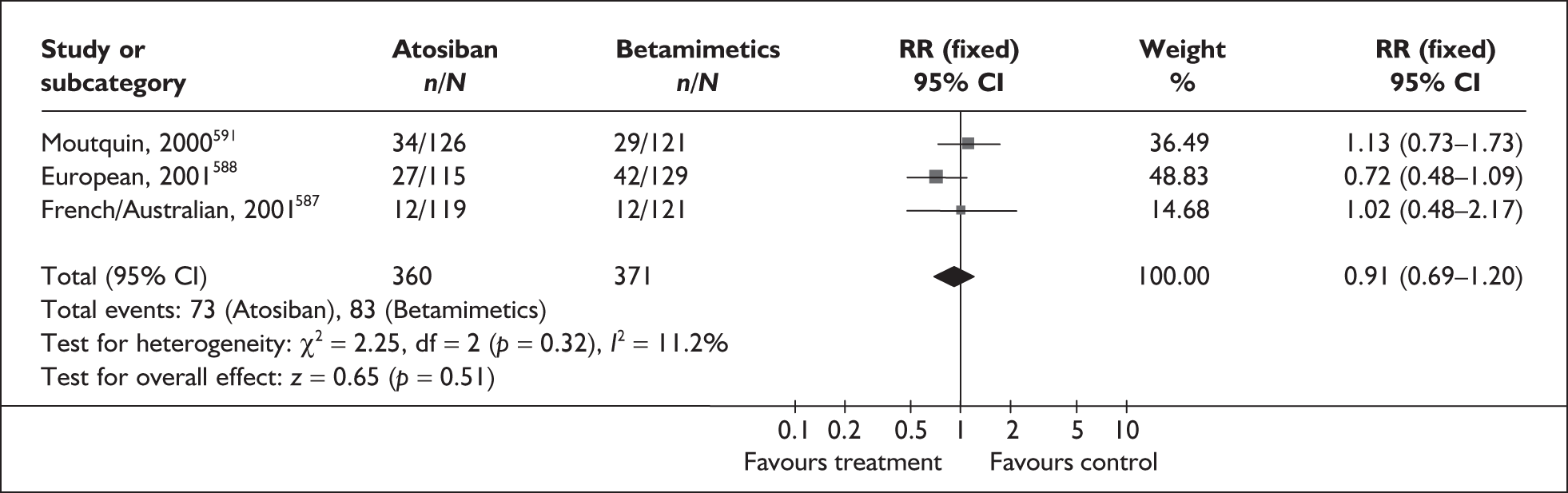
FIGURE 213.
Forest plot of the effects of atosiban versus betamimetic therapy on perinatal mortality.
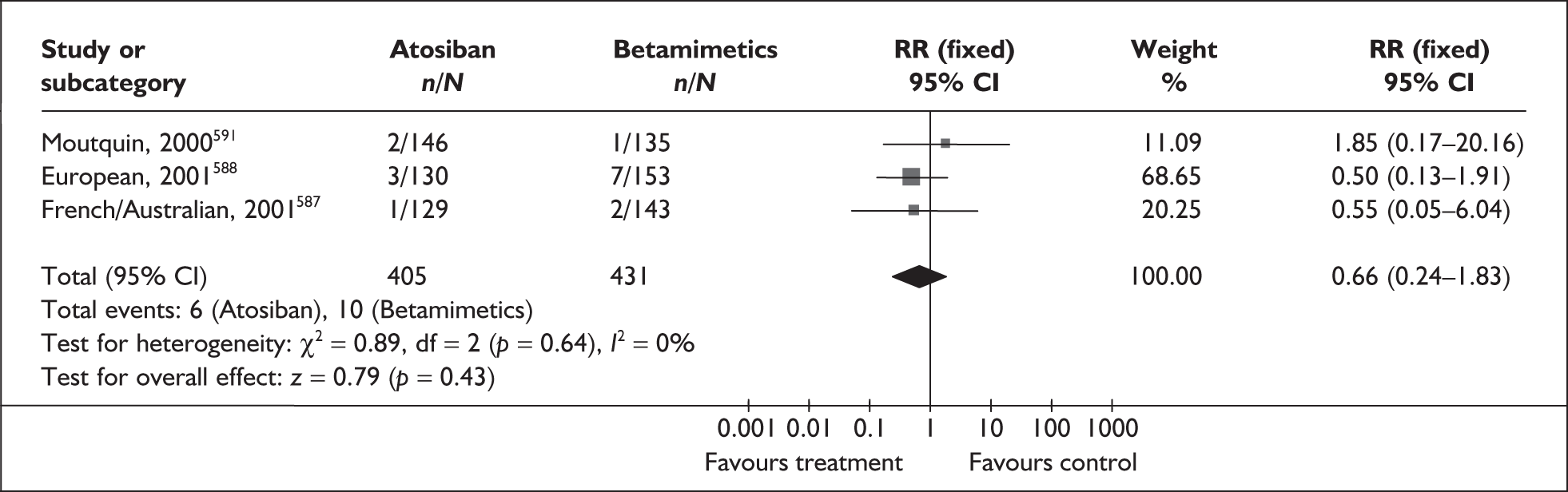
FIGURE 214.
Forest plot of the effects of atosiban versus betamimetics on neonatal admission to intensive care unit.
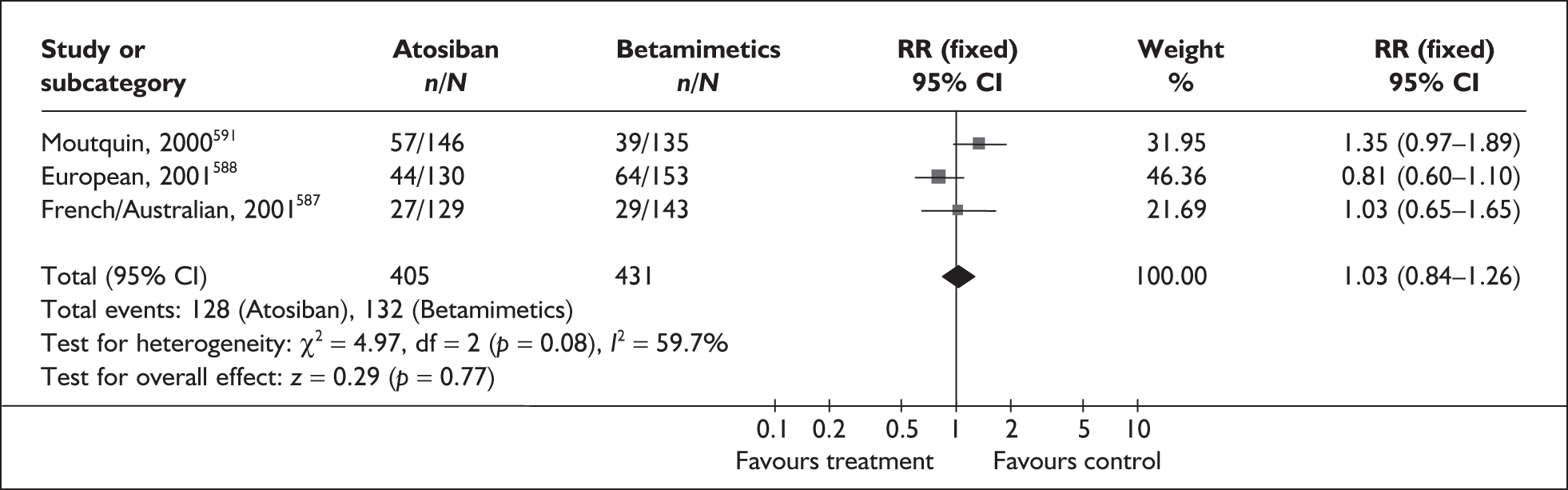
| Outcome (number of RCTs) | RR | 95% CI | I2 and p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preterm birth < 28 weeks gestation | |||
| Atosiban vs placebo (1 study, n = 585)592 | 2.25 | 0.80–6.35 | NA |
| Fetal death | |||
| Atosiban vs placebo (2 studies, n = 585)592,589 | 1.02 | 0.21–5.03 | NA* |
| Atosiban vs betamimetics (3 studies, n = 836)587,588,591 | 0.55 | 0.05–6.04 | NA* |
| Neonatal death (up to 28 days) | |||
| Atosiban vs placebo (1 study, n = 583)592 | 4.1 | 0.88–19.13 | NA |
| Atosiban vs betamimetics (4 studies, n = 1130)587–589,591 | 0.7 | 0.27–1.81 | 0%, 0.57 |
| Respiratory distress syndrome | |||
| Atosiban vs placebo (2 studies, n = 689) 589,592 | 1.28 | 0.93–1.76 | 26.2%, 0.24 |
| Atosiban vs betamimetics (4 studies, n = 1129) 587–589,591 | 0.99 | 0.76–1.29 | 55.2%, 0.08 |
| Intraventricular haemorrhage | |||
| Atosiban vs placebo (1 study, n = 489) 592 | 0.85 | 0.45–1.62 | NA |
| Necrotising enterocolitis | |||
| Atosiban vs placebo (1 study, n = 575)592 | 0.21 | 0.02–1.76 | NA |
| Atosiban vs betamimetics (2 studies, n = 576)588,590 | 0.48 | 0.12–1.98 | 0%, 0.58 |
| Hypoglycaemia | |||
| Atosiban vs placebo (1 study, n = 114) 589 | 0.75 | 0.18–3.20 | NA |
| Atosiban vs betamimetics (3 studies, n = 837)587,588,591 | 1.07 | 0.63–1.82 | 6%, 0.35 |
| Neonatal sepsis | |||
| Atosiban vs betamimetics (4 studies, n = 1129) 587–589,591 | 0.91 | 0.56–1.46 | 0%, 0.63 |
| Patent duct arteriosus | |||
| Atosiban vs placebo (2 studies, n = 689) 589,592 | 1.28 | 0.68–2.40 | 0%, 0.35 |
| Atosiban vs betamimetics (4 studies, n = 1129) 587–589,591 | 1.02 | 0.58–1.79 | 0%, 0.49 |
| Maternal adverse drug reaction requiring treatment cessation | |||
| Atosiban vs placebo (2 studies, n = 613) 592,589 | 4.02 | 2.05–7.85 | NA* |
| Atosiban vs betamimetics (4 studies, n = 1034) 587–589,591 | 0.04 | 0.02–0.11 | 0%, 0.53 |
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories and cyclo-oxygenase inhibitors
Cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitors are a subgroup of the class of non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs). They have a tocolytic effect, inhibiting uterine contractions, and are therefore an option in the treatment of threatened preterm labour. Uterine contractions are the result of an influx of extracellular calcium – COX (and in particular COX type 2) synthesises prostaglandins from arachidonic acid, resulting in the opening of myometrial cell membrane calcium channels; COX inhibitors block this effect. 593 Neither NSAIDs nor COX inhibitors specifically are currently recommended for tocolytic use by the RCOG because of concerns over their fetal adverse events profile. This assessment included the use of NSAIDs for the prevention as well as treatment of threatened preterm labour to prevent spontaneous preterm birth. In addition to acute treatment, chronic maintenance therapy is also included in the review.
The review of NSAIDs594 for treating threatened preterm labour included 13 RCTs. 595–607 A further three RCTs were added when the searches were updated and expanded to include all NSAIDs. 608–610 The quality of the studies included in the review and of the additional studies was generally high (Figure 215). Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 134. The studies included in the review examined NSAIDs and COX inhibitors for treating threatened preterm labour. 595–607 Data were available on the following comparisons:
-
COX inhibitors versus placebo (Figures 216, 218,219, 222, 223, 226, 228, 231, 234).
-
COX inhibitors versus any other tocolytic (Figures 217, 220, 224, 229, 232).
-
Non-selective COX inhibitors versus any COX-2 inhibitors (Figures 221, 225, 233).
FIGURE 215.
Methodological quality of the included trials of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
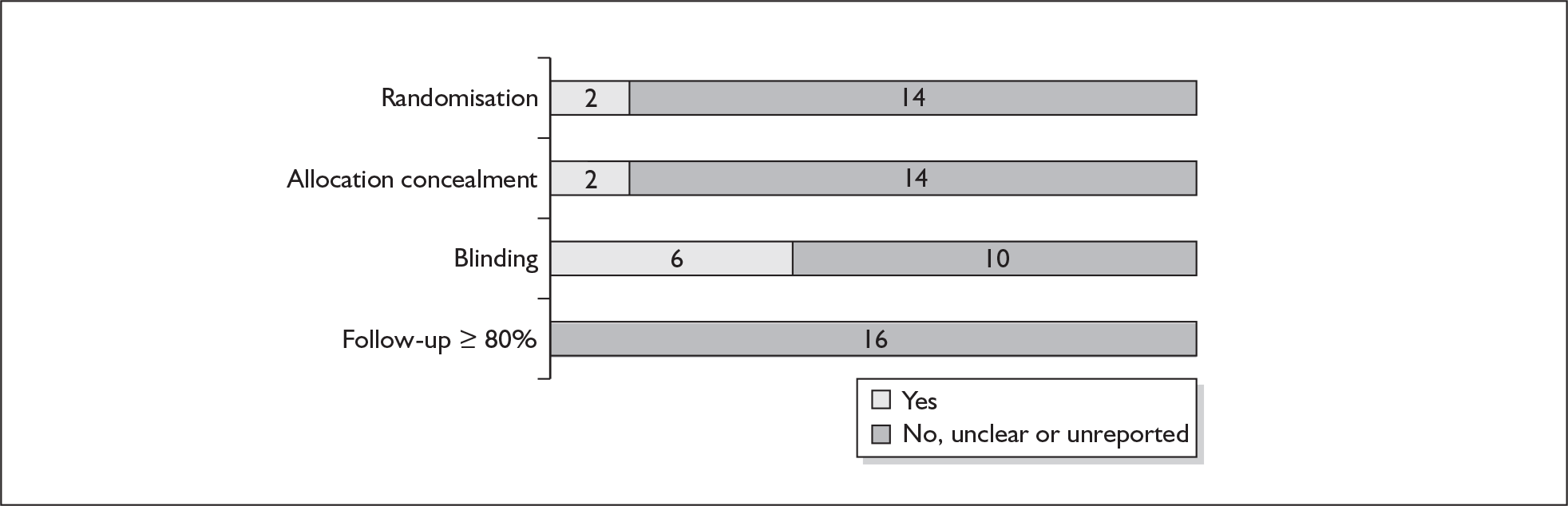
FIGURE 216.
Forest plot of the effects of any cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitor versus placebo for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of initiation of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
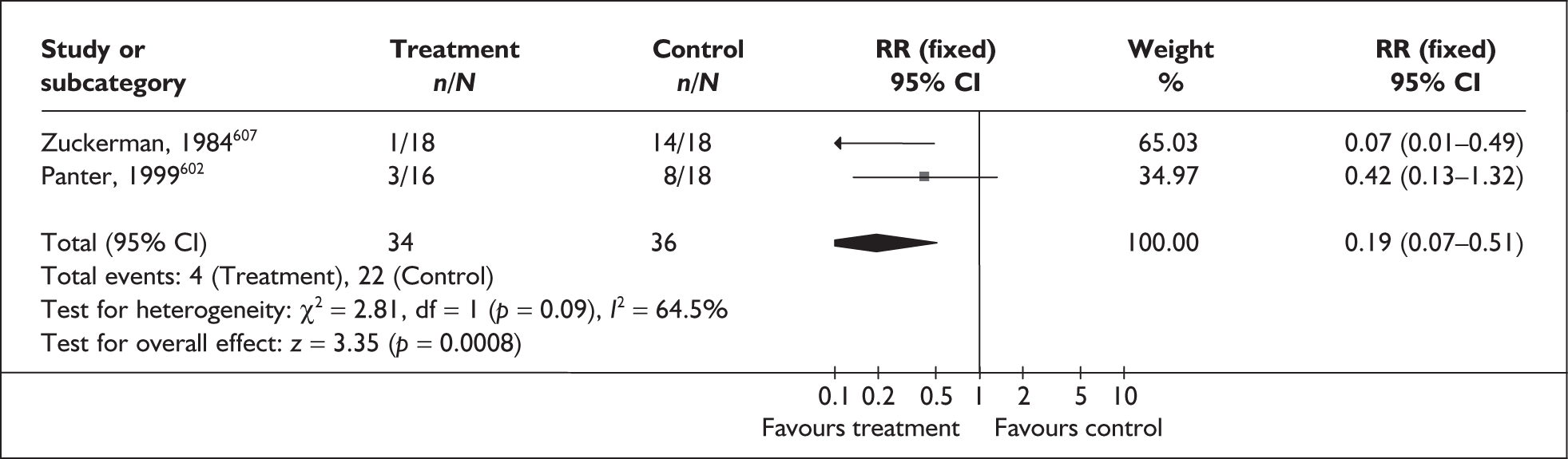
FIGURE 217.
Forest plot of the effects of any cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitor versus any other tocolytic for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of initiation of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
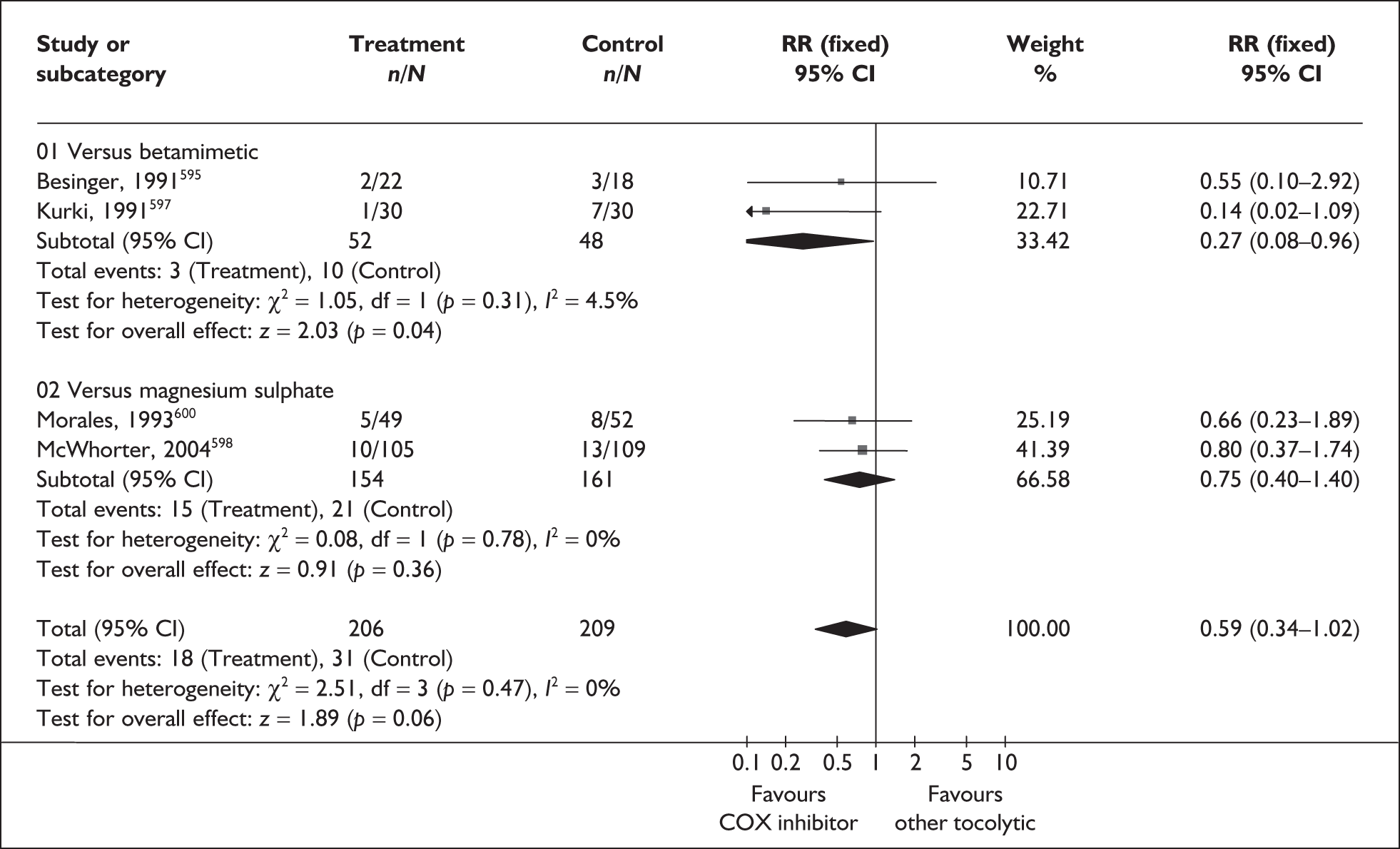
FIGURE 218.
Forest plot of the effects of sulindac versus placebo for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour (maintenance therapy after arrest of preterm labour).
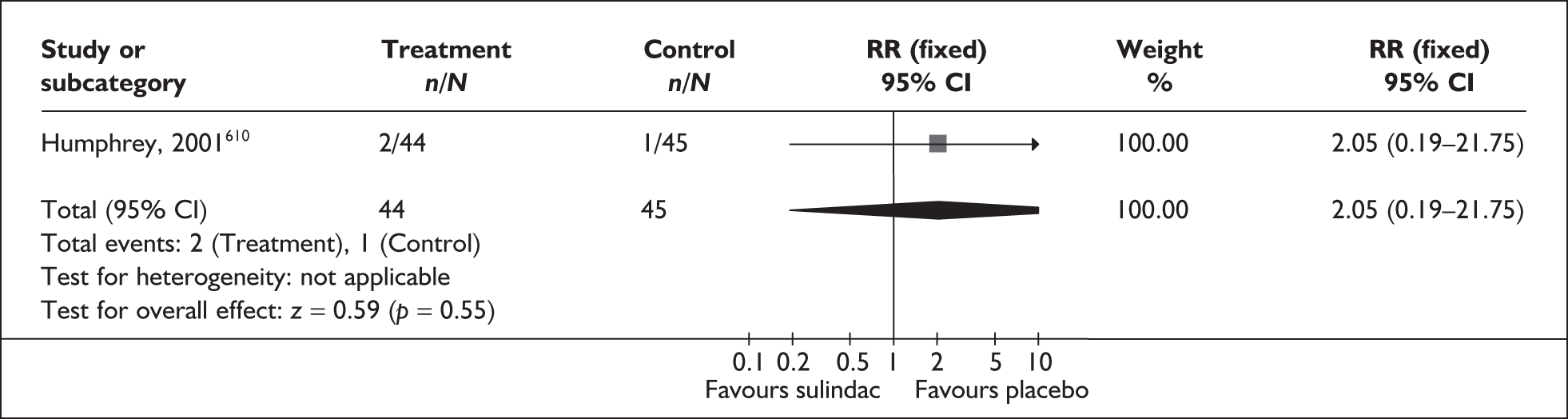
FIGURE 219.
Forest plot of the effects of any cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitor versus placebo for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
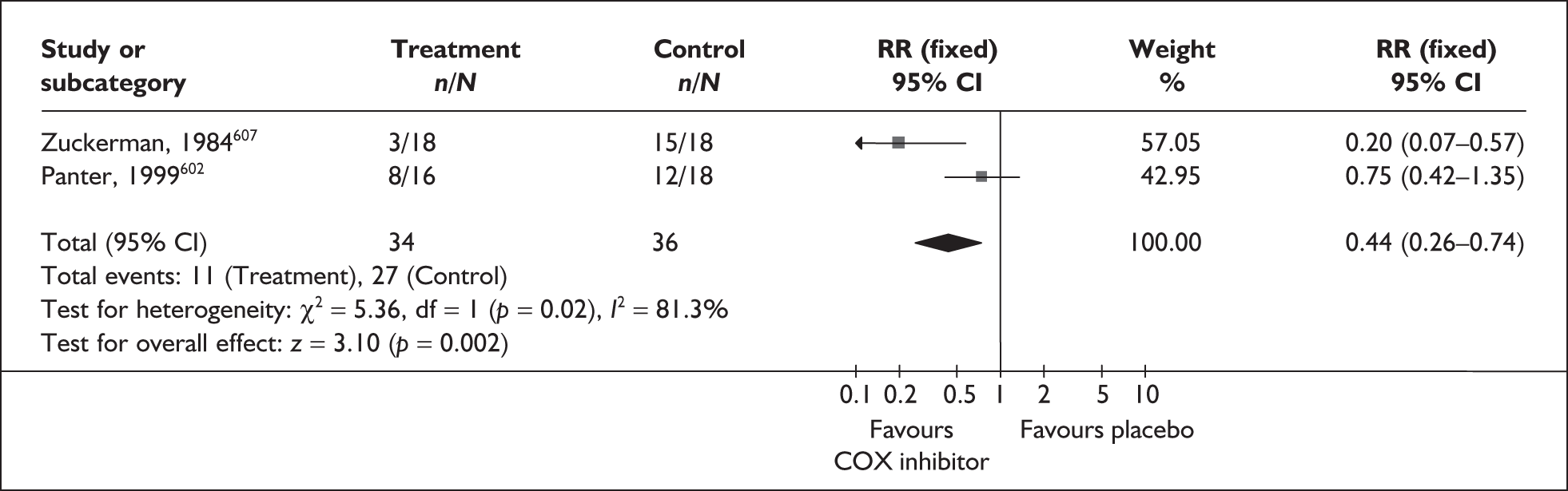
FIGURE 220.
Forest plot of the effects of any cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitor versus betamimetic for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
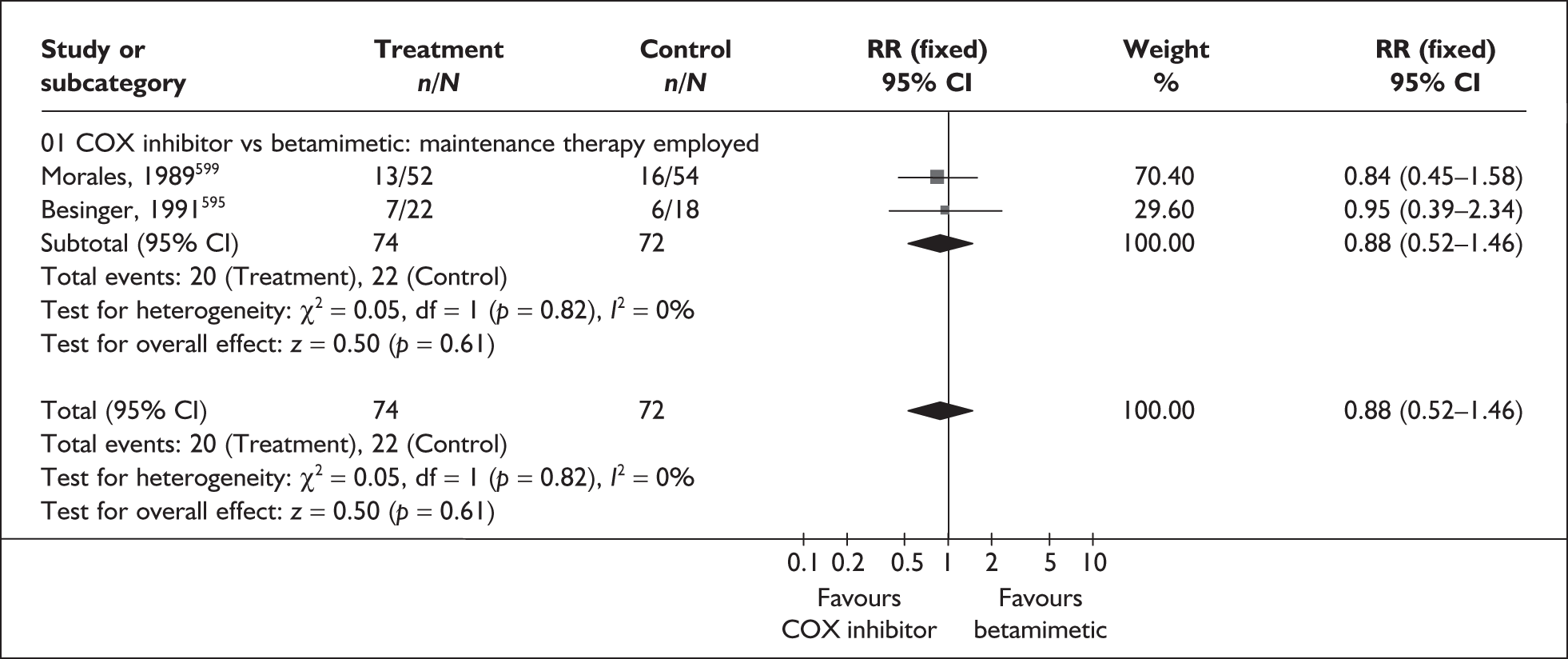
FIGURE 221.
Forest plot of the effects of indomethacin versus any cyclo-oxygenase 2 (COX-2) inhibitor for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
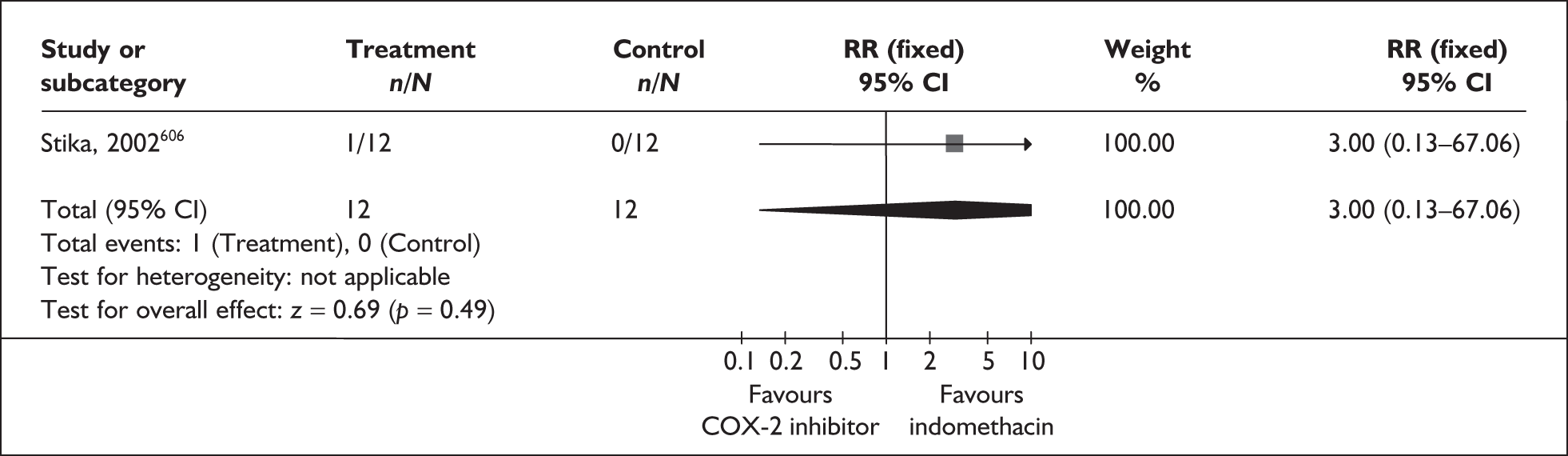
FIGURE 222.
Forest plot of the effects of sulindac versus placebo for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour (maintenance therapy after arrest of preterm labour).
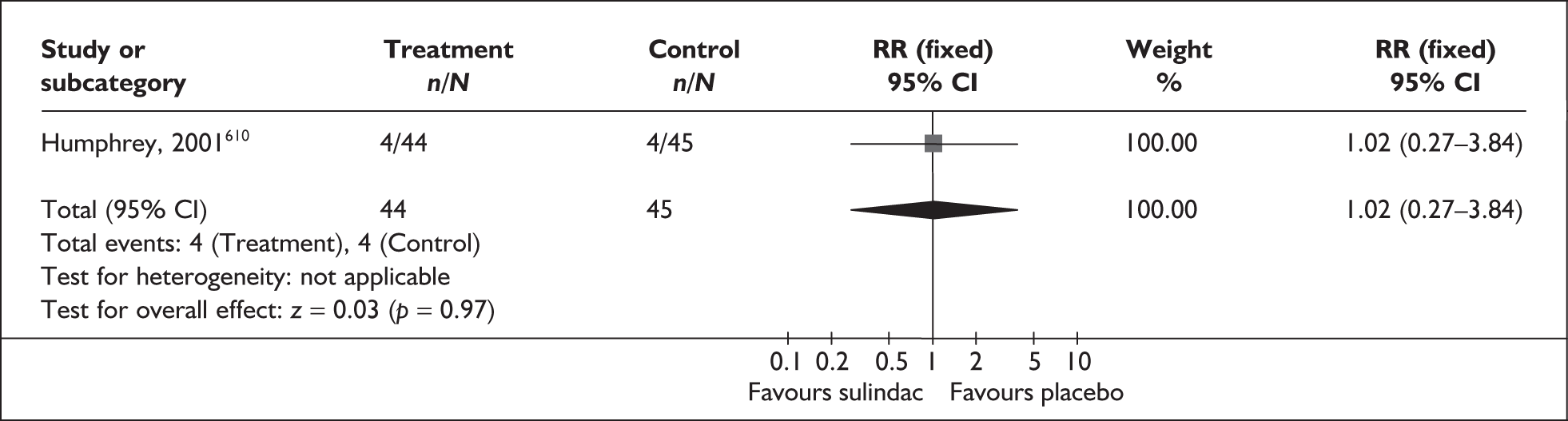
FIGURE 223.
Forest plot of the effects of any cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitor versus placebo for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
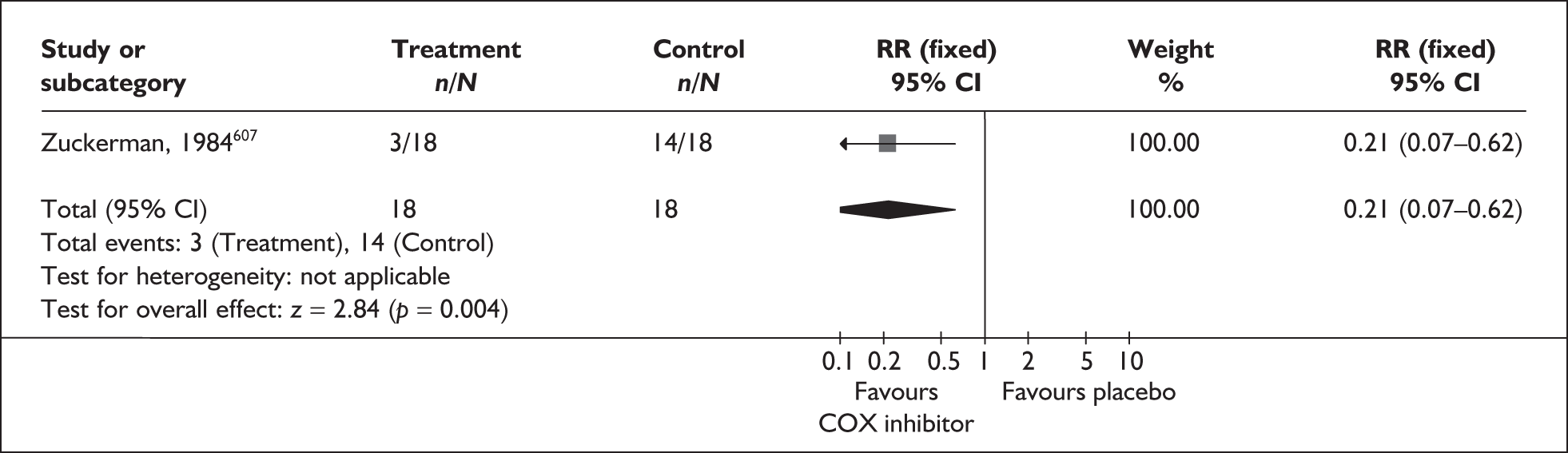
FIGURE 224.
Forest plot of the effects of any cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitor versus any other tocolytic for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
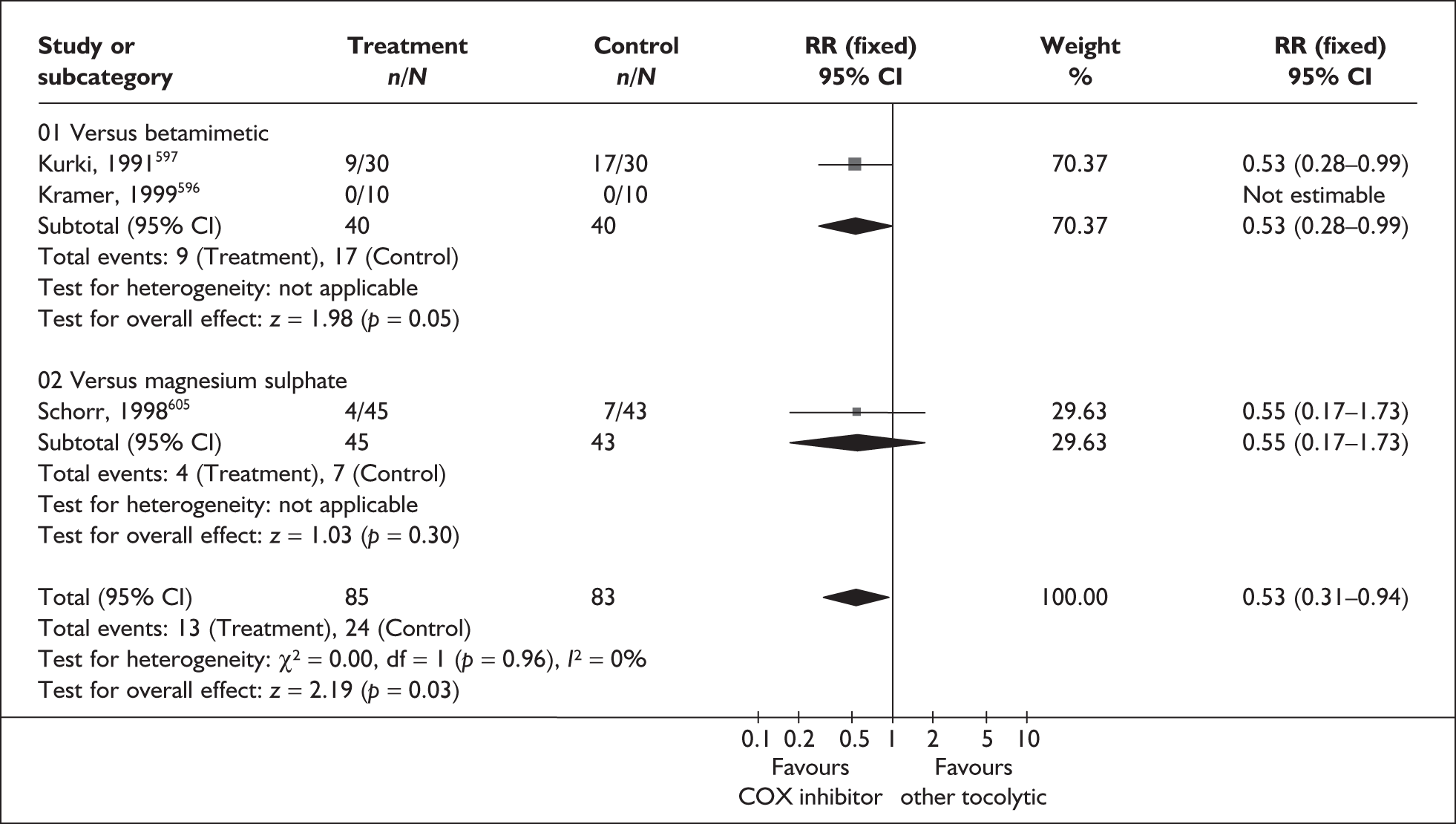
FIGURE 225.
Forest plot of the effects of indomethacin versus any cyclo-oxygenase 2 (COX-2) inhibitor for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
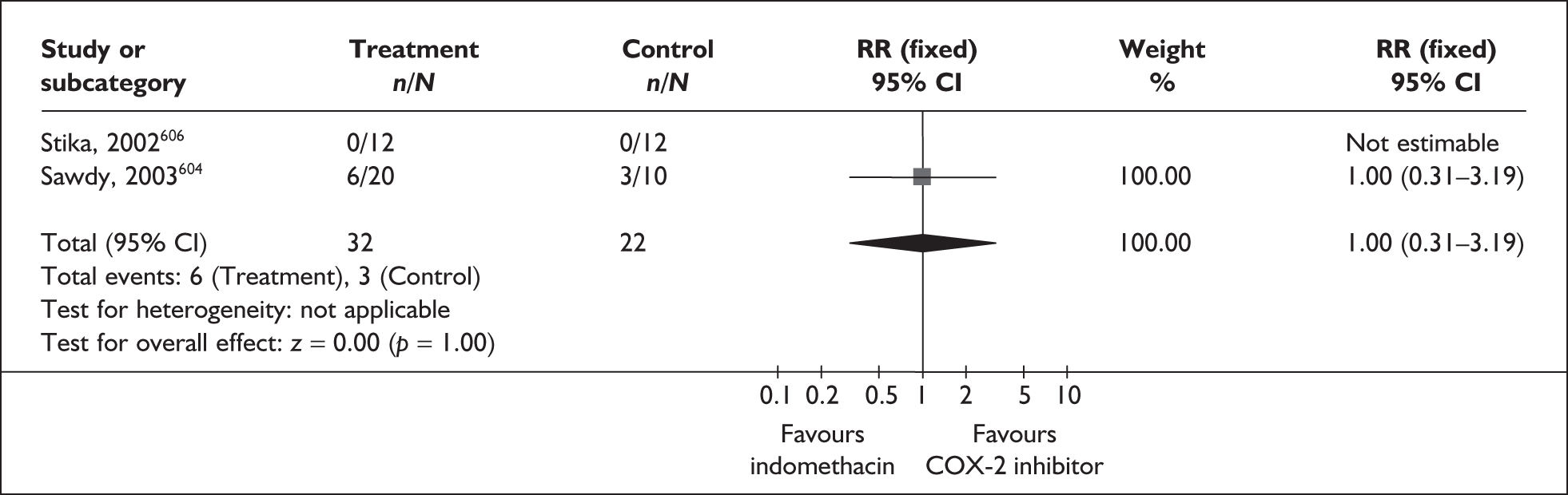
FIGURE 226.
Forest plot of the effects of prophylactic rofecoxib versus placebo for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in high-risk women.
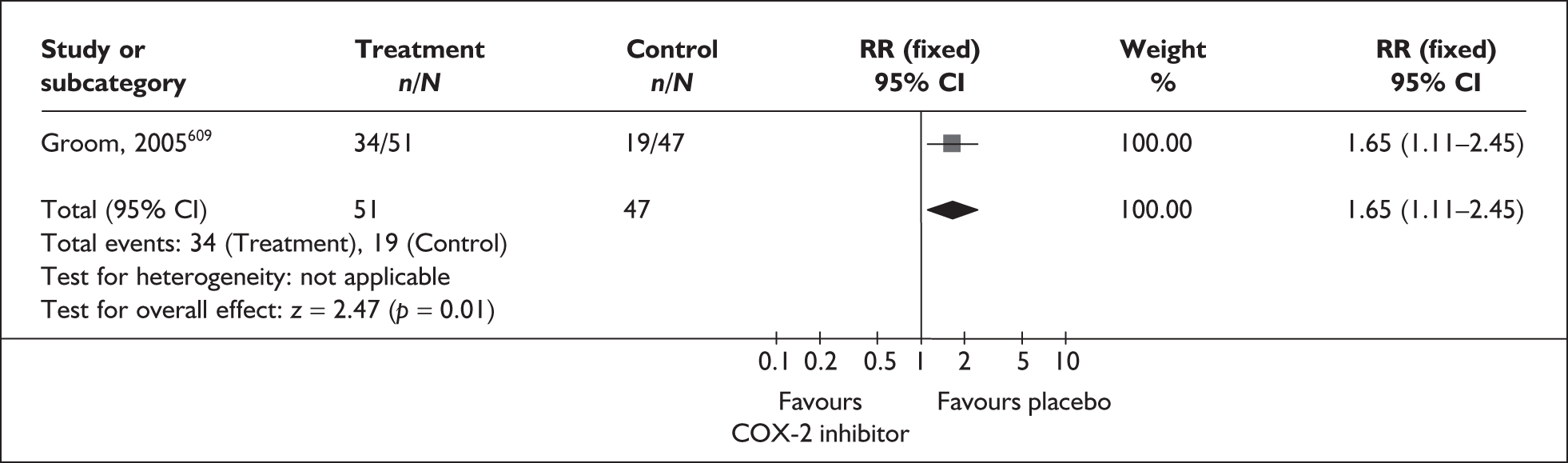
FIGURE 227.
Forest plot of the effects of prophylactic antenatal low-dose aspirin versus placebo for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
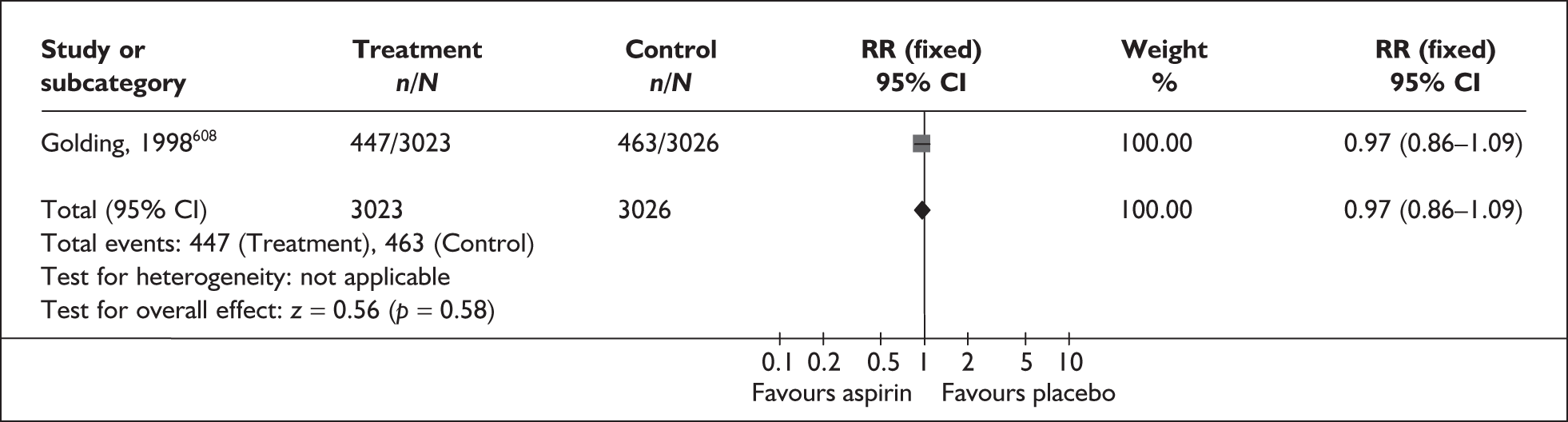
FIGURE 228.
Forest plot of the effects of any cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitor versus placebo for the prevention of perinatal mortality related to spontaneous preterm birth.
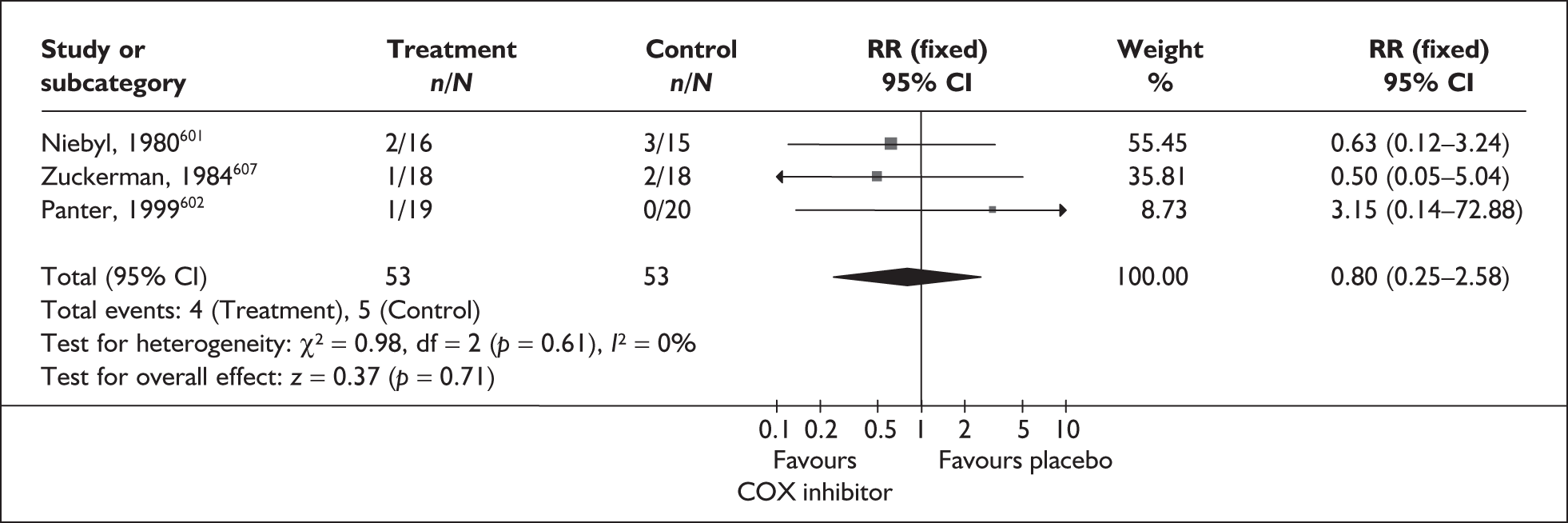
FIGURE 229.
Forest plot of the effects of any cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitor versus any other tocolytic for the prevention of perinatal mortality related spontaneous preterm birth.
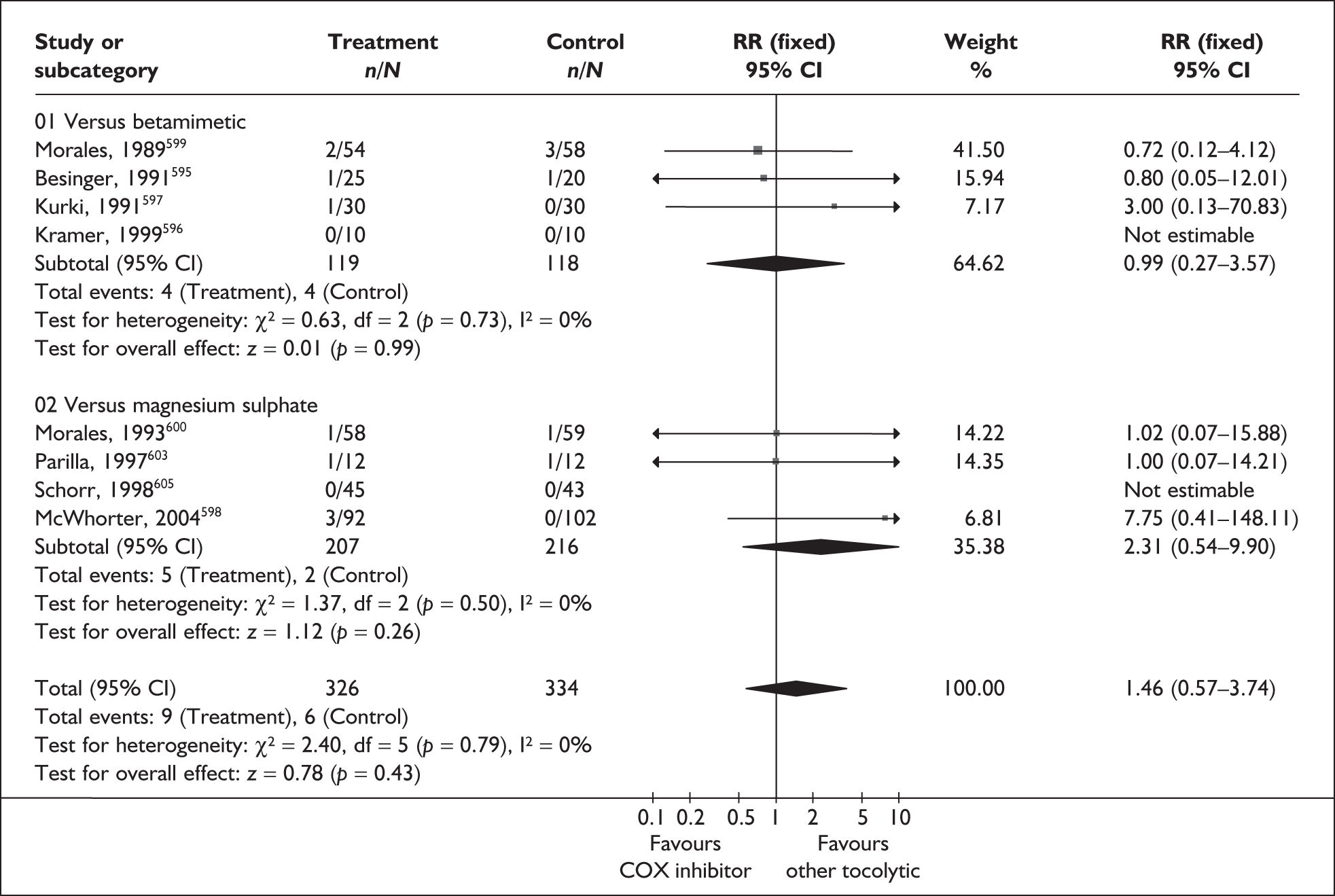
FIGURE 230.
Forest plot of the effects of prophylactic antenatal low-dose aspirin versus placebo for the prevention of perinatal mortality related to spontaneous preterm birth.
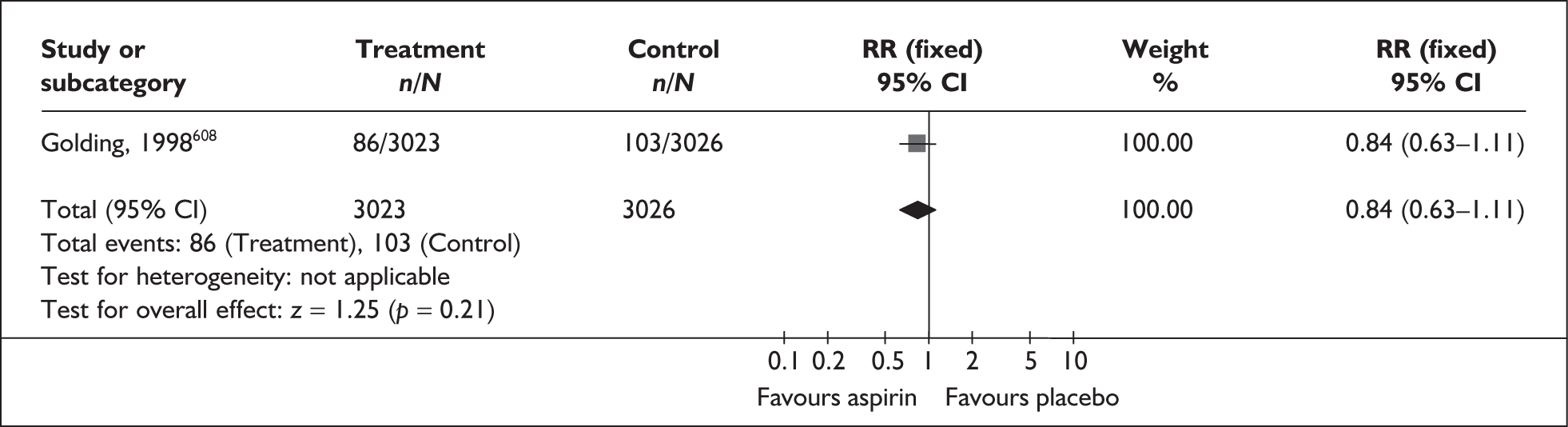
FIGURE 231.
Forest plot of the effects of any cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitor versus placebo for the prevention of neonatal intensive care admission.
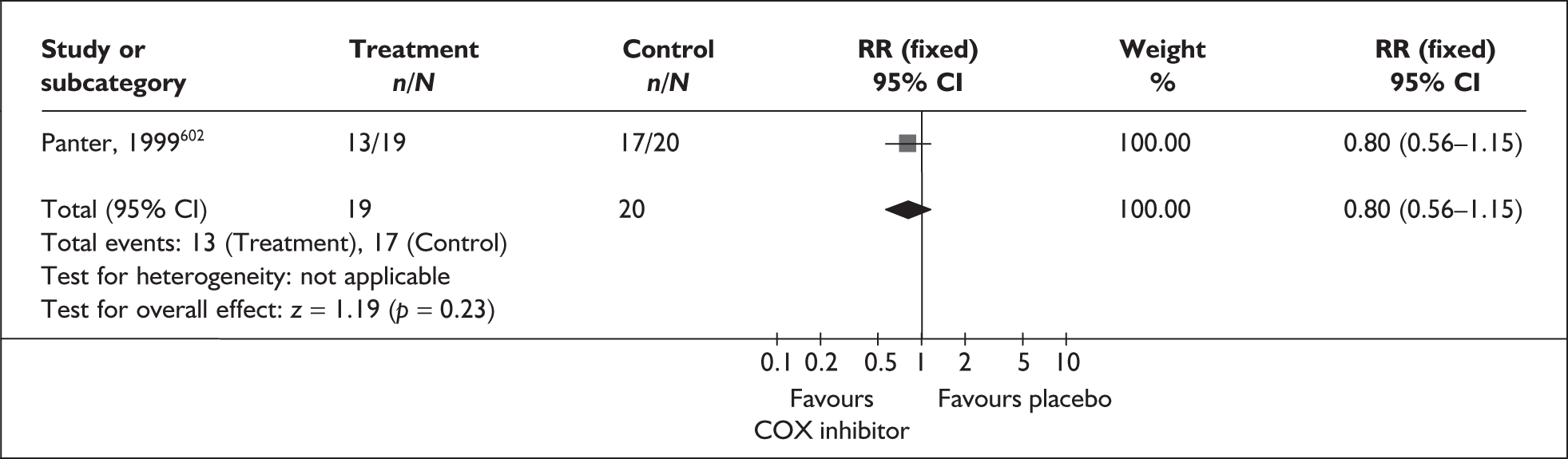
FIGURE 232.
Forest plot of the effects of any cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitor versus magnesium sulphate for the prevention of neonatal intensive care admission.
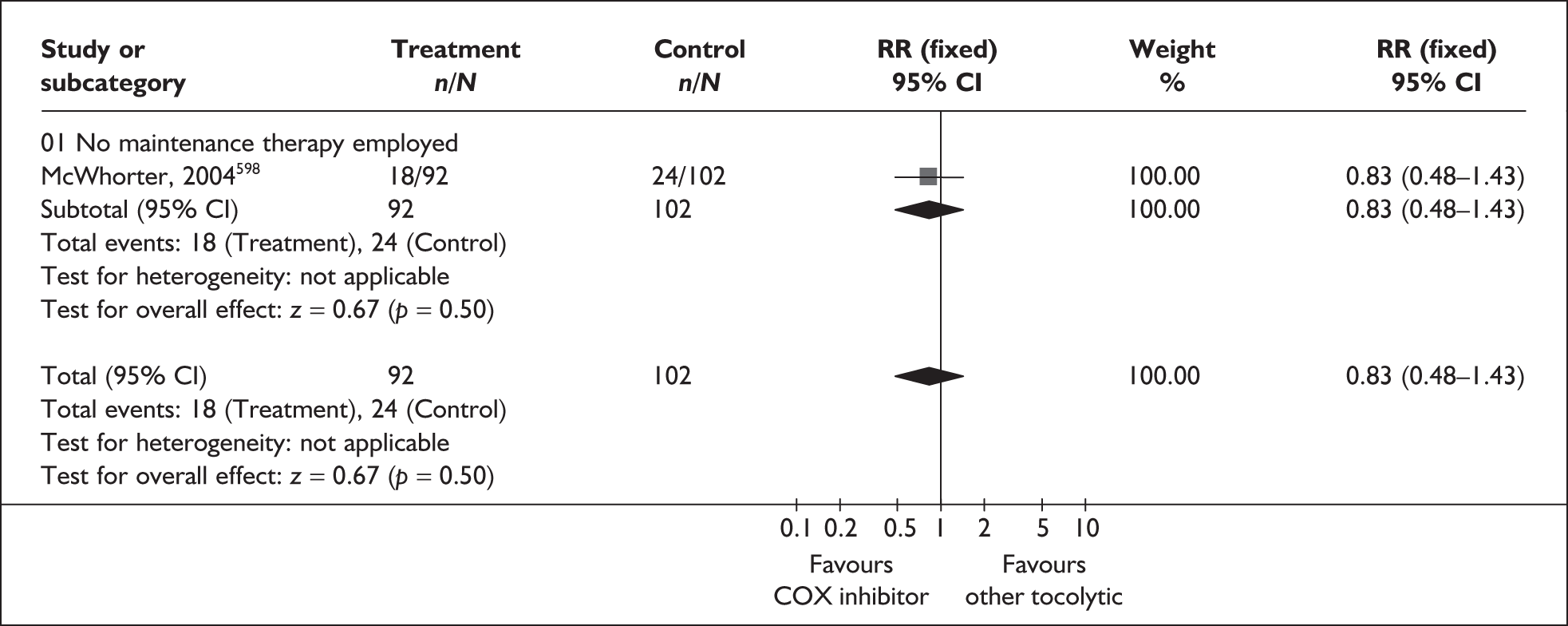
FIGURE 233.
Forest plot of the effects of indomethacin versus any cyclo-oxygenase 2 (COX-2) inhibitor for the prevention of neonatal intensive care admission.
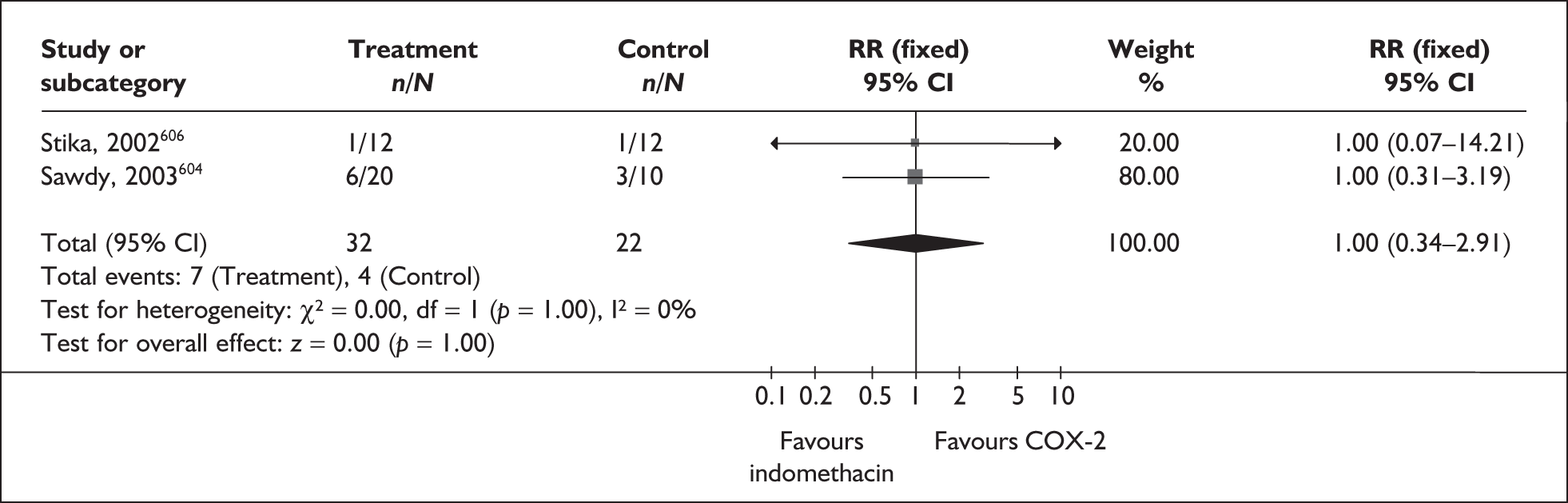
FIGURE 234.
Forest plot of the effects of prophylactic antenatal rofecoxib versus placebo for the prevention of neonatal intensive care admission in women at high risk of spontaneous preterm birth.
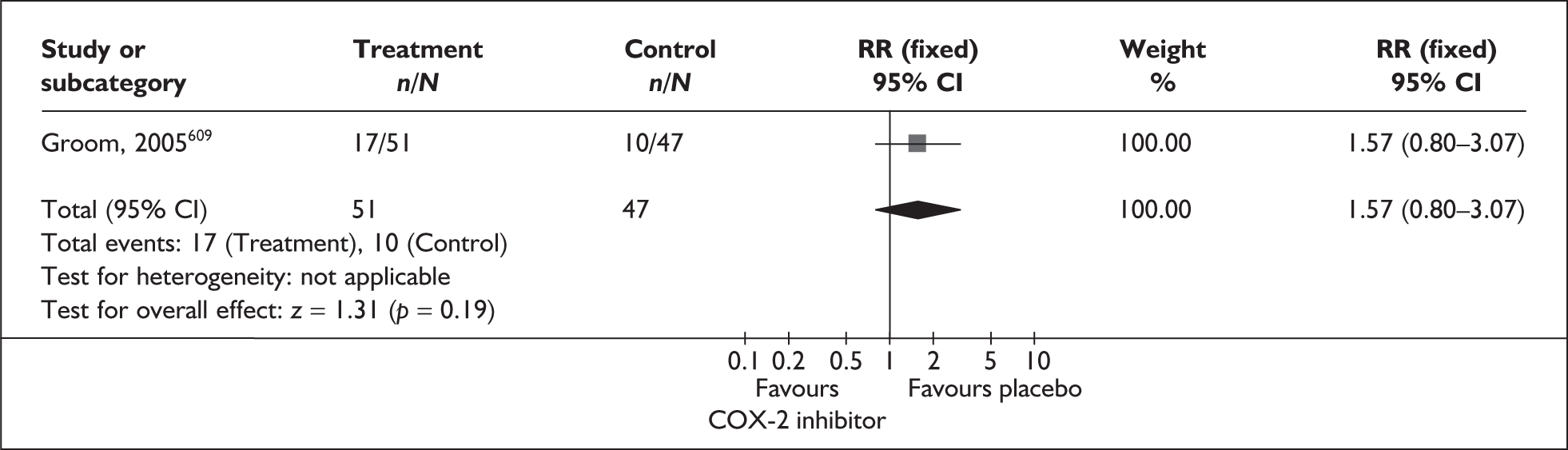
Five of the studies included in the review employed maintenance tocolysis (Table 28); three compared a COX inhibitor with a betamimetic,595,596,599 and two with magnesium sulphate. 600,605 Rescue tocolysis was employed in eight studies. 595,598–601,603,605,607 One additional study examined a COX inhibitor (sulindac) for the prevention of recurrence of spontaneous preterm birth (Figures 218, 222)610 a second additional study compared a COX-2 inhibitor (rofecoxib) with placebo in prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in high-risk women (Figures 226, 234)609 and the remaining additional study compared the use of another NSAID (aspirin) with placebo in prevention of spontaneous preterm birth labour in the general population (Figures 227, 230, 235). 608 Data were available on the following outcomes: birth within 48 hours of treatment, birth within 7 days of treatment, spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, perinatal mortality and admission to neonatal intensive care. Other maternal and perinatal outcomes are shown in Table 29.
FIGURE 235.
Forest plot of the effects of prophylactic antenatal low-dose aspirin versus placebo for the prevention of neonatal intensive care admission.
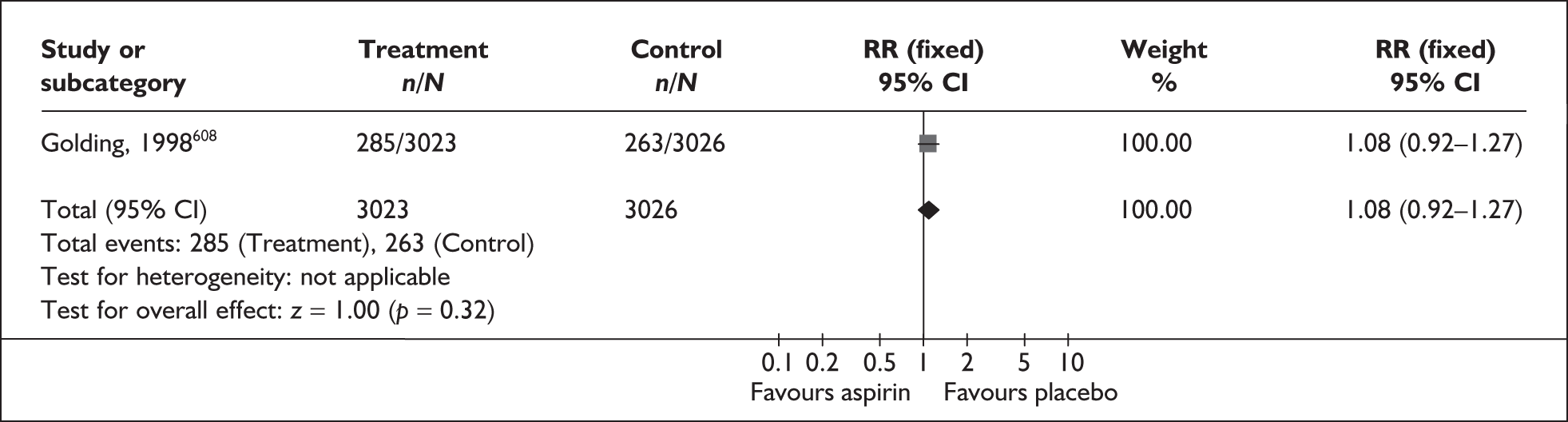
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Birth < 37 weeks gestation | |||
| Versus betamimetic (2 studies, n = 80) 596,597 | 0.53 | 0.28–0.99 | NA |
| Maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 20) 596 | Not estimable | Not estimable | NA |
| No maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 60) 597 | 0.53 | 0.28–0.99 | NA |
| Birth within 48 h of intervention | |||
| Versus betamimetic (2 studies, n = 620) 595,597 | 0.27 | 0.08–0.96 | 4.5% (0.31) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 40) 595 | 0.55 | 0.10–2.92 | NA |
| No maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 60) 597 | 0.14 | 0.02–1.09 | NA |
| Versus magnesium sulphate (2 studies, n = 315)598,600 | 0.75 | 0.40–1.40 | 0% (0.78) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 101)600 | 0.66 | 0.23–1.89 | NA |
| No maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 214)600 | 0.8 | 0.37–1.74 | NA |
| Perinatal mortality | |||
| Versus betamimetic (4 studies, n = 237)595–597,599 | 0.99 | 0.27–3.57 | 0% (0.73) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (3 studies, n = 177)595,596,599 | 0.74 | 0.17–3.21 | 0% (0.95) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 60)597 | 3 | 0.13–70.83 | NA |
| Versus magnesium sulphate (4 studies, n = 423)598,600,603,605 | 2.31 | 0.54–9.90 | 0% (0.50) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (2 studies, n = 205)598,605 | 1.02 | 0.07–15.88 | NA |
| No maintenance therapy employed (2 studies, n = 218)600,603 | 3.17 | 0.53–19.10 | 7.4% (0.30) |
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Birth within 48 h of intervention | |||
| Indomethacin vs COX-2 inhibitor (1 study, n = 24)606 | Not estimable | Not estimable | NA |
| Birth within 7 days of intervention | |||
| Indomethacin vs COX-2 inhibitor (1 study, n = 24)606 | Not estimable | Not estimable | NA |
| Perinatal mortality | |||
| Indomethacin vs COX-2 inhibitor (2 studies, n = 54)604,606 | Not estimable | Not estimable | NA |
| Low birthweight (< 2500 g) | |||
| Aspirin vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 6049)608 | 0.93 | 0.80–1.08 | NA |
| Respiratory distress syndrome | |||
| COX inhibitor vs placebo (3 studies, n = 106)601,602,607 | 1 | 0.40–2.49 | 26.2% (0.26) |
| COX inhibitor vs other tocolytic (6 studies, n = 503)596–598,600,603,605 | 1.08 | 0.66–1.76 | 0% (0.98) |
| Indomethacin vs COX-2 inhibitor (1 study, n = 24)606 | 1 | 0.07–14.21 | NA |
| Sulindac vs placebo (maintenance therapy) (1 study, n = 89)610 | 1.53 | 0.27–8.74 | NA |
| Neonatal mechanical ventilation | |||
| COX inhibitor vs other tocolytic (betamimetic, no maintenance therapy employed) (1 study, n = 60)597 | 1.5 | 0.47–4.78 | NA |
| Indomethacin vs COX-2 inhibitor (1 study, n = 24)606 | 1 | 0.07–14.21 | NA |
| Rofecoxib vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 98)609 | 1.84 | 0.49–6.96 | NA |
| Intraventricular haemorrhage: all grades | |||
| COX inhibitor vs other tocolytic (7 studies, n = 548)595–598,600,603,605 | 1.18 | 0.66–2.11 | 0% (0.58) |
| Indomethacin vs COX-2 inhibitor (1 study, n = 24)606 | 0.5 | 0.05–4.81 | NA |
| Intraventricular haemorrhage: grades 3 and 4 | |||
| COX inhibitor vs placebo (1 study, n = 39)602 | 3.15 | 0.14–72.88 | NA |
| COX inhibitor vs other tocolytic (4 studies, n = 249)596,600,603,605 | 0.61 | 0.08–4.40 | 0% (0.60) |
| Intercranial haemorrhage | |||
| Aspirin vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 6049)608 | 3 | 0.12–73.69 | NA |
| Other neonatal bleeding | |||
| Aspirin vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 6049)608 | 1.5 | 0.25–8.98 | NA |
| Necrotising enterocolitis | |||
| COX inhibitor vs placebo (2 studies, n = 70)601,602 | 0.97 | 0.21–4.43 | 0% (0.94) |
| COX inhibitor vs other tocolytic (4 studies, n = 298)596–598,603 | 3.82 | 0.65–22.51 | 0% (0.95) |
| Rofecoxib vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 98)609 | 2.77 | 0.12–66.36 | NA |
| Chronic neonatal lung disease | |||
| COX inhibitor vs placebo (2 studies, n = 70)601,602 | 1.24 | 0.39–3.94 | 60.1% (0.11) |
| Rofecoxib vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 98)609 | 0.92 | 0.20–4.34 | NA |
| Apgar score < 7 at 5 min | |||
| COX inhibitor vs placebo (1 study, n = 39)602 | 0.53 | 0.05–5.34 | NA |
| COX inhibitor vs other tocolytic (2 studies, n = 254) 597,598 | 0.53 | 0.21–1.30 | 25.2% (0.25) |
| Indomethacin vs COX-2 inhibitor (1 study, n = 24)606 | 3 | 0.13–67.06 | NA |
| Apgar score < 5 at 5 min | |||
| Aspirin vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 6049)608 | 1.52 | 0.92–2.51 | NA |
| Persistent pulmonary hypertension of newborn | |||
| COX inhibitor vs other tocolytic (5 studies, n = 488)595,596,598–600 | 2.85 | 0.56–14.38 | 0% (0.72) |
| Neonatal sepsis | |||
| COX inhibitor vs placebo (2 studies, n = 70)601,602 | 0.31 | 0.01–7.15 | NA |
| COX inhibitor vs betamimetic (2 studies, n = 80)596.597 | 1 | 0.07–15.26 | NA |
| Indomethacin vs COX-2 inhibitor (1 study, n = 24)606 | 0.33 | 0.01–7.45 | NA |
| Sulindac vs placebo (maintenance therapy) (1 study, n = 89) 610 | 1.02 | 0.15–6.94 | NA |
| Neonate discharged alive and well | |||
| Rofecoxib vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 98)609 | 0.9 | 0.73–1.10 | NA |
| Maternal adverse drug reaction | |||
| COX inhibitor vs placebo (3 studies, n = 101)601,602,607 | 1.58 | 0.66–3.78 | 0% (0.87) |
| COX inhibitor vs other tocolytic | 0.22 | 0.15–0.33 | 65.8% (0.01) |
| Total (7 studies, n = 629)595–600,603 | 0.1 | 0.05–0.20 | 5 |
| COX inhibitor vs betamimetic (4 studies, n = 226)595–597,599 | 0.03 | 0.01–0.15 | 9.1% (0.06) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (3 studies, n = 166)595,596,599 | 0.24 | 0.12–0.50 | 0% (0.56) |
| No maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 60)597 | 0.41 | 0.26–0.66 | NA |
| COX inhibitor vs magnesium sulphate (3 studies, n = 403)598,600,605 | 0.2 | 0.06–0.64 | 3.5% (0.14) |
| Maintenance therapy employed (2 studies, n = 189)600,605 | 0.51 | 0.30–0.86 | NA |
| No maintenance therapy employed (1 study, n = 214)598 | NA | ||
| Maternal adverse drug reaction requiring cessation of treatment | |||
| COX inhibitor vs other tocolytic | 0.07 | 0.02–0.29 | 0% (0.81) |
| Total (5 studies, n = 355)595,596,599,600,605 | 0.07 | 0.01–0.37 | 0% (0.63) |
| COX inhibitor vs betamimetic, maintenance therapy employed (3 studies, n = 166)595,596,599 | 0.06 | 0.00–1.05 | NA |
| COX inhibitor vs magnesium sulphate, maintenance therapy employed (2 studies, n = 189)600,605 | 1 | 0.63–1.59 | NA |
| Aspirin vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 6049)608 | |||
| Treatment required to be stopped < 32 weeks gestation | |||
| Rofecoxib vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 98)609 | 1.21 | 0.72–2.03 | na |
| Antepartum haemorrhage | |||
| Indomethacin vs COX-2 inhibitor (1 study, n = 24)606 | 0.33 | 0.01–7.45 | NA |
| Postpartum haemorrhage | |||
| COX inhibitor vs placebo (1 study, n = 34)602 | 3.94 | 0.95–16.29 | NA |
| Rofecoxib vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 98)609 | 2.77 | 0.12–66.36 | NA |
| Aspirin vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 6049)608 | 1.38 | 1.13–1.68 | NA |
| Chorioamnionitis or endometritis | |||
| COX inhibitor vs placebo (2 studies, n = 64)601,602 | 1.94 | 0.44–8.60 | 0% (0.39) |
| Indomethacin vs COX-2 inhibitor (1 study, n = 24)606 | 2 | 0.21–19.23 | NA |
| Oligohydramnios | |||
| COX inhibitor vs other tocolytic (3 studies, n = 295)599,600,605 | 2.53 | 0.76–8.84 | 0% (0.57) |
| Indomethacin vs COX-2 inhibitor (1 study, n = 24)606 | 4 | 0.52–30.76 | NA |
| Rofecoxib vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 98)609 | 8.29 | 1.09–63.00 | NA |
| PPROM | |||
| Rofecoxib vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 98)609 | 2.46 | 1.28–4.73 | NA |
| Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy | |||
| Aspirin vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 6049)608 | 1.12 | 0.81–1.55 | NA |
| Vomiting blood during pregnancy | |||
| Aspirin vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 6049)608 | 0.88 | 0.44–1.77 | NA |
| Other maternal bleeding during pregnancy | |||
| Aspirin vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 6049)608 | 1.53 | 1.02–2.29 | NA |
| Antenatal admission | |||
| Aspirin vs placebo (prophylaxis) (1 study, n = 6049)608 | 1.07 | 0.96–1.20 | NA |
COX inhibitors were significantly more effective than placebo in preventing birth within 48 hours (Figure 216), within 7 days of treatment (Figure 220), and before 37 weeks’ gestation (Figure 224). They were significantly more effective than betamimetics in preventing birth within 48 hours of treatment (Figure 217, Table 28) or before 37 weeks’ gestation (Figure 224, Table 28), but were not significantly different from magnesium sulphate on any primary outcome. COX inhibitors also caused significantly fewer maternal side effects than other tocolytic agents, both overall and those requiring cessation of treatment (Table 29). Rofecoxib given to asymptomatic women at high risk of spontaneous preterm birth increased the incidence of birth before 37 weeks’ gestation (Figure 226) and was also associated with an increased occurrence of premature pre-labour rupture of membranes and a greatly increased occurrence of oligohydramnios (Table 29). Aspirin given to asymptomatic women was associated with increased occurrence of postpartum haemorrhage and other (non-vaginal or vomiting) bleeding during pregnancy (Table 26). Summary RRs (of studies vs placebo comparators) from the forest plots presented were used in the decision analyses.
Ethanol as a tocolytic
Oxytocin is involved in the initiation and maintenance of uterine contractions in labour and alcohol appears to suppress the episodic release of oxytocin in term labour; the efficacy of ethanol in the treatment of threatened preterm labour has been credited to this mechanism of action. However, ethanol has been associated with a number of adverse events, such as respiratory depression, nausea and vomiting and urinary incontinence,611 and has not been used in clinical practice for many years.
The review of ethanol included three RCTs612–614 and two quasi-RCTs615,616 (n = 446). Further details of the studies can be found in Appendix 6, Table 135. The overall methodological quality of the studies was generally poor; the findings are shown in Figure 236. Ethanol was not found to reduce the risk of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ or 34 weeks’ gestation when compared to betamimetics (Figures 237 and 238, respectively). Although no statistically significant difference was shown between ethanol and control groups for delivery within 24 and 48 hours after intervention administration (Figures 239 and 240, respectively), ethanol was shown to increase the risk of delivery within 7 days (Figure 241). Ethanol did not improve perinatal mortality when compared to betamimetics or other comparators (Figure 242 and Table 30). A greater incidence of nausea, vomiting and loss of consciousness was shown in the ethanol group compared to controls (Table 30). There were, however, fewer cardiovascular changes (mean maternal and fetal heart acceleration, mean maternal systolic blood pressure increase, and mean fetal systolic blood pressure decrease) when compared with ritodrine (Table 30). The summary RRs were not used in the decision analyses. On the basis of the available poor-quality evidence, ethanol does not appear to be beneficial as a tocolytic in the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
FIGURE 236.
Methodological quality of the included trials of ethanol for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
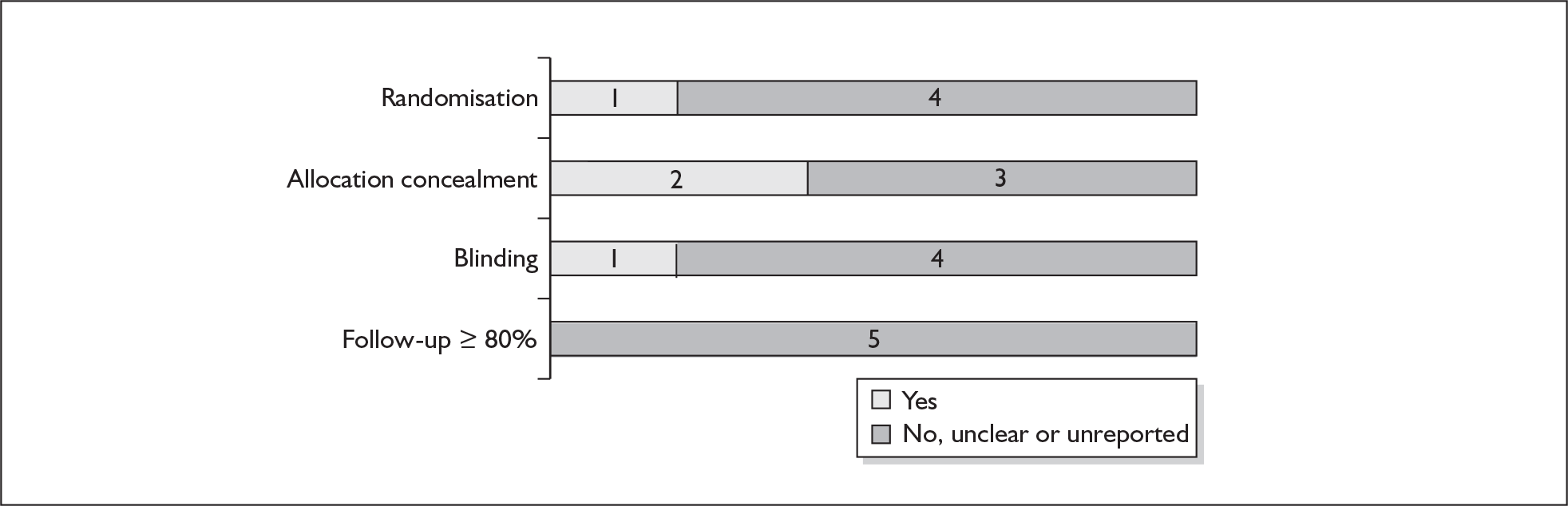
FIGURE 237.
Forest plot of the effects of ethanol versus beta-sympathomimetics for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour. a, Women with intact membranes only.
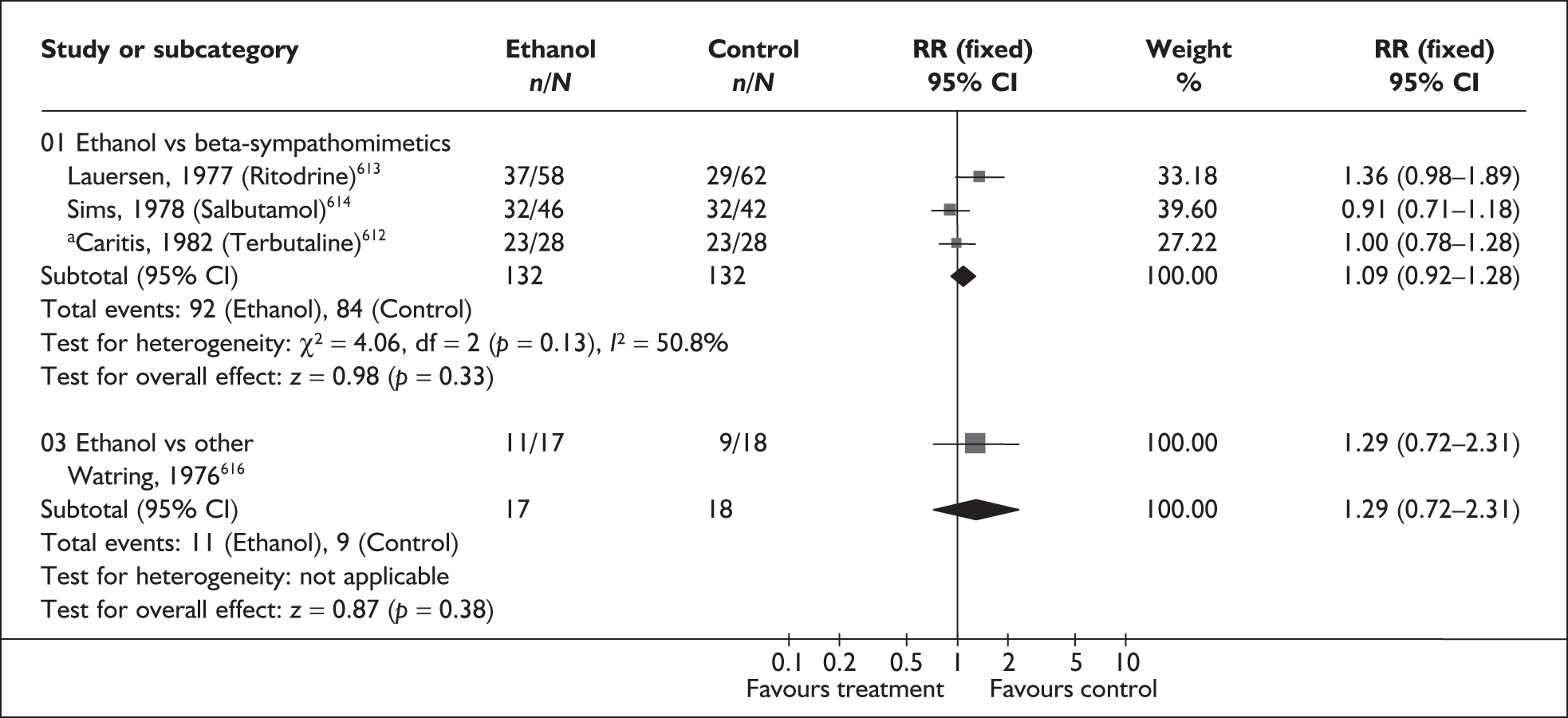
FIGURE 238.
Forest plot of the effects of ethanol versus beta-sympathomimetics for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
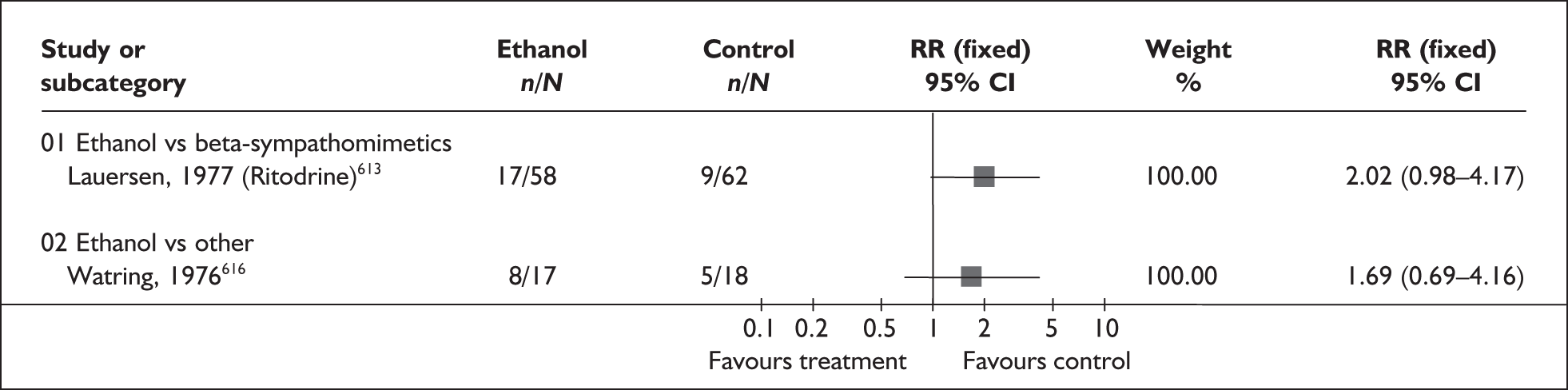
FIGURE 239.
Forest plot of the effects of ethanol versus beta-sympathomimetics for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 24 hours of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour. a, Women with intact membranes only.
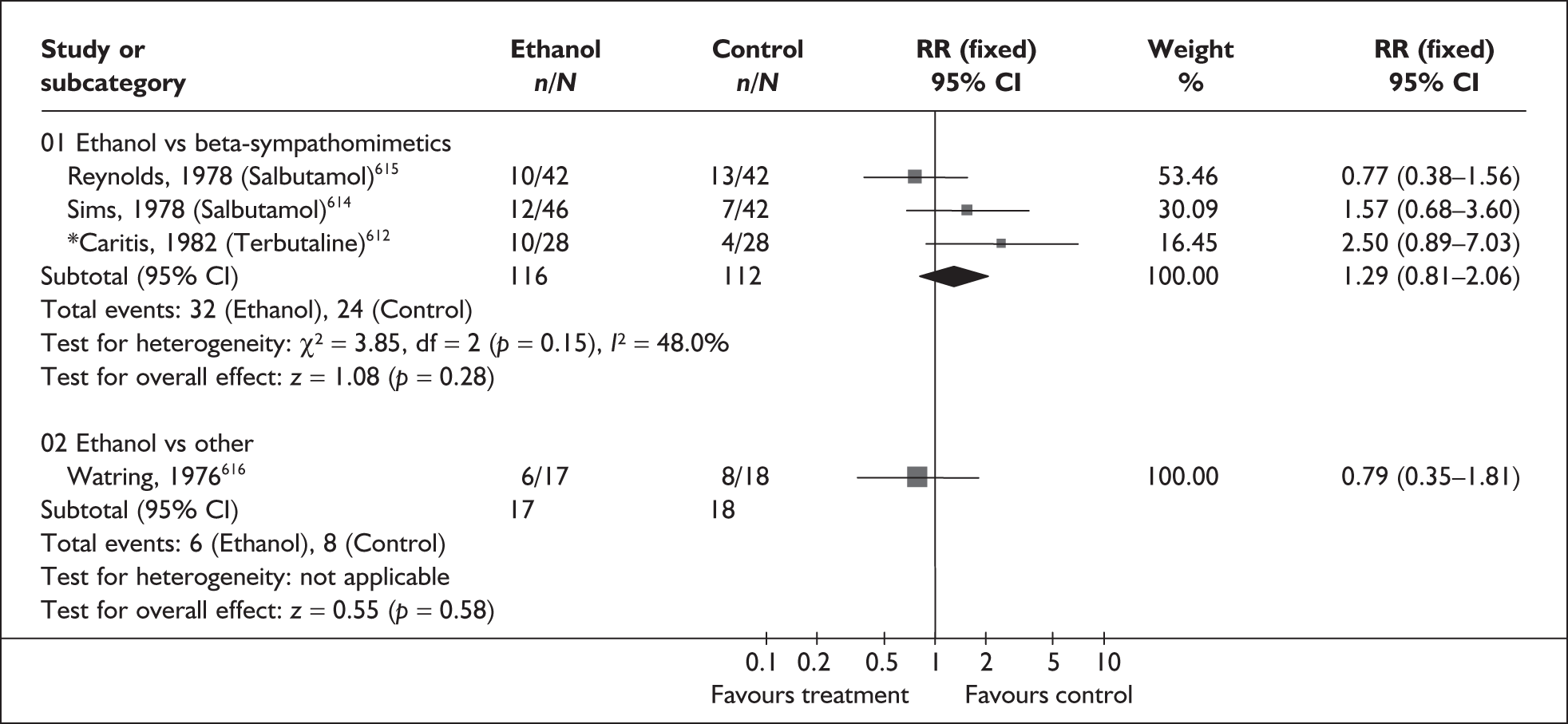
FIGURE 240.
Forest plot of the effects of ethanol versus beta-sympathomimetics for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
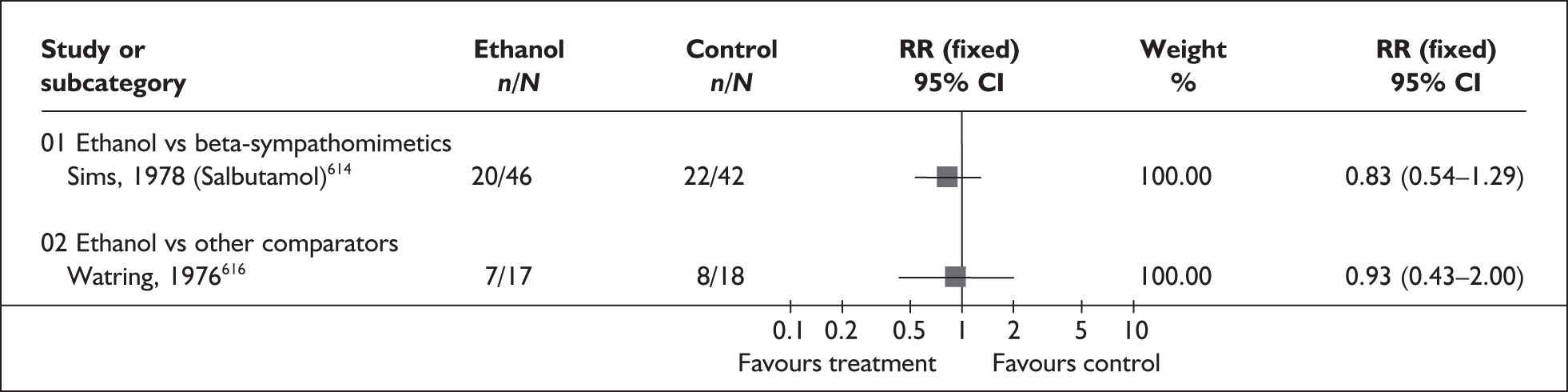
FIGURE 241.
Forest plot of the effects of ethanol versus beta-sympathomimetics for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour. a, Women with intact membranes only
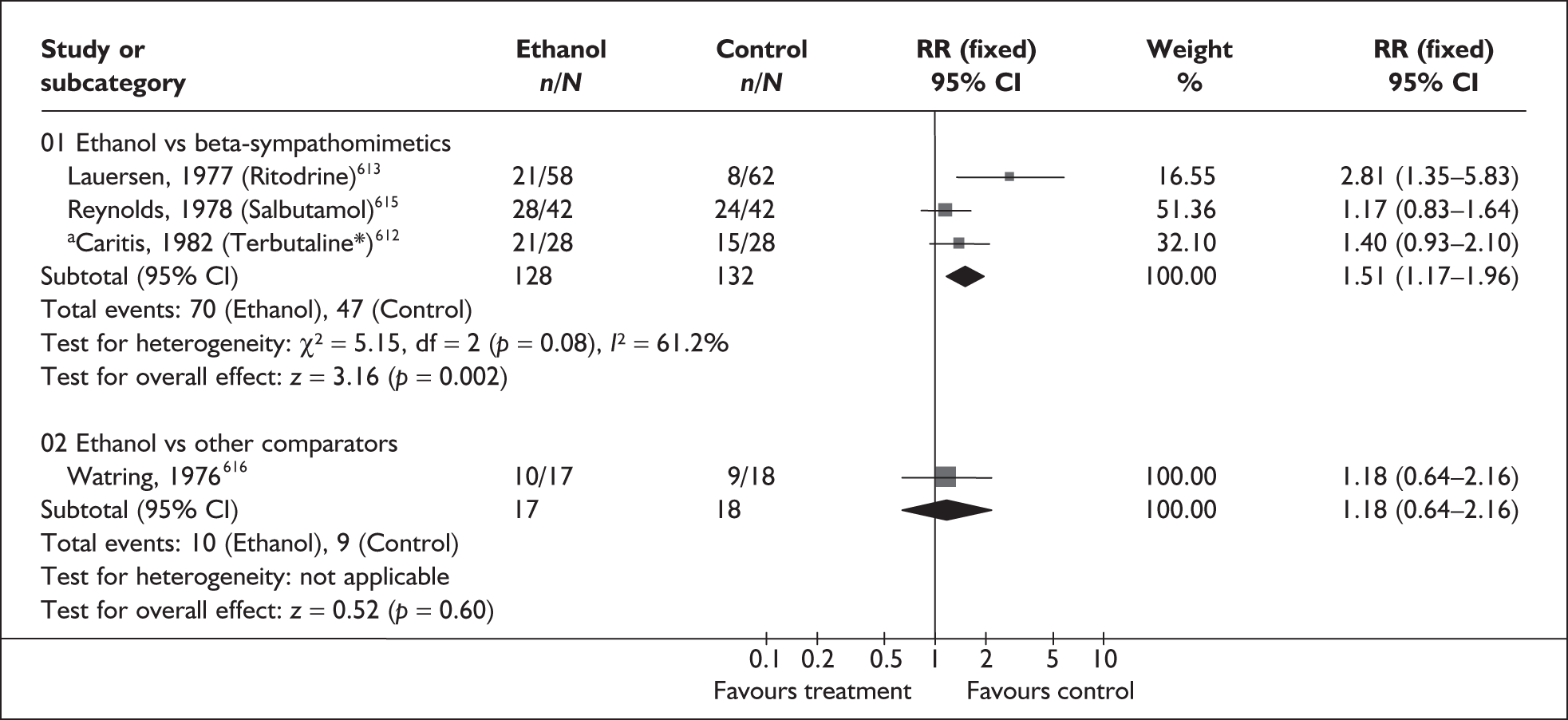
FIGURE 242.
Forest plot of the effects of ethanol versus beta-sympathomimetic tocolysis for the prevention of perinatal mortality related to spontaneous preterm birth.
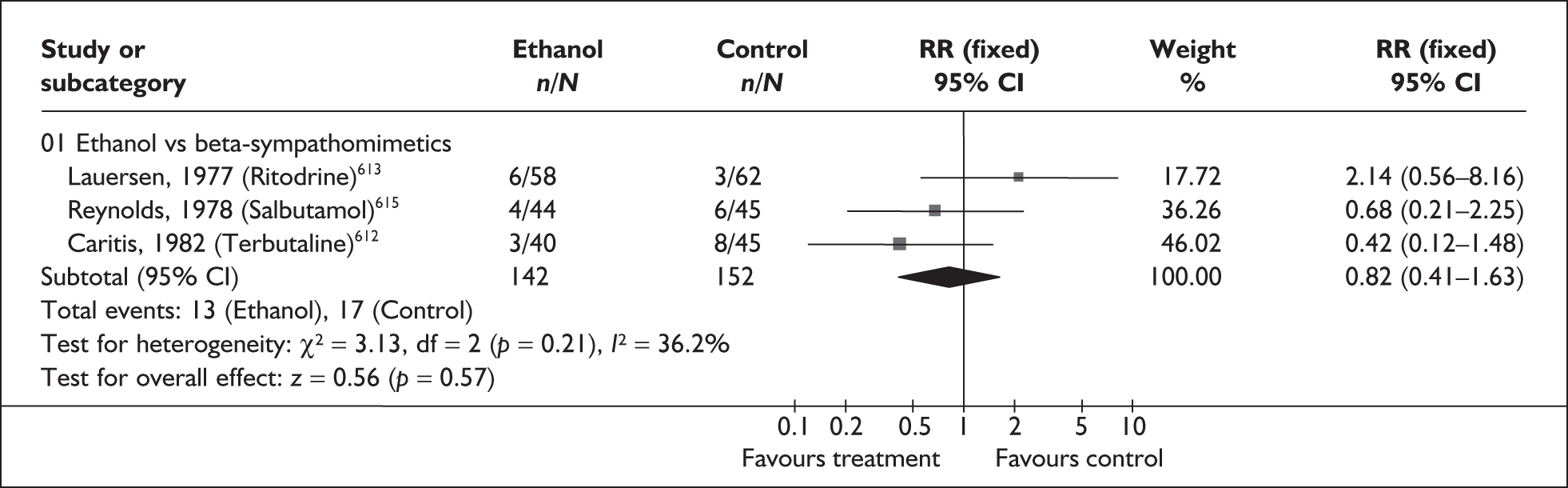
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stillbirths | |||
| Ethanol vs terbutaline (1 study, n = 56)612 | 0.5 | 0.05–5.20 | NA |
| Neonatal death | 0.33 | 0.07–1.51 | NA |
| Ethanol vs terbutaline (1 study, n = 56)612 | 2.45 | 0.67–9.04 | NA |
| Ethanol vs ritodrine (1 study, n = 119)613 | 2.28 | 0.77–6.73 | NA |
| Ethanol vs salbutamol (1 study, n = 88)614 | 1.41 | 0.37–5.40 | NA |
| Ethanol vs other comparators (1 study, n = 35)616 | |||
| Respiratory distress syndrome | |||
| Ethanol vs ritodrine (1 study, n = 149)613 | 2.4 | 0.99–5.85 | NA |
| Ethanol vs other comparators (1 study, n = 35)616 | 0.85 | 0.27–2.64 | NA |
| Hyaline membrane disease | |||
| Ethanol vs terbutaline (1 study, n = 56) 612 | 1 | 0.47–2.14 | NA |
| Birthweight | |||
| Ethanol vs other comparators (1 study, n = 35)616 | WMD – 431.43 | – 1038.63 to 175.77 | NA |
| Birthweight < 2500 g | |||
| Ethanol vs ritodrine (1 study, n = 149)613 | 2.49 | 1.57–3.93 | NA |
| Birthweight < 1500 g | |||
| Ethanol vs ritodrine (1 study, n = 149)613 | 1.76 | 0.69–4.51 | NA |
| Maternal chest pain and shortness of breath | |||
| Ethanol vs terbutaline (1 study, n = 85)613 | 0.1 | 0.01–1.79 | NA |
| Mean maternal heart acceleration (beats/min) | |||
| Ethanol vs ritodrine (1 study, n = 135)613 | WMD – 22.20 | – 26.74 to – 7.66 | NA |
| Mean fetal heart acceleration (beats/min) | |||
| Ethanol vs ritodrine (1 study, n = 149)613 | WMD – 10.40 | – 14.83 to – 5.97 | NA |
| Mean maternal systolic blood pressure increase (mmHg) | |||
| Ethanol vs ritodrine (1 study, n = 135)613 | WMD – 9.20 | – 12.73 to – 5.67 | NA |
| Mean fetal systolic blood pressure decrease (mmHg) | |||
| Ethanol vs ritodrine (1 study, n = 149)613 | WMD – 5.80 | – 9.16 to – 2.44 | NA |
| Cardiac arrhythmia | |||
| Ethanol vs terbutaline (1 study, n = 85)612 | 0.37 | 0.02–8.93 | NA |
| Maternal nausea and vomiting | |||
| Ethanol vs terbutaline (1 study, n = 85) 612 | 10.33 | 3.42–31.21 | NA |
| Ethanol vs salbutamol (1 study, n = 84)615 | 2.77 | 1.71–4.49 | NA |
| Loss of consciousness | |||
| Ethanol vs terbutaline (1 study, n = 85)612 | 21.23 | 1.28–354.96 | NA |
Magnesium sulphate acute tocolysis
Magnesium sulphate is one of a number of tocolytic agents that are used in the management of threatened preterm labour. Magnesium sulphate acts on the central nervous system to block neuromuscular transmission. However, the mechanism by which it inhibits uterine contractions is not fully understood, although it is thought to be related to calcium antagonist activity.
The review of magnesium sulphate for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth included 22 RCTs537,569,574,580,581,605,617–630 and two quasi-RCTs (n = 2036);600,631 one RCT598 was added to the primary studies identified in an earlier systematic review. 632 Further details of the review and the additional study can be found in Appendix 6, Table 136. The quality of these studies is shown in Figure 243. The quality was often poor; less than half of the included studies reported adequate randomisation or allocation concealment. Magnesium sulphate was not found to significantly reduce the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 and 34 weeks’ gestation, or admission to neonatal intensive care unit compared to other tocolytic agents, non-tocolytic therapy, or no treatment (Figures 244, 245 and 247, respectively). Similarly, when compared to other tocolytic agents, magnesium sulphate did not reduce the risk of delivery within 48 hours of treatment; however, when compared to non-tocolytic treatment a significant reduction in risk was shown (Figure 246). Relevant information relating to delivery within 24 hours or within 7 days of treatment, or perinatal mortality was not reported. A higher incidence of total infant mortality was found in mothers receiving magnesium sulphate compared with all comparators but this was not statistically significant (Table 31). Few significant differences were found for the other infant and maternal outcomes reported (Table 31); an exception was that women treated with magnesium sulphate reported fewer side effects leading to discontinuation of treatment compared to betamimetics. When data were analysed according to different dosing regimens (magnesium sulphate ≤ 2 g/hour versus > 2 g/hour), no statistically significant differences in the reported outcomes were demonstrated. It should be noted that only four of the included studies explicitly stated that only women with singleton pregnancies were included. Summary RRs from the forest plots presented (Figures 244–247) were used in the decision analysis for all primary outcomes. Overall, magnesium sulphate did not appear to significantly reduce the risk of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, and had no beneficial effect on perinatal or neonatal outcomes; however, the included studies were often of poor quality.
FIGURE 243.
Methodological quality of the included trials of magnesium sulphate tocolysis for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
FIGURE 244.
Forest plot of the effects of magnesium sulphate tocolysis for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
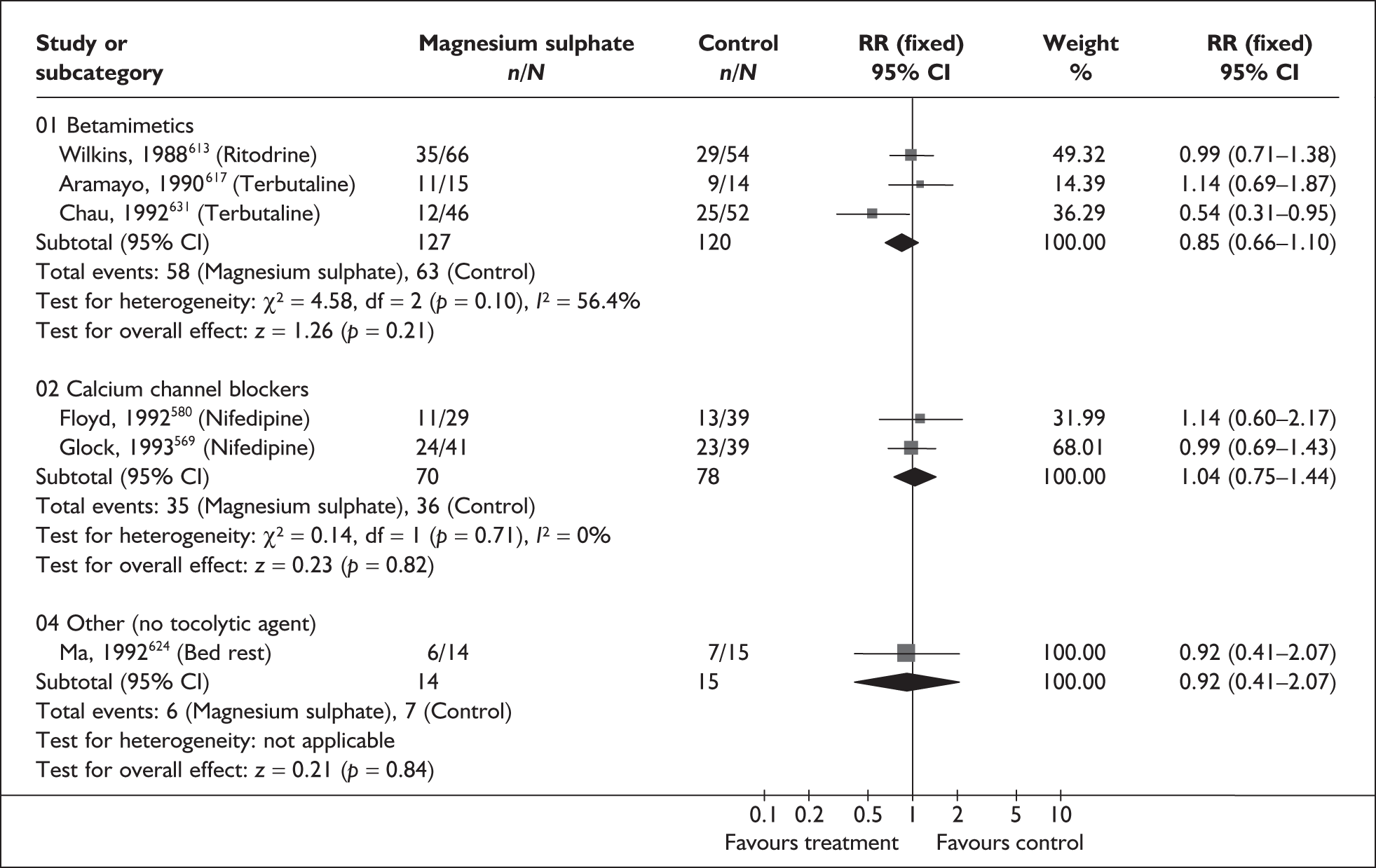
FIGURE 245.
Forest plot of the effects of magnesium sulphate tocolysis for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
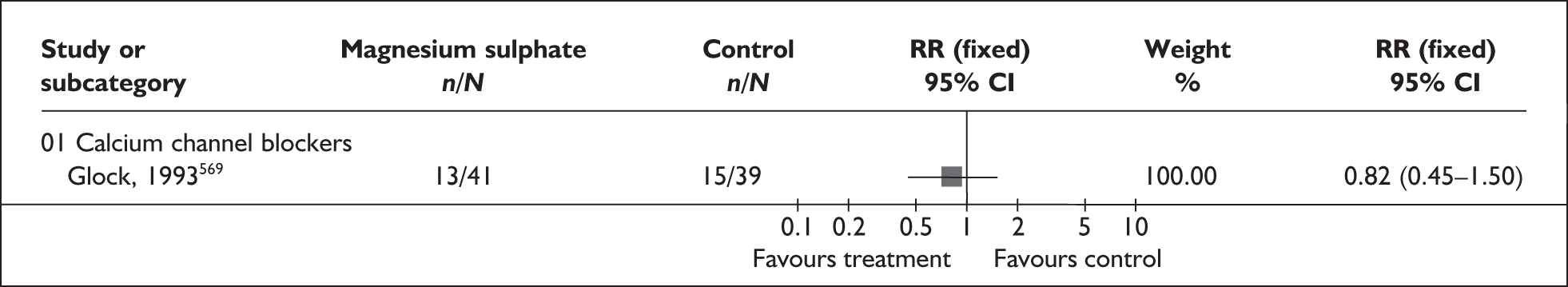
FIGURE 246.
Forest plot of the effects of magnesium sulphate tocolysis for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
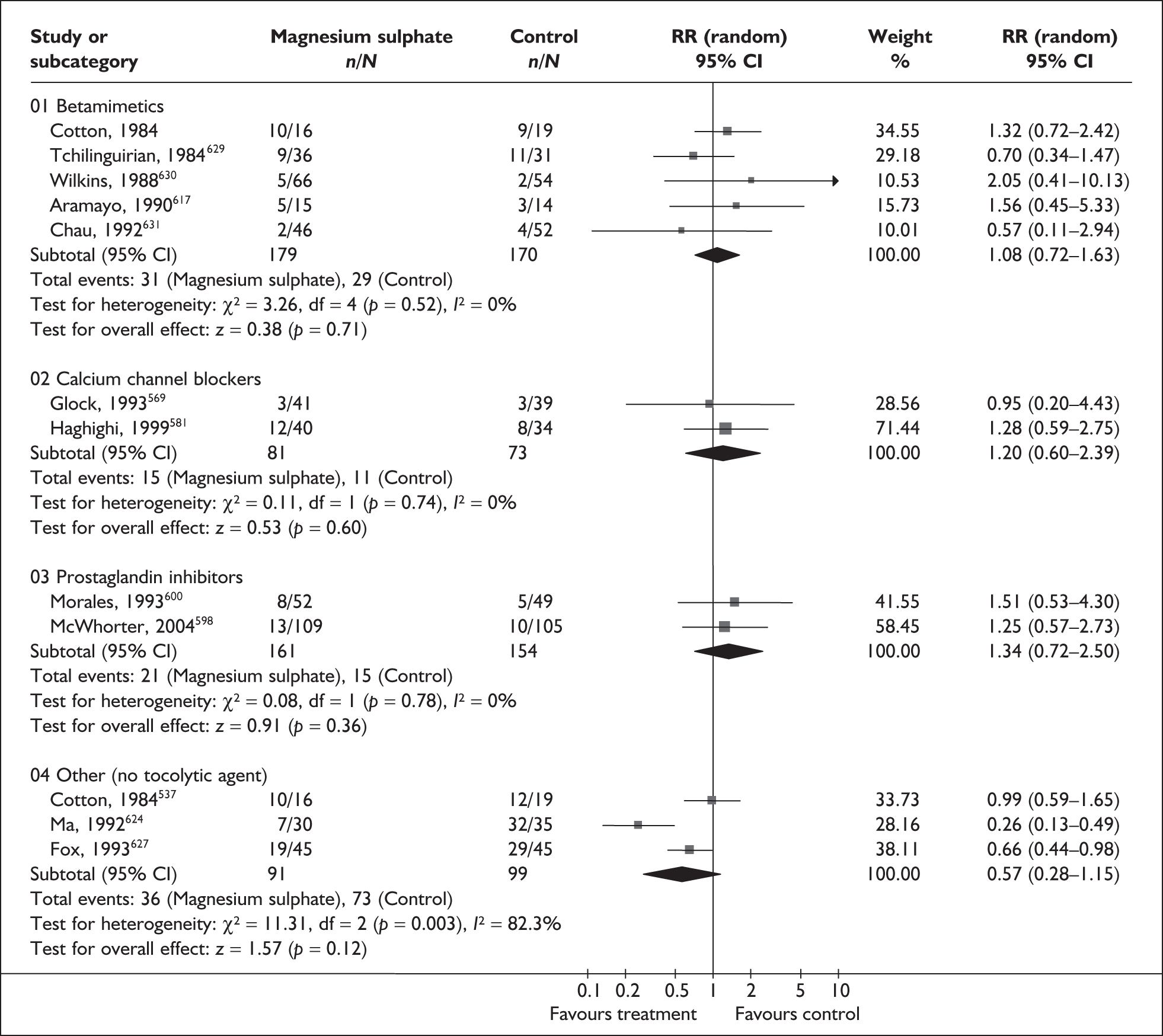
FIGURE 247.
Forest plot of the effects of magnesium sulphate tocolysis for the prevention of neonatal intensive care unit admission.
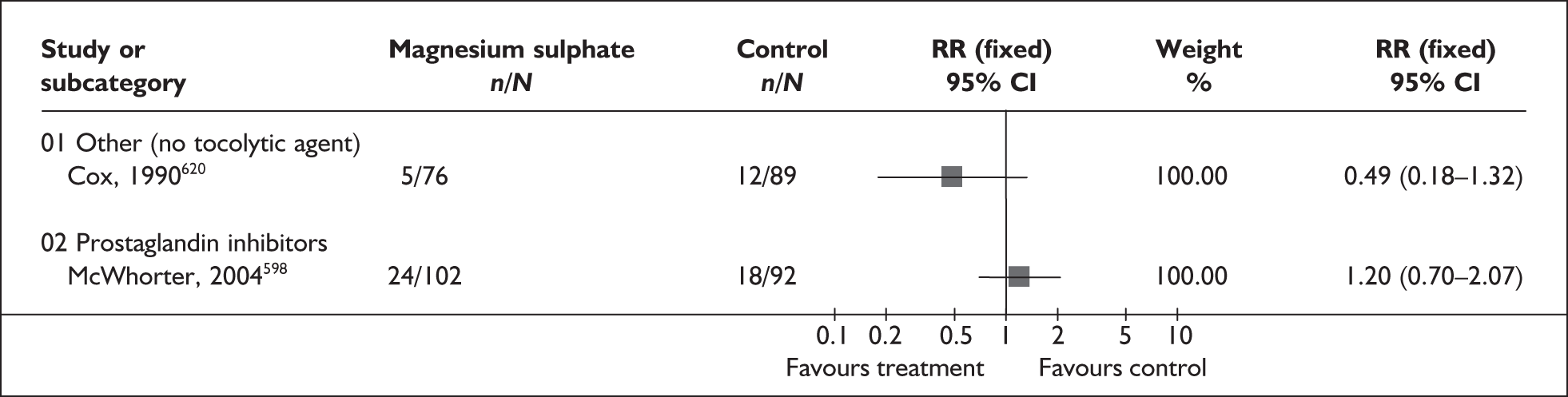
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total deaths (fetal, neonatal and infant) | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators (8 studies, n = 921)537,569,598,600,619,620,622,626 | 2.29 | 0.92–5.69 | 17.7% (0.30) |
| Magnesium sulphate vs betamimetics (2 studies, n = 166)537,619 | 1.19 | 0.08–17.51 | NA |
| Magnesium sulphate vs calcium channel blockers (1 study, n = 80)569 | 0.19 | 0.01–3.85 | NA |
| Magnesium sulphate vs prostaglandin inhibitors (2 studies, n = 311)598,600 | 3.5 | 0.56–21.64 | 12.2% (0.29) |
| Magnesium sulphate vs other (3 studies, n = 292)537,620,622 | 1.74 | 0.63–4.77 | 76.8% (0.04) |
| Respiratory distress syndrome | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs betamimetics (2 studies, n = 65)537,625 | 1.79 | 0.73–4.41 | 0% (0.86) |
| Magnesium sulphate vs prostaglandin inhibitors (2 studies, n = 311)598,600 | 0.96 | 0.57–1.61 | 0% (0.96) |
| Magnesium sulphate vs other (3 studies, n = 471)537,620,622 | 1.09 | 0.98–1.22 | 0% (0.92) |
| Need for assisted ventilation | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs other (1 study, n = 165)537 | 1.17 | 0.61–2.24 | NA |
| Cerebroventricular haemorrhage (all grades) | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs betamimetics (1 study, n = 34)537 | 0.63 | 0.06–6.34 | NA |
| Magnesium sulphate vs prostaglandin inhibitors (1 study, n = 117)600 | 0.98 | 0.26–3.75 | NA |
| Magnesium sulphate vs other (3 studies, n = 289)537,620,622 | 0.86 | 0.28–2.62 | 0% (0.43) |
| Severe cerebroventricular haemorrhage (grades 3 and 4) or periventricular leukomalacia | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs prostaglandin inhibitors (1 study, n = 117)600 | 0.98 | 0.06–15.35 | NA |
| Necrotising enterocolitis | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs betamimetics (1 study, n = 34)537 | 0.42 | 0.02–9.55 | NA |
| Magnesium sulphate vs prostaglandin inhibitors (1 study, n = 194)598 | 0.18 | 0.01–3.71 | NA |
| Magnesium sulphate vs other (3 studies, n = 289)537,620,622 | 1.19 | 0.33–4.29 | NA |
| Neonatal infection | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs betamimetics (1 study, n = 34)537 | 0.36 | 0.09–1.49 | NA |
| Magnesium sulphate vs other (1 study, n = 34)537 | 6.25 | 0.32–121.14 | NA |
| Intraventricular haemorrhage | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs prostaglandin inhibitors (1 study, n = 194)617 | 1.05 | 0.37–3.02 | NA |
| Cerebral palsy | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs other tocolytic (1 study, n = 73)626 | 0.14 | 0.01–2.60 | NA |
| Pulmonary hypertension | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs prostaglandin inhibitors (1 study, n = 194)617 | 0.9 | 0.06–14.21 | NA |
| Maternal respiratory arrest | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs other (1 study, n = 156)620 | 3.16 | 0.13–76.30 | NA |
| Nausea | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs nitric oxide donor (1 study, n = 30)621 | 1.47 | 0.75–2.90 | NA |
| Vomiting | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs nitric oxide donor (1 study, n = 30)621 | 0.86 | 0.23–3.19 | NA |
| Hypotension | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs other (1 study, n = 156)620 | 3.16 | 0.13–76.30 | NA |
| Tachycardia | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs betamimetics (2 studies, n = 133)537,631 | 0.23 | 0.03–1.9 | NA |
| Headache | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs prostaglandin inhibitors (1 study, n = 194)598 | 1.61 | 0.39–6.55 | NA |
| Shortness of breath | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs prostaglandin inhibitors (1 study, n = 194)598 | 0.19 | 0.02–1.62 | NA |
| Lethargy | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs prostaglandin inhibitors (1 study, n = 194)598 | 0.06 | 0.00–0.97 | NA |
| Flushing | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs prostaglandin inhibitors (1 study, n = 194)598 | 0.24 | 0.05–1.11 | NA |
| Any side effect of treatment | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs prostaglandin inhibitors (1 study, n = 194)598 | 0.51 | 0.30–0.86 | NA |
| Side effects leading to discontinuation of treatment | |||
| Magnesium sulphate vs betamimetics (3 studies, n = 264)537,619,631 | 0.07 | 0.02–0.31 | 0% (0.40) |
| Magnesium sulphate vs calcium channel blockers (1 study, n = 80)569 | 8.57 | 0.48–154.15 | NA |
| Magnesium sulphate vs prostaglandin inhibitors (2 studies, n = 189)598,600 | 16.04 | 0.95–270.65 | NA |
| Magnesium sulphate vs other (4 studies, n = 310)537–620,622,624 | 1.59 | 0.57–4.41 | 84.9% (0.01) |
Magnesium sulphate maintenance
Women who remain undelivered after their first course of tocolytic treatment for threatened preterm labour continue to be at increased risk of spontaneous preterm birth. Maintenance tocolysis may be given after successful treatment with acute tocolytic therapy to maintain uterine quiescence. Magnesium sulphate is one type of maintenance tocolytic therapy used after an episode of threatened preterm labour.
The review of magnesium maintenance therapy633 for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth included three randomised controlled trials (n = 303);558–560 no further trials were identified. Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 136. The quality of these studies is shown in Figure 248 where overall one trial was of good quality and the other two were of questionable quality. No statistically significant difference in risk for spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation (Figure 249), or admission to neonatal intensive care unit was shown between magnesium maintenance therapy and placebo or an alternative tocolytic maintenance therapy (Figure 250). Information relating to delivery before 34 weeks’ gestation and perinatal mortality was not reported. Women receiving magnesium maintenance therapy were more likely to report experiencing side effects of therapy than women in the placebo/no treatment group; however, they were less likely to report side effects than women in the alternative tocolytic maintenance therapy group (Table 32). Specifically, women receiving magnesium maintenance therapy were more likely to report diarrhoea than women in either control group, but women receiving alternative tocolytic maintenance therapy were more likely to report palpitations or tachycardia than women receiving magnesium maintenance therapy. Summary RRs from the forest plots presented (Figures 249 and 250) were used in the decision analyses. The limited evidence available does not indicate that magnesium maintenance therapy is effective.
FIGURE 248.
Methodological quality of the included trials of magnesium sulphate maintenance following acute tocolytic therapy for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
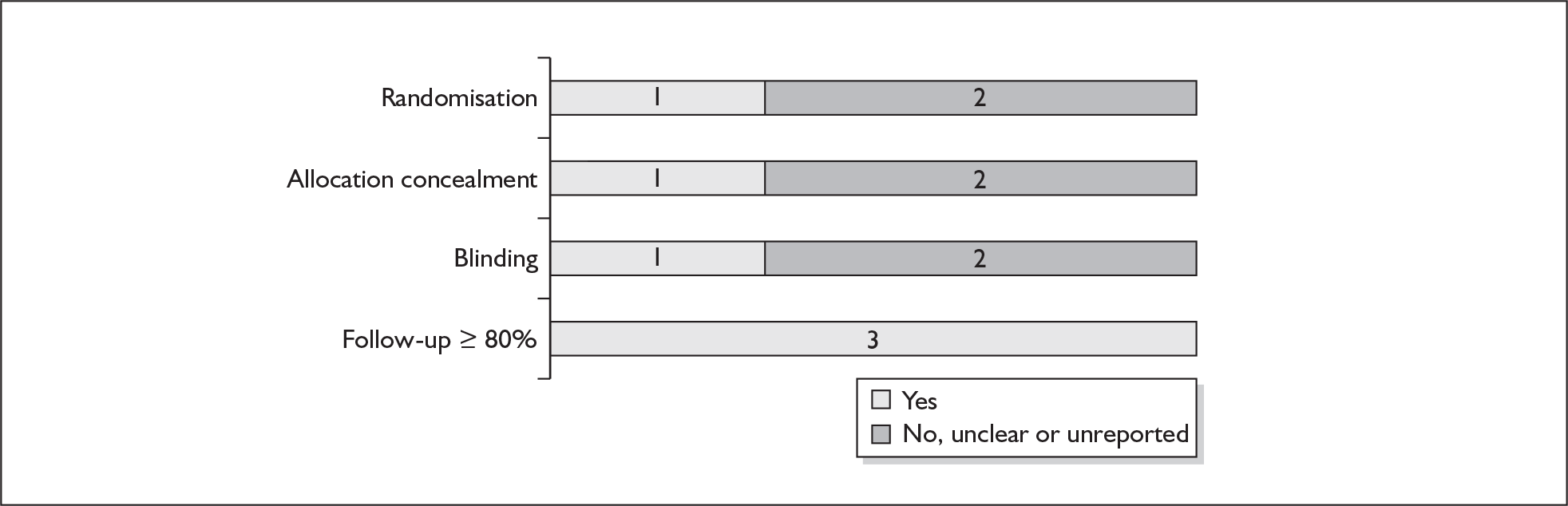
FIGURE 249.
Forest plot of the effects of magnesium sulphate maintenance following acute tocolytic therapy for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
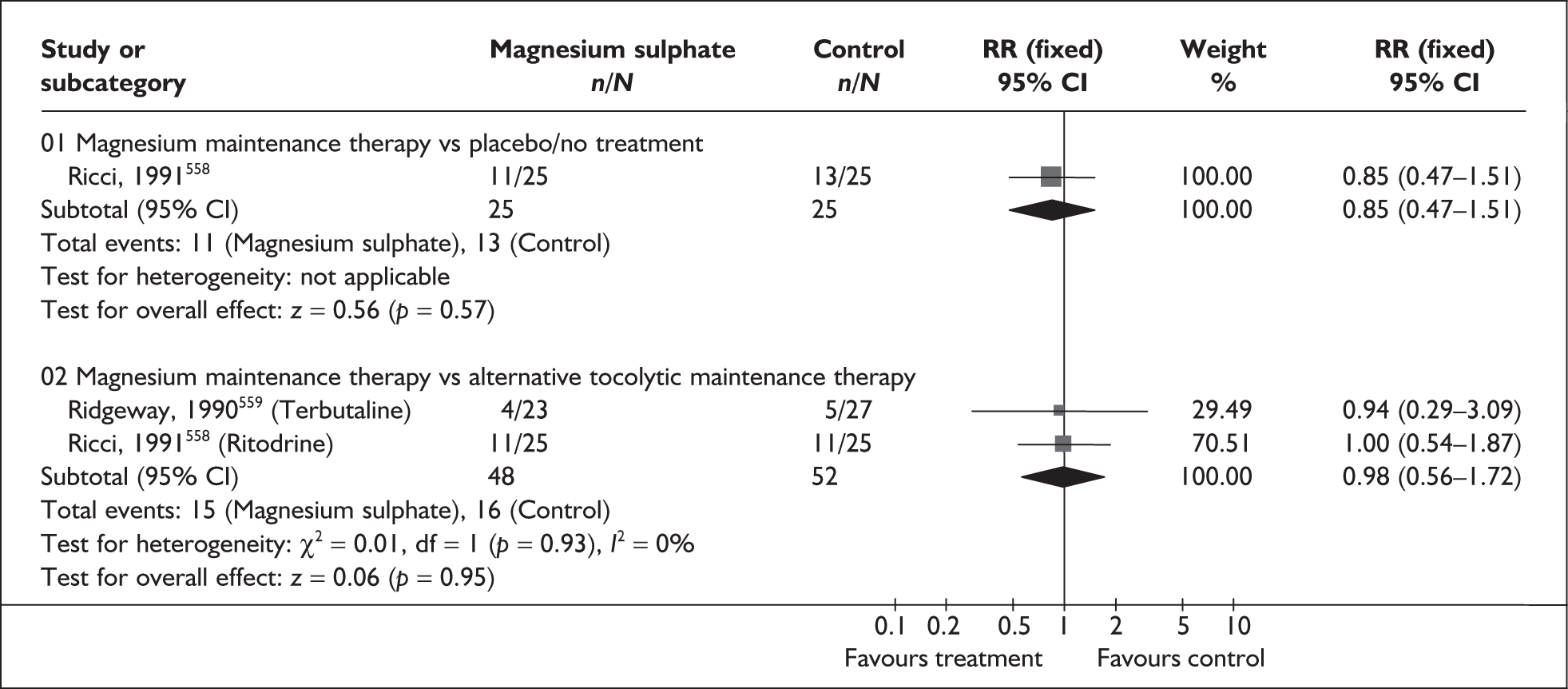
FIGURE 250.
Forest plot of the effects of magnesium sulphate maintenance following acute tocolytic therapy for the prevention of neonatal intensive care unit admission.
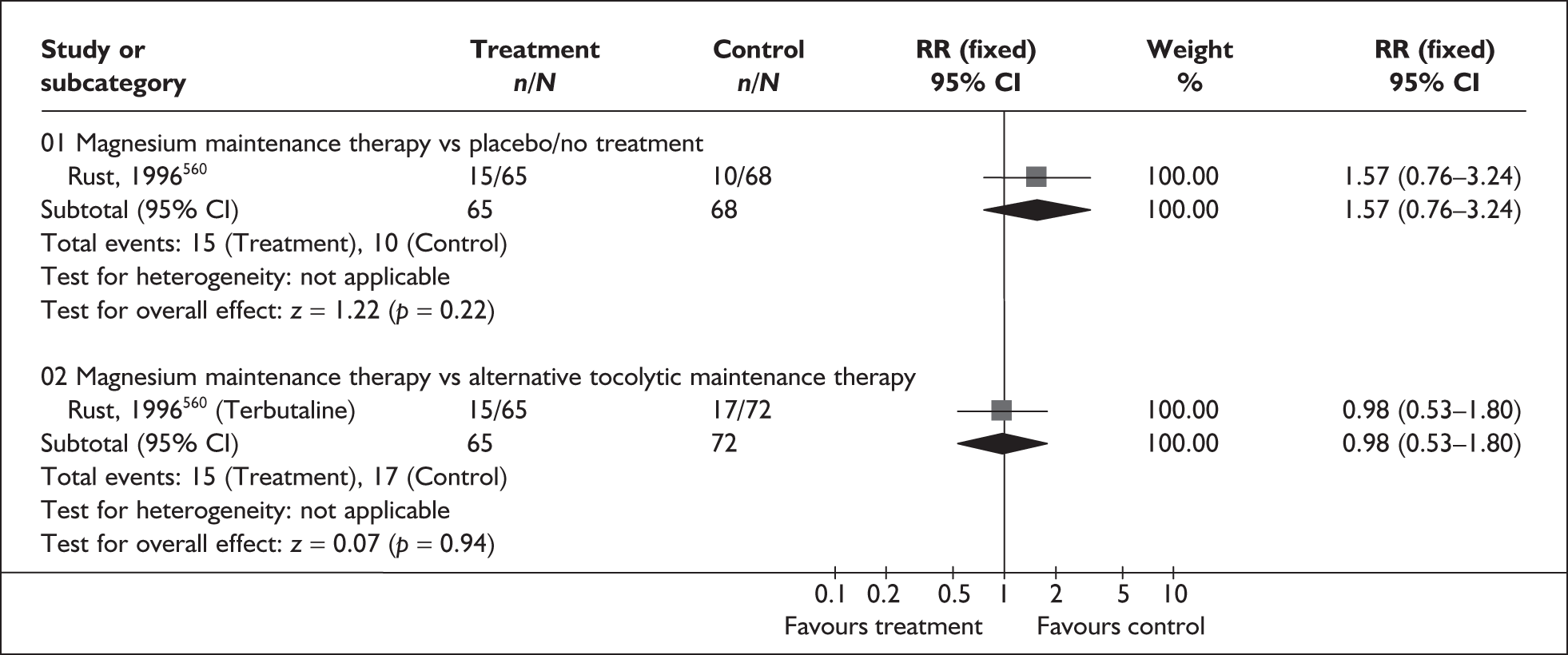
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infant death before hospital discharge | |||
| Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 50)558 | 5 | 0.25–99.16 | NA |
| Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic maintenance therapy (1 study, n = 50)558 | 5 | 0.25–99.16 | NA |
| Respiratory distress syndrome | |||
| Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 50)558 | 3 | 0.13–70.30 | NA |
| Periventricular haemorrhage | |||
| Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 50)558 | 3 | 0.13–70.30 | NA |
| Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic maintenance therapy (1 study, n = 50)558 | 1 | 0.07–15.12 | NA |
| Any maternal side effects | |||
| Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 133)560 | 1.88 | 1.11–3.20 | NA |
| Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic maintenance therapy (3 studies, n = 237)558–560 | 0.69 | 0.52–0.91 | 32.8% (0.23) |
| Nausea | |||
| Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 133)560 | 0.73 | 0.30–1.81 | NA |
| Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic maintenance therapy (3 studies, n = 237)558–560 | 0.94 | 0.50–1.75 | 0% (0.75) |
| Vomiting | |||
| Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 133)560 | 0.42 | 0.08–2.08 | NA |
| Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic maintenance therapy (3 studies, n = 237)558–560 | 0.92 | 0.39–2.17 | 61.0% (0.11) |
| Diarrhoea | |||
| Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 133)560 | 7.67 | 2.41–24.41 | NA |
| Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic maintenance therapy (3 studies, n = 237)558–560 | 10.67 | 3.35–33.99 | 46.6% (0.15) |
| Palpitations/tachycardia | |||
| Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 133)560 | 1.05 | 0.15–7.21 | NA |
| Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic maintenance therapy (3 studies, n = 237)558–560 | 0.22 | 0.11–0.44 | 0% (0.41) |
| Maternal re-admission for threatened preterm labour | |||
| Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment (1 study, n = 50)558 | 0.79 | 0.45–1.38 | NA |
| Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic maintenance therapy (2 studies, n = 100)558,559 | 1.01 | 0.63–1.65 | NA |
| Discontinued therapy | |||
| Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic maintenance therapy (2 studies, n = 100)558,559 | 1.11 | 0.29–4.23 | 0% (0.52) |
| Length of neonatal stay (days) | |||
| Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment (2 studies, n = 180)558,560 | WMD 1.18 | – 0.43–2.82 | 0% (0.39) |
| Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic maintenance therapy (2 studies, n = 180)558,560 | WMD – 2.63 | – 5.70–0.43 | 24.9% (0.25) |
Nitric oxide donors tocolysis
Nitric oxide, a gaseous free radical, has been shown to be involved in numerous aspects of female reproductive physiology. Various nitric oxide donors have been shown to inhibit myometrial contractability, probably by mimicking the action of nitric oxide. This mechanism of action appears to also affect several other organ systems, most notably the cardiovascular system.
The review of nitric oxide donors (glyceryl trinitrate; GTN) for the inhibition of threatened preterm labour included six trials (n = 704); one RCT634 was added to the five primary studies621,635–638 identified in an earlier review. 639 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 137. The quality of the studies (Figure 251) was mixed with blinding in particular being poorly reported or not carried out. GTN was not found to reduce the risk of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation when compared to any other tocolytic agent; however, a small but statistically significant reduction in risk of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation was shown in favour of GTN (Figures 252 and 253). The groups did not differ significantly with regard to risk of spontaneous preterm birth within 24 or 48 hours, or 7 days of treatment administration, although a trend favouring the control group (other tocolytic agent) was observed (Figures 254, 255, and 256, respectively). There was no statistically significant difference in rate of perinatal mortality between GTN and other tocolytics (Figure 257). A greater number of cardiovascular changes (palpitations, tachycardia, shortness of breath and chest pain) was reported in the GTN group compared with other tocolytic agents (Table 33). RRs for subgroups using a placebo comparator were used in the decision analyses. The available evidence does not indicate that the efficacy of GTN is sufficient to recommend its use.
FIGURE 251.
Methodological quality of the included trials of nitric oxide tocolytic therapy for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
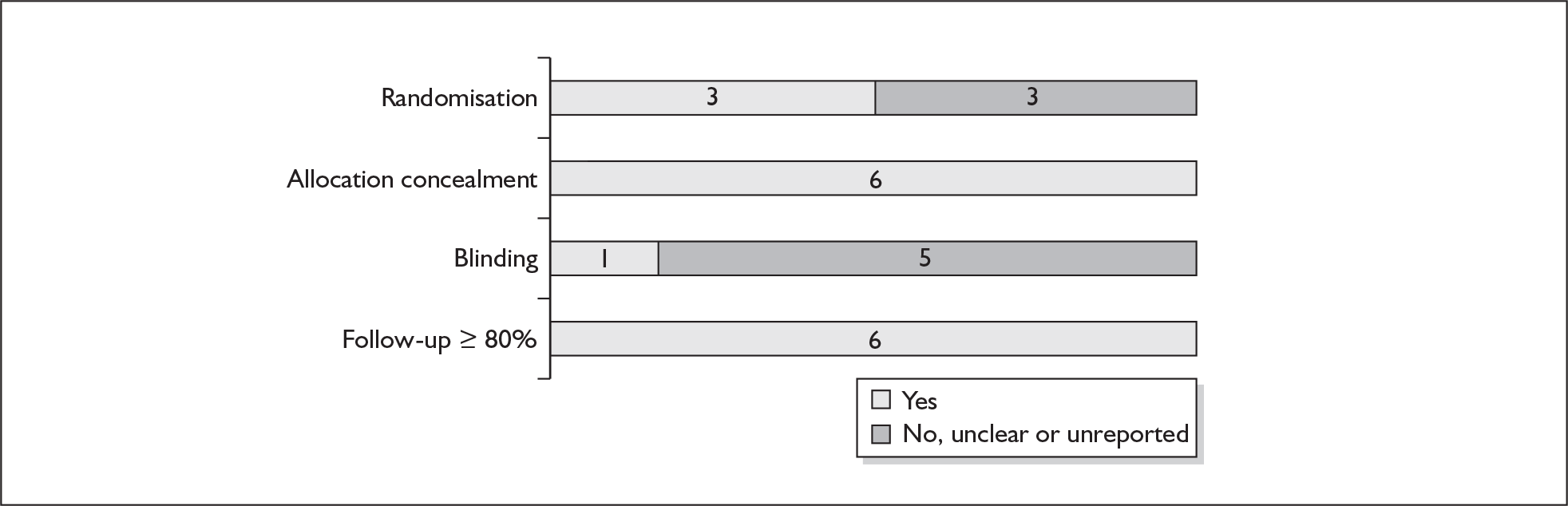
FIGURE 252.
Forest plot of the effects of nitric oxide donors versus any other tocolytic agent for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
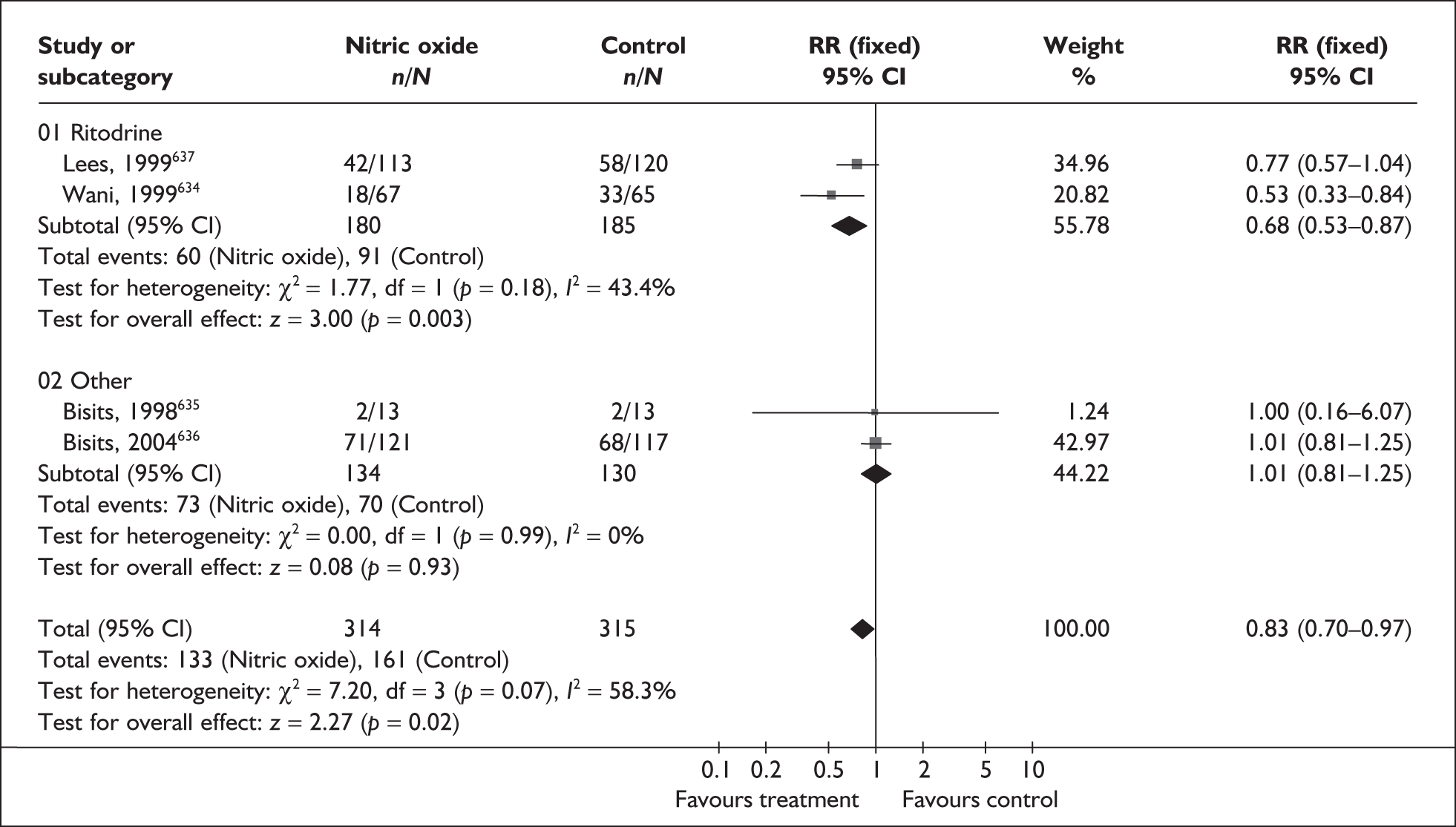
FIGURE 253.
Forest plot of the effects of nitric oxide donors versus any other tocolytic agent for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
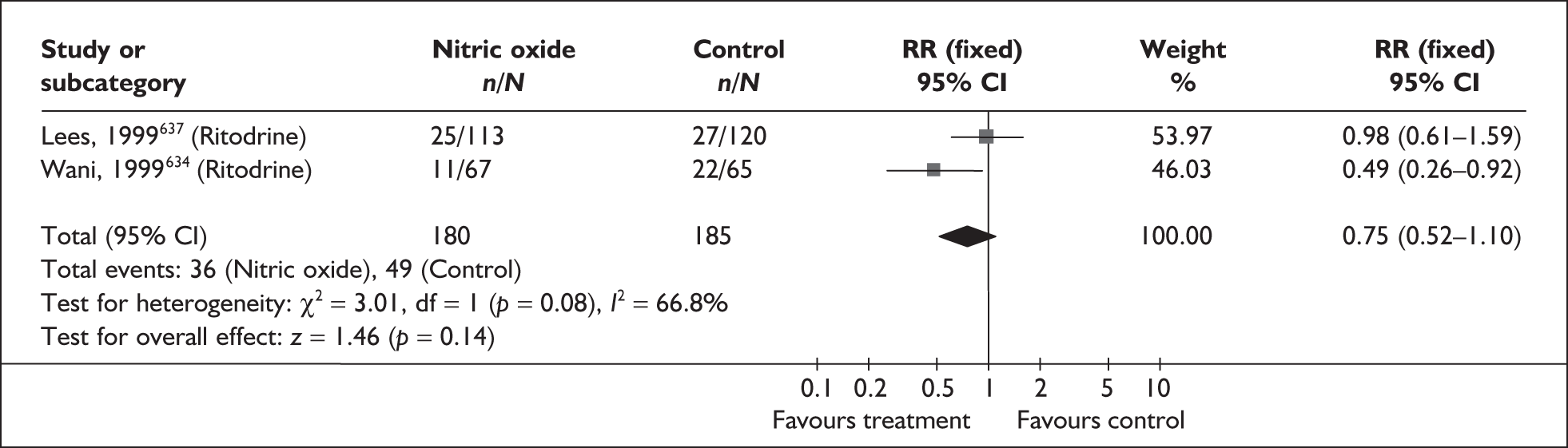
FIGURE 254.
Forest plot of the effects of nitric oxide donors versus any other tocolytic agent for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 24 hours of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
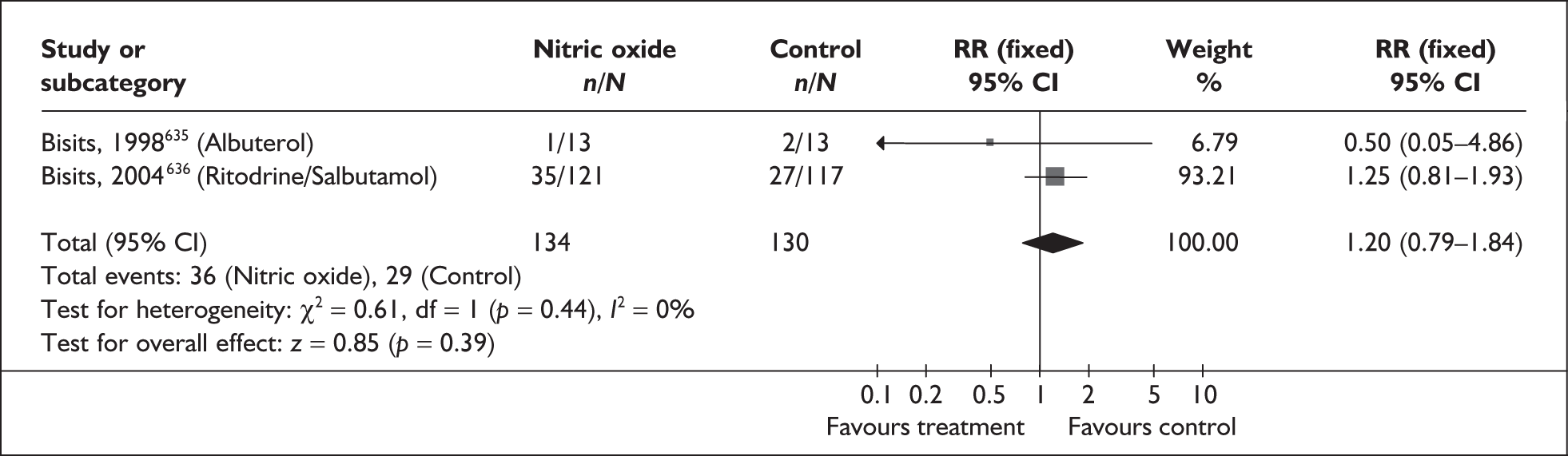
FIGURE 255.
Forest plot of the effects of nitric oxide donors versus any other tocolytic agent for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 48 hours of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
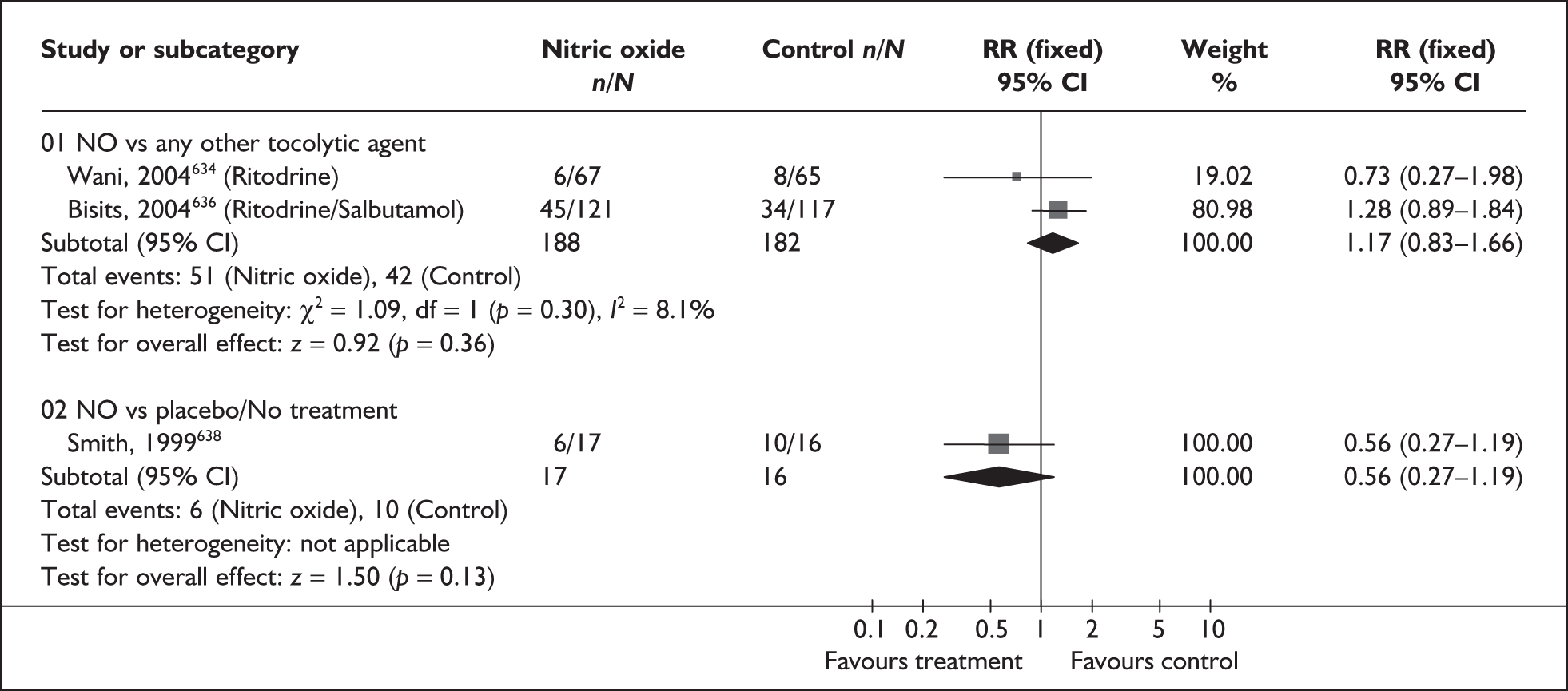
FIGURE 256.
Forest plot of the effects of nitric oxide donors versus any other tocolytic agent for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 7 days of treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
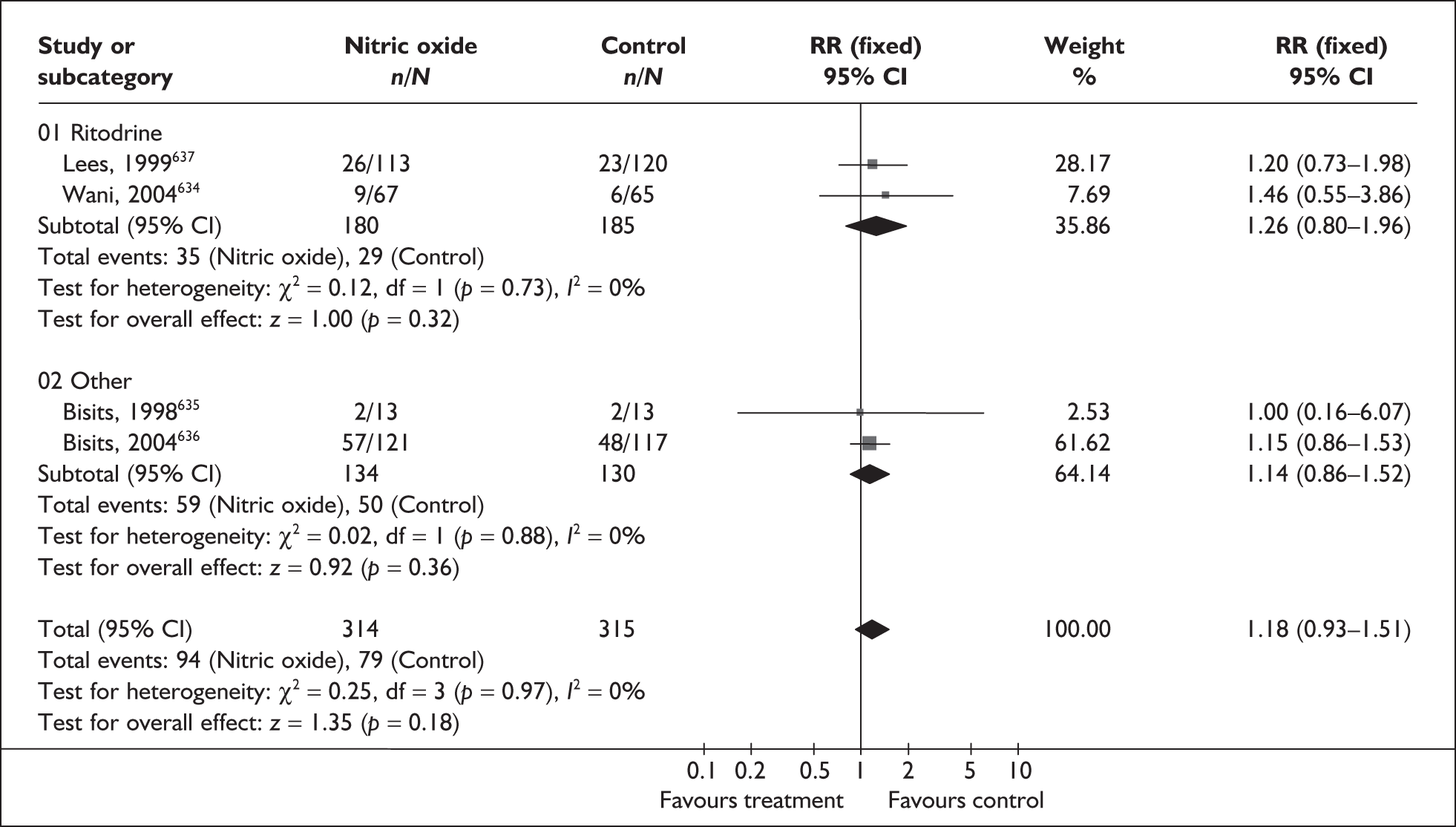
FIGURE 257.
Forest plot of the effects of nitric oxide donors versus any other tocolytic agent on perinatal mortality related to spontaneous preterm birth.
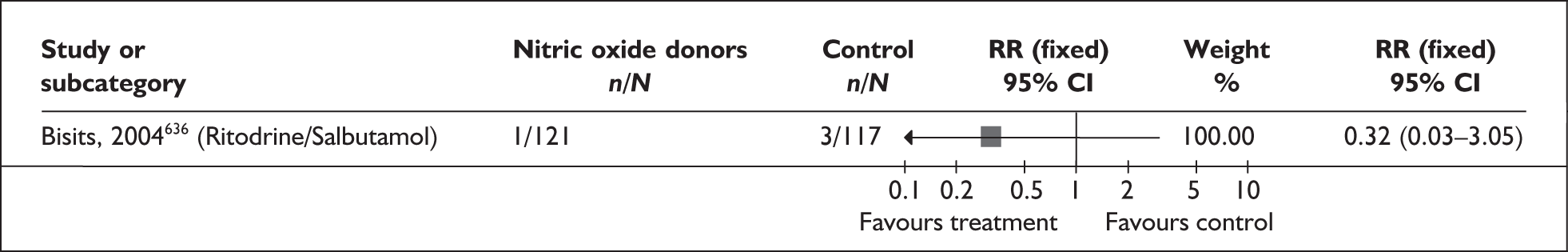
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neonatal death unrelated to congenital abnormalities (1 study, n = 33)638 | 0.94 | 0.06–13.82 | NA |
| Chronic lung disease (1 study, n = 238)636 | 0.97 | 0.40–2.35 | NA |
| Necrotising enterocolitis (1 study, n = 238)636 | 0.97 | 0.42–2.24 | NA |
| Patent duct arteriosus (1 study, n = 238)636 | 0.26 | 0.08–0.92 | NA |
| Intracerebral haemorrhage (1 study, n = 238)636 | 0.24 | 0.05–1.11 | NA |
| Cardiovascular effects | |||
| Palpitations (3 studies, n = 353)621,634,637 | 0.09 | 0.02–0.32 | 10.3% (0.33) |
| Hypotension (1 study, n = 30)621 | 7.94 | 0.46–135.65 | NA |
| Tachycardia (2 studies, n = 323)634,637 | 0.03 | 0.01–0.10 | 0% (0.64) |
| Shortness of breath (2 studies, n = 217)635,637 | 0.09 | 0.02–0.46 | 0% (0.89) |
| Chest pain/tightness (2 studies, n = 323)634,637 | 0.12 | 0.02–0.64 | 0% (0.69) |
| Headache (4 studies, n = 379)621,634,635,637 | 4.14 | 2.44–7.04 | 62.0% (0.05) |
| Nausea (3 studies, n = 227)634,637 | 0.38 | 0.09–1.55 | 0% (0.89) |
| Dizziness (2 studies, n = 221)621,637 | 2.34 | 0.76–6.89 | 0% (0.55) |
Prophylactic corticosteroids for fetal lung maturation
Antenatal corticosteroid treatment of women expected to give birth preterm significantly reduced the incidence of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and mortality among neonates, as was first reported in 1972. 640 Since then the administration of corticosteroids to pregnant women at risk of preterm birth to reduce the severity of neonatal RDS has become an established intervention. RDS occurring as a result of surfactant deficiency and immaturity of lung development is a serious complication of prematurity and a significant cause of perinatal and neonatal death.
The review of prophylactic antenatal corticosteroids to women symptomatic of threatened preterm labour24 included 17 RCTs640–657 and one quasi-RCT. 658 The latter trial was removed from the results because it did not meet the inclusion criteria for study design set out in the original review. Only corticosteroids capable of crossing the placenta were eligible for inclusion (betamethasone, dexamethasone and hydrocortisone). No additional RCTs were found when the searches were updated. Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 139. The quality of the included studies was variable, as shown in Figure 258.
FIGURE 258.
Methodological quality of the included trials of prophylactic corticosteroid therapy in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour for the prevention of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome.
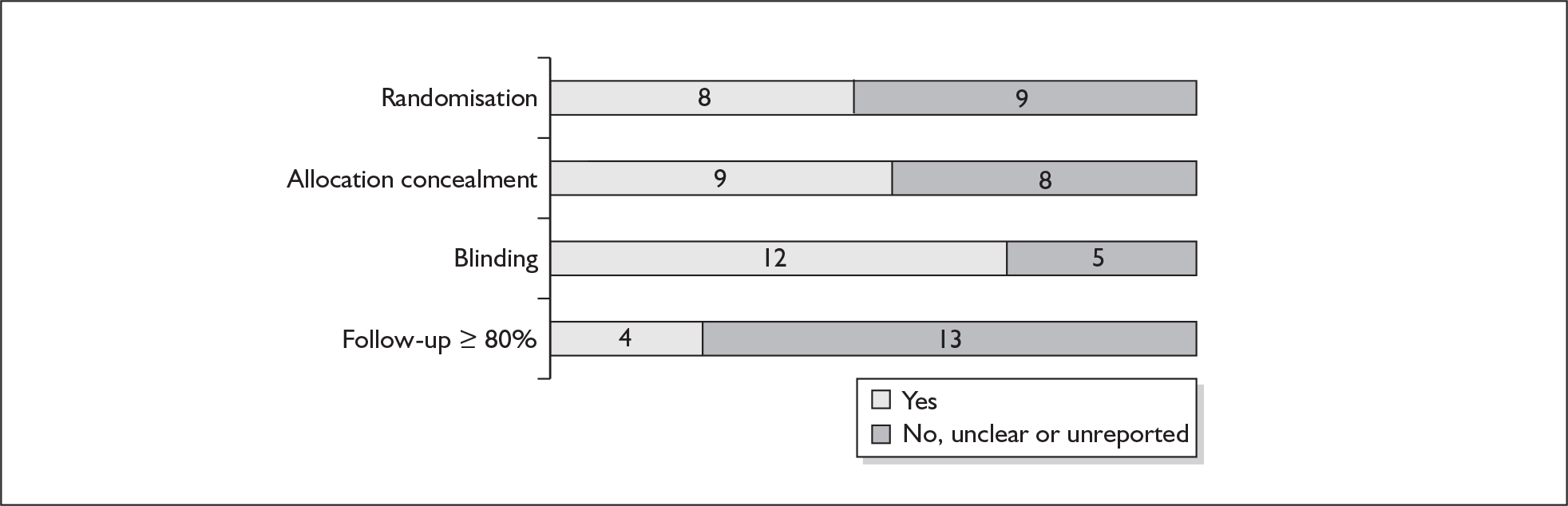
Antenatal corticosteroid given to women with expectant delivery has a beneficial effect on the incidence of RDS compared to placebo/no treatment (Figure 259). When subgrouped by type of corticosteroid used, betamethasone, dexamethasone and hydrocortisone all showed a reduction in the risk of RDS compared to placebo/no treatment, although this difference was not statistically significant for hydrocortisone. The effects are most clearly demonstrated after 28 weeks’ and before 34 weeks’ gestation, and in babies delivering 1–7 days after the intervention. (Figures 260 and 261, respectively). However, one trial did not show a statistically significant long-term reduction in neonatal chronic lung disease (Figure 262). In addition, one trial reported a significant reduction in the use of surfactant (Figure 263). No data on incidence of spontaneous preterm birth, perinatal mortality or requirement for neonatal intensive care unit admission was reported; however, a reduction in risk of neonatal mortality was shown in those receiving corticosteroid treatment (Table 34). However, antenatal corticosteroids increased the risk of maternal infection, and the likelihood of stillbirth in women with hypertension, compared to placebo/no treatment; but appeared to decrease the risk of intraventricular haemorrhage and demonstrated a trend in the reduction of necrotising enterocolitis in the premature neonates. Summary RRs for the primary outcomes of all infants assessed were used in the decision analyses. It should be noted that most of the trials included a mixed population, with infants from both singleton and multiple gestations included in the results. Overall, despite some evidence of adverse events, prophylactic corticosteroids are effective in reducing RDS in preterm babies and the current recommendation for their routine use appears justified.
FIGURE 259.
Forest plot of the effects of prophylactic corticosteroid therapy versus placebo/no treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour for the prevention of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome.
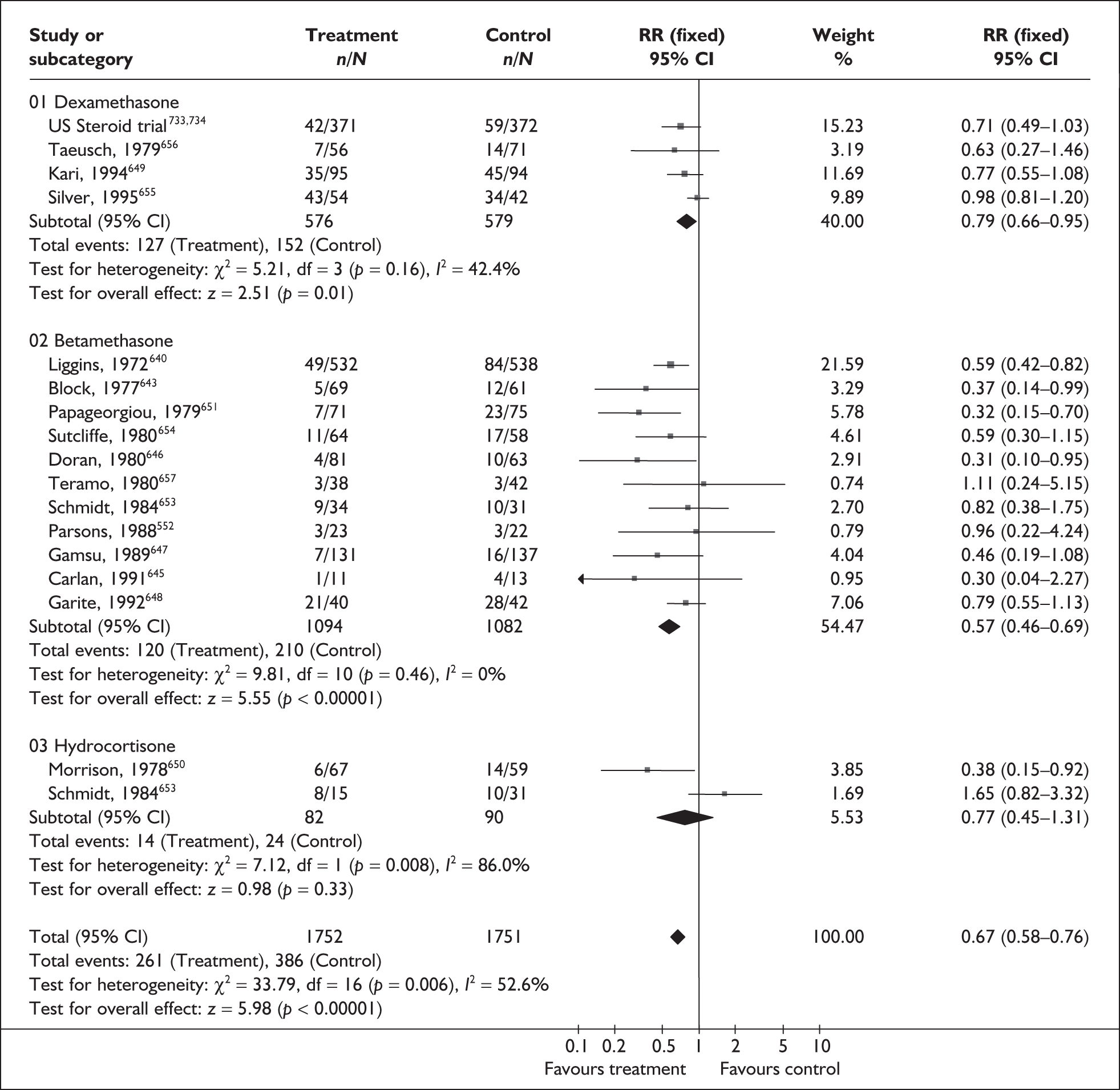
FIGURE 260.
Forest plot of the effects of prophylactic corticosteroid therapy versus placebo/no treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour for the prevention of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome subgrouped by gestational age.
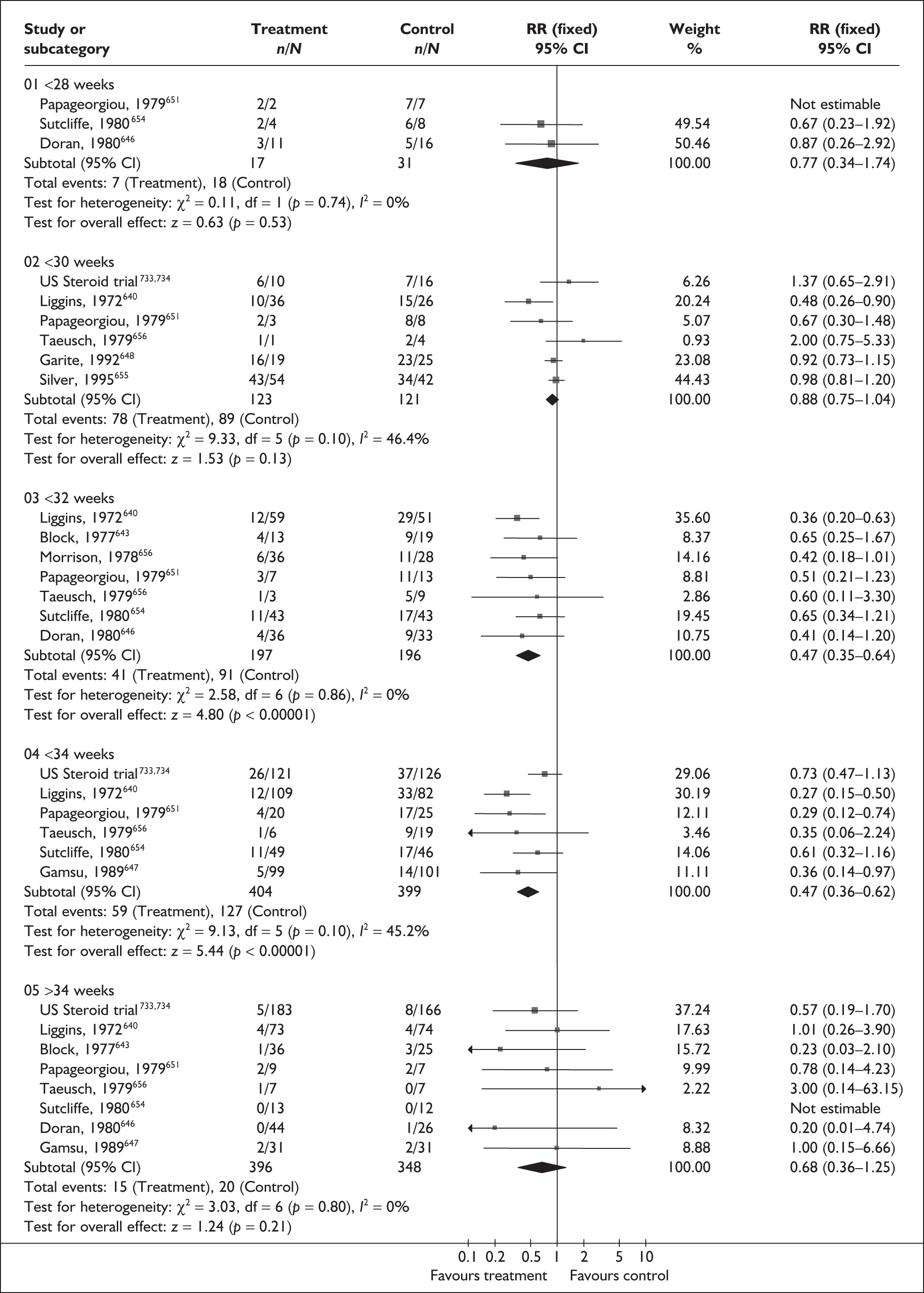
FIGURE 261.
Forest plot of the effects of prophylactic corticosteroid therapy versus placebo/no treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour for the prevention of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome subgrouped by time of delivery after first dose.
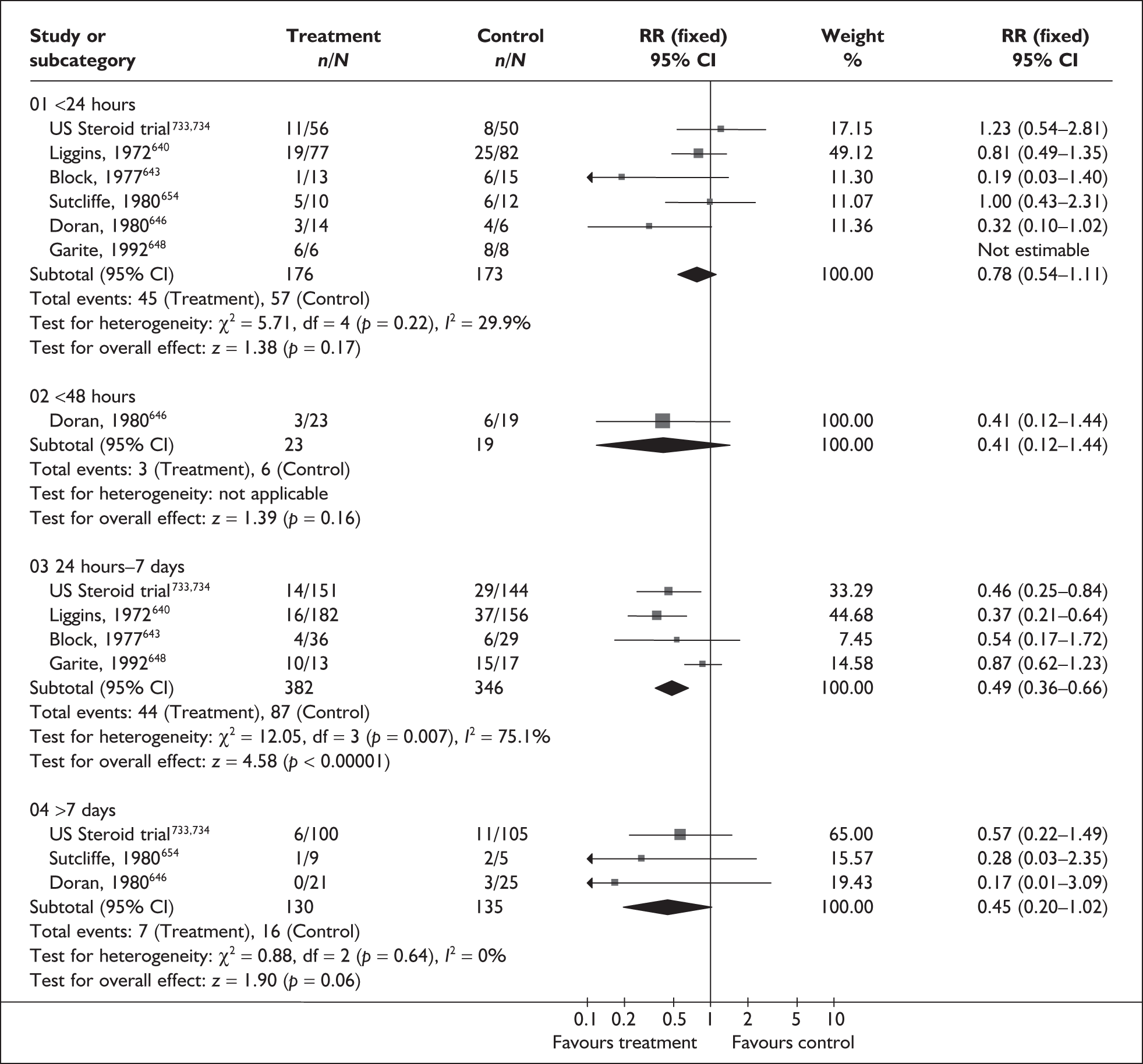
FIGURE 262.
Forest plot of the effects of prophylactic corticosteroid therapy versus placebo/no treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour for the prevention of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome for the requirement of surfactant therapy.
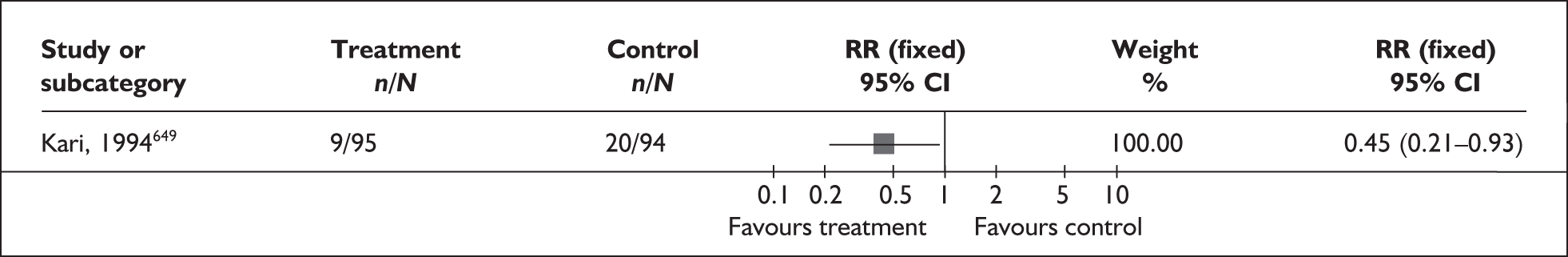
FIGURE 263.
Forest plot of the effects of prophylactic corticosteroid therapy versus placebo/no treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour for the prevention of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome on the incidence of chronic lung disease in the neonate.
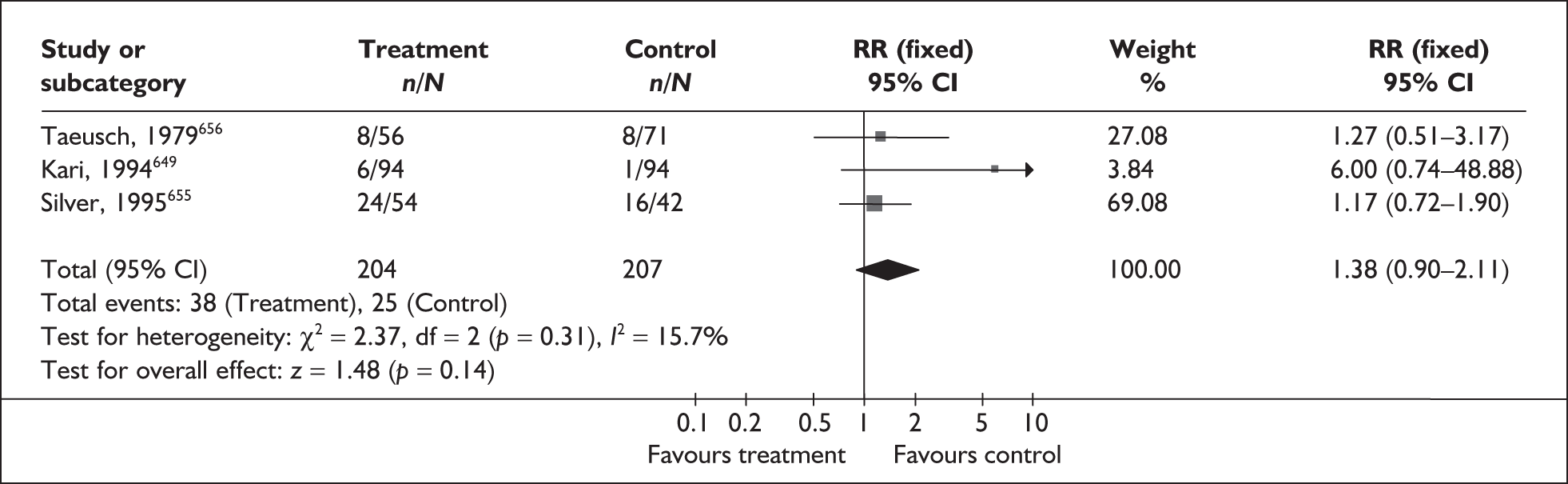
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neonatal mortality | |||
| All infants (13 studies, n = 3272)640,641,643,646–648,650–654,656 | 0.63 | 0.51–0.79 | 13.4% (0.31) |
| Treated ≤ 1980 (8 studies, n = 258)640,643–646,647,650,651,654,656 | 0.53 | 0.40–0.70 | 25.8% (0.22) |
| Treated > 1980 (5 studies, n = 1139)641,648,649,652,653 | 0.86 | 0.60–1.22 | 0% (0.93) |
| Stillbirth | |||
| All infants (11 studies, n = 3061)1,3,4,7–10,12,13,17,19,640,641,643,646–648,650,651,654,656 | 0.84 | 0.59–1.21 | 0% (0.54) |
| Women with hypertension (4 studies, n = 239)641,647,649,654 | 3.66 | 1.11–12.10 | NA |
| Intraventricular haemorrhage | |||
| All infants (7 studies, n = 1214)640,646–649,655,656 | 0.55 | 0.38–0.78 | 58.1% (0.03) |
| Diagnosed after autopsy (4 studies, n = 863)640,646,647,656 | 0.3 | 0.14–0.66 | 0% (0.86) |
| Diagnosed during ultrasound (3 studies, n = 351)648,649,655 | 0.68 | 0.46–1.01 | 76.4% (0.01) |
| Necrotising enterocoloitis | |||
| All infants (4 studies, n = 1154) 641,649,650,655 | 0.6 | 0.33–1.09 | 58.4% (0.07) |
| Long-term neurological abnormality | |||
| All infants (3 studies, 778)640,641,654 | 0.65 | 0.39–1.08 | 0% (0.94) |
| Fetal and neonatal infection | |||
| All infants (14 studies, n = 2430)641,643–649,651–656 | 0.8 | 0.55–1.16 | 2.9% (0.42) |
| After PROM > 24 h before delivery (2 studies, n = 163) 651,656 | 2.16 | 0.77–6.12 | 0% (0.96) |
| PROM at trial entry (3 studies, n = 84)644,645,652 | 1.21 | 0.34–4.23 | 46.7% (0.15) |
| Maternal infection | |||
| All infants (10 studies, n = 1864)641,645,647–651,653,654,656 | 1.44 | 1.13–1.82 | 4.7% (0.40) |
| After PROM >24 h before delivery (1 study, n = 42)656 | 4.84 | 1.16–20.14 | NA |
| PROM at trial entry (2 studies, n = 75)645,653 | 1.78 | 0.89–3.58 | 32.2% (0.22) |
Repeat corticosteroid course(s)
For women at increased risk of spontaneous preterm birth, the benefits of a single course of antenatal corticosteroids are well established, including a reduction in neonatal RDS, intraventricular haemorrhage, neonatal mortality and the need for surfactant therapy. The normal thinning of the double capillary loops, to form the thin gas exchanging walls of alveoli, is accelerated, resulting in rapid alveolisation. 659 The maturation of surfactant producing type II pneumocytes is also accelerated. 660 Repeat courses of antenatal corticosteroids are less well studied.
The review of repeat antenatal corticosteroid course(s)661 for the prevention of neonatal respiratory disease included three RCTs (n = 551);662–664 no additional trials were found. Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 139. The quality of these studies was good as shown in Figure 264. No statistically significant between-group differences were shown for any other infant or maternal outcome reported, including the risk of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 and 34 weeks’ gestation (Figures 265 and 266, respectively, and Table 35). While the use of repeat course(s) did not reduce the risk of RDS or the risk of chronic lung disease (Figures 267 and 268), a small reduction in the severity of lung disease was shown in infants receiving repeat course(s) of corticosteroids compared to placebo, based on one trial (Figure 269). In addition, fewer infants receiving repeat corticosteroid course(s) required surfactant therapy compared to placebo (Table 35). None of these studies reported outcomes of perinatal mortality or admission to a neonatal intensive care unit. Two RCTs were published after the searches were completed. 665,666 These studies were not included in the review because neither reported separate data for women with singleton pregnancies. However, both studies suggested that repeat doses of corticosteroids may be beneficial to babies at continued risk of preterm birth following initial corticosteroid treatment. Summary RRs, comparing repeat doses of antenatal corticosteroids with a single prenatal corticosteroid dose, were used in the decision analyses for all primary end points. Overall, the current benefit and risk data are insufficient to support the routine use of repeat or rescue courses of antenatal corticosteroids in clinical practice.
FIGURE 264.
Methodological quality of the included trials of repeat antenatal corticosteroid courses in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour for the prevention of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome.
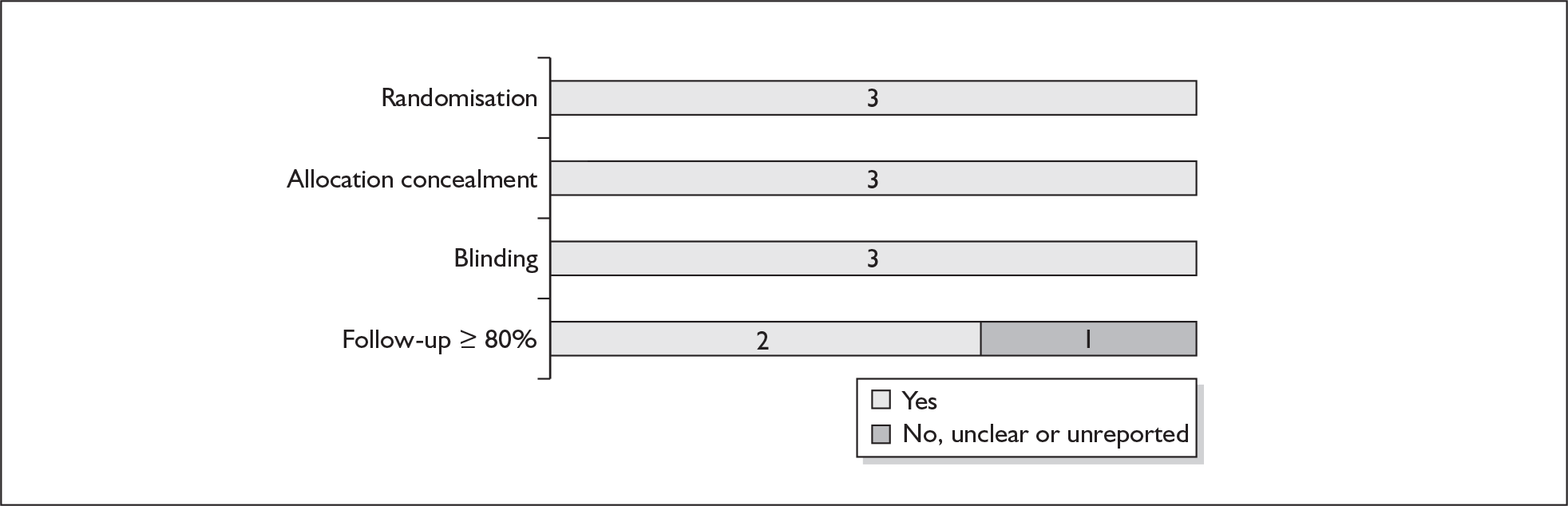
FIGURE 265.
Forest plot of the effects of repeat course(s) versus single course of antenatal corticosteroid therapy in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour for the prevention of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome on spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation.
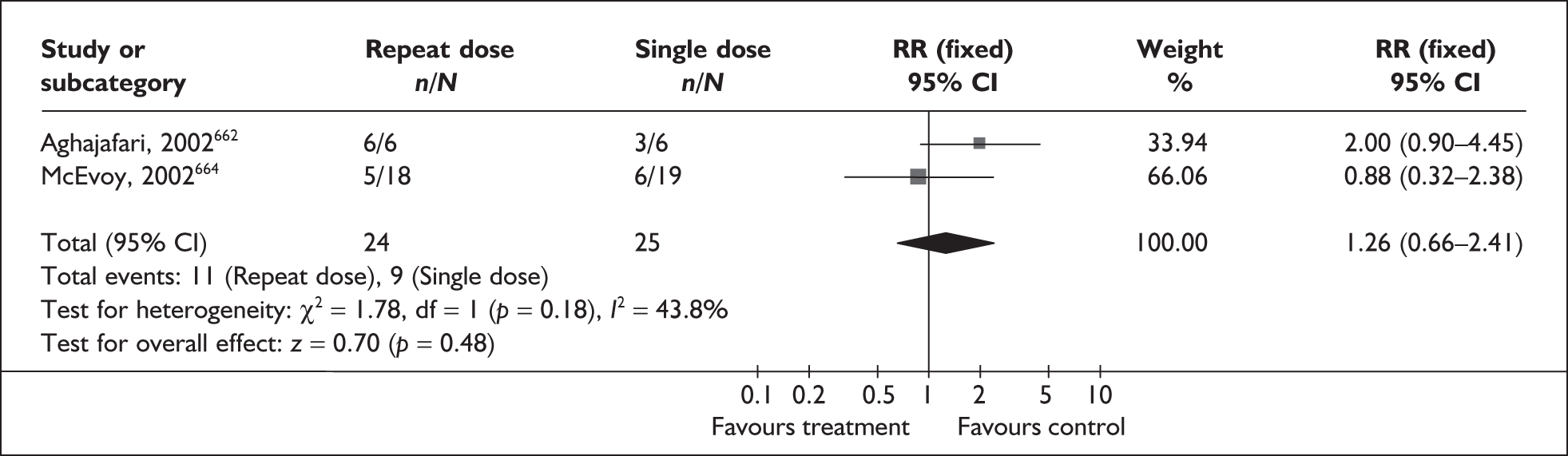
FIGURE 266.
Forest plot of the effects of repeat course(s) versus single course of antenatal corticosteroid therapy in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour for the prevention of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome on spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation.
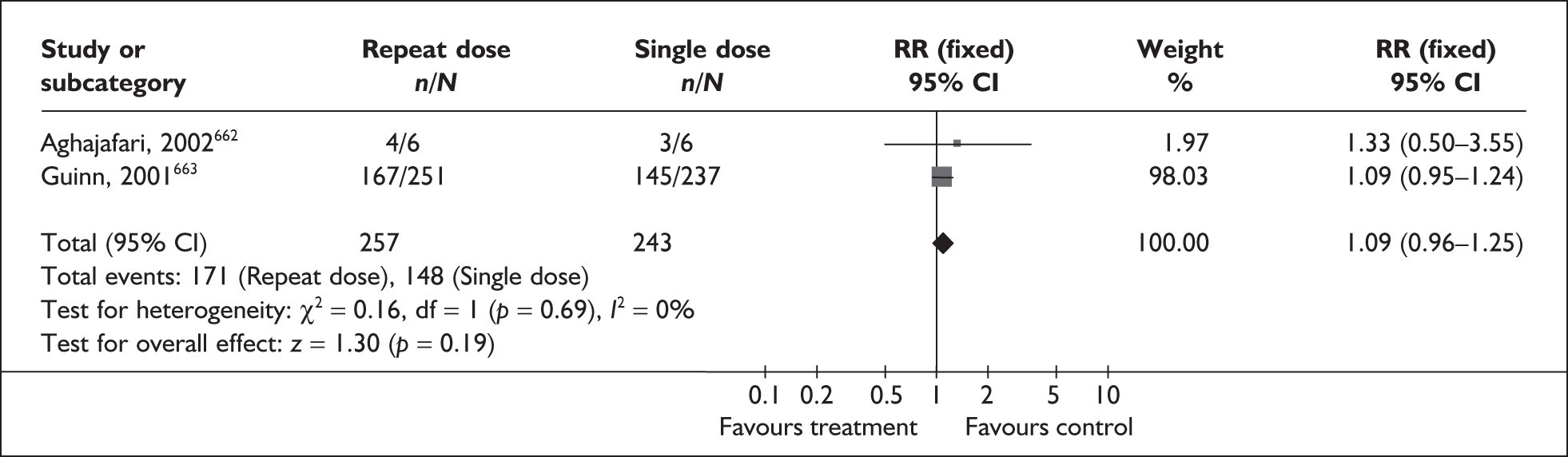
FIGURE 267.
Forest plot of the effects of repeat course(s) versus single course of antenatal corticosteroid therapy in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour on the incidence of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome.
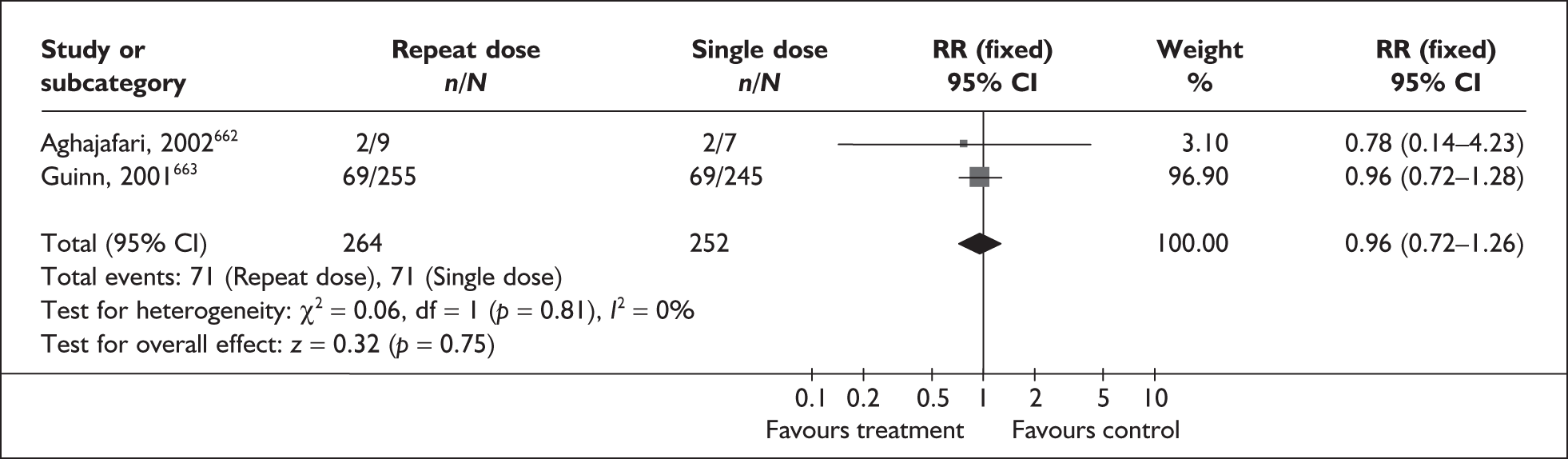
FIGURE 268.
Forest plot of the effects of repeat course(s) versus single course of antenatal corticosteroid therapy in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour on the incidence of neonatal chronic lung diease.
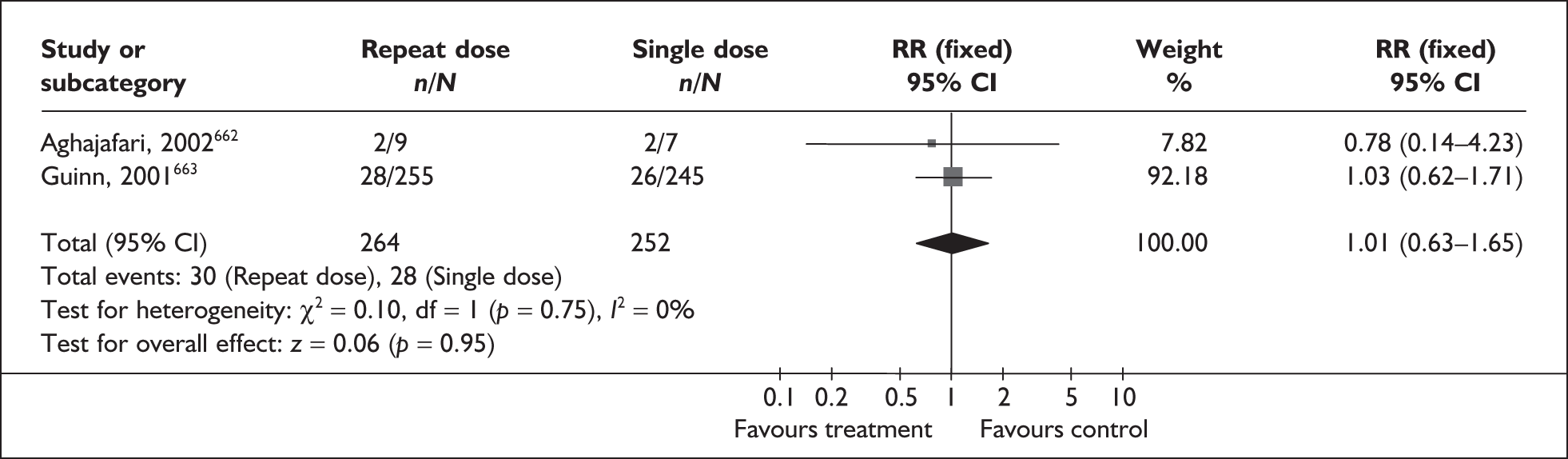
FIGURE 269.
Forest plot of the effects of repeat course(s) versus single course of antenatal corticosteroid therapy in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour on the severity of neonatal lung disease from respiratory distress.
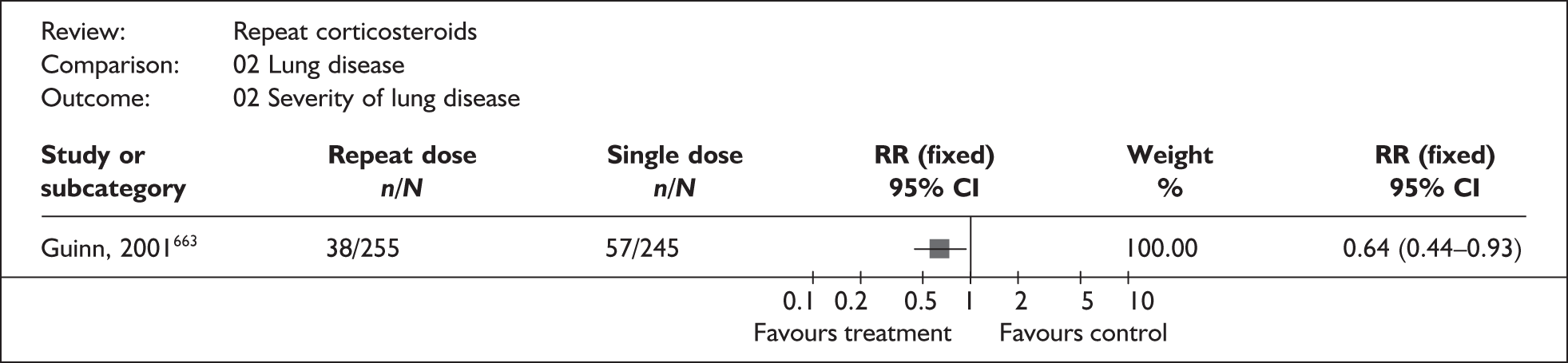
| Outcome (RCT) | RR | 95% CI | % Heterogeneity (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fetal, neonatal and infant mortality (2 studies, n = 518)662,663 | 0.53 | 0.18–1.57 | NA* |
| Periventricular haemorrhage | |||
| All grades (1 study, n = 500)663 | 1.15 | 0.70–1.90 | NA* |
| Grades 3 and 4 (2 studies, n = 516)662,663 | 2.50 | 0.76–8.22 | 60.8% (0.11) |
| Periventricular leukomalacia (2 studies, n = 516)662,663 | 0.64 | 0.11–3.80 | NA* |
| Chorioamnionitis (2 studies, n = 497)662,663 | 1.35 | 0.95–1.92 | NA* |
| Puerperal sepsis (2 studies, n = 497)662,663 | 0.88 | 0.42–1.83 | NA* |
| Preterm birth < 28 weeks gestation (1 study, n = 488)663 | 1.08 | 0.67–1.74 | NA |
| Necrotising enterocolitis (2 studies, n = 516)662,663 | 1.07 | 0.44–2.58 | NA* |
| Infection while in neonatal intensive care unit (2 studies, n = 516)662,663 | 1.09 | 0.52–2.30 | 0% (0.33) |
| Patent ductus arteriosus requiring treatment (1 study, n = 16)662 | 0.78 | 0.17–13.87 | NA |
| Retinopathy of prematurity (1 study, n = 16)662 | 0.78 | 0.22–2.74 | NA |
| Postpartum haemorrhage (1 study, n = 485)663 | 0.60 | 0.33–1.07 | NA |
| Composite serious morbidity (2 studies, n = 518)662,663 | 0.80 | 0.60–1.07 | 0% (0.56) |
| Birthweight (2 studies, n = 539)663,664 | WMD – 137.67 | – 281.53 to 6.20 | 0% (0.75) |
| Duration of oxygen supplementation, days (1 study, n = 37)664 | WMD 3.30 | – 2.31 to 8.91 | NA |
| Duration of respiratory support, days (1 study, n = 37)664 | WMD 0.30 | – 0.90 to 1.50 | NA |
| Duration of postnatal hospital stay (1 study, n = 485)663 | WMD 0.00 | – 0.22 to 0.22 | NA |
| Use of surfactant (2 studies, n = 537)663,664 | 0.65 | 0.46–0.92 | 0% (0.97) |
Magnesium sulphate for neonatal neuroprotection
Infants born preterm have increased risks of death or neurosensory impairments and disabilities. A large retrospective case–control study suggested that the prophylactic antenatal administration of low-dose magnesium sulphate may act as a neuroprotective agent;667 magnesium sulphate was associated with a lower risk of intraventricular haemorrhage, which predisposes to cerebral palsy. Subsequent trials have attempted to examine this neuroprotective ‘magnesium hypothesis’.
The review of magnesium sulphate for neuroprotection included two RCTs (n = 1119). 668,669 However, after the searches were completed, two potentially relevant clinical trials were identified, but too late for inclusion in this review. 670,671 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 140. The quality of the included studies was good and is summarised in Figure 270. When compared to placebo, antenatal administration of magnesium sulphate was not found to reduce the risk of intraventricular haemorrhage or periventricular leukomalacia (Figures 271 and 272). Although a reduction in the incidence of cerebral palsy was found in the magnesium sulphate group, this was not statistically significant (Figure 273). Summary RRs, presented in the forest plots (Figures 271–273), were used in the decision analysis. No information on perinatal mortality or admission to neonatal intensive care was reported. Results for other neonatal, infant and maternal variables are shown in Table 36. It should be noted that both the primary studies included twin gestations in their results; the proportion of multiple gestations ranged from 3.5% to 16.6%. The current evidence does not support the widespread use of magnesium sulphate for the protection of neurological morbidity in women with imminent spontaneous preterm birth; however, further randomised controlled trials are necessary before its clinical relevance can be determined.
FIGURE 270.
Methodological quality of the included trials of maternal magnesium sulphate therapy for protection against neonatal neurological morbidity in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
FIGURE 271.
Forest plot of the effect of maternal magnesium sulphate therapy for protection against neonatal neurological morbidity in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour on the incidence of intraventricular haemorrhage (all grades) in the premature neonates.
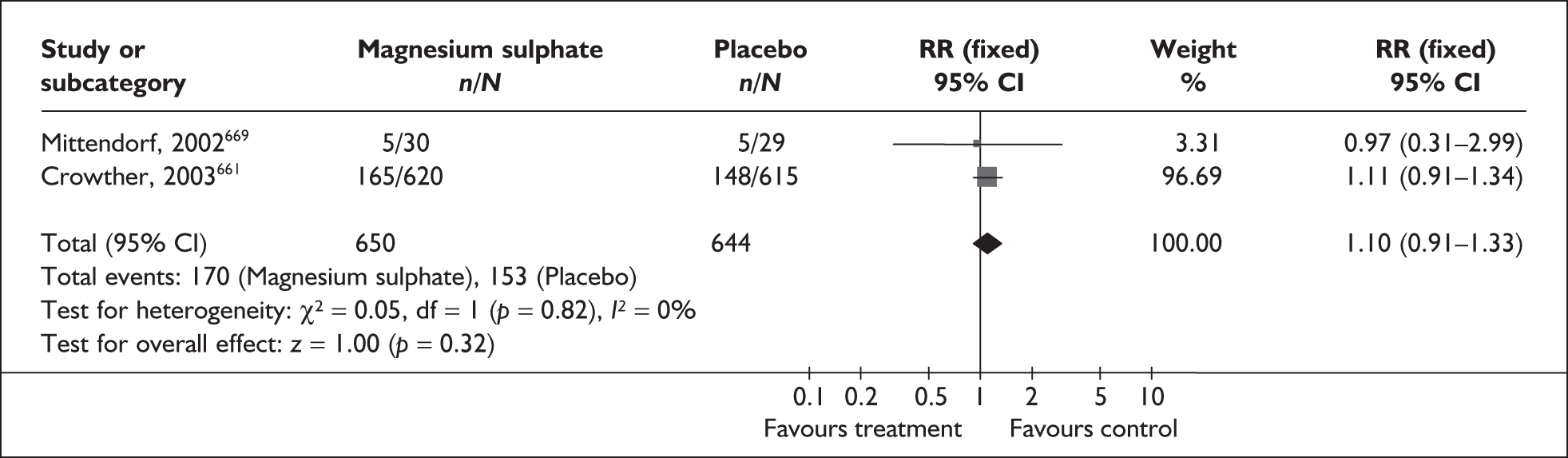
FIGURE 272.
Forest plot of the effect of maternal magnesium sulphate therapy for protection against neonatal neurological morbidity in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour on the incidence of serious periventricular leukomalacia in the premature neonates.
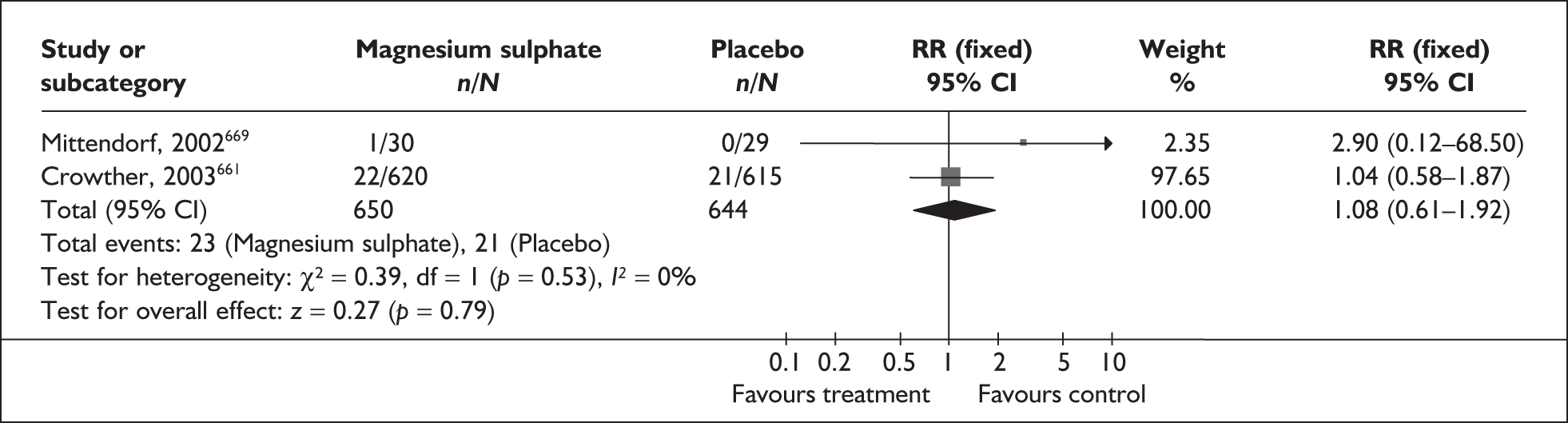
FIGURE 273.
Forest plot of the effect of maternal magnesium sulphate therapy for protection against neonatal neurological morbidity in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour on the incidence of cerebral palsy.
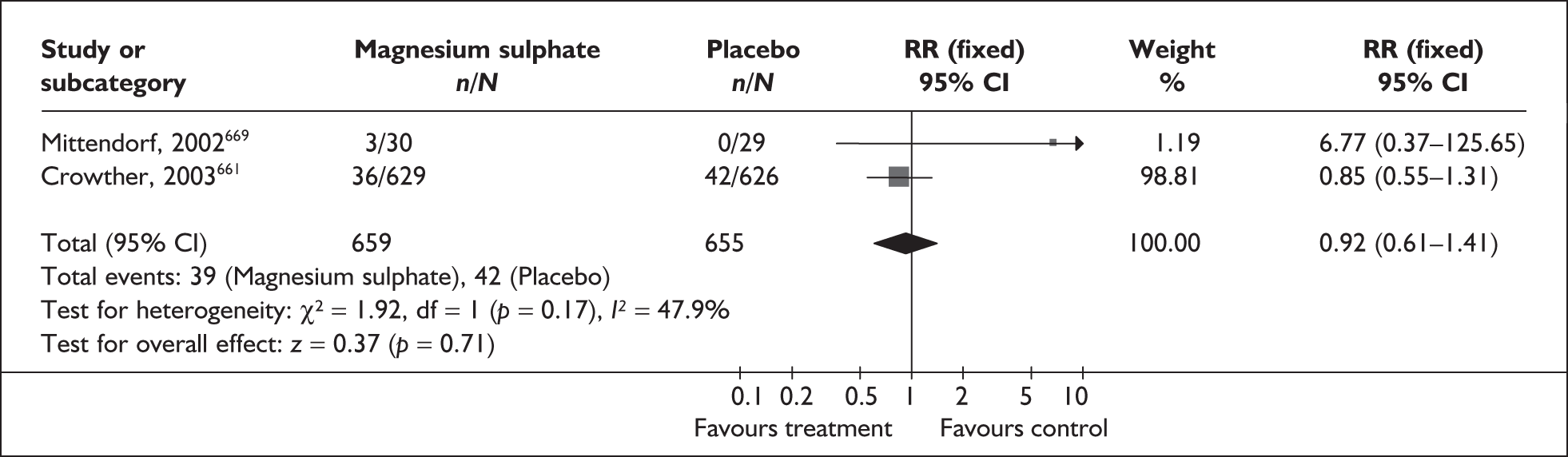
| Outcome (number of RCTs) | RR | 95% CI | I2, p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total deaths: fetal, neonatal and postnatal (2 studies, n = 1314)668,669 | 0.82 | 0.63–1.06 | 0%, 0.47 |
| Substantial gross motor dysfunction (1 study,a n = 1047) | 0.53 | 0.30–0.92 | NA |
| Neurosensory disability (1 study,a n = 1047) | 1.00 | 0.85–1.17 | NA |
| Bayley PDI (1 study,a n = 943): WMD | – 1.30 | – 3.66 to 1.06 | NA |
| Bayley MDI (1 study,a n = 949): WMD | – 1.40 | – 3.77 to 0.97 | NA |
| Delayed development (1 study,a n = 1047) | 1.00 | 0.84–1.19 | NA |
| Blindness (1 study,a n = 1047) | 0.96 | 0.06–15.38 | NA |
| Deafness (1 study,a n = 1047) | 1.10 | 0.40–3.02 | NA |
| Chronic lung disease (1 study,a n = 1235) | 1.07 | 0.94–1.21 | NA |
| Necrotising enterocolitis (1 study,a n = 1235) | 0.96 | 0.59–1.57 | NA |
| Mechanical ventilation (1 study,a n = 1235) | 1.02 | 0.99–1.05 | NA |
| Maternal infusion stopped due to adverse effects (1 study,a n = 1062) | 2.74 | 1.81–4.15 | NA |
| Any maternal adverse effects (1 study,a n = 1062) | 2.36 | 2.10–2.64 | NA |
Vitamin K before preterm birth for neuroprotection
Infants have no reserves of vitamin K at birth, and lack of this vitamin can cause potentially serious bleeding complications. Administration of vitamin K to the mother before imminent preterm birth may help to reduce the incidence of haemorrhagic disease of the newborn through improved coagulation.
The review of vitamin K672 included five RCTs and quasi-RCTs (n = 642). 673–677 Further details of the review can be found in Appendix 6, Table 141. The quality of the included studies was mixed and is presented in Figure 274. When compared to placebo or no treatment, antenatal administration of vitamin K was found to reduce the incidence of perinatal mortality (Figure 275), although this was not statistically significant; the exclusion of poorer quality trials did not change this finding. A non-significant trend for a reduction in neurological morbidity, as measured by the incidence of periventricular haemorrhage, was shown for infants receiving antenatal vitamin K compared to infants receiving placebo/no treatment (Figures 276 and 277); however, when only the higher quality trial is considered this trend disappears. 676 No information on neurodevelopment or admission to neonatal intensive care was provided. The pooled RRs presented in Figure 275 for perinatal mortality and RR 0.84 (95% CI 0.67–1.06) for the prevention of periventricular haemorrhage were used in the decision analysis. Results for other perinatal and maternal variables are shown in Table 37. It should be noted that it is unclear whether the primary studies have included multiple gestations in their results. Overall, the current evidence does not support the antenatal use of vitamin K for the prevention of neurological morbidity in preterm infants.
FIGURE 274.
Methodological quality of the included trials of maternal vitamin K therapy for protection against neonatal neurological morbidity in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
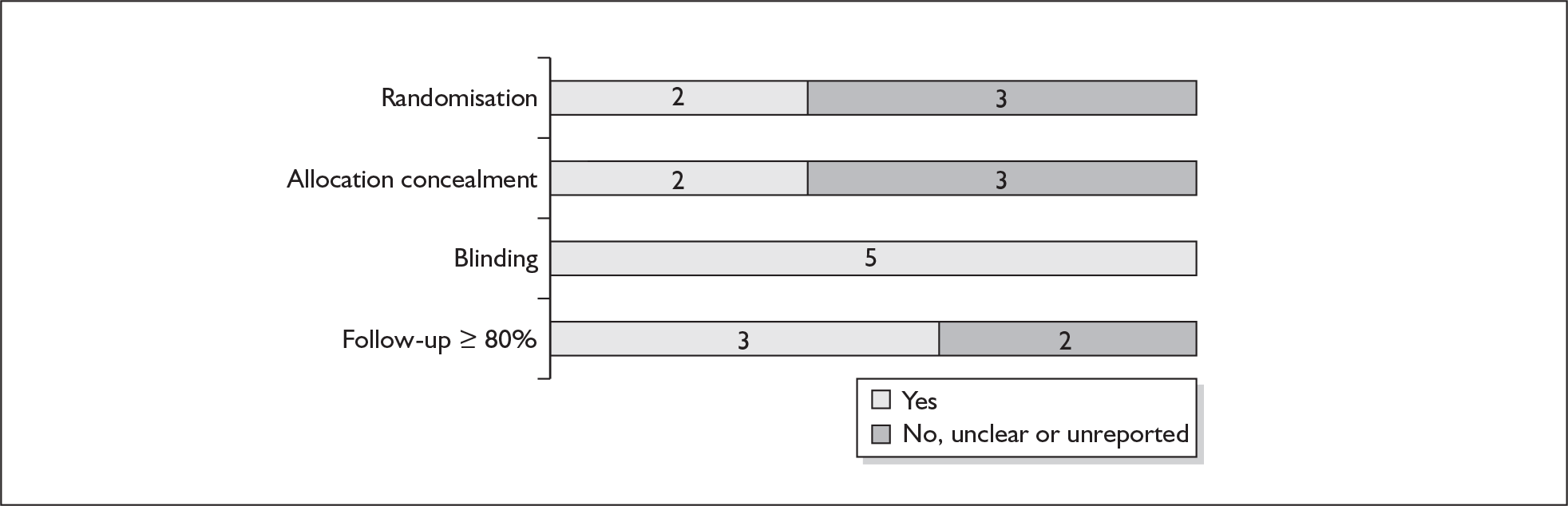
FIGURE 275.
Forest plot of the effect of maternal vitamin K therapy for protection against neonatal neurological morbidity in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour on the incidence of early neonatal mortality.
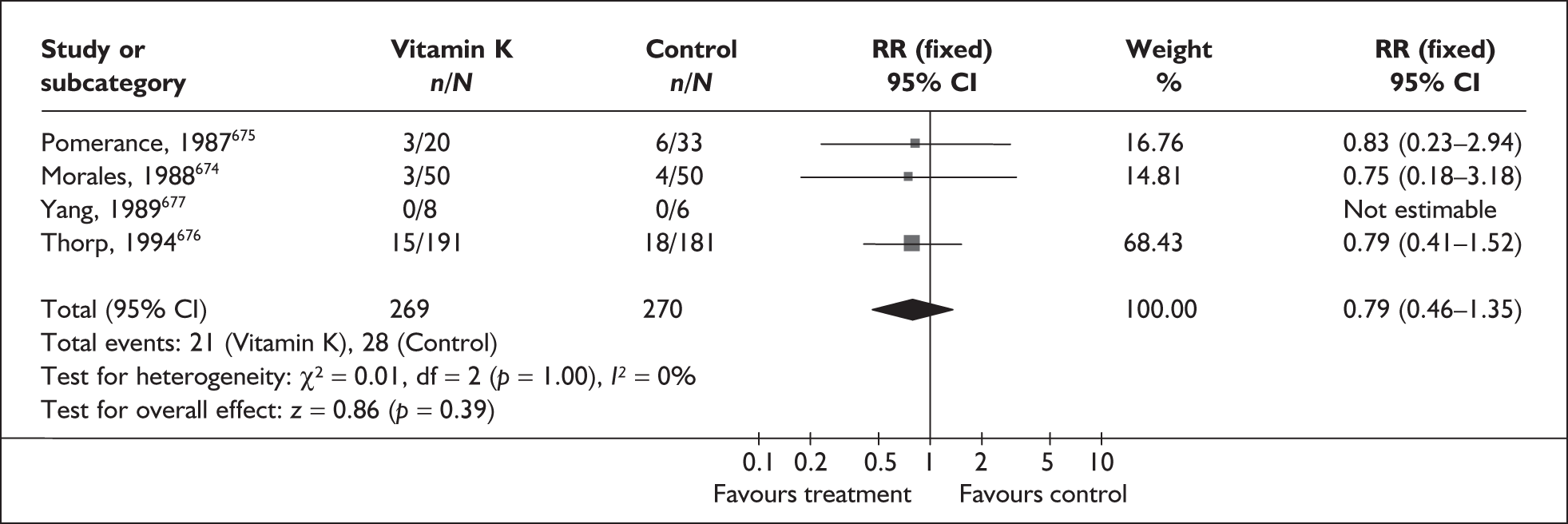
FIGURE 276.
Forest plot of the effect of maternal vitamin K therapy for protection against neonatal neurological morbidity in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour on the incidence of neonatal periventricular haemorrhage (all grades).
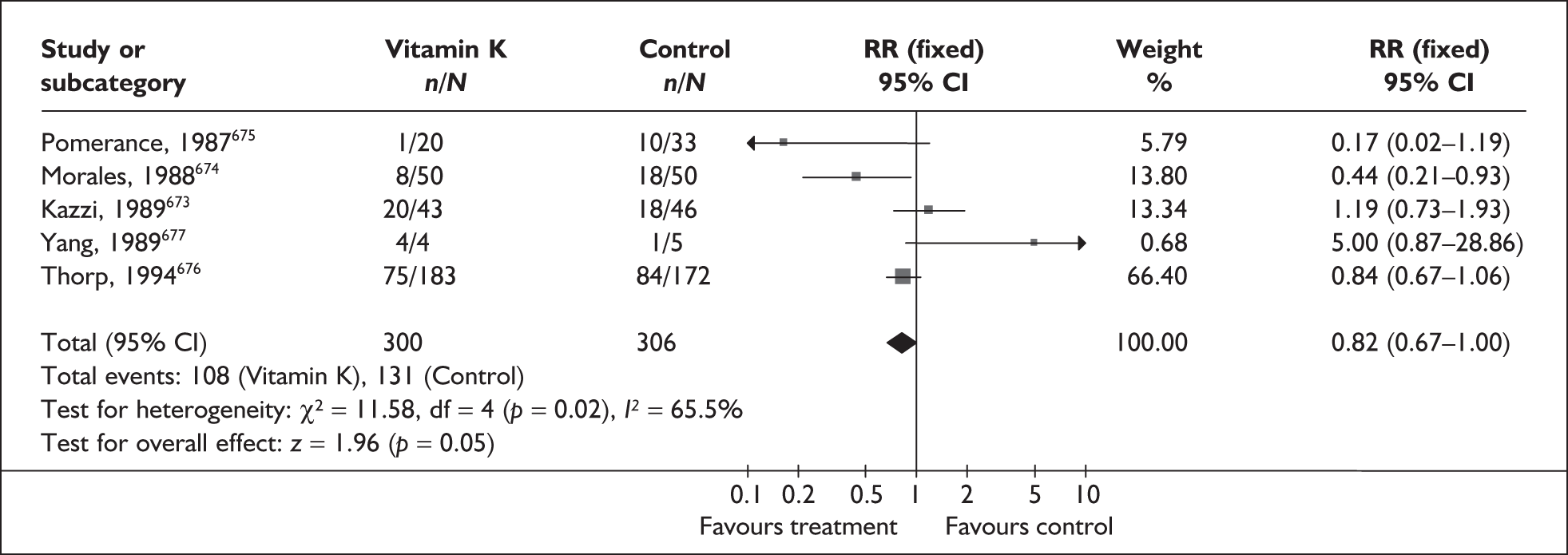
FIGURE 277.
Forest plot of the effect of maternal vitamin K therapy for protection against neonatal neurological morbidity in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour on the incidence of serious neonatal periventricular haemorrhage (grades 3 and 4).
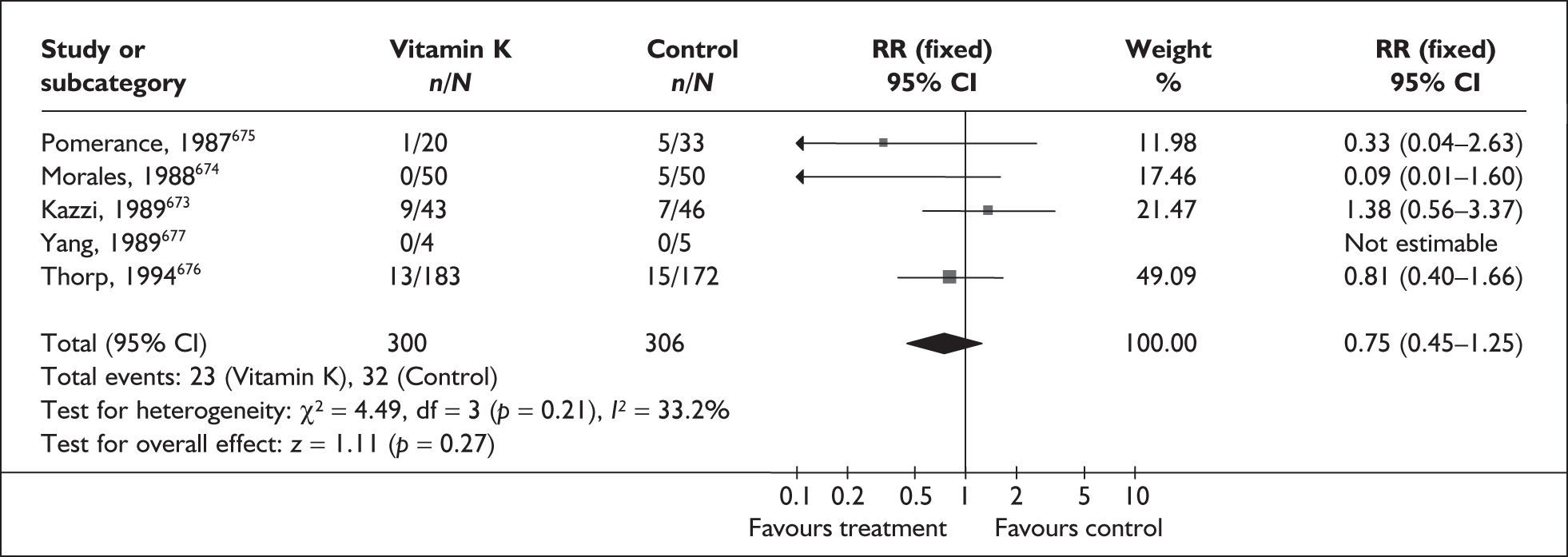
| Outcome (number of RCTs) | RR | 95% CI | I2, p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Use of mechanical ventilation (5 studies, n = 642)673–677 | 0.96 | 0.84–1.10 | 0%, 0.65 |
| Low Apgar score at 5 minutes (2 studies, n = 475)673,676 | 0.99 | 0.63–1.57 | 0%, 0.53 |
| Respiratory distress syndrome (3 studies, n = 167)674,675,677 | 1.02 | 0.76–1.37 | 0%, 0.53 |
| Pulmonary air leak (2 studies, n = 475)673,676 | 1.74 | 0.59–5.10 | 0%, 0.56 |
| Patent ductus arteriosus (3 studies, n = 528)673,676,677 | 0.96 | 0.57–1.63 | 0%, 0.61 |
| Any maternal side effects (4 studies, n = 474)673,675–677 | 3.78 | 0.41–35.07 | 0%, 0.83 |
Summary of effectiveness reviews
Summary of results of review of interventions
The evidence-based review assessed 40 interventions aimed at preventing preterm birth and its consequences. Previously published systematic reviews were identified for 33 of these topic areas. New rapid reviews were carried out for five topic areas: ethanol, home uterine monitoring, periodontal disease, fish oil and magnesium sulphate for neuroprotection. No systematic reviews or relevant RCTs were identified for two topic areas: in utero transfer and hypnotism.
Figures 279–281 indicate that most interventions which seemed to show a beneficial effect in terms of their ability to reduce the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth were aimed at treating women at high risk of spontaneous preterm birth or with symptoms of threatened preterm labour. In general, prophylactic treatment of low-risk, asymptomatic women did not appear to reduce the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth.
The main results of the methodological quality assessment as summarised in Figure 278 indicate that the quality of the included studies was often poor. Poor reporting also frequently made quality assessment difficult. Areas of concern included poor randomisation and allocation concealment, small sample sizes and lack of blinding. In addition, the number of studies per intervention area was frequently small; median number was five (range 0 to 24). Although a few interventions appeared to show some benefit towards preventing or delaying spontaneous preterm birth, the evidence base for a number of these interventions was severely limited by the quantity and/or quality of the included trials.
FIGURE 278.
Overall methodological quality of studies included in the reviews of interventions in prevention of spontaneous preterm birth. Note: (a) Some studies are included in more than one review; however, they have not been counted twice for this figure. (b) The three studies included in the reviews considering antibiotic treatment for ureaplasma and gonorrhoea were not included in this figure because they did not contribute to any of the primary outcomes sought.
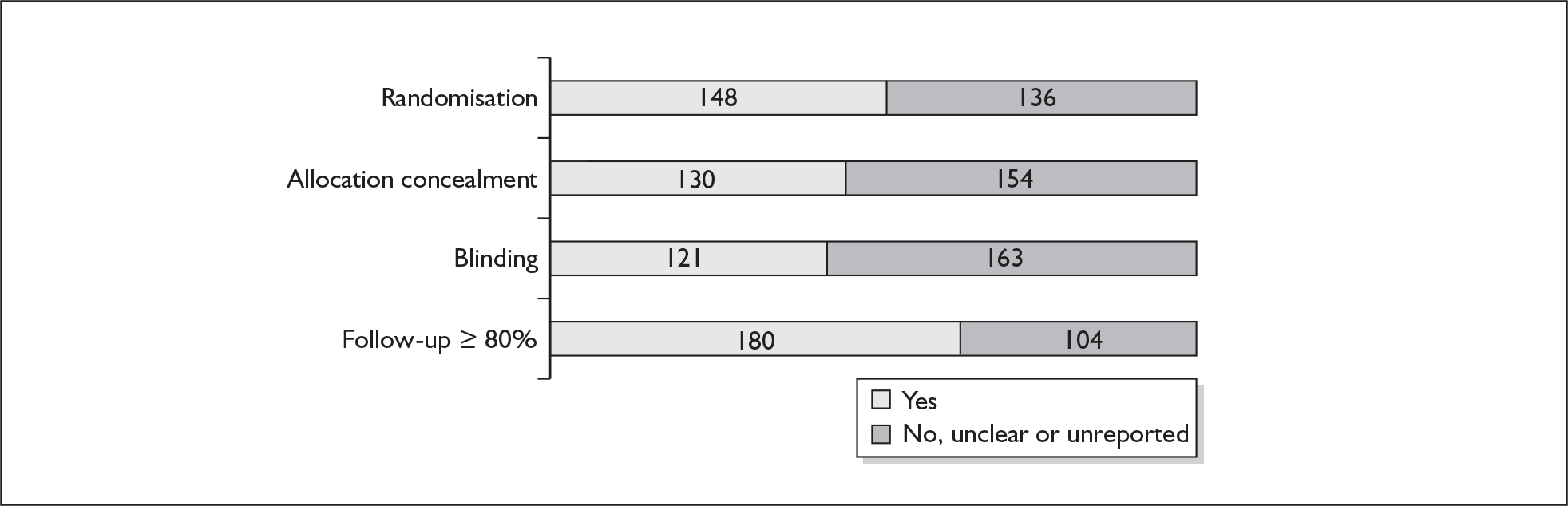
For most of the interventions evaluated, results were pooled using a fixed effect model. However, where only a single RCT contributed to the outcome(s), as in the case of bed rest, treatment for periodontal disease and ureaplasma; or where meta-analysis was not considered appropriate because of clinical variation, as in the case of zinc supplementation and home uterine monitoring, individual studies were considered. The forest plots presented here (Figures 279–281) highlight the primary outcomes for spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic and symptomatic women. The forest plots include both data that have been put forward for use in the decision analysis (highlighted in bold) and data that have not. This results section relates to clinical effectiveness. Clinical trials measure health-care outcomes to determine the efficacy or effectiveness of specific interventions. If infinite resources were available, effectiveness alone would be sufficient to determine a course of treatment. However, this is not the case; resources are finite. There is therefore a need to establish the relative cost effectiveness of interventions. Economic evaluations incorporate both costs and outcomes, and as a result the findings may differ from the results of the effectiveness review.
FIGURE 279.
Summary forest plots of relative risks of various interventions for prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation in asymptomatic women. a, Single dose vs short course.
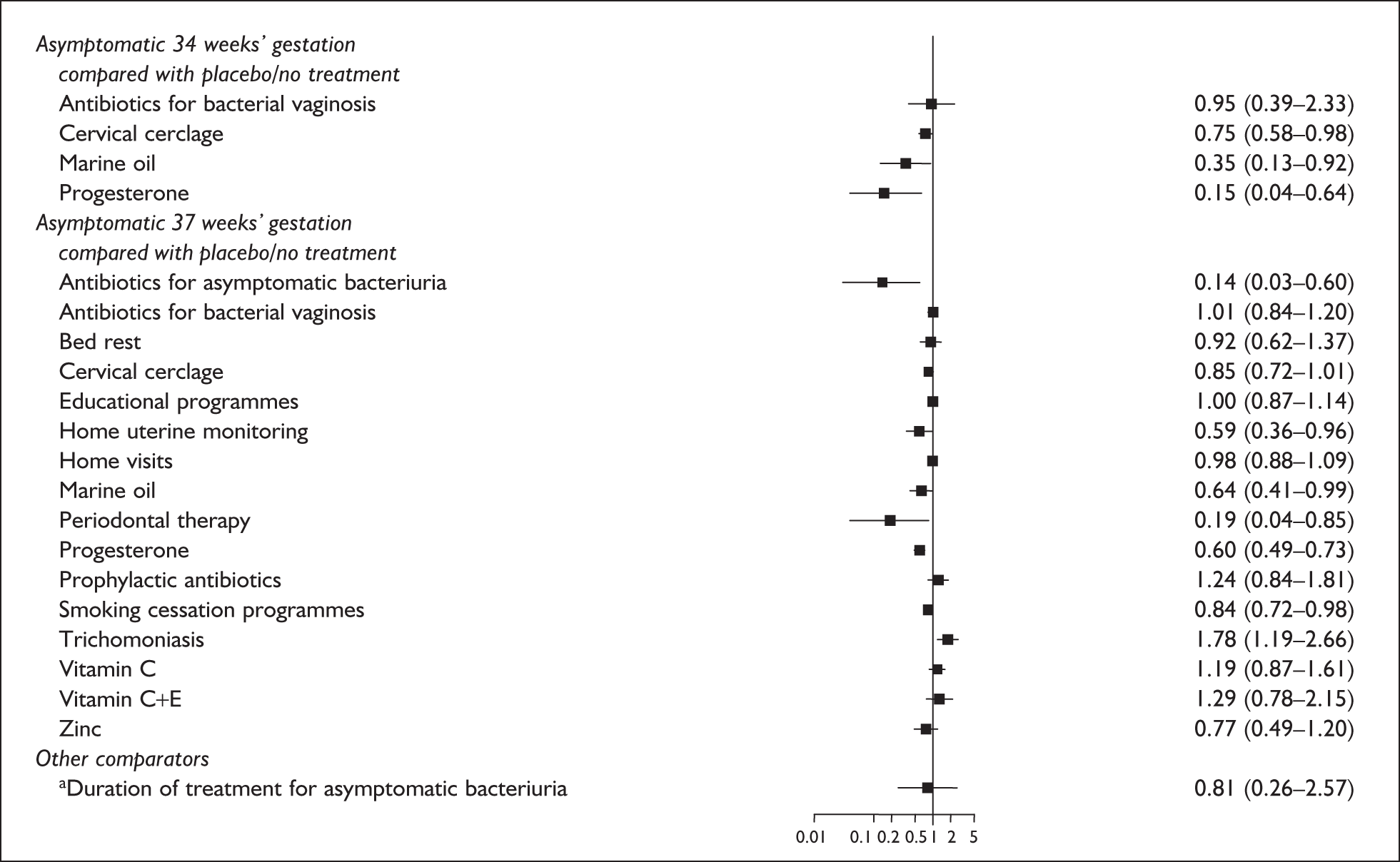
FIGURE 280.
Summary forest plots of relative risks of various interventions for prevention of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation in symptomatic women.
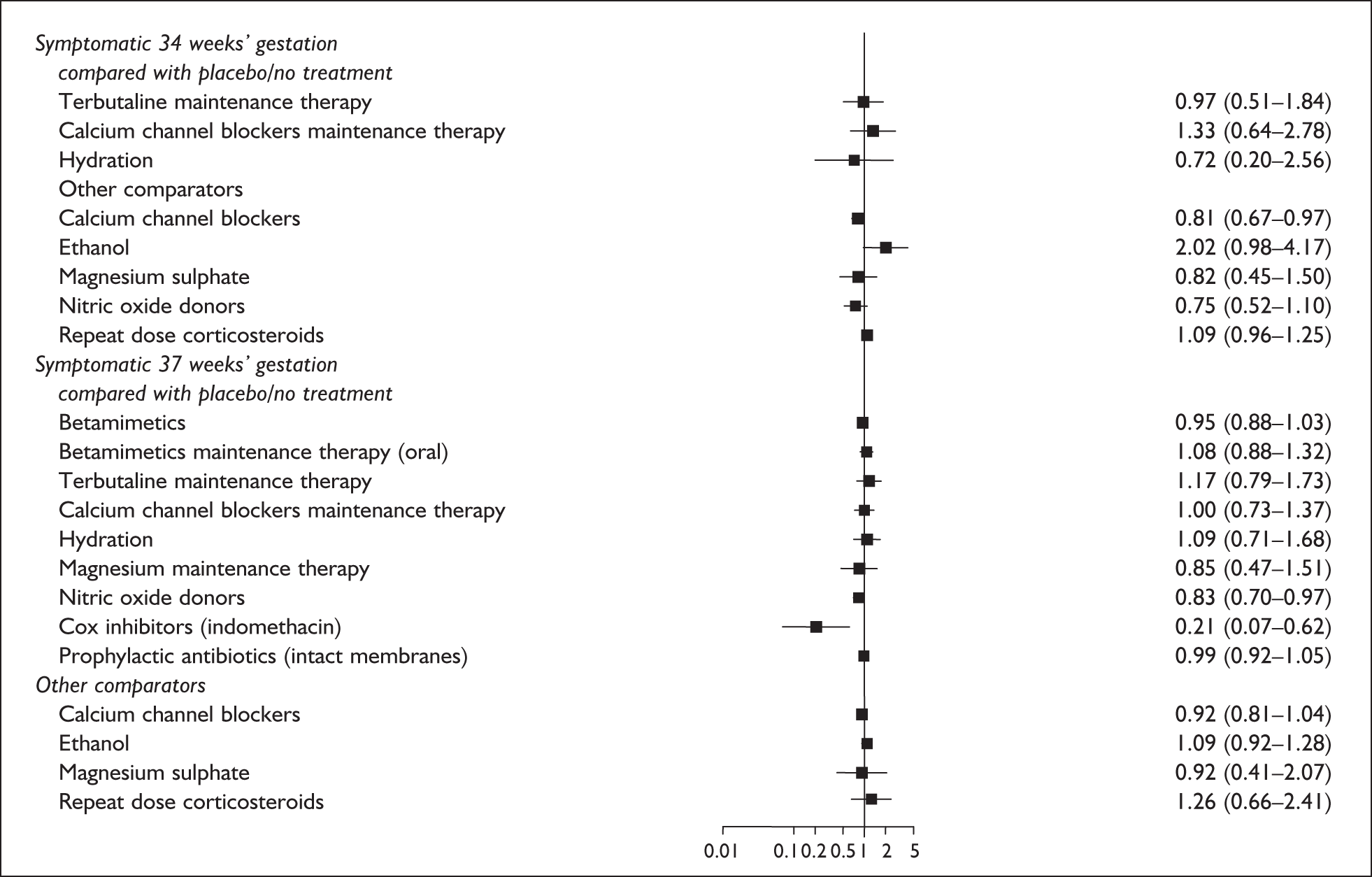
FIGURE 281.
Summary forest plots of relative risks of various interventions for prevention of spontaneous preterm birth within 24 hours 48 hours, and 7 days of initiating treatment in symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour.
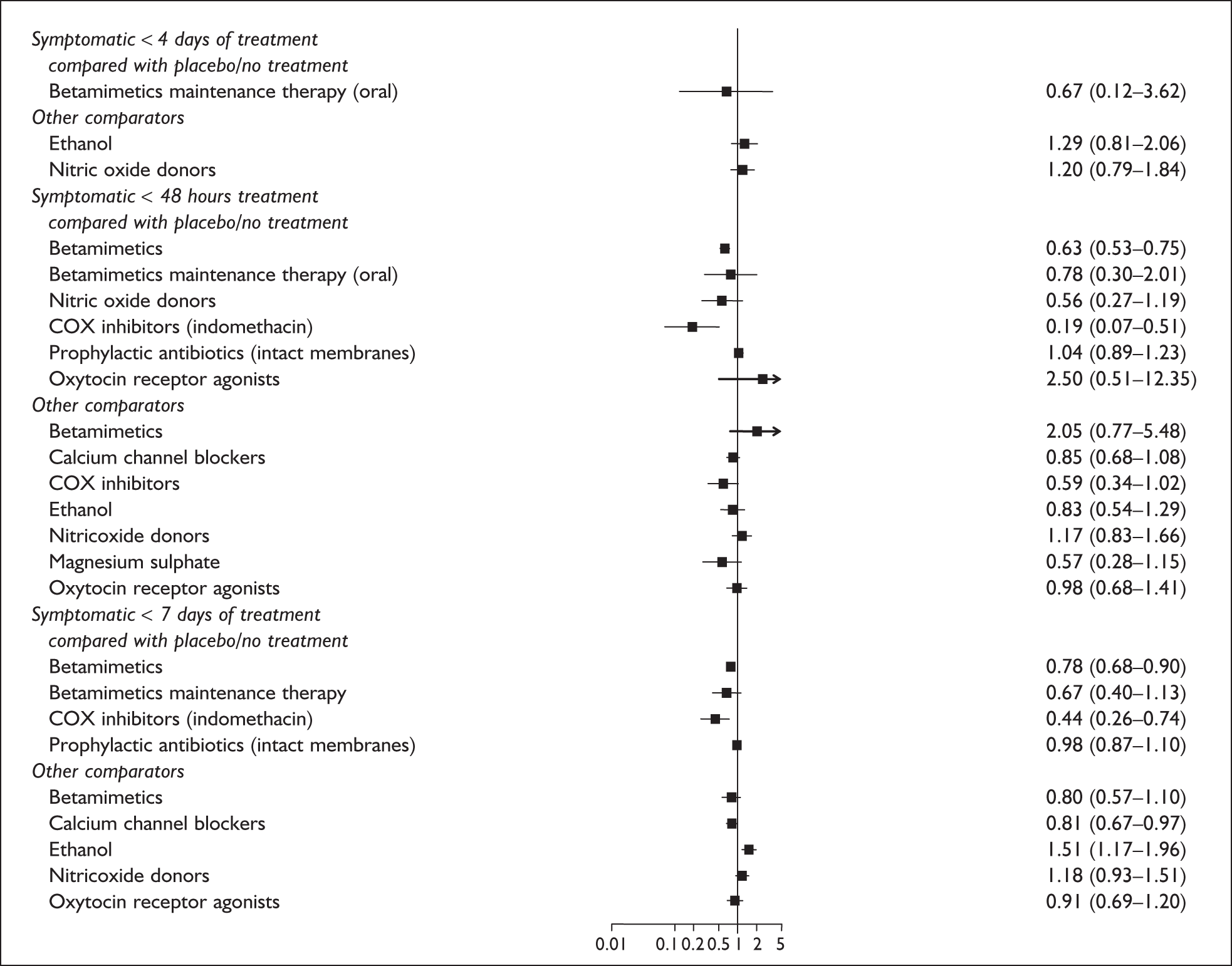
Summary of effectiveness findings
This review has sought to cover a vast area of research within a rapidly evolving field, which has been problematic given the limited resources and time available. We have employed rigorous methods but as with all systematic reviews, our findings should be interpreted in light of the restrictions imposed by both the methodology and the primary data.
The overall quality of studies across the different interventions was often poor, although whether this was because of poor reporting or poor methodology was sometimes difficult to assess. Particular areas of concern include poor randomisation and allocation concealment, lack of blinding (where appropriate), and small sample sizes. In some cases only quasi-RCTs were available (e.g. periodontal therapy), and for other interventions, assessments were based only on a limited number of small trials with fewer than 100 participants (e.g. fish oil and hydration). Sample size calculations were often not performed and so it was not possible to determine whether the lack of significant findings was the result of a true lack of effectiveness or of an inadequate sample size.
Small sample sizes also led to problems for some perinatal outcomes such as mortality, where the small number of participants often resulted in zero event rates. This often led to data being excluded from the original reviews. Consequently relative risks were in some cases based on very few trials and events, increasing the error limits and reducing the statistical power.
Reviews included in our report were restricted, where possible, to RCTs in women with singleton gestations and uncomplicated pregnancies. However, quasi-RCTs were included in a number of existing reviews, potentially diluting the quality of the included studies. Similarly, existing reviews and primary studies may have included women with multiple pregnancies, assisted pregnancies or pregnancies with maternal or fetal complications. This may limit the applicability of the findings to the general population of women’s risk of spontaneous preterm birth, as these factors are considered to increase the risk of spontaneous preterm birth678,679. In some cases, where studies were carried out in particular populations such as rural Gambian women or women with severe nutritional deficits, the degree to which the data could be generalised to the general UK population was also unclear.
Provisos/limitations arising from problems with primary data
Overall, advances in perinatal care over recent years have resulted in improvements in perinatal outcomes, yet studies included in the reviews were in some cases published over a period spanning more than three decades. This introduces problems when comparing and interpreting data because both research and clinical practice have evolved over time. These factors, in addition to heterogeneity in the outcomes, length of follow-up, dose regimens and population characteristics, hindered the interpretation of the data. For example, low birthweight was used as a proxy measure of gestational age in some earlier studies, particularly in the review of asymptomatic bacteriuria. While some concordance does exist, low birthweight and gestational age are not interchangeable; indeed, on the basis of an accumulation of epidemiological data, the World Health Organization recommended in 1961 that low birthweight no longer be used as the official definition of prematurity. 680 This appears to be supported by the results of the review of asymptomatic bacteriuria, as relative risks supported treatment for true spontaneous preterm birth but not for low birthweight. For the purposes of effectiveness, low birthweight was not considered an acceptable surrogate marker for spontaneous preterm birth.
Definitions for high-risk and low-risk women varied between studies. Women with a history of spontaneous preterm birth or threatened preterm labour, or women at risk of pre-eclampsia or diagnosed with a urogenital tract infection were largely, but not in all cases, defined as ‘high risk’. In some cases women were only considered at high risk if they had two or more second trimester miscarriages before 30 weeks’ gestation or cervical changes requiring cerclage within the current pregnancy. 609 Consequently, whether women were considered to be at low or high risk was not necessarily consistently defined across the various reviews or across studies within a review.
Threatened preterm labour was also not consistently defined across studies. Currently accepted hallmarks of threatened preterm labour include uterine contractions and concomitant changes in cervical dilatation or effacement before full-term gestation. Definitions that do not include cervical changes may inappropriately classify women as showing signs of threatened preterm labour when in fact they would subsequently deliver at term without treatment. However, in such cases waiting to confirm progressive cervical dilatation may result in the treatment being initiated too late to have any effect.
In addition a number of studies reported admission of infants to ‘special care’ or ‘neonatal care’ and, while this definition was accepted as referring to intensive care, it may in some instances refer to the lower-dependency units sometimes referred to as special care baby units, rather than to neonatal intensive care.
Provisos/limitations arising from review methods
Given the large number of potential interventions and the short timescale available it has been necessary to limit our review. Largely, this has been driven by the demands of the economic model which is the focus of the report. For instance, included interventions were chosen for their relevance according to the consensus opinions of a panel of experts. Time constraints also meant it was not feasible to carry out new reviews in each area. Indeed, in many cases this would have duplicated work already carried out by other researchers, in particular the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Review Group. The Cochrane Collaboration is an internationally recognised source of regularly updated, rigorous systematic reviews. Therefore we have used previously published good quality reviews and updated this work where required. Where no such review exists it has been necessary to carry out a rapid review for a small number of interventions (e.g. fish and marine oils, magnesium sulphate for neuroprotection, ethanol, home uterine monitoring and periodontal disease). Again the methodology used has been tailored to fit the demands of the economic model.
Our report focuses on seven key outcome measures: (1) spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation, (2) spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, (3) birth within 24 hours of intervention, (4) birth within 48 hours of intervention, (5) birth within 7 days of intervention, (6) admission to neonatal intensive care unit, and (7) perinatal mortality. These were chosen as key outcomes for the economic model as identified by consensus opinion. Trials should evaluate outcomes that are important to infants and their families as well as to health practitioners and the health service. Broadly, outcomes improve with gestational age, and the outcomes for preterm infants born at or after 34 weeks’ gestation are similar to those for term infants, although minor morbidities, which often lengthen hospitalisation, remain for neonates born between 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation. Any advantages on prolonging pregnancy in terms of morbidity and mortality may not be apparent from summary estimates of the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation; however, few studies reported on spontaneous preterm birth rates before 34 weeks’ gestation. Our review therefore has focused on short-term outcomes, largely relating to birth and the perinatal period. However, longer-term neurological effects, such as cerebral palsy, are also important to consider. In addition, the limitation of the review to RCTs may mean that relevant data on adverse events, often investigated using other study designs, may not have been included in the review. Postnatal administration of corticosteroids has been associated with improved respiratory outcomes in the short term but also a greater risk of adverse neurological effects in the longer term. 681 However, longer-term outcome data are not always available as the evaluation and follow-up of large trial cohorts can be expensive and difficult.
Given our reliance on existing reviews, it follows that the accuracy of the data presented in this report is very much dependent on that reported in the original reviews/trials. For instance, where a review required updating, searches were only carried out from the last search date reported by the original researchers. Consequently, any studies omitted from the original review are likely to remain undetected. Furthermore, data synthesis was reliant on the information reported by the original review authors or in the case of new rapid reviews, those reported by the original trial authors. Given the time and resources available attempts were only made to contact authors of newly identified primary studies where issues relating to relevance and quality were unclear. However, our success rate was low, which is not surprising given the age of some of the publications.
Provisos/limitations arising from things not done (omissions)
The prevention of spontaneous preterm birth appears to be a rapidly evolving field. This is apparent from our report as a number of new trials were published after our searches were completed but before the report was submitted for publication. Given more time it may have been possible to identify and obtain pre-publication data for inclusion in the report, but because of the aforementioned constraints this was not possible. We have referred to such studies where possible, but this does suggest that future updates of this report should be carried out relatively frequently.
There are a small number of other omissions in the report given the time limitations and the necessity to assign deadlines for the completion of each stage of the project. This has in most cases been because of difficulties in obtaining copies of original trial reports. On completion of the report only two publications remained unobtainable but a number of others did not arrive in time for assessment. However, this has been highlighted where applicable. In particular the original review of educational interventions did not provide sufficient details of the individual studies to enable figures for study quality and forest plots to be constructed. Delays in obtaining copies of the original trial reports resulted in these figures being omitted from this section of the report. In the case of interventions to treat bacterial vaginosis, delays in completing the review resulted in the relevant data missing the deadline for entry into the economic model. Again this has been made clear in the report.
Findings in the light of limitations
The interventions included in the review can broadly be divided into four categories: prevention, treatment of acute threatened preterm labour symptoms (e.g. tocolysis), maintenance therapy and interventions aimed at improving the health of the neonate (e.g. neuroprotection, reduction of RDS, and other neonatal morbidity).
Interventions given to asymptomatic women (i.e. women not experiencing symptoms of threatened preterm labour) at low risk of spontaneous preterm birth, such as prophylactic antibiotics, are aimed at preventing the occurrence of threatened preterm labour and spontaneous preterm birth. Our review suggests that there is little evidence that this approach avoids spontaneous preterm birth, and the practice of administering antibiotics to low-risk, asymptomatic women for the sole purpose of preventing spontaneous preterm birth is not supported. It may be that prophylactic administration is useful against early-onset infection, but potential harms would need to be weighed against any benefits. There is some evidence that prophylactic antibiotics given to women at high risk of spontaneous preterm birth are effective in reducing low birthweight and maternal infection rates. Similarly, antibiotic treatment for bacterial vaginosis significantly reduced the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth in women with a diagnosis of intermediate vaginal flora. No effective test was available; however, this does not impact on the effectiveness of the intervention. Should a more accurate test become available then the overall effectiveness is likely to increase. Antibiotics given to women with asymptomatic bacteriuria also significantly reduced the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth, although this was based on the results of a very small study of questionable quality. Conversely, antibiotics given for the treatment of trichomoniasis increased the risk of spontaneous preterm birth.
In many cases, non-pharmacological interventions to prevent spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic women who are at high risk of spontaneous preterm birth did not demonstrate a clear benefit for prevention of spontaneous preterm birth or other maternal or perinatal outcomes when compared to placebo or no intervention. Where reported, bed rest, education, home visits and antioxidants did not significantly reduce the risk of spontaneous preterm birth or infant mortality; however, existing studies were generally not of high quality or were of unclear methodology, making it difficult to confidently evaluate the findings. The results do, however, raise the question of whether asymptomatic women without current urogenital infection should be treated purely on the basis of their previous history.
One possible exception to the apparent ineffectiveness of prophylactic interventions was periodontal therapy, which showed potential in terms of a reduction in spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation. However, this was based on one poor-quality quasi-RCT and other relevant outcomes were not reported.
Progesterone, fish oil, home uterine activity monitoring and dietary advice also appeared to be promising interventions. Intramuscular progesterone reduced the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth before 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation, although evidence to support a reduction in perinatal mortality and morbidity was less convincing. Further research is needed regarding the use of vaginal progesterone in the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth, although the one available study showed a benefit. Fish or marine oil, given for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic women at high risk of spontaneous preterm birth, demonstrated a reduction in spontaneous preterm birth, but as data were limited to two studies of different oils and regimens, further investigation is required. Home uterine activity monitoring appeared to reduce the risk of spontaneous preterm birth; however, results were based on a single (adequately conducted) study with limited evidence of neonatal safety. Additional research is therefore required to determine support for the use of home monitoring. Dietary advice, specifically aimed at women to increase energy and protein intake, also appeared to reduce the risk of spontaneous preterm birth. However, the results are dominated by one study undertaken in rural Greece, with questionable relevance to UK practice. Interventions designed to deal with a specific problem, such as smoking or infection, known to increase spontaneous preterm birth, appeared to be beneficial whereas interventions targeted at lower-risk women to improve general health, such as antioxidants, appeared not to be. This may be a consequence of participants’ absolute risk from the cause or deficiency targeted being relatively low to start with.
Smoking cessation interventions appeared to show some benefit in reducing spontaneous preterm birth and low birthweight (< 2500 g) compared to usual care, but the quality of the studies was poor. Although no direct assessment of verified smoking cessation and spontaneous preterm birth was employed, smoking during pregnancy is one of the most clearly identifiable causes of spontaneous preterm birth, so this finding is perhaps not surprising. Future research might wish to consider the most appropriate methods of persuading pregnant women or those planning a pregnancy to stop smoking, looking at what level of intervention may become counterproductive, and whether programmes can be transferred to other areas of addiction, such as alcohol or recreational drugs. It was not possible to identify the specific aspects of these interventions that might increase the likelihood of success.
Cervical cerclage, which is aimed at asymptomatic women who are at high risk of spontaneous preterm birth, was also suggested to have some benefit in preventing spontaneous preterm birth, but this needs to be considered in light of the limited evidence concerning neonatal and maternal adverse effects. Similarly, progesterone given to asymptomatic women at high risk of spontaneous preterm birth demonstrated a reduction in the risk of spontaneous preterm birth, and perinatal mortality; however, other infant and maternal outcomes were less well reported, with many outcomes taken from a single study. A recent systematic review, which also conducted a review of adverse events, concluded that progestational agents did not show any evidence of harm. 498
Tocolytic agents are aimed at controlling the symptoms of threatened preterm labour in symptomatic women, thereby delaying spontaneous preterm birth. There was reasonable evidence to determine the effectiveness of the different tocolytic agents in the majority of cases, with the exception of ethanol, which only had one high-quality study. Evidence to support the use of hydration in symptomatic women was limited by the size of the trials. When compared with placebo, most other tocolytic classes, except ethanol, appeared effective in prolonging pregnancy. A reduced risk of spontaneous preterm birth in comparison with placebo was, however, only shown for NSAIDs (including COX inhibitors) and progesterone. NSAIDs also showed a reduced risk of spontaneous preterm birth in comparison with betamimetics and magnesium sulphate. The RCOG guidelines [Clinical guideline No. 1(B), 2002] currently recommend that if a tocolytic is used, nifedipine, a calcium channel blocker, or atosiban, an oxytocin receptor agonist, should be preferred. However, this was not supported by the data from direct comparisons in this review. Atosiban did not appear superior to placebo or betamimetics for any of the outcomes considered, although in some cases this was only based on a very limited number of small trials. However, an indirect comparison carried out during the economic modelling suggested a benefit to atosiban use. Direct comparisons were not available for calcium channel blockers versus placebo, but they were superior to betamimetics, and for some outcomes to other tocolytic agents. Indirect comparisons suggested that calcium channel blockers were more effective than placebo in preventing preterm birth up to 7 days following intervention. An indirect comparison of atosiban and calcium channel blockers was also performed and a favourable effect for admission to neonatal intensive care unit was found for calcium channel blockers (Appendix 7). This is in line with results from a meta-analysis with indirect comparisons of randomised trials. 682 Notably, rescue tocolysis was employed in a substantial number of the tocolytic studies, particularly within the reviews for NSAIDs, oxytocin receptor antagonists and magnesium sulphate. This practice may have diluted or inflated the results obtained, particularly as it was not always clear how many participants this applied to within a given trial. In addition, evidence regarding the effectiveness of the acute administration of tocolytic agents versus the effect of including a maintenance regimen was difficult to interpret because data for acute administration was often contaminated by the inclusion of maintenance regimens. Although attempts were made to separate data where information allowed, this was not always possible. Furthermore, studies often included different regimens (e.g. dose and/or route of administration); this was particularly noticeable in the reviews of calcium channel blockers. Greater standardisation in treatment regimens would be useful for future research. Differences in effect between different classes of tocolytic drug do appear to exist, but are difficult to assess because of inconsistencies across studies; therefore further research is needed.
Despite the prolongation of pregnancy and a reduction in spontaneous preterm birth, no clear evidence of a beneficial effect on perinatal mortality, or on serious morbidity as evidenced by admission to neonatal care units, was found for tocolytics in general. This may be because the trials included too many women who were so advanced in their gestation that any further prolongation would have little potential benefit, or it may be that many of the earlier studies were undertaken before the use of antenatal steroids, and therefore delay of birth may not have been used to optimum benefit. Furthermore, few RCTs comparing the effect of tocolytic agents with placebo or no treatment for these outcomes were identified, and the results are largely based on single studies with small datasets.
Overall, an increase in adverse events was observed for all tocolytic agents compared with placebo. In particular, treatment with betamimetics was found to be associated with a greater number of adverse events leading to cessation of treatment. Betamimetics are known to be potent cardiovascular stimulants, and the increased cardiovascular changes shown in this review are likely to have contributed to this finding. In consequence the review supports current clinical opinion that betamimetics are not an appropriate treatment for women with threatened preterm labour. NSAIDs compared favourably with alternative tocolytics in terms of maternal adverse events. However, the RCOG currently recommends that NSAIDs should not be used for tocolysis, this is principally because of concerns over the fetal adverse event profile. Calcium channel blockers appeared to have a good maternal and fetal safety profile. This is in line with the RCOG guidelines [Clinical guideline No. 1(B), 2002] that if a tocolytic is used, nifedipine, a calcium channel blocker, or atosiban, an oxytocin receptor antagonist, may be preferable because they have fewer adverse side effects. However, many RCTs will not detect rare, long-term effects, largely as a consequence of short-term follow-ups, or because they are not powered to detect significant differences in adverse events. There is a clear need for well-conducted studies that specifically consider the safety aspects of treatment. This is particularly important for repeated acute tocolytic therapy in women with recurring symptoms, although this was not assessed in this review.
Maintenance therapy refers to continued tocolytic treatment in women who have successfully been treated with acute tocolysis after presenting with threatened preterm labour. Prolonged oral, subcutaneous or intravenous tocolytic treatment was not associated with greater maternal or fetal benefits compared to placebo or no intervention, and in some trials a negative response to treatment was reported. Betamimetics and magnesium sulphate demonstrated greater adverse events when compared to placebo, although women receiving magnesium sulphate were less likely to report side effects than women receiving alternative tocolytics. In contrast, two trials comparing the efficacy of calcium channel blockers for acute treatment of threatened preterm labour with magnesium sulphate (both employing maintenance regimens of the same tocolytic agent used for the acute treatment) found that women receiving calcium channel blockers demonstrated significantly fewer adverse effects compared with magnesium sulphate.
In addition to interventions aimed at preventing or treating threatened preterm labour, and so delaying spontaneous preterm birth, a number of interventions included in this review were aimed at preparing the fetus for spontaneous preterm birth and trying to reduce associated neonatal morbidity. Such interventions included antenatal administration of magnesium sulphate and vitamin K for neuroprotection, neither of which demonstrated any clear beneficial effect; and prophylactic corticosteroids to prevent RDS. Antenatal corticosteroids were found to have a beneficial effect on the incidence of RDS, the risk of intraventricular haemorrhage, and may also reduce necrotising enterocolitis when compared to placebo or no treatment. The effects were most clearly demonstrated after 28 weeks’ and before 34 weeks’ gestation, and in babies delivering 1–7 days after the intervention. Whether it is beneficial to administer repeat doses of corticosteroids is currently unknown because insufficient evidence was available regarding the risks or benefits of repeat or rescue courses of antenatal corticosteroids to support their routine use in clinical practice.
Our report highlights a number of evidence gaps related to the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth. Most notable are the assessments of in utero transfer and antibiotics for urogenital infections. One of the primary aims of first-line tocolysis is to delay birth to allow transfer to a unit with more specialised facilities for premature babies. However, no RCTs were identified that assessed the efficacy and safety of in utero compared to extrauterine transfer. Few studies and fewer relevant outcomes were found by reviews of treatments for syphilis and gonorrhoea, limiting our ability to adequately assess the effectiveness of these interventions. While placebo-controlled trials would not be ethical, some research on the best therapy is required, particularly given the rising incidence of these conditions often in conjunction with HIV/AIDS. In addition, the review of ureaplasma found only one trial, which did not report any relevant primary outcomes, and no systematic reviews or relevant RCTs were identified for hypnosis, indicating a need for further research in these areas.
Recommendations for the economic model
In a number of instances, the aforementioned limitations had implications for the data entered into the economic model. Data were only entered into the model if it was in comparison with placebo and if the relative risk was favourable. Delays in completing the review of interventions for bacterial vaginosis prevented the inclusion of these data in the economic model. However, the intervention only appeared beneficial in a subgroup of women with a diagnosis of intermediate vaginal flora. In addition, no placebo comparison was available for a number of the interventions. This can in some circumstances be resolved by the inclusion of data from indirect comparisons. However, for a number of the interventions, most notably antibiotic treatments, leaving infections untreated poses ethical dilemmas and so this was not considered appropriate. Our health economists did however calculate and use an indirect comparison for calcium channel blockers versus placebo.
A further indirect comparison was used for atosiban versus placebo. A direct comparison was available but this was mainly based on one small trial of 112 participants and the data favoured placebo over atosiban. Where data are limited indirect comparisons may also offer additional information. In this case data from the direct comparison (favours placebo) and the indirect comparison (favours atosiban) are conflicting. It is important therefore to consider the internal validity and similarity of the included trials used in the indirect comparisons when interpreting the findings (Appendix 7). Direct and indirect comparisons often agree, but can, as in this circumstance, produce opposing results. This may be the result of random errors between the two estimates or deficiencies in the trials used in the direct, indirect or both comparisons. 683
The decision to use the indirect comparison in the economic model was based on the fact that atosiban is used so widely in clinical practice and indeed is favoured by the RCOG guidelines [Clinical guideline No. 1(B), 2002]. We felt it is important to consider both the direct and indirect comparisons using them as ‘worst case’ and ‘best case’ scenarios, respectively. Using the ‘worst case’ scenario (i.e. the direct comparison) the intervention would not have been effective enough to be entered into the economic model. The ‘best case’ scenario (i.e. the indirect comparison) allows the data to be entered into the model so that it can be compared with the other interventions commonly used in practice. However, the findings from the economic model need to be interpreted in light of the limitations and caveats accompanying the use of indirect comparisons, particularly when they are in conflict with evidence from direct comparisons. This also highlights the urgent need for further trials directly comparing atosiban with placebo and other relevant comparators.
Other data entered into the model also need to be considered in light of the quantity and quality of the trials included in the various reviews. For instance, the hydration review data was only based on two small trials of 228 women in total. The data for fish oil was mainly based on only two trials involving only around 250 women. The quality of the trials included in the asymptomatic bacteriuria review and smoking cessation reviews was in the main poor or questionable. The review of periodontal therapy included only one poor quality quasi-RCT (n = 351). The data for nutritional advice were mainly based on two studies of questionable quality, one of which was very small (n = 20), and neither of which defined spontaneous preterm birth. Finally, the energy/protein supplementation data were based on four trials, only one of which was considered to be of adequate quality.
In addition to problems with the internal validity of the trials, there are also issues with the external validity of certain trials. This calls into question the applicability of the findings to the UK setting. For instance the trial dominating the assessment of nutritional advice is based in a rural population of Greek women (n = 429) many of whom had nutritional problems. Similarly one of the four trials included in the assessment of energy/protein supplementation was based in a group of rural Gambian women with chronically marginal nutrition, and another looked at women in a Bogota slum.
Recommendations for practice
-
Tocolysis should be used in women symptomatic with threatened preterm labour to prevent or delay spontaneous preterm birth.
-
NSAIDs and calcium channel blockers appear to be favourable interventions to delay spontaneous preterm birth in women with symptoms of threatened preterm labour. However, evidence of contrasting maternal and fetal adverse event profiles should be taken into consideration, particularly in the light of the RCOG guideline recommendation that NSAIDs should not be used.
-
There is insufficient direct evidence to support the routine use of oxytocin receptor antagonists such as atosiban.
-
Antenatal corticosteroids are the most favourable interventions to treat symptomatic women in terms of preventing complications of prematurity in the newborn.
-
Progesterone appears to be the most favourable intervention to treat asymptomatic antenatal women in terms of preventing spontaneous preterm birth.
-
Cervical cerclage may be effective in preventing preterm birth in asymptomatic women known to be at increased risk of spontaneous preterm birth.
Recommendations for further research
Large randomised controlled trials are required for the following interventions and comparators. These should be reported according to the standards of the CONSORT statement and should carry out separate subgroup analysis for multiple pregnancies, complicated pregnancies and IVF pregnancies. Treatment regimens should be standardised; clearly defined populations and outcomes for spontaneous preterm birth before a specific stated gestation should be reported (ideally before 34 weeks’ gestation or even earlier). Additionally, spontaneous preterm birth within 24 to 48 hours of treatment (but certainly within 7 days), perinatal mortality, admission to neonatal intensive care, adverse events and longer-term neurological morbidity should also be reported.
Asymptomatic antenatal women
-
Periodontal therapy
-
Antibiotics for urogenital infections
-
Antibiotics for intermediate flora bacterial vaginosis
-
Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria
-
Fish oils
-
Progestational agents
-
Dietary advice
-
Smoking cessation interventions versus no intervention, specifically aimed at exploring which individual components of smoking cessation programmes are effective
-
Cervical cerclage versus no cerclage.
Symptomatic women with threatened preterm labour
-
In utero transfer versus extrauterine transfer
-
A systematic review should be conducted to investigate the adverse fetal events associated with NSAIDs; in case insufficient evidence is available for such a review, high-quality randomised trials should be conducted to assess adverse outcomes
-
Oxytocin antagonists versus other tocolytics (e.g. NSAIDs, calcium channel blockers)
-
Hydration versus placebo.
Conclusions of reviews of interventions
The overall quantity and quality of many of the trials was often poor or unclear because of poor reporting. No data were found to assess the effects of in utero transfer, antibiotics for urogenital infections (i.e. syphilis, gonorrhoea and ureaplasma) or hypnosis. Treatments aimed at preventing spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic women were generally less promising than those aimed at delaying birth in women displaying symptoms of threatened preterm labour (i.e. symptomatic women). Antibiotics were generally not beneficial with the exception of those used to treat bacterial vaginosis (only in women with intermediate flora) and asymptomatic bacteriuria. Trials of non-pharmacological interventions (i.e. bed rest, education, home visits and antioxidants) in asymptomatic women were generally of poor quality and did not show any reduction in spontaneous preterm birth. Smoking cessation interventions, progesterone, home uterine activity monitoring and cervical cerclage did suggest some benefit in terms of preventing spontaneous preterm birth; and the use of fish oil, dietary advice to increase energy/protein intake and periodontal therapy also appeared promising, but findings from all of these reviews were based on limited and sometimes poor quality data. An individual patient data meta-analysis of cerclage in women with a short cervix684 currently exists, the results of which suggest that cerclage may be of benefit in women with singleton gestations, particularly those with prior preterm birth or prior second trimester miscarriage.
Most tocolytic therapies aimed at delaying spontaneous preterm birth in symptomatic women appeared to show some beneficial effects with the exception of ethanol. However, there was insufficient good-quality evidence to assess the use of tocolytic maintenance therapy. The available evidence suggested that NSAIDs appeared to be the most effective treatments in terms of reducing spontaneous preterm birth and prolonging pregnancy, although evidence to support a reduction in perinatal mortality and morbidity was less convincing. However, only one placebo-controlled trial, published over 20 years ago, was available, and some caution is required in interpreting the data based on comparisons with other tocolytics. This is particularly the case because there is some evidence, from one non-randomised study and a review of largely non-randomised studies (not included in this review), which indicates that indomethacin may increase the incidence of neonatal complications, including the likelihood of the infant requiring surfactant treatment685 and an increased probability of neonatal pulmonary hypertension. 686 No data comparing calcium channel blockers with placebo was available. However, comparisons between calcium channel blockers and other tocolytics showed that calcium channel antagonists were clearly superior to betamimetics, and may be superior to other tocolytics. There appeared to be little direct evidence to support the use of oxytocin receptor antagonists in comparison with placebo or betamimetics. What evidence was available was often limited and/or of questionable quality. However, data from an indirect comparison did not support the findings from these direct comparisons, and it is therefore difficult to form definitive conclusions as to the efficacy of these interventions. Similarly, evidence to support the use of hydration in symptomatic women was limited.
Antenatal corticosteroids were found to have a beneficial effect on the incidence of RDS and the risk of intraventricular haemorrhage (between 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation), but the effects of repeat courses of corticosteroids were unclear because of insufficient data. Subsequent to the searches being completed two RCTs evaluating repeated doses of corticosteroids appeared. 665,666 These studies included some women with multiple gestations, but their results provide some support for the practice of giving repeat courses of corticosteroids to women who remain undelivered following initial therapy. However, these studies have not been fully evaluated, nor did they meet the inclusion criteria for this review. Therefore, no conclusions as to the efficacy of repeated therapy can be drawn. Additionally, there is some evidence from animal studies662 that fetal brain function and growth may be adversely affected, although caution should be exercised when extrapolating such evidence to humans. 687 There was no clear beneficial effect to support the use of antenatal magnesium sulphate or vitamin K for fetal neuroprotection.
Chapter 6 Results of decision analyses
Systematic review of economics and costs studies
Introduction
We undertook this systematic review to assess the evidence for the cost-effectiveness of different approaches for detecting risk factors and providing treatment for preterm labour. More specifically, this review aimed to assess the appropriateness of the models used and the data requirements for an economic model, and to identify areas of uncertainty that should be explored in the model-based economic evaluation of tests to identify at-risk women and interventions for prevention or delay of spontaneous preterm birth. The review formed part of a wider project: a multidisciplinary series of reviews and modelling that examined the available evidence.
Methods
Systematic reviewing and meta-analysis of clinical studies, particularly of randomised controlled trials (RCTs), is a well-established research method. The same approach to economic and cost studies is also increasingly being applied, but with marked heterogeneity typical in economic studies, data synthesis and meta-analysis are rarely possible. Usually the most appropriate method for reviewing economic studies is to use a more qualitative approach. This review followed an established method used to systematically review economic studies. 688–691
The objective of this section of the report is to describe the review of the costs and cost-effectiveness of tests and interventions aiming to predict and prevent spontaneous preterm birth, based on systematic review of the economic literature. The aim was to include all information relating to costs of all aspects of routine tests and interventions in threatened preterm labour. The cost of a spontaneous preterm birth including its calculation can be found in Appendix 8.
Inclusion criteria
To be included in this study, papers had to meet the following criteria:
-
Participants: pregnant women, singleton gestation and preterm labour
-
Tests: those included in Appendix 2 of the accuracy review
-
Interventions: those included in Appendix 3 of the effectiveness review
-
Studies: formal economic evaluations and cost studies; cost studies include studies reporting primary research on the costs and use of care, and studies that discuss economic aspects of care and contain useful primary or secondary cost or use data.
The ‘cost-generating’ events or knock-on costs influenced by threatened preterm labour were also considered. These include delivery and postnatal care for women and baby/neonatal intensive care unit. Studies were identified using the search strategy described by York CRD, University of York (Appendix 1).
Exclusion criteria
Premature pre-labour rupture of the membranes may lead to threatened preterm labour and spontaneous preterm birth but it is not the focus of this study so these papers were excluded.
Selection of papers for review
Stage I and II – initial categorisation of studies
Each study was categorised on the basis of its title, Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) and abstract when available, by one investigator (A.T.) and the results were independently assessed by a different investigator (T.R.). Where there was disagreement it was resolved by consensus. A two-stage reviewing approach was used as described in detail elsewhere. 690 In the first stage, each study was categorised on the basis of title and abstract and classified as either an economic evaluation (coded A) or a cost study (coded B) or another category deemed irrelevant to the review. In the second stage, studies were retrieved and reviewed in full, and if the initial classification was confirmed, the final classification was A1 or B1. After review, studies that were initially classified as economic evaluations but with further scrutiny were found to be cost studies were finally classified as A2. The converse occurred for cost studies that after review were found to be economic evaluations. Studies that, after full review, were confirmed to be either economic evaluations or cost studies were included in the quality assessment section of the review. Foreign language papers were included if relevant. All other papers and studies that did not fall into one of the relevant categories were rejected.
Stage III – quality criteria
The quality of the economic evaluations was assessed according to the criteria used elsewhere,690 which are presented in Appendix 4.
If the studies fulfilled all the necessary criteria they were considered for data extraction in Stage IV. Some studies that just missed fulfilling all the quality criteria, but which nevertheless contained information that might be relevant and might be the only such available data, were not rejected but were marked with a query (?).
Stage IV – data extraction
An example of a data extraction sheet is presented in Appendix 4. Cost data were then inflated to 2006 prices using the National Health Service (NHS) Executive Hospital and Community Health Services Pay and Prices inflation index. 692
Results
A total of 1157 papers were identified by the literature search. The initial and subsequent classifications of these studies, together with the result of the quality assessment, are shown in Figure 282.
FIGURE 282.
Literature search results.
In the final classification, 15 studies were confirmed as economic evaluations (ten were categorised as A1, five as B1) and there was one additional paper which was a published review. Overall the quality was not good with only one study passing all the quality criteria. 693 Eight other studies, excluding the review, were marked with a query. 56,57,694–700 The studies marked with a query were not excluded from the review and the summary data for these studies are presented in Table 38. Six studies categorised as economic evaluations failed to meet the required quality criteria and were excluded. 701–706 A summary of the excluded studies is presented in Table 39. The quality criteria were not applicable to a review,700 which was therefore not graded but discussed separately below.
| Study details, including quality | Type of economic evaluation/ Study population | Viewpoint | Effectiveness data sources | Cost data; year and currency | Model used | Test | Intervention | Primary outcome | Results | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ambrose et al. 2004694 USA B(1) Query |
Cost consequences analysis Symptomatic Women |
Not reported, it appears to be that of the third-party payer | Own primary study | US$, cost year was not reported | None | None | Inpatient vs outpatient tocolysis with continuous subcutaneous terbutaline (SQT) | Costs and outcomes were not synthesised. Primary outcomes were ‘cost of total pregnancy’, ‘rate of preterm delivery’ | Inpatient tocolysis costs $56,089 and has a preterm birth rate of 86.7%. and outpatient tocolysis costs $25,540 with a preterm birth rate of 74.4%. Therefore, outpatient management is cheaper and gives a lower preterm birth rate, and thus could be introduced | Appeared to be comprehensive with some shortcomings. Reported unit costs are incomplete. No sensitivity analysis was carried out, therefore results should be viewed with caution |
|
Egberts 1992695 The Netherlands B(1) Query |
Cost-effectiveness analysis Preterm infants (< 30 weeks) |
Not reported, it appears to be of the health-care provider | Literature | The Netherlands Dfl, 1990 | None | None | Corticosteroids; surfactant (prophylactic and therapeutic) | Cost per survivor, cost per extra survivor | Prenatal corticosteroid administration had the lowest cost per survivor of 66.3). Corticosteroids and prophylactic surfactant was the most cost-effective strategy at 63.7 (× Dfl 1000) per survivor, and gave the lowest intensive- and high-dependency-care days in hospital | There were study shortcomings. Interventions were not defined thoroughly. Results were very unclear and sensitivity analysis was not carried out. Data available to calculate ICERs but they were not calculated |
|
Ferriols et al. 2005696 Spain A(1) Query |
Cost-effectiveness analysis Symptomatic women |
Health-care system | Literature | Euro €, cost year was not reported | Decision tree | None | Ritodrine vs atosiban | Cost per preterm birth (PTB) avoided within 48 hours | The ICER for ritodrine was $194/PTB avoided and for atosiban: was$632/PTB avoided (within 48 h). Therefore it was reported that ritodrine should be the first choice agent and atosiban a rescue drug | Clear definitions of interventions and a well-defined model. However, presentation of ICER is incorrect therefore results based upon it are incorrect and misleading |
|
Kekki et al. 2004693 Finland A(1) Pass |
Cost-effectiveness analysis Asymptomatic women (early pregnancy) |
Health-care system | Two own primary studies. Published perinatal statistics | Euro €, 2000 | Decision tree | Gram-stain of the vaginal discharge | Metronidazole, clindamycin | Cost per pregnant woman | The probability of PTB was 2.8% for screening and 2.7% for no screening. The no screening strategy was marginally less costly, therefore dominated all screening strategies. Authors stated statistical uncertainty may suggest no difference between strategies, and screening and treatment may provide more health benefits | Passed all quality criteria and appears to be sound. Tests and interventions are defined thoroughly. PSA is presented in full detail. One disadvantage is the assumption of a normal distribution for the cost variables |
|
Korenbrot et al. 1984697 USA A(1) Query |
Cost consequences analysis General population |
Not stated, it seems to be that of the hospital | Hospital resources | US$, 1981 | None | None | Terbutaline or isoxsuprine (β-adrenergic drugs) vs no intervention | Costs and outcomes were not synthesised. Primary outcomes were ‘expected maternal and neonatal charges per survivor’, ‘extension of gestation’ and ‘perinatal survival rate’ | Cost-effectiveness of treatment dependent on gestational age at onset of first PTL. Treatment between 26 and 33 weeks of gestation was cost-effective, resulting in expected savings of $11,240 per birth. Treatment at 20–25 weeks cost-effective if chance of survival taken into account. Little difference in costs for treatment or no treatment over 33 weeks. β-Adrenergic tocolytic intervention should be used to prevent PTL | Comprehensive but not meeting all quality criteria. Parameters used in the statistical analysis are extensive, but no sensitivity analysis is performed. Therefore results should be viewed with caution. Final recommendations not clear |
|
Lam et al. 2003698 USA A(1) Query |
Cost consequences analysis Symptomatic women |
Not stated, it seems to be that of the health-service provider | Own primary study | US$, cost year was not reported | None | None | Oral tocolysis versus subcutaneous terbutaline infusion | Costs and outcomes were not synthesised. Primary outcomes were ‘overall cost per pregnancy’ and ‘antepartum hospitalisation charges per patient’ | Overall cost per pregnancy of subcutaneous terbutaline (SQT) infusion was $5286 less than oral tocolysis. Also there was greater pregnancy prolongation with SQT and better neonatal outcomes. Therefore SQT was cost-effective | Generally well carried out and reported, with both interventions defined thoroughly. Cost year and perspective not reported. Estimation of final costs unclear. Results should be viewed with caution because of this |
|
Mozurkewich et al. 200056 USA A(1) Query |
Cost-effectiveness analysis Symptomatic women |
Third-party payer | Literature | US$, 1999 | Decision tree |
Traditional/rapid fetal fibronectin test Cervical length measurement |
Corticosteroids, tocolytic agents | Incremental costs per additional case of RDS or neonatal death prevented by the next most effective strategy | Five strategies were dominated. Fetal fibronectin testing or cervical length assessment may be cost saving relative to treating all women. Adding corticosteroids to either rapid risk assessment strategy may lower costs by reducing morbidity among infants born to mothers with false-negative results | Costs are defined thoroughly, giving useful information Calculation of ICERs and sensitivity analysis are quite unclear. Results should be viewed with caution because of this |
|
Muller et al. 199957 Germany A(1) Query |
Cost minimisation analysis Asymptomatic women |
Third-party payer | Own primary study and standard German sources | US$, 1996 | Decision tree | Screening for bacterial vaginosis (clue cell diagnosis) | Clindamycin 2% vaginal cream; Lactobacillus preparation | Costs and outcomes were not synthesised. Primary outcomes were total cost and net savings | No screening or treatment was most expensive at $534,926. Screening and treatment with clindamycin was cheapest at $493,159. Screening and treatment with lactobacillus was $497,619. $168 can be saved per delivery if women are screened and treated | The decision tree is not used in the estimation of costs. Sensitivity analysis is carried out on prevalence and charges, but on a limited range. Costs were hospital charges for insurance funds. Cost and effectiveness could be synthesised, but no ICER was calculated |
|
Myers et al. 1997699 USA A(1) Query |
Cost-effectiveness analysis Symptomatic women |
Hospital-based | Literature and hospital resources | US$, 1996 | Markov model | Amniocentesis (test all) | Tocolysis with β-mimetic antagonists and corticosteroids (treat all) | Cost per case of RDS prevented | Tocolysis and corticosteroids strategy was most cost-effective at before 34 weeks. Amniocentesis and fetal lung maturity testing strategy was most cost-effective at 34–36 weeks and no treatment strategy after 36 weeks. Cost per case of RDS prevented for Treat all strategy ranged from $10,500 to $1 million dependent on prevalence of RDS (2–17%) | ‘Test all’ strategies were not defined thoroughly. Estimation of ‘cost of RDS’ and ‘cost of preterm delivery’ are not sound and may be underestimated. Overall, the paper would have benefited from reporting methods more fully. |
|
USA A(1) Quality criteria not applicable |
NA | NA | NA | NA | None | None | Antenatal steroids, surfactant, indomethacin, dexamethasone (postnatal) | Cost per additional survivor, additional cost per additional life year gained, additional cost per additional QALY gained | Results vary. Antenatal steroids decrease costs per additional survivor. Surfactant has decreased treatment costs and is more beneficial when given prenatally. Indomethacin results in cost savings in survivors | Criteria for including papers were unclear. Overall the conclusions were variable. Papers included in review were not subjected to critical scrutiny. No confidence in results |
| Study details, incliding quality | Type of economic evaluation/Study population | Viewpoint | Effectiveness data sources | Cost data; year and currency | Model used | Test | Intervention | Primary outcome | Results | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Abenhaim et al. 2005701 Canada B(1) Fail |
Cost consequences analysis Symptomatic women |
Not stated, it seems to be that of the health-care provider | Hospital databases | US$, cost year was not reported | None | Fetal fibronectin test vs no intervention | None | Mean cost per patient with preterm labour | Mean cost per patient with preterm labour: $581 (study group), $3666 (baseline group) | Authors acknowledge underestimation of costs, by excluding radiological and laboratory costs. Cost year is not reported. Sensitivity analysis is not carried out. Results unhelpful to this study |
|
Harrison et al. 2001702 Canada B(1) Fail |
Cost consequences analysis Symptomatic women |
Not stated | Hospital databases | Canadian $, cost year was not reported | None | Home uterine activity monitoring | Education, home care, nutrition | Total cost, total cost per woman |
In-home care group: total cost $16,556 In-hospital care group: total cost $22,891 No significant difference for total cost per woman |
The perspective is unclear. The cost year is not reported. Sensitivity analysis is not carried out. Total cost per woman is not presented for the two groups |
|
Morrison et al. 2001703 USA A(1) Fail |
Cost consequences analysis Symptomatic women |
Not stated, it seems to be that of the third-party payer | Hospital databases | US$, cost year was not reported | None | Home uterine activity monitoring, telephone nursing contact | Education, smoking cessation, nutrition, exercise | Costs and outcomes were not synthesised. Primary outcome was ‘cost per pregnancy’ | Total mean cost per pregnancy: $7,225 (telemedicine group), $21,684 (control group) average savings: $14,459 | No formal incremental analysis. Unit costs are not reported separately. Sensitivity analysis is not carried out. |
|
Moya and Goldenberg 2002704 USA A(1) Fail |
Cost-effectiveness analysis, cost utility analysis Preterm infants (not defined further) |
Societal perspective | Literature and clinical expertise | US$, cost year was not reported | Decision tree | None | Prophylactic indomethacin vs standard treatment | Cost per life expectancy, cost per QALY |
Cost per life expectancy: $7142 (prophylactic group), $7727 (standard treatment group) Cost per QALY: $9168 (prophylactic group), $8443 (standard treatment) |
Sensitivity analysis is not applied on all relevant parameters and no reason for this is given. The ICER presented is misleading. Cost per life expectancy and Cost per QALY of each alternative are estimated and then are wrongly subtracted |
|
Oswald and Mark 1996705 USA B(1) Fail |
Cost-effectiveness analysis, cost analysis High-risk women |
Not stated, it seems to be that of the third-party payer | Hospital databases | US$, 1989 | None | Previous history of preterm birth (PTB) | Education | Average cost per case of PTB avoided | Average cost per case of PTB avoided: $10,662 (control group); $28,903 (comparison group) | The PTB prevention programme evaluated is not defined thoroughly. Hence, the exclusion of its cost from the analysis is not sound. Sensitivity analysis is not carried out. No ICER is calculated. Conclusions are based on the cost analysis and net savings between groups |
|
Ross et al. 1994706 USA A(1) Fail |
Cost-effectiveness analysis High-risk women |
Not stated, it seems to be of the health-service provider | Own primary study and hospital databases | US$, 1992–1993 | None | None | Five interventions (not further defined) | Average cost per patient | Average cost per patient: $294 (prenatal care group) | The five interventions of the prenatal care group are treated as one and are compared versus no intervention. No individual information is given on the costs and benefits of the interventions. Sensitivity analysis is not carried out. No ICER is calculated. Conclusions are based on the cost analysis |
Only two studies were confirmed as cost studies, but their quality was dubious and they were both marked with a query. 123,707
Of the nine economic evaluations that remained in the final stage of the current review, five (including the review) were carried out in the USA. The remaining four studies were European; none were from the UK.
Bacterial vaginosis and antibiotic interventions
The only study to pass the required quality criteria was from Finland. 693 The authors used a decision tree to conduct an economic evaluation of screening and treatment of bacterial vaginosis (BV). The analysis was a cost-effectiveness analysis conducted from the perspective of the Finnish Health-Care System. The study population was asymptomatic women in early pregnancy at low risk for spontaneous preterm birth. Screening was carried out by detection using Gram-stain of the vaginal discharge. For treatment, two scenarios were assessed: scenario 1 was treatment with metronidazole 400 mg twice daily for 7 days and scenario 2 was treatment with clindamycin. The evaluation found that the probability of spontaneous preterm birth predicted by the model was 2.8% [95% confidence intervals (CI) 1.7–4.2] in the screening strategy and 2.7% in the no-screening strategy. Given the statistical uncertainty around point estimates, the authors’ conclusion was that there was no difference between the strategies. The authors concluded with implications for practice, which suggested that screening and treatment of BV in early pregnancy among low-risk women might not reduce costs compared to no screening.
Comment: Given that this paper passed all the quality criteria and was considered by the review team to be well carried out, there are no reasons to doubt these results from an economic perspective. The results provide no economic support for screening and treatment of BV in early pregnancy.
Muller et al. 57 also carried out an evaluation to estimate the economic impact of screening for, and treatment of, BV during early pregnancy. The results of the study suggested that $168 could be saved per delivery when women were screened in the early second trimester and, if the diagnosis was positive, treated for BV. The authors concluded that the current practice in Germany of not screening or treating positive cases should be re-evaluated.
Comment: This paper was marked with a query because it did not meet the required quality criteria. One reason for this was that the paper included a decision tree that was not used in the analysis. The authors present data on costs and effectiveness, but they do not combine them. Because of these concerns the conclusion from this study should be treated with caution.
From these two studies on BV, there is currently no clear economic evidence to support screening and treatment of BV in pregnancy to prevent spontaneous preterm birth.
Tocolytic interventions
The papers by Mozurkewich et al., Ambrose et al., Ferriols et al. , Korenbrot et al. , Lam et al. and Myers et al. 56,694,696–699 all focused on evaluating tocolytic interventions. The study by Mozurkewich et al. 56 combined the evaluation with some tests, which included the rapid fetal fibronectin test and measurement of cervical length. The study by Myers et al. 699 combined the evaluation with an amniocentesis test.
Test and tocolytic interventions
Mozurkewich et al. 56 compared the cost-effectiveness of nine strategies for the management of threatened preterm labour based on a decision tree analysis from the perspective of the third-party payer. The study population was patients diagnosed with threatened preterm labour (defined as regular uterine contractions) between 24 and 34 weeks, intact membranes, and without advanced cervical dilatation (≥ 3 cm). The paper examined a traditional fetal fibronectin test, rapid fetal fibronectin test and cervical length measurement; and treatment with corticosteroids or tocolytics. The main results of the study were that ‘Rapid fetal fibronectin testing’, ‘cervical length assessment’, ‘rapid fetal fibronectin plus cervical length’, and ‘treat none’ strategies were ‘dominated’ in the analysis of incremental cost-effectiveness, being both more costly and less effective than the next least expensive strategy which was the assessment of risk for spontaneous preterm birth with fetal fibronectin testing or cervical length assessment. They found that this assessment could result in significant cost savings relative to the current policy of treating all women who present with threatened premature onset of labour. The addition of corticosteroids to either rapid risk assessment strategy may further lower costs by reducing morbidity among infants born to mothers with false-negative results.
Comment: This paper was marked with a query because it did not meet the required quality. Although there was some useful information on costs, it was quite unclear how the authors actually calculated incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs). As a result we have to view the results with some caution although the shortcomings may be a result of poor reporting as opposed to poor analysis.
Myers et al. 699 carried out a study to determine the incremental cost-effectiveness of two strategies for preventing respiratory distress syndrome resulting from spontaneous preterm birth, from a hospital-based perspective using a Markov model. Women with preterm labour were followed over a 7-day period. Three options were compared: (1) treat all with tocolysis with betamimetic agonists and corticosteroids (TREATALL) without testing, (2) amniocentesis and testing for fetal lung maturity, with treatment based on test results (TESTALL), and (3) no treatment. Based on the model, the available literature and current costs, empirical tocolysis and corticosteroid administration before 34 weeks’ gestation was considered the most cost-effective strategy. Amniocentesis and fetal lung maturity testing appeared to be the most cost-effective strategy in this specific clinical setting within the limited time frame of 34–36 weeks’ gestation. No treatment was the most cost-effective option after 36 weeks.
Comment: Overall this was considered a relatively good paper but with some limitations, so it did not meet all of the predetermined quality criteria and was marked with a query. The reasons for this include the underestimation of costs, for example the outpatient costs for prenatal visits were omitted with the justification that these costs are small relative to hospital costs. Furthermore, the TESTALL strategy included a single or a series of tests for lung maturity, but these were not further defined or described. These items may be the result of a failure in reporting and so the results should be viewed with some limited caution but should not be rejected entirely. The use of a Markov model in this analysis was appropriate and will be discussed further.
Tocolytic interventions only
Four papers evaluated various tocolytic approaches only, without evaluating a test. 694,696–698 Only one study used a decision tree model. 696
Ferriols et al. 696 evaluated the relative cost-effectiveness of two tocolytic agents, ritodrine and atosiban. They used a decision tree model and adopted the perspective of the health service. The authors concluded that a tocolysis protocol using ritodrine as first-choice agent and atosiban as a rescue drug was the most efficient option based on available evidence.
Comment: Again, this paper was marked with a query. The strengths of the paper are that it presented clear definitions of the interventions with a well-defined model and clear information on the sources of costs and outcomes. However, the effectiveness data were not clearly defined and crucially an ICER was not presented. Instead the authors presented two effectiveness values for each agent and divided them (instead of subtracting them) to draw a comparison. This is inappropriate and consequently, the results from this study are incorrect.
Korenbrot et al. 697 compared the effectiveness and costs of care with beta-adrenergic drug treatment (terbutaline or isoxsuprine) with the expected costs in the absence of such treatment. The perspective was not clear but appeared to be that of the health-care provider. Preterm labour was defined as the occurrence of contractions leading to cervical change or premature rupture of the membranes (or both) between the 20th and 37th weeks of gestation. The authors found that: at 20–25 weeks treatment is cost-effective if the improved chances of survival of the baby are considered; at 26–33 weeks of gestation, treatment was clearly cost-effective; and after 33 weeks, expected costs with tocolytic treatment were not significantly different from costs without treatment, with or without consideration of costs per survivor. The authors conclude therefore that the beta-adrenergic tocolytic intervention should be used in the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth.
Comment: Despite being old, this paper was considered to be fairly comprehensive although it did not meet all the predetermined quality criteria and so it was marked with a query. Clinical outcomes and costs are presented for various gestational groups, but the final recommendation, in terms of appropriate gestation, was not clear.
Ambrose et al. 694 compared pregnancy and economic outcomes in women receiving inpatient with those in women receiving outpatient tocolysis with continuous subcutaneous terbutaline (SQT).
Although the perspective of the analysis was not reported it appeared to be that of the third-party payer. The study population was women hospitalised for stabilisation of an acute episode of preterm labour and thereafter prescribed continuous SQT therapy between 24.0 and 33.9 weeks’ gestation. The authors concluded that outpatient management resulted in improved pregnancy outcomes at a cost less than that of inpatient management and they suggested that outpatient management could be introduced to pregnant women.
Comment: Although this paper was marked with a query because it did not meet the predetermined quality criteria, overall it appeared to be a comprehensive evaluation. One disadvantage was that the year for the unit costs was not reported; some costs were also omitted, such as physician charges. More critically, no sensitivity analysis was performed and so we view these results with some limited caution.
In a similar analysis to that carried out by Ambrose et al. 694, Lam et al. 698 compared the clinical benefit and cost-effectiveness of using SQT and oral tocolytics following recurrent preterm labour. Again the perspective was not reported but it appeared to be that of the health-service provider. The results suggested that in this population, SQT infusion was both a clinically beneficial and a cost-effective treatment following recurrent preterm labour. Women treated with SQT infusion had greater pregnancy prolongation with better neonatal outcomes than women who were treated with oral tocolytics.
Comment: This study did not meet the predetermined quality criteria, principally because the cost year and the perspective were not reported. However, the study was otherwise considered to be generally quite well carried out and explained.
Other drug-related interventions, e.g. steroids, surfactant
The remaining paper evaluated the cost-effectiveness of corticosteroid interventions. 695 Egberts et al. 695 compared the costs and effectiveness of prenatal administration of corticosteroids and prenatal and postnatal administration of surfactant. The perspective of the analysis was not clear but appeared to be that of the health-care provider because all cost estimations were based on the number of hospitalisation days. The result showed that the estimated costs per extra survivor were the lowest for prenatal corticosteroid administration. The authors concluded that the combination of prenatal corticosteroid and postnatal prophylactic surfactant was the most cost-effective option because it produced the greater number of survivors and the lowest number of intensive and high dependency care days in hospital.
Comment: In general this cost-effectiveness study was found to have a number of omissions and so it failed to meet the predetermined quality criteria and therefore was marked with a query. In particular, no sensitivity analysis was presented; the ICERs, which could have been calculated, were not; and as a result the overall results were very unclear.
Review of economic evaluations
The published review by Rushing et al. 700 called itself a cost–benefit analysis but basically presented a summary of information from a number of studies that covered the entire perinatal period. It included summary information that applied to different points in the perinatal period including postnatal treatments. The criteria for selecting or maintaining papers in the review were not made explicit. Furthermore the papers discussed and their results were subjected to very little critical scrutiny. Given the lack of rigorous appraisal of the results it is consequently not possible either to have any faith in the results or to provide any support for the conclusions from this paper.
Discussion
In general the overall quality of the studies reviewed was poor and therefore a clear case for a test or treatment has not been supported by the results of this review of economic evaluations. All but one of the studies failed to meet all the predetermined quality criteria. However, where only one or two of the criteria were unfulfilled the paper was not excluded because it was considered that it might have some useful information and so it was marked with a query.
The main findings are summarised as follows:
-
There is no evidence to suggest that screening for and treatment of BV is a cost-effective strategy. 57,693
-
Evaluation of testing for the risk of preterm labour with either the fetal fibronectin test or cervical length measurement test found both to be cost-effective strategies. 56
-
The use of terbutaline was found to be a potentially cost-effective intervention and this result was supported by three studies although the quality of all three was defined as equivocal. 694,697,698
-
Prenatal steroids and postnatal surfactant were found to be cost-effective in reducing perinatal mortality. 695
-
The use of a Markov model by Myers et al. ,699 was noted. The authors used this model structure appropriately to model repeat doses of tocolytics in their 7-day model as women who give birth before 7 days leave the model and there is no risk of overestimating the costs of the treatment.
Methods for evaluating the relative cost-effectiveness of tests and interventions
Introduction
The objective of the economic evaluation in this study was to collate the data from the reviews on the accuracy of the tests with the data on the effectiveness of the interventions and to explore the relative cost-effectiveness of a range of different testing and treatment options. Recommendations made in previous chapters on the basis of clinical effectiveness of some of the interventions may not necessarily be reiterated on this chapter because of the introduction of cost to the analysis. All data identified from the reviews may not be included in the model. The data had to meet certain threshold criteria either in terms of the accuracy data for the tests or the effectiveness data for the interventions to be included. The final output of the modelling exercise is in terms of the dominating strategies (those achieving greater effectiveness at reduced cost) and the relative ICER for the better test and treatment options. For the symptomatic cases the results are in terms of cost per case of spontaneous preterm birth avoided and cost per perinatal death avoided as appropriate for the model. For the asymptomatic analysis the results are in terms of cost per symptom avoided and cost per perinatal death avoided as appropriate for the model. The perspective adopted for the economic evaluation was that of the NHS. Private out-of-pocket costs to women are not included in the analysis.
Methods
General
This section provides further detail about the economic modelling summarised in Chapter 3.
Model structure
The appropriate model structure for use in this study was a decision tree. The analysis for this study required nine different cases to be evaluated. This mirrored the different target populations and outcomes discussed in detail in Chapter 1, Delineation of the problem.
Symptomatic analysis:
-
Case 1 – women delivering within 24 h of being treated for symptoms of preterm labour
-
Case 2 – women delivering within 48 h of being treated for symptoms of preterm labour
-
Case 3 – women delivering within 7 days of being treated for symptoms of preterm labour
-
Case 4 – women before 34 weeks’ gestation who experience symptoms of preterm labour
-
Case 5 – women before 37 weeks’ gestation who experience symptoms of preterm labour
-
Case 6 – women experiencing symptoms of preterm labour who are at risk of perinatal mortality
Asymptomatic analysis:
-
Case 7 – Asymptomatic women before 34 weeks’ gestation who risk preterm labour
-
Case 8 – Asymptomatic women before 37 weeks’ gestation who risk preterm labour
-
Case 9 – Asymptomatic women who are at risk of perinatal mortality
The models were constructed in DATA Treeage. Space constraints do not allow all illustrations of the model structure to be presented. To illustrate the approach for each test/treatment pairing we present a subset of the model (Figure 283), used in the symptomatic analysis of women at 37 weeks’ gestation who experience symptoms of preterm labour. The subset of the model presents one test (fetal fibronectin) and one intervention (indomethacin).
FIGURE 283.
Decision tree.
In Figure 283 each branch to the right of the chance node (square symbol) indicates one way in which the test under consideration (fetal fibronectin) and treatment (indomethacin) can be brought together. All the ways in which test and treatment could in theory be used together are considered for completeness, although not all of these may have direct clinical relevance (see below for further explanation). The model considers for each test and treatment combination the number of cases of spontaneous preterm birth and the associated cost for:
-
No test and no intervention [‘No test/no treatment’]
-
Intervention, indomethacin, given to all with no preceding testing [‘No test/indomethacin_all’]
-
Test, fetal fibronectin, applied to all, but no subsequent intervention [‘Fetal fibronectin/no treatment’]
-
Test, fetal fibronectin, applied to all, followed by the intervention, indomethacin, being just given to those testing positive (having the characteristic indicated or a test value above a stated value) [‘Fetal fibronectin/indomethacin_positive’]
-
Test, fetal Fibronectin, applied to all followed by the intervention, indomethacin to all (regardless of test result) [‘Fetal fibronectin/indomethacin all’]
Branch 1, the no test, no intervention option, represents the comparison group for all the other branches 2–5, and indeed is the common comparator for all cases in the model for each test and treatment pairing considered. It indicates the number of cases of spontaneous preterm birth and the associated costs in ‘normal practice’, assuming that there is currently no systematic testing and treatment of those deemed at high risk on the basis of the test. This assumption is unlikely to be true in the NHS, which is why normal practice appears in inverted commas. Despite this, it still represents the most informative baseline against which to consider alternative strategies.
Branches 2 and 4 represent the chief clinically relevant alternative strategies for test and treatment pairings. Branch 2 considers the benefits and costs of treating all mothers, an important scenario to investigate if there is doubt about the accuracy of the available tests. Branch 4 considers the approach that attempts to focus the intervention on those indicated by the test to be at highest risk, and so avoid any adverse effects of the intervention in those thought unlikely to gain benefit, because their risk of developing spontaneous preterm birth is so low.
Branches 3 and 5 represent theoretical combinations, which have no direct clinical relevance but are nonetheless important for a complete understanding of the relationship between benefits, disbenefits and costs. Branch 3 provides an opportunity to scrutinise the costs and direct effects of testing independently of any effect of treatment. Branch 5 indicates the worst-case scenario with respect to cost, including both test and treatment costs applied to all. However, it also includes the highest level of benefit and disbenefit that might conceivably be achieved too, as all mothers receive the treatment under consideration.
In Figure 283, the right hand side of the diagram indicates the outcomes considered in measuring which of branches 1 to 5 in this and other modules is optimal. As already indicated, the main outcome for the symptomatic models (excluding the outcome of perinatal mortality) is cases of spontaneous preterm birth relative to cases without. In branches where a test result is obtained, the model considers separately the number of cases of spontaneous preterm birth occurring in those testing positive and those testing negative. Although this is shown as being a feature of the way the model works in branches 3 to 5, it is only strictly necessary in branch 4 because this is the only option where treatment is truly contingent on the test result. The box beneath the population of interest, symptomatic women, on the far left of the diagram, indicates the model parameters being used. Thus ‘c indomethacin = 1646.01’ indicates that the cost of indomethacin over the course of pregnancy is £1646.01, ‘mLR_Neg_Fibronectin=0.128’ indicates that the likelihood ratio of a negative fetal fibronectin test result estimate being used in this module of the model is 0.128 and ‘mLR_Pos_Fibronectin=7.791’ indicates that the positive likelihood ratio is 7.791. These parameters will differ depending on the module.
Test accuracy and effectiveness data
The data from the systematic reviews assessing the accuracy of all the tests reviewed as part of this project, reported in Chapter 4, were the source of the likelihood ratio model parameters. The actual values used were generally based on either pooled likelihood ratios for positive (LR+) and negative (LR–) tests or the largest highest quality individual study result, as described in the review methods section (Chapter 3). These values and their associated 95% CI are tabulated in Table 40 for asymptomatic women and Table 41 for symptomatic women. Similarly, the data from the systematic reviews of the effectiveness, reported in Chapter 5, were the source of model parameters concerning the effect of various treatments on the number of cases of spontaneous preterm birth and perinatal mortality. The values used, generally the summary relative risks (RR) from the meta-analyses, along with their 95% CI, are summarised in Table 42 for asymptomatic women and Table 43 for symptomatic women.
| Test | Detecting PTL during the first 34 weeks of gestation | Detecting PTL during the first 37 weeks of gestation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR+ | 95% CI | LR– | 95% CI | LR+ | 95% CI | LR– | 95% CI | |
| Previous history of either spontaneous or iatrogenic preterm birth | 4.624 | (3.278–6.251) | 0.677 | (0.56–0.817) | 2.259 | (1.86–2.74) | 0.715 | (0.635–0.805) |
| Digital examination | 9.247 | (3.914–21.847) | 0.457 | (0.194–1.08) | 1.15457 | (0.86–1.53) | 0.89 | (0.68 – 1.16) |
| Cervicovaginal interleukin-6 (serial testing) | – | – | – | – | 3.342 | (1.96–5.70) | 0.588 | (0.417–0.829) |
| Cervicovaginal interleukin-6 (single testing)a | – | – | – | – | 0.564 | (0.0799–3.973) | 1.0839 | (0.873–1.346) |
| Amniotic fluid interleukin-6 | 2.65 | (1.37–5.14) | 0.91 | (0.84–0.98) | 1.913 | (0.997–3.672) | 0.95 | (0.9–1.002) |
| Cervical mucus interleukin-8 (360 ng/ml) | 2.228 | (1.455–3.412) | 0.694 | (0.495–0.973) | 1.377 | (1.043–1.818) | 0.907 | (0.818–1.005) |
| Fetal fibronectin | 10.181 | (6.562–15.798) | 0.689 | (0.56–0.847) | 26.375 | (1.726–402.986) | 0.939 | (0.828–1.066) |
| Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1) | – | – | – | – | 4.167 | (2.436–7.127) | 0.208 | (0.084–0.514) |
| CV-Prolactin | 19 | (1.76–205.15) | 0.51 | (0.13–2.06) | 3.15 | (1.62–6.12) | 0.23 | (0.04–1.37) |
| Serum α-fetoprotein (threshold 2.0 MoM) | – | – | – | – | 1.63 | (0.812–3.273) | 0.957 | (0.886–1.034) |
| Serum α-fetoprotein (threshold 2.5 MoM) | 4.99 | (3.97–6.28) | 0.95 | (0.94–0.97) | 2.63 | (1.35–5.096) | 0.987 | (0.974–1.0) |
| Maternal serum β-human chorionic gonadotrophin | – | – | – | – | 2.77 | (2.07–3.69) | 0.984 | (0.98–0.99) |
| Salivary estriol (threshold 2.1 ng/ml – single) | – | – | – | – | 2.55 | (1.73–3.77) | 0.56 | (0.35–0.89) |
| Salivary estriol (threshold 2.1 ng/ml – repeat) | – | – | – | – | 5.46 | (3.18–9.40) | 0.61 | (0.43–0.88) |
| Serum estriol (threshold ≤ 0.5 MoM) a | – | – | – | – | 0.764 | (0.581–1.004) | 1.018 | (1.002–1.035) |
| Serum estriol (threshold ≤ 0.75 MoM) | – | – | – | – | 1.188 | (0.577–2.444) | 0.98 | (0.893–1.075) |
| Serum corticotrophin-releasing hormone | 3.36 | (2.298–4.918) | 0.348 | (0.133–0.914) | 1.428 | (0.863–2.362) | 0.891 | (0.735–1.082) |
| Relaxin (serum) | 1.598 | (1.241–2.059) | 0.839 | (0.74–0.952) | 1.207 | (0.725–2.1) | 0.744 | (0.285–1.947) |
| C-reactive protein | – | – | – | – | 2.061 | (1.29–3.293) | 0.767 | (0.646–0.91) |
| Amniotic fluid C-reactive protein | 2.63 | (1.85–3.75) | 0.29 | (0.08–0.99) | 4.37 | (3.03–6.29) | 0.09 | (0.01–0.60) |
| Detection of bacterial vaginosis Nugent’s (single) a | – | – | – | – | 0.804 | (0.376–1.716) | 1.04 | (0.921–1.174) |
| Detection of bacterial vaginosis Nugent’s (serial) | – | – | – | – | 1.924 | (0.625–5.918) | 0.933 | (0.794–1.095) |
| Detection of bacterial vaginosis Amsel’s (single) | – | – | – | – | 1.617 | (0.443–5.907) | 0.901 | (0.632–1.287) |
| Periodontal evaluation | – | – | – | – | 2.262 | (1.349–3.792) | 0.791 | (0.655–0.956) |
| Midstream urine culture | – | – | – | – | 2.63 | (1.54–4.50) | 0.96 | (0.92–0.99) |
| Uterine activity monitoring | 2.413 | (0.758–7.678) | 0.947 | (0.863–1.04) | 4.9 | (2.988–8.035) | 0.152 | (0.041–0.558) |
| Mammary stimulation test | 4.62 | (2.953–7.252) | 0.267 | (0.0786–0.908) | 3.3 | (1.537–7.084) | 0.489 | (0.166–1.433) |
| Measurement of cervical length – 15 mm (14–20 weeks’ gestation) | 142.856 | (3.575–5709) | 0.888 | (0.816–0.966) | – | – | – | – |
| Measurement of cervical length – 20 mm (14–20 weeks’ gestation) | 35.356 | (4.315–289.676) | 0.901 | (0.829–0.978) | – | – | – | – |
| Measurement of cervical length – 25 mm (14–20 weeks’ gestation) | 13.379 | (6.896–25.957 | 0.798 | (0.711–0.895) | – | – | – | – |
| Measurement of cervical length – 30 mm (14–20 weeks’ gestation) | 2.48 | (1.186–5.189) | 0.81 | (0.679–0.966) | – | – | – | – |
| Measurement of cervical length – 20 mm (20–24 weeks’ gestation) | 7.642 | (5.213–11.203) | 0.794 | (0.721–0.873) | – | – | – | – |
| Measurement of cervical length – 22 mm (20–24 weeks’ gestation) | 4.513 | (1.155–17.637) | 0.743 | (0.513–1.077) | – | – | – | – |
| Measurement of cervical length – 25 mm (20–24 weeks’ gestation) | 4.682 | (3.638–6.027) | 0.681 | (0.599–0.775) | – | – | – | – |
| Measurement of cervical length – 30 mm (20–24 weeks’ gestation) | 2.277 | (1.913–2.711) | 0.603 | (0.499–0.73) | – | – | – | – |
| Measurement of cervical length – 32.5 mm (20–24 weeks’ gestation) | – | – | – | – | 3.99 | (2.84–5.62) | 0.33 | (0.17–0.66) |
| Presence of funnelling (16–20 weeks’ gestation) | 5.026 | (2.534–9.968) | 0.744 | (0.559–0.992) | – | – | – | – |
| Presence of funnelling (20–24 weeks’ gestation) | 4.63 | (3.306–6.482) | 0.789 | (0.713–0.874) | – | – | – | – |
| Test | 24 ha | Delivery within 48 hb | Delivery within 7 daysb | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR+ | 95% CI | LR– | 95% CI | LR+ | 95% CI | LR– | 95% CI | ||
| Digital examination | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Serum interleukin-6 | – | 2.05 | (0.852–4.93) | 0.661 | (0.324–1.351) | 3.34 | (1.485–7.526) | 0.442 | (0.297–0.659) |
| Cervicovaginal interleukin-6 | – | 1.902 | (1.083–3.342) | 0.231 | (0.017–3.173) | 4.009 | (2.018–7.964) | 0.658 | (0.51–0.849) |
| Amniotic fluid interleukin-6 | – | 3.758 | (2.135–6.614) | 0.11 | (0.0167–0.726) | 7.013 | (2.75–17.987) | 0.171 | (0.06–0.488) |
| Interleukin-8 (15 ng/ml amniotic fluid) | – | 36 | (2.296–564.5) | 0.103 | (0.008–1.424) | 28.5 | (1.779–456.57) | 0.257 | (0.064–1.028) |
| Interleukin-8 (7.7 ng/ml cervical swab) | – | – | – | – | – | 2.34 | (1.42–3.84) | 0.52 | (0.32–0.84) |
| β-human chorionic gonadotrophin | – | – | – | – | – | 6.07 | (3.07–11.99) | 0.04 | (0.01–0.16) |
| Fetal fibronectin | – | – | – | – | – | 3.516 | (2.364–5.227) | 0.237 | (0.067–0.832) |
| Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1) | – | 1.73 | (0.92–3.252) | 0.593 | (0.242–1.451) | 2.83 | (1.571–5.092) | 0.371 | (0.133–1.038) |
| CV-Prolactin | – | – | – | – | – | 1.48 | (0.81–2.7) | 0.61 | (0.23–1.62) |
| Serum corticotrophin-releasing hormone | – | – | – | – | – | 3.12 | (1.42–6.84) | 0.63 | (0.38–1.05) |
| C-reactive protein (12.5 ng/ml) | – | – | – | – | – | 34.364 | (4.858–243.09) | 0.186 | (0.053–0.653) |
| Absence of fetal breathing movements | – | 16.077 | (5.216–49.55) | 0.162 | (0.045–0.581) | 4 | (0.73–21.84) | 0.67 | (0.32–1.38) |
| Measurement of cervical length (15 mm) | – | 6.43 | (5.17–8) | 0.027 | (0.0017–0.42) | 8.61 | (6.65–11.14) | 0.026 | (0.004–0.182) |
| Detecting PTL during the first 34 weeks of gestation | Detecting PTL during the first 37 weeks of gestation | ||||||||
| LR+ | 95% CI | LR– | 95% CI | LR+ | LR– | LR– | 95% CI | ||
| Digital examination | – | – | – | – | 2.38 | 0.47 | 0.47 | (0.29–0.79) | |
| Serum interleukin-6 | 1.437 | (0.856–2.412) | 0.585 | (0.216–1.582) | 1.125 | 0.917 | 0.917 | (0.537–1.564) | |
| Cervicovaginal interleukin-6 | 4.923 | (1.801–13.46) | 0.738 | (0.629–0.867) | 1.833 | 0.688 | 0.688 | (0.396–1.195) | |
| Amniotic fluid interleukin -6 | 7.44 | (2.01–27.52) | 0.14 | (0.056–0.36) | 28.62 | 0.659 | 0.659 | (0.54–0.81) | |
| Interleukin-8 (3.739 ng/ml cervical swab) | – | – | – | – | 1.4 | (0.83–2.35) | 0.67 | (0.3–1.5) | |
| β-human chorionic gonadotrophin | – | – | – | – | 2.11 | (1.61–2.77) | 0.45 | (0.31–0.66) | |
| Fetal fibronectin | (2.729–5.803) | 0.332 | 0.332 | (0.19–0.582) | 7.971 | (4.875–13.03) | 0.128 | (0.51–0.324) | |
| Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1) | (1.438–11.99) | 0.305 | 0.305 | (0.027–3.381) | 3.868 | (1.539–9.724) | 0.325 | (0.149–0.709) | |
| CV-Prolactin | (1.809–11.97) | 0.489 | 0.489 | (0.207–1.156) | 2.5 | (0.88–7.1) | 0.79 | (0.55–1.11) | |
| Salivary estriol (threshold 2.1 ng/ml – single) | – | – | – | – | 2.31 | (1.64–3.24) | 0.398 | (0.199–0.794) | |
| Serum corticotrophin-releasing hormone | – | – | – | – | 4.06 | (1.68–9.81) | 0.68 | (0.51–0.91) | |
| Relaxin (serum) | (0.262–8.31) | 0.861 | 0.861 | (0.378–1.96) | 0.8# | (0.193–3.31) | 1.07# | (0.72–1.57) | |
| C-reactive protein (12.5 ng/ml) | – | – | – | – | 2.316 | (1.426–3.762) | 0.468 | (0.251–0.874) | |
| C-reactive protein (15 ng/ml) | (1.34–34) | 0.66 | 0.66 | (0.38–1.14) | – | – | – | – | |
| Matrix metalloprotease-9 | – | – | – | – | 7.33 | (1.07–50.27) | 0.37 | (0.14–0.94) | |
| Detection of bacterial vaginosis Nugent’s (single) c | – | – | – | – | 0.995 | (0.359–2.756) | 1.0005 | (0.884–1.134) | |
| Rheobase (2.8 mA) | – | – | – | – | 2.29 | (1.5–3.52) | 0.6 | (0.41–0.88) | |
| Rheobase (3.4 mA) | – | – | – | – | 2.36 | (1.74–3.20) | 0.36 | (0.19–0.66) | |
| Measurement of cervical length (18 mm) | – | – | – | – | 3.36 | (1.73–6.54) | 0.35 | (0.17–0.7) | |
| Measurement of cervical length (30 mm) | (1.363–2.589) | 0.3 | 0.3 | (0.0834–1.072) | 2.29 | (1.68–3.12) | 0.29 | (0.15–0.58) | |
| Presence of funnelling | (1.90–11.66) | 0.61 | 0.61 | (0.34–1.1) | 2.53 | (1.02–6.25) | 0.86 | (0.71–1.03) | |
| Group | Test | PTL before 34 weeks’ gestation | PTL before 37 weeks’ gestation | Perinatal mortality | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RRa | 95% CI | RRa | 95% CI | RRa | 95% CI | ||
| Group 1b | Home uterine activity monitoring | – | – | 0.59 | (0.37–0.95) | – | – |
| Asymptomatic bacteriuria | – | – | 0.14 | (0.04–0.52) | – | – | |
| Periodontal therapy | – | – | 0.19 | (0.04–0.85) | – | – | |
| Cervical cerclage | 0.75 | (0.58–0.98) | – | – | – | – | |
| Progestational agents | 0.15 | (0.04–0.64) | 0.6 | (0.49–0.73) | – | – | |
| Fish oil | 0.35 | (0.13–0.92) | 0.64 | (0.41–0.99) | – | – | |
| Nutritional advice | – | – | 0.46 | (0.21–0.98) | – | – | |
| Energy/protein supplementation | – | – | – | – | 0.55 | (0.31–0.97) | |
| Smoking cessation | – | – | 0.84 | (0.72–0.98) | – | – | |
| Group 2c | Home visits | – | – | 0.98 | (0.88–1.10) | – | – |
| Bed rest (home or hospital) | – | – | 0.92 | (0.62–1.37) | – | – | |
| Antibiotics (intra amniotic infections) | – | – | – | – | 0.53 | (0.13–2.18) | |
| Cervical cerclage | – | – | 0.85 | (0.72–1.01) | 0.66 | (0.66–1.37) | |
| Progestational agents | – | – | – | – | 0.55 | (0.29–1.06) | |
| Vitamin C | – | – | – | – | 0.51 | (0.05–5.54) | |
| Zinc | – | – | 0.77 | (0.49–1.20) | – | – | |
| Nutritional advice | – | – | – | – | 0.37 | (0.07–1.90) | |
| Energy/protein supplementation | – | – | 0.83 | (0.65–1.06) | – | – | |
| Energy/protein restriction | – | – | 0.5 | (0.09–2.66) | – | – | |
| Group | Test | Delivery within 24 hoursa | Delivery within 48 hoursa | Delivery within 7 daysa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RRb | 95% CI | RRb | 95% CI | RRb | 95% CI | ||
| Group 1c | Indomethacin | – | – | 0.19 | (0.07–0.51) | 0.44 | (0.26–0.74) |
| Terbutaline (intravenously) | – | – | 0.45 | (0.25–0.81) | 0.59 | (0.40–0.87) | |
| Group 2d | Nitric oxide donors | – | – | 0.56 | (0.27–1.51) | – | – |
| Magnesium Sulphate | – | – | 0.57 | (0.28–1.15) | – | – | |
| Terbutaline (orally) | 0.67 | (0.12–3.62) | 0.78 | (0.30–2.01) | 0.67 | (0.40–1.13) | |
| Antibiotics (intact membranes) | – | – | – | – | 0.98 | (0.87–1.10) | |
| Group 3e | Calcium channel blockers | – | – | 0.44d | (0.16–(1.26) | 0.46c | (0.30–0.70) |
| Atosiban | – | – | 0.44c | (0.22–0.88) | 0.54c | (0.33–0.86) | |
| PTL before 34 weeks’ gestation | PTL before 37 weeks’ gestation | Perinatal mortality | |||||
| Effectiveness | RR | 95% CI | RR | 95% CI | RR | 95% CI | |
| Group 1c | Indomethacin | – | – | 0.21 | (0.07–0.62) | – | – |
| Terbutaline (intravenously) | – | – | 0.64 | (0.45–0.91) | – | – | |
| Group 2d | Indomethacin | – | – | – | – | 0.80 | (0.25–2.58) |
| Terbutaline pump maintenance | 0.97 | (0.51–1.84) | – | – | – | – | |
| Magnesium sulphate | – | – | 0.92 | (0.41–2.07) | – | – | |
| Antibiotics (intact membranes) | – | – | 0.99 | (0.92–1.05) | – | – | |
| Hydration | 0.72 | (0.20–2.56) | – | – | – | – | |
| Vitamin K (for neuroprotection) | – | – | – | – | 0.79 | (0.46–1.35) | |
| Prophylactic corticosteroids | – | – | – | – | 0.63 | (0.51 –0.79) | |
| Group 3e | Calcium channel blockers | 0.74d | (0.38–1.43) | 0.98d | (0.65–1.50) | – | – |
| Atosiban | – | – | 0.57c | (0.38–0.88) | – | – | |
| Feneterolf | – | – | – | – | 0.10 | (0–1.89) | |
There are two main groups of treatments differentiated because they are dealt with slightly differently by the models (see below). In group 1, the 95% CI for the RR do not include values > 1.0, indicating that a true value of the RR compatible with increased numbers of spontaneous preterm birth or perinatal mortality cases (i.e. worsened outcome) is unlikely. These are typically the only data for interventions that will be used in the probabilistic sensitivity analysis (PSA) – described in more detail in the next section. Conversely in group 2, the 95% CI for RR do include values > 1.0, i.e. a possible worsened outcome. Table 41 also gives values for the RR (group 3) obtained from indirect comparisons, where the intervention was compared with another intervention and not with placebo. In those cases the RR values were computed by combining the relevant values to obtain the intervention versus placebo RR. When relevant, data from group 3 are also included in the PSA. Typically, data on interventions from groups 1, 2 and 3 are all used in the deterministic analysis.
Test accuracy cost data
The cost estimates for each test are described in more detail (Table 44). All costs are presented in UK £ at 2005 prices. Cost data for the tests came from two main sources, the literature and the Birmingham Women’s Hospital, Birmingham, UK. The literature estimates of cost for a particular test were primarily identified from studies known to the health economics and modelling team from their work on similar topics in the past.
| Test | Description/nature of test | Duration/when is the test performed | Unit cost | Source | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previous history of either spontaneous or iatrogenic (including reason) preterm birtha |
History The midwife performs the test |
10 minutes Pre-pregnancy (at the women’s home or GP practice) or at antenatal booking (early in pregnancy) |
None | Curtis and Netten692 | This test is part of the process followed when a woman is admitted to the hospital with symptoms. We set the cost equal to zero because this test precedes all other tests below |
| Abdominal palpationb |
Examination The midwife performs the test. |
37.5 minutes (35–40 minutes) | £17.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | We used the unit cost per hour of client contact by a practice nurse (£28/hour) as a proxy for midwife |
| CDEa,b |
Examination The doctor performs the test Cervical mucus sample is taken during speculum examination with a normal swab Lab technician is required to do the analysis using ELISA reagent |
10 minutes by the doctor 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 26–30 weeks’ gestation and at 28 weeks (asymptomatic women) 24–36 weeks’ gestation (symptomatic women) |
£11.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Estimate not available for the cost of the test. We used a proxy (£7.50) based on serum CRP for the lab technician’s time and lab analysis; then added the cost of the doctor’s time (unit cost per hour on duty by a specialist registrar doctor, £23/hour) |
| Serum IL-6b |
Venous blood test The phlebotomist performs the test Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
5 minutes by the phlebotomist 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 24–36 weeks’ gestation |
£9.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Estimate not available for the cost of the test. We used a proxy (£7.50) based on Serum CRP for the lab technician’s time and lab analysis; then added the cost of the health-care assistant’s time (unit cost per hour spent with a patient, £20/hour) as a proxy for the phlebotomist |
| Cervicovaginal IL-6 (single testing)a,b |
Cervical vaginal secretion/mucus specimen The doctor performs the test Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
10 minutes by the doctor 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 24–36 weeks’ gestation (symptomatic women) 10–20 weeks’ gestation (asymptomatic women) |
£11.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Proxy based on cost of CDE |
| Cervicovaginal IL-6 (serial testing) a |
Cervical vaginal secretion/mucus specimen The doctor performs the test Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
10 minutes by the doctor 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 10–20 weeks’ gestation |
£57.50 | Curtis and Netten692 |
Proxy based on cost of CDE No information was available on how many times the test was performed, so it was assumed that it was done five times |
| Amniotic fluid IL-6 a,b |
Amniocentesis The doctor performs the test Ultrasound scan guidance is required to avoid injury of the fetus Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
30 minutes by the doctor 24–36 weeks’ gestation (symptomatic women) 14–20 weeks’ gestation (asymptomatic women) |
£216.70 | Wald et al.708 | The cost of amniocentesis was obtained by Wald et al. and then inflated to 2004/05 values using Curtis and Netten’s inflation indices |
| Amniotic fluid IL-8 a,b |
Amniocentesis The doctor performs the test Ultrasound scan guidance is required to avoid injury of the fetus Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
30 minutes by the doctor 24–36 weeks’ gestation (symptomatic women) 14–20 weeks’ gestation (asymptomatic women) |
£216.70 | Wald et al.708 | The cost of amniocentesis was obtained by Wald et al. and then inflated to 2004/05 values using Curtis and Netten’s inflation indices |
| Cervical IL-8 a |
Cervical vaginal secretion/mucus specimen The doctor performs the test. Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
10 minutes by the doctor 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 20–28 weeks’ gestation (asymptomatic women) |
£11.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Proxy based on cost of CDE |
| Serum β-human chorionic gonadotrophina |
Venous blood test The phlebotomist performs the test Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
5 minutes by the phlebotomist, 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 10 – 20 weeks’ gestation (asymptomatic women) |
£9.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Proxy based on cost of serum IL-6 |
| Cervicovaginal β-human chorionic gonadotrophinb |
Cervical vaginal secretion/mucus specimen The doctor performs the test Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
10 minutes by the doctor 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 24–36 weeks’ gestation (symptomatic women) |
£11.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Proxy based on cost of CDE |
| Cervicovaginal fetal fibronectina,b |
Cervical vaginal secretion/mucus specimen The doctor performs the test Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
10 minutes by the doctor 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 24–36 weeks’ gestation (symptomatic women) 16–24 weeks’ gestation (asymptomatic women) |
£11.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Proxy based on cost of CDE |
| Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1)a,b |
Cervical vaginal secretion/mucus specimen The doctor performs the test Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
10 minutes by the doctor 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 24–36 weeks’ gestation (symptomatic women) (16–24 weeks’ gestation (asymptomatic women) |
£11.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Proxy based on cost of CDE |
| CV-Prolactina,b |
Cervical vaginal secretion/mucus specimen The doctor performs the test Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
10 minutes by the doctor 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 24–32 weeks’ gestation (both asymptomatic and symptomatic women) |
£11.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Proxy based on cost of CDE |
| Serum α-fetoproteina |
Venous blood test The phlebotomist performs the test Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
5 minutes by the phlebotomist 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 12–20 weeks’ gestation |
£9.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Proxy based on cost of serum IL-6 |
| Salivary estriola,b |
Salivary test The midwife performs the test, by collecting saliva specimen Lab technician is required to do the analysis using the appropriate commercial assay (SalEst; Biex Inc, Dublin, CA) |
10 minutes by the midwife 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 24–36 weeks’ gestation (symptomatic women) 14–20 weeks’ gestation (asymptomatic women) |
£12.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Estimate not available for the cost of the test. We used a proxy (£7.50) based on serum CRP for the lab technician’s time and lab analysis; then added the cost of the practice nurse’s time (unit cost per hour of client contact, £28/hour) as a proxy for midwife |
| Serum estriola |
Venous blood test The phlebotomist performs the test Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
5 minutes by the phlebotomist 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 14–20 weeks’ gestation |
£9.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Proxy based on cost of serum IL-6 |
| Serum CRHa,b |
Venous blood test The phlebotomist performs the test Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
5 minutes by the phlebotomist 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 24–36 weeks’ gestation (symptomatic women) 12–20 weeks’ gestation (asymptomatic women) |
£9.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Proxy based on cost of serum IL-6 |
| Relaxin (serum)a,b |
Venous blood test The phlebotomist performs the test Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
5 minutes by the phlebotomist 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 24–34 weeks’ gestation (symptomatic women) |
£9.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Proxy based on cost of serum IL-6 |
| Serum CRPa,b |
Venous blood test The phlebotomist performs the test Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA (or other necessary materials to measure serum CRP level) |
5 minutes by the phlebotomist 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 24–36 weeks’ gestation (symptomatic women) 14–20 weeks’ gestation (asymptomatic women) |
£9.50 |
BWH Curtis and Netten692 |
Cost of serum CRP (£7.50, inclusive of reagents, equipment and technician time) was obtained by BWH Cost of the health-care assistant’s time (unit cost per hour spent with a patient, £20/hour) was used as a proxy for the phlebotomist |
| Amniotic fluid CRPa,b |
Amniocentesis The doctor performs the test Ultrasound scan guidance is required to avoid injury of the fetus Lab technician is required to do an analysis using ELISA |
30 minutes by the doctor 24–36 weeks’ gestation (symptomatic women) 14–20 weeks’ gestation (asymptomatic women) |
£216.70 | Wald et al.708 | The cost of amniocentesis was obtained by Wald et al. and then inflated to 2004/05 values by Curtis and Netten’s inflation indices |
|
MMP-9b (urine) |
Urine test Assumed self-collection by woman Lab technician is required to do the analysis using the enzyme immuno-assay for MMP-9 test kit (MediCorp, Montreal, Canada) |
1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 24–36 weeks’ gestation |
£7.50 | BWH | Estimate not available for the cost of the test. We used a proxy (£7.50) based on serum CRP for the lab technician’s time and lab analysis |
|
MMP-9b (plasma) |
Venous blood test. The phlebotomist performs the test Lab technician is required to do the analysis using the enzyme immuno-assay for MMP-9 test kit (MediCorp, Montreal, Canada) |
5 minutes by the phlebotomist 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 24–36 weeks’ gestation |
£9.50 | Curtis and Netten692 | Proxy based on cost of serum IL-6 |
| Detection of bacterial vaginosisa |
Cervical swab collection The doctor performs the test Lab technician is required to do the analysis using the necessary equipment |
10 minutes by the doctor 1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) 8–24 weeks’ gestation (asymptomatic women) |
£15.35 |
BWH Curtis and Netten692 |
We used the unit cost per hour on duty by a specialist registrar doctor (£23/hour). Cost of Detection of bacterial vaginosis (£11.52 – includes wet prep., Gram stain culture plates and technician time) was obtained by BWH |
| Periodontal screeninga | Dental hygienists or dentists perform the periodontal assessment |
30–60 minutes 8–20 weeks’ gestation (asymptomatic women) |
£15.50 | Dental & Implant Centre, UoB | We used the NHS charge of £15.50 for a ‘general examination and cleaning’ (obtained from the ‘Dental & Implant Centre’ of the University of Birmingham). |
| Midstream urine culturea |
Urine test Assumed self-collection by woman Lab technician is required to do the standard microbiology culture |
1 hour approx. by the lab technician (part of a batch) Before 16 weeks’ gestation |
£11.52 | BWH |
Cost of midstream urine culture (£4.02) was obtained by BWH We used a proxy (£7.50) based on serum C-reactive protein for the lab technician’s time and lab analysis |
| Uterine activity monitoringa |
Uterine monitoring system Women are placed in the Term Guard (Tokos Medical Corp., Santa Ana, CA) uterine monitoring system for at least one hour per day It was assumed that this is done at home and for 12 weeks in total |
1 hour per day 24–36 weeks’ gestation |
£250 |
Kosasa et al. 707 Curtis and Netten692 |
Estimate not available for the cost of the test. We have contacted Tokos Medical Corp but received no answer. Available from the literature were the ‘Ambulatory monitoring costs $60/per day’ in 1988 values. We used the 1990 Dollar to Pound conversion rate (0.62) because that was the closest to 1988 available (http://www.x-rates.com/). We used the inflation index from Curtis and Netten (234.2) to inflate the cost to 2004/05 values. This resulted in a cost of £87/day. The cost of the test was £7308 for the 12 weeks of the use of the machine. This value was considered not pragmatic. We used £250 as the cost of the test |
| Rheobaseb | The midwife performs the test using the rheobase measuring equipment |
30 minutes by the midwife 20–36 weeks’ gestation (symptomatic women) |
£20.86 |
Curtis and Netten692 Bricker et al. 709 |
Estimate of the cost of the test was not available. We used a proxy based on an inflated anomaly scan (£15.46) for the cost of the rheobase measuring equipment |
| Mammary stimulation testa |
The midwife performs the test Cardiotocogram (CTG) machine is required to monitor uterine contractions |
10 minutes by the midwife 30 minutes monitor for uterine contractions in the CTG |
£26.66 |
Curtis and Netten692 Roberts et al. 690 |
Estimate of the cost of the test was not available. We used the unit cost per hour of home visit by a practice nurse (£35/hour) as a proxy for midwife and a proxy based on an inflated anomaly scan (£15.46) for the CTG machine |
| Absence of fetal breathing movementsb |
Ultrasound scan The midwife performs the test A standard high-resolution machine is used. An image recorder may be required to record the observation |
45 minutes of ultrasound scanning 24–36 weeks’ gestation for symptomatic women 14–20 weeks’ gestation for asymptomatic women |
£69.47 |
Curtis and Netten692 Bricker et al. 709 |
Estimate of the cost of the test was not available. We used a proxy based on an inflated detailed scan (£51.47) |
| Measurement of cervical lengtha,b |
Ultrasound scan The midwife performs the test A standard high-resolution machine is used. An image recorder may be required to record the observation |
30 minutes of ultrasound scanning 14–24 weeks’ gestation for symptomatic women 24–36 weeks’ gestation for asymptomatic women |
£69.47 |
Curtis and Netten692 Bricker et al. 709 |
Estimate of the cost of the test was not available. We used a proxy based on an inflated detailed scan (£51.47) |
A cost estimate for the amniotic fluid interleukin-6 (IL-6), amniotic fluid interleukin-8 (IL-8) and amniotic fluid C-reactive protein (CRP) was obtained by Wald et al. 708 This was inflated to 2005 prices using the hospital and community health services (HCHS) pay and price inflation index.
Cost estimates for the absence of fetal breathing movements and measurement of cervical length were obtained by Bricker et al. 709 We used a proxy cost based on a detailed scan which was again inflated to 2005 prices (£69.47).
For the cost of abdominal palpation we used the unit cost per hour of client contact by a practice nurse (£28/hour) as a proxy for midwife. 692
A cost estimate for the serum CRP was obtained by the Birmingham Women’s Hospital (BWH) (£7.50 inclusive of reagents, equipment and technician’s time). The cost of the health-care assistant’s time (unit cost per hour spent with a patient, £20/hour),692 was used as a proxy for the cost of the time of the phlebotomist who performs the test. The estimated total cost was £9.50 and this was used as a proxy for all venous blood tests performed by a phlebotomist which then requires further analysis in a laboratory (e.g. serum IL-6, serum β-human chorioic gonadotrophin, serum α-fetoprotein, serum estriol, serum corticotrophin-releasing hormone, serum relaxin and plasma MMP-9 tests).
A cost estimate for ‘Cervical Digital Examination’ was not available in the literature. We used the cost of CRP (£7.50) for the laboratory technician’s time and the laboratory analysis; then added the cost of the doctor’s time (unit cost per hour on duty by a specialist registrar doctor, £23/hour). The estimated total cost was £11.50 and this was used as a proxy for all cervical vaginal secretion/mucus specimen tests performed by the doctor that then required further analysis in the laboratory. Such tests included: cervicovaginal IL-6, cervical IL-8, cervicovaginal β-human chorionic gonadotrophin, cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin, phIGFBP-1 and CV-Prolactin.
The cost of ‘previous history of either spontaneous preterm birth’ was assumed to be zero because this test is part of a process followed for all women during their routine antenatal care, and as a test, this precedes all other tests in the analysis.
A cost estimate for salivary estriol was not available in the literature. We used the cost of CRP (£7.50) as a proxy for the technician’s time and the laboratory analysis for this test; then added the cost of a practice nurse’s time (unit cost per hour of client contact, £28/hour) as a proxy for midwife time. The estimated total cost was £12.50.
No cost estimates for the urine tests (e.g. MMP-9, midstream urine culture) were available in the literature for the urine tests. We assumed self-collection for both. The cost of CRP was again used as a proxy for the cost of the MMP-9 test. The cost of midstream urine culture was obtained by BWH (£4.02) without the laboratory technician’s time and laboratory analysis. We added the cost of CRP (£7.50) as a proxy for the latter. This resulted in an estimated total cost of £11.52 for midstream urine culture.
The cost of detection of bacterial vaginosis was obtained by BWH (£11.52 – including wet preparation, Gram-stained culture plates and technician time). We added the unit cost per hour on duty by a specialist registrar doctor (£23/hour) to include the time of the doctor who performs the test. The estimated total cost was £15.35.
The cost of periodontal screening was obtained by the ‘Dental & Implant Centre’ of the University of Birmingham. We used the NHS charge of £15.50 for a ‘General examination and cleaning’.
No cost data was available for uterine activity monitoring. An attempt was made to contact the manufacturer (Tokos Medical Corp) without success. An estimate for ‘Ambulatory monitoring costs’ was available in the literature at $60/day in 1988 values. 707 The cost of the device for the 12 weeks of its use translated to £7308 in UK sterling in 2005 values. Concerned about the uncertainty associated with this cost, we actually used £250 as the cost of the test.
A cost estimate for Rheobase was not available in the literature. We used the cost of an anomaly scan (£15.46) from the literature as a proxy for the cost of the rheobase measuring equipment. 709
A cost estimate for the mammary stimulation test was not available. We used the unit cost per hour of a home visit by a practice nurse (£35/hour) as a proxy for a midwife, to estimate the midwife’s time; and we used the cost of an anomaly scan (£15.46)709 as a proxy for the cost of the cardiotocography machine. The estimated total cost for the mammary stimulation test was £26.66.
Intervention cost data
The systematic reviews of intervention effectiveness indicated the dose and duration of treatment used in the included RCTs. Where no dose or duration was available, those used in the British National Formulary (BNF) were used (after consensus with C.R.D., K.S.K. and H.H.). These are summarised in Table 45. Where a dose range was presented, the costs of the upper and lower limits of the dose were used. The treatment dose (if appropriate) and duration were applied to the treatment unit costs to give the total cost. For drugs the unit costs were taken from the BNF (Vol. 51, March 2006). The unit costs for the vitamin or herbal supplements such as fish oils were obtained from the Holland and Barrett website (a commercial health food shop) (http://www.hollandandbarrett.com/).
| Intervention | Description/nature/dose of intervention | Duration | Total cost | Comments | Source of unit cost | Relevant model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||
| Home visits | Weekly home visits of 1 hour length by the midwife. It was assumed that home visits last for 1 month | 4 weeks | £140 | We used the unit cost per hour of home visit by a practice nurse (£35/hour) as a proxy for midwife | Curtis and Netten692 | Delivery up to 37 weeks |
| Bed rest (home) | None | Bed rest at home incurs no direct cost to the NHS | Delivery up to 37 weeks | |||
| Home uterine activity monitoring | Women are placed in the Term Guard (Tokos Medical Corp., Santa Ana, CA) uterine monitoring system, twice daily (morning and evening) for 1 hour. The minimum care scheduled was a visit every 4 weeks until 30 weeks gestation, at least every 2 weeks between 30 and 36 weeks, at least weekly thereafter. Monitoring begun no earlier than 24 weeks gestation | 24–36 weeks | £250 | Estimate not available for the cost of the intervention. We used £250 as the cost of the intervention (see Table 44 for more information) |
Kosasa et al. 707 Curtis and Netten692 |
Delivery up to 37 weeks |
| Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria | Cefalexin 500 mg, 3 times a day | 7 days | £3.29 | Cefalexin 500 mg (21-cap pack) @ £3.29 (one pack required) | BNF | Delivery up to 37 weeks |
| Antibiotics for treating intra-amniotic infections |
Metronidazole 400 mg, 3 times a day Erythromycin 500 mg, 4 times a day |
14 days | £12.93 |
Metronidazole 400 mg (21-tab pack) @ £1.41 (one pack required) Erythromycin 250 mg (20 tablets) @ £1.92 (six packs required) |
BNF |
Delivery up to 37 weeks Perinatal mortality |
| Periodontal therapy | £81.50 | We used the inflated 6-monthly manual and non-fluoridated dental check | Davenport et al.716 | Delivery up to 37 weeks | ||
| Cervical cerclage | Cervical cerclage placement. Requires surgery under full anaesthesia | 1 day | £1219 | We used the ‘lower genital tract intermediate procedures’ cost, non-elective inpatient data (TNELIP) | Department of Health (2006), NHS reference costs 2005, NHS trusts and primary care trusts combined |
Delivery up to 34 weeks Delivery up to 37 weeks Perinatal mortality |
| Nutritional advice to increase energy and protein intake | None | Nutritional advice incurs no direct cost to the NHS |
Delivery up to 37 weeks Perinatal mortality |
|||
| Vitamin C | Vitamin C 100 mg, once a day from the 20th week of gestation until the 37th week | 17 weeks | £1.08 | Vitamin C 100 mg (20 tablets) @ 18p (six packs required) | BNF | Perinatal mortality |
| Zinc | One tablet in water, twice daily | 17 weeks | £34.56 | Solvazinc tablets (zinc sulphate monohydrate 125–45 mg zinc) (30-tablet pack) @ £4.32 (eight packs required) | BNF | Delivery up to 37 weeks |
| Fish oil | One capsule per day | 24 weeks | £16.99 | 250 capsules @ £16.99 | Holland and Barrett |
Delivery up to 34 weeks Delivery up to 37 weeks |
| Balanced energy/protein supplementation |
Multivitamin preparations: vitamins: ascorbic acid 15 mg, nicotinamide 7.5 mg, riboflavin 500 µg, thiamine hydrochloride 1 mg, vitamin A 2500 units, vitamin D 300 units 1 capsule per day |
17 weeks | £1.32 | Multivitamin preparations, 20-cap pack @ 22p (six packs required) | BNF |
Delivery up to 37 weeks Perinatal mortality |
| Energy/protein restriction | None | Energy/protein restriction incurs no direct cost to the NHS | Delivery up to 37 weeks | |||
| Progestational agents | Weekly intramuscular injection of 250 µg 17-hydroxyprogesterone caproate | 15 weeks from 16–20 weeks | £923.55 |
15 injections @ 57p each We used the ‘other expectant mothers ante-natal follow up outpatients’ cost (£61), available in the DoH, NHS reference costs, to include the cost of the visit (either GP or hospital) to get the injection. We used the outpatient adult follow up attendance data (TOPS FUA) |
BNF Department of Health (2006), NHS reference costs 2005, NHS trusts and primary care trusts combined |
Delivery up to 34 weeks Delivery up to 37 weeks Perinatal mortality |
| Smoking cessation | Bupropion: Start 1–2 weeks before target stop date, initially 150 mg daily for 6 days then 150 mg twice daily; max period of treatment 7–9 weeks | Bupropion: 9 weeks | £79.70 – £154.19 | Bupropion, 60-tab pack @ £39.85 (two packs required) | BNF | Delivery up to 37 weeks |
| Nicotine patches: 15 mg/16 h for 8 weeks; then 10 mg/16 h for 3 weeks | Nicotine patches: 11 weeks |
Nicotine patches 15 mg: 7 @ £9.07 (12 packs required) 10 mg: 7 @ £9.07 (five packs required) |
||||
| Symptomatic women | ||||||
| Prophylactic antibiotics (intact membranes) | Metronidazole 400 mg, 3 times per day |
£1645.41 (48 hours/37 weeks) £2479.41 (7 days) |
Metronidazole, 400 mg, 21-pack @ £1.41 (one pack required) | BNF |
Delivery within 48 hours Delivery within 7 days Delivery up to 37 weeks |
|
| Nitric oxide donors | GTN patch 9.6 mg/24 h for 48 hours | 48 hours | £1656.87 | 10 mg patch, 30 @ £12.87 (one pack required) | BNF | Delivery within 48 hours |
| Indomethacin | Indomethacin: loading dose of 50–100 mg (rectal administration) followed by 25–50 mg orally every 6 h for 24–48 hours | 48 hours |
£1646.01 (48 hours/37 weeks/perinatal mortality) £2480.01 (7 days) |
Suppositories 100 mg, 10-pack @ £1.20 (one pack required) Capsules 50 mg, 20-pack @ 81p (one pack required) |
BNF |
Delivery within 48 hours Delivery within 7 days Delivery up to 37 weeks Perinatal mortality |
| Calcium channel blockers | Nifedipine capsules 10 mg orally, repeat every 30 minutes up to a maximum of 40 mg in 2 hours; then maintenance of nifedipine (Tensipine) MR 20 mg TDS for 48 h maximum | 48 hours |
£1652.97 (48 hours/34 weeks/37 weeks) £2486.97 (7 days) |
Nifedipine 10 mg, 84-cap pack @ £3.72 (one pack required) Tensipide MR 20 mg, 56-tab pack @ £5.25 (one pack required) |
BNF |
Delivery within 48 hours Delivery within 7 days Delivery up to 34 weeks Delivery up to 37 weeks |
| Magnesium sulphate | Initial treatment 4 g over 15–30 min; then maintenance 2.5 g/h continued for 48 hours | 48 hours | £1678.95 |
Initial treatment, 10-ml (5-g) prefilled syringe @ £4.95 (one syringe required) Maintenance, 5-ml (2.5-g) amp @ £2.50 (12 amps required) |
BNF |
Delivery within 48 hours Delivery up to 37 weeks |
| Terbutaline (intravenously) | By intravenous infusion, 5 µg/min for 20 min, increased every 20 min in steps of 2.5 µg/min until contractions have ceased, continue for 1 hour; then decrease every 20 min in steps of 2.5 µg/min to lowest dose that maintains suppression, continue at this level for 12 hours; then by mouth, 5 mg every 8 hours for as long as is desirable to prolong pregnancy | 48 hours |
£1647.62 (48 hours/37 weeks) £2480.22 (7 days) |
Intravenous injections. 5-ml amp @ £1.40 (two injections required) Bricanyl, tablets, terbutaline sulphate 5mg, 20 @ 82p (one pack required) |
BNF |
Delivery within 48 hours Delivery within 7 days Delivery up to 37 weeks |
| Terbutaline pump maintenance | 1 mg of terbutaline at 0.05 ml/hour with 0.25 bolus injections every 6 hours | 5 days | £1651 | Injection, terbutaline sulphate 500 µg/ml; 5-ml amp @ £140 (five injections required) | BNF | Delivery up to 34 weeks |
| Atosiban | By intravenous injection, initially 6.75 mg over 1 min, then by intravenous infusion 18 mg/h for 3 hours, then 6 mg/h for up to 45 hours; max duration of treatment 48 hours | 48 hours |
£2555.4 (48 hours/37 weeks) £3389.4 (7 days) |
Injection, atosiban 7.5 mg/ml, 0.9-ml (6.75-mg) vial @ £18.60 (49 vials required) | BNF |
Delivery within 48 hours Delivery within 7 days Delivery up to 37 weeks |
| Terbutaline (orally) | Terbutaline 20 mg/day |
24 hours 48 hours 7 days |
£1644.82 (24/48 hours) £2479.64 (7 days) |
Terbutaline sulphate 5 mg, 20-tab pack @ 82p (one pack required – 24/48 hours) (two packs required – 7 days) |
BNF |
Delivery within 24 hours Delivery within 48 hours Delivery within 7 days |
| Hydration | Intravenous hydration with 500 ml crystalloids over 20 min, followed by 200 ml/hour | 48 hours | £1645 | No cost available for crystalloids: £1 assumed | Delivery up to 34 weeks | |
| Vitamin K for neuroprotection | Vitamin K, 10 mg intramuscularly once and then after 5 days | 48 hours | £1646 | Konakion MM Paediatric, phytomenadione 10 mg/ml, 0.2-ml amp, £1.00 | BNF | Perinatal mortality |
| Prophylactic corticosteroids | Betamethasone, two injections, 12 mg each with 24-hour interval | 48 hours | £1651.32 | Injection, betamethasone 4 mg/ml, net price 1-ml amp £1.22 (six amps required) | BNF | Perinatal mortality |
For all symptomatic women we assumed that they are hospitalised for a minimum of 5 days (based on consultation with the clinicians in the project team). This assumed hospitalisation 1 day before administration of the intervention and at least 2 days after delivery. Cost of the first day was assumed to be £532 based on HRG data ‘Admissions not Related to Delivery Event = £532 – Non-elective inpatient TNELIP sheet’ (link: http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/PublicationsPolicyAndGuidance/DH_4133221). [Source: Department of Health (2006), NHS Reference Costs 2005, NHS Trusts and Primary Care Trusts combined.] and for each of the following days the cost was assumed to be £278 based on ‘Admissions not Related to Delivery Event = £278 – Non-elective inpatient excess days TNELIPXS sheet’ (link: (http://www.dh.gov.uk/assetRoot/04/13/32/28/04133228.xls). [Source: Department of Health (2006), NHS Reference Costs 2005, NHS Trusts and Primary Care Trusts Combined.]
Hence, the total cost of hospitalisation was estimated to be £1644 based on 5 days hospitalisation for the following models: Delivery within 48 hours of intervention, delivery up to 34 weeks’ gestation, delivery up to 37 weeks’ gestation, and perinatal mortality. Finally, the total cost of hospitalisation was estimated to be £2478 based on 8 days hospitalisation, which applied to the 7-day model.
The costs of spontaneous preterm birth are required for all symptomatic models. These are estimated using a combination of data including the average birthweight by gestational age and the number of survivors by gestational age to calculate weight ranges for survivors that correspond with the costs estimated by Petrou et al. for low-birthweight infants. 60 The results of the calculations and derivation of costs are summarised in Table 46.
| Costs during the neonatal period | Birthweight | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 1000 g | 1000–1499 g | ≥ 1500 g | Total cost | Total cost – 2005 values | |
| Cost up to 34 weeks | £1873.59 | £4107.27 | £6103.90 | £12,084.76 | £15,688.75a |
| Cost up to 37 weeks | £75.96 | £166.51 | £9081.20 | £9323.67 | £12,104.23 |
The methods for the estimation of prevalence required for the model are described in detail in Appendix 9. Table 47 presents the summary of the prevalence results required for each model.
| Within 24 hours | Within 48 hours | Within 7 days | Up to 34 weeks | Up to 37 weeks | Perinatal mortality | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall prevalence of asymptomatic women having preterm birth | N/A | N/A | N/A | 3.46% (3.25–3.67) | 7.56% (7.40–7.73) | 18.37% (14.21–22.53) |
| Overall prevalence of symptomatic women having preterm birth | – | 7.55% (5.65–9.45) | 20.56% (18.26–22.85) | 24.25% (21.34–27.16) | 37.88% (36.42–39.34) | 18.37% (14.21–22.53) |
| Overall prevalence of asymptomatic women becoming symptomatic | N/A | N/A | N/A | 14.27% (14.04–14.50) | 19.97% (19.18–20.76) | N/A |
Analysis
The main objective of testing asymptomatic women for their risk of having a preterm labour and then treating them accordingly, is to prevent them from developing symptoms of preterm labour. Women who develop the symptoms of threatened preterm labour may be at risk of imminent spontaneous preterm birth. The main objective of testing women with symptoms is therefore to confirm their risk and to provide treatment to prevent or delay spontaneous preterm birth where indicated.
The main outcome of the symptomatic models is in terms of cost per spontaneous preterm birth avoided whereas the main outcome of the asymptomatic models is in terms of cost per threatened preterm labour avoided.
The cost of an asymptomatic individual becoming symptomatic is the cost associated with testing and treatment once they become symptomatic. Once symptomatic, we must assume that labour itself can be postponed by a maximum of 48 h. The results in terms of average cost per women tested and treated, which is estimated in the symptomatic model for 48 h, are required in the comparator arm of the asymptomatic model. It is this cost that the testing and treatment of asymptomatic women is attempting to avoid. It is necessary to estimate the results of the most cost-effective test and treatment in the symptomatic model for 48 h and use the average cost of the most cost-effective test and treatment combination in the asymptomatic model. This explains why analysis of symptomatic mothers, though somewhat counterintuitive, precedes the analysis of the asymptomatic scenarios.
For each model, a deterministic analysis was carried out. 710 In such an analysis, the point estimates of the probability parameters and the cost estimates for each test and each intervention relevant to the model were used. Where no effectiveness data comparing intervention with ‘placebo/no treatment’ were available from trials, the economics team estimated this from an adjusted indirect comparison. In the absence of direct data (or where direct data are limited), indirect data can provide an indication of the relative effectiveness; however, the internal validity and similarity of all of the trials involved in the indirect comparison should always be carefully examined.
The model estimated the cost-effectiveness relative to ‘no test/no treatment’ of each alternative combination of test and treatment pairing. The results, are presented in terms of the ICER, expressed as the additional cost per additional case of preterm birth avoided as a result of each test and treat combination.
In addition, for each model where possible a probabilistic sensitivity analysis was carried out to explore the effects on the ICERs of the uncertainty in accuracy of tests and effectiveness of interventions, such as implied by the 95% CI of the probability parameters. 710 In the probabilistic sensitivity analysis required for each model it was appropriate to include the interventions for which the 95% CI of the relative risk was < 1 to avoid including interventions that could be deemed harmful. Each model parameter is assigned a distribution reflecting the amount and pattern of its variation. Cost-effectiveness results are calculated by simultaneously selecting random values from each distribution. The process is repeated many times in a Monte Carlo simulation of the model to give an indication of how variation in the model parameters leads to variation in the ICERs for a given test and treatment pairing. 711
The appropriate distribution for the data on test accuracy (positive or negative likelihood ratios) was a log normal distribution. The assumption that log normal distributions are appropriate for likelihood ratios is itself an approximation and fails when the sampled value approaches 1. It is logically impossible that both likelihood ratios should be over 1, but sampling the ratios independently gives a ratio greater than 1 for a very small proportion of the samples. Since this is an artefact of the sampling, rather than a realistic extreme of the distribution, we have in such cases restricted any sampled value of the LR– (negative) to a maximum value of 0.999 and the corresponding LR+ (positive) to a minimum value of 1.001.
The appropriate distribution for data on intervention effectiveness (RR of developing spontaneous preterm birth) was a log normal distribution. A similar restriction was also applied to the relative risk of the interventions to avoid them exceeding 1 during the simulations.
A range of possible tests were identified in the literature as potentially relevant for detecting risk factors for spontaneous preterm birth, among both the symptomatic and asymptomatic women for the majority of models. The reviews provided these data in terms of likelihood ratios. The likelihood ratios were converted to their corresponding sensitivities and specificities and ranked according to their sensitivity. Starting with the test with the highest sensitivity, each test was tried in turn in the relevant model, which included all appropriate interventions for the case in question, to ensure that they would be worth including in that model. The conversion to sensitivity and specificity was for ranking only. In the actual model it was the likelihood ratios, as provided by the reviews, that were used. If tests with accuracy below a certain threshold were included in that model they risked being overlooked in favour of a strategy that would recommend ‘treating all without a preceding test’ or simply being dominated by one of the other tests, and this would not show in the results. It was only worth including tests that had a chance of providing an option where the test was recommended and so only those testing positive were treated. Use of this threshold analysis had the advantage of avoiding creating an overly large structured model with unnecessary branches.
Table 48 presents a summary on the analyses that were carried out.
| Symptomatic analysis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 24 hours | No model (no data) |
| Case 2 | 48 hours | Full model with PSA (all tests – atosiban, indomethacin, terbutaline) |
| Case 3 | 7 days | Full model with PSA (all tests – atosiban, indomethacin, calcium channel blockers, terbutaline, prophylactic antibiotics) |
| Case 4 | 34 weeks | Deterministic model on ALL tests and ALL interventions. No interventions available for the PSA – used the most effective intervention from Symptomatic 37 weeks, i.e. indomethacin (for the PSA only) |
| Case 5 | 37 weeks | Full model with PSA (one test – atosiban, indomethacin, terbutaline) |
| Case 6 | Perinatal mortality | Cost consequence only – no model |
| Asymptomatic analysis | ||
| Case 7 | 34 weeks | Full model with PSA (one test – all interventions) |
| Case 8 | 37 weeks | Full model with PSA (one test – huam, antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria, periodontal therapy, progestational agents, fish oil, nutritional advice, smoking cessation) |
| Case 9 | Perinatal mortality | Cost consequence only – no model |
Results of the decision analyses
Symptomatic analysis
Case 1 – Symptomatic women giving birth 24 hours after testing and treatment
Tables 41 and 43 present the available data from the reviews of accuracy and effectiveness of tests and interventions respectively. There were no available data for tests used to confirm diagnosis of preterm labour at 24 h and there were data available for only one intervention, namely terbutaline (orally). Therefore it was not possible to carry out an economic analysis of tests and treatments for this case.
Case 2 – Symptomatic women giving birth 48 hours after testing and treatment
The results presented in Table 49 show that five tests met the necessary criteria for inclusion in the model.
| Test | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cost of test | Cost limita | Commentb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement of cervical length (15 mm) | 0.98 | 0.85 | £69.47 | £1230 | Included |
| Amniotic fluid IL-6 | 0.92 | 0.76 | £216.70 | £929 | Included |
| IL-8 (15 ng/ml amniotic fluid) | 0.90 | 0.98 | £216.70 | £1216 | Included |
| Cervicovaginal IL-6 | 0.88 | 0.54 | £11.50 | £489 | Included |
| Absence of fetal breathing movements | 0.76 | 0.90 | £69.47 | £1032 | Included |
| phIGFBP-1 | 0.62 | 0.64 | £11.50 | £0 | Not included |
| Serum IL-6 | 0.50 | 0.76 | The combined criteria of this test did not meet the required threshold | ||
Table 50 presents the results of the deterministic model where all the included tests were combined with the full range of relevant interventions for 48 h as presented in Table 43. The results are presented incrementally compared to the previous best option. The results show that the least costly test and treat option is ‘Absence of fetal breathing movement test/Indomethacin_positive’ but this is not the most cost-effective option. The strategy of providing ‘Cervical length measurement (15 mm) test/Indomethacin_positive’ is the most cost-effective strategy. This means test everyone with the ‘cervical length measurement (15 mm)’ test and provide indomethacin to all the women who tested positive. This strategy has an average cost of £669 per woman treated (this value is also incorporated into the asymptomatic models at 34 and 37 weeks described later) and the strategy saves nearly eight cases of preterm labour per 1000 women, a number needed to treat (NNT) of 125. There is an additional cost of £5268 per case of preterm labour averted. The next preferred strategy is ‘No test/Indomethacin_all’. Given that the results are presented incrementally compared to the previous best option, ‘No test/Indomethacin_all’ avoids just over one more case of preterm labour in 1000 women than ‘Cervical length measurement (15 mm)/Indomethacin_positive’, but costs approximately £1202 more, giving an ICER of £858,334 of additional test and treatment cost per additional case of preterm labour averted. It should be noted that calcium channel blockers are one of only two treatments recommended by the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) guidelines. This option was included for evaluation in the deterministic analysis, but is dominated by the options presented in Table 50.
| Test/treatment combination | Mean cost per woman (UK £ 2005) | Difference in costs (UK £ 2005) | Effectivenessa | Absolute risk reduction | ICERb | NNT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absence of fetal breathing movements test/Indomethacin_+vec | £627.10 | 0.9763 | ||||
| Cervical length measurement (15 mm) test/Indomethacin_+ve | £669.20 | £42.1 | 0.9843 | 0.008 | £5268 | 125 |
| No test/Indomethacin_All | £1871.10 | £1201.9 | 0.9857 | 0.0014 | £858,334 | 714 |
| Cervicovaginal interleukin-6/Indomethacin_All | £1882.60 | £11.5 | 0.9857 | 0 | (Undefined) |
In Figure 284 the results of the deterministic analysis are presented diagrammatically alongside all the cost-effectiveness estimates produced by case 2. The majority of the points represent dominated options, where greater effectiveness can be achieved at lower cost by an alternative. The most cost-effective option from this analysis is shown to be ‘Cervical length measurement (15mm)/Indomethacin_positive’ which is at the bottom right corner (low cost/high effect) of the diagram.
FIGURE 284.
Case 2: Symptomatic women – 48 h. Results: costs, effects and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios on cost-effectiveness plane for all combinations of test and treatment pairs.
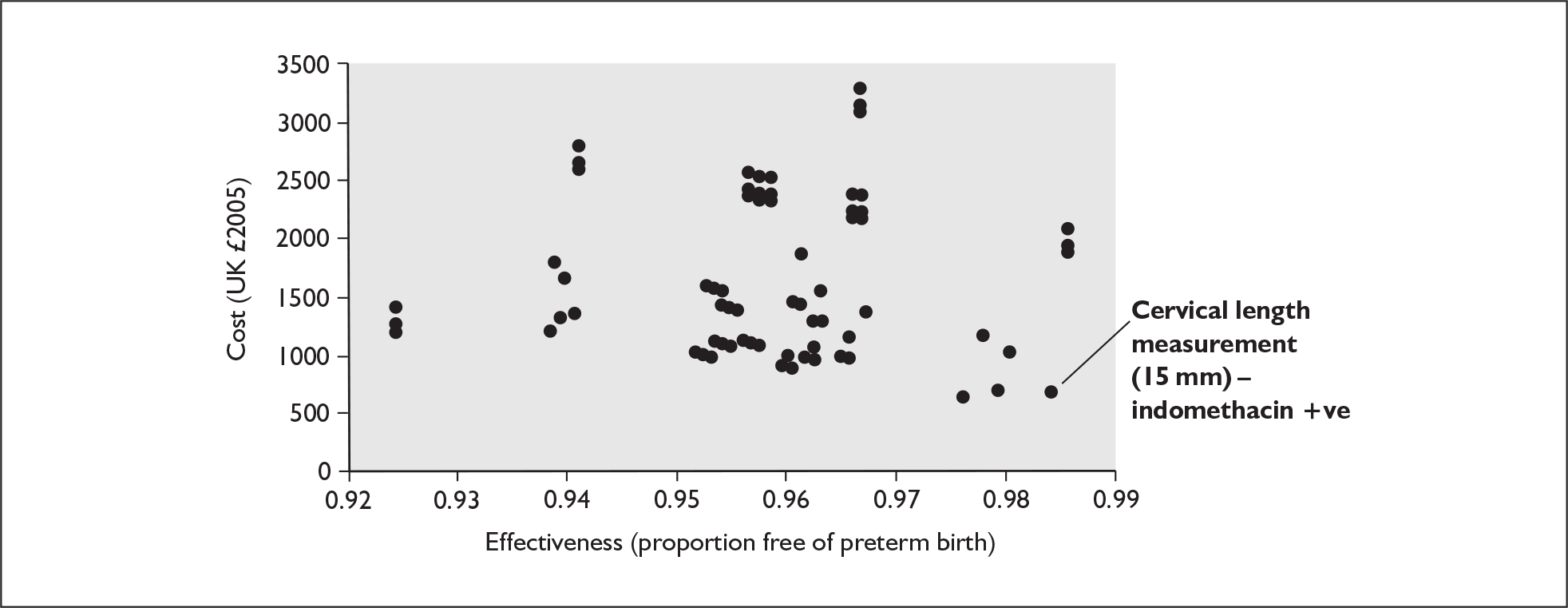
In Table 51 the results of PSA for case 2 are presented. The interventions that are included in the PSA are those for which the 95% CI for the relative risks are < 1 as shown in Table 43 and so they include only indomethacin, terbutaline (intravenously) and atosiban. The latter was estimated by an indirect comparison (Appendix 7) because the available data for atosiban from a placebo-controlled trial was based on only a small number of participants. The direct estimate was also not eligible for inclusion in the model because it did not suggest a favourable outcome for atosiban. However, atosiban is an important intervention in clinical practice so it was decided to enter the more favourable indirect estimate, which was eligible for inclusion in the model, and to use this as a ‘best-case scenario’. The results from the model reaffirm that ‘Cervical length measurement (15 mm)/Indomethacin_positive’ is the dominant option at all values of willingness to pay after £30,000.
| Test/Treatment option | Willingness to pay (UK £ 2005/6)a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10,000 | 30,000 | 50,000 | 80,000 | 100,000 | |
| Cervical length measurement (15 mm)/Indomethacin +ve | 0.2247 | 0.3919 | 0.5315 | 0.5777 | 0.6008 | 0.605 |
| Amniotic interleukin-8/Indomethacin +ve | 0.1783 | 0.1991 | 0.1971 | 0.1885 | 0.1774 | 0.1724 |
| Absence of fetal breathing movements/Indomethacin +ve | 0.5118 | 0.3149 | 0.1613 | 0.1092 | 0.0763 | 0.0656 |
| Cervical length measurement (15 mm)/Atosiban +ve | 0.0007 | 0.0035 | 0.015 | 0.0232 | 0.0323 | 0.0363 |
| Cervical length measurement (15 mm)/Terbutaline +ve | 0.0106 | 0.0226 | 0.0331 | 0.0373 | 0.0382 | 0.0376 |
| Amniotic interleukin-6/Indomethacin +ve | 0 | 0.001 | 0.0069 | 0.0129 | 0.0239 | 0.0306 |
| Amniotic interleukin-8/Atosiban +ve | 0.008 | 0.0131 | 0.0165 | 0.0178 | 0.0171 | 0.0164 |
| Amniotic interleukin-8/Terbutaline +ve | 0.0092 | 0.0105 | 0.0106 | 0.0102 | 0.0099 | 0.0097 |
| Cervicovaginal interleukin-6/Indomethacin +ve | 0.0003 | 0.0006 | 0.0019 | 0.005 | 0.0096 | 0.0118 |
| Absence of fetal breathing movements/Atosiban +ve | 0.0141 | 0.0172 | 0.0132 | 0.0096 | 0.0064 | 0.0049 |
| Absence of fetal breathing movements/Terbutaline +ve | 0.0422 | 0.0256 | 0.0124 | 0.0073 | 0.005 | 0.0044 |
For example, at a given threshold of say £30,000, which means that a policy-maker would be willing to pay £30,000 per case of spontaneous preterm birth avoided, there is a 53% chance that ‘Cervical length measurement (15 mm)/Indomethacin_positive’ is the preferred option with respect to its cost-effectiveness (Figure 285). At the same threshold there is only a 19% chance that an alternative option of ‘Amniotic interleukin-8/Indomethacin_positive’ is the preferred option and less than a 1% chance of preference for other options such as ‘Cervical length measurement (15 mm)/Atosiban_positive’. If the willingness to pay threshold is increased to £100,000 per case of spontaneous preterm birth avoided then there is now a 60% chance that ‘Cervical length measurement (15 mm)/Indomethacin_positive’ is the preferred option.
FIGURE 285.
Case 2: Symptomatic women – 48 h. Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves.
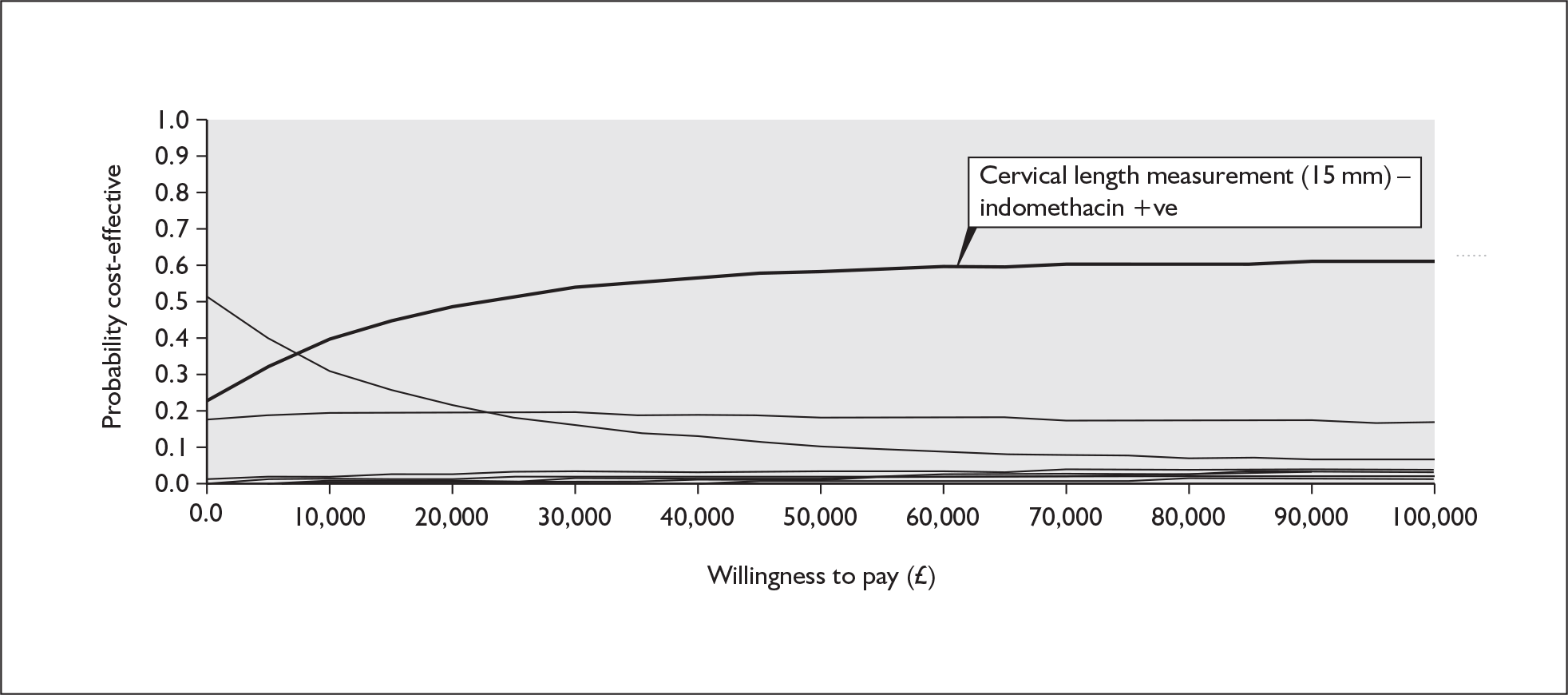
Case 3 – Symptomatic women who experience preterm labour within 7 days of testing and treatment
The results presented in the Table 52 show that six tests met the necessary criteria for inclusion in the model.
| Test | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cost of test | Cost limita | Commentb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement of cervical length (15 mm) | 0.98 | 0.89 | £69.47 | £1638 | Included |
| β-human chorionic gonadotrophin | 0.97 | 0.84 | £11.50 | £2298 | Included |
| Amniotic fluid IL-6 | 0.85 | 0.88 | £216.70 | Included | |
| Serum CRP | 0.82 | 0.98 | £9.50 | Included | |
| Fetal fibronectin | 0.82 | 0.77 | £11.50 | £648 | Included |
| IL-8 (15 ng/ml amniotic fluid) | 0.75 | 0.97 | £216.70 | £1020 | Included |
| phIGFBP-1 | 0.72 | 0.74 | £11.50 | £0 | Not included because it did not meet criteria |
| CV-Prolactin | 0.66 | 0.55 | The combined criteria of these tests did not meet the required threshold | ||
| Serum IL-6 | 0.64 | 0.81 | |||
| IL-8 (7.7 ng/ml in cervical swab) | 0.62 | 0.74 | |||
| Serum CRH | 0.46 | 0.85 | |||
| Cervicovaginal IL-6 | 0.41 | 0.90 | |||
| Absence of fetal breathing movements | 0.40 | 0.90 | |||
Table 53 presents the results of the deterministic model in which all the included tests were combined with the full range of relevant interventions for the 7-day model. The results show that the least costly test and treat option is ‘CRP test/Indomethacin_positive’ but this is not the most cost-effective option. The strategy of providing ‘Cervical length measurement (15 mm)/Indomethacin_positive’ is, like the 48-h model, the most cost-effective strategy. This strategy has an average cost of £2252 per woman treated, costs only £31 more than the least costly strategy of ‘CRP test/Indomethacin_positive’ and avoided 18 cases of spontaneous preterm birth per 1000 women, an NNT of 55. There is an additional cost of £1703 per additional case of spontaneous preterm birth averted with this strategy. The next strategy is ‘No test/Indomethacin_all’ which is marginally more effective than ‘Cervical length measurement (15 mm)/Indomethacin_positive’ but costs approximately £1647 more, giving an ICER of £620,688 of additional test and treatment cost per additional case of spontaneous preterm birth averted, which would not be deemed cost-effective.
| Test/treatment combination | Mean cost per woman (UK £ 2005) | Difference in costs (UK £ 2005) | Effectivenessa | Absolute risk reduction | ICERb | NNT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP/Indomethacin_+vec | £2221.00 | 0.889 | ||||
| Measurement of cervical length (15 mm)/Indomethacin_+ve | £2252.10 | £31.10 | 0.907 | 0.018 | £1703 | 55 |
| No test/Indomethacin | £3899.30 | £1647.20 | 0.910 | 0.003 | £620,688 | 333 |
| β-Human chorionic gonadotrophin/Indomethacin_all | £3910.80 | £11.50 | 0.910 | 0.000 | (Undefined) | |
| Fetal fibronectin/Indomethacin_all | £3910.80 | £0.0 | 0.910 | 0.000 | (Undefined) |
Figure 286 shows the results of deterministic analysis, presented diagrammatically alongside all the cost-effectiveness estimates produced by case 3. Most of the points represent dominated options, where greater effectiveness can be achieved at lower cost using an alternative. It showed that the most cost-effective option from this analysis was ‘Cervical length measurement (15 mm)/Indomethacin_positive’, which is at the bottom right hand corner (low cost/high effect) of the diagram.
FIGURE 286.
Case 3: Symptomatic women – 7 days. Results: costs, effects and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios on cost-effectiveness plane for all combinations of test and treatments pairs.
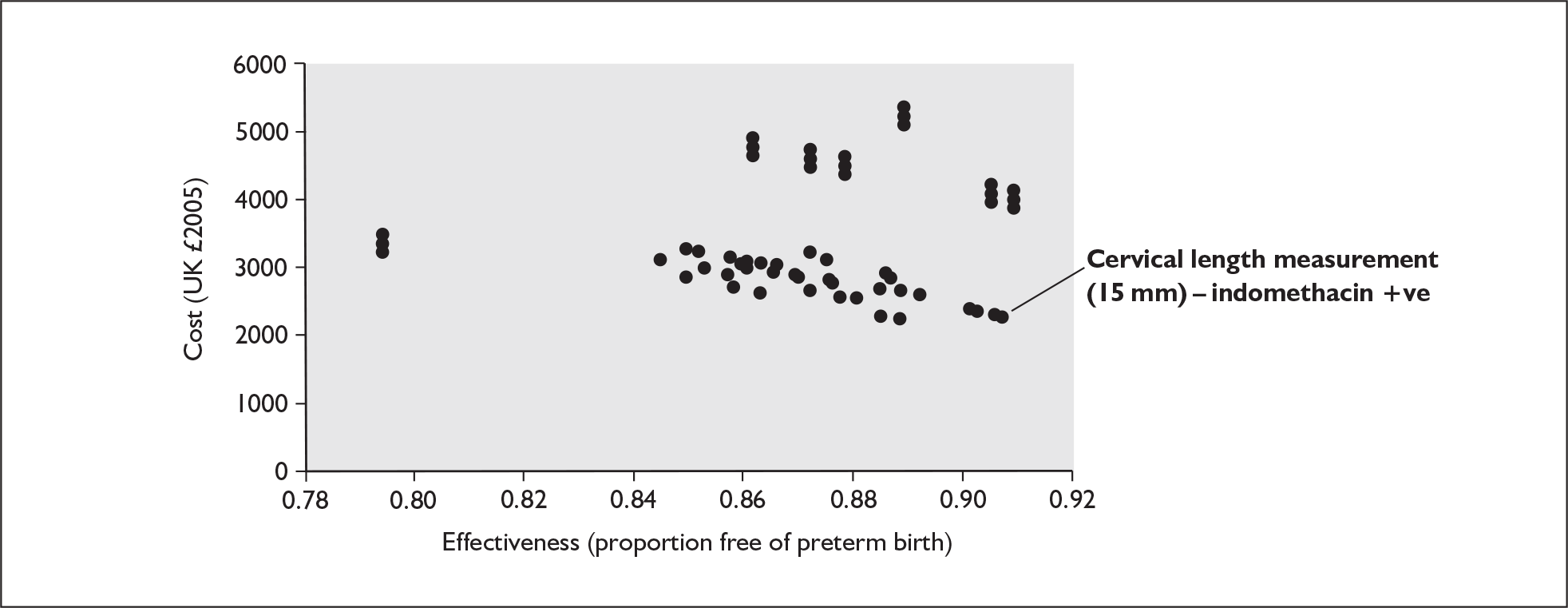
In Table 54 the results of the probabilistic sensitivity analysis for case 3 are presented. Again the PSA combines all the relevant tests with only the interventions for which the 95% CI for the relative risks was < 1, as shown in Table 43, and so includes only indomethacin, terbutaline (intravenously), calcium channel blockers (nifedipine) and atosiban. Again, appropriate data for nifedipine and atosiban were available through indirect comparison. The results reaffirm that ‘Cervical length measurement (15 mm)/Indomethacin_positive’ is the dominant option at all values of willingness to pay but the probability of it being the preferred option at the £30,000 threshold is only just over 23% (Figure 287). There are competing options for it being the most cost-effective option at all levels of willingness to pay particularly from ‘β-Human chorionic gonadotrophin test/Indomethacin_positive’, ‘Cervical length measurement (15 mm)/Calcium channel blockers_positive’ and ‘β-Human chorionic gonadotrophin test/Calcium channel blockers_positive’ test/treatment pairings.
FIGURE 287.
Case 3: Symptomatic women – 7 days. Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves.
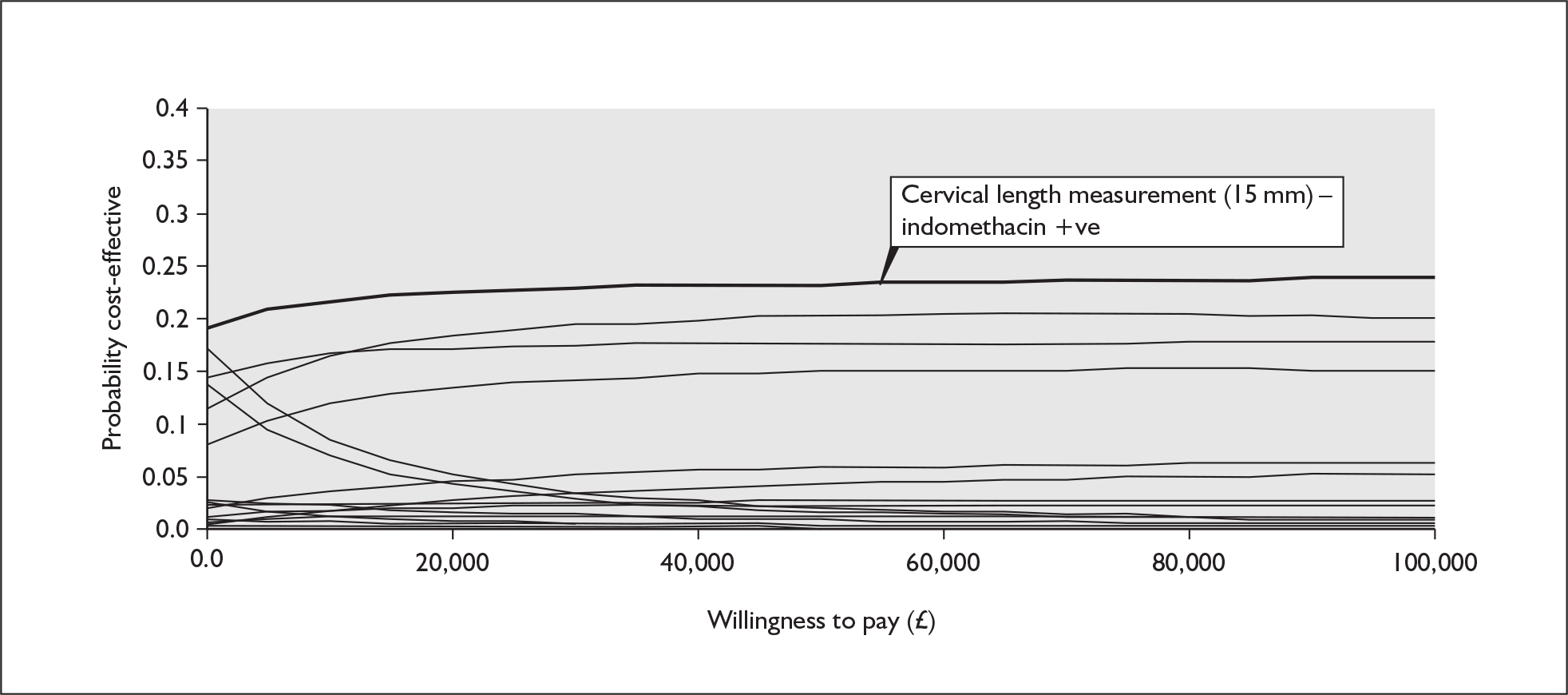
| Test/treatment option | Willingness to pay (UK £ 2005/6)a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10,000 | 30,000 | 50,000 | 80,000 | 100,000 | |
| Measurement of cervical length (15 mm)/Indomethacin +ve | 0.1938 | 0.2201 | 0.2316 | 0.2322 | 0.2358 | 0.2376 |
| β-Human chorionic gonadotrophin/Indomethacin +ve | 0.1006 | 0.1517 | 0.1842 | 0.1947 | 0.1951 | 0.194 |
| Measurement of cervical length (15 mm)/Calcium channel blockers +ve | 0.1488 | 0.1684 | 0.1734 | 0.1761 | 0.1792 | 0.1795 |
| β-Human chorionic gonadotrophin/Calcium channel blockers +ve | 0.0808 | 0.1174 | 0.1448 | 0.1506 | 0.1515 | 0.1523 |
| Measurement of cervical length (15 mm)/Atosiban +ve | 0.0179 | 0.0348 | 0.0524 | 0.0603 | 0.0656 | 0.068 |
| Measurement of cervical length (15 mm)/Terbutaline +ve | 0.0246 | 0.0285 | 0.028 | 0.0288 | 0.0287 | 0.0285 |
| Measurement of cervical length (15 mm)/Prophylactic antibiotics (intact membranes) +ve | 0.013 | 0.0152 | 0.0158 | 0.0162 | 0.0166 | 0.0166 |
| β-Human chorionic gonadotrophin/Atosiban +ve | 0.0056 | 0.0161 | 0.0306 | 0.0399 | 0.0462 | 0.0482 |
| β-Human chorionic gonadotrophin/Terbutaline +ve | 0.0113 | 0.018 | 0.0238 | 0.0242 | 0.0247 | 0.0248 |
| β-Human chorionic gonadotrophin/Prophylactic antibiotics (intact membranes) +ve | 0.0068 | 0.0103 | 0.0125 | 0.0127 | 0.0127 | 0.0127 |
| C-reactive protein/Atosiban +ve | 0.0253 | 0.0215 | 0.0127 | 0.0076 | 0.0052 | 0.0041 |
| C-reactive protein/Indomethacin +ve | 0.1753 | 0.0886 | 0.0363 | 0.0214 | 0.0133 | 0.0111 |
| C-reactive protein/Calcium channel blockers +ve | 0.1351 | 0.0707 | 0.0312 | 0.0177 | 0.0099 | 0.0079 |
| C-reactive protein/Terbutaline +ve | 0.0258 | 0.0124 | 0.0054 | 0.0028 | 0.0018 | 0.0015 |
| C-reactive protein/Prophylactic antibiotics (intact membranes) +ve | 0.0145 | 0.0076 | 0.0031 | 0.0018 | 0.001 | 0.0006 |
| Amniotic interleukin-6/Atosiban +ve | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0003 | 0.0004 | 0.0003 |
| Amniotic interleukin-6/Indomethacin +ve | 0.0013 | 0.0014 | 0.0023 | 0.0021 | 0.0024 | 0.0025 |
| Amniotic interleukin-6/Calcium channel blockers +ve | 0.0013 | 0.0013 | 0.0008 | 0.0008 | 0.0012 | 0.001 |
| Amniotic interleukin-8/Atosiban +ve | 0.0018 | 0.0021 | 0.0016 | 0.0017 | 0.0013 | 0.001 |
| Amniotic interleukin-8/Indomethacin +ve | 0.0072 | 0.0058 | 0.0035 | 0.0023 | 0.0024 | 0.0021 |
| Amniotic interleukin-8/Calcium channel blockers +ve | 0.006 | 0.0048 | 0.003 | 0.0028 | 0.002 | 0.0018 |
Case 4 – Symptomatic women at 34 weeks
All the tests that met the necessary criteria were included in the model and these are presented in Table 55.
| Tests | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cost of test | Cost limita | Commentb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amniotic fluid interleukin-6 | 0.88 | 0.88 | £216.7 | £766 | Included |
| Measurement of cervical length (30 mm) | 0.83 | 0.56 | £69.47 | £243 | Included |
| phIGFBP-1 | 0.75 | 0.82 | £11.50 | £285 | Included |
| Fetal fibronectin | 0.73 | 0.82 | £11.50 | £285 | Included |
| Serum interleukin-6 | 0.70 | 0.51 | £9.50 | £0 | Not included |
| CV-Prolactin | 0.57 | 0.88 | The combined criteria of these tests did not meet the required threshold | ||
| Presence of funnelling | 0.45 | 0.90 | |||
| CRP | 0.38 | 0.94 | |||
| Relaxin (serum) | 0.33 | 0.77 | |||
| Cervicovaginal interleukin-6 | 0.31 | 0.94 | |||
Figure 288 shows the results of the deterministic analysis, presented diagrammatically alongside all the cost-effectiveness estimates produced by case 4. The majority of the points represent dominated options, where greater effectiveness can be achieved at lower cost by an alternative. The most cost-effective option from this analysis is shown to be ‘Amniotic Fluid interleukin-6/Hydration_positive’, which is at the bottom right corner (low cost/high effect) of the diagram. Table 56 presents the results of the deterministic model where all the included tests are combined with the full range of relevant interventions for 34 weeks. The results show that the least costly test and treat option is the ‘Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 test/Hydration_positive’ option but this is not the most cost-effective option. The strategy of providing ‘Amniotic fluid interleukin-6 test/Hydration_positive’ is the most cost-effective strategy. This test and intervention have an average cost of £3584 per woman treated and the strategy saves over eight cases of spontaneous preterm birth per 1000 women, an NNT of 116. There is an additional cost of £4976 per case of preterm labour averted. The next most effective option after ‘Amniotic fluid interleukin-6 test/Hydration_positive’ is the ‘No test/Hydration_all’. This option ‘No test/Hydration_all’ (which implies treat everyone with hydration without a preceding test) avoids almost eight more cases of spontaneous preterm birth in 1000 women than ‘Amniotic fluid interleukin-6 test/Hydration_positive’, but costs £800 more, giving an ICER of £95,430 of additional test and treatment cost per additional case of preterm labour avoided.
FIGURE 288.
Case 4: Symptomatic women – 34 weeks. Results: costs, effects and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios on cost-effectiveness plane for all combinations of test and treatment pairs.
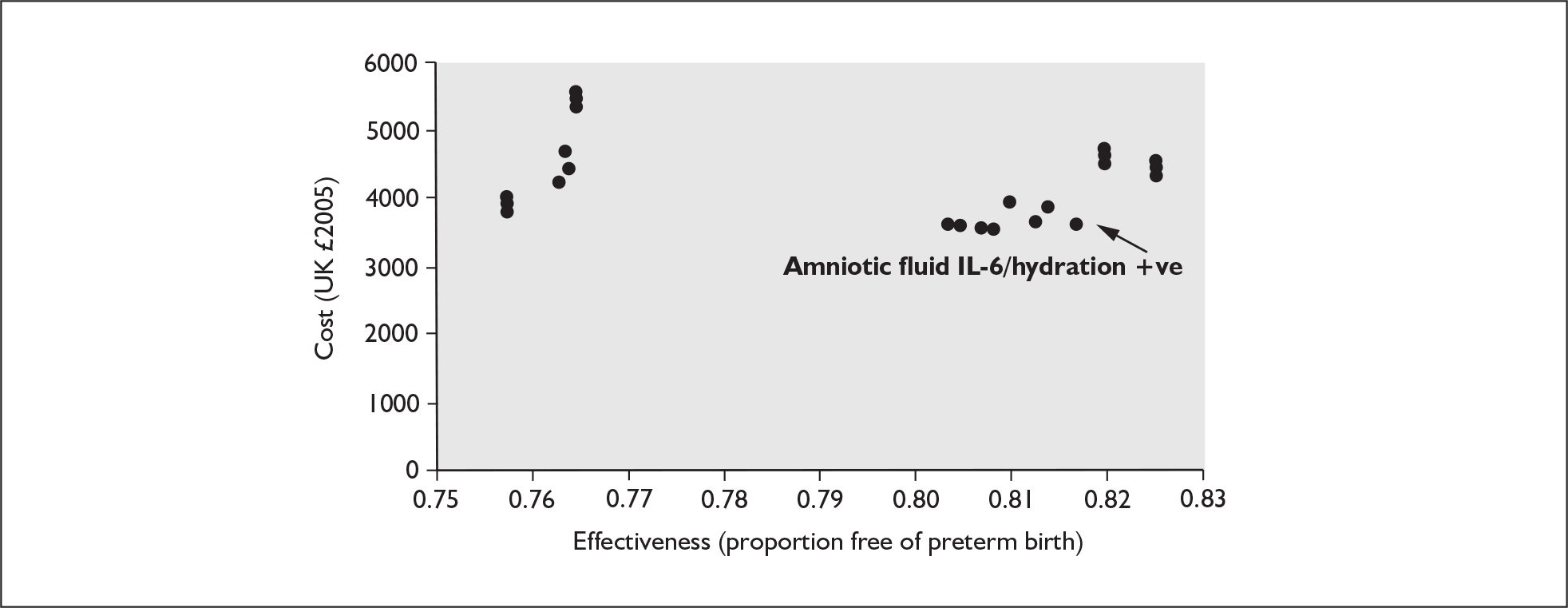
| Test/treatment combination | Mean cost per woman (UK £ 2005) | Difference in costs (UK £ 2005) | Effectivenessa | Absolute risk reduction | ICERb | NNT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| phIGFBP-1/Hydration +vec | £3541.30 | 0.8084 | ||||
| Amniotic fluid interleukin-6/Hydration +ve | £3584.00 | £42.70 | 0.817 | 0.0086 | £4976 | 116.28 |
| No test/Hydration all | £4384.30 | £800.30 | 0.8254 | 0.0084 | £95,430 | 119.05 |
The interventions that are typically included in the PSA are those for which the 95% CI for the relative risks is < 1. However, as shown in Table 43, none were available for this case and so a PSA was not carried out.
Case 5 – Symptomatic women at 37 weeks
The results presented in Table 57 show that none of the tests met the necessary criteria for inclusion in the model which suggests that the best option will be that of ‘no test/treat_all’. However, the fetal fibronectin test, which had the highest ranking sensitivity for this group, was included in the model although it did not meet the required criteria. The sensitivity and specificity of the fetal fibronectin test were adjusted to find the necessary characteristics of this or another test at the same cost as the fetal fibronectin test which was £11.50. The required characteristics for the sensitivity and specificity of this test are 0.92 and 0.99 respectively but these characteristics were not included in the model.
| Tests | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cost of test | Cost limita | Commentb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fetal fibronectin | 0.89 | 0.89 | £11.50 | £0 | Included but did not meet the required threshold |
| Measurement of cervical length (30 mm) | 0.81 | 0.65 | The combined criteria of these tests did not meet the required threshold | ||
| Rheobase (3.4 mA) | 0.76 | 0.68 | |||
| Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1) | 0.74 | 0.81 | |||
| Salivary estriol (threshold 2.1 ng/ml) | 0.73 | 0.69 | |||
| 18 mm | 0.73 | 0.78 | |||
| β-Human chorionic gonadotrophin | 0.70 | 0.67 | |||
| C-reactive protein | 0.67 | 0.71 | |||
| Matrix metalloproteases (MMP-9) | 0.66 | 0.91 | |||
| Digital examination | 0.66 | 0.72 | |||
| Interleukin-8 (3.739 ng/ml in cervical swab) | 0.63 | 0.55 | |||
| Rheobase (2.8 mA) | 0.54 | 0.76 | |||
| Cervicovaginal interleukin-6 | 0.50 | 0.73 | |||
| Serum interleukin-6 | 0.45 | 0.60 | |||
| Serum corticotrophin-releasing hormone | 0.38 | 0.91 | |||
| Amniotic fluid interleukin-6 | 0.35 | 0.99 | |||
| CV-Prolactin | 0.31 | 0.88 | |||
| Presence of funnelling | 0.21 | 0.92 | |||
| Relaxin (serum) | 0.21 | 0.74 | |||
| Sensitivity analysis | |||||
| Hypothetical test | 0.92 | 0.99 | £11.50 | ||
Table 58 presents the results of the deterministic model where only the fetal fibronectin test was included and this test was combined with the full range of relevant interventions for 37 weeks. The results show that the least costly test and treat option is ‘Fetal fibronectin test/Indomethacin_positive’ but this is not the most cost-effective option. The strategy of providing ‘No test/Indomethacin_all’ is the most cost-effective strategy, which implies that the strategy should be to provide indomethacin to all without any preceding test (as predicted by the earlier threshold analysis). The ‘No test/Indomethacin_all’ strategy has an average cost of £2609 per woman treated and the strategy saves 34 cases of spontaneous preterm birth per 1000 women, an NNT of 29. There is an additional cost of £16,336 per case of additional spontaneous preterm birth averted. Figure 289 shows the results of the deterministic analysis presented diagrammatically with all the cost-effectiveness estimates produced by case 5. The majority of the points represent dominated options, where greater effectiveness can be achieved at lower cost by an alternative. The most cost-effective option from this analysis is shown to be ‘No test/Indomethacin_all’, which is at the bottom right hand corner (low cost/high effect) of the diagram.
FIGURE 289.
Case 5: Symptomatic women – 37 weeks. Results: costs, effects and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios on cost-effectiveness plane for all combinations of test and treatment pairs.
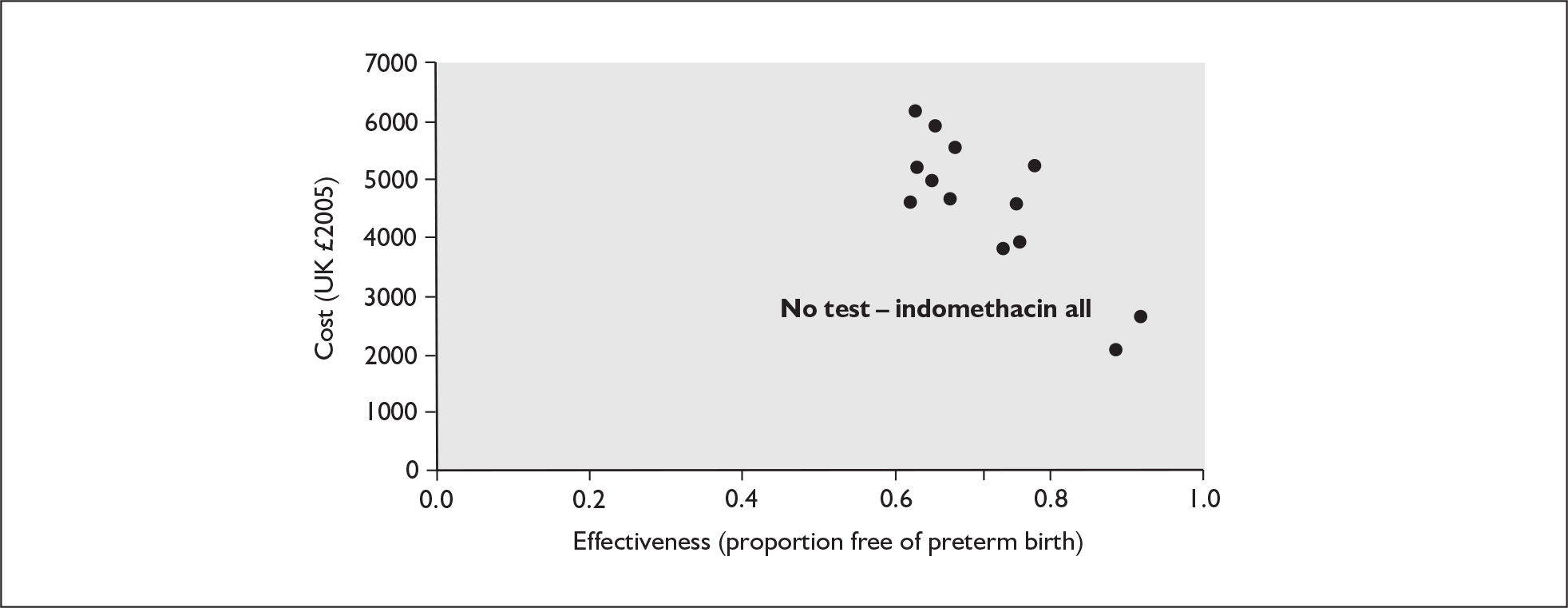
| Test/treatment combination | Mean cost per woman (UK £ 2005) | Difference in costs (UK £ 2005) | Effectivenessa | Absolute risk reduction | ICERb | NNT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fetal fibronectin test/Indomethacin_+ve c | £2052.70 | 0.886 | ||||
| No test/Indomethacin_all | £2608.90 | £556.20 | 0.92 | 0.034 | £16,336 | 29 |
In Table 59 the results of the PSA for case 5 are presented. The interventions that are included in the PSA are those for which the 95% CI for the relative risks was < 1 as shown in Table 43: this includes only indomethacin, terbutaline (intravenously) and atosiban (the latter by indirect comparison). The results reaffirm that ‘No test/Indomethacin_all’ has a 75% chance of being the preferred option at all values of willingness to pay after £30,000. The results are presented diagrammatically in Figure 290, as a cost-effectiveness acceptability curve.
FIGURE 290.
Case 5: Symptomatic women – 37 weeks. Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve.
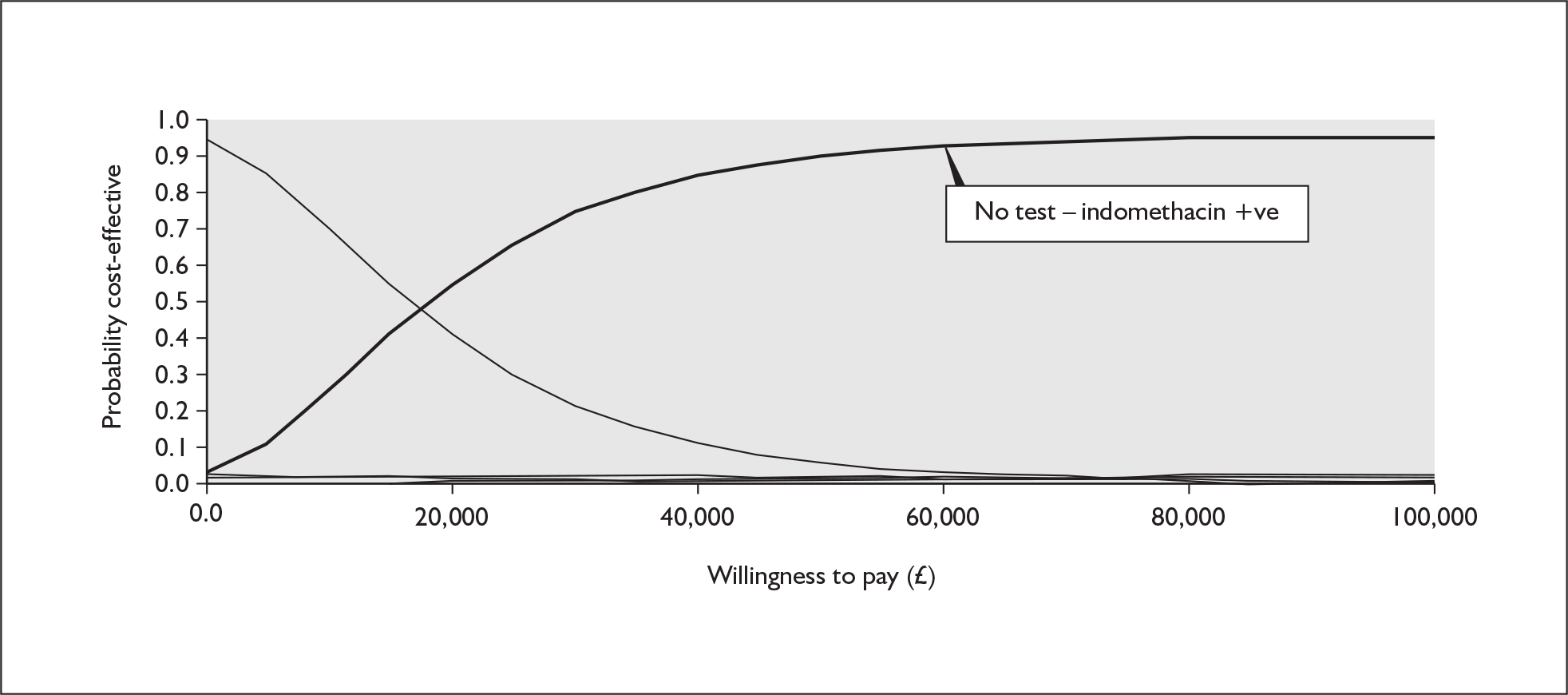
| Test/treatment option | Willingness to pay (UK £ 2005/6)a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10,000 | 30,000 | 50,000 | 80,000 | 100,000 | |
| No test/Indomethacin_all | 0.0215 | 0.271 | 0.7538 | 0.8993 | 0.9438 | 0.948 |
| No test/Atosiban_all | 0 | 0 | 0.0031 | 0.0108 | 0.0223 | 0.0266 |
| No test/Terbutaline_all | 0 | 0.0006 | 0.0073 | 0.0132 | 0.0159 | 0.0167 |
| Fetal fibronectin/Atosiban_+ve | 0.0148 | 0.0232 | 0.0244 | 0.0179 | 0.0082 | 0.0047 |
| Fetal fibronectin/Indomethacin_+ve | 0.9415 | 0.6857 | 0.2001 | 0.0537 | 0.008 | 0.0031 |
| Fetal Fibronectin/Terbutaline_+ve | 0.022 | 0.0195 | 0.0113 | 0.0051 | 0.0018 | 0.0009 |
Case 6 – Symptomatic women – perinatal mortality
From the accuracy reviews there were no data available for tests that detect risk factors for perinatal mortality in relation to spontaneous preterm birth. Data were available from the effectiveness reviews for interventions only.
Therefore the data were analysed by using a cost–consequence approach in the first instance. The interventions were ranked according to their effectiveness. If the most effective strategy was also the least costly strategy, then it would be the dominant strategy and no further economic analysis or model would be required. The results of the cost–consequence analysis for case 6 are presented in Table 60. Since all intervention strategies apply to women who are hospitalised they are all reasonably expensive and are estimated to cost approximately the same with corticosteroids being very slightly more expensive. However, it is likely that the most cost-effective intervention for treating women who are at risk of perinatal mortality in relation to spontaneous preterm birth, based on a cost–consequence analysis, is treatment with corticosteroids. Although it is very slightly more expensive than the alternatives in this group, vitamin K and indomethacin, it is much more effective and has a 95% CI upper limit < 1. A note of caution is necessary in the interpretation of corticosteroid use because the measure of mortality available is neonatal rather than perinatal mortality.
| Intervention | RR (95% CI) | Cost (UK £ 2005) (average hospital cost + unit drug costs) |
|---|---|---|
| Corticosteroidsa (betamethasone) | 0.63a (0.51–0.79) | £1651 (£1644 + £7.32) |
| Vitamin Kb | 0.79b (0.46–1.34) | £1646 (£1644 + £2.00) |
| Indomethacinc | 0.80c (0.25–2.58) | £1646 (£1644 + £2.01) |
Asymptomatic analysis
Case 7 – Asymptomatic women at 34 weeks
A range of potential possible tests were identified in the literature for detecting risk factors for spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic women at 34 weeks and these are presented in Table 61. Although the mammary stimulation test had the highest ranking sensitivity for this group, the test which ascertains a woman’s previous history of spontaneous preterm birth was the only test to meet the criteria for inclusion in the model. This was because it was assumed to have a zero cost, so that despite having a very low sensitivity of only 0.38 it met the combined required criteria because of its negligible cost.
| Test | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cost of test | Cost limita | Commentb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mammary stimulation test | 0.78 | 0.83 | £26.66 | £0 | Not included |
| Serum corticotrophin-releasing hormone | 0.73 | 0.78 | The combined criteria of these tests did not meet the required threshold | ||
| Digital examination | 0.57 | 0.94 | |||
| Measurement of cervical length – 30 mm (20–24 weeks’ gestation) | 0.54 | 0.76 | |||
| CV-Prolactin | 0.50 | 0.97 | |||
| Cervical mucus interleukin-8 (360 ng/ml) | 0.44 | 0.80 | |||
| Previous history of spontaneous preterm birth | 0.38 | 0.92 | £0 | The combined criteria of this test did meet the required threshold. In fact, this test reached the cost limit of £0 and was used in the analysis | |
| Measurement of cervical length – 25 mm (20–24 weeks’ gestation) | 0.37 | 0.92 | The combined criteria of these tests did not meet the required threshold | ||
| Relaxin (serum) | 0.34 | 0.79 | |||
| Fetal fibronectin | 0.33 | 0.97 | |||
| Measurement of cervical length – 22 mm (20–24 weeks’ gestation) | 0.31 | 0.93 | |||
| Presence of funnelling (16–20 weeks) | 0.30 | 0.94 | |||
| Measurement of cervical length – 30 mm (14–20 weeks’ gestation) | 0.28 | 0.89 | |||
| Presence of funnelling (20–24 weeks) | 0.25 | 0.95 | |||
| Measurement of cervical length – 20 mm (20–24 weeks’ gestation) | 0.23 | 0.97 | |||
| Measurement of cervical length – 25 mm (14–20 weeks’ gestation) | 0.21 | 0.98 | |||
| Amniotic fluid interleukin-6 | 0.14 | 0.95 | |||
| Measurement of cervical length – 15 mm (14–20 weeks’ gestation) | 0.11 | 1.00 | |||
| Measurement of cervical length – 20 mm (14–20 weeks’ gestation) | 0.10 | 1.00 | |||
| Serum α-fetoprotein (threshold 2.5 MoM) | 0.06 | 0.99 | |||
| Sensitivity analysis | |||||
| Hypothetical Test 1c | 0.81 c | 0.99 | £26.66 | ||
| Hypothetical Test 2c | 0.38 c | 0.92 | £0 | ||
The sensitivity of the ‘previous history’ test was also adjusted to see how low the sensitivity could be to be included in the model given that the cost was zero. The results showed that the sensitivity was already at its lowest limit to be acceptable. The sensitivity and specificity of the mammary stimulation test were also adjusted to find the necessary characteristics of this or another test (at the same cost) that would be worth including in the model. Holding the cost of the mammary stimulation test constant at £26.66 the required characteristics for the sensitivity and specificity of this test are 0.81 and 0.99 respectively, although this hypothetical test was not included in the model.
Table 62 presents the results of the deterministic model where the previous history test is combined with the full range of relevant interventions for 34 weeks. The estimated full costs of becoming symptomatic, which was estimated by the symptomatic model at 48 h to be approximately £669, is the cost in the comparator arm of the model.
| Test/treatment combination | Mean cost per woman UK £ 2005 | Difference in costs UK £ 2005 | Effectivenessa | Absolute risk reduction | ICERb | NNT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previous history of PTB/Fish oil +ve c | £19.00 | 0.9739 | ||||
| Previous history of PTB/Fish oil All | £25.10 | £6.10 | 0.9879 | 0.0140 | £434 | 71.42 |
| Previous history of PTB/Progestational agents All | £927.00 | £901.90 | 0.9948 | 0.0069 | £130,337 | 145 |
| No test/Progestational agents | £927.00 | £0.00 | 0.9948 | 0.0000 | (Undefined) |
The results show that the strategy of providing ‘Previous history test/Fish oil_positive’ is the baseline least costly option but this is not the most cost-effective strategy. According to the deterministic model the most cost-effective option is the option ‘Previous history test/Fish oil_all’. Although this result is somewhat counter intuitive it is thrown up by the deterministic model as a cost-effective option because the sensitivity of the test is so low. The results are presented incrementally compared to the previous least costly option so ‘Previous history test/Fish oil_all’ avoids nearly 14 more cases of spontaneous preterm birth in 1000 women than ‘Previous history test/Fish oil_positive’ and costs only £6 more, giving an ICER of £434 of additional test and treatment cost per additional case of spontaneous preterm birth avoided. These 14 cases would result in cases of spontaneous preterm birth if the strategy of giving fish oil to only the ‘positives’ was adopted. Figure 291 shows the results of the deterministic analysis, presented diagrammatically alongside all the cost-effectiveness estimates produced by case 7. The majority of the points represent dominated options, where greater effectiveness can be achieved at lower cost by an alternative. The most cost-effective option from this analysis is shown to be ‘Previous history of preterm birth/Fish oil_all’, which is at the bottom right hand corner (low cost/high effect) of the diagram.
FIGURE 291.
Case 7: Asymptomatic Women – 34 weeks. Results: costs, effects and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios on cost-effectiveness plane for all combinations of test and treatment pairs.
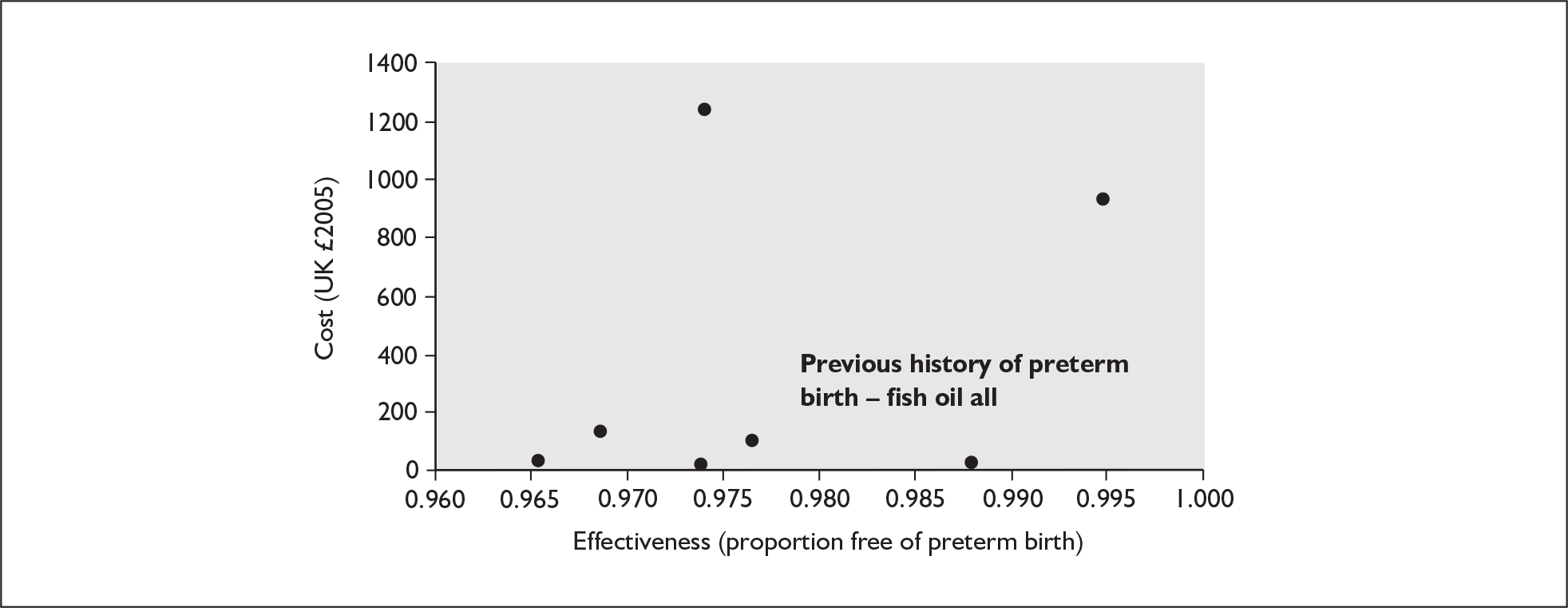
In Table 63 the results of the probabilistic sensitivity analysis for case 7 are presented. Again only one test was included in the PSA with all the relevant interventions for which the 95% CI for the relative risk was < 1. Contrary to the results of the deterministic model the results show that ‘No test/Fish oil_all’ is the dominant option at all values of willingness to pay above £10,000.
| Test/treatment option | Willingness to pay (UK £ 2005/6)a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10,000 | 30,000 | 50,000 | 80,000 | 100,000 | |
| No test/no intervention | 0.022 | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| No test/Fish oil_all | 0.0009 | 0.8418 | 0.7629 | 0.7639 | 0.648 | 0.5483 |
| No test/Progestational agents_all | 0 | 0 | 0.0001 | 0.0683 | 0.2274 | 0.305 |
| Previous history of PTB/No intervention | 0.0215 | 0.0004 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Previous history of PTB/Progestational agents_+ve | 0 | 0.0294 | 0.063 | 0.021 | 0.0017 | 0.0006 |
| Previous history of PTB/Fish oil_+ve | 0.9551 | 0.0017 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Previous history of PTB/Progestational agents_All | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0117 | 0.0302 | 0.0505 |
| Previous history of PTB/Fish oil_All | 0.0005 | 0.1242 | 0.174 | 0.1351 | 0.0927 | 0.0956 |
The results are presented diagrammatically in Figure 292.
FIGURE 292.
Case 7: Asymptomatic women – 34 weeks. Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves.
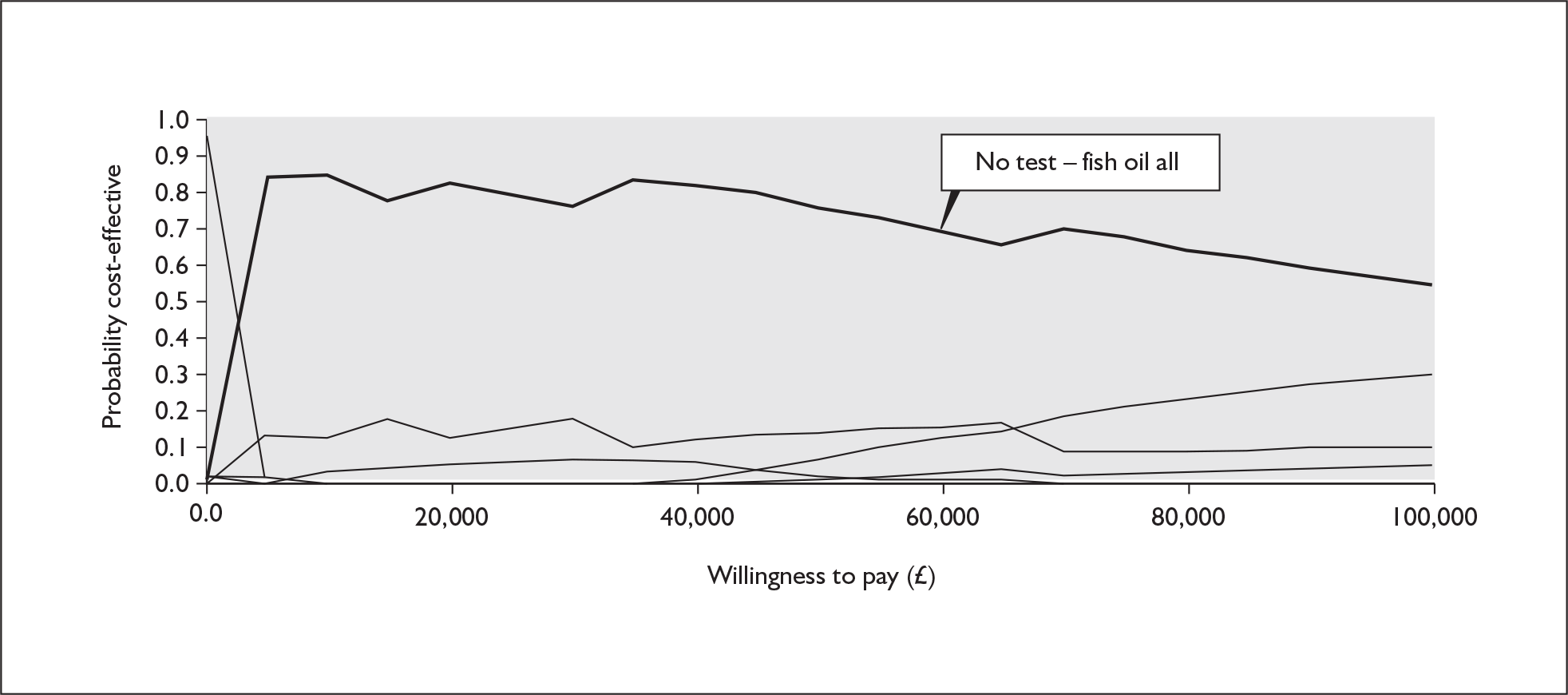
Case 8 – Asymptomatic women at 37 weeks
The range of possible tests identified in the literature as possible for detecting risk factors for spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic women at 37 weeks are presented in Table 64.
| Test | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cost of test | Cost limita | Commentb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1) | 0.83 | 0.80 | £11.50 | £0 | Not included |
| CV-Prolactin | 0.83 | 0.74 | The combined criteria of these tests did not meet the required threshold | ||
| Measurement of cervical length (32.5 mm) (20–24 weeks’ gestation) | 0.73 | 0.82 | |||
| Relaxin (serum) | 0.67 | 0.45 | |||
| Mammary stimulation test | 0.60 | 0.82 | |||
| Salivary estriol (threshold 2.1 ng/ml – single) | 0.56 | 0.78 | |||
| Cervicovaginal interleukin-6 (serial testing) | 0.50 | 0.85 | |||
| Digital examination | 0.49 | 0.58 | |||
| Salivary estriol (threshold 2.1 ng/ml – repeat) | 0.44 | 0.92 | |||
| Previous history of spontaneous preterm birth | 0.42 | 0.82 | £0 | The combined criteria of this test did meet the required threshold. In fact, this test reached the cost limit of £0 and was used in the analysis | |
| C-reactive protein | 0.37 | 0.82 | The combined criteria of these tests did not meet the required threshold | ||
| Periodontal evaluation | 0.32 | 0.86 | |||
| Serum corticotrophin-releasing hormone | 0.29 | 0.80 | |||
| Cervical mucus interleukin-8 (360 ng/ml) | 0.27 | 0.80 | |||
| Detection of bacterial vaginosis Nugent’s (single) | 0.24 | 0.87 | |||
| Detection of bacterial vaginosis Nugent’s (serial) | 0.19 | 0.86 | |||
| Detection of bacterial vaginosis Amsel’s (single) | 0.18 | 0.80 | |||
| Serum estriol (threshold ≤ 0.75 MoM) | 0.11 | 0.90 | |||
| Serum α-fetoprotein (threshold 2.0 MoM) | 0.10 | 0.94 | |||
| Amniotic fluid interleukin-6 | 0.10 | 0.95 | |||
| Cervicovaginal interleukin-6 (single testing) | 0.09 | 0.84 | |||
| Fetal fibronectin | 0.06 | 1.00 | |||
| Midstream urine culture | 0.06 | 0.98 | |||
| Serum estriol (threshold ≤ 0.5 MoM) | 0.05 | 0.93 | |||
| Maternal serum β-human chorionic gonadotrophin | 0.02 | 0.99 | |||
| Serum α-fetoprotein (threshold 2.5 MoM) | 0.02 | 0.99 | |||
| Sensitivity analysis | |||||
| Hypothetical test 1c | 0.99 c | 0.99 | £11.50 | ||
| Hypothetical test 2c | 0.20 c | 0.82 | £0 | ||
However, the results presented in the table show that the test which ascertains a woman’s previous history of spontaneous preterm birth, was again the only test that met the necessary criteria for inclusion in the model despite having a very low sensitivity of only 0.42. The sensitivity of the ‘previous history’ test was also adjusted to see how low the sensitivity could be to be included in the model given that the cost was zero. The results showed that the sensitivity in this model could fall as low as 0.20 and it would still be worth including it in the deterministic model.
Table 65 presents the results of the deterministic model where only the previous history test is included. The estimated full cost of becoming symptomatic, which was estimated by the symptomatic model for 48 h to be approximately £669, is the cost in the comparator arm of the model. The results show that the strategy of providing ‘Previous history of preterm birth/Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria_all’ and ‘No test/Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria_all’ are jointly of equal cost and effectiveness. In Table 66 the results of the probabilistic sensitivity analysis for case 8 are presented. Again, only the previous history test was combined with all the interventions for which the 95% CI for the relative risk was < 1. The results of the PSA show that ‘No test/Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria_all’ is the dominant option at all values of willingness to pay, having a probability of 52% of being the preferred option at the £30,000 threshold. The analysis shows that the next preferred option is ‘No test/Periodontal therapy_all’, which has a probability of 28% of being the preferred option at the willingness to pay threshold of £30,000.
| Test/treatment combination | Mean cost per woman (UK £ 2005) | Difference in costs (UK £ 2005) | Effectivenessa | Absolute risk reduction | ICERb | NNT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previous history of preterm birth/Asymptomatic bacteriuria_all | £22.00 | 0.972 | £23 | – | ||
| No test/Asymptomatic bacteriuria_all | £22.00 | £0.00 | 0.972 | 0.000 | £23 | – |
| Test/treatment option | Willingness to pay (UK £ 2005/6)a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10,000 | 30,000 | 50,000 | 80,000 | 100,000 | |
| No test/Asymptomatic bacteriuria_all | 0.6287 | 0.6074 | 0.5191 | 0.528 | 0.5379 | 0.5207 |
| No test/Periodontal therapy_all | 0.0007 | 0.2494 | 0.2838 | 0.3037 | 0.3225 | 0.3104 |
| No test/Fish oil_all | 0.0012 | 0.0004 | 0.0003 | 0.0003 | 0.0002 | 0.0001 |
| No test/Nutritional advice_all | 0.0467 | 0.018 | 0.0143 | 0.0145 | 0.0144 | 0.0144 |
| Previous history of PTB/Asymptomatic bacteriuria_all | 0.2979 | 0.0882 | 0.1166 | 0.0945 | 0.0773 | 0.0927 |
| Previous history of PTB/Periodontal therapy_all | 0 | 0.0341 | 0.063 | 0.0564 | 0.045 | 0.059 |
| Previous history of PTB/Nutritional advice_all | 0.0243 | 0.0022 | 0.0022 | 0.0016 | 0.0016 | 0.0015 |
The results are presented diagrammatically in Figure 293.
FIGURE 293.
Case 8: Asymptomatic women – 37 weeks. Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve.
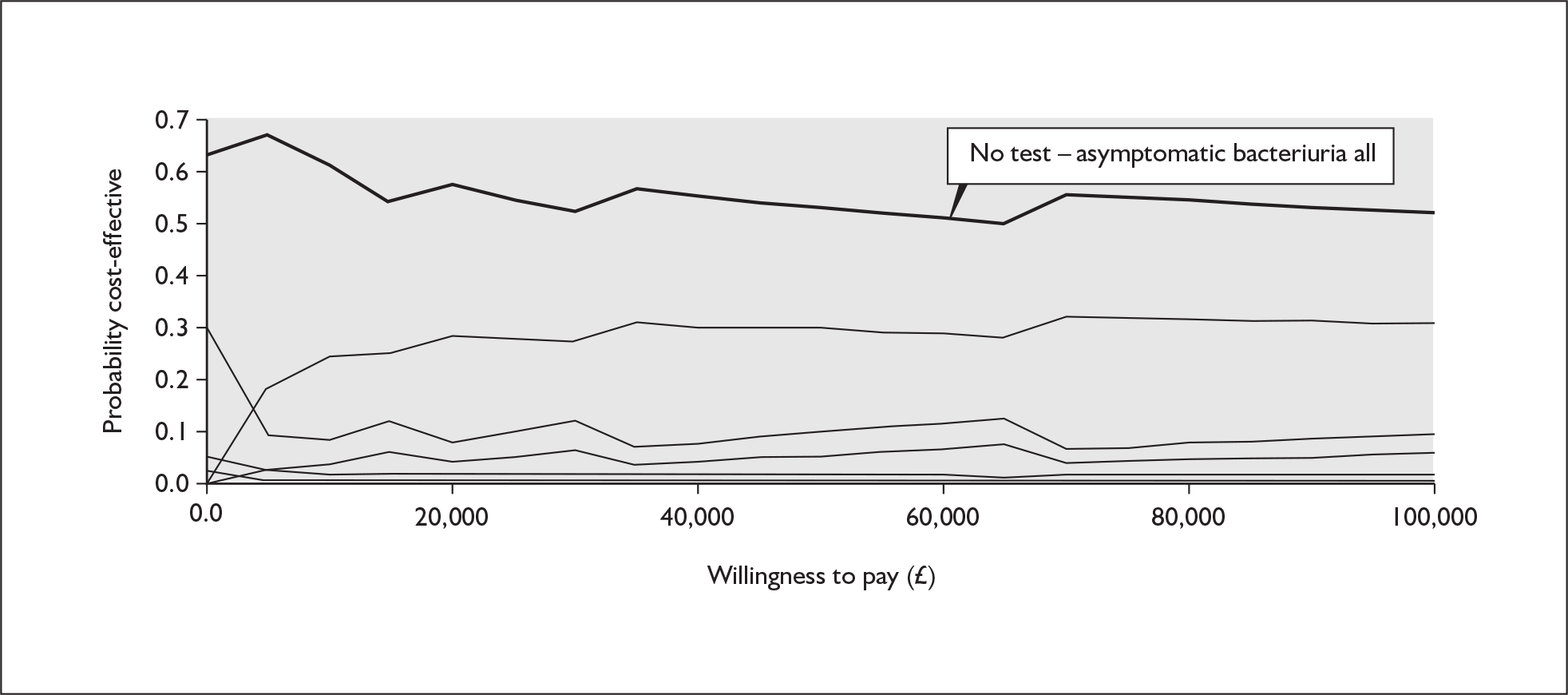
Case 9 – Asymptomatic women – perinatal mortality
From the accuracy reviews there were no data available for tests that detect risk factors for perinatal mortality. Data were available only from the effectiveness reviews for interventions. As in Case 6, the data were again analysed using a cost–consequence approach in the first instance. The interventions were first ranked according to their effectiveness. If the most effective strategy was also the least costly strategy, then it would be the dominant strategy and no further economic analysis or model would be required.
The results of the cost–consequence analysis for Case 9, are presented in Table 67. The most cost-effective intervention for treating asymptomatic women who are at risk of perinatal mortality, based on this cost–consequence analysis, is nutritional advice, which is assumed to cost zero because it could be given in a routine antenatal session. If we assumed that the cost of nutritional advice is likely to be supported by a dietician then the cost would probably in practice be greater than the next most cost-effective intervention presented in Table 67, vitamin C. However, both interventions of vitamin C and nutritional advice have 95% CI which include 1 and therefore suggest that the possibility that harm may be associated with these interventions has not been completely excluded. However, energy/protein supplementation is cheap, effective and has 95% CI for RR that do not include 1 so, on balance, it probably represents the most cost-effective strategy.
| Intervention | RR (95% CI) | Cost (UK £ 2005) |
|---|---|---|
| Nutritional advice | 0.37 (0.07–1.90) | £0a |
| Vitamin C | 0.51 (0.05–5.54) | £1.08a |
| Antibiotics (intra-amniotic infections) | 0.53 (0.13–2.18) | £12.93 |
| Progestational agents | 0.55 (0.29–1.06) | £923.55 |
| Energy/protein supplementation | 0.55 (0.31–0.97) | £1.32a,b |
| Cervical cerclage | 0.66 (0.66–1.37) | £1,219 |
Discussion
Summary of economic evaluation findings
The economic evaluation highlights a number of issues. Some of the results have pointed to areas where further research is required because they either contradict the perceived wisdom in current practice or present suggestions for interventions which have to date not been implemented at all in clinical practice. The results of the economic evaluation should not be considered in isolation and need to be considered alongside the clinical evidence and the potential weaknesses in the clinical evidence which result from either small numbers of trial participants or heterogeneity in the study populations of the dominating trials.
In the model, although the results of the deterministic analysis are noteworthy and highlight areas where further analysis may be of benefit, most confidence and weight should be given to the results of the PSA for which the full range of uncertainty in the estimates is incorporated. Furthermore, while the tests were initially subjected to analysis to ascertain tests that are of sufficient accuracy to be worth entering into the model, this was primarily performed to avoid laborious inclusion of additional redundant branches. However, for the interventions, only those for which the relative risk was < 1 were included in the PSA, also supporting greater confidence in the effectiveness of these interventions.
Cost of test/interventions/preterm birth
The key results, not already highlighted in preceding parts of the project, emerging from the health economic and modelling evaluations, were as follows. The cost of the tests for both asymptomatic and symptomatic women varied. Many were modest, particularly venous blood tests like serum IL-6, serum β-human chorionic gonadotrophin, serum estriol and serum CRP. However, they could also be substantial, in excess of £200 for tests involving amniocentesis and uterine activity monitoring.
There was also important variation in the cost of the interventions. For asymptomatic women they ranged from £1.08 for vitamin C to £14.50 for antibiotics for treating intra-amniotic infections to £140 for home visits to £1219 for cervical cerclage. The cost of all interventions for symptomatic women was significantly higher because of the inclusion of the costs of hospitalisation, estimated to be £1644. The variation in add-on costs of the interventions led to a range of total costs from £1645 for metronidazole to £2555 for atosiban (37 weeks’ gestation models).
The best estimate of additional average cost associated with a case of spontaneous preterm birth is high at approximately £15,688 for up to 34 weeks’ gestation and £12,104 for up to 37 weeks’ gestation.
Asymptomatic women
The results of the economic model for prevention of threatened preterm labour in asymptomatic women (cases 7 and 8), particularly before 34 weeks, are of especial policy relevance because it is the women who give birth without any previous symptoms or warning that are of most concern and for whom the economic burden is likely to be greatest in terms of the knock-on effects associated with premature and low-birthweight infants.
The most cost-effective options with respect to prevention of threatened preterm birth for asymptomatic women up to 34 weeks’ gestation were ‘No test/Fish oil_all’ or ‘No test/Progestational agents_all’ or ‘Previous history of preterm birth/Fish oil_all’, and up to 37 weeks‘ gestation were ‘No test/Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteruria_all’ and ‘No test/Periodontal therapy_all’. In ‘Previous history of preterm birth/Fish oil_all’, 14 cases of threatened preterm labour are averted for every 1000 mothers treated, at a mean additional cost per mother of approximately £6 relative to the least cost option of ‘Previous history of preterm birth/Fish oil_positive’ – ICER £434 per additional case of threatened preterm labour avoided.
In the asymptomatic scenarios, when the focus was prevention of perinatal death, energy and protein supplementation was arguably the most cost-effective option, although the cost–consequence analysis suggested that nutritional advice and vitamin C might also be considered from an economic perspective.
Generally stated, in the asymptomatic scenarios it appears that all the tests considered in the economic model were insufficiently accurate relative to their cost to make prior testing preferable from an economic perspective. Only when the cost of the test was assumed to be virtually zero (positive history of preterm birth) did a test feature in a potentially cost-effective test/treatment pairing. The mammary stimulation test had the highest sensitivity and specificity and although it did not feature as a recommended test in the results of this model, it may be worthy of further investigation.
Asymptomatic women – interventions
In the absence of any observed influence of testing strategy, cost-effectiveness in the asymptomatic scenarios was determined by the effectiveness relative to the cost of the interventions in isolation. The RR and cost of:
-
fish oil treatment at 34 weeks were 0.35 (95% CI 0.13–0.92; RR of preterm birth) and £16.99, respectively
-
antibiotic therapy for asymptomatic bacteruria at 37 weeks were 0.14 (95% CI 0.04–0.52; RR of preterm birth) and £3.29, respectively
-
energy protein supplementation were 0.55 (95% CI 0.31–0.97; RR of perinatal mortality) and £1.32, respectively
-
periodontal therapy at 37 weeks were 0.19 (95% CI 0.04–0.85; RR of preterm birth) and £81.50, respectively
-
progestational agents at 34 weeks were 0.15 (95% CI 0.04–0.64; RR of preterm birth) and £923.55, respectively (the RR at 37 weeks was 0.6; 95% CI 0.49–0.73).
Symptomatic women
In the symptomatic scenarios (cases 1 to 6) the most cost-effective options were:
-
delaying delivery beyond 24 h (case 1): insufficient data to model so no most cost-effective option identified
-
delaying delivery beyond 48 h (case 2): ‘Cervical length measurement < 15 mm/Indomethacin_positive’; eight additional cases of PTB are avoided for every 1000 mothers treated at an additional cost of £42 relative to the least cost option of ‘Absence of fetal breathing movements/Indomethacin_positive’
-
delaying delivery beyond 7 days (case 3): ‘Cervical length measurement < 15 mm/Indomethacin_positive’; 18 additional cases of PTB are avoided for every 1000 mothers treated at an additional cost of £42 relative to the least cost option of ‘C-reactive protein/Indomethacin_positive’
-
avoiding preterm birth at 34 weeks’ gestation (case 4): ‘Amniotic fluid interleukin-6/Hydration_positive’; nine additional cases of preterm birth are avoided for every 1000 mothers treated at an additional cost of £43 relative to the least costly option of ‘Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1/Hydration_positive’
-
avoiding preterm birth at 37 weeks (case 5): ‘No test/Indomethacin_all’; three additional cases of preterm birth are avoided for every 1000 mothers treated at an additional cost of £560 relative to the least cost option of ‘Fetal fibronection/Indomethacin_positive’
-
perinatal death (case 6): cost–consequences analysis suggested corticosteroids were the most cost-effective option.
The recommended agents by RCOG for treatment consideration in women presenting with threatened preterm labour, atosiban and nifedipine, are cost-dominated by indomethacin (but see below in Provisos/limitations arising from economic evaluation methods section).
There is incomplete consistency between the findings of the different symptomatic scenarios. However, this is in part the result of data not being available for all tests and treatments for all the cases examined. For instance there was no effectiveness data on indomethacin for the reduction in preterm birth at 34 weeks, perhaps explaining why this treatment did not feature in the most cost-effective pairing in this case.
Symptomatic women – tests
Despite this, an important general feature in contrast to the asymptomatic scenarios, is that prior testing does appear to make a useful contribution with respect to maximising cost-effectiveness, particularly where better test accuracy was achieved. The LR+, LR– and cost of some of the tests featuring in cost-effective pairings were, respectively:
-
cervical length < 15 mm (48 h): 6.43 (95% CI 5.17–8); 0.027 (95% CI 0.0017–0.42); £69.47
-
cervical length < 15 mm (7 days): 8.61 (95% CI 6.65–11.14); 0.026 (95% CI 0.004–0.182); £69.47
-
amniotic fluid interleukin-6 (34 weeks): 7.44 (95% CI 2.01–27.52); 0.14 (95% CI 0.056–0.36); £216.70.
Unfortunately test accuracy of all tests was too poor to make an impact where the focus was reducing spontaneous preterm birth at 37 weeks. No data on test accuracy were available where the focus was on reduction in perinatal deaths.
In addition to the most cost-effective options highlighted, the following results are worth noting because of clinical interest in the interventions in question.
Calcium channel blocker
It is noteworthy that the use of calcium channel blockers, a current recommendation of the RCOG, which were included in the deterministic analysis for the 48-hour, 7-day, 34-week and 37-week symptomatic models, was dominated in all models by other treatments and so was not shown to be a cost-effective intervention in any model. The data were of sufficient quality to be included in the PSA for the 7-day model only and in this case it was dominated by treatment with indomethacin. Furthermore, there were no trials identified in the review that compared calcium channel blockers directly with a placebo and so an indirect comparison was used.
Cervical cerclage
This is an acceptable treatment in UK practice which is offered to prevent preterm labour. The intervention was included in both asymptomatic deterministic models for 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation and was included in the PSA for the 34-week asymptomatic model. In the 34-week asymptomatic model, treatment with fish oil dominated treatment with cerclage. This dominance is clear because cerclage was estimated to cost £1219 compared to a cost of fish oils of £16.99. The corresponding RRs for the cerclage and fish oils were 0.75 (95% CI 0.58–0.98) and 0.35 (95% CI 0.13–0.92), respectively. This result re-iterates the importance of pursuing further research on the potential benefits of fish oil, which based on current available evidence appears to be an effective and relatively cheap intervention.
Testing for bacterial vaginosis
This was not included on any of the asymptomatic models because it did not meet the required threshold criteria. This strategy was dominated by other test/treatment options because of the low accuracy of the test for BV.
The economic model showed that the costs applied to the tests and treatments were largely superfluous to the overall results. Key drivers in the analyses included the poor sensitivities and specificities of some of the tests, which meant that in some cases (Symptomatic women 37 weeks: No test/Indomethacin_all; Asymptomatic women 34 weeks: Previous history of preterm birth/Fish oil_all; Asymptomatic women 37 weeks: No test/Asymptomatic bacteriuria_all) testing would not be recommended as ‘worthwhile’ options for ‘Test/Treat_positive’ strategies. For the treatments the key driver in the results was their relative risk, which led to the treatment with the lowest RR being recommended. The cost of spontaneous preterm birth used in the analysis was high, at approximately £15,689. The combination of poor test accuracy and relatively cheap effective interventions led to a ‘No test/Treat_all’ strategy dominating the results because spontaneous preterm birth is a serious and costly condition.
Provisos/limitations arising from economic evaluation methods
The use of an economic model fed by data on accuracy of tests and effectiveness of the interventions from the most recently available systematic reviews and meta-analyses of the evidence is a major strength of the project reported. Similarly, the model was developed by an experienced health economic and modelling team with clinical and methodological input at all stages, from the original design of the model, through its execution, to the final interpretation of its results. It has important features such as probabilistic sensitivity analysis, which helps to deal with the ever-present challenges arising from uncertainty.
However, particularly given the accelerated time-scale of the work, the complexity of the problem and the fact that there were few previous health economic models on which to build (see Systematic review of economics and costs studies at the beginning of this chapter), it is inevitable that there are limitations as follows:
Single test results
The model considers only single test results; combinations of tests or combinations of treatments may offer opportunities that are more cost-effective and these could not have been incorporated into the model as conceived unless data were available for combined tests or treatments (which they were not).
Spontaneous preterm birth outcome
The existing model primarily focuses on the outcome spontaneous preterm birth. Although there is some consideration of perinatal mortality too, the impact of test/treatment combinations on other outcomes, particularly their effects on infants that do not result in death, will be overlooked. This is especially problematic if the effect on these other outcomes counteracts or offsets the benefit implied by the reduction in preterm birth. Indomethacin, a treatment that features in a number of potentially cost-effective pairings, is a possible example where reduction in spontaneous preterm birth may be offset by effects on infant circulation (persistent patent ductus arteriosus). However, it is also possible that the current model generally underestimates the effect of test/treatment combinations because benefits attributable to reduction in outcomes like infant morbidity and disability are not fully accounted for.
Side effects
Similarly, the existing model assumes that side effects of tests and treatments are negligible. This seems a reasonable assumption for many of the tests and interventions, but may be definitely open to challenge for invasive tests involving amniocentesis (which carries the risk of rupturing the amniotic membrane and chorioamnionitis) and some pharmacological interventions like tocolytic agents. This may be particularly important in the asymptomatic scenarios where the universal use of interventions without prior testing is being speculated on, such as treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria. If these are pursued, confirmation of absence of adverse events, particularly for the baby, will require detailed investigation. It should also be noted that not incorporating adverse events into the model would accentuate the apparent superiority of ‘No test/Treat_all’ strategies. If there were associated adverse events there would be added value from avoiding false positives, such as would be achieved by a predictive test for preterm birth with high specificity; something that is not captured in the current model.
Clinical relevance of test/treatment pairings
Finally, care is required for the interpretation of some of the combinations of test/treatment pairs generated by the model. Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria provide an example in that a prior test, for bacteriuria, is implied as part of the ‘intervention’. Thus test/treatment pairings are created in the modelling process without regard to clinical relevance, which must be carefully checked when results are interpreted.
Perspective of the economic analysis
The restriction of the economic model to an NHS perspective could also be considered a potential limitation, given that there are likely to be obvious costs to patient, family and society beyond the health-care sector. The main counterargument is that because most assessments of cost-effectiveness are performed from the perspective of the health-care payer, designing the economic model from the NHS perspective remains most relevant to facilitate comparison with other uses of health-care resources. Ideally cost-effectiveness taking into account societal and individual costs is worth exploring; however, experience suggests that data to do this accurately are rarely routinely available and would require primary data collection, which was outside the original agreed protocol. It must be acknowledged that limiting the analysis to the NHS perspective may particularly lead to underestimation of certain costs, such as advice to rest or diet change where the onus is placed on the individual, their family and society to achieve implementation. However, in the absence of versions of the model from an individual and societal perspective, such considerations can only be incorporated into the conclusions qualitatively.
Provisos/limitations arising from problems with primary data
Despite features of the model like PSA, which help deal with limitations arising from the primary data, uncertainty about what the true accuracy, effectiveness or cost parameters are for particular tests and interventions remains a major challenge in this economic model. These limitations are discussed in more detail below and represent challenges and restrictions to conclusions that can be drawn concerning cost-effectiveness.
Stochastic variation in the model parameters
There is marked stochastic variation in many of the parameters, manifest in wide 95% CI. The effect of this on conclusions of the economic modelling is largely taken into account through PSA. However, the implications of the 95% CI still need to be considered, particularly where the 95% CI include values of RR > 1.0, implying that the intervention causing increased numbers of cases of spontaneous preterm birth remains a possibility based on the available data. This was the rationale for separating Group 1 interventions, where ‘harm’ was unlikely to be a possibility, from Group 2 interventions, where it was.
Uncertainty from systematic variation
In addition to chance, there is uncertainty arising from systematic variation, including operation of bias. Provisos sometimes need to be added concerning the fact that there may be threats to validity. Parameters based on single, small studies with very small numbers of outcomes raise not just concerns about the effect of chance (reflected in the 95% CI) but susceptibility to other related bias too.
Uncertainty from heterogenicity between studies
There is sometimes further uncertainty arising where estimates of accuracy or effectiveness are based on several primary studies and there is heterogeneity between the results (more variation than can be accounted for by chance alone). If the cause of this heterogeneity cannot be isolated, there may be concern about use of a summary measure from a meta-analysis. This is a theoretically important issue for many estimates of test accuracy, but effectiveness estimates based on several of the included RCTs may also be affected.
Data from indirect comparisons
Some of the estimates of effectiveness were derived from indirect comparison, e.g. atosiban. Although a useful method of deriving an estimate of effect when there is no direct comparison, in this case with placebo, caution does need to be observed as comparisons are potentially confounded despite the data being RCT based.
Uncertainty in cost estimates
There is general uncertainty about the cost estimates used for many tests and some interventions too. The routinely available information is limited, particularly accurate and specific costs for any particular test, thus removing the differentiation between these tests in the analysis. Ideally, further primary data collection of costs would have been pursued if it had been predicted to be so important when the project was first designed and the protocol devised. The relative cost of available tests to treatments is critical to the current health economic conclusions, as is the effect of test cost on the level of test accuracy needing to be demonstrated by a test for it to have a chance of a ‘Test/Treat_positive’ option becoming the preferred approach with respect to its cost-effectiveness. A particular concern is the NHS costs associated with non-pharmacological interventions like dietary advice. Independent of concerns already discussed about incorporating costs to individuals and society, is the possibility that if implemented, hospital facilities might have to be used in ways not originally envisaged, such as support from dieticians.
Unfortunately, one or other of these sources of uncertainty alone or in combination affects many of the test/treatment pairings emerging as being most cost-effective in each of the scenarios. The following are specific limitations from particular reviews:
-
Estimates of the effectiveness of fish oils are based on two studies involving around 250 women.
-
For antibiotic treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria the quality of trials was poor and the RR for the effect on preterm birth is based on just one trial of questionable quality including only 69 participants.
-
Estimates of the effect of energy/protein supplementation on perinatal mortality are based on four trials of which only one is considered to be of adequate quality. In addition, one of the trials included looks at rural Gambian women with chronically marginal nutrition, and another looked at women in a Bogota slum, so their relevance to women in the UK might be questioned. Assumptions about the low cost of this intervention (£1.32) might also be open to challenge.
-
For nutritional advice, the parameter in the model was based on two studies of questionable quality one of which was very small (n = 20) and the other, of 429 participants, was based in a rural population in Greece, many of whom had nutritional problems. Their generalisability to the UK is again questionable. Furthermore, the assumed near-zero costs to the NHS may be open to challenge because it is likely that advice/support would be required to achieve the desired dietary changes.
-
For the test of cervical length < 15 mm in threatened preterm labour, Figures 67 and 68 indicate that there is heterogeneity in the LR+ and LR– estimates among the included studies that is not completely captured by using the estimates and their 95% CI from the best quality included study.
-
The effectiveness estimate for indomethacin is based on two small RCTs involving 70 subjects in all. Furthermore, as already indicated, indomethacin has effects on the infant that may counteract the beneficial effect of reduced spontaneous preterm birth.
-
The estimates of test accuracy for amniotic fluid interleukin-6 predicting spontaneous preterm birth at 34 weeks are based on one study.
-
The effectiveness parameters for the effect of hydration are based on only two small trials of 228 women in total.
-
The evidence for periodontal therapy was provided by one quasi-RCT (n = 351).
Provisos/limitations arising from omissions
There was absence or effective absence of information on certain key parameters. There may be new or established tests or interventions that have not yet been fully evaluated. Periodontal assessment is an intervention that falls into this category. In addition to this there may well be tests and treatments in development that do not appear in the literature at all, of which we would be unaware. Finally, some systematic reviews results or updates thereof, arrived after the modelling had been completed: β-human chorionic gonadotrophin testing and treatment of bacterial vaginosis. However, the RR for treatment for bacterial vaginosis was greater than 1 and so this would be extremely unlikely to lead to changes in the main findings.
Findings in the light of limitations
The observed limitations do impinge on the initially stated main findings of the economic evaluation, particularly the confidence that can be placed on the specific tests and interventions emerging as potentially preferred from a cost-effectiveness perspective. However, the general findings probably remain unaffected.
In the asymptomatic scenarios, it seems likely that existing tests are not of sufficient accuracy relative to their cost, to improve the cost-effectiveness of strategies to reduce spontaneous preterm birth through use in all mothers of effective, low-cost interventions with low likelihood of side effects. The systematic reviews of effectiveness suggest what these might be, but confirmation of effectiveness is required for most of the front-runners, and in all cases greater scrutiny and evaluation of possible side effects would be essential. New tests may emerge that challenge the above conclusion, but the economic modelling indicates that the accuracy must be much higher than currently achieved, and any new tests must be of modest cost, less than the costs of the interventions being employed.
In the symptomatic scenarios the general possibility that prior testing may enhance the cost-effectiveness of strategies to delay delivery in threatened preterm labour again seems robust, although the specific test/treatment pairings that might achieve this definitely require further evaluation. Debatably, there may be sufficient grounds to directly evaluate the overall effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of implementing systematic use of specific test/treatment pairs – say Cervical length < 15 mm/Indomethacin_positive versus cervical length < 15 mm/Calcium channel blockers_positive versus β-human chorionic gonadotrophin/Indomethacin_positive versus β-human chorionic gonadotrophin/Calcium channel blockers_positive. However, probably, better estimates of key effectiveness and test accuracy parameters are required before proceeding to this.
As indicated at the beginning of the section, there have been some previous economic evaluations with which we can compare our findings. However, we should highlight that we believe this project to be the only economic evaluation to have attempted to assess cost-effectiveness across the complete range of test and treatment combinations which might possibly be employed, rather than focusing on specific test/treatment pairings. Direct comparison of our findings with other economic evaluations is thus impeded. However, with this caution, and noting that we assessed all but one of the past economic evaluations to be open to bias:
-
Our evaluation supports previous conclusions about lack of evidence that screening for and treatment of bacterial vaginosis is likely to be a cost-effective strategy. The systematically reviewed data on both test accuracy and effectiveness are not convincing.
-
Suggestions that fetal fibronectin test or cervical length measurement may be useful are supported, more so for cervical length measurement. This is, however, only in the context of delaying delivery in symptomatic mothers and with the proviso that better test accuracy data are probably still required.
-
Terbutaline was found to be a potentially cost-effective intervention in past evaluations, albeit in three studies with concerns about study quality. This evaluation, however, provided no direct support for the superiority of terbutaline relative to other tocolytic agents.
Recommendations for practice
The findings of the current health economic evaluation are insufficient on their own to dictate changes in practice. Further research to clarify key aspects of test accuracy, effectiveness, cost and cost-effectiveness should be the priority.
Recommendations for research
Improving estimates of effectiveness for the interventions appearing in the potentially cost-effective test/treatment pairings would appear to be the most important way of improving estimates of cost-effectiveness, particularly for:
-
fish oils
-
other dietary interventions, including nutritional advice
-
treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria
-
indomethacin
-
hydration
-
periodontal therapy.
Improved test accuracy data should also be pursued on tests such as cervical length, amniotic interleukin-6 and the mammary stimulation test. As well as new evaluations, individual data meta-analysis of existing test accuracy studies may be an approach to better understand the heterogeneity between test accuracy study estimates. Detailed examination and improved cost estimates of all tests and treatments considered in this model are also essential.
There may also be value in further developing the existing economic model to consider simultaneously maternal and child outcomes associated with spontaneous preterm birth and to capture the impact of side effects where data on these were available. More ambitiously, the model could attempt to predict the effect of interventions on all the major inter-related threats to child and maternal health, spontaneous preterm birth, intrauterine growth retardation and pre-eclampsia. A number of tests and treatments are claimed to have predictive power and effectiveness in all these entities. The complexity of such a model would be great, particularly if it attempted to explore whether combinations of tests or combinations of treatments might be more cost-effective. However, given the importance of potential research recommendations stated, any priority assignment would be relative. Rigorous evaluation of tests with modest cost and minimal invasiveness, whose initial assessments suggest that they may have high levels of accuracy (e.g. phIGFBP-1, but there may be others), and undertaking RCTs evaluating effective interventions with modest cost would represent priorities that are familiar to clinicians.
Chapter 7 Report conclusions
Introduction
This project was undertaken to identify combinations of tests and treatments that would lead to reduction in spontaneous preterm birth, a major contributor to perinatal and neonatal morbidity and mortality. This health technology assessment completed three distinct pieces of work to contribute to this goal:
-
a series of systematic reviews of test accuracy of the prediction of spontaneous preterm birth
-
a series of systematic reviews of effectiveness of interventions with potential to reduce cases of spontaneous preterm birth and its complications
-
a health economic evaluation, including an economic model, of the combined effect of tests and treatments on spontaneous preterm birth.
Each of these has been described in detail, their main findings reported and the conclusions discussed in the light of any limitations identified at the end of each of the three preceding chapters. This chapter attempts to focus on the key findings and limitations emerging from all the work undertaken. It is not a comprehensive summary of all the issues raised, for which the reader is encouraged to consult the previous three chapters.
Main findings
The methodological quality of the literature reviewed for both accuracy and effectiveness was generally poor, with few exceptions (e.g. fetal fibronectin testing, cervical length measurement, fetal breathing movements, interleukin-6 (IL-6), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents and oxytocin antagonists).
-
The accuracy of most of the tests purported to be of value in prediction of spontaneous preterm birth was disappointing. Likelihood ratios as a measure of the tests’ ability to predict all mothers who will develop preterm birth spontaneously were particularly poor.
-
The effectiveness of several interventions that might reduce the number of cases of spontaneous preterm birth or its complications was, in contrast, more promising. As well as well-known interventions like tocolysis for delaying birth and antenatal corticosteroids for lung maturity, the review has also focused attention on other interventions like bed rest, progesterone, fish oil, periodontal therapy, vitamin supplementation and antibiotic treatments.
-
By the standard of many health-care interventions, those indicated to be potentially useful in avoiding spontaneous preterm birth were noted to be affordable (costs generally less than £1650 for the whole of pregnancy even in the most expensive case of having to use an oxytocin antagonist, often substantially so).
-
From the perspective of cost-effectiveness among asymptomatic women in early pregnancy and based on the current proviso of the limited evidence, providing effective treatment, e.g. periodontal care, fish oil, progesterone etc. without prior testing is likely to be preferred to using a test followed by treating those who are positive. The provisos are that the true costs remain modest, that any effect on spontaneous preterm birth is not offset by contrary effects on important infant outcomes and that there are no serious adverse events associated with widespread use of the interventions in low-risk mothers. For women symptomatic of threatened preterm labour, prior testing before institution of therapy is likely to be more cost-effective, e.g. with ultrasound measurement of cervical length (15 mm) followed by indomethacin for those with shortened cervix.
Strengths of the project
There have been no previous attempts to systematically assess the potential cost-effectiveness of different combinations of tests and treatments for preventing spontaneous preterm birth as a whole. The particular strength of this report is that it combines the results from a wide range of test accuracy systematic reviews with a wide range of different types of interventions in one economic model. The aim is to give clinicians and researchers a much more comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge in this area than would be gained from single studies.
Limitations of the project
-
It is acknowledged that not all possibly relevant tests and interventions have been included in this report.
-
It is possible that there are new tests and treatments which have either not been fully evaluated or have not reached evaluation stage.
-
The systematic reviews of test accuracy encountered several challenges (see Chapter 3). However, none of these seriously threatened the validity of the main finding that the accuracy of most of the tests was disappointing. Better reviews and more primary research on those tests examined are unlikely to change the main conclusions (except for emerging tests, e.g. phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1), cervicovaginal β-human chorionic gonadotrophin).
-
The main limitation with the systematic reviews of effectiveness (see Chapter 4) is the poor quality of many of the studies and the paucity of direct comparative data for some of the most commonly used interventions for threatened preterm labour, e.g. tocolytics.
-
Although the direction and size of effect for the following interventions for asymptomatic women in early pregnancy: periodontal care, fish oil, progesterone and antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria, suggested their effectiveness, there is continuing uncertainty as to whether beneficial effects to the baby in reducing risk of spontaneous preterm birth are offset by contrary trends in infant outcomes such as perinatal death.
-
There are many limitations to the economic model used, partly arising from the quality of the accuracy and effectiveness data (see above), partly from lack of quality information concerning costs, and partly from the modelling approach. However, the main findings again do not seem to be highly susceptible to these limitations. It is virtually self-evident that an effective, affordable and safe intervention is unlikely to be improved upon by applying a test with poor accuracy. Furthermore, with a condition as serious and costly as spontaneous preterm birth, correct identification of those who will develop this outcome will be more important than correct categorisation of those who will not develop it (see Discussion in Chapter 4).
-
The small amount of information on adverse events associated with interventions, particularly the longer-term effects to both mother and child, is an important limitation, as is the lack of information on side effects of the tests.
Overall conclusion
The main initially stated findings appear largely unaffected by the limitations identified although it is difficult to know how much impact each of the limitations, together and in combination, would exert. Of these findings, the main driver of recommendations for practice and research is the likelihood that an effective intervention applied to all asymptomatic mothers in early pregnancy without preceding testing will be the most cost-effective approach to reducing spontaneous preterm birth. There are several candidates for an appropriate intervention: periodontal care, fish oil, progesterone and antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria, but these require further investigation because current data are limited. For women symptomatic of threatened preterm labour with a viable fetus in later pregnancy, there is a need to delineate which of the most promising tests (cervical length, fibronectin, phIGFBP-1 and absence of fetal breathing movements) is most accurate and cost-effective on its own or in combination. Some interventions, like calcium channel blockers and oxytocin antagonists, require further direct evidence on effectiveness; others, like indomethacin, need confirmation of absence of adverse events and ‘reasonableness’ of their cost.
Recommendations for practice
It is premature to suggest implementation at present. However, feasibility and acceptability to mothers and carers of application of the above strategies needs to be explored. Some consideration needs to be given to whether we should continue to do certain tests whose main perceived value up to now has been to help identify the risk of spontaneous preterm birth. Likewise, some consideration needs to be given to whether certain public health interventions e.g. smoking cessation programmes, may potentially reduce spontaneous preterm birth.
Recommendations for research
There is a need for systematic reviews to map the aetiopathogenesis of spontaneous preterm birth.
-
Researchers may wish to consult more widely to ensure that all relevant screening, testing and interventions are considered for reviews in future projects. They may wish to explore ways of involving consumers in priority setting. Consensus conferences may be needed to define important questions and study designs for the future.
-
There is a need for good-quality randomised controlled trials that directly investigate whether potentially effective interventions, e.g. periodontal care, smoking cessation, fish-oil supplementations, cervical cerclage, calcium channel blockers and oxytocin antagonists, are indeed effective not only in reducing spontaneous preterm birth but also in lowering perinatal mortality/morbidity.
-
Evaluation of pilot schemes for universal treatment of mothers with effective pharmacological interventions like progesterone should be considered. Such evaluation should include investigation of adverse events and actual costs.
-
There is a need for individual patient data meta-analyses of effectiveness literature to better delineate subgroup effects more powerfully.
-
Test accuracy individual patient data meta-analyses are required for delineating the added value of tests and for studying the value of test combinations in light of the interdependence that exists between tests.
-
Rigorous evaluation of tests with modest cost whose initial assessments suggest that they may have high levels of accuracy, e.g. phIGFBP-1, may fall into this category, but there may be other contenders in development which would need further investigation.
-
Multiple (direct and indirect) comparisons considering all the tests and interventions may help delineate their rank. Methodological research is needed to assess if this could produce outputs suitable for decision analysis.
-
There is a need for the development of an economic model that considers not just preterm birth, but other related outcomes, particularly those relevant to the infant, such as perinatal death and small-for-gestational-age. This would help to enable the development of comprehensive care pathways. Such a modelling project should make provision for primary data collection on costs.
-
There is a need to study cost-effectiveness of test/treatment combinations for prevention of preterm birth in the subgroup of multiple pregnancies; to measure iatrogenic preterm birth rate as an outcome among all preterm birth; and last but not least, to simultaneously study cost-effectiveness of test/treatment combinations for prevention of all preterm birth, pre-eclampsia and fetal growth restriction.
-
Value of information analysis is needed to determine prioritisation of future research.
Acknowledgements
Contribution of authors
All authors contributed to the idea, design and protocol for the project. K.S. Khan and H. Honest were responsible for the accuracy reviews. C.A. Forbes, K.H. Durée, G. Norman and S.B. Duffy were responsible for the effectiveness reviews. A. Tsourapas, T.E. Roberts, P.M. Barton and S.M. Jowett were responsible for the economic reviews and modelling. H. Honest was responsible for the day-to-day management of the project. All authors were involved in the final integration and interpretation of the results from the three components (accuracy, effectiveness and economics modelling) and the drafting of the report and have approved the final version.
Expert list (England, UK)
Zarko Alfirevic, Consultant Obstetrician, Liverpool Women’s Hospital; Steve Walkinshaw, Consultant Obstetrician, Liverpool Women’s Hospital; Steve Thornton, Consultant Obstetrician, Coventry Hospital; Ronnie Lamont, Consultant Obstetrician, Northwick Park.
Study selection and data extraction
Sarah Chapman, External Reviewer, Oxford; Shelley Adams, 5th MB, Birmingham University; Lucy Higgins, 5th MB, Birmingham University; Caroline Fox, Senior House Officer, Birmingham University; Lucas Bachmann, Senior Research Fellow, University of Zurich; Arravanthan Coomarasamy, Specialist Registrar, Birmingham Women’s Hospital; Pedro Cabeza, Specialist Registrar, Birmingham Women’s Hospital; Christina Schlegel, Research Fellow, University of Zurich.
Health economic analysis
Ariadna Juarez Garcia, Post-doctoral Research Fellow, Birmingham University, advised on the construction of the model, use of cost data and provided detailed advice on the probabilistic sensitivity analysis.
Investigators who provided additional data and comments on previously published reviews
With apologies if there are others who have been inadvertently missed: Roberto Eduardo Bittar, Melanie Ebber (née Essen), Shai Elizur, Suzanne Farrell, Francois Goffinet, Wendy Hansen, Peter Holbrook, Mark Klebanoff, Nestor Lopez, Rosemarie McMillon, Francois Mallard, Arun Mittal, Samarina Musaad, Melanie Plaut, Waranuch Pithipat, Lucilla Poston, Marta Radnai, Balu Rukmini, Luis Sanchez-Ramos, David Savitz, Andrew Shennan, Ida Vogel.
Local experts (Birmingham, UK)
Mark Kilby, Consultant Obstetrician, Birmingham Women’s Hospital; Martin Whittle, Consultant Obstetrician, Birmingham Women’s Hospital; Andy Ewer, Consultant Neonatologist, Birmingham Women’s Hospital.
Disclaimers
The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Morrison JJ, Rennie JM. Clinical, scientific and ethical aspects of fetal and neonatal care at extremely preterm periods of gestation. BJOG 1997;104:1341-50.
- Villar J, Abalos E, Carroli G, Giordano D, Wojdyla D, Piaggio G, et al. Heterogeneity of perinatal outcomes in the preterm delivery syndrome. Obstet Gynecol 2004;104:78-87.
- Lumley J. Defining the problem: the epidemiology of preterm birth. BJOG 2003;110:3-7.
- Kramer MS, Demissie K, Yang H, Platt RW, Sauve R, Liston R. The contribution of mild and moderate preterm birth to infant mortality. Fetal and Infant Health Study Group of the Canadian Perinatal Surveillance System. JAMA 2000;284:843-9.
- Mikkola K, Ritari N, Tommiska V, Salokorpi T, Lehtonen L, Tammela O, et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome at 5 years of age of a national cohort of extremely low birth weight infants who were born in 1996–1997. Pediatrics 2005;116:1391-400.
- Mathews TJ, Menacker F, MacDorman MF. Infant mortality statistics from the 2002 period linked birth/infant death data set. Natl Vital Stat Rep 2004;53:1-30.
- Halvorsen T, Skadberg BT, Eide GE, Roksund OD, Carlsen KH, Bakke P. Pulmonary outcome in adolescents of extreme preterm birth: a regional cohort study. Acta Paediatr 2004;93:1294-300.
- Halvorsen T, Skadberg BT, Eide GE, Roksund O, Aksnes L, Oymar K. Characteristics of asthma and airway hyper-responsiveness after premature birth. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2005;16:487-94.
- Kollee LA. Twenty-five week limit for viability of the foetus is ethically correct. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 2005;149.
- Seubert DE, Stetzer BP, Wolfe HM, Treadwell MC. Delivery of the marginally preterm infant: what are the minor morbidities?. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;181:1087-91.
- Gladstone IM, Katz VL. The morbidity of the 34- to 35-week gestation: should we reexamine the paradigm?. Am J Perinatol 2004;21:9-13.
- Schmitt SK, Sneed L, Phibbs CS. Costs of newborn care in California: a population-based study. Pediatrics 2006;117:154-60.
- Kollee LA. Rehospitalization of very preterm infants. Acta Paediatr 2004;93:1270-1.
- Escobar GJ, Clark RH, Greene JD. Short-term outcomes of infants born at 35 and 36 weeks gestation: we need to ask more questions. Semin Perinatol 2006;30:28-33.
- Byrne B, Morrison JJ. Preterm birth. Clin Evid 2004:1903-22.
- Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Sutton PD, Ventura SJ, Menacker F, Munson ML. Births: final data for 2003. Natl Vital Stat Rep 2005;54:1-116.
- McPheeters ML, Miller WC, Hartmann KE, Savitz DA, Kaufman JS, Garrett JM, et al. The epidemiology of threatened preterm labor: a prospective cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;192:1325-9.
- Office for National Statistics (ONS) . Live Births in 2004, Selected Background Data (final), England and Wales n.d. http://www.statistics.gov.uk/statbase/Product.asp?vlnk=14010 (accessed 24 August 2005).
- Escobar GJ, McCormick MC, Zupancic JA, Coleman-Phox K, Armstrong MA, Greene JD, et al. Unstudied infants: outcomes of moderately premature infants in the NICU. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2006;91:F238-44.
- Marbella AM, Chetty VK, Layde PM. Neonatal hospital lengths of stay, readmissions, and charges. Pediatrics 1998;101:32-6.
- Honest H, Bachmann LM, Coomarasamy A, Gupta JK, Kleijnen J, Khan KS. Accuracy of cervical transvaginal sonography in predicting preterm birth: a systematic review. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;22:305-22.
- Bachmann LM, Coomarasamy A, Honest H, Khan KS. Elective cervical cerclage for prevention of preterm birth: a systematic review. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2003;82:398-404.
- Honest H, Bachmann LM, Gupta JK, Kleijnen J, Khan KS. Accuracy of cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin test in predicting risk of spontaneous preterm birth: systematic review. Br Med J 2002;325.
- Crowley P. Prophylactic corticosteroids for preterm birth. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000.
- Willard D, Gandhour R, Ebtinger B, Messer J. Etiology and prevention of severe mental handicaps. Arch Fr Pediatr 1982;39:471-5.
- Lee SK, McMillan DD, Ohlsson A, Boulton J, Lee DS, Ting S, et al. The benefit of preterm birth at tertiary care centers is related to gestational age. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;188:617-22.
- Coomarasamy A, Knox EM, Gee H, Khan KS. Oxytocin antagonists for tocolysis in preterm labour – a systematic review. Med Sci Monit 2002;8:RA268-RA273.
- Egger M, Smith GD. Meta-analysis. Potentials and promise. Br Med J 1997;315:1371-4.
- Fryback DG, Thornbury JR. The efficacy of diagnostic imaging. Med Decis Making 1991;11:88-94.
- Guyatt GH, Tugwell PX, Feeny DH, Haynes RB, Drummond M. A framework for clinical evaluation of diagnostic technologies. CMAJ 1986;134:587-94.
- Sackett DL, Haynes RB. The evidence base of clinical diagnosis. London: BMJ Books; 2002.
- Honest H, Khan KS. WHO Reproductive Health Library (No.5). Geneva: WHO/RHR; 2002.
- Khan KS, Dinnes J, Kleijnen J. Systematic reviews to evaluate diagnostic tests. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2001;95:6-11.
- Khan KS, Kunz R, Kleijnen J, Antes G. Systematic reviews to support evidence-based medicine: how to review and apply findings of systematic reviews. London: Royal Society of Medicine; 2003.
- Khan KS, ter Riet G, Glanville J, Sowden AJ. Undertaking systematic reviews of research on effectiveness: CRD’s guidance for those carrying out or commissioning reviews. York: University of York; 2001.
- Cochrane Methods Group on Systematic Review of Screening and Diagnostic Tests 2005. http://www.cochrane.org/sadt/index.htm.
- Honest H, Bachmann LM, Khan K. Electronic searching of the literature for systematic reviews of screening and diagnostic tests for preterm birth. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2003;107:19-23.
- Irwig L, Macaskill P, Glasziou P, Fahey M. Meta-analytic methods for diagnostic test accuracy. J Clin Epidemiol 1995;48:119-30.
- Khan KS, Bakour SH, Bossuyt PM. Evidence-based obstetric and gynaecologic diagnosis: the STARD checklist for authors, peer-reviewers and readers of test accuracy studies. BJOG 2004;111:638-40.
- Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP, Irwig LM, et al. The STARD statement for reporting studies of diagnostic accuracy: explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med 2003;138:W1-12.
- Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Dinnes J, Reitsma J, Bossuyt PM, Kleijnen J. Development and validation of methods for assessing the quality of diagnostic accuracy studies. Health Technol Assess 2004;8:1-234.
- Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Bossuyt PM, Kleijnen J. Sources of variation and bias in studies of diagnostic accuracy: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med 2004;140:189-202.
- Honest H, Bachmann LM, Sundaram R, Gupta JK, Kleijnen J, Khan KS. The accuracy of risk scores in predicting preterm birth – a systematic review. J Obstet Gynaecol 2004;24:343-59.
- Honest H, Bachmann LM, Knox EM, Gupta JK, Kleijnen J, Khan KS. The accuracy of various tests for bacterial vaginosis in predicting preterm birth: a systematic review. BJOG 2004;111:409-22.
- Honest H, Bachmann LM, Ngai C, Gupta JK, Kleijnen J, Khan KS. The accuracy of maternal anthropometry measurements as predictor for spontaneous preterm birth – a systematic review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2005;119:11-20.
- Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kirby J, Roderick P. A methodological review of how heterogeneity has been examined in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy. Health Technol Assess 2005;9:1-113.
- Honest H, Khan KS. Reporting of measures of accuracy in systematic reviews of diagnostic literature. BMC Health Serv Res 2002;2.
- Jaeschke R, Guyatt GH, Sackett DL. Users’ guides to the medical literature. III. How to use an article about a diagnostic test. B. What are the results and will they help me in caring for my patients? The Evidence-Based Medicine Working Group. JAMA 1994;271:703-7.
- Grimes DA, Schulz KF. Refining clinical diagnosis with likelihood ratios. Lancet 2005;365:1500-5.
- Fagan TJ. Letter: nomogram for Bayes theorem. N Engl J Med 1975;293.
- Khan KS, Honest H, Bachmann LM. A generic framework for making clinical decisions integrating diagnostic and therapeutic research evidence in preterm birth. Fetal Matern Med Rev 2003;14:239-49.
- The Cochrane Manual 2005. http://www.cochrane.org/admin/manual.htm.
- Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, Stroup DF. Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Quality of reporting of meta-analyses. Lancet 1999;354:1896-900.
- Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Claxton K, Golder S, Riemsma R, et al. Review of guidelines for good practice in decision-analytic modelling in health technology assessment. Health Technol Assess 2004;8.
- Morrison JC, Pittman KP, Martin RW, McLaughlin BN. Cost/health effectiveness of home uterine activity monitoring in a Medicaid population. Obstet Gynecol 1990;76:76S-81S.
- Mozurkewich EL, Naglie G, Krahn MD, Hayashi RH. Predicting preterm birth: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182:1589-98.
- Muller E, Berger K, Dennemark N, Oleen-Burkey M. Cost of bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy. Decision analysis and cost evaluation of a clinical study in Germany. J Reprod Med 1999;44:807-14.
- Nicholson WK, Frick KD, Powe NR. Economic burden of hospitalizations for preterm labor in the United States. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:95-101.
- Petrou S, Sach T, Davidson L. The long-term costs of preterm birth and low birth weight: results of a systematic review. Child Care Health Dev 2001;27:97-115.
- Petrou S. Economic consequences of preterm birth and low birthweight. BJOG 2003;110:17-23.
- Petrou S, Mehta Z, Hockley C, Cook-Mozaffari P, Henderson J, Goldacre M. The impact of preterm birth on hospital inpatient admissions and costs during the first 5 years of life. Pediatrics 2003;112:1290-7.
- Ancel PY, Saurel-Cubizolles MJ, Di Renzo GC, Papiernik E, Breart G. Very and moderate preterm births: are the risk factors different?. BJOG 1999;106:1162-70.
- Berkowitz GS, Blackmore-Prince C, Lapinski RH, Savitz DA. Risk factors for preterm birth subtypes. Epidemiology 1998;9:279-85.
- Botsis D, Papagianni V, Vitoratos N, Makrakis E, Aravantinos L, Creatsas G. Prediction of preterm delivery by sonographic estimation of cervical length. Biol Neonate 2005;88:42-5.
- Carr-Hill RA, Hall MH. The repetition of spontaneous preterm labour. BJOG 1985;92:921-8.
- de Carvalho MH, Bittar RE, Brizot ML, Bicudo C, Zugaib M. Prediction of preterm delivery in the second trimester. Obstet Gynecol 2005;105:532-6.
- de H I, Harlow BL, Cramer DW, Frigoletto FD. Spontaneous preterm birth: a case–control study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;165:1290-6.
- Goldenberg RL, Iams JD, Mercer BM, Meis PJ, Moawad AH, Copper RL, et al. The Preterm Prediction Study: the value of new vs standard risk factors in predicting early and all spontaneous preterm births. NICHD MFMU Network. Am J Public Health 1998;88:233-8.
- Iams JD, Goldenberg RL, Mercer BM, Moawad A, Thom E, Meis PJ, et al. The Preterm Prediction Study: recurrence risk of spontaneous preterm birth. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Maternal–Fetal Medicine Units Network. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:1035-40.
- Kristensen J, Langhoff-Roos J, Kristensen FB. Implications of idiopathic preterm delivery for previous and subsequent pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol 1995;86:800-4.
- Weidinger H, Wiest W. A comparative study of the epidemiological data of pregnancies with and without tendencies to premature delivery. J Perinat Med 1974;2:276-87.
- Mercer BM, Goldenberg RL, Moawad AH, Meis PJ, Iams JD, Das AF, et al. The preterm prediction study: effect of gestational age and cause of preterm birth on subsequent obstetric outcome. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Maternal–Fetal Medicine Units Network. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;181:1216-21.
- Blondel B, Le C, X, Kaminski M, Chavigny C, Breart G, Sureau C. Prediction of preterm delivery: Is it substantially improved by routine vaginal examinations?. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;162:1042-8.
- Chambers S, Pons JC, Richard A, Chiesa M, Bouyer J, Papiernik E. Vaginal infections, cervical ripening and preterm delivery. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1991;38:103-8.
- Chhabra S, Varma P. Cervical status as a predictor of preterm labour. J Indian Med Assoc 1992;90:261-2.
- Iams JD, Newman RB, Thom EA, Goldenberg RL, Mueller-Heubach E, Moawad A, et al. Frequency of uterine contractions and the risk of spontaneous preterm delivery. N Engl J Med 2002;346:250-5.
- Leveno KJ, Cox K, Roark ML. Cervical dilatation and prematurity revisited. Obstet Gynecol 1986;68:434-5.
- Newman RB. The Preterm Prediction Study: comparison of the cervical score and bishop score for the prediction of spontaneous preterm birth (SPTB). J Soc Gynecol Invest 1997;4.
- Parikh MN, Mehta AC. Internal cervical os during the second half of pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp 1961;68:818-21.
- Schaffner F, Schanzer SN. Cervical dilatation in the early third trimester. Obstet Gynecol 1966;27:130-3.
- Stubbs TM, Van Dorsten JP, Miller MC. The preterm cervix and preterm labor: relative risks, predictive values, and change over time. Am JObstet Gynecol 1986;155:829-34.
- Onderoglu LS. Digital examination and transperineal ultrasonographic measurement of cervical length to assess risk of preterm delivery. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1997;59:223-8.
- Goldenberg RL, Klebanoff M, Carey JC, MacPherson C, Leveno KJ, Moawad AH, et al. Vaginal fetal fibronectin measurements from 8 to 22 weeks’ gestation and subsequent spontaneous preterm birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;183:469-75.
- Zamora Scorza FC, Fernandez G, de Lamanna MP, Perez MC, Maris CA. Value of fibronectin in cervical secretions in the prediction of preterm delilvery in patients with intact membranes. Rev Obstet Ginecol Venez 2000;60:15-22.
- Grandi C, Perego M, Briozzo G, Cassini A. Fetal fibronectin (fFN) in cervical secretions as a predictor of premature delivery. Rev Hosp Mat Inf Ramon Sarda 1996;15:127-36.
- Peaceman AM, Andrews WW, Thorp JM, Cliver SP, Lukes A, Iams JD, et al. Fetal fibronectin as a predictor of preterm birth in patients with symptoms: a multicenter trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:13-8.
- Faron G, Boulvain M, Lescrainier JP, Vokaer A. A single cervical fetal fibronectin screening test in a population at low risk for preterm delivery: an improvement on clinical indicators?. BJOG 1997;104:697-701.
- Heath VC, Daskalakis G, Zagaliki A, Carvalho M, Nicolaides KH. Cervicovaginal fibronectin and cervical length at 23 weeks of gestation: relative risk of early preterm delivery. BJOG 2000;107:1276-81.
- Hellemans P, Gerris J, Verdonk P. Fetal fibronectin detection for prediction of preterm birth in low risk women. BJOG 1995;102:207-12.
- LaShay N, Gilson G, Joffe G, Qualls C, Curet L. Will cervicovaginal interleukin-6 combined with fetal fibronectin testing improve the prediction of preterm delivery?. J Matern Fetal Med 2000;9:336-41.
- Morrison JC, Allbert JR, McLaughlin BN, Whitworth NS, Roberts WE, Martin RW. Oncofetal fibronectin in patients with false labor as a predictor of preterm delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;168:538-42.
- Senden IP, Owen P. Comparison of cervical assessment, fetal fibronectin and fetal breathing in the diagnosis of preterm labour. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 1996;23:5-9.
- Tekesin I, Marek S, Hellmeyer L, Reitz D, Schmidt S. Assessment of rapid fetal fibronectin in predicting preterm delivery. Obstet Gynecol 2005;105:280-4.
- Arinami Y, Hasegawa I, Takakuwa K, Tanaka K. Prediction of preterm delivery by combined use of simple clinical tests. J Matern Fetal Med 1999;8:70-3.
- Chang TC, Chew TS, Pang M, Tan AC, Yeo GS. Cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin in the prediction of preterm labour in a low-risk population. Ann Acad Med Singapore 1997;26:776-80.
- Goldenberg RL, Mercer BM, Meis PJ, Copper RL, Das A, McNellis D. The Preterm Prediction Study: fetal fibronectin testing and spontaneous preterm birth. Obstet Gynecol 1996;87:643-8.
- Goldenberg RL, Mercer BM, Iams JD, Moawad AH, Meis PJ, Das A, et al. The Preterm Prediction Study: patterns of cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin as predictors of spontaneous preterm delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:8-12.
- Hux CH, Trolice MP, Kadar N. The value of a single fetal fibronectin assay as a screen for preterm labor and delivery. J Matern Fetal Med 1995;4:100-4.
- Crane JM, Armson BA, Dodds L, Feinberg RF, Kennedy W, Kirkland SA. Risk scoring, fetal fibronectin, and bacterial vaginosis to predict preterm delivery. Obstet Gynecol 1999;93:517-22.
- Di Stefano L, Carta G, Di Paolantonio L, Palerno P, Moscarini M. Preterm delivery: predictive value of cervico-vaginal fetal fibronectin. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 1999;26:187-9.
- Garcia AA, Ayala-Mendez JA, Izquierdo-Puente JC, Jimenez SG, Sanchez MM. Presence of fetal fibronectin in cervico-vaginal secretion as predictor of premature labour. Ginecol Obstet Mex 1999;67:23-8.
- Greenhagen JB, Van Wagoner J, Dudley D, Hunter C, Mitchell M, Logsdon V, et al. Value of fetal fibronectin as a predictor of preterm delivery for a low-risk population. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;175:1054-6.
- Inglis SR, Jeremias J, Kuno K, Lescale K, Peeper Q, Chervenak FA, et al. Detection of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and fetal fibronectin in the lower genital tract during pregnancy: relation to outcome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:5-10.
- Lockwood CJ, Senyei AE, Dische MR, Casal D, Shah KD, Thung SN, et al. Fetal fibronectin in cervical and vaginal secretions as a predictor of preterm delivery. N Engl J Med 1991;325:669-74.
- Ruiz RJ, Fullerton J, Brown CE, Schoolfield J. Relationships of cortisol, perceived stress, genitourinary infections, and fetal fibronectin to gestational age at birth. Biol Res Nursing 2001;3:39-48.
- Vercoustre L, Sotter S, Bouige D, Walch R. Fibronectin as a predictor of labor, results and discussion about 206 samples. Gynecol Obstet Fertil 1996;4:23-32.
- Bartnicki J, Casal D, Kreaden US, Saling E, Vetter K. Fetal fibronectin in vaginal specimens predicts preterm delivery and very-low-birth-weight infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174:971-4.
- Benattar C, Taieb J, Fernandez H, Lindendaum A, Frydman R, Ville Y. Rapid fetal fibronectin swab-test in preterm labor patients treated by betamimetics. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1997;72:131-5.
- Closset E, Dufour P, Coeugnet P, Subtil D, Valat AS, Puech F. Fetal fibronectin as a predictor of preterm delivery. Gynecol Obstet Fertil 2001;29:808-13.
- Foxman EF, Jarolim P. Use of the fetal fibronectin test in decisions to admit to hospital for preterm labor. Clin Chem 2004;50:663-5.
- Giles W, Bisits A, Knox M, Madsen G, Smith R. The effect of fetal fibronectin testing on admissions to a tertiary maternal–fetal medicine unit and cost savings. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182:439-42.
- Gomez R, Romero R, Medina L, Nien JK, Chaiworapongsa T, Carstens M, et al. Cervicovaginal fibronectin improves the prediction of preterm delivery based on sonographic cervical length in patients with preterm uterine contractions and intact membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;192:350-9.
- Iams JD, Casal D, McGregor JA, Goodwin TM, Kreaden US, Lowensohn R, et al. Fetal fibronectin improves the accuracy of diagnosis of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:141-5.
- Lopez RL, Francis JA, Garite TJ, Dubyak JM. Fetal fibronectin detection as a predictor of preterm birth in actual clinical practice. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182:1103-6.
- Lowe MP, Zimmerman B, Hansen W. Prospective randomized controlled trial of fetal fibronectin on preterm labor management in a tertiary care center. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;190:358-62.
- Luzzi V, Hankins K, Gronowski AM. Accuracy of the rapid fetal fibronectin TLi system in predicting preterm delivery. Clin Chem 2003;49:501-2.
- Malak TM, Sizmur F, Bell SC, Taylor DJ. Fetal fibronectin in cervicovaginal secretions as a predictor of preterm birth. BJOG 1996;103:648-53.
- McKenna DS, Chung K, Iams JD. Effect of digital cervical examination on the expression of fetal fibronectin. J Reprod Med Obstet Gynecol 1999;44:796-800.
- Sakai M, Sasaki Y, Yamagishi N, Tanebe K, Yoneda S, Saito S. The preterm labor index and fetal fibronectin for prediction of preterm delivery with intact membranes. Obstet Gynecol 2003;101:123-8.
- Burrus DR, Ernest JM, Veille JC. Fetal fibronectin, interleukin-6, and C-reactive protein are useful in establishing prognostic subcategories of idiopathic preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:1258-62.
- Cox S, Little B, Dax J, Leveno K. Fetal fibronectin and preterm delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174.
- Goffeng AR, Holst E, Milsom I, Lindstedt G, Lundberg PA, Andersch B. Fetal fibronectin and microorganisms in vaginal fluid of women with complicated pregnancies. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1997;76:521-7.
- Musaad SMA, Melson CL, Boswell DR. Assessment of the impact of introducing fetal fibronectin assay in the management of preterm labour at Middlemore Hospital, New Zealand. Pathology 2005;37:226-30.
- Ni CF, Bell R, Brennecke S. Cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin testing in threatened preterm labour – translating research findings into clinical practice. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;38:399-402.
- Parker J, Bell R, Brennecke S. Fetal fibronectin in the cervicovaginal fluid of women with threatened preterm labour as a predictor of delivery before 34 weeks’ gestation. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1995;35:257-61.
- Calda P, Cibula D, Doudova D, Binder T, Peterka T, Zizka Z, et al. Fetal fibronectin in cervico-vaginal secretions – an indicator of incipient premature labor using a membrane immunoassay. Ceska Gynekol 1995;60:293-5.
- Gomez-Bravo Topete E, Castillo-Lechuga C, Villegas-Su A, Briones-Garduno JC. Predictive value of fetal fibronectin in threatened preterm delivery. Cir Ciruj 2004;72:491-4.
- Hincz P, Wilczynski J, Kozarzewski M, Szaflik K. Two-step test: the combined use of fetal fibronectin and sonographic examination of the uterine cervix for prediction of preterm delivery in symptomatic patients. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2002;81:58-63.
- Irion O, Matute J, Bischof P. Prediction of prematurity with oncofetal fibronectin: a prospective cohort study. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1995;24:624-9.
- Langer B, Boudier E, Schlaeder G. Cervico-vaginal fetal fibronectin: predictive value during false labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1997;76:218-21.
- Mansouri A, Tadjerouni A, El Rabiey G, Baube S, Garnier G, Tribalat S. Fibronectin: a predictor of preterm delivery?. Contracept Fertil Sex 1997;25:380-4.
- Pieta-Dolinska A, Jaczewski B, Wozniak P, Oszukowski P. Evaluation of fetal fibronectin concentration in identifying patients at risk for preterm delivery. Ginekologia Polska 2005;76:431-5.
- Rizzo G, Capponi A, Vlachopoulou A, Angelini E, Grassi C, Romanini C. The diagnostic value of interleukin-8 and fetal fibronectin concentrations in cervical secretions in patients with preterm labor and intact membranes. J Perinat Med 1997;25:461-8.
- Rozenberg P, Goffinet F, Malagrida L, Giudicelli Y, Perdu M, Houssin I, et al. Evaluating the risk of preterm delivery: a comparison of fetal fibronectin and transvaginal ultrasonographic measurement of cervical length. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:196-9.
- Stevens AO, Chauhan SP, Magann EF, Martin RW, Bofill JA, Cushman JL, et al. Fetal fibronectin and bacterial vaginosis are associated with preterm birth in women who are symptomatic for preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;190:1582-7.
- Vetr M, Kudela M, Prasilova J. Fetal fibronectin in patients at increased risk for premature birth. Acta Univ Palacki Olomuc Fac Med 1996;140:55-7.
- O’Brien JM, Peeler GH, Pitts DW, Salama MM, Sibai BM, Mercer BM. Cervicovaginal prolactin: a marker for spontaneous preterm delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:1107-11.
- Koca ZD, Oztekin MK, Karadadas N, Ozsener S, Asena U. Value of cervicovaginal prolactin in the prediction of spontaneous preterm delivery. Prenat Neonat Med 1999;4:120-5.
- Guvenal T, Kantas E, Erselcan T, Culhaoglu Y, Cetin A. Beta-human chorionic gonadotropin and prolactin assays in cervicovaginal secretions as a predictor of preterm delivery. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2001;75:229-34.
- Jotterand AD, Caubel P, Guillaumin D, Augereau F, Chitrit Y, Boulanger MC. Predictive value of cervical-vaginal prolactin in the evaluation of premature labor risk. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 1997;26:95-9.
- Leylek OA, Songur S, Erselcan T, Cetin A, Izgic E. Cervicovaginal washing prolactin assay in prediction of preterm delivery. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1997;59:7-12.
- Shine BK, Kim SJ, Park WI, Kim JO, Kim DW, Hong SY, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 in cervical secretion as a predictor of preterm delivery. Korean J Obstet Gynecol 2001;44:2250-6.
- Turnell R, Liu K, Blakney G, Chari R. A direct comparison of fetal fibronectin [FFN] and PIGFBP-1 [Actim Partus] in the diagnosis of preterm labor [PTL]. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2005;27.
- Bittar RE, Borges da Fonseca E, Burlacchini MH, Martinelli S, Zugaib M. Cervical Insulin Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-1 (ph IGFBP-1) in Patients at Increased Risk for Preterm Delivery: Preliminary Results (23–9–2001) n.d.:537-9.
- Kwek K, Khi C, Ting HS, Yeo GS. Evaluation of a bedside test for phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 in preterm labour. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2004;33:780-3.
- Lembet A, Eroglu D, Ergin T, Kuscu E, Zeyneloglu H, Batioglu S, et al. New rapid bed-side test to predict preterm delivery: phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 in cervical secretions. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2002;81:706-12.
- Akercan F, Kazandi M, Sendag F, Cirpan T, Mgoyi L, Terek MC, et al. Value of cervical phosphorylated insulinlike growth factor binding protein-1 in the prediction of preterm labor. J Reprod Med 2004;49:368-72.
- Choi JS, Yang JH, Ryu HM, Kim MY, Han JY, Ahn HK, et al. Evaluation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 in cervical secretion as a predictor of preterm delivery. Korean J Obstet Gynecol 2003;46:1398-403.
- Park OR, Kim JK, Chang BS, Kim HJ, Kim TS, Park IS. Usefulness of phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 for prediction of preterm delivery. Korean J Obstet Gynecol 2003;46:1378-84.
- Elizur SE, Yinon Y, Epstein GS, Seidman DS, Schiff E, Sivan E. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 detection in preterm labor: evaluation of a bedside test. Am J Perinatol 2005;22:305-9.
- Paternoster DM, Muresan D, Vitulo A, Battagliarin G, Dell’avanzo M, Nicolini U. Cervical phIGFBP-1 in the evaluation of the risk of preterm delivery. J Soc Gynecol Invest (Meeting 10–11–2005). Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2007;86:151-5.
- Halle H, Hartung J, Heling K, Albrecht C. Assessment of Risk of Premature Birth Using Phosphorylated IGFBP-L As Rapid Test, in Comparison With Fibronectin Determination n.d.
- Akinbiyi AA. Unexplained elevated maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein in singleton pregnancies as a predictor of fetal risk. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1996;53:17-21.
- Brazerol WF, Grover S, Donnenfeld AE. Unexplained elevated maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein levels and perinatal outcome in an urban clinic population. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:1030-5.
- Cho S, Durfee KK, Keel BA, Parks LH. Perinatal outcomes in a prospective matched pair study of pregnancy and unexplained elevated or low AFP screening. J Perinat Med 1997;25:476-83.
- Davis RO, Goldenberg RL, Boots L, Hoffman HJ, Copper R, Cutter GR, et al. Elevated levels of midtrimester maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein are associated with preterm delivery but not with fetal growth retardation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;167:596-601.
- Dugoff L, Hobbins JC, Malone FD, Vidaver J, Sullivan L, Canick JA, et al. Quad screen as a predictor of adverse pregnancy outcome. Obstet Gynecol 2005;106:260-7.
- Duric K, Skrablin S, Lesin J, Kalafatic D, Kuvacic I, Suchanek E. Second trimester total human chorionic gonadotropin, alpha-fetoprotein and unconjugated estriol in predicting pregnancy complications other than fetal aneuploidy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2003;110:12-5.
- Goldenberg RL, Iams JD, Mercer BM, Meis PJ, Moawad A, Das A, et al. The Preterm Prediction Study: toward a multiple-marker test for spontaneous preterm birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185:643-51.
- Hamilton MP, Abdalla HI, Whitfield CR. Significance of raised maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein in singleton pregnancies with normally formed fetuses. Obstet Gynecol 1985;65:465-70.
- Hsieh TT, Hung TH, Hsu JJ, Shau WY, Su CW, Hsieh FJ. Prediction of adverse perinatal outcome by maternal serum screening for Down syndrome in an Asian population. Obstet Gynecol 1997;89:937-40.
- Morssink LP, Kornman LH, Beekhuis JR, De Wolf BT, Mantingh A. Abnormal levels of maternal serum human chorionic gonadotropin and alpha-fetoprotein in the second trimester: relation to fetal weight and preterm delivery. Prenat Diagn 1995;15:1041-6.
- Sharara HA, Haseeb FI. ⟨-Fetoprotein elevation and prediction of pregnancy outcome. J Obstet Gynecol 1995;15:285-7.
- Simpson JL, Palomaki GE, Mercer B, Haddow JE, Andersen R, Sibai B, et al. Associations between adverse perinatal outcome and serially obtained second- and third-trimester maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein measurements. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:1742-8.
- Spencer K. Second-trimester prenatal screening for Down syndrome and the relationship of maternal serum biochemical markers to pregnancy complications with adverse outcome. Prenat Diagn 2000;20:652-6.
- Tanaka M, Natori M, Ishimoto H, Gohda N, Kiyokawa K, Yamauchi J, et al. Screening for adverse perinatal outcome by biomarkers in maternal serum; a comparison of elevated maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein versus human chorionic gonadotropin. Nippon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi 1994;46:1229-33.
- Wald N, Cuckle H, Stirrat GM, Bennett MJ, Turnbull AC. Maternal serum-alpha-fetoprotein and low birth-weight. Lancet 1977;2:268-70.
- Waller DK, Lustig LS, Cunningham GC, Feuchtbaum LB, Hook EB. The association between maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein and preterm birth, small for gestational age infants, preeclampsia, and placental complications. Obstet Gynecol 1996;88:816-22.
- Wenstrom KD, Owen J, Davis RO, Brumfield CG. Prognostic significance of unexplained elevated amniotic fluid alpha-fetoprotein. Obstet Gynecol 1996;87:213-16.
- Williams MA, Hickok DE, Zingheim RW, Luthy DA, Kimelman J, Nyberg DA, et al. Elevated maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein levels and midtrimester placental abnormalities in relation to subsequent adverse pregnancy outcomes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;167:1032-7.
- Yaron Y, Cherry M, Kramer RL, O’Brien JE, Hallak M, Johnson MP, et al. Second-trimester maternal serum marker screening: maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein, beta-human chorionic gonadotropin, estriol, and their various combinations as predictors of pregnancy outcome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;181:968-74.
- Goldenberg RL, Iams JD, Mercer BM, Meis PJ, Moawad A, Das A, et al. The Preterm Prediction Study: toward a multiple-marker test for spontaneous preterm birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185:643-51.
- Weiss G, Goldsmith LT, Sachdev R, Von Hagen S, Lederer K. Elevated first-trimester serum relaxin concentrations in pregnant women following ovarian stimulation predict prematurity risk and preterm delivery. Obstet Gynecol 1993;82:821-8.
- Goldenberg RL, Iams JD, Mercer BM, Meis PJ, Moawad A, Das A, et al. The Preterm Prediction Study: toward a multiple-marker test for spontaneous preterm birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185:643-51.
- Vogel I, Thorsen P, Hundborg HH, Uldbjerg N. Prediction of preterm delivery using changes in serum relaxin in low risk pregnancies. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2006;128:113-18.
- Vogel I, Goepfert AR, Moller HJ, Cliver S, Thorsen P, Andrews WW. Early mid-trimester serum relaxin, soluble CD163, and cervical length in women at high risk for preterm delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;195:208-14.
- Vogel I, Glavind-Kristensen M, Thorsen P, Armbruster FP, Uldbjerg N. S-relaxin as a predictor of preterm delivery in women with symptoms of preterm labour. BJOG 2002;109:977-82.
- Berkowitz GS, Lapinski RH, Lockwood CJ, Florio P, Blackmore-Prince C, Petraglia F. Corticotropin-releasing factor and its binding protein: maternal serum levels in term and preterm deliveries. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174:1477-83.
- Holzman C, Jetton J, Siler-Khodr T, Fisher R, Rip T. Second trimester corticotropin-releasing hormone levels in relation to preterm delivery and ethnicity. Obstet Gynecol 2001;97:657-63.
- Inder WJ, Prickett TC, Ellis MJ, Hull L, Reid R, Benny PS, et al. The utility of plasma CRH as a predictor of preterm delivery. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:5706-10.
- Leung TN, Chung TK, Madsen G, McLean M, Chang AM, Smith R. Elevated mid-trimester maternal corticotrophin-releasing hormone levels in pregnancies that delivered before 34 weeks. BJOG 1999;106:1041-6.
- Coleman MA, France JT, Schellenberg JC, Ananiev V, Townend K, Keelan JA, et al. Corticotropin-releasing hormone, corticotropin-releasing hormone- binding protein, and activin A in maternal serum: prediction of preterm delivery and response to glucocorticoids in women with symptoms of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;183:643-8.
- McLean M, Bisits A, Davies J, Walters W, Hackshaw A, De Voss K, et al. Predicting risk of preterm delivery by second-trimester measurement of maternal plasma corticotropin-releasing hormone and alpha-fetoprotein concentrations. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;181:207-15.
- Hsieh TT, Hung TH, Hsu JJ, Shau WY, Su CW, Hsieh FJ. Prediction of adverse perinatal outcome by maternal serum screening for Down syndrome in an Asian population. Obstet Gynecol 1997;89:937-40.
- Benn PA, Horne D, Briganti S, Rodis JF, Clive JM. Elevated second-trimester maternal serum hCG alone or in combination with elevated alpha-fetoprotein. Obstet Gynecol 1996;87:217-22.
- Brajenovic-Milic B, Tislaric D, Zuvic-Butorac M, Bacic J, Petrovic O, Ristic S, et al. Elevated second-trimester free beta-hCG as an isolated finding and pregnancy outcomes. Fetal Diagn Ther 2004;19:483-7.
- Chandra S, Scott H, Dodds L, Watts C, Blight C, Van Den Hof M. Unexplained elevated maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein and/or human chorionic gonadotropin and the risk of adverse outcomes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189:775-81.
- Dugoff L, Hobbins JC, Malone FD, Porter TF, Luthy D, Comstock CH, et al. First-trimester maternal serum PAPP-A and free-beta subunit human chorionic gonadotropin concentrations and nuchal translucency are associated with obstetric complications: a population-based screening study (the FASTER Trial). Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191:1446-51.
- Gonen R, Perez R, David M, Dar H, Merksamer R, Sharf M. The association between unexplained second-trimester maternal serum hCG elevation and pregnancy complications. Obstet Gynecol 1992;80:83-6.
- Lepage N, Chitayat D, Kingdom J, Huang T. Association between second-trimester isolated high maternal serum maternal serum human chorionic gonadotropin levels and obstetric complications in singleton and twin pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;188:1354-9.
- Lieppman RE, Williams MA, Cheng EY, Resta R, Zingheim R, Hickok DE, et al. An association between elevated levels of human chorionic gonadotropin in the midtrimester and adverse pregnancy outcome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;168:1852-6.
- Liu DF, Dickerman LH, Redline RW. Pathologic findings in pregnancies with unexplained increases in midtrimester maternal serum human chorionic gonadotropin levels. Am J Clin Pathol 1999;111:209-15.
- Onderoglu LS, Kabukcu A. Elevated second trimester human chorionic gonadotropin level associated with adverse pregnancy outcome. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1997;56:245-9.
- Ong CY, Liao AW, Spencer K, Munim S, Nicolaides KH. First trimester maternal serum free beta human chorionic gonadotrophin and pregnancy associated plasma protein A as predictors of pregnancy complications. BJOG 2000;107:1265-70.
- Wenstrom KD, Owen J, Boots LR, DuBard MB. Elevated second-trimester human chorionic gonadotropin levels in association with poor pregnancy outcome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:1038-41.
- Yaron Y, Cherry M, Kramer RL, O’Brien JE, Hallak M, Johnson MP, et al. Second-trimester maternal serum marker screening: maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein, beta-human chorionic gonadotropin, estriol, and their various combinations as predictors of pregnancy outcome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;181:968-74.
- Yaron Y, Ochshorn Y, Heifetz S, Lehavi O, Sapir Y, Orr-Urtreger A. First trimester maternal serum free human chorionic gonadotropin as a predictor of adverse pregnancy outcome. Fetal Diagn Ther 2002;17:352-6.
- Haddad B, Abirached F, Louis-Sylvestre C, Le Blond J, Paniel BJ, Zorn JR. Predictive value of early human chorionic gonadotrophin serum profiles for fetal growth retardation. Hum Reprod 1999;14:2872-5.
- Gurbuz A, Karateke A, Ozturkmen M, Kabaca C. Human chorionic gonadotropin assay in cervical secretions for accurate diagnosis of preterm labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2004;85:132-8.
- Sanchez-Ramos L, Mentel C, Bertholf R, Kaunitz AM, Delke I, Loge C. Human chorionic gonadotropin in cervicovaginal secretions as a predictor of preterm delivery. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2003;83:151-7.
- McGregor JA, Jackson GM, Lachelin GCL, Goodwin TM, Artal R, Hastings C, et al. Salivary estriol as risk assessment for preterm labor: A prospective trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:1337-42.
- Heine RP, McGregor JA, Goodwin TM, Artal R, Hayashi RH, Robertson PA, et al. Serial salivary estriol to detect an increased risk of preterm birth. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:490-7.
- Kim SY, Kim SK, Lee JS, Kim IK, Lee K. The prediction of adverse pregnancy outcome using low unconjugated estriol in the second trimester of pregnancy without risk of Down’s syndrome. Yonsei Med J 2000;41:226-9.
- Kowalczyk TD, Cabaniss ML, Cusmano L. Association of low unconjugated estriol in the second trimester and adverse pregnancy outcome. Obstet Gynecol 1998;91:396-400.
- Potkul RK, Moawad AH, Ponto KL. The association of subclinical infection with preterm labor: the role of C-reactive protein. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1985;153:642-5.
- Cammu H, Goossens A, Derde MP, Temmerman M, Foulon W, Amy JJ. C-reactive protein in preterm labour: association with outcome of tocolysis and placental histology. BJOG 1989;96:314-19.
- Cylwik B, Szmitkowski M, Bielecki M, Zdanowicz A, Poludniewski G, Arciszewski K. C-reactive protein concentration in the sera of pregnant women with imminent premature parturition and preterm amneorrhea. Rocz Akad Med Bialymst 1997;42:35-40.
- Dodds WG, Iams JD. Maternal C-reactive protein and preterm labor. J Reprod Med 1987;32:527-30.
- Foulon W, Van Liedekerke D, Demanet C, Decatte L, Dewaele M, Naessens A. Markers of infection and their relationship to preterm delivery. Am J Perinatol 1995;12:208-11.
- Ghezzi F, Franchi M, Raio L, Di Naro E, Bossi G, D’Eril GV, et al. Elevated amniotic fluid C-reactive protein at the time of genetic amniocentesis is a marker for preterm delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;186:268-73.
- Handwerker SM, Tejani NA, Verma UL, Archbald F. Correlation of maternal serum C-reactive protein with outcome of tocolysis. Obstet Gynecol 1984;63:220-4.
- Hvilsom GB, Thorsen P, Jeune B, Bakketeig LS. C-reactive protein: a serological marker for preterm delivery?. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2002;81:424-9.
- Karinen L, Pouta A, Bloigu A, Koskela P, Paldanius M, Leinonen M, et al. Serum C-reactive protein and Chlamydia trachomatis antibodies in preterm delivery. Obstet Gynecol. 2005;106:73-80.
- Mazor M, Kassis A, Horowitz S, Wiznitzer A, Kuperman O, Meril C, et al. Relationship between C-reactive protein levels and intraamniotic infection in women with preterm labor. J Reprod Med 1993;38:799-803.
- Ozer KT, Kavak ZN, Gokaslan H, Elter K, Pekin T. Predictive power of maternal serum and amniotic fluid CRP and PAPP-A concentrations at the time of genetic amniocentesis for the preterm delivery. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2005;122:187-90.
- Ruckhaberle KE, Baumann L. Infections and labor. Arch Gynecol Obstet 1991;250:690-5.
- Winkler M, Ruckhaberle KE, Baumann L, Schroder R, Schiller E. Clinical value of determining C-reactive protein in the maternal serum in pregnancies with threatened premature labour. Zentralbl Gynakol 1987;109:854-61.
- Romero R, Yoon BH, Kenney JS, Gomez R, Allison AC, Sehgal PB. Amniotic fluid interleukin-6 determinations are of diagnostic and prognostic value in preterm labor. Am J Reprod Immunol 1993;30:167-83.
- Coleman MA, Keelan JA, McCowan LM, Townend KM, Mitchell MD. Predicting preterm delivery: comparison of cervicovaginal interleukin (IL)-1beta, IL-6 and IL-8 with fetal fibronectin and cervical dilatation. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2001;95:154-8.
- Wenstrom KD, Andrews WW, Hauth JC, Goldenberg RL, DuBard MB, Cliver SP. Elevated second-trimester amniotic fluid interleukin-6 levels predict preterm delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:546-50.
- Lockwood CJ, Ghidini A, Wein R, Lapinski R, Casal D, Berkowitz RL. Increased interleukin-6 concentrations in cervical secretions are associated with preterm delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:1097-102.
- Ghidini A, Jenkins CB, Spong CY, Pezzullo JC, Salafia CM, Eglinton GS. Elevated amniotic fluid interleukin-6 levels during the early second trimester are associated with greater risk of subsequent preterm delivery. Am J Reprod Immunol 1997;37:227-31.
- Allbert JR, Naef RW, Perry KG, Magann EF, Whitworth NS, Morrison JC. Amniotic fluid interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 levels predict the success of tocolysis in patients with preterm labor. J Soc Gynecol Investig 1994;1:264-8.
- Coultrip LL, Lien JM, Gomez R, Kapernick P, Khoury A, Grossman JH. The value of amniotic fluid interleukin-6 determination in patients with preterm labor and intact membranes in the detection of microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:901-11.
- Greci LS, Gilson GJ, Nevils B, Izquierdo LA, Qualls CR, Curet LB. Is amniotic fluid analysis the key to preterm labor? A model using interleukin-6 for predicting rapid delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:172-8.
- Hillier SL, Witkin SS, Krohn MA, Watts DH, Kiviat NB, Eschenbach DA. The relationship of amniotic fluid cytokines and preterm delivery, amniotic fluid infection, histologic chorioamnionitis, and chorioamnion infection. Obstet Gynecol 1993;81:941-8.
- Rizzo G, Capponi A, Rinaldo D, Tedeschi D, Arduini D, Romanini C. Interleukin-6 concentrations in cervical secretions identify microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity in patients with preterm labor and intact membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;175:812-17.
- Romero R, Avila C, Santhanam U, Sehgal PB. Amniotic fluid interleukin 6 in preterm labor. Association with infection. J Clin Invest 1990;85:1392-400.
- Silver RM, Schwinzer B, McGregor JA. Interleukin-6 levels in amniotic fluid in normal and abnormal pregnancies: preeclampsia, small-for-gestational-age fetus, and premature labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:1101-5.
- Romero R, Yoon BH, Mazor M, Gomez R, Diamond MP, Kenney JS, et al. The diagnostic and prognostic value of amniotic fluid white blood cell count, glucose, interleukin-6, and gram stain in patients with preterm labor and intact membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:805-16.
- Goepfert AR, Goldenberg RL, Andrews WW, Hauth JC, Mercer B, Iams J, et al. The Preterm Prediction Study: association between cervical interleukin 6 concentration and spontaneous preterm birth. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units Network. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184:483-8.
- Holst RM, Mattsby-Baltzer I, Wennerholm UB, Hagberg H, Jacobsson B. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in cervical fluid in a population of Swedish women in preterm labor: relationship to microbial invasion of the amniotic fluid, intra-amniotic inflammation, and preterm delivery. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2005;84:551-7.
- Kurkinen-Raty M, Ruokonen A, Vuopala S, Koskela M, Rutanen EM, Karkkainen T, et al. Combination of cervical interleukin-6 and -8, phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 and transvaginal cervical ultrasonography in assessment of the risk of preterm birth. BJOG 2001;108:875-81.
- Lange M, Chen FK, Wessel J, Buscher U, Dudenhausen JW. Elevation of interleukin-6 levels in cervical secretions as a predictor of preterm delivery. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2003;82:326-9.
- Sozmen S, Mungan T, Micozkadioglu SD, Tapisiz OL. Predictive value of maternal serum and vaginal interleukin-6 levels in preterm labor. J Soc Gynecol Invest 2005;12:1-6.
- Trebeden H, Goffinet F, Kayem G, Maillard F, Lemoine E, Cabrol D, et al. Strip test for bedside detection of interleukin-6 in cervical secretions is predictive for impending preterm delivery. Eur Cytokine Netw 2001;12:359-60.
- Alvarez-de-la-Rosa M, Rebollo FJ, Codoceo R, Gonzalez GA. Maternal serum interleukin 1, 2, 6, 8 and interleukin-2 receptor levels in preterm labor and delivery. Eur J Obstet Gynaecol Reprod Biol 2000;88:57-60.
- Greig PC, Murtha AP, Jimmerson CJ, Herbert WN, Roitman-Johnson B, Allen J. Maternal serum interleukin-6 during pregnancy and during term and preterm labor. Obstet Gynecol 1997;90:465-9.
- Turhan NO, Karabulut A, Adam B. Maternal serum interleukin 6 levels in preterm labor: prediction of admission-to-delivery interval. J Perinat Med 2000;28:133-9.
- von Minckwitz G, Grischke EM, Schwab S, Hettinger S, Loibl S, Aulmann M, et al. Predictive value of serum interleukin-6 and -8 levels in preterm labor or rupture of the membranes. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2000;79:667-72.
- Holst E, Goffeng AR, Andersch B. Bacterial vaginosis and vaginal microorganisms in idiopathic premature labor and association with pregnancy outcome. J Clin Microbiol 1994;32:176-86.
- Gonzalez BE, Ferrer I, Valls C, Borras M, Lailla JM. The value of interleukin-8, interleukin-6 and interleukin-1beta in vaginal wash as predictors of preterm delivery. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2005;59:175-8.
- Sakai M, Ishiyama A, Tabata M, Sasaki Y, Yoneda S, Shiozaki A, et al. Relationship between cervical mucus interleukin-8 concentrations and vaginal bacteria in pregnancy. Am J Reprod Immunol 2004;52:106-12.
- Sakai M, Sasaki Y, Yoneda S, Kasahara T, Arai T, Okada M, et al. Elevated interleukin-8 in cervical mucus as an indicator for treatment to prevent premature birth and preterm, pre-labor rupture of membranes: a prospective study. Am J Reprod Immunol 2004;51:220-5.
- Agrez M, Gu X, Giles W. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 activity in urine of patients at risk for premature delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;181:387-8.
- Makrakis E, Grigoriou O, Kouskouni E, Vitoratos N, Salamalekis E, Chatzoudi E, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in plasma/serum and urine of women during term and threatened preterm labor: a clinical approach. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2003;14:170-6.
- Offenbacher S, Lieff S, Boggess KA, Murtha AP, Madianos PN, Champagne CM, et al. Maternal periodontitis and prematurity. Part I: Obstetric outcome of prematurity and growth restriction. Ann Periodontol 2001;6:164-74.
- Dasanayake AP, Boyd D, Madianos PN, Offenbacher S, Hills E. The association between Porphyromonas gingivalis-specific maternal serum IgG and low birth weight. J Periodontol 2001;72:1491-7.
- Dortbudak O, Eberhardt R, Ulm M, Persson GR. Periodontitis, a marker of risk in pregnancy for preterm birth. J Clin Periodontol 2005;32:45-52.
- Goepfert AR, Jeffcoat MK, Andrews WW, Faye-Petersen O, Cliver SP, Goldenberg RL, et al. Periodontal disease and upper genital tract inflammation in early spontaneous preterm birth. Obstet Gynecol 2004;104:777-83.
- Holbrook WP, Oskarsdottir A, Fridjonsson T, Einarsson H, Hauksson A, Geirsson RT. No link between low-grade periodontal disease and preterm birth: a pilot study in a healthy Caucasian population. Acta Odontol Scand 2004;62:177-9.
- Jarjoura K, Devine PC, Perez-Delboy A, Herrera-Abreu M, D’Alton M, Papapanou PN. Markers of periodontal infection and preterm birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;192:513-19.
- Jeffcoat MK, Geurs NC, Reddy MS, Cliver SP, Goldenberg RL, Hauth JC. Periodontal infection and preterm birth: results of a prospective study. J Am Dent Assoc 2001;132:875-80.
- Konopka T, Rutkowska M, Hirnle L, Kopec W, Karolewska E. The secretion of prostaglandin E2 and interleukin 1-beta in women with periodontal diseases and preterm low-birth-weight. Bull Group Int Rech Sci Stomatol Odontol 2003;45:18-2.
- Moore S, Ide M, Coward PY, Randhawa M, Borkowska E, Baylis R, et al. A prospective study to investigate the relationship between periodontal disease and adverse pregnancy outcome. Br Dent J 2004;197:251-8.
- Moore S, Randhawa M, Ide M. A case–control study to investigate an association between adverse pregnancy outcome and periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol 2005;32:1-5.
- Offenbacher S, Katz V, Fertik G, Collins J, Boyd D, Maynor G, et al. Periodontal infection as a possible risk factor for preterm low birth weight. J Periodontol 1996;67:1103-13.
- Radnai M, Gorzo I, Nagy E, Urban E, Novak T, Pal A. A possible association between preterm birth and early periodontitis. A pilot study. J Clin Periodontol 2004;31:736-41.
- Rajapakse PS, Nagarathne M, Chandrasekra KB, Dasanayake AP. Periodontal disease and prematurity among non-smoking Sri Lankan women. J Dent Res 2005;84:274-7.
- MacLean AB. Urinary tract infection in pregnancy. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2001;17:273-6.
- Romero R, Oyarzun E, Mazor M, Sirtori M, Hobbins JC, Bracken M. Meta-analysis of the relationship between asymptomatic bacteriuria and preterm delivery/low birth weight. Obstet Gynecol 1989;73:576-82.
- Abduljabbar H, Moumena RA, Mosli HA, Khan AS, Warda A. Urinary tract infection in pregnancy. Ann Saudi Med 1991;11:322-4.
- Bryant RE, Windom RE, Vineyard JP, Sanford JP. Asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy and its association with prematurity. J Lab Clin Med 1964;63:224-31.
- Forkman A. Bacteriuria in pregnancy: its frequency and relation to overt urinary tract infection. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1964;43:35-48.
- Gold EM, Traub FB, Daichman I, Terris M. Asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 1966;27:206-9.
- Henderson M, Reinke WA, Kass EH. Epidemiology of urinary tract infection. Progress in pyelonephritis. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis; 1965.
- Hoja WA, Hefner JD, Smith MR. Asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 1964;24:458-62.
- Kass EH. Pyelonephritis and bacteriuria. A major problem in preventive medicine. Ann Intern Med 1962;56:46-53.
- Kincaid-Smith P, Bullen M, Fussell U, Mills J, Huston N. The reliability of screening and test for bacteriuria in pregnancy. Lancet 1964;39:61-2.
- Kubicki J. Serological diagnosis of urinary tract infections in cases of premature labor. Ginekol Pol 1976;47:1269-74.
- Layton R. Infection of the urinary tract in pregnancy: an investigation of a new routine in antenatal care. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw 1964;71:927-33.
- Leblanc AL, McGanity WJ. The impact of bacteriuria in pregnancy: a survey of 1300 pregnant patients. Tex Rep Biol Med 1964;22:336-47.
- Low JA, Johnston EE, McBride RL, Tuffnell PG. The significance of asymptomatic bacteriuria in the normal obstetric patient. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1964;90:897-906.
- McDonald H, Vigneswaran R, O’Loughlin JA. Group B streptococcal colonization and preterm labour. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1989;29:291-3.
- Moller M, Thomsen AC, Borch K, Dinesen K, Zdravkovic M. Rupture of fetal membranes and premature delivery associated with group B streptococci in urine of pregnant women. Lancet 1984;2:69-70.
- Norden CW, Kilpatrick WH, Kass EH. Epidemiology of urinary tract infection. Progress in pyelonephritis. Philadelphia: FA Davis; 1965.
- Patrick MJ. Influence of maternal renal infection on the foetus and infant. Arch Dis Child 1967;42:208-13.
- Robertson JG, Livingstone JR, Isdale MH. The managment and complications of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy. Report of a study on 8,275 patients. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw 1968;75:59-65.
- Schamadan WE. Bacteriuria during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1964;89:10-5.
- Schieve LA, Handler A, Hershow R, Persky V, Davis F. Urinary tract infection during pregnancy: its association with maternal morbidity and perinatal outcome. Am J Public Health 1994;84:405-10.
- Sleigh JD, Robertson JG, Isdale MH. Asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw 1964;71:74-81.
- Stuart KL, Cummins GT, Chin WA. Bacteriuria, prematurity, and the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Br Med J 1965;5434:554-6.
- Uncu Y, Uncu G, Esmer A, Bilgel N. Should asymptomatic bacteriuria be screened in pregnancy?. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 2002;29:281-5.
- Versi E, Chia P, Griffiths DJ, Harlow BL. Bacteriuria in pregnancy: a comparison of Bangladeshi and Caucasian women. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 1997;8:8-12.
- Whalley PJ, Martin FG, Peters PC. Significance of asymptomatic bacteriuria detected during pregnancy. JAMA 1965;193:879-81.
- White CP, Wilkins EG, Roberts C, Davidson DC. Premature delivery and group B streptococcal bacteriuria. Lancet 1984;2.
- Wren BG. Subclinical renal infection and prematurity. Med J Aust 1969;2:596-600.
- Klebanoff MA, Hillier SL, Nugent RP, MacPherson CA, Hauth JC, Carey JC, et al. Is bacterial vaginosis a stronger risk factor for preterm birth when it is diagnosed earlier in gestation?. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;192:470-7.
- Mascagni JR, Miller LH. A descriptive correlational study of bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy and its association with preterm birth: implications for advanced practice nurses. J Am Acad Nurse Pract 2004;16:555-60.
- Carlini L, Somigliana E, Rossi G, Veglia F, Busacca M, Vignali M. Risk factors for spontaneous preterm birth: a Northern Italian multicenter case–control study. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2002;53:174-80.
- Balu RB, Savitz DA, Ananth CV, Hartmann KE, Miller WC, Thorp JM, et al. Bacterial vaginosis, vaginal fluid neutrophil defensins, and preterm birth. Obstet Gynecol 2003;101:862-8.
- De Seta F, Sartore A, Piccoli M, Maso G, Zicari S, Panerari F, et al. Bacterial vaginosis and preterm delivery: an open question. J Reprod Med Obstet Gynecol 2005;50:313-18.
- Oakeshott P, Kerry S, Hay S, Hay P. Bacterial vaginosis and preterm birth: a prospective community-based cohort study. Br J Gen Pract 2004;54:119-22.
- Meis PJ, Goldenberg RL, Mercer B, Moawad A, Das A, McNellis D, et al. The Preterm Prediction Study: significance of vaginal infections. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Maternal–Fetal Medicine Units Network. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:1231-5.
- Riduan JM, Hillier SL, Utomo B, Wiknjosastro G, Linnan M, Kandun N. Bacterial vaginosis and prematurity in Indonesia: association in early and late pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:175-8.
- Thorsen P, Molsted K, Jensen IP, Arpi M, Bremmelgaard A, Jeune B, et al. Bacterial vaginosis (BV) in a population of 3600 pregnant women and relations to preterm birth evaluated from their first antenatal visit. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174.
- Elliott B, Brunham RC, Laga M, Piot P, Ndinya-Achola JO, Maitha G, et al. Maternal gonococcal infection as a preventable risk factor for low birth weight. J Infect Dis 1990;161:531-6.
- Krohn MA, Hillier SL, Lee ML, Rabe LK, Eschenbach DA. Vaginal Bacteroides species are associated with an increased rate of preterm delivery among women in preterm labor. J Infect Dis 1991;164:88-93.
- Subtil D, Denoit V, Le Goueff F, Husson MO, Trivier D, Puech F. The role of bacterial vaginosis in preterm labor and preterm birth: a case–control study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2002;101:41-6.
- Eschenbach DA, Gravett MG, Chen KC, Hoyme UB, Holmes KK. Bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy. An association with prematurity and postpartum complications. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl 1984;86:213-22.
- Martius J, Krohn MA, Hillier SL, Stamm WE, Holmes KK, Eschenbach DA. Relationships of vaginal Lactobacillus species, cervical Chlamydia trachomatis, and bacterial vaginosis to preterm birth. Obstet Gynecol 1988;71:89-95.
- Cauci S, Thorsen P, Schendel DE, Bremmelgaard A, Quadrifoglio F, Guaschino S. Determination of immunoglobulin A against Gardnerella vaginalis hemolysin, sialidase, and prolidase activities in vaginal fluid: implications for adverse pregnancy outcomes. J Clin Microbiol 2003;41:435-8.
- Gratacos E, Figueras F, Barranco M, Vila J, Cararach V, Alonso PL, et al. Spontaneous recovery of bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy is not associated with an improved perinatal outcome. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1998;77:37-40.
- Helou J, Keness Y, Shalev E. Association of bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy with preterm delivery. Harefuah 1996;131:83-5.
- Govender L, Hoosen AA, Moodley J, Moodley P, Sturm AW. Bacterial vaginosis and associated infections in pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1996;55:23-8.
- Hillier SL, Nugent RP, Eschenbach DA, Krohn MA, Gibbs RS, Martin DH, et al. Association between bacterial vaginosis and preterm delivery of a low-birth-weight infant. The Vaginal Infections and Prematurity Study Group. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1737-42.
- Purwar M, Ughade S, Bhagat B, Agarwal V, Kulkarni H. Bacterial vaginosis in early pregnancy and adverse pregnancy outcome. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2001;27:175-81.
- Goffinet F, Maillard F, Mihoubi N, Kayem G, Papiernik E, Cabrol D, et al. Bacterial vaginosis: prevalence and predictive value for premature delivery and neonatal infection in women with preterm labour and intact membranes. Eur J Obstet Gynaecol Reprod Biol 2003;108:146-51.
- Eden RD, Sokol RJ, Sorokin Y, Cook HJ, Sheeran G, Chik L. The mammary stimulation test – a predictor of preterm delivery?. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:1409-17.
- Guinn DA, Wigton TR, James JA, Dunlop DD, Socol M, Frederiksen MC. Mammary stimulation test predicts preterm birth in nulliparous women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170:1809-12.
- Bell R. The prediction of preterm labour by recording spontaneous antenatal uterine activity. BJOG 1983;90:884-7.
- Iams JD, Johnson FF, O’Shaughnessy RW. A prospective random trial of home uterine activity monitoring in pregnancies at increased risk of preterm labor. Part II. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1988;159:595-603.
- Maner WL, Garfield RE, Maul H, Olson G, Saade G. Predicting term and preterm delivery with transabdominal uterine electromyography. Obstet Gynecol 2003;101:1254-60.
- Arabin B, Naschold M, Ruttgers H, Kubli F. Significance of rheobase determination in detection of threatened premature labour. Z.Geburtshilfe Perinatol 1985;189:210-16.
- Agustsson P, Patel NB. The predictive value of fetal breathing movements in the diagnosis of preterm labour. BJOG 1987;94:860-3.
- Besinger RE, Compton AA, Hayashi RH. The presence or absence of fetal breathing movements as a predictor of outcome in preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1987;157:753-7.
- Castle BM, Turnbull AC. The presence or absence of fetal breathing movements predicts the outcome of preterm labour. Lancet 1983;2:471-3.
- Devoe LD, Youssef AE, Croom CS, Watson J. Can fetal biophysical observations anticipate outcome in preterm labor or preterm rupture of membranes?. Obstet Gynecol 1994;84:432-8.
- Kanaan CM, O’Grady JP, Veille JC. Effect of maternal carbon dioxide inhalation on human fetal breathing movements in term and preterm labor. Obstet Gynecol 1991;78:9-13.
- Markwitz W, Ropacka M, Breborowicz GH. Evaluation of fetal breathing movements in prognosis of preterm labour. Ginekol Pol 2001;72:55-60.
- Schreyer P, Caspi E, Natan NB, Tal E, Weinraub Z. The predictive value of fetal breathing movement and Bishop score in the diagnosis of “true” preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1989;161:886-9.
- Iams JD, Goldenberg RL, Meis PJ, Mercer BM, Moawad A, Das A, et al. The length of the cervix and the risk of spontaneous premature delivery. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Maternal Fetal Medicine Unit Network. N Engl J Med 1996;334:567-72.
- Okitsu O, Mimura T, Nakayama T, Aono T. Early prediction of preterm delivery by transvaginal ultrasonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1992;2:402-9.
- Andersen HF, Nugent CE, Wanty SD, Hayashi RH. Prediction of risk for preterm delivery by ultrasonographic measurement of cervical length. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;163:859-67.
- Andrews WW, Copper R, Hauth JC, Goldenberg RL, Neely C, Dubard M. Second-trimester cervical ultrasound: associations with increased risk for recurrent early spontaneous delivery. Obstet Gynecol 2000;95:222-6.
- Berghella V, Tolosa JE, Kuhlman K, Weiner S, Bolognese RJ, Wapner RJ. Cervical ultrasonography compared with manual examination as a predictor of preterm delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:723-30.
- Dilek TU, Gurbuz A, Yazici G, Arslan M, Gulhan S, Pata O, et al. Comparison of cervical volume and cervical length to predict preterm delivery by transvaginal ultrasound. Am.J Perinatol. 2006;23:167-72.
- Hibbard JU, Tart M, Moawad AH. Cervical length at 16–22 weeks’ gestation and risk for preterm delivery. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:972-8.
- Leung TN, Pang MW, Leung TY, Poon CF, Wong SM, Lau TK. Cervical length at 18–22 weeks of gestation for prediction of spontaneous preterm delivery in Hong Kong Chinese women. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26:713-17.
- Mara M, Calda P, Haakova L, Zizka Z, Dohnalova A, Zivny J. Significance of ultrasound vaginal cervicometry in predicting preterm delivery. Med Sci.Monit. 2002;8:MT72-MT77.
- Owen J, Yost N, Berghella V, Thom E, Swain M, Dildy GA, et al. Mid-trimester endovaginal sonography in women at high risk for spontaneous preterm birth. JAMA 2001;286:1340-8.
- Pires CR, Moron AF, Mattar R, Diniz ALD, Andrade SGA. Bussamra LCS . Cervical gland area as an ultrasonographic marker for preterm delivery. Int.J.Gynaecol Obstet. 2006;93:214-19.
- Taipale P, Hiilesmaa V. Sonographic measurement of uterine cervix at 18–22 weeks’ gestation and the risk of preterm delivery. Obstet Gynecol 1998;92:902-7.
- To MS, Skentou C, Liao AW, Cacho A, Nicolaides KH. Cervical length and funneling at 23 weeks of gestation in the prediction of spontaneous early preterm delivery. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001;18:200-3.
- Yazici G, Yildiz A, Tiras MB, Arslan M, Kanik A, Oz U. Comparison of transperineal and transvaginal sonography in predicting preterm delivery. J Clin.Ultrasound 2004;32:225-30.
- Crane JM, Van den HM, Armson BA, Liston R. Transvaginal ultrasound in the prediction of preterm delivery: singleton and twin gestations. Obstet Gynecol 1997;90:357-63.
- Daskalakis G, Thomakos N, Hatziioannou L, Mesogitis S, Papantoniou N, Antsaklis A. Cervical assessment in women with threatened preterm labor. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2005;17:309-12.
- Fuchs IB, Henrich W, Osthues K, Dudenhausen JW. Sonographic cervical length in singleton pregnancies with intact membranes presenting with threatened preterm labor. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;24:554-7.
- Goffinet F, Rozenberg P, Kayem G, Perdu M, Philippe HJ, Nisand I. The value of intravaginal ultrasonography of the cervix uteri for evaluation of the risk of premature labour. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 1997;26:623-9.
- Gomez R, Galasso M, Romero R, Mazor M, Sorokin Y, Goncalves L, et al. Ultrasonographic examination of the uterine cervix is better than cervical digital examination as a predictor of the likelihood of premature delivery in patients with preterm labor and intact membranes. Am.J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:956-64.
- Murakawa H, Utumi T, Hasegawa I, Tanaka K, Fuzimori R. Evaluation of threatened preterm delivery by transvaginal ultrasonographic measurement of cervical length. Obstet Gynecol 1993;82:829-32.
- Rageth JC, Kernen B, Saurenmann E, Unger C. Premature contractions: possible influence of sonographic measurement of cervical length on clinical management. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997;9:183-7.
- Rizzo G, Capponi A, Arduini D, Lorido C, Romanini C. The value of fetal fibronectin in cervical and vaginal secretions and of ultrasonographic examination of the uterine cervix in predicting premature delivery for patients with preterm labor and intact membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;175:1146-51.
- Rozenberg P, Rafii A, Senat MV, Dujardin A, Rapon J, Ville Y. Predictive value of two-dimensional and three-dimensional multiplanar ultrasound evaluation of the cervix in preterm labor. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2003;13:237-41.
- Schmitz T, Maillard F, Bessard-Bacquaert S, Kayem G, Fulla Y, Cabrol D, et al. Selective use of fetal fibronectin detection after cervical length measurement to predict spontaneous preterm delivery in women with preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;194:138-43.
- Tekesin I, Eberhart LH, Schaefer V, Wallwiener D, Schmidt S. Evaluation and validation of a new risk score (CLEOPATRA score) to predict the probability of premature delivery for patients with threatened preterm labor. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26:699-706.
- Tsoi E, Akmal S, Rane S, Otigbah C, Nicolaides KH. Ultrasound assessment of cervical length in threatened preterm labor. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;21:552-5.
- Tsoi E, Geerts L, Jeffery B, Odendaal HJ, Nicolaides KH. Sonographic cervical length in threatened preterm labor in a South African population. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;24:644-6.
- Tsoi E, Fuchs IB, Rane S, Geerts L, Nicolaides KH. Sonographic measurement of cervical length in threatened preterm labor in singleton pregnancies with intact membranes. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;25:353-6.
- Vendittelli F, Mamelle N, Munoz F, Janky E. Transvaginal ultrasonography of the uterine cervix in hospitalized women with preterm labor. Int.J Gynaecol Obstet 2001;72:117-25.
- Smaill F. Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2001.
- Brumfitt W. The effects of bacteriuria in pregnancy on maternal and fetal health. Kidney Int Suppl 1975;4:S113-S119.
- Elder HA, Santamarina BA, Smith S, Kass EH. The natural history of asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy: the effect of tetracycline on the clinical course and the outcome of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1971;111:441-62.
- Foley ME, Farquharson R, Stronge JM. Is screening for bacteriuria in pregnancy worthwhile?. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987;295.
- Furness ET, McDonald PJ, Beasley NV. Urinary antiseptics in asymptomatic bacteriuria of pregnancy. N Z Med J 1975;81:417-19.
- Kincaid-Smith P, Bullen M. Bacteriuria in pregnancy. Lancet 1965;191:395-9.
- Little PJ. The incidence of urinary infection in 5000 pregnant women. Lancet 1966;2:925-8.
- Mulla N. Bacteriuria in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 1960;16:89-92.
- Pathak UN, Tang K, Williams LL, Stuart KL. Bacteriuria of pregnancy: results of treatment. J Infect Dis 1969;120:91-5.
- Thomsen AC, Morup L, Hansen KB. Antibiotic elimination of group-B streptococci in urine in prevention of preterm labour. Lancet 1987;1:591-3.
- Williams GL, Campbell H, Davies KJ. Urinary concentrating ability in women with asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy. Br Med J 1969;3:212-15.
- Zinner SH, Kass EH. Long term (10 to 14 years) follow-up of bacteriuria of pregnancy. N Engl J Med 1971;285:820-4.
- Villar J, Lydon-Rochelle MT, Gulmezoglu AM, Roganti A. Duration of treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000.
- Bailey RR, Bishop V, Peddie BA. Comparison of a single dose with a 5-day course of co-trimoxazole for asymptomatic (covert) bacteriuria of pregnancy. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynecol 1983;23:139-41.
- Bailey RR, Peddie BA, Bishop V. Comparison of a single dose with a 5-day course of trimethoprim for asymptomatic (covert) bacteriuria of pregnancy. N Z Med J 1986;99:501-3.
- Brumfitt W, Hamilton-Miller JM, Franklin IN, Anderson FM, Brown GM. Conventional and two-dose amoxycillin treatment of bacteriuria in pregnancy and recurrent bacteriuria: a comparative study. J Antimicrob Chemother 1982;10:239-48.
- Gerstner GJ, Muller G, Nahler G. Amoxicillin in the treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy: a single dose of 3g amoxicillin vs a 4-day course of 3 doses 750mg amoxicillin. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1989;27:84-7.
- Masterton RG, Evans DC, Strike PW. Single-dose amoxycillin in the treatment of bacteriuria in pregnancy and the puerperium: a controlled clinical trial. BJOG 1985;92:498-505.
- Olsen SF, Secher NJ, Tabor A, Weber T, Walker JJ, Gluud C. Randomised clinical trials of fish oil supplementation in high risk pregnancies. Fish Oil Trials In Pregnancy (FOTIP) Team. BJOG 2000;107:382-95.
- Pregazzi R, Mazzatenta E, Bouche C. Single-dose antibiotic therapy of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy. Results and complications. Minerv Ginecol 1987;39:289-92.
- Thoumsin H, Aghayan M, Lambotte R. Single dose fosfomycin trometamol versus multiple dose nitrofurantoin in pregnant women with bacteriuria: preliminary results. Infection 1990;18:94-7.
- Anderton KJ, Abbas AM, Davey A, Ancill RJ. High dose, short course amoxycillin in the treatment of bacteriuria in pregnancy. Br J Clin Pract 1983;37:212-14.
- Reeves DS. Laboratory and clinical studies with sulfametopyrazine as a treatment for bacteriuria in pregnancy. J Antimicrob Chemother 1975;1:171-86.
- Nelson DB, Macones G. Bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy: current findings and future directions. Epidemiol Rev 2002;24:102-8.
- McDonald H, Brocklehurst P, Parsons J. Antibiotics for treating bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005.
- Carey JC, Klebanoff MA, Hauth JC, Hillier SL, Thom EA, Ernest JM, et al. Metronidazole to prevent preterm delivery in pregnant women with asymptomatic bacterial vaginosis. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Network of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units. N Engl J Med 2000;342:534-40.
- Duff P, Lee ML, Hillier SL, Herd LM, Krohn MA, Eschenbach DA. Amoxicillin treatment of bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy. Obstet Gynaecol 1991;77:431-5.
- Guaschino S, Ricci E, Franchi M, Frate GD, Tibaldi C, Santo DD, et al. Treatment of asymptomatic bacterial vaginosis to prevent pre-term delivery: a randomised trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2003;110:149-52.
- Hauth JC, Goldenberg RL, Andrews WW, DuBard MB, Copper RL. Reduced incidence of preterm delivery with metronidazole and erythromycin in women with bacterial vaginosis. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1732-6.
- Joesoef MR, Hillier SL, Wiknjosastro G, Sumampouw H, Linnan M, Norojono W, et al. Intravaginal clindamycin treatment for bacterial vaginosis: effects on preterm delivery and low birth weight. Am J Obstet Gynaecol 1995;173:1527-31.
- Kekki M, Kurki T, Pelkonen J, Kurkinen-Raty M, Cacciatore B, Paavonen J. Vaginal clindamycin in preventing preterm birth and peripartal infections in asymptomatic women with bacterial vaginosis: a randomized, controlled trial. Obstet Gynaecol 2001;97:643-8.
- Lamont RF, Duncan SL, Mandal D, Bassett P. Intravaginal clindamycin to reduce preterm birth in women with abnormal genital tract flora. Obstet Gynaecol 2003;101:516-22.
- McDonald HM, O’Loughlin JA, Vigneswaran R, Jolley PT, Harvey JA, Bof A, et al. Impact of metronidazole therapy on preterm birth in women with bacterial vaginosis flora (Gardnerella vaginalis): a randomised, placebo controlled trial. BJOG 1997;104:1391-7.
- Morales WJ, Schorr S, Albritton J. Effect of metronidazole in patients with preterm birth in preceding pregnancy and bacterial vaginosis: a placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Am J Obstet Gynaecol 1994;171:345-7.
- Odendaal HJ, Popov I, Schoeman J, Smith M, Grove D. Preterm labour: is bacterial vaginosis involved?. S Afr Med J 2002;92:231-4.
- Ugwumadu A, Manyonda I, Reid F, Hay P. Effect of early oral clindamycin on late miscarriage and preterm delivery in asymptomatic women with abnormal vaginal flora and bacterial vaginosis: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2003;361:983-8.
- Vermeulen GM, Bruinse HW. Prophylactic administration of clindamycin 2% vaginal cream to reduce the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth in women with an increased recurrence risk: a randomised placebo-controlled double-blind trial. BJOG 1999;106:652-7.
- Porter K, Rambo D, Jazayeri A, Jazayeri M, Prien S. Prospective randomized trial of once versus twice a day metronidazole-vaginal in obstetrical population identified with bacterial vaginosis [meeting abstract]. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184.
- Sobel JD, Ferris D, Schwebke J, Nyirjesy P, Wiesenfeld HC, Peipert J, et al. Suppressive antibacterial therapy with 0.75% metronidazole vaginal gel to prevent recurrent bacterial vaginosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;194:1283-9.
- Mullick S, Watson-Jones D, Beksinska M, Mabey D. Sexually transmitted infections in pregnancy: prevalence, impact on pregnancy outcomes, and approach to treatment in developing countries. Sex Transm Infect 2005;81:294-302.
- Brocklehurst P. Antibiotics for gonorrhoea in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2002.
- Cavenee M, Farris JR, Spalding TR, Barnes DL, Castaneda YS, Wendel GD. Treatment of gonorrhoea in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 1993;81:33-8.
- Ramus R, Sheffield J, Mayfield J, Wendel GD. A randomized trial that compared oral cefixime and intramuscular ceftriaxone for the treatment of gonorrhea in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185:629-32.
- Walker GJ. Antibiotics for syphilis diagnosed during pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2001.
- Gulmezoglu AM. Interventions for trichomoniasis in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2002.
- Klebanoff MA, Carey JC, Hauth JC, Hillier SL, Nugent RP, Thom EA, et al. Failure of metronidazole to prevent preterm delivery among pregnant women with asymptomatic Trichomonas vaginalis infection. N Engl J Med 2001;345:487-93.
- Roos RF. Trichomoniasis treated with a single dose of benzoylmetronidazole. S Afr Med J 1978;54:869-70.
- Vazquez JC, Villar J. Treatments for symptomatic urinary tract infections during pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003.
- Brost BC, Campbell B, Stramm S, Eller D, Newman RB. Randomized clinical trial of antibiotics therapy for antenatal pyelonephritis. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol 1996;4:294-7.
- Calderon-James J, Arredondo-Garcia JL, Olvera-Salinas J, Echaniz Aviles G, Conde Gonzales C, Hernandez Nevarez P. Acute cystourethritis during pregnancy. Ginecol Obstet Mex 1989;57:57-63.
- Krcmery S, Hromec J, Demesova D. Treatment of lower urinary tract infection in pregnancy. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2001;17:279-82.
- Millar LK, Wing DA, Paul RH, Grimes DA. Outpatient treatment of pyelonephritis in pregnancy: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 1995;86:560-4.
- Nien JK, Medina L, Gomez R, Yamamoto M, Gonzalez R, Carstens M, et al. Single versus multiple doses of gentamicin in the treatment of pyelonephritis during pregnancy: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184.
- Ovalle A, Martinez MA, Wolff M, Cona E, Valderrama O, Villablanca E, et al. Prospective, randomized, comparative study of the efficacy, safety and cost of cefuroxime versus cephradine in acute pyelonephritis during pregnancy. Rev Med Chile 2000;128:749-57.
- Sanchez-Ramos L, McAlpine KJ, Adair CD, Kaunitz AM, Delke I, Briones DK. Pyelonephritis in pregnancy: once-a-day ceftriaxone versus multiple doses of cefazolin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:129-33.
- Wing DA, Hendershot CM, Debuque L, Millar LK. A randomized trial of three antibiotic regimens for the treatment of pyelonephritis in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 1998;92:249-53.
- Raynes-Greenow CH, Roberts CL, Bell JC, Peat B, Gilbert GL. Antibiotics for ureaplasma in the vagina in pregnancy. Cochrane.Database.Syst.Rev 2004.
- McCormack WM, Rosner B, Lee YH, Munoz A, Charles D, Kass EH. Effect on birth weight of erythromycin treatment of pregnant women. Obstet Gynecol 1987;69:202-7.
- Thinkhamrop J, Hofmeyr GJ, Adetoro O, Lumbiganon P. Prophylactic antibiotic administration in pregnancy to prevent infectious morbidity and mortality. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2002.
- Gichangi PB, Ndinya-Achola JO, Ombete J, Nagelkerke NJ, Temmerman M. Antimicrobial prophylaxis in pregnancy: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial with cefetamet-pivoxil in pregnant women with a poor obstetric history. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:680-4.
- McGregor JA, French JI, Richter R, Vuchetich M, Bachus V, Seo K, et al. Cervicovaginal microflora and pregnancy outcome: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of erythromycin treatment. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;163:1580-91.
- Paul VK, Singh M, Buckshee K. Erythromycin treatment of pregnant women to reduce the incidence of low birth weight and preterm deliveries. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1998;62:87-8.
- Temmerman M, Njagi E, Nagelkerke N, Ndinya-Achola J, Plummer FA, Meheus A. Mass antimicrobial treatment in pregnancy. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial in a population with high rates of sexually transmitted diseases. J Reprod Med 1995;40:176-80.
- Jones RB, Keeling PW, Hilton PJ, Thompson RP. The relationship between leucocyte and muscle zinc in health and disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981;60:237-9.
- Ghosh A, Fong LY, Wan CW, Liang ST, Woo JS, Wong V. Zinc deficiency is not a cause for abortion, congenital abnormality and small-for-gestational age infant in Chinese women. BJOG 1985;92:886-91.
- Vallee BL, Falchuk KH. The biochemical basis of zinc physiology. Physiol Rev 1993;73:79-118.
- Shah D, Sachdev HP. Effect of gestational zinc deficiency on pregnancy outcomes: summary of observation studies and zinc supplementation trials. Br J Nutr 2001;85:S101-S108.
- Mahomed K. Zinc supplementation in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000.
- Mahomed K, Gulmezoglu AM. Vitamin D supplementation in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000.
- Rumbold A, Crowther CA. Vitamin C supplementation in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005.
- Rumbold A, Crowther CA. Vitamin E supplementation in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005.
- Casanueva E, Ripoll C, Tolentino M, Morales RM, Pfeffer F, Vilchis P, et al. Vitamin C supplementation to prevent premature rupture of the chorioamniotic membranes: a randomized trial. Am J Clin Nutr 2005;81:859-63.
- Kramer MS. Determinants of low birth weight: methodological assessment and meta-analysis. Bull World Health Organ 1987;65:663-737.
- Rush D. Maternal nutrition and perinatal survival. J Health Popul Nutr 2001;19:S217-S264.
- Barker DJP. Mothers, babies and health in later life. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 1998.
- Thorsdottir I, Torfadottir JE, Birgisdottir BE, Geirsson RT. Weight gain in women of normal weight before pregnancy: complications in pregnancy or delivery and birth outcome. ObstetGynecol 2002;99:799-806.
- Kramer MS, Kakuma R. Energy and protein intake in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003.
- Atton C, Watney PJM. Selective supplementation in pregnancy: effect on birth weight. J Hum Nutr Diabetics 1990;3:381-92.
- Badrawi H, Hassanein MK, Badroui MHH, . Pregnancy outcome in obese pregnant mothers. New Egypt J Med 1993;6:1717-26.
- Blackwell RQ, Chow BF, Chinn KSK, . Prospective maternal nutrition study in Taiwan: rationale, study design, feasibility and preliminary data. Nutr Reports Intl 1973;7:517-32.
- Briley C, Flanagan NL, Lewis NM. In-home prenatal nutrition intervention increased dietary iron intakes and reduced low birthweight in low-income African-American women. J Am Diet Assoc 2002;102:984-7.
- Campbell DM, MacGillivray I. The effect of a low calorie diet or a thiazide diuretic on the incidence of pre-eclampsia and on birth weight. BJOG 1975;82:572-7.
- Campbell DM, Campbell DM, Gillmer MDG. Nutrition in pregnancy. Proceedings of the 10th Study Group of the RCOG. London: Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists; 1983.
- Campbell DM, Campbell DM, Gillmer MDG. Nutrition in pregnancy. Proceedings of the 10th Study Group of the RCOG. London: Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists; 1983.
- Ceesay SM, Prentice AM, Cole TJ, Foord F, Weaver LT, Poskitt EM, et al. Effects on birth weight and perinatal mortality of maternal dietary supplements in rural Gambia: 5 year randomised controlled trial. Br Med J 1997;315:786-90.
- Elwood PC, Haley TJL, Hughes SJ, Sweetnam PM, Gray OP, Davies DP. Child growth (0–5 years), and the effect of entitlement to a milk supplement. Arch Dis Child 1981;56:831-5.
- Girija A, Geervani P, Rao GN. Influence of dietary supplementation during pregnancy on lactation performance. J Trop Pediatr 1984;30:79-83.
- Hankin ME, Symons EM. Body weight, diet and pre-eclamptic toxaemia of pregnancy. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynecol 1962;4:156-60.
- Hunt IF, Jacob M, Ostergard NJ, Masri G, Clark VA, Coulson AH. Effect of nutrition education on the nutritional status of low-income pregnant women of Mexican descent. Am J Clin Nutr 1976;29:675-84.
- Iyengar L. Effects of dietary supplements late in pregnancy on the expectant mother and her newborn. Indian J Med Res 1967;55.
- Kafatos AG, Vlachonikolis IG, Codrington CA. Nutrition during pregnancy: the effects of an education intervention program in Greece. Am J Clin Nutr 1989;50:970-9.
- Kardjati S, Kusin JA, De With C. Energy supplementation in the last trimester of pregnancy in East Java: I. Effect on birthweight. BJOG 1988;95:783-94.
- Mardones-Santander F, Rosso P, Stekel A, Ahumada E, Llaguno S, Pizarro F, et al. Effect of a milk based food supplement on maternal nutritional status and fetal growth in underweight Chilean women. Am J Clin Nutr 1988;47:413-19.
- Mora JO, Navarro LD, Clement J, Wagner M, Paredes BD, Herrera MG. The effect of nutritional supplementation on calorie and protein intake of pregnant women. Nutr Reports Intl 1978;17:217-28.
- Ross RA, Perlzweig WA, Taylor HM, . A study of certain dietary factors of possible etiologic significance in toxaemias of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1938;35:426-40.
- Ross SM, Nel E, Naeye RL. Differing effects of low and high bulk maternal dietary supplements during pregnancy. Early Hum Dev 1985;10:295-302.
- Rush D, Stein Z, Susser M. A randomized controlled trial of prenatal nutritional supplementation in New York City. Pediatrics 1980;65:683-97.
- Sweeney C, Smith H, Foster JC, Place JC, Specht J, Kochenour NK, et al. Effects of a nutrition intervention program during pregnancy: maternal data phases 1 and 2. J Nurse Midwifery 1985;30:149-58.
- Viegas OA, Scott PH, Cole TJ, Mansfield HN, Wharton P, Wharton BA. Dietary protein energy supplementation of pregnant Asian mothers at Sorrento, Birmingham. I. Unselective during second and third trimesters. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982;285:589-92.
- Viegas OA, Scott PH, Cole TJ, Eaton P, Needham PG, Wharton BA. Dietary protein energy supplementation of pregnant Asian mothers at Sorrento, Birmingham. II. Selective during third trimester only. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982;285:592-5.
- Smuts CM, Huang M, Mundy D, Plasse T, Major S, Carlson SE. A randomized trial of docosahexaenoic acid supplementation during the third trimester of pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 2003;101:469-79.
- Saurel-Cubizolles MJ, Kaminski M, Llado-Arkhipoff J, Du MC, Estryn-Behar M, Berthier C, et al. Pregnancy and its outcome among hospital personnel according to occupation and working conditions. J Epidemiol Community Health 1985;39:129-34.
- Teitelman AM, Welch LS, Hellenbrand KG, Bracken MB. Effect of maternal work activity on preterm birth and low birth weight. Am J Epidemiol 1990;131:104-13.
- Goldenberg RL, Cliver SP, Bronstein J, Cutter GR, Andrews WW, Mennemeyer ST. Bed rest in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 1994;84:131-6.
- Sosa C, Althabe F, Belizan J, Bergel E. Bed rest in singleton pregnancies for preventing preterm birth. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2004.
- Hobel CJ, Ross MG, Bemis RL, Bragonier JR, Nessim S, Sandhu M, et al. The West Los Angeles Preterm Birth Prevention Project. I. Program impact on high-risk women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170:54-62.
- Berghella V, Odibo AO, Tolosa JE. Cerclage for prevention of preterm birth in women with a short cervix found on transvaginal ultrasound examination: a randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191:1311-17.
- To MS, Alfirevic Z, Heath VC, Cicero S, Cacho AM, Williamson PR, et al. Cervical cerclage for prevention of preterm delivery in women with short cervix: randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004;363:1849-53.
- MRC/RCOG Working Party on Cervical Cerclage . Final report of the Medical Research Council/Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists multicentre randomised trial of cervical cerclage. BJOG 1993;100:516-23.
- Althuisius SM, Dekker GA, Hummel P, Bekedam DJ, van Geijn HP. Final results of the Cervical Incompetence Prevention Randomized Cerclage Trial (CIPRACT): therapeutic cerclage with bed rest versus bed rest alone. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185:1106-12.
- Hueston WJ, Knox MA, Eilers G, Pauwels J, Lonsdorf D. The effectiveness of preterm-birth prevention educational programs for high-risk women: a meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol 1995;86:705-12.
- Multicenter randomized, controlled trial of a preterm birth prevention program . Collaborative Group on Preterm Birth Prevention. Am.J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:352-66.
- Goldenberg RL, Davis RO, Copper RL, Corliss DK, Andrews JB, Carpenter AH. The Alabama preterm birth prevention project. Obstet Gynecol 1990;75:933-9.
- Heins HC, Nance NW, McCarthy BJ, Efird CM. A randomized trial of nurse-midwifery prenatal care to reduce low birth weight. Obstet Gynecol 1990;75:341-5.
- Main DM, Gabbe SG, Richardson D, Strong S. Can preterm deliveries be prevented?. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1985;151:892-8.
- Main DM, Richardson DK, Hadley CB, Gabbe SG. Controlled trial of a Preterm Labor Detection program: efficacy and costs. Obstet Gynecol 1989;74:873-7.
- Spencer B, Berendes HW, Kessek S, Yaffe S. Advances in the prevention of low birthweight. Washington, DC: National Center for Education in Maternal and Child Health; 1991.
- Torok M. Hungarian tele-medical preterm birth prevention project: a randomized multicenter clinical trial study. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1994;46.
- Van Winter JT, Harmon MC, Atkinson EJ, Simmons PS, Ogburn PL. Young Moms’ Clinic: a multidisciplinary approach to pregnancy education in teens and in young single women. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 1997;10:28-33.
- Kollee LA, Eskes TK, Peer PG, Koppes JF. Intra- or extrauterine transport? Comparison of neonatal outcomes using a logistic model. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1985;20:393-9.
- Lamont RF, Dunlop PD, Crowley P, Levene MI, Elder MG. Comparative mortality and morbidity of infants transferred in utero or postnatally. J Perinat Med 1983;11:200-3.
- Katz M, Newman RB, Gill PJ. Assessment of uterine activity in ambulatory patients at high risk of preterm labor and delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1986;154:44-7.
- Brown HL, Britton KA, Brizendine EJ, Hiett AK, Ingram D, Turnquest MA, et al. A randomized comparison of home uterine activity monitoring in the outpatient management of women treated for preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:798-805.
- Corwin MJ, Mou SM, Sunderji SG, Gall S, How H, Patel V, et al. Multicenter randomized clinical trial of home uterine activity monitoring: pregnancy outcomes for all women randomized. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;175:1281-5.
- Dyson DC, Crites YM, Ray DA, Armstrong MA. Prevention of preterm birth in high-risk patients: the role of education and provider contact versus home uterine monitoring. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:756-62.
- Breart G, Mlika-Carbanne N, Kaminski M, , Koppe JG, Eskes TK, et al. Care, Concern and Cure in Perinatal Medicine. Carnforth: Parthenon Publishing; 1993.
- Chalmers B, Wolman W. Social support in labor – a selective review. J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol 1993;14:1-15.
- Oakley A. Social support in motherhood. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publishing; 1992.
- Blondel B, Breart G, Llado J, Chartier M. Evaluation of the home-visiting system for women with threatened preterm labor: results of a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1990;34:47-58.
- Bryce RL, Stanley FJ, Garner JB. Randomized controlled trial of antenatal social support to prevent preterm birth. BJOG 1991;98:1001-8.
- Goulet C, Gevry H, Lemay M, Gauthier RJ, Lepage L, Fraser W, et al. A randomized clinical trial of care for women with preterm labour: home management versus hospital management. CMAJ 2001;164:985-91.
- Kitzman H, Olds DL, Henderson CR, Hanks C, Cole R, Tatelbaum R, et al. Effect of prenatal and infancy home visitation by nurses on pregnancy outcomes, childhood injuries, and repeated childbearing. A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1997;278:644-52.
- Mellier G, Rudigoz RC, Dargent D, . Evaluation of the significance and effectiveness of home monitoring of pathological pregnancies by midwives. Lyon, France: ORS Rhone-Alpes; 1988.
- Oakley A, Rajan L, Grant A. Social support and pregnancy outcome. BJOG 1990;97:155-62.
- Olds DL, Henderson CR, Tatelbaum R, Chamberlin R. Improving the delivery of prenatal care and outcomes of pregnancy: a randomized trial of nurse home visitation. Pediatrics 1986;77:16-28.
- Spencer B, Thomas H, Morris J. A randomized controlled trial of the provision of a social support service during pregnancy: the South Manchester Family Worker Project. BJOG 1989;96:281-8.
- Spira N, Audras F, Chapel A, Debuisson E, Jacquelin J, Kirchhoffer C, et al. Domiciliary care of pathological pregnancies by midwives. Comparative controlled study on 996 women. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 1981;10:543-8.
- Villar J, Farnot U, Barros F, Victora C, Langer A, Belizan JM. A randomized trial of psychosocial support during high-risk pregnancies. The Latin American Network for Perinatal and Reproductive Research. N Engl J Med 1992;327:1266-71.
- Blondel B, Breart G. Home visits during pregnancy: consequences on pregnancy outcome, use of health services, and women’s situations. Semin Perinatol 1995;19:263-71.
- Lopez NJ, Smith PC, Gutierrez J. Periodontal therapy may reduce the risk of preterm low birth weight in women with periodontal disease: a randomized controlled trial. J Periodontol 2002;73:911-24.
- Dodd JM, Crowther CA, Cincotta R, Flenady V, Robinson JS. Progesterone supplementation for preventing preterm birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2005;84:526-33.
- da Fonseca EB, Bittar RE, Carvalho MH, Zugaib M. Prophylactic administration of progesterone by vaginal suppository to reduce the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth in women at increased risk: a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study. Am.J Obstet Gynecol 2003;188:419-24.
- Hartikainen-Sorri AL, Kauppila A, Tuimala R. Inefficacy of 17 alpha-hydroxyprogesterone caproate in the prevention of prematurity in twin pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 1980;56:692-5.
- Hauth JC, Gilstrap LC, Brekken AL, Hauth JM. The effect of 17 alpha-hydroxyprogesterone caproate on pregnancy outcome in an active-duty military population. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983;146:187-90.
- Johnson JW, Austin KL, Jones GS, Davis GH, King TM. Efficacy of 17alpha-hydroxyprogesterone caproate in the prevention of premature labor. N Engl J Med 1975;293:675-80.
- Meis PJ, Klebanoff M, Thom E, Dombrowski MP, Sibai B, Moawad AH, et al. Prevention of recurrent preterm delivery by 17 alpha-hydroxyprogesterone caproate. N Engl J Med 2003;348:2379-85.
- Papiernik E. Double blind study of an agent to prevent preterm delivery among women at increased risk. Serie IV, fiche 3. Edition Schering; 1970.
- Coomarasamy A, Thangaratinam S, Gee H, Khan KS. Progesterone for the prevention of preterm birth: a critical evaluation of evidence. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2006;129:111-18.
- Kyrklund-Blomberg NB, Cnattingius S. Preterm birth and maternal smoking: risks related to gestational age and onset of delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:1051-5.
- Lumley J, Oliver SS, Chamberlain C, Oakley L. Interventions for promoting smoking cessation during pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2004.
- Donovan JW. Randomised controlled trial of anti-smoking advice in pregnancy. Br J Prev Soc Med 1977;31:6-12.
- Ershoff DH, Mullen PD, Quinn VP. A randomized trial of a serialized self-help smoking cessation program for pregnant women in an HMO. Am J Public Health 1989;79:182-7.
- Haddow JE, Knight GJ, Kloza EM, Palomaki GE, Wald NJ. Cotinine-assisted intervention in pregnancy to reduce smoking and low birthweight delivery. BJOG 1991;98:859-65.
- Hegaard HK, Kjaergaard H, Moller LF, Wachmann H, Ottesen B. Multimodal intervention raises smoking cessation rate during pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2003;82:813-19.
- Hjalmarson AI, Hahn L, Svanberg B. Stopping smoking in pregnancy: effect of a self-help manual in controlled trial. BJOG 1991;98:260-4.
- LeFevre ML, Evans JK, Ewigman B. Is smoking an indication for prenatal ultrasonography? RADIUS Study Group. Arch Fam Med 1995;4:120-3.
- MacArthur C, Newton JR, Knox EG. Effect of anti-smoking health education on infant size at birth: a randomized controlled trial. BJOG 1987;94:295-300.
- Malchodi CS, Oncken C, Dornelas EA, Caramanica L, Gregonis E, Curry SL. The effects of peer counseling on smoking cessation and reduction. Obstet Gynecol 2003;101:504-10.
- Panjari M, Bell R, Bishop S, Astbury J, Rice G, Doery J. A randomized controlled trial of a smoking cessation intervention during pregnancy. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1999;39:312-17.
- Secker-Walker RH, Solomon LJ, Flynn BS, Skelly JM, Lepage SS, Goodwin GD, et al. Individualized smoking cessation counseling during prenatal and early postnatal care. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:1347-55.
- Secker-Walker RH, Solomon LJ, Flynn BS, Skelly JM, Mead PB. Smoking relapse prevention during pregnancy. A trial of coordinated advice from physicians and individual counseling. Am J Prev Med 1998;15:25-31.
- Sexton M, Hebel JR. A clinical trial of change in maternal smoking and its effect on birth weight. JAMA 1984;251:911-15.
- Tappin DM, Lumsden MA, McIntyre D, Mckay C, Gilmour WH, Webber R, et al. A pilot study to establish a randomized trial methodology to test the efficacy of a behavioural intervention. Health Educ Res 2000;15:491-502.
- Thornton L, Gogan C, McKenna P. The Rotunda stop smoking programme [abstract]. Irish J Med Sci 1997;167.
- Wisborg K, Henriksen TB, Jespersen LB, Secher NJ. Nicotine patches for pregnant smokers: a randomized controlled study. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:967-71.
- Stan C, Boulvain M, Hirsbrunner-Amagbaly P, Pfister R. Hydration for treatment of preterm labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2002.
- Guinn DA, Goepfert AR, Owen J, Brumfield C, Hauth JC. Management options in women with preterm uterine contractions: a randomized clinical trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:814-18.
- Bieniarz J, Burd L, Motew M, Scommegna A. Inhibition of uterine contractility in labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1971;111:874-9.
- Helfgott AW, Willis DC, Blanco JD. Is hydration and sedation beneficial in the treatment of threatened preterm labor? A preliminary report. J Matern Fetal Med 1994;3:37-42.
- King J, Flenady V. Prophylactic antibiotics for inhibiting preterm labour with intact membranes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2002.
- Cox SM, Bohman VR, Sherman ML, Leveno KJ. Randomized investigation of antimicrobials for the prevention of preterm birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174:206-10.
- Gordon M, Samuels P, Shubert P, Johnson F, Gebauer C, Iams J. A randomized, prospective study of adjunctive ceftizoxime in preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:1546-52.
- Kenyon SL, Taylor DJ, Tarnow-Mordi W. Broad-spectrum antibiotics for spontaneous preterm labour: the ORACLE II randomised trial. ORACLE Collaborative Group. Lancet 2001;357:989-94.
- McGregor JA, French JI, Seo K. Adjunctive clindamycin therapy for preterm labor: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;165:867-75.
- Newton ER, Dinsmoor MJ, Gibbs RS. A randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial of antibiotics in idiopathic preterm labor. Obstet Gynecol 1989;74:562-6.
- Newton ER, Shields L, Ridgway LE III, Berkus MD, Elliott BD. Combination antibiotics and indomethacin in idiopathic preterm labor: a randomized double-blind clinical trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;165:1753-9.
- Norman K, Pattinson RC, de Souza J, de Jong P, Moller G, Kirsten G. Ampicillin and metronidazole treatment in preterm labour: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. BJOG 1994;101:404-8.
- Oyarzun E, Gomez R, Rioseco A, Gonzalez P, Gutierrez P, Donoso E, et al. Antibiotic treatment in preterm labor and intact membranes: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. J Matern Fetal Med 1998;7:105-10.
- Romero R, Sibai B, Caritis S, Paul R, Depp R, Rosen M, et al. Antibiotic treatment of preterm labor with intact membranes: a multicenter, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:764-74.
- Svare J, Langhoff-Roos J, Andersen LF, Kryger-Baggesen N, Borch-Christensen H, Heisterberg L, et al. Ampicillin-metronidazole treatment in idiopathic preterm labour: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. BJOG 1997;104:892-7.
- Watts DH, Krohn MA, Hillier SL, Eschenbach DA. Randomized trial of antibiotics in addition to tocolytic therapy to treat preterm labor. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol 1994;1:220-7.
- Anotayanonth S, Subhedar NV, Garner P, Neilson JP, Harigopal S. Betamimetics for inhibiting preterm labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2004.
- Treatment of preterm labor with the beta-adrenergic agonist ritodrine. The Canadian Preterm Labor Investigators Group. N Engl J Med 1992;327:308-12.
- Adam GS. Isoxuprine and premature labour. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1966;6:294-8.
- Barden TP. Randomised Trial of Ritodrine Vs Placebo in Threatened Pre-Term Delivery 1990.
- Caritis SN, Toig G, Heddinger LA, Ashmead G. A double-blind study comparing ritodrine and terbutaline in the treatment of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1984;150:7-14.
- Cotton DB, Strassner HT, Hill LM, Schifrin BS, Paul RH. Comparison of magnesium sulfate, terbutaline and a placebo for inhibition of preterm labor. A randomized study. J Reprod Med 1984;29:92-7.
- Essed GGM, Eskes TKAB, Jongsma HW. A randomized trial of two beta-mimetic drugs for the treatment of threatening early labor. Clinical results in a prospective comparative study with ritodrine and fenoterol. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1978;8:341-8.
- Hobel CJ. Randomised Trial of Ritodrine Vs Placebo in Threatened Pre-Term Delivery 1980.
- Holleboom CA, Merkus JM, van Elferen LW, Keirse MJ. Randomised comparison between a loading and incremental dose model for ritodrine administration in preterm labour. BJOG 1996;103:695-701.
- Ingemarsson I. Effect of terbutaline on premature labor. A double-blind placebo-controlled study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1976;125:520-4.
- Larsen JF, Hansen MK, Hesseldahl H, Kristoffersen K, Larsen PK, Osler M, et al. Ritodrine in the treatment of preterm labour. A clinical trial to compare a standard treatment with three regimens involving the use of ritodrine. BJOG 1980;87:949-57.
- Leveno KJ, Klein VR, Guzick DS, Young DC, Hankins GD, Williams ML. Single-centre randomised trial of ritodrine hydrochloride for preterm labour. Lancet 1986;1:1293-6.
- Lipshitz J, Depp R, Hauth J, Hayashi R, Morrison J, Schneider J, et al. Comparison of hexoprenaline and ritodrine in the treatment of preterm labor: United States multicenter study. Rome, Italy; 1988.
- Mariona A. Randomised Trial of Ritodrine Vs Placebo in Threatened Pre-Term Delivery 1980.
- Scommegna A. Randomised Trial or Ritodrine Vs Placebo in Threatened Pre-Term Delivery 1980.
- Spellacy WN, Cruz AC, Birk SA, Buhi WC. Treatment of premature labor with ritodrine: a randomized controlled study. Obstet Gynecol 1979;54:220-3.
- Von Oeyen P, Braden G, Smith M, Garb J, Liucci L. A randomized study comparing ritodrine and terbutaline for the treatment of preterm labor [meeting abstract]. Houston, Texas; 1990.
- Dodd JM, Crowther CA, Dare MR, Middleton P. Oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy after threatened preterm labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006.
- Bivins HA, Newman RB, Fyfe DA, Campbell BA, Stramm SL. Randomized trial of oral indomethacin and terbutaline sulfate for the long-term suppression of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:1065-70.
- Brown SM, Tejani NA. Terbutaline sulfate in the prevention of recurrence of premature labor. Obstet Gynecol 1981;57:22-5.
- Creasy RK, Golbus MS, Laros RK, Parer JT, Roberts JM. Oral ritodrine maintenance in the treatment of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1980;137:212-19.
- Holleboom CA, Merkus JM, van Elferen LW, Keirse MJ. Double-blind evaluation of ritodrine sustained release for oral maintenance of tocolysis after active preterm labour. BJOG 1996;103:702-5.
- How HY, Hughes SA, Vogel RL, Gall SA, Spinnato JA. Oral terbutaline in the outpatient management of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:1518-22.
- Kopelman JN, Duff P, Read JA. Randomized comparison of oral terbutaline and ritodrine for preventing recurrent preterm labor. J Reprod Med 1989;34:225-30.
- Lewis R, Mercer BM, Salama M, Walsh MA, Sibai BM. Oral terbutaline after parenteral tocolysis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;175:834-7.
- Parilla BV, Dooley SL, Minogue JP, Socol ML. The efficacy of oral terbutaline after intravenous tocolysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:965-9.
- Ricci JM, Hariharan S, Helfgott A, Reed K, O’Sullivan MJ. Oral tocolysis with magnesium chloride: a randomized controlled prospective clinical trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;165:603-10.
- Ridgway LE, Muise K, Wright JW, Patterson RM, Newton ER. A prospective randomized comparison of oral terbutaline and magnesium oxide for the maintenance of tocolysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;163:879-82.
- Rust OA, Bofill JA, Arriola RM, Andrew ME, Morrison JC. The clinical efficacy of oral tocolytic therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;175:838-42.
- Nanda K, Cook LA, Gallo MF, Grimes DA. Terbutaline pump maintenance therapy after threatened preterm labor for preventing preterm birth. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2002.
- Guinn DA, Goepfert AR, Owen J, Wenstrom KD, Hauth JC. Terbutaline pump maintenance therapy for prevention of preterm delivery: a double-blind trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:874-8.
- Wenstrom KD, Weiner CP, Merrill D, Niebyl J. A placebo-controlled randomized trial of the terbutaline pump for prevention of preterm delivery. Am J Perinatol 1997;14:87-91.
- Saade GR, Taskin O, Belfort MA, Erturan B, Moise KJ. In vitro comparison of four tocolytic agents, alone and in combination. Obstet Gynecol 1994;84:374-8.
- King JF, Flenady VJ, Papatsonis DN, Dekker GA, Carbonne B. Calcium channel blockers for inhibiting preterm labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003.
- Bracero LA, Leikin E, Kirshenbaum N, Tejani N. Comparison of nifedipine and ritodrine for the treatment of preterm labor. Am J Perinatol 1991;8:365-9.
- Ferguson JE, Dyson DC, Schutz T, Stevenson DK. A comparison of tocolysis with nifedipine or ritodrine: analysis of efficacy and maternal, fetal, and neonatal outcome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;163:105-11.
- Garcia-Velasco JA, Gonzalez GA. A prospective, randomized trial of nifedipine vs. ritodrine in threatened preterm labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1998;61:239-44.
- Glock JL, Morales WJ. Efficacy and safety of nifedipine versus magnesium sulfate in the management of preterm labor: a randomized study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:960-4.
- Janky E, Leng JJ, Cormier PH, Salamon R, Meynard J. A randomized study of the treatment of threatened premature labor. Nifedipine versus ritodrine. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 1990;19:478-82.
- Jannet D, Abankwa A, Guyard B, Carbonne B, Marpeau L, Milliez J. Nicardipine versus salbutamol in the treatment of premature labor. A prospective randomized study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1997;73:11-6.
- Koks CA, Brolmann HA, de Kleine MJ, Manger PA. A randomized comparison of nifedipine and ritodrine for suppression of preterm labor. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1998;77:171-6.
- Kupferminc M, Lessing JB, Yaron Y, Peyser MR. Nifedipine versus ritodrine for suppression of preterm labour. BJOG 1993;100:1090-4.
- Larmon JE, Ross BS, May WL, Dickerson GA, Fischer RG, Morrison JC. Oral nicardipine versus intravenous magnesium sulfate for the treatment of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;181:1432-7.
- Papatsonis DN, van Geijn HP, Ader HJ, Lange FM, Bleker OP, Dekker GA. Nifedipine and ritodrine in the management of preterm labor: a randomized multicenter trial. Obstet Gynecol 1997;90:230-4.
- Read MD, Wellby DE. The use of a calcium antagonist (nifedipine) to suppress preterm labour. BJOG 1986;93:933-7.
- Weerakul W, Chittacharoen A, Suthutvoravut S. Nifedipine versus terbutaline in management of preterm labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2002;76:311-13.
- Al-Qattan F, Omu AE, Labeeb N. A prospective randomized study comparing nifedipine versus ritodrine for the suppression of preterm labour. Med Princ Pract 2000;9:164-73.
- Fan L, Wu GF, Huang XH. The effect of calcium entry blocker on the management of preterm labor: a randomized controlled study. Chinese J Pract Gynecol Obstet 2003;19:87-9.
- Floyd RC, McLauglin BN, Perry KG, Martin RW, Sullivan CA, Morrison JC. Magnesium sulfate or nifedipine hydrochloride for acute tocolysis of preterm labor: efficacy and side effects. J Matern Fetal Invest 1995;5:25-9.
- Haghighi L. Prevention of preterm delivery: nifedipine or magnesium sulfate. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1999;66:297-8.
- Kashanian M, Akbarian AR, Soltanzadeh M. Atosiban and nifedipine for the treatment of preterm labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;91:10-4.
- Gaunekar NN, Crowther CA. Maintenance therapy with calcium channel blockers for preventing preterm birth after threatened preterm labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2004.
- Carr DB, Clark AL, Kernek K, Spinnato JA. Maintenance oral nifedipine for preterm labor: a randomized clinical trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;181:822-7.
- Sayin NC, Varol FG, Balkanli-Kaplan P, Sayin M. Oral nifedipine maintenance therapy after acute intravenous tocolysis in preterm labor. J Perinat Med 2004;32:220-4.
- Papatsonis D, Flenady V, Cole S, Liley H. Oxytocin receptor antagonists for inhibiting preterm labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005.
- French/Australian Atosiban Investigators Group . Treatment of preterm labor with the oxytocin antagonist atosiban: a double-blind, randomized, controlled comparison with salbutamol. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2001;98:177-85.
- European Atosiban Study Group . The oxytocin antagonist atosiban versus the beta-agonist terbutaline in the treatment of preterm labor. A randomized, double-blind, controlled study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2001;80:413-22.
- Goodwin TM, Paul R, Silver H, Spellacy W, Parsons M, Chez R, et al. The effect of the oxytocin antagonist atosiban on preterm uterine activity in the human. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170:474-8.
- Goodwin TM, Valenzuela GJ, Silver H, Creasy G. Dose ranging study of the oxytocin antagonist atosiban in the treatment of preterm labor. Atosiban Study Group. Obstet Gynecol 1996;88:331-6.
- Moutquin JM, Sherman D, Cohen H, Mohide PT, Hochner-Celnikier D, Fejgin M, et al. Double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of atosiban and ritodrine in the treatment of preterm labor: a multicenter effectiveness and safety study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182:1191-9.
- Romero R, Sibai BM, Sanchez-Ramos L, Valenzuela GJ, Veille JC, Tabor B, et al. An oxytocin receptor antagonist (atosiban) in the treatment of preterm labor: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with tocolytic rescue. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182:1173-83.
- Vause S, Johnston T. Management of preterm labour. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2000;83:F79-F85.
- King J, Flenady V, Cole S, Thornton S. Cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitors for treating preterm labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005.
- Besinger RE, Niebyl JR, Keyes WG, Johnson TR. Randomized comparative trial of indomethacin and ritodrine for the long-term treatment of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:981-6.
- Kramer WB, Saade GR, Belfort M, Dorman K, Mayes M, Moise KJ. A randomized double-blind study comparing the fetal effects of sulindac to terbutaline during the management of preterm labor. AmJ Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:396-401.
- Kurki T, Eronen M, Lumme R, Ylikorkala O. A randomized double-dummy comparison between indomethacin and nylidrin in threatened preterm labor. Obstet Gynecol 1991;78:1093-7.
- McWhorter J, Carlan SJ, OLeary TD, Richichi K, O’Brien WF. Rofecoxib versus magnesium sulfate to arrest preterm labor: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 2004;103:923-30.
- Morales WJ, Smith SG, Angel JL, O’Brien WF, Knuppel RA. Efficacy and safety of indomethacin versus ritodrine in the management of preterm labor: a randomized study. Obstet Gynecol 1989;74:567-72.
- Morales WJ, Madhav H. Efficacy and safety of indomethacin compared with magnesium sulfate in the management of preterm labor: a randomized study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:97-102.
- Niebyl JR, Blake DA, White RD, Kumor KM, Dubin NH, Robinson JC, et al. The inhibition of premature labor with indomethacin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1980;136:1014-19.
- Panter KR, Hannah ME, Amankwah KS, Ohlsson A, Jefferies AL, Farine D. The effect of indomethacin tocolysis in preterm labour on perinatal outcome: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. BJOG 1999;106:467-73.
- Parilla BV, Tamura RK, Cohen LS, Clark E. Lack of effect of antenatal indomethacin on fetal cerebral blood flow. Am.J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:1166-9.
- Sawdy RJ, Lye S, Fisk NM, Bennett PR. A double-blind randomized study of fetal side effects during and after the short-term maternal administration of indomethacin, sulindac, and nimesulide for the treatment of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;188:1046-51.
- Schorr SJ, Ascarelli MH, Rust OA, Ross EL, Calfee EL, Perry KG, et al. A comparative study of ketorolac (Toradol) and magnesium sulfate for arrest of preterm labor. South Med J 1998;91:1028-32.
- Stika CS, Gross GA, Leguizamon G, Gerber S, Levy R, Mathur A, et al. A prospective randomized safety trial of celecoxib for treatment of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:653-60.
- Zuckerman H, Shalev E, Gilad G, Katzuni E. Further study of the inhibition of premature labor by indomethacin. Part II double-blind study. J Perinat Med 1984;12:25-9.
- Golding J. A randomised trial of low dose aspirin for primiparae in pregnancy. The Jamaica Low Dose Aspirin Study Group. BJOG 1998;105:293-9.
- Groom KM, Shennan AH, Jones BA, Seed P, Bennett PR. TOCOX – a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of rofecoxib (a COX-2-specific prostaglandin inhibitor) for the prevention of preterm delivery in women at high risk. BJOG 2005;112:725-30.
- Humphrey RG, Bartfield MC, Carlan SJ, O’Brien WF, O’Leary TD, Triana T. Sulindac to prevent recurrent preterm labor: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2001;98:555-62.
- Hendricks CH, Hendricks CH, Elder MG. Preterm labour. London: Butterworths; 1981.
- Caritis SN, Carson D, Greebon D, McCormick M, Edelstone DI, Mueller-Heubach E. A comparison of terbutaline and ethanol in the treatment of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1982;142:183-90.
- Lauersen NH, Merkatz IR, Tejani N, Wilson KH, Roberson A, Mann LI, et al. Inhibition of premature labor: a multicenter comparison of ritodrine and ethanol. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1977;127:837-45.
- Sims CD, Chamberlain GV, Boyd IE, Lewis PJ. A comparison of salbutamol and ethanol in the treatment of preterm labour. BJOG 1978;85:761-6.
- Reynolds JW. A comparison of salbutamol and ethanol in the treatment of premature labour. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1978;18:107-9.
- Watring WG, Benson WL, Wiebe RA, Vaughn DL. Intravenous alcohol – a single blind study in the prevention of premature delivery: a preliminary report. J Reprod Med 1976;16:35-8.
- Aramayo JFJ, Martinez FJ, Rosales CL. Tocolytic therapy with magnesium sulphate and terbutaline for inhibition of pre-term labor. Ginecol Obstet Mex 1990;58:265-9.
- Armson BA, Samuels P, Miller F, Verbalis J, Main EK. Evaluation of maternal fluid dynamics during tocolytic therapy with ritodrine hydrochloride and magnesium sulfate. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;167:758-65.
- Beall MH, Edgar BW, Paul RH, Smith-Wallace T. A comparison of ritodrine, terbutaline, and magnesium sulfate for the suppression of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1985;153:854-9.
- Cox SM, Sherman ML, Leveno KJ. Randomized investigation of magnesium sulfate for prevention of preterm birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;163:767-72.
- El Sayed YY, Riley ET, Holbrook RH, Cohen SE, Chitkara U, Druzin ML. Randomized comparison of intravenous nitroglycerin and magnesium sulfate for treatment of preterm labor. Obstet Gynecol 1999;93:79-83.
- Fox MD, Allbert JR, McCaul JF, Martin RW, McLaughlin BN, Morrison JC. Neonatal morbidity between 34 and 37 weeks’ gestation. J Perinatol 1993;13:349-53.
- Hollander DI, Nagey DA, Pupkin MJ. Magnesium sulfate and ritodrine hydrochloride: a randomized comparison. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1987;156:631-7.
- Ma L. Magnesium sulfate in prevention of preterm labor. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 1992;72:158-61.
- Miller JM, Keane MW, Horger EO III. A comparison of magnesium sulfate and terbutaline for the arrest of premature labor. A preliminary report. J Reprod Med 1982;27:348-51.
- Mittendorf R, Covert R, Boman J, Khoshnood B, Lee KS, Siegler M. Is tocolytic magnesium sulphate associated with increased total paediatric mortality?. Lancet 1997;350:1517-18.
- Sciscione A, Gorman R, Schlossman P, Colmorgen G. A randomized prospective study of intravenous magnesium sulfate, ritodrine, and subcutaneous terbutaline as treatments for preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;168.
- Steer CM, Petrie RH. A comparison of magnesium sulfate and alcohol for the prevention of premature labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1977;129:1-4.
- Tchilinguirian NG, Najem R, Sullivan GB, Craparo FJ. The use of ritodrine and magnesium sulfate in the arrest of premature labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1984;22:117-23.
- Wilkins IA, Lynch L, Mehalek KE, Berkowitz GS, Berkowitz RL. Efficacy and side effects of magnesium sulfate and ritodrine as tocolytic agents. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1988;159:685-9.
- Chau AC, Gabert HA, Miller JM. A prospective comparison of terbutaline and magnesium for tocolysis. Obstet Gynecol 1992;80:847-51.
- Crowther CA, Hiller JE, Doyle LW. Magnesium sulphate for preventing preterm birth in threatened preterm labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2002.
- Crowther CA, Moore V. Magnesium for preventing preterm birth after threatened preterm labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000.
- Wani MP, Barakzai N, Graham I. Glyceryl trinitrate vs. ritodrine for the treatment of preterm labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2004;85:165-7.
- Bisits A, Madsen G, McLean M, O’Callaghan S, Smith R, Giles W. Corticotropin-releasing hormone: a biochemical predictor of preterm delivery in a pilot randomized trial of the treatment of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:862-6.
- Bisits A, Madsen G, Knox M, Gill A, Smith R, Yeo G, et al. The Randomized Nitric Oxide Tocolysis Trial (RNOTT) for the treatment of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191:683-90.
- Lees CC, Lojacono A, Thompson C, Danti L, Black RS, Tanzi P, et al. Glyceryl trinitrate and ritodrine in tocolysis: an international multicenter randomized study. GTN Preterm Labour Investigation Group. Obstet Gynecol 1999;94:403-8.
- Smith GN, Walker MC, McGrath MJ. Randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled pilot study assessing nitroglycerin as a tocolytic. BJOG 1999;106:736-9.
- Duckitt K, Thornton S. Nitric oxide donors for the treatment of preterm labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2002.
- Liggins GC, Howie RN. A controlled trial of antepartum glucocorticoid treatment for prevention of the respiratory distress syndrome in premature infants. Pediatrics 1972;50:515-25.
- Effect of antenatal dexamethasone administration on the prevention of respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1981;141:276-87.
- Effects of antenatal dexamethasone administration in the infant: long-term follow-up. J Pediatr 1984;104:259-67.
- Block MF, Kling OR, Crosby WM. Antenatal glucocorticoid therapy for the prevention of respiratory distress syndrome in the premature infant. Obstet Gynecol 1977;50:186-90.
- Cararach V, Sentis J, Botet F, De Los Rios L. A multicentric prospective randomized study in premature rupture of membranes (PROM). Respiratory and infectious complications in the newborn. Lyon, France; 1990.
- Carlan SJ, Parsons M, O’Brien WF, Krammer J. Pharmacologic pulmonary maturation in preterm premature rupture of membranes [meeting abstract]. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164.
- Doran TA, Swyer P, MacMurray B, Mahon W, Enhorning G, Bernstein A, et al. Results of a double-blind controlled study on the use of betamethasone in the prevention of respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1980;136:313-20.
- Gamsu HR, Mullinger BM, Donnai P, Dash CH. Antenatal administration of betamethasone to prevent respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants: report of a UK multicentre trial. BJOG 1989;96:401-10.
- Garite TJ, Rumney PJ, Briggs GG, Harding JA, Nageotte MP, Towers CV, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of betamethasone for the prevention of respiratory distress syndrome at 24 to 28 weeks’ gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;166:646-51.
- Kari MA, Hallman M, Eronen M, Teramo K, Virtanen M, Koivisto M, et al. Prenatal dexamethasone treatment in conjunction with rescue therapy of human surfactant: a randomized placebo-controlled multicenter study. Pediatrics 1994;93:730-6.
- Morrison JC, Whybrew WD, Bucovaz ET, Schneider JM. Injection of corticosteroids into mother to prevent neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1978;131:358-66.
- Papageorgiou AN, Desgranges MF, Masson M, Colle E, Shatz R, Gelfand MM. The antenatal use of betamethasone in the prevention of respiratory distress syndrome: a controlled double-blind study. Pediatrics 1979;63:73-9.
- Parsons MT, Sobel D, Cummiskey K, Constantine L, Roitman J. Steroid, antibiotic and tocolytic vs no steroid, antibiotic and tocolytic management in patients with preterm PROM at 25–32 weeks [meeting abstract]. Las Vegas, Nevada; 1988.
- Schmidt PL, Sims ME, Strassner HT, Paul RH, Mueller E, McCart D. Effect of antepartum glucocorticoid administration upon neonatal respiratory distress syndrome and perinatal infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1984;148:178-86.
- Schutte MF, Treffers PE, Koppe JG, Breur W. The influence of betamethasone and orciprenaline on the incidence of respiratory distress syndrome in the newborn after preterm labour. BJOG 1980;87:127-31.
- Silver RK, Vyskocil CR, Solomon SL, Farrell EE, MacGregor SN, Neerhof MG, et al. Randomized trial of antenatal dexamethasone in surfactant-treated infants delivered prior to 30 weeks of gestation [meeting abstract]. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172.
- Taeusch HW, Frigoletto F, Kitzmiller J, Avery ME, Hehre A, Fromm B, et al. Risk of respiratory distress syndrome after prenatal dexamethasone treatment. Pediatrics 1979;63:64-72.
- Teramo K, Hallman M, Raivio KO. Maternal glucocorticoid in unplanned premature labor. Controlled study on the effects of betamethasone phosphate on the phospholipids of the gastric aspirate and on the adrenal cortical function of the newborn infant. Pediatr Res 1980;14:326-9.
- Morales WJ, Diebel ND, Lazar AJ, Zadrozny D. The effect of antenatal dexamethasone administration on the prevention of respiratory distress syndrome in preterm gestations with premature rupture of membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1986;154:591-5.
- Bunton TE, Plopper CG. Triamcinolone-induced structural alterations in the development of the lung of the fetal rhesus macaque. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1984;148:203-15.
- Adamson IY, King GM. Postnatal development of rat lung following retarded fetal lung growth. Pediatr Pulmonol 1988;4:230-6.
- Crowther CA, Harding J. Repeat doses of prenatal corticosteroids for women at risk of preterm birth for preventing neonatal respiratory disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003.
- Aghajafari F, Murphy K, Ohlsson A, Amankwah K, Matthews S, Hannah ME. Multiple versus single courses of antenatal corticosteroids for preterm birth: a pilot study. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2002;24:321-9.
- Guinn DA, Atkinson MW, Sullivan L, Lee M, MacGregor S, Parilla BV, et al. Single vs weekly courses of antenatal corticosteroids for women at risk of preterm delivery: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2001;286:1581-7.
- McEvoy C, Bowling S, Williamson K, Lozano D, Tolaymat L, Izquierdo L, et al. The effect of a single remote course versus weekly courses of antenatal corticosteroids on functional residual capacity in preterm infants: a randomized trial. Pediatrics 2002;110:280-4.
- Crowther CA, Haslam RR, Hiller JE, Doyle LW, Robinson JS. Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome after repeat exposure to antenatal corticosteroids: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2006;367:1913-19.
- Wapner RJ, Sorokin Y, Thom EA, Johnson F, Dudley DJ, Spong CY, et al. Single versus weekly courses of antenatal corticosteroids: evaluation of safety and efficacy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;195:633-42.
- Nelson KB, Grether JK. Can magnesium sulfate reduce the risk of cerebral palsy in very low birthweight infants?. Pediatrics 1995;95:263-9.
- Crowther CA, Hiller JE, Doyle LW, Haslam RR. Effect of magnesium sulfate given for neuroprotection before preterm birth: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2003;290:2669-76.
- Mittendorf R, Dambrosia J, Pryde PG, Lee KS, Gianopoulos JG, Besinger RE, et al. Association between the use of antenatal magnesium sulfate in preterm labor and adverse health outcomes in infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;186:1111-18.
- Marret S, Benichou J. Neuroprotection by Magnesium Sulfate Given to Women at Risk of Very Preterm Birth 2006. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov.
- Rouse D. Beneficial Effects of Antenatal Magnesium Sulphate (BEAM Trial) 2006. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov.
- Crowther CA, Henderson-Smart DJ. Vitamin K prior to preterm birth for preventing neonatal periventricular haemorrhage. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2001.
- Kazzi NJ, Ilagan NB, Liang KC, Kazzi GM, Poland RL, Grietsell LA, et al. Maternal administration of vitamin K does not improve the coagulation profile of preterm infants. Pediatrics 1989;84:1045-50.
- Morales WJ, Angel JL, O’Brien WF, Knuppel RA, Marsalisi F. The use of antenatal vitamin K in the prevention of early neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1988;159:774-9.
- Pomerance JJ, Teal JG, Gogolok JF, Brown S, Stewart ME. Maternally administered antenatal vitamin K1: effect on neonatal prothrombin activity, partial thromboplastin time, and intraventricular hemorrhage. Obstet Gynecol 1987;70:235-41.
- Thorp JA, Parriott J, Ferrette-Smith D, Meyer BA, Cohen GR, Johnson J. Antepartum vitamin K and phenobarbital for preventing intraventricular hemorrhage in the premature newborn: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 1994;83:70-6.
- Yang YM, Simon N, Maertens P, Brigham S, Liu P. Maternal–fetal transport of vitamin K1 and its effects on coagulation in premature infants. J Pediatr 1989;115:1009-13.
- Schieve LA, Meikle SF, Ferre C, Peterson HB, Jeng G, Wilcox LS. Low and very low birth weight in infants conceived with use of assisted reproductive technology. N Engl J Med 2002;346:731-7.
- Tucker J, McGuire W. Epidemiology of preterm birth. Br Med J 2004;329:675-8.
- World Health Organization . World Health Organization Expert Committee on Maternal and Child Health: Public Health Aspects of Low Birthweight 1961.
- Halliday HL, Ehrenkranz RA, Doyle LW. Delayed (>3 weeks) postnatal corticosteroids for chronic lung disease in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003.
- Coomarasamy A, Knox EM, Gee H, Song F, Khan KS. Effectiveness of nifedipine versus atosiban for tocolysis in preterm labour: a meta-analysis with an indirect comparison of randomised trials. BJOG 2003;110:1045-9.
- Song F, Altman DG, Glenny AM, Deeks JJ. Validity of indirect comparison for estimating efficacy of competing interventions: empirical evidence from published meta-analyses. Br Med J 2003;326.
- Berghella V, Odibo AO, To MS, Rust OA, Althuisius SM. Cerclage for short cervix on ultrasonography: meta-analysis of trials using individual patient-level data. Obstet Gynecol 2005;106:181-9.
- Abbasi S, Gerdes JS, Sehdev HM, Samimi SS, Ludmir J. Neonatal outcome after exposure to indomethacin in utero: a retrospective case cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189:782-5.
- Norton ME. Teratogen update: fetal effects of indomethacin administration during pregnancy. Teratology 1997;56:282-92.
- Perel P, Roberts I, Sena E, Wheble P, Briscoe C, Sandercock P, et al. Comparison of treatment effects between animal experiments and clinical trials: systematic review. Br Med J 2007;334.
- Henderson J, Roberts T, Sikorski J, Wilson J, Clement S. An economic evaluation comparing two schedules of antenatal visits. J Health Serv Res Policy 2000;5:69-75.
- Roberts T, Mugford M, Piercy J. Choosing options for ultrasound screening in pregnancy and comparing cost effectiveness: a decision analysis approach. BJOG 1998;105:960-70.
- Roberts T, Henderson J, Mugford M, Bricker L, Neilson J, Garcia J. Antenatal ultrasound screening for fetal abnormalities: a systematic review of studies of cost and cost effectiveness. BJOG 2002;109:44-56.
- Roberts TE, Robinson S, Barton P, Bryan S, Low N. Screening for Chlamydia trachomatis: a systematic review of the economic evaluations and modelling. Sex Transm Infect 2006;82:193-200.
- Curtis L, Netten A. Unit costs of health and social care 2005. Personal Social Services Research Unit, Canterbury: University of Kent; 2005.
- Kekki M, Kurki T, Kotomaki T, Sintonen H, Paavonen J. Cost-effectiveness of screening and treatment for bacterial vaginosis in early pregnancy among women at low risk for preterm birth. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2004;83:27-36.
- Ambrose S, Rhea DJ, Istwan NB, Collins A, Stanziano G. Clinical and economic outcomes of preterm labor management: inpatient vs outpatient. J Perinatol 2004;24:515-19.
- Egberts J. Estimated costs of different treatments of the respiratory distress syndrome in a large cohort of preterm infants of less than 30 weeks of gestation. Biol Neonate 1992;61:59-65.
- Ferriols LR, Nicolas PJ, Alos AM. Pharmacoeconomic assessment of two tocolysis protocols for the inhibition of premature delivery. Farm Hosp 2005;29:18-25.
- Korenbrot CC, Aalto LH, Laros RK. The cost effectiveness of stopping preterm labor with beta-adrenergic treatment. N Engl J Med 1984;310:691-6.
- Lam F, Istwan NB, Jacques D, Coleman SK, Stanziano GJ. Managing perinatal outcomes: the clinical benefit and cost-effectiveness of pharmacologic treatment of recurrent preterm labor. Manag Care 2003;12:39-46.
- Myers ER, Alvarez JG, Richardson DK, Ludmir J. Cost-effectiveness of fetal lung maturity testing in preterm labor. Obstet Gynecol 1997;90:824-9.
- Rushing S, Ment LR. Preterm birth: a cost–benefit analysis. Semin Perinatol 2004;28:444-50.
- Abenhaim HA, Morin L, Benjamin A. Does availability of fetal fibronectin testing in the management of threatened preterm labour affect the utilization of hospital resources?. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2005;27:689-94.
- Harrison MJ, Kushner KE, Benzies K, Kimak C, Jacobs P, Mitchell BF. In-home nursing care for women with high-risk pregnancies: outcomes and cost. Obstet Gynecol 2001;97:982-7.
- Morrison J, Bergauer NK, Jacques D, Coleman SK, Stanziano GJ. Telemedicine: cost-effective management of high-risk pregnancy. Manag Care 2001;10:42-9.
- Moya MP, Goldberg RN. Cost-effectiveness of prophylactic indomethacin in very-low-birth-weight infants. Ann Pharmacother 2002;36:218-24.
- Oswald JW, Mark PM. Assessing the costs of HMO services: a preterm birth prevention program. HMO Pract 1996;10:83-7.
- Ross MG, Sandhu M, Bemis R, Nessim S, Bragonier JR, Hobel C. The West Los Angeles Preterm Birth Prevention Project: II. Cost-effectiveness analysis of high-risk pregnancy interventions. Obstet Gynecol 1994;83:506-11.
- Kosasa TS, Abou-Sayf FK, Li-Ma G, Hale RW. Evaluation of the cost-effectiveness of home monitoring of uterine contractions. Obstet Gynecol 1990;76:71S-5S.
- Wald NJ, Kennard A, Hackshaw A, McGuire A. Antenatal screening for Down’s syndrome. Health Technol.Assess 1998;2:i-112.
- Bricker L, Garcia J, Henderson J, Mugford M, Neilson J, Roberts T, et al. Ultrasound screening in pregnancy: a systematic review of the clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and women’s views. Health Technol.Assess 2000;4:i-193.
- Drummond M, Sculpher M, Torrance GW, O’Brien BJ, Stoddart GL. Methods for the economic evaluation of health care programmes. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2005.
- Briggs A, Claxton K, Sculpher M. Decision modelling for health economic evaluation (Handbook for health economics evaluation). Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2006.
- Fenton TR. A new growth chart for preterm babies: Babson and Benda’s chart updated with recent data and a new format. BMC Pediatr 2003;3:13-2.
- Morgan MEI, Khan KS, Yarnold C. 32nd Annual Clinical Report. Birmingham: Birmingham Women’s Hospital; 2005.
- Olsen L, Nielsen IK, Zachariassen A, Sederberg-Olsen J, Frimodt-Moller N. Single-dose versus six-day therapy with sulfamethizole for asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy. A prospective randomised study. Dan Med Bull 1989;36:486-7.
- Beazley D, Ahokas R, Livingston J, . Vitamin C and E supplementation in women at high risk for pre-eclampsia: a double-blind placebo controlled trial [Abstract]. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187.
- Davenport C, Elley K, Salas C, Taylor-Weetham CL, Fry-Smith A, Bryan S, et al. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine dental checks: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 2003;7.
- Plaut MM, Smith W, Kennedy K. Fetal fibronectin: the impact of a rapid test on the treatment of women with preterm labour. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;188:1588-93.
- Dudley DJ, Hunter C, Mitchell MD, Varner MW. Clinical value of amniotic fluid interleukin-6 determinations in the management of preterm labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1994;101:592-7.
- Kass EH, Quinn EL, Kass EH. Biology of pyelonephritis. Boston, MA: Little, Brown & Co; 1960.
- Steyn P, Odendaal HJ, Schoemann J, . A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ascorbic acid supplementation for the prevention of pre-term labour. J Obstet Gynecol 2003;23:150-5.
- Hunt IF, Murphy NJ, Cleaver AE, . Zinc supplementation during pregnancy: zinc concentration of serum and hair from low-income women of Mexican descent. Am J Clin Nutr 1983;37:572-82.
- Mahomed K, James DK, Golding J, McCabe R. Zinc supplementation during pregnancy: a double-blind randomised controlled trial. BMJ 1989;48:169-75.
- Simmer K, Lort-Philips L, James C, Thompson RPH. A double blind trial of zinc supplementation in pregnancy. Eur J Clin Nutr 1991;45:139-44.
- Jonsson B, Hauge B, Larsen MF, . Zinc supplementation during pregnancy: a double blind randomised controlled trial. Acta Obstet Gynaecol Scand 1996;75:759-9.
- Christian P, Khatry SK, Katz J, . Effects of alternative maternal micronutrient supplements on low birth weight in Nepal: double-blind randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2003;326:5761-7.
- Goldenberg RL, Tamura T, Neggers Y, . The effect of zinc supplementation on pregnancy outcome. JAMA 1995;274:463-8.
- Gulmezoglu AM, Hofmeyer GJ, Oosthuisen MMJ. Antioxidants in the treatment of severe pre-eclampsia: an explanatory randomised controlled trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1997;104:689-96.
- Robertson JS, Heywood B, Atkinson SM. Zinc supplementation during preganancy. J Public Health Med 1991;13:227-9.
- Lazar P, Gueguen S, Dreyfus J, . Multicentred controlled trial of cervical cerclage in women at moderate risk of preterm delivery. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1984;91:731-5.
- Rush RW, Isaacs S, McPherson K, . A randomised controlled trial of cervical cerclage in women at high risk of spontaneous preterm delivery. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1984;91:724-30.
- Rust OA, Atlas AO, Reed J, . Revisiting the short cervix detached by vaginal ultrasound in the second trimester: why cerclage therapy may not help. Am J Obstet Gynaecol 2001;185:1098-105.
- Thornton L. Smoking and pregnancy: feasibility and effectiveness of a smoking intervention programme among pregnant women. Dublin: Department of Public Health; 1997.
- Mallet E, Gugi B, Brunelle P, . Vitamin D supplementation in pregnancy: a controlled trial of two methoods. Obstet Gynecol 1986;68:300-4.
- Odibo OA, Elkousy M, Ural SH, Macones GA. Prevention of preterm birth by cervical cerclage compared with expectant management: a systematic review. Obstet Gynecol Surv 2003;58:130-6.
- Rosenthal R. Judgement studies: designs, analysis and meta-analysis. Cambridge, MA: Cambridge University Press; 1987.
- Dodd JM, Flenady V, Cincotta R, Crowther CA. Prenatal administration of progesterone for preventing pre-term birth. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006;1.
Appendix 1 Search strategies
Scoping search strategies and results
Rapid appraisal checklist
Objective Scoping searches to identify systematic reviews, published and in progress, and ongoing primary research. Searches were undertaken on 8 March 2005. Update searches in Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effect (DARE) and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR) were undertaken on 10 August 2005.
| Completed and ongoing reviews | |
|---|---|
| Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews: Cochrane Library 2005:1 |
74 (complete) 12 (protocol) |
| Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews: Cochrane Library 2005:3. Update |
1 (complete) 3 (protocols) |
|
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) |
53 |
|
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE). Update |
6 |
| National Research Register [including Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) ongoing reviews database] | 368 |
|
Health Technology Assessment Database |
9 |
| SIGN Guidelines: http://www.sign.ac.uk/ | 0 |
| National Guideline Clearinghouse: http://www.guideline.gov/index.asp | 7 |
| National Coordinating Centre for Health Technology Assessment (also on HTA database): http://www.ncchta.org/ | 0 |
|
NICE web page (published appraisals – also on HTA database) |
0 |
| HSTAT: http://text.nlm.nih.gov/ | 3 |
| Indexes to and summaries of clinical effectiveness sources including reviews, appraisals of reviews, and evidence-based guidelines | |
| TRIP: http://www.tripdatabase.com/ | 313 (most already identified) |
| Clinical Evidence: a compendium of the best available evidence for effective health care. 2004;12 | 2 (preterm birth bacterial vaginosis) |
|
Health Evidence Bulletins Wales |
1 (chap. 13) |
| Searches for ongoing trials – to be conducted by agreement with reviewers | |
| CENTRAL (Cochrane Library) | 1248 |
| Other | |
| NHS EED: http://www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd/crddatabases.htm | 43 |
MEDLINE (Ovid Gateway), 2000–2005/Aug. week 1, 10 August 2005
186 records were retrieved.
-
Meta-Analysis/
-
Review-Literature/
-
meta analysis.pt.
-
review literature.pt.
-
(meta analy$or metaanaly$or meta-analy$).tw.
-
(systematic adj4 (review$or overview$)).tw.
-
(data adj synthesis).ti,ab.
-
(published adj studies).ti,ab.
-
(data adj extract$).ti,ab.
-
or/1–9
-
letter.pt.
-
comment.pt.
-
editorial.pt.
-
11 or 12 or 13
-
Animal/
-
Human/
-
15 not (15 and 16)
-
10 not (14 or 17)
-
Labor, Premature/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 birth$).ti,ab.
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 deliver$).ti,ab.
-
((preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 (labor or labour)).ti,ab.
-
(premature adj3 (labor or labour or parturition)).ti,ab.
-
Fetal Membranes, Premature Rupture/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 rupture$).ti,ab.
-
(PROM or PPROM).ti,ab.
-
or/19–26
-
18 and 27
Test accuracy
Diagnostic update search strategies and results
MEDLINE (Ovid Gateway), 2002/April–2005/Sept. week 1, 20 September 2005
2858 records were retrieved in MEDLINE and 184 records were retrieved in MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations.
-
Labor, Premature/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term) adj3 birth$).ti,ab.
-
((premature or preterm or pre term) adj3 deliver$).ti,ab.
-
((preterm or pre term) adj3 (labor or labour)).ti,ab.
-
(premature adj3 (labor or labour or parturition)).ti,ab.
-
or/1–5
-
exp Socioeconomic Factors/
-
Social Class/
-
Ethnic Groups/
-
risk factors/
-
Life Style/
-
exp Substance-Related Disorders/
-
exp smoking/
-
Pregnancy, High-Risk/
-
Pregnancy in Adolescence/
-
exp Pregnancy, Multiple/
-
Pregnancy Complications/
-
Parity/
-
Reproductive History/
-
Fetal Membranes, Premature Rupture/
-
Cervix Incompetence/
-
exp Abdominal Pain/
-
Uterine Contraction/
-
Uterine Hemorrhage/
-
Cervical Ripening/
-
Treponema pallidum/
-
Neisseria gonorrhoeae/
-
Chlamydia trachomatis/
-
exp Sexually Transmitted Diseases, Bacterial/
-
exp Bacteroidaceae Infections/
-
exp Chlamydiaceae Infections/
-
exp Herpes Genitalis/
-
Vaginosis, Bacterial/
-
mobiluncus/
-
Streptococcus agalactiae/
-
Mycoplasma hominis/
-
Trichomonas vaginalis/
-
Bacteroides Infections/
-
Gardnerella vaginalis/
-
Bacteriuria/
-
Granuloma Inguinale/
-
exp Mycoplasmatales Infections/
-
exp Neisseriaceae Infections/
-
exp Treponemal Infections/
-
exp Staphylococcal Infections/
-
exp Streptococcal Infections/
-
Ureaplasma Infections/
-
exp Lactobacillus/
-
exp Urinary Tract Infections/
-
exp «Diagnostic Techniques, Obstetrical and Gynecological»/
-
exp Diagnostic Equipment/
-
exp Diagnostic Imaging/
-
Diagnostic Tests, Routine/
-
exp Reagent Kits, Diagnostic/
-
exp Ultrasonography, Prenatal/
-
Medical History Taking/
-
Risk Assessment/
-
exp Physical Examination/
-
Uterine Monitoring/
-
exp Culture Techniques/
-
exp Body Constitution/
-
Body Temperature/
-
exp fever/
-
Palpation/
-
exp Corpus Luteum Hormones/
-
Relaxin/
-
exp Prostaglandins/
-
exp Estrogens/
-
exp Inhibins/
-
exp Estradiol/
-
exp Estriol/
-
exp Estrone/
-
exp Estrogen Receptor Modulators/
-
exp Receptors, Estrogen/
-
exp Prostaglandin Antagonists/
-
exp Receptors, Prostaglandin/
-
exp Leukotrienes/
-
exp Thromboxanes/
-
exp Collagenases/
-
Fetal Proteins/
-
Fibronectins/
-
exp Acute-Phase Proteins/
-
exp Immunoproteins/
-
Platelet-Derived Growth Factor/
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha/
-
Chorioamnionitis/
-
Esterases/
-
exp Cytokines/
-
exp Amniotic Fluid/
-
exp Leukocytes/
-
Saliva/
-
exp Biological Markers/
-
Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone/
-
(risk factor$or socioeconomic factor$or socioeconomic status).ti,ab.
-
(occupation$or socioeconomic or ethnic or ethnicity or manual work or long hours).ti,ab.
-
(cocaine or heroin or narcotics or crack or dope or cannabis or substance abuse$or addiction).ti,ab.
-
(substance disorder$or smoking or tobacco or alcohol$or lifestyle$or life-style$).ti,ab.
-
(low adj3 pregnancy adj3 weight).ti,ab.
-
high parity.ti,ab.
-
(early adj3 bleeding adj3 pregnancy).ti,ab.
-
vaginal bleeding.ti,ab.
-
((uterine or antepartum) adj3 (hemorrhage or haemorrhage)).ti,ab.
-
(abdominal pain or uterine contraction$).ti,ab.
-
(pyrexia or febrile or fever).ti,ab.
-
(short adj3 pregnancies).ti,ab.
-
(interpregnancy interval$or inter-pregnancy interval$).ti,ab.
-
(older women or elderly women).ti,ab.
-
(adolescent$or teenage$).ti,ab.
-
(clinical histor$or patient histor$or patient record$or pregnan$histor$or birth histor$or reproductive histor$).ti,ab.
-
(obstetric histor$or previous preterm or repeat preterm).ti,ab.
-
(premature adj3 rupture adj3 membrane$).ti,ab.
-
Chorioamnionitis.ti,ab.
-
(estriol or plasma crf or vaginal infection$).ti,ab.
-
((biophysical or biochemical) adj3 marker$).ti,ab.
-
(bishop$adj1 (score or scores)).ti,ab.
-
(cervical adj1 (change$or length or measurement)).ti,ab.
-
(endocervical adj1 (effacement or assessment or examination)).ti,ab.
-
(cervical adj1 (effacement or assessment or state or examination$)).ti,ab.
-
(risk scor$or physical examination$).ti,ab.
-
(physical exam or physical exams or cervical dilation or (cervix adj3 length)).ti,ab.
-
(dilation adj3 cervix).ti,ab.
-
tocodynamo$.ti,ab.
-
(uterine tocography or uterine anomal$or tocometry).ti,ab.
-
((cervical or cervix) adj3 (abnormal$or incompetence or incompetent)).ti,ab.
-
((cervical or cervix) adj3 (ultrasound or ultrasonography or sonography)).ti,ab.
-
((vaginal or endovaginal or transvaginal or obstetric) adj3 (ultrasound or ultrasonography or sonography)).ti,ab.
-
(uterine activity or huam or uterine excitability).ti,ab.
-
((myometrial or myometrium) adj3 excitability).ti,ab.
-
((oncofetal or c-reactive) adj3 protein$).ti,ab.
-
fibronectin.ti,ab.
-
(asymptomatic bacteriuria or genital tract infection$).ti,ab.
-
(leucocyte esterase$or cytokines).ti,ab.
-
(culture$adj3 (amniotic or blood or genital or vaginal or cervical or urine)).ti,ab.
-
(timp or collagenase or relaxin or tissue inhibitor$).ti,ab.
-
plasma corticotropin releasing hormone$.ti,ab.
-
(estrogen or oestrogen or progestogen).ti,ab.
-
(glucose concentration$adj3 amniotic).ti,ab.
-
(zinc adj3 amniotic).ti,ab.
-
or/7–138
-
exp “Sensitivity and Specificity”/
-
ROC Curve/
-
Logistic Models/
-
Likelihood Functions/
-
exp Diagnostic Errors/
-
(predictive value$or reproducibility or logistic regression).ti,ab.
-
(ability adj3 predict$).ti,ab.
-
(logistic model$or sroc or roc or positive rate or positive rates).ti,ab.
-
(likelihood ratio$or negative rate or negative rates).ti,ab.
-
(receiver operating characteristic or correlation or correlated).ti,ab.
-
((tests or test) adj3 accuracy).ti,ab.
-
(curve or curves or test outcome).ti,ab.
-
((pretest or pre-test or posttest or post-test) adj3 probabilities).ti,ab.
-
diagnosis.ti,ab.
-
or/140–153
-
6 and 139 and 154
-
6 and 139
-
Animals/
-
Humans/
-
157 not (157 and 158)
-
155 not 159
-
156 not 159
-
(200204$or 200205$or 200206$or 200207$or 200208$or 200209$or 200210$or 200211$or 200212$).ed.
-
(2003$or 2004$or 2005$).ed.
-
162 or 163
-
161 and 164
EMBASE (Ovid Gateway), 2002/Mar–2005/Sept. week 1, 20 September 2005
4004 records were retrieved.
-
Premature Labor/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 birth$).ti,ab.
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 deliver$).ti,ab.
-
((preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 (labor or labour)).ti,ab.
-
(premature adj3 (labor or labour or parturition)).ti,ab.
-
Premature Fetus Membrane Rupture/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 rupture$).ti,ab.
-
(PROM or PPROM).ti,ab.
-
or/1–8
-
exp socioeconomics/
-
Social Class/
-
Risk Factor/
-
exp “Ethnic and Racial Groups”/
-
Smoking/
-
exp Addiction/
-
Substance Abuse/
-
lifestyle/
-
High Risk Pregnancy/
-
Adolescent Pregnancy/
-
parity/
-
ANAMNESIS/
-
Pregnancy Disorder/
-
exp Pregnancy Complication/
-
Obstetric Hemorrhage/
-
Premature Fetus Membrane Rupture/
-
Abdominal Pain/
-
Uterus Contraction/
-
exp Uterine Complication/
-
Uterus Bleeding/
-
Fever/
-
exp Estrogen/
-
Relaxin/
-
Treponema Pallidum/
-
Neisseria Gonorrhoeae/
-
Streptococcus Agalactiae/
-
Mycoplasma Hominis/
-
Chlamydia Trachomatis/
-
Trichomonas Vaginalis/
-
bacteroides/
-
Vaginitis/
-
mobiluncus/
-
Gardnerella Vaginalis/
-
exp Multiple Pregnancy/
-
Uterine Cervix Incompetence/
-
Uterine Cervix Ripening/
-
Fetoprotein/
-
Fibronectin/
-
Bacteriuria/
-
exp Diagnostic Procedure/
-
exp Laboratory Diagnosis/
-
Virus Diagnosis/
-
Venereal Disease Reaction Test/
-
Transvaginal Echography/
-
equipment/
-
Diagnostic Imaging/
-
Test Strip/
-
Reagent/
-
ultrasound/
-
Diagnostic Test/
-
Risk Assessment/
-
exp Physical Examination/
-
exp examination/
-
Home Monitoring/
-
exp Urogenital System Examination/
-
Clinical Observation/
-
Fetus Monitoring/
-
Esterase/
-
exp Tissue Culture/
-
exp Cytokine/
-
Acute Phase Protein/
-
exp Immunoglobulin/
-
Platelet Derived Growth Factor/
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor/
-
Sex Hormone/
-
Progesterone/
-
Inhibin/
-
Estradiol/
-
Estriol/
-
Estrone/
-
exp Estrogen Receptor/
-
exp Prostaglandin Receptor Blocking Agent/
-
exp Leukotriene/
-
exp Thromboxane/
-
Collagenase/
-
Body Constitution/
-
exp «Physical Constitution and Health»/
-
exp Body Temperature/
-
palpation/
-
exp Sexually Transmitted Disease/
-
exp bacteroides/
-
chlamydiaceae/
-
Granuloma Inguinale/
-
mycoplasmatales/
-
Gram Negative Infection/
-
neisseriaceae/
-
Bacterial Infection/
-
Staphylococcus Infection/
-
Streptococcus Infection/
-
exp lactobacillus/
-
Genital Herpes/
-
exp Urinary Tract Infection/
-
exp Chorioamnionitis/
-
exp Amnion Fluid/
-
exp leukocyte/
-
saliva/
-
Biological Marker/
-
Blood Analysis/
-
Blood Culture/
-
exp urinalysis/
-
Amnion Fluid Analysis/
-
Image Analysis/
-
Saliva Analysis/
-
Sputum Analysis/
-
exp assay/
-
exp Chemical Analysis/
-
Corticotropin Releasing Factor/
-
(risk factor$or socioeconomic factor$or socioeconomic status).ti,ab.
-
(occupation$or socioeconomic or ethnic or ethnicity or manual work or long hours).ti,ab.
-
(cocaine or heroin or narcotics or crack or dope or cannabis or substance abuse$or addiction).ti,ab.
-
(substance disorder$or smoking or tobacco or alcohol$or lifestyle$or life-style$).ti,ab.
-
(low adj3 pregnancy adj3 weight).ti,ab.
-
high parity.ti,ab.
-
(early adj3 bleeding adj3 pregnancy).ti,ab.
-
vaginal bleeding.ti,ab.
-
((uterine or antepartum) adj3 (hemorrhage or haemorrhage)).ti,ab.
-
(abdominal pain or uterine contraction$).ti,ab.
-
(pyrexia or febrile or fever).ti,ab.
-
(short adj3 pregnancies).ti,ab.
-
(interpregnancy interval$or inter-pregnancy interval$).ti,ab.
-
(older women or elderly women).ti,ab.
-
(adolescent$or teenage$).ti,ab.
-
(clinical histor$or patient histor$or patient record$or pregnan$histor$or birth history$or reproductive history$).ti,ab.
-
(obstetric histor$or previous preterm or repeat preterm).ti,ab.
-
(premature adj3 rupture adj3 membrane$).ti,ab.
-
Chorioamnionitis.ti,ab.
-
(estriol or plasma crf or vaginal infection$).ti,ab.
-
((biophysical or biochemical) adj3 marker$).ti,ab.
-
(bishop$adj1 (score or scores)).ti,ab.
-
(cervical adj1 (change$or length or measurement)).ti,ab.
-
(endocervical adj1 (effacement or assessment or examination)).ti,ab.
-
(cervical adj1 (effacement or assessment or state or examination$)).ti,ab.
-
(risk scor$or physical examination$).ti,ab.
-
(physical exam or physical exams or cervical dilation or (cervix adj3 length)).ti,ab.
-
(dilation adj3 cervix).ti,ab.
-
tocodynamo$.ti,ab.
-
(uterine tocography or uterine anomal$or tocometry).ti,ab.
-
((cervical or cervix) adj3 (abnormal$or incompetence or incompetent)).ti,ab.
-
((cervical or cervix) adj3 (ultrasound or ultrasonography or sonography)).ti,ab.
-
((vaginal or endovaginal or transvaginal or obstetric) adj3 (ultrasound or ultrasonography or sonography)).ti,ab.
-
(uterine activity or huam or uterine excitability).ti,ab.
-
((myometrial or myometrium) adj3 excitability).ti,ab.
-
((oncofetal or c-reactive) adj3 protein$).ti,ab.
-
fibronectin.ti,ab.
-
(asymptomatic bacteriuria or genital tract infection$).ti,ab.
-
(leucocyte esterase$or cytokines).ti,ab.
-
(culture$adj3 (amniotic or blood or genital or vaginal or cervical or urine)).ti,ab.
-
(timp or collagenase or relaxin or tissue inhibitor$).ti,ab.
-
plasma corticotropin releasing hormone$.ti,ab.
-
(estrogen or oestrogen or progestogen).ti,ab.
-
(glucose concentration$adj3 amniotic).ti,ab.
-
(zinc adj3 amniotic).ti,ab.
-
or/10–161
-
Diagnostic Error/
-
Diagnostic Accuracy/
-
Diagnostic Value/
-
Differential Diagnosis/
-
Quantitative Diagnosis/
-
exp Statistical Analysis/
-
Discriminant Analysis/
-
statistics/
-
Statistical Model/
-
reliability/
-
variance/
-
Receiver Operating Characteristic/
-
Multiple Regression/
-
(predictive value$or reproducibility or logistic regression).ti,ab.
-
(ability adj3 predict$).ti,ab.
-
(logistic model$or sroc or roc or positive rate or positive rates).ti,ab.
-
(likelihood ratio$or negative rate or negative rates).ti,ab.
-
(receiver operating characteristic or correlation or correlated).ti,ab.
-
((tests or test) adj3 accuracy).ti,ab.
-
(curve or curves or test outcome).ti,ab.
-
((pretest or pre-test or posttest or post-test) adj3 probabilities).ti,ab.
-
diagnosis.ti,ab.
-
(sensitivity or specificity).ti,ab.
-
or/163–185
-
9 and 162 and 186
-
9 and 162
-
exp animal/
-
Nonhuman/
-
(rat or rats or mouse or mice or hamster or hamsters or animal or animals or dogs or dog or cats or bovine or sheep).ti,ab,sh.
-
189 or 190 or 191
-
exp human/
-
192 not (192 and 193)
-
187 not 194
-
188 not 194
-
(2002$or 2003$or 2004$or 2005$).em.
-
196 and 197
BIOSIS (DIALOG), 2002/June–2005/Sept. week 1, 22 September 2005
-
1071 records were retrieved.
-
s (premature or preterm)(3n)birth??
-
s (premature or preterm)(3n)deliver?
-
s (premature or preterm)(3n)(labo?r or parturition)
-
s risk(w)factor?? or socioeconomic(w)factor??
-
s low(3w)pregnancy(3w)weight
-
s high(w)parity
-
s early(3n)bleeding(3n)pregnancy
-
s vaginal(3n)bleeding
-
s (uterine or antepartum)(3w)(hemorrhag? or haemorrhag?)
-
s abdominal(w)pain or uterine(w)contraction??
-
s pyrexia or febrile
-
s short(3n)between(3n)pregnancies
-
s interpregnancy(w)interval??
-
s pregnancy(3n)multiple
-
s pregnancy(3n)complication??
-
s pregnancy(3n)(high(w)risk)
-
s pregnancy(3n)(adolescen? or teenage?)
-
s (older or elderly)(n)women
-
s occupation? or socioeconomic or ethnic or ethnicity or manual(w)work or long(w)hours
-
s cocaine or heroin or narcotics or crack or dope or cannabis or substance(w)abuse
-
s substance(w)disorder?? or smoking or tobacco or alcohol? or lifestyle??
-
s estriol or plasma(w)crf or vaginal(3n)infection??
-
s (biophysical or biochemical)(3w)marker??
-
s bishop?(w)score??
-
s cervical(w)(change? or length or measurement)
-
s endocervical(w)(effacement or assessment)
-
s cervical(w)(effacement or assessment or state)
-
s medical(w)histor? or clinical(w)histor? or patient(w)histor? or patient(w)record??
-
s obstetric(w)histor? or previous(w)preterm or repeat(w)preterm
-
s risk(w)scor? or risk(w)assessment
-
s physical(w)examination? or cervical(w)dilation or cervix(3n)length
-
s dilation(3n)cervix
-
s uterine(w)tocography or uterine(w)anomal? or tocometry
-
s (cervical or cervix)(3n)(abnormal? or incompetence or incompetent)
-
s (cervical or cervix)(3n)(ultrasound or ultrasonography)
-
s (vaginal or endovaginal or transvaginal or obstetric)(3n)(ultrasound or ultrasonography)
-
s diagnostic(n)(technique? or equipment or test??)
-
s uterine(3n)activity or huam or uterine(3n)excitability
-
s (myometrial or myometrium)(3n)excitability
-
s (oncofetal or c-reactive)(w)(protein?)
-
s fibronectin?
-
s sexually(w)transmitted(w)disease?
-
s asymptomatic(w)bacteriuria or genital(w)tract(w)infection?
-
s chlamydia or gonorrhea or herpes
-
s leucocyte(w)esterase? or cytokines
-
s culture?(3n)(amniotic or blood or genital or vaginal or cervical)
-
s timp or collagenase or relaxin or tissue(w)inhibitor?
-
s plasma(w)corticotropin(w)releasing(w)hormone?
-
s estrogen or oestrogen or progestogen
-
s (glucose(w)concentration?)(n)amniotic
-
s zinc(n)amniotic
-
s s1:s3
-
s s4:s51
-
s s52 and s53
-
s s54/2002–2005
PASCAL (DIALOG), 2002/June–2005/Sept. week 1, 22 September 2005
456 records were retrieved.
-
s (premature or preterm)(3n)birth??
-
s (premature or preterm)(3n)deliver?
-
s (premature or preterm)(3n)(labo?r or parturition)
-
s risk(w)factor?? or socioeconomic(w)factor??
-
s low(3w)pregnancy(3w)weight
-
s high(w)parity
-
s early(3n)bleeding(3n)pregnancy
-
s vaginal(3n)bleeding
-
s (uterine or antepartum)(3w)(hemorrhag? or haemorrhag?)
-
s abdominal(w)pain or uterine(w)contraction??
-
s pyrexia or febrile
-
s short(3n)between(3n)pregnancies
-
s interpregnancy(w)interval??
-
s pregnancy(3n)multiple
-
s pregnancy(3n)complication??
-
s pregnancy(3n)(high(w)risk)
-
s pregnancy(3n)(adolescen? or teenage?)
-
s (older or elderly)(n)women
-
s occupation? or socioeconomic or ethnic or ethnicity or manual(w)work or long(w)hours
-
s cocaine or heroin or narcotics or crack or dope or cannabis or substance(w)abuse
-
s substance(w)disorder?? or smoking or tobacco or alcohol? or lifestyle??
-
s estriol or plasma(w)crf or vaginal(3n)infection??
-
s (biophysical or biochemical)(3w)marker??
-
s bishop?(w)score??
-
s cervical(w)(change? or length or measurement)
-
s endocervical(w)(effacement or assessment)
-
s cervical(w)(effacement or assessment or state)
-
s medical(w)histor? or clinical(w)histor? or patient(w)histor? or patient(w)record??
-
s obstetric(w)histor? or previous(w)preterm or repeat(w)preterm
-
s risk(w)scor? or risk(w)assessment
-
s physical(w)examination? or cervical(w)dilation or cervix(3n)length
-
s dilation(3n)cervix
-
s uterine(w)tocography or uterine(w)anomal? or tocometry
-
s (cervical or cervix)(3n)(abnormal? or incompetence or incompetent)
-
s (cervical or cervix)(3n)(ultrasound or ultrasonography)
-
s (vaginal or endovaginal or transvaginal or obstetric)(3n)(ultrasound or ultrasonography)
-
s diagnostic(n)(technique? or equipment or test??)
-
s uterine(3n)activity or huam or uterine(3n)excitability
-
s (myometrial or myometrium)(3n)excitability
-
s (oncofetal or c-reactive)(w)(protein?)
-
s fibronectin?
-
s sexually(w)transmitted(w)disease?
-
s asymptomatic(w)bacteriuria or genital(w)tract(w)infection?
-
s chlamydia or gonorrhea or herpes
-
s leucocyte(w)esterase? or cytokines
-
s culture?(3n)(amniotic or blood or genital or vaginal or cervical)
-
s timp or collagenase or relaxin or tissue(w)inhibitor?
-
s plasma(w)corticotropin(w)releasing(w)hormone?
-
s estrogen or oestrogen or progestogen
-
s (glucose(w)concentration?)(n)amniotic
-
s zinc(n)amniotic
-
s s1:s3
-
s s4:s51
-
s s52 and s53
-
s s54/2002–2005
Science Citation Index (SCI) (DIALOG), 2002/June–2005/Sept. week 1, September/22 September 2005
643 records were retrieved.
-
s (premature or preterm)(3n)birth??
-
s (premature or preterm)(3n)deliver?
-
s (premature or preterm)(3n)(labo?r or parturition)
-
s risk(w)factor?? or socioeconomic(w)factor??
-
s low(3w)pregnancy(3w)weight
-
s high(w)parity
-
s early(3n)bleeding(3n)pregnancy
-
s vaginal(3n)bleeding
-
s (uterine or antepartum)(3w)(hemorrhag? or haemorrhag?)
-
s abdominal(w)pain or uterine(w)contraction??
-
s pyrexia or febrile
-
s short(3n)between(3n)pregnancies
-
s interpregnancy(w)interval??
-
s pregnancy(3n)multiple
-
s pregnancy(3n)complication??
-
s pregnancy(3n)(high(w)risk)
-
s pregnancy(3n)(adolescen? or teenage?)
-
s (older or elderly)(n)women
-
s occupation? or socioeconomic or ethnic or ethnicity or manual(w)work or long(w)hours
-
s cocaine or heroin or narcotics or crack or dope or cannabis or substance(w)abuse
-
s substance(w)disorder?? or smoking or tobacco or alcohol? or lifestyle??
-
s estriol or plasma(w)crf or vaginal(3n)infection??
-
s (biophysical or biochemical)(3w)marker??
-
s bishop?(w)score??
-
s cervical(w)(change? or length or measurement)
-
s endocervical(w)(effacement or assessment)
-
s cervical(w)(effacement or assessment or state)
-
s medical(w)histor? or clinical(w)histor? or patient(w)histor? or patient(w)record??
-
s obstetric(w)histor? or previous(w)preterm or repeat(w)preterm
-
s risk(w)scor? or risk(w)assessment
-
s physical(w)examination? or cervical(w)dilation or cervix(3n)length
-
s dilation(3n)cervix
-
s uterine(w)tocography or uterine(w)anomal? or tocometry
-
s (cervical or cervix)(3n)(abnormal? or incompetence or incompetent)
-
s (cervical or cervix)(3n)(ultrasound or ultrasonography)
-
s (vaginal or endovaginal or transvaginal or obstetric)(3n)(ultrasound or ultrasonography)
-
s diagnostic(n)(technique? or equipment or test??)
-
s uterine(3n)activity or huam or uterine(3n)excitability
-
s (myometrial or myometrium)(3n)excitability
-
s (oncofetal or c-reactive)(w)(protein?)
-
s fibronectin?
-
s sexually(w)transmitted(w)disease?
-
s asymptomatic(w)bacteriuria or genital(w)tract(w)infection?
-
s chlamydia or gonorrhea or herpes
-
s leucocyte(w)esterase? or cytokines
-
s culture?(3n)(amniotic or blood or genital or vaginal or cervical)
-
s timp or collagenase or relaxin or tissue(w)inhibitor?
-
s plasma(w)corticotropin(w)releasing(w)hormone?
-
s estrogen or oestrogen or progestogen
-
s (glucose(w)concentration?)(n)amniotic
-
s zinc(n)amniotic
-
s s1:s3
-
s s4:s51
-
s s52 and s53
-
s s54/2002–2005
Inside Conferences (DIALOG), 2002/June–2005/Sept. week 1, 22 September 2005
12 records were retrieved.
-
s (premature or preterm)(3n)birth??
-
s (premature or preterm)(3n)deliver?
-
s (premature or preterm)(3n)(labo?r or parturition)
-
s risk(w)factor?? or socioeconomic(w)factor??
-
s low(3w)pregnancy(3w)weight
-
s high(w)parity
-
s early(3n)bleeding(3n)pregnancy
-
s vaginal(3n)bleeding
-
s (uterine or antepartum)(3w)(hemorrhag? or haemorrhag?)
-
s abdominal(w)pain or uterine(w)contraction??
-
s pyrexia or febrile
-
s short(3n)between(3n)pregnancies
-
s interpregnancy(w)interval??
-
s pregnancy(3n)multiple
-
s pregnancy(3n)complication??
-
s pregnancy(3n)(high(w)risk)
-
s pregnancy(3n)(adolescen? or teenage?)
-
s (older or elderly)(n)women
-
s occupation? or socioeconomic or ethnic or ethnicity or manual(w)work or long(w)hours
-
s cocaine or heroin or narcotics or crack or dope or cannabis or substance(w)abuse
-
s substance(w)disorder?? or smoking or tobacco or alcohol? or lifestyle??
-
s estriol or plasma(w)crf or vaginal(3n)infection??
-
s (biophysical or biochemical)(3w)marker??
-
s bishop?(w)score??
-
s cervical(w)(change? or length or measurement)
-
s endocervical(w)(effacement or assessment)
-
s cervical(w)(effacement or assessment or state)
-
s medical(w)histor? or clinical(w)histor? or patient(w)histor? or patient(w)record??
-
s obstetric(w)histor? or previous(w)preterm or repeat(w)preterm
-
s risk(w)scor? or risk(w)assessment
-
s physical(w)examination? or cervical(w)dilation or cervix(3n)length
-
s dilation(3n)cervix
-
s uterine(w)tocography or uterine(w)anomal? or tocometry
-
s (cervical or cervix)(3n)(abnormal? or incompetence or incompetent)
-
s (cervical or cervix)(3n)(ultrasound or ultrasonography)
-
s (vaginal or endovaginal or transvaginal or obstetric)(3n)(ultrasound or ultrasonography)
-
s diagnostic(n)(technique? or equipment or test??)
-
s uterine(3n)activity or huam or uterine(3n)excitability
-
s (myometrial or myometrium)(3n)excitability
-
s (oncofetal or c-reactive)(w)(protein?)
-
s fibronectin?
-
s sexually(w)transmitted(w)disease?
-
s asymptomatic(w)bacteriuria or genital(w)tract(w)infection?
-
s chlamydia or gonorrhea or herpes
-
s leucocyte(w)esterase? or cytokines
-
s culture?(3n)(amniotic or blood or genital or vaginal or cervical)
-
s timp or collagenase or relaxin or tissue(w)inhibitor?
-
s plasma(w)corticotropin(w)releasing(w)hormone?
-
s estrogen or oestrogen or progestogen
-
s (glucose(w)concentration?)(n)amniotic
-
s zinc(n)amniotic
-
s s1:s3
-
s s4:s51
-
s s52 and s53
-
s s54/2002–2005
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR) and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Cochrane Library, Issue 2:2002–3:20 September 2005
1 new protocol was identified in CDSR and 144 records were retrieved in CENTRAL.
-
Labor, Premature (MeSH)
-
(premature or preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 birth
-
(premature or preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 deliver*
-
(preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 (labour or labor)
-
premature NEAR/3 (labour or labor or parturition)
-
Fetal Membranes, Premature Rupture (MeSH)
-
(premature or preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 ruptur*
-
PROM or PPROM
-
#1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8
-
Socioeconomic Factors (MeSH)
-
Social Class (MeSH)
-
Risk Factors (MeSH)
-
Ethnic Groups (MeSH)
-
Smoking (MeSH)
-
Life Style(MeSH)
-
Substance-Related Disorders(MeSH)
-
Pregnancy, High-Risk (MeSH)
-
Parity (MeSH)
-
Reproductive History (MeSH)
-
Abdominal Pain (MeSH)
-
Pregnancy Complications (MeSH)
-
Uterine Contraction (MeSH)
-
Uterine Hemorrhage (MeSH)
-
Fever (MeSH)
-
Estriol (MeSH)
-
Relaxin (MeSH)
-
Treponema pallidum (MeSH)
-
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (MeSH)
-
Streptococcus agalactiae (MeSH)
-
Mycoplasma hominis (MeSH)
-
Chlamydia trachomatis (MeSH)
-
Trichomonas vaginalis (MeSH)
-
Bacteroides Infections (MeSH)
-
Vaginosis, Bacterial (MeSH)
-
Mobiluncus (MeSH)
-
Gardnerella vaginalis (MeSH)
-
Prostaglandins (MeSH)
-
Pregnancy, Multiple (MeSH)
-
Cervix Incompetence (MeSH)
-
Cervical Ripening (MeSH)
-
Fetal Proteins (MeSH)
-
Bacteriuria (MeSH)
-
Diagnostic Techniques, Obstetrical and Gynecological (MeSH)
-
Diagnostic Equipment (MeSH)
-
Diagnostic Imaging (MeSH)
-
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic (MeSH)
-
Ultrasonography, Prenatal (MeSH)
-
Diagnostic Tests, Routine (MeSH)
-
Medical History Taking (MeSH)
-
Risk Assessment (MeSH)
-
Physical Examination (MeSH)
-
Uterine Monitoring (MeSH)
-
Esterases (MeSH)
-
Cytokines (MeSH)
-
Immunoproteins (MeSH)
-
Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (MeSH)
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (MeSH)
-
Gonadal Steroid Hormones (MeSH)
-
Corpus Luteum Hormones (MeSH)
-
Estrogens (MeSH)
-
Inhibins (MeSH)
-
Estradiol (MeSH)
-
Estrone (MeSH)
-
Receptors, Estrogen (MeSH)
-
Prostaglandin Antagonists (MeSH)
-
Receptors, Prostaglandin (MeSH)
-
Leukotrienes (MeSH)
-
Receptors, Thromboxane (MeSH)
-
Collagenases (MeSH)
-
Body Constitution (MeSH)
-
Body Temperature (MeSH)
-
Palpation (MeSH)
-
Sexually Transmitted Diseases, Bacterial (MeSH)
-
Bacteroidaceae Infections (MeSH)
-
Chlamydiaceae Infections (MeSH)
-
Granuloma Inguinale (MeSH)
-
Mycoplasmatales Infections (MeSH)
-
Neisseriaceae Infections (MeSH)
-
Treponemal Infections (MeSH)
-
Staphylococcal Infections (MeSH)
-
Streptococcal Infections (MeSH)
-
Ureaplasma Infections (MeSH)
-
Lactobacillus (MeSH)
-
Herpes Genitalis (MeSH)
-
Urinary Tract Infections (MeSH)
-
Chorioamnionitis (MeSH)
-
Amniotic Fluid (MeSH)
-
Leukocytes (MeSH)
-
Saliva (MeSH)
-
Biological Markers (MeSH)
-
Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (MeSH)
-
(older or elderly) NEAR women
-
fibronectin* or tocodynamo* or (risk NEAR factor*) or (socioeconomic NEAR factor*)
-
low NEAR pregnancy NEAR weight
-
(high NEAR parity) or (early NEAR bleeding) or (vaginal NEAR bleeding) or (uterine or antepartum) NEAR hemorrhage or (abdominal NEAR pain) or (uterine NEAR contraction*) or pyrexia or febrile or fever or short NEAR/3 between NEAR/3 pregnancies
-
interpregnancy and interval* or occupation* or socioeconomic or ethnic or ethnicity or (manual NEAR work) or (long NEAR hours) or cocaine or heroin or narcotics or crack or dope or cannabis or (substance NEAR abuse) or smoking or tobacco or alcohol* or lifestyle* or estriol or (plasma NEAR crf) or (vaginal NEAR infection*)
-
(biophysical or biochemical) and marker* or bishop* and (score or scores) or cervical NEAR (change* or length or measurement) or endocervical NEAR (effacement or assessment) or cervical NEAR (effacement or assessment or state)
-
(clinical NEAR histor*) or (patient NEAR histor*) or (patient NEAR record*) or (obstetric NEAR histor*) or (previous NEAR preterm) or (repeat NEAR preterm) or (risk NEAR scor*) or (physical NEAR examination*) or (physical NEAR exam) or (physical NEAR exams) or (cervical NEAR dilation) or (cervix NEAR length) or dilation NEAR cervix
-
(uterine NEAR tocography) or (uterine NEAR anomal*) or tocometry or (cervical or cervix) NEAR (abnormal* or incompetence or incompetent) or (cervical or cervix) NEAR (ultrasound or ultrasonography) or (vaginal or endovaginal or transvaginal or obstetric) NEAR (ultrasound or ultrasonography) or uterine NEAR (activity or huam or excitability)
-
(myometrial or myometrium) NEAR excitability or (oncofetal or reactive) NEAR (protein*) or (asymptomatic NEAR bacteriuria) or (genital NEAR tract NEAR infection*) or leucocyte NEAR (esterase* or cytokines) or culture* NEAR (amniotic or blood or genital or vaginal or cervical)
-
timp or collagenase or relaxin or (tissue NEAR inhibitor*) or plasma NEAR corticotropin NEAR releasing NEAR hormone* or estrogen or oestrogen or progestogen or glucose NEAR concentration* NEAR amniotic or zinc NEAR amniotic
-
#10 OR #11 OR #12 OR #13 OR #14 OR #15 OR #16 OR #17 OR #18 OR #19 OR #20
-
#21 OR #22 OR #23 OR #24 OR #25 OR #26 OR #27 OR #28 OR #29 OR #30 OR #31 OR #32 OR #33 OR #34 OR #35 OR #36 OR #37 OR #38 OR #39 OR #40
-
#41 OR #42 OR #43 OR #44 OR #45 OR #46 OR #47 OR #48 OR #49 OR #50 OR #51 OR #52 OR #53 OR #54 OR #55 OR #56 OR #57 OR #58 OR #59 OR #60
-
#61 OR #62 OR #63 OR #64 OR #65 OR #66 OR #67 OR #68 OR #69 OR #70 OR #71 OR #72 OR #73 OR #74 OR #75 OR #76 OR #77 OR #78 OR #79 OR #80
-
#81 OR #82 OR #83 OR #84 OR #85 OR #86 OR #87 OR #88 OR #89 OR #90 OR #91 OR #92 OR #93 OR #94 OR #95 OR #96 OR #97 OR #98 OR #99 OR #100 OR #101
-
#102 OR #103 OR #104 OR #105 OR #106
National Research Register (NRR), (Update Software), 2002:1–2005:21 September 2005
192 records were retrieved.
LABOR PREMATURE
-
((premature next birth) or (preterm next birth) or (preterm next birth))
-
((premature next deliver*) or (preterm next deliver*) or (preterm next deliver*))
-
((preterm next labour) or (preterm next labour))
-
((preterm next labor) or (preterm next labor))
-
((premature next labour) or (premature next labor) or (premature next parturition))
-
#1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6
-
SOCIOECONOMIC FACTORS
-
SOCIAL CLASS
-
RISK FACTORS
-
SMOKING
-
ETHNIC GROUPS
-
SUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS
-
LIFE STYLE
-
PREGNANCY HIGH RISK
-
PREGNANCY IN ADOLESCENCE
-
PARITY
-
REPRODUCTIVE HISTORY
-
PREGNANCY COMPLICATIONS
-
FETAL MEMBRANES PREMATURE RUPTURE
-
ABDOMINAL PAIN
-
UTERINE CONTRACTION
-
UTERINE HEMORRHAGE
-
FEVER
-
ESTRIOL
-
RELAXIN
-
TREPONEMA PALLIDUM
-
NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE
-
STREPTOCOCCUS AGALACTIAE
-
MYCOPLASMA HOMINIS
-
CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS
-
TRICHOMONAS VAGINALIS
-
BACTEROIDES INFECTIONS
-
VAGINOSIS BACTERIAL
-
MOBILUNCUS
-
GARDNERELLA VAGINALIS
-
PROSTAGLANDINS
-
PREGNANCY MULTIPLE
-
CERVIX INCOMPETENCE
-
CERVICAL RIPENING
-
FETAL PROTEINS
-
BACTERIURIA
-
DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES OBSTETRICAL AND GYNECOLOGICAL
-
DIAGNOSTIC EQUIPMENT
-
DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING
-
REAGENT KITS DIAGNOSTIC
-
ULTRASONOGRAPHY PRENATAL
-
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS ROUTINE
-
MEDICAL HISTORY TAKING
-
RISK ASSESSMENT
-
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
-
UTERINE MONITORING
-
ESTERASES
-
CYTOKINES
-
TISSUE CULTURE
-
ACUTE PHASE PROTEINS
-
IMMUNOPROTEINS
-
PLATELET DERIVED GROWTH FACTORS
-
TUMOR NECROSIS FACTOR
-
CORPUS LUTEUM HORMONES
-
ESTROGENS
-
INHIBINS
-
ESTRADIOL
-
ESTRIOL
-
ESTRONE
-
ESTROGEN RECEPTOR MODULATORS
-
RECEPTORS ESTROGEN
-
PROSTAGLANDIN ANTAGONISTS
-
RECEPTORS PROSTAGLANDIN
-
LEUKOTRIENES
-
THROMBOXANES
-
COLLAGENASES
-
BODY CONSTITUTION
-
BODY TEMPERATURE
-
PALPATION
-
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES BACTERIAL
-
BACTEROIDACEAE INFECTIONS
-
CHLAMYDIACEAE INFECTIONS
-
GRANULOMA INGUINALE
-
MYCOPLASMATALES INFECTIONS
-
NEISSERIACEAE INFECTIONS
-
TREPONEMAL INFECTIONS
-
STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTIONS
-
STREPTOCOCCAL INFECTIONS
-
UREAPLASMA INFECTIONS
-
LACTOBACILLUS
-
HERPES GENITALIS
-
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
-
CHORIOAMNIONITIS
-
AMNIOTIC FLUID
-
LEUKOCYTES
-
SALIVA
-
BIOLOGICAL MARKERS
-
CORTICOTROPIN RELEASING HORMONE
-
((older near women) or (elderly near women))
-
fibronectin*
-
((premature near rupture) near membrane*)
-
tocodynamo*
-
((risk near factor*) or (socioeconomic near factor*))
-
((low near pregnancy) near weight)
-
(high next parity)
-
((early near bleeding) near pregnancy)
-
(vaginal near bleeding)
-
((uterine near hemorrhage) or (antepartum near hemorrhage))
-
((abdominal next pain) or (uterine next contraction*))
-
((pyrexia or febrile) or fever)
-
((short near between) near pregnancies)
-
(interpregnancy and interval*)
-
(((((occupation* or socioeconomic) or ethnic) or ethnicity) or (manual next work)) or (long next hours))
-
((((((cocaine or heroin) or narcotics) or crack) or dope) or cannabis) or (substance next abuse))
-
(((((substance and disorder*) or smoking) or tobacco) or alcohol*) or lifestyle*)
-
((estriol or (plasma near crf)) or (vaginal near infection*))
-
((biophysical or biochemical) and marker*)
-
(bishop* and (score or scores))
-
((cervical near change*) or (cervical near length) or (cervical near measurement))
-
((endocervical near effacement) or (endocervical near assessment))
-
((cervical near effacement) or (cervical near assessment) or (cervical near state))
-
(((clinical near histor*) or (patient near histor*)) or (patient near record*))
-
(((obstetric near histor*) or (previous near preterm)) or (repeat near preterm))
-
((risk next scor*) or (physical next examination*))
-
((((physical next exam) or (physical next exams)) or (cervical next dilation)) or (cervix near length))
-
(dilation near cervix)
-
(((uterine near tocography) or (uterine near anomal*)) or tocometry)
-
((cervical near abnormal*) or (cervical near incompetence) or (cervical near incompetent))
-
((cervix near abnormal*) or (cervix near incompetence) or (cervix near incompetent))
-
((cervical near ultrasound) or (cervical near ultrasonography))
-
((cervix near ultrasound) or (cervix near ultrasonography))
-
((vaginal near ultrasound) or (ultrasound near endovaginal) or (transvaginal near ultrasound) or (obstetric near ultrasound) or (vaginal near ultrasonography) or (ultrasonography near endovaginal) or (transvaginal near ultrasonography) or (obstetric near ultrasonography))
-
((uterine near activity) or (uterine near huam) or (uterine near excitability))
-
((myometrial near excitability) or (myometrium near excitability))
-
((oncofetal near protein*) or ((c next reactive) near protein*)
-
((asymptomatic next bacteriuria) or (genital next tract next infection*))
-
((leucocyte next esterase*) or (leucocyte next cytokines))
-
((amniotic near culture*) or (blood near culture*) or (genital near culture*) or (vaginal near culture*) or (cervical near culture*))
-
(((timp or collagenase) or relaxin) or (tissue next inhibitor*))
-
(plasma next corticotropin next releasing next hormone*)
-
((estrogen or oestrogen) or progestogen)
-
((glucose next concentration*) near amniotic)
-
(zinc near amniotic)
-
(#8 or #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 or #13 or #14 or #15 or #16 or #17 or #18 or #19 or #20)
-
(#21 or #22 or #23 or #24 or #25 or #26 or #27 or #28 or #29 or #30 or #31 or #32 or #33 or #34 or #35 or #36 or #37 or #38 or #39 or #40)
-
(#21 or #22 or #23 or #24 or #25 or #26 or #27 or #28 or #29 or #30 or #31 or #32 or #33 or #34 or #35 or #36 or #37 or #38 or #39 or #40)
-
(#41 or #42 or #43 or #44 or #45 or #46 or #47 or #48 or #49 or #50 or #51 or #52 or #53 or #54 or #55 or #56 or #57 or #58 or #59 or #60)
-
(#61 or #62 or #63 or #64 or #65 or #66 or #67 or #68 or #69 or #70 or #71 or #72 or #73 or #74 or #75 or #76 or #77 or #78 or #79 or #80)
-
(#81 or #82 or #83 or #84 or #85 or #86 or #87 or #88 or #89 or #90 or #91 or #92 or #93 or #94 or #95 or #96 or #97 or #98 or #99 or #100)
-
(#101 or #102 or #103 or #104 or #105 or #106 or #107 or #108 or #109 or #110 or #111 or #112 or #113 or #114 or #115 or #116 or #117 or #118 or #119 or #120)
-
(#121 or #122 or #123 or #124 or #125 or #126 or #127 or #128 or #129 or #130 or #131 or #132 or #133 or #134 or #135 or #136 or #137 or #138 or #139)
-
(#141 or #142 or #143 or #144 or #145 or #146 or #147)
-
(#7 and #148)
MEDION. 27 September 2005
Eight records were retrieved. Separate searches were performed using the abstract, title and ICPC code fields.
ICPC code: W Pregnancy, childbearing, family planning
Abstract, Title: ‘premature’, ‘preterm’, ‘pre term’, ‘pre-term’
Effectiveness
Interventions search strategies and results
MEDLINE (Ovid Gateway), 1966–2005/Aug. week 1, 18 August 2005
5056 records were retrieved in MEDLINE and 54 records were retrieved in MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations.
-
randomized-controlled-trial.pt.
-
controlled-clinical-trial.pt.
-
randomized-controlled-trials/
-
RANDOM ALLOCATION/
-
DOUBLE-BLIND METHOD/
-
SINGLE-BLIND METHOD/
-
clinical trial.pt.
-
CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIALS/
-
CLINICAL TRIALS/
-
CLINICAL TRIALS, PHASE III/
-
CLINICAL TRIALS, PHASE IV/
-
MULTICENTER STUDIES/
-
Evaluation Studies/
-
Drug Evaluation/
-
exp PRODUCT SURVEILLANCE, POSTMARKETING/
-
(clin$adj3 trial$).ti,ab.
-
((singl$or doubl$or tripl$or trebl$) adj3 (mask$or blind$)).ti,ab.
-
Placebos/
-
placebo$.ti,ab.
-
random$.ti,ab.
-
RESEARCH DESIGN/
-
(control$adj3 (trial$or stud$)).ti,ab.
-
crossover.ti,ab.
-
Comparative Study/
-
1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 or 21 or 22 or 23 or 24
-
Animal/
-
Human/
-
26 not (26 and 27)
-
25 not 28
-
Labor, Premature/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 birth$).ti,ab.
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 deliver$).ti,ab.
-
((preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 (labor or labour)).ti,ab.
-
(premature adj3 (labor or labour or parturition)).ti,ab.
-
Fetal Membranes, Premature Rupture/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 rupture$).ti,ab.
-
(PROM or PPROM).ti,ab.
-
or/30–37
-
29 and 38
EMBASE (Ovid Gateway), 1980–2005/Aug. week 1, 18 August 2005
7830 records were retrieved.
-
Randomized Controlled Trial/
-
RANDOMIZATION/
-
Double Blind Procedure/
-
Single Blind Procedure/
-
random$control$trial$.ti,ab.
-
(clin$adj3 trial$).ti,ab.
-
exp clinical trial/
-
exp controlled study/
-
((singl$or doubl$or trebl$or tripl$) adj3 (blind$or mask$)).ti,ab.
-
placebo$.ti,ab.
-
PLACEBO/
-
EVALUATION/
-
Follow Up/
-
Prospective Study/
-
(control$or prospective$or volunteer$).ti,ab.
-
random$.ti,ab.
-
1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16
-
editorial.pt.
-
note.pt.
-
18 or 19
-
(rat or rats or mouse or mice or hamster or hamsters or animal or animals or dogs or dog or cats or bovine or sheep).ti,ab,sh.
-
exp animal/
-
Nonhuman/
-
exp human/
-
21 or 22 or 23
-
25 not (25 and 24)
-
17 not (20 or 26)
-
Premature Labor/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 birth$).ti,ab.
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 deliver$).ti,ab.
-
((preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 (labor or labour)).ti,ab.
-
(premature adj3 (labor or labour or parturition)).ti,ab.
-
Premature Fetus Membrane Rupture/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 rupture$).ti,ab.
-
(PROM or PPROM).ti,ab.
-
or/28–35
-
27 and 36
Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) (Ovid Gateway), 1982–2005/Aug. week 1, 18 August 2005
1041 records were retrieved.
-
exp Clinical Trials/
-
CLINICAL TRIAL.pt.
-
exp Random Sample/
-
(clin$adj3 trial$).ti,ab.
-
((singl$or doubl$or trebl$or tripl$) adj3 (blind$or mask$)).ti,ab.
-
PLACEBOS/
-
placebo$.ti,ab.
-
random$.ti,ab.
-
exp Study Design/
-
exp Evaluation Research/
-
exp Prospective Studies/
-
(control$or prospectiv$or volunteer$).ti,ab.
-
or/1–12
-
Labor, Premature/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 birth$).ti,ab.
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 deliver$).ti,ab.
-
((preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 (labor or labour)).ti,ab.
-
(premature adj3 (labor or labour or parturition)).ti,ab.
-
Fetal Membranes, Premature Rupture/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 rupture$).ti,ab.
-
(PROM or PPROM).ti,ab.
-
or/14–21
-
13 and 22
BIOSIS (DIALOG), 1969–2005/Aug. week 1, 19 August 2005
2317 records were retrieved.
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)birth?
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)deliver?
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)(labo?r or parturition)
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)rupture?
-
s s1:s4
-
s clinical(2w)trial?
-
s controlled(2w)(trial? or stud?)
-
s random or randomi?ation or randomi?ed
-
s (singl? or doubl? or tripl? or trebl?)(2w)(mask? or blind?)
-
s placebo?
-
s crossover
-
s evaluation
-
s (prospective(2w)stud?) or (comparative(2w)stud?)
-
s phase(w)4 or phase(w)four or phase(w)IV
-
s post(w)market?(w)surveillance
-
s follow(w)up
-
s s6:s16
-
s s5 and s17
PASCAL (DIALOG), 1973–2005/Aug. week 1, 19 August 2005
2415 records were retrieved.
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)birth?
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)deliver?
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)(labo?r or parturition)
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)rupture?
-
s s1:s4
-
s clinical(2w)trial?
-
s controlled(2w)(trial? or stud?)
-
s random or randomi?ation or randomi?ed
-
s (singl? or doubl? or tripl? or trebl?)(2w)(mask? or blind?)
-
s placebo?
-
s crossover
-
s evaluation
-
s (prospective(2w)stud?) or (comparative(2w)stud?)
-
s phase(w)4 or phase(w)four or phase(w)IV
-
s post(w)market?(w)surveillance
-
s follow(w)up
-
s s6:s16
-
s s5 and s17
Science Citation Index (SCI) (Web of Science), 1900–2005/Aug. week 1, 18 August 2005
1916 records were retrieved.
-
TS=(clinical* SAME trial*)
-
TS=(controlled SAME trial*) OR TS=(controlled SAME stud*)
-
TS=(random OR randomisation OR randomization OR randomized or randomised)
-
TS=(singl* or doubl* or tripl* or trebl*) SAME TS=(mask* or blind*)
-
TS=placebo*
-
TS=crossover
-
TS=evaluation
-
TS=(prospective SAME stud*) or TS=(comparative SAME stud*)
-
TS=(phase 4) or TS=(phase four) or TS=(phase IV)
-
TS=(post market* surveillance)
-
#10 OR #9 OR #8 OR #7 OR #6 OR #5 OR #4 OR #3 OR #2 OR #1
-
TS=(premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) SAME TS=(birth*)
-
TS=(premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) SAME TS=(deliver*)
-
TS=(preterm or pre term or pre-term) SAME TS=(labor or labour)
-
TS=premature SAME TS=(labor or labour or parturition)
-
TS=(premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) SAME TS=(rupture*)
-
#16 OR #15 OR #14 OR #13 OR #12
-
#17 AND #11
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR), Cochrane Library, Issue 3:18 August 2005
108 records were retrieved.
-
Labor, Premature (MeSH)
-
(premature or preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 birth in title
-
(premature or preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 birth in abstract
-
(premature or preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 deliver* in title
-
(premature or preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 deliver* in abstract
-
(preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 (labour or labor) in title
-
(preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 (labour or labor) in abstract
-
premature NEAR/3 (labour or labor or parturition) in title
-
premature NEAR/3 (labour or labor or parturition) in abstract
-
Fetal Membranes, Premature Rupture (MeSH)
-
(premature or preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 ruptur* in title
-
(premature or preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 ruptur* in abstract
-
(PROM or PPROM) in title
-
(PROM or PPROM) in abstract
-
#1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 or #13 or #14
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Cochrane Library, Issue 3:18 August 2005
1595 records were retrieved.
-
Labor, Premature (MeSH)
-
(premature or preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 birth
-
(premature or preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 deliver*
-
(preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 (labour or labor)
-
premature NEAR/3 (labour or labor or parturition)
-
Fetal Membranes, Premature Rupture (MeSH)
-
(premature or preterm or pre*term) NEAR/3 ruptur*
-
PROM or PPROM
-
#1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) (CRD internal databases), 1994–2005/Aug. week 1, 18 August 2005
164 records were retrieved.
-
S (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)birth$
-
S (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)deliver$
-
S (preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)(labor$or labour$)
-
S (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)(labor or labour or parturition)
-
S (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)rupture$
-
S PROM or PPROM
-
S s1 or s2 or s3 or s4 or s5 or s6
Health Technology Assessment (HTA) (CRD internal databases), 1994–2005/Aug. week 1, 18 August 2005
12 records were retrieved.
-
S (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)birth$
-
S (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)deliver$
-
S (preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)(labor$or labour$)
-
S (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)(labor or labour or parturition)
-
S (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)rupture$
-
S PROM or PPROM
-
S s1 or s2 or s3 or s4 or s5 or s6
System for Information on Grey Literature in Europe (SIGLE), (Ovid Gateway), 1980–2004/Aug. week 1, 18 August 2005
26 records were retrieved.
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) near3 birth*) in ti,ab
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) near3 deliver*) in ti,ab
-
((preterm or pre term or pre-term) near3 (labor or labour)) in ti,ab
-
(premature near3 (labor or labour or parturition)) in ti,ab
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) near3 rupture*) in ti,ab
-
#1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5
Inside Conferences (DIALOG), 1993–2005/Aug. week 1, 19 August 2005
34 records were retrieved.
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)birth?
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)deliver?
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)(labo?r or parturition)
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)rupture?
-
s s1:s4
-
s clinical(2w)trial?
-
s controlled(2w)(trial? or stud?)
-
s random or randomi?ation or randomi?ed
-
s (singl? or doubl? or tripl? or trebl?)(2w)(mask? or blind?)
-
s placebo?
-
s crossover
-
s evaluation
-
s (prospective(2w)stud?) or (comparative(2w)stud?)
-
s phase(w)4 or phase(w)four or phase(w)IV
-
s post(w)market?(w)surveillance
-
s follow(w)up
-
s s6:s16
-
s s5 and s17
Dissertation Abstracts (DIALOG), 1861–2005/Aug. week 1, 19 August 2005
124 records were retrieved.
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)birth?
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)deliver?
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)(labo?r or parturition)
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)rupture?
-
s s1:s4
-
s clinical(2w)trial?
-
s controlled(2w)(trial? or stud?)
-
s random or randomi?ation or randomi?ed
-
s (singl? or doubl? or tripl? or trebl?)(2w)(mask? or blind?)
-
s placebo?
-
s crossover
-
s evaluation
-
s (prospective(2w)stud?) or (comparative(2w)stud?)
-
s phase(w)4 or phase(w)four or phase(w)IV
-
s post(w)market?(w)surveillance
-
s follow(w)up
-
s s6:s16
-
s s5 and s17
National Research Register (NRR), (Update Software), 2005:19 August 2005
455 records were retrieved.
-
LABOR PREMATURE single term (MeSH)
-
(premature NEXT birth*) or (preterm NEXT birth*) or (pre-term NEXT birth*)
-
(premature NEXT deliver*) or (preterm NEXT deliver*) or (pre-term NEXT deliver*)
-
(preterm NEXT labour) or (pre-term NEXT labour)
-
(preterm NEXT labor) or (pre-term NEXT labor)
-
(premature NEXT labour) or (premature NEXT labor) or (premature NEXT parturition)
-
FETAL MEMBRANES PREMATURE RUPTURE single term (MeSH)
-
(premature NEXT rupture*) or (preterm NEXT rupture*) or (pre-term NEXT rupture*)
-
#1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8
National Technical Information Service (NTIS) (US Department of Commerce), 1990–2005/Aug. week 1, 19 August 2005
Seven records were retrieved. Each line was searched separately.
-
“premature birth” or “preterm birth” or “pre term birth” or “pre-term birth”
-
“premature delivery” or “preterm delivery” or “pre term delivery” or “pre-term delivery”
-
“premature labor” or “preterm labor” or “pre term labor” or “pre-term labor”
-
“premature labour” or “preterm labour” or “pre term labour” or “pre-term labour”
-
“premature parturition”
-
“premature rupture” or “preterm rupture” or “pre term rupture” or “pre-term rupture”
ClinicalTrials.gov. (US National Institutes of Health), 2005/Aug. week 1, 22 August 2005
11 records were retrieved. Each line searched was separately.
-
premature birth, preterm birth, pre term birth, pre-term birth
-
premature delivery, preterm delivery, pre term delivery, pre-term delivery
-
preterm labor, preterm labour, premature labor, premature labour
-
premature parturition
-
premature rupture, preterm rupture, pre term rupture, pre-term rupture
Economic analysis
Economic search strategies and results
NHS Economic Evaluation Database (NHS EED) (CRD internal databases), 1994–2005/Sept. week 1, 21 September 2005
113 records were retrieved.
-
S (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)birth$
-
S (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)deliver$
-
S (preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)(labor$or labour$)
-
S (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)(labor or labour or parturition)
-
S (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(w3)rupture$
-
S PROM or PPROM
-
S s1 or s2 or s3 or s4 or s5 or s6
Health Economic Evaluations Database (HEED), (Office of Health Economics), CD-ROM, 1967–2005/Sept. week 1, 21 September 2005
123 records were retrieved.
-
AX=(premature birth) or (premature births) or (preterm birth) or (preterm births) or (pre-term birth) or (pre-term births)
-
AX=(premature deliver) or (premature deliveries) or (premature delivery) or (preterm deliver) or (preterm deliveries) or (preterm delivery) or (pre-term deliver) or (pre-term deliveries) or (preterm delivery)
-
AX=(premature labor) or (premature labour) or (preterm labor) or (preterm labour) or (pre-term labor) or (pre-term labour)
-
AX=(premature parturition) or (premature rupture) or (premature ruptures) or (preterm parturition) or (preterm rupture) or (preterm ruptures) or (pre-term parturition) or (pre-term rupture) or (pre-term ruptures)
-
AX=PROM or PPROM
-
CS=1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5
MEDLINE (Ovid Gateway), 1966–2005/Sept. week 1, 21 September 2005
610 records were retrieved in MEDLINE and 15 records were retrieved in MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations.
-
economics/
-
exp “costs and cost analysis”/
-
economics, dental/
-
exp “economics, hospital”/
-
economics, medical/
-
economics, nursing/
-
economics, pharmaceutical/
-
(economic$or cost or costs or costly or costing or price or prices or pricing or pharmacoeconomic$).tw.
-
(expenditure$not energy).tw.
-
(value adj1 money).tw.
-
budget$.tw.
-
or/1–11
-
Labor, Premature/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 birth$).ti,ab.
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 deliver$).ti,ab.
-
((preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 (labor or labour)).ti,ab.
-
(premature adj3 (labor or labour or parturition)).ti,ab.
-
Fetal Membranes, Premature Rupture/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 rupture$).ti,ab.
-
(PROM or PPROM).ti,ab.
-
or/13–20
-
12 and 21
-
Animals/
-
Humans/
-
23 not (23 and 24)
-
22 not 25
EMBASE (Ovid Gateway), 1980–2005/Sept. week 1, 21 September 2005
564 records were retrieved.
-
Health Economics/
-
exp Economic Evaluation/
-
exp Health Care Cost/
-
exp PHARMACOECONOMICS/
-
or/1–4
-
(econom$or cost or costs or costly or costing or price or prices or pricing or pharmacoeconomic$).ti,ab.
-
(expenditure$not energy).ti,ab.
-
(value adj2 money).ti,ab.
-
budget$.ti,ab.
-
or/6–9
-
5 or 10
-
(metabolic adj cost).ti,ab.
-
((energy or oxygen) adj cost).ti,ab.
-
((energy or oxygen) adj expenditure).ti,ab.
-
or/12–14
-
11 not 15
-
editorial.pt.
-
note.pt.
-
letter.pt.
-
or/17–19
-
16 not 20
-
(rat or rats or mouse or mice or hamster or hamsters or animal or animals or dogs or dog or cats or bovine or sheep).ti,ab,sh.
-
exp animal/
-
Nonhuman/
-
or/22–24
-
exp human/
-
exp human experiment/
-
26 or 27
-
25 not (25 and 28)
-
21 not 29
-
Premature Labor/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 birth$).ti,ab.
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 deliver$).ti,ab.
-
((preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 (labor or labour)).ti,ab.
-
(premature adj3 (labor or labour or parturition)).ti,ab.
-
Premature Fetus Membrane Rupture/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 rupture$).ti,ab.
-
(PROM or PPROM).ti,ab.
-
or/31–38
-
30 and 39
Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) (Ovid Gateway), 1982–2005/Sept. week 1, 21 September 2005
83 records were retrieved.
-
exp “costs and cost analysis”/or “economic aspects of illness”/or “economic value of life”/or economics, pharmaceutical/
-
((cost or costs or costed or costly or costing) adj (utilit$or benefit$or effective$or stud$or minimi$or analys$)).ti,ab.
-
(economic$or pharmacoeconomic$or price$or pricing).ti,ab.
-
(expenditure$not energy).ti,ab.
-
(value adj1 money).ti,ab.
-
budget$.ti,ab.
-
or/1–6
-
Labor, Premature/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 birth$).ti,ab.
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 deliver$).ti,ab.
-
((preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 (labor or labour)).ti,ab.
-
(premature adj3 (labor or labour or parturition)).ti,ab.
-
Fetal Membranes, Premature Rupture/
-
((premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) adj3 rupture$).ti,ab.
-
(PROM or PPROM).ti,ab.
-
or/8–15
-
7 and 16
BIOSIS (Edina), 1969–2005/Sept. week 1, 21 September 2005
282 records were retrieved.
-
al:(premature n3 birth*) or (preterm n3 birth*) or (pre-term n3 birth*) or (pre term n3 birth*)
-
al:(premature n3 deliver*) or (preterm n3 deliver*) or (pre-term n3 deliver*) or (pre term n3 deliver*)
-
al:(premature n3 labo*r*) or (preterm n3 labo*r*) or (pre-term n3 labo*r*) or (pre term n3 labo*r*)
-
al:(premature n3 parturition)
-
al:(premature n3 rupture*) or (preterm n3 rupture*) or (pre-term n3 rupture*) or (pre term n3 rupture*)
-
#1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5
-
al:(economic* or cost or costs or costly or costing or price or prices or pricing or pharmacoeconomic*)
-
al:budget*
-
al:(value w1 money)
-
al:(expenditure* not energy)
-
#7 or #8 or #9 or #10
-
#6 and #11
PASCAL (DIALOG), 1973–2005/Sept. week 1, 21 September 2005
175 records were retrieved.
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)birth?
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)deliver?
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)(labo?r or parturition)
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)rupture?
-
s s1:s4
-
s economic? or cost or costs or costly or costing or price or prices or pricing or pharmacoeconomic?
-
s expenditure? not energy
-
s value(2w)money
-
s budget?
-
s s6:s9
-
s s5 and s10
Science Citation Index (SCI) (Web of Science), 1900–2005/Sept. week 1, 21 September 2005
388 records were retrieved.
-
TS=(economic* or cost or costs or costly or costing or price or prices or pricing or pharmacoeconomic*)
-
TS=(value SAME money)
-
TS=budget*
-
TS=(expenditure* NOT energy)
-
#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4
-
TS=(premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) SAME TS=(birth*)
-
TS=(premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) SAME TS=(deliver*)
-
TS=(preterm or pre term or pre-term) SAME TS=(labor or labour)
-
TS=premature SAME TS=(labor or labour or parturition)
-
TS=(premature or preterm or pre term or pre-term) SAME TS=(rupture*)
-
#6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10
-
#5 AND #11
Inside Conferences (DIALOG), 1993–2005/Sept. week 1, 21 September 2005
Four records were retrieved.
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)birth?
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)deliver?
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)(labo?r or parturition)
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)rupture?
-
s s1:s4
-
s economic? or cost or costs or costly or costing or price or prices or pricing or pharmacoeconomic?
-
s expenditure? not energy
-
s value(2w)money
-
s budget?
-
s s6:s9
-
s s5 and s10
-
s (prospective(2w)stud?) or (comparative(2w)stud?)
-
s phase(w)4 or phase(w)four or phase(w)IV
-
s post(w)market?(w)surveillance
-
s follow(w)up
-
s s6:s16
-
s s5 and s17
Dissertation Abstracts (DIALOG), 1861–2005/Sep. 21 September 2005
51 records were retrieved.
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)birth?
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)deliver?
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)(labo?r or parturition)
-
s (premature or preterm or pre(w)term)(3n)rupture?
-
s s1:s4
-
s economic? or cost or costs or costly or costing or price or prices or pricing or pharmacoeconomic?
-
s expenditure? not energy
-
s value(2w)money
-
s budget?
-
s s6:s9
-
s s5 and s10
IDEAS, the Research Papers in Economics (RePEC) database, 2005/Sept. 21 September 2005
No records were retrieved. Each line was searched separately
-
premature birth
-
preterm birth
-
preterm labor
-
preterm labour
-
premature labor
-
premature labour
-
premature parturition
-
premature rupture
-
preterm rupture
Appendix 2 List of tests for predicting spontaneous preterm birth
| Type of tests or investigation | Predictive and diagnostic tests for preterm birth | Last updated |
|---|---|---|
| History | Previous history of spontaneous preterm birtha | |
| Examination | Abdominal palpationb | |
| Cervical digital examinationb | ||
| Biochemistry | Cervicovaginal glycoproteins: | 2001 |
| Interleukins (IL-6, IL-8)b | ||
| β-human chorionic gonadotrophinb | ||
| Fetal fibronectina,b | ||
| Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1b | ||
| Serum glycoproteins: α-fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotrophin (as part of Down syndrome screening)a | ||
| Endocrine hormones: | ||
| Salivary estriolb | ||
| Cortisol-releasing hormoneb | ||
| Inflammatory markers (serum): | ||
| C-reactive proteina,b | ||
| Matrix metalloproteases (MMP)b | ||
| Interleukinsa,b | ||
| Microbiology | Detection of bacterial vaginosisa,b | 2002 |
| Periodontal screeninga | 2006 | |
| Midstream urine culturea,b | 1989 | |
| Physiological | Uterine activity monitoringa | |
| Rheobaseb | ||
| Mammary stimulation testb | ||
| Ultrasound scan | Absence of fetal breathing movementsb | 2003 |
| Measurement of cervical lengtha,b | 2003 |
Appendix 3 List of interventions preventing or improving neonatal outcome in spontaneous preterm birth
| Intervention | Comparator(s) | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women identified to be at risk of spontaneous preterm birth | ||
| Education for high-risk women | No intervention | Update |
| Home visits | No intervention | Update |
| Bed rest (home or hospital) | No intervention | Update |
| Home uterine monitoring | No intervention | New rapid review |
| Antibiotic treatment for urogenital infections, including: | ||
| Ureaplasma in vagina | No treatment or placebo | Update |
| Bacterial vaginosis | No treatment, placebo or alternative antibiotic therapy | Update |
| Asymptomatic bacteriuria | No treatment | Update |
| Syphilis | No treatment, placebo or alternative antibiotic therapy | No new trials, use existing Cochrane review |
| Gonorrhoea | Alternative antibiotic therapy | Update |
| Symptomatic urinary tract infections | Alternative antibiotic therapy | Update |
| Duration of asymptomatic bacteriuria | Antimicrobiols of varying duration, e.g. single-dose, short-course, long-course, continuous treatment | Update |
| Antibiotics for treating intra-amniotic infections | No treatment or alternative antibiotic regimen | Update |
| Periodontal disease | No treatment, placebo or alternative treatments | New rapid review |
| Cervical cerclage | No treatment, bed rest, elective versus emergency or alternative therapies (e.g. pessaries) | Update |
| Nutrition and supplements | ||
| Vitamin C | No treatment or placebo | Update |
| Vitamin D | No treatment or placebo | Update |
| Vitamin E | No treatment or placebo | Update |
| Zinc | No treatment or placebo | Update |
| Fish oil | No treatment or placebo | Update |
| Hypnosis | No treatment | New rapid review |
| Hydration | No treatment | Update |
| Prophylactic antibiotics (intact membranes) | No treatment or placebo | Update |
| Women in late pregnancy symptomatic of threatened preterm labour | ||
| Tocolytic agents | ||
| Nitric oxide donors | No treatment, placebo or alternative tocolytic agent | Update |
| Cyclo-oxygenase inhibitors | No treatment, placebo or alternative tocolytic agent | Update |
| Ethanol | No treatment, placebo or alternative tocolytic agent | Update |
| Terbutaline pump maintenance | No treatment, placebo or alternative tocolytic agent | Update |
| Oxytocin receptor agonists | No treatment, placebo or alternative tocolytic agent | Update |
| Calcium channel blockers | No treatment, placebo or alternative tocolytic agent | Update |
| Calcium channel maintenance | No treatment, placebo or alternative tocolytic agent | Update |
| Magnesium sulphate | No treatment, placebo or alternative tocolytic agent | Update |
| Progestational agents | No treatment, placebo, and different routes of administration | Use existing review |
| In utero transfer | ||
| Planned early birth versus expectant management | Planned early birth versus expectant management | Use Cochrane review (due 2006) |
| Improvement of neonatal outcomes | ||
| Magnesium sulphate for neuroprotection | No treatment or placebo | Update |
| Vitamin K for neuroprotection | No treatment or placebo | Update |
| Prophylactic corticosteroids | No treatment or placebo | |
| Repeat doses to prevent neonatal respiratory distress | No treatment or placebo | |
Appendix 4 Data extraction proforma
Test accuracy
Pro-forma for study inclusion and data extraction
| Reviewer | Language | 1st author | Publication year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selection criteria | ||||
| Population – singleton pregnancy (if threatened preterm labour – intact membrane) | Yes/No | |||
| Reference standard (outcome) – delivery gestation stated | Yes/No | |||
| 2x2 table construction possible | Yes/No | |||
| Test listed in the list of tests ( ) | Yes/No | |||
| If all the above yes – select the study (if necessary contact the corresponding author) | Yes/No | |||
| Data extraction | ||||
| Country | ||||
| Population | Asymptomatic | Symptomatic | ||
| Study design | Cohort | Case–control | Cannot tell | Others (state) |
| Data collection | Prospective | Retrospective | Cannot tell | Others (state) |
| Enrolment | Consecutive | Arbitrary | Cannot tell | Others (state) |
| Blinding | Yes | No | Cannot tell | Others (state) |
| Test description | Yes | No | Cannot tell | Others (state) |
| Inclusion criteria | ||||
| Exclusion criteria | ||||
| Testing gestation(s) | ||||
| Threshold(s) | ||||
| Reference standard(s) | ||||
| Sample size | ||||
| 2 × 2 data extraction here (reproduce table as many times as required) | ||||
| Birth < 48 h/7 days/34 weeks/37 weeks Birth > 48 h/7 days/34 weeks/37 weeks Total | ||||
| Test positive | ||||
| Test negative | ||||
Effectiveness
Proforma for study inclusion and data extraction
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Authors Title: Type of review: Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Preterm birth |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) Other sources Search restrictions Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) Population Intervention Outcomes Study selection: Data extraction: Validity assessment: Criteria used Assessment Synthesis: Heterogeneity Methods |
Number of studies included: Comparisons No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation Adequate concealment of allocation Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher Incidence of birth < 34 weeks gestation: Incidence of birth < 37 weeks gestation: Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Incidence of perinatal mortality: Incidence of adverse events: Brief summary of findings: Authors’ conclusions: Comments: |
Decision analyses – economic evaluation (systematic review)
Proforma for study inclusion and data extraction
Author(s):
Title of document:
Source:
Location:
Initial classification of study on the basis of title and abstract:
-
Study reports primary research on the costs or utilisation of care and formal economic evaluation is included.
-
Study discusses economic aspects of care, and contains useful primary or secondary cost or utilisation data.
-
Study may have useful information but does not obviously fall into (A) or (B1).
-
Study discusses economic aspects of policies for care, but is in neither (A) nor (B1).
-
E. Study does not have any relevance to the economic evaluation of preterm labour.
Final classification of study following systematic review:
-
Economic evaluation
-
Other cost study
-
Effectiveness study with some assessment of implications for cost or quantity of resources used
-
Description of methods used in aspects of economic evaluation of preterm labour
-
Review of economic aspects of care
-
Other, such as, survey of resources and facilities, survey of utilisation, estimate of economic burden of disease, discussion of health finance or policy
-
Not relevant to the economic evaluation of preterm labour
-
Foreign language
-
Quality of life study
Primary focus of study (i.e. what is it about?):
Asymptomatic/symptomatic Test/intervention
Country of origin: Document reviewed by:
Comment by reviewer:
Decision analyses – evaluation of economic systematic review quality
Quality assessment form
Author and year:
| Phillips criteria | Y/N/UC | |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | ||
| 1. | Is there a clear statement of the decision problem? | |
| 2. | Is the objective of the model specified and consistent with the stated decision problem? | |
| 3. | Is the primary decision-maker specified? | |
| 4. | Is the perspective of the model stated clearly? | |
| 5. | Are the model inputs consistent with the stated perspective? | |
| 6. | Is the structure of the model consistent with a coherent theory of the health condition under evaluation? | |
| 7. | Are the sources of the data used to develop the structure of the model specified? | |
| 8. | Are the structural assumptions reasonable given the overall objective, perspective and scope of the model? | |
| 9. | Is there a clear definition of the options under evaluation? | |
| 10. | Have all feasible and practical options been evaluated? | |
| 11. | Is there justification for the exclusion of feasible options? | |
| 12. | Is the chosen model type appropriate given the decision problem and specified casual relationships within the model? | |
| 13. | Is the time horizon of the model sufficient to reflect all the important differences between the options? | |
| 14. | Do the disease states (state transition model) or the pathways (decision tree model) reflect the underlying biological process of the disease in question and the impact of interventions? | |
| 15. | Is the cycle length defined and justified in terms of the natural history of disease? | |
| Data | ||
| 16. | Are the data identification methods transparent and appropriate given the objectives of the model? | |
| 17. | Where choices have been made between data sources are these justified appropriately? | |
| 18. | Where expert opinion has been used are the methods described and justified? | |
| 19. | Is the choice of baseline data described and justified? | |
| 20. | Are transition probabilities calculated appropriately? | |
| 21. | Has a half-cycle correction been applied to both costs and outcomes? | |
| 22. | If not, has the omission been justified? | |
| 23. | Have the methods and assumptions used to extrapolate short-term results to final outcomes been documented and justified? | |
| 24. | Are the costs incorporated into the model justified? | |
| 25. | Has the source for all costs been described? | |
| 26. | Have discount rates been described and justified given the target decision-maker? | |
| 27. | Are the utilities incorporated into the model appropriate? | |
| 28. | Is the source of utility weights referenced? | |
| 29. | If data have been incorporated as distributions, has the choice of distributions for each parameter been described and justified? | |
| 30. | If data are incorporated as point estimates, are the ranges used for sensitivity analysis stated clearly and justified? | |
| 31. | Has heterogeneity been dealt with by running the model separately for different subgroups? | |
| 32. | Have the results been compared with those of previous models and any differences in results explained? | |
Decision analyses – evaluation of economic systematic review quality
Quality assessment form
Author and year:
| Drummond adapted criteria | Y/N/UC | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Was a well-defined question posed in an answerable form? | |
| 2. | Was a comprehensive description of the competing alternatives given? | |
| 3. | Was there evidence that the programmes’ effectiveness was established? | |
| 4. | Were all the important and relevant costs and consequences for each alternative identified? | |
| 5. | Were costs and consequences measured accurately in appropriate physical units? | |
| 6. | Were costs and consequences valued credibly? | |
| 7. | Were costs and consequences adjusted for differential timing? | |
| 8. | Was an incremental analysis of costs and consequences of alternatives performed? | |
| 9. | Was allowance made for uncertainty in the estimates of costs and consequences? | |
| 10. | Did the presentation and discussion of study results include all issues of concern to users? |
Author and year:
| Cost studies criteria – based on ultrasound study | Y/N/UC | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Methods for the estimation of quantities and unit costs are described (or cited) | |
| 2. | Sources of cost data are stated/apparent | |
| 3. | Indirect costs (if included) are reported separately from direct costs | |
| 4. | Both currency and price data are recorded | |
| 5. | Details of currency or price adjustments for inflation or currency conversion are given (if appropriate) | |
| 6. | The discount rate is stated/apparent and justified (if relevant) |
Decision analyses – cost data extraction
Cost data extraction proforma
| Study details | Definition and components | Method for estimation of costs | Results/statistical analysis | Sensitivity analysis | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Author and year: Research question: Type of cost study: Country/currency: Cost year: Perspective: Study population: Intervention (including comparator): |
Definitions: Components: |
Estimation of costs: |
Costs: Statistical analysis: |
Sensitivity analysis: Appropriateness: |
Author’s conclusions: Implications for practice: Comments: |
Decision analyses – data extraction
Data extraction proforma
| Study details | Source of data | Method of estimation of benefits/costs | Results/statistical analysis | Sensitivity analysis | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Author and Year: Research question: Type of economic evaluation: Country/currency: Cost year: Perspective: Study population: Intervention (including comparator): |
Source of effectiveness data: Source of cost data: |
Valuation for clinical outcomes or benefits: Estimation of costs: Modelling: |
Clinical outcome/benefits: Costs: Synthesis of costs and benefits: Statistical analysis: |
Sensitivity analysis: Appropriateness: |
Author’s conclusions: Magnitude and direction of results: Implications for practice: Comments: |
Appendix 5 Characteristics and results of individual included test accuracy studies
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Study designs | Inclusion | Exclusion | Testing gestation | Threshold | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goldenberg68 | 1998 | USA | 1711 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Placenta praevia, congenital fetal anomaly | First antenatal appointment | Previous spontaneous preterm birth | < 35, < 37 |
| Iams69 | 1998 | USA | 1282 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | First antenatal appointment | Previous spontaneous preterm birth before 26, 31 or 36 weeks’ gestation | 37 | |
| Botsis64 | 2004 | Greece | 104 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | First antenatal appointment | Previous spontaneous preterm birth | 36 | |
| Kristensen70 | 1995 | Denmark | 13,764 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | First antenatal appointment | Previous spontaneous preterm birth | 37 | |
| Berkowitz63 | 1998 | USA | 13,197 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | First antenatal appointment | Previous spontaneous preterm birth | 37 | |
| Carr-Hill65 | 1985 | UK |
6072a 1463b |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | First antenatal appointment | One, two previous spontaneous preterm birth | 37 | |
| deCarvalho66 | 2005 | Brazil | 1958 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | First antenatal appointment | Previous spontaneous preterm birth | 34 | |
| Ancel62 | 1999 | France | 13,292 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | First antenatal appointment | Previous spontaneous preterm birth | 37 | |
| Weidinger71 | 1974 | Germany | 911 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | First antenatal appointment | One, two previous spontaneous preterm birth | 37 | |
| deHaas67 | 1991 | USA | 420 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | First antenatal appointment | Previous spontaneous preterm birth | 37 |
| Authors | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | spec | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goldenberg68 | 85 | 278 | 119 | 1229 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.49 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.83 | 2.26 | 1.86 | 2.74 | 0.72 | 0.64 | 0.81 |
| aGoldenberg68 | 55 | 308 | 32 | 1316 | 0.63 | 0.52 | 0.73 | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.83 | 3.33 | 2.76 | 4.03 | 0.45 | 0.34 | 0.60 |
| bIams69 | 15 | 83 | 67 | 1117 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 2.64 | 1.60 | 4.37 | 0.88 | 0.79 | 0.97 |
| cIams69 | 27 | 149 | 55 | 1051 | 0.33 | 0.23 | 0.44 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 2.65 | 1.88 | 3.74 | 0.77 | 0.66 | 0.89 |
| cIams69 | 55 | 323 | 27 | 877 | 0.67 | 0.56 | 0.77 | 0.73 | 0.70 | 0.76 | 2.49 | 2.09 | 2.98 | 0.45 | 0.33 | 0.61 |
| Botsis64 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 83 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.41 | 0.89 | 0.81 | 0.95 | 0.85 | 0.12 | 5.99 | 1.02 | 0.83 | 1.24 |
| Kristensen70 | 55 | 433 | 241 | 13,035 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 5.78 | 4.47 | 7.46 | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.89 |
| Berkowitz63 | 214 | 1049 | 465 | 11,469 | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.35 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 3.76 | 3.32 | 4.26 | 0.75 | 0.71 | 0.79 |
| eCarr-Hill65 | 76 | 418 | 261 | 537 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.27 | 0.56 | 0.53 | 0.59 | 0.52 | 0.42 | 0.64 | 1.38 | 1.27 | 1.49 |
| fCarr-Hill65 | 8 | 17 | 57 | 1381 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 10.12 | 4.54 | 22.59 | 0.89 | 0.81 | 0.97 |
| deCarvalho66 | 25 | 155 | 41 | 1737 | 0.38 | 0.26 | 0.51 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 4.62 | 3.28 | 6.52 | 0.68 | 0.56 | 0.82 |
| Ancel62 | 850 | 526 | 4477 | 7439 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 2.42 | 2.18 | 2.68 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.91 |
| eWeidinger71 | 73 | 18 | 370 | 450 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.20 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 4.28 | 2.60 | 7.06 | 0.87 | 0.83 | 0.91 |
| fWeidinger71 | 25 | 4 | 370 | 450 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 7.18 | 2.52 | 20.46 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.97 |
| deHaas62 | 21 | 14 | 119 | 266 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.22 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 3.00 | 1.57 | 5.72 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.96 |
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Study designs | Inclusion | Exclusion | Testing gestation (weeks) | Frequency of testing | Threshold | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Leveno77 | 1986 | USA | 185 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinded Test described |
Low risk pregnancy | 26–30 | Single | 2 cm dilated | < 34 | |
| Parikh79 | 1961 | India | 463 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Pre-eclampsia, infection, placenta praevia, previous history of miscarriages | 24–36 | Biweekly | Admit digit at internal os | < 37 |
| Iams76 | 2002 | USA | 270 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Women who had received or were scheduled to receive an ambulatory monitor or tocolytic medication or to undergo cerclage or were complicated by placenta praevia or a major fetal anomaly detected by ultrasonography. Women who did not have telephones were not enrolled, because the transmission of data collected by the monitoring system required a telephone | < 35 | Quads | Bishop score changes | < 35 |
| Stubbs81 | 1986 | USA | 108 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Uterine or fetal anomaly, previous history of IUGR, spontaneous preterm birth, or cone biopsy, PPROM, history of second-trimester miscarriage | 28, 32 and 34 | Thrice | 1 cm internal os dilatation, 30% effacement | < 37 |
| Chambers74 | 1990 | France | 5066 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Low-risk pregnancy | 28 and < 37 | Biweekly | < 1 cm long cervix at 28 weeks, > 1 cm internal os dilatation before 37 weeks | < 37 | |
| Blondel73 | 1990 | France | 3159 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies able to attend antenatal clinic at 25–28 and 29–31 weeks’ gestation, divided into nulliparous and multiparous groups | Unknown gestation, iatrogenic preterm delivery | 25–28, 29–31 | Twice | 1 cm internal os dilatation, 1 cm long cervix, mid-position, soft cervix | < 37 |
| Newman78 | 1997 | USA | 2916 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | 22–24, 26–29 | Twice | Bishop score ≥ 4 or cervical score < 1.5 | < 35 | |
| Schaffner80 | 1966 | USA | 83 |
Cohort Blinded Test described |
All pregnant women seen at routine antenatal clinic between 28–32 weeks’ gestation, divided into nulliparous and multiparous groups | Operative cervical procedure, threatened or chronic miscarriage, hormone administration during pregnancy, PPROM, previous CS, uncertain dates | 28–32 | Single | 2–3 cm dilated | < 37 |
| Chhabra75 | 1991 | India | 75 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Polyhydramnios, pre-eclampsia, vaginal bleeding, previous bad obstetrics history or history of preterm birth | 28–28 | Single | Central cervix position: ≥ 2.6, ≥ 1.5 cm long and posterior cervix position: ≥ 2.6, ≥ 1.5 cm long | < 37 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Onderoglu82 | 1997 | Turkey | 90 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singletons, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm, absence of fetal and maternal complication | 25–36 | Single | > 2 cm dilated, > 40% effacement | < 37 | |
| Authors | Testing gestation (weeks) | Threshold | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR- | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||||
| Leveno77 | 26–30 | 2 cm dilated | 4 | 11 | 3 | 167 | 0.57 | 0.18 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.97 | 9.25 | 3.91 | 21.85 | 0.46 | 0.19 | 1.08 |
| Parikh79 | 24–36 | Admit finger at internal os | 28 | 174 | 29 | 232 | 0.49 | 0.36 | 0.63 | 0.57 | 0.52 | 0.62 | 1.15 | 0.86 | 1.53 | 0.89 | 0.68 | 1.16 |
| Stubbs81 | 34 | 30% effacement | 2 | 22 | 2 | 104 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 0.93 | 0.83 | 0.75 | 0.89 | 2.86 | 1.00 | 8.19 | 0.61 | 0.23 | 1.62 |
| Stubbs81 | 32 | 30% effacement | 5 | 23 | 5 | 103 | 0.50 | 0.19 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.74 | 0.88 | 2.74 | 1.33 | 5.64 | 0.61 | 0.33 | 1.14 |
| Stubbs81 | 28 | 1 cm internal os | 2 | 15 | 6 | 85 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.76 | 0.91 | 1.67 | 0.46 | 6.04 | 0.88 | 0.59 | 1.33 |
| Stubbs81 | 32 | 1 cm internal os | 4 | 28 | 6 | 98 | 0.40 | 0.12 | 0.74 | 0.78 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 1.80 | 0.79 | 4.11 | 0.77 | 0.46 | 1.29 |
| Stubbs81 | 28 | 30% effacement | 0 | 9 | 8 | 91 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.37 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.96 | 0.59 | 0.04 | 9.34 | 1.04 | 0.88 | 1.24 |
| Stubbs81 | 34 | 1 cm internal os | 3 | 51 | 1 | 75 | 0.75 | 0.19 | 0.99 | 0.60 | 0.50 | 0.68 | 1.85 | 1.01 | 3.39 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 2.31 |
| Chambers74 | < 37 | 1 cm internal os | 65 | 846 | 109 | 4046 | 0.37 | 0.30 | 0.45 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.84 | 2.16 | 1.77 | 2.64 | 0.76 | 0.67 | 0.85 |
| Chambers74 | 28 | 1 cm long cervix | 29 | 487 | 109 | 4046 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 1.96 | 1.40 | 2.73 | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.97 |
| Chambers74 | < 37 | Combined | 30 | 146 | 109 | 4046 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 6.20 | 4.35 | 8.84 | 0.81 | 0.74 | 0.89 |
| aBlondel73 | 29–31 | 1 cm long cervix | 26 | 228 | 92 | 2271 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.31 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 2.42 | 1.68 | 3.47 | 0.86 | 0.78 | 0.95 |
| aBlondel73 | 25–28 | 1 cm long cervix | 22 | 149 | 140 | 2848 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.20 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 2.73 | 1.80 | 4.15 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.97 |
| aBlondel73 | 25–28 | Mid-position cervix | 45 | 520 | 117 | 2476 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.35 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 1.60 | 1.23 | 2.08 | 0.87 | 0.79 | 0.96 |
| aBlondel73 | 29–31 | Mid-position cervix | 34 | 427 | 84 | 2072 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.38 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 1.69 | 1.25 | 2.27 | 0.86 | 0.76 | 0.96 |
| aBlondel73 | 29–31 | 1 cm internal os | 25 | 135 | 386 | 2071 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.66 | 1.50 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 1.03 |
| aBlondel73 | 29–31 | Soft cervix | 103 | 1742 | 15 | 757 | 0.87 | 0.80 | 0.93 | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 1.25 | 1.16 | 1.35 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.68 |
| aBlondel73 | 25–28 | 1 cm internal os | 21 | 48 | 139 | 2950 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 8.20 | 5.03 | 13.35 | 0.88 | 0.83 | 0.94 |
| aBlondel73 | 25–28 | Soft cervix | 130 | 1870 | 30 | 1129 | 0.81 | 0.74 | 0.87 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.39 | 1.30 | 1.20 | 1.41 | 0.50 | 0.36 | 0.69 |
| bBlondel73 | 29–31 | 1 cm long cervix | 14 | 130 | 56 | 1509 | 0.20 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 2.52 | 1.53 | 4.14 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 0.98 |
| bBlondel73 | 25–28 | Soft cervix | 95 | 1434 | 21 | 616 | 0.82 | 0.74 | 0.88 | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 1.17 | 1.07 | 1.28 | 0.60 | 0.41 | 0.89 |
| bBlondel73 | 25–28 | Mid-position cervix | 30 | 384 | 88 | 1664 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.34 | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.83 | 1.36 | 0.98 | 1.87 | 0.92 | 0.82 | 1.02 |
| bBlondel73 | 25–28 | 1 cm long cervix | 12 | 96 | 103 | 1955 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.18 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 2.23 | 1.26 | 3.94 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 1.00 |
| bBlondel73 | 29–31 | Soft cervix | 59 | 1242 | 11 | 397 | 0.84 | 0.74 | 0.92 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 1.11 | 1.00 | 1.24 | 0.65 | 0.37 | 1.12 |
| bBlondel73 | 29–31 | 1 cm internal os | 20 | 151 | 49 | 1489 | 0.29 | 0.19 | 0.41 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 3.15 | 2.11 | 4.69 | 0.78 | 0.67 | 0.91 |
| bBlondel73 | 25–28 | 1 cm internal os | 17 | 59 | 98 | 1992 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 5.14 | 3.10 | 8.52 | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.95 |
| bBlondel73 | 29–31 | Mid-position cervix | 16 | 292 | 50 | 1351 | 0.24 | 0.15 | 0.36 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.84 | 1.36 | 0.88 | 2.12 | 0.92 | 0.80 | 1.06 |
| aSchaffner80 | 28–32 | 2–3 cm dilated | 0 | 12 | 5 | 56 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 0.82 | 0.71 | 0.91 | 0.46 | 0.03 | 6.85 | 1.12 | 0.86 | 1.46 |
| bSchaffner80 | 28–32 | 2–3cm dilated | 5 | 60 | 10 | 141 | 0.33 | 0.12 | 0.62 | 0.70 | 0.63 | 0.76 | 1.12 | 0.53 | 2.36 | 0.95 | 0.66 | 1.37 |
| Chhabra75 | 28 | Central 1.5 cm long cervix | 5 | 0 | 36 | 34 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 9.17 | 0.52 | 160.08 | 0.88 | 0.78 | 1.00 |
| Chhabra75 | 28 | Posterior 2.6 cm long cervix | 1 | 4 | 6 | 54 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.58 | 0.93 | 0.83 | 0.98 | 2.07 | 0.27 | 16.03 | 0.92 | 0.67 | 1.26 |
| Chhabra75 | 28 | Central 2.6 cm long cervix | 24 | 5 | 17 | 29 | 0.59 | 0.42 | 0.74 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 0.95 | 3.98 | 1.70 | 9.31 | 0.49 | 0.33 | 0.72 |
| Chhabra75 | 28 | Posterior 1.5 cm long cervix | 7 | 57 | 0 | 1 | 1.00 | 0.59 | 1.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.96 | 0.80 | 1.16 | 2.46 | 0.11 | 55.35 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||||
| Onderoglu82 | 25–36 | 2 cm dilated cervix | 21 | 16 | 11 | 42 | 0.66 | 0.47 | 0.81 | 0.72 | 0.59 | 0.83 | 2.38 | 1.46 | 3.87 | 0.47 | 0.29 | 0.79 |
| Onderoglu82 | 25–36 | 40% effacement | 20 | 18 | 12 | 40 | 0.63 | 0.44 | 0.79 | 0.69 | 0.55 | 0.80 | 2.01 | 1.26 | 3.22 | 0.54 | 0.34 | 0.88 |
| Authors | Year | n | Study designs | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | Testing gestation (weeks’ gestation) | Reference standards (weeks’ gestation)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | |||||||
| Ruiz105 | 2001 | 78 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Asymptomatic women | < 18 or > 40 years old, Rh iso-immunisation, multiple gestation, cervical cerclage, use of tocolytic agents in the current pregnancy, maternal medical disorders, non-English speaking, > 28 weeks’ gestation at enrolment, misses > 1 monthly antenatal check-up |
23–26, 27–30 |
< 37 weeks |
| Arinami94 | 1999 | 438 |
Prospective Consecutive Test described |
Singleton pregnancies without medical or obstetrical complications | None stated | 26–28 |
< 34 weeks < 37 weeks |
| Goldenberg96 | 1996 | 2929 |
Prospective Blind Test described |
Singleton pregnancies |
Placenta praevia Fetal anomalies |
22, 24, 26, 28, 30 | < 34 weeks |
| Goldenberg97 | 1997 | 1870 |
Prospective Blind Test described |
Singleton pregnancies of women who are not randomised to treatment for Trichomonas vaginalis or bacterial vaginosis | None stated | 8–22 | < 35 weeks |
| Goldenberg83 | 2000 | 6508 |
Prospective Blind Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | None stated | 8–22 |
< 28 weeks < 32 weeks < 35 weeks < 37 weeks |
| Hux98 | 1995 | 54 |
Prospective Blind Test described |
Intact membrane and undilated cervix | Candida infection, fetal anomalies, vaginal bleeding, placenta praevia, and threatened preterm labour | 26–29 | < 37 weeks |
| Heath88 | 2000 | 5146 |
Prospective Consecutive Blind Test described |
Singleton pregnancies of women attending an inner city antenatal clinic | Fetal abnormalities | 22–24 | < 33 weeks |
| Chang95 | 1997 | 234 |
Prospective Blind Test described |
Singleton pregnancies without previous history of spontaneous preterm labour or birth Intact membrane |
Vaginal bleeding, pre-eclampsia Placenta praevia Uncertain date Fetal anomaly |
28 |
< 34 weeks < 37 weeks |
| Faron87 | 1997 | 155 |
Prospective Consecutive Blind Test described |
All asymptomatic women in antenatal clinic with known gestation | Vaginal bleeding | 24–33 | < 37 weeks |
| Hellemans89 | 1995 | 133 |
Blind Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Low-risk singleton pregnancies Intact membrane |
Placenta praevia Vaginal bleeding Cervical dilatation > 1 cm or cervical cerclage Threatened preterm labour < 26 weeks, unknown date |
26–36 | < 37 weeks |
| Garcia101 | 1999 | 263 |
Blind Prospective Test described |
Low-risk singleton Intact membrane |
Cerclage | 24–37 |
< 32 weeks < 37 weeks |
| Greenhagen102 | 1996 | 108 |
Blind Prospective Test described |
Low-risk singleton pregnancies Intact membrane |
Previous history of spontaneous preterm labour or birth Vaginal bleeding Fetal anomaly |
24–34 | < 37 weeks |
| DiStefano100 | 1999 | 60 |
Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies Intact membrane |
Previous history of spontaneous preterm labour or birth Vaginal bleeding Fetal anomaly Cervical cerclage Genital infection Maternal or fetal complications during gestation and/or examination |
24–36 | < 37 weeks |
| Crane99 | 1999 | 140 |
Blind Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies Intact membrane |
Cerclage Fetal anomalies or death Vaginal bleeding, recently treated bacterial vaginosis |
20–24 | < 37 weeks |
| Inglis103 | 1994 | 73 |
Blind Prospective Test described |
Intact membrane | Fetal anomalies, placenta praevia, genital or urinary infection, use of antibiotics in the preceding 7 days | < 37 | < 37 weeks |
| Lockwood104 | 1993 | 429 |
Blind Prospective Test described |
Asymptomatic women from an inner city antenatal clinic | Uncertain date, placenta praevia, iatrogenic preterm delivery | 24–37 |
< 28 days of testing < 37 weeks |
| Vercoustre106 | 1996 | 58 | Test described | Asymptomatic women | Coitus < 24 h and vaginal bleeding | 27–37 | < 37 weeks |
| Zamora84 | 2000 | 20 |
Blind Test described |
Asymptomatic pregnant women Intact membrane |
Coitus < 24 h Recent usage of vaginal pessary |
28–36 | < 37 weeks |
| Symptomatic women | |||||||
| Luzzi116 | 2003 | 133 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Preterm labour, intact membrane, < 3 cm cervical dilatation | Scheduled Caesarean section, induced delivery within 21 days of testing | 24–35 | < 7, < 14 and < 21 days of testing |
| Tekesin93 | 2005 | 170 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Blinded Test described |
Preterm labour, intact membrane, < 3 cm cervical dilatation | Multiple gestations, cervical manipulations (examination, intercourse, ultrasound), vaginal bleeding, major fetal anomaly, PPROM, cervical cerclage, suspected fetal asphyxia | 24–35 | < 7, < 14, < 21 days of testing and < 34 and < 37 weeks |
| Musaad123 | 2005 | 27 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Preterm labour, intact membrane, < 3 cm cervical dilatation | Vaginal bleeding | 24–33 | < 34, < 37 |
| Dolinska132 | 2005 | 115 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton, preterm labour, intact membrane, < 3 cm cervical dilatation, no cerclage | ✗ | 24–34 | < 37 |
| Topete127 | 2004 | 74 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Preterm labour, intact membrane, < 3 cm cervical dilatation | ✗ | 24–34 | < 37 |
| Foxman110 | 2004 | 139 |
Cohort Prospective |
✗ | ✗ | ✗ | < 7 |
| Hincz128 | 2002 | 82 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Preterm labour, intact membrane, < 3 cm cervical dilatation | Cerclage, clinical criteria of intrauterine infection, vaginal bleeding, IUGR, pre-eclampsia | 24–34 | < 37 |
| Sakai119 | 2003 | 116 |
Cohort Test described |
Preterm labour, intact membrane, < 4 cm cervical dilatation | PROM, multiple pregnancy, elective preterm delivery, pre-eclampsia, abruption, placenta praevia, maternal medical conditions | 20–36 | < 7 days of testing, and < 37 weeks |
| Closset109 | 2001 | 61 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Preterm labour, intact membrane, < 3 cm cervical dilatation | ✗ | 24–36 | < 7, < 14, < 21 days of testing, and < 37 weeks |
| Gomez112 | 2005 | 215 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Preterm labour, intact membrane, < 3 cm cervical dilatation | ✗ | 22–35 | < 48 h, < 7, < 14 days of testing and < 32, < 35 weeks |
| Hansen115 | 2004 | 41 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
>16 years of age, preterm labour, < 3 cm dilatation for primigravida and < 4 cm for multiparous | Multiple gestations, major fetal anomaly, vaginal bleeding, PPROM, cervical cerclage, suspected fetal asphyxia | 23–34 | < 7, < 14 days of testing, and <37 weeks |
| Stevens135 | 2004 | 185 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Preterm labour, intact membrane, ≥ 2 cm dilatation, ≥ 50% effacement | 24–34 | < 32, < 37 weeks | |
| LaShay90 | 2000 | 118 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Blind Test described |
Singleton pregnancies Intact membrane Cervical dilatation < 3 cm |
Coitus or digital vaginal examination within 24 h Vaginal bleeding Placenta praevia Placental abruption Polyhydramnios Pre-eclampsia Known uterine or fetal abnormalities |
24–34 |
< 48 h < 7 days < 37 weeks |
| Senden92 | 1996 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Blind Test described |
Singleton pregnancies Intact membrane Cervical dilatation < 4 cm |
Vaginal bleeding Clinical chorioamnionitis Diabetes mellitus |
25–35 | < 7 days | |
| Bartnicki107 | 1996 | 112 |
Cohort Prospective Blind Test described |
Intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 2 cm | 22–35 |
< 7 days < 14 days < 21 days < 28 days < 34 weeks |
|
| Benattar108 | 1997 | 124 |
Cohort Prospective Blind Test described |
Singleton and twin pregnancies intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm |
Vaginal bleeding Coitus < 24 h |
24–36 |
< 7 days < 14 days < 21 days < 32 weeks < 34 weeks |
| Malak117 | 1996 | 112 |
Cohort Prospective Blind Test described |
Singleton pregnancies Intact membrane Cervical dilatation < 2 cm |
Placenta praevia Vaginal bleeding Coitus < 24 h |
24–34 |
< 7 days < 14 days < 21 days < 37 weeks |
| McKenna118 | 1999 | 50 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Cervical dilatation < 3 cm |
Coitus < 24 h Vaginal digital examination or transvaginal ultrasound scan procedure Cervical cerclage Uterine anomalies Placenta praevia Placental abruption |
22–34 |
< 7 days < 14 days < 37 weeks |
| Peaceman86 | 1997 | 725 |
Cohort Prospective Blind Test described |
Singleton, twin pregnancies and one triplet pregnancy Intact membrane Cervical dilatation < 3 cm |
Placenta praevia Cerclage Trauma leading to preterm labour |
24–34 |
< 7 days < 14 days < 37 weeks |
| Iams113 | 1995 | 192 |
Cohort Prospective Blind Test described |
Intact membrane Cervical dilatation < 3 cm |
Placenta praevia Cerclage Uterine anomalies Vaginal bleeding |
24–34 |
< 7 days < 37 weeks |
| Giles111 | 2000 | 150 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Intact membrane |
Vaginal bleeding Coitus < 24 h Recent digital vaginal examination |
24–34 |
< 7 days < 36 weeks |
| Lopez114 | 2000 | 85 |
Cohort Retrospective |
Singleton pregnancies Intact membrane Cervical dilatation < 3 cm |
Uncertain date Lost to follow up Incomplete data |
24–35 |
< 7 days < 14 days < 34 weeks < 37 weeks |
| Cox (abstract)121 | 1995 | 175 | Test described |
Intact membrane Cervical dilatation < 3 cm |
None stated | 24–34 | < 37 weeks |
| Chuileannain124 | 1998 | 50 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies Intact membrane Cervical dilatation < 2 cm |
Placenta praevia Placental abruption Cerclage Fetal anomalies |
< 34 | < 34 weeks |
| Goffeng122 | 1997 | 63 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies with intact membrane |
Pre-eclampsia Uterine or cervical abnormalities Placenta praevia, placental abruption Fetal anomalies Diabetes mellitus |
23–34 |
< 34 weeks < 37 weeks |
| Parker125 | 1995 | 36 |
Cohort Prospective Blind Test described |
Singleton pregnancies Intact membrane Cervical dilatation < 2 cm |
Placenta praevia Placental abruption Cerclage Fetal anomalies Coitus < 24 h |
20–34 | < 34 weeks |
| Burrus120 | 1995 | 37 |
Cohort Prospective Blind Test described |
Symptomatic women in their first pregnancy Intact membrane Cervical dilatation < 3 cm and changing, no contraindication to tocolytic |
Amnionitis Placental abruption |
< 34 | < 37 weeks |
| Grandi85 | 1996 | 26 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Blind Test described |
Singleton pregnancies Intact membrane Cervical dilatation < 2 cm |
Placenta praevia Placental abruption Fetal anomalies Coitus < 24 h Iatrogenic preterm labour |
24–36 | < 37 |
| Inglis103 | 1994 | 38 |
Cohort Prospective Blind Test described |
Singleton pregnancies Intact membrane |
Fetal anomalies Placenta praevia Genital or urinary infection Use of antibiotics in the preceding 7 days |
< 37 | < 37 |
| Irion129 | 1995 | 64 |
Cohort Prospective Blind Test described |
Intact membrane Cervical dilatation < 2 cm |
Fetal anomalies Vaginal bleeding Coitus < 24 h Iatrogenic preterm delivery |
24–36 | < 37 |
| Langer130 | 1997 | 61 |
Cohort Prospective Blind Test described |
Intact membrane |
Vaginal bleeding Coitus < 24 h Progressive cervical dilatation Abnormal fetal heart rate monitoring |
24–34 | < 37 |
| Lockwood104 | 1991 | 117 |
Cohort Prospective Blind Test described |
Intact membrane |
Fetal anomalies Placenta praevia Coitus < 24 h Intrauterine growth restriction Fetal distress Previous pregnancy terminated due to severe pre-eclampsia |
25–35 | < 37 |
| Morrison91 | 1993 | 28 |
Cohort Blind Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies Intact membrane |
Uterine or cervical abnormalities Vaginal bleeding Placenta praevia Suspected placental abruption Coitus or douching < 24 h Diabetes mellitus Unknown date Pre-eclampsia < 15 years old |
24–34 | < 37 |
| Rizzo133 | 1997 | 106 |
Cohort Prospective Blind Test described |
Singleton pregnancies Intact membrane Cervical dilatation < 3 cm |
Fetal or maternal complications Urinary or genital infection Use of antibiotic in the preceding 14 days |
24–36 | < 37 |
| Rozenberg134 | 1997 | 76 |
Cohort Prospective Blind Test described |
Singleton pregnancies Intact membrane Cervical dilatation < 2 cm |
Gestation < 24 or > 34 weeks Cerclage Placenta praevia Placental abruption Iatrogenic preterm delivery |
24–34 | < 37 |
| Calda126 | 1995 | 84 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Intact membrane | 24–34 | < 36 | |
| Mansouri131 | 1996 | 90 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Intact membrane |
Vaginal bleeding Coitus < 24 h |
24–34 | < 37 |
| Vercoustre106 | 1996 | 86 | Test described | Singleton pregnancies with threatened preterm labour |
Coitus < 24 h Vaginal bleeding |
< 37 | < 37 |
| Vetr136 | 1996 | 46 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Intact membrane |
Fetal anomalies Placenta praevia Vaginal bleeding Intrauterine growth restriction Fetal distress Diabetes mellitus Pre-eclampsia |
25–36 | < 37 |
| Authors | Outcome | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR-_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tekesin93 | 7 | 9 | 37 | 2 | 122 | 0.82 | 0.48 | 0.98 | 0.77 | 0.69 | 0.83 | 3.52 | 2.36 | 5.23 | 0.24 | 0.07 | 0.83 |
| Closset109 | 7 | 5 | 11 | 1 | 44 | 0.83 | 0.36 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.67 | 0.90 | 4.17 | 2.20 | 7.89 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 1.25 |
| LaShay90 | 7 | 3 | 10 | 2 | 103 | 0.60 | 0.15 | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.96 | 6.78 | 2.68 | 17.16 | 0.44 | 0.15 | 1.29 |
| Luzzi116 | 7 | 4 | 34 | 3 | 92 | 0.57 | 0.18 | 0.90 | 0.73 | 0.64 | 0.81 | 2.12 | 1.05 | 4.28 | 0.59 | 0.25 | 1.39 |
| Senden92 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 20 | 0.80 | 0.28 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 0.63 | 0.95 | 4.80 | 1.77 | 13.00 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 1.40 |
| Bartnicki107 | 7 | 3 | 33 | 1 | 79 | 0.75 | 0.19 | 0.99 | 0.71 | 0.61 | 0.79 | 2.55 | 1.35 | 4.80 | 0.35 | 0.06 | 1.94 |
| Benattar108 | 7 | 8 | 11 | 1 | 104 | 0.89 | 0.52 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 0.84 | 0.95 | 9.29 | 5.06 | 17.06 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.78 |
| Gomez112 | 7 | 18 | 34 | 10 | 153 | 0.64 | 0.44 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.87 | 3.54 | 2.34 | 5.33 | 0.44 | 0.26 | 0.72 |
| Hansen115 | 7 | 2 | 7 | 1 | 31 | 0.67 | 0.09 | 0.99 | 0.82 | 0.66 | 0.92 | 3.62 | 1.28 | 10.27 | 0.41 | 0.08 | 2.04 |
| Iams113 | 7 | 13 | 32 | 1 | 146 | 0.93 | 0.66 | 1.00 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.87 | 5.17 | 3.66 | 7.30 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.58 |
| Malak117 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 2 | 92 | 0.80 | 0.44 | 0.97 | 0.90 | 0.83 | 0.95 | 8.16 | 4.20 | 15.87 | 0.22 | 0.06 | 0.77 |
| McKenna118 | 7 | 5 | 13 | 1 | 35 | 0.83 | 0.36 | 1.00 | 0.73 | 0.58 | 0.85 | 3.08 | 1.71 | 5.53 | 0.23 | 0.04 | 1.38 |
| Peaceman86 | 7 | 19 | 123 | 2 | 581 | 0.90 | 0.70 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 0.80 | 0.85 | 5.18 | 4.19 | 6.40 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.43 |
| Plaut717 | 7 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 86 | 0.50 | 0.01 | 0.99 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.96 | 5.88 | 1.26 | 27.30 | 0.55 | 0.14 | 2.19 |
| Giles111 | 7 | 11 | 34 | 5 | 100 | 0.69 | 0.41 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 0.66 | 0.82 | 2.71 | 1.75 | 4.21 | 0.42 | 0.20 | 0.87 |
| Sakai119 | 7 | 11 | 27 | 7 | 71 | 0.61 | 0.36 | 0.83 | 0.72 | 0.63 | 0.81 | 2.22 | 1.36 | 3.62 | 0.54 | 0.30 | 0.97 |
| Foxman110 | 7 | 6 | 25 | 1 | 107 | 0.86 | 0.42 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.73 | 0.87 | 4.53 | 2.84 | 7.20 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 1.08 |
| Lopez114 | 7 | 8 | 12 | 1 | 64 | 0.89 | 0.52 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 0.74 | 0.92 | 5.63 | 3.19 | 9.94 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.84 |
| Musaad123 | 34 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 21 | 0.83 | 0.36 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.61 | 0.93 | 4.33 | 1.82 | 10.29 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 1.25 |
| Tekesin93 | 34 | 20 | 26 | 8 | 116 | 0.71 | 0.51 | 0.87 | 0.82 | 0.74 | 0.88 | 3.90 | 2.57 | 5.93 | 0.35 | 0.19 | 0.63 |
| Burrus120 | 34 | 23 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 0.88 | 0.70 | 0.98 | 0.45 | 0.17 | 0.77 | 1.62 | 0.93 | 2.83 | 0.25 | 0.07 | 0.88 |
| Goffeng122 | 34 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 45 | 0.64 | 0.31 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.74 | 0.94 | 4.73 | 2.08 | 10.75 | 0.42 | 0.19 | 0.93 |
| Parker125 | 34 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 25 | 0.86 | 0.42 | 1.00 | 0.78 | 0.60 | 0.91 | 3.92 | 1.90 | 8.06 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 1.13 |
| Chuileannain124 | 34 | 9 | 11 | 1 | 49 | 0.90 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 0.82 | 0.70 | 0.90 | 4.91 | 2.77 | 8.70 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.79 |
| Cox121 | 34 | 3 | 22 | 11 | 139 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 0.51 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.91 | 1.57 | 0.53 | 4.60 | 0.91 | 0.69 | 1.20 |
| Lopez114 | 34 | 11 | 9 | 4 | 61 | 0.73 | 0.45 | 0.92 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 0.94 | 5.70 | 2.88 | 11.28 | 0.31 | 0.13 | 0.71 |
| Tekesin93 | 37 | 31 | 15 | 4 | 120 | 0.89 | 0.73 | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 0.94 | 7.97 | 4.88 | 13.03 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.32 |
| Closset109 | 37 | 12 | 4 | 11 | 34 | 0.52 | 0.31 | 0.73 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 0.97 | 4.96 | 1.81 | 13.56 | 0.53 | 0.34 | 0.83 |
| Grandi85 | 37 | 4 | 9 | 4 | 9 | 0.50 | 0.16 | 0.84 | 0.50 | 0.26 | 0.74 | 1.00 | 0.43 | 2.30 | 1.00 | 0.43 | 2.30 |
| Hincz128 | 37 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 63 | 0.71 | 0.42 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.98 | 9.71 | 3.92 | 24.05 | 0.31 | 0.13 | 0.71 |
| LaShay90 | 37 | 10 | 8 | 24 | 76 | 0.29 | 0.15 | 0.47 | 0.90 | 0.82 | 0.96 | 3.09 | 1.33 | 7.15 | 0.78 | 0.62 | 0.98 |
| Morrison91 | 37 | 9 | 5 | 1 | 13 | 0.90 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 0.72 | 0.47 | 0.90 | 3.24 | 1.50 | 7.02 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.91 |
| Musaad123 | 37 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 15 | 0.50 | 0.19 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.59 | 0.96 | 3.00 | 0.90 | 10.01 | 0.60 | 0.31 | 1.15 |
| Bartnicki107 | 37 | 27 | 7 | 13 | 65 | 0.68 | 0.51 | 0.81 | 0.90 | 0.81 | 0.96 | 6.94 | 3.33 | 14.49 | 0.36 | 0.23 | 0.57 |
| Benattar108 | 37 | 9 | 9 | 16 | 90 | 0.36 | 0.18 | 0.57 | 0.91 | 0.83 | 0.96 | 3.96 | 1.76 | 8.93 | 0.70 | 0.52 | 0.95 |
| Goffeng122 | 37 | 10 | 4 | 18 | 31 | 0.36 | 0.19 | 0.56 | 0.89 | 0.73 | 0.97 | 3.13 | 1.10 | 8.91 | 0.73 | 0.54 | 0.98 |
| Hansen115 | 37 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 26 | 0.33 | 0.07 | 0.70 | 0.81 | 0.64 | 0.93 | 1.78 | 0.55 | 5.74 | 0.82 | 0.50 | 1.34 |
| Iams113 | 37 | 27 | 18 | 35 | 112 | 0.44 | 0.31 | 0.57 | 0.86 | 0.79 | 0.92 | 3.15 | 1.88 | 5.26 | 0.66 | 0.52 | 0.82 |
| Inglis103 | 37 | 7 | 2 | 9 | 20 | 0.44 | 0.20 | 0.70 | 0.91 | 0.71 | 0.99 | 4.81 | 1.15 | 20.18 | 0.62 | 0.39 | 0.97 |
| Irion129 | 37 | 15 | 11 | 7 | 31 | 0.68 | 0.45 | 0.86 | 0.74 | 0.58 | 0.86 | 2.60 | 1.45 | 4.66 | 0.43 | 0.23 | 0.82 |
| Langer130 | 37 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 35 | 0.56 | 0.31 | 0.78 | 0.81 | 0.67 | 0.92 | 2.99 | 1.41 | 6.32 | 0.55 | 0.32 | 0.93 |
| Lockwood104 | 37 | 49 | 10 | 11 | 47 | 0.82 | 0.70 | 0.90 | 0.82 | 0.70 | 0.91 | 4.66 | 2.62 | 8.28 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.38 |
| Malak117 | 37 | 17 | 5 | 10 | 109 | 0.63 | 0.42 | 0.81 | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 14.36 | 5.81 | 35.47 | 0.39 | 0.24 | 0.63 |
| Peaceman86 | 37 | 61 | 81 | 78 | 505 | 0.44 | 0.35 | 0.53 | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.89 | 3.17 | 2.41 | 4.18 | 0.65 | 0.56 | 0.76 |
| Rizzo133 | 37 | 40 | 12 | 9 | 45 | 0.82 | 0.68 | 0.91 | 0.79 | 0.66 | 0.89 | 3.88 | 2.31 | 6.52 | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.43 |
| Rozenberg134 | 37 | 14 | 17 | 6 | 39 | 0.70 | 0.46 | 0.88 | 0.70 | 0.56 | 0.81 | 2.31 | 1.41 | 3.76 | 0.43 | 0.22 | 0.86 |
| Stevens136 | 37 | 32 | 20 | 37 | 86 | 0.46 | 0.34 | 0.59 | 0.81 | 0.72 | 0.88 | 2.46 | 1.54 | 3.93 | 0.66 | 0.52 | 0.84 |
| Calda126 | 37 | 19 | 13 | 2 | 50 | 0.90 | 0.70 | 0.99 | 0.79 | 0.67 | 0.89 | 4.38 | 2.65 | 7.26 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.45 |
| Giles111 | 37 | 12 | 33 | 7 | 99 | 0.63 | 0.38 | 0.84 | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.82 | 2.53 | 1.61 | 3.97 | 0.49 | 0.27 | 0.89 |
| Sakai119 | 37 | 26 | 12 | 36 | 42 | 0.42 | 0.30 | 0.55 | 0.78 | 0.64 | 0.88 | 1.89 | 1.06 | 3.37 | 0.75 | 0.58 | 0.96 |
| Vetr136 | 37 | 5 | 11 | 4 | 26 | 0.56 | 0.21 | 0.86 | 0.70 | 0.53 | 0.84 | 1.87 | 0.87 | 4.02 | 0.63 | 0.30 | 1.35 |
| Chuileannain124 | 37 | 13 | 7 | 1 | 49 | 0.93 | 0.66 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 0.76 | 0.95 | 7.43 | 3.66 | 15.08 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.54 |
| Dolinska132 | 37 | 28 | 8 | 10 | 69 | 0.74 | 0.57 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.81 | 0.95 | 7.09 | 3.58 | 14.04 | 0.29 | 0.17 | 0.50 |
| Mansouri131 | 37 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 53 | 0.52 | 0.31 | 0.72 | 0.82 | 0.70 | 0.90 | 2.82 | 1.49 | 5.31 | 0.59 | 0.39 | 0.90 |
| Topete127 | 37 | 24 | 4 | 10 | 36 | 0.71 | 0.53 | 0.85 | 0.90 | 0.76 | 0.97 | 7.06 | 2.72 | 18.34 | 0.33 | 0.19 | 0.56 |
| Vercoustre106 | 37 | 12 | 21 | 1 | 44 | 0.92 | 0.64 | 1.00 | 0.68 | 0.55 | 0.79 | 2.86 | 1.94 | 4.20 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.75 |
| Lopez114 | 37 | 17 | 3 | 31 | 34 | 0.35 | 0.22 | 0.51 | 0.92 | 0.78 | 0.98 | 4.37 | 1.38 | 13.80 | 0.70 | 0.56 | 0.88 |
| Authors | Outcome | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34 weeks’ gestation | |||||||||||||||||
| Arinami94 | 34 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 432 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.72 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 86.60 | 6.26 | 1198.92 | 0.80 | 0.52 | 1.24 |
| Heath88 | 34 | 15 | 167 | 30 | 4934 | 0.33 | 0.20 | 0.49 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 10.18 | 6.56 | 15.80 | 0.69 | 0.56 | 0.85 |
| Chang95 | 34 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 226 | 0.50 | 0.12 | 0.88 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 57.00 | 11.57 | 280.92 | 0.50 | 0.23 | 1.12 |
| Goldenberg96 | 34 | 13 | 144 | 33 | 1680 | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.43 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 3.58 | 2.20 | 5.82 | 0.78 | 0.65 | 0.93 |
| Goldenberg97 | 34 | 29 | 88 | 98 | 2714 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.31 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 7.27 | 4.97 | 10.63 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 0.88 |
| Goldenberg83 | 34 | 79 | 457 | 331 | 5641 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 2.57 | 2.07 | 3.19 | 0.87 | 0.83 | 0.92 |
| Hux98 | 34 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 45 | 0.75 | 0.19 | 0.99 | 0.90 | 0.78 | 0.97 | 7.50 | 2.74 | 20.51 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 1.52 |
| 37 weeks’ gestation | |||||||||||||||||
| Arinami94 | 37 | 1 | 1 | 15 | 421 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 26.38 | 1.73 | 402.99 | 0.94 | 0.83 | 1.07 |
| Crane99 | 37 | 1 | 34 | 8 | 97 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.81 | 0.43 | 0.07 | 2.78 | 1.20 | 0.93 | 1.54 |
| Faron87 | 37 | 4 | 6 | 11 | 134 | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.55 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.98 | 6.22 | 1.97 | 19.60 | 0.77 | 0.56 | 1.04 |
| Hellemans89 | 37 | 6 | 18 | 4 | 105 | 0.60 | 0.26 | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 4.10 | 2.11 | 7.95 | 0.47 | 0.22 | 1.00 |
| Chang95 | 37 | 3 | 2 | 15 | 214 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.41 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 18.00 | 3.21 | 100.86 | 0.84 | 0.68 | 1.03 |
| Garcia101 | 37 | 22 | 9 | 5 | 227 | 0.81 | 0.62 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 21.37 | 10.98 | 41.57 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.42 |
| Goldenberg96 | 37 | 118 | 418 | 675 | 5297 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 2.03 | 1.68 | 2.46 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.95 |
| Goldenberg97 | 37 | 24 | 133 | 144 | 1569 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.21 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 1.83 | 1.22 | 2.74 | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.99 |
| Greenhagen83 | 37 | 5 | 16 | 3 | 84 | 0.63 | 0.24 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.75 | 0.91 | 3.91 | 1.94 | 7.87 | 0.45 | 0.18 | 1.10 |
| Inglis103 | 37 | 2 | 11 | 9 | 51 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.52 | 0.82 | 0.70 | 0.91 | 1.02 | 0.26 | 4.01 | 0.99 | 0.74 | 1.34 |
| Lockwood104 | 37 | 30 | 108 | 19 | 272 | 0.61 | 0.46 | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.67 | 0.76 | 2.15 | 1.64 | 2.83 | 0.54 | 0.38 | 0.77 |
| Ruiz103 | 37 | 0 | 8 | 6 | 62 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.46 | 0.89 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 0.60 | 0.04 | 9.28 | 1.05 | 0.84 | 1.32 |
| DiStefano100 | 37 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 46 | 0.67 | 0.22 | 0.96 | 0.85 | 0.73 | 0.93 | 4.50 | 1.92 | 10.57 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 1.22 |
| Zamora84 | 37 | 4 | 13 | 1 | 15 | 0.80 | 0.28 | 0.99 | 0.54 | 0.34 | 0.72 | 1.72 | 0.95 | 3.11 | 0.37 | 0.06 | 2.23 |
| Vercoustre106 | 37 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 58 | 1.00 | 0.03 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 0.81 | 0.96 | 7.50 | 2.54 | 22.14 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 3.07 |
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Study designs | Inclusion | Exclusion | Testing gestation (weeks) | Frequency of testing | Thresholds | Outcome (weeks’ gestation)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||
| O’Brien137 | 1994 | USA | 40 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Asymptomatic antenatal women | Rupture of membrane, fetal anomalies, vaginal bleeding, contraindication to tocolysis | 24–32 | Single | 2.0 ng/ml | < 34 |
| Koca138 | 1999 | Turkey | 40 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies, threatened preterm labour | Rupture of membrane, fetal anomalies, contraindication to tocolysis | 24–32 | Single | 1.5 ng/ml | < 37 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Jotterand140 | 1997 | France | 64 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancies, threatened preterm labour | Rupture of membrane, fetal anomalies, vaginal bleeding, fetal distress, placenta praevia, contraindication to tocolysis | 21–34 | Single | 2.0 ng/ml | < 34, < 37 |
| O’Brien137 | 1994 | USA | 40 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Threatened preterm labour | Rupture of membrane, fetal anomalies, vaginal bleeding, contraindication to tocolysis | 24–32 | Single | 2.0 ng/ml | Within 7 and 14 days of testing, < 34, < 37 weeks |
| Leylek141 | 1997 | Turkey | 66 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies, threatened preterm labour | 29–36 | Single | 50 ng/ml | Within 12 days of testing and < 37 weeks | |
| Koca138 | 1999 | Turkey | 35 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies, threatened preterm labour | Rupture of membrane, fetal anomalies, contraindication to tocolysis | 24–32 | Single | 1.5 ng/ml | < 34, < 37 |
| Guvenal139 | 2001 | Turkey | 60 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies, threatened preterm labour | Rupture of membrane, fetal anomalies, contraindication to tocolysis, maternal hypertension, IUGR, fetal distress, placenta praevia | 24–36 | Single | 1.8 ng/ml | 37 |
| Authors | Outcome | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | |||||||||||||||||
| O’Brien137 | 34 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 37 | 0.50 | 0.01 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 19.00 | 1.76 | 205.15 | 0.51 | 0.13 | 2.06 |
| Koca138 | 37 | 5 | 9 | 1 | 25 | 0.83 | 0.36 | 1.00 | 0.74 | 0.56 | 0.87 | 3.15 | 1.62 | 6.12 | 0.23 | 0.04 | 1.37 |
| Symptomatic women | |||||||||||||||||
| O’Brien137 | 7 | 6 | 14 | 3 | 17 | 0.67 | 0.30 | 0.93 | 0.55 | 0.36 | 0.73 | 1.48 | 0.81 | 2.70 | 0.61 | 0.23 | 1.62 |
| O’Brien137 | 34 | 16 | 4 | 7 | 13 | 0.70 | 0.47 | 0.87 | 0.76 | 0.50 | 0.93 | 2.96 | 1.20 | 7.26 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 0.78 |
| Koca138 | 34 | 10 | 7 | 3 | 15 | 0.77 | 0.46 | 0.95 | 0.68 | 0.45 | 0.86 | 2.42 | 1.22 | 4.77 | 0.34 | 0.12 | 0.95 |
| Jotterand140 | 34 | 4 | 7 | 3 | 50 | 0.57 | 0.18 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.76 | 0.95 | 4.65 | 1.81 | 11.97 | 0.49 | 0.21 | 1.16 |
| O’Brien137 | 37 | 17 | 3 | 11 | 9 | 0.61 | 0.41 | 0.78 | 0.75 | 0.43 | 0.95 | 2.43 | 0.87 | 6.76 | 0.52 | 0.30 | 0.92 |
| Leylek141 | 37 | 19 | 0 | 15 | 32 | 0.56 | 0.38 | 0.73 | 1.00 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 36.77 | 2.31 | 584.80 | 0.45 | 0.31 | 0.65 |
| Koca138 | 37 | 14 | 3 | 6 | 12 | 0.70 | 0.46 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 0.52 | 0.96 | 3.50 | 1.22 | 10.02 | 0.38 | 0.18 | 0.77 |
| Guvenal139 | 37 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 50 | 0.50 | 0.16 | 0.84 | 0.96 | 0.87 | 1.00 | 13.00 | 2.83 | 59.76 | 0.52 | 0.26 | 1.04 |
| Jotterand140 | 37 | 5 | 6 | 11 | 42 | 0.31 | 0.11 | 0.59 | 0.88 | 0.75 | 0.95 | 2.50 | 0.88 | 7.10 | 0.79 | 0.56 | 1.11 |
| Authors | Year | n | Study design | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | Testing gestation (weeks’ gestation) | Reference standards (weeks’ gestation)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | |||||||
| Bittar144 | 2001 | 53 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Previous premature delivery, intact membrane, no vaginal bleeding, screened and treated for Trichomonas, Candida spp, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, group B streptococcus | Lost to follow-up | 24–34, 3-weekly | < 37 |
| Symptomatic women | |||||||
| Shine142 | 2001 | 32 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Threatened preterm labour, cervix < 2 cm dilated, intact membrane | 24–36 | < 34, < 37 | |
| Lembet146 | 2002 | 36 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Threatened preterm labour | Uterine anomaly, congenital fetal abnormality, intrauterine growth restriction, pre-eclampsia, vaginal bleeding | 20–36 | < 48 h, < 7 days, and < 37 |
| Choi148 | 2003 | 42 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Threatened preterm labour | 20–36 | < 37 | |
| Park149 | 2003 | 50 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Threatened preterm labour, cervix < 3 cm dilated, intact membrane | 24–34 | < 7 days, < 34, and < 37 | |
| Akercan147 | 2004 | 45 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Threatened preterm labour | Pre-eclampsia, ruptured membrane, vaginal bleeding, intrauterine growth restriction, congenital fetal abnormality, and uterine anomaly | 24–36 | < 37 |
| Kwek145 | 2004 | 47 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Threatened preterm labour | Antepartum haemorrhage, cervix > 3 cm dilated, contraindication to tocolysis, insertion of cervical cerclage | 24–34 | < 48 h, < 7 days, and < 36 |
| Elizur150 | 2005 | 35 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Threatened preterm labour | 24–35 | < 48 hours, < 7 days, < 34, and < 37 | |
| Halle152 | 1999 | 93 |
Cohort Test described |
Threatened preterm labour | 23–32 | < 37 | |
| Paternoster151 | 2005 | 135 | Cohort | Threatened preterm labour | Pre-eclampsia, ruptured membrane, vaginal bleeding, intrauterine growth restriction, congenital fetal abnormality, and uterine anomaly | Not stated | < 37 |
| Turnell143 | 2005 | 100 |
Cohort Consecutive |
Threatened preterm labour | Not stated | < 37 | |
| Authors | Year | Quality | TP | FP | FN | TN | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | LR+ (95% CI) | LR– (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 48 hours | ||||||||||
| Lembet146 | 2002 | 4 | 14 | 4 | 1 | 17 | 0.88 (0.62–0.98) | 0.81 (0.58–0.95) | 4.59 (1.87–11.31) | 0.15 (0.04–0.57) |
| Kwek145 | 2004 | 4 | 4 | 14 | 2 | 20 | 0.67 (0.22–0.96) | 0.59 (0.41–0.75) | 1.62 (0.81–3.24) | 0.57 (0.18–1.82) |
| Elizur150 | 2005 | 4 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 29 | 0.50 (0.01–0.99) | 0.79 (0.63–0.90) | 2.38 (1.52–10.82) | 0.63 (0.16–2.56) |
| Summary LRs | 2.53 (1.17–5.48) | 0.32 (0.15–0.66) | ||||||||
| 7 days | ||||||||||
| Lembet146 | 2002 | 4 | 15 | 3 | 1 | 17 | 0.94 (0.70–1.00) | 0.85 (0.62–0.97) | 6.25 (2.19–17.88) | 0.07 (0.01–0.49) |
| Park149 | 2003 | 3 | 11 | 10 | 2 | 27 | 0.85 (0.55–0.98) | 0.73 (0.56–0.86) | 3.13 (1.76–5.58) | 0.21 (0.06–0.77) |
| Kwek145 | 2004 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 20 | 0.83 (0.52–0.98) | 0.71 (0.51–0.87) | 2.92 (1.54–5.52) | 0.23 (0.06–0.84) |
| Elizur150 | 2005 | 4 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 29 | 0.50 (0.01–0.99) | 0.79 (0.63–0.90) | 2.38 (0.52–10.82) | 0.63 (0.16–2.56) |
| Summary LRs | 3.29 (2.24–4.83) | 0.20 (0.10–0.41) | ||||||||
| 34 weeks | ||||||||||
| Shine142 | 2001 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 0 | 19 | 1.00 (0.48–1.00) | 0.70 (0.50–0.86) | 3.02 (1.64–5.56) | 0.12 (0.01–1.72) |
| Park149 | 2003 | 3 | 9 | 12 | 2 | 27 | 0.82 (0.48–0.98) | 0.69 (0.52–0.83) | 2.66 (1.54–4.60) | 0.26 (0.07–0.94) |
| Elizur150 | 2005 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 29 | 1.00 (0.03–1.00) | 0.83 (0.66–0.93) | 4.15 (1.44–11.99) | 0.31 (0.03–3.38) |
| Summary LRs | 2.96 (2.02–4.33) | 0.22 (0.08–0.64) | ||||||||
| 37 weeks | ||||||||||
| Halle152 | 1999 | 2 | 22 | 11 | 6 | 54 | 0.79 (0.59–0.92) | 0.83 (0.72–0.91) | 4.64 (2.62–8.23) | 0.26 (0.13–0.53) |
| Shine142 | 2001 | 3 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 17 | 0.80 (0.44–0.97) | 0.77 (0.55–0.92) | 3.52 (1.53–8.08) | 0.26 (0.07–0.91) |
| Lembet146 | 2002 | 4 | 17 | 1 | 2 | 16 | 0.89 (0.67–0.99) | 0.94 (0.71–1.00) | 15.21 (2.26–102.48) | 0.11 (0.03–0.42) |
| Choi148 | 2003 | 3 | 5 | 17 | 2 | 18 | 0.71 (0.29–0.96) | 0.51 (0.34–0.69) | 1.47 (0.82–2.62) | 0.56 (0.16–1.87) |
| Park149 | 2003 | 3 | 17 | 1 | 5 | 24 | 0.77 (0.55–0.92) | 0.96 (0.80–1.00) | 19.32 (2.79–133.58) | 0.24 (0.11–0.51) |
| Akercan147 | 2004 | 3 | 11 | 4 | 3 | 27 | 0.79 (0.49–0.95) | 0.87 (0.70–0.96) | 6.09 (2.34–15.82) | 0.25 (0.09–0.68) |
| Kwek145 | 2004 | 4 | 14 | 4 | 5 | 17 | 0.74 (0.49–0.91) | 0.81 (0.58–0.95) | 3.87 (1.54–9.72) | 0.33 (0.15–0.71) |
| Elizur150 | 2005 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 0.67 (0.22–0.96) | 0.67 (0.30–0.93) | 2.00 (0.68–5.91) | 0.50 (0.15–1.70) |
| Paternoster151 | 2005 | 1 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 86 | 0.69 (0.39–0.91) | 0.91 (0.83–0.96) | 7.31 (3.56–15.0)1 | 0.34 (0.15–0.77) |
| Summary LRs | 4.26 (2.54–7.17) | 0.28 (0.20–0.38) | ||||||||
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Study designs | Inclusion | Exclusion | Testing gestation (weeks’) | Frequency of testing | Thresholds | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goldenberg159 | 2001 | USA | 2929 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Pregnant women with cervical dilatation > 2 cm (nulliparous) and > 3 cm (multiparous), placenta praevia, fetal anomaly | 23–24 | Single | 90th centile | < 32, < 35 |
| Tanaka166 | 1994 | Japan | 1097 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Fetal and chromosomal abnormalities | 18–20 | Single | 2.0 MoM | < 37 |
| Simpson164 | 1995 | USA | 650 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnant women who provided specimen on the two specified occasions | Congenital anomaly |
15–20, 24–36 |
Single | 2.0 MoM | < 37 |
| Dugoff157 | 2005 | USA | 33,145 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton gestation, women > 16 years | Fetal chromosomal or structural abnormalities | 15–19 | Single | 2.0 MoM | < 32 |
| Morssink162 | 1995 | Netherlands | 7992 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singletons who underwent neural tube or Down’s syndrome screening | Congenital anomaly, delivery before 25 weeks’ gestation, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus | 15–20 | Single | 2.5 MoM | < 37 |
| Davisa156 | 1992 | USA | 843 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Non-viable pregnancy, stillbirths, fetal anomaly | 14–22 | Single | 2.5 MoM | < 37 |
| Waller168 | 1996 | USA | 51,008 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Fetal anomaly, fetal death, multiple gestations, (non-lethal chromosomal abnormalities might have been included) | 15–19 | Single | 2.0, 2.5 MoM | < 28, < 32, < 34, < 37 |
| Spencer165 | 2000 | UK | 27,129 |
Case–control Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Fetal anomaly, chromosomal abnormality, pregnancy termination, loss before 24 weeks’ gestation | 14–18 | Single | 2.0 MoM | < 35, < 37 |
| Yaron171 | 1999 | USA | 20,982 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Fetal anomaly, chromosomal abnormality | 14–22 | Single | 2.5 MoM | < 37 |
| Hsieh161 | 1997 | Taiwan | 5885 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Multiple gestation, diabetes mellitus, fetal and chromosomal abnormalities | 14–22 | Single | 2.0 MoM | < 37 |
| aDavis156 | 1992 | USA | 5555 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Non-viable pregnancy, stillbirths, fetal anomaly | 14–22 | Single | 2.5 MoM | <37 |
| Wenstorm169 | 1996 | USA | 4574 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Fetal and chromosomal abnormality | 14–20 | Single | 2.5 MoM | <37 |
| Brazerol154 | 1994 | USA | 776 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Fetal anomaly, oligohydramnios, fetal death | 15–20 | Single | 2.0 MoM | <28, <37 |
| Duric158 | 2002 | Croatia | 672 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Fetal chromosomal or structural abnormalities | 15–22 | Single | 2.02 MoM | 37 |
| Sharara163 | 1995 | Qatar | 360 |
Case–control Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Fetal anomaly, chromosomal abnormality, diabetes mellitus, pre-existing hypertension, threatened miscarriage, molar pregnancy | 16–18 | Single | 2.5 MoM | 37 |
| Akinbiyi153 | 1996 | UK | 300 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Fetal and chromosomal abnormality | 16–18 | Single | 2.0 MoM | 37 |
| Cho155 | 1997 | USA | 255 |
Case–control Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Non-viable pregnancies, fetal anomaly, chromosomal abnormality | 14–20 | Single | 2.5 MoM | 37 |
| Williams170 | 1992 | USA | 412 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Fetal anomaly, chromosomal abnormality, fetal death | 14–20 | Single | 2.0 MoM | 37 |
| Hamilton160 | 1985 | USA | 286 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Congenital anomaly | 16–20 | Single, twice | 2.5 MoM | < 34, < 37 |
| Wald167 | 1977 | UK | 188 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Congenital abnormalities | 14–22 | Single | 3.0 MoM | 37 |
| Authors | Threshold (MoM)a | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goldenberg159 | 90th centile | 32 | 18 | 184 | 32 | 2695 | 0.36 | 0.23 | 0.51 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 5.63 | 3.79 | 8.36 | 0.68 | 0.56 | 0.84 |
| Goldenberg159 | 90th centile | 35 | 45 | 389 | 82 | 2490 | 0.35 | 0.27 | 0.44 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 2.62 | 2.04 | 3.38 | 0.75 | 0.66 | 0.85 |
| Tanaka166 | 2.0 | 37 | 8 | 65 | 69 | 955 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 1.63 | 0.81 | 3.27 | 0.96 | 0.89 | 1.03 |
| bSimpson164 | 2.0 | 37 | 8 | 119 | 34 | 489 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.34 | 0.80 | 0.77 | 0.84 | 0.97 | 0.51 | 1.85 | 1.01 | 0.86 | 1.17 |
| cSimpson164 | 2.0 | 37 | 4 | 62 | 38 | 546 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.36 | 2.44 | 1.01 | 0.91 | 1.12 |
| Dugoff157 | 2.0 | 32 | 28 | 531 | 229 | 32,357 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 6.75 | 4.71 | 9.67 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.95 |
| Morssink162 | 2.5 | 37 | 10 | 60 | 467 | 7455 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 2.63 | 1.35 | 5.10 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.00 |
| Davis156 | 2.5 | 37 | 29 | 3 | 73 | 738 | 0.28 | 0.20 | 0.38 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 70.23 | 21.78 | 226.38 | 0.72 | 0.64 | 0.81 |
| Waller168 | 2.0 | 28 | 48 | 2418 | 237 | 48,305 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 3.53 | 2.72 | 4.59 | 0.87 | 0.83 | 0.92 |
| Waller168 | 2.5 | 28 | 21 | 629 | 264 | 50,094 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 5.94 | 3.91 | 9.03 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.97 |
| Waller168 | 2.0 | 32 | 118 | 2348 | 576 | 47,966 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 3.64 | 3.08 | 4.31 | 0.87 | 0.84 | 0.90 |
| Waller168 | 2.5 | 32 | 47 | 603 | 647 | 49,711 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 5.65 | 4.24 | 7.53 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.96 |
| Waller168 | 2.0 | 34 | 227 | 2239 | 1149 | 47,393 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 3.66 | 3.23 | 4.15 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.90 |
| Waller168 | 2.5 | 34 | 79 | 571 | 1297 | 49,061 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 4.99 | 3.97 | 6.28 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.97 |
| Waller168 | 2.0 | 37 | 499 | 1967 | 3212 | 45,330 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 3.23 | 2.95 | 3.55 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.91 |
| Waller168 | 2.5 | 37 | 158 | 492 | 3553 | 46,805 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 4.09 | 3.43 | 4.88 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.97 |
| Spencer165 | 2.0 | 35 | 57 | 548 | 607 | 25,917 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 4.15 | 3.19 | 5.39 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.96 |
| Spencer165 | 2.0 | 37 | 123 | 482 | 1429 | 25,095 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 4.21 | 3.47 | 5.09 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.95 |
| Yaron171 | 2.5 | 37 | 9 | 75 | 757 | 20,141 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 3.17 | 1.59 | 6.30 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 |
| Hsieh161 | 2.0 | 37 | 23 | 153 | 329 | 5380 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 2.36 | 1.55 | 3.61 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.99 |
| Davis156 | 2.5 | 37 | 87 | 19 | 393 | 5056 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 48.41 | 29.74 | 78.82 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.86 |
| Wenstorm169 | 2.5 | 37 | 62 | 99 | 609 | 3804 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 3.64 | 2.68 | 4.95 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.95 |
| Brazerol154 | 2.0 | 28 | 6 | 51 | 9 | 710 | 0.40 | 0.16 | 0.68 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 5.97 | 3.04 | 11.71 | 0.64 | 0.43 | 0.97 |
| Brazerol154 | 2.0 | 37 | 4 | 53 | 37 | 682 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 1.35 | 0.51 | 3.56 | 0.97 | 0.88 | 1.08 |
| Duric158 | 2.0 | 37 | 1 | 39 | 32 | 601 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.96 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 3.51 | 1.03 | 0.97 | 1.10 |
| Sharara163 | 2.5 | 37 | 18 | 102 | 20 | 220 | 0.47 | 0.31 | 0.64 | 0.68 | 0.63 | 0.73 | 1.50 | 1.03 | 2.17 | 0.77 | 0.56 | 1.05 |
| Akinbiyi153 | 2.0 | 37 | 9 | 91 | 4 | 196 | 0.69 | 0.39 | 0.91 | 0.68 | 0.63 | 0.74 | 2.18 | 1.46 | 3.26 | 0.45 | 0.20 | 1.02 |
| Cho155 | 2.5 | 37 | 37 | 80 | 16 | 122 | 0.70 | 0.56 | 0.82 | 0.60 | 0.53 | 0.67 | 1.76 | 1.38 | 2.25 | 0.50 | 0.33 | 0.76 |
| Williams170 | 2.0 | 37 | 43 | 158 | 23 | 188 | 0.65 | 0.52 | 0.76 | 0.54 | 0.49 | 0.60 | 1.43 | 1.16 | 1.76 | 0.64 | 0.45 | 0.90 |
| dHamilton160 | 2.5 | 34 | 19 | 81 | 1 | 185 | 0.95 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 0.70 | 0.64 | 0.75 | 3.12 | 2.53 | 3.84 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.49 |
| dHamilton160 | 2.5 | 37 | 26 | 74 | 6 | 180 | 0.81 | 0.64 | 0.93 | 0.71 | 0.65 | 0.76 | 2.79 | 2.16 | 3.60 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.55 |
| Hamilton160 | 2.5 | 34 | 9 | 78 | 1 | 185 | 0.90 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 0.70 | 0.64 | 0.76 | 3.03 | 2.30 | 4.01 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.91 |
| Hamilton160 | 2.5 | 37 | 18 | 68 | 6 | 180 | 0.75 | 0.53 | 0.90 | 0.73 | 0.67 | 0.78 | 2.74 | 2.01 | 3.72 | 0.34 | 0.17 | 0.69 |
| Wald167 | 3.0 | 37 | 23 | 4 | 71 | 90 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.34 | 0.96 | 0.89 | 0.99 | 5.75 | 2.07 | 15.99 | 0.79 | 0.70 | 0.89 |
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Study designs | Inclusion | Exclusion | Testing gestation (weeks) | Frequency of testing | Threshold | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Weiss173 | 1993 | USA | 76 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Test described |
All 18–42-year-old women who achieved singleton pregnancies from ovulatory induction either with or without IVF/ET | No previous history of preterm birth, uterine or fetal abnormalities, more than one major cervical surgery, no previous DES exposure, placenta praevia, pre-eclampsia | 6–12 | Serial | +3SD a | < 37 |
| Vogel176 | 2006 | USA | 61 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Test described |
Asymptomatic women with at least one previous late spontaneous miscarriage or early spontaneous preterm delivery between 16 and 30 weeks’ gestation | Multiple gestation, PPROM, uterine or fetal abnormalities, threatened preterm labour | 12–25 | Single | 406 mg/l | < 37 |
| Goldenberg159 | 2001 | USA | 2929 |
Case–control Retrospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancy | Cervical dilatation > 3 cm in multipara, > 2 cm in nullipara, PPROM, bulging membrane at cervical os, placenta praevia | 24 | Single | 90th centile | < 32, < 35 |
| Vogel175 | 2006 | Denmark | 483 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton asymptomatic pregnancies | Multiple gestation, PPROM, fetal abnormalities, diabetes | 18–24 | Single | 932 pg/ml | < 37 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Vogel177 | 2002 | Denmark | 34 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancy presenting with threatened preterm labour and intact membrane and without evidence of ripening cervix | Elevated blood pressure, women with major medical disease, vaginal bleeding | 24–34 | Single | 300 pg/ml | < 34, < 37 |
| Authors | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | |||||||||||||||||
| Weiss173 | 37 | 6 | 37 | 3 | 30 | 0.67 | 0.30 | 0.93 | 0.45 | 0.33 | 0.57 | 1.21 | 0.73 | 2.01 | 0.74 | 0.28 | 1.95 |
| Vogel176 | 37 | 9 | 33 | 11 | 8 | 0.45 | 0.23 | 0.68 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 0.35 | 0.56 | 0.34 | 0.93 | 2.82 | 1.35 | 5.89 |
| Vogel175 | 37 | 18 | 50 | 66 | 350 | 0.21 | 0.13 | 0.32 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 0.91 | 1.71 | 1.06 | 2.78 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 1.01 |
| Goldenberg159 | 32 | 11 | 628 | 39 | 2251 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.36 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 1.01 | 0.60 | 1.71 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 1.16 |
| Goldenberg159 | 35 | 43 | 595 | 84 | 2214 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.43 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 1.60 | 1.24 | 2.06 | 0.84 | 0.74 | 0.95 |
| Symptomatic women | |||||||||||||||||
| Vogel177 | 34 | 1 | 7 | 2 | 24 | 0.33 | 0.01 | 0.91 | 0.77 | 0.59 | 0.90 | 1.48 | 0.26 | 8.31 | 0.86 | 0.38 | 1.96 |
| Vogel175 | 37 | 2 | 6 | 8 | 18 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.56 | 0.75 | 0.53 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.19 | 3.31 | 1.07 | 0.72 | 1.57 |
| Authors | Year | Country | Population | Quality of studies | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | Testing gestation (weeks’ gestation) | Frequency of testing | Thresholds | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Leung181 | 1999 | Hong Kong | 1014 |
Blinded Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Mid-trimester miscarriage | 15–20 | Single | 1.9 MoM | < 34 |
| aBerkowitz178 | 1996 | USA | 396 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Asymptomatic Hispanic women | Multiple gestations, stillbirths, congenital malformation, iatrogenic preterm birth, women with chronic hypertension, pre-eclampsia |
20–24 24–28 29–33 33–37 |
Serial | 3.1, 41.3, 234, 665.7 pg/ml | < 37 |
| Inder180 | 2001 | USA | 297 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Antenatal women from a local area medical practice | None stated | 26 | Singleb | 50, 70, 90, 110, 130, 150 pmol/l | < 37 |
| Goldenberg159 | 2001 | USA | 2929 |
Blinded Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Fetal anomalies, chromosomal abnormalities, placenta praevia, cervical dilatation > 3 cm, or bulging membrane | 23–24 | Single | 90th centile | < 32, < 35 |
| Holzman179 | 2001 | USA | 304 (White), 181(Black) |
Blinded Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Antenatal patients at tertiary referral centre | Other ethnic groups beside black or white, multiple gestations, diabetes before pregnancy, chromosomal abnormalities | 15–19 | Single | 1.0, 1.5 MoM | < 35 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Coleman182 | 2000 | New Zealand | 94 |
Blinded Cohort Prospective Test described |
Non-diabetic singleton pregnancies presenting with preterm labour, intact membrane, and cervical dilatation < 3 cm | Fetal anomaly and chromosomal abnormality | 24–36 | Single | 90th centile | < 10 days of testing and < 37 |
| Authors | Thresholds | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||||
| Leung181 | 1.9 MoM | 34 | 8 | 217 | 3 | 786 | 0.73 | 0.39 | 0.94 | 0.78 | 0.76 | 0.81 | 3.36 | 2.30 | 4.92 | 0.35 | 0.13 | 0.91 |
| Berkowitz178 | 3.1 pg/ml | 37 | 4 | 25 | 41 | 326 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.95 | 1.25 | 0.46 | 3.42 | 0.98 | 0.89 | 1.08 |
| Berkowitz178 | 41.3 pg/ml | 37 | 11 | 71 | 34 | 280 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.84 | 1.21 | 0.69 | 2.10 | 0.95 | 0.80 | 1.13 |
| Berkowitz178 | 234 pg/ml | 37 | 13 | 71 | 32 | 280 | 0.29 | 0.16 | 0.44 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.84 | 1.43 | 0.86 | 2.36 | 0.89 | 0.73 | 1.08 |
| Berkowitz178 | 665.7 pg/ml | 37 | 9 | 74 | 36 | 277 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.35 | 0.79 | 0.74 | 0.83 | 0.95 | 0.51 | 1.76 | 1.01 | 0.87 | 1.18 |
| Inder180 | 90 pmol/l | 37 | 14 | 16 | 17 | 250 | 0.45 | 0.27 | 0.64 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 7.51 | 4.07 | 13.86 | 0.58 | 0.42 | 0.80 |
| Inder180 | 70 pmol/l | 37 | 17 | 29 | 14 | 237 | 0.55 | 0.36 | 0.73 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.93 | 5.03 | 3.15 | 8.04 | 0.51 | 0.34 | 0.75 |
| Inder180 | 110 pmol/l | 37 | 11 | 9 | 20 | 257 | 0.35 | 0.19 | 0.55 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 10.49 | 4.72 | 23.31 | 0.67 | 0.51 | 0.87 |
| Inder180 | 130 pmol/l | 37 | 8 | 6 | 23 | 260 | 0.26 | 0.12 | 0.45 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 11.44 | 4.25 | 30.82 | 0.76 | 0.62 | 0.93 |
| Inder180 | 150 pmol/l | 37 | 6 | 2 | 25 | 264 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.37 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 25.74 | 5.43 | 122.07 | 0.81 | 0.68 | 0.97 |
| Inder180 | 50 pmol/l | 37 | 21 | 60 | 10 | 206 | 0.68 | 0.49 | 0.83 | 0.77 | 0.72 | 0.82 | 3.00 | 2.16 | 4.18 | 0.42 | 0.25 | 0.70 |
| Goldenberg159 | 90th centile | 32 | 6 | 242 | 44 | 2637 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.24 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 1.43 | 0.67 | 3.05 | 0.96 | 0.87 | 1.06 |
| Goldenberg159 | 90th centile | 35 | 15 | 233 | 112 | 2569 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 1.42 | 0.87 | 2.32 | 0.96 | 0.90 | 1.03 |
| Holzman179 | 1.0 MoM (Black) | 35 | 33 | 78 | 8 | 62 | 0.80 | 0.65 | 0.91 | 0.44 | 0.36 | 0.53 | 1.44 | 1.17 | 1.78 | 0.44 | 0.23 | 0.84 |
| Holzman179 | 1.0 MoM (White) | 35 | 34 | 120 | 22 | 128 | 0.61 | 0.47 | 0.74 | 0.52 | 0.45 | 0.58 | 1.25 | 0.98 | 1.61 | 0.76 | 0.54 | 1.08 |
| Holzman179 | 1.5 MoM (Black) | 35 | 17 | 32 | 24 | 108 | 0.41 | 0.26 | 0.58 | 0.77 | 0.69 | 0.84 | 1.81 | 1.13 | 2.91 | 0.76 | 0.58 | 1.00 |
| Holzman179 | 1.5 MoM (White) | 35 | 16 | 48 | 40 | 200 | 0.29 | 0.17 | 0.42 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.85 | 1.48 | 0.91 | 2.40 | 0.89 | 0.74 | 1.06 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||||
| Coleman182 | 90th centile | 10 | 6 | 12 | 7 | 69 | 0.46 | 0.19 | 0.75 | 0.85 | 0.76 | 0.92 | 3.12 | 1.42 | 6.84 | 0.63 | 0.38 | 1.05 |
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Study designs | Inclusion | Exclusion | Testing gestation (weeks) | Frequency of testing | Threshold (MoM) | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yaron197 | 2002 | Israel | 1622 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies without fetal and chromosomal abnormalities | ✗ | 10–13 | Single | ≥ 1.0, ≥ 2.0, ≥ 3.0, ≥ 4.0, ≥ 5.0 | < 37 |
| Dugoff157 | 2005 | USA | 33,145 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies without fetal and chromosomal abnormalities | ✗ | 15–19 | Single | > 2.0 | < 32 |
| Ong194 | 2000 | UK | 5297 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies without fetal and chromosomal abnormalities | ✗ | 10–14 | Single | 5th, 10th centile | < 34, < 37 |
| Dugoff157 | 2005 | USA | 34,271 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies without fetal and chromosomal abnormalities | ✗ | 10–14 | Single | 1st, 5th, and 10th centile | < 32, < 37 |
| Morssink162 | 1995 | Netherland | 7992 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Unknown pregnancy outcome, a congenital anomaly, delivery before 25 weeks of amenorrhea, or known insulin-dependent diabetes | 15–20 | Single | ≥ 2.5 | < 37 |
| Chandra187 | 2003 | Canada | 8585 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
< 35 years, low-risk singleton pregnancies without fetal or chromosomal abnormalities | ✗ | 15–20 | Single | ≥ 2.0 | < 37 |
| Tanaka166 | 1994 | Japan | 1097 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Consecutive pregnant women in whom gestation was dated by ultrasonography, with singleton pregnancies | ✗ | 18–20 | Single | ≥ 2.0 | < 37 |
| Haddad198 | 1999 | France | 169 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
IVF singleton pregnancies | No fetal or chromosomal abnormalities | 6–7 | Serial | 90th centile | < 37 |
| Duric158 | 2002 | Croatia | 672 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
< 35 years women with singleton pregnancies without fetal or chromosomal abnormalities | ✗ | 15–22 | Single | ≥ 2.02 | < 37 |
| Spencer165 | 2000 | UK | 26,918 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Control of singleton uncomplicated pregnancies outcome. Cases were those with spontaneous preterm delivery | ✗ | 14–18 | Single | ≥ 2.0 | < 35, < 37 |
| Lieppman191 | 1993 | USA | 460 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Non-diabetic women with singleton pregnancies between 15 and 18 weeks’ gestation | Multiple gestations, diabetic pregnancies, fetal and chromosomal abnormalities | 15–18 | Single | ≥ 2.0 | < 37 |
| Onderoglu193 | 1997 | Turkey | 562 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton non-diabetic pregnancies with known outcomes | Fetal and chromosomal abnormalities or maternal serum α-fetoprotein > 2.0 MoM | 15–20 | Single | ≥ 2.0 | < 37 |
| Hsieh184 | 1997 | Taiwan | 5885 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Taiwanese women under 35 years of age with singleton pregnancies without fetal or chromosomal abnormalities | ✗ | 14–22 | Single | ≥ 2.0 | < 37 |
| Wenstorm195 | 1994 | USA | 252 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Cases were singleton pregnancies without fetal or chromosomal abnormalities who underwent amniocentesis with matched control who did not have amniocentesis | ✗ | 15–20 | Single | ≥ 2.0 | < 37 |
| Gonen189 | 1992 | Israel | 493 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Cases were singleton pregnancies with confirmed gestational age | Fetal or chromosomal abnormalities and maternal serum α-fetoprotein > 2.5 MoM | 16–20 | Single | ≥ 2.5 | < 37 |
| Yaron171 | 1999 | Israel | 45,565 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
All singleton pregnancies screened for Down syndrome risks | Fetal or chromosomal abnormalities | 14–22 | Single | > 2.5 | < 37 |
| Benn185 | 1996 | USA | 1079 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
< 35 years, singleton pregnancies without diabetes mellitus, fetal and chromosomal abnormalities | ✗ | 15–22 | Single | ≥ 3.0 | < 37 |
| Brajenovic186 | 2004 | Croatia | 1507 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies without fetal or chromosomal abnormalities | 15–20 | Single | ≥ 2.0 | < 37 | |
| Lepage190 | 2003 | Canada | 2256 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies without fetal anomalies | ✗ | 15–20 | Single | ≥ 4.0 | < 37 |
| Liu192 | 1999 | USA | 72 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Unexplained elevated maternal serum hCG levels compared with controls with normal mshCG levels delivering during the same period | ✗ | 15–20 | Not stated | ≥ 2.0 | < 36 |
| Ramos200 | 2003 | USA | 86 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Preterm labour, < 4 cm cervical dilatation, intact membrane | PPROM, presence of gross blood in vagina, cervical cerclage, fetal anomaly, IUGR, pre-eclampsia | 24–34 | Single | 25 mIU/ml | <37 |
| Gurbuz199 | 2004 | Turkey | 102 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Preterm labour, < 3 cm cervical dilatation, intact membrane | Fetal compromise, placenta praevia, abruption, fetal anomaly, PPROM, pre-eclampsia. | 25–35 | Single |
32 mIU/ml 42 mIU/ml 30 mIU/ml 33 mIU/ml 27 mIU/ml |
<100 hours <100 hours < 7 days <14 days of testing, <35 and <37 |
| Guvenal139 | 2001 | Turkey | 60 |
Case–control Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies without fetal or chromosomal abnormalities, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | Placenta praevia, vaginal bleeding, pre-eclampsia, hypertension, IUGR, fetal distress, rupture of membrane at presentation | 24–36 | Single | 27.1 mIU/ml | <37 |
| Authors | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women, threshold 2.0 MoM, < 37 weeks’ gestation | ||||||||||||||||
| Yaron197 | 32 | 1246 | 12 | 332 | 0.73 | 0.57 | 0.85 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.92 | 0.77 | 1.11 | 1.30 | 0.79 | 2.12 |
| Chandra187 | 203 | 637 | 1352 | 6393 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 1.44 | 1.24 | 1.67 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.98 |
| Duric158 | 11 | 97 | 23 | 541 | 0.32 | 0.17 | 0.51 | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.87 | 2.13 | 1.27 | 3.58 | 0.80 | 0.63 | 1.01 |
| Tanaka166 | 8 | 65 | 69 | 955 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 1.63 | 0.81 | 3.27 | 0.96 | 0.89 | 1.03 |
| Brajenovic186 | 5 | 116 | 44 | 1342 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 1.28 | 0.55 | 3.00 | 0.98 | 0.89 | 1.07 |
| Lieppman191 | 25 | 200 | 9 | 226 | 0.74 | 0.56 | 0.87 | 0.53 | 0.48 | 0.58 | 1.57 | 1.25 | 1.96 | 0.50 | 0.28 | 0.88 |
| Onderoglu193 | 27 | 54 | 39 | 442 | 0.41 | 0.29 | 0.54 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.92 | 3.76 | 2.56 | 5.52 | 0.66 | 0.54 | 0.81 |
| Shieh184 | 33 | 383 | 329 | 5140 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 1.31 | 0.94 | 1.85 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 1.01 |
| Spencer165 | 250 | 3713 | 1302 | 22,541 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 1.14 | 1.01 | 1.28 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 1.00 |
| Wenstorm195 | 4 | 18 | 37 | 193 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.95 | 1.14 | 0.41 | 3.20 | 0.99 | 0.88 | 1.10 |
| aDugoff157 | 54 | 278 | 2137 | 30,926 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 2.77 | 2.07 | 3.69 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.99 |
| bDugoff157 | 187 | 1485 | 2004 | 29,719 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 1.79 | 1.55 | 2.07 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.97 |
| cDugoff157 | 329 | 2945 | 1862 | 28,259 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 1.59 | 1.43 | 1.77 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.96 |
| Symptomatic women, threshold 30 mIU/ml, within 7 days of testing | ||||||||||||||||
| Gurbuz199 | 56 | 7 | 2 | 37 | 0.97 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 0.70 | 0.93 | 6.07 | 3.07 | 11.99 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.16 |
| Symptomatic women, threshold 30 mIU/ml, < 37 weeks’ gestation | ||||||||||||||||
| Ramos200 | 18 | 17 | 10 | 41 | 0.64 | 0.44 | 0.81 | 0.71 | 0.57 | 0.82 | 2.19 | 1.35 | 3.56 | 0.51 | 0.30 | 0.85 |
| Gurbuz199 | 61 | 10 | 19 | 12 | 0.76 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.55 | 0.32 | 0.76 | 1.68 | 1.04 | 2.69 | 0.44 | 0.25 | 0.75 |
| Guvenal139 | 7 | 18 | 1 | 34 | 0.88 | 0.47 | 1.00 | 0.65 | 0.51 | 0.78 | 2.53 | 1.60 | 3.99 | 0.19 | 0.03 | 1.21 |
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Study designs | Inclusion | Exclusion | Testing gestation (weeks’) | Frequency of testing | Threshold | Outcome (weeks’ gestation)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Heine202 | 2000 | USA | 601 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton gestation, women > 18 years | Placenta praevia, cerclage, PPROM, pre-eclampsia, medications known to affect hormone levels, planned Caesarean section, major congenital abnormalities, intrauterine growth restriction, fetal chromosomal and structural abnormalities, erythroblastosis fetalis, oral conditions that interfere with saliva collections, maternal medical complications | 21–25 | Single and twice (7 days apart) | 2.1 ng/ml | 37 |
| Dugoff157 | 2005 | USA | 33,145 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton gestation, women > 16 years | Fetal chromosomal or structural abnormalities | 15–19 | Single | 0.5 MoM | 32 |
| Yaron196 | 1999 | USA | 24,504 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
All singleton pregnancies | Fetal chromosomal or structural abnormalities | 14–22 | Single | 0.5 MoM | 37 |
| Kim203 | 2000 | Korea | 1096 |
Cohort Test described |
All singletons < 35 years old | Multiple pregnancies, diabetes mellitus, smoking abnormal α-fetoprotein and or human chorionic gonadotrophin | 15–20 | Single | 0.75 MoM | 37 |
| Duric158 | 2003 | Croatia | 672 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Fetal chromosomal or structural abnormalities | 15–22 | Single | 0.74 MoM | 37 |
| Kowalczyk204 | 1998 | USA | 399 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies, <35 years old | Elevated human chorionic gonadotrophin and/or α-fetoprotein | 15–21 | Single | 0.75 MoM | 37 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Heine202 | 2000 | USA | 115 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Symptomatic with threatened preterm labour | Placenta praevia, tocolytics therapy, cerclage, PPROM, pre-eclampsia, medications known to affect hormone levels, planned Caesarean section, major congenital abnormalities, intrauterine growth restriction, fetal chromosomal and structural abnormalities, erythroblastosis fetalis, oral conditions that interfere with saliva collections, maternal medical complications | 21–25 | Single | 1.4 ng/ml and 2.1 ng/ml | Within 14 days of testing |
| McGregor201 | 1995 | USA | 190 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies presenting with threatened preterm labour | Fetal anomalies, IUGR | 22–26 | Single | 2.1 ng/ml | 37 |
| Authors | Thresholds | Outcome (weeks’ gestation)b | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||||
| Heine202 | 2.1 ng/ml | 37 | 10 | 46 | 13 | 532 | 0.43 | 0.23 | 0.66 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 5.46 | 3.18 | 9.40 | 0.61 | 0.43 | 0.88 |
| cHeine202 | 2.1 ng/ml | 37 | 13 | 128 | 10 | 450 | 0.57 | 0.34 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.74 | 0.81 | 2.55 | 1.73 | 3.77 | 0.56 | 0.35 | 0.89 |
| Dugoff157 | 0.5 MoM | 32 | 5 | 369 | 252 | 32,519 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.73 | 0.72 | 4.15 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.01 |
| Yaron196 | 0.5 MoM | 37 | 50 | 1688 | 865 | 21,901 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.76 | 0.58 | 1.00 | 1.02 | 1.00 | 1.03 |
| Kim203 | 0.75 MoM | 37 | 7 | 100 | 54 | 935 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.92 | 1.19 | 0.58 | 2.44 | 0.98 | 0.89 | 1.07 |
| Duric158 | 0.74 MoM | 37 | 12 | 104 | 22 | 534 | 0.35 | 0.20 | 0.54 | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.86 | 2.17 | 1.33 | 3.53 | 0.77 | 0.60 | 0.99 |
| Kowalczyk204 | 0.75 MoM | 37 | 12 | 69 | 38 | 190 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.38 | 0.73 | 0.68 | 0.79 | 0.90 | 0.53 | 1.54 | 1.04 | 0.87 | 1.23 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||||
| Heine202 | 1.4 ng/ml | Within 14 days of testing | 14 | 22 | 9 | 70 | 0.61 | 0.39 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.66 | 0.84 | 2.55 | 1.56 | 4.16 | 0.51 | 0.31 | 0.87 |
| Heine202 | 2.1 ng/ml | Within 14 days of testing | 7 | 1 | 16 | 91 | 0.30 | 0.13 | 0.53 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 28.00 | 3.62 | 216.39 | 0.70 | 0.54 | 0.92 |
| McGregor201 | 2.1 ng/ml | 37 | 16 | 53 | 6 | 115 | 0.73 | 0.50 | 0.89 | 0.68 | 0.61 | 0.75 | 2.31 | 1.64 | 3.24 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 0.79 |
| Author | Year | n | Study quality | Gestation at testing (weeks) | Cut-off [ng/ml] | Reference standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amniotic fluid CRP in asymptomatic women | ||||||
| Ghezzi210 | 2002 | 306 | Cohort, blinding, test described | 14–20 | 110 | 34 weeks’ gestation |
| Ozer213 | 2005 | 141 | Cohort, consecutive, prospective, test described | 15–20 | 6.5 | 37 weeks’ gestation |
| Blood serum CRP in asymptomatic women | ||||||
| Hvilsom212 | 2002 | 484 | Case–control, test described | 14–18 | 7.6 | 37 weeks’ gestation |
| Karinen213 | 2005 | 506 | Case–control, test described | 12–16 | 4.3 | 37 weeks’ gestation |
| Rückhäberle216 | 1991 | 216 | Cohort | Not reported | pos/neg | 37 weeks’ gestation |
| Blood serum CRP in symptomatic women | ||||||
| Cammu206 | 1989 | 87 | Cohort, consecutive, blinding, test described | 22–35 | 12.5 |
7 days after testing 37 weeks’ gestation |
| Cylwik207 | 1997 | 35 | Cohort, retrospective, test described | > 24 | 10 | 37 weeks’ gestation |
| Doods208 | 1987 | 34 | Cohort, retrospective, test described | 24–35 | 8 | 7 days after testing |
| Foulon209 | 1995 | 44 | Cohort, consecutive, retrospective, test described | 20–34 | 15 | 34 weeks’ gestation |
| Handwerker211 | 1984 | 50 | Cohort, consecutive, blinding, test described | 24–34 | 0.8–1.0 | 7 days after testing |
| Mazor214 | 1993 | 48 | Cohort, consecutive, test described | 24–36 | 8 | 37 weeks’ gestation |
| Potkul205 | 1985 | 40 | Cohort, consecutive, blinding, test described | 24–36 | 7 | 37 weeks’ gestation |
| Winkler217 | 1987 | 98 | Cohort, consecutive | Not reported | 10 | 7 days after testing |
| Author | Year | Cut-off (ng/ml) | TP | FP | FN | TN | Sensitivity | 95% CI lower limit | 95% CI upper limit | Specificity | 95% CI lower limit | 95% CI upper limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amniotic fluid CRP for predicting birth before 34 weeks’ gestation | ||||||||||||
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||||
| Ghezzi210 | 2002 | 110 | 8 | 90 | 2 | 206 | 0.80 | 0.44 | 0.97 | 0.70 | 0.64 | 0.75 |
| Amniotic fluid CRP for predicting birth before 37 weeks’ gestation | ||||||||||||
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||||
| Ozer215 | 2005 | 6.5 | 13 | 27 | 1 | 100 | 0.93 | 0.66 | 0.99 | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.85 |
| Blood serum CRP for predicting birth within 7 days of testing | ||||||||||||
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||||
| Cammu206 | 1989 | 12.5 | 9 | 1 | 2 | 41 | 0.82 | 0.48 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.87 | 1.00 |
| Doods208 | 1987 | 8 | 17 | 4 | 3 | 10 | 0.85 | 0.62 | 0.97 | 0.71 | 0.42 | 0.92 |
| Handwerker211 | 1984 | 0.8–1.0 | 11 | 4 | 2 | 33 | 0.85 | 0.55 | 0.98 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 0.97 |
| Winkler217 | 1987 | 10 | 13 | 14 | 27 | 44 | 0.33 | 0.19 | 0.49 | 0.76 | 0.63 | 0.86 |
| Blood serum CRP for predicting birth before 37 weeks’ gestation | ||||||||||||
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||||
| Hvilsom212 | 2002 | 7.6 | 22 | 58 | 62 | 342 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.37 | 0.86 | 0.82 | 0.89 |
| Karinen213 | 2005 | 4.3 | 36 | 90 | 68 | 312 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 0.46 | 0.78 | 0.73 | 0.82 |
| Rückhäberle216 | 1991 | pos/neg | 39 | 20 | 66 | 91 | 0.37 | 0.28 | 0.47 | 0.82 | 0.74 | 0.89 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||||
| Cammu206 | 1989 | 12.5 | 14 | 19 | 7 | 47 | 0.67 | 0.43 | 0.85 | 0.71 | 0.59 | 0.82 |
| Cylwik207 | 1997 | 10 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 26 | 0.40 | 0.05 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.69 | 0.96 |
| bFoulon209 | 1995 | 15 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 34 | 0.38 | 0.09 | 0.76 | 0.94 | 0.81 | 0.99 |
| Mazor214 | 1993 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 22 | 0.44 | 0.22 | 0.69 | 0.73 | 0.54 | 0.88 |
| Potkul205 | 1985 | 7 | 14 | 2 | 11 | 13 | 0.56 | 0.35 | 0.76 | 0.87 | 0.60 | 0.98 |
| Author | Year | Cut-off (ng/ml) | LR+ | 95% CI lower limit | 95% CI upper limit | LR– | 95% CI lower limit | 95% CI upper limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amniotic fluid CRP for predicting birth before 34 weeks’ gestation | ||||||||
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||
| Ghezzi210 | 2002 | 110 | 2.63 | 1.85 | 3.75 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.99 |
| Ozer215 | 2005 | 6.5 | 4.37 | 3.03 | 6.29 | 0.09 | 0.014 | 0.60 |
| Blood serum CRP for predicting birth within 7 days of testing | ||||||||
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||
| Cammu206 | 1989 | 12.5 | 34.36 | 4.86 | 243.09 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.65 |
| Doods208 | 1987 | 8 | 2.98 | 1.27 | 6.95 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.63 |
| Handwerker211 | 1984 | 0.8–1.0 | 7.83 | 3.01 | 20.32 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.62 |
| Winkler214 | 1987 | 10 | 1.35 | 0.71 | 2.55 | 0.89 | 0.69 | 1.15 |
| Summary | 4.54 | 1.48 | 13.91 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 1.15 | ||
| Blood serum CRP for predicting birth before 37 weeks’ gestation | ||||||||
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||
| Hvilsom212 | 2002 | 7.6 | 1.81 | 1.17 | 2.78 | 0.86 | 0.76 | 0.98 |
| Karinen213 | 2005 | 4.3 | 1.55 | 1.22 | 2.13 | 0.84 | 0.73 | 0.98 |
| Rückhäberle216 | 1991 | pos/neg | 2.06 | 1.29 | 3.29 | 0.77 | 0.65 | 0.91 |
| Summary | 1.72 | 1.38 | 2.16 | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.91 | ||
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||
| Cammu206 | 1989 | 12,5 | 2.32 | 1.43 | 3.76 | 0.47 | 0.25 | 0.87 |
| Cylwik207 | 1997 | 10 | 3.00 | 0.73 | 12.27 | 0.69 | 0.33 | 1.44 |
| aFoulon209 | 1995 | 15 | 6.75 | 1.34 | 34.00 | 0.66 | 0.38 | 1.14 |
| Mazor214 | 1993 | 8 | 1.67 | 0.76 | 3.66 | 0.76 | 0.48 | 1.21 |
| Potkul205 | 1985 | 7 | 4.20 | 1.10 | 15.98 | 0.51 | 0.31 | 0.82 |
| Summary | 2.29 | 1.57 | 3.35 | 0.60 | 0.46 | 0.79 | ||
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Study design | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | Testing gestations | Frequency of testing | Thresholds | Outcome (weeks’ gestation)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Amniotic fluid | ||||||||||
| Wenstorm220 | 1998 | USA | 482 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies that underwent amniocentesis for various reasons (e.g. prenatal diagnosis) | Aneuploidies, anomalies, pregnancy loss within 30 days of amniocentesis | 14–18 | Single | 2.9 ng/ml | 34, 37 |
| Ghidini222 | 1997 | USA | 179 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton uncomplicated pregnancy | Multiple gestations, uterine, fetal or neonatal abnormalities, cytogenetic evidence of karyotypical abnormalities | 15–20 | Single | 1740 pg/ml | 34 |
| Cervicovaginal | ||||||||||
| Lockwood221 | 1994 | USA | 161 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinding Test described |
Singleton pregnancies, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | Unknown dates, placenta praevia, hydatidiform mole, major congenital anomaly, serious maternal medical complications | 24–36 | Serial 3–4 weekly | 125 and 250 pg/ml | 37 |
| Inglis103 | 1994 | USA | 73 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinding Test described |
All patients between 15 and 40 years old with singleton pregnancies | Congenital anomalies, placenta praevia, known genital or urinary tract infection, use of antibiotics within the past 7 days | 20–36 | Single | 50 pg/ml | 37 |
| Goepfert231 | 2001 | USA | 250 |
Case–control Retrospective Blinding Test described |
Singleton pregnancies, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | Placenta praevia, fetal abnormalities, maternal medical complications, uterine abnormalities | 22–24 | Single | 305 pg/ml | 35, 37 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Amniotic fluid | ||||||||||
| Rizzo227 | 1996 | Italy | 92 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinding Test described |
Singleton gestation in premature labour with intact membrane, cervical dilatation | Presence of other fetal or maternal complications, known genital or urinary infection, antibiotic use within the last 14 days | 24–36 | Single | 50 pg/ml | 37 |
| Romero230 | 1993 | USA | 146 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Test described |
Singleton pregnant women with threatened preterm labour | ✗ | 20–34 | Single | 0.5, 2.0 and 11.30 ng/ml | 36 |
| Coultrip224 | 1994 | USA | 89 |
Cohort Prospective Blinding Test described |
Symptomatic women singleton pregnancies with intact membrane | ✗ | 20–36 | Single | 0.38, 0.617 and 1.13 ng/ml | Within 3 days of testing (0.38 ng/ml only), 37 |
| Greig238 | 1993 | USA | 57 |
Cohort Prospective Blinding Test described |
Singleton gestation in premature labour with intact membrane | Cervical dilatation > 4 cm, antibiotic treatment in the past 7 days, any medical condition requiring antibiotic treatment | 24–34 | Single | 600 pg/ml | 3 |
| Greci225 | 1998 | USA | 53 |
Cohort Prospective Blinding Test described |
Women who presented with threatened preterm labour and intact membrane | Vaginal bleeding, placenta praevia, abruption, multiple gestations, polyhydramnios, pre-eclampsia, cervical cerclage, known uterine or fetal anomalies | 24–34 | Single | 7586 pg/ml | Within 2 and 7 days of testing |
| Burrus120 | 1995 | USA | 18 |
Cohort Prospective Blinding Test described |
Symptomatic women in first pregnancy, intact membrane cervical dilatation < 3 cm | Chorio-amnionitis, placental abruption. | 24–34 | Single | 1500 pg/ml | 48 |
| Hillier226 | 1993 | USA | 50 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Afebrile women who presented with threatened preterm labour with intact membrane | < 16 or > 40 years old, uterine or fetal abnormalities, multiple pregnancies, polyhydramnios, cervical cerclage, placenta praevia, abruption, hypertension, diabetes or had received antibiotics the previous week | 23–34 | Single | 1500 pg/ml | Within 7 days of testing, 34 |
| Silver229 | 1993 | USA | 29 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Symptomatic women singleton pregnancies with intact membrane | Additional medical or obstetrical problems, e.g. diabetes, chronic hypertension, abruptio placentae | 24–37 | Single | 400 and 500 ng/ml | 37 |
| Allbert223 | 1994 | USA | 23 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton gestation in premature labour with intact membrane | Fetal distress, IUGR, abruption, clinical amnionitis, substantial hemorrhage, fetal anomalies, or stillbirth | 20–32 | Single | 20 ng/ml | Within 2 and 7 days of testing |
| Romero218 | 1993 | USA | 120 |
Cohort Test described |
Singleton pregnant women with threatened preterm labour | Patients who received antibiotics before amniocentesis, abnormal GTT or diabetes mellitus | 22–36 | Single | 11.30 ng/ml | 37 |
| Dudley718 | 1994 | USA | 75 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Women who presented with threatened preterm labour, intact membrane who delivered within 7 days of testing | ✗ | Single | 200 pg/ml | 7 | |
| Romero228 | 1990 | USA | 56 |
Cohort Test described |
Women admitted with threatened preterm labour and intact membrane | ✗ | Single | 46 ng/ml | 35 | |
| Cervicovaginal | ||||||||||
| Inglis103 | 1994 | USA | 38 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinding Test described |
All pregnant women between 15 and 40 years, singleton, less than 37 weeks and in those who present within 7 days of testing | Fetal congenital anomalies, placenta praevia, known genital or UTI, use of antibiotics within 7 days of testing | 24–37 | Single | 50 pg/ml | 37 |
| LaShay90 | 2000 | USA | 118 |
Cohort Prospective Blinding Test described |
Singleton pregnancies, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | Coitus or digital vaginal examination within 24 h, vaginal bleeding, placenta praevia, placental abruption, polyhydramnios, pre-eclampsia, known uterine or fetal abnormalities | 24–34 | Single | 100 pg/ml | 37 |
| Kurkinen-Raty223 | 2001 | Finland | 77 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Test described |
Consecutive singleton pregnant women between 22 and 32 weeks’ gestation who present within 7 days of testing | Coitus or digital vaginal examination within 24 h, vaginal bleeding, placenta praevia, placental abruption, polyhydramnios, pre-eclampsia, known uterine or fetal abnormalities | 22–32 | Single | 61 ng/l | 37 |
| Trebeden236 | 2001 | France | 142 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Pregnant women with threatened preterm labour and intact membrane | ✗ | 22–34 | Single | 20 pg/ml | Within 7 days of testing, 34 |
| Holst232 | 2005 | Sweden | 91 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Women with singleton pregnancy presenting with threatened preterm labour and intact membrane | Uterine and fetal abnormalities, vaginal bleeding, imminent delivery and fetal distress | 22–34 | Single | 1.3 ng/ml | 7 |
| Sozmen235 | 2005 | Turkey | 40 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | Vaginal bleeding, placenta praevia, abruption, intercourse within last 24 h, signs of intrauterine infection, polyhydramnios, IUGR, hypertension, diabetes, cervical cerclage, known uterine or fetal anomalies | 28–36 | Single | 172 pg/ml | 37 |
| Lange234 | 2003 | Germany | 27 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | Multiple gestations | 24–34 | Single | 20 pg/ml | Within 2 and 7 days of testing, 34 |
| Serum | ||||||||||
| Greig238 | 1997 | USA | 56 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Pregnant women who presented to the clinic or hospital in suspected preterm labour | Refusal to participate, PPROM, multiple pregnancy, HIV infection, evidence of chorioamnionitis, UTI, pre-eclampsia, maternal age < 17 or > 40 years | 22–34 | Single | 6 pg/ml | Within 5 days of testing |
| Alvarez-de-la-Rosa237 | 2000 | Spain | 49 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Pregnant women who presented to the clinic or hospital in suspected preterm labour | Refusal to participate, multiple pregnancies, HIV infection, evidence of chorioamniontis or fetal distress | 26–37 | Single | 10 pg/ml | Within 2 days of testing, 34 |
| Turhan239 | 2000 | Turkey | 82 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies with threatened preterm labour, intact membrane | Fetal or uterine abnormalities, diabetes mellitus, placenta praevia, bleeding consistent with placental abruption, cervical cerclage, pre-eclampsia, known or suspected maternal infectious disease, positive urine culture or known maternal medical condition leading to preterm delivery | 24–36 | Single | 8.3 pg/ml | Within 2 and 7 days of testing |
| von Minckwitz240 | 2000 | Germany | 72 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies with threatened preterm labour, intact membrane | Multiple gestation, diabetes mellitus, polyhydramnios, severe concomitant disease, clotting disorders, drug addictions | 25–37 | Single | 4 pg/ml | 24 |
| Sozmen235 | 2005 | Turkey | 40 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | Vaginal bleeding, placenta praevia, abruption, intercourse within last 24 hours, signs of intrauterine infection, polyhydramnios, IUGR, hypertension, diabetes, cervical cerclage, known uterine or fetal anomalies | 28–36 | Single | 5 pg/ml | 37 |
| Authors | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||
| 34 weeks | ||||||||||||||||
| aWenstorm220 | 17 | 15 | 107 | 275 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.21 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 2.65 | 1.37 | 5.14 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.98 |
| aGhidini222 | 3 | 13 | 10 | 153 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.54 | 0.92 | 0.87 | 0.96 | 2.95 | 0.96 | 9.04 | 0.83 | 0.62 | 1.13 |
| bGoepfert231 | 10 | 3 | 39 | 46 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.34 | 0.94 | 0.83 | 0.99 | 3.33 | 0.98 | 11.38 | 0.85 | 0.72 | 0.99 |
| 37 weeks | ||||||||||||||||
| aWenstorm220 | 19 | 15 | 173 | 275 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.15 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 1.91 | 1.00 | 3.67 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 1.00 |
| bLockwood221 | 17 | 19 | 17 | 108 | 0.50 | 0.32 | 0.68 | 0.85 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 3.34 | 1.96 | 5.70 | 0.59 | 0.42 | 0.83 |
| bLockwood221 | 15 | 17 | 19 | 110 | 0.44 | 0.27 | 0.62 | 0.87 | 0.79 | 0.92 | 3.30 | 1.84 | 5.90 | 0.65 | 0.47 | 0.88 |
| bInglis103 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 52 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.41 | 0.84 | 0.72 | 0.92 | 0.56 | 0.08 | 3.97 | 1.08 | 0.87 | 1.35 |
| bGoepfert231 | 25 | 12 | 100 | 113 | 0.20 | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.90 | 0.84 | 0.95 | 2.08 | 1.10 | 3.96 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 0.98 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||
| 7–10 days | ||||||||||||||||
| aGrec225 | 17 | 4 | 3 | 29 | 0.85 | 0.62 | 0.97 | 0.88 | 0.72 | 0.97 | 7.01 | 2.75 | 17.90 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.49 |
| aHillier226 | 22 | 8 | 4 | 15 | 0.85 | 0.65 | 0.96 | 0.65 | 0.43 | 0.84 | 2.43 | 1.36 | 4.36 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.61 |
| aAllbert223 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 18 | 0.80 | 0.28 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 1.00 | 28.50 | 1.78 | 456.57 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 1.03 |
| aDudley718 | 26 | 9 | 14 | 26 | 0.65 | 0.48 | 0.79 | 0.74 | 0.57 | 0.88 | 2.53 | 1.38 | 4.64 | 0.47 | 0.30 | 0.75 |
| bTrebeden236 | 18 | 10 | 26 | 88 | 0.41 | 0.26 | 0.57 | 0.90 | 0.82 | 0.95 | 4.01 | 2.02 | 7.96 | 0.66 | 0.51 | 0.85 |
| bHolst232 | 22 | 13 | 7 | 51 | 0.76 | 0.56 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.68 | 0.89 | 3.73 | 2.21 | 6.33 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.58 |
| bLange234 | 6 | 8 | 0 | 13 | 1.00 | 0.54 | 1.00 | 0.62 | 0.38 | 0.82 | 2.40 | 1.37 | 4.23 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 1.72 |
| cTurhan239 | 36 | 5 | 20 | 21 | 0.64 | 0.50 | 0.77 | 0.81 | 0.61 | 0.93 | 3.34 | 1.48 | 7.53 | 0.44 | 0.30 | 0.66 |
| 34 weeks | ||||||||||||||||
| aHillier226 | 28 | 2 | 4 | 15 | 0.88 | 0.71 | 0.96 | 0.88 | 0.64 | 0.99 | 7.44 | 2.01 | 27.52 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.36 |
| bTrebeden236 | 24 | 4 | 54 | 60 | 0.31 | 0.21 | 0.42 | 0.94 | 0.85 | 0.98 | 4.92 | 1.80 | 13.46 | 0.74 | 0.63 | 0.87 |
| aLange234 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 13 | 1.00 | 0.59 | 1.00 | 0.65 | 0.41 | 0.85 | 2.63 | 1.44 | 4.79 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 1.45 |
| cAlvarez-de-la-Rosa237 | 7 | 19 | 3 | 20 | 0.70 | 0.35 | 0.93 | 0.51 | 0.35 | 0.68 | 1.44 | 0.86 | 2.41 | 0.59 | 0.22 | 1.58 |
| 34 weeks | ||||||||||||||||
| aRizzo227 | 18 | 0 | 34 | 40 | 0.35 | 0.22 | 0.49 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 28.62 | 1.78 | 461.04 | 0.66 | 0.54 | 0.80 |
| aCoultrip224 | 38 | 5 | 9 | 37 | 0.81 | 0.67 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.74 | 0.96 | 6.79 | 2.95 | 15.64 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.40 |
| aSilver229 | 8 | 2 | 5 | 14 | 0.62 | 0.32 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.62 | 0.98 | 4.92 | 1.26 | 19.29 | 0.44 | 0.22 | 0.90 |
| aRomero228 | 11 | 19 | 0 | 90 | 1.00 | 0.72 | 1.00 | 0.83 | 0.74 | 0.89 | 5.41 | 3.55 | 8.22 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.76 |
| bInglis103 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 52 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.41 | 0.84 | 0.72 | 0.92 | 0.56 | 0.08 | 3.97 | 1.08 | 0.87 | 1.35 |
| bLaShay90 | 21 | 59 | 13 | 25 | 0.62 | 0.44 | 0.78 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.41 | 0.88 | 0.65 | 1.19 | 1.28 | 0.75 | 2.20 |
| bKurkinen-Raty233 | 8 | 26 | 3 | 40 | 0.73 | 0.39 | 0.94 | 0.61 | 0.48 | 0.72 | 1.85 | 1.15 | 2.95 | 0.45 | 0.17 | 1.20 |
| cSozmen235 | 14 | 1 | 6 | 19 | 0.70 | 0.46 | 0.88 | 0.95 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 14.00 | 2.03 | 96.62 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.62 |
| cSozmen235 | 9 | 8 | 11 | 12 | 0.45 | 0.23 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 0.36 | 0.81 | 1.13 | 0.55 | 2.32 | 0.92 | 0.54 | 1.56 |
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Study designs | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | Testing gestation (weeks) | Frequency of testing | Thresholds | Outcomes (weeks’ gestation)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Sakai243 | 2004 | Japan | 4203 |
Cohort Prospective Blinding Test described |
Asymptomatic women with singleton pregnancy and intact membrane | Preterm pre-labour rupture of membrane, threatened or impending miscarriage or preterm delivery, genital bleeding | 20–28 |
Serial (2-weekly) |
360 ng/ml | 32, 34, 37 |
| Sakai244 | 2004 | Japan | 501 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Asymptomatic women with singleton pregnancy | Iatrogenic prematurity, fetal asphyxia, abruption, placenta praevia, pre-eclampsia | 20–24 | Single | 377 ng/ml | 37 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Kurkinen233 | 2001 | Finland | 77 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Test described |
Consecutive singleton pregnant women between 22–32 weeks’ gestation who presented with threatened preterm labour | Preterm pre-labour rupture of membrane, impending preterm delivery | 22–32 | Single | 3739 ng/l | 37 |
| Holst232 | 2005 | Sweden | 91 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Women with singleton pregnancy presenting with threatened preterm labour and intact membrane | Uterine and fetal abnormalities, vaginal bleeding, imminent delivery and fetal distress | 22–34 | Single | 7.7 ng/ml | Within 7 days of testing |
| bAllbert223 | 1994 | USA | 23 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton gestation in premature labour with intact membrane | Fetal distress, intrauterine growth restriction, abruption, clinical amnionitis, substantial haemorrhage, fetal anomalies, or stillbirth | 20–32 | Single | 15 ng/ml | Within 2 and 7 days of testing |
| Authors | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | |||||||||||||||||
| bSakai243 | 32 | 7 | 838 | 11 | 3347 | 0.39 | 0.17 | 0.64 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 1.94 | 1.08 | 3.48 | 0.76 | 0.53 | 1.10 |
| bSakai243 | 34 | 12 | 833 | 15 | 3343 | 0.44 | 0.25 | 0.65 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 2.23 | 1.46 | 3.41 | 0.69 | 0.50 | 0.97 |
| bSakai243 | 37 | 38 | 807 | 101 | 3257 | 0.27 | 0.20 | 0.36 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 1.38 | 1.04 | 1.82 | 0.91 | 0.82 | 1.01 |
| Sakai243 | 37 | 11 | 73 | 15 | 402 | 0.42 | 0.23 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 2.75 | 1.68 | 4.52 | 0.68 | 0.49 | 0.95 |
| Symptomatic women | |||||||||||||||||
| cAllbert223 | 2d | 4 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 1.00 | 0.40 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 36.00 | 2.30 | 564.54 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 1.42 |
| Holst252 | 7d | 18 | 17 | 11 | 47 | 0.62 | 0.42 | 0.79 | 0.73 | 0.61 | 0.84 | 2.34 | 1.42 | 3.84 | 0.52 | 0.32 | 0.84 |
| cAllbert223 | 7d | 4 | 0 | 1 | 18 | 0.80 | 0.28 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 1.00 | 28.50 | 1.78 | 456.57 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 1.03 |
| Kurkinen233 | 37 | 7 | 30 | 4 | 36 | 0.64 | 0.31 | 0.89 | 0.55 | 0.42 | 0.67 | 1.40 | 0.83 | 2.35 | 0.67 | 0.30 | 1.50 |
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Sample | Study designs | Inclusion | Exclusion | Testing gestation (weeks) | Frequency of testing | Threshold | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Makrakis246 | 2003 | Greece | 20 | Urine, plasma |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Symptomatic women who presented with threatened preterm labour, 20–35 years, no other pregnancy complication | Absence of cervical dilatation, no evidence of rupture membrane or chorioamnionitis | 24–36 | Single | 7.71 ng/ml (urine), 68.43 ng/ml (plasma) | < 37 |
| Agrez245 | 1999 | Australia | 15 | Urine |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Symptomatic women who presented with threatened preterm labour | ✗ | 27–34 | Single | 5 ng/ml | < 37 |
| Authors | Thresholds | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agrez245 | 5 ng/ml | 4 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 0.67 | 0.22 | 0.96 | 0.89 | 0.52 | 1.00 | 6.00 | 0.87 | 41.44 | 0.38 | 0.12 | 1.19 |
| Makrakis246 | 7.71 ng/ml | 6 | 1 | 3 | 10 | 0.67 | 0.30 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.59 | 1.00 | 7.33 | 1.07 | 50.27 | 0.37 | 0.14 | 0.94 |
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Study designs | Inclusion | Exclusion | Testing gestation | Threshold | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jeffcoat253 | 2001 | USA | 1313 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
All pregnant women being studied by the Perinatal Emphasis Research Center at UAB | Women who required antibiotic prophylaxis for dental examination or who is taking antibiotics | 21–24 | Periodontitis three or more sites with ≥ 3 mm attachment loss (AL), severe periodontitis ≥ 90 sites, and fewer than three healthy sites < 3 mm AL | 37 |
| Offenbacher247 | 2001 | USA | 812 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Pregnant women enrolled before 26 weeks’ gestation | Before 26 weeks’ gestation and within 48 h of deliveries |
Periodontitis: periodontal health (absence of any probe depth (PD) > 3 mm and no sites with AL > 2 mm), moderate severe disease (four or more sites with PD ≥ 5 mm and ≥ 2 mm AL at four or more sites), and mild periodontitis, i.e. less than the moderate to severe group but had more than the healthy group. Progression of periodontitis |
37 | |
| Moore255 | 2004 | UK | 539 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Women who attended for nuchal translucency Down syndrome screening at 12 weeks’ gestation | Pregnancy less than 10 or more than 15 weeks’ gestation, multiple pregnancy and need for antibiotics before dental treatment | 10–15 | Healthy: < 10% sites with PD ≥ 3 mm and < 5% sites with AL ≥ 2 mm, Severe: more than five sites with PD ≥ 5 mm more than three sites with AL ≥ 3 mm | 32, 37 |
| Offenbacher257 | 1996 | USA | 124 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Pregnant women under routine antenatal care in a University Hospital Prenatal Clinic | Concurrent genitourinary tract infection, use of antibiotics and if at risk for bacterial endocarditis | Day 3 postnatal | PD and AL ≥ 3 mm affecting > 60% (extent 3 : 60) in all women and in primiparous | 37 |
| Holbrook251 | 2004 | Iceland | 96 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Healthy otherwise unselected pregnant women, bacterial vaginosis testing using Amsel’s criteria was also performed on enrolled women | 28–30 | More than four pockets > 4 mm PD | 37 | |
| Rajapakse259 | 2005 | Sri Lanka | 227 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Nulliparous, 18–34 years, singleton pregnancy | Hypertension, diabetes, smoking, betel chewing, alcohol and drug abuse | 24–37 | Mean pocket depth, plaque scores and bleeding scores composite that are greater than the median value in the total cohort. | 37 |
| Moore256 | 2005 | UK | 154 |
Case–control Prospective Blinded Test described |
Cases were women who had spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, controls were uncomplicated term vaginal or elective Caesarean section delivery | Multiple pregnancy, medical history that required antibiotic cover, iatrogenic preterm delivery, hypertension, pre-eclampsia, diabetes mellitus. | Day 5 postnatal | PD ≥ 4 mm, ≥ 5 mm and AL ≥ 2 mm, ≥ 3 mm | 37 |
| Goepfert250 | 2004 | USA | 103 |
Case–control Prospective Blinded Test described |
Cases were women who delivered between 24 and 32 weeks’ gestation | Day 3 postnatal | AL > 3 mm and > 5 mm | 32 | |
| Dasanayake248 | 2001 | USA | 80 |
Case–control Prospective Blinded Test described |
Cases were women who had spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation, controls were term delivery. | Missing second trimester samples and elective preterm deliveries | 14–24 | Median and >75% immunoglobulin Porphyromonas gingivalis presence in serology. | 37 |
| Dortbudak249 | 2005 | Austria | 36 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Pregnant women undergoing amniocentesis for medical conditions | ✗ | 15–20 | PD ≥ 5 mm | 37 |
| Radnai258 | 2004 | Hungary | 85 |
Case–control Retrospective Blinded Test described |
Systemically healthy women, cases were spontaneous premature birth before 37 weeks’ gestation | Diabetes, asthma, cardiac or renal problems, thyroid problems, chronic infectious disease or multiple pregnancies, patients who needed prophylaxis antibiotics | Day 3 postnatal | PD ≥ 4 mm, bleeding on probing, and combination of probe depth, bleeding on probing | 37 |
| Jarjoura252 | 2005 | USA | 203 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Fetal or uterine anomalies, cervical incompetence, iatrogenic premature delivery, women who required antibiotics prophylaxis before dental assessment | Day 3 postnatal | Clinical attachment loss (CAL) ≥ 3 mm in five or more sites | 37 |
| Konopka254 | 2003 | Poland | 128 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Cases were women who had spontaneous preterm birth before 37 weeks’ gestation of infant who weighed < 2500 g | Multiple pregnancy, developmental defects, treated infertility patients, IVF, iatrogenic preterm births and systemic infection (apart from UTI) | Day 3 postnatal | Periodontal index > 4 | 37 |
| Authors | Thresholds | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Offenbacher247 | Mild periodontitis | 132 | 434 | 38 | 163 | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.84 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.31 | 1.07 | 0.97 | 1.17 | 0.82 | 0.60 | 1.12 |
| Offenbacher247 | Moderate to severe periodontitis | 18 | 27 | 38 | 163 | 0.32 | 0.20 | 0.46 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.90 | 2.26 | 1.35 | 3.79 | 0.79 | 0.65 | 0.96 |
| Offenbacher247 | Progressive periodontitis | 75 | 180 | 113 | 444 | 0.40 | 0.33 | 0.47 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.75 | 1.38 | 1.12 | 1.71 | 0.84 | 0.74 | 0.96 |
| aMoore255 | Severe periodontitis | 9 | 254 | 4 | 272 | 0.69 | 0.39 | 0.91 | 0.52 | 0.47 | 0.56 | 1.43 | 0.99 | 2.08 | 0.60 | 0.26 | 1.35 |
| aMoore255 | Severe periodontitis | 24 | 239 | 20 | 256 | 0.55 | 0.39 | 0.70 | 0.52 | 0.47 | 0.56 | 1.13 | 0.85 | 1.50 | 0.88 | 0.63 | 1.23 |
| Offenbacher257 | All women with periodontitis | 87 | 22 | 6 | 9 | 0.94 | 0.86 | 0.98 | 0.29 | 0.14 | 0.48 | 1.32 | 1.05 | 1.66 | 0.22 | 0.09 | 0.57 |
| Offenbacher257 | Primiparous with periodontitis | 41 | 11 | 5 | 9 | 0.89 | 0.76 | 0.96 | 0.45 | 0.23 | 0.68 | 1.62 | 1.08 | 2.44 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.63 |
| Holbrook251 | PD ≥ 4 mm in > four pockets | 0 | 16 | 6 | 74 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.46 | 0.82 | 0.73 | 0.89 | 0.39 | 0.03 | 5.90 | 1.13 | 0.90 | 1.42 |
| Rajapakse259 | PD ≥ cohort median value | 27 | 39 | 12 | 149 | 0.69 | 0.52 | 0.83 | 0.79 | 0.73 | 0.85 | 3.34 | 2.35 | 4.73 | 0.39 | 0.24 | 0.63 |
| Moore256 | PD ≥ 4 mm | 5 | 10 | 56 | 83 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.89 | 0.81 | 0.95 | 0.76 | 0.27 | 2.12 | 1.03 | 0.93 | 1.14 |
| Moore256 | LA ≥ 3 mm | 1 | 2 | 60 | 91 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0.76 | 0.07 | 8.23 | 1.01 | 0.96 | 1.05 |
| Moore256 | LA ≥ 2 mm | 3 | 7 | 58 | 86 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.92 | 0.85 | 0.97 | 0.65 | 0.18 | 2.43 | 1.03 | 0.95 | 1.12 |
| Moore256 | PD ≥ 5 mm | 1 | 4 | 60 | 89 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.96 | 0.89 | 0.99 | 0.38 | 0.04 | 3.33 | 1.03 | 0.97 | 1.08 |
| aGoepfert250 | Extent 5 | 11 | 4 | 48 | 40 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.31 | 0.91 | 0.78 | 0.97 | 2.05 | 0.70 | 6.01 | 0.89 | 0.77 | 1.04 |
| aGoepfert250 | Extent 3 | 28 | 13 | 31 | 31 | 0.47 | 0.34 | 0.61 | 0.70 | 0.55 | 0.83 | 1.61 | 0.95 | 2.73 | 0.75 | 0.55 | 1.02 |
| Dortbudak249 | PD ≥ 5 mm | 5 | 6 | 1 | 30 | 0.83 | 0.36 | 1.00 | 0.83 | 0.67 | 0.94 | 5.00 | 2.22 | 11.28 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 1.20 |
| Radnai258 | PD ≥ 4 mm | 22 | 18 | 19 | 26 | 0.54 | 0.37 | 0.69 | 0.59 | 0.43 | 0.74 | 1.31 | 0.83 | 2.07 | 0.78 | 0.52 | 1.18 |
| Radnai258 | BOP | 20 | 9 | 21 | 35 | 0.49 | 0.33 | 0.65 | 0.80 | 0.65 | 0.90 | 2.38 | 1.23 | 4.62 | 0.64 | 0.46 | 0.90 |
| Radnai258 | PD ≥ 4 mm + BOP | 19 | 5 | 22 | 39 | 0.46 | 0.31 | 0.63 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 0.96 | 4.08 | 1.68 | 9.92 | 0.61 | 0.45 | 0.82 |
| Jarjoura252 | Periodontitis | 21 | 25 | 62 | 95 | 0.25 | 0.16 | 0.36 | 0.79 | 0.71 | 0.86 | 1.21 | 0.73 | 2.02 | 0.94 | 0.81 | 1.10 |
| Konopka254 | Periodontal index greater than 4 | 27 | 12 | 57 | 32 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.43 | 0.73 | 0.57 | 0.85 | 1.18 | 0.66 | 2.09 | 0.93 | 0.74 | 1.18 |
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Study designs | Inclusion | Exclusion | Testing gestation (weeks) | Frequency of testing | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Midstream urine sample | |||||||||
| Wren287 | 1969 | Australia | 3099 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
All pregnant patients booking at their first antenatal visit | Twin pregnancies and women who moved hospital | Antenatal | Repeat if positive | < 37 |
| Robertson278 | 1968 | UK | 2184 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Miscarriages, treated women, delivered elsewhere | Booking | Single | < 37 |
| Uncu283 | 2002 | Turkey | 186 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Patients with renal disease, recent or current antibiotic treatment, current or recent asymptomatic bacteriuria | <32 | Repeat if positive | < 37 |
| Layton271 | 1964 | UK | 176 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Antenatal asymptomatic women | <32 | Single | < 37 | |
| Versi284 | 1997 | UK | 6864 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies (Caucasian and Bangladeshi populations only) | 11–14 | Single | < 37 | |
| Patrick277 | 1967 | UK | 575 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Antenatal asymptomatic women | Booking | Single | < 37 | |
| Schieve280 | 1994 | USA | 25,663 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Antenatal | Single | < 37 | |
| LeBlanc272 | 1964 | USA | 1248 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | < 20 | Single | < 37 | |
| Gold265 | 1966 | USA | 1246 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | < 20 | Single | < 37 | |
| Kass268 | 1962 | USA | 1095 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | < 20 | Single | < 37 | |
| Hoja267 | 1964 | USA | 879 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | < 20 | Single | < 37 | |
| Stuart282 | 1965 | UK | 817 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | < 20 | Single | < 37 | |
| Henderson266 | 1965 | USA | 808 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Placenta praevia, pre-eclampsia, abruption, induced labour, erythroblastosis fetalis | < 22 | Single | < 36 |
| Low273 | 1964 | USA | 771 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | < 20 | Single | < 37 | |
| Forkman264 | 1964 | Sweden | 595 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | < 20 | Single | < 37 | |
| Schamadan279 | 1965 | USA | 556 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | < 20 | Single | < 37 | |
| Kincaid269 | 1964 | USA | 556 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | < 20 | Single | < 37 | |
| Whalley285 | 1965 | USA | 283 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | < 20 | Single | < 37 | |
| Sleigh281 | 1964 | UK | 200 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | < 20 | Single | < 37 | |
| Norden276 | 1965 | USA | 197 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | < 20 | Single | < 37 | |
| Kubicki270 | 1976 | Poland | 192 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | 18–23 | Single | < 37 | |
| Bryant263 | 1964 | USA | 66 |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | < 20 | Single | < 37 | |
| Abdul-Jabbar262 | 1991 | Saudi |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Pregnant women without apparent ailments | Booking | Single | < 37 | ||
| Group B streptococcal bacteriuria | |||||||||
| Moller275 | 1984 | Denmark | 2745 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Antenatal | Single | < 37 | |
| McDonald274 | 1989 | Australia | 692 |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | 20–24 | Single | < 37 | |
| White286 | 1984 | UK | 8083 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Antenatal | Single | < 37 | |
| Authors | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Midstream urine sample | ||||||||||||||||
| Wren287 | 15 | 75 | 204 | 2805 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 2.63 | 1.54 | 4.50 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.99 |
| Robertson278 | 13 | 191 | 62 | 1918 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.28 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 1.91 | 1.15 | 3.19 | 0.91 | 0.82 | 1.01 |
| Uncu283 | 6 | 17 | 16 | 147 | 0.27 | 0.11 | 0.50 | 0.90 | 0.84 | 0.94 | 2.63 | 1.16 | 5.96 | 0.81 | 0.62 | 1.05 |
| Layton271 | 4 | 59 | 9 | 104 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.56 | 0.71 | 0.85 | 0.37 | 1.97 | 1.09 | 0.74 | 1.59 |
| aVersi284 | 13 | 139 | 624 | 6694 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.57 | 1.76 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.01 |
| bVersi284 | 39 | 393 | 512 | 5920 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 1.14 | 0.83 | 1.56 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.01 |
| Patrick277 | 7 | 68 | 21 | 479 | 0.25 | 0.11 | 0.45 | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.90 | 2.01 | 1.02 | 3.97 | 0.86 | 0.69 | 1.06 |
| Schieve280 | 293 | 1687 | 2546 | 21,137 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 1.40 | 1.24 | 1.57 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.98 |
| LeBlanc272 | 6 | 21 | 133 | 1088 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 2.28 | 0.94 | 5.55 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 1.01 |
| Gold265 | 0 | 30 | 168 | 1048 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 1.70 | 1.03 | 1.01 | 1.04 |
| Kass268 | 26 | 69 | 88 | 912 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.32 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 3.24 | 2.16 | 4.87 | 0.83 | 0.75 | 0.92 |
| Hoja287 | 1 | 21 | 54 | 803 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.71 | 0.10 | 5.21 | 1.01 | 0.97 | 1.05 |
| Stuart282 | 20 | 68 | 83 | 646 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.28 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.93 | 2.04 | 1.30 | 3.21 | 0.89 | 0.81 | 0.98 |
| Henderson266 | 33 | 15 | 371 | 389 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 2.20 | 1.21 | 3.99 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.99 |
| Low273 | 5 | 75 | 49 | 642 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.37 | 2.10 | 1.01 | 0.93 | 1.11 |
| Forkman264 | 1 | 33 | 19 | 542 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.96 | 0.87 | 0.13 | 6.06 | 1.01 | 0.91 | 1.12 |
| Schamadan279 | 8 | 48 | 25 | 475 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.42 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.93 | 2.64 | 1.36 | 5.11 | 0.83 | 0.69 | 1.01 |
| Kincaid269 | 12 | 44 | 25 | 475 | 0.32 | 0.18 | 0.50 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.94 | 3.83 | 2.22 | 6.59 | 0.74 | 0.59 | 0.92 |
| Whalley285 | 11 | 96 | 21 | 155 | 0.34 | 0.19 | 0.53 | 0.62 | 0.55 | 0.68 | 0.90 | 0.54 | 1.49 | 1.06 | 0.81 | 1.39 |
| Sleigh281 | 7 | 93 | 7 | 93 | 0.50 | 0.23 | 0.77 | 0.50 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 1.00 | 0.58 | 1.72 | 1.00 | 0.58 | 1.72 |
| Norden276 | 11 | 77 | 14 | 95 | 0.44 | 0.24 | 0.65 | 0.55 | 0.47 | 0.63 | 0.98 | 0.61 | 1.58 | 1.01 | 0.70 | 1.47 |
| Kubicki270 | 18 | 83 | 5 | 86 | 0.78 | 0.56 | 0.93 | 0.51 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 1.59 | 1.22 | 2.08 | 0.43 | 0.19 | 0.94 |
| Bryant263 | 2 | 30 | 4 | 40 | 0.33 | 0.04 | 0.78 | 0.57 | 0.45 | 0.69 | 0.78 | 0.24 | 2.49 | 1.17 | 0.64 | 2.13 |
| AbdulJabbar262 | 18 | 180 | 16 | 184 | 0.53 | 0.35 | 0.70 | 0.51 | 0.45 | 0.56 | 1.07 | 0.77 | 1.49 | 0.93 | 0.64 | 1.35 |
| Group B streptococcal bacteriuria | ||||||||||||||||
| Moller275 | 14 | 54 | 228 | 2449 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 2.68 | 1.51 | 4.76 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.99 |
| McDonald274 | 4 | 24 | 46 | 618 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 2.14 | 0.77 | 5.93 | 0.96 | 0.88 | 1.04 |
| Study | Population | Test | Reference standards | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author, publication year | Country | Study quality | n | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | Gestational age at testing | Site and frequency of testing | Criteria for diagnosis of BV | Gestational age at birth (weeks’ gestation) |
| Asymptomatic pregnant women | |||||||||
| Oakeshott 2004293 | USA |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
887 | All consecutive < 10 weeks’ gestation | Miscarriages, terminations, multiple gestations, antibiotic treatment, missing specimen slides | < 10 |
Vaginal swab Single |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) | < 37 |
| Klebanoff 2005288 | USA |
Cohort Prospective Blindeded Test described |
12,937 | Did not report genital itching, burning, malodour to questioning, no major medical or obstetric complications in current pregnancy, not received or expected to receive antibiotics, could be followed after delivery | < 13, 13–14, 15–16, 17–18, 19–20, 21–22 |
Vaginal swab Single |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) | < 37 (data were collected for 23–26 weeks’ gestation births but this was not published) | |
| DeSeta 2005292 | Italy |
Cohort Consecutive Prospective Test described |
598 | Singleton, negative urine culture the past 2 weeks, no other genitourinary tract infection | Diabetes, hypertension, cardiac or chronic renal disease, Rh iso-immunization, cervical cerclage, antibiotics treatment, unprotected intercourse or vaginal washing in the last 48 h | 13–18 |
Vaginal swab Single |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) | < 37 |
| Purwar 2001307 | India |
Cohort Blinded Prospective Test described |
938 | Arbitrary selection of singleton pregnancies | Multiple pregnancy, placenta praevia, symptomatic vaginal discharge, history suggestive of cervical incompetence, vaginal bleeding, leaking membrane, antibiotic use in the preceding 15 days, suspected uterine malformation | 16–28 |
Vaginal swab Single |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) | < 37 |
| Hillier 1995306 | USA |
Cohort Blinded Prospective Test described |
8197 | Women with singleton pregnancies who have completed 23–26 weeks’ gestation and attending routine antenatal clinic | < 16 years old; Rh iso-immunisation disease, preceding 2 weeks or current use of antibiotics, chronic renal disease, organic heart disease, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, multiple gestation, cervical cerclage, hypertension requiring treatment | 23–26 |
Posterior fornix Single |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) or vaginal pH >4.5 | < 37 |
| Govender 1996305 | S Africa |
Cohort Blinded Prospective Test described |
168 | Singleton pregnancies less than 30 weeks’ gestation | Previous spontaneous premature birth, antibiotics in the current pregnancy, symptomatic discharge, urinary tract infection, multiple pregnancy | < 30 weeks |
Vaginal swab Single |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) | < 37 |
| Kurki 1992597 | Finland |
Cohort Blinded Prospective Test described |
733 |
Singletons First pregnancy |
Antibiotics in current pregnancy, multiple pregnancy, induction before 37 weeks | 8–17 |
Posterior fornix Single |
Gram staining (Spiegel’s criteria) |
< 37 |
| Crane 199999 | Canada |
Cohort Blinded Prospective Test described |
140 | Singletons | Multiple pregnancy, pre-labour rupture of membranes, placenta praevia, previously treated for BV in current pregnancy, cervical cerclage, major fetal anomalies | 20–24 |
Posterior fornix Single |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) or clinical criteria | < 37 |
| Hay 1994737 | England |
Cohort Blinded Prospective Test described |
706 |
Singletons First antenatal visit between 9 and 24 weeks’ gestation |
Multiple pregnancy, lethal congenital malformations, antibiotics in the current pregnancy | 9–24 |
Posterior fornix Single |
Gram staining (Spiegel’s criteria) | < 37 |
| McGregor 1990411 | USA |
Cohort Blinded Prospective Test described |
194 |
Singletons Women receiving care at two prenatal clinics |
Multiple pregnancy, cerclage, placenta praevia, vaginal bleeding, preterm labour, antibiotics course in preceding 2 weeks, douching within 24 h of examination | 24 |
Mid-vaginal swab Single |
Gram staining (Spiegel’s criteria) |
< 37 |
| Gratacos 1998303 | Spain |
Cohort Blinded Prospective Test described |
635 | Singletons | Multiple pregnancy, abortion or termination, congenital malformation, lost to follow-up | <24 and <35 |
Posterior fornix Single |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) |
< 37 |
| Helou 1996304 | Israel |
Cohort Blinded Prospective Test described |
400 | Singletons | Iatrogenic preterm delivery | 15–20 and 27–32 |
Vaginal swab Serial (twice) |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) |
< 37 |
| Balu 2003291 | USA |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
646 | Singleton pregnancy, access to telephone, > 16 years old, planned to continue care in the same hospital | 24–29 | Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) | < 32, < 34, and < 37 | ||
| Riduan 1993295 | Indonesia |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
490 | Singletons | Medical conditions associated with preterm delivery, previous tocolysis or steroids treatment, antibiotics within 2 weeks of enrolment, incompetent cervix | 16–20 and 28–32 |
Vaginal swab Serial (twice) |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) |
< 37 |
| Meis 1995294 | USA |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
2929 | Singletons | Cerclage, major congenital anomaly, placenta praevia, polyhydramnios, oligohydramnios, cervix > 2 cm dilated in nulliparous and > 3 cm in multiparous women | 24 and 28 |
Posterior fornix Serial (twice) |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) |
< 35 |
| Thorsen 1996296 | USA |
Cohort Test described |
2927 | Singletons | Congenital malformations, placenta praevia, pre-eclampsia, cerclage, placental abruption, serious medical disease, Rh iso-immunisation | 7–24 |
Posterior fornix Single |
Clinical criteria | < 37 |
| Mascagni 2001289 | USA |
Retrospective Case–control |
103 | Singleton pregnancy, 18–34 years old, asymptomatic from vaginal infection | Medical or obstetrics problem requiring elective preterm delivery, cigarette smoking, diabetes, hypertension, sexually transmitted disease | 15–16 |
Vaginal swab Single |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) |
<37 |
| Women with threatened preterm labour | |||||||||
| Goffinet 2003308 | France |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
212 | Singleton with threatened preterm labour and intact membrane. | Rupture of membrane, chorioamnionitis, suspected fetal distress, fetal malformation, maternal disorder requiring delivery, > 3 cm dilatation | 24–34 |
Vaginal swab Single |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) |
< 7 days of testing, < 33, and < 35 |
| Martius 1988301 | USA |
Blinded Prospective Case–control Test described |
212 | Singletons | Age < 16 years, antibiotics within 2 weeks, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, congenital heart disease, pre-eclampsia, renal disease, essential hypertension, placental abruption, placenta praevia, multiple gestation, congenital malformation | 20–36 |
Vaginal swab Single |
Gram staining (Spiegel’s criteria) |
< 37 |
| Holst 1994241 | Sweden |
Prospective Case–control Consecutive Test described |
87 |
Women with singleton pregnancies admitted for preterm labour Control were women admitted in labour at term |
Diabetics, pre-eclampsia, placental abruption, placenta praevia, multiple gestation, cervical cerclage, pre-labour preterm rupture of membrane | 24–36 |
Vaginal swab Single |
Gram staining (Spiegel’s criteria) |
< 34 and < 37 |
| Eschenbach 1984300 | USA |
Blinded Prospective Case–control Test described |
171 |
Women admitted in labour and had vaginal exam 2 controls, women who delivered at term, were selected for each case enrolled |
Vaginal swab was not obtained Iatrogenic preterm birth Congenital malformation Placental abruption Placenta praevia Vaginal bleeding of indeterminate origin |
24–36 |
Vaginal swab Single |
Gas liquid chromatography | < 37 |
| Elliott 1990297 | Kenya |
Retrospective Case–control Test described |
276 |
Preterm singleton pregnancies who presented with preterm labour Control were women who delivered >36 weeks’ gestation |
None stated | 24–36 |
Vaginal swab Single |
Gram staining (Spiegel’s criteria) |
< 36 |
| Subtil 2002299 | France |
Prospective Case–control Test described |
102 |
Women presented with preterm labour with either cervical dilatation >2 cm or history of previous preterm labour Control matched for gestation and admitted preterm for reasons unrelated to preterm labour (e.g. pre-eclampsia, diabetes, cholestasis) |
Gestational age less than 20 or more than 34 weeks’ gestation, local or general antibiotic therapy within the past 8 days, premature rupture of membrane, bleeding, or presence of a clear cause for preterm labour (e.g. multiple pregnancy, hydramnios) | 20–34 |
Vaginal swab Single |
Clinical criteria | < 37 |
| Krohn 1991298 | USA |
Prospective Test described |
211 | Women who presented with preterm labour | Less than 16 or more than 40 years old, uterine or fetal anomaly, hypertension, diabetics, cervical cerclage, placenta praevia, placental abruption | 22–34 |
Vaginal swab Single |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) |
< 35 |
| Carlini 2003290 | USA |
Case–control Prospective Test described |
753 | Singleton with threatened preterm labour and intact membrane | Elective preterm delivery | 20–37 |
Vaginal swab Single |
Gram staining (Nugent’s criteria) |
< 37 |
| Authors | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single 37 weeks asymptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||
| Oakeshott293 | 6 | 143 | 38 | 700 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.83 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.38 | 1.72 | 1.04 | 0.92 | 1.17 |
| Crane99 | 1 | 30 | 8 | 101 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 0.77 | 0.69 | 0.84 | 0.49 | 0.07 | 3.16 | 1.15 | 0.90 | 1.48 |
| DeSeta292 | 14 | 90 | 35 | 459 | 0.29 | 0.17 | 0.43 | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.87 | 1.74 | 1.08 | 2.82 | 0.85 | 0.71 | 1.02 |
| Govender305 | 24 | 64 | 11 | 69 | 0.69 | 0.51 | 0.83 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.61 | 1.43 | 1.07 | 1.90 | 0.61 | 0.36 | 1.01 |
| Gratacos303 | 20 | 105 | 26 | 484 | 0.43 | 0.29 | 0.59 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.85 | 2.44 | 1.68 | 3.54 | 0.69 | 0.53 | 0.89 |
| Helou304 | 7 | 53 | 31 | 309 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 0.34 | 0.85 | 0.81 | 0.89 | 1.26 | 0.62 | 2.57 | 0.96 | 0.82 | 1.12 |
| Hillier306 | 77 | 1141 | 29 | 6949 | 0.73 | 0.63 | 0.81 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 5.15 | 4.53 | 5.86 | 0.32 | 0.23 | 0.43 |
| Klebanoff288 | 74 | 121 | 423 | 1156 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 1.57 | 1.20 | 2.06 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.98 |
| Purwar307 | 30 | 83 | 29 | 783 | 0.51 | 0.37 | 0.64 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.92 | 5.31 | 3.84 | 7.33 | 0.54 | 0.42 | 0.71 |
| Balu291 | 71 | 157 | 171 | 350 | 0.29 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.69 | 0.65 | 0.73 | 0.95 | 0.75 | 1.20 | 1.02 | 0.93 | 1.13 |
| Riduan295 | 17 | 67 | 48 | 358 | 0.26 | 0.16 | 0.39 | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.88 | 1.66 | 1.04 | 2.64 | 0.88 | 0.75 | 1.02 |
| Serial 37 weeks asymptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||
| Gratacos303 | 8 | 33 | 7 | 38 | 0.53 | 0.27 | 0.79 | 0.54 | 0.41 | 0.65 | 1.15 | 0.67 | 1.96 | 0.87 | 0.49 | 1.56 |
| Helou304 | 3 | 24 | 20 | 330 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.96 | 1.92 | 0.63 | 5.92 | 0.93 | 0.79 | 1.10 |
| Riduan295 | 8 | 31 | 53 | 370 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.24 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 1.70 | 0.82 | 3.52 | 0.94 | 0.85 | 1.04 |
| Amsel 37 weeks asymptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||
| Crane99 | 2 | 18 | 7 | 113 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 0.60 | 0.86 | 0.79 | 0.92 | 1.62 | 0.44 | 5.91 | 0.90 | 0.63 | 1.29 |
| Thorsen296 | 14 | 438 | 91 | 2434 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.53 | 1.43 | 1.02 | 0.95 | 1.10 |
| Cauci302 | 11 | 61 | 75 | 356 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.22 | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.48 | 1.59 | 1.02 | 0.93 | 1.12 |
| 37 weeks symptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||
| Subtil299 Amsel | 6 | 8 | 38 | 50 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.86 | 0.75 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.37 | 2.64 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 1.17 |
| Goffinet308 Nugent | 4 | 19 | 33 | 156 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.89 | 0.84 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.36 | 2.76 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 1.13 |
| Carlini290 Nugent | 85 | 39 | 321 | 308 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.92 | 1.86 | 1.31 | 2.65 | 0.89 | 0.84 | 0.95 |
| Krohn298 Nugent | 35 | 20 | 104 | 52 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.33 | 0.72 | 0.60 | 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.57 | 1.45 | 1.04 | 0.87 | 1.23 |
| Holst241 Spiegel | 9 | 3 | 13 | 24 | 0.41 | 0.21 | 0.64 | 0.89 | 0.71 | 0.98 | 3.68 | 1.13 | 11.97 | 0.66 | 0.46 | 0.96 |
| Martius301 Spiegel | 21 | 34 | 40 | 117 | 0.34 | 0.23 | 0.48 | 0.77 | 0.70 | 0.84 | 1.53 | 0.97 | 2.41 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 1.03 |
| Elliot297 Spiegel | 30 | 115 | 27 | 104 | 0.53 | 0.39 | 0.66 | 0.47 | 0.41 | 0.54 | 1.00 | 0.76 | 1.32 | 1.00 | 0.73 | 1.36 |
| Authors | Year | Country | Population | Quality of studies | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | Testing gestation (weeks’ gestation) | Frequency of testing | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eden309 | 1991 | USA | 94 |
Cohort Blinded Prospective Test described |
Inner city pregnant women | None stated | 24–32 | Single | < 5 days of testing, < 34 < 37 |
| Guinn310 | 1994 | USA | 247 |
Cohort Blinded Prospective Test described |
Nulliparous women receiving private antenatal care with singleton pregnancies | Placenta praevia, multiple gestations, preterm pre-labour rupture of membrane | 26–28 | Single | < 34 and < 37 |
| Authors | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guinn310 | 34 | 7 | 40 | 2 | 198 | 0.78 | 0.40 | 0.97 | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.88 | 4.63 | 2.95 | 7.25 | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.91 |
| Guinn310 | 37 | 3 | 44 | 2 | 198 | 0.60 | 0.15 | 0.95 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.86 | 3.30 | 1.54 | 7.08 | 0.49 | 0.17 | 1.43 |
| Eden309 | 37 | 16 | 31 | 3 | 44 | 0.84 | 0.60 | 0.97 | 0.59 | 0.47 | 0.70 | 2.04 | 1.46 | 2.84 | 0.27 | 0.09 | 0.77 |
| aEden309 | 37 | 11 | 8 | 2 | 16 | 0.85 | 0.55 | 0.98 | 0.67 | 0.45 | 0.84 | 2.54 | 1.38 | 4.68 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.85 |
| Eden309 | 5b | 12 | 35 | 0 | 47 | 1.00 | 0.74 | 1.00 | 0.57 | 0.46 | 0.68 | 2.25 | 1.71 | 2.95 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 1.02 |
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Test | Study design | Inclusion | Exclusion | Testing gestation (weeks) | Frequency of testing | Threshold | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iams76 | 2002 | USA | 270 | Tocogram |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Women who had received or were scheduled to receive an ambulatory monitor or tocolytic medication or to undergo cerclage, were complicated by placenta praevia or a major fetal anomaly detected by ultrasonography. Women who did not have telephones were not enrolled, because the transmission of data collected by the monitoring system required a telephone | 22–30 | Four times two sessions at least 2 h apart (one at night, one at day time) before 28 weeks and two more sessions between 28 and 30 weeks | Maximum night-time and day time contraction of four or more per hour | < 35 |
| Iams312 | 1988 | USA | 100 | Tocogram |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Asymptomatic singleton pregnancies data only | 20–34 | Single | Four or more contractions per hour | < 37 | |
| Symptomatic women | |||||||||||
| Bell311 | 1983 | UK | 15 | Tocogram |
Cohort Test described |
Singleton pregnancy presenting with threatened preterm labour | 20–28 | Single | Pmax ≥ 15 mmHg | < 37 | |
| Maner313 | 2003 | USA | 99 | Electromyogram |
Case–control Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies presenting with threatened preterm labour leading to vaginal deliveries, intact membrane, dilatation < 2 cm, no evidence of systemic infection or fetal distress | To ensure optimal recording, patient over 230 lb was excluded | 24–42 | Single | 0.463 | < 37 |
| Authors | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||
| aIams76 | 4 | 8 | 42 | 214 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 2.41 | 0.76 | 7.68 | 0.95 | 0.86 | 1.04 |
| bIams76 | 0 | 4 | 48 | 218 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.51 | 0.03 | 9.24 | 1.01 | 0.98 | 1.05 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||
| Bell311 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 9 | 0.75 | 0.19 | 0.99 | 0.82 | 0.48 | 0.98 | 4.13 | 1.04 | 16.32 | 0.31 | 0.05 | 1.71 |
| Maner313 | 23 | 3 | 19 | 54 | 0.55 | 0.39 | 0.70 | 0.95 | 0.85 | 0.99 | 10.40 | 3.34 | 32.38 | 0.48 | 0.34 | 0.67 |
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Quality of studies | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | Testing gestation (weeks’ gestation) | Frequency of testing | Thresholds | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Arabin314 | 1985 | Germany | 176 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies presenting with threatened preterm labour from 20 weeks’ gestation onwards | Iatrogenic preterm delivery, suspected chorioamnionitis, fetal distress, placental bleeding, polyhydramnios | 20–36 | Serial | > 2.8, > 3.4 mA | 37 |
| Authors | Threshold (mA) | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabin314 | 2.8 | 18 | 34 | 15 | 109 | 0.55 | 0.36 | 0.72 | 0.76 | 0.68 | 0.83 | 2.29 | 1.50 | 3.52 | 0.60 | 0.41 | 0.88 |
| Arabin314 | 3.4 | 25 | 46 | 8 | 97 | 0.76 | 0.58 | 0.89 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 0.75 | 2.36 | 1.73 | 3.20 | 0.36 | 0.19 | 0.66 |
| Study | Year | Language | Study quality | n | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | Frequency of testing | Testing gestation (weeks’ gestation) | Definitions of thresholds for abnormality | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senden92 | 1996 | English |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinded Test described |
25 | Singletons presenting with threatened preterm labour | PPROM, vaginal bleeding, chorioamnionitis, diabetes mellitus, cervical dilatation > 4 cm, history suggestive of cervical incompetence | Single | 25–35 | Absence of sustained FBM in a 30-s period during 30-min observations | < 7 days |
| Schreyer321 | 1988 | English |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Test described |
70 | Uncomplicated singleton pregnancies presenting with threatened preterm labour | Multiple pregnancies, PPROM, vaginal bleeding, pyrexia, non-recordable uterine contractions on tocodynamometer, non-reassuring fetal heart rate tocography | Single | 32–36 | No sustained FBM (lasting > 20 s) in a 45-min observation period |
< 24 h < 48 h < 7 days |
| Agustsson315 | 1987 | English |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
64 | Women suspected of preterm labour | Advanced cervical dilatation, regular contraction not detectable | Single | 26–36 | No sustained FBM (lasting > 20 s) in a 45-min observation period |
< 56 h < 7 days |
| Besinger316 | 1987 | English |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
50 | Women suspected of threatened preterm labour | None stated | Single | 26–34 | No sustained FBM (lasting > 20 s) in a 20-min observation period | < 48 h |
| Kanaan319 | 1991 | English |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
34 |
Singletons Healthy volunteers Regular preterm uterine contractions |
Vaginal bleeding, PPROM | Single | 24–36 | Absence of FBM in a 20-s period or decreased FBM in a 15-min observation | < 48 h |
| Markwitz320 | 2001 | Polish |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
36 | Singleton pregnancies with suspected preterm labour | None stated | Single | 28–36 | No sustained FBM (lasting > 20 s) in a 30-min observation period | < 7 days |
| Devoe318 | 1994 | English |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
25 |
Regular uterine contractions No clinical signs of chorioamnionitis No significant vaginal bleeding Singletons |
Congenital abnormalities, maternal medical or obstetrical complications | Single | 28–36 | Absence of FBM within 6-s period in a 45-min observation | < 7 days |
| Castle317 | 1983 | English |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
24 | Women suspected of preterm labour | None stated | Single | 25–34 | No sustained FBM (lasting > 20 s) in a 45-min observation period | < 7 days |
| Study | Intact membrane (Intact) or pre-labour premature rupture of membrane (PPROM) | Reference standards (hours to delivery or within days of testing) | TP | FP | FN | TN | Likelihood ratios for positive test (LR+) (95% confidence interval) | Likelihood ratios for negative test (LR–) (95% confidence interval) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agustsson315 | Intact | < 56 h | 17 | 0 | 5 | 42 | 65.43 (4.12–1039.20) | 0.23 (0.11–0.49) |
| Agustsson315 | Intact | < 7 days | 17 | 0 | 14 | 33 | 37.19 (2.33–93.09) | 0.45 (0.31–0.67) |
| Besinger316 | Intact | < 48 h | 9 | 1 | 4 | 26 | 18.69 (2.64–132.33) | 0.32 (0.14–0.72) |
| Besinger316 | PPROM | < 48 h | 7 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 7.50 (0.56–100.87) | 0.07 (0.00–1.07) |
| Castle317 | Intact | < 7 days | 5 | 0 | 2 | 17 | 24.75 (1.55–396.04) | 0.29 (0.09–0.92) |
| Castle317 | PPROM | < 7 days | 10 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 2.47 (0.22–28.05) | 0.38 (0.20–0.71) |
| Devoe318 | Intact | < 7 days | 2 | 0 | 10 | 38 | 15.00 (0.77–292.61) | 0.83 (0.65–1.07) |
| Devoe318 | Intact | < 72 h | 2 | 0 | 8 | 40 | 18.64 (0.96–360.56) | 0.80 (0.59–1.09) |
| Devoe318 | PPROM | < 7 days | 9 | 0 | 14 | 2 | 2.38 (0.18–31.28) | 0.61 (0.44–0.84) |
| Devoe318 | PPROM | < 72 h | 11 | 0 | 9 | 5 | 6.57 (0.45–96.05) | 0.45 (0.28–0.73) |
| Kanaan319 | Intact | < 48 h | 4 | 11 | 1 | 18 | 2.11 (1.11–4.00) | 0.32 (0.05–1.90) |
| Markwitz320 | Intact | < 7 days | 8 | 0 | 4 | 24 | 32.69 (2.04–522.93) | 0.33 (0.15–0.74) |
| Markwitz320 | PPROM | < 7 days | 16 | 0 | 6 | 2 | 4.30 (0.34–54.76) | 0.27 (0.14–0.54) |
| Schreyer321 | Intact | < 24 h | 7 | 7 | 1 | 55 | 7.75 (3.68–16.33) | 0.14 (0.02–0.88) |
| Schreyer321 | Intact | < 48 h | 11 | 3 | 2 | 54 | 16.08 (5.22–49.55) | 0.16 (0.05–0.58) |
| Schreyer321 | Intact | < 7 days | 12 | 2 | 4 | 52 | 20.25 (5.05–81.23) | 0.26 (0.11–0.61) |
| Senden92 | Intact | < 7 days | 2 | 2 | 3 | 18 | 4.00 (0.73–21.84) | 0.67 (0.32–1.38) |
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Study designs | Inclusion | Exclusion | Testing gestation (weeks) | Frequency of testing | Threshold (mm) | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leung329 | 2005 | HK | 2952 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancy of ethnic Chinese women only | Fetal abnormalities, non-viable pregnancies, lack of outcome information, outside test gestation | 18–22 | Single | < 15, < 20, < 25, < 27, < 30, < 35 | < 34 |
| Yazici335 | 2004 | Turkey | 357 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancies in the absence of history of cervical incompetence, PPROM or previous preterm delivery | Uterine or fetal anomalies, pregnancy-related complications, maternal systemic disease | 24 | Single | < 32.5 | < 36 |
| Owen331 | 2001 | USA | 183 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinded Test described |
Singletons with at least one previous spontaneous preterm birth | Cervical cerclage, uterine anomaly, chronic medical problem that may cause iatrogenic preterm delivery | 16–18 | Single | < 15, < 20, < 25, < 30 | < 35 |
| Berghella326 | 1997 | USA | 96 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinded Test described |
Singletons, previous spontaneous preterm birth, more than two previous abortions, previous cone biopsy, Ehlers–Danlos syndrome | Cervical cerclage, placenta praevia, major fetal anomaly | 14–22 | Single | < 16, < 25 | < 35 |
| Andrew325 | 2000 | USA | 69 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancies with previous history of spontaneous preterm birth between 16–30 weeks’ gestation | Medical or obstetrical complication, history of incompetent cervix that required cerclage, presented for antenatal care after 28 weeks | < 20 | Thrice | < 22, < 25 | < 35 |
| To334 | 2001 | UK | 6334 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | 22–24 | Single | < 15 | 33 | |
| Sakai243 | 2004 | Japan | 4203 |
Cohort Prospective Blinding Test described |
Asymptomatic women with singleton pregnancy and intact membrane | Preterm pre-labour rupture of membrane, threatened or impending miscarriage or preterm delivery, genital bleeding | 20–28 | Single | 25 | < 32, < 34, < 37 |
| Taipale333 | 1998 | Finland | 3694 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Inadequate imaging, iatrogenic preterm delivery, fetal death or malformation | 18–22 | Single | < 25, < 29, < 35, < 40, < 45, < 50 | < 35, < 37 |
| Hibbard328 | 2000 | USA | 760 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | 16–22 | Single | < 22, < 27, < 30 | < 35 | |
| Dilek327 | 2006 | Turkey | 250 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Test described |
Singleton pregnancies in the absence of history of cervical incompetence, PPROM or previous preterm delivery | Uterine or fetal anomalies, pregnancy-related complications, maternal systemic disease | 22 | Single | < 33.15 | < 37 |
| Andersen324 | 1990 | USA | 113 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singletons | Placenta praevia, patient thought to be at risk from cervical incompetence | 7–30 | Single | < 39 | < 37 |
| Carvalho66 | 2005 | Brazil | 1958 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancy attending routine antenatal care at 21–24 weeks’ gestation | Iatrogenic preterm delivery, missing outcomes | 21–24 | Single | < 10, < 15, < 20, < 25, < 30 | < 34 |
| Pires332 | 2005 | Brazil | 338 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton uncomplicated pregnancy | Previous history of preterm delivery, uterine or fetal abnormalities, miscarriage, fetal death, alteration in amniotic fluid, placenta praevia, previous uterine or cervical surgery, surgical procedures during gestation and conditions requiring iatrogenic preterm delivery | 21–24 | Single | < 20 | < 35, < 37 |
| Mara330 | 2002 | Czech Republic | 247 |
Case–control Prospective Test described |
Singleton viable pregnancy, delivering at investigating institution | Congenital or chromosomal abnormalities, history of uterine or cervix surgery, more than three previous vaginal deliveries | 18–20 | Single | < 20 | < 34 |
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Study designs | Inclusion | Exclusion | Testing gestation (weeks) | Frequency of testing | Threshold (mm) | Outcome (weeks’ gestation)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crane326 | 1997 | USA | 136 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancies whose contraction has been arrested by tocolysis | Cervical dilatation > 3 cm, placenta praevia, PPROM | 24–34 | Single | < 30 | < 34 |
| Tsoi349 | 2005 | UK | 510 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancy presenting with threatened preterm labour, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | ✗ | 24–34 | Single | < 5, < 10, < 15, < 20 | < 48 h, < 7 days of testing, < 37 |
| Schmitz345 | 2006 | France | 359 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancy presenting with threatened preterm labour, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | Cervical manipulation, PPROM, fetal or uterine anomalies, vaginal bleeding, placenta praevia, abruption, IUGR, pre-eclampsia, iatrogenic preterm delivery | 18–34 | Single | < 15, < 25, < 30 | < 7 days of testing, < 35 |
| Fuchs338 | 2004 | Germany | 253 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancy presenting with threatened preterm labour, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | PPROM, cervical cerclage, requirement for iatrogenic preterm delivery, abruption, placenta praevia, suspected fetal distress | 24–36 | Single | < 15 | < 7 days of testing |
| Tsoi347 | 2003 | UK | 216 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton viable pregnancies presenting with threatened preterm labour | Cervical dilatation > 3 cm or PPROM | 24–36 | Single | < 15 | < 7 days of testing |
| Onderoglu82 | 1997 | Turkey | 90 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singletons, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm, absence of fetal and maternal complications | ✗ | 25–36 | Single | < 28 | < 37 |
| Tekesin346 | 2005 | Germany | 85 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancy presenting with threatened preterm labour, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | Fetal abnormalities, PPROM, cervical cerclage, requirement for iatrogenic preterm delivery, abruption, placenta praevia, suspected fetal distress | 24–36 | Single | < 25 | < 37 |
| Kurkinen233 | 2001 | Finland | 76 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Test described |
Consecutive singleton pregnant women between 22 and 32 weeks’ gestation who presented with threatened preterm labour | PPROM, impending preterm delivery | 22–32 | Single | < 29.3 | < 37 |
| Tsoi348 | 2004 | UK | 63 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancy presenting with threatened preterm labour, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | PPROM | 24–36 | Single | < 15 | < 7 days of testing |
| Rozenberg134 | 2003 | France | 28 |
Cohort Prospective Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancy presenting with threatened preterm labour, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | History of cervical incompetence with cerclage, suspected chorioamnionitis, PPROM, polyhydramnios, placenta praevia, abruption, IUGR, pre-eclampsia, fetal distress, other maternal or fetal distress requiring preterm delivery | 24–34 | Single | < 26 | < 37 |
| Gomez112 | 2005 | Chile | 215 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancy presenting with threatened preterm labour, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | ✗ | 22–35 | Single | < 15, < 30 | < 48 h, < 7, < 14 days of testing, < 32, < 35 |
| Venditelli390 | 2001 | France | 174 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Cervical dilatation > 3 cm, PPROM, cervical cerclage, active vaginal bleeding, known fetal malformation or death, placenta praevia | 18–36 | Single | < 30 | < 37 |
| Daskalakis337 | 2005 | Greece | 172 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancy presenting with threatened preterm labour, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm | PPROM, cervical cerclage, requirement for iatrogenic preterm delivery, abruption, placenta praevia, suspected fetal distress | 24–34 | Single | < 20, < 25, < 30, < 35 | < 34 |
| Goffinet339 | 1997 | France | 108 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Cervical cerclage, PPROM, cervical dilatation > 2 cm, iatrogenic preterm delivery | 24–34 | Single | < 26 | < 37 |
| Rizzo227 | 1996 | Italy | 108 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm, absence of maternal or fetal complication | ✗ | 24–36 | Single | < 20 | < 37 |
| Botsis64 | 2005 | Greece | 104 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton viable pregnancy presenting with threatened preterm labour between 24 and 36 weeks’ gestation with intact fetal membrane and cervical dilatation < 2 cm | ✗ | 24–36 | Single | < 15 | < 7 days of testing |
| Murakawa341 | 1993 | Japan | 32 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Suspicion of cervical incompetence | 25–35 | Single | < 30, < 35 | < 37 |
| Rageth342 | 1997 | Switzerland | 61 |
Cohort Retrospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies whose contraction has been arrested by tocolysis | IUGR, pre-eclampsia, diabetes | 25–35 | Single | < 30 | < 34 |
| Authors | Year | Country | n | Study designs | Inclusion | Exclusion | Testing gestation (weeks) | Frequency of testing | Threshold | Outcome (weeks’ gestation)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Leung329 | 2005 | HK | 2952 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancy of ethnic Chinese women only | Fetal abnormalities, non-viable pregnancies, lack of outcome information, outside test gestation | 18–22 | Single | 5 mm length | 34 |
| Iams322 | 1996 | USA | 2915 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Multiple gestations, cervical cerclage, placenta praevia, fetal anomaly | at 28 | Twice | 3 mm length | 35 |
| Andrews325 | 2000 | USA | 69 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancies with previous history of spontaneous preterm birth between 16 and 30 weeks’ gestation | Medical or obstetrical complication, history of incompetent cervix that required cerclage, presented for antenatal care after 28 weeks | 25–29 | Twice | any | 35 |
| To334 | 2001 | UK | 6334 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | ✗ | 22–24 | Single | 5 mm width | 33 |
| Pires332 | 2005 | Brazil | 338 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton uncomplicated pregnancy | Previous history of preterm delivery, uterine or fetal abnormalities, miscarriage, fetal death, alteration in amniotic fluid, placenta praevia, previous uterine or cervical surgery, surgical procedures during gestation and conditions requiring iatrogenic preterm delivery | 21–24 | Single | any | 35 |
| Mara330 | 2002 | Czech Republic | 247 |
Case–control Prospective |
Singleton viable pregnancy, delivery at investigating institutions | Congenital or chromosomal abnormalities, history of uterine or cervix surgery, greater than 3 previous vaginal deliveries | 18–20 | Single | any | 34 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||
| Crane336 | 1997 | USA | 136 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancies whose contraction has been arrested by tocolysis | Cervical dilatation > 3 cm, placenta praevia, PPROM | 24–34 | Single | V-shaped | 37 |
| Gomez340 | 1994 | USA | 59 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Blinded Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | PPROM, cervix dilatation >3 cm | 21–35 | Single | 6 mm width | 36 |
| Kurkinen233 | 2001 | Finland | 76 |
Cohort Prospective Consecutive Test described |
Consecutive singleton pregnant women between 22 and 32 weeks’ gestation who presented with threatened preterm labour | PPROM, impending preterm delivery | 22–32 | Single | 5 mm width | 37 |
| Okitsu323 | 1992 | Japan | 130 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies | Placenta praevia | 25–36 | Single | 5 mm width | 36 |
| Rizzo227 | 1996 | Italy | 108 |
Cohort Prospective Test described |
Singleton pregnancies, intact membrane, cervical dilatation < 3 cm, absence of maternal or fetal complication | 24–36 | Single | 5 mm width | 37 | |
| Authors | Thresholds (mm) | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34 weeks’ gestation | ||||||||||||||||||
| < 20 weeks’ gestation | ||||||||||||||||||
| aAndrew325 | 25 | 35 | 5 | 0 | 10 | 38 | 0.33 | 0.12 | 0.62 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 26.81 | 1.57 | 457.07 | 0.66 | 0.47 | 0.95 |
| aAndrew325 | 22 | 35 | 4 | 0 | 11 | 38 | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 21.94 | 1.25 | 384.29 | 0.73 | 0.53 | 0.99 |
| Leung329 | 25 | 34 | 5 | 48 | 15 | 2884 | 0.25 | 0.09 | 0.49 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 15.27 | 6.80 | 34.30 | 0.76 | 0.59 | 0.98 |
| Leung329 | 15 | 34 | 2 | 0 | 18 | 2932 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.32 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 698.33 | 34.56 | 14,109.00 | 0.88 | 0.75 | 1.03 |
| Leung329 | 30 | 34 | 7 | 288 | 13 | 2644 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.59 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 3.56 | 1.94 | 6.54 | 0.72 | 0.52 | 0.99 |
| Leung329 | 35 | 34 | 12 | 1021 | 8 | 1911 | 0.60 | 0.36 | 0.81 | 0.65 | 0.63 | 0.67 | 1.72 | 1.20 | 2.47 | 0.61 | 0.36 | 1.05 |
| Leung329 | 27 | 34 | 7 | 111 | 13 | 2821 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.59 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 9.25 | 4.95 | 17.26 | 0.68 | 0.49 | 0.93 |
| Leung329 | 20 | 34 | 2 | 4 | 18 | 2928 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.32 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 73.30 | 14.23 | 377.66 | 0.90 | 0.78 | 1.04 |
| Owen331 | 20 | 35 | 5 | 1 | 42 | 135 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.23 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 14.47 | 1.73 | 120.69 | 0.90 | 0.81 | 0.99 |
| Owen331 | 25 | 35 | 9 | 3 | 39 | 132 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.33 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 8.44 | 2.38 | 29.88 | 0.83 | 0.72 | 0.95 |
| Owen331 | 30 | 35 | 12 | 24 | 29 | 118 | 0.29 | 0.16 | 0.46 | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.89 | 1.73 | 0.95 | 3.15 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 1.05 |
| Owen331 | 15 | 35 | 5 | 0 | 43 | 135 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 30.53 | 1.72 | 542.02 | 0.89 | 0.81 | 0.98 |
| Hibbard328 | 27 | 35 | 15 | 25 | 36 | 684 | 0.29 | 0.17 | 0.44 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 8.34 | 4.70 | 14.80 | 0.73 | 0.61 | 0.87 |
| Hibbard328 | 22 | 35 | 11 | 16 | 40 | 693 | 0.22 | 0.11 | 0.35 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 9.56 | 4.68 | 19.50 | 0.80 | 0.69 | 0.93 |
| Hibbard328 | 30 | 35 | 21 | 66 | 30 | 643 | 0.41 | 0.28 | 0.56 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.93 | 4.42 | 2.96 | 6.60 | 0.65 | 0.51 | 0.82 |
| Mara330 | 20 | 34 | 3 | 0 | 6 | 238 | 0.33 | 0.07 | 0.70 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 167.30 | 9.25 | 3024.97 | 0.65 | 0.41 | 1.03 |
| 20–24 weeks’ gestation | ||||||||||||||||||
| aIams322 | 20 | 35 | 29 | 84 | 97 | 2705 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.31 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 7.64 | 5.21 | 11.20 | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.87 |
| aAndrews325 | 22 | 35 | 4 | 3 | 9 | 41 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.61 | 0.93 | 0.81 | 0.99 | 4.51 | 1.15 | 17.64 | 0.74 | 0.51 | 1.08 |
| aIams322 | 25 | 35 | 47 | 218 | 79 | 2571 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.46 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 4.77 | 3.68 | 6.19 | 0.68 | 0.59 | 0.78 |
| aAndrews325 | 25 | 35 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 39 | 0.38 | 0.14 | 0.68 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 0.96 | 3.38 | 1.16 | 9.91 | 0.69 | 0.45 | 1.08 |
| aIams325 | 30 | 35 | 68 | 661 | 58 | 2128 | 0.54 | 0.45 | 0.63 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.78 | 2.28 | 1.91 | 2.71 | 0.60 | 0.50 | 0.73 |
| To334 | 15 | 33 | 21 | 80 | 38 | 6195 | 0.36 | 0.24 | 0.49 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 27.92 | 18.59 | 41.92 | 0.65 | 0.54 | 0.79 |
| Carvalho66 | 10 | 34 | 3 | 3 | 38 | 1734 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 42.37 | 8.81 | 203.65 | 0.93 | 0.85 | 1.01 |
| Carvalho66 | 10 | 34 | 5 | 5 | 61 | 1887 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 28.67 | 8.51 | 96.62 | 0.93 | 0.86 | 0.99 |
| Carvalho66 | 10 | 34 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 153 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 6.20 | 0.91 | 42.03 | 0.93 | 0.83 | 1.05 |
| Carvalho66 | 15 | 34 | 23 | 16 | 43 | 1876 | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.48 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 41.21 | 22.87 | 74.26 | 0.66 | 0.55 | 0.78 |
| Carvalho66 | 15 | 34 | 11 | 6 | 14 | 149 | 0.44 | 0.24 | 0.65 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 11.37 | 4.62 | 27.97 | 0.58 | 0.41 | 0.83 |
| Carvalho66 | 15 | 34 | 12 | 10 | 29 | 1727 | 0.29 | 0.16 | 0.46 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 50.84 | 23.31 | 110.90 | 0.71 | 0.58 | 0.87 |
| Pires332 | 20 | 37 | 4 | 10 | 17 | 307 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 6.04 | 2.07 | 17.64 | 0.84 | 0.68 | 1.03 |
| Carvalho66 | 20 | 34 | 34 | 47 | 32 | 1845 | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.64 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 20.74 | 14.37 | 29.92 | 0.50 | 0.39 | 0.64 |
| Carvalho66 | 20 | 34 | 18 | 17 | 7 | 138 | 0.72 | 0.51 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.93 | 6.56 | 3.94 | 10.94 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.59 |
| Carvalho66 | 20 | 34 | 16 | 30 | 25 | 1707 | 0.39 | 0.24 | 0.55 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 22.60 | 13.41 | 38.07 | 0.62 | 0.49 | 0.79 |
| Pires332 | 20 | 35 | 3 | 7 | 8 | 320 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0.61 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 12.74 | 3.79 | 42.80 | 0.74 | 0.52 | 1.07 |
| Carvalho66 | 25 | 34 | 38 | 171 | 28 | 1721 | 0.58 | 0.45 | 0.70 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 6.37 | 4.95 | 8.19 | 0.47 | 0.35 | 0.62 |
| Carvalho66 | 25 | 34 | 19 | 38 | 6 | 117 | 0.76 | 0.55 | 0.91 | 0.75 | 0.68 | 0.82 | 3.10 | 2.18 | 4.41 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.64 |
| Carvalho66 | 25 | 34 | 19 | 134 | 22 | 1603 | 0.46 | 0.31 | 0.63 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 6.01 | 4.16 | 8.67 | 0.58 | 0.44 | 0.77 |
| aGuzman738 | 25 | 34 | 12 | 51 | 10 | 285 | 0.55 | 0.32 | 0.76 | 0.85 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 3.59 | 2.27 | 5.68 | 0.54 | 0.34 | 0.85 |
| Carvalho66 | 30 | 34 | 42 | 442 | 24 | 1450 | 0.64 | 0.51 | 0.75 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.79 | 2.72 | 2.23 | 3.33 | 0.47 | 0.34 | 0.65 |
| Carvalho66 | 30 | 34 | 22 | 372 | 19 | 1365 | 0.54 | 0.37 | 0.69 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 2.51 | 1.86 | 3.38 | 0.59 | 0.42 | 0.82 |
| Carvalho66 | 30 | 34 | 20 | 71 | 5 | 84 | 0.80 | 0.59 | 0.93 | 0.54 | 0.46 | 0.62 | 1.75 | 1.35 | 2.27 | 0.37 | 0.17 | 0.82 |
| 37 weeks’ gestation | ||||||||||||||||||
| <20 weeks’ gestation | ||||||||||||||||||
| Hibbard328 | 22 | 37 | 11 | 10 | 74 | 665 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.22 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 8.74 | 3.82 | 19.96 | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.96 |
| Taipale333 | 25 | 37 | 5 | 8 | 83 | 3598 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 25.61 | 8.55 | 76.72 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 1.00 |
| Hibbard328 | 27 | 37 | 17 | 23 | 68 | 652 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.30 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 5.87 | 3.27 | 10.53 | 0.83 | 0.74 | 0.92 |
| Taipale333 | 29 | 37 | 14 | 96 | 74 | 3510 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.25 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 5.98 | 3.56 | 10.04 | 0.86 | 0.79 | 0.95 |
| Hibbard328 | 30 | 37 | 28 | 59 | 57 | 616 | 0.33 | 0.23 | 0.44 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 3.77 | 2.55 | 5.56 | 0.73 | 0.63 | 0.85 |
| Taipale333 | 35 | 37 | 31 | 962 | 57 | 2644 | 0.35 | 0.25 | 0.46 | 0.73 | 0.72 | 0.75 | 1.32 | 0.99 | 1.76 | 0.88 | 0.76 | 1.03 |
| Andersen324 | 39 | 37 | 13 | 39 | 4 | 56 | 0.76 | 0.50 | 0.93 | 0.59 | 0.48 | 0.69 | 1.86 | 1.30 | 2.66 | 0.40 | 0.17 | 0.96 |
| Taipale333 | 40 | 37 | 53 | 1875 | 35 | 1731 | 0.60 | 0.49 | 0.71 | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.50 | 1.16 | 0.97 | 1.38 | 0.83 | 0.64 | 1.07 |
| Taipale333 | 45 | 37 | 78 | 2731 | 10 | 875 | 0.89 | 0.80 | 0.94 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 1.17 | 1.08 | 1.26 | 0.47 | 0.26 | 0.84 |
| Taipale333 | 50 | 37 | 87 | 3261 | 1 | 345 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 1.09 | 1.07 | 1.12 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.84 |
| 20–24 weeks’ gestation | ||||||||||||||||||
| Yazici335 | 32.5 | 36 | 16 | 61 | 6 | 274 | 0.73 | 0.50 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 0.77 | 0.86 | 3.99 | 2.84 | 5.62 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 0.66 |
| Dilek327 | 33.15 | 37 | 14 | 29 | 4 | 203 | 0.78 | 0.52 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 6.22 | 4.09 | 9.48 | 0.25 | 0.11 | 0.60 |
| Authors | Thresholds (mm) | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 48 h of testing | |||||||||||||||||
| Tsoi348 | 5 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 478 | 0.43 | 0.22 | 0.66 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 19.05 | 8.87 | 40.94 | 0.58 | 0.40 | 0.85 |
| Tsoi348 | 10 | 17 | 31 | 4 | 458 | 0.81 | 0.58 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.96 | 12.77 | 8.57 | 19.03 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.49 |
| Tsoi348 | 15 | 21 | 74 | 0 | 415 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 6.43 | 5.17 | 8.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.42 |
| Tsoi348 | 20 | 21 | 150 | 0 | 339 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 0.69 | 0.65 | 0.73 | 3.18 | 2.75 | 3.69 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.51 |
| Gomez340 | 15 | 11 | 19 | 6 | 179 | 0.65 | 0.38 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.85 | 0.94 | 6.74 | 3.88 | 11.72 | 0.39 | 0.20 | 0.74 |
| Gomez340 | 30 | 15 | 93 | 2 | 105 | 0.88 | 0.64 | 0.99 | 0.53 | 0.46 | 0.60 | 1.88 | 1.50 | 2.36 | 0.22 | 0.06 | 0.82 |
| < 7 days of testing | |||||||||||||||||
| Tsoi348 | 5 | 16 | 4 | 27 | 463 | 0.37 | 0.23 | 0.53 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 43.44 | 15.20 | 124.17 | 0.63 | 0.50 | 0.80 |
| Tsoi348 | 10 | 28 | 20 | 15 | 447 | 0.65 | 0.49 | 0.79 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 15.20 | 9.40 | 24.61 | 0.36 | 0.24 | 0.55 |
| Tsoi348 | 15 | 42 | 53 | 1 | 414 | 0.98 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.91 | 8.61 | 6.65 | 11.14 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.18 |
| Tsoi348 | 20 | 42 | 129 | 1 | 338 | 0.98 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.72 | 0.68 | 0.76 | 3.54 | 3.03 | 4.12 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.22 |
| Schmitz345 | 15 | 12 | 45 | 11 | 291 | 0.52 | 0.31 | 0.73 | 0.87 | 0.82 | 0.90 | 3.90 | 2.42 | 6.27 | 0.55 | 0.36 | 0.85 |
| Schmitz345 | 25 | 20 | 131 | 3 | 205 | 0.87 | 0.66 | 0.97 | 0.61 | 0.56 | 0.66 | 2.23 | 1.81 | 2.74 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.62 |
| Schmitz345 | 30 | 23 | 193 | 0 | 143 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 1.00 | 0.43 | 0.37 | 0.48 | 1.71 | 1.53 | 1.90 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.76 |
| Fuchs338 | 15 | 17 | 19 | 4 | 213 | 0.81 | 0.58 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.95 | 9.88 | 6.13 | 15.95 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.50 |
| Tsoi348 | 15 | 16 | 27 | 1 | 172 | 0.94 | 0.71 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 0.81 | 0.91 | 6.94 | 4.79 | 10.05 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.46 |
| Tsoi348 | 15 | 20 | 10 | 0 | 33 | 1.00 | 0.83 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 0.61 | 0.88 | 4.09 | 2.40 | 6.96 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.49 |
| Gomez340 | 15 | 17 | 13 | 11 | 174 | 0.61 | 0.41 | 0.78 | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 8.73 | 4.78 | 15.96 | 0.42 | 0.27 | 0.67 |
| Gomez340 | 30 | 25 | 83 | 3 | 104 | 0.89 | 0.72 | 0.98 | 0.56 | 0.48 | 0.63 | 2.01 | 1.64 | 2.47 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.57 |
| Botsis64 | 15 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 84 | 0.91 | 0.59 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 0.82 | 0.95 | 9.39 | 4.91 | 17.97 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.65 |
| Gomez340 | 15 | 17 | 13 | 17 | 168 | 0.50 | 0.32 | 0.68 | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 6.96 | 3.74 | 12.97 | 0.54 | 0.38 | 0.76 |
| Gomez340 | 30 | 29 | 79 | 5 | 102 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 0.95 | 0.56 | 0.49 | 0.64 | 1.95 | 1.57 | 2.43 | 0.26 | 0.11 | 0.59 |
| < 34 weeks’ gestation | |||||||||||||||||
| Gomez340 | 15 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 87 | 0.78 | 0.40 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.88 | 0.98 | 14.31 | 5.70 | 35.95 | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.80 |
| Gomez340 | 30 | 9 | 40 | 0 | 52 | 1.00 | 0.66 | 1.00 | 0.57 | 0.46 | 0.67 | 2.18 | 1.66 | 2.86 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 1.33 |
| Crane336 | 30 | 30 | 35 | 7 | 64 | 0.81 | 0.65 | 0.92 | 0.65 | 0.54 | 0.74 | 2.29 | 1.68 | 3.12 | 0.29 | 0.15 | 0.58 |
| Daskalakis337 | 20 | 21 | 3 | 18 | 60 | 0.54 | 0.37 | 0.70 | 0.95 | 0.87 | 0.99 | 11.31 | 3.61 | 35.42 | 0.48 | 0.34 | 0.68 |
| Daskalakis337 | 25 | 28 | 13 | 11 | 50 | 0.72 | 0.55 | 0.85 | 0.79 | 0.67 | 0.89 | 3.48 | 2.06 | 5.87 | 0.36 | 0.21 | 0.60 |
| Daskalakis337 | 30 | 39 | 21 | 0 | 42 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.67 | 0.54 | 0.78 | 2.94 | 2.08 | 4.16 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.30 |
| Daskalakis337 | 35 | 39 | 47 | 0 | 16 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.38 | 1.33 | 1.15 | 1.54 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.79 |
| Daskalakis337 | 20 | 15 | 1 | 10 | 44 | 0.60 | 0.39 | 0.79 | 0.98 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 27.00 | 3.79 | 192.51 | 0.41 | 0.25 | 0.66 |
| Daskalakis337 | 25 | 16 | 9 | 9 | 36 | 0.64 | 0.43 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.65 | 0.90 | 3.20 | 1.66 | 6.16 | 0.45 | 0.26 | 0.77 |
| Daskalakis337 | 30 | 25 | 15 | 0 | 30 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 0.67 | 0.51 | 0.80 | 2.91 | 1.93 | 4.38 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.45 |
| Daskalakis337 | 35 | 25 | 33 | 0 | 12 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 0.27 | 0.15 | 0.42 | 1.35 | 1.12 | 1.62 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 1.15 |
| Rageth342 | 30 | 4 | 25 | 0 | 32 | 1.00 | 0.40 | 1.00 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 0.69 | 2.05 | 1.36 | 3.09 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 2.50 |
| Tsoi348 | 5 | 17 | 3 | 59 | 431 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.33 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 32.36 | 9.72 | 107.75 | 0.78 | 0.69 | 0.88 |
| Tsoi348 | 10 | 33 | 15 | 43 | 419 | 0.43 | 0.32 | 0.55 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 12.56 | 7.18 | 21.98 | 0.59 | 0.48 | 0.71 |
| Tsoi348 | 15 | 54 | 41 | 22 | 393 | 0.71 | 0.60 | 0.81 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.93 | 7.52 | 5.44 | 10.41 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.46 |
| Tsoi349 | 20 | 59 | 112 | 17 | 322 | 0.78 | 0.67 | 0.86 | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.78 | 3.01 | 2.46 | 3.67 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.46 |
| Schmitz345 | 15 | 22 | 35 | 26 | 276 | 0.46 | 0.31 | 0.61 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.92 | 4.07 | 2.63 | 6.31 | 0.61 | 0.47 | 0.79 |
| Schmitz345 | 25 | 36 | 115 | 12 | 196 | 0.75 | 0.60 | 0.86 | 0.63 | 0.57 | 0.68 | 2.03 | 1.63 | 2.52 | 0.40 | 0.24 | 0.65 |
| Schmitz345 | 30 | 43 | 173 | 5 | 138 | 0.90 | 0.77 | 0.97 | 0.44 | 0.39 | 0.50 | 1.61 | 1.40 | 1.85 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.54 |
| Gomez112 | 15 | 19 | 11 | 15 | 170 | 0.56 | 0.38 | 0.73 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.97 | 9.20 | 4.82 | 17.54 | 0.47 | 0.32 | 0.69 |
| Gomez112 | 30 | 30 | 78 | 4 | 103 | 0.88 | 0.73 | 0.97 | 0.57 | 0.49 | 0.64 | 2.05 | 1.66 | 2.52 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.52 |
| < 37 weeks’ gestation | |||||||||||||||||
| Crane336 | 30 | 30 | 35 | 7 | 64 | 0.81 | 0.65 | 0.92 | 0.65 | 0.54 | 0.74 | 2.29 | 1.68 | 3.12 | 0.29 | 0.15 | 0.58 |
| Gomez112 | 18 | 16 | 8 | 6 | 29 | 0.73 | 0.50 | 0.89 | 0.78 | 0.62 | 0.90 | 3.36 | 1.73 | 6.54 | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.70 |
| Onderoglu86 | 28 | 25 | 10 | 7 | 48 | 0.78 | 0.60 | 0.91 | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.91 | 4.53 | 2.50 | 8.20 | 0.26 | 0.14 | 0.51 |
| Tekesin346 | 25 | 17 | 22 | 6 | 40 | 0.74 | 0.52 | 0.90 | 0.65 | 0.51 | 0.76 | 2.08 | 1.38 | 3.15 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 0.82 |
| Rozenberg134 | 26 | 14 | 6 | 2 | 6 | 0.88 | 0.62 | 0.98 | 0.50 | 0.21 | 0.79 | 1.75 | 0.96 | 3.17 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 1.03 |
| Venditelli350 | 30 | 55 | 53 | 12 | 54 | 0.82 | 0.71 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 0.41 | 0.60 | 1.66 | 1.33 | 2.07 | 0.35 | 0.21 | 0.61 |
| Rizzo227 | 20 | 32 | 13 | 15 | 48 | 0.68 | 0.53 | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.66 | 0.88 | 3.19 | 1.90 | 5.38 | 0.41 | 0.26 | 0.63 |
| Goffinet339 | 26 | 19 | 28 | 5 | 56 | 0.79 | 0.58 | 0.93 | 0.67 | 0.56 | 0.77 | 2.38 | 1.65 | 3.42 | 0.31 | 0.14 | 0.69 |
| Murakawa341 | 25 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 18 | 0.64 | 0.31 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.64 | 0.97 | 4.45 | 1.43 | 13.91 | 0.42 | 0.19 | 0.95 |
| Murakawa341 | 30 | 11 | 6 | 0 | 15 | 1.00 | 0.72 | 1.00 | 0.71 | 0.48 | 0.89 | 3.24 | 1.68 | 6.25 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.90 |
| Murakawa341 | 35 | 11 | 14 | 0 | 7 | 1.00 | 0.72 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 0.15 | 0.57 | 1.45 | 1.05 | 2.01 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 1.96 |
| Authors | Thresholds | Outcome (weeks’ gestation) | TP | FP | FN | TN | sens | sens_lb | sens_ub | specs | spec_lb | spec_ub | LR+ | LR+_lb | LR+_ub | LR– | LR–_lb | LR–_ub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||||
| aLeunga | Any | 34 | 6 | 175 | 14 | 2757 | 0.30 | 0.12 | 0.54 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 5.03 | 2.53 | 9.97 | 0.74 | 0.56 | 0.99 |
| b,cAndrews325 | Any | 35 | 5 | 0 | 10 | 38 | 0.33 | 0.12 | 0.62 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 26.81 | 1.57 | 457.07 | 0.66 | 0.47 | 0.95 |
| b,cAndrews325 | Any | 35 | 7 | 8 | 2 | 24 | 0.78 | 0.40 | 0.97 | 0.75 | 0.57 | 0.89 | 3.11 | 1.55 | 6.23 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 1.02 |
| bTo334 | 5 mm width | 33 | 16 | 215 | 43 | 6103 | 0.27 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 7.97 | 5.14 | 12.35 | 0.75 | 0.65 | 0.88 |
| aPires332 | Any | 37 | 3 | 11 | 18 | 324 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.36 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 4.35 | 1.31 | 14.42 | 0.89 | 0.74 | 1.06 |
| aPires332 | Any | 35 | 3 | 11 | 8 | 316 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0.61 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 8.11 | 2.63 | 25.01 | 0.75 | 0.52 | 1.08 |
| aMara332 | Any | 34 | 7 | 33 | 2 | 205 | 0.78 | 0.40 | 0.97 | 0.86 | 0.81 | 0.90 | 5.61 | 3.50 | 8.99 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 0.88 |
| aMara332 | Any | 37 | 22 | 18 | 11 | 196 | 0.67 | 0.48 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 0.87 | 0.95 | 7.93 | 4.79 | 13.12 | 0.36 | 0.22 | 0.59 |
| Symptomatic women | ||||||||||||||||||
| Crane336 | V-shaped | 37 | 7 | 9 | 25 | 95 | 0.22 | 0.09 | 0.40 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.96 | 2.53 | 1.02 | 6.25 | 0.86 | 0.71 | 1.04 |
| Crane336 | V-shaped | 34 | 4 | 12 | 5 | 115 | 0.44 | 0.14 | 0.79 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.95 | 4.70 | 1.90 | 11.66 | 0.61 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| Gomez340 | Any | 36 | 17 | 17 | 5 | 20 | 0.77 | 0.55 | 0.92 | 0.54 | 0.37 | 0.71 | 1.68 | 1.11 | 2.55 | 0.42 | 0.18 | 0.96 |
| Gomez340 | 6 mm width | 36 | 14 | 8 | 7 | 25 | 0.67 | 0.43 | 0.85 | 0.76 | 0.58 | 0.89 | 2.75 | 1.40 | 5.40 | 0.44 | 0.23 | 0.83 |
| Gomez340 | 9 mm length | 36 | 15 | 3 | 6 | 30 | 0.71 | 0.48 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.76 | 0.98 | 7.86 | 2.58 | 23.90 | 0.31 | 0.16 | 0.62 |
| Rizzo227 | 5 mm width | 37 | 34 | 20 | 13 | 41 | 0.72 | 0.57 | 0.84 | 0.67 | 0.54 | 0.79 | 2.21 | 1.48 | 3.29 | 0.41 | 0.25 | 0.67 |
| Okitsu323 | 5 mm width | 36 | 9 | 18 | 4 | 46 | 0.69 | 0.39 | 0.91 | 0.72 | 0.59 | 0.82 | 2.46 | 1.44 | 4.20 | 0.43 | 0.19 | 0.98 |
Appendix 6 Characteristics and results of individual included effectiveness studies
Asymptomatic women
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Smaill [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 4] 351 Title: Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – OR low birthweight < 2500 g 127 (out of 879 in total) 63 (out of 431 in total) 48 (out of 300 in total) |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register (Dec 2000) Other sources None stated Search restrictions None stated Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs. Quasi-RCTs were also included in the review Population Pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria found on screening Intervention Any antibiotic regimen vs placebo/no treatment Outcomes Persistent bacteriuria, pyelonephritis, preterm delivery, low birthweight Study selection: Trials were selected for inclusion by one reviewer Data extraction: This was carried out by one reviewer Validity assessment: Criteria used Allocation concealment, randomisation, blinding of intervention and outcome, completeness of follow-up Assessment This was carried out by one reviewer Synthesis: Heterogeneity Heterogeneity was assessed using chi-squared and I-squared tests and none was found Methods Summary estimates were calculated (Peto odds ratio). Data on the number of participants with each outcome were sought to allow an intention-to-treat analysis |
No. of studies included: 14 RCTs (n = 2643) 8 studies compared treatment with placebo and six studies with no treatment. These are grouped together in the review Comparisons 01. antibiotics vs no treatment 02. continuous antibiotic therapy vs no treatment 03. short course (3–7 days) antibiotic therapy vs no treatment No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 1 Adequate concealment of allocation – 1 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 3/3/0 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported (see below) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: When defined, preterm birth defined as birthweight < 2500g 01. OR 0.60 (95% CI: 0.45–0.80) (10 studies, n = 1923) 02. OR 0.62 (95% CI: 0.42–0.93) (6 studies, n = 987) 03. OR 0.41 (95% CI: 0.25–0.67) (3 studies, n = 655) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Persistent bacteriuria 01. OR 0.07 (95% CI: 0.05–0.10) (4 studies, n = 593) 02. OR 0.21 (95% CI: 0.08–0.56) (1 study, n = 65) 03. OR 0.11 (95% CI: 0.04–0.27) (1 study, n = 69) Development of pyelonephritis 01. OR 0.24 (95% CI: 0.19–0.32) (13 studies, n = 2189) 02. OR 0.21 (95% CI: 0.15–0.31) (6 studies, n = 1005) 03. OR 0.35 (95% CI: 0.21–0.58) (5 studies, n = 725) Brief summary of findings: Antibiotic treatment compared with placebo/no treatment was effective in clearing asymptomatic bacteriuria and was associated with a reduction in the incidence of pyelonephritis, preterm birth and low birthweight where these two outcomes are conflated Authors’ conclusions: Antibiotic treatment is effective in reducing the risk of pyelonephritis in pregnancy. An apparent association with a reduction in preterm delivery should be interpreted with caution Comments: Only one person selected studies and extracted the data. The author notes methodological concern about the primary studies and reports that it is difficult to accurately assess their quality because of the lack of detail given. There was no consistent application of standard definitions for the outcomes. Preterm delivery when defined usually referred to birthweight < 2500 g |
|
Villar et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 1] 363 Title: Duration of treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Not reported |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register (April 2004) Other sources Reference lists of identified articles Search restrictions None specified Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs and quasi RCTs Population Women diagnosed during pregnancy with asymptomatic bacteriuria (1 trial included 24% symptomatic patients in both groups) Intervention Antibiotic regimens of differing duration: single-dose, short-course (4–7 days), long-course (14 days), continuous (treatment continued until after delivery). Trials comparing different therapeutic interventions with the same duration of intervention were excluded from the review. Drugs used were ampicillin, cephalexin, fosfomycin trometamol, amoxicillin, cotrimoxazole, trimethoprim and other sulphonamides Outcomes Maternal outcomes: cure rate, recurrent asymptomatic bacteriuria, pyelonephritis, need for repeat treatment Newborn outcomes including preterm birth and low birthweight. Side effects were also outcomes of interest Study selection: Carried out independently Data extraction: This was conducted independently and data were jointly reviewed before being analysed. Discrepancies were resolved by discussion Validity assessment: Criteria used Allocation concealment, blinding of outcome assessment, blinding of clinicians and patients, contamination in the control groups, attrition bias, co-intervention and protocol deviation Assessment Decisions were made by consensus Synthesis: Heterogeneity This was assessed using the chi-squared test Methods Meta-analysis using the fixed effect model. Trials were divided into two groups: trials that used the same drug in treatment and control groups and trials that used different ones. Outcomes were analysed for each group |
No. of studies included: Eight RCTs, two quasi-RCTs (n = 568) All studies compared single-dose treatment with 4–7-day treatments No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 2 Adequate concealment of allocation – 1 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 1/0/0 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Single-dose vs short-course (Fixed effects) RR 0.81 (95% CI: 0.26–2.57) (2 studies, n = 101) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: No statistically significant between-group differences found for cure rate, recurrence rate, side effects, or pyelonephritis Brief summary of findings: No statistically significant between-group differences were found for the outcomes measured (cure rate, recurrence rate, preterm births, pyelonephritis and side effects). The trials were of varying and often poor quality Authors’ conclusions: There is not enough evidence to evaluate whether single-dose or longer duration doses are equivalent in treating asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women Comments: This was a well-conducted review. The authors discuss areas of methodological concern about the primary studies, which they considered to be of poor methodological quality |
|
McDonald et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 4] 375 Title: Antibiotics for treating bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – < 37 weeks’ gestation: 01. 365 (out of 2607 in total); General population 213 (out of 1866 in total), high-risk population 102 (out of 299 in total). 02. 253 (out of 1690 in total) 03. 80 (out of 781 in total) < 34 weeks’ gestation: 01. 21 (out of 418 in total); general population 10 (out of 320 in total), high risk population 11 (out of 98 in total) 02. 20 (out of 397 in total) 03. 1 (out of 11 in total) |
Search: Databases searched (search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register (May 2004) Other sources None stated Search restrictions None stated Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Pregnant women with bacterial vaginosis, either symptomatic or asymptomatic, or intermediate vaginal flora Intervention Any antibiotic vs placebo/no treatment, or two antibiotic regimens compared Outcomes Maternal symptoms, including failure to achieve ‘microbiological cure’, chorioamnionitis, postpartum uterine infection, pregnancy loss up to 24 weeks’ gestation Neonatal outcomes, including perinatal death, severe neonatal morbidity, neonatal sepsis, preterm pre-labour rupture of membranes, preterm birth, low birthweight, admission to neonatal unit, duration of ventilatory support Maternal side effects Study selection: Two reviewers independently assessed studies for potential inclusion. Study authors were contacted for additional information Data extraction: Two authors independently extracted data Validity assessment: Criteria used Trials were assessed using standard Cochrane criteria: allocation concealment, blinding of randomisation, blinding of intervention and outcome assessment, completeness of follow-up Assessment Carried out independently by two authors Synthesis: Heterogeneity Heterogeneity was explored using the chi-squared test. Methods Trials were stratified by quality to explore the robustness of the findings. Summary estimates were calculated (Peto odds ratio) where there was no evidence of significant heterogeneity. Where significant heterogeneity was found the random effects model was used. Subgroup analyses assessed the effect of oral vs vaginal antibiotics, women with a previous preterm birth and women with intermediate flora/bacterial vaginosis Comparisons: 01. Any antibiotic vs placebo 02. Oral antibiotics vs placebo 03. Vaginal antibiotics vs placebo 04. Previous preterm delivery: antibiotics vs placebo 05. Single daily dose vs double daily dose vaginal antibiotic 06. Intermediate flora/bacterial vaginosis: antibiotics vs placebo |
No. of studies included: 13 RCTs (n = 5300) 12 trials were placebo controlled, one trial compared once daily vs twice daily regimens No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 12 Adequate concealment of allocation – 8 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 0/0/0 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: 01. OR 1.22 (95% CI: 0.67–2.19) (5 studies, n = 851); General population OR 0.95 (95% CI: 0.38–2.37), (2 studies, n = 628) high-risk women OR 1.45 (95% CI: 0.67–3.14) (3 studies, n = 223) 02. OR 1.30 (95% CI: 0.72–2.35) (3 studies, n = 819) 03. OR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.06–17.12) (1 study, n = 22) 04. OR 1.21 (95% CI: 0.59–2.49) (4 studies, n = 257) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: 01. OR 0.87 (95% CI: 0.74–1.03) (13 studies, n = 5300); General population OR 1.01 (95% CI: 0.82–1.24) (6 studies n = 3703), high-risk women OR 0.87 (95% CI: 0.74–1.03) (5 studies, n = 703) 02. OR 0.84 (95% CI: 0.69–1.02) (6 studies, n = 3481) 03. OR 0.92 (95% CI: 0.65–1.28) (4 studies, n = 1565) 04. OR 0.83 (95% CI: 0.59–1.17) (5 studies, n = 622) 05. OR 0.40 (95% CI: 0.11–1.39) (1 study, n = 94) 06. OR 0.51 (95% CI: 0.32–0.81) (1 study, n = 894) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable. Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal care admission (unclear if this is intensive care): 06. OR 0.73 (95% CI: 0.39–1.39) (1 study, n = 466) Incidence of perinatal mortality: 01. OR 2.17 (95% CI: 0.72–6.54) (2 studies, n = 749) 02. OR 2.03 (95% CI: 0.67–6.13) (2 studies, n = 739) 03. OR 0.35 (95% CI: 0.05–2.52) (1 study, n = 409) 04. OR 3.64 (95% CI: 0.86–15.45) (2 studies, n = 155) 06. OR 0.50 (95% CI: 0.10–2.48) (2 studies, n = 894) Incidence of adverse events: PPROM: 04. OR 0.14 (95% CI: 0.05–0.38) (2 studies, n = 114) Low birthweight: 01. OR 0.95 (95% CI: 0.77–1.17) (7 studies n = 4107) general pop OR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.79–1.27) (4 studies n = 3151) high risk 0.33 (95% CI: 0.11–0.93) (1 study, n = 80) 04. OR 0.31 (95% CI: 0.13–0.75) (2 studies, n = 114) Late miscarriage: 06. OR 0.25 (95% CI: 0.08–0.79) (1 study, n = 485) No other between group differences were found for the adverse events listed above, or for the other adverse events reported: postpartum infection, neonatal sepsis, side effects sufficient to stop treatment, and side effects not sufficient to stop treatment. Brief summary of findings: Antibiotic therapy was effective at eradicating bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy. It was not significant in reducing the risk of preterm birth or of preterm pre-labour rupture of membranes. In women with a previous preterm birth, treatment did not affect the risk of subsequent preterm birth but may decrease the risk of preterm pre-labour rupture of membranes and low birthweight Authors’ conclusions: Antibiotics can eradicate bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy but this review provides little evidence that screening and treating all pregnant women with asymptomatic bacterial vaginosis will prevent preterm birth and its consequences. For women with previous preterm birth there is some suggestion that treatment of bacterial vaginosis may reduce the risk of preterm pre-labour rupture of membranes and low birthweight The effect of earlier treatment needs to be studied in further trials Comments: This was a well-conducted review with clear reporting of the methodology and primary studies. The authors discuss the limitations of the trials Loss to follow-up of < 20% was reported in eight of the included trials |
|
Ugwumadu et al. [Lancet 2003; 361: 983–988] 386 Country: UK Setting: Outpatient Prevalence: Preterm birth – 28 (of 241 in total) Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: To delivery No. of participants: No. randomised – 494 No. analysed – 485 Validity: Adequate randomisation – Yes Adequate allocation concealment – Yes Blinding of clinician – Yes Blinding of patient – Yes Blinding of researcher – Yes Type of analysis: Sample size calculation showing 239 women/group would detect 9% difference in spontaneous preterm delivery/late miscarriage with 90% power and 5% significance level. Categorical variables analysed using Fisher’s exact test and continuous variables with t test. Kaplan-Meier survival curves used for time to delivery, miscarriage or last known follow-up |
Groups compared: Clindamycin vs Placebo Intervention details: Clindamycin 300 mg b.i.d. for 5 days Participants: Asymptomatic women at 12–22 weeks’ gestation who tested positive for abnormal vaginal flora and/or bacterial vaginosis Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women at their first antenatal clinic visit at between 12 and 16 weeks’ gestation (later protocol amendment to 12–22 weeks) that screened positive for abnormal vaginal flora and/or bacterial vaginosis were included. Women with multiple pregnancy, need for/had cervical cerclage, history of cone biopsy, uterine, cervical or fetal anomaly, diabetes, renal disease, collagen disease, lupus, antiphospholipid syndrome, essential hypertension, known allergy to clindamycin, < 16 years old, reported fishy smelling vaginal discharge were excluded Outcomes: Outcomes of pregnancy including spontaneous preterm delivery, late miscarriage and death in utero; admission to neonatal intensive care unit, low birthweight < 2500 g, < 1500 g |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 11 (244) No. in control group (total no.) = 28 (241) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 18 (238) No. in control group (total no.) = 23 (228) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Late miscarriage No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (244) No. in control group (total no.) = 10 (241) Death in utero No. in intervention group (total no.) = 1 (244) No. in control group (total no.) = 1 (241) Elective preterm delivery No. in intervention group (total no.) = 8 (244) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (241) Low birthweight < 2500g No. in intervention group (total no.) = 20 (240) No. in control group (total no.) = 23 (227) Low birthweight < 1500g No. in intervention group (total no.) = 10 (240) No. in control group (total no.) = 4 (227) Reported side effects No. in intervention group (total no.) = 17 (239) No. in control group (total no.) = 8 (239) Brief summary of findings: Significantly fewer preterm deliveries occurred in the clindamycin group (p = 0.001) Authors’ conclusions: Treatment of asymptomatic abnormal vaginal flora with oral clindamycin early in the 2nd trimester significantly reduces the rate of late miscarriage and spontaneous preterm birth in a general population Comments: Good quality RCT. Authors identified differences in baseline history of previous miscarriages (more women in placebo) but say previous history is not associated with increased risk as demonstrated in two previous studies. There were also differences in the number of women of black Caribbean and white origin. The authors caution that their findings may not be generalisable to other populations and state the need to replicate findings in other studies |
|
Brocklehurst [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Issue 4, 2005] 391 Title: Antibiotics for gonorrhoea in pregnancy Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Not reported |
Search: Databases searched (search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register (Feb 2004) Other sources None specified Search restrictions None specified Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Pregnant women at any stage of pregnancy with culture-confirmed genital gonococcal infection, whether symptomatic or asymptomatic Intervention Any antibiotic vs penicillin or two or more alternative antibiotics Outcomes Neonatal ophthalmia neonatorum; other neonatal gonococcal infection; post partum sepsis in the treated mothers; failure to eradicate gonorrhoea from the genital tract of treated mothers as determined by gonococcal culture after treatment; side effects Study selection: This was conducted by one reviewer Data extraction: This was conducted by one reviewer Validity assessment: Criteria used ‘Standard Cochrane criteria’ were used to assess the studies: allocation concealment, randomisation, blinding of intervention and outcome assessment and completeness of follow-up. Assessment Carried out by one reviewer Synthesis: Heterogeneity No information on how this was addressed, as no pooling took place statistical assessment was not possible Methods Summary estimates would have been calculated (Peto odds ratio) if there were no evidence of significant heterogeneity |
No. of studies included: 2 RCTs (n = 346) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 2 Adequate concealment of allocation – 0 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 0/0/0 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not reported Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: One study reported 0/43 events sufficient to stop treatment in intervention group Other outcomes: Failure to achieve microbiological cure Penicillin vs any other antibiotic: OR 2.49 (95% CI: 0.88–7.02) (1 study, n = 248) Amoxycillin and probenicid vs spectinomycin: OR 2.29 (95% CI: 0.74–7.08) (1 study, n = 168) Amoxicillin and probenicid vs ceftriaxone: OR 2.29 (95% CI: 0.74–7.08) Ceftriaxone vs cefixime: OR 1.22 (95% CI: 0.16–9.01) (1 study, n = 95) Brief summary of findings: The only outcome reported on was the incidence of ‘microbiological cure’. Failure to achieve ‘microbiological cure’ was similar for each antibiotic regimen Authors’ conclusions: No differences were seen between treatments but the trials were limited in their ability to detect important but modest differences. For women who are allergic to penicillin, this review provides some reassurance that treatment with ceftriaxone or spectinomycin appears to have similar effectiveness in producing microbiological cure Comments: There is a lack of detail about the methodology of the review. Only one person selected studies and extracted the data. Neither of the included trials used an intention-to-treat analysis, and both excluded a high proportion of participants from the analysis, which may have introduced bias. The methods of allocation concealment were not specified |
|
Walker [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 3] 394 Title: Antibiotics for syphilis diagnosed during pregnancy Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Preterm birth – |
Search: Search dates Medline 1966 – Oct. 2002, Embase 1974 – Mar. 2000, Cochrane Controlled Trials Register Mar. 2001, Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register Oct. 2002, Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group’s Specialised Register of Controlled Trials (Mar. 2001) Databases searched See above Other sources References of reviews, experts Search restrictions None Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs, quasi-RCTs (both published and unpublished) Population Pregnant women with a clinical diagnosis of primary, secondary or late-stage syphilis, confirmed by non-treponemal or treponemal tests, with and without concomitant infection with HIV Intervention No treatment, alternative antibiotic therapy Outcomes Maternal: resolution of clinical symptoms; changes in titres for quantitative reagenic serological tests. Follow-up at 3 months, 6 months, 1 year and 2 years and above Fetal/infant: miscarriage and stillbirth with/without evidence of infected fetus, neonatal death with/without evidence of congenital syphilis; baby born with congenital syphilis or suspicion of congenital syphilis Side effects: Jarisch–Herxheimer reaction in the mother with possible preterm labour, delivery and fetal or neonatal death Study selection: Titles/abstracts for each potentially relevant study were screened. The authors stated that the review drew on the strategy for the Pregnancy and Childbirth group, which includes the screening of titles/abstracts by two reviewers and resolution of disagreements by consensus or involvement of the editorial team Data extraction: The 26 papers potentially meeting the inclusion criteria were checked in full. No studies met the inclusion criteria Validity assessment: Criteria used Assessment Synthesis: Heterogeneity Methods |
No. of studies included: 26 studies met criteria for hard copy scrutiny but all were excluded. No RCTs or quasi-RCTs identified No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 0 Adequate concealment of allocation – 0 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 0 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Incidence of perinatal mortality: Incidence of adverse events: Brief summary of findings: No RCTs or quasi-RCTs found Authors’ conclusions: While there is no doubt that penicillin is effective in treatment of syphilis in pregnancy and the prevention of congenital syphilis, uncertainty remains about what are the optimal treatment regimens Future research should address treatment failure cases with recommended regimens, including the role of Hi.v. infection, and the effectiveness of various antibiotic regimens for the treatment of primary and secondary syphilis in pregnant women using RCTs Comments: The authors have provided clear details of the review methodology and of the excluded studies The authors’ conclusions about the efficacy of penicillin in the treatment of syphilis do not follow from this review, which did not include any studies and therefore cannot provide a basis for conclusions about the efficacy of the treatment. |
|
Gulmezoglu [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005 Issue 3] 395 Title: Interventions for trichomoniasis in pregnancy Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Preterm birth < 37 weeks: 31 (out of 289 in total) |
Search: The Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register (January 2004) Other sources None reported Search restrictions None reported Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs (and quasi-RCTs) Population: pregnant women with trichomoniasis diagnosed by wet-mount smear or any other laboratory test in addition to clinical findings (symptomatic women) OR asymptomatic women with a laboratory diagnosis of trichomoniasis Intervention 01. Any treatment compared with no treatment 02. Comparison of two different agents 03. Comparison of different doses of same agent 04. Systemic vs local treatment 05. Single dose vs longer (5–10 day) treatment Both included studies compared metronidazole with no treatment Outcomes Preterm birth, low birthweight, intrauterine infection. Side effects and complications of treatment Study selection: Not stated Data extraction: Performed in accordance with Cochrane reviewers’ handbook Validity assessment: Criteria used Allocation concealment, randomisation, blinding Assessment Performed in accordance with Cochrane reviewers’ handbook (Clarke 2000) Synthesis: Heterogeneity Chi-squared and I-squared tests used, trial characteristics discussed |
No. of studies included: two studies (n = 993): No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 1 Adequate concealment of allocation – 0 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 1/1/1 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: RR 1.78 (95% CI: 1.19–2.66) (1 study, n = 604) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Low birthweight < 2500 g RR 1.38 (95% 0.92–2.06) (1 study, n = 604) Brief summary of findings: Metronidazole was effective in producing parasitological cure but the risk of preterm birth was increased in the intervention group in the trial that reported it. There were no significant differences in incidence of low birthweight Authors’ conclusions: Metronidazole given as a single dose is likely to provide parasitological cure for trichomoniasis but it is not known whether this treatment will have any effect on pregnancy outcomes Comments: The review does not report how studies were selected. The conclusions are however, appropriately cautious, although given the increase in preterm birth in the good-quality study it is not appropriate to recommend treatment of trichomoniasis with metronidazole. Neither study assessed adverse events |
|
Raynes-Greenow et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 4] 407 Title: Antibiotics for ureaplasma in the vagina in pregnancy Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Not reported |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register (April 2003) Other sources None specified Search restrictions None specified Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Pregnant women < 37 weeks’ gestation with ureaplasma in the vagina. Studies of women in preterm labour were excluded Intervention Any antibiotic regimen begun before 37 weeks’ gestation vs placebo/no treatment Outcomes Primary outcome – preterm birth A range of other adverse pregnancy outcomes were sought, including preterm labour > 32 < 36 weeks, < 32 weeks, perinatal death and severe neonatal morbidity Study selection: Three reviewers independently assessed studies for potential inclusion Data extraction: Three reviewers independently extracted the data Validity assessment: Criteria used Trials were assessed using Cochrane criteria: allocation concealment, randomisation, blinding of outcome assessment and completeness of follow-up. Outcome data were to be excluded where unavailable for > 20% of participants Assessment Carried out independently by three reviewers Synthesis: Heterogeneity Not applicable Methods Categorical data were analysed using relative risk, risk difference and number needed to treat |
No. of studies included: 1 RCT, n = 1071 (1105 randomised) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 1 Adequate concealment of allocation – 0 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 1/0/0 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: No between-group differences were found for low birthweight and side effects Low birthweight < 2500 g RR 0.70 (95% CI: 0.46–1.07) (1 study, n = 825) Maternal side effects sufficient to stop or change treatment RR 1.25 (95% CI: 0.85–1.85) (1 study, n = 1071) Brief summary of findings: This trial did not report data on the primary outcome, preterm birth. Data were available on low birthweight and side effects, for which no significant between-group differences were found Authors’ conclusions: There is insufficient evidence to assess the effect of giving antibiotics to women with ureaplasma in the vagina on pregnancy outcomes including preterm birth. Well-designed RCTs are needed to determine if antibiotic treatment will reduce the risk of preterm birth in women with ureaplasma in the vagina Comments: Authors note that intention-to-treat analysis was not conducted (apart from two outcomes) as women who did not comply satisfactorily with treatment were excluded. As this includes women who had symptoms related to the study drug, the analysis is particularly open to bias |
|
Vazquez and Villar [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 4] 398 Title: Treatments for symptomatic urinary tract infections during pregnancy Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – No untreated groups |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register (Jan 2003) Other sources Reference lists of articles were checked Search restrictions None specified Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Pregnant women with any symptomatic urinary tract infection of any severity receiving treatment on either an inpatient or an outpatient basis Intervention Alternative antibiotic therapies Outcomes Primary outcomes: cure rates (symptom relief and/or urine clearance by laboratory test), recurrent infection Secondary outcomes: preterm birth, premature rupture of membranes, admission to neonatal intensive care unit, need for change of antibiotic, incidence of prolonged pyrexia. A range of other outcomes were sought including side effects, resource use and other neonatal outcomes Study selection: Two authors independently assessed studies for potential inclusion, with differences resolved by discussion Data extraction: Carried out independently by two authors with discrepancies resolved by discussion Validity assessment: Criteria used Quality ratings were assigned using Cochrane criteria. Studies were assessed for allocation concealment, blinding of outcome assessment and loss to follow-up Assessment Carried out independently by two authors with differences resolved by discussion Synthesis: Heterogeneity Heterogeneity was looked for and if found would have been explored by sensitivity analyses Methods Meta-analysis was conducted using a fixed effects model. Where numbers were given an intention-to treat analysis was performed. Numbers needed to treat were calculated from outcomes. Power calculations were extracted where available Planned subgroup analyses included an assessment of the effect of route of administration, outpatient vs inpatient regimens, dosage and duration of treatment Comparisons: 01. Intravenous (i.v.) + oral antibiotics vs i.v. only 02. Outpatient vs inpatient antibiotics 03. i.v. cephazolin vs i.v. ampicillin + gentamicin 04. Intramuscular (i.m.) ceftriaxone vs i.v. ampicillin + gentamicin 05. i.m. ceftriaxone vs i.v. cephazolin 06. Cephalosporins daily dose vs multiple doses 07. Oral ampicillin vs oral nitrofurantoin 08. i.v. plus oral cephradine vs i.v. plus oral cefuroxime 09. Oral phosphomycin trometamol vs oral ceftibuten 10. Single vs multiple dose of gentamicin |
No. of studies included: 8 studies (n = 905) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 6 Adequate concealment of allocation – 5 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – not reported Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: 02. OR 0.14 (95% CI: 0.00–6.82) (1 study, n = 120) 03. OR 1.97 (95% CI: 0.47–8.29) (1 study, n = 107) 04. OR 1.10 (95% CI: 0.21–5.68) (1 study, n = 109) 05. OR 0.56 (95% CI: 0.13–2.36) (1 study, n = 102) 06. OR 1.11 (95% CI: 0.41–3.01) (1 study, n = 178) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: 03. OR 1.50 (95% CI: 0.57–3.95) (1 study, n = 107) 04. OR 1.59 (95% CI: 0.62–4.11) (1 study, n = 109) 05. OR 1.06 (95% CI: 0.42–2.68) (1 study, n = 102) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Cefuroxime was associated with a higher rate of cure than cephradine. No other between-group differences were found for cure rates, prolonged pyrexia, need for change of antibiotic and recurrent infection Brief summary of findings: Cefuroxime was associated with a higher rate of cure and fewer recurrences than cephradine but the sample size is insufficient to give reliable findings. No other significant differences were observed between treatments in respect of any outcomes Authors’ conclusions: There are insufficient data to recommend any specific treatment regimen for symptomatic urinary tract infections during pregnancy. All the antibiotics studied were shown to be effective in decreasing the incidence of adverse outcomes. Complications were very rare Comments: Authors note that all included trials had small sample sizes and that effects seen are likely to be due to chance. Loss to follow-up is also identified as a problem |
|
Thinkhamrop et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2002, Issue 4] 409 Title: Prophylactic antibiotic administration in pregnancy to prevent infectious morbidity and mortality Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not estimable Preterm birth – 26 (out of a total of 274), based on preterm delivery (not defined) in unselected pregnant women 42 (out of a total 86), based on preterm delivery (not defined) in high-risk women with bacterial vaginosis 40 (out of a total 176), based on preterm delivery (not defined) in high-risk women with previous preterm delivery |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) The Pregnancy and Childbirth Group registry was searched for relevant articles (February 2004). Other sources Reference lists Search restrictions No search restrictions specified Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Women in their second or third trimester with a singleton gestation before labour or delivery Unselected, unspecified and high-risk women were included in the review. High-risk women were defined as: previous spontaneous preterm delivery, history of low birthweight (< 2500 g), pre-pregnancy weight < 50 kg, or associate with bacterial vaginosis Intervention Prophylactic antibiotics administered vs placebo or no antibiotics Outcomes Primary maternal and neonatal outcomes included: preterm labour (not defined), PROM, preterm delivery, chorioamnionitis, intrapartum fever, puerperal sepsis, serious maternal complication of puerperal infection requiring laparotomy for infection, hysterectomy, or death), gonococcal cervicitis, mean gestation age, low birthweight, mean birthweight, clinical neonatal sepsis, blood cultures confirming sepsis. A number of secondary maternal and neonatal outcomes were also sought including side effects, admission to neonatal intensive care unit and perinatal mortality. Study selection: The authors do not state how articles were selected for inclusion or how many reviewers performed the selection process Data extraction: The authors do not state how data was extracted or how many reviewers performed the data extraction Validity assessment: Criteria used Trials were assessed according to their allocation concealment (A=adequate, B=unclear, C=inadequate, D=not used). Blinding and loss to follow-up were also assessed Assessment The authors do not state how the methodological quality of the primary studies was assessed or how many reviewers performed the validity assessment Synthesis: Heterogeneity Chi squared analysis and I-squared statistic were used to assess heterogeneity Methods Peto ORs and their 95% CI were presented for categorical data. Sensitivity analyses were planned looking at trial quality |
No. of studies included: 6 RCTs (n = 2184) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 6 Adequate concealment of allocation – 3 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 5/6/0 (not reported) Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth preterm birth (no definition of preterm birth given): All women: Peto OR 0.83 (95% CI; 0.62–1.12) (4 studies, n = 1310) Unselected women: Peto OR 1.13 (95% CI: 0.64–1.97) (2 studies, n = 552) High-risk women with BV < 50 kg pre-pregnancy: Peto OR 0.31 (95% CI: 0.10–0.93) (1 study, n = 81) High-risk women with BV > 50 kg pre-pregnancy: Peto OR 0.48 (95% CI: 0.25–0.90) (1 study, n = 177) High-risk women with previous history of preterm delivery: Peto OR 1.06 (95% CI: 0.68–1.64) (2 studies, n = 500) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not relevant Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not relevant Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not relevant Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not estimable Incidence of perinatal mortality: All women: Peto OR 0.52 (95% CI: 0.16–1.71) (3 studies, n = 624) Unselected women: Peto OR 0.12 (95% CI: 0.01–1.99) (1 study, n = 229) High-risk women with history of preterm delivery, LBW, stillbirth or perinatal mortality: Peto OR 0.53 (95% CI: 0.13–2.16) (1 study, n = 253) High-risk women with previous preterm delivery: Peto OR 7.60 (0.15, 383.33) (1 study, n = 142) Incidence of adverse events: PPROM: Unselected women: Peto OR 0.33 (95% CI: 0.08–1.34) (1 study, n = 229) PROM: Unselected women: Peto OR 0.32 (95% CI: 0.14–0.73) (1 study, n = 229) Chorioamnionitis: Unselected women: Peto OR 0.61 (95% CI: 0.10–3.60) (1 study, n = 229) Puerperal sepsis/postpartum endometritis: Unselected women: Peto OR 0.49 (95% CI: 0.23–1.06) (2 studies, n = 431) High-risk women with history of preterm delivery, LBW, stillbirth or perinatal mortality: Peto OR 0.46 (95% CI: 0.24–0.89) (1 study, n = 196) Gonococcal infection (detected postpartum) High-risk women: Peto OR 0.35 (95% CI: 0.13–0.89) (1 study, n = 204) Low birthweight Unselected women: Peto OR 1.04 (95% CI: 0.64–1.70) (2 studies, n = 555) High-risk women with history of preterm delivery, LBW, stillbirth or perinatal mortality: Peto OR 0.48 (95% CI: 0.27–0.84) (1 study, n = 253) Neonatal sepsis: High-risk women with previous history of preterm delivery: Peto OR 8.07 (95% CI: 1.36–47.77) (1 study, n = 142) Other outcomes: Mean birthweight Unselected women: [Fixed effect] WMD – 76.00 (– 181.03 to 29.03) (2 studies, n = 555) High-risk women: WMD 155.00 (6.22, 303.78) (1 study, n = 253) Brief summary of findings: Antibiotic prophylaxis in unselected women reduced the risk of PROM. A reduced incidence of low birthweight and postpartum endometritis was reported in women with a history of previous preterm birth. A reduction in the incidence of preterm delivery was reported in women with a history of preterm birth associated with BV although no reduction was shown in women with a previous history of preterm birth without BV. Vaginal antibiotic prophylaxis did not prevent infectious pregnancy outcomes and there was a possibility of adverse events such as neonatal sepsis Authors’ conclusions: Antibiotic prophylaxis given during the second or third trimester of pregnancy reduces the risk of PROM. Beneficial effects on birthweight and risk of preterm endometritis were demonstrated in high-risk women. The authors note that the sample size for unselected women may not be sufficient to detect differences for important uncommon outcomes Comments: As the methods undertaken for study selection, data extraction and quality assessment were not described the likelihood of reviewer error or bias cannot be assessed |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Rumbold A et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 3] 420 Title: Vitamin C supplementation in pregnancy Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 54 (out of 290 in total) based on preterm birth < 37 weeks |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group trials register (June 2004), Central (Issue 2, 2004), MEDLINE (1966–May 2004), Current Contents (1998–May 2004), EMBASE (1980–May 2004) Other sources None reported. Search restrictions None. Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs, quasi-RCTs Population Asymptomatic pregnant women. Of the studies included: three trials recruited women at high risk of pre-eclampsia, one trial involved women with severe early-onset pre-eclampsia, one trial involved women at high risk of preterm birth. Intervention Vitamin C supplementation (alone or in combination with other supplements) vs placebo. Interventions using a multivitamin supplement or where the primary supplement was iron were excluded. Of the trials included in the review one trial used vitamin C only supplements, four used a combined supplement. Three trials used 1000 mg vitamin C per day and two used 500 mg vitamin C per day. Combined supplements used vitamin E (2 trials), vitamin E and allopurinal (1 trial), aspirin and fish oil (1 trial) Outcomes Primary outcomes: perinatal mortality, iron and folate status, birthweight, intrauterine growth retardation, preterm birth < 37 weeks, PROM, and pre-eclampsia. A number of secondary maternal and infant outcomes were sought, including use of health resources Study selection: Two authors independently considered trials for inclusion. Differences were resolved through discussion Data extraction: Two authors independently extracted data. Differences were resolved through discussion. Data were entered separately and double checked Validity assessment: Criteria used Quality ratings were assigned using Cochrane criteria for blinding, completeness of follow-up, use of placebo, allocation concealment. Where method of allocation concealment was unclear, attempts were made to contact authors for further details Assessment Conducted independently by two authors; differences were resolved by consensus Synthesis: Heterogeneity Tests of heterogeneity were applied (I² test) and possible causes explored. Methods Meta-analysis using a fixed effects model. Where heterogeneity was found, subgroup analyses for the main outcomes were performed. Heterogeneity that was not explained by subgroup analyses was modelled using a random effects model. Sensitivity analyses were carried out to explore the effect of trial quality |
No. of studies included: 5 RCTs (n = 766) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 3 Adequate concealment of allocation – 3 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 5/5/3 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: (Fixed effects) RR 1.38 (95% CI: 1.04–1.82) (3 studies, n = 583) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: (Fixed effects) RR 1.16 (95% CI: 0.61–2.18) (2 studies, n = 238) Incidence of adverse events: Stillbirth (Fixed effects) RR 0.87 (95% CI: 0.41–1.87) (3 studies, n = 539) Neonatal death (Random effects) RR 1.73 (95% CI: 0.25–12.12) (2 studies, n = 221). Heterogeneity χ² = 2.08 df = 1 p = 0.15 I² = 51.9% Intrauterine growth restriction (Fixed effects) RR 0.72 (95% CI: 0.49–1.04) (2 studies, n = 383) Apgar score <7 at 5 min (Fixed effects) RR 0.63 (95% CI: 0.21–1.90) (1 study, n = 39) Pre-eclampsia (Random effects) RR 0.52 (95% CI: 0.23–1.20) (4 studies, n = 710) Serious maternal morbidity (subtotals, based on one study) Eclampsia RR 1.07 (95% CI: 0.07–16.33), renal failure RR 0.36 (95% CI: 0.02–8.41), pulmonary oedema RR 0.54 (95% CI: 0.05–5.59), disseminated intravascular coagulation RR 0.36 (95% CI: 0.02–8.41) Maternal side effects (subtotals, based on one study) Acne RR 3.21 (95% CI: 0.14–75.68), transient weakness RR 5.36 (95% CI: 0.27–106.78), skin rash RR 3.21 (95% CI: 0.14–75.68). Other outcomes: Birthweight (Fixed effects) Weighted mean difference – 139.00 (95% CI: – 517.69 to 239.69) (1 study, n = 100) Sensitivity analyses: Trial quality Preterm birth RR 1.40 (95% CI: 1.02–1.93) (2 studies, n = 483) Perinatal mortality RR 1.16 (95% CI: 0.61–2.18) (2 studies, n = 238) Subgroup analyses: Gestation at trial entry Preterm birth RR 1.40 (95% CI: 1.02–1.93) (3 studies, n = 583) Perinatal mortality RR 1.16 (95% CI: 0.61–2.18) (2 studies, n = 238) Supplement type Preterm birth RR 1.38 (95% CI: 1.04–1.82) (3 studies, n = 583) Perinatal mortality RR 1.16 (95% CI: 0.61–2.18) (2 studies, n = 238) Brief summary of findings: Compared with placebo, vitamin C supplements did not reduce the incidence of stillbirth, perinatal death, neonatal death, birthweight or intrauterine growth restriction. Compared to placebo, vitamin C supplements increased the incidence of preterm birth. Women taking vitamin C were at decreased risk of pre-eclampsia using a fixed effect model This difference could not be demonstrated using a random effects model. Authors’ conclusions: The data are too few to demonstrate whether vitamin C, alone or with other supplements, is beneficial in pregnancy. Preterm birth may have been increased with vitamin C supplementation and this is an area that requires further research Comments: This was a well-conducted review and the authors appear to have taken appropriate steps to reduce bias No study reported > 20% loss to follow-up |
|
Casanueva et al. [Am J Nutr 2005; 81: 859–863] 422 Country: Mexico Setting: Prenatal clinic (Instituto Nacional de%%Perinatologia in Mexico City) Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 14 (out of a total of 57) Study design: Randomised controlled trial (RCT) Length of follow-up: Randomisation to delivery No. of participants: No. randomised – 126 No. analysed – 109 Validity: Adequate randomisation – No (Random number table used) Adequate allocation concealment – No Blinding of clinician – Yes Blinding of patient – Yes (placebo) Blinding of researcher – Yes Type of analysis: Repeated measures analysis of variance, adjusted for multiple comparisons was conducted to evaluate changes in vitamin C concentration in plasma and leucocytes. Chi-squared tests were used to compare maternal characteristics, infections and incidence of PROM. Relative risks (RRs) with their 95% CI were calculated Sample size: 60 cases per group would be needed for an 80% power to test for a 20% reduction in incidence of PROM with a 5% chance of type 1 error. Assumed 10% loss to follow-up |
Groups compared: Vitamin C (100 mg vitamin C per day) vs Placebo. Both tablet types provided by Roche Pharmaceuticals Intervention details: All women were initially assessed by nutritionist and obstetric and gynaecological personnel. General information, gynaecological and obstetric history and anthropometric data were taken. Each participant completed a food frequency questionnaire. Vitamin C intake was calculated (corrected for cooking losses by a factor of 50% for boiled/fried food, and a factor of 25% for steamed food). Women were evaluated every 4 weeks from gestation weeks 20 to 36. A vaginal examination was provided, and a swab was taken for Gram staining and microbiological testing. Where infection was diagnosed, women received appropriate antibiotic treatment. Asymptomatic participants with a positive culture did not receive treatment. Adherence to intervention was evaluated through personal record and tablet counting at each clinic visit Participants: Asymptomatic pregnant women. Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Pregnant women with no acute or chronic diseases, < 20 weeks’ gestation, singleton pregnancy, and no consumption of vitamin supplements were eligible for inclusion. Women needing uterine cerclage or having an obstetric indication for Caesarean delivery were excluded Outcomes: Incidence of incidence of premature births, incidence of PPROM, birthweight, gestational age at birth and plasma and leucocyte vitamin C concentrations |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 7 (52) No. in control group (total no.) = 14 (57) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: PROM No. in intervention group (total no.) = 4 (52) No. in control group (total no.) = 14 (57) Other outcomes: Birthweight (g) Mean weight (SD) in intervention group = 3015 (513) Mean weight (SD) in control group = 3015 (629) Brief summary of findings: A significant reduction in PPROM births was shown for women receiving vitamin C, compared to placebo (p = 0.018). No statistically significant between group differences were shown for incidence of preterm birth or birthweight Authors’ conclusions: Daily supplementation with 100 mg vitamin C after 20 weeks’ gestation reduces the incidence of PPROM. Comments: 13.5% loss to follow-up was observed, which is higher than that estimated for the power calculation Gestational age was verified by clinical examination at delivery. If a difference > 1 week was found from estimated gestational age (based on last menstrual period) the case was excluded from the study |
|
Mahomed and Gulmezoglu [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 1] 419 Title: Vitamin D supplementation in pregnancy Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Not reported |
Search: Databases searched (search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register (Oct 2001) and The Cochrane Controlled Trials Register (Issue 3, 2001) Other sources None specified Search restrictions None specified Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) Randomised controlled trials Population Pregnant women at risk of vitamin D deficiency Intervention Vitamin D supplementation vs no treatment or placebo Outcomes Low birthweight, neonatal hypocalcaemia, craniotabes (softening of the skull), perinatal mortality Study selection: The authors do not report how studies were selected for inclusion, or how many reviewers were involved in this process Data extraction: Included trial data were processed as described in the Cochrane Collaboration Handbook. This recommends that at least two reviewers extract data Validity assessment: Criteria used Authors refer to data extraction table but do not specifically state the criteria used. Allocation concealment, method of randomisation, and (sometimes) blinding were reported Assessment Included trial data were processed as described in the Cochrane Collaboration Handbook. This recommends that at least two reviewers assess the included studies for validity Synthesis: Heterogeneity Heterogeneity was assessed using H and I² tests Methods Fixed effects model, Peto odds ratio |
No. of studies included: 2 RCTs (n = 232) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 1 Adequate concealment of allocation – 1 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 1/1/1 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Low birthweight OR 0.50 (95% CI: 0.20–1.26) (1 study, n = 128) Low weight for gestation OR 0.47 (95% CI: 0.20–1.09) (1 study, n = 126) Neonatal hypocalcaemia OR 0.13 (95% CI: 0.02–0.65) (2 studies, n = 203). Heterogeneity χ² = 0.10 df = 1 p = 0.75 I² = 0.0% Craniotabes OR 0.40 (95% CI: 0.09–1.65) (1 study, n = 126) Other outcomes: Maternal daily weight gain (g) in the third trimester (Fixed effects) WMD 16.90 (95% CI: 8.08–25.72) (1 study, n = 126) Brief summary of findings: In one trial babies born to women taking vitamin D supplements had lower birthweights, and in the other trial mothers taking vitamin D had higher daily weight gain and fewer babies with low birthweights. Neonatal hypocalcaemia was less common in the supplemented group, compared to the non-supplemented group Authors’ conclusions: There is insufficient evidence to evaluate the effects of vitamin D supplementation in pregnancy Comments: There is a lack of detail on the methods used to select the primary studies, extract data, and assess trial quality. The number of women included in the trials is small and the authors point out that this may account for the conflicting data on birthweights, which could be due to chance It has also been suggested that reported SDs in one of the primary studies (Mallet et al. , 1986733) are likely to be SEs One additional trial was identified as ‘waiting to be assessed’ It is not clear whether singleton and multiple gestations were included in the primary papers |
|
Rumbold et al. [Cochrane Databse of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 4] 421 Title: Vitamin E Supplementation in Pregnancy Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 19 (out of 190 in total) based on preterm birth at <37 weeks |
Search: Databases searched (search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register (June 2004), Central (Issue 2, 2004), MEDLINE (1966 to May 2004), Current Contents (1998 to May 2004), EMBASE (1980 to May 2004) Other sources None specified Search restrictions None specified Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs and quasi-RCTs Population Asymptomatic pregnant women living in areas where there is either inadequate intake of vitamin E or presumed adequate intake. Three trials recruited women ‘at high risk of pre-eclampsia’, and two trials involved women with established severe early onset pre-eclampsia Intervention Vitamin E supplementation (alone or in combination with other separate supplements) vs placebo or no treatment or other supplements. Interventions with a multivitamin supplement (defined as more than two vitamins or minerals in the same tablet) were excluded. All included trials compared supplements of vitamins E and C with placebo Outcomes Primary outcomes: perinatal mortality, stillbirth, maternal and infant haematological measures, preterm birth < 37 weeks, pre-eclampsia, intrauterine growth restriction, birthweight, and PPROM A number of secondary maternal and infant outcomes were also sought, including use of health service resources Study selection: Two reviewers independently assessed trials for inclusion and resolved differences by discussion. Data extraction: Two reviewers independently extracted data; differences were resolved by discussion. Attempts were made to contact authors for further details if the method of allocation concealment was unclear Validity assessment: Criteria used Blinding of assessment of outcome, completeness of follow-up, use of placebo and allocation concealment were assessed using Cochrane criteria Assessment Carried out independently by two authors Synthesis: Heterogeneity Tests of heterogeneity were applied to assess the significance of any differences between trials (I² ≥ 50%) Methods Meta-analysis using the fixed effects model. Where heterogeneity was found subgroup analyses were performed for the main outcomes. Heterogeneity that was not explained by subgroup analyses was modelled using random-effects analysis. Sensitivity analyses were conducted to explore the effect of trial quality |
No. of studies included: 4 RCTs (n = 566) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 2 Adequate concealment of allocation – 2 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 3/3/2 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: (Fixed effect) RR 1.29 (95% CI: 0.78–2.15) (2 studies, n = 383) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: (Fixed effect) RR 1.29 (0.67, 2.48) (1 study, n = 56) Incidence of adverse events: Stillbirth (Fixed effect) RR 0.77 (95% CI: 0.35–1.71) (2 studies, n = 339) Neonatal death (Fixed effect) RR 5.00 (95% CI: 0.64–39.06) (1 study, n = 40) Admission to ICU (infants) (Fixed effect) RR 0.83 (95% CI: 0.30–2.29) (1 study, 40 infants) Requirement for mechanical ventilation (Fixed effect) RR 0.33 (95% CI: 0.08–1.46) (1 study, 40 infants) Clinical pre-eclampsia (Random effects) RR 0.44 (95% CI: 0.16–1.22) (3 studies, n = 510) Intrauterine growth restriction (Fixed effect) RR 0.72 (95% CI: 0.49–1.04) (2 studies, n = 383) Bleeding episodes (Fixed effect) RR 0.35 (95% CI: 0.10–1.23) (2 studies, n = 339) Apgar score less than 7 at 5 min (Fixed effect) RR 0.63 (95% CI: 0.21–1.90) (1 study, n = 39) Measures of serious maternal morbidity (subtotals only) Eclampsia RR 1.07 (95% CI: 0.07–16.33) (1 study, n = 56), Renal failure RR 0.36 (95% CI: 0.02–8.41) (1 study, n = 56), Disseminated intravascular coagulation RR 0.36 (95% CI: 0.02–8.41) (1 study, n = 56), pulmonary oedema RR 0.54 (95% CI: 0.05–5.59) Side effects of vitamin E (subtotals only) Acne RR 3.21 (95% CI: 0.14–75.68) (1 study, n = 56), transient weakness RR 5.36 (95% CI: 0.27–106.78) (1 study, n = 56), skin rash RR 3.21 (95% CI: 0.14–75.68) (1 study, n = 56) Other outcomes: Birthweight (Fixed effect) weighted mean difference – 139.00 (95% CI: – 517.69 to 239.69) (1 study, n = 100) Sensitivity analyses by trial quality: Preterm birth < 37 weeks (Fixed effects) RR 1.21 (95% CI: 0.38–3.87) (1 study, n = 283) Perinatal death (Fixed effects) RR 1.29 (0.67–2.48) (1 study, n = 56) Stillbirth (Fixed effects) RR 0.77 (95% CI: 0.35–1.71) (2 studies, n = 339) Neonatal death (Fixed effects) RR 5.00 (0.64, 39.06) (1 study, n = 40) Brief summary of findings: Compared with placebo, vitamin E did not alter the incidence of perinatal death, preterm birth, intrauterine growth restriction or birthweight. Substantial heterogeneity was found for pre-eclampsia, with a decreased risk associated with vitamin E supplementation using the fixed effects model, but no difference discernable using random-effects models. No differences were found between groups for any secondary outcomes Authors’ conclusions: There are insufficient data to determine if vitamin E supplementation is beneficial during pregnancy Comments: The authors highlight a number of considerations when interpreting the review findings: the total number of women involved in the included studies was small, and two trials were of poor quality; all of the women involved were at risk of pre-eclampsia or had established early onset pre-eclampsia; there was no information assessing vitamin E independent of other supplements so the treatment effects may not be a direct consequence of vitamin E supplementation; there are limited data on adverse event outcomes, with many results coming from a single trial; substantial heterogeneity was found for the outcome pre-eclampsia |
|
Mahomed [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1997, Issue 3] 418 Title: Zinc supplementation in pregnancy Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported. Preterm birth – 109 (out of 1280 in total) |
Search: Databases searched Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register; search date not reported Other sources None specified Search restrictions None specified Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) Controlled trials Population Asymptomatic pregnant women, at least 26 weeks’ gestation, with no systemic illness. Two trials selected women at high risk of low zinc status and one trial selected women with low plasma zinc levels Intervention Elemental zinc supplementation (20–62 mg) vs no treatment or placebo Outcomes Biochemical assessment of zinc status, plus a range of maternal and neonatal outcomes Study selection: Carried out by the one reviewer Data extraction: Additional data was sought where required by contacting the principal author. Studies in which all outcome variables were in the form of mean values with no standard deviation were excluded Validity assessment: Criteria used Satisfactory randomisation of allocation to the study or control group. In addition, studies in which >25% of participants were excluded from the final analysis were excluded from the review Assessment This was carried out by one reviewer Synthesis: Heterogeneity Heterogeneity was assessed using the H and I² test of heterogeneity Methods Peto odds ratios were calculated |
No. of studies included: 7 RCTs (n = 3486) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 4 Adequate concealment of allocation – 3 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 7/7/0 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: OR 0.73 (95% CI: 0.54–0.98) (5 studies, n = 2539) NB. Preterm delivery only defined in one trial as PTB < 37 weeks Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Stillbirth/neonatal death OR 0.97(95% CI: 0.40–2.35) (4 studies, n = 1265) Incidence of adverse events: Preterm labour OR 1.12 (95% CI: 0.72–1.74) (1 study, n = 1206) Pre-labour rupture of membranes OR 0.01 (95% CI: 0.73–1.15) (2 studies, n = 1691) Smell dysfunction OR 1.01 (95% CI: 0.47–2.16) (1 study, n = 170) Taste dysfunction OR 0.70 (95% CI: 0.31–1.59) (1 study, n = 170) Any maternal infection OR 1.26 (95% CI: 0.76–2.10) (1 study, n = 487) Antepartum haemorrhage OR 1.20 (95% CI: 0.61–2.37) (1 study, n = 1206) 5-min Apgar less than 5 OR 1.02 (95% CI: 0.25–4.08) (1 study, n = 1692) Low birthweight OR 0.89 (95% CI: 0.61–1.30) (3 studies, n = 1840) Congenital malformation OR 0.56 (95% CI: 0.21–1.53) (3 studies, n = 683) Other outcomes: A number of other outcomes were obtained, with statistically significant differences detectable only for the following: induction of labour (Peto odds ratio 0.18, 95% CI: 0.06–0.57(1 study, n = 54)) and Caesarean section (Peto odds ratio 0.69, 95% CI: 0.49–0.96 (3 studies, n = 1747)) Brief summary of findings: Compared with placebo or no treatment, zinc supplementation was associated with lower rates of labour induction, preterm delivery and Caesarean section; it had no detectable effect on any other pregnancy outcome. There was no evidence of any adverse maternal or fetal effect with zinc supplementation Authors’ conclusions: There is insufficient evidence to evaluate the affect of zinc supplementation during pregnancy. The possible beneficial effects on preterm delivery need to be evaluated in further trials Comments: This review does not appear to have been conducted using all the standard methods of the Cochrane collaboration. Only one reviewer considered trials for inclusion, evaluated trial quality and extracted the data. Search dates are not given. Results are given for ‘preterm delivery’ and ‘preterm labour’ but these are not defined. The author notes that apparent inconsistencies between trials in some of the findings (not specified) may be related to the failure to restrict the review to trials of routine zinc supplementation. The association between zinc supplementation and lower rates of induction of labour is based on one study of 54 women, so may be too small to give a reliable result It is not clear whether singleton and multiple gestations were included in the primary papers |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Sosa et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2004, Issue 1] 455 Title: Bed rest in singleton pregnancies for preventing preterm birth Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 71 (out of a total of 834), based on preterm birth less than 37 weeks’ gestation |
Search: Search dates July 2003 Databases searched Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group trials register, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Medline, Lilacs, Embase, Poplin Other sources Bibliographies Search restrictions None Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTS, quasi-RCTs Population Pregnant women at high risk of spontaneous preterm birth (asymptomatic). Definition given Women with PPROM or multiple pregnancies were not considered Intervention Bed rest (home or hospital) vs no intervention Outcomes Primary outcomes: preterm birth, perinatal mortality, low birthweight, neonatal intensive care A range of secondary perinatal and maternal outcomes were eligible for inclusion The only reported outcome is preterm birth rate Study selection: Two reviewers independently assessed the trials for inclusion. Disagreements were resolved by consensus or involvement of a third reviewer Data extraction: Two reviewers independently extracted the data Validity assessment: Criteria used Randomisation; allocation concealment (rated adequate/uncertain/inadequate); blinding and completeness of follow-up were assessed for each outcome. Quality ratings assigned using Cochrane criteria Assessment Carried out by two reviewers independently. Disagreements were resolved by consensus or involvement of a third reviewer Synthesis: Heterogeneity In the case of significant heterogeneity among study outcomes, a sensitivity analysis was to be performed and conclusions based on the results of the highest quality studies. However, only one study was included in the review Methods Where estimable, RRs and their 95% CI are reported for each outcome. The included study reported a cluster RCT designed to evaluate a programme for prevention of preterm birth that included an educational intervention plus increased clinic visits. Eight hospitals were randomised to intervention (5) or control (3) units. Besides the prevention programme, women in intervention hospitals were randomised to receive one of five interventions: bed rest, psychosocial support, progestins, placebo or no intervention. For this review the authors only considered the comparison within the intervention hospitals |
No. of studies included: 1 RCT (n = 1266). 432 were prescribed bed rest at home and 834 received a placebo (n = 412) or no intervention (n = 422) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – Unknown (not reported in primary study) Adequate concealment of allocation – Unknown (not reported in primary study) Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – Unknown (not reported in primary study) Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: (Fixed effects) RR 0.92 (95% CI: 0.62–1.37) (I study, n = 1266) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not relevant Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not relevant Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not relevant Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Not reported Brief summary of findings: No statisitically significant between group difference was found for preterm birth <37 weeks’ gestation Authors’ conclusions: There is no evidence either supporting or refuting the use of bed rest to prevent preterm birth. Due to the potential adverse effects that bed rest could have on women and their families, and the increased costs for the health-care system, clinicians should not routinely advise women to rest in bed to prevent preterm birth Comments: The authors have provided good detail about the review methodology and of the included study. Reasons are given for the exclusion of other studies The authors note that the only included trial has uncertain methodological quality and internal validity. They also note that baseline characteristics of randomised women were not reported. In addition, there are discrepancies in the number of women originally included in the intervention hospitals and those in the table of results for which they could find no adequate explanation. One study identified for possible inclusion is awaiting translation into English |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Bachmann et al. [Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2003; 82: 398–404] 22 Title: Elective cervical cerclage for prevention of preterm birth: a systematic review Type of review: Other Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Preterm birth – 182 (out of a total 1188 women), based on preterm birth at less than 34 weeks’ gestation 296 (out of a total of 1128 women), based on preterm birth at less than 37 weeks’ gestation |
Search: Databases searched (search dates) MEDLINE (1996 to 2002), EMBASE (1980 to 2002), the Cochrane Library (issue 1, 2002) and the Science Citation Index (1974 to 2001) Other sources Reference lists of relevant primary studies and review articles were also searched Search restrictions None stated Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) were eligible for inclusion. Population Pregnant women at risk of spontaneous preterm birth Intervention Cervical cerclage vs standard treatment without cerclage Outcomes Delivery before 34 weeks’ gestation was the primary outcome reported. Data on delivery before 37 weeks’ gestation and adverse events was also included Study selection: One reviewer screened citations of titles and abstracts for relevance. Complete reports of all citations deemed definitely or possibly relevant were independently assessed by two reviewers. The authors do not state how disagreements were resolved Data extraction: Two reviewers independently extracted data in duplicate Validity assessment: Criteria used: Primary studies were assessed with regard to adequacy of randomisation process, allocation concealment, blinded data analysis and intention-to-treat analysis Assessment: The authors do not state who performed the assessment Synthesis: Heterogeneity: This was assessed graphically by use of funnel plots and statistically with the chi-squared test. Planned exploration of heterogeneity included: method of cerclage used, population, study quality, clinical heterogeneity and methodological heterogeneity Methods: Outcome and harm data were abstracted into 2 × 2 tables. Were no heterogeneity was found meta-analysis of the outcome data was performed. Summary ORs and their 95% confidence intervals were presented. A narrative summary was presented for all other results |
No. of studies included: Seven RCTs were included in the review (n = 2354) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 2 Adequate concealment of allocation – 5 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 0/0/3 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: OR 0.72 (95% CI: 0.53–0.97) (1 study, n = 1292) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: OR 0.80 (95% CI: 0.63–1.02) (1 study, n = 1292) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: OR 0.66 (0.31, 1.38) (1 study, n = 1292) Mean %: cerclage vs control group 7.79% (SD 8.65) vs 10.20% (SD 7.60) (p = 0.72) Data obtained from separate review (Odibo et al. , 2003734), using six of the primary studies included in the Bachmann review Incidence of adverse events (cerclage vs control group): Cervical trauma from cerclage: 1% PROM: 18% vs 12% (p = 0.50) Chorioamnionitis: 20% vs 10.3% (p = 0.20); 16.1% vs 6.7% (p = 0.40) Puerperal pyrexia: 6% vs 3% (p = 0.03); 10% vs 3% (p = 0.07) Placental abruption: 10.9% vs 13.8% (p = 0.80); 12.9% vs 16.7% (p = 0.90) Brief summary of findings: Clinical differences between groups precluded meta-anlaysis. Five of the seven trials demonstrated a reduction in preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation. No statistically significant benefit of cerclage was found compared to standard treatment on the odds of preterm birth < 37 weeks’ gestation. Data on complications was sparse Authors’ conclusions: Elective cerclage has a significant effect in preventing spontaneous preterm birth before 34 weeks’ gestation The authors also state that further research should focus on clarifying the possible complications associated with cervical cerclage, and with the identification of risk factors and tests that identify high-risk women who are most likely to benefit from this procedure Comments: This was a well-conducted review; methods were used to minimise bias in the study selection, validity assessment and data abstraction processes. Data was appropriately pooled and heterogeneity assessed Risk of spontaneous preterm birth did not have to be verified by ultrasonographic cervical assessment to be eligible Odds ratios presented for preterm birth outcomes (delivery < 34 or 37 weeks’ gestation) and perinatal mortality relate to the largest good quality trial included in the review (MRC/RCOG trial) |
|
Berghella et al. [Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004; 191: 1311–1317] 457 Country: USA Setting: two university hospitals Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 12 (out of a total 30), based on preterm birth at < 34 weeks’ gestation Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: Not reported No. of participants: No. randomised – 61 No. analysed – 61 Validity: Adequate randomisation – Yes (Computer-generated numbers in permuted blocks of 6) Adequate allocation concealment – Yes (sealed opaque envelopes) Blinding of clinician – No Blinding of patient – No Blinding of researcher – No Type of analysis: Continuous data were analysed with the Student’s t-test; for binary variables the chi-squared test or Fisher’s Exact test was used to describe proportions between groups. Analysis was conducted on an intention-to-treat basis Power analysis: 30 participants were needed in each study arm to find a 35% reduction in preterm birth at < 35 weeks’ gestation (α = 0.05, and β = 0.20) |
Groups compared: Cervical cerclage with bed rest vs Bed rest alone Intervention details: Treatment group Women received preterm labour education. Within 3 days of randomisation women received a MacDonald cerclage (Mersiline, 5 mm, was the preferred suture). Women were advised to begin bed rest at home, and were followed with ultrasound examination until 28–30 weeks’ gestation. Betamethasone for fetal lung maturity was offered after 24 weeks’ gestation for overt preterm labour or PROM. Antibiotics, tocolytics and other interventions were left to the discretion of the obstetrician. Fetal fibronectin was not collected Control group Women were counselled about preterm labour education, and advised to start bed rest at home. Ultrasound examinations were provided until 28–30 weeks’ gestation. Treating obstetricians were allowed to offer rescue cerclage if a cervical dilatation of ≥ 1 cm was detected on digital examination. Treatment for overt preterm labour was as described in the treatment group Participants: Asymptomatic women at high risk who were identified to have short cervix (< 25 mm) or significant funnelling (> 25%), and unscreened women at low risk who were identified incidentally Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Asymptomatic women identified as having high risk factors for preterm birth (one or more preterm births between 14 and 34 weeks’ gestation, at least two curettage procedures for spontaneous/voluntary abortions, diethylstilbestrol exposure, cone biopsy, and Müllerian anomaly), and low-risk women incidentally identified as having short cervix or funnelling were eligible. Advanced cervical dilatation or membrane bulging in the vagina were not considered exclusion criteria Prophylactic cerclage due to historic high risk, previous pregnancy delivered to term, major fetal anomaly, triplets or higher order pregnancies were excluded from the study. Post-screening exclusion criteria included: previous inclusion in another trial, current drug abuse, and regular contractions leading to preterm birth after identification of abnormal cervix Outcomes: Primary outcome was preterm birth at <35 weeks’ gestation. Secondary outcomes included: gestational age at delivery, preterm labour, PROM, and interval from enrolment to delivery. Neonatal outcomes included death, admission to intensive care unit, days in intensive care unit, and composite morbidity |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 13 (31) No. in control group (total no.) = 12 (30) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 9 (34) No. in control group (total no.) = 11 (31) (includes two sets of twins) Incidence of perinatal mortality: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 9 (34) (includes three sets of twins) No. in control group (total no.) = 4 (31) Incidence of adverse events: Composite morbidity: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 7 (34) No. in control group (total no.) = 8 (31) (includes two sets of twins) PROM: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 11 (31) No. in control group (total no.) = 10 (30) Subgroup Analysis According to risk (singleton gestations): High-risk; cervical length < 25 mm: RR 0.66 (95% CI: 0.19–2.30) Previous preterm birth < 35 weeks; cervical length < 25 mm: RR 0.52 (95% CI: 0.12–2.17) Previous preterm birth < 35 weeks; cervical length ≤ 15 mm: RR 0.44 (0.03, 6.70) Brief summary of findings: Compared to bed rest alone, cerclage did not prevent preterm birth < 34 weeks’ gestation (RR 1.05; 95% CI: 0.57–1.92). No statistically significant difference between the groups was shown for incidence of mortality (p = 0.22), admission to neonatal care unit (p = 0.53), or composite morbidity (p = 0.80), birthweight (p = 0.74), or PPROM (RR 1.06, 95% CI: 0.53–2.13) Authors’ conclusions: Cerclage did not prevent preterm birth in women with a short cervix. These results should be confirmed by larger trials Comments: 52% of women eligible for inclusion declined to participate in the trial High-risk women and women without high risk were recruited; no separate analysis for the two groups was reported No loss to follow-up Women were screened with transvaginal ultrasonography |
|
To et al. [Lancet 2004; 363: 1849–1853] 458 Country: Multi-centre trial (UK, Brazil, South Africa, Slovenia, Greece, and Chille) Setting: Hospital and Home setting Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 33 (out of a total 126), based on preterm birth at < 33 weeks’ gestation in high-risk women Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: Cervical suture removed in 37th gestational week. All women followed-up until delivery No. of participants: No. randomised – 253 No. analysed – 253 Validity: Adequate randomisation – Yes (computer-generated, block randomisation) Adequate allocation concealment – Yes (telephone to central trial office) Blinding of clinician – No Blinding of patient – No Blinding of researcher – No Type of analysis: Chi-squared test or Fishers’ Exact test was used to detect between-group differences in categorical outcomes. Unpaired t-tests or Mann–Whitney tests were used for continuous variables. ITTanalysis was used Power analysis: It was calculated that 160 participants per arm would be needed to detect a 20% reduction in early preterm birth, power 90%, significance level 5% |
Groups compared: Cervical suture vs Expectant management Intervention details: Participants in the treatment group received placement of Shirodkar suture with mersilene tape under spinal anaesthesia, and received a single dose of intravenous erythromycin (500 mg) intraoperatively. Cervical suture was removed in the 37th week of pregnancy unless spontaneous onset of labour, rupture of the membranes or need for early delivery arose All women in the trial were given prophylactic steroids (two doses of dexamethasone, 12 mg intramuscularly, 12 h apart) for fetal lung maturation at 26–28 weeks’ gestation. No other interventions were routinely recommended Participants: Asymptomatic women at risk of early preterm birth Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Pregnant women with a cervical length of 15 mm or less were eligible for inclusion Women with major fetal abnormalities, painful regular uterine contractions, or history of ruptured membranes and cervical cerclage in situ were excluded from screening. Women with dilated cervix during screening were excluded from randomisation Outcomes: Preterm birth < 33 weeks’ gestation. A number of secondary outcomes were also considered: birthweight, stillbirth, neonatal death, major adverse event before discharge from hospital, maternal morbidity during antenatal hospital stay, or symptomatic vaginal discharge |
Incidence of birth < 33 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 28 (127) No. in control group (total no.) = 33 (126) Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 7 (127) No. in control group (total no.) = 10 (126) Incidence of adverse events: Stillbirth No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (127) No. in control group (total no.) = 5 (126) Retinopathy of prematurity No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (123) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (121) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia No. in intervention group (total no.) = 4 (123) No. in control group (total no.) = 4 (121) Intraventricular haemorrhage/periventricular haemorrhage No. in intervention group (total no.) = 1 (123) No. in control group (total no.) = 2 (121) Maternal pyrexia No. in intervention group (total no.) = 5 (127) No. in control group (total no.) = 1 (126) Symptomatic vaginal discharge No. in intervention group (total no.) = 8 (127) No. in control group (total no.) = 1 (126) Brief summary of findings: Cervical cerclage was not associated with a significant reduction in the rate of preterm birth < 33 weeks’ gestaion (RR 0.84, 95% CI: 0.54–1.31). A greater incidence of symptomatic vaginal discharge was shown in women with cerclage than those without (RR 7.87, 95% CI: 1.00–62.04). No other statistically significant differences in perinatal or maternal outcomes were found Authors’ conclusions: Insertion of a Shirodkar suture in women with a short cervix does not substantially reduce risk of early preterm delivery Comments: Loss to follow-up: one participant from the control group (0.01%), none from the intervention group Of the 47,123 women screened, 470 women met inclusion criteria; 217 declined to participate. Seven participants did not receive their allocated treatment: two declined cerclage, two ruptured membranes before cerclage and one recieved dummy cerclage, and two participants in the expectant management group received cerclage |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Hueston [Obstet Gynecol 1995; 86 (4, part 2):705–712] 461 Title: The effectiveness of preterm-birth prevention educational programs for high-risk women: a meta-analysis Type of review: Other Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Individual numbers were not reported. However, the authors state that the mean rate of preterm delivery in the control groups was 13%, out of a total 3187 women at risk of preterm birth |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) MEDLINE (1979 to Feb 1994) Other sources Bibliographic handsearching of relevant reviews and articles Search restrictions Only articles published in English were sought Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) ‘Well-controlled studies’ were eligible, this appeared to include: RCTs, non-RCTs and historical control studies. Only RCTs were included in the meta-analyses Population Pregnant women (asymptomatic). All the studies included in the meta-analysis included only high-risk women, and defined high risk using scoring system described by Creasy [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006 (1980) 552 Intervention Any type of preterm labour education programme. Interventions from the studies entered in the meta-analyses included provider and patient education with weekly cervical examinations or an education programme with home visitation. These programmes ranged in duration from 16 to 54 months Outcomes The primary outcomes of interest included: rate of preterm labour, rate of preterm delivery, low birthweight, rate of neonatal survival, gestational age, and birthweight Study selection: The authors do not state how the primary studies were selected for the review, or how many reviewers performed the selection Data extraction: Two reviewers independently extracted the data from the primary studies; disagreements were resolved by a third reviewer. Reviewers were blinded to the identity of the author and the journal. Validity assessment: Criteria used Studies were evaluated in terms of study design, population, study duration, sample size and control for potential confounders Assessment The authors do not state how the primary studies were assessed but report that a team of evaluators assessed the methodology of the primary studies Synthesis: Heterogeneity Heterogeneity was considered; the authors do not state what methods were used Methods Studies were entered into a meta-analysis using methods described by Rosenthal (1987)735, grouped by study design. Only results for the RCT group are presented. Risk ratios (RR), with their 95% confidence intervals, were reported for each of the primary outcomes The authors report that statistically significant heterogeneity was found for all outcomes in the meta-analyses performed for studies employing non-randomised and historical control study designs. The authors state that for this reason the analysis was limited to the RCTs |
No. of studies included: Six RCTs No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – Not reported Adequate concealment of allocation – Not reported Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – Not reported Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: RR 1.08 (95% CI: 0.92–1.27) (2 studies, n = 1345) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Preterm labour: RR 1.71 (95% CI: 1.41–2.08) (2 studies, n = 1345) Low birthweight: RR 0.99 (95% CI: 0.88–1.11) (4 studies, n = 4130) Neonatal survival: RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.99–1.01) (3 studies, n = 2949) Brief summary of findings: No statistically significant difference was found between women who received an educational programme and those who did not on the primary outcomes for preterm birth, low birthweight, and neonatal survival. When compared to no treatment, women who received a preterm birth educational programme had a greater incidence of diagnosis for preterm labour Authors’ conclusions: Preterm birth educational programmes appear to have little beneficial effect on reducing the risk of preterm birth. Educational programmes may result in an increased rate of diagnosis for preterm labour Comments: The procedures involved in study selection were not well described, the quality of the primary studies is not discussed and limited detail is provided regarding the included studies. Caution should be exercised in interpreting the observed results No loss to follow-up in any of the included studies |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Kramer et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 4] 427 Title: Energy and protein intake in pregnancy Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 18 (out of 211 in total) 118 (out of 1211 in total) 56 (out of 256 in total) 38 (out of 391 in total) 4 (out of 91 in total) Preterm birth not defined |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group trials register (Oct. 2002) Other sources Experts contacted Search restrictions None Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs, quasi-RCTs Population Pregnant women For dietary restriction, pregnant women with either high pregnancy weight or high gestational weight gain Intervention Dietary advice to increase energy and protein intakes, energy/protein supplementation, dietary restriction. For energy/protein supplementation programmes that were balanced, high protein or isocaloric were included Outcomes Dietary intake, gestational weight gain, fetal/infant outcomes (stillbirth, neonatal death, fetal growth, gestational duration), child growth and development, maternal outcomes (complications of pregnancy, labour and delivery, postpartum weight retention) Study selection: Two reviewers independently evaluated studies for inclusion Data extraction: Data were extracted independently by two reviewers, with disagreements resolved by consensus or involvement of a third party. Additional information was sought from triallists Validity assessment: Criteria used Cochrane method of assigning quality ratings to these criteria: allocation concealment, blinding of randomisation, blinding of intervention and outcome assessment, completeness of follow-up Assessment Carried out independently by two reviewers with differences resolved by consensus or involvement of third party Synthesis: Heterogeneity Meta-analysis using a fixed effect model. Where significant heterogeneity was found, pooled estimates were recalculated using a random effects model Methods Results of trials using nutritional supplements were stratified by initial nutritional status (adequate vs inadequate) of participants for the outcome of mean birthweight For two cluster RCTs with no data on the outcome-specific intra-class correlation coefficients a value of 0.1 was assumed and the corresponding sample sizes adjusted according to the design effect |
No. of studies included: 01. Five trials (n = 1134) compared nutritional advice to increase energy and protein intake with no advice 02. 13 trials (n = 4665) compared balanced energy/protein supplementation with no supplementation or vitamin/mineral only supplementation 0.3 Two trials (n = 1076) compared high protein supplementation with other supplementation 0.4 Three trials (n = 966) compared isocaloric protein supplements with no supplementation 0.5 Three trials (n = 384) compared energy/protein restriction with normal diet No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 2 Adequate concealment of allocation – 5 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – one trial reported blinding of researcher. No blinding in four trials, unknown (not reported in primary study) in 18 Incidence of preterm birth (not defined): 01. (Fixed effect) RR 0.46 (95% CI: 0.21–0.98) (2 studies, n = 449) 02. (Fixed effect) RR 0.83 (95% CI: 0.65–1.06) (5 studies, n = 2436) 03. (Fixed effect) RR 1.14 (95% CI: 0.83–1.56) (1 study, n = 505) 04. (Fixed effect) RR 1.05 (95% CI: 0.69–1.60) (1 study, n = 782) 05. (Fixed effect) RR 0.50 (95% CI: 0.09–2.66) (1 study, n = 182) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not reported Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Stillbirth 01. (Fixed effect) RR 0.37 (95% CI: 0.07–1.90) (1 study, n = 431) 02. (Fixed effect) RR 0.55 (0.31, 0.97) (4 studies, n = 2206) 03. (Fixed effect) RR 0.81 (0.31, 2.15) (1 study, n = 529) Neonatal death 01. (Fixed effect) RR 1.28 (95% CI: 0.35–4.72) (1 study, n = 448) 02. (Fixed effect) RR 0.62 (95% CI: 0.37–1.05) (4 studies, n = 2206) 03. (Fixed effect) RR 2.78 (95% CI: 0.75–10.36) (1 study, n = 529) 04. (Fixed effect) RR 0.50 (95% CI: 0.05–5.49) (1 study, n = 782) Incidence of adverse events: Pre-eclampsia 01. (Fixed effect) RR 0.89 (95% CI: 0.42–1.88) (1 study, n = 136) 02. (Fixed effect) RR 1.20 (95% CI: 0.77–1.89) (3 studies, n = 516) 04. (Fixed effect) RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.57–1.75) (1 study, n = 782) 05. (Fixed effect) RR 1.13 (95% CI: 0.59–2.18) (2 studies, n = 284) Pregnancy-induced hypertension 05. (Fixed effects) RR 0.97 (0.75, 1.26) (3 studies, n = 384) Other outcomes: Small-for-gestational-age 01. (Fixed effect) RR 0.97 (95% CI: 0.45–2.11) (1 study, n = 404) 02. (Fixed effect) RR 0.68 (95% CI: 0.56–0.84) (6 studies, n = 3396) 03. (Fixed effect) RR 1.58 (95% CI: 1.03–2.41) (1 study, n = 505) 04. (Fixed effect) RR 1.35 (95% CI: 1.12–1.61) (1 study, n = 782) Birthweight (g) 01. (Random effects) weighted mean difference 205.75 (95% CI: – 242.54 to 654.04) (2 studies, n = 426) 02. (Random effects) weighted mean difference 37.62 (– 0.21 to 75.45) (14 studies, n = 4699) 03. (Fixed effect) weighted mean difference – 58.37 (95% CI: – 146.23 to 29.50) (2 studies, n = 529) 04. (Random effects) weighted mean difference 33.45 (95% CI: – 157.88 to 224.77) (3 studies, n = 966) 05. (Random effects) weighted mean difference – 217.93 (95% CI: – 664.73 to 228.87) (2 studies, n = 282) Brief summary of findings: Nutritional advice to increase energy and protein intake was successful in achieving those goals but no consistent benefit was observed on pregnancy outcomes Balanced energy/protein supplementation was associated with modest increases in maternal weight gain and in mean birthweight and a reduction in risk of small-for-gestational-age (SGA) birth and for stillbirth and neonatal death High-protein supplementation and isocaloric protein supplementation were associated with an increased risk of SGA birth Energy/protein restriction of pregnant women who were overweight exhibited high weight gain significantly reduced weekly maternal weight gain but also mean birthweight and had no effect on pregnancy-induced hypertension or pre-eclampsia Authors’ conclusions: Dietary advice appears effective in increasing pregnant women’s energy and protein intakes but is unlikely to confer major benefits on infant or maternal health Balanced energy/protein supplementation improves fetal growth and may reduce the risk of fetal and neonatal death. High-protein or balanced protein supplementation alone is not beneficial and may be harmful to the infant Protein/energy restriction of pregnant women who are overweight or exhibit weight gain is unlikely to be beneficial and may be harmful to the infant Comments: The authors note methodological concern about the trials and highlight a number of possible sources of bias |
| Study details and design | Description of methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Olsen [BJOG 2000; 107: 382–395] 369 Country: Denmark, Scotland, Sweden, England, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Belgium and Russia Setting: 19 hospital-based centres from across participating sites Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 40 (out of a total of 120), based on preterm delivery before 37 weeks’ gestation. (Recurrence risks for sample size calculations were based on 17.5% risk of recurrence among controls). Study design: Six multicentre RCTs included (four prophylactic trials, two therapeutic trials) Length of follow-up: Four prophylactic trials: randomised at 20 weeks, followed-up until up to 4 weeks after delivery Two therapeutic trials: randomised at 33 weeks, followed-up until up to 4 weeks after delivery No. of participants: No. randomised – 1647, although only 1619 trial entry forms were received: Four prophylactic trials: 898 women with singleton pregnancies, 579 women with twin pregnancies Two therapeutic trials: 142 women (79 with threatening pre-eclampsia, 63 with suspected intrauterine growth retardation) No. analysed – 1595 women Validity: Adequate randomisation – Yes (Restricted blockwise computer-generated randomisation) Adequate allocation concealment – Yes Blinding of clinician – Yes Blinding of patient – No (although identical capsules were provided, oils would taste different: 80% allocated to fish oil group thought they had received fish oil) Blinding of researcher – Yes Type of analysis: Chi squared and Student’s t-tests were used to assess group differences. ORs were used to describe dichotomous variables. Multiple linear regression analysis was used to adjust for an observed difference in one continuous variable (gestational age). Cox regression analysis was used to assess the effects on the timing of spontaneous delivery. Intention to treat analysis was used |
Groups compared: Fish oil (Pikasol: 32% eicosapentaenoic acid, 23% docosahexaenoic acid and 2 mg tocopherol/ml) was compared with olive oil (oleric acid 72%, linoleic acid 12%). Intervention details: Prophylactic trials: Participants were given four capsules of either oil per day. For women randomised to fish oil these amounts corresponded to 2.7 g (1.3 g eicosapentaenoic acid, and 0.9 g docosahexaenoic acid) of long-chain n-3 fatty acids per day Therapeutic trials: Participants were given nine capsules of either oil per day. For women randomised to fish oil these amounts corresponded to 6.1 g (2.9 g eicosapentaenoic acid, and 2.1 g docosahexaenoic acid) of long-chain n-3 fatty acids per day Both oils were provided in identical-looking 1-g gelatine capsules Participants: Prophylactic trials: Women with uncomplicated pregnancies at high risk of preterm birth Therapeutic trials: Women with threatening pre-eclampsia, or intrauterine growth retardation Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Inclusion criteria (Prophylactic trials): > 16 weeks’ gestation; preterm delivery, intrauterine growth retardation, or pregnancy induced hypertension in a previous pregnancy; twin pregnancy (one trial) Inclusion criteria (Therapeutic trials): Women with threatening pre-eclampsia and with or without intrauterine growth restriction (one trial); women with suspected intrauterine growth restriction in current pregnancy Exclusion criteria: Diabetes (in or before pregnancy), diagnosed severe fetal malformation or hydrops in current pregnancy, suspected placental abruption in current pregnancy or occurrence in previous pregnancy, drug or alcohol abuse, regular intake of fish oil or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents or any other therapeutic agent that may have an effect on thrombocyte function or eicosanoid metabolism, or allergy to fish products. An additional exclusion criterion for the therapeutic trials was high probability of delivering within 1 week after randomisation Outcomes: Risk of preterm delivery, intrauterine growth retardation, pregnancy-induced hypertension. Therapeutic trials also assessed amelioration of threatening pre-eclampsia and suspected intrauterine growth retardation |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Earl-PD (combined prophylactic singleton pregnancy groups) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 5 (108) No. in control group (total no.) = 16 (120) Twin trial (prophylactic study) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 37 (286) No. in control group (total no.) = 44 (283) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Earl-PD No. in intervention group (total no.) = 23 (108) No. in control group (total no.) = 40 (120) Twin trial No. in intervention group (total no.) = 129 (286) No. in control group (total no.) = 127 (283) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission (figures refer to neonatal care, not stated whether intensive): a Aggregated trials No. in intervention group (total no.) = 258 (1062) No. in control group (total no.) = 283 (1076) Incidence of perinatal mortality: a Stillbirth No. in intervention group (total no.) = 16 (1056) No. in control group (total no.) = 19 (1085) Early neonatal death (aggregated trials) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (1126) No. in control group (total no.) = 2 (1144) Late neonatal death (aggregated trials) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (1125) No. in control group (total no.) = 2 (1144) Incidence of adverse events: Spontaneous abortion (aggregated trials) a No. in intervention group (total no.) = 4 (804) No. in control group (total no.) = 7 (815) Intracranial haemorrhage (aggregated trials) a No. in intervention group (total no.) = 7 (1107) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (1119) Intrauterine growth retardation (EARL-IUGR) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 43 (131) No. in control group (total no.) = 37 (132) Pregnancy-induced hypertension (EARL-PIH) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 55 (167) No. in control group (total no.) = 61 (183) Pre-eclampsia (EARL-PIH) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 11 (152) No. in control group (total no.) = 17 (169) Vaginal bleeding (aggregated trials) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 36 (802) No. in control group (total no.) = 39 (816) Maternal anaemia (aggregated trials) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 101 (407) No. in control group (total no.) = 94 (439) Low birthweight (Earl-PD) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 15 (108) No. in control group (total no.) = 26 (118) Twin trial No. in intervention group (total no.) = 238 (556) No. in control group (total no.) = 242 (566) Brief summary of findings: Compared to olive oil, a significant reduction in recurrence of preterm delivery (< 37 weeks’ gestation) for women receiving fish oil was found (OR 0.54, 95% CI: 0.30–0.98). Similarly, compared to olive oil, a reduction was found in recurrence of early preterm delivery (< 34 weeks’ gestation) (OR 0.32, 95% CI: 0.11–0.89) for women receiving fish oil. No between-group differences for preterm delivery were found in women with twin pregnancies. No statistically significant between group differences were shown for the reported adverse events Authors’ conclusions: Fish oil supplementation reduced the recurrence of preterm delivery, but had no effect on preterm delivery in twin pregnancies. Fish oil had no effect on intrauterine growth retardation and pregnancy-induced hypertension for recurrence risk in singleton or twin pregnancies Comments: Large, well-conducted study Original sample size calculation (1991): 2740 women would be needed with previous intrauterine growth retardation, pregnancy-induced hypertension/pre-eclampsia, and 2740 women with previous preterm delivery based on recurrence rate of 17.5%, risk reduction of 25%, and a 5% and 20% risk of type I/II error respectively Interim sample size calculation (1995) for six primary hypotheses; based on data from 1065 enrolled women with completed follow-up forms assuming hypothesised effects of 25% risk reductions for all end points and a 5% risk of committing a type I error. Interim analysis indicated that at least one end point would have achieved the cut-off for statistical power (0.9) by 01/01/96. Enrolment was terminated on this date |
|
Smuts et al. [Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003; 101(3): 469–479] 451 Country: USA Setting: Ambulatory clinic, Truman Medical Center, Kansas City, Missouri Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 17 (out of a total 149), based on preterm delivery < 37 weeks’ gestation Study design: Randomised, double blind, controlled trial Length of follow-up: Third trimester of pregnancy No. of participants: No. randomised – 347 (350 pregnancies, 2nd pregnancies only included for adverse events) No. analysed – 291 Withdrawal rate: 16.1% Validity: Adequate randomisation – Yes, computerised randomisation schedule, stratified by age Adequate allocation concealment – Unclear, method not reported Blinding of clinician – Yes Blinding of patient – Yes Blinding of researcher – Unclear Type of analysis: Student’s t-test was used to compare groups with regard to gestational age and birthweight. Categoric outcomes were assessed using chi-squared tests. An assessment of the relationship of selected risk factors to primary or secondary outcomes was conducted. If a relationship was found, this was included in the final regression analyses to examine the effect of docosahexaenoic acid supplementation on study outcomes. Sample size was calculated based on expected dropout of 25% to reject the null hypothesis for an increase in gestation by 5.25 days assuming an SD of 1.99 weeks, with 90% power and an α = 0.05 on a one-tailed t-test |
Groups compared: High-docosahexaenoic acid egg consumption vs Ordinary egg consumption Intervention details: Participants were given 12 eggs per week from enrolment until they gave birth, and were encouraged to eat as many of these as possible. Participants were interviewed bi-weekly to determine how many eggs had been eaten in the previous interval. Subjects were instructed to refrigerate the eggs and to cook the eggs before eating Hens were fed a nutritionally modified feed with 1% docosahexaenoic acid-rich marine microalgae (high-docosahexaenoic acid eggs; Gold Circle Farms, Boulder, CO) or fed without microalgae. Eggs were not commercially available in Kansas City and were shipped via refrigerated trucks as needed. Each batch of eggs provided during the study period was analysed for docosahexaenoic acid by the study sponsor. The high-docosahexaenoic acid eggs contained a mean of 133 mg (SD 15) docosahexaenoic acid per egg. The ordinary eggs contained a mean of 33 mg (SD 11) docosahexaenoic acid per egg Participants: Asymptomatic pregnant women Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women with a singleton gestation, 24–28 weeks’ gestation, 16–36 years old, able and willing to consume eggs with access to refrigeration and planning to deliver at Truman Medical Center were eligible Exclusion criteria: Age < 16 or > 30 years, weight > 240 lb (109 kg) at baseline, serious illness, e.g. cancer, lupus, hepatitis, untreated serious infectious disease, diabetes or gestational diabetes, elevated blood pressure Outcomes: Primary outcomes: birthweight and gestational age. A number of additional secondary maternal and infant outcomes were sought including preterm delivery < 37 weeks’ gestation and admission to neonatal intensive care |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 14 (142) No. in control group (total no.) = 17 (149) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 21 (142) No. in control group (total no.) = 21 (149) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Birthweight (< 2500 g): No. in intervention group (total no.) = 13 (142) No. in control group (total no.) = 16 (149) Pre-eclampsia/eclampsia: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 5 (142) No. in control group (total no.) = 10 (149) Gestational diabetes: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 4 (142) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (149) Meconium in amniotic fluid: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 26 (142) No. in control group (total no.) = 28 (149) Other findings: Mean gestational age in days (Did not smoke during pregnancy): Intervention group (SD) = 275.2 (11.8) Control group (SD) = 271.5 (15.3) Mean final RBC DHA (g per 100g of fatty acids): Intervention group (SD) = 5.53 (1.0) Control group (SD) = 5.35 (1.2) Mean infant RBC DHA (g per 100 g of fatty acids): Intervention group (SD) = 7.61 (3.4) Control group (SD) = 7.18 (1.4) Brief summary of findings: After controlling for various pre-defined risk factors and confounding variables, gestation was shown to significantly increase by 6.0 days (SD 2.3) (p<0.01) in the higher docosahexaenoic acid group. No other statistically significant differences were shown. No safety concerns were raised Authors’ conclusions: Modest amounts of dietary docosahexaenoic acid during pregnancy appear to extend gestational age and may lead to enhanced fetal growth Further work is necessary to understand the mechanism by which prenatal docosahexaenoic acid increases gestation and to determine what impact this increase has on developmental outcomes Comments: Mean egg intake was 7.3 (3.4 per week) for the ordinary egg group and 7.2 (3.4 per week) for the high-docosahexaenoic acid egg consumption group Study sponsored by OmegaTech Inc., Boulder, CO, USA |
| Study details and design | Description of methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Brown [Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999; 180(4): 798–805] 473 Country: USA Setting: Home monitoring Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – 997 (out of mean of 2600/year over 4.5 years – extrapolated total: 11,700) Preterm birth – 48 (out of a total of 80), based on delivery ≤ 37 weeks Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: Until birth or 37 weeks’ gestation No. of participants: No. randomised – 186 No. analysed – 162 Validity: Adequate randomisation – Unclear (process not described) Adequate allocation concealment – Yes (sealed, opaque envelopes) Blinding of clinician – No Blinding of patient – No Blinding of researcher – Unclear Type of analysis: Chi-squared test was used to analyse categoric data, Mantel–Haenszel test was used for ordinal variables, and Student’s t-test was used for continuous data. Multivariate logistic regression model was performed to determine the probability of preterm birth at < 35 weeks’ gestation Power calculation: 82 women per arm were required to determine a 20% reduction in the risk of preterm delivery with 80% power, and 5% significance level |
Groups compared: Home uterine activity monitoring vs No home uterine activity monitoring Intervention details All participants were treated with a maintenance regimen of oral terbutaline tocolysis (following i.v. magnesium sulphate treatment) for the duration of the pregnancy or until discontinuation at 37 weeks’ gestation. Before discharge from hospital all women received preterm labour and delivery education: this included recognition of signs and symptoms of preterm labour and instructions on perinatal follow-up. In addition, all participants received daily contact with a perinatal nurse who asked about any signs or symptoms of recurrent labour. Participants were followed-up weekly in a preterm labour clinic by one of the researchers. Participants in the monitored group were asked to transmit a uterine activity monitor strip by telephone to the Tokos Monitor Centre twice daily until 37 weeks’ gestation or until instructed to stop monitoring. If a participant exceeded the baseline contraction frequency of six contractions/h, the study physician, or perinatal nurse were informed by the monitoring centre, and the patient was instructed on immediate management and follow-up. Parenteral tocolysis was not reinitiated for women with recurrent preterm labour after 35 weeks’ gestation Participants: Asymptomatic women who had been treated for threatened preterm labour Participants were all being managed at Wishard Memorial Hospital, the primary hospital for disadvantaged inner-city population of Marion county Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women with a singleton gestation treated for idiopathic preterm labour between 24 and 34 weeks’ gestation, Medicaid coverage, and functioning telephone services were eligible for inclusion. Women with premature rupture of membranes or any obstetric condition warranting early delivery were excluded Outcomes: Preterm delivery < 35 weeks’ gestation and < 37 weeks’ gestation, neonatal intensive care admission, mechanical ventilation, antenatal corticosteroid treatment, birthweight, Caesarean delivery Secondary outcomes were readmissions for recurrent preterm labour necessitating parenteral tocolysis and unscheduled hospital visits lasting < 24 h |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 35 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 9 (82) No. in control group (total no.) = 12 (80) Incidence of birth ≤ 37 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 40 (82) No. in control group (total no.) = 48 (80) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not reported Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 20 (82) No. in control group (total no.) = 22 (80) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Birthweight Intervention group: 2933 (SD: 639.9) Control group: 2943.5 (SD: 547.0) Incidence of adverse events: Mechanical ventilation No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (82) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (80) Antenatal corticosteroid treatment No. in intervention group (total no.) = 56 (82) No. in control group (total no.) = 54 (80) Mean length of neonatal unit stay (days) Intervention group (SD) = 3.3 (11.4) Control group (SD) = 2.2 (6.5) Brief summary of findings: No statistically significant differences were shown for any of the measures predicting preterm birth except cervical dilatation at enrolment. Women with cervical dilatation ≥ 2 cm at enrolment had an OR of 4.35 (95% CI: 1.07–17.66) for delivery at < 35 weeks’ gestation. The OR for preterm delivery women with ≥ 2 cm dilatation was 2.07 (95% CI: 0.47–9.20); the OR for women with < 2 cm dilatation was 1.06 995% CI: 0.22–5.23) No difference was shown between groups in neonatal intensive care admissions, number of infants receiving mechanical ventilation, or percentage of women receiving corticosteroid treatment for prevention of neonatal complications Authors’ conclusions: Home uterine monitoring, as an adjunctive treatment to oral terbutaline therapy, does not reduce the likelihood of preterm delivery before 35 weeks’ gestation Comments: Mean compliance with home uterine activity monitoring (based on actual number of HUM transmissions vs expected number of transmissions) was 64.5% (delivery < 35 weeks’ gestation) and 59.7% (delivery > 35 weeks’ gestation) There was a 12.9% loss to follow-up |
|
Corwin et al. [Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996; 175: 1281–1285] 474 Country: USA Setting: Recruitment was conducted at three centres: the Truman Medical Center, Kansas City; the State University of New York, Syracuse Health Sciences Center; and the University of Illinois Hospital Chicago. Home uterine monitoring was performed in the participant’s home Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 35 (out of a total 154), based on preterm delivery at less than 37 weeks’ gestation in women at high risk of preterm birth Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: Monitoring was started no earlier than 24 weeks’ gestation, and was continued until 37 weeks’ gestation or until delivery if delivery occurred < 37 weeks No. of participants: No. randomised – 339 No. analysed – 318 (339 women with singleton pregnancies and 38 women with twin gestations were separately randomised to the trial. However, the report is limited to the outcomes for the 339 singleton gestations) Validity: Adequate randomisation – Yes (Random number table) Adequate allocation concealment – Unclear (envelopes, not stated whether opaque or sealed) Blinding of clinician – Yes Blinding of patient – No Blinding of researcher – Unclear Type of analysis: Group comparisons were assessed using Fisher’s Exact test (categorical data) and independent t-test (continuous data). Kaplan–Meier plots were used for survival curves (women remaining undelivered between 26 and 37 weeks). Group comparisons were performed with log-rank test for survival analyses Power calculation: 320 women were required to detect an improvement from 30% to 60% in the proportion of women with preterm labour with early diagnosis (alpha 0.05, and beta 0.20; power 80%). The sample obtained had a power of 80% to detect a reduction in preterm birth from 22.7% to 11% |
Groups compared: Home uterine activity monitoring (HUM) without increased nursing support vs Routine high-risk prenatal care Intervention details: Both groups received education regarding preterm labour risk and information about preterm labour precautions, including the signs and symptoms of preterm labour. Participants also received education about the monitoring protocol and self-palpation. Participants were instructed to notify their physician or the clinic if they suspected preterm labour. Treatment protocols at each site included intensive tocolytic therapy; the specific therapy provided for preterm labour was at the discretion of the treating physician The monitored group received standard high-risk obstetric care plus twice daily home uterine monitoring (Genesis System). Women were instructed in the use of this device and told to monitor for 1 h twice a day, every day. Participants were scheduled for twice-daily transmission of uterine data (morning and evening) via phone. The receiver personnel reported the number of contractions to the patient. No additional medical advice or instructions were given to the participants at these times. The control group received standard high-risk obstetric care Participants: Asymptomatic women at risk of preterm delivery Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women between 24 and 32 weeks’ gestation with an increased risk for preterm labour as judged by a Creasy risk score ≥ 10 were eligible for inclusion. Women with a psychiatric problem that precluded compliance with study protocol, or who did not speak English, and pregnancies > 32 weeks’ gestation were excluded. In addition, all participants were required to have telephone access Outcomes: Preterm birth at < 37 weeks and < 31 weeks’ gestation, birthweight and admission to neonatal care unit |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 22 (164) No. in control group (total no.) = 35 (154) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 17 (164) No. in control group (total no.) = 32 (154) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Incidence of birth < 31 weeks’ gestation No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (164) No. in control group (total no.) = 9 (154) Birthweight < 2500 g No. in intervention group (total no.) = 19 (155) No. in control group (total no.) = 37 (142) Birthweight < 2000 g No. in intervention group (total no.) = 9 (155) No. in control group (total no.) = 20 (142) Birthweight < 1500 g No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (155) No. in control group (total no.) = 7 (142) Mean length of stay in neonatal care unit (days) Intervention group = 0.89 Control group = 3.90 Brief summary of findings: Compared to routine care, home uterine monitoring was shown to reduce risk of preterm delivery at < 37 weeks’ gestation (RR 0.59, 95% CI: 0.37–0.95), and at < 31 weeks’ gestation (RR 0.21, 95% CI: 0.05–0.95). In addition, infants from women receiving home uterine monitoring were less likely to need neonatal care admission (RR 0.50, 95% CI: 0.29–0.85), or have a low birthweight (< 2500 g, < 2000 g and < 1500 g) Authors’ conclusions: The use of uterine activity monitoring improved pregnancy outcomes in women with singleton pregnancies, including: prolonged gestation, decreased risk for preterm birth, larger-birthweight infants, and a decreased need for neonatal intensive care Comments: Loss to follow-up rate: 6.19% 377 of 509 women with Creasy scores of ≥ 10 were enrolled in the trial. Reasons for lack of enrolment: 55 women refused to participate, consent for 37 women was not requested because of lack of telephone access, and 40 women were not approached because of logistical problems related to staff availability or lack of equipment |
|
Dyson et al. [Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991; 164: 756–762] 475 Country: USA Setting: Home monitoring Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – 51 (out of a total of 253), based on preterm labour at < 34 weeks in women at risk of preterm birth Preterm birth – 15 (out of a total 63), based on preterm labour at < 34 weeks in women at risk of preterm birth Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: From 24 weeks’ gestation to 36 weeks’ gestation No. of participants: No. randomised – 247 No. analysed – 247 Results presented relate to the 138 singleton pregnancies only A group of 143 participants receiving standard care were also entered in the study. Participants had received their prenatal care and were delivered of infants at the same hospital in the 30 months preceding the start of the prospective study and were selected by presence of risk factors Validity: Adequate randomisation – Unclear, method not reported Adequate allocation concealment – Unclear, not reported Blinding of clinician – No (study nurse), Unclear, not reported (obstetrician) Blinding of patient – Yes Blinding of researcher – No Type of analysis: Chi-squared test or the Student’s t-test was used as appropriate. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM |
Groups compared: Home uterine monitoring (tracings analysed and used in patient management) vs Education-palpation group (tracings not analysed or used in patient management) Intervention details: All women were contacted at least 5 days per week by a study nurse to review signs/symptoms of preterm labour, record number of contractions by palpation, and in the home monitoring group to review monitoring information. Women in the education–palpation group routinely transmitted to a monitor in such a way that the nurse could tell which participant had transmitted but could not analyse the uterine activity data All women were instructed to report to the hospital for evaluation if they experienced more than five contractions an hour that persisted for more than 1 h despite bed rest and oral hydration. Women in the home uterine monitoring group who had five contractions per hour on routine monitoring were instructed to lie down, drink fluids and remonitor for 1 h; if contractions persisted they were referred for evaluation. Women were initially asked to monitor themselves for 1 h/day and to transmit daily. Two years into the trial the protocol was changed to twice-daily monitoring and transmission. In addition, women in the home monitoring group were given the capability to transmit an emergency tracing at any time The clinical protocol recommended tocolysis for persistent uterine contractions if the cervix was dilated to 2 cm or documented cervical change before tocolysis. Prophylactic tocolytic agents were not administered. If tocolysis was successful, the participant was discharged home to bed rest taking oral tocolytic agents and maintaining pretreatment protocols. All gestational ages were confirmed by first or second trimester ultrasonography Participants: Asymptomatic women at risk of preterm birth Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women with at least one risk factor (twin gestations, premature delivery at < 34 weeks’ gestation after premature rupture of membranes in preceding pregnancy, premature labour requiring parenteral tocolysis but with term delivery in preceding pregnancy, incompetent cervix with cerclage in place, and nullipara with bicornuate, subseptate or didelphic uterus), < 28 weeks’ gestation without evidence of preterm labour in the current pregnancy were eligible Outcomes: Preterm birth (< 34 weeks), preterm labour (< 34 or < 36 weeks’ gestation), birthweight (< 2500 g and < 1500 g), respiratory distress syndrome, admission to neonatal intensive care unit, and infant hospital stay, days gained, gestational age at delivery, and delay > 48 h |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 8 (68) (11.8%) No. in control group (total no.) = 8 (70) (11.4%) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Neonatal intensive care admission (percentage): Intervention group = 22.1 (n = 15) Control group = 16.4% Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Birthweight < 2500 g (percentage) Intervention group = 20.6 (n = 14) Control group = 18.6 (n = 13) Birthweight < 1500 g (percentage) Intervention group = 5.9 (n = 4) Control group = 8.6 (n = 6) Standard care: The incidence of preterm birth < 34 weeks’ gestation was reduced in the education-palpation and home uterine monitoring group compared to standard care (p = 0.05 and 0.06, respectively). Neonatal outcomes, such as birthweight, infant hospital stay and development of respiratory distress syndrome were improved in the education-palpation and home uterine monitoring groups compared to standard care, but differences were not statistically significant except for infant hospital stay compared with education–palpation (p = 0.04) Brief summary of findings: The between-group difference in incidence of preterm birth was not statistically significant. There was no apparent difference between education–palpation and home uterine monitoring on any of the reported outcomes in women with singleton gestations Authors’ conclusions: Addition of home uterine monitoring to the educational programme was not found to significantly improve pregnancy outcomes. However, the number of singleton pregnancies was too small to rule out possible benefit from home uterine monitoring in that group Comments: Small sample sizes and unclear internal validity limit confidence in the conclusions |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Blondel [Semin Perinatol 1995; 19(4): 263–271] 489 Title: Home visits during pregnancy: consequences on pregnancy outcome, use of health services, and women’s situations. Type of review: Other Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not stated Preterm birth – 387 (out of a total 2986), based on preterm delivery rate < 37 weeks’ gestation |
Search: Search dates Not reported Databases searched Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Database Other sources Personal contacts Search restrictions No search restrictions applied Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Women at risk of pregnancy complications. Trials focusing on home visits for social support included women at risk of preterm or unfavourable social conditions. Trials focusing on home visits for medical care included mostly women at risk of preterm birth Intervention Home visits compared with no treatment. Home visits for social support: The goal of the midwife or family member was to increase emotional support, act as confidante, strengthen social networks and/or offer educational advice Home visits for medical care: The midwives’ main task was medical examination, although they also encouraged women to rest and friends/family to help with housework Outcomes Primary outcomes of interest: Preterm birth < 37 weeks’ gestation, incidence of hospital admission during pregnancy and effect on women’s health, support, attitudes, satisfaction with care and health habits Study selection: RCTs Data extraction: The authors do not state how data was extracted from the primary studies, or how many reviewers performed the data extraction. Validity assessment: Criteria used Assessment The authors do not state how the validity of the primary studies was assessed, or how many reviewers performed the quality assessment Synthesis: Heterogeneity Statistical heterogeneity does not appear to have been formally assessed Methods Odds ratios were used to measure associations for each trial. Confidence intervals were obtained using the Cornfield method. Pooled estimates and their 95% confidence intervals were obtained by meta-analysis using the Mantel–Haenzel method for each of the primary outcomes. Studies were also grouped by type of home visit (visits to provide social support, and visits to provide medical care) |
No. of studies included: Eight RCTs (n = 7401) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – Not reported Adequate concealment of allocation – Not reported Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – Not reported Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: All home visits: OR 1.0 (95% CI: 0.8–1.1) (8 studies, n = 7401) Social support: OR 0.9 (95% CI: 0.8–1.1) (5 studies, n = 6005) Medical care: OR 1.4 (95% CI: 0.9–1.9) (3 studies, n = 1403) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable. Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Prenatal hospital admission All home visits: OR 0.8 (95% CI: 0.7–1.0) (4 studies, n = 1893) Social support: OR 0.6 (95% CI: 0.4–0.9) (1 study, n = 486) Medical care: OR 0.9 (95% CI: 0.7–1.2) (3 studies, n = 1407) Brief summary of findings: Incidence of preterm delivery did not significantly differ between the intervention and control group. Home visits did not significantly reduce the incidence of prenatal hospital admission. A reduction in the number of hospital visits during pregnancy was found for home visits (social support) compared to no treatment Authors’ conclusions: Results do not support programmes offering home visits to pregnant women who are at risk for or suffering complications; visits do not improve their pregnancy outcome or reduce the rate of prenatal hospital admission Comments: Methods for the selection of the primary studies and data extraction were not reported so the possibility of reviewer error and bias cannot be assessed. Validity of the primary studies is not reported, so the quality of the included trials is uncertain. Related publication of interest: Belzian JM et al (1995). Impact of health education during pregnancy on behaviour and utilisation of health resources. Am J Obstet Gynecol 173: 894–9. This study is included in the review described but reports on different outcomes that are not of primary interest to this review |
|
Goulet et al.[CMAJ 2001; 164(7): 985–991] 481 Country: Canada Setting: Two regional perinatal centres (Montreal and Quebec City) associated with teaching hospitals Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not stated Preterm birth – 55 (out of a total of 125), based on preterm birth less than 37 weeks’ gestation Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: Women were followed-up until delivery No. of participants: No. randomised – 250 No. analysed – 250 Validity: Adequate randomisation – Yes Adequate allocation concealment – Yes Blinding of clinician – No Blinding of patient – No Blinding of researcher – Not stated Type of analysis: Student’s t-test was used to compare means, chi-squared and the Fisher exact test were used to compare proportions. One-way analysis of variance and Pearson’s chi-squared tests were used to examine differences between the two groups in neonatal and maternal outcomes. Power: A sample size of 132 per group was required based on the assumptions of a two-tailed α of 5%, a 10% probability of type II error (β), a 1-week difference between the means and standard deviation of 2.5 weeks for gestational age |
Groups compared: Home care vs Hospital care for women with preterm labour Intervention details: Intervention group (early discharge and home care): the care plan and frequency of visits was determined on an individual basis. Medical prescription was completed by attending obstetrician, external uterine monitoring and fetal heart monitoring were carried out in the home by a nurse. Visits were provided between 09.00 and 17.00 h. The average visit lasted 1 h. Blood and urine samples were also taken at each visit. Individual teaching and psychosocial support were provided. The goal was to maximise the mother’s ability to participate in her own care and to react quickly should a problem arise. Teaching was based around individual needs. Participants were given a self-monitoring diary to record uterine activity, fetal movements, maternal activity, medication etc. An assessment of additional needs was completed, including child-care. Services were arranged through family and community resources as required. The nurse could be contacted by telephone to address concerns Control group (hospital care): women received usual in-hospital medical care according to their medical status. Nurses provided the same teaching received by the experimental group. Women were also provided with a self-monitoring diary. Women discharged from the hospital were encouraged to call regarding concerns on an emergency basis or to go direct to the emergency/obstetrics ward Participants: Pregnant women with preterm labour were approached about participation after their contractions had resolved spontaneously or in response to tocolytic treatment Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women with a first episode of preterm labour, singleton pregnancy, no previous history of preterm delivery, gestational age between 20 and 35 weeks, minimum maternal age of 18, resident within 50 km of the hospital were eligible. Women were excluded if there was more than one pregnancy complication at time of randomisation, cervical dilatation was > 4 cm and effacement was > 80%, or there was a diagnosis of intrauterine death or suspicion of fetal malformation Outcomes: Primary neonatal outcomes: gestational age and birthweight Secondary neonatal outcomes: incidence of preterm birth, duration of neonatal hospital stay, admission to neonatal intensive care Maternal outcomes: incidence of maternal hospital admission and length of hospital stay |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 53 (125) No. in control group (total no.) = 55 (125) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 13 (125) No. in control group (total no.) = 11 (125) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Neonatal intermediate care No. in intervention group (total no.) = 20 (125) No. in control group (total no.) = 21 (125) Neonatal haematological problems No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (125) No. in control group (total no.) = 1 (125) Multiple neonatal problems No. in intervention group (total no.) = 30 (125) No. in control group (total no.) = 28 (125) Duration of hospital stay (neonatal) Mean (SD) number of days, intervention group= 7.9 (14.4) Mean (SD) number of days, control group= 6.1 (10.8) Number of hospital re-admissions (maternal) 1: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 14 (125) No. in control group (total no.) = 18 (125) 2: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (125) No. in control group (total no.) = 5 (125) 3: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (125) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (125) Duration of all maternal hospital stays Mean (SD) number of days, intervention group= 3.7 (3.4) Mean (SD) number of days, control group= 5.0 (5.5) Brief summary of findings: There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in incidence of preterm delivery, neonatal admission to intensive care or intermediate care, birthweight, number of maternal hospital re-admissions. The mean duration of all maternal hospital stays was slightly shorter for women in the home visit group Authors’ conclusions: Home care management is an efficient and acceptable alternative to hospital care for women experiencing preterm labour Comments: Analysis was by intention to treat A sample of 125 per group produced a power of 89% to detect a difference in the means for gestational age of more than a week |
|
Kitzman [JAMA 1997; 278(8): 644–652] 482 Country: USA Setting: Home visits for pregnant women recruited at the Regional medical centre, Memphis Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not stated Preterm birth – 13%, based on preterm birth less than 37 weeks’ gestation. Individual numbers not reported Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: Prenatal phase: until delivery Postnatal phase: 24 months postpartum No. of participants: No. randomised – 1139 (intervention group, n = 458) No. analysed – 1139, based on preterm birth, however, final numbers varied depending on outcome. Validity: Adequate randomisation – Yes (computerised programme) Adequate allocation concealment – Unknown Blinding of clinician – No Blinding of patient – No Blinding of researcher – No Type of analysis: Linear and logistic-linear models were used to analyse dependent variables. Odds ratios and their 95% confidence intervals are presented. Estimates were adjusted for all covariates, classification factors and interactions Homogeneity of regressions was considered Power: A sample of 1468 was need for the prenatal phase and a sample of 734 for the postnatal phase of the trial, based on a series of calculations using α = 0.5 and β = 0.20 for two-tailed tests |
Groups compared: Four treatment arms are described: 1. Free transport for scheduled prenatal care appointments, 2. Free transport for scheduled prenatal care appointments plus developmental screening and referral services for the child at 6, 12 and 24 months, 3. Free transportation and screening offered plus intensive nurse home visitation services during pregnancy and 1 home visit post partum, 4. Same treatment as group 3 plus nurse visits through to the child’s 2nd birthday For evaluation of the prenatal phase treatments 3 and 4 were combined to form a single comparison group (nurse visited group) and contrasted with treatments 1 and 2 (non-nurse visited group) Intervention details: Home visitation, prenatal phase: Nurses completed an average of seven home visits during pregnancy and 26 home visits postpartum. A visit-by-visit protocol was followed. Nurses helped women complete 24-h diet histories, plot weight gain, assess and facilitate reduction in smoking habits, use of alcohol and illicit drugs through behavioural analysis. Nurses taught women to identify signs and symptoms of pregnancy complications, encouraged women to inform the hospital of those conditions, and facilitated compliance with treatment. They co-ordinated care with office-based staff and measured blood flow when needed Postpartum: Nurses helped mothers and other care-givers improve the physical and emotional care of their children Participants: Pregnant women at risk of spontaneous preterm birth (asymptomatic) Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women, less than 29 weeks pregnant, with no previous history of live births, no chronic illnesses thought to contribute to fetal growth retardation or preterm delivery, and at least two sociographic risk factors (unmarried, < 12 years education, and unemployed) were eligible for inclusion Outcomes: Primary outcomes: pregnancy-induced hypertension, preterm delivery, low birthweight, and a number of infant child health-care encounters and maternal life course outcomes |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Intervention group (%) = 11 Control group (%) = 13 Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable. Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable. Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Low birthweight (< 2500 g) Intervention group (%) = 15 Control group (%) = 14 5-min Apgar Intervention group (Mean) = 8.6 Control group (Mean) = 8.7 Pregnancy-induced hypertension Intervention group (%) = 13 Control group (%) = 20 Number of yeast infections Intervention group Incidence (log-incidence) = 0.14 (– 1.94) Control group Incidence (log-incidence) = 0.19 (– 1.65) Brief summary of findings: Preterm delivery, low birthweight, and Apgar scores did not significantly differ between women receiving nurse home visit programmes and those who did not. Nurse-visited women had fewer yeast infections and lower incidence of pregnancy-induced hypertension Authors’ conclusions: Home visits by nurses can reduce pregnancy-induced hypertension, childhood injuries and subsequent pregnancies among low-income women with no previous live births Comments: Intention to treat analysis conducted The majority of participants were young, unmarried, low-income African Americans, which may limit the generalisability of the findings |
| Study details and design | Description of methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Lopez [J Periodontol 2002; 73:911–924] 490 Country: Chile Setting: Dental clinic located within the same building in which routine prenatal care was given. Women invited to participate in the study were of low socioeconomic status receiving uniform prenatal care in a public health clinic in Santiago Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Preterm birth – 12 (out of a total of 188) Study design: Quasi-RCT Length of follow-up: Periodontal therapy was completed by 28 weeks’ gestation. Maintenance therapy continued until delivery No. of participants: No. randomised – 400 (200 in each group) No. analysed – 351 (Treatment group: 163, Control group: 188) Trial stopped early, after 160 deliveries in both arms of the study Validity: Adequate randomisation – No Adequate allocation concealment – No (coin toss) Blinding of clinician – Periodontal specialist (no), obstetrician (yes) Blinding of patient – No Blinding of researcher – Not stated Type of analysis: Incidence rates were reported in relation to the outcomes of interest. In addition, univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed for a combined preterm birth/low birthweight group. ORs and their 95% CI were presented |
Groups compared: Periodontal treatment vs No treatment Intervention details: Treatment group Periodontal therapy consisted of: plaque control instructions, scaling, and root planing performed under local anaesthesia. Women were also instructed to rinse once a day with 0.12% chlorhexidine. A full periodontal examination was given before and after completing the therapy period. The same examiner performed measurements for a given participant. As a consequence of severe aggressive periodontitis, 29 women (18%) received metronidazole 250 mg and amoxicillin 500 mg for 7 days in addition to the mechanical treatment. All women in the treatment group also received routine prenatal care Control group In addition to the routine prenatal care programme women were monitored every 4–6 weeks during their pregnancy to determine any change in their periodontal condition. A full periodontal examination was performed at study entry and after 28 weeks’ gestation. Participants were to receive periodontal therapy after delivery Participants: Pregnant women (asymptomatic) Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Inclusion criteria: Pregnant women aged 18 to 35, with a singleton gestation, between 9 and 21 weeks’ gestation, with periodontal disease and fewer than 18 of their natural teeth Exclusion criteria: women with a history of congenital heart disease requiring prophylactic antibiotics for invasive procedures, diabetes, current use of corticosteroids, chronic renal disease, and the intention to deliver at a hospital other than that designated by the study Outcomes: Primary outcomes of interest: preterm birth (spontaneous delivery < 37 weeks’ gestation), and low birthweight (< 2500 g) |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (163) No. in control group (total no.) = 12 (188) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported. Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported. Incidence of adverse events: Low birthweight (< 2500 g): No. in intervention group (total no.) = 1 (163) No. in control group (total no.) = 7 (188) Fetal death (spontaneous abortion): No. in intervention group (total no.) = 8 (200) No. in control group (total no.) = 6 (200) Brief summary of findings: Compared to those not receiving treatment, the periodontal therapy group had statistically fewer preterm deliveries < 37 weeks’ gestation (p = 0.017). In addition, a reduction in infants with low birthweight was found in the periodontal therapy group, although this was not statistically significant (p = 0.083) Authors’ conclusions: Periodontal disease appears to be an independent risk factor for preterm birth and low birthweight. In addition, periodontal therapy reduced the rate of preterm birth and low birthweight in this population with periodontal disease Comments: Allocation to treatment groups was conducted by a coin toss. Residual confounding from variables such as lifetime smoking or smoking during pregnancy did not appear to be accounted for 49 participants were excluded from the analysis; 37 in the treatment group (12.7%). Reasons for exclusion included: spontaneous abortion; preterm delivery due to pre-eclampsia, gestational diabetes, placenta praevia, or polyhydramnios; withdrawal due to discomfort with treatment; or lost to follow-up Participants in the treatment group were slightly older than those in the control group (28 (SD 4.5) vs 27 9 (SD 4.3), p = 0.04; and more likely to be single (30% vs 19%; p = 0.001) |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Dodd et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Issue 1, 2006] 736 Title: Prenatal administration of progesterone for preventing preterm birth Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 130 (out of 338 in total), based on preterm birth less than 37 weeks’ gestation 13 (out of 70 in total), based on preterm birth less than 34 weeks’ gestation |
Search: Databases searched (search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register (Mar. 2005), Cochrane Controlled Trials Register (Issue 3, 2004), MEDLINE (1965 to Jan. 2005), EMBASE (1988 to Aug. 2004), Current Contents (1997 to Aug. 2004) Other sources Hand searching of bibliographic references Search restrictions None specified Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Pregnant women at high risk of preterm birth (asymptomatic) Intervention Trials comparing progesterone (administered by any route) with placebo. Trials were excluded if progesterone was administered for the treatment of preterm labour or administered in the first trimester for preventing miscarriage Outcomes Primary outcomes included: perinatal mortality, preterm birth < 34 weeks’ gestation, and major neurodevelopmental handicap at childhood follow-up A number of other maternal and neonatal outcomes were sought, including preterm birth < 37 weeks and admission to neonatal care unit Study selection: Two reviewers independently assessed studies for potential inclusion; disagreements were resolved by consensus Data extraction: Two reviewers independently extracted data from the primary studies; disagreements were resolved by consensus Validity assessment: Criteria used Four sources of potential bias were considered: Allocation concealment, randomisation, blinding, and completeness of follow-up. A quality rating for blinding of randomisation was given to each trial (A: adequate, B: unclear, C: inadequate, or D: not used). A quality rating of A: Yes, b: Cannot tell, C: No, was used for all other validity outcomes Assessment Two reviewers independently assessed the methodological quality of the primary studies; disagreements were resolved by consensus Synthesis: Heterogeneity This was assessed visually by an inspection of the outcomes tables, and statistically using the I-squared statistic and the chi-squared test. Planned subgroup analyses included: time of treatment commencement, route of administration, dose and plurality of the pregnancy Methods Pooled risk ratio (RRs), with their associated 95% confidence intervals (CIs), were calculated for each outcome using a fixed effects model |
No. of studies included: Five RCTs (n = 911). Four trials compared intramuscular 17-hydroxyprogesterone caproate with placebo one trial compared vaginal progesterone with placebo No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 2 Adequate concealment of allocation – 3 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 6/6/Not stated Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: (Fixed effects) RR 0.15 (95% CI: 0.04–0.64) (1 study, n = 142) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: (Fixed effects) RR 0.60 (95% CI: 0.49–0.73) (5 studies, n = 988). Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not reported Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Need for assisted ventilation (Fixed effects) RR 0.59 (95% CI: 0.35–1.00) (1 study, n = 454) Incidence of perinatal mortality: (Fixed effects) RR 0.55 (95% CI: 0.29–1.06) (4 studies, n = 9767) Incidence of adverse events: Intrauterine fetal death (Fixed effects) RR 0.56 (95% CI: 0.19–1.61) (3 studies, n = 671) Neonatal death (Fixed effects) RR 0.59 (95% CI: 0.27–1.30) (3 studies, n = 671) Birthweight < 2500 g (Fixed effects) RR 0.63 (95% CI: 0.49–0.81) (4 studies, n = 763). Intraventricular haemorrhage RR 0.25 (95% CI: 0.08–0.82) (1 study, n = 458) Use of antenatal corticosteroids RR 0.87 (95% CI: 0.58–1.30) (1 study, n = 459) Use of antenatal tocolytics (Fixed effects) RR 1.12 (95% CI: 0.73–1.72) (2 studies, n = 503) Respiratory distress syndrome RR 0.63 (95% CI: 0.38–1.05) (1 study, n = 457) Retinopathy of prematurity RR 0.50 (95% CI: 0.50–1.70) (1 study, n = 457) Necrotising enterocolitis RR 0.06 (95% CI: 0.00–1.03) (1 study, n = 457) Neonatal sepsis RR 1.12 (95% CI: 0.35–3.58) (1 study, n = 457) Patent duct arteriosus RR 0.43 (95% CI: 0.16–1.17) (1 study, n = 457) Subgroup analyses: Preterm birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Route of administration Intramuscular injection: (Fixed effects) RR 0.61 (95% CI: 0.50–0.75) (5 studies, n = 846) Vaginal pessary: RR 0.49 (95% CI: 0.25–0.96) (1 study, n = 142) Timing of treatment administration < 20 weeks gestation: (Fixed effects) RR 0.64 (95% CI: 0.52–0.79) (3 studies, n = 670) > 20 weeks gestation: (Fixed effects) RR 0.40 (95% CI: 0.22–0.75) (3 studies, n = 318) Cumulative weekly dose ≥ 500 mg: (Fixed effects) RR 0.50 (95% CI: 0.29–0.86) (3 studies, n = 409) < 500 mg: (Fixed effects) RR 0.63 (95% CI: 0.51–0.77) (2 studies, n = 579) Perinatal mortality: Timing of treatment administration < 20 weeks gestation: (Fixed effects) RR 0.55 (95% CI: 0.29–1.06) (3 studies, n = 671) > 20 weeks gestation: Not estimable Cumulative weekly dose ≥ 500 mg: RR 1.10 (95% CI: 0.23–5.29) (1 study, n = 168) < 500 mg: (Fixed effects) RR 0.48 (95% CI: 0.23–0.98) (2 studies, n = 503) Brief summary of findings: A reduction in the risk of preterm birth< 37 weeks’ gestation, and < 34 weeks’ gestation was shown for women prescribed progesterone compared to placebo. A reduction in the risk of birthweight < 2500 g was also shown for infants born to mothers receiving progesterone. No other differences were reported for maternal or infant outcomes Authors’ conclusions: That intramuscular progesterone is associated with reduced risk of preterm birth at < 37 weeks’ gestation and infant birthweight < 2500 g. Further research is needed on the use of vaginal progesterone for the prevention of preterm birth. Other infant and maternal outcomes are not well reported, with most outcomes reported from a single study Comments: This was a well-conducted review and the authors appear to have taken appropriate steps to reduce bias The authors note that the sample size of trials reporting outcomes is underpowered to detect significant differences in important neonatal outcomes One study, focusing on twin gestations, was excluded from the original review |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Lumley et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2004, Issue 4] 500 Title: Interventions for promoting smoking cessation during pregnancy Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not applicable Preterm birth – 341 (of 5403 in total) |
Search: Search dates: July 2003 Databases searched: Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group trials register, Cochrane Tobacco Addiction Group trials register, MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsychLIT, CINAHL, AUSTHEALTH Other sources: References of identified trials. Handsearching of journals including American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Obstetrics and Gynecology, BJOG; Acta Obstetrica et Gynecologica Scandinavica, Tobacco Control, BMJ, the Lancet Search restrictions: None reported Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs and quasi-RCTs Population Pregnant women, women seeking a pre-pregnancy consultation, health professionals in trials of strategies to change knowledge, attitudes and behaviour with respect to smoking cessation Intervention: Any programme that aimed to promote smoking cessation during pregnancy Outcomes Preterm birth < 37 weeks, preterm birth < 32 weeks, preterm birth < 30 weeks, low birthweight < 1500 g low birthweight < 2500 g, perinatal mortality. A range of outcomes relating to intervention success and maternal wellbeing and satisfaction were also included Study selection: Methods of study selection were not reported Data extraction: Two reviewers independently extracted data from the studies Validity assessment: Criteria used Cochrane reviewers’ handbook criteria, which include randomisation, allocation concealment, blinding, treatment of drop-outs and loss to follow-up, sample size calculation Assessment Two reviewers assessed studies independently Synthesis: Heterogeneity Heterogeneity was assessed using the chi-squared and I-squared tests. Subgroup analyses for treatment intensity and trial quality were conducted Methods Pooled relative risks were calculated in a fixed-effect meta-analysis |
No. of studies included: 64 of which 16 reported relevant maternal or perinatal outcomes No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – Adequate concealment of allocation – Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation RR 0.84 (95% CI: 0.72–0.98) (11 trials, n = 10932) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: RR 1.13 (95% CI 0.72–1.77) (3 studies, n = 4335) Incidence of adverse events: Low birthweight < 2500 g RR 0.82 (95% CI: 0.70–0.95) (13 studies, n = 8930) Low birthweight < 1500 g RR 1.26 (95% CI: 0.69–2.32) (3 trials, n = 4765) Stillbirth RR 1.16 (95% CI: 0.71–1.88) (5 trials, n = 4525) Neonatal death RR 1.17 (95% CI: 0.34–4.01) (3 trials, n = 4143) Brief summary of findings: Interventions to promote smoking cessation significantly reduced the incidence of preterm birth at less than 37 weeks’ gestation and the incidence of low birthweight < 2500 g, but did not significantly affect the incidence of perinatal mortality or very low birthweight < 1500 g Authors’ conclusions: Smoking cessation programmes in pregnancy reduce the proportion of women who continue to smoke and reduce low birthweight and preterm birth. Pooled trials have inadequate power to detect reductions in perinatal mortality or very low birthweight Comments: This was a well-conducted review that includes a substantial number of large trials reporting primary outcomes and the authors’ conclusions are likely to be reliable |
Symptomatic women
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Stan et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 3] 516 Title: Hydration for treatment of preterm labour Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth –Not reported Preterm birth – 24 (out of 93 in total) for preterm birth < 37 weeks’ gestation 5 (out of 56 in total) for preterm birth < 34 weeks’ gestation |
Search: Search dates June 2004 Databases searched Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register Other sources Bibliographies of identified studies were also searched Search restrictions No search restrictions reported Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs with < 20% loss to follow-up Population Pregnant women at risk of preterm birth (symptomatic) Intervention Intravenous or oral hydration compared with no treatment. Studies comparing tocolytic agents with intravenous fluids used in the control group were not considered in the review Outcomes Primary outcomes included prolongation of pregnancy (> 48 h, > 7 days), gestational age at delivery (> 28 weeks, > 32 weeks, > 34 weeks, > 37 weeks), a number of perinatal outcomes including perinatal death and admission to neonatal intensive care unit, long-term sequelae. A number of maternal outcomes were also considered Study selection: Two reviewers independently screened the titles/abstracts and full papers. Disagreements were resolved by consensus Data extraction: Two reviewers independently extracted data from the primary studies Validity assessment: Criteria used A methodological grade was given to each study primarily based on allocation concealment: grade A (adequate concealment), grade B (uncertain), grade C (inadequate concealment). Blinding and loss to follow-up were also considered Assessment Carried out independently by two reviewers, disagreements resolved by consensus Synthesis: Heterogeneity Heterogeneity was formally assessed using the chi-squared test and the I-squared test Methods Results were expressed as relative risks (RRs) for dichotomous outcomes and weighted means difference (WMD) for continuous outcomes. Where more than one study was considered, meta-analysis was performed. Separate analyses were also carried out for women included before 34 weeks |
No. of studies included: 2 RCTs (n = 228) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 2 Adequate concealment of allocation – 2 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 0/0/0 (not stated) Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: (Fixed effects) RR 0.72 (95% CI: 0.20–2.56) (1 study, n = 118) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: (Fixed effects) RR 1.09 (95% CI: 0.71–1.68) (2 studies, n = 228) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not estimable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not estimable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: (Fixed effects) RR 0.99 (95% CI: 0.46–2.16) or (1 study, n = 118) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not estimable Incidence of adverse events: Low birthweight (< 2500 g, < 1500 g), severe neonatal morbidity and maternal death were not estimable Brief summary of findings: Compared to bed rest alone, intravenous hydration did not prolong gestation; no statistical difference was found between the groups for preterm birth less than 34 or 37 weeks’ gestation. No statistical difference was found between groups for admission to neonatal intensive care unit. The impact of hydration on the other outcomes sought was not estimable Authors’ conclusions: There are insufficient data to support the use of hydration for the treatment of women presenting with preterm labour. The two included studies do not demonstrate any benefit of intravenous hydration compared to bed rest alone, even during the period of evaluation soon after admission. The authors add that women with evidence of dehydration may, however, benefit from hydration Comments: This was a well-conducted review and the authors appear to have taken appropriate steps to reduce possible biases Both included studies used intravenous hydration. No trials evaluated oral hydration It appears likely that multiple pregnancies were included as subgroup analyses were planned but not completed due to insufficient data Both studies reported less than 20% drop-out rates |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
King and Flenady [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2002, Issue 4] 520 Title: Prophylactic antibiotics for inhibiting preterm labour with intact membranes Type of review: Cochrane review Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 852 (out of a total 2087), based on delivery less than 36 or 37 weeks’ gestation |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) The Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group database (May 2002), the Cochrane Controlled Trials Registry (2002, Issue 1), and MEDLINE (1965 to May 2002) Other sources Bibliographic references of all retrieved articles were also searched. In addition the authors contacted experts in the field and cross-referenced relevant material. Search restrictions No restrictions reported Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Women thought to be in preterm labour with intact membranes Intervention Any antibiotics, administered intravenously or orally, in the management of preterm labour with intact membranes Outcomes Delivery < 28, 36 and 37 weeks’ gestation, time to delivery, chorioamnionitis, post-partum pyrexia, adverse drug reaction, length of hospital stay (maternal), adverse drug reaction, fetal death, neonatal death, perinatal mortality, Apgar scores, neonatal sepsis, admission to neonatal care unit, mechanical ventilation, respiratory distress syndrome, necrotising enterocolitis, retinopathy of prematurity, intraventricular haemorrhage, cerebral cystic lesions, chronic lung disease, long term neurosensory impairment and length of hospital stay (infant) Study selection: The authors independently selected studies for inclusion; disagreements were resolved by discussion Data extraction: The authors independently extracted data from the primary studies; disagreements were resolved by discussion. Missing or incomplete data were sought from the trial authors where necessary Validity assessment: Criteria used Blinding, allocation concealment and follow-up Assessment The authors independently assessed the methodological quality of the included studies; disagreements were resolved by discussion Synthesis: Heterogeneity Chi-squared test and I-squared statistic were used to assess differences between trials. Methods Meta-analysis was conducted using a fixed effects model; one outcome with significant heterogeneity, not explained by sensitivity analyses, was recalculated using a random effects model. Results are presented as relative risks (RR) for categorical data and weighted mean difference (WMD) for continuous data with their 95% confidence intervals Subgroup analysis was planned (treatment commenced prior to 24 weeks and between 25 and 33 weeks), treatment with macrolide antibiotics alone, treatment with beta-lactam antibiotics alone, treatment with both macrolide and beta-lactam antibiotics, treatment with antibiotics active against anaerobic bacteria |
No. of studies included: 11 RCTs (n = 7428) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 10 Adequate concealment of allocation – 10 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 9/10/10 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 36 or < 37 weeks’ gestation: Any antibiotic vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 0.99 (95% CI: 0.92–1.05) (9 studies, n = 7291) Betalactam antibiotic alone vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 0.99 (95% CI: 0.88–1.11) (4 studies, n = 2334) Macrolide antibiotics alone vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 1.02 (95% CI: 0.90–1.15) (2 studies, n = 2235) Macorilde and betalactam antibiotic vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 0.99 (95% CI: 0.89–1.10) (4 studies, n = 2613) Antibiotic active against anaerobic bacteria vs no antibiotics: [Fixed effect] RR 0.85 (95% CI: 0.68–1.05) (2 studies, n = 226) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Any antibiotic vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 1.04 (95% CI: 0.89–1.23) (4 studies, n = 6800) Betalactam antibiotic alone vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 1.01 (95% CI: 0.75–1.36) (1 study, n = 2053) Macrolide antibiotics alone vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 1.06 (95% CI: 0.78–1.42) (1 study, n = 2119) Macorilde and betalactam antibiotic vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 1.12 (95% CI: 0.86–1.45) (3 studies, n = 2520) Antibiotic active against anaerobic bacteria vs no antibiotics [Fixed effect] RR 0.55 (95% CI: 0.19–1.57) (1 study, n = 109) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Any antibiotic vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 0.98 (95% CI: 0.87–1.10) (7 studies, n = 6957) Betalactam antibiotic alone vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 0.99 (95% CI: 0.80–1.22) (3 studies, n = 2248) Macrolide antibiotics alone vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 1.04 (95% CI: 0.82–1.31) (1 study, n = 2119) Macrolide and betalactam antibiotic vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] 1.03 (95% CI: 0.84–1.26) (3 studies, n = 2401) Antibiotic active against anaerobic bacteria vs no antibiotic RR 0.62 (95% CI: 0.42–0.90) (1 study, n = 190) Incidence of neonatal intensive or special care nursery admission: Any antibiotic vs no antibiotics [Fixed effect] RR 1.03 (95% CI: 0.94–1.13) (4 studies, n = 6795) Betalactam antibiotic alone vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 1.07 (95% CI: 0.90–1.28) (1 study, n = 2053) Macrolide antibiotics alone vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 1.08 (95% CI: 0.91–1.29) (1 study, n = 2119) Macrolide and betalactam antibiotic vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 1.01 (95% CI: 0.87–1.18) (3 studies, n = 2515) Antibiotic active against anaerobic bacteria vs no antibiotics: [Fixed effect] RR 0.63 (95% CI: 0.43–0.93) (1 study, n = 109) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Any antibiotic vs no antibiotics [Fixed effect] RR 1.22 (95% CI: 0.88–1.70) (9 studies, n = 7208) Betalactam antibiotic alone vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 1.14 (95% CI: 0.63–2.04) (3 studies, n = 2227) Macrolide antibiotics alone vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 1.17 (95% CI: 0.64–2.11) (2 studies, n = 2222) Macrolide and betalactam antibiotic vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 1.39 (95% CI: 0.79–2.43) (4 studies, n = 2569) Antibiotic active against anaerobic bacteria vs no antibiotics [Fixed effect] RR 1.63 (95% CI: 0.36–7.39) (3 studies, n = 294) Incidence of adverse events: Maternal adverse drug reaction Any antibiotic vs no antibiotic [Fixed effect] RR 1.11 (95% CI: 0.99–1.24) (4 studies, n = 626) Maternal infection [Fixed effect] RR 0.74 (95% CI: 0.64–0.87) (9 studies, n = 7242) Fetal death [Fixed effect] RR 0.72 (95% CI: 0.42–1.25) (7 studies, n = 6986) (5 not estimable) Neonatal death [Fixed effect] RR 1.52 (95% CI: 0.99–2.34) (7 studies, n = 6877) (1 not estimable) Respiratory distress syndrome [Fixed effect] RR 0.99 (95% CI: 0.84–1.16) (8 studies, n = 7104) Mechanical ventilation [Fixed effect] RR 1.02 (95% CI: 0.84–1.24) (1 study, n = 6241) Chronic lung disease [Fixed effect] RR 1.17 (95% CI: 0.78–1.76) (1 study, n = 6241) Neonatal sepsis [Fixed effect] RR 0.86 (95% CI: 0.64–1.16) (9 studies, n = 7290) Necrotising enterocolitis [Fixed effect] RR 1.06 (95% CI: 0.64–1.73) (6 studies, n = 6880) Neonatal positive blood culture [Fixed effect] RR 1.01 (95% CI: 0.69–1.49) (3 studies, n = 6526) Intraventricular haemorrhage [Fixed effect] RR 0.76 (95% CI: 0.48–1.19) (4 studies, n = 6717) Major cerebral abnormality [Fixed effect] RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.66–1.51) (1 study, n = 6241) Brief summary of findings: Maternal infection was significantly reduced in the group receiving antibiotics. No statistically significant differences were reported in any other maternal outcomes. No statistically significant benefit from antibiotic administration was found in any of the neonatal outcomes including perinatal mortality and admission to neonatal intensive care unit. When grouped by type of antibiotic, a reduction in the risk of admission to neonatal intensive care unit was reported for the group receiving antibiotics active against anaerobic bacteria compared to no antibiotics; based on the results of one small study Authors’ conclusions: The review fails to demonstrate a clear overall benefit from prophylactic antibiotic treatment for preterm labour with intact membranes on neonatal outcomes and raises concerns about increased neonatal mortality for those who received antibiotics. Prophylactic antibiotic treatment for preterm labour is not recommended for routine practice. Further research may be warranted to determine if there is a subgroup of women who may benefit from this treatment when sensitive markers for subclinical infection become available Comments: This was a well-conducted review and the authors appear to have taken appropriate steps to reduce possible biases Seven of the included studies specifically stipulate singleton gestation in their inclusion criteria or multiple gestations in their exclusion criteria The review is dominated by the data from one trial (ORACLE II 2001), which is six times larger than the other 10 trials combined Nine of the studies used antibiotics as an adjunct to tocolysis Five trials were stopped early because of low recruitment rates or low baseline outcome rates |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Anotayanonth et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2004, Issue 3] 532 Title: Betamimetics for inhibiting preterm labour Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 383 (out of a total 558), based on preterm birth < 37 weeks’ gestation in women at high risk of preterm delivery |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Register (May 2003) Other sources Reference lists of retrieved articles Search restrictions Search was not restricted by language Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs with ≤ 20% loss to follow-up Population Women assessed as being in spontaneous preterm labour (defined by trial authors) and considered suitable for tocolytic therapy. Women with intact or ruptured membranes were included in the review. Intervention Betamimetics, administered by any route or any dose compared with other betamimetics, placebo or no treatment Outcomes Primary outcomes included: delivery within 48 hrs, perinatal death, neonatal morbidity, respiratory distress syndrome, chronic lung disease/bronchopulmonary dysplasia, severe neuroradiological abnormality, abnormal long-term developmental status and neonatal length of hospital stay. A number of secondary perinatal, neonatal, infant and maternal outcomes were also sought including preterm birth < 34 and < 37 weeks’ gestation, delivery within 7 days and admission to neonatal intensive care unit Study selection: Two reviewers independently selected papers for inclusion in the review; any disagreements were resolved by discussion or consultation with an additional reviewer(s) Data extraction: Two reviewers independently extracted data from the primary studies; any disagreements were resolved by discussion or consultation with an additional reviewer(s). Additional information was sought from the authors of the primary studies where necessary Validity assessment: Criteria used Quality scores were assigned to each trial for method of randomisation, method of allocation concealment, use of placebo, completeness of follow-up, and blinding of outcome Assessment At least two reviewers independently assessed the methodological quality of the primary studies; disagreements would have been resolved by discussion. Reviewers were not blinded to authorship Synthesis: Heterogeneity Chi-squared test and I-squared statistic were used to assess heterogeneity. Sensitivity analysis was carried out to assess the effect of trial quality. A funnel plot was performed to assess publication bias Methods Weighted mean difference (WMD) was used for continuous data. Relative risks (RR) were calculated with 95% confidence intervals for binary data. A 10% level of statistical significance was used. Results were pooled using a fixed effect model. If significant heterogeneity was found, a random effects model was used |
No. of studies included: 16 RCTs (n = 2282) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 9 Adequate concealment of allocation – 5 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 9/10/2 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: [Fixed effect] RR 1.02 (95% CI: 0.57–1.80) (1 study, n = 222) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 1.06 (95% CI: 0.61–1.84) (10 studies, n = 1212) Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: [Fixed effect] RR 0.78 (95% CI: 0.40–1.24) (1 study, n = 203) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 0.63 (95% CI: 0.53–0.75) (10 studies, n = 1209) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 2.05 (95% CI: 0.77–5.48) (1 study, n = 83) Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: [Fixed effect] RR 1.08 (95% CI: 0.53–2.21) (1 study, n = 203) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 0.78 (95% CI: 0.68–0.90) (5 studies, n = 911) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.80 (95% CI: 0.57–1.10) (1 study, n = 100) Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 0.84 (95% CI: 0.46–1.55) (11 studies, n = 1332) Fenoterol vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.11 (95% CI: 0.01–2.01) (1 study, n = 98) Incidence of adverse events: Preterm birth < 28 weeks’ gestation Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 2.08 (95% CI: 0.55–7.87) (1 study, n = 100) Neonatal death All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.48–2.09) (6 studies, n = 1174) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 1.27 (95% CI: 0.42–3.91) (2 studies, n = 184) Fenoterol vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] OR 0.11 (95% CI: 0.01–0.89) (1 study, n = 98) Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: [Fixed effect] RR 0.11 (95% CI: 0.01–2.04) (1 study, n = 222) Respiratory distress syndrome All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 0.87 (95% CI: 0.71–1.08) (8 studies, n = 1239) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 1.99 (95% CI: 0.93–4.27) (1 study, n = 101) Fenoterol vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 2.00 (95% CI: 0.38–10.42) (1 study, n = 98) Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: [Fixed effect] RR 0.71 (95% CI: 0.35–1.41) (1 study, n = 222) Periventricular haemorrhage (grades 3 and 4) Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: [Fixed effect] RR 0.14 (95% CI: 0.01–2.73) (1 study, n = 222) Cerebral palsy All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 0.19 (95% CI: 0.02–1.63) (1 study, n = 246) Treatment cessation due to adverse drug reaction All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 11.38 (95% CI: 5.21–24.86) (4 studies, n = 1051) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.83 (95% CI: 0.24–2.92) (1 study, n = 100) Hexoprenaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.27 (95% CI: 0.08–0.93) (1 study, n = 466) Any maternal side effects Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.95 (95% CI: 0.84–1.07) (1 study, n = 83) Hexoprenaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.83 (95% CI: 0.76–0.91) (1 study, n = 466) Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: [Fixed effect] RR 0.69 (95% CI: 0.43–1.11) (1 study, n = 203) Palpitations All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 10.11 (95% CI: 6.56–15.58) (4 studies, n = 1042) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 1.18 (95% CI: 0.78–1.79) (1 study, n = 83) Hexoprenaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.75 (95% CI: 0.60–0.94) (1 study, n = 466) Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: [Fixed effect] RR 0.50 (95% CI: 0.23–1.13) (1 study, n = 203) Tachycardia All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 4.08 (95% CI: 1.55–10.73) (2 studies, n = 229) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.66 (95% CI: 0.43–1.00) (1 study, n = 100) Fenoterol vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.71 (95% CI: 0.35–1.45) (1 study, n = 96) Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: [Fixed effect] RR 0.88 (95% CI: 0.33–2.35) (1 study, n = 203) Cardiac arrhythmias All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 3.54 (95% CI: 0.74–16.92) (1 study, n = 708) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.35 (95% CI: 0.04–3.22) (1 study, n = 100) Pulmonary oedema All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 3.03 (95% CI: 0.12–74.23) (3 studies, n = 852) Myocardial ischaemia All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 12.53 (95% CI: 0.72–216.91) (1 studies, n = 106) Chest pain All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 11.29 (95% CI: 3.81–33.46) (2 studies, n = 814) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 1.11 (95% CI: 0.55–2.25) (2 studies, n = 183) Shortness of breath/dyspnoea All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 3.86 (95% CI: 2.21–6.77) (2 studies, n = 814) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.83 (95% CI: 0.41–1.67) (2 studies, n = 183) Tremor All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 10.74 (95% CI: 6.20–18.59) (1 study, n = 708) Hypotension All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 1.77 (95% CI: 0.39–8.06) (2 studies, n = 136) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.67–1.49) (2 studies, n = 183) Hexoprenaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR0.77 (95% CI: 0.61–0.96) (1 study, n = 466) Hyperglycaemia All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 2.90 (95% CI: 2.05–4.09) (1 study, n = 708) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 1.78 (95% CI: 1.05–3.03) (1 study, n = 100) Fenoterol vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 1.33 (95% CI: 0.31–5.65) (1 study, n = 98) Hypokalaemia All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 6.07 (95% CI: 4.00–9.20) (1 study, n = 708) Nausea/vomiting All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 1.76 (95% CI: 1.29–2.42) (3 studies, n = 932) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 1.50 (95% CI: 0.71–3.20) (1 study, n = 100) Hexoprenaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.63 (95% CI: 0.45–0.89) (1 study, n = 466) Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: [Fixed effect] RR 1.23 (95% CI: 0.36–4.15) (1 study, n = 203) Headache Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.48 (95% CI: 0.23–0.99) (1 study, n = 83) Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: [Fixed effect] RR 1.01 (95% CI: 0.06–15.93) (1 study, n = 203) Anxiety Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 1.08 (95% CI: 0.67–1.75) (1 study, n = 83) Fetal hypoglycaemia All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 1.89 (95% CI: 0.35–10.04) (3 studies, n = 857) Fetal tachycardia All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 2.40 (95% CI: 1.12–5.13) (1 studies, n = 30) Increase in fetal heart rate Hexoprenaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] OR 0.65 (95% CI: 0.43–0.98) (1 study, n = 466 Sepsis/infection All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 2.72 (95% CI: 0.19–39.63) (2 studies, n = 809) Ritodrine loading dose vs incremental dose: [Fixed effect] RR 0.71 (95% CI: 0.23–2.18) (1 study, n = 222) Necrotising enterocolitis All betamimetics vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 0.42 (95% CI: 0.06–2.78) (2 studies, n = 149) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.53 (95% CI: 0.05–5.67) (1 study, n = 101) Brief summary of findings: Betamimetics vs placebo/no treatment: Betamimetics decreased the number of women in preterm labour delivering within 48 h; there was no decrease in the incidence of deliveries within 7 days after sensitivity analysis for adequate allocation concealment. No statistically significant between-group differences for perinatal death, neonatal death, respiratory distress syndrome, cerebral palsy or necrotising enterocolitis was shown. Betamimetics were significantly associated with withdrawal from treatment due to side effects: chest pains, dyspnoea, tachycardia, palpitations, headaches, hypokalaemia, hyperglycaemia, nausea/vomiting, and fetal tachycardia Authors’ conclusions: While betamimetics help delay delivery for women transferred to tertiary care or completed course of antenatal corticosteroids, the multiple adverse effects should be considered. There are insufficient data to recommend one betamimetic agent over another Comments: This was a well-conducted review and the authors appear to have taken appropriate steps to reduce possible biases Few of the primary studies included in the review were of high quality 14 of the included studies report using a maintenance regimen: of these 13 continue beyond 48 h; the duration of the remaining two trials was unclear. Maintenance therapy is treatment after the initial bolus beyond 48 h. It is therefore difficult to extract the influence of the acute tocolytic treatment from the effects of maintenance therapy for outcomes beyond this period Only one trial explicitly excluded multiple pregnancies Some studies included women with ruptured membranes |
|
Dodd et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 1] 549 Title: Oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy after threatened preterm labour Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 88 (out of a total 190), based on preterm delivery less than 37 weeks’ gestation |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) The Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register (June 2005) and MEDLINE (1966 to August 2003) were searched. Other sources None reported Search restrictions No language restrictions were applied Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) Published RCTs Population Women who have had at least one episode of threatened preterm labour that settled without delivery Intervention Oral betamimetic therapy compared with an alternative tocolytic or no tocolytic treatment for maintenance therapy. Trials in which women are administered an oral betamimetic in combination with another tocolytic agent were excluded Outcomes Primary measures included: preterm birth < 34 weeks, low birthweight (< 2500 g), admission to neonatal intensive care unit, perinatal mortality, serious infant morbidity, maternal death or serious maternal morbidity. A number of additional infant and maternal outcomes were also sought including preterm birth < 28 weeks and < 37 weeks, preterm birth within 24 h, 48 h and 7 days of treatment, and side effects Study selection: Two reviewers selected articles for inclusion in the review; any disagreements were resolved by discussion Data extraction: Two reviewers extracted and double entered data from the primary studies; any disagreements were resolved by discussion. Reviewers were not blinded to authorship Validity assessment: Criteria used Quality scores were assigned to each trial on the basis of allocation concealment (A = adequate, B = unclear, C = inadequate, D = not used). Completeness of follow-up and blinding (investigators, participants and outcome assessors) were also assessed Assessment The authors do not state how methodological quality was assessed or how many reviewers performed the quality assessment Synthesis: Heterogeneity The chi-squared and I-squared statistic was used to evaluate statistical heterogeneity. Sensitivity analyses were planned to evaluate the effect of trial quality Methods Categorical data were compared using RRs and 95% CIs using a fixed effect model. Planned subgroup analyses included: dosage administered, type of betamimetic, gestational age maintenance begun, type of therapy (control group); however, there were insufficient data to do this |
No. of studies included: 11 RCTs (n = 1238) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 6 Adequate concealment of allocation – 3 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 4/5/1 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Terbutaline vs indomethacin: [Fixed effect] RR 0.64 (95% CI: 0.24–1.76) (1 study, n = 65) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.29 (95% CI: 0.01–6.86) (1 study, n = 91) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Ritodrine/terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 1.08 (0.88, 1.32) (4 studies, n = 384) Ritodrine vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 0.98 (95% CI: 0.64–1.50) (2 studies, n = 145) Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 1.12 (95% CI: 0.89–1.41) (2 studies, n = 239) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.80 (95% CI: 0.44–1.46) (1 study, n = 91) Betamimetic vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 1.02 (95% CI: 0.58–1.79) (2 studies, n = 100) Ritodrine vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.54–1.87) (1 study, n = 50) Terbutaline vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 1.06 (95% CI: 0.32–3.50) (1 study, n = 50) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 0.67 (95% CI: 0.12–3.62) (1 study, n = 46) Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 0.78 (95% CI: 0.30–2.01) (1 study, n = 200) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Ritodrine/terbutaline vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 0.67 (95% CI: 0.40–1.13) (2 studies, n = 295) Ritodrine vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 0.23 (95% CI: 0.03–1.94) (1 study, n = 95) Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 0.75 (95% CI: 0.44–1.29) (1 study, n = 200) Terbutaline vs indomethacin: [Fixed effect] RR 0.26 (95% CI: 0.03–2.18) (1 study, n = 65) Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 1.29 (95% CI: 0.64–2.60) (1 study, n = 140) Betamimetic vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 0.80 (95% CI: 0.43–1.46) (1 study, n = 137) Incidence of perinatal mortality (death before discharge among live births): Ritodrine/terbutaline vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 2.41 (95% CI: 0.86–6.74) (6 studies, n = 681) Ritodrine vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 1.85 (95% CI: 0.41–8.39) (3 studies, n = 214) Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 2.96 (95% CI: 0.72–12.14) (3 studies, n = 467) Betamimetic vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 0.20 (95% CI: 0.01–3.97) (1 study, n = 50) Incidence of adverse events: Respiratory distress syndrome Ritodrine/terbutaline vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR1.10 (95% CI: 0.61–1.98) (5 studies, n = 577) Ritodrine vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 1.46 (95% CI: 0.57–3.73) (2 studies, n = 110) Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 0.93 (95% CI: 0.43–1.98) (3 studies, n = 467) Ritodrine vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 2.00 (95% CI: 0.19–20.67) (1 study, n = 50) Necrotising enterocolitis Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 0.98 (95% CI: 0.22–4.28) (2 studies, n = 416) Intraventricular haemorrhage Ritodrine/terbutaline vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 0.97 (95% CI: 0.27–3.58) (3 studies, n = 466) Ritodrine vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 3.00 (95% CI: 0.13–70.30) (1 study, n = 50) Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 0.72 (95% CI: 0.16–3.24) (2 studies, n = 416) Ritodrine vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.07–15.12) (1 study, n = 50) Neonatal jaundice/Hyperbilirubinaemia requiring treatment Ritodrine vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 1.67 (95% CI: 0.71–3.89) (1 study, n = 50) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 1.45 (95% CI: 0.84–2.51) (1 study, n = 91) Ritodrine vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 0.91 (95% CI: 0.47–1.75) (1 study, n = 50) Side effects to stop therapy Ritodrine vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 2.71 (95% CI: 0.11–64.79) (1 study, n = 95) Terbutaline vs indomethacin: [Fixed effect] RR 3.09 (95% CI: 0.13–73.19) (1 study, n = 65) Betamimetic vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 0.90 (95% CI: 0.24–3.46) (2 studies, n = 100) Ritodrine vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 0.50 (95% CI: 0.05–5.17) (1 study, n = 50) Terbutaline vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 1.28 (95% CI: 0.23–7.00) (1 study, n = 50) Tachycardia Ritodrine/terbutaline vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 1.55 (95% CI: 1.02–2.37) (2 studies, n = 101) Ritodrine vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 1.61 (95% CI: 0.84–3.09) (1 study, n = 55) Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 1.50 (95% CI: 0.86–2.61) (1 study, n = 46) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.57 (95% CI: 0.22–1.47) (1 study, n = 91) Betamimetic vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 5.61 (95% CI: 2.41–13.04) (3 studies, n = 237) Ritodrine vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 17.00 (95% CI: 1.03–279.53) (1 study, n = 50) Terbutaline vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 4.54 (95% CI: 1.86–11.07) (2 studies, n = 187) Tachypnoea Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 2.83 (95% CI: 0.59–13.56) (1 study, n = 140) Terbutaline vs Ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 2.57 (95% CI: 0.55–12.07) (1 study, n = 91) Terbutaline vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 1.35 (95% CI: 0.40–4.59) (1 study, n = 137) Hypotension Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 1.80 (95% CI: 1.08–3.01) (1 study, n = 46) Nausea Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 0.95 (95% CI: 0.43–2.13) (2 studies, n = 186) Betamimetic vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 1.07 (95% CI: 0.57–0.57–1.98) (3 studies, n = 237) Ritodrine vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 0.50 (95% CI: 0.05–5.17) (1 study, n = 50) Terbutaline vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 1.15 (95% CI: 0.60–2.19) (2 studies, n = 187) Vomiting Ritodrine/terbutaline vs placebo: [Fixed effect] RR 1.28 (95% CI: 0.44–3.70) (2 studies, n = 235) Ritodrine vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 2.71 (95% CI: 0.11–64.79) (1 study, n = 95) Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 1.13 (95% CI: 0.36–3.54) (1 study, n = 140) Terbutaline vs ritodrine: [Fixed effect] RR 0.57 (95% CI: 0.17–1.89) (1 study, n = 91) Terbutaline vs magnesium: [Fixed effect] RR 0.88 (95% CI: 0.39–1.98) (2 studies, n = 187) Palpitations Terbutaline vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 5.67 (95% CI: 1.32–24.40) (1 study, n = 140) Headache Ritodrine vs placebo/no treatment: [Fixed effect] RR 2.71 (95% CI: 0.11–64.79) (1 study, n = 95) Brief summary of findings: No statistically significant differences were reported for admission to neonatal care unit when betamimetics were compared with placebo or magnesium, or preterm birth < 37 weeks when ritodrine or terbutaline were compared with placebo. No statistically significant between-group differences was reported for perinatal mortality and morbidity outcomes. A number of cardiovascular effects were reported compared to placebo Authors’ conclusions: Available evidence does not support the use of oral betamimetics for maintenance therapy after threatened preterm labour Comments: This was a well-conducted review and the authors appear to have taken appropriate steps to reduce possible biases Few of the primary studies included in the review were of high quality Most trials included multiple gestations |
|
Nanda et al. [Cochrane Database of systematic Reviews 2002, Issue 4] 561 Title: Terbutaline pump maintenance therapy after threatened preterm labor for preventing preterm birth Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 17 (out of a total 28), based on preterm delivery at less than 37 weeks’ gestation in women at risk of preterm birth 12 (out of a total 28), based on preterm delivery at less than 34 weeks’ gestation in women at risk of preterm birth |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) The Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Register (May 2002), and the Cochrane Controlled Trials Register (2002, Issue 2) were searched for relevant articles Other sources Reference list and experts in the field Search restrictions No restrictions stated. Published, unpublished and ongoing trials were included Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Women with intact membranes and either singleton or multiple gestations who had had at least one episode of threatened preterm labour that was successfully stopped with tocolytic therapy before delivery Intervention Terbutaline pump maintenance therapy vs alternative drug therapy, placebo or no therapy Outcomes A number of infant maternal and health-care outcomes were sought including: gestational age, preterm, very preterm and extremely preterm birth, perinatal mortality, admission to neonatal intensive care unit, side effects (maternal), cardiovascular and other serious complications (maternal) Study selection: Two reviewers independently selected studies from inclusion in the review; discrepancies were resolved by consensus Data extraction: Two reviewers independently extracted data from the primary studies. A third reviewer checked the abstracted data for accuracy; discrepancies were resolved by discussion Validity assessment: Criteria used A quality score was given to each trial for allocation concealment. Other aspects of study quality were individually discussed for each trial in the body of the text Assessment Two reviewers independently assessed the primary studies for methodological quality; discrepancies were resolved by consensus. Reviewers were not blinded to authorship Synthesis: Heterogeneity Chi-squared test and I-squared statistic were used to assess heterogeneity Methods WMD differences with 95% confidence intervals were calculated for continuous data, and RRs were calculated with 95% confidence intervals for all dichotomous outcomes. Estimates were pooled in meta-analysis were appropriate using a fixed effects model |
No. of studies included: 2 RCTs (n = 94) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 2 Adequate concealment of allocation – 2 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 2/2/2 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Terbutaline pump vs saline pump: [Fixed effect] RR 0.97 (95% CI: 0.51–1.84) (1 study, n = 52) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Terbutaline pump vs saline pump: [Fixed effect] RR 1.17 (95% CI: 0.79–1.73) (1 study, n = 52) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission (> 24 h): Terbutaline pump vs saline pump: [Fixed effect] RR 0.94 (95% CI: 0.51–1.73) (1 study, n = 51) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Early discontinuation Terbutaline pump vs saline pump [Fixed effect] RR 1.15 (95% CI: 0.68–1.95) (2 studies, n = 79) Terbutaline pump vs oral terbutaline [Fixed effect] RR 3.00 (95% CI: 0.72–12.55) (1 study, n = 30) Respiratory distress syndrome Terbutaline pump vs saline pump [Fixed effect] RR 0.82 (95% CI: 0.23–2.93) (2 studies, n = 79) Terbutaline pump vs oral terbutaline [Fixed effect] RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.16–6.20) (1 study, n = 30) Other outcomes: Gestational age at delivery Terbutaline pump vs saline pump [Fixed effect] WMD – 0.14 (95% CI: –1.66 to 1.38) (2 studies, n = 79) Terbutaline pump vs oral terbutaline [Fixed effect] WMD 1.40 (95% CI: –1.13 to 3.93) (1 study, n = 30) Birthweight Terbutaline pump vs saline pump [Fixed effect] WMD 107.90 (95% CI: – 216.25 to 432.04) (2 studies, n = 79) Terbutaline pump vs oral terbutaline [Fixed effect] WMD 484.00 (95% CI: – 25.01 to 993.01) (1 study, n = 30) Brief summary of findings: Terbutaline pump maintenance did not offer any advantage over saline pump or oral terbutaline in preventing preterm birth or its complications. No data were reported for long-term infant outcomes, costs, or maternal assessment of therapy Authors’ conclusions: Terbutaline pump maintenance has not been shown to decrease the risk of preterm birth by prolonging pregnancy; in addition there is a lack of information on the safety of the therapy. Further well-conducted RCTs are needed Comments: This was a well-conducted review that attempted to limit reviewer error or bias Small dataset, with most results limited to one trial One of the two trials included a mixed population of singleton/multiple pregnancies. It is not stated how many multiple pregnancies were included Two additional studies were identified; the authors of these primary studies did not respond to requests for further information and so these studies could not be included in the review |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
King et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 1] 565 Title: Calcium channel blockers for inhibiting preterm labour Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Not reported No placebo/no treatment trials |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Trials Register (June 2002), Cochrane Controlled Trials Register (Issue 2, 2002), Medline (1965–June 2002), Embase (1988–June 2002), Current Contents (1997–June 2002) Other sources Experts contacted, cross-referencing of relevant material Search restrictions None Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Women in labour between 20 and 36 weeks’ gestation considered suitable for tocolysis Intervention Calcium channel blockers administered by any route vs alternative tocolytic agent. The planned comparison of calcium channel blockers and no treatment or placebo could not be conducted as no trials were found that addressed this Outcomes Maternal outcomes: pregnancy prolongation, delivery before 34 and 37 weeks, delivery within 48 h/7 days of treatment, adverse drug reaction, cessation of treatment for adverse drug reaction, antepartum/postpartum haemorrhage, maternal death, length of hospital stay, satisfaction with treatment, admission to intensive care unit Fetal outcomes: death, death excluding congenital abnormality, oligohydramnios A range of neonatal outcomes were sought, including gestation at birth, neonatal and perinatal mortality Study selection: The authors state that ‘the standard methods of the Cochrane Collaboration were used for the consideration of trials for inclusion’ i.e. independent assessment by at least two people and resolution of differences by consensus/involvement of third person Data extraction: Three authors independently extracted data with differences in interpretation resolved by discussion. Additional information was sought to enable assessment of methodology and conduct of intention-to-treat analyses Validity assessment: Criteria used Blinding of randomisation, blinding of intervention, complete follow-up, blinding of outcome assessment. Quality ratings assigned using Cochrane criteria Assessment Carried out independently by three authors with differences in interpretation resolved by discussion Synthesis: Heterogeneity Statistical heterogeneity between trials was assessed using the chi-squared test Methods Meta-analysis using the fixed effects model, or a random effects model where heterogeneity was found. One subgroup analysis was performed comparing the dihydropiridine class of calcium channel blockers with betamimetics in nine trials. An attempt was made to conduct an intention-to-treat analysis for all outcomes |
No. of studies included: 12 RCTs (n = 1029) 10 trials compared oral nifedipine with other tocolytic agents. One trial compared intravenous nicardipine with salbutamol and one compared oral nicardipine with magnesium sulphate. Results given for two comparisons: 01. Any calcium channel blocker vs any other tocolytic agent 02. Any dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker compared with any betamimetic agent No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 10 Adequate concealment of allocation – 10 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 0/0/0 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 0.83 (95% CI: 0.69–0.99) (6 studies, n = 619) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 0.79 (95% CI: 0.65–0.96) (3 studies, n = 328) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 0.95 (95% CI:0.83,1.09) (6 studies, n = 558) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 0.89 (95% CI: 0.76,1.05) (4 studies, n = 389) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 0.80 (95% CI:0.61,1.05) (9 studies, n = 761) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 0.72 (95% CI:0.53–0.97) (6 studies, n = 470) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 0.76 (95% CI: 0.60–0.97) (4 studies, n = 453) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 0.76 (95% CI: 0.59–0.99) (2 studies, n = 242) Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 0.78 (95% CI:0.64–0.95) (9 studies, n = 771) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 0.84 (95% CI:0.71–1.00) (7 studies, n = 572) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Perinatal mortality: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 1.65 (95% CI:0.74–3.64) (10 studies, n = 810) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 1.39 (95% CI: 0.60–3.24) (7 studies, n = 529) Excluding congenital abnormality: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 1.42 (95% CI: 0.61–3.31) (10 studies, n = 820) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 1.20 (95% CI: 0.49–2.94) (7 studies, n = 529) Fetal death: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 3.00 (95% CI: 0.13–71.08) (10 studies, n = 820) 02. (Fixed effects) RR3.00 (95% CI:0.13–71.08) (studies, n = 529) Neonatal death: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 1.58 (95% CI: 0.74–3.39) (11 studies, n = 883) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 1.40 (95% CI:0.63–3.12) (8 studies, n = 592) Excluding congenital abnormality: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 1.42 (95% CI: 0.61–3.31) (10 studies, n = 820) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 1.20 (95% CI: 0.49–2.94) (7 studies, n = 529) Incidence of adverse events: Maternal adverse drug reaction: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 0.32 (95% CI:0.24–0.41) (8 studies, n = 717) 02. (Fixed effects) RR0.40 (95% CI: 0.30–0.55) (5 studies, n = 426) Maternal adverse drug reaction requiring cessation of treatment: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 0.14 (95% CI: 0.05–0.36) (10 studies, n = 833) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 0.09 (95% CI:0.02–0.38) (7 studies, n = 542) Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 0.63 (95% CI: 0.46–0.88) (9 studies, n = 763) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 0.64 (95% CI: 0.45–0.91) (7 studies, n = 552) Necrotising enterocolitis: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 0.21 (95% CI: 0.05–0.96) (3 studies, n = 323) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 0.21 (95% CI: 0.04–1.25) (2 studies, n = 234) Intraventricular haemorrhage: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 0.59 (95% CI: 0.36–0.98) (3 studies, n = 340) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 0.62 (95% CI: 0.37–1.04) (2 studies, n = 251) Neonatal jaundice: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 0.73 (95% CI: 0.57–0.93) (2 studies, n = 227) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 0.73 (95% CI: 0.57–0.93) (2 studies, n = 277) Neonatal sepsis: 01. (Fixed effects) RR 0.73 (95% CI: 0.46–1.16) (4 studies, n = 375) 02. (Fixed effects) RR 0.73 (95% CI: 0.46–1.16) (4 studies, n = 375) Other: a range of other perinatal and maternal outcomes were reported Brief summary of findings: When compared with any other tocolytic agent calcium channel blockers reduced the number of women giving birth within 7 days of receiving treatment and before 34 weeks’ gestation. Calcium channel blockers also reduced the need for cessation of treatment because of maternal adverse drug reaction, frequency of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome, necrotising enterocolitis, intraventricular haemorrhage and neonatal jaundice Authors’ conclusions: When tocolysis is indicated for women in preterm labour, calcium channel blockers are preferable to other tocolytic agents compared, mainly betamimetics. They have fewer adverse effects for women and appear at least as good at postponing preterm birth. Further research should address the effects of different dosage regimens and formulations of calcium channel blockers on maternal and neonatal outcomes Comments: This was a well-conducted review with the methodology clearly reported and details given of the included studies. The authors note that a sensitivity analysis by trial quality could not be conducted because there were insufficient data. They also comment that neonatal outcomes often lacked clear definition Additional information is being sought on 12 trials for possible inclusion |
|
Al-Qattan et al. [Medical Principles and Practice 2001; 9: 164–173] 578 Country: Kuwait Setting: Hospital Prevalence: NA – no placebo group Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: To delivery and neonatal outcome No. of participants: No. randomised – 60 No. analysed – 53 Validity: Adequate randomisation – Random number table Adequate allocation concealment – No Blinding of clinician – No Blinding of patient – No Blinding of researcher – No Type of analysis: per protocol |
Groups compared: Nifedipine vs ritrodine Intervention details: Nifedipine 30 mg loading dose, second dose 20 mg after 2 h if contractions persisted, if suppressed maintenance dose 20 mg every 6 h vs Ritrodine 50 μg/min i.v. If contractions stopped 10 mg p.o. every 4–6 h started 1 h before i.v. treatment discontinued Maintenance therapy continued to 34 weeks’ gestation Participants: Women in preterm labour between 24 and 34 weeks’ gestation Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Inclusion criteria: Women in preterm labour between 24 and 34 weeks’ gestation. Preterm labour was defined as regular uterine contractions at a frequency of 2–3/10 min with documented change in cervical dilatation or effacement. Exclusion criteria: cardiac disease, placental abruption, hyperthyroidism, severe pre-eclampsia, eclampsia, clinical signs of infection like fever and vaginal discharge or white cell count > 15,000/cm3 and positive vaginal swab cultures. Medical conditions contraindicating tocolytic therapy: polyhydramnios, cervix dilated ≥ 4 cm, fetal pathology, breech presentation, PROM, intrauterine fetal death, fetal distress, congenital malformation Outcomes: Time to uterine quiescence, time to delivery, side effects, perinatal outcome, Apgar score, birthweight, respiratory distress syndrome, intraventricular haemorrhage, admission to special care baby unit |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 15 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 18 (23) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 20 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 20 (23) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 4 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 8 (23) Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 12 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 14 (23) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 15 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 18 (23) Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission (special care not intensive care): No. in intervention group (total no.) = 14 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 17 (23) Incidence of perinatal mortality: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (23) Incidence of adverse events: Neonatal Respiratory distress syndrome No. in intervention group (total no.) = 4 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 4 (23) Intraventricular haemorrhage No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (23) Low birthweight < 1500 g No. in intervention group (total no.) = 8 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 11 (23) Low birthweight < 2500g No. in intervention group (total no.) = 22 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 20 (23) Maternal Treatment stopped due to adverse events (hypotension, tachycardia, palpitations, chest pain) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 5 (28) Headache No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 1 (28) Hypotension No. in intervention group (total no.) = 1 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 2 (28) Nausea No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 11 (28) Vomiting No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 5 (28) Palpitations No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 16 (28) Chest pain No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 9 (28) Brief summary of findings: Nifedipine was more effective than ritrodine in postponing delivery for more than 24 h and in reducing births < 37 weeks. It also caused fewer maternal adverse events Authors’ conclusions: Nifedipine is an effective tocolytic with fewer side effects than ritrodine and it is easier to administer. A larger study is required to confirm these findings Comments: Small study with per protocol analysis, although it is clear why treatment was not adhered to. Allocation concealment not reported and blinding not used. A sample size calculation was conducted |
|
Fan et al. [Chinese J Practical Gynecol Obstet 2003, 19: 87–89] 579 Country: China Setting: Hospital Prevalence: Not applicable (no placebo group) Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: To delivery No. of participants: No. randomised – 61 No. analysed – 61 Validity: Adequate randomisation – Not reported Adequate allocation concealment – Not reported Blinding of clinician – No Blinding of patient – No Blinding of researcher – No Type of analysis: ITT |
Groups compared: Nifedipine vs ritodrine Intervention details: Nifedipine 20 mg p.o. (sublingual), repeated after 30 min if required. If contractions ceased, 20 mg p.o. thereafter to 35 weeks’ gestation Ritodrine 50 mg i.v. at 50 μg/min increased by 50 μg/min every 15 min until contractions ceased or a maximum of 350 μg/min was reached. The effective dose was maintained for 12 h after contractions ceased. Nifedipine 20 mg every 2 h p.o. started 30 min before i.v. ritodrine ceased, then 10 mg every 6 h until 35 weeks’ gestation Participants: Women in preterm labour Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women in preterm labour were included. Both single and multiple gestations (twins) were included Outcomes: Birth within 48 h of initiation of treatment, birth within 7 days of initiation of treatment, birth after 35 weeks’ gestation, birthweight, respiratory distress, side effects, change of treatment required |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 9 (31) No. in control group (total no.) = 9 (30) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 13 (31) No. in control group (total no.) = 14 (30) Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (31) No. in control group (total no.) = 1 (30) (twin) Incidence of adverse events: Respiratory distress No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (31) No. in control group (total no.) = 1 (30) Birth < 35 weeks’ gestation No. in intervention group (total no.) = 14 (31) No. in control group (total no.) = 16 (30) Maternal side effects (including headache, fever, weakness, palpitations and tachycardia) of mother No. in intervention group (total no.) = 8 (31) No. in control group (total no.) = 26 (30) Maternal side effects requiring treatment change No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (31) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (30) Brief summary of findings: There were no significant differences in primary outcomes including birth within 48 h and 7 days of intervention. Fewer women experienced side effects in the nifedipine group Authors’ conclusions: Nifedipine is safe and effective in the management of preterm labour Comments: Twin pregnancies were included in the study and were not identified as a subgroup for the analyses. There is no description of the methods used for randomisation so methodological quality is difficult to assess, and the sample size is small |
|
Floyd RC et al. 1995 [J Matern-Fetal Invest 1995; 5: 25–29] 580 Country: USA Setting: Hospital Prevalence: Not applicable – no placebo group Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: To delivery No. of participants: No. randomised – 90 No. analysed – 90 Validity: Adequate randomisation – computer generated Adequate allocation concealment – Yes Blinding of clinician – Yes Blinding of patient – Yes Blinding of researcher – No Type of analysis: ITT |
Groups compared: Nifedipine vs magnesium sulphate Intervention details: Nifedipine 30 mg p.o. then 20 mg every 8 h until cessation of contractions. Maintenance therapy 20 mg every 8 h until 37 weeks’ gestation or delivery Magnesium sulphate 4 g i.v. then 4–6 g i.v. for uterine quiescence. After 6 h uterine quiescence magnesium gluconate 2 g p.o every 4 h until 37 weeks’ gestation or delivery Oral medication continued to delivery or 37 weeks in both groups Participants: Women in preterm labour between 20 and 34 weeks’ gestation Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Inclusion criteria: singleton gestation, preterm labour between 20 and 34 weeks’ gestation, intact membranes Exclusion criteria: medical or obstetric problems precluding continuation of pregnancy, previous tocolytic therapy in current pregnancy, chorioamnionitis Outcomes: Primary outcomes: delivery < 34 weeks’ gestation, delivery < 37 weeks’ gestation, delivery > 37 weeks’ gestation, extension of gestation following treatment Secondary outcomes: maternal complications, birthweight, Apgar score, hypoglycaemia, respiratory complications, lethargy, depression at birth |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 10 (50) No. in control group (total no.) = 8 (40) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 18 (50) No. in control group (total no.) = 18 (40) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not reported Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Respiratory distress syndrome No. in intervention group (total no.) = 5 (50) No. in control group (total no.) = 4 (40) Transient tachypnoea of newborn No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (50) No. in control group (total no.) = 2 (40) Low birthweight < 1500 g No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (50) No. in control group (total no.) = 2 (40) Low birthweight < 2500 g No. in intervention group (total no.) = 14 (50) No. in control group (total no.) = 19 (40) Apgar < 7 at 5 min No. in intervention group (total no.) = 7 (50) No. in control group (total no.) = 6 (40) Adverse events requiring cessation of treatment No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (50) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (40) Brief summary of findings: No significant difference between groups in incidence of preterm birth < 37 weeks or other outcome Authors’ conclusions: Both nifedipine and magnesium sulphate are effective tocolytic agents. No evidence of fetal neonatal or maternal compromise in either group Comments: Small well-conducted RCT. No sample-size calculation reported |
|
Haghighi [Int J Gynecol Obstet 1999; 66: 297–298] 581 Country: Iran Setting: Hospital Prevalence: Not applicable – no placebo group Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: To delivery or neonatal intensive care unit discharge No. of participants: No. randomised – 74 No. analysed – 74 Validity: Adequate randomisation – Not reported Adequate allocation concealment – Not reported Blinding of clinician – No Blinding of patient – No Blinding of researcher – No Type of analysis: ITT |
Groups compared: Nifedipine vs magnesium sulphate Intervention details: Nifedipine 10 mg every 20 min p.o. (sublingual) up to maximum dose 40 mg in first hour of treatment if contractions persisted. If contractions stopped then 20 mg every 6 h p.o. for 24 h then 20 mg every 8 h p.o. for 24 h Magnesium sulphate loading dose 6 g i.v. over 15 min then 2 g/h increasing to a maximum of 4 g/h as required to stop contractions for up to 48 h. Infusion continued for 12 h after contractions stopped then terbutaline 5 mg every 6 h p.o. Participants: Primigravid women in preterm labour Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Inclusion criteria: Primigravid women with singleton pregnancies at 23–36 weeks’ gestation in preterm labour defined as regular contractions < 10 min apart despite bed rest, 50 mg i.v. meperidine and 500 cm3 bolus of Ringer’s solution Outcomes: Birth within 48 h of intervention, maternal side effects, birthweight, Apgar score, stay in neonatal intensive care |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 8 (34) No. in control group (total no.) = 12 (40) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not reported Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Maternal side effects (chest pain, nausea and vomiting, headache, transient hypotension) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 8 (34) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (40) Maternal side effects requiring cessation of treatment No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (34) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (40) Apgar score at 1 min: mean (SD) Intervention 7.15 (1.3) Control 7.2 (1.25) Apgar score at 5 min: mean (SD) Intervention 8.5 (1.4) Control 8.6 (1.0) Days in NICU: mean (SD) Intervention 24 (3) Control 26 (2) Brief summary of findings: There were no significant differences in birth within 48 h of intervention, maternal side effects or neonatal outcomes including length of stay in intensive care unit Authors’ conclusions: Oral nifedipine has the same efficacy and side effects and a faster action than magnesium sulphate and could be a suitable and more convenient alternative to intravenous magnesium sulphate in arresting preterm labour Comments: Methods are reported extremely briefly so it is unclear how well conducted the study was. However, a sample size calculation indicated the study was appropriately powered |
|
Kashanian et al. [Int J Gynecol Obstet 2005; 91: 10–14] 582 Country: Iran Setting: Hospital Prevalence: Not applicable, no placebo group Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: To delivery No. of participants: No. randomised – 80 No. analysed – 80 Validity: Adequate randomisation – Yes Adequate allocation concealment – No Blinding of clinician – No Blinding of patient – No Blinding of researcher – No Type of analysis: ITT |
Groups compared: Nifedipine vs atosiban Intervention details: Nifedipine 10 mg p.o. (sublingual) every 20 min for four doses. If contractions were inhibited, 20 mg every 6 h for 24 h then every 8 h for 24 h then 10 mg every 8 h for 24 h Atosiban 300 μg/min i.v. Therapy continued for a maximum of 12 h or 6 h after cessation of contractions Dexamethasone 5 mg i.m. every 12 h for 48 h in both groups No maintenance therapy in either group Participants: Symptomatic women Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Inclusion criteria: Women between 26 and 34 weeks’ gestation with pregnancy documented by a definite last menstrual period and sonography in first trimester, in preterm labour. Labour defined as contractions at a frequency of 4/20 or 8/60 min with cervical dilatation ≥ 1 cm and cervical effacement of ≥ 50%. Exclusion criteria: PROM, vaginal bleeding, fetal death, fetal distress, intrauterine growth restriction, history of trauma, cervical dilatation > 3 cm, systemic disorders of the mother, known uterine anomaly, blood pressure > 90/50 mmHg Outcomes: Birth within 48 h of intervention, birth within 7 days of intervention, time to delivery, maternal side effects |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 10 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 7 (40) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 14 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 10 (40) n = Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Total maternal side effects (women) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 16 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 7 (40) Headache No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (40) Vertigo No. in intervention group (total no.) = 9 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (40) Flank pain No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 1 (40) Hypotension No. in intervention group (total no.) = 11 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (40) Palpitation No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (40) Tachycardia No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (40) Brief summary of findings: There were no significant differences between the groups in birth within 48 h or within 7 days. Significantly more women in the nifedipine group experienced side effects Authors’ conclusions: Atosiban is an effective and safe drug for acute treatment of preterm labour with minimal side effects and may be an option Comments: Twin pregnancies were included in the study and were not identified as a subgroup for the analyses |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
King et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2005, Issue 2] 594 Title: Cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitors for treating preterm labour Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth 14 (out of a total of 18) |
Search: Search dates August 2004 Databases searched Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group trials register Other sources: Experts contacted for ongoing and unpublished trials Search restrictions None reported Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Women assessed as being in preterm labour between 20 and 36 weeks’ gestation and suitable for tocolysis Intervention COX inhibitors administered by any route for the management of preterm labour Outcomes Death or major sensoneural disability at two years of age, preterm birth < 28 weeks’ gestation, < 34 weeks, < 37 weeks, birth < 48 h after trial entry, birth < 7 days after trial entry, low birthweight < 2500 g, neonatal death, admission to neonatal intensive care unit. A range of other neonatal outcomes including respiratory distress syndrome, use and duration of mechanical ventilation, intraventricular haemorrhage, sepsis and necrotising enterocolitis were sought Maternal death, cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, admission to ICU and a range of outcomes including oligohydramnios, haemorrhage and requirement for blood transfusion Study selection: Three reviewers independently selected trials for inclusion. Differences were resolved by discussion Data extraction: Three reviewers independently extracted data. Differences were resolved by discussion Validity assessment: Criteria used: Cochrane criteria of allocation concealment, randomisation, blinding and loss to follow-up Assessment: Three reviewers independently assessed study validity. Differences were resolved by discussion Synthesis: Heterogeneity: Subgroup analyses were planned for: women < 28 weeks’ gestation vs > 28 weeks women with multiple vs singleton gestation women with ruptured vs intact membranes type of tocolytic agent used as comparator (specifically betamimetics, magnesium sulphate, calcium channel blockers, oxytocin receptor antagonists) high-quality vs low-quality trials Methods: Chi-squared tests for heterogeneity were used and an I-squared statistic was calculated. Where significant statistical heterogeneity was present a random-effects model was employed for meta-analysis in place of a fixed effect model |
No. of studies included: 13 RCTs (n = 713) 01. COX inhibitor vs placebo (3 studies, n = 106) 02. COX inhibitor vs any other tocolytic (8 studies, n = 660) 03. Indomethacin compared with COX-2 inhibitor (2 studies, n = 54) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 12 Adequate concealment of allocation – 12 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 7/7/7 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: 01. RR 0.21 (95% CI: 0.07–0.62) (1 study, n = 36) 02. RR 0.53 (95% CI: 0.31–0.94) (3 studies, n = 168) compared with betamimetic: RR 0.53 (95% CI: 0.28–0.99) (2 studies, n = 80) compared with magnesium sulphate: RR 0.55 (95% CI: 0.17–1.73) (1 study, n = 88) 03. RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.31–3.19) (2 studies, n = 54) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: 01. RR 0.19 (95% CI: 0.07–0.51) (2 studies, n = 70) 02. RR 0.59 (95% CI: 0.34–1.02) (4 studies, n = 415) compared with betamimetic: RR 0.27 (95% CI: 0.08–0.96) (2 studies, n = 100) compared with magnesium sulphate: RR 0.75 (95% CI: 0. 40–1.40) (2 studies, n = 15) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: 01. RR 0.44 (5% CI: 0.26–0.74) (2 studies, n = 70) 02. RR 0.88 (95% CI: 0.52–1.46) (2 studies, n = 146) compared with betamimetic: RR 0.88 (95% CI: 0.52–1.46) (2 studies, n = 146) 03. RR 3.00 (95% CI: 0.13–67.06) (1 study, n = 24) Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: 01. RR 0.80 (95% CI: 0.56–1.15) (1 study, n = 39) 02. RR 0.83 (95% CI: 0.48–1.43) (1 study, n = 194) compared with magnesium sulphate: RR 0.83 (95% CI: 0.48–1.43) (1 study, n = 194) 03. RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.34–2.91) (2 studies, n = 54) Incidence of perinatal mortality: 01. RR 0.80 (95% CI: 0.25–2.58) (3 studies, n = 106) 02. RR 1.46 (95% CI: 0.57–3.74) (8 studies, n = 660) compared with betamimetic: RR 0.99 (95% CI: 0.27–3.57) (4 studies, n = 237) compared with magnesium sulphate: RR 2.31 (95% CI: 0.54–9.90) (4 studies, n = 423) Incidence of adverse events: Respiratory distress syndrome 01. RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.40–2.49) (3 studies, n = 106) 02. RR 1.08 (95% CI: 0.66–1.76) (6 studies, n = 503) compared with betamimetic: RR 1.50 (95% CI: 0.27–8.34) (2 studies, n = 80) compared with magnesium sulphate: RR 1.04 (95% CI: 0.62–1.74) (4 studies, n = 423) 03. RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.07–14.21) (1 study, n = 24) Neonatal mechanical ventilation 02. RR 1.50 (95% CI: 0.47–4.78) (1 study, n = 60) 03. RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.07–14.21) (1 study, n = 24) Intraventricular haemorrhage (all grades) 02. RR 1.18 (95% CI: 0.66–2.11) (7 studies, n = 548) compared with betamimetic: RR 5.34 (95% CI: 0.66–43.10) (3 studies n = 125) compared with magnesium sulphate: RR 0.92 (95% CI: 0.49–1.73) (4 studies, n = 223) Intraventricular haemorrhage Grade III or IV 01. RR 3.15 (95% CI: 0.14–72.88) (1 study, n = 39) 02. RR 0.61(95% CI: 0.08–4.40) (3 studies, n = 249) compared with betamimetic: RR not estimable (1 study n = 20) compared with magnesium sulphate: RR 0.61(95% CI: 0.08–4.40) (3 studies, n = 229) 03. RR not estimable (1 study, n = 24) Necrotising enterocolitis 01. RR 0.97 (95% CI: 0.21–4.43) (2 studies, n = 70) 02. RR 3.82 (95% CI: 0.65–22.51) (4 studies, n = 298) compared with betamimetic: RR 3.00 (95% CI: 0.13–70.83) (2 studies, n = 80) compared with magnesium sulphate: RR 4.24 (95% CI: 0.49–36.45) (2 studies, n = 218) 03. RR not estimable (1 study, n = 24) Chronic neonatal lung disease 01. RR 1.24 (95% CI: 0.39–3.94) (2 studies, n = 70) Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn 01. RR not estimable (3 studies, n = 106) 02. RR 2.85 (95% CI: 0.56–14.38) (6 studies, n = 490) compared with betamimetic: RR 5.63 (95% CI: 0.31–103.46) (3 studies, n = 177) compared with magnesium sulphate: RR 1.78 (95% CI: 0.23–13.44) (3 studies, n = 313) Neonatal sepsis 01. RR 0.31 (95% CI: 0.01–7.15) (2 studies, n = 70) 02. RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.07–15.26) (2 studies, n = 80) 03. RR 0.33 (95% CI: 0.01–7.45) (1 study, n = 24) Apgar score < 7 at 5 min 01. RR 0.53 (95% CI: 0.05–5.34) (1 study, n = 39) 02. RR 0.53 (95% CI: 0.21–1.30) (2 studies, n = 254) compared with betamimetic: RR 3.00 (95% CI: 0.13–70.83) (1 study, n = 60) compared with magnesium sulphate: RR 0.43 (95% CI: 0.16–1.15) (1 study, n = 200) 03. RR 3.00 (95% CI: 0.13–67.06) (1 study, n = 24) Oligohydramnios 02. RR 2.53 (95% CI: 0.76–8.46) (3 studies, n = 295) compared with betamimetic: RR 2.08 (95% CI: 0.55–7.87) (1 study, n = 106) compared with magnesium sulphate: RR 5.30 (95% CI: 0.26–107.70) (2 studies, n = 189) 03. RR = 4.00 (95% CI: 0.52–30.76) (1 study, n = 24) Maternal adverse drug reaction 01. RR 1.58 (95% CI: 0.66–3.78) (3 studies, n = 101) 02. RR 0.22 (95% CI: 0.15–0.33) (7 studies, n = 629) compared with betamimetic: RR 0.10 (95% CI: 0.05–0.20) (4 studies, n = 226) compared with magnesium sulphate: RR 0.41 (95% CI: 0.26–0.66) (3 studies, n = 403) 03. RR not estimable (2 studies, n = 54) Maternal adverse drug reaction requiring cessation of treatment 02. RR 0.07 (95% CI: 0.02–0.29) (5 studies, n = 355) compared with betamimetic: RR 0.07 (95% CI: 0.01–0.37) (3 studies, n = 166) compared with magnesium sulphate: RR 0.06 (95% CI: 0.00–1.05) (2 studies, n = 189) Postpartum haemorrhage 01. RR = 3.94 (95% CI: 0.95–16.29) (1 study, n = 34) Antepartum haemorrhage 03. RR 0.33 (95% CI: 0.01–7.45) (1 study, n = 24) Chorioamnionitis or endometritis 01. RR 1.94 (95% CI: 0.44–8.60) (2 studies, n = 64) 02. RR not estimable (1 study, n = 88) 03. RR 2.00 (95% CI: 0.21–19.23) (1 study, n = 24) Brief summary of findings: COX inhibitors (indomethacin) produced a significant reduction in birth < 37 weeks compared with placebo. Compared to other tocolytics COX inhibitors reduced birth < 37 weeks’ gestation, and maternal drug reactions requiring cessation of treatment. There were no differences between selective COX-2 inhibitors and non-selective COX-2 inhibitors Authors’ conclusions: There is insufficient information on which to base decisions about the role of COX inhibition for women in preterm labour. Further well-designed trials are needed Comments: Well-conducted review. The authors are appropriately cautious about their conclusions because of the small numbers of patients involved |
|
Golding [BJOG 1998; 105: 293–299] 608 Country: Jamaica Setting: Outpatient Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth –NA Preterm birth – 463 (of 3026 in total) Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: To 6-week postnatal visit following delivery No. of participants: No. randomised – 6275 No. analysed – 6096 Validity: Adequate randomisation – Yes Adequate allocation concealment – Yes Blinding of clinician – Yes Blinding of patient – Yes Blinding of researcher – No Type of analysis: Not ITT |
Groups compared: Low-dose aspirin vs Placebo Intervention details: Aspirin 60 mg p.o. daily vs placebo Participants: Primiparae < 32 weeks’ gestation Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Primiparae < 32 weeks’ gestation at recruitment resident in two parishes in Jamaica were eligible Outcomes: Development of hypertension, proteinuric pre-eclampsia or pre-eclamptic fits; birthweight, preterm delivery < 37 weeks, perinatal mortality, bleeding in pregnancy, antepartum haemorrhage, haematemesis, postpartum haemorrhage, admission to neonatal special care, low birthweight < 2500 g, Apgar < 5 at 5 min |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 447 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 463 (3026) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 285 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 263 (3026) Incidence of perinatal mortality: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 86 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 103 (3026) Incidence of adverse events: Apgar < 5 at 5 min No. in intervention group (total no.) = 38 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 25 (3026) Low birthweight (< 2500 g) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 303 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 325 (3026) Intercranial haemorrhage No. in intervention group (total no.) = 1 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (3026) Other neonatal bleeding No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 2 (3026) Stopped medication due to adverse events No. in intervention group (total no.) = 35 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 35 (3026) Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy No. in intervention group (total no.) = 75 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 67 (3026) Vomiting blood No. in intervention group (total no.) = 15 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 17 (3026) Other maternal bleeding No. in intervention group (total no.) = 58 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 38 (3026) Severe stomach pains No. in intervention group (total no.) = 34 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 36 (3026) Skin rash No. in intervention group (total no.) = 58 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 47 (3026) Wheezing or asthma No. in intervention group (total no.) = 21 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 21 (3026) Admitted antenatally No. in intervention group (total no.) = 540 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 504 (3026) Postpartum haemorrhage No. in intervention group (total no.) = 213 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 155 (3026) Alive but ill at 6 weeks postpartum (maternal) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 38 (3023) No. in control group (total no.) = 34 (3026) Brief summary of findings: There was no effect of aspirin on rates of preterm delivery or low birthweight infants. Aspirin did show an increase in maternal bleeding disorders including postpartum haemorrhage Authors’ conclusions: Low-dose aspirin has no consistent beneficial effect in primiparae Comments: Large reasonably well-conducted study. Analysis not ITT. Multiple pregnancies were excluded from the analyses |
|
Groom et al. [BJOG 2005; 112: 725–730] 609 Country: UK Setting: Outpatient Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – 19 (of 47 in total) Preterm birth – 19 (of 47 in total) Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: To delivery (maternal); to discharge from hospital (neonatal) No. of participants: No. randomised – 92 women in 101 pregnancies No. analysed – 89 women in 98 pregnancies Validity: Adequate randomisation – computer-generated Adequate allocation concealment – yes Blinding of clinician – yes Blinding of patient – yes Blinding of researcher – no Type of analysis: Described as ITT but excluded three who did not receive treatment due to withdrawal from PPROM |
Groups compared: Rofecoxib vs placebo Intervention details: Rofecoxib 12.5 mg p.o. or placebo once daily Participants: Women at high risk of preterm delivery Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Inclusion criteria: at least one of: (1) Two or more previous second-trimester losses or preterm deliveries < 30 weeks; (2) One previous second-trimester loss or preterm delivery < 30 weeks and cervical length ≤ 15 mm from 14 to 24 weeks; (3) Cervical changes requiring cerclage in current pregnancy determined by ultrasound criteria or clinically (rescue cerclage) Women were eligible from 16 weeks’ gestation if (1) applied, and when clinically indicated in (2) and (3) up to 26 weeks Exclusion criteria were multiple pregnancy, previous allergy to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, maternal renal dysfunction Outcomes: Preterm delivery and neonatal outcome including neonatal intensive care unit admission, need for assisted ventilation, chronic lung disease. Maternal postpartum haemorrhage. Also fetal renal function and ductus arteriosus blood flow changes |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 34 (51) No. in control group (total no.) = 19 (47) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 17 (51) No. in control group (total no.) = 10 (47) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Neonate requiring assisted ventilation No. in intervention group (total no.) = 6 (51) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (47) Number of days requiring assisted ventilation: Mean (SD) Intervention: 5.2 (3.4) Control: 1.5 (16.3) Number of days given continuous positive airway pressure Mean (SD) Intervention: 10.2 (18.8) Control: 3.4 (5.1) Neonate with chronic lung disease No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (51) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (47) Necrotising enterocolitis confirmed No. in intervention group (total no.) = 1 (51) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (47) Postpartum haemorrhage No. in intervention group (total no.) = 1 (51) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (47) Stop treatment < 32 weeks No. in intervention group (total no.) = 21 (51) No. in control group (total no.) = 16 (47) Oligohydramnios No. in intervention group (total no.) = 9 (51) No. in control group (total no.) = 1 (47) PPROM No. in intervention group (total no.) = 24 (51) No. in control group (total no.) = 9 (47) Neonate discharged alive and well No. in intervention group (total no.) = 38 (51) No. in control group (total no.) = 39 (47) Brief summary of findings: Rofecoxib increased the incidence of oligohydramnios, PPROM, and the occurrence of delivery < 37 weeks in high-risk women, without reducing the risk of earlier delivery (< 30 weeks) Authors’ conclusions: Rofecoxib has a significant but reversible effect on fetal renal function and the ductus arteriosus. It does not reduce incidence of delivery < 30 weeks and is associated with an increased risk of delivery < 37 weeks in high-risk women Comments: Well conducted RCT, although true ITT analysis was not performed, sample size was small but an appropriate power calculation was performed |
|
Humphrey et al. [Obstet Gynecol 2001; 98: 555–562] 610 Country: USA Setting: Hospital Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Not reported Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: To discharge No. of participants: No. randomised – 95 No. analysed – 89 Validity: Adequate randomisation – computer generated Adequate allocation concealment – Yes Blinding of clinician – Yes Blinding of patient – Yes Blinding of researcher – Yes Type of analysis: per protocol |
Groups compared: Sulindac vs Placebo Intervention details: Sulindac 100 mg p.o b.i.d. (every 12 h) until 34 weeks’ gestation vs placebo Participants: Women with gestational age > 24 < 34 weeks, singleton gestation, intact amniotic membranes, no cerclage, diagnosis of arrested preterm labour, cervical dilatation ≤ 4 cm Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Inclusion criteria: gestational age > 24 < 34 weeks, singleton gestation, intact amniotic membranes, no cerclage, diagnosis of arrested preterm labour, cervical dilatation ≤ 4 cm. Preterm labour defined as progressive cervical dilatation or effacement associated with regular uterine contractions at a rate of ≥ 4 in 20 min or 8 in 60 min. Arrested preterm labour defined as 12-h contraction-free period after discontinuation of i.v. tocolysis Exclusion criteria were: clinical evidence of intra-amniotic infection, pyelonephritis, medical complications contraindicating tocolysis, evidence of fetal growth retardation, sonographic evidence of congenital anomalies inconsistent with life Outcomes: Birth within 48 hours intervention, birth within 7 days of intervention, birth after 35 weeks’ gestation, birth before 37 weeks’ gestation or at least one admission for repeat tocolysis before 34 weeks, birth before 34 weeks’ gestation or repeat tocolysis, readmission for tocolysis, birthweight, estimated gestational age at delivery, length of stay in neonatal intensive care, length of stay in hospital (neonatal), length of time neonate on ventilator |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (44) No. in control group (total no.) = 1 (45) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 4 (44) No. in control group (total no.) = 4 (45) Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Respiratory distress syndrome No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (44) No. in control group (total no.) = 2 (45) Neonatal sepsis No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (44) No. in control group (total no.) = 2 (45) Days in neonatal intensive care unit Intervention: 2.8 (9.2) Control: 2.4 (8.6) Days in hospital Intervention: 6.8 (10.3) Control: 4.3 (8.1) Days on ventilator Intervention: 0.3 (1.7) Control: 0.1 (0.6) Patent ductus arteriosus No. in intervention group (total no.) = 1 (44) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (45) Brief summary of findings: There were no significant differences between the groups in births within 48 h or 7 days of treatment, and no differences in incidence of adverse events Authors’ conclusions: Use of oral sulindac until 34 weeks’ gestation after successful parenteral tocolysis failed to reduce the incidence of readmission for preterm labour Comments: Well-conducted RCT, although ITT analysis was not performed. A power analysis suggested that 43 patients per group would be required |
| Study details and design | Description of methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Caritis et al. [Am J Obstet Gynecool 1982; 142(2): 183–190] 612 Country: USA Setting: Magee-Women’s Hospital, Pittsburgh Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Not estimable Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: Enrolment to neonatal period No. of participants: No. randomised – 92 No. analysed – 85 Validity: Adequate randomisation – (randomisation method not described) Adequate allocation concealment – Yes Blinding of clinician – No Blinding of patient – No Blinding of researcher – Not stated Type of analysis: Chi-squared analysis was used to assess differences between the treatment groups |
Groups compared: Ethanol vs Terbutaline Intervention details: A loading dose of 7.5 ml/kg/h of 10% ethanol in 5% dextrose was infused for 2 h. This was followed by a maintenance infusion of ethanol at a rate of 1.5 ml/kg/h for 10 h. If labour recurred, a second or third course of ethanol was given. For repeated course, the reloading dose was reduced by 10% for each hour less than 10 elapsing from the end of the previous maintenance infusion Terbutaline was diluted with physiological saline solution to a concentration of 20 µg/min. Physiological saline solution 400 ml was infused over 20 min before administering the terbutaline. The rate of terbutaline infusion was started at 5 µg/min and increased by 5 µg/min every 20 min to a maximal dosage of 30 µg/min or until uterine contractions ceased. Once contractions had stopped, the infusion was maintained for 1 h, after which the infusion rate was decreased to the minimal dose (5–10 µg/min) required to inhibit labour for an additional 8 h. If labour reoccurred during this maintenance period, the rate of infusion was increased until labour subsided, and the maintenance regimen was started again. During infusion, vital signs were recorded every 15 min. The infusion was stopped if the patient reported any tightness in the chest or shortness of breath, and the participant was evaluated by a physician All women with intact membranes in whom labour was inhibited received 5 mg terbutaline orally 30 min before the end of the intravenous maintenance infusion. This dosage was repeated four times daily for 5 days After successful inhibition with either treatment regimen, women were observed for 36 h, after which those with intact membranes were discharged Participants: Women experiencing symptoms of preterm labour Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women with regular painful contractions (documented by tocodynamometer) occurring every 5–7 min for at least 30 seconds for a minimum of 1 h, gestational age between 20 and 36 weeks in women with intact membranes and 24 and 34 weeks in women with ruptured membranes, and no obstetric or medical contraindications to the inhibition of labour or the use of labour-inhibiting drugs were eligible Women who had received an alternative labour-inhibiting drug for their current episode of preterm labour and those with cervical dilatation greater than 5 cm were excluded Outcomes: Prolongation of pregnancy, birthweight, incidence of neonatal death, fetal death and hyaline membrane disease, Apgar scores and maternal side effects |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Women with intact membranes No. in intervention group (total no.) = 23 (28) No. in control group (total no.) = 23 (28) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Women with intact membranes No. in intervention group (total no.) = 10 (28) No. in control group (total no.) = 4 (28) Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth up to and including 7 days of intervention: Women with intact membranes No. in intervention group (total no.) = 21 (28) No. in control group (total no.) = 15 (28) Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: All women No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 8 (45) Incidence of adverse events: Stillbirth: Women with intact membranes: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 1 (28) No. in control group (total no.) = 2 (28) Women with ruptured membranes: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (12) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (17) Neonatal death: Women with intact membranes: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (28) No. in control group (total no.) = 6 (28) Women with ruptured membranes: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 4 (12) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (17) Hyaline membrane disease: Women with intact membranes: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 9 (28) No. in control group (total no.) = 9 (28) Women with ruptured membranes: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 7 (12) No. in control group (total no.) = 7 (17) Loss of consciousness: All women No. in intervention group (total no.) = 9 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (45) Nausea/vomiting: All women No. in intervention group (total no.) = 32 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 13 (45) Chest pain: All women No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 7 (45) Shortness of breath: All women No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 5 (45) Cardiac arrhythmia: All women No. in intervention group (total no.) = 1 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (45) Pulmonary arrhythmia: All women No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (40) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (45) Other outcomes: Birthweight (g) Women with intact membranes: Intervention group (SD) = 1773 Control group (SD) = 1815 Women with ruptured membranes: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 1531 (436) No. in control group (total no.) = 1565 (487) Subgroup analysis: Prolongation of pregnancy by cervical dilatation (days gained) Cervix > 2 cm dilated or ≥ 75% effaced Women with intact membranes Intervention group (SD) = 2 (0.5) Control group (SD) = 9 (2.6) Cervix ≤ 2 cm dilated or < 75% effaced Women with intact membranes Intervention group (SD) = 25 (6.6) Control group (SD) = 39 (9.9) Brief summary of findings: Tocolytic success was demonstrated in 18% of both treatment groups in women with intact membranes. Terbutaline was shown to prolong pregnancy for a greater number of days than ethanol in women with intact membranes and cervix > 2 cm dilated or effacement ≥ 75%. No statistically significant difference was shown between treatment groups in women with intact membranes and cervix < 2 cm dilated or < 75% effacement. In women with ruptured membranes, the tocolytic success rate was similar in both treatment groups when all cases are considered. However, terbutaline was better at maintaining pregnancy for a minimum of 36 h in women with cervical dilatation < 4 cm. Fetal or neonatal outcomes were not significantly different between the two treatment groups when compared by gestational age Authors’ conclusions: Terbutaline is more effective than ethanol in treating preterm labour. No serious complications occurred from the use of terbutaline, either in the mother or her infant Comments: Cervical dilatation and cervical effacement were similar in the two groups at study onset Five sets of twins were recorded in the intact membrane group (two ethanol, three terbutaline), and three sets of twins were recorded in the ruptured membrane group (one ethanol, two terbutaline) 8% loss to follow-up |
|
Lauersen et al. [Am J Obstet Gynecol 1977; 127: 837–845] 613 Country: USA Setting: Three collaborating centres: The New York Hospital, University Hospitals of Cleveland, and Nassau County Medical Center Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – No non-treatment group included Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: Enrolment to neonatal period No. of participants: No. randomised – 135 No. analysed – 135 Validity: Adequate randomisation – Not reported Adequate allocation concealment – Yes Blinding of clinician – Not reported Blinding of patient – Not reported Blinding of researcher – Not reported Type of analysis: Differences between the two treatment groups were assessed using the Student t-test and chi-squared test, as appropriate |
Groups compared: Ethanol vs Ritodrine Intervention details: A loading dose of ethanol 10% in 5% dextrose (i.v.) 7.5 ml/kg/h of body weight for 2 h, followed by a maintenance dose of 1.5 ml/kg/h for 10 or more hours. If premature labour recurred after the initial ethanol infusion up to two additional courses were permitted. If labour recurred less than 10 h after discontinuation of first infusion, the repeat loading was reduced and followed by the maintenance dose described A total of 250 mg of ritodrine hydrochloride 10 mg/ml added to 450 ml of 5% dextrose in water for a final concentration of 526 µg/ml (administered intravenously). Infusion rate started at 50 µg/min and increased by 50 µg every 10 min until adequate uterine relaxation occurred (max 350 µg/min), then maintained for 12 h. 30 min before termination of the intravenous infusion, oral ritodrine was initiated at a dose schedule of up to 10 mg every 2 h and maintained for 24 h. Women were discharged from hospital receiving oral doses of ritodrine ranging from 20 to 60 mg daily. Oral therapy was maintained for up to 4 weeks or until 38th week of gestation, whichever came first. If premature labour recurred with oral therapy, up to two repeat courses of intravenous ritodrine were given Vital signs were monitored and recorded every 15 min for the first 2 h of infusion in all participants. After 2 h, vital signs were monitored and recorded every 2–4 h during the participants’ entire hospital stay Participants: Women experiencing symptoms of preterm labour Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Inclusion criteria included regular uterine contractions of 30–60 seconds at least once every 10 min and clinically judged as premature labour, gestation between 20 and 36 weeks, estimated fetal weight below 2500 g, uterine fundus above the umbilicus, intact membranes and not bulging, cervical effacement, and cervical dilatation not exceeding 4 cm Exclusion criteria included premature separation of the placenta, pre-eclampsia, chronic renal disease, diabetes mellitus and other severe maternal diseases, presence of a dead or malformed fetus, placenta praevia, if bleeding required intervention, and any maternal or fetal complication which required immediate delivery Outcomes: Labour postponed for more than 3 days, time gained, week of delivery, birthweight, infant survival, and cardiovascular effects of treatment |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: All women No. in intervention group (total no.) = 19 (67) No. in control group (total no.) = 10 (68) Singleton gestations No. in intervention group (total no.) = 17 (58) No. in control group (total no.) = 9 (62) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: All women No. in intervention group (total no.) = 41 (67) No. in control group (total no.) = 33 (68) Singleton gestations No. in intervention group (total no.) = 37 (58) No. in control group (total no.) = 29 (62) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: All women No. in intervention group (total no.) = 23 (67) No. in control group (total no.) = 9 (68) Singleton gestations No. in intervention group (total no.) = 21 (58) No. in control group (total no.) = 8 (62) Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 6 (76) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (73) Incidence of adverse events: Stillbirths No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (76) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (73) Neonatal death No. in intervention group (total no.) = 7 (76) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (73) Respiratory distress syndrome No. in intervention group (total no.) = 15 (76) No. in control group (total no.) = 6 (73) Birthweight ≤ 2500 g No. in intervention group (total no.) = 44 (76) No. in control group (total no.) = 17 (73) Birthweight ≤ 1500 g No. in intervention group (total no.) = 11 (76) No. in control group (total no.) = 6 (73) Maternal heart rate acceleration (beats per/min) Intervention group (SD) = 15.7 (10.2) Control group (SD) = 37.9 (16.1) Fetal heart rate acceleration (beats per/min) Intervention group (SD) = 11.1 (9.3) Control group (SD) = 21.5 (16.1) Maternal systolic blood pressure increase (mmHg) Intervention group (SD) = 4.2 (8.8) Control group (SD) = 13.4 (11.9) Fetal systolic blood pressure decrease (mmHg) Intervention group (SD) = 13.5 (11.2) Control group (SD) = 19.3 (9.7) Other outcomes: Postponed delivery > 72 h No. in intervention group (total no.) = 49 (67) No. in control group (total no.) = 61 (68) Brief summary of findings: Ritodrine was more effective than ethanol in singleton pregnancies (p < 0.05), but no statistically significant differences between the two treatment groups in control of premature labour in twin gestations was shown Authors’ conclusions: Ethanol and ritodrine were both found to be effective inhibitors of premature labour with ritodrine giving the most favourable results Comments: 11% had multiple pregnancies: nine sets of twins were reported in the ethanol group and six sets of twins were reported in the ritodrine group The authors’ conclusions do not seem to follow from the data presented |
|
Reynolds [Aust NZ J Obstet Gynecol 1978; 18: 107–109] 615 Country: Australia Setting: Crown Street Women’s Hospital, Sydney, Australia Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Not estimable Study design: Quasi-RCT Length of follow-up: Enrolment to delivery No. of participants: No. randomised – 84 No. analysed – 84 Validity: Adequate randomisation – No (alternate allocation) Adequate allocation concealment – No Blinding of clinician – No Blinding of patient – Not reported Blinding of researcher – No reported Type of analysis: Not reported |
Groups compared: Ethanol vs Salbutamol Intervention details: Ethanol was administered intravenously [as described by Fuchs et al. (1967), Am J Obstet Gynecol 99:672)] with a 2-h loading dose infusion, followed by an 8-h maintenance infusion. Solu-medrol 500 mg was given intravenously to all women in the ethanol group. Maternal blood pressure, pulse and fetal heart rate were recorded at 30-min intervals and degree of consciousness was closely observed. After cessation of the 10-h treatment women were observed for any uterine activity. If activity recurred within 12 h of initial treatment the maintenance dose was recommenced. If the membranes had been ruptured for more than 24 h, labour was allowed to proceed Salbutamol was diluted in a 5% dextrose solution to a concentration of 50 mg per 250 ml and intravenously infused. The initial dose was 2 µg/min which was increased by 100% increments until a rate of 40 µg/min, uterine activity ceased or a tachycardia of 140 beats/min developed. A cardiac monitor was used continuously during the infusion. Maternal pulse, blood pressure and fetal heart rate were recorded every 5 min until the maintenance infusion was achieved. Salbutamol infusion was usually stopped after 12 h, if labour had been successfully inhibited, but was recommenced if uterine activity returned. Intramuscular phenobarbitone 200 mg was given to all women in the salbutamol group Participants: Women experiencing symptoms of preterm labour Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women between 20 and 37 weeks’ gestation, with painful contractions occurring less than 10 min apart, usually verified by external tocograph were eligible. Women with major medical complications, cervix dilated more than 5 cm, amnionitis, or significant antepartum haemorrhage were excluded Outcomes: The primary outcome was inhibition of labour for more than 24 h. Secondary outcomes included: delayed delivery more than 7 days, perinatal mortality, Apgar score, and other maternal and fetal side effects |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 10 (42) No. in control group (total no.) = 13 (42) Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 28 (42) No. in control group (total no.) = 24 (42) Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 4 (44) (Two sets of twins included) No. in control group (total no.) = 6 (45) (Set of triplets and set of twins included) Incidence of adverse events: Mean Apgar score at 1 min of babies born within 24 h of treatment Intervention group (SD) = 7.4 (not reported) Control group (SD) = 7.4 (not reported) Mean Apgar score at 5 min Intervention group (SD) = 9.2 (not reported) Control group (SD) = 8.7 (not reported) Mean maternal heart rate acceleration (beats per/min) Intervention group (SD) = 4 (not reported) Control group (SD) = 40 (not reported) Mean maternal systolic blood pressure (mmHg) Intervention group (SD) = – 6 (not reported) Control group (SD) = – 5 (not reported) A number of individual maternal side effects were reported for each treatment group; 19% of the sabutamol group complained of palpitations and 29% were noted to have occasional ventricular ectopic beats, 74% of the ethanol group complained of nausea and vomiting Brief summary of findings: Ethanol was successful at suppressing labour for more than 24 h in 76% of the women receiving this treatment, compared to 69% of women in the salbutamol group. Labour was successfully delayed for more than 7 days in 33% of the ethanol group and 43% of the salbultamol group Authors’ conclusions: Ethanol and salbutamol were equally effective in the inhibition of premature labour, but the side effects were less marked with salbutamol Comments: Method of randomisation and allocation concealment was inadequate The mothers of a set of triplets and a set of twins were treated with salbutamol. Two mothers with sets of twins were treated with ethanol |
|
Sims et al. [BJOG 1978; 85: 761–766] 614 Country: UK Setting: Queen Charlotte’s Hospital, London Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – No non-treatment control group assigned. Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: Enrolment to neonatal period No. of participants: No. randomised – 100 No. analysed – 88 Validity: Adequate randomisation – Yes (randomised list) Adequate allocation concealment – Not reported Blinding of clinician – Not reported Blinding of patient – Not reported Blinding of researcher – Not reported Type of analysis: Differences between treatments were examined with the chi-squared test |
Groups compared: 01. Ethanol vs Salbutamol 01.1 Ethanol + betamethasone vs Salbutamol + betamethasone Intervention details: A solution of 10% v/v ethanol in 5% dextrose in water was prepared. 50 ml ethanol to 450 ml 5% dextrose in water was administered intravenously at a rate of 15 ml/kg of body weight over 2 h. A maintenance infusion of 1.5 ml/kg/h was administered for a further 10 h. If contractions reoccurred after discontinuation then the treatment was repeated A solution of 4 mg salbutamol in 500 ml 5% dextrose in water was prepared. The solution was administered intravenously at 5 µg of salbutamol per minute. The infusion rate was increased by 5 µg every 10 min until either contractions had ceased, a maximum of rate of 50 µg/min was attained, or until unacceptable side effects occurred. The infusion was then maintained at the lowest rate to stop contractions for a total of 12 h. Treatment was continued for 24 h in women with ruptured membranes, if the cervix showed progressive dilatation or contraction had not stopped. If contractions recurred then the treatment was repeated At commencement of therapy 23 women in each group also received either 4 mg betamethasone intramuscularly or saline placebo intramuscularly. These injections were repeated 8-hourly for six doses Participants: Women experiencing symptoms of preterm labour. Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women admitted in labour between 27 and 35 weeks’ gestation, regardless of whether the membranes were intact or not, were eligible. Women were excluded if postponement of delivery was contraindicated or if the cervix was more than 4 cm dilated. Outcomes: Delay of delivery for at least 24 h and 48 h, delivery after 37 weeks’ gestation, mean number of days delivery postponed, number of infants surviving neonatal period |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: All women No. in intervention group (total no.) = 32 (46) No. in control group (total no.) = 32 (42) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: All women No. in intervention group (total no.) = 12 (46) No. in control group (total no.) = 7 (42) Women with intact membranes with cervical dilatation 2 cm or less No. in intervention group (total no.) = 4 (29) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (21) Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: All women No. in intervention group (total no.) = 20 (46) No. in control group (total no.) = 22 (42) Women with intact membranes with cervical dilatation 2 cm or less No. in intervention group (total no.) = 7 (29) No. in control group (total no.) = 8 (21) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not reported Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported. Incidence of adverse events: Neonatal mortality: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 10 (46) No. in control group (total no.) = 4 (42) Other outcomes: Days delivery postponed Intervention group (SD) = 20.4 (24) Control group (SD.) = 15.0 (24.5) Brief summary of findings: No significant difference was found between ethanol and salbutamol, as used in this study, on prevention of premature delivery (<37 weeks), incidence of birth within 24 or 48 h of intervention, although greater maternal side effects were found with salbutamol Authors’ conclusions: Neither treatment was terribly effective. Salbutamol acted more rapidly than ethanol but produced more cardiovascular side effects Comments: Small data set with uncertain randomisation/concealment of allocation No significant differences were shown between the two treatment groups in terms of parity, gestational age, cervical dilatation, membrane status or tocolytic index at the start of the study 13 women required more than one course of salbutamol, and 10 women received two or more courses of ethanol 23 women in the salbutamol group and 23 women in the ethanol group also received betamethasone. Participants receiving betamethasone had no outcome differences, so far as delay of labour was concerned 12% loss to follow-up |
|
Watring et al. [J Reprod Med 1976; 16(1): 35–38] 616 Country: USA Setting: Tripler General Hospital, San Fransisco Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 9 (out of a total of 18 women) Study design: Single blind RCT Length of follow-up: Enrolment to postneonatal period No. of participants: No. randomised – 35 No. analysed – 35 Validity: Adequate randomisation – No (Numbered cards, selected by disinterested third party) Adequate allocation concealment – No Blinding of clinician – No Blinding of patient – Yes Blinding of researcher – No Type of analysis: Differences between the two treatment groups were assessed using the chi-squared test |
Groups compared: Intravenous alcohol vs Control Intervention details: The study group received an intravenous infusion of 5% ethanol in 5% dextrose in water. A loading dose of 15ml/lb/2 h and a maintenance dose of 10% of the total loading dose per hour until contractions had ceased for at least 6 h was administered. If contractions were still present after four hours or if they returned within 24 h, 1.5 of the loading dose was given in 1 h and the maintenance dose was continued for a total of 12 h. On cessation of contractions complete bed rest was advised for an additional 24 h. Ambulation was begun in the third 24-h period. If contractions recurred the participant was given a repeat course of ethanol as above. If contractions had ceased for 72 h following the last ethanol infusion the participant was discharged home. If contractions recurred for the third time, no attempt was made to stop labour Contractions were monitored by an external tocodynamometer. A broad liver and renal function profile was taken of all participants in the ethanol group before and after treatment. Control participants were given conventional treatment (sedation, morphine, vasodilan, bed rest, demerol, and seconal) Participants: Pregnant women experiencing symptoms of preterm labour Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women with a viable pregnancy, between 24 and 36 weeks, experiencing labour symptoms (uterine contractions less than 10 min apart for 1 h or more), regular uttering contractions determined by palpation of tocodynamometer, greater than 50% effacement of the cervix with or without dilatation, and no complications such as bleeding, PROM or fever were eligible for inclusion. Women with a history of incompetent cervical os were excluded Outcomes: Delayed delivery for 72 h, time gained, gestation age at delivery, weight at delivery, and neonatal complications including neonatal death |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 8 (17) No. in control group (total no.) = 5 (18) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 11 (17) No. in control group (total no.) = 9 (18) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 6 (17) No. in control group (total no.) = 8 (18) Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 7 (17) No. in control group (total no.) = 8 (18) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 10 (17) No. in control group (total no.) = 9 (18) Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (17) No. in control group (total no.) = 1 (18) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Neonatal death No. in intervention group (total no.) = 4 (17) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (18) Respiratory distress syndrome No. in intervention group (total no.) = 4 (17) No. in control group (total no.) = 5 (18) Other outcomes: Mean weight (g) Intervention group = 2137.35 (981.39) Control group = 2568.78 (841.31) Brief summary of findings: No statistically significant difference was found between the two treatment groups on prevention of premature delivery, neonatal mortality or respiratory distress syndrome. The ethanol group was 14% smaller, in terms of weight, than the control group at birth Authors’ conclusions: The success rate of preventing premature delivery was not statistically different between the two treatment groups Comments: Quasi-RCT although authors state that trial is an RCT. Conventional treatment varies among participants. Data set is very small |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Crowther et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2002, Issue 4] 632 Title: Magnesium sulphate for preventing preterm birth in threatened preterm labour Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported. Preterm birth – No placebo control data for this outcome |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) The Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Groups trials register (May 2002), and The Cochrane Controlled Trials Register (2002, Issue 2) were searched for relevant articles Other sources None reported Search restrictions No search restrictions stated Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs and quasi-RCTs were eligible Population Women thought to be experiencing preterm labour Intervention Magnesium sulphate given as a tocolytic, administered intravenously or orally, compared with placebo, no placebo, or alternative tocolytic agent. Trials where magnesium sulphate was used together with an alternative tocolytic were excluded Outcomes Primary outcomes included: birth < 48 h after treatment, extremely preterm birth (< 28 weeks), serious infant outcomes (death, chronic lung disease, cerebroventricular haemorrhage, periventricular leukomalacia, or major sensorineural disability), and serious maternal outcomes (death, cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, or admission to intensive care unit) A number of infant and maternal secondary outcomes were also assessed Study selection: Three reviewers independently selected the primary studies for the review; any disagreements were resolved by discussion. There was no blinding of authorship Data extraction: Two reviewers independently extracted and double entered data from the primary studies; any disagreement was resolved by discussion Validity assessment: Criteria used Quality scores were assigned to each trial for concealment of allocation, use of placebo, completeness of follow-up and blinding of outcomes assessments. Details of scoring procedures reported Assessment Two reviewers independently assessed the methodological quality of the primary studies; any disagreement was resolved by consensus. Synthesis: Heterogeneity Chi-squared test and the I-squared test were used to assess statistical heterogeneity, where appropriate Methods Data were pooled using a fixed effects model; if significant statistical heterogeneity was found pooled estimates were re-calculated using a random effects model. Categorical data were presented as relative risks (RR) and continuous data were presented as weighted mean difference (WMD) |
No. of studies included: 21 RCTs and two quasi-RCTs (n = at least 2000 women) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 10 Adequate concealment of allocation – 9 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 0/2/0 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 0.82 (95% CI: 0.45–1.50) (1 study, n = 80) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 0.91 (95% CI: 0.75–1.11) (6 studies, n = 424) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Random effects] RR 0.85 (95% CI: 0.58–1.25) (11 studies, n = 881) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not reported Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 0.49 (95% CI: 0.18–1.32) (1 study, n = 165) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Total deaths (fetal, neonatal and infant) Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 2.82 (95% CI: 1.20–6.62) (7 studies, n = 727) Respiratory distress syndrome Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 1.12 (95% CI: 0.99–1.27) (5 studies, n = 437) Need for assisted ventilation Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 1.17 (95% CI: 0.61–2.24) (1 study, n = 165) Cerebroventricular haemorrhage (all grades) Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 1.07 (95% CI: 0.56–2.05) (5 studies, n = 495) Severe cerebroventricular haemorrhage (grades 3/4) or periventricular leukomalacia Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 1.39 (95% CI: 0.24–8.21) (3 studies, n = 296) Necrotising enterocolitis Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 1.19 (95% CI: 0.33–4.29) (3 studies, n = 289) Cerebral palsy Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 0.14 (95% CI: 0.01–2.60) (1 study, n = 73) Proven neonatal infection Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 0.36 (95% CI: 0.09–1.49) (1 study, n = 34) Maternal respiratory arrest Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 3.16 (95% CI: 0.13–76.30) (1 study, n = 156) Nausea Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 1.47 (95% CI: 0.75–2.90) (2 studies, n = 128) Vomiting Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 0.86 (95% CI: 0.23–3.19) (2 studies, n = 128) Hypotension Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 3.16 (95% CI: 0.13–76.30) (2 studies, n = 171) Tachycardia Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 0.23 (95% CI: 0.03–1.90) (2 studies, n = 133) Maternal side effects leading to discontinuation of treatment Magnesium sulphate vs all comparators: [Fixed effects] RR 0.63 (95% CI: 0.37–1.06) (10 studies, n = 838) Subgroup analyses: Magnesium sulphate vs trials with good allocation concealment: Total deaths (fetal, neonatal and infant) [Fixed effects] RR 1.84 (95% CI: 0.67–5.06) (4 studies, n = 454) Maternal side effects leading to discontinuation of treatment [Fixed effects] RR 9.16 (95% CI: 2.48–33.90) (5 studies, n = 457) No other significant outcome differences were shown when only trials with good treatment allocation procedures were selected Magnesium sulphate subgrouped by alternative tocolytic therapy: Total deaths (fetal, neonatal and infant) Betamimetics [Fixed effects] RR 1.19 (95% CI: 0.08–17.51) (2 studies, n = 166) Calcium channel blockers [Fixed effects] RR 0.19 (95% CI: 0.01–3.85) (1 study, n = 80) Prostaglandin inhibitors [Fixed effects] RR 0.98 (95% CI: 0.06–15.35) (1 study, n = 117) No alternative tocolytic agent [Fixed effects] RR 1.74 (95% CI: 0.63–4.77) (3 studies, n = 292) Maternal side effects leading to discontinuation of treatment Betamimetics [Fixed effects] RR 0.07 (95% CI: 0.02–0.31) (3 studies, n = 264) No other significant outcome differences where shown when magnesium sulphate was compared to alternative tocolytic agents Magnesium sulphate subgrouped by dose: Total deaths (fetal, neonatal and infant) Dose protocol 2 g/h or less [Fixed effects] RR 1.19 (95% CI: 0.08–17.51) (1 study, n = 35) Dose protocol > 2 g/h [Fixed effects] RR 3.07 (95% CI: 1.24–7.61) (6 studies, n = 692) No other significant outcome differences were shown when magnesium sulphate was grouped by dose. Brief summary of findings: When all studies were combined, no statistically significant between group differences were shown for risk of birth within 48 h of treatment, preterm birth < 37 weeks and very preterm birth < 34 weeks’ gestation. The risk of fetal/neonatal death was higher for infants exposed to magnesium sulphate, although no statistical difference was found when categorised by tocolytic agent, dose or quality. A non-significant reduction in risk of cerebral palsy was reported at follow-up at 18 months corrected age. No beneficial effect of magnesium sulphate was found for other neonatal or maternal outcomes Authors’ conclusions: Magnesium sulphate, given to women in threatened preterm labour, does not reduce the risk of preterm birth or the risk of developing serious health problems, and is associated with an increased risk of infant death. Any further trials should be of high quality and large enough to assess serious morbidity and mortality, as well as compare different dose regimens and provide data on neurodevelopmental status Comments: This was a well-conducted review and the authors appear to have taken appropriate steps to reduce possible biases Few of the primary studies included in the review were of high quality Where stated loss to follow-up ranged from 2% to 21% |
|
Crowther and Moore [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1998, Issue 1] 633 Title: Magnesium maintenance therapy for preventing preterm birth after threatened preterm labour Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 13 (out of a total of 25), based on preterm birth < 37 weeks’ gestation |
Search: Databases searched (dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group (August 2002) Other sources None reported Search restrictions No search restrictions reported Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Women who have had at least one episode of threatened preterm labour that settled without delivery Intervention Magnesium maintenance therapy administered by any route before delivery, compared with placebo, no treatment or an alternative maintenance tocolytic therapy Trials where magnesium sulphate was used in combination with an alternative tocolytic were excluded Outcomes Primary outcomes of the trial were preterm birth, perinatal mortality and any neurological disability at follow-up. Secondary outcomes included hospital re-admission for threatened preterm labour, neonatal morbidity, maternal side effects of therapy and cost Study selection: Two reviewers independently selected the studies; any discrepancies were resolved by discussion Data extraction: Two reviewers independently extracted data from the primary studies; any discrepancies were resolved by discussion. Unpublished data was sought from authors where possible Validity assessment: Criteria used Quality scores were assigned to each trial with regard to allocation concealment, completeness of follow-up, and blinding Assessment Two reviewers independently assessed the quality of the primary studies; any discrepancies were resolved by discussion Synthesis: Heterogeneity Where appropriate, statistical heterogeneity was assessed using chi-squared test and I-squared test Methods Studies were pooled using meta-analysis (fixed effects model). Dichotomous data were presented as relative risks (RR), and continuous data were presented as weighted mean difference (WMD). Sensitivity analyses were performed (quality of trials) |
No. of studies included: 3 RCTs (n = 303) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 1 Adequate concealment of allocation – 1 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 1/1/0 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment: RR 0.85 (95% CI: 0.47–1.51) (1 study, n = 50) Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic: RR 0.98 (95% CI: 0.56–1.72) (2 studies, n = 100) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment RR 1.57 (95% CI: 0.76–3.24) (1 study, n = 133) Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic RR 0.98 (95% CI: 0.53–1.80) (1 study, n = 137) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Death before discharge Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment: RR 5.00 (95% CI: 0.25–99.16) (1 study, n = 50) Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic RR 5.00 (95% CI: 0.25–99.16) (1 study, n = 50) Maternal re-admission for threatened preterm labour Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment: RR 0.79 (95% CI: 0.45–1.38) (1 study, n = 50) Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic: RR 1.01 (95% CI: 0.63–1.65) (2 studies, n = 100) Respiratory distress syndrome Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment: RR 3.00 (95% CI: 0.13–70.30) (1 study, n = 50) Periventricular haemorrhage Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment: RR 3.00 (95% CI: 0.13–70.30) (1 study, n = 50) Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic: RR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.07–15.12) (1 study, n = 50) Any maternal side effects Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment: RR 1.88 (95% CI: 1.11–3.20) (1 study, n = 133) Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic: RR 0.69 (95% CI: 0.52–0.91) (3 studies, n = 237) Nausea Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment: RR 0.73 (95% CI: 0.30–1.81) (1 study, n = 133) Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic: RR 0.94 (95% CI: 0.50–1.75) (3 studies, n = 237) Vomiting Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment: RR 0.42 (95% CI: 0.08–2.08) (1 study, n = 133) Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic: RR 0.92 (95% CI: 0.39–2.17) (3 studies, n = 237) Diarrhoea Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment: RR 7.67 (95% CI: 2.41–24.41) (1 study, n = 133) Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic: RR 10.67 (95% CI: 3.35–33.99) (3 studies, n = 237) Palpitations/tachycardiaMagnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment: RR 1.05 (95% CI: 0.15–7.21) (1 study, n = 133) Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic: RR 0.22 (95% CI: 0.11–0.44) (3 studies, n = 237) Discontinued therapy Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic: RR 1.11 (95% CI: 0.29–4.23) (2 studies, n = 100) Neonatal length of stay (days) Magnesium maintenance vs placebo/no treatment: WMD 1.18 (95% CI: – 0.46 to 2.82) (2 studies, n = 180) Magnesium maintenance vs alternative tocolytic: WMD – 2.63 (95% CI: – 5.70 to 0.43) (2 studies, n = 180) Brief summary of findings: No statistically significant differences were shown between treatment groups in risk of preterm birth < 37 weeks’ gestation, stillbirth, death before discharge, or admission to neonatal intensive care unit. Women receiving magnesium sulphate were more likely to experience side effects than those receiving placebo/no treatment and more likely to report diarrhoea but less likely to report palpitations/tachycardia than those women on alternative maintenance tocolytic therapy or placebo/no treatment Authors’ conclusions: There is not enough evidence to show any difference between magnesium maintenance therapy and placebo or alternative tocolytic agents after threatened preterm labour Comments: This was a well-conducted review and the authors appear to have taken appropriate steps to reduce possible biases The authors note that the trials were too small to exclude either important benefits or harms from magnesium maintenance therapy Loss to follow-up was less than 20% in all included trials Only one of the trials was rated of reasonable quality |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Duckitt and Thornton [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2002, Issue 3] 639 Title: Nitric oxide donors for the treatment of preterm labour Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Not reported |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Register (March 2002), and the Cochrane Controlled Trials Register (2002, Issue 1) were searched for relevant articles Other sources None reported Search restrictions No search restrictions included Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs and quasi-RCTs were eligible. Studies where less than 20% of data was unavailable were excluded Population Pregnant women assessed as being in preterm labour and considered suitable for tocolysis. Preterm labour was defined as uterine contractions, in the presence or absence of ruptured membranes, with or without cervical dilatation Intervention Nitric oxide donors compared with placebo, no treatment or any other tocolytic agent Outcomes A number of maternal and infant outcomes were assessed including: prolongation of pregnancy greater than 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, 7 days and 14 days, delivery before 37, 34, 32 and 28 weeks’ gestation, adverse drug reactions, serious maternal outcomes, birthweight, mortality, delivery for presumed fetal distress, intraventricular haemorrhage, respiratory distress syndrome, chronic lung disease, long-term neurological development and use of health services Study selection: Two reviewers independently selected studies for inclusion; any disagreements were resolved by discussion Data extraction: Two reviewers independently extracted data form the primary studies; any disagreement was resolved by discussion Validity assessment: Criteria used Methodological quality was categorised as low, moderate or high risk of bias depending on randomisation methods, allocation concealment, blinding and use of placebo Assessment Two reviewers independently assessed the methodological quality of the primary studies; any disagreement was resolved by discussion Synthesis: Heterogeneity The chi-squared test and I-squared test were used to assess heterogeneity Methods Results are presented using relative risks for categorical data and weighted mean difference for continuous variables Subgroup analysis was planned for treatment commenced before 24 weeks’ gestation, between 24 and 34 weeks’ gestation, after 34 weeks’ gestation, treatment commenced with cervical dilatation < 3 cm, equal to or > 3 cm, treatment commenced before membrane rupture and after membrane rupture, single and multiple gestations, and nontransdermal and transdermal administration |
No. of studies included: 5 RCTs (n = 466) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 2 Adequate concealment of allocation – 5 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 1/1/1 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Nitric oxide vs any other tocolytic agent (Fixed effects) RR 0.75 (95% CI: 0.52–1.10) (3 studies, n = 365); I2 = 66.8%, p = 0.08 Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Nitric oxide vs any other tocolytic agent (Fixed effects) RR 0.69 (95% CI: 0.53–0.88) (3 studies, n = 391) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Nitric oxide vs any other tocolytic agent (Fixed effects) RR 0.50 (95% CI: 0.05–4.86) (1 study, n = 26) Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Nitric oxide vs any other tocolytic agent (Fixed effects) RR 0.73 (95% CI: 0.27–1.98) (1 study, n = 132) Nitric oxide vs placebo/no treatment (Fixed effects) RR 0.56 (95% CI: 0.27–1.19) (1 study, n = 33) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Nitric oxide vs any other tocolytic agent (Fixed effects) RR 1.24 (95% CI: 0.80–1.91) (3 studies, n = 391) Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Adverse drug reaction Nitric oxide vs any other tocolytic agent Headache (Fixed effects) RR 4.14 (95% CI: 2.44–7.04) (4 studies, n = 379) Dizziness (Fixed effects) RR 2.34 (95% CI: 0.76–6.89) (2 studies, n = 221) Flushing (Fixed effects) RR 0.15 (95% CI: 0.04–0.54) (1 study, n = 30) Palpitations (Fixed effects) RR 0.09 (95% CI: 0.02–0.32) (3 studies, n = 353) Hypotension (Fixed effects) RR 7.94 (95% CI: 0.46–135.65) (1 study, n = 30) Shortness of breath (Fixed effects) RR 0.09 (95% CI: 0.02–0.46) (1 study, n = 217) Nausea (Fixed effects) RR 0.38 (95% CI: 0.09–1.55) (2 studies, n = 227) Tachycardia (Fixed effects) RR 0.03 (95% CI: 0.01–0.10) (2 studies, n = 323) Chest pain/tightness (Fixed effects) RR 0.12 (95% CI: 0.02–0.64) (2 studies, n = 323) Nitric oxide vs placebo/no treatment (Fixed effects) RR 2.07 (95% CI: 0.92–4.64) (1 study, n = 33) Neonatal death unrelated to congenital abnormalities Nitric oxide vs placebo/no treatment (Fixed effects) RR 0.94 (95% CI: 0.06–13.82) (1 study, n = 33 Birthweight Nitric oxide vs placebo/no treatment (Fixed effects) WMD 327.00 (95% CI: – 272.13 to 926.13) (1 study, n = 33 Brief summary of findings: Nitric oxide donors did not delay delivery or improve neonatal outcomes when compared with placebo, no treatment or alternative tocolytic agents. A reduction in the number of deliveries less than 37 weeks was shown when compared with other tocolytic agents, but no statistical difference between the groups was shown for number of deliveries less than 34 weeks’ gestation. Side effects, other than headaches, were reduced in women receiving nitric oxide donors rather than other tocolytic agents Authors’ conclusions: There is currently insufficient evidence to support the routine use of nitric oxide donors in the treatment of threatened preterm labour Comments: This was a well-conducted review with clearly reported methodology and details given of the included studies Nitroglycerine was the nitric oxide donor used in all included trials Other tocolytic agents assessed: ritodrine, albuterol, and magnesium sulphate |
|
Bisits et al. [Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004; 191: 683–690] 636 Country: Australia Setting: Four tertiary obstetric care centres; two in South East Asia and two in Australia Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Not estimable Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: Randomisation to 18 months of age No. of participants: No. randomised – 238 No. analysed – 238 Validity: Adequate randomisation – Yes (random number sequence) Adequate allocation concealment – Yes (sealed opaque envelopes) Blinding of clinician – Not reported Blinding of patient – No Blinding of researcher – Not reported Type of analysis: Data were analysed by using time to delivery or with the use of rescue treatment; Kaplan–Meier survival curves were plotted. All survival curves were compared using log rank test and risk ratios with Mantel–Haenzel assessment for effect from different centres. Multivariant techniques were used to adjust for baseline differences. Subgroup analysis for women with ruptured membranes, intact membranes and closed cervices were performed Intention to treat analysis was used Sample size: It was calculated that 120 women were needed in each arm of the trial to show a median difference of 10 days in time to delivery between GTN and beta-sympathomimetic groups (80% power and two-tailed alpha 0.5) |
Groups compared: Glyceryl trinitrate (GTN) patches vs beta-sympathomimetics β2 agonists included were salbutamol and ritodrine Intervention details: GTN: Participants received one 50-g Transiderm Nitro 50 patch; patches were placed on the skin of the anterior chest wall. Steroids were administered according to local protocols. If contractions did not settle within 1 h, a second patch was administered. If contractions settled, the patch (or patches) was left on for 21 h and then removed. If contractions did not settle after 2 h of GTN treatment, the patches were removed and beta-sympathomimetic treatment was commenced Beta-sympathomimetic administration not reported Participants: Pregnant women experiencing symptoms of preterm labour Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women experiencing at least two contractions in 10 min with a singleton pregnancy between 24 and 35 weeks’ gestation, with either a positive test for cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin or the presence of ruptured membranes were eligible for inclusion. Women with multiple pregnancies, chorioamnionitis, cervical dilatation of 5 cm or more, a history of hypotension or a negative fetal fibronectin test in the presence of intact membranes were excluded Outcomes: Primary outcomes included: number of days from randomisation until delivery, delivery at 24 h, 48 h, 7 days, and before 37 weeks’ gestation. A number of maternal and infant secondary outcomes were sought, including infant mortality and admission to neonatal intensive care unit |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 71 (121) No. in control group (total no.) = 68 (117) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 35 (121) No. in control group (total no.) = 27 (117) Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 45 (121) No. in control group (total no.) = 34 (117) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 57 (121) No. in control group (total no.) = 48 (117) Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 1 (121) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (117) Incidence of adverse events: Chronic lung disease No. in intervention group (total no.) = 9 (121) No. in control group (total no.) = 9 (117) Necrotising enterocolitis No. in intervention group (total no.) = 10 (121) No. in control group (total no.) = 10 (117) Patent ductus arteriosus No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (121) No. in control group (total no.) = 11 (117) Intracerebral haemorrhage No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (121) No. in control group (total no.) = 8 (117) GTN was reported to be associated with more maternal headaches but lower incidence of cardiovascular side effects; no further details provided Subgroup analysis: The authors reported that no statistically significant differences between the treatment groups were found for time to delivery in women with ruptured membranes, intact membranes, and closed cervices Brief summary of findings: Survival curves and log rank tests showed no statistically significant differences between the two treatment groups for time to delivery or prolongation of pregnancy. A higher risk of earlier delivery was found within the GTN group, although this was not statistically significant. No statistically significant differences between the two treatment groups were found for incidence of chronic lung disease or necrotising enterocolitis, but a higher proportion of infants with patent ductus arteriosus and intracranial haemorrhage were found in the beta-sympathomimetic group Authors’ conclusions: GTN is a less efficacious tocolytic than beta-sympathomimetics Comments: 40 women from the GTN group required rescue tocolysis after unsuccessful application of a second patch |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Papatsonis et al [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 3] 586 Title: Oxytocin receptor antagonists for inhibiting preterm labour Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – 128 (out of 255 in total), based on preterm birth less than 37 weeks |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group trials register (Sept. 2004), Central (Issue 3, 2004), Medline (1966 to June 2004), Embase (1988 to June 2004) Other sources Experts contacted Search restrictions None Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Women in labour between 26 and 36 weeks’ gestation and considered suitable for tocolysis Intervention Oxytocin receptor antagonists administered as a tocolytic by any route vs placebo, no treatment or alternative tocolytic therapy Outcomes Predefined clinical outcome measures relating to the prolongation of pregnancy, infant morbidity and mortality and maternal side effects Study selection: Two authors independently considered trials for inclusion. Differences were resolved by consensus Data extraction: Two authors independently extracted data. Differences were resolved by consensus. Additional information was sought from trial authors and if there was consensus about theses data they were included in the analysis. If there was no consensus or if data were incomplete the original authors were asked for additional data or comments Validity assessment: Criteria used Quality ratings were applied to four criteria: blinding of randomisation, blinding of intervention, completeness of follow-up and blinding of outcome assessment Assessment: This was carried out independently by two authors and disagreements were resolved by consensus Synthesis: Heterogeneity Heterogeneity was assessed by visual inspection of the outcomes table and by using two statistics (H and I2 test) of heterogeneity. One trial was identified as an outlier; the authors suggest that this may be because more women with a multiple pregnancy were randomised to the atosiban group Methods Meta-analysis using the fixed effects model. Where heterogeneity was found, pooled estimates were re-calculated using a random effects model. The authors report that use of a random effects model for these outcomes did not alter their interpretation of the results. Due to insufficient data, planned subgroup analyses were not undertaken |
No. of studies included: Six RCTs Two trials compared the oxytocin receptor antagonist atosiban with placebo (n = 651) and four trials compared atosiban with betamimetic agents (n = 1044) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation –6 Adequate concealment of allocation –6 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – blinding of intervention in five trials; blinding of outcome assessment not known Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Atosiban vs placebo: < 28 weeks’ gestation (Fixed effects) RR 2.25 (95% CI: 0.80–6.35) (1 study, n = 77) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Atosiban vs placebo: (Fixed effects) RR 1.17 (95% CI: 0.99–1.37) (1 study, n = 501) Atosiban vs betamimetics (Fixed effects) RR 0.90 (95% CI: 0.71–1.13) (1 study, n = 244) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Atosiban vs placebo: (Fixed effects) RR 2.50 (95% CI: 0.51–12.35) (1 study, n = 112) Atosiban vs betamimetics (Fixed effects) RR 0.98 (95% CI: 0.68–1.41) (4 studies, n = 1033) Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Atosiban vs betamimetics: (Fixed effects) RR 0.91 (95% CI: 0.69–1.20) (3 studies, n = 731) Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Atosiban vs placebo: (Fixed effects) RR 1.09 (95% CI: 0.89–1.34) (1 study, n = 560) Atosiban vs betamimetics: (Fixed effects) RR 1.03 (95% CI: 0.84–1.26) (3 studies, n = 836) Incidence of perinatal mortality: Perinatal death Atosiban vs placebo: (Fixed effects) RR 2.25 (95% CI: 0.79–6.40) (1 study, n = 583) Atosiban vs betamimetics: (Fixed effects) RR 0.66 (95% CI: 0.24–1.83) (3 studies, n = 836). Heterogeneity: χ2 = 4.97, df = 2, p = 0.08; I2= 59.7%. Fetal death Atosiban vs placebo: (Fixed effects) RR 1.02 (95% CI: 0.21–5.03) (2 studies, n = 585) Atosiban vs betamimetics: (Fixed effects) RR 0.55 (95% CI: 0.05–6.04) (3 studies, n = 836) Neonatal death (up to 28 days) Atosiban vs placebo: (Fixed effects) RR 4.10 (95% CI: 0.88–19.13) (I study, n = 583) Atosiban vs betamimetics: (Fixed effects) RR 0.70 (95% CI: 0.27–1.81) (4 studies, n = 1130) Infant death (up to 12 months) Atosiban vs placebo: (Fixed effects) RR 6.15 (95% CI: 1.39–27.22) (1 study, n = 583) Incidence of adverse events: Maternal adverse drug reaction Atosiban vs betamimetics: (Fixed effects) RR 0.86 (95% CI: 0.72–1.03) (2 studies, n = 486) Maternal drug reaction requiring cessation of treatment Atosiban vs placebo: (Fixed effects) RR 4.02 (95% CI: 2.05–7.85) (2 studies, n = 613) Atosiban vs betamimetics: (Fixed effects) RR 0.04 (95% CI: 0.02–0.11) (4 studies, n = 1034) Respiratory distress syndrome Atosiban vs placebo: (Fixed effects) RR 1.28 (95% CI: 0.93–1.76) (2 studies, n = 689) Atosiban vs betamimetics: (Fixed effects) RR 0.99 (95% CI: 0.76–1.29) (4 studies, n = 1129). Heterogeneity: χ2 = 6.69, df = 2, p = 0.08; I2 = 55.2% Intraventricular haemorrhage Atosiban vs placebo: (Fixed effects) RR 0.21 (95% CI: 0.02–1.76) (1 study, n = 575) Necrotising enterocolitis Atosiban vs placebo: (Fixed effects) RR 0.21 (95% CI: 0.02–1.76) (1 study, n = 575) Atosiban vs betamimetics: (Fixed effects) RR 0.48 (95% CI: 0.12–1.98) (2 studies, n = 576) Hypoglycaemia Atosiban vs placebo: (Fixed effects) RR 0.75 (95% CI: 0.18–3.20) (1 study, n = 114) Atosiban vs betamimetics: (Fixed effects) RR 1.07 (95% CI: 0.63–1.82) (3 studies, n = 837) Patent ductus arteriosus Atosiban vs placebo: (Fixed effects) RR 1.28 (95% CI: 0.68–2.40) (2 studies, n = 689) Atosiban vs betamimetics: (Fixed effects) RR 1.02 (95% CI: 0.58–1.79) (4 studies, n = 1129) Neonatal sepsis Atosiban vs betamimetics: (Fixed effects) RR 0.91 (95% CI: 0.56–1.46) (4 studies, n = 1129) Brief summary of findings: Compared with placebo, atosiban did not reduce the incidence of preterm birth or improve neonatal outcomes. In one trial (583 infants) atosiban was associated with an increase in infant deaths at 12 months of age compared with placebo: RR 6.15 (95% CI: 1.39–27.22). Use of atosiban resulted in lower infant birthweight and more maternal adverse drug reactions Authors’ conclusions: This review failed to demonstrate the superiority of atosiban over betamimetics or placebo in terms of tocolytic efficacy or infant outcomes, although atosiban results in fewer maternal side effects than betamimetics. The finding of an increase in infant deaths in one placebo-controlled trial warrants caution Further RCTs of tocolytic therapy, with a placebo arm and long-term infant follow-up, are needed Comments: This was a well-conducted review and the authors appear to have taken appropriate steps to reduce bias The authors note methodological concern for one of the trials; an imbalance in the randomisation of women before 26 weeks’ gestation between atosiban and placebo groups was observed. The authors indicate this might explain results found for infant deaths. They also note that in both trials comparing atosiban with placebo the high level of rescue tocolysis used may have confounded the estimation of true effects of atosiban. Three trials identified for possible inclusion are awaiting classification pending further information from the authors |
Improving the health of the neonate
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Crowley [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1996, Issue 1] 24 Title: Prophylactic corticosteroids for preterm birth Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not applicable Preterm birth – Not applicable |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) The Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Register (search date not reported) were searched for relevant articles Other sources No other sources reported Search restrictions No search restrictions stipulated Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Women expected to deliver preterm as a result of spontaneous labour, PROM, or elective delivery Intervention Antenatal administration of corticosteroids capable of crossing the placenta (betamethasone, dexamethasone, or hydrocortisone) compared with placebo/no treatment given to women before expected preterm delivery (elective or following spontaneous labour). Trials that tested the effect of corticosteroids with other co-interventions were excluded Outcomes Primary outcomes included respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), perinatal and neonatal mortality and morbidity, and long-term neurological abnormality Study selection: Eligibility was assessed by one reviewer Data extraction: Data were extracted by one reviewer Validity assessment: Criteria used Elimination of selection bias, performance bias, exclusion bias and detection bias were assessed in each trial Assessment Trial quality was assessed by one reviewer Synthesis: Heterogeneity Chi-squared test and I-squared statistic were used to assess statistical heterogeneity Methods A weighted estimate of the treatment effect was calculated using Peto odds ratio (OR). The effect of respiratory distress syndrome in a number of infant subgroups was explored |
No. of studies included: 18 trials (n = over 3700 infants) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 6 Adequate concealment of allocation – 8 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 1/12/0 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: NA Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: NA Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: NA Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Respiratory distress syndrome All babies: OR 0.53 (95% CI: 0.44–0.63) (18 studies, n = 3735) Babies delivered at < 28 weeks: OR 0.64 (95% CI: 0.16–2.50) (2 studies, n = 48) Babies delivered at < 30 weeks: OR 0.48 (95% CI: 0.30–0.77) (7 studies, n = 349) Babies born at < 32 weeks: OR 0.33 (95% CI: 0.21–0.50) (7 studies, n = 393) Babies delivered at < 34 weeks: OR 0.36 (95% CI: 0.27–0.48) (7 studies, n = 1048) Babies delivered at > 34 weeks: OR 0.65 (95% CI: 0.33–1.29) (8 studies, n = 719) Babies born <24 h after first dose: OR 0.70 (95% CI: 0.43–1.16) (5 studies, n = 335) Babies born <48 h after first dose: OR 0.34 (95% CI: 0.08–1.47) (1 study, n = 42) Babies born 24 h to 7 days after first dose: OR 0.38 (95% CI: 0.25–0.57) (4 studies, n = 728) Babies delivered > 7 days after first dose: OR 0.41 (95% CI: 0.18–0.98) (3 studies, n = 265) Dexamethasone: OR 0.56 (95% CI: 0.43–0.73) (5 studies, n = 1400) Betamethasone: OR 0.49 (95% CI: 0.39–0.63) (11 studies, n = 2176) Hydrocortisone: OR 0.69 (95% CI: 0.32–1.47) (2 studies, 172) Male infants: OR 0.43 (95% CI: 0.29–0.64) (3 studies, n = 627) Female infants: OR 0.36 (95% CI: 0.23–0.57) (3 studies, n = 555) Twins/triplets: OR 0.72 (95% CI: 0.31–1.68) (2 studies, n = 140) Neonatal death All babies: OR 0.60 (95% CI: 0.48–0.75) (14 studies, n = 3517) Treated before 1980: OR 0.51 (95% CI: 0.38–0.68) (8 studies, n = 2133) Treated after 1980: OR 0.78 (95% CI: 0.54–1.12) (6 studies, n = 1384) Stillbirth All babies: OR 0.83 995% CI: 0.57–1.22) (12 studies, n = 3306) Women with hypertension: OR 3.75 (95% CI: 1.24–11.30) (1 study, n = 90; 3 studies unestimable) Surfactant use OR 0.41 (95% CI: 0.18–0.89) (1 study, n = 189) Chronic lung disease OR 1.57 (95% CI: 0.87–2.84) (3 studies, n = 411) Intraventricular haemorrhage Diagnosed by ultrasound OR 0.48 (95% CI: 0.32–0.72) (4 studies, n = 596) Diagnosed at autopsy OR 0.29 (95% CI: 0.14–0.61) (4 studies, n = 863) Necrotising enterocolitis OR 0.59 (95% CI: 0.32–1.09) (4 studies, n = 1154) Fetal and neonatal infection All babies: OR 0.82 (95% CI: 0.57–1.19) (15 studies, n = 2675) After PROM > 24 h: OR 2.31 (95% CI: 0.77–6.99) (2 studies, n = 163) With PROM at trial entry: OR 1.11 (95% CI: 0.50–2.43) (4 studies, n = 329) Maternal infection All mothers: OR 1.31 (95% CI: 0.99–1.73) (11 studies, n = 2109) After PROM > 24 h: OR 6.04 (95% CI: 1.47–24.71) (1 study, n = 42) With PROM at trial entry: OR 1.26 (95% CI: 0.69–2.28) (3 studies, n = 320) Long-term neurological abnormality OR 0.62 (95% CI: 0.36–1.08) (3 studies, n = 778) Brief summary of findings: Antenatal corticosteroids reduce the incidence of respiratory distress syndrome across a variety of gestational ages compared to placebo/no treatment; greatest benefits reported for babies delivered < 28 weeks to < 34 weeks’ gestation. Beneficial effect of antenatal corticosteroids appears greatest after 24 h. Administration of antenatal corticosteroids to women expected to give birth prematurely also reduces the risk of neonatal mortality compared to placebo/no treatment Authors’ conclusions: Corticosteroids given before preterm delivery are effective in preventing respiratory distress syndrome and neonatal mortality Comments: Processes undertaken for the selection of papers, data extraction and assessment of trial quality increase the possibility of reviewer error or bias Although the inclusion criteria states that only RCTs were eligible for inclusion in the review, one quasi-randomised trial has also been included Most trials included multiple gestations |
|
Crowther and Harding [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 2] 661 Title: Repeat doses of prenatal corticosteroids for women at risk of preterm birth for preventing neonatal respiratory disease Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – No untreated control group |
Search: Databases searched (Search dates) The Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group trials register (January 2003), the Cochrane Controlled Trials Register (Issue 1, 2003), MEDLINE (1965 to January 2003), EMBASE (1988 to January 2003), and Current Contents (1997 to January 2003) Other sources Bibliographic references from all retrieved articles were also searched. In addition, the authors contacted experts and searched conference abstracts Search restrictions No search restrictions stated Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs Population Pregnant women at risk of preterm birth who have already received a single course of prenatal corticosteroids seven or more days previously Intervention Repeat dose(s) of prenatal corticosteroids vs single dose of prenatal corticosteroids. Eligible comparators included: placebo or no placebo. Trials in which the fetus receives corticosteroids directly were excluded Outcomes Primary outcomes included: incidence of respiratory distress syndrome, severity of lung disease, birthweight, fetal/neonatal/infant mortality, chronic lung disease, periventricular haemorrhage, periventricular leukomalacia, disability at childhood follow-up, chorioamnionitis, and puerperal sepsis A number of secondary infant and maternal outcomes were also sought including measures of effectiveness, complications, satisfaction with care and health service use Study selection: The authors do not state how studies were selected for inclusion or how many reviewers performed the selection Data extraction: Data extraction was completed independently by two reviewers. Data were extracted from the trials on an intention to treat basis Validity assessment: Criteria used Studies were assessed in terms of randomisation, allocation concealment, blinding, use of placebo and completeness of follow-up, and assigned a score. Details of the scoring procedure were described Assessment The authors independently assessed the methodological quality of the primary studies; any disagreements were resolved by discussion. Reviewers were not blinded to authorship Synthesis: Heterogeneity Chi-squared test and I-squared test were used to assess statistical heterogeneity. Sensitivity analysis, using trial quality, was performed Methods Where appropriate studies were combined in a meta-analysis using a fixed effects model. Categorical data were presented as relative risks (RR) and continuous data were presented as weighted mean difference (WMD). If statistical heterogeneity was found, data were recalculated using a random effects model. Subgroup analyses (singletons/multiple gestation; presence or absence of ruptured membranes; type of corticosteroid given; dosage and method of administration) were planned |
No. of studies included: Three RCTs (n = 551) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 3 Adequate concealment of allocation – 3 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 3/3/3 Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: [Fixed effect] RR 1.09 (95% CI: 0.96–1.25) (2 studies, n = 500) Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: [Fixed effect] RR 1.26 (95% CI: 0.66–2.41) (2 studies, n = 49) Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Respiratory distress syndrome [Fixed effect] RR 0.96 (95% CI: 0.72–1.26) (2 studies, n = 516) Severity of lung disease [Fixed effect] RR 0.64 (95% CI: 0.44–0.93) (1 study, n = 500) Fetal, neonatal, or infant death [Fixed effect] RR 0.53 (95% CI: 0.18–1.57) (2 studies, n = 518) Chronic lung disease [Fixed effect] RR 1.01 (95% CI: 0.63–1.65) (2 studies, n = 516) Periventricular haemorrhage [Fixed effect] RR 1.15 (95% CI: 0.70–1.90) (1 study, n = 500) Periventricular haemorrhage (Grades 3/4) [Fixed effect] RR 2.50 (95% CI: 0.76–8.22) (2 studies, n = 516) Periventricular leukomalacia [Fixed effect] RR 0.64 (95% CI: 0.11–3.80) (2 studies, n = 516) Chorioamnionitis [Fixed effect] RR 1.35 (95% CI: 0.95–1.92) (2 studies, n = 497) Puerperal sepsis [Fixed effect] RR 0.88 (95% CI: 0.42–1.83) (2 studies, n = 497) Preterm birth < 28 weeks’ gestation [Fixed effect] RR 1.08 (95% CI: 0.67–1.74) (1 study, n = 488) Necrotising enterocolitis [Fixed effect] RR 1.07 (95% CI: 0.44–2.58) (2 studies, n = 516) Infection while in neonatal intensive care unit [Fixed effect] RR 1.09 (95% CI: 0.52–2.30) (2 studies, n = 516) Patent ductus arteriosus requiring treatment [Fixed effect] RR 1.56 (95% CI: 0.17–13.87) (1 study, n = 16) Retinopathy of prematurity [Fixed effect] RR 0.78 (95% CI: 0.22–2.74) (1 study, n = 16) Use of postnatal steroids [Fixed effect] RR 1.13 (95% CI: 0.61–2.11) (1 study, n = 500) Postpartum haemorrhage [Fixed effect] RR 0.60 (95% CI: 0.33–1.07) (1 study, n = 485) Composite serious morbidity [Fixed effect] RR 0.80 (95% CI: 0.60–1.07) (2 studies, n = 518) Other outcomes: Birthweight [Fixed effect] WMD – 137.67 (95% CI: – 281.54 to 6.20) (2 studies, n = 539) Length of postnatal hospitalisation [Fixed effect] WMD 0.00 (95% CI: – 0.22 to 0.22) (1 study, n = 485) Duration of oxygen supplementation (days) [Fixed effect] WMD 3.30 (95% CI: – 2.31 to 8.91) (1 study, n = 37) Duration of respiratory support (days) [Fixed effect] WMD 0.30 (95% CI: – 0.90 to 1.50) (1 study, n = 37) Use of surfactant [Fixed effect] RR 0.65 (95% CI: 0.46–0.92) (2 studies, n = 537) Brief summary of findings: A reduced risk of severe lung disease was shown for repeat dose corticosteroid administration compared to single dose, and fewer infants in the repeat-dose group received surfactant compared to the single-dose group. No statistically significant differences between the treatment groups were shown on the other infant and maternal outcomes Authors’ conclusions: Repeat dose(s) of prenatal corticosteroids may reduce the severity of neonatal lung disease. However, there is insufficient evidence regarding risks and benefits to recommend the use of repeat dose prenatal corticosteroids for women at risk of preterm birth for the prevention of neonatal respiratory disease. Further trials are needed Comments: Procedures undertaken for selection of the primary studies were not reported Datasets appeared to include both singleton and multiple pregnancies |
| Study details and design | Description of methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Crowther et al. [JAMA 2003; 290(20): 2669–2676] 668 Country: Australia and New Zealand Setting: 16 tertiary hospitals with neonatal intensive care units Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Not reported Study design: RCT Length of follow-up: From enrolment with follow-up of surviving children at 2 years No. of participants: No. randomised – 1062 (women) No. analysed – 1062 (women), 1047 (infants; 99%) Validity: Adequate randomisation – Yes (computer-generated random numbers) Adequate allocation concealment – Yes (study number placed on masked treatment packs) Blinding of clinician – Yes Blinding of patient – Yes Blinding of researcher – Yes Type of analysis: Baseline variables were included as confounders if there was an imbalance between treatment groups. Binary outcomes are presented as RRs with 95% CIs; RRs were calculated using log binomial regression. Robust variance estimation was used to account for clustering of infants within mothers Intention to treat analysis was undertaken for women randomised to the trial but not for infants Sample size: To detect a 50% reduction in risk of cerebral palsy at 2 years in survivors from 10% to 5%, with 80% probability at an alpha level of 0.5, 848 children were needed. This number was adjusted upward to 1250 infants to account for a predicted 20% mortality rate and the effect of non-independence of observations from multiple births |
Groups compared: Magnesium sulphate vs placebo (isotonic sodium chloride solution) Intervention details: Each pack contained an infusion bag of 60 ml of either a 0.5-g/ml solution of magnesium sulphate or isotonic sodium chloride solution (0.9%). Women were given a loading infusion of 8 ml [4 g (16 mmol) of magnesium sulphate or isotonic sodium chloride solution] for 20 min followed by a maintenance infusion of 2 ml/h until birth (if occurred within 24 h) or up to 24 h Pulse rate, blood pressure and respiratory rates were monitored throughout the infusion and any maternal adverse effects recorded. Loading or maintenance infusions were stopped if the respiratory rate decreased more than 4/min or diastolic blood pressure decreased more than 15 mmHg below baseline level. The infusion could be resumed once respiratory rate and blood pressure had returned to baseline levels. Magnesium levels were not measured. The care that women and infants received was otherwise according to standard practice at each centre Participants: Women with planned or expected very preterm birth within 24 h Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women with single or multiple fetuses at < 30 weeks’ gestation were eligible for inclusion. No lower limit on gestational age at enrolment was enforced. Women were excluded if they had received magnesium sulphate therapy in current pregnancy, or if there were any contraindications to magnesium sulphate Outcomes: Primary: Total paediatric mortality, cerebral palsy in survivors, and combined death or cerebral palsy Secondary: Major maternal adverse effects (e.g. death, cardiac arrest, haemorrhage or respiratory arrest), minor maternal adverse effects (e.g. nausea, sleepiness, dizziness, discomfort, sweating, blurred vision, mouth dryness and warmth over body), infant intraventricular haemorrhage, cystic periventricular leukomalacia, chronic lung disease, necrotising enterocolitis, mechanical ventilation, neurosensory disability, blindness, deafness, delayed development, and gross motor dysfunction |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not applicable Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Stillbirths No. in intervention group (total no.) = 9 (629) No. in control group (total no.) = 11 (626) Infant deaths born live before initial discharge No. in intervention group (total no.) = 76 (629) No. in control group (total no.) = 92 (626) Post discharge deaths (up to corrected age of 2 yrs) No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (629) No. in control group (total no.) = 4 (626) Total deaths No. in intervention group (total no.) = 87 (629) No. in control group (total no.) = 107 (626) Cerebral palsy No. in intervention group (total no.) = 36 (629) No. in control group (total no.) = 42 (626) Periventricular leukomalacia No. in intervention group (total no.) = 22 (620) No. in control group (total no.) = 21 (615) Intraventricular haemorrhage No. in intervention group (total no.) = 165 (620) No. in control group (total no.) = 148 (615) Primary postpartum haemorrhage No. in intervention group (total no.) = 86 (629) No. in control group (total no.) = 99 (626) Major postpartum haemorrhage No. in intervention group (total no.) = 26 (629) No. in control group (total no.) = 25 (626) Clinical and self-assessed maternal adverse effects of infusion stopped due to adverse effects No. in intervention group (total no.) = 78 (629) No. in control group (total no.) = 28 (626) Substantial gross motor dysfunction No. in intervention group (total no.) = 18 (629) No. in control group (total no.) = 34 (626) Brief summary of findings: A reduction in number of stillbirths, deaths before initial discharge home, post-discharge deaths and total paediatric mortality was observed in the magnesium sulphate group, although no statistically significant differences were found. The incidence of cerebral palsy was less frequent in the magnesium sulphate group compared to placebo, but again this difference was not statistically significant. A significant reduction in substantial gross motor dysfunction was found in the magnesium sulphate group. No statistically significant differences were shown for other neurosensory outcomes assessed at a corrected age of 2 years, or other infant outcomes. Significantly more women stopped their infusion because of adverse effects in the magnesium sulphate group. A decrease in diastolic blood pressure > 15 mmHg was found in the magnesium sulphate group compared to placebo Authors’ conclusions: Magnesium sulphate given immediately before very preterm birth may improve important paediatric outcomes but the evidence is not strong enough to recommend widespread use of magnesium sulphate. No serious harmful effects were shown Comments: Magnesium sulphate was given for neuroprotection only and not as a tocolytic 16.6% had a multiple pregnancy |
|
Mittendorf et al., 2002 [Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002; 186: 1111–1118] Country: USA Setting: Hospital based Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Not reported. Study design: Randomised, controlled trial (RCT) Length of follow-up: Infants were followed from randomisation up to 18 corrected months of age No. of participants: No. randomised – Toclysis: 92 Neuroprotection: 57 No. analysed – Toclysis: 92 Neuroprotection: 57 Validity: Adequate randomisation – Yes, 1 and 2 (computer-generated numbers) Adequate allocation concealment – Blinding of clinician – 1. No, 2. Yes Blinding of patient – Yes, 1 & 2 Blinding of researcher – Dependent on outcome Type of analysis: Chi-squared test, Student’s t-test, Mann–Whitney U-test and the Fisher exact test and multivariate logistic regression were used were appropriate. Analyses were conducted on an intention-to-treat basis. Sample size: Power analyses were based on anticipated reductions in the occurrence of neonatal intraventricular haemorrhage after the use of antenatal intravenous magnesium sulphate (18.9% to 4.4%). To obtain an alpha of 0.5 and a beta of 80%, 140 infants would be needed, increasing to 188 infants for a beta of 90% |
Groups compared: Tandem trials: Tocolytic magnesium sulphate vs Other tocolytic agents Neuroprotective magnesium sulphate vs saline Intervention details: In the tocolytic arms women were randomised to receive magnesium sulphate as a 4-g bolus followed by an infusion of 2–3 g of magnesium sulphate per hour or other tocolytic therapy (ritodrin, terbutaline, indomethacin, or nifedipine, according to the attending obstetrician’s preference) In the neuroprotective arms women were randomised to receive a 4-g intravenous bolus of magnesium sulphate without further infusion or saline solution. In the neonatal period, infants underwent a minimum of three cranial ultrasounds (weeks 1, 2 and 4 of life). Final ultrasound diagnoses were made by consensus decisions of two paediatric radiologists. Follow-up neurodevelopmental examinations were conducted in special clinic visits at 4, 8, 12 and 18 corrected months of age Participants: (Symptomatic) pregnant women Participant inclusion/exclusion criteria: Women > 24 and < 34 weeks’ gestation, reassuring fetal assessment, and absence of clinical features suggestive of infection or pre-eclampsia were eligible for the trial. Women in active labour with cervical dialation ≤ 4 cm considered legitimate candidates for aggressive tocolysis were eligible for the tocolytic arm. Women in active labour with cervical dilatation ≥ 4 cm were eligible for the prevention arm. Women with triplet or higher order gestations were excluded Outcomes: Adverse paediatric outcomes, such as mortality, cerebral palsy, neonatal intraventricular haemorrhage and periventricular haemorrhage, and obstetric and neonatal risk factors for adverse paediatric outcomes were considered |
Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not reported Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not reported Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: Not reported Incidence of adverse events: Composite adverse events Tocolytic group: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 16 (46) No. in control group (total no.) = 9 (46) Neuroprotection group: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 11 (29) No. in control group (total no.) = 6 (28) Intraventricular haemorrhage (grades 1–3) Tocolytic group: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 8 (55) No. in control group (total no.) = 6 (51) Neuroprotection group: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 5 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 5 (29) Periventricular leukomalacia Neuroprotection group: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 1 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (29) Cerebral palsy Tocolytic group: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 0 (46) No. in control group (total no.) = 3 (46) Neuroprotection group: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 3 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 0 (29) Mortality (fetal, neonatal + postnatal) Tocolytic group: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 8 No. in control group (total no.) = 0 Neuroprotection group: No. in intervention group (total no.) = 2 (30) No. in control group (total no.) = 1 (29) Brief summary of findings: A greater number of composite adverse paediatric outcomes were shown in the individual magnesium sulphate groups compared with control groups; however, between-group differences were not statistically significant When trial data were combined, multivariate regression analyses found that cord ionised magnesium was shown to be a significant risk factor for adverse paediatric outcome (i.e. intraventricular haemorrhage) Authors’ conclusions: Use of antenatal magnesium sulphate was associated with worse perinatal outcomes in a dose-dependent fashion Comments: Randomisation occurred after separation into the two parallel arms. The distributions of women in each trial arm were similar in terms of ethnicity, gestational length and fetal plurality 15.2% (14) randomised to the tocolytic arm had a multiple gestation3.5% (2) randomised to the neuroprotection arm had a multiple gestation. Individually the two arms would be underpowered to detect significant differences between the two groups The trial was stopped early because of concerns of a higher total paediatric mortality rate in the magnesium group |
| Review details | Methods | Results and conclusions |
|---|---|---|
|
Crowther et al. [Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Isssue1] 672 Title: Vitamin K prior to preterm birth for preventing neonatal periventricular haemorrhage Type of review: Cochrane Prevalence: Symptomatic for preterm birth – Not reported Preterm birth – Not reported |
Search: Search dates September 2000 Databases searched The Cochrane Controlled Trials Register and the Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Register were searched using the search term ‘vitamin’ Other sources None reported Search restrictions None specified Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Study design(s) RCTs or quasi-randomised trials were eligible for inclusion Population Women at risk of imminent very preterm labour Intervention Administration of vitamin K (parentally or orally) to the mother before preterm birth Outcomes Primary outcomes included: neonatal mortality and neonatal neurological morbidity (periventricular haemorrhage and long-term neurodevelopment). Secondary outcomes included: any maternal side effects and other neonatal morbidity Study selection: Two reviewers independently selected the studies for inclusion. There was no blinding of authorship Data extraction: Two reviewers independently extracted data from the primary studies; All data was double entered. Any disagreements were resolved through consensus. Where possible authors of the primary studies were contacted for additional information Validity assessment: Criteria used Quality scores for concealment of allocation were assigned to each study; A = adequate, B = unclear, C = inadequate and D = not used. In addition, quality scores were also assigned for completeness of follow-up, and blinding of outcome assessment; details reported Assessment Two reviewers independently assessed the included studies for methodological quality Synthesis: Heterogeneity Chi-squared test and the I-squared statistic were used to assess statistical heterogeneity. Planned sensitivity analysis was carried out, looking at trial quality Methods Categorical data were compared using RRs and their 95% CIs. Meta-analyses were used to pool data, using a fixed effects model; where statistically significant heterogeneity was found a random effects model was used |
No. of studies included: Five trials (n at least 420) No. of studies meeting quality criteria: Adequate randomisation – 2 Adequate concealment of allocation – 2 Adequate blinding of clinician/patient/researcher – 5/Unclear/Unclear Incidence of birth < 34 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth < 37 weeks’ gestation: Not reported Incidence of birth within 24 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 48 h of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of birth within 7 days of intervention: Not applicable Incidence of neonatal intensive care admission: Not reported Incidence of perinatal mortality: (Fixed effect) RR 0.79 (95% CI: 0.46–1.35) (4 studies, n = 539) Incidence of adverse events: All periventricular haemorrhage (Fixed effect) RR 0.82 (95% CI: 0.67–1.00) (5 studies, n = 606) Severe periventricular haemorrhage (grades 3–4) (Fixed effect) RR 0.75 (95% CI: 0.45–1.25) (5 studies, n = 606) Low Apgar score at 5 min (Fixed effect) RR 0.99 (95% CI: 0.63–1.57) (2 studies, n = 475) Respiratory distress syndrome (Fixed effect) RR 1.02 (95% CI: 0.76–1.37) (3 studies, n = 167) Use of mechanical ventilation (Fixed effect) RR 0.96 (95% CI: 0.84–1.10) (5 studies, n = 642) Pulmonary air leak (Fixed effect) RR 1.74 (95% CI: 0.59–5.10) (2 studies, n = 475) Patent ductus arteriosus (Fixed effect) RR 0.96 (95% CI: 0.57–1.63) (3 studies, n = 528) Maternal side effects (Fixed effect) RR 3.78 (95% CI: 0.41–35.07) (4 studies, n = 474) Sensitivity analyses: Incidence of perinatal mortality Excluding non-concealment of randomisation – (Fixed effect) RR 0.78 (95% CI: 0.43–1.42) (3 studies, n = 486) Excluding non-concealment of randomisation and unclear follow-up – (Fixed effect) RR 0.79 (95% CI: 0.41–1.52) (1 study, n = 372) Brief summary of findings: Compared to no treatment, antenatal administration of vitamin K did not statistically reduce the incidence of perinatal mortality or periventricular haemorrhage. No statistically significant between-group differences were shown on any of the other reported outcomes Neurodevelopmental outcomes were not reported in the primary studies Authors’ conclusions: Vitamin K, administered to women before very preterm birth did not significantly prevent periventricular haemorrhages in preterm infants Comments: This was a well-conducted review; methods were used to minimise bias in the study selection, validity assessment and data abstraction processes. Data were appropriately pooled and heterogeneity assessed |
Appendix 7 Adjusted indirect comparisons data
| Indirect comparison | Outcome [indirect RR (95% CI)] | Direct comparisons used in indirect estimate | RR (95% CI) | Size (n) and quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium channel blockers vs placebo |
Birth before 34 weeks 0.74 (95% CI: 1.43–0.38) |
Calcium channel blockers vs betamimetic maintenance therapy | 0.76 (95% CI: 0.64–0.91) |
Meta-analysis of five trials: n = 86, questionable quality571 n = 185, reasonable quality575 n = 57, reasonable quality572 n = 53, poor quality578 n = 89, reasonable quality577 |
| Betamimetic maintenance (terbutaline pump) vs placebo | 0.97 (95% CI: 0.51–1.84) |
One trial n = 52, good quality562 |
||
|
Birth before 37 weeks 0.98 (95% CI: 0.65–1.50) |
Calcium channel blockers vs betamimetic maintenance therapy | 0.84 (95% CI: 0.73–0.98) |
Meta-analysis of five trials: n = 90, questionable quality571 n = 52, reasonable quality568 n = 65, reasonable quality567 n = 185, reasonable quality575 n = 90, reasonable quality577 |
|
| Betamimetic maintenance (terbutaline pump) vs placebo | 1.17 (95% CI: 0.79–1.73) |
One trial n = 52, good quality562 |
||
|
Admission to neonatal intensive care unit 0.67 (95% CI: 0.35–1.26) |
Calcium channel blockers vs betamimetic maintenance therapy | 0.71 (95% CI: 0.59–0.86) |
Meta-analysis of nine trials: n = 62, reasonable quality570 n = 42, reasonable quality566 n = 82, questionable quality573 n = 86, questionable quality571 n = 173, reasonable quality575 n = 52, reasonable quality568 n = 63, reasonable quality572 n = 53, poor quality578 n = 89, reasonable quality577 |
|
| Terbutaline pump maintenance (betamimetic) vs placebo | 0.94 (95% CI: 0.51–1.73) |
One trial n = 140, good quality560 |
||
|
Birth within 48 h after treatment 0.44 (95% CI: 0.16–1.26) |
Calcium channel blockers vs magnesium sulphate – no maintenance therapy | 0.78 (95% CI: 0.36–1.69) |
One trial n = 74,questionable quality581 |
|
| Magnesium sulphate vs no tocolytic agent | 0.57 (95% CI: 0.28–1.15) |
Meta-analysis of three trials: n = 35,questionable quality578 n = 65,questionable quality624 n = 90, reasonable quality622 |
||
|
Birth within 7 days after treatment 0.46 (95% CI: 0.30–0.71) |
Calcium channel blockers vs terbutaline (betamimetic) | 0.78 (95% CI: 0.64–0.94) |
Meta-analysis of five trials: n = 185, reasonable quality575 n = 57, reasonable quality572 n = 53, poor quality578 n = 89, reasonable quality577 n = 61, questionable quality579 |
|
| Terbutaline (betamimetic) vs placebo | 0.59 (95% CI: 0.40–0.87) |
Meta-analysis of two trials: n = 30, good quality578 n = 38, questionable quality578 |
||
| Fenoterol (betamimetic) vs placebo | Perinatal mortality | Fenoterol (betamimetic) vs ritodrine (betamimetic) | 0.11 (95% CI: 0.01–2.01) |
One trial n = 98, questionable quality538 |
| Ritodrine (betamimetic) vs placebo | 0.88 (95% CI: 0.48–1.63) |
Meta-analysis of eight trials: n = 29, questionable quality547 n = 25, questionable quality535 n = 33, questionable quality539 n = 199, questionable quality539,542 n = 11, questionable quality539,545 n = 33, questionable quality539,546 |
||
| Oxytocin receptor antagonists (atosiban) vs placebo | Birth before 37 weeks | Oxytocin receptor antagonists (atosiban) vs betamimetics | 0.90 (95% CI: 0.71–1.13) |
One trial n = 244, good quality588 |
| Betamimetic (terbutaline) vs placebo | 0.64 (95% CI: 0.45–0.91) |
Meta-analysis of two trials: n = 30, good quality578 n = 38, questionable quality537 |
||
| Birth within 48 h after treatment | Oxytocin receptor antagonists (atosiban) vs betamimetics | 0.98 (95% CI: 0.68–1.41) |
Meta-analysis of four trials: n = 302, poor quality590 n = 247, good quality591 n = 244, good quality588 n = 240, good quality587 |
|
| Betamimetic (terbutaline) vs placebo | 0.45 (95% CI: 0.25–0.81) |
Meta-analysis of two trials: n = 30, good quality578 n = 38, questionable quality537 |
||
| Birth within 7 days after treatment | Oxytocin receptor antagonists (atosiban) vs betamimetics | 0.91 (95% CI: 0.69–1.20) |
Meta-analysis of three trials: n = 247, good quality591 n = 244, good quality588 n = 240, good quality587 |
|
| Betamimetic (terbutaline) vs placebo | 0.59 (95% CI: 0.40–0.87) |
Meta-analysis of two trials: n = 30, good quality578 n = 38, questionable quality537 |
Appendix 8 Estimation of cost of spontaneous preterm birth
The data presented in Table 143 represent the cost of low birthweight babies, for a specific weight range, for the neonatal period. It was derived from Petrou,60 and was used to estimate the Costs during the neonatal period (Cost of spontaneous preterm birth) for up to 34 and up to 37 weeks’ gestation, which refers to the cost of looking after the infant only and only covered the period of the initial hospitalisation.
| Average birthweight (g) | < 1000 | 1000–1499 | ≥ 1500 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Costs during the neonatal period | £29,757 | £14,896 | £9207 |
| (£19,711–£39,803) | (£9,310–£20,662) | (£4295–£14,119) |
We need to estimate the proportion of surviving infants for each of the weight ranges presented above so as to estimate the weighted mean (statistical term) of the costs during the neonatal period of the above ranges for up to 34 weeks’ and up to 37 weeks’ of gestation. Table 144 contains average birthweight for all gestational ages.
| Gestational age (weeks) | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average birthweight (g) | 500 | 590 | 690 | 790 | 900 | 1000 | 1150 | 1300 |
| Gestational age (weeks) | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 |
| Average birthweight (g) | 1500 | 1650 | 1850 | 2050 | 2300 | 2550 | 2800 | 3000 |
From Table 144, we can calculate the average birthweight per range of gestational age. For example the average birthweight of babies born up to 24 weeks is estimated by the average of the birthweight for 22, 23 and 24 weeks’ gestation.
Thus: Average birthweight up to 24 weeks = (500 + 590 + 690)/3 = 593 grams (as presented in Table 145). We proceed accordingly for the remaining gestational weeks.
| Gestational age (weeks) | ≤ 24 | 25–26 | 27–28 | 29–30 | 31–32 | 33–34 | 35–36 | ≥ 37 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average birthweight (g) | 593 | 845 | 1075 | 1400 | 1750 | 2175 | 2675 | 3000 |
Table 146 presents the number of surviving babies by gestational age.
| Gestational age (weeks) | ≤ 24 | 25–26 | 27–28 | 29–30 | 31–32 | 33–34 | 35–36 | ≥ 37 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of babies survived | 7 | 10 | 33 | 41 | 49 | 130 | 298 | 6092 | 6660 |
To estimate the proportion of survivors by weight range to correspond with Table 143 we use the data in Table 146 and Table 145.
Therefore, from Tables 145 and 146, we calculate the number of babies who survived according to their average birthweight (< 1000 g, 1000–1499 g, ≥ 1500 g) for up to 34 weeks and the same for up to 37 weeks.
For the 34 weeks: the < 1000 g range (in Table 143) corresponds to up to 26 weeks’ gestation (from Table 145). From Table 146, there are 17 (7 + 10) babies who survived to up to 26 weeks’ gestation.
The 1000–1499 g range (in Table 143) corresponds to 27–30 weeks’ gestation (from Table 145). From Table 146, there are 74 babies (i.e. 33 + 41) who survived between 27 and 30 weeks’ gestation.
The ≥ 1500-g range (in Table 143) corresponds to 31–34 weeks’ gestation (from Table 145). From Table 145, there are 179 babies (i.e. 49 + 130) who survived between 31 and 34 weeks’ gestation.
For the 37 weeks: the babies who survived for the < 1000 g and the 1000–1499 g ranges were the same as before.
The ≥ 1500-g range (in Table 143) corresponds to 31–37 weeks’ gestation (from Table 145). From Table 146, there are 6569 babies (49 + 130 + 298 + 6092) who survived between 31 and 37 weeks’ gestation.
The above as well as the weightings (statistical term) for each weight range are summarised in Table 147.
| Average birthweight (g) | < 1000 | 1000–1499 | ≥ 1500 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proportions required for up to 34 weeks | |||
| Gestational age (weeks) | ≤ 26 | 27–30 | 31–34 |
| Number of babies survived | 17 | 74 | 179 |
| Weightings (per total number of babies survived) | 0.0630 | 0.2741 | 0.6630 |
| Proportions required for up to 37 weeks | |||
| Gestational age (weeks) | ≤ 26 | 27–30 | 31–37 |
| Number of babies survived | 17 | 74 | 6569 |
| Weightings (per total number of babies survived) | 0.0026 | 0.0111 | 0.9863 |
These proportions are then used to estimate the ‘weighted’ (statistical definition) mean for weight ranges corresponding to Table 143 for both gestational weeks.
For example, for up to 34 weeks, the cost of preterm birth was estimated to be £12,084.76 (in 1998 values) which we inflated to 2005 prices:
0.0663 × £29,757 (Table 143) + 0.2741 × £14,896 (Table 143) + 0.663 × £9207 (Table 143) = £12,084.76 as shown in Table 148 for 34 weeks in 1998 prices which is then inflated to £15,688.75.
| Average birthweight (g) | 1998 values | 2005 values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 1000 | 1000–1499 | ≥1500 | Total cost | Total cost | |
| 34 weeks | |||||
| Costs during the neonatal period | £1873.59 | £4107.27 | £6103.90 | £12,084.76 | £15,688.75a |
| 37 weeks | |||||
| Costs during the neonatal period | £75.96 | £166.51 | £9,081.20 | £9,323.67 | £12,104.23 |
Appendix 9 Estimation of spontaneous preterm birth prevalence
From the meta-analysis of the accuracy data (likelihood ratios positive and negative for each test) and the effectiveness data (relative risk of each intervention) the following data were available:
-
Prevalence of symptomatic women having spontaneous preterm birth, e.g. 0.3 (30/100)
-
Prevalence of asymptomatic women having spontaneous preterm birth, e.g. 0.048 (12/250).
We had to assume that data were from separate studies (i.e. there was no overlap) and so we assumed that populations were comparable. We could then simply add the Total number of cases and divide it by the Total size of the studies. The result is the Overall Prevalence of symptomatic women having spontaneous preterm birth and the Overall Prevalence of asymptomatic women having spontaneous preterm birth. For example, Overall Prevalence of symptomatic women having spontaneous preterm birth =
where 0.3 (30/100), 0.08 (40/500) and 0.075 (30/400) are the prevalences from three separate studies. Technically the appropriate distribution for the Overall Prevalence is the β-distribution, i.e. Overall Prevalence ∼ β (n, r), where n = Total number of cases and r = Total number of studies size. In practice, the confidence intervals are expected to be sufficiently narrow that a normal distribution can be used instead. Using the β-distribution we calculate the variance of the Overall Prevalence of asymptomatic women having spontaneous preterm birth and the variance of the Overall Prevalence of symptomatic women having spontaneous preterm birth by the standard function
which will be used in the normal distribution as well as below. Next we have to determine the Overall Prevalence of asymptomatic women becoming symptomatic with threatened preterm labour.
Having calculated the Overall Prevalence of asymptomatic women having spontaneous preterm birth and the Overall Prevalence of symptomatic women having spontaneous preterm birth, we can simply divide these two and obtain the Overall Prevalence of asymptomatic women becoming symptomatic. The variance of the Overall Prevalence of asymptomatic women becoming symptomatic can be calculated using the formula:
where, y = x1/x2, y is the Overall Prevalence of asymptomatic women becoming symptomatic, x1 is the Overall Prevalence of asymptomatic women having spontaneous preterm birth and x2 is the Overall Prevalence of symptomatic women having spontaneous preterm birth.
List of abbreviations
- AIDS
- acquired immune deficiency syndrome
- BMI
- body mass index
- BNF
- British National Formulary
- BV
- bacterial vaginosis
- BWH
- Birmingham Women’s Hospital
- CDE
- cervical digital examination
- CDSR
- Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
- CEAC
- cost-effectiveness acceptability curve
- CENTRAL
- Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials
- CI
- confidence interval
- CRD
- Centre for Reviews and Dissemination
- CRH
- corticotrophin-releasing hormone
- CTG
- cardiotocography
- CRP
- C-reactive protein
- DARE
- Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effect
- ELISA
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- fFN
- fetal fibronectin
- GTN
- glyceryl trinitride
- hCG
- human chorionic gonadotrophin
- HEED
- Health Economic Evaluations Database
- ?-hCG
- beta-human chorionic gonadotrophin
- HCHS
- hospital and community health services
- HIV
- human immunodeficiency virus
- HRG
- health resources groups
- HTA
- health technology assessment
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratios
- IL-6
- interleukin-6
- IL-8
- interleukin-8
- IPD
- individual patient data (meta-analysis)
- ITT
- intention to treat
- LBW
- low birthweight
- LR
- likelihood ratio (LR+, LR for positive test result; LR–, LR for negative test result)
- MeSH
- medical subject heading (indexing)
- MMP-9
- matrix metalloprotease-9
- MSAFP
- maternal serum α-fetoprotein
- NHS EED
- NHS Economic Evaluation Database
- NNT
- number needed to treat
- NRR
- National Research Register
- NSAID
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
- NSC
- National Screening Committee
- NTIS
- National Technical Information Service
- OMNI
- Organising Medical Networked Information
- OR
- odds ratio
- phIGFBP-1
- phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1
- PROM
- pre-labour rupture of membrane
- PPROM
- premature pre-labour rupture of membrane
- PSA
- probabilistic sensitivity analysis
- PSSRU
- Personal Social Services Research Unit
- PTB
- preterm birth
- PTL
- threatened preterm labour
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- RCOG
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- RD
- risk difference
- RDS
- respiratory distress syndrome
- RR
- relative risk
- ROC
- receiver operating characteristics
- SD
- standard deviation
- SE
- standard error
- SIGLE
- Systems for Information in Grey Literature in Europe
- SQT
- subcutaneous terbutaline
- TNELIP
- non-elective inpatient HRG data
- TNELIPXS
- elective inpatient excess bed day HRG data
- WMD
- weighted mean difference
All abbreviations that have been used in this report are listed here unless the abbreviation is well known (e.g. NHS), or it has been used only once, or it is a non-standard abbreviation used only in figures/tables/appendices, in which case the abbreviation is defined in the figure legend or in the notes at the end of the table.
Notes
Health Technology Assessment reports published to date
-
Home parenteral nutrition: a systematic review.
By Richards DM, Deeks JJ, Sheldon TA, Shaffer JL.
-
Diagnosis, management and screening of early localised prostate cancer.
A review by Selley S, Donovan J, Faulkner A, Coast J, Gillatt D.
-
The diagnosis, management, treatment and costs of prostate cancer in England and Wales.
A review by Chamberlain J, Melia J, Moss S, Brown J.
-
Screening for fragile X syndrome.
A review by Murray J, Cuckle H, Taylor G, Hewison J.
-
A review of near patient testing in primary care.
By Hobbs FDR, Delaney BC, Fitzmaurice DA, Wilson S, Hyde CJ, Thorpe GH, et al.
-
Systematic review of outpatient services for chronic pain control.
By McQuay HJ, Moore RA, Eccleston C, Morley S, de C Williams AC.
-
Neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism: cost, yield and outcome.
A review by Pollitt RJ, Green A, McCabe CJ, Booth A, Cooper NJ, Leonard JV, et al.
-
Preschool vision screening.
A review by Snowdon SK, Stewart-Brown SL.
-
Implications of socio-cultural contexts for the ethics of clinical trials.
A review by Ashcroft RE, Chadwick DW, Clark SRL, Edwards RHT, Frith L, Hutton JL.
-
A critical review of the role of neonatal hearing screening in the detection of congenital hearing impairment.
By Davis A, Bamford J, Wilson I, Ramkalawan T, Forshaw M, Wright S.
-
Newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism: a systematic review.
By Seymour CA, Thomason MJ, Chalmers RA, Addison GM, Bain MD, Cockburn F, et al.
-
Routine preoperative testing: a systematic review of the evidence.
By Munro J, Booth A, Nicholl J.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness of laxatives in the elderly.
By Petticrew M, Watt I, Sheldon T.
-
When and how to assess fast-changing technologies: a comparative study of medical applications of four generic technologies.
A review by Mowatt G, Bower DJ, Brebner JA, Cairns JA, Grant AM, McKee L.
-
Antenatal screening for Down’s syndrome.
A review by Wald NJ, Kennard A, Hackshaw A, McGuire A.
-
Screening for ovarian cancer: a systematic review.
By Bell R, Petticrew M, Luengo S, Sheldon TA.
-
Consensus development methods, and their use in clinical guideline development.
A review by Murphy MK, Black NA, Lamping DL, McKee CM, Sanderson CFB, Askham J, et al.
-
A cost–utility analysis of interferon beta for multiple sclerosis.
By Parkin D, McNamee P, Jacoby A, Miller P, Thomas S, Bates D.
-
Effectiveness and efficiency of methods of dialysis therapy for end-stage renal disease: systematic reviews.
By MacLeod A, Grant A, Donaldson C, Khan I, Campbell M, Daly C, et al.
-
Effectiveness of hip prostheses in primary total hip replacement: a critical review of evidence and an economic model.
By Faulkner A, Kennedy LG, Baxter K, Donovan J, Wilkinson M, Bevan G.
-
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in colorectal surgery: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials.
By Song F, Glenny AM.
-
Bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for malignancy.
A review by Johnson PWM, Simnett SJ, Sweetenham JW, Morgan GJ, Stewart LA.
-
Screening for speech and language delay: a systematic review of the literature.
By Law J, Boyle J, Harris F, Harkness A, Nye C.
-
Resource allocation for chronic stable angina: a systematic review of effectiveness, costs and cost-effectiveness of alternative interventions.
By Sculpher MJ, Petticrew M, Kelland JL, Elliott RA, Holdright DR, Buxton MJ.
-
Detection, adherence and control of hypertension for the prevention of stroke: a systematic review.
By Ebrahim S.
-
Postoperative analgesia and vomiting, with special reference to day-case surgery: a systematic review.
By McQuay HJ, Moore RA.
-
Choosing between randomised and nonrandomised studies: a systematic review.
By Britton A, McKee M, Black N, McPherson K, Sanderson C, Bain C.
-
Evaluating patient-based outcome measures for use in clinical trials.
A review by Fitzpatrick R, Davey C, Buxton MJ, Jones DR.
-
Ethical issues in the design and conduct of randomised controlled trials.
A review by Edwards SJL, Lilford RJ, Braunholtz DA, Jackson JC, Hewison J, Thornton J.
-
Qualitative research methods in health technology assessment: a review of the literature.
By Murphy E, Dingwall R, Greatbatch D, Parker S, Watson P.
-
The costs and benefits of paramedic skills in pre-hospital trauma care.
By Nicholl J, Hughes S, Dixon S, Turner J, Yates D.
-
Systematic review of endoscopic ultrasound in gastro-oesophageal cancer.
By Harris KM, Kelly S, Berry E, Hutton J, Roderick P, Cullingworth J, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of trials and other studies.
By Sutton AJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR, Sheldon TA, Song F.
-
Primary total hip replacement surgery: a systematic review of outcomes and modelling of cost-effectiveness associated with different prostheses.
A review by Fitzpatrick R, Shortall E, Sculpher M, Murray D, Morris R, Lodge M, et al.
-
Informed decision making: an annotated bibliography and systematic review.
By Bekker H, Thornton JG, Airey CM, Connelly JB, Hewison J, Robinson MB, et al.
-
Handling uncertainty when performing economic evaluation of healthcare interventions.
A review by Briggs AH, Gray AM.
-
The role of expectancies in the placebo effect and their use in the delivery of health care: a systematic review.
By Crow R, Gage H, Hampson S, Hart J, Kimber A, Thomas H.
-
A randomised controlled trial of different approaches to universal antenatal HIV testing: uptake and acceptability. Annex: Antenatal HIV testing – assessment of a routine voluntary approach.
By Simpson WM, Johnstone FD, Boyd FM, Goldberg DJ, Hart GJ, Gormley SM, et al.
-
Methods for evaluating area-wide and organisation-based interventions in health and health care: a systematic review.
By Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ.
-
Assessing the costs of healthcare technologies in clinical trials.
A review by Johnston K, Buxton MJ, Jones DR, Fitzpatrick R.
-
Cooperatives and their primary care emergency centres: organisation and impact.
By Hallam L, Henthorne K.
-
Screening for cystic fibrosis.
A review by Murray J, Cuckle H, Taylor G, Littlewood J, Hewison J.
-
A review of the use of health status measures in economic evaluation.
By Brazier J, Deverill M, Green C, Harper R, Booth A.
-
Methods for the analysis of quality-of-life and survival data in health technology assessment.
A review by Billingham LJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR.
-
Antenatal and neonatal haemoglobinopathy screening in the UK: review and economic analysis.
By Zeuner D, Ades AE, Karnon J, Brown J, Dezateux C, Anionwu EN.
-
Assessing the quality of reports of randomised trials: implications for the conduct of meta-analyses.
A review by Moher D, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Tugwell P, Moher M, Jones A, et al.
-
‘Early warning systems’ for identifying new healthcare technologies.
By Robert G, Stevens A, Gabbay J.
-
A systematic review of the role of human papillomavirus testing within a cervical screening programme.
By Cuzick J, Sasieni P, Davies P, Adams J, Normand C, Frater A, et al.
-
Near patient testing in diabetes clinics: appraising the costs and outcomes.
By Grieve R, Beech R, Vincent J, Mazurkiewicz J.
-
Positron emission tomography: establishing priorities for health technology assessment.
A review by Robert G, Milne R.
-
The debridement of chronic wounds: a systematic review.
By Bradley M, Cullum N, Sheldon T.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (2) Dressings and topical agents used in the healing of chronic wounds.
By Bradley M, Cullum N, Nelson EA, Petticrew M, Sheldon T, Torgerson D.
-
A systematic literature review of spiral and electron beam computed tomography: with particular reference to clinical applications in hepatic lesions, pulmonary embolus and coronary artery disease.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Hutton J, Harris KM, Roderick P, Boyce JC, et al.
-
What role for statins? A review and economic model.
By Ebrahim S, Davey Smith G, McCabe C, Payne N, Pickin M, Sheldon TA, et al.
-
Factors that limit the quality, number and progress of randomised controlled trials.
A review by Prescott RJ, Counsell CE, Gillespie WJ, Grant AM, Russell IT, Kiauka S, et al.
-
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in total hip replacement: a systematic review.
By Glenny AM, Song F.
-
Health promoting schools and health promotion in schools: two systematic reviews.
By Lister-Sharp D, Chapman S, Stewart-Brown S, Sowden A.
-
Economic evaluation of a primary care-based education programme for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee.
A review by Lord J, Victor C, Littlejohns P, Ross FM, Axford JS.
-
The estimation of marginal time preference in a UK-wide sample (TEMPUS) project.
A review by Cairns JA, van der Pol MM.
-
Geriatric rehabilitation following fractures in older people: a systematic review.
By Cameron I, Crotty M, Currie C, Finnegan T, Gillespie L, Gillespie W, et al.
-
Screening for sickle cell disease and thalassaemia: a systematic review with supplementary research.
By Davies SC, Cronin E, Gill M, Greengross P, Hickman M, Normand C.
-
Community provision of hearing aids and related audiology services.
A review by Reeves DJ, Alborz A, Hickson FS, Bamford JM.
-
False-negative results in screening programmes: systematic review of impact and implications.
By Petticrew MP, Sowden AJ, Lister-Sharp D, Wright K.
-
Costs and benefits of community postnatal support workers: a randomised controlled trial.
By Morrell CJ, Spiby H, Stewart P, Walters S, Morgan A.
-
Implantable contraceptives (subdermal implants and hormonally impregnated intrauterine systems) versus other forms of reversible contraceptives: two systematic reviews to assess relative effectiveness, acceptability, tolerability and cost-effectiveness.
By French RS, Cowan FM, Mansour DJA, Morris S, Procter T, Hughes D, et al.
-
An introduction to statistical methods for health technology assessment.
A review by White SJ, Ashby D, Brown PJ.
-
Disease-modifying drugs for multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By Clegg A, Bryant J, Milne R.
-
Publication and related biases.
A review by Song F, Eastwood AJ, Gilbody S, Duley L, Sutton AJ.
-
Cost and outcome implications of the organisation of vascular services.
By Michaels J, Brazier J, Palfreyman S, Shackley P, Slack R.
-
Monitoring blood glucose control in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review.
By Coster S, Gulliford MC, Seed PT, Powrie JK, Swaminathan R.
-
The effectiveness of domiciliary health visiting: a systematic review of international studies and a selective review of the British literature.
By Elkan R, Kendrick D, Hewitt M, Robinson JJA, Tolley K, Blair M, et al.
-
The determinants of screening uptake and interventions for increasing uptake: a systematic review.
By Jepson R, Clegg A, Forbes C, Lewis R, Sowden A, Kleijnen J.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of prophylactic removal of wisdom teeth.
A rapid review by Song F, O’Meara S, Wilson P, Golder S, Kleijnen J.
-
Ultrasound screening in pregnancy: a systematic review of the clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and women’s views.
By Bricker L, Garcia J, Henderson J, Mugford M, Neilson J, Roberts T, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the taxanes used in the treatment of advanced breast and ovarian cancer.
By Lister-Sharp D, McDonagh MS, Khan KS, Kleijnen J.
-
Liquid-based cytology in cervical screening: a rapid and systematic review.
By Payne N, Chilcott J, McGoogan E.
-
Randomised controlled trial of non-directive counselling, cognitive–behaviour therapy and usual general practitioner care in the management of depression as well as mixed anxiety and depression in primary care.
By King M, Sibbald B, Ward E, Bower P, Lloyd M, Gabbay M, et al.
-
Routine referral for radiography of patients presenting with low back pain: is patients’ outcome influenced by GPs’ referral for plain radiography?
By Kerry S, Hilton S, Patel S, Dundas D, Rink E, Lord J.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (3) antimicrobial agents for chronic wounds; (4) diabetic foot ulceration.
By O’Meara S, Cullum N, Majid M, Sheldon T.
-
Using routine data to complement and enhance the results of randomised controlled trials.
By Lewsey JD, Leyland AH, Murray GD, Boddy FA.
-
Coronary artery stents in the treatment of ischaemic heart disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Meads C, Cummins C, Jolly K, Stevens A, Burls A, Hyde C.
-
Outcome measures for adult critical care: a systematic review.
By Hayes JA, Black NA, Jenkinson C, Young JD, Rowan KM, Daly K, et al.
-
A systematic review to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions to promote the initiation of breastfeeding.
By Fairbank L, O’Meara S, Renfrew MJ, Woolridge M, Sowden AJ, Lister-Sharp D.
-
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators: arrhythmias. A rapid and systematic review.
By Parkes J, Bryant J, Milne R.
-
Treatments for fatigue in multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By Brañas P, Jordan R, Fry-Smith A, Burls A, Hyde C.
-
Early asthma prophylaxis, natural history, skeletal development and economy (EASE): a pilot randomised controlled trial.
By Baxter-Jones ADG, Helms PJ, Russell G, Grant A, Ross S, Cairns JA, et al.
-
Screening for hypercholesterolaemia versus case finding for familial hypercholesterolaemia: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Marks D, Wonderling D, Thorogood M, Lambert H, Humphries SE, Neil HAW.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists in the medical management of unstable angina.
By McDonagh MS, Bachmann LM, Golder S, Kleijnen J, ter Riet G.
-
A randomised controlled trial of prehospital intravenous fluid replacement therapy in serious trauma.
By Turner J, Nicholl J, Webber L, Cox H, Dixon S, Yates D.
-
Intrathecal pumps for giving opioids in chronic pain: a systematic review.
By Williams JE, Louw G, Towlerton G.
-
Combination therapy (interferon alfa and ribavirin) in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a rapid and systematic review.
By Shepherd J, Waugh N, Hewitson P.
-
A systematic review of comparisons of effect sizes derived from randomised and non-randomised studies.
By MacLehose RR, Reeves BC, Harvey IM, Sheldon TA, Russell IT, Black AMS.
-
Intravascular ultrasound-guided interventions in coronary artery disease: a systematic literature review, with decision-analytic modelling, of outcomes and cost-effectiveness.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Hutton J, Lindsay HSJ, Blaxill JM, Evans JA, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to evaluate the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of counselling patients with chronic depression.
By Simpson S, Corney R, Fitzgerald P, Beecham J.
-
Systematic review of treatments for atopic eczema.
By Hoare C, Li Wan Po A, Williams H.
-
Bayesian methods in health technology assessment: a review.
By Spiegelhalter DJ, Myles JP, Jones DR, Abrams KR.
-
The management of dyspepsia: a systematic review.
By Delaney B, Moayyedi P, Deeks J, Innes M, Soo S, Barton P, et al.
-
A systematic review of treatments for severe psoriasis.
By Griffiths CEM, Clark CM, Chalmers RJG, Li Wan Po A, Williams HC.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine for Alzheimer’s disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Clegg A, Bryant J, Nicholson T, McIntyre L, De Broe S, Gerard K, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of riluzole for motor neurone disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Stewart A, Sandercock J, Bryan S, Hyde C, Barton PM, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Equity and the economic evaluation of healthcare.
By Sassi F, Archard L, Le Grand J.
-
Quality-of-life measures in chronic diseases of childhood.
By Eiser C, Morse R.
-
Eliciting public preferences for healthcare: a systematic review of techniques.
By Ryan M, Scott DA, Reeves C, Bate A, van Teijlingen ER, Russell EM, et al.
-
General health status measures for people with cognitive impairment: learning disability and acquired brain injury.
By Riemsma RP, Forbes CA, Glanville JM, Eastwood AJ, Kleijnen J.
-
An assessment of screening strategies for fragile X syndrome in the UK.
By Pembrey ME, Barnicoat AJ, Carmichael B, Bobrow M, Turner G.
-
Issues in methodological research: perspectives from researchers and commissioners.
By Lilford RJ, Richardson A, Stevens A, Fitzpatrick R, Edwards S, Rock F, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (5) beds; (6) compression; (7) laser therapy, therapeutic ultrasound, electrotherapy and electromagnetic therapy.
By Cullum N, Nelson EA, Flemming K, Sheldon T.
-
Effects of educational and psychosocial interventions for adolescents with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review.
By Hampson SE, Skinner TC, Hart J, Storey L, Gage H, Foxcroft D, et al.
-
Effectiveness of autologous chondrocyte transplantation for hyaline cartilage defects in knees: a rapid and systematic review.
By Jobanputra P, Parry D, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
Statistical assessment of the learning curves of health technologies.
By Ramsay CR, Grant AM, Wallace SA, Garthwaite PH, Monk AF, Russell IT.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of temozolomide for the treatment of recurrent malignant glioma: a rapid and systematic review.
By Dinnes J, Cave C, Huang S, Major K, Milne R.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of debriding agents in treating surgical wounds healing by secondary intention.
By Lewis R, Whiting P, ter Riet G, O’Meara S, Glanville J.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.
By Burns T, Knapp M, Catty J, Healey A, Henderson J, Watt H, et al.
-
How to develop cost-conscious guidelines.
By Eccles M, Mason J.
-
The role of specialist nurses in multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By De Broe S, Christopher F, Waugh N.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of orlistat in the management of obesity.
By O’Meara S, Riemsma R, Shirran L, Mather L, ter Riet G.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pioglitazone for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a rapid and systematic review.
By Chilcott J, Wight J, Lloyd Jones M, Tappenden P.
-
Extended scope of nursing practice: a multicentre randomised controlled trial of appropriately trained nurses and preregistration house officers in preoperative assessment in elective general surgery.
By Kinley H, Czoski-Murray C, George S, McCabe C, Primrose J, Reilly C, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of the effectiveness of day care for people with severe mental disorders: (1) Acute day hospital versus admission; (2) Vocational rehabilitation; (3) Day hospital versus outpatient care.
By Marshall M, Crowther R, Almaraz- Serrano A, Creed F, Sledge W, Kluiter H, et al.
-
The measurement and monitoring of surgical adverse events.
By Bruce J, Russell EM, Mollison J, Krukowski ZH.
-
Action research: a systematic review and guidance for assessment.
By Waterman H, Tillen D, Dickson R, de Koning K.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of gemcitabine for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
By Ward S, Morris E, Bansback N, Calvert N, Crellin A, Forman D, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the evidence for the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer.
By Lloyd Jones M, Hummel S, Bansback N, Orr B, Seymour M.
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.
By Brocklebank D, Ram F, Wright J, Barry P, Cates C, Davies L, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging for investigation of the knee joint.
By Bryan S, Weatherburn G, Bungay H, Hatrick C, Salas C, Parry D, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.
By Forbes C, Shirran L, Bagnall A-M, Duffy S, ter Riet G.
-
Superseded by a report published in a later volume.
-
The role of radiography in primary care patients with low back pain of at least 6 weeks duration: a randomised (unblinded) controlled trial.
By Kendrick D, Fielding K, Bentley E, Miller P, Kerslake R, Pringle M.
-
Design and use of questionnaires: a review of best practice applicable to surveys of health service staff and patients.
By McColl E, Jacoby A, Thomas L, Soutter J, Bamford C, Steen N, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.
By Clegg A, Scott DA, Sidhu M, Hewitson P, Waugh N.
-
Subgroup analyses in randomised controlled trials: quantifying the risks of false-positives and false-negatives.
By Brookes ST, Whitley E, Peters TJ, Mulheran PA, Egger M, Davey Smith G.
-
Depot antipsychotic medication in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia: (1) Meta-review; (2) Patient and nurse attitudes.
By David AS, Adams C.
-
A systematic review of controlled trials of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of brief psychological treatments for depression.
By Churchill R, Hunot V, Corney R, Knapp M, McGuire H, Tylee A, et al.
-
Cost analysis of child health surveillance.
By Sanderson D, Wright D, Acton C, Duree D.
-
A study of the methods used to select review criteria for clinical audit.
By Hearnshaw H, Harker R, Cheater F, Baker R, Grimshaw G.
-
Fludarabine as second-line therapy for B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a technology assessment.
By Hyde C, Wake B, Bryan S, Barton P, Fry-Smith A, Davenport C, et al.
-
Rituximab as third-line treatment for refractory or recurrent Stage III or IV follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wake B, Hyde C, Bryan S, Barton P, Song F, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
A systematic review of discharge arrangements for older people.
By Parker SG, Peet SM, McPherson A, Cannaby AM, Baker R, Wilson A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of inhaler devices used in the routine management of chronic asthma in older children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Peters J, Stevenson M, Beverley C, Lim J, Smith S.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of sibutramine in the management of obesity: a technology assessment.
By O’Meara S, Riemsma R, Shirran L, Mather L, ter Riet G.
-
The cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance angiography for carotid artery stenosis and peripheral vascular disease: a systematic review.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Westwood ME, Davies LM, Gough MJ, Bamford JM, et al.
-
Promoting physical activity in South Asian Muslim women through ‘exercise on prescription’.
By Carroll B, Ali N, Azam N.
-
Zanamivir for the treatment of influenza in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burls A, Clark W, Stewart T, Preston C, Bryan S, Jefferson T, et al.
-
A review of the natural history and epidemiology of multiple sclerosis: implications for resource allocation and health economic models.
By Richards RG, Sampson FC, Beard SM, Tappenden P.
-
Screening for gestational diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Scott DA, Loveman E, McIntyre L, Waugh N.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of surgery for people with morbid obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clegg AJ, Colquitt J, Sidhu MK, Royle P, Loveman E, Walker A.
-
The clinical effectiveness of trastuzumab for breast cancer: a systematic review.
By Lewis R, Bagnall A-M, Forbes C, Shirran E, Duffy S, Kleijnen J, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of vinorelbine for breast cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Lewis R, Bagnall A-M, King S, Woolacott N, Forbes C, Shirran L, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty for treatment of hip disease.
By Vale L, Wyness L, McCormack K, McKenzie L, Brazzelli M, Stearns SC.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bupropion and nicotine replacement therapy for smoking cessation: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Woolacott NF, Jones L, Forbes CA, Mather LC, Sowden AJ, Song FJ, et al.
-
A systematic review of effectiveness and economic evaluation of new drug treatments for juvenile idiopathic arthritis: etanercept.
By Cummins C, Connock M, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of growth hormone in children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Cave C, Mihaylova B, Chase D, McIntyre L, Gerard K, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of growth hormone in adults in relation to impact on quality of life: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Loveman E, Chase D, Mihaylova B, Cave C, Gerard K, et al.
-
Clinical medication review by a pharmacist of patients on repeat prescriptions in general practice: a randomised controlled trial.
By Zermansky AG, Petty DR, Raynor DK, Lowe CJ, Freementle N, Vail A.
-
The effectiveness of infliximab and etanercept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Burls A.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of computerised cognitive behaviour therapy for depression and anxiety.
By Kaltenthaler E, Shackley P, Stevens K, Beverley C, Parry G, Chilcott J.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride for ovarian cancer.
By Forbes C, Wilby J, Richardson G, Sculpher M, Mather L, Reimsma R.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of interventions based on a stages-of-change approach to promote individual behaviour change.
By Riemsma RP, Pattenden J, Bridle C, Sowden AJ, Mather L, Watt IS, et al.
-
A systematic review update of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists.
By Robinson M, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Jones L, Riemsma R, Palmer S, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and barriers to implementation of thrombolytic and neuroprotective therapy for acute ischaemic stroke in the NHS.
By Sandercock P, Berge E, Dennis M, Forbes J, Hand P, Kwan J, et al.
-
A randomised controlled crossover trial of nurse practitioner versus doctor-led outpatient care in a bronchiectasis clinic.
By Caine N, Sharples LD, Hollingworth W, French J, Keogan M, Exley A, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost – consequences of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of sex offenders.
By Adi Y, Ashcroft D, Browne K, Beech A, Fry-Smith A, Hyde C.
-
Treatment of established osteoporosis: a systematic review and cost–utility analysis.
By Kanis JA, Brazier JE, Stevenson M, Calvert NW, Lloyd Jones M.
-
Which anaesthetic agents are cost-effective in day surgery? Literature review, national survey of practice and randomised controlled trial.
By Elliott RA Payne K, Moore JK, Davies LM, Harper NJN, St Leger AS, et al.
-
Screening for hepatitis C among injecting drug users and in genitourinary medicine clinics: systematic reviews of effectiveness, modelling study and national survey of current practice.
By Stein K, Dalziel K, Walker A, McIntyre L, Jenkins B, Horne J, et al.
-
The measurement of satisfaction with healthcare: implications for practice from a systematic review of the literature.
By Crow R, Gage H, Hampson S, Hart J, Kimber A, Storey L, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of imatinib in chronic myeloid leukaemia: a systematic review.
By Garside R, Round A, Dalziel K, Stein K, Royle R.
-
A comparative study of hypertonic saline, daily and alternate-day rhDNase in children with cystic fibrosis.
By Suri R, Wallis C, Bush A, Thompson S, Normand C, Flather M, et al.
-
A systematic review of the costs and effectiveness of different models of paediatric home care.
By Parker G, Bhakta P, Lovett CA, Paisley S, Olsen R, Turner D, et al.
-
How important are comprehensive literature searches and the assessment of trial quality in systematic reviews? Empirical study.
By Egger M, Jüni P, Bartlett C, Holenstein F, Sterne J.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and economic evaluation, of home versus hospital or satellite unit haemodialysis for people with end-stage renal failure.
By Mowatt G, Vale L, Perez J, Wyness L, Fraser C, MacLeod A, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of the effectiveness of infliximab for the treatment of Crohn’s disease.
By Clark W, Raftery J, Barton P, Song F, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
A review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine anti-D prophylaxis for pregnant women who are rhesus negative.
By Chilcott J, Lloyd Jones M, Wight J, Forman K, Wray J, Beverley C, et al.
-
Systematic review and evaluation of the use of tumour markers in paediatric oncology: Ewing’s sarcoma and neuroblastoma.
By Riley RD, Burchill SA, Abrams KR, Heney D, Lambert PC, Jones DR, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of screening for Helicobacter pylori to reduce mortality and morbidity from gastric cancer and peptic ulcer disease: a discrete-event simulation model.
By Roderick P, Davies R, Raftery J, Crabbe D, Pearce R, Bhandari P, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine dental checks: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Davenport C, Elley K, Salas C, Taylor-Weetman CL, Fry-Smith A, Bryan S, et al.
-
A multicentre randomised controlled trial assessing the costs and benefits of using structured information and analysis of women’s preferences in the management of menorrhagia.
By Kennedy ADM, Sculpher MJ, Coulter A, Dwyer N, Rees M, Horsley S, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost–utility of photodynamic therapy for wet age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Meads C, Salas C, Roberts T, Moore D, Fry-Smith A, Hyde C.
-
Evaluation of molecular tests for prenatal diagnosis of chromosome abnormalities.
By Grimshaw GM, Szczepura A, Hultén M, MacDonald F, Nevin NC, Sutton F, et al.
-
First and second trimester antenatal screening for Down’s syndrome: the results of the Serum, Urine and Ultrasound Screening Study (SURUSS).
By Wald NJ, Rodeck C, Hackshaw AK, Walters J, Chitty L, Mackinson AM.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of ultrasound locating devices for central venous access: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Calvert N, Hind D, McWilliams RG, Thomas SM, Beverley C, Davidson A.
-
A systematic review of atypical antipsychotics in schizophrenia.
By Bagnall A-M, Jones L, Lewis R, Ginnelly L, Glanville J, Torgerson D, et al.
-
Prostate Testing for Cancer and Treatment (ProtecT) feasibility study.
By Donovan J, Hamdy F, Neal D, Peters T, Oliver S, Brindle L, et al.
-
Early thrombolysis for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Boland A, Dundar Y, Bagust A, Haycox A, Hill R, Mujica Mota R, et al.
-
Screening for fragile X syndrome: a literature review and modelling.
By Song FJ, Barton P, Sleightholme V, Yao GL, Fry-Smith A.
-
Systematic review of endoscopic sinus surgery for nasal polyps.
By Dalziel K, Stein K, Round A, Garside R, Royle P.
-
Towards efficient guidelines: how to monitor guideline use in primary care.
By Hutchinson A, McIntosh A, Cox S, Gilbert C.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of acute hospital-based spinal cord injuries services: systematic review.
By Bagnall A-M, Jones L, Richardson G, Duffy S, Riemsma R.
-
Prioritisation of health technology assessment. The PATHS model: methods and case studies.
By Townsend J, Buxton M, Harper G.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of tension-free vaginal tape for treatment of urinary stress incontinence.
By Cody J, Wyness L, Wallace S, Glazener C, Kilonzo M, Stearns S, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of patient education models for diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Loveman E, Cave C, Green C, Royle P, Dunn N, Waugh N.
-
The role of modelling in prioritising and planning clinical trials.
By Chilcott J, Brennan A, Booth A, Karnon J, Tappenden P.
-
Cost–benefit evaluation of routine influenza immunisation in people 65–74 years of age.
By Allsup S, Gosney M, Haycox A, Regan M.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of pulsatile machine perfusion versus cold storage of kidneys for transplantation retrieved from heart-beating and non-heart-beating donors.
By Wight J, Chilcott J, Holmes M, Brewer N.
-
Can randomised trials rely on existing electronic data? A feasibility study to explore the value of routine data in health technology assessment.
By Williams JG, Cheung WY, Cohen DR, Hutchings HA, Longo MF, Russell IT.
-
Evaluating non-randomised intervention studies.
By Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, D’Amico R, Sowden AJ, Sakarovitch C, Song F, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to assess the impact of a package comprising a patient-orientated, evidence-based self- help guidebook and patient-centred consultations on disease management and satisfaction in inflammatory bowel disease.
By Kennedy A, Nelson E, Reeves D, Richardson G, Roberts C, Robinson A, et al.
-
The effectiveness of diagnostic tests for the assessment of shoulder pain due to soft tissue disorders: a systematic review.
By Dinnes J, Loveman E, McIntyre L, Waugh N.
-
The value of digital imaging in diabetic retinopathy.
By Sharp PF, Olson J, Strachan F, Hipwell J, Ludbrook A, O’Donnell M, et al.
-
Lowering blood pressure to prevent myocardial infarction and stroke: a new preventive strategy.
By Law M, Wald N, Morris J.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of capecitabine and tegafur with uracil for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ward S, Kaltenthaler E, Cowan J, Brewer N.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of new and emerging technologies for early localised prostate cancer: a systematic review.
By Hummel S, Paisley S, Morgan A, Currie E, Brewer N.
-
Literature searching for clinical and cost-effectiveness studies used in health technology assessment reports carried out for the National Institute for Clinical Excellence appraisal system.
By Royle P, Waugh N.
-
Systematic review and economic decision modelling for the prevention and treatment of influenza A and B.
By Turner D, Wailoo A, Nicholson K, Cooper N, Sutton A, Abrams K.
-
A randomised controlled trial to evaluate the clinical and cost-effectiveness of Hickman line insertions in adult cancer patients by nurses.
By Boland A, Haycox A, Bagust A, Fitzsimmons L.
-
Redesigning postnatal care: a randomised controlled trial of protocol-based midwifery-led care focused on individual women’s physical and psychological health needs.
By MacArthur C, Winter HR, Bick DE, Lilford RJ, Lancashire RJ, Knowles H, et al.
-
Estimating implied rates of discount in healthcare decision-making.
By West RR, McNabb R, Thompson AGH, Sheldon TA, Grimley Evans J.
-
Systematic review of isolation policies in the hospital management of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a review of the literature with epidemiological and economic modelling.
By Cooper BS, Stone SP, Kibbler CC, Cookson BD, Roberts JA, Medley GF, et al.
-
Treatments for spasticity and pain in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review.
By Beard S, Hunn A, Wight J.
-
The inclusion of reports of randomised trials published in languages other than English in systematic reviews.
By Moher D, Pham B, Lawson ML, Klassen TP.
-
The impact of screening on future health-promoting behaviours and health beliefs: a systematic review.
By Bankhead CR, Brett J, Bukach C, Webster P, Stewart-Brown S, Munafo M, et al.
-
What is the best imaging strategy for acute stroke?
By Wardlaw JM, Keir SL, Seymour J, Lewis S, Sandercock PAG, Dennis MS, et al.
-
Systematic review and modelling of the investigation of acute and chronic chest pain presenting in primary care.
By Mant J, McManus RJ, Oakes RAL, Delaney BC, Barton PM, Deeks JJ, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of microwave and thermal balloon endometrial ablation for heavy menstrual bleeding: a systematic review and economic modelling.
By Garside R, Stein K, Wyatt K, Round A, Price A.
-
A systematic review of the role of bisphosphonates in metastatic disease.
By Ross JR, Saunders Y, Edmonds PM, Patel S, Wonderling D, Normand C, et al.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of capecitabine (Xeloda®) for locally advanced and/or metastatic breast cancer.
By Jones L, Hawkins N, Westwood M, Wright K, Richardson G, Riemsma R.
-
Effectiveness and efficiency of guideline dissemination and implementation strategies.
By Grimshaw JM, Thomas RE, MacLennan G, Fraser C, Ramsay CR, Vale L, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and costs of the Sugarbaker procedure for the treatment of pseudomyxoma peritonei.
By Bryant J, Clegg AJ, Sidhu MK, Brodin H, Royle P, Davidson P.
-
Psychological treatment for insomnia in the regulation of long-term hypnotic drug use.
By Morgan K, Dixon S, Mathers N, Thompson J, Tomeny M.
-
Improving the evaluation of therapeutic interventions in multiple sclerosis: development of a patient-based measure of outcome.
By Hobart JC, Riazi A, Lamping DL, Fitzpatrick R, Thompson AJ.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography compared with diagnostic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
By Kaltenthaler E, Bravo Vergel Y, Chilcott J, Thomas S, Blakeborough T, Walters SJ, et al.
-
The use of modelling to evaluate new drugs for patients with a chronic condition: the case of antibodies against tumour necrosis factor in rheumatoid arthritis.
By Barton P, Jobanputra P, Wilson J, Bryan S, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism using tandem mass spectrometry: a systematic review.
By Pandor A, Eastham J, Beverley C, Chilcott J, Paisley S.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pioglitazone and rosiglitazone in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Czoski-Murray C, Warren E, Chilcott J, Beverley C, Psyllaki MA, Cowan J.
-
Routine examination of the newborn: the EMREN study. Evaluation of an extension of the midwife role including a randomised controlled trial of appropriately trained midwives and paediatric senior house officers.
By Townsend J, Wolke D, Hayes J, Davé S, Rogers C, Bloomfield L, et al.
-
Involving consumers in research and development agenda setting for the NHS: developing an evidence-based approach.
By Oliver S, Clarke-Jones L, Rees R, Milne R, Buchanan P, Gabbay J, et al.
-
A multi-centre randomised controlled trial of minimally invasive direct coronary bypass grafting versus percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty with stenting for proximal stenosis of the left anterior descending coronary artery.
By Reeves BC, Angelini GD, Bryan AJ, Taylor FC, Cripps T, Spyt TJ, et al.
-
Does early magnetic resonance imaging influence management or improve outcome in patients referred to secondary care with low back pain? A pragmatic randomised controlled trial.
By Gilbert FJ, Grant AM, Gillan MGC, Vale L, Scott NW, Campbell MK, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of anakinra for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Clark W, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Burls A.
-
A rapid and systematic review and economic evaluation of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for treatment of mania associated with bipolar affective disorder.
By Bridle C, Palmer S, Bagnall A-M, Darba J, Duffy S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Liquid-based cytology in cervical screening: an updated rapid and systematic review and economic analysis.
By Karnon J, Peters J, Platt J, Chilcott J, McGoogan E, Brewer N.
-
Systematic review of the long-term effects and economic consequences of treatments for obesity and implications for health improvement.
By Avenell A, Broom J, Brown TJ, Poobalan A, Aucott L, Stearns SC, et al.
-
Autoantibody testing in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus.
By Dretzke J, Cummins C, Sandercock J, Fry-Smith A, Barrett T, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of prehospital intravenous fluids in trauma patients.
By Dretzke J, Sandercock J, Bayliss S, Burls A.
-
Newer hypnotic drugs for the short-term management of insomnia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Dündar Y, Boland A, Strobl J, Dodd S, Haycox A, Bagust A, et al.
-
Development and validation of methods for assessing the quality of diagnostic accuracy studies.
By Whiting P, Rutjes AWS, Dinnes J, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PMM, Kleijnen J.
-
EVALUATE hysterectomy trial: a multicentre randomised trial comparing abdominal, vaginal and laparoscopic methods of hysterectomy.
By Garry R, Fountain J, Brown J, Manca A, Mason S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Methods for expected value of information analysis in complex health economic models: developments on the health economics of interferon-β and glatiramer acetate for multiple sclerosis.
By Tappenden P, Chilcott JB, Eggington S, Oakley J, McCabe C.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of imatinib for first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia in chronic phase: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Dalziel K, Round A, Stein K, Garside R, Price A.
-
VenUS I: a randomised controlled trial of two types of bandage for treating venous leg ulcers.
By Iglesias C, Nelson EA, Cullum NA, Torgerson DJ, on behalf of the VenUS Team.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and economic evaluation, of myocardial perfusion scintigraphy for the diagnosis and management of angina and myocardial infarction.
By Mowatt G, Vale L, Brazzelli M, Hernandez R, Murray A, Scott N, et al.
-
A pilot study on the use of decision theory and value of information analysis as part of the NHS Health Technology Assessment programme.
By Claxton K, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Philips Z, Palmer S.
-
The Social Support and Family Health Study: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of two alternative forms of postnatal support for mothers living in disadvantaged inner-city areas.
By Wiggins M, Oakley A, Roberts I, Turner H, Rajan L, Austerberry H, et al.
-
Psychosocial aspects of genetic screening of pregnant women and newborns: a systematic review.
By Green JM, Hewison J, Bekker HL, Bryant, Cuckle HS.
-
Evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding: comparison of three outpatient procedures within cohorts defined by age and menopausal status.
By Critchley HOD, Warner P, Lee AJ, Brechin S, Guise J, Graham B.
-
Coronary artery stents: a rapid systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hill R, Bagust A, Bakhai A, Dickson R, Dündar Y, Haycox A, et al.
-
Review of guidelines for good practice in decision-analytic modelling in health technology assessment.
By Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Claxton K, Golder S, Riemsma R, et al.
-
Rituximab (MabThera®) for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Knight C, Hind D, Brewer N, Abbott V.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of clopidogrel and modified-release dipyridamole in the secondary prevention of occlusive vascular events: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jones L, Griffin S, Palmer S, Main C, Orton V, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Pegylated interferon α-2a and -2b in combination with ribavirin in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Brodin H, Cave C, Waugh N, Price A, Gabbay J.
-
Clopidogrel used in combination with aspirin compared with aspirin alone in the treatment of non-ST-segment- elevation acute coronary syndromes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Main C, Palmer S, Griffin S, Jones L, Orton V, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Provision, uptake and cost of cardiac rehabilitation programmes: improving services to under-represented groups.
By Beswick AD, Rees K, Griebsch I, Taylor FC, Burke M, West RR, et al.
-
Involving South Asian patients in clinical trials.
By Hussain-Gambles M, Leese B, Atkin K, Brown J, Mason S, Tovey P.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for diabetes.
By Colquitt JL, Green C, Sidhu MK, Hartwell D, Waugh N.
-
Identification and assessment of ongoing trials in health technology assessment reviews.
By Song FJ, Fry-Smith A, Davenport C, Bayliss S, Adi Y, Wilson JS, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of a long-acting insulin analogue, insulin glargine
By Warren E, Weatherley-Jones E, Chilcott J, Beverley C.
-
Supplementation of a home-based exercise programme with a class-based programme for people with osteoarthritis of the knees: a randomised controlled trial and health economic analysis.
By McCarthy CJ, Mills PM, Pullen R, Richardson G, Hawkins N, Roberts CR, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of once-daily versus more frequent use of same potency topical corticosteroids for atopic eczema: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Green C, Colquitt JL, Kirby J, Davidson P, Payne E.
-
Acupuncture of chronic headache disorders in primary care: randomised controlled trial and economic analysis.
By Vickers AJ, Rees RW, Zollman CE, McCarney R, Smith CM, Ellis N, et al.
-
Generalisability in economic evaluation studies in healthcare: a review and case studies.
By Sculpher MJ, Pang FS, Manca A, Drummond MF, Golder S, Urdahl H, et al.
-
Virtual outreach: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of joint teleconferenced medical consultations.
By Wallace P, Barber J, Clayton W, Currell R, Fleming K, Garner P, et al.
-
Randomised controlled multiple treatment comparison to provide a cost-effectiveness rationale for the selection of antimicrobial therapy in acne.
By Ozolins M, Eady EA, Avery A, Cunliffe WJ, O’Neill C, Simpson NB, et al.
-
Do the findings of case series studies vary significantly according to methodological characteristics?
By Dalziel K, Round A, Stein K, Garside R, Castelnuovo E, Payne L.
-
Improving the referral process for familial breast cancer genetic counselling: findings of three randomised controlled trials of two interventions.
By Wilson BJ, Torrance N, Mollison J, Wordsworth S, Gray JR, Haites NE, et al.
-
Randomised evaluation of alternative electrosurgical modalities to treat bladder outflow obstruction in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
By Fowler C, McAllister W, Plail R, Karim O, Yang Q.
-
A pragmatic randomised controlled trial of the cost-effectiveness of palliative therapies for patients with inoperable oesophageal cancer.
By Shenfine J, McNamee P, Steen N, Bond J, Griffin SM.
-
Impact of computer-aided detection prompts on the sensitivity and specificity of screening mammography.
By Taylor P, Champness J, Given- Wilson R, Johnston K, Potts H.
-
Issues in data monitoring and interim analysis of trials.
By Grant AM, Altman DG, Babiker AB, Campbell MK, Clemens FJ, Darbyshire JH, et al.
-
Lay public’s understanding of equipoise and randomisation in randomised controlled trials.
By Robinson EJ, Kerr CEP, Stevens AJ, Lilford RJ, Braunholtz DA, Edwards SJ, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of electroconvulsive therapy for depressive illness, schizophrenia, catatonia and mania: systematic reviews and economic modelling studies.
By Greenhalgh J, Knight C, Hind D, Beverley C, Walters S.
-
Measurement of health-related quality of life for people with dementia: development of a new instrument (DEMQOL) and an evaluation of current methodology.
By Smith SC, Lamping DL, Banerjee S, Harwood R, Foley B, Smith P, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of drotrecogin alfa (activated) (Xigris®) for the treatment of severe sepsis in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Green C, Dinnes J, Takeda A, Shepherd J, Hartwell D, Cave C, et al.
-
A methodological review of how heterogeneity has been examined in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy.
By Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kirby J, Roderick P.
-
Cervical screening programmes: can automation help? Evidence from systematic reviews, an economic analysis and a simulation modelling exercise applied to the UK.
By Willis BH, Barton P, Pearmain P, Bryan S, Hyde C.
-
Laparoscopic surgery for inguinal hernia repair: systematic review of effectiveness and economic evaluation.
By McCormack K, Wake B, Perez J, Fraser C, Cook J, McIntosh E, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness, tolerability and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for epilepsy in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wilby J, Kainth A, Hawkins N, Epstein D, McIntosh H, McDaid C, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to compare the cost-effectiveness of tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and lofepramine.
By Peveler R, Kendrick T, Buxton M, Longworth L, Baldwin D, Moore M, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of immediate angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hartwell D, Colquitt J, Loveman E, Clegg AJ, Brodin H, Waugh N, et al.
-
A randomised controlled comparison of alternative strategies in stroke care.
By Kalra L, Evans A, Perez I, Knapp M, Swift C, Donaldson N.
-
The investigation and analysis of critical incidents and adverse events in healthcare.
By Woloshynowych M, Rogers S, Taylor-Adams S, Vincent C.
-
Potential use of routine databases in health technology assessment.
By Raftery J, Roderick P, Stevens A.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of newer immunosuppressive regimens in renal transplantation: a systematic review and modelling study.
By Woodroffe R, Yao GL, Meads C, Bayliss S, Ready A, Raftery J, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene and teriparatide for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
By Stevenson M, Lloyd Jones M, De Nigris E, Brewer N, Davis S, Oakley J.
-
A systematic review to examine the impact of psycho-educational interventions on health outcomes and costs in adults and children with difficult asthma.
By Smith JR, Mugford M, Holland R, Candy B, Noble MJ, Harrison BDW, et al.
-
An evaluation of the costs, effectiveness and quality of renal replacement therapy provision in renal satellite units in England and Wales.
By Roderick P, Nicholson T, Armitage A, Mehta R, Mullee M, Gerard K, et al.
-
Imatinib for the treatment of patients with unresectable and/or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumours: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wilson J, Connock M, Song F, Yao G, Fry-Smith A, Raftery J, et al.
-
Indirect comparisons of competing interventions.
By Glenny AM, Altman DG, Song F, Sakarovitch C, Deeks JJ, D’Amico R, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of alternative strategies for the initial medical management of non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome: systematic review and decision-analytical modelling.
By Robinson M, Palmer S, Sculpher M, Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Bowens A, et al.
-
Outcomes of electrically stimulated gracilis neosphincter surgery.
By Tillin T, Chambers M, Feldman R.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pimecrolimus and tacrolimus for atopic eczema: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Stein K, Castelnuovo E, Pitt M, Ashcroft D, Dimmock P, et al.
-
Systematic review on urine albumin testing for early detection of diabetic complications.
By Newman DJ, Mattock MB, Dawnay ABS, Kerry S, McGuire A, Yaqoob M, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trial of the cost-effectiveness of water-based therapy for lower limb osteoarthritis.
By Cochrane T, Davey RC, Matthes Edwards SM.
-
Longer term clinical and economic benefits of offering acupuncture care to patients with chronic low back pain.
By Thomas KJ, MacPherson H, Ratcliffe J, Thorpe L, Brazier J, Campbell M, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness and safety of epidural steroids in the management of sciatica.
By Price C, Arden N, Coglan L, Rogers P.
-
The British Rheumatoid Outcome Study Group (BROSG) randomised controlled trial to compare the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of aggressive versus symptomatic therapy in established rheumatoid arthritis.
By Symmons D, Tricker K, Roberts C, Davies L, Dawes P, Scott DL.
-
Conceptual framework and systematic review of the effects of participants’ and professionals’ preferences in randomised controlled trials.
By King M, Nazareth I, Lampe F, Bower P, Chandler M, Morou M, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of implantable cardioverter defibrillators: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Brodin H, Loveman E, Payne E, Clegg A.
-
A trial of problem-solving by community mental health nurses for anxiety, depression and life difficulties among general practice patients. The CPN-GP study.
By Kendrick T, Simons L, Mynors-Wallis L, Gray A, Lathlean J, Pickering R, et al.
-
The causes and effects of socio-demographic exclusions from clinical trials.
By Bartlett C, Doyal L, Ebrahim S, Davey P, Bachmann M, Egger M, et al.
-
Is hydrotherapy cost-effective? A randomised controlled trial of combined hydrotherapy programmes compared with physiotherapy land techniques in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
By Epps H, Ginnelly L, Utley M, Southwood T, Gallivan S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial and cost-effectiveness study of systematic screening (targeted and total population screening) versus routine practice for the detection of atrial fibrillation in people aged 65 and over. The SAFE study.
By Hobbs FDR, Fitzmaurice DA, Mant J, Murray E, Jowett S, Bryan S, et al.
-
Displaced intracapsular hip fractures in fit, older people: a randomised comparison of reduction and fixation, bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty.
By Keating JF, Grant A, Masson M, Scott NW, Forbes JF.
-
Long-term outcome of cognitive behaviour therapy clinical trials in central Scotland.
By Durham RC, Chambers JA, Power KG, Sharp DM, Macdonald RR, Major KA, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of dual-chamber pacemakers compared with single-chamber pacemakers for bradycardia due to atrioventricular block or sick sinus syndrome: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Castelnuovo E, Stein K, Pitt M, Garside R, Payne E.
-
Newborn screening for congenital heart defects: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Knowles R, Griebsch I, Dezateux C, Brown J, Bull C, Wren C.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of left ventricular assist devices for end-stage heart failure: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clegg AJ, Scott DA, Loveman E, Colquitt J, Hutchinson J, Royle P, et al.
-
The effectiveness of the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph and laser diagnostic glaucoma scanning system (GDx) in detecting and monitoring glaucoma.
By Kwartz AJ, Henson DB, Harper RA, Spencer AF, McLeod D.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of autologous chondrocyte implantation for cartilage defects in knee joints: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clar C, Cummins E, McIntyre L, Thomas S, Lamb J, Bain L, et al.
-
Systematic review of effectiveness of different treatments for childhood retinoblastoma.
By McDaid C, Hartley S, Bagnall A-M, Ritchie G, Light K, Riemsma R.
-
Towards evidence-based guidelines for the prevention of venous thromboembolism: systematic reviews of mechanical methods, oral anticoagulation, dextran and regional anaesthesia as thromboprophylaxis.
By Roderick P, Ferris G, Wilson K, Halls H, Jackson D, Collins R, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of parent training/education programmes for the treatment of conduct disorder, including oppositional defiant disorder, in children.
By Dretzke J, Frew E, Davenport C, Barlow J, Stewart-Brown S, Sandercock J, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine and memantine for Alzheimer’s disease.
By Loveman E, Green C, Kirby J, Takeda A, Picot J, Payne E, et al.
-
FOOD: a multicentre randomised trial evaluating feeding policies in patients admitted to hospital with a recent stroke.
By Dennis M, Lewis S, Cranswick G, Forbes J.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computed tomography screening for lung cancer: systematic reviews.
By Black C, Bagust A, Boland A, Walker S, McLeod C, De Verteuil R, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of neuroimaging assessments used to visualise the seizure focus in people with refractory epilepsy being considered for surgery.
By Whiting P, Gupta R, Burch J, Mujica Mota RE, Wright K, Marson A, et al.
-
Comparison of conference abstracts and presentations with full-text articles in the health technology assessments of rapidly evolving technologies.
By Dundar Y, Dodd S, Dickson R, Walley T, Haycox A, Williamson PR.
-
Systematic review and evaluation of methods of assessing urinary incontinence.
By Martin JL, Williams KS, Abrams KR, Turner DA, Sutton AJ, Chapple C, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for children with epilepsy. A systematic review.
By Connock M, Frew E, Evans B-W, Bryan S, Cummins C, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Surveillance of Barrett’s oesophagus: exploring the uncertainty through systematic review, expert workshop and economic modelling.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Somerville M, Stein K, Price A, Gilbert N.
-
Topotecan, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride and paclitaxel for second-line or subsequent treatment of advanced ovarian cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Main C, Bojke L, Griffin S, Norman G, Barbieri M, Mather L, et al.
-
Evaluation of molecular techniques in prediction and diagnosis of cytomegalovirus disease in immunocompromised patients.
By Szczepura A, Westmoreland D, Vinogradova Y, Fox J, Clark M.
-
Screening for thrombophilia in high-risk situations: systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. The Thrombosis: Risk and Economic Assessment of Thrombophilia Screening (TREATS) study.
By Wu O, Robertson L, Twaddle S, Lowe GDO, Clark P, Greaves M, et al.
-
A series of systematic reviews to inform a decision analysis for sampling and treating infected diabetic foot ulcers.
By Nelson EA, O’Meara S, Craig D, Iglesias C, Golder S, Dalton J, et al.
-
Randomised clinical trial, observational study and assessment of cost-effectiveness of the treatment of varicose veins (REACTIV trial).
By Michaels JA, Campbell WB, Brazier JE, MacIntyre JB, Palfreyman SJ, Ratcliffe J, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of screening for oral cancer in primary care.
By Speight PM, Palmer S, Moles DR, Downer MC, Smith DH, Henriksson M, et al.
-
Measurement of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of non-invasive diagnostic testing strategies for deep vein thrombosis.
By Goodacre S, Sampson F, Stevenson M, Wailoo A, Sutton A, Thomas S, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of HealOzone® for the treatment of occlusal pit/fissure caries and root caries.
By Brazzelli M, McKenzie L, Fielding S, Fraser C, Clarkson J, Kilonzo M, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trials of conventional antipsychotic versus new atypical drugs, and new atypical drugs versus clozapine, in people with schizophrenia responding poorly to, or intolerant of, current drug treatment.
By Lewis SW, Davies L, Jones PB, Barnes TRE, Murray RM, Kerwin R, et al.
-
Diagnostic tests and algorithms used in the investigation of haematuria: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.
By Rodgers M, Nixon J, Hempel S, Aho T, Kelly J, Neal D, et al.
-
Cognitive behavioural therapy in addition to antispasmodic therapy for irritable bowel syndrome in primary care: randomised controlled trial.
By Kennedy TM, Chalder T, McCrone P, Darnley S, Knapp M, Jones RH, et al.
-
A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapies for Fabry’s disease and mucopolysaccharidosis type 1.
By Connock M, Juarez-Garcia A, Frew E, Mans A, Dretzke J, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Health benefits of antiviral therapy for mild chronic hepatitis C: randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation.
By Wright M, Grieve R, Roberts J, Main J, Thomas HC, on behalf of the UK Mild Hepatitis C Trial Investigators.
-
Pressure relieving support surfaces: a randomised evaluation.
By Nixon J, Nelson EA, Cranny G, Iglesias CP, Hawkins K, Cullum NA, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of methylphenidate, dexamfetamine and atomoxetine for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents.
By King S, Griffin S, Hodges Z, Weatherly H, Asseburg C, Richardson G, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy for Gaucher’s disease: a systematic review.
By Connock M, Burls A, Frew E, Fry-Smith A, Juarez-Garcia A, McCabe C, et al.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of salicylic acid and cryotherapy for cutaneous warts. An economic decision model.
By Thomas KS, Keogh-Brown MR, Chalmers JR, Fordham RJ, Holland RC, Armstrong SJ, et al.
-
A systematic literature review of the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions to prevent wandering in dementia and evaluation of the ethical implications and acceptability of their use.
By Robinson L, Hutchings D, Corner L, Beyer F, Dickinson H, Vanoli A, et al.
-
A review of the evidence on the effects and costs of implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in different patient groups, and modelling of cost-effectiveness and cost–utility for these groups in a UK context.
By Buxton M, Caine N, Chase D, Connelly D, Grace A, Jackson C, et al.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Takeda A, Davidson P, Price A.
-
An evaluation of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of pulmonary artery catheters in patient management in intensive care: a systematic review and a randomised controlled trial.
By Harvey S, Stevens K, Harrison D, Young D, Brampton W, McCabe C, et al.
-
Accurate, practical and cost-effective assessment of carotid stenosis in the UK.
By Wardlaw JM, Chappell FM, Stevenson M, De Nigris E, Thomas S, Gillard J, et al.
-
Etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Woolacott N, Bravo Vergel Y, Hawkins N, Kainth A, Khadjesari Z, Misso K, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of testing for hepatitis C in former injecting drug users.
By Castelnuovo E, Thompson-Coon J, Pitt M, Cramp M, Siebert U, Price A, et al.
-
Computerised cognitive behaviour therapy for depression and anxiety update: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Kaltenthaler E, Brazier J, De Nigris E, Tumur I, Ferriter M, Beverley C, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.
By Williams C, Brunskill S, Altman D, Briggs A, Campbell H, Clarke M, et al.
-
Psychological therapies including dialectical behaviour therapy for borderline personality disorder: a systematic review and preliminary economic evaluation.
By Brazier J, Tumur I, Holmes M, Ferriter M, Parry G, Dent-Brown K, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of tests for the diagnosis and investigation of urinary tract infection in children: a systematic review and economic model.
By Whiting P, Westwood M, Bojke L, Palmer S, Richardson G, Cooper J, et al.
-
Cognitive behavioural therapy in chronic fatigue syndrome: a randomised controlled trial of an outpatient group programme.
By O’Dowd H, Gladwell P, Rogers CA, Hollinghurst S, Gregory A.
-
A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling.
By Brown TJ, Hooper L, Elliott RA, Payne K, Webb R, Roberts C, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computed tomography screening for coronary artery disease: systematic review.
By Waugh N, Black C, Walker S, McIntyre L, Cummins E, Hillis G.
-
What are the clinical outcome and cost-effectiveness of endoscopy undertaken by nurses when compared with doctors? A Multi-Institution Nurse Endoscopy Trial (MINuET).
By Williams J, Russell I, Durai D, Cheung W-Y, Farrin A, Bloor K, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of oxaliplatin and capecitabine for the adjuvant treatment of colon cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Pandor A, Eggington S, Paisley S, Tappenden P, Sutcliffe P.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness.
By Chen Y-F, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Jowett S, Bryan S, Clark W, et al.
-
Telemedicine in dermatology: a randomised controlled trial.
By Bowns IR, Collins K, Walters SJ, McDonagh AJG.
-
Cost-effectiveness of cell salvage and alternative methods of minimising perioperative allogeneic blood transfusion: a systematic review and economic model.
By Davies L, Brown TJ, Haynes S, Payne K, Elliott RA, McCollum C.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancer: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.
By Murray A, Lourenco T, de Verteuil R, Hernandez R, Fraser C, McKinley A, et al.
-
Etanercept and efalizumab for the treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review.
By Woolacott N, Hawkins N, Mason A, Kainth A, Khadjesari Z, Bravo Vergel Y, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of clinical decision tools for acute abdominal pain.
By Liu JLY, Wyatt JC, Deeks JJ, Clamp S, Keen J, Verde P, et al.
-
Evaluation of the ventricular assist device programme in the UK.
By Sharples L, Buxton M, Caine N, Cafferty F, Demiris N, Dyer M, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of immunosuppressive therapy for renal transplantation in children.
By Yao G, Albon E, Adi Y, Milford D, Bayliss S, Ready A, et al.
-
Amniocentesis results: investigation of anxiety. The ARIA trial.
By Hewison J, Nixon J, Fountain J, Cocks K, Jones C, Mason G, et al.
-
Pemetrexed disodium for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Dundar Y, Bagust A, Dickson R, Dodd S, Green J, Haycox A, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of docetaxel in combination with prednisone or prednisolone for the treatment of hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer.
By Collins R, Fenwick E, Trowman R, Perard R, Norman G, Light K, et al.
-
A systematic review of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of tuberculosis infection.
By Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kunst H, Gibson A, Cummins E, Waugh N, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women.
By Stevenson M, Davis S, Lloyd-Jones M, Beverley C.
-
A systematic review of quantitative and qualitative research on the role and effectiveness of written information available to patients about individual medicines.
By Raynor DK, Blenkinsopp A, Knapp P, Grime J, Nicolson DJ, Pollock K, et al.
-
Oral naltrexone as a treatment for relapse prevention in formerly opioid-dependent drug users: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Adi Y, Juarez-Garcia A, Wang D, Jowett S, Frew E, Day E, et al.
-
Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: a systematic review and cost–utility analysis.
By Kanis JA, Stevenson M, McCloskey EV, Davis S, Lloyd-Jones M.
-
Epidemiological, social, diagnostic and economic evaluation of population screening for genital chlamydial infection.
By Low N, McCarthy A, Macleod J, Salisbury C, Campbell R, Roberts TE, et al.
-
Methadone and buprenorphine for the management of opioid dependence: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Connock M, Juarez-Garcia A, Jowett S, Frew E, Liu Z, Taylor RJ, et al.
-
Exercise Evaluation Randomised Trial (EXERT): a randomised trial comparing GP referral for leisure centre-based exercise, community-based walking and advice only.
By Isaacs AJ, Critchley JA, See Tai S, Buckingham K, Westley D, Harridge SDR, et al.
-
Interferon alfa (pegylated and non-pegylated) and ribavirin for the treatment of mild chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Hartwell D, Davidson P, Price A, Waugh N.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of bevacizumab and cetuximab for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.
By Tappenden P, Jones R, Paisley S, Carroll C.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of epoetin alfa, epoetin beta and darbepoetin alfa in anaemia associated with cancer, especially that attributable to cancer treatment.
By Wilson J, Yao GL, Raftery J, Bohlius J, Brunskill S, Sandercock J, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of statins for the prevention of coronary events.
By Ward S, Lloyd Jones M, Pandor A, Holmes M, Ara R, Ryan A, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of different models of community-based respite care for frail older people and their carers.
By Mason A, Weatherly H, Spilsbury K, Arksey H, Golder S, Adamson J, et al.
-
Additional therapy for young children with spastic cerebral palsy: a randomised controlled trial.
By Weindling AM, Cunningham CC, Glenn SM, Edwards RT, Reeves DJ.
-
Screening for type 2 diabetes: literature review and economic modelling.
By Waugh N, Scotland G, McNamee P, Gillett M, Brennan A, Goyder E, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cinacalcet for secondary hyperparathyroidism in end-stage renal disease patients on dialysis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Anderson R, Mealing S, Roome C, Snaith A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of gemcitabine for metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Takeda AL, Jones J, Loveman E, Tan SC, Clegg AJ.
-
A systematic review of duplex ultrasound, magnetic resonance angiography and computed tomography angiography for the diagnosis and assessment of symptomatic, lower limb peripheral arterial disease.
By Collins R, Cranny G, Burch J, Aguiar-Ibáñez R, Craig D, Wright K, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of treatments for children with idiopathic steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome: a systematic review.
By Colquitt JL, Kirby J, Green C, Cooper K, Trompeter RS.
-
A systematic review of the routine monitoring of growth in children of primary school age to identify growth-related conditions.
By Fayter D, Nixon J, Hartley S, Rithalia A, Butler G, Rudolf M, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness of preventing and treating Staphylococcus aureus carriage in reducing peritoneal catheter-related infections.
By McCormack K, Rabindranath K, Kilonzo M, Vale L, Fraser C, McIntyre L, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation versus electroconvulsive therapy in severe depression: a multicentre pragmatic randomised controlled trial and economic analysis.
By McLoughlin DM, Mogg A, Eranti S, Pluck G, Purvis R, Edwards D, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of direct versus indirect and individual versus group modes of speech and language therapy for children with primary language impairment.
By Boyle J, McCartney E, Forbes J, O’Hare A.
-
Hormonal therapies for early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hind D, Ward S, De Nigris E, Simpson E, Carroll C, Wyld L.
-
Cardioprotection against the toxic effects of anthracyclines given to children with cancer: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Picot J, Levitt G, Sullivan I, Baxter L, Clegg A.
-
Adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By McLeod C, Bagust A, Boland A, Dagenais P, Dickson R, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Prenatal screening and treatment strategies to prevent group B streptococcal and other bacterial infections in early infancy: cost-effectiveness and expected value of information analyses.
By Colbourn T, Asseburg C, Bojke L, Philips Z, Claxton K, Ades AE, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bone morphogenetic proteins in the non-healing of fractures and spinal fusion: a systematic review.
By Garrison KR, Donell S, Ryder J, Shemilt I, Mugford M, Harvey I, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial of postoperative radiotherapy following breast-conserving surgery in a minimum-risk older population. The PRIME trial.
By Prescott RJ, Kunkler IH, Williams LJ, King CC, Jack W, van der Pol M, et al.
-
Current practice, accuracy, effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the school entry hearing screen.
By Bamford J, Fortnum H, Bristow K, Smith J, Vamvakas G, Davies L, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of inhaled insulin in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Black C, Cummins E, Royle P, Philip S, Waugh N.
-
Surveillance of cirrhosis for hepatocellular carcinoma: systematic review and economic analysis.
By Thompson Coon J, Rogers G, Hewson P, Wright D, Anderson R, Cramp M, et al.
-
The Birmingham Rehabilitation Uptake Maximisation Study (BRUM). Homebased compared with hospital-based cardiac rehabilitation in a multi-ethnic population: cost-effectiveness and patient adherence.
By Jolly K, Taylor R, Lip GYH, Greenfield S, Raftery J, Mant J, et al.
-
A systematic review of the clinical, public health and cost-effectiveness of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection and identification of bacterial intestinal pathogens in faeces and food.
By Abubakar I, Irvine L, Aldus CF, Wyatt GM, Fordham R, Schelenz S, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial examining the longer-term outcomes of standard versus new antiepileptic drugs. The SANAD trial.
By Marson AG, Appleton R, Baker GA, Chadwick DW, Doughty J, Eaton B, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of different models of managing long-term oral anti-coagulation therapy: a systematic review and economic modelling.
By Connock M, Stevens C, Fry-Smith A, Jowett S, Fitzmaurice D, Moore D, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of interventions for preventing relapse in people with bipolar disorder.
By Soares-Weiser K, Bravo Vergel Y, Beynon S, Dunn G, Barbieri M, Duffy S, et al.
-
Taxanes for the adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ward S, Simpson E, Davis S, Hind D, Rees A, Wilkinson A.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening for open angle glaucoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burr JM, Mowatt G, Hernández R, Siddiqui MAR, Cook J, Lourenco T, et al.
-
Acceptability, benefit and costs of early screening for hearing disability: a study of potential screening tests and models.
By Davis A, Smith P, Ferguson M, Stephens D, Gianopoulos I.
-
Contamination in trials of educational interventions.
By Keogh-Brown MR, Bachmann MO, Shepstone L, Hewitt C, Howe A, Ramsay CR, et al.
-
Overview of the clinical effectiveness of positron emission tomography imaging in selected cancers.
By Facey K, Bradbury I, Laking G, Payne E.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Anderson R, Rogers G, Dyer M, Mealing S, et al.
-
Drug-eluting stents: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hill RA, Boland A, Dickson R, Dündar Y, Haycox A, McLeod C, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cardiac resynchronisation (biventricular pacing) for heart failure: systematic review and economic model.
By Fox M, Mealing S, Anderson R, Dean J, Stein K, Price A, et al.
-
Recruitment to randomised trials: strategies for trial enrolment and participation study. The STEPS study.
By Campbell MK, Snowdon C, Francis D, Elbourne D, McDonald AM, Knight R, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of functional cardiac testing in the diagnosis and management of coronary artery disease: a randomised controlled trial. The CECaT trial.
By Sharples L, Hughes V, Crean A, Dyer M, Buxton M, Goldsmith K, et al.
-
Evaluation of diagnostic tests when there is no gold standard. A review of methods.
By Rutjes AWS, Reitsma JB, Coomarasamy A, Khan KS, Bossuyt PMM.
-
Systematic reviews of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors in acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
By Leontiadis GI, Sreedharan A, Dorward S, Barton P, Delaney B, Howden CW, et al.
-
A review and critique of modelling in prioritising and designing screening programmes.
By Karnon J, Goyder E, Tappenden P, McPhie S, Towers I, Brazier J, et al.
-
An assessment of the impact of the NHS Health Technology Assessment Programme.
By Hanney S, Buxton M, Green C, Coulson D, Raftery J.
-
A systematic review and economic model of switching from nonglycopeptide to glycopeptide antibiotic prophylaxis for surgery.
By Cranny G, Elliott R, Weatherly H, Chambers D, Hawkins N, Myers L, et al.
-
‘Cut down to quit’ with nicotine replacement therapies in smoking cessation: a systematic review of effectiveness and economic analysis.
By Wang D, Connock M, Barton P, Fry-Smith A, Aveyard P, Moore D.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of strategies for reducing fracture risk in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis with additional data on long-term risk of fracture and cost of disease management.
By Thornton J, Ashcroft D, O’Neill T, Elliott R, Adams J, Roberts C, et al.
-
Does befriending by trained lay workers improve psychological well-being and quality of life for carers of people with dementia, and at what cost? A randomised controlled trial.
By Charlesworth G, Shepstone L, Wilson E, Thalanany M, Mugford M, Poland F.
-
A multi-centre retrospective cohort study comparing the efficacy, safety and cost-effectiveness of hysterectomy and uterine artery embolisation for the treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroids. The HOPEFUL study.
By Hirst A, Dutton S, Wu O, Briggs A, Edwards C, Waldenmaier L, et al.
-
Methods of prediction and prevention of pre-eclampsia: systematic reviews of accuracy and effectiveness literature with economic modelling.
By Meads CA, Cnossen JS, Meher S, Juarez-Garcia A, ter Riet G, Duley L, et al.
-
The use of economic evaluations in NHS decision-making: a review and empirical investigation.
By Williams I, McIver S, Moore D, Bryan S.
-
Stapled haemorrhoidectomy (haemorrhoidopexy) for the treatment of haemorrhoids: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burch J, Epstein D, Baba-Akbari A, Weatherly H, Fox D, Golder S, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness of diabetes education models for Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.
By Loveman E, Frampton GK, Clegg AJ.
-
Payment to healthcare professionals for patient recruitment to trials: systematic review and qualitative study.
By Raftery J, Bryant J, Powell J, Kerr C, Hawker S.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (etodolac, meloxicam, celecoxib, rofecoxib, etoricoxib, valdecoxib and lumiracoxib) for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Chen Y-F, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Fry-Smith A, Harris G, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of central venous catheters treated with anti-infective agents in preventing bloodstream infections: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hockenhull JC, Dwan K, Boland A, Smith G, Bagust A, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Stepped treatment of older adults on laxatives. The STOOL trial.
By Mihaylov S, Stark C, McColl E, Steen N, Vanoli A, Rubin G, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial of cognitive behaviour therapy in adolescents with major depression treated by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. The ADAPT trial.
By Goodyer IM, Dubicka B, Wilkinson P, Kelvin R, Roberts C, Byford S, et al.
-
The use of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hind D, Tappenden P, Tumur I, Eggington E, Sutcliffe P, Ryan A.
-
Ranibizumab and pegaptanib for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Colquitt JL, Jones J, Tan SC, Takeda A, Clegg AJ, Price A.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of 64-slice or higher computed tomography angiography as an alternative to invasive coronary angiography in the investigation of coronary artery disease.
By Mowatt G, Cummins E, Waugh N, Walker S, Cook J, Jia X, et al.
-
Structural neuroimaging in psychosis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Albon E, Tsourapas A, Frew E, Davenport C, Oyebode F, Bayliss S, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children aged 12 years and over.
By Shepherd J, Rogers G, Anderson R, Main C, Thompson-Coon J, Hartwell D, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years.
By Main C, Shepherd J, Anderson R, Rogers G, Thompson-Coon J, Liu Z, et al.
-
Ezetimibe for the treatment of hypercholesterolaemia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ara R, Tumur I, Pandor A, Duenas A, Williams R, Wilkinson A, et al.
-
Topical or oral ibuprofen for chronic knee pain in older people. The TOIB study.
By Underwood M, Ashby D, Carnes D, Castelnuovo E, Cross P, Harding G, et al.
-
A prospective randomised comparison of minor surgery in primary and secondary care. The MiSTIC trial.
By George S, Pockney P, Primrose J, Smith H, Little P, Kinley H, et al.
-
A review and critical appraisal of measures of therapist–patient interactions in mental health settings.
By Cahill J, Barkham M, Hardy G, Gilbody S, Richards D, Bower P, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening programmes for amblyopia and strabismus in children up to the age of 4–5 years: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Carlton J, Karnon J, Czoski-Murray C, Smith KJ, Marr J.
-
A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness and economic modelling of minimal incision total hip replacement approaches in the management of arthritic disease of the hip.
By de Verteuil R, Imamura M, Zhu S, Glazener C, Fraser C, Munro N, et al.
-
A preliminary model-based assessment of the cost–utility of a screening programme for early age-related macular degeneration.
By Karnon J, Czoski-Murray C, Smith K, Brand C, Chakravarthy U, Davis S, et al.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Frampton GK, Tanajewski L, Turner D, Price A.
-
Absorbent products for urinary/faecal incontinence: a comparative evaluation of key product categories.
By Fader M, Cottenden A, Getliffe K, Gage H, Clarke-O’Neill S, Jamieson K, et al.
-
A systematic review of repetitive functional task practice with modelling of resource use, costs and effectiveness.
By French B, Leathley M, Sutton C, McAdam J, Thomas L, Forster A, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectivness of minimal access surgery amongst people with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease – a UK collaborative study. The reflux trial.
By Grant A, Wileman S, Ramsay C, Bojke L, Epstein D, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Time to full publication of studies of anti-cancer medicines for breast cancer and the potential for publication bias: a short systematic review.
By Takeda A, Loveman E, Harris P, Hartwell D, Welch K.
-
Performance of screening tests for child physical abuse in accident and emergency departments.
By Woodman J, Pitt M, Wentz R, Taylor B, Hodes D, Gilbert RE.
-
Curative catheter ablation in atrial fibrillation and typical atrial flutter: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Rodgers M, McKenna C, Palmer S, Chambers D, Van Hout S, Golder S, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic modelling of effectiveness and cost utility of surgical treatments for men with benign prostatic enlargement.
By Lourenco T, Armstrong N, N’Dow J, Nabi G, Deverill M, Pickard R, et al.
-
Immunoprophylaxis against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) with palivizumab in children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wang D, Cummins C, Bayliss S, Sandercock J, Burls A.
-
Deferasirox for the treatment of iron overload associated with regular blood transfusions (transfusional haemosiderosis) in patients suffering with chronic anaemia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By McLeod C, Fleeman N, Kirkham J, Bagust A, Boland A, Chu P, et al.
-
Thrombophilia testing in people with venous thromboembolism: systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Simpson EL, Stevenson MD, Rawdin A, Papaioannou D.
-
Surgical procedures and non-surgical devices for the management of non-apnoeic snoring: a systematic review of clinical effects and associated treatment costs.
By Main C, Liu Z, Welch K, Weiner G, Quentin Jones S, Stein K.
-
Continuous positive airway pressure devices for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea–hypopnoea syndrome: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By McDaid C, Griffin S, Weatherly H, Durée K, van der Burgt M, van Hout S, Akers J, et al.
-
Use of classical and novel biomarkers as prognostic risk factors for localised prostate cancer: a systematic review.
By Sutcliffe P, Hummel S, Simpson E, Young T, Rees A, Wilkinson A, et al.
-
The harmful health effects of recreational ecstasy: a systematic review of observational evidence.
By Rogers G, Elston J, Garside R, Roome C, Taylor R, Younger P, et al.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of oesophageal Doppler monitoring in critically ill and high-risk surgical patients.
By Mowatt G, Houston G, Hernández R, de Verteuil R, Fraser C, Cuthbertson B, et al.
-
The use of surrogate outcomes in model-based cost-effectiveness analyses: a survey of UK Health Technology Assessment reports.
By Taylor RS, Elston J.
-
Controlling Hypertension and Hypotension Immediately Post Stroke (CHHIPS) – a randomised controlled trial.
By Potter J, Mistri A, Brodie F, Chernova J, Wilson E, Jagger C, et al.
-
Routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis for RhD-negative women: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Pilgrim H, Lloyd-Jones M, Rees A.
-
Amantadine, oseltamivir and zanamivir for the prophylaxis of influenza (including a review of existing guidance no. 67): a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Tappenden P, Jackson R, Cooper K, Rees A, Simpson E, Read R, et al.
-
Improving the evaluation of therapeutic interventions in multiple sclerosis: the role of new psychometric methods.
By Hobart J, Cano S.
-
Treatment of severe ankle sprain: a pragmatic randomised controlled trial comparing the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of three types of mechanical ankle support with tubular bandage. The CAST trial.
By Cooke MW, Marsh JL, Clark M, Nakash R, Jarvis RM, Hutton JL, et al. , on behalf of the CAST trial group.
-
Non-occupational postexposure prophylaxis for HIV: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Baxter L, Hird S.
-
Blood glucose self-monitoring in type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial.
By Farmer AJ, Wade AN, French DP, Simon J, Yudkin P, Gray A, et al.
-
How far does screening women for domestic (partner) violence in different health-care settings meet criteria for a screening programme? Systematic reviews of nine UK National Screening Committee criteria.
By Feder G, Ramsay J, Dunne D, Rose M, Arsene C, Norman R, et al.
-
Spinal cord stimulation for chronic pain of neuropathic or ischaemic origin: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Simpson, EL, Duenas A, Holmes MW, Papaioannou D, Chilcott J.
-
The role of magnetic resonance imaging in the identification of suspected acoustic neuroma: a systematic review of clinical and costeffectiveness and natural history.
By Fortnum H, O’Neill C, Taylor R, Lenthall R, Nikolopoulos T, Lightfoot G, et al.
-
Dipsticks and diagnostic algorithms in urinary tract infection: development and validation, randomised trial, economic analysis, observational cohort and qualitative study.
By Little P, Turner S, Rumsby K, Warner G, Moore M, Lowes JA, et al.
-
Systematic review of respite care in the frail elderly.
By Shaw C, McNamara R, Abrams K, Cannings-John R, Hood K, Longo M, et al.
-
Neuroleptics in the treatment of aggressive challenging behaviour for people with intellectual disabilities: a randomised controlled trial (NACHBID).
By Tyrer P, Oliver-Africano P, Romeo R, Knapp M, Dickens S, Bouras N, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trial to determine the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors plus supportive care, versus supportive care alone, for mild to moderate depression with somatic symptoms in primary care: the THREAD (THREshold for AntiDepressant response) study.
By Kendrick T, Chatwin J, Dowrick C, Tylee A, Morriss R, Peveler R, et al.
-
Diagnostic strategies using DNA testing for hereditary haemochromatosis in at-risk populations: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Cooper K, Picot J, Clegg A, Roderick P, Rosenberg W, et al.
-
Enhanced external counterpulsation for the treatment of stable angina and heart failure: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By McKenna C, McDaid C, Suekarran S, Hawkins N, Claxton K, Light K, et al.
-
Development of a decision support tool for primary care management of patients with abnormal liver function tests without clinically apparent liver disease: a record-linkage population cohort study and decision analysis (ALFIE).
By Donnan PT, McLernon D, Dillon JF, Ryder S, Roderick P, Sullivan F, et al.
-
A systematic review of presumed consent systems for deceased organ donation.
By Rithalia A, McDaid C, Suekarran S, Norman G, Myers L, Sowden A.
-
Paracetamol and ibuprofen for the treatment of fever in children: the PITCH randomised controlled trial.
By Hay AD, Redmond NM, Costelloe C, Montgomery AA, Fletcher M, Hollinghurst S, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to compare minimally invasive glucose monitoring devices with conventional monitoring in the management of insulin-treated diabetes mellitus (MITRE).
By Newman SP, Cooke D, Casbard A, Walker S, Meredith S, Nunn A, et al.
-
Sensitivity analysis in economic evaluation: an audit of NICE current practice and a review of its use and value in decision-making.
By Andronis L, Barton P, Bryan S.
-
Trastuzumab for the treatment of primary breast cancer in HER2-positive women: a single technology appraisal.
By Ward S, Pilgrim H, Hind D.
-
Docetaxel for the adjuvant treatment of early node-positive breast cancer: a single technology appraisal.
By Chilcott J, Lloyd Jones M, Wilkinson A.
-
The use of paclitaxel in the management of early stage breast cancer.
By Griffin S, Dunn G, Palmer S, Macfarlane K, Brent S, Dyker A, et al.
-
Rituximab for the first-line treatment of stage III/IV follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
By Dundar Y, Bagust A, Hounsome J, McLeod C, Boland A, Davis H, et al.
-
Bortezomib for the treatment of multiple myeloma patients.
By Green C, Bryant J, Takeda A, Cooper K, Clegg A, Smith A, et al.
-
Fludarabine phosphate for the firstline treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.
By Walker S, Palmer S, Erhorn S, Brent S, Dyker A, Ferrie L, et al.
-
Erlotinib for the treatment of relapsed non-small cell lung cancer.
By McLeod C, Bagust A, Boland A, Hockenhull J, Dundar Y, Proudlove C, et al.
-
Cetuximab plus radiotherapy for the treatment of locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
By Griffin S, Walker S, Sculpher M, White S, Erhorn S, Brent S, et al.
-
Infliximab for the treatment of adults with psoriasis.
By Loveman E, Turner D, Hartwell D, Cooper K, Clegg A
-
Psychological interventions for postnatal depression: cluster randomised trial and economic evaluation. The PoNDER trial.
By Morrell CJ, Warner R, Slade P, Dixon S, Walters S, Paley G, et al.
-
The effect of different treatment durations of clopidogrel in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes: a systematic review and value of information analysis.
By Rogowski R, Burch J, Palmer S, Craigs C, Golder S, Woolacott N.
-
Systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of diagnosis of heart failure, with modelling of implications of different diagnostic strategies in primary care.
By Mant J, Doust J, Roalfe A, Barton P, Cowie MR, Glasziou P, et al.
-
A multicentre randomised controlled trial of the use of continuous positive airway pressure and non-invasive positive pressure ventilation in the early treatment of patients presenting to the emergency department with severe acute cardiogenic pulmonary oedema: the 3CPO trial.
By Gray AJ, Goodacre S, Newby DE, Masson MA, Sampson F, Dixon S, et al. , on behalf of the 3CPO study investigators.
-
Early high-dose lipid-lowering therapy to avoid cardiac events: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ara R, Pandor A, Stevens J, Rees A, Rafia R.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alpha for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: an updated systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jones J, Shepherd J, Baxter L, Gospodarevskaya E, Hartwell D, Harris P, et al.
-
Methods to identify postnatal depression in primary care: an integrated evidence synthesis and value of information analysis.
By Hewitt CE, Gilbody SM, Brealey S, Paulden M, Palmer S, Mann R, et al.
-
A double-blind randomised placebocontrolled trial of topical intranasal corticosteroids in 4- to 11-year-old children with persistent bilateral otitis media with effusion in primary care.
By Williamson I, Benge S, Barton S, Petrou S, Letley L, Fasey N, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of methods of storing donated kidneys from deceased donors: a systematic review and economic model.
By Bond M, Pitt M, Akoh J, Moxham T, Hoyle M, Anderson R.
-
Rehabilitation of older patients: day hospital compared with rehabilitation at home. A randomised controlled trial.
By Parker SG, Oliver P, Pennington M, Bond J, Jagger C, Enderby PM, et al.
-
Breastfeeding promotion for infants in neonatal units: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Renfrew MJ, Craig D, Dyson L, McCormick F, Rice S, King SE, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of bariatric (weight loss) surgery for obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Picot J, Jones J, Colquitt JL, Gospodarevskaya E, Loveman E, Baxter L, et al.
-
Rapid testing for group B streptococcus during labour: a test accuracy study with evaluation of acceptability and cost-effectiveness.
By Daniels J, Gray J, Pattison H, Roberts T, Edwards E, Milner P, et al.
Health Technology Assessment programme
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
Prioritisation Strategy Group
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
-
Dr Bob Coates, Consultant Advisor, NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Andrew Cook, Consultant Advisor, NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Peter Davidson, Director of Science Support, NETSCC, HTA
-
Professor Robin E Ferner, Consultant Physician and Director, West Midlands Centre for Adverse Drug Reactions, City Hospital NHS Trust, Birmingham
-
Professor Paul Glasziou, Professor of Evidence-Based Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Dr Nick Hicks, Director of NHS Support, NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Edmund Jessop, Medical Adviser, National Specialist, National Commissioning Group (NCG), Department of Health, London
-
Ms Lynn Kerridge, Chief Executive Officer, NETSCC and NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Ruairidh Milne, Director of Strategy and Development, NETSCC
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Ms Pamela Young, Specialist Programme Manager, NETSCC, HTA
HTA Commissioning Board
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
-
Senior Lecturer in General Practice, Department of Primary Health Care, University of Oxford
-
Professor Ann Ashburn, Professor of Rehabilitation and Head of Research, Southampton General Hospital
-
Professor Deborah Ashby, Professor of Medical Statistics, Queen Mary, University of London
-
Professor John Cairns, Professor of Health Economics, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Peter Croft, Director of Primary Care Sciences Research Centre, Keele University
-
Professor Nicky Cullum, Director of Centre for Evidence-Based Nursing, University of York
-
Professor Jenny Donovan, Professor of Social Medicine, University of Bristol
-
Professor Steve Halligan, Professor of Gastrointestinal Radiology, University College Hospital, London
-
Professor Freddie Hamdy, Professor of Urology, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Allan House, Professor of Liaison Psychiatry, University of Leeds
-
Dr Martin J Landray, Reader in Epidemiology, Honorary Consultant Physician, Clinical Trial Service Unit, University of Oxford?
-
Professor Stuart Logan, Director of Health & Social Care Research, The Peninsula Medical School, Universities of Exeter and Plymouth
-
Dr Rafael Perera, Lecturer in Medical Statisitics, Department of Primary Health Care, Univeristy of Oxford
-
Professor Ian Roberts, Professor of Epidemiology & Public Health, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Mark Sculpher, Professor of Health Economics, University of York
-
Professor Helen Smith, Professor of Primary Care, University of Brighton
-
Professor Kate Thomas, Professor of Complementary & Alternative Medicine Research, University of Leeds
-
Professor David John Torgerson, Director of York Trials Unit, University of York
-
Professor Hywel Williams, Professor of Dermato-Epidemiology, University of Nottingham
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Medical Research Council
Diagnostic Technologies & Screening Panel
-
Professor of Evidence-Based Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Consultant Paediatrician and Honorary Senior Lecturer, Great Ormond Street Hospital, London
-
Professor Judith E Adams, Consultant Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Central Manchester & Manchester Children’s University Hospitals NHS Trust, and Professor of Diagnostic Radiology, Imaging Science and Biomedical Engineering, Cancer & Imaging Sciences, University of Manchester
-
Ms Jane Bates, Consultant Ultrasound Practitioner, Ultrasound Department, Leeds Teaching Hospital NHS Trust
-
Dr Stephanie Dancer, Consultant Microbiologist, Hairmyres Hospital, East Kilbride
-
Professor Glyn Elwyn, Primary Medical Care Research Group, Swansea Clinical School, University of Wales
-
Dr Ron Gray, Consultant Clinical Epidemiologist, Department of Public Health, University of Oxford
-
Professor Paul D Griffiths, Professor of Radiology, University of Sheffield
-
Dr Jennifer J Kurinczuk, Consultant Clinical Epidemiologist, National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, Oxford
-
Dr Susanne M Ludgate, Medical Director, Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency, London
-
Dr Anne Mackie, Director of Programmes, UK National Screening Committee
-
Dr Michael Millar, Consultant Senior Lecturer in Microbiology, Barts and The London NHS Trust, Royal London Hospital
-
Mr Stephen Pilling, Director, Centre for Outcomes, Research & Effectiveness, Joint Director, National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health, University College London
-
Mrs Una Rennard, Service User Representative
-
Dr Phil Shackley, Senior Lecturer in Health Economics, School of Population and Health Sciences, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Dr W Stuart A Smellie, Consultant in Chemical Pathology, Bishop Auckland General Hospital
-
Dr Nicholas Summerton, Consultant Clinical and Public Health Advisor, NICE
-
Ms Dawn Talbot, Service User Representative
-
Dr Graham Taylor, Scientific Advisor, Regional DNA Laboratory, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Professor Lindsay Wilson Turnbull, Scientific Director of the Centre for Magnetic Resonance Investigations and YCR Professor of Radiology, Hull Royal Infirmary
-
Dr Tim Elliott, Team Leader, Cancer Screening, Department of Health
-
Dr Catherine Moody, Programme Manager, Neuroscience and Mental Health Board
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Pharmaceuticals Panel
-
Consultant Physician and Director, West Midlands Centre for Adverse Drug Reactions, City Hospital NHS Trust, Birmingham
-
Professor in Child Health, University of Nottingham
-
Mrs Nicola Carey, Senior Research Fellow, School of Health and Social Care, The University of Reading
-
Mr John Chapman, Service User Representative
-
Dr Peter Elton, Director of Public Health, Bury Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Ben Goldacre, Research Fellow, Division of Psychological Medicine and Psychiatry, King’s College London
-
Mrs Barbara Greggains, Service User Representative
-
Dr Bill Gutteridge, Medical Adviser, London Strategic Health Authority
-
Dr Dyfrig Hughes, Reader in Pharmacoeconomics and Deputy Director, Centre for Economics and Policy in Health, IMSCaR, Bangor University
-
Professor Jonathan Ledermann, Professor of Medical Oncology and Director of the Cancer Research UK and University College London Cancer Trials Centre
-
Dr Yoon K Loke, Senior Lecturer in Clinical Pharmacology, University of East Anglia
-
Professor Femi Oyebode, Consultant Psychiatrist and Head of Department, University of Birmingham
-
Dr Andrew Prentice, Senior Lecturer and Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, The Rosie Hospital, University of Cambridge
-
Dr Martin Shelly, General Practitioner, Leeds, and Associate Director, NHS Clinical Governance Support Team, Leicester
-
Dr Gillian Shepherd, Director, Health and Clinical Excellence, Merck Serono Ltd
-
Mrs Katrina Simister, Assistant Director New Medicines, National Prescribing Centre, Liverpool
-
Mr David Symes, Service User Representative
-
Dr Lesley Wise, Unit Manager, Pharmacoepidemiology Research Unit, VRMM, Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Mr Simon Reeve, Head of Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness, Medicines, Pharmacy and Industry Group, Department of Health
-
Dr Heike Weber, Programme Manager, Medical Research Council
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Therapeutic Procedures Panel
-
Consultant Physician, North Bristol NHS Trust
-
Professor of Psychiatry, Division of Health in the Community, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Professor Jane Barlow, Professor of Public Health in the Early Years, Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, Coventry
-
Ms Maree Barnett, Acting Branch Head of Vascular Programme, Department of Health
-
Mrs Val Carlill, Service User Representative
-
Mrs Anthea De Barton-Watson, Service User Representative
-
Mr Mark Emberton, Senior Lecturer in Oncological Urology, Institute of Urology, University College Hospital, London
-
Professor Steve Goodacre, Professor of Emergency Medicine, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Christopher Griffiths, Professor of Primary Care, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Mr Paul Hilton, Consultant Gynaecologist and Urogynaecologist, Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Nicholas James, Professor of Clinical Oncology, University of Birmingham, and Consultant in Clinical Oncology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital
-
Dr Peter Martin, Consultant Neurologist, Addenbrooke’s Hospital, Cambridge
-
Dr Kate Radford, Senior Lecturer (Research), Clinical Practice Research Unit, University of Central Lancashire, Preston
-
Mr Jim Reece Service User Representative
-
Dr Karen Roberts, Nurse Consultant, Dunston Hill Hospital Cottages
-
Dr Phillip Leech, Principal Medical Officer for Primary Care, Department of Health
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Medical Research Council
-
Professor Tom Walley, Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Disease Prevention Panel
-
Medical Adviser, National Specialist, National Commissioning Group (NCG), London
-
Director, NHS Sustainable Development Unit, Cambridge
-
Dr Elizabeth Fellow-Smith, Medical Director, West London Mental Health Trust, Middlesex
-
Dr John Jackson, General Practitioner, Parkway Medical Centre, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Mike Kelly, Director, Centre for Public Health Excellence, NICE, London
-
Dr Chris McCall, General Practitioner, The Hadleigh Practice, Corfe Mullen, Dorset
-
Ms Jeanett Martin, Director of Nursing, BarnDoc Limited, Lewisham Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Julie Mytton, Locum Consultant in Public Health Medicine, Bristol Primary Care Trust
-
Miss Nicky Mullany, Service User Representative
-
Professor Ian Roberts, Professor of Epidemiology and Public Health, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Ken Stein, Senior Clinical Lecturer in Public Health, University of Exeter
-
Dr Kieran Sweeney, Honorary Clinical Senior Lecturer, Peninsula College of Medicine and Dentistry, Universities of Exeter and Plymouth
-
Professor Carol Tannahill, Glasgow Centre for Population Health
-
Professor Margaret Thorogood, Professor of Epidemiology, University of Warwick Medical School, Coventry
-
Ms Christine McGuire, Research & Development, Department of Health
-
Dr Caroline Stone, Programme Manager, Medical Research Council
Expert Advisory Network
-
Professor Douglas Altman, Professor of Statistics in Medicine, Centre for Statistics in Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Professor John Bond, Professor of Social Gerontology & Health Services Research, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Andrew Bradbury, Professor of Vascular Surgery, Solihull Hospital, Birmingham
-
Mr Shaun Brogan, Chief Executive, Ridgeway Primary Care Group, Aylesbury
-
Mrs Stella Burnside OBE, Chief Executive, Regulation and Improvement Authority, Belfast
-
Ms Tracy Bury, Project Manager, World Confederation for Physical Therapy, London
-
Professor Iain T Cameron, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology and Head of the School of Medicine, University of Southampton
-
Dr Christine Clark, Medical Writer and Consultant Pharmacist, Rossendale
-
Professor Collette Clifford, Professor of Nursing and Head of Research, The Medical School, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Barry Cookson, Director, Laboratory of Hospital Infection, Public Health Laboratory Service, London
-
Dr Carl Counsell, Clinical Senior Lecturer in Neurology, University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Howard Cuckle, Professor of Reproductive Epidemiology, Department of Paediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynaecology, University of Leeds
-
Dr Katherine Darton, Information Unit, MIND – The Mental Health Charity, London
-
Professor Carol Dezateux, Professor of Paediatric Epidemiology, Institute of Child Health, London
-
Mr John Dunning, Consultant Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Papworth Hospital NHS Trust, Cambridge
-
Mr Jonothan Earnshaw, Consultant Vascular Surgeon, Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Gloucester
-
Professor Martin Eccles, Professor of Clinical Effectiveness, Centre for Health Services Research, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Pam Enderby, Dean of Faculty of Medicine, Institute of General Practice and Primary Care, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Gene Feder, Professor of Primary Care Research & Development, Centre for Health Sciences, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Mr Leonard R Fenwick, Chief Executive, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Mrs Gillian Fletcher, Antenatal Teacher and Tutor and President, National Childbirth Trust, Henfield
-
Professor Jayne Franklyn, Professor of Medicine, University of Birmingham
-
Mr Tam Fry, Honorary Chairman, Child Growth Foundation, London
-
Professor Fiona Gilbert, Consultant Radiologist and NCRN Member, University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Paul Gregg, Professor of Orthopaedic Surgical Science, South Tees Hospital NHS Trust
-
Bec Hanley, Co-director, TwoCan Associates, West Sussex
-
Dr Maryann L Hardy, Senior Lecturer, University of Bradford
-
Mrs Sharon Hart, Healthcare Management Consultant, Reading
-
Professor Robert E Hawkins, CRC Professor and Director of Medical Oncology, Christie CRC Research Centre, Christie Hospital NHS Trust, Manchester
-
Professor Richard Hobbs, Head of Department of Primary Care & General Practice, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Alan Horwich, Dean and Section Chairman, The Institute of Cancer Research, London
-
Professor Allen Hutchinson, Director of Public Health and Deputy Dean of ScHARR, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Peter Jones, Professor of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge
-
Professor Stan Kaye, Cancer Research UK Professor of Medical Oncology, Royal Marsden Hospital and Institute of Cancer Research, Surrey
-
Dr Duncan Keeley, General Practitioner (Dr Burch & Ptnrs), The Health Centre, Thame
-
Dr Donna Lamping, Research Degrees Programme Director and Reader in Psychology, Health Services Research Unit, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London
-
Mr George Levvy, Chief Executive, Motor Neurone Disease Association, Northampton
-
Professor James Lindesay, Professor of Psychiatry for the Elderly, University of Leicester
-
Professor Julian Little, Professor of Human Genome Epidemiology, University of Ottawa
-
Professor Alistaire McGuire, Professor of Health Economics, London School of Economics
-
Professor Rajan Madhok, Medical Director and Director of Public Health, Directorate of Clinical Strategy & Public Health, North & East Yorkshire & Northern Lincolnshire Health Authority, York
-
Professor Alexander Markham, Director, Molecular Medicine Unit, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Dr Peter Moore, Freelance Science Writer, Ashtead
-
Dr Andrew Mortimore, Public Health Director, Southampton City Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Sue Moss, Associate Director, Cancer Screening Evaluation Unit, Institute of Cancer Research, Sutton
-
Professor Miranda Mugford, Professor of Health Economics and Group Co-ordinator, University of East Anglia
-
Professor Jim Neilson, Head of School of Reproductive & Developmental Medicine and Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, University of Liverpool
-
Mrs Julietta Patnick, National Co-ordinator, NHS Cancer Screening Programmes, Sheffield
-
Professor Robert Peveler, Professor of Liaison Psychiatry, Royal South Hants Hospital, Southampton
-
Professor Chris Price, Director of Clinical Research, Bayer Diagnostics Europe, Stoke Poges
-
Professor William Rosenberg, Professor of Hepatology and Consultant Physician, University of Southampton
-
Professor Peter Sandercock, Professor of Medical Neurology, Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Edinburgh
-
Dr Susan Schonfield, Consultant in Public Health, Hillingdon Primary Care Trust, Middlesex
-
Dr Eamonn Sheridan, Consultant in Clinical Genetics, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Dr Margaret Somerville, Director of Public Health Learning, Peninsula Medical School, University of Plymouth
-
Professor Sarah Stewart-Brown, Professor of Public Health, Division of Health in the Community, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Professor Ala Szczepura, Professor of Health Service Research, Centre for Health Services Studies, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Mrs Joan Webster, Consumer Member, Southern Derbyshire Community Health Council
-
Professor Martin Whittle, Clinical Co-director, National Co-ordinating Centre for Women’s and Children’s Health, Lymington