Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was commissioned by the HTA programme as project number 07/02/01. The contractual start date was in October 2007. The draft report began editorial review in October 2008 and was accepted for publication in May 2009. As the funder, by devising a commissioning brief, the HTA programme specified the research question and study design. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the referees for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
TRL Griffiths has attended a consensus panel meeting of bladder cancer experts which was supported by an educational grant from GE Healthcare, who market and distribute Hexvix (hexaminolevulinate). TRL Griffiths has also received honoraria from Karl Storz, manufacturers of cystoscopic equipment including the core component of the PDD light unit, for contributing to educational programmes.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© 2010 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO. This journal may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NETSCC, Health Technology Assessment, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2010 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Background
Description of health problem
Introduction
Bladder cancer, or more precisely malignant neoplasm of the bladder,1 is a disease in which the cells lining the urinary bladder lose the ability to regulate their growth and start dividing uncontrollably. 2 This abnormal growth results in a mass of cells that form a tumour. People with a suspicion of bladder cancer mainly present with urinary symptoms including gross haematuria, microscopic haematuria and urinary tract symptoms. Bladder cancers can be broadly categorised into two main groups depending upon their extent of penetration into the bladder wall: non-muscle invasive and muscle invasive. The majority of diagnosed patients (75–85%) present with non-muscle-invasive disease, which as described in the next subsection is characterised by a probability of recurrence at 5 years from 31% (95% CI 24% to 37%) to 78% (95% CI 73% to 84%) despite treatment. 3 The remaining cancers are muscle invasive and/or metastatic.
Aetiology, pathology and prognosis
Aetiology
The aetiology of bladder cancer appears to be multifactorial, with environmental and genetic factors as well as endogenous molecular factors having potential roles. The risk of developing bladder cancer before the age of 75 years is 2–4% for men and 0.5–1% for women. 4 Cigarette smoking and specific occupational exposures are the main known risk factors for bladder cancer. 5 In Europe it is estimated that up to half of bladder cancer cases in men and one-third of cases in women are caused by cigarette smoking. 6,7
Occupational exposure to chemicals in Europe accounts for up to 10% of male bladder cancers. Most carcinogens have a latent period of 15–20 years between exposure and the development of tumours. The proportion may be higher in countries with less well-regulated industrial processes. Bladder cancer has an important place in the history of occupational disease. In 1895, Rehn reported cases of bladder cancer in a German aniline dye factory. It was then recognised that aromatic amines and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, by-products of the catabolic process, were the key aetiological factors. Aromatic amines were widely used in the manufacture of dyes and pigments for textiles, paints, plastics, paper and hair dyes, and in drugs and pesticides and in the rubber industry. In 1953, bladder cancer became a prescribed industrial disease in the UK. 8 Occupational studies of hairdressers have produced conflicting results. Within the EU, the Scientific Committee on Cosmetic Products and Non-Food Products aims to set up a ‘high-risk’ permanent and semi-permanent register of hair dye formulations.
Several dietary factors have been related to bladder cancer, but the results of different studies have been controversial. A meta-analysis9 of 38 articles supported the hypothesis that vegetable and fruit intake reduced the risk of bladder cancer. Phenacetin, chlornaphazine and cyclophosphamide also increase the risk of bladder cancer. 10 In comparison to other carcinogenic agents, the latency period is relatively short. Acrolein, a metabolite of cyclophosphamide, is responsible for the ninefold increased risk of bladder cancer associated with cyclophosphamide. In addition, chronic infection by Schistosoma haematobium is a cause of squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder. Patients treated with pelvic radiotherapy for cervical and prostate cancers also have an increased risk of developing bladder cancer. 11,12
Drug- and carcinogen-metabolising enzymes are important in the processing of lipophilic chemicals to products that are more water-soluble and can be excreted. These enzyme systems are partly controlled by genetic polymorphism. In the liver, chemicals are oxidised by the cytochrome P450 superfamily and detoxified by N-acetylation, predominantly by N-acetyltransferases (NAT). Aromatic amines are usually detoxified by NAT2. NAT2 slow acetylator genotypes are at increased risk of bladder cancer [relative risk (RR) 1.4], and this may be especially true in smokers. 13 Approximately 50% of Caucasians and 25% of Asians are slow acetylators. Glutathione S-transferase (GST) is the product of the GSTM1 gene and is involved in the detoxification of polyaromatic hydrocarbons. Approximately 50% of Caucasians and Asians have a homozygous deletion of the GSTM1 gene, which is associated with a RR of 1.4. 14 There is no clear evidence that the underlying pathogenesis of bladder cancer differs by gender. 10
Pathology
Bladder cancer is a disease in which the cells lining the urinary bladder lose the ability to regulate their growth and start dividing uncontrollably. This abnormal growth results in a mass of cells that form a tumour. The most common type of bladder cancer is transitional cell carcinoma (TCC), which accounts for more than 90% of bladder cancers in the UK; other forms of bladder cancer include squamous carcinoma, adenocarcinoma (urachal and non-urachal), small cell carcinoma, sarcoma and lymphoma. TCC, also known as urothelial carcinoma, arises from changes in the urothelial cells that line the bladder, ureters, renal pelvis and proximal urethra, although TCC is approximately 50 times more common in the bladder than in other parts of the urinary tract. 15 The 2002 TNM staging system of the International Union against Cancer (UICC) 2002 is the most recent pathological staging system (Table 1). 16 About 25% of newly diagnosed TCCs of the bladder are muscle invasive (T2–T4); the remainder are non-muscle invasive, either papillary (70%) or a flat lesion of the urothelium termed carcinoma in situ (CIS) (5%).
| Primary tumour (T) | Regional lymph nodes (N) | Distant metastasis (M) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TX | Primary tumour cannot be assessed | NX | Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed | MX | Distant metastasis cannot be assessed |
| T0 | No evidence of primary tumour | N0 | No regional lymph node metastasis | M0 | No distant metastasis |
| Ta | Non-invasive papillary carcinoma | N1 | Metastasis in a single lymph node, 2 cm or less in greatest dimension | M1 | Distant metastasis |
| Tis | Carcinoma in situ: ‘flat tumour’ | N2 | Metastasis in a single lymph node, more than 2 cm but not more than 5 cm in greatest dimension; or multiple lymph nodes, none more than 5 cm in greatest dimension | ||
| T1 | Tumour invades subepithelial connective tissue | N3 | Metastasis in a lymph node, more than 5 cm in greatest dimension | ||
| T2 | Tumour invades muscle | ||||
| pT2a | Tumour invades superficial muscle | ||||
| pT2b | Tumour invades deep muscle | ||||
| T3 | Tumour invades perivesical tissue | ||||
| pT3a | As for T3 – microscopically | ||||
| pT3b | As for T3 – macroscopically | ||||
| T4 | Tumour invades any of the following – prostate, uterus, vagina, pelvic wall, abdominal wall | ||||
| T4a | Tumour invades prostate, uterus, vagina | ||||
| T4b | Tumour invades pelvic or abdominal wall | ||||
For more than three decades, the preferred grading system in the UK for bladder TCC has been the World Health Organization (WHO) 1973 classification,17 which has been repeatedly validated and shown to be of clinical relevance for treatment and prognosis. WHO 1973 divides TCC into three grades on the basis of cytological and architectural disorder, grade 1 being well differentiated, grade 2 moderately differentiated and grade 3 poorly differentiated. WHO 2004 is the latest version of the bladder TCC classification. Current reporting guidelines recommend providing the urologist with both classifications. The main differences are two grades of carcinoma (high grade and low grade) and the introduction of the term papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential (PUNLMP) to replace the best differentiated grade 1 tumours, avoiding the term carcinoma. However, there has been considerable resistance in the UK to adopting the WHO 2004 classification, which was not prospectively validated before its introduction and which has subsequently not demonstrated either improved reproducibility or clinical relevance over WHO 1973. 18 In this report we will therefore only quote the WHO 1973 classification.
Prognosis
The natural history of treated non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (Ta/T1/CIS), a group of heterogeneous cancers, can be summarised as any of the following:
-
no further recurrence
-
local recurrence, which can occur on a single occasion or on multiple occasions; it can involve single or multiple tumour recurrences, but recurrent tumours are usually of the same stage and grade as the primary tumour
-
local progression – an increase in local stage over time to muscle invasion or the appearance of distant metastases and subsequent death.
On average, non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer has a probability of recurrence at 5 years from 31% (95% CI 24% to 37%) to 78% (95% CI 73% to 84%) and of progression of between 0.8% (95% CI 0% to 1.7%) and 45% (95% CI 35% to 55%) after initial treatment. 3 The rates of recurrence and progression vary depending upon the stage, grade and number of tumours at the time of first presentation. Of the newly diagnosed non-muscle-invasive bladder tumours, approximately 30% are multifocal at presentation. There is little information on the predictive role of environmental and genetic risk factors on tumour recurrence, progression and mortality. Tumours are most likely to recur within 5 years after transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT),19 and therefore patients are closely monitored for recurrence following their initial presentation and treatment. According to the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC), the risk factors relating to recurrence and progression include the number of tumours present at diagnosis, the recurrence rate in the previous period, the tumour size (larger tumours being associated with greater risk), stage, grade and the presence of concomitant CIS. 20 The poor prognosis of T1G3 TCC is well described; 50% progression rate if associated with concomitant CIS. 21 If primary CIS is diffuse, 50% of these patients die of metastatic TCC within a year or two if maintenance intravesical immunotherapy with bacillus Calmette–Guerin (BCG) is not instituted. Once the tumour has invaded the detrusor muscle, 50% of patients have occult metastatic disease at presentation.
Epidemiology
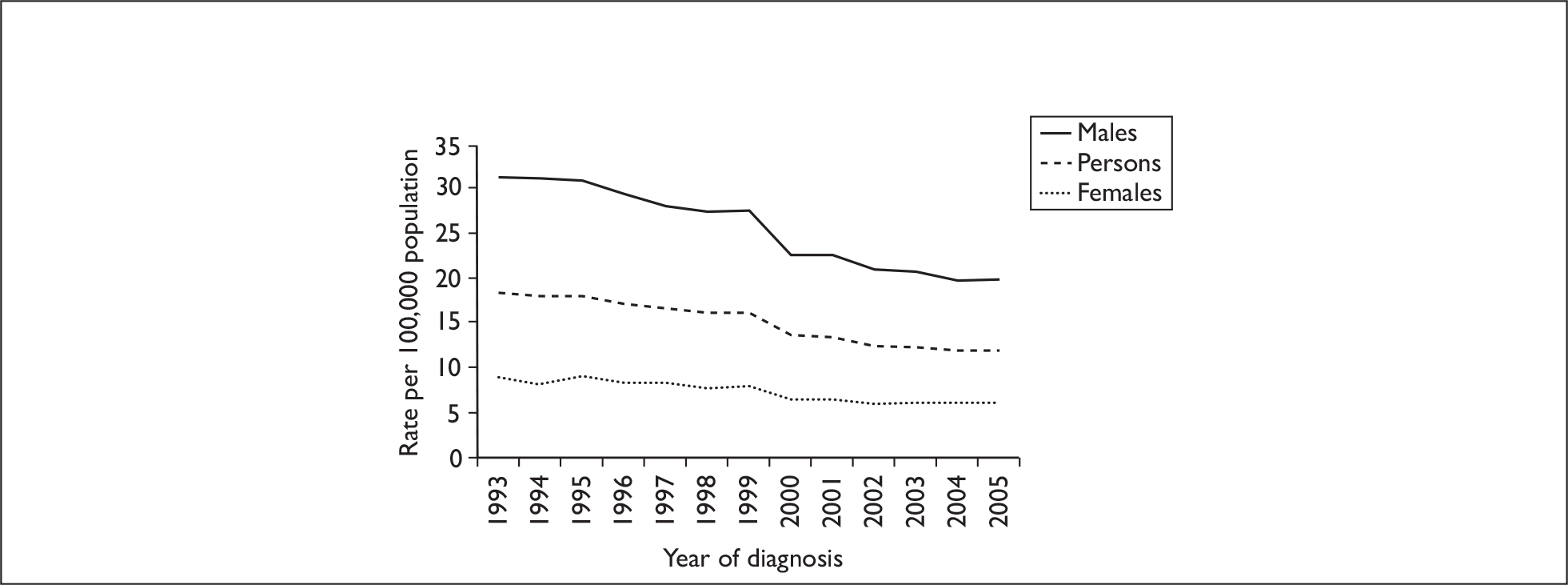
Bladder cancer is the sixth most common cancer in the UK. 22 Bladder cancer is the most frequently occurring tumour of the urinary system and accounts for 1 in every 28 new cases of cancer diagnosed each year in the UK. During the last three decades there has been a gradual decrease in the incidence of bladder cancer (Figure 1). 22 However, changing trends in the incidence of bladder cancer over time are difficult to interpret because of different and changing classifications and coding practices of the condition. 5
FIGURE 1.
Age-standardised (European) incidence rates of bladder cancer by sex, UK, 1993–2004.
Incidence and prevalence
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men and the tenth most common in women in the UK. 22 In 2005, the estimated male and female crude incidence rates of bladder cancer were 24.6 and 9.3 per 100,000 population with 6091 and 2403 new cases, respectively, in England, and 43.0 and 17.2 per 100,000 population with 619 and 260 new cases, respectively, in Wales (Table 2). 22
| England | Wales | Scotland | N. Ireland | UK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | |||||
| Male | 6091 | 619 | 468 | 132 | 7310 |
| Female | 2403 | 260 | 247 | 58 | 2968 |
| Total | 8494 | 879 | 715 | 190 | 10,278 |
| Crude rate per 100,000 population | |||||
| Male | 24.6 | 43.0 | 19.1 | 15.6 | 24.8 |
| Female | 9.3 | 17.2 | 9.4 | 6.6 | 9.7 |
| Total | 16.8 | 29.8 | 14.0 | 11.0 | 17.1 |
| Age-standardised rate (European) per 100,000 population | |||||
| Male | 19.6 | 31.6 | 15.5 | 15.0 | 19.8 |
| Female | 5.7 | 10.1 | 5.6 | 4.4 | 5.9 |
| Total | 11.7 | 19.6 | 9.8 | 9.1 | 11.9 |
Although the overall incidence of bladder cancer in the UK has remained much higher in men than in women in the last five decades, it has shown a slow decrease between 1993 and 2005 (Figure 1) following a rapid rise between 1971 and 1993. 22,23 In addition, in England and Wales, the prevalence of bladder cancer increased by 57% between 1971 and 1998, particularly in women. 23
Variation in incidence by age
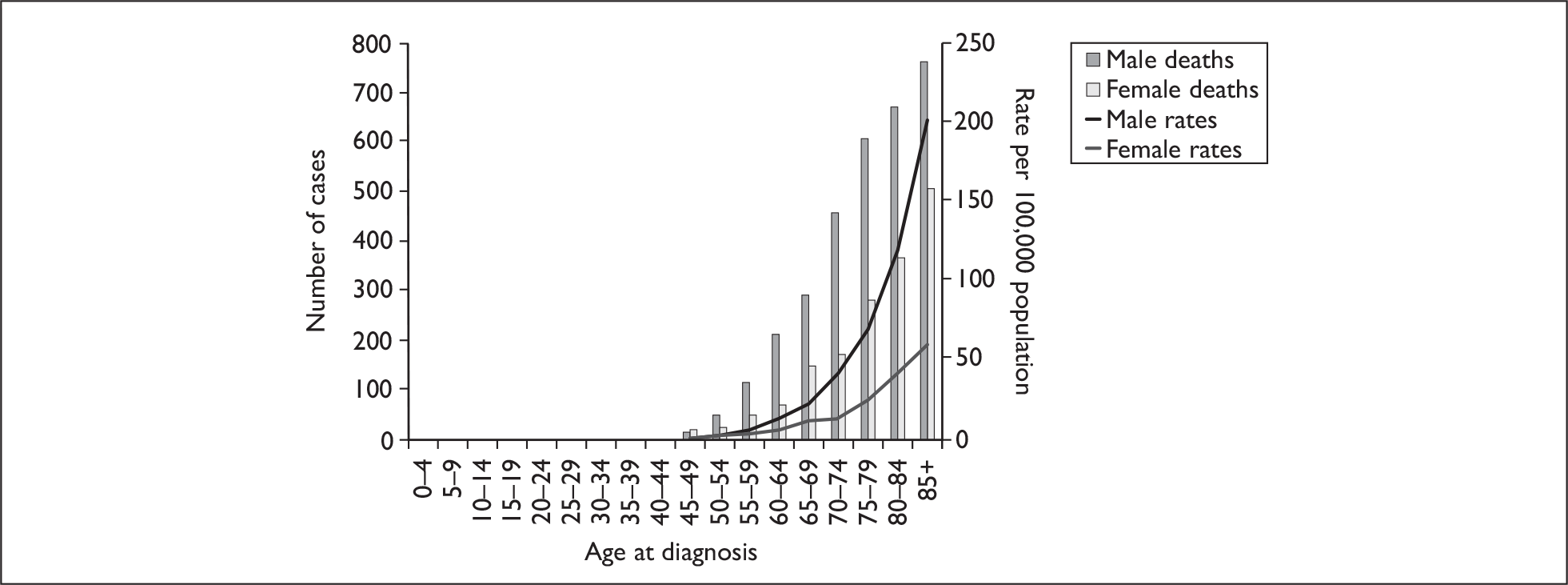
The mean age at which bladder cancer is diagnosed in the UK is 71.3 years. The incidence and mortality rate of bladder cancer rapidly increase with increasing age (Figures 2 and 3). Bladder cancer commonly occurs in older people and is rare in people under 50 years of age.
FIGURE 2.
Numbers of new cases and age-specific incidence rates of bladder cancer by sex, England and Wales, 2005.

FIGURE 3.
Numbers of deaths from and age-specific mortality rates of bladder cancer by sex, UK, 2006.
Variation in incidence by deprivation and geography
In the UK the incidence of bladder cancer also varies according to socioeconomic status and geographical area. Data from Cancer Research UK22 show that the incidence is likely to be slightly increased in areas of deprivation, with the lowest incidence found in the most affluent groups.
Geographical patterns of bladder cancer incidence are difficult to interpret because of differences in the way in which bladder tumours are classified between cancer registries, for example differences between UK and Northern Ireland. Such differences also hinder reliable international comparisons.
Impact of the health problem
Significance for patients in terms of ill-health
Although most non-muscle-invasive bladder cancers are unlikely to be life-threatening they are associated with high recurrence and variable progression rates, which result in an impaired quality of life. Untreated bladder cancer is associated with significant morbidity, such as haematuria, dysuria, irritative urinary symptoms, urinary retention, incontinence, ureteral obstruction and pelvic pain. In addition to the physical damage caused, bladder cancer also has a severe effect on work status, sexual life and mental health. A consequence of our population living longer will be an increased incidence of bladder cancer with resulting increased morbidity and mortality. At the same time, less smokers in the population may slow the rate of increase.
In the UK and also in other countries, unlike other common cancers, men with bladder cancer have consistently higher survival rates than women and this also extends to stage-specific survival. Although men seem to be diagnosed at a slightly earlier stage than women, the reasons for this male survival advantage remain unclear.
Patients with non-muscle-invasive tumours have 5-year survival rates of between 80% and 90%. 5 However, patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer have 5-year survival rates of less than 50%, because, although radical treatment deals effectively with locally invasive disease, many patients die from metastatic disease, which may have been micrometastatic at presentation. 24 Early detection while the tumour is still at a non-muscle-invasive stage is therefore very important.
Patients with early bladder cancer may fall into one of three different groups: (1) those with low-risk disease in whom the main risk is recurrent low-risk disease with a small chance of ever dying of bladder cancer; (2) those with high-risk superficial disease in whom there is a high chance of disease progression and subsequent death from bladder cancer; and (3) those with muscle-invasive disease in whom there is imminent risk of death from bladder cancer. In groups 2 and 3, inaccurate diagnosis/follow-up may have life-threatening consequences, whereas in group 1 the main impact of follow-up is to prevent morbidity rather than mortality. Therefore the clinical needs of these groups differ with respect to diagnostic performance.
Significance for the NHS
Bladder cancer is considered to be the most expensive cancer in terms of lifetime and treatment costs because of the high recurrence rates. A higher incidence of non-muscle-invasive disease, longer survival requiring lifelong surveillance and treatment of recurrences are some of the reasons for the higher cost of non-muscle-invasive disease compared with muscle-invasive bladder cancers. However, annual research fund allocation for bladder cancer from the National Cancer Research Institute (NCRI) UK is less than those for other cancers.
Current service provision
Diagnosis
Haematuria is presence of blood in the urine and is the most common symptom of bladder cancer. Bladder cancer is detected in approximately 10% of patients with gross haematuria and 3–5% of those with microscopic haematuria aged over 40 years. 25,26 Less commonly, individuals may note disturbance in their urinary habits including complaints of dysuria (painful urination), increased frequency, urgency of urination, failed attempts to urinate and urinary tract infection. These symptoms can raise suspicion of diffuse CIS. Other symptoms that may be attributed to a mass in the bladder or ureteral obstruction are likely to indicate that bladder cancer may be muscle-invasive disease. 5,24,27
History, physical examination and radiology
The clinical workup for potential bladder cancer should start with a history and a complete physical examination with careful attention to potential risk factors, such as the patient’s smoking history and occupation. Clinicians must look for cancer in all areas of the urinary tract. Most haematuria clinics in the UK perform an ultrasound of the upper tracts and kidney, ureter and bladder radiography. In some centres, intravenous pyelography (IVP) is also performed routinely; in others, computerised tomography (CT) urography has replaced ultrasound and IVP in this setting.
Cystoscopy and pathology
In many centres, voided urine for cytological analysis is usually collected before flexible cystoscopy. Flexible cystoscopy is an invasive procedure in which an endoscope is passed within the urethra, prelubricated with local anaesthetic gel. Its purpose is to evaluate the urethra and to look for tumours and irregularities in the bladder such as red patches (which may prove to be CIS on biopsy), diverticula and trabeculations. A urine culture should be performed if dipstick analysis suggests a urinary tract infection.
Transurethral resection and/or biopsy
If a bladder tumour is identified on flexible cystoscopy, arrangements are made for the patient to return as an inpatient for TURBT and/or biopsy under general anaesthesia. Depending on the location of the tumour, resection may be aided on occasion by muscle paralysis to avoid complications arising from an obturator nerve jerk. The exophytic tumour is first resected and then a separate deep resection is obtained. Both specimens are sent separately for histological assessment. Biopsies of any red areas may also be taken and submitted for analysis. Haemostasis is then achieved by using a rollerball electrode followed by insertion of an irrigating catheter. As part of clinical staging, a bimanual examination is performed to identify if there is a residual mass at the end of the procedure. If a mass is detected, it is noted whether it is mobile (clinical T3) or fixed (clinical T4).
Imaging techniques
If bladder cancer is detected, accurate disease staging and grading are critical. There is much debate over the role of imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and CT, in the staging of bladder cancer. 27 A staging CT scan of chest, abdomen and pelvis and/or MRI of pelvis are therefore not usually performed in patients with papillary non-muscle-invasive TCC. The role of CT in patients with muscle-invasive disease is primarily to provide extra information on local staging, lymph node status and visceral metastases. The primary role of MRI in patients with muscle-invasive TCC is to provide further information on local stage.
Management of disease
The management of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer is based on: (1) the pathological findings of the biopsy specimen, with attention to histological type, grade and depth of invasion; (2) the presence of associated CIS; (3) the number of tumours; (4) previous recurrence rate if applicable; and (5) size of tumour. Depending on these findings, treatment options include cystoscopic follow-up only (either flexible or rigid cystoscopy under general anaesthesia), cystoscopic follow-up and intravesical chemotherapy and immunotherapy courses or radical cystectomy.
The goals of current treatment for patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer are to prevent disease recurrence or progression to muscle-invasive disease to avoid loss of the bladder and, ultimately, to enhance survival. The current treatment strategies for patients with bladder cancer depend on three main types of bladder cancer, non-muscle-invasive disease, muscle-invasive disease and metastases, as recommended in the multidisciplinary team (MDT) guideline. 28
Non-muscle-invasive disease
Initial treatment
-
TURBT of all malignant tissue is the recommended primary treatment for non-muscle-invasive disease and should be followed as soon as possible (ideally within 6 hours, otherwise within 24 hours) by a single instillation of intravesical chemotherapy.
-
Tumours should then be assessed depending on stage, grade, size, multiplicity and the presence of recurrence at cystoscopy after 3 months:
-
– low risk – patients at low risk of recurrence and progression have TaG1 TCC or solitary T1G1 TCC
-
– intermediate risk – those at intermediate risk have TaG2 TCC or multifocal T1G1 TCC
-
– high risk – broadly speaking, patients with Ta/T1G3 TCC, CIS or multifocal T1G2 TCC are classified as being at high risk of not only recurrence but also progression.
-
Follow-up of low- and intermediate-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer
Follow-up of non-muscle-invasive disease is by cystoscopy, the frequency and duration of follow-up depending on the risk at presentation and the presence of recurrences. Multiplicity at presentation and a tumour recurrence at 3 months have consistently been shown to be key practical predictors of future recurrence, and so many urologists in the UK tailor their cystoscopic follow-up of low- and intermediate-risk patients based on these two factors:
-
If patients have a solitary tumour at diagnosis and no tumour recurrence at 3 months they are then followed up at 9 months and then annually for 4 further years. If at the end of this 5-year follow-up period they have remained tumour free they are discharged. During the follow-up visits patients undergo flexible cystoscopy and in some centres cytology and/or biomarker tests. Not all patients with a tumour recurrence will receive TURBT; some may have a cystodiathermy and biopsy.
-
Patients with multiple tumours at presentation and no recurrence at 3 months or a solitary tumour at presentation with recurrence at 3 months need more intense follow-up and are followed up every 3 months for the first year and annually if they remain tumour free until 10 years and are then discharged. During the follow-up visits patients undergo cystoscopy and in some centres cytology and/or biomarker tests. Those who present with a tumour at the follow-up visit undergo either TURBT or cystodiathermy and biopsy. These patients may be considered for a course of six intravesical instillations of mitomycin C or epirubicin.
-
Patients with multiple tumours at presentation and recurrence at 3 months have the highest risk of recurrence and are followed up every 3 months for the first 2 years and then annually thereafter. They are usually offered a course of six intravesical instillations of mitomycin C or epirubicin. Those who present with a tumour at follow-up visits undergo either TURBT or cystodiathermy and biopsy. During the follow-up visits patients undergo cystoscopy and in some centres cytology and/or biomarker tests. Cystoscopies in the first 2 years are usually under general anaesthesia using a rigid cystoscope. 29
Follow-up of high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer
If diagnosed with T1G3 TCC, patients are offered an early re-resection to ensure that the tumour is not muscle invasive. All patients in this group are usually offered an induction course of six intravesical BCG instillations followed by a maintenance regimen of a further 21 instillations over a 3-year period. Some may opt for primary radical cystectomy. Patients who opt for bladder sparing undergo their first bladder check at 3 months. If they remain tumour free they are followed up every 3 months for the first 2 years and then every 6 months thereafter. During the follow-up visits patients undergo cystoscopy and in some centres cytology and/or biomarker tests. Patients found to have a non-muscle-invasive recurrence at 3 months have four options: they can undergo cystectomy, have a second induction course of BCG and then reassess, have three further instillations of BCG and then reassess, or have endoscopic control.
Muscle-invasive disease
Initial treatment
Once again, initial treatment comprises TURBT. If muscle invasion is confirmed on histological analysis, patients undergo CT of the chest, abdomen and pelvis and in some centres MRI scanning of the pelvis. In the absence of metastatic disease and other significant comorbidity, treatment options for patients with muscle-invasive disease include radical cystectomy with ileal conduit formation, radical cystectomy with formation of a neobladder, or radical radiotherapy. Neoadjuvant systemic chemotherapy is usually recommended before radical cystectomy or radiotherapy.
Follow-up
-
Follow-up after radiotherapy is by regular (usually 6-monthly) cystoscopy. The first check cystoscopy is usually performed at about 4 months post completion of radiotherapy.
-
Follow-up after cystectomy is by clinical assessment and CT scanning.
-
A CT scan should be performed (at around 6 months following surgery for most patients) to assess for lymph or local recurrence. Subsequent CT scanning may be required in some cases but need not be carried out routinely.
-
Non-muscle-invasive recurrences are dealt with endoscopically. Intravesical chemotherapy or BCG should be considered if recurrences are multiple or frequent.
-
Non-muscle-invasive recurrences after radiotherapy are dealt with endoscopically. Intravesical chemotherapy, or in advanced cases salvage cystectomy, should be considered.
-
Muscle-invasive recurrences after radiotherapy are best dealt with by salvage cystectomy if the patient’s condition allows (in other cases chemotherapy may be appropriate).
-
Recurrence after cystectomy may be treated with radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
Metastatic disease
Radiotherapy can provide effective palliation for symptoms of locally advanced disease such as haematuria. Chemotherapy may be appropriate in cases of metastatic disease in which the patient has a good performance status and renal function. Treatment is purely palliative and should be selected according to the patient’s needs but may include systemic chemotherapy with GC (gemcitabine and cisplatin) or MVAC (methotrexate, vinblastine, adriamycin, cisplatin). Combinations with cisplatin are more effective than those without. 30,31 Gemcitabine plus cisplatin has equivalent survival to MVAC but is much less toxic.
Non-transitional cell carcinoma bladder cancer
Careful case-by-case management of non-TCC bladder cancer patients is required including discussion by the specialist MDT. Specialist histopathological review may be required, with consideration to the fact that the primary tumour may not be arising from the bladder.
Current service cost
It is difficult to estimate the current bladder cancer service cost in the UK because of the variation in practice in the diagnosis and follow-up of patients based on their risk categorisation. It is anticipated that the costs of the higher risk patients will be greater than those of the low-risk patients because of more follow-up interventions. The total cost of treatment and 5-year follow-up of patients with bladder cancer diagnosed during 2001–2 was £55.39 million; the total cost of superficial disease was £35.25 million and that of invasive disease was £20.2 million. The total cost for patients undergoing radical radiotherapy was over twice that for those undergoing cystectomy (£8.1 versus £3.6 million)32 In the USA it is estimated that $1.7 billion is spent on bladder cancer. 33
An estimate of the current cost to the UK NHS can be generated by using the total cost of each strategy (see Tables 39 and 42) and combining it with the values in Table 2. If it assumed that the current practice for diagnosis in the UK is flexible cystoscopy and cytology for initial diagnosis followed by white light rigid cystoscopy [CSC_CTL_WLC (CSC_WLC)] the cost per low-risk patient will be £6302.25. Therefore the total annual cost to the NHS will be £64,765,481. There is also evidence that costs are likely to increase with improved survival because patients need several courses of treatment.
Variation in services and/or uncertainty about best practice
All urology departments offer haematuria clinics and subsequent TURBT if appropriate either in the same hospital or in a hub hospital. Radiotherapy and systemic chemotherapy are available in cancer centres. Radical surgery for prostate and bladder cancer should be provided by teams carrying out a cumulative total of at least 50 such operations per annum. These procedures should be performed by surgeons performing at least five of either radical cystectomy or prostatectomy each year. 34
Relevant national guidelines, including National Service Frameworks
The relevant national guidelines are:
-
National Institute for Clinical Excellence (2002). Improving outcomes in urological cancers. NHS guidance on cancer services34
-
National Institute for Clinical Excellence (2003). Laparoscopic cystectomy of the urinary bladder. IPG02635
-
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) (2005). Management of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder36
-
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (2007). Intravesical microwave hyperthermia with intravesical chemotherapy for superficial bladder cancer. IPG23537
-
NHS Pan-Birmingham Cancer Network (2006/2007). Guidelines for the management of bladder cancer38
-
UK National Screening Committee (NSC) (2002). Evaluation of urinary tract malignancy (bladder cancer) screening against NSC criteria39
-
British Association of Urological Surgeons (BAUS) Section of Oncology and Uro-oncology Group (2007). MDT (multi-disciplinary team) guidance for managing bladder cancer28
-
European Association of Urology (EAU) (2009). Guidelines on TaT1 (non-muscle-invasive) bladder cancer3
-
European Association of Urology (EAU) (2009). Guidelines on bladder cancer: muscle invasive and metastatic40
-
American National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) (2009). NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. Bladder cancer including upper tract tumours and urothelial carcinoma of the prostate24
-
American Urological Association (AUA) (2007). Guideline for the management of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer (stages Ta,T1 and Tis). 5
Only two of the above guidelines specifically mention photodynamic diagnosis (PDD):
The evidence suggests potential benefits from photodynamic techniques for patients with superficial bladder cancer undergoing initial resection of their tumour. Its role in patients developing recurrence during followup is less clear.
SIGN (2005)36
The benefit of fluorescence-guided TURBT for recurrence-free survival was shown in several small randomised clinical trials, but its value remains to be proven in improving the outcome of patients for progression rates or survival. The additional costs of the equipment should be considered.
EAU (2009)3
Various guidelines, including those of the EAU and AUA, recommend the use of voided urinary cytology, both in the diagnosis and surveillance of non-muscle-invasive bladder carcinoma. However, there are no equivalent recommendations for the use of biomarkers. Although the international consensus panel on the use of biomarkers in bladder cancer realised the importance of non-invasive diagnosis and surveillance of non-muscle-invasive disease, it concluded that, although none of the non-invasive tests could replace cystoscopy, many markers together with cystoscopy could improve the current practice of managing patients with bladder cancer. 41
Description of the technologies under assessment
Summary of interventions
Photodynamic diagnosis
Principles
Fluorescence occurs when a molecule absorbs one colour of light and emits another colour. Essentially, photons of light are absorbed by tissue and excite electrons in the tissue. The electron then returns to its resting state and the photon is emitted with less energy, i.e. longer wavelength, resulting in a different colour emission. Fluorescence cystoscopy is based on the principle that specific fluorochromes have increased affinity for neoplastic tissue compared with normal urothelium. When light of an appropriate wavelength is used to look at the surface of bladder to which the fluorochrome has been applied, different signal intensities are given off by neoplastic and non-neoplastic tissue. To minimise autofluorescence from cellular components such as collagen, a longpass eye filter is needed. A filter allowing only wavelengths > 600 nm would be ideal, but this would result in the image being very dark. A compromise is therefore to use a 450-nm yellow filter and therefore accept some autofluorescence. This does not affect colour reproduction in the white light mode.
Over the last 40 years, several agents have been evaluated for their ability to improve visualisation of urothelial cancer. These include tetracyclines, fluorescein, methylene blue and synthetic porphyrin compounds. However, these have been abandoned because of several side effects, including cutaneous toxicity lasting several weeks with synthetic porphyrins.
A major breakthrough was the discovery that 5-aminolaevulinic acid (5-ALA), in a suitable dose, could be safely applied to the bladder surface and permit detection of tumours by fluorescence without serious adverse effects. 5-ALA is an initial substrate of heme biosynthesis. Exogenous application of 5-ALA induces an accumulation of fluorescent porphyrins, predominantly protoporphyrin IX (PPIX), in epithelial tissue. Using a blue–violet light with a wavelength of 450 nm, PPIX appears as fluorescent red whereas normal urothelium appears blue. This is because PPIX accumulates up to 10 times more in neoplastic cells than in normal tissue. The mechanism of accumulation of fluorescent PPIX in urothelial cancer is unclear. Several theories, including a difference in the metabolic rate of neoplastic tissue, hyperproliferation and inflammation-induced increased permeability to ALA, have been proposed. These are supported by the observations that increased PPIX can be detected in urothelial hyperplasia, inflammation and granulation tissue. 5-ALA is usually administered intravesically 2–3 hours before cystoscopy at a dose of 1.5 g. The procedure requires special endoscopes and a specific light source (D-light™, Karl Storz).
5-ALA absorption is limited because of its positive electric charge. The esterification of 5-ALA as hexylester aminolaevulinate makes ALA more lipophilic, which enables it to cross the cell membrane more easily. A consequence of this is more rapid cellular uptake and higher fluorescence than with ALA. 42 Hexaminolaevulinate (HAL) needs therefore only be administered 1 hour before cystoscopy and the dose is typically a 85-mg solution of HAL hydrochloride in 50 ml of phosphate buffered saline (Hexvix®).
Recently, hypericin has been proposed as an additional photosensitiser. Hypericin consists of a hydroxylated phenanthroperylenequinone that is extracted from the Hypericum perforatum plant, which is present in St John’s wort. Within an organic solution, hypericin produces an intense, prolonged, red fluorescence signal. This is because its pigment produces single oxygen species upon exposure to light of an appropriate wavelength. Most studies have used hypericin at a concentration of 8 μmol/l and instilled it 1–2 hours before cystoscopy.
Procedure
Before TURBT, a 12F LoFric or two-way urethral catheter is inserted by a nurse on the ward and intravesical photosensitiser instilled. The catheter is removed immediately. In theatre, under general or spinal anesthesia, the bladder is first inspected using white light rigid cystoscopy. The bladder is then reinspected using blue–violet light. Normal-appearing bladder should appear blue. Normal-appearing bladder neck and/or prostate appear red because of tangential views that cause them to be artefactually red. This, however, acts as a useful positive control. Within the bladder, any red areas are considered to be suspicious and require biopsy.
The bladder tumour is then resected in white light. A further inspection of the bladder with blue–violet light will then identify any residual tumour that may have been missed on WLC.
Equipment
-
Photosensitiser, e.g. 5-ALA, HAL, hypericin.
-
Rigid cystoscope with longpass yellow filter for wavelengths > 450 nm.
-
Fluid light cable – this blocks residual infrared light and lowers intrinsic autofluorescence; however, a disadvantage is that it cannot be autoclaved.
-
Switchable bandpass filter – this enables the surgeon to interchange between white light and blue–violet light without changing cystoscopes.
-
Xenon lamp – powerful, especially in the blue light spectra.
-
Camera controller.
-
Video monitor.
-
Colour charge-coupled device (CCD) camera (on chip integration) – this is suitable for working in low light conditions. The fluorescent image is 10 times less intense than white light; allows increased red light intensity.
-
Beam splitter cube.
Extra personnel involved
Unlike white light cystoscopy, PDD requires the instillation of a photosensitiser via a urethral catheter before TURBT. This is usually performed by a nurse on the ward.
Procedure time compared with conventional cystoscopy
On the ward, catheterisation and instillation of the photosensitiser and then removal of the catheter takes about 15 minutes. In theatre, fluorescence-guided TURBT takes an extra 10 minutes compared with conventional white light TURBT alone.
Urinary biomarkers
Urinary biomarkers are molecular substances that can be objectively measured in urine and evaluated as indicators of physiological or disease processes in the urinary tract or in various systems of the body. In principle, this could act as a source of vital information for diagnosis, prognosis and predicting response to therapies. The explosion of interest in urinary biomarker research, in particular related to bladder cancer, is driven by the fact that there is a lack of non-invasive methods of diagnosis and disease surveillance. The current standard of care – endoscopic inspection of the inside of the urinary bladder – is not only invasive but can also miss up to 10% of bladder tumours. 43 The urinary measurement of biomarkers could provide a diagnostic means that could either complement cystoscopy to enhance its performance or replace it as a mode of diagnosis and surveillance.
From a methodological perspective, urinary markers fall into a few broad groups, in particular soluble urinary proteins, cell-based biomarkers and nucleic acid biomarkers. As a complete review of each specific biomarker is beyond the scope of this chapter, the present study focused on four urinary biomarkers approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for clinical use in urological practice. These are urinary cytology, nuclear matrix protein (NMP22), fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) and ImmunoCyt.
Place of biomarkers in the treatment pathway
There are several potential strategies worth considering aimed at making use of urinary biomarkers in the care pathways of bladder cancer. They could be used:
-
Alone or as an adjunct to urinary cytology to improve the detection rate of cancer in high-risk populations.
-
To provide a less expensive and more objective alternative to the urinary cytology test.
-
To replace or supplement direct cystoscopic surveillance of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. They may also serve to decrease the number of invasive procedures, provided that adequate cancer control is maintained on follow-up, and thereby reduce the health-care cost and improve the comfort of patients.
The critical issue remains the operating characteristics of these markers compared with cystoscopy, the current standard of care. False-positive results are likely to generate further unnecessary investigations in addition to fear and anxiety in patients’ minds; alternatively, false-negative results may prove to be detrimental, such as progression to muscle invasion.
Setting
Urinary cytology involves examination of cells from the urinary tract under microscopy. A urinary sample is transported to the laboratory and cells are retrieved by a conventional cytospin method. Cells are examined under a microscope by a cytopathologist for the presence or absence of malignant changes using the standard Papanicolaou method. The test is laboratory based and results are observer dependent with the potential for inter- and intraobservational variation.
NMP22 is a patented proteomic technology that has been commercialised by Matritech. Two products are marketed for the diagnosis of bladder cancer, the NMP22® Test Kit and the NMP22® BladderChek® Test. The NMP22 BladderChek Test is the only in-office test approved by the FDA for the diagnosis of bladder cancer. It is a non-invasive test performed on a single urine sample. Bladder cancer cells release NMP22 protein into urine, which is detected by putting 4–5 drops of urine on a prepared card. A change in colour is considered as a ‘positive test’ result. The levels of NMP22 in urine from healthy individuals are very small but can be significantly elevated in patients with urothelial cancers. The test has also been approved by the FDA for point of care use in the diagnosis of bladder cancer.
The basis of this test is the detection of abnormal DNA sequences on chromosomes 3, 7, 17, and the loss of the 9p21 locus in cancer cells shed into the urine of patients with bladder cancer. The retrieved cells from voided urine specimens are fixed on microscopy slides and visualised using a four-colour, four-probe mixture of DNA probe sequences homologous to specific regions on the aforementioned chromosomes. This is a laboratory test and has been commercialised by Abbott under the market name of UroVysion™ Bladder Cancer Kit (UroVysion Kit).
The ImmunoCyt test uses a cocktail of three monoclonal antibodies labelled with fluorescent dyes that bind to two antigens, a mucin glycoprotein (green) and a carcinoembryonic antigen (red), expressed by bladder tumour cells in urine specimens. A voided urine specimen is transported to the laboratory and cells retrieved from it are fixed to a microscope slide. The antibodies are added to the slide and the stained slide examined under fluorescent microscopy by a cytopathologist.
Equipment required and personnel involved
Urine cytology requires the support of skilled laboratory cytotechnicians and cytopathologists within pathology laboratories. This means that results take longer to obtain and are not available on the same day. In addition to these requirements, the FISH and ImmunoCyt tests require specific kits and specialised fluorescence microscopes for visualisation of labelled cancer cells. Also, the FISH technique requires a special filter for cell retrieval. The only biomarker test approved for point of care diagnosis of bladder cancer is NMP22 detection using the commercially available NMP22 Test Kit. The test provides instantaneous results and can be performed by medical personnel with minimal training.
Identification of important subgroups
Photodynamic diagnosis
-
It is important to distinguish the role of fluorescence-guided TURBT for primary tumours from its role in bladder tumour recurrence. Its role in patients developing recurrence during follow-up is less clear.
-
It is important to realise that the use of different photosensitisers may lead to different results in terms of sensitivity and specificity.
Biomarkers/cytology
The diagnostic performance of urinary biomarkers can be scrutinised in the background of two clinical settings: the ability to accurately diagnose bladder cancer in high-risk populations and their potential to accurately predict recurrences in patients known to have non-muscle-invasive disease. Urinary biomarkers can either complement or replace current invasive tests such as cystoscopy. The second clinical scenario in which the diagnostic utility of urinary biomarkers comes under sharp focus is their ability to perform across all grades and stages of non-invasive bladder cancer disease. For example, urinary cytology performs well (high sensitivity) in high-grade disease, whereas its performance decreases (low sensitivity) in low-grade disease – this is why it is not a plausible replacement for cystoscopy, both at the point of diagnosis and at follow-up in the care pathways of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer disease.
Current usage in the NHS
Photodynamic diagnosis
In most UK centres PDD is not available. Moreover, in centres in which the service is available, it is used to a varying extent. In a few centres (less than five) it is used routinely for all first-time TURBTs. In others it may be used only during follow-up when CIS is suspected, such as a normal-appearing bladder on WLC but positive urine cytology.
Two further factors are likely to influence the uptake of PDD within the wider NHS:
-
Fluorescence cystoscopy has been identified as a new technology that has been signalled by the NCRI to the National Horizon Scanning Centre for early review.
-
In 2008 the NHS Technology Adoption Centre took forward a PDD implementation project involving three NHS trusts. The experience gained from the project will support the wider NHS in overseeing issues associated with the adoption of new technologies.
Biomarkers/cytology
Although urinary cytology is the most common urinary biomarker used for the diagnosis and follow-up of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer in the NHS, the practice varies across the UK. 44 There are few reports of NMP22 being used as a diagnostic biomarker in patients with haematuria from UK centres. 45 The clinical use of FISH and ImmunoCyt as urinary markers in patients with bladder cancer has not been reported in the UK.
Anticipated costs associated with the technologies
The anticipated costs associated with the technologies will depend on the strategies used in the diagnosis and follow-up of patients. The average unit cost of diagnosing bladder cancer using PDD is £1371, rigid white light cystoscopy £937, flexible cystoscopy £441, cytology £92.37, NMP22 £39.3, FISH £54.8 and ImmunoCyt £54.8; and the cost of treatment using PDD-assisted TURBT is £2436, WLC-assisted TURBT £2002, mitomycin £73, BCG £89, cystectomy £6856, chemotherapy £50.22, radical radiotherapy £1050 and palliative treatment £12,825 (see Chapter 6 for details). The modelling results indicate that using the most effective strategy (the one with the highest number of true positives and the lowest number of false negatives), which includes either of the two biomarkers FISH or ImmunoCyt and PDD as the initial strategy and either FISH or ImmunoCyt with WLC as the follow-up strategy, will cost £5919.28 per low-risk patient per year.
Chapter 2 Definition of the decision problem
Decision problem
Accurate diagnosis of bladder cancer is crucial for people who may potentially have the disease to allow for early detection and to reduce the risk of tumour recurrence and progression. The ideal test for diagnosis and follow-up of bladder cancer would be non-invasive, highly sensitive and specific, inexpensive and easy to perform and would provide reproducible results. Many of the tests meet some, but not all, of these criteria. Currently, a common diagnostic scenario in the UK is that people suspected of having bladder cancer are first examined with flexible cystoscopy and voided urine cytology, followed by white light rigid cystoscopy-assisted TURBT or biopsies for those considered positive or suspicious for the disease. However, insufficient sensitivity or specificity of the three tests can result in the incomplete detection or overtreatment of primary and recurrent disease.
As patients are living longer and recurrence of disease is becoming a major issue there is a need to identify the most appropriate methods for diagnosing patients with bladder cancer and subsequently following them up. A variety of tests have been developed that have been used as alternatives to, or alongside, existing investigations. As described in Chapter 1, urinary biomarkers for bladder cancer are non-invasive assay tests that can detect protein, genetic or chromosomal aberrations, even at early stages of disease. Some are point of care tests whereas others require laboratory analysis. These tests are considered to be attractive and potentially cost-effective as they may offer the potential to avoid unnecessary cystoscopies and labour-intensive cytology. Biomarkers have the potential to play a role in the initial diagnosis of patients either in addition to or as a replacement for urine cytology, and in monitoring during follow-up.
PDD has been used alongside rigid cystoscopy with the aim of improving detection of CIS and papillary tumours during TURBT, thereby potentially reducing the residual tumour rate at the 6-week check following TURBT and consequently also reducing recurrence and progression of disease. PDD has also been described as a safe and straightforward technique to learn.
The following sections provide a description of the care pathways that show the plausible strategies for the primary diagnosis and follow-up of people with bladder cancer.
Inclusion criteria (see Chapter 3)
Key issues
The key issues to be addressed are:
-
Can PDD improve detection of bladder cancer (1) at the time of TURBT for newly diagnosed disease and (2) during follow-up of patients with non-muscle-invasive disease?
-
Can PDD reduce recurrence and/or progression of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer compared with WLC?
-
Can urine biomarkers (FISH, ImmunoCyt, NMP22) improve detection of bladder cancer during (1) initial diagnosis of patients suspected of having bladder cancer and (2) follow-up of patients diagnosed with non-muscle-invasive disease?
-
What is the incremental cost-effectiveness of PDD during TURBT for newly diagnosed non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer and during follow-up?
-
What is the incremental cost-effectiveness of biomarkers during the initial diagnosis of patients suspected of having bladder cancer and during follow-up of those diagnosed with non-muscle-invasive disease?
Care pathways
Care pathways describing plausible strategies for the initial diagnosis and follow-up of people with bladder cancer were developed. The basic care pathway was based on discussions with the clinical experts involved in this study and a brief description of this is provided within Chapter 1.
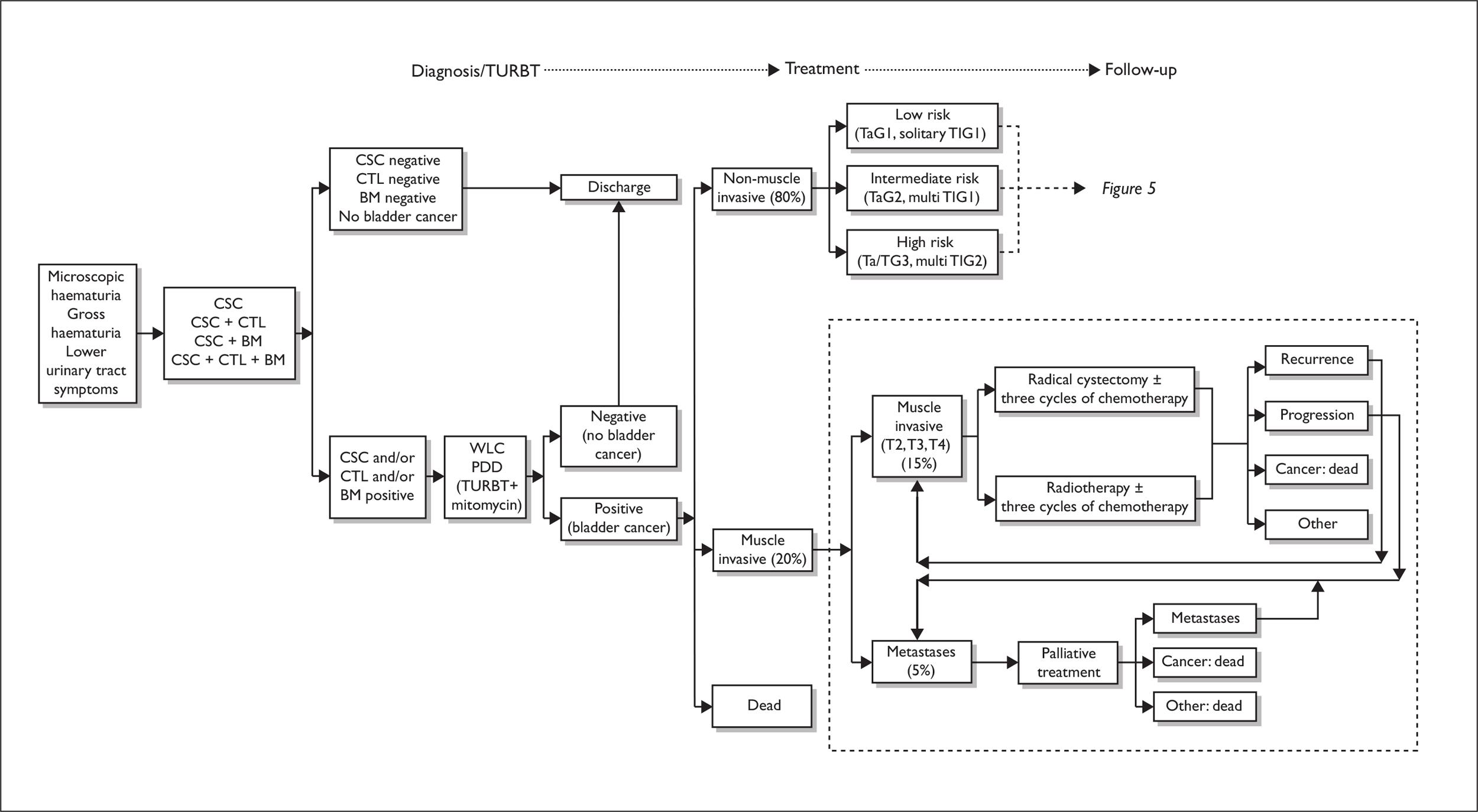
Initial diagnosis and treatment (Figure 4)
The pathway begins with an initial presentation of symptoms or asymptomatic microscopic haematuria and varies in terms of where and when biomarkers and PDD might be used. Patients who present with either microscopic or gross haematuria or lower urinary tract symptoms are tested using flexible cystoscopy and cytology. Biomarkers could be used at this point either in addition to these two tests or instead of cytology. The results of these tests can be either negative or positive. Patients who have two/three negative results are discharged. Discharged patients who later re-present with similar symptoms go back to the beginning of the care pathway. Patients with one or more positive results for these tests as outlined in Table 3 undergo TURBT during which PDD may be used with the aim of improving the detection of tumours, thereby potentially reducing the rate of residual tumours and increasing the detection of CIS and small papillary tumours.
| Cystoscopy | Cytology | Biomarkers |
|---|---|---|
| – | – | – |
| – | – | + |
| – | + | – |
| + | – | – |
| – | + | + |
| + | – | + |
| + | + | – |
| + | + | + |
After TURBT is performed for newly diagnosed bladder cancer, the standard UK management is that the patient also receives a single instillation of adjuvant intravesical mitomycin C, ideally within 6 hours of resection but not later than 24 hours if possible. Biopsies are taken and the results of the histological analysis may be either negative or positive for bladder cancer. Those who have a negative histology result are then discharged. Discharged patients whose symptoms are not resolved may subsequently re-present at the beginning of the care pathway. For the purposes of this review, although patients who have a negative bladder cancer test result are considered as discharged, it is noted that some who initially had a positive result may be at risk of upper tract urothelial cancer or renal cancer and consequently will require further tests, and, if positive, treatment.
Those patients whose histological results confirm the presence of bladder cancer are classified into muscle-invasive or non-muscle-invasive disease. For those with muscle-invasive disease, treatment options are outlined in Figure 4. Essentially, those amenable to potential cure are offered either radical cystectomy with bilateral pelvic lymphadenectomy or radiotherapy. Treatment with surgery or radiotherapy is usually preceded by three cycles of systemic neoadjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy. The rationale for chemotherapy is that over 50% of patients with muscle-invasive disease have occult metastatic disease at presentation. It is noted that practice at individual centres may vary. The decision for cystectomy or radiotherapy is primarily based on patient choice and medical fitness. The presence of concomitant CIS and upper tract dilatation are also factors that favour cystectomy. For patients with more advanced metastatic disease, the treatment is palliative.
FIGURE 4.
Developed care pathway – initial diagnosis/treatment. BM, biomarkers; CSC, flexible cystoscopy; CTL, cytology.
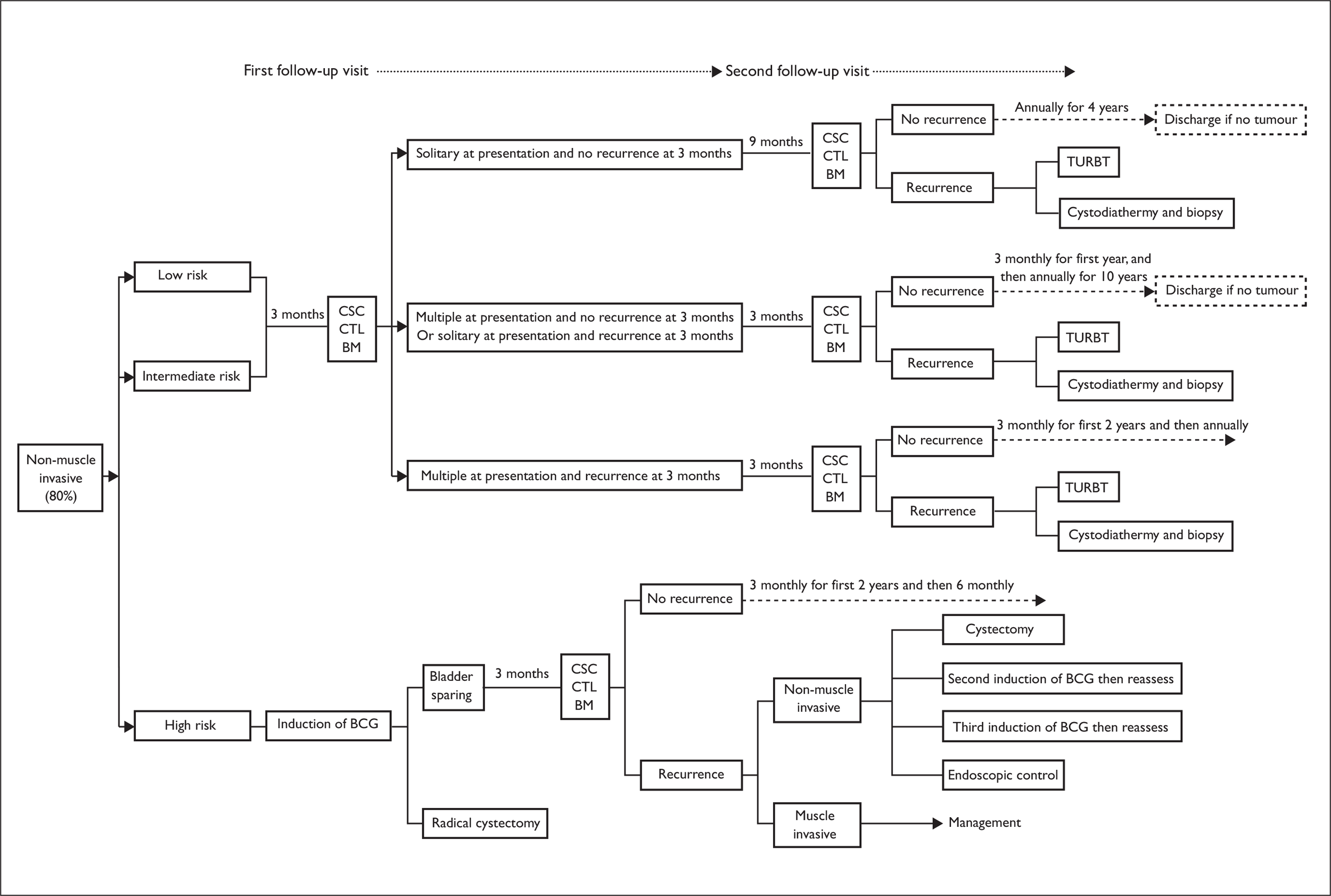
Follow-up of patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (Figure 5)
The key factors increasing the risk of recurrence and progression in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer are: (1) tumour multiplicity, (2) greater tumour diameter, (3) previous recurrence rate, (4) higher T-stage, (5) concomitant CIS and (6) higher histological grade. A brief summary is provided in the following sections and a further short review on the management of bladder cancer, required for the description of the model structure, is provided in Chapter 6 (see Model structure, Markov model).
High risk
Broadly speaking, patients with Ta/T1G3 TCC, CIS or multifocal T1G2 TCC are classified as being at high risk of not only recurrence but also progression. If diagnosed with T1G3 TCC they are offered an early re-resection to ensure that they are not muscle invasive. All patients in this group are usually offered an induction course of six intravesical BCG instillations followed by a maintenance regimen of a further 21 instillations over a 3-year period. Some may opt for primary radical cystectomy. Patients who opt for bladder sparing undergo their first bladder check at 3 months. If they remain tumour free they are followed up every 3 months for the first 2 years and then every 6 months thereafter. During the follow-up visits, patients undergo cystoscopy and in some centres cytology and/or a biomarker test. Patients found to have a non-muscle-invasive recurrence have four options: they can undergo cystectomy, have a second induction course of BCG and then reassess, have three further instillations of BCG and then reassess, or receive endoscopic control.
Low and intermediate risk
Patients at low risk of recurrence and progression have TaG1 TCC or solitary T1G1 TCC. Those at intermediate risk have TaG2 TCC or multifocal T1G1 TCC. Multiplicity at presentation and a tumour recurrence at 3 months have consistently been shown to be key practical predictors of future recurrence, and many urologists in the UK tailor their cystoscopic follow-up of low- and intermediate-risk patients based on these two factors for these reasons:
-
Patients who have a solitary tumour at diagnosis and no tumour recurrence at 3 months are followed up at 9 months and then annually for 4 further years. If at the end of this 5-year follow-up period they have remained tumour free they are discharged. During the follow-up visits these patients undergo flexible cystoscopy and in some centres cytology and/or biomarker tests. Although most patients with a tumour recurrence will receive TURBT, some may have a cystodiathermy and biopsy.
-
Patients with multiple tumours at presentation and no recurrence at 3 months or a solitary tumour at presentation with recurrence at 3 months need more intense follow-up and are followed up every 3 months for the first year and annually if they remain tumour free until 10 years and are then discharged. During the follow-up visits patients undergo cystoscopy and in some centres cytology and/or biomarker tests. Those who present with a tumour at the follow-up visit undergo either TURBT or cystodiathermy and biopsy. These patients may be considered for a course of six intravesical instillations of mitomycin C or epirubicin.
-
Patients with multiple tumours at presentation and recurrence at 3 months have the highest risk of recurrence and are followed up every 3 months for the first 2 years and then annually thereafter. They are usually offered a course of six intravesical instillations of mitomycin C or epirubicin. Those who present with a tumour at the follow-up visit undergo either TURBT or cystodiathermy and biopsy. During the follow-up visits patients undergo cystoscopy and in some centres cytology and/or biomarker tests. Cystoscopies in the first 2 years are usually under general anaesthesia using a rigid cystoscope.
During the follow-up period the status of patients may change and they may develop muscle-invasive tumours. It is also possible that patients may die at any time during follow-up from causes related to bladder cancer or from unrelated causes. The outlined care pathways in Figures 4 and 5 identify the areas in which PDD and biomarkers could be used in conjunction with the standard tests to diagnose patients with suspected bladder cancer and to follow up those who have been diagnosed with non-muscle-invasive disease. These patient care pathways will be used to inform the economic model and to establish whether the use of PDD and urine biomarkers reduces recurrence or decreases progression at follow-up as a consequence of altered treatment.
FIGURE 5.
Developed care pathway – follow-up. BM, biomarkers; CSC, flexible cystoscopy; CTL, cytology.
Aim of the review
The aim of this review is to assess the clinical and cost-effectiveness of PDD and urine biomarker tests in the detection and follow-up of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
This aim is addressed through:
-
a systematic review of PDD, and urine biomarker tests (FISH, ImmunoCyt and NMP22) and cytology alone or in combination, in the diagnosis and follow-up of bladder cancer
-
a structured review of the management of patients diagnosed with bladder cancer with associated costs and outcomes
-
economic modelling of the cost-effectiveness and cost–utility of alternative approaches in the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
The specific objectives of the review are to:
-
estimate the incremental cost-effectiveness of PDD compared with white light rigid cystoscopy, and biomarkers and urine cytology, in initial diagnosis and follow-up
-
assess the performance of PDD (1) at the time of TURBT for newly diagnosed bladder cancer and (2) during follow-up of patients with non-muscle-invasive disease
-
assess the performance of urine biomarkers and cytology in (1) initial diagnosis of bladder cancer and (2) during follow-up of patients with non-muscle-invasive disease
-
assess whether PDD reduces recurrence and/or progression of non-muscle-invasive disease compared with WLC.
Structure of the remainder of the report
The remainder of the report is structured as follows. Chapter 3 describes the methods for reviewing test performance and effectiveness, Chapter 4 assesses the diagnostic accuracy, and clinical effectiveness in terms of recurrence/progression rates, of PDD compared with WLC and Chapter 5 assesses the test performance of urine biomarkers (FISH, ImmunoCyt, NMP22) and cytology. Chapter 6 assesses the cost-effectiveness of the tests, Chapter 7 discusses factors relevant to the NHS and other parties, Chapter 8 is a discussion of the findings and Chapter 9 presents the review’s conclusions, including implications for the NHS and for research.
Chapter 3 Methods for reviewing test performance and effectiveness
Identification of studies
Studies were identified by searching electronic databases and relevant websites, contact with experts in the field and the scrutiny of bibliographies of retrieved papers. Highly sensitive electronic searches were conducted to identify reports of published and ongoing studies on the diagnostic performance of the tests of interest, as well as the effectiveness of PDD-assisted TURBT. The databases searched were MEDLINE (1966 to March Week 3 2008), MEDLINE In-Process (1 April 2008), EMBASE (1980 to Week 13 2008), BIOSIS (1985 to 27 March 2008), Science Citation Index (1970 to 1 April 2008), Health Management Information Consortium (HMIC) (March 2008) and the Cochrane Controlled Trials Register (Cochrane Library, Issue 1 2008) as well as current research registers [National Research Register (NRR) Archive (September 2007), Current Controlled Trials (CCT) (March 2008), ClinicalTrials.gov (March 2008) and WHO International Clinical Trials Registry (March 2008)]. Additional databases searched for systematic reviews and other background information included the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR) (Cochrane Library, Issue 1 2008), Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effectiveness (DARE) (March 2008), Health Technology Assessment (HTA) database (March 2008) and Medion (March 2008). A total of 5680 reports were identified (Table 4). In addition, the details of 41 potentially relevant ongoing studies were noted. Reference lists of all included studies were scanned to identify additional potentially relevant studies. Full details of the search strategies used and websites consulted are documented in Appendix 1.
| Database | Number retrieved |
|---|---|
| Primary reports | |
| MEDLINE (1966 to March Week 3 2008)/EMBASE (1980 to Week 13 2008)/MEDLINE In-Process (1 April 2008) multifile search (after deduplication in Ovid) | 5373 |
| Science Citation Index (1970 to 1 April 2008) | 206a |
| BIOSIS (1985 to 27 March 2008) | 60a |
| CENTRAL (Cochrane Library, Issue 1 2008) | 2a |
| HMIC (March 2008) | 2a |
| Total | 5643 |
| Background | |
| CDSR (Cochrane Library, Issue 1 2008) | 1 |
| DARE (March 2008) | 21 |
| HTA database (March 2008) | 15 |
| Medion (March 2008) | 0 |
| Total | 37 |
| Total assessed for review | 5680 |
| Ongoing studies | |
| NRR | 33 |
| CCT | 7 |
| ClinicalTrial.gov | 1 |
| WHO International Clinical Trials Registry | 0 |
| Total | 41 |
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Types of studies
The types of studies considered for reporting test performance were:
-
direct (head-to-head) studies in which the index test and reference standard test were performed independently in the same group of people
-
randomised controlled trials (RCTs) in which people were randomised to the index and comparator test(s) and all received the reference standard test.
In the event that there was insufficient evidence from direct and randomised studies we considered undertaking indirect (between-study) comparisons by meta-analysing studies that compared each single test or combination of tests with the reference standard test, and making comparisons between meta-analyses of the different tests. However, this type of study design is less reliable than direct studies as differences in diagnostic accuracy are susceptible to confounding factors between studies. The following types of studies were considered:
-
Observational studies, including case series, in which the sample is created by identifying all people presenting at the point of testing (without any reference to the test results).
-
Case–control studies in which two groups are created, one known to have the target disease and one known not to have the target disease, when it is reasonable for all included to go through the tests. We excluded case–control studies when the control group consisted of completely healthy volunteers, or when the control group consisted of completely healthy volunteers and people with benign urinary conditions and it was not possible to calculate results for the control group minus the healthy volunteers, such that the spectrum of disease and non-disease was unlike that to be encountered in a diagnostic situation.
Studies reporting test performance had to report the absolute numbers of true positives, false positives, false negatives and true negatives, or provide information allowing their calculation. Studies reporting patient- and/or biopsy-level analysis (for PDD) and patient- or specimen-level analysis (for biomarkers/cytology) were considered.
For assessment of the effectiveness of PDD-assisted TURBT compared with WLC-assisted TURBT in terms of outcomes such as recurrence or progression we focused on RCTs.
Types of participants
The participants considered were people (1) suspected of having bladder cancer or (2) previously diagnosed with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer and having follow-up cystoscopic examination.
Index and comparator tests
The following tests and comparators were considered:
-
PDD (using the photosensitising agents 5-ALA, HAL or hypericin) compared with WLC
-
urine biomarkers (FISH, ImmunoCyt, NMP22) or cytology either alone or compared with each other.
Studies reporting the test performance of combinations of the above tests were also considered.
If the evidence allowed, the following subgroup analyses were planned:
-
number of tumours on first cystoscopic examination
-
type (e.g. CIS) and grade of tumour (WHO 1973 or 2004 classification)
-
tumour recurrence at the first 3-month cystoscopic examination following TURBT
-
diagnostic performance of the different PDD photosensitising agents
-
diagnostic performance of the different categories of urine biomarkers
-
for urine biomarkers, whether the urine sample was voided or obtained by bladder wash.
Numerous biomarkers exist that potentially could have been included in the review but to make the task manageable within the given time frame the review’s steering committee agreed that the review should focus only on those biomarkers regarded as being most clinically relevant. These were seen as being either those approved by the US FDA or the three generally regarded as most useful – FISH, ImmunoCyt and NMP22 – with cytology also included. It was agreed that the Chairman of the BAUS Section of Oncology should be contacted to canvass the views of the Section’s Executive Committee on the most relevant biomarkers to consider. Following this, the Chairman on behalf of the Section suggested that the review should assess ImmunoCyt, NMP22, FISH and cytology, and consequently these were the tests that were included in the review.
Reference standard
The reference standard considered both for studies reporting PDD and for studies reporting biomarkers was histopathological examination of biopsied tissue.
Types of outcomes
The following outcomes were considered:
-
for PDD:
-
– test performance in detecting non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer
-
– recurrence rate of bladder tumour over time following initial resection
-
– progression to muscle-invasive disease
-
-
for urine biomarkers/cytology:
-
– test performance in detecting non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
-
In any studies reporting the above outcomes, the following outcomes were also considered if reported:
-
altered treatment as a result of the tests
-
acceptability of the tests
-
interpretability of the tests
-
quality of life (disease-specific and generic instruments)
-
adverse effects.
Exclusion criteria
The following types of report were excluded:
-
animal models
-
preclinical and biological studies
-
reviews, editorials and opinions
-
case reports
-
abstracts, as usually insufficient methodological details are reported to allow critical appraisal of study quality
-
reports investigating technical aspects of a test
-
non-English language studies.
In addition, studies reporting biomarkers or cytology in which the number of participants in the analysis was less than 100 were excluded. Studies reporting cytology that predated the publication year of the earliest of the included biomarker studies were also excluded.
Data extraction strategy
One reviewer screened the titles (and abstracts if available) of all reports identified by the search strategy. Full-text copies of all studies deemed to be potentially relevant were obtained and two reviewers independently assessed them for inclusion. Any disagreements were resolved by consensus or arbitration by a third party.
Data extraction forms for studies reporting PDD and studies reporting biomarkers/cytology were developed and piloted. One reviewer extracted details of study design, participants, index, comparator and reference standard tests and outcome data, and a second reviewer checked the data extraction. Any disagreements were resolved by consensus or arbitration by a third party.
Quality assessment strategy
Two reviewers independently assessed the quality of the included diagnostic studies using QUADAS, a quality assessment tool developed for use in systematic reviews of diagnostic studies. 46 QUADAS was developed through a formal consensus method and was based on empirical evidence. The original QUADAS checklist contained 14 questions. The QUADAS tool was adapted to make it more applicable to assessing the quality of studies of tests for detecting bladder cancer (see Appendix 2 for an example of the modified checklist for PDD).
Questions 1, 3–7 and 10–14 of the original QUADAS tool were retained (questions 1–11 in the modified version). Three questions in the original QUADAS tool that related to the quality of reporting rather than methodological quality were omitted from the modified version (questions 2, 8 and 9). These questions related to the description of: (a) the selection criteria, (b) the execution of the index test and (c) the execution of the reference standard test. Two questions were added to the modified checklist on: (a) whether the study provided a clear definition of what was considered to be a ‘positive’ result and (b) whether data on observer variation were reported and within an acceptable range. In addition, a third question was added that related only to studies reporting biomarkers and/or cytology, on whether a prespecified cut-off value was used.
Two reviewers (from GM, CB or CR) independently assessed the quality of all included diagnostic studies using the modified version of QUADAS. Each question was checked as ‘yes’, ‘no’ or ‘unclear’. Each item was worded so that a rating of ‘yes’ was always optimal in terms of methodological quality. Any disagreements were resolved by consensus or arbitration by a third party.
Two reviewers (from GM, CB or CR) independently assessed the quality of RCTs comparing WLC-assisted TURBT with PDD-assisted TURBT using a checklist adapted from Verhagen and colleagues47 and developed through the Review Body for Interventional Procedures (ReBIP). ReBIP is a joint venture between the Medical Care Research Unit at Sheffield University and the Health Services Research Unit at the University of Aberdeen and works under the auspices of the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence’s (NICE) Interventional Procedures Programme (IPP). The checklist for RCTs contained 14 questions (see Appendix 3). Any disagreements were resolved by consensus or arbitration by a third party.
Data analysis
Diagnostic accuracy of PDD/urine biomarker tests
The results of the individual studies were tabulated and sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, positive and negative likelihood ratios and diagnostic odds ratios (DORs) calculated. If reported in a given study, a separate 2 × 2 table was derived for patient-level and biopsy-level analyses.
Sensitivity describes the proportion of those with disease who have positive test results, whereas specificity is the proportion of those without disease who have negative test results. A positive likelihood ratio describes how many times more likely it is that a person with disease will receive a positive test result than a person without disease whereas a negative likelihood ratio describes how many times more likely it is that a person with disease will receive a negative test result than a person without disease. A positive predictive value (PPV) describes the proportion of those with positive test results who have the disease, whereas a negative predictive value (NPV) is the proportion of those with negative test results who do not have the disease. A DOR is a single indicator of test performance and is the ratio of the odds of testing positive in those with the disease relative to the odds of testing positive in those without the disease. It can be calculated from the sensitivity and specificity values. The DOR summarises the results into a single indicator of test performance; however, information contained in sensitivity and specificity is lost and in particular a DOR cannot distinguish between tests with high sensitivity and low specificity and vice versa.
Hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic (HSROC) curves were produced for each test when three or more studies reported sufficient data. A separate HSROC curve was derived for patient-level analysis and biopsy-level analysis when possible. Meta-analysis models were fitted using the HSROC model48 in SAS 9.1 using the NLMIXED function (SAS Institute). This HSROC model takes account of the diseased and non-diseased sample sizes in each study and allows estimation of random effects for the threshold and accuracy effects. 48,49 HSROC models for PDD and WLC were fitted individually based upon the data for the individual alone, which allowed for an asymmetric summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve. Additionally, two models that fitted the data simultaneously were also run, to formally assess the evidence for a difference in diagnostic accuracy between the tests. A fuller model was run that allowed for a difference between the tests in all three constituent diagnostic accuracy parameters (threshold, accuracy and shape of SROC curve) and also a simpler nested model was run that did not allow for a difference in diagnostic accuracy in any of the three parameters. The SROC curves from the HSROC models were produced and are shown on the corresponding SROC plots along with the individual study estimates. Summary sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios and DORs for each model were reported as point estimate and 95% confidence interval (CI).
The presentation of test performance in terms of the detection of stage and grade of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer was considered in the two broad categories of: (1) less aggressive, lower risk tumours (pTa, G1, G2) and (2) more aggressive, higher risk tumours (pT1, G3, CIS). The median (range) sensitivity of PDD and WLC across studies, for both patient- and biopsy-based detection of tumours, was reported for each category and also separately for CIS.
WLC-assisted TURBT compared with PDD-assisted TURBT
For relevant outcomes (e.g. recurrence rate after WLC-assisted TURBT compared with PDD-assisted TURBT), when appropriate, meta-analysis was employed to estimate a summary measure of effect. The dichotomous outcome data were combined using the Mantel–Haenszel (RR) method. For the estimates of RR, 95% CIs and p-values were calculated. The results were reported using a fixed-effect model in the absence of statistical heterogeneity. Chi-squared tests and I2 statistics were used to explore statistical heterogeneity across studies. Possible reasons for heterogeneity were explored using sensitivity analysis. When there was no obvious reason for heterogeneity, the results were reported using random-effects methods. In the event that a quantitative synthesis was considered to be inappropriate or not feasible, we provided a narrative synthesis of results.
Chapter 4 Results – photodynamic diagnosis
Number of studies identified
From the electronic searches for primary reports, 113 records were selected as being possibly relevant to the review of PDD. In total, 33 of these were non-English language papers and were not considered further. The full-text reports of the remaining 80 were obtained and assessed: 44 met the inclusion criteria for this review; 25 were excluded; and 11 were retained for background information. Figure 6 shows a flow diagram outlining the screening process, with reasons for exclusion of full-text papers.
FIGURE 6.
Flow diagram outlining the screening process for the photodynamic diagnosis part of the review.
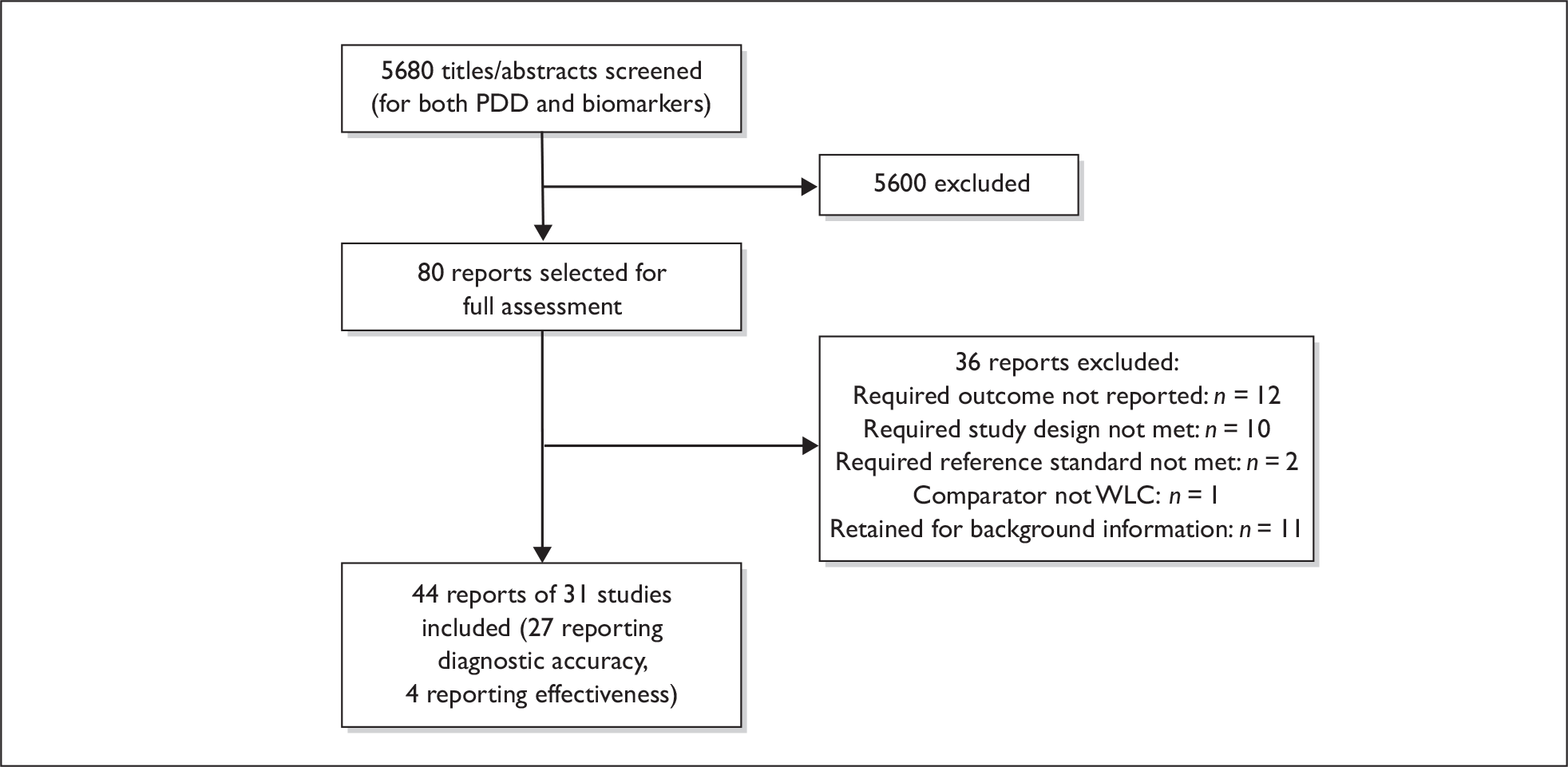
Number and type of studies included
Appendix 4 lists the 31 studies, published in 44 reports, that were included in the review of test performance and effectiveness. In total, 27 studies, published in 36 reports,50–85 met the inclusion criteria for studies reporting the diagnostic accuracy of PDD. Four RCTs, published in eight reports,86–93 met the inclusion criteria for studies comparing the effectiveness of PDD-assisted TURBT with the effectiveness of WLC-assisted TURBT in terms of outcomes such as recurrence or progression.
Number and type of studies excluded
A list of the 25 potentially relevant studies identified by the search strategy for which full-text papers were obtained but which subsequently failed to meet the inclusion criteria is given in Appendix 5. These studies were excluded because they failed to meet one or more of the inclusion criteria in terms of the type of study, participants, test, reference standard or outcomes reported.
Characteristics of the included studies
Appendix 6 shows the characteristics of the included studies. Table 5 shows summary information for the PDD studies reporting diagnostic accuracy and Table 6 shows summary information for the RCTs comparing PDD with WLC and reporting recurrence and/or progression.
| Characteristic | Number | Number of studies |
|---|---|---|
| Patients | ||
| Enrolled | 2949 | 27 |
| Analysed | 2807 | |
| Suspicion of or previously diagnosed BCa | ||
| Suspicion of BC | 946 (41%) | 19 (70%) |
| Previously diagnosed BC | 1381 (59%) | |
| Not reported | 481 | 8 (30%) |
| Age | ||
| Median (range) of means (years) | 67 (52–72) | 20 (74%) |
| Not reported | – | 7 (26%) |
| Sexb | ||
| Men | 1647 (76%) | 18 (67%) |
| Women | 510 (24%) | |
| Not reported | 656 | 9 (33%) |
| Agent used | ||
| 5-ALA | 2113 (75%) | 18 (67%) |
| HAL | 464 (17%) | 5 (19%) |
| Hypericin | 81 (3%) | 2 (7%) |
| 5-ALA or HAL | 149 (5%) | 2 (7%) |
| Characteristic | Number | Number of studies |
|---|---|---|
| Patients | ||
| Enrolled | 709 | 4 |
| Analysed | 544 | |
| Suspicion of or previously diagnosed BC | ||
| Suspicion of BC | 48 | 1 |
| Previously diagnosed BC | 74 | |
| Not reported | 422 | 3 |
| Agea | ||
| PDD groups (years) | 68 (68–69) | 3 |
| WLC groups (years) | 70 (all three studies) | |
| Whole study population (years) | 67 | 1 |
| Sex | ||
| Men | 396 (73%) | 4 |
| Women | 148 (27%) | |
| Agent used | ||
| 5-ALA | 544 | 4 |
| Outcomes reported | ||
| Recurrence-free survival | – | 2 |
| Residual tumour at first cystoscopy | – | 4 |
| Recurrence of tumour | – | 2 |
| Progression to muscle-invasive disease | – | 2 |
| Length of follow-up | ||
| 8 years | 1 | |
| 5 years | 1 | |
| 2 years | 1 | |
| 10–14 days | 1 | |
The 27 diagnostic studies enrolled 2949 participants, with 2807 included in the analysis. In 19 studies51,53,57–63,65,66,70–72,77,78,80,81,84 involving 2327 participants, 946 (41%) presented with a suspicion of bladder cancer and 1381 (59%) had previously diagnosed bladder cancer. In two72,78 of these studies the whole patient population (n = 102) had a suspicion of bladder cancer and in three51,58,84 the whole population had previously diagnosed bladder cancer (n = 117). The remaining eight studies50,52,54,56,67,73,76,85 did not report this information. In total, 1850,53,54,56,58,59,61–63,67,70–73,77,78,84,85 (67%) of 27 studies used 5-ALA as the photosensitising agent, five57,60,65,66,81 (19%) used HAL, two52,76 (7%) used hypericin and two51,80 used either 5-ALA or HAL but did report the number of patients receiving each agent.
Across 20 studies50,51,53,56,57,59–63,65–67,70,71,76,77,80,81,84 providing information on patient age, the median (range) of means was 67 years (52–72 years). In total, 18 studies50,53,54,57,60–63,65–67,70,71,76,77,80,81,84 provided information on the gender of 2157 participants, of whom 1647 (76%) were men and 510 (24%) were women.
Sixteen studies50,51,53,56,59–63,65,71,76,77,80,81,85 gave details of when they took place, with an earliest start date of February 199463 and latest end date of March 2006. 51 Nine studies took place in Germany,54,56,58,61,70,71,80,84,85 three in the Netherlands,59,60,81 two each in Italy51,53 and Singapore50,76 and one each in Belgium,52 Switzerland,63 France,72 Austria,73 Poland,78 South Korea62 and China,77 and four had multinational settings, taking place in the USA/Canada,57 Germany/the Netherlands,66 Germany/USA67 and Switzerland/Norway/Sweden/Germany. 65
The four RCTs reporting recurrence/progression enrolled 709 participants, of whom 544 were included in the analysis. In the study by Babjuk and colleagues,86 of 128 patients enrolled, six were excluded because of no histological evidence of bladder cancer (n = 2), muscle-invasive bladder cancer (n = 3) and multiple T1G3 tumour with concomitant CIS treated with immediate cystectomy (n = 1). In the study by Daniltchenko and colleagues,88 115 patients were randomised, with 13 patients subsequently excluded because of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. In the study by Denzinger and colleagues,89 301 patients were randomised to the PDD (n = 151) and WLC (n = 150) arms. A total of 63 patients were subsequently excluded from the PDD arm because of no positive tumour confirmation (n = 38), invasive tumour or indication for cystectomy (n = 23), or no follow-up examinations (n = 2), and 47 patients were excluded from the WLC arm because no tumour could be found (n = 22), muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma was diagnosed or cystectomy was indicated (n = 23) or follow-up was refused after the first resection (n = 2, one with pTaG1 and one with pT1G2). In the study by Kriegmair and colleagues,92 of 165 patients randomised, 129 patients had histological proof of TCC and were considered evaluable.
The outcomes reported for the studies included recurrence-free survival,86,89 residual tumour rate at first cystoscopy following TURBT,86,88,89,92 recurrence during follow-up88,89 and progression to muscle-invasive disease. 88,89
Although the selection criteria for all four studies allowed the inclusion of patients with either a suspicion of or previously diagnosed bladder cancer, only the study by Babjuk and colleagues86 provided details of these groups. Babjuk and colleagues reported that 20/60 (33%) of the PDD group and 28/62 (45%) of the WLC group presented with a suspicion of bladder cancer whereas 40/60 (67%) of the PDD group and 34/62 (55%) of the WLC group had previously diagnosed bladder cancer. The remaining studies by Daniltchenko and colleagues,88 Denzinger and colleagues89 and Kriegmair and colleagues92 involving 422 patients did not provide separate details of those with a suspicion of bladder cancer and those with previously diagnosed disease. All four studies used 5-ALA as the photosensitising agent.
Three studies86,89,92 provided information on patient age separately for the PDD and WLC groups, with the median (range) of means 68 years (68–69 years) for the PDD groups and 70 years (all three studies) for the WLC groups. The study by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 reported the mean age for the whole patient population as 67 years. All four studies provided information on the gender of the 544 patients analysed, of whom 396 (73%) were men and 148 (27%) were women. There were 197 men in the PDD groups and 199 in the WLC groups, and there were 67 women in the PDD groups and 81 in the WLC groups. All four studies gave details of when they took place, with an earliest start date of 199789 and latest end date of December 2003. 86 One (single centre) study took place in Germany,89 one in the Czech Republic,86 and the remaining two were multicentre, with both taking place in Germany/Austria. 88,92 The follow-up periods for the studies were 8 years for Denzinger and colleagues,89 5 years for Daniltchenko and colleagues,88 2 years for Babjuk and colleagues86 and 10–14 days for Kriegmair and colleagues,92 although Kriegmair and colleagues compared PDD and WLC with the aim of evaluating residual tumour following TURBT, hence the short follow-up period.
Quality of the included studies
Figure 7 summarises the quality assessment for the PDD diagnostic studies, and Figure 8 summarises the quality assessment for the four RCTs that compared PDD with WLC and reported recurrence/progression of disease. The results of the quality assessment of the individual studies are shown in Appendix 7.
FIGURE 7.
Summary of quality assessment of PDD diagnostic studies (n = 27).
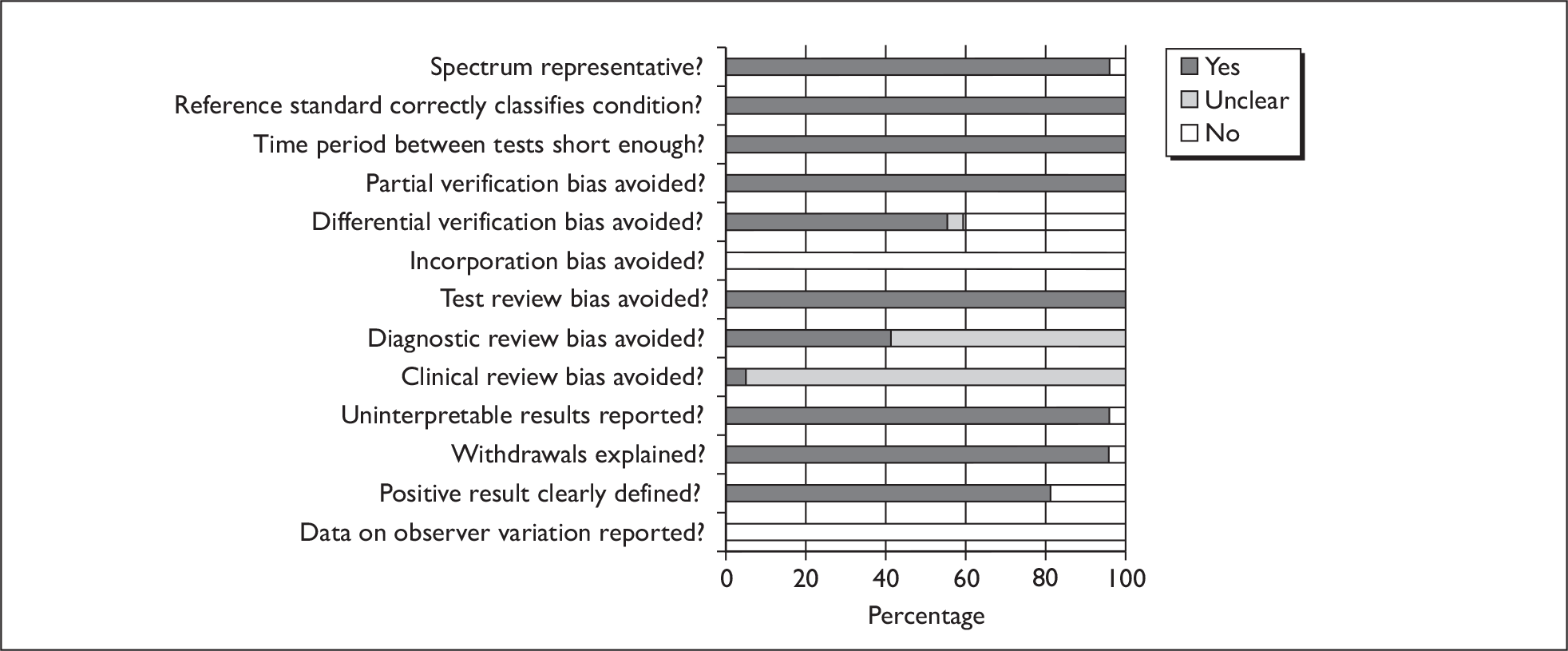
FIGURE 8.
Summary of quality assessment of RCTs reporting recurrence/progression (n = 4).
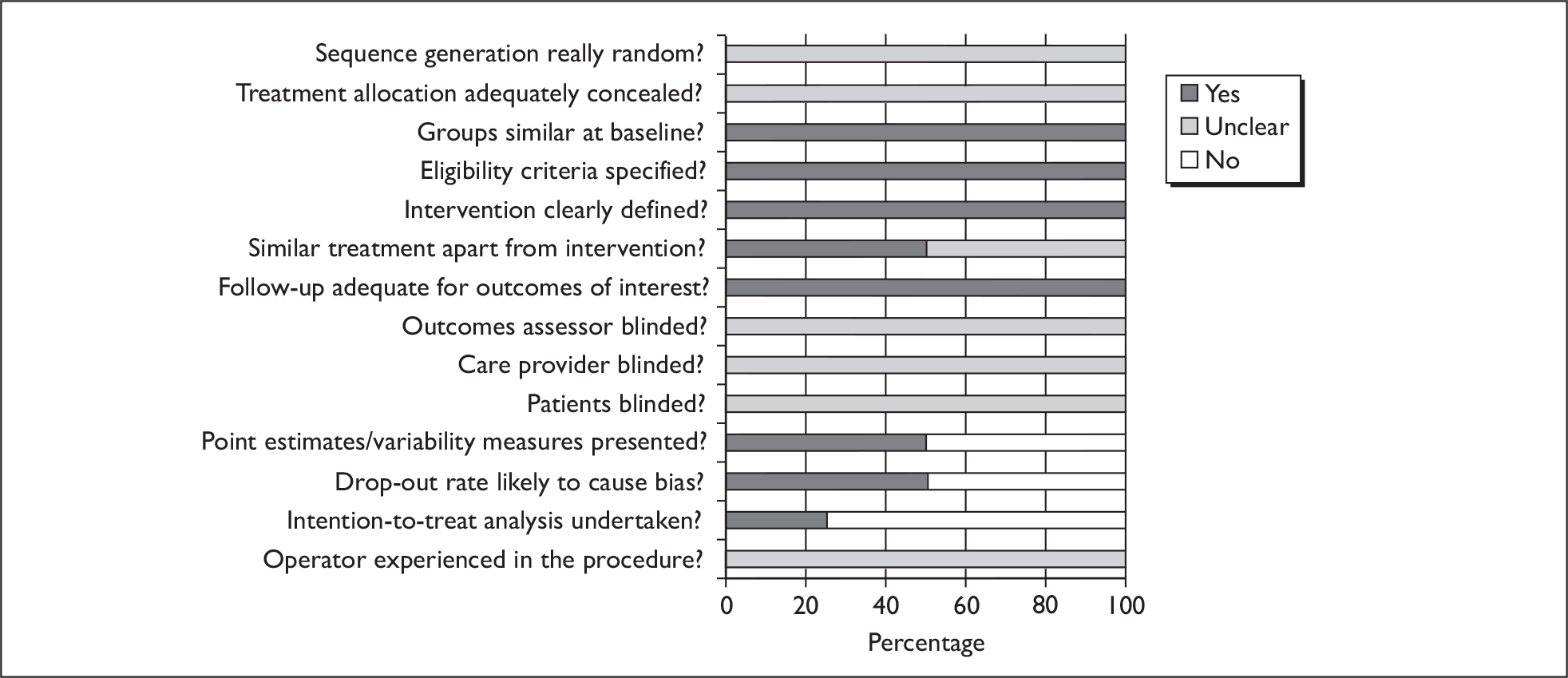
The diagnostic studies were assessed using a modified version of the QUADAS tool containing 13 questions. In 96% (26/27) of studies the spectrum of patients who received the tests was considered to be representative of those who would receive the test in practice. For this question we considered patients to be representative if the patient population either had a suspicion or a history of bladder cancer or contained patients from both groups, or the majority or all of the patient population presented with either gross or microhaematuria or contained a mixture of patients with either indication. In all studies the reference standard (histological assessment of biopsied tissue) was considered likely to correctly classify bladder cancer, and the time period between PDD and the reference standard was considered to be short enough to be reasonably sure that the patient’s condition had not changed between the tests.
In all studies partial verification bias was avoided in that all patients who underwent PDD also received a reference standard test. However, in only 55% (15/27) of studies50–54,57–60,63,65,67,70,72,84 were patients considered to have received the same reference standard regardless of the PDD test result. This question was checked ‘yes’ if random biopsies were taken from normal-appearing areas (i.e. test negative) and ‘no’ if biopsies were taken only from suspicious looking areas (i.e. test positive). In effect the patients in those studies in which random biopsies of normal-appearing areas were taken received an enhanced reference standard. In all studies test review bias was avoided in that the PDD results were interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard test. We considered that this would always be the case, as lesions considered suspicious during PDD are biopsied during the procedure and it is only later that the reference standard results are known following histological assessment of the biopsied tissue.
In 96% (26/27) of studies, either uninterpretable or intermediate test results were reported or there were no uninterpretable or intermediate test results, and withdrawals from the study were explained or there were none. The exception to this was the study by Koenig and colleagues,67 in which 55 patients were included but only 49 reported in the analysis. In 81% (22/27) of studies50,52–54,56,58–63,65–67,70–73,76–78,84 a clear definition of what was considered to be a positive result was provided. In 96% (26/27) of studies it was unclear whether the same clinical data were available when the PDD test results were interpreted as would be available when the test was used in practice, the exception being the study by Ehsan and colleagues,54 which stated that a detailed review of personal medical history was conducted for each patient before PDD. In this context clinical data were defined broadly to include any information relating to the patient such as age, gender, presence and severity of symptoms, and other test results. In 59% (16/27) of studies50,53,54,56,58,60,67,70–73,77,78,81,84,85 it was unclear whether the reference standard results were interpreted without knowledge of the results of the PDD test. All of the studies were judged to suffer from incorporation bias in that PDD was not considered to be independent of the reference standard test as the biopsies used for the reference standard were obtained via the PDD procedure. None of the studies provided information on observer variation in interpretation of test results.
The four RCTs,86,88,89,92 comparing PDD with WLC, were assessed using the 14-question checklist adapted from Verhagen and colleagues. 47 In all four studies the groups were considered to be similar at baseline in terms of prognostic factors, eligibility criteria for the study were specified, and length of follow-up was considered adequate in relation to the outcomes of interest reported by the studies.
In all four studies it was unclear whether the sequence generation was really random, whether the treatment allocation was adequately concealed, whether the outcome assessors, care providers or patients were blinded to the PDD or WLC intervention, or whether the surgeon undertaking the operation was experienced in performing the procedure. In the studies by Denzinger and colleagues89 and Kriegmair and colleagues92 the withdrawal rate was considered likely to cause bias. In the studies by Babjuk and colleagues86 and Denzinger and colleagues89 the groups were considered to have been treated in the same way apart from the intervention received, whereas in the remaining two studies88,92 this was unclear. In the studies by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 and Denzinger and colleagues89 point estimates and measures of variability were presented for the primary outcome measures. Only the study by Kriegmair and colleagues92 included an intention to treat analysis.
Assessment of diagnostic accuracy
Overview
This section reports the diagnostic accuracy of PDD compared with WLC against a reference standard of histological assessment of biopsied tissue for the detection of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. The following levels of analysis are presented: patient, biopsy, stage/grade and photosensitising agent used. For patient and biopsy levels of analysis figures are included showing the sensitivity and specificity of the individual studies, SROC curves and pooled estimates with 95% CIs for sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios and DORs for PDD and WLC. For the stage/grade level of analysis the median (range) sensitivity and specificity across studies are presented for PDD and WLC. Appendix 8 shows the studies that reported sufficient information (true and false positives and negatives for both PDD and WLC) to allow their inclusion in the pooled estimates for patient- and biopsy-level analysis, and also those studies comparing PDD with WLC that reported the sensitivity of the tests in detecting tumour stage/grade. Individual study results are given in Appendix 9. The results of studies reporting sensitivity and specificity for PDD but not WLC were examined to assess whether they differed from those of the comparative studies.
Patient-level analysis
Although biopsy-level analysis is useful to validate the accuracy of the test, patient-level data are more useful in determining management. Five studies65,66,73,80,81 comparing PDD with WLC and enrolling 386 people, with 370 included in the analysis, provided sufficient information to allow their inclusion in the pooled estimates for patient-level analysis. In four studies,65,66,80,81 of 318 patients included in the analysis, 131 (41%) had symptoms suggestive of bladder cancer and 187 (59%) had a history of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. The study by Riedl and colleagues73 did not report this information. Three of the studies65,66,81 used HAL as the photosensitising agent and two73,80 used 5-ALA. In two65,73 of the studies random biopsies of normal-appearing areas were taken.
Figure 9 shows the sensitivity and specificity of the individual studies, SROC curves and pooled estimates for the sensitivity and specificity of PDD and WLC for patient-based detection of bladder cancer. The pooled sensitivity (95% CI) for PDD was 92% (80% to 100%) compared with 71% (49% to 93%) for WLC, whereas the pooled specificity (95% CI) for PDD was 57% (36% to 79%) compared with 72% (47% to 96%) for WLC. The pooled estimates show that PDD had higher sensitivity but lower specificity than WLC, with the CIs for the two techniques overlapping. None of the five studies comparing PDD with WLC reported test performance separately for the group of patients newly presenting with a suspicion of bladder cancer or for the group with a history of non-muscle-invasive disease. The DOR values (95% CI) were 16.50 (1.00 to 42.23) for PDD and 6.44 (1.00 to 14.24) for WLC, with higher DORs indicating a better ability of the test to differentiate between those with and those without bladder cancer. Across studies the median (range) PPVs were 91% (59% to 100%) for PDD and 89% (56% to 100%) for WLC, and NPVs were 60% (32% to 100%) for PDD and 23% (20% to 87%) for WLC. However, it should be noted that predictive values are affected by disease prevalence, which is rarely constant across studies, and therefore these data should be interpreted with caution.
FIGURE 9.
Patient-level analysis: sensitivity, specificity, SROC curve and pooled estimates.
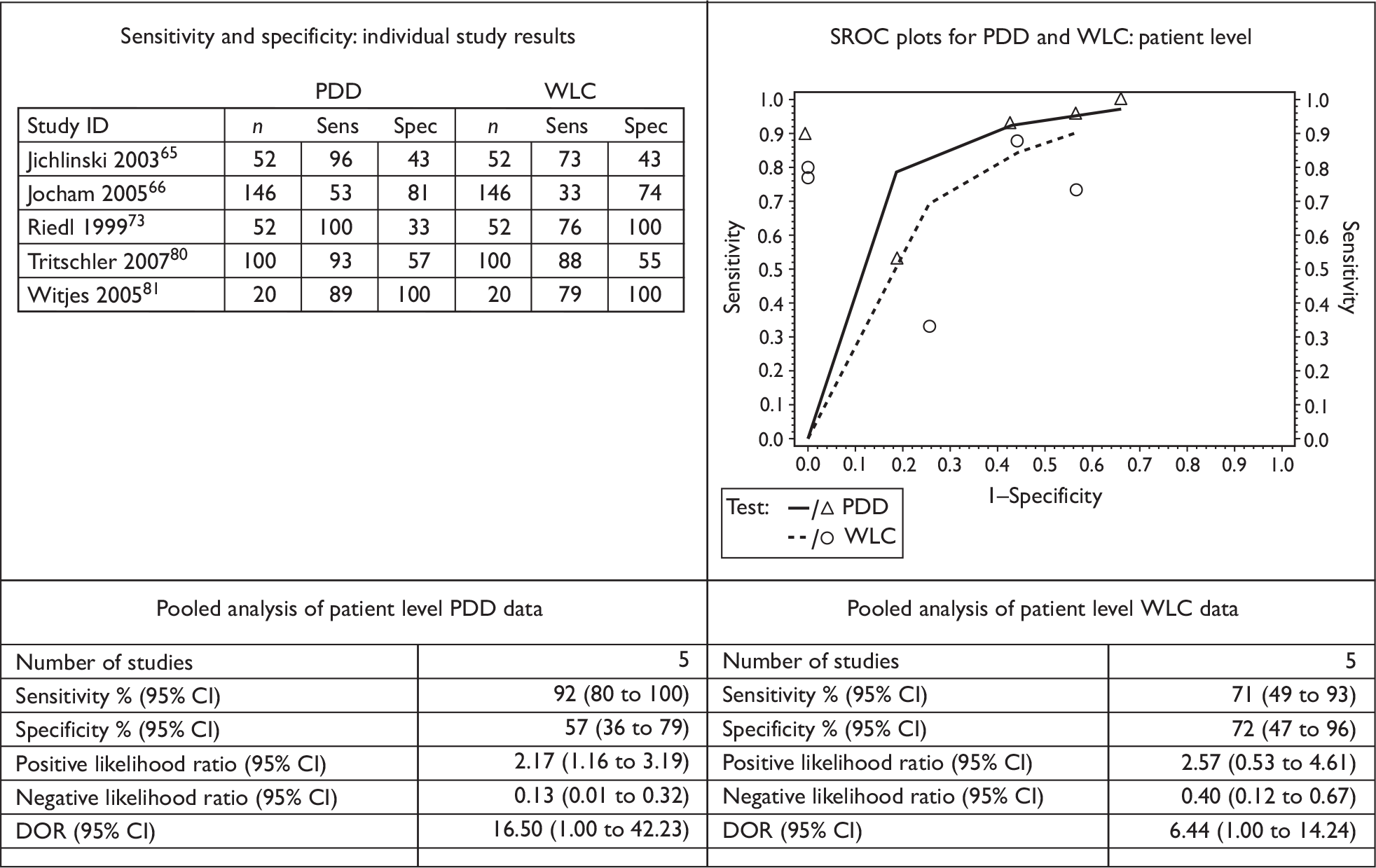
Three studies72,77,78 enrolling and analysing 153 patients reported patient-based detection for PDD only and were not included in the pooled estimates. All three studies used 5-ALA and, in one,72 random biopsies of normal-appearing areas were taken. Across these three studies the median (range) sensitivity and specificity for PDD were 91% (64% to 100%) and 67% (36% to 67%) respectively. In two72,78 of the studies the whole patient populations (n = 102) had a suspicion of bladder cancer with no previous history of the disease. Landry and colleagues72 reported a sensitivity of 64% for PDD, compared with 91% reported by Szygula and colleagues,78 whereas both studies reported a specificity of 67%.
Studies that reported patient-level analysis but only for CIS are considered in the section on stage/grade analysis.
Biopsy-level analysis
A total of 14 studies50,53,54,56,59–63,65,70,76,81,85 comparing PDD with WLC and enrolling 1751 people, with 1746 included in the analysis, provided sufficient information to allow their inclusion in the pooled estimates for biopsy-level analysis (number of biopsies: 8574 for PDD analysis, 8473 for WLC analysis). In nine studies,53,59–63,65,70,81 involving 1408 people, 560 (40%) had symptoms suggestive of bladder cancer and 848 (60%) had a history of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. The studies by Cheng and colleagues,50 Ehsan and colleagues,54 Filbeck and colleagues,56 Sim and colleagues76 and Zumbraegel and colleagues85 did not report this information. Ten studies50,53,54,56,59,61–63,70,85 used 5-ALA as the photosensitising agent and three60,65,81 used HAL, while the study by Sim and colleagues76 used hypericin. In eight studies50,53,54,59,60,63,65,70 random biopsies of normal-appearing areas were taken.
Figure 10 shows the sensitivity and specificity of the individual studies, SROC curves and pooled estimates for the sensitivity and specificity of PDD and WLC for biopsy-level detection of bladder cancer. In the pooled estimates, PDD had higher sensitivity (93%, 95% CI 90% to 96%) than WLC (65%, 95% CI 55% to 74%), whereas WLC had higher specificity (81%, 95% CI 73% to 90%) than PDD (60%, 95% CI 49% to 71%). The pair of CIs for both sensitivity and specificity did not overlap, providing evidence of a difference in diagnostic performance between the techniques. Across the 14 studies the sensitivity for PDD ranged from 76%65 to 98%54,62,70 compared with 1753 to 88%60 for WLC, and specificity ranged from 32%85 to 100%81 for PDD compared with 4685 to 100%81 for WLC. In the pooled analysis the DOR values (95% CI) were 20.29 (9.20 to 31.37) for PDD and 7.76 (3.39 to 11.93) for WLC. Across studies the median (range) PPVs were 61% (40% to 100%) for PDD and 70% (38% to 100%) for WLC, and the median (range) NPVs were 92% (20% to 99%) for PDD and 78% (13% to 91%) for WLC.
FIGURE 10.
Biopsy-level analysis: sensitivity, specificity, SROC curve and pooled estimates.
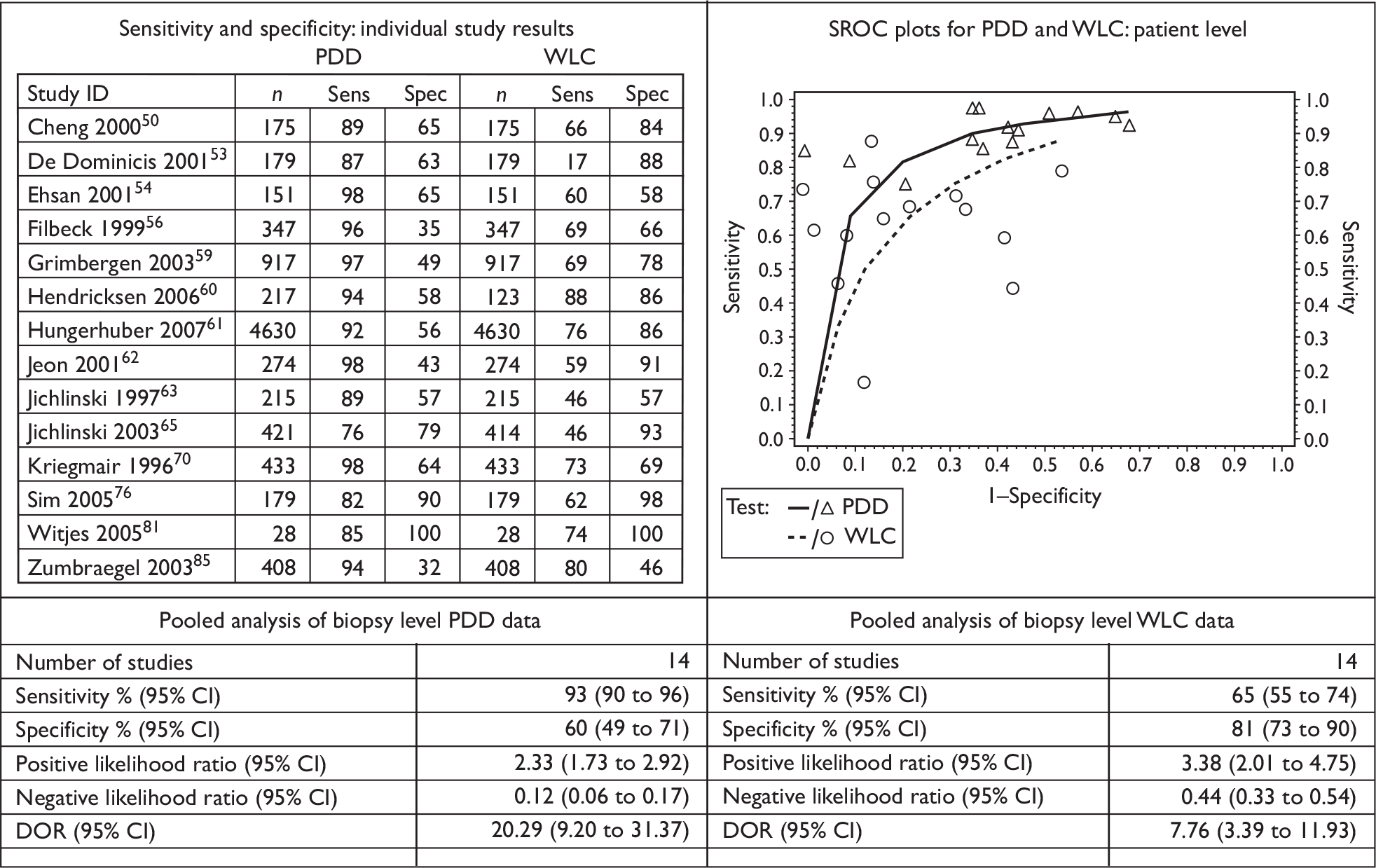
None of the 14 studies comparing PDD with WLC reported biopsy-level detection separately for the group of patients newly presenting with a suspicion of bladder cancer or for the group with a history of non-muscle-invasive disease.
Six studies58,67,71,73,77,84 involving 428 patients reported biopsy-level detection for PDD only and were not included in the pooled estimates. All six studies used 5-ALA and in four58,67,73,84 random biopsies of normal-appearing areas were taken. Across the six studies the median (range) sensitivity and specificity for PDD were 95% (87% to 98%) and 51% (36% to 67%) respectively. In two58,84 of these studies the whole patient population (n = 68) had a history of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Frimberger and colleagues58 and Zaak and colleagues84 reported sensitivities of 95% and 90% and specificities of 67% and 61%, respectively, for PDD.
Studies that reported biopsy-level analysis but only for CIS are included in the section on stage/grade analysis.
Formal comparison of PDD and WLC in patient- and biopsy-based analysis
In addition to the two HSROC models of the diagnostic accuracy of PDD and WLC individually, two HSROC models were run that simultaneously modelled PDD and WLC diagnostic accuracy using all of the data from the 14 studies. There was strong evidence of a difference in diagnostic accuracy between the tests, with the model that allowed for a difference in diagnostic accuracy in the three constituent parameters (threshold, accuracy and shape of SROC curve) having a substantially better Bayesian information criterion than the simplified diagnostic accuracy model, for both patient- and biopsy-level analysis (difference of 1408.0 and 20.7 respectively). These results are supported by noting that the intervals for the summary sensitivity and specificity at biopsy level from the models in which the tests were modelled separately (Figure 10) did not overlap for either measure. PDD had a greater sensitivity than WLC but at the cost of a lower specificity. The point estimates of the patient-level analysis were similar to those from the biopsy-level analysis, although the intervals were substantially wider, as might be expected because of the smaller number of studies and observations available for this level of analysis.
Stage/grade analysis
Studies reporting the sensitivity of PDD compared with WLC in the detection of stage and grade of tumour categorised this information in different ways, including pTa, pTaG1, pTaG1–2, pTaG2, pTaG2–3, pTaG3, pTa-T1, G1–2, pT1, pT1G1, pT1G1–2, pT1G2, pT1G3, > pT1, CIS, G3, pT2G2, pT2G3, ≥ pT2, ≥ pT2G3 and pT4G3 (see Appendix 8). Some studies reported the detection of stage/grade at the patient level and others reported this information at biopsy level.
For the purposes of this review, the presentation of test performance in terms of the detection of stage and grade of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer was considered in two broad categories:
-
less aggressive, lower risk tumours (pTa, G1, G2)
-
more aggressive, higher risk tumours (pT1, G3, CIS).
Table 7 shows the median (range) sensitivity of PDD and WLC across studies, for both patient- and biopsy-based detection of tumours, within the broad categories of less aggressive/lower risk and more aggressive/higher risk (including CIS), and also separately for CIS.
| PDD sensitivity (%), median (range) | WLC sensitivity (%), median (range) | Number of patients (biopsies)a | Number of studies | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Less aggressive/lower risk | ||||
| Patient-based detection | 92 (20 to 95) | 95 (8 to 100) | 266 | 3 |
| Biopsy-based detection | 96 (88 to 100) | 88 (74 to 100) | 1206 (5777) | 7 |
| More aggressive/higher risk including CIS | ||||
| Patient-based detection | 89 (6 to 100) | 56 (0 to 100) | 563 | 6 |
| Biopsy-based detection | 99 (54 to 100) | 67 (0 to 100) | 1756 (7506) | 13 |
| CIS | ||||
| Patient-based detection | 83 (41 to 100) | 32 (0 to 83) | 563 | 6 |
| Biopsy-based detection | 86 (54 to 100) | 50 (0 to 68) | 1756 (7506) | 13 |
Less aggressive, lower risk tumours (pTa, G1, G2)
Nine studies54,56,60–62,66,67,80,81 involving 1452 patients reported the sensitivity of PDD compared with WLC for the detection of less aggressive, lower risk tumours. The stages/grades reported by these studies included pTa,54,62,66,80 pTaG1,60,61,67 pTaG1–2,56 pTaG260,61,67,81 and G1–2. 80 Across three studies66,80,81 involving 266 patients reporting patient-based tumour detection, the median (range) sensitivities of PDD at 92% (20% to 95%) and WLC at 95% (8% to 100%) were broadly similar. Across seven studies54,56,60–62,67,81 involving 1206 patients reporting biopsy-based tumour detection (n = 5777 biopsies overall), the median (range) sensitivity of PDD at 96% (88% to 100%) was higher than that of WLC at 88% (74% to 100%) (Table 7).
None of the studies reported the specificity of PDD or WLC in detecting less aggressive, lower risk tumours.
More aggressive, higher risk tumours (pT1, G3, CIS)
Sixteen studies50,51,53,54,56,57,60–62,65–67,70,80,81,85 involving 2155 patients reported the sensitivity of PDD compared with WLC for the detection of more aggressive, higher risk tumours. The stages/grades reported by these studies included pTaG2–3,53 pTaG3,60,61,67,81 pTa-T1,50,70 pT1,54,62,66,80 pT1G1,61 pT1G1–2,60,61,67 pT1G260,61,67 pT1G3,56,60,61,67,81 > pT1,56 G380 and CIS. 50,51,53,54,56,57,60–62,65–67,70,80,81,85
Across six studies51,57,65,66,80,81 involving 563 patients reporting patient-based tumour detection, the median (range) sensitivity of PDD at 89% (6% to 100%) was much higher than that of WLC at 56% (0% to 100%). Across 13 studies50,53,54,56,57,60–62,65,67,70,81,85 involving 1756 patients reporting biopsy-based tumour detection (n = 7506 biopsies overall), the median (range) sensitivity of PDD at 99% (54% to 100%) was also much higher than that of WLC at 67% (0% to 100%) (Table 7).
None of the studies reported the specificity of PDD or WLC in detecting more aggressive, higher risk tumours, other than for CIS, discussed in the following section.
Carcinoma in situ
Although CIS is included in the more aggressive/higher risk category reported above, it may also be useful to consider separately the performance of PDD compared with WLC for the detection of CIS. The same 16 studies50,51,53,54,56,57,60–62,65–67,70,80,81,85 reporting the sensitivity of PDD compared with WLC for the detection of more aggressive/higher risk tumours also provided this information specifically for CIS.
Across six studies51,57,65,66,80,81 involving 563 patients reporting patient-based tumour detection, the median (range) sensitivity of PDD for detecting CIS was 83% (41% to 100%), much higher than the sensitivity of 32% (0% to 83%) for WLC. Across 13 studies50,53,54,56,57,60–62,65,67,70,81,85 involving 1756 patients reporting biopsy-based tumour detection (n = 7506 biopsies overall), the median (range) sensitivity of PDD was 86% (54% to 100%), also much higher than that of WLC at 50% (0% to 68%) (Table 7).
Three studies51,57,70 reported the specificity of PDD and WLC in detecting CIS and one study52 reported this information only for PDD (Table 8). The specificity reported for PDD ranged from 61%70 to 99%52 whereas that for WLC ranged from 68%70 to 97%. 51 Two51,70 of the three studies comparing PDD with WLC reported higher specificity for WLC whereas the third study57 reported similar specificities for both techniques. In the PDD studies HAL was associated with higher values than 5-ALA, with hypericin associated with the highest value. However, these results should be interpreted with caution as they are based on only a small number of studies.
Photosensitising agent used
Table 9 shows the median (range) sensitivity and specificity across studies for the different photosensitising agents used, for both patient- and biopsy-level detection of bladder cancer. Four studies using 5-ALA72,73,77,78 and three using HAL65,66,81 reported patient-level detection of bladder cancer. Across the studies using 5-ALA the median (range) sensitivity and specificity were 96% (64% to 100%) and 52% (33% to 67%), respectively, compared with 90% (53% to 96%) sensitivity and 81% (43% to 100%) specificity for HAL.
| Agent | Sensitivity (%), median (range) | Specificity (%), median (range) | Number of patients (biopsies) | Number of studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient-based detection | ||||
| 5-ALA | 96 (64 to 100) | 52 (33 to 67) | 205 | 4 |
| HAL | 90 (53 to 96) | 81 (43 to 100) | 218 | 3 |
| Hypericin | – | – | – | 0 |
| Biopsy-based detection | ||||
| 5-ALA | 95 (87 to 98) | 57 (32 to 67) | 1949 (8296) | 15 |
| HAL | 85 (76 to 94) | 80 (58 to 100) | 122 (666) | 3 |
| Hypericin | 82 | 91 | 41 (179) | 1 |
A total of 15 studies using 5-ALA,50,53,54,56,58,59,61,63,67,70,71,73,77,84,85 three using HAL60,65,81 and one using hypericin76 reported biopsy-level detection of bladder cancer. Across the studies using 5-ALA the median (range) sensitivity and specificity were 95% (87% to 98%) and 57% (32% to 67%), respectively, compared with 85% (76% to 94%) sensitivity and 80% (58% to 100%) specificity for HAL. The study by Sim and colleagues76 reported 82% sensitivity and 91% specificity for hypericin.
The results for both patient- and biopsy-based detection suggest that 5-ALA may have slightly higher sensitivity than HAL, whereas HAL may have higher specificity than 5-ALA, but this should be interpreted with caution as factors other than the photosensitising agent used may have contributed to the sensitivity and specificity values reported by the studies.
Four studies reported sensitivity and specificity at both patient and biopsy level, two using 5-ALA73,77 and two using HAL. 65,81
Side effects of photosensitising agents
5-Aminolaevulinic acid
A total of 18 studies used 5-ALA as the photosensitising agent. Seven studies53,61,63,71–73,78 involving 1320 patients reported that no side effects were associated with the instillation of 5-ALA. Jeon and colleagues,62 in a study involving 62 patients, reported that there were no systemic or serious local side effects following 5-ALA bladder instillation.
Cheng and colleagues,50 in a study involving 41 patients, reported that besides two (5%) patients who complained of urgency and were unable to retain ALA for more than 2 hours, there were no clinically significant short-term side effects such as urinary tract infections and phototoxicity. At the 1-month follow-up no phototoxicity or other complications were reported. 50 Koenig and colleagues,67 in a study involving 49 patients, reported that none showed signs of systemic side effects of PDD such as phototoxicity. One patient reported transient (< 24 hours) dysuria and one patient developed a urinary tract infection, which was treated with antibiotics. 67 Song and colleagues,77 in a study involving 51 patients, reported that one cases of acute cystitis was accompanied by haemorrhagic lesion attributed to the instillation procedure (i.e. chemical cystitis).
Kriegmair and colleagues,71 in a study involving 104 patients, reported that no serious side effects were observed during or after 5-ALA instillation. However, following instillation seven patients reported urgency. After the PDD procedure, more severe alginuresis symptoms and pollakiuria were detected in four patients. Significant gram-negative bacteriuria was detected in three patients but the symptoms improved rapidly with appropriate antibiotics and spasmolytic agents. Phototoxicity was not detected in any patient. 71
Hexaminolaevulinate
Five studies used HAL as the photosensitising agent. In the studies by Jichlinski and colleagues65 and Witjes and colleagues81 adverse events were reported in 40 of 52 and 4 of 20 patients, respectively, although none was considered to be related to HAL instillation. Fradet and colleagues57 and Jocham and colleagues66 both reported that HAL was well tolerated. In the study by Fradet and colleagues,57 800 adverse events were reported by 240 of the 298 patients in the safety set, of which 19 (2.4%) were considered to be related to HAL instillation, none of which was serious. Twenty patients experienced a total of 23 serious adverse events, including one death due to an aortic aneurysm, which was unrelated to HAL instillation. 57 In the study by Jocham and colleagues66 75 adverse events were reported by 47 of 162 patients, of which two (2.7%) were considered treatment related, with both occurring in the same patient (urinary retention and micturition urgency).
The study by Hendricksen and colleagues60 did not mention side effects.
5-Aminolaevulinic acid/hexaminolaevulinate not reported separately
Two studies51,80 involving 149 patients used 5-ALA or HAL but did not report the number of patients who received each agent. In the study by Colombo and colleagues,51 no systemic side effects related to the PDD procedure were reported and any local side effects were referred to as negligible. Tritschler and colleagues80 did not mention side effects.
Hypericin
Two studies used hypericin. D’Hallewin and colleagues,52 in a study involving 40 patients, reported that there were no significant local or systemic side effects caused by the instillation of hypericin. In the study by Sim and colleagues,76 involving 41 patients, there were no reports of urinary tract infections, contracted bladder, photosensitivity or allergies. One patient developed microscopic haematuria from cystitis, which resolved on conservative management. 76
Recurrence/progression of disease
Overview
This section presents the results of the four RCTs86,88,89,92 comparing PDD with WLC and reporting the effectiveness outcomes of recurrence-free survival, residual tumour rate at first cystoscopy following TURBT, recurrence rate during follow-up and tumour progression. Random-effects meta-analyses using RR as the effect measure are presented comparing PDD and WLC in terms of these outcomes.
The RCTs enrolled 709 participants, with 544 included in the analysis. In the study by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 the groups were randomised to WLC or PDD, whereas in the studies by Babjuk and colleagues,86 Denzinger and colleagues89 and Kriegmair and colleagues92 the groups were randomised to WLC or WLC and PDD. The follow-up periods varied from 10–14 days for the study by Kriegmair and colleagues,92 which evaluated residual tumour following TURBT, to 2 years for the study by Babjuk and colleagues,86 5 years for the study by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 and 8 years for the study by Denzinger and colleagues. 89 All four studies used 5-ALA as the photosensitising agent. Individual study results are given in Appendix 9.
In the study by Babjuk and colleagues86 none of the randomised patients with grade 1 or grade 2 tumours received adjuvant intravesical therapy during the study. All patients with grade 3 tumours (six in the PDD group and seven in the WLC group) received intravesical BCG immunotherapy, based on a standard 6-week course followed by three, weekly instillations (3-week course) at 3, 6 and 12 months. 86 In the study by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 none of the randomised patients received adjuvant intravesical therapy throughout the study. In the study by Denzinger and colleagues89 patients with a solitary primary tumour staged pTaG1–G2 did not receive recurrence prophylaxis. Patients with multifocal involvement of the bladder staged pTaG1–G2 or pT1G1–G2 underwent mitomycin therapy, and those with primary stage pT1G3, CIS or treatment failure with mitomycin received BCG therapy, with weekly instillations of 120 mg BCG given for 6 weeks. 89 The study by Kriegmair and colleagues92 did not state whether adjuvant intravesical therapy was given, although the primary outcome of this study was to evaluate residual tumour 10–14 days following TURBT.
The four RCTs were reported in eight reports. The study for which Denzinger and colleagues89 is considered the primary report was also reported by Filbeck and colleagues,91 Burger and colleagues87 and Denzinger and colleagues. 90 The primary report gave information on recurrence-free survival at 2, 4, 6 and 8 years and also tumour recurrence throughout this follow-up period, overall and for low-, intermediate- and high-risk groups, as well as reporting residual tumour rate at secondary transurethral resection (TUR). Filbeck and colleagues91 reported residual tumour rate 6 weeks after initial resection and recurrence-free survival at 12 and 24 months. Burger and colleagues87 reported recurrence-free survival, and tumour recurrence and progression at 7.1 years, and Denzinger and colleagues90 reported recurrence-free survival and tumour recurrence and progression for a subgroup of patients who presented with initial T1 high-grade bladder cancer.
The study for which Daniltchenko and colleagues88 is considered the primary report was also reported by Riedl and colleagues. 93 Daniltchenko and colleagues88 reported tumour recurrence and progression during follow-up whereas Riedl and colleagues reported residual tumour rate at the control TUR. 93
Recurrence-free survival
The studies by Babjuk and colleagues86 and Denzinger and colleagues89 involving a total of 313 patients reported recurrence-free survival at 12 and 24 months. In a random-effects meta-analysis comparing PDD and WLC in terms of recurrence-free survival, the direction of effect of the pooled estimate at both time points favoured PDD over WLC, although the difference was statistically significant only at 24 months (Figure 11). There was evidence of substantial statistical heterogeneity between the studies at the 12-month time point (I2 = 74.4%).
FIGURE 11.
Recurrence-free survival.
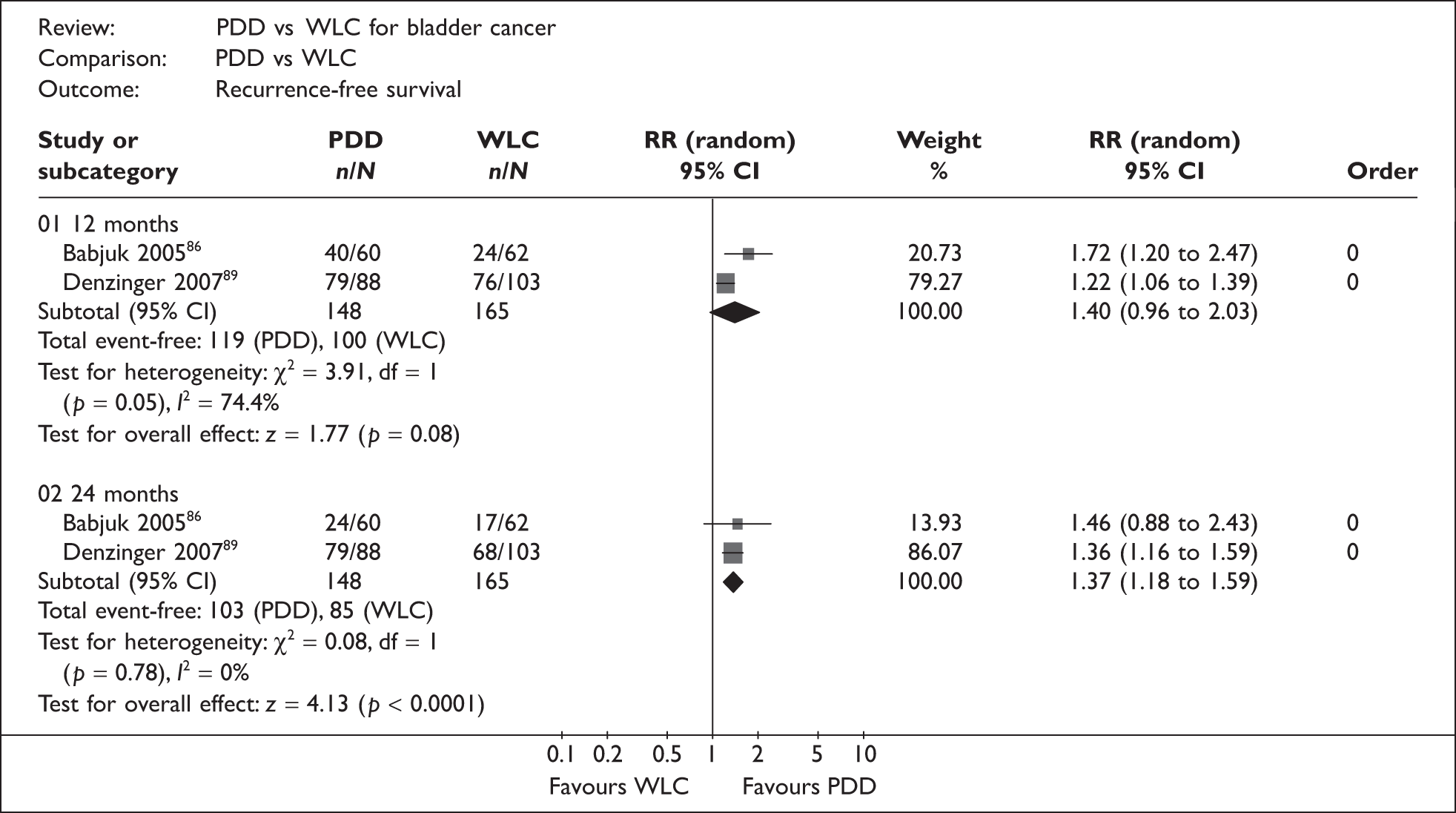
Denzinger and colleagues90 also reported on a subgroup of 46 patients who were diagnosed with T1 high-grade bladder cancer, with recurrence-free survival rates of 80% (17/21) in the PDD group compared with 52% (13/25) in the WLC group at the 8-year follow-up.
Residual tumour rate at first cystoscopy following transurethral resection
The studies by Babjuk and colleagues,86 Daniltchenko and colleagues,88 Denzinger and colleagues89 and Kriegmair and colleagues92 involving a total of 534 patients reported residual tumour rate at first cystoscopy following TUR. The timing of the cystoscopy varied between the studies, with Kriegmair and colleagues92 reporting the residual tumour rate 10–14 days after the initial resection, Denzinger and colleagues89 and Riedl and colleagues93 reporting it 6 weeks after initial resection, and Babjuk and colleagues86 assessing the residual tumour rate 10–15 weeks after TUR.
Figure 12 shows a random-effects meta-analysis comparing PDD with WLC in terms of residual tumour (pTa and pT1) detected at first cystoscopy following the initial TUR. The pooled estimates show that PDD resulted in both statistically significantly fewer residual pTa tumours (RR 0.32, 95% CI 0.15 to 0.70) and fewer pT1 tumours (RR 0.26, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.57), with an overall RR of 0.37 (95% CI 0.20 to 0.69) in favour of PDD (Kriegmair and colleagues92 reported overall rates only).
FIGURE 12.
Residual tumour (pTa and pT1) at first cystoscopy following TUR. Notes: 1. In the figure, the numbers of patients shown for the study by Denzinger and colleagues89 do not include five each from the PDD and WLC groups who at initial resection had CIS. At 6 weeks after initial resection none of the five patients in the PDD group were found to have residual CIS but four of five (80%) in the WLC group were found to have residual CIS. 2. Kriegmair and colleagues92 reported that in an intention to treat analysis 61.5% (40/65) of patients in the PDD group and 40.6% (26/64) of patients in the WLC group were tumour free. For the purposes of the meta-analysis this was interpreted as 25/64 patients in the PDD group and 38/64 patients in the WLC group having residual tumour.
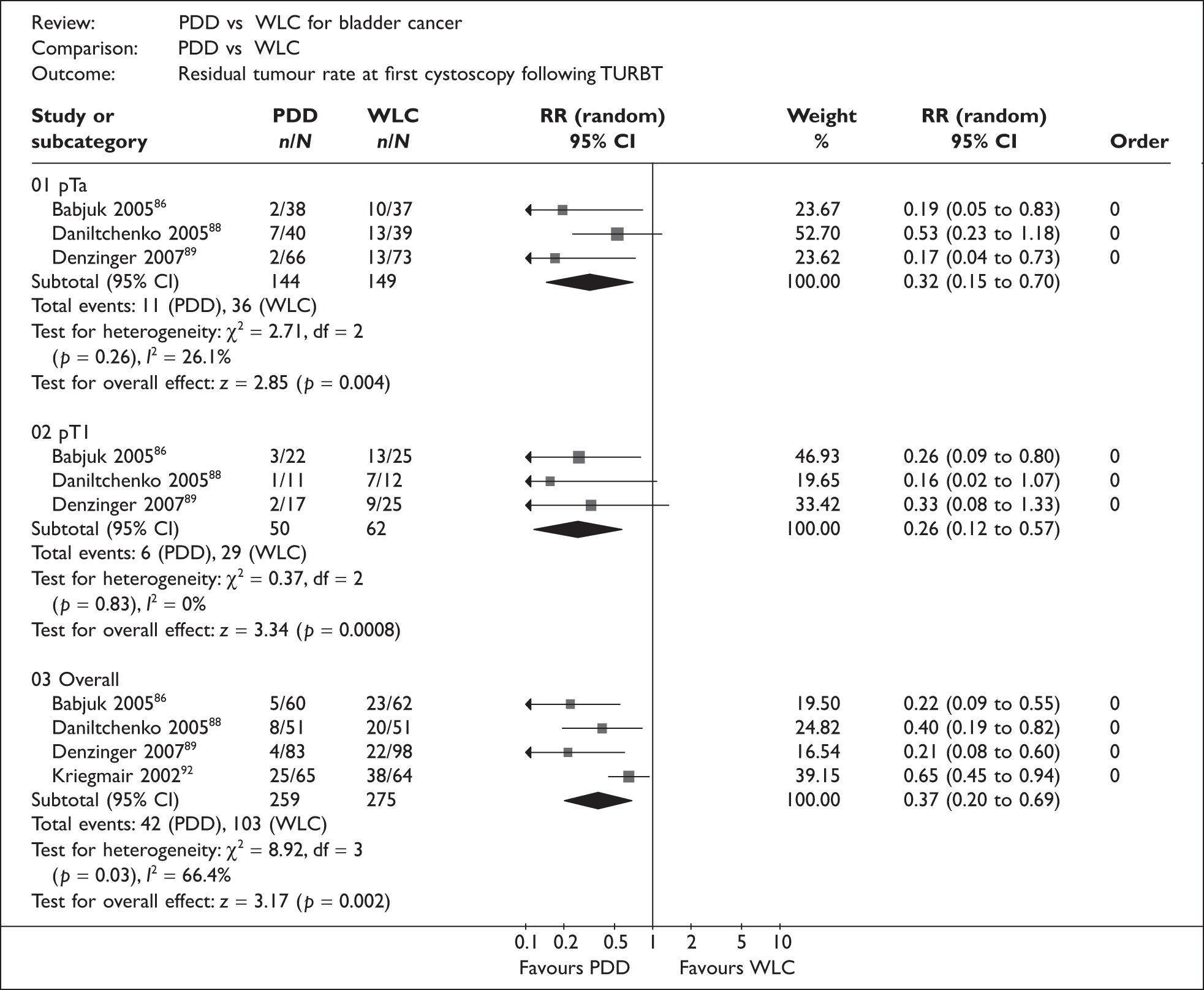
The studies by Babjuk and colleagues86 and Daniltchenko and colleagues88 also reported residual tumour according to grade, and Figure 13 shows a fixed-effect meta-analysis comparing PDD with WLC in terms of the grade of residual tumour detected at first cystoscopy following the initial TUR. The pooled estimates for G3 were not statistically significant, whereas those for G1 (RR 0.13, 95% CI 0.03 to 0.71), G2 (RR 0.32, 95% CI 0.16 to 0.64) and overall (RR 0.31, 95% CI 0.18 to 0.53) showed a statistically significant difference in favour of PDD. In the study by Babjuk and colleagues86 none of the patients with grade 1 or grade 2 tumours received adjuvant intravesical therapy whereas all those with grade 3 tumours received intravesical BCG immunotherapy. In the study by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 none of the patients received adjuvant intravesical therapy.
FIGURE 13.
Residual tumour (G1, G2 and G3) at first cystoscopy following transurethral resection.
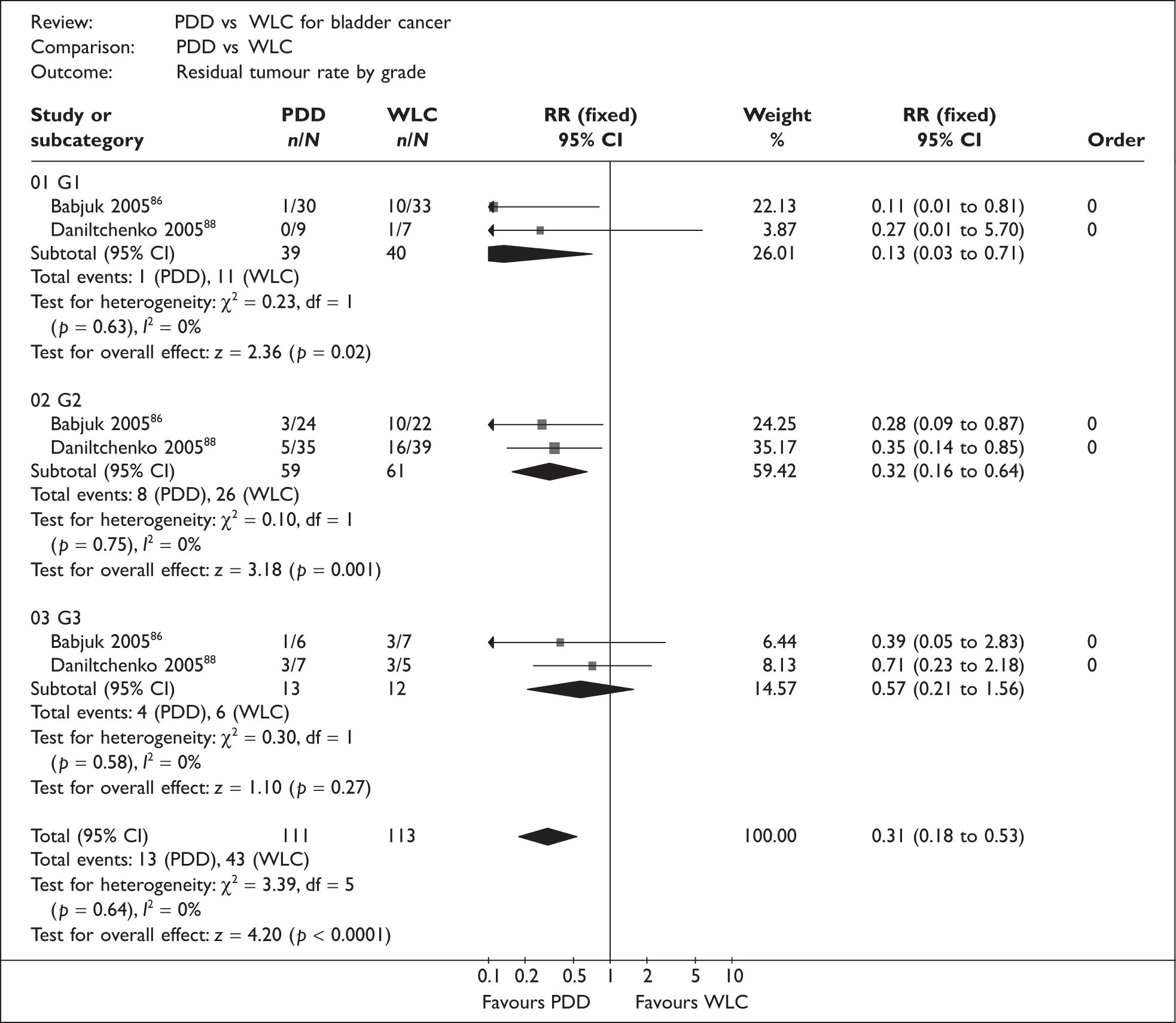
Tumour recurrence rate during follow-up
The studies by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 and Denzinger and colleagues89 involving a total of 293 patients reported tumour recurrence rate during the follow-up period. The follow-up period for the study by Daniltchenko and colleagues was 5 years88 whereas that for the study by Denzinger and colleagues was 8 years. 89
Figure 14 shows a random-effects meta-analysis comparing PDD with WLC in terms of the number of patients who experienced tumour recurrence during the follow-up period. Although the direction of effect for both studies favoured PDD it was statistically significant only in the study by Denzinger and colleagues, and the pooled estimate did not show a statistically significant difference between PDD and WLC (RR 0.64, 95% CI 0.39 to 1.06). 89 There was evidence of substantial statistical heterogeneity between the studies (I2 = 71.1%).
FIGURE 14.
Tumour recurrence rates during the follow-up period.
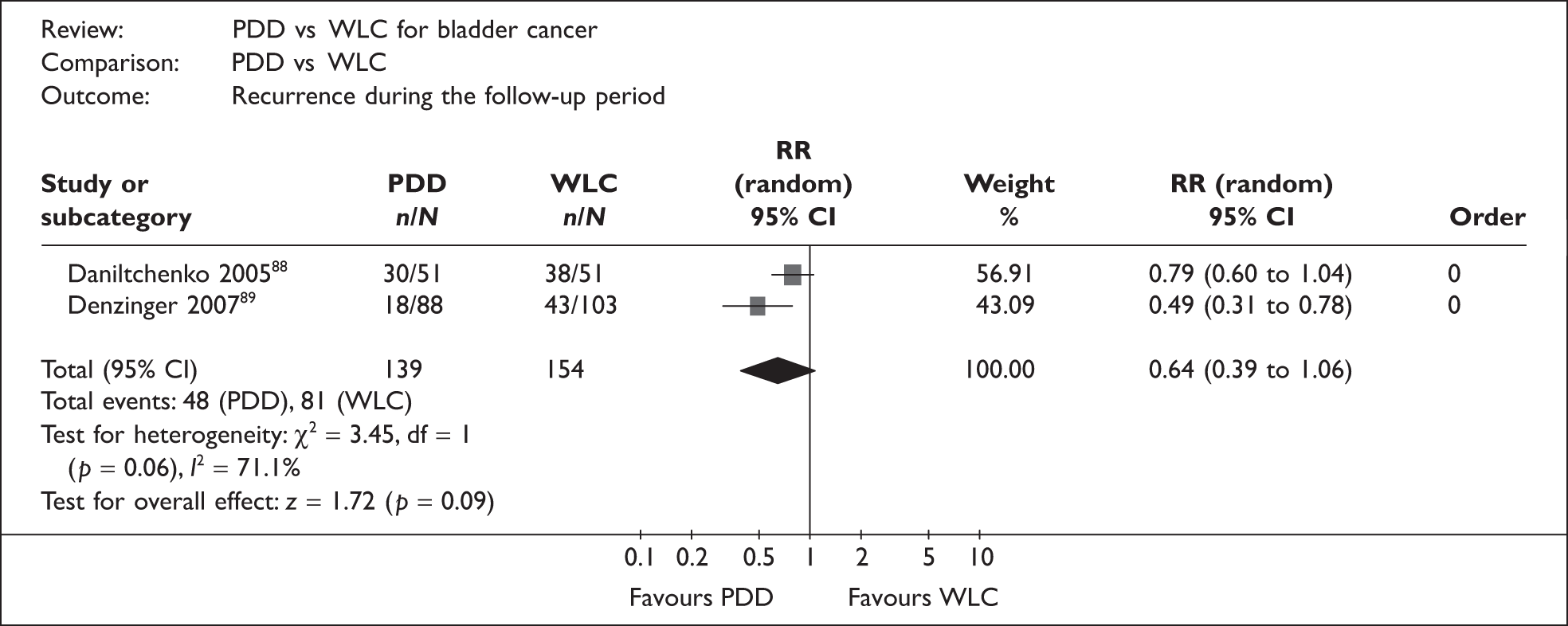
In the study by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 none of the randomised patients received adjuvant intravesical therapy. In the study by Denzinger and colleagues89 patients with a solitary primary tumour staged pTaG1–G2 (low-risk group) did not receive adjuvant intravesical therapy. Patients with multifocal involvement of the bladder staged pTaG1–G2 or pT1G1–G2 (intermediate-risk group) underwent mitomycin therapy, and those with primary stage pT1G3, CIS or treatment failure with mitomycin (high-risk group) received BCG therapy, with weekly instillations of 120 mg BCG given for 6 weeks. 89 Table 10 shows the recurrence rates for the low-, intermediate- and high-risk groups over the 8-year follow-up in the study by Denzinger and colleagues. 89 Although there were consistently fewer recurrences for PDD compared with WLC across all risk groups, the difference in recurrence rates between PDD and WLC was smaller in the intermediate- and high-risk groups, both of which received adjuvant intravesical therapy, albeit with wide CIs.
| Risk group | Intravesical therapy? | Recurrence rate (n/N) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PDD | WLC | ||
| Low | No | 7% (6/88) | 19% (20/103) |
| Intermediate | Yes | 7% (6/88) | 13% (13/103) |
| High | Yes | 7% (6/88) | 10% (10/103) |
In the subgroup of 46 patients initially diagnosed with T1 high-grade bladder cancer, Denzinger and colleagues89 reported recurrence rates of 14% (3/21) in the PDD group compared with 44% (11/25) in the WLC group during the follow-up period.
Time to recurrence
The studies by Babjuk and colleagues86 and Daniltchenko and colleagues88 reported time to recurrence of bladder tumours. In the study by Babjuk and colleagues86 this was a median of 17.05 months for the PDD group and 8.05 months for the WLC group. Babjuk and colleagues86 also reported a median time to recurrence in patients with multiple tumours of 13.54 months for the PDD group and 4.45 months for the WLC group. Daniltchenko and colleagues88 reported a median (range) time to recurrence of 12 months (2 to 58) for the PDD group and 5 months (2 to 52) for the WLC group.
Tumour progression during follow-up
The studies by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 and Denzinger and colleagues89 also reported tumour progression during their follow-up periods of 5 years and 8 years respectively.
Figure 15 shows a fixed-effect meta-analysis comparing PDD with WLC in terms of the numbers of patients who experienced tumour progression during the follow-up period. The direction of effect of the study by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 favoured PDD (four versus nine events) whereas in the study by Denzinger and colleagues89 there were two cases in each group. The pooled estimate had wide CIs reflecting the small number of events (RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.22 to 1.46).
FIGURE 15.
Tumour progression rates during the follow-up period.
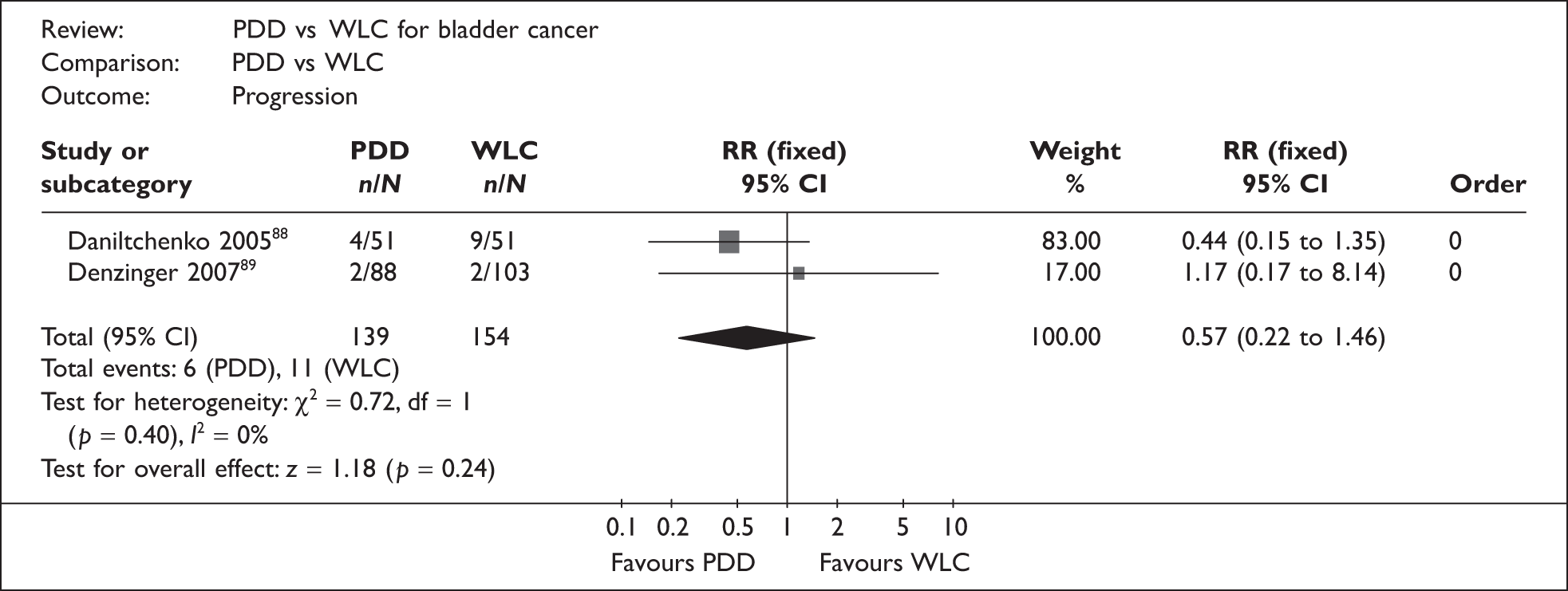
In the subgroup of patients diagnosed with T1 high-grade bladder cancer, Denzinger and colleagues90 reported progression to muscle-invasive disease (≥ T2) of 19% (4/21) in the PDD group compared with 12% (3/25) in the WLC group during the follow-up period.
Summary – assessment of diagnostic accuracy and recurrence/progression of disease
Assessment of diagnostic accuracy
A total of 31 studies, published in 44 reports, met the inclusion criteria for the PDD part of the review. In total, 27 studies (36 reports) reported the diagnostic accuracy of PDD. As measured by the modified QUADAS checklist, in all studies partial verification bias was avoided (all patients received a reference standard test) and test review bias was avoided (PDD and WLC were interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard test). In 96% (26/27) of studies uninterpretable or intermediate test results were reported or there were none, and withdrawals from the study were explained or there were none. However, all of the studies were judged to suffer from incorporation bias in that PDD was considered not to be independent of the reference standard test as biopsies used in the reference standard test were obtained via the PDD procedure.
In both patient- and biopsy-based detection of bladder cancer PDD had higher sensitivity but lower specificity than those of WLC. Five studies involving 370 patients reported patient-based detection. In the pooled estimates the sensitivity for PDD was 92% (95% CI 80% to 100%) compared with 71% (95% CI 49% to 93%) for WLC, whereas the specificity for PDD was 57% (95% CI 36% to 79%) compared with 72% (95% CI 47% to 96%) for WLC, with the CIs for the two techniques overlapping. A total of 14 studies involving 1746 patients reported biopsy-based detection (number of biopsies: 8574 for PDD analysis, 8473 for WLC analysis). In the pooled estimates the sensitivity for PDD was 93% (95% CI 90% to 96%) compared with 65% (95% CI 55% to 74%) for WLC, whereas the specificity for PDD was 60% (95% CI 49% to 71%) compared with 81% (95% CI 73% to 90%) for WLC. The pair of CIs for both sensitivity and specificity did not overlap, providing evidence of a difference in diagnostic performance between the techniques.
Studies reporting the sensitivity of PDD compared with WLC for detecting stage/grade of bladder cancer categorised this information in different ways. For the purposes of this review the detection of stage/grade was considered in two broad categories:
-
less aggressive, lower risk tumours (pTa, G1, G2)
-
more aggressive, higher risk tumours (pT1, G3, CIS).
Across three studies66,80,81 involving 266 patients reporting patient-based detection of lower risk, less aggressive tumours, the median (range) sensitivity of PDD at 92% (20% to 95%) was broadly similar to that of WLC at 95% (8% to 100%). Across seven studies54,56,60–62,67,81 involving 1206 patients reporting biopsy-based detection (n = 5777 biopsies overall), the median (range) sensitivity of PDD was slightly higher at 96% (88% to 100%) compared with 88% (74% to 100%) for WLC. Across six studies51,57,65,66,80,81 involving 563 patients reporting patient-based detection of more aggressive, higher risk tumours, the median (range) sensitivity of PDD at 89% (6% to 100%) was higher than that of WLC at 56% (0% to 100%). Across 13 studies50,53,54,56,57,60–62,65,67,70,81,85 involving 1756 patients reporting biopsy-based detection (n = 7506 biopsies overall), the median (range) sensitivity of PDD at 99% (54% to 100%) was again much higher than that of WLC at 67% (0% to 100%) (Table 7). These results suggest that PDD is much better than WLC in detecting more aggressive, higher risk tumours. However, the results for patient- and biopsy-based detection for less aggressive, lower risk tumours and patient-based detection for more aggressive, higher risk tumours should be interpreted with caution as they are based on only a small number of studies.
When CIS was considered separately, across six studies51,57,65,66,80,81 involving 563 patients reporting patient-based detection, the median (range) sensitivity of PDD for detecting CIS at 83% (41% to 100%) was much higher than that of WLC at 32% (0% to 83%). Across 13 studies50,53,54,56,57,60–62,65,67,70,81,85 involving 1756 patients reporting biopsy-based detection of CIS (n = 7506 biopsies overall), the median (range) sensitivity of PDD at 86% (54% to 100%) was also much higher than that of WLC at 50% (0% to 68%). The results for patient-based detection should be interpreted with caution as they are based on only a small number of studies. However, the median sensitivity across studies reported for patient-based detection of CIS (83%) was similar to that reported for biopsy-based detection of CIS (86%). Only three studies reported the specificity of PDD and WLC for detecting CIS. Two studies51,70 reported higher specificity for WLC (97% versus 71% and 68% versus 61% respectively), whereas the third57 reported similar specificity for both techniques (83% for WLC versus 82% for PDD).
Of the studies comparing PDD with WLC that were included in the pooled estimates in the present review, two65,73 of five reporting patient-based analysis and eight50,53,54,59,60,63,65,70 of 14 reporting biopsy-based analysis undertook random biopsies of normal-appearing areas. Ten50,53,54,56,60–62,70,81,85 of these 14 studies also reported detection of CIS lesions. Table 11 shows, for patient- and biopsy-level analysis and also for detection of CIS lesions, the sensitivity and specificity for PDD and WLC for those studies included in the pooled estimates that undertook random biopsies compared with those that did not. There did not appear to be any systematic pattern to the performance of the tests based on whether or not random biopsies were undertaken.
| Number of studies | PDD | WLC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median sensitivity (%) (range) | Median specificity (%) (range) | Median sensitivity (%) (range) | Median specificity (%) (range) | ||
| Patient-level analysis | |||||
| Random biopsies | 2 | 98 (96 to 100) | 38 (33 to 43) | 75 (73 to 76) | 72 (43 to 100) |
| No random biopsies | 3 | 89 (53 to 93) | 81 (57 to 100) | 79 (33 to 88) | 74 (55 to 100) |
| Biopsy-level analysis | |||||
| Random biopsies | 8 | 92 (76 to 98) | 64 (49 to 79) | 63 (17 to 88) | 81 (57 to 93) |
| No random biopsies | 6 | 93 (82 to 98) | 50 (32 to 100) | 72 (61 to 80) | 89 (46 to 100) |
| Detection of CIS | |||||
| Random biopsies | 5 | 77 (70 to 100) | – | 23 (0 to 67) | – |
| No random biopsies | 5 | 93 (63 to 100) | – | 57 (5 to 64) | – |
Most studies (n = 18) used 5-ALA as the photosensitising agent, with five using HAL, two hypericin and two either 5-ALA or HAL. In patient-based detection of bladder cancer, across four studies using 5-ALA72,73,77,78 and three using HAL,65,66,81 the median (range) sensitivity and specificity for 5-ALA were 96% (64% to 100%) and 52% (33% to 67%), respectively, compared with 90% (53% to 96%) sensitivity and 81% (43% to 100%) specificity for HAL. In biopsy-based detection of bladder cancer, across 15 studies50,53,54,56,58,59,61,63,67,70,71,73,77,84,85 using 5-ALA, the median (range) sensitivity and specificity for 5-ALA were 95% (87% to 98%) and 57% (32% to 67%), respectively, compared with 85% (76% to 94%) and 80% (58% to 100%) for HAL. One study, by Sim and colleagues,76 used hypericin, reporting 82% sensitivity and 91% specificity. The results for both patient- and biopsy-based detection suggest that 5-ALA may have slightly higher sensitivity than HAL, whereas HAL may have higher specificity than 5-ALA, but this should be interpreted with caution as factors other than the photosensitising agent used may have contributed to the sensitivity and specificity values reported by the studies.
In total, 20 studies reported side effects. Twelve studies51–53,61–63,65,71–73,78,81 involving 1543 patients reported that there were no side effects or no serious side effects associated with the photosensitising agent used (5-ALA, eight studies; HAL, two studies; 5-ALA/HAL not reported separately, one study; hypericin, one study). In four studies50,67,71,77 involving 245 patients and using 5-ALA, reported side effects associated with the agent included nine patients who complained of urgency,50,70 four with alginuresis symptoms and pollakiuria,70 three with significant gram-negative bacteriuria,70 one with acute cystitis accompanied by haemorrhagic lesion,77 one with transient dysuria67 and one who developed a urinary tract infection. 67 Two studies57,66 involving 460 patients and using HAL reported 21 non-serious side effects that were associated with the agent. One study76 involving 41 patients and using hypericin reported that one patient developed microscopic haematuria from cystitis.
In summary, the evidence suggests that PDD has clinically important better sensitivity but lower specificity than WLC in the detection of bladder cancer and, in terms of stage/grade, has higher sensitivity than WLC in the detection of more aggressive, higher risk tumours (pT1, G3, CIS).
Assessment of recurrence/progression of disease
Four RCTs (eight reports) reporting recurrence/progression enrolled 709 participants, with 544 included in the analysis. The follow-up periods varied from 10–14 days for the study by Kriegmair and colleagues92 (although the aim of this study was to evaluate residual tumour following TURBT) to 2 years for the study by Babjuk and colleagues,86 5 years for the study by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 and 8 years for the study by Denzinger and colleagues. 89 All four studies used 5-ALA as the photosensitising agent.
The study by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 reported that none of the patients received adjuvant intravesical therapy. In the study by Babjuk and colleagues86 only patients with grade 3 tumours received intravesical therapy. In the study by Denzinger and colleagues89 patients with a solitary primary tumour staged pTaG1–G2 did not receive intravesical therapy, whereas those with multifocal tumours staged pTaG1–G2 or pT1G1–G2 underwent mitomycin therapy and those with primary stage pT1G3, CIS or treatment failure with mitomycin received BCG therapy. The study by Kriegmair and colleagues92 did not state whether intravesical therapy was given.
In all four studies the PDD and WLC groups were similar at baseline in terms of prognostic factors, eligibility criteria for the studies were specified, and length of follow-up was considered adequate in relation to the outcomes of interest reported by the studies. However, in all four studies it was unclear whether the sequence generation was really random or whether the treatment allocation was adequately concealed.
The studies by Babjuk and colleagues86 and Denzinger and colleagues89 (involving a total of 313 patients) reported recurrence-free survival at 12 and 24 months. In a random-effects meta-analysis the direction of effect of the pooled estimate at both time points favoured PDD over WLC, although the difference was statistically significant only at 24 months (RR 1.37, 95% CI 1.18 to 1.59).
The studies by Babjuk and colleagues,86 Daniltchenko and colleagues,88 Denzinger and colleagues89 and Kriegmair and colleagues92 involving a total of 534 patients reported residual tumour rate at first cystoscopy following TURBT. In a random-effects meta-analysis PDD was associated with both statistically significantly fewer residual pTa tumours (RR 0.32, 95% CI 0.15 to 0.70) and pT1 tumours (RR 0.26, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.57), with an overall pooled estimate RR of 0.37 (95% CI 0.20 to 0.69) in favour of PDD. Babjuk and colleagues86 and Daniltchenko and colleagues88 also reported residual tumour according to grade (G1, G2 and G3). In a fixed-effect meta-analysis the pooled estimates for G1 (RR 0.13, 95% CI 0.03 to 0.71) and G2 (RR 0.32, 95% CI 0.16 to 0.64) were statistically significant in favour of PDD, as was the overall pooled estimate (RR 0.31, 95% CI 0.18 to 0.53).
Daniltchenko and colleagues88 and Denzinger and colleagues,89 in studies involving a total of 293 patients, reported tumour recurrence rate during the follow-up period (5 years and 8 years respectively). In a random-effects meta-analysis of the number of patients who experienced tumour recurrence, although the direction of effect for both studies favoured PDD it was statistically significant only in the study by Denzinger and colleagues,89 and the direction of effect in the pooled estimate also favoured PDD but was not statistically significant (RR 0.64, 95% CI 0.39 to 1.06). In the study by Denzinger and colleagues89 the recurrence rates were consistently lower for PDD than for WLC across all three risk groups. However, the difference in the recurrence rates between PDD and WLC was smaller in the intermediate-risk [PDD 7% (6/88), WLC 13% (13/103)] and high-risk [PDD 7% (6/88), WLC 10% (10/103)] groups that received adjuvant intravesical therapy than in the low-risk group that did not [PDD 7% (6/88), WLC 19% (20/103)].
Two studies86,88 reported time to recurrence, both favouring PDD. Babjuk and colleagues86 reported a median time to recurrence of 17.05 months for the PDD group and 8.05 months for the WLC group, whereas Daniltchenko and colleagues88 reported a median (range) time to recurrence of 12 (2 to 58) months for the PDD group and 5 (2 to 52) months for the WLC group.
The studies by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 and Denzinger and colleagues89 also reported tumour progression during their respective 5- and 8-year follow-up periods. In a fixed-effect meta-analysis of the number of patients who experienced tumour progression, the direction of effect of the study by Daniltchenko and colleagues favoured PDD whereas that of the study by Denzinger and colleagues favoured WLC, although neither was statistically significant. The pooled estimate favoured PDD but again was not statistically significant (RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.22 to 1.46). 88,89
In summary, the evidence suggests that, compared with WLC, the use of PDD at TURBT results in less residual tumour being found at the first cystoscopy following TURBT, longer recurrence-free survival of patients and a longer time to recurrence following TURBT, and may be associated with a lower rate of tumour recurrence over time. However, as these results are based on only a few studies they should be interpreted with caution. It should also be borne in mind that the administration of adjuvant intravesical therapy varied across the studies. Adjuvant intravesical therapy following TURBT is standard practice in the UK and much of Europe and can reduce recurrence by up to 50% in the first 2 years. The fact that in two studies86,89 only some patients received intravesical therapy and in one88 none did, while in the fourth study92 this information was not reported, makes it difficult to assess what the true added value of PDD might be in reducing recurrence rates in routine practice.
Chapter 5 Results – biomarkers and cytology
Number of studies identified
From the electronic searches for primary reports, 501 records were selected as being possibly relevant to the review of biomarkers and cytology. In total, 133 of these were non-English language papers and were excluded from further assessment. The full-text reports of the remaining papers were obtained and assessed: 83 met the inclusion criteria for this review; 241 were excluded; and 44 were retained for background information. Figure 16 shows a flow diagram outlining the screening process, with reasons for exclusion of full-text papers.
FIGURE 16.
Flow diagram outlining the screening process for the biomarkers part of the review.
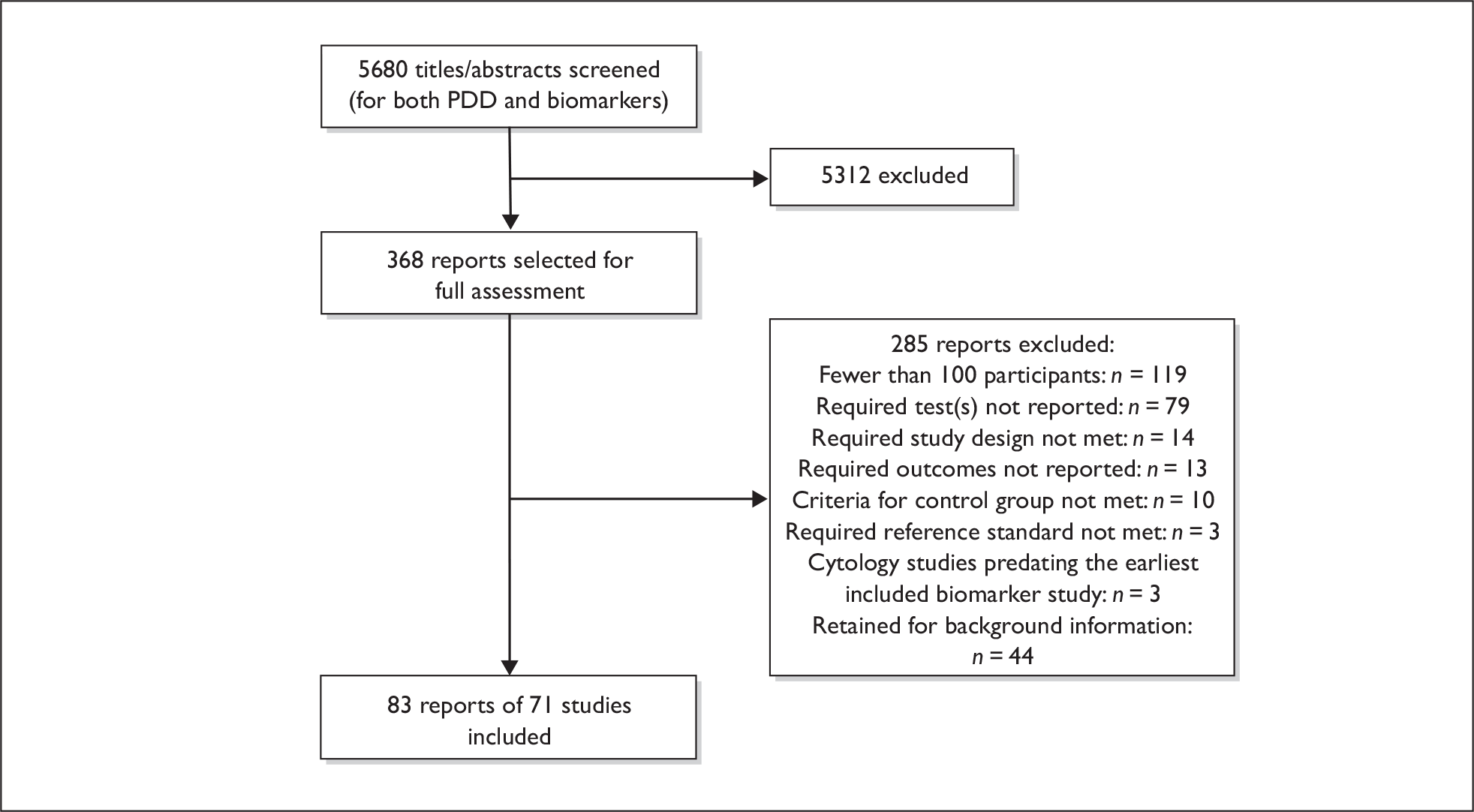
Number and type of studies included
Appendix 10 lists the 71 studies, published in 83 reports, that were included in the review of test performance.
Number and type of studies excluded
A list of the potentially relevant studies identified by the search strategy for which full-text papers were obtained but which subsequently failed to meet the inclusion criteria is given in Appendix 11. These studies were excluded because they failed to meet one or more of the inclusion criteria in terms of the type of study, participants, test(s), reference standard or outcomes reported.
Overview of the biomarkers/cytology chapter
This chapter contains a section on each of the individual tests followed by a section on studies that directly compared tests and concludes with a summary section. The section on each test contains information on the characteristics of the included studies, methodological quality of the studies, results of the pooled estimates for patient-level analysis, and also information on specimen-level analysis, stage/grade analysis and unevaluable test results. The methodological quality of the biomarker and cytology studies was assessed using a modified version of the QUADAS tool containing 14 questions. For patient-level analysis, pooled estimates with 95% CIs for sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios and DORs are presented. For specimen and stage/grade level of analysis the median (range) sensitivity and specificity across studies are presented. If the number of specimens reported by a study was one per patient included in the analysis then this was considered as a patient-level analysis. Studies reporting patient- and specimen-level analysis for CIS are included in the section on stage/grade analysis. As described in the previous chapter, for the purposes of this review, the presentation of test performance in terms of the detection of stage and grade of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer was considered in two broad categories: (1) less aggressive, lower risk tumours (pTa, G1, G2) and (2) more aggressive, higher risk tumours (pT1, G3, CIS).
Appendix 12 shows the characteristics of the included biomarker/cytology studies, Appendix 13 shows the results of the quality assessment of the individual studies, Appendix 14 shows the studies that reported sufficient information (true and false positives and negatives) to allow their inclusion in the pooled estimates for each of the tests for patient-level analysis, and also those studies that reported specimen-level analysis and also the sensitivity of the tests in detecting tumour stage/grade, Appendix 15 shows the individual study results and Appendix 16 shows the cut-offs used by the studies reporting FISH that were included in the pooled estimates.
Fluorescence in situ hybridisation
Characteristics of the included studies
A description of each of the 14 included FISH studies is given in Appendix 12, which contains the characteristics of all of the included biomarker and cytology studies listed alphabetically by surname of first author. Table 12 shows summary information for the 14 FISH studies.
| Characteristic | Number | Number of studies |
|---|---|---|
| Study designa | ||
| Cross-sectional diagnostic study | 2704 | 12 |
| Case–control | 617 | 2 |
| Patients | ||
| Enrolled | 3321 | 14 |
| Analysed | 2961 | |
| Suspicion of or previously diagnosed BCa,b | ||
| Suspicion of BC | 1012 (45%) | 12 (86%) |
| Previously diagnosed BC | 1234 (55%) | |
| Not reported | 765 | 2 (14%) |
| Age | ||
| Median (range) of means/medians (years) | 70 (63 to 72) | 7 (50%) |
| Not reported | – | 7 (50%) |
| Sexc | ||
| Men | 1073 (71%) | 7 (50%) |
| Women | 439 (29%) | |
| Not reported | 1799 | 7 (50%) |
Twelve studies, reported in 13 papers,94–106 were diagnostic cross-sectional studies, of which two101,104 reported consecutive recruitment, and the remaining two107,108 were case–control studies. Two studies were multicentre (21 centres,108 23 centres103).
The 14 studies enrolled 3321 participants, with 2961 included in the analysis. In 12 studies94,95,97,99,101–108 reporting this information, 1012 (45%) presented with a suspicion of bladder cancer and 1234 (55%) had previously diagnosed bladder cancer. In one103 of these studies the whole study population (n = 497) had a suspicion of bladder cancer and in two102,106 the whole study population had previously diagnosed bladder cancer (n = 355). Two studies98,100 did not report this information.
Across seven studies97,99,101–103,106,107 providing information on patient age for the whole study population, the median (range) of means/medians was 70 years (63 to 72 years) (Yoder and colleagues106 reported median rather than mean age). Seven studies94,97,99,102,103,106,107 provided information on the gender of 1512 participants, of whom 1073 (71%) were men and 439 (29%) were women.
Seven studies94,99,102–104,106,108 gave details of when they took place, with an earliest start date of 1996104 and latest end date of March 2007. 99 Seven studies took place in the USA,97,99,103–106,108 three in Germany95,98,107 and one each in the Netherlands102 and Israel,94 and two had multinational settings, taking place in Austria/Italy101 and the USA/Belgium. 100
Methodological quality of the included studies
Figure 17 summarises the quality assessment across the 14 FISH studies. The results for the quality assessment of the individual studies are shown in Appendix 13. In all studies the spectrum of patients who received the tests was considered to be representative of those who would receive the test in practice (Q1). For this question we considered patients to be representative if the patient population either had a suspicion or a history of bladder cancer or contained patients from both groups, or the majority or all of the patient population presented with either gross or microhaematuria or contained a mixture of patients with either indication. In all studies the reference standard (cystoscopy with histological assessment of biopsied tissue) was considered likely to correctly classify bladder cancer (Q2). In all studies partial verification bias was avoided in that all patients who underwent a FISH test also received a reference standard test (Q4), differential verification bias was avoided in that patients received the same reference standard regardless of the index test result (Q5) and incorporation bias was avoided in that the reference standard was independent of the index test (Q6). In all studies either uninterpretable or intermediate test results were reported or there were none (Q10), and withdrawals from the study were explained or there were none (Q11).
FIGURE 17.
Summary of quality assessment of FISH studies (n = 14).
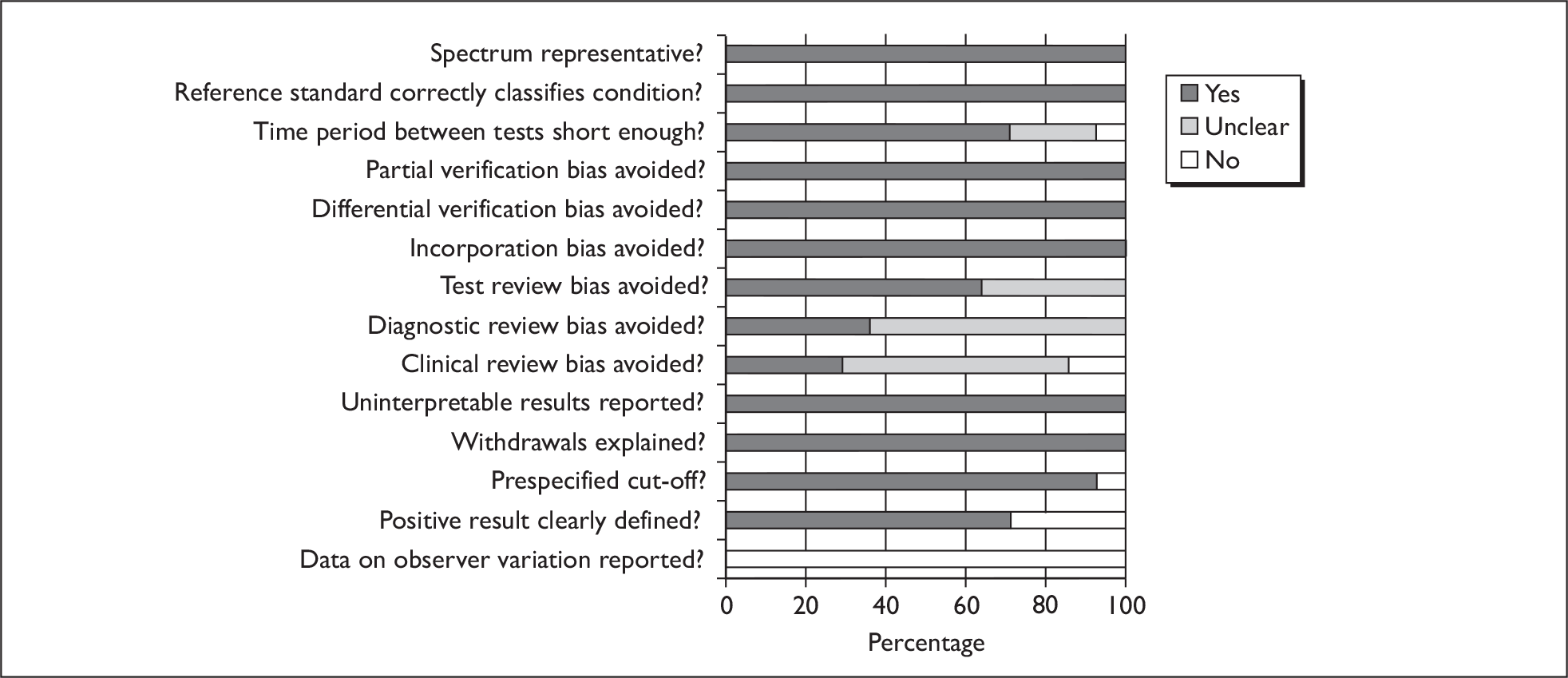
In 10 studies (71%) the time period between FISH and the reference standard was considered to be short enough (1 month or less) to be reasonably sure that the patient’s condition had not changed in the intervening period (Q3). In nine studies (64%) test review bias was avoided in that the FISH results were interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard test (Q7). However, in nine studies (64%) it was unclear whether the reference standard results were interpreted without knowledge of the results of the FISH test (diagnostic review bias, Q8) and in eight studies (57%) it was unclear whether the same clinical data were available when test results were interpreted as would be available when the test is used in practice (clinical review bias, Q9). In this context clinical data were defined broadly to include any information relating to the patient such as age, gender, presence and severity of symptoms, and other test results.
In 13 studies (93%) a prespecified cut-off value was used (Q12); in 10 studies (71%) a clear definition of what was considered to be a positive test result was provided (Q13); and none of the studies provided information on observer variation in interpretation of test results (Q14).
Assessment of diagnostic accuracy
Patient-level analysis
A total of 12 studies95,97–101,103–108 enrolling 3101 people, with 2535 included in the analysis, provided sufficient information to allow their inclusion in the pooled estimates for patient-level analysis. The cut-offs used by these studies to define a positive test result were considered sufficiently similar for all of them to be included in the pooled estimates (see Appendix 16 for a description of the cut-offs used by each of the FISH studies). Figure 18 shows the sensitivity and specificity of the individual FISH studies, pooled estimates and SROC curve for patient-based detection of bladder cancer. The pooled sensitivity and specificity (95% CI) were 76% (65% to 84%) and 85% (78% to 92%), respectively, and the DOR (95% CI) value was 18 (3 to 32). Across the 12 studies the sensitivity for FISH ranged from 53%107 to 96%,101 and specificity ranged from 45%101 to 97%. 104 The median (range) PPV across studies was 78% (27% to 99%) and the median (range) NPV was 88% (36% to 97%). However, as previously mentioned, predictive values are affected by disease prevalence, which is rarely constant across studies, and therefore these data should be interpreted with caution.
FIGURE 18.
FISH patient-level analysis: sensitivity, specificity, pooled estimates and SROC curve.
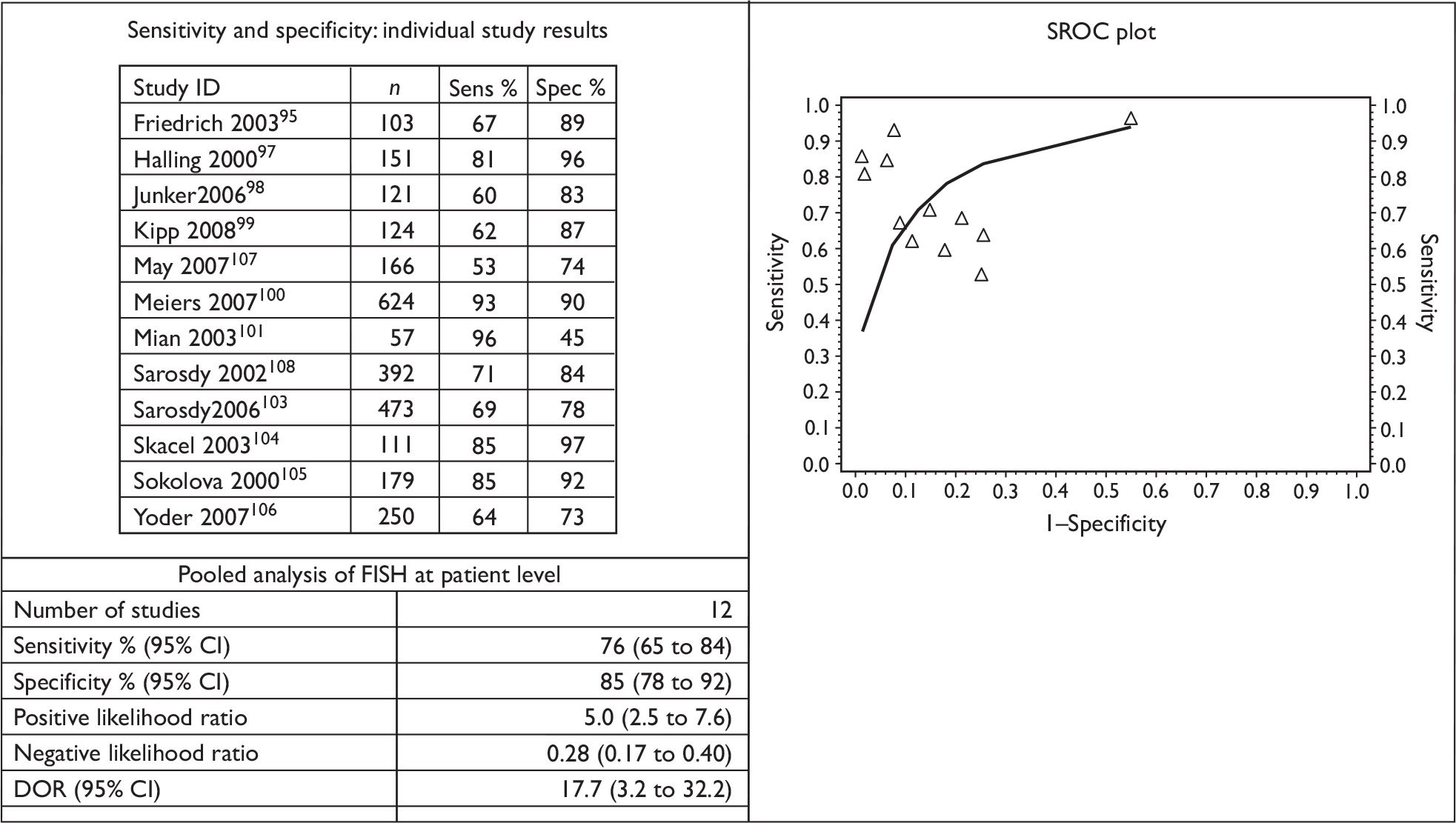
Most of the included studies in the pooled estimates contained a mixture of patients with a suspicion of bladder cancer and those with previously diagnosed bladder cancer, although two studies98,100 did not report this information. In the study by Sarosdy and colleagues103 all of the participants (n = 497) had a suspicion of bladder cancer (sensitivity 69%, specificity 78%) and in the study by Yoder and colleagues106 all of the participants (n = 250) had previously diagnosed bladder cancer (sensitivity 64%, specificity 73%).
Specimen-level analysis
The study by Moonen and colleagues,102 enrolling 105 participants, all of whom had been previously diagnosed with bladder cancer, reported specimen-level analysis (n = 103), with sensitivity and specificity of 39% and 90% respectively.
Stage/grade analysis
Studies reporting the sensitivity of FISH in the detection of stage and grade of tumour categorised this information in different ways, including pTa, pTaG1, pTaG1–2, pTaG2, pTaG3, G1, G2, pT1, pT1G2, pT1G3, pT1–4, CIS, G3, pT2, pT2–4, ≥ pT2 and pT4 (see Appendix 14). All of the studies apart from that by Moonen and colleagues102 reported the detection of stage/grade at the patient level (if the number of specimens reported by a study was one per patient included in the analysis then this was considered as a patient-level analysis).
For the purposes of this review the presentation of test performance in terms of the detection of stage and grade of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer was considered in two broad categories:
-
less aggressive, lower risk tumours (pTa, G1, G2)
-
more aggressive, higher risk tumours (pT1, G3, CIS).
Table 13 shows the median (range) sensitivity of FISH, for both patient- and specimen-based detection of tumours, within the broad categories of less aggressive/lower risk and more aggressive/higher risk (including CIS), and also separately for CIS.
| FISH sensitivity (%), median (range) | Number of patients (specimens)a | Number of studies | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Less aggressive/lower risk | |||
| Patient-based detection | 65 (32 to 100) | 2164 | 10 |
| Specimen-based detection | 27 (22 to 37) | 95 (103) | 1 |
| More aggressive/higher risk including CIS | |||
| Patient-based detection | 95 (50 to 100) | 2164 | 10 |
| Specimen-based detection | 60 (50 to 67) | 95 (103) | 1 |
| CIS | |||
| Patient-based detection | 100 (50 to 100) | 1067 | 8 |
| Specimen-based detection | NR | NR | 1 |
Less aggressive, lower risk tumours (pTa, G1, G2)
In total, 10 studies95,97,99–101,103–105,107,108 involving 2164 patients reported the sensitivity of FISH for the patient-based detection of less aggressive, lower risk tumours. Across these studies the median (range) sensitivity of FISH was 65% (32% to 100%) (Table 13). The study by Moonen and colleagues102 reported specimen-based detection (95 patients, 103 specimens), with a median (range) sensitivity of 27% (22% to 37%).
More aggressive, higher risk tumours (pT1, G3, CIS)
In total, 10 studies95,97,99–101,103–105,107,108 involving 2164 patients reported the sensitivity of FISH for the patient-based detection of more aggressive, higher risk tumours. Across these studies the median (range) sensitivity of FISH was 95% (50% to 100%) (Table 13). The study by Moonen and colleagues102 reported specimen-based detection (95 patients, 103 specimens), with a median (range) sensitivity of 60% (50% to 67%).
Carcinoma in situ
Although CIS is included in the more aggressive/higher risk category reported above, it may also be useful to consider separately the performance of biomarkers or cytology for the detection of CIS. Eight studies95,97,99,101,104,105,107,108 involving 1067 patients reported the sensitivity of FISH for the patient-based detection of CIS. Across these studies the median (range) sensitivity of FISH was 100% (50% to 100%) (Table 13).
Number of tumours
None of the included studies reported the sensitivity of FISH in detecting varying numbers of tumours.
Size of tumours
None of the included studies reported the sensitivity of FISH in detecting varying sizes of tumour.
ImmunoCyt
Characteristics of the included studies
A description of each of the 10 included ImmunoCyt studies is given in Appendix 12, which contains the characteristics of all of the included biomarker and cytology studies listed alphabetically by surname of first author. Table 14 shows summary information for the 10 ImmunoCyt studies.
| Characteristic | Number | Number of studies |
|---|---|---|
| Study design | ||
| Cross-sectional diagnostic study | 4199 | 10 |
| Patientsa | ||
| Enrolled | 4199 | 10 |
| Analysed | 3091+ | |
| Suspicion of or previously diagnosed BC | ||
| Suspicion of BC | 890 (27%) | 9 (90%) |
| Previously diagnosed BC | 2405 (73%) | |
| Not reported | 904 | 1 (10%) |
| Age | ||
| Median (range) of means (years) | 68 (66 to 73) | 6 (60%) |
| Not reported | – | 4 (40%) |
| Sexb | ||
| Men | 1076 (78%) | 4 (40%) |
| Women | 295 (22%) | 6 (60%) |
| Not reported | 2819 | |
All 10 studies, reported in 12 papers,101,109–119 were diagnostic cross-sectional studies. Six reported consecutive recruitment. 101,109,110,112,116,118 Two studies were multicentre (four centres,111 19 centres116).
The 10 studies enrolled 4199 participants, with at least 3091 included in the analysis (the study by Mian and colleagues113 enrolled 942 participants but did not report the number included in the analysis). In nine studies101,109–114,116,118 reporting this information, 890 participants (27%) presented with a suspicion of bladder cancer and 2405 (73%) had previously diagnosed bladder cancer. In one of these studies118 the whole patient population (n = 301) had a suspicion of bladder cancer and in three110,111,113 the whole population had previously diagnosed bladder cancer (n = 1499). One study119 did not report this information.
Across six studies101,109,112–114,116 providing information on patient age for the participant group as a whole, the median (range) of means was 68 years (66 to 73 years). Four studies112,114,116,118 provided information on the gender of 1371 participants, of whom 1076 (78%) were men and 295 (22%) were women.
Six studies111–114,118,119 gave details of when they took place, with an earliest start date of November 1997112 and latest end date of July 2007. 118 The studies took place in Austria,112 France,116 Germany,118 Italy,113 Sweden,114 Canada119 and the USA,111 with three having multinational settings, all taking place in Austria/Italy,101,109,110 although they did not state that they were multicentre.
Methodological quality of the included studies
Figure 19 summarises the quality assessment for the 10 ImmunoCyt studies. The results for the quality assessment of the individual studies are shown in Appendix 13. In all studies the spectrum of patients who received the tests was considered to be representative of those who would receive the test in practice (Q1). In all studies the reference standard (cystoscopy with histological assessment of biopsied tissue) was considered likely to correctly classify bladder cancer (Q2). In all studies partial verification bias was avoided in that all patients who underwent an ImmunoCyt test also received a reference standard test (Q4), differential verification bias was avoided in that patients received the same reference standard regardless of the index test result (Q5) and incorporation bias was avoided in that the reference standard was independent of the index test (Q6). In all studies either uninterpretable or intermediate test results were reported or there were none (Q10) and a prespecified cut-off value was used (Q12). In eight studies (80%) the time period between ImmunoCyt and the reference standard was considered to be short enough (1 month or less) to be reasonably sure that the patient’s condition had not changed in the intervening period (Q3). In nine studies (90%) withdrawals from the study were explained or there were none (Q11) and a clear definition of what was considered to be a positive result was provided (Q13).
FIGURE 19.
Summary of quality assessment of ImmunoCyt studies (n = 10).
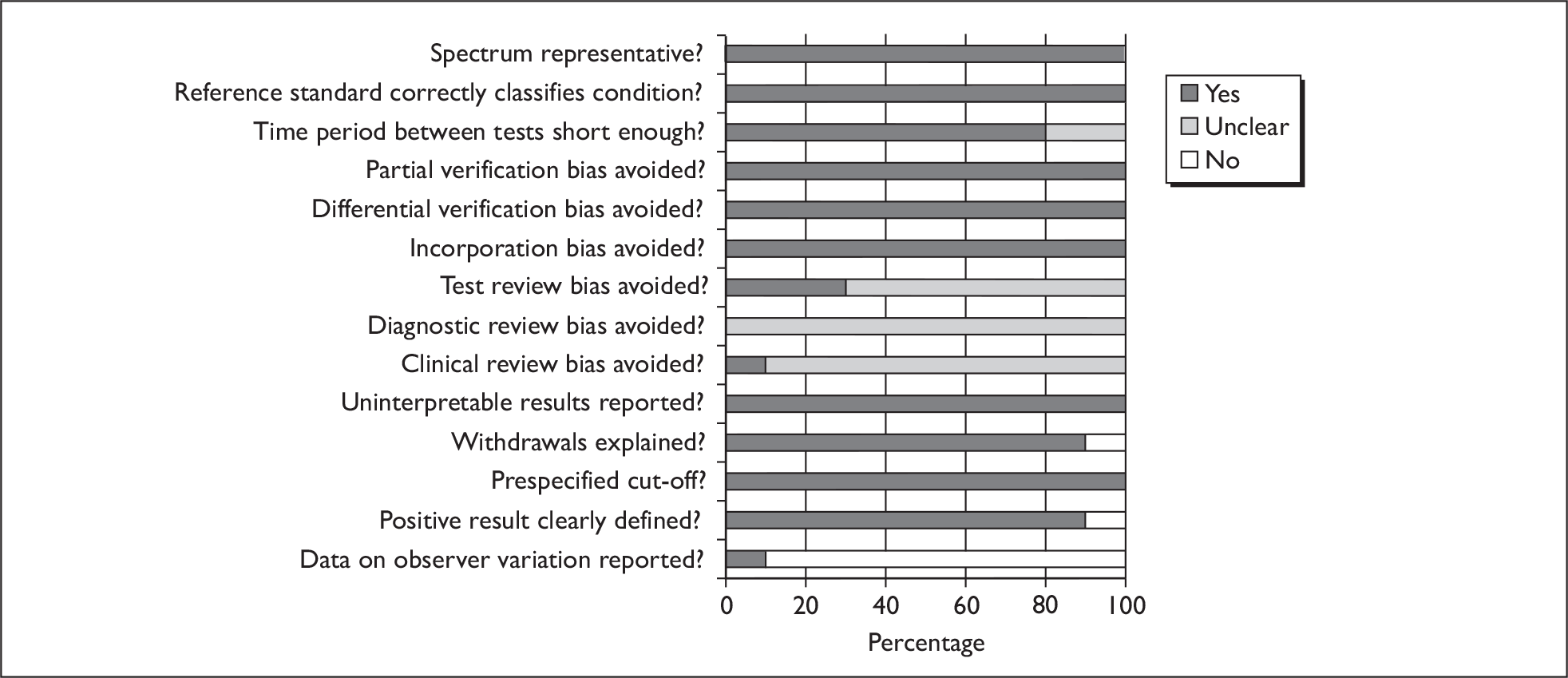
In all 10 studies (100%) it was unclear whether diagnostic review bias had been avoided (Q8), in nine studies (90%) it was unclear whether clinical review bias had been avoided (Q9) and in seven studies (70%) it was unclear whether test review bias had been avoided (Q7). One study (10%) provided information on observer variation in interpretation of test results (Q14).
Assessment of diagnostic accuracy
Patient-level analysis
Eight studies101,109,111,112,114,116,118,119 enrolling 3041 participants, with 2896 included in the analysis, provided sufficient information to allow their inclusion in the pooled estimates for patient-level analysis. The ‘common’ cut-off used by all of these studies to define a positive test result was at least one green or one red fluorescent cell. Figure 20 shows the sensitivity and specificity of the individual studies, pooled estimates and SROC curve for ImmunoCyt patient-based detection of bladder cancer. The pooled sensitivity and specificity (95% CI) were 84% (77% to 91%) and 75% (68% to 83%), respectively, and the DOR value (95% CI) was 16 (6 to 26). Across the studies the sensitivity for ImmunoCyt ranged from 73%116 to 100%,114 and specificity ranged from 62%119 to 88%. 118 The median (range) PPV across studies was 54% (26% to 70%) and the median (range) NPV was 93% (86% to 100%).
FIGURE 20.
ImmunoCyt patient-level analysis: sensitivity, specificity, pooled estimates and SROC curve.
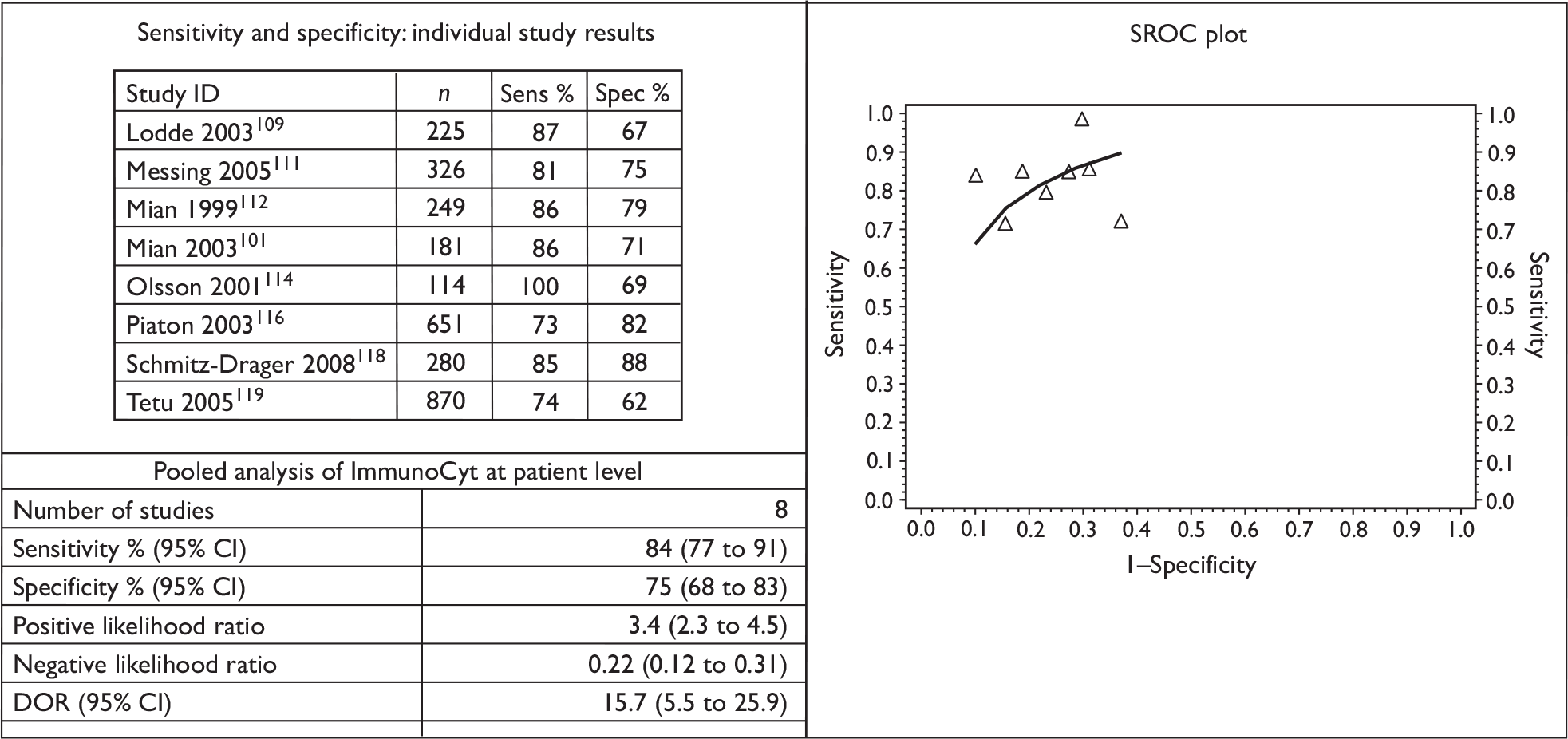
Most of the included studies in the pooled estimates contained a mixture of patients with a suspicion of bladder cancer and those with previously diagnosed bladder cancer, although one study119 did not report this information. In the study by Schmitz-Drager and colleagues118 all of the participants (n = 280) had a suspicion of bladder cancer (sensitivity 85%, specificity 88%) and in the study by Messing and colleagues111 all of the participants (n = 326) had previously diagnosed bladder cancer (sensitivity 81%, specificity 75%).
Specimen-level analysis
Two studies110,113 enrolling 1158 participants, all of whom had been previously diagnosed with bladder cancer, reported specimen-level analysis (n = 2220 specimens). Across the two studies the median (range) sensitivity and specificity were 78% (71% to 85%) and 76% (73% to 78%) respectively.
Stage/grade analysis
Studies reporting the sensitivity of ImmunoCyt in the detection of stage and grade of tumour categorised this information in different ways, including pTa, pTaG1–2, pTa pT1G3, pTa+CIS, G1, G2, pT1, pT1G1–2, CIS, G3, pT2 and ≥ pT2 (see Appendix 14). All of the studies providing this information, apart from that by Mian and colleagues,113 reported the detection of stage/grade at the patient level (if the number of specimens reported by a study was one per patient included in the analysis then this was considered as a patient-based analysis).
Table 15 shows the median (range) sensitivity of ImmunoCyt, for both patient- and specimen-based detection of tumours, within the broad categories of less aggressive/lower risk and more aggressive/higher risk (including CIS), and also separately for CIS.
| ImmunoCyt sensitivity (%), median (range) | Number of patients (specimens)a | Number of studies | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Less aggressive/lower risk | |||
| Patient-based detection | 81 (55 to 90) | 2502 | 6 |
| Specimen-based detectionb | 82 (79 to 84) | 942 (1886) | 1 |
| More aggressive/higher risk including CIS | |||
| Patient-based detection | 90 (67 to 100) | 2502 | 6 |
| Specimen-based detectionb | 91 (84 to 100) | 942 (1886) | 1 |
| CIS | |||
| Patient-based detection | 100 (67 to 100) | 2502 | 6 |
| Specimen-based detectionb | 100 | 942 (1886) | 1 |
Less aggressive, lower risk tumours (pTa, G1, G2)
Six studies101,109,111,112,116,119 involving 2502 patients reported the sensitivity of ImmunoCyt for the patient-based detection of less aggressive, lower risk tumours. Across these studies the median (range) sensitivity of ImmunoCyt was 81% (55% to 90%) (Table 15). The study by Mian and colleagues113 reported specimen-based detection (942 participants enrolled, 1886 specimens), with a median (range) sensitivity of 82% (79 to 84%).
More aggressive, higher risk tumours (pT1, G3, CIS)
Six studies101,109,111,112,116,119 involving 2502 patients reported the sensitivity of ImmunoCyt for the patient-based detection of more aggressive, higher risk tumours. Across these studies the median (range) sensitivity of ImmunoCyt was 90% (67% to 100%) (Table 15). The study by Mian and colleagues113 reported specimen-based detection (942 participants enrolled, 1886 specimens), with a median (range) sensitivity of 91% (84% to 100%).
Carcinoma in situ
Six studies101,109,111,112,116,119 involving 2502 patients reported the sensitivity of ImmunoCyt for the patient-based detection of CIS. Across these studies the median (range) sensitivity of ImmunoCyt was 100% (67% to 100%). The study by Mian and colleagues,113 with specimen as the unit of analysis, reported 100% sensitivity for detecting CIS (Table 15).
Number of tumours
None of the included studies reported the sensitivity of ImmunoCyt in detecting varying numbers of tumours.
Size of tumours
Messing and colleagues,111 in a study involving 326 patients, reported ImmunoCyt sensitivities of 71%, 84% and 60% in detecting tumours of < 1 cm, 1–3 cm and > 3 cm respectively.
Unevaluable tests
All 10 studies101,109–114,116,118,119 provided information on unevaluable tests. Overall, 279 of 5292 tests (5%) could not be evaluated. Across studies, the median (range) percentage of tests that were unevaluable was 5% (1% to 10%).
Observer variation
Messing and colleagues111 reported that after 1 day of training pathologists were able to pass an interobserver training test, achieving 100% concordance on five slides. At one participating laboratory 40% of cases were reviewed by two observers independently. There was 90% agreement between observers with the final diagnosis of disputed cases agreed on by the two pathologists who reviewed these cases together. 111
NMP22
Characteristics of the included studies
A description of each of the 41 included NMP22 studies is given in Appendix 12, which contains the characteristics of all of the included biomarker and cytology studies listed alphabetically by surname of first author. Table 16 shows summary information for the 41 NMP22 studies.
| Characteristic | Number | Number of studies |
|---|---|---|
| Study design | ||
| Cross-sectional diagnostic study | 11,236 | 31 |
| Case–control | 2649 | 10 |
| Patients | ||
| Enrolled | 13,885 | 41 |
| Analysed | 13,490 | |
| Suspicion of or previously diagnosed BCa | ||
| Suspicion of BC | 4478 (41%) | 33 (80%) |
| Previously diagnosed BC | 6536 (59%) | |
| Not reported | 1812 | 8 (20%) |
| Age | ||
| Median (range) of means (years) | 66 (53 to 71) | 24 (59%) |
| Not reported | – | 17 (41%) |
| Sexb | ||
| Men | 7818 (72%) | 29 (71%) |
| Women | 2986 (28%) | 12 (29%) |
| Not reported | 2858 | |
Thirty-one studies, reported in 37 papers,45,80,95,120–153 were diagnostic cross-sectional studies. Three45,126,127 reported consecutive recruitment. A total of 10 studies, reported in 11 papers,154–164 were case–control studies. Four studies were multicentre (23 centres,126 23 centres,127 13 centres,135 three centres149).
The 41 studies enrolled 13,885 participants, with 13,490 included in the analysis. Five studies80,126,127,131,150 involving 2426 participants used the NMP22 BladderChek point of care test. In 33 studies45,80,95,122,123,125–132,134–142,144,147–151,153,158,159,162,164 4478 participants (41%) presented with a suspicion of bladder cancer and 6536 (59%) had previously diagnosed bladder cancer. In five126,135,141,153,162 of these studies the whole patient population analysed (n = 2202) had a suspicion of bladder cancer and in 10123,127,129–131,138,142,144,147,149 the whole population analysed had previously diagnosed bladder cancer (n = 4799). Eight studies120,121,154–157,161,163 did not report this information.
Across 24 studies80,123,125–129,131,134,136,138,140,141,144,147,149–151,153,154,156,158,159,162 providing information on patient age for the whole study population, the median (range) of means was 66 years (53 to 71 years). A total of 29 studies80,121–123,125–127,129–131,135–142,144,147,149–151,153,156,158,159,162,163 provided information on the gender of 10,804 participants, of whom 7818 (72%) were men and 2986 (28%) were women.
In total, 16 studies80,121,122,126,127,135,136,139,150,151,153,155,158,159,162,164 gave details of when they took place, with an earliest start date of August 1995135 and latest end date of April 2006. 150 Nine studies took place in the USA,126,127,129,139,148,149,153,158,159 four in Italy122,123,144,154 and Spain,128,142,161,162 three in Austria,134,147,151 Germany80,95,132 and Japan,135,136,164 two in the UK,45,141 Turkey137,163 and India131,150 and one in Greece,125 Poland,130 Switzerland,121 Sweden,155 the Netherlands,138 South Korea157 and China,156 and two had multinational settings, taking place in Germany/USA140 and Saudi Arabia/USA. 120
Methodological quality of the included studies
Figure 21 summarises the quality assessment for the 41 NMP22 studies. The results for the quality assessment of the individual studies are shown in Appendix 13. In all studies the reference standard (cystoscopy with histological assessment of biopsied tissue) was considered likely to correctly classify bladder cancer (Q2) and withdrawals from the study were explained or there were none (Q11). In 40 studies (98%) the spectrum of patients who received the tests was considered to be representative of those who would receive the test in practice (Q1) and incorporation bias was avoided (Q6). In 39 studies (95%) partial verification bias was avoided (Q4), intermediate test results were reported or there were none (Q10) and a clear definition of what was considered to be a positive result was provided (Q13).
FIGURE 21.
Summary of quality assessment of NMP22 studies (n = 41).
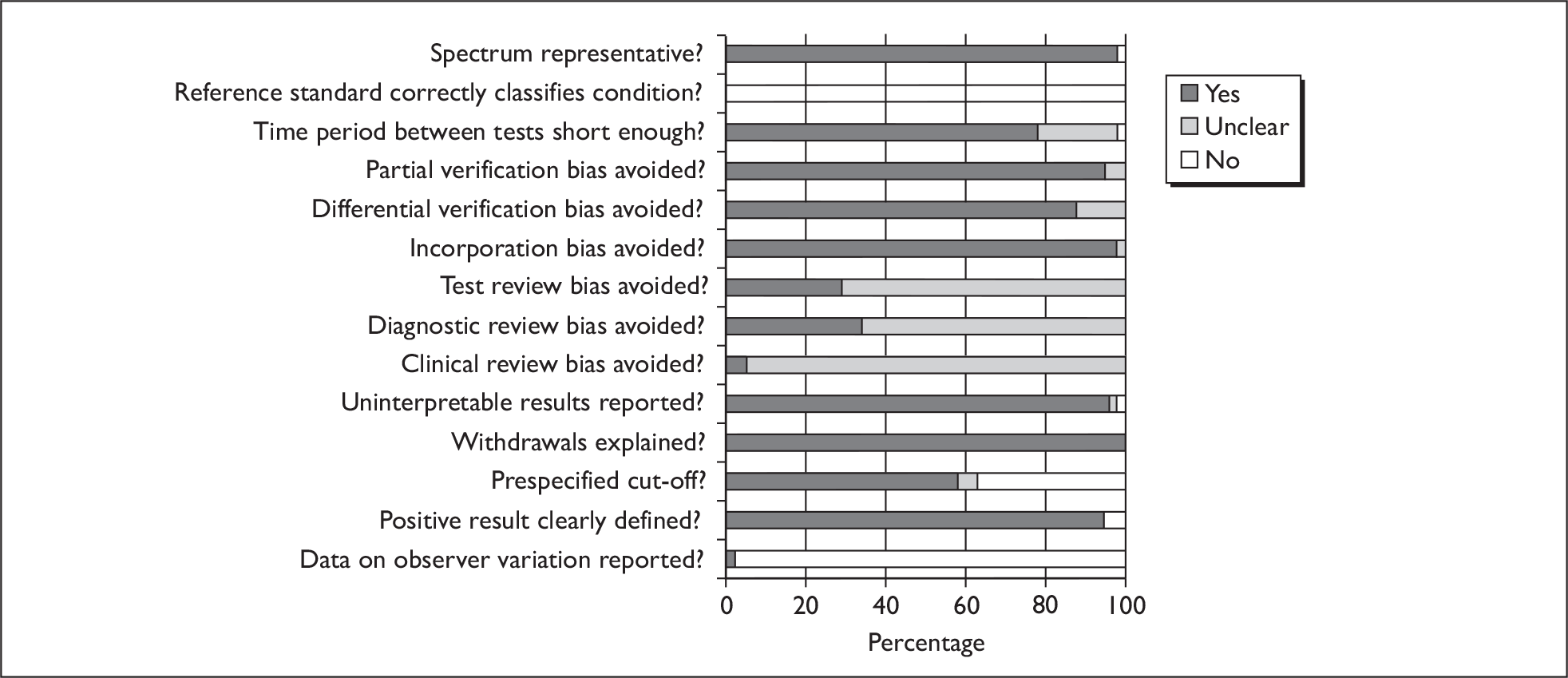
In 36 studies (88%) differential verification bias was avoided (Q5), in 32 studies (78%) the time period between NMP22 and the reference standard was considered to be short enough (1 month or less) to be reasonably sure that the patient’s condition had not changed in the intervening period (Q3) and in 24 studies (58%) a prespecified cut-off value was used (Q12).
However, in 39 studies (95%) it was unclear whether clinical review bias had been avoided (Q9), in 29 studies (71%) it was unclear whether test review bias had been avoided (Q7) and in 27 studies (66%) it was unclear whether diagnostic review bias had been avoided (Q8). A total of 40 studies (98%) did not report information on observer variation in interpretation of test results (Q14).
Assessment of diagnostic accuracy
Patient-level analysis
A total of 28 studies45,80,95,121–123,126–128,130–132,134,137,139–142,144,147,148,150,151,153,159,160,162,163 enrolling 10,565 participants, with 10,119 included in the analysis, provided sufficient information to allow their inclusion in the pooled estimates for patient-level analysis, using a ‘common’ cut-off of 10 U/ml to define a positive test result. Figure 22 shows the sensitivity and specificity of the individual studies, pooled estimates and SROC curve for NMP22 patient-based detection of bladder cancer. The pooled sensitivity and specificity (95% CI) were 68% (62% to 74%) and 79% (74% to 84%), respectively, and the DOR value (95% CI) was 8 (5 to 11). Across the 28 studies the sensitivity for NMP22 ranged from 33%45 to 100%,153 and specificity ranged from 40%80 to 93%. 142 The median (range) PPV across studies was 52% (13% to 94%) and the median (range) NPV was 82% (44% to 100%).
FIGURE 22.
NMP22 patient-level analysis: sensitivity, specificity, pooled estimates and SROC curve.
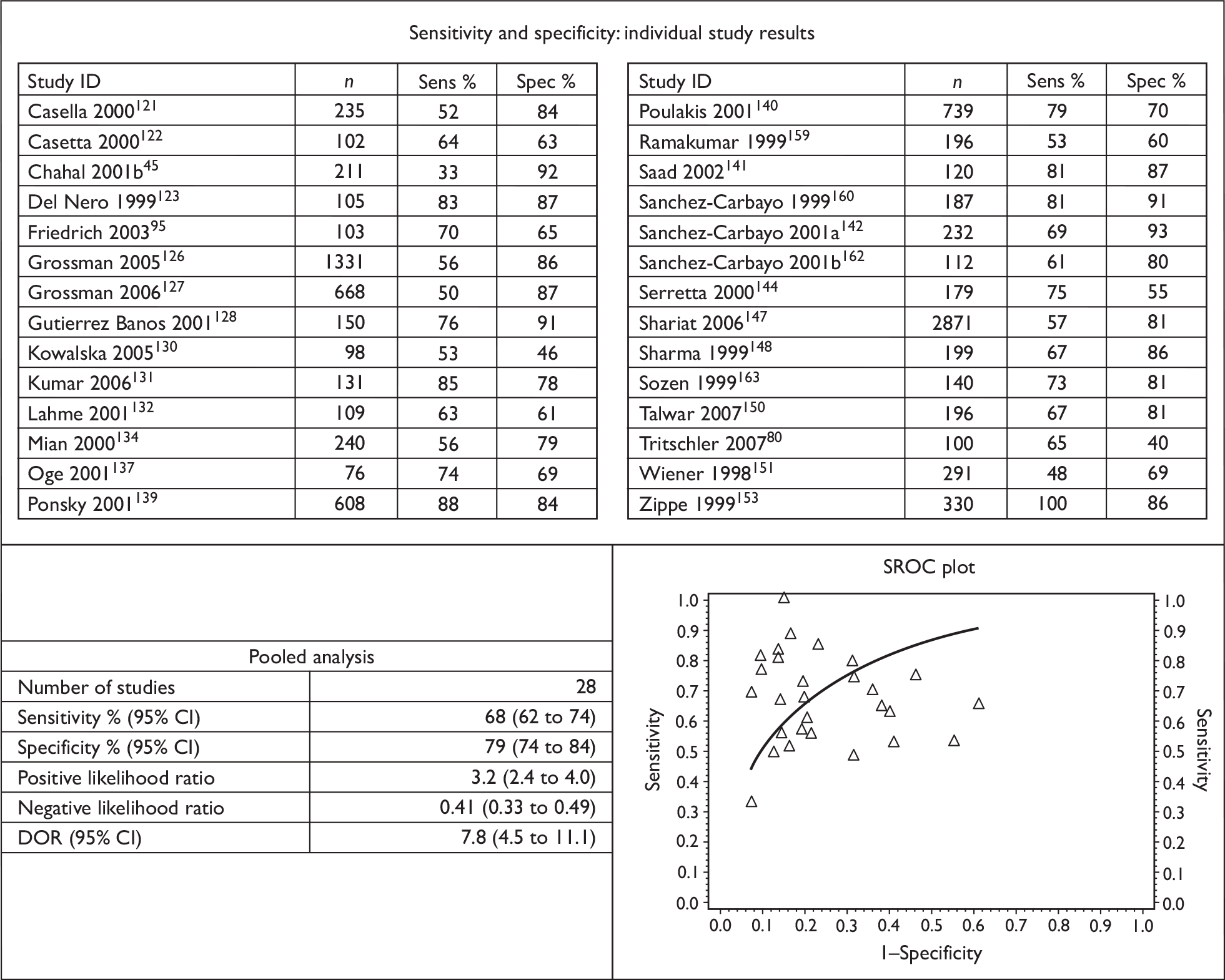
Most of the included studies in the pooled estimates contained a mixture of patients with a suspicion of bladder cancer and those with previously diagnosed bladder cancer, although three studies121,160,163 did not report this information. In four studies126,141,153,162 all of the participants (n = 1893) had a suspicion of bladder cancer [median (range) sensitivity and specificity across studies 71% (56% to 100%) and 86% (80% to 87%) respectively]. In seven studies123,127,130,131,142,144,147 all of the participants (n = 4284) had previously diagnosed bladder cancer [median (range) sensitivity and specificity across studies 69% (50% to 85%) and 81% (46% to 93%) respectively].
NMP22 BladderChek point of care test
Five studies80,126,127,131,150 involving 2426 participants used the NMP22 BladderChek point of care test. Across these studies, using a cut-off of 10 U/ml for a positive test result, the median (range) sensitivity and specificity for patient-based detection of bladder cancer were 65% (50% to 85%) and 81% (40% to 87%), respectively, compared with 68% (95% CI 62% to 74%) sensitivity and 79% (95% CI 74% to 84%) specificity for the 28 studies included in the pooled estimates. (The five studies using the NMP22 BladderChek test were also included in the pooled estimates.) In the study by Grossman and colleagues126 all of the participants (n = 1331) had a suspicion of bladder cancer (sensitivity 56%, specificity 86%). In the studies by Grossman and colleagues127 and Kumar and colleagues131 all of the participants (n = 799) had previously diagnosed bladder cancer [median (range) sensitivity and specificity across studies 68% (50% to 85%) and 83% (78% to 87%) respectively].
Specimen-level analysis
Three studies enrolling 655 participants reported specimen-level analysis (n = 705 specimens for Oosterhuis 2002138 and Stampfer 1998;149 Bhuiyan 2003120 did not report numbers) using a cut-off of 10 U/ml for a positive test result. Across the three studies the median (range) sensitivity and specificity were 49% (25% to 50%) and 92% (68% to 94%) respectively.
Stage/grade analysis
Studies reporting the sensitivity of NMP22 in the detection of stage and grade of tumour categorised this information in different ways, including pTa, pTaG1, pTaG1–2, PTaG2, pTa pT1, pTa pT1 CIS, pTa+CIS, pTaG3–pT1, G1, G2, G1–2, G1 G3, pT1, pT1G2, CIS, G3, pT2, pT2 pT2a, pT2G2, pT2–3, pT2–4, ≥ pT2, pT3, pT3a 3b and pT4 (see Appendix 14). Almost all of the studies providing this information and using a cut-off of 10 U/ml for a positive test result reported the detection of stage/grade at the patient level (if the number of specimens reported by a study was one per patient included in the analysis then this was considered as a patient-based analysis); the exception was those studies by Oosterhuis and colleagues138 and Stampfer and colleagues. 149
Table 17 shows the median (range) sensitivity of ImmunoCyt, for both patient- and specimen-based detection of tumours, within the broad categories of less aggressive/lower risk and more aggressive/higher risk (including CIS), and also separately for CIS.
| NMP22 sensitivity (%), median (range) | Number of patients (specimens)a | Number of studies | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Less aggressive/lower risk | |||
| Patient-based detection | 50 (0 to 86) | 4685 | 18 |
| Specimen-based detection | 33 | 191 (431) | 1 |
| More aggressive/higher risk including CIS | |||
| Patient-based detection | 83 (0 to 100) | 7556 | 19 |
| Specimen-based detection | 82 (25 to 100) | 191 (431) | 1 |
| CIS | |||
| Patient-based detection | 83 (0 to 100) | 3453 | 11 |
| Specimen-based detection | 25 | 191 (431) | 1 |
Less aggressive, lower risk tumours (pTa, G1, G2)
A total of 18 studies45,95,121,123,126–128,131,132,134,137,141,142,144,150,151,159,162 involving 4685 patients reported the sensitivity of NMP22 for the patient-based detection of less aggressive, lower risk tumours. Across these studies the median (range) sensitivity of NMP22 was 50% (0% to 86%) (Table 17). The study by Oosterhuis and colleagues138 reported a sensitivity of 33% for specimen-based detection (191 participants, 431 specimens).
More aggressive, higher risk tumours (pT1, G3, CIS)
A total of 19 studies45,95,121,123,126–128,131,132,134,137,141,142,144,147,150,151,159,162 involving 7556 patients reported the sensitivity of NMP22 for patient-based detection of more aggressive, higher risk tumours. Across these studies the median (range) sensitivity of NMP22 was 83% (0% to 100%) (Table 17). In the study by Oosterhuis and colleagues138 (191 participants, 431 specimens), the median (range) sensitivity for specimen-based detection was 82% (25% to 100%).
Carcinoma in situ
A total of 11 studies95,126,127,134,137,141,142,144,150,159,162 involving 3453 patients reported the sensitivity of NMP22 for the patient-based detection of CIS. Across these studies the median (range) sensitivity of NMP22 was 83% (0% to 100%). Oosterhuis and colleagues138 (191 participants, 431 specimens) reported a sensitivity of 25% for specimen-based detection of CIS.
Number of tumours
Three studies reported the sensitivity of NMP22 in detecting bladder cancer in patients with varying numbers of tumours, although none of the studies used a cut-off of 10 U/ml. Poulakis and colleagues140 in a study involving 739 patients reported NMP22 (cut-off ≥ 8.25 U/ml) sensitivities of 79%, 90% and 97% in patients with one, two to three, and more than three tumours respectively. Takeuchi and colleagues164 in a study involving 669 patients reported NMP22 (cut-off ≥ 12 U/ml) sensitivities of 44%, 60% and 91% in patients with one, two to four, and five or more tumours respectively. Sanchez-Carbayo and colleagues161 in a study involving 187 patients reported NMP22 (cut-off ≥ 14.6 U/ml) sensitivities of 72% and 75% in patients with single and multiple tumours respectively.
Size of tumours
Three studies reported the sensitivity of NMP22 in detecting bladder cancer in patients with varying sizes of tumours, although again none of the studies used a cut-off of 10 U/ml. Boman and colleagues155 in a study involving 250 patients reported NMP22 (cut-off ≥ 4 U/ml) sensitivities of 65%, 54%, 73% and 89% in detecting new tumours of ≤ 10 mm, 11–20 mm, 21–30 mm and > 30 mm, respectively, and 41%, 67% and 60% in detecting recurrent tumours of ≤ 10 mm, 11–20 mm and > 21 mm respectively. Takeuchi and colleagues164 in a study involving 669 patients reported NMP22 (cut-off ≥ 12 U/ml) sensitivities of 32%, 65% and 92% in detecting tumours < 10 mm, 10–30 mm and > 30 mm respectively. Sanchez-Carbayo and colleagues161 in a study involving 187 patients reported NMP22 (cut-off > 14.6 U/ml) sensitivities of 83%, 81% and 93% in detecting tumours < 5 mm, 5–30 mm and > 30 mm respectively.
Unevaluable tests
None of the NMP22 studies specifically reported this information.
Cytology
Characteristics of the included studies
A description of each of the 56 included cytology studies is given in Appendix 12, which contains the characteristics of all of the included biomarker and cytology studies listed alphabetically by surname of first author. Table 18 shows summary information for the 56 cytology studies.
| Characteristic | Number | Number of studies |
|---|---|---|
| Study design | ||
| Cross-sectional diagnostic study | 19,842 | 47 |
| Case–control | 2418 | 9 |
| Patients | ||
| Enrolled | 22,260 | 56 |
| Analysed | 19,219 | |
| Suspicion of or previously diagnosed BC | ||
| Suspicion of BC | 7888 (45%) | 46 (82%) |
| Previously diagnosed BC | 9487 (55%) | |
| Not reported | 3057 | 10 (18%) |
| Age | ||
| Median (range) of means (years) | 67 (54 to 73) | 33 (59%) |
| Not reported | – | 23 (41%) |
| Sex | ||
| Men | 9702 (73%) | 36 (64%) |
| Women | 3639 (27%) | 20 (36%) |
| Not reported | 8578 | |
A total of 47 studies, reported in 56 papers, were diagnostic cross-sectional studies,45,80,97,98,100–103,105,109–129,131–133,135,136,139–141,145,146,148–153,165–174 of which 1145,101,109,110,112,116,118,126,127,165,174 reported consecutive recruitment. Nine studies107,108,155,157–159,162–164 were case–control studies and 11 studies103,108,111,116,126,127,135,149,165,170,174 were multicentre (Table 19).
| Study | Number of centres |
|---|---|
| Bastacky 1999165 | 3 |
| Grossman 2005126 | 23 |
| Grossman 2006127 | 23 |
| Karakiewicz 2006170 | 10 |
| Messing 2005111 | 4 |
| Miyanaga 1999135 | 13 |
| Piaton 2003116 | 19 |
| Raitanen 2002174 | 18 |
| Sarosdy 2002108 | 21 |
| Sarosdy 2006103 | 23 |
| Stampfer 1998149 | 3 |
The 56 studies enrolled 22,260 participants, with 19,219 included in the analysis. Eight studies80,114,120,121,151,155,167,171 involving at least 872 patients reported bladder wash cytology. In 46 studies45,80,97,101–103,105,107–114,116,118,122–124,126–129,131,132,135,136,139–141,148–151,153,158,159,162,164,165,168,170–172,174 7888 participants (45%) presented with a suspicion of bladder cancer and 9487 (55%) had previously diagnosed bladder cancer. In 10103,118,126,135,141,153,162,164,168,172 of these studies the whole patient population analysed (n = 4290) had a suspicion of bladder cancer and in 11102,108,110,111,113,123,127,129,131,170,174 the whole population analysed had previously diagnosed bladder cancer (n = 5710). In total, 10 studies98,100,119–121,155,157,163,166,167 did not report this information.
Across 33 studies80,97,101–103,107,109,112–114,116,123,124,126–129,131,136,140,141,149–151,153,158,159,162,166,170–172,174 providing information on patient age for the whole study population, the median (range) of means was 67 years (54 to 73 years). A total of 36 studies provided information on the gender of 13,341 participants, of whom 9702 (73%) were men and 3639 (27%) were women.
In total, 30 studies80,102,103,108,111–114,118,119,121,122,126,127,135,136,139,150,151,153,155,158,159,162,164–168,174 gave details of when they took place, with an earliest start date of 1990165 and latest end date of July 2007. 118 Fifteen studies took place in the USA,97,103,105,108,111,126,127,129,139,148,149,153,158,159,165 seven in Germany,80,98,107,118,132,168,171 four in the UK,45,141,166,172 three each in Italy113,122,123 and Japan,135,136,164 two each in Austria,112,151 Spain,128,161 Sweden114,155 and India131,150 and one each in Belgium,167 Finland,174 France,116 Greece,124 Switzerland,121 the Netherlands,102 Turkey,163 Canada119 and South Korea,157 while seven had multinational settings, with three taking place in Austria/Italy101,109,110 and the others taking place in Germany/USA,140 USA/Belgium,100 Saudi Arabia/USA120 and Austria/Germany/Italy/Spain/Sweden/Switzerland/Egypt/Japan/Canada/USA. 170
Methodological quality of the included studies
Figure 23 summarises the quality assessment for the 56 cytology studies. The results for the quality assessment of the individual studies are shown in Appendix 13. In all studies the reference standard (cystoscopy with histological assessment of biopsied tissue) was considered likely to correctly classify bladder cancer (Q2). In 55 studies (98%) the spectrum of patients who received the tests was considered to be representative of those who would receive the test in practice (Q1), incorporation bias was avoided (Q6), uninterpretable test results were reported or there were none (Q10) and withdrawals from the study were explained or there were none (Q11). In 54 studies (96%) partial verification bias was avoided (Q4) and in 49 (88%) differential verification bias was avoided (Q5). In 41 studies (73%) the time period between cytology and the reference standard was considered to be short enough (1 month or less) to be reasonably sure that the patient’s condition had not changed in the intervening period (Q3), in 40 studies (71%) a prespecified cut-off value for a positive test result was stated (Q12) and in 37 studies (66%) a clear definition of what was considered to be a positive result was provided (Q13).
FIGURE 23.
Summary of quality assessment of cytology studies (n = 56).
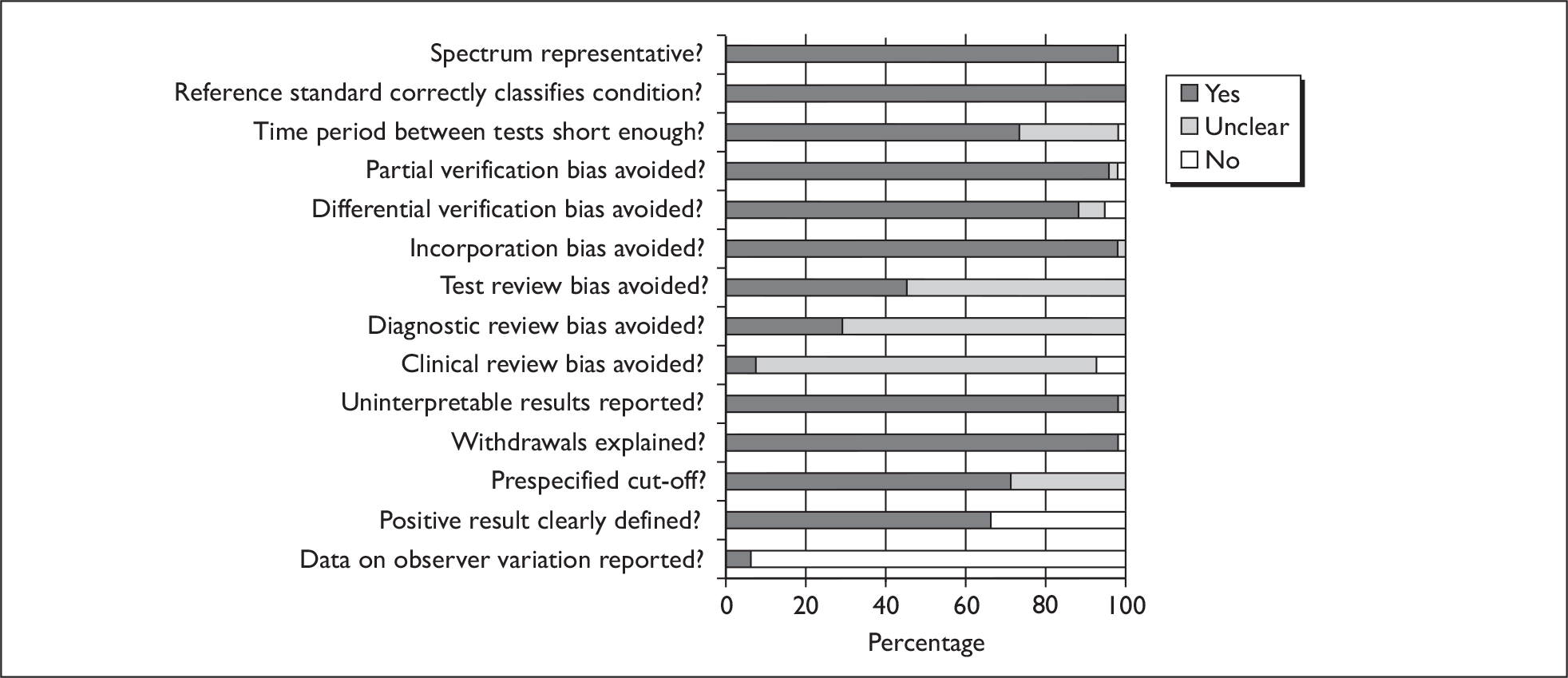
However, in 48 studies (86%) it was unclear whether clinical review bias had been avoided (Q9), in 40 studies (71%) it was unclear whether diagnostic review bias had been avoided (Q8) and in 31 studies (55%) it was unclear whether test review bias had been avoided (Q7). A total of 53 studies (95%) did not report information on observer variation in interpretation of test results (Q14).
Assessment of diagnostic accuracy
Patient-level analysis
A total of 36 studies45,80,97,100,101,107,109,111,112,116,118,119,122–124,126–128,131,132,135,136,139–141,148,150,151,153,157,159,164,166,170,172,174 reporting voided urine cytology, enrolling 15,161 participants with 14,260 included in the analysis, provided sufficient information to allow their inclusion in the pooled estimates for patient-level analysis. Figure 24 shows the sensitivity and specificity of the individual studies, pooled estimates and SROC curve for cytology patient-based detection of bladder cancer. The pooled sensitivity and specificity (95% CI) were 44% (38% to 51%) and 96% (94% to 98%), respectively, and the DOR value (95% CI) was 19 (11 to 27). Across the 36 studies the sensitivity for cytology ranged from 7%136 to 100%,172 and specificity ranged from 78%80 to 100%. 135 The median (range) PPV across studies was 80% (27% to 100%) and the median (range) NPV was also 80% (38% to 100%).
FIGURE 24.
Cytology patient-level analysis: sensitivity, specificity, pooled estimates and SROC curve.
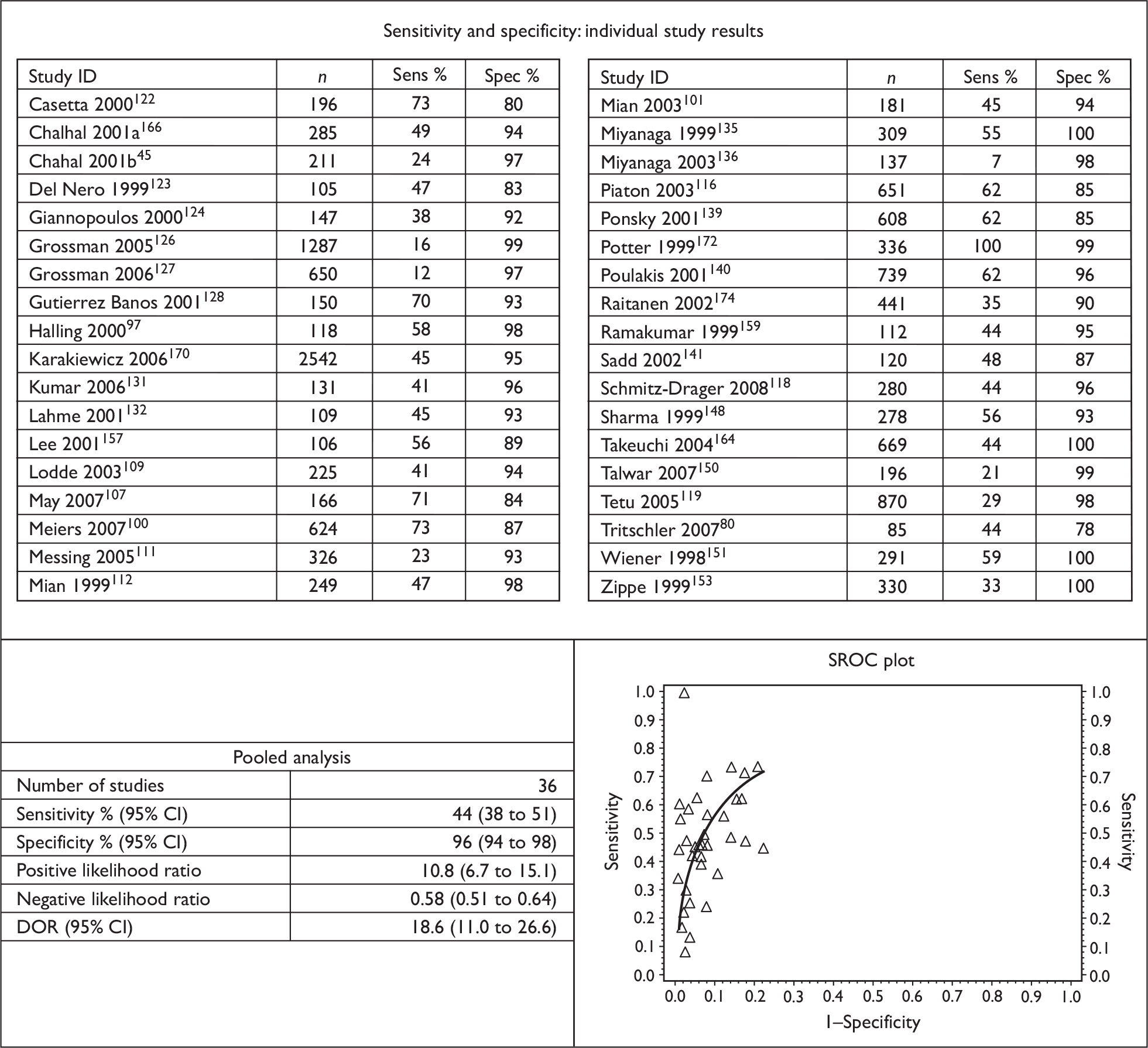
Most of the included studies in the pooled estimates contained a mixture of patients with a suspicion of bladder cancer and those with previously diagnosed bladder cancer. In seven studies118,126,135,141,153,164,172 all of the participants (n = 3331) had a suspicion of bladder cancer [median (range) sensitivity and specificity across studies 44% (16% to 100%) and 99% (87% to 100%) respectively]. In six studies111,123,127,131,170,174 all of the participants (n = 4195) had previously diagnosed bladder cancer [median (range) sensitivity and specificity across studies 38% (12% to 47%) and 94% (83% to 97%) respectively]. Four studies100,119,157,166 did not report this information.
Specimen-level analysis
Eight studies,102,110,113,120,129,149,168,171 with at least 1143 patients included in the analysis, reported specimen-level analysis (n = 3487) of voided urine cytology. (The study by Mian and colleagues113 enrolled 942 patients but did not report the number analysed, and in the study by Planz and colleagues171 it was unclear how many patients underwent voided urine cytology and how many underwent bladder wash cytology.) Across these studies the median (range) sensitivity and specificity were 42% (38% to 76%) and 94% (58% to 99%) respectively.
Cytology using bladder wash
Eight studies80,114,120,121,151,155,167,171 involving at least 872 patients reported bladder wash cytology. (It was unclear in the studies by Boman and colleagues155 and Planz and colleagues171 how many patients the specimen-based analysis related to.) Across four studies80,114,121,151 reporting patient-based detection of bladder cancer (n = 608) the median (range) sensitivity and specificity were 58% (53% to 76%) and 90% (62% to 100%) respectively (Olsson and colleagues114 did not report specificity). This compares with 44% (95% CI 38% to 51%) sensitivity and 96% (95% CI 94% to 98%) specificity for the 36 voided urine cytology studies included in the pooled estimates.
Across four studies120,155,167,171 reporting specimen-based detection of bladder cancer (n = at least 1076) the median (range) sensitivity and specificity were 50% (38% to 62%) and 94% (83% to 99%) respectively. (Bhuiyan and colleagues120 reported sensitivity and specificity but not the number of specimens upon which this was based, and Olsson and colleagues114 did not report specificity.) This compares with a median (range) sensitivity of 42% (38% to 76%) and specificity of 94% (58% to 99%) across the eight studies reporting specimen-based analysis for voided urine cytology.
All of the studies reporting bladder wash cytology contained a mixture of patients with a suspicion of bladder cancer or previously diagnosed bladder cancer, or did not report numbers for these groups of patients.
Stage/grade analysis
Studies reporting the sensitivity of cytology in the detection of stage and grade of tumour categorised this information in different ways, including pTa, pTaG1, pTaG1–2, PTaG2, pTaG3, pTa pT1, pTa pT1 CIS, pTa+CIS, ≥ pTa+CIS, pTa pT1G3, pTaG3–pT1, G1, G2, G1–2, pT1, pT1G1, pT1G2, pT1G1–2, pT1G3, pT1G3+CIS, pT1–T3b, pT1–4, CIS, CIS–pT1, G3, pT2, pT2 pT2a, pT2G2, pT2G3, pT2–3, pT2–4, ≥ pT2, pT3, pT3a 3b, pT3G3 and pT4 (see Appendix 14). If the number of specimens included in the analysis was one per patient then this was considered as a patient-based analysis.
Table 20 shows the median (range) sensitivity of voided urine cytology, for both patient- and specimen-based detection of tumours, within the broad categories of less aggressive/lower risk and more aggressive/higher risk (including CIS), and also separately for CIS.
| Cytology sensitivity (%), median (range) | Number of patients (specimens)a | Number of studies | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Less aggressive/lower risk | |||
| Patient-based detection | 27 (0 to 93) | 12,566 | 29 |
| Specimen-based detectionb | 27 (8 to 78) | 469+ (2411) | 3 |
| More aggressive/higher risk including CIS | |||
| Patient-based detection | 69 (0 to 100) | 12,566 | 29 |
| Specimen-based detectionb | 79 (68 to 93) | 608+ (3003) | 4 |
| CIS | |||
| Patient-based detection | 78 (0 to 100) | 6870 | 17 |
| Specimen-based detectionb | 81 (76 to 93) | 513+ (2895) | 3 |
Less aggressive, lower risk tumours (pTa, G1, G2)
A total of 29 studies45,97,100,101,103,107–109,111,112,116,119,123,124,126–128,131,132,140,141,150,151,157,159,164,166,170,174 involving 12,566 patients reported the sensitivity of voided urine cytology for the patient-based detection of less aggressive, lower risk tumours. Across these studies the median (range) sensitivity of cytology was 27% (0% to 93%) (Table 20). Across three studies102,113,168 reporting the sensitivity of voided urine cytology for specimen-based detection of less aggressive, lower risk tumours (469+ participants, 2411 specimens), the median (range) sensitivity was 27% (8% to 78%).
More aggressive, higher risk tumours (pT1, G3, CIS)
A total of 29 studies45,97,100,101,103,107–109,111,112,116,119,123,124,126–128,131,132,140,141,150,151,157,159,164,166,170,174 involving 12,566 patients reported the sensitivity of voided urine cytology for the patient-based detection of more aggressive, higher risk tumours. Across these studies the median (range) sensitivity of cytology was 69% (0% to 100%) (Table 20). Across four studies102,113,167,168 reporting the sensitivity of voided urine cytology for specimen-based detection of more aggressive, higher risk tumours (608+ participants, 3003 specimens), the median (range) sensitivity was 79% (68% to 93%).
Carcinoma in situ
A total of 17 studies97,101,107–109,111,112,116,119,124,126,127,140,141,150,159,174 involving 6870 patients reported the sensitivity of voided urine cytology for patient-based detection of CIS. Across these studies the median (range) sensitivity of cytology was 78% (0% to 100%). Across three studies113,167,168 reporting the sensitivity of voided urine cytology for specimen-based detection of CIS (513+ participants, 2895 specimens), the median (range) sensitivity was 81% (76% to 93%).
Number of tumours
Three studies reported the sensitivity of cytology in detecting bladder cancer in patients with varying numbers of tumours. Poulakis and colleagues140 in a study involving 739 patients reported cytology sensitivities of 48%, 68% and 86% in patients with one, two to three, and more than three tumours respectively. Raitanen and colleagues174 in a study involving 570 patients reported on a subgroup of 129 patients with no previous history of bladder cancer in which cytology sensitivities were 57%, 54% and 71% in patients with one, two and more than three tumours respectively. Takeuchi and colleagues164 in a study involving 669 patients reported cytology sensitivities of 33%, 30% and 82% in patients with one, two to four, and five or more tumours respectively.
Size of tumours
Three studies reported the sensitivity of cytology in detecting bladder cancer in patients with varying sizes of tumours. Boman and colleagues155 in a study involving 250 patients reported cytology sensitivities of 35%, 33%, 55% and 87% in detecting new tumours ≤ 10 mm, 11–20 mm, 21–30 mm and > 30 mm, respectively, and 30%, 91% and 100% in detecting recurrent tumours ≤ 10 mm, 11–20 mm and > 21 mm respectively. Messing and colleagues111 in a study involving 326 patients reported cytology sensitivities of 18%, 26% and 20% in detecting tumours < 10 mm, 10–30 mm and > 30 mm respectively. Takeuchi and colleagues164 in a study involving 669 patients reported cytology sensitivities of 21%, 47% and 75% in detecting tumours < 10 mm, 10–30 mm and > 30 mm respectively.
Unevaluable tests
Six studies101,103,114,118,119,174 specifically reported unevaluable tests. Overall, 54 of 2566 tests (2%) could not be evaluated. Across studies, the median (range) percentage of tests that were unevaluable was 1% (0.6% to 4%).
Observer variation
Two studies reported observer variation. Hughes and colleagues129 reported that all 128 specimens were independently reviewed by two cytopathologists, who were approximately 80% concordant in their interpretation of the cases. In the case of approximately 20% of specimens about which there was disagreement concerning the cytological diagnosis, the cytospin was reviewed by the two pathologists simultaneously and an agreement was reached. 129 Sarosdy and colleagues108 reported that local site results were available in 43 cases and there was agreement with study central cytology in 36 (84%). Of the remaining seven cases, four were positive at the site and negative at the study testing laboratory, and three were negative at the investigation site and positive at the study testing laboratory. 108 Study site cytology was available in three cases of CIS and eight cases of G3 tumour, with 100% agreement between study site and central laboratory cytopathology interpretation in these 11 cases. 108
Studies directly comparing tests
FISH versus cytology
Five97,98,100,101,107 of the studies included in the pooled estimates for FISH and for cytology directly compared the two tests. The studies enrolled 1377 participants, with 1119 included in the analysis for FISH and 1198 for cytology. Figure 25 shows the sensitivity and specificity of the individual studies, pooled estimates and SROC curves for these five studies. The pooled estimate (95% CI) for the sensitivity of FISH was 81% (66% to 97%) compared with 54% (39 to 80%) for cytology, whereas the pooled estimate (95% CI) for the specificity of FISH was 82% (68% to 97%) compared with 92% (84% to 99%) for cytology.
FIGURE 25.
FISH vs cytology – patient-level analysis: sensitivity, specificity, pooled estimates and SROC curve.
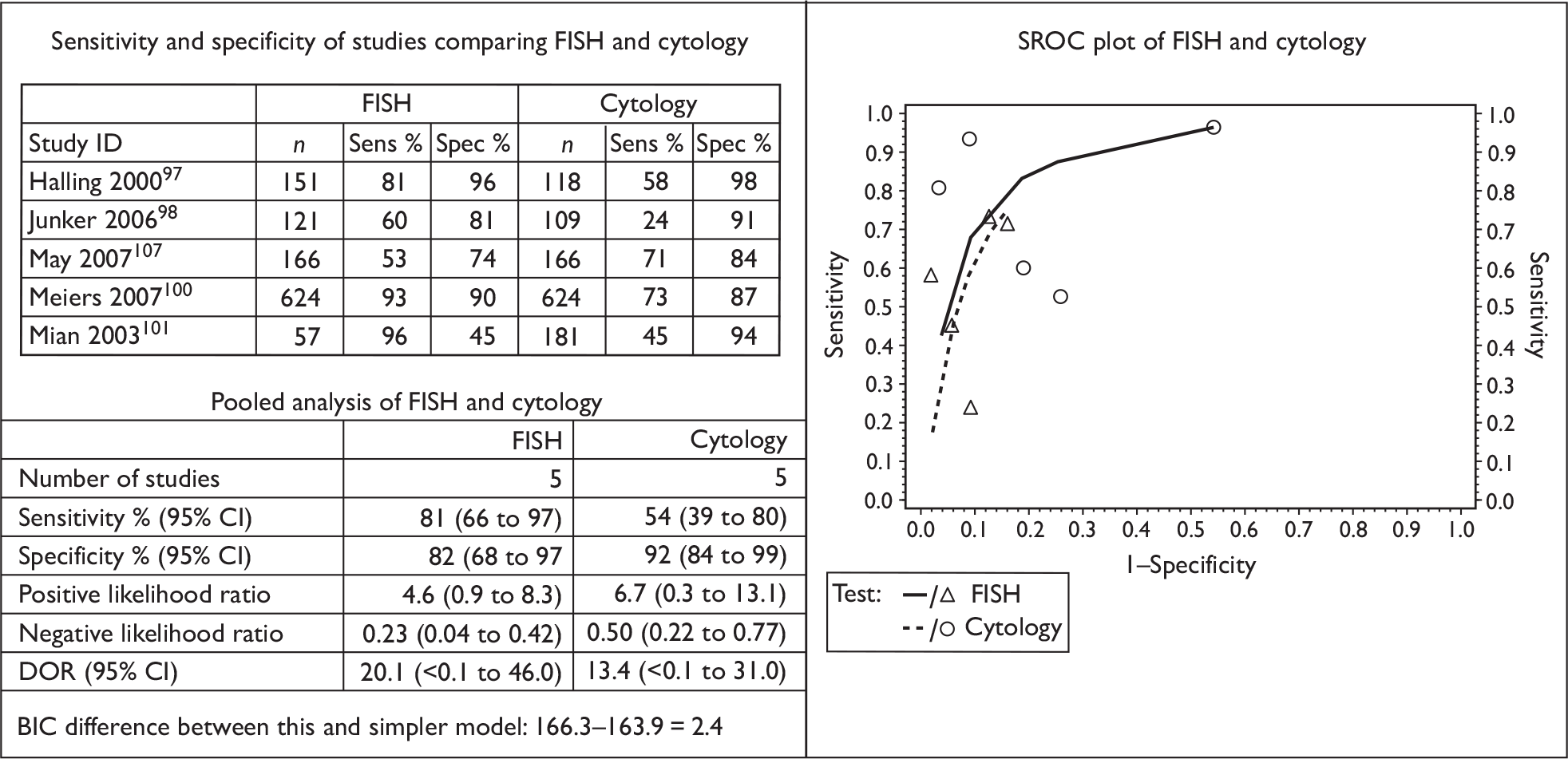
ImmunoCyt versus cytology
Six101,109,111,112,116,118 of the studies included in the pooled estimates for ImmunoCyt and for cytology directly compared the two tests. The studies enrolled 2016 participants, with 1912 included in the analysis. Figure 26 shows the sensitivity and specificity for the individual studies, pooled estimates and SROC curves for these six studies. The pooled estimate (95% CI) for the sensitivity of ImmunoCyt was 82% (76% to 89%) compared with 44% (35% to 54%) for cytology, whereas the pooled estimate (95% CI) for the specificity of ImmunoCyt was 85% (71% to 85%) compared with 94% (91% to 97%) for cytology.
FIGURE 26.
ImmunoCyt vs cytology – patient-level analysis: sensitivity, specificity, pooled estimates and SROC curve.
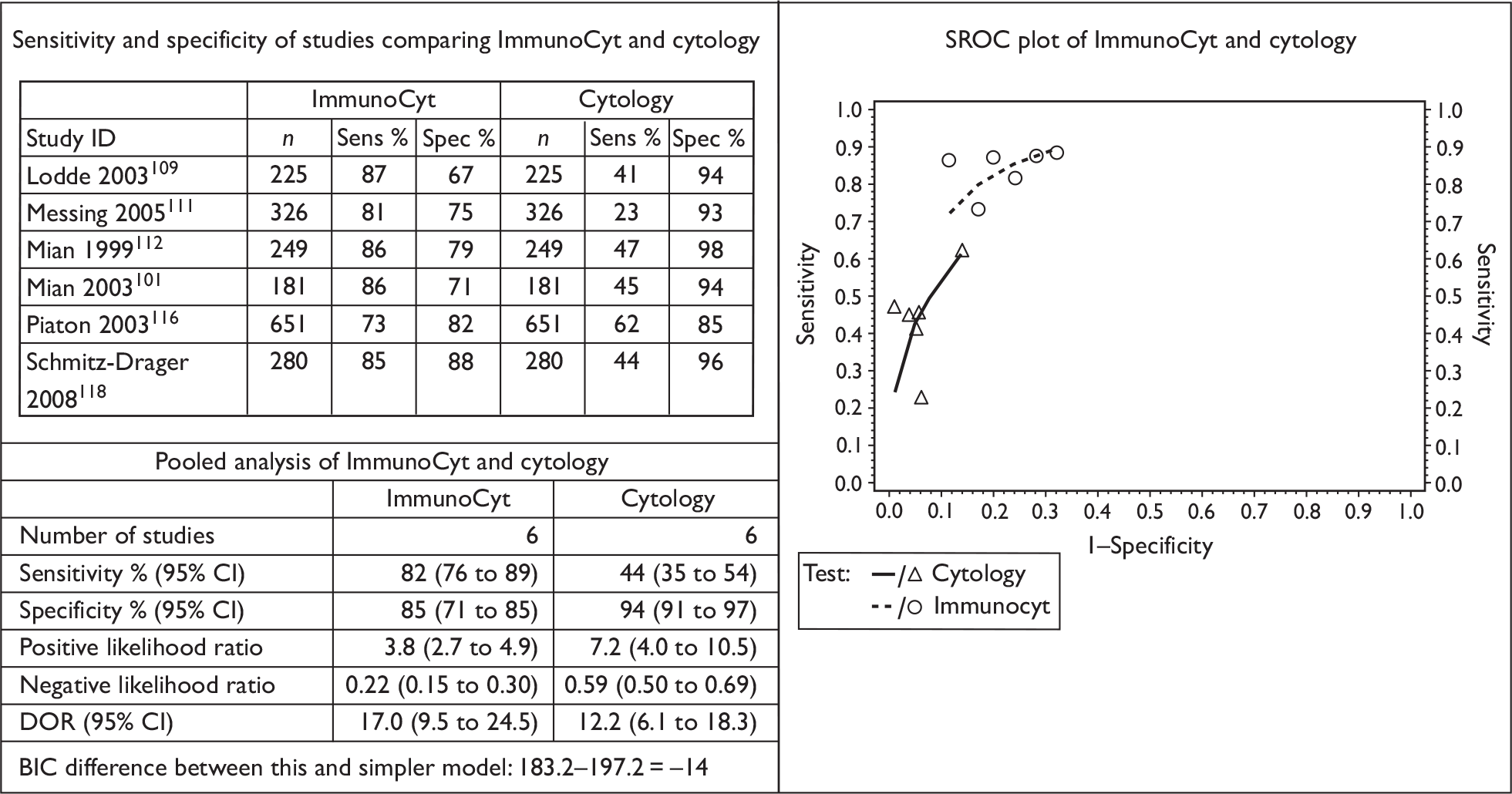
NMP22 versus cytology
In total, 1645,80,123,126–128,131,132,139–141,148,150,151,153,159 of the studies included in the pooled estimates for NMP22 and for cytology directly compared the two tests. The studies enrolled 5623 participants, with 5563 included in the analysis for NMP22 and 5402 for cytology. Figure 27 shows the sensitivity and specificity for the individual studies, pooled estimates and SROC curves for these 16 studies. The pooled estimate (95% CI) for the sensitivity of NMP22 was 70% (59% to 80%) compared with 40% (31% to 49%) for cytology, whereas the pooled estimate (95% CI) for the specificity of NMP22 was 81% (74% to 88%) compared with 97% (95% to 99%) for cytology.
FIGURE 27.
NMP22 vs cytology – patient-level analysis: sensitivity, specificity, pooled estimates and SROC curve.
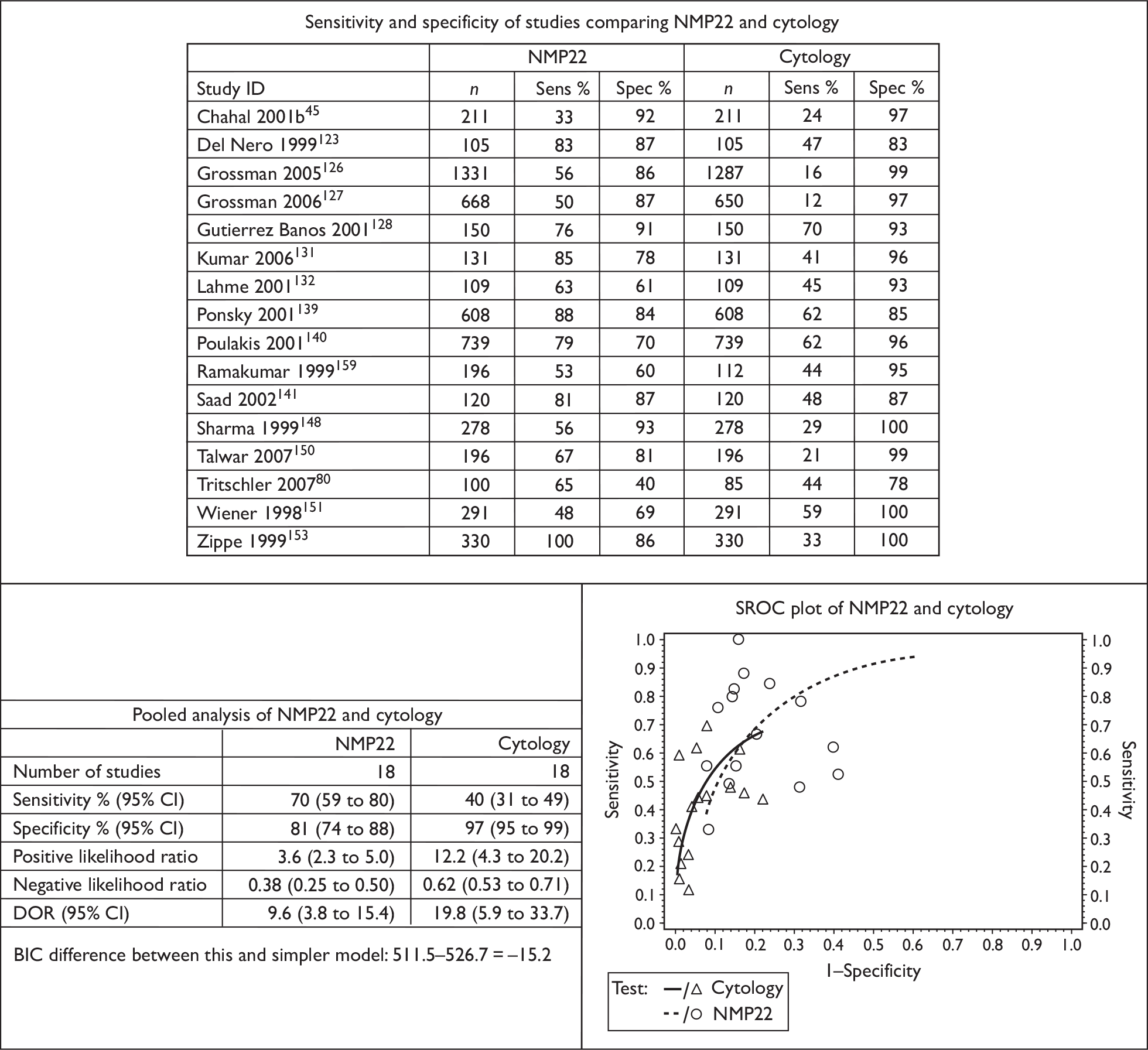
Studies reporting combinations of tests
In total, 16 studies reported the sensitivity and specificity of combinations of tests in detecting bladder cancer, including FISH and cytology,94,102 FISH and cystoscopy,99 ImmunoCyt and cytology,101,109–113,116,119 ImmunoCyt and cystoscopy,118 NMP22 and cytology,131,164 NMP22 and cystoscopy126,127 and cytology and cystoscopy. 118,127 Although not explicitly stated in the reports, the definition of a positive test result for the combined tests was a positive result on either of the tests included in the combination. The exception to this was the study by Daniely and colleagues,94 which reported the test performance of FISH combined with cytology.
FISH and cytology
Two studies94,102 reported the sensitivity and specificity of FISH and cytology used in combination. In a patient-level analysis (n = 115), Daniely and colleagues94 reported sensitivity and specificity of 100% and 50%, respectively, for FISH and cytology used in combination (results were not presented separately for the individual tests). A test was reported as positive if at least one cell abnormality in both cytology and FISH was found. In the case of abnormal FISH and normal cytology, a minimum of four cells with a gain of two or more chromosomes or 12 or more cells with homozygous loss of the 9p21 locus was required for a positive diagnosis. The study by Moonen and colleagues102 involving 105 patients reported a specimen-based analysis (n = 103), with sensitivity and specificity of 39% and 90%, respectively, for FISH, 41% and 90% for cytology and 53% and 79% for the tests used in combination.
FISH and cystoscopy
In a patient-based analysis, Kipp and colleagues99 in a study involving 124 patients reported the sensitivity and specificity of FISH and cystoscopy (not stated whether flexible or rigid) used in combination. They reported sensitivity and specificity of 62% and 87%, respectively, for FISH, 67% and 85% for cystoscopy and 87% and 79% for the tests used in combination. A definition of what constituted a positive test result for the combined tests was not given.
ImmunoCyt and cytology
Eight studies reported sensitivity and specificity for the tests of ImmunoCyt and cytology used in combination. Six studies101,109,111,112,116,119 involving 1997 patients reported patient-based detection and two studies110,113 involving 1137 patients reported specimen-based detection (2220 specimens). The median (range) sensitivities and specificities of ImmunoCyt, cytology, and ImmunoCyt and cytology across the studies reporting patient- and specimen-based detection are shown in Table 21. The sensitivity of the tests in combination for both patient- and specimen-based detection (87% and 88% respectively) was slightly higher than that of ImmunoCyt alone (84% and 78%), whereas the specificity (68% and 76%) was much lower than that of cytology alone (94% and 97%).
| Test | Sensitivity (%), median (range) | Specificity (%), median (range) |
|---|---|---|
| Patient-based detection (n = 6 studies) | ||
| ImmunoCyt | 84 (73 to 87) | 73 (62 to 82) |
| Cytology | 43 (23 to 62) | 94 (85 to 98) |
| ImmunoCyt + cytology | 87 (81 to 90) | 68 (61 to 79)a |
| Specimen-based detection (n = 2 studies) | ||
| ImmunoCyt | 78 (71 to 85) | 76 (73 to 78) |
| Cytology | 44 (39 to 49) | 97 (95 to 99) |
| ImmunoCyt + cytology | 88 (86 to 89) | 76 (73 to 78) |
ImmunoCyt and cystoscopy
In a patient-based analysis (n = 280), Schmitz-Drager and colleagues118 reported sensitivity and specificity of 85% and 88%, respectively, for ImmunoCyt, 84% and 98% for cystoscopy (not stated whether flexible or rigid) and 100% and 87% for the tests used in combination.
NMP22 and cytology
In a patient-based analysis, two studies131,164 involving 800 patients reported the sensitivity and specificity of NMP22 and cytology used in combination. The study by Kumar and colleagues131 involving 131 patients used the NMP22 BladderChek point of care test with a cut-off of 10 U/ml. They reported sensitivity and specificity of 85% and 78%, respectively, for NMP22, 41% and 96% for cytology and 91% sensitivity for the tests used in combination (specificity was not reported). 131 The study by Takeuchi and colleagues164 involving 669 patients used a cut-off of 12 U/ml for NMP22. They reported sensitivity and specificity of 58% and 80%, respectively, for NMP22, 44% and 100% for cytology and 60% sensitivity for the tests used in combination (specificity was not reported). In both studies the sensitivity for the tests in combination was slightly higher than that for NMP22 alone, although there was a wide difference in the sensitivity values for NMP22 reported by the two studies.
NMP22 and cystoscopy
In a patient-based analysis (n = 1999), two studies by Grossman and colleagues126,127 reported the sensitivity and specificity of the NMP22 BladderChek point of care test and cystoscopy (not stated whether flexible or rigid) used in combination. Both studies used a cut-off of 10 U/ml to define a positive NMP22 test result. In the first study126 sensitivity was 56% and specificity 86% for NMP22 (1331 patients), whereas in 79 patients diagnosed with bladder cancer the sensitivity of cystoscopy and the tests used in combination was 89% and 94% respectively. In the second study127 sensitivity was 50% and specificity 87% for NMP22 (668 patients), whereas in 103 patients diagnosed with bladder cancer the sensitivity of cystoscopy and the tests used in combination was 91% and 99% respectively.
Cytology and cystoscopy
In a patient-based analysis (n = 280), Schmitz-Drager and colleagues118 reported sensitivity and specificity of 44% and 96%, respectively, for cytology, 84% and 98% for cystoscopy (not stated whether flexible or rigid) and 88% and 95% for the tests used in combination. In 103 patients diagnosed with bladder cancer Grossman and colleagues127 reported sensitivity of 12% for cytology, 91% for cystoscopy and 94% for the tests used in combination.
Summary
A total of 71 studies, published in 83 reports, met the inclusion criteria for studies reporting the test performance of biomarkers (FISH, ImmunoCyt, NMP22) and cytology in detecting bladder cancer. In total, 14 studies enrolling 3321 participants reported on FISH, 10 studies enrolling 4199 participants reported on ImmunoCyt, 41 studies enrolling 13,885 participants reported on NMP22 and 56 studies enrolling 22,260 participants reported on cytology. The vast majority of the studies were diagnostic cross-sectional studies (n = 59, 83%), with the remainder being case–control studies (n = 12, 17%).
Pooled estimates with 95% CIs for sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios and DORs for each of the tests were undertaken for patient-level analysis. Table 22 shows the pooled estimates for sensitivity, specificity and DOR for each of the tests. Sensitivity was highest for ImmunoCyt at 84% (95% CI 77% to 91%) and lowest for cytology at 44% (95% CI 38% to 51%). ImmunoCyt (84%, 95% CI 77% to 91%) had higher sensitivity than NMP22 (68%, 95% CI 62% to 74%), with the lack of overlap of the CIs supporting evidence of a difference in sensitivity between the tests in favour of ImmunoCyt. FISH (76%, 95% CI 65% to 84%), ImmunoCyt (84%, 95% CI 77% to 91%) and NMP22 (68%, 95% CI 62% to 74%) all had higher sensitivity than cytology (44%, 95% CI 38% to 51%), and again the lack of overlap between the biomarker and cytology CIs supporting evidence of a difference in sensitivity in favour of the biomarkers over cytology.
| Test | Number of studies | Number analysed | Common cut-off | Sensitivity (%) (95% CI) | Specificity (%) 95% CI) | DOR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FISH | 12 | 2535 | Gain of more than one or more than two chromosomesa | 76 (65 to 84) | 85 (78 to 92) | 18 (3 to 32) |
| ImmunoCyt | 8 | 2896 | At least one green or one red fluorescent cell | 84 (77 to 91) | 75 (68 to 83) | 16 (6 to 26) |
| NMP22 | 28 | 10,119 | ≥ 10 U/ml | 68 (62 to 74) | 79 (74 to 84) | 8 (5 to 11) |
| Cytology | 36 | 14,260 | Cytologist subjective judgement | 44 (38 to 51) | 96 (94 to 98) | 19 (11 to 27) |
Although sensitivity was highest for ImmunoCyt and lowest for cytology, this situation was reversed for specificity, which was highest for cytology at 96% (95% CI 94% to 98%) and lowest for ImmunoCyt at 75% (95% CI 68% to 83%). Cytology (96%, 95% CI 94% to 98%) had higher specificity than FISH (85%, 95% CI 78% to 92%), ImmunoCyt (75%, 95% CI 68% to 83%) or NMP22 (79%, 95% CI 74% to 84%), with the lack of overlap between the cytology and biomarker CIs supporting evidence of a difference in specificity in favour of cytology over the biomarkers.
DORs (95% CI) ranged from 8 (5 to 11) to 19 (6 to 26), with higher DORs indicating a better ability of the test to differentiate between those with bladder cancer and those without. Based on the DOR values, FISH and cytology performed similarly well [18 (3 to 32) and 19 (11 to 27) respectively], ImmunoCyt slightly less so [16 (6 to 26)] and NMP22 relatively poorly [8 (5 to 11)]. However, as the DOR CIs for each of the tests all overlapped these results should be interpreted with caution.
Across studies the median (range) PPV was highest for cytology at 80% (27% to 100%) and FISH at 78% (27% to 99%), followed by ImmunoCyt at 54% (26% to 70%) and NMP22 at 52% (13% to 94%). The median (range) NPV was highest for ImmunoCyt at 93% (86% to 100%), followed by FISH at 88% (36% to 97%), NMP22 at 82% (44% to 100%) and cytology at 80% (38% to 100%).
Table 23 summarises the sensitivity of the tests in detecting stage/grade of tumour. ImmunoCyt had the highest median sensitivity across studies (81%) for detection of less aggressive/lower risk tumours whereas FISH had the highest median sensitivity across studies (95%) for detection of more aggressive/higher risk tumours. For detection of CIS the median sensitivity across studies for both FISH and ImmunoCyt was 100%. Cytology had the lowest sensitivity across studies for detecting less aggressive/lower risk tumours (27%), more aggressive/higher risk tumours (69%) and also CIS (78%). The median sensitivity across studies for each test was consistently higher for the detection of more aggressive/higher risk tumours than it was for the detection of less aggressive, lower risk tumours.
| Test | Number of studies (patients)a | Less aggressive/lower risk, median (range) sensitivity across studies | Number of studies (patients)a | More aggressive/higher risk including CIS, median (range) sensitivity across studies | Number of studies (patients)a | CIS, median (range) sensitivity across studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FISH | 10 (2164) | 65 (32 to 100) | 10 (2164) | 95 (50 to 100) | 8 (1067) | 100 (50 to 100) |
| ImmunoCyt | 6 (2502) | 81 (55 to 90) | 6 (2502) | 90 (67 to 100) | 6 (2502) | 100 (67 to 100) |
| NMP22 | 18 (4685) | 50 (0 to 86) | 19 (7556) | 83 (0 to 100) | 11 (3453) | 83 (0 to 100) |
| Cytology | 29 (12,566) | 27 (0 to 93) | 29 (12,566) | 69 (0 to 100) | 17 (6870) | 78 (0 to 100) |
Some of the studies included in the pooled estimates for the individual tests also directly compared tests, e.g. FISH versus cytology. Table 24 shows the pooled estimates for sensitivity and specificity for those tests being directly compared in studies and reporting a patient-level analysis. In each set of comparisons cytology had lower sensitivity but higher specificity than the biomarker with which it was being compared. ImmunoCyt had a statistically significant higher sensitivity (82%, 95% CI 76% to 89%) than that of cytology (44%, 95% CI 35% to 54%), whereas cytology had a statistically significant higher specificity (94%, 95% CI 91% to 97%) than that of ImmunoCyt (85%, 95% CI 71% to 85%). Similarly, NMP22 had a statistically significant higher sensitivity (70%, 95% CI 59% to 80%) than that of cytology (40%, 95% CI 31% to 49%), whereas cytology had a statistically significant higher specificity (97%, 95% CI 95% to 99%) than that of NMP22 (81%, 95% CI 74% to 88%).
| Comparison | Number of studies (patients)a | Test | Sensitivity (%) (95% CI) | Specificity (%) (95% CI) | Test | Sensitivity (%) (95% CI) | Specificity (%) (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FISH vs cytology | 5 (1119; 1198) | FISH | 81 (66 to 79) | 82 (68 to 97) | Cytology | 54 (39 to 80) | 92 (84 to 99) |
| ImmunoCyt vs cytology | 6 (1912; 1912) | ImmunoCyt | 82 (76 to 89) | 85 (71 to 85) | Cytology | 44 (35 to 54) | 94 (91 to 97) |
| NMP22 vs cytology | 16 (5563; 5402) | NMP22 | 70 (59 to 80) | 81 (74 to 88) | Cytology | 40 (31 to 49) | 97 (95 to 99) |
In studies reporting the sensitivity and specificity of tests used in combination, sensitivity was generally higher but specificity lower for the combined tests compared with the higher value of the individual tests. Most combinations of tests were reported by only one or two studies, apart from the combination of ImmunoCyt and cytology, which was reported by eight studies.
In studies specifically reporting unevaluable tests, rates were 6.1% (65/1059, five studies) for FISH, 5% (279/5292, 10 studies) for ImmunoCyt and 2% (54/2566, six studies) for cytology. None of the NMP22 studies specifically reported unevaluable tests.
Chapter 6 Assessment of cost-effectiveness
Using the care pathways described in Chapter 2, an economic model was developed to estimate the cost-effectiveness of several management strategies for the initial diagnosis and follow-up of bladder cancer. This chapter describes how the data to estimate cost-effectiveness were derived and how these data were used in the economic model. The perspective adopted for the cost-effectiveness analysis was that of the NHS.
Economic model for initial diagnosis and follow-up of bladder cancer
Model structure
Based on the care pathway described in Chapter 2, the model structure was developed following consultation with clinicians and taking into consideration the approaches adopted by the existing economic evaluations153,158,175–180 identified from the literature. The approach attempts to model patients passing through the whole sequence of care and determine the overall impact on costs and the clinical consequences. Figure 28 shows a simplified model structure for the primary diagnosis and follow-up management of bladder cancer. Within this model people with suspected bladder cancer will receive tests and investigations to diagnose bladder cancer. Subsequent management will depend upon the findings of these tests and the nature of any bladder cancer detected. The absorbing state in the model is death from either bladder cancer or other causes.
FIGURE 28.
Model structure.
The cost-effectiveness analysis was performed in two parts. The first part considered the diagnostic tests and consisted of a decision tree model element and the second part considered the follow-up of patients after diagnosis using a Markov model.
Decision tree model
The decision tree, constructed using TreeAge Software, displays the temporal and logical sequence of a clinical decision problem. Although this decision tree does not explicitly specify the time over which diagnosis takes as part of the model structure, going from initial presentation to final diagnosis may take weeks or even months.
As described in Chapters 1 and 2 there does not appear to be a single standard strategy in the UK. Flexible cystoscopy alone or combined with cytology followed by white light rigid cystoscopy are the main diagnostic tests performed. Cytology or biomarkers followed by WLC or PDD for the initial diagnosis of bladder cancer are less commonly used in the UK, but the use of cytology or biomarkers followed by WLC or PDD may be feasible. The aim of this model is to reflect the costs and consequences of these tests compared with one ‘standard’ strategy, ‘flexible cystoscopy followed by WLC’.
Interventions of diagnosis and follow-up
The interventions included in the model were flexible cystoscopy, cytology, three types of biomarkers (NMP22, FISH, ImmunoCyt), WLC and PDD. Although flexible cystoscopy combined with cytology and a biomarker as the first suite of tests may be an option for the primary diagnosis of bladder cancer, there is little information about the results of these tests used in combination, as reported in Chapters 4 and 5. Table 25 summarises the potential strategies that are considered in the model. These options were based on advice from clinical experts about strategies that are currently in use or those that can potentially be used.
| Strategy | Primary diagnosis | Follow-up surveillance | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial test | Second test | Initial test | Second test | |||||||
| CSC | CTL | BM | WLC | PDD | CSC | CTL | BM | WLC | PDD | |
| 1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| 2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| 3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| 5 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| 6 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| 7 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 8 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 9 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 10 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 11 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 12 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 13 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 14 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 15 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 16 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
Strategies 1–6 consider the use of a single test for initial diagnosis. These options might represent situations that clinical practice might move towards although they may not be currently used in practice. Strategies 7–16 represent alternative situations in which two or more tests are used in the initial phase of diagnosis. Across all strategies the choice of second level diagnostic test varies between WLC and PDD. The strategies also differ in terms of the tests used for follow-up surveillance. In our study we have assumed that a single test is used for initial surveillance with any positives confirmed by WLC.
It should be noted that none of our strategies explicitly considers the use of ultrasound. Ultrasound might be considered part of all of the strategies when the patient population is restricted to haematuria. In such a situation this would have no impact on incremental costs (as all patients under all strategies incur the test) although it may alter the likelihood of subsequent testing.
Figure 29 illustrates a simplified model structure for the decision tree model for diagnosis of bladder cancer when a single test is used as part of the initial diagnosis (i.e. strategies 1–6). Figure 30 illustrates the model structure for the situation in which two tests are used as part of the initial testing (strategies 7–14). When three tests are used in combination (strategies 15 and 16) a similar model structure to that in Figure 30 is developed (figure not shown).
FIGURE 29.
Decision tree model structure for single diagnostic technology as the first test. BM, biomarker; CSC, flexible cystoscopy; CTL, cytology.
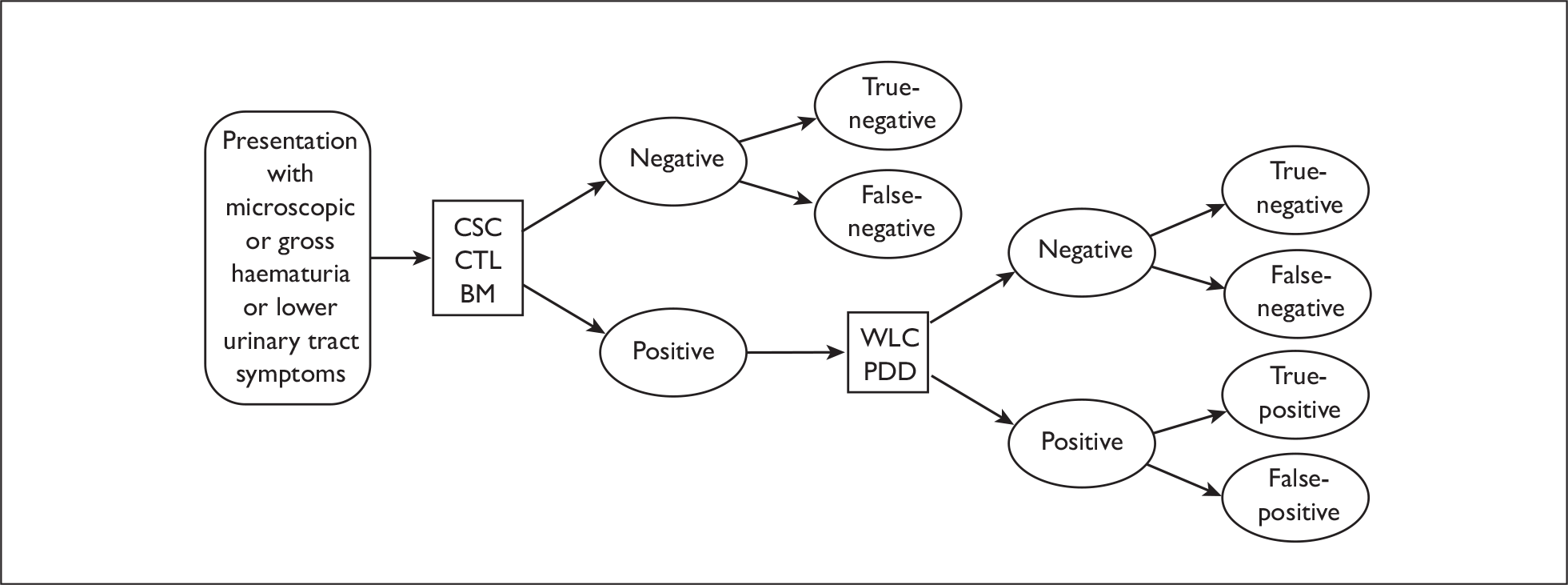
FIGURE 30.
Decision tree model structure for flexible cystoscopy combined with cytology or biomarker as the first test. BM, biomarker; CSC, flexible cystoscopy; CTL, cytology.
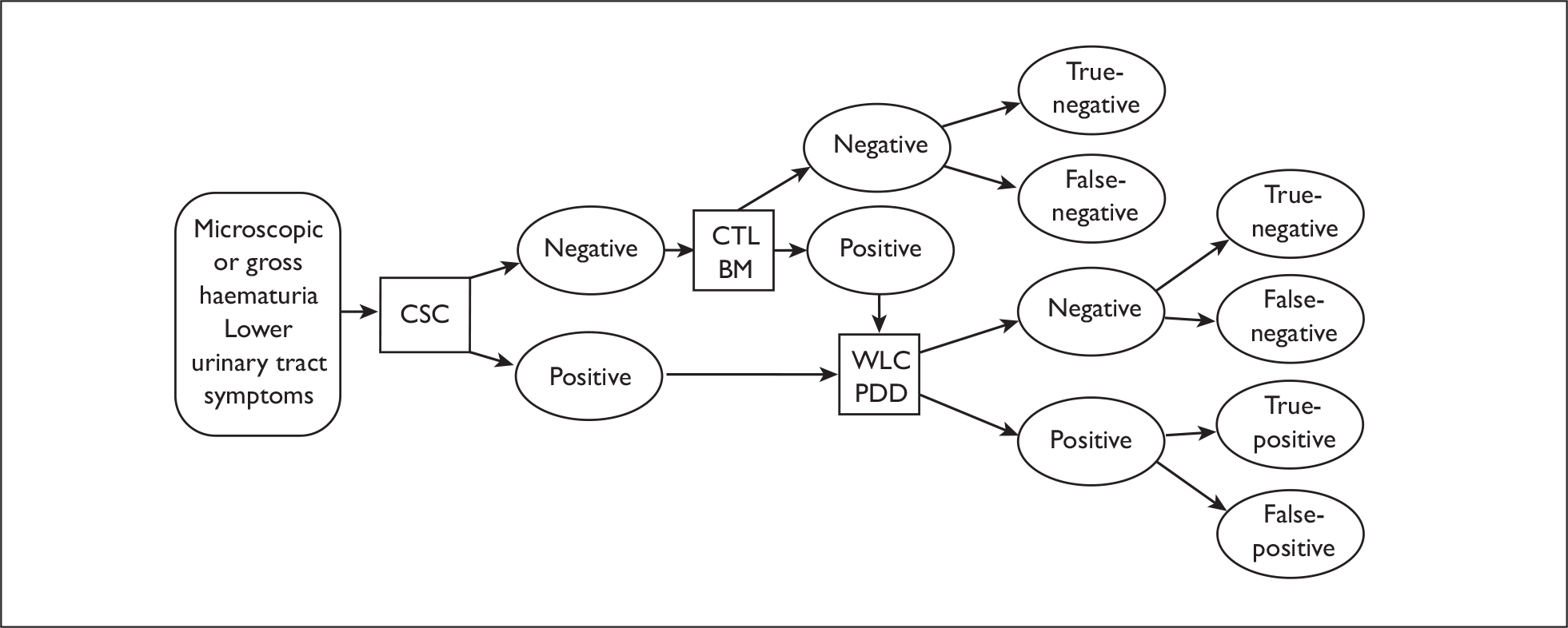
In Figure 29 a patient may, for example, arrive in a hospital with symptoms of haematuria. Taking the patient’s history and symptoms into account, the physician may perform an invasive test (flexible cystoscopy) or a non-invasive test (e.g. cytology and biomarkers). The results of these tests could be either negative or positive. The negative test result could be either a false or a true negative. If the first single test in Figure 29 is negative, it is assumed that there appears to be no evidence of bladder cancer and the patient is deemed not to have bladder cancer. If the result of the first test is positive (which might be either a true or a false positive) the patient will be further investigated using the second test, which will be either PDD or WLC. As with the first test there are four potential test results: true negative, false negative, true positive and false positive. As there is a risk of death associated with the use of general anaesthesia required for rigid cystoscopy, there is a chance that the patient may die whilst undergoing or as a result of undergoing the second test.
For the strategies in which two tests form part of the initial diagnosis (strategies 7–14) the first test that a patient receives will be flexible cystoscopy (Figure 30). If the result is negative (it might be either a true or a false negative) it is assumed that the patient will be further tested using cytology or a biomarker. If the result of cytology or a biomarker is negative the patient will be deemed not to have bladder cancer. If the result of the first test is positive (which might be either a true or a false positive) the patient will be further investigated using the second test, which will be either PDD or WLC. Patients who test positive with cytology or a biomarker will be handled in a similar manner. As with the first test there are four potential test results: true negative, false negative, true positive and false positive. As there is a risk of death associated with the use of general anaesthesia required for rigid cystoscopy, there is a chance that the patient may die whilst undergoing or as a result of undergoing the second test.
Strictly speaking, Figure 30 describes the situation in which only those negative on flexible cystoscopy (CSC) receive either cytology (CTL) or a biomarker (BM) test. In practice, because of the way that services might be organised, the different tests may be performed during the same visit, i.e. those who are positive with flexible cystoscopy may also receive either cytology or a biomarker test. The implications of this are that, given the cost data available for this study, the average cost per patient in actual practice would be increased compared with the practice described in Figure 29 (there will be no impact on effectiveness as all positives go through to the next level of testing). It should be noted that the practice of conducting additional tests at the same time as flexible cystoscopy is likely to be adopted because it is logistically easier to organise, i.e. the real opportunity costs of current practice are less than would be predicted from the unit costs available for this study. For this reason we have assumed that a more realistic estimate of costs will be provided by a model following the structure set out in Figure 30 but we have provided an additional analysis to illustrate the effect on costs when two or more tests are conducted on all patients presenting for initial diagnosis.
Estimation of probabilities required for the decision tree model
The probabilities used to populate the decision model were calculated according to the standard conventions of Bayes’ theorem. The essence of the calculations is that, once the sensitivity and specificity of a test are known, along with the a priori probability of disease, the posterior probabilities of disease and absence of disease can be determined. Accordingly, if a patient has an abnormal test result, the probability of disease – the ‘true positive rate’, also referred to as the ‘positive predictive value’ (PPV) – is represented as p(BC+|T+), and if the patient has a normal test result, the probability of disease – the ‘false-negative rate’ – is similarly presented as p(BC+|T–). These are calculated as follows:
where BC = bladder cancer, T+ = test positive, T– = test negative, p(T+|BC+) = sensitivity, p(BC+) = prior probability of disease (prevalence or incidence), p(T+|BC–) = 1 – specificity, p(BC–) = 1 – prevalence (or incidence), p(T–|BC+) = 1 – sensitivity and p(T–|BC–) = specificity.
When two tests are connected in series, the calculations are the same except that the prior probability of disease (prevalence or incidence) for the second test is the calculated ‘true positive rate’ of the first test.
To illustrate this in the construction and analysis of the bladder cancer primary diagnosis tree (Appendix 17, Figure 37), the strategy ‘flexible cystoscopy (CSC) followed by WLC’ is considered. The probability of a test positive result following flexible cystoscopy is:
where Sens_CSC = sensitivity of flexible cystoscopy, Spec_CSC = specificity of flexible cystoscopy and priori is the prevalence or incidence rate for patients with suspected bladder cancer before the flexible cystoscopy test.
From this, the probability of a:
-
negative result for flexible cystoscopy is 1 – pPos_CSC
-
false negative for flexible cystoscopy is pFN_CSC = (1 – Sens_CSC)*priori/((1 – Sens_CSC)* priori + Spec_CSC*(1 – priori))
-
true negative is 1 – pFN_CSC
-
positive result for WLC following a positive flexible cystoscopy result is pPos_CSC_WLC = (Sens_WLC*pPPV_CSC) + (1 – Spec_WLC)*(1 – pPPV_CSC), where Sens_WLC = sensitivity of WLC, Spec_WLC = specificity of WLC and pPPV_CSC = positive predictive value of flexible cystoscopy = (Sens_CSC*priori)/pPos_CSC
-
true positive for WLC following a positive flexible cystoscopy result is pTP_CSC_WLC = (Sens_WLC*pPPV_CSC)/pPos_CSC_WLC
-
false positive for WLC following flexible cystoscopy is 1 – pTP_CSC_WLC
-
false negative for WLC following flexible cystoscopy is pFN_CSC_WLC = [Spec_WLC*(1 – pPPV_CSC)]/(1 – pPos_CSC_WLC)
-
true negative is 1 – pFN_CSC_WLC
-
the NPV after a negative result for CSC is pNPV_CSC = [Spec_CSC*(1 – priori)]/(1 – pPos_CSC).
The probabilities for the remaining strategies in the tree are calculated in a similar manner.
It is important to quantify the false-positive and false-negative values for each strategy, as these provide valuable information to the clinician in addition to the cost and number of true cases detected. The implications of false-positive results within the model are the cost of testing and treating patients and the associated morbidity and discomfort of further investigation and treatment. False-positive results may also induce adverse psychological responses in patients in terms of the needless distress that a positive result might cause and by leading to questioning of future results that are negative. In the case of false-negative results the patient may have a serious or life-threatening condition that is missed, resulting in a potentially poorer prognosis following late detection, such as CIS missed by WLC, as well as psychological distress from false reassurance. In the decision model patients with a false-negative evaluation following the first (flexible cystoscopy, cytology or biomarkers) or second (PDD/WLC) test may be subsequently correctly diagnosed as their continuing symptoms worsen. In the case of true negative results, it is assumed that the patients will not need further investigation.
Management of bladder cancer
Patients with true-positive results (confirmed bladder cancer) are classified into two types: non-muscle-invasive and muscle-invasive disease (Figure 31). Those with muscle-invasive tumours will not be discharged but are managed usually with either surgery (radical cystectomy) or radical radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy and routine checking thereafter and treatment. All patients with non-muscle-invasive tumours will undergo a follow-up test at 3 months after the primary diagnosis because of the high chance of recurrence and a chance of progression. For each risk group there are similar outcomes considered in initial diagnosis: true positive, false positive, true negative and false negative (Appendix 17, Figure 37).
FIGURE 31.
Classification of bladder cancer.
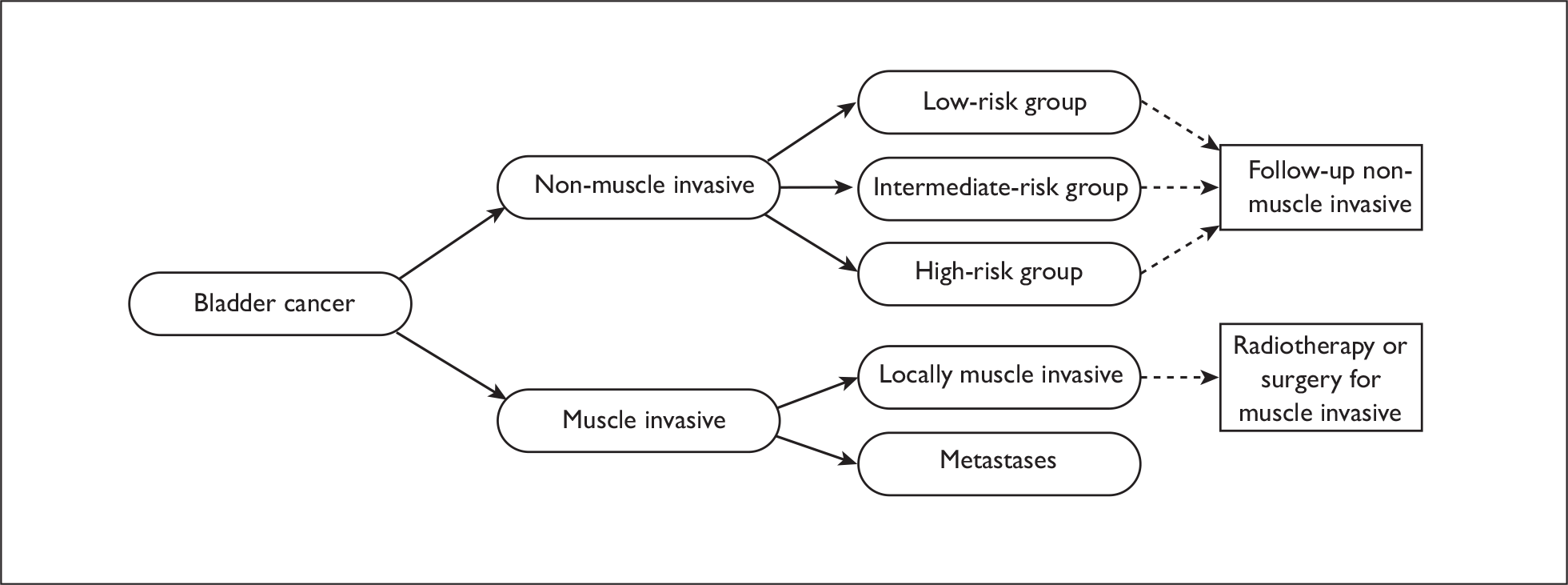
It is assumed that the first test used in the follow-up of patients will be the same as the test used for primary diagnosis and the second test will be WLC. To illustrate the construction and analysis of each risk group, strategy ‘flexible cystoscopy (CSC) followed by WLC in primary diagnosis and follow-up by CSC’ is considered. In the case of each group, the probability of:
-
true positive is pTP_Riskgroup = Sens_CSC* Recurrence rate of risk group at 3 months
-
true negative is pTN_Riskgroup = Spec_CSC*(1 – Recurrence rate of risk group at 3 months)
-
false negative is pTP_Riskgroup = (1 – Sens_CSC)* Recurrence rate of risk group at 3 months
-
false positive is pFN_Riskgroup = (1 – Spec_CSC)*(1 – Recurrence rate of risk group at 3 months).
As described in the care pathway reported in Chapter 2, bladder cancer treatment options will depend on classification of disease (Table 26).
| Type of bladder cancer | Initial treatment | |
|---|---|---|
| Non-muscle invasive | Low risk | TURBT and one dose of mitomycin |
| Intermediate risk | TURBT and one dose of mitomycin | |
| High risk | TURBT, one dose of mitomycin and BCG induction | |
| Muscle invasive | Three cycles of chemotherapy and cystectomy or three cycles of chemotherapy and radiotherapy or palliative treatment | |
To determine the efficiency of each strategy the terminal nodes (Appendix 17, Figure 37) of the tree were assigned a value of either ‘1’ or ‘0’. This enabled the following solutions to be calculated: mean cost per case detected – achieved by assigning the value ‘0’ to dead terminal node and the value ‘1’ to the others.
Markov model
At the end of each branch of the decision tree the patients will enter one of the predefined states of the Markov model (Appendix 17, Figures 36 and 38). The health states within the Markov model are considered to reflect possible paths of recurrence and progression of bladder cancer based on information of the primary diagnosis and following the follow-up visit carried out 3 months after initial treatment of the bladder cancer.
As indicated in the care pathways described in Chapter 2, there are two elements in the Markov models: non-muscle invasive (TaT1) and muscle invasive (T2 or > T2). In the case of muscle-invasive disease, patients have a serious and life-threatening condition and high mortality and morbidity rates; they are thus not discharged from care but receive regular checks with CT or MRI and they receive either radiotherapy or chemotherapy treatment. Alternatively, the patient may receive palliative care after the initial major treatment if there is recurrence or progression of the tumour (Table 26).
Although a non-muscle-invasive tumour is not as likely to result in a serious life-threatening condition, it has high recurrence rates. As discussed in Chapter 1, the recurrence rate of non-muscle-invasive disease depends upon a number of prognostic risk factors: stage, grade, size of the tumour and number of previous recurrences. Prognostic risk factors are essential to predict future courses of the tumour in terms of recurrence and progression. Prognostic factors for recurrence and progression have been investigated by several clinical groups. The most frequent factor related to recurrence, in almost all series, has been multiplicity (Appendix 18, Table 55). Intravesical instillations have been defined as a protective factor. Kurth and colleagues181 reported factors affecting recurrence and progression from the data of two trials involving 576 patients. The trials considered factors such as tumour size, grade, and recurrence rate per year and concluded that the most significant prognostic factors for recurrence were multiplicity, recurrence at 3 months, size of the tumour and site of involvement (Appendix 18, Table 55). 20,181–195 Parmar and colleagues191 considered multiplicity and recurrence at 3 months as the main prognostic factors in recurrence. These two parameters provided the most predictive information related to recurrence, and they were independent of the stage (Table 27). However, the Medical Research Council classification in Parmar’s study is only used to predict the risk of recurrence, not progression. 191
| Study | Risk factors | Proportion (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Millán-Rodriguez 2000187 | Low risk | TaG1, single T1G1 | 11.5 |
| Intermediate risk | TaG2, multi T1G1 | 44.6 | |
| High risk | Multi T1G2 | 43.9 | |
| TaG3, T1G3 | |||
| CIS | |||
| Oosterlinck 2001190 | Low risk | Single TaG1 and < 3 cm diameter | NA |
| Intermediate risk | TaT1 excluding low and high risks | NA | |
| High risk | T1G3, CIS, multifocal or highly recurrent | NA | |
| Parmar 1989191 | Low risk | Single tumour and no recurrence at first follow-up | 60 |
| Intermediate risk | Single tumour and no recurrence at first follow-up or multiple tumour no recurrence at first follow-up | 30 | |
| High risk | Multiple or highly recurrent | 10 | |
| Kurth 1995181 | Low risk | G1 and no recurrence in 2 years | 52.5 |
| G1, size (< 1.5 cm) and recurrence (< 3 cm) in 2 years | |||
| G2, small size (< 1.5 cm) and no recurrence in 2 years | |||
| Intermediate risk | The others excluding low and high risks | 40.7 | |
| High risk | G1, great size (> 3 cm) and > 3 recurrences in 2 years | 6.7 | |
| G2, great size (> 3 cm) and recurrence in 2 years | |||
| G3 |
Grade, associated CIS and stage are factors globally related to progression in the series that have investigated prognostic factors (Appendix 18, Table 56). 20,181,183–185,187,192,196 Millán-Rodriguez and colleagues187 developed three risk groups based on 1529 patients with primary non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. The trial used recurrence prognostic factors such as multiplicity, tumour size and CIS and progression prognostic factors such as grade, CIS and multiplicity.
Although different studies have analysed the factors involved in recurrence and progression, there is no universally agreed prognostic risk group classification (Table 27). It is not possible to use the risk stratification illustrated in Kurth’s study181 in the model because of the complexity of data requirements for recurrence and progression. The risk groups and their proportions will be defined later in this chapter depending on the two studies that have the best data available for recurrence and progression.
Markov model structure for non-muscle-invasive disease
At the end of each risk group branch of non-muscle-invasive disease in the decision tree (Appendix 17, Figure 36) the patient will enter one of the following states of the Markov model shown in Figure 32: (1) no tumour recurrence; (2) recurrence; (3) progression to muscle-invasive disease; and (4) death. There are two diagnostic results of non-tumour recurrence, i.e. true negative and false negative, as well as true positive and false positive for tumour recurrence.
FIGURE 32.
Markov model structure for non-muscle-invasive tumour.
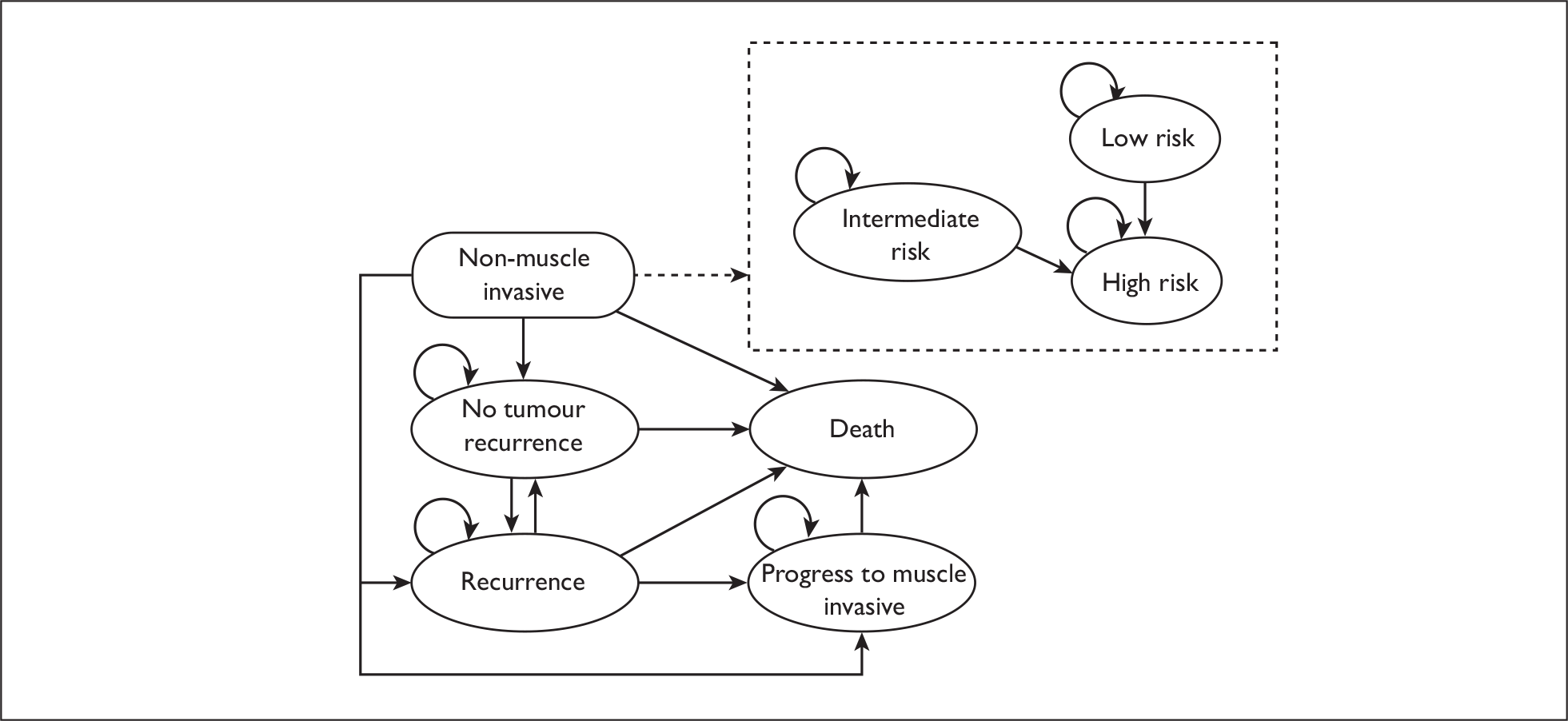
The patients with a false-negative result in the model will be followed using the follow-up strategy of non-tumour recurrence. The cycle length considered is 1 year, although the risk groups in the care pathway will be followed at different time periods: 12 months for low risk, 6 months for intermediate risk and 3 months for high risk. The absorbing state is ‘death’, which can be reached from any of the other states.
Markov model for local muscle-invasive disease
At the end of each risk group branch of local muscle-invasive disease in the decision tree (Appendix 17, Figure 38) the patient will enter one of the following states of the Markov model shown in Figure 33: (1) no tumour; (2) recurrence; (3) progression to metastases; and (4) death. Cycle length will be the same as that of non-muscle-invasive disease.
FIGURE 33.
Markov model for local muscle-invasive follow-up.
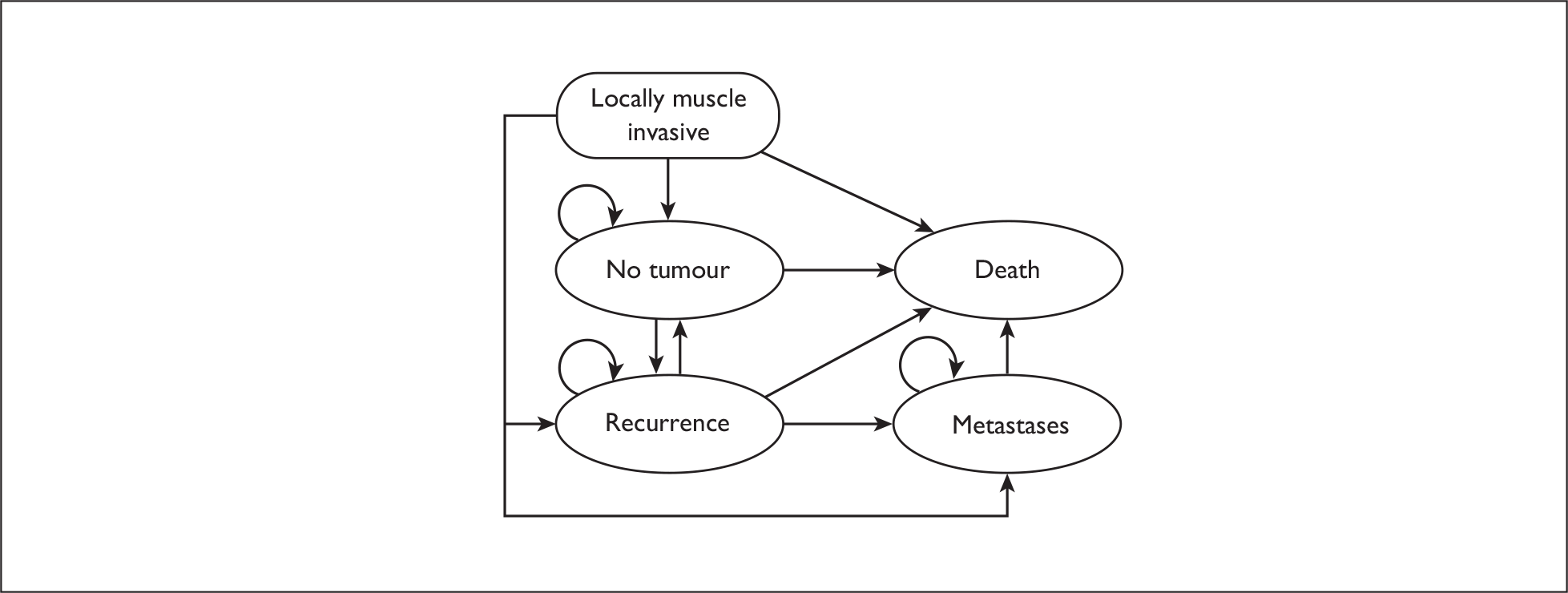
Estimation of parameters used in the model
Parameters used in the decision tree and Markov models were calculated within the model or estimated from the systematic reviews of diagnostic performance reported in Chapters 4 and 5 and the epidemiology of bladder cancer reported in Chapter 1, as well as other relevant cost-effectiveness data identified from the literature. The details of the data for the probabilities, costs and utilities used in the models are described below.
Probabilities
Sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic test
The data on the sensitivity and specificity of each diagnostic test were taken from the systematic review and are summarised in Table 28. For flexible cystoscopy assessment there were no data available from the systematic review. It is therefore assumed that the accuracy of flexible cystoscopy used in the models is the same as that of white light rigid cystoscopy. This assumption is relaxed in the sensitivity analysis in which the performance of flexible cystoscopy is increased by 5%, 10% and an extreme 20% compared with white light rigid cystoscopy.
| Diagnosis | Sensitivity | 95% CI | Specificity | 95% CI | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSC | 0.71 | 0.49 to 0.93 | 0.72 | 0.47 to 0.96 | Systematic review based on WLC |
| CTL | 0.44 | 0.38 to 0.51 | 0.96 | 0.94 to 0.98 | Systematic review |
| NMP22 | 0.68 | 0.62 to 0.74 | 0.79 | 0.74 to 0.84 | Systematic review |
| ImmunoCyt | 0.84 | 0.79 to 0.91 | 0.75 | 0.68 to 0.83 | Systematic review |
| FISH | 0.76 | 0.65 to 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.78 to 0.92 | Systematic review |
| PDD | 0.92 | 0.8 to 1.0 | 0.57 | 0.36 to 0.79 | Systematic review |
| WLC | 0.71 | 0.49 to 0.93 | 0.72 | 0.47 to 0.96 | Systematic review |
Prevalence rate
The prevalence rate was not derived from existing data in the literature as the prevalence of bladder cancer varies considerably among subgroups with different symptoms, from 1% to 20% (for men over 50 years of age). 179 In the model base-case analysis it was assumed that the prevalence rate is 5% and in a sensitivity analysis a range of prevalence rates was considered to identify those prevalence rates for which different diagnostic strategies may be considered worthwhile. This approach of repeating the analysis for different prevalence rates was felt to be more informative than defining prevalence using a wide uniform (i.e. uninformative) distribution.
Proportions of types and their subgroups for bladder cancer
The proportions of the two main types of bladder cancer were assessed based on the literature and clinical opinions detailed in Chapter 1. With reference to the available information presented in the previous section and in Table 27, as well as discussions with the clinical members of the research team, prognostic risk groups in non-muscle-invasive disease within this model have been categorised by using a combination of Millán-Rodriguez and colleagues’187 classification at initial diagnosis and Parmar and colleagues’191 classifications at 3 months’ follow-up, i.e. low risk, intermediate risk and high risk. These classifications are shown in Table 29, which also provides details on the proportions of patients in each risk group of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
| Risk groups | Subgroups (cancer at diagnosis) | Factors defined in follow-up at 3 months | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low: TaG1, single T1G1 | Group 1: single TaG1, single T1G1 | No tumour recurrence | 10 |
| Group 2a: single TaG1, single T1G1 | Tumour recurrencea | ||
| Group 2b: multi TaG1 | No tumour recurrence | ||
| Group 3: multi TaG1 | Tumour recurrencea | ||
| Intermediate: TaG2, multi T1G1, single T1G2 | Group 1: single TaG2, single T1G2 | No tumour recurrence | 45 |
| Group 2a: single TaG2, single T1G2 | Tumour recurrencea | ||
| Group 2b: multi TaG2, multi T1G1 | No tumour recurrence | ||
| Group 3: multi TaG2, multi T1G1 | Tumour recurrencea | ||
| High: TaG3, T1G3, CIS, multi T1G2 | Tumour recurrence or not | 45 |
Table 30 summarises the values of these proportions used in the decision tree and Markov models.
| Type of bladder cancer | Proportion | Subgroups of bladder cancer considered | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-muscle invasive | 75% | Low risk | 10% |
| Intermediate risk | 45% | ||
| High risk | 45% | ||
| Muscle invasive | 25% | Local muscle invasive | 75% |
| Metastases | 25% |
Recurrence, progression and mortality of non-muscle-invasive disease
Table 31 shows the probabilities of recurrence, progression and mortality for the three risk groups of non-muscle-invasive disease used in the model for a 20-year time horizon. As referred to above, the first 5-year probabilities of recurrence, progression and mortality caused by cancer of the three risk groups used in the model were calculated from the study by Millán-Rodriguez and colleagues. 187 The following 15-year probabilities of recurrence, progression and mortality caused by cancer in these groups were estimated by using mean values of relevant data of the last 3 years in the 5-year data available in the study by Millán-Rodriguez and colleagues. 187 This was a retrospective cohort study of 1529 patients with primary non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer in Spain in the years 1968–96. Of the patients treated with TURBT and random biopsy, half were treated using additional BCG and one-third using additional intravesical instillation (mainly mitomycin C, thiotepa and doxorubicin). However, the characteristics of the patients, such as gender and mean age, were not reported, and the follow-up was less than 5 years. 187
| Time (years) | Recurrence (%) | Progression (%) | Mortality caused by cancer (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Intermediate | High | Low | Intermediate | High | Low | Intermediate | High | |
| 3 months | 2 | 4 | 9.4 | 0 | 0.2 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 15 | 26 | 39 | 0 | 0.4 | 8 | 0 | 0.4 | 1 |
| 2 | 10 | 13 | 11 | 0 | 0.8 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| 3 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.6 | 3 | 0 | 0.3 | 1 |
| 4 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0.8 | 1 | 0 | 0.3 | 2 |
| 5 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 6 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 7 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 8 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 9 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 10 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 11 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 12 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 13 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 14 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 15 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 16 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 17 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 18 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 19 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 20 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 0.2 | 2 |
Recurrence, progression and mortality of muscle-invasive disease
When patients move into the Markov model for muscle-invasive disease, the model requires estimates of the annual rates of recurrence, progression and mortality caused by cancer. The probabilities of recurrence, progression and mortality of muscle-invasive disease and metastases used in the model for 20 years are presented in Table 32. The first 5-year probabilities of recurrence, progression and mortality caused by local muscle-invasive disease used in the model were obtained from a retrospective cohort study in Canada by Stein and colleagues197 in which a cohort of 1054 patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer were treated by radical cystectomy between 1971 and 1997. The mean age of the patients was 66 years, 80% of the patients were male197 and data were available for 10 years of follow-up. The last 10-year probabilities used in the model are assumed to be the same as the data reported for between 5 and 10 years in the study by Stein and colleagues. The last column of Table 32 presents the probabilities of mortality for metastases provided by von der Maase and colleagues198 and there are data available for 5 years of follow-up. The last 5-year probabilities used in the model are assumed to be the same as rates reported for between 3 and 5 years in von der Maase and colleagues. 198 This RCT investigated the long-term survival of patients with metastatic bladder cancer treated with chemotherapy in Denmark. Of the 405 patients, 137 had locally advanced disease and 268 had metastatic disease. The median survival time was 8.3 months.
| Time (years) | Local muscle-invasive disease after cystectomy | Metastases | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recurrence (%) | Progression (%) | Mortality (%) | Mortality (%) | |
| 3 months | 0 | 6.25 | 3 | 10.5 |
| 1 | 0 | 25 | 12 | 42 |
| 2 | 0 | 13 | 11 | 80 |
| 3 | 0 | 8 | 9 | 50 |
| 4 | 0 | 4 | 8 | 50 |
| 5 | 0 | 4 | 8 | 50 |
| 6 | 0 | 4 | 7 | 50 |
| 7 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 50 |
| 8 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 50 |
| 9 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 50 |
| 10 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 50 |
| 11 | 0 | 4 | 5 | |
| 12 | 0 | 4 | 5 | |
| 13 | 0 | 4 | 5 | |
| 14 | 0 | 4 | 5 | |
| 15 | 0 | 4 | 5 | |
| 16 | 0 | 4 | 5 | |
| 17 | 0 | 4 | 5 | |
| 18 | 0 | 4 | 5 | |
| 19 | 0 | 4 | 5 | |
| 20 | 0 | 4 | 5 | |
All-cause mwortality rates in the UK
As patients progress through the model over time, values of annual rates of age-specific general or all-cause mortality are required. These were taken from the published UK life tables for the years 2004–6. 199 As discussed in Chapter 1, Cancer Research UK reported that 70% of all primary bladder cancer affects men and therefore the all-cause mortality for the model cohort was weighted to reflect this (Figure 34). Further data related to the rate of all-cause mortality are shown in Table 57 in Appendix 18.
FIGURE 34.
Kaplan–Meier plot for sex- and age-adjusted survival (30% female, 70% male) in the UK.
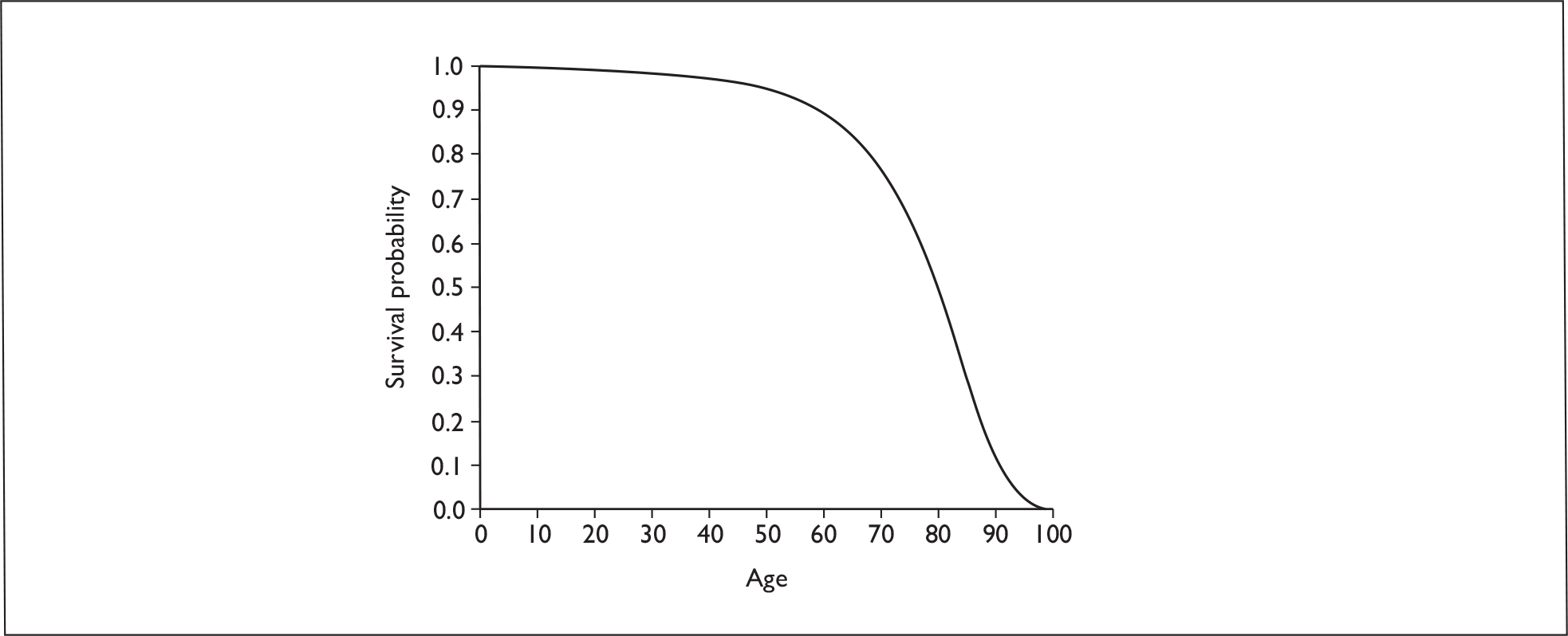
Other probabilities
White light rigid cystoscopy (WLC), PDD and TURBT are invasive procedures. As with all surgical procedures requiring general anaesthetic, death due to complications in the perioperative period is a potential risk. There are no available data on mortality rates associated with WLC or PDD. The probability of death during WLC and PDD in Table 33 was therefore obtained from a study by Farrow and collegues,200 which examined 108,878 anaesthetic cases in Cardiff between 1972 and 1977. The probability of death during TURBT in Table 33 was obtained from Kondas and colleagues,201 which evaluated 1250 TURBT cases in Cardiff during 18 years.
| Other probabilities | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Mortality rate of WLC/PDD | 0.5% | Farrow 1982200 |
| Mortality rate of TURBT | 0.8% | Kondas 1992201 |
| False negatives: probability detected in first 3 months | 50% | Assumption |
| Relative risk for progression (no treatment vs treatment) | 2.56 | Millán-Rodriguez 2000187 |
| Relative risk for recurrence (PDD vs WLC) | 1 | Assumption |
| Relative risk for progression (PDD vs WLC) | 1 | Assumption |
| False negatives: probability detected in first year | 50% | Assumption |
| False negatives: probability detected in second year | 75% | Assumption |
| False negatives: probability detected after second year | 100% | Assumption |
As some patients who have bladder cancer show negative results during the initial diagnosis or follow-up, it was believed that the risk of progression in the case of a false negative without relevant treatment was higher than that of a true positive with treatment. However, there are no data available in relation to false-negative diagnoses. Although there are some studies investigating disease-free survival or survival for different types of drug treatment as an adjunct to initial treatment (TURBT) for bladder cancer, there is no identified study that compares survival with and without TURBT. Using information from the Millán-Rodriguez and colleagues’ study187 it was assumed that the base-case RR for progression comparing no treatment (TURBT) with treatment (TURBT) was 2.56, that is the RR compared TURBT plus BCG with TURBT alone. The uncertainty around this value was tested as part of the sensitivity analysis.
One of the issues that could be considered in the model is whether the recurrence and progression rates of non-muscle-invasive disease differ based on the type of intervention used in the treatment (PDD or WLC). Although there is some evidence in Chapter 4 that PDD may reduce recurrence and progression for non-muscle-invasive disease compared with WLC, there are no reliable data related to recurrence and progression of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer following PDD or WLC in primary diagnosis. It was therefore assumed that recurrence and progression rates are not different between PDD and WLC so that the base-case RR for recurrence and progression comparing PDD and WLC is 1. This assumption was tested as part of the sensitivity analysis.
There is no evidence to suggest when patients who have false-negative results should be detected. Therefore assumptions were made about when such patients were identified. The probabilities of detecting false-negative cases are described in Table 33.
Costs
Table 34 shows the cost estimates for the tests and investigations used within the model. The costs of flexible cystoscopy, WLC or WLC-assisted TURBT were identified from 2006 NHS reference costs. 202 The cost of flexible cystoscopy was based on the NHS reference cost with Healthcare Resource Group (HRG) (day case) code L21 ‘Bladder cancer endoscopic procedure without complications (cc)’. The cost of WLC was based on the NHS reference cost with HRG (elective inpatient) code LB15C ‘Bladder minor procedure 19 years and over without cc’. The day unit cost of WLC-assisted TURBT was based on the NHS reference cost with HRG (elective inpatient) code L21 ‘Bladder intermediate endoscopic procedure without cc’. Based on the 2006 report by Karl Storz Endoscopy (UK), the cost of WLC-assisted TURBT is calculated by multiplying the cost per day by 2 days. [Karl Storz Endoscopy (UK), 2006, personal communication]. Also reported in Table 34 are the costs of PDD. Compared with WLC, PDD incurs the following additional costs:
-
extra equipment: photosensitiser (HAL, ALA), colour CCD camera (on chip integration), xenon lamp, fluid light cable
-
extra personnel involved: unlike WLC, PDD requires the instillation of a photosensitiser via a urethral catheter prior to TURBT; this is usually performed by a nurse on the ward
-
procedure time: on the ward, catheterisation and instillation of photosensitiser and then removal of catheter takes about 15 minutes; in theatres, fluorescence-guided TURBT takes an extra 10 minutes compared with conventional white light TURBT alone.
| Parameter | Base case (£) | Range | Unit | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDD | 1371 | 1136 to 1758 | Procedure | Health Care Financial |
| WLC | 937 | 702 to 1324 | Procedure | NHS reference costs202 |
| CSC | 441 | 362 to 680 | Session | NHS reference costs202 |
| Cytology | 92.37 | Uniform distribution | Session | NHS reference costs202 |
| NMP22 | 39.30 | 25 to 54.8 | Test | MediChecks.com |
| ImmunoCyt | 54.8 | Uniform distribution | Session | NHS reference costs202 |
| FISH | 54.8 | 40 to 60 | Test | NHS reference costs202 |
| PDD-assisted TURBT | 2436 | 2006 to 2994 | Procedure | Health Care Financial |
| WLC-assisted TURBT | 2002 | 1572 to 2560 | Procedure | NHS reference costs202 |
| CT scan | 325 | Uniform distribution | Procedure | Rodgers 2006179 |
The additional cost of extra equipment, personnel and time of PDD were obtained from a business report prepared by Karl Storz (UK) [Karl Storz Endoscopy (UK), 2006, personal communication] (Table 35). It was assumed that the lifespan of PDD equipment is 5 years, a 3.5% discount rate is used in equivalent annual cost and the average number of PDD tests per year is 100.
| Additional capital resource | Cost |
|---|---|
| Total cost of the extra equipment for PDD | £17,950 |
| Lifespan of the equipment (years) | 5 |
| Average number of PDD tests per year | 100 |
| 3.5% discount rate for 5 years | 0.2215 |
| Equivalent annual cost | £3976 |
| Additional cost per test | £40 |
| Cost of hexyl-5-aminolaevulinic acid per test | £286 |
| Annual service and maintenance costs (after year 1) | £1795 |
| Cost of service and maintenance per patient | £18 |
| Total average cost per test | £344 |
The costs associated with the additional resources are shown in Table 36 and these costs were added to the costs of WLC to obtain the costs of PDD and PDD-assisted TURBT.
| Additional procedure | Additional cost |
|---|---|
| Extra nurse time for catheterising patients and instillation of 5-ALA | £40 |
| Extra staffing cost (operation) | £35 |
| Additional equipment of PDD | £344 |
| Consumables (catheter, etc.) | £15 |
| Total | £434 |
The states related to ‘true negative’ and ‘false negative’ only incur diagnostic costs. However, the states for ‘true positive’ and ‘false positive’ incur both diagnostic and relevant treatment costs. For example, for strategy CSC_WLC, the costs of ‘true positive of low risk’ and ‘false positive of low risk’ are equal to cost_CSC. The costs of ‘true negative of low risk’ and ‘false negative of low risk’ are equal to cost_CSC + cost_TURBT. For muscle-invasive disease relevant diagnostic and treatment costs were also considered.
The cost of NMP22 was based on the marketing price in the UK. 203 As the costs of ImmunoCyt and FISH are not available in the UK market, these costs were calculated from a systematic review conducted for NICE179 as well as from 2005 NHS reference costs202 with HRG code L13 ‘Minor pathology test’. The cost of cytology was estimated using HRG code L14 ‘Intermediate pathology test’179 and the cost of a CT scan was estimated by using data from the same source. 179
Table 37 reports the costs of treatments for bladder cancer. The cost of cystectomy was based on 2006 NHS reference costs with HRG code LB389B ‘Cystectomy with urinary diversion and reconstruction without cc’. The unit day cost of palliative treatment was also obtained from NHS reference costs with HRG code SD01A ‘Inpatient specialist palliative care 19 years and over’. Following consultation with clinical experts, an assumption was made that the palliative treatment requires a range of 3–6 months. The cost of palliative treatment was estimated by multiplying the unit cost per day by 135 days. This figure is uncertain as it would of course depend upon the type of care necessary. However, the proportion of patients likely to need this care is relatively small and the likely differences between strategies will also be small.
| Parameter | Base case (£) | Range | Quantity | Unit | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitomycin | 73.88 | Uniform distribution | 40 mg | Cycle | British National Formulary |
| BCG | 89 | Uniform distribution | 12.5 mg | Cycle | British National Formulary |
| Cystectomy (w/o cc) | 6856 | 3656 to 8437 | Procedure | NHS reference costs202 | |
| Chemotherapy (cisplatin) | 50.22 | 25.37 to 100 | Cycle | British National Formulary | |
| Radical radiotherapy | 1050 | 900 to 1200 | 35 (30–40) | £30/day | Aberdeen Royal Infirmary |
| Palliative treatment (outpatient) | 12,825 | 8550 to 17,100 | £95/day | NHS reference costs202 | |
| Discount | 3.5% | 0% to 6% | NICE guideline204 |
The unit cost of radical radiotherapy was obtained from Aberdeen Royal Infirmary (Dr Ghulam Nabi, University of Aberdeen, May 2008, personal communication). Radical radiotherapy requires from 30 to 40 sessions. The cost of radiotherapy was calculated by multiplying the unit cost by 35 sessions. The costs of the three drug treatments – mitomycin, BCG and cisplatin – were derived from the British National Formulary (http://bnf.org).
Discount rate
Discount rates used for costs and outcomes were those recommended in the recent NICE guideline204 on the conduct of technology assessment reviews. Annual discount rates of 3.5% with a range from 0% to 6% were used in the model.
Estimation of total cost of strategies
The total cost for each strategy was determined using recursive costing in the decision tree and the Markov model. At the end point in the decision tree model this is achieved by setting the cost variable as 0 at the root node. As the tree expands from left to right, the ‘cost’ variable is modified by adding new cost variables to the variable ‘cost’. In this way, the value of ‘cost’ at each terminal node is unique to the path from the root node to that terminal node. In the example strategy being used, flexible cystoscopy followed by WLC, the value of ‘cost’ at the ‘true-positive’ terminal node would be the costs of flexible cystoscopy and WLC and the additional treatment cost depending on the type of bladder cancer.
Discounted costs are considered in the Markov model to estimate the cost for each diagnostic strategy by using the following formulation:
Distribution of parameters
For probabilities of recurrence, progression and mortality of bladder cancer and all-cause mortality rate, no distribution was assigned, as the number of observations or studies used to calculate the risk was very large. The estimates of sensitivity and specificity of the three biomarker tests and cytology were assigned normal distributions, which appear to fit the data that have small and symmetric ranges. The estimates for the performance of flexible cystoscopy, WLC and PDD were assigned beta distributions, which are more flexible to deal with data that have large and skewed ranges. Diagnoses and treatment costs were assigned log-normal distributions as this distribution appeared to best fit the data that have skewed or symmetric ranges.
Quality of life measures
To conduct a cost–utility analysis, quality of life (QoL) (utilities) data are required. The best estimates of QoL (utilities) data for a UK setting may be provided by using generic measures such as EQ-5D or SF-6D (which might be derived from responses to the SF-36 or SF-12). A structured literature search was conducted in EMBASE, MEDLINE and other relevant databases using the key words related to urological cancer, EQ-5D and SF-36 (Appendix 1). However, no QoL data were identified relating to bladder cancer. The only available QoL data were for other urological cancers. After discussions with clinical experts involved in this study it was decided not to use QoL estimates for other urological cancers as a proxy as these values were not considered to be generalisable to the population who have bladder cancer, although as reported later sensitivity analysis was conducted that explored the impact of using these data.
Data analysis
Cost-effectiveness analysis
The base-case analysis was based on the costs and outcomes for a hypothetical cohort of 1000 people with a mean age of 67 years reported in the systematic review in Chapter 4. The base-case model analysis was run for 5% prevalence rates and a 20-year time horizon. Two different measures of incremental cost-effectiveness have been considered as they provide slightly different information. These measures are the incremental cost per true positive case detected and incremental cost per life-year gained. The cases of true positives might be considered to be the key clinical outcome to reflect the diagnostic performance and life-years are a natural outcome to reflect survival.
The incremental cost-effectiveness is presented both with and without dominated and extendedly dominated options. For the estimation of incremental cost per life-year gained the results are presented as cost-effectiveness scatter plots and cost-effectiveness acceptability curves (CEACs). CEACs illustrate the likelihood that the strategy is cost-effective at various threshold values for society’s willingness to pay for an additional life-year. Probabilistic sensitivity analysis was based mainly on the non-dominated strategies in the base-case model as changes in the estimates of parameters in these particular strategies are more likely to change the conclusions.
Cost–consequence analysis
The cost-effectiveness analysis results were presented as true positive cases detected and life-years. Further information can be obtained by considering the different outcome of diagnostic performance and longer-term effectiveness within the model for each strategy included in this study. The diagnostic performance of each strategy is reported in terms of false negative, false positive, true negative, correct diagnosis and incorrect diagnosis. Here, data along with information on life expectancy and cost can be presented in the form of a cost–consequence analysis. As such these data can be useful to aid in the interpretation of cost-effectiveness analyses and, had one been possible as part of the base-case analysis, a cost-utility analysis as they help to identify what factors might be drivers of the results.
Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analyses were carried out to explore uncertainties within the model. Sensitivity analyses concentrated on various assumptions made about estimates of main parameters used in the base-case model. As mentioned above the results of the sensitivity analyses focused on the non-dominated strategies in the base-case model. A cost–consequence analysis can be used to highlight the choices and trade-offs that can be made between outcomes.
Prevalence rates of patients who have symptoms of bladder cancer
Although considerable efforts were made to identify estimates for prevalence rates for patients who have symptoms of bladder cancer, no reliable data were available. In the base-case analysis a prevalence rate of 5% was used. Existing data in the literature suggest that prevalence rates range from 1% to 20%. Sensitivity analysis was performed to explore the effects of a decrease to 1% and increases to 10% and 20%. The same distribution of parameters adopted in the base-case analysis was used.
Relative risk of progression comparing no treatment (false negative) and treatment (true positive)
As mentioned earlier there was little information available to investigate the risk of progression of no treatment for patients who have bladder cancer when they have negative results in the initial diagnosis. Bladder cancer missed in the initial diagnosis and at follow-up would not be treated and would subsequently have a higher risk of progression and mortality. The base-case analysis assumed that the RR of no treatment (TURBT) compared with treatment would be 2.56 based on the Millán-Rodriguez and colleagues’ study. 187 A range of this RR was considered to investigate those values for which diagnostic strategies may be considered worthwhile. Based on available evidence on the RR for progression comparing TURBT with TURBT plus BCG or other drugs, a sensitivity analysis was performed with the assumption that the RR for progression comparing TURBT with no TURBT decreased to 1.
Relative risks of recurrence and progression comparing PDD with WLC
There are no reliable data on recurrence and progression when PDD is used for initial diagnosis and follow-up, although PDD is likely to reduce recurrence and progression compared with WLC as described in Chapter 4. It was assumed in the base-case model that the RRs of recurrence and progression comparing PDD with WLC would be 1, i.e. any gains from the use of PDD would flow from improvements in diagnostic performance as measured by sensitivity and specificity alone, as opposed to gains that might arise from a more complete removal of the cancer facilitated by the increased information provided by PDD. Results in Chapter 4 suggested that the RRs of recurrence and progression comparing PDD with WLC were 0.64 and 0.56 and these values were used in the sensitivity analysis.
Sensitivity and specificity of flexible cystoscopy
There were no data related to the sensitivity and specificity of flexible cystoscopy, although it is likely that the performance of flexible cystoscopy could be better than that of WLC. The assumption was made in the base-case analysis that the performance of flexible cystoscopy would be the same as that of WLC. Expert opinion (TR Leyston Griffiths, University of Leicester, July 2008, personal communication) suggested that the performance of flexible cystoscopy is better than that of WLC; sensitivity analysis was therefore performed assuming that both sensitivity and specificity of flexible cystoscopy are increased from 5% to 25% compared with WLC.
Proportion of risk groups for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer
The risk groups used in the model were defined by combining two classifications based on the best available data. There were large differences in the proportions for risk groups in the two studies. The base case assumed that the proportion of risk would be the same as in the Millán-Rodriguez and colleagues’ study,187 in which the proportion of the high-risk group is much higher than that of the low-risk group. As mentioned in Chapter 1 it is likely that the proportion of the low-risk group in non-muscle-invasive disease is the same as that in the study by Parmar and colleagues. 191 Thus, it was assumed in the sensitivity analysis that the proportion of the high-risk group decreased from 30% in the base-case analysis to 10% and that the proportion of the low-risk group increased from 10% in the base-case analysis to 30%. The distributions of parameters were the same as those used in the base case.
Starting age and 10-year time horizon
As mentioned in Chapter 1 the incidence and mortality rate of bladder cancer are likely to increase as age increases. The base-case analysis was carried out on the assumption that the starting age of the cohort would be 67 years, based on the results from the systematic review, and considered a 20-year time horizon with constant mortality rates of bladder cancer except for the first 5 years. The sensitivity analysis used the reported mean age of bladder cancer patients in the UK of 71 years. The prevalence and mortality rate of bladder cancer associated with age may imply that the most cost-effective strategy in the base case may no longer be considered to be cost-effective.
Annual discount rate
As recommended in the NICE guidelines, an annual discount rate of 3.5% for cost and outcomes was used in the base-case model. A range from 0% to 6% for discount rate was considered in the sensitivity analysis.
Follow-up diagnostic strategies
White light rigid cystoscopy was considered as the second-line test in follow-up for each strategy in the base-case model as it is commonly used to follow bladder cancer in the UK if the result of the first test in follow-up is positive. Sensitivity analysis was performed to investigate whether alternative strategies associated with PDD in follow-up may be more cost-effective than those involving WLC, although PDD is more expensive than WLC.
Quality of life measures
As addressed in the previous section cost–utility analysis was not conducted in the base case. Sensitivity analysis was performed using the QoL data from other urological cancers to produce quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). The utility values identified for urological cancers are included in Table 38. A prediagnosis utility value of 0.78 was identified and the rest of the values were based on a reduction in utility for undergoing the different tests and treatments.
| Utility and disutility | Assumption of reduction in utility | Value | Range | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prediagnosis | NAa | 0.78 | 0.52 to 1.0 | UK EQ-5D |
| CSC | –0 | 0.78 | 0.518 to 1.0 | Kulkarni 2007205 |
| CTL | –0 | 0.78 | 0.52 to 1.0 | Assumption |
| NMP22 | –0 | 0.78 | 0.52 to 1.0 | Assumption |
| ImmunoCyt | –0 | 0.78 | 0.52 to 1.0 | Assumption |
| FISH | –0 | 0.78 | 0.52 to 1.0 | Assumption |
| WLC | –0.05 | 0.73 | 0.66 to 0.73 | Kulkarni 2007205 |
| PDD | –0.05 | 0.73 | 0.66 to 0.73 | Kulkarni 2007205 |
| TURBT | –0.05 | 0.73 | 0.66 to 0.73 | Kulkarni 2007205 |
| BCG | –0.016 | 0.764 | 0.534 to 0.764 | Kulkarni 2007205 |
| Cystectomy (alone) | NAb | 0.624 | 0.39 to 0.78 | Kulkarni 2007205 |
| Chemotherapy | –0.28 | 0.60 | 0.08 to 0.62 | Kulkarni 2007205 |
| Radiotherapy | –0.13 | 0.65 | 0.49 to 0.65 | Pickard 2007206 |
| Non-muscle-invasive | –0 | 0.78 | 0.24 to 0.73 | Kulkarni 2007205 |
| Muscle-invasive | –0 | 0.78 | 0.52 to 1.0 | UK EQ-5D |
| Metastases with palliative treatment | –0.29 | 0.49 | 0.518 to 1.0 | Kulkarni 2007205 |
Subgroup analysis
Depending on data availability it was intended that subgroup analysis would be performed on:
-
type of tumour detected, e.g. CIS, low risk and high risk
-
tumour recurrence at the first 3-month cystoscopic examination following TURBT
-
diagnostic performance of the different PDD photosensitising agents.
Results
Deterministic and probabilistic results
The cost-effectiveness analysis aggregates the diagnostic performance and the time spent in the various health states of the model. As described previously cost–utility analysis was not performed because QoL data suitable for incorporation into the economic model were not available.
Deterministic results
The cost-effectiveness of the 26 strategies for initial diagnosis and follow-up were considered over a 20-year time horizon.
Base case: diagnostic performance and life-years and costs per patient
Table 39 shows the results for a hypothetical cohort of 1000 patients. The table reports performance of the strategies, from the least to the most costly. For each strategy the diagnostic performance of the strategy and the average cost and life expectancy over a 20-year time horizon are shown. It is important to remember when interpreting these data that in the base-case analysis the prevalence of disease is 5% (i.e. 50 people out of the 1000 in the cohort have bladder cancer).
| Strategy | Diagnostic performance | Average limitation outcome | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First line tests (second line tests) | True positive | True negative | False positive | False negative | Correct diagnosis | Incorrect diagnosis | Life-years | Cost | |
| 1 | CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | 16 | 939 | 11 | 34 | 955 | 45 | 11.59 | £1043 |
| 2 | CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | 20 | 934 | 16 | 30 | 954 | 46 | 11.6 | £1094 |
| 3 | FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | 27 | 910 | 40 | 23 | 937 | 63 | 11.62 | £1171 |
| 4 | FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | 35 | 889 | 61 | 15 | 924 | 76 | 11.64 | £1235 |
| 5 | NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | 24 | 894 | 56 | 26 | 918 | 82 | 11.61 | £1242 |
| 6 | NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | 31 | 864 | 86 | 19 | 895 | 105 | 11.62 | £1321 |
| 7 | IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | 30 | 884 | 67 | 20 | 913 | 87 | 11.63 | £1345 |
| 8 | IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | 39 | 848 | 102 | 11 | 887 | 113 | 11.65 | £1458 |
| 9 | CSC_CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | 30 | 868 | 82 | 20 | 898 | 102 | 11.62 | £1662 |
| 10 | CSC_FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | 33 | 847 | 103 | 17 | 880 | 120 | 11.63 | £1807 |
| 11 | CSC_NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | 32 | 835 | 115 | 18 | 867 | 133 | 11.62 | £1851 |
| 12 | CSC_CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | 39 | 824 | 126 | 11 | 863 | 137 | 11.65 | £1859 |
| 13 | CSC_WLC (CSC_WLC) | 25 | 876 | 75 | 25 | 901 | 99 | 11.6 | £1920 |
| 14 | CSC_IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | 34 | 828 | 122 | 16 | 862 | 138 | 11.63 | £1941 |
| 15 | CSC_CTL_WLC (CSC_WLC) | 30 | 868 | 82 | 20 | 898 | 102 | 11.62 | £1997 |
| 16 | CSC_FISH_WLC (CSC_WLC) | 33 | 847 | 103 | 17 | 880 | 120 | 11.66 | £2005 |
| 17 | CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | 43 | 792 | 158 | 7 | 835 | 165 | 11.63 | £2042 |
| 18 | CSC_NMP22_WLC (CSC_WLC) | 32 | 835 | 115 | 18 | 867 | 133 | 11.62 | £2070 |
| 19 | CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | 33 | 836 | 114 | 17 | 869 | 131 | 11.63 | £2082 |
| 20 | CSC_NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | 42 | 774 | 176 | 8 | 816 | 184 | 11.65 | £2089 |
| 21 | CSC_IMM_WLC (CSC_WLC) | 34 | 828 | 122 | 16 | 862 | 138 | 11.63 | £2105 |
| 22 | CSC_CTL_PDD (CSC_WLC) | 39 | 818 | 132 | 11 | 857 | 143 | 11.64 | £2145 |
| 23 | CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | 44 | 762 | 188 | 6 | 806 | 194 | 11.66 | £2195 |
| 24 | CSC_FISH_PDD (CSC_WLC) | 43 | 792 | 158 | 7 | 835 | 165 | 11.66 | £2270 |
| 25 | CSC_NMP22_PDD (CSC_WLC) | 42 | 774 | 176 | 8 | 816 | 184 | 11.65 | £2318 |
| 26 | CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | 44 | 762 | 188 | 6 | 806 | 194 | 11.66 | £2370 |
Of the strategies shown, strategy 26, flexible cystoscopy and ImmunoCyt followed by PDD in initial diagnosis and flexible cystoscopy followed by WLC in follow-up [CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC)], has the best performance in terms of the highest number of true positives and lowest number of false negatives and the highest number of life-years but it also has the worst performance in terms of the highest number of false positives (n = 188), the lowest number of true negatives and the highest cost. Strategy 1, CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC), reports the lowest numbers of true positives and false positives and life-years saved and the highest values for true negatives and false negatives.
Cost–consequence analysis
The results presented in Table 39 can be used to consider the trade-offs between the different treatment strategies and this can be further illustrated using the data presented in Table 40. Table 40 reports the strategies that perform the best in terms of the different outcome measures considered. The results for all strategies are reported in Appendix 19 (Tables 58 and 59). For example, CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) is the best-performing strategy in terms of having the lowest false-negative and the highest true-positive rates and longest survival. However, it is associated with the highest rates of false positives and the lowest rates of true negatives.
| Ranking | True negative | True positive | False positive | False negative | Correct diagnosis | Incorrect diagnosis | Life-years | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CTL_WLC | CSC_IMM_PDD | CTL_WLC | CSC_IMM_PDD | CTL_WLC | CTL_WLC | CSC_IMM_PDD | CTL_WLC |
| (CTL_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | |
| 2 | CTL_PDD | CSC_IMM_PDD | CTL_PDD | CSC_IMM_PDD | CTL_PDD | CTL_PDD | CSC_IMM_PDD | CTL_PDD |
| (CTL_WLC) | (IMM_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | (IMM_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | (IMM_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | |
| 3 | FISH_WLC | CSC_FISH_PDD | FISH_WLC | CSC_FISH_PDD | FISH_WLC | FISH_WLC | CSC_FISH_PDD | FISH_WLC |
| (FISH_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) | |
| 4 | NMP22_WLC | CSC_FISH_PDD | NMP22_WLC | CSC_FISH_PDD | FISH_PDD | FISH_PDD | CSC_FISH_PDD | FISH_PDD |
| (NMP22_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (NMP22_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) | |
| 5 | FISH_PDD | CSC_NMP22_PDD | FISH_PDD | CSC_NMP22_PDD | NMP22_WLC | NMP22_WLC | CSC_NMP22_PDD | NMP22_WLC |
| (FISH_WLC) | (NMP22_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) | (NMP22_WLC) | (NMP22_WLC) | (NMP22_WLC) | (NMP22_WLC) | (NMP22_WLC) | |
| 6 | IMM_WLC | CSC_NMP22_PDD | IMM_WLC | CSC_NMP22_PDD | IMM_WLC | IMM_WLC | CSC_NMP22_PDD | NMP22_PDD |
| (IMM_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (IMM_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (IMM_WLC) | (IMM_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (NMP22_WLC) | |
| 7 | CSC_WLC | IMM_PDD | CSC_WLC | IMM_PDD | CSC_WLC | CSC_WLC | IMM_PDD | IMM_WLC |
| (CSC_WLC) | (IMM_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (IMM_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (IMM_WLC) | (IMM_WLC) | |
| 8 | CSC_CTL_WLC | CSC_CTL_PDD | CSC_CTL_WLC | CSC_CTL_PDD | CSC_CTL_WLC | CSC_CTL_WLC | CSC_CTL_PDD | IMM_PDD |
| (CSC_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | (IMM_WLC) | |
| 9 | CSC_CTL_WLC | CSC_CTL_PDD | CSC_CTL_WLC | CSC_CTL_PDD | CSC_CTL_WLC | CSC_CTL_WLC | CSC_CTL_PDD | CSC_CTL_WLC |
| (CTL_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | (CSC_WLC) | (CTL_WLC) | |
| 10 | NMP22_PDD | FISH_PDD | NMP22_PDD | FISH_PDD | NMP22_PDD | NMP22_PDD | FISH_PDD | CSC_FISH_WLC |
| (NMP22_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) | (NMP22_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) | (NMP22_WLC) | (NMP22_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) | (FISH_WLC) |
This table and Table 39 illustrate the trade-offs that exists between those strategies that can correctly identify those without disease but will result in all of the harms from an incorrect diagnosis compared with those strategies that are better able to identify disease if it is present but also result in additional anxiety and cost for those incorrectly initially diagnosed as positive.
Cost-effectiveness analysis
Incremental cost per true positive case detected
The cost-effectiveness results for diagnostic performance are presented in Table 41 using incremental cost per true positive detected. In terms of mean true positive cases and costs, most of the strategies associated with flexible cystoscopy or WLC in the initial diagnosis [except for CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) and FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC)] are dominated by those that involve PDD or biomarkers and can be eliminated because they are less effective and more costly than the non-dominated strategies. The lower part of the table reports the incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) when dominated and extendedly dominated strategies are omitted.
| Strategy number | Strategy | Average cost | Incremental cost | True positive cases detected | Incremental number of cases detected | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 16 | |||
| 2 | CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 20 | 4 | £13 |
| 3 | FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | £1171 | £77 | 27 | 7 | £11 |
| 4 | FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £64 | 35 | 8 | £8 |
| 5 | NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | £1242 | £6 | 24 | –11 | Dominated |
| 6 | IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | £1321 | £86 | 30 | –5 | Dominated |
| 7 | NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | £1345 | £109 | 32 | –3 | Dominated |
| 8 | IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 39 | 4 | £56 |
| 9 | CSC_CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1662 | £204 | 30 | –9 | Dominated |
| 10 | CSC_FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | £1807 | £349 | 33 | –5 | Dominated |
| 11 | CSC_NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | £1851 | £393 | 32 | –7 | Dominated |
| 12 | CSC_CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1859 | £401 | 39 | 0 | Dominated |
| 13 | CSC_WLC (CSC_WLC) | £1920 | £462 | 25 | –14 | Dominated |
| 14 | CSC_IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | £1941 | £483 | 34 | –5 | Dominated |
| 15 | CSC_CTL_WLC (CSC_WLC) | £1997 | £539 | 30 | –9 | Dominated |
| 16 | CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2005 | £547 | 43 | 4 | £137 |
| 17 | CSC_FISH_WLC (CSC_WLC) | £2042 | £37 | 33 | –10 | Dominated |
| 18 | CSC_NMP22_WLC (CSC_WLC) | £2070 | £65 | 32 | –11 | Dominated |
| 19 | CSC_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | £2082 | £77 | 33 | –10 | Dominated |
| 20 | CSC_NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | £2089 | £84 | 42 | –1 | Dominated |
| 21 | CSC_IMM_WLC (CSC_WLC) | £2105 | £100 | 34 | –9 | Dominated |
| 22 | CSC_CTL_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2145 | £140 | 39 | -4 | Dominated |
| 23 | CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2195 | £190 | 44 | 1 | £190 |
| 24 | CSC_FISH_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2270 | £75 | 43 | –1 | Dominated |
| 25 | CSC_NMP22_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2318 | £123 | 42 | –2 | Dominated |
| 26 | CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2370 | £175 | 44 | 0 | Dominated |
| Results without dominated and extendedly dominated options | ||||||
| 1 | CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 16 | |||
| 2 | CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 20 | 4 | £13 |
| 3 | FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | £1171 | £77 | 27 | 7 | £11 |
| 4 | FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £64 | 35 | 8 | £8 |
| 8 | IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 39 | 4 | £56 |
| 16 | CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2005 | £547 | 43 | 4 | £137 |
| 23 | CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2195 | £190 | 44 | 1 | £190 |
The results in Table 41 show that strategy 26 (CSC_IMM_PDD) has the highest number of true positive cases detected (n = 44) and is the most costly strategy (£2370) per patient. Strategy 1 (CTL_WLC) has the lowest cost per patient (£1043) and produces the least number of true positives (n = 16). It is also highlighted in the table that total cost increases when moving from WLC to PDD and the number of cases detected also increases when PDD is used.
Incremental cost per life-year
The base-case analysis was also presented in terms of incremental cost per life-year (Table 42). The results presented for life-years are similar to those presented in Table 41. As can be seen from Table 42 many strategies are dominated, that is they provide no more or even less benefits at the same or increased cost. Further strategies are extendedly dominated, that is providing a mix of a lower cost but less effective strategy and a higher cost but more effective strategy would be more efficient. The strategy of FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) is extendedly dominated by the strategy of CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) and it can be eliminated as its ICER is greater than that of FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) as well as CSC_IMM_PDD. Furthermore, even for those strategies that are not dominated or extendedly dominated the incremental cost per life-year gained might be higher than society is willing to pay. Reference values for society’s willingness to pay for a life-year are not available but given that people will be in less than full health it is likely that the incremental cost per QALY would be greater than £20,000 for all strategies apart from 2, 3 and 4. The incremental cost per QALY for strategy 8 may be greater than £20,000 but less than £30,000 as long as the average annual QoL score is 0.65.
| Strategy number | Strategy | Cost | Incremental cost | Life-years | Incremental years | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | |||
| 2 | CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3423 |
| 3 | FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | £1171 | £77 | 11.62 | 0.01 | £5575a |
| 4 | FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £64 | 11.64 | 0.02 | £2762 |
| 5 | NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | £1242 | £6 | 11.61 | –0.03 | Dominated |
| 6 | IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | £1321 | £86 | 11.62 | –0.02 | Dominated |
| 7 | NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | £1345 | £109 | 11.63 | –0.01 | Dominated |
| 8 | IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,864 |
| 9 | CSC_CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1662 | £204 | 11.62 | –0.03 | Dominated |
| 10 | CSC_FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | £1807 | £349 | 11.63 | –0.02 | Dominated |
| 11 | CSC_NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | £1851 | £393 | 11.62 | –0.02 | Dominated |
| 12 | CSC_CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1859 | £401 | 11.65 | 0 | Dominated |
| 13 | CSC_WLC (CSC_WLC) | £1920 | £462 | 11.60 | –0.04 | Dominated |
| 14 | CSC_IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | £1941 | £483 | 11.63 | –0.02 | Dominated |
| 15 | CSC_CTL_WLC (CSC_WLC) | £1997 | £539 | 11.62 | –0.03 | Dominated |
| 16 | CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2005 | £547 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £60,284 |
| 17 | CSC_FISH_WLC (CSC_WLC) | £2042 | £37 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated |
| 18 | CSC_NMP22_WLC (CSC_WLC) | £2070 | £65 | 11.62 | –0.03 | Dominated |
| 19 | CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2082 | £77 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated |
| 20 | CSC_NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | £2089 | £84 | 11.65 | –0.01 | Dominated |
| 21 | CSC_IMM_WLC (CSC_WLC) | £2105 | £100 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated |
| 22 | CSC_CTL_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2145 | £140 | 11.64 | –0.01 | Dominated |
| 23 | CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2195 | £190 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £309,256a |
| 24 | CSC_FISH_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2270 | £75 | 11.66 | 0 | Dominated |
| 25 | CSC_NMP22_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2318 | £123 | 11.65 | –0.01 | Dominated |
| 26 | CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2370 | £175 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £237,863 |
| Results without dominated and extendedly dominated options | ||||||
| 1 | CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | |||
| 2 | CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3423 |
| 4 | FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £141 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3806 |
| 8 | IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,864 |
| 16 | CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2005 | £547 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £60,284 |
| 26 | CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2370 | £365 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £270,375 |
Probabilistic results
The cost-effectiveness point estimates do not provide any information on uncertainty surrounding the model parameters. The results of the probabilistic analysis revealed the level of uncertainty concerning results as illustrated in the CEACs in Figure 35.
FIGURE 35.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves determined by society’s willingness to pay for a life-year for the eight strategies.
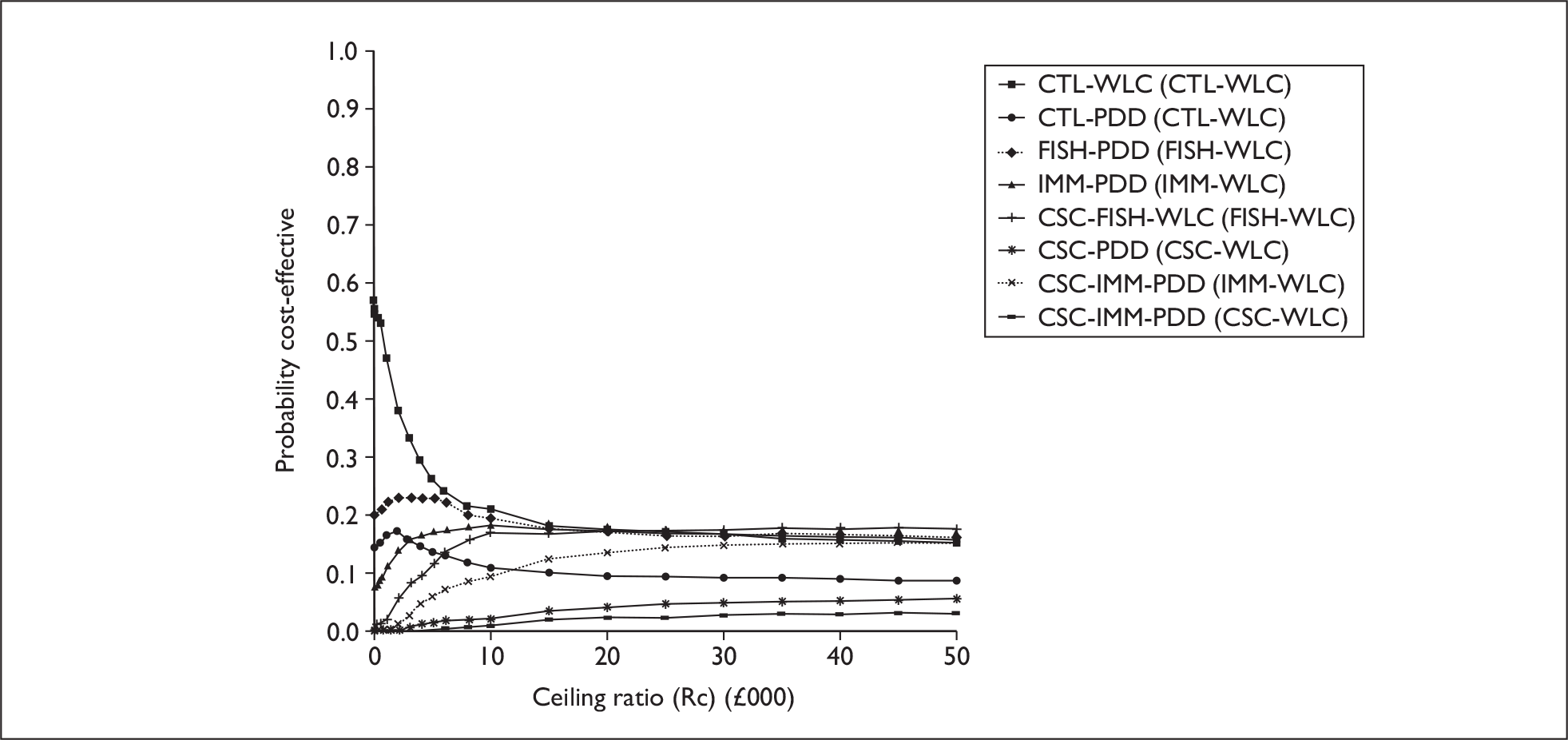
As can be seen in Figure 35 none of the eight strategies considered is likely to be cost-effective more than 50% of the time when society is willing to pay relatively little for an additional life-year except for strategy 1 [CTL_WLC (CTL-WLC)]. Nevertheless, there are four strategies that are each associated with an approximately 20% chance of being considered cost-effective over much of the range of willingness to pay values considered. It is notable that three of the four strategies involve the use of biomarkers for diagnosis and follow-up, while the fourth uses cytology.
As mentioned in the methods section of this chapter, the cost-effectiveness estimates for those strategies that involve more than one test as part of the initial diagnosis may be underestimated. Adding in these potential extra costs had virtually no effect on the point estimates of cost-effectiveness or on the likelihood that a particular strategy would be likely to be considered cost-effective.
Sensitivity analysis and subgroup analysis
Changing prevalence rates in patients who have symptoms of bladder cancer
As prevalence rates increase, people with suspected bladder cancer have more positive results and the costs and outcomes associated with diagnostic performance for each strategy are increased. However, the outcomes associated with long-term survival may be decreased, because fewer people within the cohort are disease free. Table 43 describes the results of the sensitivity analysis for changes in the prevalence rate. The non-dominated or non-extendedly dominated strategies are the same as in the base-case analysis and are excluded from the table. At low probabilities of disease (i.e. 1%) it is likely that the least costly strategy, strategy 1 [CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC)], is likely to be cost-effective. The probability of IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC), FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) and CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) being also considered as cost-effective strategies at different thresholds of society’s willingness to pay for an additional life-year in the base case did not vary greatly when either lower or higher prevalence rates were used in the analysis. However, Figure 35 shows that CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) had an increased probability of being considered cost-effective when the prevalence rate increased to 20%. For example, the probability of CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) being considered the most cost-effective strategy would be greater than 22% when society is willing to pay more than £20,000 per extra life-year. The CEACs for these sensitivity analyses are shown in Appendix 20.
| Strategy | Deterministic results | Probability of cost-effectiveness for different threshold values for society’s willingness to pay for a life-year (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average cost | Incremental cost | Average life-years | Incremental life-years | Incremental cost/ life-year | £10,000 | £20,000 | £30,000 | £40,000 | £50,000 | |
| Base case, prevalence = 5% | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 21 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3423 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £141 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3806 | 20 | 17 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,864 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2005 | £547 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £60,284 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2082 | £77 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2195 | £190 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 9 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 16 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2370 | £365 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £270,375 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Prevalence = 1% | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £319 | 11.79 | 35 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £349 | £30 | 11.79 | < 0.01 | £12,120 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £499 | £150 | 11.79 | < 0.01 | £51,884 | 18 | 15 | 14 | 14 | 13 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £680 | £180 | 11.79 | 0 | Dominated | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 12 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £1148 | £648 | 11.78 | –0.01 | Dominated | 16 | 19 | 19 | 21 | 21 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1306 | £806 | 11.79 | –0.01 | Dominated | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1427 | £928 | 11.78 | –0.01 | Dominated | 10 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 16 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £1450 | £951 | 11.78 | –0.01 | Dominated | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Prevalence = 10% | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1951 | 11.34 | 15 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 11 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £2033 | £82 | 11.37 | 0.03 | Extendedly dominated | 11 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2168 | £217 | 11.45 | 0.11 | £2018 | 19 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2449 | £281 | 11.47 | 0.02 | £13,597 | 18 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2899 | £451 | 11.50 | 0.03 | £17,555 | 22 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 22 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £3177 | £278 | 11.50 | 0.01 | £48,035 | 12 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £3271 | £93 | 11.43 | –0.08 | Dominated | 2 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £3545 | £368 | 11.50 | < 0.01 | £235,672 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Prevalence = 20% | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £3765 | 10.85 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £3904 | £139 | 10.90 | 0.06 | Extendedly dominated | 9 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £4019 | £254 | 11.07 | 0.22 | £1150 | 19 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 15 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £4411 | £392 | 11.12 | 0.05 | Extendedly dominated | 19 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £4667 | £648 | 11.17 | 0.11 | £6148 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £5119 | £452 | 11.19 | 0.02 | £28,183 | 17 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £5628 | £509 | 11.03 | –0.16 | Dominated | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £5871 | £751 | 11.19 | < 0.01 | £233,858 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 9 |
Changes in the sensitivity and specificity of flexible cystoscopy
When the sensitivity and specificity of flexible cystoscopy were increased, life-years associated with ‘flexible cystoscopy’ strategies increased and relevant costs decreased. Results of the changes in the sensitivity and specificity of flexible cystoscopy are presented in Table 44 and, as this table shows, the strategies involving flexible cystoscopy generally become more likely to be considered cost-effective as its diagnostic performance increases. Nonetheless, at perhaps the most plausible increase of 5% in sensitivity and specificity for flexible cystoscopy compared with those of WLC the probabilities that strategies involving flexible cystoscopy are cost-effective are not greatly changed. The CEACs for these sensitivity analyses are shown in Appendix 21.
| Strategy | Deterministic results | Probability of cost-effectiveness for different threshold values for society’s willingness to pay for a life-year (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average cost | Incremental cost | Average life-years | Incremental life-years | Incremental cost/ life-year | £10,000 | £20,000 | £30,000 | £40,000 | £50,000 | |
| Base case, CSC = WLC (sens = 0.71, spec = 0.72) | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 21 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3423 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £141 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3806 | 20 | 17 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,864 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2005 | £547 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £60,284 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2082 | £77 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2195 | £190 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 9 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 16 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2370 | £365 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £270,375 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| CSC = WLC + 5.0% (sens = 0.76, spec = 0.77) | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 22 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3423 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £141 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3806 | 20 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,864 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1952 | £494 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £55,236 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £1986 | £34 | 11.63 | –0.02 | Dominated | 3 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2149 | £197 | 11.66 | 0 | Dominated | 12 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2293 | £341 | 11.66 | 0 | Dominated | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| CSC = WLC + 10.0% (sens = 0.81, spec = 0.82) | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 21 | 18 | 16 | 15 | 15 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3423 | 9 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 7 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £141 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3806 | 20 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 16 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,864 | 17 | 16 | 17 | 17 | 16 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £1881 | £423 | 11.64 | 0 | Dominated | 3 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 7 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1892 | £434 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £49,145 | 17 | 19 | 19 | 20 | 20 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2096 | £204 | 11.66 | 0 | Dominated | 12 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 17 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2211 | £319 | 11.65 | 0 | Dominated | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| CSC = WLC + 25.0% (sens = 0.96, spec = 0.97) | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 14 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 9 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3423 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £141 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3806 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 14 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 17 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £1552 | £317 | 11.67 | 0.03 | £10,485 | 17 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1706 | £154 | 11.66 | –0.01 | Dominated | 17 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1931 | £379 | 11.65 | –0.02 | Dominated | 8 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £1964 | £412 | 11.65 | –0.02 | Dominated | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
Relative risk rate of progression of bladder cancer comparing no treatment with treatment
In the sensitivity analysis the speed of progression and rate of mortality for those falsely diagnosed as negative and hence not treated were altered. As might be expected, reducing these rates would decrease the cost-effectiveness of those strategies associated with fewer false negatives. Hence, the probability that CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) would be considered cost-effective increased from 18% in the base-case analysis (RR 2.56) to 28% when the RR was 1 and society’s willingness to pay for a life-year was £20,000 (Table 45). The CEACs for these sensitivity analyses are shown in Appendix 22.
| Strategy | Deterministic result | Probability of cost-effectiveness for different threshold values for society’s willingness to pay for a life-year (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average cost | Incremental cost | Average life-years | Incremental life-years | Incremental cost/life-year | £10,000 | £20,000 | £30,000 | £40,000 | £50,000 | |
| Base case, RR = 2.56 | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 21 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3423 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £141 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3806 | 20 | 17 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,864 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2005 | £547 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £60,284 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2082 | £77 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2195 | £190 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 9 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 16 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2370 | £365 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £270,375 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| RR = 2.0 | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1040 | 11.63 | 24 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1092 | £52 | 11.64 | 0.01 | £5707 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1242 | £150 | 11.66 | 0.02 | £7115 | 20 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1464 | £222 | 11.66 | 0 | £51,443 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 14 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2008 | £544 | 11.66 | 0 | £127,281 | 16 | 18 | 18 | 19 | 19 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2110 | £102 | 11.64 | –0.02 | Dominated | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2198 | £190 | 11.66 | 0.00 | Dominated | 10 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 14 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2378 | £370 | 11.67 | < 0.01 | £897,929 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| RR = 1.5 | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1026 | 11.66 | 30 | 26 | 24 | 23 | 23 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1081 | £55 | 11.66 | 0 | £11,311 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1243 | £162 | 11.67 | 0.01 | £24,861 | 19 | 18 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1465 | £223 | 11.67 | < 0.01 | £204,841 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2008 | £543 | 11.67 | < 0.01 | £2,836,313 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 17 | 18 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2133 | £124 | 11.66 | –0.01 | Dominated | 3 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2200 | £191 | 11.67 | 0 | Dominated | 8 | 11 | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2384 | £376 | 11.67 | 0 | Dominated | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| RR = 1.0 | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £999 | 11.69 | 32 | 28 | 26 | 25 | 25 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1066 | £67 | 11.69 | < 0.01 | £123,479 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1239 | £173 | 11.68 | –0.01 | Dominated | 17 | 15 | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1463 | £398 | 11.68 | –0.01 | Dominated | 14 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 12 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2006 | £940 | 11.68 | –0.01 | Dominated | 14 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2149 | £1083 | 11.68 | –0.02 | Dominated | 3 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2200 | £1134 | 11.68 | –0.02 | Dominated | 8 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2389 | £1323 | 11.68 | –0.02 | Dominated | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
Relative risk rate of recurrence and progression comparing PDD with WLC
As indicated in Chapter 4, PDD is more likely to reduce the recurrence and progression of bladder cancer, decreasing these rates, and would therefore increase the cost-effectiveness of strategies associated with it. FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) had an increased probability of being considered cost-effective when the RRs of recurrence and progression were decreased to 0.64 and 0.56 respectively (Tables 46 and 47 respectively). The CEACs for these sensitivity analyses are shown in Appendices 23 and 24 respectively.
| Strategy | Deterministic result | Probability of cost-effectiveness for different threshold values for society’s willingness to pay for a life-year (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average cost | Incremental cost | Average life-years | Incremental life-years | Incremental cost/life-year | £10,000 | £20,000 | £30,000 | £40,000 | £50,000 | |
| Base case (RR_R = 1.0) | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 21 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3423 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £141 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3806 | 20 | 17 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,864 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2005 | £547 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £60,284 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2082 | £77 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2195 | £190 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 9 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 16 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2370 | £365 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £270,375 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| RR_R = 0.9 | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 21 | 18 | 16 | 16 | 16 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1090 | £47 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3301 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1227 | £136 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3650 | 20 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1451 | £224 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,840 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1999 | £548 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £60,008 | 18 | 20 | 20 | 21 | 21 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2080 | £81 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2190 | £191 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 11 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2367 | £368 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £277,574 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| RR_R = 0.8 | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 17 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 12 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1084 | £41 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £2773 | 13 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1215 | £131 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3469 | 23 | 21 | 19 | 18 | 18 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1439 | £224 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,553 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1986 | £547 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £59,527 | 16 | 18 | 19 | 19 | 19 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2071 | £85 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 4 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 8 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2177 | £191 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £267,929 | 11 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2357 | £180 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £304,531 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| RR_R = 0.64 | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 18 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 12 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1075 | £31 | 11.61 | 0.02 | £2005 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 11 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1197 | £122 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3181 | 21 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1420 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,083 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1965 | £545 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £58,791 | 15 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2058 | £93 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2156 | £190 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £239,084 | 11 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 17 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2341 | £185 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £395,494 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Strategy | Deterministic result | Probability of cost-effectiveness for different threshold values for society’s willingness to pay for a life-year (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average cost | Incremental cost | Average life-years | Incremental life-years | Incremental cost/life-year | £10,000 | £20,000 | £30,000 | £40,000 | £50,000 | |
| Base case (RR_P = 1.0) | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 21 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3423 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £141 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3806 | 20 | 17 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,864 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2005 | £547 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £60,284 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2082 | £77 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2195 | £190 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 9 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 16 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2370 | £365 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £270,375 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| RR_P = 0.9 | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 20 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 14 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1095 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3697 | 12 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1236 | £141 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3797 | 21 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1460 | £225 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £29,123 | 15 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 14 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2009 | £549 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £60,273 | 15 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 19 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2086 | £77 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 4 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 8 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2200 | £191 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 11 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 16 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2376 | £366 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £272,285 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| RR_P = 0.8 | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 19 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 14 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1093 | £50 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3529 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1233 | £140 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3760 | 25 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 20 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £225 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £29,122 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2006 | £548 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £60,046 | 16 | 18 | 19 | 19 | 20 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2085 | £78 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 3 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2197 | £191 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2374 | £367 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £273,525 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| RR_P = 0.56 | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 22 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1089 | £46 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3148 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1227 | £137 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3671 | 21 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1452 | £225 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £29,110 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 14 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1999 | £547 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £59,522 | 16 | 18 | 18 | 19 | 19 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2080 | £81 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 4 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 7 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2191 | £192 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 10 | 13 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2369 | £370 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £276,805 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
Discount rate
Another sensitivity analysis was conducted by changing the discount rate. The cost-effectiveness of the different strategies did not markedly change when the discount rate was changed between 0% and 6% (Table 48). The CEACs for these sensitivity analyses are shown in Appendix 25.
| Strategy | Deterministic result | Probability of cost-effectiveness for different threshold values for society’s willingness to pay for a life-year (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average cost | Incremental cost | Average life-years | Incremental life-years | Incremental cost/life-year | £10,000 | £20,000 | £30,000 | £40,000 | £50,000 | |
| Base case (discount rate = 3.5%) | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 21 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3423 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £141 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3806 | 20 | 17 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,864 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2005 | £547 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £60,284 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2082 | £77 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2195 | £190 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 9 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 16 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2370 | £365 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £270,375 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Discount rate = 6% | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £978 | 9.84 | 21 | 17 | 15 | 15 | 14 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1031 | £53 | 9.85 | 0.01 | £4364 | 12 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1166 | £134 | 9.88 | 0.03 | £4509 | 23 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1382 | £217 | 9.88 | 0.01 | £36,596 | 16 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1940 | £558 | 9.89 | 0.01 | £80,682 | 16 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 22 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £1987 | £46 | 9.87 | –0.03 | Dominated | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2122 | £181 | 9.89 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 10 | 13 | 15 | 15 | 16 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2278 | £337 | 9.89 | < 0.01 | £408,489 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Discount rate = 1% | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1124 | 13.95 | 19 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 15 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1172 | £48 | 13.97 | 0.02 | £2607 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1323 | £151 | 14.02 | 0.05 | £3215 | 20 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 15 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1554 | £231 | 14.03 | 0.01 | £22,648 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 15 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2088 | £533 | 14.04 | 0.01 | £44,272 | 18 | 20 | 21 | 21 | 21 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2203 | £115 | 14.00 | –0.04 | Dominated | 4 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 8 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2289 | £201 | 14.04 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 12 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2487 | £399 | 14.04 | < 0.01 | £190,983 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Discount rate = 0% | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1162 | 15.13 | 17 | 15 | 14 | 14 | 14 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1209 | £47 | 15.15 | 0.02 | £2316 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1365 | £156 | 15.20 | 0.05 | £3009 | 21 | 19 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1600 | £235 | 15.21 | 0.01 | £20,526 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2127 | £527 | 15.23 | 0.01 | £38,899 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2261 | £134 | 15.18 | –0.04 | Dominated | 4 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2334 | £207 | 15.23 | < 0.01 | £162,110 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2543 | £209 | 15.23 | < 0.01 | £174,776 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
Proportions in each prognostic risk group for non-muscle-invasive disease
Changes to the proportions in each prognostic risk group for non-muscle-invasive disease were also considered (note that as the proportion in the low-risk group was increased, the proportion in the high-risk group decreased). The likelihood that CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC), IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC), FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) or CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) would be considered cost-effective did not change although some non-dominated or non-extendedly dominated strategies in the base-case analysis became dominated or extendedly dominated (Table 49). The CEACs for these sensitivity analyses are shown in Appendix 26.
| Strategy | Deterministic results | Probability of cost-effectiveness for different threshold values for society’s willingness to pay for a life-year (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average cost | Incremental cost | Average life-years | Incremental life-years | Incremental cost/life-year | £10,000 | £20,000 | £30,000 | £40,000 | £50,000 | |
| Base case, low = 0.1, high = 0.45 | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 21 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3423 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £141 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3806 | 20 | 17 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,864 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2005 | £547 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £60,284 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2082 | £77 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2195 | £190 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 9 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 16 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2370 | £365 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £270,375 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Low = 0.3, high = 0.3 | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1020 | 11.60 | 21 | 17 | 15 | 15 | 15 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1071 | £51 | 11.61 | 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1190 | £170 | 11.65 | 0.05 | £3254 | 22 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 18 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1400 | £210 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £27,170 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1957 | £557 | 11.67 | 0.01 | £58,259 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 20 | 21 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2011 | £54 | 11.64 | –0.03 | Dominated | 4 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2132 | £175 | 11.67 | < 0.01 | £224,407 | 9 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 14 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2283 | £151 | 11.67 | < 0.01 | £389,886 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Low = 0.6, high = 0.1 | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £979 | 11.61 | 18 | 16 | 14 | 14 | 13 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1029 | £49 | 11.63 | 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 10 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1111 | £132 | 11.67 | 0.05 | £2487 | 23 | 21 | 20 | 18 | 18 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1302 | £190 | 11.67 | 0.01 | £28,973 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1867 | £565 | 11.68 | 0.01 | £51,823 | 19 | 20 | 20 | 21 | 21 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £1883 | £17 | 11.65 | –0.03 | Dominated | 2 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 7 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2036 | £170 | 11.68 | < 0.01 | £296,812 | 8 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2117 | £80 | 11.68 | < 0.01 | £420,138 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
Starting age of population and time horizon
Sensitivity analysis was used to investigate the effects of changing the starting age of the patient population or changing the number of years that the model was performed. None of these sensitivity analyses altered the likelihood of a given strategy being considered cost-effective (Table 50). However, as the time horizon was reduced, the incremental cost per life-year gained for each non-dominated strategy increased. This is because the majority of costs are incurred in earlier years but of course as the time horizon increases it is possible to gain more life-years. The CEACs for the sensitivity analyses are shown in Appendix 27.
| Strategy | Deterministic results | Probability of cost-effectiveness for different threshold values for society’s willingness to pay for a life-year (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average cost | Incremental cost | Average life-years | Incremental life-years | Incremental cost/life-year | £10,000 | £20,000 | £30,000 | £40,000 | £50,000 | |
| Base case, starting age 67 years | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 21 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3423 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £141 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3806 | 20 | 17 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,864 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2005 | £547 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £60,284 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2082 | £77 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2195 | £190 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 9 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 16 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2370 | £365 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £270,375 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Starting age 57 years | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1095 | 13.34 | 21 | 18 | 16 | 16 | 15 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1145 | £50 | 13.35 | 0.02 | £2821 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1294 | £149 | 13.40 | 0.04 | £3376 | 25 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 20 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1522 | £228 | 13.41 | 0.01 | £23,832 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2061 | £539 | 13.42 | 0.01 | £47,517 | 17 | 19 | 21 | 21 | 21 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2162 | £101 | 13.38 | –0.04 | (Dominated) | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2258 | £197 | 13.42 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 8 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2447 | £386 | 13.42 | < 0.01 | £197,884 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Starting age 77 years | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £951 | 8.84 | 23 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 18 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1005 | £54 | 8.85 | 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 11 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1135 | £184 | 8.87 | 0.04 | £5041 | 20 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 15 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1349 | £214 | 8.88 | 0 | £44,105 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 11 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1911 | £562 | 8.88 | 0.01 | £100,340 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 19 | 19 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £1946 | £35 | 8.86 | –0.02 | Dominated | 3 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2089 | £178 | 8.88 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 12 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2239 | £328 | 8.89 | < 0.01 | £709,968 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Time horizon 10 years | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £983 | 8.37 | 25 | 19 | 16 | 15 | 14 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1034 | £51 | 8.38 | 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 11 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1155 | £121 | 8.40 | 0.02 | £5255 | 26 | 21 | 21 | 20 | 19 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1369 | £213 | 8.40 | < 0.01 | £54,101 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1926 | £557 | 8.41 | < 0.01 | £121,083 | 13 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £1972 | £46 | 8.39 | –0.02 | Dominated | 2 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 7 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2105 | £179 | 8.41 | 0 | Dominated | 6 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2259 | £333 | 8.41 | < 0.01 | £4,183,060 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
Strategy used in follow-up and quality of life measures
The final sensitivity analyses performed involved including the use of PDD in follow-up and conducting cost–utility analysis using the values reported in Table 38. The CEACs for these two sensitivity analyses are shown in Appendices 28 and 29 respectively. These results did not change much and there was no strategy that was likely to be considered the most cost-effective as shown in Table 51. It was noted that the strategies associated with flexible cystoscopy were dominated by others when using QoL measures.
| Strategy | Deterministic results | Probability of cost-effectiveness for different threshold values for society’s willingness to pay for a life-year (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average cost | Incremental cost | Average life-years | Incremental life-years | Incremental cost/life-year | £10,000 | £20,000 | £30,000 | £40,000 | £50,000 | |
| Base case, second test in follow-up is WLC | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 11.59 | 21 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3423 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £141 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £3806 | 20 | 17 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £28,864 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2005 | £547 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £60,284 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2082 | £77 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2195 | £190 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 9 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 16 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2370 | £365 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £270,375 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Second test in follow-up is PDD | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_PDD) | £1069 | 11.59 | 20 | 17 | 15 | 15 | 14 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_PDD) | £1119 | £50 | 11.60 | 0.01 | £3372 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1279 | £160 | 11.64 | 0.04 | £4314 | 20 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_PDD) | £1517 | £238 | 11.65 | 0.01 | £30,839 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_PDD) | £2051 | £533 | 11.66 | 0.01 | £58,765 | 18 | 20 | 21 | 21 | 21 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_PDD) | £2140 | £90 | 11.63 | –0.03 | Dominated | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_PDD) | £2257 | £207 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 10 | 13 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_PDD) | £2433 | £383 | 11.66 | < 0.01 | £284,001 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Cost–utility analysis | ||||||||||
| CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | £1043 | 9.00 | 25 | 20 | 18 | 18 | 18 | |||
| CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | £1094 | £51 | 9.01 | 0.01 | £4678 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 |
| FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £1235 | £141 | 9.04 | 0.03 | £5051 | 22 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 |
| IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £1458 | £223 | 9.04 | < 0.01 | Extendedly dominated | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | £2005 | £770 | 9.05 | 0.01 | £66,905 | 16 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 |
| CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2082 | £77 | 9.01 | –0.04 | Dominated | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | £2195 | £190 | 9.05 | 0 | Dominated | 8 | 12 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | £2370 | £365 | 9.05 | 0 | Dominated | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
Subgroup analyses
No subgroup analyses were conducted because of lack of relevant data.
Summary of results
The economic model presented in this chapter considered some strategies involving PDD, WLC, biomarkers, cytology and flexible cystoscopy that are potentially relevant for the diagnosis and follow-up of bladder cancer patients. The effectiveness data for diagnostic tests came from the effectiveness review. However, there were no data available on the performance of flexible cystoscopy alone or combined with cytology or biomarkers. Therefore, the sensitivity and specificity of flexible cystoscopy were assumed to be the same as those of WLC as it was likely that flexible and rigid cystoscopies would identify similar types of cancer at the same rate. Plausible changes in this rate did not change the results to any extent. For the strategies relating to combined tests it was assumed that flexible cystoscopy was combined with cytology and/or biomarkers and then followed by WLC or PDD if any one of the previous tests performed was positive.
The base-case analysis model suggests that, for a prevalence rate of 5% in a population with suspected bladder cancer, the diagnostic strategy that would be cost-effective depends upon the value that society would be willing to pay to obtain an additional unit of outcome. Broadly speaking the results based on cases detected were similar to those based upon life-years. The strategy of flexible cystoscopy and ImmunoCyt followed by PDD in initial diagnosis and flexible cystoscopy followed by WLC in follow-up [CSC_IMM_PDD(CSC_WLC)], which produced 11.66 life-years and had a mean cost of £2370 per patient, was the most costly among the diagnostic strategies in the base-case analysis. The CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) strategy was the least costly (£1043) and least effective (11.59 life-years). Although the differences between strategies in terms of costs and effects appear to be small, the important issue is the results of the willingness to pay for additional gain. CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) had a greater chance of being cost-effective when the willingness to pay was less than £20,000 per life-year. IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC), FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) and CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) had a greater probability of being cost-effective when the willingness to pay was increased to £30,000. Nevertheless, over most of the range of willingness to pay values there appeared to be no strategy that would have a likelihood of being cost-effective more than 50% of the time. For example, when the willingness to pay was over £10,000 per life-year the cost-effectiveness of FISH_PDD ranged from 16% to 20%. It should be noted, however, that four out of the eight strategies considered in the sensitivity analyses each had a probability of being considered cost-effective of approximately 20%. Three of these four strategies involved a biomarker and PDD.
The results of probabilistic sensitivity analyses performed to handle the uncertainty around the parameters within the model were broadly consistent with the point estimates in the base-case analysis and did not change the order of strategies in terms of cost. The likelihood that different strategies might be considered cost-effective, however, did change in some sensitivity analyses. For example, the CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) strategy had a 31% chance of being considered cost-effective when the prevalence rate was increased to 20% and society’s willingness to pay for a life-year was £20,000. Furthermore, CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) and CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) had an increased chance of being cost-effective in the situation in which the sensitivity and specificity of flexible cystoscopy were increased. This is important because in the base-case analysis it was assumed that the sensitivity and specificity of flexible cystoscopy would be the same as those of WLC. Both methods of cystoscopy use white light so it might be appropriate to assume that they would identify (and miss) similar types of cancer at the same rates. However, flexible cystoscopy may be able to visualise more of the bladder than rigid cystoscopy. This means that it may be possible for flexible cystoscopy to detect more cancers. Whether this is true and, if it is true, to what extent it improves sensitivity and specificity is unclear. Overall, a potentially plausible 5% gain in performance would not greatly alter the conclusions drawn on the basis of the cost-effectiveness results.
In sensitivity analyses the results did not change greatly when the QoL estimates were used to determine QALYs. The strategies associated with flexible cystoscopy were dominated and there was a decreased chance of them being considered cost-effective. This is because flexible cystoscopy, being an invasive surgical procedure, is more likely to reduce QoL than cytology or biomarkers.
In the model WLC was considered the second test in follow-up in each strategy if the result of the first test in follow-up was positive. Sensitivity analysis suggested that the non-dominated or non-extendedly dominated strategies had slightly improved life-years with higher costs compared with the base case when WLC in follow-up was replaced by PDD. However, strategies did not markedly change in how likely they were to be cost-effective.
Chapter 7 Assessment of factors relevant to the NHS and other parties
Factors relevant to the NHS
Should strategies that involve PDD be adopted by the NHS then costs to the NHS would increase and new capital equipment would be required. It is likely, however, that learning to use PDD should be straightforward for an experienced cystoscopist and hence the training period should be short. Replacing WLC with PDD should increase the number of cancers detected but this comes at the price of an increasing number of false positives. These false positives lead to an increased workload as unnecessary tests and investigations are performed and, because these tests are unlikely to be without risk, a potential increase in complications.
The results of the economic evaluation suggest that the use of cytology as part of a diagnostic strategy might be reduced. Furthermore, the results suggest that there may be merit in the increased use of biomarkers. Changes in the use of such tests would have resource implications for the NHS and would suggest transfers of resources between those parts of the NHS involved in the conduct, analysis and interpretation of these tests.
The adoption of less invasive tests in place of more invasive tests may also allow shifts in the balance of care between secondary and primary care, at least for initial diagnosis and potentially also for follow-up. Whether such changes are desirable would of course depend upon a host of other factors in addition to feasibility, such as a desire to maintain continuity of care amongst those who have been treated for bladder cancer.
One consequence of any adoption of a more effective diagnostic test is that it may result in greater survival (as estimated in the economic evaluation). Although this outcome is desirable it is important to remember that these patients will require continuing care and follow-up over a longer period. Therefore, it is possible that workload will increase for those specialties involved in follow-up. Other longer-term effects, for example the effect on palliative services, are less easy to predict.
The results of the cost-effectiveness analysis suggest that the strategies involving PDD were likely to detect more true positive cases and produce more life-years at higher costs.
Factors relevant to other parties
Quality of life for patients
The use of strategies involving PDD, ImmunoCyt and FISH could provide advantages to patients in terms of early detection of disease and (for strategies that replace an invasive procedure with a biomarker) provide a reduction in the number of invasive procedures that they may have to undergo. These strategies are also likely to decrease the number of false negatives, which will reduce the risks from false reassurance and the psychological distress following a subsequent correct diagnosis. However, there is a price to pay for this in that strategies involving these tests are also associated with an increased chance of a false-positive diagnosis. Such a diagnosis may have health effects as further tests and investigations performed are not without risk. The false-positive diagnosis may also cause considerable anxiety and distress, not only for the patients but also for their families.
Patients and their families may also have views about which diagnostic strategy they prefer that go beyond preferences over different aspects of diagnostic performance or longer-term health effects. In particular, there may be preferences about the process of care. All things being equal patients would prefer the use of non-invasive biomarker tests to the use of unpleasant, less convenient and potentially risky invasive tests. Nevertheless, all things are not equal and there are choices and trade-offs to be made between process, short-term outcomes and long-term outcomes. Currently there are no data with which to inform decision-makers about how these different outcomes might be traded off against each other.
Chapter 8 Discussion
Statement of principal findings
Photodynamic diagnosis
Diagnostic accuracy
The included diagnostic accuracy studies reported true and false positive and negative results or provided information that allowed these data to be calculated, thereby allowing further calculation of sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios, DORs and positive and negative predictive values. Most studies compared PDD with WLC. Studies comparing PDD with WLC were included in the pooled estimates (meta-analyses) using a HSROC curve model. This method takes into account the inherent trade-off between sensitivity and specificity and also allows for differences in accuracy between studies. Summary pooled estimates of the sensitivity and the specificity were calculated. Meta-analyses were performed on two levels:
-
patient
-
biopsy.
In addition to the meta-analysis models of the diagnostic accuracy of PDD and WLC individually, two HSROC models were run for patient- and biopsy-level analysis that simultaneously modelled PDD and WLC diagnostic accuracy from all of the studies included in the pooled estimates. Analysis was also undertaken on the sensitivity of PDD and WLC for the detection of stage and grade of bladder cancer, which was considered in two broad categories:
-
less aggressive, lower risk tumours (pTa, G1, G2)
-
more aggressive, higher risk tumours (pT1, G3, CIS).
The sensitivity of PDD and WLC for the detection of CIS alone was also considered. Stage and grade analysis was undertaken for both patient- and biopsy-level detection of bladder cancer. An analysis of the sensitivity of PDD according to the type of photosensitising agent used (5-ALA, HAL or hypericin) was also undertaken. Information on stage and grade analysis and type of agent used was presented as median and range across studies.
In terms of methodological quality, in all studies the spectrum of patients who received the tests was considered to be representative of those who would receive the tests in practice, partial verification bias was avoided in that all patients who underwent PDD also received a reference standard test, and test review bias was avoided in that the PDD results were considered to have been interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard test. However, in only 55% (15/27) of studies were patients considered to have received the same reference standard regardless of the index test result. All of the studies were judged to have suffered from incorporation bias in that PDD was not considered to be independent of the reference standard test as the biopsies used for the reference standard were obtained via the PDD procedure.
Although biopsy-level analysis of the accuracy of the test is more commonly reported, patient-level data are more useful in determining management. Most studies took multiple biopsies from participants, leading to clustering within participants. We were unable to account for this clustering in the biopsy-level analysis and therefore estimates from the biopsy-level analysis will be to some degree artificially precise. In the pooled estimates for patient-level analysis, based on direct evidence, PDD had higher sensitivity than WLC [92% (95% CI 80% to 100%) versus 71% (95% CI 49% to 93%)] but lower specificity [57% (95% CI 36% to 79%) versus 72% (95% CI 47% to 96%)]. As for patient-level analysis, in the pooled estimates for biopsy-level analysis, based on direct evidence, PDD also had higher sensitivity than WLC [93% (95% CI 90% to 96%) versus 65% (95% CI 55% to 74%)] but lower specificity [60% (95% CI 49% to 71%) versus 81% (95% CI 73% to 90%)]. In terms of sensitivity the upper CI for WLC did not overlap with the lower CI for PDD, supporting evidence of a difference in sensitivity in favour of PDD, and for specificity the upper CI for PDD did not overlap with the lower CI for WLC, supporting evidence of a difference in specificity in favour of WLC. The corresponding CIs for the patient-level analysis were wider because of the reduced number of studies although the direction was consistent. Although at least four of the five studies included for patient-level analysis and at least nine of the 14 studies included for biopsy-level analysis in the pooled estimates contained a mixture of patients with a suspicion of bladder cancer and those with previously diagnosed non-muscle-invasive disease, test performance in these groups was not reported separately. The formal comparison of PDD and WLC in patient- and biopsy-based analysis supported strong evidence of a difference in sensitivity in favour of PDD and in specificity in favour of WLC.
The consequence of underdiagnosis at a patient level would mean that a patient’s treatment path may be detrimentally affected (e.g. discharged from follow-up or chanelled to an inappropriately low-risk follow-up pathway). The consequence of underdiagnosis at a biopsy level is that a patient may have suboptimal treatment of their known bladder cancer, for example by failure to remove an occult lesion or failure to institute a therapy because of underestimating the patient’s risk category (e.g. by failing to diagnose concomitant CIS).
Across studies the median sensitivities (range) of PDD and WLC for detecting lower risk, less aggressive tumours were broadly similar for patient-level detection [92% (20% to 95%) versus 95% (8% to 100%)], but sensitivity was higher for PDD for biopsy-level detection [96% (88% to 100%) versus 88% (74% to 100%)]. However, for the detection of more aggressive, higher risk tumours the median sensitivities of PDD for both patient-level [89% (6% to 100%)] and biopsy-level [99% (54% to 100%)] detection were much higher than those of WLC [56% (0% to 100%) and 67% (0% to 100%) respectively]. The superior sensitivity of PDD was also reflected in the detection of CIS alone, both for patient-level [83% (41% to 100%) versus 32% (0% to 83%)] and biopsy-level [86% (54% to 100%) versus 50% (0% to 68%)] detection. However, these results should be interpreted with caution as, other than for PDD biopsy-based detection of lower risk disease, the range of sensitivities for both tests was very wide. [It may also be useful to note that, although not meeting the inclusion criteria for this review as information was not provided on false positives and true negatives, Schmidbauer and colleagues,207 in a European multicentre study (19 centres), reported that, of 83 patients with CIS lesions, CIS was detected in 80 (96%) by PDD (HAL) compared with 64 (77%) by WLC.]
In terms of the relative sensitivities of the photosensitising agents used, for patient-level detection of bladder cancer, the median sensitivity (range) of 5-ALA was slightly higher than that of HAL [96% (64% to 100%) versus 90% (53% to 96%)] whereas HAL had higher specificity than 5-ALA [81% (43% to 100%) versus 52% (33% to 67%)]. This situation was also reflected in biopsy-based detection, with 5-ALA associated with higher sensitivity [95% (87% to 98%) versus 85% (76% to 94%)] but lower specificity [57% (32 to 67%) versus 80% (58 to 100%)] than HAL. One study, by Sim and colleagues,76 reporting biopsy-based detection of bladder cancer, used hypericin, reporting sensitivity of 82% and specificity of 91%. These results suggest that 5-ALA may be associated with slightly higher sensitivity than HAL and that HAL has higher specificity than 5-ALA, but this should be interpreted with caution as a number of factors other than the photosensitising agent used may have contributed to the sensitivity and specificity values reported by the studies.
Twelve studies51–53,61–63,65,71–73,78,81 involving 1543 patients reported that there were no side effects or no serious side effects associated with the photosensitising agent used. Seven studies50,57,66,67,71,76,77 involving 746 patients reported 41 side effects associated with the agent (5-ALA, 19; HAL, 21; hypericin, 1), none of which was considered to be serious.
No other systematic reviews of PDD for detecting bladder cancer or reporting effectiveness outcomes such as tumour recurrence were identified.
In summary, compared with WLC, PDD has higher sensitivity (fewer false negatives) and so will detect cases of bladder cancer that are missed by WLC. However, compared with WLC, PDD’s lower specificity (more false positives) will result in additional, unnecessary biopsies of non-cancerous tissue being taken and sent for analysis. Reasons cited in the literature for PDD false-positive results include: (1) inexperience in using PDD, in which the application of tangential fluorescence light may cause fluorescence in normal urothelium, (2) simple hyperplasia, (3) lesions with inflammation or scarring after previous TURBT when PDD was carried out within 6 weeks of the previous procedure and (4) previous instillation therapy within 3–6 months of PDD. 208,209 De Dominicis and colleagues53 noted that a greater number of false-positive lesions were detected during the period when the authors were still not sufficiently trained in the PDD procedure, particularly in the first 15 patients. In terms of the detection of stage and grade of tumour, the results suggest that PDD is much more sensitive than WLC in the detection of more aggressive, higher risk tumours, and the superior performance of PDD is also reflected in the detection of CIS alone. From a clinical point of view, compared with WLC, the advantages of PDD’s higher overall sensitivity in detecting bladder cancer and also its higher sensitivity in detecting more aggressive, higher risk tumours have to be weighed against the disadvantages of a higher false-positive rate leading to additional, unnecessary biopsies of normal tissue being taken and potentially additional unnecessary investigations being carried out and the resulting anxiety caused to patients and their families.
Recurrence/progression of disease
Jain and Kockelbergh210 noted that the high recurrence rate of superficial bladder cancer, up to 70% at 5 years, was responsible for a huge workload for urologists and much inconvenience for patients. They stated that the recurrence rate at the first check cystoscopy varied enormously, suggesting that incomplete resection or failure to detect small additional tumours may be a risk factor. 210 The evidence from the diagnostic accuracy part of this review suggests that PDD has a higher sensitivity for the detection of bladder cancer than WLC. Therefore, compared with WLC, the use of PDD during initial TURBT may be expected to result in lower recurrence and progression rates, given that some tumours, including more aggressive, higher risk tumours such as CIS, that might be missed by WLC will be detected by PDD.
For the assessment of PDD-assisted TURBT compared with WLC in terms of effectiveness outcomes such as recurrence and progression, this review focused on RCTs. Four RCTs (reported in eight papers) involving 544 participants met the inclusion criteria. In terms of methodological quality, in all four studies the groups were considered to be similar at baseline in terms of prognostic factors, eligibility criteria for the studies were specified and the length of follow-up was considered adequate in relation to the outcomes of interest. However, in all studies it was unclear whether the sequence generation was really random or whether treatment allocation was adequately concealed.
When meta-analysis was undertaken, the results were reported using RR as the effect measure and a fixed-effect model in the absence of statistical heterogeneity, otherwise a random-effects model was used. Two studies86,89 reported recurrence-free survival at 12 and 24 months. In pooled estimates the direction of effect for both time points favoured PDD, although the difference was statistically significant only at the 24-month time point (RR 1.37, 95% CI 1.18 to 1.59).
Four studies86,88,89,92 reported residual tumour rate at first cystoscopy following TURBT. In pooled estimates PDD was associated with both statistically significantly fewer residual pTa tumours (RR 0.32, 95% CI 0.15 to 0.70) and fewer residual pT1 tumours (RR 0.26, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.57) than WLC (overall pooled estimate RR 0.37, 95% CI 0.20 to 0.69). Two of the studies86,88 also reported residual tumour according to grade (G1, G2 and G3). Pooled estimates for G1 (RR 0.13, 95% CI 0.03 to 0.71) and G2 (RR 0.32, 95% CI 0.16 to 0.64) were statistically significant in favour of PDD, with the direction of effect for G3 favouring PDD without reaching statistical significance (RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.21 to 1.56), and the overall pooled estimate was statistically significant in favour of PDD (RR 0.31, 95% CI 0.18 to 0.53).
Two studies88,89 reported tumour recurrence rate during follow-up (5 years and 8 years respectively). In pooled estimates the direction of effect favoured PDD without reaching statistical significance (RR 0.64, 95% CI 0.39 to 1.06). Both studies88,89 also reported tumour progression during their respective follow-up periods and again in the pooled estimates the direction of effect favoured PDD without reaching statistical significance (RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.22 to 1.46).
Two studies86,88 reported time to recurrence, both favouring PDD. Babjuk and colleagues86 reported a median time to recurrence of 17.05 months for the PDD group and 8.05 months for the WLC group, whereas Daniltchenko and colleagues88 reported a median (range) time to recurrence of 12 (2 to 58) months for the PDD group and 5 (2 to 52) months for the WLC group.
In summary, the evidence from the RCTs86,88,89,92 suggests that, compared with WLC, the use of PDD during TURBT results in a statistically significant and large reduction in residual pTa and pT1 tumours, longer recurrence-free survival of patients at 2 years following surgery and a longer interval between TURBT and tumour recurrence. However, these results should be interpreted with caution as they are based on data from only four small studies. Based on the limited evidence it is unclear whether PDD compared with WLC is associated with lower tumour recurrence and progression rates in the longer term. Also, as discussed in the section on uncertainties, the administration of adjuvant intravesical therapy varied across the studies, making it difficult to assess what the true added value of PDD might be in reducing recurrence rates in routine clinical practice.
Biomarkers and cytology
The included diagnostic accuracy studies reported true and false positive and negative results or provided information that allowed these data to be calculated, thereby allowing the further calculation of sensitivity and specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios, DORs and positive and negative predictive values for the three included urine biomarkers (FISH, ImmunoCyt and NMP22) and cytology. Meta-analyses were undertaken for each of the individual biomarkers and cytology for patient-based detection of bladder cancer using the HSROC model. Additional meta-analyses were also undertaken on the subset of studies included in the pooled estimates that directly compared biomarkers with cytology. Analysis was also undertaken on the sensitivity of the biomarkers and cytology for the detection of stage and grade of bladder cancer, which was considered in the two broad categories previously referred to (less aggressive/lower risk tumours and more aggressive/higher risk tumours), and also for detection of CIS alone.
For each biomarker only those studies that were considered to have a similar (‘common’) cut-off, which was generally taken to be the most frequently used cut-off across studies, were included in the meta-analyses. The common cut-off was also used when studies reported results using a number of different cut-offs. The following common cut-offs were used: FISH, gains of two or more chromosomes or five or more cells with polysomy or four or more aneusomic of 25 counted cells; ImmunoCyt, at least one green or one red fluorescent cell; NMP22, 10 U/ml; urine cytology, cytologist subjective assessment.
In terms of methodological quality, in all 71 studies the reference standard (cystoscopy with histological assessment of biopsied tissue) was considered likely to correctly classify bladder cancer. In 99% (70/71) of studies the spectrum of patients receiving the tests was considered to be representative of those who would receive the test in practice, and incorporation bias was avoided in that the reference standard was independent of the biomarker/cytology test. In 96% (68/71) of studies partial verification bias was avoided in that all patients who received a biomarker/cytology test also received a reference standard test, and in 87% (62/71) of studies differential verification bias was avoided in that all patients received the same reference standard regardless of the index test result. However, only 69% (49/71) of studies were considered to have given a clear definition of what constituted a positive result.
Table 52 shows the pooled estimates (sensitivity, specificity, DORs) as well as the median (range) positive and negative predictive values across studies for the biomarkers and cytology for patient-based detection of bladder cancer. In the pooled estimates, based on indirect evidence, sensitivity was highest for ImmunoCyt at 84% (95% CI 77% to 91%) and lowest for cytology at 44% (95% CI 38% to 51%). ImmunoCyt (84%, 95% CI 77% to 91%) had higher sensitivity than NMP22 (68%, 95% CI 62% to 74%), with the lack of overlap between the CIs supporting evidence of a difference in sensitivity in favour of ImmunoCyt over NMP22. FISH (76%, 95% CI 65% to 84%), ImmunoCyt (84%, 95% CI 77% to 91%) and NMP22 (68%, 95% CI 62% to 74%) all had higher sensitivity than cytology (44%, 95% CI 38% to 51%), and again the lack of overlap of the CIs between the three biomarkers and cytology supported evidence of a difference in sensitivity in favour of the three biomarkers over cytology. This situation was reversed for specificity, which was highest for cytology at 96% (95% CI 94% to 98%) and lowest for ImmunoCyt at 75% (68% to 83%). Cytology (96%, 95% CI 94% to 98%) had higher specificity than FISH (85%, 95% CI 78% to 92%), ImmunoCyt (75%, 95% CI 68% to 83%) or NMP22 (79%, 95% CI 74% to 84%), with the lack of overlap of the CIs between cytology and the three biomarkers supporting evidence of a difference in specificity in favour of cytology over the biomarkers.
| Test | Number of studies | Number analysed | Sensitivity (%) (95% CI) | Specificity (%) (95% CI) | DOR (95% CI) | PPV (%), median (range) | NPV (%), median (range) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FISH | 12 | 2535 | 76 (65 to 84) | 85 (78 to 92) | 18 (3 to 32) | 78 (27 to 99) | 88 (36 to 97) |
| ImmunoCyt | 8 | 2896 | 84 (77 to 91) | 75 (68 to 83) | 16 (6 to 26) | 54 (26 to 70) | 93 (86 to 100) |
| NMP22 | 28 | 10,119 | 68 (62 to 74) | 79 (74 to 84) | 8 (5 to 11) | 52 (13 to 94) | 82 (44 to 100) |
| Cytology | 36 | 14,260 | 44 (38 to 51) | 96 (94 to 98) | 19 (11 to 27) | 80 (27 to 100) | 80 (38 to 100) |
DORs (95% CI) ranged from 8 (5 to 11) to 19 (6 to 26), with higher DORs indicating a better ability of the test to differentiate between those with and those without bladder cancer. Based on the DOR values, FISH and cytology performed similarly well [18 (3 to 32) and 19 (11 to 27) respectively], ImmunoCyt slightly less so [16 (6 to 26)] and NMP22 relatively poorly [8 (5 to 11)]. However, as the DOR confidence intervals for each of the tests all overlapped these results should be interpreted with caution.
Across studies the median (range) PPVs were 80% (27% to 100%) for cytology (36 studies), 78% (27% to 99%) for FISH (12 studies), 54% (26% to 70%) for ImmunoCyt (eight studies) and 52% (13% to 94%) for NMP22 (28 studies). NPVs were 93% (86% to 100%) for ImmunoCyt, 88% (36% to 97%) for FISH, 82% (44% to 100%) for NMP22 and 80% (38% to 100%) for cytology. However, it should be noted that predictive values are affected by disease prevalence, which is rarely constant across studies.
Five studies80,126,127,131,150 reporting NMP22 used the BladderChek point of care test. Across these studies, using a cut-off of 10 U/ml for a positive test result, the median (range) sensitivity and specificity for patient-based detection of bladder cancer were 65% (50% to 85%) and 81% (40% to 87%) respectively. This is broadly similar to the 68% (95% CI 62% to 74%) sensitivity and 79% (95% CI 74% to 84%) specificity for the 28 studies included in the pooled estimates.
In terms of the detection of stage/grade of tumour, ImmunoCyt had the highest median sensitivity across studies (81%) for the detection of less aggressive/lower risk tumours whereas FISH had the highest median sensitivity across studies (95%) for the detection of more aggressive/higher risk tumours. For detection of CIS the median sensitivity across studies for both FISH and ImmunoCyt was 100%. Cytology had the lowest sensitivity across studies for detecting less aggressive/lower risk tumours (27%), more aggressive/higher risk tumours (69%) and also CIS (78%). For each of the tests, the median sensitivity across studies was consistently higher for the detection of more aggressive/higher risk tumours than for the detection of less aggressive, lower risk tumours. The results for the stage/grade analysis should be interpreted with caution, however, as they are based on a relatively small number of studies for ImmunoCyt (n = 6) and FISH (n = 10), as are the results for the detection of CIS (ImmunoCyt, n = 6; FISH, n = 8; NMP22, n = 11). Additionally, for all of the tests the range of sensitivities across the studies for detecting stage/grade (both lower and higher risk) and CIS was very wide.
Some studies included in the pooled estimates for the individual tests also directly compared tests, comparing FISH with cytology (five studies), ImmunoCyt with cytology (six studies) and NMP22 with cytology (16 studies). In each set of comparisons cytology had lower sensitivity but higher specificity than the biomarker with which it was being compared. ImmunoCyt had higher sensitivity (82%, 95% CI 76% to 89%) than cytology (44%, 95% CI 35% to 54%), whereas cytology had higher specificity (94%, 95% CI 91% to 97%) than ImmunoCyt (85%, 95% CI 71% to 85%), with the lack of overlap of the CIs supporting evidence of differences in sensitivity in favour of ImmunoCyt and in specificity in favour of cytology. Similarly, NMP22 had higher sensitivity (70%, 95% CI 59% to 80%) than cytology (40%, 95% CI 31% to 49%), whereas cytology had higher specificity (97%, 95% CI 95% to 99%) than NMP22 (81%, 95% CI 74% to 88%), with the lack of overlap of the CIs supporting evidence of differences in sensitivity in favour of NMP22 and in specificity in favour of cytology. The pooled estimates for the sensitivity and specificity of the tests in the direct comparison studies were broadly similar to those reported for the individual tests. The formal comparison for a difference between tests supported a difference between both ImmunoCyt and NMP22, and cytology, but there was no evidence for a difference between FISH and cytology. The latter finding was based upon a small number of studies and therefore a real difference may exist as implied by the results for the individual tests, which were based upon a larger number of studies.
In studies reporting the sensitivity and specificity of tests used in combination, sensitivity was generally higher but specificity lower for the combined tests compared with the higher value of the two individual tests. Most combinations of tests were reported by only one or two studies apart from the combination of ImmunoCyt and cytology, which was reported by eight studies.
In studies specifically reporting unevaluable tests, rates were 6.1% (65/1059, five studies) for FISH, 5% (279/5292, 10 studies) for ImmunoCyt and 2% (54/2566, six studies) for cytology. None of the NMP22 studies specifically reported unevaluable tests.
A few other systematic reviews have reported the sensitivity and specificity of biomarkers and cytology for detecting bladder cancer (Table 53). In a systematic review and meta-analysis of biomarkers for the surveillance monitoring of previously diagnosed bladder cancer Lotan and Roehrborn211 reported, amongst other biomarkers, ImmunoCyt, NMP22 and cytology. A systematic review by Glas and colleagues212 of tumour markers in the diagnosis of primary bladder cancer reported, amongst others, NMP22 and cytology. A systematic review by van Rhijn and colleagues213 of urine markers for bladder cancer surveillance reported, amongst others, FISH, ImmunoCyt, NMP22 and cytology. Our results for the sensitivity and specificity of FISH, ImmunoCyt, NMP22 and cytology were mostly similar to those reported by the other reviews, other than we reported higher specificity for FISH (85% compared with 70%), higher sensitivity for ImmunoCyt (84% compared with 67%) and slightly higher specificity for NMP22 (79% compared with 73%) than van Rhijn and colleagues,213 respectively, and, for cytology, higher sensitivity than Lotan and Roehrborn211 and van Rhijn and colleagues213 (44% compared with 34% and 35% respectively) but lower sensitivity than Glas and colleagues (44% compared with 55% respectively). 212
| FISH | ImmunoCyt | NMP22 | Cytology | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of studies | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | No. of studies | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | No. of studies | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | No. of studies | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | |
| Present review | 12 | 76 (65 to 84) | 85 (78 to 92) | 8 | 84 (77 to 91) | 75 (68 to 83) | 28 | 68 (62 to 74) | 79 (74 to 84) | 36 | 44 (38 to 51) | 96 (94 to 98) |
| Glas 2003212 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 14 | 67 (60 to 73) | 78 (72 to 83) | 26 | 55 (48 to 62) | 94 (90 to 96) |
| Lotan 2003211 | – | – | – | 1 | 86 | 79 | 15 | 73 (47 to 87) | 80 (58 to 91) | 18 | 34 (20 to 53) | 99 (83 to 99) |
| van Rhijn 2005213 | 4 | 79 (70 to 86) | 70 (66 to 93) | 6 | 67 (52 to 100) | 75 (62 to 82) | 15 | 71 (47 to 100) | 73 (55 to 98) | 26 | 35 (13 to 75) | 94 (85 to 100) |
Strengths and limitations of the assessment
Diagnostic accuracy/effectiveness
In terms of strengths, for PDD/WLC effectiveness outcomes such as recurrence we focused only on RCTs. In biomarker/cytology case–control studies in which the control group contained a proportion of completely healthy controls, the control group was reanalysed minus the healthy controls to try to make it more representative of the types of people who would receive the tests in practice. If this was not possible the study was excluded. Case–control studies in which the whole control group consisted of healthy volunteers were excluded.
In terms of limitations, non-English language studies were excluded, as were biomarker studies with fewer than 100 patients included in the analysis. Cytology studies whose publication year predated the publication year of the earliest included biomarker study were excluded. Although most studies contained a mixture of patients with a suspicion of bladder cancer and those with a history of previously diagnosed bladder cancer, few studies reported results for these groups separately. Only five of the 41 included NMP22 studies used the BladderChek point of care test.
Uncertainties
Diagnostic accuracy/effectiveness
PDD in the clinical pathway
PDD could potentially be used in conjunction with rigid WLC at different stages in the clinical pathway, including initial diagnosis and treatment and surveillance monitoring. As with rigid WLC, PDD is not only a diagnostic test but also involves treatment in that during the procedure suspicious lesions are not only identified but also removed. Although most of the studies included in the pooled estimates for both patient- and biopsy-level analysis contained a mixture of patients with a suspicion of bladder cancer and those with previously diagnosed non-muscle-invasive disease, test performance in these groups was not reported separately. In the pooled estimates for both patient- and biopsy-level analysis, PDD had higher sensitivity than WLC but lower specificity. Across studies the median sensitivities (range) of PDD and WLC for detecting lower risk, less aggressive tumours were broadly similar for patient-level detection but the sensitivity of PDD was higher than that of WLC for biopsy-level detection. However, for the detection of more aggressive, higher risk tumours the median sensitivities of PDD for both patient- and biopsy-level detection were much higher than those of WLC and this superior sensitivity of PDD was also reflected in the detection of CIS alone. This suggests that the appropriate point in the clinical pathway for PDD to be used is in conjunction with rigid WLC during the initial TURBT, and possibly also in conjunction with rigid WLC during surveillance monitoring of some high-risk patients.
In the four studies reporting effectiveness outcomes, PDD was used during the initial TURBT. Patients were randomised to WLC- or WLC- and PDD-assisted TURBT,86,89,92 or WLC- or PDD-assisted TURBT. 88 In the studies by Babjuk and colleagues,86 Denzinger and colleagues89 and Kriegmair and colleagues92 residual tumour in both groups was evaluated by WLC-assisted resection. However, in the study by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 residual tumour in both groups was evaluated by PDD-assisted resection. In three studies the patients were followed up using WLC and urinary cytology. 86,88,89 (As the aim of the study by Kriegmair and colleagues92 was to assess residual tumour 10–14 days following TURBT there was no longer-term follow-up).
Adjuvant chemotherapy
Adjuvant single-dose chemotherapy administered within the first 24 hours and ideally within the first 6 hours following TURBT is standard practice in the UK and much of Europe and can reduce recurrence rates by up to 50% in the first 2 years. However, the administration of adjuvant intravesical therapy varied across the four studies reporting effectiveness outcomes. The study by Kriegmair and colleagues92 did not state whether intravesical therapy was given. The study by Daniltchenko and colleagues88 reported that none of the patients received adjuvant intravesical therapy. In the study by Babjuk and colleagues86 none of the patients with grade 1 or grade 2 tumours received intravesical therapy, whereas all those with grade 3 tumours received intravesical BCG immunotherapy. In the study by Denzinger and colleagues89 patients with a solitary primary tumour staged pTaG1–G2 (low-risk group) did not receive intravesical therapy, whereas those with multifocal tumours staged pTaG1–G2 or pT1G1–G2 (intermediate-risk group) underwent mitomycin therapy and those with primary stage pT1G3, CIS or treatment failure with mitomycin (high-risk group) received BCG therapy. In this study, although there were consistently fewer recurrences for PDD compared with WLC across all risk groups, the difference in recurrence rates between PDD and WLC was smaller in the intermediate- and high-risk groups, both of which received adjuvant intravesical therapy, than it was in the low-risk group. 89 The fact that adjuvant intravesical therapy was not given to all of the patients in all of the studies makes it difficult to assess what the true added value of PDD might be in reducing bladder tumour recurrence rates in routine practice.
Biomarker/cytology test performance in patients with a suspicion of bladder cancer and those with a history of non-muscle-invasive disease
It is possible that the diagnostic accuracy of urine biomarkers/cytology may differ in patients newly presenting with a suspicion of bladder cancer compared with those with a previous history of non-muscle-invasive disease. Most of the included studies contained a mixture of patients with a suspicion of bladder cancer and those with previously diagnosed disease but did not report results for these groups separately. However, in a few of the studies included in the pooled estimates that reported patient-level analysis the whole patient population consisted either of one or other of these groups. Table 54 shows, for each test, the median (range) sensitivity and specificity across studies containing those newly presenting with symptoms of bladder cancer and those with previously diagnosed non-muscle-invasive disease. For each test, both sensitivity and specificity were slightly higher for the studies containing patients newly presenting with symptoms of bladder cancer, although these results should be interpreted with caution as they are based on limited evidence, especially for FISH and ImmunoCyt.
| Test | Suspicion/previous history of BC | Number of studies | Number analysed | Sensitivity (%), median (range) | Specificity (%), median (range) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FISH | Suspicion of BC | 1 | 497 | 69 | 78 |
| Previous history of BC | 1 | 250 | 64 | 73 | |
| ImmunoCyt | Suspicion of BC | 1 | 280 | 85 | 88 |
| Previous history of BC | 1 | 326 | 81 | 75 | |
| NMP22 | Suspicion of BC | 4 | 1893 | 71 (56 to 100) | 86 (80 to 87) |
| Previous history of BC | 7 | 4284 | 69 (50 to 85) | 81 (46 to 93) | |
| Cytology | Suspicion of BC | 7 | 3331 | 44 (16 to 100) | 99 (87 to 100) |
| Previous history of BC | 6 | 4195 | 38 (12 to 47) | 94 (83 to 97) |
Biomarkers as a replacement for cytology
In the pooled estimates the lack of overlap of the CIs between the three biomarkers and cytology supported evidence of the biomarkers’ superior sensitivity over cytology. ImmunoCyt had the highest sensitivity (84%, 95% CI 77% to 91%), followed by FISH (76%, 95% CI 65% to 84%) and NMP22 (68%, 95% CI 62% to 74%), with cytology having the lowest sensitivity (44%, 95% CI 38% to 51%). This situation was reversed for specificity, with the lack of overlap of the CIs between cytology and the three biomarkers supporting evidence of cytology’s superior specificity over all three biomarkers. The specificity of cytology was 96% (95% CI 94% to 98%), compared with 85% (95% CI 78% to 92%) for FISH, 79% (95% CI 74% to 84%) for NMP22 and 75% (95% CI 68% to 73%) for ImmunoCyt. The question of whether biomarkers might replace cytology depends on the relative importance of higher sensitivity (fewer false-negative results) compared with higher specificity (fewer false-positive results). If the sensitivity of the test was seen as being more important than its specificity then a test such as ImmunoCyt could be regarded as a potential candidate for replacing cytology. However, if the specificity of the test was seen as being more important then cytology would remain the test of choice, given its superior specificity over all three biomarkers. A highly sensitive test will have few false negatives, whereas a highly specific test will have few false positives. In the case of high-risk bladder cancer, for example, the consequences of a false-negative test result are potentially great, whereas those of a false-positive test result are relatively low, inasmuch as these patients are unlikely to progress to a significantly morbid treatment without a further diagnostic test.
Biomarkers as a replacement for flexible cystoscopy in monitoring patients with a history of low-risk bladder cancer
There have been suggestions that, given appropriate sensitivity, a biomarker might replace the use of some flexible cystoscopy for monitoring patients with a history of low-risk bladder cancer. In the pooled estimates the median (95% CI) sensitivity was 84% (77% to 91%) for ImmunoCyt, 76% (65% to 84%) for FISH and 68% (62% to 74%) for NMP22. ImmunoCyt at 84% had the highest sensitivity but this may still be regarded as too low for its consideration as a replacement for flexible cystoscopy. Messing and colleagues111 stated that for all biomarkers the lowest sensitivity was for detecting low-grade tumours, which would be of concern if these tests were used to replace some cystoscopic examinations for monitoring patients with a history of low-risk bladder cancer. Also, a study by Yossepowitch and colleagues214 interviewed 200 consecutive patients previously diagnosed with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer who were undergoing outpatient flexible cystoscopy at follow-up. The authors reported that, of the 200 patients, 75% would accept the results of a urine test as a replacement for cystoscopy only if it was capable of detecting more than 95% of recurrent bladder tumours. Anxiety associated with the possibility of missing cancer was given as the major determinant of the minimal accepted accuracy. 214 However, these findings may not take account of the fact that cystoscopy itself may not have perfect sensitivity.
Random biopsies
There appears to be no general consensus on whether random biopsies of normal-appearing areas of the bladder should be undertaken during cystoscopy. Some authors54,68 argue that flat lesions such as dysplasias and CIS may be difficult to visualise and therefore random biopsies should be undertaken. Kiemeney and colleagues,215 in a study involving 854 patients with superficial bladder cancer, noted that random biopsies from normal-appearing areas revealed important histological findings that were of high prognostic value. However, Witjes and colleagues,194 in a study of 1026 patients, claimed that random biopsies were of little value in determining patients’ prognosis. In a study by van der Meijden and colleagues,216 the authors stated that in approximately 90% of patients the biopsies of normal-appearing urothelium in patients with stage Ta or T1 bladder cancer showed no abnormalities and therefore did not contribute to staging or to the correct choice of adjuvant therapy following TURBT. Jichlinski and colleagues65 stated that random biopsies of normal urothelium remained a subject of controversy and did not recommend their use in the general population of patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Cost-effectiveness analysis
Statement of principal findings
The base-case analysis was based on a 5% prevalence rate of bladder cancer regardless of whether the cost-effectiveness measure was presented in terms of either cost per true positive case detected or cost per life-year. Flexible cystoscopy and ImmunoCyt followed by PDD in initial diagnosis and flexible cystoscopy followed by WLC in follow-up [CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC)], which produced on average 11.66 life-years and had a mean cost of £2370 per patient, was the most costly among the diagnostic strategies considered in this study. The CTL_WLC strategy was the least costly (£1043) and least effective (11.59 life-years). There were six ‘non-dominated’ or non-extendedly dominated strategies in the base-case model when outcomes were measured in terms of incremental cost per life-year: CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC), CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC), FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC), IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC), CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) and CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC). Although the differences between these appear to be small in terms of cost and effects, it is important to remember that in only 5% of patients in the base-case analysis would testing provide any gain. The important issue is what society would be willing to pay for additional gain. The base-case results of the economic model indicated that the diagnostic strategy that would be cost-effective depends upon the value that society would be willing to pay to obtain an additional life-year. Cytology followed by WLC as the initial diagnosis and follow-up using the same interventions [CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC)] had a greater chance of being cost-effective when the willingness to pay was less than £20,000 per life-year. However, when the willingness to pay was increased to £30,000 per life-year IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC), FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) and CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_PDD) also had a greater probability of being cost-effective. Nevertheless, over most of the range of willingness to pay values there appeared to be no strategy that would have a likelihood of being cost-effective more than 50% of the time. For example, when the willingness to pay was over £10,000 per life-year the cost-effectiveness of FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) ranged from 16% to 20%. Of note, however, is that four of the eight strategies considered in the probabilistic analysis were each associated with a 20% probability of being considered cost-effective at a range of values that society might be willing to pay. Three of these four strategies involved the use of a biomarker and PDD.
Results of probabilistic sensitivity analyses performed to handle the uncertainty around the parameters within the model were broadly consistent with the point estimates in the base-case analysis and did not change the order of strategies in terms of cost. However, the likelihood that different strategies might be considered cost-effective changed when some of the parameters were varied. For example, the CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) strategy had a 25% chance of being considered cost-effective when the prevalence rate was increased to 20% and society’s willingness to pay for a life-year was £20,000. There was some concern that, because of lack of data, the performance of flexible cystoscopy might be underestimated. Sensitivity analyses suggest that plausible (but contentious) increases in diagnostic performance would not alter the conclusions drawn.
In the cost–consequence analysis presented as part of the economic evaluation it was shown that the different strategies were likely to vary not only in terms of long-term performance but also in terms of short-term diagnostic performance. It is likely that patients will have preferences about these different short-term outcomes that would not be reflected in estimates of life-years or indeed in QALYs based upon standard generic instruments such as the EQ-5D. Furthermore, as indicated in Chapter 7 patients may also have preferences about the process of care (including the use of non-invasive tests). The net impact of including these other potential benefits is unclear at present and might be considered as an area for further research.
Strengths and limitations
This work is important as it is the first study to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the diagnostic and follow-up strategies in patients with bladder cancer. The analysis considered the use of PDD, biomarkers and cytology, in a variety of combinations, using a decision tree and a Markov model.
A structured literature search was performed to identify existing economic analyses of the diagnosis and management of patients with bladder cancer. No studies were identified that directly compared the interventions under consideration. The approach adopted in this study provides an explicit, reproducible methodology with which to consider the interventions under consideration. Based on the relevant guidelines and detailed discussion with clinical experts involved in this study, the care pathways were developed to build up the structure of an economic model. The methods used to estimate the parameters used in the model were explicit and systematic and sought to identify the best available evidence.
Although the methods adopted to obtain the parameter estimates sought to identify the best evidence available, the results should be interpreted with caution as there are uncertainties and assumptions made in the economic model. For example, there was no evidence of what happens to patients who have false-negative results. It is likely that bladder cancers missed in initial diagnosis would not be treated until later, resulting in the risk of faster progression of disease. It was also difficult to identify suitable data on how quickly untreated bladder cancer progresses compared with treated bladder cancer. In the model a RR of progression or mortality comparing no treatment (false-negative results) with treatment (treatment of true positives) was used. In the base-case analysis it was assumed that the rate of RRs for progression (to muscle-invasive disease) and mortality for patients who did not receive treatment (i.e. those falsely diagnosed as negative) compared with those who did receive treatment (i.e. those correctly diagnosed as positive) was 2.56. It should be noted, however, that the sensitivity analysis that addressed this assumption had very little impact on the results because there were small differences in false-negative cases (or proportions) between strategies at the level of prevalence (5%) of bladder cancer considered in the base-case analysis, indicating that this variable might not be that important as a determinant of cost-effectiveness.
The model structure focused on the diagnosis and management of bladder cancer. The costs and benefits of identifying and treating other causes of the symptoms (e.g. upper urinary tract problems, etc.) that patients presented with have not been included. The net effect of not including this in a model is uncertain.
Besides the uncertainties surrounding the parameter estimates there were several other limitations to the report. One of the limitations of the economic evaluation was that it was not possible to perform analysis on the impact of diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer on QoL as there were no data based on a generic economic tool. Although QoL data for other urological cancers were available, after discussion with clinical experts they were deemed not to be generalisable to this group of patients. A simple sensitivity analysis suggested that the inclusion of QoL estimates may not greatly change the results. However, further research to elicit relevant health rate utilities would be useful.
Another challenge was that it was not possible to conduct subgroup analysis because of a lack of data relating to subgroups. The subgroups considered in this study were number of tumours on first cystoscopic examination; type of tumour; tumour recurrence at the first 3-month cystoscopic examination following TURBT; and diagnostic performance of the different PDD photosensitising agents. Also considered were types of tumour and tumour recurrence on diagnostic performance of the different categories of urine biomarker; and whether the urine sample for urine biomarkers was voided or obtained by bladder wash. More data are needed to perform these subgroup analyses.
Another limitation was the lack of evidence on the performance of flexible cystoscopy, although it is the most commonly used test in current UK practice. The reasons for lack of evidence for flexible cystoscopy may be attributable to the fact that it is an invasive procedure purely based on the judgement of the person performing it, making it difficult to evaluate the subjective outcome. Sensitivity analysis showed that potentially plausible improvements in the performance of flexible cystoscopy may not be meaningful.
Another limitation was the determination of the most appropriate value for the prevalence rate of bladder cancer in the population that presents with various symptoms of bladder cancer. There is evidence that the prevalence rate may vary depending on the symptoms that the patients present with. Ideally the population in the model should have been based on patients who had primary bladder cancer without a cancer history. However, it was difficult to establish relevant numbers from the review of effectiveness as the results were based on both first-time presentations as well as repeat patients. It can be argued that the prevalence rate considered in the model may either overestimate or underestimate the number of people with primary bladder cancer. Sensitivity analysis results indicated that the prevalence rate has a big impact on the cost-effectiveness results. At a low level of prevalence (e.g. 1%) it is most likely that the least costly strategy [CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC)] would be cost-effective over most of the strategy range for a cost per life-year that society might be willing to pay. At higher prevalences (e.g. 20%) it is more likely that the more costly but more effective strategies would be considered worthwhile. One implication of the sensitivity of the model to prevalence rates is that it suggests that should a subgroup of the population be identified that has a higher expected prevalence rate then it is possible that more effective (but more costly) strategies would be worthwhile for such patients. Further research could consider whether such subgroups could be identified.
The economic evaluation may suffer from other limitations in addition to those related to the evidence base. A number of assumptions were made with respect to the way that the decision tree and the Markov model were constructed. These assumptions were mostly made because of the lack of data to populate the model. As mentioned in Chapter 6, it was assumed that the cycle lengths for risk groups were the same during follow-up. Given the different intensities of follow-up for different types of bladder cancer, in practice there would be more than one opportunity per cycle for recurrent cancer to be diagnosed for some risk groups.
A further assumption was made regarding the management of patients following recurrent disease. During follow-up following treatment for bladder cancer, individuals could be incorrectly identified as still clear of cancer at a follow-up visit (i.e. be a false-negative). There were no data to help model the impact of missing a cancer on follow-up on mortality and progression. However, in our model all patients would have relatively frequent repeat testing during follow-up so the impact of this limitation is debatable.
Uncertainty in cost-effectiveness
Although cost-effectiveness analysis was performed using the best available data there was some uncertainty surrounding some of the parameters used in the model. One of these parameters was the risk group categorisation of non-muscle-invasive disease. The ideal categorisation would need to be based on all six prognostic risk factors and include long-term survival and disease-free information. As mentioned in Chapter 1, although the EORTC classification was the most recently recommended version and may have been the ideal one to be adopted in the model, it was not possible to use because of its complexity. Also, there were no reliable data associated with the risk groups. In addition, the diagnostic technology for follow-up of bladder cancer may depend on the risk level for progression and recurrence, for example T1G3 and CIS will always be followed up using rigid cystoscopy. It is acknowledged that the definition of risk groups may affect the judgement of cost-effectiveness in the model. However, the sensitivity analysis suggested that there is only a slight impact on base-case analysis when the proportions of risk group are changed.
There was also uncertainty relating to survival and recurrence-free and progression-free survival data as they were only available up to 5 years post initial diagnosis. These data were extrapolated to predict cost-effectiveness up to 20 years. Data at 5 years suggested little difference in terms of survival and recurrence- and progression-free survival. However, results would be greatly strengthened if longer-term randomised data were available. For the purposes of the model the mortality, progression and recurrence rates were assumed to be constant over time. Given that data were extrapolated for 20 years in total, this assumption is perhaps unrealistic. However, it is unlikely that the effect of holding the recurrence, progression and mortality rates constant would have any impact on the direction of results.
The cost data used were also imprecise because the costs of diagnosis and treatments were mainly identified from NHS reference costs. As mentioned there were very few studies that collected data on resource utilisation and, what published data there were, were not generalisable to the UK. A further issue regarding costs was that inflation was not taken into account. For the purposes of the analysis all prices were taken for the year 2007. However, the costs identified from NHS reference costs, the paper by Rodgers and colleagues179 and the unpublished report for PDD were all 2006 costs. Normal practice within an economic evaluation would argue that such costs be inflated to the same base year allowing all costs to be comparable. The analyses conducted as part of this review, however, did not take into account inflation over time. However, it is anticipated that the failure to inflate the costs, given the similar price years of the data, may have little impact on the results.
One final point of uncertainty was the discount rate. The discount rates utilised followed published guidance relevant at the time that the technology assessment report was commissioned. Increases to the discount rate (mentioned in the methods chapter) would not change the overall direction of effects but are likely to make the more effective strategies (in terms of life-years) less likely to be cost-effective. This is because these additional benefits accrue over time and hence are given less weight when the discount rate is increased.
Chapter 9 Conclusions
Implications for service provision
In terms of test performance, PDD has higher sensitivity than WLC [pooled estimates for biopsy-level analysis: 93% (95% CI 90% to 96%) versus 65% (95% CI 55% to 74%) respectively] in detecting bladder cancer in patients with symptoms such as haematuria and is better at detecting more aggressive, higher risk tumours, including CIS [median (range) sensitivity across studies for biopsy-level analysis: 99% (54% to 100%) versus 67% (0% to 100%) respectively]. However, PDD has lower specificity than WLC [pooled estimates for biopsy-level analysis: 60% (95% CI 49% to 71%) versus 81% (95% CI 73% to 90%) respectively]. The advantages of higher sensitivity (fewer false-negative results, better detection of higher risk tumours) have to be weighed against the disadvantages of lower specificity (more false-positive results, leading to additional unnecessary biopsies and potentially additional unnecessary investigations and the resulting anxiety caused to patients and their families).
In terms of the photosensitising agents used, across studies the median (range) specificity reported for HAL was higher than that of 5-ALA for both patient-level [81% (43% to 100%) compared with 52% (33 to 67%)] and biopsy-level [80% (58% to 100%) compared with 57% (32% to 67%)] detection of bladder cancer, although the ranges were wide and factors other than the agent used may also have contributed to the specificity values reported.
Compared with WLC, the use of PDD at TURBT results in fewer residual tumours at check cystoscopy (pooled estimate RR 0.37, 95% CI 0.20 to 0.69) and longer recurrence-free survival (pooled estimate RR 1.37, 95% CI 1.18 to 1.59), although these results are based on limited evidence (three and two studies respectively) and should be interpreted with caution. The advantages of PDD at TURBT in reducing tumour recurrence (pooled estimate RR 0.64, 95% CI 0.39 to 1.06) and progression (pooled estimate RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.22 to 1.46) in the longer term were less clear (based on two studies, one with 5 years’ and one with 8 years’ follow-up). In addition, as adjuvant single-dose intravesical therapy following TURBT (standard practice in the UK and much of Europe) was not given to all of the patients in all of the studies it is difficult to assess what the true added value of PDD over WLC might be in routine clinical practice in terms of outcomes such as residual tumour at check cystoscopy, tumour recurrence and progression. However, single-dose intravesical chemotherapy is known to be ineffective against high-risk tumours, the types more likely to be detected by PDD.
All three biomarkers had higher sensitivity but lower specificity than cytology for detecting bladder cancer in patients with symptoms such as haematuria. In the pooled estimates (95% CI) ImmunoCyt had the highest sensitivity [84% (77% to 91%)], followed by FISH [76% (65% to 84%)], NMP22 [68% (62% to 74%)] and cytology [44% (38% to 51%)], whereas cytology had the highest specificity [96% (94% to 98%)], followed by FISH [85% (78% to 92%)], NMP22 [79% (74% to 84%)] and ImmunoCyt [75% (68% to 83%)]. ImmunoCyt [84% (95% CI 77% to 91%)] had higher sensitivity than NMP22 [68% (95% CI 62% to 74%)], with the lack of overlap between the CIs supporting evidence of a difference in sensitivity in favour of ImmunoCyt. FISH [76% (95% CI 65% to 84%)] also had higher sensitivity than NMP22 although the difference in sensitivity was more uncertain as the CIs overlapped. All three biomarkers and cytology were better at detecting more aggressive, higher risk tumours [median (range) sensitivity across studies: FISH 95% (50% to 100%), ImmunoCyt 90% (67% to 100%), NMP22 83% (0% to 100%), cytology 69% (0% to 100%)] than lower risk, less aggressive tumours [ImmunoCyt 81% (55% to 90%), FISH 65% (32% to 100%), NMP22 50% (0% to 86%), cytology 27% (0% to 93%)]. A urine biomarker test such as ImmunoCyt could potentially replace some cytology tests if higher sensitivity (fewer false negatives) was considered more important than higher specificity (fewer false positives). However, if higher specificity was considered to be more important then cytology would remain the test of choice.
The most cost-effective strategy for diagnosis and follow-up of bladder cancer patients amongst PDD, WLC, biomarkers, cytology and flexible cystoscopy was evaluated. Based on currently available data and taking into account the assumptions made in the model, the strategy of flexible cystoscopy and ImmunoCyt followed by PDD in initial diagnosis and flexible cystoscopy followed by WLC in follow-up is likely to be the most costly and the most effective (£2370 per patient and 11.66 life-years). The strategy of cytology followed by WLC in initial diagnosis and follow-up is likely to be the least costly (£1043 per patient) and least effective in terms of life-years (11.59) per patient. Compared with WLC in each strategy, PDD is more likely to be cost-effective. However, it should be noted that the diagnostic strategy that would be cost-effective depends upon the value that society would be willing to pay to obtain an additional life-year. There appeared to be no strategy that would have a likelihood of being cost-effective more than 50% of the time over most of the range of willingness to pay values. Nevertheless, the four strategies involving PDD and biomarkers were cumulatively associated with over a 70% likelihood of being considered cost-effective. The strategies of ImmunoCyt or FISH followed by PDD in initial diagnosis and ImmunoCyt or FISH followed by WLC in follow-up may be considered to be the most cost-effective when the willingness to pay is over £20,000.
In summary, given the evidence presented a judgement needs to be made as to whether the current ‘standard’ strategies with regard to diagnosis and follow-up of bladder cancer should be altered. Currently, there is no standard strategy for the detection and follow-up of primary bladder cancer. The implications of the finding that diagnostic strategies involving ImmunoCyt or FISH and PDD appear to have potential long-term outcome benefits compared with current commonly used strategies involving cytology or flexible cystoscopy need to be considered. Diagnostic strategies involving ImmunoCyt or FISH and PDD may also have potential short-term benefits, such as more true-positive cases detected and less false-negative cases missed. However, any decision needs to take into account the extra costs associated with PDD and indeed whether the probable gains in QoL justify this increased cost.
In the sensitivity analyses no strategy was likely to have more than a 50% probability of being cost-effective. This suggests that either the evidence base is insufficient to warrant a change in practice or we are indifferent between several strategies in terms of cost-effectiveness, or more likely a combination of these two factors.
There were no data on the combination of flexible cystoscopy and cytology, the tests that are involved in current commonly used strategies. Also, as there were no data available with which to explicitly incorporate QoL within the model, a judgement needs to be made as to whether the expected gain in QoL is sufficient to offset any extra cost.
Currently, PDD is used in only a few centres in the UK and therefore the impact on the use of operating theatres arising from an increase in the use of PDD would need to be considered. Learning to use PDD should be straightforward for an experienced cystoscopist and the training period should be relatively short.
Suggested research priorities
Further research is required in the following areas:
-
RCTs comparing PDD with rigid WLC plus adjuvant intravesical therapy at TURBT in patients presumed to have non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. The design of such studies should take into account participant characteristic risk groups, for example smoking and age, and allow outcomes to be reported based on risk categories at randomisation. Clinical effectiveness outcomes should include residual tumour rates at first check cystoscopy, recurrence-free survival, tumour recurrence rates, time to first recurrence, and progression. Such studies should make provision for longer-term follow-up (up to 10 years) and as a matter of course include an economic evaluation and measurement of health state utilities for incorporation into a cost–utility analysis.
-
Diagnostic cross-sectional studies comparing FISH with ImmunoCyt, NMP22 BladderChek point of care test and voided urine cytology, and also combinations of these tests, against a reference standard of cystoscopy with histological assessment of biopsied tissue in the same patient population. The patient population would be those newly presenting with symptoms suspicious for bladder cancer and those with previously diagnosed non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. The studies should report true and false positives and negatives for a patient-level analysis of the whole patient group and also for the suspicion of bladder cancer/previously diagnosed disease subgroups. For each of these groups the studies should report the sensitivity of the tests in detecting stage (pTa, pT1, ≥ pT2, CIS) and grade (G1, G2, G3) of tumour, and size (< 1 cm, 1–3 cm, > 3cm) and number (one, two to three, more than three) of tumours. Upper tract end points should also be considered. Observer variability in the interpretation of tests should also be reported. There should be formal follow-up of patients who are categorised as negative for bladder cancer to better understand the consequences of false-negative case ascertainment. The results of such studies should be incorporated into a refined economic model that fully reflects the pragmatic factors listed above.
-
In addition, BAUS and the Renal Association have recently produced a new diagnostic algorithm for the diagnosis of patients with haematuria. This would be an appropriate setting for further evaluating novel urinary biomarkers such as ImmunoCyt and FISH and also for assessing their performance in specific populations with a higher prevalence of bladder cancer, such as men aged over 60 years who smoke.
-
The level of QoL data suitable for incorporation into an economic model. Consideration should be given to the collection of data suitable to expand on economic evaluations from cost-effectiveness analyses. Such data may be derived from further prospective studies or stand-alone studies that seek to identify health state utilities relevant to a refined economic model.
-
The different strategies differ in terms of longer-term outcomes and also in terms of the process of care and short-term outcomes. This suggests that consideration should be given to preference elicitation studies using recognised methodology that explore the trade-offs and valuations between processes and health outcomes. Such analysis should be conducted in such a way that it can be incorporated into future models based on trial-based analysis.
-
False-negative results, either at diagnosis or at follow-up, will prevent or at least delay those patients from receiving potentially beneficial treatment. Further information is required as to what would happen to these patients in practice and the impact of an incorrect diagnosis on future survival, QoL and costs. Such information could be identified through follow-up of patients who are discharged following an initial negative result.
Acknowledgements
We thank Satchi Swami for advice on clinical aspects of the review, Adrian Grant for commenting on drafts, Clare Robertson and Susan Wong for assistance with assessing full-text studies for inclusion, data extraction and quality assessment, Clare Robertson for preparation of the characteristics of the included studies tables and Kathleen McIntosh and Karen McLeod for secretarial support. We thank the British Association of Urological Surgeons (BAUS) Section of Oncology Executive Committee for its suggestions as to which biomarkers the review might consider. The Health Services Research Unit and Health Economics Research Unit, Institute of Applied Health Sciences, University of Aberdeen, are core funded by the Chief Scientist Office of the Scottish Government Health Directorates. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the funding bodies. Any errors are the responsibility of the authors.
Contribution of authors
Graham Mowatt (Research Fellow) screened the search results, assessed full-text studies for inclusion, undertook data extraction and quality assessment, drafted the chapters on photodynamic diagnosis and biomarkers, and coordinated the review. Shihua Zhu (TAR Training Fellow) and Mary Kilonzo (Research Fellow) drafted the chapter on cost-effectiveness, supervised by Luke Vale (Professor of Health Technology Assessment). Shihua Zhu, TR Leyshon Griffiths (Senior Lecturer and Honorary Consultant Urological Surgeon) and Ghulam Nabi (Clinical Lecturer in Urology) drafted the background chapter. Charles Boachie (Statistician) drafted the data analysis section of the review and conducted the statistical analysis, supervised by Jonathan Cook (Statistician). TR Leyshon Griffiths, James N’Dow (Professor of Urology) and Ghulam Nabi provided expert advice on clinical aspects of the review. Cynthia Fraser (Information Officer) developed and ran the search strategies, obtained papers and formatted the references. All authors assisted in preparing the manuscript, reading and commenting on drafts, and reading the final draft.
Disclaimers
The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- World Health Organization . International Classificiation of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD) 10th Revision 2007. www.who.int/classifications/apps/icd/icd10online/ (accessed July 2008).
- UroVysion Fluorescence in Situ Hybridisation (FISH) Assay. MSAC Application 1084 2005. www.msac.gov.au/internet/msac/publishing.nsf/Content/4753418A5C8F33DDCA25745E000A3933/$File/1084%20-%20UroVysion%20Report.pdf (accessed September 2008).
- Babjuk M, Oosterlinck W, Sylvester R, Kaasinen E, Bohle A, Palou J. Guidelines on TaT1 (non-muscle-invasive) bladder cancer. Arnhem: European Association of Urology; 2009.
- Kirkali Z, Chan T, Manoharan M, Algaba F, Busch C, Cheng L, et al. Bladder cancer: epidemiology, staging and grading, and diagnosis. Urology 2005;66:4-34.
- Hall MC, Chang SS, Dalbagni G, Pruthi RS, Schellhammer PF, Seigne JD, et al. Guideline for the management of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer: (stages Ta,T1 and Tis). 2007 update. Linthicum, MD: American Urological Association; 2007.
- Brennan P, Bogillot O, Cordier S, Greiser E, Schill W, Vineis P, et al. Cigarette smoking and bladder cancer in men: a pooled analysis of 11 case–control studies. Int J Cancer 2000;86:289-94.
- Brennan P, Bogillot O, Greiser E, Chang-Claude J, Wahrendorf J, Cordier S, et al. The contribution of cigarette smoking to bladder cancer in women (pooled European data). Cancer Causes Control 2001;12:411-7.
- Occupational bladder cancer: a guide for clinicians. The BAUS Subcommittee on Industrial Bladder Cancer. Br J Urol 1988;61:183-91.
- Steinmaus CM, Nunez S, Smith AH. Diet and bladder cancer: a meta-analysis of six dietary variables. Am J Epidemiol 2000;151:693-702.
- Murta-Nascimento C, Schmitz-Drager BJ, Zeegers MP, Steineck G, Kogevinas M, Real FX, et al. Epidemiology of urinary bladder cancer: from tumor development to patient’s death. World J Urol 2007;25:285-95.
- Boorjian S, Cowan JE, Konety BR, DuChane J, Tewari A, Carroll PR, et al. Bladder cancer incidence and risk factors in men with prostate cancer: results from Cancer of the Prostate Strategic Urologic Research Endeavor. J Urol 2007;177:883-7.
- Duncan RE, Bennett DW, Evans AT, Aron BS, Schellhas HF. Radiation-induced bladder tumors. J Urol 1977;118:43-5.
- Garcia-Closas M, Malats N, Silverman D, Dosemeci M, Kogevinas M, Hein DW, et al. NAT2 slow acetylation, GSTM1 null genotype, and risk of bladder cancer: results from the Spanish Bladder Cancer Study and meta-analyses. Lancet 2005;366:649-59.
- Engel LS, Taioli E, Pfeiffer R, Garcia-Closas M, Marcus PM, Lan Q, et al. Pooled analysis and meta-analysis of glutathione S-transferase M1 and bladder cancer: a HuGE review. Am J Epidemiol 2002;156:95-109.
- Newling DW, Robinson MR, Smith PH, Byar D, Lockwood R, Stevens I, et al. Tryptophan metabolites, pyridoxine (vitamin B6) and their influence on the recurrence rate of superficial bladder cancer. Results of a prospective, randomised phase III study performed by the EORTC GU Group. EORTC Genito-Urinary Tract Cancer Cooperative Group. Eur Urol 1995;27:110-6.
- Sobin DH, Witteking CH. TNM classification of malignant tumours. New York: Wiley-Liss; 2002.
- Mostofi FK. International histologic classification of tumors. A report by the Executive Committee of the International Council of Societies of Pathology. Cancer 1974;33:1480-4.
- Harnden P. A critical appraisal of the classification of urothelial tumours: time for a review of the evidence and a radical change?. BJU Int 2007;99:723-5.
- Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP, Lamm DL. Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin reduces the risk of progression in patients with superficial bladder cancer: a meta-analysis of the published results of randomized clinical trials. J Urol 2002;168:1964-70.
- Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP, Oosterlinck W, Witjes JA, Bouffioux C, Denis L, et al. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: a combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur Urol 2006;49:466-77.
- Heney NM, Ahmed S, Flanagan MJ, Frable W, Corder MP, Hafermann MD, et al. Superficial bladder cancer: progression and recurrence. J Urol 1983;130:1083-6.
- Cancer Research UK . UK Bladder Cancer Statistics 2007. http://info.cancerresearchuk.org/cancerstats/types/bladder/?a=5441 (accessed July 2008).
- Hayne D, Arya M, Quinn MJ, Babb PJ, Beacock CJ, Patel HR. Current trends in bladder cancer in England and Wales. J Urol 2004;172:1051-5.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network . NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Bladder Cancer Including Upper Tract Tumours and Urothelial Carcinoma of the Prostate. V.2.2008 2008. www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/bladder.pdf (accessed July 2008).
- Edwards TJ, Dickinson AJ, Natale S, Gosling J, McGrath JS. A prospective analysis of the diagnostic yield resulting from the attendance of 4020 patients at a protocol-driven haematuria clinic. BJU Int 2006;97:301-5.
- Khadra MH, Pickard RS, Charlton M, Powell PH, Neal DE. A prospective analysis of 1,930 patients with hematuria to evaluate current diagnostic practice. J Urol 2000;163:524-7.
- Pashos CL, Botteman MF, Laskin BL, Redaelli A. Bladder cancer: epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. Cancer Pract 2002;10:311-22.
- BAUS Section of Oncology, British Uro-oncology Group (BUG) . MDT (multi-Disciplinary Team) Guidance for the Managing of Bladder Cancer 2007. www.bauslibrary.co.uk/PDFS/BSONC/MDT%20guidance%20for%20bladder%20cancer.pdf.
- Hall RR, . Proposal for changes in cystoscopic follow up of patients with bladder cancer and adjuvant intravesical chemotherapy. BMJ 1994;308:257-60.
- Mead GM, Russell M, Clark P, Harland SJ, Harper PG, Cowan R, et al. A randomized trial comparing methotrexate and vinblastine (MV) with cisplatin, methotrexate and vinblastine (CMV) in advanced transitional cell carcinoma: results and a report on prognostic factors in a Medical Research Council study. MRC Advanced Bladder Cancer Working Party. Br J Cancer 1998;78:1067-75.
- Saxman SB, Propert KJ, Einhorn LH, Crawford ED, Tannock I, Raghavan D, et al. Long-term follow-up of a phase III intergroup study of cisplatin alone or in combination with methotrexate, vinblastine, and doxorubicin in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a cooperative group study. J Clin Oncol 1997;15:2564-9.
- Sangar VK, Ragavan N, Matanhelia SS, Watson MW, Blades RA. The economic consequences of prostate and bladder cancer in the UK. BJU Int 2005;95:59-63.
- Bosanquet N, Sikora K. The economics of cancer care in the UK. Lancet Oncol 2004;5:568-74.
- Impoving outcomes in urological cancers. Guidance on cancer services: the manual. London: National Institute for Clinical Excellence; 2002.
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence . Laparoscopic Cystectomy. Interventional Procedures Guidance IPG026 2003. www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/pdf/ip/ipg026guidance.pdf (accessed July 2008).
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network . Management of Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder. SIGN Guideline No. 85 2005. www.sign.ac.uk/pdf/sign85.pdf (accessed July 2008).
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence . Intravesical Microwave Hyperthermia With Intravesical Chemotherapy for Superficial Bladder Cancer. Interventional Procedure Guidance IPG235 2007. www.nice.org.uk/Guidance/IPG235/Guidance/pdf/English (accessed July 2008).
- Foster M, Barnish L, Tudway D, Guest P, James N, McGarr C, et al. Guidelines for the management of bladder. Birmingham: NHS Pan-Birmingham Cancer Network; 2007.
- National Screening Committee . Evaluation of Urinary Tract Malignancy (bladder Cancer) Screening Against NSC Criteria 2002. www.library.nhs.uk/screening/ViewResource.aspx?resID=60477%26tabID=288 (accessed July 2008).
- Stenzl A, Cowan NC, de Santis M, Jakse G, Kuczyk M, Merseburger MS, et al. Guideline on bladder cancer: muscle-invasive and metastatic. Arnhem: European Association of Urology; 2009.
- Lokeshwar VB, . Bladder tumor markers beyond cytology: International Consensus Panel on bladder tumor markers. Urology 2005;66:35-63.
- Marti A, Jichlinski P, Lange N, Ballini JP, Guillou L, Leisinger HJ, et al. Comparison of aminolevulinic acid and hexylester aminolevulinate induced protoporphyrin IX distribution in human bladder cancer. J Urol 2003;170:428-32.
- Grossman HB, Blute ML, Dinney CP, Jones JS, Liou LS, Reuter VE, et al. The use of urine-based biomarkers in bladder cancer. Urology 2006;67:62-4.
- Wazait HD, Al Bhueissi SZ, Patel HR, Nathan MS, Miller RA. Long-term surveillance of bladder tumours: current practice in the United Kingdom and Ireland. Eur Urol 2003;43:485-8.
- Chahal R, Darshane A, Browning AJ, Sundaram SK. Evaluation of the clinical value of urinary NMP22 as a marker in the screening and surveillance of transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Eur Urol 2001;40:415-20.
- Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PM, Kleijnen J. The development of QUADAS: a tool for the quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol 2003;3.
- Verhagen AP, de Vet HC, de Bie RA, Kessels AG, Boers M, Bouter LM, et al. The Delphi list: a criteria list for quality assessment of randomized clinical trials for conducting systematic reviews developed by Delphi consensus. J Clin Epidemiol 1998;51:1235-41.
- Macaskill P. Empirical Bayes estimates generated in a hierarchical summary ROC analysis agreed closely with those of a full Bayesian analysis. J Clin Epidemiol 2004;57:925-32.
- Rutter CM, Gatsonis CA. A hierarchical regression approach to meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy evaluations. Stat Med 2001;20:2865-84.
- Cheng CW, Lau WK, Tan PH, Olivo M. Cystoscopic diagnosis of bladder cancer by intravesical instillation of 5-aminolevulinic acid induced porphyrin fluorescence – the Singapore experience. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2000;29:153-8.
- Colombo R, Naspro R, Bellinzoni P, Fabbri F, Guazzoni G, Scattoni V, et al. Photodynamic diagnosis for follow-up of carcinoma in situ of the bladder. Therap Clin Risk Manag 2007;3:1003-7.
- D’Hallewin MA, De Witte PA, Waelkens E, Merlevede W, Baert L. Fluorescence detection of flat bladder carcinoma in situ after intravesical instillation of hypericin. J Urol 2000;164:349-51.
- De Dominicis C, Liberti M, Perugia G, De Nunzio C, Sciobica F, Zuccala A, et al. Role of 5-aminolevulinic acid in the diagnosis and treatment of superficial bladder cancer: improvement in diagnostic sensitivity. Urology 2001;57:1059-62.
- Ehsan A, Sommer F, Haupt G, Engelmann U. Significance of fluorescence cystoscopy for diagnosis of superficial bladder cancer after intravesical instillation of delta aminolevulinic acid. Urol Int 2001;67:298-304.
- Filbeck T, Roessler W, Knuechel R, Straub M, Kiel HJ, Wieland WF. 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence endoscopy applied at secondary transurethral resection after conventional resection of primary superficial bladder tumors. Urology 1999;53:77-81.
- Filbeck T, Roessler W, Knuechel R, Straub M, Kiel HJ, Wieland WF. Clinical results of the transurethral resection and evaluation of superficial bladder carcinomas by means of fluorescence diagnosis after intravesical instillation of 5-aminolevulinic acid. J Endourol 1999;13:117-21.
- Fradet Y, Grossman HB, Gomella L, Lerner S, Cookson M, Albala D, et al. A comparison of hexaminolevulinate fluorescence cystoscopy and white light cystoscopy for the detection of carcinoma in situ in patients with bladder cancer: a phase III, multicenter study. J Urol 2007;178:68-73.
- Frimberger D, Zaak D, Stepp H, Knuchel R, Baumgartner R, Schneede P, et al. Autofluorescence imaging to optimize 5-ALA-induced fluorescence endoscopy of bladder carcinoma. Urology 2001;58:372-5.
- Grimbergen MC, van Swol CF, Jonges TG, Boon TA, van Moorselaar RJ. Reduced specificity of 5-ALA induced fluorescence in photodynamic diagnosis of transitional cell carcinoma after previous intravesical therapy. Eur Urol 2003;44:51-6.
- Hendricksen K, Moonen PM, der Heijden AG, Witjes JA. False-positive lesions detected by fluorescence cystoscopy: any association with p53 and p16 expression?. World J Urol 2006;24:597-601.
- Hungerhuber E, Stepp H, Kriegmair M, Stief C, Hofstetter A, Hartmann A, et al. Seven years’ experience with 5-aminolevulinic acid in detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urology 2007;69:260-4.
- Jeon SS, Kang I, Hong JH, Choi HY, Chai SE. Diagnostic efficacy of fluorescence cystoscopy for detection of urothelial neoplasms. J Endourol 2001;15:753-9.
- Jichlinski P, Forrer M, Mizeret J, Glanzmann T, Braichotte D, Wagnieres G, et al. Clinical evaluation of a method for detecting superficial surgical transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder by light-induced fluorescence of protoporphyrin IX following the topical application of 5-aminolevulinic acid: preliminary results. Lasers Surg Med 1997;20:402-8.
- Jichlinski P, Wagnieres G, Forrer M, Mizeret J, Guillou L, Oswald M, et al. Clinical assessment of fluorescence cytoscopy during transurethral bladder resection in superficial bladder cancer. Urol Res 1997;25:S3-6.
- Jichlinski P, Guillou L, Karlsen SJ, Malmstrom PU, Jocham D, Brennhovd B, et al. Hexyl aminolevulinate fluorescence cystoscopy: new diagnostic tool for photodiagnosis of superficial bladder cancer – a multicenter study. J Urol 2003;170:226-9.
- Jocham D, Witjes F, Wagner S, Zeylemaker B, van Moorselaar J, Grimm MO, et al. Improved detection and treatment of bladder cancer using hexaminolevulinate imaging: a prospective, phase III multicenter study. J Urol 2005;174:862-6.
- Koenig F, McGovern FJ, Larne R, Enquist H, Schomacker KT, Deutsch TF. Diagnosis of bladder carcinoma using protoporphyrin IX fluorescence induced by 5-aminolaevulinic acid. BJU Int 1999;83:129-35.
- Kriegmair M, Baumgartner R, Knuechel R, Steinbach P, Ehsan A, Lumper W, et al. Fluorescence photodetection of neoplastic urothelial lesions following intravesical instillation of 5-aminolevulinic acid. Urology 1994;44:836-41.
- Kriegmair M, Stepp H, Steinbach P, Lumper W, Ehsan A, Stepp HG, et al. Fluorescence cystoscopy following intravesical instillation of 5-aminolevulinic acid: a new procedure with high sensitivity for detection of hardly visible urothelial neoplasias. Urol Int 1995;55:190-6.
- Kriegmair M, Baumgartner R, Knuchel R, Stepp H, Hofstadter F, Hofstetter A. Detection of early bladder cancer by 5-aminolevulinic acid induced porphyrin fluorescence. J Urol 1996;155:105-9.
- Kriegmair M, Zaak D, Stepp H, Stepp H, Baumgartner R, Knuechel R, et al. Transurethral resection and surveillance of bladder cancer supported by 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence endoscopy. Eur Urol 1999;36:386-92.
- Landry JL, Gelet A, Bouvier R, Dubernard JM, Martin X, Colombel M. Detection of bladder dysplasia using 5-aminolaevulinic acid-induced porphyrin fluorescence. BJU Int 2003;91:623-6.
- Riedl CR, Plas E, Pfluger H. Fluorescence detection of bladder tumors with 5-amino-levulinic acid. J Endourol 1999;13:755-9.
- Schneeweiss S, Kriegmair M, Stepp H. Is everything all right if nothing seems wrong? A simple method of assessing the diagnostic value of endoscopic procedures when a gold standard is absent. J Urol 1999;161:1116-9.
- Schneeweiss S. Sensitivity analysis of the diagnostic value of endoscopies in cross-sectional studies in the absence of a gold standard. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 2000;16:834-41.
- Sim HG, Lau WK, Olivo M, Tan PH, Cheng CW. Is photodynamic diagnosis using hypericin better than white-light cystoscopy for detecting superficial bladder carcinoma?. BJU Int 2005;95:1215-8.
- Song X, Ye Z, Zhou S, Yang W, Zhang X, Liu J, et al. The application of 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence for cystoscopic diagnosis and treatment of bladder carcinoma. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2007;4:39-43.
- Szygula M, Wojciechowski B, Adamek M, Pietrusa A, Kawczyk-Krupka A, Cebula W, et al. Fluorescent diagnosis of urinary bladder cancer – a comparison of two diagnostic modalities. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2004;1:23-6.
- Szygula M, Wojciechowski B, Adamek M, Kawczyk-Krupka A, Cebula W, Zieleznik W, et al. Photodynamic vs autofluorescent diagnosis of urinary bladder using Xillix LIFE system. Phys Med 2004;20:55-7.
- Tritschler S, Scharf S, Karl A, Tilki D, Knuechel R, Hartmann A, et al. Validation of the diagnostic value of NMP22 BladderChek test as a marker for bladder cancer by photodynamic diagnosis. Eur Urol 2007;51:403-7.
- Witjes JA, Moonen PM, van der Heijden AG. Comparison of hexaminolevulinate based flexible and rigid fluorescence cystoscopy with rigid white light cystoscopy in bladder cancer: results of a prospective Phase II study. Eur Urol 2005;47:319-22.
- Zaak D, Kriegmair M, Stepp H, Stepp H, Baumgartner R, Oberneder R, et al. Endoscopic detection of transitional cell carcinoma with 5-aminolevulinic acid: results of 1012 fluorescence endoscopies. Urology 2001;57:690-4.
- Zaak D, Hungerhuber E, Schneede P, Stepp H, Frimberger D, Corvin S, et al. Role of 5-aminolevulinic acid in the detection of urothelial premalignant lesions. Cancer 2002;95:1234-8.
- Zaak D, Stepp H, Baumgartner R, Schneede P, Waidelich R, Frimberger D, et al. Ultraviolet-excited (308 nm) autofluorescence for bladder cancer detection. Urology 2002;60:1029-33.
- Zumbraegel A, Bichler KH, Krause FS, Feil G, Nelde HJ. The photodynamic diagnosis (PDD) for early detection of carcinoma and dysplasia of the bladder. Adv Exp Med Biol 2003;539:61-6.
- Babjuk M, Soukup V, Petrik R, Jirsa M, Dvoracek J. 5-aminolaevulinic acid-induced fluorescence cystoscopy during transurethral resection reduces the risk of recurrence in stage Ta/T1 bladder cancer. BJU Int 2005;96:798-802.
- Burger M, Zaak D, Stief CG, Filbeck T, Wieland WF, Roessler W, et al. Photodynamic diagnostics and noninvasive bladder cancer: is it cost-effective in long-term application? A Germany-based cost analysis. Eur Urol 2007;52:142-7.
- Daniltchenko DI, Riedl CR, Sachs MD, Koenig F, Daha KL, Pflueger H, et al. Long-term benefit of 5-aminolevulinic acid fluorescence assisted transurethral resection of superficial bladder cancer: 5-year results of a prospective randomized study. J Urol 2005;174:2129-33.
- Denzinger S, Burger M, Walter B, Knuechel R, Roessler W, Wieland WF, et al. Clinically relevant reduction in risk of recurrence of superficial bladder cancer using 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence diagnosis: 8-year results of prospective randomized study. Urology 2007;69:675-9.
- Denzinger S, Wieland WF, Otto W, Filbeck T, Knuechel R, Burger M. Does photodynamic transurethral resection of bladder tumour improve the outcome of initial T1 high-grade bladder cancer? A long-term follow-up of a randomized study. BJU Int 2008;101:566-9.
- Filbeck T, Pichlmeier U, Knuechel R, Wieland WF, Roessler W. Clinically relevant improvement of recurrence-free survival with 5-aminolevulinic acid induced fluorescence diagnosis in patients with superficial bladder tumors. J Urol 2002;168:67-71.
- Kriegmair M, Zaak D, Rothenberger KH, Rassweiler J, Jocham D, Eisenberger F, et al. Transurethral resection for bladder cancer using 5-aminolevulinic acid induced fluorescence endoscopy versus white light endoscopy. J Urol 2002;168:475-8.
- Riedl CR, Daniltchenko D, Koenig F, Simak R, Loening SA, Pflueger H. Fluorescence endoscopy with 5-aminolevulinic acid reduces early recurrence rate in superficial bladder cancer. J Urol 2001;165:1121-3.
- Daniely M, Rona R, Kaplan T, Olsfanger S, Elboim L, Freiberger A, et al. Combined morphologic and fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of voided urine samples for the detection and follow-up of bladder cancer in patients with benign urine cytology. Cancer 2007;111:517-24.
- Friedrich MG, Toma MI, Hellstern A, Pantel K, Weisenberger DJ, Noldus J, et al. Comparison of multitarget fluorescence in situ hybridization in urine with other noninvasive tests for detecting bladder cancer. BJU Int 2003;92:911-4.
- Friedrich MG, Hellstern A, Hautmann SH, Graefen M, Conrad S, Huland E, et al. Clinical use of urinary markers for the detection and prognosis of bladder carcinoma: a comparison of immunocytology with monoclonal antibodies against Lewis X and 486p3/12 with the BTA STAT and NMP22 tests. J Urol 2002;168:470-4.
- Halling KC, King W, Sokolova IA, Meyer RG, Burkhardt HM, Halling AC, et al. A comparison of cytology and fluorescence in situ hybridization for the detection of urothelial carcinoma. J Urol 2000;164:1768-75.
- Junker K, Fritsch T, Hartmann A, Schulze W, Schubert J. Multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization (M-FISH) on cells from urine for the detection of bladder cancer. Cytogenet Genome Res 2006;114:279-83.
- Kipp BR, Halling KC, Campion MB, Wendel AJ, Karnes RJ, Zhang J, et al. Assessing the value of reflex fluorescence in situ hybridization testing in the diagnosis of bladder cancer when routine urine cytological examination is equivocal. J Urol 2008;179:1296-301.
- Meiers I, Singh H, Hossain D, Lang K, Liu L, Qian JQ, et al. Improved filter method for urine sediment detection of urothelial carcinoma by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:1574-7.
- Mian C, Lodde M, Comploj E, Negri G, Egarter-Vigl E, Lusuardi L, et al. Liquid-based cytology as a tool for the performance of uCyt+ and Urovysion Multicolour-FISH in the detection of urothelial carcinoma. Cytopathology 2003;14:338-42.
- Moonen PM, Merkx GF, Peelen P, Karthaus HF, Smeets DF, Witjes JA. UroVysion compared with cytology and quantitative cytology in the surveillance of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol 2007;51:1275-80.
- Sarosdy MF, Kahn PR, Ziffer MD, Love WR, Barkin J, Abara EO, et al. Use of a multitarget fluorescence in situ hybridization assay to diagnose bladder cancer in patients with hematuria. J Urol 2006;176:44-7.
- Skacel M, Fahmy M, Brainard JA, Pettay JD, Biscotti CV, Liou LS, et al. Multitarget fluorescence in situ hybridization assay detects transitional cell carcinoma in the majority of patients with bladder cancer and atypical or negative urine cytology. J Urol 2003;169:2101-5.
- Sokolova IA, Halling KC, Jenkins RB, Burkhardt HM, Meyer RG, Seelig SA, et al. The development of a multitarget, multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization assay for the detection of urothelial carcinoma in urine. J Mol Diagn 2000;2:116-23.
- Yoder BJ, Skacel M, Hedgepeth R, Babineau D, Ulchaker JC, Liou LS, et al. Reflex UroVysion testing of bladder cancer surveillance patients with equivocal or negative urine cytology: a prospective study with focus on the natural history of anticipatory positive findings. Am J Clin Pathol 2007;127:295-301.
- May M, Hakenberg OW, Gunia S, Pohling P, Helke C, Lubbe L, et al. Comparative diagnostic value of urine cytology, UBC-ELISA, and fluorescence in situ hybridization for detection of transitional cell carcinoma of urinary bladder in routine clinical practice. Urology 2007;70:449-53.
- Sarosdy MF, Schellhammer P, Bokinsky G, Kahn P, Chao R, Yore L, et al. Clinical evaluation of a multi-target fluorescent in situ hybridization assay for detection of bladder cancer. J Urol 2002;168:1950-4.
- Lodde M, Mian C, Negri G, Berner L, Maffei N, Lusuardi L, et al. Role of uCyt+ in the detection and surveillance of urothelial carcinoma. Urology 2003;61:243-7.
- Lodde M, Mian C, Comploj E, Palermo S, Longhi E, Marberger M, et al. uCyt+ test: alternative to cystoscopy for less-invasive follow-up of patients with low risk of urothelial carcinoma. Urology 2006;67:950-4.
- Messing EM, Teot L, Korman H, Underhill E, Barker E, Stork B, et al. Performance of urine test in patients monitored for recurrence of bladder cancer: a multicenter study in the United States. J Urol 2005;174:1238-41.
- Mian C, Pycha A, Wiener H, Haitel A, Lodde M, Marberger M. Immunocyt: a new tool for detecting transitional cell cancer of the urinary tract. J Urol 1999;161:1486-9.
- Mian C, Maier K, Comploj E, Lodde M, Berner L, Lusuardi L, et al. uCyt+/ImmunoCyt in the detection of recurrent urothelial carcinoma: an update on 1991 analyses. Cancer 2006;108:60-5.
- Olsson H, Zackrisson B. ImmunoCyt a useful method in the follow-up protocol for patients with urinary bladder carcinoma. Scand J Urol Nephrol 2001;35:280-2.
- Pfister C, Chautard D, Devonec M, Perrin P, Chopin D, Rischmann P, et al. Immunocyt test improves the diagnostic accuracy of urinary cytology: results of a French multicenter study. J Urol 2003;169:921-4.
- Piaton E, Daniel L, Verriele V, Dalifard I, Zimmermann U, Renaudin K, et al. Improved detection of urothelial carcinomas with fluorescence immunocytochemistry (uCyt+ assay) and urinary cytology: results of a French Prospective Multicenter Study. Lab Invest 2003;83:845-52.
- Schmitz-Drager BJ, Beiche B, Tirsar LA, Schmitz-Drager C, Bismarck E, Ebert T. Immunocytology in the assessment of patients with asymptomatic microhaematuria. Eur Urol 2007;51:1582-8.
- Schmitz-Drager BJ, Tirsar LA, Schmitz-Drager C, Dorsam J, Mellan Z, Bismarck E, et al. Immunocytology in the assessment of patients with asymptomatic hematuria. World J Urol 2008;26:31-7.
- Tetu B, Tiguert R, Harel F, Fradet Y. ImmunoCyt/uCyt+ improves the sensitivity of urine cytology in patients followed for urothelial carcinoma. Mod Pathol 2005;18:83-9.
- Bhuiyan J, Akhter J, O’Kane DJ. Performance characteristics of multiple urinary tumor markers and sample collection techniques in the detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Clin Chim Acta 2003;331:69-77.
- Casella R, Huber P, Blochlinger A, Stoffel F, Dalquen P, Gasser TC, et al. Urinary level of nuclear matrix protein 22 in the diagnosis of bladder cancer: experience with 130 patients with biopsy confirmed tumor. J Urol 2000;164:1926-8.
- Casetta G, Gontero P, Zitella A, Pelucelli G, Formiconi A, Priolo G, et al. BTA quantitative assay and NMP22 testing compared with urine cytology in the detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urol Int 2000;65:100-5.
- Del Nero A, Esposito N, Curro A, Biasoni D, Montanari E, Mangiarotti B, et al. Evaluation of urinary level of NMP22 as a diagnostic marker for stage pTa-pT1 bladder cancer: comparison with urinary cytology and BTA test. Eur Urol 1999;35:93-7.
- Giannopoulos A, Manousakas T, Mitropoulos D, Botsoli-Stergiou E, Constantinides C, Giannopoulou M, et al. Comparative evaluation of the BTA stat test, NMP22, and voided urine cytology in the detection of primary and recurrent bladder tumors. Urology 2000;55:871-5.
- Giannopoulos A, Manousakas T, Gounari A, Constantinides C, Choremi-Papadopoulou H, Dimopoulos C. Comparative evaluation of the diagnostic performance of the BTA stat test, NMP22 and urinary bladder cancer antigen for primary and recurrent bladder tumors [see comment]. J Urol 2001;166:470-5.
- Grossman HB, Messing E, Soloway M, Tomera K, Katz G, Berger Y, et al. Detection of bladder cancer using a point-of-care proteomic assay. JAMA 2005;293:810-6.
- Grossman HB, Soloway M, Messing E, Katz G, Stein B, Kassabian V, et al. Surveillance for recurrent bladder cancer using a point-of-care proteomic assay. JAMA 2006;295:299-305.
- Gutierrez Banos JL, Rebollo Rodrigo MH, Antolin Juarez FM, Martin GB. NMP 22, BTA stat test and cytology in the diagnosis of bladder cancer: a comparative study. Urol Int 2001;66:185-90.
- Hughes JH, Katz RL, Rodriguez-Villanueva J, Kidd L, Dinney C, Grossman HB, et al. Urinary nuclear matrix protein 22 (NMP22): a diagnostic adjunct to urine cytologic examination for the detection of recurrent transitional-cell carcinoma of the bladder. Diagn Cytopathol 1999;20:285-90.
- Kowalska M, Kaminska J, Kotowicz B, Fuksiewicz M, Rysinska A, Demkow T, et al. Evaluation of the urinary nuclear matrix protein (NMP22) as a tumour marker in bladder cancer patients. Nowotwory 2005;55:300-2.
- Kumar A, Kumar R, Gupta NP. Comparison of NMP22 BladderChek test and urine cytology for the detection of recurrent bladder cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 2006;36:172-5.
- Lahme S, Bichler KH, Feil G, Krause S. Comparison of cytology and nuclear matrix protein 22 for the detection and follow-up of bladder cancer. Urol Int 2001;66:72-7.
- Lahme S, Bichler KH, Feil G, Zumbragel A, Gotz T. Comparison of cytology and nuclear matrix protein 22 (NMP 22) for the detection and follow-up of bladder-cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 2003;539:111-9.
- Mian C, Lodde M, Haitel A, Vigl EE, Marberger M, Pycha A. Comparison of the monoclonal UBC-ELISA test and the NMP22 ELISA test for the detection of urothelial cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urology 2000;55:223-6.
- Miyanaga N, Akaza H, Tsukamoto T, Ishikawa S, Noguchi R, Ohtani M, et al. Urinary nuclear matrix protein 22 as a new marker for the screening of urothelial cancer in patients with microscopic hematuria. Int J Urol 1999;6:173-7.
- Miyanaga N, Akaza H, Tsukamoto S, Shimazui T, Ohtani M, Ishikawa S, et al. Usefulness of urinary NMP22 to detect tumor recurrence of superficial bladder cancer after transurethral resection. Int J Clin Oncol 2003;8:369-73.
- Oge O, Atsu N, Kendi S, Ozen H. Evaluation of nuclear matrix protein 22 (NMP22) as a tumor marker in the detection of bladder cancer. Int Urol Nephrol 2001;32:367-70.
- Oosterhuis JWA, Pauwels RPE, Schapers RFM, Van Pelt J, Smeets W, Newling DWW. Detection of recurrent transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder with nuclear matrix protein-22 in a follow-up setting. Urooncology 2002;2:137-42.
- Ponsky LE, Sharma S, Pandrangi L, Kedia S, Nelson D, Agarwal A, et al. Screening and monitoring for bladder cancer: refining the use of NMP22. J Urol 2001;166:75-8.
- Poulakis V, Witzsch U, De Vries R, Altmannsberger HM, Manyak MJ, Becht E. A comparison of urinary nuclear matrix protein-22 and bladder tumour antigen tests with voided urinary cytology in detecting and following bladder cancer: the prognostic value of false-positive results. BJU Int 2001;88:692-701.
- Saad A, Hanbury DC, McNicholas TA, Boustead GB, Morgan S, Woodman AC. A study comparing various noninvasive methods of detecting bladder cancer in urine. BJU Int 2002;89:369-73.
- Sanchez-Carbayo M, Urrutia M, Gonzalez de Buitrago JM, Navajo JA. Utility of serial urinary tumor markers to individualize intervals between cystoscopies in the monitoring of patients with bladder carcinoma. Cancer 2001;92:2820-8.
- Serretta V, Lo PD, Vasile P, Gange E, Esposito E, Menozzi I. Urinary NMP22 for the detection of recurrence after transurethral resection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: experience on 137 patients. Urology 1998;52:793-6.
- Serretta V, Pomara G, Rizzo I, Esposito E. Urinary BTA-stat, BTA-trak and NMP22 in surveillance after TUR of recurrent superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol 2000;38:419-25.
- Shariat SF, Casella R, Monoski MA, Sulser T, Gasser TC, Lerner SP. The addition of urinary urokinase-type plasminogen activator to urinary nuclear matrix protein 22 and cytology improves the detection of bladder cancer. J Urol 2003;170:2244-7.
- Shariat SF, Casella R, Khoddami SM, Hernandez G, Sulser T, Gasser TC, et al. Urine detection of survivin is a sensitive marker for the noninvasive diagnosis of bladder cancer. J Urol 2004;171:626-30.
- Shariat SF, Marberger MJ, Lotan Y, Sanchez-Carbayo M, Zippe C, Ludecke G, et al. Variability in the performance of nuclear matrix protein 22 for the detection of bladder cancer. J Urol 2006;176:919-26.
- Sharma S, Zippe CD, Pandrangi L, Nelson D, Agarwal A. Exclusion criteria enhance the specificity and positive predictive value of NMP22 and BTA stat. J Urol 1999;162:53-7.
- Stampfer DS, Carpinito GA, Rodriguez-Villanueva J, Willsey LW, Dinney CP, Grossman HB, et al. Evaluation of NMP22 in the detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol 1998;159:394-8.
- Talwar R, Sinha T, Karan SC, Doddamani D, Sandhu A, Sethi GS, et al. Voided urinary cytology in bladder cancer: is it time to review the indications?. Urology 2007;70:267-71.
- Wiener HG, Mian C, Haitel A, Pycha A, Schatzl G, Marberger M. Can urine bound diagnostic tests replace cystoscopy in the management of bladder cancer?. J Urol 1998;159:1876-80.
- Zippe C, Pandrangi L, Potts JM, Kursh E, Novick A, Agarwal A. NMP22: a sensitive, cost-effective test in patients at risk for bladder cancer. Anticancer Res 1999;19:2621-3.
- Zippe C, Pandrangi L, Agarwal A. NMP22 is a sensitive, cost-effective test in patients at risk for bladder cancer. J Urol 1999;161:62-5.
- Abbate I, D’Introno A, Cardo G, Marano A, Addabbo L, Musci MD, et al. Comparison of nuclear matrix protein 22 and bladder tumor antigen in urine of patients with bladder cancer. Anticancer Res 1998;18:3803-5.
- Boman H, Hedelin H, Holmang S. Four bladder tumor markers have a disappointingly low sensitivity for small size and low grade recurrence. J Urol 2002;167:80-3.
- Chang YH, Wu CH, Lee YL, Huang PH, Kao YL, Shiau MY. Evaluation of nuclear matrix protein-22 as a clinical diagnostic marker for bladder cancer. Urology 2004;64:687-92.
- Lee KH. Evaluation of the NMP22 test and comparison with voided urine cytology in the detection of bladder cancer. Yonsei Med J 2001;42:14-8.
- Parekattil SJ, Fisher HA, Kogan BA. Neural network using combined urine nuclear matrix protein-22, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and urinary intercellular adhesion molecule-1 to detect bladder cancer. J Urol 2003;169:917-20.
- Ramakumar S, Bhuiyan J, Besse JA, Roberts SG, Wollan PC, Blute ML, et al. Comparison of screening methods in the detection of bladder cancer. J Urol 1999;161:388-94.
- Sanchez-Carbayo M, Herrero E, Megias J, Mira A, Soria F. Evaluation of nuclear matrix protein 22 as a tumour marker in the detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. BJU Int 1999;84:706-13.
- Sanchez-Carbayo M, Herrero E, Megias J, Mira A, Soria F. Comparative sensitivity of urinary CYFRA 21–1, urinary bladder cancer antigen, tissue polypeptide antigen, tissue polypeptide antigen and NMP22 to detect bladder cancer. J Urol 1999;162:1951-6.
- Sanchez-Carbayo M, Urrutia M, Silva JM, Romani R, De Buitrago JM, Navajo JA. Comparative predictive values of urinary cytology, urinary bladder cancer antigen, CYFRA 21–1 and NMP22 for evaluating symptomatic patients at risk for bladder cancer. J Urol 2001;165:1462-7.
- Sozen S, Biri H, Sinik Z, Kupeli B, Alkibay T, Bozkirli I. Comparison of the nuclear matrix protein 22 with voided urine cytology and BTA stat test in the diagnosis of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol 1999;36:225-9.
- Takeuchi Y, Sawada Y. A clinical study of urinary NMP22 in urinary epithelial cancer. J Med Soc Toho Univ 2004;51:332-8.
- Bastacky S, Ibrahim S, Wilczynski SP, Murphy WM. The accuracy of urinary cytology in daily practice. Cancer 1999;87:118-28.
- Chahal R, Gogoi NK, Sundaram SK. Is it necessary to perform urine cytology in screening patients with haematuria?. Eur Urol 2001;39:283-6.
- Garbar C, Mascaux C, Wespes E. Is urinary tract cytology still useful for diagnosis of bladder carcinomas? A large series of 592 bladder washings using a five-category classification of different cytological diagnoses. Cytopathology 2007;18:79-83.
- Hakenberg OW, Franke P, Froehner M, Manseck A, Wirth MP. The value of conventional urine cytology in the diagnosis of residual tumour after transurethral resection of bladder carcinomas. Onkologie 2000;23:252-7.
- Hutterer GC, Karakiewicz PI, Zippe C, Ludecke G, Boman H, Sanchez-Carbayo M, et al. Urinary cytology and nuclear matrix protein 22 in the detection of bladder cancer recurrence other than transitional cell carcinoma. BJU Int 2008;101:561-5.
- Karakiewicz PI, Benayoun S, Zippe C, Ludecke G, Boman H, Sanchez-Carbayo M, et al. Institutional variability in the accuracy of urinary cytology for predicting recurrence of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. BJU Int 2006;97:997-1001.
- Planz B, Jochims E, Deix T, Caspers HP, Jakse G, Boecking A. The role of urinary cytology for detection of bladder cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 2005;31:304-8.
- Potter JM, Quigley M, Pengelly AW, Fawcett DP, Malone PR. The role of urine cytology in the assessment of lower urinary tract symptoms. BJU Int 1999;84:30-1.
- Raitanen M-P, Aine R, Rintala E, Kallio J, Rajala P, Juusela H, et al. Differences between local and review urinary cytology in diagnosis of bladder cancer. An interobserver multicenter analysis. Eur Urol 2002;41:284-9.
- Raitanen MP, Aine RA, Kaasinen ES, Liukkonen TJ, Kylmala TM, Huhtala H, et al. Suspicious urine cytology (class III) in patients with bladder cancer: should it be considered as negative or positive?. Scand J Urol Nephrol 2002;36:213-7.
- Botteman MF, Pashos CL, Redaelli A, Laskin B, Hauser R. The health economics of bladder cancer: a comprehensive review of the published literature. Pharmacoeconomics 2003;21:1315-30.
- Corwin HL, Silverstein MD. The diagnosis of neoplasia in patients with asymptomatic microscopic hematuria: a decision analysis. J Urol 1988;139:1002-6.
- Ellwein LB, Farrow GM. Urinary cytology screening: the decision facing the asymptomatic patient. Med Decis Making 1988;8:110-9.
- Novicki DE, Stern JA, Nemec R, Lidner TK. Cost-effective evaluation of indeterminate urinary cytology. J Urol 1998;160:734-6.
- Rodgers M, Nixon J, Hempel S, Aho T, Kelly J, Neal D, et al. Diagnostic tests and algorithms used in the investigation of haematuria: systematic reviews and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 2006;10.
- Lotan Y, Svatek RS, Sagalowsky AI. Should we screen for bladder cancer in a high-risk population? A cost per life-year saved analysis. Cancer 2006;107:982-90.
- Kurth KH, Denis L, Bouffioux C, Sylvester R, Debruyne FMJ, Pavone-Macaluso M, et al. Factors affecting recurrence and progression in superficial bladder tumours. Eur J Cancer 1995;31:1840-6.
- Dalesio O, Schulman CC, Sylvester R, De Pauw M, Robinson M, Denis L, et al. Prognostic factors in superficial bladder tumors. A study of the European Organization for Research on Treatment of Cancer: Genitourinary Tract Cancer Cooperative Group. J Urol 1983;129:730-3.
- García RJ, Fernandez Gomez JM, Escaf BS, Jalon MA, Alvarez MM, Regadera SJ. Pronostic factors on recurrence and progression of superficial bladder cancer. Risk groups (part II). Actas Urol Esp 2006;30:1009-16.
- Kiemeney LA, Witjes JA, Heijbroek RP, Verbeek AL, Debruyne FM. Predictability of recurrent and progressive disease in individual patients with primary superficial bladder cancer. J Urol 1993;150:60-4.
- Kiemeney LA, Witjes JA, Heijbroek RP, Debruyne FM, Verbeek AL. Dysplasia in normal-looking urothelium increases the risk of tumour progression in primary superficial bladder cancer. Eur J Cancer 1994;30A:1621-5.
- Loening S, Narayana A, Yoder L, Slymen D, Penick G, Culp D. Analysis of bladder tumor recurrence in 178 patients. Urology 1980;16:137-41.
- Millán-Rodriguez F, Chéchile-Toniolo G, Salvador-Bayarri J, Palou J, Algaba F, Vicente-Rodriguez J. Primary superficial bladder cancer risk groups according to progression, mortality and recurrence. J Urol 2000;164:680-4.
- Mulders PF, Meyden AP, Doesburg WH, Oosterhof GO, Debruyne FM. Prognostic factors in pTa-pT1 superficial bladder tumours treated with intravesical instillations. The Dutch South-Eastern Urological Collaborative Group. Br J Urol 1994;73:403-8.
- Narayana AS, Loening SA, Slymen DJ, Culp DA. Bladder cancer: factors affecting survival. J Urol 1983;130:56-60.
- Oosterlinck W, Lobel B, Jakse G, Malmstrom PU, Stockle M, Sternberg CO. Guidelines on bladder cancer. Arnhem: European Association of Urology; 2001.
- Parmar H, Charlton C, Phillips RH, Lightman SL. Management of advanced prostatic cancer. Lancet 1989;2:1338-9.
- Pawinski A, Sylvester R, Kurth KH, Bouffioux C, Van der MA, Parmar MK, et al. A combined analysis of European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, and Medical Research Council randomized clinical trials for the prophylactic treatment of stage TaT1 bladder cancer. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Genitourinary Tract Cancer Cooperative Group and the Medical Research Council Working Party on Superficial Bladder Cancer. J Urol 1996;156:1934-40.
- Shinka T, Matsumoto M, Ogura H, Hirano A, Ohkawa T. Recurrence of primary superficial bladder cancer treated with prophylactic intravesical Tokyo 172 bacillus Calmette-Guerin: a long-term follow-up. Int J Urol 1997;4:139-43.
- Witjes JA, Kiemeney LALM, Verbeek ALM, Heijbroek RP, Debruyne FMJ. Random bladder biopsies and the risk of recurrent superficial bladder cancer: a prospective study in 1026 patients. World J Urol 1992;10:231-4.
- Witjes JA, Kiemeney LA, Schaafsma HE, Debruyn FM. The influence of review pathology on study outcome of a randomized multicentre superficial bladder cancer trial. Members of the Dutch South East Cooperative Urological Group. Br J Urol 1994;73:172-6.
- Herr HW. Natural history of superficial bladder tumors: 10- to 20-year follow-up of treated patients. World J Urol 1997;15:84-8.
- Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R, Groshen S, Feng A-C, Boyd S, et al. Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: long-term results in 1,054 patients. J Clin Oncol 2001;19:666-75.
- von der Maase H, Sengelov L, Roberts JT, Ricci S, Dogliotti L, Oliver T, et al. Long-term survival results of a randomized trial comparing gemcitabine plus cisplatin, with methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, plus cisplatin in patients with bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol 2005;23:4602-8.
- Government Actuary’s Department . Interim Life Tables 2004–6 2008. www.gad.gov.uk/Demography%5FData/Life_Tables/Interim_life_tables.asp (accessed September 2008).
- Farrow SC, Fowkes FGR, Lunn JN. Epidemiology in anaesthesia. II. Factors affecting mortality in hospital. Br J Anaesth 1982;54:811-7.
- Kondas J, Szentgyorgyi E. Transurethral resection of 1250 bladder tumours. Int Urol Nephrol 1992;24:35-42.
- Department of Health . NHS Reference Costs 2005–6 2006. www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/PublicationsPolicyAndGuidance/DH_062884 (accessed September 2008).
- Tumour-marker NMP22 (NMP). Nottingham: MediChecks.com; 2008.
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence . Guide to the Methods of Technology Appraisal 2008. www.nice.org.uk/media/B52/A7/TAMethodsGuideUpdatedJune2008.pdf (accessed September 2008).
- Kulkarni GS, Finelli A, Fleshner NE, Jewett MAS, Lopushinsky SR, Alibhai SMH. Optimal management of high-risk T1G3 bladder cancer: a decision analysis. PLoS Med 2007;4:1538-49.
- Pickard AS, Neary MP, Cella D. Estimation of minimally important differences in EQ-5D utility and VAS scores in cancer. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2007;5.
- Schmidbauer J, Witjes F, Schmeller N, Donat R, Susani M, Marberger M, et al. Improved detection of urothelial carcinoma in situ with hexaminolevulinate fluorescence cystoscopy. J Urol 2004;171:135-8.
- Spiess PE, Grossman HB. Fluorescence cystoscopy: is it ready for use in routine clinical practice?. Curr Opin Urol 2006;16:372-6.
- Zaak D, Karl A, Knuchel R, Stepp H, Hartmann A, Reich O, et al. Diagnosis of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder using fluorescence endoscopy. BJU Int 2005;96:217-22.
- Jain S, Kockelbergh RC. The role of photodynamic diagnosis in the contemporary management of superficial bladder cancer. BJU Int 2005;96:17-21.
- Lotan Y, Roehrborn CG. Sensitivity and specificity of commonly available bladder tumor markers versus cytology: results of a comprehensive literature review and meta-analyses. Urology 2003;61:109-18.
- Glas AS, Roos D, Deutekom M, Zwinderman AH, Bossuyt PM, Kurth KH. Tumor markers in the diagnosis of primary bladder cancer. A systematic review. J Urol 2003;169:1975-82.
- van Rhijn BW, van der Poel HG, van der Kwast TH. Urine markers for bladder cancer surveillance: a systematic review. Eur Urol 2005;47:736-48.
- Yossepowitch O, Herr HW, Donat SM. Use of urinary biomarkers for bladder cancer surveillance: patient perspectives. J Urol 2007;177:1277-82.
- Kiemeney LALM, Witjes JA, Heijbroek RP, Koper NP, Verbeek ALM, Debruyne FMJ. Should random urothelial biopsies be taken from patients with primary superficial bladder cancer? A decision analysis. Br J Urol 1994;73:164-71.
- van der Meijden A, Oosterlinck W, Brausi M, Kurth K-H, Sylvester R, de Balincourt C. Significance of bladder biopsies in Ta,T1 bladder tumors: a report from the EORTC genito-urinary tract cancer cooperative group. Eur Urol 1999;35:267-71.
Appendix 1 Search strategies
Clinical effectiveness
MEDLINE (1966 to March Week 3 2008), EMBASE (1980 to 2008 Week 13), Medline In-Process (31 March 2008)
Ovid Multifile Search
URL: http://gateway.ovid.com/athens
-
urinary bladder neoplasms/use mesz
-
exp bladder cancer/use emez
-
hematuria/
-
(bladder adj3 (cancer$or neoplasms$or carci$)).tw.
-
(hematuria or haematuria).tw.
-
or/1–5
-
*urinary bladder neoplasms/su use mesz
-
exp *bladder cancer/su use emez
-
cystectomy/
-
((bladder adj3 resect$) or cystectomy or turbt).tw.
-
or/7–10
-
cystoscopy/
-
cystoscop$.tw.
-
(photo dynamic$or photodynamic$or fluorescence$).tw.
-
(12 or 13) and 14
-
hypericin.tw.
-
548–04–9.rn.
-
hexvix.tw.
-
hexaminolevulinate.tw.
-
(hexyl$adj3 aminolevulinate).tw.
-
106–60–5.rn.
-
5-ALA.tw.
-
5-aminolevulinic acid.tw.
-
5-aminolevulinic acid hexyl ester.tw,rn.
-
or/15–24
-
(6 or 11) and 25
-
tumor markers,biological/use mesz
-
exp tumor marker/or biological marker/or disease marker/use emez
-
((tumo?r or biological or molecular or histolog$or biochem$or genetic$or urine or disease) adj3 marker$).tw.
-
6 and (27 or 28 or 29))
-
In Situ Hybridization, Fluorescence/
-
fluorescence in situ hybridization.tw.
-
urovysion.tw
-
or/31–33
-
6 and 34
-
nuclear proteins/
-
(nuclear matrix protein 22 or nmp22).tw,rn.
-
or/36–37
-
6 and 38
-
urine/cy
-
urine cytology/use emez
-
cytodiagnosis/use mesz
-
cancer cytodiagnosis/use emez
-
cell count/
-
immunocyt$or ucyt$.tw.
-
or/40–45
-
6 and 46
-
26 or 30 or 35 or 39 or 47
-
(animals/or nonhuman/) not humans/
-
48 not 49
-
(editorial or letter or comment or case reports).pt.
-
editorial/or letter/or note/or case report/use emez
-
50 not (51 or 52)
-
“sensitivity and specificity”/
-
roc curve/
-
receiver operating characteristic/use emez
-
predictive value of tests/
-
diagnostic errors/use emez
-
false positive reactions/use mesz
-
false negative reactions/use mesz
-
diagnostic accuracy/use emez
-
diagnostic value/use emez
-
du.fs. use mesz
-
sensitivity.tw.
-
distinguish$.tw.
-
differentiate.tw.
-
identif$.tw.
-
detect$.tw.
-
diagnos$.tw.
-
(predictive adj4 value$).tw.
-
accura$.tw.
-
comparison.tw.
-
or/54–72
-
53 and 73
-
exp diagnostic errors/
-
reproducibility of results/
-
observer variation
-
exp reliability/
-
diagnosis, differential/
-
early diagnosis/
-
(reliab$or reproduc$).tw.
-
or/75–81
-
53 and 82
-
prognosis/
-
(predict$or prognosis or prognostic).tw.
-
84 or 85
-
53 and 86
-
26 or 74 or 83 or 87
Science Citation Index (1970 to 1 April 2006), BIOSIS (1985 to 3 April 2008)
Web of Knowledge
-
#1 TS=(bladder SAME (cancer* or neoplasm* or carci*))
-
#2 TS=(hematuria OR haematuria)
-
#3 #1 or #2
-
#4 TS=((bladder SAME resect*) or cystectomy or turbt)
-
#5 #3 or #4
-
#6 TS=(cystoscop* AND (photo* dynamic* OR photodynamic* OR fluorescence*))
-
#7 #5 AND #6
-
#8 TS=(hypericin or hexvix or hexaminolevulin*or hexyl* aminolevulin* or 5-ala or 5-aminolevulin*)
-
#9 #5 and #8
-
#10 #7 or #9
-
#11 TS=(marker* SAME (tumor or tumour or biological or molecular or histolog* or biochem* or genetic* or urine or disease))
-
#12 #3 and #11
-
#13 TS=(immunocyt* or ucyt*)
-
#14 TS=cytolog*
-
#15 TS=(nmp22 or nuclear matrix protein 22)
-
#16 TS=urovysion
-
#17 TS=(fluorescence SAME hybridization)
-
#18 #13 or #14 or #15 or #16 or #17
-
#19 #3 and #18
-
#20 #10 or #12 or #19
-
#21 TS=((bladder or hemauturia or haematuria) SAME (predict* or prognosis or prognostic or reliab* or reproduc*))
-
#22 TS=((bladder or hemauturia or haematuria) SAME (sensitivity or specificity or roc))
-
#23 TS=((bladder or hemauturia or haematuria) SAME (identif* or accura* or compara*))
-
#24 TS=((bladder or hemauturia or haematuria) SAME detect*)
-
#25 TS=((bladder or hemauturia or haematuria) SAME diagnos*)
-
#26 #21 or #22 or #23 or #24 or #25
-
#27 #20 and #26
-
#28 #10 or #27
Health Management Information Consortium (1979 to March 2008)
Ovid Multifile Search
URL: http://gateway.ovid.com/athens
-
bladder cancer/
-
haematuria/
-
1 or 2
-
(photo$dynamic$or photodynamic or fluorescence).tw. (17)
-
(hypericin or hexvix or hexyl$or 5-ala$or aminolevulonate).tw.
-
(marker$or biomarker$).tw.
-
(nmp22 or immunocyt$or ucyt$or urovysion or fish).tw. (
-
cytology/
-
or/4–8
-
3 and 9
Cochrane Library (Issue 1 2008)
URL: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/mrwhome/106568753/HOME
-
#1 URINARY BLADDER NEOPLASMS single term (MeSH)
-
#2 HEMATURIA single term (MeSH)
-
#3 (#1 or #2)
-
#4 ((photo* next dynamic*) or photodynamic* or fluoresence*)
-
#5 (hypericin or hexvix or hexyl* or ala)
-
#6 (#4 or #5)
-
#7 (#3 and #6)
-
#8 marker*
-
#9 #9 nmp22 or immunocyt or urovysion or fish
-
#10 (#3 and (#8 or #9))
-
#11 (#7 or #10)
DARE and HTA databases (March 2008)
NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination
URL: http://nhscrd.york.ac.uk/welcome.htm
-
1 MeSH Bladder Neoplasms EXPLODE 1 2 3 4 49
-
# 2 MeSH Hematuria EXPLODE 1 2 15
-
# 4 nmp22 OR immunocyt OR ucyt OR urovysion OR fish 93
-
# 5 marker* or biomarker* 419
-
# 7 #1 or #2 63
-
# 8 #5 and #7 11
-
# 9 photo AND dynamic OR photodynamic 83
-
# 10 #7 and #9 2
-
# 12 fluorescence OR hexvix OR hexyl OR hypericin OR 5-ala 34
-
# 13 #1 or #2 or #4 or #8 or #10 or #12 171
National Research Register Archive (September 2007)
URL: www.update-software.com/National/
-
#1 URINARY BLADDER NEOPLASMS single term (MeSH)
-
#2 HEMATURIA single term (MeSH)
-
#3 (#1 or #2)
-
#4 ((photo* next dynamic*) or photodynamic* or fluoresence*)
-
#5 (hypericin or hexvix or hexyl* or ala)
-
#6 (#4 or #5)
-
#7 (#3 and #6)
-
#8 marker*
-
#9 #9 nmp22 or immunocyt or urovysion or fish
-
#10 (#3 and (#8 or #9))
-
#11 (#7 or #10)
ClinicalTrials.gov (March 2008)
URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct/gui/c/r
“bladder cancer”:Topic AND (photodynamic OR fluoresence OR ALA OR hexvix OR hexyl OR hypericin or NMP22 or Immunocyt or urovysion or fish): Search terms
Current Controlled Trials (March 2008)
URL: www.controlled-trials.com/
bladder AND (marker% OR photo% OR fluoresence OR ALA OR hexvix OR hexyl OR hypericin or NMP22 or Immunocyt or urovysion or fish)
WHO ICTRP (March 2008)
(photodynamic OR fluoresence OR ALA OR hexvix OR hexyl OR hypericin or NMP22 or Immunocyt or urovysion or fish):TI AND bladder cancer:Condition
Cost-effectiveness
MEDLINE (1966 to March Week 3 2008), EMBASE (1980 to 2008 Week 13), Medline In-Process (1 April 2008)
Ovid Multifile Search
URL: http://gateway.ovid.com/athens
-
urinary bladder neoplasms/use mesz
-
exp bladder cancer/use emez
-
hematuria/
-
(bladder adj3 (cancer$or neoplasm$or carci$)).tw.
-
(hematuria or haematuria).tw.
-
or/1–5
-
*urinary bladder neoplasms/su use mesz
-
exp *bladder cancer/su use emez
-
cystectomy/
-
((bladder adj3 resect$) or cystectomy or turbt).tw.
-
or/7–10
-
cystoscopy/
-
cystoscop$.tw.
-
(photo dynamic$or photodynamic$or fluorescence$).tw.
-
(12 or 13) and 14
-
hypericin.tw.
-
548–04–9.rn.
-
hexvix.tw.
-
hexaminolevulinate.tw.
-
(hexyl$adj3 aminolevulinate).tw.
-
106–60–5.rn.
-
5-ALA.tw.
-
5-aminolevulinic acid.tw.
-
5-aminolevulinic acid hexyl ester.tw,rn.
-
or/15–24
-
(6 or 11) and 25
-
tumor markers,biological/use mesz
-
exp tumor marker/or biological marker/or disease marker/use emez
-
((tumo?r or biological or molecular or histolog$or biochem$or genetic$or urine or disease) adj3 marker$).tw.
-
6 and (27 or 28 or 29)
-
In Situ Hybridization, Fluorescence/
-
fluorescence in situ hybridization.tw.
-
urovysion.tw.
-
or/31–33
-
6 and 34
-
nuclear proteins/
-
(nuclear matrix protein 22 or nmp22).tw,rn.
-
or/36–37
-
6 and 38
-
urine/cy
-
urine cytology/use emez
-
cytodiagnosis/use mesz
-
cancer cytodiagnosis/use emez
-
cell count/
-
immunocyt$.tw.
-
or/40–45
-
6 and 46
-
26 or 30 or 35 or 39 or 47
-
exp “costs and cost analysis”/
-
economics/
-
exp economics,hospital/
-
exp economics,medical/
-
economics,pharmaceutical/
-
exp budgets/
-
exp models, economic/
-
exp decision theory/
-
ec.fs. use mesz
-
monte carlo method/
-
markov chains/
-
exp health status indicators/
-
cost$.ti.
-
(cost$adj2 (effective$or utilit$or benefit$or minimis$)).ab.
-
economic$model$.tw.
-
(economics$or pharmacoeconomic$or pharmo-economic$).ti.
-
(price$or pricing$).tw.
-
(financial or finance or finances or financed).tw.
-
(value adj2 (money or monetary)).tw.
-
markov$.tw.
-
monte carlo.tw.
-
(decision$adj2 (tree? or analy$or model$)).tw.
-
(standard adj1 gamble).tw.
-
trade off.tw.
-
or/49–72
-
48 and 73
-
remove duplicates from 74
Science Citation Index (1970 to 1 April 2008)
Web of Knowledge
-
#1 TS=(bladder SAME (cancer* or neoplasm* or carci*))
-
#2 TS=(hematuria OR haematuria)
-
#3 #1 or #2
-
#4 TS=((bladder SAME resect*) or cystectomy or turbt)
-
#5 #3 or #4
-
#6 TS=(cystoscop* AND (photo* dynamic* OR photodynamic* OR fluorescence*))
-
#7 #5 AND #6
-
#8 TS=(hypericin or hexvix or hexaminolevulin*or hexyl aminolevulin* or 5-ala or 5-aminolevulin*)
-
#9 #5 and #8
-
#10 #7 or #9
-
#11 TS=(marker* SAME (tumor or tumour or biological or molecular or histolog* or biochem* or genetic* or urine or disease))
-
#12 #3 and #11
-
#13 45,591 TS=(immunocyt* or ucyt)
-
#14 35,989 TS=cytolog*
-
#15 221 TS=(nmp22 or nuclear matrix protein 22)
-
#16 33 TS=urovysion
-
#17 13,601 TS=(fluorescence SAME hybridization)
-
#18 #13 or #14 or #15 or #16 or #17
-
#19 #3 and #18
-
#20 #10 or #12 or #19
-
#21 TS=economic*
-
#22 TS=cost*
-
#23 TS=(price* OR pricing*)
-
#24 TS=(financial or finance*)
-
#25 TS=(decision* SAME (tree* OR analy* or model*))
-
#26 TS=markov*
-
#27 TS=monte carlo
-
#28 #21 or #22 or #23 or #24 or #25 or #26 or #27
-
#29 #20 and #28
NHS Economic Evaluation Database (March 2008)
NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination
URL:http://nhscrd.york.ac.uk/welcome.htm
-
1 MeSH Bladder Neoplasms EXPLODE 1 2 3 4 49
-
# 2 MeSH Hematuria EXPLODE 1 2 15
-
# 4 nmp22 OR immunocyt OR ucyt OR urovysion OR fish 93
-
# 5 marker* or biomarker* 419
-
# 7 #1 or #2 63
-
# 8 #5 and #7 11
-
# 9 photo AND dynamic OR photodynamic 83
-
# 10 #7 and #9 2
-
# 12 fluorescence OR hexvix OR hexyl OR hypericin OR 5-ala 34
-
# 13 #1 or #2 or #4 or #8 or #10 or #12 171
Health Management Information Consortium (1979 to March 2008)
Ovid Multifile Search
URL: http://gateway.ovid.com/athens
-
bladder cancer/
-
haematuria/
-
1 or 2
-
(photo$dynamic$or photodynamic or fluorescence).tw. (17)
-
(hypericin or hexvix or hexyl$or 5-ala$or aminolevulonate).tw.
-
(marker$or biomarker$).tw.
-
(nmp22 or immunocyt$or ucyt$or urovysion or fish).tw. (
-
cytology/
-
or/4–8
-
3 and 9
CEA Registry (March 2008)
Centre for the Evaluation of Value and Risk in Health
URL: https://research.tufts-nemc.org/cear/default.aspx
bladder or hemauria or haematuria
Quality of life and cost data for model
MEDLINE (1966 to March Week 3 2008), EMBASE (1980 to 2008 Week 13), Medline In-Process (1 April 2008)
Ovid Multifile Search
URL: http://gateway.ovid.com/athens
-
urinary bladder neoplasms/di, pc
-
exp bladder cancer/di, dm
-
*hematuria/
-
(hematuria or haematuria).ti.
-
(bladder adj1 (cancer$or neoplasm$or carci$)).ti.
-
*cystoscopy/
-
or/1–6
-
exp “costs and cost analysis”/
-
economics/
-
exp economics,hospital/
-
exp economics,medical/
-
economics,pharmaceutical/
-
exp budgets/
-
exp models, economic/
-
exp decision theory/
-
ec.fs. use mesz
-
monte carlo method/
-
markov chains/
-
exp health status indicators/
-
cost$.ti.
-
(cost$adj2 (effective$or utilit$or benefit$or minimis$)).ab.
-
economic$model$.tw.
-
(economics$or pharmacoeconomic$or pharmo-economic$).ti
-
(price$or pricing$).tw.
-
(financial or finance or finances or financed).tw.
-
(value adj2 (money or monetary)).tw.
-
markov$.tw.
-
monte carlo.tw.
-
(decision$adj2 (tree? or analy$or model$)).tw.
-
(standard adj1 gamble).tw.
-
trade off.tw.
-
or/8–31
-
7 and 32
-
quality of life/
-
quality adjusted life year/
-
“Value of Life”/use mesz
-
health status indicators/use mesz
-
health status/use emez
-
sickness impact profile/use mesz
-
disability evaluation/use mesz
-
disability/use emez
-
activities of daily living/use mesz
-
exp daily life activity/use emez
-
cost utility analysis/use emez
-
rating scale/
-
questionnaires/
-
(quality adj1 life).tw.
-
quality adjusted life.tw.
-
disability adjusted life.tw.
-
(qaly? or qald? or qale? or qtime? or daly?).tw.
-
(euroqol or euro qol or eq5d or eq 5d).tw.
-
(hql or hqol or h qol or hrqol or hr qol).tw.
-
(hye or hyes).tw.
-
health$year$equivalent$.tw.
-
(hui or hui1 or hui2 or hui3).tw.
-
(health adj3 (utilit$or disutili$)).tw.
-
(health adj3 (state or status)).tw.
-
(sf36 or sf 36 or short form 36 or shortform 36).tw.
-
(sf6 or sf 6 or short form 6 or shortform 6).tw.
-
(sf12 or sf 12 or short form 12 or shortform 12).tw.
-
(sf16 or sf 16 or short form 16 or shortform 16).tw.
-
(sf20 or sf 20 or short form 20 or shortform 20).tw.
-
willingness to pay.tw.
-
standard gamble.tw.
-
or/34–64
-
7 and 65
-
33 or 66
-
(case report or editorial or letter).pt.
-
case report/
-
67 not (68 or 69)
-
limit 70 to english language
-
remove duplicates from 71
Websites consulted
Cancer Research UK – URL: www.cancerresearchuk.org/
European Association of Urology – URL: www.uroweb.org/
European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) – URL: www.eortc.be/
Hexvix, GE Healthcare Medical Diagnostics – URL: www.hexvix.com/cont.shtml
National Cancer Institute, US National Institutes of Health – URL: www.cancer.gov/
National Comprehensive Cancer Network – URL: www.nccn.org/default.asp
National Insitute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) – URL: http://www2.niddk.nih.gov/Research/ScientificAreas/Urology/
NHS National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence – URL: www.nice.org.uk/
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, NHS Quality Improvement Scotland – URL: www.sign.ac.uk/
Appendix 2 PDD quality assessment checklist (QUADAS tool)
Study id: Assessor initials:
Date assessed:
| Item | Yes | No | Unclear | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Was the spectrum of patients representative of the patients who will receive the test in practice? | |||
| 2 | Is the reference standard likely to correctly classify the target condition? | |||
| 3 | Is the time period between the reference standard and index test short enough to be reasonably sure that the target condition did not change between the two tests? | |||
| 4 | Did the whole sample or a random selection of the sample receive verification using a reference standard of diagnosis? | |||
| 5 | Did patients receive the same reference standard regardless of the index test result? | |||
| 6 | Was the reference standard independent of the index test (i.e. the index test did not form part of the reference standard)? | |||
| 7 | Were the index test results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard? | |||
| 8 | Were the reference standard results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test? | |||
| 9 | Were the same clinical data available when test results were interpreted as would be available when the test is used in practice? | |||
| 10 | Were uninterpretable/intermediate test results reported? | |||
| 11 | Were withdrawals from the study explained? | |||
| 12 | Did the study provide a clear definition of what was considered to be a ‘positive’ result? | |||
| 13 | Were data on observer variation reported and within an acceptable range? | |||
Appendix 3 PDD quality assessment checklist (RCTs)
Study id: Assessor initials:
Date assessed:
| Criteria | Yes | No | Unclear | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Was the assignment to the treatment groups really random? (Adequate approaches to sequence generation: computer-generated random tables, random number tables; inadequate approaches to sequence generation: use of alternation, case record numbers, birth dates or week days) | |||
| 2 | Was the treatment allocation concealed? [Adequate approaches to concealment of randomisation: centralised or pharmacy-controlled randomisation, serially numbered identical containers, on-site computer-based system with a randomisation sequence that is not readable until allocation, other approaches with robust methods to prevent foreknowledge of the allocation sequence to clinicians and patients; inadequate approaches to concealment of randomisation: use of alternation, case record numbers, birth dates or week days, open random numbers lists, serially numbered envelopes (even sealed opaque envelopes can be subject to manipulation)] | |||
| 3 | Were the groups similar at baseline in terms of prognostic factors? | |||
| 4 | Were the eligibility criteria specified? | |||
| 5 | Was the intervention (and comparison) clearly defined? | |||
| 6 | Were the groups treated in the same way apart from the intervention received? | |||
| 7 | Was follow-up long enough to detect important effects on outcomes of interest? | |||
| 8 | Was the outcome assessor blinded to the treatment allocation? | |||
| 9 | Was the care provider blinded? | |||
| 10 | Were the patients blinded? | |||
| 11 | Were the point estimates and measures of variability presented for the primary outcome measures? | |||
| 12 | Was the withdrawal/dropout rate likely to cause bias? | |||
| 13 | Did the analyses include an intention to treat analysis? | |||
| 14 | Was the operation undertaken by somebody experienced in performing the procedure? | |||
Appendix 4 Photodynamic diagnosis (PDD) included studies
Diagnostic accuracy
Cheng 2000
Cheng CW, Lau WK, Tan PH, Olivo M. Cystoscopic diagnosis of bladder cancer by intravesical instillation of 5-aminolevulinic acid induced porphyrin fluorescence – the Singapore experience. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2000;29:153–8.
Colombo 2007
Colombo R, Naspro R, Bellinzoni P, Fabbri F, Guazzoni G, Scattoni V, et al. Photodynamic diagnosis for follow-up of carcinoma in situ of the bladder. Ther Clin Risk Manage 2007;3:1003–7.
De Dominicis 2001
De Dominicis C, Liberti M, Perugia G, De Nunzio C, Sciobica F, Zuccala A, et al. Role of 5-aminolevulinic acid in the diagnosis and treatment of superficial bladder cancer: improvement in diagnostic sensitivity. Urology 2001;57:1059–62.
D’Hallewin 2000
D’Hallewin MA, De Witte PA, Waelkens E, Merlevede W, Baert L. Fluorescence detection of flat bladder carcinoma in situ after intravesical instillation of hypericin. J Urol 2000;164:349–51.
Ehsan 2001
Ehsan A, Sommer F, Haupt G, Engelmann U. Significance of fluorescence cystoscopy for diagnosis of superficial bladder cancer after intravesical instillation of delta aminolevulinic acid. Urol Int 2001;67:298–304.
Filbeck 1999
Primary reference
Filbeck T, Roessler W, Knuechel R, Straub M, Kiel HJ, Wieland WF. Clinical results of the transurethral resection and evaluation of superficial bladder carcinomas by means of fluorescence diagnosis after intravesical instillation of 5-aminolevulinic acid. J Endourol 1999;13:117–21.
Secondary reference
Filbeck T, Roessler W, Knuechel R, Straub M, Kiel HJ, Wieland WF. 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence endoscopy applied at secondary transurethral resection after conventional resection of primary superficial bladder tumors. Urology 1999;53:77–81.
Fradet 2007
Fradet Y, Grossman HB, Gomella L, Lerner S, Cookson M, Albala D, et al. A comparison of hexaminolevulinate fluorescence cystoscopy and white light cystoscopy for the detection of carcinoma in situ in patients with bladder cancer: a phase III, multicenter study. J Urol 2007;178:68–73.
Frimberger 2001
Frimberger D, Zaak D, Stepp H, Knuchel R, Baumgartner R, Schneede P, et al. Autofluorescence imaging to optimize 5-ALA-induced fluorescence endoscopy of bladder carcinoma. Urology 2001;58:372–5.
Grimbergen 2003
Grimbergen MC, van Swol CF, Jonges TG, Boon TA, van Moorselaar RJ. Reduced specificity of 5-ALA induced fluorescence in photodynamic diagnosis of transitional cell carcinoma after previous intravesical therapy. Eur Urol 2003;44:51–6.
Hendricksen 2006
Hendricksen K, Moonen PM, der Heijden AG, Witjes JA. False-positive lesions detected by fluorescence cystoscopy: any association with p53 and p16 expression? World J Urol 2006;24:597–601.
Hungerhuber 2007
Primary reference
Hungerhuber E, Stepp H, Kriegmair M, Stief C, Hofstetter A, Hartmann A, et al. Seven years’ experience with 5-aminolevulinic acid in detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urology 2007;69:260–4.
Secondary references
Zaak D, Kriegmair M, Stepp H, Stepp H, Baumgartner R, Oberneder R, et al. Endoscopic detection of transitional cell carcinoma with 5-aminolevulinic acid: results of 1012 fluorescence endoscopies. Urology 2001;57:690–4.
Zaak D, Hungerhuber E, Schneede P, Stepp H, Frimberger D, Corvin S, et al. Role of 5-aminolevulinic acid in the detection of urothelial premalignant lesions. Cancer 2002;95:1234–8.
Jeon 2001
Jeon SS, Kang I, Hong JH, Choi HY, Chai SE. Diagnostic efficacy of fluorescence cystoscopy for detection of urothelial neoplasms. J Endourol 2001;15:753–9.
Jichlinski 1997
Primary reference
Jichlinski P, Forrer M, Mizeret J, Glanzmann T, Braichotte D, Wagnieres G, et al. Clinical evaluation of a method for detecting superficial surgical transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder by light-induced fluorescence of protoporphyrin IX following the topical application of 5-aminolevulinic acid: preliminary results. Lasers Surg Med 1997;20:402–8.
Secondary reference
Jichlinski P, Wagnieres G, Forrer M, Mizeret J, Guillou L, Oswald M, et al. Clinical assessment of fluorescence cytoscopy during transurethral bladder resection in superficial bladder cancer. Urol Res 1997;25(Suppl. 1):S3–6.
Jichlinski 2003
Jichlinski P, Guillou L, Karlsen SJ, Malmstrom PU, Jocham D, Brennhovd B, et al. Hexyl aminolevulinate fluorescence cystoscopy: new diagnostic tool for photodiagnosis of superficial bladder cancer – a multicenter study. J Urol 2003;170:226–9.
Jocham 2005
Jocham D, Witjes F, Wagner S, Zeylemaker B, van Moorselaar J, Grimm MO, et al. Improved detection and treatment of bladder cancer using hexaminolevulinate imaging: a prospective, phase III multicenter study. J Urol 2005;174:862–6.
Koenig 1999
Koenig F, McGovern FJ, Larne R, Enquist H, Schomacker KT, Deutsch TF. Diagnosis of bladder carcinoma using protoporphyrin IX fluorescence induced by 5-aminolaevulinic acid. BJU Int 1999;83:129–35.
Kriegmair 1996
Primary reference
Kriegmair M, Baumgartner R, Knuchel R, Stepp H, Hofstadter F, Hofstetter A. Detection of early bladder cancer by 5-aminolevulinic acid induced porphyrin fluorescence. J Urol 1996;155:105–9.
Secondary references
Kriegmair M, Baumgartner R, Knuechel R, Steinbach P, Ehsan A, Lumper W, et al. Fluorescence photodetection of neoplastic urothelial lesions following intravesical instillation of 5-aminolevulinic acid. Urology 1994;44:836–41.
Kriegmair M, Stepp H, Steinbach P, Lumper W, Ehsan A, Stepp HG, et al. Fluorescence cystoscopy following intravesical instillation of 5-aminolevulinic acid: a new procedure with high sensitivity for detection of hardly visible urothelial neoplasias. Urol Int 1995;55:190–6.
Kriegmair 1999
Primary reference
Kriegmair M, Zaak D, Stepp H, Stepp H, Baumgartner R, Knuechel R, et al. Transurethral resection and surveillance of bladder cancer supported by 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence endoscopy. Eur Urol 1999;36:386–92.
Secondary references
Schneeweiss S, Kriegmair M, Stepp H. Is everything all right if nothing seems wrong? A simple method of assessing the diagnostic value of endoscopic procedures when a gold standard is absent. J Urol 1999;161:1116–9.
Schneeweiss S. Sensitivity analysis of the diagnostic value of endoscopies in cross-sectional studies in the absence of a gold standard. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 2000;16:834–41.
Landry 2003
Landry JL, Gelet A, Bouvier R, Dubernard JM, Martin X, Colombel M. Detection of bladder dysplasia using 5-aminolaevulinic acid-induced porphyrin fluorescence. BJU Int 2003;91:623–6.
Riedl 1999
Riedl CR, Plas E, Pfluger H. Fluorescence detection of bladder tumors with 5-amino-levulinic acid. J Endourol 1999;13:755–9.
Sim 2005
Sim HG, Lau WK, Olivo M, Tan PH, Cheng CW. Is photodynamic diagnosis using hypericin better than white-light cystoscopy for detecting superficial bladder carcinoma? BJU Int 2005;95:1215–18.
Song 2007
Song X, Ye Z, Zhou S, Yang W, Zhang X, Liu J, et al. The application of 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence for cystoscopic diagnosis and treatment of bladder carcinoma. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2007;4:39–43.
Szygula 2004
Primary reference
Szygula M, Wojciechowski B, Adamek M, Pietrusa A, Kawczyk-Krupka A, Cebula W, et al. Fluorescent diagnosis of urinary bladder cancer – a comparison of two diagnostic modalities. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2004;1:23–6.
Secondary reference
Szygula M, Wojciechowski B, Adamek M, Kawczyk-Krupka A, Cebula W, Zieleznik W, et al. Photodynamic vs autofluorescent diagnosis of urinary bladder using Xillix LIFE system. Physica Medica 2004;20(Suppl. 1):55–7.
Tritschler 2007
Tritschler S, Scharf S, Karl A, Tilki D, Knuechel R, Hartmann A, et al. Validation of the diagnostic value of NMP22 BladderChek test as a marker for bladder cancer by photodynamic diagnosis. Eur Urol 2007;51:403–7.
Witjes 2005
Witjes JA, Moonen PM, van der Heijden AG. Comparison of hexaminolevulinate based flexible and rigid fluorescence cystoscopy with rigid white light cystoscopy in bladder cancer: results of a prospective phase II study. Eur Urol 2005;47:319–22.
Zaak 2002
Zaak D, Stepp H, Baumgartner R, Schneede P, Waidelich R, Frimberger D, et al. Ultraviolet-excited (308 nm) autofluorescence for bladder cancer detection. Urology 2002;60:1029–33.
Zumbraegel 2003
Zumbraegel A, Bichler KH, Krause FS, Feil G, Nelde HJ. The photodynamic diagnosis (PDD) for early detection of carcinoma and dysplasia of the bladder. Adv Exp Med Biol 2003;539:61–6.
Effectiveness
Babjujk 2005
Babjuk M, Soukup V, Petrik R, Jirsa M, Dvoracek J. 5-aminolaevulinic acid-induced fluorescence cystoscopy during transurethral resection reduces the risk of recurrence in stage Ta/T1 bladder cancer. BJU Int 2005;96:798–802.
Daniltchenko 2005
Primary reference
Daniltchenko DI, Riedl CR, Sachs MD, Koenig F, Daha KL, Pflueger H, et al. Long-term benefit of 5-aminolevulinic acid fluorescence assisted transurethral resection of superficial bladder cancer: 5-year results of a prospective randomized study. J Urol 2005;174:2129–33.
Secondary reference
Riedl CR, Daniltchenko D, Koenig F, Simak R, Loening SA, Pflueger H. Fluorescence endoscopy with 5-aminolevulinic acid reduces early recurrence rate in superficial bladder cancer. J Urol 2001;165:1121–3.
Denzinger 2007
Primary reference
Denzinger S, Burger M, Walter B, Knuechel R, Roessler W, Wieland WF, et al. Clinically relevant reduction in risk of recurrence of superficial bladder cancer using 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence diagnosis: 8-year results of prospective randomized study. Urology 2007;69:675–9.
Secondary references
Burger M, Zaak D, Stief CG, Filbeck T, Wieland WF, Roessler W, et al. Photodynamic diagnostics and noninvasive bladder cancer: is it cost-effective in long-term application? A Germany-based cost analysis. Eur Urol 2007;52:142–7.
Denzinger S, Wieland WF, Otto W, Filbeck T, Knuechel R, Burger M. Does photodynamic transurethral resection of bladder tumour improve the outcome of initial T1 high-grade bladder cancer? A long-term follow-up of a randomized study. BJU Int 2008;101:566–9.
Filbeck T, Pichlmeier U, Knuechel R, Wieland WF, Roessler W. Clinically relevant improvement of recurrence-free survival with 5-aminolevulinic acid induced fluorescence diagnosis in patients with superficial bladder tumors. J Urol 2002;168:67–71.
Kriegmair 2002
Kriegmair M, Zaak D, Rothenberger KH, Rassweiler J, Jocham D, Eisenberger F, et al. Transurethral resection for bladder cancer using 5-aminolevulinic acid induced fluorescence endoscopy versus white light endoscopy. J Urol 2002;168:475–8.
Appendix 5 Photodynamic diagnosis excluded studies
Required outcomes not reported (n = 12)
Chin WW, Ramaswamy B, Thong PSP, Heng PWS, Gan YY, Olivo M, et al. Preclinical and pilot clinical cancer studies using fluorescence-guided photodynamic therapy with chlorin e6-polyvinylpyrrolidone and hypericin. Singapore Gen Hosp Proc 2007;16:118–26.
D’Hallewin MA, Vanherzeele H, Baert L. Fluorescence detection of flat transitional cell carcinoma after intravesical instillation of aminolevulinic acid. Am J Clin Oncol 1998;21:223–5.
D’Hallewin MA, Kamuhabwa AR, Roskams T, De Witte PA, Baert L. Hypericin-based fluorescence diagnosis of bladder carcinoma. BJU Int 2002;9:760–3.
Filbeck T, Pichlmeier U, Knuechel R, Wieland WF, Roessler W. Do patients profit from 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence diagnosis in transurethral resection of bladder carcinoma? Urology 2002;60:1025–8.
Grossman HB, Gomella L, Fradet Y, Morales A, Presti J, Ritenour C, et al. A phase III, multicenter comparison of hexaminolevulinate fluorescence cystoscopy and white light cystoscopy for the detection of superficial papillary lesions in patients with bladder cancer. J Urol 2007;178:62–7.
Junker K, Kania K, Fiedler W, Hartmann A, Schubert J, Werner W. Molecular genetic evaluation of fluorescence diagnosis in bladder cancer. Int J Oncol 2002;20:647–53.
Kriegmair M, Zaak D, Knuechel R, Baumgartner R, Hofstetter A. 5-Aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence endoscopy for the detection of lower urinary tract tumors. Urol Int 1999;63:27–31.
Kriegmair M, Zaak D, Knuechel R, Baumgartner R, Hofstetter A. Photodynamic cystoscopy for detection of bladder tumors. Semin Laparosc Surg 1999;6:100–3.
Loidl W, Schmidbauer J, Susani M, Marberger M. Flexible cystoscopy assisted by hexaminolevulinate induced fluorescence: a new approach for bladder cancer detection and surveillance? Eur Urol 2005;47:323–6.
Petrik R, Jirsa M, Dvorak E, Skoda V, Stadnik B. Fluorescence cystoscopy in the diagnostics and treatment of bladder tumors. Biomed Tech (Berl) 1998;43(Suppl.):74–5.
Schmidbauer J, Witjes F, Schmeller N, Donat R, Susani M, Marberger M, et al. Improved detection of urothelial carcinoma in situ with hexaminolevulinate fluorescence cystoscopy. J Urol 2004;171:135–8.
van der Meijden APM. Does hexaminolevulinate imaging improve the detection and treatment of bladder cancer? Nature Clin PractUrol 2006;3:22–3.
Required study design not met (n = 10)
Batlle A, Peng Q. Preface: special issue of photodynamic therapy and photodetection with porphyrin precursors for the Journal of Environmental Pathology, Toxicology, and Oncology. J Env Pathol Toxicol Oncol 2007;26:ix–xii.
Chatterton K, Ray E, O’Brien TS. Fluorescence diagnosis of bladder cancer. Br J Nurs 2006;15:595–7.
Collaud S, Jichlinski P, Marti A, Aymon D, Gurny R, Lange N. An open pharmacokinetic study of hexylaminolevulinate-induced photodiagnosis after intravesical administration. Drugs R D 2006;7:173–86.
Grossman H. Re: Long-term benefit of 5-aminolevulinic acid fluorescence-assisted transurethral resection of superficial bladder cancer: 5-year results of a prospective randomised study. Eur Urol 2006;50:861–2.
Jichlinski P. Hexyl aminolevulinate in the detection of bladder cancer. Drugs 2006;66:579–80.
Koenig F, McGovern FJ. Fluorescence detection of bladder carcinoma. Urology 1997;50:778–9.
Witjes JA, Jichlinski P, Zaak D, Stief CG. Hexyl aminolevulinate in the detection of bladder cancer. Drugs 2006;66:579–80.
Zaak D, Frimberger D, Stepp H, Wagner S, Baumgartner R, Schneede P, et al. Quantification of 5-aminolevulinic acid induced fluorescence improves the specificity of bladder cancer detection. J Urol 2001;166:1665–8.
Zaak D, Stief CG. Hexyl aminolevulinate in the detection of bladder cancer. Drugs 2006;66(4).
Zlotta A. Fluorescence cystoscopy: is flexible scope as effective as rigid? Eur Urol 2005;47:318.
Required reference standard not met (n = 2)
Olivo M, Lau W, Manivasager V, Hoon TP, Christopher C. Fluorescence confocal microscopy and image analysis of bladder cancer using 5-aminolevulinic acid. Int J Oncol 2003;22:523–8.
Olivo M, Lau W, Manivasager V, Tan PH, Soo KC, Cheng C. Macro-microscopic fluorescence of human bladder cancer using hypericin fluorescence cystoscopy and laser confocal microscopy. Int J Oncol 2003;23:983–90.
Comparator test not white light cystoscopy (n = 1)
Lipinski M, Jeromin L. Comparison of the bladder tumour antigen test with photodynamic diagnosis in patients with pathologically confirmed recurrent superficial urinary bladder tumours. BJU Int 2002;89:757–9.
Appendix 6 Characteristics of the PDD diagnostic studies
| Studya | Participants | Tests | Outcomes summary |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cheng 200050 Time period: Jan 1997 to Dec 1998 Country: Singapore |
Enrolled: 41; analysed: 41 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): mean 66.8, range 42 to 89 Sex: M 24; F 17 |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes for PDD |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 175) Sensitivity: PDD 89%, WLC 66% Specificity: PDD 65%, WLC 84% |
|
Colombo 200751 Time period: Feb 2004 to Mar 2006 Country: Italy |
Enrolled: 49; analysed: 49 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 49 Age (years): mean 70, SD 12 Sex: NS Notes: All patients were suffering from CIS alone at inclusion and undergoing BCG therapy |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA, HAL Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes (NS whether PDD or WLC or both) |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 49) Sensitivity: PDD 100%, WLC 0% Specificity: PDD 71%, WLC 97% |
|
De Dominicis 200153 Time period: May 1997 to NS Country: Italy |
Enrolled: 49; analysed: 49 No previous history of BC: 17; history of BC: 32 Age (years): mean 60, range 31 to 77 Sex: M 42; F 7 |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes for both PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 179) Sensitivity: PDD 87%, WLC 17% Specificity: PDD 63%, WLC 88% |
|
D’Hallewin 200052 Time period: NS Country: Belgium |
Enrolled: 40; analysed: 40 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Index test: PDD Agent: hypericin Comparator: none ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes for PDD |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (CIS) (n = 281) Sensitivity: PDD 93% Specificity: PDD 99% |
|
Ehsan 200154 Time period: NS Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 30; analysed: 30 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): mean NS, range 55 to 85 Sex: M 19; F 11 |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 151) Sensitivity: PDD 59%, WLC 60% Specificity: PDD 98%, WLC 58% |
|
Filbeck 199956 Time period: NS Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 123; analysed: 120 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): mean 64.5, range 28 to 86 Sex: NS Notes: 60 of the patients were having a secondary resection 6 weeks after primary tumour resection |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no (except in cases of a resection in areas of a primary tumour) |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 347) Sensitivity: PDD 96% Specificity: PDD 35% |
|
[Filbeck 199955] Time period: Jan 1997 to Oct 1997 Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 50; analysed: 50 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): mean 63.4, range 32 to 88 Sex: M 36, F 14 Notes: Patients had undergone conventional TUR of primary tumour 6 weeks earlier |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 347) Sensitivity: WLC 69% Specificity: WLC 66% Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 130) Sensitivity: PDD 78% Specificity: PDD 33% Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 18) Sensitivity: WLC 64% Specificity: NS |
|
Fradet 200757 Time period: NS Country: USA, Canada |
Enrolled: 311; analysed: 196 (1 NS?) No previous history of BC: 62; history of BC: 133 Age (years): mean 67, SD 11 Sex: M 148, F 48 Notes: 49 patients received previous chemotherapy and 77 received previous BCG treatment |
Index test: PDD Agent: HAL Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 196) Sensitivity: PDD 87%, WLC 83% Specificity: PDD 82%, WLC 72% Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = NS, CIS 113) Sensitivity: PDD 92%, WLC 68% Specificity: NS |
|
Frimberger 200158 Time period: NS Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 25; analysed: 25 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 25 Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 19) Sensitivity: PDD 95% Specificity: PDD 67% NS for WLC |
|
Grimbergen 200359 Time period: Nov 1998 to Jun 2002 Country: Netherlands |
Enrolled: 160; analysed: 160 No previous history of BC: 87?; history of BC: 73? Age (years): mean 67, range 30 to 91 Sex: NS Notes: 73 patients received previous BCG, mitomycin C or epirubicin treatment |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 917) Sensitivity: PDD 97%, WLC 69% Specificity: PDD 49%, WLC 78% |
|
Hendricksen 200660 Time period: Oct 2001 to Apr 2002 Country: Netherlands |
Enrolled: 50; analysed: 50 No previous history of BC: 23; history of BC: 27 Age (years): mean 67, range 35 to 86 Sex: M 40, F 10 Notes: This study takes the patient data from the Radbound University Medical Centre, Nijmesen that contributed to Jocham 2005 and Schmidbauer 2004 |
Index test: PDD Agent: HAL Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes (NS whether PDD or WLC or both) |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (PDD n = 217, WLC n = 123) Sensitivity: PDD 94%, WLC 88% Specificity: PDD 58%, WLC 86% |
|
Hungerhuber 200761 Time period: Feb 1995 to Feb 2002 Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 875; analysed: 875 No previous history of BC: 327; history of BC: 548 Age (years): mean 65.3, range 16 to 99 Sex: M 671, F 204 Notes: Patients with a history of recurrent disease had undergone multiple TURs (mean 3.6, range 1 to 22) |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 4630) Sensitivity: PDD 92%, WLC 76% Specificity: PDD 56%, WLC 86% |
|
[Zaak 200283] Time period: Jan 1995 to Dec 2000 Country: Germany, Austria |
Enrolled: 713; analysed: 713 No previous history of BC: 270; history of BC: 443 Age (years): NS Sex: NS Notes: Patients previously treated for BC had a history of undergoing multiple TURs (mean 3.5, range 1 to 20) |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (PDD n = 3834, WLC NS) Sensitivity: PDD 98%, WLC 47% Specificity: PDD 21%, WLC NS |
|
[Zaak 200182] Time period: 1995 to 1999 Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 605; analysed: 605 No previous history of BC: 212; history of BC: 393 Age (years): mean 65.6, range 16 to 99 Sex: M 472, F 133 Notes: Patients previously treated for BC had a history of undergoing multiple TURs (mean 3.5, range 1 to 20) |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (PDD n = 1012, WLC n = 552) Sensitivity: PDD 86%, WLC 66% Specificity: PDD 23%, WLC NS |
|
Jeon 200162 Time period: Dec 1997 to Aug 1999 Country: South Korea |
Enrolled: 62; analysed: 62 No previous history of BC: 36; history of BC: 26 Age (years): mean 61.9, range 32 to 80 Sex: M 57, F 5 Notes: Of the patients with a history of BC, five had nephrourterectomy performed with a bladder cuff resection for upper urinary tract carcinoma and six had BCG |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 274) Sensitivity: PDD 98%, WLC 61 Specificity: PDD 41%, WLC 92% |
|
Jichlinski 199763 Time period: Feb 1994 to NS Country: Switzerland |
Enrolled: 34; analysed: 34 No previous history of BC: 13; history of BC: 21 Age (years): mean 67.9, range 44 to 84 Sex: M 21, F 13 |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes for PDD only |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 215) Sensitivity: PDD 89%, WLC 46%? Specificity: PDD 57% WLC 57%? |
|
[Jichlinski 199764] Time period: Jan 1995 to NS Country: Switzerland |
Enrolled: 31; analysed: 31 No previous history of BC: 11; history of BC: 22 Age (years): mean 66.1, range 44 to 84 Sex: M 23, F 8 Notes: Topical chemotherapy or immunotherapy with BCG was added to the previous surgical treatments in 19 patients |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: biopsies of apparently normal mucosa under WLC |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 132) Sensitivity: PDD 83% Specificity: PDD 81% |
|
Jichlinski 200365 Time period: Dec 2000 to Apr 2001 Country: Switzerland, Norway, Sweden, Germany |
Enrolled: 52; analysed: 52 No previous history of BC: 18; history of BC: 34 Age (years): mean 72, SD 12 Sex: M 38, F 14 |
Index test: PDD Agent: HAL Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes for WLC |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 52) Sensitivity: PDD 96%, WLC 73% Specificity: PDD 43%, WLC 43% Unit of analysis: biopsy (PDD n = 421, WLC n = 414) Sensitivity: PDD 76%, WLC 80% Specificity: PDD 46%, WLC 93% |
|
Jocham 200566 Time period: NS Country: Germany, Netherlands |
Enrolled: 162; analysed: 146 No previous history of BC: 73; history of BC: 73 Age (years): mean 67, range 33 to 91 Sex: M 107, F 39 Notes: 18% received previous BCG immunotherapy and 18% received previous intravesical chemotherapy |
Index test: PDD Agent: HAL Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 146) Sensitivity: PDD 53%, WLC 33% Specificity: PDD 81%, WLC 74% |
|
Koenig 199967 Time period: NS Country: Germany, USA |
Enrolled: 55; analysed: 49 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): mean 66, range 31 to 87 Sex: M 44, F 11 |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes (NS whether PDD or WLC or both) |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (PDD n = 130, WLC n = 67) Sensitivity: PDD 87%, WLC 84% Specificity: PDD 59%, WLC NS |
|
Kriegmair 199670 Time period: NS Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 106; analysed: 106 No previous history of BC: 29; history of BC: 77 Age (years): mean 68, range 41 to 85 Sex: M 80, F 24 |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes for PDD |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 433) Sensitivity: PDD 98%, WLC 73% Specificity: PDD 64%, WLC 69% Unit of analysis: patient (n = 308 – all patients) Sensitivity: PDD 93%, WLC 70% Specificity: PDD 53%, WLC 75% Unit of analysis: patient (n = 165 – history of BCG or chemotherapy) Sensitivity: PDD 96%, WLC 62% Specificity: PDD 72%, WLC 71% |
|
[Kriegmair 199468] Time period: NS Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 68; analysed: 68 No previous history of BC: 6; history of BC: 62 Age (years): mean 66.2, range 43 to 83 Sex: M 51, F 17 Notes: 47 patients received previous intravesical chemotherapy or BCG |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: none ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes for PDD |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 285) Sensitivity: PDD 100% Specificity: PDD 76% |
|
[Kriegmair 199569] Time period: NS Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 90; analysed: 90 No previous history of BC: 26; history of BC: 64 Age (years): mean 65, range 41 to 85 Sex: NS Notes: 64 patients with history of BC had received previous intravesical therapy with BCG or cytostatics |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes for PDD |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 294) Sensitivity: PDD 98% Specificity: PDD 71% |
|
Kriegmair 199971 Time period: NS Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 208; analysed: 208 No previous history of BC: 72; history of BC: 136 Age (years): mean 64.8, range 16 to 89 Sex: M 170, F 38 Notes: Patients previously treated for BC had a history of multiple TURS (mean 3.5, range 1 to 20) and intravesical instillation with BCG (n = 50) or mitomycin C (n = 49) |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (PDD n = 328, WLC n = 163) Sensitivity: PDD 98%, WLC 47% Specificity: PDD 41%, WLC NS |
|
[Schneeweiss 199974] Time period: Jan 1995 to Aug 1996 Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 208; analysed: 208 No previous history of BC: 72; history of BC: 136 Age (years): mean 64.8, SD 12.4, range 16 to 89 Sex: M 170, F 38 |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 328) Sensitivity: PDD 98%, WLC 47% Specificity: PDD 41%, WLC NS |
|
[Schneeweiss 200075] As above |
|||
|
Landry 200372 Time period: NS Country: France |
Enrolled: 50; analysed: 50 No previous history of BC: 50; history of BC: 0 Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes for WLC |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 50) Sensitivity: PDD 64%, WLC NS Specificity: PDD 67%, WLC NS |
|
Riedl 199973 Time period: NS Country: Austria |
Enrolled: 52; analysed: 52 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): range 44 to 79 Sex: NS |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes (NS whether PDD or WLC or both) |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 52) Sensitivity: PDD 100%, WLC 76% Specificity: PDD 67%, WLC 100% Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 123) Sensitivity: PDD 95%, WLC 76% Specificity: PDD 43%, WLC NS |
|
Sim 200576 Time period: Jan 2001 to Oct 2004 Country: Singapore |
Enrolled: 41; analysed: 41 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): mean 66.1, SD 9.1, range 46 to 81 Sex: M 34, F 7 |
Index test: PDD Agent: hypericin Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 179) Sensitivity: PDD 82%, WLC 62% Specificity: PDD 91%, WLC 98% |
|
Song 200777 Time period: Mar 2002 to Oct 2005 Country: China |
Enrolled: 51; analysed: 51 No previous history of BC: 47; history of BC: 4 Age (years): mean 52 Sex: M 32, F 19 Notes: All patients had typical whole range anodynia gross haematuria |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: patient (PDD n = 51, WLC n = 40) Sensitivity: PDD 100%, WLC 53% Specificity: PDD 36%, WLC NS |
|
Szygula 200478 Time period: NS Country: Poland |
Enrolled: 52 (PDD group); analysed: 52 No previous history of BC: 52; history of BC: 0 Age (years): NS Sex: NS Notes: All patients received TURBT 3 months before investigative procedure. All patients received WLC |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: LIF ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no Notes: unclear whether comparing PDD with LIF or PDD + WLC with LIF; no WLC only comparison |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 52) Sensitivity: PDD 91%, WLC NS Specificity: PDD 67%, WLC NS |
|
[Szygula 200479] As above |
|||
|
Tritschler 200780 Time period: Sep 2004 to Apr 2005 Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 100; analysed: 100 No previous history of BC: 30; history of BC: 70 Age (years): mean 67.9 Sex: M 71, F 29 |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA/HAL Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 100) Sensitivity: PDD 93%, WLC 88% Specificity: PDD 57%, WLC 55% |
|
Witjes 200581 Time period: Jan 2004 to Mar 2004 Country: Netherlands |
Enrolled: 20; analysed: 20 No previous history of BC: 10; history of BC: 10 Age (years): mean 71, range 49 to 89 Sex: M 17, F 3 Notes: Seven patients received previous intravesical chemotherapy or BCG for superficial papillary tumours |
Index test: PDD Agent: HAL Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no for PDD and WLC |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 20) Sensitivity: PDD 90%, WLC 79% Specificity: PDD 100%, WLC 100% Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 28) Sensitivity: PDD 85%, WLC 74% Specificity: PDD 100%, WLC 100% |
|
Zaak 200284 Time period: NS Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 43; analysed: 43 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 43 Age (years): mean 70, range 49 to 89 Sex: M 31, F 12 |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: excimer laser-induced autofluorescence; no WLC comparison ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: yes for PDD |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 114) Sensitivity: PDD 90% Specificity: PDD 61% |
|
Zumbraegel 200385 Time period: Jan 1997 to Jul 1999 Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 108; analysed: 152 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Index test: PDD Agent: 5-ALA Comparator: WLC ‘Random’ biopsies of normal-appearing areas: no for PDD or WLC |
Unit of analysis: biopsy (n = 408) Sensitivity: PDD 94%, WLC 80% Specificity: PDD 32%, WLC 46% |
Appendix 7 Quality assessment results for the individual PDD studies
Diagnostic studies
| Study | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Q6 | Q7 | Q8 | Q9 | Q10 | Q11 | Q12 | Q13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cheng 200050 | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Colombo 200751 | – | + | + | + | + | – | + | + | ? | + | + | – | – |
| De Dominicis 200153 | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | – |
| D’Hallewin 200052 | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | + | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Ehsan 200154 | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Filbeck 199956 | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Fradet 200757 | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | + | ? | + | + | – | – |
| Frimberger 200158 | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Grimbergen 200359 | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | + | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Hendricksen 200660 | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Hungerhuber 200761 | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | + | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Jeon 200162 | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | + | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Jichlinski 199763 | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | + | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Jichlinski 200365 | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | + | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Jocham 200566 | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | + | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Koenig 199967 | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | ? | ? | – | – | + | – |
| Kriegmair 199670 | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Kriegmair 199971 | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Landry 200372 | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Riedl 199973 | + | + | + | + | ? | – | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Sim 200576 | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | + | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Song 200777 | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Szygula 200478 | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Tritschler 200780 | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | + | ? | + | + | – | – |
| Witjes 200581 | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | ? | ? | + | + | – | – |
| Zaak 200284 | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | – |
| Zumbraegel 200385 | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | ? | ? | + | + | – | – |
RCTs reporting recurrence/progression
Appendix 8 Studies of PDD versus WLC included in pooled estimates for patient- and biopsy-level analysis and also those reporting stage/grade
| Patient | Biopsy | pTa | pTaG1 | pTaG1–2 | pTaG2 | pTaG2–3 | pTaG3 | pTa–T1 | G1–2 | pT1 | pT1G1 | pT1G1–2 | pT1G2 | pT1G3 | > pT1 | CIS | G3 | pT2G2 | pT2G3 | ≥ pT2 | ≥ pT2G3 | pT4G3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cheng 200050 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Colombo 200751 | ✓P | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| De Dominicis 200153 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ehsan 200154 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Filbeck 199956 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Fradet 200757 | ✓P,B | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Grimbergen 200359 | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hendricksen 200660 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||
| Hungerhuber 200761 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Jeon 200162 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Jichlinski 199763 | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jichlinski 200365 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓P,B | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Jocham 200566 | ✓ | ✓P | ✓P | ✓P | ✓P | ||||||||||||||||||
| Koenig 199967 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Kriegmair 199670 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Riedl 199973 | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sim 200576 | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tritschler 200780 | ✓ | ✓P | ✓P | ✓P | ✓P | ✓P | ✓P | ||||||||||||||||
| Witjes 200581 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓P,B | ✓P,B | ✓P,B | ✓P,B | ✓P,B | ||||||||||||||||
| Zumbraegel 200385 | ✓ | ✓ |
Appendix 9 PDD and WLC test performance for detecting bladder cancer, results table with 2 × 2 data
| Studya,b,c | Test | Unit of analysis | Number analysed | TP | FP | FN | TN | Sens (%) | Spec (%) | LR+ | LR– |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cheng 200050 No. of patients 41, of whom primary NS, recurrent NS PDD ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 175 | 57 | 39 | 7 | 72 | 89 | 65 | 2.5 | 0.2 |
| Flat lesions | 136 | 20 | 38 | 7 | 71 | 74 | 65 | 2.1 | 0.4 | ||
| CIS lesions | 7 | 5 | 2 | 71 | |||||||
| pTa–T1 lesions | 36 | 36 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| ≥ pT2 lesions | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| WLC | Biopsy | 175 | 42 | 18 | 22 | 93 | 66 | 84 | 4.0 | 0.4 | |
| Flat lesions | 136 | 5 | 16 | 22 | 93 | 23 | 85 | 1.5 | 0.9 | ||
| CIS lesions | 7 | 1 | 6 | 14 | |||||||
| pTa–T1 lesions | 36 | 30 | 6 | 83 | |||||||
| ≥ pT2 lesions | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
|
Colombo 200751 No. of patients 49, of whom primary 0, recurrent 49 (all being followed up for CIS) ‘Random’ biopsies (NS whether PDD or WLC or both) |
PDD (5-ALA, HAL) | Patients with CIS | 49 | 18 | 9 | 0 | 22 | 100 | 71 | 3.4 | 0.0 |
| WLC | Patients with CIS | 49 | 0 | 1 | 18 | 30 | 0 | 97 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
|
De Dominicis 200153 No. of patients 49, of whom primary 17, recurrent 32 PDD and WLC ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 179 | 45 | 47 | 7 | 80 | 87 | 63 | 2.3 | 0.2 |
| Dysplasia | 19 | 16 | 3 | 84 | |||||||
| CIS | 13 | 10 | 3 | 77 | |||||||
| SNA | 2 | 1 | 1 | 50 | |||||||
| pTaG2–3 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 0 | ||||||||||
| pT1G2–3 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| WLC | Biopsy | 179 | 9 | 15 | 43 | 112 | 17 | 88 | 1.5 | 0.9 | |
| Dysplasia | 19 | 6 | 13 | 32 | |||||||
| CIS | 13 | 3 | 10 | 23 | |||||||
| SNA | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | |||||||
| pTaG2–3 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 8 | 0 | 8 | 0 | |||||||
| pT1G2–3 | 0 | ||||||||||
|
D’Hallewin 200052 No. of patients 40, of whom primary NS, recurrent NS PDD ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (hypericin) | Biopsy | |||||||||
| CIS | 281 | 132 | 2 | 10 | 137 | 93 | 99 | 93.0 | 0.1 | ||
|
Ehsan 200154 No. of patients 30, of whom primary NS, recurrent NS PDD and WLC ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 151 | 59 | 32 | 1 | 59 | 98 | 65 | 2.8 | 0.0 |
| CIS | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pTa | 20 | 20 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT1 | 28 | 28 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| WLC | Biopsy | 151 | 36 | 38 | 24 | 53 | 60 | 58 | 1.4 | 0.7 | |
| CIS | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | |||||||
| pTa | 20 | 18 | 2 | 90 | |||||||
| pT1 | 28 | 14 | 14 | 50 | |||||||
|
Filbeck 199956 No. of patients 120, of whom primary NS, recurrent NS (60 of the patients were having a secondary resection 6 weeks after primary tumour resection) No ‘random’ biopsies (except in cases of a resection in areas of primary tumour) |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy (primary/recurrent/secondary tumour resection) | 347 | 119 | 145 | 5 | 78 | 96 | 35 | 1.5 | 0.1 |
| pTaG1–2 | 77 | 74 | 3 | 96 | |||||||
| pT1G1–2 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 90 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 11 | 11 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| CIS | 7 | 7 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| > pT1 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| Dysplasia | 13 | 12? | 1? | 92? | |||||||
| Biopsy (primary/recurrent tumour resection) | |||||||||||
| pTaG1–2 | 64 | 64 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT1G1–2 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| CIS | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| > pT1 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| Dysplasia | 6 | 6 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| Biopsy (secondary tumour resection) | |||||||||||
| pTaG1–2 | 13 | 10 | 3 | 77 | |||||||
| pT1G1–2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 50 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| CIS | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| Dysplasia | 7 | 6 | 1 | 86 | |||||||
| WLC | Biopsy (primary/recurrent/secondary tumour resection) | 347 | 85 | 75 | 39 | 148 | 69 | 66 | 2.0 | 0.5 | |
| pTaG1–2 | 77 | 57 | 20 | 74 | |||||||
| pT1G1–2 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 80 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 11 | 8 | 3 | 73 | |||||||
| CIS | 7 | 4 | 3 | 57 | |||||||
| > pT1 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | |||||||
| Dysplasia | 13 | 3 | 10 | 30 | |||||||
| Biopsy (primary/recurrent tumour resection) | |||||||||||
| pTaG1–2 | 64 | 54 | 10 | 84 | |||||||
| pT1G1–2 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 88 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 80 | |||||||
| CIS | 5 | 4 | 1 | 80 | |||||||
| >pT1 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | |||||||
| Dysplasia | 6 | 2 | 4 | 33 | |||||||
| Biopsy (secondary tumour resection) | |||||||||||
| pTaG1–2 | 13 | 3 | 10 | 23 | |||||||
| pT1G1–2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 50 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| CIS | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | |||||||
| Dysplasia | 7 | 1 | 6 | 14 | |||||||
|
[Filbeck 199955] (secondary TUR) No. of patients 50, all of whom were having a secondary TUR of the former resection area 6 weeks after conventional TUR No ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 130 | 14 | 75 | 4 | 37 | 78 | 33 | 1.2 | 0.7 |
| WLC | Biopsy | 18 | 7? | 11? | 64? | ||||||
|
Fradet 200757 No. of patients 196, of whom primary 62, recurrent 133 (missing, 1) PDD and WLC ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (HAL) | Patient | |||||||||
| CIS | 196 | 50 | 25 | 8 | 113 | 87 | 82 | 4.8 | 0.2 | ||
| Biopsy | |||||||||||
| CIS | 113 | 104 | 223 | 9 | 92 | ||||||
| WLC | Patient | ||||||||||
| CIS | 196 | 48 | 39 | 10 | 99 | 83 | 72 | 3.0 | 0.2 | ||
| Biopsy | |||||||||||
| CIS | 113 | 77 | 137 | 36 | 68 | ||||||
|
Frimberger 200158 No. of patients 25, all of whom were recurrent PDD and WLC ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 43 | 18 | 8 | 1 | 16 | 95 | 67 | 2.9 | 0.1 |
| CIS | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | |||||||
| pTa | 10 | 10 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
|
Grimbergen 200359 No. of patients 160, of whom primary 87?, recurrent 73? PDD and WLC ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 917 | 378 | 270 | 12 | 257 | 97 | 49 | 1.9 | 0.1 |
| WLC | Biopsy | 917 | 270 | 115 | 120 | 412 | 69 | 78 | 3.2 | 0.4 | |
|
Hendricksen 200660 No. of patients 50, of whom primary 23, recurrent 27 ‘Random’ biopsies (unclear whether PDD or WLC or both) |
PDD (HAL) | Biopsy | 217 | 88 | 52 | 6 | 71 | 94 | 58 | 2.2 | 0.1 |
| CIS | 10 | 7 | 3 | 70 | |||||||
| pTaG1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pTaG2 | 39 | 37 | 2 | 95 | |||||||
| pTaG3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT1G2 | 13 | 12 | 1 | 92 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT2G2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT2G3 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT4G3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| WLC | Biopsy | 123 | 83 | 17 | 11 | 106 | 88 | 86 | 6.4 | 0.1 | |
| CIS | 10 | 3 | 7 | 30 | |||||||
| pTaG1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pTaG2 | 39 | 39 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pTaG3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT1G2 | 13 | 12 | 1 | 92 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 88 | |||||||
| pT2G2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT2G3 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT4G3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
|
Hungerhuber 200761 No. of patients 875, of whom primary 327, recurrent 548 No ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 4630 | 1484 | 1339 | 129 | 1678 | 92 | 56 | 2.1 | 0.1 |
| pTxG1 | 47 | 42 | 5 | 89 | |||||||
| pTxG2 | 28 | 26 | 2 | 93 | |||||||
| pTxG3 | 18 | 15 | 3 | 83 | |||||||
| pTaG1 | 495 | 466 | 29 | 94 | |||||||
| pTaG2 | 205 | 196 | 9 | 96 | |||||||
| pTaG3 | 45 | 42 | 3 | 93 | |||||||
| pT1G1 | 12 | 11 | 1 | 92 | |||||||
| pT1G2 | 53 | 52 | 1 | 98 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 149 | 144 | 5 | 97 | |||||||
| ≥ T2G3 | 101 | 90 | 11 | 89 | |||||||
| CIS | 274 | 254 | 20 | 93 | |||||||
| Dysplasia grade 2 | 186 | 146 | 40 | 78 | |||||||
| WLC | Biopsy | 4630 | 1231 | 430 | 382 | 2587 | 76 | 86 | 5.4 | 0.3 | |
| pTxG1 | 47 | 40 | 7 | 85 | |||||||
| pTxG2 | 28 | 23 | 5 | 82 | |||||||
| pTxG3 | 18 | 15 | 3 | 83 | |||||||
| pTaG1 | 495 | 408 | 87 | 82 | |||||||
| pTaG2 | 205 | 175 | 30 | 85 | |||||||
| pTaG3 | 45 | 34 | 11 | 76 | |||||||
| pT1G1 | 12 | 8 | 4 | 67 | |||||||
| pT1G2 | 53 | 38 | 15 | 72 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 149 | 119 | 30 | 80 | |||||||
| ≥ T2G3 | 101 | 87 | 14 | 86 | |||||||
| CIS | 274 | 155 | 119 | 57 | |||||||
| Dysplasia grade 2 | 186 | 129 | 57 | 69 | |||||||
|
[Zaak 200283] No. of patients 713, of whom primary 270, recurrent 443 No ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Lesion (same as biopsy) | 3834 | 1222 | 2049 | 28 | 535 | 98 | 21 | 1.2 | 0.1 |
| CIS | 159 | 145 | 14 | 91 | |||||||
| WLC | Lesion (same as biopsy) | ||||||||||
| CIS | 159 | 75 | 84 | 47 | |||||||
|
[Zaak 200182] No. of patients 605, of whom primary 212, recurrent 393 No ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Endoscopy | 1012 | 477 | 352 | 75 | 108 | 86 | 23 | 1.1 | 0.6 |
| Dysplasia grade 2 | 52 | 30 | 22 | 58 | |||||||
| CIS | 88 | 84 | 4 | 95 | |||||||
| pTxGx | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pTxG1 | 13 | 11 | 2 | 85 | |||||||
| pTxG2 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pTxG3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pTaG1 | 178 | 146 | 32 | 82 | |||||||
| pTaG2 | 80 | 69 | 11 | 86 | |||||||
| pTaG3 | 11 | 11 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT1G1 | 9 | 8 | 1 | 89 | |||||||
| pT1G2 | 26 | 26 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 46 | 43 | 3 | 93 | |||||||
| > pT1G2–3 | 37 | 37 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| WLC | Endoscopy | 552 | 363 | 189 | 66 | ||||||
| Dysplasia grade 2 | 52 | 32 | 20 | 62 | |||||||
| CIS | 88 | 38 | 50 | 43 | |||||||
| pTxGx | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pTxG1 | 13 | 12 | 1 | 92 | |||||||
| pTxG2 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 60 | |||||||
| pTxG3 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 69 | |||||||
| pTaG1 | 178 | 118 | 60 | 66 | |||||||
| pTaG2 | 80 | 61 | 19 | 76 | |||||||
| pTaG3 | 11 | 6 | 5 | 55 | |||||||
| pT1G1 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 67 | |||||||
| pT1G2 | 26 | 15 | 11 | 58 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 46 | 34 | 12 | 74 | |||||||
| > pT1G2–3 | 37 | 32 | 5 | 86 | |||||||
|
Jeon 200162 No. of patients 62, of whom primary 36, recurrent 26 No ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | |||||||||
| CIS or more | 274 | 140 | 77 | 3 | 54 | 98 | 41 | 1.7 | 0.0 | ||
| Dysplasia or more | 274 | 145 | 72 | 3 | 54 | 98 | 43 | 1.7 | 0.0 | ||
| Dysplasia | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| CIS | 20 | 20 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| Ta | 64 | 63 | 1 | 98 | |||||||
| T1 | 42 | 40 | 2 | 95 | |||||||
| ≥ T2 | 17 | 17 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| WLC | Biopsy | ||||||||||
| CIS or more | 274 | 87 | 11 | 56 | 120 | 61 | 92 | 7.6 | 0.4 | ||
| Dysplasia or more | 274 | 87 | 11 | 61 | 115 | 59 | 91 | 6.6 | 0.5 | ||
| Dysplasia | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | |||||||
| CIS | 20 | 1 | 19 | 5 | |||||||
| Ta | 64 | 48 | 16 | 75 | |||||||
| T1 | 42 | 25 | 17 | 60 | |||||||
| ≥ T2 | 17 | 13 | 4 | 76 | |||||||
|
Jichlinski 199763 No. of patients 34, of whom primary 13, recurrent 21 PDD ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 215 | 97 | 46 | 12 | 60 | 89 | 57 | 2.1 | 0.2 |
| WLC | Biopsy | 215 | 50? | 46?? | 59? | 60?? | 46? | 57? | 1.1 | 0.9 | |
|
[Jichlinski 199764] No. of patients 31, of whom primary 11, recurrent 22 (data as reported) WLC ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsies of apparently normal mucosa under WLC | 132 | 34 | 17 | 7 | 74 | 83 | 81 | 4.4 | 0.2 |
|
Jichlinski 200365 No. of patients 52, of whom primary 18, recurrent 34 WLC ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (HAL) | Patient | 52 | 43 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 96 | 43 | 1.7 | 0.1 |
| CIS | 13 | 12 | 1 | 92 | |||||||
| Biopsy | 421 | 108 | 57 | 35 | 221 | 76 | 79 | 3.7 | 0.3 | ||
| CIS | 57 | 31? | 26? | 54? | |||||||
| WLC | Patient | 52 | 33 | 4 | 12 | 3 | 73 | 43 | 1.3 | 0.6 | |
| CIS | 13 | 3 | 10 | 30 | |||||||
| Biopsy | 414 | 65 | 19 | 75 | 255 | 46 | 93 | 6.7 | 0.6 | ||
| CIS | 57 | 3 | 54 | 5 | |||||||
|
Jocham 200566 No. of patients 146, of whom primary 73, recurrent 73 No ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (HAL) | Patient | 146 | 61 | 6 | 54 | 25 | 53 | 81 | 2.7 | 0.6 |
| CIS | 29 | 12 | 17 | 41 | |||||||
| pTa | 66 | 13 | 53 | 20 | |||||||
| pT1 (pT1a + pT1b) | 16 | 1 | 15 | 6 | |||||||
| pT2–4 | 22 | 3 | 19 | 14 | |||||||
| WLC | Patient | 146 | 38 | 8 | 77 | 23 | 33 | 74 | 1.3 | 0.9 | |
| CIS | 29 | 2 | 27 | 7 | |||||||
| pTa | 66 | 5 | 61 | 8 | |||||||
| pT1 (pT1a + pT1b) | 16 | 1 | 15 | 6 | |||||||
| pT2–4 | 22 | 1 | 21 | 5 | |||||||
|
Koenig 199967 No. of patients 55, of whom primary NS, recurrent NS ‘Random’ biopsies (unclear whether PDD or WLC or both) |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 130 | 58 | 26 | 9 | 37 | 87 | 59 | 2.1 | 0.2 |
| CIS | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | |||||||
| pTaG1 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 88 | |||||||
| pTaG2 | 25 | 22 | 3 | 88 | |||||||
| pTaG3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT1G2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT2G3 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | |||||||
| WLC | Biopsy | 67 | 56 | 11 | 84 | ||||||
| CIS | 6 | 4 | 2 | 67 | |||||||
| pTaG1 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 75 | |||||||
| pTaG2 | 25 | 24 | 1 | 96 | |||||||
| pTaG3 | 0 | ||||||||||
| pT1G2 | 0 | ||||||||||
| pT1G3 | 0 | ||||||||||
| pT2G3 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | |||||||
|
Kriegmair 199670 No. of patients 106, of whom primary 29, recurrent 77 PDD ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 433 | 126 | 110 | 2 | 195 | 98 | 64 | 2.7 | 0.0 |
| Dysplasia grade 1 + CIS | 329 | 23 | 110 | 1 | 195 | 96 | 64 | 2.7 | 0.1 | ||
| Dysplasia grade 2 + CIS | 221 | 13 | 12 | 0 | 196 | 100 | 94 | 17.2 | 0.0 | ||
| CIS | 329 | 6 | 127 | 0 | 196 | 100 | 61 | 2.5 | 0.0 | ||
| pTa–T1 | 399 | 93 | 110 | 1 | 195 | 99 | 64 | 2.7 | 0.0 | ||
| Patients with dysplasia or TCC from normal bladder wall or bladder wall with non-specific inflammation – all patients | 308 | 28 | 83 | 2 | 195 | 93 | 70 | 3.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Patients with dysplasia or TCC from normal bladder wall or bladder wall with non-specific inflammation – patients with a history of BCG instillation or chemotherapy | 165 | 25 | 39 | 1 | 100 | 96 | 72 | 3.4 | 0.1 | ||
| WLC | Biopsy | 433 | 93 | 96 | 35 | 209 | 73 | 69 | 2.3 | 0.4 | |
| Dysplasia grade 1 + CIS | 329 | 10 | 96 | 14 | 209 | 42 | 69 | 1.3 | 0.9 | ||
| Dysplasia grade 2 + CIS | 329 | 7 | 99 | 6 | 217 | 54 | 69 | 1.7 | 0.7 | ||
| CIS | 329 | 4 | 102 | 2 | 221 | 67 | 68 | 2.1 | 0.5 | ||
| pTa–T1 | 399 | 74 | 96 | 20 | 209 | 79 | 69 | 2.5 | 0.3 | ||
| Patients with dysplasia or TCC from normal bladder wall or bladder wall with non-specific inflammation – all patients | 308 | 16 | 69 | 14 | 209 | 53 | 75 | 2.1 | 0.6 | ||
| Patients with dysplasia or TCC from normal bladder wall or bladder wall with non-specific inflammation – patients with a history of BCG instillation or chemotherapy | 165 | 16 | 41 | 10 | 98 | 62 | 71 | 2.1 | 0.5 | ||
|
[Kriegmair 199468] No. of patients 68, of whom primary 6, recurrent 62 PDD ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 285 | 93 | 46 | 0 | 146 | 100 | 76 | 4.2 | N/C |
|
[Kriegmair 199569] No. of patients 90, of whom primary 26, recurrent 64 PDD ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 294 | 43 | 73 | 1 | 177 | 98 | 71 | 3.4 | 0.0 |
|
No. of patients 208, of whom primary 72, recurrent 136 No ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 328 | 159 | 97 | 4 | 68 | 98 | 41 | 1.7 | 0.0 |
| WLC | Biopsy | 163 | 77 | 86 | 47 | ||||||
|
Landry 200372 No. of patients 50, of whom primary 50, recurrent 0 WLC ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Patient | 50 | 9 | 12 | 5 | 24 | 64 | 67 | 1.9 | 0.5 |
|
Riedl 199973 No. of patients 52, of whom primary NS, recurrent NS ‘Random’ biopsies (unclear whether PDD or WLC or both) |
PDD (5-ALA) | Patient | 52 | 34 | 12 | 0 | 6 | 100 | 33 | 1.5 | N/C |
| Biopsy | 123 | 50? | 40? | 3? | 30? | 95 | 43 | 1.7 | 0.1 | ||
| WLC | Patient | 52 | 26 | 0 | 8 | 18 | 76 | 100 | N/C | 0.2 | |
| Biopsy | 70 | 53? | 17? | 76 | |||||||
|
Sim 200576 No. of patients 41, of whom primary NS, recurrent NS No ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (hypericin) | Biopsy | 179 | 61 | 10 | 13 | 95 | 82 | 90 | 8.7 | 0.2 |
| WLC | Biopsy | 179 | 46 | 2 | 28 | 103 | 62 | 98 | 32.7 | 0.4 | |
|
Song 200777 No. of patients 51, of whom primary 47, recurrent 4 No ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Patient | 51 | 40 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 100 | 36 | 1.6 | N/C |
| Biopsy | 103 | 68 | 21 | 2 | 12 | 97 | 36 | 1.5 | 0.1 | ||
| WLC | Patient | 40 | 21 | 19 | 53 | ||||||
|
No. of patients 52, of whom primary 52?, recurrent 0? No ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Patient | 52 | 20 | 10 | 2 | 20 | 91 | 67 | 2.7 | 0.1 |
|
Tritschler 200780 No. of patients 100, of whom primary 30, recurrent 70 No ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA/HAL) | Patient | 100 | 37 | 26 | 3 | 34 | 93 | 57 | 2.1 | 0.1 |
| pTa | 22? | 21? | 1? | 95 | |||||||
| CIS | 9? | 7? | 2? | 78 | |||||||
| pT1 | 4? | 4? | 0? | 100? | |||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 3? | 3? | 0? | 100? | |||||||
| G1–2 | 22? | 21? | 1? | 95? | |||||||
| G3 | 18? | 16? | 2? | 89? | |||||||
| WLC | Patient | 100 | 35 | 27 | 5 | 33 | 88 | 55 | 1.9 | 0.2 | |
| pTa | 22? | 21? | 1? | 95? | |||||||
| CIS | 9? | 5? | 4? | 56? | |||||||
| pT1 | 4? | 4? | 0? | 100? | |||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 3? | 3? | 0? | 100? | |||||||
| G1–2 | 22? | 21? | 1? | 95? | |||||||
| G3 | 18? | 14? | 4? | 78? | |||||||
|
Witjes 200581 No. of patients 20, of whom primary 10, recurrent 10 No ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (HAL) | Patient | 20 | 17 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 89 | 100 | N/C | 0.1 |
| pTaG2 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 88 | |||||||
| pTaG3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| CIS | 3 | 2 | 1 | 67 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT2G3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| Lesion (same as biopsy) | 28 | 23 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 85 | 100 | N/C | 0.1 | ||
| pTaG2 | 11 | 10 | 1 | 91 | |||||||
| pTaG3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| CIS | 8 | 5 | 3 | 63 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT2G3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| WLC | Patient | 20 | 15 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 79 | 100 | N/C | 0.2 | |
| pTaG2 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pTaG3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| CIS | 3 | 1 | 2 | 33 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT2G3 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 67 | |||||||
| Lesion | 28 | 20 | 0 | 7 | 1 | 74 | 100 | N/C | 0.3 | ||
| pTaG2 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 91 | |||||||
| pTaG3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| CIS | 8 | 4 | 4 | 50 | |||||||
| pT1G3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| pT2G3 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 67 | |||||||
|
Zaak 200284 No. of patients 43, of whom primary 0, recurrent 43 PDD ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 114 | 19 | 36 | 2 | 57 | 90 | 61 | 2.3 | 0.2 |
|
Zumbraegel 200385 No. of patients 108, of whom primary NS, recurrent NS No ‘random’ biopsies |
PDD (5-ALA) | Biopsy | 408 | 125 | 186 | 8 | 89 | 94 | 32 | 1.4 | 0.1 |
| CIS | 14 | 12 | 2 | 86 | |||||||
| Dysplasia | 48 | 43 | 5 | 90 | |||||||
| WLC | Biopsy | 408 | 107 | 148 | 26 | 127 | 80 | 46 | 1.5 | 0.4 | |
| CIS | 14 | 9 | 5 | 64 | |||||||
| Dysplasia | 48 | 15 | 33 | 31 | |||||||
Appendix 10 Biomarker/cytology included studies
Abbate 1998
Abbate I, D’Introno A, Cardo G, Marano A, Addabbo L, Musci MD, et al. Comparison of nuclear matrix protein 22 and bladder tumor antigen in urine of patients with bladder cancer. Anticancer Res 1998;18:3803–5.
Bastacky 1999
Bastacky S, Ibrahim S, Wilczynski SP, Murphy WM. The accuracy of urinary cytology in daily practice. Cancer 1999;87:118–28.
Bhuiyan 2003
Bhuiyan J, Akhter J, O’Kane DJ. Performance characteristics of multiple urinary tumor markers and sample collection techniques in the detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Clin Chim Acta 2003;331:69–77.
Boman 2002
Boman H, Hedelin H, Holmang S. Four bladder tumor markers have a disappointingly low sensitivity for small size and low grade recurrence. J Urol 2002;167:80–3.
Casella 2000
Primary reference
Casella R, Huber P, Blochlinger A, Stoffel F, Dalquen P, Gasser TC, et al. Urinary level of nuclear matrix protein 22 in the diagnosis of bladder cancer: experience with 130 patients with biopsy confirmed tumor. J Urol 2000;164:1926–8.
Secondary references
Shariat SF, Casella R, Monoski MA, Sulser T, Gasser TC, Lerner SP. The addition of urinary urokinase-type plasminogen activator to urinary nuclear matrix protein 22 and cytology improves the detection of bladder cancer. J Urol 2003;170:2244–7.
Shariat SF, Casella R, Khoddami SM, Hernandez G, Sulser T, Gasser TC, et al. Urine detection of survivin is a sensitive marker for the noninvasive diagnosis of bladder cancer. J Urol 2004;171:626–30.
Casetta 2000
Casetta G, Gontero P, Zitella A, Pelucelli G, Formiconi A, Priolo G, et al. BTA quantitative assay and NMP22 testing compared with urine cytology in the detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urol Int 2000;65:100–5.
Chahal 2001a
Chahal R, Gogoi NK, Sundaram SK. Is it necessary to perform urine cytology in screening patients with haematuria? Eur Urol 2001;39:283–6.
Chahal 2001b
Chahal R, Darshane A, Browning AJ, Sundaram SK. Evaluation of the clinical value of urinary NMP22 as a marker in the screening and surveillance of transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Eur Urol 2001;40:415–20.
Chang 2004
Chang YH, Wu CH, Lee YL, Huang PH, Kao YL, Shiau MY. Evaluation of nuclear matrix protein-22 as a clinical diagnostic marker for bladder cancer. Urology 2004;64:687–92.
Daniely 2007
Daniely M, Rona R, Kaplan T, Olsfanger S, Elboim L, Freiberger A, et al. Combined morphologic and fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of voided urine samples for the detection and follow-up of bladder cancer in patients with benign urine cytology. Cancer 2007;111:517–24.
Del Nero 1999
Del Nero A, Esposito N, Curro A, Biasoni D, Montanari E, Mangiarotti B, et al. Evaluation of urinary level of NMP22 as a diagnostic marker for stage pTa-pT1 bladder cancer: comparison with urinary cytology and BTA test. Eur Urol 1999;35:93–7.
Friedrich 2003
Primary reference
Friedrich MG, Toma MI, Hellstern A, Pantel K, Weisenberger DJ, Noldus J, et al. Comparison of multitarget fluorescence in situ hybridization in urine with other noninvasive tests for detecting bladder cancer. BJU Int 2003;92:911–4.
Secondary reference
Friedrich MG, Hellstern A, Hautmann SH, Graefen M, Conrad S, Huland E, et al. Clinical use of urinary markers for the detection and prognosis of bladder carcinoma: a comparison of immunocytology with monoclonal antibodies against Lewis X and 486p3/12 with the BTA STAT and NMP22 tests. J Urol 2002;168:470–4.
Garbar 2007
Garbar C, Mascaux C, Wespes E. Is urinary tract cytology still useful for diagnosis of bladder carcinomas? A large series of 592 bladder washings using a five-category classification of different cytological diagnoses. Cytopathology 2007;18:79–83.
Giannopoulos 2001
Primary reference
Giannopoulos A, Manousakas T, Gounari A, Constantinides C, Choremi-Papadopoulou H, Dimopoulos C. Comparative evaluation of the diagnostic performance of the BTA stat test, NMP22 and urinary bladder cancer antigen for primary and recurrent bladder tumors [see comment]. J Urol 2001;166:470–5.
Secondary reference
Giannopoulos A, Manousakas T, Mitropoulos D, Botsoli-Stergiou E, Constantinides C, Giannopoulou M, et al. Comparative evaluation of the BTAstat test, NMP22, and voided urine cytology in the detection of primary and recurrent bladder tumors. Urology 2000;55:871–5.
Grossman 2005
Grossman HB, Messing E, Soloway M, Tomera K, Katz G, Berger Y, et al. Detection of bladder cancer using a point-of-care proteomic assay. JAMA 2005;293:810–16.
Grossman 2006
Grossman HB, Soloway M, Messing E, Katz G, Stein B, Kassabian V, et al. Surveillance for recurrent bladder cancer using a point-of-care proteomic assay. JAMA 2006;295:299–305.
Guttierez Banos 2001
Gutierrez Banos JL, Rebollo Rodrigo MH, Antolin Juarez FM, Martin GB. NMP 22, BTA stat test and cytology in the diagnosis of bladder cancer: a comparative study. Urol Int 2001;66:185–90.
Hakenberg 2000
Hakenberg OW, Franke P, Froehner M, Manseck A, Wirth MP. The value of conventional urine cytology in the diagnosis of residual tumour after transurethral resection of bladder carcinomas. Onkologie 2000;23:252–7.
Halling 2000
Halling KC, King W, Sokolova IA, Meyer RG, Burkhardt HM, Halling AC, et al. A comparison of cytology and fluorescence in situ hybridization for the detection of urothelial carcinoma. J Urol 2000;164:1768–75.
Hughes 1999
Hughes JH, Katz RL, Rodriguez-Villanueva J, Kidd L, Dinney C, Grossman HB, et al. Urinary nuclear matrix protein 22 (NMP22): a diagnostic adjunct to urine cytologic examination for the detection of recurrent transitional-cell carcinoma of the bladder. Diagn Cytopathol 1999;20:285–90.
Junker 2006
Junker K, Fritsch T, Hartmann A, Schulze W, Schubert J. Multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization (M-FISH) on cells from urine for the detection of bladder cancer. Cytogenet Genome Res 2006;114:279–83.
Karakiewicz 2006
Primary reference
Karakiewicz PI, Benayoun S, Zippe C, Ludecke G, Boman H, Sanchez-Carbayo M, et al. Institutional variability in the accuracy of urinary cytology for predicting recurrence of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. BJU Int 2006;97:997–1001.
Secondary reference
Hutterer GC, Karakiewicz PI, Zippe C, Ludecke G, Boman H, Sanchez-Carbayo M, et al. Urinary cytology and nuclear matrix protein 22 in the detection of bladder cancer recurrence other than transitional cell carcinoma. BJU Int 2008;101:561–5.
Kipp 2008
Kipp BR, Halling KC, Campion MB, Wendel AJ, Karnes RJ, Zhang J, et al. Assessing the value of reflex fluorescence in situ hybridization testing in the diagnosis of bladder cancer when routine urine cytological examination is equivocal. J Urol 2008;179:1296–301.
Kowalska 2005
Kowalska M, Kaminska J, Kotowicz B, Fuksiewicz M, Rysinska A, Demkow T, et al. Evaluation of the urinary nuclear matrix protein (NMP22) as a tumour marker in bladder cancer patients. Nowotwory 2005;55:300–2.
Kumar 2006
Kumar A, Kumar R, Gupta NP. Comparison of NMP22 BladderChek test and urine cytology for the detection of recurrent bladder cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 2006;36:172–5.
Lahme 2001
Primary reference
Lahme S, Bichler KH, Feil G, Krause S. Comparison of cytology and nuclear matrix protein 22 for the detection and follow-up of bladder cancer. Urol Int 2001;66:72–7.
Secondary reference
Lahme S, Bichler KH, Feil G, Zumbragel A, Gotz T. Comparison of cytology and nuclear matrix protein 22 (NMP 22) for the detection and follow-up of bladder-cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 2003;539:111–19.
Lee 2001
Lee KH. Evaluation of the NMP22 test and comparison with voided urine cytology in the detection of bladder cancer. Yonsei Med J 2001;42:14–18.
Lodde 2003
Lodde M, Mian C, Negri G, Berner L, Maffei N, Lusuardi L, et al. Role of uCyt+ in the detection and surveillance of urothelial carcinoma. Urology 2003;61:243–7.
Lodde 2006
Lodde M, Mian C, Comploj E, Palermo S, Longhi E, Marberger M, et al. uCyt+ test: alternative to cystoscopy for less-invasive follow-up of patients with low risk of urothelial carcinoma. Urology 2006;67:950–4.
May 2007
May M, Hakenberg OW, Gunia S, Pohling P, Helke C, Lubbe L, et al. Comparative diagnostic value of urine cytology, UBC-ELISA, and fluorescence in situ hybridization for detection of transitional cell carcinoma of urinary bladder in routine clinical practice. Urology 2007;70:449–53.
Meiers 2007
Meiers I, Singh H, Hossain D, Lang K, Liu L, Qian JQ, et al. Improved filter method for urine sediment detection of urothelial carcinoma by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007;131:1574–7.
Messing 2005
Messing EM, Teot L, Korman H, Underhill E, Barker E, Stork B, et al. Performance of urine test in patients monitored for recurrence of bladder cancer: a multicenter study in the United States. J Urol 2005;174:1238–41.
Mian 1999
Mian C, Pycha A, Wiener H, Haitel A, Lodde M, Marberger M. Immunocyt: a new tool for detecting transitional cell cancer of the urinary tract. J Urol 1999;161:1486–9.
Mian 2000
Mian C, Lodde M, Haitel A, Vigl EE, Marberger M, Pycha A. Comparison of the monoclonal UBC-ELISA test and the NMP22 ELISA test for the detection of urothelial cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urology 2000;55:223–6.
Mian2003
Mian C, Lodde M, Comploj E, Negri G, Egarter-Vigl E, Lusuardi L, et al. Liquid-based cytology as a tool for the performance of uCyt+ and Urovysion Multicolour-FISH in the detection of urothelial carcinoma. Cytopathology 2003;14:338–42.
Mian 2006
Mian C, Maier K, Comploj E, Lodde M, Berner L, Lusuardi L, et al. uCyt+/ImmunoCyt in the detection of recurrent urothelial carcinoma: an update on 1991 analyses. Cancer 2006;108:60–5.
Miyanaga 1999
Miyanaga N, Akaza H, Tsukamoto T, Ishikawa S, Noguchi R, Ohtani M, et al. Urinary nuclear matrix protein 22 as a new marker for the screening of urothelial cancer in patients with microscopic hematuria. Int J Urol 1999;6:173–7.
Miyanaga 2003
Miyanaga N, Akaza H, Tsukamoto S, Shimazui T, Ohtani M, Ishikawa S, et al. Usefulness of urinary NMP22 to detect tumor recurrence of superficial bladder cancer after transurethral resection. Int J Clin Oncol 2003;8:369–73.
Moonen 2007
Moonen PM, Merkx GF, Peelen P, Karthaus HF, Smeets DF, Witjes JA. UroVysion compared with cytology and quantitative cytology in the surveillance of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol 2007;51:1275–80.
Oge 2001
Oge O, Atsu N, Kendi S, Ozen H. Evaluation of nuclear matrix protein 22 (NMP22) as a tumor marker in the detection of bladder cancer. Int Urol Nephrol 2001;32:367–70.
Olsson 2001
Olsson H, Zackrisson B. ImmunoCyt a useful method in the follow-up protocol for patients with urinary bladder carcinoma. Scand J Urol Nephrol 2001;35:280–2.
Oosterhuis 2002
Oosterhuis JWA, Pauwels RPE, Schapers RFM, Van Pelt J, Smeets W, Newling DWW. Detection of recurrent transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder with nuclear matrix protein-22 in a follow-up setting. UroOncology 2002;2:137–42.
Parekattil 2003
Parekattil SJ, Fisher HA, Kogan BA. Neural network using combined urine nuclear matrix protein-22, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and urinary intercellular adhesion molecule-1 to detect bladder cancer. J Urol 2003;169:917–20.
Piaton 2003
Primary reference
Piaton E, Daniel L, Verriele V, Dalifard I, Zimmermann U, Renaudin K, et al. , French Prospective MS. Improved detection of urothelial carcinomas with fluorescence immunocytochemistry (uCyt+ assay) and urinary cytology: results of a French Prospective Multicenter Study. Lab Invest 2003;83:845–52.
Secondary reference
Pfister C, Chautard D, Devonec M, Perrin P, Chopin D, Rischmann P, et al. Immunocyt test improves the diagnostic accuracy of urinary cytology: results of a French multicenter study. J Urol 2003;169:921–4.
Planz 2005
Planz B, Jochims E, Deix T, Caspers HP, Jakse G, Boecking A. The role of urinary cytology for detection of bladder cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 2005;31:304–8.
Ponsky 2001
Ponsky LE, Sharma S, Pandrangi L, Kedia S, Nelson D, Agarwal A, et al. Screening and monitoring for bladder cancer: refining the use of NMP22. J Urol 2001;166:75–8.
Potter 1999
Potter JM, Quigley M, Pengelly AW, Fawcett DP, Malone PR. The role of urine cytology in the assessment of lower urinary tract symptoms. BJU Int 1999;84:30–1.
Poulakis 2001
Poulakis V, Witzsch U, De Vries R, Altmannsberger HM, Manyak MJ, Becht E. A comparison of urinary nuclear matrix protein-22 and bladder tumour antigen tests with voided urinary cytology in detecting and following bladder cancer: the prognostic value of false-positive results. BJU Int 2001;88:692–701.
Raitanen 2002
Primary reference
Raitanen MP, Aine RA, Kaasinen ES, Liukkonen TJ, Kylmala TM, Huhtala H, et al. Suspicious urine cytology (class III) in patients with bladder cancer: should it be considered as negative or positive? Scand J Urol Nephrol 2002;36:213–7.
Secondary reference
Raitanen M-P, Aine R, Rintala E, Kallio J, Rajala P, Juusela H, et al. Differences between local and review urinary cytology in diagnosis of bladder cancer. An interobserver multicenter analysis. Eur Urol 2002;41:284–9.
Ramakumar 1999
Ramakumar S, Bhuiyan J, Besse JA, Roberts SG, Wollan PC, Blute ML, et al. Comparison of screening methods in the detection of bladder cancer. J Urol 1999;161:388–94.
Saad 2002
Saad A, Hanbury DC, McNicholas TA, Boustead GB, Morgan S, Woodman AC. A study comparing various noninvasive methods of detecting bladder cancer in urine. BJU Int 2002;89:369–73.
Sanchez-Carbayo 1999
Primary reference
Sanchez-Carbayo M, Herrero E, Megias J, Mira A, Soria F. Comparative sensitivity of urinary CYFRA 21–1, urinary bladder cancer antigen, tissue polypeptide antigen, tissue polypeptide antigen and NMP22 to detect bladder cancer. J Urol 1999;162:1951–6.
Secondary reference
Sanchez-Carbayo M, Herrero E, Megias J, Mira A, Soria F. Evaluation of nuclear matrix protein 22 as a tumour marker in the detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. BJU Int 1999;84:706–13.
Sanchez-Carbayo 2001a
Sanchez-Carbayo M, Urrutia M, Gonzalez de Buitrago JM, Navajo JA. Utility of serial urinary tumor markers to individualize intervals between cystoscopies in the monitoring of patients with bladder carcinoma. Cancer 2001;92:2820–8.
Sanchez-Carbayo 2001b
Sanchez-Carbayo M, Urrutia M, Silva JM, Romani R, De Buitrago JM, Navajo JA. Comparative predictive values of urinary cytology, urinary bladder cancer antigen, CYFRA 21–1 and NMP22 for evaluating symptomatic patients at risk for bladder cancer. J Urol 2001;165:1462–7.
Sarosdy 2002
Sarosdy MF, Schellhammer P, Bokinsky G, Kahn P, Chao R, Yore L, et al. Clinical evaluation of a multi-target fluorescent in situ hybridization assay for detection of bladder cancer. J Urol 2002;168:1950–4.
Sarosdy 2006
Sarosdy MF, Kahn PR, Ziffer MD, Love WR, Barkin J, Abara EO, et al. Use of a multitarget fluorescence in situ hybridization assay to diagnose bladder cancer in patients with hematuria. J Urol 2006;176:44–7.
Schmitz-Drager 2008
Primary reference
Schmitz-Drager BJ, Tirsar LA, Schmitz-Drager C, Dorsam J, Mellan Z, Bismarck E, et al. Immunocytology in the assessment of patients with asymptomatic hematuria. World J Urol 2008;26:31–7.
Secondary reference
Schmitz-Drager BJ, Beiche B, Tirsar LA, Schmitz-Drager C, Bismarck E, Ebert T. Immunocytology in the assessment of patients with asymptomatic microhaematuria. Eur Urol 2007;51:1582–8.
Serretta 2000
Primary reference
Serretta V, Pomara G, Rizzo I, Esposito E. Urinary BTA-stat, BTA-trak and NMP22 in surveillance after TUR of recurrent superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol 2000;38:419–25.
Secondary reference
Serretta V, Lo PD, Vasile P, Gange E, Esposito E, Menozzi I. Urinary NMP22 for the detection of recurrence after transurethral resection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: experience on 137 patients. Urology 1998;52:793–6.
Shariat 2006
Shariat SF, Marberger MJ, Lotan Y, Sanchez-Carbayo M, Zippe C, Ludecke G, et al. Variability in the performance of nuclear matrix protein 22 for the detection of bladder cancer. J Urol 2006;176:919–26.
Sharma 1999
Sharma S, Zippe CD, Pandrangi L, Nelson D, Agarwal A. Exclusion criteria enhance the specificity and positive predictive value of NMP22 and BTA stat. J Urol 1999;162:53–7.
Skacel 2003
Skacel M, Fahmy M, Brainard JA, Pettay JD, Biscotti CV, Liou LS, et al. Multitarget fluorescence in situ hybridization assay detects transitional cell carcinoma in the majority of patients with bladder cancer and atypical or negative urine cytology. J Urol 2003;169:2101–5.
Sokolova 2000
Sokolova IA, Halling KC, Jenkins RB, Burkhardt HM, Meyer RG, Seelig SA, et al. The development of a multitarget, multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization assay for the detection of urothelial carcinoma in urine. J Mol Diagn 2000;2:116–23.
Sozen 1999
Sozen S, Biri H, Sinik Z, Kupeli B, Alkibay T, Bozkirli I. Comparison of the nuclear matrix protein 22 with voided urine cytology and BTA stat test in the diagnosis of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol 1999;36:225–9.
Stampfer 1998
Stampfer DS, Carpinito GA, Rodriguez-Villanueva J, Willsey LW, Dinney CP, Grossman HB, et al. Evaluation of NMP22 in the detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol 1998;159:394–8.
Takeuchi 2004
Takeuchi Y, Sawada Y. A clinical study of urinary NMP22 in urinary epithelial cancer. J Med Soc Toho Univ 2004;516:332–8.
Talwar 2007
Talwar R, Sinha T, Karan SC, Doddamani D, Sandhu A, Sethi GS, et al. Voided urinary cytology in bladder cancer: is it time to review the indications? Urology 2007;70:267–71.
Tetu 2005
Tetu B, Tiguert R, Harel F, Fradet Y. ImmunoCyt/uCyt+ improves the sensitivity of urine cytology in patients followed for urothelial carcinoma. Mod Pathol 2005;18:83–9.
Tritschler 2007
Tritschler S, Scharf S, Karl A, Tilki D, Knuechel R, Hartmann A, et al. Validation of the diagnostic value of NMP22 BladderChek test as a marker for bladder cancer by photodynamic diagnosis. Eur Urol 2007;51:403–7.
Wiener 1998
Wiener HG, Mian C, Haitel A, Pycha A, Schatzl G, Marberger M. Can urine bound diagnostic tests replace cystoscopy in the management of bladder cancer? J Urol 1998;159:1876–80.
Yoder 2007
Yoder BJ, Skacel M, Hedgepeth R, Babineau D, Ulchaker JC, Liou LS, et al. Reflex UroVysion testing of bladder cancer surveillance patients with equivocal or negative urine cytology: a prospective study with focus on the natural history of anticipatory positive findings. Am J Clin Pathol 2007;127:295–301.
Zippe 1999
Primary reference
Zippe C, Pandrangi L, Agarwal A. NMP22 is a sensitive, cost-effective test in patients at risk for bladder cancer. J Urol 1999;161:62–5.
Secondary reference
Zippe C, Pandrangi L, Potts JM, Kursh E, Novick A, Agarwal A. NMP22: a sensitive, cost-effective test in patients at risk for bladder cancer. Anticancer Res 1999;19:2621–3.
Appendix 11 Biomarker/cytology excluded studies
Less than 100 participants included in the analysis (n = 119)
Abd El Gawad IA, Moussa HS, Nasr MI, El Gemae EH, Masooud AM, Ibrahim IK, et al. Comparative study of NMP-22, telomerase, and BTA in the detection of bladder cancer. J Egypt Natl Cancer Inst 2005;17:193–202.
Atsu N, Ekici S, Oge OO, Ergen A, Hascelik G, Ozen H. False-positive results of the NMP22 test due to hematuria. J Urol 2002;167:555–8.
Bakhos R, Shankey TV, Flanigan RC, Fisher S, Wojcik EM. Comparative analysis of DNA flow cytometry and cytology of bladder washings: review of discordant cases. Diagn Cytopathol 2000;22:65–9.
Baltaci S, Suzer O, Ozer G, Beduk Y, Gou O. The efficacy of urinary cytology in the detection of recurrent bladder tumours. Int Urol Nephrol 1996;28:649–53.
Baron A, Mastroeni F, Moore PS, Bonetti F, Orlandini S, Manfrin E, et al. Detection of bladder cancer by semi-automated microsatellite analysis of urine sediment. Adv Clin Pathol 2000;4:19–24.
Bartlett JMS, White A, Stewart CJR, McNicol AM, Underwood MA. Molecular genetic screening for urine detection of bladder cancer. UroOncology 2002;2:81–5.
Bartoletti R, Dal Canto M, Cai T, Piazzini M, Travaglini F, Gavazzi A, et al. Early diagnosis and monitoring of superficial transitional cell carcinoma by microsatellite analysis on urine sediment. Oncol Rep 2005;13:531–7.
Bass RA, Hemstreet GP, III, Honker NA, Hurst RE, Doggett RS. DNA cytometry and cytology by quantitative fluorescence image analysis in symptomatic bladder cancer patients. Int J Cancer 1987;40:698–705.
Bialkowska-Hobrzanska H, Bowles L, Bukala B, Joseph MG, Fletcher R, Razvi H. Comparison of human telomerase reverse transcriptase messenger RNA and telomerase activity as urine markers for diagnosis of bladder carcinoma. Mol Diagn 2000;5:267–77.
Bianco FJ, Jr, Gervasi DC, Tiguert R, Grignon DJ, Pontes JE, Crissman JD, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in bladder washes from bladder cancer patients predicts pathological stage and grade. Clin Cancer Res 1998;4:3011–6.
Bollmann M, Heller H, Bankfalvi A, Griefingholt H, Bollmann R. Quantitative molecular urinary cytology by fluorescence in situ hybridization: a tool for tailoring surveillance of patients with superficial bladder cancer? BJU Int 2005;95:1219–25.
Bowles L, Bialkowska-Hobrzanska H, Bukala B, Nott L, Razvi H. A prospective evaluation of the diagnostic and potential prognostic utility of urinary human telomerase reverse transcriptase mRNA in patients with bladder cancer. Can J Urol 2004;11:2438–44.
Cajulis RS, Haines GK, III, Frias-Hidvegi D, McVary K. Interphase cytogenetics as an adjunct in the cytodiagnosis of urinary bladder carcinoma. A comparative study of cytology, flow cytometry and interphase cytogenetics in bladder washes. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 1994;16:1–10.
Cajulis RS, Haines GK, III, Frias-Hidvegi D, McVary K, Bacus JW. Cytology, flow cytometry, image analysis, and interphase cytogenetics by fluorescence in situ hybridization in the diagnosis of transitional cell carcinoma in bladder washes: a comparative study. Diagn Cytopathol 1995;13:214–23.
Chan MW, Chan LW, Tang NL, Tong JH, Lo KW, Lee TL, et al. Hypermethylation of multiple genes in tumor tissues and voided urine in urinary bladder cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 2002;8:464–70.
Chang SH, Kim YH, Kim ME. Urinary survivin test compared to the nuclear matrix protein (NMP)-22 test and urine cytology for the diagnosis of bladder cancer. Korean J Urol 2006;47:1041–5.
Chen GL, El Gabry EA, Bagley DH. Surveillance of upper urinary tract transitional cell carcinoma: the role of ureteroscopy, retrograde pyelography, cytology and urinalysis. J Urol 2000;164:1901–4.
Cheng L, Reiter RE, Jin Y, Sharon H, Wieder J, Lane TF, et al. Immunocytochemical analysis of prostate stem cell antigen as adjunct marker for detection of urothelial transitional cell carcinoma in voided urine specimens. J Urol 2003;169:2094–100.
Chow NH, Tzai TS, Cheng HL, Chan SH, Lin JS. Urinary cytodiagnosis: can it have a different prognostic implication than a diagnostic test? Urol Int 1994;53:18–23.
Constantinou M, Binka-Kowalska A, Borkowska E, Zajac E, Jalmuzna P, Matych J, et al. Application of multiplex FISH, CGH and MSSCP techniques for cytogenetic and molecular analysis of transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) cells in voided urine specimens. J Applied Genet 2006;47:273–5.
Dal Canto M, Bartoletti R, Travaglini F, Piazzini M, Lodovichi G, Rizzo M, et al. Molecular urinary sediment analysis in patients with transitional cell bladder carcinoma. Anticancer Res 2003;23:5095–100.
Dalbagni G, Han W, Zhang ZF, Cordon-Cardo C, Saigo P, Fair WR, et al. Evaluation of the telomeric repeat amplification protocol (TRAP) assay for telomerase as a diagnostic modality in recurrent bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 1997;3:1593–8.
Daniely M, Rona R, Kaplan T, Olsfanger S, Elboim L, Zilberstien Y, et al. Combined analysis of morphology and fluorescence in situ hybridization significantly increases accuracy of bladder cancer detection in voided urine samples. Urology 2005;66:1354–9.
Desgrippes A, Izadifar V, Assailly J, Fontaine E, Beurton D. Diagnosis and prediction of recurrence and progression in superficial bladder cancers with DNA image cytometry and urinary cytology. BJU Int 2000;85:434–6.
D’Hallewin M-A, Baert L. Initial evaluation of the bladder tumor antigen test in superficial bladder cancer. J Urol 1996;155:475–6.
Di Carlo A, Terracciano D, Mariano A, Macchia V. Urinary gelatinase activities (matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9) in human bladder tumors. Oncol Rep 2006;15:1321–6.
Feil G, Zumbragel A, Paulgen-Nelde HJ, Hennenlotter J, Maurer S, Krause S, et al. Accuracy of the ImmunoCyt assay in the diagnosis of transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Anticancer Res 2003;23:963–7.
Fornari D, Steven K, Hansen AB, Vibits H, Jepsen JV, Poulsen AL, et al. Microsatellite analysis of urine sediment versus urine cytology for diagnosing transitional cell tumors of the urinary bladder. APMIS 2004;112:148–52.
Frau DV, Usai P, Dettori T, Caria P, De Lisa A, Vanni R. Fluorescence in situ hybridization patterns in newly diagnosed superficial bladder lesions and corresponding bladder washings. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2006;169:21–6.
Friedrich MG, Hellstern A, Toma MI, Hammerer P, Huland H. Are false-positive urine markers for the detection of bladder carcinoma really wrong or do they predict tumor recurrence? Eur Urol 2003;43:146–50.
Frigerio S, Padberg BC, Strebel RT, Lenggenhager DM, Messthaler A, Abdou MT, et al. Improved detection of bladder carcinoma cells in voided urine by standardized microsatellite analysis. Int J Cancer 2007;121:329–38.
Gibanel R, Ribal MJ, Filella X, Ballesta AM, Molina R, Alcaraz A, et al. BTA TRAK urine test increases the efficacy of cytology in the diagnosis of low-grade transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Anticancer Res 2002;22:1157–60.
Gilbert SM, Veltri RW, Sawczuk A, Shabsigh A, Knowles DR, Bright S, et al. Evaluation of DD23 as a marker for detection of recurrent transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder in patients with a history of bladder cancer. Urology 2003;61:539–43.
Godekmerdan A, Yahsi S, Semercioz A, Ilhan F, Akpolat N, Yekeler H. Determination of nuclear matrix protein 22 levels in cystitis, urothelial dysplasia and urothelial carcinoma. Turk J Med Sci 2006;36:93–6.
Halling KC, King W, Sokolova IA, Karnes RJ, Meyer RG, Powell EL, et al. A comparison of BTA stat, hemoglobin dipstick, telomerase and Vysis UroVysion assays for the detection of urothelial carcinoma in urine. J Urol 2002;167:2001–6.
Hautmann S, Toma M, Lorenzo Gomez MF, Friedrich MG, Jaekel T, Michl U, et al. Immunocyt and the HA-HAase urine tests for the detection of bladder cancer: a side-by-side comparison. Eur Urol 2004;46:466–71.
Hoshi S, Takahashi T, Satoh M, Numahata K, Suzuki K-I, Ohyama C, et al. Telomerase activity. Simplification of assay and detection in bladder tumor and urinary exfoliated cells. Urol Oncol 2000;5:25–30.
Hwang EC, Park SH, Jung SI, Kwon DD, Park K, Ryu SB, et al. Usefulness of liquid-based preparation in urine cytology. Intl J Urol 2007;14:626–9.
Ianari A, Sternberg CN, Rossetti A, Van Rijn A, Deidda A, Giannarelli D, et al. Results of Bard BTA test in monitoring patients with a history of transitional cell cancer of the bladder. Urology 1997;49:786–9.
Inoue T, Nasu Y, Tsushima T, Miyaji Y, Murakami T, Kumon H. Chromosomal numerical aberrations of exfoliated cells in the urine detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization: clinical implication for the detection of bladder cancer. Urol Res 2000;28:57–61.
Ishiwata S, Takahashi S, Homma Y, Tanaka Y, Kameyama S, Hosaka Y, et al. Noninvasive detection and prediction of bladder cancer by fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of exfoliated urothelial cells in voided urine. Urology 2001;57:811–15.
Kang JU, Koo SH, Jeong TE, Kwon KC, Park JW, Jeon CH. Multitarget fluorescence in situ hybridization and melanoma antigen genes analysis in primary bladder carcinoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2006;164:32–8.
Katz RL, Sinkre PA, Zhang HH, Kidd L, Johnston D. Clinical significance of negative and equivocal urinary bladder cytology alone and in combination with DNA image analysis and cystoscopy. Cancer 1997;81:354–64.
Kibar Y, Goktas S, Kilic S, Yaman H, Onguru O, Peker AF. Prognostic value of cytology, nuclear matrix protein 22 (NMP22) test, and urinary bladder cancer II (UBC II) test in early recurrent transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Ann Clin Lab Sci 2006;36:31–8.
Kinoshita H, Ogawa O, Kakehi Y, Mishina M, Mitsumori K, Itoh N, et al. Detection of telomerase activity in exfoliated cells in urine from patients with bladder cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 1997;89:724–30.
Kipp BR, Karnes RJ, Brankley SM, Harwood AR, Pankratz VS, Sebo TJ, et al. Monitoring intravesical therapy for superficial bladder cancer using fluorescence in situ hybridization. J Urol 2005;173:401–4.
Kirollos MM, McDermott S, Bradbrook RA. The performance characteristics of the bladder tumour antigen test. Br J Urol 1997;80:30–4.
Konety BR, Metro MJ, Melham MF, Salup RR. Diagnostic value of voided urine and bladder barbotage cytology in detecting transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary tract. Urol Int 1999;62:26–30.
Krause FS, Rauch A, Schrott KM, Engehausen DG. Clinical decisions for treatment of different staged bladder cancer based on multitarget fluorescence in situ hybridization assays? World J Urol 2006;24:418–22.
Krupski T, Moskaluk C, Boyd JC, Theodorescu D. A prospective pilot evaluation of urinary and immunohistochemical markers as predictors of clinical stage of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. BJU Int 2000;85:1027–32.
Kumar NU, Dey P, Mondal AK, Singh SK, Vohra H. DNA flow cytometry and bladder irrigation cytology in detection of bladder carcinoma. Diagn Cytopathol 2001;24:153–6.
Landman J, Chang Y, Kavaler E, Droller MJ, Liu BC. Sensitivity and specificity of NMP-22, telomerase, and BTA in the detection of human bladder cancer. Urology 1998;52:398–402.
Larsson PC, Beheshti B, Sampson HA, Jewett MA, Shipman R. Allelic deletion fingerprinting of urine cell sediments in bladder cancer. Mol Diagn 2001;6:181–8.
Laudadio J, Keane TE, Reeves HM, Savage SJ, Hoda RS, Lage JM, et al. Fluorescence in situ hybridization for detecting transitional cell carcinoma: implications for clinical practice. BJU Int 2005;96:1280–5.
Lee DH, Yang SC, Hong SJ, Chung BH, Kim IY. Telomerase: a potential marker of bladder transitional cell carcinoma in bladder washes. Clin Cancer Res 1998;4:535–8.
Lekili M, Sener E, Demir MA, Temelta G, Muezzinolu T, Buyuksu C. Comparison of the nuclear matrix protein 22 with voided urine cytology in the diagnosis of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urol Res 2004;32:124–8.
Lubbe L, Nowack R, May M, Ullmann K, Gunia S, Kaufmann O, et al. FISH – a new noninvasive method for the diagnosis of urinary bladder carcinomas. Clin Lab 2004;50:395–402.
Mack D, Frick J. Diagnostic problems of urine cytology on initial follow-up after intravesical immunotherapy with Calmette-Guérin bacillus for superficial bladder cancer. Urol Int 1994;52:204–7.
Mao L, Schoenberg MP, Scicchitano M, Erozan YS, Merlo A, Schwab D, Sidransky D, et al. Molecular detection of primary bladder cancer by microsatellite analysis. Science 1996;271:659–62.
Marin-Aguilera M, Mengual L, Ribal MJ, Burset M, Arce Y, Ars E, et al. Utility of a multiprobe fluorescence in situ hybridization assay in the detection of superficial urothelial bladder cancer. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2007;173:131–5.
Mattioli S, Seregni E, Caperna L, Botti C, Savelli G, Bombardieri E. BTA-TRAK combined with urinary cytology is a reliable urinary indicator of recurrent transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) of the bladder. Int J Biol Markers 2000;15:219–25.
Meloni AM, Peier AM, Haddad FS, Powell IJ, Block AW, Huben RP, et al. A new approach in the diagnosis and follow-up of bladder cancer. FISH analysis of urine, bladder washings, and tumors. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1993;71:105–18.
Menendez V, Filella X, Alcover JA, Molina R, Mallafre JM, Ballesta AM, et al. Usefulness of urinary nuclear matrix protein 22 (NMP22) as a marker for transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Anticancer Res 2000;20:1169–72.
Menendez V, Fernandez-Suarez A, Galan JA, Perez M, Garcia-Lopez F. Diagnosis of bladder cancer by analysis of urinary fibronectin. Urology 2005;65:284–9.
Mezzelani A, Dagrada G, Alasio L, Sozzi G, Pilotti S. Detection of bladder cancer by multitarget multicolour FISH: comparative analysis on archival cytology and paraffin-embedded tissue. Cytopathology 2002;13:317–25.
Mian C, Lodde M, Comploj E, Palermo S, Mian M, Maier K, et al. The value of the ImmunoCyt/uCyt+ test in the detection and follow-up of carcinoma in situ of the urinary bladder. Anticancer Res 2005;25:3641–4.
Minimo C, Tawfiek ER, Bagley DH, McCue PA, Bibbo M. Grading of upper urinary tract transitional cell carcinoma by computed DNA content and p53 expression. Urology 1997;50:869–74.
Misra V, Gupta SC, Tandon SP, Gupta AK, Sircar S. Cytohistological study of urinary bladder neoplasms. Ind J Pathol Microbiol 2000;43:303–9.
Mora LB, Nicosia SV, Pow-Sang JM, Ku NK, Diaz JI, Lockhart J, et al. Ancillary techniques in the followup of transitional cell carcinoma: a comparison of cytology, histology and deoxyribonucleic acid image analysis cytometry in 91 patients. J Urol 1996;156:49–55.
Mungan NA, Kulacoglu S, Basar M, Sahin M, Witjes JA. Can sensitivity of voided urinary cytology or bladder wash cytology be improved by the use of different urinary portions? Urol Int 1999;62:209–12.
Oge O, Atsu N, Sahin A, Ozen H. Comparison of BTA stat and NMP22 tests in the detection of bladder cancer. Scand J Urol Nephrol 2000;34:349–51.
Paez A, Coba JM, Murillo N, Fernandez P, de la Cal MA, Lujan M, et al. Reliability of the routine cytological diagnosis in bladder cancer. Eur Urol 1999;35:228–32.
Pajor G, Sule N, Alpar D, Kajtar B, Kneif M, Bollmann D, et al. Increased efficiency of detecting genetically aberrant cells by UroVysion test on voided urine specimens using automated immunophenotypical preselection of uroepithelial cells. Cytometry A 2008;73:259–65.
Panani AD, Kozirakis D, Anastasiou J, Babanaraki A, Malovrouvas D, Roussos C. Is aneusomy of chromosome 9 alone a valid biomarker for urinary bladder cancer screening? Anticancer Res 2006;26:1161–5.
Paoluzzi M, Cuttano MG, Mugnaini P, Salsano F, Giannotti P. Urinary dosage of nuclear matrix protein 22 (NMP22) like biologic marker of transitional cell carcinoma (TCC): a study on patients with hematuria. Arch Ital Urol Androl 1999;71:13–18.
Placer J, Espinet B, Salido M, Sole F, Gelabert-Mas A. Clinical utility of a multiprobe FISH assay in voided urine specimens for the detection of bladder cancer and its recurrences, compared with urinary cytology. Eur Urol 2002;42:547–52.
Planz B, Striepecke E, Jakse G, Bocking A. Use of Lewis X antigen and deoxyribonucleic acid image cytometry to increase sensitivity of urinary cytology in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol 1998;159:384–7.
Planz B, Synek C, Robben J, Bocking A, Marberger M. Diagnostic accuracy of DNA image cytometry and urinary cytology with cells from voided urine in the detection of bladder cancer. Urology 2000;56:782–6.
Planz B, Synek C, Deix T, Bocking A, Marberger M. Diagnosis of bladder cancer with urinary cytology, immunocytology and DNA-image-cytometry. Anal Cell Pathol 2001;22:103–9.
Pu YS, Tsai TC, Hsieh TS, Huang HH, Kuo SH, Hsueh WC. Role of urinary cytology and urinary deoxyribonucleic acid flow cytometry in the diagnosis of bladder cancer. J Formos Med Assoc 1994;93:216–21.
Raab SS, Lenel JC, Cohen MB. Low grade transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Cytologic diagnosis by key features as identified by logistic regression analysis. Cancer 1994;74:1621–6.
Raab SS, Slagel DD, Jensen CS, Teague MW, Savell VH, Ozkutlu D, et al. Transitional cell carcinoma: cytologic criteria to improve diagnostic accuracy. Modern Pathol 1996;9:225–32.
Raica M, Zylis D, Cimpean AM. Cytokeratin 20, 34betaE12 and overexpression of HER-2/neu in urine cytology as predictors of recurrences in superficial urothelial carcinoma. Romanian J Morphol Embryol 2005;46:11–15.
Rieger-Christ KM, Mourtzinos A, Lee PJ, Zagha RM, Cain J, Silverman M, et al. Identification of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 mutations in urine sediment DNA samples complements cytology in bladder tumor detection. Cancer 2003;98:737–44.
Sadek S, Soloway MS, Hook S, Civantos F. The value of upper tract cytology after transurethral resection of bladder tumor in patients with bladder transitional cell cancer. J Urol 1999;161:77–9.
Sagerman PM, Saigo PE, Sheinfeld J, Charitonowics E, Cordon-Cardo C. Enhanced detection of bladder cancer in urine cytology with Lewis X, M344 and 19A211 antigens. Acta Cytol 1994;38:517–23.
Sanchez-Carbayo M, Urrutia M, Romani R, Herrero M, Gonzalez de Buitrago JM, Navajo JA. Serial urinary IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, TNFalpha, UBC, CYFRA 21–1 and NMP22 during follow-up of patients with bladder cancer receiving intravesical BCG. Anticancer Res 2001;21:3041–7.
Sawczuk IS, Bagiella E, Sawczuk AT, Yun EJ. Clinical application of NMP22 in the management of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Cancer Detect Prevent 2000;24:364–8.
SchmittConrad M, Fornara P, Bohle A, Knipper A, Jocham D. Clinical experience with immunocytology using monoclonal antibody 486 P (Medaquic(R)) in detection of bladder cancer. Aktuelle Urol 1997;28:29–33.
Selli C, Travaglini F, Dal Canto M, Piazzini M, Frontera S, Bartoletti R. Microsatellite analysis in the detection of bladder carcinoma: a preliminary report. Acta Urol Ital 1999;13:117–20.
Seripa D, Parrella P, Gallucci M, Gravina C, Papa S, Fortunato P, et al. Sensitive detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder by microsatellite analysis of cells exfoliated in urine. Int J Cancer 2001;95:364–9.
Serretta V, Vasile P, Gange E, Lino E, Esposito E, Menozzi I. The NMP22 (nuclear matrix protein) test for surveillance of superficial bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Experience in 84 patients. Acta Urol Ital 1998;12:201–3.
Sharkey FE, Sarosdy MF. The significance of central pathology review in clinical studies of transitional cell carcinoma in situ. J Urol 1997;157:68–71.
Soloway MS, Briggman V, Carpinito GA, Chodak GW, Church PA, Lamm DL, et al. Use of a new tumor marker, urinary NMP22, in the detection of occult or rapidly recurring transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary tract following surgical treatment. J Urol 1996;156:363–7.
Song Z, Sun X, Wu D. Significance of flow cytometry in the diagnosis and treatment of bladder tumors. Chin Med Sci J 1995;10:38–41.
Su CK, Yang CR, Horng YY, Kao YL, Ho HC, Ou YC, et al. NMP22 in transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. J Chin Med Assoc 2003;66:294–8.
Sumi S, Arai K, Kitahara S, Yoshida KI. Preliminary report of the clinical performance of a new urinary bladder cancer antigen test: comparison to voided urine cytology in the detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Clin Chim Acta 2000;296:111–20.
Takeuchi Y, Sawada Y, Yabuki D, Masuda E, Satou D, Kuroda K, et al. Clinical study of urine NMP 22 (nuclear matrix protein 22) as a tumor marker in urinary epithelial cancer. Aktuelle Urol 2003;34:265–6.
Tang CS, Tang CM, Lau YY, Kung IT. Alcoholic carbowax prefixation and formal alcohol fixation. A new technique for urine cytology. Acta Cytol 1997;41:1183–8.
Trott PA, Edwards L. Comparison of bladder washings and urine cytology in the diagnosis of bladder cancer. J Urol 1973;110:664–6.
van Rhijn BW, Lurkin I, Kirkels WJ, van der Kwast TH, Zwarthoff EC. Microsatellite analysis – DNA test in urine competes with cystoscopy in follow-up of superficial bladder carcinoma: a phase II trial. Cancer 2001;92:768–75.
van Rhijn BW, Smit M, van Geenen D, Wijnmaalen A, Kirkels WJ, van der Kwast TH, et al. Surveillance with microsatellite analysis of urine in bladder cancer patients treated by radiotherapy. Eur Urol 2003;43:369–73.
Varella-Garcia M, Akduman B, Sunpaweravong P, Di Maria MV, Crawford ED. The UroVysion fluorescence in situ hybridization assay is an effective tool for monitoring recurrence of bladder cancer. Urol Oncol 2004;22:16–19.
Veeramachaneni R, Nordberg ML, Shi R, Herrera GA, Turbat-Herrera EA. Evaluation of fluorescence in situ hybridization as an ancillary tool to urine cytology in diagnosing urothelial carcinoma. Diagn Cytopathol 2003;28:301–7.
Vriesema JL, Atsma F, Kiemeney LA, Peelen WP, Witjes JA, Schalken JA. Diagnostic efficacy of the ImmunoCyt test to detect superficial bladder cancer recurrence. Urology 2001;58:367–71.
Walsh IK, Keane PF, Ishak LM, Flessland KA. The BTA stat test: a tumor marker for the detection of upper tract transitional cell carcinoma. Urology 2001;58:532–5.
Weikert S, Christoph F, Schrader M, Krause H, Miller K, Muller M. Quantitative analysis of survivin mRNA expression in urine and tumor tissue of bladder cancer patients and its potential relevance for disease detection and prognosis. Int J Cancer 2005;116:100–4.
Werner W, Ebert W, Wunderlich H, Schubert J, Junker K. Fluorescence in situ hybridization in the diagnosis of transitional cell carcinoma. Onkologie 1999;22:216–20.
Whisnant RE, Bastacky SI, Ohori NP. Cytologic diagnosis of low-grade papillary urothelial neoplasms (low malignant potential and low-grade carcinoma) in the context of the 1998 WHO/ISUP classification. Diagn Cytopathol 2003;28:186–90.
Witjes JA, van der Poel HG, van Balken MR, Debruyne FM, Schalken JA. Urinary NMP22 and karyometry in the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with superficial bladder cancer. Eur Urol 1998;33:387–91.
Wolman SR, Goldman B, Slovak ML, Tangen C, Persons DL, Wood D. Aneusomy for detection of bladder cancer recurrence: a Southwest Oncology Group study. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2007;176:22–7.
Xu K, Tam PC, Hou S, Wang X, Bai W. The role of nuclear matrix protein 22 combined with bladder tumor antigen stat test in surveillance of recurring bladder cancer. Chin Med J (Engl) 2002;115:1736–8.
Yang SC, Lee DH, Hong SJ, Chung BH, Kim IY. Telomerase activity: a potential marker of bladder transitional cell carcinoma in bladder washes. Yonsei Med J 1997;38:155–9.
Yokota K, Kanda K, Inoue Y, Kanayama H, Kagawa S. Semi-quantitative analysis of telomerase activity in exfoliated human urothelial cells and bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Br J Urol 1998;82:727–32.
Zancan M, Franceschini R, Mimmo C, Vianello M, Di Tonno F, Mazzariol C, et al. Free DNA in urine: a new marker for bladder cancer? Preliminary data. Int J Biol Markers 2005;20:134–6.
Zargar M, Soleimani M, Moslemi M. Comparative evaluation of urinary bladder cancer antigen and urine cytology in the diagnosis of bladder cancer. Urol J 2005;2:137–40.
Zhang FF, Arber DA, Wilson TG, Kawachi MH, Slovak ML. Toward the validation of aneusomy detection by fluorescence in situ hybridization in bladder cancer: comparative analysis with cytology, cytogenetics, and clinical features predicts recurrence and defines clinical testing limitations. Clin Cancer Res 1997;3:2317–28.
Zhang J, Zheng S, Fan Z, Gao Y, Di X, Wang D, et al. A comparison between microsatellite analysis and cytology of urine for the detection of bladder cancer. Cancer Lett 2001;172:55–8.
Ziaee SA, Moula SJ, Hosseini Moghaddam SM, Eskandar-Shiri D. Diagnosis of bladder cancer by urine survivin, an inhibitor of apoptosis: a preliminary report. Urol J 2006;3:150–3.
Required test(s) not reported (n = 79)
The use of the bladder-tumour associated analyte test to determine the type of cystoscopy in the follow-up of patients with bladder cancer. The United Kingdom and Eire Bladder Tumour Antigen Study Group. Br J Urol 1997;79:362–6.
Akao T, Kakehi Y, Wu X-X, Kinoshita H, Takahashi T, Ogawa O, et al. Semi-quantitative analysis of telomerase activity of exfoliated cells in urine of patients with urothelial cancers: causative factors affecting sensitivity and specificity. Urol Oncol 1998;3:118–24.
Attallah AM, Sakr HA, Ismail H, Abdel-Hady E, El Dosoky I. An office-based immunodiagnostic assay for detecting urinary nuclear matrix protein 52 in patients with bladder cancer. BJU Int 2005;96:334–9.
Babjuk M, Kostirova M, Mudra K, Pecher S, Smolova H, Pecen L, et al. Qualitative and quantitative detection of urinary human complement factor H-related protein (BTA stat and BTA TRAK) and fragments of cytokeratins 8, 18 (UBC rapid and UBC IRMA) as markers for transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol 2002;41:34–9.
Barlandas-Rendon E, Muller MM, Garcia-Latorre E, Heinschink A. Comparison of urine cell characteristics by flow cytometry and cytology in patients suspected of having bladder cancer. Clin Chem Lab Med 2002;40:817–23.
Bian W, Xu Z. Combined assay of CYFRA21–1, telomerase and vascular endothelial growth factor in the detection of bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Int J Urol 2007;14:108–11.
Billerey C, Lamy B, Bittard H, Rozan S, Carbillet JP. Flow cytometry versus urinary cytology in the diagnosis and follow-up of bladder tumors: critical review of a 5-year experience. World J Urol 1993;11:156–60.
Bonner RB, Hemstreet GP, III, Fradet Y, Rao JY, Min KW, Hurst RE. Bladder cancer risk assessment with quantitative fluorescence image analysis of tumor markers in exfoliated bladder cells. Cancer 1993;72:2461–9.
Casella R, Shariat SF, Monoski MA, Lerner SP. Urinary levels of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its receptor in the detection of bladder carcinoma. Cancer 2002;95:2494–9.
Chautard D, Daver A, Bocquillon V, Verriele V, Colls P, Bertrand G, et al. Comparison of the Bard Trak test with voided urine cytology in the diagnosis and follow-up of bladder tumors. Eur Urol 2000;38:686–90.
Chong TW, Cheng C. The role of the bladder tumour antigen test in the management of gross haematuria. Singapore Med J 1999;40:578–80.
Eissa S, Kenawy G, Swellam M, El Fadle AA, Abd El-Aal AA, El Ahmady O. Comparison of cytokeratin 20 RNA and angiogenin in voided urine samples as diagnostic tools for bladder carcinoma. Clin Biochem 2004;37:803–10.
Eissa S, Labib RA, Mourad MS, Kamel K, El Ahmady O. Comparison of telomerase activity and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in voided urine and bladder wash samples as a useful diagnostic tool for bladder cancer. Eur Urol 2003;44:687–94.
Eissa S, Kassim SK, Labib RA, El Khouly IM, Ghaffer TM, Sadek M, et al. Detection of bladder carcinoma by combined testing of urine for hyaluronidase and cytokeratin 20 RNAs. Cancer 2005;103:1356–62.
Eissa S, Swellam M, el Mosallamy H, Mourad MS, Hamdy N, Kamel K, et al. Diagnostic value of urinary molecular markers in bladder cancer. Anticancer Res 2003;23:4347–55.
Ellis WJ, Blumenstein BA, Ishak LM, Enfield DL. Clinical evaluation of the BTA TRAK assay and comparison to voided urine cytology and the Bard BTA test in patients with recurrent bladder tumors. The Multi Center Study Group. Urology 1997;50:882–7.
Fernandez-Gomez J, Rodriguez-Martinez JJ, Barmadah SE, Garcia RJ, Allende DM, Jalon A, et al. Urinary CYFRA 21.1 is not a useful marker for the detection of recurrences in the follow-up of superficial bladder cancer. Eur Urol 2007;51:1267–74.
Fitzgerald JM, Ramchurren N, Rieger K, Levesque P, Silverman M, Libertino JA, et al. Identification of H-ras mutations in urine sediments complements cytology in the detection of bladder tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 1995;87:129–33.
Fracasso ME, Franceschetti P, Doria D, Talamini G, Bonetti F. DNA breaks as measured by the alkaline comet assay in exfoliated cells as compared to voided urine cytology in the diagnosis of bladder cancer: a study of 105 subjects. Mutat Res 2004;564:57–64.
Frick J, Aulitzky W, Fuchs D. The value of urinary neopterin as an immunological parameter in patients with malignant tumors of the genitourinary tract. Urol Int 1985;40:155–9.
Golijanin D, Shapiro A, Pode D. Immunostaining of cytokeratin 20 in cells from voided urine for detection of bladder cancer. J Urol 2000;164:1922–5.
Gourlay W, Chan V, Gilks CB. Screening for urothelial malignancies by cytologic analysis and flow cytometry in a community urologic practice: a prospective study. Mod Pathol 1995;8:394–7.
Gregoire M, Fradet Y, Meyer F, Tetu B, Bois R, Bedard G, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of urinary cytology, and deoxyribonucleic acid flow cytometry and cytology on bladder washings during followup for bladder tumors. J Urol 1997;157:1660–4.
Gutierrez Banos JL, Henar Rebollo RM, Antolin Juarez FM, Garcia BM. Usefulness of the BTA STAT test for the diagnosis of bladder cancer. Urology 2001;57:685–9.
Guy L, Savareux L, Molinie V, Botto H, Boiteux J-P, Lebret T. Should bladder biopsies be performed routinely after bacillus Calmette-Guérin treatment for high-risk superficial transitional cell cancer of the bladder? Eur Urol 2006;50:516–20.
Hakenberg OW, Fuessel S, Richter K, Froehner M, Oehlschlaeger S, Rathert P, et al. Qualitative and quantitative assessment of urinary cytokeratin 8 and 18 fragments compared with voided urine cytology in diagnosis of bladder carcinoma. Urology 2004;64:1121–6.
Heino A, Aaltomaa S, Ala-Opas M. BTA test is superior to voided urine cytology in detecting malignant bladder tumours. Ann Chir Gynaecol 1999;88:304–7.
Jayachandran S, Unni Mooppan MM, Wax SH, Kim H. The value of urinary fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products as tumor markers in urothelial carcinoma. J Urol 1984;132:21–3.
Johnston B, Morales A, Emerson L, Lundie M. Rapid detection of bladder cancer: a comparative study of point of care tests. J Urol 1997;158:2098–101.
Kavaler E, Landman J, Chang Y, Droller MJ, Liu BC. Detecting human bladder carcinoma cells in voided urine samples by assaying for the presence of telomerase activity. Cancer 1998;82:708–14.
Khalbuss W, Goodison S. Immunohistochemical detection of hTERT in urothelial lesions: a potential adjunct to urine cytology. Cytojournal 2006;3:18.
Leyh H, Mazeman E. Bard BTA test compared with voided urine cytology in the diagnosis of recurrent bladder cancer. Eur Urol 1997;32:425–8.
Leyh H, Hall R, Mazeman E, Blumenstein BA. Comparison of the Bard BTA test with voided urine and bladder wash cytology in the diagnosis and management of cancer of the bladder. Urology 1997;50:49–53.
Leyh H, Marberger M, Conort P, Sternberg C, Pansadoro V, Pagano F, et al. Comparison of the BTA stat test with voided urine cytology and bladder wash cytology in the diagnosis and monitoring of bladder cancer. Eur Urol 1999;35:52–6.
Liedl T. Flow cytometric DNA/cytokeratin analysis of bladder lavage: methodical aspects and clinical implications. Urol Int 1995;54:22–47.
Liu J, Katz R, Shin HJ, Johnston DA, Zhang HZ, Caraway NP. Use of mailed urine specimens in diagnosing urothelial carcinoma by cytology and DNA image analysis. Acta Cytol 2005;49:157–62.
Maier U, Simak R, Neuhold N. The clinical-value of urinary cytology – 12 years of experience with 615 patients. J Clin Pathol 1995;48:314–7.
Melissourgos N, Kastrinakis NG, Davilas I, Foukas P, Farmakis A, Lykourinas M. Detection of human telomerase reverse transcriptase mRNA in urine of patients with bladder cancer: evaluation of an emerging tumor marker. Urology 2003;62:362–7.
Melissourgos ND, Kastrinakis NG, Skolarikos A, Pappa M, Vassilakis G, Gorgoulis VG, et al. Cytokeratin-20 immunocytology in voided urine exhibits greater sensitivity and reliability than standard cytology in the diagnosis of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urology 2005;66:536–41.
Miyake H, Hara I, Gohji K, Yamanaka K, Arakawa S, Kamidono S. Urinary cytology and competitive reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis of a specific CD44 variant to detect and monitor bladder cancer. J Urol 1998;160:2004–8.
Miyanaga N, Akaza H, Kameyama S, Hachiya T, Ozono S, Kuroda M, et al. Significance of the BTA test in bladder cancer: a multicenter trial. BTA Study Group Japan. Int J Urol 1997;4:557–60.
Morsi MI, Youssef AI, Hassouna ME, El Sedafi AS, Ghazal AA, Zaher ER. Telomerase activity, cytokeratin 20 and cytokeratin 19 in urine cells of bladder cancer patients. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst 2006;18:82–92.
Nasuti JF, Gomella LG, Ismial M, Bibbo M. Utility of the BTA stat test kit for bladder cancer screening. Diagn Cytopathol 1999;21:27–9.
Neves M, Ciofu C, Larousserie F, Fleury J, Sibony M, Flahault A, et al. Prospective evaluation of genetic abnormalities and telomerase expression in exfoliated urinary cells for bladder cancer detection. J Urol 2002;167:1276–81.
Pode D, Shapiro A, Wald M, Nativ O, Laufer M, Kaver I. Noninvasive detection of bladder cancer with the BTA stat test. J Urol 1999;161:443–6.
Pogacnik A, Us-Krasovec M. Cytomorphology and flow cytometry in monitoring patients treated for bladder cancer; preliminary results. Radiolo Oncol 1997;31:155–7.
Priolo G, Gontero P, Martinasso G, Mengozzi G, Formiconi A, Pelucelli G, et al. Bladder tumor antigen assay as compared to voided urine cytology in the diagnosis of bladder cancer. Clin Chim Acta 2001;305:47–53.
Quek P, Chin CM, Lim PH. The role of BTA stat in clinical practice. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2002;31:212–6.
Radkhah K, Nowroozi MR, Jabalameli P. Sensitivity and specificity of urinary bladder cancer antigen for diagnosis of bladder tumor; a comparative study with urinary cytology. Acta Medica Iranica 2005;43:169–72.
Raitanen MP, Marttila T, Kaasinen E, Rintala E, Aine R, Tammela TL. Sensitivity of human complement factor H related protein (BTA stat) test and voided urine cytology in the diagnosis of bladder cancer. J Urol 2000;163:1689–92.
Raitanen MP, Hellstrom P, Marttila T, Korhonen H, Talja M, Ervasti J, et al. Effect of intravesical instillations on the human complement factor H related protein (BTA stat) test. Eur Urol 2001;40:422–6.
Raitanen MP, Kaasinen E, Lukkarinen O, Kauppinen R, Viitanen J, Liukkonen T, et al. Analysis of false-positive BTA STAT test results in patients followed up for bladder cancer. Urology 2001;57:680–4.
Raitanen MP, Leppilahti M, Tuhkanen K, Forssel T, Nylund P, Tammela T, et al. Routine follow-up cystoscopy in detection of recurrence in patients being monitored for bladder cancer. Ann Chir Gynaecol 2001;90:261–5.
Raitanen MP, Marttila T, Nurmi M, Ala-Opas M, Nieminen P, Aine R, et al. Human complement factor H related protein test for monitoring bladder cancer. J Urol 2001;165:374–7.
Saika T, Tsushima T, Nasu Y, Kumon H, Ohmori H. Epidermal growth factor in urine from patients with bladder cancer. Urol Res 2000;28:230–4.
Sanchez-Carbayo M, Urrutia M, Gonzalez de Buitrago JM, Navajo JA. Evaluation of two new urinary tumor markers: bladder tumor fibronectin and cytokeratin 18 for the diagnosis of bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2000;6:3585–94.
Sanchini MA, Gunelli R, Nanni O, Bravaccini S, Fabbri C, Sermasi A, et al. Relevance of urine telomerase in the diagnosis of bladder cancer. JAMA 2005;294:2052–6.
Sarosdy MF, deVere White RW, Soloway MS, Sheinfeld J, Hudson MA, Schellhammer PF, et al. Results of a multicenter trial using the BTA test to monitor for and diagnose recurrent bladder cancer. J Urol 1995;154:379–83.
Sarosdy MF, Hudson MA, Ellis WJ, Soloway MS, deVere WR, Sheinfeld J, et al. Improved detection of recurrent bladder cancer using the Bard BTA stat test. Urology 1997;50:349–53.
Sawczuk IS, Pickens CL, Vasa UR, Ralph DA, Norris KA, Miller MC, et al. DD23 Biomarker: a prospective clinical assessment in routine urinary cytology specimens from patients being monitored for TCC. Urol Oncol 2002;7:185–90.
Schamhart DH, de Reijke TM, van der Poel HG, Witjes JA, de Boer EC, Kurth K, et al. The Bard BTA test: its mode of action, sensitivity and specificity, compared to cytology of voided urine, in the diagnosis of superficial bladder cancer. Eur Urol 1998;34:99–106.
Schmetter BS, Habicht KK, Lamm DL, Morales A, Bander NH, Grossman HB, et al. A multicenter trial evaluation of the fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products test for detection and monitoring of bladder cancer. J Urol 1997;158:801–5.
Schroeder GL, Lorenzo-Gomez MF, Hautmann SH, Friedrich MG, Ekici S, Huland H, et al. A side by side comparison of cytology and biomarkers for bladder cancer detection. J Urol 2004;172:1123–6.
Shariat SF, Herman MP, Casella R, Lotan Y, Karam JA, Stenman UH. Urinary levels of tumor-associated trypsin inhibitor (TATI) in the detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Eur Urol 2005;48:424–31.
Shariat SF, Matsumoto K, Casella R, Jian W, Lerner SP. Urinary levels of soluble e-cadherin in the detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Eur Urol 2005;48:69–76.
Slaton JW, Dinney CPN, Veltri RW, Miller MC, Liebert M, O’Dowd et al. Deoxyribonucleic acid ploidy enhances the cytological prediction of recurrent transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol 1997;158:806–11.
Sole M, Alos L, Mallofre C, Romero JA, Muntane J, Cardesa A. Bladder wash flow cytometry in transitional cell carcinoma: useful or misleading? Urol Res 1995;22:361–5.
Takashi M, Schenck U, Kissel K, Leyh H, Treiber U. Use of diagnostic categories in urinary cytology in comparison with the bladder tumour antigen (BTA) test in bladder cancer patients. Int Urol Nephrol 1999;31:189–96.
Tanaka K, Takashi M, Miyake K, Koshikawa T. Immunocytochemically demonstrated expression of epithelial membrane antigen and carcinoembryonic antigen by exfoliated urinary cells in patients with bladder cancer. Urol Int 1994;52:140–4.
Tauber S, Schneede P, Liedl B, Liesmann F, Zaak D, Hofstetter A. Fluorescence cytology of the urinary bladder. Urology 2003;61:1067–71.
Thomas L, Leyh H, Marberger M, Bombardieri E, Bassi P, Pagano F, et al. Multicenter trial of the quantitative BTA TRAK assay in the detection of bladder cancer. Clin Chem 1999;45:472–7.
Topsakal M, Karadeniz T, Anac M, Donmezer S, Besisik A. Assessment of fibrin-fibrinogen degradation products (Accu-Dx) test in bladder cancer patients. Eur Urol 2001;39:287–91.
van der Poel HG, Boon ME, van Stratum P, Ooms EC, Wiener H, Debruyne FM, et al. Conventional bladder wash cytology performed by four experts versus quantitative image analysis. Mod Pathol 1997;10:976–82.
van der Poel HG, van Balken MR, Schamhart DH, Peelen P, de Reijke T, Debruyne FM, et al. Bladder wash cytology, quantitative cytology, and the qualitative BTA test in patients with superficial bladder cancer. Urology 1998;51:44–50.
van der Poel HG, van Rhijn BW, Peelen P, Debruyne FM, Boon ME, Schalken JA. Consecutive quantitative cytology in bladder cancer. Urology 2000;56:584–8.
Varaldo M, Moretti M, Malcangi B, Cichero A, Pittaluga P. Flow cytometry in the follow-up of superficial bladder cancer. Acta Urol Ital 1995;9:207–9.
Weikert S, Krause H, Wolff I, Christoph F, Schrader M, Emrich T, et al. Quantitative evaluation of telomerase subunits in urine as biomarkers for noninvasive detection of bladder cancer. Int J Cancer 2005;117:274–80.
Wu WJ, Liu LT, Huang CH, Chang SF, Chang LL. Telomerase activity in human bladder tumors and bladder washing specimens. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 2001;17:602–9.
Zhao J, He D, Yang L, He H, Nan X. The study of microsatellites alteration in diagnoses of bladder cancer. Acad J Xi’an Jiaotong Univ 2006;18:73–7.
Required study design not met (n = 14)
New clinical data further supports accuracy of the Vysis UroVysion test. Expert RevMol Diagn 2002;2:93–4.
Akhtar M, Gallagher L, Rohan S. Survivin: role in diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of bladder cancer. Adv Anat Pathol 2006;13:122–6.
Barak V, Goike H, Panaretakis KW, Einarsson R. Clinical utility of cytokeratins as tumor markers. Clin Biochem 2004;37:529–40.
Clarke NW, Sangar VK. Urine telomerase activity for the diagnosis of bladder cancer: commentary. Nature Clin Pract Urol 2006;3:192–3.
Delanghe J. New screening diagnostic techniques in urinalysis. Acta Clin Belg 2007;62:155–61.
Duffy MJ, O’Donovan N, Brennan DJ, Gallagher WM, Ryan BM. Survivin: a promising tumor biomarker. Cancer Lett 2007;249:49–60.
Ellwein LB. Bladder cancer screening: lessons from a biologically based model of bladder cancer progression and therapeutic intervention. J Occup Med 1990;32:806–11.
Getzenberg RH. Urine-based assays for bladder cancer. Lab Med 2003;34:613–7.
Grossman HB. Bladder cancer markers: translating discovery to the clinic. J Clin Ligand Assay 2004;26:184–6.
Grossman HB. Fluorescence in situ hybridization for detecting transitional cell carcinoma: implications for clinical practice. In: Laudadio J, Keane TE, Reeves HM, Savage SJ, Hoda RS, Lage JM, Wolff DJ, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC. Urol Oncol 2006;24:270–1.
Master VA, Meng MV, Koppie TM, Carroll PR, Grossfeld GD. Origin of urothelial carcinoma after renal transplant determined by fluorescence in situ hybridization. J Urol 2002;167:2521–2.
Mellon JK. Can nomograms using urinary NMP22 predict recurrence and progression of superficial bladder cancer? Commentary. Nature Clin Pract Urol 2005;2:370–1.
Moonen PM, Kiemeney LA, Witjes JA. Urinary NMP22 BladderChek test in the diagnosis of superficial bladder cancer. Eur Urol 2005;48:951–6.
Yossepowitch O, Herr HW, Donat SM. Use of urinary biomarkers for bladder cancer surveillance: patient perspectives. J Urol 2007;177:1277–82.
Required outcomes not reported (n = 13)
Boman H, Hedelin H, Jacobsson S, Holmang S. Newly diagnosed bladder cancer: the relationship of initial symptoms, degree of microhematuria and tumor marker status. J Urol 2002;168:1955–9.
Britton JP, Dowell AC, Whelan P, Harris CM. A community study of bladder cancer screening by the detection of occult urinary bleeding. J Urol 1992;148:788–90.
Chen Y-T, Hayden CL, Marchand KJ, Makuch RW. Comparison of urine collection methods for evaluating urinary nuclear matrix protein, NMP22, as a tumor marker. J Urol 1997;158:1899–901.
Mahnert B, Tauber S, Kriegmair M, Nagel D, Holdenrieder S, Hofmann K, et al. Measurements of complement factor H-related protein (BTA-TRAK assay) and nuclear matrix protein (NMP22 assay) – useful diagnostic tools in the diagnosis of urinary bladder cancer? Clin Chem Lab Med 2003;41:104–10.
Mansoor I. Analysis of urine cytology at a community hospital. JAMC 2003;15:20–3.
Murphy WM, Rivera-Ramirez I, Medina CA, Wright NJ, Wajsman Z. The bladder tumor antigen (BTA) test compared to voided urine cytology in the detection of bladder neoplasms. J Urol 1997;158:2102–6.
Pariente JL, Bordenave L, Michel P, Latapie MJ, Ducassou D, Le Guillou M. Initial evaluation of CYFRA 21–1 diagnostic performances as a urinary marker in bladder transitional cell carcinoma. J Urol 1997;158:338–41.
Shariat SF, Zippe C, Ludecke G, Boman H, Sanchez-Carbayo M, Casella R, et al. Nomograms including nuclear matrix protein 22 for prediction of disease recurrence and progression in patients with Ta, T1 or CIS transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol 2005;173:1518–25.
Svatek RS, Lee D, Lotan Y. Correlation of office-based cystoscopy and cytology with histologic diagnosis: how good is the reference standard? Urology 2005;66:65–8.
Toma MI, Friedrich MG, Hautmann SH, Jakel KT, Erbersdobler A, Hellstern A, et al. Comparison of the ImmunoCyt test and urinary cytology with other urine tests in the detection and surveillance of bladder cancer. World J Urol 2004;22:145–9.
Tut VM, Hildreth AJ, Kumar M, Mellon JK. Does voided urine cytology have biological significance? Br J Urol 1998;82:655–9.
Wiener HG, Vooijs GP, Hof-Grootenboer B. Accuracy of urinary cytology in the diagnosis of primary and recurrent bladder cancer. Acta Cytol 1993;37:163–9.
Wiener HG, Remkes GW, Schatzl G, Susani M, Breitenecker G. Quick-staining urinary cytology and bladder wash image analysis with an integrated risk classification: a worthwhile improvement in the follow-up of bladder cancer? Cancer 1999;87:263–9.
Criteria for control group not met (n = 10)
Houskova L, Zemanova Z, Babjuk M, Melichercikova J, Pesl M, Michalova K. Molecular cytogenetic characterization and diagnostics of bladder cancer. Neoplasma 2007;54:511–16.
Junker K, Werner W, Mueller C, Ebert W, Schubert J, Claussen U. Interphase cytogenetic diagnosis of bladder cancer on cells from urine and bladder washing. Int J Oncol 1999;14:309–13.
Lee MY, Tsou MH, Cheng MH, Chang DS, Yang AL, Ko JS. Clinical application of NMP22 and urinary cytology in patients with hematuria or a history of urothelial carcinoma. World J Urol 2000;18:401–5.
Shiff C, Veltri R, Naples J, Quartey J, Otchere J, Anyan W, et al. Ultrasound verification of bladder damage is associated with known biomarkers of bladder cancer in adults chronically infected with Schistosoma haematobium in Ghana. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hygiene 2006;100:847–54.
Sun Y, He DL, Ma Q, Wan XY, Zhu GD, Li L, et al. Comparison of seven screening methods in the diagnosis of bladder cancer. Chin Med J (Engl) 2006;119:1763–71.
Svatek RS, Karam J, Karakiewicz PI, Gallina A, Casella R, Roehrborn CG, et al. Role of urinary cathepsin B and L in the detection of bladder urothelial cell carcinoma. J Urol 2008;179:478–84.
Svatek RS, Herman MP, Lotan Y, Casella R, Hsieh JT, Sagalowsky AI, et al. Soluble Fas – a promising novel urinary marker for the detection of recurrent superficial bladder cancer. Cancer 2006;106:1701–7.
Tsui KH, Chen SM, Wang TM, Juang HH, Chen CL, Sun GH, et al. Comparisons of voided urine cytology, nuclear matrix protein-22 and bladder tumor associated antigen tests for bladder cancer of geriatric male patients in Taiwan, China. Asian J Androl 2007;9:711–15.
Upendra KN, Dey P, Mondal AK, Singh SK, Vohra H. DNA flow cytometry and bladder irrigation cytology in detection of bladder carcinoma. Diagn Cytopathol 2001;24:153–6.
Zellweger T, Benz G, Cathomas G, Mihatsch MJ, Sulser T, Gasser TC, et al. Multi-target fluorescence in situ hybridization in bladder washings for prediction of recurrent bladder cancer. Int J Cancer 2006;119:1660–5.
Required reference standard not met (n = 3)
Alishahi S, Byrne D, Goodman CM, Baxby K. Haematuria investigation based on a standard protocol: emphasis on the diagnosis of urological malignancy. J R Coll Surg Edinb 2002;47:422–7.
Hofland CA, Mariani AJ. Is cytology required for a hematuria evaluation? J Urol 2004;171:324–6.
Sanchini MA, Gunelli R, Nanni O, Bravaccini S, Fabbri C, Sermasi A, et al. Relevance of urine telomerase in the diagnosis of bladder cancer. JAMA 2005;294:2052–6.
Cytology studies predating the publication year of the earliest included biomarker study (n = 3)
Loh CS, Spedding AV, Ashworth MT, Kenyon WE, Desmond AD. The value of exfoliative urine cytology in combination with flexible cystoscopy in the diagnosis of recurrent transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Br J Urol 1996;77:655–8.
Renshaw AA, Nappi D, Weinberg DS. Cytology of grade 1 papillary transitional cell carcinoma. A comparison of cytologic, architectural and morphometric criteria in cystoscopically obtained urine. Acta Cytol 1996;40:676–82.
Sack MJ, Artymyshyn RL, Tomaszewski JE, Gupta PK. Diagnostic-value of bladder wash cytology, with special reference to low-grade urothelial neoplasms. Acta Cytol 1995;39:187–94.
Appendix 12 Characteristics of the biomarker and cytology studies
| Study | Participants | Tests | Outcomes summary |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Abbate 1998154 Study design: case–control Time period: NS Country: Italy |
Enrolled: 182; analysed: 135 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): mean 63, range 41 to 89 Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22, 12 U/ml |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 135) Sensitivity: 54% Specificity: 87% |
|
Bastacky 1999165 Study design: CC-SD (three centres) Time period: 1990–4 Country: USA |
Enrolled: 1672; analysed: 743 No previous history of BC: 752; history of BC: 485 Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: cytology (VU or BW), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 743) Sensitivity: 64% Specificity: 93% |
|
Bhuiyan 2003120 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Saudi Arabia/USA |
Enrolled: 233; analysed: 231 NMP22, 125 cytology No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22, 3.6 U/ml, ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: specimen (n = 231, NMP22; n = 125, cytology) Sensitivity: 25% (NMP22 10 U/ml), 40% (cytology) Specificity: 94% (NMP22 10 U/ml), 95% (cytology) |
|
Study design: case–control Time period: Jan 1998 to Nov 1999 Country: Sweden |
Enrolled: 250; specimens analysed: 297 NMP22, 293 cytology No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: 174 Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22, ≥ 4 U/ml; cytology (BW), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: specimen (n = 297, NMP22; n = 293, cytology) Sensitivity: 54% (NMP22), 40% (cytology) Specificity: 68 (NMP22), 93% (cytology) |
|
Study design: C-SD Time period: Jan 1997 to Jun 1999 Country: Switzerland |
Enrolled: 235; analysed: 235 NMP22, 200 cytology No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): mean 72, range 37 to 97 (M); mean 69, range 23 to 96 (F) Sex: 164 M, 71 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (BW), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 235, NMP22; n = 200, cytology) Sensitivity: 52% (NMP22), 53% (cytology) Specificity: 84% (NMP22), 90% (cytology) |
|
Casetta 2000122 Study design: C-SD Time period: Jan 1997 to Dec 1998 Country: Italy |
Enrolled: 196; analysed: 196 No previous history of BC: 94; history of BC: 102 Age (years): mean 68, no history BC; mean 69, history BC; range NS Sex: 170 M, 26 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥10 U/ml, 11 U/ml, 12 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 196) Sensitivity: 64% (NMP22 10 U/ml), 73% (cytology) Specificity: 63% (NMP22 10 U/ml), 80% (cytology) |
|
Chahal 2001166 Study design: C-SD Time period: Jan 1998 to Jan 2000 Country: UK |
Enrolled: 285; analysed: 285 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): mean 62, range NS Sex: 171 M, 114 F |
Tests and cut-off used: cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 285) Sensitivity: 49% Specificity: 94% |
|
Chahal 200145 Study design: CC-SD Time period: NS Country: UK |
Enrolled: 211; analysed: 211 No previous history of BC: 96; history of BC: 115 Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 211) Sensitivity: 33% (NMP22), 24% (cytology) Specificity: 92 (NMP22), 97% (cytology) |
|
Study design: case–control (no history of disease) Time period: NS Country: China |
Enrolled: 399; analysed: 314 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): mean 53, range 3 to 91 Sex: 220 M, 111 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 7.5 U/ml |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 314) Sensitivity: 36% Specificity: 83% |
|
Daniely 200794 Study design: C-SD Time period: 2003–4 Country: Israel |
Enrolled: 115; analysed: 115 No previous history of BC: 49; history of BC: 66 Age (years): NS Sex: 73 M, 42 F |
Tests and cut-off used: FISH, minimum of four cells with gains of two or more chromosomes or 12 or more cells with homozygous loss of the 9p21 locus + cytology |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 115) Sensitivity: 100% Specificity: 50% |
|
Del Nero 1999123 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Italy |
Enrolled: 105; analysed: 105 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 105 Age (years): mean 54, range 42 to 73 Sex: 92 M, 13 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 5 U/ml, 6 U/ml, 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 105) Sensitivity: 83% (NMP22 10 U/ml), 47% (cytology) Specificity: 87% (NMP22 10 U/ml), 83% (cytology) |
|
Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 103; analysed: 103 No previous history of BC: 55; history of BC: 48 Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; FISH, 20% of cells had a gain of two or more chromosomes (3, 7 or 17) or 40% of cells had a gain of one chromosome or 40% loss of 9p21 locus |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 103) Sensitivity: 70% (NMP22), 67% (FISH) Specificity: 65% (NMP22), 89% (FISH) |
|
Garbar 2007167 Study design: C-SD Time period: 2002–4 Country: Belgium |
Enrolled: 139; analysed: 139 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): mean 69 (men), range NS; mean 68 (female), range NS Sex: 90 M, 49 F |
Tests and cut-off used: cytology (BW), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: specimen (n = 592) Sensitivity: 60% Specificity: 95% |
|
Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Greece |
Enrolled: 234; analysed: 213 No previous history of BC: 118; history of BC: 95 Age (years): mean 66, range 25 to 93 Sex: 200 M, 34 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 8 U/ml |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 213) Sensitivity: 64% Specificity: 72% |
|
Grossman 2005126 Study design: CC-SD (23 centres) Time period: Sep 2001 to May 2002 Country: USA |
Enrolled: 1331; analysed: 1331 No previous history of BC:1331; history of BC: 1331 Age (years): mean 59, range 18 to 96 Sex: 759 M, 572 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 1331, NMP22; n = 1287, cytology) Sensitivity: 56% (NMP22), 16% (cytology) Specificity: 86% (NMP22), 99% (cytology) |
|
Grossman 2006127 Study design: CC-SD (23 centres) Time period: Sep 2001 to Feb 2002 Country: USA |
Enrolled: 668; analysed: 668 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 668 Age (years): mean 71, range 30 to 95 Sex: 503 M, 165 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 668, NMP22; n = 650, cytology) Sensitivity: 50% (NMP22), 12% (cytology) Specificity: 87% (NMP22), 97% (cytology) |
|
Guttierez Banos 2001128 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Spain |
Enrolled: 150; analysed: 150 No previous history of BC: 64; history of BC: 86 Age (years): mean 68, range 20 to 91 Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 6 U/ml, 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment; cystoscopy (rigid) |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 150) Sensitivity: 76% (NMP22 10 U/ml), 70% (cytology), 100% (cystoscopy) Specificity: 91% (NMP22 10 U/ml), 93% (cytology), 89% (cystoscopy) |
|
Hakenberg 2000168 Study design: C-SD Time period: Jun 1996 to Dec 1997 Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 374; analysed: 374 No previous history of BC: 374; history of BC: 0 Age (years): mean 68 (men), 74 (female), range NS Sex: 276 M, 98 F |
Tests and cut-off used: cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: specimen (n = 417) Sensitivity: 76% Specificity: 80% |
|
Halling 200097 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: USA |
Enrolled: 265; analysed: 118 No previous history of BC: 115; history of BC: 150 Age (years): mean 70, range 36 to 94 Sex: 200 M, 65 F |
Tests and cut-off used: FISH five or more cells polysomy; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 151, FISH; n = 118, cytology) Sensitivity: 81% (FISH), 58% (cytology) Specificity: 96% (FISH), 98% (cytology) |
|
Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: USA |
Enrolled: 107; analysed: 107 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 107 Age (years): mean 66, range 33 to 86 Sex: 84 M, 23 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 6.4 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: specimen (n = 128) Sensitivity: 47% (NMP22), 60% (cytology) Specificity: 79% (NMP22), 58% (cytology) |
|
Junker 200698 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 141; analysed: 121 FISH, 109 cytology No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: FISH, five or more cells showed gains of more than one chromosome (3, 7 or 17), or 10 or more cells showed gains of a single chromosome (3, 7 or 17) or 10 or more cells showed homozygous loss of 9p21 locus; cytology (NS) |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 121, FISH; n = 109, cytology) Sensitivity: 60% (FISH), 24% (cytology) Specificity: 81% (FISH), 91% (cytology) |
|
Study design: C-SD (10 centres) Time period: NS Country: Austria |
Enrolled: 2686; analysed: 2542 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 2542 Age (years): mean 65, range 18 to 97 Sex: 1910 M, 632 F |
Tests and cut-off used: cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 2542) Sensitivity: 45% Specificity: 95% |
|
Kipp 200899 Study design: C-SD Time period: Mar 2006 to Mar 2007 Country: USA |
Enrolled: 124; analysed: 124 No previous history of BC: 41; history of BC: 81 Age (years): mean 72, range 45 to 89 Sex: 103 M, 21 F |
Tests and cut-off used: FISH, four or more cells had polysomic signal patterns (gain of two or more of the four chromosomes in an individual cell), 10 or more cells demonstrated tetrasomy (four signal patterns for all four probes) or > 20% of the cells demonstrated 9p21 homozygous deletion (loss of two 9p21 signals) |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 124) Sensitivity: 62% Specificity: 87% |
|
Kowalska 2005130 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Poland |
Enrolled: 98; analysed: 98 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 98 Age (years): mean 67 (male), 64 (female), range 36 to 96 Sex: 84 M, 14 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 98) Sensitivity: 53% Specificity: 46% |
|
Kumar 2006131 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: India |
Enrolled: 131; analysed: 131 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 131 Age (years): mean 67, range 32 to 91 Sex: 117 M, 14 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 131) Sensitivity: 85% (NMP22), 41% (cytology) Specificity: 78% (NMP22), 96% (cytology) |
|
Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 169; analysed: 109 No previous history of BC: 40; history of BC: 44 Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 109) Sensitivity: 63% (NMP22), 45% (cytology) Specificity: 61% (NMP22), 93% (cytology) |
|
Study design: case–control (nhd) Time period: NS Country: South Korea |
Enrolled: 106; analysed: 106 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): mean 60 (cases), 62 (control), range 30 to 78 Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 7.7 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 106) Sensitivity: 76% (NMP22), 56% (cytology) Specificity: 72% (NMP22), 89% (cytology) |
|
Lodde 2003109 Study design: CC-SD Time period: NS Country: Austria, Italy |
Enrolled: 235; analysed: 225 No previous history of BC: 98; history of BC: 137 Age (years): mean 72, range 32 to 86 Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: ImmunoCyt, at least one green or one red fluorescent cell; cytology (VU), subjective assessment ; ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 225) Sensitivity: 87% (ImmunoCyt), 41% (cytology), 90% (ImmunoCyt + cytology) Specificity: 67% (ImmunoCyt), 94% (cytology), 68% (ImmunoCyt + cytology) |
|
Lodde 2006110 Study design: CC-SD Time period: NS Country: Austria, Italy |
Enrolled: 216; analysed: 195 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 216 Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: ImmunoCyt, at least one green or one red fluorescent cell; cytology (VU), subjective assessment ; ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) |
Unit of analysis: tumour recurrence (n = 334, ImmunoCyt; n = 277, cytology; n = 334, ImmunoCyt + cytology) Sensitivity: 71% (ImmunoCyt), 49% (cytology), 86% (ImmunoCyt + cytology) Specificity: 78% (ImmunoCyt), 95% (cytology), 78% (ImmunoCyt + cytology) |
|
May 2007107 Study design: case–control (nhd) Time period: NS Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 166; analysed: 166 No previous history of BC: 62; history of BC: 71 Age (years): mean 68, range 37 to 90 Sex: 139 M, 27 F |
Tests and cut-off used: FISH, gain of two or more chromosomes in five or more cases per slide, or in cases of isolated gains of chromosome 3, 7 or 17 when the proportion of cells with such a gain was 10% or more of at least 100 cells evaluated, or when there were 10 or more cells with 9p21 loss; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 166) Sensitivity: 53% (FISH), 71% (cytology) Specificity: 74% (FISH), 84% (cytology) |
|
Meiers 2007100 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: USA, Belgium |
Enrolled: 624; analysed: 624 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: FISH, chromosomal gain of two or more chromosomes (+3, +7, +17) in four or more cells or deletion of 9p21 in 12 or more cells; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 624) Sensitivity: 93% (FISH), 73% (cytology) Specificity: 90% (FISH), 87% (cytology) |
|
Messing 2005111 Study design: C-SD (four centres) Time period: Nov 2000 to Nov 2003 Country: USA |
Enrolled: 341; analysed: 326 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 341 Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: ImmunoCyt, one green or one red fluorescent cell; cytology (VU), subjective assessment; ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 326) Sensitivity: 81% (ImmunoCyt), 23% (cytology), 81% (ImmunoCyt + cytology) Specificity: 75% (ImmunoCyt), 93% (cytology), 73% (ImmunoCyt + cytology) |
|
Mian 1999112 Study design: CC-SD Time period: Nov 1997 to Mar 1998 Country: Austria |
Enrolled: 264; analysed: 249 No previous history of BC: 114; history of BC: 150 Age (years): mean 66, range 21 to 93 Sex: 204 M, 60 F |
Tests and cut-off used: ImmunoCyt, one green or one red fluorescent cell; cytology (VU), subjective assessment ; ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 249) Sensitivity: 86% (ImmunoCyt), 47% (cytology), 90% (ImmunoCyt + cytology) Specificity: 79% (ImmunoCyt), 98% (cytology), 79% (ImmunoCyt + cytology) |
|
Mian 2000134 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Austria |
Enrolled: 240; analysed: 240 No previous history of BC: 81; history of BC: 159 Age (years): mean 66, range 22 to 92 Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 240) Sensitivity: 56% Specificity: 79% |
|
Mian 2003101 Study design: CC-SD Time period: NS Country: Austria, Italy |
Enrolled: 181; analysed: 181 ImmunoCyt, cytology; 57 FISH No previous history of BC: 81; history of BC: 100 Age (years): 67, range 32 to 83 Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: ImmunoCyt, one green or one red fluorescent cell; FISH, four or more aneusomic of 25 counted cells; cytology (VU), subjective assessment; ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 181, ImmunoCyt; n = 57, FISH; n = 181, cytology; n = 181, ImmunoCyt + cytology) Sensitivity: 86% (ImmunoCyt), 96% (FISH), 45% (cytology), 90% (ImmunoCyt + cytology) Specificity: 71% (ImmunoCyt), 45% (FISH), 94% (cytology), 66% (ImmunoCyt + cytology) |
|
Mian 2006113 Study design: C-SD Time period: Jan 2002 to Oct 2004 Country: Italy |
Enrolled: 942; analysed: NS No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 942 Age (years): mean 73, range 32 to 87 Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: ImmunoCyt, one green or one red fluorescent cell; cytology (VU), subjective assessment; ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) |
Unit of analysis: specimen (n = 1886) Sensitivity: 85% (ImmunoCyt), 39% (cytology), 89% (ImmunoCyt + cytology) Specificity: 73% (ImmunoCyt), 99% (cytology), 73% (ImmunoCyt + cytology) |
|
Study design: C-SD (13 centres) Time period: Aug 1995 to Mar 1997 Country: Japan |
Enrolled: 309; analysed: 309 No previous history of BC: 309; history of BC: 0 Age (years): NS Sex: 145 M, 164 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 12 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 309) Sensitivity: 91% (NMP22), 55% (cytology) Specificity: 76% (NMP22), 100% (cytology) |
|
Study design: C-SD Time period: Jan 2000 to Mar 2002 Country: Japan |
Enrolled: 156; analysed: 137 No previous history of BC: 99; history of BC: 57 Age (years): mean 69, range 37 to 91 Sex: 120 M, 36 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 5 U/ml, 12 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 137) Sensitivity: 19% (NMP22 12 U/ml), 7% (cytology) Specificity: 85% (NMP22 12 U/ml), 98% (cytology) |
|
Moonen 2007102 Study design: C-SD Time period: Mar 2005 to Apr 2006 Country: the Netherlands |
Enrolled: 105; analysed: 95 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 105 Age (years): mean 70, range 44 to 93 Sex: 73 M, 22 F |
Tests and cut-off used: FISH, four or more of the 25 morphologically abnormal cells showed gains of two or more chromosomes (3, 7 or 17) or 12 or more of the 25 cells had no 9p21 signals; cytology (VU), subjective assessment; FISH + cytology (VU) |
Unit of analysis: specimen (n = 103, FISH; n = 108, cytology; n = 103, FISH + cytology) Sensitivity: 39% (FISH), 41% (cytology), 53% (FISH + cytology) Specificity: 90% (FISH), 90% (cytology), 79% (FISH + cytology) |
|
Oge 2001137 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Turkey |
Enrolled: 114; analysed: 76 No previous history of BC: 37; history of BC: 39 Age (years): mean 59 (groups 1–3), range 26 to 87 Sex: 93 M, 21 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 76) Sensitivity: 74% Specificity: 69% |
|
Olsson 2001114 Study design: C-SD Time period: Jun 1999 to Jul 2000 Country: Sweden |
Enrolled: 121; analysed: 114 No previous history of BC: 60; history of BC: 61 Age (years): mean 68, range 15 to 93 Sex: 95 M, 26 F |
Tests and cut-off used: ImmunoCyt, one green or one red fluorescent cell; cytology (BW), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 114) Sensitivity: 100% (ImmunoCyt), 58% (cytology) Specificity: 69% (ImmunoCyt), NS (cytology) |
|
Oosterhuis 2002138 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: the Netherlands |
Enrolled: 191; analysed: 191 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 191 Age (years): mean 65, range 32 to 89 Sex: 146 M, 45 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml |
Unit of analysis: specimen (n = 431) Sensitivity: 50% Specificity: 68% |
|
Study design: case–control (nhd) Time period: Nov 1999 to Sep 2000 Country: USA |
Enrolled: 253; analysed: 253 No previous history of BC: 155; history of BC: 98 Age (years): mean 63, range 16 to 89 Sex: 182 M, 71 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 2.5 U/ml; cytology (VU or BW), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 252, NMP22; n = 253, cytology) Sensitivity: 70% (NMP22), 67% (cytology) Specificity: 45% (NMP22), 81% (cytology) |
|
Study design: CC-SD (19 centres) Time period: NS Country: France |
Enrolled: 694; analysed: 651 No previous history of BC: 236; history of BC: 458 Age (years): mean 66, range 32 to 92 Sex: 550 M, 144 F |
Tests and cut-off used: ImmunoCyt, one green or one red fluorescent cell; cytology (VU), subjective assessment ; ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 651, ImmunoCyt; n = 651, cytology; n = 146, ImmunoCyt + cytology) Sensitivity: 73% (ImmunoCyt), 62% (cytology), 82% (ImmunoCyt + cytology) Specificity: 82% (ImmunoCyt), 85% (cytology), NS (ImmunoCyt + cytology) |
|
Planz 2005171 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 626; analysed: 495 No previous history of BC: 353; history of BC: 273 Age (years): mean 62, range NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: cytology (VU), subjective assessment; cytology (BW), subjective assessment; cytology (VU + BW) |
Unit of analysis: specimen (n = 346, cytology (VU); n = 191 cytology (BW); n = 535, cytology (VU) + cytology (BW)) Sensitivity: 38% (cytology (VU)), 38% (cytology (BW)), 39% (cytology (VU) + cytology (BW)) Specificity: 98% (cytology (VU)), 99% (cytology (BW)), 98% (cytology (VU) + cytology (BW)) |
|
Ponsky 2001139 Study design: C-SD Time period: May 1996 to Dec 1998 Country: USA |
Enrolled: 608; analysed: 608 No previous history of BC: 529; history of BC: 79 Age (years): mean 70 (malignant group), 61 (benign group), range NS Sex: 438 M, 170 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 608) Sensitivity: 88% (NMP22), 62% (cytology) Specificity: 84% (NMP22), 85% (cytology) |
|
Potter 1999172 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: UK |
Enrolled: 336; analysed: 336 No previous history of BC: 336; history of BC: 0 Age (years): mean 64, range NS Sex: 336 M |
Tests and cut-off used: cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 336) Sensitivity: 100% Specificity: 99% |
|
Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Germany, USA |
Enrolled: 739; analysed: 739 No previous history of BC: 353; history of BC: 386 Age (years): mean 67, range 37 to 90 Sex: 485 M, 254 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 8.25 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 739) Sensitivity: 85% (NMP22), 62% (cytology) Specificity: 68% (NMP22), 96% (cytology) |
|
Study design: CC-SD (18 centres) Time period: 1997–9 Country: Finland |
Enrolled: 652; analysed: 570 No previous history of BC: 151; history of BC: 501 Age (years): mean 69, range 21 to 92 Sex: 449 M, 121 F |
Tests and cut-off used: cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 129 no history of BC; n = 441, previous BC history) Sensitivity: 57% (no history), 35% (BC history) Specificity: NS (no history), 90% (BC history) |
|
Ramakumar 1999159 Study design: case–control (nhd) Time period: Sep 1997 to Dec 1997 Country: USA |
Enrolled: 196; analysed: 196 NMP22, 112 cytology No previous history of BC: 19; history of BC: 38 Age (years): mean 66, range 29 to 102 Sex: 152 M, 44 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 196, NMP22; n = 112, cytology) Sensitivity: 53% (NMP22), 44% (cytology) Specificity: 60% (NMP22), 95% (cytology) |
|
Saad 2002141 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: UK |
Enrolled: 120; analysed: 120 No previous history of BC: 120; history of BC: 0 Age (years): mean 70, range 30 to 88 Sex: 100 M, 20 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 120) Sensitivity: 81% (NMP22), 48% (cytology) Specificity: 87% (NMP22), 87% (cytology) |
|
Sanchez-Carbayo 1999161a (primary report) Study design: case–control (nhd) Time period: NS Country: Spain |
Enrolled: 267; analysed: 187 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 14.6 U/ml |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 187) Sensitivity: 76% Specificity: 95% |
|
[Sanchez-Carbayo 1999160] (secondary report) Study design: case–control (nhd) Time period: NS Country: Spain |
Enrolled: 267; analysed: 187 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 6.4, 7, 10, 12, 13.7 U/ml |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 187) Sensitivity: 81% (NMP22 10 U/ml) Specificity: 91% (NMP22 10 U/ml) |
|
Sanchez-Carbayo 2001142 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Spain |
Enrolled: 232; analysed: 232 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 232 Age (years): NS Sex: 201 M, 31 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 232) Sensitivity: 69% Specificity: 93% |
|
Sanchez-Carbayo 2001162 Study design: case–control (nhd) Time period: Jan1999 to Jul 1999 Country: Spain |
Enrolled: 187; analysed: 187 No previous history of BC: 112; history of BC: 0 Age (years): mean 66, range 24 to 89 Sex: 87 M, 25 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (VU or catheterised) |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 187, NMP22; n = 112, cytology) Sensitivity: 61% (NMP22), 35% (cytology) Specificity: 80% (NMP22), 97% (cytology) |
|
Sarosdy 2002108 Study design: case–control (nhd) (21 centres) Time period: NS to Apr 2000 Country: USA |
Enrolled: 451; analysed: 392 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 176 Age (years): mean 71 (cases), 58 (control), range 25 to 98 Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: FISH, aneuploidy of chromosomes 3, 7 and 17 or loss of the 9p21 locus; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 392, FISH) Sensitivity: 71% (FISH) Specificity: 84% (FISH) |
|
Sarosdy 2006103 Study design: C-SD (23 centres) Time period: NS to Apr 2003 Country: USA |
Enrolled: 497; analysed: 473 No previous history of BC: 497; history of BC: 0 Age (years): mean 63, range 40 to 97 Sex: 298 M, 199 F |
Tests and cut-off used: FISH, NS; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 473) Sensitivity: 69% (FISH), 38% (cytology) Specificity: 78% (FISH), NS (cytology) |
|
Study design: CC-SD Time period: Oct 2000 to Jul 2007 Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 301; analysed: 280 No previous history of BC: 301; history of BC: 0 Age (years): mean 59 (gross hematuria group), 57 (microhematuria group), range 24 to 89 Sex: 227 M, 65 F |
Tests and cut-off used: ImmunoCyt, more than one green or red urothelial cell; cytology (VU), subjective assessment; cystoscopy, NS; ImmunoCyt + cystoscopy; cystoscopy + cytology (VU) |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 280, ImmunoCyt; n = 280, cytology; n = 278, cystoscopy; n = 280, ImmunoCyt+ cystoscopy; n = 280, cystoscopy + cytology) Sensitivity: 85% (ImmunoCyt), 44% (cytology), 84% (cystoscopy), 100% (ImmunoCyt + cystoscopy), 88% (cystoscopy + cytology) Specificity: 88% (ImmunoCyt), 96% (cytology), 98% (cystoscopy), 87% (ImmunoCyt + cystoscopy), 95% (cystoscopy + cytology) |
|
Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Italy |
Enrolled: 179; analysed: 179 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 179 Age (years): mean 65, range 31 to 84 Sex: 151 M, 28 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 179) Sensitivity: 75% Specificity: 55% |
|
Shariat 2006147 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: Austria |
Enrolled: 2951; analysed: 2871 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 2871 Age (years): mean 68, range 21 to 97 Sex: 2166 M, 705 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml and 1–30 U/ml |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 2871) Sensitivity: 57% (NMP22 10 U/ml) Specificity: 81% (NMP22 10 U/ml) |
|
Sharma 1999148 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: USA |
Enrolled: 278; analysed: 278 No previous history of BC: 199; history of BC: 79 Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml for patients with no previous history of BC, ≥ 6 U/ml for patients with previous history of BC; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 199, NMP22 10 U/ml; n = 278, cytology) Sensitivity: 67% (NMP22 10 U/ml), 56% (cytology) Specificity: 86% (NMP22 10 U/ml), 93% (cytology) |
|
Skacel 2003104 Study design: CC-SD Time period: 1996–2001 Country: USA |
Enrolled: 120; analysed: 111 No previous history of BC: 26; history of BC: 94 Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: FISH, chromosomal gain of two or more chromosomes in five or more cells per slide, or in cases of isolated gains of chromosome 3, 7 or 17 when the number of cells with such gain was ≥ 10%, or when 12 or more cells with 9p21 loss was the only abnormality |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 111) Sensitivity: 85% Specificity: 97% |
|
Sokolova 2000105 Study design: C-SD Time period: NS Country: USA |
Enrolled: 179; analysed: 179 No previous history of BC: 86; history of BC: 93 Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: FISH, five or more cells with polysomy; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 179) Sensitivity: 85% Specificity: 92% |
|
Sozen 1999163 Study design: case–control (nhd) Time period: NS Country: Turkey |
Enrolled: 140; analysed: 140 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): mean 71 (cases), 62 (controls), range NS Sex: 127 M, 13 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 5, 6.4, 7, 10, 12, 15 U/ml; cytology (VU or catheterised), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 140) Sensitivity: 73% (NMP22 10 U/ml), 35% (cytology) Specificity: 81% (NMP22 10 U/ml), 90% (cytology) |
|
Stampfer 1998149 Study design: C-SD (three centres) Time period: NS Country: USA |
Enrolled: 231; analysed: 217 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 231 Age (years): mean 68, range NS Sex: 166 M, 65 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 5, 6.4, 7, 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: cystoscopy (n = 274, NMP22 10 U/ml; n = 200, cytology) Sensitivity: 49% (NMP22 10 U/ml), 43% (cytology) Specificity: 92% (NMP22 10 U/ml), 92% (cytology) |
|
Study design: case–control (nhd) Time period: Nov 1999 to May 2004 Country: Japan |
Enrolled: 669; analysed: 669 No previous history of BC: 48; history of BC: 0 Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 12 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment; NMP22 + cytology (VU) |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 669, NMP22; n = 699, cytology; n = 48, NMP22 + cytology) Sensitivity: 58% (NMP22), 44% (cytology), 60% (NMP22 + cytology) Specificity: 80% (NMP22), 100% (Cytology), NS (NMP22 + cytology) |
|
Talwar 2007150 Study design: C-SD Time period: Mar 2004 to Apr 2006 Country: India |
Enrolled: 196; analysed: 196 No previous history of BC: 127; history of BC: 63 Age (years): mean 63, range 39 to 78 Sex: 142 M, 54 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 196) Sensitivity: 67% (NMP22), 22% (cytology) Specificity: 81% (NMP22), 99% (cytology) |
|
Tetu 2005119 Study design: C-SD Time period: May 2000 to Jul 2002 Country: Canada |
Enrolled: 904; analysed: 870 No previous history of BC: NS; history of BC: NS Age (years): NS Sex: NS |
Tests and cut-off used: ImmunoCyt, one green or one red fluorescent cell; cytology (VU), subjective assessment; ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 870) Sensitivity: 74% (ImmunoCyt), 29% (Cytology), 84% (ImmunoCyt + cytology) Specificity: 62% (ImmunoCyt), 98% (cytology), 61% (Immunocyt + cytology) |
|
Tritschler 200780 Study design: C-SD Time period: Sep 2004 to Apr 2005 Country: Germany |
Enrolled: 100; analysed: 100 NMP22; 94 cytology No previous history of BC: 30; history of BC: 70 Age (years): mean 68, range NS Sex: 71 M, 29 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment; cytology (BW), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 100, NMP22; n = 85, cytology (VU); n = 94, cytology (BW)) Sensitivity: 65% (NMP22), 44% (cytology (VU)), 76% (cytology (BW)) Specificity: 40% (NMP22), 78% (cytology (VU)), 62% (cytology (BW)) |
|
Wiener 1998151 Study design: C-SD Time period: Jan 1996 to Oct 1996 Country: Austria |
Enrolled: 291; analysed: 291 No previous history of BC: 190; history of BC: 101 Age (years): mean 62, range 17 to 90 Sex: 199 M, 92 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment; cytology (BW), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 291, NMP22; n = 291, cytology (VU); n = 200, cytology (BW)) Sensitivity: 48% (NMP22), 59% (cytology (VU)), 58% (cytology (BW)) Specificity: 69% (NMP22), 100% (cytology (VU)), 100% (cytology (BW)) |
|
Yoder 2007106 Study design: C-SD Time period: Jun 2002 to Dec 2003 Country: USA |
Enrolled: 250; analysed: 250 No previous history of BC: 0; history of BC: 250 Age (years): median 72, range NS Sex: 187 M, 63 F |
Tests and cut-off used: FISH, more than two chromosomal gains of chromosomes 3, 7 or 17 in at least four analysed cells, or homozygous 9p21 deletion in at least 12 analysed cells, or isolated trisomy of chromosome 3, 7 or 17 in at least 10% of analysed cells |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 250) Sensitivity: 64% Specificity: 73% |
|
Study design: C-SD Time period: Apr 1997 to Feb 1998 Country: USA |
Enrolled: 330; analysed: 330 No previous history of BC: 330; history of BC: 0 Age (years): mean 63, range NS Sex: 254 M, 76 F |
Tests and cut-off used: NMP22 ≥ 10 U/ml; cytology (VU), subjective assessment |
Unit of analysis: patient (n = 330) Sensitivity: 100% (NMP22) 33% (cytology) Specificity: 86% (NMP22) 100% (cytology) |
Appendix 13 Quality assessment results for the biomarker and cytology studies
| Study | Marker | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Q6 | Q7 | Q8 | Q9 | Q10 | Q11 | Q12 | Q13 | Q14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbate 1998154 | N | + | + | + | + | ? | + | ? | + | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Bastacky 1999165 | C | + | + | ? | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Bhuiyan 2003120 | N, C | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | –N, ?C | +N, –C | – |
| Boman 2002155 | N, C | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | + | – |
| Casella 2000121 | N,a C | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Casetta 2000122 | N,a Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | +C, –N | + | – |
| Chahal 2001166 | Ca | + | + | + | + | – | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Chahal 200145 | N,a Ca | + | + | + | + | ? | + | + | + | ? | + | + | +C, –N | + | – |
| Chang 2004156 | N | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | – | + | – |
| Daniely 200794 | F+C | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Del Nero 1999123 | N,a Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | –N, ?C | +N, –C | – |
| Friedrich 200395 | N,a Fa | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Garbar 2007167 | C | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Giannopoulos 2001125 | N | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | – | + | – |
| [Giannopoulos 2000124] | N, Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | –N, +C | + | – |
| Grossman 2005126 | N,a Ca | – | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Grossman 2006127 | N,a Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Guttierez Banos 2001128 | N,a Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | +N, ?C | +N, –C | – |
| Hakenberg 2000168 | C | + | + | ? | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | – | – |
| Halling 200097 | F,a Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | – | + | + | + | + | – |
| Hughes 1999129 | N, C | + | + | – | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | + |
| Junker 200698 | F,a C | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Karakiewicz 2006170 | Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | – | + | + | + | + | – |
| Kipp 200899 | Fa | + | + | – | + | + | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + | – | – |
| Kowalska 2005130 | Na | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | ? | – | – |
| Kumar 2006131 | N,a C,a N+C | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Lahme 2001132 | N,a Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | –N, ?C | +N, –C | – |
| Lee 2001157 | N, Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Lodde 2003109 | I,a C,a I+C | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Lodde 2006110 | I, C, I+C | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| May 2007107 | F,a Ca | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + | – | – |
| Meiers 2007100 | F,a Ca | + | + | ? | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Messing 2005111 | I,a C,a I+C | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | + |
| Mian 1999112 | I,a C,a I+C | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Mian 2000134 | Na | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Mian 2003101 | F,a I,a C,a I+C | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – | – |
| Mian 2006113 | I, C, I+C | + | + | ? | + | – | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Miyanaga 1999135 | N, Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Miyanaga 2003136 | N, Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Moonen 2007102 | F, C, F+C | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | + | + | +F, ?C | +F, –C | – |
| Oge 2001137 | Na | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Olsson 2001114 | I,a C | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | +I, ?C | +I, –C | – |
| Oosterhuis 2002138 | N | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | – | + | – |
| Parekattil 2003158 | N, C | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + | + | ? | +C, –N | + | +C, –N | +C, –N | – |
| Piaton 2003116 | I,a C,a I+C | + | + | + | + | + | + | +C, ?I | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Planz 2005171 | C | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | ? | + | + | + | – | – |
| Ponsky 2001139 | N,a Ca | + | + | ? | + | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | + | + | +N, ?C | +N, –C | – |
| Potter 1999172 | Ca | + | + | ? | – | – | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | ? | – | – |
| Poulakis 2001140 | N,a Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | +C, –N | + | – |
| Raitanen 2002174b | Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | – | + | + | + | + | – |
| Ramakumar 1999159 | N,a Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | ? | + | + | +C, –N | + | – |
| Saad 2002141 | N,a Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | +N, ?C | +N, –C | – |
|
Sanchez-Carbayo 1999161 (primary report) [Sanchez-Carbayo 1999160] (secondary report) |
N, [Na] | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + | ? | + | – |
| Sanchez-Carbayo 2001142 | Na | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | – | + | – |
| Sanchez-Carbayo 2001162 | N,a C | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | ? | + | + | –N, ?C | +N, –C | – |
| Sarosdy 2002108 | F,a C | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | + | +F, ?C | +F, –C | +C, –F |
| Sarosdy 2006103 | F,a C | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | + | +F, ?C | – | – |
| Schmitz–Drager 2008118 | I,a Ca | + | + | ? | + | ? | + | + | ? | ? | + | – | + | + | – |
| Serretta 2000144 | Na | + | + | ? | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Shariat 2006147 | Na | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Sharma 1999148 | N,a Ca | + | + | ? | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | +N, ?C | + | – |
| Skacel 2003104 | Fa | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Sokolova 2000105 | F,a C | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | + | –F, ?C | +F, –C | – |
| Sozen 1999163 | N,a C | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | ? | + | + | –N, ?C | +N, –C | – |
| Stampfer 1998149 | N, C | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | +C, –N | + | – |
| Takeuchi 2004164 | N, C,a N+C | + | + | ? | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Talwar 2007150 | N,a Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | +C, ?N | ? | + | + | +N, ?C | +N, –C | – |
| Tetu 2005119 | I,a C,a I+C | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Tritschler 200780 | N,a Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | +N, ?C | + | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Wiener 1998151 | N,a Ca | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Yoder 2007106 | Fa | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
| Zippe 1999153 | N,a Ca | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | – |
Appendix 14 Studies of biomarkers included in pooled estimates for patient-level analysis and also those reporting specimen and stage/grade
| Study | Marker | Patient | Specimen | pTa | pTaG1 | pTaG1–2 | pTaG2 | pTaG3 | pTa, pT1 | pTa, pT1, CIS | pTa, pT1G3 | pTaG3–pT1 | G1 | G2 | G1–2 | G1 G3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | pT1 | pT1G1 | pT1G2 | pT1G3 | pT1G3 + CIS | pT1–4 | CIS | G3 | pT2 | pT2, pT2a | pT2G2 | pT2G3 | pT2–3 | pT2–4 | ≥ pT2 | pT3 | pT3a, 3b | pT3G3 | pT4 |
| Abbate 1998154 | N | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Bastacky 1999165 | C | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Bhuiyan 2003120 | N, C | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Boman 2002155 | N, C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Casella 2000121 | N,a C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Casetta 2000122b | N,a Ca | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Chahal 2001166 | Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Chahal 200145 | N,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Chang 2004156 | N | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Daniely 200794 | F+C | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Del Nero 1999123 | N,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Friedrich 200395 | N,a Fa | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| [Friedrich 200296] | N | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Garbar 2007167 | C | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Giannopoulos 2001125 | N | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| [Giannopoulos 2000124] | Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Grossman 2005126 | N,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||
| Grossman 2006127 | N,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Guttierez Banos 2001128 | N,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Hakenberg 2000168 | C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Halling 200097 | F,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Hughes 1999129 | N, C | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| [Hutterer 2008169] | N, C | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Junker 200698 | F,a C | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Karakiewicz 2006170 | Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Kipp 200899 | Fa | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Kowalska 2005130 | Na | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Kumar 2006131 | N,a C,a N+C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||
| Lahme 2001132 | N,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||
| Lee 2001157 | N, Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Lodde 2003109 | I,a C,a I+C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Lodde 2006110c | I, C, I+C | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| May 2007107 | F,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Meiers 2007100 | F,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Messing 2005111 | I,a C,a I+C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Mian 1999112 | I,a C,a I+C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Mian 2000134 | Na | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Mian 2003101 | F,a I,a C,a I+C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Mian 2006113 | I, C, I+C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Miyanaga 1999135 | N, Ca | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Miyanaga 2003136 | N, Ca | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Moonen 2007102 | F, C, F+C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Oge 2001137 | Na | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Olsson 2001114 | I,a C | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Oosterhuis 2002138 | N | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Parekattil 2003158 | N, C | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| dPiaton 2003116 | I,a C,a I+C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||
| Planz 2005171 | C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Ponsky 2001139 | N,a Ca | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Potter 1999172 | Ca | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Poulakis 2001140 | N,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||
| dRaitanen 2002174 | Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| dRamakumar 1999159 | N,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Saad 2002141 | N,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Sanchez-Carbayo 1999161 | N | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| [Sanchez-Carbayo 1999160] | Na | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Sanchez-Carbayo 2001142 | Na | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Sanchez-Carbayo 2001162e | N,a C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Sarosdy 2002108 | F,a C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||
| Sarosdy 2006103 | F,a C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||
| Schmitz-Drager 2008118 | I,a Ca | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Serretta 2000144 | Na | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Shariat 2006147 | Na | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Sharma 1999148 | N,a Ca | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Skacel 2003104f | Fa | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Sokolova 2000105 | F,a C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Sozen 1999163 | N,a C | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Stampfer 1998149g | N, C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||
| dTakeuchi 2004164 | N, C,a N+C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Talwar 2007150 | N,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Tetu 2005119 | I,a C,a I+C | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Tritschler 200780h | N,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Wiener 1998151 | N,a Ca | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Yoder 2007106 | Fa | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Zippe 1999153 | N,a Ca | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Abbate 1998154 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Bastacky 1999165 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Bhuiyan 2003120 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Boman 2002155 | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Casella 2000121 | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Casetta 2000122b | |||||||||||||||||||
| Chahal 2001166 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||
| Chahal 200145 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Chang 2004156 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Daniely 200794 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Del Nero 1999123 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Friedrich 200395 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| [Friedrich 200296] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Garbar 2007167 | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Giannopoulos 2001125 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| [Giannopoulos 2000124] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Grossman 2005126 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||
| Grossman 2006127 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||
| Guttierez Banos 2001128 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hakenberg 2000168 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Halling 200097 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hughes 1999129 | |||||||||||||||||||
| [Hutterer 2008169] | |||||||||||||||||||
| Junker 200698 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Karakiewicz 2006170 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Kipp 200899 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Kowalska 2005130 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Kumar 2006131 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Lahme 2001132 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Lee 2001157 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Lodde 2003109 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Lodde 2006110c | |||||||||||||||||||
| May 2007107 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Meiers 2007100 | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Messing 2005111 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Mian 1999112 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Mian 2000134 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Mian 2003101 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Mian 2006113 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Miyanaga 1999135 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Miyanaga 2003136 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Moonen 2007102 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Oge 2001137 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Olsson 2001114 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Oosterhuis 2002138 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Parekattil 2003158 | |||||||||||||||||||
| dPiaton 2003116 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Planz 2005171 | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ponsky 2001139 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Potter 1999172 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Poulakis 2001140 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||
| dRaitanen 2002174 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| dRamakumar 1999159 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Saad 2002141 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Sanchez-Carbayo 1999161 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||
| [Sanchez-Carbayo 1999160] | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Sanchez-Carbayo 2001142 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Sanchez-Carbayo 2001162e | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||
| Sarosdy 2002108 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Sarosdy 2006103 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Schmitz-Drager 2008118 | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Serretta 2000144 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Shariat 2006147 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sharma 1999148 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Skacel 2003104f | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Sokolova 2000105 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sozen 1999163 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Stampfer 1998149g | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| dTakeuchi 2004164 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Talwar 2007150 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Tetu 2005119 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Tritschler 200780h | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||
| Wiener 1998151 | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Yoder 2007106 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Zippe 1999153 |
Appendix 15 Biomarker and cytology test performance for detecting bladder cancer, results table with 2 × 2 data
| Study | Test | Cut-off | Unit of analysis | Number analysed | TP | FP | FN | TN | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Abbate 1998154 No. of patients 109, of whom No previous History of BC NS, History of BC NS, plus benign genitourinary disorders 26 |
NMP22 (Matritech test kit) Laboratory analysis |
12 U/ml | Patient | 135 | 59 | 4 | 50 | 22 | 54 | 85 |
|
Bastacky 1999165 No. of patients 1672, of whom No previous History of BC 752, History of BC 485, other 435 |
Cytology (VU or BW) | Patient | 743 | 115 | 39 | 65 | 524 | 64 | 93 | |
|
Bhuiyan 2003120 No. of patients 233, of whom No previous History of BC NS, History of BC NS |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
≥ 10 U/ml | Specimen | 25 | 94 | |||||
| NMP22 (voided) | 3.6 U/ml | Specimen | 231 | 42 | 66 | 27 | 96 | 61 | 59 | |
| NMP22 (cystoscopically collected) | 3.6 U/ml | Specimen | 54 | 61 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Specimen | 125 | 27 | 3 | 40 | 55 | 40 | 95 | ||
| Cytology (cystoscopically collected) | Specimen | 62 | 83 | |||||||
|
Boman 2002155 No. of patients 250, of whom No previous History of BC NS, History of BC 174 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
≥ 4 U/ml | Specimen? | 297 | 83 | 46 | 71 | 97 | 54 | 68 |
| No previous History of BC | 127 | 42 | 16 | 23 | 46 | 65 | 74 | |||
| pTaG1–2 | 39 | 23 | 16 | 59 | ||||||
| pTaG3–pT1 | 20 | 13 | 7 | 65 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≤ 10 mm | 17 | 11 | 6 | 65 | ||||||
| 11–20 mm | 24 | 13 | 11 | 54 | ||||||
| 21–30 mm | 15 | 11 | 4 | 73 | ||||||
| > 30 mm | 9 | 8 | 1 | 89 | ||||||
| Previous History of BC | 170 | 41 | 30 | 48 | 51 | 46 | 63 | |||
| pTaG1–2 | 68 | 25 | 43 | 37 | ||||||
| pTaG3–pT1 | 13 | 10 | 3 | 77 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 75 | ||||||
| ≤ 10 mm | 73 | 30 | 43 | 41 | ||||||
| 11–20 mm | 12 | 8 | 4 | 67 | ||||||
| > 21 mm | 5 | 3 | 2 | 60 | ||||||
| Cytology (BW) | Specimen? | 293 | 60 | 12 | 90 | 131 | 40 | 93 | ||
| No previous History of BC | 125 | 26 | 4 | 37 | 58 | 41 | 94 | |||
| pTaG1–2 | 38 | 8 | 30 | 21 | ||||||
| pTaG3–pT1 | 19 | 13 | 6 | 68 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| ≤ 10 mm | 17 | 6 | 11 | 35 | ||||||
| 11–20 mm | 24 | 8 | 16 | 33 | ||||||
| 21–30 mm | 9 | 5 | 4 | 55 | ||||||
| > 30 mm | 8 | 7 | 1 | 87 | ||||||
| Previous History of BC | 168 | 34 | 8 | 53 | 73 | 39 | 92 | |||
| pTaG1–2 | 67 | 20 | 47 | 30 | ||||||
| pTaG3–pT1 | 12 | 9 | 3 | 75 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 63 | ||||||
| ≤ 10 mm | 74 | 22 | 52 | 30 | ||||||
| 11–20 mm | 11 | 10 | 1 | 91 | ||||||
| > 21 mm | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
|
Casella 2000121 No. of patients 235, of whom No previous History of BC NS, History of BC NS |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
10 U/ml | Patient | 235 | 67 | 17 | 63 | 88 | 52 | 84 |
| Superficial (non-invasive) | 77 | 28 | 49 | 36 | ||||||
| G1 | 42 | 13 | 29 | 31 | ||||||
| G2 | 50 | 28 | 22 | 56 | ||||||
| G3 | 38 | 26 | 12 | 68 | ||||||
| Cytology (BW) | Patient | 200 | 50 | 11 | 45 | 94 | 53 | 90 | ||
| Superficial (non-invasive) | 65 | 25 | 40 | 38 | ||||||
| G1 | 30 | 9 | 21 | 30 | ||||||
| G2 | 38 | 19 | 19 | 50 | ||||||
| G3 | 24 | 22 | 2 | 92 | ||||||
|
[Shariat 2003145] No. of patients 229, of whom No previous History of BC NS, History of BC NS |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
≥ 10 U/ml | Patient | 229 | 85 | 25 | 37 | 82 | 70 | 77 |
| Cytology (BW) | Only high-grade atypia was considered positive | Patient | 191 | 50 | 10 | 43 | 88 | 54 | 90 | |
|
[Shariat 2004146] No. of patients 209, of whom No previous History of BC NS, History of BC NS, controls 92 |
NMP22 | ≥ 10 U/ml | Patient | 209 | 58 | 14 | 59 | 78 | 50 | 85 |
| pTa | 65 | 23 | 42 | 35 | ||||||
| pT1 | 31 | 23 | 8 | 74 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 17 | 12 | 5 | 71 | ||||||
| CIS | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 | ||||||
| G1 | 41 | 12 | 29 | 29 | ||||||
| G2 | 41 | 22 | 19 | 54 | ||||||
| G3 | 35 | 24 | 11 | 69 | ||||||
| Cytology (BW) | Only high-grade atypia was considered positive | Patient | 174 | 46 | 8 | 43 | 77 | 52 | 91 | |
| pTa | 65 | 23 | 42 | 35 | ||||||
| pT1 | 31 | 25 | 6 | 81 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 17 | 16 | 1 | 92 | ||||||
| CIS | 4 | 3 | 1 | 75 | ||||||
| G1 | 41 | 12 | 29 | 29 | ||||||
| G2 | 41 | 18 | 23 | 45 | ||||||
| G3 | 35 | 33 | 2 | 95 | ||||||
|
Casetta 2000122 No. of patients 196, of whom No previous History of BC 94, History of BC 102 |
NMP22 | 11 U/ml | Patient | 196 | 84 | 20 | 66 | 26 | 56 | 57 |
| NMP22 | 12 U/ml | No previous History of BC | 94 | 35 | 8 | 45 | 6 | 44 | 43 | |
| NMP22 | 10 U/ml | History of BC | 102 | 45 | 12 | 25 | 20 | 64 | 63 | |
| Cytology (VU) | Dubious cases considered positive | Patient | 196 | 110 | 9 | 40 | 37 | 73 | 80 | |
| No previous History of BC | 94 | 61 | 1 | 19 | 13 | 76 | 93 | |||
| History of BC | 102 | 49 | 8 | 21 | 24 | 70 | 75 | |||
| Cytology (VU) | Dubious cases considered negative | Patient | 196 | 88 | 5 | 62 | 41 | 59 | 89 | |
| No previous History of BC | 94 | 48 | 1 | 32 | 13 | 60 | 93 | |||
| History of BC | 102 | 40 | 4 | 30 | 28 | 58 | 88 | |||
|
Chahal 2001166 No. of patients 285, of whom No previous History of BC NS, History of BC NS |
Cytology (VU) | Suspicious classed with positive | Patient | 285 | 23 | 14 | 24 | 224 | 49 | 94 |
| pTaG1 | 11 | 3 | 8 | 27 | ||||||
| pTaG2 | 12 | 3 | 9 | 25 | ||||||
| pTaG3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 67 | ||||||
| pT1G1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||
| pT1G2 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 80 | ||||||
| pT1G3 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 67 | ||||||
| pT1G3 and CIS | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pT2G2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pT2G3 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 60 | ||||||
| pT3G3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
|
Chahal 200145 No. of patients 211, of whom No previous History of BC 96, History of BC 115 |
NMP22 (test kit) Laboratory analysis |
10 U/ml | Patient | 211 | 11 | 14 | 22 | 164 | 33 | 92 |
| pTa | 22 | 2 | 20 | 9 | ||||||
| pT1 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 43 | ||||||
| pT2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 33 | ||||||
| pT3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 19 | 1 | 18 | 5 | ||||||
| G2 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 33 | ||||||
| G3 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 50 | ||||||
| No previous History of BC | 96 | 7 | 7 | 9 | 73 | 44 | 91 | |||
| Previous History of BC | 115 | 4 | 8 | 13 | 90 | 24 | 92 | |||
| Cytology (VU) (these patients already included for cytology in Chahal 2001166?) | Patient | 211 | 8 | 5 | 25 | 173 | 24 | 97 | ||
| pTa | 22 | 4 | 18 | 18 | ||||||
| pT1 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 72 | ||||||
| pT2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 33 | ||||||
| pT3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 19 | 3 | 16 | 16 | ||||||
| G2 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 33 | ||||||
| G3 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 67 | ||||||
| No previous History of BC | 96 | 5 | 4 | 11 | 76 | 31 | 95 | |||
| Previous History of BC | 115 | 2 | 1 | 15 | 97 | 13 | 99 | |||
|
Chang 2004156 No. of patients 399, of whom benign urothelial disease or urogenital cancer 331 (11 BC), No previous History of BC NS, History of BC NS |
NMP22 (Sancordon) Laboratory analysis |
≥ 7.5 U/ml | Patient | 314 | 4 | 52 | 7 | 251 | 36 | 83 |
|
Daniely 200794 No. of patients 115, of whom No previous History of BC 49, History of BC 66 |
FISH (UroVysion) + cytology (VU) | FISH: minimum of four cells with gains of two or more chromosomes or ≥ 12 cells with homozygous loss of the 9p21 locus | Patient | 115 | 12 | 51 | 0 | 52 | 100 | 50 |
|
Del Nero 1999123 No. of patients 105, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 105 |
NMP22 Laboratory analysis |
10 U/ml | Patient | 105 | 62 | 4 | 13 | 26 | 83 | 87 |
| pTa | 30 | 20 | 10 | 67 | ||||||
| pT1 | 45 | 42 | 3 | 93 | ||||||
| G1 | 29 | 20 | 9 | 69 | ||||||
| G2 | 36 | 34 | 2 | 94 | ||||||
| G3 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 80 | ||||||
| 6 U/ml | Patient | 105 | 69 | 7 | 6 | 23 | 92 | 76 | ||
| pTa | 30 | 25 | 5 | 83 | ||||||
| pT1 | 45 | 44 | 1 | 98 | ||||||
| G1 | 29 | 25 | 4 | 86 | ||||||
| G2 | 36 | 35 | 1 | 97 | ||||||
| G3 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 90 | ||||||
| 5 U/ml | Patient | 105 | 70 | 11 | 5 | 19 | 94 | 63 | ||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 105 | 35 | 5 | 40 | 25 | 47 | 83 | ||
| pTa | 30 | 6 | 24 | 20 | ||||||
| pT1 | 45 | 29 | 16 | 64 | ||||||
| G1 | 29 | 11 | 18 | 38 | ||||||
| G2 | 36 | 16 | 20 | 44 | ||||||
| G3 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 80 | ||||||
|
Friedrich 200395 No. of patients 103, of whom No previous History of BC 55, History of BC 48 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
≥ 10 U/ml | Patient | 103 | 32 | 20 | 14 | 37 | 70 | 65 |
| pTa | 21 | 11 | 10 | 52 | ||||||
| pT1 | 18 | 17 | 1 | 94 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| CIS | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 43 | ||||||
| G2 | 28 | 20 | 8 | 70 | ||||||
| G3 | 11 | 9 | 2 | 83 | ||||||
| FISH (UroVysion) | If 20% of the cells had a gain of two or more chromosomes (3, 7 or 17) or 40% of the cells had a gain of one chromosome or 40% loss of 9p21 locus | Patient | 103 | 31 | 6 | 15 | 51 | 67 | 89 | |
| pTa | 21 | 13 | 8 | 62 | ||||||
| pT1 | 18 | 12 | 6 | 67 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| CIS | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 57 | ||||||
| G2 | 28 | 18 | 10 | 63 | ||||||
| G3 | 11 | 9 | 2 | 83 | ||||||
|
[Friedrich 200296] No. of patients 115, of whom No previous History of BC 70, History of BC 45 |
NMP22 | 10 U/ml | Specimen | 146 | 37 | 32 | 17 | 60 | 69 | 65 |
| pTa | 25 | 13 | 12 | 52 | ||||||
| pT1 | 20 | 18 | 2 | 90 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 75 | ||||||
| CIS | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||
| G1 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 43 | ||||||
| G2 | 31 | 22 | 9 | 71 | ||||||
| G3 | 16 | 12 | 4 | 75 | ||||||
|
Garbar 2007167 No. of patients 139, of whom No previous History of BC NS (82 BW), History of BC NS (510 BW) |
Cytology (BW) | Suspicious classed as positive | Specimen | 592 | 98 | 22 | 65 | 407 | 60 | 95 |
| CIS | 50 | 38 | 12 | 76 | ||||||
| Low-grade atypia | 59 | 22 | 37 | 37 | ||||||
| High-grade atypia | 14 | 3 | 11 | 21 | ||||||
|
Giannopoulos 2001125 No. of patients 234, of whom No previous History of BC 118, History of BC 95, healthy volunteers 21 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
> 8 U/ml | Patient (excluding healthy volunteers) | 213 | 75 | 27 | 43 | 68 | 64 | 72 |
| pTa | 57 | 30 | 27 | 53 | ||||||
| pT1 | 32 | 21 | 11 | 66 | ||||||
| pT2–4 | 20 | 18 | 2 | 90 | ||||||
| CIS | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| G1 | 30 | 15 | 15 | 50 | ||||||
| G2 | 45 | 25 | 20 | 56 | ||||||
| G3 | 43 | 35 | 8 | 81 | ||||||
| No previous History of BC | 68 | 50 | 18 | 74 | ||||||
| History of BC | 50 | 28 | 22 | 56 | ||||||
| Healthy volunteers | 21 | 2 | 19 | 90 | ||||||
| Urological disease | 50 | 16 | 34 | 68 | ||||||
| No evidence of disease | 45 | 11 | 34 | 76 | ||||||
| Excluding stones, urinary tract infection and urological malignancies other than BC | 211 | 75 | 18 | 43 | 75 | 64 | 81 | |||
|
[Giannopoulos 2000124] No. of patients 168, of whom No previous History of BC 85, History of BC 62, healthy volunteers 21 |
NMP22 | > 8 U/ml | Patient | 168 | 62 | 18 | 37 | 51 | 63 | 74 |
| pTa | 49 | 26 | 23 | 53 | ||||||
| pT1 | 26 | 17 | 9 | 65 | ||||||
| pT2–T4 | 16 | 14 | 2 | 88 | ||||||
| CIS | 5 | 4 | 1 | 80 | ||||||
| G1 | 26 | 14 | 12 | 54 | ||||||
| G2 | 39 | 21 | 18 | 54 | ||||||
| G3 | 34 | 27 | 7 | 79 | ||||||
| No evidence of disease | 25 | 7 | 18 | 72 | ||||||
| Urological disease | 23 | 9 | 14 | 72 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient (excluding 21 healthy volunteers) | 147 | 38 | 4 | 61 | 44 | 38 | 92 | ||
| pTa | 49 | 8 | 41 | 16 | ||||||
| pT1 | 26 | 12 | 14 | 46 | ||||||
| pT2–T4 | 16 | 11 | 5 | 69 | ||||||
| CIS | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 26 | 2 | 24 | 8 | ||||||
| G2 | 39 | 10 | 29 | 26 | ||||||
| G3 | 34 | 26 | 8 | 77 | ||||||
| No evidence of disease | 25 | 4 | 21 | 84 | ||||||
| Urological disease | 9 | 0 | 9 | 100 | ||||||
|
Grossman 2005126 No. of patients 1331, of whom No previous History of BC 1331, History of BC 0 |
NMP22 (Matritech) BladderChek | 10 U/ml | Patient | 1331 | 44 | 179 | 35 | 1073 | 56 | 86 |
| pTa | 30 | 14 | 16 | 47 | ||||||
| pT1 | 27 | 13 | 14 | 48 | ||||||
| pTa, T1 | 62 | 31 | 31 | 50 | ||||||
| pT2, T2a | 6 | 6 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pT3a, T3b | 4 | 3 | 1 | 75 | ||||||
| pT2–T3 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 90 | ||||||
| CIS | 5 | 4 | 1 | 80 | ||||||
| pTx | 7 | 4 | 3 | 57 | ||||||
| G1 | 27 | 13 | 14 | 48 | ||||||
| G2 | 18 | 9 | 9 | 50 | ||||||
| G3 | 25 | 18 | 7 | 72 | ||||||
| Gx (grade unknown) | 9 | 4 | 5 | 44 | ||||||
| No urinary tract disease | 567 | 55 | 512 | 90 | ||||||
| Benign prostatic hypertrophy/prostatitis | 280 | 49 | 231 | 83 | ||||||
| Cystitis/inflammation/trigonitis/urinary tract infection | 125 | 28 | 97 | 78 | ||||||
| Erythema | 51 | 9 | 42 | 82 | ||||||
| Hyperplasia/squamous metaplasia/cysts and polyps | 53 | 12 | 41 | 77 | ||||||
| Calculi | 40 | 11 | 29 | 73 | ||||||
| Trabeculations | 217 | 42 | 175 | 81 | ||||||
| Other benign diseases, kidney and genitourinary | 220 | 41 | 179 | 81 | ||||||
| Other cancer history, non-bladder | 8 | 1 | 7 | 88 | ||||||
| Other active cancer, non-bladder | 38 | 5 | 33 | 87 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 1287 | 12 | 10 | 64 | 1201 | 16 | 99 | ||
| pTa | 28 | 2 | 26 | 7 | ||||||
| pT1 | 27 | 5 | 22 | 19 | ||||||
| pTa, T1 | 60 | 10 | 50 | 17 | ||||||
| pT2, T2a | 6 | 2 | 4 | 33 | ||||||
| pT3a, T3b | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | ||||||
| pT2–T3 | 9 | 2 | 7 | 22 | ||||||
| CIS | 5 | 3 | 2 | 60 | ||||||
| pTx | 7 | 0 | 7 | 0 | ||||||
| G1 | 25 | 0 | 25 | 0 | ||||||
| G2 | 18 | 3 | 15 | 17 | ||||||
| G3 | 24 | 9 | 15 | 38 | ||||||
| Gx (grade unknown) | 9 | 0 | 9 | 0 | ||||||
| Cystoscopy (NS) | Patient | 79 | 70 | 9 | 89 | |||||
| NMP22 + cystoscopy | Patient | 79 | 74 | 5 | 94 | |||||
|
Grossman 2006127 No. of patients 668, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 668 |
NMP22 (Matritech) BladderChek | ≥ 10 U/ml | Patient | 668 | 51 | 72 | 52 | 493 | 50 | 87 |
| pTa | 50 | 18 | 32 | 36 | ||||||
| pT1 | 17 | 11 | 6 | 65 | ||||||
| pT2 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 88 | ||||||
| pT3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pT4 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 8 | 4 | 4 | 50 | ||||||
| pTx | 17 | 8 | 9 | 47 | ||||||
| pTa, pT1, CIS | 75 | 33 | 42 | 44 | ||||||
| pTa, pT1, CIS, G1 | 53 | 19 | 34 | 36 | ||||||
| pT2–T4 | 11 | 10 | 1 | 91 | ||||||
| G1 | 38 | 12 | 26 | 32 | ||||||
| G2 | 16 | 7 | 9 | 44 | ||||||
| G3 | 32 | 24 | 8 | 75 | ||||||
| All grades | 86 | 43 | 43 | 50 | ||||||
| Poorly differentiated muscle-invasive G3, T2–T4 | 33 | 24 | 9 | 73 | ||||||
| No evidence of urinary tract disease | 264 | 28 | 236 | 89 | ||||||
| Benign prostatic hyperplasia/prostatitis | 120 | 17 | 103 | 86 | ||||||
| Erythema/cystitis/inflammation | 82 | 12 | 70 | 85 | ||||||
| Urinary tract infection | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| Hyperplasia/squamous metaplasia/cyst/polyp/carbuncle | 23 | 2 | 21 | 91 | ||||||
| Calculi | 6 | 1 | 5 | 83 | ||||||
| Trabeculations | 49 | 6 | 43 | 88 | ||||||
| Diverticulum/pouch/cellule | 18 | 3 | 15 | 83 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 650 | 12 | 17 | 86 | 535 | 12 | 97 | ||
| pTa | 48 | 3 | 45 | 6 | ||||||
| pT1 | 16 | 2 | 14 | 13 | ||||||
| pT2 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 0 | ||||||
| pT3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||
| pT4 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | ||||||
| CIS | 8 | 3 | 5 | 38 | ||||||
| pTx | 16 | 4 | 12 | 25 | ||||||
| pTa, pT1, CIS | 72 | 8 | 64 | 11 | ||||||
| pTa, pT1, CIS, G1 | 50 | 2 | 48 | 4 | ||||||
| pT2–T4 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0 | ||||||
| G1 | 37 | 2 | 35 | 5 | ||||||
| G2 | 14 | 0 | 14 | 0 | ||||||
| G3 | 31 | 6 | 25 | 19 | ||||||
| All grades | 82 | 8 | 74 | 10 | ||||||
| Poorly differentiated muscle-invasive G3, T2–T4 | 32 | 6 | 26 | 19 | ||||||
| Cystoscopy (NS) | Patient | 103 | 94 | 9 | 91 | |||||
| G3 | 32 | 24 | 8 | 75 | ||||||
| NMP22 + cystoscopy | Patient | 103 | 102 | 1 | 99 | |||||
| G3 | 32 | 31 | 1 | 97 | ||||||
| Cytology + cystoscopy | Patient | 103 | 97 | 6 | 94 | |||||
|
Gutierrez Banos 2001128 No. of patients 150, of whom No previous History of BC 64, History of BC 86 |
NMP22 Laboratory analysis |
10 U/ml | Patient | 150 | 58 | 7 | 18 | 67 | 76 | 91 |
| pTa | 16 | 8 | 8 | 50 | ||||||
| pT1 | 46 | 39 | 7 | 80 | ||||||
| pT2–T4 | 14 | 13 | 1 | 93 | ||||||
| G1 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 50 | ||||||
| G2 | 29 | 20 | 9 | 69 | ||||||
| G3 | 31 | 30 | 1 | 97 | ||||||
|
NMP22 Laboratory analysis |
6 U/ml | Patient | 150 | 64 | 10 | 12 | 64 | 84 | 87 | |
| pTa | 16 | 11 | 5 | 69 | ||||||
| pT1 | 46 | 39 | 7 | 85 | ||||||
| pT2–T4 | 14 | 14 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 16 | 11 | 5 | 69 | ||||||
| G2 | 29 | 22 | 7 | 76 | ||||||
| G3 | 31 | 31 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 150 | 53 | 5 | 23 | 69 | 70 | 93 | ||
| pTa | 16 | 6 | 10 | 38 | ||||||
| pT1 | 46 | 35 | 1 | 76 | ||||||
| pT2–T4 | 14 | 12 | 2 | 86 | ||||||
| G1 | 16 | 7 | 9 | 44 | ||||||
| G2 | 29 | 18 | 11 | 62 | ||||||
| G3 | 31 | 28 | 3 | 90 | ||||||
| Cystoscopy (R) | Patient | 150 | 76 | 8 | 0 | 66 | 100 | 89 | ||
|
Hakenberg 2000168 No. of patients 374, of whom No previous History of BC 374, History of BC 0 |
Cytology (VU) | Specimen | 417 | 257 | 16 | 80 | 64 | 76 | 80 | |
| CIS | 16 | 13 | 3 | 81 | ||||||
| G1 | 57 | 27 | 30 | 47 | ||||||
| G2 | 166 | 130 | 36 | 78 | ||||||
| G3 | 98 | 87 | 11 | 89 | ||||||
| Undergoing primary TUR | 326 | 213 | 11 | 65 | 37 | 77 | 77 | |||
| CIS | 11 | 8 | 3 | 73 | ||||||
| G1 | 48 | 26 | 22 | 54 | ||||||
| G2 | 136 | 106 | 30 | 78 | ||||||
| G3 | 83 | 73 | 10 | 88 | ||||||
| Undergoing secondary TUR | 91 | 44 | 5 | 15 | 27 | 75 | 84 | |||
| CIS | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 9 | 1 | 8 | 11 | ||||||
| G2 | 30 | 24 | 6 | 80 | ||||||
| G3 | 15 | 14 | 1 | 93 | ||||||
|
Halling 200097 No. of patients 265, of whom No previous History of BC 115, previous History of BC 150 |
FISH (UroVysion) | Five or more cells with polysomy | Patient | 151 | 59 | 3 | 14 | 75 | 81 | 96 |
| pTa | 37 | 24 | 13 | 65 | ||||||
| pT1–T4 | 19 | 18 | 1 | 95 | ||||||
| CIS | 17 | 17 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 11 | 4 | 7 | 36 | ||||||
| G2 | 25 | 19 | 6 | 76 | ||||||
| G3 | 37 | 36 | 1 | 97 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Suspicious classed with positive | Patient | 118 | 40 | 1 | 29 | 48 | 58 | 98 | |
| pTa | 36 | 17 | 19 | 47 | ||||||
| pT1–T4 | 15 | 9 | 6 | 60 | ||||||
| CIS | 18 | 14 | 4 | 78 | ||||||
| G1 | 11 | 3 | 8 | 27 | ||||||
| G2 | 24 | 13 | 11 | 54 | ||||||
| G3 | 34 | 24 | 10 | 71 | ||||||
|
Hughes 1999129 No. of patients 107, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 107 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
≥ 6.4 U/ml | Specimen | 128 | 25 | 16 | 28 | 59 | 47 | 79 |
| Cytology (VU) | Indeterminate results were classed as negative | Specimen | 128 | 32 | 31 | 21 | 44 | 60 | 58 | |
|
Junker 200698 No. of patients 141, of whom No previous History of BC NS, History of BC NS |
FISH (UroVysion) | Five or more cells showed gains of more than one chromosome (3, 7 or 17), or ≥ 10 cells showed gains of a single chromosome (3, 7 or 17), or ≥ 10 cells showed homozygous loss of 9p21 locus | Patient | 121 | 57 | 5 | 38 | 21 | 60 | 81 |
| Cytology (NS) | Patient | 109 | 21 | 2 | 66 | 20 | 24 | 91 | ||
|
Karakiewicz 2006170 No. of patients 2686, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 2686 |
Cytology (VU) | Patient | 2542 | 404 | 87 | 494 | 1557 | 45 | 95 | |
| pTa–T1, CIS | 2542 | 284 | 92 | 408 | 1758 | 41 | 95 | |||
| ≥ pT2 | 2542 | 122 | 117 | 84 | 2219 | 59 | 95 | |||
| G1–G2 | 2542 | 211 | 97 | 393 | 1841 | 35 | 95 | |||
| G3 | 2542 | 197 | 112 | 97 | 2136 | 67 | 95 | |||
|
[Hutterer 2008169] No. of patients 1731, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 1731 |
NMP22 Laboratory analysis |
10 U/ml | Patients with non-TCC recurrence | 1731 | 62 | 301 | 18 | 1350 | 78 | 82 |
| Cytology (VU) | Patients with non-TCC recurrence | 1731 | 16 | 86 | 64 | 1565 | 20 | 95 | ||
|
Kipp 200899 No. of patients 124, of whom No previous History of BC 41, History of BC 81, previous cancer of the upper urinary tract 2 |
FISH (UroVysion) | Four or more cells had polysomic signal patterns (gain of two or more of the four chromosomes in an individual cell), ≥ 10 cells demonstrated tetrasomy (four signal patterns for all four probes) or > 20% of the cells demonstrated 9p21 homozygous deletion (loss of the two 9p21 signals) | Patient | 124 | 53 | 5 | 32 | 34 | 62 | 87 |
| pTaG1 | 22 | 7 | 15 | 32 | ||||||
| pTaG2 | 11 | 7 | 4 | 64 | ||||||
| pTaG3 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 75 | ||||||
| pT1 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 80 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 16 | 14 | 2 | 88 | ||||||
| CIS | 21 | 13 | 8 | 62 | ||||||
| Small cell carcinoma | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| With muscle-invasive BC | 17 | 15 | 2 | 88 | ||||||
| Cystoscopy (NS) | Suspicious classed with positive | Patient | 124 | 57 | 6 | 28 | 33 | 67 | 85 | |
| pTaG1 | 22 | 21 | 1 | 96 | ||||||
| pTaG2 | 11 | 9 | 2 | 82 | ||||||
| pTaG3 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 75 | ||||||
| pT1 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 16 | 13 | 3 | 81 | ||||||
| CIS | 21 | 16 | 5 | 76 | ||||||
| Small cell carcinoma | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| With muscle-invasive BC | 17 | 10 | 7 | 59 | ||||||
| FISH (UroVysion) + cystoscopy | Patient | 124 | 74 | 8 | 11 | 31 | 87 | 79 | ||
| With muscle-invasive BC | 17 | 16 | 1 | 94 | ||||||
|
Kowalska 2005130 No. of patients 98, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 98 |
NMP22 Laboratory analysis |
10 U/ml? | Patient | 98 | 10 | 43 | 9 | 36 | 53 | 46 |
|
Kumar 2006131 No. of patients 131, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 131 |
NMP22 (Matritech) BladderChek | 10 U/ml | Patient | 131 | 39 | 19 | 7 | 66 | 85 | 78 |
| pTa | 21 | 16 | 5 | 76 | ||||||
| pT1 | 17 | 15 | 2 | 88 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 11 | 9 | 2 | 82 | ||||||
| G2 | 22 | 18 | 4 | 81 | ||||||
| G3 | 13 | 12 | 1 | 92 | ||||||
| Low risk (pTaG1–G2) | 18 | 15 | 3 | 83 | ||||||
| High risk (pTaG3, T1) | 20 | 16 | 4 | 80 | ||||||
| ≥ invasive pT2 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 131 | 19 | 3 | 27 | 82 | 41 | 96 | ||
| pTa | 21 | 3 | 18 | 14 | ||||||
| pT1 | 17 | 8 | 9 | 47 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 11 | 2 | 9 | 19 | ||||||
| G2 | 22 | 6 | 16 | 27 | ||||||
| G3 | 13 | 11 | 2 | 85 | ||||||
| Low risk (pTaG1–G2) | 18 | 2 | 16 | 11 | ||||||
| High risk (pTaG3, T1) | 20 | 9 | 11 | 45 | ||||||
| ≥ invasive pT2 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| NMP22 + cytology (VU) | Patient | 46 | 42 | 4 | 91 | |||||
|
Lahme 2001132 No. of patients 169, of whom No previous History of BC 40, History of BC 44, other 25, healthy controls 60 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
10 U/ml | Patient (excluding healthy controls) | 109 | 25 | 27 | 15 | 42 | 63 | 61 |
| With BC or being followed up | 84 | 25 | 15 | 15 | 29 | 63 | 66 | |||
| Ta | 22 | 9 | 13 | 41 | ||||||
| T1 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 63 | ||||||
| Ta-T1 | 30 | 14 | 16 | 47 | ||||||
| T2–4 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 90 | ||||||
| G1 | 25 | |||||||||
| G2 | 68 | |||||||||
| G3 | 100 | |||||||||
| Healthy controls | 60 | 4 | 56 | 93 | ||||||
| With benign lesions | 25 | 12 | 13 | 51 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient (excluding healthy controls) | 109 | 18 | 5 | 22 | 64 | 45 | 93 | ||
| With BC or being followed up | 84 | 18 | 5 | 22 | 39 | 45 | 89 | |||
| Ta | 22 | 6 | 16 | 27 | ||||||
| T1 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 63 | ||||||
| Ta-T1 | 30 | 11 | 19 | 37 | ||||||
| T2–4 | 10 | 7 | 3 | 70 | ||||||
| G1 | 20 | |||||||||
| G2 | 59 | |||||||||
| G3 | 67 | |||||||||
| Healthy controls | 60 | 0 | 60 | 100 | ||||||
| With benign lesions | 25 | 0 | 25 | 100 | ||||||
|
Lee 2001157 No. of patients 106, of whom No previous History of BC NS, History of BC NS (cases 70; controls 36 with History of BC) |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
7.7 U/ml | Patient | 106 | 53 | 10 | 17 | 26 | 76 | 72 |
| pTa | 23 | 13 | 10 | 57 | ||||||
| pT1 | 23 | 18 | 5 | 78 | ||||||
| p ≥ T2 | 24 | 22 | 2 | 92 | ||||||
| G1 | 19 | 11 | 8 | 58 | ||||||
| G2 | 34 | 27 | 7 | 79 | ||||||
| G3 | 17 | 15 | 2 | 88 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 106 | 39 | 4 | 31 | 32 | 56 | 89 | ||
| pTa | 23 | 8 | 15 | 35 | ||||||
| pT1 | 23 | 13 | 10 | 57 | ||||||
| p ≥ T2 | 24 | 18 | 6 | 75 | ||||||
| G1 | 19 | 4 | 15 | 21 | ||||||
| G2 | 34 | 22 | 12 | 65 | ||||||
| G3 | 17 | 13 | 4 | 77 | ||||||
|
Lodde 2003109 No. of patients 235, of whom No previous History of BC 98, History of BC 137 |
ImmunoCyt | At least one green or one red fluorescent cell | Patient | 225 | 89 | 40 | 13 | 83 | 87 | 67 |
| pTa | 62 | 50 | 12 | 81 | ||||||
| pT1 | 16 | 15 | 1 | 94 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 11 | 10 | 1 | 91 | ||||||
| CIS | 13 | 13 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 43 | 35 | 8 | 81 | ||||||
| G2 | 28 | 25 | 3 | 89 | ||||||
| G3 | 31 | 29 | 2 | 94 | ||||||
| No previous History of BC | 91 | 47 | 10 | 4 | 30 | 92 | 75 | |||
| pTa | 29 | 25 | 4 | 86 | ||||||
| pT1 | 13 | 13 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| CIS | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 20 | 17 | 3 | 85 | ||||||
| G2 | 18 | 18 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G3 | 13 | 12 | 1 | 92 | ||||||
| History of BC | 134 | 42 | 30 | 9 | 53 | 82 | 64 | |||
| pTa | 33 | 25 | 8 | 76 | ||||||
| pT1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 67 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 10 | 10 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 23 | 18 | 5 | 78 | ||||||
| G2 | 10 | 7 | 3 | 70 | ||||||
| G3 | 18 | 17 | 1 | 94 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 225 | 42 | 7 | 60 | 116 | 41 | 94 | ||
| pTa | 62 | 7 | 55 | 11 | ||||||
| pT1 | 16 | 14 | 2 | 88 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 11 | 10 | 1 | 91 | ||||||
| CIS | 13 | 12 | 1 | 92 | ||||||
| G1 | 43 | 2 | 41 | 5 | ||||||
| G2 | 28 | 12 | 16 | 43 | ||||||
| G3 | 31 | 28 | 3 | 90 | ||||||
| No previous History of BC | 91 | 22 | 2 | 29 | 38 | 43 | 95 | |||
| pTa | 29 | 4 | 25 | 14 | ||||||
| pT1 | 13 | 11 | 2 | 85 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| CIS | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 20 | 1 | 19 | 5 | ||||||
| G2 | 18 | 10 | 8 | 56 | ||||||
| G3 | 13 | 11 | 2 | 85 | ||||||
| History of BC | 134 | 20 | 5 | 31 | 78 | 39 | 94 | |||
| pTa | 33 | 3 | 30 | 9 | ||||||
| pT1 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 10 | 9 | 1 | 90 | ||||||
| G1 | 23 | 1 | 22 | 4 | ||||||
| G2 | 10 | 2 | 8 | 20 | ||||||
| G3 | 18 | 17 | 1 | 94 | ||||||
| ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) | Patient | 225 | 92 | 40 | 10 | 83 | 90 | 68 | ||
| pTa | 62 | 52 | 10 | 84 | ||||||
| pT1 | 16 | 16 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 11 | 11 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 13 | 13 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 43 | 35 | 8 | 81 | ||||||
| G2 | 28 | 27 | 1 | 55 | ||||||
| G3 | 31 | 31 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| No previous History of BC | 91 | 48 | 10 | 3 | 94 | 75 | ||||
| pTa | 29 | 25 | 4 | 86 | ||||||
| pT1 | 13 | 13 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 20 | 17 | 3 | 85 | ||||||
| G2 | 18 | 18 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G3 | 13 | 13 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| History of BC | 134 | 44 | 30 | 7 | 53 | 86 | 64 | |||
| pTa | 33 | 27 | 6 | 82 | ||||||
| pT1 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 10 | 10 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 23 | 18 | 5 | 78 | ||||||
| G2 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 90 | ||||||
| G3 | 18 | 18 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
|
Lodde 2006110 No. of patients 216, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 216 |
ImmunoCyt | At least one green or one red fluorescent cell | Specimen | 334 | 85 | 51 | 16 | 182 | 71 | 78 |
| Low-risk group | 132 | 26 | 21 | 4 | 81 | 87 | 79 | |||
| Intermediate-risk group | 124 | 35 | 19 | 8 | 62 | 81 | 77 | |||
| High-risk group | 78 | 24 | 11 | 4 | 39 | 86 | 78 | |||
| Cytology (VU) | Specimen | 277 | 49 | 9 | 52 | 167 | 49 | 95 | ||
| Low-risk group | 132 | 5 | 1 | 25 | 101 | 17 | 99 | |||
| Intermediate-risk group | 67 | 20 | 4 | 23 | 20 | 47 | 83 | |||
| High-risk group | 78 | 24 | 4 | 4 | 46 | 86 | 92 | |||
| ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) | Specimen | 334 | 87 | 52 | 14 | 181 | 86 | 78 | ||
| Low-risk group | 132 | 26 | 21 | 4 | 81 | 87 | 79 | |||
| Intermediate-risk group | 124 | 36 | 20 | 7 | 61 | 84 | 75 | |||
| High-risk group | 78 | 25 | 11 | 3 | 39 | 89 | 78 | |||
|
May 2007107 No. of patients 166, of whom No previous History of BC 62, History of BC 71 and other 33 |
FISH (UroVysion) | Gain of two or more chromosomes in five or more cells per slide, or in cases of isolated gains of chromosome 3, 7, or 17 when the proportion of cells with such a gain was 10% or more of at least 100 cells evaluated, or when there were ≥ 10 cells with 9p21 loss | Patient | 166 | 33 | 27 | 29 | 77 | 53 | 74 |
| pTa | 38 | 16 | 22 | 42 | ||||||
| pT1 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 80 | ||||||
| pT2 | 12 | 8 | 4 | 67 | ||||||
| CIS | 2 | 1 | 1 | 50 | ||||||
| G1 | 33 | 14 | 19 | 42 | ||||||
| G2 | 14 | 5 | 9 | 36 | ||||||
| G3 | 15 | 14 | 1 | 93 | ||||||
| No previous History of BC group | 58 | 32 | 26 | 55 | ||||||
| History of BC group | 4 | 1 | 3 | 25 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 166 | 44 | 17 | 18 | 87 | 71 | 84 | ||
| pTa | 38 | 16 | 22 | 58 | ||||||
| pT1 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pT2 | 12 | 10 | 2 | 83 | ||||||
| CIS | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 33 | 17 | 16 | 52 | ||||||
| G2 | 14 | 13 | 1 | 93 | ||||||
| G3 | 15 | 14 | 1 | 93 | ||||||
| No previous History of BC group | 58 | 41 | 17 | 71 | ||||||
| History of BC group | 4 | 3 | 1 | 75 | ||||||
|
Meiers 2007100 No. of patients 624, of whom No previous History of BC NS, History of BC NS |
FISH (UroVysion) | Chromosomal gain of two or more chromosomes (+3, +7, +17) in four or more cells or deletion of 9p21 in 12 or more cells | Patient | 624 | 158 | 44 | 12 | 410 | 93 | 90 |
| G1 | 42 | 36 | 6 | 42 | ||||||
| G2 | 48 | 45 | 3 | 94 | ||||||
| G3 | 80 | 77 | 3 | 96 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 624 | 124 | 59 | 46 | 395 | 73 | 87 | ||
| G1 | 42 | 21 | 21 | 50 | ||||||
| G2 | 48 | 38 | 10 | 79 | ||||||
| G3 | 80 | 65 | 15 | 81 | ||||||
|
Messing 2005111 No. of patients 341, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 341 |
ImmunoCyt | One confirmed red or green fluorescent cell | Patient | 326 | 42 | 68 | 10 | 206 | 81 | 75 |
| pTa | 35 | 29 | 6 | 83 | ||||||
| pT1 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 75 | ||||||
| pT2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 28 | 22 | 6 | 79 | ||||||
| G2 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 90 | ||||||
| G3 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 67 | ||||||
| Tumour | ||||||||||
| < 1 cm | 17 | 12 | 5 | 71 | ||||||
| 1–3 cm | 19 | 16 | 3 | 84 | ||||||
| > 3 cm | 5 | 3 | 2 | 60 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 326 | 12 | 19 | 40 | 255 | 23 | 93 | ||
| pTa | 35 | 2 | 33 | 6 | ||||||
| pT1 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 50 | ||||||
| pT2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | ||||||
| CIS | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 28 | 2 | 26 | 7 | ||||||
| G2 | 10 | 1 | 9 | 10 | ||||||
| G3 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 67 | ||||||
| Tumour | ||||||||||
| < 1 cm | 17 | 3 | 14 | 18 | ||||||
| 1–3 cm | 19 | 5 | 14 | 26 | ||||||
| > 3 cm | 5 | 1 | 4 | 20 | ||||||
| ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) | Patient | 326 | 42 | 73 | 10 | 201 | 81 | 73 | ||
| pTa | 35 | 29 | 6 | 83 | ||||||
| pT1 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 75 | ||||||
| pT2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 28 | 22 | 6 | 79 | ||||||
| G2 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 90 | ||||||
| G3 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 67 | ||||||
|
Mian 1999112 No. of patients 264, of whom No previous History of BC 114, History of BC 150 |
ImmunoCyt | At least one green or one red fluorescent cell | Patient | 249 | 68 | 35 | 11 | 135 | 86 | 79 |
| pTa | 43 | 37 | 6 | 86 | ||||||
| pT1 | 20 | 17 | 3 | 85 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 12 | 10 | 2 | 83 | ||||||
| CIS | 4 | 4 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 25 | 21 | 4 | 84 | ||||||
| G2 | 25 | 21 | 4 | 84 | ||||||
| G3 | 29 | 26 | 3 | 90 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 249 | 37 | 3 | 42 | 167 | 47 | 98 | ||
| pTa | 43 | 9 | 34 | 21 | ||||||
| pT1 | 20 | 14 | 6 | 70 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 12 | 10 | 2 | 83 | ||||||
| CIS | 4 | 4 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 25 | 1 | 24 | 4 | ||||||
| G2 | 25 | 13 | 12 | 52 | ||||||
| G3 | 29 | 23 | 6 | 79 | ||||||
| ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) | Patient | 249 | 71 | 35 | 8 | 135 | 90 | 79 | ||
| pTa | 43 | 38 | 5 | 88 | ||||||
| pT1 | 20 | 18 | 2 | 90 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 12 | 11 | 1 | 92 | ||||||
| CIS | 4 | 4 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 25 | 21 | 4 | 84 | ||||||
| G2 | 25 | 22 | 3 | 88 | ||||||
| G3 | 29 | 28 | 1 | 97 | ||||||
|
Mian 2000134 No. of patients 240, of whom No previous History of BC 81, History of BC 159 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
≥ 10 U/ml | Patient | 240 | 30 | 39 | 24 | 147 | 56 | 79 |
| pTa | 29 | 15 | 14 | 52 | ||||||
| pT1 | 13 | 6 | 7 | 46 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 10 | 7 | 3 | 70 | ||||||
| CIS | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 18 | 9 | 9 | 50 | ||||||
| G2 | 20 | 10 | 10 | 50 | ||||||
| G3 | 16 | 11 | 5 | 69 | ||||||
|
Mian 2003101 No. of patients 181, of whom No previous History of BC 81, History of BC 100 |
ImmunoCyt | At least one green or one red fluorescent cell | Patient | 181 | 69 | 29 | 11 | 72 | 86 | 71 |
| pTa | 47 | 38 | 9 | 81 | ||||||
| pT1 | 13 | 12 | 1 | 92 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 90 | ||||||
| CIS | 10 | 10 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 31 | 25 | 6 | 81 | ||||||
| G2 | 24 | 21 | 3 | 88 | ||||||
| G3 | 25 | 23 | 2 | 92 | ||||||
| FISH (UroVysion) | Four or more aneusomic of 25 counted cells | Patient | 57 | 27 | 16 | 1 | 13 | 96 | 45 | |
| pTa | 26 | 25 | 1 | 96 | ||||||
| pT1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 88 | ||||||
| G2 | 19 | 19 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 181 | 36 | 6 | 44 | 95 | 45 | 94 | ||
| pTa | 47 | 6 | 41 | 13 | ||||||
| pT1 | 13 | 12 | 1 | 92 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 90 | ||||||
| CIS | 10 | 9 | 1 | 90 | ||||||
| G1 | 31 | 2 | 29 | 6 | ||||||
| G2 | 24 | 11 | 13 | 46 | ||||||
| G3 | 25 | 23 | 2 | 92 | ||||||
| ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) | Patient | 181 | 72 | 34 | 8 | 67 | 90 | 66 | ||
| pTa | 47 | 39 | 8 | 83 | ||||||
| pT1 | 13 | 13 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 10 | 10 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 31 | 26 | 5 | 84 | ||||||
| G2 | 24 | 22 | 2 | 92 | ||||||
| G3 | 25 | 24 | 1 | 96 | ||||||
|
Mian 2006113 No. of patients 942, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 942 |
ImmunoCyt | At least one green or one red fluorescent cell | Specimen | 1886 | 253 | 436 | 45 | 1152 | 85 | 73 |
| pTa | 202 | 165 | 37 | 82 | ||||||
| pT1 | 47 | 42 | 5 | 89 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 19 | 16 | 3 | 84 | ||||||
| CIS | 28 | 28 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 121 | 96 | 25 | 79 | ||||||
| G2 | 88 | 74 | 14 | 84 | ||||||
| G3 | 89 | 82 | 7 | 92 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Specimen | 1886 | 116 | 10 | 182 | 1578 | 39 | 99 | ||
| pTa | 202 | 41 | 161 | 20 | ||||||
| pT1 | 47 | 31 | 16 | 68 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 19 | 17 | 2 | 90 | ||||||
| CIS | 28 | 26 | 2 | 93 | ||||||
| G1 | 121 | 10 | 111 | 8 | ||||||
| G2 | 88 | 39 | 49 | 43 | ||||||
| G3 | 89 | 67 | 22 | 75 | ||||||
| ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) | Specimen | 1886 | 266 | 436 | 32 | 1152 | 89 | 73 | ||
| pTa | 202 | 172 | 30 | 85 | ||||||
| pT1 | 47 | 46 | 1 | 98 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 19 | 17 | 2 | 90 | ||||||
| CIS | 28 | 28 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 121 | 96 | 25 | 79 | ||||||
| G2 | 88 | 80 | 8 | 91 | ||||||
| G3 | 89 | 88 | 1 | 99 | ||||||
|
Miyanaga 1999135 No. of patients 309, of whom No previous History of BC 309, History of BC 0 |
NMP22 (Konica-Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
12 U/ml | Patient (urothelial cancer, not just BC) | 309 | 20 | 68 | 2 | 219 | 91 | 76 |
| Cytology (VU) | Patient (urothelial cancer, not just BC) | 309 | 12 | 1 | 10 | 286 | 55 | 100 | ||
|
Miyanaga 2003136 No. of patients 156, of whom No previous History of BC 99, History of BC 57 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
≥ 12 U/ml | Patient | 137 | 8 | 14 | 35 | 80 | 19 | 85 |
| ≥ 5 U/ml | Patient | 137 | 21 | 32 | 22 | 62 | 49 | 66 | ||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 137 | 3 | 2 | 40 | 92 | 7 | 98 | ||
|
Moonen 2007102 No. of patients 105, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 105 |
FISH (UroVysion) | Four or more of the 25 morphologically abnormal cells showed gains of two or more chromosomes (3, 7 or 17) or ≥ 12 of the 25 cells had no 9p21 signals | Specimen | 103 | 25 | 4 | 39 | 35 | 39 | 90 |
| pTa | 44 | 12 | 32 | 27 | ||||||
| pT1 | 10 | 6 | 4 | 60 | ||||||
| pT2–4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 50 | ||||||
| G1 | 27 | 6 | 21 | 22 | ||||||
| G2 | 19 | 7 | 12 | 37 | ||||||
| G3 | 18 | 12 | 6 | 67 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Specimen | 108 | 26 | 4 | 38 | 40 | 41 | 90 | ||
| pTa | 44 | 12 | 32 | 27 | ||||||
| pT1 | 10 | 7 | 3 | 70 | ||||||
| pT2–4 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 75 | ||||||
| G1 | 27 | 6 | 21 | 22 | ||||||
| G2 | 19 | 5 | 14 | 26 | ||||||
| G3 | 18 | 15 | 3 | 83 | ||||||
| FISH (UroVysion) + cytology (VU) | Specimen | 103 | 34 | 8 | 30 | 31 | 53 | 79 | ||
| pTa | 44 | 18 | 26 | 40 | ||||||
| pT1 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 80 | ||||||
| pT2–4 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 75 | ||||||
| G1 | 27 | 8 | 19 | 30 | ||||||
| G2 | 19 | 10 | 9 | 53 | ||||||
| G3 | 18 | 16 | 2 | 89 | ||||||
|
Oge 2001137 No. of patients 114, of whom No previous History of BC 37, History of BC 39, benign urological conditions 18, healthy subjects 20 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
10 U/ml (study also reports sensitivity and specificity at 5 and 20 U/ml) | Patient (excluding those with benign urological disease and healthy volunteers) | 76 | 37 | 8 | 13 | 18 | 74 | 69 |
| pTaG1 | 12 | 5 | 7 | 42 | ||||||
| pTaG2 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 75 | ||||||
| pT1G2 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| G1 G3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pT2G2 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS G3 | 18 | 15 | 3 | 83 | ||||||
|
Olsson 2001114 No. of patients 121, of whom No previous History of BC 60, History of BC 61 |
ImmunoCyt | At least one green or one red cell | Patient | 114 | 31 | 26 | 0 | 57 | 100 | 69 |
| Cytology (BW) | Patient | 114 | 18 | 13 | 58 | |||||
|
Oosterhuis 2002138 No. of patients 191, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 191 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
10 U/ml | Specimen | 431 | 32 | 116 | 32 | 251 | 50 | 68 |
| pTa | 39 | 13 | 26 | 33 | ||||||
| Low grade | 32 | 7 | 25 | 22 | ||||||
| High grade | 7 | 6 | 1 | 86 | ||||||
| pT1 | 17 | 14 | 3 | 82 | ||||||
| Low grade | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||
| High grade | 16 | 14 | 2 | 88 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 4 | 1 | 3 | 25 | ||||||
|
Parekattil 2003158 No. of patients 253, of whom No previous History of BC 155, History of BC 98 |
NMP22 Laboratory analysis |
2.5 U/ml | Patient | 252 | 19 | 123 | 8 | 102 | 70 | 45 |
| Cytology (VU or BW) | Atypia classed with positive | Patient | 253 | 18 | 43 | 9 | 183 | 67 | 81 | |
|
Piaton 2003116 No. of patients 694, of whom No previous History of BC 236, History of BC 458 |
ImmunoCyt | At least one green or one red fluorescent cell | Patient | 651 | 106 | 89 | 40 | 416 | 73 | 82 |
| With No previous History of BC | 215 | 44 | 26 | 15 | 130 | 75 | 83 | |||
| pTaG1–G2 | 22 | 15 | 7 | 68 | ||||||
| pTa–1 G3 | 14 | 11 | 3 | 79 | ||||||
| pT1G1–G2 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 75 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 11 | 8 | 3 | 73 | ||||||
| CIS | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pTa + CIS | 5 | 4 | 1 | 80 | ||||||
| pTxGx (bladder) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pTxGx (UUT) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 10 | 4 | 6 | 40 | ||||||
| G2 | 17 | 15 | 2 | 88 | ||||||
| G3 | 30 | 23 | 7 | 77 | ||||||
| Gx | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| With previous History of BC | 436 | 62 | 63 | 25 | 286 | 71 | 82 | |||
| pTaG1–G2 | 42 | 27 | 15 | 64 | ||||||
| pTa–1 G3 | 18 | 16 | 2 | 89 | ||||||
| pT1G1–G2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 67 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 16 | 10 | 6 | 63 | ||||||
| CIS | 2 | 1 | 1 | 50 | ||||||
| ≥ pTa + CIS | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pTxGx (bladder) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pTxGx (UUT) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 21 | 13 | 8 | 62 | ||||||
| G2 | 24 | 16 | 8 | 67 | ||||||
| G3 | 39 | 30 | 9 | 77 | ||||||
| Gx | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 651 | 90 | 74 | 56 | 431 | 62 | 85 | ||
| With No previous History of BC | 215 | 42 | 26 | 17 | 130 | 71 | 83 | |||
| pTaG1–G2 | 22 | 10 | 12 | 45 | ||||||
| pTa–1 G3 | 14 | 13 | 1 | 93 | ||||||
| pT1G1–G2 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 11 | 9 | 2 | 82 | ||||||
| CIS | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||
| ≥ pTa + CIS | 5 | 4 | 1 | 80 | ||||||
| pTxGx (bladder) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pTxGx (UUT) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 10 | 3 | 7 | 30 | ||||||
| G2 | 17 | 12 | 5 | 71 | ||||||
| G3 | 30 | 25 | 5 | 83 | ||||||
| Gx | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| With previous History of BC | 436 | 48 | 48 | 39 | 301 | 55 | 86 | |||
| pTaG1–G2 | 42 | 19 | 23 | 45 | ||||||
| pTa–1 G3 | 18 | 14 | 4 | 78 | ||||||
| pT1G1–G2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 16 | 9 | 7 | 56 | ||||||
| CIS | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pTa + CIS | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | ||||||
| pTxGx (bladder) | 1 | N/S | ||||||||
| pTxGx (UUT) | 2 | 1 | 1 | 50 | ||||||
| G1 | 21 | 8 | 13 | 38 | ||||||
| G2 | 24 | 14 | 10 | 58 | ||||||
| G3 | 39 | 25 | 14 | 64 | ||||||
| Gx | 3 | 1 | 2 | 33 | ||||||
| ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) | Patient | 146 | 120 | 26 | 82 | |||||
| With No previous History of BC | 59 | 51 | 8 | 86 | ||||||
| pTaG1–G2 | 22 | 16 | 6 | 73 | ||||||
| pTa–1 G3 | 14 | 14 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pT1G1–G2 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 11 | 9 | 2 | 82 | ||||||
| CIS | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pTa + CIS | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pTxGx (bladder) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pTxGx (UUT) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 50 | ||||||
| G2 | 17 | 16 | 1 | 94 | ||||||
| G3 | 30 | 28 | 2 | 93 | ||||||
| Gx | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| With previous History of BC | 87 | 69 | 18 | 79 | ||||||
| pTaG1–G2 | 42 | 30 | 10 | 71 | ||||||
| pTa–1 G3 | 18 | 16 | 2 | 89 | ||||||
| pT1G1–G2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 16 | 13 | 3 | 81 | ||||||
| CIS | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pTa + CIS | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pTxGx (bladder) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pTxGx (UUT) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 21 | 13 | 8 | 62 | ||||||
| G2 | 24 | 19 | 5 | 79 | ||||||
| G3 | 39 | 34 | 5 | 87 | ||||||
| Gx | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
|
[Pfister 2003115] No. of patients 694, of whom No previous History of BC 236, History of BC 458 |
ImmunoCyt | At least one green or one red fluorescent cell | Patient | 691 | 102 | 87 | 41 | 461 | 71 | 84 |
| pTa | 75 | 52 | 23 | 75 | ||||||
| pT1 | 28 | 19 | 9 | 67 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 28 | 20 | 8 | 73 | ||||||
| CIS | 8 | 8 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 31 | 19 | 12 | 61 | ||||||
| G2 | 40 | 30 | 10 | 76 | ||||||
| G3 | 68 | 52 | 16 | 77 | ||||||
| No previous History of BC | 58 | 42 | 16 | 72 | ||||||
| History of BC | 85 | 60 | 25 | 71 | ||||||
| Cystoscopy | Patient | 691 | 141 | 79 | 2 | 469 | 99 | 86 | ||
| No previous History of BC | 58 | 58 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 691 | 70 | 30 | 73 | 518 | 49 | 95 | ||
| pTa | 75 | 27 | 48 | 36 | ||||||
| pT1 | 28 | 17 | 11 | 59 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 28 | 25 | 3 | 91 | ||||||
| CIS | 8 | 3 | 5 | 33 | ||||||
| G1 | 31 | 6 | 25 | 18 | ||||||
| G2 | 40 | 19 | 21 | 46 | ||||||
| G3 | 68 | 43 | 25 | 64 | ||||||
| No previous History of BC | 58 | 37 | 21 | 64 | ||||||
| History of BC | 85 | 33 | 52 | 39 | ||||||
| ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) | Patient | 691 | 113 | 106 | 30 | 442 | 79 | 81 | ||
| pTa | 75 | 56 | 19 | 75 | ||||||
| pT1 | 28 | 22 | 6 | 78 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 28 | 25 | 3 | 91 | ||||||
| CIS | 8 | 8 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 31 | 21 | 10 | 67 | ||||||
| G2 | 40 | 31 | 9 | 78 | ||||||
| G3 | 68 | 59 | 9 | 87 | ||||||
| No previous History of BC | 58 | 49 | 9 | 84 | ||||||
| History of BC | 85 | 64 | 21 | 75 | ||||||
|
Planz 2005171 No. of patients 626, of whom No previous History of BC 353, History of BC 273 |
Cytology (VU) | Specimen | 346 | 54 | 4 | 88 | 200 | 38 | 98 | |
| One specimen | 142 | 25 | 1 | 32 | 84 | 44 | 99 | |||
| Two specimens | 142 | 32 | 1 | 25 | 84 | 56 | 99 | |||
| Three specimens | 142 | 38 | 3 | 44 | 82 | 67 | 97 | |||
| Cytology (BW) | Specimen | 191 | 16 | 2 | 26 | 147 | 38 | 99 | ||
| One specimen | 20 | 4 | 0 | 6 | 10 | 40 | 100 | |||
| Two specimens | 20 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 50 | 100 | |||
| Three specimens | 20 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 10 | 60 | 100 | |||
| Cytology (VU + BW) | Specimen | 535 | 70 | 6 | 112 | 347 | 39 | 98 | ||
| G1 | 42 | 5 | 37 | 12 | ||||||
| One specimen | 13 | 2 | 11 | 15 | ||||||
| Two specimens | 13 | 2 | 11 | 15 | ||||||
| Three specimens | 13 | 2 | 11 | 15 | ||||||
| G2 | 55 | 23 | 32 | 42 | ||||||
| One specimen | 27 | 13 | 14 | 48 | ||||||
| Two specimens | 27 | 16 | 11 | 59 | ||||||
| Three specimens | 27 | 20 | 7 | 74 | ||||||
| G3 | 45 | 26 | 19 | 58 | ||||||
| One specimen | 23 | 12 | 11 | 52 | ||||||
| Two specimens | 23 | 15 | 8 | 65 | ||||||
| Three specimens | 23 | 18 | 5 | 78 | ||||||
|
Ponsky 2001139 No. of patients 608, of whom No previous History of BC 529, History of BC 79 |
NMP22 Laboratory analysis |
> 10 U/ml | Patient | 608 | 46 | 89 | 6 | 467 | 88 | 84 |
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 608 | 32 | 85 | 20 | 471 | 62 | 85 | ||
|
Potter 1999172 No. of patients 336, of whom No previous History of BC 336, History of BC 0 |
Cytology (VU) | Patient | 336 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 331 | 100 | 99 | |
|
Poulakis 2001140 No. of patients 739, of whom No previous History of BC 353, History of BC 386 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
≥ 8.25 U/ml (study also gives sensitivity and specificity from 6.4 to 20 U/ml) | Patient | 739 | 347 | 107 | 59 | 226 | 85 | 68 |
| pTa | 210 | 174 | 36 | 83 | ||||||
| pT1 | 47 | 40 | 7 | 85 | ||||||
| pT2 | 58 | 55 | 3 | 95 | ||||||
| pT3 | 45 | 43 | 2 | 96 | ||||||
| pT4 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 31 | 23 | 8 | 74 | ||||||
| Superficial invasive (pTa, pT1, CIS) | 286 | 237 | 49 | 83 | ||||||
| Superficial invasive (pT2–T4) | 111 | 107 | 4 | 96 | ||||||
| G1 | 129 | 106 | 23 | 82 | ||||||
| G2 | 167 | 149 | 18 | 89 | ||||||
| G3 | 70 | 66 | 4 | 94 | ||||||
| With one tumour | 208 | 165 | 43 | 79 | ||||||
| With two to three tumours | 92 | 83 | 9 | 90 | ||||||
| With more than three tumours | 99 | 96 | 3 | 97 | ||||||
| With no History of BC | 179 | 154 | 25 | 86 | ||||||
| With History of BC | 220 | 190 | 30 | 86 | ||||||
| ≥ 10 U/ml | Patient | 739 | 321 | 101 | 85 | 232 | 79 | 70 | ||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 739 | 253 | 14 | 153 | 319 | 62 | 96 | ||
| pTa | 211 | 93 | 118 | 44 | ||||||
| pT1 | 47 | 33 | 14 | 70 | ||||||
| pT2 | 58 | 45 | 13 | 78 | ||||||
| pT3 | 45 | 42 | 3 | 93 | ||||||
| pT4 | 9 | 8 | 1 | 89 | ||||||
| CIS | 31 | 26 | 5 | 84 | ||||||
| Superficial invasive (pTa, pT1, CIS) | 287 | 152 | 135 | 53 | ||||||
| Superficial invasive (pT2–T4) | 112 | 95 | 17 | 85 | ||||||
| G1 | 129 | 49 | 80 | 38 | ||||||
| G2 | 160 | 109 | 51 | 68 | ||||||
| G3 | 70 | 63 | 7 | 90 | ||||||
| With one tumour | 208 | 99 | 109 | 48 | ||||||
| With two to three tumours | 92 | 63 | 29 | 68 | ||||||
| With more than three tumours | 99 | 85 | 14 | 86 | ||||||
| With no History of BC | 179 | 140 | 39 | 78 | ||||||
| With History of BC | 220 | 107 | 113 | 49 | ||||||
|
Raitanen 2002173 No. of patients 652, of whom No previous History of BC 151, History of BC 501 |
Cytology (VU) | Papanicolaou I–II classed as negative and III–V classed as positive (suspicious classed as positive) | Patient | |||||||
| With No previous History of BC | 129 | 73 | 56 | 57 | ||||||
| pTa | 51 | 16 | 35 | 35 | ||||||
| pT1 | 49 | 33 | 16 | 67 | ||||||
| pT2–T4 | 22 | 19 | 3 | 86 | ||||||
| pTx | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS (no suspicious) | 4 | 2 | 2 | 50 | ||||||
| G1 | 44 | 10 | 34 | 23 | ||||||
| G2 | 45 | 28 | 17 | 62 | ||||||
| G3 | 39 | 34 | 5 | 87 | ||||||
| Gx (only suspicious) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| One tumour | 86 | 49 | 37 | 57 | ||||||
| Two tumours | 26 | 14 | 12 | 54 | ||||||
| More than three tumours | 14 | 10 | 4 | 71 | ||||||
| With previous History of BC | 441 | 41 | 32 | 77 | 291 | 35 | 90 | |||
| pTa | 54 | 9 | 45 | 16 | ||||||
| pT1 | 20 | 6 | 14 | 30 | ||||||
| > pT2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 67 | ||||||
| pTx | 33 | 13 | 20 | 39 | ||||||
| CIS | 8 | 6 | 2 | 75 | ||||||
| G1 | 48 | 10 | 38 | 21 | ||||||
| G2 | 35 | 16 | 19 | 46 | ||||||
| G3 (no suspicious) | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| Gx | 32 | 12 | 20 | 38 | ||||||
| Papanicolaou I–III classed as negative and IV–V classed as positive (suspicious classed as negative) | Patient | |||||||||
| With No previous History of BC | 129 | 40 | 89 | 31 | ||||||
| pTa | 51 | 6 | 45 | 12 | ||||||
| pT1 | 49 | 19 | 30 | 39 | ||||||
| pT2-T4 | 22 | 11 | 11 | 50 | ||||||
| pTx | 3 | 2 | 1 | 67 | ||||||
| CIS (no suspicious) | 4 | 2 | 2 | 50 | ||||||
| G1 | 44 | 5 | 39 | 11 | ||||||
| G2 | 45 | 12 | 33 | 27 | ||||||
| G3 | 39 | 23 | 16 | 59 | ||||||
| Gx (only suspicious) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||
| One tumour | 86 | 27 | 59 | 31 | ||||||
| Two tumours | 26 | 5 | 21 | 19 | ||||||
| More than three tumours | 14 | 8 | 6 | 57 | ||||||
| With previous History of BC | 441 | 21 | 11 | 97 | 312 | 18 | 97 | |||
| pTa | 54 | 8 | 46 | 15 | ||||||
| pT1 | 20 | 4 | 16 | 20 | ||||||
| > pT2 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | ||||||
| pTx | 33 | 5 | 28 | 15 | ||||||
| CIS | 8 | 4 | 4 | 50 | ||||||
| G1 | 48 | 6 | 42 | 13 | ||||||
| G2 | 35 | 7 | 28 | 20 | ||||||
| G3 (no suspicious) | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| Gx | 32 | 5 | 27 | 16 | ||||||
| [Raitanen 2002174] | Cytology (VU) | Papanicolaou I–III classed as negative and IV–V classed as positive (suspicious classed as negative) (local analysis) | Patient | 575 | 71 | 8 | 177 | 319 | 29 | 98 |
| With No previous History of BC | 129 | 50 | 79 | 39 | ||||||
| pTa–T1 | 100 | 32 | 68 | 32 | ||||||
| G1 | 44 | 3 | 41 | 7 | ||||||
| G2–3 | 84 | 47 | 37 | 56 | ||||||
| With History of BC | 446 | 21 | 8 | 98 | 319 | 18 | 98 | |||
| Papanicolaou I–III classed as negative and IV–V classed as positive (suspicious classed as negative) (review analysis) | Patient | 575 | 61 | 11 | 187 | 316 | 25 | 97 | ||
| With No previous History of BC | 129 | 40 | 89 | 31 | ||||||
| pTa–T1 | 100 | 25 | 75 | 25 | ||||||
| G1 | 44 | 5 | 39 | 11 | ||||||
| G2–3 | 84 | 35 | 49 | 42 | ||||||
| With History of BC | 446 | 21 | 11 | 98 | 316 | 18 | 97 | |||
|
Ramakumar 1999159 No. of patients 196, of whom No previous History of BC 19, History of BC 38 and control (others undergoing cystoscopy who were negative for BC and with negative urine specimen) 139 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
10 U/ml | Patient | 196 | 30 | 56 | 27 | 83 | 53 | 60 |
| pTa | 25 | 12 | 13 | 48 | ||||||
| pT1–T3b | 14 | 11 | 3 | 79 | ||||||
| CIS | 11 | 5 | 6 | 45 | ||||||
| G1 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 44 | ||||||
| G2 | 26 | 16 | 10 | 62 | ||||||
| G3 | 13 | 8 | 5 | 62 | ||||||
| No previous History of BC tumour | 19 | 14 | 5 | 74 | ||||||
| History of BC tumour | 38 | 16 | 22 | 42 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 112 | 24 | 3 | 30 | 55 | 44 | 95 | ||
| pTa | 24 | 7 | 17 | 29 | ||||||
| pT1–T3b | 12 | 8 | 4 | 67 | ||||||
| CIS | 11 | 8 | 3 | 73 | ||||||
| G1 | 9 | 2 | 7 | 22 | ||||||
| G2 | 24 | 9 | 15 | 38 | ||||||
| G3 | 12 | 10 | 2 | 83 | ||||||
| No previous History of BC tumour | 17 | 10 | 7 | 59 | ||||||
| History of BC tumour | 37 | 14 | 23 | 38 | ||||||
|
Saad 2002141 No. of patients 120, of whom No previous History of BC 120, History of BC 0 |
NMP22 Laboratory analysis |
≥ 10 U/ml | Patient | 120 | 42 | 9 | 10 | 59 | 81 | 87 |
| pTa | 23 | 16 | 7 | 70 | ||||||
| pT1 | 20 | 18 | 2 | 90 | ||||||
| pT2 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 6 | 6 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 13 | 8 | 5 | 62 | ||||||
| G2 | 22 | 19 | 3 | 86 | ||||||
| G3 | 17 | 15 | 2 | 88 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 120 | 25 | 9 | 27 | 59 | 48 | 87 | ||
| pTa | 23 | 7 | 16 | 30 | ||||||
| pT1 | 20 | 10 | 10 | 50 | ||||||
| pT2 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 88 | ||||||
| CIS | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| G1 | 13 | 2 | 11 | 15 | ||||||
| G2 | 22 | 9 | 13 | 41 | ||||||
| G3 | 17 | 14 | 3 | 82 | ||||||
|
Sanchez-Carbayo 1999160 No. of patients 267, of whom No previous History of BC NS, History of BC NS, other urological diseases 25, malignancies of non-bladder origin 25, healthy volunteers 30 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
> 14.6 U/ml | Patient (from group 1: 111 with positive cystoscopy for TCC of the bladder; from group 2: 76 with previous BC and free of disease at time of study) | 187 | 84 | 4 | 27 | 72 | 76 | 95 |
| Patient (from group 1) | ||||||||||
| pTa | 24 | 15 | 9 | 63 | ||||||
| pT1 | 53 | 42 | 11 | 79 | ||||||
| pT2 | 11 | 9 | 2 | 82 | ||||||
| pT3 | 13 | 13 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pT4 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 3 | 2 | 1 | 67 | ||||||
| G1 | 33 | 25 | 8 | 76 | ||||||
| G2 | 33 | 27 | 6 | 82 | ||||||
| G3 | 40 | 33 | 7 | 83 | ||||||
| Single tumour | 25 | 18 | 7 | 72 | ||||||
| Multiple tumours | 81 | 61 | 20 | 75 | ||||||
| < 0.5 cm | 23 | 19 | 4 | 83 | ||||||
| 0.5–3 cm | 42 | 34 | 8 | 81 | ||||||
| > 3 cm | 41 | 38 | 3 | 93 | ||||||
| Papillary tumour | 78 | 63 | 15 | 81 | ||||||
| Solid tumour | 28 | 28 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| No previous History of BC | 43 | 33 | 10 | 77 | ||||||
| Previous History of BC | 64 | 54 | 10 | 84 | ||||||
|
[Sanchez-Carbayo 1999161] No. of patients as for Sanchez-Carbayo 1999160 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
6.4 U/ml | Patient | 187 | 95 | 15 | 16 | 61 | 85 | 80 |
| 7 U/ml | Patient | 187 | 95 | 13 | 16 | 63 | 85 | 83 | ||
| 10 U/ml | Patient | 187 | 90 | 7 | 21 | 69 | 81 | 91 | ||
| 12 U/ml | Patient | 187 | 87 | 6 | 24 | 70 | 78 | 92 | ||
| 13.7 U/ml | Patient | 187 | 87 | 3 | 24 | 73 | 78 | 96 | ||
|
Sanchez-Carbayo 2001162 No. of patients 232, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 232 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
≥ 10 U/ml | Patient | 232 | 38 | 13 | 17 | 164 | 69 | 93 |
| Not receiving intravesical instillations | 106 | 25 | 5 | 6 | 70 | 81 | 93 | |||
| Receiving intravesical instillations | 126 | 13 | 8 | 11 | 94 | 65 | 92 | |||
| CIS | 4 | 1 | 3 | 25 | ||||||
| G1 | 29 | 8 | 21 | 27 | ||||||
| G2 | 37 | 21 | 16 | 58 | ||||||
| G3 | 40 | 30 | 10 | 76 | ||||||
|
Sanchez-Carbayo 2001142 No. of patients 187, of whom No previous History of BC 112, History of BC 0, other 75 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
≥ 10 U/ml | Patient | 187 | 26 | 29 | 17 | 115 | 61 | 80 |
| Patients with No previous History of BC | 112 | 26 | 7 | 17 | 62 | 60 | 90 | |||
| pTa | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | ||||||
| pT1 | 28 | 16 | 12 | 57 | ||||||
| CIS | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||
| pT2 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 86 | ||||||
| pT3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 11 | 2 | 9 | 18 | ||||||
| G2 | 15 | 9 | 6 | 60 | ||||||
| G3 | 17 | 14 | 3 | 82 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU or catheterised) | Patients with No previous History of BC | 112 | 15 | 23 | 28 | 46 | 35 | 97 | ||
|
Sarosdy 2002108 No. of patients 451, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 176 and other 275 |
FISH (UroVysion) | Aneuploidy of chromosomes 3, 7 and 17 or loss of the 9p21 locus | Patient (whole group excluding 59 healthy donors) | 392 | 44 | 54 | 18 | 276 | 71 | 84 |
| Patients with History of BC | 176 | 44 | 39 | 18 | 75 | 71 | 66 | |||
| pTaG1–G2 | 26 | 16 | 10 | 62 | ||||||
| pTaG3 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| pT1G2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pT1G3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 75 | ||||||
| pT2 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 7 | 7 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 22 | 12 | 10 | 55 | ||||||
| G2 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 78 | ||||||
| G3 | 18 | 17 | 1 | 94 | ||||||
| Control group | 275 | 15 | 260 | 95 | ||||||
| Healthy donors | 59 | 0 | 59 | 100 | ||||||
| Non-genitourinary benign disease | 48 | 4 | 44 | 92 | ||||||
| Non-genitourinary cancer | 3 | 1 | 2 | 67 | ||||||
| Benign prostatic hyperplasia | 58 | 5 | 53 | 92 | ||||||
| Microhaematuria | 15 | 2 | 13 | 87 | ||||||
| Infections, inflammation | 28 | 1 | 27 | 96 | ||||||
| Prostate and renal cancer | 61 | 5 | 56 | 92 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | |||||||||
| pTaG1–G2 | 26 | 6 | 20 | 23 | ||||||
| pTaG3 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 33 | ||||||
| pT1G2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pT1G3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 50 | ||||||
| pT2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 33 | ||||||
| CIS | 6 | 2 | 4 | 33 | ||||||
| G1 | 22 | 4 | 18 | 18 | ||||||
| G2 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 44 | ||||||
| G3 | 17 | 7 | 10 | 41 | ||||||
|
Sarosdy 2006105 No. of patients 497, of whom No previous History of BC 497, History of BC 0 |
FISH (UroVysion) | NS (assay was performed according to instructions on the product labelling) | Patient | 473 | 35 | 94 | 16 | 328 | 69 | 78 |
| pTaG1 | 21 | 10 | 11 | 48 | ||||||
| pTaG2 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| pTaG3 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pT1 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 86 | ||||||
| pT2 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 90 | ||||||
| Unknown stage | 2 | 1 | 1 | 50 | ||||||
| G1 | 21 | 10 | 11 | 48 | ||||||
| G2 | 10 | 7 | 3 | 70 | ||||||
| G3 | 17 | 15 | 2 | 88 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 473 | 19 | 32 | 38 | |||||
| pTaG1 | 21 | 5 | 16 | 24 | ||||||
| pTaG2 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 50 | ||||||
| pTaG3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 50 | ||||||
| pT1 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 43 | ||||||
| pT2 | 10 | 6 | 4 | 60 | ||||||
| Unknown stage | 2 | 1 | 1 | 50 | ||||||
| G1 | 21 | 5 | 16 | 24 | ||||||
| G2 | 10 | 3 | 7 | 30 | ||||||
| G3 | 17 | 9 | 8 | 53 | ||||||
|
No. of patients 301, of whom No previous History of BC 301, History of BC 0 |
ImmunoCyt | More than one green or one red urothelial cell | Patient | 280 | 23 | 31 | 4 | 222 | 85 | 88 |
| Gross haematuria | 63 | 15 | 8 | 2 | 38 | 88 | 83 | |||
| High grade | 11 | 9 | 2 | 82 | ||||||
| Low grade | 5 | 5 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| Microhaematuria | 217 | 8 | 23 | 2 | 184 | 80 | 89 | |||
| High grade | 4 | 4 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| Low grade | 6 | 4 | 2 | 67 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 280 | 12 | 11 | 15 | 242 | 44 | 96 | ||
| Gross haematuria | 63 | 8 | 4 | 9 | 42 | 47 | 91 | |||
| High grade | 11 | 6 | 5 | 55 | ||||||
| Low grade | 5 | 2 | 3 | 40 | ||||||
| Microhaematuria | 217 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 200 | 40 | 97 | |||
| High grade | 4 | 2 | 2 | 50 | ||||||
| Low grade | 6 | 4 | 2 | 67 | ||||||
| Cystoscopy (NS) | Patient | 278 | 21 | 4 | 4 | 249 | 84 | 98 | ||
| Gross haematuria | 61 | 13 | 2 | 2 | 44 | 87 | 96 | |||
| High grade | 11 | 8 | 3 | 73 | ||||||
| Low grade | 5 | 4 | 1 | 80 | ||||||
| Microhaematuria | 217 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 205 | 80 | 99 | |||
| ImmunoCyt + cystoscopy | Patient | 280 | 27 | 32 | 0 | 221 | 100 | 87 | ||
| Gross haematuria | 63 | 17 | 9 | 0 | 37 | 100 | 80 | |||
| Microhaematuria | 217 | 10 | 23 | 0 | 184 | 100 | 89 | |||
| Cystoscopy + cytology (VU) | Patient | 280 | 22 | 13 | 5 | 240 | 88 | 95 | ||
| Gross haematuria | 63 | 14 | 6 | 3 | 40 | 82 | 87 | |||
| Microhaematuria | 217 | 8 | 7 | 2 | 200 | 80 | 97 | |||
|
Serretta 2000144 No. of patients 179, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 179 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
10 U/ml | Patient | 179 | 41 | 56 | 14 | 68 | 75 | 55 |
| pTa | 13 | 7 | 6 | 54 | ||||||
| pT1 | 27 | 20 | 7 | 74 | ||||||
| pT2–T3 | 12 | 10 | 2 | 83 | ||||||
| CIS | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 43 | ||||||
| G2 | 19 | 12 | 7 | 63 | ||||||
| G3 | 29 | 26 | 3 | 90 | ||||||
|
[Serretta 1998143] No. of patients 137, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 137 |
NMP22 | ≥ 10 U/ml | Patient | 137 | 30 | 37 | 12 | 58 | 71 | 61 |
| 20 U/ml | Patient | 137 | 24 | 18 | 18 | 77 | 57 | 81 | ||
|
Shariat 2006147 No. of patients 2871, of whom No previous History of BC 0, History of BC 2871 |
NMP22 Laboratory analysis |
≥ 10 U/ml (study also gives sensitivity and specificity for cut-offs from 1 to 30 U/ml) | Patient | 2871 | 596 | 347 | 449 | 1479 | 57 | 81 |
| ≥ pT2 | 220 | 183 | 37 | 83 | ||||||
| G3 | 329 | 247 | 82 | 75 | ||||||
|
Sharma 1999148 No. of patients 278, of whom No previous History of BC 199, History of BC 79 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
≥ 10 U/ml for patients with No previous History of BC, ≥ 6 U/ml for patients with History of BC | Patient | 278 | 28 | 44 | 6 | 200 | 82 | 82 |
| ≥ 10 U/ml | With No previous History of BC | 199 | 4 | 27 | 2 | 166 | 67 | 86 | ||
| ≥ 6 U/ml | With previous History of BC | 79 | 24 | 17 | 4 | 34 | 86 | 67 | ||
| Cytology (VU) | Atypical classed with positive | Patient | 278 | 19 | 17 | 15 | 227 | 56 | 93 | |
| With No previous History of BC | 199 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 185 | 33 | 96 | |||
| With previous History of BC | 79 | 17 | 9 | 11 | 42 | 61 | 82 | |||
| Cytology (VU) | Atypical classed with negative | Patient | 278 | 10 | 1 | 24 | 243 | 29 | 100 | |
| With No previous History of BC | 199 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 193 | 17 | 100 | |||
| With previous History of BC | 79 | 9 | 1 | 19 | 50 | 32 | 98 | |||
|
Skacel 2003104 No. of patients 120, of whom no previous history of BC 26, history of BC 94 |
FISH (UroVysion) | Chromosomal gain of two or more chromosomes in five or more cells per slide, or in cases of isolated gain of chromosome 3, 7 or 17 when the number of cells with such gain was ≥ 10%, or when 9p21 loss was the only abnormality, ≥ 12 cells with such loss | Patient | 111 | 70 | 1 | 12 | 28 | 85 | 97 |
| pTa | 64 | 53 | 11 | 83 | ||||||
| pT1 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| pT2 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| pT4 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 23 | 19 | 4 | 83 | ||||||
| G2 | 35 | 28 | 7 | 80 | ||||||
| G3 | 24 | 23 | 1 | 96 | ||||||
|
Sokolova 2000105 No. of patients 179, of whom no previous history of BC 86, history of BC 93 |
FISH (UroVysion) | Five or more cells with polysomy | Patient (urothelial carcinoma) | 179 | 39 | 11 | 7 | 122 | 85 | 92 |
| pTa | 22 | 14 | 8 | 65 | ||||||
| pT1–T4 | 12 | 11 | 1 | 95 | ||||||
| CIS | 12 | 12 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G2 | 14 | 11 | 3 | 76 | ||||||
| G3 | 22 | 21 | 1 | 97 | ||||||
| 2.8% of cells with tetrasomy | CEP3 | 19 | 14 | 5 | 74 | |||||
| 6.5% of cells with tetrasomy | CEP7 | 21 | 16 | 5 | 76 | |||||
| 7.1% of cells with tetrasomy | CEP8 | 19 | 11 | 8 | 58 | |||||
| CEP9 | 21 | 11 | 10 | 52 | ||||||
| CEP11 | 19 | 10 | 9 | 53 | ||||||
| 6.2% of cells with tetrasomy | CEP17 | 21 | 13 | 8 | 62 | |||||
| 7.0% of cells with tetrasomy | CEP18 | 19 | 8 | 11 | 42 | |||||
| 16.9% of cells with homozygous deletion | 9p21 | 21 | 6 | 15 | 29 | |||||
| Four or more cells with polysomy | Patient (urothelial carcinoma) | 179 | 41 | 16 | 5 | 117 | 90 | 88 | ||
| CEP3, 7, 17 and 9p21 | 21 | 20 | 1 | 95 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient (urothelial carcinoma) | |||||||||
| pTa | 22 | 10 | 12 | 47 | ||||||
| pT1–T4 | 12 | 7 | 5 | 60 | ||||||
| CIS | 12 | 9 | 3 | 78 | ||||||
| G2 | 14 | 8 | 6 | 54 | ||||||
| G3 | 22 | 16 | 6 | 71 | ||||||
|
Sozen 1999163 No. of patients 140, of whom no previous history of BC NS, history of BC NS, control group of 100 with benign urological disease or renal or prostate cancer |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
5 U/ml | Patient | 140 | 36 | 37 | 4 | 63 | 90 | 63 |
| 6.4 U/ml | Patient | 140 | 35 | 31 | 5 | 69 | 88 | 69 | ||
| 7 U/ml | Patient | 140 | 34 | 28 | 6 | 72 | 85 | 72 | ||
| 10 U/ml | Patient | 140 | 29 | 19 | 11 | 81 | 73 | 81 | ||
| 12 U/ml | Patient | 140 | 29 | 15 | 11 | 85 | 73 | 85 | ||
| 15 U/ml | Patient | 140 | 28 | 13 | 12 | 87 | 70 | 87 | ||
| Cytology (VU or catheterised) | Patient | 140 | 14 | 10 | 26 | 90 | 35 | 90 | ||
|
Stampfer 1998149 No. of patients 231, of whom no previous history of BC 0, history of BC 231 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
> 6.4 U/ml | Specimen | 274 | 45 | 42 | 21 | 166 | 68 | 80 |
| pTa | 44 | 27 | 17 | 61 | ||||||
| pT1 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| CIS | 10 | 7 | 3 | 70 | ||||||
| G1 | 13 | 4 | 9 | 31 | ||||||
| G2 | 27 | 20 | 7 | 74 | ||||||
| G3 | 26 | 21 | 5 | 81 | ||||||
| Low risk (pTaG1, pTaG2) | 39 | 23 | 16 | 59 | ||||||
| High risk (pTaG3, T1) | 11 | 10 | 1 | 90 | ||||||
| Invasive (pT2–T4) | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| 5 U/ml | Specimen | 274 | 48 | 59 | 18 | 149 | 73 | 72 | ||
| 7 U/ml | Specimen | 274 | 43 | 34 | 23 | 174 | 65 | 84 | ||
| 10 U/ml | Specimen | 274 | 32 | 17 | 34 | 191 | 49 | 92 | ||
| Cytology (VU) | Specimen | 200 | 18 | 12 | 24 | 146 | 43 | 92 | ||
|
Takeuchi 2004164 No. of patients 669, of whom no previous history of BC 48, history of BC 0, benign disease 621 |
NMP22 (Konica-Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
12 U/ml | Patient | 669 | 28 | 124 | 20 | 497 | 58 | 80 |
| CIS–pT1 | 39 | 19 | 20 | 49 | ||||||
| pT2–T4 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 50 | ||||||
| G2 | 35 | 19 | 16 | 54 | ||||||
| G3 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 78 | ||||||
| < 10 mm | 19 | 6 | 13 | 32 | ||||||
| 10–30 mm | 17 | 11 | 6 | 65 | ||||||
| > 30 mm | 12 | 11 | 1 | 92 | ||||||
| Single | 27 | 12 | 15 | 44 | ||||||
| Two to four | 10 | 6 | 4 | 60 | ||||||
| Five or more | 11 | 10 | 1 | 91 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 669 | 21 | 0 | 27 | 621 | 44 | 100 | ||
| CIS–pT1 | 39 | 15 | 24 | 39 | ||||||
| pT2–T4 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 67 | ||||||
| G1 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 25 | ||||||
| G2 | 35 | 13 | 22 | 37 | ||||||
| G3 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 78 | ||||||
| < 10 mm | 19 | 4 | 15 | 21 | ||||||
| 10–30 mm | 17 | 8 | 9 | 47 | ||||||
| > 30 mm | 12 | 9 | 3 | 75 | ||||||
| Single | 27 | 9 | 18 | 33 | ||||||
| Two to four | 10 | 3 | 7 | 30 | ||||||
| Five or more | 11 | 9 | 2 | 82 | ||||||
| NMP22 + cytology (VU) | Patient | 48 | 29 | 19 | 60 | |||||
| CIS–pT1 | 39 | 20 | 19 | 51 | ||||||
| pT2–T4 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| G1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 50 | ||||||
| G2 | 35 | 20 | 15 | 57 | ||||||
| G3 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 78 | ||||||
| < 10 mm | 19 | 7 | 12 | 37 | ||||||
| 10–30 mm | 17 | 11 | 6 | 65 | ||||||
| > 30 mm | 12 | 11 | 1 | 92 | ||||||
| Single | 27 | 13 | 14 | 48 | ||||||
| Two to four | 10 | 6 | 4 | 60 | ||||||
| Five or more | 11 | 10 | 1 | 91 | ||||||
|
Talwar 2007150 No. of patients 196, of whom no previous history of BC 69, history of BC 127 |
NMP22 (Matritech) BladderChek | ≥ 10 U/ml | Patient | 196 | 35 | 28 | 17 | 116 | 67 | 81 |
| pTa | 24 | 14 | 10 | 58 | ||||||
| pT1 | 14 | 10 | 4 | 71 | ||||||
| pT2 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 75 | ||||||
| pT3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| With well-differentiated tumours | 21 | 11 | 10 | 52 | ||||||
| With poorly-differentiated tumours | 7 | 6 | 1 | 86 | ||||||
| With moderately-differentiated tumours | 22 | 17 | 5 | 77 | ||||||
| No previous history of BC | 69 | 9 | 7 | 1 | 52 | 90 | 88 | |||
| History of BC | 127 | 27 | 21 | 15 | 64 | 64 | 75 | |||
| Non-invasive | 39 | 25 | 14 | 64 | ||||||
| Muscle invasive | 1 | 9 | 2 | 82 | ||||||
| Cystitis, inflammation, UTI | 58 | 17 | 41 | 71 | ||||||
| Benign prostatic hyperplasia | 38 | 5 | 33 | 87 | ||||||
| Calculi | 44 | 7 | 37 | 84 | ||||||
| Non-TCC malignancies | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| No urinary tract disease | 51 | 2 | 49 | 96 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 196 | 11 | 2 | 41 | 142 | 21 | 99 | ||
| pTa | 24 | 14 | 10 | 58 | ||||||
| pT1 | 14 | 2 | 12 | 14 | ||||||
| pT2 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 25 | ||||||
| pT3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| CIS | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||
| With well-differentiated tumours | 21 | 2 | 19 | 10 | ||||||
| With poorly-differentiated tumours | 7 | 4 | 3 | 57 | ||||||
| With moderately-differentiated tumours | 22 | 4 | 18 | 18 | ||||||
| No previous history of BC | 69 | 1 | 0 | 9 | 59 | 10 | 100 | |||
| History of BC | 127 | 9 | 0 | 33 | 85 | 21 | 100 | |||
| Non-invasive | 39 | 5 | 34 | 13 | ||||||
| Muscle invasive | 11 | 5 | 6 | 45 | ||||||
| Cystitis, inflammation, UTI | 58 | 1 | 57 | 98 | ||||||
| Benign prostatic hyperplasia | 38 | 0 | 38 | 100 | ||||||
| Calculi | 44 | 0 | 44 | 100 | ||||||
| Non-TCC malignancies | 2 | 1 | 1 | 50 | ||||||
| No urinary tract disease | 51 | 0 | 51 | 100 | ||||||
|
Tetu 2005119 No. of patients 904, of whom no previous history of BC NS, history of BC NS |
ImmunoCyt | Presence of one green or one red fluorescent cell | Patient | 870 | 100 | 281 | 36 | 453 | 74 | 62 |
| pTa | 65 | 51 | 14 | 79 | ||||||
| pT1 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 19 | 13 | 6 | 68 | ||||||
| CIS | 14 | 13 | 1 | 93 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | (The study included cases with atypias suspicious for malignancy in the negative category) | Patient | 870 | 39 | 17 | 97 | 814 | 29 | 98 | |
| pTa | 65 | 8 | 57 | 12 | ||||||
| pT1 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 67 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 19 | 9 | 10 | 47 | ||||||
| CIS | 14 | 7 | 7 | 50 | ||||||
| ImmunoCyt + cytology (VU) | Patient | 870 | 114 | 284 | 22 | 450 | 84 | 61 | ||
| pTa | 65 | 51 | 14 | 79 | ||||||
| pT1 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 83 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 19 | 15 | 4 | 79 | ||||||
| CIS | 14 | 14 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
|
Tritschler 200780 No. of patients 100, of whom no previous history of BC 30, history of BC 70 |
NMP22 (Matritech) BladderChek | 10 U/ml | Patient | 100 | 26 | 36 | 14 | 24 | 65 | 40 |
| Tumour | ||||||||||
| G1–2 | 22 | 12 | 10 | 55 | ||||||
| G3 | 18 | 14 | 4 | 78 | ||||||
| pTa | 22 | 12 | 10 | 55 | ||||||
| CIS | 9 | 7 | 2 | 78 | ||||||
| Invasive T1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 50 | ||||||
| Invasive ≥ T2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 85 | 15 | 11 | 19 | 40 | 44 | 78 | ||
| Cytology (BW) | Patient | 94 | 26 | 23 | 8 | 37 | 76 | 62 | ||
| Tumour | ||||||||||
| G1–2 | 22 | 17 | 5 | 83 | ||||||
| G3 | 18 | 15 | 3 | 83 | ||||||
| pTa | 22 | 18 | 4 | 82 | ||||||
| CIS | 9 | 7 | 2 | 78 | ||||||
| T1 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 75 | ||||||
| ≥ T2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 67 | ||||||
|
Wiener 1998151 No. of patients 291, of whom no previous history of BC 190, history of BC 101 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
10 U/ml | Patient | 291 | 44 | 62 | 47 | 138 | 48 | 69 |
| pTa | 47 | 23 | 24 | 49 | ||||||
| pT1 | 25 | 11 | 14 | 44 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 19 | 10 | 9 | 53 | ||||||
| G1 | 23 | 12 | 11 | 52 | ||||||
| G2 | 38 | 17 | 21 | 45 | ||||||
| G3 | 30 | 15 | 15 | 50 | ||||||
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 291 | 54 | 0 | 37 | 200 | 59 | 100 | ||
| pTa | 47 | 23 | 24 | 49 | ||||||
| pT1 | 25 | 16 | 9 | 64 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 19 | 15 | 4 | 79 | ||||||
| G1 | 23 | 4 | 19 | 17 | ||||||
| G2 | 38 | 23 | 15 | 61 | ||||||
| G3 | 30 | 27 | 3 | 90 | ||||||
| Cytology (BW) | Patient | 200 | 48 | 0 | 35 | 117 | 58 | 100 | ||
| pTa | 47 | 22 | 25 | 47 | ||||||
| pT1 | 25 | 18 | 7 | 25 | ||||||
| ≥ pT2 | 19 | 15 | 4 | 79 | ||||||
| G1 | 23 | 5 | 18 | 22 | ||||||
| G2 | 38 | 21 | 17 | 55 | ||||||
| G3 | 30 | 27 | 3 | 90 | ||||||
|
Yoder 2007106 No. of patients 250, of whom no previous history of BC 0, history of BC 250 |
FISH (UroVysion) | More than two chromosomal gains of chromosomes 3, 7 or 17 in at least four analysed cells, or homozygous 9p21 deletion in at least 12 analysed cells, or isolated trisomy of chromosome 3, 7, or 17 in at least 10% of analysed cells | Patient | 250 | 25 | 56 | 14 | 155 | 64 | 73 |
|
Zippe 1999152 No. of patients 330, of whom no previous history of BC 330, history of BC 0 |
NMP22 (Matritech) Laboratory analysis |
> 10 U/ml | Patient | 330 | 18 | 45 | 0 | 267 | 100 | 86 |
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 330 | 6 | 0 | 12 | 312 | 33 | 100 | ||
|
[Zippe 1999153] No. of patients 146, of whom no previous history of BC 146, history of BC 0 |
NMP22 | > 10 U/ml | Patient | 146 | 8 | 14 | 0 | 124 | 100 | 90 |
| Cytology (VU) | Patient | 146 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 138 | 25 | 100 | ||
Appendix 16 Cut-offs for a positive test used in studies reporting FISH
| Study | Cut-off |
|---|---|
| Daniely 200794 | Minimum of four cells with gains of two or more chromosomes, or 12 or more cells with homozygous loss of the 9p21 locus |
| Friedrich 200395 | If 20% of the cells had a gain of two or more chromosomes (3, 7 or 17), or 40% of the cells had a gain of one chromosome or 40% loss of 9p21 locus |
| Halling 200097 | Five or more cells with polysomy |
| Junker 200698 | Five or more cells showed gains of more than one chromosome (3, 7 or 17), or 10 or more cells showed gains of a single chromosome (3, 7 or 17), or 10 or more cells showed homozygous loss of the 9p21 locus |
| Kipp 200899 | Four or more cells had polysomic signal patterns (gain of two or more of the four chromosomes in an individual cell), 10 or more cells demonstrated tetrasomy (four signal patterns for all four probes), or > 20% of the cells demonstrated 9p21 homozygous deletion (loss of the two 9p21 signals) |
| May 2007107 | Gain of two or more chromosomes in five or more cells per slide, or in cases of isolated gains of chromosome 3, 7, or 17 when the proportion of cells with such a gain was 10% or more of at least 100 cells evaluated, or when there were 10 or more cells with 9p21 loss |
| Meiers 2007100 | Chromosomal gain of two or more chromosomes (+3, +7, +17) in four or more cells, or deletion of 9p21 in 12 or more cells |
| Mian 2003101 | Four or more aneusomic of 25 counted cells |
| Moonen 2007102 | Four or more of the 25 morphologically abnormal cells showed gains of two or more chromosomes (3, 7 or 17), or 12 or more of the 25 cells had no 9p21 signals |
| Sarosdy 2002108 | Aneuploidy of chromosomes 3, 7 and 17 or loss of the 9p21 locus |
| Sarosdy 2006103 | Assay was performed according to product instructions [the UroVysion Bladder Cancer Kit (UroVysion Kit) is designed to detect aneuploidy for chromosomes 3, 7, 17, and loss of the 9p21 locus] |
| Skacel 2003104 | Chromosomal gain of two or more chromosomes in five or more cells per slide, or in cases of isolated gain of chromosome 3, 7 or 17 when the number of cells with such gain was ≥ 10%, or when 9p21 loss was the only abnormality, 12 or more cells with such loss |
| Sokolova 2000105 | Five or more cells with polysomy |
| Yoder 2007106 | More than two chromosomal gains of chromosomes 3, 7 or 17 in at least four analysed cells, or homozygous 9p21 deletion in at least 12 analysed cells, or isolated trisomy of chromosome 3, 7, or 17 in at least 10% of analysed cells |
Appendix 17 Model structure
FIGURE 36.
Diagram of Markov model for non-muscle-invasive disease.
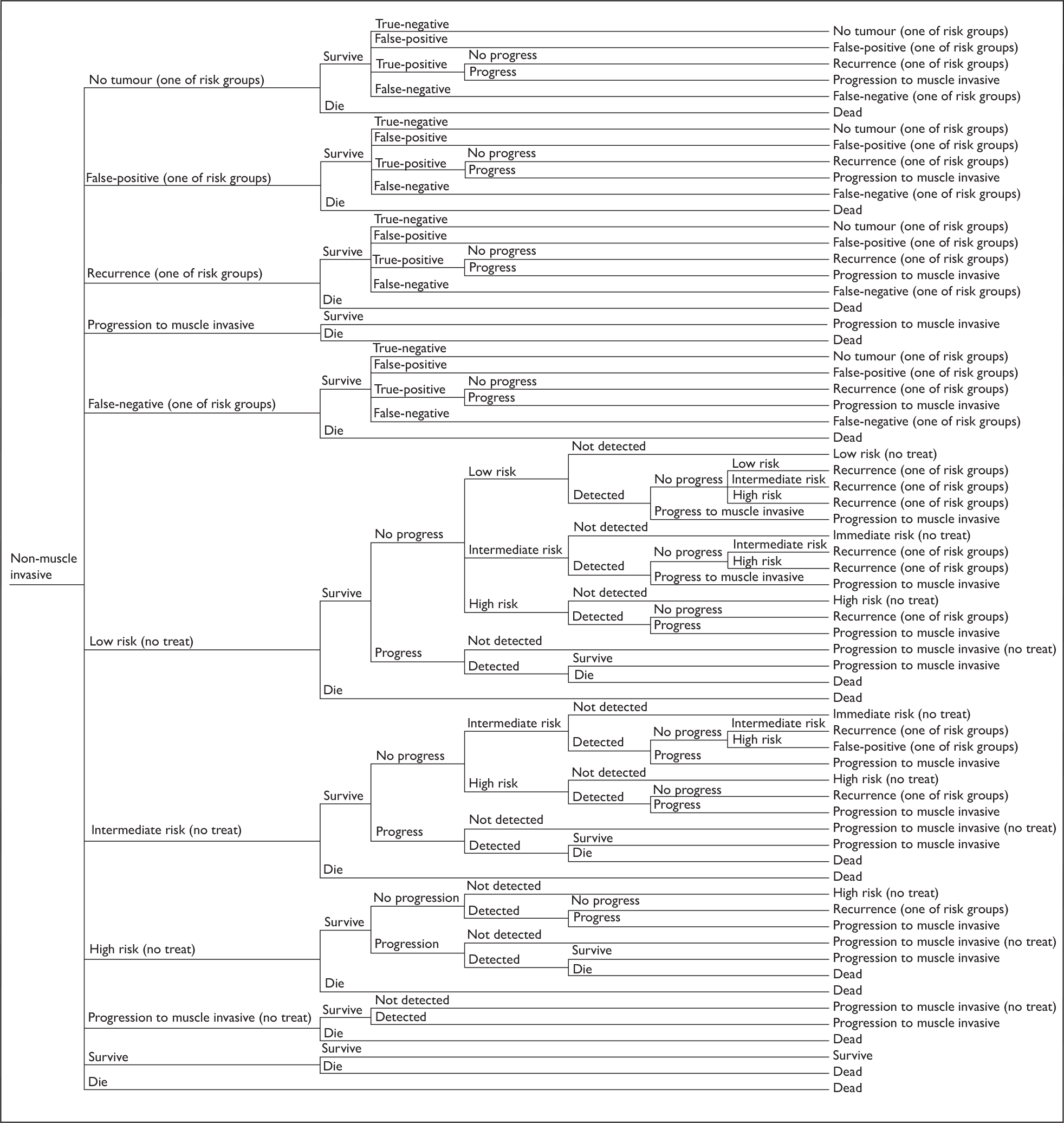
FIGURE 37.
Diagram of decision model.
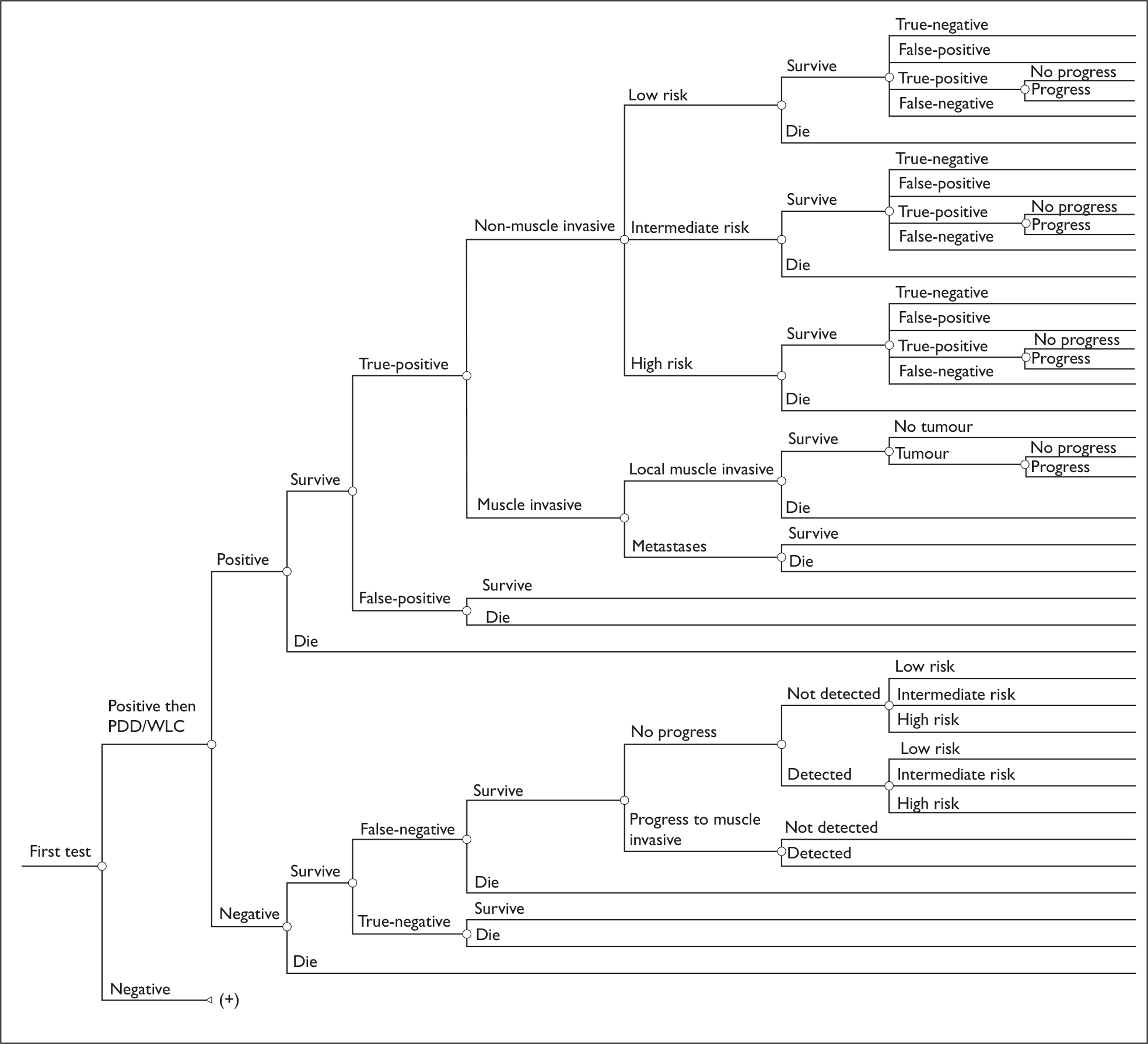
FIGURE 38.
Diagram of Markov model for muscle-invasive disease.
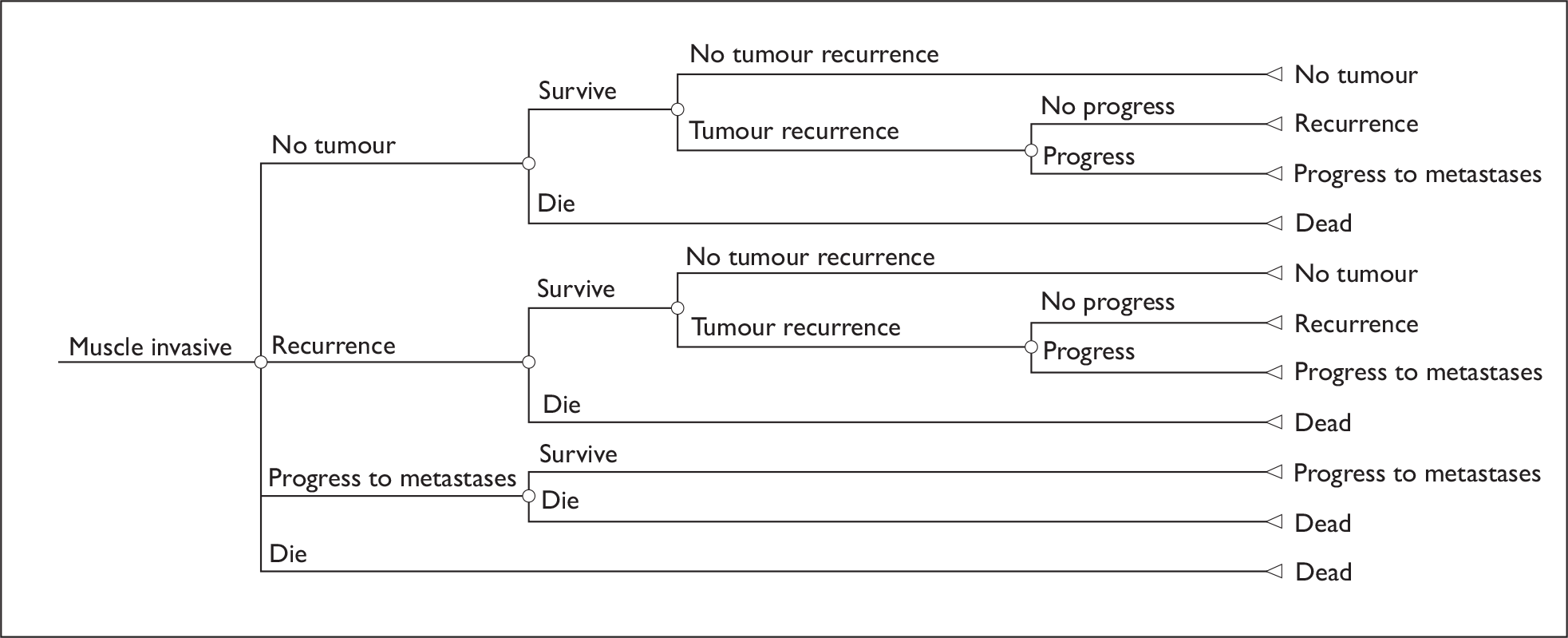
Appendix 18 Summary of studies reporting prognosis and all-cause mortality rates for the UK
| Study | Study type | Tumour status | No. of cases | Grade | T stage | CIS | Multiplicity | Tumour size | Intravesical instillations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loening 1980186 | Retrospective | Primary and recurrent | 178 | No | Yes | – | No | No | – |
| Narayana 1983189 | Prospective | Primary and recurrent | 468 | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | – |
| Yes | Yes | – | No | No | – | ||||
| Dalesio 1983182 | Prospective | Primary and recurrent | 308 | No | – | – | Yes | Yes | – |
| Parmar 1989191 | Prospective | Primary | 305 | No | No | – | Yes | No | – |
| Witjes 1992194 | Prospective | Primary | 1026 | No | Yes | No | No | – | Yes |
| Kiemeney 1993184 | Prospective | Primary | 1674 | No | Yes | No | Yes | – | Yes |
| Kiemeney 1994185 | Prospective | Primary | 1674 | Yes | Yes | No | – | – | Yes |
| Witjes 1994195 | Prospective | Primary and recurrent | 469 | No | No | – | Yes | No | – |
| Mulders 1994188 | Prospective | Primary and recurrent | 371 | No | No | – | Yes | No | – |
| Kurth 1995181 | Retrospective | Primary and recurrent | 576 | Yes | No | – | Yes | No | – |
| Pawinski 1996192 | Meta-analysis | Primary and recurrent | 2535 | – | – | – | – | – | Yes |
| Shinka 1997193 | Prospective | Primary | 141 | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | – |
| Millán-Rodriguez 2000187 | Retrospective | Primary | 1529 | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Oosterlinck 2001190 | Guideline | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Sylvester 200620 | Retrospective | Primary and recurrent | 2596 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| García 2006183 | Retrospective | Primary and recurrent | 473 | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Study | Study type | Tumour status | No. of cases | Grade | T stage | CIS | Multiplicity | Tumour size | Intravesical instillations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herr 1997196 | – | Primary and recurrent | 221 | – | Yes | – | – | – | – |
| Kiemeney 1993184 | Prospective | Primary | 1674 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | – | No |
| Kiemeney 1994185 | Prospective | Primary and recurrent | 1674 | Yes | Yes | Yes | – | – | No |
| Kurth 1995181 | Retrospective | Primary and recurrent | 576 | Yes | – | – | No | Yes | – |
| Pawinski 1996192 | Meta-analysis | Primary and recurrent | 2535 | – | – | – | – | – | No |
| Millán-Rodriguez 2000187 | Retrospective | Primary | 1529 | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Sylvester 200620 | Retrospective | Primary and recurrent | 2596 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| García 2006183 | Retrospective | Primary and recurrent | 473 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Age (years) | Female | Male | 30% female/70% male |
|---|---|---|---|
| 57 | 0.004643 | 0.007311 | 0.0065106 |
| 58 | 0.005050 | 0.007850 | 0.0070100 |
| 59 | 0.005639 | 0.008787 | 0.0078426 |
| 60 | 0.006160 | 0.010172 | 0.0089684 |
| 61 | 0.006807 | 0.011002 | 0.0097435 |
| 62 | 0.007443 | 0.012545 | 0.0110144 |
| 63 | 0.008116 | 0.013460 | 0.0118568 |
| 64 | 0.009152 | 0.015029 | 0.0132659 |
| 65 | 0.010041 | 0.016189 | 0.0143446 |
| 66 | 0.011114 | 0.017829 | 0.0158145 |
| 67 | 0.012173 | 0.019784 | 0.0175007 |
| 68 | 0.013430 | 0.021671 | 0.0191987 |
| 69 | 0.014893 | 0.024025 | 0.0212854 |
| 70 | 0.016138 | 0.026284 | 0.0232402 |
| 71 | 0.018145 | 0.029844 | 0.0263343 |
| 72 | 0.020737 | 0.032942 | 0.0292805 |
| 73 | 0.023061 | 0.036532 | 0.0324907 |
| 74 | 0.026217 | 0.041049 | 0.0365994 |
| 75 | 0.029660 | 0.045240 | 0.0405660 |
| 76 | 0.033232 | 0.050620 | 0.0454036 |
| 77 | 0.037046 | 0.056696 | 0.0508010 |
| 78 | 0.041599 | 0.062325 | 0.0561072 |
| 79 | 0.046364 | 0.069874 | 0.0628210 |
| 80 | 0.051959 | 0.076846 | 0.0693799 |
| 81 | 0.058465 | 0.085981 | 0.0777262 |
| 82 | 0.065710 | 0.094133 | 0.0856061 |
| 83 | 0.073339 | 0.103537 | 0.0944776 |
| 84 | 0.080283 | 0.111409 | 0.1020712 |
| 85 | 0.090944 | 0.121991 | 0.1126769 |
| 86 | 0.102260 | 0.136694 | 0.1263638 |
| 87 | 0.119838 | 0.159120 | 0.1473354 |
| 88 | 0.132897 | 0.174064 | 0.1617139 |
| 89 | 0.148659 | 0.192931 | 0.1796494 |
| 90 | 0.163740 | 0.201010 | 0.1898290 |
| 91 | 0.182212 | 0.220958 | 0.2093342 |
| 92 | 0.202965 | 0.243762 | 0.2315229 |
| 93 | 0.228008 | 0.269145 | 0.2568039 |
| 94 | 0.251579 | 0.281937 | 0.2728296 |
| 95 | 0.275949 | 0.319381 | 0.3063514 |
| 96 | 0.300473 | 0.342860 | 0.3301439 |
| 97 | 0.329979 | 0.371213 | 0.3588428 |
Appendix 19 Results of cost–consequence analysis
| Ranking | True negative | True positive | False positive | False negative |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) |
| 2 | CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) |
| 3 | FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) |
| 4 | NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_FISH_PDD (CSC_WLC) | NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_FISH_PDD (CSC_WLC) |
| 5 | FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) |
| 6 | IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_PDD (CSC_WLC) | IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_PDD (CSC_WLC) |
| 7 | CSC_WLC (CSC_WLC) | IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | CSC_WLC (CSC_WLC) | IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) |
| 8 | CSC_CTL_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_CTL_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CSC_CTL_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_CTL_PDD (CSC_WLC) |
| 9 | CSC_CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | CSC_CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | CSC_CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | CSC_CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) |
| 10 | NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) |
| 11 | CSC_FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | CSC_IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | CSC_FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | CSC_IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) |
| 12 | CSC_FISH_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_IMM_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_FISH_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_IMM_WLC (CSC_WLC) |
| 13 | IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | CSC_FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | CSC_FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) |
| 14 | CSC_NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_FISH_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_FISH_WLC (CSC_WLC) |
| 15 | CSC_NMP22_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) |
| 16 | CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) |
| 17 | CSC_IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_WLC (CSC_WLC) |
| 18 | CSC_IMM_WLC (CSC_WLC) | NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_IMM_WLC (CSC_WLC) | NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) |
| 19 | CSC_CTL_PDD (CSC_WLC) | IMM_WLC(IMM_WLC) | CSC_CTL_PDD (CSC_WLC) | IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) |
| 20 | CSC_CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | CSC_CTL_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | CSC_CTL_WLC (CSC_WLC) |
| 21 | CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | CSC_CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | CSC_CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) |
| 22 | CSC_FISH_PDD (CSC_WLC) | FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | CSC_FISH_PDD (CSC_WLC) | FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) |
| 23 | CSC_NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_WLC (CSC_WLC) |
| 24 | CSC_NMP22_PDD (CSC_WLC) | NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_PDD (CSC_WLC) | NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) |
| 25 | CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) |
| 26 | CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) |
| Ranking | Correct diagnosis | Incorrect diagnosis | Life-years | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) |
| 2 | CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) |
| 3 | FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | CSC_FISH_PDD (CSC_WLC) | FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) |
| 4 | FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) |
| 5 | NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) |
| 6 | IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_PDD (CSC_WLC) | NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) |
| 7 | CSC_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_WLC (CSC_WLC) | IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) |
| 8 | CSC_CTL_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_CTL_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) |
| 9 | CSC_CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | CSC_CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | CSC_CTL_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CSC_CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) |
| 10 | NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | CSC_FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) |
| 11 | IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | CSC_IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) |
| 12 | CSC_FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | CSC_FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | CSC_IMM_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) |
| 13 | CSC_FISH_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_FISH_WLC (CSC_WLC) | NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_WLC (CSC_WLC) |
| 14 | CSC_NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_FISH_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) |
| 15 | CSC_NMP22_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | CSC_CTL_WLC (CSC_WLC) |
| 16 | CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CSC_FISH_WLC (CSC_WLC) |
| 17 | CSC_IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | CSC_IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | CSC_PDD (CSC_PDD) | CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) |
| 18 | CSC_IMM_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_IMM_WLC (CSC_WLC) | IMM_WLC (IMM_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_WLC (CSC_WLC) |
| 19 | CSC_CTL_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CSC_CTL_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_PDD (CSC_WLC) |
| 20 | CSC_CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | CSC_CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_IMM_WLC (CSC_WLC) |
| 21 | CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | CSC_FISH_PDD (FISH_WLC) | CSC_CTL_WLC (CTL_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) |
| 22 | CSC_FISH_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CSC_FISH_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CSC_CTL_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_CTL_PDD (CSC_WLC) |
| 23 | CSC_NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_PDD (NMP22_WLC) | FISH_WLC (FISH_WLC) | CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) |
| 24 | CSC_NMP22_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_PDD (CSC_WLC) | NMP22_WLC (NMP22_WLC) | CSC_FISH_PDD (CSC_WLC) |
| 25 | CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | CSC_IMM_PDD (IMM_WLC) | CSC_WLC (CSC_WLC) | CSC_NMP22_PDD (CSC_WLC) |
| 26 | CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) | CTL_PDD (CTL_WLC) | CSC_IMM_PDD (CSC_WLC) |
Appendix 20 Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves for the eight strategies for changes in the incidence rate (base case = 5%)
FIGURE 39.
Incidence rate is 1%.
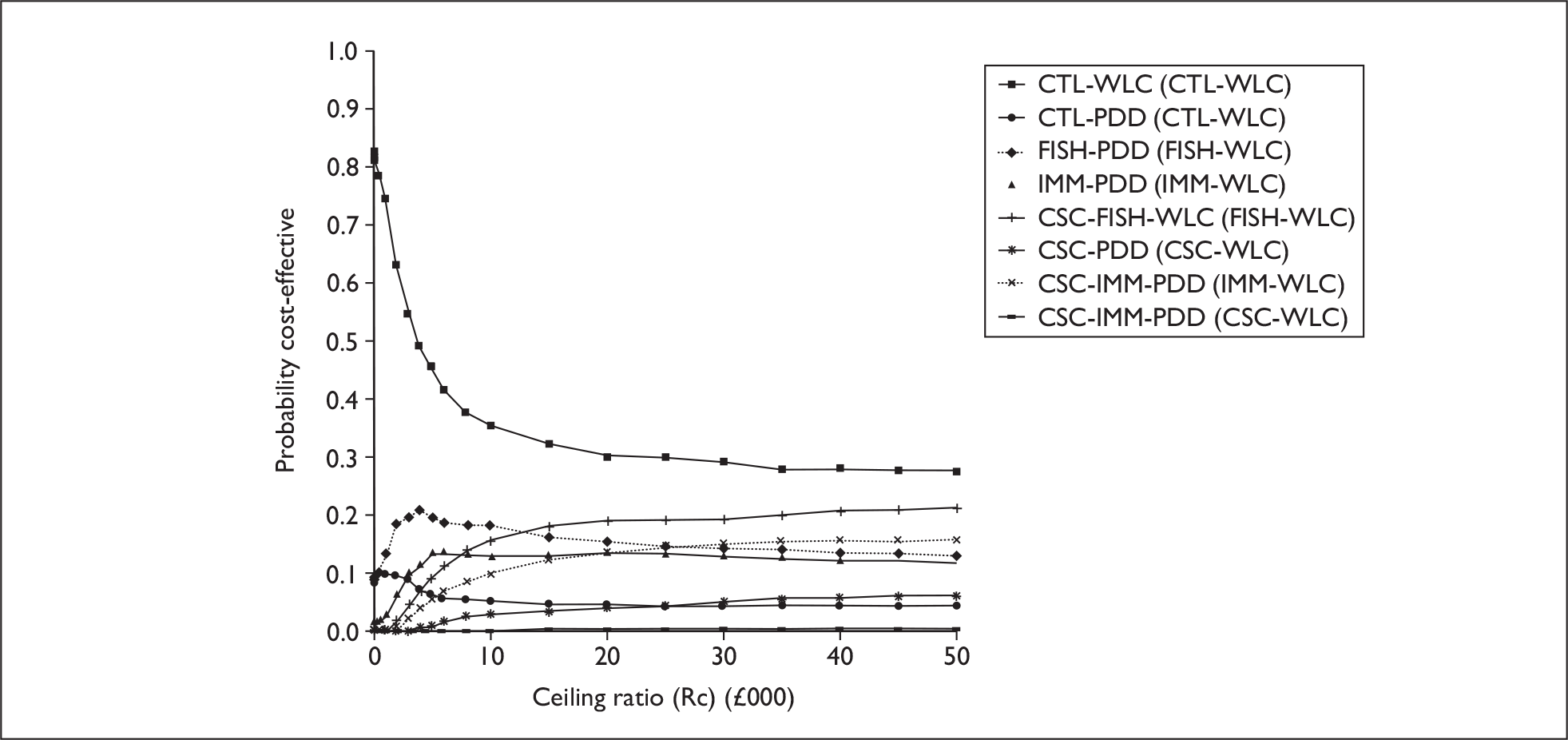
FIGURE 40.
Incidence rate is 10%.
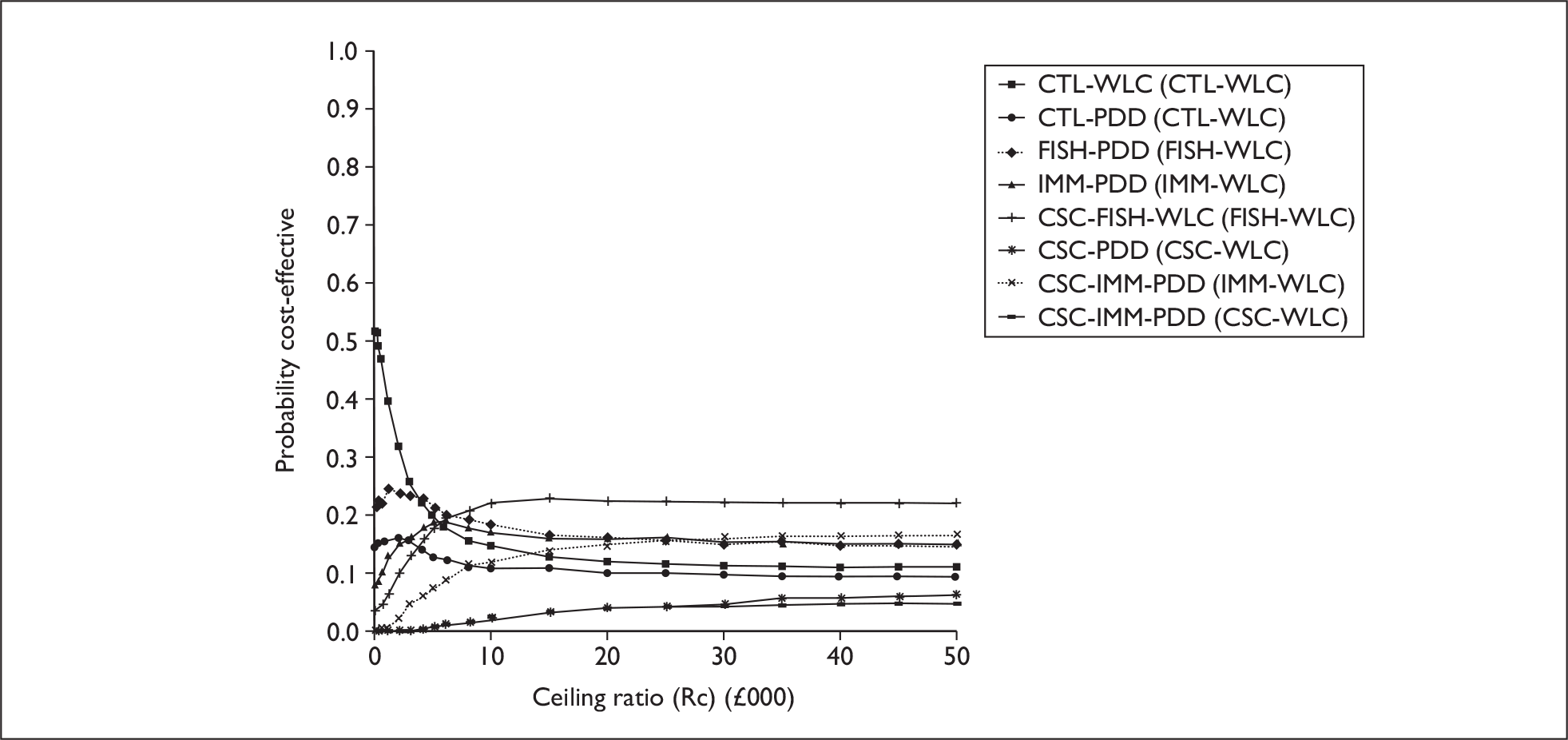
FIGURE 41.
Incidence rate is 20%.
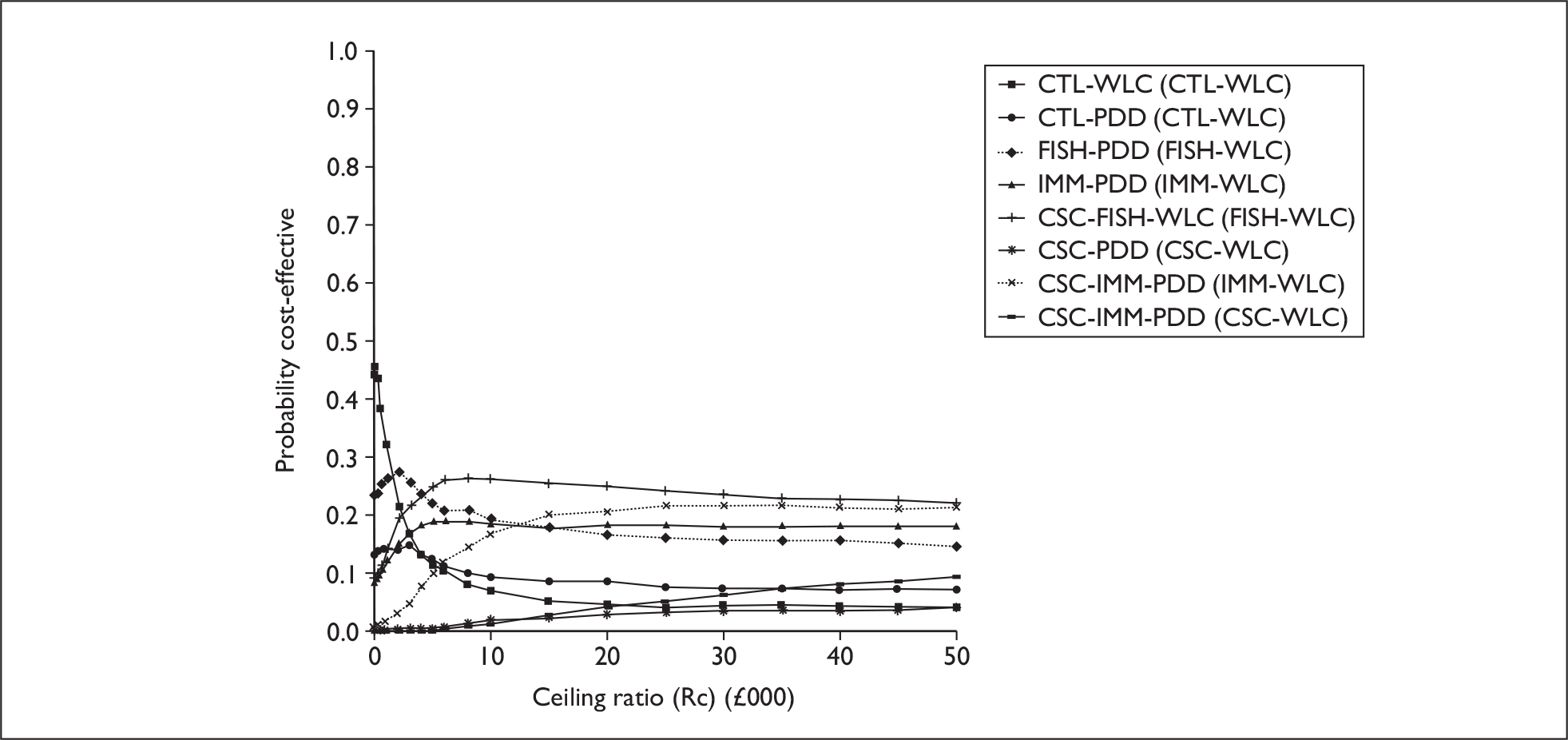
Appendix 21 Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves for changes to the performance of flexible cystoscopy (base-case flexible cystoscopy is the same as white light rigid cystoscopy)
FIGURE 42.
Sensitivity and specificity of flexible cystoscopy are increased by 5% from base case.
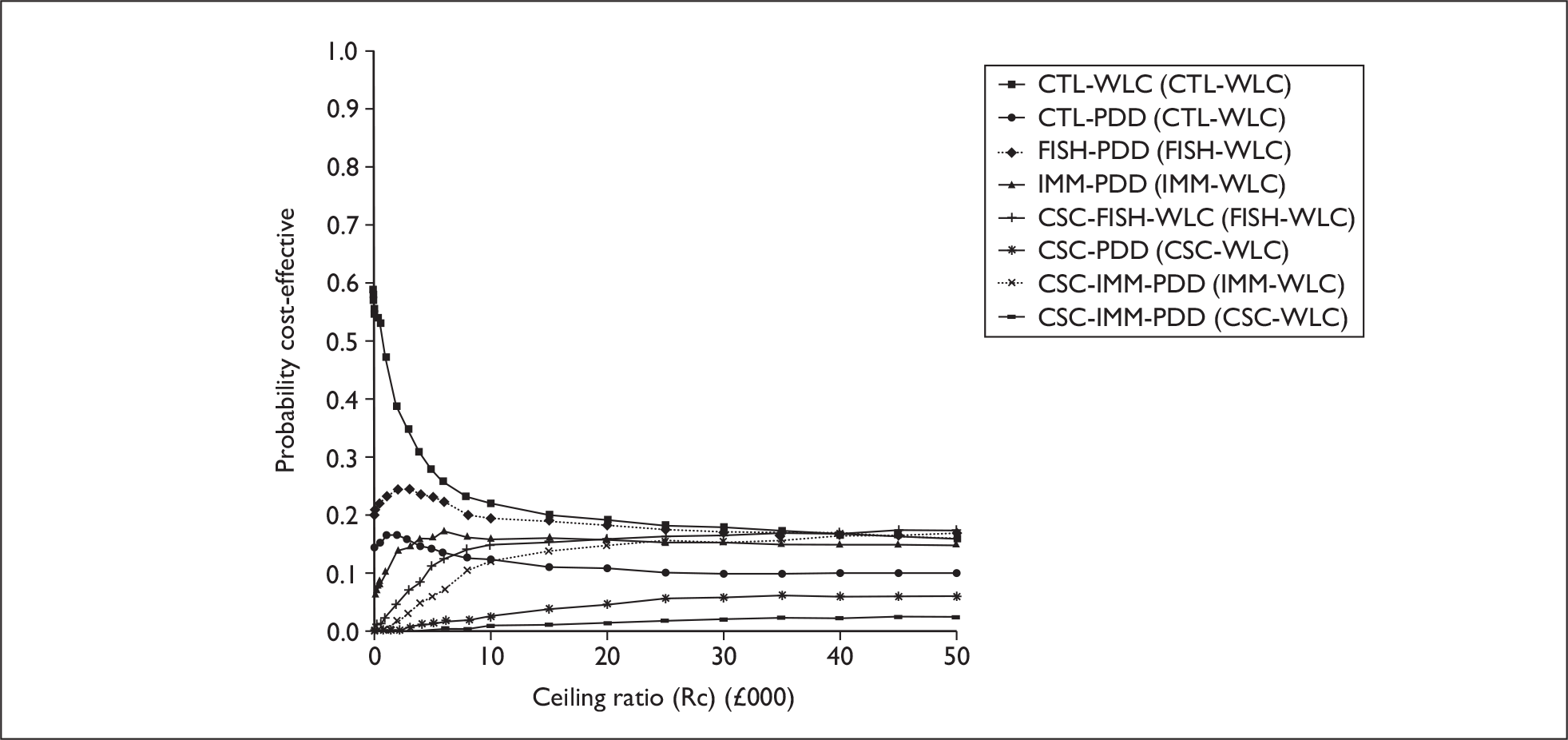
FIGURE 43.
Sensitivity and specificity of flexible cystoscopy are increased by 10% from base case.
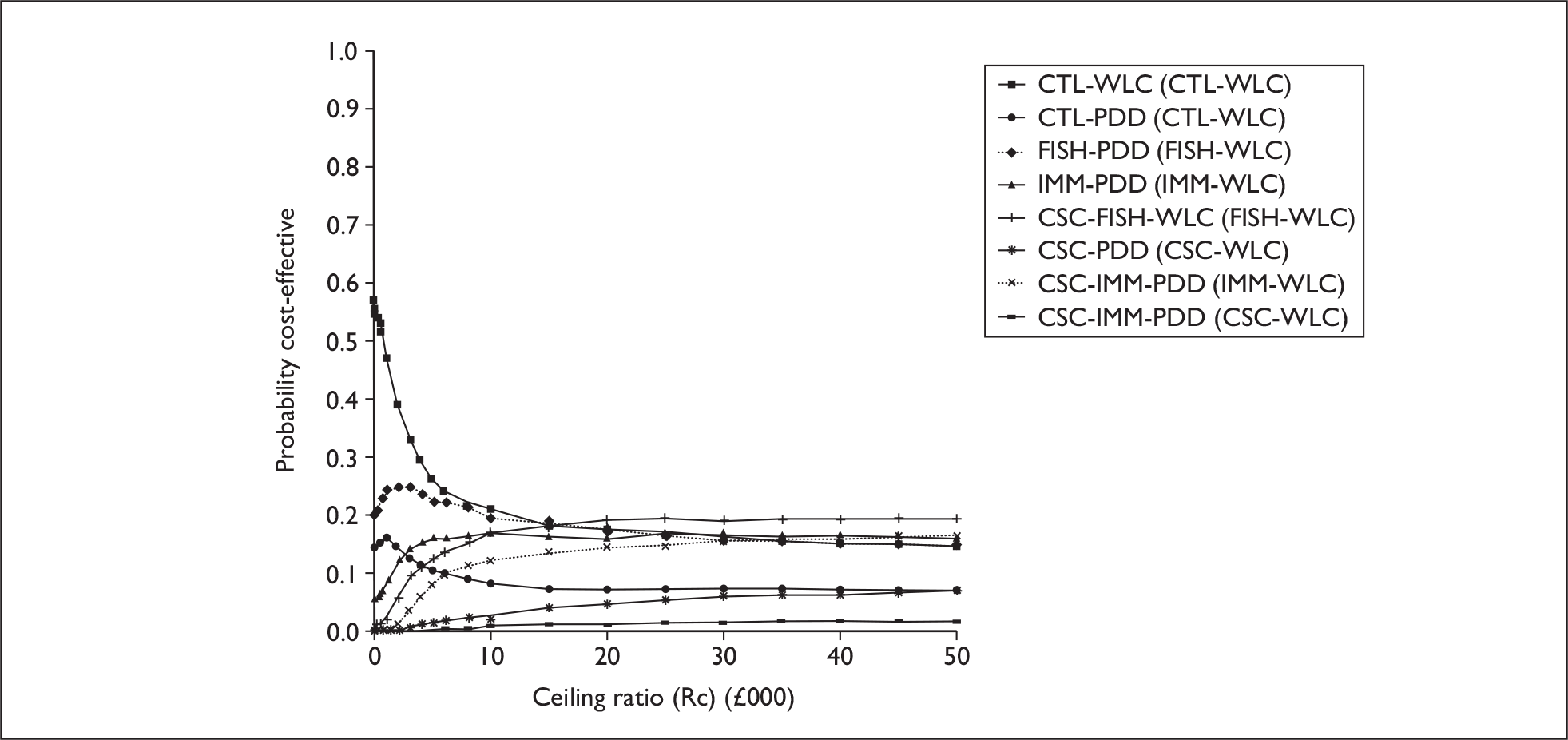
FIGURE 44.
Sensitivity and specificity of flexible cystoscopy are increased by 25% from base case.
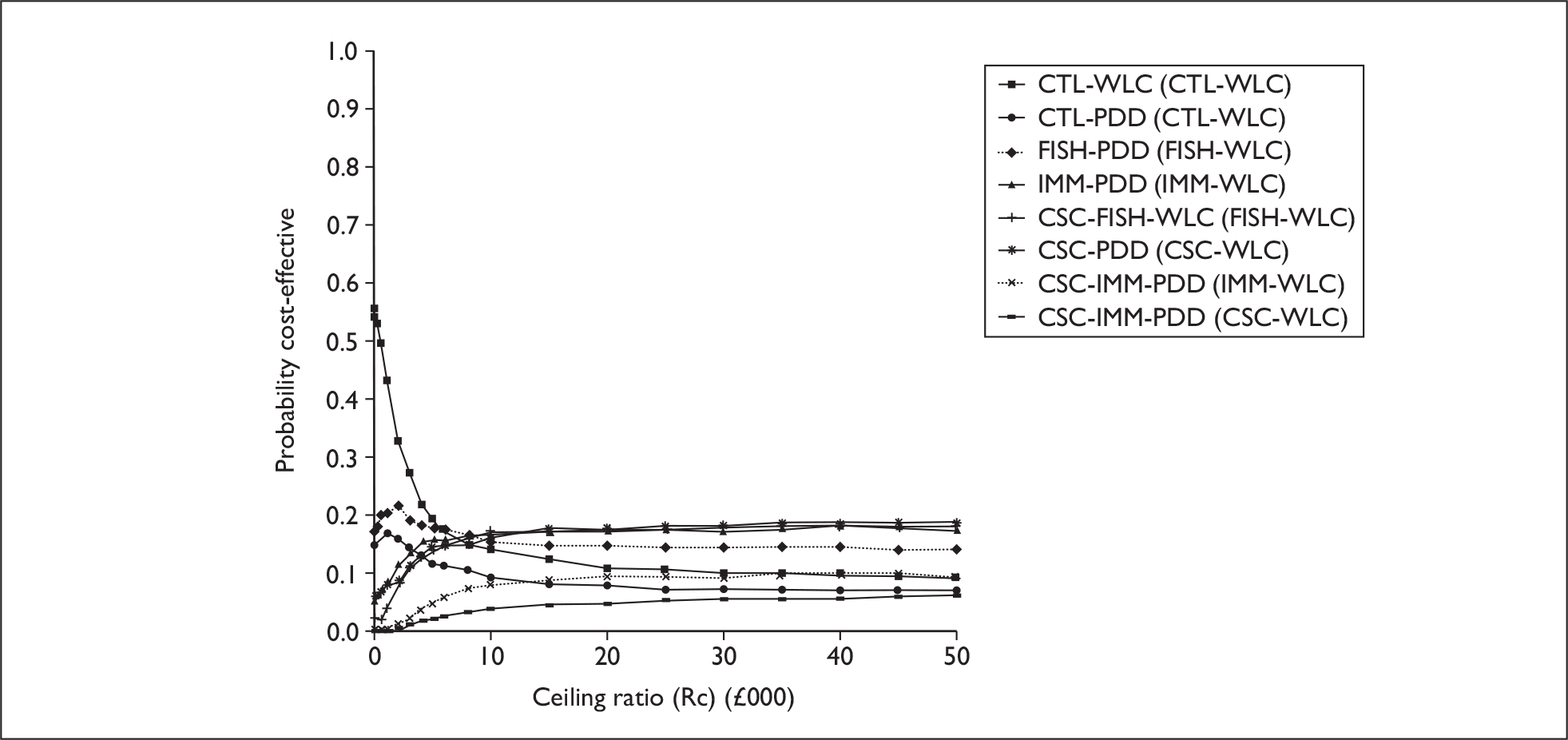
Appendix 22 Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves for changes to the relative risk (RR) of progression of bladder cancer for no treatment of bladder cancer compared with treatment of bladder cancer (base-case RR = 2.56)
FIGURE 45.
The relative risk for progression comparing no treatment with treatment is decreased to 2.0.
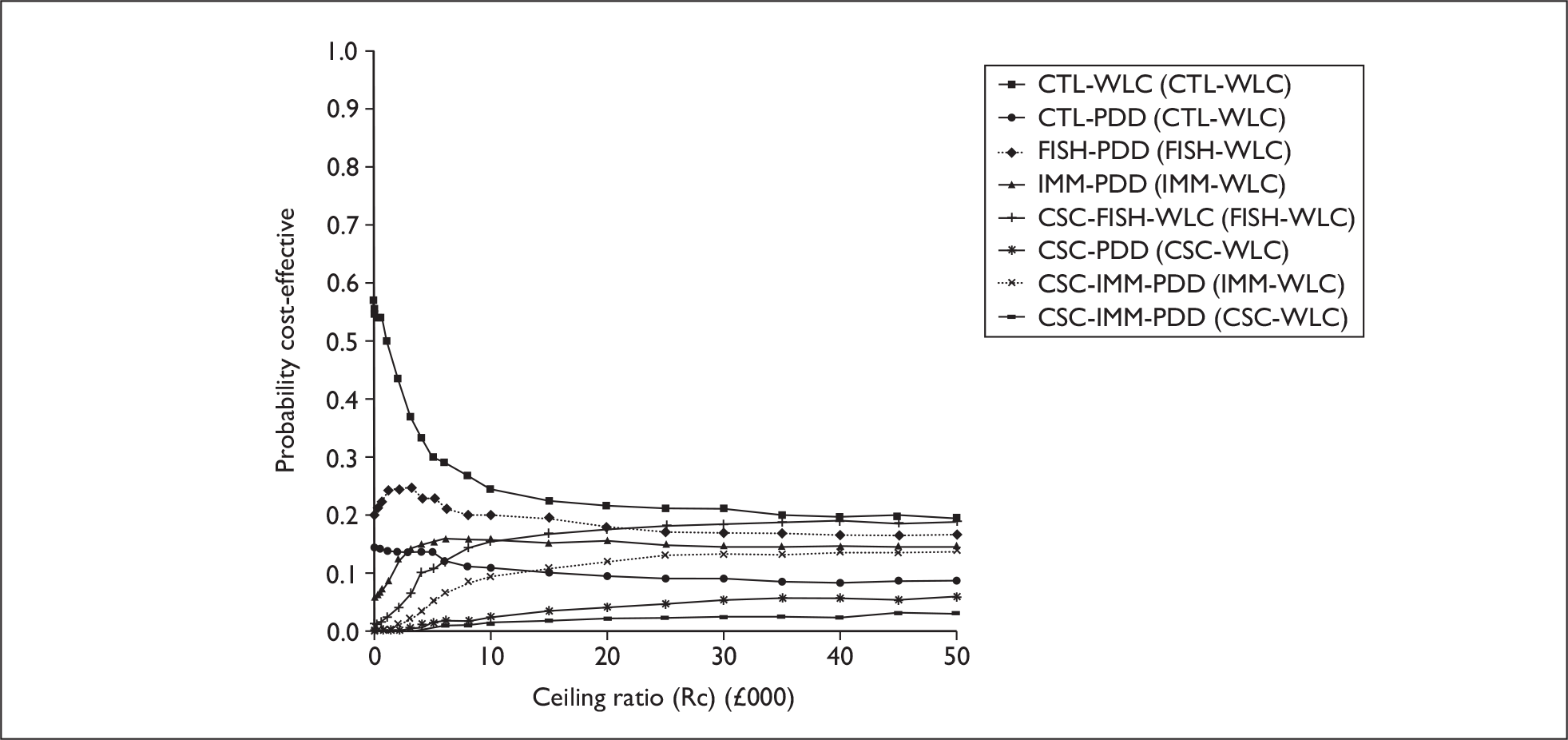
FIGURE 46.
The relative risk for progression comparing no treatment with treatment is decreased to 1.5.
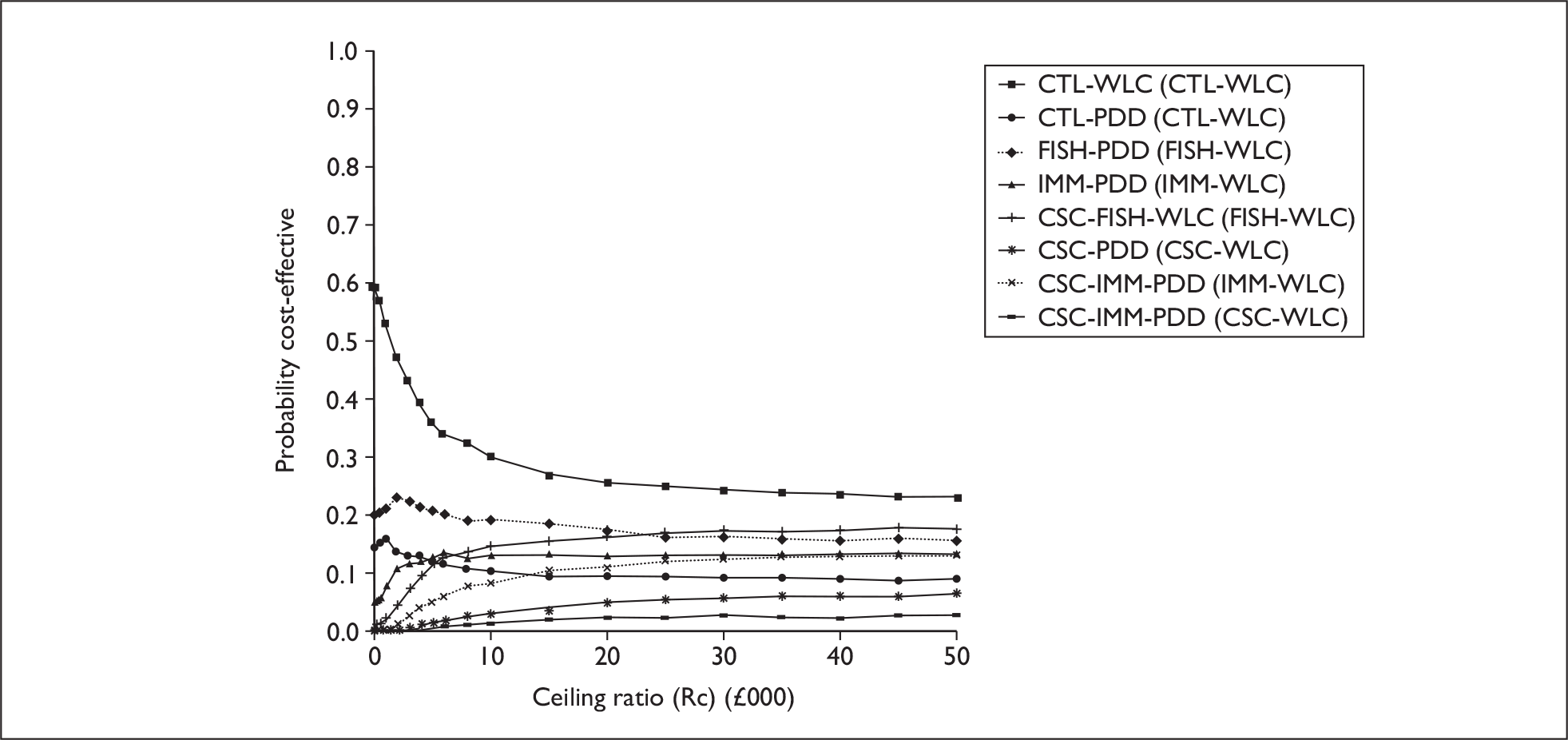
FIGURE 47.
The relative risk for progression comparing no treatment with treatment is decreased to 1.0.
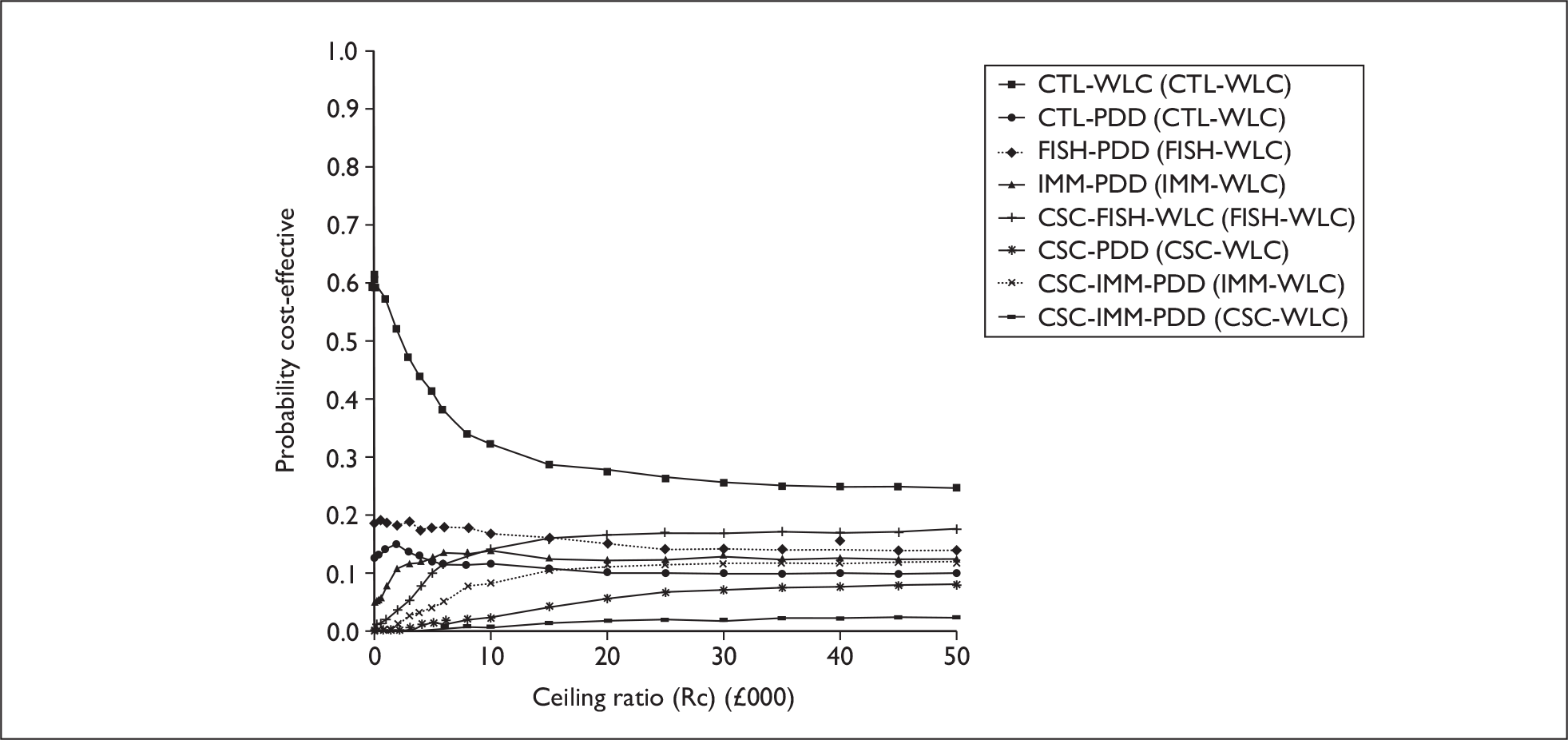
Appendix 23 Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves for the eight strategies for changes in the relative risk (RR) for recurrence comparing PDD with WLC (base-case RR = 1)
FIGURE 48.
The relative risk for recurrence for the comparison of PDD with WLC is 0.9.
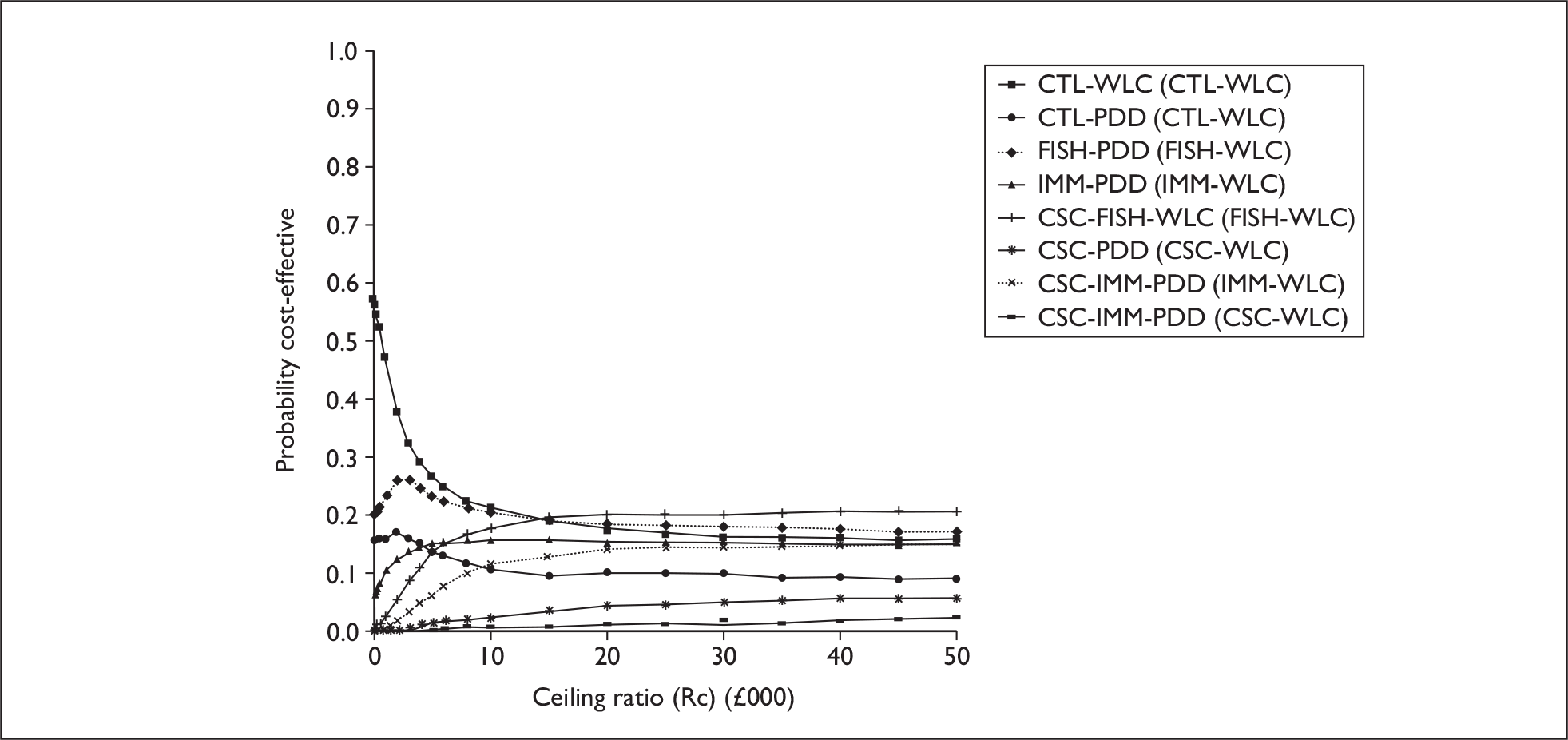
FIGURE 49.
The relative risk for recurrence for the comparison of PDD with WLC is 0.8.
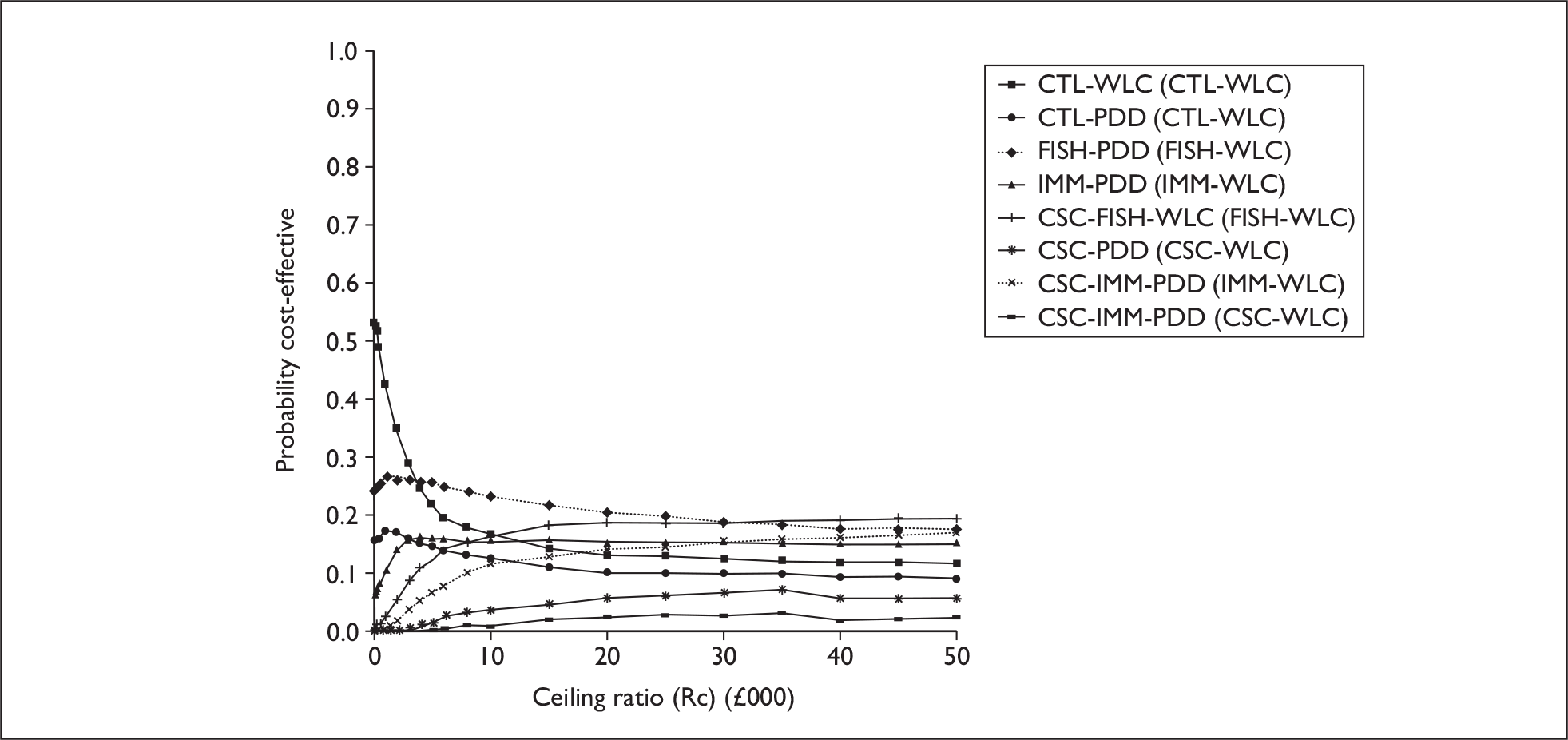
FIGURE 50.
The relative risk for recurrence for the comparison of PDD with WLC is 0.64.
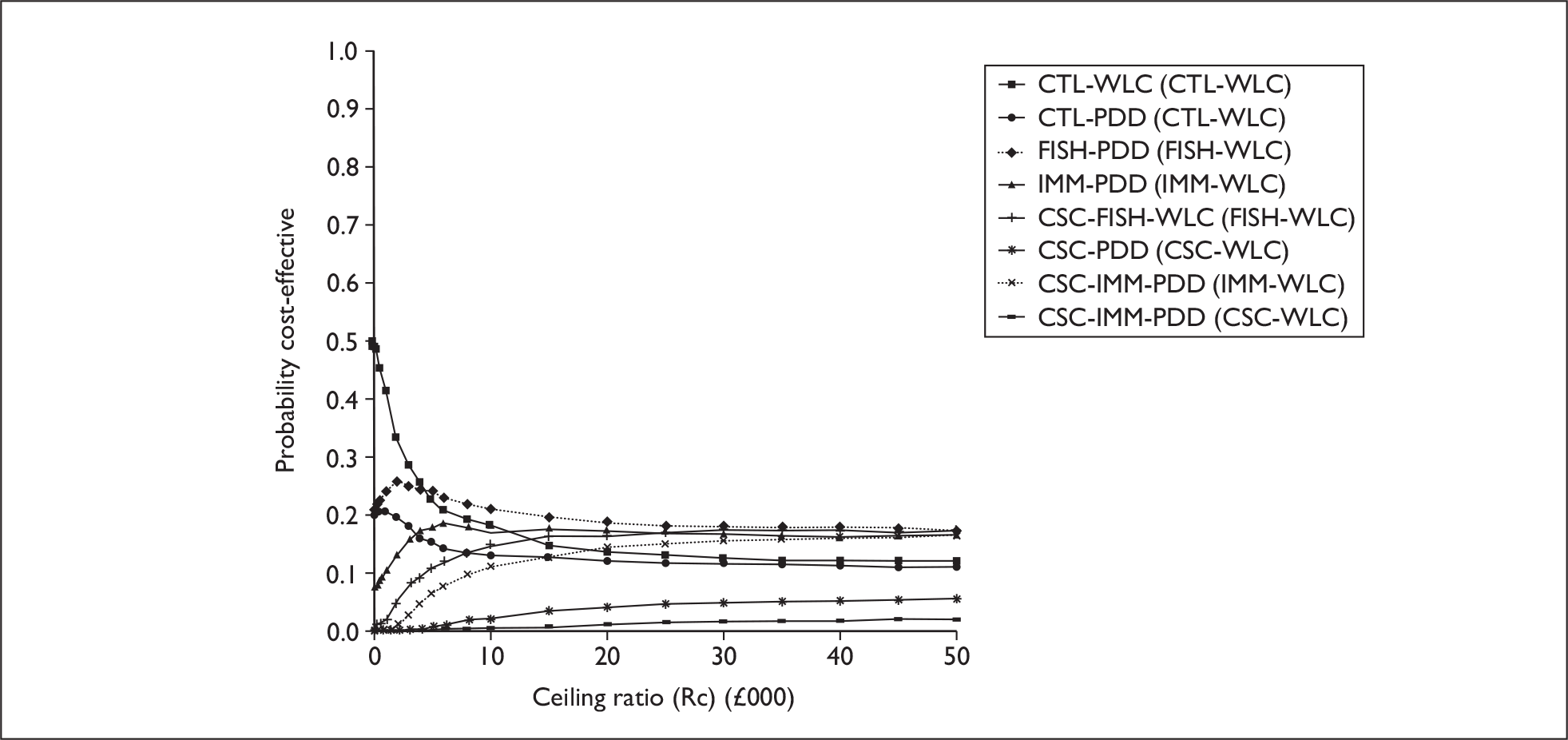
Appendix 24 Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves for the eight strategies for changes in the relative risk (RR) for progression comparing PDD with WLC (base-case RR = 1)
FIGURE 51.
The relative risk for progression for the comparison of PDD with WLC is 0.9.
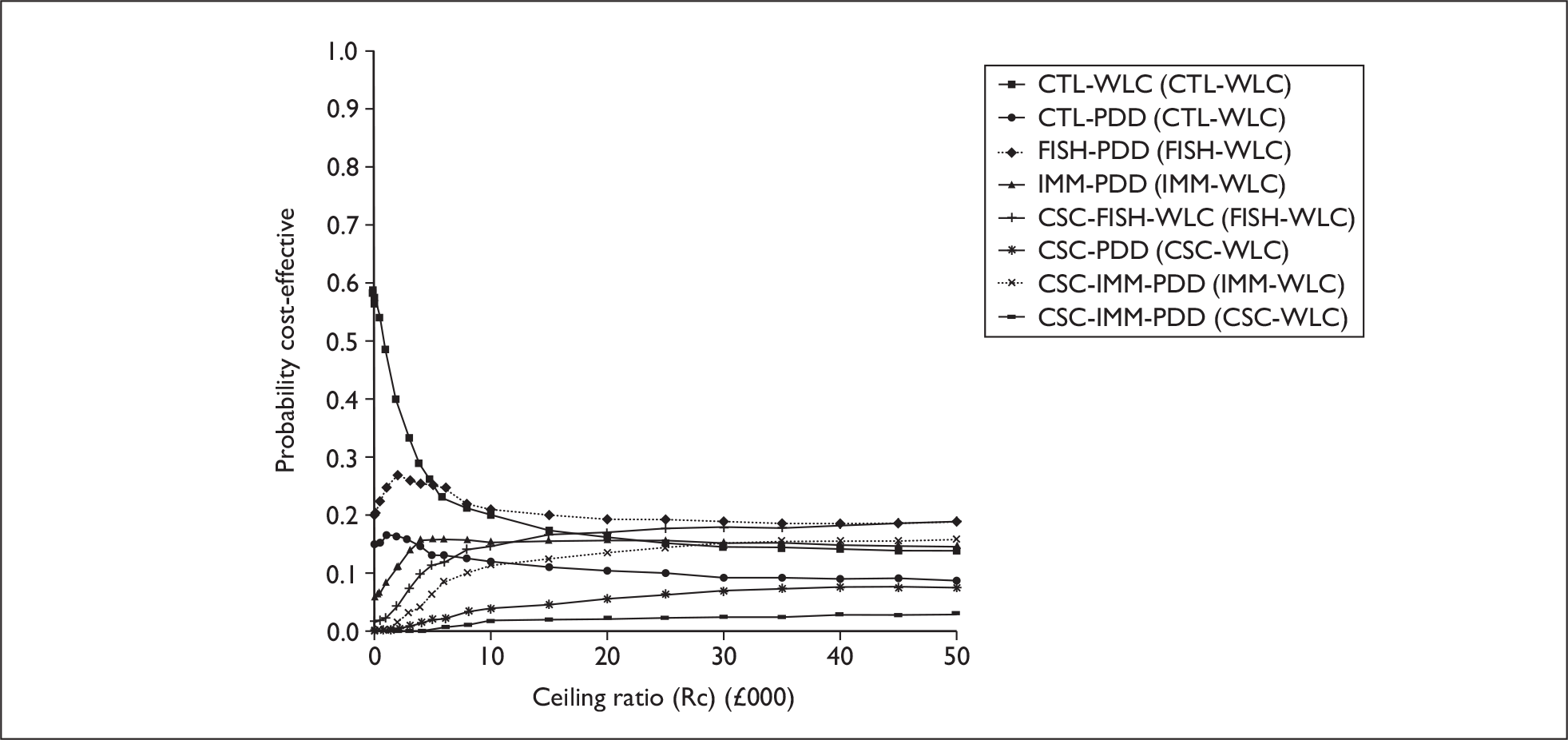
FIGURE 52.
The relative risk for progression for the comparison of PDD with WLC is 0.8.

FIGURE 53.
The relative risk for progression for the comparison of PDD with WLC is 0.56.
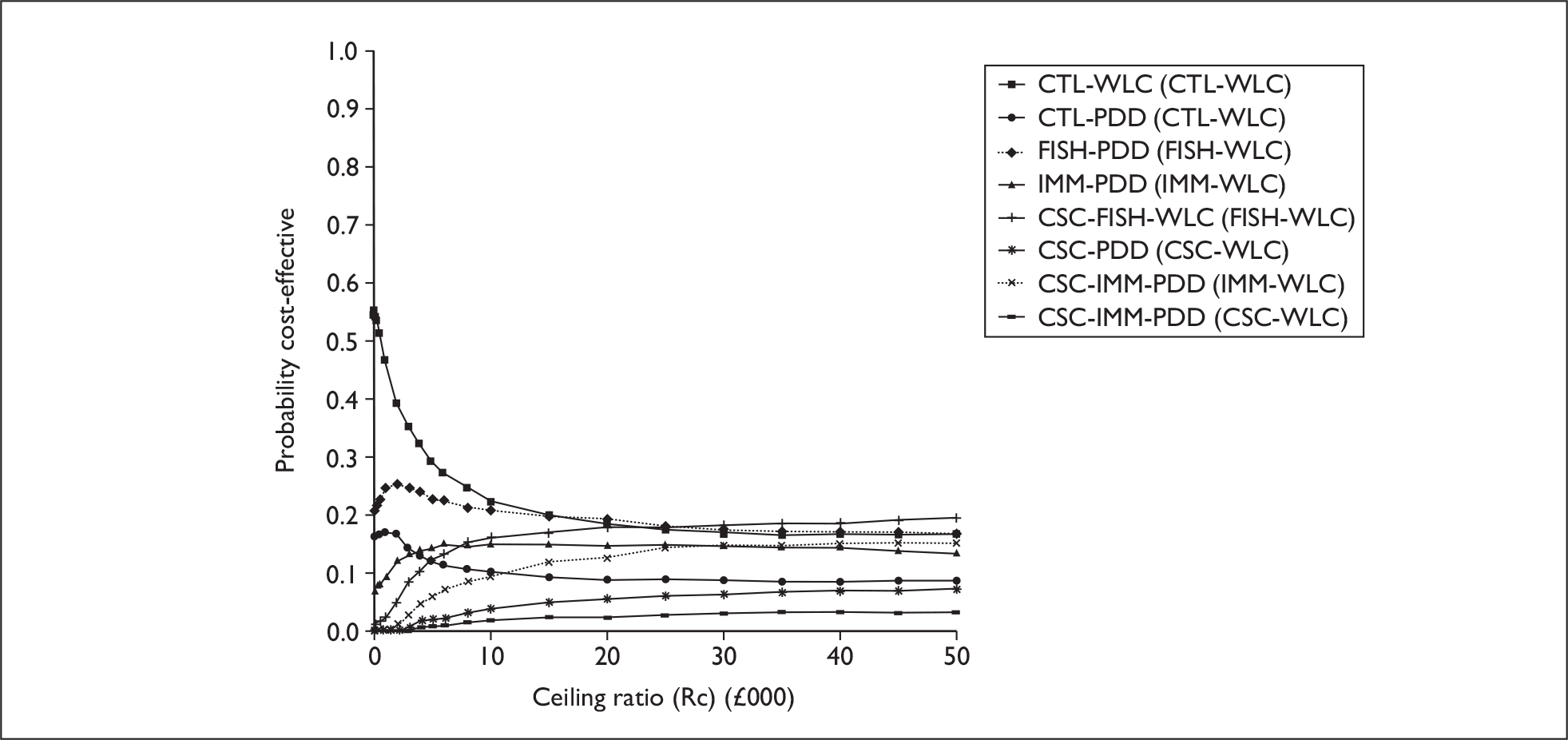
Appendix 25 Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves for the eight strategies for changes in the discount rate (base-case discount rate = 3.5%)
FIGURE 54.
The discount rate is 6%.
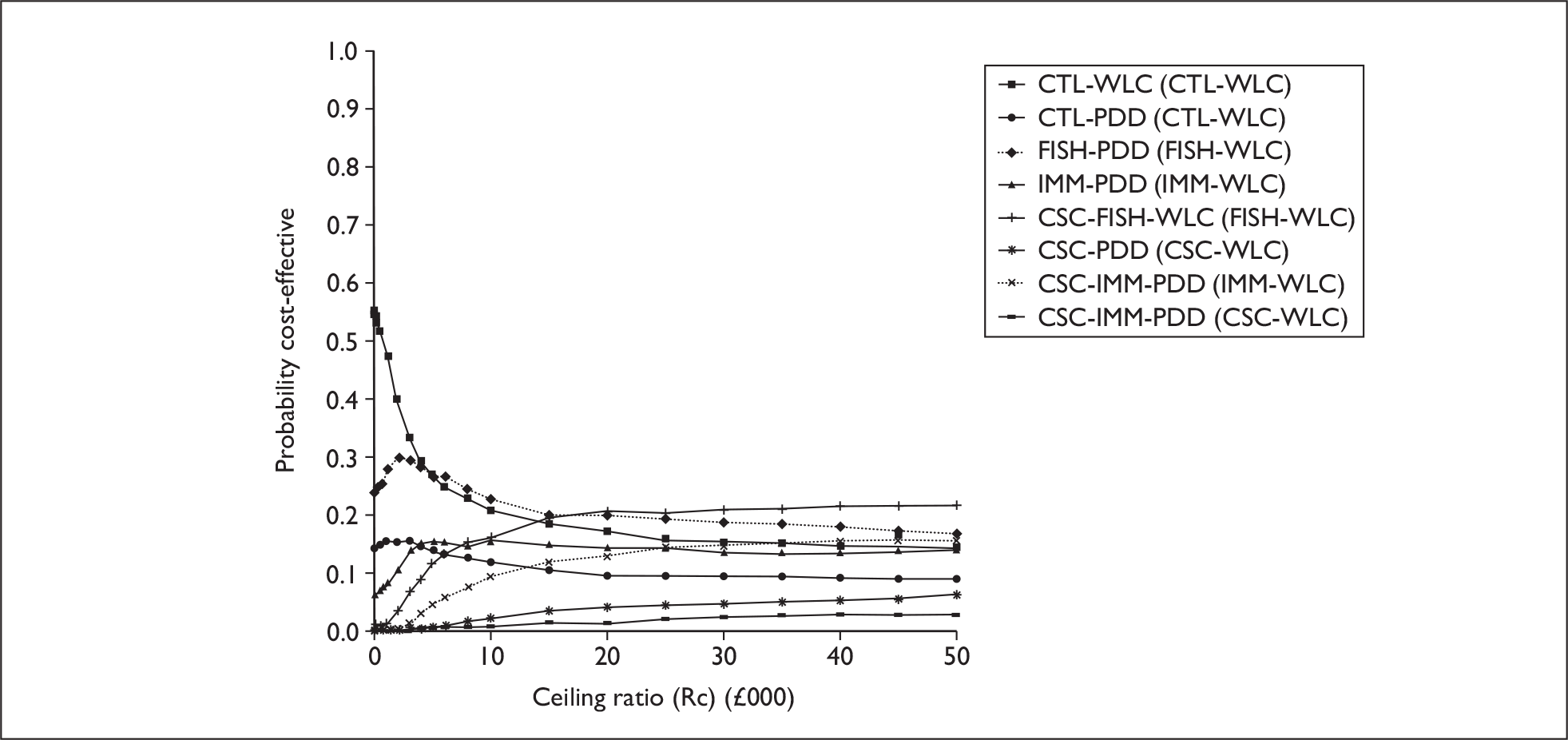
FIGURE 55.
The discount rate is 1%.
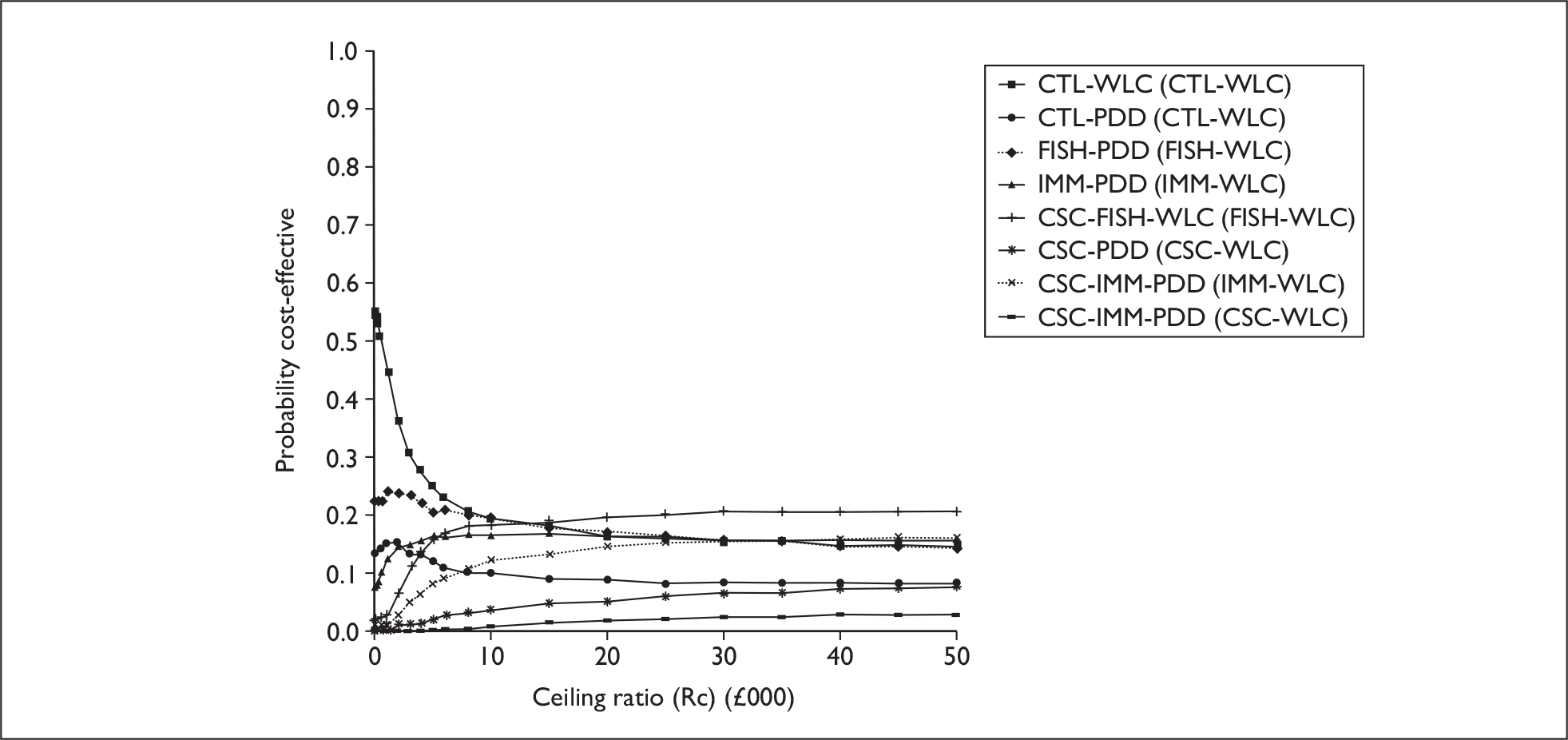
FIGURE 56.
The discount rate is 0%.
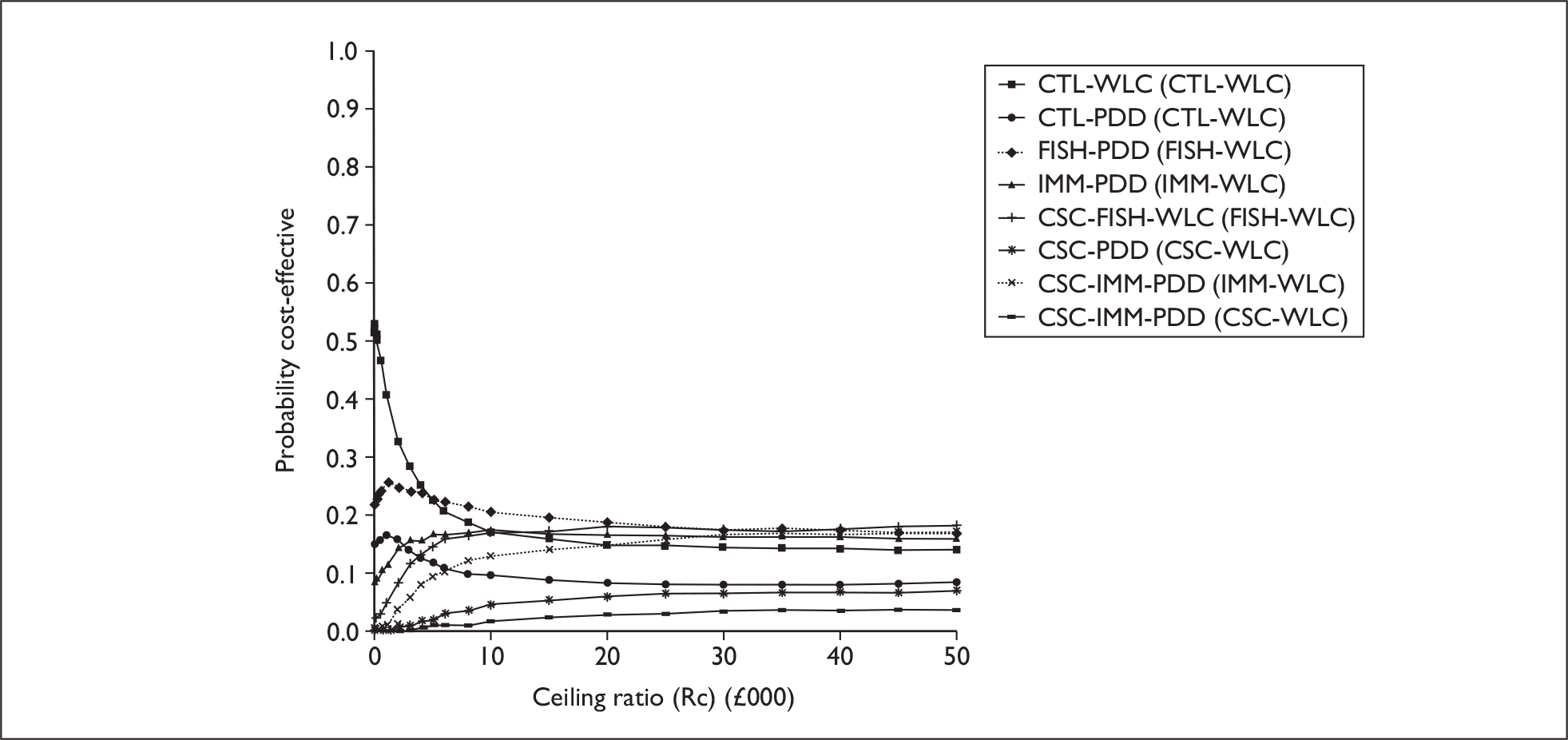
Appendix 26 Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves for the eight strategies for changes in proportions in the risk groups for non-invasive disease (base case: proportion in low-risk group is 0.1 and proportion is high-risk group is 0.45)
FIGURE 57.
Proportions in the high- and low-risk groups are 30%.
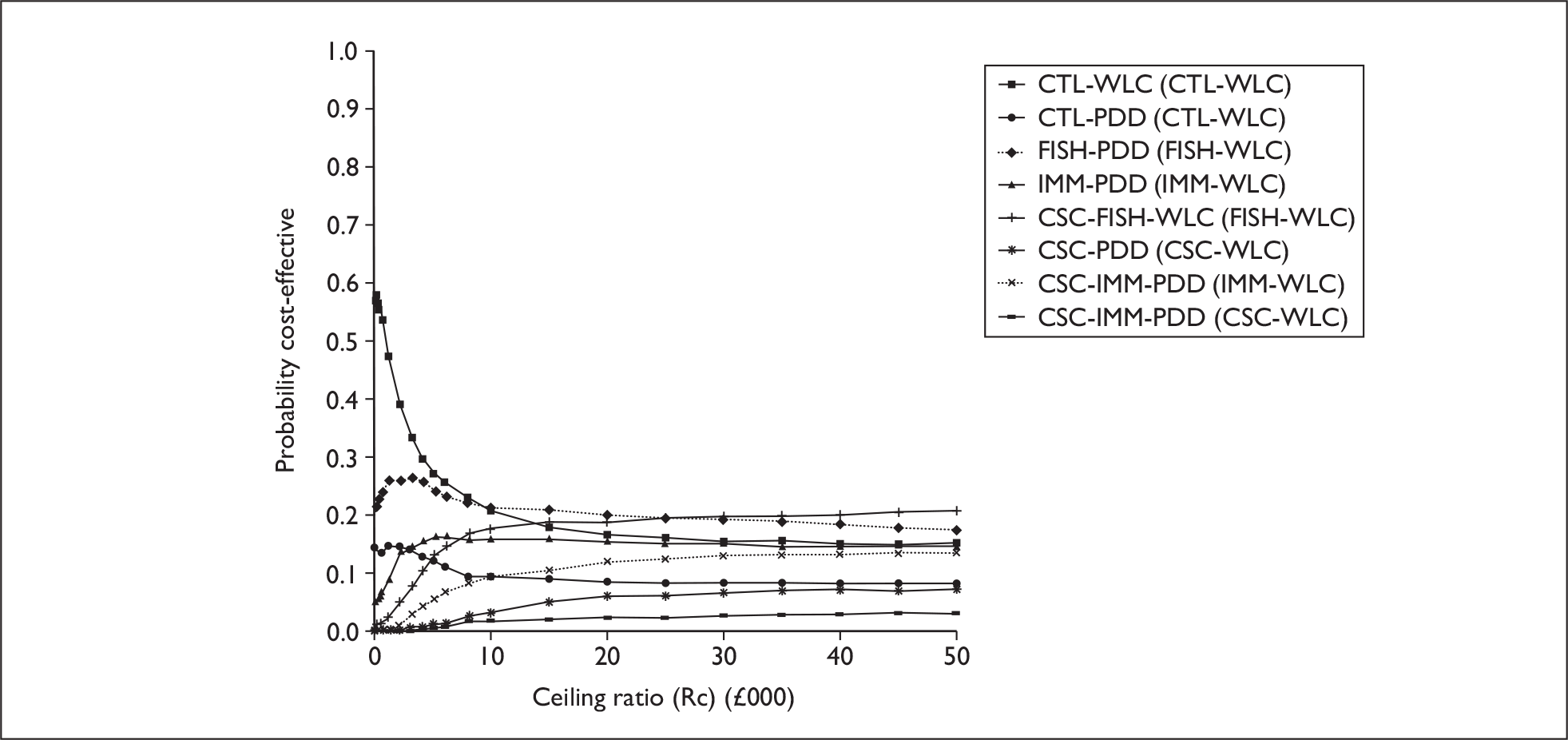
FIGURE 58.
Proportions in the high- and low-risk groups are 10% and 60% respectively.
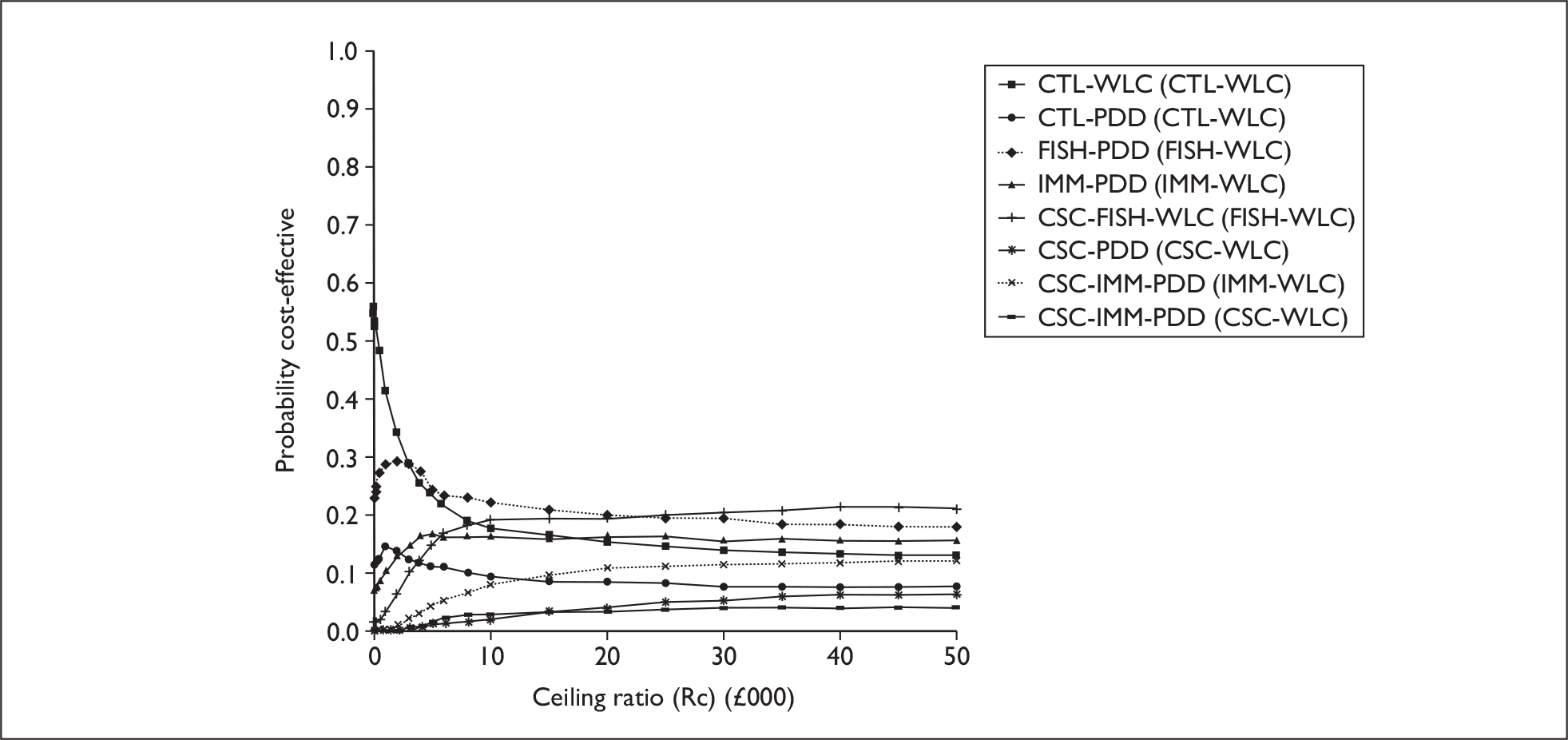
Appendix 27 Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves for the eight strategies for changes in the starting age and time horizon
FIGURE 59.
Starting age is 57 years.
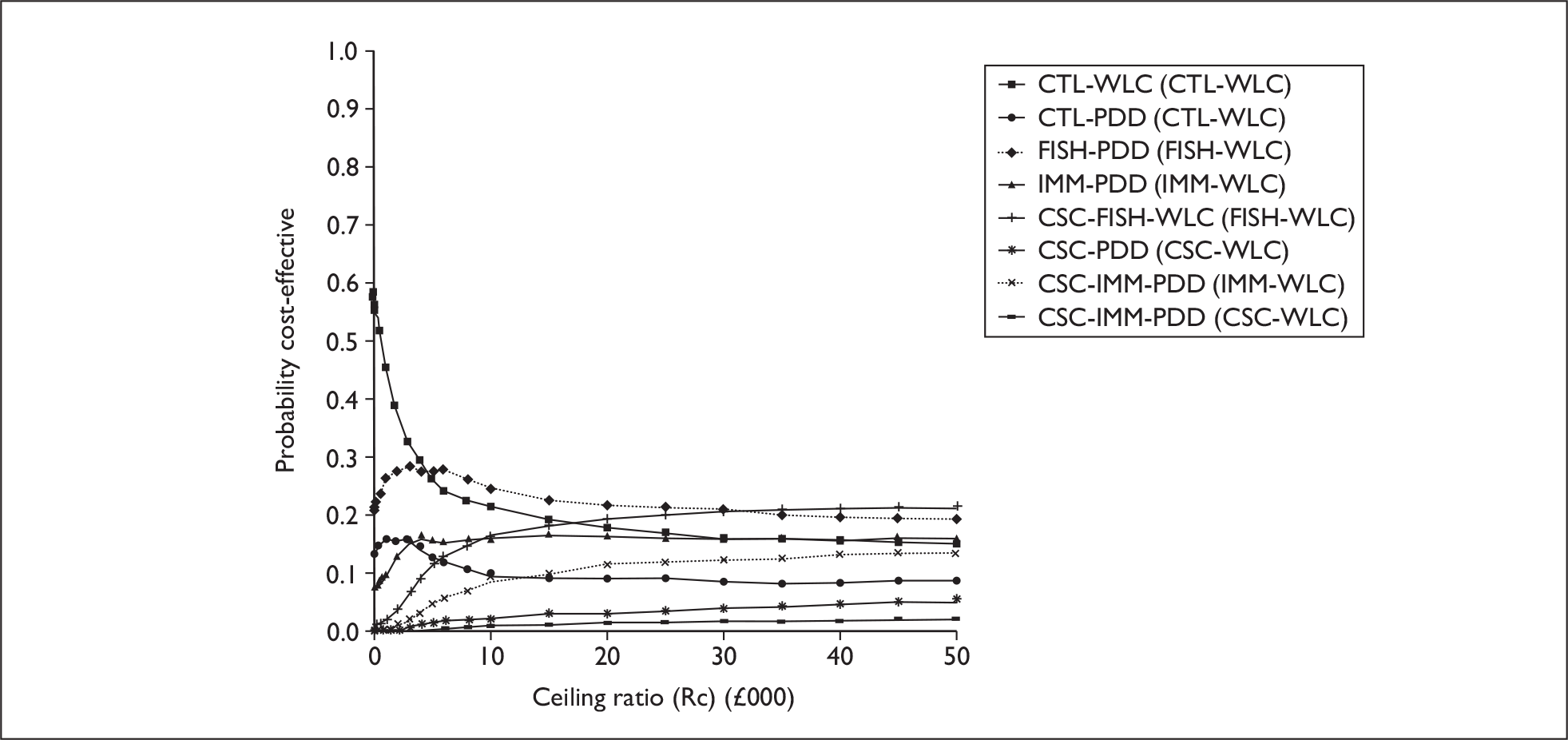
FIGURE 60.
Starting age is 77 years.
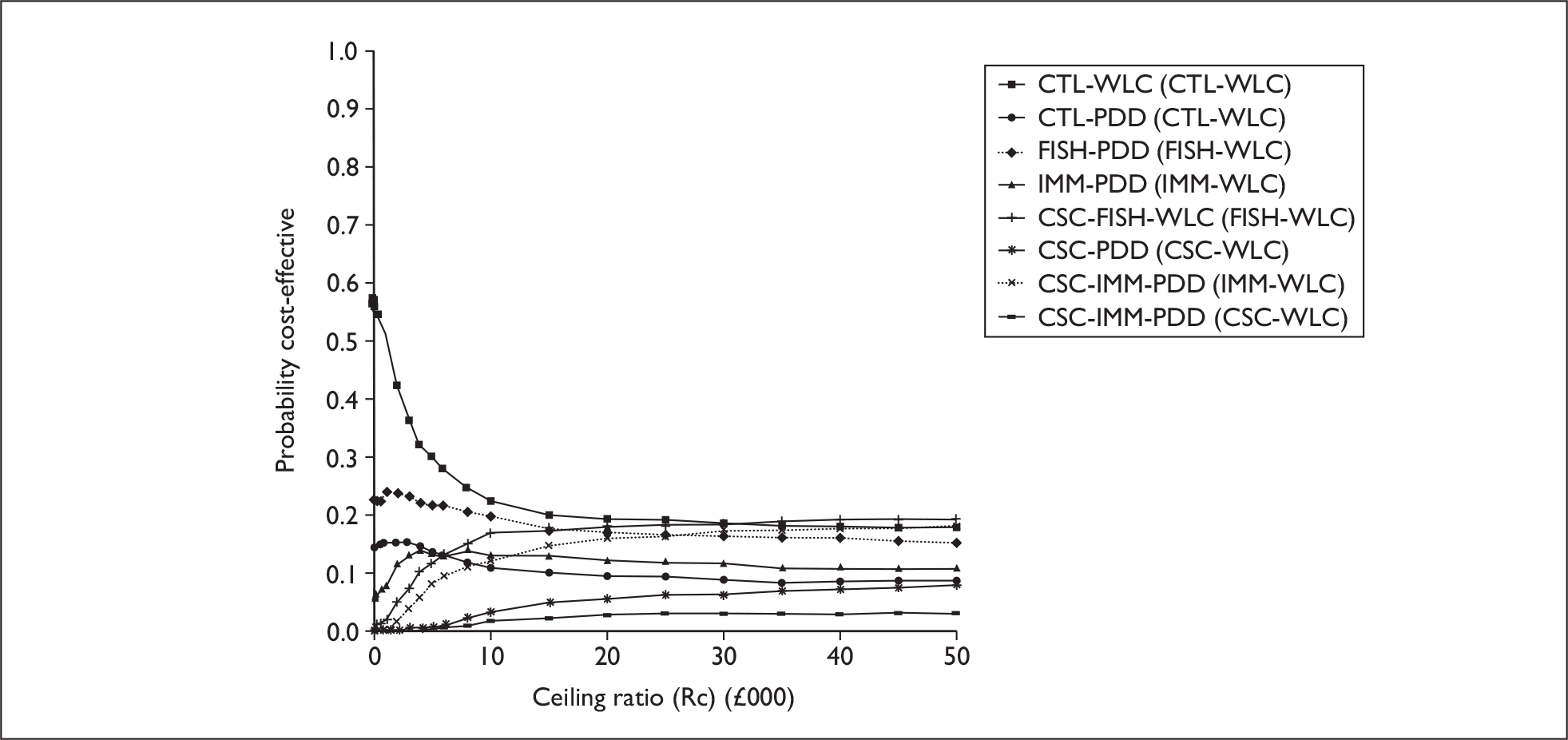
FIGURE 61.
Time horizon is 10 years.
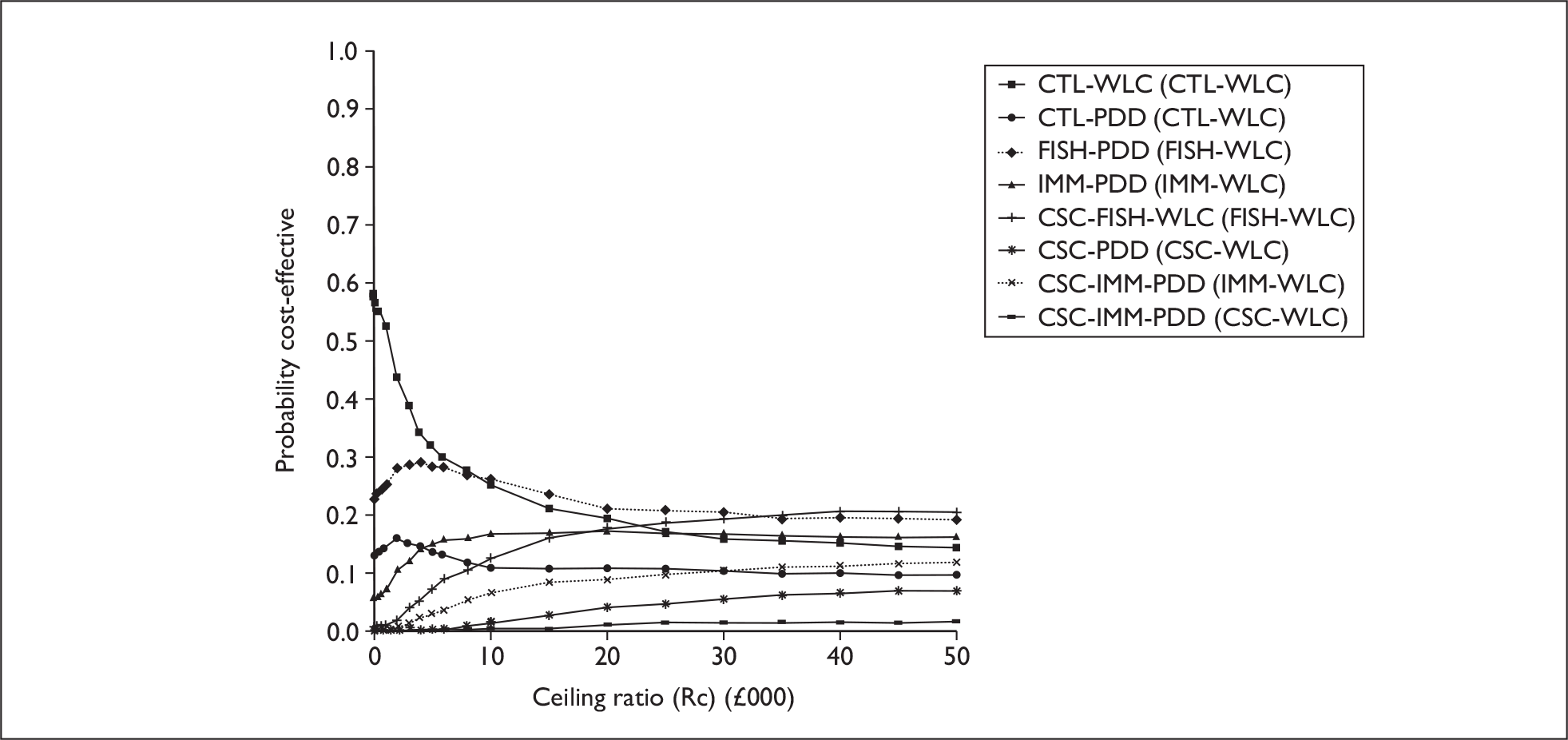
Appendix 28 Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves for the eight strategies when WLC is replaced by PDD in follow-up for each strategy
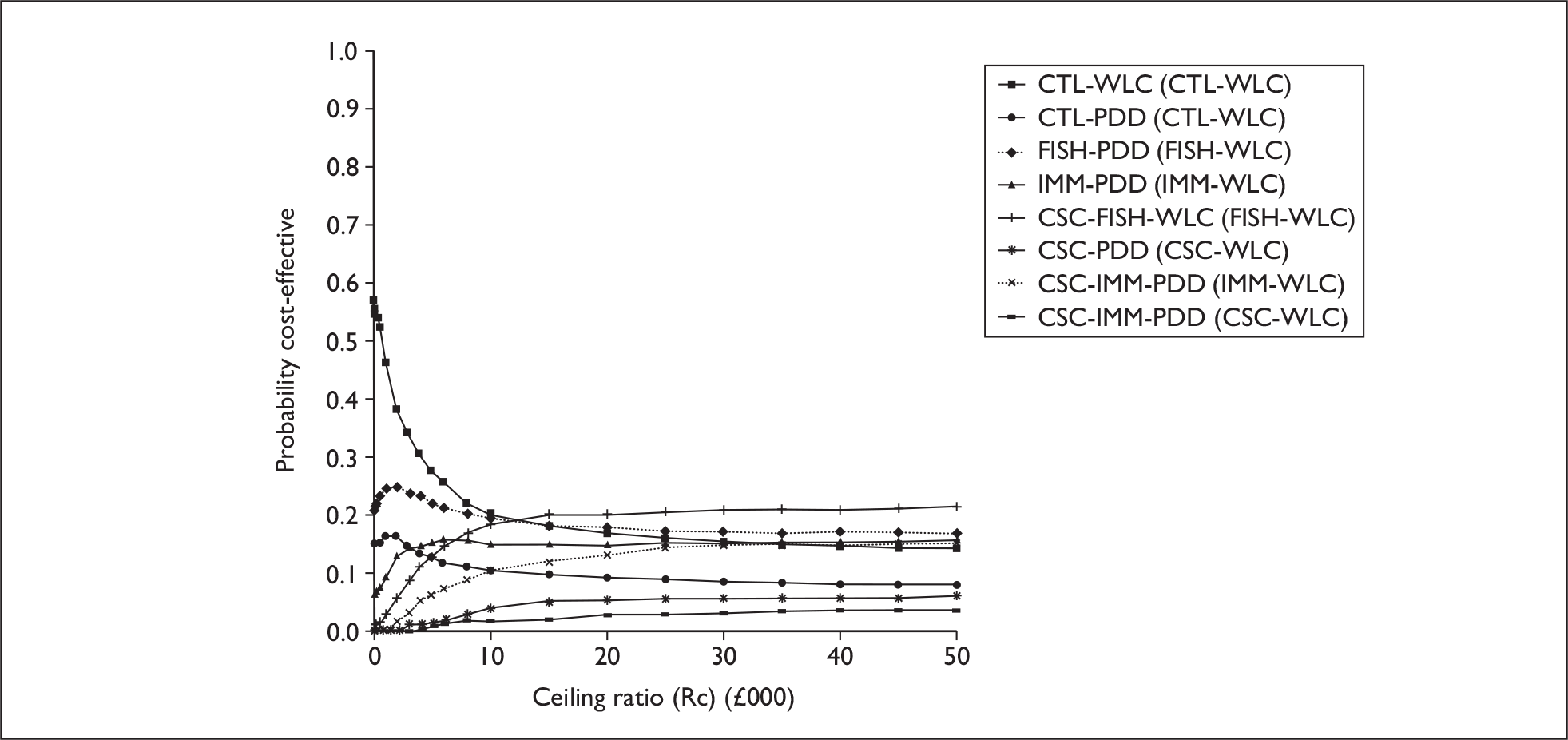
Appendix 29 Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves for the eight strategies when quality of life measures are incorporated to produce quality-adjusted life-years
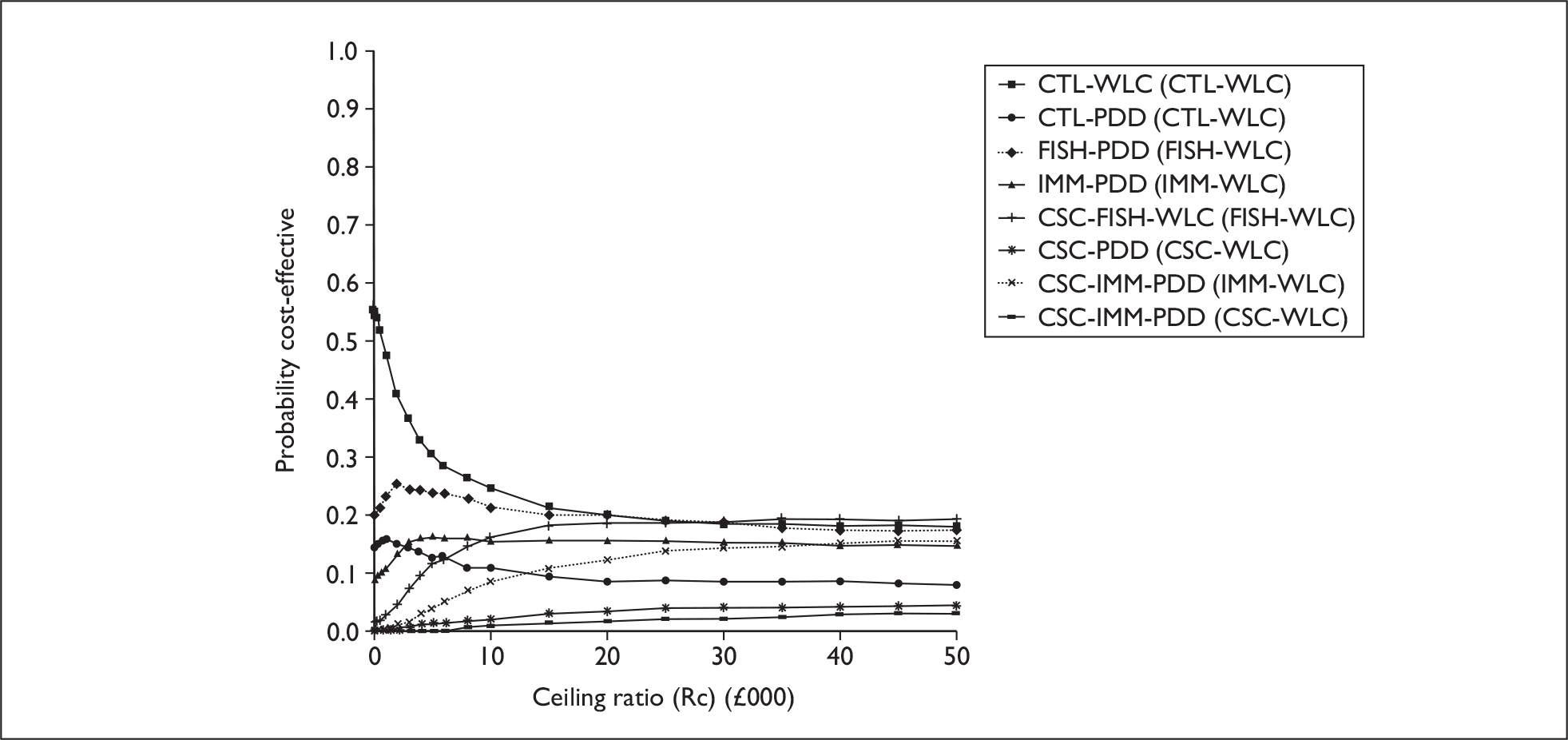
List of abbreviations
- 5-ALA
- 5-aminolaevulinic acid
- AUA
- American Urological Association
- BAUS
- British Association of Urological Surgeons
- BCG
- bacillus Calmette–Guerin
- BM
- biomarker
- CEAC
- cost-effectiveness acceptability curve
- CI
- confidence interval
- CIS
- carcinoma in situ
- CSC
- flexible cystoscopy
- CT
- computerised tomography
- CTL
- cytology
- DOR
- diagnostic odds ratio
- EAU
- European Association of Urology
- EORTC
- European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer
- FDA
- Food and Drug Administration
- FISH
- fluorescence in situ hybridisation
- GC
- gemcitabine, cisplatin
- GST
- glutathione S-transferase
- HAL
- hexaminolaevulinate
- HRG
- Healthcare Resource Group
- HSROC
- hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- IVP
- intravenous pyelography
- MDT
- multidisciplinary team
- MRI
- magnetic resonance imaging
- MVAC
- methotrexate, vinblastine, adriamycin, cisplatin
- NAT
- N-acetyltransferase
- NCRI
- National Cancer Research Institute
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
- NMP22
- nuclear matrix protein
- NPV
- negative predictive value
- PDD
- photodynamic diagnosis
- PPIX
- protoporphyrin IX
- PPV
- positive predictive value
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- QoL
- quality of life
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- ReBIP
- Review Body for Interventional Procedures
- RR
- relative risk
- SIGN
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network
- SROC
- summary receiver operating characteristic
- TCC
- transitional cell carcinoma
- TUR
- transurethral resection
- TURBT
- transurethral resection of bladder tumour
- WHO
- World Health Organization
- WLC
- white light cystoscopy
- WMD
- weighted mean difference
All abbreviations that have been used in this report are listed here unless the abbreviation is well known (e.g. NHS), or it has been used only once, or it is a non-standard abbreviation used only in figures/tables/appendices, in which case the abbreviation is defined in the figure legend or in the notes at the end of the table.
Notes
Health Technology Assessment reports published to date
-
Home parenteral nutrition: a systematic review.
By Richards DM, Deeks JJ, Sheldon TA, Shaffer JL.
-
Diagnosis, management and screening of early localised prostate cancer.
A review by Selley S, Donovan J, Faulkner A, Coast J, Gillatt D.
-
The diagnosis, management, treatment and costs of prostate cancer in England and Wales.
A review by Chamberlain J, Melia J, Moss S, Brown J.
-
Screening for fragile X syndrome.
A review by Murray J, Cuckle H, Taylor G, Hewison J.
-
A review of near patient testing in primary care.
By Hobbs FDR, Delaney BC, Fitzmaurice DA, Wilson S, Hyde CJ, Thorpe GH, et al.
-
Systematic review of outpatient services for chronic pain control.
By McQuay HJ, Moore RA, Eccleston C, Morley S, de C Williams AC.
-
Neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism: cost, yield and outcome.
A review by Pollitt RJ, Green A, McCabe CJ, Booth A, Cooper NJ, Leonard JV, et al.
-
Preschool vision screening.
A review by Snowdon SK, Stewart-Brown SL.
-
Implications of socio-cultural contexts for the ethics of clinical trials.
A review by Ashcroft RE, Chadwick DW, Clark SRL, Edwards RHT, Frith L, Hutton JL.
-
A critical review of the role of neonatal hearing screening in the detection of congenital hearing impairment.
By Davis A, Bamford J, Wilson I, Ramkalawan T, Forshaw M, Wright S.
-
Newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism: a systematic review.
By Seymour CA, Thomason MJ, Chalmers RA, Addison GM, Bain MD, Cockburn F, et al.
-
Routine preoperative testing: a systematic review of the evidence.
By Munro J, Booth A, Nicholl J.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness of laxatives in the elderly.
By Petticrew M, Watt I, Sheldon T.
-
When and how to assess fast-changing technologies: a comparative study of medical applications of four generic technologies.
A review by Mowatt G, Bower DJ, Brebner JA, Cairns JA, Grant AM, McKee L.
-
Antenatal screening for Down’s syndrome.
A review by Wald NJ, Kennard A, Hackshaw A, McGuire A.
-
Screening for ovarian cancer: a systematic review.
By Bell R, Petticrew M, Luengo S, Sheldon TA.
-
Consensus development methods, and their use in clinical guideline development.
A review by Murphy MK, Black NA, Lamping DL, McKee CM, Sanderson CFB, Askham J, et al.
-
A cost–utility analysis of interferon beta for multiple sclerosis.
By Parkin D, McNamee P, Jacoby A, Miller P, Thomas S, Bates D.
-
Effectiveness and efficiency of methods of dialysis therapy for end-stage renal disease: systematic reviews.
By MacLeod A, Grant A, Donaldson C, Khan I, Campbell M, Daly C, et al.
-
Effectiveness of hip prostheses in primary total hip replacement: a critical review of evidence and an economic model.
By Faulkner A, Kennedy LG, Baxter K, Donovan J, Wilkinson M, Bevan G.
-
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in colorectal surgery: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials.
By Song F, Glenny AM.
-
Bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for malignancy.
A review by Johnson PWM, Simnett SJ, Sweetenham JW, Morgan GJ, Stewart LA.
-
Screening for speech and language delay: a systematic review of the literature.
By Law J, Boyle J, Harris F, Harkness A, Nye C.
-
Resource allocation for chronic stable angina: a systematic review of effectiveness, costs and cost-effectiveness of alternative interventions.
By Sculpher MJ, Petticrew M, Kelland JL, Elliott RA, Holdright DR, Buxton MJ.
-
Detection, adherence and control of hypertension for the prevention of stroke: a systematic review.
By Ebrahim S.
-
Postoperative analgesia and vomiting, with special reference to day-case surgery: a systematic review.
By McQuay HJ, Moore RA.
-
Choosing between randomised and nonrandomised studies: a systematic review.
By Britton A, McKee M, Black N, McPherson K, Sanderson C, Bain C.
-
Evaluating patient-based outcome measures for use in clinical trials.
A review by Fitzpatrick R, Davey C, Buxton MJ, Jones DR.
-
Ethical issues in the design and conduct of randomised controlled trials.
A review by Edwards SJL, Lilford RJ, Braunholtz DA, Jackson JC, Hewison J, Thornton J.
-
Qualitative research methods in health technology assessment: a review of the literature.
By Murphy E, Dingwall R, Greatbatch D, Parker S, Watson P.
-
The costs and benefits of paramedic skills in pre-hospital trauma care.
By Nicholl J, Hughes S, Dixon S, Turner J, Yates D.
-
Systematic review of endoscopic ultrasound in gastro-oesophageal cancer.
By Harris KM, Kelly S, Berry E, Hutton J, Roderick P, Cullingworth J, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of trials and other studies.
By Sutton AJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR, Sheldon TA, Song F.
-
Primary total hip replacement surgery: a systematic review of outcomes and modelling of cost-effectiveness associated with different prostheses.
A review by Fitzpatrick R, Shortall E, Sculpher M, Murray D, Morris R, Lodge M, et al.
-
Informed decision making: an annotated bibliography and systematic review.
By Bekker H, Thornton JG, Airey CM, Connelly JB, Hewison J, Robinson MB, et al.
-
Handling uncertainty when performing economic evaluation of healthcare interventions.
A review by Briggs AH, Gray AM.
-
The role of expectancies in the placebo effect and their use in the delivery of health care: a systematic review.
By Crow R, Gage H, Hampson S, Hart J, Kimber A, Thomas H.
-
A randomised controlled trial of different approaches to universal antenatal HIV testing: uptake and acceptability. Annex: Antenatal HIV testing – assessment of a routine voluntary approach.
By Simpson WM, Johnstone FD, Boyd FM, Goldberg DJ, Hart GJ, Gormley SM, et al.
-
Methods for evaluating area-wide and organisation-based interventions in health and health care: a systematic review.
By Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ.
-
Assessing the costs of healthcare technologies in clinical trials.
A review by Johnston K, Buxton MJ, Jones DR, Fitzpatrick R.
-
Cooperatives and their primary care emergency centres: organisation and impact.
By Hallam L, Henthorne K.
-
Screening for cystic fibrosis.
A review by Murray J, Cuckle H, Taylor G, Littlewood J, Hewison J.
-
A review of the use of health status measures in economic evaluation.
By Brazier J, Deverill M, Green C, Harper R, Booth A.
-
Methods for the analysis of quality-of-life and survival data in health technology assessment.
A review by Billingham LJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR.
-
Antenatal and neonatal haemoglobinopathy screening in the UK: review and economic analysis.
By Zeuner D, Ades AE, Karnon J, Brown J, Dezateux C, Anionwu EN.
-
Assessing the quality of reports of randomised trials: implications for the conduct of meta-analyses.
A review by Moher D, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Tugwell P, Moher M, Jones A, et al.
-
‘Early warning systems’ for identifying new healthcare technologies.
By Robert G, Stevens A, Gabbay J.
-
A systematic review of the role of human papillomavirus testing within a cervical screening programme.
By Cuzick J, Sasieni P, Davies P, Adams J, Normand C, Frater A, et al.
-
Near patient testing in diabetes clinics: appraising the costs and outcomes.
By Grieve R, Beech R, Vincent J, Mazurkiewicz J.
-
Positron emission tomography: establishing priorities for health technology assessment.
A review by Robert G, Milne R.
-
The debridement of chronic wounds: a systematic review.
By Bradley M, Cullum N, Sheldon T.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (2) Dressings and topical agents used in the healing of chronic wounds.
By Bradley M, Cullum N, Nelson EA, Petticrew M, Sheldon T, Torgerson D.
-
A systematic literature review of spiral and electron beam computed tomography: with particular reference to clinical applications in hepatic lesions, pulmonary embolus and coronary artery disease.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Hutton J, Harris KM, Roderick P, Boyce JC, et al.
-
What role for statins? A review and economic model.
By Ebrahim S, Davey Smith G, McCabe C, Payne N, Pickin M, Sheldon TA, et al.
-
Factors that limit the quality, number and progress of randomised controlled trials.
A review by Prescott RJ, Counsell CE, Gillespie WJ, Grant AM, Russell IT, Kiauka S, et al.
-
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in total hip replacement: a systematic review.
By Glenny AM, Song F.
-
Health promoting schools and health promotion in schools: two systematic reviews.
By Lister-Sharp D, Chapman S, Stewart-Brown S, Sowden A.
-
Economic evaluation of a primary care-based education programme for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee.
A review by Lord J, Victor C, Littlejohns P, Ross FM, Axford JS.
-
The estimation of marginal time preference in a UK-wide sample (TEMPUS) project.
A review by Cairns JA, van der Pol MM.
-
Geriatric rehabilitation following fractures in older people: a systematic review.
By Cameron I, Crotty M, Currie C, Finnegan T, Gillespie L, Gillespie W, et al.
-
Screening for sickle cell disease and thalassaemia: a systematic review with supplementary research.
By Davies SC, Cronin E, Gill M, Greengross P, Hickman M, Normand C.
-
Community provision of hearing aids and related audiology services.
A review by Reeves DJ, Alborz A, Hickson FS, Bamford JM.
-
False-negative results in screening programmes: systematic review of impact and implications.
By Petticrew MP, Sowden AJ, Lister-Sharp D, Wright K.
-
Costs and benefits of community postnatal support workers: a randomised controlled trial.
By Morrell CJ, Spiby H, Stewart P, Walters S, Morgan A.
-
Implantable contraceptives (subdermal implants and hormonally impregnated intrauterine systems) versus other forms of reversible contraceptives: two systematic reviews to assess relative effectiveness, acceptability, tolerability and cost-effectiveness.
By French RS, Cowan FM, Mansour DJA, Morris S, Procter T, Hughes D, et al.
-
An introduction to statistical methods for health technology assessment.
A review by White SJ, Ashby D, Brown PJ.
-
Disease-modifying drugs for multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By Clegg A, Bryant J, Milne R.
-
Publication and related biases.
A review by Song F, Eastwood AJ, Gilbody S, Duley L, Sutton AJ.
-
Cost and outcome implications of the organisation of vascular services.
By Michaels J, Brazier J, Palfreyman S, Shackley P, Slack R.
-
Monitoring blood glucose control in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review.
By Coster S, Gulliford MC, Seed PT, Powrie JK, Swaminathan R.
-
The effectiveness of domiciliary health visiting: a systematic review of international studies and a selective review of the British literature.
By Elkan R, Kendrick D, Hewitt M, Robinson JJA, Tolley K, Blair M, et al.
-
The determinants of screening uptake and interventions for increasing uptake: a systematic review.
By Jepson R, Clegg A, Forbes C, Lewis R, Sowden A, Kleijnen J.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of prophylactic removal of wisdom teeth.
A rapid review by Song F, O’Meara S, Wilson P, Golder S, Kleijnen J.
-
Ultrasound screening in pregnancy: a systematic review of the clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and women’s views.
By Bricker L, Garcia J, Henderson J, Mugford M, Neilson J, Roberts T, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the taxanes used in the treatment of advanced breast and ovarian cancer.
By Lister-Sharp D, McDonagh MS, Khan KS, Kleijnen J.
-
Liquid-based cytology in cervical screening: a rapid and systematic review.
By Payne N, Chilcott J, McGoogan E.
-
Randomised controlled trial of non-directive counselling, cognitive–behaviour therapy and usual general practitioner care in the management of depression as well as mixed anxiety and depression in primary care.
By King M, Sibbald B, Ward E, Bower P, Lloyd M, Gabbay M, et al.
-
Routine referral for radiography of patients presenting with low back pain: is patients’ outcome influenced by GPs’ referral for plain radiography?
By Kerry S, Hilton S, Patel S, Dundas D, Rink E, Lord J.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (3) antimicrobial agents for chronic wounds; (4) diabetic foot ulceration.
By O’Meara S, Cullum N, Majid M, Sheldon T.
-
Using routine data to complement and enhance the results of randomised controlled trials.
By Lewsey JD, Leyland AH, Murray GD, Boddy FA.
-
Coronary artery stents in the treatment of ischaemic heart disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Meads C, Cummins C, Jolly K, Stevens A, Burls A, Hyde C.
-
Outcome measures for adult critical care: a systematic review.
By Hayes JA, Black NA, Jenkinson C, Young JD, Rowan KM, Daly K, et al.
-
A systematic review to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions to promote the initiation of breastfeeding.
By Fairbank L, O’Meara S, Renfrew MJ, Woolridge M, Sowden AJ, Lister-Sharp D.
-
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators: arrhythmias. A rapid and systematic review.
By Parkes J, Bryant J, Milne R.
-
Treatments for fatigue in multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By Brañas P, Jordan R, Fry-Smith A, Burls A, Hyde C.
-
Early asthma prophylaxis, natural history, skeletal development and economy (EASE): a pilot randomised controlled trial.
By Baxter-Jones ADG, Helms PJ, Russell G, Grant A, Ross S, Cairns JA, et al.
-
Screening for hypercholesterolaemia versus case finding for familial hypercholesterolaemia: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Marks D, Wonderling D, Thorogood M, Lambert H, Humphries SE, Neil HAW.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists in the medical management of unstable angina.
By McDonagh MS, Bachmann LM, Golder S, Kleijnen J, ter Riet G.
-
A randomised controlled trial of prehospital intravenous fluid replacement therapy in serious trauma.
By Turner J, Nicholl J, Webber L, Cox H, Dixon S, Yates D.
-
Intrathecal pumps for giving opioids in chronic pain: a systematic review.
By Williams JE, Louw G, Towlerton G.
-
Combination therapy (interferon alfa and ribavirin) in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a rapid and systematic review.
By Shepherd J, Waugh N, Hewitson P.
-
A systematic review of comparisons of effect sizes derived from randomised and non-randomised studies.
By MacLehose RR, Reeves BC, Harvey IM, Sheldon TA, Russell IT, Black AMS.
-
Intravascular ultrasound-guided interventions in coronary artery disease: a systematic literature review, with decision-analytic modelling, of outcomes and cost-effectiveness.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Hutton J, Lindsay HSJ, Blaxill JM, Evans JA, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to evaluate the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of counselling patients with chronic depression.
By Simpson S, Corney R, Fitzgerald P, Beecham J.
-
Systematic review of treatments for atopic eczema.
By Hoare C, Li Wan Po A, Williams H.
-
Bayesian methods in health technology assessment: a review.
By Spiegelhalter DJ, Myles JP, Jones DR, Abrams KR.
-
The management of dyspepsia: a systematic review.
By Delaney B, Moayyedi P, Deeks J, Innes M, Soo S, Barton P, et al.
-
A systematic review of treatments for severe psoriasis.
By Griffiths CEM, Clark CM, Chalmers RJG, Li Wan Po A, Williams HC.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine for Alzheimer’s disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Clegg A, Bryant J, Nicholson T, McIntyre L, De Broe S, Gerard K, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of riluzole for motor neurone disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Stewart A, Sandercock J, Bryan S, Hyde C, Barton PM, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Equity and the economic evaluation of healthcare.
By Sassi F, Archard L, Le Grand J.
-
Quality-of-life measures in chronic diseases of childhood.
By Eiser C, Morse R.
-
Eliciting public preferences for healthcare: a systematic review of techniques.
By Ryan M, Scott DA, Reeves C, Bate A, van Teijlingen ER, Russell EM, et al.
-
General health status measures for people with cognitive impairment: learning disability and acquired brain injury.
By Riemsma RP, Forbes CA, Glanville JM, Eastwood AJ, Kleijnen J.
-
An assessment of screening strategies for fragile X syndrome in the UK.
By Pembrey ME, Barnicoat AJ, Carmichael B, Bobrow M, Turner G.
-
Issues in methodological research: perspectives from researchers and commissioners.
By Lilford RJ, Richardson A, Stevens A, Fitzpatrick R, Edwards S, Rock F, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (5) beds; (6) compression; (7) laser therapy, therapeutic ultrasound, electrotherapy and electromagnetic therapy.
By Cullum N, Nelson EA, Flemming K, Sheldon T.
-
Effects of educational and psychosocial interventions for adolescents with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review.
By Hampson SE, Skinner TC, Hart J, Storey L, Gage H, Foxcroft D, et al.
-
Effectiveness of autologous chondrocyte transplantation for hyaline cartilage defects in knees: a rapid and systematic review.
By Jobanputra P, Parry D, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
Statistical assessment of the learning curves of health technologies.
By Ramsay CR, Grant AM, Wallace SA, Garthwaite PH, Monk AF, Russell IT.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of temozolomide for the treatment of recurrent malignant glioma: a rapid and systematic review.
By Dinnes J, Cave C, Huang S, Major K, Milne R.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of debriding agents in treating surgical wounds healing by secondary intention.
By Lewis R, Whiting P, ter Riet G, O’Meara S, Glanville J.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.
By Burns T, Knapp M, Catty J, Healey A, Henderson J, Watt H, et al.
-
How to develop cost-conscious guidelines.
By Eccles M, Mason J.
-
The role of specialist nurses in multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By De Broe S, Christopher F, Waugh N.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of orlistat in the management of obesity.
By O’Meara S, Riemsma R, Shirran L, Mather L, ter Riet G.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pioglitazone for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a rapid and systematic review.
By Chilcott J, Wight J, Lloyd Jones M, Tappenden P.
-
Extended scope of nursing practice: a multicentre randomised controlled trial of appropriately trained nurses and preregistration house officers in preoperative assessment in elective general surgery.
By Kinley H, Czoski-Murray C, George S, McCabe C, Primrose J, Reilly C, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of the effectiveness of day care for people with severe mental disorders: (1) Acute day hospital versus admission; (2) Vocational rehabilitation; (3) Day hospital versus outpatient care.
By Marshall M, Crowther R, Almaraz- Serrano A, Creed F, Sledge W, Kluiter H, et al.
-
The measurement and monitoring of surgical adverse events.
By Bruce J, Russell EM, Mollison J, Krukowski ZH.
-
Action research: a systematic review and guidance for assessment.
By Waterman H, Tillen D, Dickson R, de Koning K.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of gemcitabine for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
By Ward S, Morris E, Bansback N, Calvert N, Crellin A, Forman D, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the evidence for the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer.
By Lloyd Jones M, Hummel S, Bansback N, Orr B, Seymour M.
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.
By Brocklebank D, Ram F, Wright J, Barry P, Cates C, Davies L, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging for investigation of the knee joint.
By Bryan S, Weatherburn G, Bungay H, Hatrick C, Salas C, Parry D, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.
By Forbes C, Shirran L, Bagnall A-M, Duffy S, ter Riet G.
-
Superseded by a report published in a later volume.
-
The role of radiography in primary care patients with low back pain of at least 6 weeks duration: a randomised (unblinded) controlled trial.
By Kendrick D, Fielding K, Bentley E, Miller P, Kerslake R, Pringle M.
-
Design and use of questionnaires: a review of best practice applicable to surveys of health service staff and patients.
By McColl E, Jacoby A, Thomas L, Soutter J, Bamford C, Steen N, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.
By Clegg A, Scott DA, Sidhu M, Hewitson P, Waugh N.
-
Subgroup analyses in randomised controlled trials: quantifying the risks of false-positives and false-negatives.
By Brookes ST, Whitley E, Peters TJ, Mulheran PA, Egger M, Davey Smith G.
-
Depot antipsychotic medication in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia: (1) Meta-review; (2) Patient and nurse attitudes.
By David AS, Adams C.
-
A systematic review of controlled trials of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of brief psychological treatments for depression.
By Churchill R, Hunot V, Corney R, Knapp M, McGuire H, Tylee A, et al.
-
Cost analysis of child health surveillance.
By Sanderson D, Wright D, Acton C, Duree D.
-
A study of the methods used to select review criteria for clinical audit.
By Hearnshaw H, Harker R, Cheater F, Baker R, Grimshaw G.
-
Fludarabine as second-line therapy for B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a technology assessment.
By Hyde C, Wake B, Bryan S, Barton P, Fry-Smith A, Davenport C, et al.
-
Rituximab as third-line treatment for refractory or recurrent Stage III or IV follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wake B, Hyde C, Bryan S, Barton P, Song F, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
A systematic review of discharge arrangements for older people.
By Parker SG, Peet SM, McPherson A, Cannaby AM, Baker R, Wilson A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of inhaler devices used in the routine management of chronic asthma in older children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Peters J, Stevenson M, Beverley C, Lim J, Smith S.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of sibutramine in the management of obesity: a technology assessment.
By O’Meara S, Riemsma R, Shirran L, Mather L, ter Riet G.
-
The cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance angiography for carotid artery stenosis and peripheral vascular disease: a systematic review.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Westwood ME, Davies LM, Gough MJ, Bamford JM, et al.
-
Promoting physical activity in South Asian Muslim women through ‘exercise on prescription’.
By Carroll B, Ali N, Azam N.
-
Zanamivir for the treatment of influenza in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burls A, Clark W, Stewart T, Preston C, Bryan S, Jefferson T, et al.
-
A review of the natural history and epidemiology of multiple sclerosis: implications for resource allocation and health economic models.
By Richards RG, Sampson FC, Beard SM, Tappenden P.
-
Screening for gestational diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Scott DA, Loveman E, McIntyre L, Waugh N.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of surgery for people with morbid obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clegg AJ, Colquitt J, Sidhu MK, Royle P, Loveman E, Walker A.
-
The clinical effectiveness of trastuzumab for breast cancer: a systematic review.
By Lewis R, Bagnall A-M, Forbes C, Shirran E, Duffy S, Kleijnen J, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of vinorelbine for breast cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Lewis R, Bagnall A-M, King S, Woolacott N, Forbes C, Shirran L, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty for treatment of hip disease.
By Vale L, Wyness L, McCormack K, McKenzie L, Brazzelli M, Stearns SC.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bupropion and nicotine replacement therapy for smoking cessation: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Woolacott NF, Jones L, Forbes CA, Mather LC, Sowden AJ, Song FJ, et al.
-
A systematic review of effectiveness and economic evaluation of new drug treatments for juvenile idiopathic arthritis: etanercept.
By Cummins C, Connock M, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of growth hormone in children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Cave C, Mihaylova B, Chase D, McIntyre L, Gerard K, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of growth hormone in adults in relation to impact on quality of life: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Loveman E, Chase D, Mihaylova B, Cave C, Gerard K, et al.
-
Clinical medication review by a pharmacist of patients on repeat prescriptions in general practice: a randomised controlled trial.
By Zermansky AG, Petty DR, Raynor DK, Lowe CJ, Freementle N, Vail A.
-
The effectiveness of infliximab and etanercept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Burls A.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of computerised cognitive behaviour therapy for depression and anxiety.
By Kaltenthaler E, Shackley P, Stevens K, Beverley C, Parry G, Chilcott J.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride for ovarian cancer.
By Forbes C, Wilby J, Richardson G, Sculpher M, Mather L, Reimsma R.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of interventions based on a stages-of-change approach to promote individual behaviour change.
By Riemsma RP, Pattenden J, Bridle C, Sowden AJ, Mather L, Watt IS, et al.
-
A systematic review update of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists.
By Robinson M, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Jones L, Riemsma R, Palmer S, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and barriers to implementation of thrombolytic and neuroprotective therapy for acute ischaemic stroke in the NHS.
By Sandercock P, Berge E, Dennis M, Forbes J, Hand P, Kwan J, et al.
-
A randomised controlled crossover trial of nurse practitioner versus doctor-led outpatient care in a bronchiectasis clinic.
By Caine N, Sharples LD, Hollingworth W, French J, Keogan M, Exley A, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost – consequences of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of sex offenders.
By Adi Y, Ashcroft D, Browne K, Beech A, Fry-Smith A, Hyde C.
-
Treatment of established osteoporosis: a systematic review and cost–utility analysis.
By Kanis JA, Brazier JE, Stevenson M, Calvert NW, Lloyd Jones M.
-
Which anaesthetic agents are cost-effective in day surgery? Literature review, national survey of practice and randomised controlled trial.
By Elliott RA Payne K, Moore JK, Davies LM, Harper NJN, St Leger AS, et al.
-
Screening for hepatitis C among injecting drug users and in genitourinary medicine clinics: systematic reviews of effectiveness, modelling study and national survey of current practice.
By Stein K, Dalziel K, Walker A, McIntyre L, Jenkins B, Horne J, et al.
-
The measurement of satisfaction with healthcare: implications for practice from a systematic review of the literature.
By Crow R, Gage H, Hampson S, Hart J, Kimber A, Storey L, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of imatinib in chronic myeloid leukaemia: a systematic review.
By Garside R, Round A, Dalziel K, Stein K, Royle R.
-
A comparative study of hypertonic saline, daily and alternate-day rhDNase in children with cystic fibrosis.
By Suri R, Wallis C, Bush A, Thompson S, Normand C, Flather M, et al.
-
A systematic review of the costs and effectiveness of different models of paediatric home care.
By Parker G, Bhakta P, Lovett CA, Paisley S, Olsen R, Turner D, et al.
-
How important are comprehensive literature searches and the assessment of trial quality in systematic reviews? Empirical study.
By Egger M, Jüni P, Bartlett C, Holenstein F, Sterne J.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and economic evaluation, of home versus hospital or satellite unit haemodialysis for people with end-stage renal failure.
By Mowatt G, Vale L, Perez J, Wyness L, Fraser C, MacLeod A, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of the effectiveness of infliximab for the treatment of Crohn’s disease.
By Clark W, Raftery J, Barton P, Song F, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
A review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine anti-D prophylaxis for pregnant women who are rhesus negative.
By Chilcott J, Lloyd Jones M, Wight J, Forman K, Wray J, Beverley C, et al.
-
Systematic review and evaluation of the use of tumour markers in paediatric oncology: Ewing’s sarcoma and neuroblastoma.
By Riley RD, Burchill SA, Abrams KR, Heney D, Lambert PC, Jones DR, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of screening for Helicobacter pylori to reduce mortality and morbidity from gastric cancer and peptic ulcer disease: a discrete-event simulation model.
By Roderick P, Davies R, Raftery J, Crabbe D, Pearce R, Bhandari P, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine dental checks: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Davenport C, Elley K, Salas C, Taylor-Weetman CL, Fry-Smith A, Bryan S, et al.
-
A multicentre randomised controlled trial assessing the costs and benefits of using structured information and analysis of women’s preferences in the management of menorrhagia.
By Kennedy ADM, Sculpher MJ, Coulter A, Dwyer N, Rees M, Horsley S, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost–utility of photodynamic therapy for wet age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Meads C, Salas C, Roberts T, Moore D, Fry-Smith A, Hyde C.
-
Evaluation of molecular tests for prenatal diagnosis of chromosome abnormalities.
By Grimshaw GM, Szczepura A, Hultén M, MacDonald F, Nevin NC, Sutton F, et al.
-
First and second trimester antenatal screening for Down’s syndrome: the results of the Serum, Urine and Ultrasound Screening Study (SURUSS).
By Wald NJ, Rodeck C, Hackshaw AK, Walters J, Chitty L, Mackinson AM.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of ultrasound locating devices for central venous access: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Calvert N, Hind D, McWilliams RG, Thomas SM, Beverley C, Davidson A.
-
A systematic review of atypical antipsychotics in schizophrenia.
By Bagnall A-M, Jones L, Lewis R, Ginnelly L, Glanville J, Torgerson D, et al.
-
Prostate Testing for Cancer and Treatment (ProtecT) feasibility study.
By Donovan J, Hamdy F, Neal D, Peters T, Oliver S, Brindle L, et al.
-
Early thrombolysis for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Boland A, Dundar Y, Bagust A, Haycox A, Hill R, Mujica Mota R, et al.
-
Screening for fragile X syndrome: a literature review and modelling.
By Song FJ, Barton P, Sleightholme V, Yao GL, Fry-Smith A.
-
Systematic review of endoscopic sinus surgery for nasal polyps.
By Dalziel K, Stein K, Round A, Garside R, Royle P.
-
Towards efficient guidelines: how to monitor guideline use in primary care.
By Hutchinson A, McIntosh A, Cox S, Gilbert C.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of acute hospital-based spinal cord injuries services: systematic review.
By Bagnall A-M, Jones L, Richardson G, Duffy S, Riemsma R.
-
Prioritisation of health technology assessment. The PATHS model: methods and case studies.
By Townsend J, Buxton M, Harper G.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of tension-free vaginal tape for treatment of urinary stress incontinence.
By Cody J, Wyness L, Wallace S, Glazener C, Kilonzo M, Stearns S, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of patient education models for diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Loveman E, Cave C, Green C, Royle P, Dunn N, Waugh N.
-
The role of modelling in prioritising and planning clinical trials.
By Chilcott J, Brennan A, Booth A, Karnon J, Tappenden P.
-
Cost–benefit evaluation of routine influenza immunisation in people 65–74 years of age.
By Allsup S, Gosney M, Haycox A, Regan M.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of pulsatile machine perfusion versus cold storage of kidneys for transplantation retrieved from heart-beating and non-heart-beating donors.
By Wight J, Chilcott J, Holmes M, Brewer N.
-
Can randomised trials rely on existing electronic data? A feasibility study to explore the value of routine data in health technology assessment.
By Williams JG, Cheung WY, Cohen DR, Hutchings HA, Longo MF, Russell IT.
-
Evaluating non-randomised intervention studies.
By Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, D’Amico R, Sowden AJ, Sakarovitch C, Song F, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to assess the impact of a package comprising a patient-orientated, evidence-based self- help guidebook and patient-centred consultations on disease management and satisfaction in inflammatory bowel disease.
By Kennedy A, Nelson E, Reeves D, Richardson G, Roberts C, Robinson A, et al.
-
The effectiveness of diagnostic tests for the assessment of shoulder pain due to soft tissue disorders: a systematic review.
By Dinnes J, Loveman E, McIntyre L, Waugh N.
-
The value of digital imaging in diabetic retinopathy.
By Sharp PF, Olson J, Strachan F, Hipwell J, Ludbrook A, O’Donnell M, et al.
-
Lowering blood pressure to prevent myocardial infarction and stroke: a new preventive strategy.
By Law M, Wald N, Morris J.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of capecitabine and tegafur with uracil for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ward S, Kaltenthaler E, Cowan J, Brewer N.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of new and emerging technologies for early localised prostate cancer: a systematic review.
By Hummel S, Paisley S, Morgan A, Currie E, Brewer N.
-
Literature searching for clinical and cost-effectiveness studies used in health technology assessment reports carried out for the National Institute for Clinical Excellence appraisal system.
By Royle P, Waugh N.
-
Systematic review and economic decision modelling for the prevention and treatment of influenza A and B.
By Turner D, Wailoo A, Nicholson K, Cooper N, Sutton A, Abrams K.
-
A randomised controlled trial to evaluate the clinical and cost-effectiveness of Hickman line insertions in adult cancer patients by nurses.
By Boland A, Haycox A, Bagust A, Fitzsimmons L.
-
Redesigning postnatal care: a randomised controlled trial of protocol-based midwifery-led care focused on individual women’s physical and psychological health needs.
By MacArthur C, Winter HR, Bick DE, Lilford RJ, Lancashire RJ, Knowles H, et al.
-
Estimating implied rates of discount in healthcare decision-making.
By West RR, McNabb R, Thompson AGH, Sheldon TA, Grimley Evans J.
-
Systematic review of isolation policies in the hospital management of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a review of the literature with epidemiological and economic modelling.
By Cooper BS, Stone SP, Kibbler CC, Cookson BD, Roberts JA, Medley GF, et al.
-
Treatments for spasticity and pain in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review.
By Beard S, Hunn A, Wight J.
-
The inclusion of reports of randomised trials published in languages other than English in systematic reviews.
By Moher D, Pham B, Lawson ML, Klassen TP.
-
The impact of screening on future health-promoting behaviours and health beliefs: a systematic review.
By Bankhead CR, Brett J, Bukach C, Webster P, Stewart-Brown S, Munafo M, et al.
-
What is the best imaging strategy for acute stroke?
By Wardlaw JM, Keir SL, Seymour J, Lewis S, Sandercock PAG, Dennis MS, et al.
-
Systematic review and modelling of the investigation of acute and chronic chest pain presenting in primary care.
By Mant J, McManus RJ, Oakes RAL, Delaney BC, Barton PM, Deeks JJ, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of microwave and thermal balloon endometrial ablation for heavy menstrual bleeding: a systematic review and economic modelling.
By Garside R, Stein K, Wyatt K, Round A, Price A.
-
A systematic review of the role of bisphosphonates in metastatic disease.
By Ross JR, Saunders Y, Edmonds PM, Patel S, Wonderling D, Normand C, et al.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of capecitabine (Xeloda®) for locally advanced and/or metastatic breast cancer.
By Jones L, Hawkins N, Westwood M, Wright K, Richardson G, Riemsma R.
-
Effectiveness and efficiency of guideline dissemination and implementation strategies.
By Grimshaw JM, Thomas RE, MacLennan G, Fraser C, Ramsay CR, Vale L, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and costs of the Sugarbaker procedure for the treatment of pseudomyxoma peritonei.
By Bryant J, Clegg AJ, Sidhu MK, Brodin H, Royle P, Davidson P.
-
Psychological treatment for insomnia in the regulation of long-term hypnotic drug use.
By Morgan K, Dixon S, Mathers N, Thompson J, Tomeny M.
-
Improving the evaluation of therapeutic interventions in multiple sclerosis: development of a patient-based measure of outcome.
By Hobart JC, Riazi A, Lamping DL, Fitzpatrick R, Thompson AJ.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography compared with diagnostic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
By Kaltenthaler E, Bravo Vergel Y, Chilcott J, Thomas S, Blakeborough T, Walters SJ, et al.
-
The use of modelling to evaluate new drugs for patients with a chronic condition: the case of antibodies against tumour necrosis factor in rheumatoid arthritis.
By Barton P, Jobanputra P, Wilson J, Bryan S, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism using tandem mass spectrometry: a systematic review.
By Pandor A, Eastham J, Beverley C, Chilcott J, Paisley S.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pioglitazone and rosiglitazone in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Czoski-Murray C, Warren E, Chilcott J, Beverley C, Psyllaki MA, Cowan J.
-
Routine examination of the newborn: the EMREN study. Evaluation of an extension of the midwife role including a randomised controlled trial of appropriately trained midwives and paediatric senior house officers.
By Townsend J, Wolke D, Hayes J, Davé S, Rogers C, Bloomfield L, et al.
-
Involving consumers in research and development agenda setting for the NHS: developing an evidence-based approach.
By Oliver S, Clarke-Jones L, Rees R, Milne R, Buchanan P, Gabbay J, et al.
-
A multi-centre randomised controlled trial of minimally invasive direct coronary bypass grafting versus percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty with stenting for proximal stenosis of the left anterior descending coronary artery.
By Reeves BC, Angelini GD, Bryan AJ, Taylor FC, Cripps T, Spyt TJ, et al.
-
Does early magnetic resonance imaging influence management or improve outcome in patients referred to secondary care with low back pain? A pragmatic randomised controlled trial.
By Gilbert FJ, Grant AM, Gillan MGC, Vale L, Scott NW, Campbell MK, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of anakinra for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Clark W, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Burls A.
-
A rapid and systematic review and economic evaluation of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for treatment of mania associated with bipolar affective disorder.
By Bridle C, Palmer S, Bagnall A-M, Darba J, Duffy S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Liquid-based cytology in cervical screening: an updated rapid and systematic review and economic analysis.
By Karnon J, Peters J, Platt J, Chilcott J, McGoogan E, Brewer N.
-
Systematic review of the long-term effects and economic consequences of treatments for obesity and implications for health improvement.
By Avenell A, Broom J, Brown TJ, Poobalan A, Aucott L, Stearns SC, et al.
-
Autoantibody testing in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus.
By Dretzke J, Cummins C, Sandercock J, Fry-Smith A, Barrett T, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of prehospital intravenous fluids in trauma patients.
By Dretzke J, Sandercock J, Bayliss S, Burls A.
-
Newer hypnotic drugs for the short-term management of insomnia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Dündar Y, Boland A, Strobl J, Dodd S, Haycox A, Bagust A, et al.
-
Development and validation of methods for assessing the quality of diagnostic accuracy studies.
By Whiting P, Rutjes AWS, Dinnes J, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PMM, Kleijnen J.
-
EVALUATE hysterectomy trial: a multicentre randomised trial comparing abdominal, vaginal and laparoscopic methods of hysterectomy.
By Garry R, Fountain J, Brown J, Manca A, Mason S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Methods for expected value of information analysis in complex health economic models: developments on the health economics of interferon-β and glatiramer acetate for multiple sclerosis.
By Tappenden P, Chilcott JB, Eggington S, Oakley J, McCabe C.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of imatinib for first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia in chronic phase: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Dalziel K, Round A, Stein K, Garside R, Price A.
-
VenUS I: a randomised controlled trial of two types of bandage for treating venous leg ulcers.
By Iglesias C, Nelson EA, Cullum NA, Torgerson DJ, on behalf of the VenUS Team.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and economic evaluation, of myocardial perfusion scintigraphy for the diagnosis and management of angina and myocardial infarction.
By Mowatt G, Vale L, Brazzelli M, Hernandez R, Murray A, Scott N, et al.
-
A pilot study on the use of decision theory and value of information analysis as part of the NHS Health Technology Assessment programme.
By Claxton K, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Philips Z, Palmer S.
-
The Social Support and Family Health Study: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of two alternative forms of postnatal support for mothers living in disadvantaged inner-city areas.
By Wiggins M, Oakley A, Roberts I, Turner H, Rajan L, Austerberry H, et al.
-
Psychosocial aspects of genetic screening of pregnant women and newborns: a systematic review.
By Green JM, Hewison J, Bekker HL, Bryant, Cuckle HS.
-
Evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding: comparison of three outpatient procedures within cohorts defined by age and menopausal status.
By Critchley HOD, Warner P, Lee AJ, Brechin S, Guise J, Graham B.
-
Coronary artery stents: a rapid systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hill R, Bagust A, Bakhai A, Dickson R, Dündar Y, Haycox A, et al.
-
Review of guidelines for good practice in decision-analytic modelling in health technology assessment.
By Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Claxton K, Golder S, Riemsma R, et al.
-
Rituximab (MabThera®) for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Knight C, Hind D, Brewer N, Abbott V.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of clopidogrel and modified-release dipyridamole in the secondary prevention of occlusive vascular events: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jones L, Griffin S, Palmer S, Main C, Orton V, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Pegylated interferon α-2a and -2b in combination with ribavirin in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Brodin H, Cave C, Waugh N, Price A, Gabbay J.
-
Clopidogrel used in combination with aspirin compared with aspirin alone in the treatment of non-ST-segment- elevation acute coronary syndromes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Main C, Palmer S, Griffin S, Jones L, Orton V, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Provision, uptake and cost of cardiac rehabilitation programmes: improving services to under-represented groups.
By Beswick AD, Rees K, Griebsch I, Taylor FC, Burke M, West RR, et al.
-
Involving South Asian patients in clinical trials.
By Hussain-Gambles M, Leese B, Atkin K, Brown J, Mason S, Tovey P.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for diabetes.
By Colquitt JL, Green C, Sidhu MK, Hartwell D, Waugh N.
-
Identification and assessment of ongoing trials in health technology assessment reviews.
By Song FJ, Fry-Smith A, Davenport C, Bayliss S, Adi Y, Wilson JS, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of a long-acting insulin analogue, insulin glargine
By Warren E, Weatherley-Jones E, Chilcott J, Beverley C.
-
Supplementation of a home-based exercise programme with a class-based programme for people with osteoarthritis of the knees: a randomised controlled trial and health economic analysis.
By McCarthy CJ, Mills PM, Pullen R, Richardson G, Hawkins N, Roberts CR, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of once-daily versus more frequent use of same potency topical corticosteroids for atopic eczema: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Green C, Colquitt JL, Kirby J, Davidson P, Payne E.
-
Acupuncture of chronic headache disorders in primary care: randomised controlled trial and economic analysis.
By Vickers AJ, Rees RW, Zollman CE, McCarney R, Smith CM, Ellis N, et al.
-
Generalisability in economic evaluation studies in healthcare: a review and case studies.
By Sculpher MJ, Pang FS, Manca A, Drummond MF, Golder S, Urdahl H, et al.
-
Virtual outreach: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of joint teleconferenced medical consultations.
By Wallace P, Barber J, Clayton W, Currell R, Fleming K, Garner P, et al.
-
Randomised controlled multiple treatment comparison to provide a cost-effectiveness rationale for the selection of antimicrobial therapy in acne.
By Ozolins M, Eady EA, Avery A, Cunliffe WJ, O’Neill C, Simpson NB, et al.
-
Do the findings of case series studies vary significantly according to methodological characteristics?
By Dalziel K, Round A, Stein K, Garside R, Castelnuovo E, Payne L.
-
Improving the referral process for familial breast cancer genetic counselling: findings of three randomised controlled trials of two interventions.
By Wilson BJ, Torrance N, Mollison J, Wordsworth S, Gray JR, Haites NE, et al.
-
Randomised evaluation of alternative electrosurgical modalities to treat bladder outflow obstruction in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
By Fowler C, McAllister W, Plail R, Karim O, Yang Q.
-
A pragmatic randomised controlled trial of the cost-effectiveness of palliative therapies for patients with inoperable oesophageal cancer.
By Shenfine J, McNamee P, Steen N, Bond J, Griffin SM.
-
Impact of computer-aided detection prompts on the sensitivity and specificity of screening mammography.
By Taylor P, Champness J, Given- Wilson R, Johnston K, Potts H.
-
Issues in data monitoring and interim analysis of trials.
By Grant AM, Altman DG, Babiker AB, Campbell MK, Clemens FJ, Darbyshire JH, et al.
-
Lay public’s understanding of equipoise and randomisation in randomised controlled trials.
By Robinson EJ, Kerr CEP, Stevens AJ, Lilford RJ, Braunholtz DA, Edwards SJ, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of electroconvulsive therapy for depressive illness, schizophrenia, catatonia and mania: systematic reviews and economic modelling studies.
By Greenhalgh J, Knight C, Hind D, Beverley C, Walters S.
-
Measurement of health-related quality of life for people with dementia: development of a new instrument (DEMQOL) and an evaluation of current methodology.
By Smith SC, Lamping DL, Banerjee S, Harwood R, Foley B, Smith P, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of drotrecogin alfa (activated) (Xigris®) for the treatment of severe sepsis in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Green C, Dinnes J, Takeda A, Shepherd J, Hartwell D, Cave C, et al.
-
A methodological review of how heterogeneity has been examined in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy.
By Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kirby J, Roderick P.
-
Cervical screening programmes: can automation help? Evidence from systematic reviews, an economic analysis and a simulation modelling exercise applied to the UK.
By Willis BH, Barton P, Pearmain P, Bryan S, Hyde C.
-
Laparoscopic surgery for inguinal hernia repair: systematic review of effectiveness and economic evaluation.
By McCormack K, Wake B, Perez J, Fraser C, Cook J, McIntosh E, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness, tolerability and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for epilepsy in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wilby J, Kainth A, Hawkins N, Epstein D, McIntosh H, McDaid C, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to compare the cost-effectiveness of tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and lofepramine.
By Peveler R, Kendrick T, Buxton M, Longworth L, Baldwin D, Moore M, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of immediate angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hartwell D, Colquitt J, Loveman E, Clegg AJ, Brodin H, Waugh N, et al.
-
A randomised controlled comparison of alternative strategies in stroke care.
By Kalra L, Evans A, Perez I, Knapp M, Swift C, Donaldson N.
-
The investigation and analysis of critical incidents and adverse events in healthcare.
By Woloshynowych M, Rogers S, Taylor-Adams S, Vincent C.
-
Potential use of routine databases in health technology assessment.
By Raftery J, Roderick P, Stevens A.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of newer immunosuppressive regimens in renal transplantation: a systematic review and modelling study.
By Woodroffe R, Yao GL, Meads C, Bayliss S, Ready A, Raftery J, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene and teriparatide for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
By Stevenson M, Lloyd Jones M, De Nigris E, Brewer N, Davis S, Oakley J.
-
A systematic review to examine the impact of psycho-educational interventions on health outcomes and costs in adults and children with difficult asthma.
By Smith JR, Mugford M, Holland R, Candy B, Noble MJ, Harrison BDW, et al.
-
An evaluation of the costs, effectiveness and quality of renal replacement therapy provision in renal satellite units in England and Wales.
By Roderick P, Nicholson T, Armitage A, Mehta R, Mullee M, Gerard K, et al.
-
Imatinib for the treatment of patients with unresectable and/or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumours: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wilson J, Connock M, Song F, Yao G, Fry-Smith A, Raftery J, et al.
-
Indirect comparisons of competing interventions.
By Glenny AM, Altman DG, Song F, Sakarovitch C, Deeks JJ, D’Amico R, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of alternative strategies for the initial medical management of non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome: systematic review and decision-analytical modelling.
By Robinson M, Palmer S, Sculpher M, Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Bowens A, et al.
-
Outcomes of electrically stimulated gracilis neosphincter surgery.
By Tillin T, Chambers M, Feldman R.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pimecrolimus and tacrolimus for atopic eczema: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Stein K, Castelnuovo E, Pitt M, Ashcroft D, Dimmock P, et al.
-
Systematic review on urine albumin testing for early detection of diabetic complications.
By Newman DJ, Mattock MB, Dawnay ABS, Kerry S, McGuire A, Yaqoob M, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trial of the cost-effectiveness of water-based therapy for lower limb osteoarthritis.
By Cochrane T, Davey RC, Matthes Edwards SM.
-
Longer term clinical and economic benefits of offering acupuncture care to patients with chronic low back pain.
By Thomas KJ, MacPherson H, Ratcliffe J, Thorpe L, Brazier J, Campbell M, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness and safety of epidural steroids in the management of sciatica.
By Price C, Arden N, Coglan L, Rogers P.
-
The British Rheumatoid Outcome Study Group (BROSG) randomised controlled trial to compare the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of aggressive versus symptomatic therapy in established rheumatoid arthritis.
By Symmons D, Tricker K, Roberts C, Davies L, Dawes P, Scott DL.
-
Conceptual framework and systematic review of the effects of participants’ and professionals’ preferences in randomised controlled trials.
By King M, Nazareth I, Lampe F, Bower P, Chandler M, Morou M, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of implantable cardioverter defibrillators: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Brodin H, Loveman E, Payne E, Clegg A.
-
A trial of problem-solving by community mental health nurses for anxiety, depression and life difficulties among general practice patients. The CPN-GP study.
By Kendrick T, Simons L, Mynors-Wallis L, Gray A, Lathlean J, Pickering R, et al.
-
The causes and effects of socio-demographic exclusions from clinical trials.
By Bartlett C, Doyal L, Ebrahim S, Davey P, Bachmann M, Egger M, et al.
-
Is hydrotherapy cost-effective? A randomised controlled trial of combined hydrotherapy programmes compared with physiotherapy land techniques in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
By Epps H, Ginnelly L, Utley M, Southwood T, Gallivan S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial and cost-effectiveness study of systematic screening (targeted and total population screening) versus routine practice for the detection of atrial fibrillation in people aged 65 and over. The SAFE study.
By Hobbs FDR, Fitzmaurice DA, Mant J, Murray E, Jowett S, Bryan S, et al.
-
Displaced intracapsular hip fractures in fit, older people: a randomised comparison of reduction and fixation, bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty.
By Keating JF, Grant A, Masson M, Scott NW, Forbes JF.
-
Long-term outcome of cognitive behaviour therapy clinical trials in central Scotland.
By Durham RC, Chambers JA, Power KG, Sharp DM, Macdonald RR, Major KA, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of dual-chamber pacemakers compared with single-chamber pacemakers for bradycardia due to atrioventricular block or sick sinus syndrome: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Castelnuovo E, Stein K, Pitt M, Garside R, Payne E.
-
Newborn screening for congenital heart defects: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Knowles R, Griebsch I, Dezateux C, Brown J, Bull C, Wren C.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of left ventricular assist devices for end-stage heart failure: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clegg AJ, Scott DA, Loveman E, Colquitt J, Hutchinson J, Royle P, et al.
-
The effectiveness of the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph and laser diagnostic glaucoma scanning system (GDx) in detecting and monitoring glaucoma.
By Kwartz AJ, Henson DB, Harper RA, Spencer AF, McLeod D.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of autologous chondrocyte implantation for cartilage defects in knee joints: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clar C, Cummins E, McIntyre L, Thomas S, Lamb J, Bain L, et al.
-
Systematic review of effectiveness of different treatments for childhood retinoblastoma.
By McDaid C, Hartley S, Bagnall A-M, Ritchie G, Light K, Riemsma R.
-
Towards evidence-based guidelines for the prevention of venous thromboembolism: systematic reviews of mechanical methods, oral anticoagulation, dextran and regional anaesthesia as thromboprophylaxis.
By Roderick P, Ferris G, Wilson K, Halls H, Jackson D, Collins R, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of parent training/education programmes for the treatment of conduct disorder, including oppositional defiant disorder, in children.
By Dretzke J, Frew E, Davenport C, Barlow J, Stewart-Brown S, Sandercock J, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine and memantine for Alzheimer’s disease.
By Loveman E, Green C, Kirby J, Takeda A, Picot J, Payne E, et al.
-
FOOD: a multicentre randomised trial evaluating feeding policies in patients admitted to hospital with a recent stroke.
By Dennis M, Lewis S, Cranswick G, Forbes J.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computed tomography screening for lung cancer: systematic reviews.
By Black C, Bagust A, Boland A, Walker S, McLeod C, De Verteuil R, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of neuroimaging assessments used to visualise the seizure focus in people with refractory epilepsy being considered for surgery.
By Whiting P, Gupta R, Burch J, Mujica Mota RE, Wright K, Marson A, et al.
-
Comparison of conference abstracts and presentations with full-text articles in the health technology assessments of rapidly evolving technologies.
By Dundar Y, Dodd S, Dickson R, Walley T, Haycox A, Williamson PR.
-
Systematic review and evaluation of methods of assessing urinary incontinence.
By Martin JL, Williams KS, Abrams KR, Turner DA, Sutton AJ, Chapple C, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for children with epilepsy. A systematic review.
By Connock M, Frew E, Evans B-W, Bryan S, Cummins C, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Surveillance of Barrett’s oesophagus: exploring the uncertainty through systematic review, expert workshop and economic modelling.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Somerville M, Stein K, Price A, Gilbert N.
-
Topotecan, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride and paclitaxel for second-line or subsequent treatment of advanced ovarian cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Main C, Bojke L, Griffin S, Norman G, Barbieri M, Mather L, et al.
-
Evaluation of molecular techniques in prediction and diagnosis of cytomegalovirus disease in immunocompromised patients.
By Szczepura A, Westmoreland D, Vinogradova Y, Fox J, Clark M.
-
Screening for thrombophilia in high-risk situations: systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. The Thrombosis: Risk and Economic Assessment of Thrombophilia Screening (TREATS) study.
By Wu O, Robertson L, Twaddle S, Lowe GDO, Clark P, Greaves M, et al.
-
A series of systematic reviews to inform a decision analysis for sampling and treating infected diabetic foot ulcers.
By Nelson EA, O’Meara S, Craig D, Iglesias C, Golder S, Dalton J, et al.
-
Randomised clinical trial, observational study and assessment of cost-effectiveness of the treatment of varicose veins (REACTIV trial).
By Michaels JA, Campbell WB, Brazier JE, MacIntyre JB, Palfreyman SJ, Ratcliffe J, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of screening for oral cancer in primary care.
By Speight PM, Palmer S, Moles DR, Downer MC, Smith DH, Henriksson M, et al.
-
Measurement of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of non-invasive diagnostic testing strategies for deep vein thrombosis.
By Goodacre S, Sampson F, Stevenson M, Wailoo A, Sutton A, Thomas S, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of HealOzone® for the treatment of occlusal pit/fissure caries and root caries.
By Brazzelli M, McKenzie L, Fielding S, Fraser C, Clarkson J, Kilonzo M, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trials of conventional antipsychotic versus new atypical drugs, and new atypical drugs versus clozapine, in people with schizophrenia responding poorly to, or intolerant of, current drug treatment.
By Lewis SW, Davies L, Jones PB, Barnes TRE, Murray RM, Kerwin R, et al.
-
Diagnostic tests and algorithms used in the investigation of haematuria: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.
By Rodgers M, Nixon J, Hempel S, Aho T, Kelly J, Neal D, et al.
-
Cognitive behavioural therapy in addition to antispasmodic therapy for irritable bowel syndrome in primary care: randomised controlled trial.
By Kennedy TM, Chalder T, McCrone P, Darnley S, Knapp M, Jones RH, et al.
-
A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapies for Fabry’s disease and mucopolysaccharidosis type 1.
By Connock M, Juarez-Garcia A, Frew E, Mans A, Dretzke J, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Health benefits of antiviral therapy for mild chronic hepatitis C: randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation.
By Wright M, Grieve R, Roberts J, Main J, Thomas HC, on behalf of the UK Mild Hepatitis C Trial Investigators.
-
Pressure relieving support surfaces: a randomised evaluation.
By Nixon J, Nelson EA, Cranny G, Iglesias CP, Hawkins K, Cullum NA, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of methylphenidate, dexamfetamine and atomoxetine for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents.
By King S, Griffin S, Hodges Z, Weatherly H, Asseburg C, Richardson G, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy for Gaucher’s disease: a systematic review.
By Connock M, Burls A, Frew E, Fry-Smith A, Juarez-Garcia A, McCabe C, et al.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of salicylic acid and cryotherapy for cutaneous warts. An economic decision model.
By Thomas KS, Keogh-Brown MR, Chalmers JR, Fordham RJ, Holland RC, Armstrong SJ, et al.
-
A systematic literature review of the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions to prevent wandering in dementia and evaluation of the ethical implications and acceptability of their use.
By Robinson L, Hutchings D, Corner L, Beyer F, Dickinson H, Vanoli A, et al.
-
A review of the evidence on the effects and costs of implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in different patient groups, and modelling of cost-effectiveness and cost–utility for these groups in a UK context.
By Buxton M, Caine N, Chase D, Connelly D, Grace A, Jackson C, et al.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Takeda A, Davidson P, Price A.
-
An evaluation of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of pulmonary artery catheters in patient management in intensive care: a systematic review and a randomised controlled trial.
By Harvey S, Stevens K, Harrison D, Young D, Brampton W, McCabe C, et al.
-
Accurate, practical and cost-effective assessment of carotid stenosis in the UK.
By Wardlaw JM, Chappell FM, Stevenson M, De Nigris E, Thomas S, Gillard J, et al.
-
Etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Woolacott N, Bravo Vergel Y, Hawkins N, Kainth A, Khadjesari Z, Misso K, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of testing for hepatitis C in former injecting drug users.
By Castelnuovo E, Thompson-Coon J, Pitt M, Cramp M, Siebert U, Price A, et al.
-
Computerised cognitive behaviour therapy for depression and anxiety update: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Kaltenthaler E, Brazier J, De Nigris E, Tumur I, Ferriter M, Beverley C, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.
By Williams C, Brunskill S, Altman D, Briggs A, Campbell H, Clarke M, et al.
-
Psychological therapies including dialectical behaviour therapy for borderline personality disorder: a systematic review and preliminary economic evaluation.
By Brazier J, Tumur I, Holmes M, Ferriter M, Parry G, Dent-Brown K, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of tests for the diagnosis and investigation of urinary tract infection in children: a systematic review and economic model.
By Whiting P, Westwood M, Bojke L, Palmer S, Richardson G, Cooper J, et al.
-
Cognitive behavioural therapy in chronic fatigue syndrome: a randomised controlled trial of an outpatient group programme.
By O’Dowd H, Gladwell P, Rogers CA, Hollinghurst S, Gregory A.
-
A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling.
By Brown TJ, Hooper L, Elliott RA, Payne K, Webb R, Roberts C, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computed tomography screening for coronary artery disease: systematic review.
By Waugh N, Black C, Walker S, McIntyre L, Cummins E, Hillis G.
-
What are the clinical outcome and cost-effectiveness of endoscopy undertaken by nurses when compared with doctors? A Multi-Institution Nurse Endoscopy Trial (MINuET).
By Williams J, Russell I, Durai D, Cheung W-Y, Farrin A, Bloor K, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of oxaliplatin and capecitabine for the adjuvant treatment of colon cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Pandor A, Eggington S, Paisley S, Tappenden P, Sutcliffe P.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness.
By Chen Y-F, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Jowett S, Bryan S, Clark W, et al.
-
Telemedicine in dermatology: a randomised controlled trial.
By Bowns IR, Collins K, Walters SJ, McDonagh AJG.
-
Cost-effectiveness of cell salvage and alternative methods of minimising perioperative allogeneic blood transfusion: a systematic review and economic model.
By Davies L, Brown TJ, Haynes S, Payne K, Elliott RA, McCollum C.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancer: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.
By Murray A, Lourenco T, de Verteuil R, Hernandez R, Fraser C, McKinley A, et al.
-
Etanercept and efalizumab for the treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review.
By Woolacott N, Hawkins N, Mason A, Kainth A, Khadjesari Z, Bravo Vergel Y, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of clinical decision tools for acute abdominal pain.
By Liu JLY, Wyatt JC, Deeks JJ, Clamp S, Keen J, Verde P, et al.
-
Evaluation of the ventricular assist device programme in the UK.
By Sharples L, Buxton M, Caine N, Cafferty F, Demiris N, Dyer M, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of immunosuppressive therapy for renal transplantation in children.
By Yao G, Albon E, Adi Y, Milford D, Bayliss S, Ready A, et al.
-
Amniocentesis results: investigation of anxiety. The ARIA trial.
By Hewison J, Nixon J, Fountain J, Cocks K, Jones C, Mason G, et al.
-
Pemetrexed disodium for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Dundar Y, Bagust A, Dickson R, Dodd S, Green J, Haycox A, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of docetaxel in combination with prednisone or prednisolone for the treatment of hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer.
By Collins R, Fenwick E, Trowman R, Perard R, Norman G, Light K, et al.
-
A systematic review of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of tuberculosis infection.
By Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kunst H, Gibson A, Cummins E, Waugh N, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women.
By Stevenson M, Davis S, Lloyd-Jones M, Beverley C.
-
A systematic review of quantitative and qualitative research on the role and effectiveness of written information available to patients about individual medicines.
By Raynor DK, Blenkinsopp A, Knapp P, Grime J, Nicolson DJ, Pollock K, et al.
-
Oral naltrexone as a treatment for relapse prevention in formerly opioid-dependent drug users: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Adi Y, Juarez-Garcia A, Wang D, Jowett S, Frew E, Day E, et al.
-
Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: a systematic review and cost–utility analysis.
By Kanis JA, Stevenson M, McCloskey EV, Davis S, Lloyd-Jones M.
-
Epidemiological, social, diagnostic and economic evaluation of population screening for genital chlamydial infection.
By Low N, McCarthy A, Macleod J, Salisbury C, Campbell R, Roberts TE, et al.
-
Methadone and buprenorphine for the management of opioid dependence: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Connock M, Juarez-Garcia A, Jowett S, Frew E, Liu Z, Taylor RJ, et al.
-
Exercise Evaluation Randomised Trial (EXERT): a randomised trial comparing GP referral for leisure centre-based exercise, community-based walking and advice only.
By Isaacs AJ, Critchley JA, See Tai S, Buckingham K, Westley D, Harridge SDR, et al.
-
Interferon alfa (pegylated and non-pegylated) and ribavirin for the treatment of mild chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Hartwell D, Davidson P, Price A, Waugh N.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of bevacizumab and cetuximab for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.
By Tappenden P, Jones R, Paisley S, Carroll C.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of epoetin alfa, epoetin beta and darbepoetin alfa in anaemia associated with cancer, especially that attributable to cancer treatment.
By Wilson J, Yao GL, Raftery J, Bohlius J, Brunskill S, Sandercock J, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of statins for the prevention of coronary events.
By Ward S, Lloyd Jones M, Pandor A, Holmes M, Ara R, Ryan A, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of different models of community-based respite care for frail older people and their carers.
By Mason A, Weatherly H, Spilsbury K, Arksey H, Golder S, Adamson J, et al.
-
Additional therapy for young children with spastic cerebral palsy: a randomised controlled trial.
By Weindling AM, Cunningham CC, Glenn SM, Edwards RT, Reeves DJ.
-
Screening for type 2 diabetes: literature review and economic modelling.
By Waugh N, Scotland G, McNamee P, Gillett M, Brennan A, Goyder E, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cinacalcet for secondary hyperparathyroidism in end-stage renal disease patients on dialysis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Anderson R, Mealing S, Roome C, Snaith A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of gemcitabine for metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Takeda AL, Jones J, Loveman E, Tan SC, Clegg AJ.
-
A systematic review of duplex ultrasound, magnetic resonance angiography and computed tomography angiography for the diagnosis and assessment of symptomatic, lower limb peripheral arterial disease.
By Collins R, Cranny G, Burch J, Aguiar-Ibáñez R, Craig D, Wright K, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of treatments for children with idiopathic steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome: a systematic review.
By Colquitt JL, Kirby J, Green C, Cooper K, Trompeter RS.
-
A systematic review of the routine monitoring of growth in children of primary school age to identify growth-related conditions.
By Fayter D, Nixon J, Hartley S, Rithalia A, Butler G, Rudolf M, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness of preventing and treating Staphylococcus aureus carriage in reducing peritoneal catheter-related infections.
By McCormack K, Rabindranath K, Kilonzo M, Vale L, Fraser C, McIntyre L, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation versus electroconvulsive therapy in severe depression: a multicentre pragmatic randomised controlled trial and economic analysis.
By McLoughlin DM, Mogg A, Eranti S, Pluck G, Purvis R, Edwards D, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of direct versus indirect and individual versus group modes of speech and language therapy for children with primary language impairment.
By Boyle J, McCartney E, Forbes J, O’Hare A.
-
Hormonal therapies for early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hind D, Ward S, De Nigris E, Simpson E, Carroll C, Wyld L.
-
Cardioprotection against the toxic effects of anthracyclines given to children with cancer: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Picot J, Levitt G, Sullivan I, Baxter L, Clegg A.
-
Adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By McLeod C, Bagust A, Boland A, Dagenais P, Dickson R, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Prenatal screening and treatment strategies to prevent group B streptococcal and other bacterial infections in early infancy: cost-effectiveness and expected value of information analyses.
By Colbourn T, Asseburg C, Bojke L, Philips Z, Claxton K, Ades AE, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bone morphogenetic proteins in the non-healing of fractures and spinal fusion: a systematic review.
By Garrison KR, Donell S, Ryder J, Shemilt I, Mugford M, Harvey I, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial of postoperative radiotherapy following breast-conserving surgery in a minimum-risk older population. The PRIME trial.
By Prescott RJ, Kunkler IH, Williams LJ, King CC, Jack W, van der Pol M, et al.
-
Current practice, accuracy, effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the school entry hearing screen.
By Bamford J, Fortnum H, Bristow K, Smith J, Vamvakas G, Davies L, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of inhaled insulin in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Black C, Cummins E, Royle P, Philip S, Waugh N.
-
Surveillance of cirrhosis for hepatocellular carcinoma: systematic review and economic analysis.
By Thompson Coon J, Rogers G, Hewson P, Wright D, Anderson R, Cramp M, et al.
-
The Birmingham Rehabilitation Uptake Maximisation Study (BRUM). Homebased compared with hospital-based cardiac rehabilitation in a multi-ethnic population: cost-effectiveness and patient adherence.
By Jolly K, Taylor R, Lip GYH, Greenfield S, Raftery J, Mant J, et al.
-
A systematic review of the clinical, public health and cost-effectiveness of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection and identification of bacterial intestinal pathogens in faeces and food.
By Abubakar I, Irvine L, Aldus CF, Wyatt GM, Fordham R, Schelenz S, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial examining the longer-term outcomes of standard versus new antiepileptic drugs. The SANAD trial.
By Marson AG, Appleton R, Baker GA, Chadwick DW, Doughty J, Eaton B, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of different models of managing long-term oral anti-coagulation therapy: a systematic review and economic modelling.
By Connock M, Stevens C, Fry-Smith A, Jowett S, Fitzmaurice D, Moore D, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of interventions for preventing relapse in people with bipolar disorder.
By Soares-Weiser K, Bravo Vergel Y, Beynon S, Dunn G, Barbieri M, Duffy S, et al.
-
Taxanes for the adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ward S, Simpson E, Davis S, Hind D, Rees A, Wilkinson A.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening for open angle glaucoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burr JM, Mowatt G, Hernández R, Siddiqui MAR, Cook J, Lourenco T, et al.
-
Acceptability, benefit and costs of early screening for hearing disability: a study of potential screening tests and models.
By Davis A, Smith P, Ferguson M, Stephens D, Gianopoulos I.
-
Contamination in trials of educational interventions.
By Keogh-Brown MR, Bachmann MO, Shepstone L, Hewitt C, Howe A, Ramsay CR, et al.
-
Overview of the clinical effectiveness of positron emission tomography imaging in selected cancers.
By Facey K, Bradbury I, Laking G, Payne E.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Anderson R, Rogers G, Dyer M, Mealing S, et al.
-
Drug-eluting stents: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hill RA, Boland A, Dickson R, Dündar Y, Haycox A, McLeod C, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cardiac resynchronisation (biventricular pacing) for heart failure: systematic review and economic model.
By Fox M, Mealing S, Anderson R, Dean J, Stein K, Price A, et al.
-
Recruitment to randomised trials: strategies for trial enrolment and participation study. The STEPS study.
By Campbell MK, Snowdon C, Francis D, Elbourne D, McDonald AM, Knight R, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of functional cardiac testing in the diagnosis and management of coronary artery disease: a randomised controlled trial. The CECaT trial.
By Sharples L, Hughes V, Crean A, Dyer M, Buxton M, Goldsmith K, et al.
-
Evaluation of diagnostic tests when there is no gold standard. A review of methods.
By Rutjes AWS, Reitsma JB, Coomarasamy A, Khan KS, Bossuyt PMM.
-
Systematic reviews of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors in acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
By Leontiadis GI, Sreedharan A, Dorward S, Barton P, Delaney B, Howden CW, et al.
-
A review and critique of modelling in prioritising and designing screening programmes.
By Karnon J, Goyder E, Tappenden P, McPhie S, Towers I, Brazier J, et al.
-
An assessment of the impact of the NHS Health Technology Assessment Programme.
By Hanney S, Buxton M, Green C, Coulson D, Raftery J.
-
A systematic review and economic model of switching from nonglycopeptide to glycopeptide antibiotic prophylaxis for surgery.
By Cranny G, Elliott R, Weatherly H, Chambers D, Hawkins N, Myers L, et al.
-
‘Cut down to quit’ with nicotine replacement therapies in smoking cessation: a systematic review of effectiveness and economic analysis.
By Wang D, Connock M, Barton P, Fry-Smith A, Aveyard P, Moore D.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of strategies for reducing fracture risk in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis with additional data on long-term risk of fracture and cost of disease management.
By Thornton J, Ashcroft D, O’Neill T, Elliott R, Adams J, Roberts C, et al.
-
Does befriending by trained lay workers improve psychological well-being and quality of life for carers of people with dementia, and at what cost? A randomised controlled trial.
By Charlesworth G, Shepstone L, Wilson E, Thalanany M, Mugford M, Poland F.
-
A multi-centre retrospective cohort study comparing the efficacy, safety and cost-effectiveness of hysterectomy and uterine artery embolisation for the treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroids. The HOPEFUL study.
By Hirst A, Dutton S, Wu O, Briggs A, Edwards C, Waldenmaier L, et al.
-
Methods of prediction and prevention of pre-eclampsia: systematic reviews of accuracy and effectiveness literature with economic modelling.
By Meads CA, Cnossen JS, Meher S, Juarez-Garcia A, ter Riet G, Duley L, et al.
-
The use of economic evaluations in NHS decision-making: a review and empirical investigation.
By Williams I, McIver S, Moore D, Bryan S.
-
Stapled haemorrhoidectomy (haemorrhoidopexy) for the treatment of haemorrhoids: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burch J, Epstein D, Baba-Akbari A, Weatherly H, Fox D, Golder S, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness of diabetes education models for Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.
By Loveman E, Frampton GK, Clegg AJ.
-
Payment to healthcare professionals for patient recruitment to trials: systematic review and qualitative study.
By Raftery J, Bryant J, Powell J, Kerr C, Hawker S.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (etodolac, meloxicam, celecoxib, rofecoxib, etoricoxib, valdecoxib and lumiracoxib) for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Chen Y-F, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Fry-Smith A, Harris G, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of central venous catheters treated with anti-infective agents in preventing bloodstream infections: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hockenhull JC, Dwan K, Boland A, Smith G, Bagust A, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Stepped treatment of older adults on laxatives. The STOOL trial.
By Mihaylov S, Stark C, McColl E, Steen N, Vanoli A, Rubin G, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial of cognitive behaviour therapy in adolescents with major depression treated by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. The ADAPT trial.
By Goodyer IM, Dubicka B, Wilkinson P, Kelvin R, Roberts C, Byford S, et al.
-
The use of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hind D, Tappenden P, Tumur I, Eggington E, Sutcliffe P, Ryan A.
-
Ranibizumab and pegaptanib for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Colquitt JL, Jones J, Tan SC, Takeda A, Clegg AJ, Price A.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of 64-slice or higher computed tomography angiography as an alternative to invasive coronary angiography in the investigation of coronary artery disease.
By Mowatt G, Cummins E, Waugh N, Walker S, Cook J, Jia X, et al.
-
Structural neuroimaging in psychosis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Albon E, Tsourapas A, Frew E, Davenport C, Oyebode F, Bayliss S, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children aged 12 years and over.
By Shepherd J, Rogers G, Anderson R, Main C, Thompson-Coon J, Hartwell D, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years.
By Main C, Shepherd J, Anderson R, Rogers G, Thompson-Coon J, Liu Z, et al.
-
Ezetimibe for the treatment of hypercholesterolaemia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ara R, Tumur I, Pandor A, Duenas A, Williams R, Wilkinson A, et al.
-
Topical or oral ibuprofen for chronic knee pain in older people. The TOIB study.
By Underwood M, Ashby D, Carnes D, Castelnuovo E, Cross P, Harding G, et al.
-
A prospective randomised comparison of minor surgery in primary and secondary care. The MiSTIC trial.
By George S, Pockney P, Primrose J, Smith H, Little P, Kinley H, et al.
-
A review and critical appraisal of measures of therapist–patient interactions in mental health settings.
By Cahill J, Barkham M, Hardy G, Gilbody S, Richards D, Bower P, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening programmes for amblyopia and strabismus in children up to the age of 4–5 years: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Carlton J, Karnon J, Czoski-Murray C, Smith KJ, Marr J.
-
A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness and economic modelling of minimal incision total hip replacement approaches in the management of arthritic disease of the hip.
By de Verteuil R, Imamura M, Zhu S, Glazener C, Fraser C, Munro N, et al.
-
A preliminary model-based assessment of the cost–utility of a screening programme for early age-related macular degeneration.
By Karnon J, Czoski-Murray C, Smith K, Brand C, Chakravarthy U, Davis S, et al.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Frampton GK, Tanajewski L, Turner D, Price A.
-
Absorbent products for urinary/faecal incontinence: a comparative evaluation of key product categories.
By Fader M, Cottenden A, Getliffe K, Gage H, Clarke-O’Neill S, Jamieson K, et al.
-
A systematic review of repetitive functional task practice with modelling of resource use, costs and effectiveness.
By French B, Leathley M, Sutton C, McAdam J, Thomas L, Forster A, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectivness of minimal access surgery amongst people with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease – a UK collaborative study. The reflux trial.
By Grant A, Wileman S, Ramsay C, Bojke L, Epstein D, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Time to full publication of studies of anti-cancer medicines for breast cancer and the potential for publication bias: a short systematic review.
By Takeda A, Loveman E, Harris P, Hartwell D, Welch K.
-
Performance of screening tests for child physical abuse in accident and emergency departments.
By Woodman J, Pitt M, Wentz R, Taylor B, Hodes D, Gilbert RE.
-
Curative catheter ablation in atrial fibrillation and typical atrial flutter: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Rodgers M, McKenna C, Palmer S, Chambers D, Van Hout S, Golder S, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic modelling of effectiveness and cost utility of surgical treatments for men with benign prostatic enlargement.
By Lourenco T, Armstrong N, N’Dow J, Nabi G, Deverill M, Pickard R, et al.
-
Immunoprophylaxis against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) with palivizumab in children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wang D, Cummins C, Bayliss S, Sandercock J, Burls A.
-
Deferasirox for the treatment of iron overload associated with regular blood transfusions (transfusional haemosiderosis) in patients suffering with chronic anaemia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By McLeod C, Fleeman N, Kirkham J, Bagust A, Boland A, Chu P, et al.
-
Thrombophilia testing in people with venous thromboembolism: systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Simpson EL, Stevenson MD, Rawdin A, Papaioannou D.
-
Surgical procedures and non-surgical devices for the management of non-apnoeic snoring: a systematic review of clinical effects and associated treatment costs.
By Main C, Liu Z, Welch K, Weiner G, Quentin Jones S, Stein K.
-
Continuous positive airway pressure devices for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea–hypopnoea syndrome: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By McDaid C, Griffin S, Weatherly H, Durée K, van der Burgt M, van Hout S, Akers J, et al.
-
Use of classical and novel biomarkers as prognostic risk factors for localised prostate cancer: a systematic review.
By Sutcliffe P, Hummel S, Simpson E, Young T, Rees A, Wilkinson A, et al.
-
The harmful health effects of recreational ecstasy: a systematic review of observational evidence.
By Rogers G, Elston J, Garside R, Roome C, Taylor R, Younger P, et al.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of oesophageal Doppler monitoring in critically ill and high-risk surgical patients.
By Mowatt G, Houston G, Hernández R, de Verteuil R, Fraser C, Cuthbertson B, et al.
-
The use of surrogate outcomes in model-based cost-effectiveness analyses: a survey of UK Health Technology Assessment reports.
By Taylor RS, Elston J.
-
Controlling Hypertension and Hypotension Immediately Post Stroke (CHHIPS) – a randomised controlled trial.
By Potter J, Mistri A, Brodie F, Chernova J, Wilson E, Jagger C, et al.
-
Routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis for RhD-negative women: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Pilgrim H, Lloyd-Jones M, Rees A.
-
Amantadine, oseltamivir and zanamivir for the prophylaxis of influenza (including a review of existing guidance no. 67): a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Tappenden P, Jackson R, Cooper K, Rees A, Simpson E, Read R, et al.
-
Improving the evaluation of therapeutic interventions in multiple sclerosis: the role of new psychometric methods.
By Hobart J, Cano S.
-
Treatment of severe ankle sprain: a pragmatic randomised controlled trial comparing the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of three types of mechanical ankle support with tubular bandage. The CAST trial.
By Cooke MW, Marsh JL, Clark M, Nakash R, Jarvis RM, Hutton JL, et al. , on behalf of the CAST trial group.
-
Non-occupational postexposure prophylaxis for HIV: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Baxter L, Hird S.
-
Blood glucose self-monitoring in type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial.
By Farmer AJ, Wade AN, French DP, Simon J, Yudkin P, Gray A, et al.
-
How far does screening women for domestic (partner) violence in different health-care settings meet criteria for a screening programme? Systematic reviews of nine UK National Screening Committee criteria.
By Feder G, Ramsay J, Dunne D, Rose M, Arsene C, Norman R, et al.
-
Spinal cord stimulation for chronic pain of neuropathic or ischaemic origin: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Simpson, EL, Duenas A, Holmes MW, Papaioannou D, Chilcott J.
-
The role of magnetic resonance imaging in the identification of suspected acoustic neuroma: a systematic review of clinical and costeffectiveness and natural history.
By Fortnum H, O’Neill C, Taylor R, Lenthall R, Nikolopoulos T, Lightfoot G, et al.
-
Dipsticks and diagnostic algorithms in urinary tract infection: development and validation, randomised trial, economic analysis, observational cohort and qualitative study.
By Little P, Turner S, Rumsby K, Warner G, Moore M, Lowes JA, et al.
-
Systematic review of respite care in the frail elderly.
By Shaw C, McNamara R, Abrams K, Cannings-John R, Hood K, Longo M, et al.
-
Neuroleptics in the treatment of aggressive challenging behaviour for people with intellectual disabilities: a randomised controlled trial (NACHBID).
By Tyrer P, Oliver-Africano P, Romeo R, Knapp M, Dickens S, Bouras N, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trial to determine the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors plus supportive care, versus supportive care alone, for mild to moderate depression with somatic symptoms in primary care: the THREAD (THREshold for AntiDepressant response) study.
By Kendrick T, Chatwin J, Dowrick C, Tylee A, Morriss R, Peveler R, et al.
-
Diagnostic strategies using DNA testing for hereditary haemochromatosis in at-risk populations: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Cooper K, Picot J, Clegg A, Roderick P, Rosenberg W, et al.
-
Enhanced external counterpulsation for the treatment of stable angina and heart failure: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By McKenna C, McDaid C, Suekarran S, Hawkins N, Claxton K, Light K, et al.
-
Development of a decision support tool for primary care management of patients with abnormal liver function tests without clinically apparent liver disease: a record-linkage population cohort study and decision analysis (ALFIE).
By Donnan PT, McLernon D, Dillon JF, Ryder S, Roderick P, Sullivan F, et al.
-
A systematic review of presumed consent systems for deceased organ donation.
By Rithalia A, McDaid C, Suekarran S, Norman G, Myers L, Sowden A.
-
Paracetamol and ibuprofen for the treatment of fever in children: the PITCH randomised controlled trial.
By Hay AD, Redmond NM, Costelloe C, Montgomery AA, Fletcher M, Hollinghurst S, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to compare minimally invasive glucose monitoring devices with conventional monitoring in the management of insulin-treated diabetes mellitus (MITRE).
By Newman SP, Cooke D, Casbard A, Walker S, Meredith S, Nunn A, et al.
-
Sensitivity analysis in economic evaluation: an audit of NICE current practice and a review of its use and value in decision-making.
By Andronis L, Barton P, Bryan S.
-
Trastuzumab for the treatment of primary breast cancer in HER2-positive women: a single technology appraisal.
By Ward S, Pilgrim H, Hind D.
-
Docetaxel for the adjuvant treatment of early node-positive breast cancer: a single technology appraisal.
By Chilcott J, Lloyd Jones M, Wilkinson A.
-
The use of paclitaxel in the management of early stage breast cancer.
By Griffin S, Dunn G, Palmer S, Macfarlane K, Brent S, Dyker A, et al.
-
Rituximab for the first-line treatment of stage III/IV follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
By Dundar Y, Bagust A, Hounsome J, McLeod C, Boland A, Davis H, et al.
-
Bortezomib for the treatment of multiple myeloma patients.
By Green C, Bryant J, Takeda A, Cooper K, Clegg A, Smith A, et al.
-
Fludarabine phosphate for the firstline treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.
By Walker S, Palmer S, Erhorn S, Brent S, Dyker A, Ferrie L, et al.
-
Erlotinib for the treatment of relapsed non-small cell lung cancer.
By McLeod C, Bagust A, Boland A, Hockenhull J, Dundar Y, Proudlove C, et al.
-
Cetuximab plus radiotherapy for the treatment of locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
By Griffin S, Walker S, Sculpher M, White S, Erhorn S, Brent S, et al.
-
Infliximab for the treatment of adults with psoriasis.
By Loveman E, Turner D, Hartwell D, Cooper K, Clegg A
-
Psychological interventions for postnatal depression: cluster randomised trial and economic evaluation. The PoNDER trial.
By Morrell CJ, Warner R, Slade P, Dixon S, Walters S, Paley G, et al.
-
The effect of different treatment durations of clopidogrel in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes: a systematic review and value of information analysis.
By Rogowski R, Burch J, Palmer S, Craigs C, Golder S, Woolacott N.
-
Systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of diagnosis of heart failure, with modelling of implications of different diagnostic strategies in primary care.
By Mant J, Doust J, Roalfe A, Barton P, Cowie MR, Glasziou P, et al.
-
A multicentre randomised controlled trial of the use of continuous positive airway pressure and non-invasive positive pressure ventilation in the early treatment of patients presenting to the emergency department with severe acute cardiogenic pulmonary oedema: the 3CPO trial.
By Gray AJ, Goodacre S, Newby DE, Masson MA, Sampson F, Dixon S, et al. , on behalf of the 3CPO study investigators.
-
Early high-dose lipid-lowering therapy to avoid cardiac events: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ara R, Pandor A, Stevens J, Rees A, Rafia R.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alpha for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: an updated systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jones J, Shepherd J, Baxter L, Gospodarevskaya E, Hartwell D, Harris P, et al.
-
Methods to identify postnatal depression in primary care: an integrated evidence synthesis and value of information analysis.
By Hewitt CE, Gilbody SM, Brealey S, Paulden M, Palmer S, Mann R, et al.
-
A double-blind randomised placebocontrolled trial of topical intranasal corticosteroids in 4- to 11-year-old children with persistent bilateral otitis media with effusion in primary care.
By Williamson I, Benge S, Barton S, Petrou S, Letley L, Fasey N, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of methods of storing donated kidneys from deceased donors: a systematic review and economic model.
By Bond M, Pitt M, Akoh J, Moxham T, Hoyle M, Anderson R.
-
Rehabilitation of older patients: day hospital compared with rehabilitation at home. A randomised controlled trial.
By Parker SG, Oliver P, Pennington M, Bond J, Jagger C, Enderby PM, et al.
-
Breastfeeding promotion for infants in neonatal units: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Renfrew MJ, Craig D, Dyson L, McCormick F, Rice S, King SE, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of bariatric (weight loss) surgery for obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Picot J, Jones J, Colquitt JL, Gospodarevskaya E, Loveman E, Baxter L, et al.
-
Rapid testing for group B streptococcus during labour: a test accuracy study with evaluation of acceptability and cost-effectiveness.
By Daniels J, Gray J, Pattison H, Roberts T, Edwards E, Milner P, et al.
-
Screening to prevent spontaneous preterm birth: systematic reviews of accuracy and effectiveness literature with economic modelling.
By Honest H, Forbes CA, Durée KH, Norman G, Duffy SB, Tsourapas A, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cochlear implants for severe to profound deafness in children and adults: a systematic review and economic model.
By Bond M, Mealing S, Anderson R, Elston J, Weiner G, Taylor RS, et al.
-
Gemcitabine for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer.
By Jones J, Takeda A, Tan SC, Cooper K, Loveman E, Clegg A.
-
Varenicline in the management of smoking cessation: a single technology appraisal.
By Hind D, Tappenden P, Peters J, Kenjegalieva K.
-
Alteplase for the treatment of acute ischaemic stroke: a single technology appraisal.
By Lloyd Jones M, Holmes M.
-
Rituximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
By Bagust A, Boland A, Hockenhull J, Fleeman N, Greenhalgh J, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Omalizumab for the treatment of severe persistent allergic asthma.
By Jones J, Shepherd J, Hartwell D, Harris P, Cooper K, Takeda A, et al.
-
Rituximab for the treatment of relapsed or refractory stage III or IV follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
By Boland A, Bagust A, Hockenhull J, Davis H, Chu P, Dickson R.
-
Adalimumab for the treatment of psoriasis.
By Turner D, Picot J, Cooper K, Loveman E.
-
Dabigatran etexilate for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in patients undergoing elective hip and knee surgery: a single technology appraisal.
By Holmes M, C Carroll C, Papaioannou D.
-
Romiplostim for the treatment of chronic immune or idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a single technology appraisal.
By Mowatt G, Boachie C, Crowther M, Fraser C, Hernández R, Jia X, et al.
-
Sunitinib for the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumours: a critique of the submission from Pfizer.
By Bond M, Hoyle M, Moxham T, Napier M, Anderson R.
-
Vitamin K to prevent fractures in older women: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Stevenson M, Lloyd-Jones M, Papaioannou D.
-
The effects of biofeedback for the treatment of essential hypertension: a systematic review.
By Greenhalgh J, Dickson R, Dundar Y.
-
A randomised controlled trial of the use of aciclovir and/or prednisolone for the early treatment of Bell’s palsy: the BELLS study.
By Sullivan FM, Swan IRC, Donnan PT, Morrison JM, Smith BH, McKinstry B, et al.
-
Lapatinib for the treatment of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer.
By Jones J, Takeda A, Picot J, von Keyserlingk C, Clegg A.
-
Infliximab for the treatment of ulcerative colitis.
By Hyde C, Bryan S, Juarez-Garcia A, Andronis L, Fry-Smith A.
-
Rimonabant for the treatment of overweight and obese people.
By Burch J, McKenna C, Palmer S, Norman G, Glanville J, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Telbivudine for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection.
By Hartwell D, Jones J, Harris P, Cooper K.
-
Entecavir for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection.
By Shepherd J, Gospodarevskaya E, Frampton G, Cooper, K.
-
Febuxostat for the treatment of hyperuricaemia in people with gout: a single technology appraisal.
By Stevenson M, Pandor A.
-
Rivaroxaban for the prevention of venous thromboembolism: a single technology appraisal.
By Stevenson M, Scope A, Holmes M, Rees A, Kaltenthaler E.
-
Cetuximab for the treatment of recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
By Greenhalgh J, Bagust A, Boland A, Fleeman N, McLeod C, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Mifamurtide for the treatment of osteosarcoma: a single technology appraisal.
By Pandor A, Fitzgerald P, Stevenson M, Papaioannou D.
-
Ustekinumab for the treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis.
By Gospodarevskaya E, Picot J, Cooper K, Loveman E, Takeda A.
-
Endovascular stents for abdominal aortic aneurysms: a systematic review and economic model.
By Chambers D, Epstein D, Walker S, Fayter D, Paton F, Wright K, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of epoprostenol, iloprost, bosentan, sitaxentan and sildenafil for pulmonary arterial hypertension within their licensed indications: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Chen Y-F, Jowett S, Barton P, Malottki K, Hyde C, Gibbs JSR, et al.
-
Cessation of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder drugs in the young (CADDY) – a pharmacoepidemiological and qualitative study.
By Wong ICK, Asherson P, Bilbow A, Clifford S, Coghill D, R DeSoysa R, et al.
-
ARTISTIC: a randomised trial of human papillomavirus (HPV) testing in primary cervical screening.
By Kitchener HC, Almonte M, Gilham C, Dowie R, Stoykova B, Sargent A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness of glucosamine and chondroitin supplements in slowing or arresting progression of osteoarthritis of the knee: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Black C, Clar C, Henderson R, MacEachern C, McNamee P, Quayyum Z, et al.
-
Randomised preference trial of medical versus surgical termination of pregnancy less than 14 weeks’ gestation (TOPS).
By Robson SC, Kelly T, Howel D, Deverill M, Hewison J, Lie MLS, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trial of the use of three dressing preparations in the management of chronic ulceration of the foot in diabetes.
By Jeffcoate WJ, Price PE, Phillips CJ, Game FL, Mudge E, Davies S, et al.
-
VenUS II: a randomised controlled trial of larval therapy in the management of leg ulcers.
By Dumville JC, Worthy G, Soares MO, Bland JM, Cullum N, Dowson C, et al.
-
A prospective randomised controlled trial and economic modelling of antimicrobial silver dressings versus non-adherent control dressings for venous leg ulcers: the VULCAN trial
By Michaels JA, Campbell WB, King BM, MacIntyre J, Palfreyman SJ, Shackley P, et al.
-
Communication of carrier status information following universal newborn screening for sickle cell disorders and cystic fibrosis: qualitative study of experience and practice.
By Kai J, Ulph F, Cullinan T, Qureshi N.
-
Antiviral drugs for the treatment of influenza: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burch J, Paulden M, Conti S, Stock C, Corbett M, Welton NJ, et al.
-
Development of a toolkit and glossary to aid in the adaptation of health technology assessment (HTA) reports for use in different contexts.
By Chase D, Rosten C, Turner S, Hicks N, Milne R.
-
Colour vision testing for diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review of diagnostic accuracy and economic evaluation.
By Rodgers M, Hodges R, Hawkins J, Hollingworth W, Duffy S, McKibbin M, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of weight management schemes for the under fives: a short report.
By Bond M, Wyatt K, Lloyd J, Welch K, Taylor R.
-
Are adverse effects incorporated in economic models? An initial review of current practice.
By Craig D, McDaid C, Fonseca T, Stock C, Duffy S, Woolacott N.
-
Multicentre randomised controlled trial examining the cost-effectiveness of contrast-enhanced high field magnetic resonance imaging in women with primary breast cancer scheduled for wide local excision (COMICE).
By Turnbull LW, Brown SR, Olivier C, Harvey I, Brown J, Drew P, et al.
-
Bevacizumab, sorafenib tosylate, sunitinib and temsirolimus for renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Thompson Coon J, Hoyle M, Green C, Liu Z, Welch K, Moxham T, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of testing for cytochrome P450 polymorphisms in patients with schizophrenia treated with antipsychotics: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Fleeman N, McLeod C, Bagust A, Beale S, Boland A, Dundar Y, et al.
Health Technology Assessment programme
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
Prioritisation Strategy Group
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
-
Dr Bob Coates, Consultant Advisor, NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Andrew Cook, Consultant Advisor, NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Peter Davidson, Director of Science Support, NETSCC, HTA
-
Professor Robin E Ferner, Consultant Physician and Director, West Midlands Centre for Adverse Drug Reactions, City Hospital NHS Trust, Birmingham
-
Professor Paul Glasziou, Professor of Evidence-Based Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Dr Nick Hicks, Director of NHS Support, NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Edmund Jessop, Medical Adviser, National Specialist, National Commissioning Group (NCG), Department of Health, London
-
Ms Lynn Kerridge, Chief Executive Officer, NETSCC and NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Ruairidh Milne, Director of Strategy and Development, NETSCC
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Ms Pamela Young, Specialist Programme Manager, NETSCC, HTA
HTA Commissioning Board
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
-
Senior Lecturer in General Practice, Department of Primary Health Care, University of Oxford
-
Professor Ann Ashburn, Professor of Rehabilitation and Head of Research, Southampton General Hospital
-
Professor Deborah Ashby, Professor of Medical Statistics, Queen Mary, University of London
-
Professor John Cairns, Professor of Health Economics, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Peter Croft, Director of Primary Care Sciences Research Centre, Keele University
-
Professor Nicky Cullum, Director of Centre for Evidence-Based Nursing, University of York
-
Professor Jenny Donovan, Professor of Social Medicine, University of Bristol
-
Professor Steve Halligan, Professor of Gastrointestinal Radiology, University College Hospital, London
-
Professor Freddie Hamdy, Professor of Urology, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Allan House, Professor of Liaison Psychiatry, University of Leeds
-
Dr Martin J Landray, Reader in Epidemiology, Honorary Consultant Physician, Clinical Trial Service Unit, University of Oxford?
-
Professor Stuart Logan, Director of Health & Social Care Research, The Peninsula Medical School, Universities of Exeter and Plymouth
-
Dr Rafael Perera, Lecturer in Medical Statisitics, Department of Primary Health Care, Univeristy of Oxford
-
Professor Ian Roberts, Professor of Epidemiology & Public Health, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Mark Sculpher, Professor of Health Economics, University of York
-
Professor Helen Smith, Professor of Primary Care, University of Brighton
-
Professor Kate Thomas, Professor of Complementary & Alternative Medicine Research, University of Leeds
-
Professor David John Torgerson, Director of York Trials Unit, University of York
-
Professor Hywel Williams, Professor of Dermato-Epidemiology, University of Nottingham
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Medical Research Council
Diagnostic Technologies & Screening Panel
-
Professor of Evidence-Based Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Consultant Paediatrician and Honorary Senior Lecturer, Great Ormond Street Hospital, London
-
Professor Judith E Adams, Consultant Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Central Manchester & Manchester Children’s University Hospitals NHS Trust, and Professor of Diagnostic Radiology, Imaging Science and Biomedical Engineering, Cancer & Imaging Sciences, University of Manchester
-
Ms Jane Bates, Consultant Ultrasound Practitioner, Ultrasound Department, Leeds Teaching Hospital NHS Trust
-
Dr Stephanie Dancer, Consultant Microbiologist, Hairmyres Hospital, East Kilbride
-
Professor Glyn Elwyn, Primary Medical Care Research Group, Swansea Clinical School, University of Wales
-
Dr Ron Gray, Consultant Clinical Epidemiologist, Department of Public Health, University of Oxford
-
Professor Paul D Griffiths, Professor of Radiology, University of Sheffield
-
Dr Jennifer J Kurinczuk, Consultant Clinical Epidemiologist, National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, Oxford
-
Dr Susanne M Ludgate, Medical Director, Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency, London
-
Dr Anne Mackie, Director of Programmes, UK National Screening Committee
-
Dr Michael Millar, Consultant Senior Lecturer in Microbiology, Barts and The London NHS Trust, Royal London Hospital
-
Mr Stephen Pilling, Director, Centre for Outcomes, Research & Effectiveness, Joint Director, National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health, University College London
-
Mrs Una Rennard, Service User Representative
-
Dr Phil Shackley, Senior Lecturer in Health Economics, School of Population and Health Sciences, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Dr W Stuart A Smellie, Consultant in Chemical Pathology, Bishop Auckland General Hospital
-
Dr Nicholas Summerton, Consultant Clinical and Public Health Advisor, NICE
-
Ms Dawn Talbot, Service User Representative
-
Dr Graham Taylor, Scientific Advisor, Regional DNA Laboratory, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Professor Lindsay Wilson Turnbull, Scientific Director of the Centre for Magnetic Resonance Investigations and YCR Professor of Radiology, Hull Royal Infirmary
-
Dr Tim Elliott, Team Leader, Cancer Screening, Department of Health
-
Dr Catherine Moody, Programme Manager, Neuroscience and Mental Health Board
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Pharmaceuticals Panel
-
Consultant Physician and Director, West Midlands Centre for Adverse Drug Reactions, City Hospital NHS Trust, Birmingham
-
Professor in Child Health, University of Nottingham
-
Mrs Nicola Carey, Senior Research Fellow, School of Health and Social Care, The University of Reading
-
Mr John Chapman, Service User Representative
-
Dr Peter Elton, Director of Public Health, Bury Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Ben Goldacre, Research Fellow, Division of Psychological Medicine and Psychiatry, King’s College London
-
Mrs Barbara Greggains, Service User Representative
-
Dr Bill Gutteridge, Medical Adviser, London Strategic Health Authority
-
Dr Dyfrig Hughes, Reader in Pharmacoeconomics and Deputy Director, Centre for Economics and Policy in Health, IMSCaR, Bangor University
-
Professor Jonathan Ledermann, Professor of Medical Oncology and Director of the Cancer Research UK and University College London Cancer Trials Centre
-
Dr Yoon K Loke, Senior Lecturer in Clinical Pharmacology, University of East Anglia
-
Professor Femi Oyebode, Consultant Psychiatrist and Head of Department, University of Birmingham
-
Dr Andrew Prentice, Senior Lecturer and Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, The Rosie Hospital, University of Cambridge
-
Dr Martin Shelly, General Practitioner, Leeds, and Associate Director, NHS Clinical Governance Support Team, Leicester
-
Dr Gillian Shepherd, Director, Health and Clinical Excellence, Merck Serono Ltd
-
Mrs Katrina Simister, Assistant Director New Medicines, National Prescribing Centre, Liverpool
-
Mr David Symes, Service User Representative
-
Dr Lesley Wise, Unit Manager, Pharmacoepidemiology Research Unit, VRMM, Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Mr Simon Reeve, Head of Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness, Medicines, Pharmacy and Industry Group, Department of Health
-
Dr Heike Weber, Programme Manager, Medical Research Council
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Therapeutic Procedures Panel
-
Consultant Physician, North Bristol NHS Trust
-
Professor of Psychiatry, Division of Health in the Community, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Professor Jane Barlow, Professor of Public Health in the Early Years, Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, Coventry
-
Ms Maree Barnett, Acting Branch Head of Vascular Programme, Department of Health
-
Mrs Val Carlill, Service User Representative
-
Mrs Anthea De Barton-Watson, Service User Representative
-
Mr Mark Emberton, Senior Lecturer in Oncological Urology, Institute of Urology, University College Hospital, London
-
Professor Steve Goodacre, Professor of Emergency Medicine, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Christopher Griffiths, Professor of Primary Care, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Mr Paul Hilton, Consultant Gynaecologist and Urogynaecologist, Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Nicholas James, Professor of Clinical Oncology, University of Birmingham, and Consultant in Clinical Oncology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital
-
Dr Peter Martin, Consultant Neurologist, Addenbrooke’s Hospital, Cambridge
-
Dr Kate Radford, Senior Lecturer (Research), Clinical Practice Research Unit, University of Central Lancashire, Preston
-
Mr Jim Reece Service User Representative
-
Dr Karen Roberts, Nurse Consultant, Dunston Hill Hospital Cottages
-
Dr Phillip Leech, Principal Medical Officer for Primary Care, Department of Health
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Medical Research Council
-
Professor Tom Walley, Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Disease Prevention Panel
-
Medical Adviser, National Specialist, National Commissioning Group (NCG), London
-
Director, NHS Sustainable Development Unit, Cambridge
-
Dr Elizabeth Fellow-Smith, Medical Director, West London Mental Health Trust, Middlesex
-
Dr John Jackson, General Practitioner, Parkway Medical Centre, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Mike Kelly, Director, Centre for Public Health Excellence, NICE, London
-
Dr Chris McCall, General Practitioner, The Hadleigh Practice, Corfe Mullen, Dorset
-
Ms Jeanett Martin, Director of Nursing, BarnDoc Limited, Lewisham Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Julie Mytton, Locum Consultant in Public Health Medicine, Bristol Primary Care Trust
-
Miss Nicky Mullany, Service User Representative
-
Professor Ian Roberts, Professor of Epidemiology and Public Health, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Ken Stein, Senior Clinical Lecturer in Public Health, University of Exeter
-
Dr Kieran Sweeney, Honorary Clinical Senior Lecturer, Peninsula College of Medicine and Dentistry, Universities of Exeter and Plymouth
-
Professor Carol Tannahill, Glasgow Centre for Population Health
-
Professor Margaret Thorogood, Professor of Epidemiology, University of Warwick Medical School, Coventry
-
Ms Christine McGuire, Research & Development, Department of Health
-
Dr Caroline Stone, Programme Manager, Medical Research Council
Expert Advisory Network
-
Professor Douglas Altman, Professor of Statistics in Medicine, Centre for Statistics in Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Professor John Bond, Professor of Social Gerontology & Health Services Research, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Andrew Bradbury, Professor of Vascular Surgery, Solihull Hospital, Birmingham
-
Mr Shaun Brogan, Chief Executive, Ridgeway Primary Care Group, Aylesbury
-
Mrs Stella Burnside OBE, Chief Executive, Regulation and Improvement Authority, Belfast
-
Ms Tracy Bury, Project Manager, World Confederation for Physical Therapy, London
-
Professor Iain T Cameron, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology and Head of the School of Medicine, University of Southampton
-
Dr Christine Clark, Medical Writer and Consultant Pharmacist, Rossendale
-
Professor Collette Clifford, Professor of Nursing and Head of Research, The Medical School, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Barry Cookson, Director, Laboratory of Hospital Infection, Public Health Laboratory Service, London
-
Dr Carl Counsell, Clinical Senior Lecturer in Neurology, University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Howard Cuckle, Professor of Reproductive Epidemiology, Department of Paediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynaecology, University of Leeds
-
Dr Katherine Darton, Information Unit, MIND – The Mental Health Charity, London
-
Professor Carol Dezateux, Professor of Paediatric Epidemiology, Institute of Child Health, London
-
Mr John Dunning, Consultant Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Papworth Hospital NHS Trust, Cambridge
-
Mr Jonothan Earnshaw, Consultant Vascular Surgeon, Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Gloucester
-
Professor Martin Eccles, Professor of Clinical Effectiveness, Centre for Health Services Research, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Pam Enderby, Dean of Faculty of Medicine, Institute of General Practice and Primary Care, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Gene Feder, Professor of Primary Care Research & Development, Centre for Health Sciences, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Mr Leonard R Fenwick, Chief Executive, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Mrs Gillian Fletcher, Antenatal Teacher and Tutor and President, National Childbirth Trust, Henfield
-
Professor Jayne Franklyn, Professor of Medicine, University of Birmingham
-
Mr Tam Fry, Honorary Chairman, Child Growth Foundation, London
-
Professor Fiona Gilbert, Consultant Radiologist and NCRN Member, University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Paul Gregg, Professor of Orthopaedic Surgical Science, South Tees Hospital NHS Trust
-
Bec Hanley, Co-director, TwoCan Associates, West Sussex
-
Dr Maryann L Hardy, Senior Lecturer, University of Bradford
-
Mrs Sharon Hart, Healthcare Management Consultant, Reading
-
Professor Robert E Hawkins, CRC Professor and Director of Medical Oncology, Christie CRC Research Centre, Christie Hospital NHS Trust, Manchester
-
Professor Richard Hobbs, Head of Department of Primary Care & General Practice, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Alan Horwich, Dean and Section Chairman, The Institute of Cancer Research, London
-
Professor Allen Hutchinson, Director of Public Health and Deputy Dean of ScHARR, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Peter Jones, Professor of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge
-
Professor Stan Kaye, Cancer Research UK Professor of Medical Oncology, Royal Marsden Hospital and Institute of Cancer Research, Surrey
-
Dr Duncan Keeley, General Practitioner (Dr Burch & Ptnrs), The Health Centre, Thame
-
Dr Donna Lamping, Research Degrees Programme Director and Reader in Psychology, Health Services Research Unit, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London
-
Mr George Levvy, Chief Executive, Motor Neurone Disease Association, Northampton
-
Professor James Lindesay, Professor of Psychiatry for the Elderly, University of Leicester
-
Professor Julian Little, Professor of Human Genome Epidemiology, University of Ottawa
-
Professor Alistaire McGuire, Professor of Health Economics, London School of Economics
-
Professor Rajan Madhok, Medical Director and Director of Public Health, Directorate of Clinical Strategy & Public Health, North & East Yorkshire & Northern Lincolnshire Health Authority, York
-
Professor Alexander Markham, Director, Molecular Medicine Unit, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Dr Peter Moore, Freelance Science Writer, Ashtead
-
Dr Andrew Mortimore, Public Health Director, Southampton City Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Sue Moss, Associate Director, Cancer Screening Evaluation Unit, Institute of Cancer Research, Sutton
-
Professor Miranda Mugford, Professor of Health Economics and Group Co-ordinator, University of East Anglia
-
Professor Jim Neilson, Head of School of Reproductive & Developmental Medicine and Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, University of Liverpool
-
Mrs Julietta Patnick, National Co-ordinator, NHS Cancer Screening Programmes, Sheffield
-
Professor Robert Peveler, Professor of Liaison Psychiatry, Royal South Hants Hospital, Southampton
-
Professor Chris Price, Director of Clinical Research, Bayer Diagnostics Europe, Stoke Poges
-
Professor William Rosenberg, Professor of Hepatology and Consultant Physician, University of Southampton
-
Professor Peter Sandercock, Professor of Medical Neurology, Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Edinburgh
-
Dr Susan Schonfield, Consultant in Public Health, Hillingdon Primary Care Trust, Middlesex
-
Dr Eamonn Sheridan, Consultant in Clinical Genetics, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Dr Margaret Somerville, Director of Public Health Learning, Peninsula Medical School, University of Plymouth
-
Professor Sarah Stewart-Brown, Professor of Public Health, Division of Health in the Community, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Professor Ala Szczepura, Professor of Health Service Research, Centre for Health Services Studies, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Mrs Joan Webster, Consumer Member, Southern Derbyshire Community Health Council
-
Professor Martin Whittle, Clinical Co-director, National Co-ordinating Centre for Women’s and Children’s Health, Lymington