Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was commissioned by the HTA programme as project number 08/54/01. The contractual start date was in December 2008. The draft report began editorial review in April 2009 and was accepted for publication in August 2009. As the funder, by devising a commissioning brief, the HTA programme specified the research question and study design. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the referees for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
None
Permissions
Copyright statement
© 2010 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO. This journal is a member of and subscribes to the principles of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) (http://www.publicationethics.org/). This journal may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NETSCC, Health Technology Assessment, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2010 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Background
Description of health problem
Introduction
Chlamydia is the most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI) in the world. 1 In 1999, it was estimated that there were almost 92 million new infections of genital chlamydia among adults worldwide. 2
Within the UK, in 2006, there were 112,473 chlamydia diagnoses made in England and Wales, and a further 17,962 made in Scotland. 3 Chlamydia accounts for 30% of all new STI diagnoses made in UK genito-urinary medicine (GUM) clinics3 and yet it is easily treated with a single oral dose of azithromycin. 4
Incidence, prevalence and infection epidemiology
Targeted testing, monitoring of prevalence and reaching particular risk groups are all key to ensuring effective chlamydia testing for a population. The collection of data relating to chlamydia is most robust around the specialist GUM clinics, laboratories and the National Chlamydia Screening Programme (NCSP). Data from primary care and community venues are limited, particularly for those aged over 25 years. Previous population-based studies indicate a prevalence of 2–6% for both men and women aged between 15 and 24 years old,5 although some estimate prevalence to be higher6,7 and recent data suggest that it could be greater than 10% among those aged between 18 and 25 years old. 8
The number of cases of chlamydia diagnosed has increased markedly over recent years, but in part this may be explained by an increase in the number of tests carried out. The introduction of more sensitive nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) to diagnose chlamydia has also been a major contributory factor. The number and variety of testing venues have also increased to improve access to testing and, in England and Wales in 2006, 27% of all chlamydia infections were diagnosed outside a GUM clinic setting. 3 In Scotland the proportion diagnosed in non-GUM clinic settings is higher (53%). 9
There are still differences in the characteristics of the groups being diagnosed. For example, the ratio of new diagnoses in women compared with men is 1.6:1 in England and Wales. 3 The ratio in Scotland is similar (1.7:1). 10
Also, with regard to age, the focus of chlamydia testing should be directed towards young people under 25 years of age (as is current practice within the NCSP), as it is recognised that young people are at most risk of chlamydia infection through a combination of their risk-taking behaviour11 and biological susceptibility to infection. 12 There is therefore an ongoing challenge to increase testing rates among those aged less than 25 years. People below 25 years account for 12% of the total population, but accounted for 65% of all chlamydia diagnoses made in GUM clinics in 2007. 13
The available diagnostic data on chlamydia also show clear geographical variation in infection rates3,8 as well as variation by ethnic group (with the highest positive rates among mixed race or Black-Caribbean populations, and the lowest rates among Asian populations). 3,8,13
Aetiology, pathology and the impact of the health problem
The natural history of chlamydia infection and the frequency of reproductive tract complications is not known. 14–16 This knowledge gap exists (and is unlikely to be resolved) because long-term follow-up of untreated chlamydia infection would be unethical, and diagnosed infections that are treated alter the natural history of the infection.
The sexually transmitted strains of the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis (strains D–K) cause cervicitis and urethritis in women and urethritis in men, and can also cause rectal and pharyngeal infections, as well as having the potential to be transmitted in labour, causing pneumonia and eye infections in neonates. 4 There is clear recognition that untreated infection ascending the reproductive tract is influenced by immunological factors and can cause tubal damage predisposing to ectopic pregnancy, tubal infertility and chronic pelvic pain. 15 Ascending infection in males may cause epididymitis, but the effect on future fertility is less clear. 14,16 This report does not consider the strains that cause the tropical STI lymphogranuloma venereum that have been responsible for outbreaks of ulcerative proctitis mainly in men who have sex with men. 17
Genital tract infection with chlamydia often remains asymptomatic in at least 70% of women and 50% of men. 18 Current thinking is that the majority of infections clear spontaneously without any associated significant morbidity. Around 50% of infections resolve within 1 year. 19 Resolved infection is not thought to confer a lasting immunity, so re-infection remains a possibility. 20,21 Worryingly, as with other STIs, chlamydia can facilitate human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) transmission. 22
Very early studies based on clinic populations considered that 30% of untreated chlamydia infections would lead to acute pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) within weeks and that complications of chlamydia infection were common, particularly in women. 23 More recent research suggests that the complication rate is much lower than previously believed. 15 There now exists uncertainty regarding the prognosis for any positive chlamydia test, but it is established that previous probability estimates for long-term sequelae associated with chlamydia infection were too high. Currently, there is significant debate about the frequency of upper reproductive tract complications following lower genital tract infection with chlamydia. 14–16 It should be noted, however, that most of this research has been conducted in specialist GUM clinic and hospital populations and has therefore been affected by selection bias. 24 Furthermore, the sound and objective diagnosis of PID is notoriously difficult. 25 It is also difficult to be certain that any subsequent sequelae can be directly attributed to chlamydia, particularly where time has elapsed from a diagnosis or acute infection.
Early studies suggested that the complications associated with chlamydia were common, particularly in women. 23 However, despite dramatic increases in the number of chlamydia tests and diagnoses, there has been no accompanying rise in PID. In fact, the number of hospital admissions for PID has fallen by 43% [figures calculated using the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th revision (ICD-10) codes N70–N73 inclusive] over the last decade, from 19,367 in 1998/9 to 13,502 in 2007/8. 26 Most PID diagnoses will be made in primary care, but the reported incidence of PID is falling in primary care settings also. 3 However, it is important to note that regardless of any previous overestimates of the impact of chlamydia infection, it still remains a significant cause of morbidity for women of reproductive age and has significant resource implications for health-care provision and planning.
Little is known about the psychosocial impact of a diagnosis of chlamydia infection, but there is some evidence to suggest that it creates considerable anxiety, particularly with regard to possible stigmatisation, the need to inform sexual partners of possible infection, and the risk of infertility. 27,28
Significance for the NHS
The impact of the health problem caused by chlamydia is considerable. Undiagnosed and untreated chlamydia infection is a serious public health concern, with the potential for those infected and untreated to further spread the infection, including possibly re-infecting previously treated cases.
The health-care services costs related to chlamydia include the cost of screening and the cost of treating chlamydia or complications arising from chlamydia infection described above. The complications can be grouped into female, neonatal and male sequelae. 29 The female sequelae include PIDs, chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancy and infertility. Neonatal sequelae are conjunctivitis and pneumonia, and the male sequelae are epididymytis and urethritis. In the UK, the costs of complications of Chlamydia trachomatis in women were estimated as at least £50M annually in the late 1990s. 30 The total cost burden of chlamydia to UK health services was estimated to exceed £100M in 2002 prices. 29
Current service provision
Management of infection
Chlamydia screening programmes operate in some countries, for example, Sweden, the USA and Canada. England introduced a NCSP in 200331 and Northern Ireland plans to introduce a similar system (the Chlamydia Testing Programme in Northern Ireland; CTPNI) in the near future. Scotland and Wales currently do not have screening programmes in place, although targeted opportunistic testing is provided in a varied and increasing number of settings. The screening and opportunistic programmes both share an aim to reduce morbidity in individuals and achieve longer term infection control through a sustained reduction in the onward transmission of infections.
Chlamydia testing itself currently uses NAAT methods, which are laboratory dependant and therefore have an inherent processing delay between testing and advising the health provider of a positive result. Test results must be relayed to the patient tested in order for treatment and partner notification (and partner treatment) to take place. Management of confirmed chlamydia infection requires appropriate antimicrobial treatment, partner notification advice and abstinence from sexual intercourse until both the patient and any current partner(s) have been treated.
All the drug treatments available to treat chlamydia showed a cure rate of more than 90%. 4 It is well recognised that compliance is better with a single oral dose, and therefore azithromycin as an oral 1-g stat dose is the first choice for treating uncomplicated infection. 18,32 There are other regimes extending over 7 days, using ofloxacin, minocycline, lymecycline and doxycycline. Erythromycin is another alternative, but is less well tolerated and therefore has a greater likelihood of non-completion of treatment. 33
Partner notification and treatment is essential to reducing re-infection rates, as the highest prevalence of chlamydia infection occurs in the partners of patients with diagnosed chlamydia infection. However, partner notification has inherent difficulties and there is evidence that it reaches only 50–60% of partners. 34 Indeed, in 2007/8 in England and Wales, of the 18,497 partners reported to NCSP venues, 11,596 (63%) were contacted and 7533 (40.7% of those originally reported) were eventually treated. 8 Current clinical recommendations are that for symptomatic patients, all partners from the 4 weeks prior to the onset of symptoms should be contacted. For asymptomatic patients, it is suggested that all partners over the preceding 6 months or the most recent sexual partner outside that time frame should be contacted. 4 Within the NCSP, there are additional targets to verify at least 0.6 partners per index case as treated (except within London where the standard is 0.4 partners), but recent indications suggest a decline in the proportion of programme areas achieving this rate, and it has been noted that future monitoring is required. 8 The latest Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) guideline on chlamydia also includes a key recommendation for more active management and follow-up of positive cases and contacts. 18
In terms of preventing re-infection, there is only limited evidence regarding the effectiveness of follow-up and the role of test of cure (where a repeat test is carried out to confirm the absence of the infection). Routine test of cure is recommended in pregnancy and where non-compliance or re-exposure is suspected (although this should not be done using a NAAT until after 5 weeks of initiation of therapy to avoid a false-positive result due to the persistence of non-viable chlamydia organisms). 4
In limiting re-infection, there is accumulating evidence that, after partners of index cases, the next highest prevalence of chlamydia is caused by the re-infection of treated index cases. One study has shown re-infection rates of between 21.1 and 29.9 per 100 people treated, depending on the original treatment setting. 35 It is therefore recommended that testing for re-infection be conducted at between 6 and 12 months after initial treatment. 18
A follow-up interview can also serve to ensure adherence to treatment, confirm avoidance of risk of the exposure to infection and maximise the opportunity to contact all sexual partners. The success rate for partner notification has been shown in one UK study of 200 GUM clinic attendees to have significantly improved from 0.46 to 0.66 contacts per index case after specific follow-up was introduced (p = 0.005). 36
Current service cost
Different health services’ cost estimates for the UK have been reported in three recent studies. 29,37,38 Estimates are provided on the average costs of acute chlamydia infections and complications associated with chlamydia (Table 1). These cost estimates vary owing to assumptions made about the resources used. Adams and colleagues37 based their estimates on the Department of Health 2004 reference costs. 39
| Conditions | Estimated costs (and standard deviation) at 2004 prices (£)37 | Estimated unit costs at 2001 prices (£)29 | Estimated unit costs at 2005 prices (£)38 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symptomatically infected and seeking treatment (men) | 64 (6) | ||
| Symptomatically infected and seeking treatment (women) | 61 (5) | ||
| Screened and treated for those infected (men and women) | 31 (2) | ||
| PIDs | 137 (46) | 190 | 3014 (HRG costs)a |
| Epididymitis | 142 (67) | 15 | 790 |
| Chronic pelvic pain | – | 111 | |
| Ectopic pregnancy | 762 (329) | 2530 | 2456 (HRG costs) |
| Tubal factor infertility | 10,798 (4279) | ||
| Infertility | – | 4540 | 453 (NICE guideline) |
| Neonatal conjunctivitis | 41 (4) | 8 | |
| Neonatal pneumonia | 612 (555) | 303 | |
| Neonatal complications | 749 (HRG costs) |
It should also be noted that aside from the index patient costs included in the table, there are also the additional costs of partner notification and treatment. It has been estimated that the average health service cost of partner notification for each index case is £11.72, and for treatment would be £32.55 at 2003 prices. 34
Variation in services and/or uncertainty about best practice
Nucleic acid amplification tests are undoubtedly the most sensitive and specific, and therefore most accurate, tests for use in practice. They have replaced the older less reliable assays, including culture and antigen detection. The high sensitivity of these tests means that specimens can be taken non-invasively, e.g. as a urine sample or from vaginal (or other) secretions. It should be noted that all NAATs currently available for use perform very well diagnostically, although there are some differences between them. 40 In terms of the type of NAAT method used, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was the laboratory method used for 160,683 (48.3%) of the 332,403 chlamydia tests conducted in the NCSP in 2007/8. A further 95,966 (28.9%) were conducted using strand displacement amplification (SDA), 68,027 (20.5%) were conducted using transcription-mediated amplification (TMA), and the method for the remaining 7727 tests (2.3%) was predominantly reported as being unknown. 8
These tests, although diagnostically excellent, are expensive, and the need for separate laboratory testing necessitates a return visit for treatment following a positive diagnosis. The delay causes inherent difficulties in contacting patients once the diagnosis has been made, as well as difficulties for partner notification, and it is these latter steps that are critical to reducing the pool of infection. Therefore, there are clear advantages to developing immediate near-patient technologies for testing chlamydia, as theoretically they could have public health advantages and be more cost-effective than current practice. However, in practice, point-of-care enzyme immunoassays are not currently recommended on account of their reduced sensitivity in comparison with NAAT methods. The immediacy of a result for any new point-of-care tests (POCTs) would have to be balanced against the proportion of false-negative results (and the need for full NAAT screening for test-negative individuals would need to be determined), but finding an effective, reliable and low-cost near-patient test that gives an immediate result remains attractive to health-care providers and policy-makers.
Relevant national guidelines, including national service frameworks
Current guidelines on the management of chlamydia infection are available from the British Association of Sexual Health and HIV. 4 In addition, the NCSP publishes a set of core requirements, as standards required to be met by all screening venues performing chlamydia testing in England. 32 Both guidelines tend to provide uniform advice on chlamydia management, as does the SIGN guideline on the management of chlamydia infection, which was updated in March 2009. 18
More information on chlamydia infection can be found in the national strategic policy work undertaken for sexual health. National sexual health policy in England is set out within the National Strategy for Sexual Health and HIV,41 which is currently in the process of being reviewed. 42 Scotland has had it’s own national strategy and action plan in place since 2005,43 and NHS Quality Improvement Scotland has also developed a set of national standards for the treatment of STIs in Scotland44 (although HIV standards are taken to be equivalent to those available from the British HIV Association);45 Wales46 and Northern Ireland47 also have their own sexual health strategies.
Description of the technologies under assessment
Summary of interventions
As noted above, POCTs are attractive to health-care providers and policy-makers because of their potential to deliver an immediate result, creating an opportunity for immediate treatment and discussion of partner notification and thereby reducing the pool of infection. Given the poor sensitivity of current POCTs, for a POCT to become part of the current care pathway for testing chlamydia infection, it would have to show enhanced sensitivity, or otherwise be used only in situations where those with negative results would be retested using a NAAT method to confirm the result.
The length of treatment required for a POCT is measurable in hours, although follow-up may be required if confirmatory laboratory testing using a NAAT method is required, and this could take several days/weeks. The tests could be undertaken in the same settings as current practice, but there is the potential to expand the number of chlamydia testing venues using POCTs, as little equipment is required. Trained personnel would be needed to administer the test, provide the result, treatment and advice, and administer contact tracing to allow partner notification.
Identification of important subgroups
Regardless of the test used, the most important subgroup with regard to chlamydia infection is those aged under 25 years, as this population is disproportionately affected by the infection.
Current usage in the NHS
Some POCTs may not be available currently. Others may be available to buy, but it is unlikely that they are sold to the NHS, as their use is not recommended under current guidelines.
Chapter 2 Definition of the decision problem
Decision problem
As described in Chapter 1, Introduction, genital chlamydia is the most common bacterial STI in the world. It creates a significant health burden for the NHS with regard to testing and treatment. However, left untreated, the health burden is potentially even greater, as the infection can cause PID, ectopic pregnancy and infertility in women and epididymo-orchitis and reactive arthritis in men. 48
Current practice in detecting chlamydia involves analysing specimens in a laboratory setting, using NAATs. The delay in processing results caused by the need to send them to a laboratory for analysis means that there is the potential for positively diagnosed patients not to return for treatment and contact tracing of previous partners, as individuals receiving their test results at a later date have to make a return visit for treatment to be initiated and contacts identified. 49 POCTs may have lower sensitivity than the NAAT methods of current practice, but as their use would allow positively diagnosed patients to have treatment initiated during the same session in which testing was carried out, the proportion of positive cases receiving treatment would increase. Therefore, even with reduced sensitivity, POCTs could still potentially lead to the treatment of more infected people than is the case at present.
In addition, new POCTs may report improved levels of sensitivity which could make them viable alternatives to laboratory methods. One such test is the Chlamydia Rapid Test (CRT), a POCT developed by the Diagnostics Development Unit at the University of Cambridge, UK. 50 Whether this test represents an efficient, reliable and cost-effective alternative to current laboratory diagnosis of genital chlamydia is unclear.
Key issues
The key issues to be addressed were:
-
Can the CRT improve detection of genital chlamydia?
-
Is the CRT more effective than current practice for testing and diagnosing genital chlamydia infection in terms of (i) the number of cases detected and treated, and (ii) the proportion of partners identified and treated?
-
What is the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of the CRT (compared with current practice) for the testing and diagnosis of genital chlamydia infection?
-
What are patients’ own preferences with regard to chlamydia testing services?
Care pathways
To address the above key economic issues, a care pathway was developed. The first point on this pathway is attendance at different facilities where testing is available. Patients are then faced with the choice of accepting or not accepting the offer of a test, and providing the sample for the test. It is likely that not all will accept the offer and a small proportion of those who do will be unable to provide the sample required, or the sample may not be properly collected. The group that does not accept the offer and those who cannot provide the sample will have a terminal stage in the pathway and would remain untested. The prevalence rate will be used to determine the proportion of those tested who are expected to have genital chlamydia. The sensitivity and specificity of the tests that are being compared will identify the proportion of the patients correctly or incorrectly identified. It is assumed that positive cases and any partners are treated.
Overall aims and objectives
The aim of this review was to assess the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the CRT, a POCT for detecting genital chlamydia infection.
The aim was addressed through:
-
A systematic review of the accuracy of the CRT in the diagnosis of genital Chlamydia trachomatis infection.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of the CRT in terms of the number of infected individuals diagnosed and treated.
-
A systematic review of patient preferences for the organisation and outcomes of chlamydia testing services.
-
Economic modelling of the cost-effectiveness of the CRT.
The specific objectives of the review were to:
-
Assess the performance of the CRT in the detection of genital chlamydia infection.
-
Assess the effectiveness of the CRT in identifying cases of chlamydia infection (and cases resulting in treatment), compared with current practice.
-
Estimate the ICER of the CRT compared with current practice for the testing, diagnosis and treatment of genital chlamydia infection.
-
Assess patients’ own preferences for chlamydia testing services.
Chapter 3 Methods for reviewing diagnostic accuracy and clinical effectiveness
Identification of studies
Studies were identified by searching electronic databases and relevant websites, contact with experts in the field and the scrutiny of bibliographies of retrieved papers. Highly sensitive electronic searches were conducted to identify reports of published and ongoing studies on POCTs for chlamydia. A preliminary search that included only terms related to the tests produced a small set of records, therefore no restrictions in terms of study type or publication date were used subsequently, although the results were restricted to articles written in English. The databases searched were: MEDLINE (1966 to week 3 November 2008), MEDLINE In-Process (26 November 2008), EMBASE (1980 to week 48 2008), BIOSIS (1985 to 27 November 2008), Science Citation Index (1970 to 22 November 2008), ISI Conference Proceedings (1990 to 22 November 2008), Health Management Information Consortium (October 2008) and Cochrane Controlled Trials Register (The Cochrane Library, Issue 4, 2008), as well as current research registers, Current Controlled Trials (November 2008), Clinical Trials (November 2008), CRISP (November 2008) and World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry (November 2008). Additional databases searched for systematic reviews and other background information included the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (The Cochrane Library, Issue 4, 2008), Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (November 2008) and Health Technology Assessment Database (November 2008). Recent conference proceedings were also searched. Full details of the search strategies used and websites consulted are documented in Appendix 1.
A total of 235 reports were identified (see Table 2). In addition, the details of 13 potentially relevant ongoing studies were noted. Reference lists of all included studies were scanned to identify additional potentially relevant studies.
| Database | Number retrieved |
|---|---|
| Primary reports | |
| MEDLINE (1966 to week 3 November 2008)/EMBASE (1980 to week 48 2008)/MEDLINE In-Process (26 November 2008) multifile search (after deduplication in Ovid) | 111 |
| Science Citation Index (1970 to 22 November 2008) | 77a |
| BIOSIS (1985 27 November 2008) | 19a |
| CENTRAL (Cochrane Library, Issue 4, 2008) | 4a |
| Health Management Information Consortium (October 2008) | 0a |
| ISI Conference Proceedings (1990 to 22 November 2008) | 4 |
| Recent conference proceedings | 3 |
| Total | 218 |
| Background | |
| CDSR (The Cochrane Library, Issue 4 2008) | 14 |
| DARE (November 2008) | 2 |
| HTA Database (November 2008) | 1 |
| Total | 17 |
| Total assessed for review | 235 |
| Ongoing studies | |
| Controlled Clinical Trial | 3 |
| Clinical Trials | 5 |
| CRISP | 5 |
| WHO International Clinical Trials Registry | 0 |
| Total | 13 |
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The types of studies considered for reporting diagnostic accuracy were:
-
Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) in which people were randomised to the index and comparator test(s) and all received the reference standard test.
-
Direct (head-to-head) studies in which the same group of people received the index test and/or any other comparator POCT(s), and all received the reference standard test.
In the event that there was insufficient evidence from direct or randomised studies, we considered undertaking indirect (between-study) comparisons by meta-analysing studies that compared the index test (or the identified and relevant comparators) with the reference standard test, and making comparisons between meta-analyses of the different tests. However, we were aware that this type of study design is less reliable than direct studies, as differences in diagnostic accuracy are susceptible to confounding factors between studies. Studies reporting test performance had to report the absolute numbers of true-positives, false-positives, false-negatives and true-negatives, or provide information allowing their calculation.
For assessing the CRT in terms of effectiveness outcomes, we decided to focus on RCTs unless they provided insufficient evidence, in which case we agreed to consider non-randomised comparative studies.
The participants considered for both the reviews of effectiveness and diagnostic accuracy were sexually active adolescent and adult men and women suspected of, or being tested for, genital chlamydia infection. If sufficient evidence was available, subgroup analysis was planned for high-risk participants, defined as those aged under 25 years.
The index test considered for both the reviews of effectiveness and diagnostic accuracy was the CRT, a new ‘rapid’ POCT developed by the Diagnostics Development Unit at the University of Cambridge for the detection of genital chlamydia infection.
For the review of diagnostic accuracy, the reference standard test(s) considered were NAATs, including PCR, TMA, SDA and ligase chain reaction (LCR). Comparator tests considered were:
-
non-POCTs (i.e. NAATs), which is equivalent to a comparison with any of the reference standard test(s) mentioned above
-
other alternative rapid POCTs identified for the diagnosis of genital chlamydia infection.
For the review of effectiveness, the comparator(s) considered were tests used in current practice.
The following outcomes were considered for the review of diagnostic accuracy:
-
sensitivity (the proportion of those infected who have positive test results)
-
specificity (the proportion of those not infected who have negative test results)
-
positive predictive value (the proportion of those with positive test results who are infected)
-
negative predictive value (proportion of those with negative test results who are not infected)
-
positive likelihood ratio (how many times an infected person is more likely to receive a positive test result)
-
negative likelihood ratios (how many times an infected person is more likely to receive a negative test result)
-
diagnostic odds ratios (DORs; the ratio of the odds of testing positive in those with infection relative to the odds of testing positive in those without infection)
-
acceptability of the tests
-
interpretability of the tests.
The following outcomes were considered for the review of effectiveness:
-
numbers of chlamydia cases detected
-
the number of infections diagnosed that are treated (including return/non-return rates for treatment in different settings and locations throughout the UK, following diagnosis using non-POCTs)
-
the proportion of partners identified and treated
-
acceptability of the tests
-
interpretability of the tests.
The following types of report were excluded from both the reviews of effectiveness and diagnostic accuracy:
-
studies published in languages other than English
-
narrative reviews, editorials, letters and opinions
-
animal models
-
preclinical and biological studies
-
case reports
-
abstracts published before 2006
-
reports investigating the technical aspects of a test.
Data extraction strategy
Citations identified by the search strategy were screened by one reviewer on the basis of title and, where available, the abstract. Full-text copies of all studies deemed to be potentially relevant were obtained, and two reviewers independently assessed them for inclusion, using a full-text screening form that had been developed and piloted. Any disagreements were resolved by consensus or arbitration by a third party. Reviewers were not blinded to authors, institutions or publications. Where there was insufficient information in the published report, no attempt was made to contact the authors for clarification, owing to time constraints.
Data extraction forms were developed and piloted. One reviewer extracted details of study design, participants, tests used and outcome data, and a second reviewer checked the data extraction. Any disagreements were resolved by consensus or arbitration by a third party.
Quality assessment strategy
Two reviewers independently assessed the quality of both the included full text and published diagnostic studies using QUADAS (Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies), a quality assessment tool developed for use in systematic reviews of diagnostic studies. 51 QUADAS was developed through a formal consensus method and was based on empirical evidence. The original QUADAS checklist contained 14 questions. The QUADAS tool was adapted to make it more applicable to assessing the quality of studies of tests for detecting genital chlamydia infection (see Appendix 3 for an example of the modified checklist). Abstracts were not quality assessed because it was felt unlikely that they would provide sufficient information about their methods to allow for quality assessment.
Questions 1, 3–7 and 10–14 of the original checklist were retained (questions 1–11 in the modified version). Three questions in the original QUADAS tool that related to the quality of reporting rather than methodological quality were omitted from the modified version (questions 2, 8 and 9). These questions related to the description of (a) the selection criteria, (b) the execution of the index test and (c) the execution of the reference standard. Two questions were added to the modified checklist on (a) whether data on observer variation were reported and within an acceptable range and (b) whether data were presented on the subgroup of interest in this review, those under 25 years of age.
For the review of effectiveness, the intention was to assess the study quality of RCTs using a Delphi criteria list adapted from Verhagen and colleagues. 52 In the event that there was insufficient evidence from RCTs and a subsequent need to assess the quality of non-randomised comparative studies, it was intended to use a separate checklist to assess study quality. The checklist was adapted from several sources, including the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination’s guidance for those carrying out or commissioning reviews,53 Verhagen and colleagues,52 Downs and Black54 and the Generic Appraisal Tool for Epidemiology (GATE).
It was intended that two reviewers would independently assess the quality of all included full-text studies for the reviews of effectiveness and diagnostic accuracy. Each question would be checked ‘Yes’, ‘No’ or ‘Unclear’ (with space for comments), and each item was worded so that a rating of ‘Yes’ was always optimal in terms of methodological quality. Any disagreements would be resolved by consensus or arbitration by a third party.
Data analysis
For diagnostic accuracy, the results of the individual studies were tabulated and the outcomes described in Inclusion and exclusion criteria were calculated.
There are a number of different methods available for meta-analysis of diagnostic studies that allow for between-study variability. Two methods are generally accepted as the most rigorous: the hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristics (HSROCs) model55 and bivariate random-effects meta-analysis56,57 The HSROC model approach was considered appropriate for this analysis. 58 HSROC curves were produced for each test where three or more studies reported sufficient data. Meta-analysis models were to be fitted using the HSROC model59 in sas version 9.1 using the NLMIXED function (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). This HSROC model takes account of the infected and non-infected sample sizes in each study, and allows estimation of random effects for the threshold and accuracy effects. 55,59 The summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curves from the HSROC models were produced and are shown on the corresponding SROC plots along with the individual study estimates. Summary sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios and DORs for each model were reported as median and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Sensitivity and specificity were pooled using the weighted average method,60 where there was no evidence of a threshold effect. Pooled likelihood ratios and DORs were calculated using the DerSimonian and Laird random effects method. 61 Where a study had an empty cell, a correction of 0.5 was added to all four cells. These analyses were carried out using meta-disc software. 62 Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic, which describes the percentage of variability in effect estimates that is due to heterogeneity rather than sampling error. A value greater than 50% was considered to represent substantial heterogeneity. 63
For the review of effectiveness, where appropriate, it was intended that meta-analysis be used to estimate a summary measure of effect for relevant outcomes. Dichotomous outcome data were to be combined using the Mantel–Haenszel relative risk (RR) method, and any continuous outcomes were to be combined using the inverse-variance weighted mean difference (WMD) method. For the estimates of RR and WMD it was planned to calculate 95% CIs and p-values, and report results using a fixed effect model. Statistical heterogeneity across studies was to be explored using chi-squared and I2 statistics, and possible reasons for heterogeneity explored using sensitivity analysis. If no obvious reasons for heterogeneity were found, it was planned to explore the implications using random effects methods. Where a quantitative synthesis was considered inappropriate or not feasible, the intention was to provide a narrative synthesis of results.
Chapter 4 Results of diagnostic accuracy and effectiveness
Quantity and quality of research available
Number of studies identified
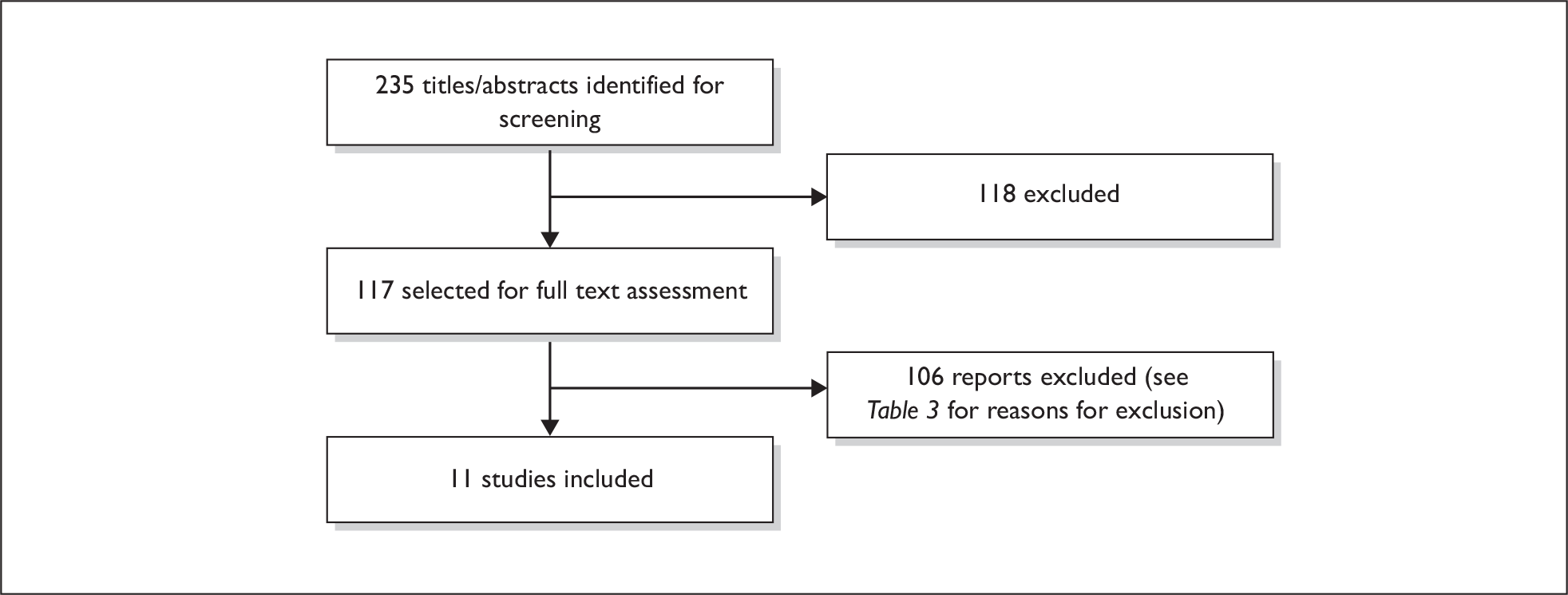
From the electronic searches for primary reports, 235 records were selected as possibly relevant to the reviews of diagnostic accuracy and clinical effectiveness. Following the screening of titles and abstracts, 118 of the 235 records were not considered further. The full-text reports of the remaining 117 records were obtained and assessed. Eleven met the inclusion criteria for this review, 82 were excluded and 24 were retained for background information. The main reasons for exclusion can be found in Table 3. Of the 11 studies that met our inclusion criteria, all met the inclusion criteria for the review of diagnostic accuracy. Figure 1 shows a flow diagram outlining the screening process, with reasons for exclusion of full-text papers.
| Reason | Number of papers excluded from diagnostic accuracy review on this basis | Number of papers excluded from review of effectiveness on this basis |
|---|---|---|
| Not a diagnostic accuracy study/not a comparative study | 13 | 25 |
| Pre-2006 abstracts | 12 | 12 |
| NAAT not used/NAAT not used as reference standard | 6 | 10 |
| Uses an obsolete POCT | 5 | 5 |
| No POCT used | 3 | 13 |
| Not a study on chlamydia | 2 | 3 |
| POCT cannot distinguish between chlamydia and other infections | 1 | 1 |
| Not all participants received both tests | 2 | 1 |
| Not a study on genital chlamydia | 1 | 1 |
| Animal study | 1 | 1 |
| No outcomes of relevance/pre-specified outcomes not reported | 3 | 3 |
| TOTAL EXCLUDED | 49 | 75 |
| Of which were duplicates (i.e. assessed for both reviews)a | 42 | 42 |
| Of which were not duplicates (i.e. assessed for only one of the two reviews)a | 7 | 33 |
| TOTAL INCLUDED | 11 | 11 |
| TOTAL ASSESSED FOR EACH REVIEWb | 60 | 86 |
FIGURE 1.
Flow diagram outlining the screening process for the reviews of diagnostic accuracy and effectiveness.
Number and type of studies included
Appendix 4 lists the 11 studies identified by the search strategy that were included in the reviews of diagnostic accuracy and effectiveness. All of these studies50,64–72 met the inclusion criteria for reporting the diagnostic accuracy of POCTs, of which 10 were full-text papers50,64–72 and one73 was a conference abstract.
Three studies reported results for the CRT against a NAAT (PCR),50,65,72 and a further eight reported results64,66–71,73 for other POCTs, either still available on the market (as confirmed by their respective manufacturers) or possibly still available on the market (where no confirmation had been received from the manufacturer regarding whether or not the test was still available). In addition, reports of two unpublished studies were provided for this review by the Diagnostics Development Unit at the University of Cambridge, under the condition that they be treated as academic-in-confidence. Both have since been published. 74,75
We did not identify any RCTs that assessed the effectiveness of POCTs compared with current practice, and therefore decided to include non-randomised comparative studies. No additional studies assessing the effectiveness of point-of-care testing compared with current practice were found.
Number and type of studies excluded
A list of the 82 potentially relevant studies identified by the search strategy but which subsequently failed to meet the inclusion criteria is given in Appendix 5. These studies were excluded because they failed to meet one or more of the inclusion criteria in terms of the types of study, participants, test, reference standard or outcomes reported. Forty-two of the excluded studies had been screened and excluded from both reviews, whilst the remaining 40 had been screened only for either the diagnostic accuracy review or the effectiveness review.
Characteristics of included studies
Appendix 6 shows the characteristics of the individual included studies. Table 4 shows summary information for the 13 studies reporting diagnostic accuracy outcomes. 50,64–75
| Characteristic | Number | Number of studies |
|---|---|---|
| Patients | ||
| Enrolled | 8904 | 13 |
| Analysed | 8717 | |
| Sex | ||
| Men | 2156 (24.7%) | 13 |
| Women | 6561 (75.3%) | |
| Agea | ||
| Median age | 25.8 years | 4 |
| Age range | 15–56 years | 5 |
| Not reported | – | 7 |
| Symptomatic of STD infectionb | ||
| Shows symptoms | 2104 (24.1%) | 6 |
| Asymptomatic | 1701 (19.5%) | |
| Not reported | 4912 (56.4%) | 9 |
| NAAT usedc | ||
| PCR | 8029 | 8 |
| SDA | 737 | 2 |
| TMA | 65 | 1 |
| LCR | 588 | 3 |
| Point-of-care test usedc | ||
| Chlamydia Rapid Test | 4223 | 4 |
| Clearview Chlamydia | 3956 | 7 |
| Chlamydia Wand/HandiLab C | 331 | 2 |
| QuickVue | 199 | 1 |
| Magic Lite Chlamydia | 1007 | 1 |
| SureCell Chlamydia | 128 | 1 |
| Type of specimen used for POCTc | ||
| Vaginal swab (self-collected) | 2282 | 3 |
| Vaginal swab (clinician-collected) | 3094 | 4 |
| Cervical/endocervical swab | 4533 | 7 |
| Urethral swab | 283 | 1 |
| First void urine (routine cup collection) | 790 | 2 |
| First void urine (using ‘FirstBurst’) | 1745 | 2 |
Nine studies50,64,65,68–70,72,74,75 involving 5914 participants provided details of when they took place, with an earliest start date of September 1996 and a latest end date of May 2008. However, it should be noted that one study71 was published before the earliest specified start date, although it did not actually report details of when the study took place.
Six studies, involving a total of 3788 participants took place in the UK,50,67,68,72,73,75 two studies (involving 2282 participants) took place in the Philippines,65,74 and one study each took place in Canada (involving 128 participants),69 the Netherlands (involving 1007 participants),71 the USA (involving 65 participants),70 Egypt (involving 50 participants)64 and China (involving 1497 participants). 66
All 13 studies reported testing venues, and six studies50,65–67,74,75 involving 4996 participants were held at multiple venues. Of the six UK-based studies, four studies (involving 1642 participants) included testing in at least one GUM clinic,50,67,73,75 whilst three (involving 1651 participants) included a Young People’s Sexual Health Centre venue. 50,72,75 In addition, one study (involving 395 participants) used a British Pregnancy Advisory Service Clinic,68 and another (involving 100 participants) included a hospital gynaecology department venue. 67
All studies reported the gender of participants. Nine studies (involving 5937 participants)50,64–68,70,73,74 had exclusively female populations, whilst a further three studies (involving 1873 participants)69,72,75 comprised only male participants. Therefore only one study71 investigated the diagnostic accuracy of point of care testing in both genders.
In six studies providing information on patient age, four (involving 6008 participants) reported a mean or median age,50,65,66,75 four (involving 4561 participants) reported specific age ranges50,64,65,75 and one study (involving 395 participants)68 reported the number of participants falling into different age bands (six age bands, each comprising 5 years starting at ages 15–19 years). Of the ranges reported (including the Hopwood study), participants were aged between 15 and 56 years. It should also be noted that although the age of participants was not explicitly specified in two further studies, one (involving 65 participants) had been conducted within campus venues at a university,70 and the other (involving 534 participants) had been undertaken at a venue used specifically for young people under the age of 25 years, and participants had been at least 16 years of age or older. 72
In six studies50,64–66,70,75 reporting whether participants had symptoms or not, 3805 participants were included in the analysis, of whom 2104 (55.3%) had symptoms (including all 50 patients in one study who had been diagnosed with PID). 64
Three of the 13 studies (involving 1873 participants) used only first void urine (FVU) samples,69,72,75 two (involving 431 participants) used only vaginal swab samples,73,74 whilst four (involving 709 participants) used only endocervical samples. 64,67,68,70 A further three studies (involving 4797 participants)50,65,66 collected endocervical and vaginal specimens, and one study (involving 1007 participants) collected endocervical and urethral specimens. 71
Eight of the 13 studies (involving 6760 participants)64–67,71,72,74,75 used PCR as the reference standard NAAT. In addition, one study (involving 1349 participants) used PCR as the reference standard but also reported data for 637 participants using SDA as the reference standard. 50 One study (with 100 participants) used SDA as the only reference standard. 73 The remaining three studies (involving 588 participants) used LCR as the reference standard test, although one (with 65 participants) also used a TMA test70 and another study with 128 participants used the LCR method with additional confirmation using a direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) test. 69
Quality of the included studies
Figure 2 summarises the quality assessment for the 12 full-text published diagnostic studies. 50,64–72 The results of the quality assessment of the individual studies are shown in Appendix 7.
FIGURE 2.
Summary of quality assessment of chlamydia diagnostic studies.
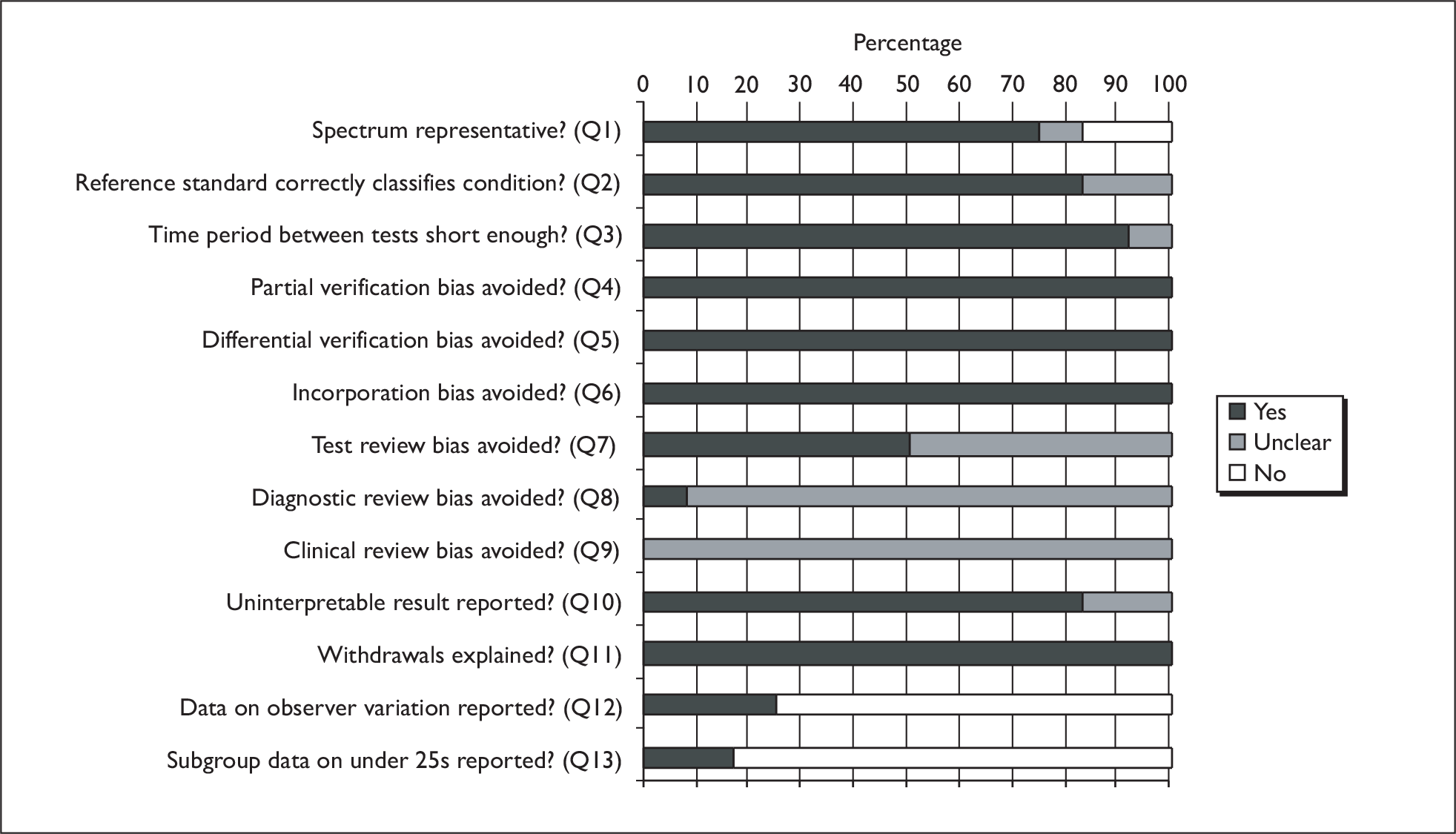
The diagnostic studies were assessed using a modified version of the QUADAS tool containing 13 questions. In 75% (9/12) of studies the spectrum of patients who received the tests was considered to be representative of those who would receive the test in practice (question 1). For this question we considered patients to be representative if the patient population was women and/or men suspected of having or being tested for genital chlamydia. Specific population subsets (e.g. pregnant women) were not considered to be representative. In the study by Chernesky and colleagues69 it was unclear whether the patient spectrum was representative, and in the studies by Hopwood and colleagues68 and Shaarawy and colleagues64 it was considered not to be representative. In 83.3% (10/12) of studies the reference standard NAAT was considered likely to classify correctly genital chlamydia (question 2). This was considered to be unclear in the studies by Chernesky and colleagues69 and Hopwood and colleagues. 68 These two studies used the Abbott LCx (Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, IL, USA) for LCR NAAT, which was withdrawn from the market in 2002 because of reproducibility problems. 76 In 91.7% (11/12) of studies the time period between the POCT and reference standard was considered to be short enough to be reasonably sure that the target condition had not changed between the tests (question 3), whilst this was unclear in the study by Shaarawy and colleagues. 64
In all studies, partial verification bias was avoided as all patients who received a POCT also received a reference standard test (question 4); differential verification bias was avoided as all patients received the same reference standard (a NAAT) regardless of the index test result (question 5); and incorporation bias was avoided as the reference standard test was independent of the POCT index test (question 6). In 50% (6/12) of studies,50,65,66,70,74,75 test review bias was avoided as the POCT results were interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard test, whilst in the remaining six studies this was unclear (question 7). In the study by Saison and colleagues,65 diagnostic review bias was avoided as the reference standard results were interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test, whilst in the remaining 11 studies this was unclear (question 8).
In all 12 studies it was unclear whether the same clinical data were available when the POCT results were interpreted as would be available when the test was used in practice (question 9). In this context, clinical data were defined broadly to include any information relating to the patient such as age, gender, presence and severity of symptoms, and other test results. In 83.3% (10/12) of studies, either uninterpretable or intermediate test results were reported or there were none, whilst in the remaining two studies64,65 this was unclear (question 10). In all studies either withdrawals from the study were explained or there were none (question 11). In 75% (9/12) of studies, data on observer variation were not reported (question 12), the exceptions being the studies by Mahilum-Tapay and colleagues,50 Nadala and colleagues75 and Yin and colleagues. 66 Two of the 12 studies (16.7%), Mahilum-Tapay and colleagues50 and Nadala and colleagues,75 presented data on the specific subgroup of interest in the review, which was those under 25 years of age (question 13), as one of the venues used in both studies was a Young People’s Sexual Health Centre, treating only those aged under 25 years old.
Assessment of diagnostic accuracy
Overview
This section reports the diagnostic accuracy of POCTs compared with a reference standard of nucleic acid amplification testing. Specimen level analysis was undertaken instead of patient level analysis, as several of the included studies conducted analysis at specimen level. Figures are included showing the sensitivity and specificity of the individual studies, SROC curves and pooled estimates with 95% CIs for sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios and DORs for each POCT for which pooled analysis could be undertaken. Results were pooled only where there were four or more studies comparing the same technique. Owing to the low number of studies, Stata’s (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA) Metandi procedure was used for the analysis instead of sas NLMIXED, as stated in the original protocol. Metandi requires a minimum of four sets of specimens. Individual study results are given in Appendix 8.
In addition, information on the acceptability of the tests is provided in Table 5.
| Patient outcome | Number/total (%) | Number of studies reporting outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Willingness to wait for POCT results | ||
| < 30 minutes | 1293/2378 (54.4) | Two (Mahilum-Tapay et al.50 and Yin et al.66) |
| ≤ 1 hour only | 30/683 (4.4) | One (Nadala et al.75) |
| Between 30 minutes and 2 hours | 912/2378 (38.4) | Two (Mahilum-Tapay et al.50 and Yin et al.66) |
| ≥ 1 hour | 653/683 (95.6) | One (Nadala et al.75) |
| > 2 hours | 96/881 (10.9) | One (Mahilum-Tapay et al.50) |
| > 1 day | 63/881 (7.2) | One (Mahilum-Tapay et al.50) |
| Preferences for collection method | ||
| Preferred ‘FirstBurst’ to routine cup | 736/936 (78.6) | Two (Wisniewski et al.72 and Nadala et al.75) |
| Preferred routine cup collection to ‘FirstBurst’ | 124/687 (18.0) | One (Nadala et al.75) |
| Were willing to use either ‘FirstBurst’ or routine cup to collect FVU sample | 38/687 (5.5) | One (Nadala et al.75) |
| Preferred a urine sample to giving a urethral swaba | 619/697 (88.8) | One (Nadala et al.75) |
| Would have preferred to give a urethral swaba | 49/697 (7.0) | One (Nadala et al.75) |
| Were willing to provide either a urine or a urethral swaba sample | 29/697 (4.2) | One (Nadala et al.75) |
| Preferred self-collecting vaginal swabs to giving a urine sample | 435/1068 (40.7) | One (Mahilum-Tapay et al.50) |
| Preferred giving a urine sample to self-collecting vaginal swabs | 401/1068 (37.5) | One (Mahilum-Tapay et al.50) |
| No preference for either self-collecting vaginal swabs or providing a urine sample | 232/1068 (21.7) | One (Mahilum-Tapay et al.50) |
| Ease of understanding/comfort | ||
| Found instructions for urine collection easy to understand | 741/759 (97.6) | One (Nadala et al.75) |
| Found collection of their urine easy | 735/755 (97.4) | One (Nadala et al.75) |
| Found instructions for self-collecting vaginal swab specimens easy to understand | 1813/1837 (98.7) | One (Mahilum-Tapay et al.50) |
| Felt comfortable self-collecting vaginal swab specimens | 1039/1083 (95.9) | One (Mahilum-Tapay et al.50) |
| Staff outcome | Number/total (%) | Number of studies reporting outcome |
| Use of the test | ||
| Thought the kit had clear instructions from the manufacturer | 13/14 (92.9) | One (Yin et al.66) |
| Thought the test was easy to use | 12/14 (85.7) | One (Yin et al.66) |
| Felt the test had a 10 minutes ‘hands-on’ time | 12/14 (85.7) | One (Yin et al.66) |
| Thought it was ‘rapid’ (i.e. < 20 minutes until the result was displayed) | 14/14 (100) | One (Yin et al.66) |
| Felt that the training on operational procedures took < 30 minutes | 13/14 (92.9) | One (Yin et al.66) |
Chlamydia Rapid Test
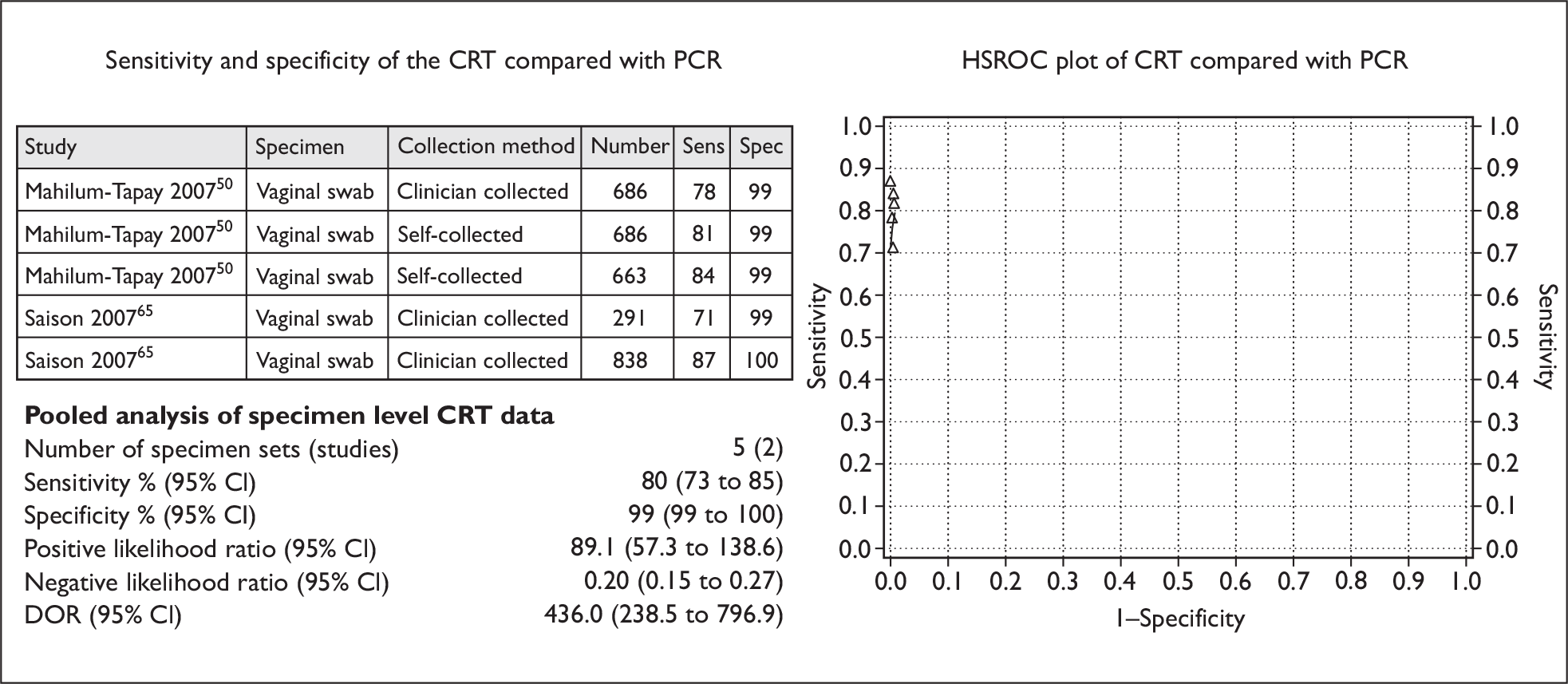
Two studies (involving 2478 participants) compared the accuracy of the CRT with a NAAT [PCR using the Roche AMPLICOR CT/NG Test (Hoffman-La Roche AG, Basel, Switzerland)] for detecting genital chlamydia in five sets of vaginal swab specimens. 50,65 This provided sufficient information to allow their inclusion in the pooled estimates for specimen level analysis. Of the five sets of vaginal swab specimens, three sets (two from the study by Saison and colleagues, and one from the study by Mahilum-Tapay and colleagues) were clinician-collected, whilst the remaining two sets from one study50 were self-collected specimens taken from patients at two different testing venues (a social hygiene clinic for female sex workers, and an obstetrics and gynaecology clinic mostly attended by women for antenatal care).
Figure 3 shows the sensitivity and specificity of the individual studies, SROC curves and pooled estimates for the sensitivity and specificity of the CRT for detecting genital chlamydia infection in vaginal swab specimens. The pooled sensitivity (95% CI) for the CRT was 80% (73% to 85%), whilst the pooled specificity (95% CI) was 99% (99% to 100%). The DOR (95% CI) was 436.0 (238.5 to 796.9).
FIGURE 3.
The Chlamydia Rapid Test (vaginal swab specimens): sensitivity, specificity, HSROC plot and pooled estimates.
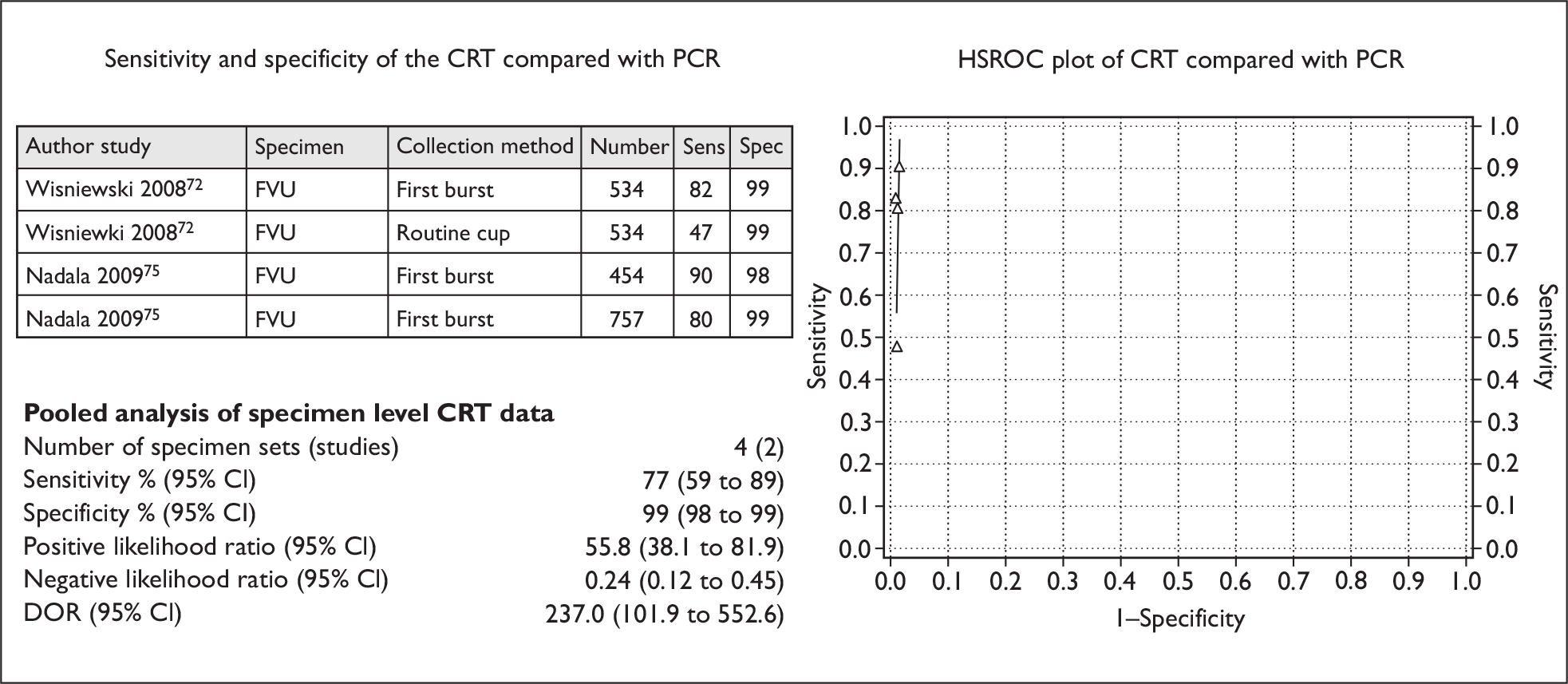
Two studies (involving 1745 participants) compared the CRT with a NAAT (PCR using the Roche AMPLICOR CT/NG Test) for detecting genital chlamydia, using four sets of FVU specimens. 72,75 This provided sufficient information to allow their inclusion in the pooled estimates for specimen level analysis. Of the four sets of FVU specimens, three sets (two from Nadala and colleagues’ 2009 study75 and one from Wisniewski and colleagues’ 2008 study)72 used the ‘FirstBurst’ method of collection whilst the remaining set (from the study by Wisniewski and colleagues) used routine cup collection of urine.
Figure 4 shows the sensitivity and specificity for the individual studies, SROC curves and pooled estimates for the sensitivity and specificity of the CRT for the detection of genital chlamydia infection in FVU specimens. The pooled sensitivity (95% CI) for the CRT was 77% (59% to 89%), whilst the pooled specificity (95% CI) was 99% (98% to 99%). The DOR (95% CI) was 237.0 (101.9 to 552.6).
FIGURE 4.
The Chlamydia Rapid Test (FVU specimens): sensitivity, specificity, HSROC plot and pooled estimates.
In addition to the specimens discussed above, there was one additional set of specimens from 637 participants in one study50 comparing the CRT with a NAAT method. As this NAAT method was SDA and not PCR (as used for all other specimen sets), it was not possible to pool estimates of diagnostic accuracy for this particular comparison. Data from the study itself show that the specimens were compared using the two tests. For the POCT, the specimens were self-collected vaginal swabs taken by women attending two GUM clinics in the UK, compared with clinician collected endocervical specimens for SDA analysis. The sensitivity (95% CI) of the CRT compared with SDA was 81.6% (70.8% to 92.5%), whilst the specificity (95% CI) was 98.3% (97.2% to 99.3%).
Clearview Chlamydia test
Four studies comparing the Clearview® Chlamydia test (Inverness Medical Professional Diagnostics, Princeton, NJ, USA) with a NAAT, and using eight sets of swab specimens (from a total of 3368 participants), provided sufficient information to allow their inclusion in the pooled estimates for specimen level analysis. The NAAT method reportedly used in two of the studies (involving 1547 participants) was PCR using the ‘Roche AMPLICOR’,64,66 whilst one study involving 822 participants reported using PCR with the Roche AMPLICOR CT/NG method. 65 It is highly likely that these tests are the same technique and were merely reported differently (Roche Diagnostics, January 2009, personal communication). The remaining study, with 999 participants, did not specify the type of PCR method used. 71 Of the eight sets of swab specimens, four sets, from four different studies involving 3368 participants,64–66,71 were cervical specimens. Three sets, from two different studies involving 1830 participants,65,66 were vaginal swab specimens (of which one set65 was self-collected specimens whilst the remaining two sets were clinician-collected). 65,66 The remaining set of 283 specimens came from urethral swabs. 71
Figure 5 shows the sensitivity and specificity of the individual studies, SROC curves and pooled estimates for the sensitivity and specificity of the Clearview Chlamydia test for specimen level detection of genital chlamydia infection. The pooled sensitivity (95% CI) of the test was 52% (39% to 65%), whilst the pooled specificity (95% CI) was 97% (94% to 100%). The DOR (95% CI) was 32.7 (13.0 to 82.2).
FIGURE 5.
The Clearview Chlamydia test (various types of swab specimens): sensitivity, specificity, HSROC plot and pooled estimates.
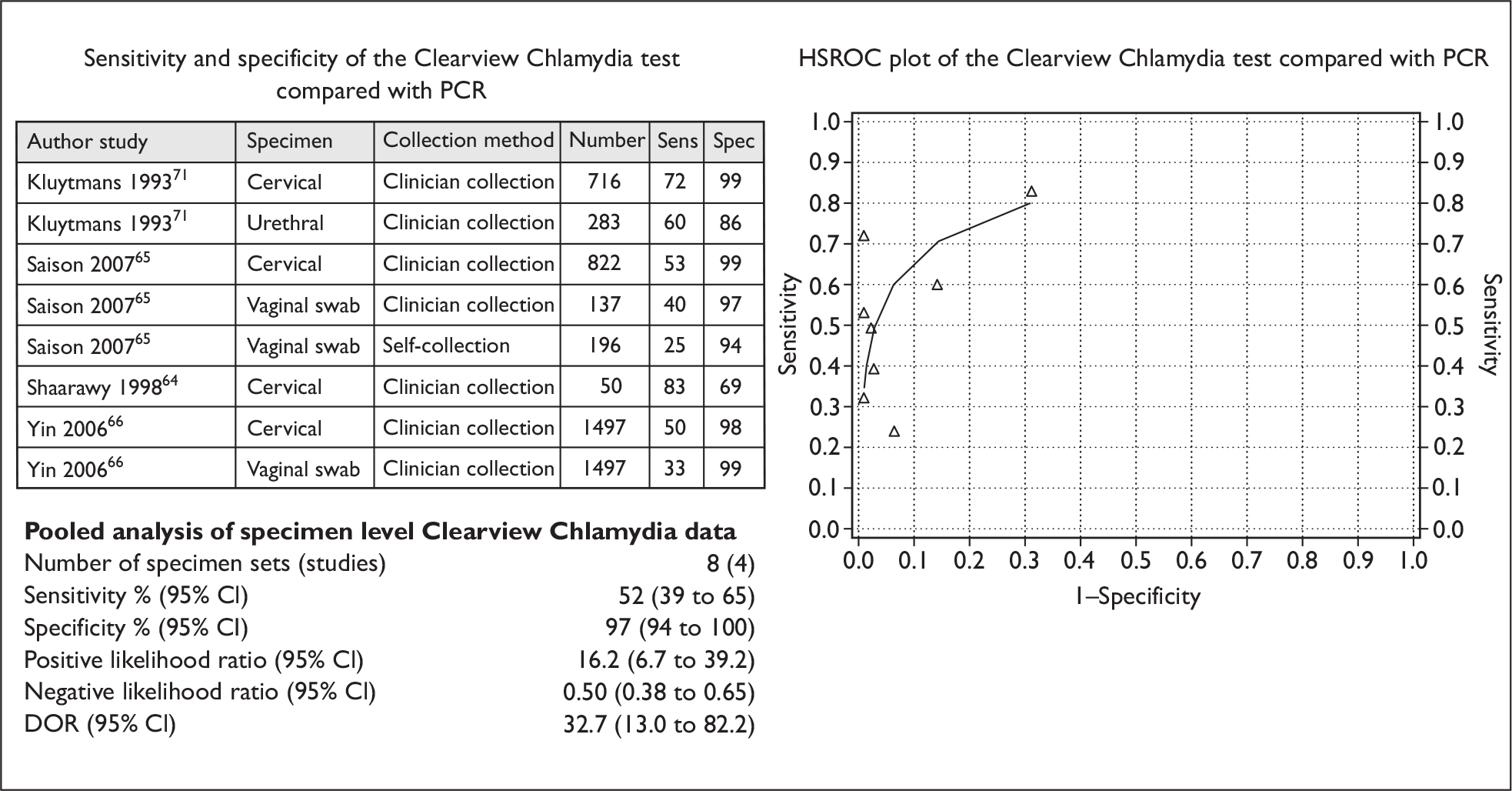
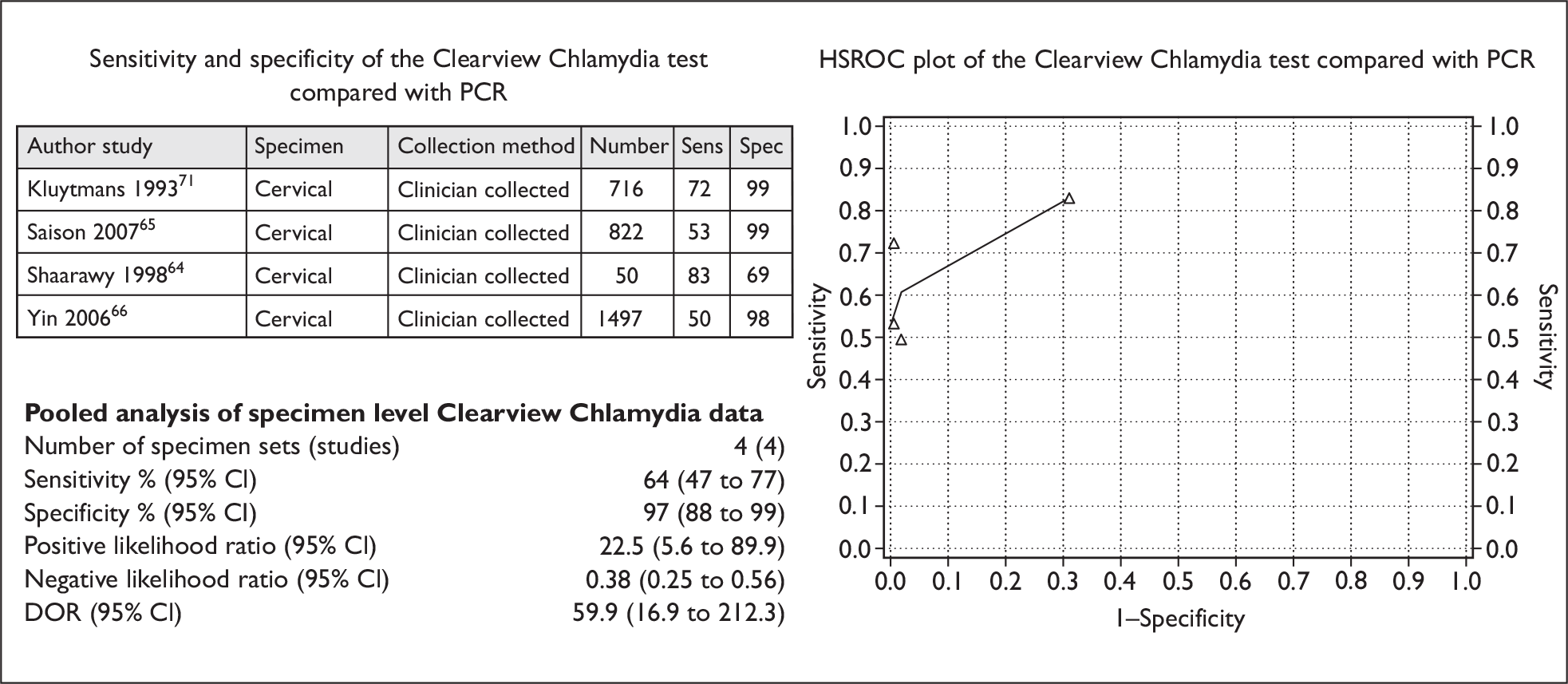
Figure 6 shows separate pooled analysis results conducted on sets of cervical swab specimens only. The pooled sensitivity (95% CI) of the Clearview test using cervical specimens was 64% (47% to 77%), whilst the pooled specificity (95% CI) was 97% (88% to 99%). The DOR (95% CI) was 59.9 (16.9 to 212.3).
FIGURE 6.
The Clearview Chlamydia test (cervical specimens only): sensitivity, specificity, HSROC plot and pooled estimates.
In addition to the specimens available for pooled estimates, three other studies compared four sets of specimens (from a total of 588 participants) tested using the Clearview Chlamydia POCT against a NAAT. 68–70 The NAAT method used in three sets of specimens was the LCx assay (Abbott Laboratories),68–70 although in one instance69 a DFA test was used to confirm the LCx result, and data were not available separately for these comparator tests. In the remaining set of specimens, the NAAT method used was TMA [using the Gen-Probe AMP-CT test (Gen-Probe Inc., San Diego, CA, USA)]. Three sets of specimens from two studies (involving 460 participants) were endocervical samples from women,68,70 whilst the remaining set were FVU samples from 128 men. 69 There were insufficient data to enable the pooling of estimates for the diagnostic accuracy for these comparisons.
However, individual data from the studies are available, and show that 128 FVU specimens compared the diagnostic accuracy of the Clearview Chlamydia test with the LCx assay. All the specimens were from males, but had been selected from an original sample of 762 male FVU specimens that had been submitted for testing in a private laboratory in Canada. The sensitivity of the Clearview Chlamydia test compared with the LCx assay for FVU specimens was 67.7%, whilst the specificity was 95.5%. 69
In addition, two studies, one using 395 endocervical specimens from women attending a clinic of the British Pregnancy Advisory Service (BPAS) for an abortion procedure68 and the other using 65 endocervical specimens from one of four outpatient obstetric and gynaecology clinics at the University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL, USA,70 compared the diagnostic accuracy of the Clearview Chlamydia test with the LCx assay. The sensitivity of the Clearview Chlamydia test compared with the LCx assay for endocervical specimens in those attending the BPAS clinic for an abortion procedure was 75.0%, whilst the specificity was 99.2%. 68 The sensitivity for endocervical specimens in those attending the outpatient obstetric and gynaecology clinics was 50%, whilst specificity was 100%. 70
Also, a set of endocervical specimens was taken from the 65 participants in the study by Lauderdale and colleagues,70 to compare data from the same population of women attending one of four outpatient obstetric and gynaecology clinics at the University of South Alabama, using the Clearview Chlamydia POCT against a different NAAT as the reference standard (TMA using the Gen-Probe AMP-CT test). The sensitivity and specificity for endocervical specimens in this instance were the same as when the LCx assay was used as the reference standard (i.e. 50% and 100% respectively).
SureScreen Chlamydia Wand
Two studies compared the diagnostic accuracy of the SureScreen Chlamydia Wand (SureScreen, Derby, UK) with a NAAT as the reference standard. There were not enough available data to allow the pooling of estimates, but data were available from the individual studies for this test (also sometimes marketed as the ‘HandiLab C’ test and ‘SELFCheck’ test). One study compared the SureScreen Chlamydia Wand with PCR using the Roche AMPLICOR CT/NG with clinician-collected vaginal swab samples of 231 women in the Philippines (in one social hygiene clinic with 131 female sex workers and one obstetric and gynaecology clinic setting with 100 women mostly attending for antenatal care). The sensitivity and specificity of the SureScreen Chlamydia Wand were 18.4% and 90.7% respectively. 74 Another study73 compared the SureScreen Chlamydia Wand with SDA using the Becton-Dickinson ProbeTec ET™ (Becton-Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), with self-collected vaginal swab specimens taken by 100 women attending a GUM clinic in the UK. The sensitivity and specificity of the SureScreen Chlamydia Wand in this case were 36.4% and 79.8% respectively.
QuickVue Chlamydia test
One study involving 199 participants67 compared the diagnostic accuracy of the QuickVue® Chlamydia test (Quidel, San Diego, CA, USA) with the PCR NAAT method of testing (Roche COBAS® AMPLICOR test) using endocervical specimens, of which 99 were taken from consecutive women attending a UK GUM clinic, and a further 100 were taken from women attending the gynaecology department of a UK hospital. The sensitivity of the QuickVue test for the GUM clinic specimens was 64.7%, whilst specificity was 100%. For the hospital gynaecology department specimens, sensitivity and specificity were 25% and 100% respectively.
Magic Lite Chlamydia test
One study71 used two sets of specimens (one urethral and one cervical) from 1007 patients to assess the diagnostic accuracy of the Magic Lite Chlamydia test at a hospital sexually transmitted disease clinic in the Netherlands, using PCR (not further specified) as the reference standard NAAT. For the 283 urethral specimens, the sensitivity and specificity of the Magic Lite were 72.1% and 99.6% respectively. For the 724 cervical specimens, the sensitivity of the Magic Lite Chlamydia test was 60.5% whilst specificity was 99.9%.
SureCell Chlamydia test
One study with 128 participants69 compared the diagnostic accuracy of the Kodak SureCell Chlamydia test with the LCx assay. A DFA test was then used to confirm the LCx result, but data were not available separately for these comparator tests. One hundred and twenty-eight selected FVU specimens from males (which were taken from an original sample of 762 specimens submitted for testing in a private laboratory in Canada) were used to compare the SureCell Chlamydia test with the LCx assay. The sensitivity of the SureCell Chlamydia test was reported as 62.9%, whilst the specificity was 100%.
Acceptability outcomes
All additional outcomes reported by those studies included in the review of diagnostic accuracy are included below (Table 5). Aside from the outcome of ‘number of chlamydia cases detected’, five studies, involving a total of 3688 participants, provided additional information on acceptability outcomes for participants,50,66,72,73,75 and one study provided information on acceptability outcomes for staff. 66 For study participants, the studies by Yin and colleagues,66 Mahilum-Tapay and colleagues50 and Nadala and colleagues75 reported preferences for waiting time. The studies by Mahilum-Tapay and colleagues,50 Wisniewksi and colleagues72 and Nadala and colleagues75 reported participants’ preferences for providing different types of specimens, and these studies, along with the study by Kegg and colleagues,73 also reported participants’ views on the process of specimen collection itself.
These acceptability outcomes are listed in Table 5.
Interpretability outcomes
Three of the included studies reported interpretability (or reproducibility) outcomes. 50,66,75 Two of these studies reported reproducibility outcomes for the CRT, by having an independent laboratory repeat testing with randomised and masked panels, using two independent operators. 50,75 Both found 100% concordance between the expected results and the results from independent laboratory testing. The remaining study66 reported kappa statistics on the agreement of results of the Clearview test read by two independent staff. Agreement ranged from 0.94 to 1.00 for vaginal specimens and from 0.96 to 1.00 for cervical specimens, and was found to be statistically significant (p < 0.001). 66
Review of effectiveness
Although all studies included in the diagnostic accuracy review also met the criteria for inclusion in the review of effectiveness inasmuch as they provided information on the number of chlamydia cases detected, as the results for this outcome have been discussed above they will not be repeated here. No studies were identified that provided additional data that met the inclusion criteria for the review of effectiveness. Therefore, it was not possible to provide information on the clinical effectiveness of point-of-care testing compared with the current practice of nucleic acid amplification testing.
Summary of results
There were 13 studies enrolling 8817 participants in the analysis. In the pooled estimates for the CRT, two studies compared five separate sets of vaginal swab specimens, and a further two studies compared four sets of FVU specimens. The sensitivity (95% CI) of the CRT was 80% (73% to 85%) for vaginal swab specimens and 77% (59% to 89%) for FVU specimens. Specificity was 99% (99% to 100%) for vaginal swab specimens and 99% (98% to 99%) for FVU specimens.
In the pooled estimates for a comparator POCT (Clearview Chlamydia), four studies compared eight separate sets of vaginal, cervical and urethral specimens. For cervical specimens alone, there were four sets of specimens from the four studies. The sensitivity (95% CI) was 52% (39% to 65%) for vaginal, cervical and urethral swab specimens combined, and 64% (47% to 77%) for cervical specimens alone. Specificity was 97% (94% to 100%) for vaginal, cervical and urethral swab specimens combined, and 97% (88% to 99%) for cervical specimens alone.
Chapter 5 Assessment of patient preferences
Methods
The review of the preferences of patients was confined to studies that had reported willingness to pay (WTP; which may or may not have been determined using contingent valuation) or reported preferences between different relevant screening test regimens. Few relevant studies were expected to be identified but any data identified might be used to assign a value to the health benefits from a patient’s perspective. Such data might then be related to cost (estimated from a NHS perspective) to provide an estimate of relative efficiency.
Identification of studies
The review on preferences was based on electronic searches to identify reports of patient preference studies for different ways of organising chlamydia screening/testing. The searches were restricted to articles written in English, but without publication date limits. The databases searched were: MEDLINE (1966 to week 3 November 2008), MEDLINE In-Process (26 November 2008), EMBASE (1980 to week 48 2008), Science Citation Index (1970 to 1 November 2008), ISI Conference Proceedings (1990 to 22 November 2008), and Health Management Information Consortium (November 2008). Full details of the search strategies used and websites consulted are documented in Appendix 1. A total of 294 reports were identified (see Table 6).
| Database | Number retrieved |
|---|---|
| Patient preference | |
| MEDLINE (1966 to week 3 November 2008)/EMBASE (1980 to week 48 2008)/MEDLINE In-Process (26 November 2008) multifile search (after deduplication in Ovid) | 220 |
| Science Citation Index (1970 to 1 November 2008) | 19a |
| Health Management Information Consortium (1979 to November 2008) | 55a |
| Total | 294 |
One reviewer assessed these studies and found that most did not meet our inclusion criteria. Only two relevant studies77,78 were identified from the search conducted.
Summary of the review on patient preferences
Study selection
The review of patient preferences considered studies conducted in similar populations to those considered relevant to a UK health setting. Only economic measures of preference based on population values were considered, as such data would be most useful for priority setting. Individuals may have strong preferences not just for the outcomes of testing but also about how such a service might be organised in different settings. The studies, covering the different characteristics of screening (type of test, setting, diagnostic and long-term outcomes, etc.) and considering how patients value such characteristics and hence value alternative methods of diagnosing chlamydia, are included in this part of the review.
Ryan and Watson77 conducted an experimental study to examine women’s preferences for chlamydia screening, and compared the WTP estimates from two different methods: a discrete choice experiment (DCE) and a contingent valuation (using a payment card method). A total of 174 women attending family planning clinics were recruited for the study. In the DCE, the women were requested to choose between sets of hypothetical scenarios that differed in terms of location of screening (family planning clinic, GUM clinic, home, GP practice), the ways in which the collection sample would be collected (full pelvic examination, perineal swab, urine test), support from providers (trained health-care provider or not) and costs (options being £0, £5, £10 and £25). These screening attributes or characteristics were derived from literature searches, policy variations and advice from family planning doctors, and can be considered to represent factors relevant to organising a screening service in the UK. The combination of different characteristics described above produced a large number of scenarios, and a fractional factorial design (generated by experimental design software) was used to reduce this down to 16 scenarios.
The payment card attempted to elicit respondents’ WTP for a defined screening test: screening to be carried out at a family planning clinic, using a urine test, with a 25% risk of PID, and a trained health advisor providing support to the woman when results are obtained. Results from 130 respondents could be analysed, after incomplete questionnaires and protesters to the WTP were excluded. Results from the DCE and payment card methods could be compared for 110 women.
Summary of contingent valuation
A general preference to be screened was observed. Mean WTP was £23.71 (95% CI £22.89 to £24.54) with the payment card method and £34.18 (95% CI £27.29 to £51.19) for the DCE. It was found that WTP was £22 (95% CI £20.92 to £27.17) for those with an annual income of less than £15,000 and £26 (95% CI £24.64 to £27.17) for those with an annual income above £15,000 (Table 7). Screening at both the family planning clinic and GUM clinic had a positive impact on utility, whereas screening in general practice or at home reduces the utility of screening services at the family planning clinics and GUM clinics.
| Payment card method (all income groups) | Payment card method (< £15,000) (n = 59) | Payment card method (> £15,000) (n = 58) | Discrete choice experiment (n = 130) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean WTP | £23.71 | £22.20 | £25.90 | £34.18 |
| 95% confidence interval | £22.89 to £24.54 | £20.92 to £23.48 | £24.64 to £27.17 | £27.29 to £51.19 |
Discrete choice experiment
Watson and colleagues78 used a DCE to examine how the characteristics of a screening programme for chlamydia affected the value of the screening programme. For the 16 profiles in the choice set, patients were asked to answer whether they would or would not accept the screening. The total respondents to the DCE survey were 149 women out of the 175 who were recruited, and these respondents generated 2142 observations for the experiments. The respondents from the family planning clinics valued the screening for chlamydia, on average at £15.23. The study also provided the estimates of marginal WTP. It was found that a less invasive screening test increased WTP by £7.09 from the average of £15.23, and more invasive tests would reduce WTP by £3.51 for a perineal swab, and by £3.58 when pelvic examination was used. The most preferred screening location was family planning clinics and this choice would increase the average WTP by £5.32, whilst a home location would reduce WTP by £4.14. The GUM clinic as location did not have any significant effect on patients’ WTP. The support from a trained health-care professional after receiving the results would increase the average WTP by £4.26. 78 Predicted uptake of urine testing at family planning clinics with support was 91%, and 87% at a GUM clinic. In a sensitivity analysis it was found that respondents aged below 25 years and having casual relationships had less preference for screening and have obtained less utility from screening.
Relationship between planned and actual behaviour
Comparison of the stated intention and actual behaviour suggested that 77% of those providing payment card responses behaved in the same way as they intended when they were actually offered the test. In the case of the discrete choice experiment respondents, 81% behaved in the same way as predicted. The hypothetical response patterns were significantly different among the respondents for both the payment card methods and the DCEs, and the findings from the Ryan and Watson77 study suggest that in both cases the hypothetical data overestimated the actual screening test uptake.
The review suggests that, from a patient’s point of view, the preferable location for testing would be a family planning clinic. The method of sample collection would ideally be non-invasive and, out of the methods of sampling considered, a urine sample would be favoured most.
Chapter 6 Assessment of cost-effectiveness
The principal research question addressed is: ‘what testing strategies, using the new CRT, for detecting genital chlamydia infection will increase the number of infections effectively treated in index patients and contacts, and be cost-effective compared with current detection practice?’
Methods
Relevant patient population
The cost-effectiveness and cost–consequence analyses were based on a cohort modelling approach that reflects the prevalence of chlamydia in a population of people presenting or a specified subgroup presenting for testing. The time horizon of the model covers only the period of initial diagnosis and subsequent treatment for chlamydia infection. The model also includes another short-term element: the identification of contacts for those tested as positive. As the time horizon is short (< 1 year), no discounting of costs or effects was necessary.
The target population considered is sexually active adolescent and adult men and women suspected of having or being tested for chlamydia infection. Where data were available, the following subgroups would have been considered: those aged under 25 years old; men who have sex with men; sex workers; and high-risk African populations. Given the lack of data, separate models were not constructed for these groups. However, by changing the pre-test probability of the prevalence of chlamydia, the effect of the screening for these groups might be considered.
Screening options to be evaluated
A decision analytic model was developed to compare the CRT to other relevant POCTs and one non-POCT (current practice assumed to involve NAATs). This model displays the logical sequence of the clinical decision problem.
Based on the results of the systematic review of test performance (see Chapter 4), the use of the best two POCTs in terms of diagnostic performance (and quantity of evidence available) were considered within the model. The two POCTs considered for the decision model were Clearview and the CRT. For the decision model, the test performance (and cost) of the comparator test(s) considered is PCR, which is the most frequently used NAAT in current practice.
The setting considered for the reviews of test performance and effectiveness is a family planning clinic. This has not been explored in a sensitivity analysis as no data are available to assess how parameter estimates might change as the setting varies.
Screening and treatment pathway: the model
The different strategies were compared in terms of the number of chlamydia cases detected, diagnosed and treated in index patients and contacts, and the costs of the different strategies used to detect chlamydia. The model compares three basic strategies: screening A (the Clearview POCT); screening B (CRT POCT); and screening C (current practice – PCR – see Figure 7).
FIGURE 7.
Pathway of the patient.
The model describes the pathway of individuals covering the period of offer of screening, testing and the costs and consequences of any subsequent short-term outcomes. The structure of the economic model is based on care pathways developed in consultation with our expert advisors, and describes alternative ways in which a service for chlamydia testing may be organised.
The decision model for the three screening options is also used to identify the costs and consequences of contact tracing (Figure 7). For illustrative purposes, the structure for only one test is shown. The structure for the other tests would be identical.
The assumed pathway of the model
When a test is offered in a particular setting, a proportion of the target population is assumed to accept the offer. Of those who do not take up the offer of testing, some will have chlamydia that remains undetected. The health service incurs the costs of offering the test, i.e. the cost of inviting the target population to receive the test. Of those who do decide to take up the test, it is possible that a proportion may not be able, or willing, to provide a suitable sample for testing. Those for whom samples were not obtained remain undiagnosed and untreated. For those who do provide a sample, some will test positive and some negative. The proportion of people in each group will depend upon the prevalence of infection and the diagnostic performance of the test. Those with a positive result, which might have been a true- or a false-positive result, are expected to be treated and their partners are notified. The model assumes that all those who test negative (true or false) are not treated, and for these people no contact tracing is performed. The model also assumes that a certain proportion of partners of those who test positive are contacted.
Data requirements for the model
Effectiveness, as included in the model, is largely influenced by the performance of the test, i.e. the sensitivity and specificity of the different types of the test and also the type of setting. These factors may result in different levels of acceptance and proportions of those in the different risk groups presenting for testing.
Effectiveness within the model was measured in terms of the absolute numbers of true-positives, false-positives, false-negatives (and other positive cases missed) and true-negatives detected. We have also considered the two other different measures of outcome: (1) cases of chlamydia correctly diagnosed and treated and the index patients’ partners notified and (2) correct diagnosis with those with chlamydia treated and the index patients’ partners notified. In this latter situation, testing is considered to be effective if it could also correctly identify true-negatives.
The diagnostic performance of the tests was based upon the data reported in Chapter 4. We used simple equations to determine the true-positive and true-negative rates:
Resource use, cost data and unit costs
Cost information is derived by combining information on resource use with information on the unit costs for the different POCTs and comparators in different settings (GUM clinics, chlamydia screening clinics/programmes, GP surgery, pharmacies) where the testing will be conducted and diagnosed. Data were obtained from the manufacturers of the different tests, the literature (e.g. the ClaSS studies5) and expert opinion. Costs include resource material costs incurred in offering the test (e.g. the time of personnel in a clinical setting, the costs of education leaflets, the cost of kits and other supplies, laboratory personnel time, treatment and partner notification). The model assumes a pre-test probability of presence of chlamydia which is the prevalence rate of the age group of 15–24 years old. Table 8 gives a list of the parameters and their associated values that were used in the model.
| Parameters | Description | Value | Value used for sensitivity analysis | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | ||||
| Uptake of screening and prevalence | |||||
| tst_acpCPCR | Proportion accepting test offer for current practice (PCR) | 0.189 | 0.16 | 0.233 | Low et al.5 |
| tst_acpCRT | Proportion accepting the offer of test B (CRT) | 0.189 | 0.16 | 0.25 | Same uptake used for PCR (from Low et al.5) |
| tst_acpCV | Proportion accepting the offer of test A (Clearview) | 0.189 | 0.16 | 0.25 | Same uptake used for PCR (from Low et al.5) |
| Prev_1 | Prevalence in the population group | 0.078 | 0.069 | 0.091 | NHS Vital Signs79 |
| num_part | Average number of partners | 1.5 | 1.3 | 2 | Assumption |
| part_rep | Percentage of partners reported | 0.988 | 0.968 | 0.991 | Assumption |
| p_treated | Proportion of index patient treated | 0.95 | 0.65 | 1 | Assumption |
| samp_obt | Sample obtained | 0.98 | 0.97 | 1 | Assumption |
| Cost parameters | |||||
| c_acptst | Cost of accepting test | £2.78 | £2.00 | £5.00 | Adams et al.6 |
| c_offtst | Cost of offering test | £2.21 | £1.80 | £2.50 | Adams et al.6 |
| c_partrep | Cost of partner notifications | £6.10 | £3.06 | £8.10 | Adams et al.6 |
| c_samobA | Cost of sample obtained | £0.72 | £0.70 | £0.75 | Low et al.5 |
| c_testCPCR | Cost of current practice (PCR) | £20.56 | £19.50 | £21.50 | Low et al.5 |
| c_testCRT | Cost of screening test (CRT) | £21.74 | £20.50 | £22.50 | Low et al.5 and cost of test kit price assumed to same as Clearview |
| c_testCV | Cost of screening test (Clearview) | £21.74 | £20.50 | £22.50 | Low et al.5,80 |
| c_treat | Cost of treating patient – drugs+ | £13.58 | £12.50 | £14.80 | Low et al.5 |
| T_CostA | Total cost of test A (Clearview) | Estimates derived within the model | |||
| T_CostB | Total cost of test B (CRT) | Estimates derived within the model | |||
| T_CostC | Total cost of current practice | Estimates derived within the model | |||
| Sensitivity and specificity | |||||
| sens_cPCR | Sensitivity of current practice | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.96 | Roberts38 |
| sens_CRT | Sensitivity of test B (CRT) | 0.8 | 0.73 | 0.85 | From the review, Chapter 4 |
| sens_CV | Sensitivity of test A (Clearview) | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.65 | From the review, Chapter 4 |
| spec_cPCR | Specificity of current practice (PCR) | 0.97 | 0.96 | 1 | Roberts38 |
| spec_CRT | Specificity of test B (CRT) | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1 | From the review |
| spec_CV | Specificity of test A (Clearview) | 0.97 | 0.94 | 1 | From the review |
| Tot_num | Total cohort | 1000 | |||
Assumptions
In addition to those parameters taken from other studies, assumptions had to be made for some other parameters. For the numbers of partners per index case, a number of different figures are found in different studies. The number of partners per index case was an assumption based on expert opinion, from a small unpublished survey. In many economic evaluations of chlamydia screening, a 100% rate of partner notification was assumed. We have used a value of 98%. However, there are reports (e.g. NCSP Five Years: 5th annual report of the National Chlamydia Screening Programme8) suggesting that only 63% of partners might be contacted. A second assumption related to the cost of testing using the CRT was that the cost of testing using the CRT would be same as, or close to, the cost using Clearview Chlamydia kit. We took the market price (March 2009) of this kit. 80
Model analysis
The analysis compares the cost-effectiveness of testing of two POCTs with a current practice option. The results of the analysis are presented as the costs and the number of true cases (i.e. true-positive) detected and treated with partners notified. The difference in costs and effectiveness is also compared with the effectiveness and measured in terms of true cases (including true-negative) identified. The cost-effectiveness analysis is based on health service provider (the NHS) perspectives.
Sensitivity analysis
The sensitivity of the findings was tested using one-way sensitivity analysis to examine the impact of varying key assumptions and/or values of the following parameters:
-
The proportion of patients taking the test (accepting the offer) in order to capture the likely difference in preferences of different settings which may also vary among different risk groups of the population.
-
The pre-test prevalence of chlamydia.
-
Sensitivity analysis in relation to the sensitivity and specificity of different POCTs.
-
Sensitivity analysis in relation to the changes in the costs of the screening test.
-
The rates showing the details of these sensitivity analyses are reported in Sensitivity analysis (see page 34).
Results
Cost–consequences analysis
Current practice performed better in terms of the number of true-positives identified, and hence the number of true-positives treated compared with the POCTs. It also resulted in fewer false-negatives and hence missed fewer people with chlamydia. The current practice and the Clearview test would result in a similar number of false-positives (who would then receive unnecessary treatment and have contacts treated needlessly). Among the two POCTs, the CRT performed better in terms identifying more true-positives, fewer false-negatives, more true-negatives, more partners of true-positive cases notified and fewer partners notified among those falsely identified as positive (Table 9).
| Current practice (PCR)-C | Clearview (POCT)-A | Chlamydia Rapid Test (CRT-POCT)-B | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of false-positives | 5.123 | 5.123 | 1.708 |
| Number of false-negatives | 1.156 | 6.934 | 2.889 |
| Number of false-positives treated | 4.867 | 4.867 | 1.622 |
| Number of true-positives | 13.291 | 7.5125 | 11.558 |
| Number of true-negatives | 165.649 | 165.649 | 169.065 |
| Number of true-positives treated | 12.627 | 7.137 | 10.979 |
| Number of partners reported for true-positives | 18.712 | 10.577 | 16.272 |
| Number of partners reported for false-positives | 7.213 | 7.123 | 2.404 |
| Total costs of offering, screening and treating index patients and their partners | 7070 | 7170 | 7180 |
Cost-effectiveness analysis
The results of the cost-effectiveness analysis using the two different outcome measures are shown in Table 10. If effectiveness is measured in terms of the number of true-positives identified and treated and their partners notified, then current practice performs better than the two POCTS considered in our model.
| Total costs (£)a | Total effectivenessb | ICER | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness measured as number of true-positive cases identified and treated and their partners notified | |||
| Current practice (PCR) | 7070 | 12.63 | |
| Clearview (POCT) | 7170 | 7.14 | Dominated |
| Chlamydia Rapid Test (CRT-POCT) | 7180 | 10.98 | Dominated |
| Effectiveness measured as number of cases correctly identified and treated if necessary and partners of positive cases notified | |||
| Current practice (PCR) | 7070 | 178.27 | |
| Clearview (POCT) | 7170 | 172.79 | Dominated |
| Chlamydia Rapid Test (CRT-POCT) | 7180 | 180.05 | 62.18 |
If effectiveness is measured in terms of the number of people correctly diagnosed by the test (i.e. true-positives and true-negatives), including notifying the partners of the true-positives and treating the positive cases where necessary, then the CRT performs better than current practice with a marginal increase in costs.
Sensitivity analysis
The sensitivity analyses are conducted with respect to the outcome defined as the number of cases of chlamydia correctly identified and treated, and partners notified. A summary of the sensitivity analyses is given in Table 11.
| Parameters’ value and strategies | Values of the parameters | Total costs | Effectivenessa | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acceptance rate of the test offer | ||||
| Current practice (PCR) | 22.3% | £7880 | 14.9 | |
| Clearview (CV) | 25% | £8710 | 9.44 | Dominated |
| Chlamydia Rapid Test (CRT) | 25% | £8730 | 14.52 | Dominated |
| Keeping the acceptance rate fixed at 18.9% for PCR and CV, changing CRT’s to 22.75% | ||||
| Current practice (PCR) | 18.9% | £7010 | 12.63 | |
| Clearview (CV) | 18.9% | £7130 | 7.14 | Dominated |
| Chlamydia Rapid Test (CRT) | 22.75% | £8730 | 14.52 | 906.69 |
| Pre-test prevalence = 0.069 (6.9%) | ||||
| Current practice (PCR) | 6.9% | £6990 | 11.17 | |
| Clearview (CV) | 6.9% | £7110 | 6.31 | Dominated |
| Chlamydia Rapid Test (CRT) | 6.9% | £7120 | 9.71 | Dominated |
| Pre-test prevalence = 0.091(9.1%) | ||||
| Current practice (PCR) | 9.1% | £7050 | 14.73 | |
| Clearview (CV) | 9.1% | £7150 | 8.32 | Dominated |
| Chlamydia Rapid Test (CRT) | 9.1% | £7170 | 12.81 | Dominated |
| Costs of tests at lower value of £19.50 | ||||
| Clearview (CV) | £6752 | 7.14 | 22.58 | |
| Chlamydia Rapid Test (CRT) | £6766 | 10.98 | 3.65 | |
| Current practice (PCR) | £6876 | 12.63 | 66.66 | |
| Costs of the POCTs reduced to £19.50 keeping PCR unchanged at £20.56 | ||||
| Clearview (CV) | £6752 | 7.14 | ||
| Chlamydia Rapid Test (CRT) | £6766 | 10.98 | 3.65 | |
| Current practice (PCR) | £7072 | 12.63 | 185.45 | |
| Sensitivity of Chlamydia Rapid Test = 0.85 | 0.85 | |||
| Current practice (PCR) | £7070 | 12.63 | ||
| Clearview (CV) | £7170 | 7.14 | Dominated | |
| Chlamydia Rapid Test (CRT) | £7200 | 11.67 | Dominated | |
| Specificity of Chlamydia Rapid Test = 1.00 | 1.00 | £7070 | 12.63 | |
| Chlamydia Rapid Test (CRT) | £7140 | 10.98 | Dominated | |
| Clearview (CV) | £7170 | 7.14 | Dominated | |
| Sensitivity of Clearview = 0.65 | 0.65 | |||
| Current practice (PCR) | £7070 | 12.63 | ||
| Chlamydia Rapid Test (CRT) | £7180 | 10.98 | Dominated | |
| Clearview (CV) | £7210 | 8.92 | Dominated | |
| Specificity of Clearview = 1.00 | 1.00 | |||
| Clearview (CV) | £7060 | 7.14 | ||
| Current practice (PCR) | £7070 | 12.63 | 2.74 | |
| Chlamydia Rapid Test (CRT) | £7180 | 10.98 | Dominated | |
Change in the uptake of the test offer
The current practice of using PCR will remain cost-effective even if the rate of acceptance of the offer of the test is increased for all the three tests reported in Table 8. If we assume that the acceptance rate for PCR and Clearview was 18.9% and that the acceptance for the CRT was 22.75%, the sensitivity analysis suggests that the CRT would be more effective but more costly than PCR and that the incremental cost per case of chlamydia correctly identified and treated and partners traced was £906.
Sensitivity of pre-test prevalence
One-way sensitivity analysis also suggests that at both the high and low pre-test prevalence rate of chlamydia (low = 6.9%, high = 9.1%), the current practice of using PCR for screening is less costly and more effective (i.e. it is dominant).
Change in sensitivity of the point-of-care tests
Similarly, the lower and higher values for sensitivity and specificity (see Table 8) were considered in a sensitivity analysis. In none of these analyses would the conclusion change from that based on the base-case analysis (results shown in Table 11).
Sensitivity analysis using higher and lower levels of sensitivity and specificity of the POCTs does not change the relative cost-effectiveness against PCR.
There are two different assumptions used for the sensitivity of costs, in one instance we lowered the cost of all tests to £19.50 and in another we kept the cost of testing for PCR unchanged at £20.56. We found the results were sensitive to changes.
The model used is only deterministic. It is important to show the changes in the value of the parameters simultaneously, and a probabilistic model needs to be used.
Discussion
The cost-effectiveness study compared two POCTs and one non-POCT. In our analysis we provided the estimates of the total costs of screening for a cohort of 1000 men and women aged 16–24 years. Our findings suggest that the current types of screening using PCR would identify more true-positive cases than the other two POCTs, namely CRT and Clearview. The CRT performs better than Clearview in identifying more true-positives, fewer false-negatives and more true-negatives, and is the more effective POCT. The current practice of using PCR would be the least costly method of detecting chlamydia at a total cost for the cohort of £7070. Furthermore, it was the most effective method – 12.63 people per 1000 offered the test (and assuming a prevalence of chlamydia of 7.8%) would be correctly treated and their partners contacted.
The CRT POCT may be worth considering over current practice when the acceptance of offer for the CRT tests by the patients visiting a chlamydia screening facility is higher at 22.75% (the base-case uptake rate of testing for CRT was 18.9% and the uptake rates for the other tests were kept at 18.9%). Such a situation might arise if the POCT was deemed to be more acceptable to patients because it was more convenient (in terms of location of testing and speed of obtaining a result).
The results were also (as might be expected) sensitive to reductions in the cost of the POCT, and the Clearview test has a higher ICER.
Limitations of the analysis
The short-time horizon has led to a focus on diagnostic outcomes, the likelihood of receiving treatment and contact tracing. The impact on health has not been considered nor has the effect of testing on the overall burden of the infection. It might be expected however that the more effective test in terms of the outcomes modelled would be the test that results in the highest health gain and the greatest reduction in the prevalence of infection in the population.
The analysis conducted has been deterministic in nature but has been supplemented by various sensitivity analyses. Ideally, further sensitivity analysis might be useful to explore more fully threshold values for key parameters. However, the sensitivity analysis conducted has highlighted some of the key areas for further investigation (e.g. uptake rates and costs of the tests).
Ideally, we would have liked to incorporate patient preferences into our model. Unfortunately few data are available and what data there were, were not suitable for incorporation into the model. Nevertheless, the results of the DCE suggest that family planning clinics are the preferred facility for screening, and less invasive techniques are favoured. However, no information was elicited to show if a POCT would be preferred or not. Ideally, further research investigating preferences for setting, diagnostic accuracy and waiting time for results could be performed. A DCE comparing variation in these attributes would be useful because, as we reported earlier, people have a preference for a short waiting time for the result, but we do not know how this might be traded off against diagnostic performance or other characteristics of the service by people receiving the test.
Chapter 7 Assessment of factors relevant to the NHS and other parties
Factors relevant to the NHS
There is currently insufficient evidence to suggest that using POCTs within the NHS would increase the overall number of cases of chlamydia detected. Tests used in current practice (i.e. NAATs) have been shown to have greater sensitivity and specificity than POCTs. This loss in diagnostic performance might be offset if POCTs increased the likelihood that individuals would come forward for testing (because the whole process of detecting and if necessary treating chlamydia was perceived as being less onerous) and/or that once tested individuals are more likely to receive treatment as required. There is an absence of evidence to suggest that either of these two changes is likely to occur. This suggests that there will still be a considerable amount of undiagnosed chlamydia infections which will result in a continuing burden on the NHS to manage patients who experience complications.
The use of POCTs would also increase the number of people incorrectly diagnosed as having chlamydia. There will be costs incurred of counselling and treating these people as well as of subsequent contact tracing.
Given the burden of chlamydia in the community, it is unlikely that the introduction of a point-of-care service would allow any reduction in the scale of existing testing services. Therefore, the introduction of POCTs will result in a net increase in costs. Nevertheless, for the NHS, any improvement in uptake rates would be beneficial, particularly where certain population groups are disproportionately affected by chlamydia as a result of the current low uptake of testing. This would potentially reduce the number of complications arising from undiagnosed chlamydia infection that require NHS treatment. The introduction of point-of-care testing in settings where uptake rates are low may require the provision of testing at a wider range of venues than is currently available. The NHS would incur the additional costs of such increased provision (e.g. capital costs, training health professionals to undertake the tests, providing immediate treatment and advice, and immediate contact tracing of the partners of each index case) and it is likely that different venues would incur different costs depending on the extent of uptake at each type of venue. However, in order to provide a service that is as accessible as possible, the NHS would be required to meet these costs.
The results of the economic evaluation suggested point-of-care testing may be more cost-effective than current practice if the cost of the POCT is reduced. Given the potential market power of the NHS the cost may be reduced if any economies of scale in purchasing the test can be realised.
New or improved technology that results in greater sensitivity of point-of-care tests would be of benefit to the NHS, but currently there is insufficient evidence to support the widespread adoption of POCTs as an alternative to current practice.
Factors relevant to other parties
Given that NAATs have been shown to be superior to POCTs in terms of diagnostic accuracy, changing practice within the NHS to diagnose chlamydia using POCTs may (because of the number of false-positives) cause physical and psychological distress to patients and their partners. POCTs may be a more acceptable method of testing as they offer the opportunity to get a result quickly (the available evidence suggests that most people would be willing to wait for a period of up to 2 hours for a test result) and hence avoid the need to make a further visit to receive treatment and perform contact tracing if necessary. The net impact of these two factors on the health of, and the costs incurred by, individuals is uncertain.
The use of POCTs may provide advantages to individuals (and their partners) in terms of earlier detection and treatment of the infection. This would rely on an increase in uptake of testing, which might be facilitated if point-of-care testing can be provided in venues that are more acceptable to potential clients.
Chapter 8 Discussion
Statement of principal findings
Review of test performance – pooled estimates
Most studies compared Clearview Chlamydia with PCR as the NAAT reference standard. Studies comparing the CRT with PCR, and those comparing Clearview Chlamydia with PCR were included in the pooled estimates (meta-analyses) using a HSROC model.
In terms of methodological quality, most populations in the studies included in the analysis50,64–72 were considered representative of those who would receive the test in practice. Two studies considered specific population groups (e.g. pregnant women, women receiving hospital treatment for PID)64,68 and one reported an unspecified population. 69 All NAATs were considered to be able to correctly classify chlamydia, except LCx, which was used in two studies68,69 but withdrawn from the market in 2002 because of reproducibility problems. 76,81 None of the quality assessed studies presented data on the specific subgroup of interest (those aged under 25 years).
A summary of the results of the pooled estimates is shown in Table 12.
| POCT | Type of point-of-care specimen included | Type of NAAT test used | Number of specimen sets included (number of studies from which specimens came) | Number of participants included (number of specimens included) | Sensitivity % (95% CI) | Specificity % (95% CI) | DOR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlamydia Rapid Test | Vaginal | PCR | 5 (2) | 2478 (3164) | 80 (73 to 85) | 99 (99 to 100) | 436.0 (238.5 to 796.9) |
| Chlamydia Rapid Test | FVU | PCR | 4 (2) | 1745 (2279) | 77 (59 to 89) | 99 (98 to 99) | 237.0 (101.9 to 552.6) |
| Clearview Chlamydia | Vaginal, cervical and urethral | PCR | 8 (4) | 3368 (5198) | 52 (39 to 65) | 97 (94 to 100) | 32.7 (13.0 to 82.2) |
| Clearview Chlamydia | Cervical | PCR | 4 (4) | 3085 (3085) | 64 (47 to 77) | 97 (88 to 99) | 59.9 (16.9 to 212.3) |
There was sufficient evidence available to pool estimates for the diagnostic accuracy of the CRT for both vaginal swab and FVU samples. For vaginal swabs, there was insufficient evidence to separate the pooled analysis by whether swabs were self- or clinician-collected, although the study by Mahilum-Tapay and colleagues,50 included in the diagnostic accuracy analysis, had compared these swab collection methods (using 686 self-collected and 686 clinician-collected specimens) and found no statistically significant difference between them (p = 0.096). 50 For FVU samples, there was also insufficient evidence to allow separation of the pooled analysis of routine cup collected urine and urine collected using the ‘FirstBurst’ device. The study by Wisniewski and colleagues72 compared these collection methods (using 534 specimens collected using ‘FirstBurst’ and 534 specimens collected using routine cup collection), and reported that more cases of chlamydia were identified using the ‘FirstBurst’ device. This result was statistically significant (p = 0.0015)72 and should be taken into account when considering the results of the diagnostic accuracy of the CRT when compared with PCR testing.
The pooled sensitivity (95% CI) of the CRT compared with PCR was 80% (73% to 85%) using vaginal swab samples and 77% (59% to 89%) when using FVU samples. Specificity (95% CI) was also similar at 99% (99% to 100%) using vaginal swab samples and 99% (98% to 99%) using FVU samples. DORs (95% CI) were also higher for vaginal swab samples at 436.0 (238.5 to 796.9) than for FVU samples at 237.0 (101.9 to 552.6). Although the reduced sensitivity of the CRT using FVU specimens might be explained by the difference in the method of specimen collection (‘FirstBurst’ versus routine cup collection), the CIs for the POCTs compared with the reference standard overlap for the sensitivity, specificity and DOR. Such indirect comparisons are difficult to interpret but these data suggest that there is no evidence of a difference in sensitivity between vaginal swab and FVU specimens.
For the Clearview Chlamydia test estimates, we originally pooled those studies containing comparisons with PCR as the reference standard, using vaginal, cervical or urethral swab specimens. This provided a sensitivity (95% CI) estimate of 52% (39% to 65%), a specificity (95% CI) estimate of 97% (94% to 100%) and a DOR (95% CI) of 32.7 (13.0 to 82.2). However, the resulting HSROC plot (see Figure 5) indicated that type of specimen can make a difference to the diagnostic accuracy results. Therefore, the results of the Clearview Chlamydia test compared with PCR using cervical samples were reported separately from those comparing Clearview Chlamydia with PCR using vaginal or urethral samples. There were insufficient comparisons available to conduct pooled analysis of the results using vaginal swabs (separately from the results using urethral and cervical specimens), and this was also true for urethral samples (as there was only one comparison available comparing the Clearview Chlamydia test using urethral samples with PCR testing). When the estimates were pooled for the Clearview Chlamydia test using cervical specimens only, sensitivity (95% CI) increased to 64% (44% to 77%), specificity (95% CI) was slightly reduced at 97% (88% to 99%) and the DOR (95% CI) increased to 59.9 (16.9 to 212.3). It should be noted that the study by Shaarawy and colleagues,64 which had a much smaller sample size than the other specimen sets, had much reduced specificity compared with the other three studies. It is likely that the small sample size accounted for this relatively low specificity.
The Clearview Chlamydia test is meant for use only in women, although the Clearview Chlamydia MF test can also be used with male FVU specimens. 82 This may explain the reduced sensitivity and specificity of the test when vaginal swab specimens are used instead of cervical swab specimens. 65,66 Use with a clinician-collected urethral swab71 did not appear to compromise diagnostic accuracy, although the test is not validated for this type of sample. 82,83
No studies were identified that directly compared the diagnostic accuracy of the CRT with Clearview Chlamydia. Evidence that one test is superior to the other can only be inferred from the indirect comparison of the results of each test compared with the reference standard. For the pooled estimates of Clearview Chlamydia’s sensitivity using cervical, vaginal and urethral swab specimens combined, the upper 95% CI for the Clearview Chlamydia test did not overlap with the lower 95% CI for the CRT using vaginal swab specimens, suggesting that the CRT might be a more sensitive test. However, when only cervical specimens were pooled, the CIs overlapped. For specificity, overlap in the CIs was present (regardless of whether the pooled results for the Clearview Chlamydia test were based upon combined or cervical only specimens) when Clearview Chlamydia results were compared with CRT results (using either vaginal swab or FVU samples).
Diagnostic odds ratios for the pooled analysis of Clearview Chlamydia using combined (vaginal, cervical and urethral) specimen types had an upper 95% CI that did not overlap with the lower 95% CI for either the pooled analysis of the CRT using vaginal swab samples or the pooled analysis of the CRT using FVU samples. The pooled analysis of Clearview Chlamydia using cervical only specimens had an upper 95% CI that did not overlap with the lower 95% CI for the pooled analysis of the CRT using vaginal swab samples.
Interpretation of these results therefore largely depends on the emphasis placed on the value of the DOR as a measure of diagnostic accuracy. The DOR is used to summarise diagnostic accuracy into a single value, but compared with values of sensitivity and/or specificity, it is less directly interpretable from a clinical point of view. Given the limited number of studies eligible for inclusion in this review and the limited amount of data that could be used in the pooled analysis, the DOR results should be interpreted with caution, as there is currently insufficient evidence to determine whether the CRT (using either vaginal swab or FVU specimens) performs better than the Clearview Chlamydia test (using cervical specimens) as a POCT for detecting genital chlamydia. Further research is required to determine which test is more accurate in diagnosing chlamydia infection.
Review of test performance – data that were not pooled
A summary of the results of data that could not be pooled is shown in Table 13.
| POCT | Type of point-of-care specimen included | Type of NAAT test used | Number of specimen sets included (from number of studies) | Number of participants included (number of specimens included) | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlamydia Rapid Test | Vaginal | SDA | 1 (1) | 637 (637) | 81.6% | 98.3% |
| Clearview Chlamydia | FVU | LCR | 1 (1) | 128 (128) | 67.7%, | 95.5% |
| Clearview Chlamydia | Cervical | LCR | 1 (1) | 395 (395) | 75.0% | 99.2% |
| Clearview Chlamydia | Cervical | LCR | 1 (1) | 65 (65) | 50.0% | 100% |
| Clearview Chlamydia | Cervical | TMA | 1 (1) | 65 (65) | 50.0% | 100% |
| Chlamydia Wand/HandiLab C | Vaginal | SDA | 1 (1) | 100 (100) | 36.4% | 79.8% |
| Chlamydia Wand/HandiLab C | Vaginal | PCR | 1 (1) | 231 (231) | 18.4% | 90.7% |
| QuickVue Chlamydia | Cervical | PCR | 1 (1) | 99 (99) | 64.7% | 100% |
| QuickVue Chlamydia | Cervical | PCR | 1 (1) | 100 (100) | 25.0% | 100% |
| Magic Lite Chlamydia | Urethral | PCR | 1 (1) | 283 (283) | 72.1% | 99.6% |
| Magic Lite Chlamydia | Cervical | PCR | 1 (1) | 724 | 60.5% | 99.9% |
| SureCell Chlamydia | FVU | LCR | 1 | 128 | 62.9% | 100% |
The study by Mahilum-Tapay and colleagues50 provides one additional set of self-collected vaginal swab specimens that could not be included in the pooled analysis for the CRT because a different reference standard (SDA) was used. The study did investigate if there was any significant difference depending on whether the SDA or PCR nucleic acid amplification method was used, and found that there was no evidence of a difference (p = 0.317). 50 The sensitivity and specificity of self-collected vaginal swabs using the CRT compared with SDA, as reported by Mahilum-Tapay and colleagues,50 lay within the CIs of the pooled analysis (see above) for vaginal swab specimens using the CRT compared with PCR testing.
Data from studies by Chernesky and colleagues,69 Hopwood and colleagues68 and Lauderdale and colleagues70 provided four additional sets of specimens on the diagnostic accuracy of Clearview Chlamydia. One set used FVU samples from men,69 whilst the remaining three sets used cervical specimens from women. 68,70 One of the cervical specimen sets70 was compared with the TMA method as the NAAT reference standard, whilst the remaining sets used the LCx assay which was withdrawn in 2002 following concerns over its reproducibility. 76,81 The sensitivity of the cervical specimen sets ranged from 50% to 75%, whilst specificity ranged from 99.2% to 100%. For sensitivity, these results are within the CIs for the pooled analysis of the sensitivity of the Clearview Chlamydia test using cervical samples alone. However, the specificities cited by these individual studies are higher than the pooled result. This is perhaps explained by low specificity in the Shaarawy study64 included in the pooled estimates.
There are no FVU samples eligible for inclusion in the pooled analysis of Clearview Chlamydia results using all specimen types. The sensitivity of the study comparing Clearview Chlamydia using FVU specimens, with the LCx assay (with a DFA test as confirmation)69 at 67.7% was above the upper 95% CI limit of the pooled estimate for all specimen types (65%). However, the specificity was within the 95% CI for the pooled estimate, and both sensitivity and specificity were within the 95% CI limits for the pooled estimates of Clearview Chlamydia using cervical specimens compared with PCR. These results could indicate that using Clearview Chlamydia with an FVU sample may, like cervical samples, be more sensitive than using the test with vaginal swab specimens. More evidence, however, is needed to be able to draw reliable conclusions. Furthermore, it should be noted that the study in question was the first to analyse use of the Clearview Chlamydia test with FVU specimens, using modifications to the original test (meant only for cervical specimens) and not the Clearview Chlamydia MF test which is validated for use with FVU specimens. 69,83
In addition to the two POCTs for which pooled analysis could be undertaken, results were available for another four POCTs. The Magic Lite test using urethral specimens reported the highest sensitivity (72.1%) compared with PCR as the reference standard, in the study by Kluytmans and colleagues. 71 The test with the lowest reported sensitivity was the Surescreen Chlamydia wand (18.4%), where PCR was again the reference standard, in the study by Michel and colleagues. 74 The highest specificity reported was 100% for the QuickVue Chlamydia test (using both the GUM clinic and hospital gynaecology department venues) compared with PCR, in the study by Rani and colleagues,67 and the SureCell Chlamydia test, using the LCx as the reference standard, in the study by Chernesky and colleagues. 69 The lowest specificity reported (79.8%) used the Surescreen Chlamydia wand compared with PCR as the reference standard, in the study by Kegg and colleagues. 73
Review of effectiveness
The comparative effectiveness of point-of-care testing with current practice in terms of the number of cases detected, treated and the number of partners identified, notified, tested and treated was not possible because of a lack of available evidence. This review found no RCTs or non-randomised studies comparing any of the identified POCTs with current practice using NAATs, for any of these outcomes. Therefore, it was not possible to determine whether or not the CRT was more effective than current practice for testing and diagnosing genital chlamydia infection in terms of the number of cases detected and treated, and the proportion of partners notified and treated. Further research is required to evaluate the practical use of point-of-care testing compared with laboratory testing methods currently in use throughout the NHS. The need for this research on non-diagnostic outcomes is particularly important because the relevance of point-of-care testing methods to diagnose chlamydia in clinical practice extends beyond their diagnostic accuracy, owing to what Gift and colleagues49 referred to as ‘the rapid test paradox’, whereby the non-return rate of positively infected patients (from the time of being tested to the time of requested attendance for treatment after a delay caused by waiting for a laboratory-based diagnosis) exceeds any relative diagnostic superiority, in terms of sensitivity and specificity, of the laboratory-based testing method over a POCT. In this way, even with poorer diagnostic accuracy, more positive cases could potentially be treated using the POCT than with a laboratory-based method,84 as treatment of the patient would take place immediately and contact tracing of sexual partners could also begin without delay.
Acceptability outcomes and patient preferences
Five studies provided information on the acceptability of the tests used,50,66,72,73,75 but no more than two studies reported data on the same outcome using the same criteria (e.g. cut-offs for waiting time categories), and the methods used for collecting acceptability data were not well reported by any of the studies.
The data collected showed that the majority of those surveyed would be willing to wait for up to 2 hours for the results of a POCT. Results also suggested that the vast majority (over 90% in each instance) were comfortable collecting either vaginal swab or urine samples for testing, and found instructions for collection of these specimens easy to understand. In terms of preferred type of specimen to provide (urine sample or urethral swab), most (88.8%, 619/697) would prefer to provide a urine sample. For cup collection methods, both studies comparing preference between the new ‘FirstBurst’ method and routine cup collection found that most participants (78.6%, 736/936) preferred the ‘FirstBurst’ method. Between providing a vaginal swab specimen or a urine specimen, there was no clear method favoured by most participants, but 40.7% (435/1068) would prefer to provide a self-collected vaginal swab, whilst 37.6% (401/1068) would prefer to provide a urine sample and the remaining 21.7% (232/1068) had no preference.
Acceptability outcomes for staff were only available from the study by Yin and colleagues,66 questioning 14 staff members on use of the Clearview Chlamydia test. Most responded that the test had clear instructions from the manufacturer, was easy to use, took around 10 minutes of ‘hands-on’ time to perform, gave a ‘rapid’ result in less than 20 minutes and required less than 30 minutes of training time.
There is a need for more research to be conducted on the acceptability of POCTs to both patients and staff, to provide more robust evidence of the acceptability of these tests, particularly in comparison with current practice.
The results of the DCE suggest that, in terms of patients’ own preferences for chlamydia testing services, family planning clinics are preferred as a facility for screening, and less invasive techniques are favoured. Further research investigating preferences for setting, type of tests, diagnostic accuracy and waiting time for results is needed. A DCE comparing variation in these attributes would be useful to consider how patients might trade off these attributes against poorer diagnostic performance of a test providing a faster result (e.g. POCTs). Such information would also be useful for improving the economic model to incorporate patient preferences, as those data available were sparse and not suitable for incorporation into the economic model for this review.
Three studies reported interpretability or reproducibility outcomes. 50,66,75 For both POCTs, reproducibility and/or interpretability outcomes were good. There was 100% concordance between the expected results and the results generated at an independent laboratory by two operators using randomised masked panels in both the studies by Mahilum-Tapay and colleagues50 and Nadala and colleagues. 75 The study by Yin and colleagues66 found statistically significant agreement between the results of the Clearview Chlamydia test, when interpreted by two different members of staff (p < 0.001). These results indicate that the interpretability of both the CRT and the Clearview Chlamydia test is good, although the fact that only three of the 13 included studies reported any interpretability outcomes suggests that further data on this would be beneficial.
Cost-effectiveness
The cost-effectiveness analysis compared two POCTs (the CRT and Clearview Chlamydia) and one NAAT method (PCR testing) in a setting where screening would generally be offered. In the analysis, the estimates of the total costs of screening a cohort of 1000 men and women aged 16–24 years were provided. The findings suggest that the current methods of testing using PCR would identify more true-positive cases than either of the POCTs. The CRT performs better than Clearview Chlamydia in identifying more true-positives, fewer false-negatives and more true-negatives, and is the more effective POCT. The current practice of using PCR would be the least costly method of detecting chlamydia, at a total cost for the cohort of £7070, and it would result in the most people correctly treated and their partners contacted (12.63 people per 1000 who are offered the test assuming a prevalence of chlamydia of 7.8%). Therefore no incremental cost-effectiveness of the CRT was found when compared with current practice.
Nevertheless, the CRT may still be worth considering (compared with current practice), if the acceptance rate of the offer of testing using this method could be increased. For example, if acceptance rate of the offer was 22.75% or greater (the base-case uptake rate of the testing for CRT was 18.9% and the uptake rates for the other tests was kept at 18.9%) then the CRT would be more effective but more costly than current practice. A judgement would be required as to whether the extra effectiveness would be worth the extra cost. Such a situation might arise if the POCT was deemed to be more acceptable to patients, for example if it was more convenient to them (in terms of location of testing and the speed in obtaining a result).
The results were also (as might be expected) sensitive to reductions in the cost of the POCT. This showed that increases in uptake rates and reductions in cost could make the CRT worthwhile, although results were not sensitive to changes in diagnostic accuracy for the levels used in the analysis. The sensitivity analysis conducted has highlighted some of the key areas for further investigation, including prevalence and uptake rates. These are discussed in Strengths and limitations of the assessment.
Strengths and limitations of the assessment
In terms of strengths of the research, a NAAT method was used as the reference standard, and the results for only people who received both the POCT and the reference standard were included in the pooled estimates. The use of point-of-care testing in a variety of different settings (e.g. GUM clinics, hospital obstetric and gynaecology venues, social hygiene clinics for female sex workers and sexual health centres providing contraceptive advice) was considered. The manufacturers of the CRT were contacted for information on any ongoing studies, and provided ‘in confidence’ reports of two studies awaiting publication. This provided sufficient information for pooled estimate analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of the CRT for more than one type of specimen (i.e. vaginal swab and FVU samples).
In terms of limitations, non-English studies were excluded, as were abstracts published prior to 2006. Most (nine of the 13) included studies had entirely female populations, and therefore may not be relevant to evaluating POCTs in male populations. Also, although age group is considered important in terms of risk, not all studies reported the age groups of participants and, of those who did, most did not report any information by age group. Therefore, subgroup analysis could not be performed on the high-risk age group (18–24 years), for the review of diagnostic accuracy.
It has been assumed that all the strains of chlamydia identified in Chapter 1 – Aetiology, pathology and the impact of the health problem – are equally detected by NAATs. It has also been assumed that all cases of chlamydia are of equal importance, but it is possible that some untreated positive cases clear spontaneously.
No comparative studies were identified that reported effectiveness outcomes for the POCTs under consideration (for example, the number of cases detected and treated and the number of partners notified and treated). Therefore, it was not possible to undertake a review of effectiveness. It was also not possible to consider the public health implications of effectiveness, e.g. re-infection, which is of particular relevance to high-risk populations (i.e. those aged less than 25 years). In addition, methods used in evaluating the acceptability and interpretability of POCTs within diagnostic accuracy studies were poorly reported, and few DCE studies were eligible for inclusion in this review.
For the economic evaluation, the short time horizon has led to a focus on diagnostic outcomes of test performance, likelihood of receiving treatment and contact tracing. The impact on health has not been considered nor has the effect of testing on the overall burden of the infection. It is possible that a herd immunity from chlamydia could occur if the vast majority of a population is tested and treated regularly, preventing the overall spread of infection. However, it is more likely that re-infection would create a longer term burden on services. It might be expected, however, that the more effective test in terms of the outcomes modelled would be the test that results in the highest health gain and the greatest reduction in the prevalence of infection in the population.
The focus of this review is point-of-care testing; therefore, other possible options for providing chlamydia testing services through altering the current NAAT service were not examined. Several alternatives could be considered, for example reducing transport times between the testing centre and the laboratory, reducing laboratory processing times, and undertaking dual testing of chlamydia alongside testing for gonorrhoea. However, it is likely that enhancing the way in which chlamydia testing services are currently provided would incur capital costs and also require additional staff.
The analysis conducted has been deterministic in nature but has been supplemented by various sensitivity analyses. Ideally, further sensitivity analysis might be useful to explore threshold values for key parameters more fully. For example, the cost estimates for testing are applicable to venues where testing is currently carried out, but further investigation on the implications on cost of conducting testing in each of these different venues could improve the model. It was not possible to include these parameters in the sensitivity analysis because of the lack of evidence on uptake rates at different testing venues.
However, the sensitivity analysis conducted has highlighted this and other key areas for further investigation (e.g. uptake rates, prevalence and costs of the tests).
Uncertainties
The dearth of available evidence hinders the interpretability of results. For the diagnostic accuracy review there is insufficient evidence available to conclude whether or not the CRT is a POCT with enhanced diagnostic capabilities compared with other POCTs. There were insufficient comparative studies available to conduct a review of effectiveness. For the review of patient preferences, there were few data available that were suitable enough to allow preferences to be incorporated into the economic model. For the economic evaluation, the impact of different methods of chlamydia testing on patients’ health has not been considered, nor has the effect of different testing methods on the overall burden of infection.
The withdrawal of the LCx assay in 2002 because of reproducibility issues76,81 means that the diagnostic accuracy results for studies using this method as the reference standard should be interpreted with caution (although in any event there were insufficient comparable specimen sets for pooled analysis using this test as the reference standard).
Chapter 9 Conclusions
Implications for service provision
In terms of diagnostic accuracy, the sensitivity of the CRT was higher than that of the Clearview Chlamydia test, but the sensitivity of POCTs was inferior to the current reference standard of NAAT testing for detecting genital chlamydia infection, and there was insufficient evidence available to suggest a clear difference in the performance of the point-of-care methods. However, both POCTs reported levels of specificity that were similar to the current reference standard, suggesting that all tests are effective in ruling out the presence of infection in uninfected patients. In addition, as things stand, NAAT methods currently used for diagnosing chlamydia remain the most cost-effective for service providers.
Nevertheless, even with relatively poorer diagnostic accuracy than in NAATs, POCTs could potentially still treat more infected people in instances where non-return rates for treatment using laboratory-based testing methods are particularly high or, as suggested by the economic evaluation, where uptake rates are increased by using the CRT method. However, this review found no comparative studies that had compared outcomes other than diagnostic accuracy for POCTs against NAATs. Until there is more robust evidence on the clinical effectiveness of POCTs beyond their diagnostic accuracy, service providers would need to provide point-of-care testing as a preliminary adjunct to existing laboratory testing with NAATs, and not as a replacement for current service provision for chlamydia diagnosis.
There is a very limited amount of evidence on the acceptability of POCTs, but the results suggest that most patients find these methods of testing acceptable. Evidence from a selective sample shows that women preferred having chlamydia testing services provided in family planning clinics, and preferred less invasive techniques for specimen collection. If services accommodate these preferences as far as possible, there is potentially an opportunity to increase uptake rates for testing. Further research is needed to determine whether increasing uptake rates would make point-of-care testing a viable alternative to current practice.
Suggested research priorities
This review did not identify any studies comparing point-of-care testing with NAATs that reported effectiveness outcomes, therefore research on this subject is required. Until this is done, the extent to which the ability of POCTs to provide an immediate result compensates for reduced diagnostic accuracy will not be known.
Research on uptake rates using point-of-care testing would be beneficial as there is evidence to suggest that if the CRT can improve uptake rates for testing, it could become more cost-effective than current practice using NAATs. A DCE would be useful for this type of research, as it is a research method that could predict uptake rates for a particular service, based on the preferences elicited from respondents. Further research on patients’ preferences, and the extent to which they find point-of-care testing acceptable, would also be necessary to evaluate this type of testing, and could perhaps also be used in instances where the cost-effectiveness of point-of-care testing is being considered.
Further studies are needed to confirm the relative diagnostic accuracy of the CRT compared with other POCTs, as there is currently not enough evidence available (from clinically similar sets of specimens) to allow a robust comparison of POCTs and NAATs.
The evidence on the long-term effects of undiagnosed chlamydia infection is confusing, as it is now estimated that the early evidence overestimated the proportion of infected patients who develop long-term complications from infection. There is a need to precisely determine the correct scale of the problem, as the potential for future ill-health resulting from undiagnosed chlamydia is what provides the rationale for prioritising research on effective testing.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ambreen Butt, Margaret Watson, Allan Templeton and Hamish McKenzie for advice on clinical aspects of the review; Jonathan Cook for advice on statistical aspects of the review; Luke Vale, Margaret Watson, Ambreen Butt and Allan Templeton for commenting on drafts; Jen Burr for advice on the development of the protocol; and Kathleen McIntosh and Lara Kemp for secretarial support. We thank Lourdes Mahilum-Tapay, Diagnostics Development Unit, University of Cambridge, for providing details of unpublished studies, and Robin Harbour and Michele Hilton Boon, Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, for providing an early draft of the updated guideline for chlamydia infection. The Health Services Research Unit and Health Economics Research Unit, Institute of Applied Health Sciences, University of Aberdeen, are core-funded by the Chief Scientist Office of the Scottish Government Health Directorates.
Contribution of authors
Jenni Hislop (Research Fellow) screened the search results, assessed full text studies for inclusion, undertook data extraction and quality assessment, drafted the chapters on diagnostic accuracy and clinical effectiveness, and co-ordinated the review. Zahidul Quayyum (Research Fellow) drafted the chapters on patient preferences and cost-effectiveness, supervised by Luke Vale (Professor of Health Technology Assessment). Gillian Flett (Clinical Lead for Sexual Health, NHS Grampian) drafted the background chapter with assistance from Jenni Hislop and Zahidul Quayyum. Charles Boachie (Statistician) drafted the data analysis section of the review and conducted the statistical analysis. Gillian Flett provided expert advice on clinical aspects of the review. Cynthia Fraser (Information Officer) developed and ran the search strategies, obtained papers and formatted the references. Graham Mowatt (Senior Research Fellow) screened full-text papers, checked data extraction, undertook quality assessment and drafted quality assessment results and tables. All authors assisted in preparing the manuscript, reading and commenting on drafts and reading the final draft.
Disclaimers
The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- World Health Organization . Chlamydia Trachomatis 2009. www.who.int/vaccine_research/diseases/chlamydia_trachomatis/en/ (accessed March 2009).
- World Health Organization . Global Prevalence and Incidence of Selected Curable Sexually Transmitted Infections: Chlamydia 2009. www.who.int/docstore/hiv/GRSTI/003.htm (accessed March 2009).
- The UK Collaborative Group for HIV and STI Surveillance . Testing Times – HIV and Other Sexually Transmitted Infections in the United Kingdom: 2007 2007. www.hpa.org.uk/web/HPAwebFile/HPAweb_C/1203496897276 (accessed March 2009).
- British Association of Sexual Health and HIV . 2006 UK National Guideline for the Management of Genital Tract Infection With Chlamydia Trachomatis 2009. www.bashh.org/documents/61/61.pdf (accessed March 2009).
- Low N, McCarthy A, Macleod J, Salisbury C, Campbell R, Roberts TE, et al. Epidemiological, social, diagnostic and economic evaluation of population screening for genital chlamydial infection. Health Technol Assess 2007;11.
- Adams EJ, Charlett A, Edmunds WJ, Hughes G. Chlamydia trachomatis in the United Kingdom: a systematic review and analysis of prevalence studies. Sex Transm Infect 2004;80:354-62.
- Fenton KA, Korovessis C, Johnson AM, McCadden A, McManus S, Wellings K, et al. Sexual behaviour in Britain: reported sexually transmitted infections and prevalent genital Chlamydia trachomatis infection. Lancet 2001;358:1851-4.
- Health Protection Agency National Chlamydia Screening Programme . NCSP Five Years: 5th Annual Report of the National Chlamydia Screening Programme 2007 08 2008. www.chlamydiascreening.nhs.uk/ps/assets/pdfs/core_req/NSCP_CoreReq_4th_edition_latest.pdf (accessed March 2009).
- Health Protection Scotland . Sexually Transmitted Infections and Other Sexual Health Information for Scotland 2007. www.documents.hps.scot.nhs.uk/bbvsti/sti/publications/sexual-health-2007.pdf (accessed March 2009).
- Cullen BL, Wallace LE, Palmer H, Codere G, Goldberg DJ. Genital herpes simplex, genital chlamydia, and gonorrhoea infection in Scotland: Laboratory diagnoses 1998–2007. Health Protection Scotland Weekly Data Reports 2008;42:102-9.
- Johnson AM, Mercer CH, Erens B, Copas AJ, McManus S, Wellings K, et al. Sexual behaviour in Britain: partnerships, practices, and HIV risk behaviours. Lancet 2001;358:1835-42.
- Kaestle CE, Halpern CT, Miller WC, Ford CA. Young age at first sexual intercourse and sexually transmitted infections in adolescents and young adults. Am J Epidemiol 2005;161:774-80.
- Health Protection Agency . Sexually Transmitted Infections and Young People in the United Kingdon: 2008 Report 2008. www.hpa.org.uk/web/HPAwebFile/HPAweb_C/1216022461534 (accessed March 2009).
- Low N, Egger M. What should we do about screening for genital chlamydia?. Int J Epidemiol 2002;31:891-3.
- Low N, Egger M, Sterne JA, Harbord RM, Ibrahim F, Lindblom B, et al. Incidence of severe reproductive tract complications associated with diagnosed genital chlamydial infection: the Uppsala Women’s Cohort Study. Sex Transm Infect 2006;82:212-18.
- van Valkengoed IG, Morre SA, van den Brule AJ, Meijer CJ, Bouter LM, Boeke AJ. Overestimation of complication rates in evaluations of Chlamydia trachomatis screening programmes – implications for cost-effectiveness analyses. Int J Epidemiol 2004;33:416-25.
- UK Collaborative Group for HIV and STI Surveillance UK Collaborative Group for HIV and STI Surveillance . Mapping the Issues: HIV and Other Sexually Transmitted Infections in the United Kingdom 2005 2005. www.hpa.org.uk/web/HPAwebFile/HPAweb_C/1194947372107 (accessed March 2009).
- Management of genital Chlamydia trachomatis infection. Edinburgh: Scottish Intercollegiate Guideline Network; 2009.
- Geisler WM, Wang C, Morrison SG, Black CM, Bandea CI, Hook EW. The natural history of untreated Chlamydia trachomatis infection in the interval between screening and returning for treatment. Sex Transm Dis 2008;35:119-23.
- Parks KS, Dixon PB, Richey CM, Hook EW. Spontaneous clearance of Chlamydia trachomatis infection in untreated patients. Sex Transm Dis 1997;24:229-35.
- Rogers SM, Miller WC, Turner CF, Ellen J, Zenilman J, Rothman R, et al. Concordance of Chlamydia trachomatis infections within sexual partnerships. Sex Transm Infect 2008;84:23-8.
- Weatherburn P, Bonell C, Hickson F, Stewart, Weatherburn P, Bonell C, et al. The Facilitation of HIV Transmission by Other Sexually Transmitted Infections During Sex Between Gay Men 1999. www.sigmaresearch.org.uk/files/report1999c.pdf (accessed March 2009).
- Risser WL, Risser JM. The incidence of pelvic inflammatory disease in untreated women infected with Chlamydia trachomatis: a structured review. Int J STD AIDS 2007;18:727-31.
- Froom P, Froom J. Selection bias in using data from one population to another: common pitfalls in the interpretation of medical literature. Theor Med 1992;13:255-9.
- Simms I, Warburton F, Westrom L. Diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease: time for a rethink. Sex Transm Infect 2003;79:491-14.
- NHS Information Centre . HESonline: Hospital Episode Statistics [database on the Internet] 2009. www.hesonline.nhs.uk/ (accessed March 2009).
- Duncan B, Hart G, Scoular A, Bigrigg A. Qualitative analysis of psychosocial impact of diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis: implications for screening. BMJ 2001;322:195-9.
- Mills N, Daker-White G, Graham A, Campbell R. Population screening for Chlamydia trachomatis infection in the UK: a qualitative study of the experiences of those screened. Fam Pract 2006;23:550-7.
- Norman JE, Wu O, Twaddle S, Macmillan S, McMillan L, Templeton A, et al. An evaluation of economics and acceptability of screening for Chlamydia trachomatis infection, in women attending antenatal, abortion, colposcopy and family planning clinics in Scotland, UK. BJOG 2004;111:1261-8.
- Aldeen T. Urine based screening for asymptomatic/undiagnosed genital chlamydial infection in young people visiting the accident and emergency department is feasible, acceptable, and can be epidemiologically helpful. Sex Transm Infect 2003;79:229-33.
- National Chlamydia Screening Programme (NCSP). London: Centre for Infections, Health Protection Agency; 2009.
- The National Chlamydia Screening Programme in England: Core Requirements. London: Health Protection Agency National Chlamydia Screening Programme; 2008.
- Linnemann CC, Heaton CL, Ritchey M. Treatment of Chlamydia trachomatis infections: comparison of 1- and 2-g doses of erythromycin daily for seven days. Sex Transm Dis 1987;14:102-6.
- Low N, McCarthy A, Roberts TE, Huengsberg M, Sanford E, Sterne JA, et al. Partner notification of chlamydia infection in primary care: randomised controlled trial and analysis of resource use. BMJ 2006;332:14-9.
- Scott LD, Baster K, Emmett L, Nichols T, Randall S, McLean L, et al. Incidence and reinfection rates of genital chlamydial infection among women aged 16–24 years attending general practice, family planning and genitourinary medicine clinics in England: a prospective cohort study by the Chlamydia Recall Study Advisory Group. Sex Transm Infect 2007;83:292-303.
- Raval B, Challenor R. Clinching the contacts: a tale of two audits before and after the introduction of a contacts’ clinic. Int J STD AIDS 2006;17:772-5.
- Adams EJ, Turner KME, Edmunds WJ, Roberts TE, Low N. The cost effectiveness of opportunistic chlamydia screening in England. Sex Transm Infect 2007;83:267-75.
- Roberts TE. Cost effectiveness of home based population screening for Chlamydia trachomatis in the UK: economic evaluation of chlamydia screening studies [C.l.a.S.S.] project. BMJ 2007;335:291-4.
- NHS reference costs 2004 [database on the Internet]. London: Department of Health; 2005.
- White R, Perry K, White R. Chlamydia Trachomatis Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs): Review of Evaluation Literature. Report MHRA 04122 2004. www.pasa.nhs.uk/pasa/Doc.aspx?Path=%5BMN%5D%5BSP%5D/NHSprocurement/CEP/Analytical/MHRA%2004122.pdf (accessed March 2009).
- The national strategy for sexual health and HIV: better prevention, better services, better sexual health. London: Department of Health; 2001.
- Christophers HM, Mann S, Christophers HM. Progress and Priorities – Working Together for High Quality Sexual Health: Review of the National Strategy for Sexual and Health and HIV 2008. www.medfash.org.uk/publications/documents/Progress_and_priorities_working_together_for_high%20quality_sexual_health_FULL_REPORT.pdf (accessed March 2009).
- Respect and responsibility: Strategy and action plan for improving sexual health. Edinburgh: Scottish Executive; 2005.
- Sexual health services standards. Edinburgh: NHS Quality Improvement Scotland; 2008.
- Standards for HIV clinical care. London: British HIV Association; 2007.
- A Strategic Framework for Promoting Sexual Health in Wales 1999. www.wales.nhs.uk/sites3/Documents/568/WAGStrategicFramework.pdf (accessed March 2009).
- Sexual health promotion: strategy and action plan 2008–2013. Belfast: Department of Health and Social Services and Public Safety for Northern Ireland; 2008.
- Management of Genital Chlamydia trachomatis Infection. Edinburgh: Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network; 2000.
- Gift TL, Pate MS, Hook EW, Kassler WJ. The rapid test paradox: when fewer cases detected lead to more cases treated: a decision analysis of tests for Chlamydia trachomatis. Sex Transm Dis 1999;26:232-40.
- Mahilum-Tapay L, Laitila V, Wawrzyniak JJ, Lee HH, Alexander S, Ison C, et al. New point of care Chlamydia Rapid Test – bridging the gap between diagnosis and treatment: performance evaluation study. BMJ 2007;335:1190-4.
- Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PM, Kleijnen J. The development of QUADAS: a tool for the quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol 2003;3.
- Verhagen AP, de Vet HC, de Bie RA, Kessels AG, Boers M, Bouter LM, et al. The Delphi list: a criteria list for quality assessment of randomized clinical trials for conducting systematic reviews developed by Delphi consensus. J Clin Epidemiol 1998;51:1235-41.
- Systematic reviews: CRD’s guidance for undertaking systematic reviews in health care. University of York: Centre for Reviews and Dissemination; 2009.
- Downs SH, Black N. The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J Epidemiol Community Health 1998;52:377-84.
- Rutter CM, Gatsonis CA. A hierarchical regression approach to meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy evaluations. Stat Med 2001;20:2865-84.
- Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten RJ, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol 2005;58:982-90.
- van Houwelingen HC, Arends LR, Stijnen T. Advanced methods in meta-analysis: multivariate approach and meta-regression. Stat Med 2002;21:589-624.
- Harbord RM, Deeks JJ, Egger M, Whiting P, Sterne JA. A unification of models for meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy studies. Biostatistics 2007;8:239-51.
- Macaskill P. Empirical Bayes estimates generated in a hierarchical summary ROC analysis agreed closely with those of a full Bayesian analysis. J Clin Epidemiol 2004;57:925-32.
- Deeks J. Systematic reviews in health care: systematic reviews of evaluations of diagnostic and screening tests. BMJ 2001;323:157-62.
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Cont Clin Trial 1986;7:177-88.
- Zamora J, Muriel A, Zamora J. Meta-DiSc for Windows: A Software Package for the Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Tests 2003. www.hrc.es/investigacion/metadisc_en.htm (accessed March 2009).
- Higgins JP, Green S, Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1. London: Cochrane Collaboration; 2008.
- Shaarawy M. Chlamydia trachomatis infection in pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) prevalence and comparative methodology. Clin Lab 1998;44:285-90.
- Saison F, Mahilum-Tapay L, Michel CE, Buttress ND, Nadala EC, Magbanua JP, et al. Prevalence of Chlamydia trachomatis infection among low- and high-risk Filipino women and performance of Chlamydia rapid tests in resource-limited settings. J Clin Microbiol 2007;45:4011-17.
- Yin YP, Peeling RW, Chen XS, Gong KL, Zhou H, Gu WM, et al. Clinic-based evaluation of Clearview Chlamydia MF for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in vaginal and cervical specimens from women at high risk in China. Sex Transm Infect 2006;82:v33-7.
- Rani R, Corbitt G, Killough R, Curless E. Is there any role for rapid tests for Chlamydia trachomatis?. Int J STD AIDS 2002;13:22-4.
- Hopwood J, Mallinson H, Gleave T. Evaluation of near patient testing for Chlamydia trachomatis in a pregnancy termination service. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care 2001;27:127-30.
- Chernesky M, Jang D, Krepel J, Sellors J, Mahony J. Impact of reference standard sensitivity on accuracy of rapid antigen detection assays and a leukocyte esterase dipstick for diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis infection in first-void urine specimens from men. J Clin Microbiol 1999;37:2777-80.
- Lauderdale TL, Landers L, Thorneycroft I, Chapin K. Comparison of the PACE 2 assay, two amplification assays, and Clearview EIA for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in female endocervical and urine specimens. J Clin Microbiol 1999;37:2223-9.
- Kluytmans JA, Goessens WH, Mouton JW, Rijsoort-Vos JH, Niesters HG, Quint WG, et al. Evaluation of Clearview and Magic Lite tests, polymerase chain reaction, and cell culture for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in urogenital specimens. J Clin Microbiol 1993;31:3204-10.
- Wisniewski CA, White JA, Michel CE, Mahilum-Tapay L, Magbanua JP, Nadala EC, et al. Optimal method of collection of first-void urine for diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis infection in men. J Clin Microbiol 2008;46:1466-9.
- Kegg S, Roberts C. Evaluation of a rapid self-administered test for Chlamydia trachomatis: caveat emptor. Int J STD AIDS 2006;17:39-40.
- Michel CE, Saison FG, Joshi H, Mahilum-Tapay LM, Lee HH. Pitfalls of internet-accessible diagnostic tests: inadequate performance of a CE-marked Chlamydia test for home use. Sex Transm Infect 2009;85:187-9.
- Nadala EC, Goh BT, Magbanua JP, Barber P, Swain A, Alexander S, et al. Performance evaluation of a new rapid urine test for chlamydia in men: prospective cohort study. BMJ 2009;339.
- Recall of LCx® Neisseria gonorrhoeae Assay and Implications for Laboratory Testing for N. gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2002;51.
- Ryan M, Watson V. Comparing welfare estimates from payment card contingent valuation and discrete choice experiments. Health Econ 2009;18:389-401.
- Watson V, Ryan M, Watson E. Valuing experience factors in the provision of chlamydia screening: an application to women attending the family planning clinic. Value Health 2009. www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/121402661/HTMLSTART (accessed March 2009).
- National Chlamydia Screening Programme NHS Vital Signs 2008 9. Primary Care Trust (PCT) and Strategic Health Authority (SHA) Specific Tables 1st April 2008–31st December 2008 2009. www.chlamydiascreening.nhs.uk/ps/assets/pdfs/data/Vital_Signs%20_PCT_%20April_Dec%2008.pdf (accessed March 2009).
- Clearview Chlamydia M F Kits [website on the Internet] 2009. www.medisave.co.uk/ (accessed March 2009).
- Gronowski AM, Copper S, Baorto D, Murray PR. Reproducibility problems with the Abbott laboratories LCx assay for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol 2000;38:2416-18.
- Clearview Chalmydia – features and benefits [website on the Internet]. Louisville, CO: Inverness Medical; 2009.
- Clearview Chlamydia MF. Bedford, UK: Inverness Medical Innovations; 2009.
- Vickerman P, Watts C, Alary M, Mabey D, Peeling RW. Sensitivity requirements for the point of care diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in women. Sex Transm Infect 2003;79:363-7.
Appendix 1 Search strategies
Clinical effectiveness
MEDLINE (1966 – Week 3 November 2008), EMBASE (1980 – Week 48 2008), Medline In-Process (26 November 2008)
Ovid multifile search URL: gateway.ovid.com/athens
-
chlamydia infection/use mesz
-
chlamydiasis/use emez
-
chlamydia/use mesz
-
chlamydia trachomatis/
-
chlamydia.tw.
-
or/1–5
-
“Point-of-Care Systems”/use mesz
-
“Point of Care Testing”/use emez
-
point of care.tw.
-
poct?.tw.
-
near patient?.tw.
-
(rapid adj1 test$).tw.
-
(clearview or surecell or quickvue or biostar or oia or handilab or nptgold or insticheck).tw.
-
or/7–13
-
6 and 14
-
limit 15 to english language
-
remove duplicates from 16
Science Citation Index (1970 – 22 November 2008)
BIOSIS (1985 – 27 November 2008)
ISI Proceedings (1990 – 22 November 2008)
Web of Knowledge URL: wok.mimas.ac.uk/
-
#1 TS=chlamydia AND Language=(English)
-
#2 TS=point of care AND Language=(English)
-
#3 TS=poct* AND Language=(English)
-
#4 TS=(rapid SAME test*) AND Language=(English)
-
#5 TS=(clearview OR surecell or quickvue or biostar or oia or handilab or nptgold or instcheck) AND Language=(English)
-
#6 #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 AND Language=(English)
-
#7 #1 and #6 AND Language=(English) and TA=humans
Cochrane Library Issue 4, 2008
URL: www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/mrwhome/106568753/HOME
-
#1 MeSH descriptor Chlamydia Infections, this term only
-
#2 MeSH descriptor Chlamydia, this term only
-
#3 MeSH descriptor Chlamydia trachomatis, this term only
-
#4 (chlamydia)
-
#5 (#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4)
-
#6 MeSH descriptor Point-of-Care Systems, this term only
-
#7 (point of care) or (poct*)
-
#8 “near patient*” or (rapid NEAR/3 test*)
-
#9 (clearview) or (surecell) or (quickvue) or (biostar) or (oia)
-
#10 (handilab) or (nptgold or insticheck)
-
#11 (#6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10)
-
#12 (#5 AND #11)
DARE and HTA Databases (November 2008)
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination URL: www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd
-
#1 MeSH Chlamydia
-
#2 MeSH Chlamydia Infections
-
#3 MeSH Chlamydia trachomatis
-
#4 chlamydia
-
#5 #1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4
-
#6 MeSH Health Services Administration EXPLODE 1 2
-
#7 MeSH Point-of-Care Systems
-
#8 “point of care”
-
#9 “near patient*”
-
#10 poct*
-
#11 “rapid test*”
-
#12 clearview OR surecell OR quickvue OR biostar
-
#13 oia OR handilab OR nptgold or insticheck
-
#14 #7 or #8 or #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 or #13
-
#15 #5 and #14
Health Management Information Consortium (1979 – October 2008)
Ovid Gateway URL: gateway.ovid.com/athens
-
chlamydia infections/
-
chlamydia.tw.
-
1 or 2
-
point of care.tw.
-
poct*.tw.
-
near patient*.tw.
-
(rapid adj1 test*).tw.
-
(clearview or surecell or quickvue or biostar or oia or handilab or nptgold).tw.
-
or/4–8
-
3 and 9
Clinical Trials (November 2008)
URL: clinicaltrials.gov/ct/gui/c/r
“chlamydia infections”:Topic
Current Controlled Trials (November 2008)
URL: www.controlled-trials.com/
Chlamydia AND test%
World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (November 2008)
URL: www.who.int/ictrp/en/
chlamydia:Condition
Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects (November 2008)
URL: crisp.cit.nih.gov/
Chlamydia AND test*
Conference proceedings
European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases
16th European Congress, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2–5 April 2005
16th European Congress, Nice, France, 1–4 April 2006
17th European Congress, Munich, Germany, 31 March–3 April 2007
18th European Congress, Barcelona, Spain, 19–22 April 2008
American Association for Clinical Chemistry
Annual meeting, Orlando, FL, USA, 25–28 July 2005
Annual meeting, Chicago, IL, USA, 23–27 July 2006
Annual meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 15–19 July 2007
Annual meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 27–31 July 2008
International Society for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Research
16th Biennial meeting, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 11–13 July 2005
17th Biennial meeting, Seattle, WA, USA, 30 July–1 August 2007
British Association for Sexual Health and HIV
Spring Meeting, Blackpool, UK, 2–4 May 2006
Spring Meeting, Nottingham, UK, 17–19 May 2007
Patient preferences
MEDLINE (1966 – Week 3 November 2008), EMBASE (1980 – Week 48 2008), Medline In-Process (1 December 2008)
Ovid multifile search URL: gateway.ovid.com/athens
-
chlamydia infection/use mesz
-
chlamydiasis/use emez
-
chlamydia/use mesz
-
chlamydia trachomatis/
-
chlamydia.tw.
-
or/1–5
-
“Point-of-Care Systems”/use mesz
-
“Point of Care Testing”/use emez
-
point of care.tw.
-
poct?.tw.
-
near patient?.tw.
-
(rapid adj1 test$).tw.
-
(clearview or surecell or quickvue or biostar or oia or handilab or nptgold).tw.
-
mass screening/
-
screen$.tw.
-
(opportun$adj3 test$).tw.
-
or/7–16
-
6 and 17
-
patient satisfaction/
-
patient attitude/use emez
-
attitude/use mesz
-
decision making/
-
choice behavior/
-
willing$to pay.tw.
-
willing$to wait.tw.
-
(discrete adj3 choice$).tw.
-
standard gamble.tw.
-
contingennt valu$.tw
-
((preference$or opinion$or choice$) adj3 (elicit$or measure$or obtain$or technique$)).tw.
-
rating scale/
-
questionnaires/
-
(hui or hui1 or hui2 or hui3).tw.
-
(health adj3 (utilit$or disutili$)).tw.
-
or/19–32
-
18 and 33
-
limit 34 to english language
Science Citation Index (1970 – 1 November 2008)
Web of Knowledge URL: wok.mimas.ac.uk/
-
#1 TS=chlamydia AND Language=(English)
-
#2 TS=point of care AND Language=(English)
-
#3 TS=poct AND Language=(English)
-
#4 TS=(rapid SAME test*) AND Language=(English)
-
#5 TS=(clearview or surecell or quickvue or biostar or oia or handilab or nptgold or insticheck) AND Language=(English)
-
#6 1,312 TS=(chlamydia and screen*) AND Language=(English)
-
#7 TS=(opportun* SAME test*) AND Language=(English)
-
#8 #1 and (#2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7) AND Language=(English)
-
#9 TS=willing* to pay AND Language=(English)
-
#10 TS=willing* to wait AND Language=(English)
-
#11 TS=standard gamble AND Language=(English)
-
#12 TS=(discrete SAME choice) AND Language=(English)
-
#13 TS=((preference* SAME elicit*) or (preference* SAME measure*) or (preference* SAME obtain*) or (preference* SAME technique*)) AND Language=(English)
-
#14 TS=((opinion* SAME elicit*) or (opinion* SAME measure*) or (opinion* SAME obtain*) or (opinion* SAME technique*)) AND Language=(English)
-
#15 TS=((elicit* SAME elicit*) or (elicit* SAME measure*) or (elicit* SAME obtain*) or (elicit* SAME technique*)) AND Language=(English)
-
#16 TS=((choice* SAME elicit*) or (choice* SAME measure*) or (choice* SAME obtain*) or (choice* SAME technique*)) AND Language=(English)
-
#17 TS=(utilit* or disutilit*) AND Language=(English)
-
#18 #8 and (#9 or #10 or #11 or #12 or #13 or #14 or #15 or #16 or #17) AND Language=(English) AND Document Type=(Article)
Health Management Information Consortium (1979 – November 2008)
Ovid multifile search URL: gateway.ovid.com/athens
-
chlamydia infections/
-
chlamydia.tw.
-
1 or 2
-
point of care.tw
-
poct*.tw
-
near patient*.tw.
-
(rapid adj1 test*).tw.
-
(clearview or surecell or quickvue or biostar or oia or handilab or nptgold).tw.
-
mass screening/
-
screen*.tw
-
(opportun* adj3 test*).tw
-
or/4–11
-
3 and 12
Economic evaluation
NHS Economic Evaluation Database (November 2008)
Health Technology Assessment Database (November 2008)
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination URL: www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd
-
#1 MeSH Chlamydia
-
#2 MeSH Chlamydia Infections
-
#3 MeSH Chlamydia trachomatis
-
#4 chlamydia
-
#5 #1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4
IDEAS (November 2008)
RePeC URL: ideas.repec.org/
chlamydia
Websites consulted (accessed January 2009)
Australia and New Zealand Horizon Scanning Network URL: www.horizonscanning.gov.au/
Biostar OIA Chlamydia, Inverness Medical Professional Diagnostics URL: www.invernessmedicalpd.com/poc/products/oia_chlamydia.html
British Association for Sexual Health and HIV URL: www.bashh.org/
Clearview Chlamydia, Inverness Medical Professional Diagnostics URL: www.invernessmedicalpd.com/poc/products/clr_chlamydia.html
Department of Health URL: www.dh.gov.uk/en/index.htm
Enigma Diagnostics URL: www.enigmadiagnostics.com/
HandiLab, Zonca Incorporated URL: www.zondaincusa.com/index2.php?id=spproducts
Health Protection Agency (HPA) URL: www.hpa.org.uk/
Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency URL: www.mhra.gov.uk/
National Chlamydia Screening Programme URL: www.chlamydiascreening.nhs.uk/
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence URL: www.nice.org.uk/nice-web/Cat.asp?c=20
NHS Quality Improvement Scotland URL: www.nhshealthquality.org/nhsqis/
Quickvue Chlamydia, bioMérieux UK Ltd URL: www.quickvue.co.uk/en/gbr/contact.html
Scottish Intercollegiate Guideline Network URL: www.sign.ac.uk/
US National Institute of Health: Sexually Transmited Diseases URL: health.nih.gov/result.asp/588
US Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality URL: www.ahrq.gov/
Appendix 2 Data extraction form – diagnostic accuracy
Appendix 3 Quality assessment checklist – diagnostic accuracy
Appendix 4 List of included studies
Charnesky et al. 1999
Chernesky M, Jang D, Krepel J, Sellors J, Mahony J. Impact of reference standard sensitivity on accuracy of rapid antigen detection assays and a leukocyte esterase dipstick for diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis infection in first-void urine specimens from men. J Clin Microbiol 1999;37:2777–80.
Hopwood et al. 2001
Hopwood J, Mallinson H, Gleave T. Evaluation of near patient testing for Chlamydia trachomatis in a pregnancy termination service. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care 2001;27:127–30.
Kegg and Roberts 2006
Kegg S, Roberts C. Evaluation of a rapid self-administered test for Chlamydia trachomatis: caveat emptor. Int J STD AIDS 2006;17(Suppl. 1):39–40.
Kluytmans et al. 1993
Kluytmans JA, Goessens WH, Mouton JW, Rijsoort-Vos JH, Niesters HG, Quint WG, et al. Evaluation of Clearview and Magic Lite tests, polymerase chain reaction, and cell culture for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in urogenital specimens. J Clin Microbiol 1993;31:3204–10.
Lauderdale et al. 1999
Lauderdale TL, Landers L, Thorneycroft I, Chapin K. Comparison of the PACE 2 assay, two amplification assays, and Clearview EIA for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in female endocervical and urine specimens. J Clin Microbiol 1999;37:2223–9.
Mahilum-Tapay et al. 2007
Mahilum-Tapay L, Laitila V, Wawrzyniak JJ, Lee HH, Alexander S, Ison C, et al. New point of care Chlamydia Rapid Test – bridging the gap between diagnosis and treatment: performance evaluation study. BMJ 2007;335:1190–4.
Michel et al. 2009
Michel CE, Saison FG, Joshi H, Mahilum-Tapay LM, Lee HH. Pitfalls of internet-accessible diagnostic tests: inadequate performance of a CE-marked Chlamydia test for home use. Sex Transm Infect 2009;85:187–9.
Nadala et al. 2009
Nadala EC, Goh BT, Magbanua JP, Barber P, Swain A, Alexander S, et al. Performance evaluation of a new rapid urine test for chlamydia in men: prospective cohort study. BMJ 2009;339:b2655
Rani et al. 2002
Rani R, Corbitt G, Killough R, Curless E. Is there any role for rapid tests for Chlamydia trachomatis? Int J STD AIDS 2002;13:22–4.
Saison et al. 2007
Saison F, Mahilum-Tapay L, Michel CE, Buttress ND, Nadala EC, Jr., Magbanua JP, et al. Prevalence of Chlamydia trachomatis infection among low- and high-risk Filipino women and performance of Chlamydia rapid tests in resource-limited settings. J Clin Microbiol 2007;45:4011–17.
Shaarawy 1998
Shaarawy M. Chlamydia trachomatis infection in pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) prevalence and comparative methodology. Clin Lab 1998;44:285–90.
Wisniewski et al. 2008
Wisniewski CA, White JA, Michel CE, Mahilum-Tapay L, Magbanua JP, Nadala EC, Jr., et al. Optimal method of collection of first-void urine for diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis infection in men. J Clin Microbiol 2008;46:1466–9.
Yin et al. 2006
Yin YP, Peeling RW, Chen XS, Gong KL, Zhou H, Gu WM, et al. Clinic-based evaluation of Clearview Chlamydia MF for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in vaginal and cervical specimens from women at high risk in China. Sex Transm Infect 2006;82(Suppl. 5):v33–7.
Appendix 5 List of excluded studies
| Study | Reason for exclusion from review | |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic accuracy | Effectiveness | |
| Alary M, Gbenafa-Agossa C, Aina G, Ndour M, Labbe AC, Fortin D, et al. Evaluation of a rapid point-of-care test for the detection of gonococcal infection among female sex workers in Benin. Sex Transm Infect 2006;82:V29–32. | Not a study on chlamydia | Not applicable |
| Andersen B, Gundgaard J, Kretzschmar M, Olsen J, Welte R, Oster-Gaard L. Prediction of costs, effectiveness, and disease control of a population-based program using home sampling for diagnosis of urogenital Chlamydia trachomatis infections (Structured abstract). Sex Transm Dis 2006;33:407–15. | Not applicable | No POCT used |
| Blanding J, Aarnaes S, Darrow V, De La Maza L, Peterson E. The evaluation of the chlamydia optical immunoassay (OIA) for the direct detection of Chlamydia in cervical specimens. Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1995;35. | Pre-2006 abstract | Pre-2006 abstract |
| Bowden FJ. Reappraising the value of urine leukocyte esterase testing in the age of nucleic acid amplification. Sex Transm Dis 1998;25:322–6. | POCT cannot distinguish between chlamydia and other infections | POCT cannot distinguish between chlamydia and other infections |
| Braverman PK, Schwarz DF, Mph M, Deforest A, Hodinka RL, McGowan KL, et al. Use of ligase chain reaction for laboratory identification of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in adolescent women. J Ped Adoles Gynecol 2002;15:37–41. | No POCT used | No POCT used |
| Carder C, Mercey D, Benn P. Chlamydia trachomatis. Sex Transm Infect 2006;82(Suppl. 4):iv10–12. | Not a diagnostic accuracy study | Not a comparative study |
| Coleman P, Varitek V, Mushahwar IK, Marchlewicz B, Safford J, Hansen J, et al. Testpack Chlamydia, a new rapid assay for the direct detection of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Clin Microbiol 1989;27:2811–14. | NAAT not used as reference standard | No NAAT used |
| de Vries R, van Bergen JE, de Jong-van den Berg, Postma MJ. Systematic screening for Chlamydia trachomatis: estimating cost-effectiveness using dynamic modeling and Dutch data. Value in Health 2006;9:1–11. | Not applicable | Not a comparative study |
| Dean GL. Near-patient testing will not improve the control of sexually transmitted infections. Sex Transm Infect 2006;82:509–12. | Not applicable | Not a comparative study |
| Dean D, Ferrero D, McCarthy M. Comparison of performance and cost-effectiveness of direct fluorescent-antibody, ligase chain reaction, and PCR assays for verification of chlamydial enzyme immunoassay results for populations with a low to moderate prevalence of Chlamydia trachomatis infection. J Clin Microbiol 1998;36:94–9. | Not all participants received both tests | No outcomes of relevance |
| Diallo MO, Ghys PD, Vuylsteke B, Ettiegne-Traore V, Gnaore E, Soroh D, et al. Evaluation of simple diagnostic algorithms for Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis cervical infections in female sex workers in Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire. Sex Transm Infect 1998;74:S106–111. | No POCT used | Not a comparative study |
| Ferris DG, Petry LJ, Fischer PM. Sensitivity of rapid antigen-detection tests for Chlamydia trachomatis screening. JAMA 1995;273:917–18. | Not a diagnostic accuracy study | Not a comparative study |
| Forward KR. The impact of switching to polymerase chain reaction for the diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis infections in women. Can J Pub Health 2003;94:229–32. | Not all participants received both tests | Not all participants received both tests |
| Gift TL, Walsh C, Haddix A, Irwin KL. A cost-effectiveness evaluation of testing and treatment of Chlamydia trachomatis infection among asymptomatic women infected with Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Sex Transm Dis 2002;29:542–51. | Not applicable | No POCT used |
| Gift TL, Pate MS, Hook EW, III, Kassler WJ. The rapid test paradox: when fewer cases detected lead to more cases treated: a decision analysis of tests for Chlamydia trachomatis. Sex Transm Dis 1999;26:232–40. | Not a diagnostic accuracy study | Not a comparative study |
| Gilbert G. Chlamydia rapid test as accurate as conventional testing. J Natl Med Assoc 2008;100:459–60. | Not a diagnostic accuracy study | Not a comparative study |
| Goeree R, Jang D, Blackhouse G, Chong S, Mahony J, Sellors J, et al. Cost-effectiveness of screening swab or urine specimens for Chlamydia trachomatis from young Canadian women in Ontario. Sex Transm Dis 2001;28:701–9. | Not applicable | Not a comparative study |
| Groody E, Leszczynski J, Hendricks K, Spesard J, IXth International Conference on Aids and the IVth Std World Congress. Evaluation of Testpack Chlamydia, Kodak SureCell Chlamydia and Clearview Chlamydia across multiple clinical studies. IXth International Conference on AIDS in affiliation with the IVth STD World Congress, 1993. | Pre-2006 abstract | Not applicable |
| Greer L, Wendel GD, Jr. Rapid diagnostic methods in sexually transmitted infections. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2008;22:601–17. | Not a diagnostic accuracy study | Not applicable |
| Heath CB, Heath JM. Chlamydia trachomatis infection update. Am Fam Physician 1995;52:1455–61. | Not applicable | Not a comparative study |
| Herring A, Ballard R, Mabey D, Peeling RW. Evaluation of rapid diagnostic tests: chlamydia and gonorrhoea. Nature Rev Microbiol 2006;6:S41–8. | Not applicable | Not a comparative study |
| Hesterberg LK. An overview of rapid immunoassays. Lab Med 1996;27:41–6. | Not applicable | Not a comparative study |
| Hobbs FD, Delaney BC, Fitzmaurice DA, Wilson S, Hyde CJ, Thorpe GH, et al. A review of near patient testing in primary care. Health Technol Assess 1997;1(5). | Not applicable | Not a comparative study |
| Hogan DR, Baltussen R, Hayashi C, Lauer JA, Salomon JA. Cost effective analysis of strategies to combat HIV/AIDS in developing countries (Structured abstract). BMJ 2005;331:1431–5. | Not applicable | Not about chlamydia |
| Hossain A. Rapid diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis infections by a monoclonal-antibody direct immunofluorescence test. J Trop Med Hyg 1987;90:307–10. | No NAAT used | No NAAT used |
| Howell MR, Mckee KT, Gaydos JC, Quinn TC, Gaydos CA. Point-of-entry screening for C. trachomatis in female army recruits: who derives the cost savings? Am J Prev Med 2000;19:160–6. | Not applicable | No POCT used |
| Howell MR, Gaydos JC, Mckee KT, Quinn TC, Gaydos CA. Control of Chlamydia trachomatis infections in female army recruits: cost-effective screening and treatment in training cohorts to prevent pelvic inflammatory disease. Sex Transm Dis 1999;26:519–26. | Not applicable | No POCT used |
| Howell MR, Kassler WJ, Haddix A. Partner notification to prevent pelvic inflammatory disease in women: cost-effectiveness of two strategies. Sex Transm Dis 1997;24:287–92. | Not applicable | Not a comparative study |
| Jones HE, Altini L, de Kock A, Young T, van de Wijgert JH. Home-based versus clinic-based self-sampling and testing for sexually transmitted infections in Gugulethu, South Africa: randomised controlled trial. Sex Transm Infect 2007;83:552–7. | Not applicable | No POCT used |
| Khare VK, Consonni R, Martin DC, Winfield AC. Use of algorithmic pathways to develop quality, cost-effective clinical care. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc 1995;2:169–74. | Not applicable | Not about chlamydia |
| Kubo R, Kaneko T, Nomura A, Kouda M, Matsuzaki H, Murahashi I. Comparison of new simple immunochromatography test and conventional assay for detecting chlamydia in urine specimens. Gen Meet Am Soc Microbiol 1998;98. | Pre-2006 abstract | Pre-2006 abstract |
| Landers L, Lauderdale T, Thorneycroft I, Chapin K. Comparison of PACE and amplified Chlamydia trachomatis (Amp CT) assays, ligase chain reaction (LCx) and clearview EIA for CT. Gen Meet Am Soc Microbiol 1998;98. | Pre-2006 abstract | Pre-2006 abstract |
| Lewis DA. The burden of asymptomatic sexually transmitted infections among men in Carletonville, South Africa: Implications for syndromic management. Sex Transm Infect 2008;84:371–6. | Not applicable | No POCT used |
| Lippman SA, Jones HE, Luppi CG, Pinho AA, Veras MA, van de Wijgert JH. Home-based self-sampling and self-testing for sexually transmitted infections: acceptable and feasible alternatives to provider-based screening in low-income women in São Paulo, Brazil. Sex Transm Dis 2007;34:421–8. | Not applicable | No POCT used |
| Mabey D. Rapid and simple point of care diagnostics for STIs. Sex Transm Infect 2001;77:397–8. | Not a diagnostic accuracy study | Not a comparative study |
| Magbanua JP, Goh BT, Michel CE, Aguirre-Andreasen A, Alexander S, Ushiro-Lumb I, et al. Chlamydia trachomatis variant not detected by plasmid based nucleic acid amplification tests: molecular characterisation and failure of single dose azithromycin. Sex Transm Infect 2007;83:339–43. | Not a diagnostic accuracy study | Not a comparative study |
| Machungo F, Zanconato G, Persson K, Lind I, Jorgensen B, Herrmann B, et al. Syphilis, gonorrhoea and chlamydial infection among women undergoing legal or illegal abortion in Maputo. Int J STD AIDS 2002;13:326–30. | Not applicable | No NAAT used |
| Marions L, Rotzen-Ostlund M, Grillner L, Edgardh K, Tiveljung-Lindell A, Wikstrom A, et al. High occurrence of a new variant of Chlamydia trachomatis escaping diagnostic tests among STI clinic patients in Stockholm, Sweden. Sex Transm Dis 2008;35:61–4. | No point-of-care test used | Not applicable |
| Martin JL, Alexander SY, Selwood TS, Cross GF. Use of the polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in clinical specimens and its comparison to commercially available tests. Genitourin Med 1995;71:169–71. | No outcomes of relevance | No outcomes of relevance |
| Matthews R, Wise R, Radcliffe K, Temple C, Sheard P, Davidson I. Evaluation of a new prototype rapid immunoassay (Clearview Chlamydia) for the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in male urine samples and female endocervical swabs. Gen Meet Am Soc Microbiol 1995;95. | Pre-2006 abstract | Pre-2006 abstract |
| Matthews R, Ridgway G, Carder C, Hooki E, Pate M, Gleason B, et al. Evaluation of a new rapid immunoassay (Clearview™ Chlamydia) for the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in male urine samples and female endocervical swabs. Gen Meet Am Soc Microbiol 1996;96. | Pre-2006 abstract | Pre-2006 abstract |
| Noguchi M, Okamoto T, Aoyama N, Hieda S, Yabushita H, Nakanishi M. Rapid diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis infection in obstetrics and gynecology – evaluation of chlamydia test pack. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp 1989;46:462–70. | No NAAT used | No NAAT used |
| Nyari T, Woodward M, Kovacs L. Should all sexually active young women in Hungary be screened for Chlamydia trachomatis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2003;106:55–9. | Not applicable | No NAAT used |
| Pate MS, Dixon PB, Hardy K, Crosby M, Hook EW, III. Evaluation of the Biostar Chlamydia OIA assay with specimens from women attending a sexually transmitted disease clinic. J Clin Microbiol 1998;36:2183–6. | Uses an obsolete POCT | Uses an obsolete POCT |
| Philips DR, McCarthy O, Pakianathan MR, Sadiq ST. A computer based non-urine, non-swab simple point of care diagnostic test for Chlamydia trachomatis. Sex Transm Infect 2006;82:A11. | Not a diagnostic accuracy study | No NAAT used |
| Pittrof R, McLellan J. Test Not Talk screening for asymptomatic men. Int J STD AIDS 2007;18:274–5. | Not applicable | Not a comparative study |
| Postma MJ, Welte R, van den Hoek JA, van Doornum GJ, Coutinho RA, Jager JC. Opportunistic screening for genital infections with Chlamydia trachomatis in sexually active population of Amsterdam. II: Cost-effectiveness analysis of screening women. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 1999;143:677–81. | Not applicable | No POCT used |
| Reichart CA, Moncada J, Schachter J, Koshakow M, Sedmak G, Reising S, et al. Multicenter Evaluation of Clearview Chlamydia for Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in Women. Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1992;32. | Pre-2006 abstract | Pre-2006 abstract |
| Romoren M, Hussein F, Steen TW, Velauthapillai M, Sundby J, Hjortdahl P, et al. Costs and health consequences of chlamydia management strategies among pregnant women in sub-Saharan Africa. Sex Transm Infect 2007;83:558–66. | Not applicable | No NAAT used |
| Romoren M. Chlamydia and gonorhea in pregnancy: effectiveness of diagnosis and treatment in Botswana. Sex Transm Infect 2004;80:395–400. | Not applicable | No NAAT used |
| Sahin-Hodoglugil NN, Woods R, Pettifor A, Walsh J. A comparison of cost-effectiveness of three protocols for diagnosis and treatment of gonococcal and chlamydial infections in women in Africa. Sex Transm Dis 2003;30:455–69. | Not applicable | No POCT used |
| Schachter J. We must be realistic in evaluating rapid diagnostic tests. Sex Transm Dis 1999;26:241–2. | Not a diagnostic accuracy study | Not a comparative study |
| Schubiner HH, LeBar WD, Joseph S, Taylor C, Jemal C. Evaluation of two rapid tests for the diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis genital infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 1992;11:553–6. [Erratum appears in Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 1992;11:872]. | Not applicable | No NAAT used |
| Schubiner H, Taylor C, Ritchie J, Jemal C, Lebar W, Herschman B. Comparison of two membrane enzyme immunoassays for the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in clinical samples. Ann Meet Am Soc Microbiol 1990;90. | Not applicable | Pre-2006 abstract |
| Sharma M, Nayak N, Malhotra S, Kumar B, Hemal A. Chlamydiazyme test for rapid detection of Chlamydia trachomatis. Ind J Med Res A-Infect Dis 1989;89:87–91. | No NAAT used | No NAAT used |
| Skidmore S, Randall S, Mallinson H. Testing for Chlamydia trachomatis: self-test or laboratory-based diagnosis? J Fam Plan Reprod Health Care 2007;33:231–2. | Not a diagnostic accuracy study | Not a comparative study |
| Sloan NL, Winikoff B, Haberland N, Coggins C, Elias C. Screening and syndromic approaches to identify gonorrhea and chlamydial infection among women. Stud Fam Plan 31(1) 2000:55–68. | No NAAT used | Not applicable |
| Steingrimsson O, Olafsson J, Dolphin L, Pals-Dottir R, Davidsson S, Pawlak C, et al. Clinical evaluation of two immunoassay methods for the rapid detection of Chlamydia trachomatis antigen in endocervical specimens from high risk female patients. Gen Meet Am Soc Microbiol 1995;95. | Pre-2006 abstract | Pre-2006 abstract |
| Stratton N, Hirsch L, Harris F, Condon F, De La MAZA, Peterson EM. Evaluation of the Rapid Clearview Test for the direct detection of Chlamydia from cervical specimens. Gen Meet Am Soc Microbiol 1991;91. | No NAAT used | Not applicable |
| Svanas G, Boisen M, Brien J, Cox C, Frisch L, Hopkins D, et al. Thermo BioStar™ rapid immunoassays for Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (GC) from a single male or female specimen. Int J STD AIDS 2001;12. | Pre-2006 abstract | Pre-2006 abstract |
| Swain GR, McDonald RA, Pfister JR, Gradus MS, Sedmak GV, Singh A. Decision analysis: point-of-care Chlamydia testing vs. laboratory-based methods. Clin Med Res 2004;2:29–35. | Uses an obsolete POCT | Uses an obsolete POCT |
| Tao G, Abban BK, Gift TL, Chen G, Irwin KL. Applying a mixed-integer program to model re-screening women who test positive for C. trachomatis infection (Structured abstract). Health Care Manag Sci 2004;7:135–44. | Not applicable | No POCT used |
| Taylor-Robinson D. The value of nonculture techniques for diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis infections – making the best of a bad job. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 1992;11:499–503. | Not a diagnostic accuracy study | Not a comparative study |
| Theodore M, Hook E, Mableton S, Whittington W, Gaydos C. Use of Thermo BioStar™ optical immunoassay (OIA®) as a point of care assay for Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (GC) in sexually transmitted disease clinics. Int J STD AIDS 2001;12. | Pre-2006 abstract | Pre-2006 abstract |
| Thomas BJ, MacLeod EJ, Taylor-Robinson D. Evaluation of sensitivity of 10 diagnostic assays for Chlamydia trachomatis by use of a simple laboratory procedure. J Clin Pathol 1993;46:408–10. | No outcomes of relevance | No outcomes of relevance |
| Thomas BJ, MacLeod EJ, Taylor-Robinson D. Evaluation of sensitivity of 10 diagnostic assays for Chlamydia trachomatis by use of a simple laboratory procedure. J Clin Pathol 1993;46:912–14. | No outcomes of relevance | Not applicable |
| Tison DL. Evaluation of the Kodak SureCell Chlamydia Test Kit for the Direct Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis. Genl Meet Am Soc Microbiol 1991;91. | Pre-2006 abstract | Pre-2006 abstract |
| Veringa EM. Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in clinical specimens. Comparison of culture, direct antigen detection, DNA probe hybridization and PCR. J Microbiol Methods 1994;19:117–25. | Uses an obsolete POCT | Uses an obsolete POCT |
| Vickerman P, Watts C, Alary M, Mabey D, Peeling RW. Sensitivity requirements for the point of care diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in women. Sex Transm Infect 2003;79:363–7. | Not applicable | Not a comparative study |
| Wang LY, Burstein GR, Cohen DA. An economic evaluation of a school-based sexually transmitted disease screening program. Sex Transm Dis 2002;29:737–45. | Not applicable | Not a comparative study |
| Wang LY, Davis M, Robin L, Collins J, Coyle K, Baumler E. Economic evaluation of Safer Choices: a school-based human immunodeficiency virus, other sexually transmitted diseases, and pregnancy prevention program. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2000;154:1017–24. | Not applicable | Not about chlamydia |
| Warszawski J, Meyer L, Weber P. CLEARVIEW Chlamydia test for detection of chlamydiae in cervical specimens. J Clin Microbiol 1992;30:2216. | Not a diagnostic accuracy study | Not a comparative study |
| Wells A. Evaluation of the BioStar Chlamydia OIA assay for Chlamydia trachomatis in an outpatient setting. Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1995;35. | Pre-2006 abstract | Pre-2006 abstract |
| Welte R, Kretzschmar M, Leidl R, Van den HA, Jager JC, Postma MJ. Cost-effectiveness of screening programs for Chlamydia trachomatis: a population-based dynamic approach. Sex Transm Dis 2000;27:518–29. | Not applicable | No POCT used |
| Widjaja S, Cohen S, Brady WE, O’reilly K, Susanto, Wibowo A et al. Evaluation of a rapid assay for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis infections in outpatient clinics in South Kalimantan, Indonesia. J Clin Microbiol 1999;37:4183–5. | Uses an obsolete POCT | Uses an obsolete POCT |
| Wilsmore AJ, Davidson I. ‘Clearview’ rapid test compared with other methods to diagnose chlamydial infection. Vet Rec 1991;128:503–4. | Animal study | Animal study |
| Witkin SS, Bongiovanni AM, Inglis SR. Detection of endocervical anti-Chlamydia trachomatis immunoglobulin A in pregnant women by a rapid, 6-minute enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: Comparison with PCR and chlamydial antigen detection methods. J Clin Microbiol 1997;35:1781–3. | Uses an obsolete POCT | Uses an obsolete POCT |
| You JH, Wong WC, Sin CW, Woo J. The cost-effectiveness of an outreach clinical model in the management and prevention of gonorrhea and chlamydia among Chinese female sex workers in Hong Kong (Structured abstract). Sex Transm Dis 2006;33:220–7. | Not applicable | No POCT used |
| Point of care testing opportunities: Chlamydia screening. Pharm J 2007;279:506. | Not applicable | Not a comparative study |
| Adelaide Health Technology Assessment on behalf of National Horizon Scanning Unit (HealthPACT and MSAC). Rapid point-of-care test for the detection of chlamydia; horizon scanning prioritising summary – volume 13 (Brief record). Adelaide: Adelaide Health Technology Assessment (AHTA) on behalf of National Horizon Scanning Unit (HealthPACT and MSAC) 2006. | Not genital chlamydia | Not genital chlamydia |
| Kaye D. New rapid test developed to detect chlamydia. Clin Infect Dis 2004;38:iv. | Not a diagnostic accuracy study | Not a comparative study |
| Point-of-care tests should be quick and cheap. Pharm J 2002;269:185. | Not about chlamydia | Not a comparative study |
Appendix 6 Characteristics of the included studies
| Study ID | Participants | Intervention test(s) and comparator | Outcomes summary |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Study: Chernesky et al. 69 Year: 1999 Time period: 1997 (not specified further) Country: Canada |
Enrolled: 128 Analysed: 128 (100%) Gender: male 128 (100%); female 0 (0%) Age (mean, SD): not specified Baseline characteristics (e.g. symptoms, etc.): not specified Venue: private laboratory in Toronto, Ontario Setting (prevalence): 43% (sample of positive samples from the private laboratory were chosen for this study) |
POCT used: Clearview Chlamydia by Unipath (now Inverness Medical) Specimen type for POCT: FVU POCT used: SureCell Chlamydia by Kodak Specimen type for POCT: FVU NAAT reference standard: LCR using LCx assay by Abbott, confirmed with DFA staining (not specified further) Specimen type for NAAT: FVU |
Unit of analysis: specimen Using Clearview: Sensitivity (%): 42/62 (67.7) Specificity (%): 63/66 (95.5) Positive predictive value (%): 42/45 (93.3) Negative predictive value (%): 63/83 (75.9) Positive likelihood ratio: 14.90 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.34 Using SureCell: Sensitivity (%): 39/62 (62.9) Specificity (%): 66/66 (100) Positive predictive value (%): 39/39 (100) Negative predictive value (%): 66/89 (74.2) Positive likelihood ratio: – Negative likelihood ratio: 0.37 |
|
Study: Hopwood et al. 68 Year: 2001 Time period: February – March 2000 (2 months) Country: England (UK) |
Enrolled: 400 Analysed: 395 (98.8%) Gender: male 0 (0%); female 395 (100%) Age (mean, SD): age groups provided for 378 participants, of which: 15–19 years old – 89/378 (23.5%) 20–24 years old – 119/378 (31.5%) 25–29 years old – 65/378 (17.2%) 30–34 years old – 67/378 (17.7%) 35–39 years old – 29/378 (7.7%) 40–44 years old – 9/378 (2.4%) Baseline characteristics (e.g. symptoms, etc.): all participants were pregnant women undergoing a termination of pregnancy procedure. Venue: British Pregnancy Advisory Service clinic Setting (prevalence): not specified |
POCT used: Clearview Chlamydia MF by Unipath (now Inverness Medical) Specimen Type for POCT: endocervical swab NAAT reference standard: LCR using LCx assay by Abbott Laboratories Specimen type for NAAT: endocervical swab |
Unit of analysis: specimen/patient Sensitivity (%): 24/32 (75.0) Specificity (%): 360/363 (99.2) Positive predictive value (%): 24/27 (88.9) Negative predictive value (%): 360/368 (97.8) Positive likelihood ratio: 90.75 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.25 Additional outcomes: 270/397 (68.0%) asked for their results to be sent to their home address 23/397 (5.8%) asked for their results to be sent to another address 104/397 (26%) were ‘harder to reach’, of which: 15/397 (3.8%) gave a contact telephone number 80/397 (20.2%) wanted to simply telephone the clinic to find out their results 9/397 (2.3%) wanted to be contacted at various other places |
|
Study: Kegg and Roberts73 Year: 2006 Time period: not specified Country: England, UK |
Enrolled: 100 Analysed: 100 (100%) Gender: male 0 (0%); female 100 (100%) Age (mean, SD): not specified Baseline characteristics (e.g. symptoms, etc.): not specified Venue: GUM clinic Setting (prevalence): not specified |
POCT used: Chlamydia Wand by Surescreen Specimen type: Vaginal swab (self-collected) NAAT reference standard: SDA by Becton Dickinson ProbeTec Specimen type: cervical |
Unit of analysis: specimen/patient Sensitivity (%): 4/11 (36.4) Specificity (%): 71/89 (79.8) Positive predictive value (%): 4/22 (18.2) Negative predictive value (%): 71/78 (91.0) Positive likelihood ratio: 1.80 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.80 Additional outcomes: ‘Our experienced nursing staff encountered significant difficulties in manipulating the test device and is [sic] interpreting the colour change denoting a positive result’ |
|
Study: Kluytmans et al. 71 Year: 1993 Time period: not specified Country: the Netherlands |
Enrolled: 1007 Analysed: Magic Lite test – 1007/1007 (100%); Clearview Chlamydia test – 999/1007 (99.2%) Gender: male 283/1007 (28.1%); female 724/1007 (71.9%) Age (mean, SD): not specified Baseline characteristics (e.g. symptoms, etc.): not specified Venue: sexually transmitted disease clinic based in a hospital (University Hospital Rotterdam) Setting (prevalence): not specified |
POCT used: Clearview Chlamydia by Unipath (now Inverness Medical) Specimen type: urethral (for men); cervical (for women) POCT used: Magic Lite by CIBA Corning (now part of Novartis/Chiron) NAAT reference standard: PCR (not specified further) Specimen type: urethral (for men); cervical (for women) |
Unit of analysis: specimen Using Clearview: Sensitivity (%): women 31/43 (72.1); men: 26/44 (59.1) Specificity (%): women 667/673 (99.1); men 206/239 (86.2) Positive predictive value (%): women 31/37 (83.8); men 26/60 (43.3) Negative predictive value (%): women 667/679 (98.2); men 206/223 (92.4) Positive likelihood ratio: women 80.86; men 4.28 Negative likelihood ratio: women 0.28; men 0.47 Using Magic Lite: Sensitivity (%): women 26/43 (60.5); men 31/44 (70.5) Specificity (%): women 680/681 (99.9); men 239/239 (100) Positive predictive value (%): women 26/27 (96.3); men 31/32 (96.9) Negative predictive value (%): women 680/697 (97.6); men 239/251 (95.2) Positive likelihood ratio: women 411.77; men – Negative likelihood ratio: women 0.40; men 0.30 Additional outcomes: – |
|
Study: Lauderdale et al. 70 Year: 1999 Time period: June 1997 to November 1997 (6 months) Country: USA |
Enrolled: 68 Analysed: 65 Gender: male 0 (0%); female 68 (100%) Age (mean, SD): not specified (but likely university students) Baseline characteristics (e.g. symptoms etc): 87% asymptomatic (‘had no STD related symptoms’) Venue: Local OB-GYN outpatient clinics at the University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL Setting (prevalence): ‘low to moderate’ prevalence of between 3.0% and 6.5% |
POCT used: Clearview enzyme immunoassay by Wampole (now made by Inverness Medical) Specimen type: endocervical NAAT reference standard: TMA using AMP CT assay by Gen-Probe Specimen type: endocervical NAAT reference standard: LCR using LCx assay by Abbott Laboratories Specimen type: endocervical |
Unit of analysis: specimen Using either LCR or TMA as reference standard (results identical): Sensitivity (%): 5/10 (50) Specificity (%): 55/55 (100) Positive predictive value (%): 5/5 (100) Negative predictive value (%): 55/60 (91.7) Positive likelihood ratio: – Negative likelihood ratio: 0.50 Additional outcomes: – |
|
Study: Mahilum-Tapay et al. 50 Year: 2007 Time period: November 2005 to March 2006 (5 months) Country: England, UK |
Enrolled: 1458 Analysed: 1349 (using PCR as reference standard); 637 (using SDA as reference standard) Gender: male 0 (0%); female 1349 (100%) Age (mean, SD): ranged from 16 to 54 years: At site 1: 18.5 years (16.0–27.4 years) At site 2: 25.4 years (16.0–49.7 years) At site 3: 27.8 years (17.1–54.8 years) Baseline characteristics (e.g. symptoms, etc.): Of the 662 attending GUM clinic venues, 441/662 (66.6%) had symptoms. However, ‘most’ were asymptomatic at the Young People’s Sexual Health Centre venue Venue: One Sexual Health Centre for Young People (providing contraceptive advice etc) as ‘Site 1’ – 663; and two GUM clinics, as ‘Site 2’ and ‘Site 3’ – 686 Setting (prevalence): not specified |
POCT used: Chlamydia Rapid Test Specimen type: vaginal swabs (both self-collected and clinician-collected) NAAT reference standard: PCR using AMPLICOR CT/NG by Roche, and SDA (not further specified) Specimen type: FVU (for PCR samples) and endocervical swabs (for SDA samples) |
Unit of analysis: specimen Using clinician-collected vaginal swabs at sites 2 and 3 (with PCR as reference standard): Sensitivity (%): 42/54 (77.8) Specificity (%): 627/632 (99.2) Positive predictive value (%): 42/47 (89.4) Negative predictive value (%): 627/632 (98.1) Positive likelihood ratio: 98.31 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.22 Using self-collected vaginal swabs at sites 2 and 3 (with PCR as reference standard): Sensitivity (%): 44/54 (81.5) Specificity (%): 624/632 (98.7) Positive predictive value (%): 44/52 (84.6) Negative predictive value (%): 624/632 (98.4) Positive likelihood ratio: 64.37 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.19 Using self-collected vaginal swabs at site 1 (with PCR as reference standard): Sensitivity (%): 47/56 (83.9) Specificity (%): 600/607 (98.8) Positive predictive value (%): 47/54 (87.0) Negative predictive value (%): 600/609 (98.5) Positive likelihood ratio: 72.78 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.16 Using self-collected vaginal swabs (total for all sites as listed above), with PCR as reference standard: Sensitivity (%): 91/110 (82.7) Specificity (%): 1224/1239 (98.8) Positive predictive value (%): 91/106 (85.8) Negative predictive value (%): 1224/1243 (98.5) Positive likelihood ratio: 68.92 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.18 Using self-collected vaginal swabs at sites 2 and 3 (with SDA as reference standard): Sensitivity (%): 40/49 (81.6) Specificity (%): 578/588 (98.3) Positive predictive value (%): 40/50 (80.0) Negative predictive value (%): 578/587 (98.5) Positive likelihood ratio: 48.00 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.19 Additional outcomes: 1083/1349 (80.3%) of participants completed a questionnaire after testing 1072/1078 (99.4%) found instructions easy to understand 1039/1083 (95.9%) felt comfortable collecting their own vaginal swab specimens 435/1068 (40.7%) preferred self-collected vaginal swabs 401/1068 (37.5%) preferred giving a urine sample 232/1068 (21.7%) had no preference for type of sample they preferred (there was no significant difference between sites p = 0.069) 61/881 (6.9%) were willing to wait less than 30 minutes for their results 661/881 (75.0%) were willing to wait between 30 minutes and 2 hours for their results 96/881 (10.9%) were willing to wait more than 2 hours for their results 63/881 (7.2%) were willing to wait more than 1 day for their results |
|
Study: Michel et al. 74 Year: 2009 Time period: not specified Country: the Philippines |
Enrolled: 231 Analysed: 231 Gender: male 0 (0%), female 231 (100%) Age (mean, SD): not specified Baseline characteristics (e.g. symptoms, etc.): most of the Social Hygiene Clinic participants were commercial sex workers who attended the clinic for a weekly health check, whereas participants at the OB-GYN clinic were mostly pregnant women attending for antenatal care Venue: Social Hygiene Clinic 131/231 (56.7%), OB-GYN Clinic 100/231 (43.3%) Setting (prevalence): not specified |
POCT used: Handilab C test, also known as ‘SureScreen’ and ‘SELFCheck’ Specimen type: vaginal swab NAAT reference standard: PCR using AMPLICOR CT/NG by Roche Specimen type: vaginal swab |
Unit of analysis: specimen/patient For Social Hygiene Clinic setting: Sensitivity (%): 6/30 (20.0) Specificity (%): 89/101 (88.1) Positive predictive value (%): 6/18 (33.3) Negative predictive value (%): 89/113 (78.8%) Positive likelihood ratio: 1.68 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.91 For OB-GYN setting: Sensitivity (%): 1/8 (12.5) Specificity (%): 86/92 (93.5) Positive predictive value (%): 1/7 (14.3) Negative predictive value (%): 86/93 (92.5) Positive likelihood ratio: 1.92 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.94 For both settings combined: Sensitivity (%): 7/38 (18.4) Specificity (%): 175/193 (90.7) Positive predictive value (%): 7/25 (28.0) Negative predictive value (%): 175/206 (85.0) Positive likelihood ratio: 1.98 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.90 Additional outcomes: not specified |
|
Study: Nadala et al. 75 Year: 2009 Time Period: March to November 2007 Country: England, UK |
Enrolled: 1277 Analysed: 1211 Gender: male 1211 (100%), female 0 (0%) Age (mean, SD): Baseline characteristics (e.g. symptoms, etc.): At site 1 (Sexual Health Centre), most participants were attending for contraception/advice and were asymptomatic. At site 2 (GUM Clinic) 62% (467/469) were symptomatic. 21% (155/741) had urethral discharge, 23% (169/744) had dysuria. 2.6% (20/757) of participants attended with contact slips Venue: site 1 was a Sexual Health Centre. Site 2 was a GUM clinic. There were significant differences in the negative and positive predictive values of the Chlamydia Rapid Test between the two sites (p = 0.0089 and p = 0.0283 respectively) Setting (prevalence): not specified |
POCT used: Chlamydia Rapid Test Specimen type: first void urine using the ‘FirstBurst’ collection method NAAT reference standard: PCR using AMPLICOR CT/NG by Roche Specimen type: first void urine collected using routine cup collection |
Unit of analysis: specimen/patient For site 1 (Sexual Health Centre): Sensitivity (%): 18/20 (90.0) Specificity (%): 426/434 (98.2) Positive predictive value (%): 18/26 (69.2) Negative predictive value (%): 426/428 (99.5) Positive likelihood ratio: 50.0 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.10 For site 2 (GUM clinic): Sensitivity (%): 72/90 (80.0) Specificity (%): 658/667 (98.7) Positive predictive value (%): 72/81 (88.9) Negative predictive value (%): 658/676 (97.3) Positive likelihood ratio: 61.5 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.20 For both settings combined: Sensitivity (%): 90/110 (81.8) Specificity (%): 1084/1101 (98.5) Positive predictive value (%): 90/107 (84.1) Negative predictive value (%): 1084/1104 (98.2) Positive likelihood ratio: 54.5 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.19 Additional outcomes: ‘A concordance of 100% was found between the expected results and the results generated from randomised and masked panels by two independent operators performing the Chlamydia Rapid Test’ Of the 20 attending with contact slips, 30% (6/20) tested positive using PCR and 25% (5/20) tested positive using the Chlamydia Rapid Test. At site 1, 18/20 (90%) of PCR positive participants were without genitourinary symptoms at time of recruitment to the study. At site 2, 31.1% (28/90) were without symptoms. The CRT picked up 16/18 (88.9%) of these participants at site 1, and 20/28 (71.4%) at site 2, giving the CRT a sensitivity of 78.3% for asymptomatic men, and 84.4% for symptomatic men 812 participants were offered a questionnaire, of which 767 (94.5%) responded (though not to all questions). Of them: 97.6% (741/759) of respondents found the instructions easy to understand 97.4% (735/755) found collection of their urine easy 88.8% (619/697) of respondents preferred to give a urine sample 7.0% (49/697) would have preferred to give a urethral swaba 4.2% (29/697) were willing to provide either sample 76.4% (525/687) of respondents preferred the FirstBurst device 18.0% (124/687) preferred the urine cup 5.5% (38/687) were willing to use either device 95.6% (653/683) of respondents indicated that they were willing to wait 1 hour or more 4.4% (30/683) indicated that they would not wait more than 1 hour |
|
Study: Rani et al. 67 Year: 2002 Time period: not specified Country: England, UK |
Enrolled: 200 Analysed: 199 Gender: male 0 (0%); female 200 (100%) Age (mean, SD): not specified Baseline characteristics (e.g. symptoms, etc.): not specified Venue: one GUM clinic and the Gynaecology Department of hospital Setting (prevalence): GUM clinic considered ‘high prevalence’ and Gynaecology Department considered ‘low prevalence’ but no further detail |
POCT used: QuickVue Chlamydia (Quidel) Specimen type: endocervical NAAT reference standard: PCR using the COBAS Amplicor by Roche Specimen type: endocervical |
Unit of analysis: specimen/patient For GUM Clinic setting: Sensitivity (%): 11/17 (62.5) Specificity (%): 83/83 (100) Positive predictive value (%): 11/11 (100) Negative predictive value (%): 83/89 (93.3) Positive likelihood ratio: – Negative likelihood ratio: 0.38 For Gynaecology Department setting: Sensitivity (%): 1/4 (25.0) Specificity (%): 96/96 (100) Positive predictive value (%): 1/1 (100) Negative predictive value (%): 96/99 (97.0) Positive likelihood ratio: – Negative likelihood ratio: 0.75 Additional outcomes: – |
|
Study: Saison et al. 65 Year: 2007 Time period: August 2002 to March 2006 (six 2- to 3-week periods within these dates for data collection at the Social Hygiene Clinic; 6 months within these dates for data collection at the OB-GYN clinic) Country: the Philippines |
Enrolled: 2322 Analysed: 822 (using Clearview); 1129 (using the Chlamydia Rapid Test) Gender: male 0 (0%); female 2322 (100%) Age (mean, SD): given for 782 attendees at the Social Hygiene Clinic, where the median (range) was 25.8 years (18–56 years) Baseline characteristics (e.g. symptoms, etc.): 219/782 (28%) had symptoms Venue: a Social Hygiene Clinic for Female Sex Workers and an OB-GYN Clinic at a Medical Centre Setting (prevalence): for female sex workers, the prevalence range was estimated to be between 27% and 36%. The OB-GYN setting was considered ‘low-risk’ |
POCT used: Chlamydia Rapid Test Specimen type: vaginal swabs (×2) POCT used: Clearview Chlamydia MF by Inverness Medical Specimen type: vaginal (×2) and endocervical (×1) NAAT reference standard: PCR using the AMPLICOR CT/NG by Roche Specimen type: vaginal (×4) and endocervical (×1) |
Unit of analysis: specimen Using Clearview at SHC setting, with endocervical swabs: Sensitivity (%): 85/159 (53.5) Specificity (%): 657/663 (99.1) Positive predictive value (%): 85/91 (93.4) Negative predictive value (%): 657/731 (89.9) Positive likelihood ratio: 59.07 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.47 Using Clearview at the SHC setting with clinician-collected vaginal swabs: Sensitivity (%): 10/25 (40.0) Specificity (%): 109/112 (97.3) Positive predictive value (%): 10/13 (76.9) Negative predictive value (%): 109/124 (87.9) Positive likelihood ratio: 14.93 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.62 Using Clearview at the SHC setting with self-collected vaginal swabs: Sensitivity (%): 9/36 (25.0) Specificity (%): 150/160 (93.8) Positive predictive value (%): 9/19 (47.4) Negative predictive value (%): 150/177 (84.7) Positive likelihood ratio: 4.00 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.80 Using the Chlamydia Rapid Test at the SHC setting with clinician-collected vaginal swabs: Sensitivity (%): 66/93 (71.0) Specificity (%): 196/198 (99.0) Positive predictive value (%): 66/68 (97.1) Negative predictive value (%): 196/223 (87.9) Positive likelihood ratio: 70.26 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.29 Using the Chlamydia Rapid Test at the OB-GYN clinic with clinician-collected vaginal swabs: Sensitivity (%): 46/53 (86.8) Specificity (%): 782/785 (99.6) Positive predictive value (%): 46/49 (93.9) Negative predictive value (%): 782/789 (99.1) Positive likelihood ratio: 227.11 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.13 Additional outcomes: – |
|
Study: Shaarawy64 Year: 1998 Time period: September 1996 to December 1996 (4 months) Country: Egypt |
Enrolled: 50 Analysed: 50 Gender: male 0 (0%); female 50 (100%) Age (mean, SD): ranged from 25 to 35 years old Baseline characteristics (e.g. symptoms, etc.): all participants had pelvic inflammatory disease Venue: the OB-GYN department of a hospital Setting (prevalence): not specified |
POCT used: Clearview Specimen type: cervical NAAT reference standard: PCR using AMPLICOR by Roche Specimen type: cervical |
Unit of analysis: specimen/patient Sensitivity (%): 15/18 (83.3) Specificity (%): 22/32 (68.8) Positive predictive value (%): 15/25 (60.0) Negative predictive value (%): 22/25 (88.0) Positive likelihood ratio: 2.67 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.24 Additional outcomes: – |
|
Study: Wisniewski et al. 72 Year: 2008 Time period: September 2005 to December 2006 (4 months) Country: England, UK |
Enrolled: 534 Analysed: 534 Gender: male 534 (100%); female 0 (0%) Age (mean, SD): greater than 16 years old (not further specified) Baseline characteristics (e.g. symptoms, etc.): not specified Venue: Young People’s Sexual Health Centre Setting (prevalence): not specified |
POCT used: Chlamydia Rapid Test Specimen type: FVU (using routine cup collection and the ‘FirstBurst’ device) NAAT reference standard: PCR using the AMPLICOR CT/NG by Roche Specimen type: FVU |
Unit of analysis: specimen Using the ‘FirstBurst’ device: Sensitivity (%): 28/34 (82.4) Specificity (%): 494/500 (98.8) Positive predictive value (%): 28/34 (82.4) Negative predictive value (%): 494/500 (98.8) Positive likelihood ratio: 68.63 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.18 Using routine urine cup collection: Sensitivity (%): 16/34 (47.1) Specificity (%): 494/500 (98.8) Positive predictive value (%): 16/22 (72.7) Negative predictive value (%): 494/512 (96.5) Positive likelihood ratio: 39.22 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.54 Additional outcomes: – |
|
Study: Yin et al. 66 Year: 2006 Time period: not specified Country: China |
Enrolled: 1500 Analysed: 1497 Gender: male 0 (0%); female 1500 (100%) Age (mean, SD): 28 years (median) Baseline characteristics (e.g. symptoms, etc.): 920/1497 (61.5%) had symptoms Venue: sexually transmitted disease clinics, female re-education centres and sex entertainment venues in six cities in China Setting (prevalence): not specified |
POCT used: Clearview Chlamydia MF by Unipath (now made by Inverness Medical) Specimen type: vaginal and cervical specimens NAAT reference standard: PCR using AMPLICOR by Roche Specimen type: vaginal and cervical specimens |
Unit of analysis: specimen Using cervical specimens: Sensitivity (%): 98/197 (49.7) Specificity (%): 1273/1300 (97.9) Positive predictive value (%): 98/125 (78.4) Negative predictive value (%): 1273/1300 (92.8) Positive likelihood ratio: 23.95 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.51 Using vaginal specimens: Sensitivity (%): 66/201 (32.8) Specificity (%): 1285/1296 (99.2) Positive predictive value (%): 66/77 (85.7) Negative predictive value (%): 1285/1296 (90.5) Positive likelihood ratio: 38.69 Negative likelihood ratio: 0.68 Additional outcomes: ‘The vast majority of the patients (99.1%) were willing to wait up to two hours for the result, of whom 83.1% preferred waiting for 30 min’ 14 staff members were surveyed, of which: 13/14 (92.9%) recognised that the kit provided very clear manufacturers’ instructions 12/14 (85.7%) felt the test had a 10-minute ‘hands on’ time 12/14 (85.7%) felt the test was very easy to use 14/14 (100%) thought it was quick (< 20 minutes) to display the results 13/14 (92.9%) thought the training of operational procedures took ≤ 30 minutes |
Appendix 7 Quality assessment results for the individual full text, published chlamydia diagnostic studies
| Study ID | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Q6 | Q7 | Q8 | Q9 | Q10 | Q11 | Q12 | Q13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chernesky et al.,69 1999 | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | – | – |
| Hopwood et al.,68 1991 | – | ? | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | – | – |
| Kluytmans et al.,71 1993 | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | – | – |
| Lauderdale et al.,70 1999 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | – | – |
| Mahilum-Tapay et al.,50 2007 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | + |
| Michel et al.,74 2009 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | – | – |
| Nadala et al.,75 2009 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | + |
| Rani et al.,67 2002 | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | – | – |
| Saison et al.,65 2007 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | – | – |
| Shaarawy,64 1998 | – | + | ? | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | ? | + | – | – |
| Wisniewski et al.,72 2008 | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | – | – |
| Yin et al.,66 2006 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | + | + | – |
Appendix 8 Test accuracy results for the individual studies
| Study | POCT | Type of specimen | Method of collection | NAAT method | Specimens analysed | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Positive LR | Negative LR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chernesky et al.,69 1999 | Clearview | FVU | Self-collected | LCR | 128 | 67.7% | 95.5% | 93.3% | 75.9% | 14.90 | 0.34 |
| Chernesky et al.,69 1999 | SureCell | FVU | Self-collected | LCR | 128 | 62.9% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 74.2% | – | 0.37 |
| Hopwood et al.,68 2001 | Clearview | Endocervical | Clinician-collected | LCR | 395 | 75.0% | 99.2% | 88.9% | 97.8% | 90.75 | 0.25 |
| Kegg and Roberts,73 2006 | Chlamydia Wand | Vaginal | Self-collected | SDA | 100 | 36.4% | 79.8% | 18.2% | 91.0% | 1.80 | 0.80 |
| Kluytmans et al.,71 1993 | Clearview | Cervical | Clinician-collected | PCR | 716 | 72.1% | 99.1% | 83.8% | 98.2% | 80.86 | 0.28 |
| Kluytmans et al.,71 1993 | Clearview | Urethral | Clinician-collected | PCR | 283 | 59.1% | 86.2% | 43.3% | 92.4% | 4.28 | 0.47 |
| Kluytmans et al.,71 1993 | Magic Lite | Cervical | Clinician-collected | PCR | 724 | 60.5% | 99.9% | 96.3% | 97.6% | 411.77 | 0.40 |
| Kluytmans et al.,71 1993 | Magic Lite | Urethral | Clinician-collected | PCR | 283 | 70.5% | 100.0% | 96.9% | 95.2% | – | 0.30 |
| Lauderdale et al.,70 1999 | Clearview | Endocervical | Clinician-collected | LCR | 65 | 50.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 91.7% | – | 0.50 |
| Lauderdale et al.,70 1999 | Clearview | Endocervical | Clinician-collected | TMA | 65 | 50.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 91.7% | – | 0.50 |
| Mahilum-Tapay et al.,50 2007 | Chlamydia Rapid Test | Vaginal | Clinician-collected | PCR | 686 | 77.8% | 99.2% | 89.4% | 98.1% | 98.31 | 0.22 |
| Mahilum-Tapay et al.,50 2007 | Chlamydia Rapid Test | Vaginal | Self-collected | PCR | 686 | 81.5% | 98.7% | 84.6% | 98.4% | 64.37 | 0.19 |
| Mahilum-Tapay et al.,50 2007 | Chlamydia Rapid Test | Vaginal | Self-collected | PCR | 663 | 83.9% | 98.8% | 87.0% | 98.5% | 72.78 | 0.16 |
| Mahilum-Tapay et al.,50 2007 | Chlamydia Rapid Test | Vaginal | Self-collected | SDA | 637 | 81.6% | 98.3% | 80.0% | 98.5% | 48.00 | 0.19 |
| Michel et al.,74 2009 | Chlamydia Wand | Vaginal | Clinician-collected | PCR | 131 | 20.0% | 88.1% | 33.3% | 78.8% | 1.68 | 0.91 |
| Michel et al.,74 2009 | Chlamydia Wand | Vaginal | Clinician-collected | PCR | 100 | 12.5% | 93.5% | 14.3% | 92.5% | 1.92 | 0.94 |
| Nadala et al.,75 2009 | Chlamydia Rapid Test | FVU | Self-collected | PCR | 454 | 90.0% | 98.2% | 69.2% | 99.5% | 48.83 | 0.10 |
| Nadala et al.,75 2009 | Chlamydia Rapid Test | FVU | Self-collected | PCR | 757 | 80.0% | 98.7% | 88.9% | 97.3% | 59.29 | 0.20 |
| Rani et al.,67 2002 | QuickVue | Endocervical | Clinician-collected | PCR | 99 | 62.5% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 93.3% | – | 0.38 |
| Rani et al.,67 2002 | QuickVue | Endocervical | Clinician-collected | PCR | 100 | 25.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 97.0% | – | 0.75 |
| Saison et al.,65 2007 | Clearview | Endocervical | Clinician-collected | PCR | 822 | 53.5% | 99.1% | 93.4% | 89.9% | 59.07 | 0.47 |
| Saison et al.,65 2007 | Clearview | Vaginal | Clinician-collected | PCR | 137 | 40.0% | 97.3% | 76.9% | 87.9% | 14.93 | 0.62 |
| Saison et al.,65 2007 | Clearview | Vaginal | Self-collected | PCR | 196 | 25.0% | 93.8% | 47.4% | 84.7% | 4.00 | 0.80 |
| Saison et al.,65 2007 | Chlamydia Rapid Test | Vaginal | Clinician-collected | PCR | 291 | 71.0% | 99.0% | 97.1% | 87.9% | 70.26 | 0.29 |
| Saison et al.,65 2007 | Chlamydia Rapid Test | Vaginal | Clinician-collected | PCR | 838 | 86.8% | 99.6% | 93.9% | 99.1% | 227.11 | 0.13 |
| Shaarawy,64 1998 | Clearview | Endocervical | Clinician-collected | PCR | 50 | 83.3% | 68.8% | 60.0% | 88.0% | 2.67 | 0.24 |
| Wisniewski et al.,72 2008 | Chlamydia Rapid Test | FVU | FirstBurst | PCR | 534 | 82.4% | 98.8% | 82.4% | 98.8% | 68.63 | 0.18 |
| Wisniewski et al.,72 2008 | Chlamydia Rapid Test | FVU | Routine Cup | PCR | 534 | 47.1% | 98.8% | 72.7% | 96.5% | 39.22 | 0.54 |
| Yin et al.,66 2006 | Clearview | Endocervical | Clinician-collected | PCR | 1497 | 49.7% | 97.9% | 78.4% | 92.8% | 23.95 | 0.51 |
| Yin et al.,66 2006 | Clearview | Vaginal | Clinician-collected | PCR | 1497 | 32.8% | 99.2% | 85.7% | 90.5% | 38.69 | 0.68 |
List of abbreviations
- CI
- confidence interval
- CRT
- Chlamydia Rapid Test
- DCE
- discrete choice experiment
- DFA
- direct fluorescent antibody
- DOR
- diagnostic odds ratio
- FVU
- first void urine
- GATE
- Generic Appraisal Tool for Epidemiology
- GUM
- genito-urinary medicine
- HIV
- human immunodeficiency virus
- HSROC
- hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- LCR
- ligase chain reaction
- NAAT
- nucleic acid amplification test
- NCSP
- National Chlamydia Screening Programme
- PCR
- polymerase chain reaction
- PID
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- POCT
- point-of-care test
- QUADAS
- Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- RR
- relative risk
- SDA
- strand displacement amplification
- SIGN
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network
- SROC
- summary receiver operating characteristic
- STI
- sexually transmitted infection
- TMA
- transcription-mediated amplification
- WMD
- weighted mean difference
- WTP
- willingness to pay
All abbreviations that have been used in this report are listed here unless the abbreviation is well known (e.g. NHS), or it has been used only once, or it is a non-standard abbreviation used only in figures/tables/appendices, in which case the abbreviation is defined in the figure legend or in the notes at the end of the table.
NoteSome of the point-of-care tests referenced in this report are now obsolete and it has not been possible to verify their trademark. The trademark symbols are used at first mention only for current tests for which they can be verified.
Notes
Health Technology Assessment reports published to date
-
Home parenteral nutrition: a systematic review.
By Richards DM, Deeks JJ, Sheldon TA, Shaffer JL.
-
Diagnosis, management and screening of early localised prostate cancer.
A review by Selley S, Donovan J, Faulkner A, Coast J, Gillatt D.
-
The diagnosis, management, treatment and costs of prostate cancer in England and Wales.
A review by Chamberlain J, Melia J, Moss S, Brown J.
-
Screening for fragile X syndrome.
A review by Murray J, Cuckle H, Taylor G, Hewison J.
-
A review of near patient testing in primary care.
By Hobbs FDR, Delaney BC, Fitzmaurice DA, Wilson S, Hyde CJ, Thorpe GH, et al.
-
Systematic review of outpatient services for chronic pain control.
By McQuay HJ, Moore RA, Eccleston C, Morley S, de C Williams AC.
-
Neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism: cost, yield and outcome.
A review by Pollitt RJ, Green A, McCabe CJ, Booth A, Cooper NJ, Leonard JV, et al.
-
Preschool vision screening.
A review by Snowdon SK, Stewart-Brown SL.
-
Implications of socio-cultural contexts for the ethics of clinical trials.
A review by Ashcroft RE, Chadwick DW, Clark SRL, Edwards RHT, Frith L, Hutton JL.
-
A critical review of the role of neonatal hearing screening in the detection of congenital hearing impairment.
By Davis A, Bamford J, Wilson I, Ramkalawan T, Forshaw M, Wright S.
-
Newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism: a systematic review.
By Seymour CA, Thomason MJ, Chalmers RA, Addison GM, Bain MD, Cockburn F, et al.
-
Routine preoperative testing: a systematic review of the evidence.
By Munro J, Booth A, Nicholl J.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness of laxatives in the elderly.
By Petticrew M, Watt I, Sheldon T.
-
When and how to assess fast-changing technologies: a comparative study of medical applications of four generic technologies.
A review by Mowatt G, Bower DJ, Brebner JA, Cairns JA, Grant AM, McKee L.
-
Antenatal screening for Down’s syndrome.
A review by Wald NJ, Kennard A, Hackshaw A, McGuire A.
-
Screening for ovarian cancer: a systematic review.
By Bell R, Petticrew M, Luengo S, Sheldon TA.
-
Consensus development methods, and their use in clinical guideline development.
A review by Murphy MK, Black NA, Lamping DL, McKee CM, Sanderson CFB, Askham J, et al.
-
A cost–utility analysis of interferon beta for multiple sclerosis.
By Parkin D, McNamee P, Jacoby A, Miller P, Thomas S, Bates D.
-
Effectiveness and efficiency of methods of dialysis therapy for end-stage renal disease: systematic reviews.
By MacLeod A, Grant A, Donaldson C, Khan I, Campbell M, Daly C, et al.
-
Effectiveness of hip prostheses in primary total hip replacement: a critical review of evidence and an economic model.
By Faulkner A, Kennedy LG, Baxter K, Donovan J, Wilkinson M, Bevan G.
-
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in colorectal surgery: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials.
By Song F, Glenny AM.
-
Bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for malignancy.
A review by Johnson PWM, Simnett SJ, Sweetenham JW, Morgan GJ, Stewart LA.
-
Screening for speech and language delay: a systematic review of the literature.
By Law J, Boyle J, Harris F, Harkness A, Nye C.
-
Resource allocation for chronic stable angina: a systematic review of effectiveness, costs and cost-effectiveness of alternative interventions.
By Sculpher MJ, Petticrew M, Kelland JL, Elliott RA, Holdright DR, Buxton MJ.
-
Detection, adherence and control of hypertension for the prevention of stroke: a systematic review.
By Ebrahim S.
-
Postoperative analgesia and vomiting, with special reference to day-case surgery: a systematic review.
By McQuay HJ, Moore RA.
-
Choosing between randomised and nonrandomised studies: a systematic review.
By Britton A, McKee M, Black N, McPherson K, Sanderson C, Bain C.
-
Evaluating patient-based outcome measures for use in clinical trials.
A review by Fitzpatrick R, Davey C, Buxton MJ, Jones DR.
-
Ethical issues in the design and conduct of randomised controlled trials.
A review by Edwards SJL, Lilford RJ, Braunholtz DA, Jackson JC, Hewison J, Thornton J.
-
Qualitative research methods in health technology assessment: a review of the literature.
By Murphy E, Dingwall R, Greatbatch D, Parker S, Watson P.
-
The costs and benefits of paramedic skills in pre-hospital trauma care.
By Nicholl J, Hughes S, Dixon S, Turner J, Yates D.
-
Systematic review of endoscopic ultrasound in gastro-oesophageal cancer.
By Harris KM, Kelly S, Berry E, Hutton J, Roderick P, Cullingworth J, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of trials and other studies.
By Sutton AJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR, Sheldon TA, Song F.
-
Primary total hip replacement surgery: a systematic review of outcomes and modelling of cost-effectiveness associated with different prostheses.
A review by Fitzpatrick R, Shortall E, Sculpher M, Murray D, Morris R, Lodge M, et al.
-
Informed decision making: an annotated bibliography and systematic review.
By Bekker H, Thornton JG, Airey CM, Connelly JB, Hewison J, Robinson MB, et al.
-
Handling uncertainty when performing economic evaluation of healthcare interventions.
A review by Briggs AH, Gray AM.
-
The role of expectancies in the placebo effect and their use in the delivery of health care: a systematic review.
By Crow R, Gage H, Hampson S, Hart J, Kimber A, Thomas H.
-
A randomised controlled trial of different approaches to universal antenatal HIV testing: uptake and acceptability. Annex: Antenatal HIV testing – assessment of a routine voluntary approach.
By Simpson WM, Johnstone FD, Boyd FM, Goldberg DJ, Hart GJ, Gormley SM, et al.
-
Methods for evaluating area-wide and organisation-based interventions in health and health care: a systematic review.
By Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ.
-
Assessing the costs of healthcare technologies in clinical trials.
A review by Johnston K, Buxton MJ, Jones DR, Fitzpatrick R.
-
Cooperatives and their primary care emergency centres: organisation and impact.
By Hallam L, Henthorne K.
-
Screening for cystic fibrosis.
A review by Murray J, Cuckle H, Taylor G, Littlewood J, Hewison J.
-
A review of the use of health status measures in economic evaluation.
By Brazier J, Deverill M, Green C, Harper R, Booth A.
-
Methods for the analysis of quality-of-life and survival data in health technology assessment.
A review by Billingham LJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR.
-
Antenatal and neonatal haemoglobinopathy screening in the UK: review and economic analysis.
By Zeuner D, Ades AE, Karnon J, Brown J, Dezateux C, Anionwu EN.
-
Assessing the quality of reports of randomised trials: implications for the conduct of meta-analyses.
A review by Moher D, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Tugwell P, Moher M, Jones A, et al.
-
‘Early warning systems’ for identifying new healthcare technologies.
By Robert G, Stevens A, Gabbay J.
-
A systematic review of the role of human papillomavirus testing within a cervical screening programme.
By Cuzick J, Sasieni P, Davies P, Adams J, Normand C, Frater A, et al.
-
Near patient testing in diabetes clinics: appraising the costs and outcomes.
By Grieve R, Beech R, Vincent J, Mazurkiewicz J.
-
Positron emission tomography: establishing priorities for health technology assessment.
A review by Robert G, Milne R.
-
The debridement of chronic wounds: a systematic review.
By Bradley M, Cullum N, Sheldon T.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (2) Dressings and topical agents used in the healing of chronic wounds.
By Bradley M, Cullum N, Nelson EA, Petticrew M, Sheldon T, Torgerson D.
-
A systematic literature review of spiral and electron beam computed tomography: with particular reference to clinical applications in hepatic lesions, pulmonary embolus and coronary artery disease.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Hutton J, Harris KM, Roderick P, Boyce JC, et al.
-
What role for statins? A review and economic model.
By Ebrahim S, Davey Smith G, McCabe C, Payne N, Pickin M, Sheldon TA, et al.
-
Factors that limit the quality, number and progress of randomised controlled trials.
A review by Prescott RJ, Counsell CE, Gillespie WJ, Grant AM, Russell IT, Kiauka S, et al.
-
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in total hip replacement: a systematic review.
By Glenny AM, Song F.
-
Health promoting schools and health promotion in schools: two systematic reviews.
By Lister-Sharp D, Chapman S, Stewart-Brown S, Sowden A.
-
Economic evaluation of a primary care-based education programme for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee.
A review by Lord J, Victor C, Littlejohns P, Ross FM, Axford JS.
-
The estimation of marginal time preference in a UK-wide sample (TEMPUS) project.
A review by Cairns JA, van der Pol MM.
-
Geriatric rehabilitation following fractures in older people: a systematic review.
By Cameron I, Crotty M, Currie C, Finnegan T, Gillespie L, Gillespie W, et al.
-
Screening for sickle cell disease and thalassaemia: a systematic review with supplementary research.
By Davies SC, Cronin E, Gill M, Greengross P, Hickman M, Normand C.
-
Community provision of hearing aids and related audiology services.
A review by Reeves DJ, Alborz A, Hickson FS, Bamford JM.
-
False-negative results in screening programmes: systematic review of impact and implications.
By Petticrew MP, Sowden AJ, Lister-Sharp D, Wright K.
-
Costs and benefits of community postnatal support workers: a randomised controlled trial.
By Morrell CJ, Spiby H, Stewart P, Walters S, Morgan A.
-
Implantable contraceptives (subdermal implants and hormonally impregnated intrauterine systems) versus other forms of reversible contraceptives: two systematic reviews to assess relative effectiveness, acceptability, tolerability and cost-effectiveness.
By French RS, Cowan FM, Mansour DJA, Morris S, Procter T, Hughes D, et al.
-
An introduction to statistical methods for health technology assessment.
A review by White SJ, Ashby D, Brown PJ.
-
Disease-modifying drugs for multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By Clegg A, Bryant J, Milne R.
-
Publication and related biases.
A review by Song F, Eastwood AJ, Gilbody S, Duley L, Sutton AJ.
-
Cost and outcome implications of the organisation of vascular services.
By Michaels J, Brazier J, Palfreyman S, Shackley P, Slack R.
-
Monitoring blood glucose control in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review.
By Coster S, Gulliford MC, Seed PT, Powrie JK, Swaminathan R.
-
The effectiveness of domiciliary health visiting: a systematic review of international studies and a selective review of the British literature.
By Elkan R, Kendrick D, Hewitt M, Robinson JJA, Tolley K, Blair M, et al.
-
The determinants of screening uptake and interventions for increasing uptake: a systematic review.
By Jepson R, Clegg A, Forbes C, Lewis R, Sowden A, Kleijnen J.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of prophylactic removal of wisdom teeth.
A rapid review by Song F, O’Meara S, Wilson P, Golder S, Kleijnen J.
-
Ultrasound screening in pregnancy: a systematic review of the clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and women’s views.
By Bricker L, Garcia J, Henderson J, Mugford M, Neilson J, Roberts T, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the taxanes used in the treatment of advanced breast and ovarian cancer.
By Lister-Sharp D, McDonagh MS, Khan KS, Kleijnen J.
-
Liquid-based cytology in cervical screening: a rapid and systematic review.
By Payne N, Chilcott J, McGoogan E.
-
Randomised controlled trial of non-directive counselling, cognitive–behaviour therapy and usual general practitioner care in the management of depression as well as mixed anxiety and depression in primary care.
By King M, Sibbald B, Ward E, Bower P, Lloyd M, Gabbay M, et al.
-
Routine referral for radiography of patients presenting with low back pain: is patients’ outcome influenced by GPs’ referral for plain radiography?
By Kerry S, Hilton S, Patel S, Dundas D, Rink E, Lord J.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (3) antimicrobial agents for chronic wounds; (4) diabetic foot ulceration.
By O’Meara S, Cullum N, Majid M, Sheldon T.
-
Using routine data to complement and enhance the results of randomised controlled trials.
By Lewsey JD, Leyland AH, Murray GD, Boddy FA.
-
Coronary artery stents in the treatment of ischaemic heart disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Meads C, Cummins C, Jolly K, Stevens A, Burls A, Hyde C.
-
Outcome measures for adult critical care: a systematic review.
By Hayes JA, Black NA, Jenkinson C, Young JD, Rowan KM, Daly K, et al.
-
A systematic review to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions to promote the initiation of breastfeeding.
By Fairbank L, O’Meara S, Renfrew MJ, Woolridge M, Sowden AJ, Lister-Sharp D.
-
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators: arrhythmias. A rapid and systematic review.
By Parkes J, Bryant J, Milne R.
-
Treatments for fatigue in multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By Brañas P, Jordan R, Fry-Smith A, Burls A, Hyde C.
-
Early asthma prophylaxis, natural history, skeletal development and economy (EASE): a pilot randomised controlled trial.
By Baxter-Jones ADG, Helms PJ, Russell G, Grant A, Ross S, Cairns JA, et al.
-
Screening for hypercholesterolaemia versus case finding for familial hypercholesterolaemia: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Marks D, Wonderling D, Thorogood M, Lambert H, Humphries SE, Neil HAW.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists in the medical management of unstable angina.
By McDonagh MS, Bachmann LM, Golder S, Kleijnen J, ter Riet G.
-
A randomised controlled trial of prehospital intravenous fluid replacement therapy in serious trauma.
By Turner J, Nicholl J, Webber L, Cox H, Dixon S, Yates D.
-
Intrathecal pumps for giving opioids in chronic pain: a systematic review.
By Williams JE, Louw G, Towlerton G.
-
Combination therapy (interferon alfa and ribavirin) in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a rapid and systematic review.
By Shepherd J, Waugh N, Hewitson P.
-
A systematic review of comparisons of effect sizes derived from randomised and non-randomised studies.
By MacLehose RR, Reeves BC, Harvey IM, Sheldon TA, Russell IT, Black AMS.
-
Intravascular ultrasound-guided interventions in coronary artery disease: a systematic literature review, with decision-analytic modelling, of outcomes and cost-effectiveness.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Hutton J, Lindsay HSJ, Blaxill JM, Evans JA, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to evaluate the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of counselling patients with chronic depression.
By Simpson S, Corney R, Fitzgerald P, Beecham J.
-
Systematic review of treatments for atopic eczema.
By Hoare C, Li Wan Po A, Williams H.
-
Bayesian methods in health technology assessment: a review.
By Spiegelhalter DJ, Myles JP, Jones DR, Abrams KR.
-
The management of dyspepsia: a systematic review.
By Delaney B, Moayyedi P, Deeks J, Innes M, Soo S, Barton P, et al.
-
A systematic review of treatments for severe psoriasis.
By Griffiths CEM, Clark CM, Chalmers RJG, Li Wan Po A, Williams HC.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine for Alzheimer’s disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Clegg A, Bryant J, Nicholson T, McIntyre L, De Broe S, Gerard K, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of riluzole for motor neurone disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Stewart A, Sandercock J, Bryan S, Hyde C, Barton PM, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Equity and the economic evaluation of healthcare.
By Sassi F, Archard L, Le Grand J.
-
Quality-of-life measures in chronic diseases of childhood.
By Eiser C, Morse R.
-
Eliciting public preferences for healthcare: a systematic review of techniques.
By Ryan M, Scott DA, Reeves C, Bate A, van Teijlingen ER, Russell EM, et al.
-
General health status measures for people with cognitive impairment: learning disability and acquired brain injury.
By Riemsma RP, Forbes CA, Glanville JM, Eastwood AJ, Kleijnen J.
-
An assessment of screening strategies for fragile X syndrome in the UK.
By Pembrey ME, Barnicoat AJ, Carmichael B, Bobrow M, Turner G.
-
Issues in methodological research: perspectives from researchers and commissioners.
By Lilford RJ, Richardson A, Stevens A, Fitzpatrick R, Edwards S, Rock F, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (5) beds; (6) compression; (7) laser therapy, therapeutic ultrasound, electrotherapy and electromagnetic therapy.
By Cullum N, Nelson EA, Flemming K, Sheldon T.
-
Effects of educational and psychosocial interventions for adolescents with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review.
By Hampson SE, Skinner TC, Hart J, Storey L, Gage H, Foxcroft D, et al.
-
Effectiveness of autologous chondrocyte transplantation for hyaline cartilage defects in knees: a rapid and systematic review.
By Jobanputra P, Parry D, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
Statistical assessment of the learning curves of health technologies.
By Ramsay CR, Grant AM, Wallace SA, Garthwaite PH, Monk AF, Russell IT.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of temozolomide for the treatment of recurrent malignant glioma: a rapid and systematic review.
By Dinnes J, Cave C, Huang S, Major K, Milne R.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of debriding agents in treating surgical wounds healing by secondary intention.
By Lewis R, Whiting P, ter Riet G, O’Meara S, Glanville J.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.
By Burns T, Knapp M, Catty J, Healey A, Henderson J, Watt H, et al.
-
How to develop cost-conscious guidelines.
By Eccles M, Mason J.
-
The role of specialist nurses in multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By De Broe S, Christopher F, Waugh N.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of orlistat in the management of obesity.
By O’Meara S, Riemsma R, Shirran L, Mather L, ter Riet G.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pioglitazone for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a rapid and systematic review.
By Chilcott J, Wight J, Lloyd Jones M, Tappenden P.
-
Extended scope of nursing practice: a multicentre randomised controlled trial of appropriately trained nurses and preregistration house officers in preoperative assessment in elective general surgery.
By Kinley H, Czoski-Murray C, George S, McCabe C, Primrose J, Reilly C, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of the effectiveness of day care for people with severe mental disorders: (1) Acute day hospital versus admission; (2) Vocational rehabilitation; (3) Day hospital versus outpatient care.
By Marshall M, Crowther R, Almaraz- Serrano A, Creed F, Sledge W, Kluiter H, et al.
-
The measurement and monitoring of surgical adverse events.
By Bruce J, Russell EM, Mollison J, Krukowski ZH.
-
Action research: a systematic review and guidance for assessment.
By Waterman H, Tillen D, Dickson R, de Koning K.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of gemcitabine for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
By Ward S, Morris E, Bansback N, Calvert N, Crellin A, Forman D, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the evidence for the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer.
By Lloyd Jones M, Hummel S, Bansback N, Orr B, Seymour M.
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.
By Brocklebank D, Ram F, Wright J, Barry P, Cates C, Davies L, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging for investigation of the knee joint.
By Bryan S, Weatherburn G, Bungay H, Hatrick C, Salas C, Parry D, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.
By Forbes C, Shirran L, Bagnall A-M, Duffy S, ter Riet G.
-
Superseded by a report published in a later volume.
-
The role of radiography in primary care patients with low back pain of at least 6 weeks duration: a randomised (unblinded) controlled trial.
By Kendrick D, Fielding K, Bentley E, Miller P, Kerslake R, Pringle M.
-
Design and use of questionnaires: a review of best practice applicable to surveys of health service staff and patients.
By McColl E, Jacoby A, Thomas L, Soutter J, Bamford C, Steen N, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.
By Clegg A, Scott DA, Sidhu M, Hewitson P, Waugh N.
-
Subgroup analyses in randomised controlled trials: quantifying the risks of false-positives and false-negatives.
By Brookes ST, Whitley E, Peters TJ, Mulheran PA, Egger M, Davey Smith G.
-
Depot antipsychotic medication in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia: (1) Meta-review; (2) Patient and nurse attitudes.
By David AS, Adams C.
-
A systematic review of controlled trials of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of brief psychological treatments for depression.
By Churchill R, Hunot V, Corney R, Knapp M, McGuire H, Tylee A, et al.
-
Cost analysis of child health surveillance.
By Sanderson D, Wright D, Acton C, Duree D.
-
A study of the methods used to select review criteria for clinical audit.
By Hearnshaw H, Harker R, Cheater F, Baker R, Grimshaw G.
-
Fludarabine as second-line therapy for B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a technology assessment.
By Hyde C, Wake B, Bryan S, Barton P, Fry-Smith A, Davenport C, et al.
-
Rituximab as third-line treatment for refractory or recurrent Stage III or IV follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wake B, Hyde C, Bryan S, Barton P, Song F, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
A systematic review of discharge arrangements for older people.
By Parker SG, Peet SM, McPherson A, Cannaby AM, Baker R, Wilson A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of inhaler devices used in the routine management of chronic asthma in older children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Peters J, Stevenson M, Beverley C, Lim J, Smith S.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of sibutramine in the management of obesity: a technology assessment.
By O’Meara S, Riemsma R, Shirran L, Mather L, ter Riet G.
-
The cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance angiography for carotid artery stenosis and peripheral vascular disease: a systematic review.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Westwood ME, Davies LM, Gough MJ, Bamford JM, et al.
-
Promoting physical activity in South Asian Muslim women through ‘exercise on prescription’.
By Carroll B, Ali N, Azam N.
-
Zanamivir for the treatment of influenza in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burls A, Clark W, Stewart T, Preston C, Bryan S, Jefferson T, et al.
-
A review of the natural history and epidemiology of multiple sclerosis: implications for resource allocation and health economic models.
By Richards RG, Sampson FC, Beard SM, Tappenden P.
-
Screening for gestational diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Scott DA, Loveman E, McIntyre L, Waugh N.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of surgery for people with morbid obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clegg AJ, Colquitt J, Sidhu MK, Royle P, Loveman E, Walker A.
-
The clinical effectiveness of trastuzumab for breast cancer: a systematic review.
By Lewis R, Bagnall A-M, Forbes C, Shirran E, Duffy S, Kleijnen J, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of vinorelbine for breast cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Lewis R, Bagnall A-M, King S, Woolacott N, Forbes C, Shirran L, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty for treatment of hip disease.
By Vale L, Wyness L, McCormack K, McKenzie L, Brazzelli M, Stearns SC.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bupropion and nicotine replacement therapy for smoking cessation: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Woolacott NF, Jones L, Forbes CA, Mather LC, Sowden AJ, Song FJ, et al.
-
A systematic review of effectiveness and economic evaluation of new drug treatments for juvenile idiopathic arthritis: etanercept.
By Cummins C, Connock M, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of growth hormone in children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Cave C, Mihaylova B, Chase D, McIntyre L, Gerard K, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of growth hormone in adults in relation to impact on quality of life: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Loveman E, Chase D, Mihaylova B, Cave C, Gerard K, et al.
-
Clinical medication review by a pharmacist of patients on repeat prescriptions in general practice: a randomised controlled trial.
By Zermansky AG, Petty DR, Raynor DK, Lowe CJ, Freementle N, Vail A.
-
The effectiveness of infliximab and etanercept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Burls A.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of computerised cognitive behaviour therapy for depression and anxiety.
By Kaltenthaler E, Shackley P, Stevens K, Beverley C, Parry G, Chilcott J.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride for ovarian cancer.
By Forbes C, Wilby J, Richardson G, Sculpher M, Mather L, Riemsma R.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of interventions based on a stages-of-change approach to promote individual behaviour change.
By Riemsma RP, Pattenden J, Bridle C, Sowden AJ, Mather L, Watt IS, et al.
-
A systematic review update of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists.
By Robinson M, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Jones L, Riemsma R, Palmer S, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and barriers to implementation of thrombolytic and neuroprotective therapy for acute ischaemic stroke in the NHS.
By Sandercock P, Berge E, Dennis M, Forbes J, Hand P, Kwan J, et al.
-
A randomised controlled crossover trial of nurse practitioner versus doctor-led outpatient care in a bronchiectasis clinic.
By Caine N, Sharples LD, Hollingworth W, French J, Keogan M, Exley A, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost – consequences of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of sex offenders.
By Adi Y, Ashcroft D, Browne K, Beech A, Fry-Smith A, Hyde C.
-
Treatment of established osteoporosis: a systematic review and cost–utility analysis.
By Kanis JA, Brazier JE, Stevenson M, Calvert NW, Lloyd Jones M.
-
Which anaesthetic agents are cost-effective in day surgery? Literature review, national survey of practice and randomised controlled trial.
By Elliott RA Payne K, Moore JK, Davies LM, Harper NJN, St Leger AS, et al.
-
Screening for hepatitis C among injecting drug users and in genitourinary medicine clinics: systematic reviews of effectiveness, modelling study and national survey of current practice.
By Stein K, Dalziel K, Walker A, McIntyre L, Jenkins B, Horne J, et al.
-
The measurement of satisfaction with healthcare: implications for practice from a systematic review of the literature.
By Crow R, Gage H, Hampson S, Hart J, Kimber A, Storey L, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of imatinib in chronic myeloid leukaemia: a systematic review.
By Garside R, Round A, Dalziel K, Stein K, Royle R.
-
A comparative study of hypertonic saline, daily and alternate-day rhDNase in children with cystic fibrosis.
By Suri R, Wallis C, Bush A, Thompson S, Normand C, Flather M, et al.
-
A systematic review of the costs and effectiveness of different models of paediatric home care.
By Parker G, Bhakta P, Lovett CA, Paisley S, Olsen R, Turner D, et al.
-
How important are comprehensive literature searches and the assessment of trial quality in systematic reviews? Empirical study.
By Egger M, Jüni P, Bartlett C, Holenstein F, Sterne J.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and economic evaluation, of home versus hospital or satellite unit haemodialysis for people with end-stage renal failure.
By Mowatt G, Vale L, Perez J, Wyness L, Fraser C, MacLeod A, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of the effectiveness of infliximab for the treatment of Crohn’s disease.
By Clark W, Raftery J, Barton P, Song F, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
A review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine anti-D prophylaxis for pregnant women who are rhesus negative.
By Chilcott J, Lloyd Jones M, Wight J, Forman K, Wray J, Beverley C, et al.
-
Systematic review and evaluation of the use of tumour markers in paediatric oncology: Ewing’s sarcoma and neuroblastoma.
By Riley RD, Burchill SA, Abrams KR, Heney D, Lambert PC, Jones DR, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of screening for Helicobacter pylori to reduce mortality and morbidity from gastric cancer and peptic ulcer disease: a discrete-event simulation model.
By Roderick P, Davies R, Raftery J, Crabbe D, Pearce R, Bhandari P, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine dental checks: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Davenport C, Elley K, Salas C, Taylor-Weetman CL, Fry-Smith A, Bryan S, et al.
-
A multicentre randomised controlled trial assessing the costs and benefits of using structured information and analysis of women’s preferences in the management of menorrhagia.
By Kennedy ADM, Sculpher MJ, Coulter A, Dwyer N, Rees M, Horsley S, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost–utility of photodynamic therapy for wet age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Meads C, Salas C, Roberts T, Moore D, Fry-Smith A, Hyde C.
-
Evaluation of molecular tests for prenatal diagnosis of chromosome abnormalities.
By Grimshaw GM, Szczepura A, Hultén M, MacDonald F, Nevin NC, Sutton F, et al.
-
First and second trimester antenatal screening for Down’s syndrome: the results of the Serum, Urine and Ultrasound Screening Study (SURUSS).
By Wald NJ, Rodeck C, Hackshaw AK, Walters J, Chitty L, Mackinson AM.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of ultrasound locating devices for central venous access: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Calvert N, Hind D, McWilliams RG, Thomas SM, Beverley C, Davidson A.
-
A systematic review of atypical antipsychotics in schizophrenia.
By Bagnall A-M, Jones L, Lewis R, Ginnelly L, Glanville J, Torgerson D, et al.
-
Prostate Testing for Cancer and Treatment (ProtecT) feasibility study.
By Donovan J, Hamdy F, Neal D, Peters T, Oliver S, Brindle L, et al.
-
Early thrombolysis for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Boland A, Dundar Y, Bagust A, Haycox A, Hill R, Mujica Mota R, et al.
-
Screening for fragile X syndrome: a literature review and modelling.
By Song FJ, Barton P, Sleightholme V, Yao GL, Fry-Smith A.
-
Systematic review of endoscopic sinus surgery for nasal polyps.
By Dalziel K, Stein K, Round A, Garside R, Royle P.
-
Towards efficient guidelines: how to monitor guideline use in primary care.
By Hutchinson A, McIntosh A, Cox S, Gilbert C.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of acute hospital-based spinal cord injuries services: systematic review.
By Bagnall A-M, Jones L, Richardson G, Duffy S, Riemsma R.
-
Prioritisation of health technology assessment. The PATHS model: methods and case studies.
By Townsend J, Buxton M, Harper G.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of tension-free vaginal tape for treatment of urinary stress incontinence.
By Cody J, Wyness L, Wallace S, Glazener C, Kilonzo M, Stearns S, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of patient education models for diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Loveman E, Cave C, Green C, Royle P, Dunn N, Waugh N.
-
The role of modelling in prioritising and planning clinical trials.
By Chilcott J, Brennan A, Booth A, Karnon J, Tappenden P.
-
Cost–benefit evaluation of routine influenza immunisation in people 65–74 years of age.
By Allsup S, Gosney M, Haycox A, Regan M.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of pulsatile machine perfusion versus cold storage of kidneys for transplantation retrieved from heart-beating and non-heart-beating donors.
By Wight J, Chilcott J, Holmes M, Brewer N.
-
Can randomised trials rely on existing electronic data? A feasibility study to explore the value of routine data in health technology assessment.
By Williams JG, Cheung WY, Cohen DR, Hutchings HA, Longo MF, Russell IT.
-
Evaluating non-randomised intervention studies.
By Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, D’Amico R, Sowden AJ, Sakarovitch C, Song F, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to assess the impact of a package comprising a patient-orientated, evidence-based self- help guidebook and patient-centred consultations on disease management and satisfaction in inflammatory bowel disease.
By Kennedy A, Nelson E, Reeves D, Richardson G, Roberts C, Robinson A, et al.
-
The effectiveness of diagnostic tests for the assessment of shoulder pain due to soft tissue disorders: a systematic review.
By Dinnes J, Loveman E, McIntyre L, Waugh N.
-
The value of digital imaging in diabetic retinopathy.
By Sharp PF, Olson J, Strachan F, Hipwell J, Ludbrook A, O’Donnell M, et al.
-
Lowering blood pressure to prevent myocardial infarction and stroke: a new preventive strategy.
By Law M, Wald N, Morris J.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of capecitabine and tegafur with uracil for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ward S, Kaltenthaler E, Cowan J, Brewer N.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of new and emerging technologies for early localised prostate cancer: a systematic review.
By Hummel S, Paisley S, Morgan A, Currie E, Brewer N.
-
Literature searching for clinical and cost-effectiveness studies used in health technology assessment reports carried out for the National Institute for Clinical Excellence appraisal system.
By Royle P, Waugh N.
-
Systematic review and economic decision modelling for the prevention and treatment of influenza A and B.
By Turner D, Wailoo A, Nicholson K, Cooper N, Sutton A, Abrams K.
-
A randomised controlled trial to evaluate the clinical and cost-effectiveness of Hickman line insertions in adult cancer patients by nurses.
By Boland A, Haycox A, Bagust A, Fitzsimmons L.
-
Redesigning postnatal care: a randomised controlled trial of protocol-based midwifery-led care focused on individual women’s physical and psychological health needs.
By MacArthur C, Winter HR, Bick DE, Lilford RJ, Lancashire RJ, Knowles H, et al.
-
Estimating implied rates of discount in healthcare decision-making.
By West RR, McNabb R, Thompson AGH, Sheldon TA, Grimley Evans J.
-
Systematic review of isolation policies in the hospital management of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a review of the literature with epidemiological and economic modelling.
By Cooper BS, Stone SP, Kibbler CC, Cookson BD, Roberts JA, Medley GF, et al.
-
Treatments for spasticity and pain in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review.
By Beard S, Hunn A, Wight J.
-
The inclusion of reports of randomised trials published in languages other than English in systematic reviews.
By Moher D, Pham B, Lawson ML, Klassen TP.
-
The impact of screening on future health-promoting behaviours and health beliefs: a systematic review.
By Bankhead CR, Brett J, Bukach C, Webster P, Stewart-Brown S, Munafo M, et al.
-
What is the best imaging strategy for acute stroke?
By Wardlaw JM, Keir SL, Seymour J, Lewis S, Sandercock PAG, Dennis MS, et al.
-
Systematic review and modelling of the investigation of acute and chronic chest pain presenting in primary care.
By Mant J, McManus RJ, Oakes RAL, Delaney BC, Barton PM, Deeks JJ, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of microwave and thermal balloon endometrial ablation for heavy menstrual bleeding: a systematic review and economic modelling.
By Garside R, Stein K, Wyatt K, Round A, Price A.
-
A systematic review of the role of bisphosphonates in metastatic disease.
By Ross JR, Saunders Y, Edmonds PM, Patel S, Wonderling D, Normand C, et al.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of capecitabine (Xeloda®) for locally advanced and/or metastatic breast cancer.
By Jones L, Hawkins N, Westwood M, Wright K, Richardson G, Riemsma R.
-
Effectiveness and efficiency of guideline dissemination and implementation strategies.
By Grimshaw JM, Thomas RE, MacLennan G, Fraser C, Ramsay CR, Vale L, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and costs of the Sugarbaker procedure for the treatment of pseudomyxoma peritonei.
By Bryant J, Clegg AJ, Sidhu MK, Brodin H, Royle P, Davidson P.
-
Psychological treatment for insomnia in the regulation of long-term hypnotic drug use.
By Morgan K, Dixon S, Mathers N, Thompson J, Tomeny M.
-
Improving the evaluation of therapeutic interventions in multiple sclerosis: development of a patient-based measure of outcome.
By Hobart JC, Riazi A, Lamping DL, Fitzpatrick R, Thompson AJ.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography compared with diagnostic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
By Kaltenthaler E, Bravo Vergel Y, Chilcott J, Thomas S, Blakeborough T, Walters SJ, et al.
-
The use of modelling to evaluate new drugs for patients with a chronic condition: the case of antibodies against tumour necrosis factor in rheumatoid arthritis.
By Barton P, Jobanputra P, Wilson J, Bryan S, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism using tandem mass spectrometry: a systematic review.
By Pandor A, Eastham J, Beverley C, Chilcott J, Paisley S.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pioglitazone and rosiglitazone in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Czoski-Murray C, Warren E, Chilcott J, Beverley C, Psyllaki MA, Cowan J.
-
Routine examination of the newborn: the EMREN study. Evaluation of an extension of the midwife role including a randomised controlled trial of appropriately trained midwives and paediatric senior house officers.
By Townsend J, Wolke D, Hayes J, Davé S, Rogers C, Bloomfield L, et al.
-
Involving consumers in research and development agenda setting for the NHS: developing an evidence-based approach.
By Oliver S, Clarke-Jones L, Rees R, Milne R, Buchanan P, Gabbay J, et al.
-
A multi-centre randomised controlled trial of minimally invasive direct coronary bypass grafting versus percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty with stenting for proximal stenosis of the left anterior descending coronary artery.
By Reeves BC, Angelini GD, Bryan AJ, Taylor FC, Cripps T, Spyt TJ, et al.
-
Does early magnetic resonance imaging influence management or improve outcome in patients referred to secondary care with low back pain? A pragmatic randomised controlled trial.
By Gilbert FJ, Grant AM, Gillan MGC, Vale L, Scott NW, Campbell MK, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of anakinra for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Clark W, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Burls A.
-
A rapid and systematic review and economic evaluation of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for treatment of mania associated with bipolar affective disorder.
By Bridle C, Palmer S, Bagnall A-M, Darba J, Duffy S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Liquid-based cytology in cervical screening: an updated rapid and systematic review and economic analysis.
By Karnon J, Peters J, Platt J, Chilcott J, McGoogan E, Brewer N.
-
Systematic review of the long-term effects and economic consequences of treatments for obesity and implications for health improvement.
By Avenell A, Broom J, Brown TJ, Poobalan A, Aucott L, Stearns SC, et al.
-
Autoantibody testing in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus.
By Dretzke J, Cummins C, Sandercock J, Fry-Smith A, Barrett T, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of prehospital intravenous fluids in trauma patients.
By Dretzke J, Sandercock J, Bayliss S, Burls A.
-
Newer hypnotic drugs for the short-term management of insomnia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Dündar Y, Boland A, Strobl J, Dodd S, Haycox A, Bagust A, et al.
-
Development and validation of methods for assessing the quality of diagnostic accuracy studies.
By Whiting P, Rutjes AWS, Dinnes J, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PMM, Kleijnen J.
-
EVALUATE hysterectomy trial: a multicentre randomised trial comparing abdominal, vaginal and laparoscopic methods of hysterectomy.
By Garry R, Fountain J, Brown J, Manca A, Mason S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Methods for expected value of information analysis in complex health economic models: developments on the health economics of interferon-β and glatiramer acetate for multiple sclerosis.
By Tappenden P, Chilcott JB, Eggington S, Oakley J, McCabe C.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of imatinib for first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia in chronic phase: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Dalziel K, Round A, Stein K, Garside R, Price A.
-
VenUS I: a randomised controlled trial of two types of bandage for treating venous leg ulcers.
By Iglesias C, Nelson EA, Cullum NA, Torgerson DJ, on behalf of the VenUS Team.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and economic evaluation, of myocardial perfusion scintigraphy for the diagnosis and management of angina and myocardial infarction.
By Mowatt G, Vale L, Brazzelli M, Hernandez R, Murray A, Scott N, et al.
-
A pilot study on the use of decision theory and value of information analysis as part of the NHS Health Technology Assessment programme.
By Claxton K, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Philips Z, Palmer S.
-
The Social Support and Family Health Study: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of two alternative forms of postnatal support for mothers living in disadvantaged inner-city areas.
By Wiggins M, Oakley A, Roberts I, Turner H, Rajan L, Austerberry H, et al.
-
Psychosocial aspects of genetic screening of pregnant women and newborns: a systematic review.
By Green JM, Hewison J, Bekker HL, Bryant, Cuckle HS.
-
Evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding: comparison of three outpatient procedures within cohorts defined by age and menopausal status.
By Critchley HOD, Warner P, Lee AJ, Brechin S, Guise J, Graham B.
-
Coronary artery stents: a rapid systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hill R, Bagust A, Bakhai A, Dickson R, Dündar Y, Haycox A, et al.
-
Review of guidelines for good practice in decision-analytic modelling in health technology assessment.
By Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Claxton K, Golder S, Riemsma R, et al.
-
Rituximab (MabThera®) for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Knight C, Hind D, Brewer N, Abbott V.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of clopidogrel and modified-release dipyridamole in the secondary prevention of occlusive vascular events: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jones L, Griffin S, Palmer S, Main C, Orton V, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Pegylated interferon α-2a and -2b in combination with ribavirin in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Brodin H, Cave C, Waugh N, Price A, Gabbay J.
-
Clopidogrel used in combination with aspirin compared with aspirin alone in the treatment of non-ST-segment- elevation acute coronary syndromes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Main C, Palmer S, Griffin S, Jones L, Orton V, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Provision, uptake and cost of cardiac rehabilitation programmes: improving services to under-represented groups.
By Beswick AD, Rees K, Griebsch I, Taylor FC, Burke M, West RR, et al.
-
Involving South Asian patients in clinical trials.
By Hussain-Gambles M, Leese B, Atkin K, Brown J, Mason S, Tovey P.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for diabetes.
By Colquitt JL, Green C, Sidhu MK, Hartwell D, Waugh N.
-
Identification and assessment of ongoing trials in health technology assessment reviews.
By Song FJ, Fry-Smith A, Davenport C, Bayliss S, Adi Y, Wilson JS, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of a long-acting insulin analogue, insulin glargine
By Warren E, Weatherley-Jones E, Chilcott J, Beverley C.
-
Supplementation of a home-based exercise programme with a class-based programme for people with osteoarthritis of the knees: a randomised controlled trial and health economic analysis.
By McCarthy CJ, Mills PM, Pullen R, Richardson G, Hawkins N, Roberts CR, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of once-daily versus more frequent use of same potency topical corticosteroids for atopic eczema: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Green C, Colquitt JL, Kirby J, Davidson P, Payne E.
-
Acupuncture of chronic headache disorders in primary care: randomised controlled trial and economic analysis.
By Vickers AJ, Rees RW, Zollman CE, McCarney R, Smith CM, Ellis N, et al.
-
Generalisability in economic evaluation studies in healthcare: a review and case studies.
By Sculpher MJ, Pang FS, Manca A, Drummond MF, Golder S, Urdahl H, et al.
-
Virtual outreach: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of joint teleconferenced medical consultations.
By Wallace P, Barber J, Clayton W, Currell R, Fleming K, Garner P, et al.
-
Randomised controlled multiple treatment comparison to provide a cost-effectiveness rationale for the selection of antimicrobial therapy in acne.
By Ozolins M, Eady EA, Avery A, Cunliffe WJ, O’Neill C, Simpson NB, et al.
-
Do the findings of case series studies vary significantly according to methodological characteristics?
By Dalziel K, Round A, Stein K, Garside R, Castelnuovo E, Payne L.
-
Improving the referral process for familial breast cancer genetic counselling: findings of three randomised controlled trials of two interventions.
By Wilson BJ, Torrance N, Mollison J, Wordsworth S, Gray JR, Haites NE, et al.
-
Randomised evaluation of alternative electrosurgical modalities to treat bladder outflow obstruction in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
By Fowler C, McAllister W, Plail R, Karim O, Yang Q.
-
A pragmatic randomised controlled trial of the cost-effectiveness of palliative therapies for patients with inoperable oesophageal cancer.
By Shenfine J, McNamee P, Steen N, Bond J, Griffin SM.
-
Impact of computer-aided detection prompts on the sensitivity and specificity of screening mammography.
By Taylor P, Champness J, Given- Wilson R, Johnston K, Potts H.
-
Issues in data monitoring and interim analysis of trials.
By Grant AM, Altman DG, Babiker AB, Campbell MK, Clemens FJ, Darbyshire JH, et al.
-
Lay public’s understanding of equipoise and randomisation in randomised controlled trials.
By Robinson EJ, Kerr CEP, Stevens AJ, Lilford RJ, Braunholtz DA, Edwards SJ, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of electroconvulsive therapy for depressive illness, schizophrenia, catatonia and mania: systematic reviews and economic modelling studies.
By Greenhalgh J, Knight C, Hind D, Beverley C, Walters S.
-
Measurement of health-related quality of life for people with dementia: development of a new instrument (DEMQOL) and an evaluation of current methodology.
By Smith SC, Lamping DL, Banerjee S, Harwood R, Foley B, Smith P, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of drotrecogin alfa (activated) (Xigris®) for the treatment of severe sepsis in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Green C, Dinnes J, Takeda A, Shepherd J, Hartwell D, Cave C, et al.
-
A methodological review of how heterogeneity has been examined in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy.
By Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kirby J, Roderick P.
-
Cervical screening programmes: can automation help? Evidence from systematic reviews, an economic analysis and a simulation modelling exercise applied to the UK.
By Willis BH, Barton P, Pearmain P, Bryan S, Hyde C.
-
Laparoscopic surgery for inguinal hernia repair: systematic review of effectiveness and economic evaluation.
By McCormack K, Wake B, Perez J, Fraser C, Cook J, McIntosh E, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness, tolerability and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for epilepsy in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wilby J, Kainth A, Hawkins N, Epstein D, McIntosh H, McDaid C, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to compare the cost-effectiveness of tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and lofepramine.
By Peveler R, Kendrick T, Buxton M, Longworth L, Baldwin D, Moore M, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of immediate angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hartwell D, Colquitt J, Loveman E, Clegg AJ, Brodin H, Waugh N, et al.
-
A randomised controlled comparison of alternative strategies in stroke care.
By Kalra L, Evans A, Perez I, Knapp M, Swift C, Donaldson N.
-
The investigation and analysis of critical incidents and adverse events in healthcare.
By Woloshynowych M, Rogers S, Taylor-Adams S, Vincent C.
-
Potential use of routine databases in health technology assessment.
By Raftery J, Roderick P, Stevens A.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of newer immunosuppressive regimens in renal transplantation: a systematic review and modelling study.
By Woodroffe R, Yao GL, Meads C, Bayliss S, Ready A, Raftery J, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene and teriparatide for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
By Stevenson M, Lloyd Jones M, De Nigris E, Brewer N, Davis S, Oakley J.
-
A systematic review to examine the impact of psycho-educational interventions on health outcomes and costs in adults and children with difficult asthma.
By Smith JR, Mugford M, Holland R, Candy B, Noble MJ, Harrison BDW, et al.
-
An evaluation of the costs, effectiveness and quality of renal replacement therapy provision in renal satellite units in England and Wales.
By Roderick P, Nicholson T, Armitage A, Mehta R, Mullee M, Gerard K, et al.
-
Imatinib for the treatment of patients with unresectable and/or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumours: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wilson J, Connock M, Song F, Yao G, Fry-Smith A, Raftery J, et al.
-
Indirect comparisons of competing interventions.
By Glenny AM, Altman DG, Song F, Sakarovitch C, Deeks JJ, D’Amico R, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of alternative strategies for the initial medical management of non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome: systematic review and decision-analytical modelling.
By Robinson M, Palmer S, Sculpher M, Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Bowens A, et al.
-
Outcomes of electrically stimulated gracilis neosphincter surgery.
By Tillin T, Chambers M, Feldman R.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pimecrolimus and tacrolimus for atopic eczema: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Stein K, Castelnuovo E, Pitt M, Ashcroft D, Dimmock P, et al.
-
Systematic review on urine albumin testing for early detection of diabetic complications.
By Newman DJ, Mattock MB, Dawnay ABS, Kerry S, McGuire A, Yaqoob M, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trial of the cost-effectiveness of water-based therapy for lower limb osteoarthritis.
By Cochrane T, Davey RC, Matthes Edwards SM.
-
Longer term clinical and economic benefits of offering acupuncture care to patients with chronic low back pain.
By Thomas KJ, MacPherson H, Ratcliffe J, Thorpe L, Brazier J, Campbell M, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness and safety of epidural steroids in the management of sciatica.
By Price C, Arden N, Coglan L, Rogers P.
-
The British Rheumatoid Outcome Study Group (BROSG) randomised controlled trial to compare the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of aggressive versus symptomatic therapy in established rheumatoid arthritis.
By Symmons D, Tricker K, Roberts C, Davies L, Dawes P, Scott DL.
-
Conceptual framework and systematic review of the effects of participants’ and professionals’ preferences in randomised controlled trials.
By King M, Nazareth I, Lampe F, Bower P, Chandler M, Morou M, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of implantable cardioverter defibrillators: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Brodin H, Loveman E, Payne E, Clegg A.
-
A trial of problem-solving by community mental health nurses for anxiety, depression and life difficulties among general practice patients. The CPN-GP study.
By Kendrick T, Simons L, Mynors-Wallis L, Gray A, Lathlean J, Pickering R, et al.
-
The causes and effects of socio-demographic exclusions from clinical trials.
By Bartlett C, Doyal L, Ebrahim S, Davey P, Bachmann M, Egger M, et al.
-
Is hydrotherapy cost-effective? A randomised controlled trial of combined hydrotherapy programmes compared with physiotherapy land techniques in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
By Epps H, Ginnelly L, Utley M, Southwood T, Gallivan S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial and cost-effectiveness study of systematic screening (targeted and total population screening) versus routine practice for the detection of atrial fibrillation in people aged 65 and over. The SAFE study.
By Hobbs FDR, Fitzmaurice DA, Mant J, Murray E, Jowett S, Bryan S, et al.
-
Displaced intracapsular hip fractures in fit, older people: a randomised comparison of reduction and fixation, bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty.
By Keating JF, Grant A, Masson M, Scott NW, Forbes JF.
-
Long-term outcome of cognitive behaviour therapy clinical trials in central Scotland.
By Durham RC, Chambers JA, Power KG, Sharp DM, Macdonald RR, Major KA, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of dual-chamber pacemakers compared with single-chamber pacemakers for bradycardia due to atrioventricular block or sick sinus syndrome: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Castelnuovo E, Stein K, Pitt M, Garside R, Payne E.
-
Newborn screening for congenital heart defects: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Knowles R, Griebsch I, Dezateux C, Brown J, Bull C, Wren C.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of left ventricular assist devices for end-stage heart failure: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clegg AJ, Scott DA, Loveman E, Colquitt J, Hutchinson J, Royle P, et al.
-
The effectiveness of the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph and laser diagnostic glaucoma scanning system (GDx) in detecting and monitoring glaucoma.
By Kwartz AJ, Henson DB, Harper RA, Spencer AF, McLeod D.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of autologous chondrocyte implantation for cartilage defects in knee joints: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clar C, Cummins E, McIntyre L, Thomas S, Lamb J, Bain L, et al.
-
Systematic review of effectiveness of different treatments for childhood retinoblastoma.
By McDaid C, Hartley S, Bagnall A-M, Ritchie G, Light K, Riemsma R.
-
Towards evidence-based guidelines for the prevention of venous thromboembolism: systematic reviews of mechanical methods, oral anticoagulation, dextran and regional anaesthesia as thromboprophylaxis.
By Roderick P, Ferris G, Wilson K, Halls H, Jackson D, Collins R, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of parent training/education programmes for the treatment of conduct disorder, including oppositional defiant disorder, in children.
By Dretzke J, Frew E, Davenport C, Barlow J, Stewart-Brown S, Sandercock J, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine and memantine for Alzheimer’s disease.
By Loveman E, Green C, Kirby J, Takeda A, Picot J, Payne E, et al.
-
FOOD: a multicentre randomised trial evaluating feeding policies in patients admitted to hospital with a recent stroke.
By Dennis M, Lewis S, Cranswick G, Forbes J.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computed tomography screening for lung cancer: systematic reviews.
By Black C, Bagust A, Boland A, Walker S, McLeod C, De Verteuil R, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of neuroimaging assessments used to visualise the seizure focus in people with refractory epilepsy being considered for surgery.
By Whiting P, Gupta R, Burch J, Mujica Mota RE, Wright K, Marson A, et al.
-
Comparison of conference abstracts and presentations with full-text articles in the health technology assessments of rapidly evolving technologies.
By Dundar Y, Dodd S, Dickson R, Walley T, Haycox A, Williamson PR.
-
Systematic review and evaluation of methods of assessing urinary incontinence.
By Martin JL, Williams KS, Abrams KR, Turner DA, Sutton AJ, Chapple C, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for children with epilepsy. A systematic review.
By Connock M, Frew E, Evans B-W, Bryan S, Cummins C, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Surveillance of Barrett’s oesophagus: exploring the uncertainty through systematic review, expert workshop and economic modelling.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Somerville M, Stein K, Price A, Gilbert N.
-
Topotecan, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride and paclitaxel for second-line or subsequent treatment of advanced ovarian cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Main C, Bojke L, Griffin S, Norman G, Barbieri M, Mather L, et al.
-
Evaluation of molecular techniques in prediction and diagnosis of cytomegalovirus disease in immunocompromised patients.
By Szczepura A, Westmoreland D, Vinogradova Y, Fox J, Clark M.
-
Screening for thrombophilia in high-risk situations: systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. The Thrombosis: Risk and Economic Assessment of Thrombophilia Screening (TREATS) study.
By Wu O, Robertson L, Twaddle S, Lowe GDO, Clark P, Greaves M, et al.
-
A series of systematic reviews to inform a decision analysis for sampling and treating infected diabetic foot ulcers.
By Nelson EA, O’Meara S, Craig D, Iglesias C, Golder S, Dalton J, et al.
-
Randomised clinical trial, observational study and assessment of cost-effectiveness of the treatment of varicose veins (REACTIV trial).
By Michaels JA, Campbell WB, Brazier JE, MacIntyre JB, Palfreyman SJ, Ratcliffe J, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of screening for oral cancer in primary care.
By Speight PM, Palmer S, Moles DR, Downer MC, Smith DH, Henriksson M, et al.
-
Measurement of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of non-invasive diagnostic testing strategies for deep vein thrombosis.
By Goodacre S, Sampson F, Stevenson M, Wailoo A, Sutton A, Thomas S, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of HealOzone® for the treatment of occlusal pit/fissure caries and root caries.
By Brazzelli M, McKenzie L, Fielding S, Fraser C, Clarkson J, Kilonzo M, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trials of conventional antipsychotic versus new atypical drugs, and new atypical drugs versus clozapine, in people with schizophrenia responding poorly to, or intolerant of, current drug treatment.
By Lewis SW, Davies L, Jones PB, Barnes TRE, Murray RM, Kerwin R, et al.
-
Diagnostic tests and algorithms used in the investigation of haematuria: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.
By Rodgers M, Nixon J, Hempel S, Aho T, Kelly J, Neal D, et al.
-
Cognitive behavioural therapy in addition to antispasmodic therapy for irritable bowel syndrome in primary care: randomised controlled trial.
By Kennedy TM, Chalder T, McCrone P, Darnley S, Knapp M, Jones RH, et al.
-
A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapies for Fabry’s disease and mucopolysaccharidosis type 1.
By Connock M, Juarez-Garcia A, Frew E, Mans A, Dretzke J, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Health benefits of antiviral therapy for mild chronic hepatitis C: randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation.
By Wright M, Grieve R, Roberts J, Main J, Thomas HC, on behalf of the UK Mild Hepatitis C Trial Investigators.
-
Pressure relieving support surfaces: a randomised evaluation.
By Nixon J, Nelson EA, Cranny G, Iglesias CP, Hawkins K, Cullum NA, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of methylphenidate, dexamfetamine and atomoxetine for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents.
By King S, Griffin S, Hodges Z, Weatherly H, Asseburg C, Richardson G, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy for Gaucher’s disease: a systematic review.
By Connock M, Burls A, Frew E, Fry-Smith A, Juarez-Garcia A, McCabe C, et al.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of salicylic acid and cryotherapy for cutaneous warts. An economic decision model.
By Thomas KS, Keogh-Brown MR, Chalmers JR, Fordham RJ, Holland RC, Armstrong SJ, et al.
-
A systematic literature review of the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions to prevent wandering in dementia and evaluation of the ethical implications and acceptability of their use.
By Robinson L, Hutchings D, Corner L, Beyer F, Dickinson H, Vanoli A, et al.
-
A review of the evidence on the effects and costs of implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in different patient groups, and modelling of cost-effectiveness and cost–utility for these groups in a UK context.
By Buxton M, Caine N, Chase D, Connelly D, Grace A, Jackson C, et al.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Takeda A, Davidson P, Price A.
-
An evaluation of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of pulmonary artery catheters in patient management in intensive care: a systematic review and a randomised controlled trial.
By Harvey S, Stevens K, Harrison D, Young D, Brampton W, McCabe C, et al.
-
Accurate, practical and cost-effective assessment of carotid stenosis in the UK.
By Wardlaw JM, Chappell FM, Stevenson M, De Nigris E, Thomas S, Gillard J, et al.
-
Etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Woolacott N, Bravo Vergel Y, Hawkins N, Kainth A, Khadjesari Z, Misso K, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of testing for hepatitis C in former injecting drug users.
By Castelnuovo E, Thompson-Coon J, Pitt M, Cramp M, Siebert U, Price A, et al.
-
Computerised cognitive behaviour therapy for depression and anxiety update: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Kaltenthaler E, Brazier J, De Nigris E, Tumur I, Ferriter M, Beverley C, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.
By Williams C, Brunskill S, Altman D, Briggs A, Campbell H, Clarke M, et al.
-
Psychological therapies including dialectical behaviour therapy for borderline personality disorder: a systematic review and preliminary economic evaluation.
By Brazier J, Tumur I, Holmes M, Ferriter M, Parry G, Dent-Brown K, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of tests for the diagnosis and investigation of urinary tract infection in children: a systematic review and economic model.
By Whiting P, Westwood M, Bojke L, Palmer S, Richardson G, Cooper J, et al.
-
Cognitive behavioural therapy in chronic fatigue syndrome: a randomised controlled trial of an outpatient group programme.
By O’Dowd H, Gladwell P, Rogers CA, Hollinghurst S, Gregory A.
-
A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling.
By Brown TJ, Hooper L, Elliott RA, Payne K, Webb R, Roberts C, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computed tomography screening for coronary artery disease: systematic review.
By Waugh N, Black C, Walker S, McIntyre L, Cummins E, Hillis G.
-
What are the clinical outcome and cost-effectiveness of endoscopy undertaken by nurses when compared with doctors? A Multi-Institution Nurse Endoscopy Trial (MINuET).
By Williams J, Russell I, Durai D, Cheung W-Y, Farrin A, Bloor K, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of oxaliplatin and capecitabine for the adjuvant treatment of colon cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Pandor A, Eggington S, Paisley S, Tappenden P, Sutcliffe P.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness.
By Chen Y-F, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Jowett S, Bryan S, Clark W, et al.
-
Telemedicine in dermatology: a randomised controlled trial.
By Bowns IR, Collins K, Walters SJ, McDonagh AJG.
-
Cost-effectiveness of cell salvage and alternative methods of minimising perioperative allogeneic blood transfusion: a systematic review and economic model.
By Davies L, Brown TJ, Haynes S, Payne K, Elliott RA, McCollum C.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancer: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.
By Murray A, Lourenco T, de Verteuil R, Hernandez R, Fraser C, McKinley A, et al.
-
Etanercept and efalizumab for the treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review.
By Woolacott N, Hawkins N, Mason A, Kainth A, Khadjesari Z, Bravo Vergel Y, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of clinical decision tools for acute abdominal pain.
By Liu JLY, Wyatt JC, Deeks JJ, Clamp S, Keen J, Verde P, et al.
-
Evaluation of the ventricular assist device programme in the UK.
By Sharples L, Buxton M, Caine N, Cafferty F, Demiris N, Dyer M, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of immunosuppressive therapy for renal transplantation in children.
By Yao G, Albon E, Adi Y, Milford D, Bayliss S, Ready A, et al.
-
Amniocentesis results: investigation of anxiety. The ARIA trial.
By Hewison J, Nixon J, Fountain J, Cocks K, Jones C, Mason G, et al.
-
Pemetrexed disodium for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Dundar Y, Bagust A, Dickson R, Dodd S, Green J, Haycox A, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of docetaxel in combination with prednisone or prednisolone for the treatment of hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer.
By Collins R, Fenwick E, Trowman R, Perard R, Norman G, Light K, et al.
-
A systematic review of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of tuberculosis infection.
By Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kunst H, Gibson A, Cummins E, Waugh N, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women.
By Stevenson M, Davis S, Lloyd-Jones M, Beverley C.
-
A systematic review of quantitative and qualitative research on the role and effectiveness of written information available to patients about individual medicines.
By Raynor DK, Blenkinsopp A, Knapp P, Grime J, Nicolson DJ, Pollock K, et al.
-
Oral naltrexone as a treatment for relapse prevention in formerly opioid-dependent drug users: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Adi Y, Juarez-Garcia A, Wang D, Jowett S, Frew E, Day E, et al.
-
Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: a systematic review and cost–utility analysis.
By Kanis JA, Stevenson M, McCloskey EV, Davis S, Lloyd-Jones M.
-
Epidemiological, social, diagnostic and economic evaluation of population screening for genital chlamydial infection.
By Low N, McCarthy A, Macleod J, Salisbury C, Campbell R, Roberts TE, et al.
-
Methadone and buprenorphine for the management of opioid dependence: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Connock M, Juarez-Garcia A, Jowett S, Frew E, Liu Z, Taylor RJ, et al.
-
Exercise Evaluation Randomised Trial (EXERT): a randomised trial comparing GP referral for leisure centre-based exercise, community-based walking and advice only.
By Isaacs AJ, Critchley JA, See Tai S, Buckingham K, Westley D, Harridge SDR, et al.
-
Interferon alfa (pegylated and non-pegylated) and ribavirin for the treatment of mild chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Hartwell D, Davidson P, Price A, Waugh N.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of bevacizumab and cetuximab for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.
By Tappenden P, Jones R, Paisley S, Carroll C.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of epoetin alfa, epoetin beta and darbepoetin alfa in anaemia associated with cancer, especially that attributable to cancer treatment.
By Wilson J, Yao GL, Raftery J, Bohlius J, Brunskill S, Sandercock J, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of statins for the prevention of coronary events.
By Ward S, Lloyd Jones M, Pandor A, Holmes M, Ara R, Ryan A, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of different models of community-based respite care for frail older people and their carers.
By Mason A, Weatherly H, Spilsbury K, Arksey H, Golder S, Adamson J, et al.
-
Additional therapy for young children with spastic cerebral palsy: a randomised controlled trial.
By Weindling AM, Cunningham CC, Glenn SM, Edwards RT, Reeves DJ.
-
Screening for type 2 diabetes: literature review and economic modelling.
By Waugh N, Scotland G, McNamee P, Gillett M, Brennan A, Goyder E, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cinacalcet for secondary hyperparathyroidism in end-stage renal disease patients on dialysis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Anderson R, Mealing S, Roome C, Snaith A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of gemcitabine for metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Takeda AL, Jones J, Loveman E, Tan SC, Clegg AJ.
-
A systematic review of duplex ultrasound, magnetic resonance angiography and computed tomography angiography for the diagnosis and assessment of symptomatic, lower limb peripheral arterial disease.
By Collins R, Cranny G, Burch J, Aguiar-Ibáñez R, Craig D, Wright K, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of treatments for children with idiopathic steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome: a systematic review.
By Colquitt JL, Kirby J, Green C, Cooper K, Trompeter RS.
-
A systematic review of the routine monitoring of growth in children of primary school age to identify growth-related conditions.
By Fayter D, Nixon J, Hartley S, Rithalia A, Butler G, Rudolf M, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness of preventing and treating Staphylococcus aureus carriage in reducing peritoneal catheter-related infections.
By McCormack K, Rabindranath K, Kilonzo M, Vale L, Fraser C, McIntyre L, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation versus electroconvulsive therapy in severe depression: a multicentre pragmatic randomised controlled trial and economic analysis.
By McLoughlin DM, Mogg A, Eranti S, Pluck G, Purvis R, Edwards D, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of direct versus indirect and individual versus group modes of speech and language therapy for children with primary language impairment.
By Boyle J, McCartney E, Forbes J, O’Hare A.
-
Hormonal therapies for early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hind D, Ward S, De Nigris E, Simpson E, Carroll C, Wyld L.
-
Cardioprotection against the toxic effects of anthracyclines given to children with cancer: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Picot J, Levitt G, Sullivan I, Baxter L, Clegg A.
-
Adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By McLeod C, Bagust A, Boland A, Dagenais P, Dickson R, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Prenatal screening and treatment strategies to prevent group B streptococcal and other bacterial infections in early infancy: cost-effectiveness and expected value of information analyses.
By Colbourn T, Asseburg C, Bojke L, Philips Z, Claxton K, Ades AE, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bone morphogenetic proteins in the non-healing of fractures and spinal fusion: a systematic review.
By Garrison KR, Donell S, Ryder J, Shemilt I, Mugford M, Harvey I, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial of postoperative radiotherapy following breast-conserving surgery in a minimum-risk older population. The PRIME trial.
By Prescott RJ, Kunkler IH, Williams LJ, King CC, Jack W, van der Pol M, et al.
-
Current practice, accuracy, effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the school entry hearing screen.
By Bamford J, Fortnum H, Bristow K, Smith J, Vamvakas G, Davies L, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of inhaled insulin in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Black C, Cummins E, Royle P, Philip S, Waugh N.
-
Surveillance of cirrhosis for hepatocellular carcinoma: systematic review and economic analysis.
By Thompson Coon J, Rogers G, Hewson P, Wright D, Anderson R, Cramp M, et al.
-
The Birmingham Rehabilitation Uptake Maximisation Study (BRUM). Homebased compared with hospital-based cardiac rehabilitation in a multi-ethnic population: cost-effectiveness and patient adherence.
By Jolly K, Taylor R, Lip GYH, Greenfield S, Raftery J, Mant J, et al.
-
A systematic review of the clinical, public health and cost-effectiveness of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection and identification of bacterial intestinal pathogens in faeces and food.
By Abubakar I, Irvine L, Aldus CF, Wyatt GM, Fordham R, Schelenz S, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial examining the longer-term outcomes of standard versus new antiepileptic drugs. The SANAD trial.
By Marson AG, Appleton R, Baker GA, Chadwick DW, Doughty J, Eaton B, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of different models of managing long-term oral anti-coagulation therapy: a systematic review and economic modelling.
By Connock M, Stevens C, Fry-Smith A, Jowett S, Fitzmaurice D, Moore D, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of interventions for preventing relapse in people with bipolar disorder.
By Soares-Weiser K, Bravo Vergel Y, Beynon S, Dunn G, Barbieri M, Duffy S, et al.
-
Taxanes for the adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ward S, Simpson E, Davis S, Hind D, Rees A, Wilkinson A.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening for open angle glaucoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burr JM, Mowatt G, Hernández R, Siddiqui MAR, Cook J, Lourenco T, et al.
-
Acceptability, benefit and costs of early screening for hearing disability: a study of potential screening tests and models.
By Davis A, Smith P, Ferguson M, Stephens D, Gianopoulos I.
-
Contamination in trials of educational interventions.
By Keogh-Brown MR, Bachmann MO, Shepstone L, Hewitt C, Howe A, Ramsay CR, et al.
-
Overview of the clinical effectiveness of positron emission tomography imaging in selected cancers.
By Facey K, Bradbury I, Laking G, Payne E.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Anderson R, Rogers G, Dyer M, Mealing S, et al.
-
Drug-eluting stents: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hill RA, Boland A, Dickson R, Dündar Y, Haycox A, McLeod C, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cardiac resynchronisation (biventricular pacing) for heart failure: systematic review and economic model.
By Fox M, Mealing S, Anderson R, Dean J, Stein K, Price A, et al.
-
Recruitment to randomised trials: strategies for trial enrolment and participation study. The STEPS study.
By Campbell MK, Snowdon C, Francis D, Elbourne D, McDonald AM, Knight R, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of functional cardiac testing in the diagnosis and management of coronary artery disease: a randomised controlled trial. The CECaT trial.
By Sharples L, Hughes V, Crean A, Dyer M, Buxton M, Goldsmith K, et al.
-
Evaluation of diagnostic tests when there is no gold standard. A review of methods.
By Rutjes AWS, Reitsma JB, Coomarasamy A, Khan KS, Bossuyt PMM.
-
Systematic reviews of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors in acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
By Leontiadis GI, Sreedharan A, Dorward S, Barton P, Delaney B, Howden CW, et al.
-
A review and critique of modelling in prioritising and designing screening programmes.
By Karnon J, Goyder E, Tappenden P, McPhie S, Towers I, Brazier J, et al.
-
An assessment of the impact of the NHS Health Technology Assessment Programme.
By Hanney S, Buxton M, Green C, Coulson D, Raftery J.
-
A systematic review and economic model of switching from nonglycopeptide to glycopeptide antibiotic prophylaxis for surgery.
By Cranny G, Elliott R, Weatherly H, Chambers D, Hawkins N, Myers L, et al.
-
‘Cut down to quit’ with nicotine replacement therapies in smoking cessation: a systematic review of effectiveness and economic analysis.
By Wang D, Connock M, Barton P, Fry-Smith A, Aveyard P, Moore D.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of strategies for reducing fracture risk in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis with additional data on long-term risk of fracture and cost of disease management.
By Thornton J, Ashcroft D, O’Neill T, Elliott R, Adams J, Roberts C, et al.
-
Does befriending by trained lay workers improve psychological well-being and quality of life for carers of people with dementia, and at what cost? A randomised controlled trial.
By Charlesworth G, Shepstone L, Wilson E, Thalanany M, Mugford M, Poland F.
-
A multi-centre retrospective cohort study comparing the efficacy, safety and cost-effectiveness of hysterectomy and uterine artery embolisation for the treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroids. The HOPEFUL study.
By Hirst A, Dutton S, Wu O, Briggs A, Edwards C, Waldenmaier L, et al.
-
Methods of prediction and prevention of pre-eclampsia: systematic reviews of accuracy and effectiveness literature with economic modelling.
By Meads CA, Cnossen JS, Meher S, Juarez-Garcia A, ter Riet G, Duley L, et al.
-
The use of economic evaluations in NHS decision-making: a review and empirical investigation.
By Williams I, McIver S, Moore D, Bryan S.
-
Stapled haemorrhoidectomy (haemorrhoidopexy) for the treatment of haemorrhoids: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burch J, Epstein D, Baba-Akbari A, Weatherly H, Fox D, Golder S, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness of diabetes education models for Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.
By Loveman E, Frampton GK, Clegg AJ.
-
Payment to healthcare professionals for patient recruitment to trials: systematic review and qualitative study.
By Raftery J, Bryant J, Powell J, Kerr C, Hawker S.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (etodolac, meloxicam, celecoxib, rofecoxib, etoricoxib, valdecoxib and lumiracoxib) for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Chen Y-F, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Fry-Smith A, Harris G, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of central venous catheters treated with anti-infective agents in preventing bloodstream infections: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hockenhull JC, Dwan K, Boland A, Smith G, Bagust A, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Stepped treatment of older adults on laxatives. The STOOL trial.
By Mihaylov S, Stark C, McColl E, Steen N, Vanoli A, Rubin G, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial of cognitive behaviour therapy in adolescents with major depression treated by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. The ADAPT trial.
By Goodyer IM, Dubicka B, Wilkinson P, Kelvin R, Roberts C, Byford S, et al.
-
The use of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hind D, Tappenden P, Tumur I, Eggington E, Sutcliffe P, Ryan A.
-
Ranibizumab and pegaptanib for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Colquitt JL, Jones J, Tan SC, Takeda A, Clegg AJ, Price A.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of 64-slice or higher computed tomography angiography as an alternative to invasive coronary angiography in the investigation of coronary artery disease.
By Mowatt G, Cummins E, Waugh N, Walker S, Cook J, Jia X, et al.
-
Structural neuroimaging in psychosis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Albon E, Tsourapas A, Frew E, Davenport C, Oyebode F, Bayliss S, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children aged 12 years and over.
By Shepherd J, Rogers G, Anderson R, Main C, Thompson-Coon J, Hartwell D, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years.
By Main C, Shepherd J, Anderson R, Rogers G, Thompson-Coon J, Liu Z, et al.
-
Ezetimibe for the treatment of hypercholesterolaemia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ara R, Tumur I, Pandor A, Duenas A, Williams R, Wilkinson A, et al.
-
Topical or oral ibuprofen for chronic knee pain in older people. The TOIB study.
By Underwood M, Ashby D, Carnes D, Castelnuovo E, Cross P, Harding G, et al.
-
A prospective randomised comparison of minor surgery in primary and secondary care. The MiSTIC trial.
By George S, Pockney P, Primrose J, Smith H, Little P, Kinley H, et al.
-
A review and critical appraisal of measures of therapist–patient interactions in mental health settings.
By Cahill J, Barkham M, Hardy G, Gilbody S, Richards D, Bower P, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening programmes for amblyopia and strabismus in children up to the age of 4–5 years: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Carlton J, Karnon J, Czoski-Murray C, Smith KJ, Marr J.
-
A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness and economic modelling of minimal incision total hip replacement approaches in the management of arthritic disease of the hip.
By de Verteuil R, Imamura M, Zhu S, Glazener C, Fraser C, Munro N, et al.
-
A preliminary model-based assessment of the cost–utility of a screening programme for early age-related macular degeneration.
By Karnon J, Czoski-Murray C, Smith K, Brand C, Chakravarthy U, Davis S, et al.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Frampton GK, Tanajewski L, Turner D, Price A.
-
Absorbent products for urinary/faecal incontinence: a comparative evaluation of key product categories.
By Fader M, Cottenden A, Getliffe K, Gage H, Clarke-O’Neill S, Jamieson K, et al.
-
A systematic review of repetitive functional task practice with modelling of resource use, costs and effectiveness.
By French B, Leathley M, Sutton C, McAdam J, Thomas L, Forster A, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectivness of minimal access surgery amongst people with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease – a UK collaborative study. The reflux trial.
By Grant A, Wileman S, Ramsay C, Bojke L, Epstein D, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Time to full publication of studies of anti-cancer medicines for breast cancer and the potential for publication bias: a short systematic review.
By Takeda A, Loveman E, Harris P, Hartwell D, Welch K.
-
Performance of screening tests for child physical abuse in accident and emergency departments.
By Woodman J, Pitt M, Wentz R, Taylor B, Hodes D, Gilbert RE.
-
Curative catheter ablation in atrial fibrillation and typical atrial flutter: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Rodgers M, McKenna C, Palmer S, Chambers D, Van Hout S, Golder S, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic modelling of effectiveness and cost utility of surgical treatments for men with benign prostatic enlargement.
By Lourenco T, Armstrong N, N’Dow J, Nabi G, Deverill M, Pickard R, et al.
-
Immunoprophylaxis against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) with palivizumab in children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wang D, Cummins C, Bayliss S, Sandercock J, Burls A.
-
Deferasirox for the treatment of iron overload associated with regular blood transfusions (transfusional haemosiderosis) in patients suffering with chronic anaemia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By McLeod C, Fleeman N, Kirkham J, Bagust A, Boland A, Chu P, et al.
-
Thrombophilia testing in people with venous thromboembolism: systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Simpson EL, Stevenson MD, Rawdin A, Papaioannou D.
-
Surgical procedures and non-surgical devices for the management of non-apnoeic snoring: a systematic review of clinical effects and associated treatment costs.
By Main C, Liu Z, Welch K, Weiner G, Quentin Jones S, Stein K.
-
Continuous positive airway pressure devices for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea–hypopnoea syndrome: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By McDaid C, Griffin S, Weatherly H, Durée K, van der Burgt M, van Hout S, Akers J, et al.
-
Use of classical and novel biomarkers as prognostic risk factors for localised prostate cancer: a systematic review.
By Sutcliffe P, Hummel S, Simpson E, Young T, Rees A, Wilkinson A, et al.
-
The harmful health effects of recreational ecstasy: a systematic review of observational evidence.
By Rogers G, Elston J, Garside R, Roome C, Taylor R, Younger P, et al.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of oesophageal Doppler monitoring in critically ill and high-risk surgical patients.
By Mowatt G, Houston G, Hernández R, de Verteuil R, Fraser C, Cuthbertson B, et al.
-
The use of surrogate outcomes in model-based cost-effectiveness analyses: a survey of UK Health Technology Assessment reports.
By Taylor RS, Elston J.
-
Controlling Hypertension and Hypotension Immediately Post Stroke (CHHIPS) – a randomised controlled trial.
By Potter J, Mistri A, Brodie F, Chernova J, Wilson E, Jagger C, et al.
-
Routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis for RhD-negative women: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Pilgrim H, Lloyd-Jones M, Rees A.
-
Amantadine, oseltamivir and zanamivir for the prophylaxis of influenza (including a review of existing guidance no. 67): a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Tappenden P, Jackson R, Cooper K, Rees A, Simpson E, Read R, et al.
-
Improving the evaluation of therapeutic interventions in multiple sclerosis: the role of new psychometric methods.
By Hobart J, Cano S.
-
Treatment of severe ankle sprain: a pragmatic randomised controlled trial comparing the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of three types of mechanical ankle support with tubular bandage. The CAST trial.
By Cooke MW, Marsh JL, Clark M, Nakash R, Jarvis RM, Hutton JL, et al. , on behalf of the CAST trial group.
-
Non-occupational postexposure prophylaxis for HIV: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Baxter L, Hird S.
-
Blood glucose self-monitoring in type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial.
By Farmer AJ, Wade AN, French DP, Simon J, Yudkin P, Gray A, et al.
-
How far does screening women for domestic (partner) violence in different health-care settings meet criteria for a screening programme? Systematic reviews of nine UK National Screening Committee criteria.
By Feder G, Ramsay J, Dunne D, Rose M, Arsene C, Norman R, et al.
-
Spinal cord stimulation for chronic pain of neuropathic or ischaemic origin: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Simpson, EL, Duenas A, Holmes MW, Papaioannou D, Chilcott J.
-
The role of magnetic resonance imaging in the identification of suspected acoustic neuroma: a systematic review of clinical and cost-effectiveness and natural history.
By Fortnum H, O’Neill C, Taylor R, Lenthall R, Nikolopoulos T, Lightfoot G, et al.
-
Dipsticks and diagnostic algorithms in urinary tract infection: development and validation, randomised trial, economic analysis, observational cohort and qualitative study.
By Little P, Turner S, Rumsby K, Warner G, Moore M, Lowes JA, et al.
-
Systematic review of respite care in the frail elderly.
By Shaw C, McNamara R, Abrams K, Cannings-John R, Hood K, Longo M, et al.
-
Neuroleptics in the treatment of aggressive challenging behaviour for people with intellectual disabilities: a randomised controlled trial (NACHBID).
By Tyrer P, Oliver-Africano P, Romeo R, Knapp M, Dickens S, Bouras N, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trial to determine the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors plus supportive care, versus supportive care alone, for mild to moderate depression with somatic symptoms in primary care: the THREAD (THREshold for AntiDepressant response) study.
By Kendrick T, Chatwin J, Dowrick C, Tylee A, Morriss R, Peveler R, et al.
-
Diagnostic strategies using DNA testing for hereditary haemochromatosis in at-risk populations: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Cooper K, Picot J, Clegg A, Roderick P, Rosenberg W, et al.
-
Enhanced external counterpulsation for the treatment of stable angina and heart failure: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By McKenna C, McDaid C, Suekarran S, Hawkins N, Claxton K, Light K, et al.
-
Development of a decision support tool for primary care management of patients with abnormal liver function tests without clinically apparent liver disease: a record-linkage population cohort study and decision analysis (ALFIE).
By Donnan PT, McLernon D, Dillon JF, Ryder S, Roderick P, Sullivan F, et al.
-
A systematic review of presumed consent systems for deceased organ donation.
By Rithalia A, McDaid C, Suekarran S, Norman G, Myers L, Sowden A.
-
Paracetamol and ibuprofen for the treatment of fever in children: the PITCH randomised controlled trial.
By Hay AD, Redmond NM, Costelloe C, Montgomery AA, Fletcher M, Hollinghurst S, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to compare minimally invasive glucose monitoring devices with conventional monitoring in the management of insulin-treated diabetes mellitus (MITRE).
By Newman SP, Cooke D, Casbard A, Walker S, Meredith S, Nunn A, et al.
-
Sensitivity analysis in economic evaluation: an audit of NICE current practice and a review of its use and value in decision-making.
By Andronis L, Barton P, Bryan S.
-
Trastuzumab for the treatment of primary breast cancer in HER2-positive women: a single technology appraisal.
By Ward S, Pilgrim H, Hind D.
-
Docetaxel for the adjuvant treatment of early node-positive breast cancer: a single technology appraisal.
By Chilcott J, Lloyd Jones M, Wilkinson A.
-
The use of paclitaxel in the management of early stage breast cancer.
By Griffin S, Dunn G, Palmer S, Macfarlane K, Brent S, Dyker A, et al.
-
Rituximab for the first-line treatment of stage III/IV follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
By Dundar Y, Bagust A, Hounsome J, McLeod C, Boland A, Davis H, et al.
-
Bortezomib for the treatment of multiple myeloma patients.
By Green C, Bryant J, Takeda A, Cooper K, Clegg A, Smith A, et al.
-
Fludarabine phosphate for the firstline treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.
By Walker S, Palmer S, Erhorn S, Brent S, Dyker A, Ferrie L, et al.
-
Erlotinib for the treatment of relapsed non-small cell lung cancer.
By McLeod C, Bagust A, Boland A, Hockenhull J, Dundar Y, Proudlove C, et al.
-
Cetuximab plus radiotherapy for the treatment of locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
By Griffin S, Walker S, Sculpher M, White S, Erhorn S, Brent S, et al.
-
Infliximab for the treatment of adults with psoriasis.
By Loveman E, Turner D, Hartwell D, Cooper K, Clegg A
-
Psychological interventions for postnatal depression: cluster randomised trial and economic evaluation. The PoNDER trial.
By Morrell CJ, Warner R, Slade P, Dixon S, Walters S, Paley G, et al.
-
The effect of different treatment durations of clopidogrel in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes: a systematic review and value of information analysis.
By Rogowski R, Burch J, Palmer S, Craigs C, Golder S, Woolacott N.
-
Systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of diagnosis of heart failure, with modelling of implications of different diagnostic strategies in primary care.
By Mant J, Doust J, Roalfe A, Barton P, Cowie MR, Glasziou P, et al.
-
A multicentre randomised controlled trial of the use of continuous positive airway pressure and non-invasive positive pressure ventilation in the early treatment of patients presenting to the emergency department with severe acute cardiogenic pulmonary oedema: the 3CPO trial.
By Gray AJ, Goodacre S, Newby DE, Masson MA, Sampson F, Dixon S, et al. , on behalf of the 3CPO study investigators.
-
Early high-dose lipid-lowering therapy to avoid cardiac events: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ara R, Pandor A, Stevens J, Rees A, Rafia R.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alpha for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: an updated systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jones J, Shepherd J, Baxter L, Gospodarevskaya E, Hartwell D, Harris P, et al.
-
Methods to identify postnatal depression in primary care: an integrated evidence synthesis and value of information analysis.
By Hewitt CE, Gilbody SM, Brealey S, Paulden M, Palmer S, Mann R, et al.
-
A double-blind randomised placebo-controlled trial of topical intranasal corticosteroids in 4- to 11-year-old children with persistent bilateral otitis media with effusion in primary care.
By Williamson I, Benge S, Barton S, Petrou S, Letley L, Fasey N, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of methods of storing donated kidneys from deceased donors: a systematic review and economic model.
By Bond M, Pitt M, Akoh J, Moxham T, Hoyle M, Anderson R.
-
Rehabilitation of older patients: day hospital compared with rehabilitation at home. A randomised controlled trial.
By Parker SG, Oliver P, Pennington M, Bond J, Jagger C, Enderby PM, et al.
-
Breastfeeding promotion for infants in neonatal units: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Renfrew MJ, Craig D, Dyson L, McCormick F, Rice S, King SE, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bariatric (weight loss) surgery for obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Picot J, Jones J, Colquitt JL, Gospodarevskaya E, Loveman E, Baxter L, et al.
-
Rapid testing for group B streptococcus during labour: a test accuracy study with evaluation of acceptability and cost-effectiveness.
By Daniels J, Gray J, Pattison H, Roberts T, Edwards E, Milner P, et al.
-
Screening to prevent spontaneous preterm birth: systematic reviews of accuracy and effectiveness literature with economic modelling.
By Honest H, Forbes CA, Durée KH, Norman G, Duffy SB, Tsourapas A, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cochlear implants for severe to profound deafness in children and adults: a systematic review and economic model.
By Bond M, Mealing S, Anderson R, Elston J, Weiner G, Taylor RS, et al.
-
Gemcitabine for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer.
By Jones J, Takeda A, Tan SC, Cooper K, Loveman E, Clegg A.
-
Varenicline in the management of smoking cessation: a single technology appraisal.
By Hind D, Tappenden P, Peters J, Kenjegalieva K.
-
Alteplase for the treatment of acute ischaemic stroke: a single technology appraisal.
By Lloyd Jones M, Holmes M.
-
Rituximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
By Bagust A, Boland A, Hockenhull J, Fleeman N, Greenhalgh J, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Omalizumab for the treatment of severe persistent allergic asthma.
By Jones J, Shepherd J, Hartwell D, Harris P, Cooper K, Takeda A, et al.
-
Rituximab for the treatment of relapsed or refractory stage III or IV follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
By Boland A, Bagust A, Hockenhull J, Davis H, Chu P, Dickson R.
-
Adalimumab for the treatment of psoriasis.
By Turner D, Picot J, Cooper K, Loveman E.
-
Dabigatran etexilate for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in patients undergoing elective hip and knee surgery: a single technology appraisal.
By Holmes M, C Carroll C, Papaioannou D.
-
Romiplostim for the treatment of chronic immune or idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a single technology appraisal.
By Mowatt G, Boachie C, Crowther M, Fraser C, Hernández R, Jia X, et al.
-
Sunitinib for the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumours: a critique of the submission from Pfizer.
By Bond M, Hoyle M, Moxham T, Napier M, Anderson R.
-
Vitamin K to prevent fractures in older women: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Stevenson M, Lloyd-Jones M, Papaioannou D.
-
The effects of biofeedback for the treatment of essential hypertension: a systematic review.
By Greenhalgh J, Dickson R, Dundar Y.
-
A randomised controlled trial of the use of aciclovir and/or prednisolone for the early treatment of Bell’s palsy: the BELLS study.
By Sullivan FM, Swan IRC, Donnan PT, Morrison JM, Smith BH, McKinstry B, et al.
-
Lapatinib for the treatment of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer.
By Jones J, Takeda A, Picot J, von Keyserlingk C, Clegg A.
-
Infliximab for the treatment of ulcerative colitis.
By Hyde C, Bryan S, Juarez-Garcia A, Andronis L, Fry-Smith A.
-
Rimonabant for the treatment of overweight and obese people.
By Burch J, McKenna C, Palmer S, Norman G, Glanville J, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Telbivudine for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection.
By Hartwell D, Jones J, Harris P, Cooper K.
-
Entecavir for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection.
By Shepherd J, Gospodarevskaya E, Frampton G, Cooper, K.
-
Febuxostat for the treatment of hyperuricaemia in people with gout: a single technology appraisal.
By Stevenson M, Pandor A.
-
Rivaroxaban for the prevention of venous thromboembolism: a single technology appraisal.
By Stevenson M, Scope A, Holmes M, Rees A, Kaltenthaler E.
-
Cetuximab for the treatment of recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
By Greenhalgh J, Bagust A, Boland A, Fleeman N, McLeod C, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Mifamurtide for the treatment of osteosarcoma: a single technology appraisal.
By Pandor A, Fitzgerald P, Stevenson M, Papaioannou D.
-
Ustekinumab for the treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis.
By Gospodarevskaya E, Picot J, Cooper K, Loveman E, Takeda A.
-
Endovascular stents for abdominal aortic aneurysms: a systematic review and economic model.
By Chambers D, Epstein D, Walker S, Fayter D, Paton F, Wright K, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of epoprostenol, iloprost, bosentan, sitaxentan and sildenafil for pulmonary arterial hypertension within their licensed indications: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Chen Y-F, Jowett S, Barton P, Malottki K, Hyde C, Gibbs JSR, et al.
-
Cessation of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder drugs in the young (CADDY) – a pharmacoepidemiological and qualitative study.
By Wong ICK, Asherson P, Bilbow A, Clifford S, Coghill D, R DeSoysa R, et al.
-
ARTISTIC: a randomised trial of human papillomavirus (HPV) testing in primary cervical screening.
By Kitchener HC, Almonte M, Gilham C, Dowie R, Stoykova B, Sargent A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness of glucosamine and chondroitin supplements in slowing or arresting progression of osteoarthritis of the knee: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Black C, Clar C, Henderson R, MacEachern C, McNamee P, Quayyum Z, et al.
-
Randomised preference trial of medical versus surgical termination of pregnancy less than 14 weeks’ gestation (TOPS).
By Robson SC, Kelly T, Howel D, Deverill M, Hewison J, Lie MLS, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trial of the use of three dressing preparations in the management of chronic ulceration of the foot in diabetes.
By Jeffcoate WJ, Price PE, Phillips CJ, Game FL, Mudge E, Davies S, et al.
-
VenUS II: a randomised controlled trial of larval therapy in the management of leg ulcers.
By Dumville JC, Worthy G, Soares MO, Bland JM, Cullum N, Dowson C, et al.
-
A prospective randomised controlled trial and economic modelling of antimicrobial silver dressings versus non-adherent control dressings for venous leg ulcers: the VULCAN trial
By Michaels JA, Campbell WB, King BM, MacIntyre J, Palfreyman SJ, Shackley P, et al.
-
Communication of carrier status information following universal newborn screening for sickle cell disorders and cystic fibrosis: qualitative study of experience and practice.
By Kai J, Ulph F, Cullinan T, Qureshi N.
-
Antiviral drugs for the treatment of influenza: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burch J, Paulden M, Conti S, Stock C, Corbett M, Welton NJ, et al.
-
Development of a toolkit and glossary to aid in the adaptation of health technology assessment (HTA) reports for use in different contexts.
By Chase D, Rosten C, Turner S, Hicks N, Milne R.
-
Colour vision testing for diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review of diagnostic accuracy and economic evaluation.
By Rodgers M, Hodges R, Hawkins J, Hollingworth W, Duffy S, McKibbin M, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of weight management schemes for the under fives: a short report.
By Bond M, Wyatt K, Lloyd J, Welch K, Taylor R.
-
Are adverse effects incorporated in economic models? An initial review of current practice.
By Craig D, McDaid C, Fonseca T, Stock C, Duffy S, Woolacott N.
-
Multicentre randomised controlled trial examining the cost-effectiveness of contrast-enhanced high field magnetic resonance imaging in women with primary breast cancer scheduled for wide local excision (COMICE).
By Turnbull LW, Brown SR, Olivier C, Harvey I, Brown J, Drew P, et al.
-
Bevacizumab, sorafenib tosylate, sunitinib and temsirolimus for renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Thompson Coon J, Hoyle M, Green C, Liu Z, Welch K, Moxham T, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of testing for cytochrome P450 polymorphisms in patients with schizophrenia treated with antipsychotics: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Fleeman N, McLeod C, Bagust A, Beale S, Boland A, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of photodynamic diagnosis and urine biomarkers (FISH, ImmunoCyt, NMP22) and cytology for the detection and follow-up of bladder cancer.
By Mowatt G, Zhu S, Kilonzo M, Boachie C, Fraser C, Griffiths TRL, et al.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of arthroscopic lavage in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a mixed methods study of the feasibility of conducting a surgical placebo-controlled trial (the KORAL study).
By Campbell MK, Skea ZC, Sutherland AG, Cuthbertson BH, Entwistle VA, McDonald AM, et al.
-
A randomised 2 × 2 trial of community versus hospital pulmonary rehabilitation for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease followed by telephone or conventional follow-up.
By Waterhouse JC, Walters SJ, Oluboyede Y, Lawson RA.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of behavioural interventions for the prevention of sexually transmitted infections in young people aged 13–19: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Kavanagh J, Picot J, Cooper K, Harden A, Barnett-Page E, et al.
-
Dissemination and publication of research findings: an updated review of related biases.
By Song F, Parekh S, Hooper L, Loke YK, Ryder J, Sutton AJ, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of biomarkers for the prioritisation of patients awaiting coronary revascularisation: a systematic review and decision model.
By Hemingway H, Henriksson M, Chen R, Damant J, Fitzpatrick N, Abrams K, et al.
-
Comparison of case note review methods for evaluating quality and safety in health care.
By Hutchinson A, Coster JE, Cooper KL, McIntosh A, Walters SJ, Bath PA, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for diabetes: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Cummins E, Royle P, Snaith A, Greene A, Robertson L, McIntyre L, et al.
-
Self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes: systematic review.
By Clar C, Barnard K, Cummins E, Royle P, Waugh N.
-
North of England and Scotland Study of Tonsillectomy and Adeno-tonsillectomy in Children (NESSTAC): a pragmatic randomised controlled trial with a parallel non-randomised preference study.
By Lock C, Wilson J, Steen N, Eccles M, Mason H, Carrie S, et al.
-
Multicentre randomised controlled trial of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of a bypass-surgery-first versus a balloon-angioplasty-first revascularisation strategy for severe limb ischaemia due to infrainguinal disease. The Bypass versus Angioplasty in Severe Ischaemia of the Leg (BASIL) trial.
By Bradbury AW, Adam DJ, Bell J, Forbes JF, Fowkes FGR, Gillespie I, et al.
-
A randomised controlled multicentre trial of treatments for adolescent anorexia nervosa including assessment of cost-effectiveness and patient acceptability – the TOuCAN trial.
By Gowers SG, Clark AF, Roberts C, Byford S, Barrett B, Griffiths A, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trials for policy interventions: a review of reviews and meta-regression.
By Oliver S, Bagnall AM, Thomas J, Shepherd J, Sowden A, White I, et al.
-
Paracetamol and selective and non-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for the reduction of morphine-related side effects after major surgery: a systematic review.
By McDaid C, Maund E, Rice S, Wright K, Jenkins B, Woolacott N.
-
A systematic review of outcome measures used in forensic mental health research with consensus panel opinion.
By Fitzpatrick R, Chambers J, Burns T, Doll H, Fazel S, Jenkinson C, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Loveman E, Jones J, Hartwell D, Bird A, Harris P, Welch K, et al.
-
Antenatal screening for haemoglobinopathies in primary care: a cohort study and cluster randomised trial to inform a simulation model. The Screening for Haemoglobinopathies in First Trimester (SHIFT) trial.
By Dormandy E, Bryan S, Gulliford MC, Roberts T, Ades T, Calnan M, et al.
-
Early referral strategies for management of people with markers of renal disease: a systematic review of the evidence of clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and economic analysis.
By Black C, Sharma P, Scotland G, McCullough K, McGurn D, Robertson L, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial of cognitive behaviour therapy and motivational interviewing for people with Type 1 diabetes mellitus with persistent sub-optimal glycaemic control: A Diabetes and Psychological Therapies (ADaPT) study.
By Ismail K, Maissi E, Thomas S, Chalder T, Schmidt U, Bartlett J, et al.
-
A randomised controlled equivalence trial to determine the effectiveness and cost–utility of manual chest physiotherapy techniques in the management of exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (MATREX).
By Cross J, Elender F, Barton G, Clark A, Shepstone L, Blyth A, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of aldosterone antagonists for postmyocardial infarction heart failure.
By McKenna C, Burch J, Suekarran S, Walker S, Bakhai A, Witte K, et al.
-
Avoiding and identifying errors in health technology assessment models: qualitative study and methodological review.
By Chilcott JB, Tappenden P, Rawdin A, Johnson M, Kaltenthaler E, Paisley S, et al.
-
BoTULS: a multicentre randomised controlled trial to evaluate the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of treating upper limb spasticity due to stroke with botulinum toxin type A.
By Shaw L, Rodgers H, Price C, van Wijck F, Shackley P, Steen N, et al. , on behalf of the BoTULS investigators.
-
Weighting and valuing quality-adjusted life-years using stated preference methods: preliminary results from the Social Value of a QALY Project.
By Baker R, Bateman I, Donaldson C, Jones-Lee M, Lancsar E, Loomes G, et al.
-
Cetuximab for the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.
By Meads C, Round J, Tubeuf S, Moore D, Pennant M and Bayliss S.
-
Infliximab for the treatment of acute exacerbations of ulcerative colitis.
By Bryan S, Andronis L, Hyde C, Connock M, Fry-Smith A and Wang D.
-
Sorafenib for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
By Connock M, Round J, Bayliss S, Tubeuf S, Greenheld W and Moore D.
-
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection.
By Jones J, Colquitt J, Shepherd J, Harris P and Cooper K.
-
Prasugrel for the treatment of acute coronary artery syndromes with percutaneous coronary intervention.
By Greenhalgh J, Bagust A, Boland A, Saborido CM, Fleeman N, McLeod C, et al.
-
Alitretinoin for the treatment of severe chronic hand eczema.
By Paulden M, Rodgers M, Griffin S, Slack R, Duffy S, Ingram JR, et al.
-
Pemetrexed for the first-line treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer.
By Fleeman N, Bagust A, McLeod C, Greenhalgh J, Boland A, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Topotecan for the treatment of recurrent and stage IVB carcinoma of the cervix.
By Paton F, Paulden M, Saramago P, Manca A, Misso K, Palmer S, et al.
-
Trabectedin for the treatment of advanced metastatic soft tissue sarcoma.
By Simpson EL, Rafia R, Stevenson MD and Papaioannou D.
-
Azacitidine for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome, chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia and acute myeloid leukaemia.
By Edlin R, Connock M, Tubeuf S, Round J, Fry-Smith A, Hyde C, et al.
-
The safety and effectiveness of different methods of earwax removal: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clegg AJ, Loveman E, Gospodarevskaya E, Harris P, Bird A, Bryant J, et al.
Health Technology Assessment programme
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
Prioritisation Strategy Group
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
-
Dr Bob Coates, Consultant Advisor, NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Andrew Cook, Consultant Advisor, NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Peter Davidson, Director of NETSCC, Health Technology Assessment
-
Professor Robin E Ferner, Consultant Physician and Director, West Midlands Centre for Adverse Drug Reactions, City Hospital NHS Trust, Birmingham
-
Professor Paul Glasziou, Professor of Evidence-Based Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Dr Nick Hicks, Consultant Adviser, NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Edmund Jessop, Medical Adviser, National Specialist, National Commissioning Group (NCG), Department of Health, London
-
Ms Lynn Kerridge, Chief Executive Officer, NETSCC and NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Ruairidh Milne, Director of NETSCC External Relations
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Senior NIHR Programme Manager, Department of Health
-
Ms Pamela Young, Specialist Programme Manager, NETSCC, HTA
HTA Commissioning Board
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Warwick Clinical Trials Unit
-
Director, Nottingham Clinical Trials Unit
-
Senior Lecturer in General Practice, Department of Primary Health Care, University of Oxford
-
Professor Ann Ashburn, Professor of Rehabilitation and Head of Research, Southampton General Hospital
-
Professor Deborah Ashby, Professor of Medical Statistics, Queen Mary, University of London
-
Professor John Cairns, Professor of Health Economics, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Peter Croft, Director of Primary Care Sciences Research Centre, Keele University
-
Professor Nicky Cullum, Director of Centre for Evidence-Based Nursing, University of York
-
Professor Jenny Donovan, Professor of Social Medicine, University of Bristol
-
Professor Steve Halligan, Professor of Gastrointestinal Radiology, University College Hospital, London
-
Professor Freddie Hamdy, Professor of Urology, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Allan House, Professor of Liaison Psychiatry, University of Leeds
-
Dr Martin J Landray, Reader in Epidemiology, Honorary Consultant Physician, Clinical Trial Service Unit, University of Oxford?
-
Professor Stuart Logan, Director of Health & Social Care Research, The Peninsula Medical School, Universities of Exeter and Plymouth
-
Dr Rafael Perera, Lecturer in Medical Statisitics, Department of Primary Health Care, University of Oxford
-
Professor Ian Roberts, Professor of Epidemiology & Public Health, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Mark Sculpher, Professor of Health Economics, University of York
-
Professor Helen Smith, Professor of Primary Care, University of Brighton
-
Professor Kate Thomas, Professor of Complementary & Alternative Medicine Research, University of Leeds
-
Professor David John Torgerson, Director of York Trials Unit, University of York
-
Ms Kay Pattison, NHS R&D Programme/DH, Leeds
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Medical Research Council
Diagnostic Technologies and Screening Panel
-
Professor of Evidence-Based Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Consultant Paediatrician and Honorary Senior Lecturer, Great Ormond Street Hospital, London
-
Professor Judith E Adams, Consultant Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Central Manchester & Manchester Children’s University Hospitals NHS Trust, and Professor of Diagnostic Radiology, Imaging Science and Biomedical Engineering, Cancer & Imaging Sciences, University of Manchester
-
Mr A S Arunkalaivanan, Honorary Senior Lecturer, University of Birmingham and Consultant Urogynaecologist and Obstetrician, City Hospital
-
Dr Dianne Baralle, Consultant & Senior Lecturer in Clinical Genetics, Human Genetics Division & Wessex Clinical Genetics Service, Southampton, University of Southampton
-
Dr Stephanie Dancer, Consultant Microbiologist, Hairmyres Hospital, East Kilbride
-
Dr Ron Gray, Consultant, National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, Institute of Health Sciences, University of Oxford
-
Professor Paul D Griffiths, Professor of Radiology, Academic Unit of Radiology, University of Sheffield
-
Mr Martin Hooper, Service User Representative
-
Professor Anthony Robert Kendrick, Professor of Primary Medical Care, University of Southampton
-
Dr Susanne M Ludgate, Director, Medical Devices Agency, London
-
Dr Anne Mackie, Director of Programmes, UK National Screening Committee
-
Dr David Mathew Service User Representative
-
Dr Michael Millar, Lead Consultant in Microbiology, Department of Pathology & Microbiology, Barts and The London NHS Trust, Royal London Hospital
-
Mr Stephen Pilling, Director, Centre for Outcomes, Research & Effectiveness, University College London
-
Mrs Una Rennard, Service User Representative
-
Ms Jane Smith, Consultant Ultrasound Practitioner, Ultrasound Department, Leeds Teaching Hospital NHS Trust, Leeds
-
Dr W Stuart A Smellie, Consultant, Bishop Auckland General Hospital
-
Professor Lindsay Wilson Turnbull, Scientific Director of the Centre for Magnetic Resonance Investigations and YCR Professor of Radiology, Hull Royal Infirmary
-
Dr Alan J Williams, Consultant in General Medicine, Department of Thoracic Medicine, The Royal Bournemouth Hospital
-
Dr Tim Elliott, Team Leader, Cancer Screening, Department of Health
-
Dr Catherine Moody, Programme Manager, Neuroscience and Mental Health Board
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Disease Prevention Panel
-
Medical Adviser, National Specialist Commissioning Advisory Group (NSCAG), Department of Health
-
Professor of Epidemiology, University of Warwick Medical School, Coventry
-
Dr Robert Cook Clinical Programmes Director, Bazian Ltd, London
-
Dr Elizabeth Fellow-Smith, Medical Director, West London Mental Health Trust, Middlesex
-
Dr Colin Greaves Senior Research Fellow, Peninsular Medical School (Primary Care)
-
Dr John Jackson, General Practitioner, Parkway Medical Centre, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Dr Russell Jago, Senior Lecturer in Exercise, Nutrition and Health, Centre for Sport, Exercise and Health, University of Bristol
-
Dr Chris McCall, General Practitioner, The Hadleigh Practice, Corfe Mullen, Dorset
-
Miss Nicky Mullany, Service User Representative
-
Dr Julie Mytton, Locum Consultant in Public Health Medicine, Bristol Primary Care Trust
-
Professor Irwin Nazareth, Professor of Primary Care and Director, Department of Primary Care and Population Sciences, University College London
-
Professor Ian Roberts, Professor of Epidemiology and Public Health, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Carol Tannahill, Glasgow Centre for Population Health
-
Mrs Jean Thurston, Service User Representative
-
Professor David Weller, Head, School of Clinical Science and Community Health, University of Edinburgh
-
Ms Christine McGuire, Research & Development, Department of Health
-
Ms Kay Pattison Senior NIHR Programme Manager, Department of Health
-
Dr Caroline Stone, Programme Manager, Medical Research Council
External Devices and Physical Therapies Panel
-
Consultant Physician North Bristol NHS Trust, Bristol
-
Reader in Wound Healing and Director of Research, University of Leeds, Leeds
-
Professor Bipin Bhakta Charterhouse Professor in Rehabilitation Medicine, University of Leeds, Leeds
-
Mrs Penny Calder Service User Representative
-
Professor Paul Carding, Professor of Voice Pathology, Newcastle Hospital NHS Trust, Newcastle
-
Dr Dawn Carnes, Senior Research Fellow, Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry, London
-
Dr Emma Clark, Clinician Scientist Fellow & Cons. Rheumatologist, University of Bristol, Bristol
-
Mrs Anthea De Barton-Watson, Service User Representative
-
Professor Christopher Griffiths, Professor of Primary Care, Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry, London
-
Dr Shaheen Hamdy, Clinical Senior Lecturer and Consultant Physician, University of Manchester, Manchester
-
Dr Peter Martin, Consultant Neurologist, Addenbrooke’s Hospital, Cambridge
-
Dr Lorraine Pinnigton, Associate Professor in Rehabilitation, University of Nottingham, Nottingham
-
Dr Kate Radford, Division of Rehabilitation and Ageing, School of Community Health Sciences. University of Nottingham, Nottingham
-
Mr Jim Reece, Service User Representative
-
Professor Maria Stokes, Professor of Neuromusculoskeletal Rehabilitation, University of Southampton, Southampton
-
Dr Pippa Tyrrell, Stroke Medicine, Senior Lecturer/Consultant Stroke Physician, Salford Royal Foundation Hospitals’ Trust, Salford
-
Dr Sarah Tyson, Senior Research Fellow & Associate Head of School, University of Salford, Salford
-
Dr Nefyn Williams, Clinical Senior Lecturer, Cardiff University, Cardiff
-
Dr Phillip Leech, Principal Medical Officer for Primary Care, Department of Health , London
-
Ms Kay Pattison Senior NIHR Programme Manager, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, MRC, London
-
Dr Ursula Wells PRP, DH, London
Interventional Procedures Panel
-
Consultant Surgeon & Honorary Clinical Lecturer, University of Sheffield
-
Mr David P Britt, Service User Representative, Cheshire
-
Mr Sankaran ChandraSekharan, Consultant Surgeon, Colchester Hospital University NHS Foundation Trust
-
Professor Nicholas Clarke, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust
-
Mr Seamus Eckford, Consultant in Obstetrics & Gynaecology, North Devon District Hospital
-
Professor David Taggart, Consultant Cardiothoracic Surgeon, John Radcliffe Hospital
-
Dr Matthew Hatton, Consultant in Clinical Oncology, Sheffield Teaching Hospital Foundation Trust
-
Dr John Holden, General Practitioner, Garswood Surgery, Wigan
-
Dr Nadim Malik, Consultant Cardiologist/ Honorary Lecturer, University of Manchester
-
Mr Hisham Mehanna, Consultant & Honorary Associate Professor, University Hospitals Coventry & Warwickshire NHS Trust
-
Dr Jane Montgomery, Consultant in Anaesthetics and Critical Care, South Devon Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust
-
Dr Simon Padley, Consultant Radiologist, Chelsea & Westminster Hospital
-
Dr Ashish Paul, Medical Director, Bedfordshire PCT
-
Dr Sarah Purdy, Consultant Senior Lecturer, University of Bristol
-
Mr Michael Thomas, Consultant Colorectal Surgeon, Bristol Royal Infirmary
-
Professor Yit Chiun Yang, Consultant Ophthalmologist, Royal Wolverhampton Hospitals NHS Trust
-
Mrs Isabel Boyer, Service User Representative, London
Pharmaceuticals Panel
-
Professor in Child Health, University of Nottingham
-
Unit Manager, Pharmacoepidemiology Research Unit, VRMM, Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency
-
Mrs Nicola Carey, Senior Research Fellow, School of Health and Social Care, The University of Reading
-
Mr John Chapman, Service User Representative
-
Dr Peter Elton, Director of Public Health, Bury Primary Care Trust
-
Professor Robin Ferner, Consultant Physician and Director, West Midlands Centre for Adverse Drug Reactions, City Hospital NHS Trust, Birmingham
-
Dr Ben Goldacre, Research Fellow, Division of Psychological Medicine and Psychiatry, King’s College London
-
Dr Bill Gutteridge, Medical Adviser, London Strategic Health Authority
-
Dr Dyfrig Hughes, Reader in Pharmacoeconomics and Deputy Director, Centre for Economics and Policy in Health, IMSCaR, Bangor University
-
Dr Yoon K Loke, Senior Lecturer in Clinical Pharmacology, University of East Anglia
-
Professor Femi Oyebode, Consultant Psychiatrist and Head of Department, University of Birmingham
-
Dr Andrew Prentice, Senior Lecturer and Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, The Rosie Hospital, University of Cambridge
-
Dr Martin Shelly, General Practitioner, Leeds, and Associate Director, NHS Clinical Governance Support Team, Leicester
-
Dr Gillian Shepherd, Director, Health and Clinical Excellence, Merck Serono Ltd
-
Mrs Katrina Simister, Assistant Director New Medicines, National Prescribing Centre, Liverpool
-
Mr David Symes, Service User Representative
-
Ms Kay Pattison Senior NIHR Programme Manager, Department of Health
-
Mr Simon Reeve, Head of Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness, Medicines, Pharmacy and Industry Group, Department of Health
-
Dr Heike Weber, Programme Manager, Medical Research Council
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Psychological and Community Therapies Panel
-
Professor of Psychiatry, University of Warwick
-
Professor Jane Barlow, Professor of Public Health in the Early Years, Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School
-
Dr Sabyasachi Bhaumik, Consultant Psychiatrist, Leicestershire Partnership NHS Trust
-
Mrs Val Carlill, Service User Representative, Gloucestershire
-
Dr Steve Cunningham, Consultant Respiratory Paediatrician, Lothian Health Board
-
Dr Anne Hesketh, Senior Clinical Lecturer in Speech and Language Therapy, University of Manchester
-
Dr Yann Lefeuvre, GP Partner, Burrage Road Surgery, London
-
Dr Jeremy J Murphy, Consultant Physician & Cardiologist, County Durham & Darlington Foundation Trust
-
Mr John Needham, Service User, Buckingmashire
-
Ms Mary Nettle, Mental Health User Consultant, Gloucestershire
-
Professor John Potter, Professor of Ageing and Stroke Medicine, University of East Anglia
-
Dr Greta Rait, Senior Clinical Lecturer and General Practitioner, University College London
-
Dr Paul Ramchandani, Senior Research Fellow/Cons. Child Psychiatrist, University of Oxford
-
Dr Howard Ring, Consultant & University Lecturer in Psychiatry, University of Cambridge
-
Dr Karen Roberts, Nurse/Consultant, Dunston Hill Hospital, Tyne and Wear
-
Dr Karim Saad, Consultant in Old Age Psychiatry, Coventry & Warwickshire Partnership Trust
-
Dr Alastair Sutcliffe, Senior Lecturer, University College London
-
Dr Simon Wright, GP Partner, Walkden Medical Centre, Manchester
-
Ms Kay Pattison Senior NIHR Programme Manager, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, MRC, London
-
Professor Tom Walley, HTA Programme Director, Liverpool
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Policy Research Programme, DH, London
Expert Advisory Network
-
Professor Douglas Altman, Professor of Statistics in Medicine, Centre for Statistics in Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Professor John Bond, Professor of Social Gerontology & Health Services Research, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Andrew Bradbury, Professor of Vascular Surgery, Solihull Hospital, Birmingham
-
Mr Shaun Brogan, Chief Executive, Ridgeway Primary Care Group, Aylesbury
-
Mrs Stella Burnside OBE, Chief Executive, Regulation and Improvement Authority, Belfast
-
Ms Tracy Bury, Project Manager, World Confederation for Physical Therapy, London
-
Professor Iain T Cameron, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology and Head of the School of Medicine, University of Southampton
-
Dr Christine Clark, Medical Writer and Consultant Pharmacist, Rossendale
-
Professor Collette Clifford, Professor of Nursing and Head of Research, The Medical School, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Barry Cookson, Director, Laboratory of Hospital Infection, Public Health Laboratory Service, London
-
Dr Carl Counsell, Clinical Senior Lecturer in Neurology, University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Howard Cuckle, Professor of Reproductive Epidemiology, Department of Paediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynaecology, University of Leeds
-
Dr Katherine Darton, Information Unit, MIND – The Mental Health Charity, London
-
Professor Carol Dezateux, Professor of Paediatric Epidemiology, Institute of Child Health, London
-
Mr John Dunning, Consultant Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Papworth Hospital NHS Trust, Cambridge
-
Mr Jonothan Earnshaw, Consultant Vascular Surgeon, Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Gloucester
-
Professor Martin Eccles, Professor of Clinical Effectiveness, Centre for Health Services Research, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Pam Enderby, Dean of Faculty of Medicine, Institute of General Practice and Primary Care, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Gene Feder, Professor of Primary Care Research & Development, Centre for Health Sciences, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Mr Leonard R Fenwick, Chief Executive, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Mrs Gillian Fletcher, Antenatal Teacher and Tutor and President, National Childbirth Trust, Henfield
-
Professor Jayne Franklyn, Professor of Medicine, University of Birmingham
-
Mr Tam Fry, Honorary Chairman, Child Growth Foundation, London
-
Professor Fiona Gilbert, Consultant Radiologist and NCRN Member, University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Paul Gregg, Professor of Orthopaedic Surgical Science, South Tees Hospital NHS Trust
-
Bec Hanley, Co-director, TwoCan Associates, West Sussex
-
Dr Maryann L Hardy, Senior Lecturer, University of Bradford
-
Mrs Sharon Hart, Healthcare Management Consultant, Reading
-
Professor Robert E Hawkins, CRC Professor and Director of Medical Oncology, Christie CRC Research Centre, Christie Hospital NHS Trust, Manchester
-
Professor Richard Hobbs, Head of Department of Primary Care & General Practice, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Alan Horwich, Dean and Section Chairman, The Institute of Cancer Research, London
-
Professor Allen Hutchinson, Director of Public Health and Deputy Dean of ScHARR, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Peter Jones, Professor of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge
-
Professor Stan Kaye, Cancer Research UK Professor of Medical Oncology, Royal Marsden Hospital and Institute of Cancer Research, Surrey
-
Dr Duncan Keeley, General Practitioner (Dr Burch & Ptnrs), The Health Centre, Thame
-
Dr Donna Lamping, Research Degrees Programme Director and Reader in Psychology, Health Services Research Unit, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London
-
Mr George Levvy, Chief Executive, Motor Neurone Disease Association, Northampton
-
Professor James Lindesay, Professor of Psychiatry for the Elderly, University of Leicester
-
Professor Julian Little, Professor of Human Genome Epidemiology, University of Ottawa
-
Professor Alistaire McGuire, Professor of Health Economics, London School of Economics
-
Professor Rajan Madhok, Medical Director and Director of Public Health, Directorate of Clinical Strategy & Public Health, North & East Yorkshire & Northern Lincolnshire Health Authority, York
-
Professor Alexander Markham, Director, Molecular Medicine Unit, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Dr Peter Moore, Freelance Science Writer, Ashtead
-
Dr Andrew Mortimore, Public Health Director, Southampton City Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Sue Moss, Associate Director, Cancer Screening Evaluation Unit, Institute of Cancer Research, Sutton
-
Professor Miranda Mugford, Professor of Health Economics and Group Co-ordinator, University of East Anglia
-
Professor Jim Neilson, Head of School of Reproductive & Developmental Medicine and Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, University of Liverpool
-
Mrs Julietta Patnick, National Co-ordinator, NHS Cancer Screening Programmes, Sheffield
-
Professor Robert Peveler, Professor of Liaison Psychiatry, Royal South Hants Hospital, Southampton
-
Professor Chris Price, Director of Clinical Research, Bayer Diagnostics Europe, Stoke Poges
-
Professor William Rosenberg, Professor of Hepatology and Consultant Physician, University of Southampton
-
Professor Peter Sandercock, Professor of Medical Neurology, Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Edinburgh
-
Dr Susan Schonfield, Consultant in Public Health, Hillingdon Primary Care Trust, Middlesex
-
Dr Eamonn Sheridan, Consultant in Clinical Genetics, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Dr Margaret Somerville, Director of Public Health Learning, Peninsula Medical School, University of Plymouth
-
Professor Sarah Stewart-Brown, Professor of Public Health, Division of Health in the Community, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Professor Ala Szczepura, Professor of Health Service Research, Centre for Health Services Studies, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Mrs Joan Webster, Consumer Member, Southern Derbyshire Community Health Council
-
Professor Martin Whittle, Clinical Co-director, National Co-ordinating Centre for Women’s and Children’s Health, Lymington