Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the HTA programme as project number 12/02/01. The contractual start date was in March 2012. The draft report began editorial review in July 2012 and was accepted for publication in January 2013. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors' report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Aileen Clarke is a member of the NIHR Journals Library Editorial Board.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen's Printer and Controller of HMSO 2013. This work was produced by Sutcliffe et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
Chapter 1 Background
Introduction
Heart failure (HF) is a common condition in which the heart does not pump blood properly limiting an individual's quality of life (QoL) and length of life. 1 This chapter describes definition, epidemiology, causes, classification and management of HF.
Definition of heart failure
There are many definitions of HF2 which have changed over the years. Changes have caused difficulties in undertaking epidemiological studies in this area. 2
In 1989, HF was defined as a ‘syndrome which develops as a consequence of cardiac disease and is recognised clinically by a constellation of symptoms and signs produced by complex circulatory and neurohormonal responses to cardiac dysfunction’. 3 A Health Technology Assessment (HTA) report published in 2005 described HF as ‘a disease characterised by a decline in the heart's ability to pump blood around a person's body at normal filling pressures to meet its metabolic needs’. 4
Symptoms of HF typically include shortness of breath at rest or during exertion and/or fatigue, signs of fluid retention such as pulmonary congestion and ankle swelling, and objective evidence of an abnormality of the structure or function of the heart at rest (Box 1). 5,6 Over time, as HF advances, the severity of symptoms worsens. The condition is sometimes known as advanced or end-stage HF. For consistency in this report we will refer to advanced HF.
Heart failure is a clinical syndrome in which patients have the following features:
-
symptoms typical of HF: breathlessness at rest or on exercise, fatigue, tiredness, ankle swelling; and
-
signs typical of HF: tachycardia, tachypnoea, pulmonary rales, pleural effusion, raised jugular venous pressure, peripheral oedema, hepatomegaly; and
-
objective evidence of a structural or functional abnormality of the heart at rest: cardiomegaly, third heart sound, cardiac murmurs, abnormality on the echocardiogram, raised natriuretic peptide concentration.
Epidemiology of heart failure
Heart failure is a major health problem worldwide. It has a considerable impact on health-care costs and patients' lives. It has been estimated that there are currently approximately 750,000 people with HF in the UK. 1 According to the General Practice Research Database, the overall incidence rates of HF are 37.5 and 23 per 100,000 person-years for men and women, respectively, and there are an estimated 27,000 new cases of HF per year in the UK. 7 The overall prevalence of HF in the UK at age 65–74 years is 1 in 35 people, which increases to 1 in 15 in those aged 75–84 years, and just over 1 in 7 in those aged ≥ 85 years. 8 Parameshwar et al. found that the prevalence of HF in the UK in patients aged < 65 years was 0.6 per 1000 patients but rose to 27.2 per 1000 in those aged ≥ 65 years. 9 Similarly, the Hillingdon Heart Failure Study, a contemporary population-based study, identified the median age at presentation of HF as 76 years10 indicating that risk increases with increasing age. This is in accordance with recorded higher rates of hospital admission for HF at older ages in the UK. 11
In the year 2000, the direct health-care costs of HF to the NHS were estimated to be £0.75B annually. Total expenditure was estimated to be approximately 4% of the total health-care expenditure in the UK. 11 The impact on health-care costs in the UK is owing to the high prevalence of cardiovascular diseases in older age groups coupled with ageing of the population. 4
Over the last 10 years HF admission rates in England increased by around 5% and 4% in men and women respectively. 12 It has been predicted that the burden of HF will rise over the next 20–30 years. Hospital admissions due to HF are estimated to increase by approximately 50% in the next 25 years. 12,13
Aetiology and pathophysiology of heart failure
Any anatomical or physiological conditions which affect ventricular function can cause HF. In a survey conducted in Hillingdon, West London, which included a population of 151,000 people, researchers found that the most common cause of HF was ischaemic or coronary heart disease (CHD). 10 Similarly, in a UK-based population, a study of coronary artery angiography in new patients aged < 75 years,14 CHD was found to be the commonest cause of HF. Other causes of HF include hypertension, valvular heart disease, myocardial toxins, myocarditis and cardiomyopathy. 4,10,14
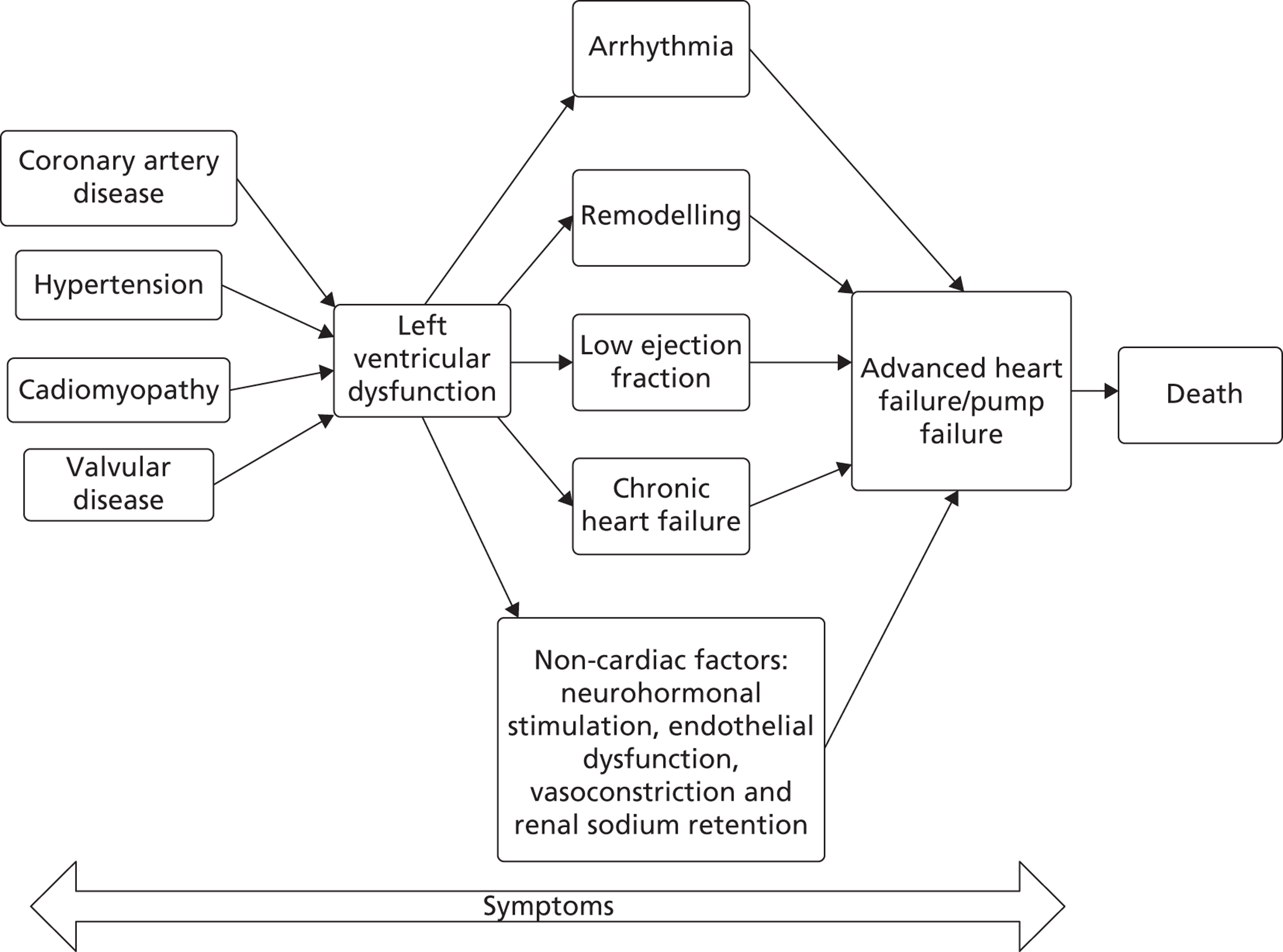
The final common pathway for all pathophysiology of HF (CHD, poorly controlled hypertension, cardiomyopathy or valvular heart disease) is ventricular dysfunction. The left ventricle (LV) is most commonly affected with eventual myocardial injury and remodelling leading to a dilated ventricular chamber with a low ejection fraction, activation of non-cardiac factors such as the neurohormonal systems with vasoconstriction and renal sodium retention, and further symptoms such as dyspnoea, fatigue and oedema (Figure 1). 15,16 This can lead to episodes of arrhythmia, increasing pump failure and, finally, premature death. However, aetiology of HF varies by age group, as also do the criteria used to identify its presence. 10,17
Symptoms and signs of heart failure
The most common symptoms of HF are breathlessness, tiredness, loss of appetite, and signs of peripheral oedema, raised jugular venous pressure, tachycardia or tachypnoea. 5,6 The severity of HF is usually assessed using the New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional classification, which is based on the severity of symptoms patients develop in relation to physical activity. Severity of HF can be classified into four grades using the NYHA classification. Patients with NYHA class I are considered to be less severely affected and can perform ordinary physical activity without developing symptoms of HF. Patients with NYHA class IV have advanced HF, are unable to carry out any physical activity and have symptoms at rest (Box 2).
Class I: No limitation of physical activity. Ordinary physical activity does not cause undue fatigue, palpitation or dyspnoea.
Class II: Slight limitation of physical activity. Comfortable at rest, but ordinary physical activity results in fatigue, palpitation or dyspnoea.
Class III: Marked limitation of physical activity. Comfortable at rest, but less than ordinary activity results in fatigue, palpitation or dyspnoea.
Class IV: Unable to carry on any physical activity without discomfort. Symptoms at rest. If any physical activity is undertaken, discomfort is increased.
Adapted from the Criteria Committee of the NYHA, Nomenclature and Criteria for Diagnosis of Diseases of the Heart and Great Vessels. 18
Diagnosis of heart failure
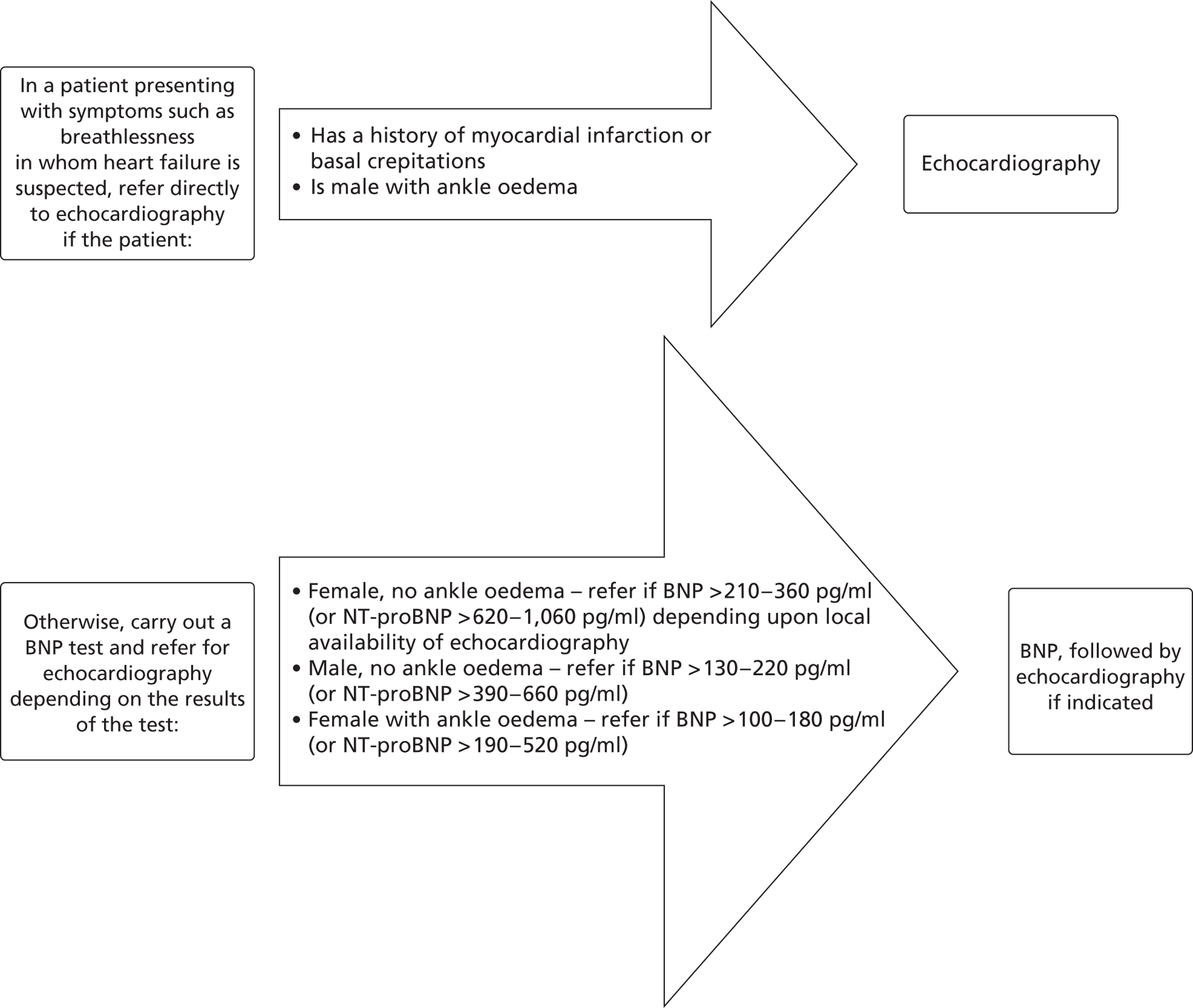
There is no ‘gold standard’ for diagnosis of HF. Initially, it is assessed by patient history and physical examination. 8 In addition, there are no signs and symptoms that are both sensitive and specific for the diagnosis of HF. 19 Investigations such as electrocardiography, measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) or both are recommended depending on the condition. If the above tests are abnormal then echocardiography (to measure ventricular performance) and chest radiography (to detect cardiomegaly, pulmonary congestion and pleural fluid accumulation) are undertaken to confirm the diagnosis of HF. BNP and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-pro-BNP) are useful biomarker hormones in the diagnosis of HF. Levels of these biomarkers are raised in patients with HF and the concentrations vary with NYHA class. 5,19,20 Figure 2 gives a schematic representation of recommendations on the diagnosis of HF (adapted from Sutherland). 21
FIGURE 2.
A schematic diagram of HF diagnosis recommendations (redrawn and adapted from Sutherland21).
Quality of life and prognosis of heart failure
People with HF are often heavy users of primary care services. 17,22 The mortality rate of HF is comparable to that of cancer. 17,23 de Giuli et al. 24 studied primary care patients in the UK and found that people with HF have a very poor prognosis, especially the elderly. The Hillingdon Heart Failure study also reported that around 40% of people die within 1 year of a diagnosis of HF. 10 In the Echocardiographic Heart of England Screening Study, QoL was measured by Short Form questionnaire-36 items (SF-36), and impairment in both mental and physical QoL was reported. Impairment was found to be worse in those with more severe HF as measured by NYHA severity assessment class25 and reduction in QoL was particularly evident among elderly people. 21
Management of heart failure
Treatment of patients with HF depends on type and stage of HF.
Medical management
Medical therapy is beneficial and used for symptomatic relief in patients with HF. 26 Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and beta-blockers are recommended as first-line therapy in patients with chronic HF caused by systolic LV dysfunction. Alternatively, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) can be given to patients to reduce morbidity and mortality. 5,27,28 Other drugs, such as beta-adrenoceptor antagonists, inhibitors of the renin–angiotensin system and aldosterone antagonists, can also be used. Diuretics such as thiazides or loop diuretics are given for symptomatic benefit. 6 Simultaneously, it is important to control intake of fluid and sodium in these patients. In severely ill patients who do not respond to other medical treatment, inotropic drugs, such as dobutamine (Dobutrex®, Abbott Healthcare Pvt. Ltd), milrinone (Primacor®, Sanofi-Aventis) or enoximone (Perfan®, Hoechst Marion Roussel), may be considered. 27,28 In England, for example, inotropic drugs are given only on specialist advice for treatment of decompensating HF to reduce hypoperfusion or congestion and if patients are resistant to vasodilators and/or diuretics. 5,6 Some patients can become inotropic dependent while waiting for a donor heart to become available.
Electrical device treatment and heart transplant
Cardiac resynchronisation treatment (CRT) is recommended to improve symptoms and survival of patients with HF, but there remains a subgroup of patients who, despite optimal medical therapy, progress to more severe HF equivalent to NYHA class III or IV. 26
The prognosis for patients with advanced HF who do not respond to pharmacological and electrical resynchronising therapies is poor. Therefore, heart transplant (HT) is the ultimate surgical approach for the treatment of patients with advanced HF. HT can increase long-term survival for these patients. Patients with NYHA class III or IV are eligible for HT. 28 Survival after HT is estimated at approximately 50% at 10 years. In contrast, for similar patients who do not receive a HT, survival is < 50% at 1 year. 29 In the UK HT has been offered to patients with advanced HF over the last 30 years. However, overall numbers and rates of HT have decreased more recently, i.e. over the last 10 years. 1
It has been estimated that, although approximately 30,000 patients are waiting for a HT worldwide, only 3500 donor hearts are available annually. 26 The increasing number of patients with HF coupled with the shortage of donor hearts has led to an increased mortality rates among patients waiting for HT. It is estimated that approximately 30% of patients die while waiting for a HT. 26 Following HT, patients are at high risk of developing complications such as infection, bleeding, lung congestion, liver congestion, renal failure, neurological complications (NCs) and device failure. In order to prevent allograft rejection,6 patients are also given a variety of immunosuppressant and prophylactic drugs, which in turn increases their susceptibility to opportunistic infection. 30
Mechanical circulatory devices (MCDs) have increasingly been used in the last decade or so in order to increase survival and QoL for patients awaiting HT. 4,30 These devices are used as either short- or long-term support in patients awaiting HT. 31 When a VAD is implanted for a short duration of time, while the patient waits for a suitable heart to become available for transplantation, the procedure is called bridge to transplant (BTT). VADs are currently approved as BTT in the UK. When a VAD is implanted temporarily to support blood flow to allow the heart to recover from a condition, such as post-myocardial infarction or post-cardiotomy shock, the procedure is known as bridge to recovery (BTR). When recovery is impossible and patients are ineligible for HT, then VADs are used as destination therapy (DT). 32 Currently the NHS does not fund VADs as DT;28 however, VADs are increasingly used for this purpose in some non-UK countries. 33
Unfortunately, not all patients are eligible for HT. As reported in the Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support (INTERMACS) study,34 contraindications to HT can be due to either modifiable or non-modifiable factors. In the INTERMACS study, the most commonly reported contraindications included advanced age, renal dysfunction or high body mass index (BMI). It should be noted that > 50% of the contraindications identified in the INTERMACS study were modifiable. Approximately 10% of patients originally considered unsuitable for HT and selected for DT subsequently improved sufficiently to undergo HT after 12 months. 34
In this report, we are considering only patients who are eligible for HT. We are investigating two situations:
-
The use of VADs as BTT in patients eligible for HT.
-
The use of VADs as an alternative to transplant in patients who are eligible for transplant – a procedure not currently used in the UK. We have coined a new acronym for this situation, ‘alternative to transplant’ (ATT). ATT should be clearly distinguished from DT as patients receiving ATT are eligible for HT. Patients receiving VADs as DT are not eligible for HT.
Mechanical circulatory devices or ventricular assist devices
Mechanical circulatory devices or VADs are categorised into (a) left ventricular assist devices (LVADs), (b) right ventricular assist devices (RVADs) or (c) devices designed to support both ventricles (biventricular assist devices; BiVADs). Other types include the percutaneous ventricular assist device (PVAD) and the total artificial heart (TAH). Device use depends on the patient's condition and the type of HF. As mentioned above, indications for the use of MCD are:
-
BTT
-
BTR
-
DT
-
ATT.
Descriptions of ventricular assist devices
An LVAD has inflow and outflow cannulae which help to regulate blood flow from the LV or left atrium to the ascending aorta. Similarly, in the RVAD, an inflow cannula regulates blood from the right ventricle (RV) or right atrium to the pulmonary artery.
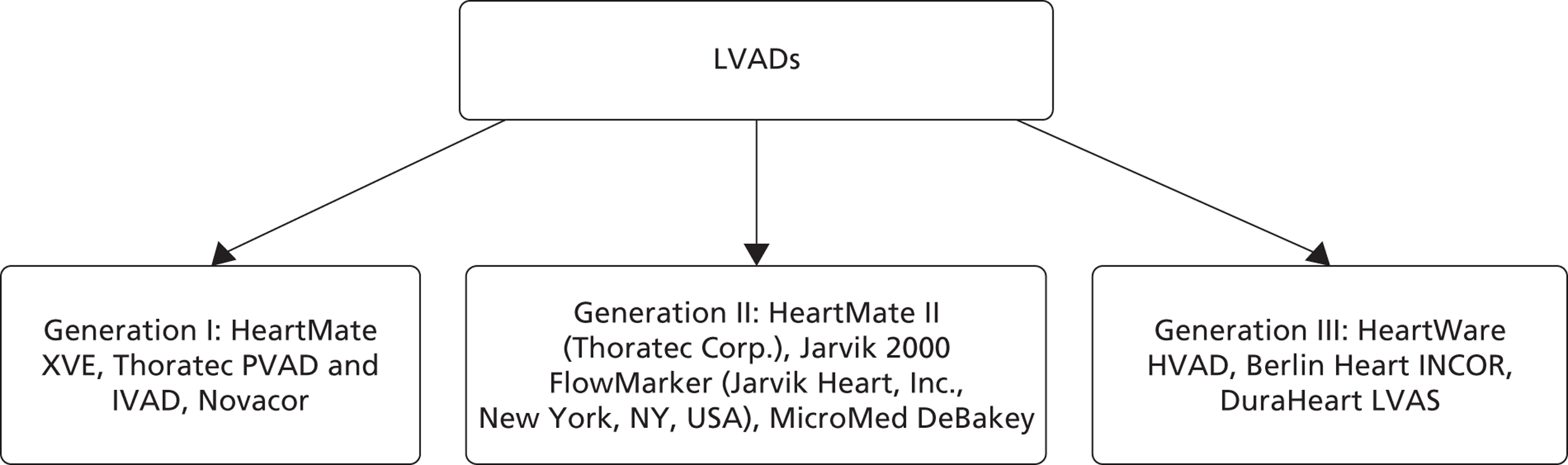
Left ventricular assist devices help to pump blood from the LV of the heart to the rest of the body in patients with advanced HF. 35 In the UK, LVAD patients with advanced HF wait for a donor heart to become available. 1,36 These devices as are not currently licensed for use as DT in the UK, although they are approved in the USA and in parts of Europe. 1,35 LVADs can be broadly categorised as generation I, generation II and generation III (Figure 3).
FIGURE 3.
A schematic diagram of HF diagnosis recommendations.
Second- and third-generation LVADs are magnetic continuous flow (CF) rotary pumps whereas first-generation LVADs are pulsatile volume displacement devices. 35,37 Compared with first-generation devices, second- and third-generation devices are smaller, quieter and more reliable. Second- and third-generation devices are inserted through a small dissection. They are easier to insert and less traumatic than previous types and are associated with less bleeding and infection. Third-generation LVADs are attached with an impeller which uses magnetic forces or hydrodynamic levitation without mechanical contact. They therefore have greater durability, with no mechanical wear and tear compared with second-generation LVADs. 35,37 In this report the interventions of interest are second- and third-generation devices which have either US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or Conformité Européenne (CE) approval or both; therefore, this section will describe characteristics only of these devices.
Table 1 shows the VADs which have FDA or CE approval.
| Name of devices | Manufacturer |
|---|---|
| LVADs | |
| MicroMed DeBakey VAD (HeartAssist 5®) | MicroMed, Uden, Netherlands |
| DuraHeart LVAS® | Terumo Heart Inc., Ann Arbor, MI, USA |
| HeartMate II® | Thoratec Inc., Pleasanton, CA, USA |
| aHeartWare HVAD® | HeartWare Inc., Framingham, MA, USA |
| INCOR® | Berlin Heart, Berlin, Germany |
| bJarvik Heart 2000® | Jarvik Heart Inc., New York, NY, USA |
| RVADs | |
| bJarvik 2000 Flow Maker® | Jarvik Heart Inc., New York, NY, USA |
| BiVADs | |
| bJarvik 2000® | Jarvik Heart Inc., New York, NY, USA |
| aHeartWare HVAD® | HeartWare Inc., Framingham, MA, USA |
Second-generation devices
HeartMate II
This is the only CF axial device. It has an internal rotator with helical blades which curve around the central shaft. It is reported that the device has been implanted in more than 3000 patients worldwide. 35 According to Thoratec Inc., HeartMate (HM) II received FDA approval as a BTT and DT in April 2008 and on 20 January 2010 respectively. The device received CE approval in November 2005, allowing its commercial sale in Europe. 35,38
Jarvik 2000
This is a long-term implantable, axial, CF pump and has been approved by both the FDA and the CE as a BTT and as a DT in Europe only. It is inserted intrapericardially, regulating blood flow from the LV apex to either the ascending or descending aorta.
MicroMed DeBakey
The design of MicroMed DeBakey has been improved over the years and it is now marketed as HeartAssist 5, which has both CE and FDA approval as a BTT. 39 HeartAssist 5 represent the new-generation device that includes new features such as flow accurate diagnostics and heart assist remote, which provide direct online measurement of blood flow. This is an improvement over MicroMed DeBakey in terms of designs, prevention of pump thrombosis and power fluctuation. In 2002, the MicroMed DeBakey was used in the USA as a BTT. 39
Third-generation devices
Berlin Heart ‘INCOR’
The INCOR LVAD is a magnetic bearing, flow pump with axial design which circulates blood from the LV apex to the ascending aorta. This device was first implanted in 2002 at the German Heart Institute. After this, the device gained CE approval in 2003. Since then it has been implanted in more than 500 patients worldwide. At present, the device is not available in the USA. 37,40
DuraHeart left ventricular assist system
The DuraHeart left ventricular assist system (LVAS) is a small continuous, radial flow pump connected to a magnetically levitated impeller which helps pump blood from the left side of the heart, improving circulation throughout the body. 37,40,43 The device is generated in such a way that magnetic levitation uses electromagnetic coils to position the movement of impeller within the pump to generate ‘gentle and consistent blood flow’ as the manufacture suggests. 41 According to the review published by Morshuis et al. ,42 DuraHeart LVAS is the world's first third-generation implantable LVAS to obtain market approval (CE) in February 2007.
HeartWare HVAD
The HeartWare® (HW) HVAD is a small, implantable centrifugal pump, designed to draw blood from the LV and pump it towards the ascending aorta with the help of an outflow graft. The pump has only one moving part, a wide-blade impeller suspended within the pump housing by the combination of passive magnetic and hydrodynamic bearing systems. A thin blood film created by the hydrodynamic thrust bearing prevents physical contact between the housing and the impeller. 37,40,43 The first human implant was performed in March 200643 and a clinical trial began in 2008 in the USA, which consisted of 150 participants for whom the device was indicated as a BTT. The device received CE mark approval in 2009. 37,40,43
The most frequently used CF left VADs in the UK are the HMII and HW. 44 Table 2 summarises characteristics of second- and third-generation devices.
| Devices | Type | Weight gram (g) | Size (cm) | Circulatory support | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length | Diameter | RPM | Flow (l/minute) | ||||
| Second generation | |||||||
| A | Thoratec HMII | CF axial blood pumps with magnetically suspended axial flow rotor. The device is placed just below the diaphragm in the abdomen | 350 | 7.0 | 4.0 | 6000 –15,000 | 10 |
| B | Jarvik Heart 2000 Flow Maker | CF axial blood pump which placed in the ventricular cavity | 85 | 5.5 | 2.4 | 8000–12,000 | 7 |
| C | MicroMed DeBakey VAD | Continuous axial flow rotary pump, implants above the diaphragm | 92 | 7.1 | 3.8 | 10,000 | 2–10 |
| Third generation | |||||||
| D | Berlin Heart INCOR | CF pumps with an axial design, with free floating impeller with magnetic connection | 200 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 5000–10,000 | 5 |
| E | Terumo DuraHeart LVAS | A CF centrifugal pump with a magnetically levitated impeller implanted in an abdominal pocket | 540 | 7.2 | 4.5 | 1200–2600 | 2 |
| F | HW HVAD | Small CF, centrifugal pump inserted in the pericardial space | 145 | < 2.0 | 4.0 | 1800–3000 | 10 |
Randomised controlled trials of left ventricular assist devices
Two randomised controlled trials (RCTs)45,46 have been performed which examined the effectiveness of LVADs. In each of these the LVAD was used as DT for patients who were not eligible for HT and in whom HT was contraindicated, and these studies therefore do not satisfy the remit for the current report. However, these studies are included here as they provide the only randomised evidence on VADs. Results from the first trial, Randomized Evaluation of Mechanical Assistance for the Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure (REMATCH), were published by Rose et al. 45 The study compared the pulsatile HMXVE® device (Thoratec Inc., Pleasanton, CA, USA) (n = 68) with optimum medical management (MM) (n = 61) for patients described as having ‘end stage heart failure’ (all participants were classified as experiencing NYHA class IV HF). Kaplan–Meier (K–M) analysis of death by any cause was superior in the HMXVE group [relative risk (RR) 0.52, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.34 to 0.78; p = 0.001]. The survival rate at 1 year was 52% and 25% in the LVAD and MM groups respectively (p = 0.002). Similarly, 2-year survival rates were 23% in the LVAD group and 8% in the MM group (p = 0.09). Adverse events (infection, bleeding and device failure) were 2.35 times more common in the LVAD group (95% CI 1.86 to 2.95), partly reflecting greater time at risk. The QoL according to the Minnesota Living With Heart Failure Questionnaire (MLWHF), the SF-36 and the NYHA classification was improved in the LVAD group at 1 year after implant. Stevenson et al. 46 recently reported results from post-hoc analyses of the REMATCH data in which participants were stratified according to inotrope use at baseline. K–M analysis indicated poorer survival for MM patients receiving inotrope treatment at baseline than for MM patients who did not receive inotropes at baseline.
Slaughter et al. 47 extended the REMATCH study design to compare the CF HMII device (n = 134) with the HMXVE pulsatile flow device (n = 66). Again, in this study, LVADs were used as DT for patients for whom HT was contraindicated. The primary end point was survival, freedom from disabling stroke and reoperation for repair or replacement of the device. At 2 years this outcome was significantly superior for the HMII group (46% vs. 11%). The hazard ratio comparing treatments for this outcome was 0.38 (95% CI 0.27 to 0.54; p < 0.001). The actuarial survival rate at 2 years was superior for the HMII group (58% vs. 24%; p = 0.008). Rates of adverse events and of repeat hospitalisations were lower for the HMII group. Post-implant improvement in the QoL and functional status were similar in both groups.
Complications of ventricular assist devices
This section summarises papers by Potapov et al. 48 and Barnes,49 which describe complications which can occur for patients with VADs. Complications in patients with VADs can be categorised as acute or late.
Acute complications
Acute complications occur shortly after implantation of the device and include thromboembolism, haemorrhage, right ventricular failure and altered immune response.
Thromboembolism: The incidence of thromboembolism after VADs implantation ranges between 10% and 25%. The risk depends on many factors such as presence of infection, type of device used and type of anticoagulation regimen used. 49 Most thromboembolic events in this situation are reported as cerebrovascular. Contact between the surface of the device and the patient's blood is the cause of the thromboembolism. This interaction triggers immune cells and coagulation pathways, thus ultimately causing clot formation. Because of this risk, it is important to administer adequate anticoagulation therapy in these patients. Recent HM devices have a special coating and patients implanted with these devices are considered to need only antiplatelet therapy.
Haemorrhage: Haemorrhage is common post-operatively. It has been reported in more than half of patients with VADs. It also occurs in those undergoing reoperation to treat haemorrhage (∼ 20–40% of patients). Risk of bleeding can be increased by anticoagulation, prolonged surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass and extensive surgical incision. Some of the CF devices cause arteriovenous malformation, leading to increased gastrointestinal bleeding. 50 Early and appropriate intervention to control bleeding is important. If untreated, this may lead to further complications such as multiple organ failure. Patients with haemorrhage are given blood transfusion; however, fluid overload can be a problem for some, potentially causing right heart problems and right HF.
Immune response: The interaction between the surface of the device and the patient's blood can activate defective proliferation of T cells, causing activation-induced cell death. This can affect a patient's immunity, and thus he/she may become more susceptible to infection or thromboembolic events. The foreign material of the device can also cause B cell hyperactivity, thus activating an autoimmune reaction. These patients also have an increased risk of post-transplantation organ rejection.
Multiorgan failure: Multiorgan failure is a cause of death after VADs use. It occurs because patients with advanced heart disease in a compromised health state may already have reduced kidney and liver function. Some may also have reduced pulmonary function and may be on mechanical ventilation. It has been suggested that multiple mechanisms and events may be responsible for the development of multiorgan failure including inflammatory reactions, infection, prolonged surgery time, blood transfusion and hypothermia.
Right ventricle failure: RV failure occurs in approximately a tenth of patients receiving VADs. It may develop suddenly after implantation or may already be present in some patients, becoming apparent only after VAD implantation. Various mechanisms can lead to right ventricular failure. One possibility is that the intraventricular septum bulges into the LV, decreasing right ventricular efficiency or the increased efficiency of the LV may increase venous return to the right side of the heart causing failure. Other causes are thought to include myocardial stunning, ischaemia, arrhythmias and increased pulmonary vascular resistance.
Long-term complications
Infection: This occurs commonly and may present as pneumonia, mediastinitis, urinary tract infections or line sepsis. Some infections may also be device related, such as driveline or pump pocket infections, endocarditis or sepsis. After surgery, patients' immunity is considerably reduced, and this can make them susceptible to infection. In addition, existing diseases such as diabetes mellitus and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can increase susceptibility. Risk of infection increases as some parts of the devices are exposed to external pathogens. Some devices may have cavities and pockets which can harbour pathogens. Staphylococcus species, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candida are the most common pathogens. It is very important to treat infection early. If not treated, it can increase the risk of other complications such as thromembolic events and strokes.
Abdominal complications: Risk of abdominal complications increases when VAD hardware is placed in the abdomen. Abdominal hardware infection is the most common complication and is usually acquired in hospital. Other abdominal complications include fistula formation, gastrointestinal haemorrhage, bowel obstruction and abdominal herniation (incisional or diaphragmatic hernia). Diaphragmatic hernia usually occurs after the VAD is removed and a heart has been transplanted. Serious abdominal complications such as cholecystitis, pancreatitis, gastric ulceration and perforation can also occur.
Device malfunction: Over the years, modifications to the devices have been made to reduce this complication. However, patients implanted with VADs can still suffer significant morbidity and mortality. It has been estimated that device failure occurs in approximately 35% of patients during the 24 months after implantation. In half of these, external components such as the controller, batteries or the Y-connector are involved, whereas in the remaining patients internal VAD components such as inflow or outflow cannulae are involved. Malposition of the inflow cannula can occur over time as a result of pericardial changes or inappropriate preparation of the pocket for the pump causing partial blockage of the cannula and haemolysis, low pump flow, arrhythmias and, finally, right ventricular failure due to reduced LV loading. 50
Malnutrition: Almost half of patients with HF are already malnourished. The term ‘cardiac cachexia’ is used to describe this condition, in which the body's inflammatory and metabolic response leads to malnutrition, muscle wasting and weight loss. Implantation of VADs further increases the risk of malnutrition. Other factors, such as poor appetite, delayed gastric emptying, nausea and vomiting, also contribute to malnourishment.
Psychosocial issues: In most patients, VADs have been found to improve QoL. However, some patients and carers are found to be anxious and concerned about physical limitations and complications which may occur as a result of the device. Some patients deteriorate with time and some may develop more severe psychiatric problems. 50
In conclusion, driveline infection, post-operative bleeding and thromboembolism are the main complications related to use of LVADs. 50 The use of modern technology and new materials has ensured that complications have reduced in recent years.
Current service provision
With increasing demand for HT, the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) has coded waiting list (WL) patients as Status 1A, 1B or 2 on the basis of medical urgency. Patients who are in a clinically stable condition and patients with LVAD-related complications (infection, thromboembolism or device malfunction) are categorised as Status 1A patients for 30 days. Status 1B is assigned to patients supported by LVAD who do not meet the criteria for Status 1A. Status 2 patients are those receiving long-term LVAD support. 51
In the UK, WL management is based on the urgent and non-urgent WL, developed by the Cardiothoracic Advisory Group of NHS Blood and Transplant (Box 3). 28
Need for:
-
continuous inotropic treatment at high dose or in combination
-
IABP with or without inotropic support
-
mechanical circulatory support with a short-term device including venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
-
long-term LVAD support with device-related complications.
Or:
-
exceptional cases outwith these criteria may be listed with permission from the chair of the advisory group.
IABP, intra-aortic balloon pump.
Evolving LVAD technology from first generation to second and third generation has led to development of devices which are considerably smaller, more durable and associated with fewer adverse events. As pulsatile and first-generation LVADs have been modified to CF devices, the improvements have been marked with a lower incidence of infection and complications. Use of these devices as a BTT has led to considerable improvements in QoL among patients with advanced HF. 52,53
Patient pathways for management of heart failure
Treatment of patients with HF depends on the type and stage of HF. The following examples of patient pathways indicate how patients are treated at different stages: BTT to VAD (Box 4), BTT to HT (Box 5) and MM (Box 6). The National Protocol for Assessment of Cardiothoracic patients lists below the medical indications for patients eligible for a HT.
-
End-stage heart disease with a life expectancy of between 12 and 18 months.
-
NYHA class III or IV.
-
Refractory to medical therapy, including, if necessary, cardiac resynchronisation therapy. (This assessment should be made by a cardiologist with a special interest in HF.)
-
Usually < 60 years of age as there is an increase in comorbidity with the ageing process. However, consider biologically fit older patients.
In the next section of this report we describe the decision problem and research questions.
Patients who are on the WL with rapidly deteriorating heart function and would not survive to get a HT or who are at increased risk of adverse events after HT.
Ventricular assist device implantPatients receiving a VAD implant as a semi-elective procedure stay in an ICU approximately 3–5 days and spend 2 weeks in the ward. At the end of the second week they are discharged and called for regular follow-up.
Follow-up procedure 1. Drug treatment for heart failurePatients are treated with the following drugs: diuretics, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonist, beta-blockers, spironolactone (Aldactone®, Pharmacia Ltd), warfarin, statins, digoxin.
2. Follow-up visitFortnightly visits occur for 1 month, and then the patient has monthly visits for 3–4 months and then every 3 months.
Serious adverse eventsPatients' post-VAD implant survive with relatively few adverse events. Ten per cent of the patients present with bleeding from either nose or gut and they get admitted and are transfused with blood products for 4–5 weeks. Incidence of infection is relatively rare and occasionally patients present with infection at the VAD exit site are treated with intravenous antibiotics for 1 week.
ICU, intensive care unit.
Appropriate candidate for HT.
Heart transplantPatients' post-HT stay in an ICU for approximately 3–5 days and spend 2 weeks in a ward. At the end of the hospital stay they are discharged and called for regular follow-up visits.
Follow-up procedure 1. Follow-up medicationPatients are treated with the following drugs: patients receive antiviral prophylaxis against cytomegalovirus, valganciclovir (Valcyte®, Roche) 900 mg once daily for 3 months (about one-third of the patients will need it for 6 months). All patients receive rabbit antithymocyte globulin, three doses per day, tacrolimus (Prograf®, Astellas Pharma US, Inc.) 1 mg per day, mycophenolate mofetil (Cellcept®, Roche) 2.5 g per day and prednisolone 12.5 mg per day.
2. Follow-up visitsFortnightly visits occur for 1 month, then monthly visits for 3–4 months and after that visits are every 3 months.
3. InvestigationsPatients have approximately 12–14 endomyocardial biopsies per year and coronary angiography is usually performed once a year.
Serious adverse eventsAdverse events post HT are relatively rare. A patient may experience rejection or infection in the first year and is treated with methylprednisolone 750 mg per day and ganciclovir (Cytovene®, Roche) 5 mg/kg. Fifteen per cent of patients post HT are at risk of getting skin cancer and as the overall survival increases, patients are prone to coronary artery disease in 6–10 years' time.
ICU, intensive care unit.
Patients are medically managed at home with oral medications while awaiting HT. Forty-five per cent of patients are admitted to hospital with severe HF and are treated with intravenous inotropes. They are admitted to the ICU approximately once per 6 months and either improve or are given urgent VAD implant in 10–15% of cases.
1. Patients are medically managed at home with oral medicationsPatients are treated with the following drugs: diuretics, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonist, beta-blockers, spironolactone, warfarin, statins, digoxin.
Some HF patients are managed with implantable cardioverter defibrillators and biventricular pacemaker.
2. Patients who are admitted to hospital are managed with intravenous inotropesEnoximone 5 µg/kg/minute and dopamine 5 µg/kg/minute.
Fifty per cent of patients admitted to ICU with acute HF are treated with an IABP, 30% require haemofiltration and a few patients with end stage HF are treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
IABP, intra-aortic balloon pump; ICU, intensive care unit.
Chapter 2 Definition of the decision problem
The purpose of this section is to specify the decision problem and to translate it into research objectives. A copy of the protocol is included in Appendix 1.
Decision problem
In patients with advanced HF who are eligible for HT, VADs are used as a BTT in patients in the UK. There are a number of newer devices and it is important to know the cost-effectiveness of devices used in this way in comparison with MM.
Research suggests that HT is likely to offer the best treatment option in terms of both improved survival and QoL for these patients. 1 However, HT is dependent on the availability of donor hearts and availability appears to be diminishing. Therefore, it is valuable to know the comparative cost-effectiveness of VADs used as an ATT compared with HT. (Note: it is our understanding that VADs are currently funded for use in the UK as a BTT and not as an ATT or as a DT.) Outcomes to be investigated include survival, adverse events, reasons for death, QoL and functional status.
Research questions
In patients aged ≥ 16 years with advanced HF who are eligible for HT:
-
What is the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of second- and third-generation VADs used as a BTT compared with MM?
-
Where data permit, what is the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of second- and third-generation VADs used as an ATT in comparison with their use as a BTT therapy?
Overall aims and objectives of assessment
Objectives
-
To summarise previously published HTA reports by Clegg et al. 4 and Sharples et al. 30 on VADs.
-
To undertake a systematic review and evidence synthesis of the relevant clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness literature.
-
To further develop the cost-effectiveness and cost–utility models developed in the 2006 HTA: Evaluation of the ventricular assist device programme in the UK and where possible to compare the use of VADs as BTT firstly to MM and secondly as ATT.
-
To investigate the factors that drive cost-effectiveness estimates.
-
To report on findings and make recommendations for future research.
Chapter 3 Review of clinical effectiveness
In this chapter we describe the methods and results of the clinical effectiveness systematic reviews.
Methods for reviewing clinical effectiveness
Identification of literature
Identification of publications
Initial scoping searches were undertaken to assess the volume and type of literature relating to the assessment question. A search strategy was then developed which focused the searches on VADs meeting the inclusion and exclusion criteria (see Inclusion criteria and Exclusion criteria). All searches were undertaken in February and March 2012.
Scoping searches were undertaken to inform the development of the search strategy. An iterative procedure was used, with input from clinical advisors and previous HTAs (e.g. Clegg et al. 4 and Sharples et al. 30).
A copy of the search strategy that was used in each of the major databases is provided in Appendix 2. This search strategy developed for MEDLINE was adapted as appropriate for other databases. The strategy was designed to capture generic terms for VADs and the specific product names of second- or third-generation, FDA- or CE-approved devices. The search was date limited from 2003 to February/March 2012 (this avoided the retrieval of a large number of literature concerning first-generation VADs, which were outside the remit of the report; see Clegg et al. 4 and Sharples et al. 30 for further information on first-generation VADs). Studies of patients aged < 16 years and non-English-language studies were excluded. There were no limits for study design at the searching stage. All retrieved papers were screened for potential inclusion.
The search strategy involved the following main elements:
-
searching of electronic bibliographic databases
-
contact with experts in the field
-
scrutiny of references of included studies
-
screening of manufacturers websites for relevant publications.
Databases searched
Databases searched included MEDLINE; MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations; EMBASE; Cochrane Database [including Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR), Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE), NHS Economic Evaluation Database (NHS EED), and HTA databases]; Science Citation Index and Conference Proceedings (Web of Science); UK Clinical Research Network (UKCRN) Portfolio Database; Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL); PsycINFO; and the National Library of Medicine (NLM) Gateway (US Meeting Abstracts and Health Services Research Projects in Progress) were searched. The following trial databases were also searched: Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL); Current Controlled Trials; and ClinicalTrials.gov.
In addition, the reference lists of relevant articles were checked, and the manufacturers' websites screened for relevant publications. Also, the online resources of various regulatory bodies, health services research agencies and professional societies were consulted via the Internet. These included:
-
HTA organisations (including the National Institute for Health Research and the National Research Register Archive)
-
INTERMACS
-
NHS Blood and Transplant (including the Cardiothoracic Transplant Advisory Group)
-
Ventricular Assist Device Forum, National Specialised Commissioning Team
-
The International Society Heart & Lung Transplantation
-
Eurotransplant
-
Scandiatransplant
-
US Transplant
-
The Transplantation Society
-
British Transplantation Society
-
Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency
-
US FDA.
Citation searches of included studies were undertaken using the Web of Science citation search facility. The reference lists of included studies and relevant review articles were also checked.
Inclusion criteria
Study design
We included:
-
studies of VADs with FDA/CE approval
-
studies with a minimum of 50 participants in the approved VAD group
-
studies including both FDA/CE-approved and multiple unapproved VADs
-
approved VADs had to be recorded and analysed separately or
-
if they were not analysed separately, at least 80% of the included devices had to be FDA/CE approved.
-
Studies with control groups (i.e. RCTs, cohort studies, case–control studies) and systematic reviews of studies with control groups were included. Case series were included if they reported on adverse events and if they reported on consecutive patients.
Interventions
Interventions included second-generation axial CF pumps and third-generation bearingless CF pumps; LVADs, RVADs and BiVADs currently approved by the FDA and/or CE and in current clinical use in the UK as a BTT; and LVADs, RVADs and BiVADs currently approved by FDA and/or CE and used as potential long-term ATT for people with advanced HF. Studies with a mixture of generation devices were considered if data for second- or third-generation devices were presented separately to first-generation devices (see Study design).
Comparators
Comparators included MM and HT; studies that compared two different VADs approved for intervention were also included. Studies comparing first-generation devices with second- or third-generation devices were used to extract data on second- or third-generation devices only.
Population
Participants (aged ≥ 16 years) with advanced HF and considered suitable for receipt of a LVAD, RVAD and BiVAD as a BTT or as potential long-term ATT. Studies which reported BTT and DT participants, but which did not distinguish outcomes according to therapy, were included for purpose of complete information, but outcome data were not included in the main text.
Outcomes
We investigated survival, adverse events, reasons for death, QoL and functional status (e.g. change in NYHA functional classification).
Exclusion criteria
The following exclusion criteria were applied:
-
studies in which 20% patients were known to be receiving VADs as DT
-
PVAD
-
TAH
-
first-generation pulsatile volume displacement pumps
-
devices yet to be FDA or CE approved
-
devices for ‘bridge to decision’
-
post-transplant mechanical circulatory support devices for primary graft failure
-
studies involving VADs in conjunction with other interventions where it was not possible to separate out the effects of the different interventions on outcomes
-
animal models and post-mortem studies
-
preclinical and biological studies
-
editorials and opinions
-
reports published as meeting abstracts only, where insufficient methodological details were reported to allow critical appraisal of study quality
-
studies not in English
-
studies before the year 2003
-
case series reports with < 50 cases or where patient recruitment was not consecutive.
Data abstraction strategy
A record of all papers rejected at full-text stage and reasons for exclusion was documented. Titles and abstracts of retrieved studies were examined for inclusion by two reviewers independently. Disagreement was resolved by retrieval of the full publication and consensus agreement.
The full data were extracted independently by one reviewer using a data extraction form informed by the NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD)54 and previous HTA reports4,30 (see Appendix 3 for the complete data extraction forms, this includes publications which did not separate outcomes for BTT patients from DT patients and which are not included in the main text of the report). All studies were checked by a second researcher, and any disagreements were resolved by discussion. Further discrepancies were resolved with involvement of a third reviewer. Data were extracted to allow quality assessment of the included studies.
Critical appraisal strategy
Quality criteria were applied independently by two reviewers and an agreed overall quality assessment was determined for each paper. Any disagreements were resolved by independent assessment by a third reviewer. Included studies were assessed using the following recognised quality assessment scales and/or checklists. Systematic reviews were assessed using criteria developed by NHS CRD. 54 Experimental and non-experimental studies were assessed using an adapted set of criteria developed by Thomas et al. 55 Each study was scored according to (a) selection of participants; (b) study design; (c) confounders; (d) blinding; (e) data collection methods; (f) withdrawal and dropout; and (g) integrity and analysis (see Appendix 4 for further details on quality assessment).
Methods of data synthesis
Data were tabulated and discussed in a narrative review based on indication for treatment, type of VAD, quantity and quality of research evidence, representativeness and outcomes. The remit of this report was to consider BTT but not DT. Some publications presented aggregate results for both groups; such aggregate results are not relevant to BTT, but for completeness we report such results in Appendix 3. Where data specific to BTT patients could be extracted from any publication these are also included in the main text of the report. Outcome results are given for BTT patients with published data selected so as to avoid double counting from overlapping populations.
We analysed patient populations in each included study for overlap between studies, and developed a ‘family tree’ to ascertain which data set included the most recent data on the largest number of unique patient records (as earlier, smaller studies fed into larger, later studies). For each device, we used the largest/latest data set of separately identifiable patients to report baseline characteristics and adverse events.
Baseline characteristics were listed as means for continuous variables and percentages for binary variables. Ninety-five per cent CIs were calculated. Where possible, the reported data for subgroups were combined to obtain a value for the whole study population. Pooling of study baseline characteristic values was undertaken using a random-effects model in MetaAnalyst Version Beta 3.13 (Tufts Medical Centre, Boston, MA, USA) software. Narrative syntheses were used to describe outcomes.
Clinical effectiveness results
Outcomes for each device are reported separately. Outcomes assessed included adverse events, causes of death, functional status and QoL. Again, we adjusted our reporting for double counting caused by inclusion of multiple, overlapping patient populations in studies. Survival analyses findings were included as reported and are further described in the results section by device.
Quantity and quality of research available
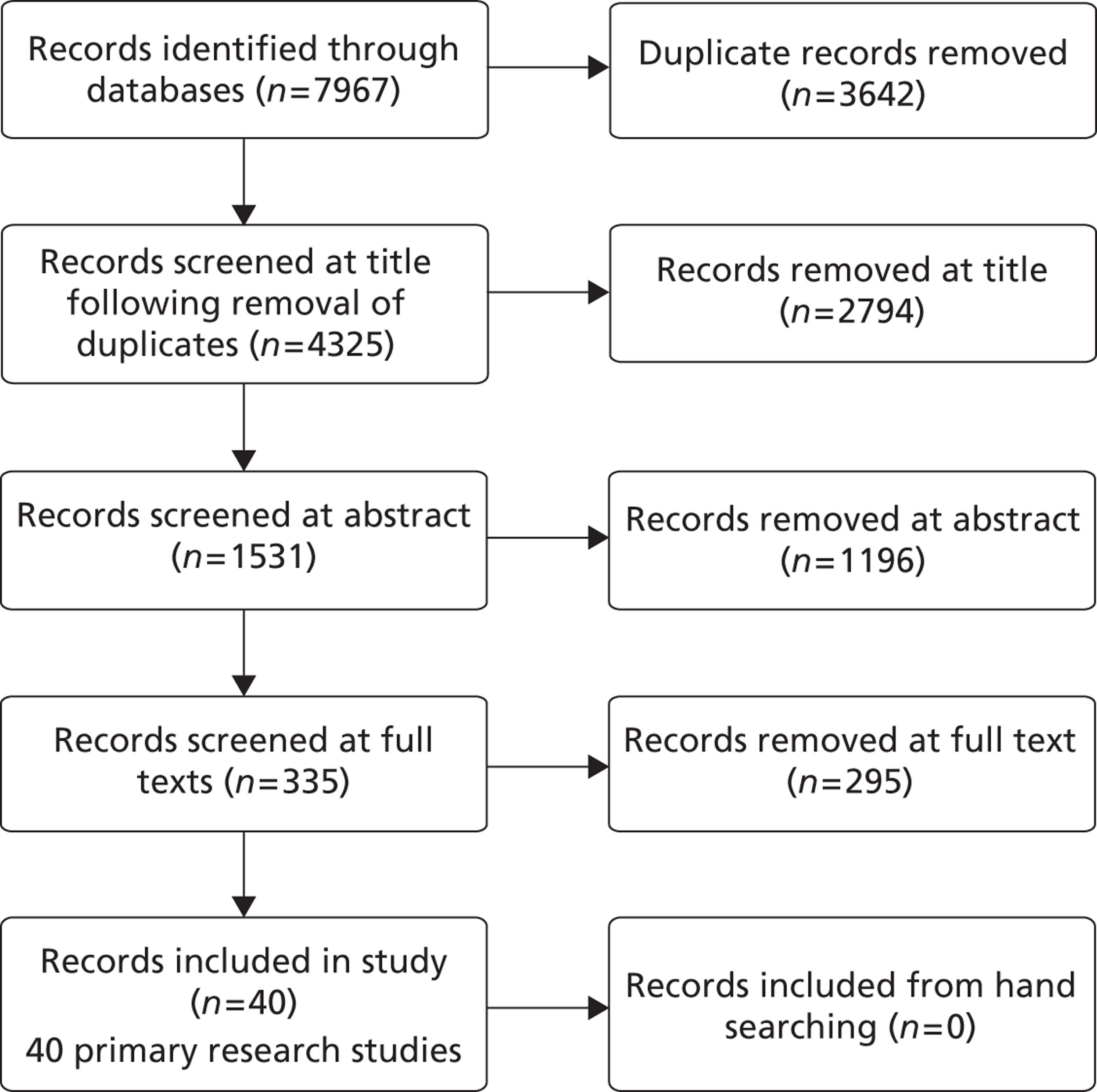
A flow chart describing the process of identifying relevant literature on the clinical effectiveness of VADs can be found in Figure 4. Following the removal of duplicates, our searches identified 4325 potentially relevant articles. We removed 2794 articles which did not meet our inclusion criteria at title sift, leaving 1531 articles to be screened at abstract sifting stage. A total of 1196 articles were removed at abstract sift because they did not meet inclusion criteria, leaving 335 articles to be sifted at full-paper stage. A total of 40 publications42,52,53,56–92 met the current inclusion criteria and reported findings on the following devices: HMII (n = 29);52,53,56–82 HW (n = 1);83 Berlin Heart INCOR (n = 1);86 DuraHeart (n = 2);42,85 MicroMed DeBakey (n = 1);84 and mixed devices (n = 6). 87–92 Included papers were published between 2003 and 2012.
Seven systematic reviews were identified. After full investigation it was concluded for each one that the majority of their included studies and patients did not meet the inclusion criteria and these reviews were therefore rejected.
A list of the 288 articles that were excluded at full paper sift with reasons for exclusion is provided in Appendix 5.
FIGURE 4.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses diagram: summary of study selection and inclusion.
Tables 3–8 provide a summary of the 40 included publications by type of VADs reported and reasons for VAD use.
| First author | Date | Country | Reference number | n | VADs reported | Reason for VAD use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adamson | 2011 | USA | 56 | 55 | HMII only | Both DT and BTT Results NR separately |
| Bogaev | 2011 | USA | 57 | 465 | HMII only | BTT |
| Boyle | 2009 | USA | 58 | 331 (from 469 HMII population) | HMII only | BTT |
| Brewer | 2012 | USA | 59 | 896 (486 BTT) | HMII only | Both DT and BTT BTT: underweight 23 (48%); normal 305 (51%); obese 108 (66%); extremely obese 50 (57%) |
| Cowger | 2010 | USA | 60 | 78 | HMXVE and HMII | Both DT and BTT BTT: 69 (88%) [HMII: 54 (90%); HMXVE: 21 (84%)] |
| Demirozu | 2011 | USA | 61 | 172 | HMII only | NR |
| Hasin | 2012 | USA | 62 | 83 | HMII only | Both DT and BTT BTT: overall sample 27/83 (32%); GFR < 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 group 15/54 (28%); GFR > 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 group 12/29 (41%) |
| John | 2010 | USA | 63 | 486, of whom 250 underwent HT | HMII only | NR |
| John | 2011 | USA | 64 | 102 | HMII only | BTT |
| John | 2011 | USA | 65 | 1982 | HMII only | BTT |
| Kato | 2012 | USA | 66 | 342 | HMI and HMII | NR |
| Kormos | 2010 | Unclear | 67 | 484 | HMII only | BTT |
| Lahpor | 2010 | European countries | 68 | 184 | HMII only | DT, BTT and BTR BTT (73%); DT (21%); BTR (6%) |
| Martin | 2010 | USA | 69 | 145 | HMII only | NR |
| Miller | 2007 | USA | 70 | 133 | HMII only | BTT |
| Pagani | 2009 | USA | 71 | 281 | HMII only | BTT |
| Pak | 2010 | USA | 72 | 130 | HMXVE and HMII | Both DT and BTT 13 HMXVE patients (19.4%) and 10 HMII patients (15.9%) received devices with DT as the initial goal (p = 0.530) |
| Pal | 2009 | USA | 73 | 281 | HMII only | BTT |
| Petrucci | 2009 | USA | 74 | 93 | HMII only | BTT |
| Rogers | 2010 | USA | 53 | 655 | HMII only | Both DT and BTT BTT 281; DT 374 |
| Russell | 2009 | USA | 75 | 309 | HMII only | BTT |
| Schaffer | 2011 | USA | 76 | 133 | HMXVE and HMII | Both DT and BTT BTT 93/133; DT 40/133 Results NR separately |
| Schaffer | 2009 | USA | 77 | 86 | HMII only | Both DT and BTT 57/86 BTT; 29/86 DT Results NR separately |
| Starling | 2011 | USA | 52 | 338 (169 HMII) | HMII compared with other devices (not specified) | BTT |
| Strueber | 2008 | Multiple | 78 | 101 | HMII only | Both BTT and DT (split for survival only) |
| Topilsky | 2011 | USA | 79 | 110 | HMII only | Both DT and BTT 47 DT; 29 BTT |
| Topilsky | 2011 | USA | 80 | 76 | HMII only | Both DT and BTT RCM/HCM: 6/8 BTT; I/D: 21/75 BTT; others DT |
| Uriel | 2010 | France | 81 | 79 | HMXVE and HMII | Both DT and BTT Results NR separately |
| Ventura | 2011 | USA | 82 | 1157 | HMXVE and HMII | BTT |
| First author | Date | Country | Reference number | n | VADs reported | Reason for VAD use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strueber | 2011 | Multiple | 83 | 50 | HW only | BTT |
| First author | Date | Country | Reference number | n | VADs reported | Reason for VAD use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goldstein | 2003 | European countries | 84 | 150 | MicroMed DeBakey VAD | BTT |
| First author | Date | Country | Reference number | n | VADs reported | Reason for VAD use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morshuis | 2009 | Multiple | 85 | 68 | DuraHeart only | BTT |
| Morshuis | 2010 | Multiple | 43 | 82 | DuraHeart only | BTT |
| First author | Date | Country | Reference number | n | VADs reported | Reason for VAD use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schmid | 2008 | Multiple | 86 | 216 | INCOR (Berlin Heart) | Both DT and BTT |
| First author | Date | Country | Reference number | n | VADs reported | Reason for VAD use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drews | 2010 | Germany | 87 | 174 | Berlin Heart EXCOR® (Berlin Heart, The Woodlands, TX, USA), Novacor® (World Heart Corp., CA, USA), LionHeart LVD 2000® (Arrow International, PA, USA), HMI, Berlin Heart INCOR, MicroMed DeBakey, HMII, DuraHeart and Jarvik 2000 | All devices were implanted primarily for long-term support and not as a BTT |
| Klotz | 2006 | Germany | 88 | 130 | Continuous LVAD: MicroMed DeBakey or INCOR Berlin Heart Pulsatile LVAD: Novacor or HM |
NR |
| Nativi | 2011 | USA | 89 | 8557 | Pulsatile LVAD: HMIP® (Thoratec Inc., Pleasanton, CA, USA), HMVE® (Thoratec Inc., Pleasanton, CA, USA), HMXVE, Novacor PC® (Novacor, Oakland, CA, USA), Novacor PCq® (Novacor, Oakland, CA, USA), Thoratec® (Thoratec Inc., Pleasanton, CA, USA) and Toyobo® (Toyobo-National Cardiovascular Centre, Osaka, Japan) Continuous LVAD: HMII, Jarvik 2000, MicroMed DeBakey and VentrAssist® (Ventracor Ltd, Sydney, Australia) |
BTT |
| Oswald | 2010 | Germany | 90 | 61 | HMII and HW | NR |
| Sandner | 2009 | Austria | 91 | 86 | MicroMed DeBakey VAD, HVAD® (HeartWare Inc., Miami Lakes, FL, USA) and DuraHeart LVAD | BTT |
| Sandner | 2009 | Austria | 92 | 86 | MicroMed DeBakey VAD, HVAD and DuraHeart LVAD | BTT |
Types of device used
Of the 29 included studies52,53,56–82 involving HMII, 22 studies53,56–59,61–65,67–71,73–75,77–80 presented data on HMII alone. Five studies60,72,76,81,82 compared HMXVE with HMII. One study66 compared HMI with HMII, and a further study52 compared HMII with other devices (type not reported). One study83 reported on HW only, one study84 involved MicroMed DeBakey VAD only, one study86 involved Berlin Heart INCOR only, and two studies42,85 involved DuraHeart only.
A further six studies87–92 reported a mixture of devices but data by device were not reported separately.
Reasons for use of ventricular assist devices in included studies
Studies reported mixed reasons for use of VADs. For example, of the 29 HMII studies,52,53,56–82 12 studies52,57,58,64,65,67,70,71,73–75,82 reported that treatment was for BTT, 12 studies53,56,59,60,62,72,76–81 reported that treatment was for BTT and DT, one study68 reported that treatment was for BTT or DT or BTR and the remaining four studies61,63,66,69 did not report reason for treatment.
Delineating multiple overlapping populations between publications
Many of the identified publications investigated overlapping populations; this was especially true for studies of HMII, most of which were conducted in the USA. Also, in some studies the patient group received different devices and authors did not report results separately for each of the several devices investigated. There were many studies in which different patients were given bridge or destination therapies; however, in most of these outcomes were not reported according to indication.
The US HMII publications can be classified as (a) from single centres (n = 14); (b) deriving from the multicentre FDA approval study and its extension (n = 12); and (c) multicentre registry studies.
Starling et al. 52 and John et al. 65 reported on HMII, while Nativi et al. 89 indicated the number of HMII recipients but reported data for a mix of different VADs. In 12 of the single-centre studies53,56,59,60,62,72,76–81 both DT and BTT patients were included, or indication was not clearly defined; none of these analysed results separately for BTT patients. The other two single-centre publications (Petrucci et al. 74 and John et al. 64) reported results for BTT patients, but these single centres appear to have contributed participants to the FDA approval group of multicentre publications. The FDA approval study publications reflect the gradual accrual of more patients and multiple publications have been produced for overlapping groups of patients. Five of these publications58,59,65,67,82 report on the same 469–486 participants by either dichotomising the population by various criteria,67,82 focusing on a particular outcome,58 combining BTT patients with HMII DT patients,59 or not separating the outcome data according to therapy received. Registry studies, including John et al. 65 and Starling et al. ,52 reported on post-approval HMII BTT patients who were not participants in the FDA extension study. We consider it likely that the 169 patients reported in Starling et al. 52 are participants in the analysis by John et al. 65 The International Society for Heart & Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) registry report by Nativi et al. 89 included 417 patients who received later generation LVADs for BTT. Of these, 291 were implanted with the HMII device and some were likely to also be participants in the FDA approval study or its extension although outcome results for HMII were not reported.
FIGURE 5.
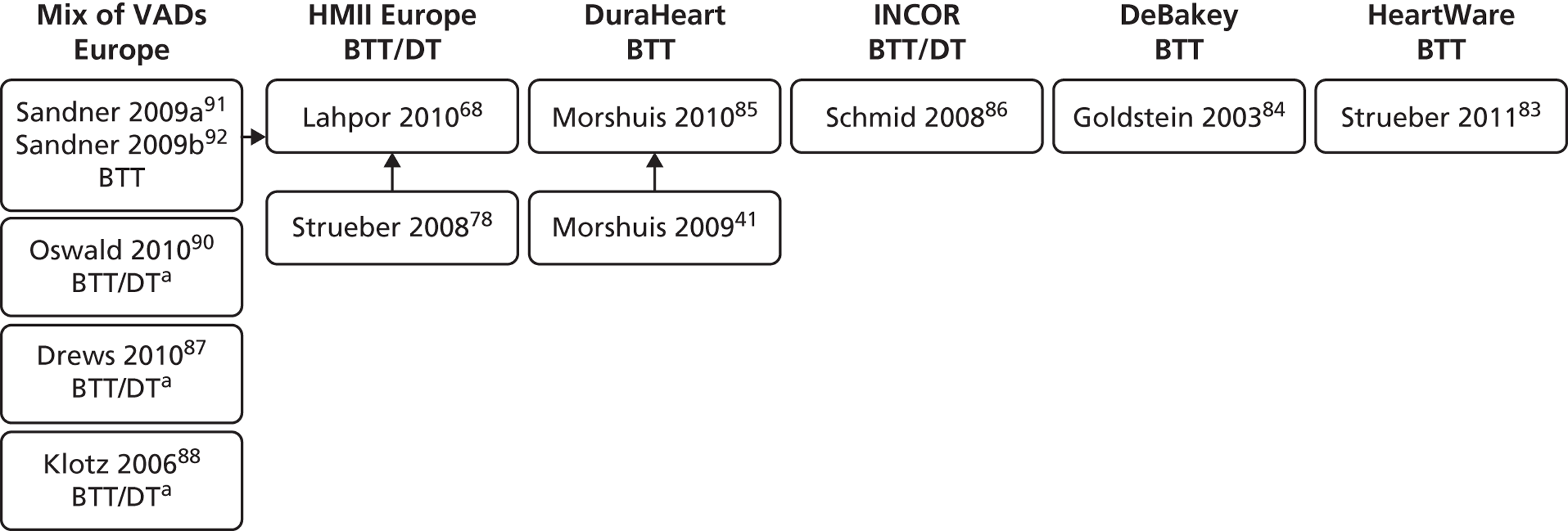
Summary of relationships between the included US HMII publications. All US multicentre BTT HMII FDA protocol publications shared patients with each other; the John 201063 publication reported on 250 patients who received a HT out of 486 BTT participants. The multicentre study by Brewer 201259 combined the 486 FDA study patients with 410 DT patients but did not report results separately according to therapy, some of the DT patients may have come from the single-centre studies. Among the US HMII single-centre publications, those of Petrucci 200974 and John 201164 contributed patients to the multicentre BTT HMII FDA protocol study. All other US HMII single-centre studies (n = 12) included both BTT and DT patients in single analyses (i.e. results not separated according to therapy) or did not state if patients received BTT or DT (Demirozu 2011,61 Martin 201069 and Kato 201266). The two studies of Topilsky 201179,80 investigated overlapping populations as also did the two studies by Schaffer 2009,77 2011. 76 The Nativi 201189 registry study may have included HMII patients from the FDA protocol study extension and may have included patients common to John 201165 which in turn included the patients from Starling 2011. 52 Solid arrows indicate publications that almost certainly shared participants and dashed arrows represent publications that probably shared patients. Numbers of patients are shown in brackets. a, CF VAD numbers only, data for HMII not reported separately; pulsatile VADs (n = 1980) excluded.
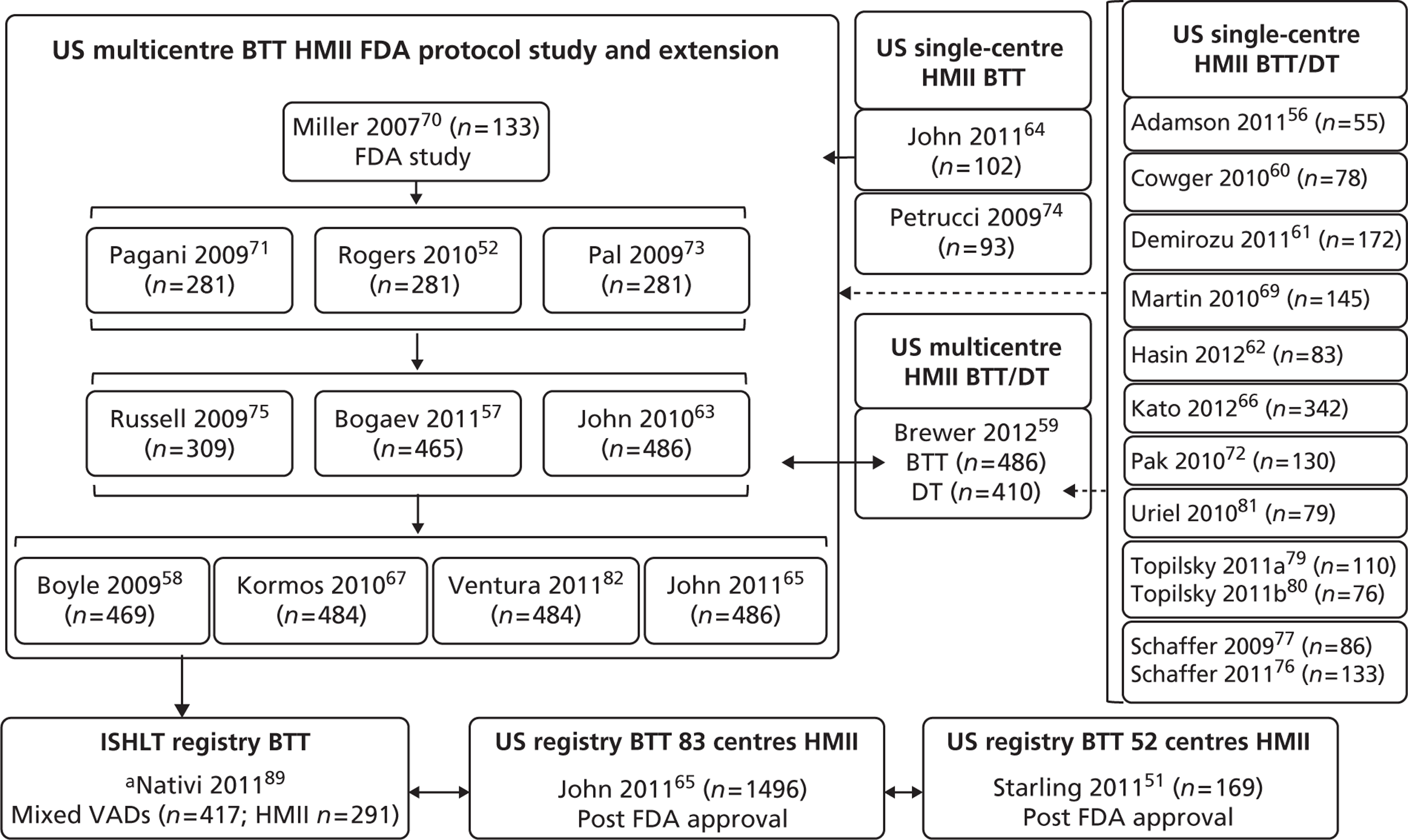
Figure 5 attempts to summarise the ‘family tree’ of the large number of US HMII VAD publications. As publications lacked sufficient detail, these relationships between publications cannot be stated with total certainty and it would be valuable to confirm this diagram with the authors. A similar situation of overlapping patient populations applies to the other included publications. These reported on a single device other than HMII, or reported results from studies conducted at European centres employing a mix of LVADs or the HMII device. There were two publications about HMII use with European patients;68,78 these included both BTT and DT patients. In Lahpor et al. 68 outcomes were not stratified by therapy and in Strueber et al. 78 the only outcome reported according to therapy was survival. The relationship between these is summarised in Figure 6. The European multicentre study of patients implanted with the HMII device for BTT, DT or BTR, by Lahpor et al. 68 (n = 184), included the patients (n = 101) reported separately by Strueber et al. ,78 and possibly some of the patients in the mixed VAD studies by Drews et al. 87 and Oswald et al. 90 The two BTT publications by Sandner et al. 91,92 examined the same 86 patient population (who received an amalgam of several devices which did not include HMII and results were not stratified according to device). The source of patients for the multiple device studies by Klotz et al. 88 and Drews et al. 87 were single German centres. Two publications of the DuraHeart (Morshuis et al. 42,85) investigated almost identical patient populations differing slightly in size (n = 6885 and n = 8242). A single-centre publication describing 79 HMII patients (BTT n = 64, BTT and DT n = 15) did not identify the centre and it was uncertain if this was a French or US study. 81
FIGURE 6.
Summary publication relationships: non-HMII single-device publications and European centre studies. One single-device publication was included for each of the INCOR, HW (centres in Europe and Australia) and MicroMed DeBakey devices. The INCOR study included both BTT and DT patients but results were not reported by therapy. The two DuraHeart publications had overlapping populations. Solid arrows indicate publications that almost certainly shared participants and dashed arrows represent publications that probably shared patients. a, The Drews 201087 population was ‘relatively contraindicated for HT’; the reports of Oswald 201090 and Klotz 200688 were also unclear on proportions BTT or DT patients.
The overlapping inter-relationship of populations described above, especially notable for HMII studies, renders any summary of baseline characteristics or of outcome results problematic if double counting is to be avoided. Therefore, where duplication of patients was judged to occur we have included the largest and/or most recent study of the cohort, conditional on availability of data. However, because of the multicentre nature of many of the HMII studies and authors' contention that experience with LVADs over time has influenced study results for some outcomes, we have occasionally also discussed earlier and smaller studies. We have organised baseline characteristics and outcome results according to device; in the main text we have not considered results for DT patients, or where results combine DT and BTT patients, or where this distinction was unclear. For full data on all baseline characteristics, and on outcome results irrespective of therapy, please consult Appendix 3.
Overall quality assessment
The 40 primary included publications42,52,53,56–92 were each quality assessed using an adapted set of criteria developed by Thomas et al. 55 For completeness, see Appendix 4 for copies of the quality assessment sheets for each publication.
Selection of participants
The methodological strength of the studies in terms of population representativeness and selection bias varied: 38 studies42,52,53,56–58,60–89,91,92 were rated moderate and two studies59,90 were rated weak. Individuals selected to participate in the studies were considered to be ‘somewhat likely’ to be representative of the target population in just under half of the studies (n = 17). 52,53,56,59,64–67,70,71,73–75,82–84,87 Two studies69,88 were not likely to be representative, and in 21 studies42,57,58,60–63,68,72,76–81,85,86,89–92 it was not possible to tell.
Study design
There were no RCTs included in the 40 publications. 42,51,52,56–92 No publications reported on a comparison group who received MM or best supportive care. Likewise, no publications reported on direct comparisons between VADs and HT. Some publications reported outcomes (e.g. on clinical functioning or functional assessment/QoL) using patients as their own controls (before–after designs) or within-study comparison on the basis of baseline characteristics such as age > 70 years.
Fourteen publications42,52,53,63,64,70,71,73–75,83–85,90 used a prospective design; mostly these were single-arm studies either using routine-collected data in registry studies or collecting de novo data. Some of these prospective studies reported used a mixture of data collection methods including both prospective and retrospective data.
Twenty-five publications42,52,53,63,64,70,71,73,74,75,83–85,90 reported a retrospective design (e.g. based on retrospective case note review).
Confounders
Two publications73,80 were rated as strong in relation to dealing with confounding factors and 3342,52,53,56–67,69–71,75–79,82–88,91,92 of the 40 publications were rated as moderate overall. Problems related to important differences between groups prior to the intervention and the percentage of relevant confounders that were adjusted for in analysis. Five publications68,72,81,89,90 were rated weak on this quality criterion.
Blinding
It was considered that 3742,52,53,56–73,76–81,83–92 of the 40 publications had weak overall blinding, one publication82 was rated moderate and two publications74,75 as strong. In the 37 publications42,52,53,56–73,76–81,83–92 the outcome assessor was aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants. Interestingly, only 12 publications42,57,61,63,65,70,71,73,74,83–85 reported that participants were aware of the research question.
Data collection methods
Overall, the data collection methods of eight42,73,75,76,85,89,91,92 of the studies were rated strong, of 2352,53,56,57,59–65,67,70–72,74,79,82–84,86,87,90 as moderate and of nine as weak. 58,66,68,69,77,78,80,81,88 In 24 publications42,52,53,56,59,62–64,67,69–76,83–85,89–92 the data collection tools were shown to be valid; in the other 16 publications57,58,60,61,65,66,68,77–82,86–88 it was not possible to tell. Eighteen publications42,52,63,64,70,71,73–76,79,83–86,89,91,92 reported that the data collection tools were shown to be reliable, three were not reliable,58,60,80 and in the remaining 19 publications53,56,57,59,61,62,65–69,72,77,78,81,82,87,88,90 it was not clear.
Withdrawal and dropout
Thirty-seven publications42,52,56–81,83–86,88–92 reported an 80–100% completion rate for study participants. Of these, 15 studies57–60,62–65,70–74,83,90 detailed numbers of dropouts and reasons. Overall, the methodological considerations relating to dropouts were considered strong in 17 publications,57–65,70,71,73,74,83,84,87,90 moderate in 21 publications42,52,66–69,72,75–82,85,86,88,89,91,92 and the remaining two weak. 53,56
Integrity
In all but one study 80–100% of participants received the intervention of interest. 42,52,53,56–82,84–92 Two publications62,89 measured the consistency of intervention, five56,65,69,85,87 did not and in 33 publications42,52,53,57–61,63,64,66–68,70–84,86,88,90–92 it was not possible to tell either way. Eighteen publications42,56,66,68,69,72,76–81,85,86,88,89,91,92 reported that participants were likely to have received an unintended intervention that may have influenced the results. In the remainder it was not possible to tell. 52,53,57–65,67,70,71,73–75,82–84,87,90
Analysis
This section of quality assessment included unit of allocation, unit of analysis, use of appropriate statistical method and whether the analysis was performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received. In all 40 publications,42,52,53,56–92 the unit of allocation and analysis was the patient. Twenty-eight publications42,52,53,56,57,59,61,62,64–67,69–76,80,83–85,87,89,91,92 reported statistical methods that were deemed appropriate, in four60,63,68,88 statistical methods were not appropriate and in eight58,77–79,81,82,86,90 it was not possible to tell. In 30 publications42,57–71,73,76–81,85–87,89–92 it was not possible to tell how the analysis was performed.
Summary
For the 40 included publications, overall quality ratings were as follows: one study was rated strong,75 15 studies as strong to moderate,42,52,53,64,70,71,73,76,80,83–85,89,91,92 13 studies as moderate,56,57,59,62,63,65–67,74,79,82,86,87 10 studies as moderate to weak58,60,61,68,69,72,77,78,88,90 and one study as weak. 81
Overall, the study designs were not strong: studies were likely to be only moderately representative of underlying populations, there were no randomised trials and blinding of outcomes assessors was weak. Most patients received the intervention they were anticipated to receive although this criterion is not relevant for the 25 retrospective designs. Data collection methods and recording of withdrawal and dropout were moderate. Analysis was deemed appropriate for the majority of studies and most studies attempted to deal with confounding. Detailed quality assessment reports for each study are presented in Appendix 4.
Baseline characteristics
An apparent 19,161 participants were described in the 40 included publications; however, please see Delineating multiple overlapping populations between publications, which explains the issue of multiple reporting of patients by publications. The majority of the studies took place in the USA (n = 27); others were listed as taking place in Germany (n = 3), Europe specifically (n = 2), Austria (n = 2), unclear (n = 1) and multiple counties (n = 5).
All included studies reported some baseline characteristic values for the population investigated, one study reported five84 baseline characteristics while two others reported 43. 79,80 Method of reporting varied; for example, age was reported as a mean (standard deviation; SD), a median with range, a proportion or percentage within each of several defined age bands or as a combination of these methods. Some authors reported data for subgroups only but, where possible, subgroups have been combined to provide a value for the whole study population. Authors frequently used baseline characteristics in regression analyses attempting to identify factors that influence outcomes of particular interest in their study (e.g. aortic insufficiency,60,72 renal function62 and stroke58,81).
The baseline characteristics of BTT patients are presented in Figures 7–13. To avoid double counting caused by overlapping populations, the largest or most recent publication from each known cohort, conditional on the availability of data, has been included. Pooled estimates are provided. If the two large registry studies by Nativi et al. 89 and John et al. 65 were to be included in pooling then pooled estimates would merely reflect their input; therefore, these have been omitted from pooling but where possible have been compared with the pooled estimate. A further difficulty concerns whether or not mixed-device studies should be included. We have included data from Sandner et al. 91,92 when reported, as overlap with other studies is likely to be minimal. Pooled estimates should be treated with extreme caution as they:
-
may miss studies that should be included
-
may not be representative either of all included studies or of all patients within a particular VAD study (most studies defined sampling frames and patient selection methods poorly)
-
may include clinical heterogeneity and missing information (not all studies provided analysable information and we excluded studies with fewer than 50 patients).
Nevertheless, pooled estimates provide a picture of baseline characteristics of relevant populations receiving VADs.
Age
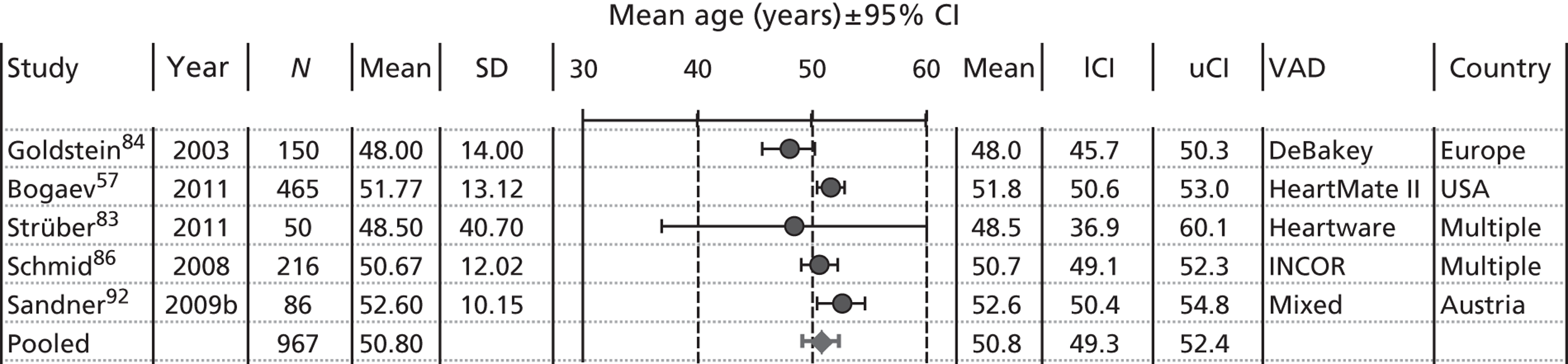
Where mean age was reported it varied between 45 years (Klotz et al. 88) and 65 years (Adamson et al. 56). Two large studies involving 115782 and 855789 participants reported comparable mean ages of 51 years. The distribution of mean age in the included non-overlapping studies of BTT patients is summarised in Figure 7. The pooled estimate was 50.8 years, and this is similar to the large registry study by Nativi et al. 89 of 8557 BTT LVAD patients, which found mean ages of 50.1, 50.2, 50.8, 51.4 and 51.8 years, respectively, in patients who received pulsatile first-generation LVADs, pulsatile second-generation LVADs, continuous second-generation LVADs and for second-generation patients (no LVADs) on inotropes and second-generation patients (no LVADs) not on inotropes.
FIGURE 7.
Mean age at baseline for individual studies. (Note: studies with minimal population overlap with other studies; only BTT patients included.) There was statistical heterogeneity between studies (I2 = 64%). lCI, lower CI; uCI, upper CI.
Gender
The percentage of males in all these studies ranged from 68.5% (Lahpor et al. 68) to 91.5% (Morshuis et al. 85) (summarised in Figure 8).
FIGURE 8.
Baseline number (%) of patients reported to be male. (Note: studies with minimal population overlap with other studies; only BTT patients included.) lCI, lower CI; uCI, upper CI.
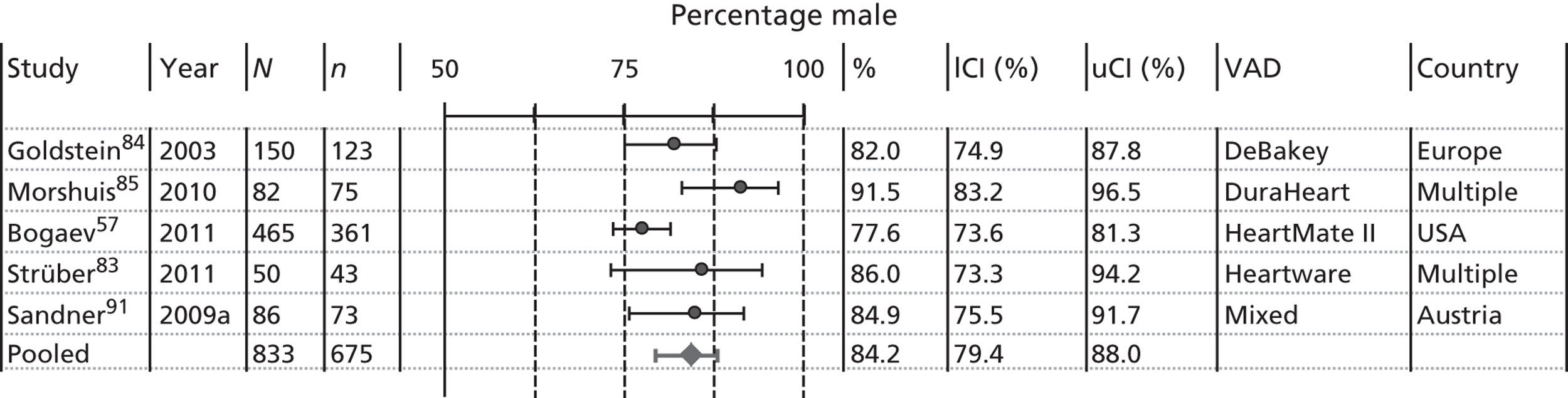
The pooled estimate was 84% with moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 40%). Again, the combined result is similar to the large registry study of 8557 LVAD BTT patients reported by Nativi et al. 89 which found percentages of males to be 85.5%, 86.1%, 82.3%, 75.0% and 74.9% for pulsatile first-generation LVADs, pulsatile second-generation LVADs, continuous second-generation LVADs, second-generation patients on inotropes and second-generation patients not on inotropes respectively.
Race
White or Caucasian patients constituted 44.2% (Schaffer et al. 77) to 95.1% (Oswald et al. 90) of patient populations. The proportion of African American or black patients ranged between 6.6% (Topilsky et al. 79) and 22.6% (Miller et al. 70). All studies reporting race were undertaken in the USA. Studies were overlapping in terms of population and most reported a mix of destination and bridged therapies. Overall, there was limited reporting of race across all devices. The large registry studies (Nativi et al. 89 and John et al. 65) (n = 1496) did not report race of patients.
Body mass index
Fourteen studies59,62–65,71,72,77,81,83,86,88,89,91 reported baseline BMI (kg/m2) of patients. All but one of the studies reported BMIs suggestive that patients were overweight. 59,62–65,71,72,77,81,83,86,89,91 The results reported in non-overlapping studies of BTT patients are shown in Figure 9.
FIGURE 9.
Baseline BMI (kg/m2). (Note: studies with minimal population overlap with other studies; only BTT patients included.) lCI, lower CI; uCI, upper CI.
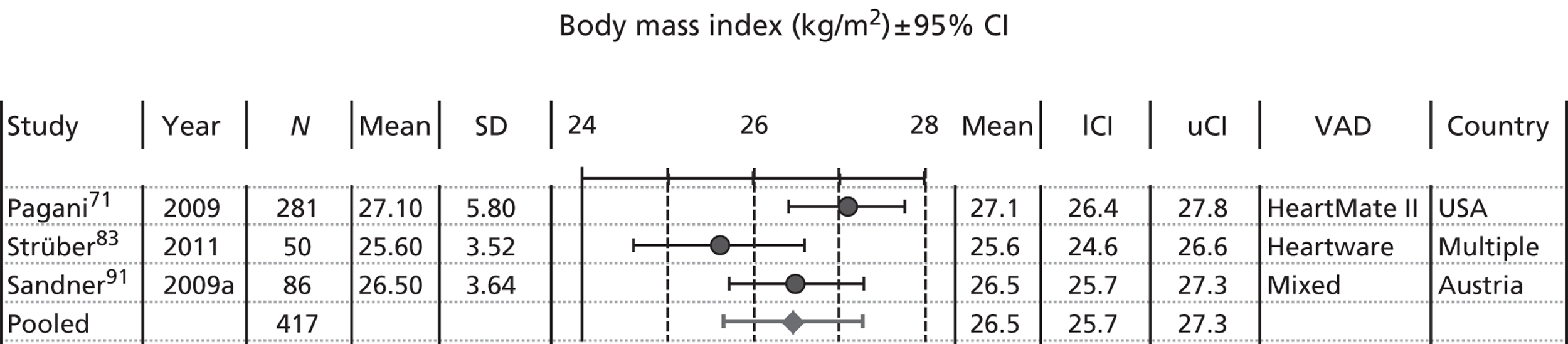
The pooled estimate of 26.5 kg/m2 is similar to the value in the large registry study of 8557 LVAD patients reported by Nativi et al. ,89 which found values of 26.7, 27.4, 26.8, 26.2 and 26.3 kg/m2, respectively, for BTT patients who received pulsatile first-generation LVADs, pulsatile second-generation LVADs, continuous second-generation LVADs, and for second-generation patients on inotropes and second-generation patients not on inotropes. A somewhat larger value of 28.8 kg/m2 was reported by John et al. 65 for 1496 registry patients. It should be noted that in HF BMI may be misleading, owing to the underlying fluid retention of HF.
New York Heart Association functional classification of the extent of heart failure
A minority of studies (n = 16) reported baseline information on the NYHA functional classification of patients and where this was reported, the majority of patients were reported as having NYHA class IV. Overall, there was limited reporting of NHYA classification across all devices. Four-fifths (83.5%) of BTT patients had a rating of NYHA class IV assessed from non-overlapping studies (Figure 10).
FIGURE 10.
Baseline number (%) of patients with NYHA IV classification. (Note: studies with minimal population overlap with other studies; only BTT patients included.) lCI, lower CI; uCI, upper CI.
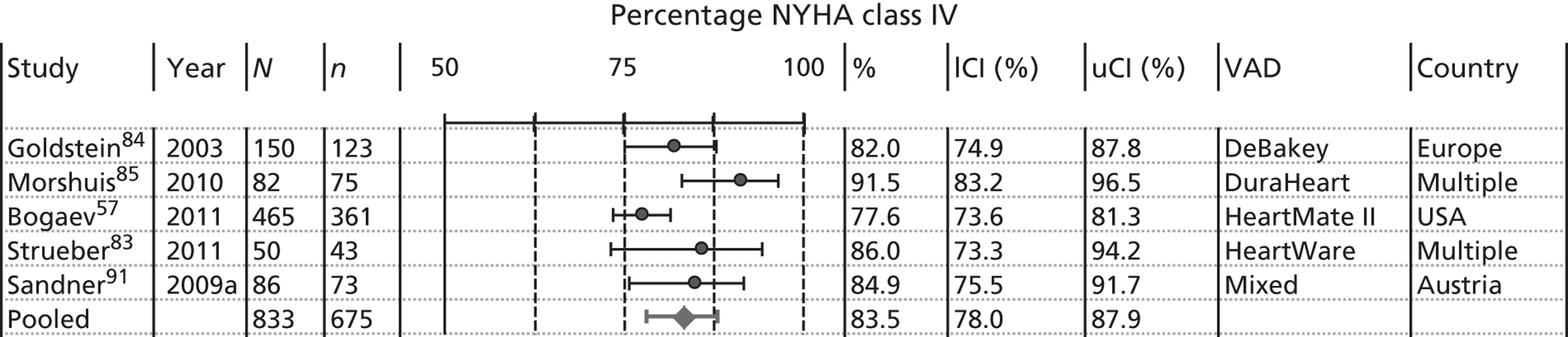
There was some heterogeneity among studies (I2 = 38%). Neither large registry study65,89 included usable NYHA class information.
Diabetes mellitus
A total of 12 studies reported the number of patients with diabetes mellitus at baseline (HMII, n = 8; HW, n = 1; mixed devices, n = 3). The percentage of patients with diabetes mellitus at baseline in these studies ranged from 14% (Strueber et al. 83) to 38.5% (Pak et al. 72). In some studies, subgroups with different rates of diabetes mellitus were reported at baseline [e.g. Sandner et al. 91 reported 17.9% compared with 53.3% (group 1 aged < 60 years vs. group 2 aged > 60 years respectively)]. Figure 11 summarises results reported in non-overlapping studies of BTT patients.
FIGURE 11.
Baseline number (%) of patients with diabetes mellitus. (Note: studies with minimal population overlap with other studies; only BTT patients included.) lCI, lower CI; uCI, upper CI.
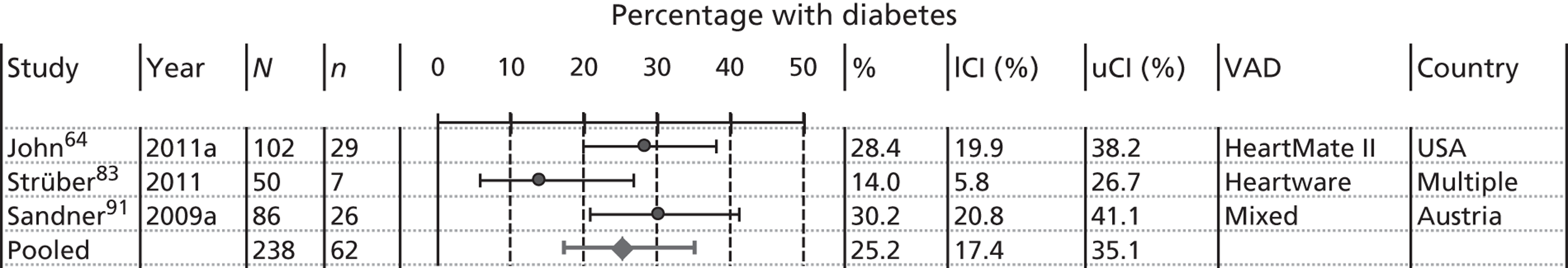
The pooled value of 25.2% is similar to reported values, ranging between 20.5% and 28.3%, for patients who received pulsatile first-generation LVADs, pulsatile second-generation LVADs or continuous second-generation LVADs, and for second-generation patients taking inotropes and second-generation patients not taking inotropes, in the large registry study of 8557 LVAD patients (Nativi et al. 89).
Inotropes
The baseline numbers (and percentages) of patients receiving inotropes in non-overlapping studies of BTT patients are shown in Figure 12.
FIGURE 12.
Baseline number (%) of patients using inotropes in non-overlapping studies of BTT patients. lCI, lower CI; uCI, upper CI.
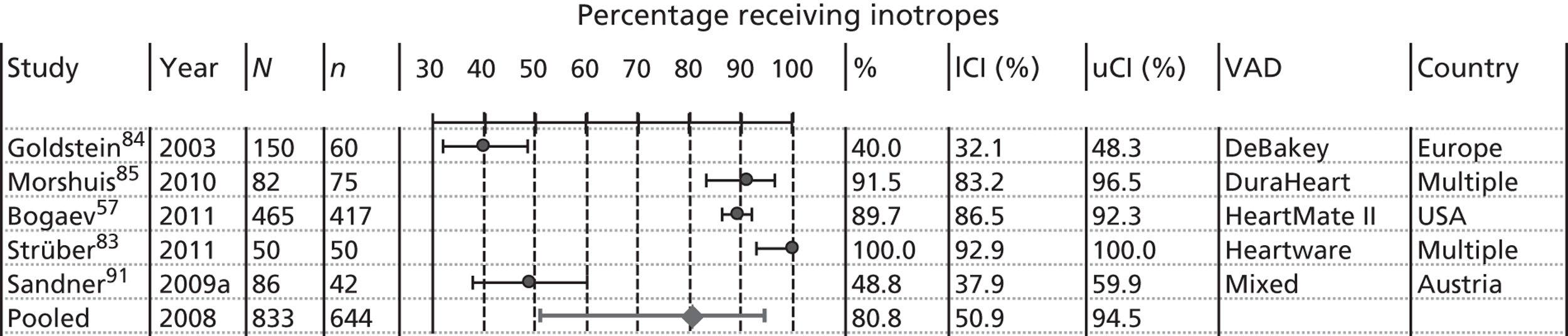
There was heterogeneity between studies (I2 = 49%) and percentage values ranged widely, from 40% to 100% of patients receiving inotropes; the pooled estimate of 81% is similar to the value of 80.4% reported for 1496 HMII patients in the large registry study by John et al. 65
Systolic blood pressure
Baseline systolic blood pressure (BP) was reported in 15 studies. 42,52,53,56,59,63,65,70,71,74,75,79,80,83,85 Figure 13 summarises the results reported in non-overlapping studies of BTT patients. Systolic BP can be seen to be low compared with normal physiological levels, reflecting the severity of HF in these patients, with a pooled estimate of 97.3 mmHg.
FIGURE 13.
Baseline systolic BP (mmHg). (Note: Studies with minimal population overlap with other studies; only BTT patients included.) lCI, lower CI; uCI, upper CI.
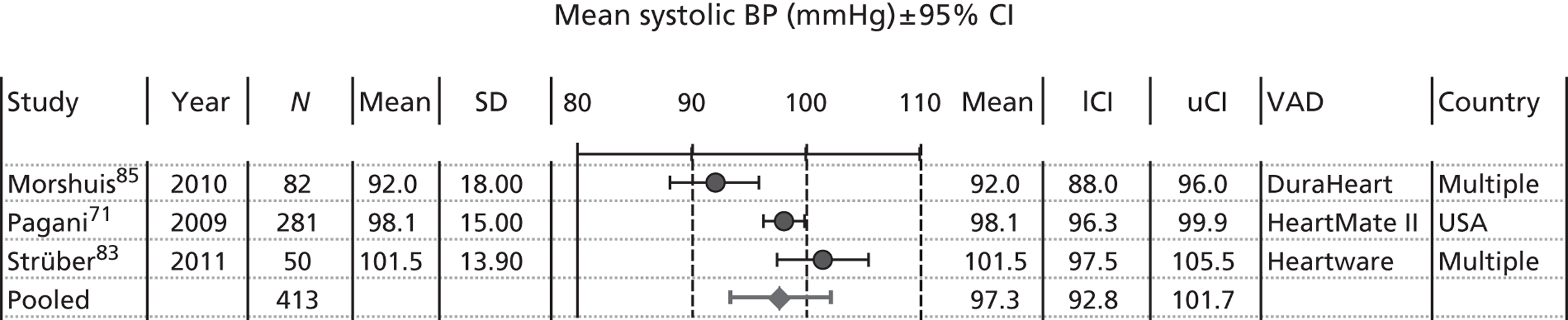
Heterogeneity (I2 = 83%) between studies arose mainly from the study by Morshuis et al. 85 The pooled estimate is similar to the value of 100.9 mmHg reported for 1496 HMII patients in the large registry study by John et al. 65 Nativi et al. 89 did not report this characteristic for registry patients.
Summary of baseline characteristics
In so far as it was possible to separately identify non-overlapping groups of patients, we identified the following baseline characteristics. The majority of patients were white (78–94%), male [84.2% (95% CI 79.4% to 88.0%)] and middle aged [mean age 50.8 years (95% CI 49.3 to 52.4 years)]. Mean BMI was in the overweight range [mean BMI 26.5 kg/m2 (95% CI 25.7 to 27.3 kg/m2)] and about one-quarter of patients [25.2% (95% CI 17.4% to 35.1%)] had diabetes mellitus. Study patients had very severe HF, with 83.5% (95% CI 78.0% to 87.9%) overall rated as NYHA class IV. This was supported by the proportion receiving inotrope medication [80.8% (95% CI 50.9% to 94.5%)] and the low mean systolic BP of 97.3 mmHg (95% CI 92.8 to 101.7 mmHg).
Outcomes by device
In this section we describe outcomes including adverse events, survival, causes of death and QoL for each device.
Outcomes for HeartMate II
A total of 29 studies52,53,56–82 met the current inclusion criteria concerning HMII (see Table 3).
Adverse events
Twenty-three studies52,56–61,64–73,75,76,78,79,82 reported adverse events or complications during the follow-up of HMII implantation. Given the problems of reporting on overlapping populations within studies (see Delineating multiple overlapping populations between publications), adverse events for HMII are best described by John et al. 65 (Table 9).
| Adverse event | John et al.65 trial group (n = 486), 511.1 patient-years | |
|---|---|---|
| Incidence (% of patients) | Event rate/patient-year | |
| Bleeding requiring re-exploration | 21 | 0.23 |
| Infection | ||
| Percutaneous lead infection | 20 | 0.33 |
| Pump pocket infection | 3 | 0.03 |
| Right-side HF requiring RVAD | 7 | 0.06 |
| Stroke | ||
| Ischaemic | 5 | 0.05 |
| Haemorrhagic | 5 | 0.05 |
| Other | 0 | 0.00 |
| Device replacement | 5 | 0.06 |
Adverse events with HMII affect high proportions of patients. Twenty-one per cent of patients had bleeding requiring re-exploration; 20% had percutaneous lead infection and 3% pump pocket infection. Stroke is a very serious adverse event affecting approximately 10% of patients (it is assumed the ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke did not occur in the same patient). Event rates per year should be treated with caution as follow-up rates are variable and events are highest in the first year after surgery.
Survival
Table 10 summarises the K–M survival results as reported in the HMII studies (see Table 3).
| Study | Population | n | % (SE) alive | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month 1 | Month 6 | Month 12 | Month 18 | |||
| aBogaev 201157 | Women | 104 | 96 ± 2 | 87 ± 4 | 76 ± 3 | 73 ± 3 |
| aBogaev 201157 | Men | 361 | 93 ± 1 | 83 ± 2 | 74 ± 5 | 73 ± 5 |
| John 201165 | HMII FDA approval trial extension | 486 | NR | 83.8 ± 1.8 | 75.6 ± 2.4 | NR |
| John 201165 | INTERMACS post-FDA approval | 1496 | NR | 89.4 ± 0.9 | 84.9 ± 1.1 | NR |
| aKormos 201067 | With early RV failure | 65 | 89 ± 4 | 66 ± 6 | 59 ± 7 | NR |
| aKormos 201067 | Without early RV failure | 386 | 94 ± 1 | 87 ± 2 | 78 ± 3 | NR |
| bMiller 200770 | HMII FDA approval trial | 133 | 90 | 75 | 68.5 | NR |
| Pagani 200971 | HMII FDA approval trial extension | 281 | 92 ± 2 | 83 ± 3 | 73 ± 3 | 72 ± 3 |
| aPal 200973 | Concurrent cardiac procedures | 111 | 89 ± 4 | 77 ± 5 | 66 ± 7 | NR |
| aPal 200973 | No concurrent cardiac procedures | 271 | 94 ± 2 | 84 ± 3 | 77 ± 4 | NR |
| bStarling 201152 | INTERMACS post-approval study for FDAc (first 169 patients post Miller 200770) | 169 | 96 | 90 | 85 | NR |
The most recent and largest study of survival in the HMII BTT programme for HF appears to be that of John et al. ,65 who included 486 patients from the extension of the HMII FDA approval study and 1496 post-approval patients in the INTERMACS registry. This analysis indicated superior survival for the latter patients (p < 0.0001 for log-rank test comparison). These results led the authors to propose that increasing experience with the HMII device has led to a gradual improvement in survival (Figure 14).
FIGURE 14.
Kaplan–Meier survival results reported by John et al. 65 for patients who received an HMII LVAD.
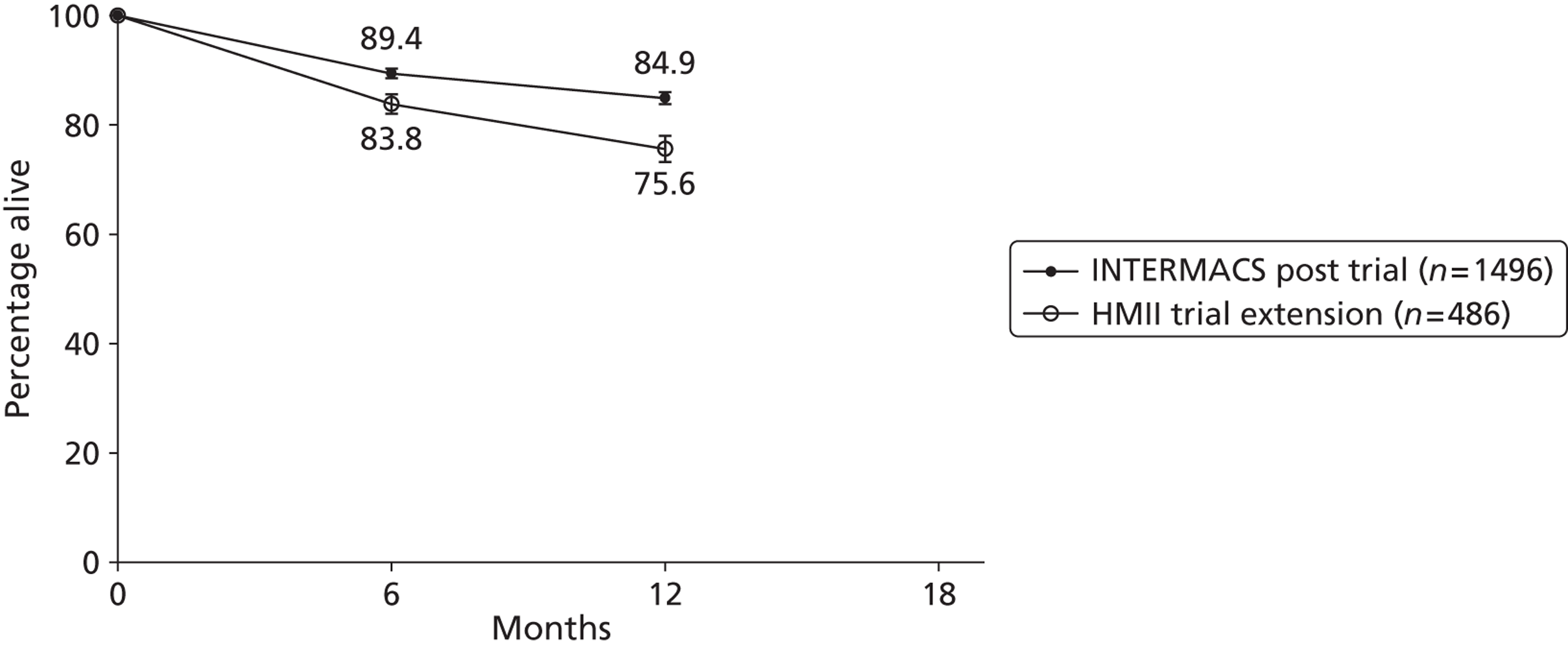
Earlier publications in the HMII FDA approval series included those of Miller et al. ,70 with 133 patients, and Pagani et al. ,71 with 281 patients; they represent samples from John et al. ,65 a growing cohort of the HMII approval study patients which accumulated 486 patients. The survival results reported are shown in Figure 15 together with those for the first 169 post-approval patients analysed in Starling et al. 52 The results tend to support the proposition that a so-called learning curve leads to improving survival as the cohort grows. Survival at 1 year was 68.5% in Miller et al. ,70 73% in Pagani et al. ,71 75.6% in John et al. 65 and 85% in Starling et al. 52 as well as for the 1496 registry post-approval patients in John et al. 65
FIGURE 15.
Kaplan–Meier survival results for the HMII FDA approval trial and registry patients.
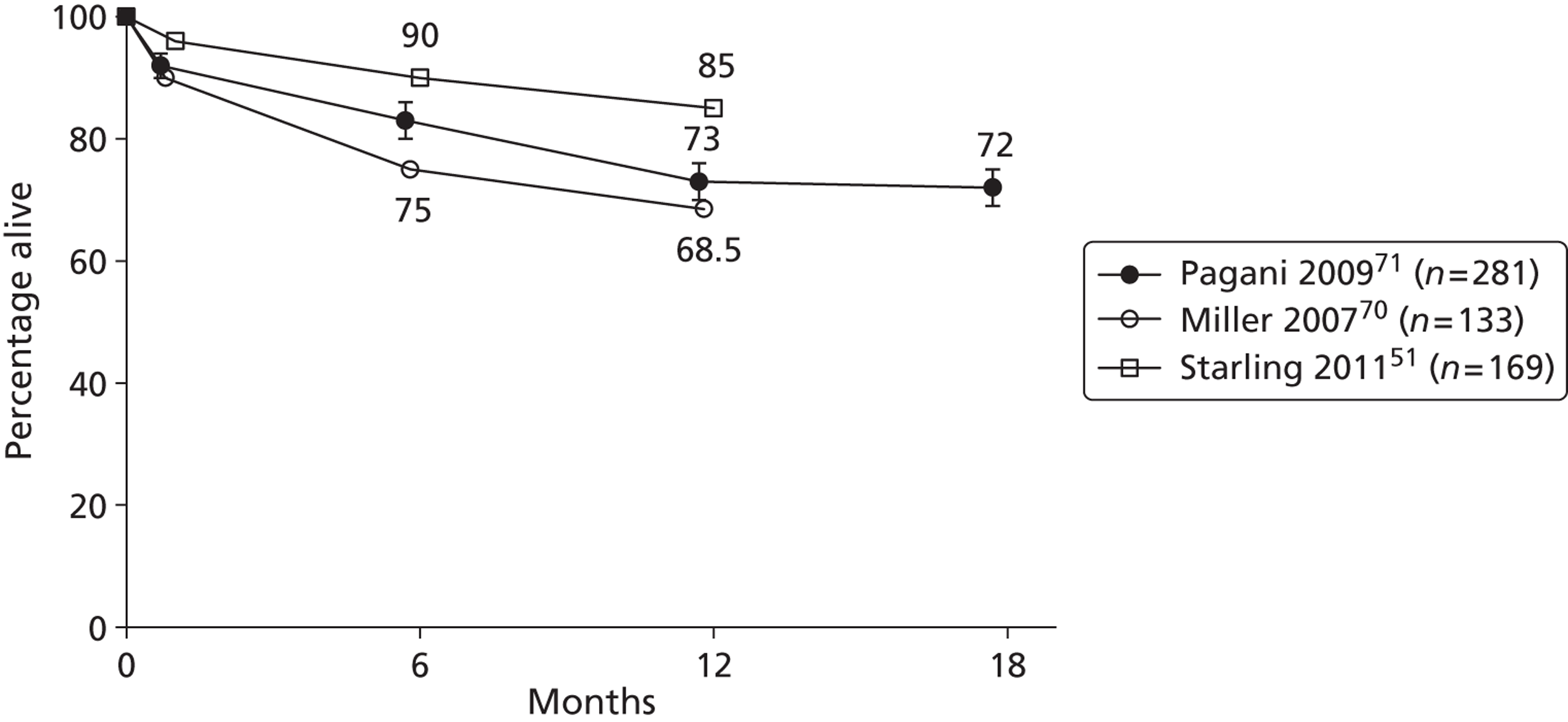
Greater experience with the device offers one explanation for the apparently improving survival; however, the similarity of these populations at baseline is difficult to gauge.
FIGURE 16.
Kaplan–Meier results reported for subgroups of patients receiving HMII LVAD.
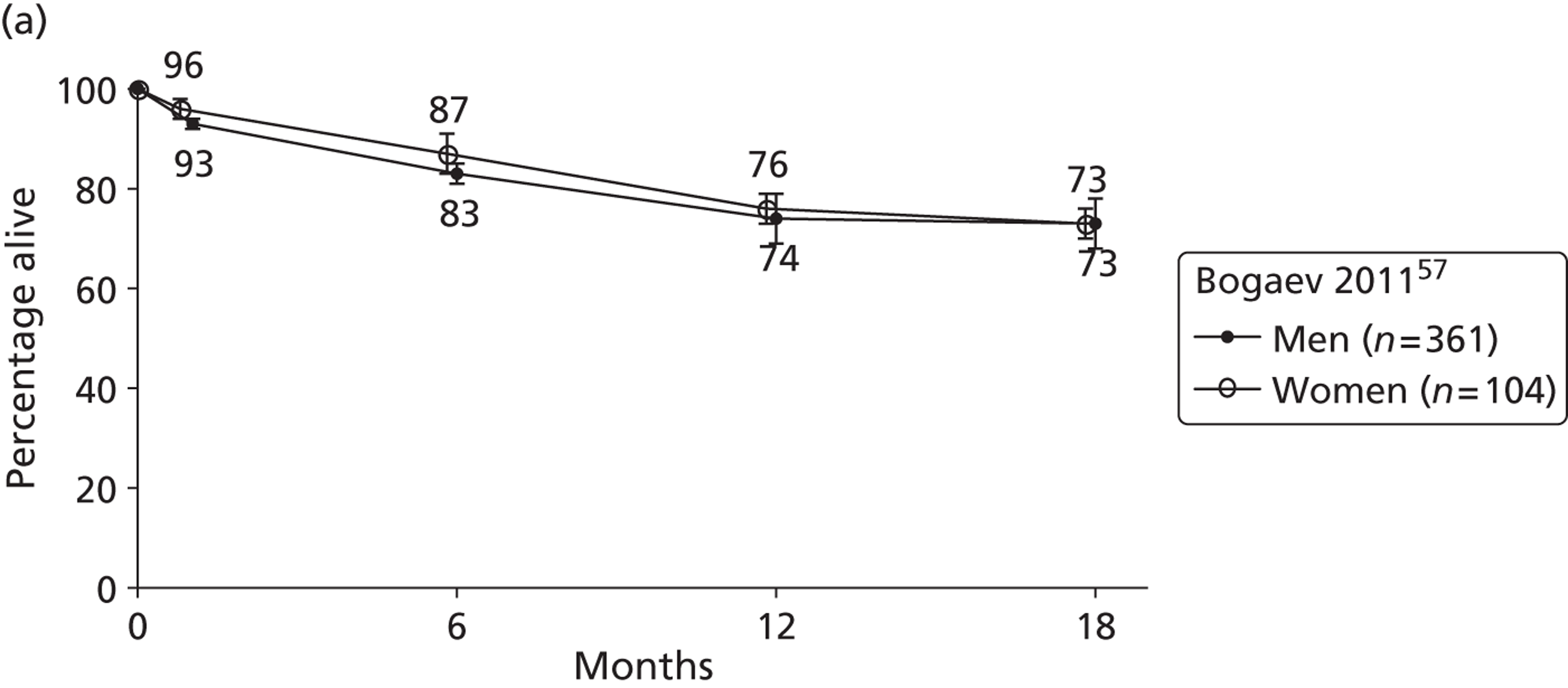
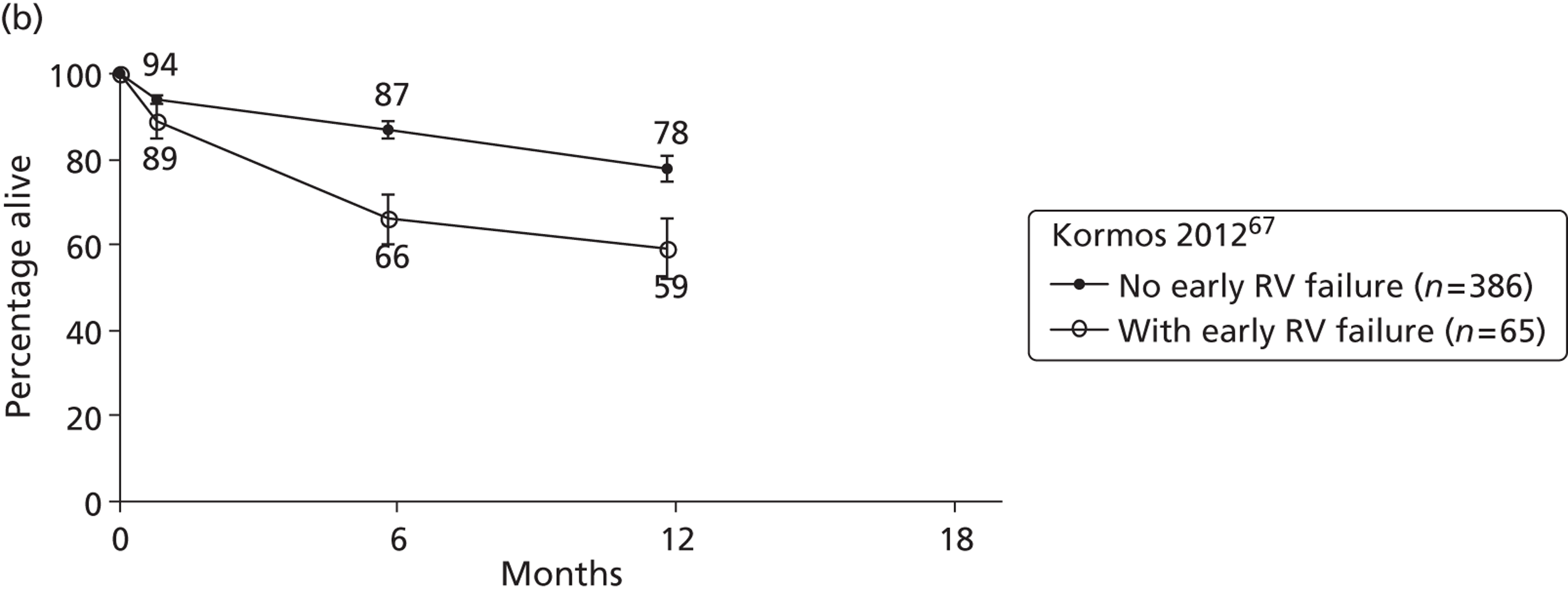
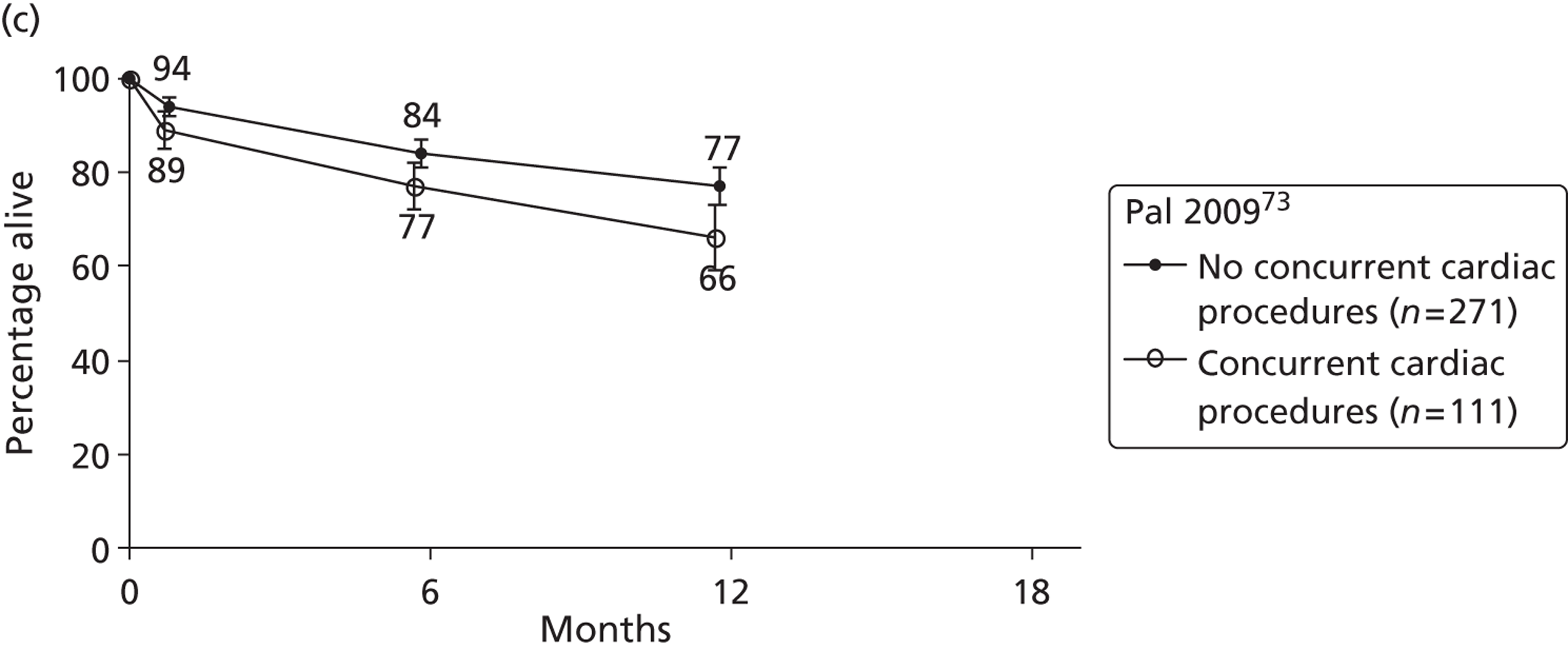
Three publications reported survival for subgroups of patients in the extension of the HMII FDA approval study (Bogaev et al. ,57 Kormos et al. 67 and Pal et al. 73). In each of these studies participants were dichotomised according to a single variable. The results are summarised in Figure 16. No significant difference was observed between genders, although early RV failure was associated with poorer survival (p = 0.026), as were concurrent cardiac procedures undertaken (p = 0.048).
In summary, publications suggest that survival at 1 year is approximately 75% but may improve with gain in surgical experience. These K–M analyses censor patients when they receive a HT. The problem here is that if the chance of receiving a donor heart depends on a patient's prognosis, for example if more seriously ill patients are selectively removed from follow-up and receive priority for transplantation, then survival estimates are susceptible to informative censoring and may thereby represent overestimates.
Causes of death
Twelve of the included HMII papers reported causes of death. 56,57,64,68,70–73,78–80,82 Of these, the most recent and largest publication reporting this outcome in the HMII BTT programme for HF appears to be that of Bogaev et al. 57 This publication dichotomised participants according to gender. The reported leading causes of death in men were sepsis (3.9%), right HF (2.8%) and multisystem organ failure (2.2%). The leading causes of death in women were multisystem organ failure (3.8%), haemorrhagic stroke (2.9%), ischaemic stroke (1.9%), right HF (1.9%) and external component device malfunction (1.9%; percutaneous lead trauma in one patient and pump disconnection in another). 57 Table 11 provides a summary of the causes of death reported in the 12 HMII studies.
| First author | Date | Country | Causes of death |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adamson56 | 2011 | USA | Anoxic brain injury, cardiomyopathy, sepsis, respiratory failure, multiorgan failure, ischaemic stroke, haemorrhagic stroke, device thrombosis, patient disconnected power, cancer, withdrawal of support, unknown causes |
| Bogaev57 | 2011 | USA | Sepsis, right HF, multisystem organ failure, ischaemic stroke, haemorrhagic stroke (thrombi, pump disconnection, twisted inflow graft, pump pocket infection, loss of power, percutaneous lead trauma), respiratory failure, cardiac failure, bleeding, cancer, elective withdrawal of support, death during transplantation, unknown causes |
| John64 | 2011a | USA | Multisystem organ failure, subclavian vein haemorrhage, ventricular fibrillation, respiratory failure, RV failure, intracranial bleed |
| Lahpor68 | 2010 | Europe | Multiorgan failure mainly occurring as a result of septic complications or right-HF, CVAs |
| Miller70 | 2007 | USA | Sepsis, ischaemic stroke, multisystem organ failure, haemorrhagic stroke, anoxic brain injury, right HF, miscellaneous other causes, device-related death caused by an inflow graft that was accidentally twisted during implantation |
| Pagani71 | 2009 | USA | Sepsis, stroke (ischaemic, haemorrhagic), right HF, device related, multiorgan failure, anoxic brain injury, bleeding, cancer, respiratory failure, hyperthermia, air embolism |
| Pak72 | 2010 | USA | Aortic insufficiency onset of multiorgan system failure |
| Pal73 | 2009 | USA | Bleeding, sepsis, driveline infection, ventricular arrhythmias, perioperative stroke, renal failure |
| Strueber78 | 2008 | Multiple | Multiorgan failure, right HF, CVAs, respiratory failure, driveline disconnection, bleeding after ventricular rupture, suffocation after epistaxis (nose bleed) |
| Topilsky79 | 2011a | USA | Multiorgan failure, intractable right HF, hyperperfusion brain injury, sepsis, uncontrollable bleeding |
| Topilsky80 | 2011b | USA | Uncontrolled right HF, multiorgan failure, intracerebellar bleeding, traumatic head trauma injury, haemorrhagic stroke, unexplained sudden death, RV failure, embolic stroke, complication of myocardial biopsy after transplant, patient withdrawal of support owing to persistent RV failure and need for dialysis |
| Ventura82 | 2011 | USA | Graft failure, infection, cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, multiorgan failure, haemorrhage, malignancy, unknown causes |
Common causes of death included (a) multiorgan failure (n = 12 studies), (b) right heart (ventricular) failure (n = 8 studies), (c) bleeding (n = 7 studies) and (d) stroke and cerebrovascular accident (CVAs) (n = 9 studies).
Quality of life
The HMII studies used several instruments for monitoring QoL and functional status of HF patients. Table 12 provides a summary of HMII studies indicating which QoL measures were used.
| First author | Date | Country | MLWHF | KCCQ | METs | VAS | NYHA functional class | 6-minute walk test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rogers53 | 2010 | USA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Topilsky79 | 2011 | USA | ✓ | |||||
| Topilsky80 | 2011 | USA | ✓ | |||||
| Adamson56 | 2011 | USA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Bogaev57 | 2011 | USA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| John65 | 2011 | USA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Miller70 | 2007 | USA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Pagani71 | 2009 | USA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Starling52 | 2011 | USA | ✓ |
For this variety of QoL measures, data were presented as group means at various time points, change in group mean from baseline, or as change in mean or median for paired measures for individual patients. The number of patients investigated during individual studies gradually diminished as a result of death, transplantation with a donor heart and loss to follow-up or withdrawal. Baseline values were not always complete because some patients may not have been sufficiently well to participate. Full QoL results can be found in Appendix 3.
Five of the nine studies (Rogers et al. ,53 Bogaev et al. ,57 John et al. ,65 Miller et al. 70 and Pagani et al. 71) contribute to the multicentre HMII BTT FDA approval programme with overlapping populations. By far the fullest QoL information was provided in Rogers et al. 53 (n = 281). Although the largest BTT patient groups were investigated in Bogaev et al. 57 (n = 465) and John et al. 65 (n = 486), relatively limited results were presented and neither report paired measures; therefore, here we focus on the data presented in Rogers et al. 53 (for this study information in Pagani et al. 71 can be used to gauge the completeness of the reported data). Rogers et al. 53 presented results separately for 281 BTT and 374 DT patients; the DT results were similar to those for BTT patients. (They are not considered further here but can be found in Appendix 3.) In the following section, the QoL results presented by Rogers et al. 53 are summarised and considered separately according to the investigatory instrument. Comments on the results from Bogaev et al. 57 and John et al. 65 should be viewed in the knowledge that the populations in these studies included participants from Rogers et al. 53
Minnesota Living With Heart Failure Questionnaire
Scores on the MLWHF questionnaire ranged from 0 to 105, with lower values signifying improved QoL. Scores reported by Rogers et al. 53 decreased over time relative to baseline scores (–10 points at 1 month and –29 points at 6 months; median per cent improvement at 6 months of 38%), indicating an improvement in QoL (p < 0.05). These results for MLWHF scores at 1, 3 and 6 months for BTT patients are summarised in Figure 17.
Reading from the graph in Pagani et al. 71 the number of patients supported on HMII at 6 months was about 132, so that the return of 115 questionnaires at 6 months represents a data set approximately 87% complete.
Rogers et al. 53 also reported paired change (i.e. mean change from baseline for patients with measures at both time points) (Table 13).
| BTT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | n | Mean ± SD | Median [25th, 75th percentiles] | % improvement of median |
| 1 | 167 | −12 ± 27 | −10 [−28, 4] | 13 |
| 3 | 126 | −24 ± 31 | −30 [−47, −4] | 39 |
| 6 | 87 | −28 ± 28 | −29 [−50, −9] | 38 |
FIGURE 17.
Changes in MLWHF for the BTT group over time (Rogers et al. 53). Bars indicate 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles, and the whiskers indicate fifth and 95th percentiles.
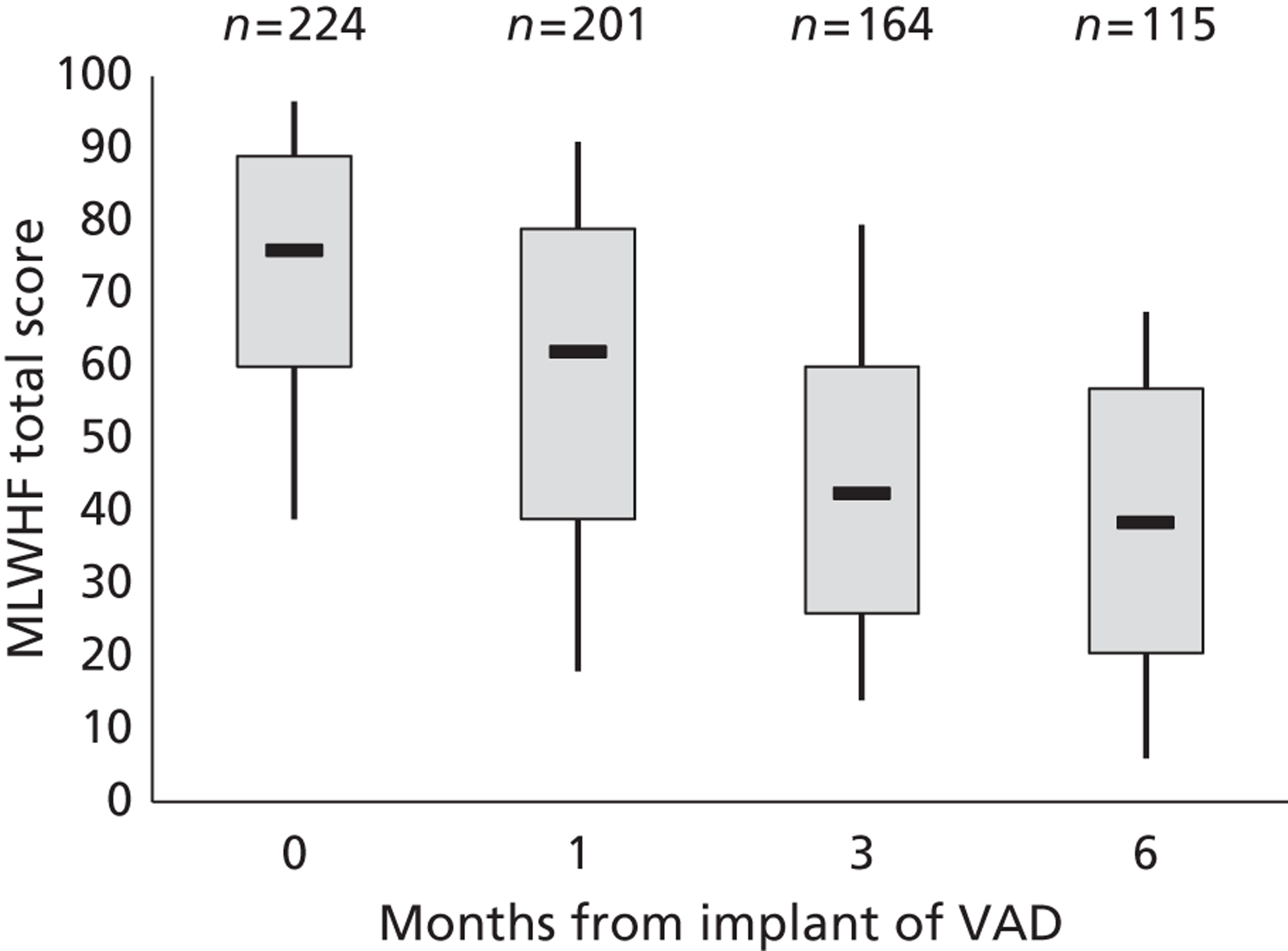
Borgaev et al. ,57 who subdivided the population by gender, reported similar results: a significant improvement (both genders group) between baseline and 6 months (female: 73 ± 22 to 35 ± 22; male: 71 ± 22 to 40 ± 23). There was no significant difference between the sexes (p = 0.661).
The Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) overall summary score (OSS) and clinical summary score (CSS) improved during HMII support. The median KCCQ OSS showed improvements at 1, 3 and 6 months compared with baseline and (p < 0.05 at each time point). KCCQ group OSS also showed similar improvements (p < 0.05 at each time point) (Figure 18).
FIGURE 18.
Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire scores (Rogers et al. 53). Bars indicate 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles, and the whiskers indicate fifth and 95th percentiles. (a) OSS; and (b) CSS.
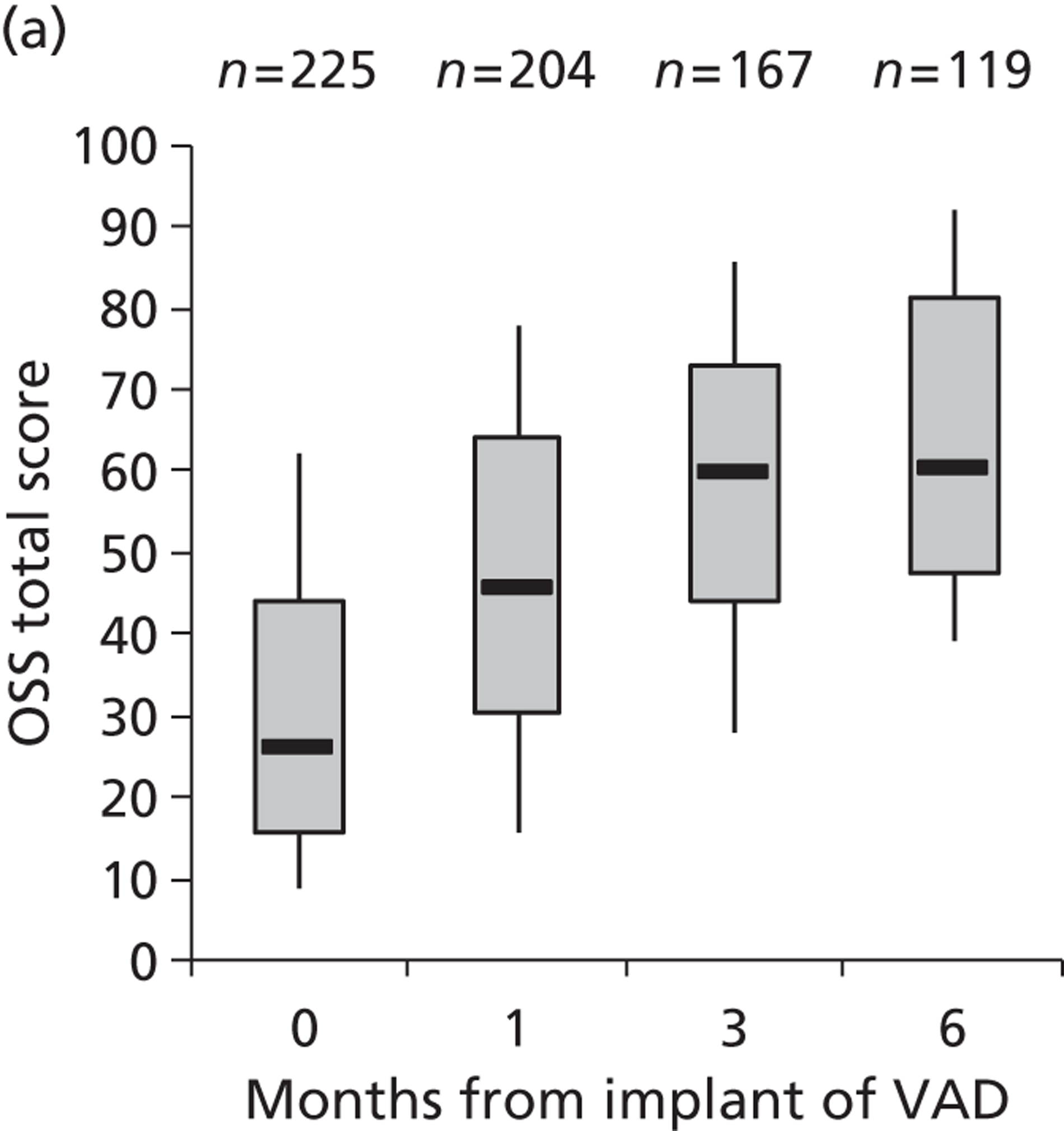
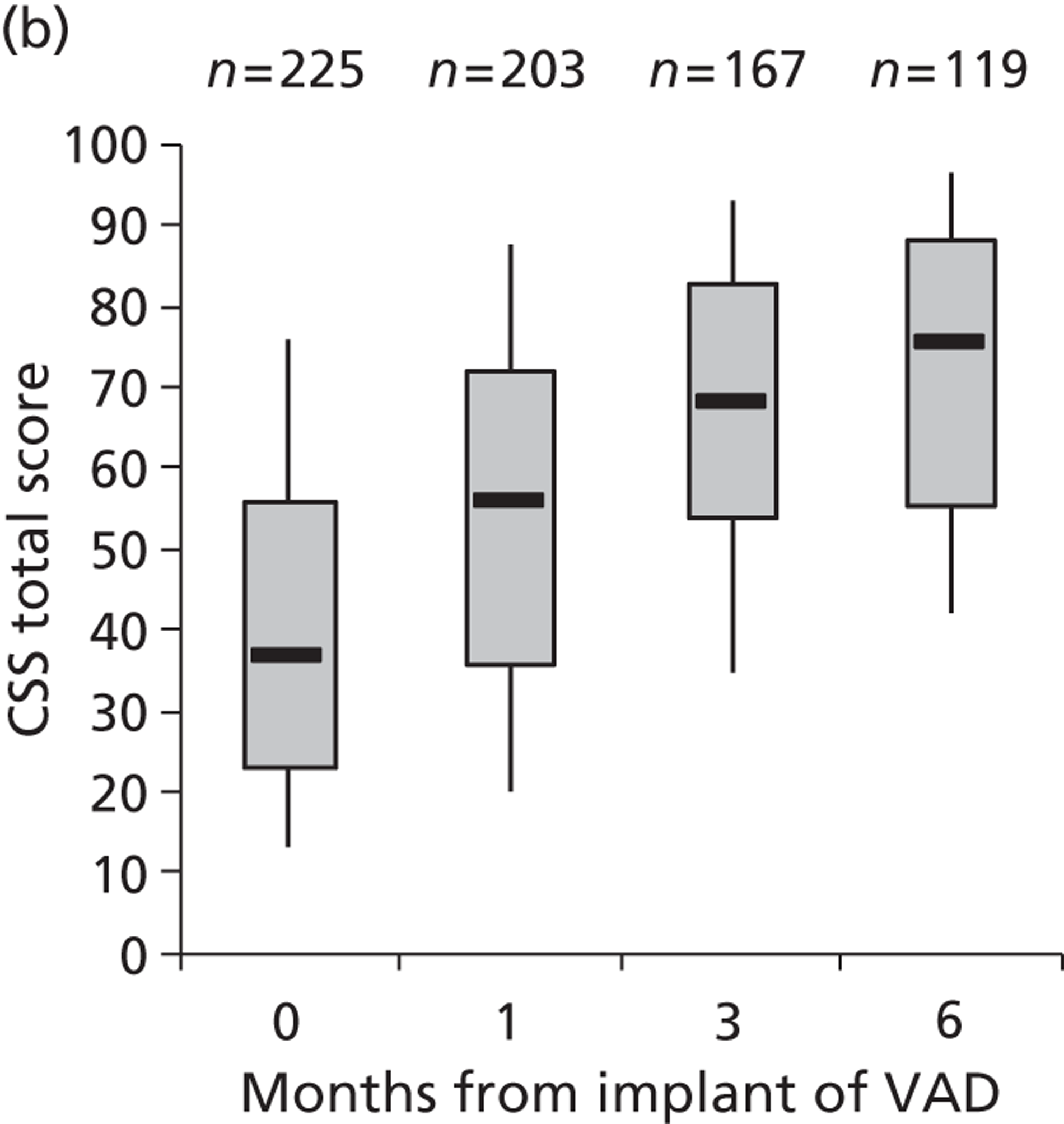
Rogers et al. 53 reported paired KCCQ score changes (i.e. mean of change from baseline for patients with measures at both time points). These results are summarised in Table 14.
| OSS | CSS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | n | Mean ± SD | Median [25th, 75th percentiles] | Improvement of median | Month | n | Mean ± SD | Median [25th, 75th percentiles] | Improvement of median |
| 1 | 172 | 13 ± 25 | 14 [−3, 29] | 0.54 | 1 | 170 | 12 ± 27 | 11 [−6, 31] | 0.3 |
| 3 | 132 | 22 ± 26 | 20 [9, 42] | 0.77 | 3 | 132 | 21 ± 28 | 21 [4, 42] | 0.57 |
| 6 | 90 | 27 ± 28 | 28 [7, 45] | 1.08 | 6 | 90 | 25 ± 31 | 24 [8, 43] | 0.65 |
Again, paired measures support the evidence for an improvement in QoL for patients surviving after implant of the HMII VAD (p-value and statistical significance were not reported).
Borgaev et al. ,57 who subdivided the population by gender, reported significant improvements for both men and women in mean values on the KCCQ OSS and CSS between baseline and 6 months (there was no significant difference between the sexes).
Metabolic equivalent task score
The metabolic equivalent task score (METs) measures patient-reported exercise ability. Rogers et al. 53 presented serial assessments of METs following HMII (Figure 19). At baseline, > 90% of patients described their level of function as low or very low. At 6 months, about two-thirds of patients described their level of function as moderate to very high (p < 0.001 vs. baseline).
Borgaev et al. 57 found no significant difference between males and females in METs improvements (p = 0.348).
Quality of life visual analogue scale
Rogers et al. 53 did not report on this outcome. For purposes of completeness, results from other studies are reported here. The data presented by Starling et al. 52 for the first 169 post-FDA-approval HMII patients are summarised in Figure 20. Visual analogue scale (VAS) scores (scale 0–100; best QoL = 100) improved at 3, 6 and 12 months relative to baseline. Changes were large, but p-value and statistical significance were not reported. Results were based on 253 tests (50%) completed in 508 potential test sessions.
FIGURE 20.
Visual analogue scale for HMII and comparator VADs at different time points (Starling et al. 52). Note: the comparator group consisted of patients who received other LVADs than HMII approved for BTT.
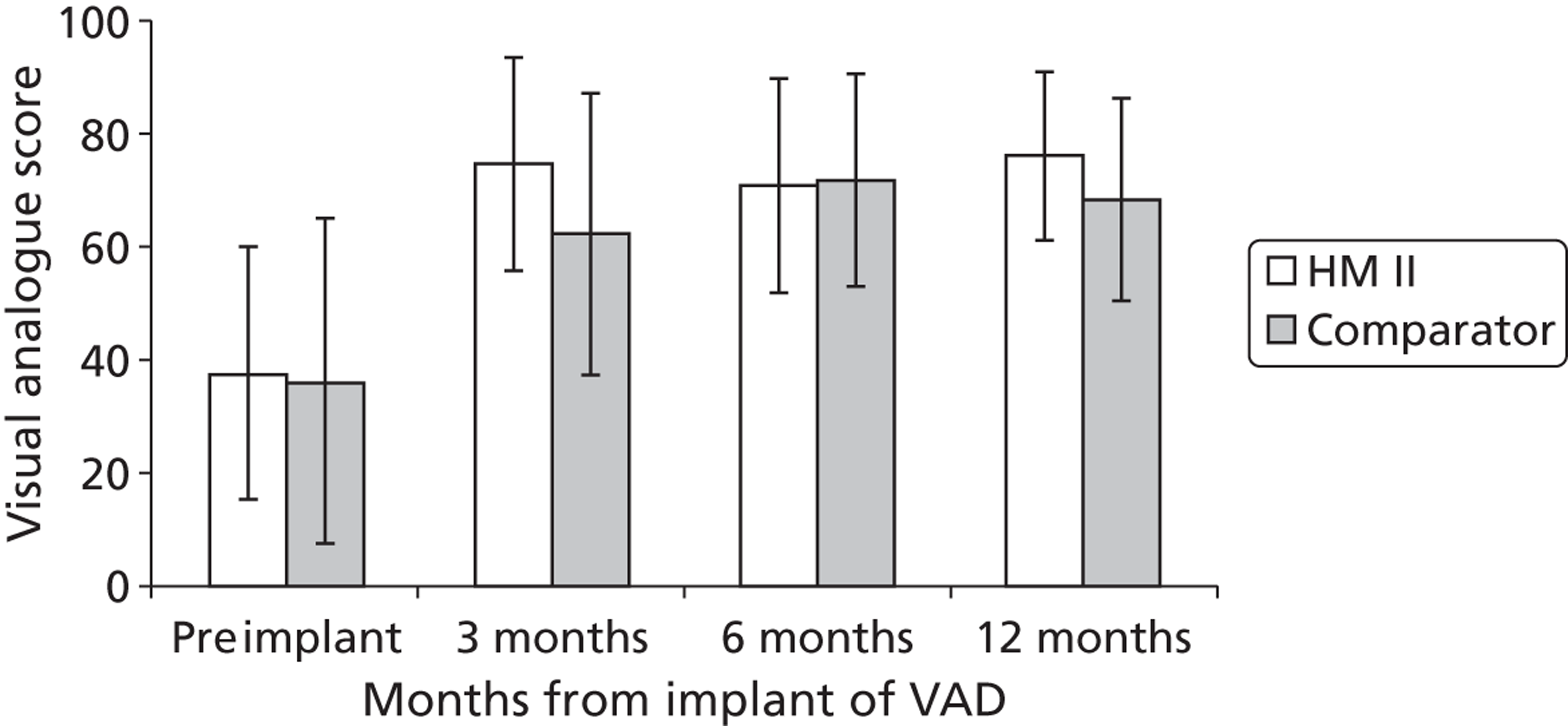
John et al. 65 presented METs QoL data for a sample from the INTERMACS registry BTT post-approval HMII patients (Table 15). Improvements of 32 points at 3 months were sustained at 12 months. The authors provided limited discussion of these findings. The overlapping underlying populations preclude development of a summary estimate combining results with those of Starling et al. 52
| Item | Pre implant | 3 months | 6 months | 12 months |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (at risk) | 1498 | 1142 | 822 | 393 |
| n (completing test) | 777 | 617 | 432 | 192 |
| Per cent (completing test) | 52 | 54 | 53 | 49 |
| VAS score | 42 | 74 | 75 | 76 |
Functional status
Rogers et al. 53 reported that at baseline patients were classified as NYHA class IV, by 1 month 59% had improved to NYHA class I or II, and at 6 months 82% were NYHA classified as class I or II (Figure 21). Relative to baseline scores, highly significant improvements in NYHA functional class were observed at all study intervals (p < 0.001).
FIGURE 21.
Summary of NYHA classification at each time point reported (Rogers et al. 53). Ratings were determined by an independent clinician.
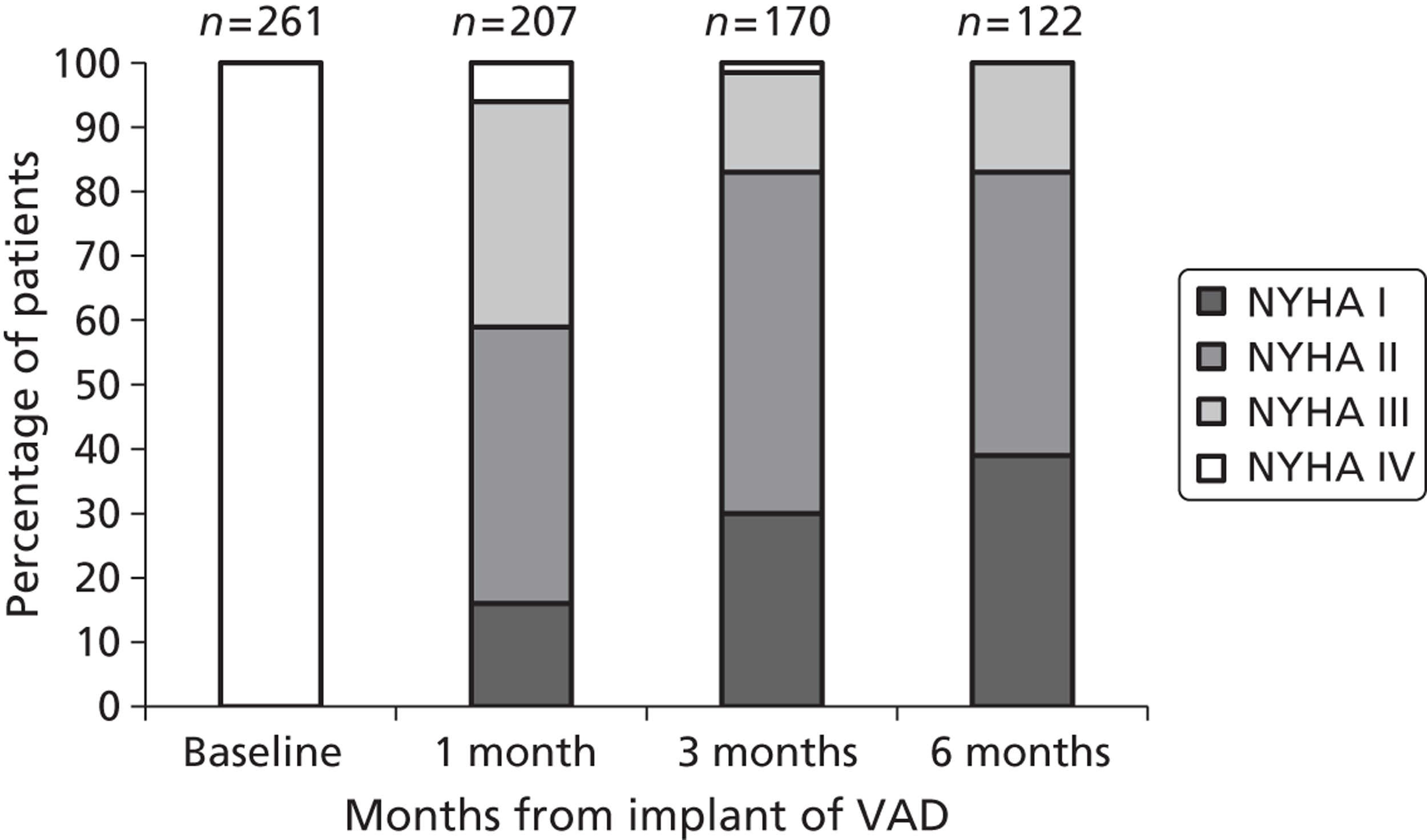
Bogaev et al. 57 reported significant improvements from baseline in the proportion of patients classified as NYHA functional class I/II for both women [0–49 (83%)] and men [0–147 (85%)] (p < 0.001). No significant differences were observed between men and women (p = 0.55).
At baseline, Rogers et al. 53 reported that of 281 BTT patients 38 (14%) were able to perform the 6-minute walk test. Baseline distance walked for was 214 ± 125 metres. At 6 months the distance walked was 372 ± 199 metres although only 97 patients completed the test. There was a statistically significant improvement over time.
Bogaev et al. 57 reported that before LVAD implantation, many patients were unable to walk and could not provide baseline values. Group means exhibited significant change for both women and men at 1, 3, and 6 months. Distance walked at all times was further for men (p = 0.037). Registry data for the 6-minute walk test results reported by John et al. 65 similarly indicated improvement from baseline. No statistical analysis was reported.
The results presented by Rogers et al. 53 provide a persuasive indication that those patients who survive implantation of the HMII device as BTT experience an improvement in QoL by 3 months sustained at 6 months. Some of the changes are substantial and statistically significant (e.g. improvements in MLWHF, KCCQ, NYHA and METs in Rogers et al. 53), but data sets were not complete and this may have skewed results.
These results were supported in other publications with somewhat larger populations and where measures are extended to 12 months.
Summary of outcomes for HeartMate II
The relatively modest quality and diversity of reporting of outcomes and the occurrence of overlapping populations in the 29 publications of HMII have precluded numerical synthesis of results. Outcomes for HMII overall show a profile of substantial adverse events. One in five patients had bleeding requiring re-exploration and almost one in three patients had infection. Stroke is a very serious adverse event affecting 1 in 10 patients. The K–M estimates of survival post implant of the HMII device suggest improvement with growing experience. The best 1-year survival estimate for this device was 85%. It should be borne in mind that in estimating survival of BTT patients during VAD support using K–M analyses, those patients who receive a HT are censored at the time of transplant; if these patients have poorer prognosis than uncensored patients then survival may be overestimated (or vice versa). Furthermore, any comparison between device types for any outcome may be confounded by differences in underlying populations (e.g. owing to geography, time period, eligibility criteria).
Set against this, however, is reported improvements in QoL and functional status reported using a number of different measures in a number of different studies.
Outcomes for HeartWare
One study reporting on 50 patients implanted with a HW VAD as a BTT fulfilled our inclusion criteria (Strueber et al. 83).
Adverse events
Adverse events were reported in detail and are shown in Table 16. Overall, 22 infections occurred among 50 patients; 20% of patients required repeat surgery for bleeding. Six of the 50 patients suffered from stroke and seven device replacements were required. Other important adverse events suffered by smaller numbers of patients included renal and hepatic dysfunction, haemolysis and right HF. Some patients may have experienced multiple events; therefore, summing percentages within categories may be misleading.
| Adverse events | Patients with events (%) | Number of events, overall | Number of events, 0–30 days | Number of events, > 30 days |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infection | ||||
| Localised non-device related | 7 (14) | 7 | 2 | 5 |
| Sepsis | 5 (10) | 5 | 1 | 4 |
| Driveline exit site | 9 (18) | 10 | 0 | 10 |
| Bleeding | ||||
| Requiring surgery | 10 (20) | 11 | 8 | 3 |
| Requiring transfusion ≥ 2 units | 2 (4) | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Requiring hospital stay | 3 (6) | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Ventricular arrhythmias | 2 (4) | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Neurological dysfunction | ||||
| Ischaemic stroke | 2 (4) | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Haemorrhagic stroke | 4 (8) | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| TIA | 2 (4) | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Pulmonary dysfunction | 8 (16) | 9 | 8 | 1 |
| Device replacement | ||||
| Manufacturing defect | 2 (4) | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Left heart embolus | 4 (8) | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| Inflow occlusion | 1 (2) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Pleural effusion | 6 (12) | 7 | 5 | 2 |
| Right HF | ||||
| RVAD | 3 (6) | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Intravenous inotropes | 3 (6) | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Other serious adverse events | ||||
| Renal dysfunction | 5 (10) | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| Hepatic dysfunction | 3 (6) | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Haemolysis | 1 (2) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| HF | 3 (6) | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Chest pain | 1 (2) | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Femoral embolism | 2 (4) | 2 | 1 | 1 |
Survival
Table 17 provides a summary of the K–M survival results for patients who received the HW VAD in the study by Strueber et al. 83
| Study population | Group | n | Month 6 | Month 12 | Month 18 | Month 24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strueber et al.83 BTT (patients from Europe and Australia) | HW | 50 | 90% | 85% | NR | 79% |
| Virtual control | 50 | 73% | 58% | 48% | 40% |
Strueber et al. 83 reported K–M survival results for HW BTT patients (n = 50; Figure 22). Relative to HMII studies (shown in Figures 14 and 15), survival with HW appears to be at least comparable, with 85% of patients alive at 1 year after implant. When compared with the earlier HMII publications, survival appears superior for HW. Strueber et al. 83 also provided a survival curve for a ‘virtual control’ group; this was based on the application of the Seattle Heart Failure Model (SHFM) to the baseline characteristics of the intervention group. This virtual control data fits well when a SHFM score of 2.416 is applied. These results are summarised in Figure 22.
Causes of death
Reports on nine deaths from the 50 eligible patients in the HW study78 suggested that three were caused by sepsis, three by multiorgan failure and three were thought to be caused by haemorrhagic stroke.
Quality of life
Strueber et al. 83 reported KCCQ data for stated sample sizes of 38, 37, 36 and 21 presurgery and 1, 3 and 6 months post surgery for the 50 patients in their study. Results are summarised in Figure 23. It was unclear if these were paired data.
FIGURE 23.
Group mean scores for the KCCQ (Strueber et al. 83). Bars indicate means with 95% CIs and asterisks indicate 90th percentiles. *Statistically significant improvement reported in KCCQ score at p < 0.05.
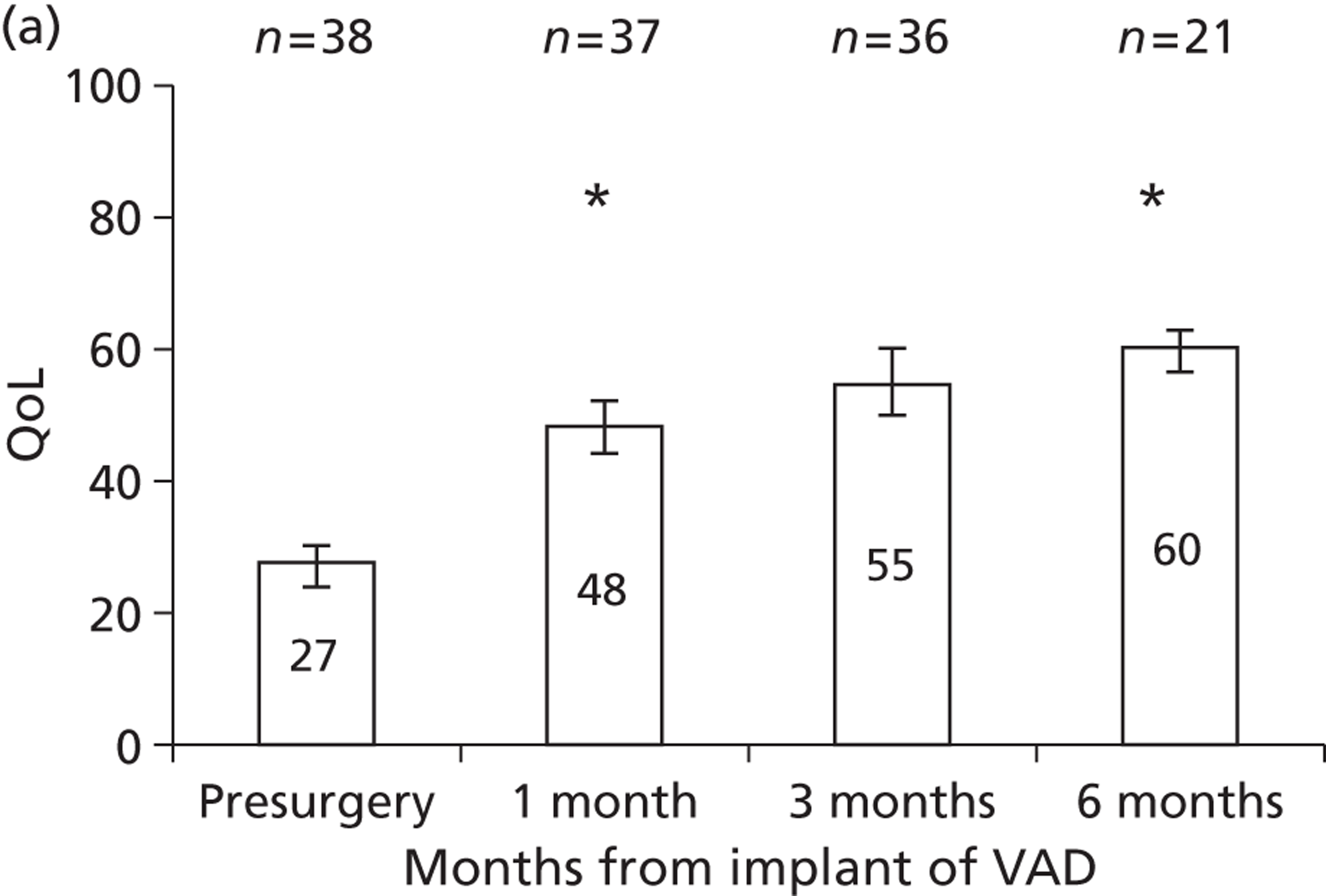
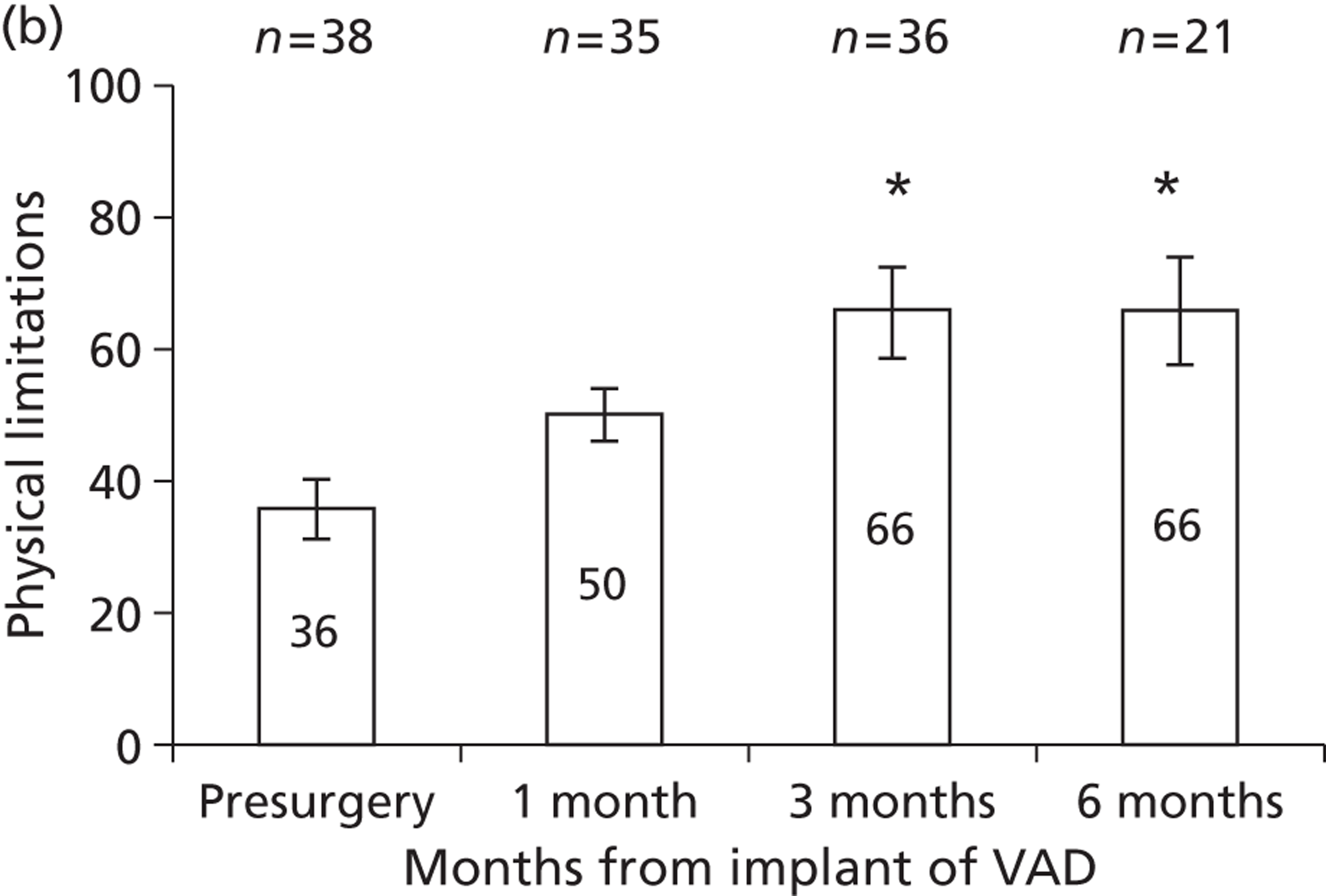
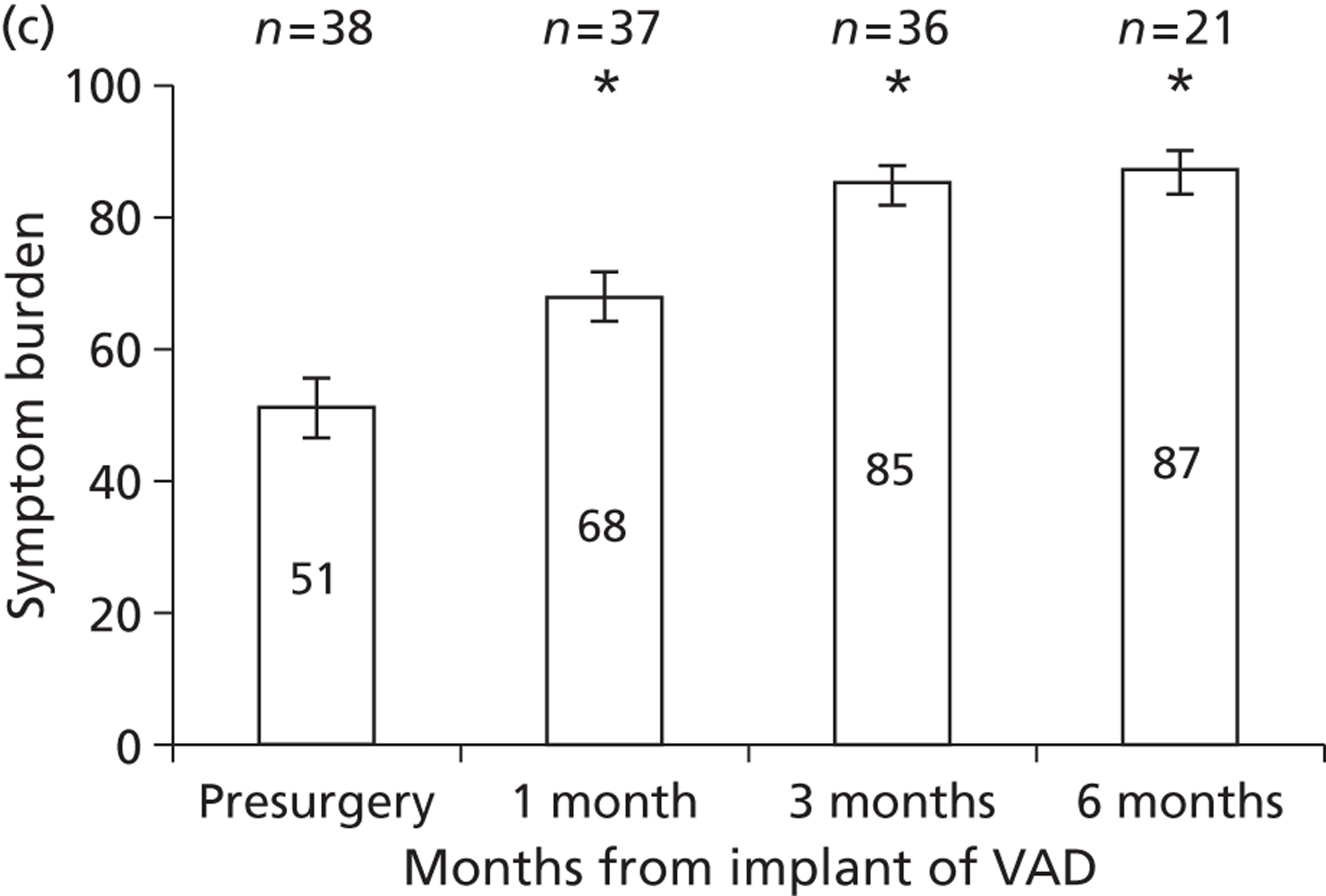
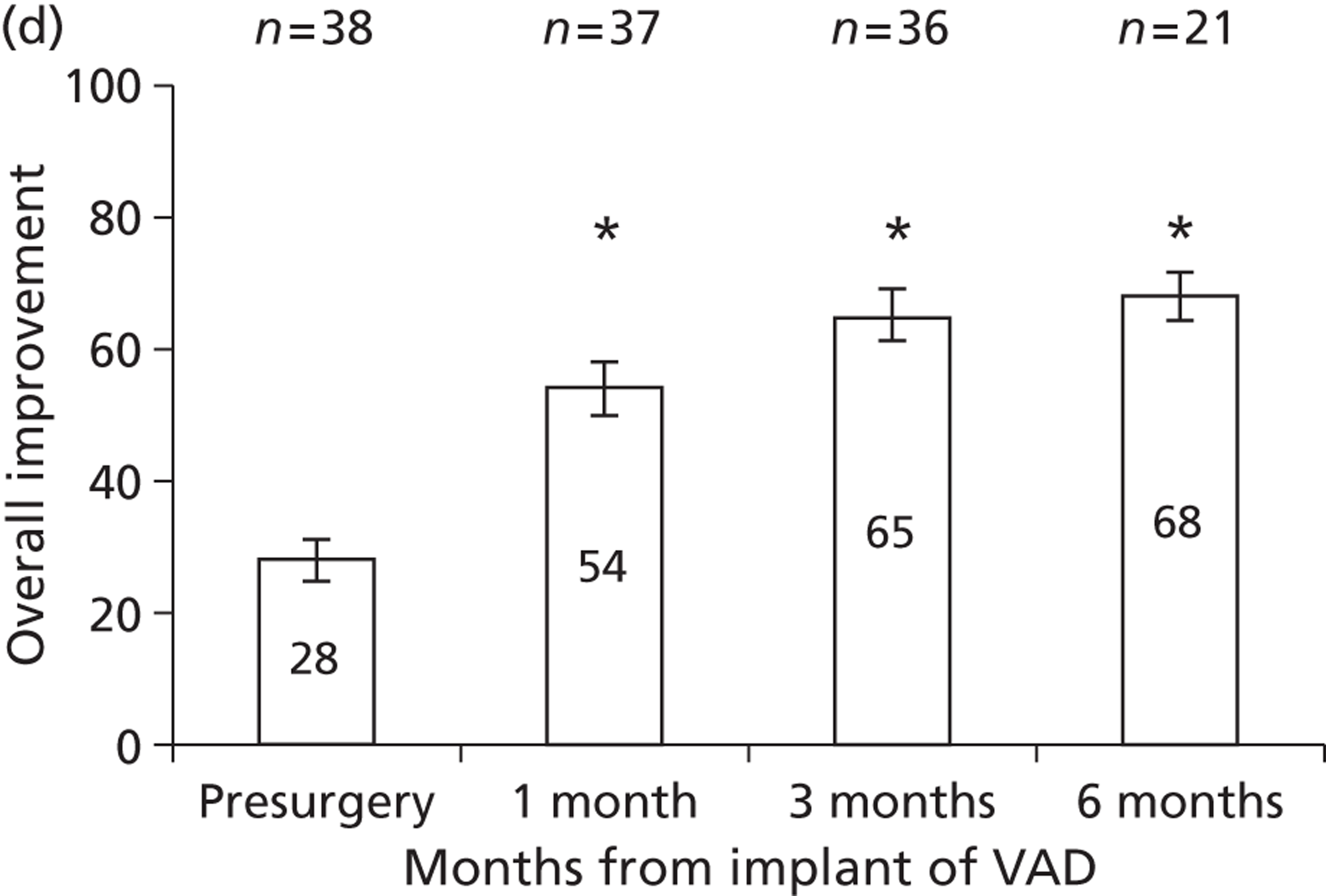
Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) improved significantly by 1 month for all subscales of the KCCQ. The authors found statistically significant (p = 0.05) improvement in physical limitations, QoL, symptom burden, and overall functional status across all time points. Greater improvements were found during the first 30 days following the HW implant.
Summary of outcomes for HeartWare
Only one small publication reported on the HW VAD; there is a profile of substantial adverse events and mortality due to infection, bleeding and stroke, and one in seven patients with a HW device was reported as requiring the device to be replaced. Although it is possible that mortality within the first year is slightly less than as reported in HMII analyses published during earlier years of experience with that device (e.g. Miller et al. 70 and Pagani et al. 71), it should be borne in mind that the K–M estimates are subject to censoring for receipt of a HT. Significantly improved QoL and functional status were reported over the first 6 months after a HW implant.
Outcomes for the Berlin Heart INCOR
One study by Schmid et al. 86 of the Berlin Heart INCOR fulfilled our inclusion criteria. This study reported on 138 patients who received a short cannula device and 78 patients who received a long cannula device.
Adverse events
Table 18 shows adverse events for the Berlin Heart INCOR. Nearly one in four patients (23.2%) with a short cannula suffered a thromboembolic stroke. This rate appeared to be significantly lower in the smaller group of patients with a long cannula (3.8%). The authors distinguished stroke from intracerebral bleeding, again finding higher rates in the short cannula group – although not significantly so.
| Adverse events | Short cannula (N = 138) | Long cannula (N = 78) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thromboembolic stroke, n | 35 | 4 | |
| Patients affected, n (%) | 32 (23.2) | 3 (3.8) | < 0.001 |
| Events/patient-year | 0.5 | 0.11 | |
| Time to event (days), mean (range; SD) | 73 (2–429; ± 86) | 38 (4–66; ± 31) | |
| Intracerebral bleeding, n | 15 | 4 | |
| Patients affected, n (%) | 14 (10.1) | 4 (5.1) | 0.152 |
| Events/patient year | 0.21 | 0.11 | |
| Time to event (days), mean (range; SD) | 118 (18–330; ± 110) | 271 (15–933; ± 442) |
Survival
Kaplan–Meier analysis of survival was performed for 78 patients with a short cannula device and 138 who received a long cannula device in this study. 86 Survival reported at 12 and 24 months for each device type is summarised in Table 19, showing that even in the improved survival (long cannula) group, 39% of the patients had died by 12 months.
Causes of death
In this study there were 92 deaths including 48 from multiorgan failure; 13 due to a cerebrovascular event; eight from right ventricular artery failure; two owing to cancer; two to trauma; and one each from pulmonary artery embolism and bleeding. Seventeen additional deaths were reported with ‘other’ or ‘unknown’ cause.
Quality of life and functional status
No data were reported on QoL or functional status.
Summary of outcomes for the Berlin Heart INCOR ventricular assist device
Only one relatively small study reported on the Berlin Heart INCOR VAD with a profile of substantial adverse events caused by intracerebral bleeding and stroke. Mortality within the first year was high. No data were reported on QoL and functional status.
Outcomes for the DuraHeart ventricular assist device
Two publications fulfilled our inclusion criteria. 42,85 These reported on overlapping populations.
Adverse events
The 2010 study (Morshuis et al. 42) reported adverse events in more detail and these are shown in Table 20. Almost all patients (31/33; 94%) suffered at least one serious adverse event. There were 114 serious adverse events in all, equivalent to each patient suffering nearly four events. Infections, cardiovascular complications and bleeding were the most commonly reported.
| Serious adverse events | Patients with events (%) | Number of events, overall | Number of events, 0–30 days | Number of events, > 30 days |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All serious adverse events | 31 (94) | 114 | 50 | 64 |
| Infection | ||||
| Local non-device-related infection | 14 (42) | 14 | 6 | 8 |
| Driveline infection | 5 (15) | 7 | 1 | 6 |
| Pocket infection | 1 (3) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Sepsis | 6 (18) | 6 | 3 | 3 |
| Cardiovascular complications | ||||
| Right HF requiring RVAD | 1 (3) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Right HF extended inotropes | 9 (27) | 10 | 7 | 3 |
| Ventricular arrhythmiaa | 8 (24) | 8 | 5 | 4 |
| Myocardial infarctiona | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Cerebrovascular complications | ||||
| Ischaemic CVA | 2 (6) | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Haemorrhagic CVA | 4 (12) | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| TIA | 5 (15) | 5 | 1 | 4 |
| Bleeding | ||||
| Total bleeding | 8 (24) | 11 | 4 | 7 |
| Bleeding requiring surgery | 4 (12) | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Other | ||||
| Renal failure | 5 (15) | 5 | 3 | 2 |
| Respiratory failure | 4 (12) | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| Pump replacement | 2 (6) | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Hepatic dysfunction | 2 (6) | 2 | 2 | 0 |
Survival
Both publications reported K–M survival results for BTT patients who received the DuraHeart VAD. 42,85 Populations in the studies overlapped. The 2009 study85 provided survival results for the greater number of patients (n = 68) as follows: 87% (95% CI 77% to 94%) at 3 months, 81% (95% CI 67% to 89%) at 6 months and 77% (95% CI 34% to 78%) at 1 year.
These figures are comparable with studies reporting early experience with the HMII VAD.
Causes of death
Morshuis et al. 86 reported on 20 deaths from 82 eligible patients, 13 of which were adjudicated by the Clinical Event Committee. The causes of death in the 13 patients were as follows: CVA, six patients (four haemorrhagic; two ischaemic); sepsis, three patients; non-traumatic subdural haematoma, one patient; accidental fall, one patient; acute myocardial infarction, one patient; and one patient was unknown.
Quality of life and functional status
No data were reported on QoL or functional status.
Summary of outcomes for the DuraHeart ventricular assist device
Two relatively small publications with overlapping populations reported on the DuraHeart VAD with a profile of substantial serious adverse events. Major causes of adverse events and death were CVA bleeding and infection, as with the other devices. Mortality within the first year was apparently similar to that reported in the publications describing earlier experience with the HMII device. No data were reported on QoL and functional status.
Outcomes for the MicroMed DeBakey ventricular assist device
One relatively small international study of 150 patients in 14 centres (of which 11 centres were European) by Goldstein84 reported on the MicroMed DeBakey VAD.
Adverse events
Table 21 shows adverse events in this study. One-third of patients required reoperation for surgery and one-third suffered a thromboembolic event. Adverse event reporting in this study was mainly restricted to those related to the device. Complications not directly related to the device were not reported.
| Adverse event | Incidence | Rate/patient-year |
|---|---|---|
| Reoperation for bleeding | 32.0% (48/150) | 2.03 |
| Haemolysisa | 12.0% (18/150) | 0.61 |
| Device infection | 3.3% (5/150) | 0.16 |
| Thromboembolic eventb | 10.7% (16/150) | 0.61 |
| Pump thrombus | 11.3% (17/150) | 0.61 |
| Mechanical failure | 2.7% (4/150) | 0.13 |
Survival
This study84 did not provide K–M survival data.
Causes of death
Unclear.
Quality of life and functional status
No data were reported.
Summary of outcomes for the MicroMed DeBakey ventricular assist device
Only one study reported on this device with a profile of substantial adverse events. No data were reported on survival or on QoL or functional status. Little can be concluded on outcomes from this device as yet.
Outcomes for the publications reporting on mixed devices
This section reports findings from six studies88–93 of different VADs (where > 80% of patients received a VAD type which met the inclusion criteria and where results are not reported separately by VAD type).
Adverse events
Table 22 provides a list of the adverse events and complications reported in the six studies88–93 concerning a mixture of devices. All six studies reported adverse events or complications. The most common adverse events reported were death (n = 4 studies), bleeding (n = 2 studies), stroke (n = 3 studies), renal failure (n = 2 studies), and right heart (RV) failure (n = 2 studies).
Drews et al. 87 reported details of device malfunction. Pump thrombosis occurred in five patients (four patients fitted with the MicroMed DeBakey LVAD; one patient who received the Jarvik 2000 device) and three patients had pump-stop due to technical failure (MicroMed DeBakey, Berlin Heart INCOR) or due to pannus on inflow cannula (DuraHeart). Two patients had bearing problems (Berlin Heart INCOR), one patient had a broken driveline and in five patients pump exchange was performed. Two patients died and four patients underwent successful HT.
| First author, year, country | Reference number | Adverse events and complications | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drews, 2010, Germany | 87 | Population (n = 110) received non-pulsatile devices Technical complicationsn (%)Device failure2 (2)Pump thrombosis5 (4.5)Inflow-thrombosis1 (1)Bearing problem2 (2)Driveline broken1 (1)Total11 (10)Pump exchange5 (5)Rehospitalisation (patient/year)3.6 |
Technical complications | n (%) | Device failure | 2 (2) | Pump thrombosis | 5 (4.5) | Inflow-thrombosis | 1 (1) | Bearing problem | 2 (2) | Driveline broken | 1 (1) | Total | 11 (10) | Pump exchange | 5 (5) | Rehospitalisation (patient/year) | 3.6 | ||||||||||||||
| Technical complications | n (%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device failure | 2 (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump thrombosis | 5 (4.5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inflow-thrombosis | 1 (1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bearing problem | 2 (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline broken | 1 (1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 11 (10) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump exchange | 5 (5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rehospitalisation (patient/year) | 3.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Klotz, 2006, Germany | 88 | Reported that risk of severe rejection post HT was higher for pulsatile than non-pulsatile devices | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nativi, 2011, USA | 89 | Post-HT adverse events included: treated rejection, stroke, hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, diabetes mellitus, vasculopathy, malignancy, severe renal dysfunctions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oswald, 2010, Germany | 90 | Population (n = 61) received HMII or HW LVAD Patient safety and complicationsn (%)Non-lethal cerebrovascular event3 (5)Death from thromboembolic events9 (15)LVAD cable infection (total)14 (23)Conservatively managed13 (21)Requiring surgical revision1 (2) |
Patient safety and complications | n (%) | Non-lethal cerebrovascular event | 3 (5) | Death from thromboembolic events | 9 (15) | LVAD cable infection (total) | 14 (23) | Conservatively managed | 13 (21) | Requiring surgical revision | 1 (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient safety and complications | n (%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-lethal cerebrovascular event | 3 (5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Death from thromboembolic events | 9 (15) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD cable infection (total) | 14 (23) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conservatively managed | 13 (21) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Requiring surgical revision | 1 (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sandner, 2009, Austria | 91 | Data as: n (%); p-value for difference between age groups Adverse eventsGroup aged < 60 years, n = 56Group aged ≥ 60 years, n = 30p-valueDeath < 30 days4 (7.1)3 (10.0)0.644Bleeding requiring surgery15 (26.8)7 (23.3)0.727Stroke11 (19.6)8 (26.7)0.454Ischaemic5 (8.9)4 (13.3)0.525Haemorrhagic6 (10.7)4 (13.3)0.718Renal failure requiring CVVHD14 (25.0)16 (53.3)0.009HF requiring RVAD2 (3.6)3 (10.0)0.225 |
Adverse events | Group aged < 60 years, n = 56 | Group aged ≥ 60 years, n = 30 | p-value | Death < 30 days | 4 (7.1) | 3 (10.0) | 0.644 | Bleeding requiring surgery | 15 (26.8) | 7 (23.3) | 0.727 | Stroke | 11 (19.6) | 8 (26.7) | 0.454 | Ischaemic | 5 (8.9) | 4 (13.3) | 0.525 | Haemorrhagic | 6 (10.7) | 4 (13.3) | 0.718 | Renal failure requiring CVVHD | 14 (25.0) | 16 (53.3) | 0.009 | HF requiring RVAD | 2 (3.6) | 3 (10.0) | 0.225 |
| Adverse events | Group aged < 60 years, n = 56 | Group aged ≥ 60 years, n = 30 | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Death < 30 days | 4 (7.1) | 3 (10.0) | 0.644 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding requiring surgery | 15 (26.8) | 7 (23.3) | 0.727 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke | 11 (19.6) | 8 (26.7) | 0.454 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic | 5 (8.9) | 4 (13.3) | 0.525 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic | 6 (10.7) | 4 (13.3) | 0.718 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure requiring CVVHD | 14 (25.0) | 16 (53.3) | 0.009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HF requiring RVAD | 2 (3.6) | 3 (10.0) | 0.225 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sandner, 2009, Austria | 92 | Data as: n (%); p-value for difference between renal function groups Adverse eventGFR > 60, n = 46GFR < 60, n = 40p-valueBleeding requiring surgery11 (23.9)11 (27.5)0.704HF requiring RVAD2 (4.3)3 (7.5)0.533Stroke6 (13.0)13 (32.5)0.03Ischaemic4 (8.7)5 (12.5)0.565Haemorrhagic2 (4.3)8 (20.0)0.024Renal failure requiring continuous venovenous haemofiltration13 (28.3)17 (42.5)0.167 |
Adverse event | GFR > 60, n = 46 | GFR < 60, n = 40 | p-value | Bleeding requiring surgery | 11 (23.9) | 11 (27.5) | 0.704 | HF requiring RVAD | 2 (4.3) | 3 (7.5) | 0.533 | Stroke | 6 (13.0) | 13 (32.5) | 0.03 | Ischaemic | 4 (8.7) | 5 (12.5) | 0.565 | Haemorrhagic | 2 (4.3) | 8 (20.0) | 0.024 | Renal failure requiring continuous venovenous haemofiltration | 13 (28.3) | 17 (42.5) | 0.167 | ||||
| Adverse event | GFR > 60, n = 46 | GFR < 60, n = 40 | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding requiring surgery | 11 (23.9) | 11 (27.5) | 0.704 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HF requiring RVAD | 2 (4.3) | 3 (7.5) | 0.533 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke | 6 (13.0) | 13 (32.5) | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic | 4 (8.7) | 5 (12.5) | 0.565 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic | 2 (4.3) | 8 (20.0) | 0.024 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure requiring continuous venovenous haemofiltration | 13 (28.3) | 17 (42.5) | 0.167 |
Among 86 patients common to both Sandner et al. publications,91,92 22 episodes of bleeding requiring surgery, 19 strokes, 30 instances of renal failure requiring continuous venovenous haemofiltration, and five cases of right HF requiring a RVAD were reported; these outcomes were reported by risk groups according to baseline age and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) status (see Table 22). The studies by Oswald et al. 90 and by Nativi et al. 89 reported adverse events post HT; these are listed in Table 22.
Survival
Of the six studies,88–93 two studies88,90 did not provide survival results. The population in Drews et al. 87 mostly received the VAD as DT patients and results could not be separated for BTT patients; post-HT survival only was reported. Likewise, Nativi et al. 89 reported post-HT survival only. Results for the remaining two studies, Sandner et al. 91,92 are summarised in Table 23. The two studies91,92 appear to have analysed the same populations which were dichotomised according to age in one study and according to renal function status in the other. It was unclear if patients were censored on receipt of a donor heart. Survival appears to be worse for younger patients,91 but these findings are not adjusted for severity or case mix and these studies lack power; numbers are too small to provide definitive information.
| Study | Population | n | % survival | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month 1 | Month 3 | Month 6 | |||
| Sandner 200991 | BTT (Austria) aged ≥ 60 years | 30 | 92.9 | 79.9 | 74 |
| Sandner 200991 | BTT (Austria) aged < 60 years | 56 | 90.0 | 62.0 | 37.0 |
| Sandner 200992 | BTT (Austria) normal renal function | 46 | 91.3 | 79.9 | 72.6 |
| Sandner 200992 | BTT (Austria) abnormal renal function | 50 | 92.5 | 66.5 | 47.9 |
Causes of death
All six of the included papers83–93 reporting on a mixture of devices provided information on the causes of death. Table 24 summarises the causes of death. Common causes of death included (a) multiorgan failure; (b) right heart (ventricular) failure; (c) bleeding; and (d) stroke/CVA. Because the proportion of different devices varied from study to study, or was not reported, events rates could not be attributed to a particular device.
| First author | Date | Country | Reference number | Causes of death |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drews | 2010 | Germany | 87 | Cardiomyopathy, ischaemic cardiomyopathy, other heart diseases |
| Klotz | 2006 | Germany | 88 | Multiorgan failure, cerebral, right HF, sepsis, bleeding, rejection |
| Nativi | 2011 | USA | 89 | Head trauma, stroke, infection, graft failure, CAV, acute rejection, technical, multiorgan failure, renal failure, pulmonary, cerebrovascular, malignancy |
| Oswald | 2010 | Germany | 90 | Thromboembolic events and haemorrhage, in particular stroke |
| Sandner | 2009 | Austria | 92 | Sepsis, haemorrhagic stroke, multiorgan failure, ischaemic stroke, unknown causes |
Quality of life and functional status
None of the included studies with mixed devices reported QoL or functional status measures.
Summary of outcomes for studies reporting on more than one ventricular assist device
Among these studies, outcomes were not reported by device and the mixture of devices varied from study to study. Therefore it was difficult to derive meaningful conclusions. Overall rates of survival and adverse events are in line with findings reported earlier in this chapter. None of the studies reported on QoL or functional status.
Summary of clinical effectiveness findings
We have reported outcomes for the 40 included publications (for full details see Appendix 3). The lack of prospective comparative study design, modest study quality, diversity of reporting of outcomes, and overlap between populations investigated, render it difficult to draw firm overall conclusions. The only comparisons between devices reported were between early generation VADs and second-/third-generation devices. (See also Appendix 3. )
For all the devices there was a profile of substantial serious adverse events caused by infection, thrombosis, bleeding and stroke, and of mortality from various causes in this already frail population. By 12 months patients had suffered a variety of serious complications. Studies reported the following ranges for adverse events: 4–27% bleeding requiring transfusion; 1.5–40% stroke; 3.3–48% infection (sepsis); 1–14% device failure; 3–30% HF; 11–32% reoperation; and 3–53% renal failure. Table 25 gives a summary of the range of rates of the main adverse events by device type per patient-year demonstrating these high rates of adverse events.
| Devicea | Bleeding requiring transfusion | Stroke | Infection (sepsis) | Device failure | HF | Reoperation | Renal failure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMII | 11–21% | 4–40% | 17–48%b | 1–10% | 3–28% | 11–27% | 3–40% |
| HW (one study only83) | 4%c | 12% | 10% | 14% | 6% | 20%c | 10% |
| MicroMed DeBakey (one study only84) | NRd | 12%e | 3.3%f | 3% | NR | 32%d | NR |
| DuraHeart (two studies42,85) | 24% | 18% | 18% | 6% | 30% | NR | 15% |
| Mixture of devices (six studies83–93) | 23–27% | 1.5–32% | NR | 2% | 3.6–10% | 24–28% | 6–53% |
The wide range of rates for stroke, with a very high upper end, represents data from a variety of studies. Higher rates of stroke emanate from shorter studies, as stroke is more likely to occur in the first 3 months after an implant (Figure 24).
FIGURE 24.
Hazard analysis depicting varying incidence over time of four major adverse events: stroke, reoperation for bleeding, pump thrombus and haemolysis (redrawn from Goldstein 200384).
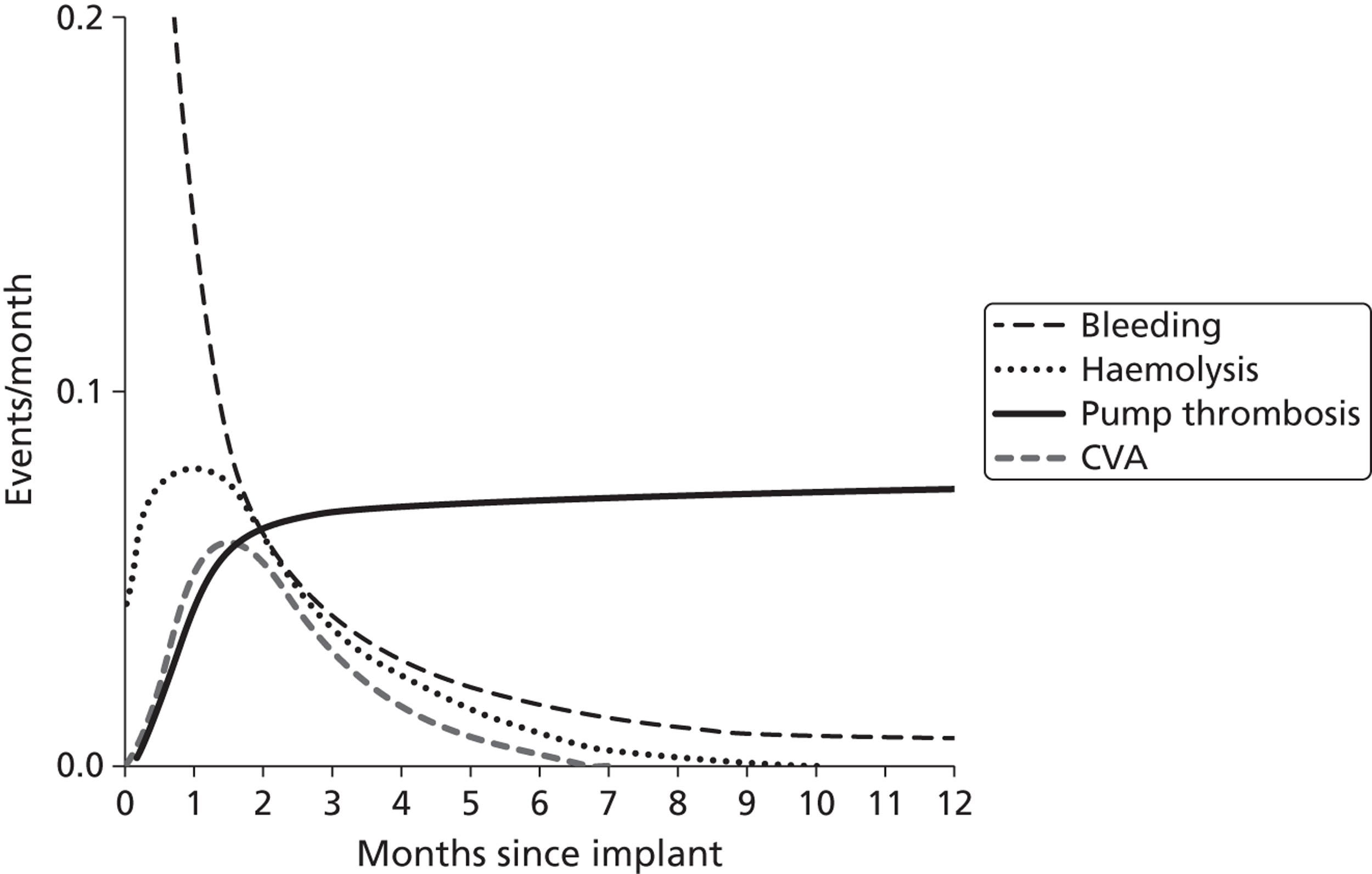
Early follow-up data (e.g. at 1–3 months) cannot reliably be extrapolated to longer time periods (e.g. over 6 months) owing to the changing adverse event profile over time. Also, as few of the papers reported outcomes beyond 12 months, numbers and percentages in Table 25 represent the best estimate of adverse events likely in the first year after the VAD intervention, but cannot reliably be extrapolated to later years after the intervention.
Kaplan–Meier estimates of survival post implant of the HMII device suggest improvement with growing experience. The best 1-year survival estimate for this device was 85%. A similar estimate of 85% survival at 1 year was reported for 50 HW patients (investigated at centres in Europe and Australia). While preparing this report, Aaronson et al. 94 published a larger study of 140 US HW patients and estimated survival at 1 year to be 86%. Estimates of survival at 1 year for other devices as reported in the included publications were less impressive (INCOR 61% and DuraHeart 76%). It should be borne in mind that in estimating survival of BTT patients during VAD support using K–M analyses, those patients who receive a HT are censored at the time of transplant; if these patients are unrepresentative of the overall population studied (e.g. have a poorer prognosis than uncensored patients) then survival may be overestimated (and vice versa). Furthermore, any comparison across device types for any outcome may be confounded by differences in underlying populations (e.g. geography, time period, eligibility criteria, case mix, etc.)
Quality of life and functional status, where these were measured for patients who were still alive, showed a trajectory of improvement in the first year after implant for all groups of patients especially over the first 3 months. Improvements at 6 months were statistically significant in studies of HW and HMII.
In the next chapter we describe the individual patient data (IPD) set provided by the NHS Blood and Transplant National Registry (BTNR) from the UK Blood and Transplant Database (BTDB) maintained on behalf of the UK transplant community and explain derivation of parameters for the Warwick Evidence cost-effectiveness model.
Chapter 4 Individual patient data set
This chapter provides a narrative description of the IPD set provided by the BTNR form the BTDB maintained on behalf of the UK transplant community as part of the National Specialist Commissioning Advisory Group (NSCAG)-funded VAD programme. The data set is known here as the BTDB. Data are included from May 2002 to December 2011. The data are collected for patients from six UK centres (listed below) which are responsible for carrying out VAD implantation surgery:
-
Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust (RB)
-
Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
-
Newcastle upon Tyne Hospital NHS Foundation Trust (NUT)
-
Glasgow Golden Jubilee National Hospital (GJNH)
-
University Hospital of Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust (UNB)
-
University Hospital of South Manchester NHS Foundation Trust (UHSM).
Within this report VADs used for BTT in the UK have been considered. This chapter explains the BTDB data sets used for calculating parameter values in order to evaluate cost-effectiveness of the VAD economic model. For the purpose of this report and in line with the scope, information and analyses have not been stratified by centre.
Selection of patients
Ventricular assist devices are implanted in patients who have deteriorating advanced HF according to NSCAG's service specification. The clinical guidance recommends VAD implantation for patients as a BTT until a suitable heart donor becomes available. The specified indications are for patients with:
-
Low cardiac output (cardiac index < 2.2 l/minute/m2) despite an adequate preload [central venous pressure (CVP) > 12 mmHg or pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) > 16 mmHg] and who require inotropic and/or intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) support for:
-
symptomatic hypotension (systolic BP < 90 mmHg)
-
secondary organ dysfunction (especially renal and hepatic).
-
-
Better haemodynamic status than mentioned above, but in a rapid rate of deterioration such that the patient is unlikely to survive until transplantation.
Structure of the database
The clinical data were collected at different centres and at different time intervals and have been collated into four categories. These data sets are:
The WL constitutes all the advanced HF patients who are registered for a HT. This data set contains patient information regarding previous medical history and baseline characteristics of the patients. This information is then matched with donor hearts to decide on the feasibility of HT. A hypothetical comparator group was formed by removing the BTT patients from the WL. This group constitutes the MM group.
The information for the VAD patients in the BTDB is entered in two subsets. The first data set in the BTDB is a consolidated representation of all VADs surgery and outcomes. This data set contains basic information for VADs patients such as unique reference number, diagnosis details, implant details, dates, current status, etc. All this information relates to the VADs surgery phase. The second data set in the BTDB gives further information for patients in each time phase from VAD implant until the end of follow-up or explant (if the patient is still alive and has not received a HT), HT (if transplanted), or death. A diagrammatic representation of the second data set is shown in Figure 25. The second data set was useful for derivation of transition probabilities between health states for use in the economic model.
FIGURE 25.
Ventricular assist devices detailed data set.
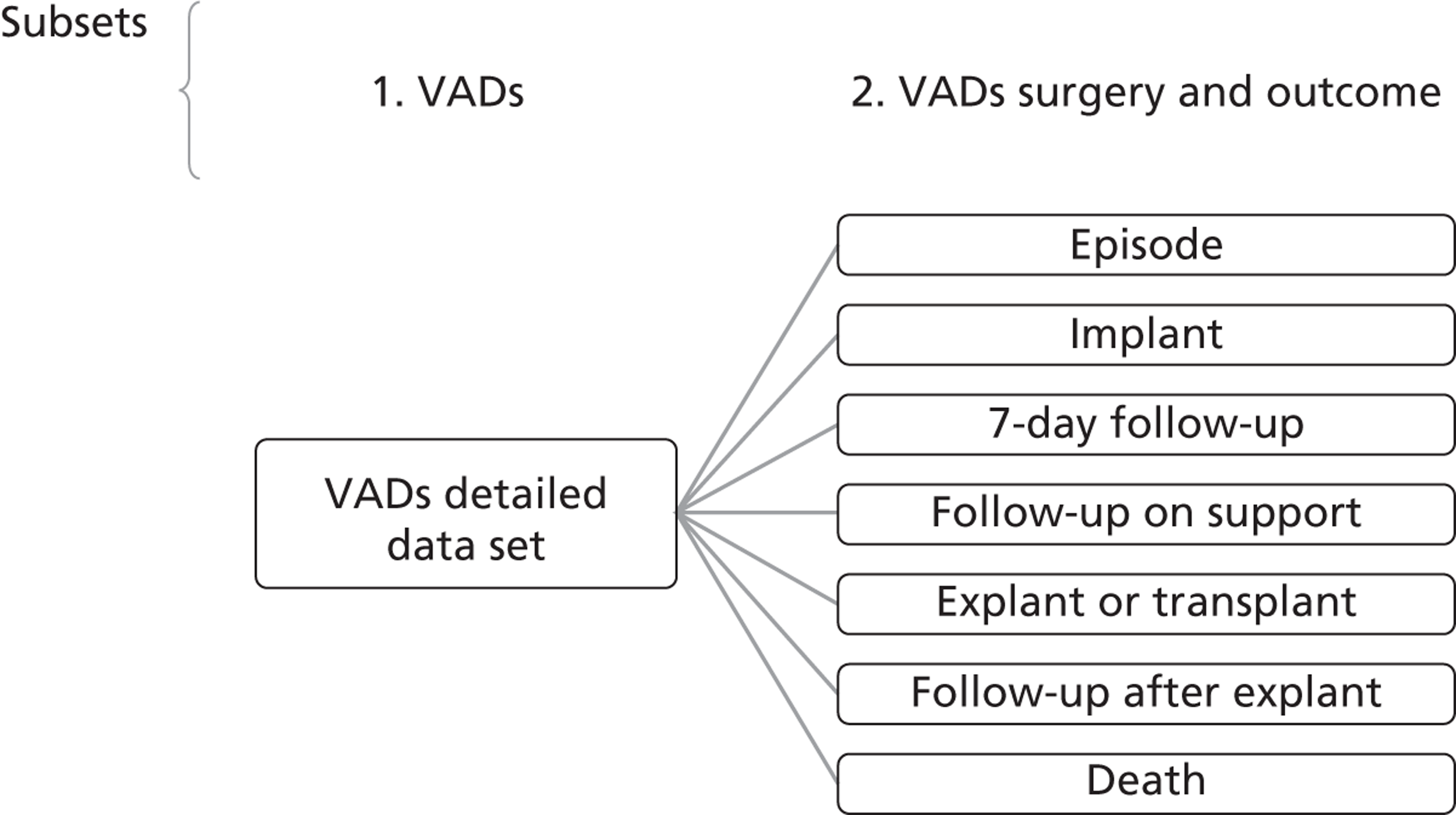
The HT data set pools information on patients from the BTT group as well as the MM group along with others, for which registration details were missing, although they received a HT. The next section provides detailed numbers. This data set also provides patient information at different time intervals (i.e. registration, transplant and follow-up post HT). The patient information includes both clinical measurements as well as demographic information.
Contents of the database
In order to evaluate cost-effectiveness of VADs, we identified two patient groups: BTT and MM.
-
BTT. This group includes patients who fulfilled the eligibility criteria for VAD implants (see indications above) who received a VAD implant as a BTT.
-
MM. This group includes patients who fulfil the eligibility criteria for HT but who do not receive a VAD and who are supported on MM until a suitable heart donor becomes available.
On the basis of clinicians' suggestions, we divided the patients in the MM data set into three subcategories (Figure 26). These categories are listed below:
-
patients who had not received inotropes (non-inotrope)
-
patients who had received inotropes (inotrope)
-
a third group (others for whom no information was available about inotrope treatment).
FIGURE 26.
Classification of MM patients.
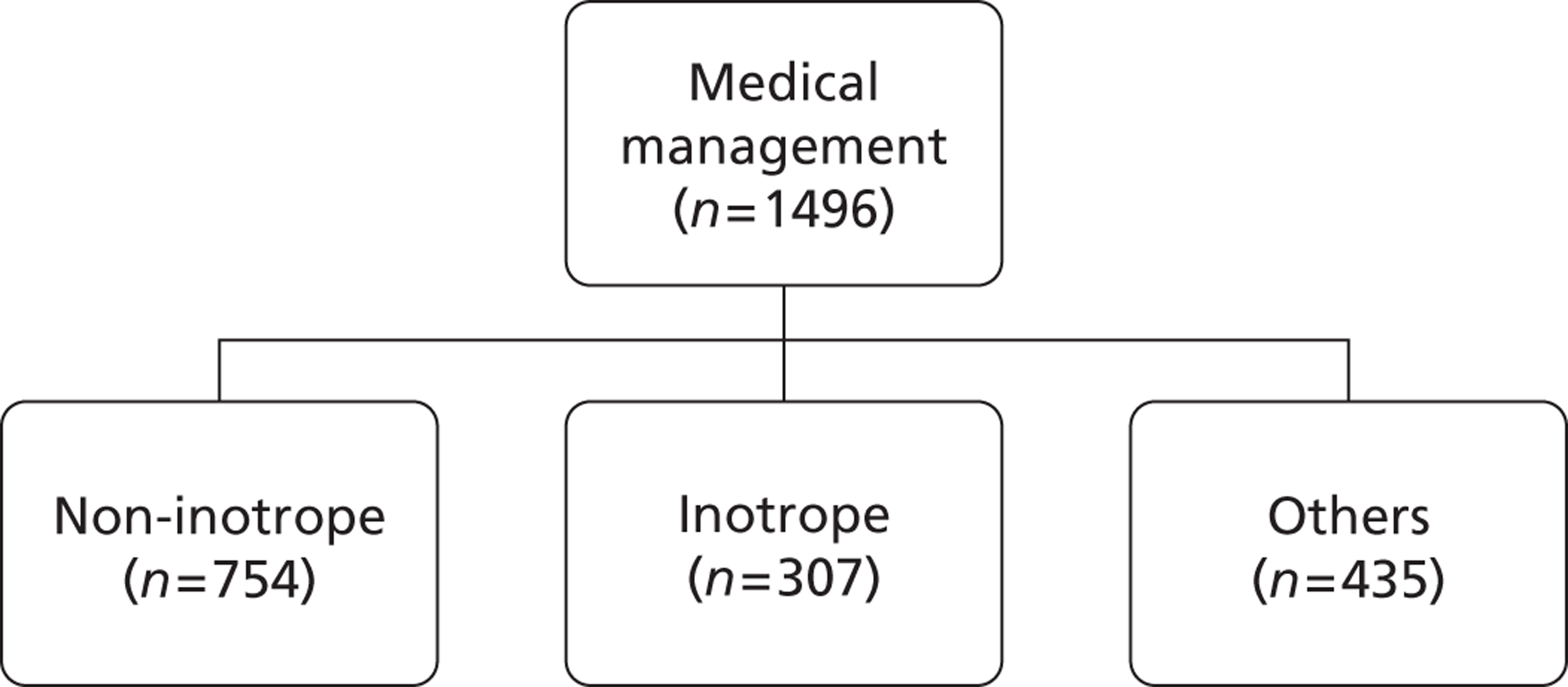
Results
Waiting list patients
The WL data set reported analysable registration data for 33 BTT patients and 1496 MM patients collected during the period January 2002 to December 2011. Figure 27 illustrates the outcomes for the MM subgroup as reported in the data set.
Of the 1496 MM patients, 1005 (67.18%) patients received a HT (Transplanted) and 154 (10.3%) patients died while on the WL (Died on WL) before receiving a HT. The data set included 207 (13.84%) patients who were completely removed from the WL because of substantial improvement in their condition, deterioration in their condition or through patient choice. These patients were referred to as Removed from WL in the data set. Of the remaining 130 (8.69%) patients, some were temporarily removed (Suspended) from the WL due to serious illness such that a HT was inadvisable or because further medical testing was required, while others (Active) were still waiting for a transplant.
FIGURE 27.
Medical management patients.
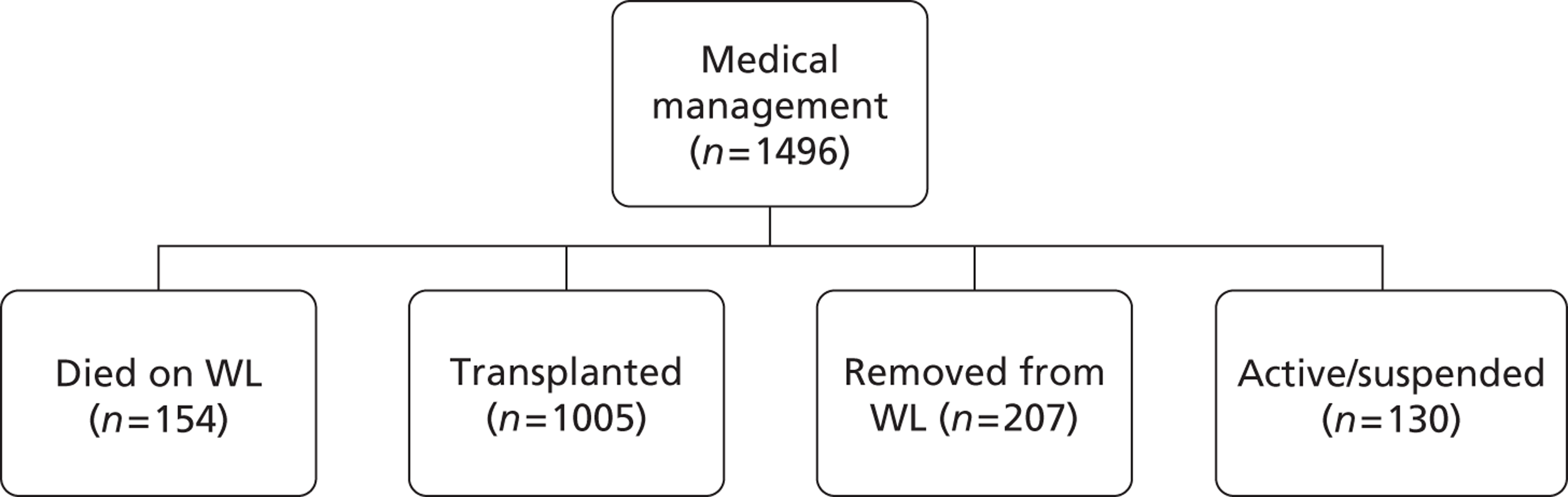
The next section gives outcomes for the various subgroups identified in the MM arm.
FIGURE 28.
Non-inotrope subgroup.
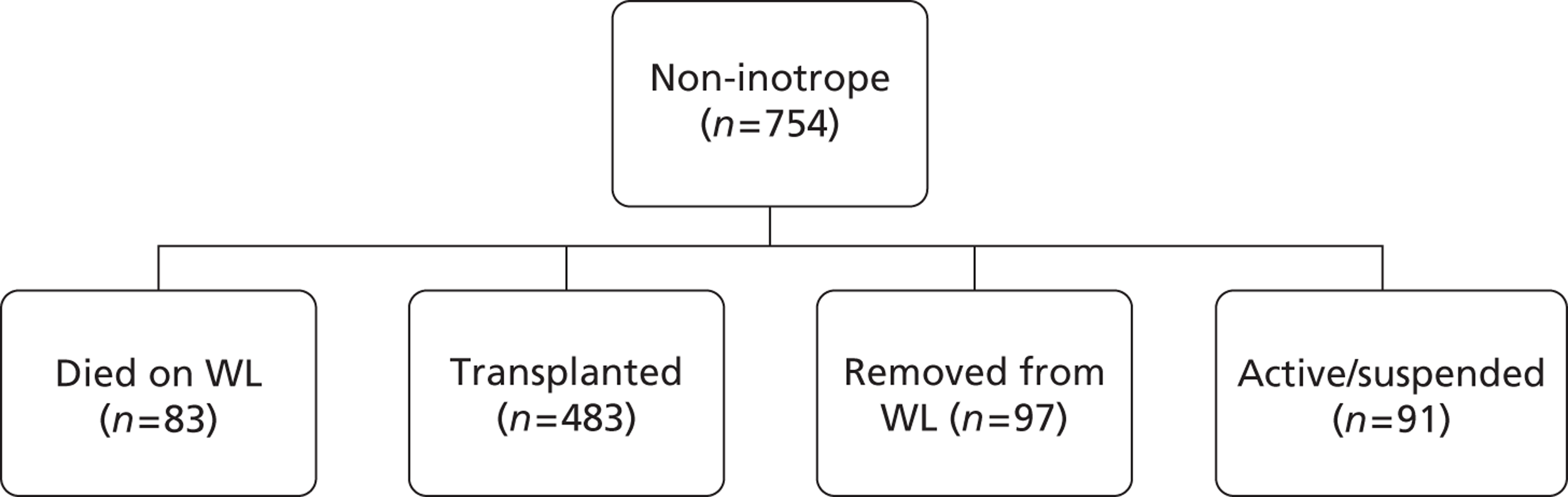
Baseline characteristics for the non-inotrope group (Figure 28) are reported in Table 26. The median reported age of the patients in this non-inotrope group was 48 years. Almost three-quarters of the group were male. These patients had poor health as evidenced by their NYHA class. More than 95% of the patient groups were categorised either NYHA class III or class IV. Approximately one-third of the patients had had an automatic implantable cardioverter defibrillator (AICD) before registration for a HT. Hypertension was present in a fifth of the patients. One-third of the patients in this subgroup had already had open heart surgery. Just over 3% of patients had diabetes mellitus prior to HT registration.
Patients in the inotrope group were older than those in non-inotrope group; the median age in the inotrope group was 58 years. Almost three-quarters of patients were male. The patients in this subgroup had much poorer health than the non-inotrope group. The NYHA class confirm this, as > 99% of the patients were either NYHA class III or class IV. Almost a fifth of the patients had AICD before registration. A small number (22%) of patients had already undergone open heart surgery and a very small number had already undergone a previous HT. Table 26 reports the baseline characteristics of the ‘other’ group illustrated in Figure 29.
FIGURE 29.
The ‘other’ group.
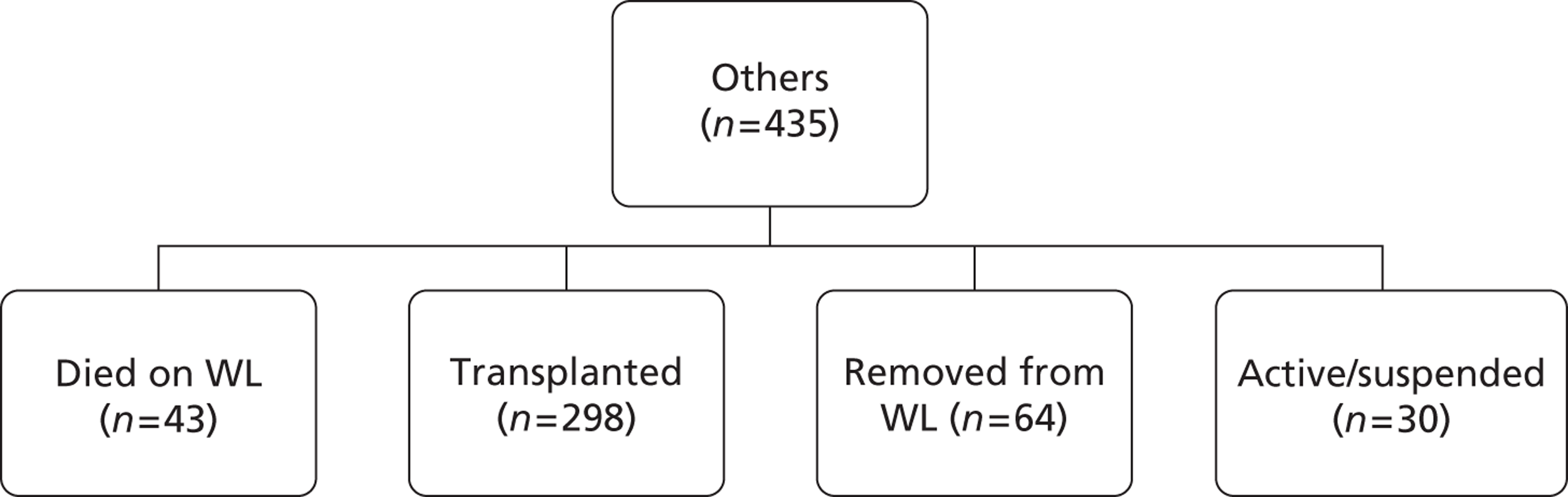
Patients in the ‘other’ group have a median age of 50 years. Three-quarters were male. Approximately three-quarters of the patients (∼ 73%) in this group belonged to NYHA class III with fewer (∼ 24%) belonging to NYHA class IV. There were some patients for whom NYHA class was not reported. One-quarter of these patients had already had an open heart surgery and three patients had already undergone HT surgery.
Summary table
Baseline characteristics for each of the three groups of MM patients are given in Table 26.
| Characteristics | Subcategory | Non-inotrope, n (%) | Inotrope, n (%) | Others, n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | Mean | 45.34 | 41.98 | 47.89 |
| Median | 48 | 58 | 50 | |
| SD | 13.49 | 14.16 | 12.18 | |
| Range | 16–68 | 16–66 | 16–68 | |
| Gender | Male | 564/754 (74.8) | 236/307 (76.87) | 318/435 (73.1) |
| Female | 190/754 (25.2) | 71/307 (23.13) | 117/435 (26.9) | |
| Ethnicity | White | 676/754 (89.66) | 266/307 (86.64) | 395/435 (90.8) |
| Asian – Asian British | 41/754 (5.44) | 26/307 (8.47) | 26/435 (5.98) | |
| Black – Black British | 28/754 (3.71) | 6/307 (1.95) | 10/435 (2.3) | |
| Others | 9/754 (1.2) | 9/307 (2.93) | 4/435 (0.92) | |
| NYHA classa | I | 2/753 (0.27) | 1/307 (0.33) | 2/422 (0.47) |
| II | 40/753 (5.31) | 1/307 (0.33) | 12/422 (2.84) | |
| III | 504/753 (66.93) | 43/307 (14.01) | 307/422 (72.75) | |
| IV | 207/753 (27.49) | 262/307 (85.34) | 101/422 (23.93) | |
| Previous open heart surgeryb | None | 493/750 (65.73) | 244/305 (80) | 316/424 (74.53) |
| 1 or more | 257/750 (34.27) | 61/305 (20) | 108/424 (25.47) | |
| AICD | 247/754 (32.76) | 58/307 (18.89) | 114/435 (26.21) | |
| Hypertension | 142/754 (18.83) | 43/307 (14.01) | 96/435 (22.07) | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 25/754 (3.32) | 7/307 (2.28) | 22/435 (5.06) | |
| Previous HT | 12/754 (1.59) | 2/307 (2.39) | 3/435 (0.69) |
Baseline characteristics for inotrope patients (Figure 30) are reported in Table 26.
FIGURE 30.
Inotrope subgroup.
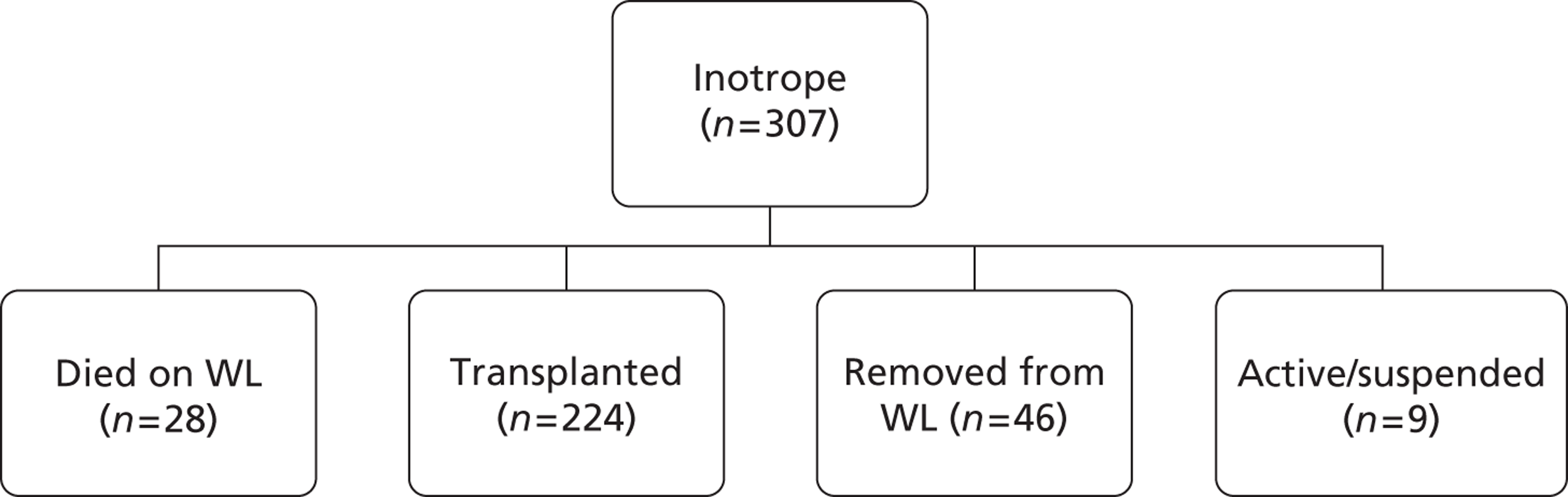
Bridge to transplant patients
To gain a better understanding of the BTT patients the data were cleaned and merged. Individual identifiers in separate data sheets were matched and then combined so that individual patient characteristics of patients who received a VAD implant were amenable for further analysis.
Figure 31 illustrates the case mix of patients who had received a VAD. The cleaned data set included 235 of the total 389 VAD patients. All these patients were further categorised into three main categories depending on the current status of their VAD implant. If patients still had a VAD and were awaiting HT they were categorised as VAD patients; just over three-quarters of the patients (n = 181; 77%) belonged in this category. Thirty-three patients (14%) had received a HT and are referred to as Transplanted. The remaining patients had had their VAD removed and are referred to as Explanted.
FIGURE 31.
Ventricular assist device patient set.
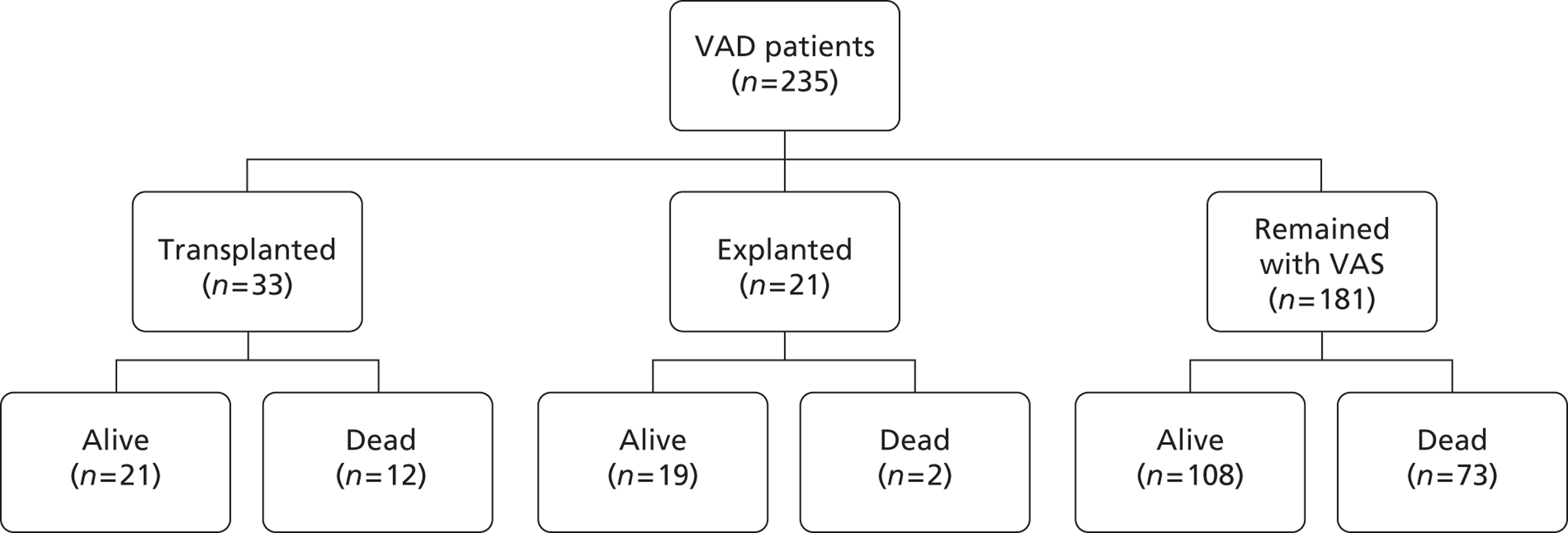
The number of VAD implants has grown with an overall eightfold increase over a period of 10 years and with significant growth over the last 3 years. The year-over-year graph (Figure 32) illustrates this trend.
FIGURE 32.
Trends of rising VAD implants over a period of 10 years.
Current practice in the UK is to use a second- or higher-generation VAD implant in patients. Table 27 lists the second or higher generation FDA-/CE-approved VADs used for the UK patient cohort. The two most commonly used VADs are HW and HMII.
| Rank of commonly used devices | Types of devices | Number used |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | HW | 125 |
| 2 | HMII | 82 |
| 3 | Jarvik 2000 LVAD | 23 |
| 5 | MicroMed DeBakey | 5 |
| Total | 235 |
Baseline characteristics of VAD patients are reported in Table 28. Information mainly includes patient demographics, past medical history and some clinical measurements. The median age for VAD patients was 47 years and > 80% were male. Almost three-quarters of VAD patients had received intravenous inotrope therapy. ARB use was reported for 10% of patients. Beta-blockers were used in more than one-third of the patients, as were ACE inhibitors.
| Patient characteristic | Subcategory | VAD, mean number (%) | HT, mean number (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | Mean | 44 | 45.46 |
| Median | 47 | 48 | |
| SD | 13.41 | 13.12 | |
| Range | 16–66 | 15–68 | |
| Gender | Male | 189/235 (80.43) | 814/1101 (73.93) |
| Female | 46/235 (19.57) | 287/1101 (26.07) | |
| Ethnicitya | White | 204/225 (90.67) | 991/1101 (90.01) |
| Asian – Asian British | 10 (4.44) | 71/1101 (6.45) | |
| Black – Black British | 7/225 (3.11) | 18/1101 (1.63) | |
| Others | 4/225 (1.78) | 21/1101 (1.91) | |
| NYHA classb | I | 0 (0) | 1/1089 (0.1) |
| II | 1/31 (3.23) | 30/1089 (2.75) | |
| III | 12/31 (38.71) | 549/1089 (50.41) | |
| IV | 18/31 (58.06) | 509/1089 (46.74) | |
| Systolic BP | Mean | 97 | |
| Median | 97 | ||
| SD | 14.07 | ||
| Range | 60–130 | ||
| Inotrope use | 180/235 (76.6) | 305/1101 (27.70) | |
| Beta-blocker use | 106/235 (45.1) | ||
| ARB use | 25/235 (10.64) | ||
| ICD use | 112/235 (47.7) | ||
| Pre IABP | 68/235 (28.94) | ||
| Pre VAD | 15/235 (6.39) | ||
| Pre ECMO | 8/235 (3.4) | ||
| Ace inhibitors | 94/235 (40) |
Previous medical history also included previous VAD implant, use of IABP or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). Just over 25% of VADs patients already had IABP before implant. A very small number (∼ 3%) of the patients were on ECMO support during the pre-operative phase.
Within the first 7 days a number of adverse events were reported in BTT patients. These are shown in Table 29. Right HF as well as renal failure were the most common problems faced by these patients. Infection and neurological dysfunction were other prominent adverse events which occurred in the VAD-supported patients. A few patients (n = 3) also suffered from device malfunction.
| Adverse events after VAD implant | No. (%) of patients (n = 235) |
|---|---|
| Infection | 26 (11.06) |
| Neurological dysfunction | 10 (4.26) |
| Device malfunction | 3 (1.28) |
| Haemolysis | 1 (0.4) |
| Right HF | 32 (13.62) |
| Renal failure | 46 (19.57) |
Adverse events reported during the follow-up period post 7 days VAD implant are reported in Table 30. Infection was the most common, ∼ 15% patients suffered with infection. Other patients had neurological dysfunction and right HF. During the follow-up period two patients were rehospitalised each due to infection and right HF.
| Adverse events after VAD implant | No. (%) of patients (n = 235) |
|---|---|
| Infection | 38 (16.17) |
| Neurological dysfunction | 10 (4.3) |
| Device malfunction | 7 (2.98) |
| Haemolysis | 3 (1.28) |
| Right HF | 9 (3.83) |
| Hypertension | 1 (0.43) |
Some of the VAD explanted patients had adverse events. Infection (n = 3) and neurological disorder (n = 3) were the two main adverse events among patients after the VAD explant surgery.
During follow-up period of the VADs patients received a HT while some remained on VAD implants. Some patients (n = 68) died. The main reasons reported for death are given in Table 31.
| Reasons listed for death | No. (%) of patients (n = 235) |
|---|---|
| Pulmonary | 3 (1.28) |
| Bleeding | 14 (5.96) |
| Cardiovascular | 6 (2.55) |
| Infection | 7 (2.98) |
| Liver failure | 2 (0.85) |
| Other | 34 (14.47) |
| Device malfunction | 1 (0.43) |
| CNS | 1 (0.43) |
Heart transplant patients
Figure 33 explains patient mix of the HT patients. There were 1101 patients, including BTT patients as well as MM patients, on the WL for HT. Of these, 33 of the patients were in the BTT arm and had received a VAD implant later followed by a HT. The majority of patients (91.2%), however, were from the MM subgroup. Almost half were in the non-inotrope patient subgroup. The remaining half was shared between the inotrope and the ‘other’ subgroup. There were 64 unregistered patients who spent no time on the WL but went straight to a HT.
FIGURE 33.
Heart transplant patients.
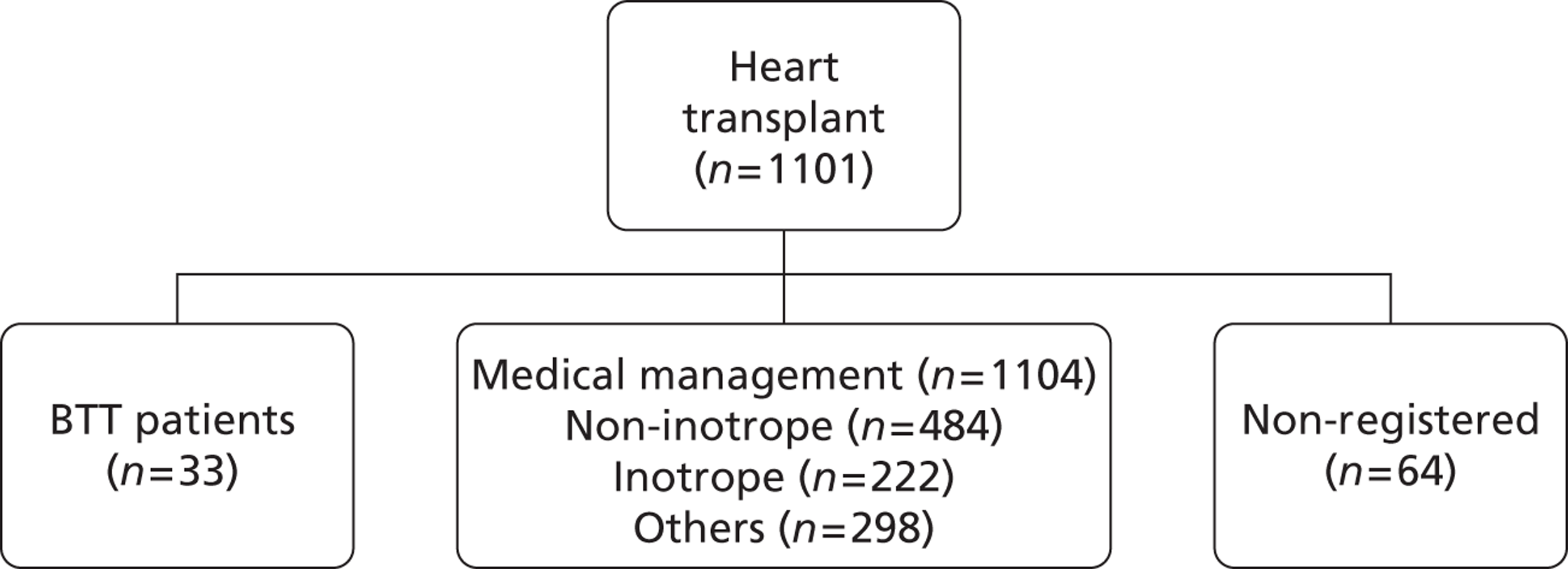
Baseline characteristics for the HT patients are given in Table 28. The reported median age for a HT patient was 48 years. Almost three-quarters of the patients were male. Almost all the patients belonged to either NYHA class III or class IV, although there were a few in NYHA class I and class II. Of note are the differences in NYHA classification between transplant patients and VAD patients in Table 28, with very different inotrope usage (∼ 75% for the VAD patients compared with ∼ 25% for the HT patients).
Intra-aortic balloon pump use was reported in almost 10% of transplant patients and ECMO support in 1% of transplant patients during the pre-transplant phase.
Assessment of the utility and quality of the UK Blood and Transplant Database
This section considers the utility and quality of the data set from the perspective of the requirements for the present report. Unsurprisingly, the database structure of this resource was not tailored specifically for the task in hand. Therefore, to extract relevant information for the economic model required some readjustment and modification. The strengths and weakness of the data sets are briefly summarised below.
Strengths
-
The database was comprehensive in that it contained information on all patients listed for HT within the six designated UK NHS centres between May 2002 and December 2011.
-
It was possible to identify which VAD had been implanted into BTT patients.
-
It was possible to distinguish between BTT and MM patients. The patients who fulfilled the eligibility criteria (see Appendix 6) for HT were clearly registered for HT.
-
The data set reported information about the various important events occurring at different time intervals during the BTT and post-transplant phases.
-
Mortality and time of transplant were recorded in an efficient manner in that patients were followed up routinely and at each time point, current transplant and mortality status were reported. It has therefore been possible to make reasonable estimates of transition probabilities between health states necessary for economic modelling.
Limitations
-
The data set had no information about patients during the pre-VAD phase. Assumptions about clinical treatment and events during that phase had to be made in order to carry out economic modelling.
-
The data set had missing values for some of the important covariates for some of the patients. It had been hoped to use the full set of SHFM covariates in order to make use of the SHFM95 to model survival for VADs patients in the database, but because of incompleteness of data it was necessary to undertake modelling with those few covariate values that were available in the database.
-
A few of the patients (n = 15) in the data set had an apparent negative waiting time for receipt of a donor heart. This happened because such patients are taken off the WL on receiving a VAD and then put on the WL for receiving a HT, and only recent registration dates are available.
-
NYHA stage was not reported for all BTT patients. A full data set for this variable would have allowed a more rigorous assessment of QoL and utility values for use in the economic model.
-
In the systematic review of clinical effectiveness the adverse events were considered according to the type of device. However, we have described here adverse events experienced post-VAD implantation for all devices as the BTDB data did not clarify these in an interpretable format after 7 days of implantation.
-
There were no cost data in the database.
-
It was hoped to use the database to estimate resource-use incidence and intensity for each health state so that an estimate of current costs associated with the NHS transplant programme could be made in conjunction with NHS reference costs and based on the BTDB. However, as data sets were not complete in terms of resource use – especially for hospital stay and duration, and frequency of medication use in the different health states – alternative modelling procedures were necessary.
Quality assessment
Quality assessment of the BTDB was carried out96 (Table 32). It should be noted that the four data sets were updated over a period of 10 years.
| Quality criterion | Subcategory | No. of data sets |
|---|---|---|
| Completeness of recruitment | Few (< 80%) or unknown | 0 |
| Some (80–89%) | 0 | |
| Most (90–96%) | 1 | |
| All or almost all (≥ 97%) | 3 | |
| Completeness of data | Few (< 80%) or unknown | 1 |
| Some (80–89%) | 0 | |
| Most (90–97%) | 1 | |
| All or almost all (≥ 97%) | 2 | |
| Use of explicit definitions of the variables | None | 0 |
| Some | 0 | |
| Most (90–97%) | 0 | |
| All or almost all (≥ 97%) | 4 | |
| Independence of observations of the primary outcome | Observer not included | N/A |
| Observer neither independent nor included | N/A | |
| Independent observer not blinded | N/A | |
| Independent observer blinded or outcome is objective | N/A | |
| Extent of data validation | No validation | 1 |
| Range or consistency checks | 0 | |
| Range and consistency checks | 0 | |
| Range and consistency checks and validity checks | 3 |
Quality assessment was carried out with the help of the statisticians at the BTNR. The completeness of recruitment is very high for all data sets. Three data sets reported 97% catchment of the target population, and one data set captured most of them (90–97%). However, there is some concern about completeness of data in all the data sets. As already mentioned, several important covariates (n = 16) of the SHFM95 model were not reported and only 5 of the total of 21 covariates used for SHFM analysis were reported. The data sets used explicit definitions for covariates which were well explained for each of the four data sets. Three data sets reported thorough range, consistency and validity checks.
Comparison of individual patient data with literature estimates
Table 33 gives a comparison of the BTDB individual patient baseline characteristics for the 235 UK VAD patients with values for similar patients reported in the international literature (see Chapter 3). The UK population implanted with VADs and awaiting a donor heart appear to be younger in mean age, with a less severe NYHA class rating and are more likely to be white.
| Baseline characteristics | BTDB (VAD) estimate (95% CI) | Pooled published studies estimate (95% CI) | Registry studies (Nativi 201189 or John 201165) estimate (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean, years) | 44.00 (42.72 to 45.28) | 50.80 (49.30 to 52.38) | 50.80 (49.84 to 51.76) |
| Gender (% male) | 80.40 (74.77 to 84.99) | 84.20 (79.40 to 88.00) | 82.30 (78.24 to 85.81) |
| % NYHA (class IV) | 58.10 (39.07 to 75.45) | 83.50 (78.00 to 87.90) | Not available |
| Ethnicity (% white) | 89.70 (81.80 to 90.86) | 69.20 (60.60 to 76.90)a | Not available |
| % use of inotropes | 76.60 (70.65 to 81.85) | 80.10 (50.90 to 94.50) | 80% |
| % use of beta-blockers | 45.10 (38.63 to 51.71) | 38.30 (30.10 to 47.20)a | Not available |
| % use of ACE inhibitors | 40.00 (33.69 to 46.57) | 30.10 (22.40 to 94.50)a | Not available |
| % use of systolic BP | 97.00 (95.71 to 98.28) | 97.30 (92.80 to 101.71) | Not available |
The proportion of patients using inotropes is of particular relevance to the economic model used in this report. More than three-quarters of BTDB VAD recipients used inotropes, whereas the pooled estimate for published BTT studies with non-overlapping populations and the estimate reported in the registry study by John et al. 65 was slightly higher, at 80%. Just over 20% (307) of the 1496 BTDB MM patients were categorised as using ‘inotrope’ treatment; this lower use of inotropes relative to the BTDB BTT patients tends to support the use of the ‘inotrope’ category group patients for the base-case comparator group in the economic model.
Conclusion
The BTDB provides valuable information about patient subgroups and the timing of important events for all patients listed for HT under the UK transplant programme for the period May 2002 to December 2011. There were insufficient complete data to estimate resource use or costs associated with the programme.
The following chapter reports the cost-effectiveness review of the literature. The subsequent chapters describe further analysis of this database for use in the Warwick Evidence model.
Chapter 5 Review of cost-effectiveness publications
Introduction
A previous HTA report by Clegg et al. 4 investigated LVADs as a BTT, as a BTR or as a long-term chronic support for people with advanced HF. The authors undertook a systematic review with searches up to 2003. Sixteen studies assessed VADs as BTT, with the majority relating to first-generation devices. The methodological quality of studies was considered to be weak. The authors found limited differences in survival between different types of VADs.
Clegg et al. 4 found that patients receiving the pulsatile HM ‘experienced some benefit in actuarial survival’ and functional status when compared with inotropic agents. They considered that there is a paucity of data in this area. The authors also undertook a systematic review of cost–utility analyses, identifying no relevant cost-effectiveness studies. They developed two models to evaluate the use of VADs: (1) as a BTT and (2) as long-term chronic support for patients suffering from advanced HF, finding that VADs were not cost-effective for either of the indications.
They found the baseline cost per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) of the first-generation HM to be £170,616. Sensitivity analyses had little effect on this value. Clegg et al. 4 suggested that, given the decline in the number of hearts available for transplant that rather than further developing VADs, researching how to improve organ donation may be more prudent and valuable.
In 2006, Sharples et al. 30 undertook an evaluation of the VADs programme in the UK. 30 The objectives of the study included summarising the relevant clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness literature and constructing cost-effectiveness and cost–utility models of VADs in a UK context, using data on outcomes (including survival, transplantation rates, HRQoL and resource use) to assess the factors that drive costs and survival.
Sharples et al. 30 updated the Clegg et al. 4 review. Most of the included studies were of first-generation VADs, with only a few reporting mixed use of first- and second-generation devices. Sharples et al. 30 found the evidence for effectiveness of VADs used for all indications ‘limited’. 30 They reported that the ‘methodological quality of the studies for assessing the effectiveness of VADs as a BTT, a BTR or a long-term circulatory support was weak’ because of the small-scale observational nature of the studies and their potential for bias. They concluded that evidence for second-generation devices was not yet available. As far as studies of the cost-effectiveness or cost–utility of VADs were concerned, at that time the authors concluded that both for BTT or for longer-term support methodology was also weak and that further studies based on actual resource use were needed.
Sharples et al. 30 developed cost-effectiveness and cost–utility models using IPD from the UK NHS funded VAD programme on all 70 patients with VADs implanted during the period April 2002 to December 2004. 30 Comparator groups were drawn from those on the WL for HT [non-VAD-supported transplant candidates (n = 250)] who were divided into two groups – those on standard supportive MM (n = 179) and those on inotropic support alongside MM (n = 71). A final hypothetical group was used in models, which comprised a worst case scenario, where, without VAD technology, all eligible patients would otherwise die in the intensive care unit (ICU) within 1 month. Individual patient-based QoL and resource data were collected and a multistate model of VAD and transplant activity was constructed populated with the data described.
The authors found that survival after a VAD was 74% at 30 days and 52% at 12 months which compared with a survival at 12 months after a transplant of 84%. VAD patients experienced on average between five and six adverse events each, mostly in the first month after VAD implant. Main adverse events were respiratory problems, bleeding and infections. Subsequent HT had similar outcomes for both VAD and MM (non-VAD) groups in terms of survival at 1 year, functional status (NYHA) and European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D).
At that time, the mean VAD implantation cost, including the device and the main cost drivers (e.g. staffing, lengths of ICU and hospital stay and adverse events), was £63,830. Sharples et al. 30 concluded that for the base case:
-
For a VAD patient, extrapolating over the patient's lifetime, mean cost was £173,841, with a mean survival of 5.63 years and mean QALYs of 3.27.
-
For MM inotrope-dependent patients, costs were £130,905, with a mean survival of 8.62 years and mean QALYs of 4.99 (this intervention was considered to be dominant).
-
For non-inotrope-dependent patients who had a HT, similar survival rates to patients on inotropes with lower costs meant that this scenario was also dominant.
-
For the ‘worst case scenario’ the mean lifetime incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) for VADs was £49,384 per QALY. However, as neither the inotrope-dependent transplant candidates nor the worst case scenario were considered fair controls, a mixture of these scenarios was investigated, here the ICER for VADs ranged from £79,212 per QALY to the non-VAD group being both cheaper and more effective. 30
The authors concluded that there were ‘insufficient data from either published studies or the current study to construct a fair comparison group for VADs’, but that in as far as comparisons could be made, VADs would not be cost-effective at traditional thresholds. They suggested, however, that VADs could be justified in selected cases based on survival and for maintaining ‘skills required for implantation and management’. 30
Cost-effectiveness studies: literature searches
The HTA reports by Clegg et al. 4 and Sharples et al. ,30 as well as the economic studies which they describe, concerned first-generation or a mixture of first- and second-generation devices. 4,30 We therefore searched for cost-effectiveness studies of second- and third-generation VADs. The keyword search strategies developed in the review of clinical effectiveness were used. The same limits and restrictions used in the review of clinical effectiveness were employed (see Chapter 3). Search filters were applied to restrict the search results to economic and cost-related studies. The search strategy is described in Appendix 2. Searches were undertaken in February and March 2012.
Two reviewers independently screened all titles and abstracts for inclusion. Disagreements were resolved through discussion. The full texts of papers considered potentially relevant were retrieved for further assessment.
Studies were selected for inclusion if they reported cost-effectiveness estimates for BTT which employed second- or third-generation VADs. Studies which reported insufficient detail or which failed to provide an estimate of cost-effectiveness were excluded. Data were extracted by one reviewer using a predefined extraction form, and were checked by a second reviewer. The quality of the included study was investigated by a single reviewer using the Drummond assessment tool. 97
Results
FIGURE 34.
Flow chart for identification of cost-effectiveness studies.
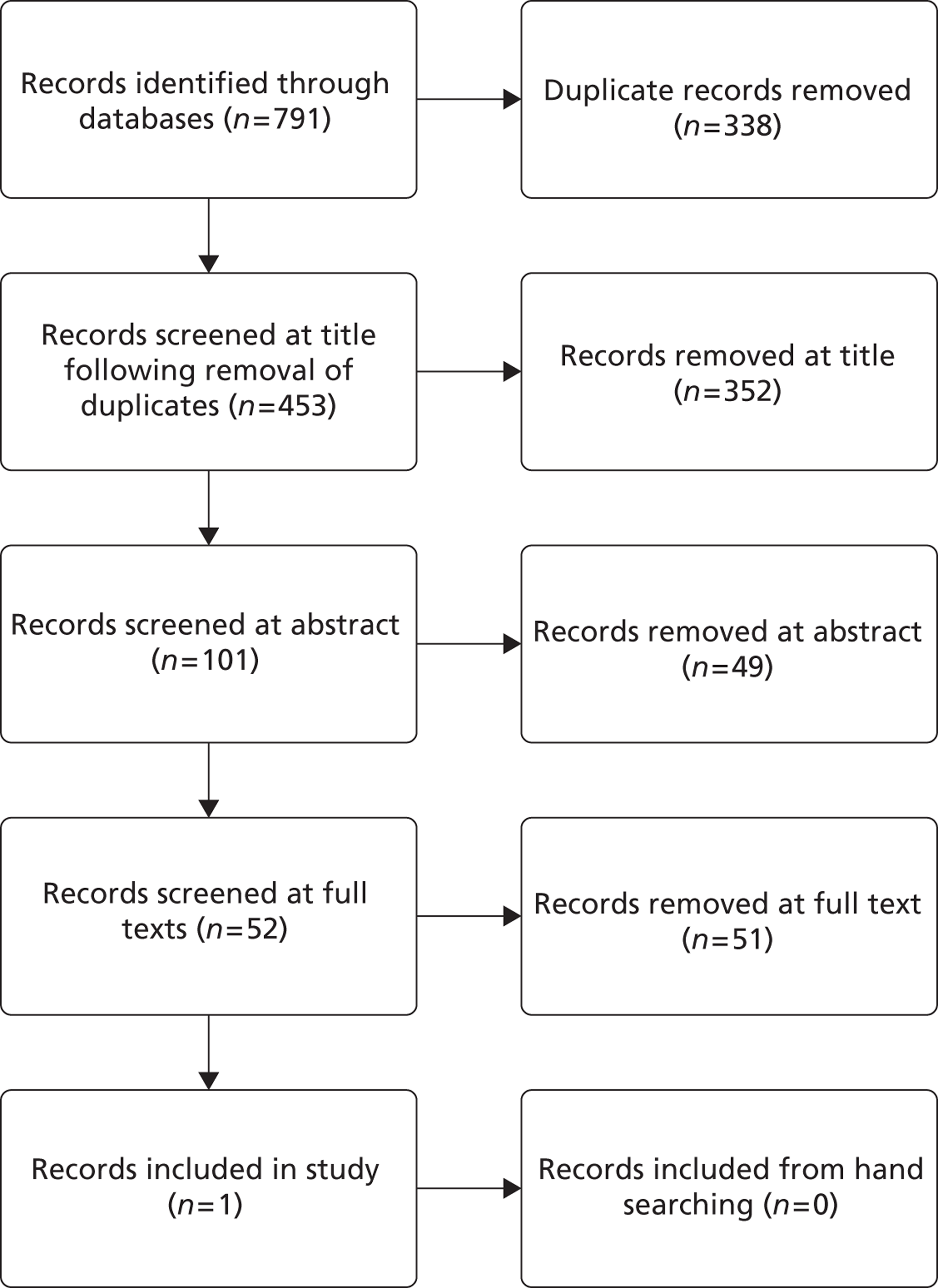
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) flow chart is summarised in (Figure 34). One identified study, Moreno et al. ,98 satisfied the inclusion criteria and is summarised below. 98
Aim of analysis
The authors aimed to estimate the cost-effectiveness of the HMII using the most robust and recently published evidence about its comparative performance compared with conventional therapy for patients with advanced HF.
Model structure
The model was a semi-Markov discrete-time multistate model with monthly cycles; the model design was the same as used by Sharples et al. 30 The health states were:
-
support on VAD to HT
-
support on conventional care to HT
-
support in the HT state
-
dead.
Model inputs
Transition probabilities between health states 1 and 4 (VAD to dead), 2 and 4 (conventional care to dead) and 3 to 4 (transplanted to dead) were based on data in published studies describing survival rates: these are summarised in Table 34.
| Time from VAD or HT | Mean survival rates (%) | SE | Beta distribution used for probabilistic sensitivity analysis | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional therapy | |||||
| 6 months | 76 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Lietz et al. (2007)99 |
| 6–12 months | 69 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 12–18 months | 63 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| LVAD implant | |||||
| 1 month | 92 | 0.016 | 258 | 23 | Pagani et al. (2009)71 |
| 1–6 months | 82 | 0.033 | 109 | 24 | |
| 6–18 months | 72 | 0.059 | 42 | 16 | |
| Post-HT survival | |||||
| 3 months | 93 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Russo et al. (2009)100 |
| 7 years | 65 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
For the base-case analysis, all patients alive in each arm at 6 months received a HT [92% and 76%, respectively, for BTT with VAD and conventional therapy patients; transition probability (TP) at 6 months = 1]. For sensitivity analyses receipt of a transplant took place at 12 months or at 18 months. In this way the model did not require extrapolation of survival for patients with BTT or conventional care beyond the observed 18 months of data. Survival after HT was fitted with exponential distributions at 3 months and 7 years using data from Russo et al. ,100 extrapolated to a lifetime horizon.
The utilities attached to the health states used by Moreno et al. 98 were taken from Sharples et al. 30 and are summarised in Table 35. 30
| Health state (time) | Mean | SE | Beta distribution for probabilistic sensitivity analyses | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional therapy | 0.500 | 0.092 | 6.5 | 6.5 |
| LVAD implant | ||||
| Month 1 | 0.510 | 0.056 | 35.7 | 34.3 |
| Month 2+ | 0.660 | 0.015 | 46.2 | 23.8 |
| Post HT | 0.760 | 0.015 | 58.5 | 18.5 |
Cost inputs (Table 36) were based on those of Sharples et al. 30 inflated to 2012 prices with the cost of the HMII device set at £94,200, the remaining cost items were given gamma distributions for the probabilistic sensitivity analysis.
| Event | Mean (£) | SE (£) |
|---|---|---|
| HMII device | 94,200 | N/A |
| LVAD implant procedure | 19,628 | 2120 |
| Post LVAD implant | ||
| Month 1 | 25,601 | 1669 |
| Month 2 | 13,348 | 1297 |
| Month 3 | 5075 | 759 |
| Month 4 | 3810 | 602 |
| Month 5 | 3226 | 457 |
| Month 6 | 2310 | 354 |
| Month 7+ | 1880 | 901 |
| Conventional therapy | ||
| HT assessment | ||
| Treated Month 1 | 12,133 | 2526 |
| Treated Month 2 | 6350 | 1320 |
| Treated Month 3+ | 5925 | 423 |
| HT surgery (both groups), perioperative/post operative | 16,933 | N/A |
| Theatre for HT | ||
| LVAD patient | 16,550 | N/A |
| Conventional therapy patient | 11,317 | N/A |
| Post-HT patients | ||
| LVAD, month 1 | 15,471 | 1667 |
| Conventional therapy, month 1 | 13,120 | 969 |
| Post HT, both groups | ||
| Month 2 | 4301 | 694 |
| Month 3 | 2591 | 407 |
| Month 4 | 2808 | 226 |
| Month 5 | 2164 | 374 |
| Month 6 | 1634 | 119 |
| Month 7+ | 1401 | 154 |
Discounting of costs and benefits used a rate of 3.5% and results were expressed as ICERs calculated as cost per life-year gained (LYG) and cost per QALY.
Results
The base-case results (HT received at 6 months) are summarised in Table 37.
| Base-casea results | |
|---|---|
| Intervention | Survival in life-years (95% CI) |
| LVAD | 9.19 (8.48 to 9.91) |
| Conventional therapy | 8.54 |
| Diff. survival (LYG) | 0.65 (−0.06 to 1.36) |
| Intervention | QALYs (95% CI) |
| LVAD | 6.93 (5.94 to 7.93) |
| Conventional therapy | 6.38 (5.61 to 7.16) |
| Diff. QALYs | 0.55 (−0.01 to 1.11) |
| Intervention | Costs (£) (95% CI) |
| LVAD | 350,939 (311,726 to 390,151). |
| Conventional therapy | 208,444 (178,835 to 238,053) |
| Diff. costs | 142,495 (116,413 to 168,578) |
| Economic outcome | Mean ICER (£/LYG or £/QALY) |
| For a LYG | 219,705 |
| For a QALY gained | 258,922 |
Probabilistic sensitivity analysis of the base case indicated a 50% probability of cost-effectiveness at a willingness to pay of £247,000 per QALY. Other sensitivity analyses used 12- and 18-month intervals before receipt of a donor heart. The deterministic results for these are summarised in Table 38.
| Waiting time for HT | 12-month interval (95% CI) | 18-month interval (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| (Time horizon; device cost) | Lifetime horizon; £94,200 | Lifetime horizon; £94,200 |
| Survival (life-years) | ||
| LVAD | 8.99 (8.34 to 9.65) | 8.87 (7.84 to 9.91) |
| Conventional therapy | 8.19 | 7.95 |
| Diff. survival (LYG) | 0.8 (0.15 to 1.46) | 0.92 (−0.11 to 1.96) |
| QALYs | ||
| LVAD | 6.76 (5.84 to 7.69) | 6.62 (5.54 to 7.69) |
| Conventional therapy | 6.04 (5.31 to 6.78) | 5.76 (5.04 to 6.48) |
| Diff. QALYs | 0.72 (0.16 to 1.28) | 0.86 (0.02 to 1.69) |
| Costs (£) | ||
| LVAD | 347,216 (313,018 to 381,414) | 344,170 (303,118 to 385,222) |
| Conventional therapy | 218,630 (190,796 to 246,464) | 229,638 (198,472 to 260,804) |
| Diff. costs | 128,586 (108,801 to 148,371) | 114,532 (80,689 to 148,376) |
| Mean ICER (£) | ||
| For a LYG | 160,388 | 124,066 |
| For a QALY gained | 178,829 | 133,860 |
Base-case results were also reported for a 10-year time horizon; the ICER was £411,227 per QALY. A further analysis was undertaken in which the HMII was provided free of charge; this reduced the lifetime horizon ICER from £133,860 per QALY to £24,063 per QALY when the waiting time for transplant was set at 18 months, indicating that a major driver in these analyses is the cost of the device.
Authors conclusions
The authors concluded that HMII implantation does not offer better value for money than conventional MM and that it is unlikely to be cost-effective with current cost of the device. For a 50% probability of being cost-effective with 6 month transplant delay and lifetime horizon, a payer would need to be willing to pay about £247,000 per QALY.
Quality assessment and comment
This was a good-quality study using model inputs taken wholly from the published literature (refer to authors for full quality assessment according to the Drummond et al. assessment tool97). The clinical effectiveness studies used for input to the model did not derive from a systematic review of the literature; however, in comparing the studies discussed in the study with those which we identified in our own review of the literature it appears that appropriate and relevant studies were identified.
A weakness of this study that is common to all studies of VADs for BTT for advanced HF is the lack of a randomised comparative study in which an appropriate population of patients is randomised to each treatment strategy. A critical element in these economic studies therefore concerns the choice of the comparator population and its associated prognosis (i.e. survival). In the Moreno et al. 98 analysis 76%, 69% and 63% of conventional care patients survived to 6, 12 and 18 months respectively. This survival is somewhat inferior to that of the total MM population in the BTDB, but considerably superior to that of BTDB ‘inotrope’ patients when their survival is modelled on the robust part of the observed K–M survival plot.
A further noteworthy element of the Moreno et al. 98 study is the allocation of a donor heart with equal probability to both groups of live patients; this contrasts with the analysis of Sharples et al. ,30 in which MM patients received a donor heart with much greater probability than BTT patients. 30 It appears sensible for the purposes of a fair comparison between treatment options that each should have an equal opportunity of receiving benefits of a transplant; however, in medical practice, MM patients do in fact receive transplants much earlier than BTT patients, mainly because it makes little sense to remove a VAD from a patient who is doing relatively well to give them a donor heart which is much more urgently required by other patients. Once the premise that equal opportunity of transplant should prevail for both BTT and MM patients is accepted, then the issue becomes one of ‘At what rate should this be set?’ In the Moreno et al. 98 base case all live patients received a transplant at 6 months; in the BTDB the proportion of live BTT patients who had received a donor heart by 6 months was < 20%. It appears possible that the 18-month delay to transplant used by Moreno et al. 98 in sensitivity analysis is more likely to represent a real-world likelihood of receiving a transplant and may have represented a better choice for the base-case analysis (this reduces the estimated ICER to nearly half).
In the next chapter we describe design of the Warwick Evidence model.
Chapter 6 Description of model including definition of scenarios
Overview
This chapter describes the structure of the economic model, the scenarios evaluated and the probabilistic sensitivity analysis. The main assumptions of the model are also presented in this section. The underlying model is based on the study by Sharples et al. 30 which has been adapted for our decision problem and updated with new data. For more detailed information, readers are referred to Chapter 7 and 8 in the Sharples et al. 30 report.
Model structure
An economic model was developed based on a multistate model of patient experience from the UK during the period April 2005 to November 2011. The aim of the economic model was to compare BTT with MM treatment for patients eligible for HT.
The model is a semi-Markov, multistate model as shown in Figure 35. In the model each patient can be in one of three mutually exclusive health states, namely alive with VAD (or MM) support (state 1), alive after HT (state 2) or dead (state 3). Each individual may move between health states or remain in the same state. State 3 (dead) is an absorbing health state. The transition between each of these health states, referred to as the TP, is represented by the quantities p12, p13 and p23. Transition probabilities are not fixed but depend on time t since the VAD was implanted (p12, p13) or the time t* since transplantation (p23). 30 For patients on MM support, a precisely similar model was constructed, with different estimates of pre-transplantation transition probabilities (p12, p13), but the same estimates of post-transplantation transition probabilities (p22 and p23).
FIGURE 35.
Discrete-time, semi-Markov, multistate model of health states for VAD patients. For patients on MM instead of a VAD, a precisely similar model was constructed, with different estimates of the pre-transplantation transition probabilities (p12, p13), but the same estimates of post-transplantation transition probabilities (p22 and p23). p11(t), transplantation listing t in state 1; p22(t*), time since HT t* in state 2.
Cycle length was set at 1 month and transition between each health state occurs at the end of each cycle.
The model was evaluated over several time horizons. For the base-case scenario, a lifetime horizon, spanning approximately 50 years, was used. The model was also run for shorter time horizons of 3 and 10 years. The model evaluates costs from the perspective of the NHS. Thus, only direct costs related to VAD implants have been included and indirect costs are excluded. All costs are at 2010/11 UK prices in pounds sterling (£). Health outcomes were measured in QALYs. In accordance with current UK guidelines,101 an annual discount rate of 3.5% was applied to both costs and health outcomes. Both deterministic and probabilistic approaches were used to estimate the cost-effectiveness of VADs. The probabilistic approach was used to account for uncertainty in the various variables within the model.
Base-case analysis
For the base-case analysis we used observed survival data from the BTDB. We hypothesised that although survival rates are different for each group (patients who received a second- or third-generation approved VAD as a BTT or patients who received MM support to transplant), they would have common post-transplant survival rates, with a constant death rate for months 3–12. In the base-case analysis survival up to 3 years from VAD implantation/listing were estimated using data from the BTDB based on constant death rates beyond 6 months post transplantation. Several assumptions were made when estimating longer-term survival rates after 42 months (see Chapter 7).
Structural assumptions
Disease state/pathways
Two pathways were modelled for this economic evaluation of VADs. In the base case, patients with more severe HF (based on inotrope medication) either followed the VAD pathway or were allocated to the MM pathway. In both pathways patients received a HT after a certain period of time (which was varied according to different sensitivity analyses). Some of the patients died before receiving a HT.
Strategies/comparators
For the two research questions we compared:
-
use of VADs as a BTT with MM using the inotrope subgroup of patients as the comparator group
-
use of VADs as an ATT with use of VADs as a BTT. For an ATT, transition probabilities were kept the same as for patients in the BTT base-case arm, except that the probability of receiving a donor heart was set to zero.
For the sensitivity analyses we included comparisons of:
-
use of the HW only, as a BTT with MM using the inotrope subgroup of patients as the comparator group as in the base case
-
use of VADs as a BTT with all MM patients (both inotrope and non-inotrope)
-
use of VADs as a BTT with an artificially constructed MM group using the VAD patients as their own controls. (Based on predicted survival of the VADs group – had they been treated with MM not VADs. Predictions were made using the SHFM; see Chapter 7, Selection of comparator group and sensitivity analyses.)
Cost-effectiveness summaries
Incremental costs and QALYs gained were estimated and summarised as the ICER, the additional cost per QALY gained. Specifically, given mean costs CA, CB, CC and CD and mean benefits (QALYs) QA, QB, QC and QD for the groups, the ICER for group A relative to group B, say, is:
The mean costs and benefits for each group were estimated from the economic model using data from the BTDB.
The joint distribution of incremental mean costs and benefits was plotted on the cost-effectiveness plane and used to estimate both the incremental net benefit (INB), for example:
and the cost-effectiveness acceptability curve (CEAC), for example:
where λ represents the maximum acceptable cost for one unit of benefit, in this case one QALY.
Estimation of model parameters
Three types of input were considered for the economic analysis: transition probabilities estimated from the BTDB, utilities derived from the published literature, and costs computed from UK data. The following assumptions were made in the base-case analysis and subsequent scenarios.
Transitions to the HT state were assumed to occur at monthly intervals and a whole month of pre-transplantation survival and costs were included. However, in practice, a transplant may take place at any time during the month and, on average, at the mid-point of the relevant month. Also, costs and utilities associated with death were assigned zero. A half-cycle correction was added to reflect the fact that a death could occur at any time during the month, although transitions were assumed to occur at monthly intervals. Thus, a transition to death would result in a reduction in survival time of 0.5 months. For the month in which death occurred no reduction in costs was required, as only costs up to death were included in these months.
In summary, for the economic model, a simple discrete-time, discrete-state model was constructed. Cost-effectiveness summaries of interest were estimated by weighting time in each state of the model by the utility and cost associated with that state. Transition probabilities, costs and utilities have been estimated using data from the NHS BTDB (see Chapter 7).
Quality of life and utilities
Health-related quality of life remains relatively static in HF patients who are medically managed,102 and improves after receiving a VAD53,103,104 or HT,104–106 with improvements maintained for several years. 103,105,107–109 Recipients of HT report better HRQoL than recipients of VAD. 104 In the model, health outcomes were measured in QALYs, in accordance with current UK guidelines. 101 The EuroQoL EQ-5D110 is the preferred measure of decision-making bodies such as the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). 101 The literature revealed two applicable sources of EQ-5D utility scores derived from patients suffering from chronic HF: Sharples et al. 30 and Gohler et al. 111
Sharples et al. 30 derived EQ-5D utility scores from UK patients suffering from chronic HF who were either implanted with a VAD or medically managed while waiting for HT. A subset of the group were reassessed post HT. Table 39 shows the extracted data.
| Group | EQ-5D utility score (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| Medically managed | |
| All months | 0.50 (0.32 to 0.68) |
| Post VAD | |
| Month 1 | 0.51 (0.40 to 0.62) |
| Month 2+ | 0.66 (0.63 to 0.69) |
| Post HT | |
| All months | 0.76 (0.73 to 0.79) |
Gohler et al. 111 collected EQ-5D data on a subsample of the Eplerenone Post-AMI Heart Failure Efficacy and Survival Trial (EPHESUS) trial participants. EPHESUS was a multinational RCT which investigated the effect of the aldosterone antagonist eplerenone (Inspra®, Pharmacia) in patients with chronic HF after acute myocardial infarction. Responses to the EQ-5D descriptive system were used to generate an EQ-5D utility score by applying the appropriate tariff based on participant's country of origin. Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to investigate the association of EQ-5D utility scores with NYHA class. The findings highlight the utility loss associated with worsening NYHA class, with excellent model fit found in the multivariate models. The association between NYHA class and HRQoL, including EQ-5D utility scores, is supported in the literature. 25,112,113 Table 40 shows the relationship between NYHA class and utility.
| NYHA class | EQ-5D utility score (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| I | 0.855 (0.845 to 0.864) |
| II | 0.771 (0.761 to 0.781) |
| III | 0.673 (0.665 to 0.690) |
| IV | 0.532 (0.480 to 0.584) |
For the purposes of this analysis we used the data provided by the BTBD to determine EQ-5D utility scores for health states in the model. The HT data set recorded NYHA class for 1011 patients who received a HT (from 2002 till the end of 2011). NYHA class was entered at initial registration and 3 months after VAD implant (for the 83 of 235 patients who subsequently received a HT). For those who received a HT, NYHA class was recorded post transplant at their 3, 12 and 24 months outpatient visits. The BTDB suggests that there is some improvement in NYHA class after HT; however, this translates into very minor changes in the weighted EQ-5D utility scores over time. Table 41 summarises the data.
| NYHA class | Post VAD | Post HT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 months | 3 months | 12 months | 24 months | |||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| 83 | 100.0 | 931 | 100.0 | 832 | 100.0 | 719 | 100.0 | |
| I | 18 | 21.7 | 710 | 76.3 | 683 | 82.1 | 615 | 85.5 |
| II | 36 | 43.4 | 175 | 18.8 | 116 | 13.9 | 90 | 12.51 |
| III | 21 | 25.3 | 25 | 2.7 | 24 | 2.9 | 10 | 1.4 |
| IV | 8 | 9.6 | 21 | 2.3 | 9 | 1.1 | 4 | 0.6 |
For the model, the weighted derived EQ-5D utility score was based on the proportions of patients for each NYHA class for VAD patients (3 months post implant) and HT patients (3 months post transplant) (see Table 41). Thereafter, utility was assumed to remain constant.
| NYHA class | Inotrope | All MM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | n | |||
| 225 | % | 978 | % | |
| I | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.2 |
| II | 0 | 0 | 40 | 4.1 |
| III | 24 | 10. 7 | 528 | 54.0 |
| IV | 201 | 89.3 | 408 | 41.7 |
A weighted EQ-5D utility score for all MM patients and for those MM patients receiving inotropes was similarly determined using NYHA data recorded at registration (Table 42) and, as with previous analysis, EQ-5D utility score was assumed to remain constant thereafter (Table 43). Table 43 shows the EQ-5D utility scores used for the base-case analysis. For the sensitivity analysis, data reported by Sharples et al. 30 were used (see Table 39).
| Group | EQ-5D | Distribution | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Lowa | Higha | ||
| All medically managed patients: all months | 0.62 | 0.59 | 0.65 | Beta |
| Medically managed receiving inotropes: all months | 0.55 | 0.50 | 0.6 | Beta |
| Post VAD: all months | 0.74 | 0.73 | 0.76 | Beta |
| Post HT: all months | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.84 | Beta |
In the next chapter we describe derivation of transition probabilities between model states in more detail.
Chapter 7 Transition probabilities between health states
This section describes the derivation of the transition probabilities between health states used in the economic model.
The transitions required are:
-
supported on VAD to death
-
supported on MM to death
-
supported on VAD to supported on HT
-
supported on MM to supported on HT
-
supported on HT to death.
For the purposes of this report survival after HT is assumed to be the same whether preceded by VAD support or MM support.
The main source of information is the BTDB. In addition, published literature sources and UK population survival data are used, especially for extrapolation beyond observed data, for sensitivity analyses and to place the current analyses in context.
Transition from support on ventricular assist device to death (bridge to transplant)
The BTDB contained analysable data for 235 patients who had received an approved second- or third-generation VAD. The mortality of these patients while on VAD support was investigated using K–M analysis in which patients were censored at the time of receiving a HT, at the time alive at last follow-up while on VAD support, or at the time of explantation of the VAD. This was necessary because there are no observed survival data for a cohort of UK patients who receive a VAD but who never receive a donor heart. The K–M plot is shown in Figure 36. Median survival was 32.1 months; < 25 (∼ 10%) patients remained at risk after 23 months.
Because patients are removed from the cohort as they receive a HT, and because these patients are likely to be unrepresentative of original cohort (perhaps either more or less ill), then estimated survival is likely to be biased. Clinical opinion varies, but one of our clinical advisors suggested that more severely ill patients are more likely to receive a transplant and therefore the estimated survival shown in Figure 36 may be an overestimate; on the other hand, patients must be deemed well enough to benefit from HT and this bias will also operate in the comparator (MM) arm.
FIGURE 36.
Observed survival and 95% CI while supported on a VAD. Two hundred and thirty-five BTDB patients receiving second- or third-generation approved VADs. Patients were censored on receipt of transplant, device removal, or if alive at end of follow-up without receiving a transplant.
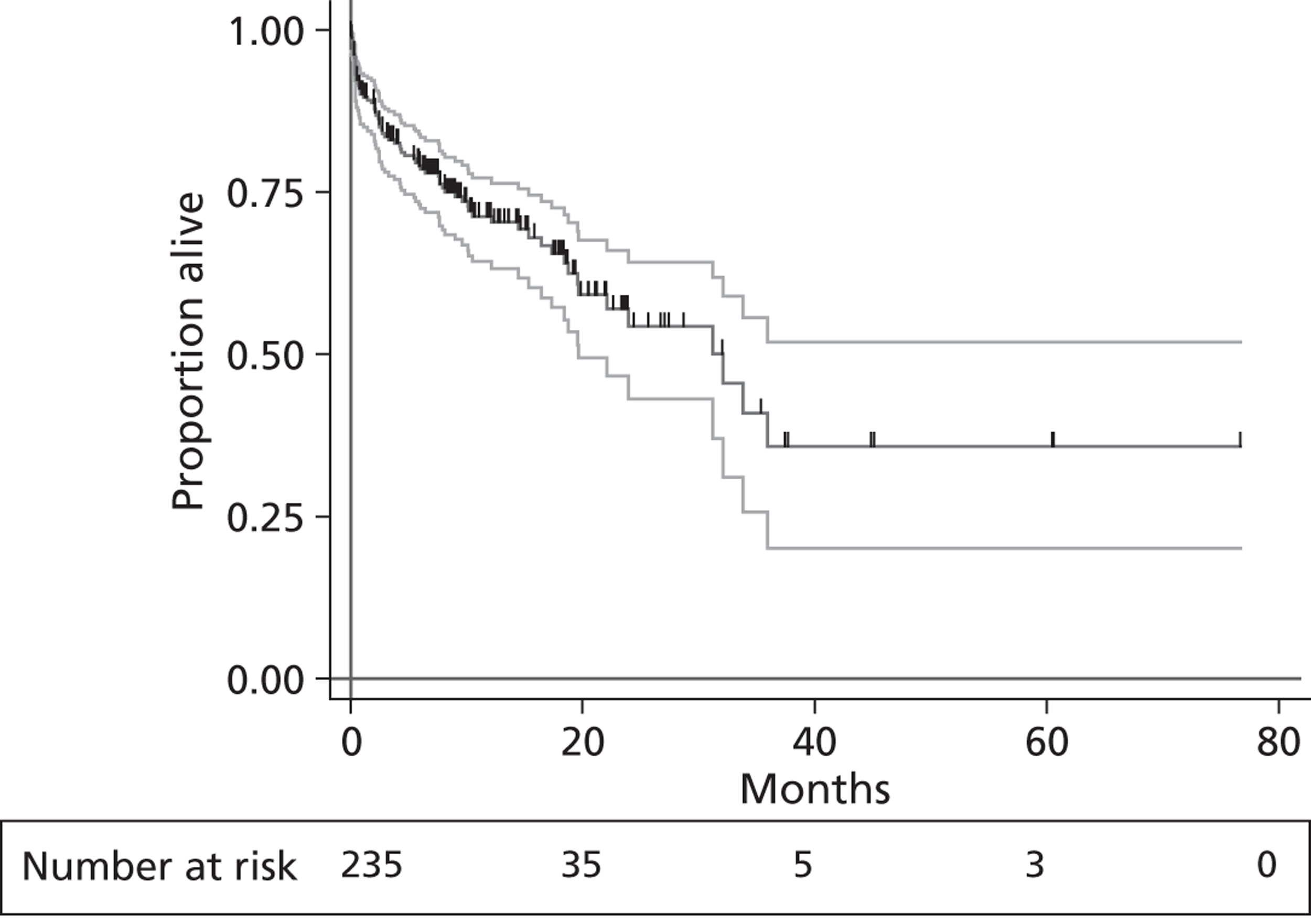
Most patients had received HMII (n = 82) or HW (n = 125) devices. There were sufficient data for these patients to be analysed separately; the results are shown in Figures 37 and in 38 respectively.
FIGURE 37.
Survival while supported by HMII. Patients were censored on receipt of transplant, device removal or if alive at end of follow-up without receiving a transplant.
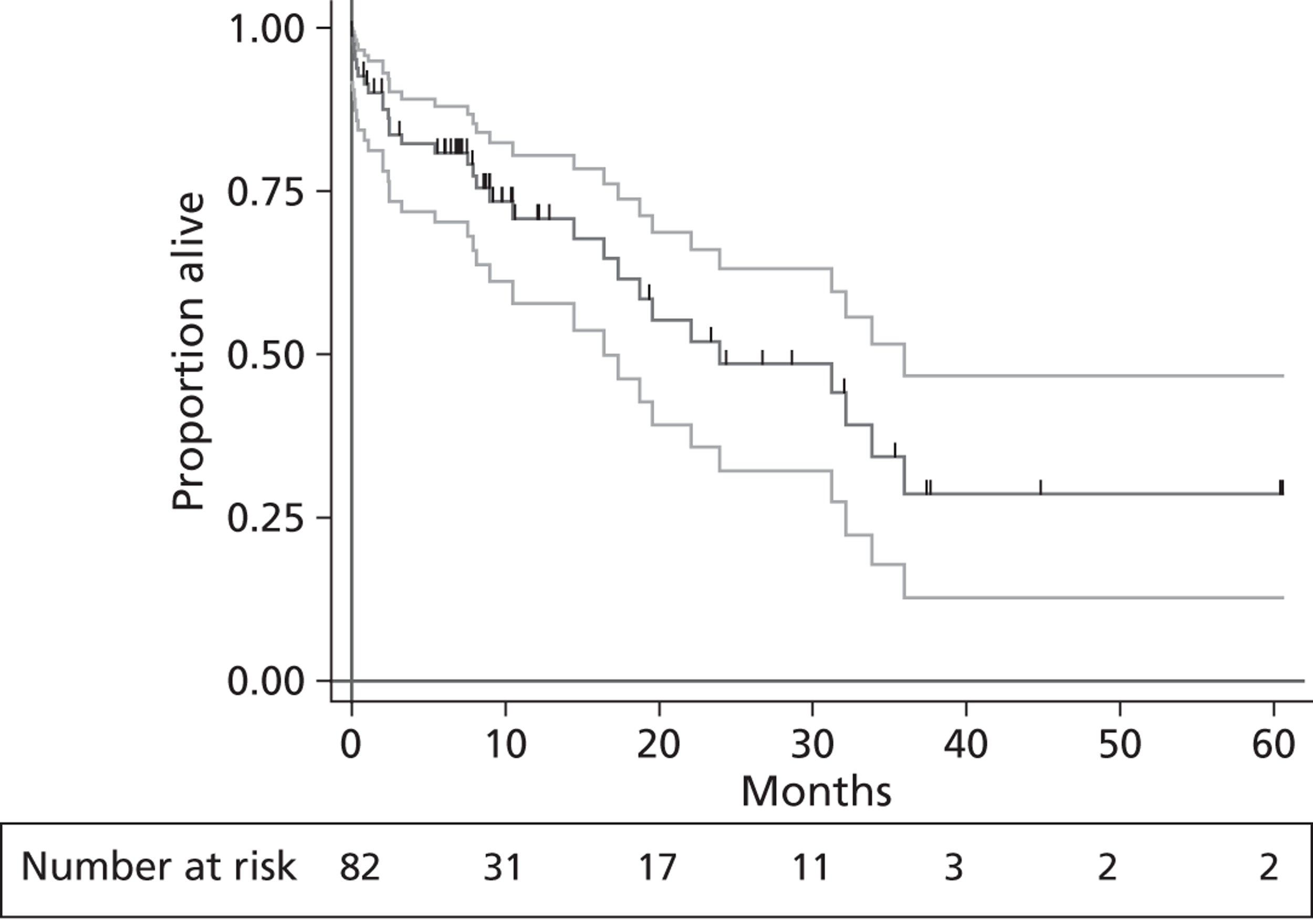
FIGURE 38.
Survival while supported by a HW VAD.
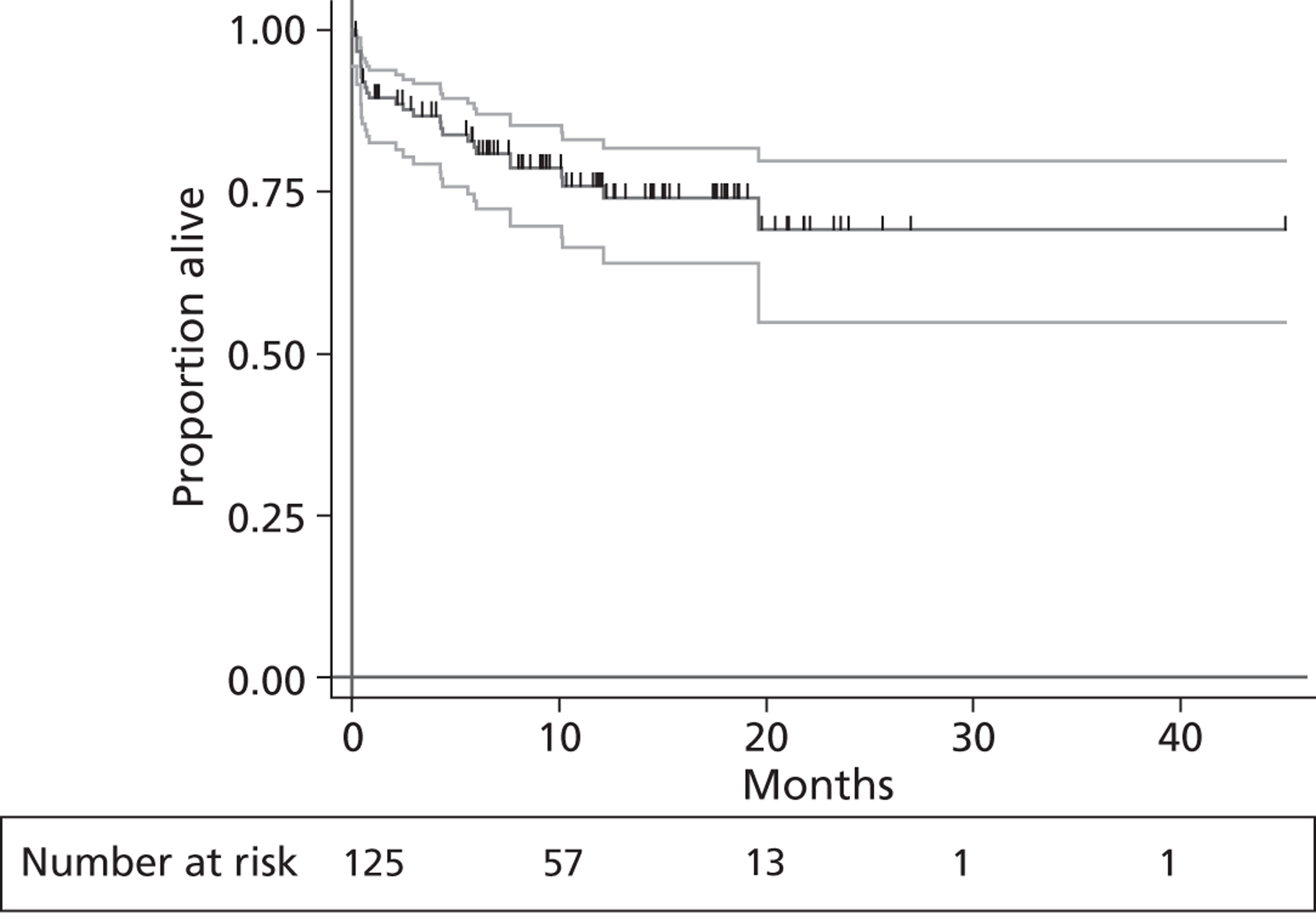
Median survival with HMII was 23.95 months but was not reached for HW, 75% of patients with the HW survived to 12 months.
As previously observed by others, survival over the first 90 days post VAD implant was poor relative to the remaining time span. For the whole population (n = 235), in common with previous economic analyses (Sharples et al. 30 and Moreno et al. 98), we explored fitting a constant hazard for the first 3 months and a second constant hazard for the period 3–23 months (∼ 700 days beyond which fewer than 10% of patients remained at risk and the observed data were more uncertain). The fit produced relative to observed survival is shown in Figure 39a.
FIGURE 39.
All BTDB BTT patients. (a) Survival curve derived from corresponding transition probabilities; and(b) exponential fits to observed data month 3 and from month 3 to 23.
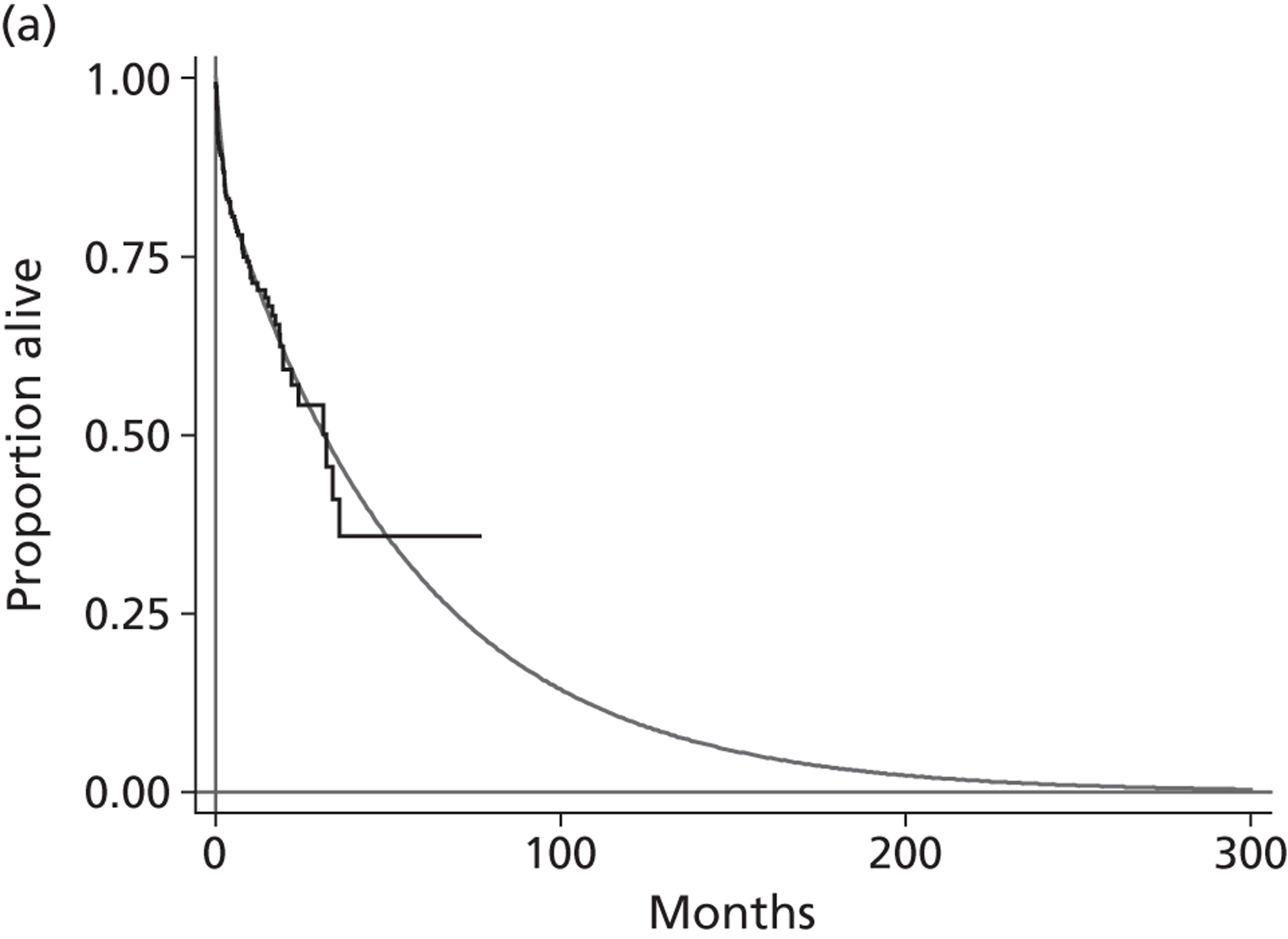
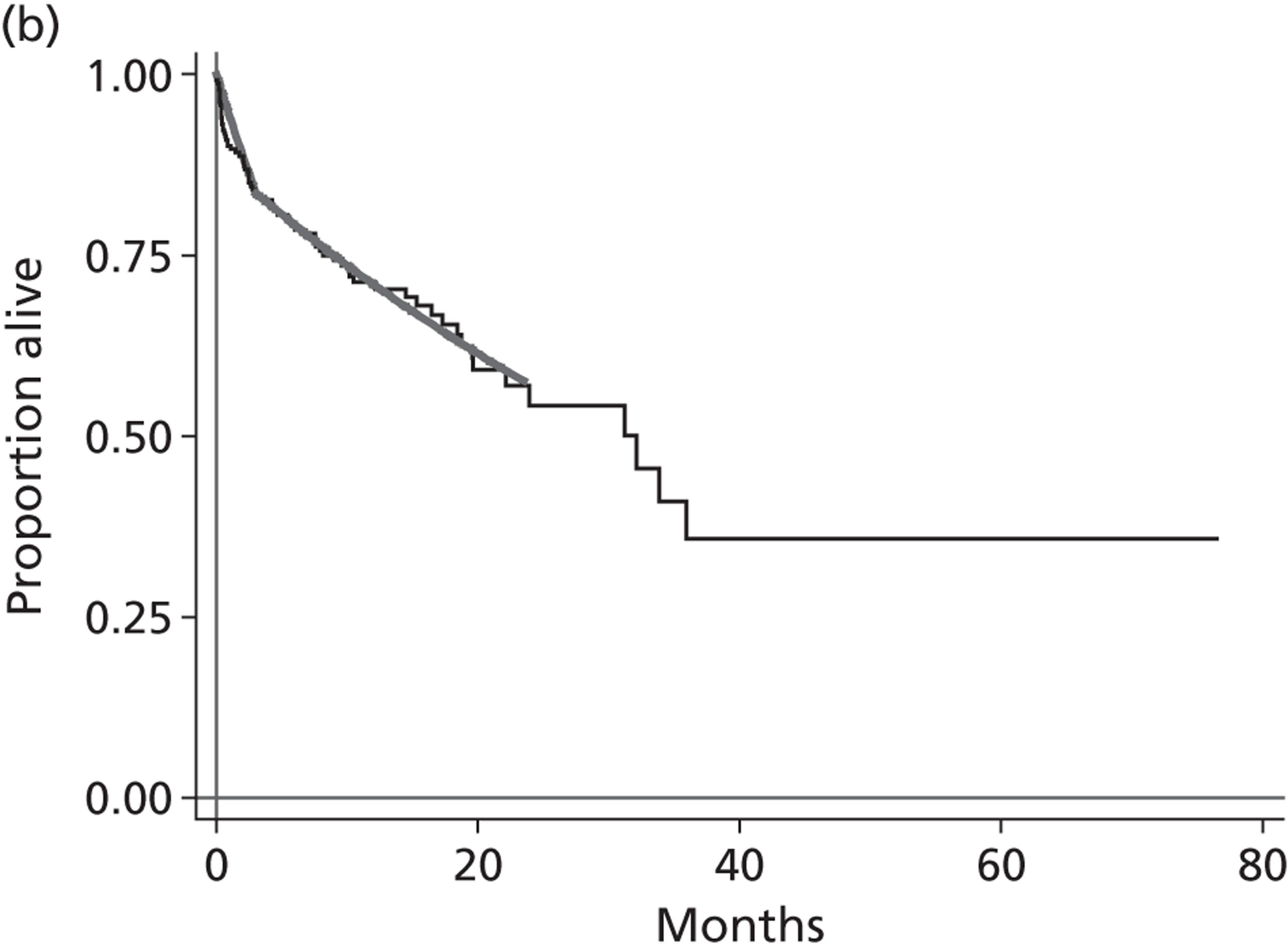
Several options were considered for extrapolation beyond 23 months observed data. The simplest extrapolation was to retain the constant hazard fitted from 3 months to 23 months to lifetime horizon.
This generated the extrapolation shown in Figure 39b and the monthly probability of death, conditional on surviving to the start of the month, as shown in Table 44. These probabilities for the more recent analysis of VAD recipients indicates superior prognosis to the probabilities reported by Sharples et al. 30 and this presumably reflects improved performance of the second- and third-generation devices together with the cumulative experience of procedures. This constant hazard model was selected for the base-case analysis.
| Present model input | Sharples et al.30 model input | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Month | TP | Month | TP |
| 1 | 0.0577197 | 1 | 0.20 |
| 2 | 0.0577197 | 2+ | 0.04 |
| 3 | 0.0577197 | 3 | 0.04 |
| 4+ | 0.0179873 | 4+ | 0.04 |
For sensitivity analysis, an alternative approach of employing a parametric fit was explored. Weibull, exponential, log-normal, log-logistic and Gompertz distributions were all fitted to the observed data, with the Weibull producing the lowest Akaike information criterion (AIC) values. The Weibull fit is illustrated in Figure 40. As the Weibull fit generated a hazard that decreased with time, a better survival was obtained than with the exponential distribution. Decreasing hazard extending to 50 years appears implausible. Therefore, the Weibull distribution was adjusted at the time when the probability of death became less than that for the UK general population matched by age and gender,114 after which the extrapolation followed the survival for the latter; this made insubstantial difference to the extrapolated curve. These extrapolated survival curves are summarised in Figure 40.
FIGURE 40.
Extrapolated constant hazard and Weibull fits for survival of 235 VAD patients. The Weibull curve also shows the adjustment to that of the general population after 380 months. The modelled survival curve for VAD patients employed by Sharples et al. 30 is included for comparison.
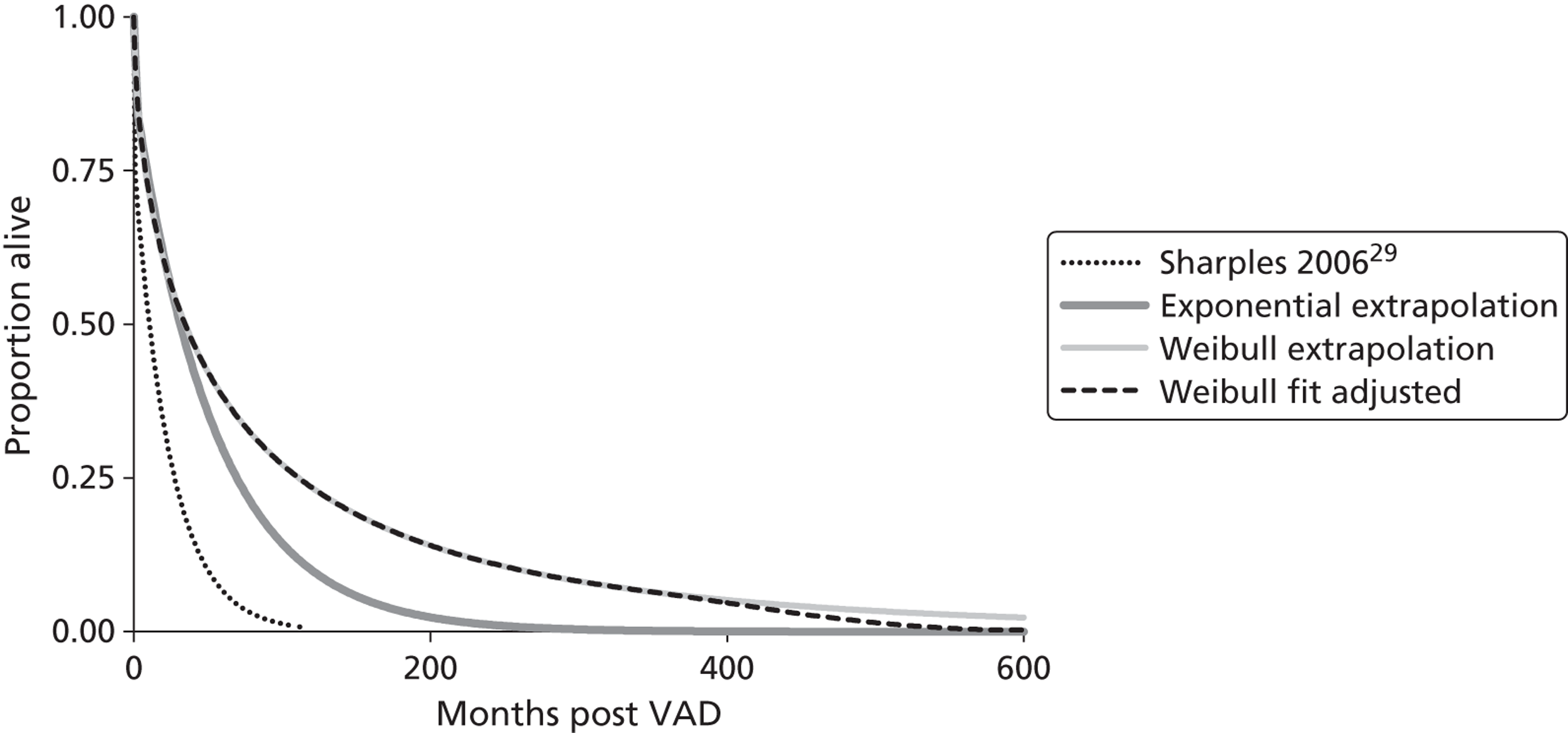
For further sensitivity analysis, the observed survival for the 125 BTDB patients who received a HW device was investigated. Weibull and log-normal fits provided the lowest AIC values for goodness of fit, but generated implausible proportions of survivors after extrapolation to 50 years because of continuously decreasing hazard. An alternative approach was adopted in which an exponential distribution was used to fit the K–M survival at 1 month and at 3 months, and then a second exponential distribution was fitted to the K–M function from either 1 month or 3 months, respectively, to 10 months when ∼ 10% of patients remained at risk, this latter constant hazard was then extrapolated beyond 10 months. This generated the transition probabilities shown in Table 45 and the extrapolation shown in Figure 41.
FIGURE 41.
HeartWare VAD. Exponential fits to observed data. (a) Extrapolation fit to month 3 and from months 3 to 10; (b) extrapolation derived from corresponding transition probabilities; (c) fit to month 1 and months 1 to 10; and (d) extrapolation derived from corresponding transition probabilities.
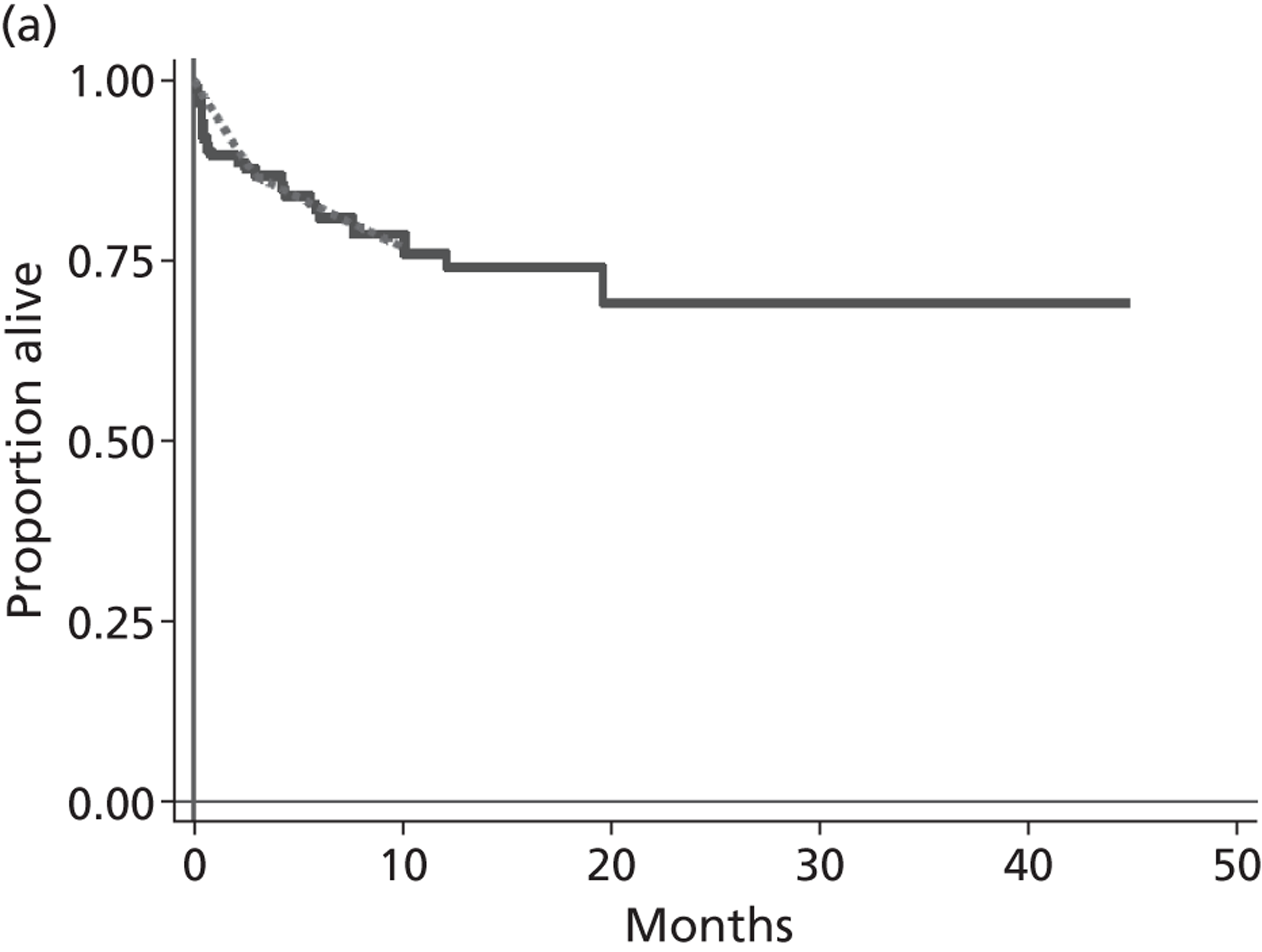
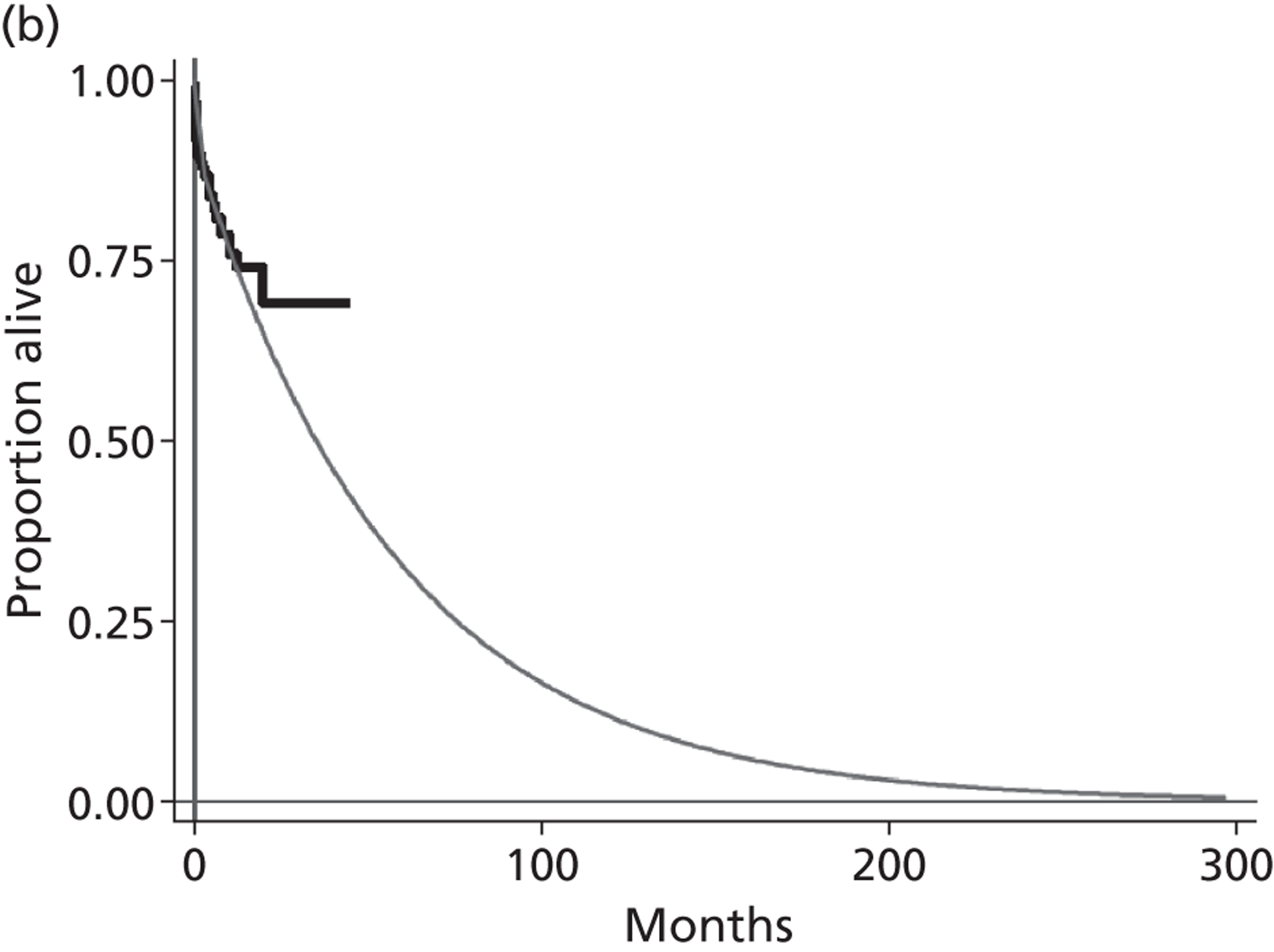
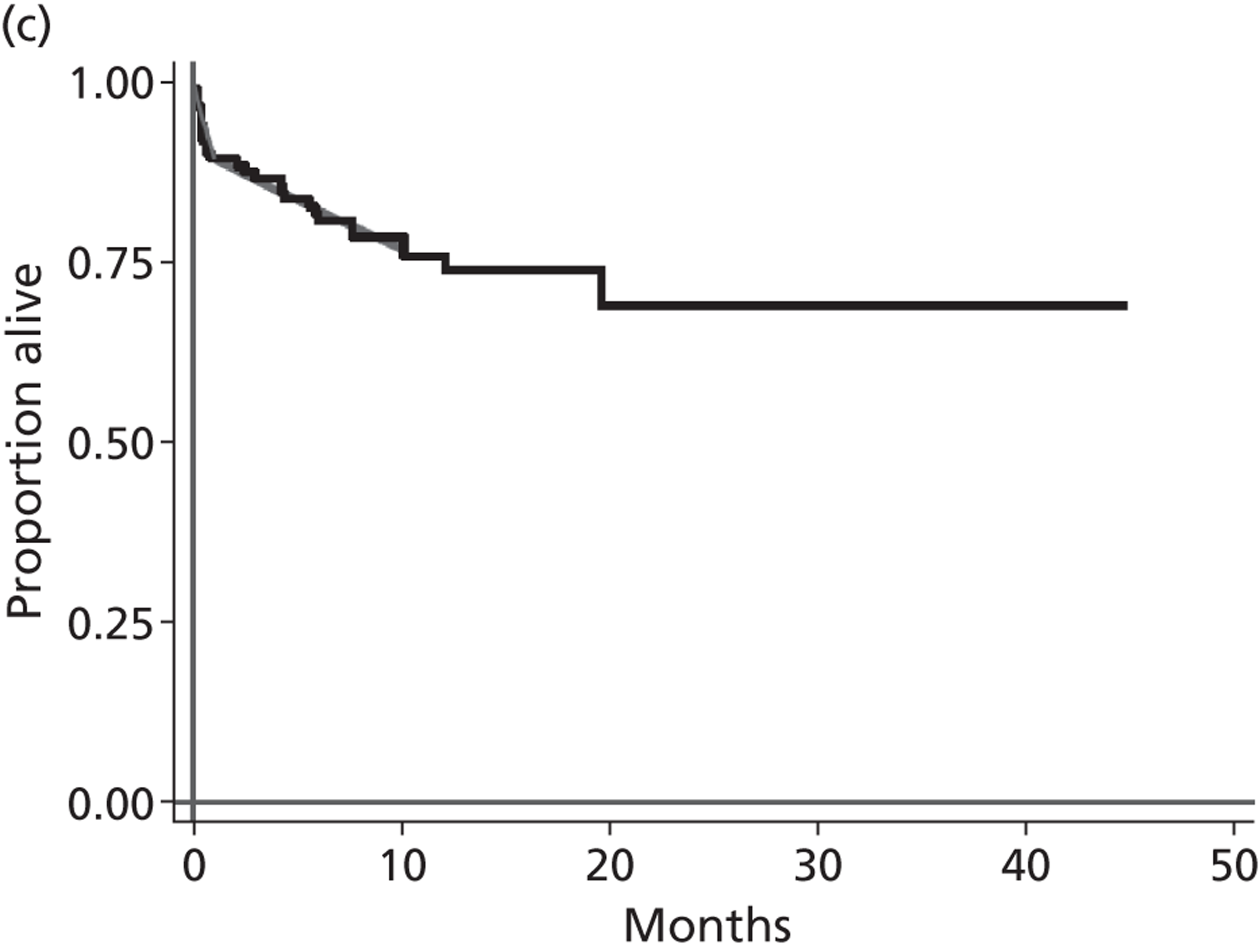
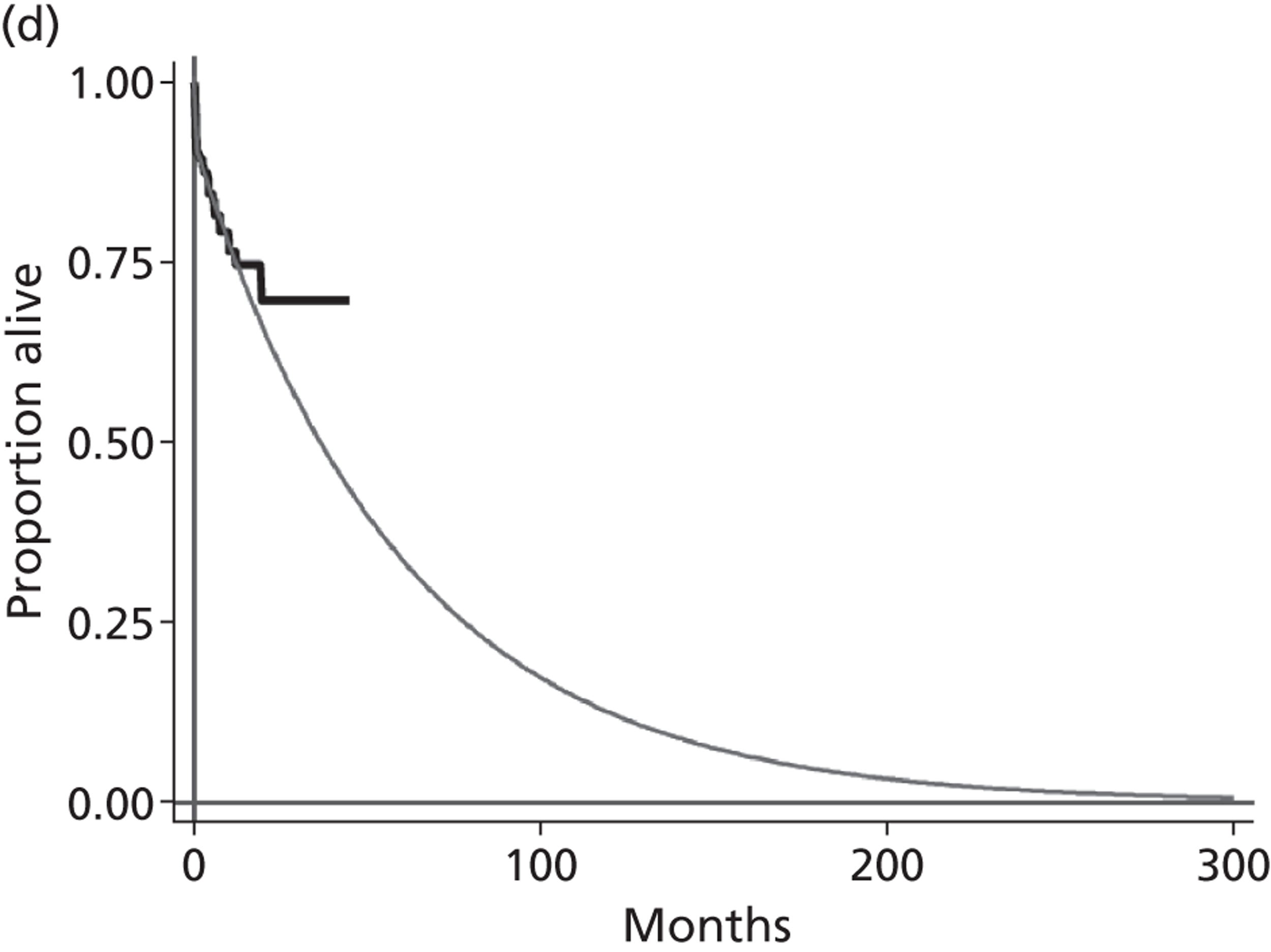
| Based on fit to month 1 and months 1–10 | Based on fit to month 3 and months 3–10 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Month | TP | Month | TP |
| 1 | 0.103196666 | 1, 2 and 3 | 0.046859463 |
| 2+ | 0.016531431 | 4+ | 0.016966028 |
Transition from support on medical management to death
We explored survival for the BTDB MM patients to try and establish transition probabilities for MM to death using an appropriate comparison group. There are no observed survival data for a cohort of MM patients suitable for HT who never receive a donor heart.
The estimate of survival may be biased as a subcategory of patients, possibly those who are more ill, are lost from the cohort to HT.
The BTDB contained data for nearly 1500 patients registered for HT while supported on MM; patients were censored at the time of receiving a HT and at the time alive at last follow-up while on MM support. The K–M analysis for these patients is shown in Figure 42; median survival was not reached, 75% survived to 19.5 months. Fewer than 10% of patients remained at risk after about 17 months.
FIGURE 42.
Observed survival and 95% CI while supported on a MM (1496 BTDB patients).
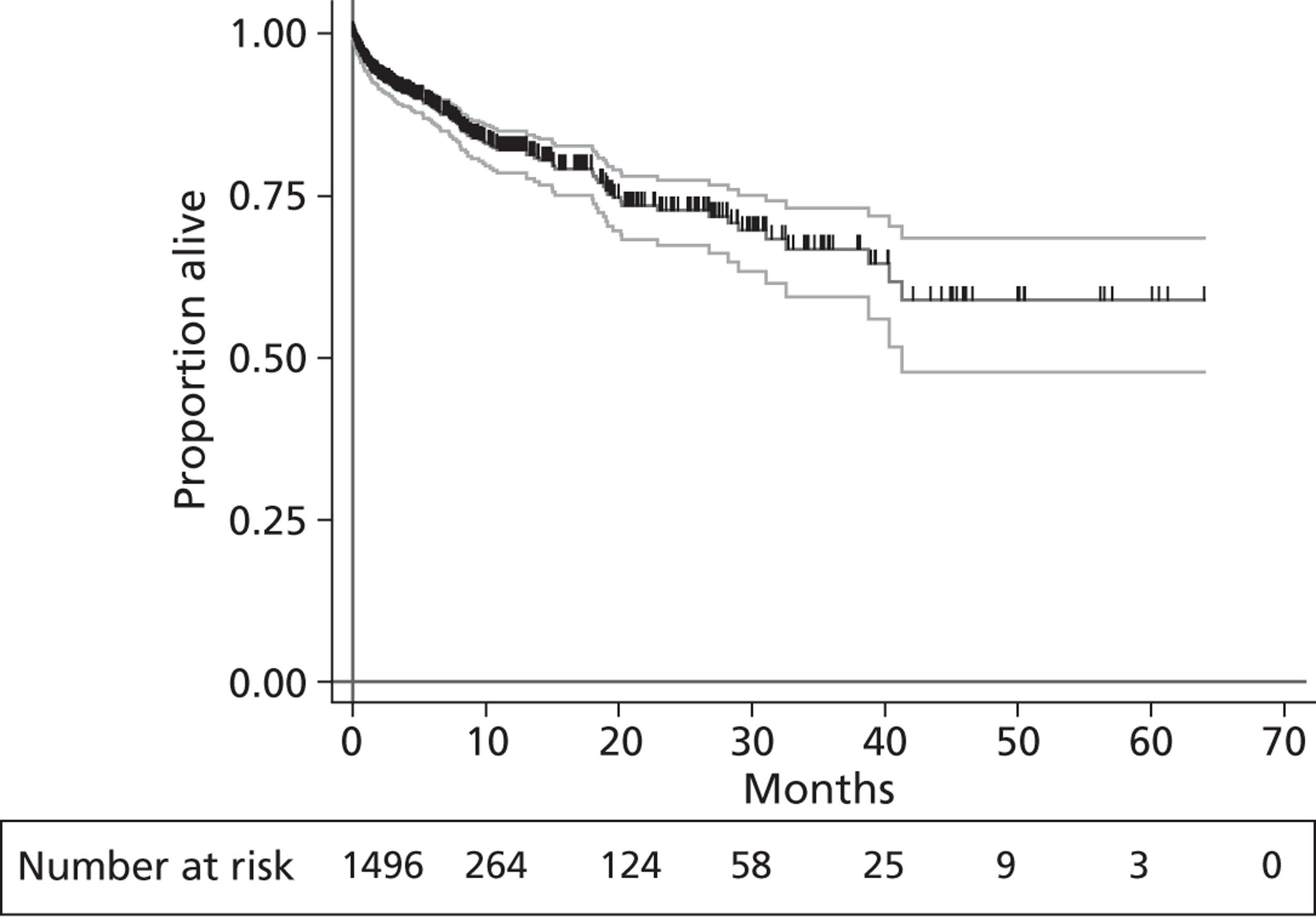
It is recommended by the NICE Decision Support Unit115 that the same modelling approach for survival should be applied for compared groups (in this case BTT and MM). Therefore, the K–M survival at 3 months was fitted with an exponential distribution, and a second exponential was fitted to the K–M function for the time period from 3 months until 10% of patients remained at risk. This exponential was used to extrapolate beyond the observed data to a lifetime horizon. The fit is shown in Figure 43. The resulting survival curve is shown in Figure 43 and, in Figure 44 is compared with the survival for medically managed ‘inotrope-dependent’ and ‘non-inotrope’ patients as modelled by Sharples et al. 30 The monthly transition probabilities are shown in Table 46.
| Month | TP |
|---|---|
| 1, 2 and 3 | 0.027716183 |
| 4+ | 0.012493303 |
FIGURE 43.
Medical management, all patients. Exponential fits to observed data. (a) Fit to month 3 and from months 3 to 17; and (b) extrapolation derived from corresponding transition probabilities.
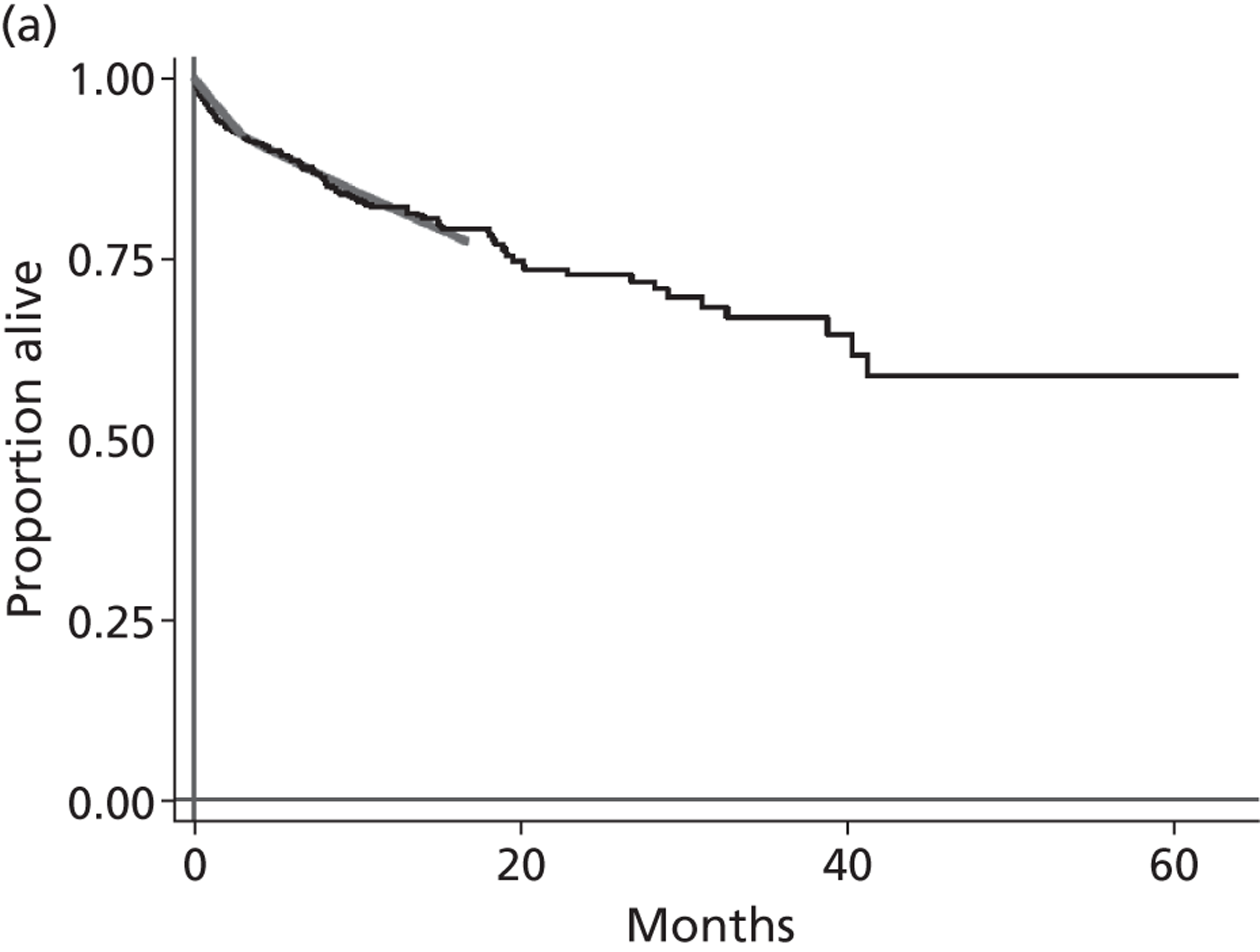
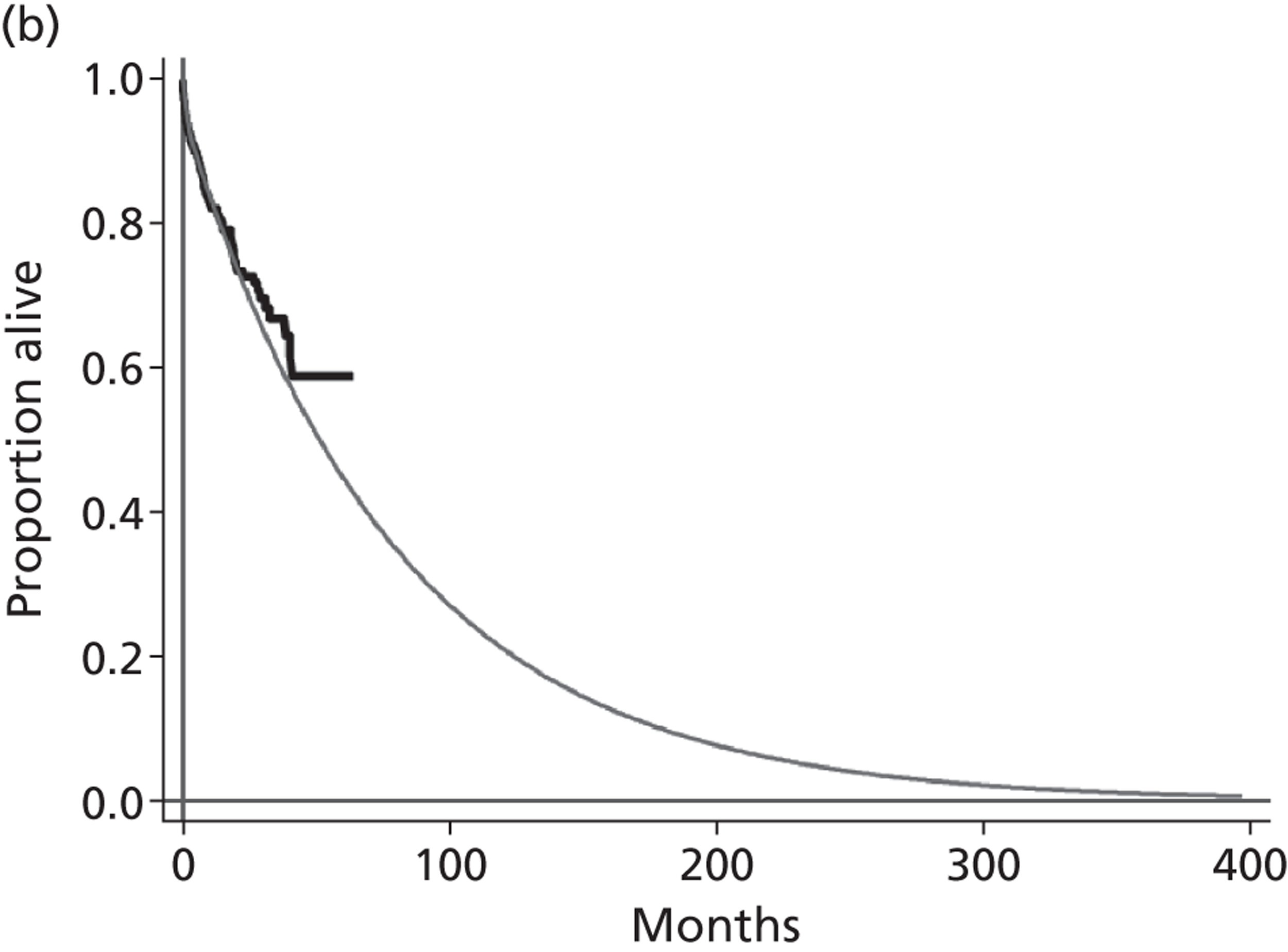
FIGURE 44.
Extrapolated survival for 1496 BTDB MM patients. Comparison with MM patients modelled by Sharples et al. 30 and 307 BTDB ‘inotrope’ patients. (Note: 4-month and 2-week/2-month BTDB fits overlap). Sharples et al. 30 curves were calculated from the reported monthly transition probabilities.
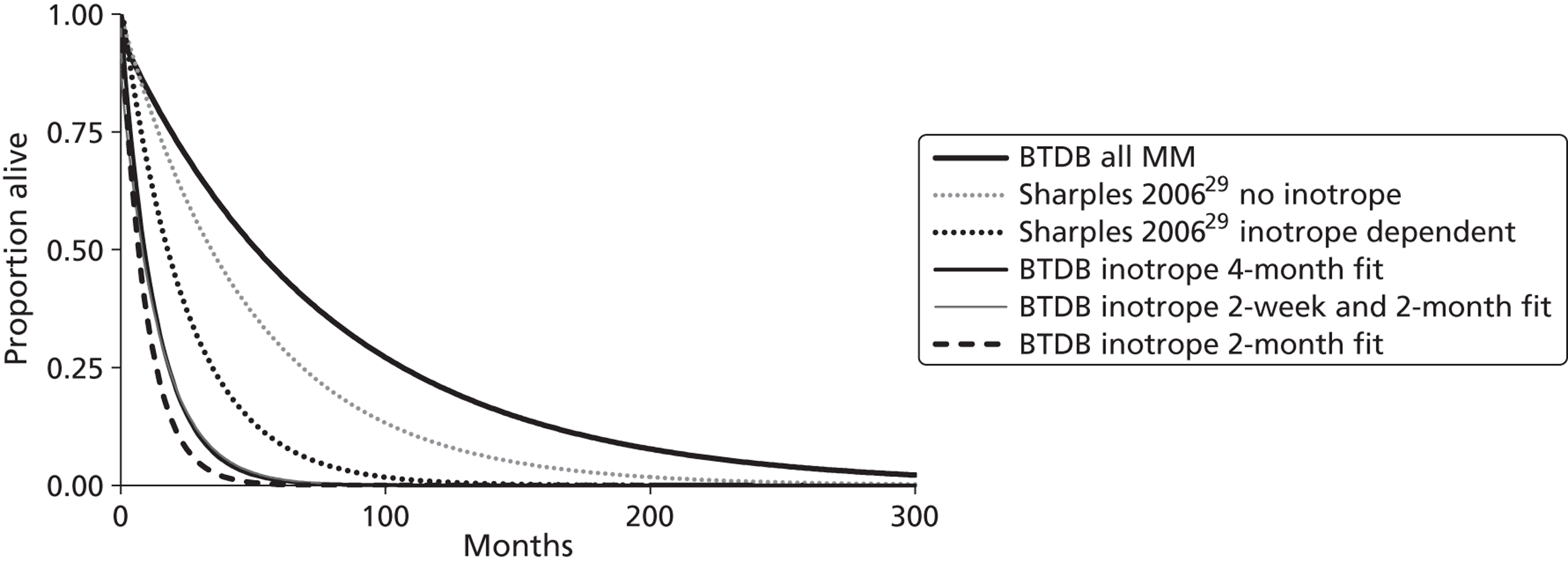
The survival of the three BTDB database subgroups (inotrope, no inotrope, or unknown) is shown in Figure 45. The survival of the ‘inotrope’ group (n = 307) appears less good than that of either the ‘no inotrope’ or ‘unknown’ groups; the median survival for the inotrope group was 28.2 months, but uncertainty at this time was extreme, with only two patients remaining at risk after this time.
FIGURE 45.
Survival of MM patients according to inotrope classification. Seven hundred and fifty-four ‘no-inotrope’ patients, 307 ‘inotrope’ patients and 435 ‘unknown’ patients.
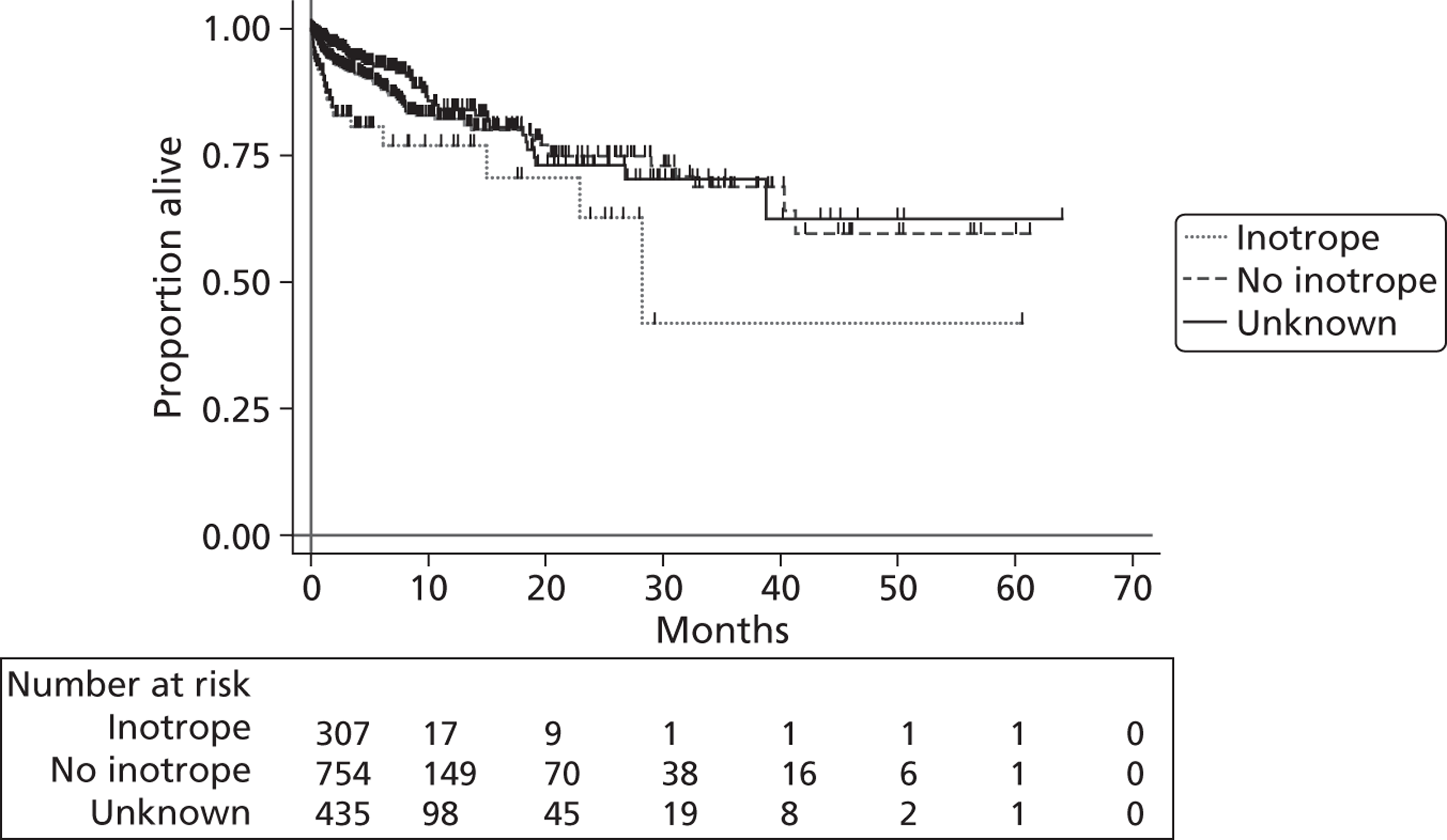
The K–M plot for ‘inotrope’ patients shows distinct phases (Figure 46): in the first 2 weeks there was poor survival; between 2 weeks and 2 months survival improved slightly; and after 2 months the plot is increasingly associated with great uncertainty. Of a total of 28 events, only five occurred after 2 months. Fewer than 10% of ‘inotrope’ patients remained at risk after 4 months and uncertainty in the plot then becomes very substantial. We judged, therefore, that the data beyond 4 months was too unreliable to be used for modelling survival of the ‘inotrope’ population.
FIGURE 46.
Observed survival and 95% CI for BTDB inotrope patients.
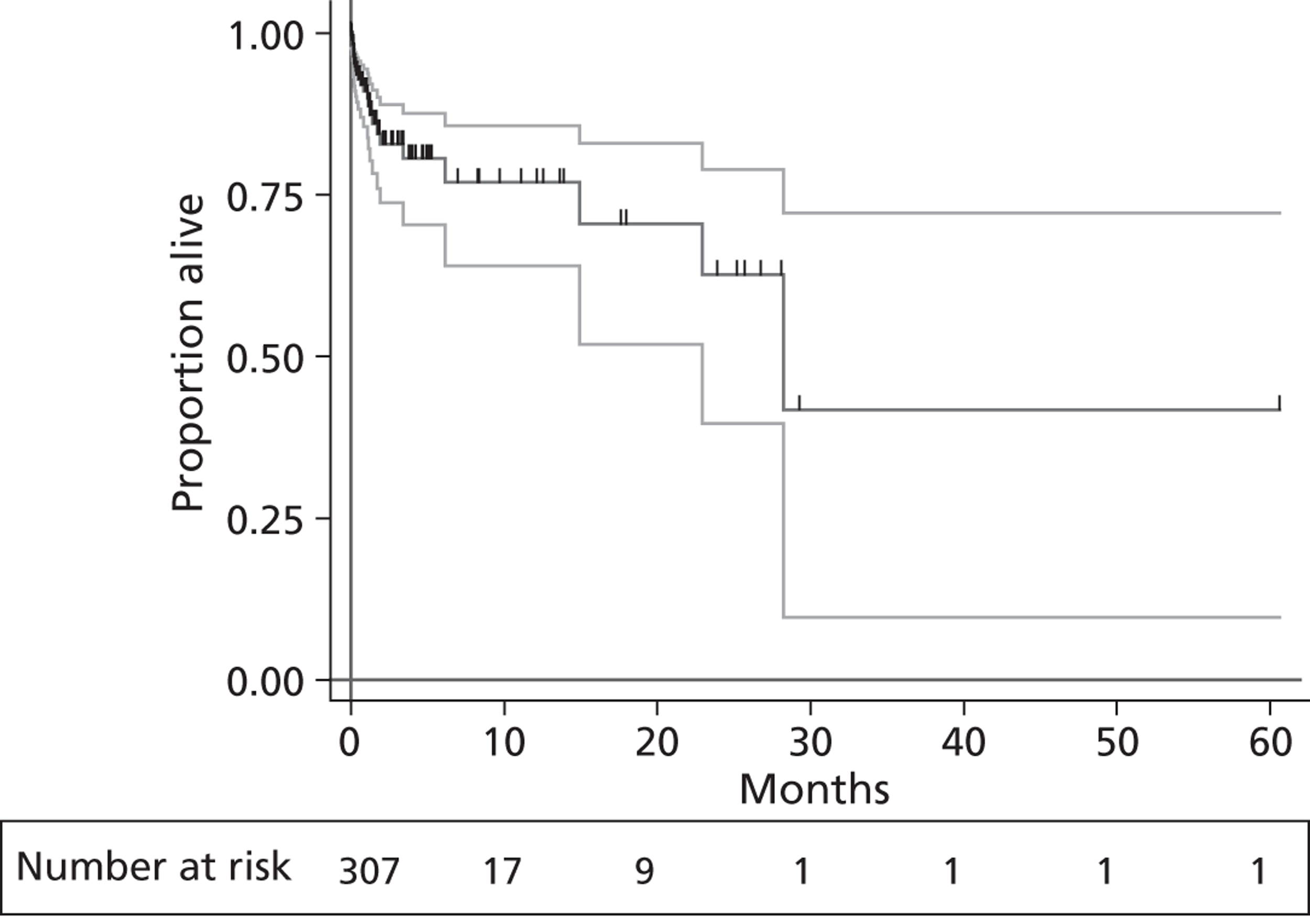
When Weibull and exponential distributions were fitted to all the observed ‘inotrope’ patients' data, the survival curves generated were poorly related to the more robust part of the K–M plot. Therefore, for consistency of approach, exponential distribution fits to the K–M function to 2 months, 3.4 months and 4 months were explored (Figure 47). Up to 4 months the fitted curves correspond well with the K–M data. Transition probabilities are shown in Table 47.
FIGURE 47.
Exponential fits to observed data for ‘inotrope’ BTDB patients. (a) Fit to 2, 3.4 and 4 month K–M function; and (b) extrapolated curves.
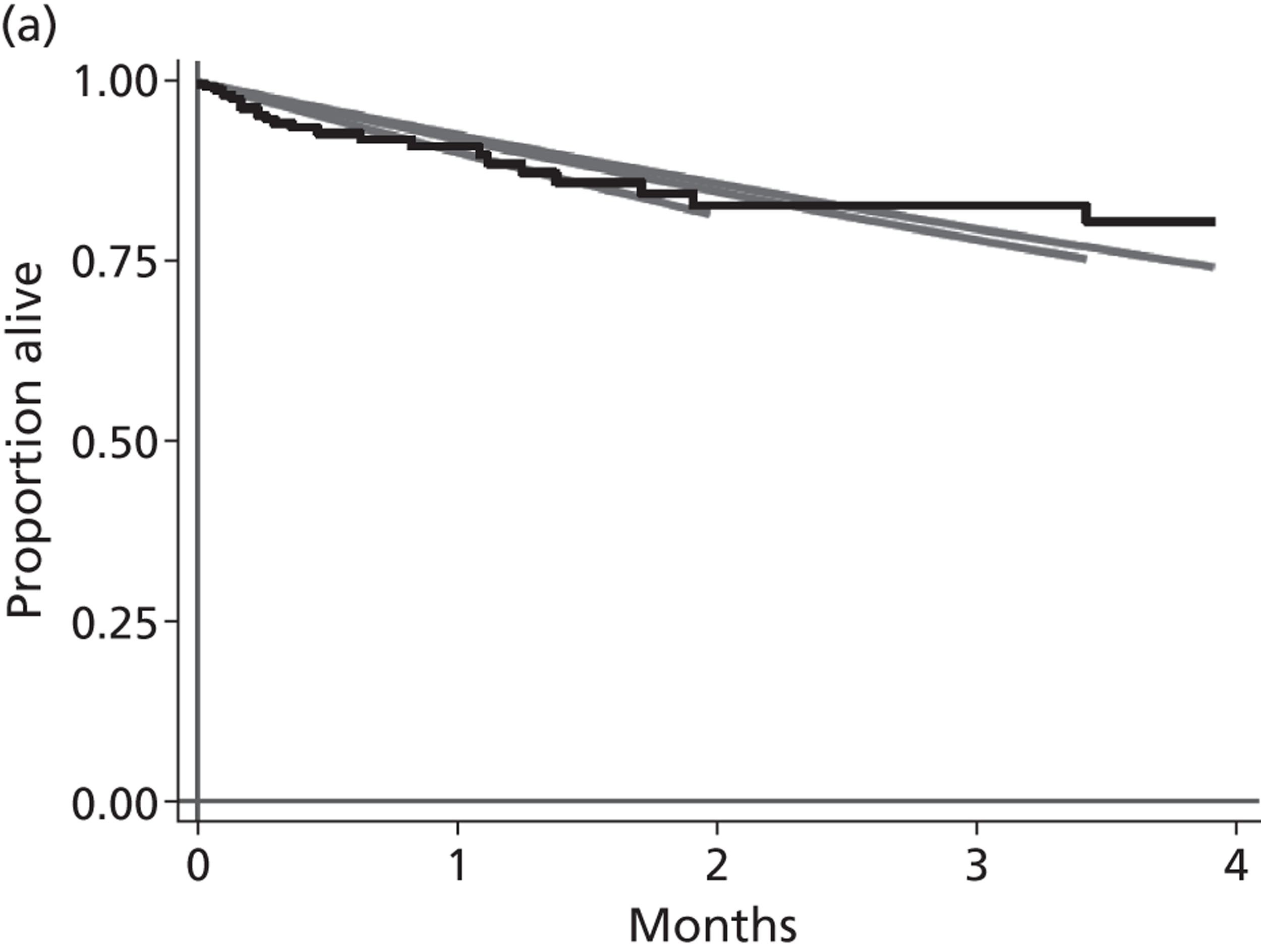
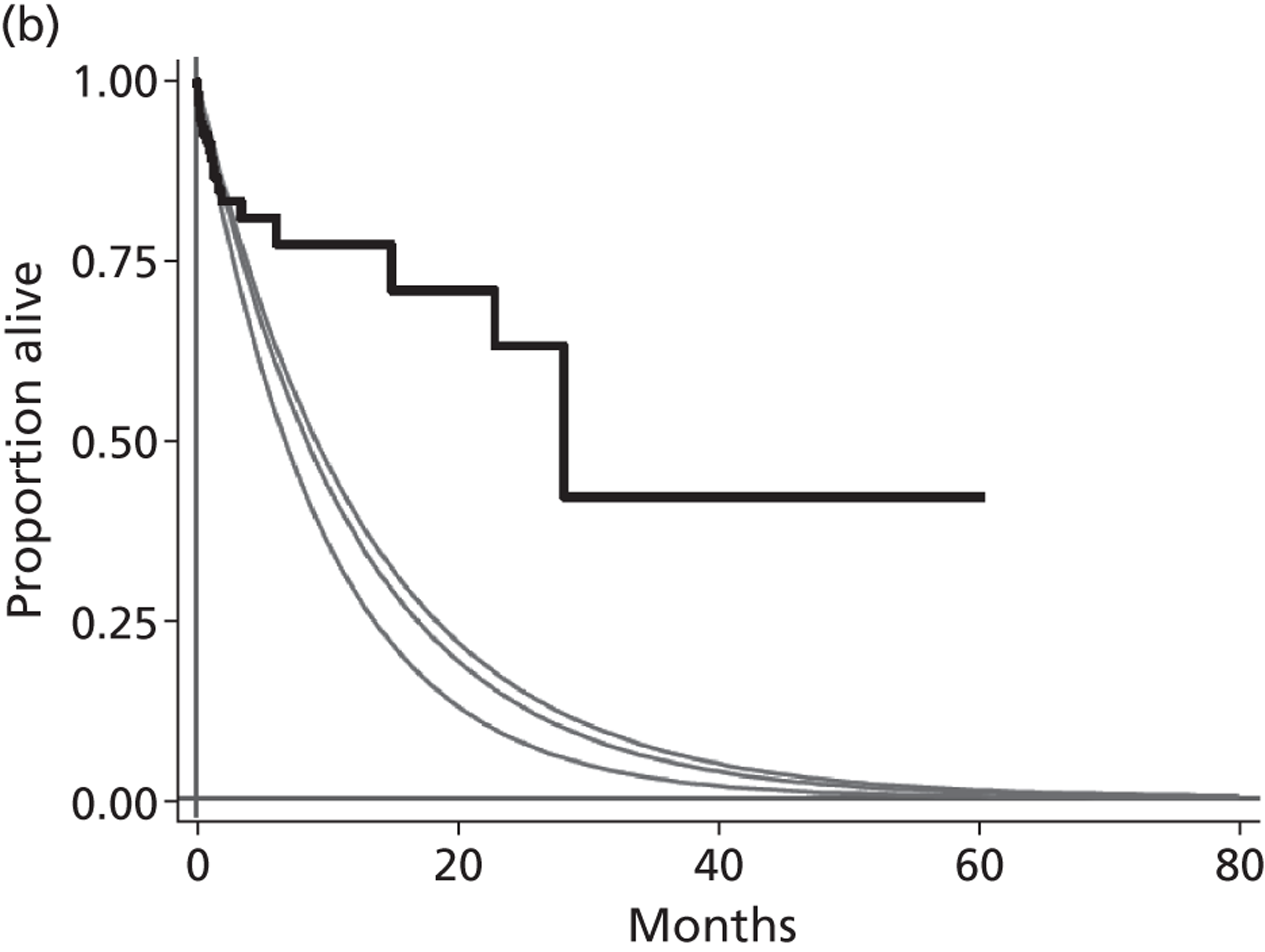
| Month | Monthly TP |
|---|---|
| 2-month fit | 0.097618 |
| 3.4-month fit | 0.079359 |
| 4-month fit | 0.073344 |
In addition, because the early part of the observed survival exhibited two distinct phases, to 2 weeks and 2 weeks to 2 months, these were fitted separately with exponential distributions and the latter (2 weeks to 2 months) used for extrapolation. The results are shown in Figure 48 and transition probabilities in Table 48. The extrapolated curve is almost the same as that using the 4-month fit described above.
FIGURE 48.
Exponential fits to observed data for ‘inotrope’ BTDB patients. (a) Exponential distributions fit to 2 weeks and from 2 weeks to 2 months; and (b) extrapolation derived from corresponding transition probabilities.
| Month | TP | Lambda (months) | SE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.148552692 × 0.5 | 0.160817662 | |
| 0.5 to 1.5+ | 0.067042844 | 0.069396 | 0.0019133 |
Selection of comparator group and sensitivity analyses
As mentioned above, the absence of a RCT in which patients have been randomised to VAD or to MM makes it difficult to select an appropriate MM group to act as a comparator for VAD implantation. Of the 1496 BTDB HT-listed patients who received MM, the poorest prognosis (survival) was associated with those patients who were categorised as ‘inotrope’ (see Figure 45). Without randomised evidence it is uncertain if these are equivalent to the 235 BTDB patients who were selected to receive a VAD as BTT; however, in view of comments in the literature (Slaughter and Rogers116) and from our clinical advisors, it is clear that patients who are selected for BTT are perceived as being less well than the generality of patients who are supported with MM.
For this reason the ‘inotrope’ subgroup was selected for the base case in the present economic analysis. This follows previous analysis by Sharples et al. 30 Furthermore, among the MM BTDB patients only 20% were categorised as ‘inotrope’, whereas among BTDB BTT patients 77% were classified as ‘inotrope’ at baseline; this implies that the inotrope subgroup of MM patients may represent a reasonable comparator group for VAD recipients. Sharples et al. 30 found that ‘inotrope-dependent’ patients in their study were associated with greater costs than their ‘no inotrope’ subgroup (mainly because of hospital stays). Therefore, with minor adjustment, we have used Sharples et al. 30 costs for this subgroup, assessed in the light of information provided by Dr Mark Petrie of GJNH, Glasgow. Clinical experts advised that medications used will have remained similar as the previous analysis (Dr Jayan Parameshwar, Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, 2012, personal communication).
Several options of choice of MM comparator group were selected for sensitivity analysis:
-
All MM: using the K–M function for all MM patients with a constant hazard fitted to 3 months and from 3 months to the time when 10% of patients remained at risk. The monthly transition probabilities are shown in Table 46 and the resulting extrapolation in Figure 46.
-
Exponential fit to 2 months: using exponential distribution fit to 2 months K–M survival for the ‘inotrope’ patients (see Table 47).
-
Predicted survival using the SHFM: survival based on the SHFM (Levy et al. 95).
In this analysis we constructed an artificial ‘MM’ comparator group using the characteristics of the BTDB VAD patients so that the VADs patients could, in effect, act as their own controls. The assumption underlying this use of SHFM scores calculated from baseline characteristics for patients who go on to receive a VAD is that patients with this score would represent the most appropriate comparator group.
The SHFM score is based on multiple baseline covariates and survival may be predicted according to the following equation (Levy et al. 95):
where t is in years and SC is the mean SHFM for a group of patients. This may be modified to predict monthly survival:
Given an SHFM score it is possible to predict survival in order to be able to compare survival with and without a VAD. An SHFM score was obtained for representative populations of VAD patients in the following three ways:
-
Schaffer: Shaffer et al. 77 reported the frequency of SHFM scores at baseline among all VAD patients at a single centre for the period June 2000 to May 2009. The results reported were used to calculate a mean score of 3.036. The resulting survival curves are shown in Figure 49.
-
Strueber: Strueber et al. 83 presented survival to 24 months for a ‘virtual’ comparator group for patients who were implanted with the HW VAD; the survival estimate was based on the SHFM score. These data fitted the equation above when the score was set at 2.416 and generated the curve shown in Figure 49.
-
BTDB SHFM: some covariates required for the calculation of an SHFM score were available at baseline for VAD patients in the BTDB. These were used to estimate a mean score using a Cox's model by using the probability value of ≤ 0.05. The SHFM score was evaluated from the outcomes of the multivariate model, by using the products of the variables, and their β coefficients (natural log of the hazard ratio) were summed. The resulting score was 3.372. Baseline survival was estimated using the equation above and the resulting curve is shown in Figure 49.
The monthly transition probabilities for each of these sensitivity analyses are provided in Table 49.
| Source | SHFM score | Median survival (months) | Monthly TP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base-case inotrope MM | 3.011a | 9.1 | 0.073344 |
| Schaffer et al.77 | 3.036b | 8.9 | 0.075111 |
| Strueber et al.83 | 2.146c | 16.59 | 0.041134 |
| BTDB SHFM | 3.372d | 6.343 | 0.09366 |
| REMATCH MM | 3.625e | 4.9 | 0.13121 |
FIGURE 49.
Modelled survival using SHFM and REMATCH control group.
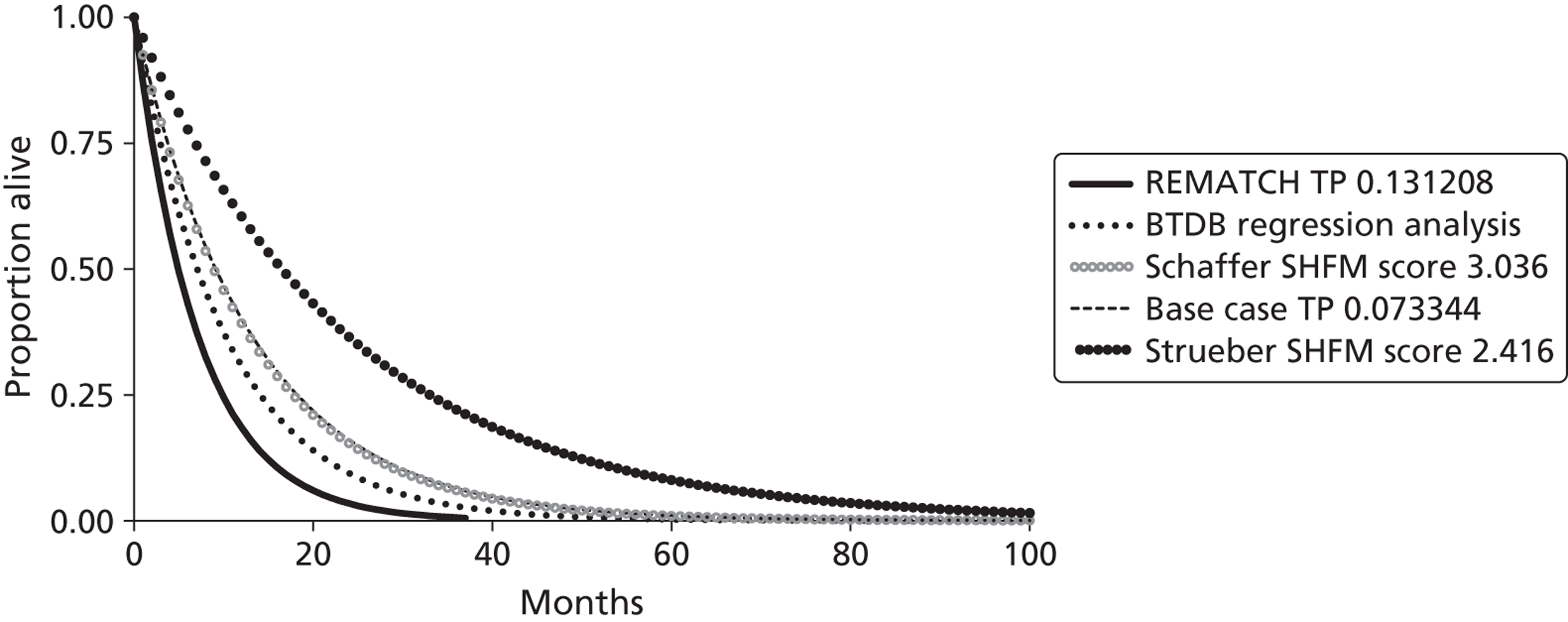
Informative censoring
Clinical experts advised that among MM patients, those most likely to receive a donor heart are those with the poorest prognosis. This means that censoring these patients in the analysis of survival under MM may represent informative censoring (i.e. those not transplanted would have better prognosis leading to an over estimate of survival).
The distribution of times between listing for transplant and receiving a transplant for the inotrope MM patients is shown in Figure 50. About one-quarter were transplanted within 2–3 days of being listed, half were transplanted within a week of listing and 86% within 4 weeks.
FIGURE 50.
Distribution of times from listing to transplant for BTDB MM patients receiving inotropes.
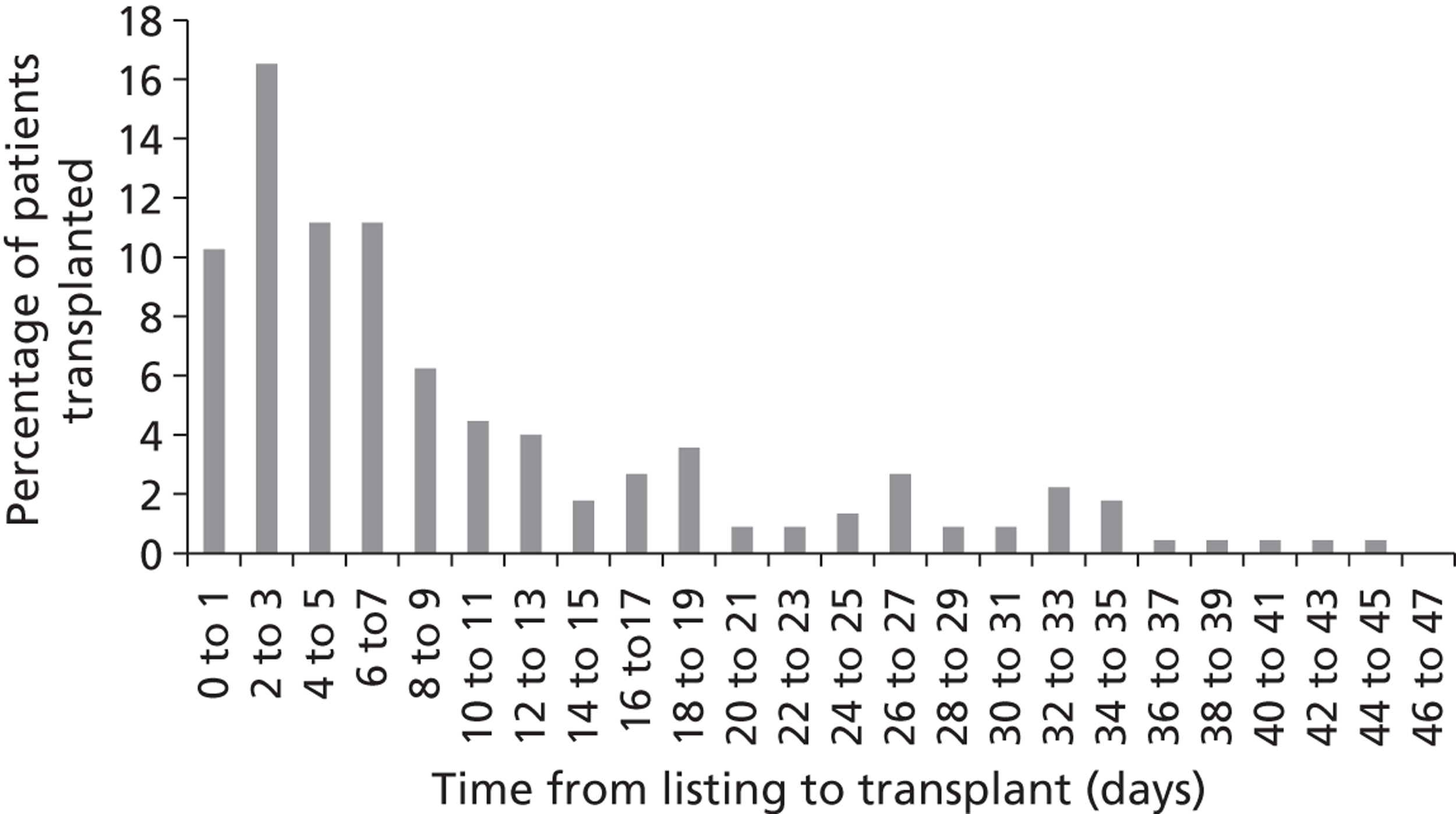
This is a short delay to transplant and it seems unlikely to reflect variations in likely survival. However, we further investigated the presence of informative censoring and whether or not it is likely to cause a problem in our analysis by considering the sensitivity analysis approach described by Collet117 in which patients censored for transplant were (a) assumed instead to die 1 day after their date of transplant; and (b) assumed instead to die at the last event time for uncensored patients. The resulting K–M plots exhibited median survival times of 0.39 months and 28 months, respectively, clearly indicating a large effect on survival estimates if censoring times are equated to predicted survival (Figure 51).
The median survival in graph Figure 51a mostly reflects the short time between being listed for transplant and receipt of a transplant for those patients transplanted. Although this could be indicative of informative censoring, this could, however, also be partly due to delayed listing of eligible patients so that recorded times between listing and transplantation were too close. Thus, the deviation between the two K–M curves seen is unlikely to be caused by poor prognosis of transplanted patients only, but may also be caused by delayed entry onto the transplant list; this might be interpreted as lead-time bias.
FIGURE 51.
Analysis of inotrope MM patients' survival using modified censoring according to Collet. (a) HT recipients assumed instead to die 1-day post-HT date; and (b) HT recipients assumed instead to die at time of last observed event.
In view of a possible overestimate of survival for the MM group we followed advice from clinical experts to explore the use of the ‘optimum MM’ group from the REMATCH RCT (Rose et al. 45) as our control group. In the REMATCH trial the median survival for optimum MM patients (for whom HT was contraindicated) was 150 days (4.93 months), the data were mature (54 deaths among 61 patients), most were receiving inotropes at baseline, and there was little censoring. Using this median survival value we calculated the exponent (lambda) for a constant hazard fit: λ = (ln 0.5)/4.93 = 0.14065; the fit to observed data is shown in Figure 52 and the corresponding monthly TP of 0.131207633 was used in our economic model for sensitivity analysis. Table 49 and Figure 52 show the survival curve and TP together with other sensitivity analyses.
FIGURE 52.
Constant hazard fit to REMATCH control group based on median survival of 150 days.
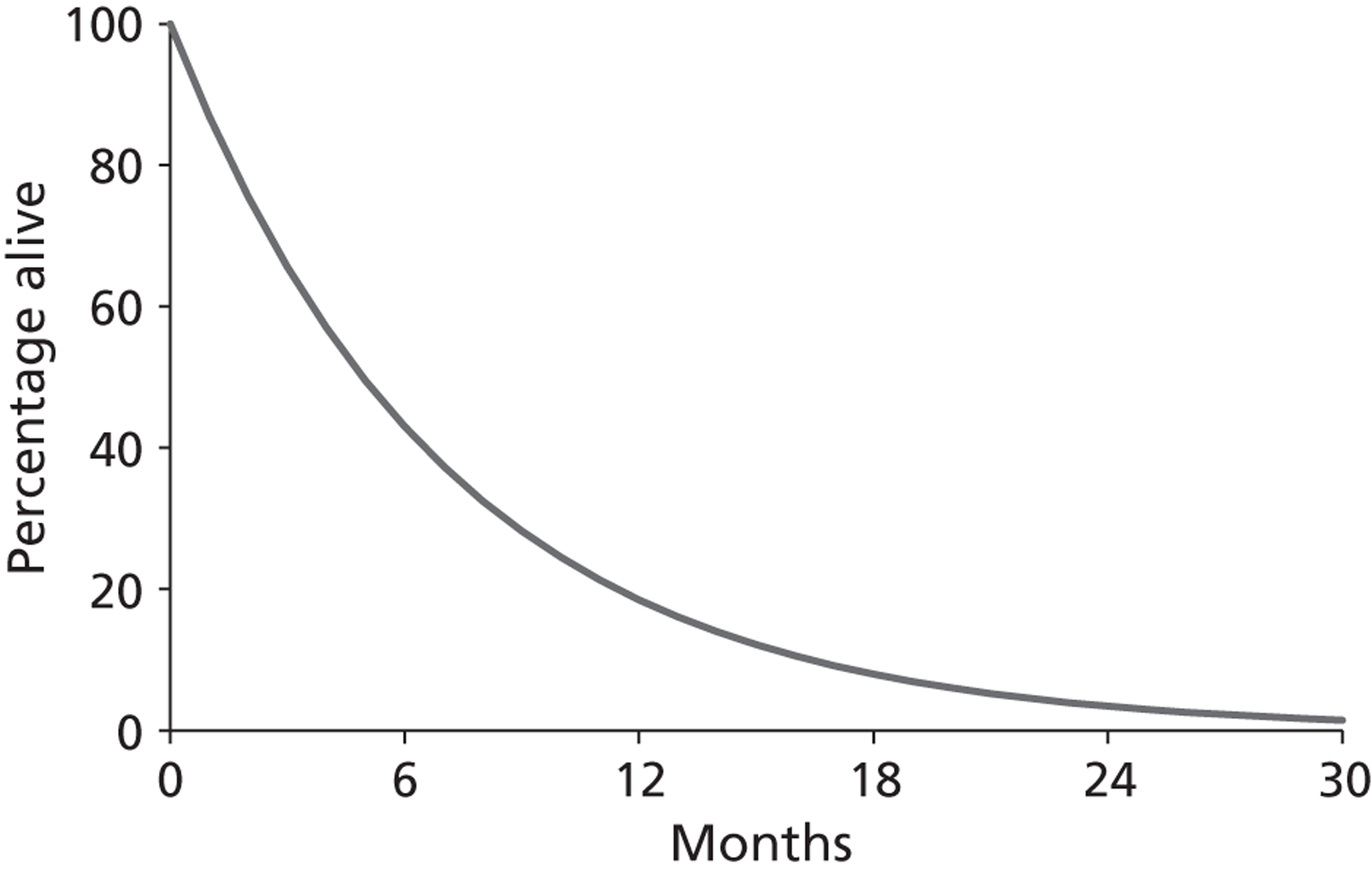
Stevenson et al. 46 performed a post-hoc analysis of survival data from the REMATCH trial. Patients were stratified by baseline treatment with inotropes. Among MM patients, survival was poorer for those receiving inotropes; median survival was 120 days (3.94 months). When fitted with a constant hazard model this provided a monthly TP of 0.161217 which was also used for sensitivity analysis in our economic model.
Transition to heart transplant from ventricular assist device or medical management
The BTDB provided sufficient data for analysis of time to HT for 1731 patients. Of these, 235 BTT patients with approved second- or third-generation VADs provided sufficient data for analysis. K–M analysis of time to transplant for all 1731 patients is shown in Figure 53.
FIGURE 53.
Time to HT for all patients in the BTDB with log-logistic and log-normal distribution fits.
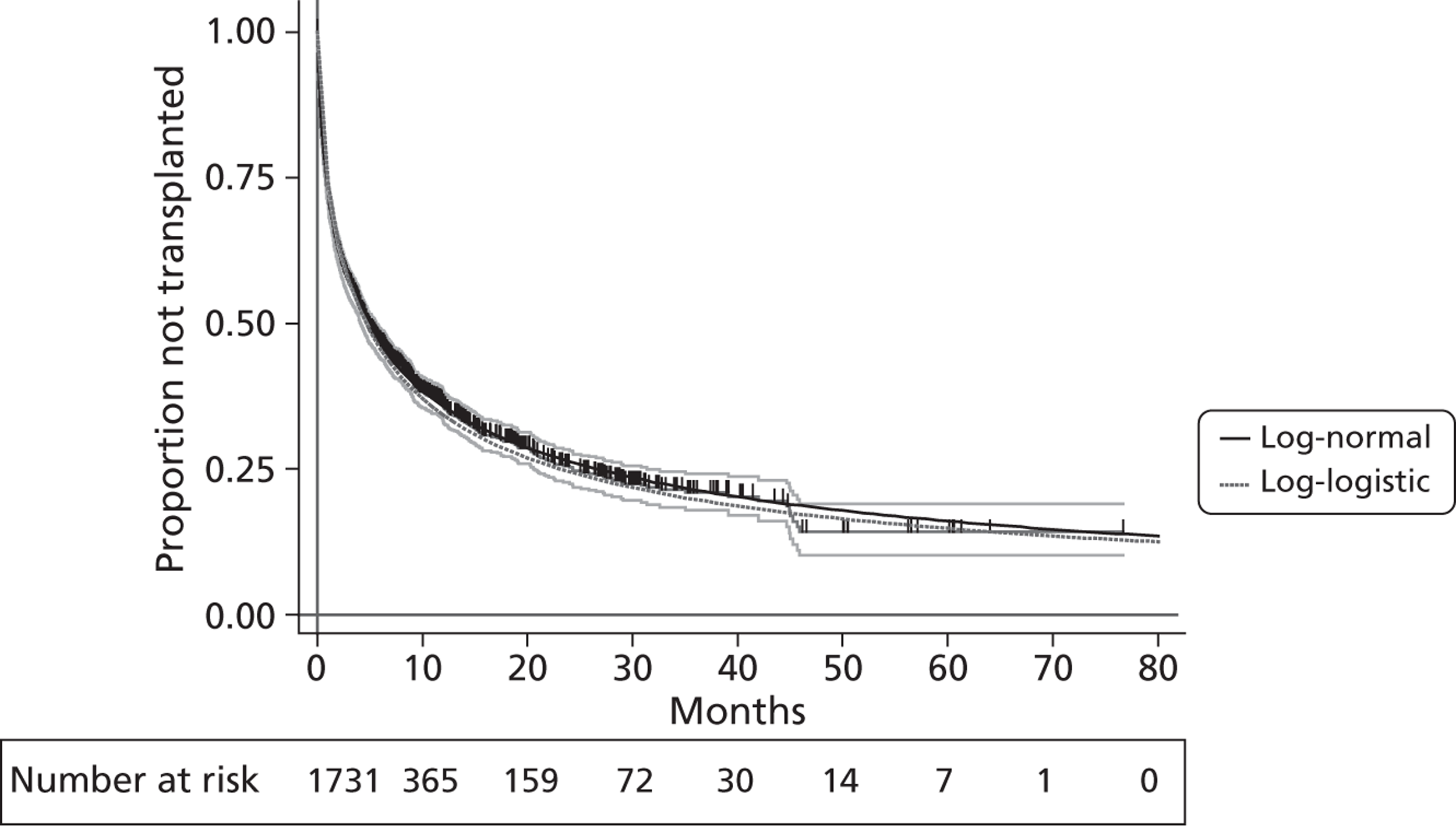
The median time to transplant was 4.76 months; by 40 months fewer than 2% of patients remained at risk. After 42 months no further patients received a donor heart except for an atypical cluster. Clinical advisors suggested that transplantation beyond 42 months was unlikely and for this reason the model set the probability beyond this time as zero.
The log-logistic and log-normal distributions yielded the lowest AIC values (Table 50) for parametric fits to the observed data. And these distributions generated almost indistinguishable fits (see Figure 53). For sensitivity analysis transition probabilities were calculated from the log-normal distribution.
| AIC | BIC | Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| 5963.861 | 5974.795 | Weibull |
| 5915.031 | 5925.966 | Log-normal |
| 5906.04 | 5916.974 | Log-logistic |
| 6863.469 | 6868.937 | Exponential |
The time to receipt of a HT in the BTDB was considerably longer for VAD patients (median time to transplant was 44.7 months) than for MM patients (median time to transplant was 3.25 months) (Figure 54), and similar results were reflected in the inputs used in the Sharples et al. 30 economic analysis. However, in the recent analysis proposed by Moreno et al. 98 the probability of receiving a donor heart was kept the same for both VAD (BTT) and MM patients.
FIGURE 54.
Time to HT for BTT (BTT with VAD) and MM patients.
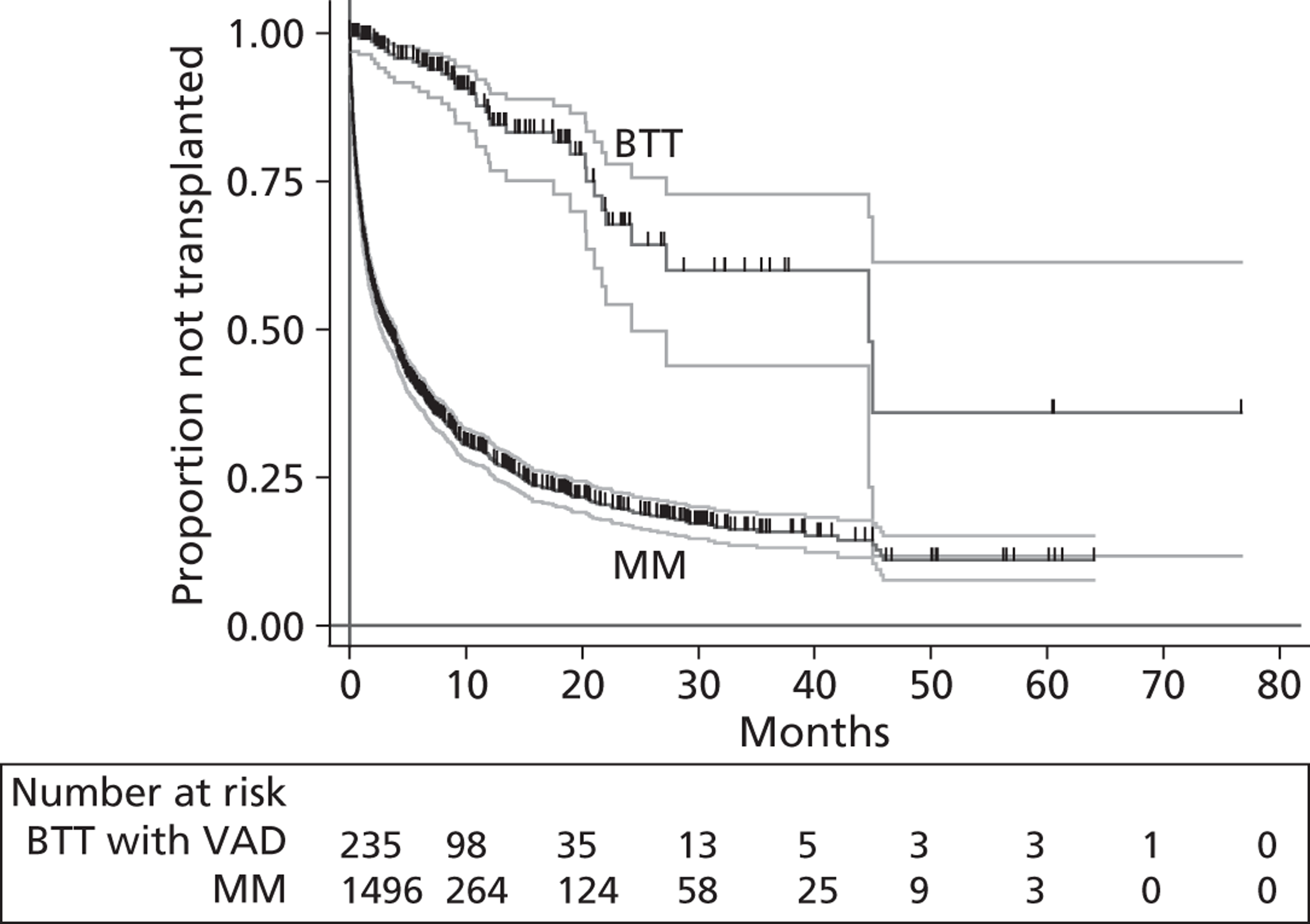
For MM patients only, log-logistic and log-normal distributions exhibited the lowest AIC values and a good fit to the observed data (as for all BTDB patients; Figure 55 and Table 51).
| AIC | BIC | Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| 5413.291 | 5423.912 | Weibull |
| 5361.457 | 5372.078 | Log-normal |
| 5342.205 | 5352.826 | Log-logistic |
| 6277.83 | 6283.14 | Exponential |
FIGURE 55.
Log-normal distribution fitted to time to transplant for MM patients.
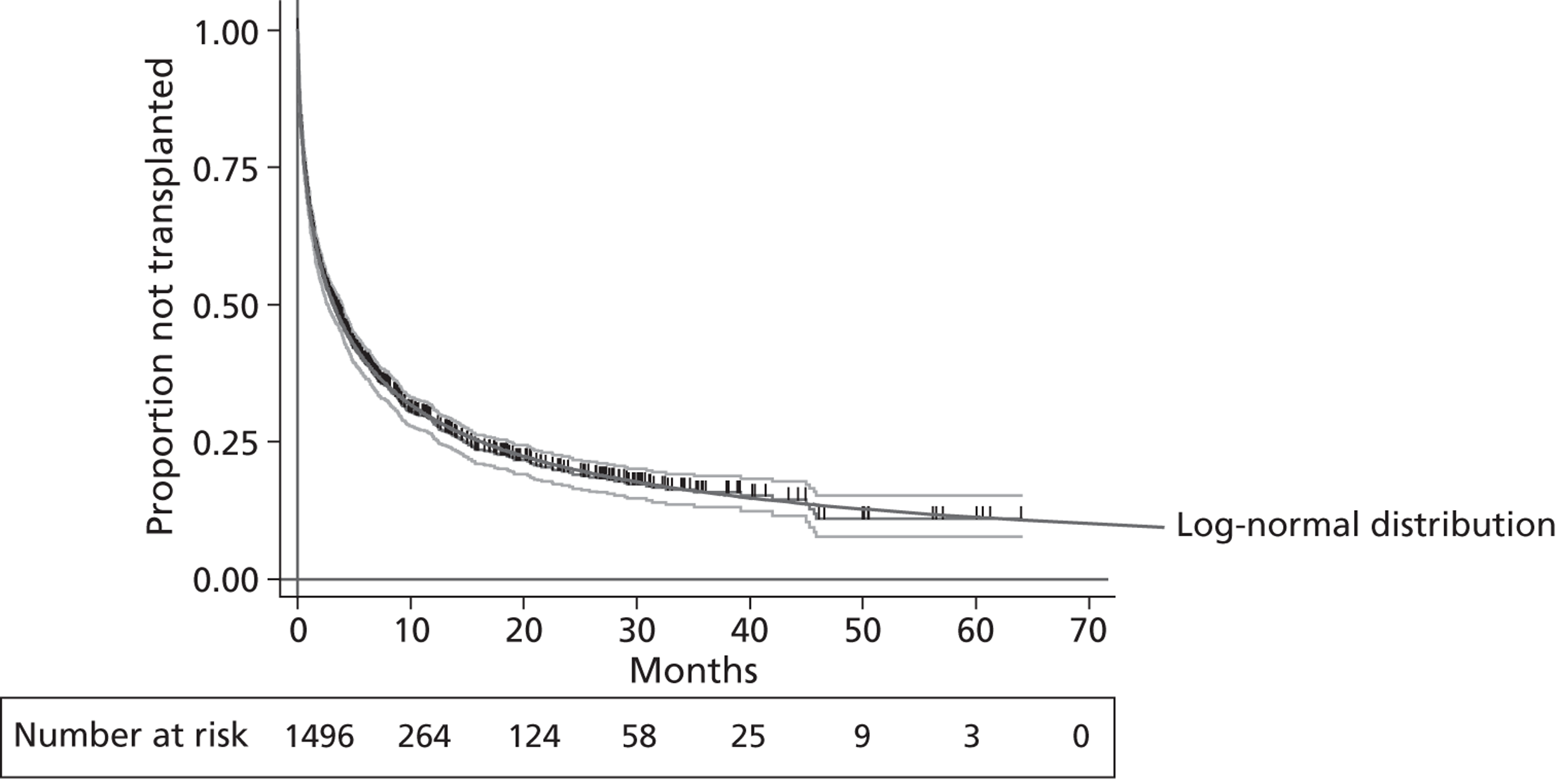
For the BTT patients exponential and Weibull parametric distributions provided similarly low AIC values (Table 52), these and log-normal fitted curves are shown in Figure 56.
FIGURE 56.
Time to HT. Log-normal, Weibull and exponential distributions fitted to time to HT for VAD patients.
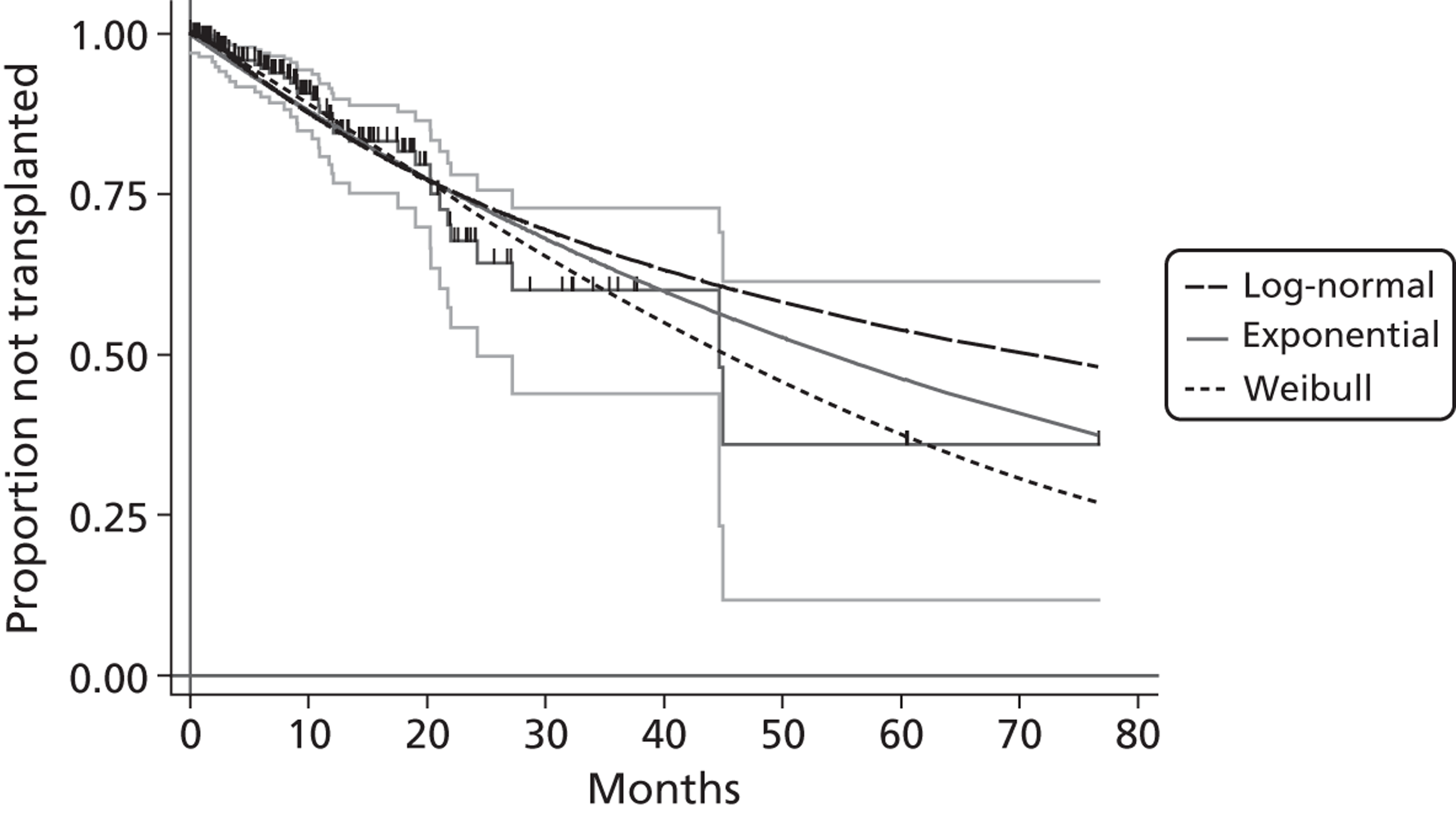
| AIC | BIC | Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| 224.4692 | 231.3883 | Log-normal |
| 217.4888 | 224.4079 | Weibull |
| 217.2066 | 220.6661 | Exponential |
For the base-case analysis the same probability of transition to the transplanted state was used for both arms and was calculated from the exponential distribution for the BTT patients; see Figure 56). This is in line with Moreno et al. 98 and is judged to allow a fairer comparison between management strategies.
The effect of using transition probabilities based on time to HT for all BTDB patients (log-normal fit) for both compared groups was explored in sensitivity analysis. Further sensitivity analyses used transition probabilities based on time to HT for all BTDB patients (log-normal fit) for the MM arm and TP based on the exponential fit to the time to transplant for BTT patients for the BTT arm.
Transition from heart transplant support to death
The BTDB provided appropriate data for K–M analysis of post-transplant survival for 1101 patients. The plot is shown in Figure 57.
FIGURE 57.
Post-HT survival for patients in the BTDB.
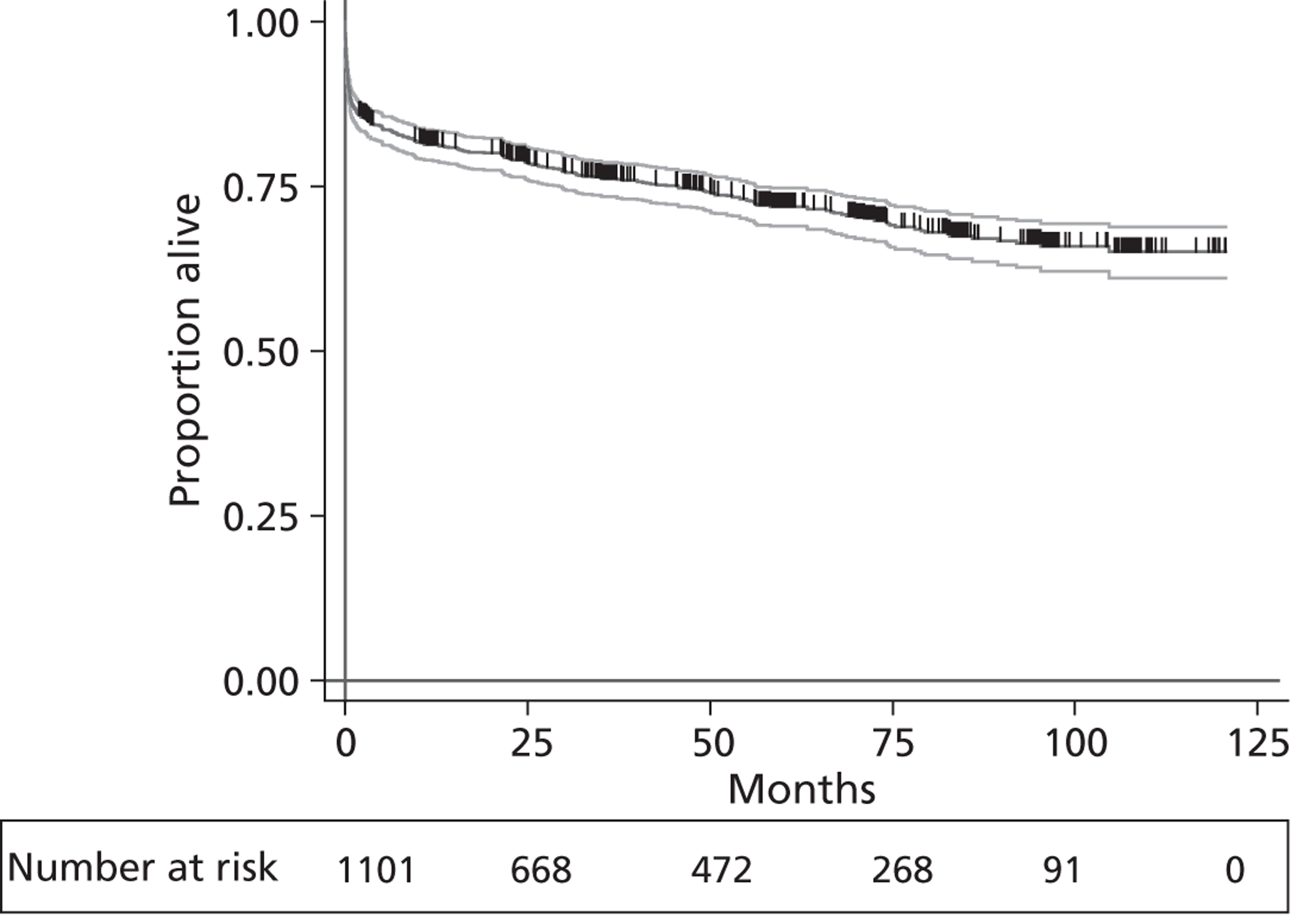
Median survival was not reached, 75% survived to 45.6 months. The K–M survival curve follows two phases, an initial phase of poor survival during the first few months post surgery, followed by good survival for up to about 10 years of follow-up. A similar pattern has been reported for 25 years of follow-up for patients transplanted at Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust (Goldsmith et al. 118). In the Goldsmith et al. 118 study about 20–25% of patients died within the first 3 months (depending on the era for analysis). At 3 months K–M survival was about 85% for the BTDB patients. We compared BTDB patients with the survival from 3 months reported by Goldsmith et al. 118 by assuming 85% survival at 3 months for the latter (Figure 58). The recent economic analysis by Moreno et al. 98 used post-transplant survival data from the study of Russo et al. ;100 the Russo et al. 100 data are also shown in Figure 58.
FIGURE 59.
Post-HT survival of BTDB patients: exponential distributions fitted to observed data. (a) Exponential distributions fit to 3 months and 3–84 months; and (b) exponential distributions fitted to 6 months and 6–84 months.
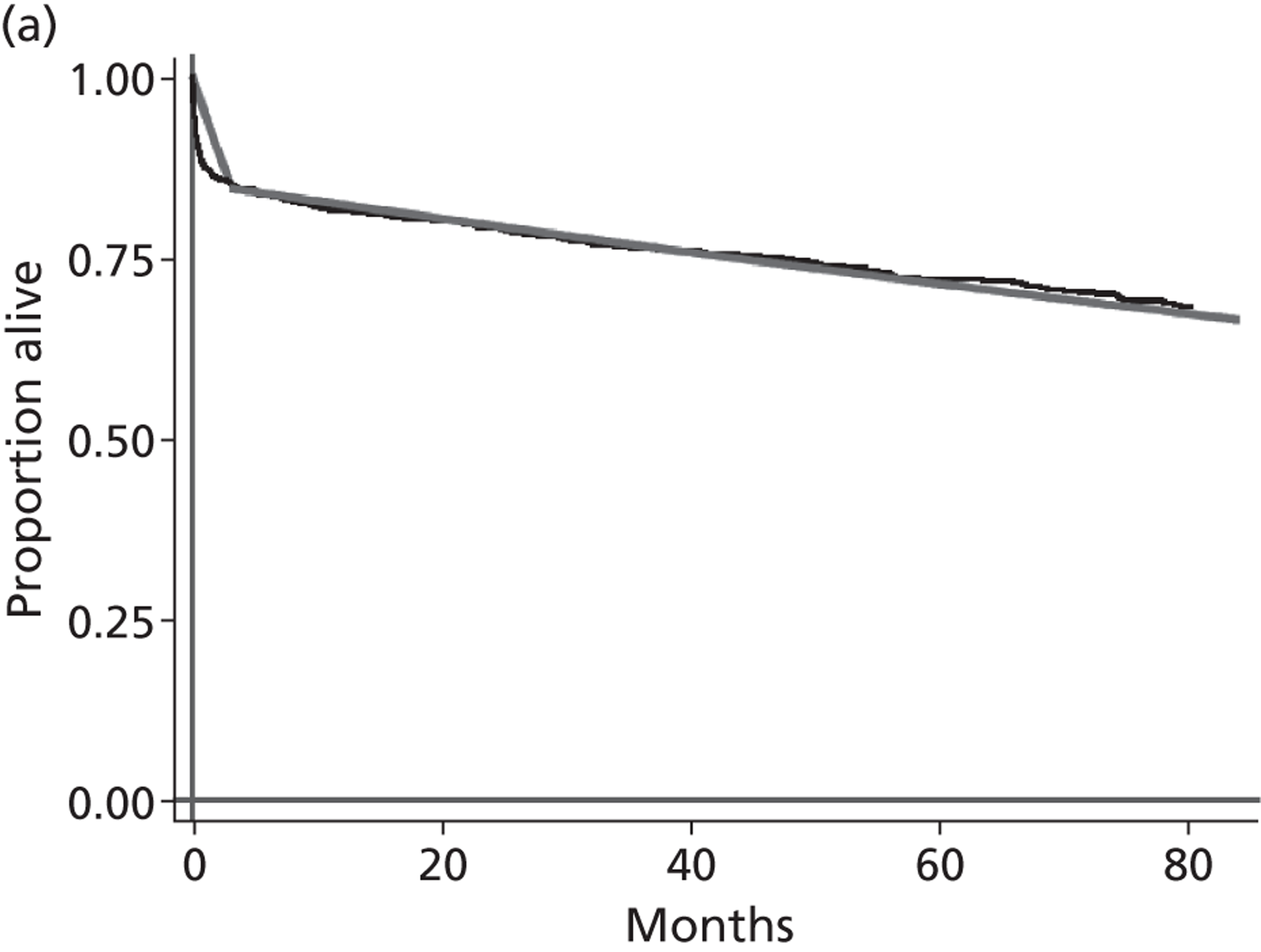
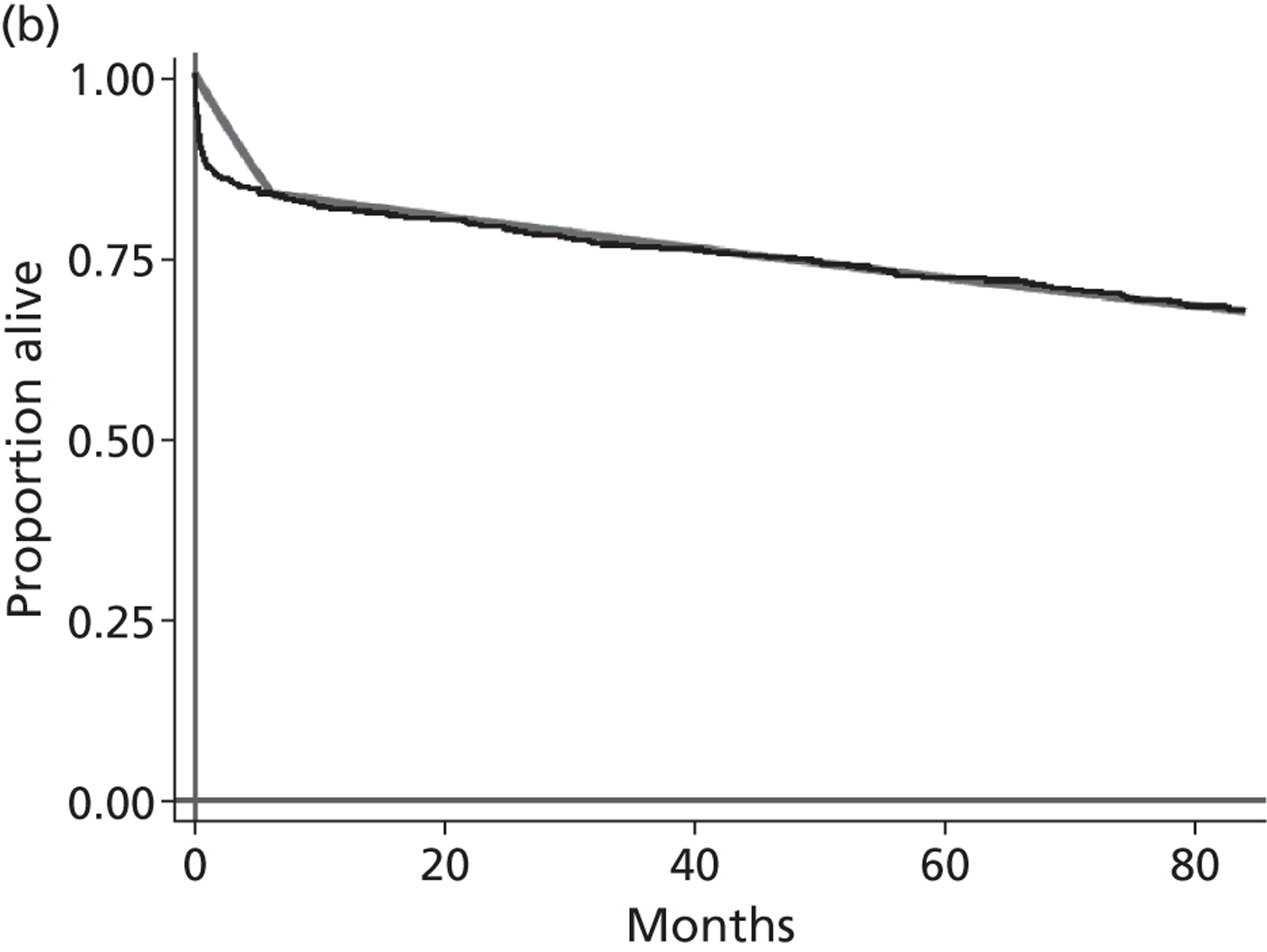
Extrapolating survival beyond the observed data is problematic because the K–M plot extends to only about 68% survival and is flat. To remain consistent with previous approaches we fitted a constant hazard to the K–M at 3 months and a second fit to the K–M function from 3 months to 7 years (at which time the proportion of patients at risk has depleted to near 10%). The fits are shown in Figure 59a. This generated TP for the first 3 months of 0.070366726, and for months 4–84 of 0.002980948. A second constant hazard fit was made to 6 months and from 6 to 84 months (see Figure 59a). Extrapolation beyond 84 months with the 3–84 month and 6–84 month exponentials generated unrealistic proportions of survivors by 50 years. The probability of death after 24 years was less than that for the UK general population matched according to gender and age (corresponding to the BTDB mean age at transplant + 7 years). Therefore from that time, the probability of death was taken to be the same as the UK general population (matched by age and gender). The curves generated from the transition probabilities are shown in Figure 60. The 3–84-month model was used for the base-case analysis.
FIGURE 60.
Modelled post-HT survival of BTDB patients. The upper curve refers to the 6-month plus 6–84 months-fit to observed data and the lower curve refers to the 3-month plus 3–84-months fit to observed data. The grey lines indicate survival if the constant hazard continued to operate beyond 24 years. The black lines beyond 24 years (288 months) indicate survival according to the probability of death for the UK general population (matched by age and gender).
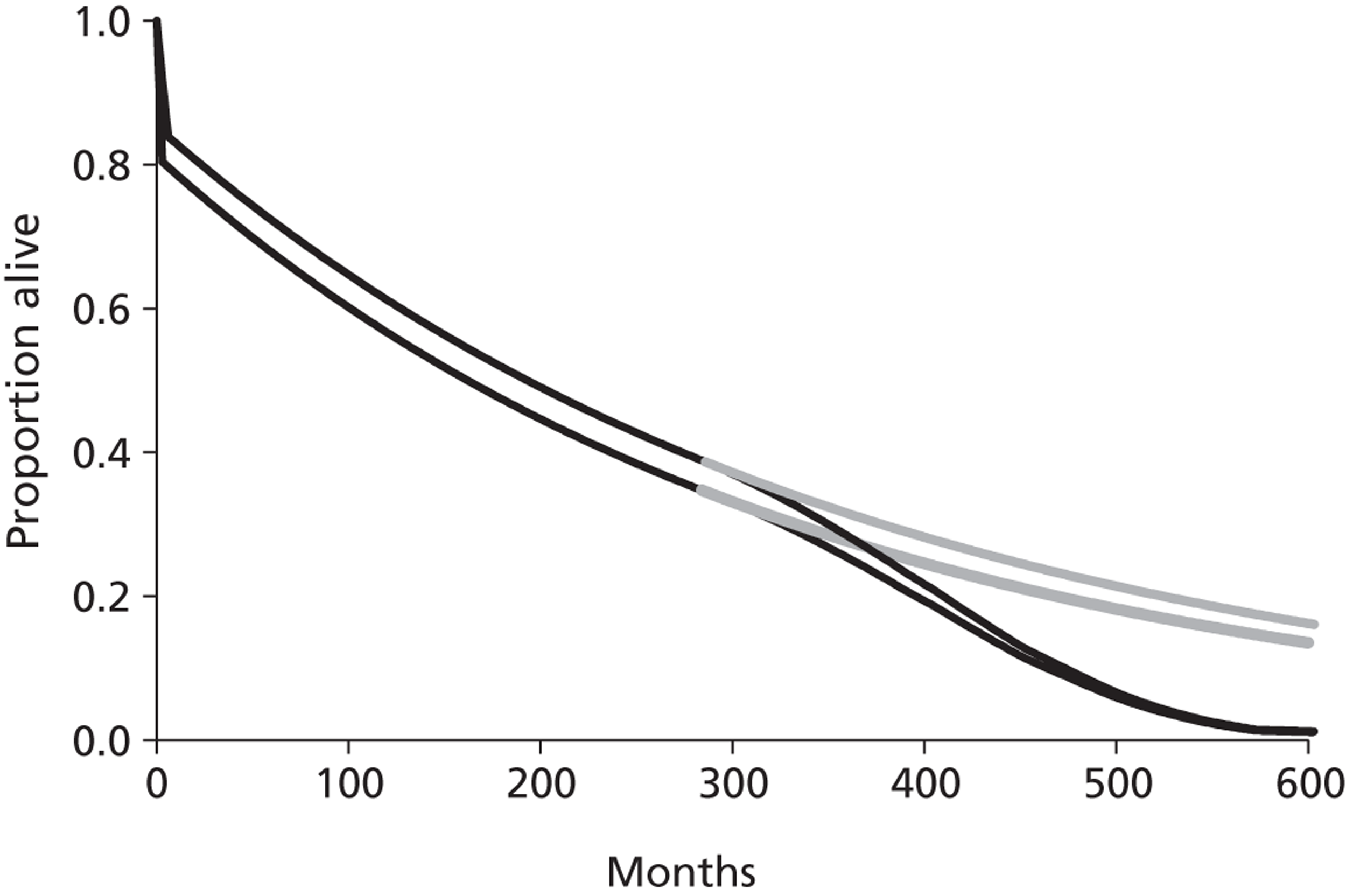
The transition probabilities between health states employed for the base case and for sensitivity analyses are summarised in Tables 53 and 54.
| Health state transition | Monthly TP | Source |
|---|---|---|
| VAD support to death | Months 1–3: 0.0577197 | Constant hazard fit to K–M at 3 months, and exponential fit to the K–M function from 3 months until 10% of patients remain at risk for all BTDB VAD recipientsa (see Figure 39) |
| Months 4+: 0.0179873 | ||
| MM support to death | Months 1+: 0.073344 | Constant hazard fit to K–M function to 4 months for inotrope BTDB MM patients (see Figure 47) |
| MM and VAD support to HT | All months: 0.012745641 | Exponential parametric fit to observed time to HT for BTDB BTT patients (see Figure 56). Probability set at zero after 42 months |
| Support on HT to death (both BTT and MM groups) | Months 1–3: 0.070366726 | Constant hazard fit to K–M at 3 months and exponential fit to the K–M function from 3 months until 10% of patients remain at risk (84 months) for those BTDB patients who received a HT (see Figure 59). Office of National Statistics survival data114 |
| Months 4–284: 0.002980948 | ||
| Months 284+: as UK population (matched for age and gender; available from authors on request) |
Sensitivity analyses around transition probabilities are designated I for purposes of reporting results. The following analyses were applied for transition probabilities:
-
I A] for the transition from MM support to death.
-
I B] for the transition from VAD support to death.
-
I C] for transition from VAD or MM support to HT.
-
I D] bivariate sensitivity analyses.
| Input parameter | Monthly TP | Source |
|---|---|---|
| I A1] MM support to death | Months 1–3: 0.027716183 | Constant hazard fit to K–M at 3 months and to K–M function from 4 months to 10% at risk for all MM patients |
| Months 4+: 0.012493303 | ||
| I A2] MM support to death | Based on SHFM95 analyses using data from: | |
| (i) 0.075111 | (i) Mean SHFM score derived from Schaffer et al.,77 single-centre study of patients given VADs | |
| (ii) 0.041133 | (ii) Mean SHFM score derived from the ‘virtual’ comparator group for HW VAD patients reported by Strueber et al.83 | |
| (iii) 0.09366 | (iii) Mean SHFM score derived from Cox regression analysis of baseline covariates for 34 BTDB patients who received a VAD | |
| I A3] MM support to death | Months 1+: 0.097618 | Constant hazard fit to K–M function to 2 months for BTDB MM inotrope patients (see Figure 47) |
| I A4] MM support to death | (i) Months 1+: 0.131210 | Constant hazard fit to REMATCH all MM arm |
| (ii) Months 1+: 0.161217 | Constant hazard fit to REMATCH inotrope MM patients | |
| I B1] VAD support to death | Available from authors on request | Weibull distribution fitted to the observed survival for all BTDB VAD patients, with correction after 420 months to survival for age- and gender-matched UK population |
| I B2] VAD support to death | Months 1–3: 0.046859463 | Constant hazard fit to K–M at 3 months and from 4 months to 10% at risk for those BTDB patients who received a HW VAD |
| Months 4+: 0.016966028 | ||
| I C1] VAD or MM support to HT | (i) For MM: log-normal fit to time to HT for all BTDB patients (available on request) For BTT patients: months 1+ 0.012745649 |
For MM patients (log-normal fit to time to HT all BTDB patients); for BTT patients as base case (i.e. based on exponential fit to time to HT for BTT patients) |
| (ii) For both MM and BTT: log-normal fit to time to HT for all BTDB patients (available on request) | For both arms log-normal parametric fit to observed time to HT for all listed BTDB patients (see Figure 53). Probability set at zero after 42 months |
Two bivariate sensitivity analyses were conducted:
-
[I D1] Survival supported by MM based on constant hazard fit to K–M function to 2 months for inotrope patients (as I A3], and for survival on VAD support using Weibull fit to data for all VAD patients (as I B1]).
-
[I D2] Survival supported by MM based on Schaffer et al. 77 data, SHFM (as I A2 i]) and survival on VAD support based on Weibull fit to data for all VAD patients (as B1).
Probabilistic sensitivity analysis was undertaken for the base case. Details of the inputs are provided in Table 70.
Research question 2 (alternative to transplant compared with bridge to transplant)
What is the cost-effectiveness of second- and third-generation VADs used as an alternative to HT in comparison with their use as a BTT therapy for patients with advanced HF who are eligible for HT?
In the intervention arm for this comparison, patients with HF and eligible for HT receive a VAD as an alternative to proceeding with VAD as a BTT. Although RCTs for patients not eligible for HT (REMATCH study119 and Slaughter et al. 47) have been undertaken, no comparative evidence is available for a population eligible for transplant. For this research question the comparator arm patients eligible for HT receive a VAD as a bridge to future intended transplant with a donor heart, whereas the intervention arm patients are also eligible for a HT and receive a VAD as an ATT.
For economic modelling of the comparator arm (BTT) we adopted the base-case TP inputs listed above for the BTT arm of the first research question (as listed in Table 53; corresponding costs and utilities also applied). For the intervention arm (ATT) all inputs were the same as the comparator except that the probability of receiving a donor heart was set at zero.
The difference in costs between arms derives from the cost of HT in the comparator arm for BTT patients who survive long enough to receive a donor heart. The intervention (ATT) will therefore always remain cost saving (unless donor hearts cease to become available, in which case the two arms become identical). At present, survival is more favourable after receiving a donor heart, therefore the comparator (BTT) is likely to remain more effective than the intervention (ATT) until survival with a VAD becomes as favourable as that after receiving a donor heart. The ICER for this comparison estimates the savings to the payer for each QALY sacrificed, should ATT be adopted in favour of BTT.
Transition probabilities summary and comment
Kaplan–Meier survival plots of BTDB patients supported by VADs and post HT exhibited two phases – a poor survival for several months post surgery and a following longer phase of better survival. Similar poor short-term survival, though less pronounced, was also seen for MM patients. When log-normal or Weibull distributions were fitted to these data they tended to generate implausible proportions of long-term survivors. Therefore, following the approaches of Sharples et al. 30 and Moreno et al. 98 we used constant hazard fits to segments of the K–M plots up to the time when the proportion of patients at risk was depleted to about 10%.
Time to HT was very different between BTDB MM and BTT patients. In order to retain an equitable comparison between treatment strategies we employed the same transplant probability for both groups. It appears sensible for the purposes of a fair comparison between treatment options that each should have an equal opportunity of receiving benefits of a transplant; however, in clinical practice MM patients do in fact receive transplants much earlier than BTT patients, mainly because it makes little sense to remove a VAD from a patient who is doing well to give them a donor heart much more urgently required by other patients.
Once the premise that equal opportunity of transplant should prevail in economic modelling for both BTT and MM patients then the issue becomes one of ‘at what rate should this be set?’ In the base case we used data for the BTT group because the much higher probability observed for the MM patients in the BTDB was judged inappropriate as it would dictate that within only about 4 months of receiving a VAD implant, most BTT patients would have undergone device removal so as to receive a donor heart.
In the absence of randomised evidence the selection of an appropriate MM population as comparator is open to debate. Modelling K–M data from the BTDB inotrope MM patients yielded a median survival of 9.1 months. This was almost the same as that calculated from the distribution of SHFM scores reported in Schaffer et al. 77 for a series of BTT patients at a single US centre. Aaronson et al. 94 reported median survival of 9.86 months for a MM ‘virtual comparison’ group, again, using the SHFM with data for 140 HW recipients in a multicentre US study. Similar methods used by Strueber et al. 83 for 50 HW recipients (at European and Australian centres) yielded a median survival of 16.5 months. Some clinical advisors asserted their opinion that median survival of 9 months was excessively generous, and suggested the poorer survival observed for MM patients in the REMATCH trial of 4.9 months for all REMATCH controls and of 3.94 months for the inotrope subgroup of MM patients, respectively, as more appropriate. These have therefore been employed within sensitivity analyses.
In the next chapter we describe resource and cost inputs to the model.
Chapter 8 Overview of resource and cost inputs to the model
Nature of the inputs required
Resource use and associated costs are required for the following health states
-
Support on BTT with VAD until HT.
-
Support on MM until HT.
-
Support on HT.
States 1 and 3 have two phases:
-
a short-term phase associated with preparation for surgery and the immediate aftermath of surgery
-
a prolonged phase of maintenance.
Sources of cost inputs; base case and summary of sensitivity analyses
In our economic evaluation, resource use and costs were estimated from the perspective of the NHS. All costs reported in this chapter are based on 2010/11 prices unless otherwise specified.
Base case
Our main source of information on cost and resource use was from a previous HTA report undertaken by Sharples et al. 30 In the Sharples et al. 30 study, patient-specific resource-use data were collected for VAD implant, HT, and patients on MM while awaiting transplant. For all three patient groups, costs were collected as monthly costs from the date of VAD implantation, or the date the patients were accepted on to the transplant WL, until the study cut–off date. Post-transplantation and VAD monthly cost were assumed to be constant from month 7 onwards in all groups. Importantly, the study recorded actual costs incurred by patients and, hence, provides a more accurate representation of costs. For our model, these costs were inflated to current levels by applying the projected health services costs. 120 VAD costs were obtained from five UK centres operating under the auspices of the National Specialist Commissioning Team (NSCT), which commissions the VAD programme. We did not include the cost of the VAD supplied by GJNH which was based on a single VAD used at this centre; however, this was used in scenario analysis. The base-case cost inputs for the three health states are summarised in Table 55. It is worth mentioning that Sharples et al. 30 estimated resource use from the perspective of the NHS and centre. In such settings, the cost does not include setting-up costs for a new centre and we would emphasise that setting up a new service would incur additional set-up costs.
| Item | Period | Mean cost (£) | SE | Gamma distribution parameter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | β | ||||
| Supported by VAD | |||||
| VAD | 80,569a | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| VAD implant procedure | 3728b | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Post-VAD hospital stay and follow-up | Month 1 | 25,777 | 2518 | 2029.08 | 55.90 |
| Month 2 | 13,440 | 1306 | 105.95 | 126.84 | |
| Month 3 | 5110 | 764 | 44.69 | 114.32 | |
| Month 4 | 3836 | 607 | 40.00 | 95.89 | |
| Month 5 | 3248 | 460 | 49.89 | 65.09 | |
| Month 6 | 2326 | 356 | 42.69 | 54.48 | |
| Months 7+ | 1893 | 907 | 4.35 | 434.97 | |
| Supported by MM | |||||
| Support on MM (inotrope)c | Month 1 | 12,216 | 1156 | 111.67 | 109.39 |
| Month 2 | 6393 | 604 | 112.03 | 57.06 | |
| Months 3+ | 5965 | 193 | 951.25 | 6.27 | |
| Supported by HT | |||||
| HT theatre cost | |||||
| BTT | 16,663 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| MM | 11,395 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| HT assessment cost | |||||
| BTT | 0 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| MM | 1633 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Post-HT hospital stay and follow-up | Month 1: BTT | 15,577 | 1117 | 832.97 | 38.70 |
| Month 1: MM | 13,211 | 961 | 730.39 | 33.68 | |
| Post-HT hospital stay and follow-up | BTT and MM | ||||
| Month 2 | 4331 | 802 | 29.18 | 148.40 | |
| Month 3 | 2609 | 470 | 30.77 | 84.79 | |
| Month 4 | 2828 | 260 | 117.87 | 23.99 | |
| Month 5 | 2179 | 432 | 25.42 | 85.70 | |
| Month 6 | 1646 | 138 | 142.69 | 11.53 | |
| Months 7+ | 1410 | 177 | 62.91 | 22.41 | |
State 1: Support on bridge to transplant with a ventricular assist device until heart transplant
This health state consists of an early short-term phase associated with the VAD implant procedure cost which includes the cost of the device, theatre cost and cost of immediate post-operative hospital stay, and a second long-term follow-up phase that includes the costs of outpatient visits, adverse events and rehospitalisation.
We obtained costs of VADs from five centres (listed below) providing long-term VAD support:
-
NUT
-
Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
-
RB
-
UNB
-
UHSM.
The base-case cost per VAD (£80,569) was a weighted value according to the number of devices used by BTDB BTT patients and costs of different devices. Details of unit cost of VADs used in this study are given in Table 56.
| Name of device | Average cost/device (£) | Source |
|---|---|---|
| HMII | 89,831a | NHS designated provider cost (Dr Mark Petrie, Golden Jubilee National Hospital, 2012, personal communication) |
| HW | 80,076 | NHS designated provider cost (Dr Mark Petrie, Golden Jubilee National Hospital, 2012, personal communication) |
| Jarvik Heart | 50,273 | Clegg et al.4 |
| MicroMed DeBakey/(HeartAssist 5) | 80,400 | NHS designated provider cost (Dr Mark Petrie, Golden Jubilee National Hospital, 2012, personal communication) |
Device maintenance cost
The costs of maintaining the VAD per patient and associated costs of replacing batteries, cables and other hardware are not incorporated in any of the published cost-effectiveness models. We contacted two long-standing VAD manufacturers, who suggested that the yearly VAD maintenance and other hardware costs were trivial. Although we obtained costs of VADs from six centres, only two centres provided an annual maintenance cost (of £4000/year from year 2 onwards). All other centres reported that the purchase price of the device included a maintenance element and that they did not incur any additional cost on maintenance. We again contacted the device manufactures to verify the maintenance element, but no response was forthcoming. We therefore did not adjust the Sharples et al. 30 estimate for the cost of device maintenance.
We estimated the VAD implant procedure cost based on a GJNH finance department costings (£3728.20) supplied to us on request. Detailed information on this is given in Table 57.
| Resource area | Description of resource | Number of hours required per average patient | Number of units/tests required per average patient | Estimated average cost per hour/cost per case (£) | Estimated % of patients requiring this input | Total estimated average cost for VAD (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment by medical staff | ||||||
| Cardiac MDT | Referred to AHF clinic | 0.85 | 528.26 | 50 | 224.51 | |
| Pre-VAD tests/checks | Consultant surgeon | 0.21 | 68.32 | 100 | 14.35 | |
| SPR | 0.21 | 22.18 | 100 | 4.66 | ||
| Consultant anaesthetist | 0.42 | 61.80 | 100 | 25.95 | ||
| Surgical procedure | ||||||
| Theatre – pay | Theatre nursing team | 5.00 | 78.00 | 100 | 390.00 | |
| Theatre – average consumables | 1.00 | 755.85 | 100 | 755.85 | ||
| Hardware | Pump | 1 | 250.00 | 100 | 250.00 | |
| Perfusion – pay | Perfusionist – Band 7 | 7.50 | 35.31 | 100 | 264.85 | |
| Perfusion – supplies | Consumables per average case | 1.00 | 798.44 | 100 | 798.44 | |
| Surgeon | 6.25 | 61.80 | 100 | 386.22 | ||
| Anaesthetist | 6.25 | 61.80 | 100 | 386.22 | ||
| Pharmacy (theatre) | Drugs costs | 1.00 | 227.15 | 100 | 227.15 | |
| Total cost per VAD implant: £3728.20 | ||||||
State 2: Support on medical management until heart transplant
The input required is an estimate of the average monthly cost while patients are medically managed. This includes medication, such as inotropes, and follow-up assessment as inpatient or out-patient visits.
An inotrope-dependent patient subgroup of BTDB MM patients was selected for the base-case analysis. We consulted our clinical advisors and they advised that medications and inotropes used will have remained similar as the previous analysis. 30 The intravenous inotropes used were enoximone 5 μg/kg/minute and dopamine 5 μg/kg/minute. We inflated the cost of inotrope-dependent patients' medications to 2011 prices by applying the projected Health Services Cost Index. 120 The resulting monthly costs with distribution parameters where appropriate are shown in Table 55.
State 3: Support on heart transplant
The cost inputs include average presurgery preparatory cost, procedural cost and short-term post-surgery cost. The transplantation procedure cost was considered to be different between groups to address the increase in theatre time for VAD explant. Post-transplant monthly costs were assumed to be the same for both groups from month 2 onwards. Post-HT support costs include follow-up outpatient visits, investigation, blood test and drugs (see Table 55).
Clinical experts advised that the costs of the transplant donor procedure were trivial and we therefore did not include this cost in our model.
Sources of cost inputs: summary of sensitivity analyses
Sensitivity analyses around cost inputs
A sensitivity analysis (I A1] in Table 54) was conducted around the TP for MM to death which assumed the MM group was constituted of all BTDB MM patients (both 307 inotrope patients and 1189 non-inotrope patients). The monthly cost for these is shown in Table 58.
| Event | Components of cost | Mean cost/patient (£) |
|---|---|---|
| All MM | Month 1a | 4517 |
| Month 2 | 1673 | |
| Month 3 | 1759 | |
| Month 4 | 329 | |
| Month 5 | 220 | |
| Month 6 | 245 | |
| Months 7+ | 287 |
The monthly cost of all MM was a weighted value according to the number of both inotrope and non-inotrope patients from the BTDB. We used previously reported costs30 for inotrope- and non-inotrope-supported MM patients, inflated to 2010/11 prices for the sensitivity analysis Table 59.
| Event | Components of cost | Mean cost/patient (£) |
|---|---|---|
| MM – inotrope-dependent | Transplant assessment cost | 1633 |
| Month 1 | 12,216 | |
| Month 2 | 6393 | |
| Months 3+ | 5965 | |
| MM – non-inotrope-dependent | Transplant assessment cost | 1633 |
| Month 1 | 475 | |
| Month 2 | 454 | |
| Month 3 | 672 | |
| Month 4 | 413 | |
| Month 5 | 277 | |
| Month 6 | 308 | |
| Months 7+ | 361 |
Sensitivity analyses II A and II B around cost inputs
In univariate sensitivity analyses, the cost of the VAD was varied from that in the base case as shown in Table 60. This analysis is designated II A in the results section.
| Analysis II A: input parameter | Cost (£) | Source |
|---|---|---|
| VAD cost (% reduction) | ||
| 10 | 72,513 | Base-case inputs cost of £80,569 |
| 15 | 68,484 | |
| 20 | 64,456 | |
| 30 | 56,399 | |
| 40 | 48,342 | |
| 50 | 40,285 | |
| 60 | 32,228 | |
| 76 | 19,337 | |
| Analysis II B: VAD immediate and long-term monthly cost reduced by 30% | ||
| Month 1 | 102,342a | Base-case inputs |
| Month 2 | 9408 | |
| Month 3 | 3577 | |
| Month 4 | 2686 | |
| Month 5 | 2274 | |
| Month 6 | 1628 | |
| Months 7+ | 1325 | |
In a further sensitivity analysis (designated II B) the cost of patient maintenance on a VAD was decreased from base case by 30%.
This was undertaken because clinical experts advised that patients on second- and third-generation VADs experience relatively fewer adverse events than those supported with earlier VAD designs. To address the potential cost savings of reduced adverse events, we lowered the monthly post-VAD implantation cost by 30% in sensitivity analysis.
Sensitivity analyses (II C and II D) around costs for both arm using Golden Jubilee National Hospital and national schedule of reference costs data
Further sensitivity analyses used a detailed list of resource use and associated costs which were supplied from Glasgow the Glasgow centre, the GJNH, one of the UK centres operating with the NSCT (analysis II C). The GJNH cost data and definitions used are all presented exactly as provided by GJNH. This provided information on all three health states. In addition, we also sourced the mean cost for three health states from the national schedule of reference costs (NSRC) 2010/11 (analysis II D). 122 These alternative sources are described in further detail below.
Support on medical management until heart transplant
Resource-use data from the Glasgow GJNH finance department were collected on hospital stay, drugs, investigations and outpatient visits for patients with advanced HF. The GJNH finance department reported a total cost of £10,111.66 per hospital stay per patient with advanced HF for the year 2009/10, based on a total of 92 patients costing £842.63 (£10,111.66/12) per patient in month 1. Further detailed information on the resource use and costs supplied by GJNH involved in managing patients in hospital with advanced HF is shown in Table 61.
| Resource area | Description of resource | Number of OBD per average patient | Number of units/tests/hours required per average patient | Estimated average cost per hour/cost per case (£) | Estimated % of patients requiring this input | Estimated average cost for HT (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medical assessment and review on admission | Consultant surgeon | 0.42 | 68.32 | 100 | 28.70 | |
| Consultant physician | 20.00 | 68.32 | 100 | 1366.44 | ||
| Anaesthetist/intensivist | 0.43 | 61.80 | 100 | 26.57 | ||
| Cardiology registrar | 1.25 | 22.18 | 100 | 27.72 | ||
| Inpatient stay (excluding drugs) | Ward staffing and supplies | 12.30 | 461.25 | 77 | 4368.49 | |
| Outlier ward staffing and supplies | 6.90 | 194.74 | 23 | 309.05 | ||
| ITU staffing and supplies | 6.67 | 1268.54 | 15 | 1269.17 | ||
| HDU staffing and supplies | 5.70 | 420.18 | 8 | 191.60 | ||
| CCU staffing and supplies | 1.50 | 448.67 | 2 | 13.46 | ||
| IABP | 2 | 696.32 | 23 | 320.30 | ||
| Drugs | Prescribed in hospital | 226.82 | ||||
| Tests | Radiology | 459.26 | ||||
| Cardiology/catheterisation laboratory | 608.04 | |||||
| Respiratory medicine | 24.85 | |||||
| Laboratory | 572.83 | |||||
| AHP contact | Physiotherapy staff – Band 6 | 11.33 | 17.83 | 100 | 202.01 | |
| Cardiology rehabilitation staff – Band 3 | 3.00 | 10.16 | 100 | 30.48 | ||
| Occupational therapy staff – Band 6 | 3.00 | 17.83 | 100 | 53.49 | ||
| Occupational therapy rehabilitation staff – Band 3 | 1.00 | 10.16 | 100 | 10.16 | ||
| Clinical nutrition – Band 7 | 0.10 | 22.15 | 100 | 2.22 | ||
| Total cost: £10,111.66 | ||||||
From the cost provided by the GJNH finance department, it was not possible to identify the drugs and inotropes used in hospital at the time of admission. We assumed that patients admitted to hospital for advanced HF were inotrope-dependent and patients at home on the WL were non-inotrope-dependent (Dr Mark Petrie, GJNH, 2012, personal communication).
Patients at home and on the WL were seen in the HF clinic every third month. The cost per initial visit was £437.79, and after 3 months patients are reassessed by a multidisciplinary team consisting of a cardiologist, a cardiac surgeon and a specialist nurse. The cost for every other consecutive follow-up was £160.11 per visit.
We also sourced the mean cost of MM (from the NSRC) 2010/11 and these were explored in the sensitivity analysis (see Table 66).
Support on bridge to transplant with a ventricular assist device until heart transplant
A detailed description of resource-use data and unit cost estimates were collected for VAD implant from the GJNH finance department. Resource-use data were collected on VAD assessment cost, implant procedure cost, cost associated with ward and ICU stay, follow-up outpatient visits, investigation, blood test and drugs. The cost was based on one long-term VAD (HMII) patient for 2009/10. We recommend caution in interpreting this result partly because of this and partly as we believe that the cost from the GJNH might be overestimated (as throughput for this intervention is at present insufficient for economies of scale to be in evidence). However, the GJNH data give us details of the cost component for immediate post-operative hospital stay following VAD implant, and are shown in Table 62.
| Resource area | Description of resource | Number of OBD per patient | Number of units/tests/hours required per patient | Estimated average cost per hour/cost per case/cost per OBD (£) | Estimated % of patients requiring this input | Total estimated cost for VAD (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inpatient stay (excluding drugs) | ITU staffing and supplies | 14.66 | 1268.54 | 100 | 18,596.79 | |
| ITU specialist consumables incurred by VAD patients | 1 | 3882 | 100 | 3882.00 | ||
| Ward staffing and supplies | 12.67 | 461.25 | 100 | 58,440.03 | ||
| IABP | 2 | 696.32 | 66 | 919.14 | ||
| Medical staff rounds to VAD patients | Surgeon | 51.25 | 61.80 | 100 | 3167.00 | |
| Junior surgeon | 51.25 | 22.18 | 100 | 1136.65 | ||
| Consultant cardiologist | 27 | 61.80 | 100 | 1668.47 | ||
| Junior cardiologist | 25 | 22.18 | 100 | 554.46 | ||
| Anaesthetist/intensivist | 1.25 | 428.05 | 100 | 535.06 | ||
| Pharmacy | Surgery drugs – ITU | 1 | 149.53 | 100 | 149.53 | |
| Surgery drugs – ward | 1 | 43.51 | 39.55 | |||
| Tests | Radiology | 132.33 | ||||
| Laboratory | 310.91 | |||||
| AHP contact | Physiotherapy staff – Band 6 | 25.17 | 17.83 | 100 | 448.78 | |
| Cardiology rehabilitation staff – Band 3 | 7.67 | 10.16 | 100 | 77.93 | ||
| Occupational therapy staff –Band 6 | 10.50 | 17.83 | 100 | 187.22 | ||
| Occupational therapy rehabilitation staff – Band 3 | 3.33 | 10.16 | 100 | 33.83 | ||
| Total cost per VAD implant: £37,683.71 | ||||||
Following a VAD implant, patients were requested to attend fortnightly for a follow-up visit for 1 month, then to visit monthly for 3–4 months and then to visit 3-monthly for 6 months. Outpatient follow-up visit was estimated at £894.06 per visit (an outpatient visit post VAD is resource intensive with several invasive tests and non-invasive test undertaken during a follow-up visit).
We also sourced the mean cost of VAD implantation from the NSRC 2010/11 and this was explored in the sensitivity analysis (see Table 66).
Support on heart transplant
We determined the transplantation procedure cost for both VAD and MM patients from the GJNH finance department. The theatre cost of retrieving a donor heart was reported as £16,811.66. This includes the cost of surgical support for organ retrieval and does not include the cost of investigations; Tables 63 and 64 summarise HT theatre cost and immediate post-operative hospital stay cost following four HTs. We recommend caution in interpreting this result partly because of these small numbers and partly as we believe that the cost from the GJNH might be overestimated owing to lack of economies of scale.
| Resource area | Description of resource | Number of hours required per average patient | Number of units/tests required per average patient | Estimated average cost per hour/cost per case (£) | Estimated % of patients requiring this input | Total estimated cost attached to HT (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donor heart retrieval | ||||||
| Organ Retrieval team | Transplant co-ordinator call-outsa | 1 | 6311.66 | 100 | 6311.66 | |
| SAS surgeon transport of recipient and donor organ | 1 | 10,500.00 | 100 | 10,500.00 | ||
| Theatre cost | ||||||
| Theatre | Theatre nursing team | 15.00 | 78.00 | 100 | 1170.00 | |
| Theatre consumables and drugs | 100 | 2770.77 | ||||
| Consultant transplant surgeon | 15.00 | 68.32 | 100 | 1024.83 | ||
| Consultant anaesthetist | 15.00 | 61.80 | 100 | 926.93 | ||
| Perfusionist – Band 7 | 22.50 | 35.31 | 100 | 794.56 | ||
| Perfusion consumables | 1603.44 | 100 | 1603.44 | |||
| Cardiac physiologist – switch-off device | 3.00 | 26.90 | 100 | 80.70 | ||
| Total cost per HT: £25,182.88 | ||||||
| Resource area | Description of resource | Number of OBD per average patient | Number of units/tests/hours required per average patient | Estimated average cost per hour/cost per case (£) | Estimated % of patients requiring this input | Total estimated average cost for HT (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inpatient stay (excluding drugs) | ITU staffing and supplies | 3.50 | 1268.54 | 100 | 4439.89 | |
| HDU staffing and supplies | 3.00 | 420.18 | 25 | 315.13 | ||
| Ward staffing and supplies | 19.00 | 461.25 | 100 | 8763.75 | ||
| Outlier ward staffing and supplies | 3.00 | 194.74 | 50 | 292.11 | ||
| Medical staff rounds to transplant patients | Surgeon | 51.25 | 61.80 | 100 | 3167.00 | |
| Junior surgeon | 51.25 | 22.18 | 100 | 1136.65 | ||
| Consultant cardiologist | 27 | 61.80 | 100 | 1668.47 | ||
| Junior cardiologist | 25 | 22.18 | 100 | 554.46 | ||
| Anaesthetist/intensivist | 1.25 | 428.05 | 100 | 535.06 | ||
| Drugs | Post operative | 15,700.76 | ||||
| Tests | Radiology | 141.96 | ||||
| Laboratory | 358.38 | |||||
| Cardiac physiology | 528 | |||||
| AHP contact | Physiotherapy staff – Band 6 | 25.17 | 17.83 | 100 | 448.78 | |
| Cardiology rehabilitation staff – Band 3 | 7.67 | 10.16 | 100 | 77.93 | ||
| Occupational therapy staff – Band 6 | 10.50 | 17.83 | 100 | 187.22 | ||
| Occupational therapy rehabilitation staff – Band 3 | 3.33 | 10.16 | 100 | 33.83 | ||
| Discharge element | Hotel stay | 2.50 | 45.00 | 100 | 112.50 | |
| Transport | 15.00 | 15.00 | ||||
| Total cost per patient: £27,136.95 | ||||||
Following a HT, the follow-up management for both VAD and MM patients was assumed to be the same. The transplant management guidelines from the GJNH detailing follow-up outpatient visits, blood tests, chest radiograph and the biopsy regimen are provided in Table 65.
| Time after transplant | Clinic visits | Biopsy (endomyocardial) |
|---|---|---|
| 0–6 weeks | Weekly | Weekly |
| 6 weeks to 3 months | Fortnightly | Fortnightly |
| 3 months to 1 year | 6-weekly | 6-weekly |
| Year 1 to year 2 | 3-monthly | Regular biopsies will cease at 1 year |
| Year 2+ | 6-monthly |
We also sourced the mean cost of HT from the NSRC 2010/11 and this was explored in the sensitivity analysis. These are summarised in Table 66.
| Item | Period | Mean cost based on GJNH finance department 2011 price (£) | Period | Mean cost based on NSRC 2010/11 price (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAD | 78,877 | N/A | ||
| VAD implant procedure | 3728 | N/A | ||
| Post-VAD implant support | Month 1 | 120,289a | Month 1 | 67,003b |
| Month 2 | 1788.12 | Month 2 | N/A | |
| Month 3 | 894.06 | Month 3 | N/A | |
| Month 4 | 894.06 | Month 4 | N/A | |
| Months 5+ | 298.02 | Month 5 | N/A | |
| Month 6 | N/A | |||
| Months 7+ | N/A | |||
| Support on MM (inotrope) | Month 1 | 843 | Months 1+ | 1479 |
| Month 2 | 438 | |||
| Months 3+ | 160 | |||
| HT assessment and theatre cost | BTT and MM | 25,183 | BTT and MM | N/A |
| Post-HT hospital stay and follow-up | Month 1 | 27,137 | Month 1 | 37,871 |
| Month 2 | 3576 | Month 2 | N/A | |
| Month 3 | 1788 | Month 3 | N/A | |
| Months 4+ | 894 | Months 4–7+ | N/A |
Model assumptions for transition probabilities, utilities and cost inputs
A summary of the transition probabilities, utilities and cost inputs to the cost–utility model is detailed in Table 67. We also include here a list of model assumptions.
Model assumptions – transition probabilities
-
The model was simplified by assuming all patients have the same survival post HT despite receiving a donor heart at different times (up to maximum of 42 months) and despite different treatment (VAD or MM) prior to transplant. The assumption is supported by data published by Russo et al. 100 and Nativi et al. 89 The same assumption has been made in previous economic analyses. 30,98
-
In our base-case analysis < 1% of patients are alive supported by a VAD beyond 70 months.
-
In the base case, the model assumes that for an equitable comparison of the compared therapies the same probability of receiving a donor heart should be applied for both treatment and comparator groups.
-
In the base case, survival of BTDB MM and VAD-supported patients who were censored on receipt of a HT was assumed to represent survival of patients eligible for HT who never received one; the impact of this was examined in extensive sensitivity analysis. Furthermore, constant hazard extrapolations were assumed to be reasonable estimates for extension of survival beyond the observed data. The same assumption has been made in previous economic analyses. 30,98
-
It is assumed that the MM patients in the BTDB who were classified as baseline users of ‘inotropes’ represent a distinct subpopulation of all MM patients in the database.
-
The model assumes that post-HT survival remains the same irrespective of previous therapy (BTT with VAD or MM) and can be estimated from observed survival of UK BTDB patients who receive a donor heart.
Model assumptions – costs
-
The model assumes that, other than for VAD cost, resource use associated with MM and VAD support have remained essentially the same as the previous analysis30 so that relative costs merely require inflating to current prices. Expert clinical advice supported this assumption.
-
We simplified assumptions on adverse event costs occurring in the long term (due to lack of reliable data).
-
For costing we assumed that patients on second- and third-generation VADs rarely require a VAD replacement within a 7-year period; this was based on personal communication with HW manufacturers (Mr Timothy Homer, Global Market Access, 2012, personal communication).
Model assumptions – utilities
-
It was assumed that in the absence of direct EQ-5D information, the modelling of utilities for health states using from NYHA classification of patients in the BTDB represents a reasonable compromise.
The base-case model assumptions were explored in sensitivity analyses. In the next section we describe results from the cost-effectiveness model.
| Health state transition | Period | Monthly TP | SE | Beta distribution parameter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | β | ||||
| VAD support to death p13 | Months 1–3 | 0.0577197 | 0.028 | 3.91 | 63.93 |
| Months 4+ | 0.0179873 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| MM support to death p13 | Months 1+ | 0.073344 | 0.058 | 7.38 | 93.35 |
| Time to HTa p12 | Months 1–42: probability set to zero after 42 months | 0.012745641 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Support on HT to death p23 | Months 1–3 | 0.070366726 | 0.0163 | 17.20 | 227.25 |
| Months 4–284 | 0.002980948 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Utility inputs | |||||
| Health state | Period | Mean utility | SE | Beta distribution parameter | |
| α | β | ||||
| MMb (inotrope) | All months | 0.55 | 0.023 | 237.89 | 194.63 |
| Post VAD | All months | 0.74 | 0.075 | 24.57 | 8.63 |
| Post HT | All months | 0.83 | 0.005 | 4683.69 | 959.31 |
| Item | Period | Mean cost (£) | SE (£) | Gamma distribution parameter | |
| α | β | ||||
| Cost inputs (2011 prices) | |||||
| VAD | 80,569 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| VAD implant procedure | 3728 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Post-VAD implant supportc | Month 1 | 110,075 | 2518 | 2029.08 | 55.90 |
| Month 2 | 13,440 | 1306 | 105.95 | 126.84 | |
| Month 3 | 5110 | 764 | 44.69 | 114.32 | |
| Month 4 | 3836 | 607 | 40.0 | 95.89 | |
| Month 5 | 3248 | 460 | 49.89 | 65.09 | |
| Month 6 | 2326 | 356 | 42.69 | 54.48 | |
| Months 7+ | 1893 | 907 | 4.35 | 434.97 | |
| Support on MM (inotrope)d | Month 1 | 12,216 | 1156 | 111.67 | 109.39 |
| Month 2 | 6393 | 604 | 112.03 | 57.06 | |
| Months 3+ | 5965 | 193 | 951.25 | 6.27 | |
| HT theatre cost | BTT | 16,663 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| MM | 11,395 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| HT assessment cost | BTT | 0 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| MM | 1633 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Post-transplant hospital stay and follow-up | Month 1: BTT | 15,577 | 1117 | 832.97 | 38.70 |
| Month 1: MM | 13,211 | 961 | 730.39 | 33.68 | |
| BTT and MM | |||||
| Month 2 | 4331 | 802 | 29.18 | 148.40 | |
| Month 3 | 2609 | 470 | 30.77 | 84.79 | |
| Month 4 | 2828 | 260 | 117.87 | 23.99 | |
| Month 5 | 2179 | 432 | 25.42 | 85.70 | |
| Month 6 | 1646 | 138 | 142.69 | 11.53 | |
| Months 7+ | 1410 | 177 | 62.91 | 22.41 | |
Assessment of quality of cost inputs
The Sharples et al. 30 study was a good-quality study estimating cost inputs by combining two methods: direct observation of patients cost and cost estimated from NHS finance departments. The estimated unit costs were specific to the intervention and events of interest, and were generalisable to the study population. The resource use was measured for all three patient groups from the perspective of the NHS until the study cut-off date. Quality and validity of the cost data are good in relation to criteria suggested by Drummond et al. 97 The study by Sharples et al. 30 was the only study to report patient-specific resource-use data for the VAD procedure and subsequent stay in ICU and cardiac ward. The unit cost reflected the level of resource aggregation for procedure and itemised subsequent costs appropriately (e.g. stay in ICU and cardiac ward; device cost; HT procedure and associated ICU and ward stay; transplant assessment; follow-up readmission to ICU or ward; outpatient visits; investigation and drugs). A weakness of the study for the purposes of the current report is that it describes the results of a mixture of first- and second-generation VADs; however, it is the only available comparable study with the most recent resource-use data and unit cost estimates published in the UK setting.
Chapter 9 Results from the cost-effectiveness model
We present here deterministic and probabilistic results for the two research questions. For the base case(s) we also present probabilistic results plotted on the cost-effectiveness plane showing the joint distribution of differences in costs and QALYs, and CEACs indicating the probability that the interventions (BTT or ATT) are cost-effective at different thresholds of willingness to pay.
We adopted 3-, 10- and 50-year time horizons for both research questions. The 3-year horizon approximately reflects the period over which eligible patients are likely to receive a transplant, the 10-year horizon approximately reflects the maximum follow-up of BTT patients, and the 50-year horizon follows recommendations by NICE that the time horizon should be sufficiently extended to capture all benefits likely to accrue from the intervention. As about 60% of BTDB patients remained alive 10 years after transplant, a 50-year horizon was judged appropriate.
Results for research question 1
In patients aged ≥ 16 years with advanced HF who are eligible for HT:
-
What is the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of second- and third-generation VADs used as BTT compared with MM?
Base-case deterministic results: research question 1
For the base case we compared the cost-effectiveness of BTT based on all VAD recipients compared with the MM patients in the BTDB who were classified as ‘inotrope’. Derivation of utilities is reported in Chapter 4, transition probabilities between health states in Chapter 7, and resources and costs are reported in Chapter 8. Model inputs are summarised at the end of Chapter 8.
Results are tabulated (Table 68) in terms of mean cost, mean LYG and mean QALYs gained in each treatment group for 3-year, 10-year and lifetime (50-year) horizons. Also presented are the ICERs for these time horizons. The perspective is from the UK NHS and discounting of benefits and costs at 3.5% was undertaken according to UK guidelines. 115
| Time horizon | Mean cost (£) | Mean years survival | Mean QALYs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-year time horizon | |||
| VAD | 176,594 | 1.95 | 1.48 |
| MM | 79,637 | 1.13 | 0.69 |
| Difference | 96,957 | 0.82 | 0.79 |
| ICERs (£/LYG) | 117,728 | ||
| ICERs (£/QALY) | 122,730 | ||
| 10-year time horizon | |||
| VAD | 212,648 | 3.81 | 2.95 |
| MM | 91,450 | 1.72 | 1.17 |
| Difference | 121,198 | 2.09 | 1.78 |
| ICERs (£/LYG) | 57,989 | ||
| ICERs (£/QALY) | 68,088 | ||
| Lifetime model | |||
| VAD | 239,832 | 5.40 | 4.26 |
| MM | 104,106 | 2.47 | 1.80 |
| Difference | 135,726 | 2.93 | 2.46 |
| ICERs (£/LYG) | 46,322 | ||
| ICERs (£/QALY) | 55,173 | ||
For VAD patients compared with the inotrope subgroup of the MM patients the ICER is £122,730 per QALY over a 3-year time horizon. At the 10-year time horizon the ICER increases to £68,088 per QALY, and at a lifetime horizon of 50 years the ICER is £55,1730 per QALY.
The cost of the VAD and of the implantation procedure together make a substantial contribution to the costs. The impact of this and of other inputs is explored in sensitivity analysis. Undiscounted LYG in the BTT and the MM arms are summarised in Figures 61 and 62.
FIGURE 61.
Undiscounted LYG with VAD – BTT.
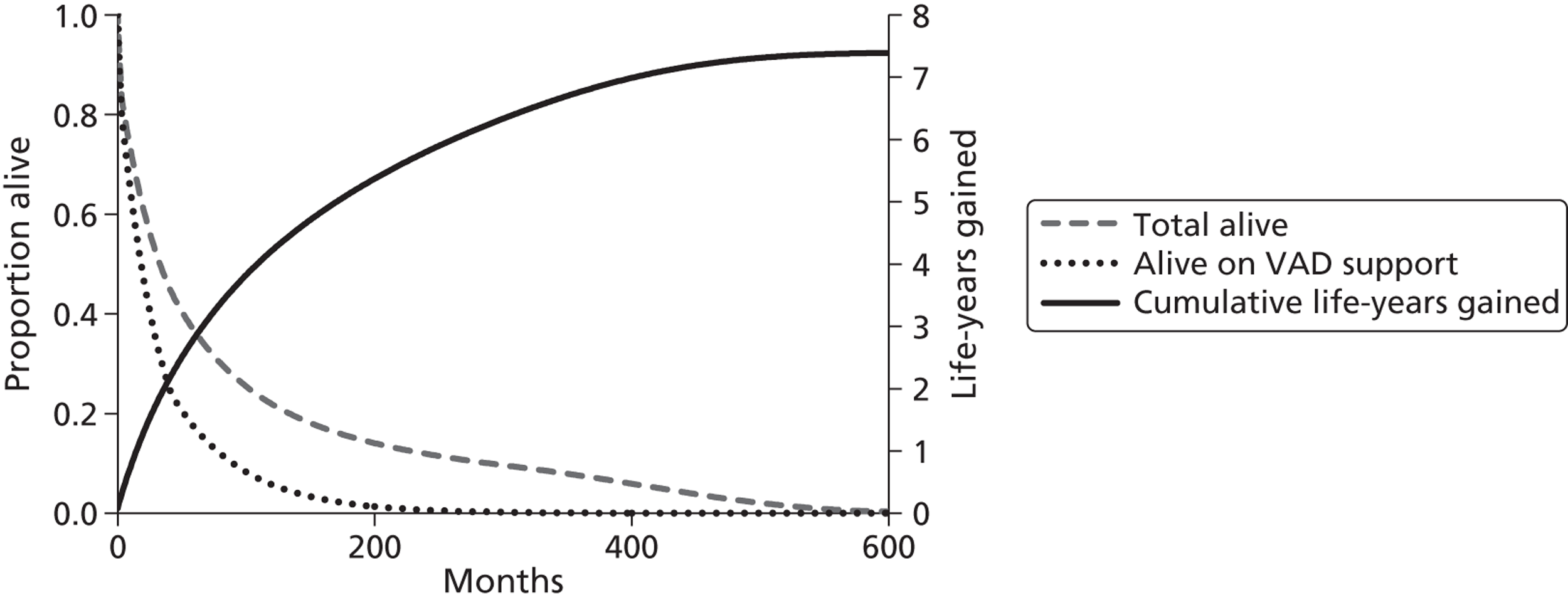
FIGURE 62.
Undiscounted LYG with MM support.
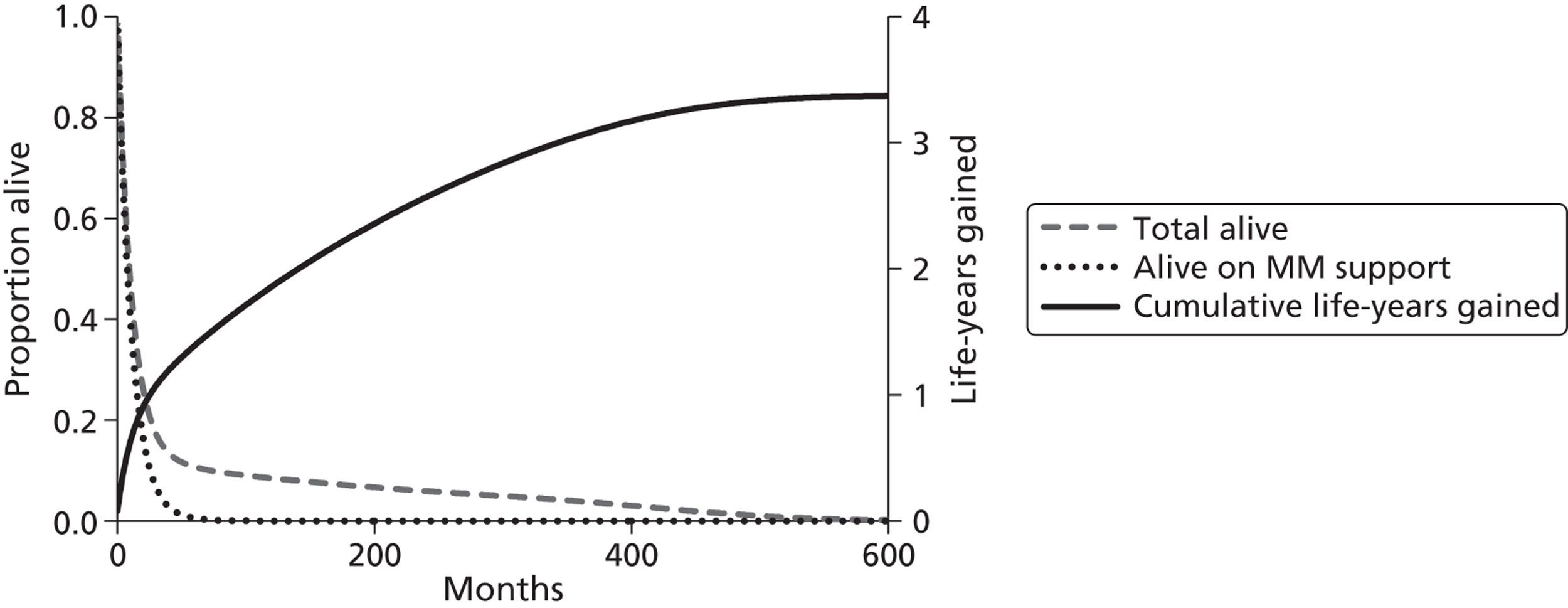
Base-case probabilistic results: research question 1
Base-case probabilistic inputs are shown in Table 67. The base-case probabilistic results summarised in Table 69 indicate a lifetime horizon ICER of £53,527 per QALY. Deterministic and probabilistic ICER estimates are similar for all three time horizons with the ICER increasing as the time horizon decreases.
| Time horizon | Mean cost (£) (95% CI) | Mean years survival (95% CI) | Mean QALYs (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-year time horizon | |||
| VAD | 177,009 (154,922 to 210,495) | 1.96 (1.60 to 2.22) | 1.49 (1.14 to 1.80) |
| MM | 83,010 (49,888 to 124,933) | 1.18 (0.68 to 1.81) | 0.72 (0.42 to 1.12) |
| Difference | 93,999 (45,307 to 139,435) | 0.78 (0.09 to 1.36) | 0.77 (0.26 to 1.21) |
| ICERs (£/LYG) | 114,631 (78,800 to 374,982) | ||
| ICERs (£/QALY) | 120,510 (79,560 to 251,285) | ||
| 10-year time horizon | |||
| VAD | 212,000 (175,724 to 264,432) | 3.83 (3.07 to 4.41) | 2.95 (2.26 to 3.55) |
| MM | 99,240 (57,026 to 169,449) | 1.87 (1.05 to 3.19) | 1.27 (0.73 to 2.15) |
| Difference | 112,760 (33,076 to 179,395) | 1.96 (0.55 to 2.97) | 1.68 (0.63 to 2.51) |
| ICERs (£/LYG) | 57,530 (35,881 to 99,572) | ||
| ICERs (£/QALY) | 67,119 (38,756 to 116,681) | ||
| Lifetime model | |||
| VAD | 240,193 (196,411 to 306,883) | 5.46 (4.29 to 6.56) | 4.32 (3.31 to 5.31) |
| MM | 112,802 (65,086 to 197,666) | 2.67 (1.49 to 4.59) | 1.94 (1.07 to 3.33) |
| Difference | 127,391 (36,782 to 179,736) | 2.79 (0.61 to 4.33) | 2.38 (0.78 to 3.59) |
| ICERs (£/LYG) | 45,659 (30,159 to 86,586) | ||
| ICERs (£/QALY) | 53,527 (31,802 to 94,853) | ||
The joint distribution of the difference in costs and the differences in QALYs for the three time horizons is shown in Figure 63. Each point is a simulation from the joint distribution; the plot illustrates the uncertainty surrounding incremental costs and benefits for the two groups being compared.
FIGURE 63.
Cost-effectiveness plane for 3-year, 10-year and lifetime horizons: base-case probabilistic results.
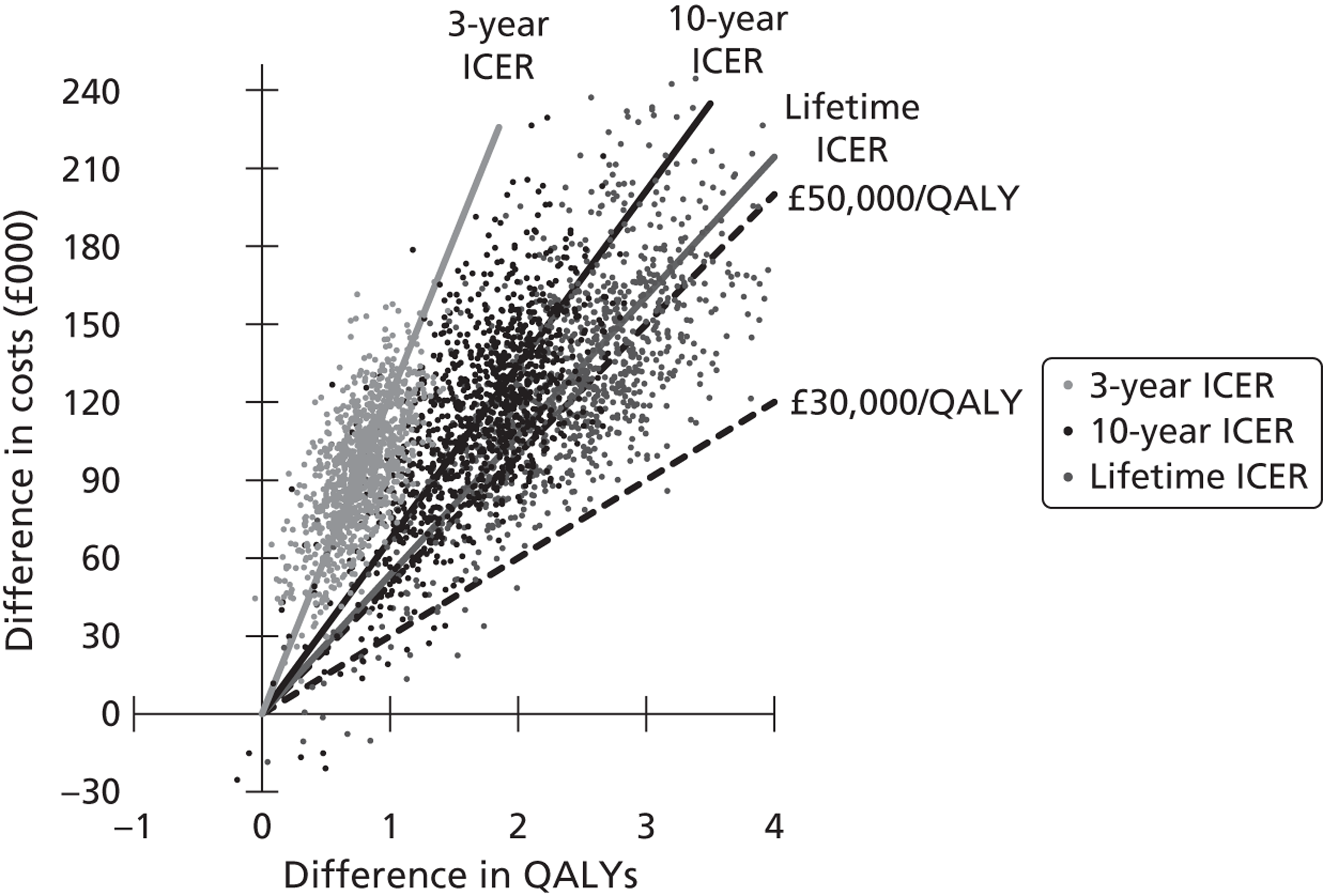
Figure 64 presents the CEACs for the 3-year, 10-year and 50-year time horizons. NICE guidance,101 although not explicit, suggests a benchmark of approximately £30,000 per QALY as the usual upper limit for the NHS. At a willingness to pay of £50,000 per QALY BTT approaches cost-effectiveness compared with MM (see Figure 63). Although, again not explicit, NICE appears to have applied a threshold of £50,000 per QALY for interventions which satisfy recommended criteria as end of life treatments. These include:
-
predicted survival of < 2 years in the absence of the intervention
-
the intervention prolongs survival by at least 3 months
-
a small population eligible for the treatment.
FIGURE 64.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves for 3-year, 10-year and lifetime models.
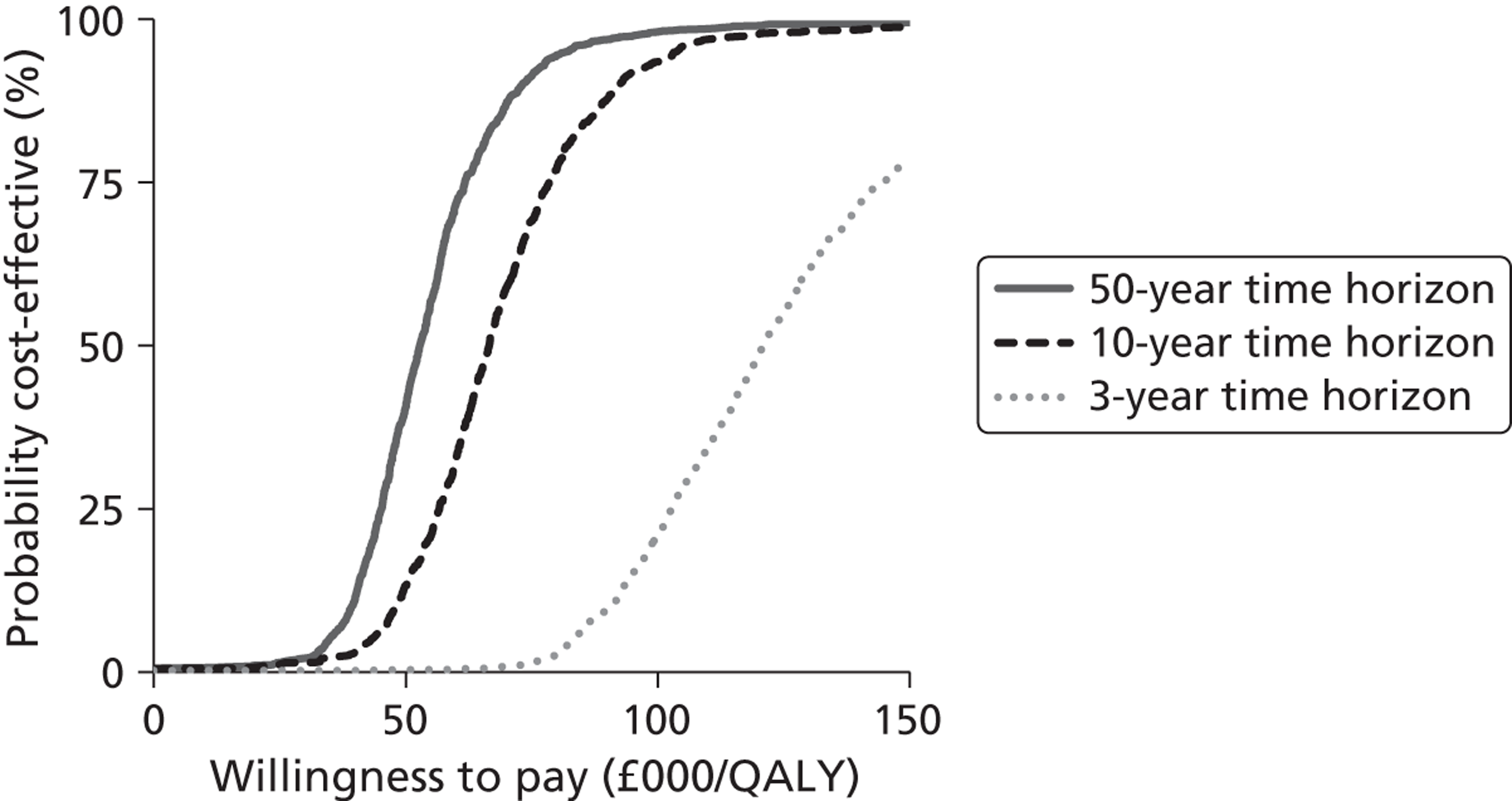
Sensitivity analyses: base-case analysis-research question 1
Sensitivity analyses were conducted by altering base-case inputs to the model. Several types of sensitivity analysis were explored encompassing changes to:
-
I] TPs between health states (I A to I D)
-
II] inputs for costs (II A to II D)
-
III] utility inputs for health states.
I] Impact of changing the transition probabilities between health states
The results for these sensitivity analyses are summarised in Table 70.
| Input parameter | Horizon (years) | ICERa (£/QALY) | Difference in QALYs | Difference in costs (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1] TP MM to death based on K–M for all BTDB MM patients (n = 1496) using constant hazard fit to 3 months and then 3 months to 10% at risk (costs input appropriate for mix of inotrope and non-inotrope patients) | 3 | 7,423,100 | −0.02 | 148,462 |
| 10 | −430,700b | −0.37 | 159,359 | |
| 50 | −207,054b | −0.76 | 157,361 | |
| A2 i] TP MM to death from SHFM95 making use of data from Schaffer et al.77 | 3 | 122,814 | 0.80 | 98,251 |
| 10 | 68,268 | 1.80 | 122,882 | |
| 50 | 55,058 | 2.50 | 137,644 | |
| A2 ii] TP MM to death from SHFM95 making use of data from Strueber et al.83 | 3 | 129,178 | 0.50 | 64,589 |
| 10 | 61,539 | 1.17 | 72,001 | |
| 50 | 51,731 | 1.55 | 80,183 | |
| A2 iii] TP MM to death from SHFM92 making use of BTDB MM patients' data | 3 | 121,309 | 0.90 | 109,781 |
| 10 | 68,967 | 1.99 | 137,302 | |
| 50 | 55,148 | 2.79 | 154,125 | |
| A3] TP MM to death based on K–M for BTDB inotrope MM patients using constant hazard fit to 2 months | 3 | 121,560 | 0.92 | 111,835 |
| 10 | 69,196 | 2.02 | 139,776 | |
| 50 | 55,074 | 2.85 | 156,961 | |
| A4 i] TP MM to death based on the optimum MM arm of the REMATCH trial using constant hazard fit to reported median survival of 150 days | 3 | 119,305 | 1.05 | 125,270 |
| 10 | 69,413 | 2.24 | 155,484 | |
| 50 | 55,203 | 3.17 | 174,994 | |
| A4 ii] TP MM to death based on the optimum MM arm of the REMATCH trial using constant hazard fit to reported median survival of 120 days | 3 | 118,968 | 1.12 | 133,244 |
| 10 | 69,723 | 2.36 | 164,547 | |
| 50 | 55,178 | 3.36 | 185,398 | |
| B1] TP VAD to death based on Weibull fit to survival for all BTDB VAD patients | 3 | 128,556 | 0.75 | 96,432 |
| 10 | 69,947 | 1.73 | 121,030 | |
| 50 | 56,221 | 2.40 | 134,853 | |
| B2] TP VAD to death based on K–M for BTDB HW patients, using hazard fit to 4 months, and from 4 months to 10% at risk (with associated HW costs)c | 3 | 115,794 | 0.86 | 99,032 |
| 10 | 64,663 | 1.95 | 126,064 | |
| 50 | 52,344 | 2.72 | 142,545 | |
| C1i] TP MM to HT based on log-normal fit to data for all BTDB transplant recipients (MM and BTT); TP VAD to HT based on exponential fit to data for BTDB BTT transplant recipients | 3 | 627, 644 | 0.16 | 100,423 |
| 10 | −404,858b | −0.24 | 97,166 | |
| 50 | −54,168b | −1.37 | 74,210 | |
| C1ii] TP from MM or VAD to HT based on log-normal fit to data for all BTDB transplant recipients (i.e. equal opportunity of donor heart in both arms based on log-normal fit) | 3 | 283,924 | 0.38 | 107,891 |
| 10 | 135,726 | 0.88 | 119,439 | |
| 50 | 96,319 | 1.34 | 129,068 | |
| Bivariate sensitivity analysis | ||||
| D1] TP MM to death based on K–M for BTDB inotrope MM patients using constant hazard fit to 2 months to death using a constant hazard fit to 2 months (A3] above)TP VAD to death based on Weibull fit to survival for all BTDB VAD patients (as B1] above) | 3 | 125,880 | 0.88 | 111,309 |
| 10 | 70,621 | 1.97 | 139,419 | |
| 50 | 56,172 | 2.78 | 155,897 | |
| D2] TP MM to death based on SHFM using data from Schaffer et al.77 (as A2i] above) TP VAD to death based on Weibull fit to survival for all BTDB VAD patients (as B1] above) | 3 | 128,300 | 0.76 | 97,725 |
| 10 | 70,026 | 1.75 | 122,686 | |
| 50 | 56,224 | 2.43 | 136,744 |
In analyses A2, the survival under MM was modelled according to the SHFM score after Levy et al. 95 for BTT patients. Using data from Schaffer et al. 77 and from Strueber et al. 83 the resulting modelled median survivals were 8.9 months and 16.5 months, respectively, providing values both higher and lower than that modelled for the BTDB inotrope patients (9.1 months). The resulting lifetime ICERs of £55,058 per QALY and £51,731 per QALY differed little from the deterministic base-case value of £55,173 per QALY. More recently Aaronson et al. 94 reported that the SHFM predicted 43% survival at 1 year for a MM group equivalent to the 140 BTT patients investigated in a HW study. This equates to a median predicted survival of 9.86 months, again very close to that modelled from our BTDB inotrope patients. Thus, when survival under MM is modelled according to these SHFM scores, the ICER estimates remain similar to that of the base case.
Some UK clinical experts expressed the view that a median survival of 9 months was too generous an estimate for inotrope-dependent MM patients entered onto UK lists for HT. On their suggestion sensitivity analysis was therefore undertaken in which the TP for MM to death was modelled on the survival of the optimum MM control group of the REMATCH trial (median survival 4.94 months); the resulting lifetime ICER (£55,203/QALY) was hardly different to that in the base case. The reason for this is that although the poorer survival of the MM arm results in an increase in the difference in QALYs between BTT and MM this poorer survival also results in lower costs in the MM group and an increase in the difference in costs between BTT and MM, and these factors tend to cancel out when calculating the ICER. It is interesting that under the base-case scenario, varying the survival of the MM arm between 3.9 and 16.5 months has negligible impact on the resulting lifetime ICER.
When the comparator population is constituted from the whole BTDB MM population (analysis A1), the ICER indicates that BTT is dominated, that is BTT is found to be more costly and less beneficial than MM. Similarly when a high probability of receiving a HT is applied to both groups (C1i), or if the MM arm is allocated a high probability but the BTT arm a low probability as in previous analyses (C1ii), BTT is dominated or the ICER becomes extremely large. These results indicate the critical importance of both the selection of an appropriate comparator population and of ensuring that an equal opportunity of receiving a HT is allocated to both groups.
These alternative scenarios have been modelled over the lifetime of the patient (i.e. until all patients have died). As in the base case, models with shorter time-horizons result in higher ICERs.
II] Impact of changing inputs for cost
Analysis II A change to device cost
We reduced the mean cost of the VAD by 10–76% to identify its impact on the ICER. The largest reduction in ICER was noticed at 76% reduction, where the 10-year and lifetime horizons of the model were more cost-effective (Table 71). Although the device has already been priced and marketed, this sensitivity analysis may inform reimbursement agencies in identifying the maximum price they may be willing to accept on the basis of cost-effectiveness.
| % reduction in device cost | Time period | VAD mean cost (£) | New ICER (£/QALY) | Deterministic base-case ICER (£/QALY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 3 years | 168,537 | 112,605 | 122,730 |
| 10 years | 204,591 | 63,613 | 68,088 | |
| Lifetime | 231,774 | 51,739 | 55,173 | |
| 15 | 3 years | 164,509 | 107,502 | 122,730 |
| 10 years | 200,563 | 61,348 | 68,088 | |
| Lifetime | 227,746 | 50,106 | 55,173 | |
| 20 | 3 years | 160,481 | 102,400 | 122,730 |
| 10 years | 196,534 | 59,083 | 68,088 | |
| Lifetime | 223,718 | 48,474 | 55,173 | |
| 30 | 3 years | 152,424 | 92,194 | 122,730 |
| 10 years | 188,477 | 54,553 | 68,088 | |
| Lifetime | 215,661 | 45,209 | 55,173 | |
| 40 | 3 years | 144,367 | 81,989 | 122,730 |
| 10 years | 180,420 | 50,023 | 68,088 | |
| Lifetime | 207,604 | 41,943 | 55,173 | |
| 50 | 3 years | 136,310 | 71,784 | 122,730 |
| 10 years | 172,364 | 45,493 | 68,088 | |
| Lifetime | 199,547 | 38,678 | 55,173 | |
| 76 | 3 years | 115,361 | 45,250 | 122,730 |
| 10 years | 151,415 | 33,715 | 68,088 | |
| Lifetime | 178,599 | 30,189 | 55,173 |
These results indicate that under the base-case scenario a modest reduction in device cost of 15% reduces the ICER to a threshold of ∼ £50,000 per QALY, which is close to values used by NICE for treatments which satisfy end of life criteria. To bring the ICER to a threshold of £30,000 per QALY requires a very substantial reduction to the cost of the device of 76%.
Analysis II A: Change to patient maintenance cost supported on ventricular assist device
A sensitivity analysis considered that patients implanted with second- and third-generation VADs rather than first-generation devices experience fewer adverse events. The base-case monthly cost of immediate and long-term follow-up under VAD support was based on appropriately adjusted data from a previous study obtained in an era of transition between use of early and later generation devices. A reduction of 30% to this base-case cost resulted in an ICER of £42,914 over a lifetime time horizon (Table 72). It should be borne in mind that to date there are no firm data to support a conclusion that patients experience 30% fewer adverse events after implantation of second- and third-generation VADs. However, one publication identified in the clinical effectiveness systematic review (Ventura et al. 82) reported a non-randomised comparative study of HMII (n = 484) compared with the pulsatile HMXVE (n = 673) finding a significantly higher rate of hospitalisation for infection post implant for the pulsatile device. In addition, the RCT of DT with patients ineligible for HT conducted by Slaughter et al. ,47 comparing HMII with the pulsatile HMXVE device, reported lower risk in the HMII group for a wide range of adverse events (bleeding, stroke, rehospitalisation) and statistically lower rates of infection.
| Time period | Mean cost (£) | Cost difference (£) | New ICER (£/QALY) | Base-case ICER (£/QALY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-year time horizon | ||||
| VAD | 153,381 | |||
| MM | 79,637 | 73,744 | 94,529 | 122,730 |
| 10-year time horizon | ||||
| VAD | 183,939 | |||
| MM | 91,450 | 92,488 | 51,960 | 68,088 |
| Lifetime model | ||||
| VAD | 209,998 | |||
| MM | 104,106 | 105,892 | 42,914 | 55,173 |
Analysis II C: Sensitivity analysis around costs for both arms using Golden Jubilee National Hospital data
Sensitivity analysis used variations on cost inputs for both arms based on the GJNH finance department costs; results are shown in Table 73. All ICERs (3 year, 10 year and lifetime) are higher than base case with these alternative costings.
| Time period | Mean cost (£) | Cost difference (£) | New ICER (£/QALY) | Deterministic base-case ICER (£/QALY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-year time horizon | ||||
| VAD | 145,431 | |||
| MM | 12,954 | 132,477 | 167,692 | 122,730 |
| 10-year time horizon | ||||
| VAD | 159,856 | |||
| MM | 19,048 | 140,808 | 79,106 | 68,088 |
| Lifetime model | ||||
| VAD | 175,303 | |||
| MM | 27,069 | 148,234 | 60,014 | 55,173 |
Analysis II D: Sensitivity analysis around costs for both arms using national schedule of reference costs data
In this sensitivity analysis we altered costs for both arms using variations in cost inputs based on the NSRC for 2010/11;122 results are shown in Table 74. All ICERs (3 year, 10 year and lifetime) are higher than base case with these alternative costings.
| Time period | Mean cost (£) | Cost difference (£) | New ICER (£/QALY) | Deterministic base-case ICER (£/QALY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-year time horizon | ||||
| VAD | 134,907 | |||
| MM | 25,832 | 109,075 | 138,158 | 122,730 |
| 10-year time horizon | ||||
| VAD | 171,016 | |||
| MM | 35,879 | 135,137 | 75,980 | 68,088 |
| Lifetime model | ||||
| VAD | 198,200 | |||
| MM | 48,533 | 149,667 | 60,654 | 55,173 |
III] Impact of changing utility values for health states
Univariate sensitivity analysis was undertaken replacing base-case utilities by those reported by Sharples et al. ;30 no large deviation in ICER was noticed (Table 75).
| Time period | Mean QALY | QALY difference | New ICER (£/QALY) | Deterministic base-case ICER (£/QALY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-year time horizon | ||||
| VAD | 1.31 | |||
| MM | 0.63 | 0.69 | 141,360 | 122,730 |
| 10-year time horizon | ||||
| VAD | 2.65 | |||
| MM | 1.07 | 1.58 | 76,823 | 68,088 |
| Lifetime model | ||||
| VAD | 3.85 | |||
| MM | 1.64 | 2.21 | 61,536 | 55,173 |
Tornado diagram
In sensitivity analysis the sources of all major base-case inputs were retained, but their values were raised and lowered at a fixed rate of 30% from their original values. For each parameter change, the percentage impact on the ICER is shown graphically in the form of a tornado diagram (Figure 65).
FIGURE 65.
Tornado diagram. The bars indicate the effect on the base-case deterministic ICER (£55,173/QALY) of a 30% increase or decrease in input values for each of the input parameters listed on the right-hand side of the figure. Note: change to monthly cost of the BTT and MM arms included 30% increase or decrease to both pre-HT and post-HT costs.
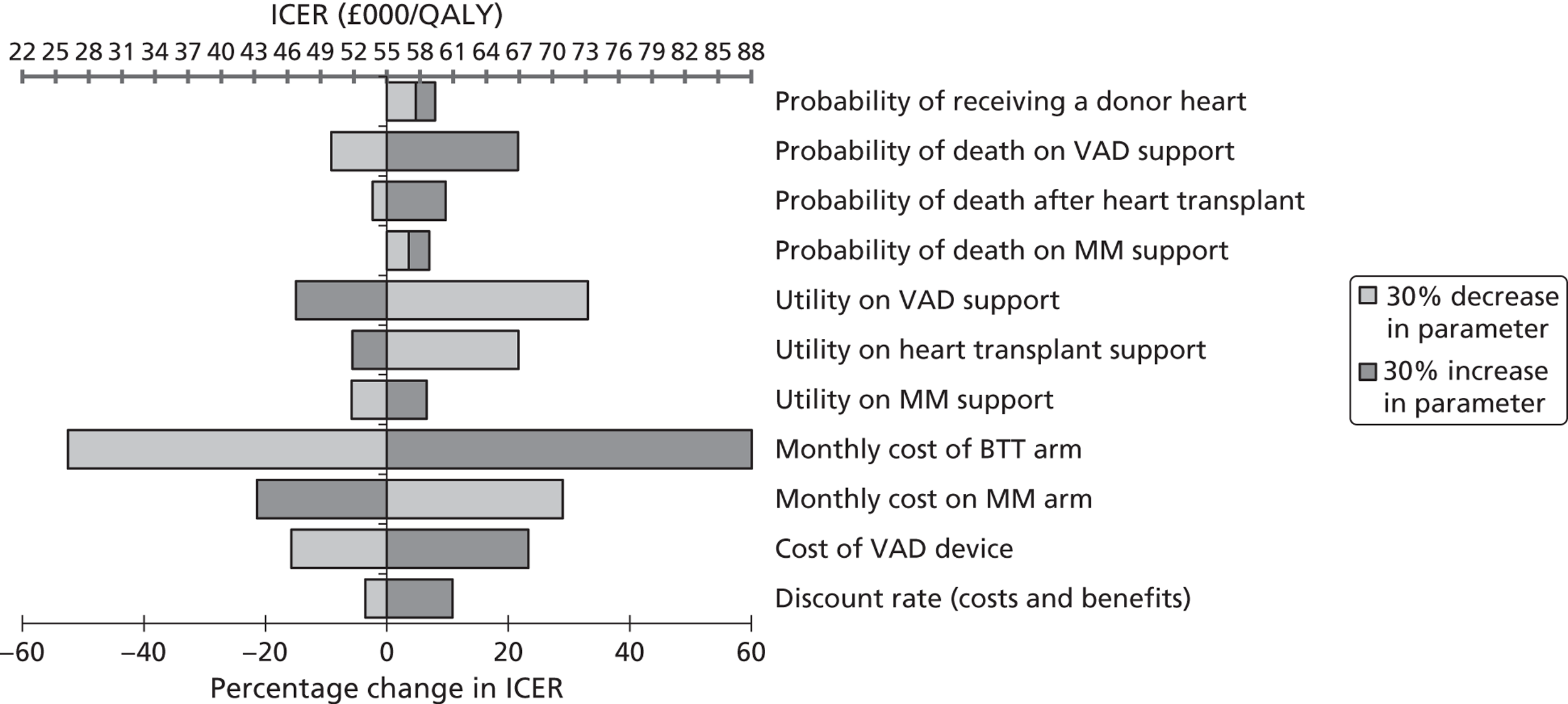
These analyses indicate that the most influential inputs were the monthly cost on BTT support, the monthly cost on MM support, and utility on VAD support. The probability of death while supported with a VAD was not influential in this over a ± 30% range of change. These results coincide with findings from the previous sensitivity analyses except that the time to HT is not influential in this analysis. This is because here the opportunity of receiving a donor heart has been kept the same for both VAD (BTT) and MM arms.
Base-case results for research question 2
Where data permit, what is the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of second- and third-generation VADs used as ATT in comparison with their use as BTT therapy? This comparison addresses a hypothetical scenario in which VAD recipients in one arm (ATT) have no opportunity of receiving a donor heart, whereas the BTT arm retains the same chance of a transplant as observed for BTDB BTT patients.
Base-case deterministic results: research question 2
The base-case TP inputs as listed for BTT VAD recipients for research question 1, and corresponding costs and utilities were applied to the comparator arm. For the ATT arm all inputs were the same as for the BTT arm except that the probability of receiving a donor heart was set to zero. It is recognised that ATT for patients suitable for HT is not currently a therapeutic option for the UK HF patients.
The base-case results for the deterministic model are represented for 3-year, 10-year and lifetime time horizons of the model, and these are tabulated in Tables 76 and 77. We have also presented results on a cost-effectiveness plane together with a CEAC (see Figures 66 and 67).
| Time horizon | Mean cost (£) | Mean survival (years) | Mean QALYs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-year time horizon | |||
| VAD – ATT | 165,990 | 1.96 | 1.45 |
| BTT | 176,594 | 1.96 | 1.48 |
| Difference | −10,604 | 0 | −0.03 |
| ICERs (£/LYG) | Cannot be calculated | ||
| ICERs (£/QALY) | 353,467 | ||
| 10-year time horizon | |||
| VAD – ATT | 197,319 | 3.33 | 2.47 |
| BTT | 212,648 | 3.81 | 2.96 |
| Difference | −15,329 | −0.48 | −0.48 |
| ICERs (£/LYG) | 31,685 | ||
| ICERs (£/QALY) | 31,685 | ||
| Lifetime model | |||
| VAD – ATT | 207,019 | 3.62 | 2.60 |
| BTT | 239,831 | 5.41 | 4.27 |
| Difference | −32,812 | −1.79 | −1.59 |
| ICERs (£/LYG) | 18,331 | ||
| ICERs (£/QALY) | 20,637 | ||
The ICERs (cost/QALY) for VAD as an ATT compared with VAD as a BTT over the 3-year, 10-year and lifetime study periods are £353,467, £31,685 and £20,637, respectively, but it should be noted that ATT costs less than BTT and delivers reduced benefit.
Over 3 years the ATT arm cost £10,604 less than the BTT arm and generated 0.03 fewer QALYs. At 10 years the ATT arm cost £15,329 less than the BTT arm and generated 0.48 fewer QALYs, and over a lifetime the VAD as ATT arm cost £32,813 less and generated 1.59 fewer QALYs. Thus, over a 50-year time horizon 1.59 QALYs are sacrificed at a cost saving rate of £20,637 per QALY.
Base-case probabilistic results: research question 2
Base-case probabilistic results are summarised in Table 77 and indicate a lifetime horizon ICER of £21,393 per QALY. The ICER falls mainly across the south-west quadrant, with a few results in the north-west quadrant, indicating that a VAD as an ATT is less effective and in some of the simulations is more costly. VADs as an ATT is, on the whole, cheaper – but confers less health gain. These findings are illustrated graphically in Figures 66 and 67. The cost-effectiveness plane for 3-year, 10-year and lifetime probabilistic estimates for VAD as an ATT compared with VAD as a BTT are shown in Figure 66 and base-case results are presented as CEACs for 3-year, 10-year and lifetime time horizons of the model in Figure 67.
| Costs | Mean cost (£) | Mean survival (years) | Mean QALYS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-year time horizon | |||
| VAD – ATT | 167,400 | 1.97 | 1.46 |
| BTT | 177,430 | 1.97 | 1.50 |
| Difference | −10,030 | 0 | −0.04 |
| ICERs (£/LYG) | Cannot be calculated | ||
| ICERs (£/QALY) | 309,561 | ||
| 10-year time horizon | |||
| VAD – ATT | 195,745 | 3.34 | 2.48 |
| BTT | 213,626 | 3.84 | 2.97 |
| Difference | −17,881 | −0.49 | −0.50 |
| ICERs (£/LYG) | 36,490 | ||
| ICERs (£/QALY) | 35,760 | ||
| Lifetime Model | |||
| VAD – ATT | 206,153 | 3.62 | 2.68 |
| BTT | 241,023 | 5.47 | 4.32 |
| Difference | −34,870 | −1.85 | −1.63 |
| ICERs (£/LYG) | 18,849 | ||
| ICERs (£/QALY) | 21,393 | ||
FIGURE 66.
Cost-effectiveness planes for 3-year, 10-year and lifetime time horizons. The dashed line indicates a saving of £30,000 for the sacrifice of 1 QALY.
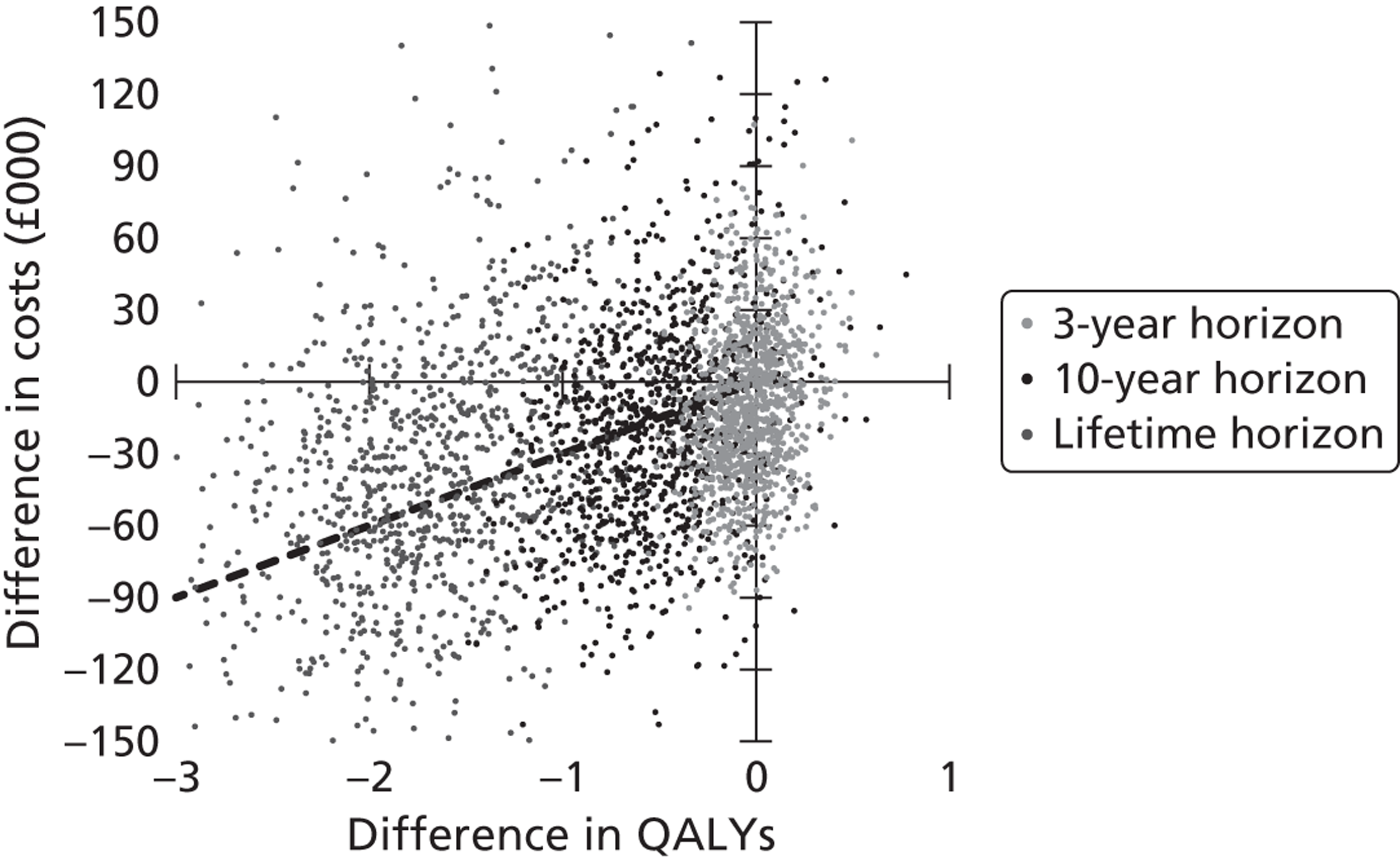
FIGURE 67.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for VAD as an ATT vs. VAD as a BTT.
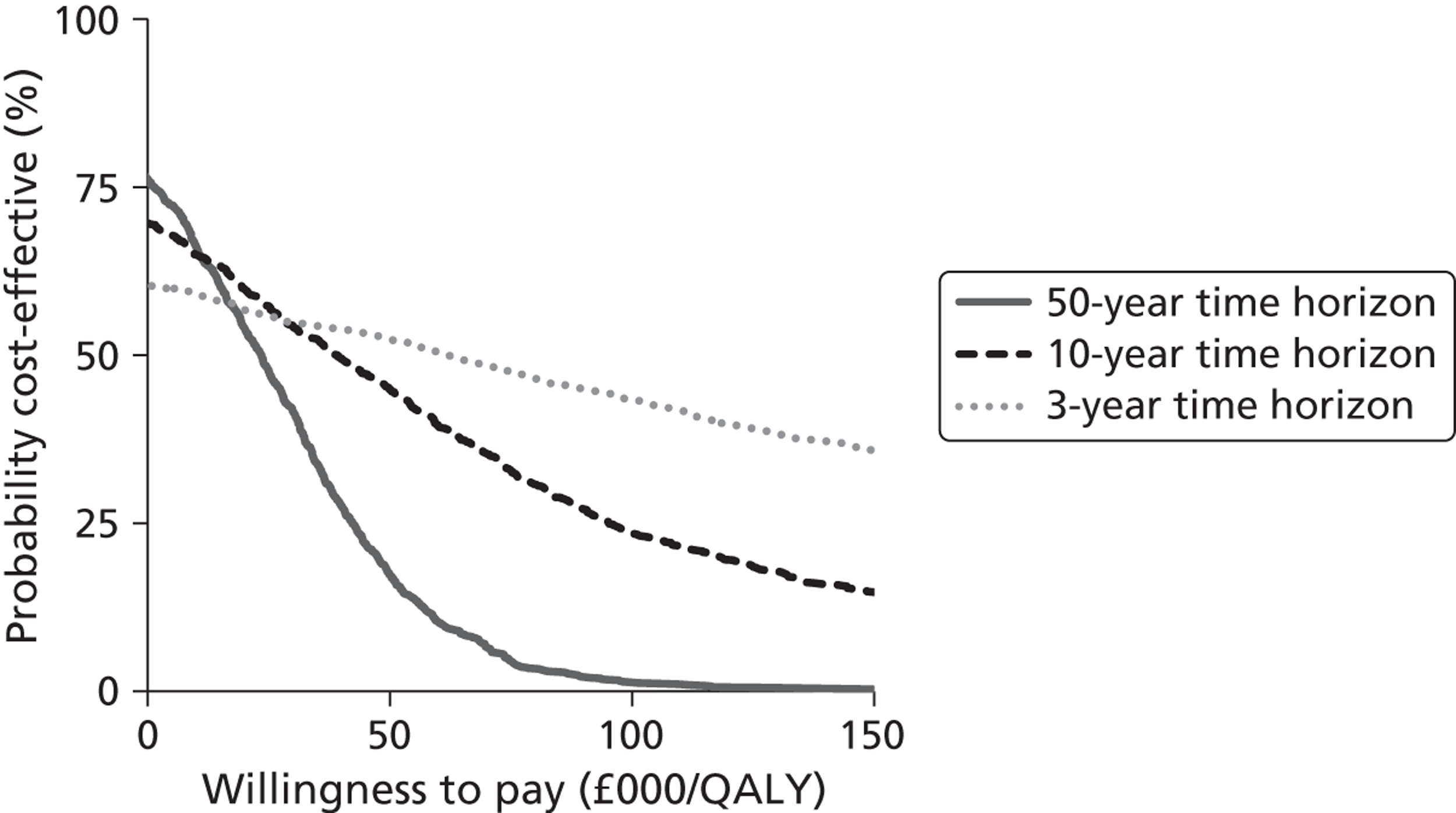
These findings tell us that, relative to VAD for a BTT, VAD as an ATT over a 10-year or lifetime time horizon costs less and confers less benefit. At 10 years the intervention is just above ∼ £30,000 per QALY plane – albeit mainly within the ‘south-west’ rather than the ‘north-east’ quadrant.
In the final chapter we summarise our findings, discuss the strengths and limitations of the work and make recommendations for future research.
Chapter 10 Discussion
Summary of research questions and methods
We aimed to answer two research questions:
In patients aged ≥ 16 years with advanced HF who are eligible for HT:
-
What is the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of second- and third-generation VADs used as a BTT compared with MM?
-
Where data permit, what is the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of second- and third-generation VADs used as an ATT in comparison with their use as a BTT therapy?
Our objectives were:
-
to summarise previously published HTA reports by Clegg et al. 4 and Sharples et al. 30 on VADs
-
to undertake a systematic review and evidence synthesis of the relevant clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness literature
-
to further develop the cost-effectiveness and cost–utility models developed in the 2006 HTA: Evaluation of the ventricular assist device programme in the UK30 and where possible to compare the use of VADs as a BTT firstly with MM and secondly as an ATT
-
to investigate the factors that drive cost-effectiveness estimates
-
to report on findings and make recommendations for future research.
We summarised previous research in the area and undertook systematic reviews of the evidence on the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of second- and third-generation VADs, including studies which had control groups, or were case series with ≥ 50 patients. Studies had to relate to patients with advanced HF suitable for receipt of an LVAD, RVAD or BiVAD as a BTT or as potential long-term alternative to HT. We investigated potential comparators. Patient outcomes included survival, functional capacity (e.g. change in NYHA functional classification), QoL and adverse events. We used recognised quality assessment methods and produced a narrative review.
Data from the NHS BTDB were obtained from the BTNR maintained on behalf of the UK transplant community. We used review findings and IPD to build a model to compare costs and effectiveness of VADs firstly used as a BTT with MM and secondly used as an ATT. To estimate quality-adjusted survival a discrete-time, semi-Markov, multistate model was developed. The discount rate was 3.5%, the time horizon varied (with 3-year, 10-year and lifetime time horizons investigated) and the analysis was undertaken from the perspective of the NHS. We reported the findings using both deterministic and probabilistic methods and undertook multiple sensitivity analyses varying survival, utilities and costs inputs to the model.
Summary of clinical effectiveness evidence
A total of 40 observational publications42,52,53,56–92 were included; 2952,53,56–82 involved HMII, one83 involved HW, one84 involved the MicroMed DeBakey VAD, one86 involved Berlin Heart INCOR, two42,85 involved DuraHeart, and six further studies reported on a mixture of devices. Nineteen studies reported that the patients received a BTT; the remaining studies reported results for a mix of patients some receiving a BTT and some DT. In some studies the reason for VAD implantation was not clearly reported.
No direct comparative evidence was found for the clinical effectiveness of second- and third-generation VADs used as a BTT compared with MM or best supportive care. Furthermore, there was no direct evidence for the clinical effectiveness of second- and third-generation VADs used as an ATT in comparison with their use (1) as a BTT and (2) with MM and subsequent HT. This is in line with previous findings on first-generation devices (Clegg et al. 4 and Sharples et al. 30).
The 40 included publications reported outcomes for repeatedly overlapping populations. Therefore, to avoid double counting, the results presented have focussed on the study or studies with the largest relevant population that reported on outcome results with sufficient rigour and coverage. The results from such studies are difficult to interpret in an assessment of the clinical effectiveness of BTT.
The majority of studies were rated as of moderate quality or less. In over half of the studies, it was not possible to tell if the participants were representative of the target population. This was mainly due to limited or no information on baseline characteristics.
All included studies were observational in design and were potentially at risk of bias. Studies were mostly non-comparative, always non-randomised, non-blinded and often retrospective. Although several studies did compare the findings of different VADs (e.g. HMII vs. HMXVE and HMII vs. HMI) these studies often provided insufficient detail to judge the adequacy or relevance of the comparator groups and so the potential for bias remained. The technology is changing rapidly in this area. We have highlighted the evidence currently available on the effectiveness of second- and third-generation devices. However, with the exception of HMII, evidence is limited although we are aware of a recently published study of HW by Aaronson et al. 94
Analyses of included publications suggested the following estimates for baseline characteristics of participants in BTT studies: the majority of participants were white (78–94%), male 84.2% (95% CI 79.4% to 88.0%) and middle aged [mean age was estimated at 50.8 years (95% CI 49.3 to 52.4 years)]; mean BMI was in the overweight range, estimated at 26.5 kg/m2 (95% CI 25.7 to 27.3 kg/m2); one-quarter of patients, 25.2% (95% CI 17.4% to 35.1%) were estimated to have diabetes mellitus; study participants had very severe HF, with 83.5% (95% CI 78.0% to 87.9%) overall rated as NYHA class IV; most participants were supported with inotrope medication (80.8%; 95% CI 50.9% to 94.5%) and had low mean systolic BP (97.3 mmHg; 95% CI 92.8 to 101.7 mmHg).
By 12 months patients had suffered a variety of serious complications. Studies reported the following ranges for adverse events: 4–27% bleeding requiring transfusion; 1.5–40% stroke; 3.3–48% infection (sepsis); 1–14% device failure; 3–30% HF; 11–32% reoperation; and 3–53% renal failure. Publications reported results from a variety of QoL and functional status measures; these indicated that patients supported by HMII and HW VADs for up to 6 and 12 months, respectively, experienced an improved QoL and functional status relative to their condition pre implantation. Overall, patients who were supported by a VAD and survived appeared to have an improved QoL and functional status from before implantation of the device.
The adverse event rates reported (including, for example, stroke and renal failure) are high. However, this needs to be read in the context of patients with advanced HF, whose vascular and renal function are likely to have been poor prior to intervention, and whose QoL and life expectancy are poor (e.g. a substantial chance of dying within a year with conventional therapy without VAD; see Chapters 6 and 10). These patients are receiving VADs as a BTT, their options without the intervention may be limited and they may be prepared to accept a high risk of adverse events in an attempt to achieve a better QoL post transplant.
Strengths of systematic review of clinical effectiveness evidence
Our review was rigorous and followed clear systematic methods to ensure robust coverage and quality assessment of available evidence. We were informed by clinical and methodological experts who advised about the development of the research protocol and the report.
Limitations of systematic review of clinical effectiveness evidence
Studies in this area reported on heterogeneous populations, were of modest or poor quality and reported on diverse outcomes over diverse time periods. This made synthesis and/or pooling of study data problematic and use of meta-analysis of outcome measures was not an option.
Mixed populations receiving destination and bridge to transplant therapies
The reason for VAD use varied across the 40 publications. It was not always clear what the indication for treatment was. Although every attempt was made to identify papers concerned with BTT, in those studies that involved both a BTT and a DT, results were frequently not reported separately.
Different numbers of patients at each period
Analysis of different time periods in several publications was undertaken on different numbers of participants. This was likely to be attributable to several factors (e.g. death and transplantation). It was also noted that outcomes (e.g. survival) were often reported at different follow-up time points across the included studies, which presented difficulties when analysing findings. Attrition rates were difficult to determine. Some studies did report missing data and withdrawals. However, owing to the nature of the studies (i.e. retrospective), there was limited reporting of dropouts and their reasons.
Duplication of data and heterogeneity
As many publications reported on patients who were participants in other studies, the extent of duplication was difficult to determine precisely. We were unable to contact authors to clarify overlaps.
Summary of cost-effectiveness evidence
Using rigorous systematic review methods we identified only one relevant study of cost-effectiveness of second- and third-generation VADs. 98 This was a good-quality, cost-effectiveness modelling study which allocated equal probability of receiving a HT to both groups of patients (VADs and MM); this contrasts with the analysis of Sharples et al. 30 in which MM patients received a donor heart with much greater probability than BTT patients reflecting actual UK clinical practice. It appears sensible for the purposes of a fair comparison between treatment options that each should have an equal opportunity of receiving the benefits of a transplant.
Our model was built using data from a UK database (BTDB) with large sample size reflecting UK practice and under a range of model scenarios and sensitivity analyses. We investigated cost-effectiveness of BTT for patients implanted with a second- or third-generation VAD, compared with MM candidates. BTT patients had higher mean costs with higher survival benefit. This was the case for nearly all the various scenarios examined for BTT patients compared with MM patients and for all time horizons considered (3 years, 10 years and lifetime), exceptions occurring when the MM arm was represented by all BTDB MM patients or when chance of a transplant was much greater for MM patients than for BTT patients. Both our probabilistic and deterministic results were confirmatory of these results.
In the base-case scenario with a deterministic analysis, for the lifetime model, the ICER for VAD patients compared with MM patients was £55,173. For a shorter time horizon of 3 years the ICER was much higher at £122,730. Using a wide range of model assumptions and scenarios the three time horizons gave us costs per QALY in the range £55,173–122,730 in the base case. The base-case probabilistic lifetime ICER was £53,527 per QALY. The base-case ICER was notably stable to sensitivity analyses in which the median survival during MM was varied between 3.9 and 16.5 months.
We found that, relative to currently employed willingness-to-pay thresholds, VADs as a BTT cannot be considered cost-effective compared with MM. However, for the lifetime horizon the ICER approaches willingness-to-pay thresholds that have been applied by NICE under specified end of life criteria. The cost of VADs would need to be reduced by 15% in order to bring the base-case lifetime ICER to £50,000 per QALY. To bring the ICER to £30,000 per QALY would require a reduction in device cost of 76%.
Sensitivity analyses demonstrated that the model inputs most influential in affecting the estimated ICER of BTT with a VAD compared with MM to transplant were:
-
The choice of the comparator population For the base case we selected BTDB MM patients classified as ‘inotrope’ as the comparator population and the resulting ICER was £55,173 per QALY. This choice can be justified on the following grounds: (a) there was no direct comparative or randomised evidence to inform choice of comparator; (b) 77% of BTT patients in the BTDB were using inotropes at baseline, while only 20% of MM patients were classified as using inotropes; (c) the SHFM95 score for VAD patients taken from the published literature (Schaffer et al. 77 and Strueber et al. 83) and for BTT patients, the BTDB predict survival that is consistent with that of the ‘inotrope’ MM patients; (c) clinical advice and published opinion116 indicate that patients who receive BTT therapy have poorer prognosis than the generality of MM patients. This choice was critical in determining the cost-effectiveness estimate; this was demonstrated when all MM patients were compared with all BTT patients – the former exhibited superior delivery of benefit and was less costly. It should be noted that varying median survival from 3.9 months to 16.5 months had little impact on the estimated ICER under base-case conditions.
-
The probability of receiving a donor heart For the base case we adopted an equal probability of receiving a donor heart for both arms and based this on the probability of HT observed for the BTDB BTT patients. However, in current clinical practice BTT patients have a much longer waiting time to transplant than patients supported on MM. When these probabilities are applied in the economic model, MM was cheaper and yielded more QALYs than VADs as a BTT therapy.
-
Cost of the VAD When the cost of the device is reduced by 30% the ICER reduces by 18%.
-
Cost of lifetime treatment for BTT When the overall cost of VAD support was reduced by 30% the ICER was halved to £42,914 per QALYs.
One of the ‘fairest’ comparisons made, modelling a situation nearest to a RCT, was to use the SHFM95 to predict the BTDB VADs patients' survival using data from their own baseline values in order to construct an artificial ‘matched’ control group. Even with this comparison, VADs were not cost-effective at standard levels of willingness to pay, with an ICER of £55,148 at a lifetime time horizon.
For research question 2 we investigated the cost-effectiveness of VADs used as an ATT compared with VADs used as a BTT. The ICERS (cost/QALY) for a VAD as an ATT compared with a VAD as a BTT over the 3-year, 10-year and lifetime study periods were £353,467, £31,685, and £20,637, respectively, but these should be viewed carefully as ATT was cost saving while delivering less benefit than BTT. Probabilistic analysis yielded similar results over the lifetime horizon.
Strengths of the cost-effectiveness analysis
We undertook a rigorous systematic review of cost-effectiveness studies of VADs. The individual patient database from the BTDB was used for the derivation of the prediction model and for transition probabilities between health states. The use of IPD from the NHS for > 1000 patients provided substantial key clinical characteristics of patients for VAD implantation and relevant associated mortality.
All patients in the UK receiving a relevant VAD and included in the BTDB database until 2011 were included in the study. First-generation VADs were excluded. Compared with Sharples et al. 30 the BTDB database now has a large sample size to provide more robust clinical effectiveness estimates for patients from UK VADs practice. We built a discrete-time, semi-Markov, multistate cost-effectiveness model and undertook both deterministic and probabilistic analysis and extensive sensitivity analyses.
Limitations of the cost-effectiveness analysis
No randomised or controlled evidence was available to inform the choice of an appropriate MM population to act as a comparator to BTT with a VAD. The ongoing long-term cost of support with modern VADs is uncertain. It is difficult to establish the cost of adverse events experienced by patients who receive the newer generation VADs. There was a lack of sufficient IPD resource-use data; however, we have been able to update device costs and certain other costs related to resources. In some cases, when there was a complete lack of data, we have used Sharples et al. 's30 costs and inflated them to the current prices. The GJNH was the only centre that shared its cost data with us. GJNH provided detailed cost for immediate and post-operative hospital stay following VAD implant and HT, but the cost was based on one VAD implant and four HT cases. Hence, we used the cost only as a scenario analysis.
The length of follow-up of patients supported by either MM or a VAD was short and required extrapolation to model survival. We extrapolated survival data beyond observed data (especially post HT), leading to uncertainty regarding the estimation of transition probabilities in the longer term. The use of a simple constant hazard model may also be problematic in analysis. The problem is a result of poor parametric fits to the biphasic survival data seen post surgery.
We made a number of assumptions in the model, although the base-case model assumptions were explored in sensitivity analyses. The disadvantage of the BTDB is that limited clinical variables were reported for the patients in this data set to allow us to use published predictive survival models (e.g. the SHFM). 95 In addition, the BTDB did not collect information on QoL measures such as the EQ-5D or EuroQoL. The lack of individual QoL data for individuals from the BTDB meant that we had to use values from the literature for different health states. This will continue to hamper economic evaluations of VADs in the UK until these data can be routinely collected as part of the BTDB.
Conclusions and recommendations for future research
Despite the lack of randomised trials and the consequent weak design of effectiveness studies, the systematic review of clinical evidence provides support for an improvement in QoL and functional status for patients who survive implantation of a HMII or HW second-/third-generation LVAD. The lack of a comparator means that survival advantage from VAD implantation remains to be demonstrated unequivocally. There is randomised evidence from the REMATCH study that VAD implantation improves survival in patients ineligible for transplant. 119 A lack of survival benefit for some BTT patients would therefore be surprising.
We found that VADs considered as a BTT yields ICERs of £122,730, £68,088 and £55,173, respectively, when compared with MM. We found that at a lifetime time horizon, using VADs as an ATT rather than as a BTT was complex. VADs as an ATT has a reduced cost and reduced QALYs. When considered over a lifetime horizon ATT as compared with BTT is £20,637 cheaper for each QALY lost.
Future research
No RCT has yet been conducted comparing BTT with MM for patients eligible for HT; furthermore, the long-term survival after these therapies is uncertain. For ethical reasons a RCT offering equal probability of HT for each group would not be feasible. The REMATCH randomised trial119 made the comparison of VADs with MM, but only for patients for whom HT was counterindicated. REMATCH also employed a pulsatile VAD of an earlier generation than those currently used. In the context of the results from the REMATCH trial, and from a UK NHS perspective, Girling et al. 123 explored the expected value of further information (i.e. from a RCT) and considered that a further RCT was likely to be justified only for devices that cost < £60,000.
Although the REMATCH result cannot be applied for second-generation devices, and in any case was based on results from a population ineligible for transplant, it indicates that although a RCT can provide the best information on effectiveness it would need to be justified in terms of the value of information provided to bodies responsible for reimbursement decisions. However, an adequately powered trial of BTT with VAD compared with BTT with MM (or alternative VAD) with second- and third-generation devices would, if undertaken, provide far superior information for decision-makers than that currently available.
Therefore attention should be directed towards:
-
How any future evaluations of second- or third-generation VADs might be conducted. Future studies should fully assess costs, long-term patient survival, QoL, functional ability, adverse events so these may be incorporated into economic evaluation.
-
Agreement on outcome measures across future studies; in particular, length of follow-up, time points for data collection, agreed QoL and functional ability measures.
-
Consideration of support for BTBD so as to ensure that full and accurate records of all patients are kept, and that regular analyses and comparative assessments of performance with other international centres are undertaken.
-
Consideration of extending the BTDB data collection process so as to include QoL data (e.g. using the EQ-5D), and to include resource-use data in order to facilitate future cost-effectiveness evaluation.
-
Development of guidance in the use of VADs as technology and management continue to change. It will be important to monitor and update this assessment regularly.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the following for their advice and expert contribution to the report:
-
Dr Mark Petrie, Consultant Cardiologist GJNH, Glasgow and Director of the Scottish National Advanced Heart Failure Service.
-
Dr Jayan Parameshwar, Consultant Cardiologist, Transplant Physician, Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
-
Dr Guy MacGowan, Consultant Cardiologist, Freeman Hospital, the Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
-
Mr Steven Tsui, Clinical Director of Transplant Services, Papworth Hospital NHS Foundations Trust.
-
Mr Saleem Haj-Yahia, Consultant Transplant Surgeon and deputy Director of the Scottish National Advanced Heart Failure Service.
-
Professor Stephen Schueler, Consultant Cardiac Surgeon, the Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
-
Professor John Wallwork, retired transplant surgeon.
-
Dr Nicholas R Banner, Chair of UK Cardiothoracic Transplant Audit Steering Group, Royal Brompton and Harefield NHS Trust, Harefield Hospital, Middlesex UK and Imperial College.
-
Professor Martin Buxton, Professor of Health Economics, Health Economics Research Group, Brunel University.
-
Dr Linda Sharples, Programme Leader, Medical Research Council Biostatistics Unit, Institute of Public Health, University of Cambridge.
-
Dr Ewen Cummings, McMDC Consulting, Glasgow.
-
Dr Jacoby Patterson, Research Consultant, Windsor.
-
Mr Duncan Ambrose, Senior Commissioning Manager at NHS National Specialised Commissioning Team.
We are extremely grateful to:
-
NHS Blood and Transplant staff for continuing advice and support through the project including advice on the BTDB.
-
Dr Santiago Moreno (Fundació Clínic, Barcelona) for constructive discussion of the economic model and generous sharing of data.
-
Mrs Hannah Fraser for her input in assembling material and formatting the report.
Contributions of authors
Paul Sutcliffe (Associate Professor), Martin Connock (Senior Research Fellow) and Aileen Clarke (Professor of Public Health and Health Services Research) co-ordinated the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness systematic reviews.
Tara Gurung (Research Fellow) wrote the background section of the report.
Simon Briscoe (Information Specialist) developed the search strategy and undertook searches.
Paul Sutcliffe and Martin Connock screened search results and with Deepson Shyangdan (Research Fellow) screened retrieved papers against inclusion criteria, appraised the quality of papers and abstracted data from papers.
Gaurav Suri (Research Associate) and Kandala Ngianga-Bakwin analysed and critiqued the BTDB.
Martin Connock, Kandala Ngianga-Bakwin (Principal Research Fellow) and Gaurav Suri analysed the data and developed transition probabilities.
Ruth Pulikottil-Jacob, Martin Connock and Aileen Clarke developed the economic model and Hendramoorthy Maheswaran (Academic Clinical Fellow) assisted in developing and analysing the economic model.
Aileen Clarke provided advice on design and analysis, wrote the abstract, summary and discussion and with Amy Grove (Research Project Manager) co-ordinated the project.
All authors were involved in writing draft and final versions of the report.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- MacGowan G, Schueler S, Parry G. The decline in heart transplantation in the UK. BMJ 2011;342. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d2483.
- Davis RC, Hobbs FD, Lip GY. ABC of heart failure. History and epidemiology. BMJ 2000;320:39-42. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.320.7226.39.
- Poole-Wilson PA, Julian DG, Camm AJ, Fox KF, Hall RJC. Diseases of the Heart. London: Bailliere Tindall; 1989.
- Clegg AJ, Scott DA, Loveman E, Colquitt J, Hutchinson J, Royle P, et al. The clinical and cost-effectiveness of left ventricular assist devices for end-stage heart failure: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 2005;9.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Chronic Heart Failure: Management of Chronic Heart Failure in Adults in Primary and Secondary Care: Clinical Guideline No. 108 2010. www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/live/13099/50517/50517.pdf (accessed 24 May 2012).
- Dickstein K, Cohen-Solal A, Filippatos G, McMurray JJ, Ponikowski P, Poole-Wilson PA, et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008 of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail 2008;10:933-89. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejheart.2008.08.005.
- British Heart Foundation Health Promotion Research Group . Coronary Heart Disease Statistics: 2010 Edition 2010. www.bhf.org.uk/research/statistics.aspx (accessed 24 May 2012).
- McMurray JJV, Stewart S. The burden of heart failure. Eur Heart J Suppl 2002;4:D50-D58. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1520-765X(02)90160-4.
- Parameshwar J, Shackell MM, Richardson A, Poole-Wilson PA, Sutton GC. Prevalence of heart failure in three general practices in north west London. Br J Gen Pract 1992;42:287-9.
- Cowie MR, Wood DA, Coats AJ, Thompson SG, Poole-Wilson PA, Suresh V, et al. Incidence and aetiology of heart failure; a population-based study. Eur Heart J 1999;20:421-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/euhj.1998.1280.
- Stewart S, Jenkins A, Buchan S, McGuire A, Capewell S, McMurray JJ. The current cost of heart failure to the National Health Service in the UK. Eur J Heart Fail 2002;4:361-71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1388-9842(01)00198-2.
- Petersen S, Rayner M, Wolstenholme J. Coronary heart disease statistics: heart failure supplement. London: British Heart Foundation; 2002.
- Stewart S, Blue L, Walker A, Morrison C, McMurray JJ. An economic analysis of specialist heart failure nurse management in the UK: can we afford not to implement it?. Eur Heart J 2002;23:1369-78.
- Fox KF, Cowie MR, Wood DA, Coats AJ, Gibbs JS, Underwood SR, et al. Coronary artery disease as the cause of incident heart failure in the population. Eur Heart J 2001;22:228-36. http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/euhj.2000.2289.
- Palazzuoli A, Nuti R. Heart failure: pathophysiology and clinical picture. Contrib Nephrol 2010;164:1-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000313714.
- Cohn JN. The management of chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 1996;335:490-8.
- McMurray JJV, Stewart S. Epidemiology, aetiology, and prognosis of heart failure. Heart 2000;83:596-602. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/heart.83.5.596.
- Nomenclature and criteria for diagnosis of diseases of the heart and great vessels. Boston, MA: Little Brown & Co; 1994.
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network . Management of Chronic Heart Failure: a National Clinical Guideline: No. 95 2007. www.sign.ac.uk/pdf/sign95.pdf (accessed 24 May 2012).
- Mant J, Al-Mohammad A, Swain S, Laramee P. Management of chronic heart failure in adults: synopsis of the National Institute For Health and clinical excellence guideline. Ann Intern Med 2011;155:252-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-155-4-201108160-00009.
- Sutherland K. Bridging the Quality Gap: Heart Failure 2010. www.health.org.uk/publications/bridging-the-quality-gap-heart-failure/ (accessed 28 May 2012).
- Murphy NF, Simpson CR, McAlister FA, Stewart S, MacIntyre K, Kirkpatrick M, et al. National survey of the prevalence, incidence, primary care burden, and treatment of heart failure in Scotland. Heart 2004;90:1129-36. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/hrt.2003.029553.
- O’Leary N, Murphy NF, O’Loughlin C, Tiernan E, McDonald K. A comparative study of the palliative care needs of heart failure and cancer patients. Eur J Heart Fail 2009;11:406-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/eurjhf/hfp007.
- de Giuli F, Khaw KT, Cowie MR, Sutton GC, Ferrari R, Poole-Wilson PA. Incidence and outcome of persons with a clinical diagnosis of heart failure in a general practice population of 696,884 in the United Kingdom. Eur J Heart Fail 2005;7:295-302.
- Hobbs FD, Kenkre JE, Roalfe AK, Davis RC, Hare R, Davies MK. Impact of heart failure and left ventricular systolic dysfunction on quality of life: a cross-sectional study comparing common chronic cardiac and medical disorders and a representative adult population. Eur Heart J 2002;23:1867-76. http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/euhj.2002.3255.
- Bartoli CR, Dowling RD. The future of adult cardiac assist devices: novel systems and mechanical circulatory support strategies. Cardiol Clin 2011;29:559-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ccl.2011.08.013.
- Friedrich EB, Bohm M. Management of end stage heart failure. Heart 2007;93:626-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/hrt.2006.098814.
- Banner NR, Bonser RS, Clark AL, Clark S, Cowburn PJ, Gardner RS, et al. UK guidelines for referral and assessment of adults for heart transplantation. Heart 2011;97:1520-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2011-300048.
- Stehlik J, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, Aurora P, Christie JD, Kirk R, et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: twenty-seventh official adult heart transplant report – 2010. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29:1089-103. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2010.08.007.
- Sharples LD, Buxton M, Caine N, Cafferty F, Demiris N, Dyer M, et al. Evaluation of the ventricular assist device programme in the UK. Health Technol Assess 2006;10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2006.09.011.
- Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures – Surgical (ASERNIP-S) . Continuous Flow Ventricular Assist Devices for Bridge to Transplantation 2008. www.horizonscanning.gov.au/internet/horizon/publishing.nsf/Content/211ABF81A69CA39DCA2575AD0080F3DC/$File/HSR%20%20Continuous%20flowVADs%20HSR%20Nov%2008.pdf (accessed 14 June 2013).
- Stewart GC, Givertz MM. Mechanical circulatory support for advanced heart failure: patients and technology in evolution. Circulation 2012;125:1304-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.060830.
- Shams OF, Ventura HO. Device therapy for heart failure: when and for whom?. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 2008;8:147-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.2165/00129784-200808030-00001.
- Kirklin JK, Naftel D, Kormos R, Stevenson LW, Pagani FD, Miller MA, et al. Third INTERMACS annual report: the evolution of destination therapy in the United States. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;302:115-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2010.12.001.
- Birks EJ. Left ventricular assist devices. Heart 2010;96:63-71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/hrt.2007.130740.
- Birks EJ. The comparative use of ventricular assist devices: differences between Europe and the United States. Tex Heart Inst J 2010;37:565-7.
- Nguyen DQ, Thourani VH. Third-generation continuous flow left ventricular assist devices. Innov Technol Tech Cardiothorac Vasc Surg 2010;5:250-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/IMI.0b013e3181ee77a1.
- Thoratec . A New Era for the Treatment of Advanced Heart Failure: 2008 Annual Report 2008. http://phx.corporate-ir.net/External.File?item=UGFyZW50SUQ9MzMyMjk4fENoaWxkSUQ9MzE0ODY5fFR5cGU9MQ==&t=1 (accessed 28 May 2012).
- Noon GP, Loebe M. Current status of the MicroMed DeBakey Noon Ventricular Assist Device. Tex Heart Inst J 2010;37:652-3.
- Timms D. A review of clinical ventricular assist devices. Med Eng Phys 2011;33:1041-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2011.04.010.
- Terumo Heart . How DuraHeart Works 2012. www.terumoheart.com/us/index.php/medical-professionals/how-it-works (accessed 31 May 2012).
- Morshuis M, Schoenbrodt M, Nojiri C, Roefe D, Schulte-Eistrup S, Boergermann J, et al. DuraHeart magnetically levitated centrifugal left ventricular assist system for advanced heart failure patients. Expert Rev Med Devices 2010;7:173-83. http://dx.doi.org/10.1586/erd.09.68.
- Krishnamani R, DeNofrio D, Konstam MA. Emerging ventricular assist devices for long-term cardiac support. Nat Rev Cardiol 2010;7:71-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2009.222.
- Felix SE, Martina JR, Kirkels JH, Klopping C, Nathoe H, Sukkel E, et al. Continuous flow left ventricular assist device support in patients with advanced heart failure: points of interest for the daily management. Eur J Heart Fail 2012;14:351-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/eurjhf/hfs012.
- Rose EA, Gelijns AC, Moskowitz AJ, Heitjan DF, Stevenson LW, Dembitsky W, et al. Long-term use of a left ventricular assist device for end-stage heart failure. N Engl J Med 2001;345:1435-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa012175.
- Stevenson LW, Miller LW, Desvigne-Nickens P, Ascheim DD, Parides MK, Renlund DG, et al. Left ventricular assist device as destination for patients undergoing intravenous inotropic therapy: a subset analysis from REMATCH (Randomized Evaluation of Mechanical Assistance in Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure). Circulation 2004;110:975-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000139862.48167.23.
- Slaughter MS, Rogers JG, Milano CA, Russell SD, Conte JV, Feldman D, et al. Advanced heart failure treated with continuous flow left ventricular assist device. New Engl J Med 2009;361:2241-51. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0909938.
- Potapov EV, Stepanenko A, Krabatsch T, Hetzer R. Managing long-term complications of left ventricular assist device therapy. Curr Opin Cardiol 2011;26:237-44. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/HCO.0b013e328345af80.
- Barnes K. Complications in patients with ventricular assist devices. Dimens Critic Care Nurs 2008;27:233-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.DCC.0000338867.24293.20.
- Pepper JR. Update on mechanical circulatory support in heart failure. Heart 2012;98:663-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2011-300735.
- Slaughter MS. UNOS status of heart transplant patients supported with a left ventricular assist device: is it time to reconsider the status criteria?. Tex Heart Inst J 2011;38:549-51.
- Starling RC, Naka Y, Boyle AJ, Gonzalez-Stawinski G, John R, Jorde U, et al. Results of the post-U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approval study with a continuous flow left ventricular assist device as a bridge to heart transplantation: a prospective study using the INTERMACS (Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support). J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;57:1890-8.
- Rogers JG, Aaronson KD, Boyle AJ, Russell SD, Milano CA, Pagani FD, et al. Continuous flow left ventricular assist device improves functional capacity and quality of life of advanced heart failure patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;55:1826-34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2009.12.052.
- Centre for Reviews and Dissemination . CRD'S Guidance for Undertaking Reviews in Health Care 2008. www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd/pdf/Systematic_Reviews.pdf (accessed 18 June 2012).
- Thomas BH, Ciliska D, Dobbins M, Micucci S. A process for systematically reviewing the literature: providing the research evidence for public health nursing interventions. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs 2004;1:176-84. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-475X.2004.04006.x.
- Adamson RM, Stahovich M, Chillcott S, Baradarian S, Chammas J, Jaski B, et al. Clinical strategies and outcomes in advanced heart failure patients older than 70 years of age receiving the HeartMate II left ventricular assist device: a community hospital experience. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;57:2487-95.
- Bogaev RC, Pamboukian SV, Moore SA, Chen L, John R, Boyle AJ, et al. Comparison of outcomes in women versus men using a continuous flow left ventricular assist device as a bridge to transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:515-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2010.12.009.
- Boyle AJ, Russell SD, Teuteberg JJ, Slaughter MS, Moazami N, Pagani FD, et al. Low thromboembolism and pump thrombosis with the HeartMate II left ventricular assist device: analysis of outpatient anti-coagulation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28:881-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2009.05.018.
- Brewer RJ, Lanfear DE, Sai-Sudhakar CB, Sundareswaran KS, Ravi Y, Farrar DJ, et al. Extremes of body mass index do not impact mid-term survival after continuous flow left ventricular assist device implantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2012;31:167-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2011.11.006.
- Cowger J, Pagani FD, Haft JW, Romano MA, Aaronson KD, Kolias TJ. The development of aortic insufficiency in left ventricular assist device-supported patients. Circ Heart Fail 2010;3:668-74.
- Demirozu ZT, Radovancevic R, Hochman LF, Gregoric ID, Letsou GV, Kar B, et al. Arteriovenous malformation and gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with the HeartMate II left ventricular assist device. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:849-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2011.03.008.
- Hasin T, Topilsky Y, Schirger JA, Li Z, Zhao Y, Boilson BA, et al. Changes in renal function after implantation of continuous flow left ventricular assist devices. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012;59:26-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2011.09.038.
- John R, Pagani FD, Naka Y, Boyle A, Conte JV, Russell SD, et al. Post-cardiac transplant survival after support with a continuous flow left ventricular assist device: impact of duration of left ventricular assist device support and other variables. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2010;140:174-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.03.037.
- John R, Kamdar F, Eckman P, Colvin-Adams M, Boyle A, Shumway S, et al. Lessons learned from experience with over 100 consecutive HeartMate II left ventricular assist devices. Ann Thorac Surg 2011;92:1593-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2011.06.081.
- John R, Naka Y, Smedira NG, Starling R, Jorde U, Eckman P, et al. Continuous flow left ventricular assist device outcomes in commercial use compared with the prior clinical trial. Ann Thorac Surg 2011;92:1406-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2011.05.080.
- Kato TS, Schulze PC, Yang J, Chan E, Shahzad K, Takayama H, et al. Pre-operative and post-operative risk factors associated with neurologic complications in patients with advanced heart failure supported by a left ventricular assist device. J Heart Lung Transplant 2012;31:1-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2011.08.014.
- Kormos RL, Teuteberg JJ, Pagani FD, Russell SD, John R, Miller LW, et al. Right ventricular failure in patients with the HeartMate II continuous flow left ventricular assist device: incidence, risk factors, and effect on outcomes. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2010;139:1316-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2009.11.020.
- Lahpor J, Khaghani A, Hetzer R, Pavie A, Friedrich I, Sander K, et al. European results with a continuous flow ventricular assist device for advanced heart-failure patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2010;37:357-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcts.2009.05.043.
- Martin SI, Wellington L, Stevenson KB, Mangino JE, Sai-Sudhakar CB, Firstenberg MS, et al. Effect of body mass index and device type on infection in left ventricular assist device support beyond 30 days. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2010;11:20-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1510/icvts.2009.227801.
- Miller LW, Pagani FD, Russell SD, John R, Boyle AJ, Aaronson KD, et al. Use of a continuous flow device in patients awaiting heart transplantation. New Engl J Med 2007;357:885-96. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa067758.
- Pagani FD, Miller LW, Russell SD, Aaronson KD, John R, Boyle AJ, et al. Extended mechanical circulatory support with a continuous flow rotary left ventricular assist device. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009;54:312-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2009.03.055.
- Pak S-W, Uriel N, Takayama H, Cappleman S, Song R, Colombo PC, et al. Prevalence of de novo aortic insufficiency during long-term support with left ventricular assist devices. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29:1172-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2010.05.018.
- Pal JD, Klodell CT, John R, Pagani FD, Rogers JG, Farrar DJ, et al. Low operative mortality with implantation of a continuous flow left ventricular assist device and impact of concurrent cardiac procedures. Circulation 2009;120:S215-19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.844274.
- Petrucci RJ, Wright S, Naka Y, Idrissi KA, Russell SD, Dordunoo D, et al. Neurocognitive assessments in advanced heart failure patients receiving continuous flow left ventricular assist devices. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28:542-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2009.02.007.
- Russell SD, Rogers JG, Milano CA, Dyke DB, Pagani FD, Aranda JM, et al. Renal and hepatic function improve in advanced heart failure patients during continuous flow support with the HeartMate II left ventricular assist device. Circulation 2009;120:2352-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.814863.
- Schaffer JM, Allen JG, Weiss ES, Arnaoutakis GJ, Patel ND, Russell SD, et al. Infectious complications after pulsatile-flow and continuous flow left ventricular assist device implantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:164-74. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2010.08.003.
- Schaffer JM, Allen JG, Weiss ES, Patel ND, Russell SD, Shah AS, et al. Evaluation of risk indices in continuous flow left ventricular assist device patients. Ann Thorac Surg 2009;88:1889-96. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2009.08.011.
- Strueber M, Sander K, Lahpor J, Ahn H, Litzler PY, Drakos SG, et al. HeartMate II left ventricular assist device; early European experience. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2008;34:289-94. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcts.2008.05.011.
- Topilsky Y, Pereira NL, Shah DK, Boilson B, Schirger JA, Kushwaha SS, et al. Left ventricular assist device therapy in patients with restrictive and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circ Heart Fail 2011;4:266-75. http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.110.959288.
- Topilsky Y, Hasin T, Oh JK, Borgeson DD, Boilson BA, Schirger JA, et al. Echocardiographic variables after left ventricular assist device implantation associated with adverse outcome. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2011;4:648-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.111.965335.
- Uriel N, Pak SW, Jorde UP, Jude B, Susen S, Vincentelli A, et al. Acquired von Willebrand syndrome after continuous flow mechanical device support contributes to a high prevalence of bleeding during long-term support and at the time of transplantation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;56:1207-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2010.05.016.
- Ventura PA, Alharethi R, Budge D, Reid BB, Horne BD, Mason NO, et al. Differential impact on post-transplant outcomes between pulsatile- and continuous flow left ventricular assist devices. Clin Transplant 2011;25:E390-E395. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0012.2011.01433.x.
- Strueber M, O’Driscoll G, Jansz P, Khaghani A, Levy WC, Wieselthaler GM, et al. Multicenter evaluation of an intrapericardial left ventricular assist system. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;57:1375-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2010.10.040.
- Goldstein DJ. Worldwide experience with the MicroMed DeBakey Ventricular Assist Device as a bridge to transplantation. Circulation 2003;108:II272-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000087387.02218.7e.
- Morshuis M, El-Banayosy A, Arusoglu L, Koerfer R, Hetzer R, Wieselthaler G, et al. European experience of DuraHeart magnetically levitated centrifugal left ventricular assist system. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2009;35:1020-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcts.2008.12.033.
- Schmid C, Jurmann M, Birnbaum D, Colombo T, Falk V, Feltrin G, et al. Influence of inflow cannula length in axial-flow pumps on neurologic adverse event rate: results from a multicenter analysis. J Heart Lung Transplant 2008;27:253-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2007.12.007.
- Drews T, Stepanenko A, Dandel M, Buz S, Lehmkuhl HB, Hetzer R. Mechanical circulatory support in patients of advanced age. Eur J Heart Fail 2010;12:990-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/eurjhf/hfq076.
- Klotz S, Stypmann J, Welp H, Schmid C, Drees G, Rukosujew A, et al. Does continuous flow left ventricular assist device technology have a positive impact on outcome pretransplant and posttransplant?. Ann Thorac Surg 2006;82:1774-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2006.05.079.
- Nativi JN, Drakos SG, Kucheryavaya AY, Edwards LB, Selzman CH, Taylor DO, et al. Changing outcomes in patients bridged to heart transplantation with continuous- versus pulsatile-flow ventricular assist devices: an analysis of the registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:854-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2011.03.019.
- Oswald H, Schultz-Wildelau C, Gardiwal A, Lusebrink U, Konig T, Meyer A, et al. Implantable defibrillator therapy for ventricular tachyarrhythmia in left ventricular assist device patients. Eur J Heart Fail 2010;12:593-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/eurjhf/hfq048.
- Sandner SE, Zimpfer D, Zrunek P, Rajek A, Schima H, Dunkler D, et al. Age and outcome after continuous flow left ventricular assist device implantation as bridge to transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28:367-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2009.01.008.
- Sandner SE, Zimpfer D, Zrunek P, Rajek A, Schima H, Dunkler D, et al. Renal function and outcome after continuous flow left ventricular assist device implantation. Ann Thorac Surg 2009;87:1072-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2009.01.022.
- Duncan BW, Lorenz M, Kopcak MW, Fukamachi K, Ootaki Y, Chen HM, et al. The PediPump: a new ventricular assist device for children. Artif Organs 2005;29:527-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1594.2005.29088.x.
- Aaronson KD, Slaughter MS, Miller LW, McGee EC, Cotts WG, Acker MA, et al. Use of an intrapericardial, continuous flow, centrifugal pump in patients awaiting heart transplantation/clinical perspective. Circulation 2012;125:3191-200.
- Levy WC, Mozaffarian D, Linker DT, Sutradhar SC, Anker SD, Cropp AB, et al. The Seattle Heart Failure Model: prediction of survival in heart failure. Circulation 2006;113:1424-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.584102.
- Black N, Barker M, Payne M. Cross sectional survey of multicentre clinical databases in the United Kingdom. BMJ 2004;328. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.328.7454.1478.
- Drummond A, Bachman T, Antaki J. Three-dimensional virtual anatomic fit study for an implantable pediatric ventricular assist device. Comput Sci 2006;3994:855-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/11758549_114.
- Moreno SG, Novielli N, Cooper NJ. Cost-effectiveness of the implantable HeartMate II left ventricular assist device for patients awaiting heart transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2012;31:450-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2011.10.017.
- Lietz K, Long JW, Kfoury AG, Slaughter MS, Silver MA, Milano CA, et al. Outcomes of left ventricular assist device implantation as destination therapy in the post-REMATCH era: implications for patient selection. Circulation 2007;116:497-505. http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.691972.
- Russo MJ, Hong KN, Davies RR, Chen JM, Sorabella RA, Ascheim DD, et al. Posttransplant survival is not diminished in heart transplant recipients bridged with implantable left ventricular assist devices. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2009;138:1425-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2009.07.034.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Guide to the Methods of Technology Appraisal 2008. www.nice.org.uk/media/B52/A7/TAMethodsGuideUpdatedJune2008.pdf (accessed 29 May 2012).
- Rogers WJ, Johnstone DE, Yusuf S, Weiner DH, Gallagher P, Bittner VA, et al. Quality of life among 5,025 patients with left ventricular dysfunction randomized between placebo and enalapril: the Studies Of Left Ventricular Dysfunction. The SOLVD Investigators. J Am Coll Cardiol 1994;23:393-400. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0735-1097(94)90426-X.
- Miller K, Myers TJ, Robertson K, Shah N, Delgado RM, Gregoric ID. Quality of life in bridge-to-transplant patients with chronic heart failure after implantation of an axial flow ventricular assist device. Congestive Heart Fail 2004;10:226-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1527-5299.2004.03258.x.
- Kugler C, Malehsa D, Tegtbur U, Guetzlaff E, Meyer AL, Bara C, et al. Health-related quality of life and exercise tolerance in recipients of heart transplants and left ventricular assist devices: a prospective, comparative study. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:204-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2010.08.030.
- Ortega T, Diaz-Molina B, Montoliu MA, Ortega F, Valdes C, Rebollo P, et al. The utility of a specific measure for heart transplant patients: reliability and validity of the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire. Transplantation 2008;86:804-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e318183eda4.
- Almenar-Pertejo M, Almenar L, Martinez-Dolz L, Campos J, Galan J, Girones P, et al. Study on health-related quality of life in patients with advanced heart failure before and after transplantation. Transplant Proc 2006;38:2524-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2006.08.017.
- Grady KL, Naftel DC, Kobashigawa J, Chait J, Young JB, Pelegrin D, et al. Patterns and predictors of quality of life at 5 to 10 years after heart transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2007;26:535-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2007.01.042.
- Kugler C, Tegtbur U, Gottlieb J, Bara C, Malehsa D, Dierich M, et al. Health-related quality of life in long-term survivors after heart and lung transplantation: a prospective cohort study. Transplantation 2010;90:451-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e3181e72863.
- Politi P, Piccinelli M, Poli PF, Klersy C, Campana C, Goggi C, et al. Ten years of ‘extended’ life: quality of life among heart transplantation survivors. Transplantation 2004;78:257-63. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.TP.0000133537.87951.F2.
- EuroQol Group . EuroQol – a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy 1990;16:199-208.
- Gohler A, Geisler BP, Manne JM, Kosiborod M, Zhang Z, Weintraub WS, et al. Utility estimates for decision-analytic modeling in chronic heart failure--health states based on New York Heart Association classes and number of rehospitalizations. Value Health 2009;12:185-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4733.2008.00425.x.
- Dyer MT, Goldsmith KA, Sharples LS, Buxton MJ. A review of health utilities using the EQ-5D in studies of cardiovascular disease. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2010;8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-8-13.
- Juenger J, Schellberg D, Kraemer S, Haunstetter A, Zugck C, Herzog W, et al. Health related quality of life in patients with congestive heart failure: comparison with other chronic diseases and relation to functional variables. Heart 2002;87:235-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/heart.87.3.235.
- Office for National Statistics . Topic Guide To: Mortality Rates 2001. www.statistics.gov.uk/hub/population/deaths/mortality-rates (accessed 25 June 2012).
- NICE Decision Support Unit . Technical Support Documents 2011. www.nicedsu.org.uk/Technical-Support-Documents(1985314).htm (accessed 19 June 2012).
- Slaughter MS, Rogers JG. Editorial commentary: determining the cost-effectiveness of mechanical circulatory support. J Heart Lung Transplant 2012;31:448-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2012.02.013.
- Collett D. Modelling survival data in medical research. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press LLC; 2003.
- Goldsmith K, Sharples L, Sudarshan C, Parameshwar J, Tsui S, Wallwork J, et al. Twenty-five years of heart transplantation at a single centre: changes in factors influencing short- and long-term survival over time. J Heart Lung Transplant 2007;262. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2006.11.426.
- Rose EA, Moskowitz AJ, Packer M, Sollano JA, Williams DL, Tierney AR, et al. The REMATCH trial: rationale, design, and end points. Randomized Evaluation of Mechanical Assistance for the Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure. Ann Thorac Surg 1999;67:723-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0003-4975(99)00042-9.
- Curtis L. Unit costs of health and social care 2011. Kent: University of Kent; Personal Social Services Research Unit; 2011.
- Personal Social Services Research Unit . Unit Costs of Health & Social Care 2010. www.education.gov.uk/publications/eOrderingDownload/PSSRU-1368-230X.pdf (accessed 18 June 2012).
- Appendix NSRC04: NHS Trusts and PTs combined reference cost schedules. London: Department of Health; n.d.
- Girling AJ, Freeman G, Gordon JP, Poole-Wilson P, Scott DA, Lilford RJ. Modeling payback from research into the efficacy of left-ventricular assist devices as destination therapy. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 2007;23:269-77. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0266462307070365.
- Assessment of neurological/neurocognitive function: guidance for industry and FDFA reviewers. Washington, DC: USDHHS; 2003.
Appendix 1 Protocol: National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment programme project number 12/02/01
1. Research questions
In patients aged 16 years and over with end-stage heart failure who are eligible for heart transplant:
-
What is the clinical and cost-effectiveness of second and third generation ventricular assist devices used as bridge to transplant compared to medical management?
-
Where data permit, what is the clinical and cost-effectiveness of second and third generation ventricular assist devices used as destination therapy (alternative to transplant (ATT)) in comparison to their use i) as bridge to transplant therapy ii) with medical management and subsequent heart transplant?
2. Name of TAR team and project ‘lead’
Produced by:
Warwick Evidence
Health Sciences Research Institute
Medical School
University of Warwick
Coventry
CV4 7AL
Lead Author:
Paul Sutcliffe
Co-authors:
Deepson Shyangdan
Martin Connock
Pamela Royle
Simon Briscoe
Helen Hall
Tara Gurung
Kandala Ngianga-Bakwin
Ruth Jacob
Gaurav Suri
Norman Waugh
Amy Grove
Aileen Clarke
Correspondence to:
Dr Paul Sutcliffe
Warwick Evidence, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry, CV4 7AL
Tel: 02476 150189
Fax: 02476 528375
Email: p.a.sutcliffe@warwick.ac.uk
Date completed: 23 February 2012
This project is commissioned by the NIHR HTA Programme as project number 12/02/01. The views expressed in this protocol are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NIHR HTA Programme. Any errors are the responsibility of the authors. The authors have no conflicts of interest.
3. Plain English Summary
Heart failure is the debilitating condition when the heart does not pump blood properly thereby limiting an individual's life activities. End-stage heart failure (ESHF) is life threatening but heart transplant (HT) offers a last resort treatment for patients not well controlled on medical therapies. Unfortunately donor hearts are in short supply and some patients are not suitable to receive one for a variety of reasons. Patients receive medicines aimed at reducing symptoms, improving quality of life and slowing progression of disease. If these fail, and a donor heart is not available, they may have surgery to receive a device (a ‘ventricular assist device’, VAD) which partly or wholly takes over the job of the heart. There are many types of device and this report aims to find out how successful they are in prolonging survival and providing good quality of life. If data permit, we will consider which devices are best. Patients who are suitable for a HT may receive a device until a donor heart becomes available. This latter option is called bridging therapy or bridge to transplant (BTT). There have been technical advances in device design and it would be useful to know which are best for bridging. Surgery and devices are expensive treatments. For the NHS to best allocate and deliver its services, relative costs and benefits of various treatments need to be estimated. Therefore another aim of this report is to relate patient's extra benefits from these treatments to the costs of the treatments and to reach an idea of their cost-effectiveness.
4. Decision problem
-
In patients with ESHF who are eligible for HT, VADS are used as BTT in patients in the UK. There are a number of newer devices and it is important to know the comparative cost-effectiveness of devices used in this way, and to know how the use of devices compares to medical management (MM).
-
Research suggests that HT is likely to offer the best treatment option in terms of both length and quality of life for these patients. However, HT is dependent on availability of donor hearts whose availability appears to be diminishing. Therefore, it will be valuable to know the comparative cost-effectiveness of VADs used as alternative to transplant (ATT) in comparison to their use as BTT. (Note: VADs are currently used in the UK as BTT and are not commissioned as ATT. This means that UK data may not be available for populating models to investigate question 1b. We will therefore use published international data where available, to make direct comparisons between VADs i) used as bridge to transplant therapy ii) with medical management and subsequent HT).
Objectives:
To:
-
Summarise previously published HTA reports1,2 on ventricular assist devices (VADs).
-
Undertake a systematic review and evidence synthesis of the relevant clinical and cost-effectiveness literature.
-
Further develop the cost-effectiveness and cost-utility models developed in the 2006 HTA: “Evaluation of the ventricular assist device programme in the UK” using findings from objectives i. and ii. and NHS Blood and Transplant, Organ Donation and Transplant Directorate data.
-
Where data permit, compare the use of VADs as ATT in comparison to their use as BTT and with medical management and subsequent HT.
-
Investigate the factors that drive costs and survival.
-
Report on findings and make recommendations on future research.
4.1 Background
Heart failure is defined as ‘a disease characterised by a decline in the heart's ability to pump blood around a person's body at normal filling pressures to meet its metabolic needs’. 1 Any anatomical or physiological condition that affects the function of ventricle can cause heart failure. This mainly includes coronary heart disease. 1 Other causes include hypertension, valvular heart diseases, myocardial toxins, myocarditis, or idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. 1 The severity of heart failure is usually assessed using the New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional classification which is based on the severity of symptoms patients develop after undertaking physical activity. The severity of the heart failure is classified into four grades of increasing severity using the NYHA classification. NYHA grade I heart failure is the least severe category. 1
Heart failure can have a considerable impact on patients' lives and also on overall health care costs. 3 In 2005, it was estimated that there would be between 250,000 and 400,000 people with heart failure in England and Wales, with approximately 7,000 to 8,000 people with ESHF. 1 The impact on overall health care cost to the NHS is high as the incidence and prevalence of heart failure is increasing due to the ageing population and the high prevalence of cardiovascular diseases. 1
Medical management with inotropic agents, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, angiotensin 2 inhibitors and aldosterone antagonists together with resynchronisation therapy has improved the survival of many with heart failure, but there remain a subgroup of patients who, despite optimal medical therapy, progress to NYHA Class III or IV heart failure. 3,4
HT offers the best effective surgical treatment for long-term survival in suitable patients with ESHF. 4 The number of HTs is severely limited by the availability of suitable donor hearts. It has been estimated that approximately 30,000 patients are waiting for HT, with approximately 3,500 donor hearts being available in the whole world annually. 4
When heart failure occurs, patients may show signs and symptoms of inadequate cardiovascular functioning, pulmonary or peripheral oedema and under perfusion of other organs such as the kidney and liver. Pulmonary hypertension can make patients ineligible for HT. Even if patients undergo HT, there is a chance of allograft rejection. In order to prevent this, patients are given variety of immunosuppressant and prophylactic drugs which in turn increases their susceptibility to opportunistic infections. 2
In order to increase survival and quality of life among selected patients waiting for HT (BTT) VADs are increasingly being used. 1–3 These include: a) left ventricular assist device (LVAD), b) right ventricular assist device (RVAD) and c) Biventricular assist device (BiVAD). Destination therapy (DT) describes a course of treatment for severe (e.g., NYHA stage IV/ACC stage D) heart failure patients using a mechanical circulatory support in place of HT. Devices are increasingly used in some non-UK countries as DT in these patients. 3,5 However, since devices are used in this way when patients are no longer eligible for HT, DT is outside the scope of this review.
As the number of donor hearts available for transplant is decreasing, there is a suggested need within the UK to determine the place of VAD as ATT in the clinical management of patients with ESHF (see Figure 1). 6
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of research questions. HT: heart transplant, BTT: bridge to transplant, VAD: ventricular assist device, ESHF: end-stage heart failure, ATT: alternative to transplant.
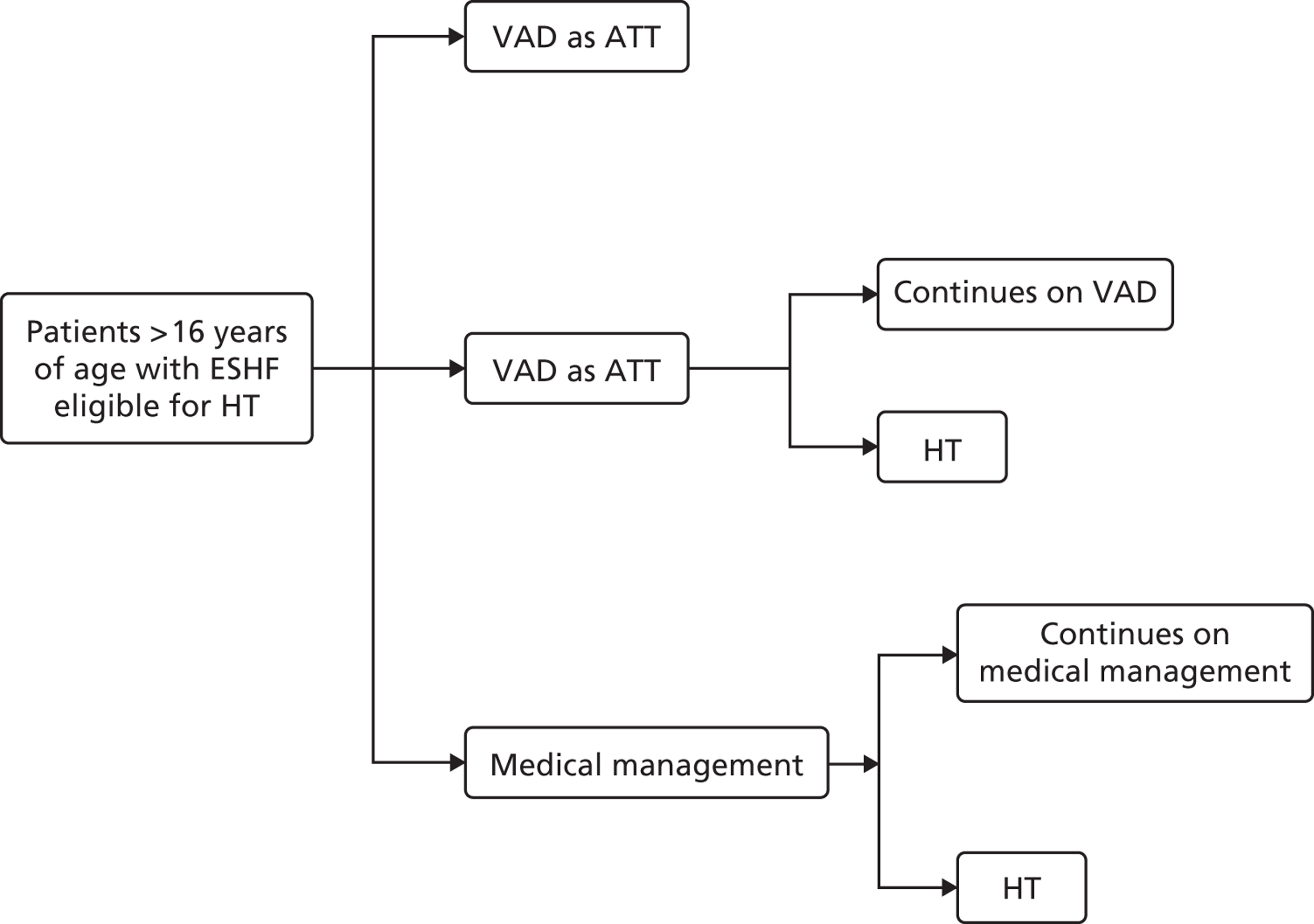
4.2 Scoping searches
The aim of the scoping searches was to establish all known devices and determine their approval status with the Conformité Européenne (CE) and Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Scoping searches were undertaken in MEDLINE (2000 to date) and on identified VAD manufacturer websites in February 2012. The scoping searches identified a range of VADs and manufacturers, which were discussed with our clinical advisors. The following tables provide a summary of the findings.
| Name of Device | Manufacturer |
|---|---|
| Coraide | Arrow International Inc |
| C-Pulse | Sunshine Heart |
| CircuLite Synergy Pump | CiculLite |
| DeBakey VAD | MicroMed |
| DuraHeart LVAS | Terumo |
| Evaheart LVAS | Evaheart Medical |
| HeartAssist5 | MicroMed |
| HeartMate II | Thoratec |
| HeartMate III | Thoratec |
| HeartMate X | Thoratec |
| HeartMate XVE, VE, and IP1000 | Thoratec |
| HeartQuest | MedQuest Products |
| Heartware MVAD | HeartWare Inc |
| HVAD | HeartWare Inc |
| INCOR | Berlin Heart |
| Implantable Ventricular Assist Device (IVAD) | Thoratec |
| Jarvik 2000 | Jarvik Heart |
| Levacor VAD | World Heart Inc |
| LionHeart | Arrow International Inc |
| MTIHeartLVAD | MiTiHeart Corporation |
| Novacor | World Heart Inc |
| Procyon circulatory assist device (CAD) | Procyon Inc |
| Rotary VAD | World Heart |
| Symphony | SCR Inc |
| Synergy | CircuLite Inc |
| TandemHeart | Cardiac Assist |
| Thoratec PVAD or IVAD | Thoratec |
| VentrAssist | Ventracor |
| Name of Device | Manufacturer |
|---|---|
| Jarvik 2000 Flow Maker | Jarvik |
| IVAD | Thoractec |
| DexAide RVAD | Cleveland Heart |
| Impella Recover RD | Abiomed |
| Impella Right Peripheral | Abiomed |
| Name of Device | Manufacturer |
|---|---|
| Impella Recover LP 2.5 | Abiomed |
| TandemHeart | Cardiac Assist |
| Name of Device | Manufacturer |
|---|---|
| Abiomed BVS5000 and AB5000 | Abiomed |
| Thoratec PVAD and IVAD | Thoratec |
| Berlin Heart EXCOR | Berlin Heart |
| Medos HIA-VAD | MEDOS Medizintechnik |
| Levitronx CentiMag | Levitronx |
| Jarvik 2000 | Jarvik |
| HeartWare HVAD | HeartWare Inc |
| CorAide/DexAide | Arrow International Inc |
| Korean AnyHeart | BiomedLab Co |
| Gyro | Baylor College of Medicine, Miwatec, NEDO |
| BiVACOR BV Assist | BiVACOR Pty Ltd |
The current scoping searches identified seven LVAD, one RVAD, two pVAD, and two BiVAD that have been approved by the FDA and/or CE.
Report methods for synthesis of clinical evidence
A systematic review of the evidence for each included VAD will be undertaken following the general principles recommended in the PRISMA statement. 7,8 Previous systematic reviews of included VAD will be identified and summarised in the current report.
5.1 Identification and selection of studies
Initial scoping searches were undertaken to assess the volume and type of literature relating to the assessment question. A search strategy was then developed which focuses the searches to ventricular assist devices meeting the inclusion and exclusion criteria (see below). All searches will be undertaken in February and March 2012.
5.1.1 Search strategy for clinical effectiveness
Scoping searches have been undertaken to inform the development of the search strategy. An iterative procedure was used, with input from clinical advisors and previous HTAs (e.g. Clegg et al., 20051; Sharples et al., 20062). A copy of the draft search strategy that is likely to be used in the major databases is provided in Appendix A. This search strategy developed for MEDLINE will be adapted as appropriate for other databases. The strategy has been designed to capture generic terms for VADs and the specific product names of second or third generation and FDA or CE approved devices. The search will be date-limited from 2003 to current. Studies of patients under 16 years and non-English language studies will be excluded. There will be no limits for study design at the searching stage. All retrieved papers will be screened for potential inclusion.
The search strategy will comprise the following main elements:
-
Searching of electronic bibliographic databases.
-
Contact with experts in the field.
-
Scrutiny of references of included studies.
-
Screening of manufacturers websites for relevant publications.
Databases will include:
MEDLINE; MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations; EMBASE; Cochrane Database (including Cochrane Systematic Reviews, DARE, NHS EED, and HTA databases); Science Citation Index and Conference Proceedings (Web of Science); UKCRN Portfolio Database; CINAHL; PsycINFO; and NLM gateway (US Meeting Abstracts and Health Services Research Projects in Progress). The following trial databases will also be searched: CENTRAL; Current Controlled Trials; and ClinicalTrials.gov.
In addition, the reference lists of relevant articles will be checked, and the manufacturers' websites will be screened for relevant publications. Also the online resources of various regulatory bodies, health services research agencies and professional societies will be consulted via the Internet. These are likely to include:
-
HTA organisations, including the NIHR and the National Research Register (NRR) Archive.
-
Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support (INTERMACS).
-
NHS Blood and Transplant, including the Cardiothoracic Transplant Advisory Group.
-
Ventricular Assist Device Forum, National Specialised Commissioning Team.
-
International Society Heart and Lung Transplantation.
-
Eurotransplant.
-
Scandia Transplant.
-
US Transplant.
-
The Transplantation Society.
-
British Transplantation Society.
-
Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Authority (MHRA).
-
US Food and Drug Administration.
Citation searches of included studies will be undertaken using the Web of Science citation search facility. The reference lists of included studies and relevant review articles will also be checked.
5.1.2 Inclusion of relevant studies
Study design:
-
Studies with control groups (i.e. randomised controlled trials, cohort studies, case controlled studies), systematic reviews of studies with control groups.
-
Case series will be included if they report adverse events and if they report on consecutive patients. In the first instance we will limit the inclusion of case series to those including over 50 patients and published since 2003.
Population:
-
People (aged > 16 years) with ESHF and considered suitable for receipt of an LVAD, RVAD and BiVAD as BTT or as potential long-term ATT.
Intervention:
-
Second generation axial continuous flow pumps.
-
Third generation bearingless continuous flow pumps.
-
LVAD, RVAD and BiVAD currently approved by FDA and/or CE and in current clinical use in the UK as a BTT.
-
LVAD, RVAD and BiVAD currently approved by FDA and/or CE and used as potential long-term ATT for people with ESHF.
-
Studies with a mixture of generation devices will be considered if data for second or third generation devices are presented separately to first generation devices.
Comparator:
-
Medical management.
-
Studies comparing HT with other interventions listed above.
-
Comparing two different interventions listed above.
-
Studies comparing first generation devices with second or third generation devices will be used to extract data on second or third generation devices only.
Outcomes:
-
Patient outcomes will include survival, functional capacity (e.g. change in NYHA functional classification), quality of life (QoL) and adverse events.
5.1.3 Exclusion criteria
-
pVAD.
-
Total artificial heart (TAH).
-
First generation pulsatile volume displacement pumps.
-
Devices yet to be FDA or CE approved.
-
Devices for “bridge to decision”.
-
Post-transplant mechanical circulatory support devices for primary graft failure.
-
Studies involving VADs in conjunction with other interventions where it is not possible to separate out the effects of the different interventions on outcomes.
-
Animal models and post-mortem studies.
-
Preclinical and biological studies.
-
Editorials and opinions.
-
Reports published as meeting abstracts only, where insufficient methodological details are reported to allow critical appraisal of study quality.
-
Studies not in English.
-
Studies before the year 2003.
-
Case series reports with less than 30 cases or where patient recruitment is not consecutive.
5.2 Review methods
A record of all papers rejected at full text stage and reasons for exclusion will be documented. Titles and abstracts of retrieved studies will be examined for inclusion by two reviewers independently. Disagreement will be resolved by retrieval of the full publication and consensus agreement.
5.3 Data extraction strategy
The full data will be extracted independently by one reviewer using a data extraction form informed by the NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination9 and previous HTA reports (e.g. Clegg et al., 20051; Sharples et al., 20062; see Appendix B). Studies that give rise to uncertainty will be reviewed by a second researcher, and any disagreements will be resolved by discussion. Further discrepancies will be resolved with involvement of a third reviewer when necessary. Summary tables will detail information about study design, participant, intervention, comparator and outcomes. In addition we will provide a summary of the findings and authors conclusions.
Data will be extracted to allow quality assessment of the included studies (see below).
5.4 Quality assessment strategy
Quality criteria will be applied independently by two reviewers, with any disagreements resolved by independent assessment by a third reviewer. Included studies will be assessed using recognised quality assessment scales and/or checklists. Systematic reviews will be assessed using criteria developed by NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD). 10 Experimental and nonexperimental studies will be assessed using the criteria developed by Thomas et al. 11 See Appendix C.
5.5 Methods of analysis/synthesis
Data will be tabulated and discussed in a narrative review through subgroup analysis based on the indication for treatment, type of VAD and quality of studies. Each device will be looked at separately for the VAD categories (e.g. LVAD, RVAD and BiVAD). Subanalyses will be undertaken (if possible) of the different populations captured in the studies (e.g. demographics, reasons for VADs, co-morbidities such as diabetes mellitus). It is unlikely that a meta-analysis will be appropriate due to clinical heterogeneity. However, if appropriate studies are available, meta-analyses will be undertaken using random effect models using STATA software. 12 The possibility of using mixed treatment comparison (MTC) methods will be considered if appropriate studies are available using WINBUGS.
Report methods for synthesising evidence of cost-effectiveness
The structure of the economic evaluation will be informed by previous work undertaken by Clegg et al. (2005)1 and Sharples et al. (2006). 2 Therefore the content of this section has been adapted from their protocols and published reports.
6.1 Published economic studies
Published economic studies of HT and second and third generation VADs in the treatment of ESHF will be identified. The keyword search strategy developed in the review of clinical effectiveness of VADs will be used and an additional two searches will be conducted for studies on HT and ESHF. The same limits and restrictions used in the review of clinical effectiveness will be applied. Search filters will be applied to restrict the search results to economic and cost-related studies (Appendix A). The primary objective will be to investigate second and third generation VADs currently approved by FDA and/or CE and in current clinical use in the UK as a BTT. However, additional searches will be undertaken to identify high-quality evidence on second and third generation VADS which do not have FDA/CE approval to provide controls for cost-effectiveness models, where appropriate. All searches will be undertaken in February and March 2012. Two reviewers will independently screen all titles and abstracts for inclusion. Disagreement will be resolved through discussion. The full text of papers considered potentially relevant will be retrieved for further assessment. Studies will be selected for inclusion if they report cost-effectiveness estimates for second or third generation VADs. Studies considered methodologically unsound, that report insufficient detail or that fail to provide an estimate of cost-effectiveness, will be excluded. The quality of included economic studies will be investigated by a single reviewer using the Drummond assessment tool (Appendix C). 13
6.2 Approach to economic evaluation
Availability of requisite data permitting, we will undertake an economic evaluation through a decision analytic approach to estimate: a) the incremental cost effectiveness of second and third generation VADs used as BTT compared to medical management; and b) the incremental cost effectiveness of second and third generation VADs used as ATT in comparison to their use as BTT.
The models will take the form of EXCEL spreadsheets and will be transparent in order that changes/updates to any attribute of provision can be incorporated and the model can be continually updated.
Our analyses will involve the following data:
-
The clinical pathways for the different patient groups will need to be clarified with support from our clinical advisors.
-
The different treatment options will need to be defined (i.e. HT, LVAD, RVAD, BiVAD, usual care on WL or best supportive care [BSC]).
-
All cause mortality according to treatment received.
-
The resources and costs required to manage the care of the patients.
The analyses will be informed by previous models completed by Clegg et al. (2005)1 and Sharples et al. (2006)2 for the UK HTA programme and will be guided and informed by advice from the authors of the Sharples model. Our initial intention is to provide estimates for a life time horizon from the perspective of the NHS and Social Services. Information for the analysis will be identified through searching for literature and support from clinical experts and manufacturer's of devices. This will be supplemented with data from NHS Blood and Transplant, Organ Donation and Transplant Directorate, Bristol, if individual patients' data (IPD) is available, appropriate and accessible within the predicted time scale.
If UK NHS Blood and Transplant VAD database data are adequate, the report will include an analysis of data on survival from listing for transplant, transplantation rates, post-transplant survival, and resource use for patients with and without mechanical circulatory support. Analysis of the database will be undertaken in collaboration with our clinical advisors.
Key inputs will be costs (of devices, of surgery, of associated medications and adverse events, of device maintenance, of consumables, of specialist staff pay costs, of infrastructure including staff training/skill maintenance); life years gained; frequency of cost-incurring events; and the utility associated with health states. All resource-use data will be in monetary terms using UK unit costs. Costs will be presented in a base year with discounting of costs and benefits in subsequent years.
Where available, outcomes will be analysed for different subgroups, the type of VAD used and the severity of the patient condition, to allow assessment of the most appropriate treatment for the different patient groups. The underlying assumptions and robustness of the developed models will be examined through sensitivity and threshold analyses.
6.3 Effectiveness of treatment
The model will use efficacy data extracted from the studies included in the systematic review of clinical effectiveness and/or IPD provided by NHS Blood & Transplant. Outcomes will be extracted for patients receiving VADs and for the comparators of HT and WL/supportive care.
The primary effectiveness end-point for the economic evaluation will be patient survival defined in terms of mean (or possibly median) life-years. In addition, the economic evaluation may use information on functional capacity and QoL if available to assess utilities of health states following various interventions.
Studies of QoL for people with ESHF undergoing different types of treatment will be identified concurrently with cost-effectiveness studies (Appendix A and section 6.1). Initial scoping searches suggest the information on QoL may be limited. In addition, searches will be made to identify whether any studies have mapped measures of functional status, such as the NYHA values, with utility weights. If necessary information from the literature may be supplemented by patient-, clinician- and/or expert based estimates of utility by patient perception data held by NHS Blood and Transplant and by published UK population norms for the EQ-5D. The nature and quality of the data will be assessed and, if adequate, will be used to inform the economic evaluation.
6.4 Cost and resource use
Costs will be identified from published sources, supplemented by contact with NHS Blood and Transplant, the National Specialised Commissioning Team, and advice from clinical experts. Costs can be divided into a number of categories: materials; operational or implantation procedures; maintenance; hospitalisation. Material costs include the costs of the VAD devices, up-to-date costs of these, including discounts available, will be obtained from manufacturers; LVADs are not reused. The cost and frequency of device re-implantation following failure will be considered. Drug costs associated with treatments will be obtained from the British National Formulary. Cost of HT will be obtained from the National Specialised Commissioning Team. Other procedural costs will include the costs of implantation and removal of the LVAD. Hospitalisation will incorporate length of inpatient/outpatient attendance for implantation, side-effects, infection, complications, drugs, maintenance of the VADs and routine check-ups. Patients may require home visits by GPs or district nurses. These costs will be obtained from published data. 14 For simplification, costs of side-effects (e.g. haemorrhage, thromboembolism, infections) will be aggregated depending on their likelihood.
Resource use will require the patients' clinical and treatment pathways for the different treatment options to be clarified. Literature searches and advice from experts will provide the evidence to construct the appropriate scenarios. Where applicable, survival analysis or the DEALE method15,16 will be used to estimate prospective resource use over patients' lives. Likewise, UK NHS Blood and Transplant will be approached for data on WL patients.
Expertise in this TAR team
Warwick Evidence is a newly developed technology assessment group located within Warwick Medical School. Warwick Evidence brings together experts in clinical and cost effectiveness reviewing, medical statistics, health economics and modelling. The team planned for the work includes: Dr Paul Sutcliffe, Dr Deepson Shyangdan, Dr Martin Connock, Dr Pam Royle, Dr Tara Gurung and Professor Norman Waugh who are experienced systematic reviewers; Dr Helen Hall and Mr Simon Briscoe, information specialists; Professor Aileen Clarke, Dr Kandala Ngianga-Bakwin, Ms Ruth Jacobs, Mr Gaurav Suri provide modelling and health economic expertise; Mr Steven Tsui, Professor John Wallwork, Dr Jayan Parameshwar, Professor Stephan Schueler, Dr Guy MacGowan, Dr Mark Petrie, Mr Saleem Haj-Yahia provide clinical advice; Professor Martin Buxton and Dr Linda Sharples provide methodological modelling and economic advice; and Ms Amy Grove will provide project management support.
Competing interests of authors and advisors
None of the authors have any competing interests. One of our clinical advisors holds consultancy agreements with a number of LVAD manufacturers.
Timetable/milestones
The project will be undertaken in phases, including: literature search, study selection, data extraction and critical appraisal, evidence synthesis, and dissemination of the results. A progress report including a draft clinical effectiveness section will be submitted on the 30 March 2012, this is conditional upon the rapid approval of the protocol. The final assessment report including the clinical and cost-effectiveness sections will be submitted on 31 May 2012. There will be fortnightly team meetings and correspondence with the clinical advisors will take place every 2–3 weeks via email.
Draft protocol finalised: 21 February 2012
Commissioning decision: TBC
Progress report including draft clinical effectiveness section: 30 March 2012
Final assessment report including clinical and cost-effectiveness sections: 31 May 2012
10. Team members' contributions
Research team: Warwick Evidence
Lead: Dr Paul Sutcliffe
Title: Senior Research Fellow
Address: Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL
Tel: 02476 574505
Email: p.a.sutcliffe@warwick.ac.uk
Contribution: Co-ordinate review process, protocol development, assessment for eligibility, quality assessment of trials, data extraction, data entry, data analysis, and report writing
Name: Dr Deepson Shyangdan
Title: Research Fellow
Address: Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL
Tel: 02476 151183
Email: d.s.shyangdan@warwick.ac.uk
Contribution: Protocol development, assessment for eligibility, quality assessment of trials, data extraction, data entry, data analysis, and report writing
Name: Dr Martin Connock
Title: Senior Research Fellow
Address: Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL
Tel: 02476 574940
Email: M.Connock@warwick.ac.uk
Contribution: Protocol development, assessment for eligibility, quality assessment of trials, data extraction, data entry, data analysis, and report writing
Name: Dr Pamela Royle
Title: Senior Research Fellow
Address: Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL
Tel: 02476 50984
Email: p.l.royle@warwick.ac.uk
Contribution: Protocol development, data extraction and report writing
Name: Dr Tara Gurung
Title: Research Fellow
Address: Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL
Tel: 02476 150711
Email: t.gurung@warwick.ac.uk
Contribution: Assessment for eligibility, quality assessment of trials, data extraction and report writing
Name: Simon Briscoe
Title: Information Specialist
Address: Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL
Tel: 02476 151184
Email: Simon.Briscoe@warwick.ac.uk
Contribution: Protocol development, develop search strategy and undertake the electronic literature searches
Name: Helen Hall
Title: Information specialist
Address: Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL
Tel: 02476 574639
Email: H.E.Hall@warwick.ac.uk
Contribution: Protocol development, develop search strategy and undertake the electronic literature searches
Name: Dr Kandala Ngianga-Bakwin
Title: Principal Research Fellow
Address: Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL
Tel: 02476 575054
Email: N-B.Kandala@warwick.ac.uk
Contribution: Data entry, data analysis, and statistical modeller
Name: Ms Ruth Jacob
Title: Research Fellow Health Economics
Address: Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL
Tel: 02476 151902
Email: R.Jacob@warwick.ac.uk
Contribution: Health economics modeller, assessment for eligibility and data extraction
Name: Mr Gaurav Suri
Title: Research Associate
Address: Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL
Tel: 02476 73163
Email: G.Suri@warwick.ac.uk
Contribution: Operations research modeller, assessment for eligibility and data extraction
Name: Amy Grove
Title: Project Manager
Address: Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL
Tel: 02476 528375
Email: A.L.Grove@warwick.ac.uk
Contribution: Retrieval of papers and help in preparing and formatting the report
Name: Professor Norman Waugh
Title: Professor of Public Health and Health Technology Assessment
Address: Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL
Tel: 02476 151585
Email: norman.waugh@warwick.ac.uk
Contribution: Protocol development and report writing
Name: Professor Aileen Clarke
Title: Director of Warwick Evidence
Address: Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL
Tel: 02476 150189
Email: Aileen.Clarke@warwick.ac.uk
Contribution: Co-ordinate review process, protocol development, data analysis, synthesis of findings and report writing
10.1 Methodological advisors
Professor Martin Buxton, Professor of Health Economics and founder of Brunel's Health Economics Research Group.
Dr Linda Sharples, MRC Biostatistics Unit, Institute of Public Health, University Forvie Site, Robinson Way, Cambridge. UK.
Contribution of methodological advisors: previous experience of modelling in this area, multistate models, general evidence synthesis, statistics issues in health economic modelling, application of statistical methods to cardiothoracic medicine and surgery.
10.2 Clinical Advisors
Mr Steven Tsui, Clinical Director of Transplant Services, Consultant Surgeon, Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
Professor John Wallwork, retired transplant surgeon.
Dr Jayan Parameshwar, Consultant Respiratory, Transplant Physician, Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
Professor Stephan Schueler, Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Freeman Hospital, The Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
Dr Guy MacGowan, Consultant Cardiologist, Freeman Hospital, The Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
Dr Mark Petrie, Consultant Cardiologist, The GJNH, Glasgow.
Mr Saleem Haj-Yahia, Consultant Cardiac and Transplant Surgeon, The GJNH, Glasgow.
Contribution of clinical advisors: protocol development, help interpret data, provide a methodological, policy and clinical perspective on data and review development of background information and clinical effectiveness and review of report drafts.
11. References
- Clegg AJ, Scott DA, Loveman E, Colquitt J, Hutchinson J, Royle P, et al. The clinical and cost-effectiveness of left ventricular assist devices for end-stage heart failure: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 2005;9:1-iv.
- Sharples L, Buxton M, Caine N, Cafferty F, Demiris N, Dyer M, et al. Evaluation of the ventricular assist device programme in the UK. Health Technol Assess 2006;10:1-iv.
- Strueber M, O’Driscoll G, Jansz P, Khaghani A, Levy WC, Wieselthaler GM. Multicenter evaluation of an intrapericardial left ventricular assist system. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;57:1375-82.
- Bartoli CR, Dowling RD. The future of adult cardiac assist devices: novel systems and mechanical circulatory support strategies. Cardiol Clin 2011;29:559-82.
- Macgowan GA, Parry G, Schueler S, Hasan A. The decline in heart transplantation in the UK. BMJ 2011;342.
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol 2009;62.
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009;339.
- Khan KS, Ter Riet G, Galnville J, Snowdon AJ, Kleijnen J. Undertaking Systematic Reviews of Research on Effectiveness. CRD's Guidance for Carrying Out or Commissioning Reviews. York: NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD), University of York; 2001.
- Undertaking systematic reviews of research on effectiveness: CRD guidelines for those carrying out or commissioning reviews. York: NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York; 1999.
- Thomas BH, Ciliska D, Dobbins M, Micucci S. A process for systematically reviewing the literature: providing the research evidence for public health nursing interventions. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs 2004;1.
- STATA . Data analysis and statistical software 2012. URL: http://www.stata.com/.
- Drummond MF, Jefferson TO. Guidelines for authors and peer reviewers of economic submissions to the BMJ. The BMJ Economic Evaluation Working Party. BMJ 1996;313.
- Curtis L. Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2011. Personal Social Services Research Unit, University of Kent; 2011.
- Beck JR, Kassirer JP, Pauker SG. A convenient approximation of life expectancy (the “DEALE”). I. Validation of the method. Am J Med 1982;73:883-8.
- Beck JR, Pauker SG, Gottlieb JE, Klein K, Kassirer JP. A convenient approximation of life expectancy (the “DEALE”). II. Use in medical decision-making. Am J Med 1982;73.
Appendix A Search strategies
Search for clinical-effectiveness of VADs
-
*Heart-Assist Devices/
-
(lvad or biVAD or bvad or vad or vads or rvad).tw.
-
(ventricular support or biventricular support or ventric* assist device* or ventric* assist system* or biventricular assist device* or ventricular assistance or heart assist device*).tw.
-
(heartassist* or debakey or heartmate II or HVAD or incor or jarvik 2000 or jarvik flowmaker or duraheart).tw.
-
2 or 3
-
1 and 5
-
4 or 6
-
limit 7 to (English language and yr=“2003 -Current”)
Search for cost effectiveness of VADs
Lines 1–8 as above
-
9. “costs and cost analysis”/
-
10. “cost of illness”/
-
11. exp Economics/
-
12. (pharmacoeconomic$ or pharmaco-economic$ or cost$ or economic$).tw
-
13. exp “Quality of Life”/
-
14. exp “quality adjusted life years”/
-
15. (qaly$ or EQ5D or EQ-5D or well-being or wellbeing or health status or satisfaction or euroqol or euro-qol or SF-36 or SF36 or hrql or hrqol).tw
-
16. (quality adj2 life).tw
-
17. (“resource use” or “resource utili?ation”).tw
-
18. (utilit* or hrql or hrqol).tw
-
19. health status/
-
20. (health state* or health status).tw
-
21. 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20
-
22. 8 and 21
Searches for cost-effectiveness and quality of life for heart transplantation
-
(heart and transplant*).ti,ab and *HEART TRANSPLANTATION/ [limit to human only]
-
“costs and cost analysis”/
-
“cost of illness”/
-
exp Economics/
-
(pharmacoeconomic$ or pharmaco-economic$ or cost$ or economic$).tw
-
exp “Quality of Life”/
-
exp “quality adjusted life years”/
-
(qaly$ or EQ5D or EQ-5D or well-being or wellbeing or health status or satisfaction or euroqol or euro-qol or SF-36 or SF36 or hrql or hrqol).tw
-
(quality adj2 life).tw
-
(“resource use” or “resource utili?ation”).tw
-
(utilit* or hrql or hrqol).tw
-
health status/
-
(health state* or health status).tw
-
2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13
-
1 and 14
-
limit 15 to (English language and yr=“2003 -Current”)
Searches for cost-effectiveness and quality of life for end-stage heart failure
-
(“heart failure” and (“end stage” or “end-stage”)).mp and heart failure/
-
“costs and cost analysis”/
-
“cost of illness”/
-
exp Economics/
-
(pharmacoeconomic$ or pharmaco-economic$ or cost$ or economic$).tw
-
exp “quality of Life”/
-
exp “quality adjusted life years”/
-
(qaly$ or EQ5D or EQ-5D or well-being or wellbeing or health status or satisfaction or euroqol or euro-qol or SF-36 or SF36 or hrql or hrqol).tw
-
(quality adj2 life).tw
-
(“resource use” or “resource utili?ation”).tw
-
(utilit* or hrql or hrqol).tw
-
health status/
-
(health state* or health status).tw
-
2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13
-
1 and 14
-
limit 15 to (English language and yr=“2003 -Current”)
Searches for prospective studies, cohort studies and RCTs of specific product names of VADs that do not have FDA/CE approval to provide controls for cost-effectiveness models, where appropriate
-
*Heart-Assist Devices/
-
(lvad or biVAD or bvad or vad or vads or rvad).tw.
-
(ventricular support or biventricular support or ventric* assist device* or ventric* assist system* or biventricular assist device* or ventricular assistance or heart assist device*).tw.
-
(CircuLite Synergy Pump or Coraide or Evaheart LVAS or HeartMate III or HeartMate X or HeartQuest or Heartware MVAD or Levacor VAD or MTIHeartLVAD or Procyon circulatory assist device or Rotary VAD or Symphony or Synergy or VentrAssist or DexAide RVAD or Impella Right Peripheral or CorAide or DexAide or BiVACOR BV Assist).tw.
-
2 or 3
-
1 and 5
-
4 or 6
-
limit 7 to (English language and yr=“2003 -Current”)
-
random$.mp
-
8 and 9
-
Epidemiologic studies/
-
Exp case control studies/
-
Exp cohort studies/
-
Case control.tw.
-
(cohort adj (study or studies)).tw.
-
Cohort analy$.tw.
-
(Follow up adj (study or studies)).tw.
-
(observational adj (study or studies)).tw.
-
Longitudinal.tw.
-
Retrospective.tw.
-
Cross sectional.tw.
-
Prospective.tw
-
Cross-sectional studies/
-
Or/11-23
-
8 and 24
-
10 or 25
Appendix B Data extraction form
Data extraction form for primary studies
| Study details | ||
|---|---|---|
| Study ID (Ref man): First author surname: Year of publication: Country: Study design: Study setting: Number of centres: Duration of study: Follow-up period: Funding: |
||
| Aim of the study: | ||
| Participants | ||
| Total number of participants: Sample attrition/dropout: Inclusion criteria: Exclusion criteria: Characteristics of participants: Mean age: Mean sex: Race: Diagnosis: |
||
| Intervention | ||
| Indication for treatment: Type of device used: Any comparison: Duration of treatment: Other interventions used: Any FDA or CE approval: Yes/No; which one? |
||
| Outcomes | ||
| Primary outcomes: Secondary outcomes: Method of assessing outcomes: Timing of assessment: Study end point: Survival analysis: Yes/No Mortality: Yes/No Physiological data: Yes/No Adverse event: Yes/No HRQoL: Yes/No; which measures used? Length of follow-up: |
||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present |
| Screened | ||
| Randomised/included | ||
| Excluded | ||
| Missing participants | ||
| Withdrawals | ||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | Intervention | Comparator, if present |
| Age, years | ||
| Sex | ||
| BSA, m2 | ||
| Weight, kg, BMI | ||
| Ischaemic causes of heart failure | ||
| Survival data | Intervention | Comparator, if present |
| Actuarial survival | ||
| Overall survival | ||
| Kaplan-Meier estimates | ||
| Survival by era (at 5 year intervals) | ||
| Heart transplantation without prior mechanical circulatory support | ||
| Mechanical circulatory support without subsequent heart transplantation | ||
| Mechanical circulatory support with subsequent heart transplantation | ||
| Physiological data | Intervention | Comparator, if present |
| New York Heart Association class | ||
| Six minute walk test | ||
| American United Network for Organ Sharing classification | ||
| Short-term complications | ||
| Long-term complications | ||
| Adverse events | Intervention | Comparator, if present |
| Bleeding | ||
| Stroke | ||
| Hypertension | ||
| Infection | ||
| Heart failure | ||
| VAD failure | ||
| Renal failure | ||
| Haemorrhagic stroke | ||
| Other neurological dysfunction | ||
| Haemolysis | ||
| Cause of death | ||
| ≤12 months | ||
| ≥12 months | ||
| Quality of life | Intervention | Comparator, if present |
| Authors conclusion | ||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||
Data extraction form for economic studies1
| Study intervention (clearly defined?) |
|---|
| Objective (clearly defined?) |
| Design |
| Analytical framework (type of model): |
| Patient population: |
| Comparator (clearly defined?) |
| Analytic horizon: |
| Perspective: |
| Setting: |
| Clinical measures: |
| Effectiveness measures: |
| Economic measures: |
| Methods |
| Health care system: |
| Model description: |
| Data sources (efficacy, resource use, costs, appropriately measured, all costs included?: |
| Data collection (primary data collection, if appropriate): |
| Probabilities: |
| Healthcare use: |
| Sensitivity analysis (allowance made for uncertainty): |
| Discounting (costs/benefits?): |
| Results (incremental analysis of costs and consequences?) |
| Conclusion: Assessment: |
| Authors conclusion |
| Reviewer's conclusion |
Data extraction form for systematic reviews
| Study details |
|---|
| Study ID (Ref man): First author surname: Year of publication: Country: Funding: |
| Aim of the study: |
| Methods |
| Databases searched: Last date of search: Inclusion criteria: Participants: Interventions: Comparators: Outcome measures: Types of studies included: Quality assessment criteria used: Application of methods: Methods of analysis: 1. narrative, 2. meta-analysis, 3. indirect comparison, 4. others |
| Results |
| Quantity and quality of included studies: Treatment effect: Economic evaluation: Conclusions: Implications of the review: |
| Methodological comments |
| Search strategy: Participants: Inclusion/exclusion criteria: Quality assessment of studies: Method of synthesis: |
| General comment |
| Generalisability: Funding: |
| Authors conclusion |
| Reviewer's conclusion |
Appendix C Quality assessment forms
Quality assessment form for primary studies
[Based on the quality criteria given by Thomas et al. 2004]11 – Used by Clegg et al. 20051
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate?) | 80–100% | 60–79%, | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, go to Section C Confounders. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. race, sex, marital status, age, income, social class, education, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (If the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60%) | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| Overall rating (To be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) | |||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
The different criteria were rated following the guidelines provided by Thomas and colleagues. Where criteria are rated as weak, moderate, or strong, it relates to the study's methodological control of the criteria. As such, if a study is rated as strong it indicates that there is a low risk of bias for the particular criteria.
Quality assessment criteria for systematic reviews:
[Based on NHS CRD Report 4]10 – used by Clegg et al. 20051
| Question | Score |
|---|---|
| 1. Are any inclusion/exclusion criteria reported to the primary studies which address the review question? | Yes or No |
| 2. Is there evidence of a substantial effort to search for all relevant research? | Yes or No |
| 3. Is the validity of included studies adequately assessed? | Yes or No |
| 4. Is sufficient detail of the individual studies presented? | Yes or No |
| 5. Are the primary studies summarised appropriately? | Yes or No |
Quality assessment criteria for economic studies: Drummond checklist (Drummond, 1996)13
| Item | Yes | No | Not clear | Not appropriate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study design | |||||
| 1. | The research question is stated. | ||||
| 2. | The economic importance of the research question is stated. | ||||
| 3. | The viewpoint(s) of the analysis are clearly stated and justified. | ||||
| 4. | The rationale for choosing alternative programmes or interventions compared is stated. | ||||
| 5. | The alternatives being compared are clearly described. | ||||
| 6. | The form of economic evaluation used is stated. | ||||
| 7. | The choice of form of economic evaluation is justified in relation to the questions addressed. | ||||
| Data collection | |||||
| 8. | The source(s) of effectiveness estimates used are stated. | ||||
| 9. | Details of the design and results of effectiveness study are given (if based on a single study). | ||||
| 10. | Details of the methods of synthesis or meta-analysis of estimates are given (if based on a synthesis of a number of effectiveness studies). | ||||
| 11. | The primary outcome measure(s) for the economic evaluation are clearly stated. | ||||
| 12. | Methods to value benefits are stated. | ||||
| 13. | Details of the subjects from whom valuations were obtained were given. | ||||
| 14. | Productivity changes (if included) are reported separately. | ||||
| 15. | The relevance of productivity changes to the study question is discussed. | ||||
| 16. | Quantities of resource use are reported separately from their unit costs. | ||||
| 17. | Methods for the estimation of quantities and unit costs are described. | ||||
| 18. | Currency and price data are recorded. | ||||
| 19. | Details of currency of price adjustments for inflation or currency conversion are given. | ||||
| 20. | Details of any model used are given. | ||||
| 21. | The choice of model used and the key parameters on which it is based are justified. | ||||
| Analysis and interpretation of results | |||||
| 22. | Time horizon of costs and benefits is stated. | ||||
| 23. | The discount rate(s) is stated. | ||||
| 24. | The choice of discount rate(s) is justified. | ||||
| 25. | An explanation is given if costs and benefits are not discounted. | ||||
| 26. | Details of statistical tests and confidence intervals are given for stochastic data. | ||||
| 27. | The approach to sensitivity analysis is given. | ||||
| 28. | The choice of variables for sensitivity analysis is justified. | ||||
| 29. | The ranges over which the variables are varied are justified. | ||||
| 30. | Relevant alternatives are compared. | ||||
| 31. | Incremental analysis is reported. | ||||
| 32. | Major outcomes are presented in a disaggregated as well as aggregated form. | ||||
| 33. | The answer to the study question is given. | ||||
| 34. | Conclusions follow from the data reported. | ||||
| 35. | Conclusions are accompanied by the appropriate caveats. | ||||
Appendix 2 Search strategies
MEDLINE via Ovid interface
Search for clinical effectiveness of ventricular assist devices
-
*Heart-Assist Devices/
-
(lvad or biVAD or bvad or vad or vads or rvad).tw.
-
(ventricular support or biventricular support or ventric* assist device* or ventric* assist system* or biventricular assist device* or ventricular assistance or heart assist device*).tw.
-
(heartassist* or debakey or heartmate II or HVAD or incor or jarvik 2000 or jarvik flowmaker or duraheart).tw.
-
2 or 3
-
1 and 5
-
4 or 6
-
limit 7 to (English language and yr=“2003 -Current”)
(2350 results, search run 22 February 2012.)
Search for cost-effectiveness of ventricular assist devices
Lines 1–8 as above.
-
9. “costs and cost analysis”/
-
10. “cost of illness”/
-
11. exp Economics/
-
12. (pharmacoeconomic$ or pharmaco-economic$ or cost$ or economic$).tw
-
13. exp “Quality of Life”/
-
14. exp “quality adjusted life years”/
-
15. (qaly$ or EQ5D or EQ-5D or well-being or wellbeing or health status or satisfaction or euroqol or euro-qol or SF-36 or SF36 or hrql or hrqol).tw
-
16. (quality adj2 life).tw
-
17. (“resource use” or “resource utili?ation”).tw
-
18. (utilit* or hrql or hrqol).tw
-
19. health status/
-
20. (health state* or health status).tw
-
21. 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20
-
22. 8 and 21
(243 results, search run 22 February 2012.)
Search for cost-effectiveness and quality of life for heart transplantation
-
(heart and transplant*).ti,ab and *heart transplantation/ [limit to human only]
-
“costs and cost analysis”/
-
“cost of illness”/
-
exp Economics/
-
(pharmacoeconomic$ or pharmaco-economic$ or cost$ or economic$).tw
-
exp “Quality of Life”/
-
exp “quality adjusted life years”/
-
(qaly$ or EQ5D or EQ-5D or well-being or wellbeing or health status or satisfaction or euroqol or euro-qol or SF-36 or SF36 or hrql or hrqol).tw
-
(quality adj2 life).tw
-
(“resource use” or “resource utili?ation”).tw
-
(utilit* or hrql or hrqol).tw
-
health status/
-
(health state* or health status).tw
-
2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13
-
1 and 14
-
limit 15 to (English language and yr=“2003 -Current”)
(388 results, search run 23 February 2012.)
Search for cost-effectiveness and quality of life for end-stage heart failure
-
(“heart failure” and “end stage” and “end-stage”).mp and heart failure/
Lines 2–16 as above.
(172 results, search run 23 February 2012.)
MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations via Ovid interface
Search for clinical effectiveness of ventricular assist devices
-
(lvad or biVAD or bvad or vad or vads or rvad).tw.
-
(ventricular support or biventricular support or ventric* assist device* or ventric* assist system* or biventricular assist device* or ventricular assistance or heart assist device*).tw.
-
(heartassist* or debakey or heartmate II or HVAD or incor or jarvik 2000 or jarvik flowmaker or duraheart).tw.
-
1 or 2
-
3 or 4
-
limit 5 (english language and yr=”2003 –Current)
(363 results, search run 23 February 2012.)
Search for cost-effectiveness of ventricular assist devices
Lines 1–6 as above.
-
7. (pharmacoeconomic$ or pharmaco-economic$ or cost$ or economic$).tw
-
8. (qaly$ or EQ5D or EQ-5D or well-being or wellbeing or health status or satisfaction or euroqol or euro-qol or SF-36 or SF36 or hrql or hrqol).tw
-
9. (quality adj2 life).tw
-
10. (“resource use” or “resource utili?ation”).tw
-
11. (utilit* or hrql or hrqol).tw
-
12. (health state* or health status).tw
-
13. 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12
-
14. 6 and 14
(33 results, search run 23 February 2012.)
EMBASE via Ovid interface
Search for clinical effectiveness of ventricular assist devices
-
*heart assist device/
-
(lvad or biVAD or bvad or vad or vads or rvad).tw.
-
(ventricular support or biventricular support or ventric* assist device* or ventric* assist system* or biventricular assist device* or ventricular assistance or heart assist device*).tw.
-
(heartassist* or debakey or heartmate II or HVAD or incor or jarvik 2000 or jarvik flowmaker or duraheart).tw.
-
2 or 3
-
1 and 5
-
4 or 6
-
limit 7 to (English language and yr=“2003 -Current”)
(2330 results, search run 29 February 2012.)
Search for cost-effectiveness of ventricular assist devices
Lines 1–8 as above.
-
9. “cost”/
-
10. “cost benefit analysis”/
-
11. “cost of illness”/
-
12. exp Health Economics/
-
13. (pharmacoeconomic$ or pharmaco-economic$ or cost$ or economic$).tw
-
14. exp “quality of life”/
-
15. exp quality adjusted life year/
-
16. (qaly$ or EQ5D or EQ-5D or well-being or wellbeing or health status or satisfaction or euroqol or euro-qol or SF-36 or SF36 or hrql or hrqol).tw
-
17. (quality adj2 life).tw
-
18. (“resource use” or “resource utili?ation”).tw
-
19. (utilit* or hrql or hrqol).tw
-
20. health status/
-
21. (health state* or health status).tw
-
22. 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 or 21
-
23. 8 and 22
(320 results, search run 29 February 2012.)
Cumaltive Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature via EBSCOhost interface
Search for clinical effectiveness of ventricular assist devices
-
(MM “Heart Assist Devices”)
-
TI ( lvad or biVAD or bvad or vad or vads or rvad ) OR AB ( lvad or biVAD or bvad or vad or vads or rvad) OR TI ( ventricular support or biventricular support or ventric* assist device* or ventric* assist system* or biventricular assist device* or ventricular assistance or heart assist device* ) OR AB (ventricular support or biventricular support or ventric* assist device* or ventric* assist system* or biventricular assist device* or ventricular assistance or heart assist device* )
-
TI ( heartassist* or debakey or heartmate II or HVAD or incor or jarvik 2000 or jarvik flowmaker or duraheart ) OR AB ( heartassist* or debakey or heartmate II or HVAD or incor or jarvik 2000 or jarvik flowmaker or duraheart )
-
(S1 and S2)
-
S3 or S4
-
S3 or S4 [Limiters - Published Date from: 20030101-20121231; English Language]
(387 results, search run 22 February 2012.)
Search for cost-effectiveness of ventricular assist devices
Lines 1–6 as above.
-
7. (MH “Costs and Cost Analysis”)
-
8. (MH “Economic Aspects of Illness”)
-
9. (MH “Economics+”)
-
10. (MH “Quality of Life+”)
-
11. (MH “Quality-Adjusted Life Years+”)
-
12. (MH “Health Status”)
-
13. TI ( pharmacoeconomic* or pharmaco-economic* or cost* or economic* ) OR AB ( pharmacoeconomic* or pharmaco-economic* or cost* or economic* ) OR TI ( qaly* or EQ5D or EQ-5D or well-being or wellbeing or health status or satisfaction or euroqol or euro-qol or SF-36 or SF36 or hrql or hrqol ) OR AB ( qaly* or EQ5D or EQ-5D or well-being or wellbeing or health status or satisfaction or euroqol or euro-qol or SF-36 or SF36 or hrql or hrqol ) OR TI quality N2 life OR AB quality N2 life OR TI ( “resource use" or "resource utili?ation” ) OR AB ( “resource use” or “resource utili?ation” ) OR TI ( utilit* or hrql or hrqol ) OR AB ( utilit* or hrql or hrqol ) OR TI ( health state* or health status ) OR TI ( health state* or health status )
-
14. S7 or S8 or S9 or S10 or S11 or S12 or S13
-
15. 6 and 14
(81 results, search run 22 February 2012.)
PsycINFO via ProQuest interface
Search for clinical effectiveness of ventricular assist devices
-
ab(ventricular support OR biventricular support OR ventric* assist device* OR cardiac assist device* or cardiac assist system* or ventric* assist system* OR biventricular assist device* OR ventricular assistance OR heart assist device* OR heartassist* OR debakey OR heartmate II OR HVAD OR incor OR jarvik 2000 OR jarvik flowmaker OR duraheart) OR ti(ventricular support OR biventricular support OR ventric* assist device* OR cardiac assist device* OR cardiac assist system* OR ventric* assist system* OR biventricular assist device* OR ventricular assistance OR heart assist device* OR heartassist* OR debakey OR heartmate II OR HVAD OR incor OR jarvik 2000 OR jarvik flowmaker OR duraheart)
-
Additional limits - Date: After 31 December 2002; Population: Human; Language: English
(151 results, search run 24 February 2012.)
Search for cost-effectiveness of ventricular assist devices
Lines 1–2 as above.
-
3. EXACT.EXPLODE(“Costs and Cost Analysis”)
-
4. EXACT.EXPLODE(“Economics”)
-
5. EXACT.EXPLODE(“Quality of Life”)
-
6. ab(pharmacoeconomic* or pharmaco-economic* or cost* or economic* or qaly* or EQ5D or EQ-5D or well-being or wellbeing or health state* or health status or satisfaction or euroqol or euro-qol or SF-36 or SF36 or hrql or hrqol or utilit* or resource use or resource utili?ation) or ti(pharmacoeconomic* or pharmaco-economic* or cost* or economic* or qaly* or EQ5D or EQ-5D or well-being or wellbeing or health state* or health status or satisfaction or euroqol or euro-qol or SF-36 or SF36 or hrql or hrqol or utilit* or resource use or resource utili?ation)
-
7. ti(quality W/2 life) or ab(quality W/2 life)
-
8. 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7
-
9. 2 and 8
(20 results, search run 24 February 2012.)
Cochrane database
Cochrane database includes:
-
CDSR (Cochrane reviews)
-
DARE (other reviews)
-
HTA database (technology assessments)
-
NHS EED (economic evaluations).
Search for clinical effectiveness of ventricular assist devices
-
Heart-Assist Devices/
-
(lvad or biVAD or bvad or vad or vads or rvad):ti,ab,kw
-
(ventricular support or biventricular support or ventric* assist device* or ventric* assist system* or biventricular assist device* or ventricular assistance or heart assist device*):ti,ab,kw
-
(heartassist* or debakey or heartmate II or HVAD or incor or jarvik 2000 or jarvik flowmaker or duraheart):ti,ab,kw
-
2 or 3
-
1 and 5
-
4 or 6
-
limit 7 to (yr=“2003 -Current”)
(Results: CDSR = 0; DARE = 3; HTA database = 22; NHS EED = 3, search run 27 February 2012.)
Search for cost-effectiveness of ventricular assist devices
Lines 1–8 as above.
-
9. (pharmacoeconomic* or pharmaco-economic* or cost* or economic* or qaly* or EQ5D or EQ-5D or well-being or wellbeing or health state* or health status or satisfaction or euroqol or euro-qol or SF-36 or SF36 or hrql or hrqol or utilit* or resource use or resource utili?ation):ti,ab,kw
-
10. 8 and 9
(Results: CDSR = 0; DARE = 0; HTA database = 4; NHS EED = 2, search run 27 February 2012.)
Appendix 3 Data extraction form for primary studies
Adamson 201156
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Adamson Year of publication: 2011 Country: CA, USA Study design: Retrospective case series Study setting: Small community hospital Number of centres: Single centre Duration of study: 5 October 2005 and 1 January 2010 Follow-up period: Patients were followed up until HT, recovery of native heart function with device removal, or withdrawal from the study Funding: Not reported |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To determine outcomes of LVAD patients aged > 70 years | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inclusion criteria: All patients studied met the clinical trial enrolment criteria and the general criteria for BTT/DT LVAD implantation as published by the Centres for Medicare & Medicaid Services, including chronic end-stage HF (NYHA functional class IV symptoms, failing to respond to optimal MM, end-stage left ventricular failure for at least 90 days, and a life expectancy of < 2 years), LVEF < 25%, demonstrated functional limitation with peak VO2 < 12 ml/kg/minute, continued need for intravenous in inotropic therapy, and an appropriate body size to support LVAD implantation Exclusion criteria: Not reported Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): < 70 years group 56.7 ± 14.3 (16–69) years; ≥ 70 years group 76.3 ± 3.9 (70–87) years Median age: Not reported Age range: See above Sex: Not reported Race: Not reported Diagnosis: HF |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT/DT for advanced HF Type of device used: HMII LVADs Any comparison: HMII not compared against another device, but all the participants were divided into two groups according to age at the time of implant: (1) aged < 70 years and (2) aged ≥ 70 years Duration of treatment: Until HT, recovery of native heart function with device removal, or withdrawal from the study Percentage of patients using inotropes: 17/25 and 18/30 Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Groups were compared with regard to pre-operative patient characteristics and outcome measures, including K–M survival, prevalence and incidence of adverse events, QoL metrics (KCCQ CSS and OSS, MLWHF), and functional status (6-minute walk distance, NYHA functional class, and patient activity levels with the METs) Secondary outcomes: Not applicable Method of assessing outcomes: Prospective data collection Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: Yes Length of follow-up: Patients were followed up until HT, recovery of native heart function with device removal, or withdrawal from the studyNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reportedNot reportedRandomised/includedAged < 70 years group: n = 25Aged ≥ 70 years group: n = 30ExcludedNot reportedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawals01 |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported | Not reported | Randomised/included | Aged < 70 years group: n = 25 | Aged ≥ 70 years group: n = 30 | Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | 0 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | Aged < 70 years group: n = 25 | Aged ≥ 70 years group: n = 30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | 0 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ParameterAged < 70 years (n = 25)Aged ≥ 70 years (n = 30)p-valuePatients enrolled25 (45%)30 (55%)Age, years (minimum–maximum)56.7 ± 14.3 (16–69)76.3 ± 3.9 (70–87)< 0.001Ischaemic15 (60%)24 (80%)0.140BSA (m2)1.98 ± 0.211.95 ± 0.190.671Weight (kg)83 ± 1579 ± 150.276LVEF (%)21 ± 920 ± 60.651Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)1.95 ± 0.721.67 ± 0.490.139PCWP (mmHg)27 ± 927 ± 90.824Systolic BP (mmHg)104 ± 19108 ± 150.438Creatinine (mg/dl)1.76 ± 1.171.47 ± 0.610.420BUN (mg/dl)34.3 ± 20.132.8 ± 15.40.939ALT (U/l)81 ± 20962 ± 1230.205AST (U/l)98 ± 16544 ± 480.141Total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.08 ± 0.780.99 ± 0.530.932Albumin (g/dl)3.55 ± 0.523.76 ± 0.520.137Pre-albumin (mg/dl)16 ± 721 ± 60.030Na (mmol/l)135.3 ± 5.5136.9 ± 4.60.297Beta-blockers6 (24%)13 (43%)0.163ACE inhibitors2 (8%)13 (43%)0.005Intravenous inotrope agents17 (68%)18 (60%)0.585 Single inotrope10 (40%)14 (47%)0.785 More than one inotrope7 (28%)4 (13%)0.198CRT9 (36%)19 (63%)0.060ICD16 (64%)25 (83%)0.128Ventilator support5 (20%)0 (0%)0.015IABP3 (12%)0 (0%)0.088DTRS10.5 ± 6.38.3 ± 5.80.205 DTRS low risk10 (40%)15 (50%)0.588 DTRS high/very high risk5 (20%)4 (13%)0.716 BSA, cardiac index, PCWP, systolic BP, albumin, pre-albumin and DTRS were normally distributed and evaluated using the t-test. The remaining continuous variables, LVEF, creatinine, BUN, ALT, AST, total bilirubin and Na, were evaluated using the non-parametric Mann–Whitney U-test |
Parameter | Aged < 70 years (n = 25) | Aged ≥ 70 years (n = 30) | p-value | Patients enrolled | 25 (45%) | 30 (55%) | Age, years (minimum–maximum) | 56.7 ± 14.3 (16–69) | 76.3 ± 3.9 (70–87) | < 0.001 | Ischaemic | 15 (60%) | 24 (80%) | 0.140 | BSA (m2) | 1.98 ± 0.21 | 1.95 ± 0.19 | 0.671 | Weight (kg) | 83 ± 15 | 79 ± 15 | 0.276 | LVEF (%) | 21 ± 9 | 20 ± 6 | 0.651 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.95 ± 0.72 | 1.67 ± 0.49 | 0.139 | PCWP (mmHg) | 27 ± 9 | 27 ± 9 | 0.824 | Systolic BP (mmHg) | 104 ± 19 | 108 ± 15 | 0.438 | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.76 ± 1.17 | 1.47 ± 0.61 | 0.420 | BUN (mg/dl) | 34.3 ± 20.1 | 32.8 ± 15.4 | 0.939 | ALT (U/l) | 81 ± 209 | 62 ± 123 | 0.205 | AST (U/l) | 98 ± 165 | 44 ± 48 | 0.141 | Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.08 ± 0.78 | 0.99 ± 0.53 | 0.932 | Albumin (g/dl) | 3.55 ± 0.52 | 3.76 ± 0.52 | 0.137 | Pre-albumin (mg/dl) | 16 ± 7 | 21 ± 6 | 0.030 | Na (mmol/l) | 135.3 ± 5.5 | 136.9 ± 4.6 | 0.297 | Beta-blockers | 6 (24%) | 13 (43%) | 0.163 | ACE inhibitors | 2 (8%) | 13 (43%) | 0.005 | Intravenous inotrope agents | 17 (68%) | 18 (60%) | 0.585 | Single inotrope | 10 (40%) | 14 (47%) | 0.785 | More than one inotrope | 7 (28%) | 4 (13%) | 0.198 | CRT | 9 (36%) | 19 (63%) | 0.060 | ICD | 16 (64%) | 25 (83%) | 0.128 | Ventilator support | 5 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 0.015 | IABP | 3 (12%) | 0 (0%) | 0.088 | DTRS | 10.5 ± 6.3 | 8.3 ± 5.8 | 0.205 | DTRS low risk | 10 (40%) | 15 (50%) | 0.588 | DTRS high/very high risk | 5 (20%) | 4 (13%) | 0.716 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Aged < 70 years (n = 25) | Aged ≥ 70 years (n = 30) | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients enrolled | 25 (45%) | 30 (55%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, years (minimum–maximum) | 56.7 ± 14.3 (16–69) | 76.3 ± 3.9 (70–87) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic | 15 (60%) | 24 (80%) | 0.140 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 1.98 ± 0.21 | 1.95 ± 0.19 | 0.671 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight (kg) | 83 ± 15 | 79 ± 15 | 0.276 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF (%) | 21 ± 9 | 20 ± 6 | 0.651 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.95 ± 0.72 | 1.67 ± 0.49 | 0.139 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 27 ± 9 | 27 ± 9 | 0.824 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 104 ± 19 | 108 ± 15 | 0.438 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.76 ± 1.17 | 1.47 ± 0.61 | 0.420 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 34.3 ± 20.1 | 32.8 ± 15.4 | 0.939 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT (U/l) | 81 ± 209 | 62 ± 123 | 0.205 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST (U/l) | 98 ± 165 | 44 ± 48 | 0.141 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.08 ± 0.78 | 0.99 ± 0.53 | 0.932 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albumin (g/dl) | 3.55 ± 0.52 | 3.76 ± 0.52 | 0.137 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-albumin (mg/dl) | 16 ± 7 | 21 ± 6 | 0.030 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Na (mmol/l) | 135.3 ± 5.5 | 136.9 ± 4.6 | 0.297 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beta-blockers | 6 (24%) | 13 (43%) | 0.163 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACE inhibitors | 2 (8%) | 13 (43%) | 0.005 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intravenous inotrope agents | 17 (68%) | 18 (60%) | 0.585 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Single inotrope | 10 (40%) | 14 (47%) | 0.785 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More than one inotrope | 7 (28%) | 4 (13%) | 0.198 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CRT | 9 (36%) | 19 (63%) | 0.060 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICD | 16 (64%) | 25 (83%) | 0.128 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventilator support | 5 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 0.015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP | 3 (12%) | 0 (0%) | 0.088 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DTRS | 10.5 ± 6.3 | 8.3 ± 5.8 | 0.205 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DTRS low risk | 10 (40%) | 15 (50%) | 0.588 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DTRS high/very high risk | 5 (20%) | 4 (13%) | 0.716 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall survival Survival of patients, including those who had a HMXVE replaced with a HMII: K–M survival for both groups were comparable (log-rank p = 0.806). Survival rates for the < 70-year age group vs. ≥ 70-year age group were similar at 30 days (96% vs. 97%), 6 months (88% vs. 83%), 1 year (72% vs. 75%) and 2 years (65% vs. 70%) Survival rates for patients receiving the HMII as their initial device, after excluding those who received it as an exchange for the HMXVE, were also similar (p = 0.898) at 1 year (65% vs. 70%) and 2 years (65% vs. 70%) (log-rank p = 0.898) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average length of stay in the hospital was similar for the < 70-year age group and ≥ 70-year age group (23 ± 14 days vs. 24 ± 15 days, respectively) 6-minute walk testParameterAged < 70 yearsAged ≥ 70 yearsBaseline1 month3 months6 monthsp-value ABaseline1 month3 months6 monthsp-value APatients tested at interval, n6141817< 0.001151717150.004Distance walked (m)256 ± 96188 ± 113354 ± 162275 ± 135233 ± 100162 ± 114256 ± 100295 ± 97p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.221. Patient activity levels (METs)ParameterAged < 70 yearsAged ≥ 70 yearsBaseline1 month3 months6 monthsp-value ABaseline1 month3 months6 monthsp-value APatients tested at interval, n25232319< 0.00130272320<0 .001% METs ≥ 33 (12%)4 (17%)15 (65%)12 (63%)2 (7%)4 (15%)12 (52%)17 (85%)p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.205. 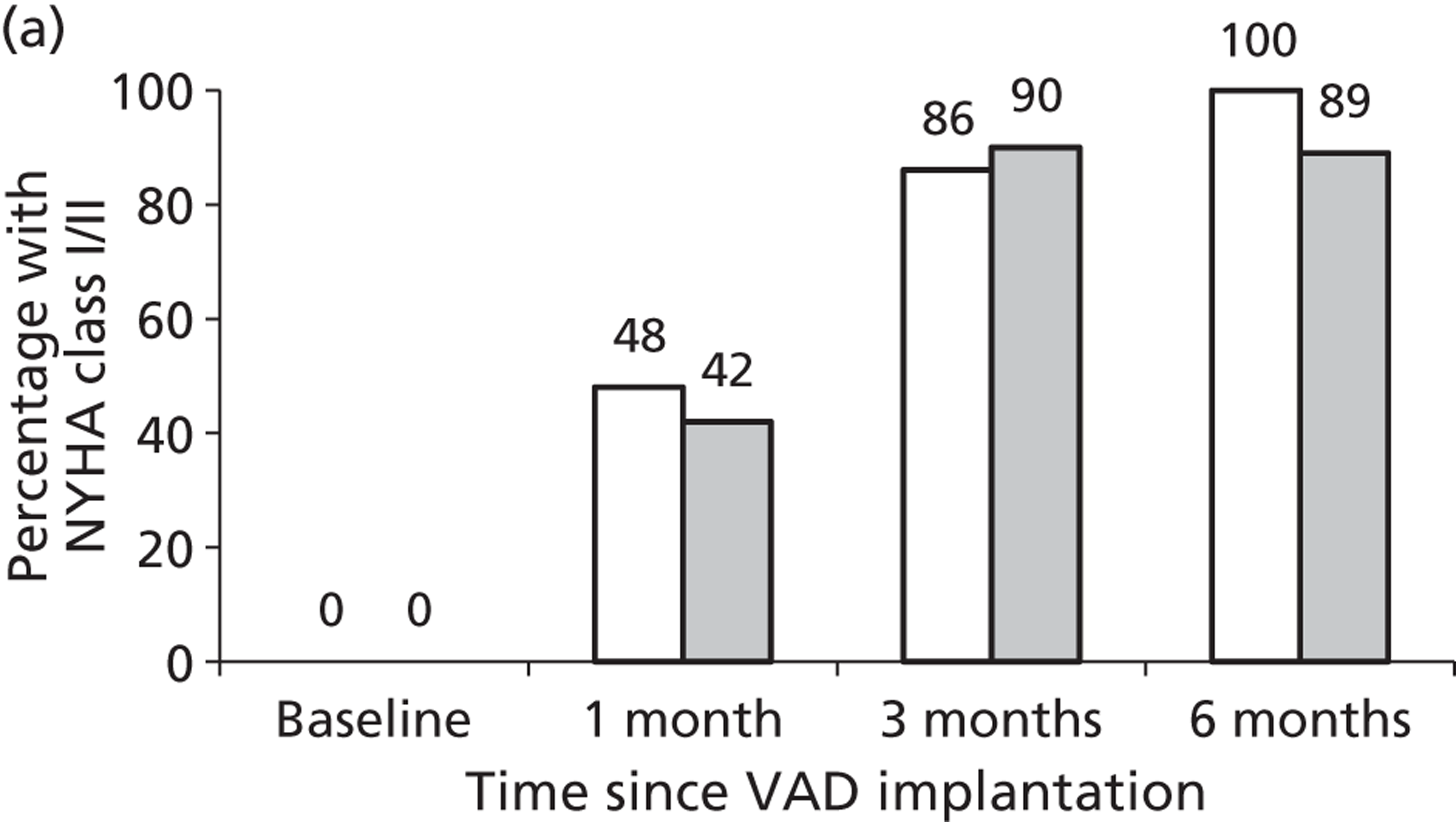 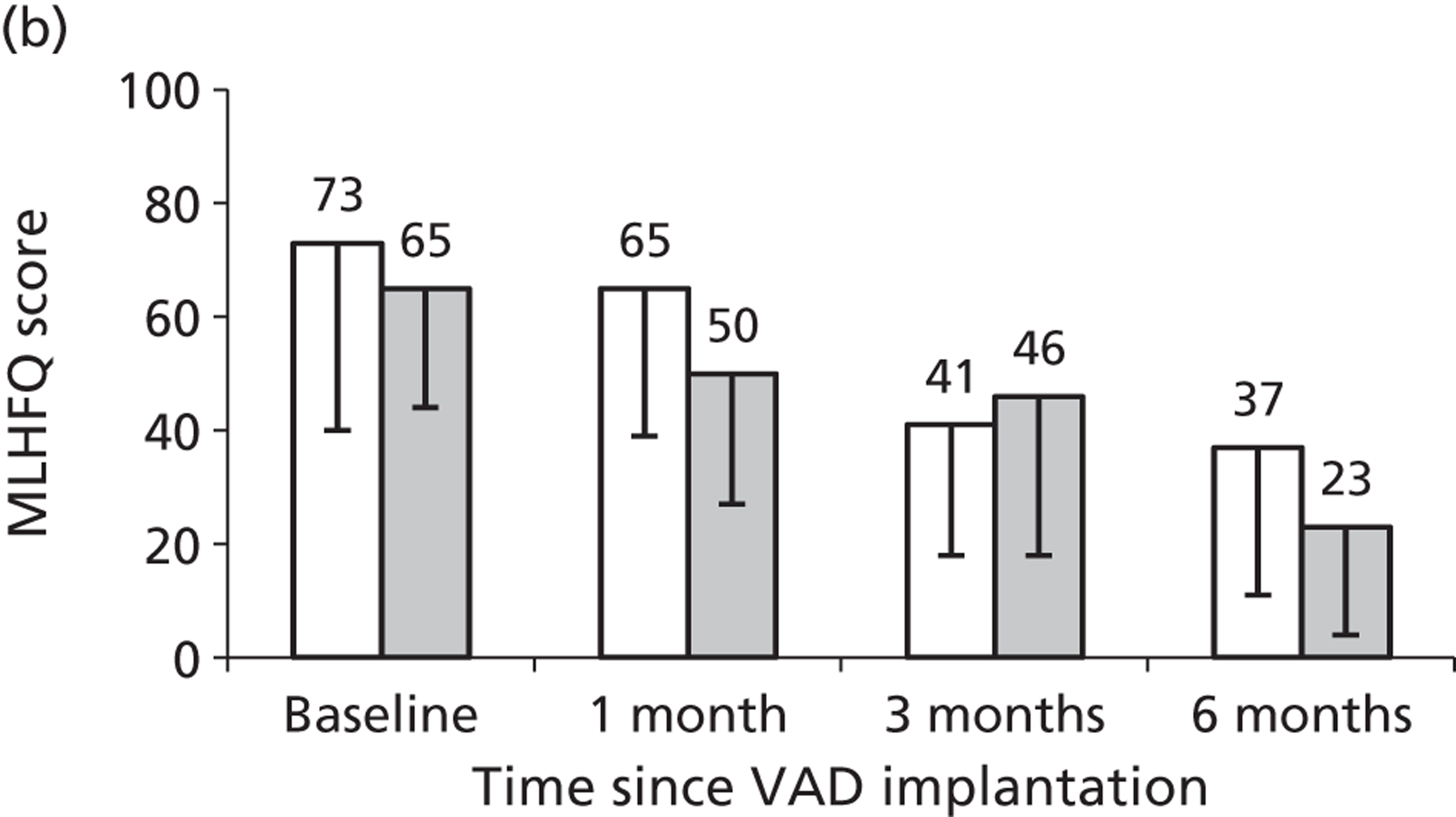 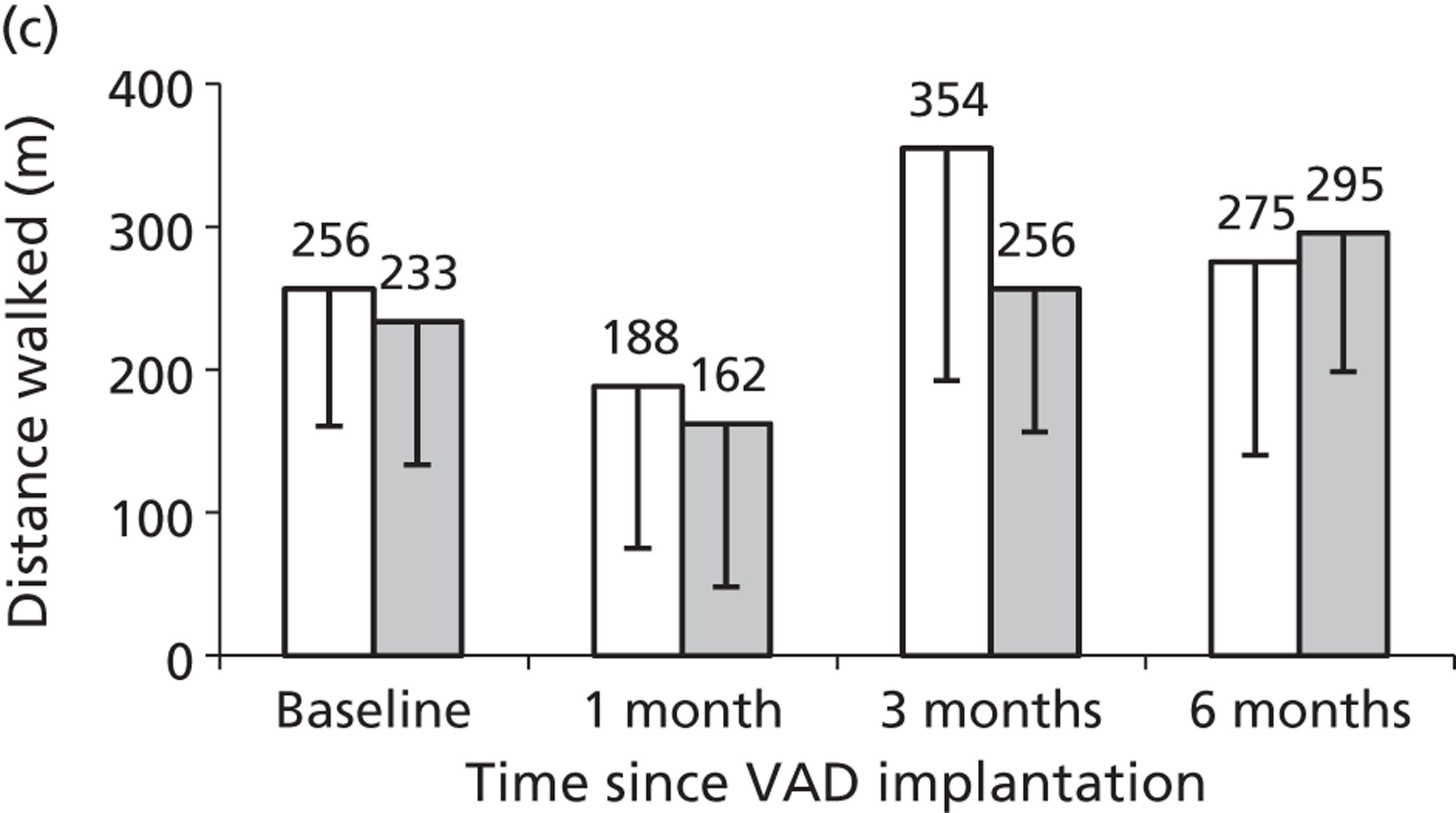 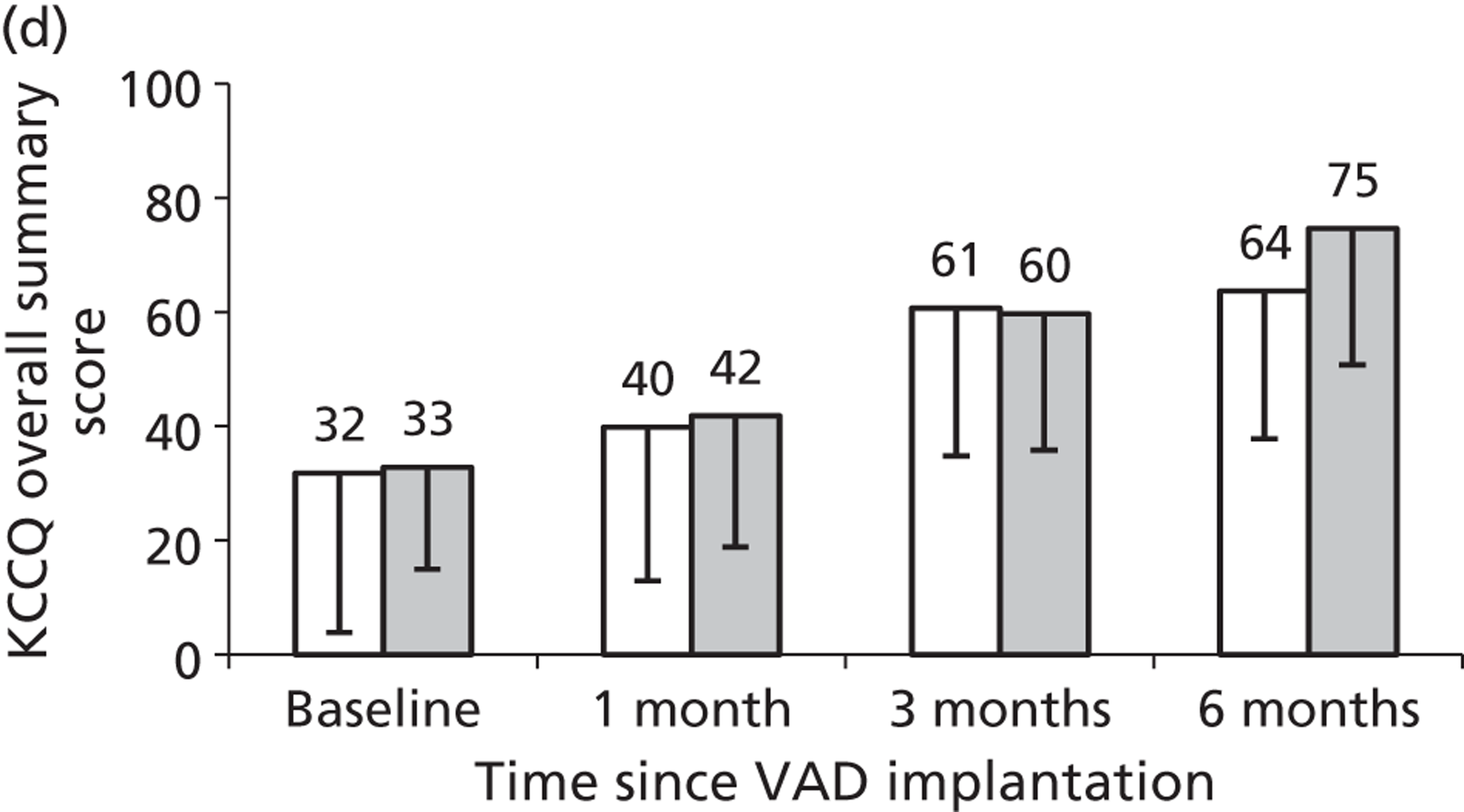 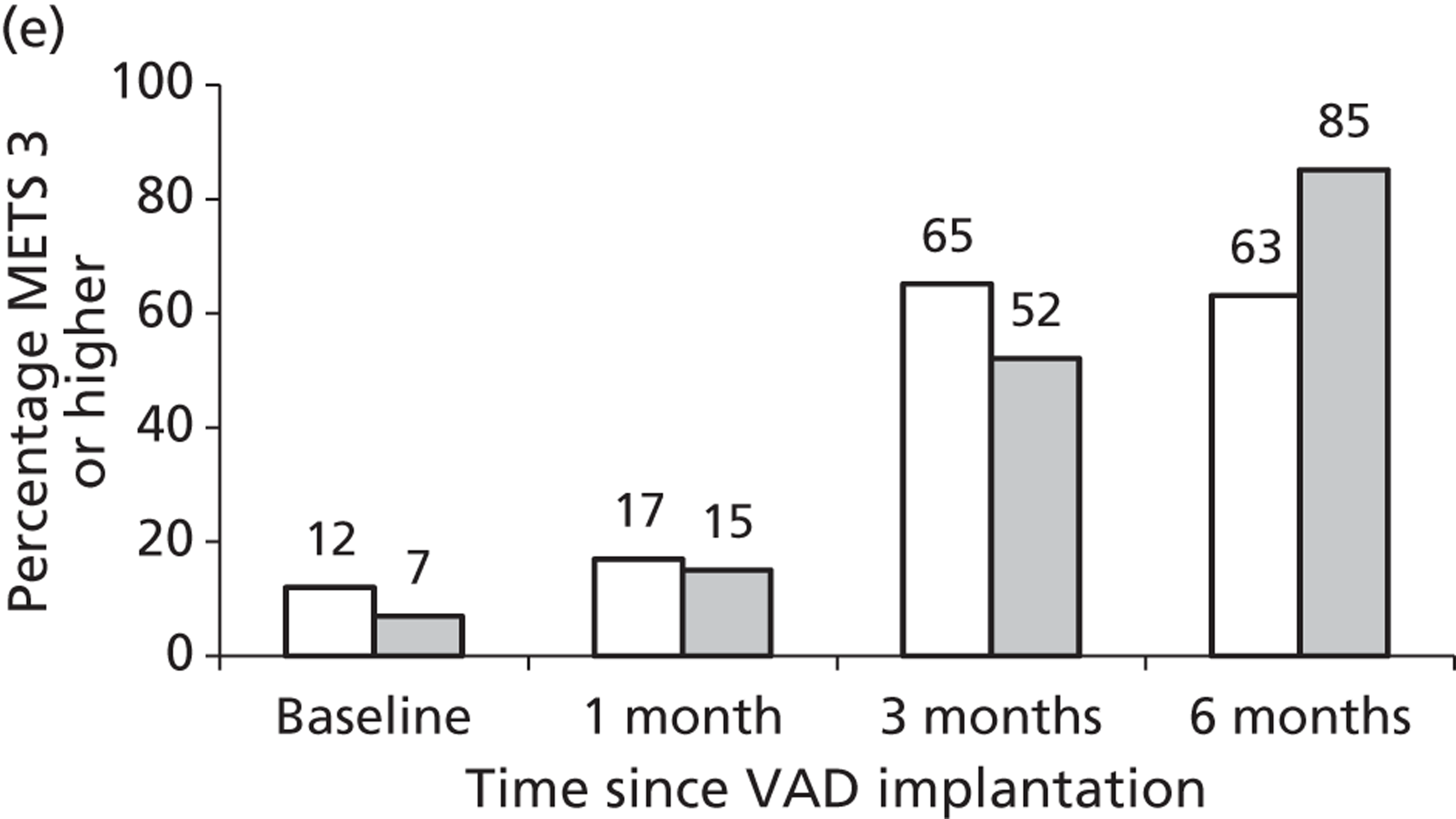 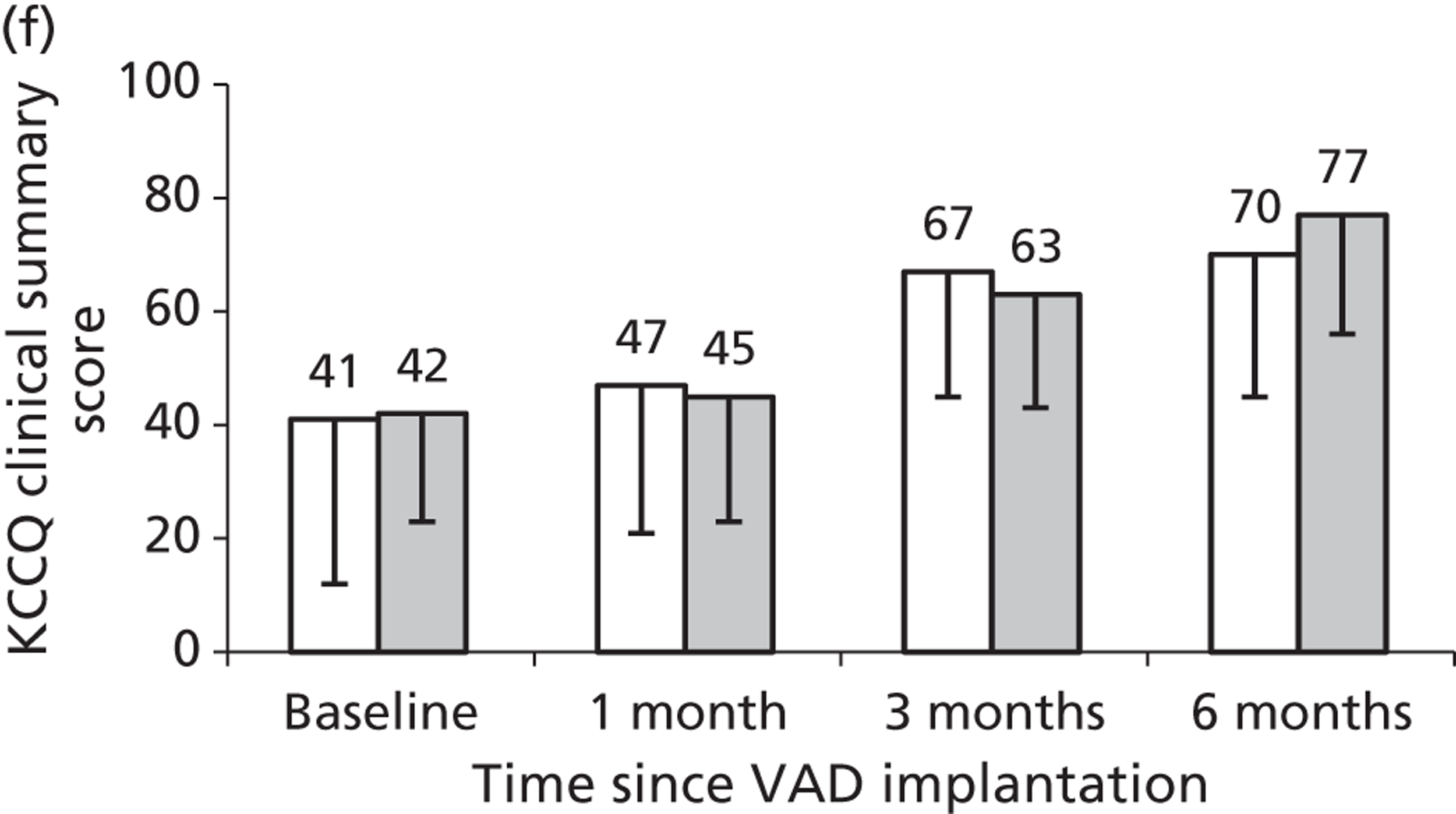 |
Parameter | Aged < 70 years | Aged ≥ 70 years | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | Patients tested at interval, n | 6 | 14 | 18 | 17 | < 0.001 | 15 | 17 | 17 | 15 | 0.004 | Distance walked (m) | 256 ± 96 | 188 ± 113 | 354 ± 162 | 275 ± 135 | 233 ± 100 | 162 ± 114 | 256 ± 100 | 295 ± 97 | p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.221. | Parameter | Aged < 70 years | Aged ≥ 70 years | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | Patients tested at interval, n | 25 | 23 | 23 | 19 | < 0.001 | 30 | 27 | 23 | 20 | <0 .001 | % METs ≥ 3 | 3 (12%) | 4 (17%) | 15 (65%) | 12 (63%) | 2 (7%) | 4 (15%) | 12 (52%) | 17 (85%) | p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.205. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Aged < 70 years | Aged ≥ 70 years | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval, n | 6 | 14 | 18 | 17 | < 0.001 | 15 | 17 | 17 | 15 | 0.004 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance walked (m) | 256 ± 96 | 188 ± 113 | 354 ± 162 | 275 ± 135 | 233 ± 100 | 162 ± 114 | 256 ± 100 | 295 ± 97 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.221. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Aged < 70 years | Aged ≥ 70 years | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval, n | 25 | 23 | 23 | 19 | < 0.001 | 30 | 27 | 23 | 20 | <0 .001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| % METs ≥ 3 | 3 (12%) | 4 (17%) | 15 (65%) | 12 (63%) | 2 (7%) | 4 (15%) | 12 (52%) | 17 (85%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.205. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention)EventsAged < 70 years (n = 25), 38.8 patient-yearsAged > 70 years (n = 30), 37.7 patient-yearsp-valueIncidence (%)Rate events/patient-yearIncidence (%)Rate events/patient-yearBleeding requiring PRBCs7 (28)0.339 (30)0.420.591Bleeding requiring re-exploration5 (20)0.153 (10)0.110.583Infection Sepsis12 (48)0.6714 (47)0.720.853 Local non-device related6 (24)0.216 (20)0.190.854 Device related5 (20)0.155 (17)0.130.813Cardiac arrhythmias (cardioversion/defibrillation)8 (32)0.2610 (33)0.290.802Renal failure1 (4)0.031 (3)0.030.984Right side HF1 (4)0.031 (3)0.030.984RVAD0 (0)01 (3)0.030.317Ischaemic stroke1 (4)0.031 (3)0.030.984Haemorrhagic stroke1 (4)0.032 (7)0.050.557Other neurological events (TIA, seizures, confusion, etc.)4 (16)0.13 (10)0.080.746Haemolysis0 (0)00 (0)0Not reported | Events | Aged < 70 years (n = 25), 38.8 patient-years | Aged > 70 years (n = 30), 37.7 patient-years | p-value | Incidence (%) | Rate events/patient-year | Incidence (%) | Rate events/patient-year | Bleeding requiring PRBCs | 7 (28) | 0.33 | 9 (30) | 0.42 | 0.591 | Bleeding requiring re-exploration | 5 (20) | 0.15 | 3 (10) | 0.11 | 0.583 | Infection | Sepsis | 12 (48) | 0.67 | 14 (47) | 0.72 | 0.853 | Local non-device related | 6 (24) | 0.21 | 6 (20) | 0.19 | 0.854 | Device related | 5 (20) | 0.15 | 5 (17) | 0.13 | 0.813 | Cardiac arrhythmias (cardioversion/defibrillation) | 8 (32) | 0.26 | 10 (33) | 0.29 | 0.802 | Renal failure | 1 (4) | 0.03 | 1 (3) | 0.03 | 0.984 | Right side HF | 1 (4) | 0.03 | 1 (3) | 0.03 | 0.984 | RVAD | 0 (0) | 0 | 1 (3) | 0.03 | 0.317 | Ischaemic stroke | 1 (4) | 0.03 | 1 (3) | 0.03 | 0.984 | Haemorrhagic stroke | 1 (4) | 0.03 | 2 (7) | 0.05 | 0.557 | Other neurological events (TIA, seizures, confusion, etc.) | 4 (16) | 0.1 | 3 (10) | 0.08 | 0.746 | Haemolysis | 0 (0) | 0 | 0 (0) | 0 | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Events | Aged < 70 years (n = 25), 38.8 patient-years | Aged > 70 years (n = 30), 37.7 patient-years | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incidence (%) | Rate events/patient-year | Incidence (%) | Rate events/patient-year | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding requiring PRBCs | 7 (28) | 0.33 | 9 (30) | 0.42 | 0.591 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding requiring re-exploration | 5 (20) | 0.15 | 3 (10) | 0.11 | 0.583 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 12 (48) | 0.67 | 14 (47) | 0.72 | 0.853 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Local non-device related | 6 (24) | 0.21 | 6 (20) | 0.19 | 0.854 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device related | 5 (20) | 0.15 | 5 (17) | 0.13 | 0.813 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac arrhythmias (cardioversion/defibrillation) | 8 (32) | 0.26 | 10 (33) | 0.29 | 0.802 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure | 1 (4) | 0.03 | 1 (3) | 0.03 | 0.984 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right side HF | 1 (4) | 0.03 | 1 (3) | 0.03 | 0.984 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVAD | 0 (0) | 0 | 1 (3) | 0.03 | 0.317 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic stroke | 1 (4) | 0.03 | 1 (3) | 0.03 | 0.984 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic stroke | 1 (4) | 0.03 | 2 (7) | 0.05 | 0.557 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other neurological events (TIA, seizures, confusion, etc.) | 4 (16) | 0.1 | 3 (10) | 0.08 | 0.746 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemolysis | 0 (0) | 0 | 0 (0) | 0 | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention)Causes of deathAged < 70 yearsAged ≥ 70 yearsp-value< 12 monthsn = 6/25 (24%)n = 7/30 (23%)Sepsis1 (4%)1 (3%)1Respiratory failure2 (8%)1 (3%)0.586Multiorgan failure0 (0%)1 (3%)1Ischaemic stroke1 (4%)0 (0%)0.455Haemorrhagic stroke0 (0%)1 (3%)1Device thrombosis1 (4%)0 (0%)0.455Patient disconnected power1 (4%)0 (0%)0.455Cancer0 (0%)1 (3%)1Withdrawal of support0 (0%)1 (3%)1Unknown0 (0%)1 (3%)1> 12 monthsn = 2/25 (8%)n = 3/30 (10%)Anoxic brain injury0 (0%)1 (3%)1Cardiomyopathy1 (4%)0 (0%)0.455Sepsis1 (4%)0 (0%)0.455Unknown0 (0%)1 (3%)1Respiratory failure0 (0%)1 (3%)1 | Causes of death | Aged < 70 years | Aged ≥ 70 years | p-value | < 12 months | n = 6/25 (24%) | n = 7/30 (23%) | Sepsis | 1 (4%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | Respiratory failure | 2 (8%) | 1 (3%) | 0.586 | Multiorgan failure | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | Ischaemic stroke | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.455 | Haemorrhagic stroke | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | Device thrombosis | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.455 | Patient disconnected power | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.455 | Cancer | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | Withdrawal of support | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | Unknown | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | > 12 months | n = 2/25 (8%) | n = 3/30 (10%) | Anoxic brain injury | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | Cardiomyopathy | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.455 | Sepsis | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.455 | Unknown | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | Respiratory failure | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Causes of death | Aged < 70 years | Aged ≥ 70 years | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < 12 months | n = 6/25 (24%) | n = 7/30 (23%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 1 (4%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory failure | 2 (8%) | 1 (3%) | 0.586 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Multiorgan failure | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic stroke | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.455 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic stroke | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device thrombosis | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.455 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient disconnected power | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.455 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cancer | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawal of support | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unknown | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 12 months | n = 2/25 (8%) | n = 3/30 (10%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Anoxic brain injury | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiomyopathy | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.455 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.455 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unknown | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory failure | 0 (0%) | 1 (3%) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLWHFParameterAged < 70 yearsAged ≥ 70 yearsBaseline1 month3 months6 monthsp-value ABaseline1 month3 months6 monthsp-value APatients tested at interval, n18202220< 0.00126232017< 0.001Score73 ± 3365 ± 2641 ± 2337 ± 2665 ± 2150 ± 2346 ± 2823 ± 19p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.072. KCCQParameterAged < 70 yearsAged ≥ 70 yearsBaseline1 month3 months6 monthsp-value ABaseline1 month3 months6 monthsp-value APatients tested at interval, n18202220< 0.00125232218< 0.001OSS32 ± 2840 ± 2761 ± 2664 ± 2633 ± 1842 ± 2360 ± 2475 ± 24CSS41 ± 2947 ± 2667 ± 2270 ± 25< 0.00142 ± 1945 ± 2263 ± 2077 ± 21< 0.001p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.587 (OSS), 0.881 (CSS). NYHA functional class: patients tested at interval class I/IIParameterAged < 70 yearsAged ≥ 70 yearsBaseline1 month3 months6 monthsp-valueBaseline1 months3 months6 monthsp-value APatients tested at interval, n24212120< 0.00129262019< 0.001Class I/II0 (0%)10 (48%)18 (86%)20 (100%)0 (0%)11 (42%)18 (90%)17 (89%)p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.35. 6-minute walk test by age across time pointsParameterAged < 70 yearsAged ≥ 70 yearsBaseline1 month3 months6 monthsp-valueBaseline1 month3 months6 monthsp-value APatients tested at interval, n614181715171715Distance walked (m)256 ± 96188 ± 113354 ± 162275 ± 135<0.001233 ± 100162 ± 114256 ± 100295 ± 970.004p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.221. |
Parameter | Aged < 70 years | Aged ≥ 70 years | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | Patients tested at interval, n | 18 | 20 | 22 | 20 | < 0.001 | 26 | 23 | 20 | 17 | < 0.001 | Score | 73 ± 33 | 65 ± 26 | 41 ± 23 | 37 ± 26 | 65 ± 21 | 50 ± 23 | 46 ± 28 | 23 ± 19 | p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.072. | Parameter | Aged < 70 years | Aged ≥ 70 years | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | Patients tested at interval, n | 18 | 20 | 22 | 20 | < 0.001 | 25 | 23 | 22 | 18 | < 0.001 | OSS | 32 ± 28 | 40 ± 27 | 61 ± 26 | 64 ± 26 | 33 ± 18 | 42 ± 23 | 60 ± 24 | 75 ± 24 | CSS | 41 ± 29 | 47 ± 26 | 67 ± 22 | 70 ± 25 | < 0.001 | 42 ± 19 | 45 ± 22 | 63 ± 20 | 77 ± 21 | < 0.001 | p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.587 (OSS), 0.881 (CSS). | Parameter | Aged < 70 years | Aged ≥ 70 years | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value | Baseline | 1 months | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | Patients tested at interval, n | 24 | 21 | 21 | 20 | < 0.001 | 29 | 26 | 20 | 19 | < 0.001 | Class I/II | 0 (0%) | 10 (48%) | 18 (86%) | 20 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 11 (42%) | 18 (90%) | 17 (89%) | p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.35. | Parameter | Aged < 70 years | Aged ≥ 70 years | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | Patients tested at interval, n | 6 | 14 | 18 | 17 | 15 | 17 | 17 | 15 | Distance walked (m) | 256 ± 96 | 188 ± 113 | 354 ± 162 | 275 ± 135 | <0.001 | 233 ± 100 | 162 ± 114 | 256 ± 100 | 295 ± 97 | 0.004 | p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.221. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Aged < 70 years | Aged ≥ 70 years | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval, n | 18 | 20 | 22 | 20 | < 0.001 | 26 | 23 | 20 | 17 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Score | 73 ± 33 | 65 ± 26 | 41 ± 23 | 37 ± 26 | 65 ± 21 | 50 ± 23 | 46 ± 28 | 23 ± 19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.072. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Aged < 70 years | Aged ≥ 70 years | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval, n | 18 | 20 | 22 | 20 | < 0.001 | 25 | 23 | 22 | 18 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OSS | 32 ± 28 | 40 ± 27 | 61 ± 26 | 64 ± 26 | 33 ± 18 | 42 ± 23 | 60 ± 24 | 75 ± 24 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CSS | 41 ± 29 | 47 ± 26 | 67 ± 22 | 70 ± 25 | < 0.001 | 42 ± 19 | 45 ± 22 | 63 ± 20 | 77 ± 21 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.587 (OSS), 0.881 (CSS). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Aged < 70 years | Aged ≥ 70 years | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value | Baseline | 1 months | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval, n | 24 | 21 | 21 | 20 | < 0.001 | 29 | 26 | 20 | 19 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class I/II | 0 (0%) | 10 (48%) | 18 (86%) | 20 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 11 (42%) | 18 (90%) | 17 (89%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.35. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Aged < 70 years | Aged ≥ 70 years | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval, n | 6 | 14 | 18 | 17 | 15 | 17 | 17 | 15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance walked (m) | 256 ± 96 | 188 ± 113 | 354 ± 162 | 275 ± 135 | <0.001 | 233 ± 100 | 162 ± 114 | 256 ± 100 | 295 ± 97 | 0.004 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-value A, change over time. p-value older vs. younger = 0.221. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Advanced HF patients receiving an HMII LVAD who were aged ≥ 70 years had outcomes similar to those of patients aged < 70 years. Older patients had acceptable length of hospital stays, adverse events and functional recovery. Advanced age should not be used as an independent contraindication when selecting a patient for LVAD therapy. As this technology continues to improve, increasing numbers of older patients will seek centres for DT. Analysis of the referral data suggests that more patients should be referred for LVAD evaluation at an experienced centre, because good outcomes can be achieved in this patient cohort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The population consisted of both DT and BTT patients; results were not reported separately. The results were similar for patients aged < 70 and aged ≥ 70 years | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Bogaev 201157
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Bogaev Year of publication: 2011 Country: USA Study design: Retrospective Study setting: Unclear Number of centres: 35 Duration of study: March 2005 and April 2008 Follow-up period: First 18 months of support Funding: The HMII BTT trial was sponsored by Thoratec Inc. Dr Bogaev is a consultant to Thoratec Inc. Dr Pamboukian has received honoraria from Thoratec Inc. Dr John has received research support from Thoratec Inc. Dr Moore served on the Clinical Events Committee of the HMII clinical trial while the trial was in progress. Dr Farrar and Dr Sundareswaran are employees and stockholders of Thoratec Inc. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To compare the survival outcomes, QoL and adverse events in 465 patients (104 women, 361 men) with advanced systolic HF in their first 18 months of support with the HMII CF LVAD for BTT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 465 Sample attrition/dropout: Unclear Inclusion criteria: Patients had NYHA functional class IV symptoms and UNOS status 1a or 1b Exclusion criteria: Patients were excluded for severe renal (serum creatinine > 3.5 mg/dl or long-term dialysis), hepatic (INR > 2.5, total bilirubin > 5 mg/dl, or transaminases > 2000 U/litre), or pulmonary (severe chronic obstructive or restrictive disease) dysfunction. Patients were also excluded if they had uncontrolled infections, previous strokes, mechanical aortic valves, irreparable aortic insufficiency, aortic aneurysm > 5.0 cm, or other mechanical circulatory support devices, except IABPs Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): Women 49.6 ± 14.2 years; men 52.4 ± 12.8 years Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: 104 women, 361 men Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Advanced systolic HF |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT patients enrolled in the HMII clinical trial. For patients who underwent transplantation, recovered their native heart function, died, underwent pump explantation, or withdrew from the study before 18 months, data measurements until the date of outcome were used Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: Male vs. female Duration of treatment: 18 months Percentage of patients using inotropes: Approximately 90% of patients were receiving inotropic support [women n = 89 (86%); men n = 328 (91%)] Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Differences in outcomes and adverse events between women and men were evaluated at follow-up 18 months Secondary outcomes: Hospital readmissions and adverse events, causes of death, QoL questionnaires and functional assessments were obtained when possible for all patients before LVAD implantation (baseline) and at 1, 3 and 6 months. Functional status measurements included NYHA functional class, METs and 6-minute walk distances. HF-related QoL was assessed using responses from the MLWHF and KCCQs Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records and interviews with family members Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: Yes Length of follow-up: 18 monthsNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreened465 HF patientsNot applicableRandomised/included465 HF patientsNot applicableExcludedNot applicableNot applicableMissing participantsNot applicableNot applicableWithdrawalsFive men underwent pump replacement and were withdrawnNot applicable |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | 465 HF patients | Not applicable | Randomised/included | 465 HF patients | Not applicable | Excluded | Not applicable | Not applicable | Missing participants | Not applicable | Not applicable | Withdrawals | Five men underwent pump replacement and were withdrawn | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | 465 HF patients | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 465 HF patients | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not applicable | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not applicable | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Five men underwent pump replacement and were withdrawn | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VariableWomenMenp-valuePatients enrolled104 (22%)361 (78%)Age (years)49.6 ± 14.252.4 ± 12.80.075Ischaemic cardiomyopathy32 (31%)177 (49%)0.001BSA (m2)1.76 ± 0.272.05 ± 0.23< 0.001BSA < 1.5 (m2)15 (14%)3 (1%)< 0.001Weight (kg)68.6 ± 18.487.3 ± 18.1< 0.001LVEF (%)16.4 ± 7.016.5 ± 6.40.803Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)2.07 ± 0.622.06 ± 0.680.699PCWP (mmHg)23 ± 726 ± 80.001SBP (mmHg)97 ± 1599 ± 160.230Creatinine (mg/dl)1.32 ± 0.521.46 ± 0.520.006BUN (mg/dl)26.9 ± 15.231.4 ± 17.10.013ALT (U/l)106 ± 22696 ± 2500.841AST (U/l)107 ± 23877 ± 2400.007Total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.08 ± 0.791.31 ± 0.840.003Albumin (g/dl)3.40 ± 0.583.59 ± 1.410.037Pre-albumin (mg/dl)17.2 ± 6.918.3 ± 7.60.288Na (mmol/l)134.6 ± 5.4133.4 ± 4.80.028Beta-blockers30 (29%)147 (41%)0.030ACE inhibitors26 (25%)100 (28%)0.619Inotropes89 (86%)328 (91%)0.142CRT45 (43%)185 (51%)0.182ICD68 (65%)287 (80%)0.004Ventilatory support14 (13%)25 (7%)0.044IABP48 (46%)147 (41%)0.367 Continuous data are reported as mean ± SD; categorical data as number (%) Fewer women had ischaemic cardiomyopathy (31% vs. 49%; p = 0.001); women had significantly smaller BSAs (1.76 ± 0.27 vs. 2.05 ± 0.23 m2; p < 0.001); 15 out of 104 women had BSAs < 1.5 m2 compared with 3 out of 361 men |
Variable | Women | Men | p-value | Patients enrolled | 104 (22%) | 361 (78%) | Age (years) | 49.6 ± 14.2 | 52.4 ± 12.8 | 0.075 | Ischaemic cardiomyopathy | 32 (31%) | 177 (49%) | 0.001 | BSA (m2) | 1.76 ± 0.27 | 2.05 ± 0.23 | < 0.001 | BSA < 1.5 (m2) | 15 (14%) | 3 (1%) | < 0.001 | Weight (kg) | 68.6 ± 18.4 | 87.3 ± 18.1 | < 0.001 | LVEF (%) | 16.4 ± 7.0 | 16.5 ± 6.4 | 0.803 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.07 ± 0.62 | 2.06 ± 0.68 | 0.699 | PCWP (mmHg) | 23 ± 7 | 26 ± 8 | 0.001 | SBP (mmHg) | 97 ± 15 | 99 ± 16 | 0.230 | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.32 ± 0.52 | 1.46 ± 0.52 | 0.006 | BUN (mg/dl) | 26.9 ± 15.2 | 31.4 ± 17.1 | 0.013 | ALT (U/l) | 106 ± 226 | 96 ± 250 | 0.841 | AST (U/l) | 107 ± 238 | 77 ± 240 | 0.007 | Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.08 ± 0.79 | 1.31 ± 0.84 | 0.003 | Albumin (g/dl) | 3.40 ± 0.58 | 3.59 ± 1.41 | 0.037 | Pre-albumin (mg/dl) | 17.2 ± 6.9 | 18.3 ± 7.6 | 0.288 | Na (mmol/l) | 134.6 ± 5.4 | 133.4 ± 4.8 | 0.028 | Beta-blockers | 30 (29%) | 147 (41%) | 0.030 | ACE inhibitors | 26 (25%) | 100 (28%) | 0.619 | Inotropes | 89 (86%) | 328 (91%) | 0.142 | CRT | 45 (43%) | 185 (51%) | 0.182 | ICD | 68 (65%) | 287 (80%) | 0.004 | Ventilatory support | 14 (13%) | 25 (7%) | 0.044 | IABP | 48 (46%) | 147 (41%) | 0.367 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variable | Women | Men | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients enrolled | 104 (22%) | 361 (78%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 49.6 ± 14.2 | 52.4 ± 12.8 | 0.075 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic cardiomyopathy | 32 (31%) | 177 (49%) | 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 1.76 ± 0.27 | 2.05 ± 0.23 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA < 1.5 (m2) | 15 (14%) | 3 (1%) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight (kg) | 68.6 ± 18.4 | 87.3 ± 18.1 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF (%) | 16.4 ± 7.0 | 16.5 ± 6.4 | 0.803 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.07 ± 0.62 | 2.06 ± 0.68 | 0.699 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 23 ± 7 | 26 ± 8 | 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SBP (mmHg) | 97 ± 15 | 99 ± 16 | 0.230 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.32 ± 0.52 | 1.46 ± 0.52 | 0.006 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 26.9 ± 15.2 | 31.4 ± 17.1 | 0.013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT (U/l) | 106 ± 226 | 96 ± 250 | 0.841 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST (U/l) | 107 ± 238 | 77 ± 240 | 0.007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.08 ± 0.79 | 1.31 ± 0.84 | 0.003 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albumin (g/dl) | 3.40 ± 0.58 | 3.59 ± 1.41 | 0.037 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-albumin (mg/dl) | 17.2 ± 6.9 | 18.3 ± 7.6 | 0.288 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Na (mmol/l) | 134.6 ± 5.4 | 133.4 ± 4.8 | 0.028 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beta-blockers | 30 (29%) | 147 (41%) | 0.030 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACE inhibitors | 26 (25%) | 100 (28%) | 0.619 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inotropes | 89 (86%) | 328 (91%) | 0.142 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CRT | 45 (43%) | 185 (51%) | 0.182 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICD | 68 (65%) | 287 (80%) | 0.004 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventilatory support | 14 (13%) | 25 (7%) | 0.044 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP | 48 (46%) | 147 (41%) | 0.367 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| During the 18 months, 21 women (20%) and 70 men (21%) died No differences in K–M survival (log-rank test p = 0.855) during support, with similar survival at 30 days (96% vs. 93%), 180 days (87% vs. 83%) and 365 days (74% vs. 76%) after HMII implantation No difference in 1-year survival after HT for women (32/37, 86%) or men (157/174, 90%) (p = 0.553) Similar survival rates during device support and lower transplantation rates compared with that of men, more women remained on LVAD support at 18 months (36% vs. 23%; p = 0.007) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| During the 18-month period, 42 women (40%) had HT compared with 200 men (55%) (p = 0.001) For women who had HT, median duration of support before transplantation was similar to men (155 vs. 141 days) No differences in BSA between women who had a HT and those on device support Five men underwent pump replacement for a different device and were withdrawn from the study Before LVAD implantation, fewer women were taking P-blockers (29% vs. 41%) Fewer women had ICDs (65% vs. 80%), and more women required pre-operative ventilatory support (13% vs. 7%) More than 40% of all patients were receiving IABP support. Cardiac resynchronisation therapy had failed in > 40% of all patients No difference in pre-operative cardiac index or SBP measurements, although PCWP was lower in women (23 vs. 26 mmHg) Serum creatinine and BUN levels were lower in women, and serum sodium levels were slightly higher. AST in women was elevated, but men had higher total bilirubin levels Mean duration of LVAD support was 422 ± 370 days for women (median 238 days; longest duration 4.3 years) and 315 ± 322 days for men (median 184 days; longest duration 4.2 years; p = 0.003) Pulsatility index, measured from pump console, also was higher in women (5.0 ± 0.7 vs. 4.8 ± 0.8; p = 0.009) No difference in average SBP measurement during support (98 ± 12 vs. 96 ± 13 mmHg; p = 0.317) Average pump speed during LVAD support was significantly lower for women (9204 ± 421 vs. 9420 ± 524 RPM; p < 0.001) Mean estimated pump blood flow index was higher in women (2.9 ± 0.4 vs. 2.7 ± 0.4 litre/minute/m2; p < 0.001) Significant differences were observed between women and men in the transplantation rate (p = 0.001) and in ongoing LVAD support (p = 0.007). There were no significant differences among other outcomes |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Most frequent adverse events were bleeding, arrhythmias and infection (see below) Average duration of LVAD support before an ischaemic stroke did not differ (207 ± 289 vs. 156 ± 260 days; p = 0.441) No difference in ischaemic stroke rate between sexes (0.06 vs. 0.05 events/patient-year), but the haemorrhagic stroke rate was higher in women (0.10 vs. 0.04 events/patient-year; p = 0.02) Event rates associated with sepsis, non-device-related infections (e.g. central line or urinary tract infections, pneumonias) and right HF requiring the use of a VAD or extended inotropic support (> 14 days) did not differ between sexes The rate of device-related infection was lower in women (0.23 vs. 0.44 events/patient-year; p = 0.006) compared with men Duration of LVAD support before a haemorrhagic stroke did not differ (170 ± 177 vs. 170 ± 166 days; p = 0.977), nor did average systolic BP in patients who had a haemorrhagic stroke (99 ± 15 vs. 98 ± 12 mmHg; p = 0.891). At time of haemorrhagic stroke, no difference in mean INR (1.82 ± 0.70 vs. 1.98 ± 0.78; p = 0.648), partial thromboplastic time (55 ± 12 vs. 50 ± 27 seconds; p = 0.197), or platelet count (229 ± 66 vs. 213 ± 117 × 1000/mm3; p = 0.750) In BSA-matched subanalysis, haemorrhagic stroke occurred more frequently in women (12%) than in smaller-sized men (4%), but difference in event rates did not reach statistical significance (0.10 vs. 0.06 events/patient-year; p = 0.317)Adverse eventWomen (n = 104) 120.1 patient-yearsMen (n = 361) 311.1 patient-yearsp-valueIncidence, patients (%)Event rate/patient-yearIncidence, patients (%)Event rate/patient-yearBleeding requiring PRBC68 (65)1.4200 (55)1.240.398Bleeding requiring re-exploration23 (22)0.2377 (21)0.270.546Infection Local non-device related49 (47)0.74117 (32)0.690.674 Sepsis20 (19)0.2278 (22)0.340.062 Device related20 (19)0.2377 (21)0.440.006 Arrhythmias cardioversion/defibrillation59 (57)0.93208 (58)1.150.168Renal failure9 (9)0.0842 (12)0.140.145Right HF25 (24)0.2267 (19)0.220.970RVAD7 (7)22 (6)Ischaemic stroke7 (7)0.0616 (4)0.050.788 < 30 days3 (3)0.369 (2)0.320.886 > 30 days4 (4)0.047 (2)0.030.704Haemorrhagic stroke12 (12)0.112 (3)0.040.020 < 30 days3 (3)0.362 (1)0.070.086 > 30 days9 (9)0.0810 (3)0.040.109Other neurological eventsa13 (13)0.1334 (9)0.130.910Haemolysis8 (8)0.112 (3)0.050.090a TIA, seizures, confusion, etc. |
Adverse event | Women (n = 104) 120.1 patient-years | Men (n = 361) 311.1 patient-years | p-value | Incidence, patients (%) | Event rate/patient-year | Incidence, patients (%) | Event rate/patient-year | Bleeding requiring PRBC | 68 (65) | 1.4 | 200 (55) | 1.24 | 0.398 | Bleeding requiring re-exploration | 23 (22) | 0.23 | 77 (21) | 0.27 | 0.546 | Infection | Local non-device related | 49 (47) | 0.74 | 117 (32) | 0.69 | 0.674 | Sepsis | 20 (19) | 0.22 | 78 (22) | 0.34 | 0.062 | Device related | 20 (19) | 0.23 | 77 (21) | 0.44 | 0.006 | Arrhythmias cardioversion/defibrillation | 59 (57) | 0.93 | 208 (58) | 1.15 | 0.168 | Renal failure | 9 (9) | 0.08 | 42 (12) | 0.14 | 0.145 | Right HF | 25 (24) | 0.22 | 67 (19) | 0.22 | 0.970 | RVAD | 7 (7) | 22 (6) | Ischaemic stroke | 7 (7) | 0.06 | 16 (4) | 0.05 | 0.788 | < 30 days | 3 (3) | 0.36 | 9 (2) | 0.32 | 0.886 | > 30 days | 4 (4) | 0.04 | 7 (2) | 0.03 | 0.704 | Haemorrhagic stroke | 12 (12) | 0.1 | 12 (3) | 0.04 | 0.020 | < 30 days | 3 (3) | 0.36 | 2 (1) | 0.07 | 0.086 | > 30 days | 9 (9) | 0.08 | 10 (3) | 0.04 | 0.109 | Other neurological eventsa | 13 (13) | 0.13 | 34 (9) | 0.13 | 0.910 | Haemolysis | 8 (8) | 0.1 | 12 (3) | 0.05 | 0.090 | a TIA, seizures, confusion, etc. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse event | Women (n = 104) 120.1 patient-years | Men (n = 361) 311.1 patient-years | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incidence, patients (%) | Event rate/patient-year | Incidence, patients (%) | Event rate/patient-year | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding requiring PRBC | 68 (65) | 1.4 | 200 (55) | 1.24 | 0.398 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding requiring re-exploration | 23 (22) | 0.23 | 77 (21) | 0.27 | 0.546 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Local non-device related | 49 (47) | 0.74 | 117 (32) | 0.69 | 0.674 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 20 (19) | 0.22 | 78 (22) | 0.34 | 0.062 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device related | 20 (19) | 0.23 | 77 (21) | 0.44 | 0.006 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arrhythmias cardioversion/defibrillation | 59 (57) | 0.93 | 208 (58) | 1.15 | 0.168 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure | 9 (9) | 0.08 | 42 (12) | 0.14 | 0.145 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HF | 25 (24) | 0.22 | 67 (19) | 0.22 | 0.970 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVAD | 7 (7) | 22 (6) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic stroke | 7 (7) | 0.06 | 16 (4) | 0.05 | 0.788 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < 30 days | 3 (3) | 0.36 | 9 (2) | 0.32 | 0.886 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 30 days | 4 (4) | 0.04 | 7 (2) | 0.03 | 0.704 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic stroke | 12 (12) | 0.1 | 12 (3) | 0.04 | 0.020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < 30 days | 3 (3) | 0.36 | 2 (1) | 0.07 | 0.086 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 30 days | 9 (9) | 0.08 | 10 (3) | 0.04 | 0.109 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other neurological eventsa | 13 (13) | 0.13 | 34 (9) | 0.13 | 0.910 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemolysis | 8 (8) | 0.1 | 12 (3) | 0.05 | 0.090 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a TIA, seizures, confusion, etc. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In men, the leading causes of death were sepsis (3.9%), right HF (2.8%) and multisystem organ failure (2.2%). The leading causes of death in women were multisystem organ failure (3.8%), haemorrhagic stroke (2.9%), ischaemic stroke (1.9%), right HF (1.9%) and external component device malfunction (1.9%; percutaneous lead trauma in one patient and pump disconnection in another). See below Causes of death at 18 monthsCauseDeaths in LVAD patientsWomen, n (%)Men, n (%)p-valueTotal21/104 (20.2)70/361 (19.4)Sepsis1 (1.0)14 (3.9)0.208Right HF2 (1.9)10 (2.8)1.000Multisystem organ failure4 (3.8)8 (2.2)0.480Ischaemic stroke2 (1.9)4 (1.1)0.620Haemorrhagic stroke3 (2.9)3 (0.8)0.129Internal componentsa1 (1.0)5 (1.4)1.000External componentsb2 (1.9)2 (0.3)0.037Otherc6 (5.8)24 (7.2)1.000a Three thrombi, one pump disconnection, one twisted inflow graft and one pump-pocket infection.b Three loss of power and one percutaneous lead trauma.c Other causes of death included respiratory failure, cardiac failure, bleeding, cancer, elective withdrawal of support, death during transplantation and unknown causes. |
Cause | Deaths in LVAD patients | Women, n (%) | Men, n (%) | p-value | Total | 21/104 (20.2) | 70/361 (19.4) | Sepsis | 1 (1.0) | 14 (3.9) | 0.208 | Right HF | 2 (1.9) | 10 (2.8) | 1.000 | Multisystem organ failure | 4 (3.8) | 8 (2.2) | 0.480 | Ischaemic stroke | 2 (1.9) | 4 (1.1) | 0.620 | Haemorrhagic stroke | 3 (2.9) | 3 (0.8) | 0.129 | Internal componentsa | 1 (1.0) | 5 (1.4) | 1.000 | External componentsb | 2 (1.9) | 2 (0.3) | 0.037 | Otherc | 6 (5.8) | 24 (7.2) | 1.000 | a Three thrombi, one pump disconnection, one twisted inflow graft and one pump-pocket infection. | b Three loss of power and one percutaneous lead trauma. | c Other causes of death included respiratory failure, cardiac failure, bleeding, cancer, elective withdrawal of support, death during transplantation and unknown causes. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause | Deaths in LVAD patients | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Women, n (%) | Men, n (%) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 21/104 (20.2) | 70/361 (19.4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 1 (1.0) | 14 (3.9) | 0.208 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HF | 2 (1.9) | 10 (2.8) | 1.000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Multisystem organ failure | 4 (3.8) | 8 (2.2) | 0.480 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic stroke | 2 (1.9) | 4 (1.1) | 0.620 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic stroke | 3 (2.9) | 3 (0.8) | 0.129 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Internal componentsa | 1 (1.0) | 5 (1.4) | 1.000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External componentsb | 2 (1.9) | 2 (0.3) | 0.037 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Otherc | 6 (5.8) | 24 (7.2) | 1.000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Three thrombi, one pump disconnection, one twisted inflow graft and one pump-pocket infection. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Three loss of power and one percutaneous lead trauma. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c Other causes of death included respiratory failure, cardiac failure, bleeding, cancer, elective withdrawal of support, death during transplantation and unknown causes. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NOTE: Before LVAD implantation, many patients were unable to walk and were therefore omitted from this analysis Significant improvements from baseline in 6-minute walk distances for both women (219–327 m) and men (247–356 m) Overall distance walked at all times was further for men (p = 0.037). Improvement for both sexes in QoL metrics related to HF Percentage of patients with NYHA functional class I or II symptoms improved from 0% at baseline to 83% for females and 85% for males at 6 months (see below) The number of patients achieving METs of ≥ 3 increased from 5% in women and 8% in men at baseline to 67% in women and 74% in men at 6 months Functional capacity and QoL femaleVariableWomenBaseline1 month3 months6 monthsp-valueaNYHA functional class Patients tested at interval98807859< 0.001 Class I/II0 (0)47 (59)60 (77)49 (83)6-minute walk test Patients tested at interval15565647 Distance walked, metres219 ± 173238 ± 108306 ± 147327 ± 114< 0.001QuestionnairesMLWHF Patients tested at interval77787356 Score73 ± 2263 ± 2744 ± 2535 ± 22< 0.001KCCQ Patients tested at interval75807559 OSS29 ± 2144 ± 2457 ± 2268 ± 21< 0.001 CSS37 ± 2450 ± 2565 ± 2374 ± 21< 0.001METs Patients tested at interval103927963 METs ≥ 35 (5)15 (16)45 (57)42 (67)< 0.001a p-value for changes over time.Continuous data are presented as mean ± SD; categorical data as number (%). Functional capacity and QoL maleVariableMenBaseline1 month3 month6 monthp-valueap-valuebNYHA functional class Patients tested at interval342276227172 Class I/II0 (0)165 (60)188 (83)147 (85)< 0.0010.5506-minute walk test Patients tested at interval59208177152 Distance walked, m247 ± 112275 ± 162351 ± 163356 ± 179< 0.0010.037QuestionnairesMLWHF Patients tested at interval297268224161 Score71 ± 2258 ± 2742 ± 2440 ± 23< 0.0010.661KCCQ Patients tested at interval300304233170 OSS31 ± 2046 ± 2260 ± 2165 ± 21< 0.0010.706 CSS40 ± 2254 ± 2468 ± 2173 ± 21< 0.0010.371METs Patients tested at interval349304233170 METs ≥ 327 (8)76 (25)157 (67)125 (74)< 0.0010.348a p-value for changes over time.b p-value for differences between men and women. |
Variable | Women | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-valuea | NYHA functional class | Patients tested at interval | 98 | 80 | 78 | 59 | < 0.001 | Class I/II | 0 (0) | 47 (59) | 60 (77) | 49 (83) | 6-minute walk test | Patients tested at interval | 15 | 56 | 56 | 47 | Distance walked, metres | 219 ± 173 | 238 ± 108 | 306 ± 147 | 327 ± 114 | < 0.001 | Questionnaires | MLWHF | Patients tested at interval | 77 | 78 | 73 | 56 | Score | 73 ± 22 | 63 ± 27 | 44 ± 25 | 35 ± 22 | < 0.001 | KCCQ | Patients tested at interval | 75 | 80 | 75 | 59 | OSS | 29 ± 21 | 44 ± 24 | 57 ± 22 | 68 ± 21 | < 0.001 | CSS | 37 ± 24 | 50 ± 25 | 65 ± 23 | 74 ± 21 | < 0.001 | METs | Patients tested at interval | 103 | 92 | 79 | 63 | METs ≥ 3 | 5 (5) | 15 (16) | 45 (57) | 42 (67) | < 0.001 | a p-value for changes over time. | Continuous data are presented as mean ± SD; categorical data as number (%). | Variable | Men | Baseline | 1 month | 3 month | 6 month | p-valuea | p-valueb | NYHA functional class | Patients tested at interval | 342 | 276 | 227 | 172 | Class I/II | 0 (0) | 165 (60) | 188 (83) | 147 (85) | < 0.001 | 0.550 | 6-minute walk test | Patients tested at interval | 59 | 208 | 177 | 152 | Distance walked, m | 247 ± 112 | 275 ± 162 | 351 ± 163 | 356 ± 179 | < 0.001 | 0.037 | Questionnaires | MLWHF | Patients tested at interval | 297 | 268 | 224 | 161 | Score | 71 ± 22 | 58 ± 27 | 42 ± 24 | 40 ± 23 | < 0.001 | 0.661 | KCCQ | Patients tested at interval | 300 | 304 | 233 | 170 | OSS | 31 ± 20 | 46 ± 22 | 60 ± 21 | 65 ± 21 | < 0.001 | 0.706 | CSS | 40 ± 22 | 54 ± 24 | 68 ± 21 | 73 ± 21 | < 0.001 | 0.371 | METs | Patients tested at interval | 349 | 304 | 233 | 170 | METs ≥ 3 | 27 (8) | 76 (25) | 157 (67) | 125 (74) | < 0.001 | 0.348 | a p-value for changes over time. | b p-value for differences between men and women. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variable | Women | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-valuea | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA functional class | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval | 98 | 80 | 78 | 59 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class I/II | 0 (0) | 47 (59) | 60 (77) | 49 (83) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-minute walk test | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval | 15 | 56 | 56 | 47 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance walked, metres | 219 ± 173 | 238 ± 108 | 306 ± 147 | 327 ± 114 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Questionnaires | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLWHF | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval | 77 | 78 | 73 | 56 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Score | 73 ± 22 | 63 ± 27 | 44 ± 25 | 35 ± 22 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KCCQ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval | 75 | 80 | 75 | 59 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OSS | 29 ± 21 | 44 ± 24 | 57 ± 22 | 68 ± 21 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CSS | 37 ± 24 | 50 ± 25 | 65 ± 23 | 74 ± 21 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| METs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval | 103 | 92 | 79 | 63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| METs ≥ 3 | 5 (5) | 15 (16) | 45 (57) | 42 (67) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a p-value for changes over time. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Continuous data are presented as mean ± SD; categorical data as number (%). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variable | Men | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | 1 month | 3 month | 6 month | p-valuea | p-valueb | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA functional class | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval | 342 | 276 | 227 | 172 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class I/II | 0 (0) | 165 (60) | 188 (83) | 147 (85) | < 0.001 | 0.550 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-minute walk test | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval | 59 | 208 | 177 | 152 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance walked, m | 247 ± 112 | 275 ± 162 | 351 ± 163 | 356 ± 179 | < 0.001 | 0.037 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Questionnaires | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLWHF | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval | 297 | 268 | 224 | 161 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Score | 71 ± 22 | 58 ± 27 | 42 ± 24 | 40 ± 23 | < 0.001 | 0.661 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KCCQ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval | 300 | 304 | 233 | 170 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OSS | 31 ± 20 | 46 ± 22 | 60 ± 21 | 65 ± 21 | < 0.001 | 0.706 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CSS | 40 ± 22 | 54 ± 24 | 68 ± 21 | 73 ± 21 | < 0.001 | 0.371 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| METs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients tested at interval | 349 | 304 | 233 | 170 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| METs ≥ 3 | 27 (8) | 76 (25) | 157 (67) | 125 (74) | < 0.001 | 0.348 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a p-value for changes over time. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b p-value for differences between men and women. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTT women with the HMII were equivalent to that of men, despite significantly fewer women who eventually underwent transplantation. Women had longer wait times for suitable donor hearts, they also had longer LVAD support times and usually continued LVAD support beyond the 18-month period (36% of women vs. 23% of men continued support at 18 months). In addition, there were significant improvements in functional capacity and HF-related QoL metrics for both sexes during LVAD support. CF LV assistance as a BTT was associated with similar survival rates in both women and men. Further research is needed to examine the differences observed in higher stroke rates and fewer infections among women | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL and functional capacity data were reported on different numbers of patients at each period because of several factors (e.g. death and transplantation). Interesting observation of higher stroke rates and fewer infections among women than men. Caution is needed when interpreting the findings as there were differences in baseline characteristics between the male and female samples (e.g. BSA, weight, ischaemic cardiomyopathy) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Boyle 200958
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Boyle Year of publication: 2009 Country: USA Study design: Retrospective Study setting: Not reported Number of centres: Not reported Duration of study: Unclear – 6-month analysis period Follow-up period: INR was measured monthly for 6 months in all discharged HMII BTT patients and at an event. Three hundred and thirty-one patients had follow-up for at least 1 month since their initial discharge on support and formed the cohort for analysis Funding: Data from this study were from a clinical trial sponsored and managed by Thoratec Inc. Authors have the following disclosures related to this article: three were consultants to Thoratec Inc.; five received grant support from Thoratec Inc.; and two are employees of Thoratec Inc. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To evaluate the risk of thromboembolism and pump thrombosis related to the degree of anticoagulation as reflected by the INR in HMII BTT patients after their initial discharge To assess the frequency of major bleeding events once a patient is discharged and its relationship with the degree of anticoagulation with warfarin |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 331 Sample attrition/dropout: 1 (0.3%). Of the 469 patients who received an implant, 138 had outcomes before discharge, 46 received a transplant, 3 were exchanged to other types of LVADs and withdrew, 50 died, and 39 remained on device support in hospital Inclusion criteria: At least 1 month since their initial discharge on support and form cohort for analysis Exclusion criteria: Blood transfusions for events related to trauma, surgical procedures, or haemolysis were excluded from bleeding analysis Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): 55 years Median age: 55 years Age range: 15–74 years Sex: Male (n = 252, 76%); female (n = 79, 24%) Race: African American 22% Diagnosis: 45% ischaemic cardiomyopathy |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT Type of device used: HMII LVAD Any comparison: Comparisons against 469 patients enrolled in BTT arm of US HMII pivotal trial Duration of treatment: Mean duration of mechanical circulatory support in these patients was 272 ± 201 days (median 211 days; range 31–1088 days), for an accumulated duration of support for entire cohort of 246 patient-years Percentage of patients using inotropes: Intravenous inotropes, 89.1% Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: INR, haemoglobin, platelet count and partial thromboplastin time Secondary outcomes: Adverse events. Thrombotic events analysed included ischaemic stroke and pump thrombosis. Haemorrhagic events analysed included haemorrhagic stroke, bleeding requiring surgical exploration, and bleeding requiring at least 2 units of PRBC within 24 hours. Stroke was defined as any neurological event lasting longer than 24 hours and then categorised as having a haemorrhagic or thromboembolic aetiology according to the results of intracranial imaging. Pump thrombosis was defined as any thrombus within the device or its conduits associated with clinical signs of impaired pump performance Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records. INRs recorded at the time of adverse events. Adverse events related to thromboembolism, thrombosis and major bleeding were independently adjudicated by the Clinical Events Committee of the main trial. Adverse events for each INR range during the 6-month analysis period were calculated in events per patient-year Survival: No Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: 331 participants had follow-up for at least 1 month since their initial discharge on support and form the cohort for analysisNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreened469 patients enrolled in the BTT arm of the US HMII pivotal trialNot applicableRandomised/included331 patients who have had follow-up for at least 1 month since their initial discharge on supportNot applicableExcludedNot reportedNot applicableMissing participantsNot reportedNot applicableWithdrawalsThree patients were exchanged to other types of LVADs and withdrew from the study, 50 patients diedNot applicable |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | 469 patients enrolled in the BTT arm of the US HMII pivotal trial | Not applicable | Randomised/included | 331 patients who have had follow-up for at least 1 month since their initial discharge on support | Not applicable | Excluded | Not reported | Not applicable | Missing participants | Not reported | Not applicable | Withdrawals | Three patients were exchanged to other types of LVADs and withdrew from the study, 50 patients died | Not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | 469 patients enrolled in the BTT arm of the US HMII pivotal trial | Not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 331 patients who have had follow-up for at least 1 month since their initial discharge on support | Not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Three patients were exchanged to other types of LVADs and withdrew from the study, 50 patients died | Not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Demographics for patients successfully dischargedCharacteristicValueTotal N331Sex, n (%) Male252 (76) Female79 (24)Age, mean years (range)55 (15–74)lschaemic aetiology (%)45African American (%)22BSA, mean (range), m22.0 ± 0.3 (1.33–2.62)LVEF, mean ± SD (%)16.5 ± 6.5LVEDD, mean ± SD (mm)70 ± 12ACE inhibitors (%)29ARBs (%)5P-blockers (%)37.2CRT (%)45,3Intravenous inotropes (%)89.1IABP (%)41Lab/haematology, mean ± SD BUN (mg/dl)29 ± 16 Creatinine (mg/dl)1.4 ± 0.5 Total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.3 ± 0.8 ALT (U/l)96 ± 246 AST (IU/l)76 ± 217 INR1.3 ± 0.4 PTT (seconds)48.8 ± 31.2 Haemoglobin (g/dl)11.7 ± 1.9 Flematocrit35.1 ± 5.5 WBC count (1000/mm3)8.7 ± 3.5 Platelets (1000/mm3)225 ± 85 |
Characteristic | Value | Total N | 331 | Sex, n (%) | Male | 252 (76) | Female | 79 (24) | Age, mean years (range) | 55 (15–74) | lschaemic aetiology (%) | 45 | African American (%) | 22 | BSA, mean (range), m2 | 2.0 ± 0.3 (1.33–2.62) | LVEF, mean ± SD (%) | 16.5 ± 6.5 | LVEDD, mean ± SD (mm) | 70 ± 12 | ACE inhibitors (%) | 29 | ARBs (%) | 5 | P-blockers (%) | 37.2 | CRT (%) | 45,3 | Intravenous inotropes (%) | 89.1 | IABP (%) | 41 | Lab/haematology, mean ± SD | BUN (mg/dl) | 29 ± 16 | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.3 ± 0.8 | ALT (U/l) | 96 ± 246 | AST (IU/l) | 76 ± 217 | INR | 1.3 ± 0.4 | PTT (seconds) | 48.8 ± 31.2 | Haemoglobin (g/dl) | 11.7 ± 1.9 | Flematocrit | 35.1 ± 5.5 | WBC count (1000/mm3) | 8.7 ± 3.5 | Platelets (1000/mm3) | 225 ± 85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristic | Value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total N | 331 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex, n (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male | 252 (76) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Female | 79 (24) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, mean years (range) | 55 (15–74) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| lschaemic aetiology (%) | 45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| African American (%) | 22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA, mean (range), m2 | 2.0 ± 0.3 (1.33–2.62) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF, mean ± SD (%) | 16.5 ± 6.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEDD, mean ± SD (mm) | 70 ± 12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACE inhibitors (%) | 29 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ARBs (%) | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P-blockers (%) | 37.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CRT (%) | 45,3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intravenous inotropes (%) | 89.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP (%) | 41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lab/haematology, mean ± SD | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 29 ± 16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.3 ± 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT (U/l) | 96 ± 246 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST (IU/l) | 76 ± 217 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INR | 1.3 ± 0.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PTT (seconds) | 48.8 ± 31.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemoglobin (g/dl) | 11.7 ± 1.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Flematocrit | 35.1 ± 5.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WBC count (1000/mm3) | 8.7 ± 3.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets (1000/mm3) | 225 ± 85 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall survival: 30 (9.1%) patients died Mechanical circulatory support without subsequent HT: 137 (41.4%) Mechanical circulatory support with subsequent HT: 154 (46.5%) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean duration of mechanical circulatory support was 272 ± 201 days (median 211 days; range 31–1088 days), for an accumulated duration of support for the entire cohort of 246 patient-years Mean duration of time outside the hospital once a patient was discharged was 221 ± 191 days, or 93% of total support time Overall cumulative support time after discharge was 200.2 patient-years Cumulative support period for INR analysis from hospital discharge through 6 months was 111 patient-years |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thrombotic and haemorrhagic adverse events after initial hospital discharge (n = 331)Events after dischargeAll events (220 patient-years)Discharge to 6 month (111 patient-years)Patients (%)EventsEvents/patient-yearPatients (%)EventsEvents/patient-yearThrombotic events lschaemic stroke8 (2.4)90.0416 (1.8)60.054 Pump thrombosis3 (0.9)30.0143 (0.9)30.027Haemorrhagic events Haemorrhagic stroke7 (2.1)70.0326 (1.8)60.054 Bleeding requiring surgery4 (1.2)40.0184 (1.2)40.037Transfusion > 2 units PRBC/24 hours For bleedinga40 (12.1)60c0.27331 (9.4)43d0.387 For anaemiab21 (6.3)42c0.19117 (5.1)25d0.225a With identified sites of bleeding.b Without identified site of bleeding.c The combined 60 + 42 = 102 events occurred in 51 patients (15.4%).d The combined 43 + 25 = 48 events occurred in 40 patients (12.9%). The frequency of thromboembolic events in HMII patients is extremely low, in patients with INRs > 1.5. The risk of lowering the target INR in selected patients who demonstrated a repeated tendency towards significant bleeding, such as those with recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding, appears to below. The frequency of thromboembolic events in this study was very low despite the infrequent use of clopidogrel (Plavix®, Bristol-Myers Squibb) Patient outcomes before and after hospital dischargeVariableBefore discharge, n (%)After discharge, n (%)Patients on LVAD support469331Transplantation46 (9.8)154 (46.5)Recovery0 (0.0)9 (2.7)Withdrew from study3 (0.6)1 (0.3)Death50 (10.7)30 (9.1)Ongoing device support39 (8.3)137 (41.4)Transplantation, recovery, or ongoing support device416 (88.7)300 (90.6) |
Events after discharge | All events (220 patient-years) | Discharge to 6 month (111 patient-years) | Patients (%) | Events | Events/patient-year | Patients (%) | Events | Events/patient-year | Thrombotic events | lschaemic stroke | 8 (2.4) | 9 | 0.041 | 6 (1.8) | 6 | 0.054 | Pump thrombosis | 3 (0.9) | 3 | 0.014 | 3 (0.9) | 3 | 0.027 | Haemorrhagic events | Haemorrhagic stroke | 7 (2.1) | 7 | 0.032 | 6 (1.8) | 6 | 0.054 | Bleeding requiring surgery | 4 (1.2) | 4 | 0.018 | 4 (1.2) | 4 | 0.037 | Transfusion > 2 units PRBC/24 hours | For bleedinga | 40 (12.1) | 60c | 0.273 | 31 (9.4) | 43d | 0.387 | For anaemiab | 21 (6.3) | 42c | 0.191 | 17 (5.1) | 25d | 0.225 | a With identified sites of bleeding. | b Without identified site of bleeding. | c The combined 60 + 42 = 102 events occurred in 51 patients (15.4%). | d The combined 43 + 25 = 48 events occurred in 40 patients (12.9%). | Variable | Before discharge, n (%) | After discharge, n (%) | Patients on LVAD support | 469 | 331 | Transplantation | 46 (9.8) | 154 (46.5) | Recovery | 0 (0.0) | 9 (2.7) | Withdrew from study | 3 (0.6) | 1 (0.3) | Death | 50 (10.7) | 30 (9.1) | Ongoing device support | 39 (8.3) | 137 (41.4) | Transplantation, recovery, or ongoing support device | 416 (88.7) | 300 (90.6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Events after discharge | All events (220 patient-years) | Discharge to 6 month (111 patient-years) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients (%) | Events | Events/patient-year | Patients (%) | Events | Events/patient-year | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thrombotic events | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| lschaemic stroke | 8 (2.4) | 9 | 0.041 | 6 (1.8) | 6 | 0.054 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump thrombosis | 3 (0.9) | 3 | 0.014 | 3 (0.9) | 3 | 0.027 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic events | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic stroke | 7 (2.1) | 7 | 0.032 | 6 (1.8) | 6 | 0.054 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding requiring surgery | 4 (1.2) | 4 | 0.018 | 4 (1.2) | 4 | 0.037 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transfusion > 2 units PRBC/24 hours | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For bleedinga | 40 (12.1) | 60c | 0.273 | 31 (9.4) | 43d | 0.387 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For anaemiab | 21 (6.3) | 42c | 0.191 | 17 (5.1) | 25d | 0.225 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a With identified sites of bleeding. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Without identified site of bleeding. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c The combined 60 + 42 = 102 events occurred in 51 patients (15.4%). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| d The combined 43 + 25 = 48 events occurred in 40 patients (12.9%). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variable | Before discharge, n (%) | After discharge, n (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients on LVAD support | 469 | 331 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transplantation | 46 (9.8) | 154 (46.5) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recovery | 0 (0.0) | 9 (2.7) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrew from study | 3 (0.6) | 1 (0.3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Death | 50 (10.7) | 30 (9.1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ongoing device support | 39 (8.3) | 137 (41.4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transplantation, recovery, or ongoing support device | 416 (88.7) | 300 (90.6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rates of thromboembolism and pump thrombosis are low with the HMII as a BTT. The low number of thrombotic events appears to be offset by a greater number of haemorrhagic events, particularly in patients with higher INRs. Hence, an appropriate universal target INR to minimise the risk of both thromboembolic and haemorrhagic events appears to be 1.5–2.5 in addition to the routine use of aspirin therapy. In patients with recurrent episodes of bleeding, the risk of lowering the target INR appears to be small. Therefore, a patient's target INR, taking into account their own risk factors for and history of thrombosis and bleeding, may be difficult from the universal target INR and should be individualised to minimise the risks of both thromboembolism and haemorrhage | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INR levels were recorded at monthly intervals and at time of a clinical event. However, it was noted that INRs for outpatients can change widely and over much shorter time periods according to patient conditions. There is a question of how appropriate it is to assign data into INR ranges. Generalisability of adverse event findings – caution is needed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Brewer 201259
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Brewer Year of publication: 2012 Country: USA Study design: Retrospective analysis of patients enrolled in the multicentre HMII BTT and DT Study setting: USA Number of centres: Multicentre Duration of study: Not reported Follow-up period: Not reported Funding: Lead author has received research support and travel reimbursement from Thoratec Inc.; one author has received speaking honoraria and travel reimbursement from Thoratec Inc.; two authors are employees of Thoratec Corporation; and another author has received grant support from Thoratec Inc. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To assess the association of BMI with survival and major morbidity after CF LVAD implantation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 896 Sample attrition/dropout: Four patients were withdrawn: obese 2 (1%); extremely obese 2 (2%) Inclusion criteria: The authors report that inclusion and exclusion criteria have been published elsewhere (Slaughter et al. 200947 and Miller et al. 200770). To be eligible to participate, patients have to be enrolled in the multicentre HMII BTT and DT trials, and received HMII devices Exclusion criteria: Patients who received the HMII as an exchange for a HMXVE Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): Underweight (< 18.5): 53 ± 16 years; normal (≤ 18.5 to < 30): 59 ± 14 years; obese (≤ 30 to < 35): 54 ± 13 years and extremely obese (≥ 35): 49 ± 12 years Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: n (%) of females reported – underweight 22 (46); normal 144 (24); obese 32 (20); extremely obese 18 (20) Race: n (%) reported – Caucasian race, underweight 29 (60); normal 428 (72); obese 125 (76); extremely obese: 62 (70); African American race, underweight 13 (27); normal 117 (20); obese 31 (19); extremely obese 20 (23) Diagnosis: n (%) reported – ischaemic aetiology, underweight 17 (35); normal 307 (52); obese 91 (55); extremely obese 36 (41) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT and DT [BTT indication, n (%) – underweight 23 (48); normal 305 (51); obese 108 (66); extremely obese 50 (57)] Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: Patients were divided based on their BMI into four groups: underweight (< 18.5); normal (≤ 18.5 to < 30); obese (≤ 30 to < 35) and extremely obese (≥ 35) Duration of treatment: Not clear Percentage of patients using inotropes: Not reported Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Survival; association of BMI group with survival; adverse events Secondary outcomes: Unclear Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: 2 yearsNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reportedNot reportedRandomised/included896: underweight 48; normal 596; obese 164; extremely obese 88Refer to left columnExcludedNot reportedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsUnderweight 0 (0%); normal 0 (0%); obese 2 (1%); extremely obese 2 (2%)Refer to left column |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported | Not reported | Randomised/included | 896: underweight 48; normal 596; obese 164; extremely obese 88 | Refer to left column | Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Underweight 0 (0%); normal 0 (0%); obese 2 (1%); extremely obese 2 (2%) | Refer to left column | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 896: underweight 48; normal 596; obese 164; extremely obese 88 | Refer to left column | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Underweight 0 (0%); normal 0 (0%); obese 2 (1%); extremely obese 2 (2%) | Refer to left column | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristicsParameterUnderweightNormalObeseExtremely obesep-valueN4859616488BTT indication (%)23 (48)305 (51)108 (66)50 (57)0.007Age (years)53 ± 1659 ± 1454 ± 1349 ± 12a< 0.001Female (%)22 (46)144 (24)32 (20)18 (20)0.002Caucasian race (%)29 (60)428 (72)125 (76)62 (70)0.192African American race (%)13 (27)117 (20)31 (19)20 (2%)0.562BMI (kg/m2)17 ± 1a24 ± 332 ± la38 ± 3a< 0.001BSA (m2)1.57 ± 0.181.88 ± 0.212.16 ± 0.182.35 ± 0.23a< 0.001Ischaemic aetiology (%)17 (35)307 (52)91 (55)36 (41)0.024LVEF (%)17 ± 717 ± 617 ± 716 ± 60.405Systolic BP (mmHg)97 ± 18100 ± 15102 ± 15100 ± 160.316Diastolic BP (mmHg)59 ± 1461 ± 1263 ± 1263 ± 110.064PCWP (mmHg)21 ± 724 ± 827 ± 927 ± 7< 0.001CVP (mmHg)12 ± 612 ± 714 ± 6a15 ± 7a< 0.001Serum sodium (mmol/l)133.2 ± 5.7134.1 ± 4.9134.8 ± 4.5134.5 ± 4.40.478Serum albumin (g/dl)3.18 ± 0.603.48 ± 1.163.57 ± 0.593.51 ± 0.64< 0.001Pre-albumin (mg/dl)15.2 ± 5.418.2 ± 7.519.3 ± 7.317.6 ± 16.90.011Cholesterol (mg/dl)119 ± 36126 ± 39126 ± 44124 ± 410.774Serum creatinine (mg/dl)1.35 ± 0.591.45 ± 0.571.53 ± 0.511.58 ± 0.620.004Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dl)30.5 ± 18.632.0 ± 19.433.1 ± 17.832.6 ± 18.30.423ALT (IU/l)80 ± 18579 ± 20867 ± 15661 ± 920.382AST (IU/l)72 ± 14467 ± 18666 ± 22349 It 660.742Total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.39 ± 1.651.27 ± 0.901.24 ± 0.801.18 ± 0.740.845LDH (mg/dl)783 ± 1,643435 ± 942412 ± 410330 ± 1870.696Haematocrit (%)33 ± 535 ± 635 ± 636 ± 50.001WBC (× 1000)/ml8.7 ± 3.48.3 ± 3.38.7 ± 3.28.8 ± 3.20.196Platelets (× 1000)/ml225 ± 95216 ± 90224 ± 82241 ± 870.013INR1.35 ± 0.481.34 ± 0.641.31 ± 0.311.33 ± 0.380.913ACE inhibitors (%)13 (27)168 (28)45 (27)26 (30)0.985Beta-blockers (%)15 (31)238 (40)78 (48)45 (51)0.038CRT (%)24 (50)319 (54)90 (55)53 (60)0.622IABP (%)13 (27)200 (34)52 (32)25 (28)0.646Prior cardiac procedures (%)12 (25)165 (28)48 (29)17 (19)0.347a < 0.001 vs. normal BMI group as control. | Parameter | Underweight | Normal | Obese | Extremely obese | p-value | N | 48 | 596 | 164 | 88 | BTT indication (%) | 23 (48) | 305 (51) | 108 (66) | 50 (57) | 0.007 | Age (years) | 53 ± 16 | 59 ± 14 | 54 ± 13 | 49 ± 12a | < 0.001 | Female (%) | 22 (46) | 144 (24) | 32 (20) | 18 (20) | 0.002 | Caucasian race (%) | 29 (60) | 428 (72) | 125 (76) | 62 (70) | 0.192 | African American race (%) | 13 (27) | 117 (20) | 31 (19) | 20 (2%) | 0.562 | BMI (kg/m2) | 17 ± 1a | 24 ± 3 | 32 ± la | 38 ± 3a | < 0.001 | BSA (m2) | 1.57 ± 0.18 | 1.88 ± 0.21 | 2.16 ± 0.18 | 2.35 ± 0.23a | < 0.001 | Ischaemic aetiology (%) | 17 (35) | 307 (52) | 91 (55) | 36 (41) | 0.024 | LVEF (%) | 17 ± 7 | 17 ± 6 | 17 ± 7 | 16 ± 6 | 0.405 | Systolic BP (mmHg) | 97 ± 18 | 100 ± 15 | 102 ± 15 | 100 ± 16 | 0.316 | Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 59 ± 14 | 61 ± 12 | 63 ± 12 | 63 ± 11 | 0.064 | PCWP (mmHg) | 21 ± 7 | 24 ± 8 | 27 ± 9 | 27 ± 7 | < 0.001 | CVP (mmHg) | 12 ± 6 | 12 ± 7 | 14 ± 6a | 15 ± 7a | < 0.001 | Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 133.2 ± 5.7 | 134.1 ± 4.9 | 134.8 ± 4.5 | 134.5 ± 4.4 | 0.478 | Serum albumin (g/dl) | 3.18 ± 0.60 | 3.48 ± 1.16 | 3.57 ± 0.59 | 3.51 ± 0.64 | < 0.001 | Pre-albumin (mg/dl) | 15.2 ± 5.4 | 18.2 ± 7.5 | 19.3 ± 7.3 | 17.6 ± 16.9 | 0.011 | Cholesterol (mg/dl) | 119 ± 36 | 126 ± 39 | 126 ± 44 | 124 ± 41 | 0.774 | Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.35 ± 0.59 | 1.45 ± 0.57 | 1.53 ± 0.51 | 1.58 ± 0.62 | 0.004 | Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dl) | 30.5 ± 18.6 | 32.0 ± 19.4 | 33.1 ± 17.8 | 32.6 ± 18.3 | 0.423 | ALT (IU/l) | 80 ± 185 | 79 ± 208 | 67 ± 156 | 61 ± 92 | 0.382 | AST (IU/l) | 72 ± 144 | 67 ± 186 | 66 ± 223 | 49 It 66 | 0.742 | Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.39 ± 1.65 | 1.27 ± 0.90 | 1.24 ± 0.80 | 1.18 ± 0.74 | 0.845 | LDH (mg/dl) | 783 ± 1,643 | 435 ± 942 | 412 ± 410 | 330 ± 187 | 0.696 | Haematocrit (%) | 33 ± 5 | 35 ± 6 | 35 ± 6 | 36 ± 5 | 0.001 | WBC (× 1000)/ml | 8.7 ± 3.4 | 8.3 ± 3.3 | 8.7 ± 3.2 | 8.8 ± 3.2 | 0.196 | Platelets (× 1000)/ml | 225 ± 95 | 216 ± 90 | 224 ± 82 | 241 ± 87 | 0.013 | INR | 1.35 ± 0.48 | 1.34 ± 0.64 | 1.31 ± 0.31 | 1.33 ± 0.38 | 0.913 | ACE inhibitors (%) | 13 (27) | 168 (28) | 45 (27) | 26 (30) | 0.985 | Beta-blockers (%) | 15 (31) | 238 (40) | 78 (48) | 45 (51) | 0.038 | CRT (%) | 24 (50) | 319 (54) | 90 (55) | 53 (60) | 0.622 | IABP (%) | 13 (27) | 200 (34) | 52 (32) | 25 (28) | 0.646 | Prior cardiac procedures (%) | 12 (25) | 165 (28) | 48 (29) | 17 (19) | 0.347 | a < 0.001 vs. normal BMI group as control. | ||||||
| Parameter | Underweight | Normal | Obese | Extremely obese | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| N | 48 | 596 | 164 | 88 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTT indication (%) | 23 (48) | 305 (51) | 108 (66) | 50 (57) | 0.007 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 53 ± 16 | 59 ± 14 | 54 ± 13 | 49 ± 12a | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Female (%) | 22 (46) | 144 (24) | 32 (20) | 18 (20) | 0.002 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caucasian race (%) | 29 (60) | 428 (72) | 125 (76) | 62 (70) | 0.192 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| African American race (%) | 13 (27) | 117 (20) | 31 (19) | 20 (2%) | 0.562 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 17 ± 1a | 24 ± 3 | 32 ± la | 38 ± 3a | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 1.57 ± 0.18 | 1.88 ± 0.21 | 2.16 ± 0.18 | 2.35 ± 0.23a | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic aetiology (%) | 17 (35) | 307 (52) | 91 (55) | 36 (41) | 0.024 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF (%) | 17 ± 7 | 17 ± 6 | 17 ± 7 | 16 ± 6 | 0.405 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 97 ± 18 | 100 ± 15 | 102 ± 15 | 100 ± 16 | 0.316 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 59 ± 14 | 61 ± 12 | 63 ± 12 | 63 ± 11 | 0.064 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 21 ± 7 | 24 ± 8 | 27 ± 9 | 27 ± 7 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CVP (mmHg) | 12 ± 6 | 12 ± 7 | 14 ± 6a | 15 ± 7a | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 133.2 ± 5.7 | 134.1 ± 4.9 | 134.8 ± 4.5 | 134.5 ± 4.4 | 0.478 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum albumin (g/dl) | 3.18 ± 0.60 | 3.48 ± 1.16 | 3.57 ± 0.59 | 3.51 ± 0.64 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-albumin (mg/dl) | 15.2 ± 5.4 | 18.2 ± 7.5 | 19.3 ± 7.3 | 17.6 ± 16.9 | 0.011 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cholesterol (mg/dl) | 119 ± 36 | 126 ± 39 | 126 ± 44 | 124 ± 41 | 0.774 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.35 ± 0.59 | 1.45 ± 0.57 | 1.53 ± 0.51 | 1.58 ± 0.62 | 0.004 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dl) | 30.5 ± 18.6 | 32.0 ± 19.4 | 33.1 ± 17.8 | 32.6 ± 18.3 | 0.423 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT (IU/l) | 80 ± 185 | 79 ± 208 | 67 ± 156 | 61 ± 92 | 0.382 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST (IU/l) | 72 ± 144 | 67 ± 186 | 66 ± 223 | 49 It 66 | 0.742 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.39 ± 1.65 | 1.27 ± 0.90 | 1.24 ± 0.80 | 1.18 ± 0.74 | 0.845 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LDH (mg/dl) | 783 ± 1,643 | 435 ± 942 | 412 ± 410 | 330 ± 187 | 0.696 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haematocrit (%) | 33 ± 5 | 35 ± 6 | 35 ± 6 | 36 ± 5 | 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WBC (× 1000)/ml | 8.7 ± 3.4 | 8.3 ± 3.3 | 8.7 ± 3.2 | 8.8 ± 3.2 | 0.196 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets (× 1000)/ml | 225 ± 95 | 216 ± 90 | 224 ± 82 | 241 ± 87 | 0.013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INR | 1.35 ± 0.48 | 1.34 ± 0.64 | 1.31 ± 0.31 | 1.33 ± 0.38 | 0.913 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACE inhibitors (%) | 13 (27) | 168 (28) | 45 (27) | 26 (30) | 0.985 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beta-blockers (%) | 15 (31) | 238 (40) | 78 (48) | 45 (51) | 0.038 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CRT (%) | 24 (50) | 319 (54) | 90 (55) | 53 (60) | 0.622 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP (%) | 13 (27) | 200 (34) | 52 (32) | 25 (28) | 0.646 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prior cardiac procedures (%) | 12 (25) | 165 (28) | 48 (29) | 17 (19) | 0.347 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a < 0.001 vs. normal BMI group as control. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actuarial survival: Not reported Overall survival: Death at 1 year, n (%) – underweight 12 (25); normal 149 (25); obese 33 (20); extremely obese 16 (18) (p = 0.357) K–M estimates: 1 year – underweight 73% ± 7%; normal 71% ± 2%; obese 76% ± 4%; extremely obese 79% ± 5%; 2 year – underweight 59% ± 9%; normal 60% ± 2%; obese 66% ± 5%; extremely obese 68% ± 6% (p = 0.83) Proportional hazards regression modelling was used to assess survival compared with the normal BMI group, adjusting for baseline characteristics that differed between BMI groups (age, gender, race, aetiology, CVP, albumin, creatinine, haematocrit, platelet, beta-blocker and BTT/DT indication) In adjusted analyses there were no differences observed for the underweight patients [HR 1.23 (95% CI 0.72 to 2.10); p = 0.452], obese patients [HR 0.94 (95% CI 0.68 to 1.31); p = 0.723] or extremely obese patients [HR 1.29 (95% CI 0.85 to 1.97); p = 0.231] when compared with normal-weight patients Using same Cox proportional hazard model, if an age of 59 years is entered (this was the mean age of normal group), predicted 1-year survival for underweight group drops to 69%, obese group remains at 76% and extremely obese group drops to 69% Higher K–M survival estimate in extremely obese patients is likely owing to confounding variables, primarily related to significantly younger age of patients in extremely obese group |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comparisons of outcomes at 1 year for the four BMI groupsOutcomes at 1 yearUnderweight (%)Normal (%)Obese (%)Extremely obesep-valueTransplantation, ongoing or recovery36 (75)445 (75)129 (79)70 (80)0.606Ongoing21 (44)270 (45)73 (45)47 (53)0.512Transplanted12 (25)169 (28)54 (33)23 (26)0.560Transplanted (BTT)10/23 (43)155/305 (51)48/108 (44)18/50 (36)0.208Transplanted (DT)2/25 (8)14/291 (5)6/56 (11)5/38 (13)0.122Expired12 (25)149 (25)33 (20)16 (18)0.357Explanteda0 (0)2 (0)0 (0)0 (0)Recovereda3 (6)6 (1)2 (1)0 (0)Withdrawna0 (0)0 (0)2 (1)2 (2)a Total number of events too small to evaluate a meaningful p-value. | Outcomes at 1 year | Underweight (%) | Normal (%) | Obese (%) | Extremely obese | p-value | Transplantation, ongoing or recovery | 36 (75) | 445 (75) | 129 (79) | 70 (80) | 0.606 | Ongoing | 21 (44) | 270 (45) | 73 (45) | 47 (53) | 0.512 | Transplanted | 12 (25) | 169 (28) | 54 (33) | 23 (26) | 0.560 | Transplanted (BTT) | 10/23 (43) | 155/305 (51) | 48/108 (44) | 18/50 (36) | 0.208 | Transplanted (DT) | 2/25 (8) | 14/291 (5) | 6/56 (11) | 5/38 (13) | 0.122 | Expired | 12 (25) | 149 (25) | 33 (20) | 16 (18) | 0.357 | Explanteda | 0 (0) | 2 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | Recovereda | 3 (6) | 6 (1) | 2 (1) | 0 (0) | Withdrawna | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (1) | 2 (2) | a Total number of events too small to evaluate a meaningful p-value. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes at 1 year | Underweight (%) | Normal (%) | Obese (%) | Extremely obese | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transplantation, ongoing or recovery | 36 (75) | 445 (75) | 129 (79) | 70 (80) | 0.606 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ongoing | 21 (44) | 270 (45) | 73 (45) | 47 (53) | 0.512 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transplanted | 12 (25) | 169 (28) | 54 (33) | 23 (26) | 0.560 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transplanted (BTT) | 10/23 (43) | 155/305 (51) | 48/108 (44) | 18/50 (36) | 0.208 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transplanted (DT) | 2/25 (8) | 14/291 (5) | 6/56 (11) | 5/38 (13) | 0.122 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Expired | 12 (25) | 149 (25) | 33 (20) | 16 (18) | 0.357 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Explanteda | 0 (0) | 2 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recovereda | 3 (6) | 6 (1) | 2 (1) | 0 (0) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawna | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (1) | 2 (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Total number of events too small to evaluate a meaningful p-value. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical circulatory support without subsequent HT: (a) ongoing, n (%) – underweight 21 (44); normal 270 (45); obese 73 (45); extremely obese 47 (53) (p = 0.512); (b) explanted, n (%) – underweight 0 (0); normal 2 (0); obese 0 (0); extremely obese 0 (0) (p = 0.357) Mechanical circulatory support with subsequent HT: (a) total transplant, n (%) – underweight 12 (25); normal 169 (28); obese 54 (33); extremely obese 23 (26) (p = 0.560); (b) BTT, n/N (%) – underweight 10/23 (43); normal 155/305 (51); obese 48/108 (44); extremely obese 18/50 (36) (p=0.208); (c) DT, n/N (%) – underweight 2/25 (8); normal 14/291 (5); obese 6/56 (11); extremely obese 5/38 (13) (p = 0.122) No differences between groups in percentage of patients who were transplanted (p = 0.560), died (p = 0.357) or had ongoing device support (p = 0.512) at 1 year |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comparisons of adverse events for the four groupsAdverse eventsUnderweight (66.4 patient-years)Normal (731.8 patient-years)Obese (192.9 patient-years)Extremely obese (129.0 patient-years)p-valueIncidenceEvent rateIncidenceEvent rateIncidenceEvent rateIncidenceEvent rateBleeding requiring packed red blood cells31 (65%)1.67399 (67%)1.40100 (61%)1.3057 (65%)1.12< 0.001Bleeding: requiring re-exploration20 (42%)0.35130 (22%)0.2141 (25%)0.2216 (18%)0.130.010InfectionLocal non-device related20 (42%)0.65229 (38%)0.6066 (40%)0.7238 (43%)0.670.660Sepsis13 (27%)0.30136 (23%)0.2843 (26%)0.3328 (32%)0.500.032Device related10 (21%)0.29144 (24%)0.3445 (27%)0.3831 (35%)0.510.041Cardiac arrhythmias: cardioversion/defibrillation25 (52%)0.62339 (57%)0.7983 (51%)0.7956 (64%)0.860.179Renal failure8 (17%)0.1460 (10%)0.0923 (14%)0.1215 (17%)0.120.959Right HF11 (23%)0.17110 (18%)0.1737 (23%)0.2024 (27%)0.210.749RVAD4 (8%)0.0632 (5%)0.0413 (8%)0.075 (6%)0.040.403Ischaemic stroke6 (13%)0.0932 (5%)0.0510 (6%)0.069 (10%)0.070.838Haemorrhagic stroke3 (6%)0.0532 (5%)0.0512 (7%)0.075 (6%)0.040.394Other neurological events (TIA, seizures, confusion, etc.)9 (19%)0.1493 (16%)0.1517 (10%)0.1111 (13%)0.100.731Haemolysis4 (8%)0.0622 (4%)0.039 (5%)0.087 (8%)0.070.617Respiratory failure21 (44%)0.45183 (31%)0.3442 (26%)0.2333 (38%)0.350.055Rehospitalisations33 (69%)1.91417 (70%)2.02114 (70%)2.2667 (76%)2.540.014p = evaluated based on event rates using Poisson regression. Adverse event comparisons of four BMI groups are shown above. Extremely obese patients had a higher incidence of sepsis (p = 0.032) and device-related infection (p = 0.041). Extremely obese patients also had highest rate of rehospitalisation (2.54 hospitalisations/patient-year), which differed significantly from other three groups (p = 0.014). In terms of bleeding requiring transfusion, rates were 1.67, 1.40, 1.30 and 1.12 bleeding events per patient-year for same groups respectively (p < 0.001). Bleeding was significantly associated with BMI, with underweight patients having highest risk and extremely obese patients having the lowest risk. For bleeding requiring re-exploration, the incidence was 42%, 22%, 25% and 18% in the underweight, normal, obese and extremely obese groups respectively (p < 0.01). Incidence of respiratory failure was borderline significant across the four BMI groups (p = 0.055), with underweight patients having highest risk (underweight 44%, normal 31%, obese 26%, very obese 38%). No differences were observed in development of cardiac arrhythmias, renal failure, right HF, stroke or haemolysis |
Adverse events | Underweight (66.4 patient-years) | Normal (731.8 patient-years) | Obese (192.9 patient-years) | Extremely obese (129.0 patient-years) | p-value | Incidence | Event rate | Incidence | Event rate | Incidence | Event rate | Incidence | Event rate | Bleeding requiring packed red blood cells | 31 (65%) | 1.67 | 399 (67%) | 1.40 | 100 (61%) | 1.30 | 57 (65%) | 1.12 | < 0.001 | Bleeding: requiring re-exploration | 20 (42%) | 0.35 | 130 (22%) | 0.21 | 41 (25%) | 0.22 | 16 (18%) | 0.13 | 0.010 | Infection | Local non-device related | 20 (42%) | 0.65 | 229 (38%) | 0.60 | 66 (40%) | 0.72 | 38 (43%) | 0.67 | 0.660 | Sepsis | 13 (27%) | 0.30 | 136 (23%) | 0.28 | 43 (26%) | 0.33 | 28 (32%) | 0.50 | 0.032 | Device related | 10 (21%) | 0.29 | 144 (24%) | 0.34 | 45 (27%) | 0.38 | 31 (35%) | 0.51 | 0.041 | Cardiac arrhythmias: cardioversion/defibrillation | 25 (52%) | 0.62 | 339 (57%) | 0.79 | 83 (51%) | 0.79 | 56 (64%) | 0.86 | 0.179 | Renal failure | 8 (17%) | 0.14 | 60 (10%) | 0.09 | 23 (14%) | 0.12 | 15 (17%) | 0.12 | 0.959 | Right HF | 11 (23%) | 0.17 | 110 (18%) | 0.17 | 37 (23%) | 0.20 | 24 (27%) | 0.21 | 0.749 | RVAD | 4 (8%) | 0.06 | 32 (5%) | 0.04 | 13 (8%) | 0.07 | 5 (6%) | 0.04 | 0.403 | Ischaemic stroke | 6 (13%) | 0.09 | 32 (5%) | 0.05 | 10 (6%) | 0.06 | 9 (10%) | 0.07 | 0.838 | Haemorrhagic stroke | 3 (6%) | 0.05 | 32 (5%) | 0.05 | 12 (7%) | 0.07 | 5 (6%) | 0.04 | 0.394 | Other neurological events (TIA, seizures, confusion, etc.) | 9 (19%) | 0.14 | 93 (16%) | 0.15 | 17 (10%) | 0.11 | 11 (13%) | 0.10 | 0.731 | Haemolysis | 4 (8%) | 0.06 | 22 (4%) | 0.03 | 9 (5%) | 0.08 | 7 (8%) | 0.07 | 0.617 | Respiratory failure | 21 (44%) | 0.45 | 183 (31%) | 0.34 | 42 (26%) | 0.23 | 33 (38%) | 0.35 | 0.055 | Rehospitalisations | 33 (69%) | 1.91 | 417 (70%) | 2.02 | 114 (70%) | 2.26 | 67 (76%) | 2.54 | 0.014 | p = evaluated based on event rates using Poisson regression. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events | Underweight (66.4 patient-years) | Normal (731.8 patient-years) | Obese (192.9 patient-years) | Extremely obese (129.0 patient-years) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incidence | Event rate | Incidence | Event rate | Incidence | Event rate | Incidence | Event rate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding requiring packed red blood cells | 31 (65%) | 1.67 | 399 (67%) | 1.40 | 100 (61%) | 1.30 | 57 (65%) | 1.12 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding: requiring re-exploration | 20 (42%) | 0.35 | 130 (22%) | 0.21 | 41 (25%) | 0.22 | 16 (18%) | 0.13 | 0.010 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Local non-device related | 20 (42%) | 0.65 | 229 (38%) | 0.60 | 66 (40%) | 0.72 | 38 (43%) | 0.67 | 0.660 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 13 (27%) | 0.30 | 136 (23%) | 0.28 | 43 (26%) | 0.33 | 28 (32%) | 0.50 | 0.032 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device related | 10 (21%) | 0.29 | 144 (24%) | 0.34 | 45 (27%) | 0.38 | 31 (35%) | 0.51 | 0.041 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac arrhythmias: cardioversion/defibrillation | 25 (52%) | 0.62 | 339 (57%) | 0.79 | 83 (51%) | 0.79 | 56 (64%) | 0.86 | 0.179 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure | 8 (17%) | 0.14 | 60 (10%) | 0.09 | 23 (14%) | 0.12 | 15 (17%) | 0.12 | 0.959 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HF | 11 (23%) | 0.17 | 110 (18%) | 0.17 | 37 (23%) | 0.20 | 24 (27%) | 0.21 | 0.749 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVAD | 4 (8%) | 0.06 | 32 (5%) | 0.04 | 13 (8%) | 0.07 | 5 (6%) | 0.04 | 0.403 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic stroke | 6 (13%) | 0.09 | 32 (5%) | 0.05 | 10 (6%) | 0.06 | 9 (10%) | 0.07 | 0.838 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic stroke | 3 (6%) | 0.05 | 32 (5%) | 0.05 | 12 (7%) | 0.07 | 5 (6%) | 0.04 | 0.394 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other neurological events (TIA, seizures, confusion, etc.) | 9 (19%) | 0.14 | 93 (16%) | 0.15 | 17 (10%) | 0.11 | 11 (13%) | 0.10 | 0.731 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemolysis | 4 (8%) | 0.06 | 22 (4%) | 0.03 | 9 (5%) | 0.08 | 7 (8%) | 0.07 | 0.617 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory failure | 21 (44%) | 0.45 | 183 (31%) | 0.34 | 42 (26%) | 0.23 | 33 (38%) | 0.35 | 0.055 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rehospitalisations | 33 (69%) | 1.91 | 417 (70%) | 2.02 | 114 (70%) | 2.26 | 67 (76%) | 2.54 | 0.014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p = evaluated based on event rates using Poisson regression. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unclear | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The reported data from the HMII clinical trial suggest both cachectic and obese patients who are appropriately selected and managed can undergo CF LVAD implantation with good intermediate-term results. Extremely obese patients (BMI ≥ 35) can also achieve good outcomes but have a higher risk of infection | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This was a post-hoc analysis of trial data. The authors did attempt to adjust for factors that might differ across groups. The population looks comparable to other study samples in terms of demographics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cowger 201060
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Cowger Year of publication: 2010 Country: USA Study design: Retrospective Study setting: University hospital, UMHS Number of centres: One Duration of study: May 2004 and May 2008 Follow-up period: Studies were obtained pre-operatively and at 1, 3, 6, 12, 18 and 24 months after surgery Funding: National Institutes of Health T32-HL007853 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To examine the temporal trend of AI following LVAD implant and to identify correlates of AI development and progression | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: Echocardiograms (n = 315) from 78 subjects undergoing HMXVE [n = 25 (32%)] or HMII [n = 53 (68%)] implantations Sample attrition/dropout: All subjects with pre-operative AI of moderate or worse severity undergo intraoperative aortic valve repair, bioprosthetic valve replacement, or patch closure of the aortic valve (n = 8) were excluded Inclusion criteria: Transthoracic or transesophageal echocardiograms from consecutive HMXVE and HMII LVADs implanted at the UMHS between May 2004 and May 2008 Exclusion criteria: Subjects were excluded from the analysis if they did not have a pre-operative echocardiogram plus at least one echocardiogram within 1 year of device placement from which AI could be accurately assessed Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): Total cohort 54 ± 13; HMII 54 ± 13; HMXVE 52 ± 13 Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: Male, n (%): total cohort 68 (87); HMII 44 (83); HMXVE 24 (96) Race: Caucasian, n (%): total cohort 57 (73); HMII 17 (68); HMXVE 40 (75) Diagnosis: Not clear |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT – 69 (88%) [HMII 54 (90%); HMXVE 21 (84%)] Type of device used: HMXVE and HMII Any comparison: HMXVE and HMII Duration of treatment: Echocardiograms were performed pre-operatively within 30 days of LVAD implant and at approximate intervals of 1, 3, 6, 12, 18 and 24 months post operative or until LVAD explant for any cause Percentage of patients using inotropes: Not reported Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Temporal trend of AI following LVAD implant and AI development and progression Secondary outcomes: Device replacement and AI Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: No Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: Echocardiograms were performed pre-operatively within 30 days of LVAD implant and at approximate intervals of 1, 3, 6, 12, 18 and 24 months post operative or until LVAD explant for any causeNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reportedNot reportedRandomised/includedHMII [n = 53 (68%)]HMXVE [n = 25 (32%)]Excluded8 participants were excluded from the analysisNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reportedNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported | Not reported | Randomised/included | HMII [n = 53 (68%)] | HMXVE [n = 25 (32%)] | Excluded | 8 participants were excluded from the analysis | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | HMII [n = 53 (68%)] | HMXVE [n = 25 (32%)] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | 8 participants were excluded from the analysis | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline characteristics and demographics of the total cohort and by LVAD model type (mean ± SD)ParameterTotal cohort (n = 78)HMXVE (n = 25)HMII (n = 53)p-valueAge, years54 ± 1352 ± 1354 ± 130.60Male, n (%)68 (87)24 (96)44 (83)0.16Caucasian, n (%)57 (73)17 (68)40 (75%)0.41BSA, m22.0 ± 0.32.1 ± 0.22.0 ± 0.30.36Diabetes mellitus, n (%)28 (36)10 (40)18 (34)0.62Hypertension, n (%)34 (44)10 (40)24 (45)0.81Hyperlipidemia, n (%)52 (67)15 (60)37 (70)0.45Non-ischaemic HF, n (%)39 (50)16 (64)23 (43)0.14Pre-operative IABP, n (%)30 (38)11 (44)19 (36)0.62BTT, n (%)69 (88)21 (84)54 (90)0.46 | Parameter | Total cohort (n = 78) | HMXVE (n = 25) | HMII (n = 53) | p-value | Age, years | 54 ± 13 | 52 ± 13 | 54 ± 13 | 0.60 | Male, n (%) | 68 (87) | 24 (96) | 44 (83) | 0.16 | Caucasian, n (%) | 57 (73) | 17 (68) | 40 (75%) | 0.41 | BSA, m2 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 0.36 | Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 28 (36) | 10 (40) | 18 (34) | 0.62 | Hypertension, n (%) | 34 (44) | 10 (40) | 24 (45) | 0.81 | Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 52 (67) | 15 (60) | 37 (70) | 0.45 | Non-ischaemic HF, n (%) | 39 (50) | 16 (64) | 23 (43) | 0.14 | Pre-operative IABP, n (%) | 30 (38) | 11 (44) | 19 (36) | 0.62 | BTT, n (%) | 69 (88) | 21 (84) | 54 (90) | 0.46 | |||||
| Parameter | Total cohort (n = 78) | HMXVE (n = 25) | HMII (n = 53) | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, years | 54 ± 13 | 52 ± 13 | 54 ± 13 | 0.60 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male, n (%) | 68 (87) | 24 (96) | 44 (83) | 0.16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caucasian, n (%) | 57 (73) | 17 (68) | 40 (75%) | 0.41 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA, m2 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 0.36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 28 (36) | 10 (40) | 18 (34) | 0.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 34 (44) | 10 (40) | 24 (45) | 0.81 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 52 (67) | 15 (60) | 37 (70) | 0.45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-ischaemic HF, n (%) | 39 (50) | 16 (64) | 23 (43) | 0.14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative IABP, n (%) | 30 (38) | 11 (44) | 19 (36) | 0.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTT, n (%) | 69 (88) | 21 (84) | 54 (90) | 0.46 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Profile plot of aortic insufficiency for LVAD support subjects are reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAD failure = 8 (10%) in the entire cohort, six leading to reoperation AI grade for the cohort at follow-up. The within-subject change in AI (ΔAI) is also shownTimenAI total cohortΔAI from baselinep-valuea ΔAIPre operative780.0 [0.0, 0.0]1 month750.0 [0.0, 0.5]0.0 [0.0, 0.5]< 0.0013 months660.5 [0.0, 1.0]0.0 [0.0, 1.0]< 0.0016 months491.0 [0.5, 1.5]0.5 [0.0, 1.0]< 0.00112 months291.0 [0.0, 1.5]1.0 [0.0, 1.0]< 0.00118 months132.0 [0.0, 2.0]1.0 [0.0, 2.0]0.00424 months52.0 [1.0, 2.0]1.5 [1.0, 2.0]0.13a via Wilcoxon signed-rank tests. Data expressed as median [25th, 75th]; AI was graded: 0 = none, 0.5 = trivial, 1.0 = mild, 1.5 = mild–moderate, 2.0 = moderate, 2.5 = moderate–severe, 3.0 = severe. Correlates of worsening aortic insufficiency in LVAD supported subjectsParameterChange in AI p-value, slope ± SEp-valueAge, per 10 years0.0004 ± 0.0020.069Female sex0.002 ± 0.0010.010HMII vs. HMXVE0.002 ± 0.0010.039LVAD flow (l/minute)0.090 ± 0.0440.044 |
Time | n | AI total cohort | ΔAI from baseline | p-valuea ΔAI | Pre operative | 78 | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | 1 month | 75 | 0.0 [0.0, 0.5] | 0.0 [0.0, 0.5] | < 0.001 | 3 months | 66 | 0.5 [0.0, 1.0] | 0.0 [0.0, 1.0] | < 0.001 | 6 months | 49 | 1.0 [0.5, 1.5] | 0.5 [0.0, 1.0] | < 0.001 | 12 months | 29 | 1.0 [0.0, 1.5] | 1.0 [0.0, 1.0] | < 0.001 | 18 months | 13 | 2.0 [0.0, 2.0] | 1.0 [0.0, 2.0] | 0.004 | 24 months | 5 | 2.0 [1.0, 2.0] | 1.5 [1.0, 2.0] | 0.13 | a via Wilcoxon signed-rank tests. Data expressed as median [25th, 75th]; AI was graded: 0 = none, 0.5 = trivial, 1.0 = mild, 1.5 = mild–moderate, 2.0 = moderate, 2.5 = moderate–severe, 3.0 = severe. | Parameter | Change in AI p-value, slope ± SE | p-value | Age, per 10 years | 0.0004 ± 0.002 | 0.069 | Female sex | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.010 | HMII vs. HMXVE | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.039 | LVAD flow (l/minute) | 0.090 ± 0.044 | 0.044 | ||||||
| Time | n | AI total cohort | ΔAI from baseline | p-valuea ΔAI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre operative | 78 | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 month | 75 | 0.0 [0.0, 0.5] | 0.0 [0.0, 0.5] | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 months | 66 | 0.5 [0.0, 1.0] | 0.0 [0.0, 1.0] | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 months | 49 | 1.0 [0.5, 1.5] | 0.5 [0.0, 1.0] | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 months | 29 | 1.0 [0.0, 1.5] | 1.0 [0.0, 1.0] | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 months | 13 | 2.0 [0.0, 2.0] | 1.0 [0.0, 2.0] | 0.004 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 months | 5 | 2.0 [1.0, 2.0] | 1.5 [1.0, 2.0] | 0.13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a via Wilcoxon signed-rank tests. Data expressed as median [25th, 75th]; AI was graded: 0 = none, 0.5 = trivial, 1.0 = mild, 1.5 = mild–moderate, 2.0 = moderate, 2.5 = moderate–severe, 3.0 = severe. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Change in AI p-value, slope ± SE | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, per 10 years | 0.0004 ± 0.002 | 0.069 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Female sex | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII vs. HMXVE | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.039 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD flow (l/minute) | 0.090 ± 0.044 | 0.044 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AI progresses over time in LVAD supported participants. Post-operative progression of AI is likely multifactorial. More studies are needed to determine the clinical significance of these findings | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This was a single-centre study. There may be potential bias in selection, image interpretation and LVAD management which could impact on AI development and assessment. Caution when interpreting the unadjusted p-values. Also failure to apply Bonferroni correction to the multiple comparisons reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Demirozu 201161
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Demirozu Year of publication: 2011 Country: USA Study design: Retrospective Study setting: Texas Heart Institute at St. Luke's Episcopal Hospital Number of centres: One Duration of study: October 2003 and June 2010 Follow-up period: Unclear Funding: Not reported |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To identify the prevalence of GI bleeding and the role of AVMs in patients with the CF HMII LVAD | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 172 Sample attrition/dropout: None Inclusion criteria: Patients with severe HF associated with compromised systolic left ventricular cardiac function who underwent implantation of a CF HMII LVAD at authors hospital between October 2003 and June 2010 Exclusion criteria: Not reported Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): GI bleeding group 58 ± 12 years; non-GI bleeding group 49 ± 15 years Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: Men/women – GI bleeding group 24/8; non-GI bleeding group 110/30 Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Ischaemic cardiomyopathy – GI bleeding group 18 (56%); non-GI bleeding group 59 (42%); idiopathic cardiomyopathy – GI bleeding group 14 (44%); non-GI bleeding group 81 (58%) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: CF LVAD support was initiated as therapy for patients with severe HF associated with compromised systolic left ventricular cardiac function Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: Two groups – GI bleeding group (n = 31) and non-GI bleeding group (n = 140) Duration of treatment: Unclear Percentage of patients using inotropes: Not reported Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below. Post-operative anticoagulation therapy included aspirin (81 mg/day), dipyridamole (Persantine®, Actavis) (75 mg, three times a day) and warfarin (maintaining an INR of 1.5 to 2.5). A proton pump inhibitor was administered intravenously for peptic ulcer prophylaxis until extubation and then was continued orally Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: GI bleeding Secondary outcomes: None Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: No Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: UnclearNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedGI bleeding group: n = 32Non-GI bleeding group: n = 140Randomised/includedGI bleeding group: n = 32Non-GI bleeding group: n = 140ExcludedNoneNoneMissing participantsNoneNoneWithdrawalsNoneNone |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | GI bleeding group: n = 32 | Non-GI bleeding group: n = 140 | Randomised/included | GI bleeding group: n = 32 | Non-GI bleeding group: n = 140 | Excluded | None | None | Missing participants | None | None | Withdrawals | None | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | GI bleeding group: n = 32 | Non-GI bleeding group: n = 140 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | GI bleeding group: n = 32 | Non-GI bleeding group: n = 140 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | None | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | None | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | None | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics Demographic and pre-implantation characteristics of patients with and without GI bleedingParameterGI bleeding (n = 32)No GI bleeding (n = 140)p-valueAge (years)58 ± 1249 ± 150.001Weight (kg)81 ± 1987 ± 210.175BSA (m2)1.9 ± 0.32.0 ± 0.30.234Men/women24/8110/300.839Heart disease0.211Ischaemic cardiomyopathy18 (56)59 (42)Idiopathic cardiomyopathy14 (44)81 (58)Diabetes mellitus10 (31)50 (36)0.581Hypertension21 (66)72 (51)0.209Myocardial infarction15 (47)38 (27)0.049LVEF (%)19 ± 420 ± 50.944Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)1.7 ± 0.31.7 ± 0.50.224BUN (mg/dl)40 ± 29a30 ± 17a0.055Creatinine (mg/dl)1.8 ± 1.31.3 ± 0.40.066Use of haemodialysis4 (13)4 (3)0.123Previous cardiac surgery13 (41)65 (46)0.691HMXVE LVAD implantation5 (16)27 (19)0.819Pre-implantation supportIABP12 (38)57 (41)0.893Tandem heart1 (3)18 (13)0.203Pre-existing hepatic dysfunction5 (5)18 (13)0.899Gastric ulcer4 (4)11 (8)0.622a Normal range 10–26 mg/dl.Results are presented as mean ± SD or number of patients. |
Parameter | GI bleeding (n = 32) | No GI bleeding (n = 140) | p-value | Age (years) | 58 ± 12 | 49 ± 15 | 0.001 | Weight (kg) | 81 ± 19 | 87 ± 21 | 0.175 | BSA (m2) | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 0.234 | Men/women | 24/8 | 110/30 | 0.839 | Heart disease | 0.211 | Ischaemic cardiomyopathy | 18 (56) | 59 (42) | Idiopathic cardiomyopathy | 14 (44) | 81 (58) | Diabetes mellitus | 10 (31) | 50 (36) | 0.581 | Hypertension | 21 (66) | 72 (51) | 0.209 | Myocardial infarction | 15 (47) | 38 (27) | 0.049 | LVEF (%) | 19 ± 4 | 20 ± 5 | 0.944 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 0.224 | BUN (mg/dl) | 40 ± 29a | 30 ± 17a | 0.055 | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.8 ± 1.3 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 0.066 | Use of haemodialysis | 4 (13) | 4 (3) | 0.123 | Previous cardiac surgery | 13 (41) | 65 (46) | 0.691 | HMXVE LVAD implantation | 5 (16) | 27 (19) | 0.819 | Pre-implantation support | IABP | 12 (38) | 57 (41) | 0.893 | Tandem heart | 1 (3) | 18 (13) | 0.203 | Pre-existing hepatic dysfunction | 5 (5) | 18 (13) | 0.899 | Gastric ulcer | 4 (4) | 11 (8) | 0.622 | a Normal range 10–26 mg/dl. | Results are presented as mean ± SD or number of patients. | |||||||||||||
| Parameter | GI bleeding (n = 32) | No GI bleeding (n = 140) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 58 ± 12 | 49 ± 15 | 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight (kg) | 81 ± 19 | 87 ± 21 | 0.175 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 0.234 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Men/women | 24/8 | 110/30 | 0.839 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heart disease | 0.211 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic cardiomyopathy | 18 (56) | 59 (42) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Idiopathic cardiomyopathy | 14 (44) | 81 (58) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 10 (31) | 50 (36) | 0.581 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension | 21 (66) | 72 (51) | 0.209 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myocardial infarction | 15 (47) | 38 (27) | 0.049 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF (%) | 19 ± 4 | 20 ± 5 | 0.944 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 0.224 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 40 ± 29a | 30 ± 17a | 0.055 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.8 ± 1.3 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 0.066 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Use of haemodialysis | 4 (13) | 4 (3) | 0.123 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Previous cardiac surgery | 13 (41) | 65 (46) | 0.691 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMXVE LVAD implantation | 5 (16) | 27 (19) | 0.819 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-implantation support | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP | 12 (38) | 57 (41) | 0.893 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tandem heart | 1 (3) | 18 (13) | 0.203 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-existing hepatic dysfunction | 5 (5) | 18 (13) | 0.899 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gastric ulcer | 4 (4) | 11 (8) | 0.622 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Normal range 10–26 mg/dl. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Results are presented as mean ± SD or number of patients. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arteriovenous malformations were source of GI bleeding in 10 of 32 (31%) patients; mean duration of LVAD support was 439 ± 315 (range 108–996) days Average age of 10 AVM patients was 63 ± 7 (range 54–75) years; these patients were significantly older than 162 HMII recipients (mean age 50 ± 15 years, range 14–76 years; p = 0.0001) Eight of the 10 patients with AVMs as cause of bleeding were supported by HMII LVAD at most recent follow-up (mean duration 468 ± 339 days, range 108–996 days). Five of the 10 patients had had recurrent GI bleeding from a different location in each episode: three patients had two episodes of bleeding from a jejunal AVM, and two patients had five episodes of bleeding from a gastric AVM |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No thromboembolic events occurred GI bleeding: 32 (19%); 53 episodes Upper GI bleeding: 16 Lower GI bleeding: 15 Upper and lower GI bleeding: 1 Compared with 140 patients not having GI bleeding, patients with GI bleeding were significantly older (p = 0.001) and had more myocardial infarctions before LVAD implantation (p = 0.049) On multivariate regression analysis, the only significant risk factor was age > 51 years (odds ratio = 2.8, 95% CI 1.1 to 7.3; p = 0.031) The first AVM bleeding episode occurred at an average of 67 (range 17–241) days after device implantation. In 10 patients with bleeding from GI AVMs, 6 had jejuna AVMs and 4 had gastric AVMs. At first GI bleeding episode, mean INR was 1.8 ± 1.0 and mean haemoglobin was 9.0 ± 1.4 g/dl. Two of the 10 patients with AVM bleeding subsequently underwent HT; no GI bleeding occurred after transplantation |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location of GI bleeding in 32 patients after HMII implantationLocationNumber of patientsUpper GI16Haemorrhagic gastritis10Mallory–Weiss tear2Gastric AVM4Lower GI15Jejuna AVM6Diverticulosis6Driveline erosion of colon1Ischaemic colitis1Sigmoid polyp1Upper and lower GI1Colocutaneous and gastrocutaneous fistula1 | Location | Number of patients | Upper GI | 16 | Haemorrhagic gastritis | 10 | Mallory–Weiss tear | 2 | Gastric AVM | 4 | Lower GI | 15 | Jejuna AVM | 6 | Diverticulosis | 6 | Driveline erosion of colon | 1 | Ischaemic colitis | 1 | Sigmoid polyp | 1 | Upper and lower GI | 1 | Colocutaneous and gastrocutaneous fistula | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Number of patients | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Upper GI | 16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic gastritis | 10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mallory–Weiss tear | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gastric AVM | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lower GI | 15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jejuna AVM | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diverticulosis | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline erosion of colon | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic colitis | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sigmoid polyp | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Upper and lower GI | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Colocutaneous and gastrocutaneous fistula | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AVM-related GI bleeding is a significant but medically manageable complication, the possibility of which should be considered in patients with CF LVADs. The overall incidence of GI bleeding associated with this technology is similar to that associated with other implantable LVADs that require anticoagulation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The study provides no information on survival or QoL. The main consideration is that arteriovenous malformations can cause GI bleeding in patients with HMII. Limited statistical analysis was reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drews 201087
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Drews Year of publication: 2010 Country: Germany Study design: Retrospective Study setting: Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery, Deutsches Herzzentrum Berlin Number of centres: One Duration of study: January 1999 and January 2009 Follow-up period: 3 years Funding: Funding to reproduce the figures in colour was provided by Berlin Heart GmbH |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To find out whether or not pulsatile and non-pulsatile VADs can ensure a low rate of complications for extended periods of time in elderly patients | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 174 – group A 64; group B 110 Sample attrition/dropout: Not clear Inclusion criteria: 174 consecutive patients presenting with catecholamine-dependent terminal HF who underwent implantation of a left ventricular MCS system and who were aged > 60 years Exclusion criteria: Not clear Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): Group A 65 ± 3; group B: 67 ± 4 Median age: Not reported Age range, years: Group A 60–73; group B 60–80 Sex (male/female): Group A 61/3; group B 98/12 Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Group A – ischaemic CMP = 33, dilated CMP = 28 and post-cardiotomy syndrome = 3; group B – ischaemic CMP = 50, dilated CMP = 50, acute myocarditis = 2, post-cardiotomy syndrome = 2 and restrictive CMP = 1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: Owing to the shortage of organs available for transplantation, this age is a relative contraindication for HT; therefore, all these patients received the device primarily for permanent support. All devices were implanted primarily for long-term support and not as a BTT Type of device used: Berlin Heart EXCOR, Novacor, LionHeart, HMI, Berlin Heart INCOR, MicroMed DeBakey, HMII, DuraHeart and Jarvik 2000 Any comparison: Two groups – group A 64 patients who underwent implantation of a first-generation pulsatile system (Berlin Heart EXCOR n = 39, Novacor n = 18, LionHeart n = 4 and HMI 3) between January 1994 and October 2008; group B 110 patients with implantation of a second- or third-generation non-pulsatile VAD (Berlin Heart INCOR n = 65, MicroMed DeBakey n = 18, HMII n = 14, DuraHeart n = 7 and Jarvik 2000 n = 6) Duration of treatment: Group A were implanted during 1994–2008 and the non-pulsatile devices during 1999–2009 Percentage of patients using inotropes: Not reported Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – Berlin Heart INCOR, MicroMed DeBakey, HMII, DuraHeart and Jarvik 2000 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Survival Secondary outcomes: Discharge from hospital, technical complications Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: 3 yearsNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreened943 pulsatile have been implanted in the institution567 non-pulsatile have been implanted in our institutionRandomised/included64110ExcludedNot reportedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reportedNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | 943 pulsatile have been implanted in the institution | 567 non-pulsatile have been implanted in our institution | Randomised/included | 64 | 110 | Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | 943 pulsatile have been implanted in the institution | 567 non-pulsatile have been implanted in our institution | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 64 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ParameterGroup A: pulsatile deviceGroup B: non-pulsatile devicePatients, n64110Age (years)65 ± 3 (60–73)67 ± 4 (60–80)Sex (male/female)61/398/12Date of implantationJanuary 1994 to October 2008January 1999 to January 2009Heart diseaseIschaemic CMP52% (33)50% (55)Dilated CMP44% (28)45% (50)Other4% (3)5% (5)Assist device Berlin Heart EXCOR LVAD61% (39)Novacor28% (18)LionHeart6% (4)HMI5% (3)Berlin Heart INCOR59% (65)MicroMed DeBakey LVAD16% (18)HMII13% (14)DuraHeart7% (7)Jarvik 20005% (6)Data are presented as mean ± SD (range, minimum–maximum) or % (z). | Parameter | Group A: pulsatile device | Group B: non-pulsatile device | Patients, n | 64 | 110 | Age (years) | 65 ± 3 (60–73) | 67 ± 4 (60–80) | Sex (male/female) | 61/3 | 98/12 | Date of implantation | January 1994 to October 2008 | January 1999 to January 2009 | Heart disease | Ischaemic CMP | 52% (33) | 50% (55) | Dilated CMP | 44% (28) | 45% (50) | Other | 4% (3) | 5% (5) | Assist device Berlin Heart EXCOR LVAD | 61% (39) | Novacor | 28% (18) | LionHeart | 6% (4) | HMI | 5% (3) | Berlin Heart INCOR | 59% (65) | MicroMed DeBakey LVAD | 16% (18) | HMII | 13% (14) | DuraHeart | 7% (7) | Jarvik 2000 | 5% (6) | Data are presented as mean ± SD (range, minimum–maximum) or % (z). | ||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Group A: pulsatile device | Group B: non-pulsatile device | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients, n | 64 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 65 ± 3 (60–73) | 67 ± 4 (60–80) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex (male/female) | 61/3 | 98/12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Date of implantation | January 1994 to October 2008 | January 1999 to January 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heart disease | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic CMP | 52% (33) | 50% (55) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dilated CMP | 44% (28) | 45% (50) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 4% (3) | 5% (5) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assist device Berlin Heart EXCOR LVAD | 61% (39) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Novacor | 28% (18) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LionHeart | 6% (4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMI | 5% (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Berlin Heart INCOR | 59% (65) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MicroMed DeBakey LVAD | 16% (18) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII | 13% (14) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DuraHeart | 7% (7) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jarvik 2000 | 5% (6) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Data are presented as mean ± SD (range, minimum–maximum) or % (z). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-month survival rate of pulsatile (group A) was 11% and non-pulsatile (group B) was 42% (p = 0.0017) Differences in survival between the group A and group B: The 1-year survival was 15% in group A and 36% in group B The 2-year survival was 12% in group A and 26% in group B The 3-year survival was 12% in group A and 16% in group B The difference was significant (log-rank test p = 0.0017) Most deaths occurred during the early post-operative period In group A 63% of patients died during first 3 months and in group B 42% (p = 0.0017). Death was mainly multiorgan failure and infections (significantly more frequent in group A, p = 0.0036/p = 0.015). Other reasons included stroke, right ventricular failure and bleeding complications. The rate of stroke, right ventricular failure and bleeding complications did not differ between groups |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Only 17% of patients in group A and 41% in group B could be discharged home (p = 0.017) The mean time to first discharge was 79 ± 38 (33–146) days in group A and 50 ± 33 (9–160) days in group B (p = 0.007) The frequency of rehospitalisation in group A was 2.8 rehospitalisations per patient per year and group B was 3.6 rehospitalisations per patient per year (p > 0.05) Reasons for rehospitalisation were mainly anticoagulation disorders, wound infections and other non-cardiac problems For group A mean duration of support was 157 ± 343 (1–1836) days (see below); 17 patients (27%) were supported for > 6 months, 7 (11%) for > 1 year; 3 (5%) for > 2 years; and 3 (5%) for > 3 years For group B patients were on MCS for mean of 281 ± 336 (1–1619) days (significantly longer than group A; p = 0.0004); 46 patients (42%) were supported for > 6 months; 34 (28%) for > 1 year; 14 (13%) for > 2 years; and 4 (3.6%) for > 3 years Duration of support and discharge from hospitalParameterGroup A: pulsatile deviceGroup B: non-pulsatile deviceNumber of patients64110Duration of support, mean (days)157 ± 343 (1–1836)a281 ± 336 (1–1619)a > 6 months27% (17)42% (46) > 1 year11% (7)28% (34) > 2 years5% (3)13% (14) > 3 years5% (3)3.6% (4)Discharge from hospital Number of patients17% (11)b41% (45)b Mean (days)632 ± 635 (7–1688)442 ± 344 (7–1487) > 6 months13% (8)31% (34) > 1 year11% (7)19% (21) > 2 years6% (4)10% (11) > 3 years5% (3)2% (2)Time to first discharge (days)79 ± 38 (33–146)c50 ± 33 (9–160)cRehospitalisation (patient/year)2.8 ×3.6 ×a p = 0.00043.b p = 0.0173.c p = 0.007.Data are presented as mean ± SD (range, minimum–maximum) or % (z). |
Parameter | Group A: pulsatile device | Group B: non-pulsatile device | Number of patients | 64 | 110 | Duration of support, mean (days) | 157 ± 343 (1–1836)a | 281 ± 336 (1–1619)a | > 6 months | 27% (17) | 42% (46) | > 1 year | 11% (7) | 28% (34) | > 2 years | 5% (3) | 13% (14) | > 3 years | 5% (3) | 3.6% (4) | Discharge from hospital | Number of patients | 17% (11)b | 41% (45)b | Mean (days) | 632 ± 635 (7–1688) | 442 ± 344 (7–1487) | > 6 months | 13% (8) | 31% (34) | > 1 year | 11% (7) | 19% (21) | > 2 years | 6% (4) | 10% (11) | > 3 years | 5% (3) | 2% (2) | Time to first discharge (days) | 79 ± 38 (33–146)c | 50 ± 33 (9–160)c | Rehospitalisation (patient/year) | 2.8 × | 3.6 × | a p = 0.00043. | b p = 0.0173. | c p = 0.007. | Data are presented as mean ± SD (range, minimum–maximum) or % (z). | ||||||||||
| Parameter | Group A: pulsatile device | Group B: non-pulsatile device | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of patients | 64 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Duration of support, mean (days) | 157 ± 343 (1–1836)a | 281 ± 336 (1–1619)a | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 6 months | 27% (17) | 42% (46) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 1 year | 11% (7) | 28% (34) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 2 years | 5% (3) | 13% (14) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 3 years | 5% (3) | 3.6% (4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discharge from hospital | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of patients | 17% (11)b | 41% (45)b | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean (days) | 632 ± 635 (7–1688) | 442 ± 344 (7–1487) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 6 months | 13% (8) | 31% (34) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 1 year | 11% (7) | 19% (21) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 2 years | 6% (4) | 10% (11) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 3 years | 5% (3) | 2% (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time to first discharge (days) | 79 ± 38 (33–146)c | 50 ± 33 (9–160)c | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rehospitalisation (patient/year) | 2.8 × | 3.6 × | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a p = 0.00043. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b p = 0.0173. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c p = 0.007. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Data are presented as mean ± SD (range, minimum–maximum) or % (z). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical complications were observed in group B only (p = 0.0175), see below. Pump thrombosis occurred in five patients (MicroMed DeBakey LVAD n = 4; Jarvik 2000 n = 1) and 3 patients had pump-stop due to technical failure (MicroMed DeBakey, Berlin Heart INCOR) and due to pannus on inflow cannula (DuraHeart); two patients had bearing problems (Berlin Heart INCOR); one patient had a broken driveline; five patients pump exchange could be performed; two patients died; and four patients underwent a successful HT Technical complications and outcomeParameterGroup A: pulsatile deviceGroup B: non-pulsatile deviceNumber of patients64110Technical complications Device failureNot reported2% (2) Pump thrombosisNot reported4.5% (5) Inflow-thrombosisNot reported1% (1) Bearing problemNot reported2% (2) Driveline brokenNot reported1% (1) Total0a10% (11)aPump exchangeNot reported5% (5)Outcome On device5% (3)15% (17) Transplanted5% (3)8% (9) Weaned5% (3)3% (3)a p = 0.0175.Data are presented as mean ± SD (range, minimum–maximum) or % (z). |
Parameter | Group A: pulsatile device | Group B: non-pulsatile device | Number of patients | 64 | 110 | Technical complications | Device failure | Not reported | 2% (2) | Pump thrombosis | Not reported | 4.5% (5) | Inflow-thrombosis | Not reported | 1% (1) | Bearing problem | Not reported | 2% (2) | Driveline broken | Not reported | 1% (1) | Total | 0a | 10% (11)a | Pump exchange | Not reported | 5% (5) | Outcome | On device | 5% (3) | 15% (17) | Transplanted | 5% (3) | 8% (9) | Weaned | 5% (3) | 3% (3) | a p = 0.0175. | Data are presented as mean ± SD (range, minimum–maximum) or % (z). | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Group A: pulsatile device | Group B: non-pulsatile device | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of patients | 64 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical complications | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device failure | Not reported | 2% (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump thrombosis | Not reported | 4.5% (5) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inflow-thrombosis | Not reported | 1% (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bearing problem | Not reported | 2% (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline broken | Not reported | 1% (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 0a | 10% (11)a | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump exchange | Not reported | 5% (5) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcome | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| On device | 5% (3) | 15% (17) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transplanted | 5% (3) | 8% (9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weaned | 5% (3) | 3% (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a p = 0.0175. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Data are presented as mean ± SD (range, minimum–maximum) or % (z). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall, 88 patients had dilated CMP, 78 patients had ischaemic CMP and 8 patients had other heart diseases leading to device implantation. For patients with CMP (n = 88): 59 died, 6 were transplanted and 4 were still on the device. For patients with ischaemic CMP: 72 died, 5 were transplanted, 2 were weaned and 9 are still on support. For patients with other heart diseases: 5 died and 2 were weaned. Outcome in relation to differences in aetiology were not significant | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Although pulsatile (Berlin Heart EXCOR, Novacor, LionHeart and HMI) and non-pulsatile VADs (Berlin Heart INCOR, MicroMed DeBakey, HMII, DuraHeart and Jarvik2000) can be used for extended periods of time, non-pulsatile systems resulted in significantly higher survival rate in elderly patients. The authors suggested that this may allow elderly patients additional years of life in their familiar environment. The authors recognised that a limitation of the study was that the pulsatile devices in group A were implanted during an earlier period (1994–2008) and the non-pulsatile devices between 1999 and 2009. Therefore, improved understanding during recent years in the care of these elderly patients on MCS may have contributed to the better results in the non-pulsatile device group | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All devices were implanted primarily for long-term support and not as a BTT. Devices were implanted during different time periods. Cox proportional hazards were not reported. Caution when interpreting the findings related to survival | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Goldstein 200384
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Goldstein Year of publication: 2003 Country: Europe (Germany, Austria, France, Switzerland and Italy) and USA (Texas, Cleveland and Newark) Study design: Prospective single arm study Study setting: Multicentre Number of centres: Europe (11 centres) and USA (3 centres) Duration of study: Unclear Follow-up period: Unclear Funding: Unclear |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To explore if second-generation VAD, MicroMed DeBakey, can overcome the shortcomings of pulsatile first-generation pumps such as applicability to small patients, noise, and high incidence of infection and pump malfunction | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 150 Sample attrition/dropout: None Inclusion criteria: All patients in the US groups (n = 24, 3 centres) and in the European groups (n = 126, 11 centres) underwent implantation of the MicroMed VAD with the intention of BTT as part of a clinical trial between 13 November 1998 and 7 July 2002 Exclusion criteria: Post-cardiotomy cardiac failure, cardiogenic shock due to acute myocardial infarction of < 48 hours duration, as well as any criteria that contraindicated future cardiac transplantation Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): 48 ± 14 years Age range: 12–73 years Sex: 18% (n = 27) were female Race: Not reported Diagnosis: The most common aetiology of HF was ischaemic, followed by dilated cardiomyopathy |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT Type of device used: MicroMed DeBakey VAD Any comparison: 103 patients who had complete data were divided into two groups according to BSA. Outcomes such as mean pump speed, mean pump flow and indices of renal (BUN and creatinine) and hepatic (total bilirubin) function for duration of support were extracted from each patient's datasheet and comparisons were made between small (BSA < 1.9 m2) and large (BSA ≥ 1.9 m2) patients Duration of treatment: Unclear, the authors stated given that the longest support time was 441 days Percentage of patients using inotropes: 40% of patients were on at least two inotropes Other interventions used: Unclear Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – MicroMed DeBakey VAD |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Adverse events and outcome of the support (BTT, death, ongoing support, recovery) Secondary outcomes: Not clear Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records – haemolysis defined as plasma–free haemoglobin > 40 mg/dl. Thromboembolic event is a composite of embolic stroke, TIA and peripheral embolism Survival: No Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: Longest support time was 441 days. Cumulative support time was 30.4 patient-years. Twelve patients (8%) have been supported for at least 6 monthsNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedUnclearNot applicableRandomised/included150Not applicableExcluded47 patients from the subgroup analysisNot applicableMissing participantsNot reportedNot applicableWithdrawalsNot reportedNot applicablePatient's baseline characteristicsAge, years48 ± 14 years (range 12–73)Not applicableSex18% (n = 27) were femaleNot applicableBSA (m2)Range 1.4–2.34Not applicableWeight (kg), BMINot reportedNot applicableIschaemic causes of HFNo data. However, the paper reports that most common aetiology of HF was ischaemic, followed by dilated cardiomyopathyNot applicable |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Unclear | Not applicable | Randomised/included | 150 | Not applicable | Excluded | 47 patients from the subgroup analysis | Not applicable | Missing participants | Not reported | Not applicable | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not applicable | Patient's baseline characteristics | Age, years | 48 ± 14 years (range 12–73) | Not applicable | Sex | 18% (n = 27) were female | Not applicable | BSA (m2) | Range 1.4–2.34 | Not applicable | Weight (kg), BMI | Not reported | Not applicable | Ischaemic causes of HF | No data. However, the paper reports that most common aetiology of HF was ischaemic, followed by dilated cardiomyopathy | Not applicable | |||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Unclear | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 150 | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | 47 patients from the subgroup analysis | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, years | 48 ± 14 years (range 12–73) | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex | 18% (n = 27) were female | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | Range 1.4–2.34 | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight (kg), BMI | Not reported | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic causes of HF | No data. However, the paper reports that most common aetiology of HF was ischaemic, followed by dilated cardiomyopathy | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A baseline characteristics table was not presented. All patients in the US groups (n = 24, 3 centres) and in the European groups (n = 126, 11 centres) underwent implantation of the MicroMed VAD with intention of BTT as part of a clinical trial. Demographic, adverse event and outcome data were collected for each participant in case report forms | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Linearisation and hazard function analysis were performed to calculate the incidence of adverse events. t-tests were used for comparison of means and a two-tailed probability value < 0.05 was considered significant Outcomes of 150 patients receiving the MicroMed DeBakey VAD as a BTTOutcomeEuropeUSACarmedaaTotalBTT4116562Died4581568Ongoing101819BTR1001Total882438150a Pumps with covalently coated heparin, recently available. |
Outcome | Europe | USA | Carmedaa | Total | BTT | 41 | 16 | 5 | 62 | Died | 45 | 8 | 15 | 68 | Ongoing | 1 | 0 | 18 | 19 | BTR | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Total | 88 | 24 | 38 | 150 | a Pumps with covalently coated heparin, recently available. | ||||||||
| Outcome | Europe | USA | Carmedaa | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTT | 41 | 16 | 5 | 62 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Died | 45 | 8 | 15 | 68 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ongoing | 1 | 0 | 18 | 19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTR | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 88 | 24 | 38 | 150 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Pumps with covalently coated heparin, recently available. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) Comparison of pump speed, flow and end-organ function between smaller (BSA < 1.9) and larger (BSA ≥ 1.9) patientsParameterBSA< 1.9 m2 (n = 46)∼ 1.9 m2 (n = 57)p-valueMean BSA (m2)1.7 ± 0.12.0 ± 0.1< 0.05Range BSA (m2)1.4–1.891.9–2.34Mean pump speed (RPM)9500 ± 6009700 ± 4000.08Mean pump flow (l/minute)4.2 ± 0.94.8 ± 0.90.005Mean BUN26 ± 4238 ± 310.57Mean serum creatinine (mg/dl)1.0 ± 0.51.4 ± 0.50.14Mean total bilirubin (mg/dl)2.8 ± 5.32.4 ± 2.00.009All figures are average values for duration of MicroMed VAD support. |
Parameter | BSA | < 1.9 m2 (n = 46) | ∼ 1.9 m2 (n = 57) | p-value | Mean BSA (m2) | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | < 0.05 | Range BSA (m2) | 1.4–1.89 | 1.9–2.34 | Mean pump speed (RPM) | 9500 ± 600 | 9700 ± 400 | 0.08 | Mean pump flow (l/minute) | 4.2 ± 0.9 | 4.8 ± 0.9 | 0.005 | Mean BUN | 26 ± 42 | 38 ± 31 | 0.57 | Mean serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 0.14 | Mean total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 2.8 ± 5.3 | 2.4 ± 2.0 | 0.009 | All figures are average values for duration of MicroMed VAD support. | ||||||
| Parameter | BSA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < 1.9 m2 (n = 46) | ∼ 1.9 m2 (n = 57) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean BSA (m2) | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | < 0.05 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Range BSA (m2) | 1.4–1.89 | 1.9–2.34 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean pump speed (RPM) | 9500 ± 600 | 9700 ± 400 | 0.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean pump flow (l/minute) | 4.2 ± 0.9 | 4.8 ± 0.9 | 0.005 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean BUN | 26 ± 42 | 38 ± 31 | 0.57 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 0.14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 2.8 ± 5.3 | 2.4 ± 2.0 | 0.009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All figures are average values for duration of MicroMed VAD support. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reoperation for bleeding was most common complication following VAD placement Low incidence of device-related infection and pump failure Infections were all related to the driveline site as no real preperitoneal pocket exists The causes of mechanical failure were: recessed connector pin (n = 2); broken wire (n = 1); controller failure (n = 1) 17 cases of pump thrombus, 11 (64%) cases had a successful resolution with transplantation, pump exchange or thrombolysis No strokes associated with pump thrombus Two patients haemolysis was association with pump thrombus BTT was successful in nearly 50% of patients (European series) and 66% of patients (US cohort) No statistically significant difference was present with regard to pump speed, larger patients had statistically significant higher pump flows. Renal function did not differ significantly between smaller and larger patients but larger patients had lower total bilirubin levels. Patients with larger BSAs had higher pump output Incidence and linearised rate of adverse events following MicroMed DeBakey VAD replacementAdverse eventIncidenceRate/patient-yearReoperation for bleeding32.0% (48/150)2.03Haemolysisa12.0% (18/150)0.61Device infection3.3% (5/150)0.16Thromboembolic eventb10.7% (16/150)0.61Pump thrombus11.3% (17/150)0.61Mechanical failure2.7% (4/150)0.13a Defined as plasma-free haemoglobin > 40 mg/dl.b Composite of embolic stroke, TIA and peripheral embolism. 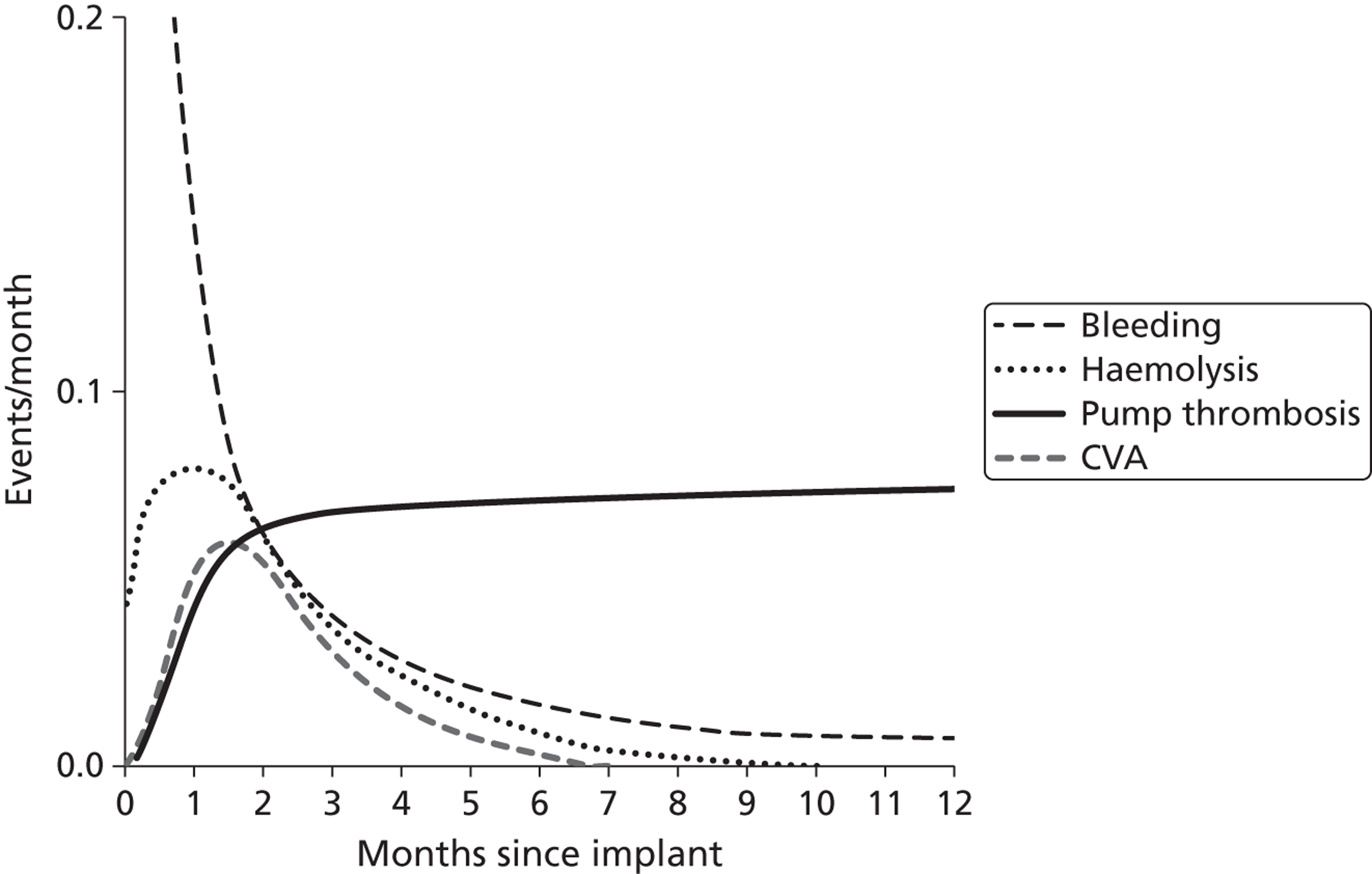 Hazard analysis depicting varying incidence over time of four major adverse eventsa |
Adverse event | Incidence | Rate/patient-year | Reoperation for bleeding | 32.0% (48/150) | 2.03 | Haemolysisa | 12.0% (18/150) | 0.61 | Device infection | 3.3% (5/150) | 0.16 | Thromboembolic eventb | 10.7% (16/150) | 0.61 | Pump thrombus | 11.3% (17/150) | 0.61 | Mechanical failure | 2.7% (4/150) | 0.13 | a Defined as plasma-free haemoglobin > 40 mg/dl. | b Composite of embolic stroke, TIA and peripheral embolism. | ||||||||||||||||
| Adverse event | Incidence | Rate/patient-year | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reoperation for bleeding | 32.0% (48/150) | 2.03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemolysisa | 12.0% (18/150) | 0.61 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device infection | 3.3% (5/150) | 0.16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thromboembolic eventb | 10.7% (16/150) | 0.61 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump thrombus | 11.3% (17/150) | 0.61 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical failure | 2.7% (4/150) | 0.13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Defined as plasma-free haemoglobin > 40 mg/dl. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Composite of embolic stroke, TIA and peripheral embolism. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unclear | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MicroMed DeBakey VAD is promising and supports continued evaluation of axial flow pumps for long-term support. Low incidence of pump failure and infection and pumps are applicable to many patient sizes. The patients appreciate the easy mobility and quiet operation and outpatient support is possible. Incidence of pump thrombus and thromboembolism is being examined through heparin coating to all device surfaces. Many challenges including elucidation of pathogenesis of pump thrombus, its prevention and treatment, as well as better patient selection and development of a physiologically responsive controller remain | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Did not clearly report the patient baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Hasin 201262
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Hasin Year of publication: 2012 Country: USA (Rochester, MN) Study design: Retrospective Study setting: Mayo Clinic (University hospital) Number of centres: Single centre Duration of study: February 2007 to June 2010 Follow-up period: 6 months Funding: Unclear |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To evaluate the effects of LVAD support on renal function in our cohort of BTT and DT patients implanted with CF HMII devices and to identify pre-operative predictors for improved renal function within this population | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 83 Sample attrition/dropout: None Inclusion criteria: Patients implanted with HMII CF devices (n = 83) from February 2007 to June 2010 in a single centre were followed. Included both BTT and DT patients Exclusion criteria: 20 patients with other devices (8 with Jarvik 2000, 6 with VentrAssist and 6 with HMXVE were excluded from analysis) Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): All patients 63.0 ± 12.3 years; GFR < 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 65.9 ± 8.8 years; GFR > 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2: 57.7 ± 15.8 years Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: Male – all patients 68/83 (81%); GFR < 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 41/54 (76%); GFR > 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 27/29 (93%) Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Ischaemic aetiology – all patients 46/83 (55%); GFR < 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 30/54 (56%); GFR > 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 16/29 (55%) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT – all patients 27/83 (32%); GFR < 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 15/54 (28%); GFR > 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 12/29 (41%) Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: Two groups – GFR < 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 and GFR > 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2: 12/29 (41%) Duration of treatment: Unclear Percentage of patients using inotropes: 59/83 (71%) Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Renal function; predictors of RD Secondary outcomes: Not relevant Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records – renal function was assessed at admission for LVAD implantation (determined as baseline renal function), the morning before LVAD implantation, and 1 month (range 14–46 days), 3 months (range 56–120 days) and 6 months (range 150–240 days) after implantation during routine follow-up visits. Stages of RD were determined according to calculated GFR in accordance with established guidelines. A GFR cut-off of > 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 was used to differentiate mild or normal renal function from more severe RD. Patients requiring haemodialysis were considered in stage 5 (GFR 15 ml/minute/1.73 m2). As the actual GFRs in these patients were undetermined, they were considered missing for analysis requiring numerical GFR measurement Survival: Yes Adverse event: No. Eight patients developed ARF. In addition, it is reported that ‘all patients had significant post-operative complications, including right ventricular dysfunction, infections, bleeding, and need for prolonged inotropic support’. No data given HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: UnclearNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreened103Randomised/included83; 80% of adult LVAD implantationsExcluded20 patients with other devices (8 with Jarvik 2000, 6 with VentrAssist and 6 with HMXVE were excluded from analysisMissing participantsNoneWithdrawalsNone |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | 103 | Randomised/included | 83; 80% of adult LVAD implantations | Excluded | 20 patients with other devices (8 with Jarvik 2000, 6 with VentrAssist and 6 with HMXVE were excluded from analysis | Missing participants | None | Withdrawals | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 83; 80% of adult LVAD implantations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | 20 patients with other devices (8 with Jarvik 2000, 6 with VentrAssist and 6 with HMXVE were excluded from analysis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics Demographic characteristics of patients needing chronic dialysis after LVAD implantationPatient no.Age (years)SexMedical historyTransplantation candidacySmall kidney (< 10 cm)NYHA functional classRhythmLM Score159FemaleHTN, CKD (CVVHD), severe lung diseaseBTTYesIVAF13262MaleCKD s/p transplantation, (Fabry), lung disease, s/p TVRBTTNAIIIbAF21374MaleHTN, CKD, IHDDTNoIIIbAF22461MaleHTN, DMDTNoIVSinus6567MaleComplex congenital heart disease, recurrent VT, CKD (CVVHD)BTTNoIVSinus24673Males/p B-cell lymphoma, s/p CABG, DM, CKD, on continuous milrinone infusion (4 years)DTNoIVAF4745FemaleRecent mitral repair + Maze procedure, shock, acute renalBTTNoIVAF20848MaleRecent mitral repair + Maze procedure, shock, acute renalBTTNoIIIPaced10 |
Patient no. | Age (years) | Sex | Medical history | Transplantation candidacy | Small kidney (< 10 cm) | NYHA functional class | Rhythm | LM Score | 1 | 59 | Female | HTN, CKD (CVVHD), severe lung disease | BTT | Yes | IV | AF | 13 | 2 | 62 | Male | CKD s/p transplantation, (Fabry), lung disease, s/p TVR | BTT | NA | IIIb | AF | 21 | 3 | 74 | Male | HTN, CKD, IHD | DT | No | IIIb | AF | 22 | 4 | 61 | Male | HTN, DM | DT | No | IV | Sinus | 6 | 5 | 67 | Male | Complex congenital heart disease, recurrent VT, CKD (CVVHD) | BTT | No | IV | Sinus | 24 | 6 | 73 | Male | s/p B-cell lymphoma, s/p CABG, DM, CKD, on continuous milrinone infusion (4 years) | DT | No | IV | AF | 4 | 7 | 45 | Female | Recent mitral repair + Maze procedure, shock, acute renal | BTT | No | IV | AF | 20 | 8 | 48 | Male | Recent mitral repair + Maze procedure, shock, acute renal | BTT | No | III | Paced | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient no. | Age (years) | Sex | Medical history | Transplantation candidacy | Small kidney (< 10 cm) | NYHA functional class | Rhythm | LM Score | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 59 | Female | HTN, CKD (CVVHD), severe lung disease | BTT | Yes | IV | AF | 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 62 | Male | CKD s/p transplantation, (Fabry), lung disease, s/p TVR | BTT | NA | IIIb | AF | 21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 74 | Male | HTN, CKD, IHD | DT | No | IIIb | AF | 22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 61 | Male | HTN, DM | DT | No | IV | Sinus | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 67 | Male | Complex congenital heart disease, recurrent VT, CKD (CVVHD) | BTT | No | IV | Sinus | 24 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 73 | Male | s/p B-cell lymphoma, s/p CABG, DM, CKD, on continuous milrinone infusion (4 years) | DT | No | IV | AF | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | 45 | Female | Recent mitral repair + Maze procedure, shock, acute renal | BTT | No | IV | AF | 20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | 48 | Male | Recent mitral repair + Maze procedure, shock, acute renal | BTT | No | III | Paced | 10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline characteristicsCharacteristicAll patients (n = 83)GFR < 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 (n = 54)GFR ≥ 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 (n = 29)p-valueDemographic Age (years)63.0 ± 12.365.9 ± 8.857.7 ± 15.80.020 Men68/83 (81%)41/54 (76%)27/29 (93%)0.053 HTN31/83 (37%)20/54 (37%)11/29 (38%)0.936 HM24/83 (29%)19/54 (35%)5/29 (17%)0.086 CKD45/83 (54%)41/54 (76%)4/29 (14%)< 0.001 Ischaemic aetiology46/83 (55%)30/54 (56%)16/29 (55%)0.973 BTT27/83 (32%)15/54 (28%)12/29 (41%)0.207Clinical GFR (ml/minute/1.73 m2)53.2 ± 21.440.5 ± 12.376.8 ± 12.7< 0.001 Pre-operative GFR64.5 ± 22.555.4 ± 18.281.3 ± 20.2< 0.001 Admission to operation time (days)9.4 ± 9.3 (n = 83)10.8 ± 10.2 (n = 54)6.8 ± 6.6 (n = 29)0.039 BMI (kg/m2)28.9 ± 5.628.8 ± 5.829.2 ± 5.30.782 NYHA class IV50/81 (62%)31/52 (60%)19/29 (66%)0.577 Prior sternotomy42/83 (51%)28/54 (52%)14/29 (48%)0.756 AF14/83 (17%)8/54 (15%)16/29 (21%)0.500Kidney length (cm) Left11.7 ± 1.211.5 ± 1.211.9 ± 1.30.287 Right11.5 ± 1.111.5 ± 1.111.5 ± 1.30.868Pre-operative IABP use28/83 (37%)20/54 (37%)8/29 (28%)0.385Need for inotropes59/83 (71%)41/54 (76%)18/29 (62%)0.184ACE inhibitors or ARBs54/78 (69%)34/51 (67%)20/29 (69%)0.585Spironolactone43/81 (53%)29/53 (55%)14/28 (50%)0.686Beta-blockers68/81 (84%)44/53 (83%)24/28 (86%)0.753Loop diuretic agents69/75 (92%)44/48 (92%)25/27 (93%)0.887Digoxin43/75 (57%)28/48 (58%)15/27 (56%)0.815Urine protein (mg/dl)7 (4–23) (n = 71)7 (4–30) (n = 45)7 (4–18) (n = 26)0.756Haemoglobin (g/dl)11.9 ± 1.911.7 ± 2.012.4 ± 1.70.100Platelet count (× 1000)175.6 ± 70.0167.1 ± 61.0191.0 ± 83.00.286Bilirubin (mg/dl)1.2 ± 0.71.2 ± 0.71.4 ± 0.80.171NT-pro-BNP (pg/ml)6004 ± 5812 (n = 47)7521 ± 6578 (n = 29)3559 ± 3143 (n = 18)0.014Albumin (g/dl)3.8 ± 0.63.7 ± 0.53.8 ± 0.70.486BUN (mg/dl)31.6 ± 16.835.2 ± 17.625.0 ± 12.90.005Creatinine (mg/dl)1.6 ± 0.71.9 ± 0.71.1 ± 0.2< 0.001LM score9.6 ± 6.010.3 ± 6.08.6 ± 5.70.156VO2 max. (% predicted)39.4 ± 11.3 (n = 42)39.6 ± 8.5 (n = 25)39.1 ± 11.8 (n = 17)0.885Pre-operative echocardiography Left ventricular diastolic diameter (mm)67.2 ± 9.5 (n = 82)67.9 ± 9.4 (n = 53)66.0 ± 9.60.379 Ejection fraction (%)19.8 ± 8.6 (n = 83)19.2 ± 6.3 (n = 54)20.9 ± 11.7 (n = 29)0.908 RIMP0.6 ± 0.2 (n = 75)0.6 ± 0.2 (n = 48)0.5 ± 0.3 (n = 27)0.440 RV dysfunction more than moderate54/81 (67%)40/52 (77%)14/29 (48%)0.009Pre-operative catheterisation Mean right atrial pressure (mmHg)15.4 ± 6.7 (n = 80)15.9 ± 6.5 (n = 52)14.5 ± 7.2 (n = 28)0.388 Mean pulmonary pressure (mmHg)36.1 ± 9.3 (n = 80)36.8 ± 9.0 (n = 52)34.8 ± 9.9 (n = 28)0.350 RVSWI (g/m2/beat)7.1 ± 3.9 (n = 74)7.0 ± 3.7 (n = 49)7.3 ± 4.3 (n = 27)0.776 Mean wedge pressure (mmHg)23.5 ± 6.9 (n = 77)24.6 ± 6.6 (n = 50)21.4 ± 7.1 (n = 27)0.049 Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)1.9 ± 0.5 (n = 78)1.9 ± 0.6 (n = 50)2.1 ± 0.5 (n = 28)0.073Operation Bypass time (minutes)103.6 ± 33.7 (n = 82)105.6 ± 32.9 (n = 54)99.8 ± 35.5 (n = 28)0.350 Duration of hospitalisation (days)21.4 ± 13.3 (n = 75)22.2 ± 14.2 (n = 47)20.1 ± 11.8 (n = 28)0.576Values are mean ± SD or n/N (%). The above table depicts baseline characteristics of 83 patients implanted with HMII LVADs and of the subgroups of patients with baseline GFRs < 60 or > 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 All comparisons are between patients with baseline GFR < 60 and > 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 At baseline the mean age was 63 ± 12 years, and majority of patients were men (82%). Majority of LVADs (70%) were DT, and approximately half had ischaemic aetiology Main reason for DT was older age (median 70 years vs. 55 years for BTT patients; p < 0.0001) Compared with patients with preserved renal function (GFR ml/minute/1.73 m2), those with low baseline GFRs were significantly older, with more CKD and longer pre-operative hospital stays Pre-operative clinical characteristics of patients needing chronic dialysis after LVAD implantationPatient no.GFR (ml/minute/1.73 m2)Pre-operative GFR improvementHb (mg)Albumin (g%)IABPTRMRRVSWIRAP (mmHg)Wedge pressure (mmHg)124+249.23.1NoSevereModerate to severe52521220+1011.22.8SevereModerate1.31222339+1710.23.3NoModNone11.71119438+09.83.8YesModNone1.93432532−1311.13.3YesNoneNoneNANANA640+1812.43.5YesModMild5.12327741+439.83.3YesSevereNone2.42025876+010.9NAYesModMild1.43535 |
Characteristic | All patients (n = 83) | GFR < 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 (n = 54) | GFR ≥ 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 (n = 29) | p-value | Demographic | Age (years) | 63.0 ± 12.3 | 65.9 ± 8.8 | 57.7 ± 15.8 | 0.020 | Men | 68/83 (81%) | 41/54 (76%) | 27/29 (93%) | 0.053 | HTN | 31/83 (37%) | 20/54 (37%) | 11/29 (38%) | 0.936 | HM | 24/83 (29%) | 19/54 (35%) | 5/29 (17%) | 0.086 | CKD | 45/83 (54%) | 41/54 (76%) | 4/29 (14%) | < 0.001 | Ischaemic aetiology | 46/83 (55%) | 30/54 (56%) | 16/29 (55%) | 0.973 | BTT | 27/83 (32%) | 15/54 (28%) | 12/29 (41%) | 0.207 | Clinical | GFR (ml/minute/1.73 m2) | 53.2 ± 21.4 | 40.5 ± 12.3 | 76.8 ± 12.7 | < 0.001 | Pre-operative GFR | 64.5 ± 22.5 | 55.4 ± 18.2 | 81.3 ± 20.2 | < 0.001 | Admission to operation time (days) | 9.4 ± 9.3 (n = 83) | 10.8 ± 10.2 (n = 54) | 6.8 ± 6.6 (n = 29) | 0.039 | BMI (kg/m2) | 28.9 ± 5.6 | 28.8 ± 5.8 | 29.2 ± 5.3 | 0.782 | NYHA class IV | 50/81 (62%) | 31/52 (60%) | 19/29 (66%) | 0.577 | Prior sternotomy | 42/83 (51%) | 28/54 (52%) | 14/29 (48%) | 0.756 | AF | 14/83 (17%) | 8/54 (15%) | 16/29 (21%) | 0.500 | Kidney length (cm) | Left | 11.7 ± 1.2 | 11.5 ± 1.2 | 11.9 ± 1.3 | 0.287 | Right | 11.5 ± 1.1 | 11.5 ± 1.1 | 11.5 ± 1.3 | 0.868 | Pre-operative IABP use | 28/83 (37%) | 20/54 (37%) | 8/29 (28%) | 0.385 | Need for inotropes | 59/83 (71%) | 41/54 (76%) | 18/29 (62%) | 0.184 | ACE inhibitors or ARBs | 54/78 (69%) | 34/51 (67%) | 20/29 (69%) | 0.585 | Spironolactone | 43/81 (53%) | 29/53 (55%) | 14/28 (50%) | 0.686 | Beta-blockers | 68/81 (84%) | 44/53 (83%) | 24/28 (86%) | 0.753 | Loop diuretic agents | 69/75 (92%) | 44/48 (92%) | 25/27 (93%) | 0.887 | Digoxin | 43/75 (57%) | 28/48 (58%) | 15/27 (56%) | 0.815 | Urine protein (mg/dl) | 7 (4–23) (n = 71) | 7 (4–30) (n = 45) | 7 (4–18) (n = 26) | 0.756 | Haemoglobin (g/dl) | 11.9 ± 1.9 | 11.7 ± 2.0 | 12.4 ± 1.7 | 0.100 | Platelet count (× 1000) | 175.6 ± 70.0 | 167.1 ± 61.0 | 191.0 ± 83.0 | 0.286 | Bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.2 ± 0.7 | 1.2 ± 0.7 | 1.4 ± 0.8 | 0.171 | NT-pro-BNP (pg/ml) | 6004 ± 5812 (n = 47) | 7521 ± 6578 (n = 29) | 3559 ± 3143 (n = 18) | 0.014 | Albumin (g/dl) | 3.8 ± 0.6 | 3.7 ± 0.5 | 3.8 ± 0.7 | 0.486 | BUN (mg/dl) | 31.6 ± 16.8 | 35.2 ± 17.6 | 25.0 ± 12.9 | 0.005 | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.6 ± 0.7 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | < 0.001 | LM score | 9.6 ± 6.0 | 10.3 ± 6.0 | 8.6 ± 5.7 | 0.156 | VO2 max. (% predicted) | 39.4 ± 11.3 (n = 42) | 39.6 ± 8.5 (n = 25) | 39.1 ± 11.8 (n = 17) | 0.885 | Pre-operative echocardiography | Left ventricular diastolic diameter (mm) | 67.2 ± 9.5 (n = 82) | 67.9 ± 9.4 (n = 53) | 66.0 ± 9.6 | 0.379 | Ejection fraction (%) | 19.8 ± 8.6 (n = 83) | 19.2 ± 6.3 (n = 54) | 20.9 ± 11.7 (n = 29) | 0.908 | RIMP | 0.6 ± 0.2 (n = 75) | 0.6 ± 0.2 (n = 48) | 0.5 ± 0.3 (n = 27) | 0.440 | RV dysfunction more than moderate | 54/81 (67%) | 40/52 (77%) | 14/29 (48%) | 0.009 | Pre-operative catheterisation | Mean right atrial pressure (mmHg) | 15.4 ± 6.7 (n = 80) | 15.9 ± 6.5 (n = 52) | 14.5 ± 7.2 (n = 28) | 0.388 | Mean pulmonary pressure (mmHg) | 36.1 ± 9.3 (n = 80) | 36.8 ± 9.0 (n = 52) | 34.8 ± 9.9 (n = 28) | 0.350 | RVSWI (g/m2/beat) | 7.1 ± 3.9 (n = 74) | 7.0 ± 3.7 (n = 49) | 7.3 ± 4.3 (n = 27) | 0.776 | Mean wedge pressure (mmHg) | 23.5 ± 6.9 (n = 77) | 24.6 ± 6.6 (n = 50) | 21.4 ± 7.1 (n = 27) | 0.049 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.9 ± 0.5 (n = 78) | 1.9 ± 0.6 (n = 50) | 2.1 ± 0.5 (n = 28) | 0.073 | Operation | Bypass time (minutes) | 103.6 ± 33.7 (n = 82) | 105.6 ± 32.9 (n = 54) | 99.8 ± 35.5 (n = 28) | 0.350 | Duration of hospitalisation (days) | 21.4 ± 13.3 (n = 75) | 22.2 ± 14.2 (n = 47) | 20.1 ± 11.8 (n = 28) | 0.576 | Values are mean ± SD or n/N (%). | Patient no. | GFR (ml/minute/1.73 m2) | Pre-operative GFR improvement | Hb (mg) | Albumin (g%) | IABP | TR | MR | RVSWI | RAP (mmHg) | Wedge pressure (mmHg) | 1 | 24 | +24 | 9.2 | 3.1 | No | Severe | Moderate to severe | 5 | 25 | 21 | 2 | 20 | +10 | 11.2 | 2.8 | Severe | Moderate | 1.3 | 12 | 22 | 3 | 39 | +17 | 10.2 | 3.3 | No | Mod | None | 11.7 | 11 | 19 | 4 | 38 | +0 | 9.8 | 3.8 | Yes | Mod | None | 1.9 | 34 | 32 | 5 | 32 | −13 | 11.1 | 3.3 | Yes | None | None | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 40 | +18 | 12.4 | 3.5 | Yes | Mod | Mild | 5.1 | 23 | 27 | 7 | 41 | +43 | 9.8 | 3.3 | Yes | Severe | None | 2.4 | 20 | 25 | 8 | 76 | +0 | 10.9 | NA | Yes | Mod | Mild | 1.4 | 35 | 35 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristic | All patients (n = 83) | GFR < 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 (n = 54) | GFR ≥ 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 (n = 29) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demographic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 63.0 ± 12.3 | 65.9 ± 8.8 | 57.7 ± 15.8 | 0.020 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Men | 68/83 (81%) | 41/54 (76%) | 27/29 (93%) | 0.053 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HTN | 31/83 (37%) | 20/54 (37%) | 11/29 (38%) | 0.936 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HM | 24/83 (29%) | 19/54 (35%) | 5/29 (17%) | 0.086 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CKD | 45/83 (54%) | 41/54 (76%) | 4/29 (14%) | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic aetiology | 46/83 (55%) | 30/54 (56%) | 16/29 (55%) | 0.973 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTT | 27/83 (32%) | 15/54 (28%) | 12/29 (41%) | 0.207 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Clinical | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GFR (ml/minute/1.73 m2) | 53.2 ± 21.4 | 40.5 ± 12.3 | 76.8 ± 12.7 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative GFR | 64.5 ± 22.5 | 55.4 ± 18.2 | 81.3 ± 20.2 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Admission to operation time (days) | 9.4 ± 9.3 (n = 83) | 10.8 ± 10.2 (n = 54) | 6.8 ± 6.6 (n = 29) | 0.039 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.9 ± 5.6 | 28.8 ± 5.8 | 29.2 ± 5.3 | 0.782 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class IV | 50/81 (62%) | 31/52 (60%) | 19/29 (66%) | 0.577 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prior sternotomy | 42/83 (51%) | 28/54 (52%) | 14/29 (48%) | 0.756 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AF | 14/83 (17%) | 8/54 (15%) | 16/29 (21%) | 0.500 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kidney length (cm) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left | 11.7 ± 1.2 | 11.5 ± 1.2 | 11.9 ± 1.3 | 0.287 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right | 11.5 ± 1.1 | 11.5 ± 1.1 | 11.5 ± 1.3 | 0.868 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative IABP use | 28/83 (37%) | 20/54 (37%) | 8/29 (28%) | 0.385 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Need for inotropes | 59/83 (71%) | 41/54 (76%) | 18/29 (62%) | 0.184 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACE inhibitors or ARBs | 54/78 (69%) | 34/51 (67%) | 20/29 (69%) | 0.585 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spironolactone | 43/81 (53%) | 29/53 (55%) | 14/28 (50%) | 0.686 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beta-blockers | 68/81 (84%) | 44/53 (83%) | 24/28 (86%) | 0.753 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loop diuretic agents | 69/75 (92%) | 44/48 (92%) | 25/27 (93%) | 0.887 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Digoxin | 43/75 (57%) | 28/48 (58%) | 15/27 (56%) | 0.815 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Urine protein (mg/dl) | 7 (4–23) (n = 71) | 7 (4–30) (n = 45) | 7 (4–18) (n = 26) | 0.756 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemoglobin (g/dl) | 11.9 ± 1.9 | 11.7 ± 2.0 | 12.4 ± 1.7 | 0.100 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelet count (× 1000) | 175.6 ± 70.0 | 167.1 ± 61.0 | 191.0 ± 83.0 | 0.286 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.2 ± 0.7 | 1.2 ± 0.7 | 1.4 ± 0.8 | 0.171 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NT-pro-BNP (pg/ml) | 6004 ± 5812 (n = 47) | 7521 ± 6578 (n = 29) | 3559 ± 3143 (n = 18) | 0.014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albumin (g/dl) | 3.8 ± 0.6 | 3.7 ± 0.5 | 3.8 ± 0.7 | 0.486 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 31.6 ± 16.8 | 35.2 ± 17.6 | 25.0 ± 12.9 | 0.005 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.6 ± 0.7 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LM score | 9.6 ± 6.0 | 10.3 ± 6.0 | 8.6 ± 5.7 | 0.156 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VO2 max. (% predicted) | 39.4 ± 11.3 (n = 42) | 39.6 ± 8.5 (n = 25) | 39.1 ± 11.8 (n = 17) | 0.885 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative echocardiography | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left ventricular diastolic diameter (mm) | 67.2 ± 9.5 (n = 82) | 67.9 ± 9.4 (n = 53) | 66.0 ± 9.6 | 0.379 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ejection fraction (%) | 19.8 ± 8.6 (n = 83) | 19.2 ± 6.3 (n = 54) | 20.9 ± 11.7 (n = 29) | 0.908 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RIMP | 0.6 ± 0.2 (n = 75) | 0.6 ± 0.2 (n = 48) | 0.5 ± 0.3 (n = 27) | 0.440 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RV dysfunction more than moderate | 54/81 (67%) | 40/52 (77%) | 14/29 (48%) | 0.009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative catheterisation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean right atrial pressure (mmHg) | 15.4 ± 6.7 (n = 80) | 15.9 ± 6.5 (n = 52) | 14.5 ± 7.2 (n = 28) | 0.388 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean pulmonary pressure (mmHg) | 36.1 ± 9.3 (n = 80) | 36.8 ± 9.0 (n = 52) | 34.8 ± 9.9 (n = 28) | 0.350 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVSWI (g/m2/beat) | 7.1 ± 3.9 (n = 74) | 7.0 ± 3.7 (n = 49) | 7.3 ± 4.3 (n = 27) | 0.776 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean wedge pressure (mmHg) | 23.5 ± 6.9 (n = 77) | 24.6 ± 6.6 (n = 50) | 21.4 ± 7.1 (n = 27) | 0.049 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.9 ± 0.5 (n = 78) | 1.9 ± 0.6 (n = 50) | 2.1 ± 0.5 (n = 28) | 0.073 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bypass time (minutes) | 103.6 ± 33.7 (n = 82) | 105.6 ± 32.9 (n = 54) | 99.8 ± 35.5 (n = 28) | 0.350 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Duration of hospitalisation (days) | 21.4 ± 13.3 (n = 75) | 22.2 ± 14.2 (n = 47) | 20.1 ± 11.8 (n = 28) | 0.576 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Values are mean ± SD or n/N (%). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient no. | GFR (ml/minute/1.73 m2) | Pre-operative GFR improvement | Hb (mg) | Albumin (g%) | IABP | TR | MR | RVSWI | RAP (mmHg) | Wedge pressure (mmHg) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 24 | +24 | 9.2 | 3.1 | No | Severe | Moderate to severe | 5 | 25 | 21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 20 | +10 | 11.2 | 2.8 | Severe | Moderate | 1.3 | 12 | 22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 39 | +17 | 10.2 | 3.3 | No | Mod | None | 11.7 | 11 | 19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 38 | +0 | 9.8 | 3.8 | Yes | Mod | None | 1.9 | 34 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 32 | −13 | 11.1 | 3.3 | Yes | None | None | NA | NA | NA | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 40 | +18 | 12.4 | 3.5 | Yes | Mod | Mild | 5.1 | 23 | 27 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | 41 | +43 | 9.8 | 3.3 | Yes | Severe | None | 2.4 | 20 | 25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | 76 | +0 | 10.9 | NA | Yes | Mod | Mild | 1.4 | 35 | 35 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Of the 51 patients with GFRs < 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 before LVAD surviving at 1 month, 34 (67%) improved to GFRs > 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2. Univariate pre-operative predictors for improvement in renal function at 1 month included younger age (p = 0.049), GFR improvement with optimal medical therapy (p < 0.001), IABP use (p = 0.004), kidney length > 10 cm (p = 0.023), no treatment with ACE inhibitors or ARBs (p = 0.029), higher bilirubin (p = 0.002), higher LM score (p = 0.019) and AF (p = 0.007). Multivariate analysis indicated pre-operative improved GFR (slope = 0.5 U/unit improved, 95% CI 0.2 to 0.8; p = 0.003), AF (slope = 27, 95% CI 8 to 46; p = 0.006) and IABP use (slope = 14, 95% CI 2 to 26; p = 0.02) as independent predictors Post-operative characteristics of patients who succumbed to chronic need for haemodialysisPatient numberComplicationsDuration of inotropic supportHospital stayLate outcome1GI bleeding, pneumonia, prolonged intubation, RV dysfunction, MR (moderate), continued need for dialysis16065 daysDied (sepsis) 2.5 years after implantation2Early RV failure, sepsis, prolonged intubation, VT1032Death 76 daysIn-hospital death3Early HMXVE failure, emergent HMII implantation, mediastinitis, RV dysfunction44628 daysWithdrew support 1.5 years after implantation4Early RV failure, prolonged intubation, sepsis, RV dysfunction50452 daysRecovered renal function 6 months after implantation5Early RV failure, prolonged intubation, recurrent VT encephalopathy, sepsis, ileus, hyperbilirubinemia1488Death 37 daysIn-hospital death6Delayed chest closure, prolonged intubation, encephalopathy, biliary sepsis1056Death 44 daysIn-hospital death7Early RV failure, delayed chest closure, prolonged ventilation132061 daysRecovered renal function 45 days after implantation8Chest reopening for severe bleeding, shock168Death 7 daysIn-hospital death |
Patient number | Complications | Duration of inotropic support | Hospital stay | Late outcome | 1 | GI bleeding, pneumonia, prolonged intubation, RV dysfunction, MR (moderate), continued need for dialysis | 160 | 65 days | Died (sepsis) 2.5 years after implantation | 2 | Early RV failure, sepsis, prolonged intubation, VT | 1032 | Death 76 days | In-hospital death | 3 | Early HMXVE failure, emergent HMII implantation, mediastinitis, RV dysfunction | 446 | 28 days | Withdrew support 1.5 years after implantation | 4 | Early RV failure, prolonged intubation, sepsis, RV dysfunction | 504 | 52 days | Recovered renal function 6 months after implantation | 5 | Early RV failure, prolonged intubation, recurrent VT encephalopathy, sepsis, ileus, hyperbilirubinemia | 1488 | Death 37 days | In-hospital death | 6 | Delayed chest closure, prolonged intubation, encephalopathy, biliary sepsis | 1056 | Death 44 days | In-hospital death | 7 | Early RV failure, delayed chest closure, prolonged ventilation | 1320 | 61 days | Recovered renal function 45 days after implantation | 8 | Chest reopening for severe bleeding, shock | 168 | Death 7 days | In-hospital death | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient number | Complications | Duration of inotropic support | Hospital stay | Late outcome | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | GI bleeding, pneumonia, prolonged intubation, RV dysfunction, MR (moderate), continued need for dialysis | 160 | 65 days | Died (sepsis) 2.5 years after implantation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Early RV failure, sepsis, prolonged intubation, VT | 1032 | Death 76 days | In-hospital death | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | Early HMXVE failure, emergent HMII implantation, mediastinitis, RV dysfunction | 446 | 28 days | Withdrew support 1.5 years after implantation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | Early RV failure, prolonged intubation, sepsis, RV dysfunction | 504 | 52 days | Recovered renal function 6 months after implantation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | Early RV failure, prolonged intubation, recurrent VT encephalopathy, sepsis, ileus, hyperbilirubinemia | 1488 | Death 37 days | In-hospital death | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | Delayed chest closure, prolonged intubation, encephalopathy, biliary sepsis | 1056 | Death 44 days | In-hospital death | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | Early RV failure, delayed chest closure, prolonged ventilation | 1320 | 61 days | Recovered renal function 45 days after implantation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | Chest reopening for severe bleeding, shock | 168 | Death 7 days | In-hospital death | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall, GFR significantly improved 1 month after LVAD implantation (from 53.2 ± 21.4 to 87.4 ± 27.9 ml/minute/1.73 m2; p < 0.0001). GFR partially declined at 3 months in 41 of 66 patients with GFR estimates at both time points (77.6 ± 22.8 ml/minute/1.73 m2; p = 0.0001, compared with 1 month). Between 3 and 6 months, GFR further declined in 36 of 55 patients (71.2 ± 21.0 ml/minute/1.73 m2; p = 0.0032, compared with 3 months). Only six patients had continuous GFR improvements without any decline over the study period (67 had some decline or no recovery of RD, and data were missing for 10 patients) Overall, GFR remained significantly higher at 6 months compared with pre-operative GFR (p < 0.0001) Eight patients (10%) developed ARF after LVAD implantation necessitating acute haemodialysis. Two died in the early post-operative period, and two recovered renal function. Four patients (5%) continued with chronic haemodialysis The subset with pre-operative RD had a significant increase at 1 month (p < 0.0001), a partial decline (1–3 months, p = 0.0059; 3–6 months, p = 0.0258), and overall improvement > 6 months (p < 0.0001) For patients with available renal staging at 1 month, 57 patients (72%) improved their RD stages or remained at stage 1 14 patients (18%) remained in their pre-operative renal stages (10 in stage 2, 4 in stage 3), and 8 (10%) deteriorated (2 from stages 4–5, 5 from stages 3–5, and 1 from stages 2–3) Renal dysfunction stage distribution – all patientsRenal dysfunction stage (GFR range)Baseline1 month3 months6 monthsn%n%n%n%Stage 1 (> 90)5632381518810Stage 2 (60–90)2429293535423137Stage 3 (30–60)4251111315181822Stage 4 (15–30)1113001100Stage 5 (< 15)11783434Missing004514172328 Renal dysfunction stage distribution – subset with stage 3 at baselineRenal dysfunction stage (GFR range)Baseline1 month3 months6 monthsn%n%n%n%Stage 1 (> 90)00133141037Stage 2 (60–90)00184322521740Stage 3 (30–60)42100410717819Stage 4 (15–30)00000000Stage 5 (< 15)005122525Missing00257171229 Univariate linear regression analysis for prediction of increase in GFR 1 month after LVAD implantationParameternParameter estimate95% CIp-valueGeneral Age44−0.8−1.6 to 0.00.049 Malea444.2−12.8 to 21.10.630 HTNa44−0.4−15.1 to 14.20.954 DMa44−0.6−15.4 to 14.20.936 CKDa44−11.5−27.1 to 4.10.151 BTTa449.1−6.6 to 24.90.256 Ischaemic aetiologya444.5−10.1 to 19.00.549 Weight44−0.2−0.6 to 0.20.300 BSA44−18.1−46.0 to 9.80.204 Diastolic BP44−0.2−1.2 to 0.50.474 Systolic BP44−0.2−0.7 to 0.30.413 Heart rate440.0−0.5 to 0.50.974 AFa4431.88.8 to 54.70.007 NYHA class IVa4410.0−4.1 to 24.10.163 Small kidney (< 10 cm)a40−24.7−46.0 to −3.50.023 VO2 max. (% predicted)200.6−0.5 to 1.70.294 GFR increase, admission to pre-operative440.60.3 to 0.9< 0.001Scores LM score441.60.2 to 2.90.019 Matthews score442.4−0.4 to 5.20.091 Kormos score413.5−1.2 to 8.20.149Treatment before surgery IABP useda4420.56.7 to 34.20.004 Inotropesa43−2.8−20.1 to 14.40.745 ACE inhibitors or ARBsa44−15.5−29.4 to −1.60.029 Beta-blockersa44−5.4−23.9 to 13.00.562 Aldosterone inhibitorsa445.6−8.5 to 19.80.435 Diuretic agentsa40−14.4−39.4 to 10.60.258 Amiodaronea40−6.9−22.8 to 8.90.390 ICD/CRTa40−4.7−20.0 to 10.70.550 Digoxina40−8.1−23.6 to 7.40.307 Statinsa407.0−9.5 to 23.50.404Laboratory results Urine protein360.1−0.1 to 0.30.466 GFR on admission44−0.1−0.7 to 0.40.626 Haemoglobin44−0.5−4.0 to 3.00.779 Bilirubin4414.65.6 to 23.70.002 AST440.00.0 to 0.10.193 ALT410.00.0 to 0.00.157 LDH370.00.0 to 0.00.210 BNP250.00.0 to 0.00.768 Platelets440.0−0.1 to 0.10.943 BUN440.0−0.4 to 0.40.975 Albumin43−13.2−28.1 to 1.70.082Echocardiography RIMP39−3.2−38.5 to 32.20.861 TR time (corrected)42−0.1−0.2 to 0.00.174 LVEDD44−0.4−1.3 to 0.40.320 Mitral E-wave395.3−17.7 to 28.20.653 LA volume index43−0.1−0.5 to 0.40.794 EF44−0.2−1.4 to 0.90.684 LV mass340.0−0.1 to 0.00.130 TR (more than moderate)44−0.5−14.8 to 13.70.941 AR (more than moderate)44−7.1−35.3 to 21.10.623 MR (more than moderate)443.5−10.9 to 17.80.633Catheterisation Stroke volume index42−0.2−0.9 to 0.60.682 RVSWI42−0.7−2.8 to 1.50.537 Cardiac index42−2.7−16.7 to 11.30.704 SVR31−0.6−1.5 to 0.40.242 PVR42−0.4−2.7 to 2.00.757 RA pressure (mean)430.7−0.5 to 2.00.262 Wedge pressure (mean)41−0.4−1.5 to 0.70.452 PA pressure (mean)430.1−0.7 to 0.90.821Surgery and pump settings Bypass time440.0−0.2 to 0.20.928 Discharge pump flow430.5−9.5 to 10.50.920 Discharge LVAD pulsatility index4212.60.5 to 24.80.042 Discharge pump speed (200 RPM)427.41.8 to 13.00.009 Discharge pump speed > 9200 RPMa4222.06.9 to 37.20.004a Categorical predictors were assessed using one-way analysis of variance.Table shows the results of a univariate linear regression analysis for prediction of increase in GFR 1 month after LVAD implantation. GFR was evaluated as a continuous variable. Authors estimated associations of various pre-operative variables with increased GFR (operative time and LVAD settings were also included). Estimates were calculated depicting the change in mean GFR associated with the variable measured before and 1 month after operation. Estimates for continuous variables are for change in mean per unit increase in evaluated variable.TR time was corrected for pulse; RIMP = (TR time − RV ejection time)/RV ejection time; RVSWI = [0.0136 × (MPAP − RAP) × stroke volume index]; kidney size was assessed by pre-operative abdominal ultrasound. Predictors of improved GFR 1 month after LVAD implantation. Authors used a univariate model for predicting an increase in GFR for 72 patients with available GFR measurements at 1 month. Five significant positive predictors associated with GFR improvement were: (1) use of an IABP before surgery (slope = 17; p = 0.003); (2) higher bilirubin (slope = 12.1; p = 0.002); (3) alanine transaminase (slope = 0.03; p = 0.041); (4) LM score (slope = 1.5; p = 0.003); and (5) higher right atrial pressure (slope = 0.97; p = 0.048) An increase in GFR with optimal medical treatment before surgery was associated with further improvement 1 month after surgery (slope = 0.6/ml/minute/1.73 m2; p < 0.001). Higher pump speed at discharge (slope = 5.9/200 RPM increase; p = 0.01) was also associated with improved GFR. Negative predictors were: (1) having at least one kidney < 10 cm on ultrasound (slope = −23.7; p = 0.01); and (2) treatment with an angiotensin pathway inhibitor before surgery (slope = −15.7; p = 0.006) Multivariate model suggested that LM score (slope = 1.2/unit increase, 95% CI 0.25 to 2.11; p = 0.013) having at least one kidney < 10 cm (slope = −21, 95% CI −37.7 to −4.6; p = 0.012), and use of an IABP (slope = 11.8, 95% CI 0.8 to 22.8; p = 0.035) and were independent predictors |
Renal dysfunction stage (GFR range) | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | Stage 1 (> 90) | 5 | 6 | 32 | 38 | 15 | 18 | 8 | 10 | Stage 2 (60–90) | 24 | 29 | 29 | 35 | 35 | 42 | 31 | 37 | Stage 3 (30–60) | 42 | 51 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 18 | 18 | 22 | Stage 4 (15–30) | 11 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Stage 5 (< 15) | 1 | 1 | 7 | 8 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 | Missing | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 14 | 17 | 23 | 28 | Renal dysfunction stage (GFR range) | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | Stage 1 (> 90) | 0 | 0 | 13 | 31 | 4 | 10 | 3 | 7 | Stage 2 (60–90) | 0 | 0 | 18 | 43 | 22 | 52 | 17 | 40 | Stage 3 (30–60) | 42 | 100 | 4 | 10 | 7 | 17 | 8 | 19 | Stage 4 (15–30) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Stage 5 (< 15) | 0 | 0 | 5 | 12 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 5 | Missing | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 17 | 12 | 29 | Parameter | n | Parameter estimate | 95% CI | p-value | General | Age | 44 | −0.8 | −1.6 to 0.0 | 0.049 | Malea | 44 | 4.2 | −12.8 to 21.1 | 0.630 | HTNa | 44 | −0.4 | −15.1 to 14.2 | 0.954 | DMa | 44 | −0.6 | −15.4 to 14.2 | 0.936 | CKDa | 44 | −11.5 | −27.1 to 4.1 | 0.151 | BTTa | 44 | 9.1 | −6.6 to 24.9 | 0.256 | Ischaemic aetiologya | 44 | 4.5 | −10.1 to 19.0 | 0.549 | Weight | 44 | −0.2 | −0.6 to 0.2 | 0.300 | BSA | 44 | −18.1 | −46.0 to 9.8 | 0.204 | Diastolic BP | 44 | −0.2 | −1.2 to 0.5 | 0.474 | Systolic BP | 44 | −0.2 | −0.7 to 0.3 | 0.413 | Heart rate | 44 | 0.0 | −0.5 to 0.5 | 0.974 | AFa | 44 | 31.8 | 8.8 to 54.7 | 0.007 | NYHA class IVa | 44 | 10.0 | −4.1 to 24.1 | 0.163 | Small kidney (< 10 cm)a | 40 | −24.7 | −46.0 to −3.5 | 0.023 | VO2 max. (% predicted) | 20 | 0.6 | −0.5 to 1.7 | 0.294 | GFR increase, admission to pre-operative | 44 | 0.6 | 0.3 to 0.9 | < 0.001 | Scores | LM score | 44 | 1.6 | 0.2 to 2.9 | 0.019 | Matthews score | 44 | 2.4 | −0.4 to 5.2 | 0.091 | Kormos score | 41 | 3.5 | −1.2 to 8.2 | 0.149 | Treatment before surgery | IABP useda | 44 | 20.5 | 6.7 to 34.2 | 0.004 | Inotropesa | 43 | −2.8 | −20.1 to 14.4 | 0.745 | ACE inhibitors or ARBsa | 44 | −15.5 | −29.4 to −1.6 | 0.029 | Beta-blockersa | 44 | −5.4 | −23.9 to 13.0 | 0.562 | Aldosterone inhibitorsa | 44 | 5.6 | −8.5 to 19.8 | 0.435 | Diuretic agentsa | 40 | −14.4 | −39.4 to 10.6 | 0.258 | Amiodaronea | 40 | −6.9 | −22.8 to 8.9 | 0.390 | ICD/CRTa | 40 | −4.7 | −20.0 to 10.7 | 0.550 | Digoxina | 40 | −8.1 | −23.6 to 7.4 | 0.307 | Statinsa | 40 | 7.0 | −9.5 to 23.5 | 0.404 | Laboratory results | Urine protein | 36 | 0.1 | −0.1 to 0.3 | 0.466 | GFR on admission | 44 | −0.1 | −0.7 to 0.4 | 0.626 | Haemoglobin | 44 | −0.5 | −4.0 to 3.0 | 0.779 | Bilirubin | 44 | 14.6 | 5.6 to 23.7 | 0.002 | AST | 44 | 0.0 | 0.0 to 0.1 | 0.193 | ALT | 41 | 0.0 | 0.0 to 0.0 | 0.157 | LDH | 37 | 0.0 | 0.0 to 0.0 | 0.210 | BNP | 25 | 0.0 | 0.0 to 0.0 | 0.768 | Platelets | 44 | 0.0 | −0.1 to 0.1 | 0.943 | BUN | 44 | 0.0 | −0.4 to 0.4 | 0.975 | Albumin | 43 | −13.2 | −28.1 to 1.7 | 0.082 | Echocardiography | RIMP | 39 | −3.2 | −38.5 to 32.2 | 0.861 | TR time (corrected) | 42 | −0.1 | −0.2 to 0.0 | 0.174 | LVEDD | 44 | −0.4 | −1.3 to 0.4 | 0.320 | Mitral E-wave | 39 | 5.3 | −17.7 to 28.2 | 0.653 | LA volume index | 43 | −0.1 | −0.5 to 0.4 | 0.794 | EF | 44 | −0.2 | −1.4 to 0.9 | 0.684 | LV mass | 34 | 0.0 | −0.1 to 0.0 | 0.130 | TR (more than moderate) | 44 | −0.5 | −14.8 to 13.7 | 0.941 | AR (more than moderate) | 44 | −7.1 | −35.3 to 21.1 | 0.623 | MR (more than moderate) | 44 | 3.5 | −10.9 to 17.8 | 0.633 | Catheterisation | Stroke volume index | 42 | −0.2 | −0.9 to 0.6 | 0.682 | RVSWI | 42 | −0.7 | −2.8 to 1.5 | 0.537 | Cardiac index | 42 | −2.7 | −16.7 to 11.3 | 0.704 | SVR | 31 | −0.6 | −1.5 to 0.4 | 0.242 | PVR | 42 | −0.4 | −2.7 to 2.0 | 0.757 | RA pressure (mean) | 43 | 0.7 | −0.5 to 2.0 | 0.262 | Wedge pressure (mean) | 41 | −0.4 | −1.5 to 0.7 | 0.452 | PA pressure (mean) | 43 | 0.1 | −0.7 to 0.9 | 0.821 | Surgery and pump settings | Bypass time | 44 | 0.0 | −0.2 to 0.2 | 0.928 | Discharge pump flow | 43 | 0.5 | −9.5 to 10.5 | 0.920 | Discharge LVAD pulsatility index | 42 | 12.6 | 0.5 to 24.8 | 0.042 | Discharge pump speed (200 RPM) | 42 | 7.4 | 1.8 to 13.0 | 0.009 | Discharge pump speed > 9200 RPMa | 42 | 22.0 | 6.9 to 37.2 | 0.004 | a Categorical predictors were assessed using one-way analysis of variance. | Table shows the results of a univariate linear regression analysis for prediction of increase in GFR 1 month after LVAD implantation. GFR was evaluated as a continuous variable. Authors estimated associations of various pre-operative variables with increased GFR (operative time and LVAD settings were also included). Estimates were calculated depicting the change in mean GFR associated with the variable measured before and 1 month after operation. Estimates for continuous variables are for change in mean per unit increase in evaluated variable. | TR time was corrected for pulse; RIMP = (TR time − RV ejection time)/RV ejection time; RVSWI = [0.0136 × (MPAP − RAP) × stroke volume index]; kidney size was assessed by pre-operative abdominal ultrasound. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal dysfunction stage (GFR range) | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 1 (> 90) | 5 | 6 | 32 | 38 | 15 | 18 | 8 | 10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 2 (60–90) | 24 | 29 | 29 | 35 | 35 | 42 | 31 | 37 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 3 (30–60) | 42 | 51 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 18 | 18 | 22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 4 (15–30) | 11 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 5 (< 15) | 1 | 1 | 7 | 8 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 14 | 17 | 23 | 28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal dysfunction stage (GFR range) | Baseline | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 1 (> 90) | 0 | 0 | 13 | 31 | 4 | 10 | 3 | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 2 (60–90) | 0 | 0 | 18 | 43 | 22 | 52 | 17 | 40 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 3 (30–60) | 42 | 100 | 4 | 10 | 7 | 17 | 8 | 19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 4 (15–30) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 5 (< 15) | 0 | 0 | 5 | 12 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 17 | 12 | 29 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | n | Parameter estimate | 95% CI | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age | 44 | −0.8 | −1.6 to 0.0 | 0.049 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Malea | 44 | 4.2 | −12.8 to 21.1 | 0.630 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HTNa | 44 | −0.4 | −15.1 to 14.2 | 0.954 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DMa | 44 | −0.6 | −15.4 to 14.2 | 0.936 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CKDa | 44 | −11.5 | −27.1 to 4.1 | 0.151 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTTa | 44 | 9.1 | −6.6 to 24.9 | 0.256 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic aetiologya | 44 | 4.5 | −10.1 to 19.0 | 0.549 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight | 44 | −0.2 | −0.6 to 0.2 | 0.300 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA | 44 | −18.1 | −46.0 to 9.8 | 0.204 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic BP | 44 | −0.2 | −1.2 to 0.5 | 0.474 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic BP | 44 | −0.2 | −0.7 to 0.3 | 0.413 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heart rate | 44 | 0.0 | −0.5 to 0.5 | 0.974 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AFa | 44 | 31.8 | 8.8 to 54.7 | 0.007 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class IVa | 44 | 10.0 | −4.1 to 24.1 | 0.163 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Small kidney (< 10 cm)a | 40 | −24.7 | −46.0 to −3.5 | 0.023 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VO2 max. (% predicted) | 20 | 0.6 | −0.5 to 1.7 | 0.294 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GFR increase, admission to pre-operative | 44 | 0.6 | 0.3 to 0.9 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scores | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LM score | 44 | 1.6 | 0.2 to 2.9 | 0.019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Matthews score | 44 | 2.4 | −0.4 to 5.2 | 0.091 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kormos score | 41 | 3.5 | −1.2 to 8.2 | 0.149 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment before surgery | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP useda | 44 | 20.5 | 6.7 to 34.2 | 0.004 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inotropesa | 43 | −2.8 | −20.1 to 14.4 | 0.745 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACE inhibitors or ARBsa | 44 | −15.5 | −29.4 to −1.6 | 0.029 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beta-blockersa | 44 | −5.4 | −23.9 to 13.0 | 0.562 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aldosterone inhibitorsa | 44 | 5.6 | −8.5 to 19.8 | 0.435 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diuretic agentsa | 40 | −14.4 | −39.4 to 10.6 | 0.258 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amiodaronea | 40 | −6.9 | −22.8 to 8.9 | 0.390 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICD/CRTa | 40 | −4.7 | −20.0 to 10.7 | 0.550 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Digoxina | 40 | −8.1 | −23.6 to 7.4 | 0.307 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Statinsa | 40 | 7.0 | −9.5 to 23.5 | 0.404 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Laboratory results | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Urine protein | 36 | 0.1 | −0.1 to 0.3 | 0.466 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GFR on admission | 44 | −0.1 | −0.7 to 0.4 | 0.626 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemoglobin | 44 | −0.5 | −4.0 to 3.0 | 0.779 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilirubin | 44 | 14.6 | 5.6 to 23.7 | 0.002 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST | 44 | 0.0 | 0.0 to 0.1 | 0.193 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT | 41 | 0.0 | 0.0 to 0.0 | 0.157 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LDH | 37 | 0.0 | 0.0 to 0.0 | 0.210 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BNP | 25 | 0.0 | 0.0 to 0.0 | 0.768 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets | 44 | 0.0 | −0.1 to 0.1 | 0.943 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN | 44 | 0.0 | −0.4 to 0.4 | 0.975 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albumin | 43 | −13.2 | −28.1 to 1.7 | 0.082 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Echocardiography | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RIMP | 39 | −3.2 | −38.5 to 32.2 | 0.861 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TR time (corrected) | 42 | −0.1 | −0.2 to 0.0 | 0.174 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEDD | 44 | −0.4 | −1.3 to 0.4 | 0.320 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mitral E-wave | 39 | 5.3 | −17.7 to 28.2 | 0.653 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LA volume index | 43 | −0.1 | −0.5 to 0.4 | 0.794 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EF | 44 | −0.2 | −1.4 to 0.9 | 0.684 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LV mass | 34 | 0.0 | −0.1 to 0.0 | 0.130 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TR (more than moderate) | 44 | −0.5 | −14.8 to 13.7 | 0.941 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AR (more than moderate) | 44 | −7.1 | −35.3 to 21.1 | 0.623 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MR (more than moderate) | 44 | 3.5 | −10.9 to 17.8 | 0.633 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Catheterisation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke volume index | 42 | −0.2 | −0.9 to 0.6 | 0.682 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVSWI | 42 | −0.7 | −2.8 to 1.5 | 0.537 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index | 42 | −2.7 | −16.7 to 11.3 | 0.704 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SVR | 31 | −0.6 | −1.5 to 0.4 | 0.242 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PVR | 42 | −0.4 | −2.7 to 2.0 | 0.757 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RA pressure (mean) | 43 | 0.7 | −0.5 to 2.0 | 0.262 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wedge pressure (mean) | 41 | −0.4 | −1.5 to 0.7 | 0.452 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PA pressure (mean) | 43 | 0.1 | −0.7 to 0.9 | 0.821 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surgery and pump settings | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bypass time | 44 | 0.0 | −0.2 to 0.2 | 0.928 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discharge pump flow | 43 | 0.5 | −9.5 to 10.5 | 0.920 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discharge LVAD pulsatility index | 42 | 12.6 | 0.5 to 24.8 | 0.042 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discharge pump speed (200 RPM) | 42 | 7.4 | 1.8 to 13.0 | 0.009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discharge pump speed > 9200 RPMa | 42 | 22.0 | 6.9 to 37.2 | 0.004 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Categorical predictors were assessed using one-way analysis of variance. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Table shows the results of a univariate linear regression analysis for prediction of increase in GFR 1 month after LVAD implantation. GFR was evaluated as a continuous variable. Authors estimated associations of various pre-operative variables with increased GFR (operative time and LVAD settings were also included). Estimates were calculated depicting the change in mean GFR associated with the variable measured before and 1 month after operation. Estimates for continuous variables are for change in mean per unit increase in evaluated variable. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TR time was corrected for pulse; RIMP = (TR time − RV ejection time)/RV ejection time; RVSWI = [0.0136 × (MPAP − RAP) × stroke volume index]; kidney size was assessed by pre-operative abdominal ultrasound. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unclear | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See above | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For most patients with end-stage HF considered for LVAD, RD appears to be reversible. The present study found that ARF after LVAD was less common than previously reported and is related with a complicated post-operative course. Prediction of post-operative improvement in RD should consider the contribution of renal hypo-perfusion and congestion, irreversible renal injury and response to medical treatment pre implant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GFR estimates later in the post-implantation course might be biased to healthier patients. No consideration of QoL measures | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
John 2011a64
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: John Year of publication: 2011 Country: USA (MN) Study design: Retrospective (data prospectively collected and retrospectively analysed) Study setting: Medical Centre at University of Minnestota Number of centres: One centre Duration of study: From June 2005 to June 2010 Follow-up period: Total duration of follow-up was 137.5 patient-years Funding: Not reported |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To report the outcomes in patients receiving the HMII LVAD at a single centre and review lessons learned from this experience | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 102 BTT patients; pre-FDA approval (n = 38) and post-FDA approval (n = 64) Sample attrition/dropout: None Inclusion criteria: Patients who received the HMII LVAD at the University of Minnesota Medical Centre as BTT therapy from June 2005 through June 2010 Exclusion criteria: DT and exchange therapy for a failed HMXVE Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): 52.6 ± 12.8 years Median age: Not reported Age range: 17–71 years Sex: 76 male : 26 female Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Coronary artery disease 53 (51.9%) [causes of HF – ischaemic 58 (56.8%); non-ischaemic 36 (35.3%); other 8 (7.8%)] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT. HF resulting from causes such as: ischaemic 58 (56.8%); non-ischaemic 36 (35.3%); and other 8 (7.8%; including postpartum cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, congenital heart disease and post-cardiotomy shock) Type of device used: HMII LVAD Any comparison: Patients were divided into pre-FDA and post-FDA approval groups Duration of treatment: Duration of LVAD support (days) 327 ± 286 (range 10–1538 days) Percentage of patients using inotropes: Not reported Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below. Anticoagulation therapy – initially (first 14 patients) intravenous infusion of unfractionated heparin as a bridge to warfarin therapy was used, titrating dose to an INR of 2–3. However, it was changed to include only warfarin therapy starting on post-operative day 2 or 3, titrating dose to an INR of 1.5–2, in addition to antiplatelet therapy with aspirin Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII LVAD |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Haemodynamic and end-organ function; adverse events (BTT therapy); survival; impact of FDA approval on BTT outcomes Secondary outcomes: Not relevant Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records, data were also prospectively collected and retrospectively analysed. Baseline and follow-up data were collected, including patient characteristics, blood chemistry analyses, haematological findings, neurological status and concomitant medication use. After discharged from hospital, patients returned for follow-up, device review and clinical assessment. Data were prospectively collected and retrospectively analysed. Continuous data are presented as mean and SD. Categorical data were presented as a percentage. Continuous data were compared with analysis of variance or the t-test as indicated. The chi-squared or the Fisher's exact test was used for categorical variables. Survival estimates were based on the K–M method and compared using log-rank statistics. Hospital readmission and patient adverse events were recorded throughout the study period as they occurred, using standardised definitions. After FDA approval, data continued to be collected for all patients using similar definitions Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: Total duration of follow-up was 137.5 patient-years. Duration of LVAD support (days) 327 ± 286 (range 10–1538)Number of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreened130 patientsRandomised/included102 patientsExcluded28 patients – 17 DT patients and 11 exchange patientsMissing participantsNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | 130 patients | Randomised/included | 102 patients | Excluded | 28 patients – 17 DT patients and 11 exchange patients | Missing participants | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | 130 patients | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 102 patients | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | 28 patients – 17 DT patients and 11 exchange patients | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of BTT patients prior to LVAD implantation (n = 102)Variablen (%)Mean age (years)52.6 ± 12.8 (range 17–71)Gender ratio (male : female)76 : 26Aetiology of HF Ischaemic58 (56.8%) Non-ischaemic36 (35.3%) Other8 (7.8%)Diabetes mellitus29 (28.4%)Hypertension37 (36.2%)Coronary artery disease53 (51.9%)BMI28.7 ± 6.8 (range 15–44)Duration of LVAD support (days)327 ± 286 (range 10–1538)Haemodynamics mean ± SD Systolic PAP (mmHg)54.55 ± 14.86 Diastolic PAP (mmHg)28.11 ± 7.35 Right atrial mean (mmHg)13.46 ± 6.28 PCWP (mmHg)24.80 ± 6.58 PVR (Wood units)3.75 ± 2.14 Cardiac output (l/minute)3.77 ± 1.11 Cardiac index1.86 ± 0.49End-organ parameters (mean ± SD)Renal Sodium134.8 ± 5.1 Creatinine1.39 ± 0.59 BUN33.4 ± 20.4Liver ALT80.49 ± 236 AST79.16 ± 224 Total bilirubin1.15 ± 1.00INTERMACS profiles (n = 97) 117 (17.5) 213 (13.4) 313 (13.4) 416 (16.5) 525 (25.7) 612 (12.7) 71 (1.03) | Variable | n (%) | Mean age (years) | 52.6 ± 12.8 (range 17–71) | Gender ratio (male : female) | 76 : 26 | Aetiology of HF | Ischaemic | 58 (56.8%) | Non-ischaemic | 36 (35.3%) | Other | 8 (7.8%) | Diabetes mellitus | 29 (28.4%) | Hypertension | 37 (36.2%) | Coronary artery disease | 53 (51.9%) | BMI | 28.7 ± 6.8 (range 15–44) | Duration of LVAD support (days) | 327 ± 286 (range 10–1538) | Haemodynamics mean ± SD | Systolic PAP (mmHg) | 54.55 ± 14.86 | Diastolic PAP (mmHg) | 28.11 ± 7.35 | Right atrial mean (mmHg) | 13.46 ± 6.28 | PCWP (mmHg) | 24.80 ± 6.58 | PVR (Wood units) | 3.75 ± 2.14 | Cardiac output (l/minute) | 3.77 ± 1.11 | Cardiac index | 1.86 ± 0.49 | End-organ parameters (mean ± SD) | Renal | Sodium | 134.8 ± 5.1 | Creatinine | 1.39 ± 0.59 | BUN | 33.4 ± 20.4 | Liver | ALT | 80.49 ± 236 | AST | 79.16 ± 224 | Total bilirubin | 1.15 ± 1.00 | INTERMACS profiles (n = 97) | 1 | 17 (17.5) | 2 | 13 (13.4) | 3 | 13 (13.4) | 4 | 16 (16.5) | 5 | 25 (25.7) | 6 | 12 (12.7) | 7 | 1 (1.03) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variable | n (%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean age (years) | 52.6 ± 12.8 (range 17–71) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gender ratio (male : female) | 76 : 26 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aetiology of HF | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic | 58 (56.8%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-ischaemic | 36 (35.3%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 8 (7.8%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 29 (28.4%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension | 37 (36.2%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coronary artery disease | 53 (51.9%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI | 28.7 ± 6.8 (range 15–44) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Duration of LVAD support (days) | 327 ± 286 (range 10–1538) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemodynamics mean ± SD | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic PAP (mmHg) | 54.55 ± 14.86 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic PAP (mmHg) | 28.11 ± 7.35 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right atrial mean (mmHg) | 13.46 ± 6.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 24.80 ± 6.58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PVR (Wood units) | 3.75 ± 2.14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac output (l/minute) | 3.77 ± 1.11 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index | 1.86 ± 0.49 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| End-organ parameters (mean ± SD) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sodium | 134.8 ± 5.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine | 1.39 ± 0.59 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN | 33.4 ± 20.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Liver | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT | 80.49 ± 236 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST | 79.16 ± 224 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin | 1.15 ± 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INTERMACS profiles (n = 97) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 17 (17.5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 13 (13.4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 13 (13.4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 16 (16.5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 25 (25.7) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 12 (12.7) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | 1 (1.03) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30-day and 6-month survival in 38 patients in the clinical trial (pre-FDA approval) was 97.4% and 88.8%, and were not significant when compared with the 93.7% and 76.2% 30-day and 6-month survival in the 64 patients in the post-FDA approval period (p = 0.1) K–M estimates: 30-day, 6-month and 1-year survival for the BTT patients by K–M estimate was 95.1%, 83.5%, and 78.8%, respectively |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical circulatory support with subsequent HT: Of 102 BTT patients, 48 had cardiac transplantation with mean duration to transplant period of 329.8 ± 265.6 days (range 96–1230 days) In pre-FDA approval period, 30 of 38 were patients transplanted with mean duration to transplant period of 331.2 ± 322 days; in post-FDA approval period, 18 of 64 were patients transplanted with mean duration to transplant period of 327.78 ± 132 days (no significant difference in mean duration to transplant between both groups; p = 0.9) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Major adverse events among 102 BTT patients included right ventricular failure requiring RVAD support in 5 patients (4.9%), LVAD driveline infections in 25 patients (24.5%), neurological events in 10 patients (9.8%) and gastrointestinal bleeding in 18 patients (17.6%) One patient had pump thrombosis, and this patient required a device replacement (for pump thrombosis) Incidence of adverse outcomes in pre-FDA approval group was not statistically different from that in the post-FDA approval group Adverse events in BTT patients during LVAD support (n = 102)Eventsn (%)NeurologicalStroke/TIA9 (8.8)Paraplegia1 (0.98)HaemorrhagicGastrointestinal bleeding18 (17.6)Mediastinal bleeding requiring reoperation17 (16.7)InfectiousDriveline infection22 (21.5)Pocket infection0Pump infection0RV failure requiring RVAD5 (4.9)Pump thrombosis1 (0.98)Device malfunction2 (1.9)Device replacement1 (0.98)Renal failure2 (1.9) Adverse events in BTT patients during LVAD support by the US FDA approval statusEventsPre-FDA approval (n = 38)Post-FDA approval (n = 64)n%n%Neurological stroke/TIA25.3710.9Haematological Gastrointestinal bleeding923.79(14.1)Infectious Driveline infection1026.31218.8RV failure requiring RVAD25.334.7Pump thrombosis011.6Device replacement011.6 Summary of adverse eventsAdverse eventsInterventionComparator, if presentBleedingGastrointestinal bleeding in 18 (17.6%) patients; mediastinal bleeding requiring reoperation 17 (16.7%)Gastrointestinal bleeding – pre-FDA approval 9 (23.7%) and post-FDA approval 9 (14.1%)StrokeStroke/TIA 9 (8.8%)Stroke/TIA – pre-FDA approval 2 (5.3%) and post-FDA approval 7 (10.9%)HypertensionSome of the patients already had hypertension at baselineInfectionDriveline infections in 25 (24.5%) patients; pocket infection 0; pump infection 0Driveline infection – pre-FDA approval 10 (26.3%) and post-FDA approval 12 (18.8%)HFRight ventricular failure requiring RVAD support in 5 (4.9%) patientsRV failure requiring RVAD – pre-FDA approval 2 (5.3%) and post-FDA approval 3 (4.7%)VAD failureDevice malfunction 2 (1.9%)Renal failureRenal failure 2 (1.9%)Other neurological dysfunctionParaplegia 1 (0.98%) |
Events | n (%) | Neurological | Stroke/TIA | 9 (8.8) | Paraplegia | 1 (0.98) | Haemorrhagic | Gastrointestinal bleeding | 18 (17.6) | Mediastinal bleeding requiring reoperation | 17 (16.7) | Infectious | Driveline infection | 22 (21.5) | Pocket infection | 0 | Pump infection | 0 | RV failure requiring RVAD | 5 (4.9) | Pump thrombosis | 1 (0.98) | Device malfunction | 2 (1.9) | Device replacement | 1 (0.98) | Renal failure | 2 (1.9) | Events | Pre-FDA approval (n = 38) | Post-FDA approval (n = 64) | n | % | n | % | Neurological stroke/TIA | 2 | 5.3 | 7 | 10.9 | Haematological | Gastrointestinal bleeding | 9 | 23.7 | 9 | (14.1) | Infectious | Driveline infection | 10 | 26.3 | 12 | 18.8 | RV failure requiring RVAD | 2 | 5.3 | 3 | 4.7 | Pump thrombosis | 0 | 1 | 1.6 | Device replacement | 0 | 1 | 1.6 | Adverse events | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Bleeding | Gastrointestinal bleeding in 18 (17.6%) patients; mediastinal bleeding requiring reoperation 17 (16.7%) | Gastrointestinal bleeding – pre-FDA approval 9 (23.7%) and post-FDA approval 9 (14.1%) | Stroke | Stroke/TIA 9 (8.8%) | Stroke/TIA – pre-FDA approval 2 (5.3%) and post-FDA approval 7 (10.9%) | Hypertension | Some of the patients already had hypertension at baseline | Infection | Driveline infections in 25 (24.5%) patients; pocket infection 0; pump infection 0 | Driveline infection – pre-FDA approval 10 (26.3%) and post-FDA approval 12 (18.8%) | HF | Right ventricular failure requiring RVAD support in 5 (4.9%) patients | RV failure requiring RVAD – pre-FDA approval 2 (5.3%) and post-FDA approval 3 (4.7%) | VAD failure | Device malfunction 2 (1.9%) | Renal failure | Renal failure 2 (1.9%) | Other neurological dysfunction | Paraplegia 1 (0.98%) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Events | n (%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neurological | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke/TIA | 9 (8.8) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paraplegia | 1 (0.98) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gastrointestinal bleeding | 18 (17.6) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mediastinal bleeding requiring reoperation | 17 (16.7) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infectious | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline infection | 22 (21.5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pocket infection | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump infection | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RV failure requiring RVAD | 5 (4.9) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump thrombosis | 1 (0.98) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device malfunction | 2 (1.9) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device replacement | 1 (0.98) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure | 2 (1.9) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Events | Pre-FDA approval (n = 38) | Post-FDA approval (n = 64) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | % | n | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neurological stroke/TIA | 2 | 5.3 | 7 | 10.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haematological | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gastrointestinal bleeding | 9 | 23.7 | 9 | (14.1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infectious | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline infection | 10 | 26.3 | 12 | 18.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RV failure requiring RVAD | 2 | 5.3 | 3 | 4.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump thrombosis | 0 | 1 | 1.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device replacement | 0 | 1 | 1.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding | Gastrointestinal bleeding in 18 (17.6%) patients; mediastinal bleeding requiring reoperation 17 (16.7%) | Gastrointestinal bleeding – pre-FDA approval 9 (23.7%) and post-FDA approval 9 (14.1%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke | Stroke/TIA 9 (8.8%) | Stroke/TIA – pre-FDA approval 2 (5.3%) and post-FDA approval 7 (10.9%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension | Some of the patients already had hypertension at baseline | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection | Driveline infections in 25 (24.5%) patients; pocket infection 0; pump infection 0 | Driveline infection – pre-FDA approval 10 (26.3%) and post-FDA approval 12 (18.8%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HF | Right ventricular failure requiring RVAD support in 5 (4.9%) patients | RV failure requiring RVAD – pre-FDA approval 2 (5.3%) and post-FDA approval 3 (4.7%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAD failure | Device malfunction 2 (1.9%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure | Renal failure 2 (1.9%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other neurological dysfunction | Paraplegia 1 (0.98%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| There were eight early deaths (≤ 30 days or prior to hospital discharge); four patients with multisystem organ failure, one with subclavian vein haemorrhage, one patient with ventricular fibrillation, one patient with respiratory failure, and one patient with RV failure and intracranial bleed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Despite significant morbidity, use of HMII LVAD as a BTT provides excellent haemodynamic support and is associated with excellent survival and low mortality. Improvement and focused strategies are needed in areas of gastrointestinal bleeding, driveline infections, and adverse neurological events for devices to provide a long-term alternative to HT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neurological problems were present in approximately 10% patients and around 5% experiencing right ventricular failure requiring RVAD. Survival findings did not reach significance, but note the small numbers used. There was a 12% difference in 1-year survival pre-FDA and post-FDA approval | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
John 201063
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: John Year of publication: 2010 Country: USA, Canada Study design: Retrospective Study setting: Multicentre Number of centres: 35 centres (abstract states 36 centres) Duration of study: Between March 2005 and April 2008 Follow-up period: Each centre followed up patients based on their own post-transplant follow-up schedule. Each centre completed a form to document 1-month and 1-year post-transplant survival. Of transplanted patients, 229 patients completed a 30-day follow-up and 190 patients completed a 1-year follow-up Funding: Not reported |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To determine factors related to post-transplant survival in patients supported with CF LVADs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 250 Sample attrition/dropout: Unclear Inclusion criteria: Patients with end-stage HF and listed for HT at each centre. Patients were required to have NYHA class IV HF symptoms and to be ill enough to have high priority for transplantation (UNOS status 1a or 1b). Detailed inclusion and exclusion criteria published elsewhere (Miller et al. 200770). Only patients who underwent cardiac transplantation after VAD support are included in this paper Exclusion criteria: Severe renal, pulmonary or hepatic dysfunction, active uncontrolled infection, a mechanical aortic valve, aortic insufficiency, an aortic aneurysm, other mechanical circulatory support (except an IABP) and technical obstacles thought by investigator to pose an increase surgical risk Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): 51 ± 13 years Median age: 54 years Age range: Not reported Sex: Male 204 (82%) Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Ischaemic causes of HF – 107 (43%); the paper reports that most of the HF were caused by non-ischaemic cardiomyopathy |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: Most frequent aetiology of HF was non-ischaemic cardiomyopathy. All patients had symptoms of advanced HF despite optimal MM with oral medications Type of device used: HMII LVAD Any comparison: None Duration of treatment: Unclear for each centre. Of 468 patients, 250 (53%) underwent cardiac transplantation after a median duration of LVAD support of 151 days (longest 3.2 years). Of the patients undergoing transplantation, 229 patients completed a 30-day follow-up and 190 patients completed a 1-year follow-up Percentage of patients using inotropes: Intravenous inotrope agents = 91% (n = 228); intolerant to inotropes owing to arrhythmias = 9% (n = 22) Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below. After device implantation, a standardised antithrombotic regimen was implemented with initiation of heparin followed by transition to warfarin as well as aspirin. Post-operative MM, including inotropic, antiarrhythmic and HF therapy was performed according to each investigator's preference and usual practice Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII LVAD |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival after transplantation at two specific time points: 30 days and 1 year. Survival after transplantation was also compared with the survival for patients continuing on LVAD support, starting at 6 months of support and continuing through 18 months support (censored for transplantation) Secondary outcomes: The post-transplant survival was also stratified according to age, aetiology, BMI, duration of device support, and by adverse events during support Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records. This study was supervised by sponsor (Thoratec Inc.). Co-ordinators at each site collected all study data, which were then forwarded to data analysis centre of sponsor. Academic authors vouch for completeness and accuracy of data and analyses. Data and safety monitoring board consisting of four independent physicians and one biostatistician who were not investigators met routinely to review study compliance, adverse events, QoL and outcomes of patients. A clinical events committee of four independent physicians reviewed, classified and adjudicated causes of death and all adverse events Survival: Yes Adverse event: No HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: 30 days and 1 year (229 patients completed a 30-day follow-up and 190 patients completed a 1-year follow-up)Number of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreened468 patentsNot applicableRandomised/included250 (53%) patients that underwent cardiac transplantationNot applicableExcludedOut of 468 patients, 218 patients were excluded: 106 (23%) patients died, 12 (2.6%) patients recovered ventricular function and the device was removed, and 100 (21%) patients were still receiving LVAD supportNot applicableMissing participantsNot applicableNot applicableWithdrawalsNot applicableNot applicable |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | 468 patents | Not applicable | Randomised/included | 250 (53%) patients that underwent cardiac transplantation | Not applicable | Excluded | Out of 468 patients, 218 patients were excluded: 106 (23%) patients died, 12 (2.6%) patients recovered ventricular function and the device was removed, and 100 (21%) patients were still receiving LVAD support | Not applicable | Missing participants | Not applicable | Not applicable | Withdrawals | Not applicable | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | 468 patents | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 250 (53%) patients that underwent cardiac transplantation | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Out of 468 patients, 218 patients were excluded: 106 (23%) patients died, 12 (2.6%) patients recovered ventricular function and the device was removed, and 100 (21%) patients were still receiving LVAD support | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not applicable | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not applicable | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline characteristics of the 250 LVAD patients who underwent HTCharacteristicMean ± SD or n (%) (n = 250)Age (years)51 ± 13Male (%)204 (82)BMI (kg/m2)27 ± 5.6BSA (m2)2.0 ± 0.3Ischaemic aetiology of HF (%)107 (43)LVEF (%)16.1 ± 6.5Arterial BP (mmHg) Systolic98.2 ± 15.4 Diastolic62.3 ± 12.1PCWP (mmHg)25.4 ± 8.2Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)2.1 ± 0.7Heart rate (b.p.m.)92 ± 18 Pulmonary artery pressure (mmHg) Systolic51.5 ± 13.2 Diastolic26.7 ± 8.0 Mean35.8 ± 9.0Pulmonary vascular resistance (Wood units)2.8 ± 1.4CVP (mmHg)12 ± 6NYHA classIV (221/250)Serum sodium (mmol/l)133.3 ± 5.2Serum albumin (g/dl)3.6 ± 1.8Pre-albumin (mg/dl)18.5 ± 7.7Cholesterol (mg/dl)129 ± 41Serum creatinine (mg/dl)1.4 ± 0.5BUN (mg/dl)29.8 ± 16.7ALT (IU/l)106 ± 278AST (IU/l)91 ± 223Total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.3 ± 0.8LDH (mg/dl)567 ± 1538Haematocrit (%)34.8 ± 5.7White blood count (× 1000/ml)8.8 ± 3.3Platelets (1000/ml)225 ± 87INR1.3 ± 0.3Concomitant medications Intravenous inotrope agents228 (91) Intolerant to inotropes owing to arrhythmias22 (9) Biventricular pacemaker119 (48) ICD192 (77) IABP115 (46) Mechanical ventilation18 (7) Of 468 patients, 250 (53%) underwent cardiac transplantation, 106 (23%) died, 12 (2.6%) recovered ventricular function and device was removed, and 100 (21%) were still receiving LVAD support Of transplanted patients, 229 patients completed a 30-day follow-up and 190 patients completed a 1-year follow-up; 46% of patients had concomitant support with IABP, many had previously received biventricular pacing therapy Majority of patients were listed at UNOS status 1a |
Characteristic | Mean ± SD or n (%) (n = 250) | Age (years) | 51 ± 13 | Male (%) | 204 (82) | BMI (kg/m2) | 27 ± 5.6 | BSA (m2) | 2.0 ± 0.3 | Ischaemic aetiology of HF (%) | 107 (43) | LVEF (%) | 16.1 ± 6.5 | Arterial BP (mmHg) | Systolic | 98.2 ± 15.4 | Diastolic | 62.3 ± 12.1 | PCWP (mmHg) | 25.4 ± 8.2 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.1 ± 0.7 | Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 92 ± 18 | Pulmonary artery pressure (mmHg) | Systolic | 51.5 ± 13.2 | Diastolic | 26.7 ± 8.0 | Mean | 35.8 ± 9.0 | Pulmonary vascular resistance (Wood units) | 2.8 ± 1.4 | CVP (mmHg) | 12 ± 6 | NYHA class | IV (221/250) | Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 133.3 ± 5.2 | Serum albumin (g/dl) | 3.6 ± 1.8 | Pre-albumin (mg/dl) | 18.5 ± 7.7 | Cholesterol (mg/dl) | 129 ± 41 | Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | BUN (mg/dl) | 29.8 ± 16.7 | ALT (IU/l) | 106 ± 278 | AST (IU/l) | 91 ± 223 | Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.3 ± 0.8 | LDH (mg/dl) | 567 ± 1538 | Haematocrit (%) | 34.8 ± 5.7 | White blood count (× 1000/ml) | 8.8 ± 3.3 | Platelets (1000/ml) | 225 ± 87 | INR | 1.3 ± 0.3 | Concomitant medications | Intravenous inotrope agents | 228 (91) | Intolerant to inotropes owing to arrhythmias | 22 (9) | Biventricular pacemaker | 119 (48) | ICD | 192 (77) | IABP | 115 (46) | Mechanical ventilation | 18 (7) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristic | Mean ± SD or n (%) (n = 250) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 51 ± 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male (%) | 204 (82) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27 ± 5.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 2.0 ± 0.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic aetiology of HF (%) | 107 (43) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF (%) | 16.1 ± 6.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arterial BP (mmHg) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic | 98.2 ± 15.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic | 62.3 ± 12.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 25.4 ± 8.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.1 ± 0.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 92 ± 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary artery pressure (mmHg) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic | 51.5 ± 13.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic | 26.7 ± 8.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean | 35.8 ± 9.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary vascular resistance (Wood units) | 2.8 ± 1.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CVP (mmHg) | 12 ± 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class | IV (221/250) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 133.3 ± 5.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum albumin (g/dl) | 3.6 ± 1.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-albumin (mg/dl) | 18.5 ± 7.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cholesterol (mg/dl) | 129 ± 41 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 29.8 ± 16.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT (IU/l) | 106 ± 278 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST (IU/l) | 91 ± 223 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.3 ± 0.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LDH (mg/dl) | 567 ± 1538 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haematocrit (%) | 34.8 ± 5.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| White blood count (× 1000/ml) | 8.8 ± 3.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets (1000/ml) | 225 ± 87 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INR | 1.3 ± 0.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concomitant medications | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intravenous inotrope agents | 228 (91) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intolerant to inotropes owing to arrhythmias | 22 (9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biventricular pacemaker | 119 (48) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICD | 192 (77) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP | 115 (46) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 18 (7) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post-transplant survival: Of 468 patients, 250 (53%) patients had cardiac transplantation after LVAD support median duration of 151 days (longest 3.2 years). In patient's receiving transplantation, 229 patients completed a 30-day follow-up and 190 patients completed a 1-year follow-up. Overall 30-day and 1-year survivals are 97% and 87%, respectively. 1-year survival was 88% for men and 82% for women. No significant differences in 30-day and 1-year post-transplant survivals in patients when stratified by demographics (e.g. age, gender, aetiology of HF, and BMI) Post-transplant survival vs. patient demographicsParameterDemographicLVAD durationSurvival at 30 daysp-valueSurvival at 1 yearp-valueOverallAll151 (3.2 years)222/229 (97%)165/190 (87%)Aetiologylschaemic152 (13 years)100/102 (98%)0.4774/85 (87%)1.00Non-ischaemic143 (3.2 years)122/127 (96%)91/105 (87%)GenderMale145 (3.2 years)182/187 (97%)0.36136/155 (88%)0.41Female159 (1.7 years)38/40 (95%)28/34 (82%)Age (years)< 50131 (3.2 years)82/85 (97%)0.9266/75 (88%)0.9350–59172 (3.2 years)79/81 (98%)56/65 (86%)> 60151 (1.8 years)61/63 (97%)43/50 (86%)BMI (kg/m2)< 20131 (1.4 years)19/21 (91%)0.1016/19 (84%)0.7520–29136 (3.2 years)136/138 (99%)99/112 (88%)> 30173 (3.2 years)66/69 (96%)50/59 (85%) Patients undergoing transplantation were stratified into four groups on basis of duration of LVAD support ranging from < 30 days to > 180 days (see below). No significant differences in 30-day or 1-year post-transplant survivals among groups Post-transplant survival vs. LVAD durationLVAD durationMedian days (maximum)Survival at 30 daysp-valueSurvival at 1 yearp-value< 30 days18 (28)17/17 (100%)0.2816/17 (94%)0.1830–89 days58 (89)62/62 (100%)55/59 (93%)90–179 days135 (179)57/60 (95%)46/55 (84%)180–365 days227 (363)64/68 (94%)37/45 (82%)> 365 days507 (3.2 years)22/22 (100%)11/14 (79%) No significant difference in 30-day or 1-year post-transplant survivals when patients supported for > 180 days were subdivided into 180–365 days and > 365 days Post-transplant survival vs. adverse events during LVAD supportAdverse eventLVAD durationSurvival at 30 daysp-valueSurvival at 1 yearp-valueAny infection during LVAD supportNo120 (3.2 years)132/135 (98%)0.45102/115 (89%)0.38Yes192 (2.1 years)90/94 (96%)63/75 (84%)Percutaneous lead infection during LVAD supportNo126 (3.2 years)185/189 (98%)0.10144/162 (89%)0.07Yes253 (2.1 years)37/40 (93%)21/28 (75%)Reoperation for bleeding during LVAD supportNo149 (3.2 years)180/184 (98%)0.14133/152 (88%)0.60Yes152 (3.2 years)42/45 (93%)32/38 (84%)Bleeding requiring > 2 units PRBC/24 hours during LVAD supportNo130 (2.1 years)88/90 (98%)0.7i74/79 (94%)0.03Yes162 (3.2 years)134/139 (96%)91/111 (82%)Last creatinine value during LVAD support< 1.7 mg/dl (1.1 ± 0.1)143 (3.2 years)202/209 (97%)1.00154/175 (88%)0.12> 1.7 mg/dl (2.2 ± 0.5)194 (1.5 years)20/20 (100%)11/15 (73%)Last BUN value during LVAD support< 30 mg/dl (17 ± 5)143 (3.2 years)200/206 (97%)0.53151/172 (88%)0.27> 30 mg/dl (46 ± 19)178 (1.3 years)22/23 (96%)14/18 (78%)Last ALT value during LVAD support< 40 IU (24 ± 8)157 (3.2 years)171/177 (97%)1.00124/142 (87%)0.81> 40 IU (62 ± 38)120 (1.8 years)51/52 (98%)41/48 (85%) Post-transplant survival was stratified on basis of occurrence of adverse events during LVAD support as well as end-organ function before transplantation (see above). Patients needing > 2 units of PRBCs in 24 hours during LVAD support had a significant decreased 1-year survival (82% vs. 94%) compared with patients not requiring > 2 units of PRBCs in 24 hours during LVAD support (p = 0.03). There was lower survival at 1 year (75%) in 28 patients with percutaneous lead infections during LVAD support vs. no infection (89%) (p = 0.07), and in 15 patients with last creatinine level before transplant > 1.7 mg/dl (73% vs. 88%) when compared with patients with creatinine level before transplant was < 1.7 mg/dl (p = 0.12). No significant differences in 30-day or 1-year post-transplant survivals among other groups (see above) Post-transplant survival vs. survival after 6 months of LVAD support: 30-day and 1-year survivals for patients continuing on LVAD support were 98% and 87%. This was not significantly different from 30-day and 1-year post-transplant survivals of 97% and 87%. (Note: starting point of 6 months was used for analysis as median duration for timing of transplant on LVAD support was 151 days) Summary of survival dataSurvival dataInterventionComparator, if presentOverall survivalOverall 30-day and 1-year post-transplant survival was 97% (222/229) and 87% (165/190) respectively. LVAD support duration was 151 days (longest 3.2 years)1-year post-transplant survival for men was 88% (136/155) and 82% (28/34) for women (LVAD support in men was 145 days, longest 3.2 years; and in women 159 days, longest 1.7 years)There was no statistically significant differences in 30-day and 1-year post-transplant survivals among these patientsThe 30-day and 1-year survival for patients continuing on LVAD support (starting from 6 months of support, through 18 months, and censored for transplantation) were 98% and 87%. This was not statistically significantly different from the 30-day and 1-year post-transplant survivals of 97% and 87%. The starting point of 6 months for this analysis was used as the median duration of timing of transplant on LVAD support was 151 daysNot applicableK–M estimatesNot applicableNot applicableSurvival by era (at 5-year intervals)Not applicableNot applicableHT without prior mechanical circulatory supportOnly included patients who had a HT after LVAD supportNot applicableMechanical circulatory support without subsequent HTOnly included patients who had a HT after LVAD supportNot applicableMechanical circulatory support with subsequent HT250 patientsNot applicable |
Parameter | Demographic | LVAD duration | Survival at 30 days | p-value | Survival at 1 year | p-value | Overall | All | 151 (3.2 years) | 222/229 (97%) | 165/190 (87%) | Aetiology | lschaemic | 152 (13 years) | 100/102 (98%) | 0.47 | 74/85 (87%) | 1.00 | Non-ischaemic | 143 (3.2 years) | 122/127 (96%) | 91/105 (87%) | Gender | Male | 145 (3.2 years) | 182/187 (97%) | 0.36 | 136/155 (88%) | 0.41 | Female | 159 (1.7 years) | 38/40 (95%) | 28/34 (82%) | Age (years) | < 50 | 131 (3.2 years) | 82/85 (97%) | 0.92 | 66/75 (88%) | 0.93 | 50–59 | 172 (3.2 years) | 79/81 (98%) | 56/65 (86%) | > 60 | 151 (1.8 years) | 61/63 (97%) | 43/50 (86%) | BMI (kg/m2) | < 20 | 131 (1.4 years) | 19/21 (91%) | 0.10 | 16/19 (84%) | 0.75 | 20–29 | 136 (3.2 years) | 136/138 (99%) | 99/112 (88%) | > 30 | 173 (3.2 years) | 66/69 (96%) | 50/59 (85%) | LVAD duration | Median days (maximum) | Survival at 30 days | p-value | Survival at 1 year | p-value | < 30 days | 18 (28) | 17/17 (100%) | 0.28 | 16/17 (94%) | 0.18 | 30–89 days | 58 (89) | 62/62 (100%) | 55/59 (93%) | 90–179 days | 135 (179) | 57/60 (95%) | 46/55 (84%) | 180–365 days | 227 (363) | 64/68 (94%) | 37/45 (82%) | > 365 days | 507 (3.2 years) | 22/22 (100%) | 11/14 (79%) | Adverse event | LVAD duration | Survival at 30 days | p-value | Survival at 1 year | p-value | Any infection during LVAD support | No | 120 (3.2 years) | 132/135 (98%) | 0.45 | 102/115 (89%) | 0.38 | Yes | 192 (2.1 years) | 90/94 (96%) | 63/75 (84%) | Percutaneous lead infection during LVAD support | No | 126 (3.2 years) | 185/189 (98%) | 0.10 | 144/162 (89%) | 0.07 | Yes | 253 (2.1 years) | 37/40 (93%) | 21/28 (75%) | Reoperation for bleeding during LVAD support | No | 149 (3.2 years) | 180/184 (98%) | 0.14 | 133/152 (88%) | 0.60 | Yes | 152 (3.2 years) | 42/45 (93%) | 32/38 (84%) | Bleeding requiring > 2 units PRBC/24 hours during LVAD support | No | 130 (2.1 years) | 88/90 (98%) | 0.7i | 74/79 (94%) | 0.03 | Yes | 162 (3.2 years) | 134/139 (96%) | 91/111 (82%) | Last creatinine value during LVAD support | < 1.7 mg/dl (1.1 ± 0.1) | 143 (3.2 years) | 202/209 (97%) | 1.00 | 154/175 (88%) | 0.12 | > 1.7 mg/dl (2.2 ± 0.5) | 194 (1.5 years) | 20/20 (100%) | 11/15 (73%) | Last BUN value during LVAD support | < 30 mg/dl (17 ± 5) | 143 (3.2 years) | 200/206 (97%) | 0.53 | 151/172 (88%) | 0.27 | > 30 mg/dl (46 ± 19) | 178 (1.3 years) | 22/23 (96%) | 14/18 (78%) | Last ALT value during LVAD support | < 40 IU (24 ± 8) | 157 (3.2 years) | 171/177 (97%) | 1.00 | 124/142 (87%) | 0.81 | > 40 IU (62 ± 38) | 120 (1.8 years) | 51/52 (98%) | 41/48 (85%) | Survival data | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Overall survival | Overall 30-day and 1-year post-transplant survival was 97% (222/229) and 87% (165/190) respectively. LVAD support duration was 151 days (longest 3.2 years) 1-year post-transplant survival for men was 88% (136/155) and 82% (28/34) for women (LVAD support in men was 145 days, longest 3.2 years; and in women 159 days, longest 1.7 years) There was no statistically significant differences in 30-day and 1-year post-transplant survivals among these patients The 30-day and 1-year survival for patients continuing on LVAD support (starting from 6 months of support, through 18 months, and censored for transplantation) were 98% and 87%. This was not statistically significantly different from the 30-day and 1-year post-transplant survivals of 97% and 87%. The starting point of 6 months for this analysis was used as the median duration of timing of transplant on LVAD support was 151 days |
Not applicable | K–M estimates | Not applicable | Not applicable | Survival by era (at 5-year intervals) | Not applicable | Not applicable | HT without prior mechanical circulatory support | Only included patients who had a HT after LVAD support | Not applicable | Mechanical circulatory support without subsequent HT | Only included patients who had a HT after LVAD support | Not applicable | Mechanical circulatory support with subsequent HT | 250 patients | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Demographic | LVAD duration | Survival at 30 days | p-value | Survival at 1 year | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall | All | 151 (3.2 years) | 222/229 (97%) | 165/190 (87%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aetiology | lschaemic | 152 (13 years) | 100/102 (98%) | 0.47 | 74/85 (87%) | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-ischaemic | 143 (3.2 years) | 122/127 (96%) | 91/105 (87%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gender | Male | 145 (3.2 years) | 182/187 (97%) | 0.36 | 136/155 (88%) | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Female | 159 (1.7 years) | 38/40 (95%) | 28/34 (82%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | < 50 | 131 (3.2 years) | 82/85 (97%) | 0.92 | 66/75 (88%) | 0.93 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 50–59 | 172 (3.2 years) | 79/81 (98%) | 56/65 (86%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 60 | 151 (1.8 years) | 61/63 (97%) | 43/50 (86%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | < 20 | 131 (1.4 years) | 19/21 (91%) | 0.10 | 16/19 (84%) | 0.75 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20–29 | 136 (3.2 years) | 136/138 (99%) | 99/112 (88%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 30 | 173 (3.2 years) | 66/69 (96%) | 50/59 (85%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD duration | Median days (maximum) | Survival at 30 days | p-value | Survival at 1 year | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < 30 days | 18 (28) | 17/17 (100%) | 0.28 | 16/17 (94%) | 0.18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30–89 days | 58 (89) | 62/62 (100%) | 55/59 (93%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 90–179 days | 135 (179) | 57/60 (95%) | 46/55 (84%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 180–365 days | 227 (363) | 64/68 (94%) | 37/45 (82%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 365 days | 507 (3.2 years) | 22/22 (100%) | 11/14 (79%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse event | LVAD duration | Survival at 30 days | p-value | Survival at 1 year | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Any infection during LVAD support | No | 120 (3.2 years) | 132/135 (98%) | 0.45 | 102/115 (89%) | 0.38 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | 192 (2.1 years) | 90/94 (96%) | 63/75 (84%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Percutaneous lead infection during LVAD support | No | 126 (3.2 years) | 185/189 (98%) | 0.10 | 144/162 (89%) | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | 253 (2.1 years) | 37/40 (93%) | 21/28 (75%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reoperation for bleeding during LVAD support | No | 149 (3.2 years) | 180/184 (98%) | 0.14 | 133/152 (88%) | 0.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | 152 (3.2 years) | 42/45 (93%) | 32/38 (84%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding requiring > 2 units PRBC/24 hours during LVAD support | No | 130 (2.1 years) | 88/90 (98%) | 0.7i | 74/79 (94%) | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | 162 (3.2 years) | 134/139 (96%) | 91/111 (82%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Last creatinine value during LVAD support | < 1.7 mg/dl (1.1 ± 0.1) | 143 (3.2 years) | 202/209 (97%) | 1.00 | 154/175 (88%) | 0.12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 1.7 mg/dl (2.2 ± 0.5) | 194 (1.5 years) | 20/20 (100%) | 11/15 (73%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Last BUN value during LVAD support | < 30 mg/dl (17 ± 5) | 143 (3.2 years) | 200/206 (97%) | 0.53 | 151/172 (88%) | 0.27 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 30 mg/dl (46 ± 19) | 178 (1.3 years) | 22/23 (96%) | 14/18 (78%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Last ALT value during LVAD support | < 40 IU (24 ± 8) | 157 (3.2 years) | 171/177 (97%) | 1.00 | 124/142 (87%) | 0.81 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 40 IU (62 ± 38) | 120 (1.8 years) | 51/52 (98%) | 41/48 (85%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival data | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall survival | Overall 30-day and 1-year post-transplant survival was 97% (222/229) and 87% (165/190) respectively. LVAD support duration was 151 days (longest 3.2 years) 1-year post-transplant survival for men was 88% (136/155) and 82% (28/34) for women (LVAD support in men was 145 days, longest 3.2 years; and in women 159 days, longest 1.7 years) There was no statistically significant differences in 30-day and 1-year post-transplant survivals among these patients The 30-day and 1-year survival for patients continuing on LVAD support (starting from 6 months of support, through 18 months, and censored for transplantation) were 98% and 87%. This was not statistically significantly different from the 30-day and 1-year post-transplant survivals of 97% and 87%. The starting point of 6 months for this analysis was used as the median duration of timing of transplant on LVAD support was 151 days |
Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K–M estimates | Not applicable | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival by era (at 5-year intervals) | Not applicable | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HT without prior mechanical circulatory support | Only included patients who had a HT after LVAD support | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical circulatory support without subsequent HT | Only included patients who had a HT after LVAD support | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical circulatory support with subsequent HT | 250 patients | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported – post-transplant survival was stratified according to adverse events that developed during LVAD support | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported – the causes of post-transplant death were unknown | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post-cardiac transplant survival in patients supported with CF devices such as HMII LVAD was found to be equivalent to that with conventional transplantation. Furthermore, post-transplant survival was not influenced by duration of LVAD support. Improved durability and reduced short- and long-term morbidity associated with HMII LVAD reduced the need for urgent cardiac transplantation, which may have adversely influenced survival in the pulsatile LVAD era. This information may have significant implications for changing current UNOS criteria regarding listing of HT candidates | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This was a non-randomised study which did not have a risk-adjusted group for direct comparison. The authors stated that the comparison of efficacy of LVADs as a BTT therapy with a medical control group would be unethical. Several key variables not examined in this study could potentially influence transplant survival (e.g. HLA sensitisation and pulmonary vascular resistance). There were no data evaluated on post-transplant morbidity such as rejections, infections, and post-transplant length of stay and hospital readmissions. This study had a limited 1-year post-transplant follow-up. Further multivariate analyses are needed to identify the clinically significant variables: infection, sensitisation, increased duration, or a combination of these risk factors | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
John 2011b65
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: John Year of publication: 2011 Country: Multicentre Study design: Retrospective analysis of outcome data from 1982 patients supported by the HMII LVAD as a BTT Study setting: Multicentre Number of centres: Trial group = 32 centres; post-trial group = 83 centres Duration of study: Trial group (March 2005 to April 2008) – 6 months; post-trial group (April 2008 to October 2010) – 12 months Follow-up period: For the trial period patients were followed up at 1, 3 and 6 months; for the post-trial period patients were followed up at 3, 6 and 12 months Funding: Thoratec Inc. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To determine changes in post-trial outcomes in widespread commercial use since the clinical trial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 1982 patients (trial group 486 patients; post-trial group 1496 patients) Sample attrition/dropout: Unclear Inclusion criteria: Patients supported by the HMII LVAD as a BTT between 2005 and 2010 Exclusion criteria: Unclear Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): aged < 40 years = trial group 96 (20%), post-trial group 255 (17%); aged 40–59 years = trial group 234 (48%), post-trial group 787 (53%) Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: Male – trial group 377 (78%); post-trial group 1154 (77%) Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Unclear |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT Type of device used: HMII LVAD Any comparison: Patients were divided into two groups: those supported during the clinical trial (trial group) and those supported after commercial approval by the FDA (post-trial group) as reported to the INTERMACs registry Duration of treatment: Average support duration for the trial period 12.6 ± 14.0 months; post-trial period 8.7 ± 7.1 months Percentage of patients using inotropes: n = 297 (19.9%) were stable but inotrope dependent. A smaller percentage of post-trial patients (80%) required intravenous inotropes than did trial patients (90%; p < 0.0001) Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below. IABP = trial 204 (42%), post trial 490 (33%); mechanical ventilation = trial 41 (8%), post trial 138 (9%); ACE inhibitors = trial 134 (28%), post trial not reported; beta-blockers = trial 182 (37%), post trial not reported; intravenous inotropic agents = trial 436 (90%), post trial 1203 (80%) Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Overall survival from the LVAD implant, ongoing LVAD support, transplant, device removal after myocardial recovery, and death. Adverse events were recorded (for trial patients KCCQ OSSs and for post-trial patients EuroQol EQ-5D) to assess QoL. 6-minute walk test was used in both groups to assess functional status Secondary outcomes: Not applicable Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records. No clear details on how outcomes were assessed. In the trial period, data were collected before implant and 1, 3 and 6 months after implant. In the post-trial period, data were collected before implant and at 3, 6 and 12 months Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: Yes. For trial patients the KCCQ OSSs; for post-trial patients the EuroQol EQ-5D Length of follow-up: For trial patients 6 months; for post-trial patients 12 monthsNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reportedNot reportedRandomised/includedTrial group: 486Post-trial group: 1496ExcludedNot applicableNot applicableMissing participantsNot applicableNot applicableWithdrawalsNot applicableNot applicable |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported | Not reported | Randomised/included | Trial group: 486 | Post-trial group: 1496 | Excluded | Not applicable | Not applicable | Missing participants | Not applicable | Not applicable | Withdrawals | Not applicable | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | Trial group: 486 | Post-trial group: 1496 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not applicable | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not applicable | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not applicable | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline characteristics of the trial and post-trial groupsCharacteristicTrial groupPost-trial groupp-valuen4861496Male, n (%)377 (78)1154 (77)0.9009Age (years), n (%)0.4048 < 4096 (20)255 (17) 40–59234 (48)787 (53) > 60156 (32)454 (30)Height (cm)174.7 ± 9.8174.8 ± 11.50.8631Weight (kg)83.5 ± 20.187.4 ± 21.40.0004BSA (m2)1.99 ± 0.272.05 ± 0.290.0001BMI (kg/m2)27.2 ± 5.928.8 ± 10.00.0008BSA (< 1.5 m2), n (%)18 (3.7)24 (2)0.0098INTERMACS category, n (%) 1 = critical cardiogenic shockNA252 (16.8) 2 = progressive declineNA667 (44.6) 3 = stable but inotrope dependentNA297 (19.9) 4 = resting symptomsNA174 (11.6) 5 = exertion intolerantNA42 (2.8) 6 = exertion limitedNA33 (2.2) 7 = advanced NYHA class IIINA31 (2.1)Haemodynamics Heart rate (b.p.m.)91.2 ± 18.689.9 ± 18.40.1773 Systolic BP (mmHg)98.5 ± 15.5100.9 - ± 15.60.0032 Diastolic BP (mmHg)62.3 ± 11.663.0 ± 11.60.2479 Mean BP (mmHg)74.4 ± 11.275.7 ± 11.40.0304 Systolic PAP (mmHg)51.4 ± 13.550.0 ± 115.00.0258 Diastolic PAP (mmHg)26.8 ± 8.225.7 it 8.60.0133 Mean PAP (mmHg)35.9 ± 9.433.8 ± 10.10.0002 Pulmonary wedge pressure (mmHg)25.5 ± 8.024.5 ± 8.60.0236 PVR (Wood units)2.89 ± 1.572.76 ± 2.230.2973 Right atrial pressure (mmHg)12.8 ± 6.612.8 ± 6.81.0000 Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)2.06 ± 0.672.13 ± 0.660.0705Laboratory BUN (mg/l)30.3 ± 16.728.4 ± 18.00.0398 Creatinine (mg/l)1.42 ± 0.521.39 ± 0.760.4176 Total bilirubin (mg/l)1.26 ± 0.831.49 ± 1.830.0074 Sodium (mg/l)133.6 ± 4.9134.5 ± 5.10.0007 INR1.34 ± 0.411.34 ± 0.461.0000 White blood cell count (K/μl)8.9 ± 3.68.8 ± 3.60.5948 Platelets (K/μl)225.7 ± 87.6206.2 ± 89.70.0001 SGOT/AST, (unclear units)84.0 ± 237.983.9 ± 336.80.9952 Haemoglobin (mg/dl)11.6 ± 2.011.3 ± 2.00.0041 Albumin (mg/dl)3.5 ± 1.23.4 ± 0.680.0224Concomitant procedures, n (%) IABP204 (42)490 (33)0.0002 Mechanical ventilation41 (8)138 (9)0.6493 ACE inhibitors134 (28)Not reported Beta-blockers182 (37)Not reported Intravenous inotropic agents436 (90)1203 (80)0.0001 | Characteristic | Trial group | Post-trial group | p-value | n | 486 | 1496 | Male, n (%) | 377 (78) | 1154 (77) | 0.9009 | Age (years), n (%) | 0.4048 | < 40 | 96 (20) | 255 (17) | 40–59 | 234 (48) | 787 (53) | > 60 | 156 (32) | 454 (30) | Height (cm) | 174.7 ± 9.8 | 174.8 ± 11.5 | 0.8631 | Weight (kg) | 83.5 ± 20.1 | 87.4 ± 21.4 | 0.0004 | BSA (m2) | 1.99 ± 0.27 | 2.05 ± 0.29 | 0.0001 | BMI (kg/m2) | 27.2 ± 5.9 | 28.8 ± 10.0 | 0.0008 | BSA (< 1.5 m2), n (%) | 18 (3.7) | 24 (2) | 0.0098 | INTERMACS category, n (%) | 1 = critical cardiogenic shock | NA | 252 (16.8) | 2 = progressive decline | NA | 667 (44.6) | 3 = stable but inotrope dependent | NA | 297 (19.9) | 4 = resting symptoms | NA | 174 (11.6) | 5 = exertion intolerant | NA | 42 (2.8) | 6 = exertion limited | NA | 33 (2.2) | 7 = advanced NYHA class III | NA | 31 (2.1) | Haemodynamics | Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 91.2 ± 18.6 | 89.9 ± 18.4 | 0.1773 | Systolic BP (mmHg) | 98.5 ± 15.5 | 100.9 - ± 15.6 | 0.0032 | Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 62.3 ± 11.6 | 63.0 ± 11.6 | 0.2479 | Mean BP (mmHg) | 74.4 ± 11.2 | 75.7 ± 11.4 | 0.0304 | Systolic PAP (mmHg) | 51.4 ± 13.5 | 50.0 ± 115.0 | 0.0258 | Diastolic PAP (mmHg) | 26.8 ± 8.2 | 25.7 it 8.6 | 0.0133 | Mean PAP (mmHg) | 35.9 ± 9.4 | 33.8 ± 10.1 | 0.0002 | Pulmonary wedge pressure (mmHg) | 25.5 ± 8.0 | 24.5 ± 8.6 | 0.0236 | PVR (Wood units) | 2.89 ± 1.57 | 2.76 ± 2.23 | 0.2973 | Right atrial pressure (mmHg) | 12.8 ± 6.6 | 12.8 ± 6.8 | 1.0000 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.06 ± 0.67 | 2.13 ± 0.66 | 0.0705 | Laboratory | BUN (mg/l) | 30.3 ± 16.7 | 28.4 ± 18.0 | 0.0398 | Creatinine (mg/l) | 1.42 ± 0.52 | 1.39 ± 0.76 | 0.4176 | Total bilirubin (mg/l) | 1.26 ± 0.83 | 1.49 ± 1.83 | 0.0074 | Sodium (mg/l) | 133.6 ± 4.9 | 134.5 ± 5.1 | 0.0007 | INR | 1.34 ± 0.41 | 1.34 ± 0.46 | 1.0000 | White blood cell count (K/μl) | 8.9 ± 3.6 | 8.8 ± 3.6 | 0.5948 | Platelets (K/μl) | 225.7 ± 87.6 | 206.2 ± 89.7 | 0.0001 | SGOT/AST, (unclear units) | 84.0 ± 237.9 | 83.9 ± 336.8 | 0.9952 | Haemoglobin (mg/dl) | 11.6 ± 2.0 | 11.3 ± 2.0 | 0.0041 | Albumin (mg/dl) | 3.5 ± 1.2 | 3.4 ± 0.68 | 0.0224 | Concomitant procedures, n (%) | IABP | 204 (42) | 490 (33) | 0.0002 | Mechanical ventilation | 41 (8) | 138 (9) | 0.6493 | ACE inhibitors | 134 (28) | Not reported | Beta-blockers | 182 (37) | Not reported | Intravenous inotropic agents | 436 (90) | 1203 (80) | 0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristic | Trial group | Post-trial group | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | 486 | 1496 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male, n (%) | 377 (78) | 1154 (77) | 0.9009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years), n (%) | 0.4048 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < 40 | 96 (20) | 255 (17) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40–59 | 234 (48) | 787 (53) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 60 | 156 (32) | 454 (30) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Height (cm) | 174.7 ± 9.8 | 174.8 ± 11.5 | 0.8631 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight (kg) | 83.5 ± 20.1 | 87.4 ± 21.4 | 0.0004 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 1.99 ± 0.27 | 2.05 ± 0.29 | 0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.2 ± 5.9 | 28.8 ± 10.0 | 0.0008 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (< 1.5 m2), n (%) | 18 (3.7) | 24 (2) | 0.0098 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INTERMACS category, n (%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 = critical cardiogenic shock | NA | 252 (16.8) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 = progressive decline | NA | 667 (44.6) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 = stable but inotrope dependent | NA | 297 (19.9) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 = resting symptoms | NA | 174 (11.6) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 = exertion intolerant | NA | 42 (2.8) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 = exertion limited | NA | 33 (2.2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 = advanced NYHA class III | NA | 31 (2.1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemodynamics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 91.2 ± 18.6 | 89.9 ± 18.4 | 0.1773 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 98.5 ± 15.5 | 100.9 - ± 15.6 | 0.0032 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 62.3 ± 11.6 | 63.0 ± 11.6 | 0.2479 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean BP (mmHg) | 74.4 ± 11.2 | 75.7 ± 11.4 | 0.0304 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic PAP (mmHg) | 51.4 ± 13.5 | 50.0 ± 115.0 | 0.0258 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic PAP (mmHg) | 26.8 ± 8.2 | 25.7 it 8.6 | 0.0133 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean PAP (mmHg) | 35.9 ± 9.4 | 33.8 ± 10.1 | 0.0002 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary wedge pressure (mmHg) | 25.5 ± 8.0 | 24.5 ± 8.6 | 0.0236 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PVR (Wood units) | 2.89 ± 1.57 | 2.76 ± 2.23 | 0.2973 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right atrial pressure (mmHg) | 12.8 ± 6.6 | 12.8 ± 6.8 | 1.0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.06 ± 0.67 | 2.13 ± 0.66 | 0.0705 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Laboratory | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/l) | 30.3 ± 16.7 | 28.4 ± 18.0 | 0.0398 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/l) | 1.42 ± 0.52 | 1.39 ± 0.76 | 0.4176 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/l) | 1.26 ± 0.83 | 1.49 ± 1.83 | 0.0074 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sodium (mg/l) | 133.6 ± 4.9 | 134.5 ± 5.1 | 0.0007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INR | 1.34 ± 0.41 | 1.34 ± 0.46 | 1.0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| White blood cell count (K/μl) | 8.9 ± 3.6 | 8.8 ± 3.6 | 0.5948 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets (K/μl) | 225.7 ± 87.6 | 206.2 ± 89.7 | 0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SGOT/AST, (unclear units) | 84.0 ± 237.9 | 83.9 ± 336.8 | 0.9952 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemoglobin (mg/dl) | 11.6 ± 2.0 | 11.3 ± 2.0 | 0.0041 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albumin (mg/dl) | 3.5 ± 1.2 | 3.4 ± 0.68 | 0.0224 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concomitant procedures, n (%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP | 204 (42) | 490 (33) | 0.0002 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 41 (8) | 138 (9) | 0.6493 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACE inhibitors | 134 (28) | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beta-blockers | 182 (37) | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intravenous inotropic agents | 436 (90) | 1203 (80) | 0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MeasureTrial patientsPost-trial patientsK–M estimates83.8% at 6 months and 75.6% at 12 months89.4% at 6 months and 84.9% at 12 monthsK–M survival significantly improved for the post-trial group (p = 0.001) compared with the trial group, with 1-year survival estimates increasing from 76% to 85%Mechanical circulatory support without subsequent HTOngoing support: 53% at 6 months and 32% at 12 monthsOngoing support: 66% at 6 months and 45% at 12 monthsMechanical circulatory support with subsequent HT32% at 6 months and 48% at 12 months22% at 6 months and 39% at 12 monthsDeaths30-day operative mortality: 6.6%Deaths: 14% at 6 months and 18% at 12 months30-day operative mortality: 4.5%Deaths: 10% at 6 months and 13% at 12 months. (Please note 1-year data of only 892 patients available in this group) | Measure | Trial patients | Post-trial patients | K–M estimates | 83.8% at 6 months and 75.6% at 12 months | 89.4% at 6 months and 84.9% at 12 months K–M survival significantly improved for the post-trial group (p = 0.001) compared with the trial group, with 1-year survival estimates increasing from 76% to 85% |
Mechanical circulatory support without subsequent HT | Ongoing support: 53% at 6 months and 32% at 12 months | Ongoing support: 66% at 6 months and 45% at 12 months | Mechanical circulatory support with subsequent HT | 32% at 6 months and 48% at 12 months | 22% at 6 months and 39% at 12 months | Deaths | 30-day operative mortality: 6.6% Deaths: 14% at 6 months and 18% at 12 months |
30-day operative mortality: 4.5% Deaths: 10% at 6 months and 13% at 12 months. (Please note 1-year data of only 892 patients available in this group) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Measure | Trial patients | Post-trial patients | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K–M estimates | 83.8% at 6 months and 75.6% at 12 months | 89.4% at 6 months and 84.9% at 12 months K–M survival significantly improved for the post-trial group (p = 0.001) compared with the trial group, with 1-year survival estimates increasing from 76% to 85% |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical circulatory support without subsequent HT | Ongoing support: 53% at 6 months and 32% at 12 months | Ongoing support: 66% at 6 months and 45% at 12 months | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical circulatory support with subsequent HT | 32% at 6 months and 48% at 12 months | 22% at 6 months and 39% at 12 months | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deaths | 30-day operative mortality: 6.6% Deaths: 14% at 6 months and 18% at 12 months |
30-day operative mortality: 4.5% Deaths: 10% at 6 months and 13% at 12 months. (Please note 1-year data of only 892 patients available in this group) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See included tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events in the post-trial period were presented using INTERMACS definitions. Adverse events in the trial period were only presented for events having comparable definitions with the INTERMACS registry Bleeding and infection were the most frequently reported adverse events Adverse events for the post-trial patients (n = 1496)aAdverse eventPatients, n (%)No. of eventsEvents/patient-yearArterial non-CNS thromboembolism8 (1)90.01Bleeding539 (36)13761.27 Bleeding requiring surgery101 (7)1270.12 Gastrointestinal bleeding157 (10)4150.38Cardiac arrhythmia418 (28)6430.59Device malfunction156 (10)2250.21Haemolysis45 (3)540.05Hepatic dysfunction59 (4)630.06Hypertension78 (5)940.09Infectionb566 (38)11131.03 Driveline192 (13)3030.28 Pump pocket28 (2)330.03 Pump interior4 (0)50.00 Blood167 (11)2330.22 Line sepsis38 (3)410.04 Other infection386 (26)6530.60Myocardial infarction10 (1)100.01Stroke97 (6)1100.10 Haemorrhagic stroke23 (2)240.02 Ischaemic stroke57 (4)620.06 Unknown17 (1)240.02Other neurological dysfunction64 (4)700.06 Pericardial drainage91 (6)1030.10 Psychiatric episode125 (8)1530.14 Rehospitalisation744 (50)18821.74 Renal dysfunction129 (9)1510.14 Respiratory failure241 (16)3030.28Right-side HF173 (12)1970.18RVAD14 (1)150.01Venous thromboembolism88 (6)960.09 Wound dehiscence19 (1)220.02 Device replacement21 (1)220.02a Cumulative support = 1081.8 patient-years.b Infection events can have multiple sites. Adverse events comparable by definition for trial group (n = 486) and post-trial group (n = 1496)Adverse eventTrial (n = 486) 511.1 patient-yearsPost-trial group (n = 1496) 1081.8 patient-yearsIncidence (%)aEvent ratebIncidence (%)aEvent ratebBleeding requiring re-exploration210.2370.12Infection Percutaneous lead200.33130.28 Pump pocket30.0320.03 Right-side HF requiring RVAD70.0610.01Stroke Ischaemic50.0540.06 Haemorrhagic50.0520.02 Other00.0010.02Device replacement50.0610.02a Per cent of patients.b Events per patient-year. |
Adverse event | Patients, n (%) | No. of events | Events/patient-year | Arterial non-CNS thromboembolism | 8 (1) | 9 | 0.01 | Bleeding | 539 (36) | 1376 | 1.27 | Bleeding requiring surgery | 101 (7) | 127 | 0.12 | Gastrointestinal bleeding | 157 (10) | 415 | 0.38 | Cardiac arrhythmia | 418 (28) | 643 | 0.59 | Device malfunction | 156 (10) | 225 | 0.21 | Haemolysis | 45 (3) | 54 | 0.05 | Hepatic dysfunction | 59 (4) | 63 | 0.06 | Hypertension | 78 (5) | 94 | 0.09 | Infectionb | 566 (38) | 1113 | 1.03 | Driveline | 192 (13) | 303 | 0.28 | Pump pocket | 28 (2) | 33 | 0.03 | Pump interior | 4 (0) | 5 | 0.00 | Blood | 167 (11) | 233 | 0.22 | Line sepsis | 38 (3) | 41 | 0.04 | Other infection | 386 (26) | 653 | 0.60 | Myocardial infarction | 10 (1) | 10 | 0.01 | Stroke | 97 (6) | 110 | 0.10 | Haemorrhagic stroke | 23 (2) | 24 | 0.02 | Ischaemic stroke | 57 (4) | 62 | 0.06 | Unknown | 17 (1) | 24 | 0.02 | Other neurological dysfunction | 64 (4) | 70 | 0.06 | Pericardial drainage | 91 (6) | 103 | 0.10 | Psychiatric episode | 125 (8) | 153 | 0.14 | Rehospitalisation | 744 (50) | 1882 | 1.74 | Renal dysfunction | 129 (9) | 151 | 0.14 | Respiratory failure | 241 (16) | 303 | 0.28 | Right-side HF | 173 (12) | 197 | 0.18 | RVAD | 14 (1) | 15 | 0.01 | Venous thromboembolism | 88 (6) | 96 | 0.09 | Wound dehiscence | 19 (1) | 22 | 0.02 | Device replacement | 21 (1) | 22 | 0.02 | a Cumulative support = 1081.8 patient-years. | b Infection events can have multiple sites. | Adverse event | Trial (n = 486) 511.1 patient-years | Post-trial group (n = 1496) 1081.8 patient-years | Incidence (%)a | Event rateb | Incidence (%)a | Event rateb | Bleeding requiring re-exploration | 21 | 0.23 | 7 | 0.12 | Infection | Percutaneous lead | 20 | 0.33 | 13 | 0.28 | Pump pocket | 3 | 0.03 | 2 | 0.03 | Right-side HF requiring RVAD | 7 | 0.06 | 1 | 0.01 | Stroke | Ischaemic | 5 | 0.05 | 4 | 0.06 | Haemorrhagic | 5 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.02 | Other | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 0.02 | Device replacement | 5 | 0.06 | 1 | 0.02 | a Per cent of patients. | b Events per patient-year. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse event | Patients, n (%) | No. of events | Events/patient-year | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arterial non-CNS thromboembolism | 8 (1) | 9 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding | 539 (36) | 1376 | 1.27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding requiring surgery | 101 (7) | 127 | 0.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gastrointestinal bleeding | 157 (10) | 415 | 0.38 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac arrhythmia | 418 (28) | 643 | 0.59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device malfunction | 156 (10) | 225 | 0.21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemolysis | 45 (3) | 54 | 0.05 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hepatic dysfunction | 59 (4) | 63 | 0.06 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension | 78 (5) | 94 | 0.09 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infectionb | 566 (38) | 1113 | 1.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline | 192 (13) | 303 | 0.28 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump pocket | 28 (2) | 33 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump interior | 4 (0) | 5 | 0.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blood | 167 (11) | 233 | 0.22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line sepsis | 38 (3) | 41 | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other infection | 386 (26) | 653 | 0.60 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myocardial infarction | 10 (1) | 10 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke | 97 (6) | 110 | 0.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic stroke | 23 (2) | 24 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic stroke | 57 (4) | 62 | 0.06 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unknown | 17 (1) | 24 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other neurological dysfunction | 64 (4) | 70 | 0.06 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pericardial drainage | 91 (6) | 103 | 0.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Psychiatric episode | 125 (8) | 153 | 0.14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rehospitalisation | 744 (50) | 1882 | 1.74 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal dysfunction | 129 (9) | 151 | 0.14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory failure | 241 (16) | 303 | 0.28 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right-side HF | 173 (12) | 197 | 0.18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVAD | 14 (1) | 15 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Venous thromboembolism | 88 (6) | 96 | 0.09 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wound dehiscence | 19 (1) | 22 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device replacement | 21 (1) | 22 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Cumulative support = 1081.8 patient-years. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Infection events can have multiple sites. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse event | Trial (n = 486) 511.1 patient-years | Post-trial group (n = 1496) 1081.8 patient-years | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incidence (%)a | Event rateb | Incidence (%)a | Event rateb | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding requiring re-exploration | 21 | 0.23 | 7 | 0.12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Percutaneous lead | 20 | 0.33 | 13 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump pocket | 3 | 0.03 | 2 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right-side HF requiring RVAD | 7 | 0.06 | 1 | 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic | 5 | 0.05 | 4 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic | 5 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device replacement | 5 | 0.06 | 1 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Per cent of patients. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Events per patient-year. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unclear – bleeding and infection were the most frequently reported adverse events | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For the trial patients, the KCCQ OSSs were used to assess QoL. For post-trial patients, the EuroQol EQ-5D METs, as used by INTERMACS, was used. Functional status was evaluated using 6-minute walk test in both groups. Comparisons over time for functional and QoL measures used linear mixed-effects modelling Results of 6-minute walk test showed similar improvements in distance walked after LVAD support in both groups. Although using different instruments, similar improvements were found during LVAD support in the KCCQ (used in trial) and the EQ-5D METs 6-minute walk test results for the trial and post-trial groups (data read off histogram)ParameterPre implant3 months6 months12 monthsTrial groupPost-trial groupTrial groupPost-trial groupTrial groupPost-trial groupTrial groupn at risk14964861147347822258393n available data points1189486428283469222111n able to do test1397635625343220991% able to do test13168389929482Distance (m)240230340310350370380 KCCQ OSSs for the trial group (data read off histogram)ParameterPre implant1 month3 months6 monthsn at risk486432342258n completing teat393369317246% completing test81859393OSS30456068 EuroQoL EQ-5D METs results for the post-trial cohort (note: the EuroQoL and KCCQ reporting intervals are different; data read off histogram)ParameterPre implant3 months6 months12 monthsn at risk14981142822393n completing test777617432192% completing test52545349EuroQoL results42747576 |
Parameter | Pre implant | 3 months | 6 months | 12 months | Trial group | Post-trial group | Trial group | Post-trial group | Trial group | Post-trial group | Trial group | n at risk | 1496 | 486 | 1147 | 347 | 822 | 258 | 393 | n available data points | 1189 | 486 | 428 | 283 | 469 | 222 | 111 | n able to do test | 139 | 76 | 356 | 253 | 432 | 209 | 91 | % able to do test | 13 | 16 | 83 | 89 | 92 | 94 | 82 | Distance (m) | 240 | 230 | 340 | 310 | 350 | 370 | 380 | Parameter | Pre implant | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | n at risk | 486 | 432 | 342 | 258 | n completing teat | 393 | 369 | 317 | 246 | % completing test | 81 | 85 | 93 | 93 | OSS | 30 | 45 | 60 | 68 | Parameter | Pre implant | 3 months | 6 months | 12 months | n at risk | 1498 | 1142 | 822 | 393 | n completing test | 777 | 617 | 432 | 192 | % completing test | 52 | 54 | 53 | 49 | EuroQoL results | 42 | 74 | 75 | 76 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Pre implant | 3 months | 6 months | 12 months | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trial group | Post-trial group | Trial group | Post-trial group | Trial group | Post-trial group | Trial group | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n at risk | 1496 | 486 | 1147 | 347 | 822 | 258 | 393 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n available data points | 1189 | 486 | 428 | 283 | 469 | 222 | 111 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n able to do test | 139 | 76 | 356 | 253 | 432 | 209 | 91 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| % able to do test | 13 | 16 | 83 | 89 | 92 | 94 | 82 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance (m) | 240 | 230 | 340 | 310 | 350 | 370 | 380 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Pre implant | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n at risk | 486 | 432 | 342 | 258 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n completing teat | 393 | 369 | 317 | 246 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| % completing test | 81 | 85 | 93 | 93 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OSS | 30 | 45 | 60 | 68 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Pre implant | 3 months | 6 months | 12 months | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n at risk | 1498 | 1142 | 822 | 393 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n completing test | 777 | 617 | 432 | 192 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| % completing test | 52 | 54 | 53 | 49 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EuroQoL results | 42 | 74 | 75 | 76 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Results demonstrate that survival rates of BTT patients with HMII LVAD improved since the clinical trial. Findings indicate excellent outcomes have been maintained with dissemination of new LVAD technology from a clinical trial phase to more broad based use in post-market-approval period | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Limited reporting of QoL measures. Important to note that individual centres may have their own variations in patient selection criteria, implantation techniques, and post-operative management of patients. The authors recognised that this is a limitation of multicentre trials; however, this was not accounted for within the analysis. Furthermore, caution should be made when interpreting the adverse events and QoL results as it is possible that the definitions and tools used may have varied between the clinical trial and INTERMACS registry | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Kato 201266
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Kato Year of publication: 2012 Country: USA Study design: Retrospective Study setting: Columbia University Medical Centre Number of centres: One Duration of study: November 2000 to December 2010 Follow-up period: Mean post-operative observation period was 259 ± 304 days. Mean observation periods were 138 ± 224 days (range 3–1434 days) for HMI patients and 277 ± 333 days (range 3–2069 days) for HMII patients Funding: Unclear. One author reports received consulting fees from Thoratec Inc. and Terumo Heart and another from Thoratec Inc. and Jarvik Heart |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This study was initiated to assess pre-operative and post-operative factors associated with the development of NCs in patients undergoing LVAD placement, and investigated factors associated with NCs after LVAD surgery | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 307 patients (167 patients with HMI device and 140 patients with HMII device) Sample attrition/dropout: Not applicable Inclusion criteria: Patients who underwent placement of a HMI or HMII device were divided into two groups: those with any NC, including TIA (group NC), and those who did not develop NC after the surgery (group non-NC). After excluding patients with only TIA episodes, patients with ischaemic or haemorrhagic CVA were classified as group CVA Exclusion criteria: Patients who underwent other types of LVAD surgery and patients with only TIA episodes Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): Overall 54 ± 14 years at time of surgery; group non-NC (n = 264) = 53.6 ± 12.6 years; group NC (n = 43) = 54.4 ± 13.1 years; group CVA (n = 35) = 54.1 ± 15.6 years Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: Males: Group non-NC n = 216 (79.1%); group NC n = 33 (76.7%); group CVA n = 29 (82.9%) Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Not clear |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: Not clear Type of device used: HMI or HMII Any comparison: Patients who underwent placement of a HMI or HMII device were divided into two groups: those with any NC, including TIA (group NC), and those who did not develop NC after the surgery (group non-NC). After excluding patients with only TIA episodes, patients with ischaemic or haemorrhagic CVA were classified as group CVA Duration of treatment: The mean observation periods were 138 ± 224 days (range 3–1434 days) for HMI patients and 277 ± 333 days (range 3–2069 days) for HMII patients Percentage of patients using inotropes: Not reported Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII patients |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Factors associated with NC or CVA; variables that discriminated patients with NC or CVA from those without any episodes of NC Secondary outcomes: Clinical characteristics, haemodynamic and laboratory data were compared among groups Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records. Pre-operative variables were obtained within 7 days before surgery. Post-operative laboratory data for patients with NC or CVA were collected within 7 days before events, and data for patients without NC were collected within 7 days from end of observation or device removal owing to transplant, recovery or death Survival: No Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: Mean post-operative observation period was 259 ± 304 days. Mean observation periods were 138 ± 224 days (range 3–1434 days) for HMI patients and 277 ± 333 days (range 3–2069 days) for HMII patientsNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reportedNot reportedRandomised/included167140ExcludedNot reportedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reportedNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported | Not reported | Randomised/included | 167 | 140 | Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 167 | 140 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Clinical characteristicsVariablesGroup non-NC (n = 264)Group NC (n = 43)p-value (non-NC vs. NC)Group CVA (n = 35)p-value (non-NC vs. CVA)Age, years53.6 ± 12.654.4 ± 13.10.70154.1 ± 15.60.830Male sex216 (79.1)33 (76.7)0.12629 (82.9)0.266BSA, m21.96 ± 0.241.91 ± 0.210.5781.93 ± 0.220.484Medical history Stroke41 (15.5)12 (27.9)0.04610 (28.6)0.054 Diabetes mellitus77 (29.1)12 (27.9)0.86610 (28.6)0.941 Hypertension120 (47.0)18 (40.9)0.66018 (51.4)0.505 Hyperlipidaemia84 (31.8)13 (30.2)0.83613 (37.4)0.527 PVD29 (11.0)8 (18.6)0.2257 (20.0)0.124 Renal failure76 (28.8)11 (25.0)0.6659 (25.7)0.704 Atrial fibrillation134 (50.8)25 (58.1)0.36923 (62.8)0.096Aetiology of heart disease Ischaemic207 (78.8)28 (65.1)0.05625 (71.4)0.352 Non-ischaemic57(21.2)15 (34.9)0.05610 (28.6)0.352Type of LVAD HMI143 (54.2)24 (55.8)0.80419 (54.3)0.989 HMII121 (55.8)19 (44.2)0.80416 (45.7)0.989 Results of pre-operative haemodynamic and laboratory examinationsParameterGroup non-NC (n = 264)Group NC (n = 43)p-value (non-NC vs. NC)Group CVA (n = 35)p-value (non-NC vs. CVA)Haemodynamic variables Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)1.8 ± 0.41.7 ± 0.30.1181.7 ± 0.50.179 PCWP (mmHg)28.4 ± 8.12.3 ± 8.90.26828.8 ± 10.00.790Mean pressure (mmHg) Pulmonary artery36.2 ± 9.438.5 ± 9.70.14037.2 ± 12.00.568 Right atrial12.9 ± 7.913.2 ± 7.80.81712.6 ± 8.00.833 Atrial79.1 ± 12.876.3 ± 9.60.17177.1 ± 10.00.375Vascular resistance (Wood units) Peripheral3.8 ± 2.23.9 ± 2.40.7853.7 ± 2.50.804 Systemic23.1 ± 6.323.8 ± 9.20.53023.8 ± 7.90.550Laboratory examinations White cell count (× 103/pl)8.2 ± 2.39.0 ± 3.90.0609.0 ± 3.80.078 Lymphocytes (%)11.4 ± 5.210.9 ± 3.70.54510.3 ± 4.60.234 Haematocrit (%)33.2 ± 5.932.4 ± 6.20.30432.1 ± 6.30.414 Platelets (× 103/111)191 ± 86190 ± 800.898189. ± 850.876Bilirubin (mg/dl) Total1.7 ± 1.31.8 ± 1.50.6781.6 ± 1.60.375 Direct0.6 ± 0.50.7 ± 0.70.2540.7 ± 0.90.322Sodium (mEq/l)132.1 ± 8.1129.0 ± 7.00.018129.1 ± 7.10.038Potassium (mEq/l)4.3 ± 0.54.4 ± 0.50.2254.4 ± 0.40.257BUN (mg/dl)37 ± 1835 ± 190.46034 ± 180.442Creatinine (mg/dl)1.6 ± 0.41.5 ± 0.90.2241.5 ± 0.70.212Albumin (mg/dl)3.7 ± 0.63.5 ± 0.70.0493.5 ± 0.70.030ALT (IU/l)99 ± 10088 ± 960.50991 ± 910.661AST (IU/l)72 ± 8655 ± 770.23160 ± 770.428BNP (pg/ml)1835 ± 11172101 ± 10460.1451921 ± 9460.663INR1.4 ± 0.51.3 ± 0.40.2131.3 ± 0.30.249Echocardiographic parameters LVEDD (mm)69.5 ± 12.171.9 ± 12.80.24070.7 ± 12.50.588 LVEF (%)18.4 ± 10.020.0 ± 12.40.35319.1 ± 10.80.713 |
Variables | Group non-NC (n = 264) | Group NC (n = 43) | p-value (non-NC vs. NC) | Group CVA (n = 35) | p-value (non-NC vs. CVA) | Age, years | 53.6 ± 12.6 | 54.4 ± 13.1 | 0.701 | 54.1 ± 15.6 | 0.830 | Male sex | 216 (79.1) | 33 (76.7) | 0.126 | 29 (82.9) | 0.266 | BSA, m2 | 1.96 ± 0.24 | 1.91 ± 0.21 | 0.578 | 1.93 ± 0.22 | 0.484 | Medical history | Stroke | 41 (15.5) | 12 (27.9) | 0.046 | 10 (28.6) | 0.054 | Diabetes mellitus | 77 (29.1) | 12 (27.9) | 0.866 | 10 (28.6) | 0.941 | Hypertension | 120 (47.0) | 18 (40.9) | 0.660 | 18 (51.4) | 0.505 | Hyperlipidaemia | 84 (31.8) | 13 (30.2) | 0.836 | 13 (37.4) | 0.527 | PVD | 29 (11.0) | 8 (18.6) | 0.225 | 7 (20.0) | 0.124 | Renal failure | 76 (28.8) | 11 (25.0) | 0.665 | 9 (25.7) | 0.704 | Atrial fibrillation | 134 (50.8) | 25 (58.1) | 0.369 | 23 (62.8) | 0.096 | Aetiology of heart disease | Ischaemic | 207 (78.8) | 28 (65.1) | 0.056 | 25 (71.4) | 0.352 | Non-ischaemic | 57(21.2) | 15 (34.9) | 0.056 | 10 (28.6) | 0.352 | Type of LVAD | HMI | 143 (54.2) | 24 (55.8) | 0.804 | 19 (54.3) | 0.989 | HMII | 121 (55.8) | 19 (44.2) | 0.804 | 16 (45.7) | 0.989 | Parameter | Group non-NC (n = 264) | Group NC (n = 43) | p-value (non-NC vs. NC) | Group CVA (n = 35) | p-value (non-NC vs. CVA) | Haemodynamic variables | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 0.118 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 0.179 | PCWP (mmHg) | 28.4 ± 8.1 | 2.3 ± 8.9 | 0.268 | 28.8 ± 10.0 | 0.790 | Mean pressure (mmHg) | Pulmonary artery | 36.2 ± 9.4 | 38.5 ± 9.7 | 0.140 | 37.2 ± 12.0 | 0.568 | Right atrial | 12.9 ± 7.9 | 13.2 ± 7.8 | 0.817 | 12.6 ± 8.0 | 0.833 | Atrial | 79.1 ± 12.8 | 76.3 ± 9.6 | 0.171 | 77.1 ± 10.0 | 0.375 | Vascular resistance (Wood units) | Peripheral | 3.8 ± 2.2 | 3.9 ± 2.4 | 0.785 | 3.7 ± 2.5 | 0.804 | Systemic | 23.1 ± 6.3 | 23.8 ± 9.2 | 0.530 | 23.8 ± 7.9 | 0.550 | Laboratory examinations | White cell count (× 103/pl) | 8.2 ± 2.3 | 9.0 ± 3.9 | 0.060 | 9.0 ± 3.8 | 0.078 | Lymphocytes (%) | 11.4 ± 5.2 | 10.9 ± 3.7 | 0.545 | 10.3 ± 4.6 | 0.234 | Haematocrit (%) | 33.2 ± 5.9 | 32.4 ± 6.2 | 0.304 | 32.1 ± 6.3 | 0.414 | Platelets (× 103/111) | 191 ± 86 | 190 ± 80 | 0.898 | 189. ± 85 | 0.876 | Bilirubin (mg/dl) | Total | 1.7 ± 1.3 | 1.8 ± 1.5 | 0.678 | 1.6 ± 1.6 | 0.375 | Direct | 0.6 ± 0.5 | 0.7 ± 0.7 | 0.254 | 0.7 ± 0.9 | 0.322 | Sodium (mEq/l) | 132.1 ± 8.1 | 129.0 ± 7.0 | 0.018 | 129.1 ± 7.1 | 0.038 | Potassium (mEq/l) | 4.3 ± 0.5 | 4.4 ± 0.5 | 0.225 | 4.4 ± 0.4 | 0.257 | BUN (mg/dl) | 37 ± 18 | 35 ± 19 | 0.460 | 34 ± 18 | 0.442 | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 0.224 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 0.212 | Albumin (mg/dl) | 3.7 ± 0.6 | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 0.049 | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 0.030 | ALT (IU/l) | 99 ± 100 | 88 ± 96 | 0.509 | 91 ± 91 | 0.661 | AST (IU/l) | 72 ± 86 | 55 ± 77 | 0.231 | 60 ± 77 | 0.428 | BNP (pg/ml) | 1835 ± 1117 | 2101 ± 1046 | 0.145 | 1921 ± 946 | 0.663 | INR | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 0.213 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 0.249 | Echocardiographic parameters | LVEDD (mm) | 69.5 ± 12.1 | 71.9 ± 12.8 | 0.240 | 70.7 ± 12.5 | 0.588 | LVEF (%) | 18.4 ± 10.0 | 20.0 ± 12.4 | 0.353 | 19.1 ± 10.8 | 0.713 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variables | Group non-NC (n = 264) | Group NC (n = 43) | p-value (non-NC vs. NC) | Group CVA (n = 35) | p-value (non-NC vs. CVA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, years | 53.6 ± 12.6 | 54.4 ± 13.1 | 0.701 | 54.1 ± 15.6 | 0.830 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male sex | 216 (79.1) | 33 (76.7) | 0.126 | 29 (82.9) | 0.266 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA, m2 | 1.96 ± 0.24 | 1.91 ± 0.21 | 0.578 | 1.93 ± 0.22 | 0.484 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Medical history | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke | 41 (15.5) | 12 (27.9) | 0.046 | 10 (28.6) | 0.054 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 77 (29.1) | 12 (27.9) | 0.866 | 10 (28.6) | 0.941 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension | 120 (47.0) | 18 (40.9) | 0.660 | 18 (51.4) | 0.505 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hyperlipidaemia | 84 (31.8) | 13 (30.2) | 0.836 | 13 (37.4) | 0.527 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PVD | 29 (11.0) | 8 (18.6) | 0.225 | 7 (20.0) | 0.124 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure | 76 (28.8) | 11 (25.0) | 0.665 | 9 (25.7) | 0.704 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atrial fibrillation | 134 (50.8) | 25 (58.1) | 0.369 | 23 (62.8) | 0.096 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aetiology of heart disease | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic | 207 (78.8) | 28 (65.1) | 0.056 | 25 (71.4) | 0.352 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-ischaemic | 57(21.2) | 15 (34.9) | 0.056 | 10 (28.6) | 0.352 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type of LVAD | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMI | 143 (54.2) | 24 (55.8) | 0.804 | 19 (54.3) | 0.989 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII | 121 (55.8) | 19 (44.2) | 0.804 | 16 (45.7) | 0.989 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Group non-NC (n = 264) | Group NC (n = 43) | p-value (non-NC vs. NC) | Group CVA (n = 35) | p-value (non-NC vs. CVA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemodynamic variables | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 0.118 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 0.179 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 28.4 ± 8.1 | 2.3 ± 8.9 | 0.268 | 28.8 ± 10.0 | 0.790 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean pressure (mmHg) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary artery | 36.2 ± 9.4 | 38.5 ± 9.7 | 0.140 | 37.2 ± 12.0 | 0.568 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right atrial | 12.9 ± 7.9 | 13.2 ± 7.8 | 0.817 | 12.6 ± 8.0 | 0.833 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atrial | 79.1 ± 12.8 | 76.3 ± 9.6 | 0.171 | 77.1 ± 10.0 | 0.375 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vascular resistance (Wood units) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Peripheral | 3.8 ± 2.2 | 3.9 ± 2.4 | 0.785 | 3.7 ± 2.5 | 0.804 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systemic | 23.1 ± 6.3 | 23.8 ± 9.2 | 0.530 | 23.8 ± 7.9 | 0.550 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Laboratory examinations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| White cell count (× 103/pl) | 8.2 ± 2.3 | 9.0 ± 3.9 | 0.060 | 9.0 ± 3.8 | 0.078 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lymphocytes (%) | 11.4 ± 5.2 | 10.9 ± 3.7 | 0.545 | 10.3 ± 4.6 | 0.234 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haematocrit (%) | 33.2 ± 5.9 | 32.4 ± 6.2 | 0.304 | 32.1 ± 6.3 | 0.414 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets (× 103/111) | 191 ± 86 | 190 ± 80 | 0.898 | 189. ± 85 | 0.876 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilirubin (mg/dl) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 1.7 ± 1.3 | 1.8 ± 1.5 | 0.678 | 1.6 ± 1.6 | 0.375 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct | 0.6 ± 0.5 | 0.7 ± 0.7 | 0.254 | 0.7 ± 0.9 | 0.322 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sodium (mEq/l) | 132.1 ± 8.1 | 129.0 ± 7.0 | 0.018 | 129.1 ± 7.1 | 0.038 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Potassium (mEq/l) | 4.3 ± 0.5 | 4.4 ± 0.5 | 0.225 | 4.4 ± 0.4 | 0.257 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 37 ± 18 | 35 ± 19 | 0.460 | 34 ± 18 | 0.442 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 0.224 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 0.212 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albumin (mg/dl) | 3.7 ± 0.6 | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 0.049 | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 0.030 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT (IU/l) | 99 ± 100 | 88 ± 96 | 0.509 | 91 ± 91 | 0.661 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST (IU/l) | 72 ± 86 | 55 ± 77 | 0.231 | 60 ± 77 | 0.428 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BNP (pg/ml) | 1835 ± 1117 | 2101 ± 1046 | 0.145 | 1921 ± 946 | 0.663 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INR | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 0.213 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 0.249 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Echocardiographic parameters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEDD (mm) | 69.5 ± 12.1 | 71.9 ± 12.8 | 0.240 | 70.7 ± 12.5 | 0.588 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF (%) | 18.4 ± 10.0 | 20.0 ± 12.4 | 0.353 | 19.1 ± 10.8 | 0.713 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Malnutrition and inflammation, pre-LVAD and post-LVAD factors known to be associated with severity of HF were also associated with development of major complications after LVAD placement such as NC and infection. The authors suggest that major complications after LVAD placement, such as NC and infection, may also have a cause-and-effect relationship with each other | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 51 NC events occurred in 43 patients (14.0%, 0.23 events/patient/year) after a mean of 92 ± 116 days after LVAD surgery, consisting of 27 events in 24 patients (14.4%) with HMI and 24 events in 19 patients (13.6%) with HMII. These 43 patients were classified as those in group NC A total of 39 CVA events occurred in 33 patients (10.7%, 0.18 events/patient/year) at 80 ± 103 days after surgery, consisting of 22 events in 19 patients (11.4%, 0.34 events/patient/year) with HMI and 17 events in 14 patients (10.0%, 0.16 events/patient/year) with HMII. These patients were classified as those in group CVA Duration from LVAD surgery to all NC events revealed that 37 of 51 events (72.5%) occurred within 6 months after LVAD surgery Multiple NCs occurred in six patients (2.0%) Stepwise forward selection analysis found that history of CVA and post-operative infection was independently associated with the development of NCs after LVAD surgery. A discriminant function test found that a discriminant score (z-value), yielded a discriminant probability of 76.6% Post-operative infection data in all patientsInfection typeGroup non-NC (n = 264)Group NC (n = 43)p-value (non-NC vs. NC)Group CVA (n = 35)p-value (non-NC vs. CVA)All forms, n (%)51 (19.3)17 (39.5)0.00313 (37.1)0.016Sepsis, n (%)41 (15.1)9 (20.9)0.3777 (20.0)0.498LVAD related, n (%)30 (11.4)10 (23.3)0.0317 (20.0)0.145Urinary tract, n (%)45 (17.0)11 (25.6)0.1799 (25.7)0.082Respiratory, n (%)30 (11.4)6 (14.0)0.6245 (14.2)0.613Others, n (%)14 (5.3)4 (9.3)0.8742 (5.7)0.577 Stepwise forward selection analysis of factors associated with NC and CVA after LVAD placementFactorsOR (95% CI)p-valueAssociated with overall NC developmentHistory of CVA2.37 (1.24 to 5.29)0.011Pre-operative factor Sodium0.93 (0.90 to 1.12)0.208 Albumin0.51 (0.21 to 1.37)0.079Post-operative factor Haematocrit0.96 (0.71 to 1.22)0.184 Sodium0.84 (0.68 to 1.21)0.075 Albumin0.71 (0.46 to 2.42)0.143 Infection2.99 (1.16 to 10.49)0.011Associated with CVA developmentPre-operative factor Sodium0.95 (0.92 to 1.01)0.057Post-operative factor Sodium0.92 (0.90 to 1.02)0.060 Albumin0.43 (0.23 to 0.98)0.050 Infection4.24 (1.69 to 14.58)0.0005 |
Infection type | Group non-NC (n = 264) | Group NC (n = 43) | p-value (non-NC vs. NC) | Group CVA (n = 35) | p-value (non-NC vs. CVA) | All forms, n (%) | 51 (19.3) | 17 (39.5) | 0.003 | 13 (37.1) | 0.016 | Sepsis, n (%) | 41 (15.1) | 9 (20.9) | 0.377 | 7 (20.0) | 0.498 | LVAD related, n (%) | 30 (11.4) | 10 (23.3) | 0.031 | 7 (20.0) | 0.145 | Urinary tract, n (%) | 45 (17.0) | 11 (25.6) | 0.179 | 9 (25.7) | 0.082 | Respiratory, n (%) | 30 (11.4) | 6 (14.0) | 0.624 | 5 (14.2) | 0.613 | Others, n (%) | 14 (5.3) | 4 (9.3) | 0.874 | 2 (5.7) | 0.577 | Factors | OR (95% CI) | p-value | Associated with overall NC development | History of CVA | 2.37 (1.24 to 5.29) | 0.011 | Pre-operative factor | Sodium | 0.93 (0.90 to 1.12) | 0.208 | Albumin | 0.51 (0.21 to 1.37) | 0.079 | Post-operative factor | Haematocrit | 0.96 (0.71 to 1.22) | 0.184 | Sodium | 0.84 (0.68 to 1.21) | 0.075 | Albumin | 0.71 (0.46 to 2.42) | 0.143 | Infection | 2.99 (1.16 to 10.49) | 0.011 | Associated with CVA development | Pre-operative factor | Sodium | 0.95 (0.92 to 1.01) | 0.057 | Post-operative factor | Sodium | 0.92 (0.90 to 1.02) | 0.060 | Albumin | 0.43 (0.23 to 0.98) | 0.050 | Infection | 4.24 (1.69 to 14.58) | 0.0005 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection type | Group non-NC (n = 264) | Group NC (n = 43) | p-value (non-NC vs. NC) | Group CVA (n = 35) | p-value (non-NC vs. CVA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All forms, n (%) | 51 (19.3) | 17 (39.5) | 0.003 | 13 (37.1) | 0.016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis, n (%) | 41 (15.1) | 9 (20.9) | 0.377 | 7 (20.0) | 0.498 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD related, n (%) | 30 (11.4) | 10 (23.3) | 0.031 | 7 (20.0) | 0.145 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Urinary tract, n (%) | 45 (17.0) | 11 (25.6) | 0.179 | 9 (25.7) | 0.082 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory, n (%) | 30 (11.4) | 6 (14.0) | 0.624 | 5 (14.2) | 0.613 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others, n (%) | 14 (5.3) | 4 (9.3) | 0.874 | 2 (5.7) | 0.577 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Factors | OR (95% CI) | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Associated with overall NC development | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History of CVA | 2.37 (1.24 to 5.29) | 0.011 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative factor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sodium | 0.93 (0.90 to 1.12) | 0.208 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albumin | 0.51 (0.21 to 1.37) | 0.079 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post-operative factor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haematocrit | 0.96 (0.71 to 1.22) | 0.184 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sodium | 0.84 (0.68 to 1.21) | 0.075 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albumin | 0.71 (0.46 to 2.42) | 0.143 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection | 2.99 (1.16 to 10.49) | 0.011 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Associated with CVA development | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative factor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sodium | 0.95 (0.92 to 1.01) | 0.057 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post-operative factor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sodium | 0.92 (0.90 to 1.02) | 0.060 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albumin | 0.43 (0.23 to 0.98) | 0.050 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection | 4.24 (1.69 to 14.58) | 0.0005 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unclear | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The overall frequency of NC including TIA was 14.0% after LVAD placement and that the frequency of ischaemic/haemorrhagic CVA was 11.4%; the frequency of NC was not different between patients with HMI vs HMII devices; the history of CVA and post-operative infection were factors independently associated with development of NCs after LVAD placement; the combination of prior CVA, pre-operative sodium and albumin, post-operative sodium, haematocrit and albumin, and post-operative infection could discriminate patients who develop NCs with a discriminant probability of 76.6%; and an analysis done for CVA patients after excluding patients with only TIA yielded similar results. Previous CVA, persistent malnutrition, persistent inflammation, severity of HF, and post-LVAD infections were found to be key factors associated with NC as well as CVA development after LVAD implantation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The study did not reveal differences in frequency of NC development between devices in different generation. The authors claim that these findings provide helpful guidance for risk stratification and clinical management strategies of patients with advanced HF receiving LVAD support. Furthermore, previous stroke, persistent malnutrition and inflammation, severity of HF, and post-LVAD infections were considered to be key factors associated with the development of NCs after LVAD implantation. However, owing to limitations of the statistical analyses in terms of a failure to adjust for the large number of multiple analyses caution should be made when interpreting these findings | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Klotz 200688
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Klotz Year of publication: 2006 Country: Germany Study design: Retrospective Study setting: University hospital in Münster Number of centres: One Duration of study: Unclear Follow-up period: Unclear Funding: No information |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To find out if the pre- and post-transplant outcomes of CF LVADs are similar to pulsatile LVADs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: CF LVAD n = 50 (MicroMed DeBakey n = 30 and INCOR Berlin Heart n = 20); pulsatile LVAD n = 80 (Novacor n = 61 and HM n = 19) Sample attrition/dropout: Presumably none Inclusion criteria: Unclear. It included patients receiving pulsatile LVAD from the year 1993 and continuous LVAD from the year 2000 at the Münster University hospital Exclusion criteria: Patients with extracorporeal LVAD systems and patients aged < 17 years Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): MicroMed DeBakey 43.0 ± 14.6; INCOR 46.1 ± 11.1; Novacor 45.0 ± 11.9; HM 49.4 ± 7.2 Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: Male – MicroMed DeBakey 87%; INCOR 70%; Novacor 85%; HM 95% Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Dilated cardiomyopathy – MicroMed DeBakey 37%; INCOR 45%; Novacor 51%; HM 42% |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: Elective – MicroMed DeBakey 13%, INCOR 30%, Novacor 16%, HM 26%; urgent – MicroMed DeBakey 43%, INCOR 35%, Novacor 54%, HM 42%; emergency – MicroMed DeBakey 44%, INCOR 35%, Novacor 30%, HM 32% Type of device used: Continuous LVAD – MicroMed DeBakey or INCOR Berlin Heart; pulsatile LVAD – Novacor or HM Any comparison: Patients with a CF device was compared with an age-, disease-, and LVAD duration-matched control group supported with a pulsatile device. Mortality data compared with patients after cardiac transplantation without previous LVAD support Duration of treatment: Unclear Percentage of patients using inotropes: Unclear Other interventions used: No information Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – MicroMed DeBakey; INCOR |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Mortality data compared with patients after cardiac transplantation without previous LVAD support Secondary outcomes: Adverse events Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records. No clear information Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: UnclearNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reportedNot reportedRandomised/included50 patients with a CF device (MicroMed DeBakey, n = 30 and INCOR Berlin Heart, n = 20)LVAD duration-matched control group (n = 80) supported with a pulsatile device (Novacor, n = 61 and HM, n = 19)ExcludedNot reportedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reportedNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported | Not reported | Randomised/included | 50 patients with a CF device (MicroMed DeBakey, n = 30 and INCOR Berlin Heart, n = 20) | LVAD duration-matched control group (n = 80) supported with a pulsatile device (Novacor, n = 61 and HM, n = 19) | Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 50 patients with a CF device (MicroMed DeBakey, n = 30 and INCOR Berlin Heart, n = 20) | LVAD duration-matched control group (n = 80) supported with a pulsatile device (Novacor, n = 61 and HM, n = 19) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, yearsCF: MicroMed DeBakey 43.0 ± 14.6; INCOR 46.1 ± 11.1Pulsatile flow: Novacor 45.0 ± 11.9; HM 49.4 ± 7.2Sex, maleCF: MicroMed DeBakey 87%; INCOR 70%Pulsatile flow: Novacor 85%; HM 95%BSA, m2CF: MicroMed DeBakey 1.92 ± 0.18; INCOR 1.91 ± 0.23Pulsatile flow: Novacor 1.94 ± 0.19; HM 2.02 ± 0.21Weight, kg, BMICF: MicroMed DeBakey 24.5 ± 3.2; INCOR 24.9 ± 3.9Pulsatile flow: Novacor 24.6 ± 3.6; HM 25.2 ± 4.8Ischaemic causes of HFDilated cardiomyopathy: MicroMed DeBakey 37%; INCOR 45%Dilated cardiomyopathy: Novacor 51%; HM 42% Demographics and clinical characteristics at study entryDemographicsCFPulsatilep-valueMicroMed DeBakeyINCORNovacorHMn30206119Age (years)43.0 ± 14.646.1 ± 11.145.0 ± 11.949.4 ± 7.2NSGender, male (%)87708595NSDisease, DCM (%)37455142NSBMI (kg/m2)24.5 ± 3.224.9 ± 3.924.6 ± 3.625.2 ± 4.8NSBSA (m2)1.92 ± 0.181.91 ± 0.231.94 ± 0.192.02 ± 0.21Inotropic agents (%)83758679IABP (%)27251621ECC (%)20151611Status of implantation (%)30NS Elective13301626 Urgent43355442 Emergency44353032LVAD duration, days (death prior HT)69 ± 6368 ± 3480 ± 10468 ± 68NSLVAD duration, days (BTT)240 ± 115194 ± 177160 ± 87195 ± 120NS |
Age, years | CF: MicroMed DeBakey 43.0 ± 14.6; INCOR 46.1 ± 11.1 | Pulsatile flow: Novacor 45.0 ± 11.9; HM 49.4 ± 7.2 | Sex, male | CF: MicroMed DeBakey 87%; INCOR 70% | Pulsatile flow: Novacor 85%; HM 95% | BSA, m2 | CF: MicroMed DeBakey 1.92 ± 0.18; INCOR 1.91 ± 0.23 | Pulsatile flow: Novacor 1.94 ± 0.19; HM 2.02 ± 0.21 | Weight, kg, BMI | CF: MicroMed DeBakey 24.5 ± 3.2; INCOR 24.9 ± 3.9 | Pulsatile flow: Novacor 24.6 ± 3.6; HM 25.2 ± 4.8 | Ischaemic causes of HF | Dilated cardiomyopathy: MicroMed DeBakey 37%; INCOR 45% | Dilated cardiomyopathy: Novacor 51%; HM 42% | Demographics | CF | Pulsatile | p-value | MicroMed DeBakey | INCOR | Novacor | HM | n | 30 | 20 | 61 | 19 | Age (years) | 43.0 ± 14.6 | 46.1 ± 11.1 | 45.0 ± 11.9 | 49.4 ± 7.2 | NS | Gender, male (%) | 87 | 70 | 85 | 95 | NS | Disease, DCM (%) | 37 | 45 | 51 | 42 | NS | BMI (kg/m2) | 24.5 ± 3.2 | 24.9 ± 3.9 | 24.6 ± 3.6 | 25.2 ± 4.8 | NS | BSA (m2) | 1.92 ± 0.18 | 1.91 ± 0.23 | 1.94 ± 0.19 | 2.02 ± 0.21 | Inotropic agents (%) | 83 | 75 | 86 | 79 | IABP (%) | 27 | 25 | 16 | 21 | ECC (%) | 20 | 15 | 16 | 11 | Status of implantation (%)30 | NS | Elective | 13 | 30 | 16 | 26 | Urgent | 43 | 35 | 54 | 42 | Emergency | 44 | 35 | 30 | 32 | LVAD duration, days (death prior HT) | 69 ± 63 | 68 ± 34 | 80 ± 104 | 68 ± 68 | NS | LVAD duration, days (BTT) | 240 ± 115 | 194 ± 177 | 160 ± 87 | 195 ± 120 | NS | ||||||||||||||
| Age, years | CF: MicroMed DeBakey 43.0 ± 14.6; INCOR 46.1 ± 11.1 | Pulsatile flow: Novacor 45.0 ± 11.9; HM 49.4 ± 7.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex, male | CF: MicroMed DeBakey 87%; INCOR 70% | Pulsatile flow: Novacor 85%; HM 95% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA, m2 | CF: MicroMed DeBakey 1.92 ± 0.18; INCOR 1.91 ± 0.23 | Pulsatile flow: Novacor 1.94 ± 0.19; HM 2.02 ± 0.21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight, kg, BMI | CF: MicroMed DeBakey 24.5 ± 3.2; INCOR 24.9 ± 3.9 | Pulsatile flow: Novacor 24.6 ± 3.6; HM 25.2 ± 4.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic causes of HF | Dilated cardiomyopathy: MicroMed DeBakey 37%; INCOR 45% | Dilated cardiomyopathy: Novacor 51%; HM 42% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demographics | CF | Pulsatile | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MicroMed DeBakey | INCOR | Novacor | HM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | 30 | 20 | 61 | 19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 43.0 ± 14.6 | 46.1 ± 11.1 | 45.0 ± 11.9 | 49.4 ± 7.2 | NS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gender, male (%) | 87 | 70 | 85 | 95 | NS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Disease, DCM (%) | 37 | 45 | 51 | 42 | NS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.5 ± 3.2 | 24.9 ± 3.9 | 24.6 ± 3.6 | 25.2 ± 4.8 | NS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 1.92 ± 0.18 | 1.91 ± 0.23 | 1.94 ± 0.19 | 2.02 ± 0.21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inotropic agents (%) | 83 | 75 | 86 | 79 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP (%) | 27 | 25 | 16 | 21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ECC (%) | 20 | 15 | 16 | 11 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status of implantation (%)30 | NS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elective | 13 | 30 | 16 | 26 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Urgent | 43 | 35 | 54 | 42 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emergency | 44 | 35 | 30 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD duration, days (death prior HT) | 69 ± 63 | 68 ± 34 | 80 ± 104 | 68 ± 68 | NS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD duration, days (BTT) | 240 ± 115 | 194 ± 177 | 160 ± 87 | 195 ± 120 | NS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term survival was similar in both LVAD groups compared with patients without previous LVAD support From transplanted patients with prior CF LVAD support who survived longer than 30 days, 89% had rejections equal to or higher than ISHLT grade III K–M survival analysis for transplanted patient with previous CF LVAD support log-rank = 0.7085 Patients at riskIntervalsPulsatile flowCFControl group0452526222913169428614662011581587101558 |
Intervals | Pulsatile flow | CF | Control group | 0 | 45 | 25 | 262 | 2 | 29 | 13 | 169 | 4 | 28 | 6 | 146 | 6 | 20 | 115 | 8 | 15 | 87 | 10 | 15 | 58 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervals | Pulsatile flow | CF | Control group | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 45 | 25 | 262 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 29 | 13 | 169 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 28 | 6 | 146 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 20 | 115 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | 15 | 87 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | 15 | 58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Successful BTT was similar with CF in comparison with pulsatile device support (52% vs. 56%; p = NS) Severe rejections were more frequent in patients with a CF LVAD (p < 0.001) Patients who died during LVAD support were significantly older compared with patients who could be transplanted (p < 0.05) The rate of rejection ISHLT grade III or greater in the pulsatile group was 33% (p < 0.001) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre transplantation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall mortality rate pre transplant was 48% (n = 24) in CF group and 44% (n = 35) in pulsatile group (p = NS). Time interval from LVAD implantation to death in the CF group was not significant to pulsatile group (68 ± 54 days vs. 76 ± 95 days; p = NS). In analyses of patients who received an LVAD under emergency conditions in acute cardiogenic shock, in 20 patients in CF group, BTT or weaning was possible in n = 10 (50%). In pulsatile group this was possible in 14 out of 24 patients (58%) of the emergency implants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post transplantation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In CF group, 23 patients (46%) transplanted and 3 patients (6%) weaned from device. In pulsatile group, 45 patients (56%) transplanted (p = NS). The time from LVAD implantation to cardiac transplant was 220 ± 147 days in CF group and 167 ± 96 days in the pulsatile group (p = 0.084). Post-transplant 30-day mortality was 21.7% in CF group and 22.2% in pulsatile LVAD group In both groups, age was significantly higher in patients who died during LVAD support BMI was significantly higher in pulsatile LVAD group in patients who died before cardiac transplant compared with patients who BTT successfully (25.7 ± 4.5 vs. 24.0 ± 3.2 kg/m2; p < 0.05), while there was no difference between the CF LVAD and control groups Pulsatile LVADs in this study were implanted from the year 1993 to 2000 while CF LVADs were implanted starting from year 2000 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The risk of severe rejection was increased threefold after CF LVAD support, compared with pulsatile LVAD support | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reasons for death were similar among the different LVAD groups | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre transplant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CF device vs. pulsatile device (read off graphs – approximations): multiorgan failure (∼ 35 vs. ∼ 45 deaths); cerebral (∼ 47 vs. ∼ 33 deaths); device related (∼ 9 vs. 0); right HF (∼ 6 vs. ∼ 13); sepsis (∼ 10 vs. ∼ 11); bleeding (∼ 0 vs. ∼ 6). No significant difference between CF and pulsatile LVAD group | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post transplant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CF vs. pulsatile device (read off graphs – approximations): multiorgan failure (∼ 22 vs. ∼ 42 deaths); cerebral (∼ 42 vs. ∼ 0 deaths); right HF (∼ 42 vs. ∼ 31); rejection (∼ 0 vs. ∼ 12); sepsis (∼ 0 vs. ∼ 22). Reasons for death post transplant showed no significant difference between CF and pulsatile LVAD groups. Trend towards lower incidence of rejection, sepsis, and multiorgan failure while the incidence of cerebral accident is elevated | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| New generation of cardiac assist devices with CF pattern has a similar rate of pre- and post-transplant mortality in comparison with pulsatile LVADs. The rate and severity of post-transplant rejection was significantly higher in with CF device group. Further studies are needed to explain the higher rate of severe rejections | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall the analyses generally support the author's conclusions; however, patients were not randomised to different VADs. Authors did use age-, disease- and LVAD duration-match controls. Regression and Cox's proportional hazards were not undertaken to accommodate confounders and identify influential variables. Exact p-values were not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Kormos 201067
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Kormos Year of publication: 2010 Country: Unclear Study design: Presumably retrospective analysis of data from multicentre trial. Data were then divided into different groups and compared against each other Study setting: Not reported Number of centres: Multicentre Duration of study: 1 year Follow-up period: 1 year Funding: Unclear |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To evaluate incidence, risk factors and effect on outcomes of RVF in patients implanted with HMII CF LVAD | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: Total n = 484 – no RVF n = 386 and RVF subgroups n = 98 (RVF-RVAD n = 30; RVF-early inotropes n = 35; RVF-late inotropes n = 33). Data from RVF-RVAD and RVF-early inotropes were combined to form an early RVF group (n = 65) Sample attrition/dropout: None Inclusion criteria: Patients receiving HMII LVAD in the multicentre HMII pivotal clinical trial for BTT between March 2005 and April 2008. Patients were listed as status 1A or 1B on the HT list Exclusion criteria: Not stated Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): No RVF 51.8 ± 13.5 years; RVF-RVAD 51.0 ± 13.3 years; RVF-early inotropes 55.0 ± 11.0 years; RVF-late inotropes 48.6 ± 12.0 years Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex (female): No RV: 80 (21%); RVF-RVAD 7 (23%); RVF-early inotropes 8 (23%); RVF-late inotropes 13 (39%) Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Ischaemic cause – no RVF 174 (75%); RVF-RVAD 15 (50%); RVF-early inotropes 15 (43%); RVF-late inotropes 10 (30%) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT Type of device used: HMII LVAD Any comparison: RVF was defined in HMII clinical trial as either need for a RVAD. In addition: group 1, need of an LVAD support; group 2, continuous inotropic support for at least 14 days after implantation; group 3, late inotropic support starting 14 days after implantation. Data from groups 1 and 2 were combined to form an early RVF group, whereas group 3 patients were examined separately (late RVF group). Rationale for differentiating early and late occurrences of RVF is that cause of the RVF is likely triggered by different mechanisms Duration of treatment: Durations of support for all RVADs ranged from 0 to 408 days. Most RVADs were implanted within 24 hours of LVAD surgery. Eight patients received RVAD after 24 hours, with one patient receiving RVAD 38 days after LVAD surgery. Three of these eight patients underwent transplantation, four died and one withdrew Percentage of patients using inotropes: Inotropes, early 35 (7%); inotropes, late 33 (7%) Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Identify the potential risk factors for early RVF, survival on HMII, adverse events (intra- and post-operative complications) Secondary outcomes: Not relevant Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records. RVF was defined in HMII clinical trial as either need for a RVAD in addition to LVAD, continuous inotropic support for at least 14 days after implantation, or late inotropic support starting 14 days after implantation Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes – intraoperative and post operative HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: 1 yearNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reportedRandomised/includedNo RVF n = 386 and RVF subgroups n = 98 (RVF-RVAD n = 30, RVF-early inotropes n = 35, RVF-late inotropes n = 33); data from RVF-RVAD and RVF-early inotropes were combined to form an early RVF group (n = 65)See column to leftExcludedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported | Randomised/included | No RVF n = 386 and RVF subgroups n = 98 (RVF-RVAD n = 30, RVF-early inotropes n = 35, RVF-late inotropes n = 33); data from RVF-RVAD and RVF-early inotropes were combined to form an early RVF group (n = 65) | See column to left | Excluded | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | No RVF n = 386 and RVF subgroups n = 98 (RVF-RVAD n = 30, RVF-early inotropes n = 35, RVF-late inotropes n = 33); data from RVF-RVAD and RVF-early inotropes were combined to form an early RVF group (n = 65) | See column to left | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-implantation characteristics for all groupsParameterNo RVF (n = 386)RVF subgroupsp-valueaAny early RVF (n = 65)RVF-RVAD (n = 30)RVF-early inotropes (n = 35)RVF-late inotropes (n = 33)Percentage of total patients (n = 484)8067713Sex, female80 (21%)7 (23%)8 (23%)13 (39%)0.1015 (23%)Ischaemic cause174 (45%)15 (50%)15 (43%)10 (30%)0.3730 (46%)Age (years)51.8 ± 13.551.0 ± 13.355.0 ± 11.048.6 I 12.00.1253.0 ± 12.0BSA1.99 ± 0.261.94 +.0.281.98 ± 0.302.11 ± 0.630.581.96 ± 0.29Cardiac index2.1 ± 0.72.0 ± 0.62.2 ± 0.82.0 ± 0.50.962.1 ± 0.7PCWP (mmHg)25 ± 826 ± 826 ± 824 ± 70.6026 ± 6PAPm (mmHg)36 ± 935 ± 935 ± 935 ± 110.9435 ± 9PAPs (mmHg)52 + 1349 + 1250 ± 1650 ± 170.5450 ± 14PAPd (mmHg)27 ± 827 ± 826 ± 826 ± 90.8727 ± 8CVP (mmHg)12.3 ± 6.416.1 ± 6.4b14.5 ± 7.1c12.9 ± 7.70.0115.2 ± 6.8dCVP/PCWP ratio0.51 ± 0.460.64 ± 0.210.57 + 0.270.51 ± 0.230.100.60 ± 0.20dRVSWI (mmHg/ml/m2)556 ± 298391 ± 226c541 ± 344.1560 ± 3350.04477 ± 306cPVR (Wood units)2.91 ± 1.612.93 + 1.4172.79 ± 1.552.94 ± 1.670.972.85 + 1.48BPs (mmHg)99 ± 16102 ± 1898 ± 1595 ± 140.51100 ± 16Heart rate (b.p.m.)91 ± 1998 ± 1989 ± 1787 ± 190.1493 1 18IABP161 (42%)18 (60%)15 (43%)9 (27%)0.0733 (51%)Ventitatory support21 (5%)11 (37%)d5 (14%)c3 (9%)< 0.00116 (25%)dPacing188 (49%)10 (33%)20 (57%)18 (55%)0.2330 (46%)Creatinine (mg/dl)1.41 ± 0.501.54 ± 0.521.53 ± 0.591.47 ± 0.630.341.53 ± 0.56BUN (mg/dl)29.6 + 16.636.1 ± 17.5c32.0 ± 13.633.1 ± 19.70.0533.8 ± 15.0cAST (mg/dl)74 + 201236 ± 557b78 ± 23689 ± 164c0.02148 ± 415TBILL (mg/dl)1.25 + 0.781.39 + 1.431.34 ± 0.711.25 ± 0.980.551.36 ± 1.07Haematocrit (%)34.9 ± 5.533.5 ± 7.435.3 ± 6.034.5 ± 5.40.264.5 ± 6.6WBC (× 103/ml)8.7 ± 3.611.2 ± 4.6b9.3 ± 3.28.4 ± 3.20.0110.1 ± 4.0bPlatelet count (× 103/ml)226 ± 88221 ± 90220 ± 74225 ± 930.98220 ± 81INR (IU)1.32 ± 0.331.57 ± 1.011.35 ± 0.321.37 ± 0.440.891.5 ± 0.71MRVFRS1.14 ± 1.882.04 ± 2.341.34 ± 1.701.38 ± 1.800.080.65 ± 2.00ca p-value for differences between the four subgroups.b p < 0.01.c p < 0.05.d p < 0.001 compared with no-RVF group. | Parameter | No RVF (n = 386) | RVF subgroups | p-valuea | Any early RVF (n = 65) | RVF-RVAD (n = 30) | RVF-early inotropes (n = 35) | RVF-late inotropes (n = 33) | Percentage of total patients (n = 484) | 80 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 13 | Sex, female | 80 (21%) | 7 (23%) | 8 (23%) | 13 (39%) | 0.10 | 15 (23%) | Ischaemic cause | 174 (45%) | 15 (50%) | 15 (43%) | 10 (30%) | 0.37 | 30 (46%) | Age (years) | 51.8 ± 13.5 | 51.0 ± 13.3 | 55.0 ± 11.0 | 48.6 I 12.0 | 0.12 | 53.0 ± 12.0 | BSA | 1.99 ± 0.26 | 1.94 +.0.28 | 1.98 ± 0.30 | 2.11 ± 0.63 | 0.58 | 1.96 ± 0.29 | Cardiac index | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 2.2 ± 0.8 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 0.96 | 2.1 ± 0.7 | PCWP (mmHg) | 25 ± 8 | 26 ± 8 | 26 ± 8 | 24 ± 7 | 0.60 | 26 ± 6 | PAPm (mmHg) | 36 ± 9 | 35 ± 9 | 35 ± 9 | 35 ± 11 | 0.94 | 35 ± 9 | PAPs (mmHg) | 52 + 13 | 49 + 12 | 50 ± 16 | 50 ± 17 | 0.54 | 50 ± 14 | PAPd (mmHg) | 27 ± 8 | 27 ± 8 | 26 ± 8 | 26 ± 9 | 0.87 | 27 ± 8 | CVP (mmHg) | 12.3 ± 6.4 | 16.1 ± 6.4b | 14.5 ± 7.1c | 12.9 ± 7.7 | 0.01 | 15.2 ± 6.8d | CVP/PCWP ratio | 0.51 ± 0.46 | 0.64 ± 0.21 | 0.57 + 0.27 | 0.51 ± 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.60 ± 0.20d | RVSWI (mmHg/ml/m2) | 556 ± 298 | 391 ± 226c | 541 ± 344.1 | 560 ± 335 | 0.04 | 477 ± 306c | PVR (Wood units) | 2.91 ± 1.61 | 2.93 + 1.41 | 72.79 ± 1.55 | 2.94 ± 1.67 | 0.97 | 2.85 + 1.48 | BPs (mmHg) | 99 ± 16 | 102 ± 18 | 98 ± 15 | 95 ± 14 | 0.51 | 100 ± 16 | Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 91 ± 19 | 98 ± 19 | 89 ± 17 | 87 ± 19 | 0.14 | 93 1 18 | IABP | 161 (42%) | 18 (60%) | 15 (43%) | 9 (27%) | 0.07 | 33 (51%) | Ventitatory support | 21 (5%) | 11 (37%)d | 5 (14%)c | 3 (9%) | < 0.001 | 16 (25%)d | Pacing | 188 (49%) | 10 (33%) | 20 (57%) | 18 (55%) | 0.23 | 30 (46%) | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.41 ± 0.50 | 1.54 ± 0.52 | 1.53 ± 0.59 | 1.47 ± 0.63 | 0.34 | 1.53 ± 0.56 | BUN (mg/dl) | 29.6 + 16.6 | 36.1 ± 17.5c | 32.0 ± 13.6 | 33.1 ± 19.7 | 0.05 | 33.8 ± 15.0c | AST (mg/dl) | 74 + 201 | 236 ± 557b | 78 ± 236 | 89 ± 164c | 0.02 | 148 ± 415 | TBILL (mg/dl) | 1.25 + 0.78 | 1.39 + 1.43 | 1.34 ± 0.71 | 1.25 ± 0.98 | 0.55 | 1.36 ± 1.07 | Haematocrit (%) | 34.9 ± 5.5 | 33.5 ± 7.4 | 35.3 ± 6.0 | 34.5 ± 5.4 | 0.26 | 4.5 ± 6.6 | WBC (× 103/ml) | 8.7 ± 3.6 | 11.2 ± 4.6b | 9.3 ± 3.2 | 8.4 ± 3.2 | 0.01 | 10.1 ± 4.0b | Platelet count (× 103/ml) | 226 ± 88 | 221 ± 90 | 220 ± 74 | 225 ± 93 | 0.98 | 220 ± 81 | INR (IU) | 1.32 ± 0.33 | 1.57 ± 1.01 | 1.35 ± 0.32 | 1.37 ± 0.44 | 0.89 | 1.5 ± 0.71 | MRVFRS | 1.14 ± 1.88 | 2.04 ± 2.34 | 1.34 ± 1.70 | 1.38 ± 1.80 | 0.08 | 0.65 ± 2.00c | a p-value for differences between the four subgroups. | b p < 0.01. | c p < 0.05. | d p < 0.001 compared with no-RVF group. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | No RVF (n = 386) | RVF subgroups | p-valuea | Any early RVF (n = 65) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVF-RVAD (n = 30) | RVF-early inotropes (n = 35) | RVF-late inotropes (n = 33) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Percentage of total patients (n = 484) | 80 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex, female | 80 (21%) | 7 (23%) | 8 (23%) | 13 (39%) | 0.10 | 15 (23%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic cause | 174 (45%) | 15 (50%) | 15 (43%) | 10 (30%) | 0.37 | 30 (46%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 51.8 ± 13.5 | 51.0 ± 13.3 | 55.0 ± 11.0 | 48.6 I 12.0 | 0.12 | 53.0 ± 12.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA | 1.99 ± 0.26 | 1.94 +.0.28 | 1.98 ± 0.30 | 2.11 ± 0.63 | 0.58 | 1.96 ± 0.29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 2.2 ± 0.8 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 0.96 | 2.1 ± 0.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 25 ± 8 | 26 ± 8 | 26 ± 8 | 24 ± 7 | 0.60 | 26 ± 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PAPm (mmHg) | 36 ± 9 | 35 ± 9 | 35 ± 9 | 35 ± 11 | 0.94 | 35 ± 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PAPs (mmHg) | 52 + 13 | 49 + 12 | 50 ± 16 | 50 ± 17 | 0.54 | 50 ± 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PAPd (mmHg) | 27 ± 8 | 27 ± 8 | 26 ± 8 | 26 ± 9 | 0.87 | 27 ± 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CVP (mmHg) | 12.3 ± 6.4 | 16.1 ± 6.4b | 14.5 ± 7.1c | 12.9 ± 7.7 | 0.01 | 15.2 ± 6.8d | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CVP/PCWP ratio | 0.51 ± 0.46 | 0.64 ± 0.21 | 0.57 + 0.27 | 0.51 ± 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.60 ± 0.20d | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVSWI (mmHg/ml/m2) | 556 ± 298 | 391 ± 226c | 541 ± 344.1 | 560 ± 335 | 0.04 | 477 ± 306c | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PVR (Wood units) | 2.91 ± 1.61 | 2.93 + 1.41 | 72.79 ± 1.55 | 2.94 ± 1.67 | 0.97 | 2.85 + 1.48 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BPs (mmHg) | 99 ± 16 | 102 ± 18 | 98 ± 15 | 95 ± 14 | 0.51 | 100 ± 16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 91 ± 19 | 98 ± 19 | 89 ± 17 | 87 ± 19 | 0.14 | 93 1 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP | 161 (42%) | 18 (60%) | 15 (43%) | 9 (27%) | 0.07 | 33 (51%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventitatory support | 21 (5%) | 11 (37%)d | 5 (14%)c | 3 (9%) | < 0.001 | 16 (25%)d | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pacing | 188 (49%) | 10 (33%) | 20 (57%) | 18 (55%) | 0.23 | 30 (46%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.41 ± 0.50 | 1.54 ± 0.52 | 1.53 ± 0.59 | 1.47 ± 0.63 | 0.34 | 1.53 ± 0.56 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 29.6 + 16.6 | 36.1 ± 17.5c | 32.0 ± 13.6 | 33.1 ± 19.7 | 0.05 | 33.8 ± 15.0c | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST (mg/dl) | 74 + 201 | 236 ± 557b | 78 ± 236 | 89 ± 164c | 0.02 | 148 ± 415 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TBILL (mg/dl) | 1.25 + 0.78 | 1.39 + 1.43 | 1.34 ± 0.71 | 1.25 ± 0.98 | 0.55 | 1.36 ± 1.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haematocrit (%) | 34.9 ± 5.5 | 33.5 ± 7.4 | 35.3 ± 6.0 | 34.5 ± 5.4 | 0.26 | 4.5 ± 6.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WBC (× 103/ml) | 8.7 ± 3.6 | 11.2 ± 4.6b | 9.3 ± 3.2 | 8.4 ± 3.2 | 0.01 | 10.1 ± 4.0b | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelet count (× 103/ml) | 226 ± 88 | 221 ± 90 | 220 ± 74 | 225 ± 93 | 0.98 | 220 ± 81 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INR (IU) | 1.32 ± 0.33 | 1.57 ± 1.01 | 1.35 ± 0.32 | 1.37 ± 0.44 | 0.89 | 1.5 ± 0.71 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MRVFRS | 1.14 ± 1.88 | 2.04 ± 2.34 | 1.34 ± 1.70 | 1.38 ± 1.80 | 0.08 | 0.65 ± 2.00c | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a p-value for differences between the four subgroups. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b p < 0.01. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c p < 0.05. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| d p < 0.001 compared with no-RVF group. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actuarial survival | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At 1 year: No RVF 79%; RVF-RVAD 59% (p = 0.004); RVF-early inotropes 56% (p = 0.007); RVF-late inotropes 75% (p = 0.81). Actuarial survival at 1 year was also significantly better for patients without RVF (79%) compared with that in patients requiring RVADs (group 1, 59%; p = 0.004) or extended inotropes (group 2, 56%; p = 0.007) No difference for patients with late inotrope use (group 3, 75%; p = 0.81) Overall survival K–M estimates: At 0 days: No RVF, remaining at risk 386; RVF, remaining at risk 65 At 30 days: No RVF, remaining at risk 348, 94% ± 1%; RVF, remaining at risk 52, 89% ± 4% At 180 days: No RVF, remaining at risk 206, 87% ± 3%; RVF, remaining at risk 30, 66% ± 6% At 365 days: No RVF, remaining at risk 105, 78% ± 3%; RVF, remaining at risk 18, 59% ± 7% At 1 year: No RVF, 78% ± 3%; RVF-RVAD, 59% ± 9% (p < 0.01); RVF-early inotropes, 56% ± 9% (p < 0.01); RVF-late inotropes, 75% ± 9%; any early RVF, 59% ± 7% (p < 0.01) Decreased survival for patients with early RVF is evident in grouped K–M survival curve Patients without RVF, 342 (89%) survived to transplantation, recovery, or continuing support at 180 days. Patients with early RVF had worse survival to same end points (n = 46, 71%; p = 0.001), with those requiring RVADs having lowest percentage reaching these outcomes (n = 20, 67%; p < 0.001) Within RVAD group, 17 (77%) of 22 patients who received a RVAD within first 24 hours survived to primary outcome at 180 days, whereas only 3 (38%) of 8 patients who received a RVAD later survived to the same end point |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other outcomesParameterPatients (n = 484)Length of stay for discharged patients (days)Transplant, recovery or ongoing at 180 daysK–M survival at 1 yearNo RVF386 (80%)22 (8–180)342 (89%)78% ± 3%RVF subgroups RVAD30 (6%)32 (0–158)20 (67%)59% ± 9% Inotropes, early35 (7%)35 (17–73)25 (71%)56% ± 9% Inotropes, late33 (7%)32 (12–86)29 (88%)75% ± 9% Any early RVF65 (13%)32 (0–173)46 (71%)59% ± 7% Hospital length of stay for discharged patients was longer for those requiring a RVAD than for those without RVF (32 vs. 22 days; p < 0.001). Those who required inotropic support for > 14 days after LVAD implantation and those with late inotropic support had an average length of stay of 35 and 32 days, respectively Any RVF resulted in a significantly longer hospitalisation time before discharge than seen in those without any RVF (p < 0.001) |
Parameter | Patients (n = 484) | Length of stay for discharged patients (days) | Transplant, recovery or ongoing at 180 days | K–M survival at 1 year | No RVF | 386 (80%) | 22 (8–180) | 342 (89%) | 78% ± 3% | RVF subgroups | RVAD | 30 (6%) | 32 (0–158) | 20 (67%) | 59% ± 9% | Inotropes, early | 35 (7%) | 35 (17–73) | 25 (71%) | 56% ± 9% | Inotropes, late | 33 (7%) | 32 (12–86) | 29 (88%) | 75% ± 9% | Any early RVF | 65 (13%) | 32 (0–173) | 46 (71%) | 59% ± 7% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Patients (n = 484) | Length of stay for discharged patients (days) | Transplant, recovery or ongoing at 180 days | K–M survival at 1 year | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No RVF | 386 (80%) | 22 (8–180) | 342 (89%) | 78% ± 3% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVF subgroups | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVAD | 30 (6%) | 32 (0–158) | 20 (67%) | 59% ± 9% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inotropes, early | 35 (7%) | 35 (17–73) | 25 (71%) | 56% ± 9% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inotropes, late | 33 (7%) | 32 (12–86) | 29 (88%) | 75% ± 9% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Any early RVF | 65 (13%) | 32 (0–173) | 46 (71%) | 59% ± 7% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Univariate analysis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The haemodynamic variables of CVP > 15 mmHg, RVSWI < 300 mmHg/ml/m2, and a CVP/PCWP ratio > 0.63 were statistically significant predictors that indicated a higher risk of RVF. No statistically significant differences in pulmonary artery pressures or pulmonary vascular resistance between groups With a baseline CVP of > 15 mmHg, 19% of patients had early RVF compared with 10% of patients with a CVP of < 15 mmHg (OR 2.1, 95% CI 1.2 to 3.6; p < 0.01) 22% of patients with a CVP/PCWP ratio of > 0.63 had early RVF compared with 11% with a CVP/PCWP ratio of < 0.63, and 26% of patients with an RVSWI of < 300 mmHg/ml/m2 had RVF compared with 10% of patients with an RVSWI of > 300 mmHg/ml/m2 Increased WBC and lower haematocrit values were also statistically significant between those who required RVAD support and those who did not Patients on pre-operative ventilator support were five times more likely to have RVF compared with those without ventilator support Multivariate analysis found that CVP/PCWP ratio of > 0.63 (OR 2.3, 95% CI 1.2 to 4.3; p < 0.009), need for ventilatory support (OR 5.5, 95% CI 2.3 to 13.2; p < 0.001), and a pre-operative BUN value of > 39 mg/dl (OR 2.1, 95% CI 1.1 to 4.1; p < 0.02) were the independent pre-operative predictors of early RVF after LVAD implantation The area under the receiver operating curve was 0.68 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No significant differences in bleeding and transfusion requirements during implantation or within the first 48 hours of LVAD implantation for those who eventually had RVF Patients implanted with a RVAD required a greater number of units of packed red blood cell transfusions compared with those without RVF (14.3 ± 18.9 vs. 5.6 ± 5.8 units; p < 0.03) and more often required a reoperation for bleeding (40% vs. 19%; p < 0.04) 53% of patients who needed a RVAD required > 6 units of PRBCs during implantation procedure, only 26% of those without RVF required similar transfusion Cardio-pulmonary bypass times were higher in those requiring a RVAD (149 ± 76 vs. 106 ± 61 minutes; p < 0.005) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unclear | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rates of RVF and RVAD requirement in patients with HMII were low compared with previous results with pulsatile LVADs and support use of this device in those with end-stage HF. The development of RVF remains difficult to predict. Both clinical and haemodynamic factors affect the development of RVF. RVF in HMII recipients was associated with worse clinical outcomes than in patients without RVF, which highlights the importance of appropriate RVF management and prevention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No concurrent control group for comparison with pulsatile devices. It was noted that the late inotrope group (group 3) was excluded from RVF group for most of analyses | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lahpor 201068
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Lahpor Year of publication: 2010 Country: European countries Study design: Presumably retrospective analysis of data from a multicentre trial Study setting: Multicentre study Number of centres: 64 European institutions Duration of study: March 2004 until August 2008 Follow-up period: All 411 patients were followed for a minimum of 180 days or until either transplantation, explantation after recovery or death Funding: Not reported |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Report on the European experience with the HMII as a BTT and as a destination device | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: HMII was implanted in 571 patients at 64 European institutions. 411 patients (72%) had implantation at least 6 months before closing date of the study (1 August 2008) Sample attrition/dropout: None, although analysis focussed on the 411 patients (72%) that had implantation at least 6 months before end of study Inclusion criteria: Unclear. Patients suffering from end-stage HF secondary to cardiomyopathy; all patients were NYHA class IIIb or IV and were on maximum medical treatment including intravenous inotropic support Exclusion criteria: Unclear Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): mean of 51 ± 14 years Median age: Not reported Age range: 14–75 years Sex: 81% male and 19% female Race: Not reported Diagnosis: All patients were NYHA class IIIb or IV and were on maximum medical treatment including intravenous inotropic support |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: The intention of support was BTT (73%), DT (21%) and a BTR (6%) Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: HMII CE mark study (group A), a European multicentric study (group B), and a Dutch single-centre study (group C) Duration of treatment: Duration of support ranged from 0 to 1019 days with a mean of 236 ± 214 days and a total of 293 patient-years support time Percentage of patients using inotropes: Not reported Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below. Patients (19% female, 70% ischaemic aetiology) were on maximum medical therapy, including inotropic support Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Overall survival to transplantation, recovery of the natural heart function with device removal or ongoing device support Secondary outcomes: Not reported Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records or prospective data collection Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: All 411 patients were followed for a minimum of 180 days or until either transplantation, explantation after recovery or deathNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreened571Not reportedRandomised/included411Not reportedExcluded160Not reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reportedNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | 571 | Not reported | Randomised/included | 411 | Not reported | Excluded | 160 | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | 571 | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 411 | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | 160 | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient characteristics and LVAD support durationParameterGroup A, n = 53Group B, n = 101Group C, n = 30Mean age (years)46 ± 1248 ± 1345 ± 12Male (%)607174Mean support duration (days)347 ± 214166 ± 175264 ± 192Range (days)1–15561–9721–615Total experience (years)51.344.622.4 | Parameter | Group A, n = 53 | Group B, n = 101 | Group C, n = 30 | Mean age (years) | 46 ± 12 | 48 ± 13 | 45 ± 12 | Male (%) | 60 | 71 | 74 | Mean support duration (days) | 347 ± 214 | 166 ± 175 | 264 ± 192 | Range (days) | 1–1556 | 1–972 | 1–615 | Total experience (years) | 51.3 | 44.6 | 22.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Group A, n = 53 | Group B, n = 101 | Group C, n = 30 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean age (years) | 46 ± 12 | 48 ± 13 | 45 ± 12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male (%) | 60 | 71 | 74 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean support duration (days) | 347 ± 214 | 166 ± 175 | 264 ± 192 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Range (days) | 1–1556 | 1–972 | 1–615 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total experience (years) | 51.3 | 44.6 | 22.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All 411 patients were followed for a minimum of 180 days or until either transplantation, explantation after recovery or death Overall survival to transplantation, recovery or ongoing device support at end of study was 69% (n = 284) with an early mortality of 17.5% and late mortality of 13.5% Of surviving patients, 23% had been transplanted, 4% had their device removed after recovery of LV and 42% were still ongoing A total of 249 (61%) patients were supported for > 6 months, 119 (29%) patients for > 1 year and 12 (3.0%) patients for > 2 years Overall survival to transplantation, recovery of natural heart function with device removal or ongoing device support was 69% (284) at end of study, with an early mortality (30 days) of 18% and late mortality of 13% Survival rate at 6 months = 74% and at 1 year = 71.5%. Of the surviving patients by end of follow-up period, 23% were transplanted, 4% had device removed after recovery of LV and 42% were still ongoing 6 months following implant Actuarial survival: taken from curve Number at risk: 0 days = 409; 90 days = 297; 180 days = 249; 270 days = 181; 360 days = 121 Survival probability (%):180 days = 72% ± 2%; 360 days = 65% ± 3% Competing-outcomes analysis of survival to transplantation, recovery of the natural heart, or ongoing device (percentage of patients): Recovery at 180 days = 2.5% and 1 year = 5%; transplanted at 180 days = 11% and 1 year = 23%; expired at 180 days = 26% and 1 year = 31%; ongoing at 180 days = 61% and 1 year = 41%; positive outcomes at 180 days = 74% and 1 year = 69% |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events occurred in first 53 patients in original HMII CE mark study (group A), in 101 patients of European multicentric study (group B) and 30 patients in a Dutch single-centre study (group C) Most common adverse events occurring following implantation of a HM VAD are shown below NCs occurred primarily in first 6 weeks following implantation Adverse events included bleeding (ranging from 42% in group C to 59% in group A), percutaneous lead infections (group A 0.19, group B 0.61 and group C 0.18 events/patient-year), pocket infections (group A 0.08, group B 0.07 and group C 0.09 events/patient-year), ischaemic stroke (group A 0.06, group B 0.09 and group C 0.04 events/patient-year), haemorrhagic stroke (group B 0.07 and group C 0.04 events/patient-year) and TIAs (group A 0.08, group B 0.02 and group C 0.13 events/patient-year) Rethoracotomy or multiple blood transfusions (6 units/24 hours) due to bleeding, mainly due to coagulopathy was found in all groups (e.g. group C = 43% and group A = 59%) Other frequent adverse events are cardiac arrhythmias, right-HF, renal failure and haemolysis Pocket infections was a more serious complication with incidences of 0.08, 0.07 and 0.09 events per patient-year Incidence of sepsis varied from 0.13% (group C) to 0.62% (group B) per patient-year Isolated percutaneous lead infections were most frequently seen in all three groups with incidences of 0.19, 0.61 and 0.18 per patient-year Adverse events and events per patient yearAdverse eventsNumber of adverse events (events/patient year)Group A, n = 53Group B, n = 101Group C, n = 30Bleeding31 (0.59)51 (1.14)13 (0.58)Ventricular arrhythmias14 (0.27)41 (0.92)3 (0.13)Infections47 (0.92)77 (1.73)11 (0.49)Local non-device related16 (0.31)19 (0.43)2 (0.09)Sepsis24 (0.47)28 (0.62)3 (0.13)Percutaneous lead10 (0.19)27 (0.61)4 (0.18)Pump pocket4 (0.08)3 (0.07)2 (0.09)NCs7 (0.14)8 (0.18)5 (0.22)Ischaemic stroke3 (0.06)4 (0.09)1 (0.04)Haemorrhagic stroke03 (0.05)1 (0.04)TIA4 (0.08)1 (0.02)3 (0.13)Device thrombosis1 (0.02)1 (0.02)1 (0.05)Right ventricular failure17 (0.33)10 (0.22)9 (0.40)Renal failure8 (0.16)18 (0.40)1 (0.04)Haemolysis7 (0.14)6 (0.13)4 (0.18) |
Adverse events | Number of adverse events (events/patient year) | Group A, n = 53 | Group B, n = 101 | Group C, n = 30 | Bleeding | 31 (0.59) | 51 (1.14) | 13 (0.58) | Ventricular arrhythmias | 14 (0.27) | 41 (0.92) | 3 (0.13) | Infections | 47 (0.92) | 77 (1.73) | 11 (0.49) | Local non-device related | 16 (0.31) | 19 (0.43) | 2 (0.09) | Sepsis | 24 (0.47) | 28 (0.62) | 3 (0.13) | Percutaneous lead | 10 (0.19) | 27 (0.61) | 4 (0.18) | Pump pocket | 4 (0.08) | 3 (0.07) | 2 (0.09) | NCs | 7 (0.14) | 8 (0.18) | 5 (0.22) | Ischaemic stroke | 3 (0.06) | 4 (0.09) | 1 (0.04) | Haemorrhagic stroke | 0 | 3 (0.05) | 1 (0.04) | TIA | 4 (0.08) | 1 (0.02) | 3 (0.13) | Device thrombosis | 1 (0.02) | 1 (0.02) | 1 (0.05) | Right ventricular failure | 17 (0.33) | 10 (0.22) | 9 (0.40) | Renal failure | 8 (0.16) | 18 (0.40) | 1 (0.04) | Haemolysis | 7 (0.14) | 6 (0.13) | 4 (0.18) | ||
| Adverse events | Number of adverse events (events/patient year) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group A, n = 53 | Group B, n = 101 | Group C, n = 30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding | 31 (0.59) | 51 (1.14) | 13 (0.58) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventricular arrhythmias | 14 (0.27) | 41 (0.92) | 3 (0.13) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infections | 47 (0.92) | 77 (1.73) | 11 (0.49) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Local non-device related | 16 (0.31) | 19 (0.43) | 2 (0.09) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 24 (0.47) | 28 (0.62) | 3 (0.13) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Percutaneous lead | 10 (0.19) | 27 (0.61) | 4 (0.18) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump pocket | 4 (0.08) | 3 (0.07) | 2 (0.09) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NCs | 7 (0.14) | 8 (0.18) | 5 (0.22) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic stroke | 3 (0.06) | 4 (0.09) | 1 (0.04) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic stroke | 0 | 3 (0.05) | 1 (0.04) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TIA | 4 (0.08) | 1 (0.02) | 3 (0.13) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device thrombosis | 1 (0.02) | 1 (0.02) | 1 (0.05) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right ventricular failure | 17 (0.33) | 10 (0.22) | 9 (0.40) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure | 8 (0.16) | 18 (0.40) | 1 (0.04) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemolysis | 7 (0.14) | 6 (0.13) | 4 (0.18) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Most frequent cause of death was multiorgan failure mainly occurring as a result of septic complications or right-HF; the second most common cause was CVAs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| These results support the use of HMII for long-term support as a BTT and possibly for DT. Future emphasis should focus on minimising adverse events such as infections, bleeding and neurological events. The authors recognise the limitations of the Thoratec Inc. Registry as it is retrospective and does not provide adequate information concerning adverse events and causes of mortality. The data were derived from institutional studies with HMII | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Limited reporting of baseline characteristics and lack of statistical analyses which suggests caution is needed when interpreting these findings | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Martin 201069
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Martin Year of publication: 2010 Country: USA Study design: Retrospective Study setting: The OSUMC Number of centres: Not reported Duration of study: April 2000 through to March 2009 Follow-up period: Unclear Funding: Not reported |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Examine a series of LVAD recipients at a single institution to assess the impact of targeted risk factors on the development of infection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 145 cases, of which 52 (35.9%) were HMII Sample attrition/dropout: None Inclusion criteria: For inclusion in the final analysis, the device had to be in place for > 30 days. The six categories of LVADs identified were: device 1 (HMXVE), device 2 (HMII), device 3 (Thoratec Inc. IVAD), device 4 (VentrAssist LVAS), device 5 [ABIOMED VADs (ABIOMED Inc., MA, USA)], and device 6 (MicroMed) Exclusion criteria: Not clear Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): Not reported Median age: Overall 52 years; HMII details are not provided Age range: Overall 18–75 years; HMII details are not provided Sex: Not reported Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Unclear |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: Not reported Type of device used: The six categories of LVADs identified were: device 1 (HMXVE), device 2 (HMII), device 3 (Thoratec Inc. IVAD), device 4 (VentrAssist LVAS), device 5 (ABIOMED VADs), and device 6 (MicroMed) Any comparison: See above devices which were reported in terms of baseline characteristics and risk of infection Duration of treatment: Unclear, > 30 days Percentage of patients using inotropes: Not reported Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Risk for infection Secondary outcomes: None Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: No Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: UnclearNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedThrough to March 2009, there were 202 LVADs placed in 163 patients at OSUMC since the programme's inception in April 2000. Of the 202 device placements, 150 remained in place for > 30 days. Five had no BMI dataNot applicableRandomised/included145 cases for analysisNot applicableExcludedNot reportedNot applicableMissing participantsNot reportedNot applicableWithdrawalsNot reportedNot applicable |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Through to March 2009, there were 202 LVADs placed in 163 patients at OSUMC since the programme's inception in April 2000. Of the 202 device placements, 150 remained in place for > 30 days. Five had no BMI data | Not applicable | Randomised/included | 145 cases for analysis | Not applicable | Excluded | Not reported | Not applicable | Missing participants | Not reported | Not applicable | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Through to March 2009, there were 202 LVADs placed in 163 patients at OSUMC since the programme's inception in April 2000. Of the 202 device placements, 150 remained in place for > 30 days. Five had no BMI data | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 145 cases for analysis | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comparison between patients with infection vs those without after LVAD placement for long-term supportParameterALL LVAD placements (n = 145)LVAD placements with infections (n = 51)LVAD placements without infections (n = 94)p-valueaAge, median years (range)52 (18–75)50 (20–74)53 (18–75)0.316Male gender107 (73.8%)39 (76.5%)67 (71.3%)0.351Median BMI, kg/m2 (range)28.41 (14.92–48.35)29.35 (18.56–47.13)28.32 (14.92–48.35)0.372Underweight3 (2.1%)03 (3.2%)Not applicableNormal weight39 (26.9%)12 (23.5%)27 (28.7%)0.501Overweight41 (28.3%)14 (27.5%)27 (28.7%)0.871Obese33 (22.8%)14 (27.5%)19 (20.2%)0.322Severely obese15 (10.3%)5 (9.8%)10 (10.6%)0.875Morbidly obese14 (9.7%)6 (11.8%)8 (8.5%)0.528Device type164 (44.1%)34 (66.7%)30 (31.9%)0.0001252 (35.9%)8 (15.7%)44 (46.8%)0.0001313 (9%)2 (3.9%)11 (11.7%)0.136410 (6.9%)6 (11.8%)4 (4.3%)0.10154 (2.8%)1 (2%)3 (3.2%)0.66962 (1.4%)02 (2.1%)Not applicablea p-value based on univariate logistical regression analysis.Please note: device 1 (HMXVE), device 2 (HMII), device 3 (Thoratec Inc. IVAD), device 4 (VentrAssist LVAS), device 5 (ABIOMED VADs), and device 6 (MicroMed). | Parameter | ALL LVAD placements (n = 145) | LVAD placements with infections (n = 51) | LVAD placements without infections (n = 94) | p-valuea | Age, median years (range) | 52 (18–75) | 50 (20–74) | 53 (18–75) | 0.316 | Male gender | 107 (73.8%) | 39 (76.5%) | 67 (71.3%) | 0.351 | Median BMI, kg/m2 (range) | 28.41 (14.92–48.35) | 29.35 (18.56–47.13) | 28.32 (14.92–48.35) | 0.372 | Underweight | 3 (2.1%) | 0 | 3 (3.2%) | Not applicable | Normal weight | 39 (26.9%) | 12 (23.5%) | 27 (28.7%) | 0.501 | Overweight | 41 (28.3%) | 14 (27.5%) | 27 (28.7%) | 0.871 | Obese | 33 (22.8%) | 14 (27.5%) | 19 (20.2%) | 0.322 | Severely obese | 15 (10.3%) | 5 (9.8%) | 10 (10.6%) | 0.875 | Morbidly obese | 14 (9.7%) | 6 (11.8%) | 8 (8.5%) | 0.528 | Device type | 1 | 64 (44.1%) | 34 (66.7%) | 30 (31.9%) | 0.0001 | 2 | 52 (35.9%) | 8 (15.7%) | 44 (46.8%) | 0.0001 | 3 | 13 (9%) | 2 (3.9%) | 11 (11.7%) | 0.136 | 4 | 10 (6.9%) | 6 (11.8%) | 4 (4.3%) | 0.101 | 5 | 4 (2.8%) | 1 (2%) | 3 (3.2%) | 0.669 | 6 | 2 (1.4%) | 0 | 2 (2.1%) | Not applicable | a p-value based on univariate logistical regression analysis. | Please note: device 1 (HMXVE), device 2 (HMII), device 3 (Thoratec Inc. IVAD), device 4 (VentrAssist LVAS), device 5 (ABIOMED VADs), and device 6 (MicroMed). | ||||||||||||
| Parameter | ALL LVAD placements (n = 145) | LVAD placements with infections (n = 51) | LVAD placements without infections (n = 94) | p-valuea | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, median years (range) | 52 (18–75) | 50 (20–74) | 53 (18–75) | 0.316 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male gender | 107 (73.8%) | 39 (76.5%) | 67 (71.3%) | 0.351 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median BMI, kg/m2 (range) | 28.41 (14.92–48.35) | 29.35 (18.56–47.13) | 28.32 (14.92–48.35) | 0.372 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Underweight | 3 (2.1%) | 0 | 3 (3.2%) | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal weight | 39 (26.9%) | 12 (23.5%) | 27 (28.7%) | 0.501 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overweight | 41 (28.3%) | 14 (27.5%) | 27 (28.7%) | 0.871 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Obese | 33 (22.8%) | 14 (27.5%) | 19 (20.2%) | 0.322 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Severely obese | 15 (10.3%) | 5 (9.8%) | 10 (10.6%) | 0.875 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Morbidly obese | 14 (9.7%) | 6 (11.8%) | 8 (8.5%) | 0.528 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 64 (44.1%) | 34 (66.7%) | 30 (31.9%) | 0.0001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 52 (35.9%) | 8 (15.7%) | 44 (46.8%) | 0.0001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 13 (9%) | 2 (3.9%) | 11 (11.7%) | 0.136 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 10 (6.9%) | 6 (11.8%) | 4 (4.3%) | 0.101 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 4 (2.8%) | 1 (2%) | 3 (3.2%) | 0.669 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 2 (1.4%) | 0 | 2 (2.1%) | Not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a p-value based on univariate logistical regression analysis. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Please note: device 1 (HMXVE), device 2 (HMII), device 3 (Thoratec Inc. IVAD), device 4 (VentrAssist LVAS), device 5 (ABIOMED VADs), and device 6 (MicroMed). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The overall time to infection post-device placement was a median 50 days (range 6–524 days) HMII showed a decreased risk of infection, OR 0.21 with 95% CI 0.09 to 0.50 (p = 0.0001). Adjusting for age, gender and BMI as either a continuous variable or by individual weight categories using multivariable logistical regression confirmed this association with infection for both of these devices with device 1 and device 2 (see below) Results of multivariable regression model on infectious risk and LVAD typeDevice typeOR (95% CI)p-valueHMXVE4.63 (2.14 to 10.03)0.0006HMII0.20 (0.08 to 0.49)0.0005 Infections among recipients of LVAD long-term supportInfectionsNumber of infections (n = 51)Source Bacteraemia21 (41.2%) Driveline19 (37.3%) LVAD pocket5 (9.8%) Sternal wound6 (11.8%)Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus14 (27.5%) Pseudomonas aeruginosa7 (13.7%) Staphylococcus epidermidis6 (11.8%) Enteric Gram-negative rods6 (11.8%) Enterococcus species6 (11.8%) Candida species5 (9.8%) Culture negative5 (9.8%) Lactobacillus species1 (2%) Aspergillus species1 (2%)Although the table below does not subdivide the number of infections by device, HMII appeared to have a decreased risk of infection compared with the other device types in the study. |
Device type | OR (95% CI) | p-value | HMXVE | 4.63 (2.14 to 10.03) | 0.0006 | HMII | 0.20 (0.08 to 0.49) | 0.0005 | Infections | Number of infections (n = 51) | Source | Bacteraemia | 21 (41.2%) | Driveline | 19 (37.3%) | LVAD pocket | 5 (9.8%) | Sternal wound | 6 (11.8%) | Pathogen | Staphylococcus aureus | 14 (27.5%) | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 7 (13.7%) | Staphylococcus epidermidis | 6 (11.8%) | Enteric Gram-negative rods | 6 (11.8%) | Enterococcus species | 6 (11.8%) | Candida species | 5 (9.8%) | Culture negative | 5 (9.8%) | Lactobacillus species | 1 (2%) | Aspergillus species | 1 (2%) | Although the table below does not subdivide the number of infections by device, HMII appeared to have a decreased risk of infection compared with the other device types in the study. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type | OR (95% CI) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMXVE | 4.63 (2.14 to 10.03) | 0.0006 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII | 0.20 (0.08 to 0.49) | 0.0005 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infections | Number of infections (n = 51) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bacteraemia | 21 (41.2%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline | 19 (37.3%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD pocket | 5 (9.8%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sternal wound | 6 (11.8%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathogen | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Staphylococcus aureus | 14 (27.5%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 7 (13.7%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 6 (11.8%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enteric Gram-negative rods | 6 (11.8%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enterococcus species | 6 (11.8%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Candida species | 5 (9.8%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Culture negative | 5 (9.8%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lactobacillus species | 1 (2%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aspergillus species | 1 (2%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Although the table below does not subdivide the number of infections by device, HMII appeared to have a decreased risk of infection compared with the other device types in the study. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Certain device types may have an effect infection risk in long-term support. Patients with HMXVE had a greater risk compared with patients with HMII who had a smaller risk. This effect was considered independent of BMI. Understanding risk factors for infection post-LVAD placement for long-term support remains much-needed area of study. Patient selection for long-term LVAD support is a complex decision-making process. In this cohort, there were likely to be a variety of issues that contributed to infectious risk in long-term support | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This single-centre retrospective analysis presents useful findings related to BMI and infection in patients with various LVADs (including HMII – n = 52). Limited information was provided about sample. Caution is needed when comparing the findings as definitions of infections may vary across studies | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Miller 200770
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Miller Year of publication: 2007 Country: USA Study design: Prospective study Study setting: Multicentres in USA Number of centres: 26 Duration of study: March 2005 to March 2006 Follow-up period: Data on performance of the device and haemodynamics of patients were recorded every 8 hours for 3 days, daily through day 14, and weekly through day 30 while the patient was hospitalised. Physical assessment and laboratory tests and medications were recorded on days 1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 14, 21 and 28 after implantation of the device while the patient was hospitalised. After 30 days, device measurements, laboratory evaluations, and physical assessments were recorded monthly. After discharge, patients were assessed over the telephone at least every 2 weeks; they returned to the investigational study site for follow-up, equipment review, and general status assessment weekly for first 4 weeks and then monthly. Assessment of QoL and a 6-minute walk test were completed at baseline and 1, 3 and 6 months after implantation of device. Deaths of patients and causes of death were determined at autopsy when possible or by examination of medical records or by interviews with family members. Final adjudication was determined by the clinical events committee Funding: Supervised by the sponsor (Thoratec Inc.) – Investigators in the clinical affairs and biostatistics departments at Thoratec Inc. designed this trial in consultation with FDA and clinical investigators |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To report on results from a large observational clinical study of a CF LVAD | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 133 patients with end-stage HF Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported Inclusion criteria: The following was taken from the supplementary appendix:
Patients will be excluded from study participation for any one or more of the following:
Mean age (SD): 50.1 ± 13.1 years Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: Male, n = 105 (79%) Race: White n = 92 (69%); Black n = 30 (23%) Diagnosis: Patients with end-stage HF who were on a WL for HT |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: Not clear – some discussion about comparison with studies involving pulsatile pumps Duration of treatment: Median duration of support was 126 days (range 1–600 days) Percentage of patients using inotropes: All patients were receiving intravenous inotropic therapy, with 25% requiring more than one inotrope. 11% of patients could not tolerate inotropes owing to cardiac arrhythmias. Median duration of post-operative inotropic support was 7 days. 17 patients (13%) required inotropic support for > 14 days for right ventricular dysfunction Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Proportions of patients who, at 180 days, had undergone transplantation, had cardiac recovery, or had ongoing mechanical support while remaining eligible for transplantation Secondary outcomes: Overall survival, survival while receiving device support, survival after transplantation, frequency of adverse events, assessment of functional class by a 6-minute walk test, independent evaluation of NYHA functional class by a physician and QoL Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records and prospective data collection Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: Yes Length of follow-up: Data on performance of the device and haemodynamics of patients were recorded every 8 hours for 3 days, daily through day 14, and weekly through day 30 while the patient was hospitalised. Physical assessment and laboratory tests and medications were recorded on days 1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 14, 21 and 28 after implantation of the device while the patient was hospitalised. After 30 days, device measurements, laboratory evaluations and physical assessments were recorded monthly. After discharge, patients were assessed over the telephone at least every 2 weeks; they returned to the investigational study site for follow-up, equipment review and general status assessment weekly for first 4 weeks and then monthly. Assessment of QoL and a 6-minute walk test were completed at baseline and 1, 3 and 6 months after implantation of device. Deaths of patients and causes of death were determined at autopsy when possible or by examination of medical records or by interviews with family members. Final adjudication was determined by the clinical events committeeNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedUnclearRandomised/included133ExcludedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedWithdrawalsThree patients underwent replacement of CF pump with a different type of VAD (because of surgical complications that occurred shortly after pump implantation) and were withdrawn from study |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Unclear | Randomised/included | 133 | Excluded | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Withdrawals | Three patients underwent replacement of CF pump with a different type of VAD (because of surgical complications that occurred shortly after pump implantation) and were withdrawn from study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Unclear | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 133 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Three patients underwent replacement of CF pump with a different type of VAD (because of surgical complications that occurred shortly after pump implantation) and were withdrawn from study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline characteristics of the 133 patientsaCharacteristicValueCharacteristicValueAge, years50.1 ± 13.1Haematologic valuesSex, male, n (%)105 (79)Haematocrit, %34.8 ± 5.2Race, n (%)bWhite cell count/mm38900 ± 3200 White92 (69)Platelets/mm3228,000 ± 86,000 Black30 (23)Concomitant medications, n (%)BSA, m22.0 ± 0.3Inotropic agentsIschaemic cause of HF, n (%)49 (37)Intravenous118 (89)LVEF, %16.3 ± 5.7Intolerance to inotropic agents owing to arrhythmias15 (11)Arterial BP (mmHg)Two or more inotropic agents33 (25) Systolic95.8 ± 14.6Diuretic109 (82) Diastolic61.7 ± 11.3ACE inhibitor40 (30)PCWP (mmHg)26.1 ± 7.9Angiotensin II-receptor antagonist7 (5)Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)2.0 ± 0.6Beta-blocker51 (38)Heart rate (b.p.m.)91.8 ± 18.5Digoxin61 (46)Pulmonary artery pressure (mmHg)Hydralazine25 (19) Systolic53.0 ± 14.1Amiodarone54 (41) Diastolic28.2 ± 8.8Heparin84 (63) Mean36.5 ± 9.7Warfarin2 (2)PVR, Wood units3.0 ± 1.5Aspirin40 (30)CVP, mmHg13.5 ± 7.8Mechanical device, n (%)RVSWI564 ± 272Biventricular pacemaker64 (48)NYHA classIVICD98 (74)Laboratory valuesIABP55 (41) Serum sodium (mmol/l)132.9 ± 5.1Mechanical ventilation8 (6) Serum albumin (g/dl)3.7 ± 3.3 Serum pre-albumin (mg/dl)18.8 ± 8.0 Serum cholesterol (mg/dl)126 ± 41 Serum creatinine (mg/dl)1.4 ± 0.5 Estimated creatinine clearance (ml/minute)75.1 ± 36.8 BUN (mg/dl)31.4 ± 17.6 Serum ALT (U/l)104 ± 287 Serum AST (U/l)67 ± 168 Serum total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.2 ± 0.8 Serum lactate dehydrogenase (mg/dl)376 ± 371a Plus–minus values are means ± SD.b Race was reported by the patient. | Characteristic | Value | Characteristic | Value | Age, years | 50.1 ± 13.1 | Haematologic values | Sex, male, n (%) | 105 (79) | Haematocrit, % | 34.8 ± 5.2 | Race, n (%)b | White cell count/mm3 | 8900 ± 3200 | White | 92 (69) | Platelets/mm3 | 228,000 ± 86,000 | Black | 30 (23) | Concomitant medications, n (%) | BSA, m2 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | Inotropic agents | Ischaemic cause of HF, n (%) | 49 (37) | Intravenous | 118 (89) | LVEF, % | 16.3 ± 5.7 | Intolerance to inotropic agents owing to arrhythmias | 15 (11) | Arterial BP (mmHg) | Two or more inotropic agents | 33 (25) | Systolic | 95.8 ± 14.6 | Diuretic | 109 (82) | Diastolic | 61.7 ± 11.3 | ACE inhibitor | 40 (30) | PCWP (mmHg) | 26.1 ± 7.9 | Angiotensin II-receptor antagonist | 7 (5) | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.0 ± 0.6 | Beta-blocker | 51 (38) | Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 91.8 ± 18.5 | Digoxin | 61 (46) | Pulmonary artery pressure (mmHg) | Hydralazine | 25 (19) | Systolic | 53.0 ± 14.1 | Amiodarone | 54 (41) | Diastolic | 28.2 ± 8.8 | Heparin | 84 (63) | Mean | 36.5 ± 9.7 | Warfarin | 2 (2) | PVR, Wood units | 3.0 ± 1.5 | Aspirin | 40 (30) | CVP, mmHg | 13.5 ± 7.8 | Mechanical device, n (%) | RVSWI | 564 ± 272 | Biventricular pacemaker | 64 (48) | NYHA class | IV | ICD | 98 (74) | Laboratory values | IABP | 55 (41) | Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 132.9 ± 5.1 | Mechanical ventilation | 8 (6) | Serum albumin (g/dl) | 3.7 ± 3.3 | Serum pre-albumin (mg/dl) | 18.8 ± 8.0 | Serum cholesterol (mg/dl) | 126 ± 41 | Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | Estimated creatinine clearance (ml/minute) | 75.1 ± 36.8 | BUN (mg/dl) | 31.4 ± 17.6 | Serum ALT (U/l) | 104 ± 287 | Serum AST (U/l) | 67 ± 168 | Serum total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.2 ± 0.8 | Serum lactate dehydrogenase (mg/dl) | 376 ± 371 | a Plus–minus values are means ± SD. | b Race was reported by the patient. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristic | Value | Characteristic | Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, years | 50.1 ± 13.1 | Haematologic values | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex, male, n (%) | 105 (79) | Haematocrit, % | 34.8 ± 5.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Race, n (%)b | White cell count/mm3 | 8900 ± 3200 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| White | 92 (69) | Platelets/mm3 | 228,000 ± 86,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Black | 30 (23) | Concomitant medications, n (%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA, m2 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | Inotropic agents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic cause of HF, n (%) | 49 (37) | Intravenous | 118 (89) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF, % | 16.3 ± 5.7 | Intolerance to inotropic agents owing to arrhythmias | 15 (11) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arterial BP (mmHg) | Two or more inotropic agents | 33 (25) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic | 95.8 ± 14.6 | Diuretic | 109 (82) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic | 61.7 ± 11.3 | ACE inhibitor | 40 (30) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 26.1 ± 7.9 | Angiotensin II-receptor antagonist | 7 (5) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.0 ± 0.6 | Beta-blocker | 51 (38) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 91.8 ± 18.5 | Digoxin | 61 (46) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary artery pressure (mmHg) | Hydralazine | 25 (19) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic | 53.0 ± 14.1 | Amiodarone | 54 (41) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic | 28.2 ± 8.8 | Heparin | 84 (63) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean | 36.5 ± 9.7 | Warfarin | 2 (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PVR, Wood units | 3.0 ± 1.5 | Aspirin | 40 (30) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CVP, mmHg | 13.5 ± 7.8 | Mechanical device, n (%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVSWI | 564 ± 272 | Biventricular pacemaker | 64 (48) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class | IV | ICD | 98 (74) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Laboratory values | IABP | 55 (41) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 132.9 ± 5.1 | Mechanical ventilation | 8 (6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum albumin (g/dl) | 3.7 ± 3.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum pre-albumin (mg/dl) | 18.8 ± 8.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum cholesterol (mg/dl) | 126 ± 41 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Estimated creatinine clearance (ml/minute) | 75.1 ± 36.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 31.4 ± 17.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum ALT (U/l) | 104 ± 287 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum AST (U/l) | 67 ± 168 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.2 ± 0.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum lactate dehydrogenase (mg/dl) | 376 ± 371 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Plus–minus values are means ± SD. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Race was reported by the patient. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rate of death was 20–25% before transplantation Overall rate of survival to transplantation, recovery, or continued support with no pump replacement was 75% at 180 days K–M analysis of survival for patients who continued to receive mechanical support, with data censored for HT and recovery of ventricular function were reported in a figure. Withdrawal from the study was counted as a death. Overall survival of patients who underwent transplantation, recovered cardiac function, or continued to receive mechanical support while remaining a candidate for transplantation was estimated to be 70% at 1 year Additional estimates of actuarial survival taken from the K–M curve were: 1 month = 89%; 2 months = 88%; 3 months = 84%; 4 months = 79%; 5 months = 75%; 6 months = 75%; 7 months = 74%; 8 months = 74%; 9 months = 74%; 10 months = 74%; 11 months = 68%; 12 months = 68% |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median duration of support was 126 days (range 1–600 days), with a mean of 168 ± 148 days during a cumulative follow-up of 61.7 patient-years. Median time to transplantation was 97 days (range 15–498 days), and the median time to cardiac recovery for three patients was 347 days (range 161–380 days) All 133 patients were followed for ≥ 180 days or until transplantation or death: 100 patients (75%) reached HT, cardiac recovery, or survival at 180 days with ongoing mechanical support and eligibility for transplantation Of 100 patients: 56 underwent a HT, 43 received support and were eligible for transplantation, and one did not need transplantation after recovery of cardiac function and explantation of device Of 43 patients remaining on device support at 180 days: 32 were on active list for a HT, and 11 remained eligible for transplantation, including four who removed themselves from transplantation list Among 33 patients with unsuccessful outcomes were 25 patients who died before 180 days of support, with a median time to death of 38 days (range, 6–144) days: five patients became ineligible for transplantation during mechanical support owing to irreversible medical complications, and three patients underwent replacement of the CF pump with a different type of VAD (because of surgical complications that occurred shortly after pump implantation) and were withdrawn from the study Two patients who underwent replacement of CF pump with a second identical pump remained in study were alive on mechanical support at 216 and 367 days after replacement Twelve patients (9%) underwent transplantation during their initial hospital stay, and 18 patients (14%) died before discharge while receiving mechanical support. One-hundred patients (75%) were discharged from hospital while receiving mechanical support, with a median hospital stay after surgery of 25 days (range 10–114 days) Median number of days out of hospital before transplantation, readmission, or death was 60 days (range 0–418 days). Forty-four discharged patients required rehospitalisation for complications, with a median duration of rehospitalisation of 4 days (range 0–57 days) Outcomes of the 133 patientsaOutcomeValuePrincipal outcomes at 180 days, n (%)100 (75)HT, n (%)b56 (42)Cardiac recovery with device explanted, n (%)c1 (1)Ongoing device support > 180 days, n (%)43 (32)On WL for transplantation, n (%)d32 (24)Eligible for transplantation, n (%)e11 (8)Other outcomes, n (%)33 (25)Death at < 180 days, n (%)25 (19)Ongoing device support at > 180 days but ineligible for transplantation owing to medical issues, n (%)f5 (4)Device replaced with another LVAD; patient withdrawn from study, n (%)3 (2)Transplantation, recovery of cardiac function, or ongoing support at 180 days, n (%)g105 (79)With no pump replacement, n (%)h100 (75)Alive with LVAD support, %i At 1 month89 ± 3 At 6 month75 ± 4 At 1 year68 ± 6Alive after transplantation, n (%)j At 30 days64/68 (94) At 1 year12/15 (80)a LVAD denotes left ventricular assist device.b An additional 12 patients underwent transplantation after 180 days.c An additional two patients had recovery with the device removed at 347 and 380 days.d One patient subsequently died at 326 days.e Of 11 patients who were eligible for transplantation, four removed themselves from the WL owing to a preference to continue mechanical support (one of whom underwent transplantation at 21 months); three were not on the list because of inadequate social support and smoking, alcohol abuse, or a failed drug test; three had reversible illness (one of whom subsequently underwent transplantation at 16 months and one of whom was on the WL at 7 months); and one was being evaluated for potential cardiac recovery but was placed on the WL at 13 months.f Two patients subsequently died at 184 and 191 days.g This category includes the 100 patients who met the principal outcomes plus five patients who remained on device support but were not eligible for transplantation owing to medical issues.h This category includes the 105 patients listed above minus five patients who received pump replacements (three who withdrew from the study and two who remained in the study on CF LVAD support).i Plus–minus values are means ± SE for actuarial survival.j For patients who reached the stated interval (actual survival). The authors present a figure showing the outcomes of 133 patients after implantation of HMII. It shows all outcomes over time. After 6 months of mechanical support, outcomes were as follows: 56 patients had undergone a HT (42%); 48 patients continued to receive mechanical support (36%), five of whom were ineligible for transplantation; 25 patients had died while receiving mechanical support (19%); three had withdrawn from study; and one patient had recovery of ventricular function after explantation of device (1%). A total of 105 patients (79%) had undergone transplantation, had undergone explantation of device with recovery of ventricular function, or continued to receive mechanical support |
Outcome | Value | Principal outcomes at 180 days, n (%) | 100 (75) | HT, n (%)b | 56 (42) | Cardiac recovery with device explanted, n (%)c | 1 (1) | Ongoing device support > 180 days, n (%) | 43 (32) | On WL for transplantation, n (%)d | 32 (24) | Eligible for transplantation, n (%)e | 11 (8) | Other outcomes, n (%) | 33 (25) | Death at < 180 days, n (%) | 25 (19) | Ongoing device support at > 180 days but ineligible for transplantation owing to medical issues, n (%)f | 5 (4) | Device replaced with another LVAD; patient withdrawn from study, n (%) | 3 (2) | Transplantation, recovery of cardiac function, or ongoing support at 180 days, n (%)g | 105 (79) | With no pump replacement, n (%)h | 100 (75) | Alive with LVAD support, %i | At 1 month | 89 ± 3 | At 6 month | 75 ± 4 | At 1 year | 68 ± 6 | Alive after transplantation, n (%)j | At 30 days | 64/68 (94) | At 1 year | 12/15 (80) | a LVAD denotes left ventricular assist device. | b An additional 12 patients underwent transplantation after 180 days. | c An additional two patients had recovery with the device removed at 347 and 380 days. | d One patient subsequently died at 326 days. | e Of 11 patients who were eligible for transplantation, four removed themselves from the WL owing to a preference to continue mechanical support (one of whom underwent transplantation at 21 months); three were not on the list because of inadequate social support and smoking, alcohol abuse, or a failed drug test; three had reversible illness (one of whom subsequently underwent transplantation at 16 months and one of whom was on the WL at 7 months); and one was being evaluated for potential cardiac recovery but was placed on the WL at 13 months. | f Two patients subsequently died at 184 and 191 days. | g This category includes the 100 patients who met the principal outcomes plus five patients who remained on device support but were not eligible for transplantation owing to medical issues. | h This category includes the 105 patients listed above minus five patients who received pump replacements (three who withdrew from the study and two who remained in the study on CF LVAD support). | i Plus–minus values are means ± SE for actuarial survival. | j For patients who reached the stated interval (actual survival). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcome | Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Principal outcomes at 180 days, n (%) | 100 (75) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HT, n (%)b | 56 (42) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac recovery with device explanted, n (%)c | 1 (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ongoing device support > 180 days, n (%) | 43 (32) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| On WL for transplantation, n (%)d | 32 (24) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eligible for transplantation, n (%)e | 11 (8) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other outcomes, n (%) | 33 (25) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Death at < 180 days, n (%) | 25 (19) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ongoing device support at > 180 days but ineligible for transplantation owing to medical issues, n (%)f | 5 (4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device replaced with another LVAD; patient withdrawn from study, n (%) | 3 (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transplantation, recovery of cardiac function, or ongoing support at 180 days, n (%)g | 105 (79) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| With no pump replacement, n (%)h | 100 (75) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alive with LVAD support, %i | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At 1 month | 89 ± 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At 6 month | 75 ± 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At 1 year | 68 ± 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alive after transplantation, n (%)j | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At 30 days | 64/68 (94) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At 1 year | 12/15 (80) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a LVAD denotes left ventricular assist device. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b An additional 12 patients underwent transplantation after 180 days. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c An additional two patients had recovery with the device removed at 347 and 380 days. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| d One patient subsequently died at 326 days. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| e Of 11 patients who were eligible for transplantation, four removed themselves from the WL owing to a preference to continue mechanical support (one of whom underwent transplantation at 21 months); three were not on the list because of inadequate social support and smoking, alcohol abuse, or a failed drug test; three had reversible illness (one of whom subsequently underwent transplantation at 16 months and one of whom was on the WL at 7 months); and one was being evaluated for potential cardiac recovery but was placed on the WL at 13 months. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| f Two patients subsequently died at 184 and 191 days. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| g This category includes the 100 patients who met the principal outcomes plus five patients who remained on device support but were not eligible for transplantation owing to medical issues. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| h This category includes the 105 patients listed above minus five patients who received pump replacements (three who withdrew from the study and two who remained in the study on CF LVAD support). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| i Plus–minus values are means ± SE for actuarial survival. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| j For patients who reached the stated interval (actual survival). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events per patient-year with HMII showed an acceptable risk profile with respect to bleeding requiring surgery (0.78 events/patient-year), driveline infection (0.37 events/patient-year), stroke (0.19 events/patient-year), other non-stroke neurological events (0.26 events/patient-year), and right HF requiring a RVAD (0.08 events/patient-year) Most common adverse event was bleeding (mainly early post-operative period) Eight patients (6%) had ischaemic stroke, three (2%) had a haemorrhagic stroke Five additional patients had TIAs that were completely reversed Nine patients were reported to have psychological symptoms Eight patients had other neurological events Localised infection not related to device implantation occurred in 28% of patients Device-related infection occurred in 14% of patients, with all infections involving the percutaneous lead and none involving the pump pocket Five devices were replaced: two for pump thrombosis at 24 and 56 days after implantation and three for complications related to surgical implantation at 1, 15 and 32 days Adverse events in the 133 study patientsaAdverse eventOverall0–30 days> 30 daysPatients with event (%)No. of eventsEvent rate/patient-yearPatients with event (%)No. of eventsEvent rate/patient-yearPatients with eventNo. of with eventsEvent rate/patient-yearBleedingRequiring surgery41 (31)480.7840454.41130.06Requiring ≥ 2 units of PRBCs only70 (53)1292.0960858.3310440.85Ventricular arrhythmiasb32 (24)490.7924262.558230.45InfectionLocal, not related to device37 (28)701.1328373.639330.64Sepsis27 (20)380.6218181.779200.39Percutaneous lead18 (14)230.37000.0018230.45Pump pocket000.00000.00000.00Respiratory failure34 (26)430.7029323.145110.21Renal failure18 (14)190.3115151.47340.08Right HFNeed for RVAD5 (4)50.08440.39110.02Need for extended inotropic supportc17 (13)170.2812121.18550.10StrokeIschaemic8 (6)80.135d50.49330.06Haemorrhagic3 (2)30.05220.20110.02Spinal cord infarct1 (1)10.02000.00110.02TIA5 (4)60.10220.20340.08Psychological9 (7)110.18660.59350.10Other neurological8 (6)100.16330.29570.14Peripheral non-neurologic thromboembolic event9 (7)90.15880.78110.02Device replacemente5 (4)50.08330.29220.04Device thrombosesf2 (2)20.03110.10110.02Complications of surgical implantationg3 (2)30.05220.20110.02Haemolysis4 (3)40.06330.29110.02Hepatic dysfunction3 (2)30.05220.20110.02a The cumulative duration of device support was 61.7 patient-years overall, 10.2 patient-years for 0–30 days, and 51.5 patient-years for > 30 days.b This event required cardioversion or defibrillation.c The duration of support was for a period longer than 14 days or starting after day 14.d All events took place within the first 2 days after implantation.e Devices were replaced with another HMII in two patients and with another LVAD in three patientsf Events occurred on days 24 and 56.g Complications included a surgical pledget that was trapped in the pump (day 1), a temporary RVAD that caused a kink in outflow graft (day 15), and malpositioning of the inflow cannula (day 32). |
Adverse event | Overall | 0–30 days | > 30 days | Patients with event (%) | No. of events | Event rate/patient-year | Patients with event (%) | No. of events | Event rate/patient-year | Patients with event | No. of with events | Event rate/patient-year | Bleeding | Requiring surgery | 41 (31) | 48 | 0.78 | 40 | 45 | 4.41 | 1 | 3 | 0.06 | Requiring ≥ 2 units of PRBCs only | 70 (53) | 129 | 2.09 | 60 | 85 | 8.33 | 10 | 44 | 0.85 | Ventricular arrhythmiasb | 32 (24) | 49 | 0.79 | 24 | 26 | 2.55 | 8 | 23 | 0.45 | Infection | Local, not related to device | 37 (28) | 70 | 1.13 | 28 | 37 | 3.63 | 9 | 33 | 0.64 | Sepsis | 27 (20) | 38 | 0.62 | 18 | 18 | 1.77 | 9 | 20 | 0.39 | Percutaneous lead | 18 (14) | 23 | 0.37 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 18 | 23 | 0.45 | Pump pocket | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | Respiratory failure | 34 (26) | 43 | 0.70 | 29 | 32 | 3.14 | 5 | 11 | 0.21 | Renal failure | 18 (14) | 19 | 0.31 | 15 | 15 | 1.47 | 3 | 4 | 0.08 | Right HF | Need for RVAD | 5 (4) | 5 | 0.08 | 4 | 4 | 0.39 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | Need for extended inotropic supportc | 17 (13) | 17 | 0.28 | 12 | 12 | 1.18 | 5 | 5 | 0.10 | Stroke | Ischaemic | 8 (6) | 8 | 0.13 | 5d | 5 | 0.49 | 3 | 3 | 0.06 | Haemorrhagic | 3 (2) | 3 | 0.05 | 2 | 2 | 0.20 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | Spinal cord infarct | 1 (1) | 1 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | TIA | 5 (4) | 6 | 0.10 | 2 | 2 | 0.20 | 3 | 4 | 0.08 | Psychological | 9 (7) | 11 | 0.18 | 6 | 6 | 0.59 | 3 | 5 | 0.10 | Other neurological | 8 (6) | 10 | 0.16 | 3 | 3 | 0.29 | 5 | 7 | 0.14 | Peripheral non-neurologic thromboembolic event | 9 (7) | 9 | 0.15 | 8 | 8 | 0.78 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | Device replacemente | 5 (4) | 5 | 0.08 | 3 | 3 | 0.29 | 2 | 2 | 0.04 | Device thrombosesf | 2 (2) | 2 | 0.03 | 1 | 1 | 0.10 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | Complications of surgical implantationg | 3 (2) | 3 | 0.05 | 2 | 2 | 0.20 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | Haemolysis | 4 (3) | 4 | 0.06 | 3 | 3 | 0.29 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | Hepatic dysfunction | 3 (2) | 3 | 0.05 | 2 | 2 | 0.20 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | a The cumulative duration of device support was 61.7 patient-years overall, 10.2 patient-years for 0–30 days, and 51.5 patient-years for > 30 days. | b This event required cardioversion or defibrillation. | c The duration of support was for a period longer than 14 days or starting after day 14. | d All events took place within the first 2 days after implantation. | e Devices were replaced with another HMII in two patients and with another LVAD in three patients | f Events occurred on days 24 and 56. | g Complications included a surgical pledget that was trapped in the pump (day 1), a temporary RVAD that caused a kink in outflow graft (day 15), and malpositioning of the inflow cannula (day 32). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse event | Overall | 0–30 days | > 30 days | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with event (%) | No. of events | Event rate/patient-year | Patients with event (%) | No. of events | Event rate/patient-year | Patients with event | No. of with events | Event rate/patient-year | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Requiring surgery | 41 (31) | 48 | 0.78 | 40 | 45 | 4.41 | 1 | 3 | 0.06 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Requiring ≥ 2 units of PRBCs only | 70 (53) | 129 | 2.09 | 60 | 85 | 8.33 | 10 | 44 | 0.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventricular arrhythmiasb | 32 (24) | 49 | 0.79 | 24 | 26 | 2.55 | 8 | 23 | 0.45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Local, not related to device | 37 (28) | 70 | 1.13 | 28 | 37 | 3.63 | 9 | 33 | 0.64 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 27 (20) | 38 | 0.62 | 18 | 18 | 1.77 | 9 | 20 | 0.39 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Percutaneous lead | 18 (14) | 23 | 0.37 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 18 | 23 | 0.45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump pocket | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory failure | 34 (26) | 43 | 0.70 | 29 | 32 | 3.14 | 5 | 11 | 0.21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure | 18 (14) | 19 | 0.31 | 15 | 15 | 1.47 | 3 | 4 | 0.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HF | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Need for RVAD | 5 (4) | 5 | 0.08 | 4 | 4 | 0.39 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Need for extended inotropic supportc | 17 (13) | 17 | 0.28 | 12 | 12 | 1.18 | 5 | 5 | 0.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic | 8 (6) | 8 | 0.13 | 5d | 5 | 0.49 | 3 | 3 | 0.06 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic | 3 (2) | 3 | 0.05 | 2 | 2 | 0.20 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spinal cord infarct | 1 (1) | 1 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TIA | 5 (4) | 6 | 0.10 | 2 | 2 | 0.20 | 3 | 4 | 0.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Psychological | 9 (7) | 11 | 0.18 | 6 | 6 | 0.59 | 3 | 5 | 0.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other neurological | 8 (6) | 10 | 0.16 | 3 | 3 | 0.29 | 5 | 7 | 0.14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Peripheral non-neurologic thromboembolic event | 9 (7) | 9 | 0.15 | 8 | 8 | 0.78 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device replacemente | 5 (4) | 5 | 0.08 | 3 | 3 | 0.29 | 2 | 2 | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device thrombosesf | 2 (2) | 2 | 0.03 | 1 | 1 | 0.10 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Complications of surgical implantationg | 3 (2) | 3 | 0.05 | 2 | 2 | 0.20 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemolysis | 4 (3) | 4 | 0.06 | 3 | 3 | 0.29 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hepatic dysfunction | 3 (2) | 3 | 0.05 | 2 | 2 | 0.20 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a The cumulative duration of device support was 61.7 patient-years overall, 10.2 patient-years for 0–30 days, and 51.5 patient-years for > 30 days. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b This event required cardioversion or defibrillation. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c The duration of support was for a period longer than 14 days or starting after day 14. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| d All events took place within the first 2 days after implantation. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| e Devices were replaced with another HMII in two patients and with another LVAD in three patients | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| f Events occurred on days 24 and 56. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| g Complications included a surgical pledget that was trapped in the pump (day 1), a temporary RVAD that caused a kink in outflow graft (day 15), and malpositioning of the inflow cannula (day 32). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Causes of death in first 180 days after device implantation were: sepsis (n = 5); ischaemic stroke (n = 5); multisystem organ failure (n = 4); haemorrhagic stroke (n = 3); anoxic brain injury (n = 2; 1 after a protamine reaction and 1 after a hemothorax with cardiac arrest), right HF (n = 2), and miscellaneous other causes (n = 4). Also one device-related death caused by an inflow graft that was accidentally twisted during implantation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Most patients who were evaluated at 3 months after device implantation had improvement in two or more NYHA functional classes and improvement in a 6-minute walk test by a distance > 200 m. Measures of QoL significantly improved after device implantation on basis of both survey instruments used (p < 0.001) Functional status and QoLaVariable valueBaseline3 monthsp-valueNYHA functional classPatients evaluated, n13378bMean class4.0 ± 0.01.9 ± 0.7Patients with paired measurements, nNA78Class, n (96%) I025 (32) II040 (51) III011 (14) IV133 (100)2 (3)Improvement in functional class in paired measurementsNA2.1 ± 0.7< 0.001Distance walked in 6 minutesPatients performing test, n2556Patients not performing test, n Unable for medical reasonc10513 For other reasond313Values included in mean distance, n13069Mean distance, m42 ± 97292 ± 212Patients with paired data Patients, nNA66 Mean paired change, mNA250 ± 232< 0.001 Patients with improved distance > 200 m, nNA38 (58)QoLMLWHFe Patients completing questionnaire, nd11477 Mean score73 ± 2545 ± 25Patients with paired dataf Patients, nNA61 Mean paired change in scoreNA−27 ± 26< 0.001KCCQg Patients completing questionnaire, nf11377 OSS33 ± 1957 ± 20 CSS39 ± 2265 ± 22Patients with paired data Patients, nNA60 Mean paired change in overall scoreNA22 ± 19< 0.001 Mean paired change in clinical scoreNA25 ± 22< 0.001NA, not applicable.a Plus–minus values are means ± SD.b Of the 82 patients who were alive at 3 months, four patients did not undergo NYHA evaluation because of issues related to staff availability, scheduling, or oversight.c Patients in this category were assigned 0 m in distance walked.d Some patients did not perform the indicated tests or complete the questionnaire because of issues related to staff availability, scheduling, or oversight; other patients underwent a HT or died during the interval.e Scores on the MLWHF range from 0 to 105, with higher scores indicating a worse QoL.f Performance was compared with that at baseline measurement.g Scores on the KCCQ range from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating a better QoL. |
Variable value | Baseline | 3 months | p-value | NYHA functional class | Patients evaluated, n | 133 | 78b | Mean class | 4.0 ± 0.0 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | Patients with paired measurements, n | NA | 78 | Class, n (96%) | I | 0 | 25 (32) | II | 0 | 40 (51) | III | 0 | 11 (14) | IV | 133 (100) | 2 (3) | Improvement in functional class in paired measurements | NA | 2.1 ± 0.7 | < 0.001 | Distance walked in 6 minutes | Patients performing test, n | 25 | 56 | Patients not performing test, n | Unable for medical reasonc | 105 | 13 | For other reasond | 3 | 13 | Values included in mean distance, n | 130 | 69 | Mean distance, m | 42 ± 97 | 292 ± 212 | Patients with paired data | Patients, n | NA | 66 | Mean paired change, m | NA | 250 ± 232 | < 0.001 | Patients with improved distance > 200 m, n | NA | 38 (58) | QoL | MLWHFe | Patients completing questionnaire, nd | 114 | 77 | Mean score | 73 ± 25 | 45 ± 25 | Patients with paired dataf | Patients, n | NA | 61 | Mean paired change in score | NA | −27 ± 26 | < 0.001 | KCCQg | Patients completing questionnaire, nf | 113 | 77 | OSS | 33 ± 19 | 57 ± 20 | CSS | 39 ± 22 | 65 ± 22 | Patients with paired data | Patients, n | NA | 60 | Mean paired change in overall score | NA | 22 ± 19 | < 0.001 | Mean paired change in clinical score | NA | 25 ± 22 | < 0.001 | NA, not applicable. | a Plus–minus values are means ± SD. | b Of the 82 patients who were alive at 3 months, four patients did not undergo NYHA evaluation because of issues related to staff availability, scheduling, or oversight. | c Patients in this category were assigned 0 m in distance walked. | d Some patients did not perform the indicated tests or complete the questionnaire because of issues related to staff availability, scheduling, or oversight; other patients underwent a HT or died during the interval. | e Scores on the MLWHF range from 0 to 105, with higher scores indicating a worse QoL. | f Performance was compared with that at baseline measurement. | g Scores on the KCCQ range from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating a better QoL. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variable value | Baseline | 3 months | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA functional class | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients evaluated, n | 133 | 78b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean class | 4.0 ± 0.0 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with paired measurements, n | NA | 78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class, n (96%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I | 0 | 25 (32) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| II | 0 | 40 (51) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| III | 0 | 11 (14) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IV | 133 (100) | 2 (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Improvement in functional class in paired measurements | NA | 2.1 ± 0.7 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance walked in 6 minutes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients performing test, n | 25 | 56 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients not performing test, n | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unable for medical reasonc | 105 | 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For other reasond | 3 | 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Values included in mean distance, n | 130 | 69 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean distance, m | 42 ± 97 | 292 ± 212 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with paired data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients, n | NA | 66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean paired change, m | NA | 250 ± 232 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with improved distance > 200 m, n | NA | 38 (58) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLWHFe | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients completing questionnaire, nd | 114 | 77 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean score | 73 ± 25 | 45 ± 25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with paired dataf | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients, n | NA | 61 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean paired change in score | NA | −27 ± 26 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KCCQg | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients completing questionnaire, nf | 113 | 77 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OSS | 33 ± 19 | 57 ± 20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CSS | 39 ± 22 | 65 ± 22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with paired data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients, n | NA | 60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean paired change in overall score | NA | 22 ± 19 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean paired change in clinical score | NA | 25 ± 22 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NA, not applicable. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Plus–minus values are means ± SD. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Of the 82 patients who were alive at 3 months, four patients did not undergo NYHA evaluation because of issues related to staff availability, scheduling, or oversight. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c Patients in this category were assigned 0 m in distance walked. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| d Some patients did not perform the indicated tests or complete the questionnaire because of issues related to staff availability, scheduling, or oversight; other patients underwent a HT or died during the interval. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| e Scores on the MLWHF range from 0 to 105, with higher scores indicating a worse QoL. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| f Performance was compared with that at baseline measurement. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| g Scores on the KCCQ range from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating a better QoL. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII provided effective mechanical circulatory support in patients with refractory HF. Circulatory support with this device significantly improved haemodynamic status and improvements in functional status, as assessed with a 6-minute walk test, and in NYHA functional class and QoL, as measured by MLWHF and KCCQs. A CF LVAD can provide effective haemodynamic support for a period of at least 6 months in patients awaiting a HT, with improved functional status and QoL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| It was noted that the authors were not able to assess the functional status and QoL of all patients, which raises the concern that the estimates of typical benefit with respect to these end points may be subject to ascertainment bias. The criteria for selection of patients for ventricular assist is subjective and may present difficulties in comparison with other studies | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Morshuis 200985
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Morshuis Year of publication: 2009 Country: Multiple Study design: Prospective, multicentre, non-randomised trial Study setting: Germany, Austria and France Number of centres: Four Duration of study: Between 15 January 2004 and 7 March 2007 Follow-up period: All 33 CE mark study patients were followed for ≥ 3 months or until either transplant or death at time of database closure. All 68 patients of both CE mark and post-market studies were followed until 25 August 2008 Funding: Not reported |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Report clinical outcomes of 68 patients implanted with DuraHeart as a bridge to cardiac transplantation in Europe | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: A total of 68 patients were implanted with DuraHeart between January 2004 and July 2008. Of those, 33 patients who met inclusion criteria were enrolled in CE mark study and 35 patients were enrolled in post-market study in four centres (48 patients were enrolled at Heart & Diabetes Centre, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, 14 at German Heart Institute Berlin, Germany, five at University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, and one at Pitie Salpetriere Hospital, Paris, France) Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported Inclusion criteria: Patient referred for, and eligible for, cardiac transplantation: BSA 1.1 m2; NYHA functional class IV; cardiac index 2.2 l/minute/m2 with either systolic BP 80 mmHg or LAP (PCWP) or PAD ∼ 18 mmHg; receiving optimal medical treatment, including inotropes and/or IABP; gives informed consent; all laboratory and physiologic data used for evaluation of patient status were collected within 48 hours of enrolment Exclusion criteria: Surgical contraindications to LVAD implantation; high-risk cardiothoracic surgery within 30 days of enrolment; myocardial infarction within 30 days of enrolment; aortic regurgitation ∼ grade 1; evidence of recent or life-limiting malignant disease; patients with either an implanted mechanical aortic or mitral heart valve; fixed pulmonary hypertension with a PVR ∼ 480 dynes/second/cm5; severe COPD as evidenced by FEV1 1.5 l/minute; on ventilator support for ∼ 1 week within 30 days of enrolment Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): Not reported Median age: 58 years Age range: 29–74 years. Note: 43% of patients were aged > 60 years and 31% were aged > 65 years Sex: Male 90% Race: Not reported Diagnosis: End-stage left ventricular failure |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: Bridge to cardiac transplantation Type of device used: DuraHeart Any comparison: CE mark study vs. post-market study Duration of treatment: Unclear – 13 weeks end point and all 68 patients in CE mark and post-market studies were followed until 25 August 2008. The mean support duration was 338 ± 311 days (range 17—1148 days, median 201 days) Percentage of patients using inotropes: Unclear, all patients were receiving optimal medical treatment (e.g. inotropes and/or IABP) Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – DuraHeart |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Survival of patients either to cardiac transplantation or at 13 weeks (3 months) of device support Secondary outcomes: Adverse events, device performance, and overall patient status throughout period of DuraHeart support Method of assessing outcomes: Prospective data collection Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: All 33 CE mark study patients were followed for ≥ 3 months or until either transplant or death at time of database closure. All 68 patients of both CE mark and post-market studies were followed until 25 August 2008Number of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedUnclearNot reportedRandomised/included33 patients were enrolled in CE mark study35 patients were enrolled in post-market studyExcludedNot reportedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reportedNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Unclear | Not reported | Randomised/included | 33 patients were enrolled in CE mark study | 35 patients were enrolled in post-market study | Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Unclear | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 33 patients were enrolled in CE mark study | 35 patients were enrolled in post-market study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline characteristics of the trial and post-market patientsCharacteristicsAll (n = 68)Trial (n = 33)Post-market study (n = 35)Age, years (median)56.7 ± 11.3 (57.6)55.5 ± 12.5 (57.0)57.8 ± 10.4 (58.2)Male (%)908596BSA (m2)1.9 ± 0.21.9 ± 0.22.0 ± 0.2NYHA class IV (%)100100100Ischaemic cause of HF (%)514262LVEF (%)20.2 ± 6.920.2 ± 6.720.2 ± 7.0LVEDD (mm)74.6 ± 11.674.7 ± 12.974.3 ± 9.8Arterial BP (mmHg) Systolic98.1 ± 16.697.2 ± 16.299.3 ± 21.7 Diastolic61.0 ± 13.259.2 ± 16.263.2 ± 15.6 Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)1.8 ± 0.31 PCWP (mmHg)22 ± 6.7 CVP (mmHg)10.0 ± 4.8 PVR (dyne/second/cm5)265 ± 98Blood chemistry values Serum albumin (g/dl)3.4 ± 1.03.5 ± 1.03.0 ± 0.2 Serum sodium (mmol/l)132.9 ± 10.4131.2 ± 12.3135.4 ± 6.0 Serum creatinine (mg/dl)1.5 ± 0.71.5 ± 0.51.6 ± 1.0 BUN (mg/dl)39.1 ± 24.738.7 ± 26.039.7 ± 23.4 Serum ALT (U/l)80.9 ± 231.188.9 ± 285.667.5 ± 91.8 Serum AST (U/l)96.7 ± 347.3114.9 ± 429.362.4 ± 53.4 Serum lactate dehydrogenase (mg/dl)313.7 ± 163.1294.6 ± 120.3344.9 ± 215.9 Serum total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.5 ± 1.61.4 ± 1.11.7 ± 2.2Haematologic values Haematocrit (%)36.2 ± 6.337.1 ± 6.734.8 ± 5.5 Platelets (per mm3)198,000 ± 82,000202,000 ± 91,000193,000 ± 69,000 INR1.4 ± 0.51.5 ± 0.61.3 ± 0.3 Intravenous inotropic support (%)97Mechanical support prior to implant surgery ICD/biventricular pacemaker82 IABP18 Mechanical ventilation6 | Characteristics | All (n = 68) | Trial (n = 33) | Post-market study (n = 35) | Age, years (median) | 56.7 ± 11.3 (57.6) | 55.5 ± 12.5 (57.0) | 57.8 ± 10.4 (58.2) | Male (%) | 90 | 85 | 96 | BSA (m2) | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | NYHA class IV (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | Ischaemic cause of HF (%) | 51 | 42 | 62 | LVEF (%) | 20.2 ± 6.9 | 20.2 ± 6.7 | 20.2 ± 7.0 | LVEDD (mm) | 74.6 ± 11.6 | 74.7 ± 12.9 | 74.3 ± 9.8 | Arterial BP (mmHg) | Systolic | 98.1 ± 16.6 | 97.2 ± 16.2 | 99.3 ± 21.7 | Diastolic | 61.0 ± 13.2 | 59.2 ± 16.2 | 63.2 ± 15.6 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.8 ± 0.31 | PCWP (mmHg) | 22 ± 6.7 | CVP (mmHg) | 10.0 ± 4.8 | PVR (dyne/second/cm5) | 265 ± 98 | Blood chemistry values | Serum albumin (g/dl) | 3.4 ± 1.0 | 3.5 ± 1.0 | 3.0 ± 0.2 | Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 132.9 ± 10.4 | 131.2 ± 12.3 | 135.4 ± 6.0 | Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 1.0 | BUN (mg/dl) | 39.1 ± 24.7 | 38.7 ± 26.0 | 39.7 ± 23.4 | Serum ALT (U/l) | 80.9 ± 231.1 | 88.9 ± 285.6 | 67.5 ± 91.8 | Serum AST (U/l) | 96.7 ± 347.3 | 114.9 ± 429.3 | 62.4 ± 53.4 | Serum lactate dehydrogenase (mg/dl) | 313.7 ± 163.1 | 294.6 ± 120.3 | 344.9 ± 215.9 | Serum total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.5 ± 1.6 | 1.4 ± 1.1 | 1.7 ± 2.2 | Haematologic values | Haematocrit (%) | 36.2 ± 6.3 | 37.1 ± 6.7 | 34.8 ± 5.5 | Platelets (per mm3) | 198,000 ± 82,000 | 202,000 ± 91,000 | 193,000 ± 69,000 | INR | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | Intravenous inotropic support (%) | 97 | Mechanical support prior to implant surgery | ICD/biventricular pacemaker | 82 | IABP | 18 | Mechanical ventilation | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristics | All (n = 68) | Trial (n = 33) | Post-market study (n = 35) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, years (median) | 56.7 ± 11.3 (57.6) | 55.5 ± 12.5 (57.0) | 57.8 ± 10.4 (58.2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male (%) | 90 | 85 | 96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class IV (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic cause of HF (%) | 51 | 42 | 62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF (%) | 20.2 ± 6.9 | 20.2 ± 6.7 | 20.2 ± 7.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEDD (mm) | 74.6 ± 11.6 | 74.7 ± 12.9 | 74.3 ± 9.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arterial BP (mmHg) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic | 98.1 ± 16.6 | 97.2 ± 16.2 | 99.3 ± 21.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic | 61.0 ± 13.2 | 59.2 ± 16.2 | 63.2 ± 15.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.8 ± 0.31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 22 ± 6.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CVP (mmHg) | 10.0 ± 4.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PVR (dyne/second/cm5) | 265 ± 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blood chemistry values | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum albumin (g/dl) | 3.4 ± 1.0 | 3.5 ± 1.0 | 3.0 ± 0.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 132.9 ± 10.4 | 131.2 ± 12.3 | 135.4 ± 6.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 39.1 ± 24.7 | 38.7 ± 26.0 | 39.7 ± 23.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum ALT (U/l) | 80.9 ± 231.1 | 88.9 ± 285.6 | 67.5 ± 91.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum AST (U/l) | 96.7 ± 347.3 | 114.9 ± 429.3 | 62.4 ± 53.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum lactate dehydrogenase (mg/dl) | 313.7 ± 163.1 | 294.6 ± 120.3 | 344.9 ± 215.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.5 ± 1.6 | 1.4 ± 1.1 | 1.7 ± 2.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haematologic values | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haematocrit (%) | 36.2 ± 6.3 | 37.1 ± 6.7 | 34.8 ± 5.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets (per mm3) | 198,000 ± 82,000 | 202,000 ± 91,000 | 193,000 ± 69,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INR | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intravenous inotropic support (%) | 97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical support prior to implant surgery | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICD/biventricular pacemaker | 82 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP | 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Some disagreements in reporting of the overall survival for CE mark study: ‘The K–M survival for CE-mark study at time of 15 June 2007 was 81% (95% CI 63% to 91%) at 13 weeks end point and 76% (95% CI 55% to 88%) at 1 year’ and ‘K–M survival estimates for the CE mark study were 81% (95% CI 63% to 91%) at 3 months, 77% (95% CI 58% to 89%) at 6 months, 72% (95% CI 51% to 85%) at 1 year, and 57% (95% CI 31% to 76%) at 2 years’ The overall K–M survival estimate of all 68 patients was 87% (95% CI 77% to 94%) at 3 months, 81% (95% CI 67% to 89%) at 6 months, 77% at 1 year, and 61% (95% CI 34% to 78%) at 2 years |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The median time to transplantation was 142 days (range 43–497 days); 35 patients (51%) were awaiting HT with a mean support duration of 317 days (range 19–1148 days, median 216 days) At 1 year of support 16 patients (38%) had undergone transplant, while 13 patients (31%) remained on device support End-organ function and haemolysis during supportParameterBaseline (n = 33)a4 weeks (n = 30)a13 weeks (n = 24)a6 months (n = 15)aBUN (mg/dl)38.7 ± 26.022.0 ± 19.624.1 ± 21.127.9 ± 14.5Creatinine (mg/dl)1.5 ± 0.51.2 ± 0.41.3 ± 0.71.4 ± 0.6Total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.4 ± 1.11.2 ± 2.10.7 ± 0.40.6 ± 0.2GOT (U/l)89 ± 28636 ± 2232 ± 1039 ± 37GPT (U/l)115 ± 42931 ± 2328 ± 1121 ± 14Free haemoglobin (mg/dl)10.0 ± 10.68.1 ± 5.811.0 ± 10.09.0 ± 7.5LDH (U/l)295 ± 120323 ± 96267 ± 73260 ± 77a Mean ± SD. |
Parameter | Baseline (n = 33)a | 4 weeks (n = 30)a | 13 weeks (n = 24)a | 6 months (n = 15)a | BUN (mg/dl) | 38.7 ± 26.0 | 22.0 ± 19.6 | 24.1 ± 21.1 | 27.9 ± 14.5 | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.7 | 1.4 ± 0.6 | Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 1.1 | 1.2 ± 2.1 | 0.7 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | GOT (U/l) | 89 ± 286 | 36 ± 22 | 32 ± 10 | 39 ± 37 | GPT (U/l) | 115 ± 429 | 31 ± 23 | 28 ± 11 | 21 ± 14 | Free haemoglobin (mg/dl) | 10.0 ± 10.6 | 8.1 ± 5.8 | 11.0 ± 10.0 | 9.0 ± 7.5 | LDH (U/l) | 295 ± 120 | 323 ± 96 | 267 ± 73 | 260 ± 77 | a Mean ± SD. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Baseline (n = 33)a | 4 weeks (n = 30)a | 13 weeks (n = 24)a | 6 months (n = 15)a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 38.7 ± 26.0 | 22.0 ± 19.6 | 24.1 ± 21.1 | 27.9 ± 14.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.7 | 1.4 ± 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 1.1 | 1.2 ± 2.1 | 0.7 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GOT (U/l) | 89 ± 286 | 36 ± 22 | 32 ± 10 | 39 ± 37 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GPT (U/l) | 115 ± 429 | 31 ± 23 | 28 ± 11 | 21 ± 14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Free haemoglobin (mg/dl) | 10.0 ± 10.6 | 8.1 ± 5.8 | 11.0 ± 10.0 | 9.0 ± 7.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LDH (U/l) | 295 ± 120 | 323 ± 96 | 267 ± 73 | 260 ± 77 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Mean ± SD. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incidence of serious adverse events during support for 33 trial patientsSerious adverse eventOverall (n = 33) 17.8 patient-yearsInitial 11 patients 4.8 patient-yearsLast 22 patients 13.0 patient-yearsNo. of eventsNo. of patients (%)Event rate/ patient-yearNo. of eventsNo. of patients (%)Event rate/ patient-yearNo. of eventsNo. of patients (%)Event rate/ patient-yearAll serious adverse events9228 (85)5.173410 (91)7.115818 (82)4.45Infection, total2420 (61)1.3587 (64)1.671613 (59)1.23Local, non-device related1111 (33)0.6244 (36)0.8476 (27)0.54Driveline65 (15)0.3421 (9)0.4244 (18)0.31Pocket11 (3)0.0600 (0)011 (5)0.08Sepsis66 (18)0.3422 (18)0.4244 (18)0.31Right HF, total109 (27)0.5643 (27)0.8466 (27)0.46Requiring RVAD11 (3)0.0600 (0)011 (5)0.08Neurological dysfunction, total109 (27)0.5676 (55)1.4633 (14)0.23CVA55 (15)0.2855 (45)1.0500 (0)0TIA55 (15)0.2822 (18)0.4133 (14)0.23Ventricular arrhythmia77 (21)0.3922 (18)0.4255 (23)0.38Renal dysfunction – acute44 (12)0.2333 (27)0.6311 (5)0.08Bleeding, total88 (24)0.4522 (18)0.4266 (27)0.46Requiring surgery44 (12)0.2211 (9)0.2133 (14)0.23Respiratory failure44 (12)0.2211 (9)0.2133 (14)0.23Temporary flow interruption32 (6)0.1700 (0)032 (9)0.23Hepatic dysfunction22 (6)0.1111 (9)0.2111 (5)0.08Other, total1612 (36)0.9055 (45)1.05118 (36)0.84 | Serious adverse event | Overall (n = 33) 17.8 patient-years | Initial 11 patients 4.8 patient-years | Last 22 patients 13.0 patient-years | No. of events | No. of patients (%) | Event rate/ patient-year | No. of events | No. of patients (%) | Event rate/ patient-year | No. of events | No. of patients (%) | Event rate/ patient-year | All serious adverse events | 92 | 28 (85) | 5.17 | 34 | 10 (91) | 7.11 | 58 | 18 (82) | 4.45 | Infection, total | 24 | 20 (61) | 1.35 | 8 | 7 (64) | 1.67 | 16 | 13 (59) | 1.23 | Local, non-device related | 11 | 11 (33) | 0.62 | 4 | 4 (36) | 0.84 | 7 | 6 (27) | 0.54 | Driveline | 6 | 5 (15) | 0.34 | 2 | 1 (9) | 0.42 | 4 | 4 (18) | 0.31 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.06 | 0 | 0 (0) | 0 | 1 | 1 (5) | 0.08 | Sepsis | 6 | 6 (18) | 0.34 | 2 | 2 (18) | 0.42 | 4 | 4 (18) | 0.31 | Right HF, total | 10 | 9 (27) | 0.56 | 4 | 3 (27) | 0.84 | 6 | 6 (27) | 0.46 | Requiring RVAD | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.06 | 0 | 0 (0) | 0 | 1 | 1 (5) | 0.08 | Neurological dysfunction, total | 10 | 9 (27) | 0.56 | 7 | 6 (55) | 1.46 | 3 | 3 (14) | 0.23 | CVA | 5 | 5 (15) | 0.28 | 5 | 5 (45) | 1.05 | 0 | 0 (0) | 0 | TIA | 5 | 5 (15) | 0.28 | 2 | 2 (18) | 0.41 | 3 | 3 (14) | 0.23 | Ventricular arrhythmia | 7 | 7 (21) | 0.39 | 2 | 2 (18) | 0.42 | 5 | 5 (23) | 0.38 | Renal dysfunction – acute | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.23 | 3 | 3 (27) | 0.63 | 1 | 1 (5) | 0.08 | Bleeding, total | 8 | 8 (24) | 0.45 | 2 | 2 (18) | 0.42 | 6 | 6 (27) | 0.46 | Requiring surgery | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.22 | 1 | 1 (9) | 0.21 | 3 | 3 (14) | 0.23 | Respiratory failure | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.22 | 1 | 1 (9) | 0.21 | 3 | 3 (14) | 0.23 | Temporary flow interruption | 3 | 2 (6) | 0.17 | 0 | 0 (0) | 0 | 3 | 2 (9) | 0.23 | Hepatic dysfunction | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.11 | 1 | 1 (9) | 0.21 | 1 | 1 (5) | 0.08 | Other, total | 16 | 12 (36) | 0.90 | 5 | 5 (45) | 1.05 | 11 | 8 (36) | 0.84 | |||||||
| Serious adverse event | Overall (n = 33) 17.8 patient-years | Initial 11 patients 4.8 patient-years | Last 22 patients 13.0 patient-years | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No. of events | No. of patients (%) | Event rate/ patient-year | No. of events | No. of patients (%) | Event rate/ patient-year | No. of events | No. of patients (%) | Event rate/ patient-year | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All serious adverse events | 92 | 28 (85) | 5.17 | 34 | 10 (91) | 7.11 | 58 | 18 (82) | 4.45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection, total | 24 | 20 (61) | 1.35 | 8 | 7 (64) | 1.67 | 16 | 13 (59) | 1.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Local, non-device related | 11 | 11 (33) | 0.62 | 4 | 4 (36) | 0.84 | 7 | 6 (27) | 0.54 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline | 6 | 5 (15) | 0.34 | 2 | 1 (9) | 0.42 | 4 | 4 (18) | 0.31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 (3) | 0.06 | 0 | 0 (0) | 0 | 1 | 1 (5) | 0.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 6 | 6 (18) | 0.34 | 2 | 2 (18) | 0.42 | 4 | 4 (18) | 0.31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HF, total | 10 | 9 (27) | 0.56 | 4 | 3 (27) | 0.84 | 6 | 6 (27) | 0.46 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Requiring RVAD | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.06 | 0 | 0 (0) | 0 | 1 | 1 (5) | 0.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neurological dysfunction, total | 10 | 9 (27) | 0.56 | 7 | 6 (55) | 1.46 | 3 | 3 (14) | 0.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CVA | 5 | 5 (15) | 0.28 | 5 | 5 (45) | 1.05 | 0 | 0 (0) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TIA | 5 | 5 (15) | 0.28 | 2 | 2 (18) | 0.41 | 3 | 3 (14) | 0.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventricular arrhythmia | 7 | 7 (21) | 0.39 | 2 | 2 (18) | 0.42 | 5 | 5 (23) | 0.38 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal dysfunction – acute | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.23 | 3 | 3 (27) | 0.63 | 1 | 1 (5) | 0.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding, total | 8 | 8 (24) | 0.45 | 2 | 2 (18) | 0.42 | 6 | 6 (27) | 0.46 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Requiring surgery | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.22 | 1 | 1 (9) | 0.21 | 3 | 3 (14) | 0.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory failure | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.22 | 1 | 1 (9) | 0.21 | 3 | 3 (14) | 0.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Temporary flow interruption | 3 | 2 (6) | 0.17 | 0 | 0 (0) | 0 | 3 | 2 (9) | 0.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hepatic dysfunction | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.11 | 1 | 1 (9) | 0.21 | 1 | 1 (5) | 0.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other, total | 16 | 12 (36) | 0.90 | 5 | 5 (45) | 1.05 | 11 | 8 (36) | 0.84 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Majority of deaths (six patients, 85%) occurred in initial 11 patients enrolled in study. Majority of patients who died had multiple comorbidities Seven deaths occurred during device support, six before primary end point and one after primary end point Median time to death was 29 days One ischaemic and three haemorrhagic CVA were determined to be cause of death in four patients (57%) Summary of deaths during supportImplant orderAge (years)Time to death (day)Cause of deathOther complicationsDevice relatedness#26728Ischaemic CVAHIT II, Left atrial thrombus, chronic atrial fibrillationPossibly related#56029Haemorrhagic CVAaMultiorgan failurePossibly related#66321Subdural haematomaa (non-traumatic bleeding)Multiorgan failureUnrelated#77317Cardiovascular failure (traumatic fall)Carotid stenosis, confusionPossibly related#106686Haemorrhagic CVAaSepsis (Staphylococcus aureus)Possibly related#115637Haemorrhagic CVAaSepsis (Candida albicans)Possibly related#1661178SepsisMultiorgan failureUnrelateda Three haemorrhagic CVAs with massive intracerebral bleeding and one subdural haematoma resulted in immediate deaths; likely associated with excessive anticoagulation therapy. |
Implant order | Age (years) | Time to death (day) | Cause of death | Other complications | Device relatedness | #2 | 67 | 28 | Ischaemic CVA | HIT II, Left atrial thrombus, chronic atrial fibrillation | Possibly related | #5 | 60 | 29 | Haemorrhagic CVAa | Multiorgan failure | Possibly related | #6 | 63 | 21 | Subdural haematomaa (non-traumatic bleeding) | Multiorgan failure | Unrelated | #7 | 73 | 17 | Cardiovascular failure (traumatic fall) | Carotid stenosis, confusion | Possibly related | #10 | 66 | 86 | Haemorrhagic CVAa | Sepsis (Staphylococcus aureus) | Possibly related | #11 | 56 | 37 | Haemorrhagic CVAa | Sepsis (Candida albicans) | Possibly related | #16 | 61 | 178 | Sepsis | Multiorgan failure | Unrelated | a Three haemorrhagic CVAs with massive intracerebral bleeding and one subdural haematoma resulted in immediate deaths; likely associated with excessive anticoagulation therapy. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Implant order | Age (years) | Time to death (day) | Cause of death | Other complications | Device relatedness | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #2 | 67 | 28 | Ischaemic CVA | HIT II, Left atrial thrombus, chronic atrial fibrillation | Possibly related | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #5 | 60 | 29 | Haemorrhagic CVAa | Multiorgan failure | Possibly related | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #6 | 63 | 21 | Subdural haematomaa (non-traumatic bleeding) | Multiorgan failure | Unrelated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #7 | 73 | 17 | Cardiovascular failure (traumatic fall) | Carotid stenosis, confusion | Possibly related | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #10 | 66 | 86 | Haemorrhagic CVAa | Sepsis (Staphylococcus aureus) | Possibly related | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #11 | 56 | 37 | Haemorrhagic CVAa | Sepsis (Candida albicans) | Possibly related | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #16 | 61 | 178 | Sepsis | Multiorgan failure | Unrelated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Three haemorrhagic CVAs with massive intracerebral bleeding and one subdural haematoma resulted in immediate deaths; likely associated with excessive anticoagulation therapy. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The study demonstrated that the DuraHeart LVAS appears to be safe and provides an adequate circulatory support with an acceptable adverse event rate for patients eligible for cardiac transplantation. The device may have a potential for long-term circulatory support not only as a bridge to cardiac transplantation, but also for older patient cohort as a DT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Limitations of study include a limited clinical experience with 68 patients and lack of direct randomised comparison with other LVADs or optimal medical therapy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Morshuis 201042
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Morshuis Year of publication: 2010 Country: Multiple Study design: Prospective, multicentre, non-randomised trial Study setting: Germany, Austria and France Number of centres: Four Duration of study: between 15 January 2004 and 7 March 2007 Follow-up period: Adverse events were analysed for CE mark study patients (n = 33) for extended follow-up periods of at least 15 months at time of database closure on 15 June 2008 Funding: Not reported |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Review the clinical outcome of 82 patients implanted with DuraHeart LVAS in Europe | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 82 patients were implanted with the DuraHeart LVAS between January 2004 and May 2009 in Europe. Of these, 33 patients who met inclusion criteria were enrolled in approval CE mark study, and 49 patients were implanted after CE mark Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported Inclusion criteria: Patients referred for, and eligible for, cardiac transplantation: BSA 1.1 m2; NYHA functional class IV; cardiac index 2.2 l/minute/m2 with either systolic BP 80 mmHg or LAP (PCWP) or PAD ∼ 18 mmHg; receiving optimal medical treatment, including inotropes and/or IABP; gives informed consent; all laboratory and physiologic data used for evaluation of patient status were collected within 48 hours of enrolment Exclusion criteria: Surgical contraindications to LVAD implantation; high-risk cardiothoracic surgery within 30 days of enrolment; myocardial infarction within 30 days of enrolment; aortic regurgitation ∼ grade 1; evidence of recent or life-limiting malignant disease; patients with either an implanted mechanical aortic or mitral heart valve; fixed pulmonary hypertension with a PVR ∼ 480 dyne/second/cm5; severe COPD as evidenced by FEV1 1.5 l/minute; on ventilator support for ∼ 1 week within 30 days of enrolment Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): Not reported Median age: 57 ± 11 years (59 years) Age range: Not reported Sex: Male 91% Race: Not reported Diagnosis: End-stage left ventricular failure |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: Bridge to cardiac transplantation Type of device used: DuraHeart Any comparison: CE mark study vs. post-market study. The authors relate to comparisons of pulsatile devices Duration of treatment: Median duration of device support was 261 days (range 17–1494 days), with a cumulative duration of 78 patient-years Percentage of patients using inotropes: Unclear. All patients were receiving optimal medical treatment (e.g. inotropes and/or IABP) Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – DuraHeart |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Survival of patients either to cardiac transplantation or at 13 weeks (3 months) of device support Secondary outcomes: Adverse events, device performance and overall patient status throughout period of DuraHeart support Method of assessing outcomes: Prospective data collection Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: Adverse events were analysed for CE mark study patients (n = 33) for extended follow-up periods of at least 15 months at time of database closure on 15 June 2008Number of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedUnclearUnclearRandomised/includedn = 82Trial n = 33; post-market study n = 49ExcludedMissing participantsWithdrawalsOne patient (2%) was withdrawn from study after original device was replaced |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Unclear | Unclear | Randomised/included | n = 82 | Trial n = 33; post-market study n = 49 | Excluded | Missing participants | Withdrawals | One patient (2%) was withdrawn from study after original device was replaced | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Unclear | Unclear | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | n = 82 | Trial n = 33; post-market study n = 49 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | One patient (2%) was withdrawn from study after original device was replaced | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-implant characteristics of the trial and post-market patientsCharacteristicsAll ± SD (n = 82)Trial ± SD (n = 33)Post-market study ± SD (n = 49)p-value (trial vs. post-market study)Age, years (median)57 ± 11 (59)55 ± 13 (57)58 ± 10 (59)0.6462Male (%)9185960.161BSA (m2)1.9 ± 0.21.9 ± 0.22.0 ± 0.20.8986NYHA class IV (%)92100850.0303Ischaemic cause of HF (%)5242570.1207LVEF (%)20 ± 720 ± 720 ± 70.8986LVEDD (mm)72 ± 1175 ± 1370 ± 100.0689Systolic arterial BP (mmHg)92 ± 1 897 ± 1676 ± 150.0007Diastolic arterial BP (mmHg)54 ± 1559 ± 1638 ± 140.0004Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)2.0 ± 0.51.8 ± 0.32.2 ± 0.60.0018PCWP (mmHg)20 ± 6.622 ± 6.719 ± 6.40.165CVP (mmHg)9 ± 510 ± 58 ± 50.1762Pulmonary vascular resistance (dyne/second/cm5)232 ± 106265 ± 98200 ± 1050.0068Blood chemistry values Serum sodium (mmol/l)134 ± 10131 ± 12136 ± 60.0132 Serum creatinine (mg/dl)1.5 ± 0.71.5 ± 0.51.5 ± 0.70.9042 BUN (mg/dl)37 ± 2239 ± 2636 ± 190.9808 Serum ALT (U/l)82 ± 28789 ± 28657 ± 620.0827 Serum AST (U/l)71 ± 191115 ± 42956 ± 680.3388 Serum lactate dehydrogenase (mg/dl)372 ± 288295 ± 120437 ± 3640.0732 Serum total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.4 ± 1.11.4 ± 1.11.2 ± 0.80.7925Haematological values Haematocrit (%)35 ± 637 ± 733 ± 50.0152 Platelets per mm3199,000 ± 84,000202,000 ± 91,000199,000 ± 80,0000.9311Inotrope values Intravenous inotropic support (%)9197880.1329 Number of inotropes/patient1.8 ± 1.01.8 ± 0.81.8 ± 1.10.9517Mechanical support prior to implant surgery (%) ICD5348560.5069 Biventricular pacemaker3736381 IABP2618330.2033 Mechanical ventilation106130.462 | Characteristics | All ± SD (n = 82) | Trial ± SD (n = 33) | Post-market study ± SD (n = 49) | p-value (trial vs. post-market study) | Age, years (median) | 57 ± 11 (59) | 55 ± 13 (57) | 58 ± 10 (59) | 0.6462 | Male (%) | 91 | 85 | 96 | 0.161 | BSA (m2) | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 0.8986 | NYHA class IV (%) | 92 | 100 | 85 | 0.0303 | Ischaemic cause of HF (%) | 52 | 42 | 57 | 0.1207 | LVEF (%) | 20 ± 7 | 20 ± 7 | 20 ± 7 | 0.8986 | LVEDD (mm) | 72 ± 11 | 75 ± 13 | 70 ± 10 | 0.0689 | Systolic arterial BP (mmHg) | 92 ± 1 8 | 97 ± 16 | 76 ± 15 | 0.0007 | Diastolic arterial BP (mmHg) | 54 ± 15 | 59 ± 16 | 38 ± 14 | 0.0004 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 0.6 | 0.0018 | PCWP (mmHg) | 20 ± 6.6 | 22 ± 6.7 | 19 ± 6.4 | 0.165 | CVP (mmHg) | 9 ± 5 | 10 ± 5 | 8 ± 5 | 0.1762 | Pulmonary vascular resistance (dyne/second/cm5) | 232 ± 106 | 265 ± 98 | 200 ± 105 | 0.0068 | Blood chemistry values | Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 134 ± 10 | 131 ± 12 | 136 ± 6 | 0.0132 | Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 0.9042 | BUN (mg/dl) | 37 ± 22 | 39 ± 26 | 36 ± 19 | 0.9808 | Serum ALT (U/l) | 82 ± 287 | 89 ± 286 | 57 ± 62 | 0.0827 | Serum AST (U/l) | 71 ± 191 | 115 ± 429 | 56 ± 68 | 0.3388 | Serum lactate dehydrogenase (mg/dl) | 372 ± 288 | 295 ± 120 | 437 ± 364 | 0.0732 | Serum total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 1.1 | 1.4 ± 1.1 | 1.2 ± 0.8 | 0.7925 | Haematological values | Haematocrit (%) | 35 ± 6 | 37 ± 7 | 33 ± 5 | 0.0152 | Platelets per mm3 | 199,000 ± 84,000 | 202,000 ± 91,000 | 199,000 ± 80,000 | 0.9311 | Inotrope values | Intravenous inotropic support (%) | 91 | 97 | 88 | 0.1329 | Number of inotropes/patient | 1.8 ± 1.0 | 1.8 ± 0.8 | 1.8 ± 1.1 | 0.9517 | Mechanical support prior to implant surgery (%) | ICD | 53 | 48 | 56 | 0.5069 | Biventricular pacemaker | 37 | 36 | 38 | 1 | IABP | 26 | 18 | 33 | 0.2033 | Mechanical ventilation | 10 | 6 | 13 | 0.462 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristics | All ± SD (n = 82) | Trial ± SD (n = 33) | Post-market study ± SD (n = 49) | p-value (trial vs. post-market study) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, years (median) | 57 ± 11 (59) | 55 ± 13 (57) | 58 ± 10 (59) | 0.6462 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male (%) | 91 | 85 | 96 | 0.161 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 0.8986 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class IV (%) | 92 | 100 | 85 | 0.0303 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic cause of HF (%) | 52 | 42 | 57 | 0.1207 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF (%) | 20 ± 7 | 20 ± 7 | 20 ± 7 | 0.8986 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEDD (mm) | 72 ± 11 | 75 ± 13 | 70 ± 10 | 0.0689 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic arterial BP (mmHg) | 92 ± 1 8 | 97 ± 16 | 76 ± 15 | 0.0007 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic arterial BP (mmHg) | 54 ± 15 | 59 ± 16 | 38 ± 14 | 0.0004 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 0.6 | 0.0018 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 20 ± 6.6 | 22 ± 6.7 | 19 ± 6.4 | 0.165 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CVP (mmHg) | 9 ± 5 | 10 ± 5 | 8 ± 5 | 0.1762 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary vascular resistance (dyne/second/cm5) | 232 ± 106 | 265 ± 98 | 200 ± 105 | 0.0068 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blood chemistry values | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 134 ± 10 | 131 ± 12 | 136 ± 6 | 0.0132 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 0.9042 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 37 ± 22 | 39 ± 26 | 36 ± 19 | 0.9808 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum ALT (U/l) | 82 ± 287 | 89 ± 286 | 57 ± 62 | 0.0827 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum AST (U/l) | 71 ± 191 | 115 ± 429 | 56 ± 68 | 0.3388 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum lactate dehydrogenase (mg/dl) | 372 ± 288 | 295 ± 120 | 437 ± 364 | 0.0732 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 1.1 | 1.4 ± 1.1 | 1.2 ± 0.8 | 0.7925 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haematological values | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haematocrit (%) | 35 ± 6 | 37 ± 7 | 33 ± 5 | 0.0152 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets per mm3 | 199,000 ± 84,000 | 202,000 ± 91,000 | 199,000 ± 80,000 | 0.9311 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inotrope values | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intravenous inotropic support (%) | 91 | 97 | 88 | 0.1329 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of inotropes/patient | 1.8 ± 1.0 | 1.8 ± 0.8 | 1.8 ± 1.1 | 0.9517 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical support prior to implant surgery (%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICD | 53 | 48 | 56 | 0.5069 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biventricular pacemaker | 37 | 36 | 38 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP | 26 | 18 | 33 | 0.2033 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 10 | 6 | 13 | 0.462 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 (24%) patients died on support with a median time to death of 167 days (range 17–1066 days) 70% of deaths occurred within 1 year of support As of August 2009, 36 patients (45%) were alive using device support, with a median duration of 442 days, with a longest duration of 4.1 years Overall K–M survival for patients who continued on device support was 90% (95% CI 81% to 95%) at 13 weeks end point; 85% (95% CI 75% to 92%) at 6 months; 79% (95% CI 67% to 87%) at 1 year; and 58% (95% CI 37% to 74%) at 2 years Overall survival for 62 patients (76% of all patients) implanted at Heart and Diabetes Centre had survival outcome of 85% (95% CI 71% to 92%) at 12 months and 69% (95% CI 48% to 84%) at 24 months; this was significantly better than other centres (log-rank p = 0.05 at 12 months and p = 0.0365 at 24 months) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 patients (28%) received a HT, with a median time to HT of 157 days (range 43–497 days) 87% of patients received a HT within 1 year of device support, 13% received a HT after 1 year Median age of patients who received a HT was 52 years (range 29–68 years) Median age of patients with ongoing device support was 60 years (range 30–73 years), with 12 patients (31%) aged > 65 years and 4 patients (11%) aged > 70 years (p = 0.009) Two patients recovered and devices were removed at 283 and 344 days of support At 1 year, 20 patients (29%) received a HT, 31 patients (46%) remained on device support with median support duration of 1.5 years; 14 patients (21%) died, 2 patients (3%) recovered and underwent device explantation 66 patients (80% of all patients, n = 82; 86% survived > 30 days) were discharged from hospital with DuraHeart, with a median hospital stay after implantation of 36 days (range 20−147 days). Median time of out of hospital was 260 days (range 29–410 days) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 114 adverse events were observed in 31 patients (94%) during device support Highest rates of adverse events and deaths were observed within 30 days, and significantly lower levels of adverse events and deaths were observed after 1 month, and further decreased over time during late follow-up periods (91–180 days and > 180 days) 28 infections occurred in 22 patients (67%): 14 (50%) were localised and non-device related (pneumonia, urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections and decubitus ulceration); six patients (18%) had device-related infections (six driveline and one driveline/pocket infection); and six patients (18%) had sepsis Events of right HF were found 11 times in 10 patients (30%), and one patient (3%) required a RVAD [Thoratec PVAD™ (Thoratec Inc., Pleasanton, CA, USA)] A total of 11 neurological events occurred in 10 patients (33%), six were CVA and five were TIAs. Of these six CVAs (four haemorrhagic and two ischaemic), five were determined to be the cause of death. One intracerebral bleeding that followed an accidental fall was resolved without permanent neurological deficit In the initial 11 patients, five CVAs were reported (1.05/patient-year), whereas only one CVA was found in the last 22 patients (0.04/patient-year) after implementing less intensive anticoagulation and antiplatelet therapy Five CVAs occurred within the first 3 months and only one haemorrhagic CVA occurred at 549 days post implant Perioperatively, four patients developed acute renal dysfunction (12%); however, all events resolved within a few days. One patient (3%) had chronic renal failure and the patient later died of multiorgan failure Bleeding events occurred 11 times in eight patients (24%) Four events (two cardiac tamponades and two pump pocket bleedings) required surgical interventions Three patients (9%) had GI bleeding Three events of sudden temporary flow interruption occurred in two patients (6%) The authors state that the event rates for major adverse events during DuraHeart support were acceptable in comparison with the first-generation pulsatile and the second-generation axial flow devices. For example, event rate of bleeding requiring surgery (0.14/patient-year) was considerably lower in DuraHeart than first- and second-generation LVADs (1.47/patient-year and 0.78/patient-year, respectively) Three GI bleedings (9%; 0.10/patient-year) at 197, 275 and 113 days after implantation DuraHeart LVAS showed a lower rate of GI bleedings compared with those reported previously with other rotary blood pumps (0.10 vs. 0.63) and comparable to pulsatile pumps Driveline or pocket infection rate was reduced by 90% compared with pulsatile device (0.27 vs. 3.49) and was comparable to the small axial flow devices (0.27 vs. 0.37) Incidence of serious adverse events of 33 CE mark trial patients for extended duration of supportSerious adverse eventsOverall (n = 33) 28.7 patient-years0–30 days 2.6 patient years> 30 days 26.1 patient yearsNumber of eventsNumber of patients (%)Event rateNumber of eventsNumber of patients (%)Event rateNumber of eventsNumber of patients (%)Event rateAll serious adverse events11431 (94)3.965019 (58)18.96423 (70)2.45Local non-device-related infection1414 (42)0.4966 (18)2.2787 (21)0.31Driveline infection75 (15)0.2411 (3)0.3864 (12)0.23Pocket infection11 (3)0.0311 (3)0.38000Sepsis66 (18)0.2133 (9)1.1333 (9)0.11Right HF requiring RVAD11 (3)0.0611 (3)0.38000Right HF extended inotropes109 (27)0.3577 (21)2.6533 (9)0.11Ischaemic CVA22 (6)0.0722 (6)0.76000Haemorrhagic CVA44 (12)0.1411 (3)0.3833 (9)0.11TIA55 (15)0.1711 (3)0.3844 (12)0.15Ventricular arrhythmia88 (24)0.2855 (15)1.8944 (12)0.15Renal failure55 (15)0.1733 (9)1.1422 (6)0.08Total bleeding118 (24)0.3844 (12)1.5176 (12)0.27Bleeding requiring surgery44 (12)0.1422 (6)0.7622 (6)0.07Respiratory failure44 (12)0.1433 (9)1.1311 (3)0.04Pump replacement22 (6)0.0700022 (6)0.08Hepatic dysfunction22 (6)0.0722 (6)0.76000Myocardial infarction00000011 (3)0.04Other, total3421 (63)1.1833 (9)1.17209 (27)0.77 |
Serious adverse events | Overall (n = 33) 28.7 patient-years | 0–30 days 2.6 patient years | > 30 days 26.1 patient years | Number of events | Number of patients (%) | Event rate | Number of events | Number of patients (%) | Event rate | Number of events | Number of patients (%) | Event rate | All serious adverse events | 114 | 31 (94) | 3.96 | 50 | 19 (58) | 18.9 | 64 | 23 (70) | 2.45 | Local non-device-related infection | 14 | 14 (42) | 0.49 | 6 | 6 (18) | 2.27 | 8 | 7 (21) | 0.31 | Driveline infection | 7 | 5 (15) | 0.24 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.38 | 6 | 4 (12) | 0.23 | Pocket infection | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.03 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.38 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Sepsis | 6 | 6 (18) | 0.21 | 3 | 3 (9) | 1.13 | 3 | 3 (9) | 0.11 | Right HF requiring RVAD | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.06 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.38 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Right HF extended inotropes | 10 | 9 (27) | 0.35 | 7 | 7 (21) | 2.65 | 3 | 3 (9) | 0.11 | Ischaemic CVA | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.07 | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.76 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Haemorrhagic CVA | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.14 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.38 | 3 | 3 (9) | 0.11 | TIA | 5 | 5 (15) | 0.17 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.38 | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.15 | Ventricular arrhythmia | 8 | 8 (24) | 0.28 | 5 | 5 (15) | 1.89 | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.15 | Renal failure | 5 | 5 (15) | 0.17 | 3 | 3 (9) | 1.14 | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.08 | Total bleeding | 11 | 8 (24) | 0.38 | 4 | 4 (12) | 1.51 | 7 | 6 (12) | 0.27 | Bleeding requiring surgery | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.14 | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.76 | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.07 | Respiratory failure | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.14 | 3 | 3 (9) | 1.13 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.04 | Pump replacement | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.08 | Hepatic dysfunction | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.07 | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.76 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Myocardial infarction | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.04 | Other, total | 34 | 21 (63) | 1.18 | 3 | 3 (9) | 1.17 | 20 | 9 (27) | 0.77 | ||||||
| Serious adverse events | Overall (n = 33) 28.7 patient-years | 0–30 days 2.6 patient years | > 30 days 26.1 patient years | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of events | Number of patients (%) | Event rate | Number of events | Number of patients (%) | Event rate | Number of events | Number of patients (%) | Event rate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All serious adverse events | 114 | 31 (94) | 3.96 | 50 | 19 (58) | 18.9 | 64 | 23 (70) | 2.45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Local non-device-related infection | 14 | 14 (42) | 0.49 | 6 | 6 (18) | 2.27 | 8 | 7 (21) | 0.31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline infection | 7 | 5 (15) | 0.24 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.38 | 6 | 4 (12) | 0.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pocket infection | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.03 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.38 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 6 | 6 (18) | 0.21 | 3 | 3 (9) | 1.13 | 3 | 3 (9) | 0.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HF requiring RVAD | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.06 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.38 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HF extended inotropes | 10 | 9 (27) | 0.35 | 7 | 7 (21) | 2.65 | 3 | 3 (9) | 0.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic CVA | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.07 | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.76 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic CVA | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.14 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.38 | 3 | 3 (9) | 0.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TIA | 5 | 5 (15) | 0.17 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.38 | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventricular arrhythmia | 8 | 8 (24) | 0.28 | 5 | 5 (15) | 1.89 | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure | 5 | 5 (15) | 0.17 | 3 | 3 (9) | 1.14 | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bleeding | 11 | 8 (24) | 0.38 | 4 | 4 (12) | 1.51 | 7 | 6 (12) | 0.27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding requiring surgery | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.14 | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.76 | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory failure | 4 | 4 (12) | 0.14 | 3 | 3 (9) | 1.13 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump replacement | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hepatic dysfunction | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.07 | 2 | 2 (6) | 0.76 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myocardial infarction | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 (3) | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other, total | 34 | 21 (63) | 1.18 | 3 | 3 (9) | 1.17 | 20 | 9 (27) | 0.77 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Of 20 deaths reported, 13 were adjudicated by the Clinical Event Committee. The primary causes of these 13 deaths were CVA in six patients (four haemorrhagic; two ischaemic) and sepsis in three patients Other causes included non-traumatic subdural haematoma, accidental fall, acute myocardial infarction and unknown |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Third-generation DuraHeart LVAS combined with a centrifugal pump and active magnetic levitation provided adequate circulatory support with improved survival and reduced adverse event rates during extended follow-up periods for patients who are eligible for transplantation. Better survival outcomes, reduced adverse event rates and long-term device reliability in present study with DuraHeart LVADs compared with first-generation pulsatile LVADs. DuraHeart may have significant potential for long-term circulatory support for both BTT and DT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Several limitations were identified including limited clinical experience with 82 patients, with few patients supported beyond 2 years, and lack of a direct, randomised comparison with other LVADs, including second- and third-generation LVAS or optimal medical therapy. These patients appear to have been included in the earlier study by this author | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nativi 201189
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Nativi Year of publication: 2011 Country: USA Study design: Retrospective Study setting: Unclear Number of centres: Unclear. Data taken from ISHLT. The centres participating in data collection were listed on ISHLT website Duration of study: January 2000 to May 2008 Follow-up period: 4 years Funding: Part funded by the 2010 ISHLT ‘Branislav Radovancevic Memorial’ Best Mechanical Circulatory Support Abstract Award |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Determine whether or not post-transplant survival in BTT patients with newer CF LVADs differed from BTT patients bridged with first-generation pulsatile LVADs. Aimed to determine whether or not the era of LVAD implantation influenced survival rates | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 8557 patients underwent a HT between January 2000 and May 2008. Of these, 2397 required mechanical assist support as a BTT. In first era, 1100 BTT patients were bridged with pulsatile-flow LVADs. In second era, 880 BTT patients were bridged with pulsatile-flow LVADs and 417 BTT patients were bridged with CF LVADs. Control groups consisted of 3432 second-era patients who did not receive LVAD but needed continuous inotropic support before transplant and 2728 patients who did not need LVAD or inotropes Sample attrition/dropout: None reported Inclusion criteria: Included adult patients who underwent a HT from January 2000 to May 2008. No further details were provided Exclusion criteria: 568 patients were excluded from analysis, those who required biventricular support (both LVAD and RVAD or TAH) and those with temporary extracorporeal LVADs [ABIOMED BVS or TandemHeart™ (CardiacAssist Inc., Pittsburgh, PA, USA)]. Excluded patients bridged with CF LVADs transplanted in first era Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): Pulsatile LVAD 50.1 ± 11.6 years; pulsatile LVAD 50.2 ± 11.7 years; continuous LVAD 50.8 ± 12 years; no LVAD, on inotropes 51.4 ± 12.9 years; no LVAD, no inotropes 51.8 ± 12.6 years Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: % male – Pulsatile LVAD 85.5%; pulsatile LVAD 86.1%; continuous LVAD 82.3%; no LVAD, on inotropes 75.0%; no LVAD, no inotropes 74.9% Race: Not reported Diagnosis: HF |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT Type of device used: See below Devices and numberDevicenPulsatile LVAD, first era HMIP, HMVE, HMXVE1029 Novacor PC, PCq17 Thoratec33 Toyobo12 Other total9 Total1100Pulsatile LVAD, second era HM IP, VE, XVE605 Novacor PC, PCq58 Thoratec196 Toyobo9 Other12 Total880Continuous LVAD, second era HMII291 Jarvik 200039 MicroMed DeBakey34 VentrAssist31 Other22 Total417Note: first era January 2000 to June 2004; second era July 2004 to May 2008. Any comparison: Pulsatile LVAD, first era vs. pulsatile LVAD, second era vs. continuous LVAD, second era. Patients who required intravenous inotropes but not LVAD support (n = 2728) and patients who did not require either LVAD or inotropes (n = 3432) were controls Duration of treatment: Unclear Percentage of patients using inotropes: Unclear in the intervention groups. In the control groups: (a) no LVAD, on inotropes (n = 2728); and (b) no LVAD, no inotropes (n = 3432) Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII, Jarvik 2000, MicroMed MicroMed DeBakey |
Device | n | Pulsatile LVAD, first era | HMIP, HMVE, HMXVE | 1029 | Novacor PC, PCq | 17 | Thoratec | 33 | Toyobo | 12 | Other total | 9 | Total | 1100 | Pulsatile LVAD, second era | HM IP, VE, XVE | 605 | Novacor PC, PCq | 58 | Thoratec | 196 | Toyobo | 9 | Other | 12 | Total | 880 | Continuous LVAD, second era | HMII | 291 | Jarvik 2000 | 39 | MicroMed DeBakey | 34 | VentrAssist | 31 | Other | 22 | Total | 417 | Note: first era January 2000 to June 2004; second era July 2004 to May 2008. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device | n | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulsatile LVAD, first era | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMIP, HMVE, HMXVE | 1029 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Novacor PC, PCq | 17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thoratec | 33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toyobo | 12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other total | 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 1100 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulsatile LVAD, second era | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HM IP, VE, XVE | 605 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Novacor PC, PCq | 58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thoratec | 196 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toyobo | 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 880 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Continuous LVAD, second era | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII | 291 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jarvik 2000 | 39 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MicroMed DeBakey | 34 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VentrAssist | 31 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 417 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note: first era January 2000 to June 2004; second era July 2004 to May 2008. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: All-cause mortality. Secondary analyses focused on Secondary outcomes: Causes of mortality and non-fatal post-transplant events Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: 4 yearsNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reportedNot reportedRandomised/includedFirst era: Pulsatile LVAD (n = 1100)Second era: Pulsatile LVAD (n = 880); continuous LVAD (n = 417); no LVAD, on inotropes (n = 2728); no LVAD, no inotropes (n = 3432)See left columnExcludedIn total 568 patients were excluded from analysis: those who required biventricular support (both LVAD and RVAD or TAH) and those with temporary extracorporeal LVADs (ABIOMED BVS or TandemHeart). In addition, authors excluded patients bridged with CF LVADs transplanted in first era, as significant clinical use of CF devices did not occur until 2004 (n was not reported)See left columnMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reportedNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported | Not reported | Randomised/included | First era: Pulsatile LVAD (n = 1100) Second era: Pulsatile LVAD (n = 880); continuous LVAD (n = 417); no LVAD, on inotropes (n = 2728); no LVAD, no inotropes (n = 3432) |
See left column | Excluded | In total 568 patients were excluded from analysis: those who required biventricular support (both LVAD and RVAD or TAH) and those with temporary extracorporeal LVADs (ABIOMED BVS or TandemHeart). In addition, authors excluded patients bridged with CF LVADs transplanted in first era, as significant clinical use of CF devices did not occur until 2004 (n was not reported) | See left column | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | First era: Pulsatile LVAD (n = 1100) Second era: Pulsatile LVAD (n = 880); continuous LVAD (n = 417); no LVAD, on inotropes (n = 2728); no LVAD, no inotropes (n = 3432) |
See left column | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | In total 568 patients were excluded from analysis: those who required biventricular support (both LVAD and RVAD or TAH) and those with temporary extracorporeal LVADs (ABIOMED BVS or TandemHeart). In addition, authors excluded patients bridged with CF LVADs transplanted in first era, as significant clinical use of CF devices did not occur until 2004 (n was not reported) | See left column | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, years: See below Sex: See below BSA, m2: See below Weight, kg, BMI: See below Ischaemic causes of HF: See below |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First eraSecond erap-valuesPulsatile LVAD (n = 1100)Pulsatile LVAD (n = 880)Continuous LVAD (n = 417)No LVAD, on inotropes (n = 2728)No LVAD, no inotropes (n = 3432)RecipientAge, years50.1 ± 11.650.2 ± 11.750.8 ± 1251.4 ± 12.951.8 ± 12.6< 0.01BMI26.7 ± 4.327.4 ± 4.626.8 ± 4.726.2 ± 4.526.3 ± 4.4< 0.01Gender (% male)85.586.182.375.074.9< 0.01PRA (%)b7.5 ± 2010.4 ± 247.3 ± 194.8 ± 154.1 ± 14< 0.01 0–10%84.779.884.789.090.9< 0.01 > 10–30%6.77.76.164.3< 0.01 > 30–90%6.59.27.94.44.2< 0.01 > 90%2.23.21.30.70.7< 0.01Blood type< 0.01 A36.532.638.641.744.2 B11.112.210.113.915.7 AB3.33.12.66.07.3 O49.152.248.738.432.8Diagnosis< 0.01 DCM45.950.653.752.545.7 ICM51.645.044.437.642.0 VHD1.21.80.72.52.2 CHD0.40.50.02.93.6 Retransplant0.50.20.03.03.9 Other0.51.91.21.52.5Medical condition (%)< 0.01 In ICU27.623.116.447.312.9 Hospitalised not in ICU35.728.216.418.310.9 Not hospitalised36.748.767.234.476.3Diabetes mellitus20.527.428.325.521.7< 0.01Creatinine1.2 ± 0.51.2 ± 0.51.3 ± 0.51.3 ± 0.51.3 ± 0.5< 0.01 Ischaemic time (hours)3.2 ± 1.03.4 ± 1.13.4 ± 1.13.3 ± 1.03.2 ± 1.0< 0.01DonorAge (years)31.3 ± 12.130.9 ± 11.530.7 ± 11.831.6 ± 12.432.2 ± 12.70.08BMI (kg/m2)26.3 ± 4.726.9 ± 4.726.3 ± 4.526.1 ± 4.726.0 ± 4.6< 0.01Gender (% male)75.279.178.972.271.2< 0.01Blood type (%)< 0.01 A30.428.535.335.339.8 AB1.20.30.02.24.0 B6.47.27.710.012.1 O62.164.057.152.544.1Cause of deathHead trauma62.665.660.461.159.50.01Stroke27.021.924.024.826.90.02Other10.312.415.614.213.60.01First era: January 2000 to June 2004; second era: July 2004 to June 2006. | First era | Second era | p-values | Pulsatile LVAD (n = 1100) | Pulsatile LVAD (n = 880) | Continuous LVAD (n = 417) | No LVAD, on inotropes (n = 2728) | No LVAD, no inotropes (n = 3432) | Recipient | Age, years | 50.1 ± 11.6 | 50.2 ± 11.7 | 50.8 ± 12 | 51.4 ± 12.9 | 51.8 ± 12.6 | < 0.01 | BMI | 26.7 ± 4.3 | 27.4 ± 4.6 | 26.8 ± 4.7 | 26.2 ± 4.5 | 26.3 ± 4.4 | < 0.01 | Gender (% male) | 85.5 | 86.1 | 82.3 | 75.0 | 74.9 | < 0.01 | PRA (%)b | 7.5 ± 20 | 10.4 ± 24 | 7.3 ± 19 | 4.8 ± 15 | 4.1 ± 14 | < 0.01 | 0–10% | 84.7 | 79.8 | 84.7 | 89.0 | 90.9 | < 0.01 | > 10–30% | 6.7 | 7.7 | 6.1 | 6 | 4.3 | < 0.01 | > 30–90% | 6.5 | 9.2 | 7.9 | 4.4 | 4.2 | < 0.01 | > 90% | 2.2 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 0.7 | 0.7 | < 0.01 | Blood type | < 0.01 | A | 36.5 | 32.6 | 38.6 | 41.7 | 44.2 | B | 11.1 | 12.2 | 10.1 | 13.9 | 15.7 | AB | 3.3 | 3.1 | 2.6 | 6.0 | 7.3 | O | 49.1 | 52.2 | 48.7 | 38.4 | 32.8 | Diagnosis | < 0.01 | DCM | 45.9 | 50.6 | 53.7 | 52.5 | 45.7 | ICM | 51.6 | 45.0 | 44.4 | 37.6 | 42.0 | VHD | 1.2 | 1.8 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 2.2 | CHD | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 2.9 | 3.6 | Retransplant | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 3.0 | 3.9 | Other | 0.5 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 2.5 | Medical condition (%) | < 0.01 | In ICU | 27.6 | 23.1 | 16.4 | 47.3 | 12.9 | Hospitalised not in ICU | 35.7 | 28.2 | 16.4 | 18.3 | 10.9 | Not hospitalised | 36.7 | 48.7 | 67.2 | 34.4 | 76.3 | Diabetes mellitus | 20.5 | 27.4 | 28.3 | 25.5 | 21.7 | < 0.01 | Creatinine | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | < 0.01 | Ischaemic time (hours) | 3.2 ± 1.0 | 3.4 ± 1.1 | 3.4 ± 1.1 | 3.3 ± 1.0 | 3.2 ± 1.0 | < 0.01 | Donor | Age (years) | 31.3 ± 12.1 | 30.9 ± 11.5 | 30.7 ± 11.8 | 31.6 ± 12.4 | 32.2 ± 12.7 | 0.08 | BMI (kg/m2) | 26.3 ± 4.7 | 26.9 ± 4.7 | 26.3 ± 4.5 | 26.1 ± 4.7 | 26.0 ± 4.6 | < 0.01 | Gender (% male) | 75.2 | 79.1 | 78.9 | 72.2 | 71.2 | < 0.01 | Blood type (%) | < 0.01 | A | 30.4 | 28.5 | 35.3 | 35.3 | 39.8 | AB | 1.2 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 2.2 | 4.0 | B | 6.4 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 10.0 | 12.1 | O | 62.1 | 64.0 | 57.1 | 52.5 | 44.1 | Cause of death | Head trauma | 62.6 | 65.6 | 60.4 | 61.1 | 59.5 | 0.01 | Stroke | 27.0 | 21.9 | 24.0 | 24.8 | 26.9 | 0.02 | Other | 10.3 | 12.4 | 15.6 | 14.2 | 13.6 | 0.01 | First era: January 2000 to June 2004; second era: July 2004 to June 2006. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First era | Second era | p-values | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulsatile LVAD (n = 1100) | Pulsatile LVAD (n = 880) | Continuous LVAD (n = 417) | No LVAD, on inotropes (n = 2728) | No LVAD, no inotropes (n = 3432) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recipient | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, years | 50.1 ± 11.6 | 50.2 ± 11.7 | 50.8 ± 12 | 51.4 ± 12.9 | 51.8 ± 12.6 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI | 26.7 ± 4.3 | 27.4 ± 4.6 | 26.8 ± 4.7 | 26.2 ± 4.5 | 26.3 ± 4.4 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gender (% male) | 85.5 | 86.1 | 82.3 | 75.0 | 74.9 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PRA (%)b | 7.5 ± 20 | 10.4 ± 24 | 7.3 ± 19 | 4.8 ± 15 | 4.1 ± 14 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0–10% | 84.7 | 79.8 | 84.7 | 89.0 | 90.9 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 10–30% | 6.7 | 7.7 | 6.1 | 6 | 4.3 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 30–90% | 6.5 | 9.2 | 7.9 | 4.4 | 4.2 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > 90% | 2.2 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 0.7 | 0.7 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blood type | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | 36.5 | 32.6 | 38.6 | 41.7 | 44.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B | 11.1 | 12.2 | 10.1 | 13.9 | 15.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AB | 3.3 | 3.1 | 2.6 | 6.0 | 7.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| O | 49.1 | 52.2 | 48.7 | 38.4 | 32.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diagnosis | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DCM | 45.9 | 50.6 | 53.7 | 52.5 | 45.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICM | 51.6 | 45.0 | 44.4 | 37.6 | 42.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VHD | 1.2 | 1.8 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 2.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CHD | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 2.9 | 3.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Retransplant | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 3.0 | 3.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 0.5 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 2.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Medical condition (%) | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In ICU | 27.6 | 23.1 | 16.4 | 47.3 | 12.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hospitalised not in ICU | 35.7 | 28.2 | 16.4 | 18.3 | 10.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not hospitalised | 36.7 | 48.7 | 67.2 | 34.4 | 76.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 20.5 | 27.4 | 28.3 | 25.5 | 21.7 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic time (hours) | 3.2 ± 1.0 | 3.4 ± 1.1 | 3.4 ± 1.1 | 3.3 ± 1.0 | 3.2 ± 1.0 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Donor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 31.3 ± 12.1 | 30.9 ± 11.5 | 30.7 ± 11.8 | 31.6 ± 12.4 | 32.2 ± 12.7 | 0.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.3 ± 4.7 | 26.9 ± 4.7 | 26.3 ± 4.5 | 26.1 ± 4.7 | 26.0 ± 4.6 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gender (% male) | 75.2 | 79.1 | 78.9 | 72.2 | 71.2 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blood type (%) | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | 30.4 | 28.5 | 35.3 | 35.3 | 39.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AB | 1.2 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 2.2 | 4.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B | 6.4 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 10.0 | 12.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| O | 62.1 | 64.0 | 57.1 | 52.5 | 44.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Head trauma | 62.6 | 65.6 | 60.4 | 61.1 | 59.5 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke | 27.0 | 21.9 | 24.0 | 24.8 | 26.9 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 10.3 | 12.4 | 15.6 | 14.2 | 13.6 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First era: January 2000 to June 2004; second era: July 2004 to June 2006. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No significant difference in survival among patients bridged with CF LVADs compared with patients in control groups; patients without LVAD and not on inotropic support (RR = 1.19; p = 0.32) or on inotropic support (RR = 1.16; p = 0.41) No statistically significant difference in post-transplant survival of patients bridged in second era with CF LVADs compared with those bridged with pulsatile-flow LVADs (RR = 1.25; p = 0.26) To adjust for possible confounders of relationship between LVAD use and post-transplant survival, a proportional hazards multivariate regression analysis was undertaken, exploring donor and recipient characteristics collected at time of transplant. The results of this analysis are consistent with the univariate results below Comparison of mortality risk within 4 years in patients bridged with LVADs, for patients transplanted between 1 January 2000 and 30 June 2006: univariate analysisVariablesRR95% CIp-valueFirst-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes1.211.02 to 1.430.03First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes1.251.07 to 1.470.01First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era pulsatile LVAD1.301.03 to 1.650.03Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era pulsatile LVAD1.250.85 to 1.830.26Second-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes0.930.74 to 1.170.51Second-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes0.960.76 to 1.200.70Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes1.160.82 to 1.650.41Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes1.190.84 to 1.690.32 Even after adjustment, in the multivariate model, post-transplant survival in second era was similar among all groups of interest BTT patients with pulsatile-flow LVADs, patients bridged with CF LVADs, and patients not requiring LVAD support. See below Risk factors for mortality within 4 years of transplant, for patients transplanted between 1 January 2000 through 30 June 2006: multivariate analysisVariablesRR95% CIp-valueComparison between groups First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes1.281.05 to 1.580.02 First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes1.180.97 to 1.440.09 First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era pulsatile LVAD1.281.00 to 1.630.05 Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era pulsatile LVAD1.290.85 to 1.950.24 Second-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes1.010.78 to 1.300.96 Second-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes0.930.72 to 1.190.55 Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes1.290.88 to 1.910.19 Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes1.190.81 to 1.750.37Categorical Recipient on ventilator at time of transplant1.851.29 to 2.64< 0.01 Recipient history of dialysis1.731.33 to 2.26< 0.01 Congenital vs. cardiomyopathy1.541.07 to 2.230.02 Coronary artery disease vs. cardiomyopathy1.211.04 to 1.410.01Continuous Recipient age< 0.01 Donor age< 0.01 Recipient height< 0.01 Serum creatinine< 0.01 Serum bilirubin< 0.01 |
Variables | RR | 95% CI | p-value | First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes | 1.21 | 1.02 to 1.43 | 0.03 | First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes | 1.25 | 1.07 to 1.47 | 0.01 | First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era pulsatile LVAD | 1.30 | 1.03 to 1.65 | 0.03 | Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era pulsatile LVAD | 1.25 | 0.85 to 1.83 | 0.26 | Second-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes | 0.93 | 0.74 to 1.17 | 0.51 | Second-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes | 0.96 | 0.76 to 1.20 | 0.70 | Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes | 1.16 | 0.82 to 1.65 | 0.41 | Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes | 1.19 | 0.84 to 1.69 | 0.32 | Variables | RR | 95% CI | p-value | Comparison between groups | First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes | 1.28 | 1.05 to 1.58 | 0.02 | First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes | 1.18 | 0.97 to 1.44 | 0.09 | First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era pulsatile LVAD | 1.28 | 1.00 to 1.63 | 0.05 | Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era pulsatile LVAD | 1.29 | 0.85 to 1.95 | 0.24 | Second-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes | 1.01 | 0.78 to 1.30 | 0.96 | Second-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes | 0.93 | 0.72 to 1.19 | 0.55 | Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes | 1.29 | 0.88 to 1.91 | 0.19 | Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes | 1.19 | 0.81 to 1.75 | 0.37 | Categorical | Recipient on ventilator at time of transplant | 1.85 | 1.29 to 2.64 | < 0.01 | Recipient history of dialysis | 1.73 | 1.33 to 2.26 | < 0.01 | Congenital vs. cardiomyopathy | 1.54 | 1.07 to 2.23 | 0.02 | Coronary artery disease vs. cardiomyopathy | 1.21 | 1.04 to 1.41 | 0.01 | Continuous | Recipient age | < 0.01 | Donor age | < 0.01 | Recipient height | < 0.01 | Serum creatinine | < 0.01 | Serum bilirubin | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variables | RR | 95% CI | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes | 1.21 | 1.02 to 1.43 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes | 1.25 | 1.07 to 1.47 | 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era pulsatile LVAD | 1.30 | 1.03 to 1.65 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era pulsatile LVAD | 1.25 | 0.85 to 1.83 | 0.26 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Second-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes | 0.93 | 0.74 to 1.17 | 0.51 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Second-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes | 0.96 | 0.76 to 1.20 | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes | 1.16 | 0.82 to 1.65 | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes | 1.19 | 0.84 to 1.69 | 0.32 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variables | RR | 95% CI | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comparison between groups | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes | 1.28 | 1.05 to 1.58 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes | 1.18 | 0.97 to 1.44 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era pulsatile LVAD | 1.28 | 1.00 to 1.63 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era pulsatile LVAD | 1.29 | 0.85 to 1.95 | 0.24 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Second-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes | 1.01 | 0.78 to 1.30 | 0.96 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Second-era pulsatile LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes | 0.93 | 0.72 to 1.19 | 0.55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD on inotropes | 1.29 | 0.88 to 1.91 | 0.19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Second-era continuous LVAD vs. second-era no LVAD/no inotropes | 1.19 | 0.81 to 1.75 | 0.37 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Categorical | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recipient on ventilator at time of transplant | 1.85 | 1.29 to 2.64 | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recipient history of dialysis | 1.73 | 1.33 to 2.26 | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Congenital vs. cardiomyopathy | 1.54 | 1.07 to 2.23 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coronary artery disease vs. cardiomyopathy | 1.21 | 1.04 to 1.41 | 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Continuous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recipient age | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Donor age | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recipient height | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum creatinine | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum bilirubin | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Significant differences in morbidity after transplant in patients in five different groups Before discharge, most reported adverse event was drug-treated infection Risk of fatal or non-fatal stroke before discharge was roughly double (3–5%) in patients bridged with LVADs compared with patients without LVADs (< 2%; p < 0.01) Risk of renal failure requiring haemodialysis before discharge was higher in patients bridged with LVADs (11–13%) compared with patients not needing LVAD bridging (9–10%; p = 0.02) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post-transplant events | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post-transplant eventsFirst eraSecond erap-valuePulsatile LVAD, n (%)Pulsatile LVAD, n (%)Continuous LVAD, n (%)No LVAD, on inotropes, n (%)No LVAD, no inotropes, n (%)Prior to discharge Drug-treated infection365 (34.4)298 (37.0)116 (35.0)571 (22.8)606 (19.9)< 0.01 Stroke34 (3.2)41 (4.8)13 (3.4)43 (1.7)51 (1.6)< 0.01 Dialysis113 (10.6)101 (11.9)49 (12.7)255 (9.7)287 (8.9)0.0212 months post discharge Treated rejection163 (24.8)61 (24.3)415 (22.2)500 (21.5)0.27 Stroke13 (1.5)18 (3.1)5 (2.7)19 (1.1)25 (1.2)< 0.01 Hypertension658 (75.7)410 (71.1)148 (77.9)1215 (73.2)1511 (73.5)0.21 Hyperlipidaemia646 (74.0)400 (68.7)135 (68.5)1203 (71.1)1530 (72.3)0.11 Diabetes mellitus254 (29.0)222 (33.5)84 (33.31)657 (34.9)742 (31.7)0.03 Vascutopathy52 (6.5)38 (6.2)15 (6.6)129 (7.7)156 (7.4)0.68 Malignancy17 (1.9)11 (1.6)2 (0.8)45 (2.4)54 (2.4)0.36 Severe renal dysfunctions81 (9.2)40 (6.0)25 (9.9)75 (4.0)104 (4.5)< 0.01p-values compare all groups. | Post-transplant events | First era | Second era | p-value | Pulsatile LVAD, n (%) | Pulsatile LVAD, n (%) | Continuous LVAD, n (%) | No LVAD, on inotropes, n (%) | No LVAD, no inotropes, n (%) | Prior to discharge | Drug-treated infection | 365 (34.4) | 298 (37.0) | 116 (35.0) | 571 (22.8) | 606 (19.9) | < 0.01 | Stroke | 34 (3.2) | 41 (4.8) | 13 (3.4) | 43 (1.7) | 51 (1.6) | < 0.01 | Dialysis | 113 (10.6) | 101 (11.9) | 49 (12.7) | 255 (9.7) | 287 (8.9) | 0.02 | 12 months post discharge | Treated rejection | 163 (24.8) | 61 (24.3) | 415 (22.2) | 500 (21.5) | 0.27 | Stroke | 13 (1.5) | 18 (3.1) | 5 (2.7) | 19 (1.1) | 25 (1.2) | < 0.01 | Hypertension | 658 (75.7) | 410 (71.1) | 148 (77.9) | 1215 (73.2) | 1511 (73.5) | 0.21 | Hyperlipidaemia | 646 (74.0) | 400 (68.7) | 135 (68.5) | 1203 (71.1) | 1530 (72.3) | 0.11 | Diabetes mellitus | 254 (29.0) | 222 (33.5) | 84 (33.31) | 657 (34.9) | 742 (31.7) | 0.03 | Vascutopathy | 52 (6.5) | 38 (6.2) | 15 (6.6) | 129 (7.7) | 156 (7.4) | 0.68 | Malignancy | 17 (1.9) | 11 (1.6) | 2 (0.8) | 45 (2.4) | 54 (2.4) | 0.36 | Severe renal dysfunctions | 81 (9.2) | 40 (6.0) | 25 (9.9) | 75 (4.0) | 104 (4.5) | < 0.01 | p-values compare all groups. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post-transplant events | First era | Second era | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulsatile LVAD, n (%) | Pulsatile LVAD, n (%) | Continuous LVAD, n (%) | No LVAD, on inotropes, n (%) | No LVAD, no inotropes, n (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prior to discharge | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug-treated infection | 365 (34.4) | 298 (37.0) | 116 (35.0) | 571 (22.8) | 606 (19.9) | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke | 34 (3.2) | 41 (4.8) | 13 (3.4) | 43 (1.7) | 51 (1.6) | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dialysis | 113 (10.6) | 101 (11.9) | 49 (12.7) | 255 (9.7) | 287 (8.9) | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 months post discharge | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treated rejection | 163 (24.8) | 61 (24.3) | 415 (22.2) | 500 (21.5) | 0.27 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke | 13 (1.5) | 18 (3.1) | 5 (2.7) | 19 (1.1) | 25 (1.2) | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension | 658 (75.7) | 410 (71.1) | 148 (77.9) | 1215 (73.2) | 1511 (73.5) | 0.21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hyperlipidaemia | 646 (74.0) | 400 (68.7) | 135 (68.5) | 1203 (71.1) | 1530 (72.3) | 0.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 254 (29.0) | 222 (33.5) | 84 (33.31) | 657 (34.9) | 742 (31.7) | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vascutopathy | 52 (6.5) | 38 (6.2) | 15 (6.6) | 129 (7.7) | 156 (7.4) | 0.68 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Malignancy | 17 (1.9) | 11 (1.6) | 2 (0.8) | 45 (2.4) | 54 (2.4) | 0.36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Severe renal dysfunctions | 81 (9.2) | 40 (6.0) | 25 (9.9) | 75 (4.0) | 104 (4.5) | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-values compare all groups. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Causes of death at 1 year after transplantCause of deathFirst eraSecond erap-valuePulsatile LVAD (n = 1100), n (%)Pulsatile LVAD (n = 880), n (%)Continuous LVAD (n = 417), n (%)No LVAD, on inotropes (n = 2728), n (%)No LVAD, no inotropes (n = 3432), n (%)Infection39 (3.6)24 (2.7)11 (2.6)57 (2.1)74 (2.3)0.10Graft failure41 (3.7)32 (3.6)15 (3.6)75 (2.7)96 (2.8)0.31CAV3 (0.3)1 (0.1)1 (0.2)5 (0.2)6 (0.2)0.85Acute rejection9 (0.8)5 (0.6)7 (1.7)27 (1.0)29 (0.8)0.36Technical9 (0.8)3 (0.3)4 (1.0)10 (0.4)14 (0.4)0.18Multiorgan failure13 (1.2)15 (1.7)5 (1.2)31 (1.1)47 (1.4)0.74Renal failure1 (0.1)2 (0.2)0 (0.0)2 (0.1)3 (0.1)0.69Pulmonary6 (0.5)4 (0.5)4 (1.0)18 (0.7)21 (0.6)0.85Cerebrovascular8 (0.7)0 (0.0)2 (0.5)17 (0.6)22 (0.6)0.20Malignancy1 (0.1)1 (0.1)1 (0.2)6 (0.2)7 (0.2)0.71Other15 (1.4)8 (0.9)5 (1.2)34 (1.2)27 (0.8)0.33All causes of death145 (13.2)95 (10.8)55 (13.2)282 (10.3)346 (10.1)p-values compare all groups. No adjustments were made for multiple comparisons. | Cause of death | First era | Second era | p-value | Pulsatile LVAD (n = 1100), n (%) | Pulsatile LVAD (n = 880), n (%) | Continuous LVAD (n = 417), n (%) | No LVAD, on inotropes (n = 2728), n (%) | No LVAD, no inotropes (n = 3432), n (%) | Infection | 39 (3.6) | 24 (2.7) | 11 (2.6) | 57 (2.1) | 74 (2.3) | 0.10 | Graft failure | 41 (3.7) | 32 (3.6) | 15 (3.6) | 75 (2.7) | 96 (2.8) | 0.31 | CAV | 3 (0.3) | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.2) | 5 (0.2) | 6 (0.2) | 0.85 | Acute rejection | 9 (0.8) | 5 (0.6) | 7 (1.7) | 27 (1.0) | 29 (0.8) | 0.36 | Technical | 9 (0.8) | 3 (0.3) | 4 (1.0) | 10 (0.4) | 14 (0.4) | 0.18 | Multiorgan failure | 13 (1.2) | 15 (1.7) | 5 (1.2) | 31 (1.1) | 47 (1.4) | 0.74 | Renal failure | 1 (0.1) | 2 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.1) | 3 (0.1) | 0.69 | Pulmonary | 6 (0.5) | 4 (0.5) | 4 (1.0) | 18 (0.7) | 21 (0.6) | 0.85 | Cerebrovascular | 8 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.5) | 17 (0.6) | 22 (0.6) | 0.20 | Malignancy | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.2) | 6 (0.2) | 7 (0.2) | 0.71 | Other | 15 (1.4) | 8 (0.9) | 5 (1.2) | 34 (1.2) | 27 (0.8) | 0.33 | All causes of death | 145 (13.2) | 95 (10.8) | 55 (13.2) | 282 (10.3) | 346 (10.1) | p-values compare all groups. No adjustments were made for multiple comparisons. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death | First era | Second era | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulsatile LVAD (n = 1100), n (%) | Pulsatile LVAD (n = 880), n (%) | Continuous LVAD (n = 417), n (%) | No LVAD, on inotropes (n = 2728), n (%) | No LVAD, no inotropes (n = 3432), n (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection | 39 (3.6) | 24 (2.7) | 11 (2.6) | 57 (2.1) | 74 (2.3) | 0.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Graft failure | 41 (3.7) | 32 (3.6) | 15 (3.6) | 75 (2.7) | 96 (2.8) | 0.31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAV | 3 (0.3) | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.2) | 5 (0.2) | 6 (0.2) | 0.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acute rejection | 9 (0.8) | 5 (0.6) | 7 (1.7) | 27 (1.0) | 29 (0.8) | 0.36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | 9 (0.8) | 3 (0.3) | 4 (1.0) | 10 (0.4) | 14 (0.4) | 0.18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Multiorgan failure | 13 (1.2) | 15 (1.7) | 5 (1.2) | 31 (1.1) | 47 (1.4) | 0.74 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure | 1 (0.1) | 2 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.1) | 3 (0.1) | 0.69 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary | 6 (0.5) | 4 (0.5) | 4 (1.0) | 18 (0.7) | 21 (0.6) | 0.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cerebrovascular | 8 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.5) | 17 (0.6) | 22 (0.6) | 0.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Malignancy | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.2) | 6 (0.2) | 7 (0.2) | 0.71 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 15 (1.4) | 8 (0.9) | 5 (1.2) | 34 (1.2) | 27 (0.8) | 0.33 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All causes of death | 145 (13.2) | 95 (10.8) | 55 (13.2) | 282 (10.3) | 346 (10.1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-values compare all groups. No adjustments were made for multiple comparisons. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post-transplant survival of BTT patients with LVADs has improved. In most recent era, the use of either pulsatile- or CF LVADs did not result in increased mortality up to 4 years after transplant. The key finding of this study is the demonstration of improved post-transplant survival of patients bridged with LVADs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Large number of confounding factors as shown by the statistically significant differences in baseline characteristics. Cox's proportional hazards assumption may not have been tested | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Oswald 201090
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Oswald Year of publication: 2010 Country: Germany Study design: Prospective Study setting: Unclear Number of centres: Unclear Duration of study: July 2005 and October 2008 Follow-up period: Median follow-up of 12 months of ICD protection during ongoing LVAD support (range 13–1167 days). Outpatient routine follow-up was performed at 3-month intervals Funding: Not reported |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To investigate incidence and prevalence of VA, defined as ICD interventions, in patients with CF LVADs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 61 – HMII was implanted in 44 patients and 17 patients received HW LVAD system Sample attrition/dropout: None Inclusion criteria: Consecutive patients with drug refractory highly symptomatic congestive HF and successful implantation of a CF LVAD between July 2005 and October 2008 were included Exclusion criteria: Not reported Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): 50 ± 12 years Median age: Not reported Age range: 17–75 years Sex: Male n = 58 (95%) Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Drug refractory highly symptomatic congestive HF: 46 (75%) patients underwent ICD implantation for primary prophylaxis of VA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: Unclear Type of device used: HMII and the HW Any comparison: Outcomes of HMII and HW were not compared Duration of treatment: ICDs were implanted on average 17 ± 15 days after LVAD implantation Percentage of patients using inotropes: Not reported Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII and the HW |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Safety and efficacy of primary prevention ICD therapy and the rate of appropriate ICD interventions Secondary outcomes: Unclear Method of assessing outcomes: Prospective data collection Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: Median follow-up of 12 months of ICD protection during ongoing LVAD support (range 13–1167 days)Number of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reportedNot reportedRandomised/includedHMII n = 44 and HW n = 17Not reportedExcludedNot reportedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reportedNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported | Not reported | Randomised/included | HMII n = 44 and HW n = 17 | Not reported | Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | HMII n = 44 and HW n = 17 | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variablen%Total patients61Age (years)50 ± 12 (range 17–75)12 (range 17–75)Male sex5895Heart disease ICM3049 NICM3151Medication Beta-blockers4269 ACE inhibitors4167 Aldosterone antagonists2541 Diuretics4777 Calcium channel blockers58 Oral anticoagulation61100 Platelet inhibitors1118 Amiodarone4371 Digitalis1220LVAD HMII4472 HW1728 | Variable | n | % | Total patients | 61 | Age (years) | 50 ± 12 (range 17–75) | 12 (range 17–75) | Male sex | 58 | 95 | Heart disease | ICM | 30 | 49 | NICM | 31 | 51 | Medication | Beta-blockers | 42 | 69 | ACE inhibitors | 41 | 67 | Aldosterone antagonists | 25 | 41 | Diuretics | 47 | 77 | Calcium channel blockers | 5 | 8 | Oral anticoagulation | 61 | 100 | Platelet inhibitors | 11 | 18 | Amiodarone | 43 | 71 | Digitalis | 12 | 20 | LVAD | HMII | 44 | 72 | HW | 17 | 28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variable | n | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total patients | 61 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 50 ± 12 (range 17–75) | 12 (range 17–75) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male sex | 58 | 95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heart disease | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICM | 30 | 49 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NICM | 31 | 51 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Medication | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beta-blockers | 42 | 69 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACE inhibitors | 41 | 67 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aldosterone antagonists | 25 | 41 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diuretics | 47 | 77 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Calcium channel blockers | 5 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oral anticoagulation | 61 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelet inhibitors | 11 | 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amiodarone | 43 | 71 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Digitalis | 12 | 20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII | 44 | 72 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HW | 17 | 28 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with a secondary prevention indication for ICD implantation [ICD was implanted before LVAD implantation (12 patients, mean ICD treatment before LVAD 16 ± 16 months)], a monthly event rate was calculated (number of spontaneous VA divided by observation time) for the period before LVAD implantation (0.65 ± 1.56 VA events/month) and after LVAD implantation (0.65 ± 1.58 VA events/month) This calculated event rate did not differ for the period of time before vs. after implantation of the LVAD (P 0.99) Patients with no previous arrhythmia history had an estimated 1-year risk of 24% for appropriate ICD treatment Patients with a secondary prevention indication had an even higher 1-year risk of 50% |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICD devices and settingsICD devices and settingsn (%)Primary prevention ICD46 (75)Secondary prevention ICD15 (25)VVI-ICD43 (71)DDD-ICD5 (8)CRTD13 (21)VT-zone interval (ms)345 ± 31VT detection duration (intervals)24 ± 1VF-zone interval (ms)286 ± 13VF detection duration (intervals)24 ± 1 ResultsOutcomen%Patient status Alive with ongoing LVAD4472 Alive with explanted LVAD (recovered)12 HT711 Death915Patient safety and complications Non-lethal cerebrovascular event35 LVAD cable infection (total)1423 Conservatively managed1321 Requiring surgical revision12 Operation for ICD system revision (total)1423 HMII and ICD interaction47 ICD replacement for battery depletion47 Right ventricular lead failure35 ICD pocket haematoma revision35VA burden Patients with appropriate ICD Therapy (total)21 With monomorphic VT52 With polymorphic VT13With VF Patients with inappropriate ICD therapy (after 7-days in hospital blanking period)1525 |
ICD devices and settings | n (%) | Primary prevention ICD | 46 (75) | Secondary prevention ICD | 15 (25) | VVI-ICD | 43 (71) | DDD-ICD | 5 (8) | CRTD | 13 (21) | VT-zone interval (ms) | 345 ± 31 | VT detection duration (intervals) | 24 ± 1 | VF-zone interval (ms) | 286 ± 13 | VF detection duration (intervals) | 24 ± 1 | Outcome | n | % | Patient status | Alive with ongoing LVAD | 44 | 72 | Alive with explanted LVAD (recovered) | 1 | 2 | HT | 7 | 11 | Death | 9 | 15 | Patient safety and complications | Non-lethal cerebrovascular event | 3 | 5 | LVAD cable infection (total) | 14 | 23 | Conservatively managed | 13 | 21 | Requiring surgical revision | 1 | 2 | Operation for ICD system revision (total) | 14 | 23 | HMII and ICD interaction | 4 | 7 | ICD replacement for battery depletion | 4 | 7 | Right ventricular lead failure | 3 | 5 | ICD pocket haematoma revision | 3 | 5 | VA burden | Patients with appropriate ICD Therapy (total) | 21 | With monomorphic VT | 52 | With polymorphic VT | 13 | With VF | Patients with inappropriate ICD therapy (after 7-days in hospital blanking period) | 15 | 25 | |||||||||||
| ICD devices and settings | n (%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary prevention ICD | 46 (75) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary prevention ICD | 15 (25) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VVI-ICD | 43 (71) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DDD-ICD | 5 (8) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CRTD | 13 (21) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VT-zone interval (ms) | 345 ± 31 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VT detection duration (intervals) | 24 ± 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VF-zone interval (ms) | 286 ± 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VF detection duration (intervals) | 24 ± 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcome | n | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient status | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alive with ongoing LVAD | 44 | 72 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alive with explanted LVAD (recovered) | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HT | 7 | 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Death | 9 | 15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient safety and complications | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-lethal cerebrovascular event | 3 | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD cable infection (total) | 14 | 23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conservatively managed | 13 | 21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Requiring surgical revision | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operation for ICD system revision (total) | 14 | 23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII and ICD interaction | 4 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICD replacement for battery depletion | 4 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right ventricular lead failure | 3 | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICD pocket haematoma revision | 3 | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VA burden | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with appropriate ICD Therapy (total) | 21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| With monomorphic VT | 52 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| With polymorphic VT | 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| With VF | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with inappropriate ICD therapy (after 7-days in hospital blanking period) | 15 | 25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 71% of VA were terminated by overdrive pacing, 29% by shock Nine patients died from thromboembolism or haemorrhage Overall, the rate of appropriate ICD interventions was 34%, mostly for treatment of monomorphic VT in 52%, polymorphic VT in 13%, and VF in 35% Patients with a history of VA before LVAD implantation had a significantly higher 1-year rate for ICD therapy compared with LVAD patients with a primary prevention ICD indication LVAD patients (50% vs. 24%) Patients with NICM had a significantly higher risk for ICD therapy than patients with ischaemic heart disease (50% vs. 22%) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nine deaths (15%) due to thromboembolic events and haemorrhage, in particular stroke | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More than one-third of LVAD recipients experience appropriate ICD therapy in the first year. Patients with a secondary prophylactic ICD indication have a twofold increased risk for appropriate shocks compared with patients with a primary prophylactic ICD indication. Patients with NICM have a higher risk of appropriate ICD therapies than patients with ICM. ICD therapy is safe and effective in LVAD patients. VAs leading to ICD intervention occur frequently in LVAD patients over 1 year of follow-up, with large differences depending on underlying cardiac disease and previous arrhythmia history | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This is the first paper to show prospective data for a large cohort of primary prevention ICD indication patients after LVAD implantation. The author states that it is unclear how often VF in LVAD patients leads to cardiogenic shock and how often LVAD support is sufficient to sustain long-term circulation in non-pulsatile LVADs. Baseline characteristics are not described separately for each group. Regression and Cox's proportional hazards were not undertaken to accommodate confounders and identify influential variables – limited reporting of p-values | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pagani 200971
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Pagani Year of publication: 2009 Country: USA Study design: Prospective non-comparative trial Study setting: Hospital Number of centres: 33 centres in the USA Duration of study: Unclear. Enrolment was between March 2005 and April 2008 Follow-up period: Up to 18 months Funding: Industry, Thoratec Inc. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To evaluate the use of a CF rotary LVAD (HMII) as a BTT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 281 Sample attrition/dropout: Three participants were withdrawn because of HMII replacement with an alternative device Inclusion criteria: Patients with HF who were on a WL for a HT at each centre were eligible for study enrolment. Patients were required to have symptoms of NYHA functional class IV HF and to be ill enough to have high priority for transplantation (UNOS status 1a or 1b). A complete list of study inclusion and exclusion criteria have been reported in Miller et al.70 Exclusion criteria: See Miller et al.70 Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): 50 years (13) Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: Male 214/281 (76%) Race: Caucasian n = 194 (69%)/African American n = 61 (22%) Diagnosis: HF |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: No Duration of treatment: Various Percentage of patients using inotropes: 90% (252/281) Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: The principal outcomes assessed, through 18 months after enrolment, were the proportions of patients who had undergone transplantation, had undergone explantation of the device because of recovery of ventricular function, or continued with ongoing MCS Secondary outcomes: QoL, adverse events Method of assessing outcomes: Prospective data collection Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: Yes Length of follow-up: To 18 months; cumulative follow-up of 181 patient-yearsNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreened469 enrolledRandomised/included281 (completed study end points or had 18 months follow-up)ExcludedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedWithdrawals3 |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | 469 enrolled | Randomised/included | 281 (completed study end points or had 18 months follow-up) | Excluded | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Withdrawals | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | 469 enrolled | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 281 (completed study end points or had 18 months follow-up) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ParameterValueAge (years)50 ± 13Male214 (76)Caucasian/African American194 (69)/61 (22)BMI (kg/m2)27.1 ± 5.8BSA (m2)2.0 ± 0.3Ischaemic aetiology of HF121 (43)LVEF (%)16.3 ± 6.5Arterial BP (mmHg) Systolic98.1 ± 15.0 Diastolic61.4 ± 11.2Pulmonary-capillary wedge pressure (mmHg)25.4 ± 7.9Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)2.1 ± 0.6Heart rate (b.p.m.)92.2 ± 18.8Pulmonary artery pressure (mmHg) Systolic51.4 ± 13.7 Diastolic26.8 ± 8.4 Mean35.9 ± 9.6Pulmonary vascular resistance (Wood units)2.8 ± 1.4CVP (mmHg)12.6 ± 6.5RVSWI (mmHg/ml/m2)548 ± 291NYHA functional classIVSerum sodium (mmol/l)133.7 ± 5.2Serum albumin (g/dl)3.5 ± 0.6Pre-albumin (mg/dl)18.4 ± 7.6Cholesterol (mg/dl)129 ± 41Serum creatinine (mg/dl)1.4 ± 0.5Estimated creatinine clearance (ml/minute)78.6 ± 35.1BUN (mg/dl)30.4 ± 17.1ALT (IU/l)106 ± 278AST (IU/l)92 ± 281Total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.3 ± 0.9LDH (mg/dl)584 ± 1,489Haematocrit (%)34.8 ± 5.5White blood count (× 1000/ml)9.0 ± 3.4Platelets (× 1000/ml)223 ± 88INR1.3 ± 0.5Concomitant medications Intravenous inotrope agents252 (90) Intolerant to inotropes due to arrhythmias29 (10) Two or more inotrope agents91 (32) Diuretics228 (81) ACE inhibitors73 (26) Angiotensin-II receptor antagonists17 (6) Beta-blockers100 (36) Digoxin111 (40) Hydralazine37 (13) Amiodarone105 (37) Heparin174 (62) Warfarin6 (2) Aspirin89 (32) CRT135 (48) ICD213 (76) IABP126 (45) Mechanical ventilation26 (9) | Parameter | Value | Age (years) | 50 ± 13 | Male | 214 (76) | Caucasian/African American | 194 (69)/61 (22) | BMI (kg/m2) | 27.1 ± 5.8 | BSA (m2) | 2.0 ± 0.3 | Ischaemic aetiology of HF | 121 (43) | LVEF (%) | 16.3 ± 6.5 | Arterial BP (mmHg) | Systolic | 98.1 ± 15.0 | Diastolic | 61.4 ± 11.2 | Pulmonary-capillary wedge pressure (mmHg) | 25.4 ± 7.9 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.1 ± 0.6 | Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 92.2 ± 18.8 | Pulmonary artery pressure (mmHg) | Systolic | 51.4 ± 13.7 | Diastolic | 26.8 ± 8.4 | Mean | 35.9 ± 9.6 | Pulmonary vascular resistance (Wood units) | 2.8 ± 1.4 | CVP (mmHg) | 12.6 ± 6.5 | RVSWI (mmHg/ml/m2) | 548 ± 291 | NYHA functional class | IV | Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 133.7 ± 5.2 | Serum albumin (g/dl) | 3.5 ± 0.6 | Pre-albumin (mg/dl) | 18.4 ± 7.6 | Cholesterol (mg/dl) | 129 ± 41 | Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | Estimated creatinine clearance (ml/minute) | 78.6 ± 35.1 | BUN (mg/dl) | 30.4 ± 17.1 | ALT (IU/l) | 106 ± 278 | AST (IU/l) | 92 ± 281 | Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.3 ± 0.9 | LDH (mg/dl) | 584 ± 1,489 | Haematocrit (%) | 34.8 ± 5.5 | White blood count (× 1000/ml) | 9.0 ± 3.4 | Platelets (× 1000/ml) | 223 ± 88 | INR | 1.3 ± 0.5 | Concomitant medications | Intravenous inotrope agents | 252 (90) | Intolerant to inotropes due to arrhythmias | 29 (10) | Two or more inotrope agents | 91 (32) | Diuretics | 228 (81) | ACE inhibitors | 73 (26) | Angiotensin-II receptor antagonists | 17 (6) | Beta-blockers | 100 (36) | Digoxin | 111 (40) | Hydralazine | 37 (13) | Amiodarone | 105 (37) | Heparin | 174 (62) | Warfarin | 6 (2) | Aspirin | 89 (32) | CRT | 135 (48) | ICD | 213 (76) | IABP | 126 (45) | Mechanical ventilation | 26 (9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 50 ± 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male | 214 (76) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caucasian/African American | 194 (69)/61 (22) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.1 ± 5.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 2.0 ± 0.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic aetiology of HF | 121 (43) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF (%) | 16.3 ± 6.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arterial BP (mmHg) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic | 98.1 ± 15.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic | 61.4 ± 11.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary-capillary wedge pressure (mmHg) | 25.4 ± 7.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.1 ± 0.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 92.2 ± 18.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary artery pressure (mmHg) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic | 51.4 ± 13.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic | 26.8 ± 8.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean | 35.9 ± 9.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary vascular resistance (Wood units) | 2.8 ± 1.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CVP (mmHg) | 12.6 ± 6.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVSWI (mmHg/ml/m2) | 548 ± 291 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA functional class | IV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 133.7 ± 5.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum albumin (g/dl) | 3.5 ± 0.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-albumin (mg/dl) | 18.4 ± 7.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cholesterol (mg/dl) | 129 ± 41 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Estimated creatinine clearance (ml/minute) | 78.6 ± 35.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 30.4 ± 17.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT (IU/l) | 106 ± 278 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST (IU/l) | 92 ± 281 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.3 ± 0.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LDH (mg/dl) | 584 ± 1,489 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haematocrit (%) | 34.8 ± 5.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| White blood count (× 1000/ml) | 9.0 ± 3.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets (× 1000/ml) | 223 ± 88 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INR | 1.3 ± 0.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concomitant medications | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intravenous inotrope agents | 252 (90) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intolerant to inotropes due to arrhythmias | 29 (10) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Two or more inotrope agents | 91 (32) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diuretics | 228 (81) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACE inhibitors | 73 (26) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Angiotensin-II receptor antagonists | 17 (6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beta-blockers | 100 (36) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Digoxin | 111 (40) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydralazine | 37 (13) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amiodarone | 105 (37) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heparin | 174 (62) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warfarin | 6 (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aspirin | 89 (32) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CRT | 135 (48) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICD | 213 (76) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP | 126 (45) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 26 (9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
K–M survival analysis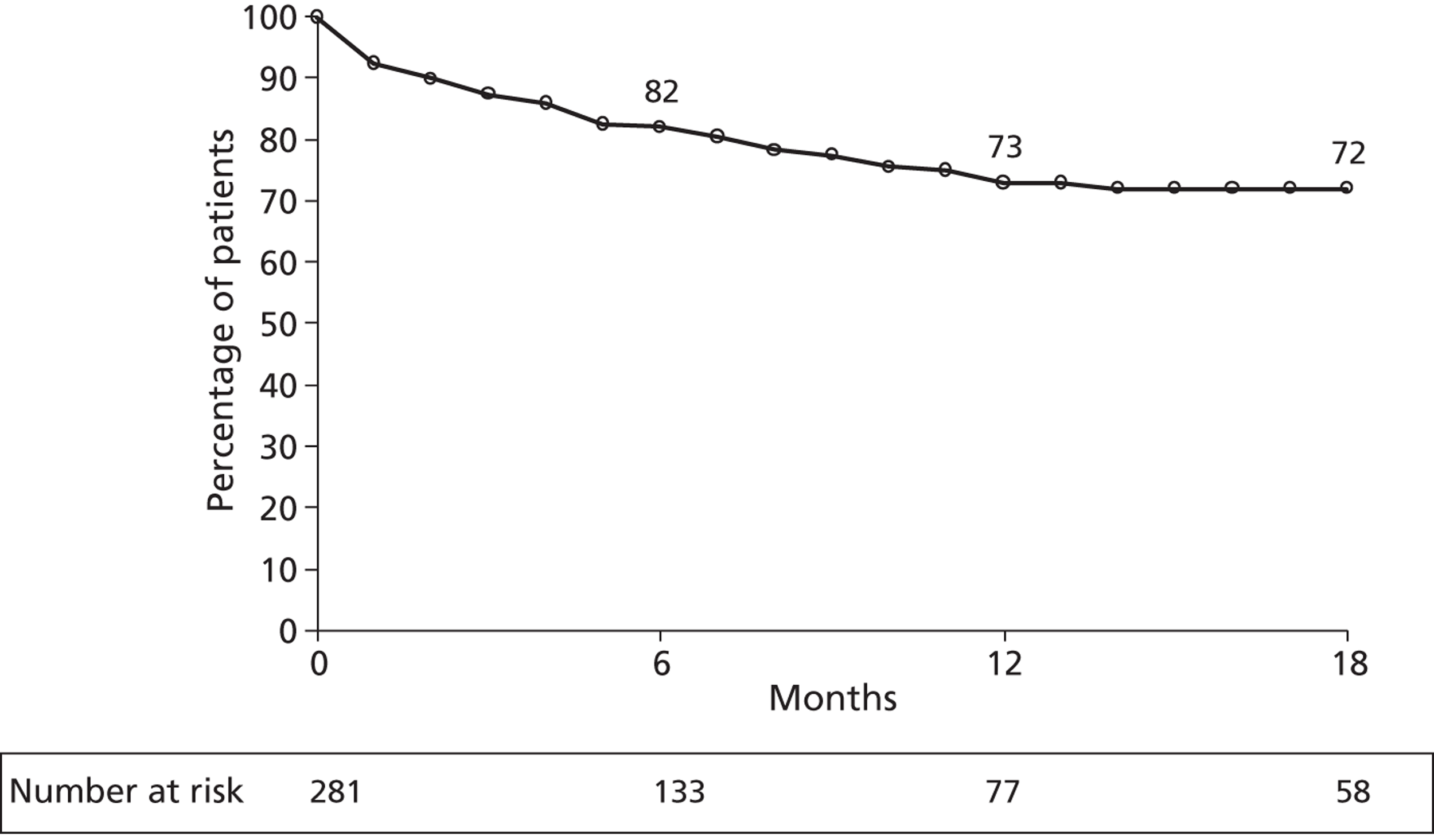 As of June 2008, 42 patients were alive with device support with a median duration of 1.6 years (longest duration 3.1 years). Of these patients, 71% remained active on the transplant list and 29% were not listed (see below). Three patients were not listed for irreversible medical conditions or degree of organ dysfunction Thirty-three patients (11.7%) died on LVAD support before discharge from hospital. Twenty-five patients (8.9%) underwent transplantation during their initial hospital stay and 220 patients (78%) were discharged from the hospital with the LVAD, with a median hospital stay after surgery of 25 days (range 8–180 days) Characteristics of patients alive with ongoing device support as of June 2008 (n = 42)ParameterValueDuration of LVAD support (years)1.6 (1.3–3.1)Age (years)51 (15–70)Men/women26 (62)/16 (38)Listed for cardiac transplantation30 (71.4)Not listed for cardiac transplantation12 (28.6)Reasons not listed Irreversible medical condition3 Non-compliance3 Obesity2 Elevated panel reactive antibody screen2 Preference to stay on device1 Insurance1Median (range), or n (%). |
Parameter | Value | Duration of LVAD support (years) | 1.6 (1.3–3.1) | Age (years) | 51 (15–70) | Men/women | 26 (62)/16 (38) | Listed for cardiac transplantation | 30 (71.4) | Not listed for cardiac transplantation | 12 (28.6) | Reasons not listed | Irreversible medical condition | 3 | Non-compliance | 3 | Obesity | 2 | Elevated panel reactive antibody screen | 2 | Preference to stay on device | 1 | Insurance | 1 | Median (range), or n (%). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Duration of LVAD support (years) | 1.6 (1.3–3.1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 51 (15–70) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Men/women | 26 (62)/16 (38) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Listed for cardiac transplantation | 30 (71.4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not listed for cardiac transplantation | 12 (28.6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reasons not listed | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Irreversible medical condition | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-compliance | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Obesity | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elevated panel reactive antibody screen | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preference to stay on device | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Insurance | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median (range), or n (%). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Competing outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Of the 281 patients, 222 (79%) either received a transplant, recovered cardiac function and underwent device explantation, or remained alive with ongoing LVAD support at 18-month follow-up (see figure below; data for 6 and 12 months read from graph)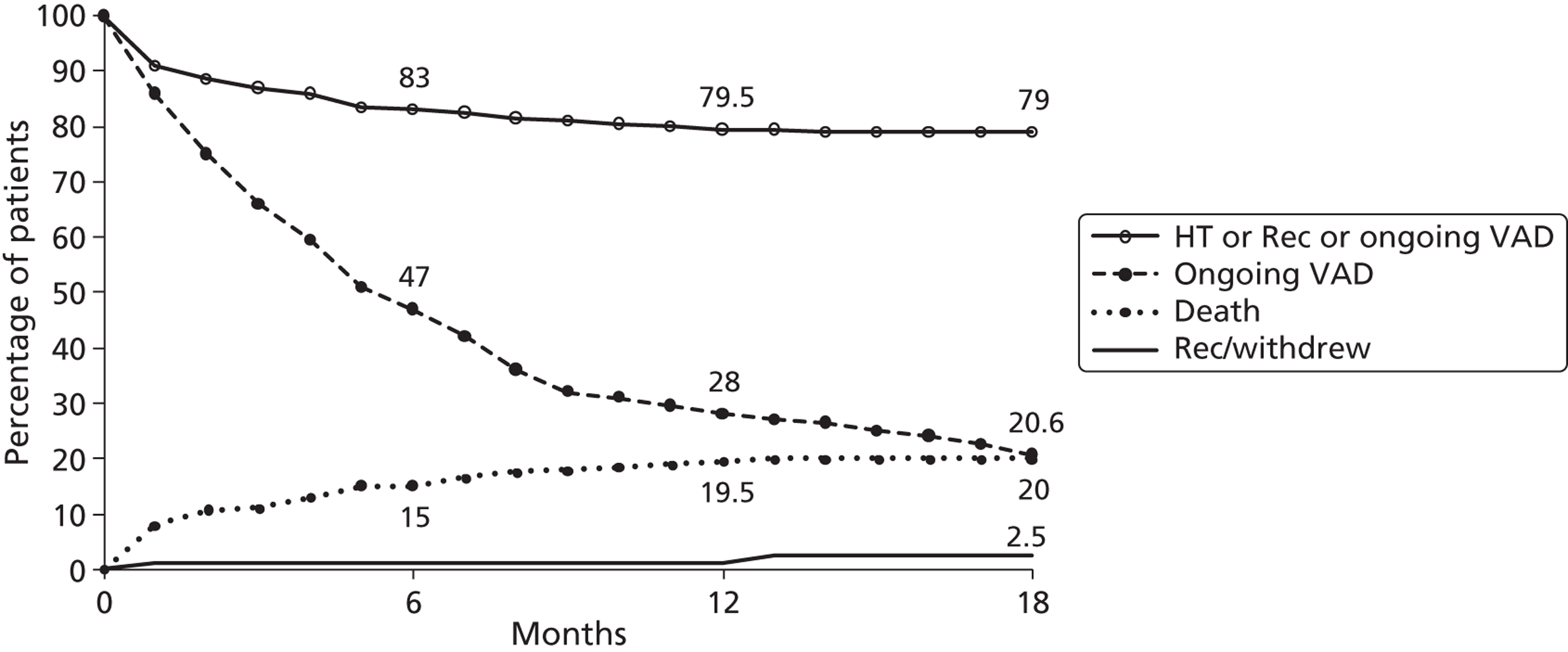 At 18 months, 157 patients (55.8%) had received a HT, 58 patients (20.6%) remained alive with ongoing LVAD support, 56 patients (19.9%) died, seven patients (2.5%) recovered cardiac function and underwent device explantation, and three patients (1%) were withdrawn from the study after device explantation and exchange for another type of LVAD Median time to transplantation: 118 days (range 10–545 days) Median time to death was 64 days (range 0–797 days) Median time to pump removal after cardiac recovery was 302 days (range 161–558 days) Median duration of support for all patients was 155 days (range 0–1026 days), with a cumulative follow-up of 181 patient-years Average LVAD estimated blood flow at 6 months of support = 5.6 ± 0.9 l/minute (flow index 2.83 ± 0.45 l/minute/m2) at a pump speed of 9467 ± 499 RPM LVEDD determined by echocardiography reduced: Baseline 69.7 ± 12.3 mm At 1 week 59.2 ± 15.1 mm At 6 months 56.7 ± 14.5 mm Anticoagulation with warfarin resulted in an average INR throughout support of 2.1 ± 0.8 (median 2.0), baseline INR was 1.3 ± 0.5 Twenty-five patients (8.9%) underwent transplantation during their initial hospital stay, and 33 patients (11.7%) died on LVAD support before discharge (see above) Two hundred and twenty patients (78%) were discharged from the hospital with the LVAD (see above), with a median hospital stay after surgery of 25 days (range 8–180 days). The median number of days out of hospital before transplantation, readmission, or death was 55.5 days (range 1–892 days). One hundred and forty-nine patients (68%) required rehospitalisation after discharge, with a median duration of rehospitalisation of 5 days (range 0–209 days) There were no failures of the mechanical pumping mechanism Median time to pump replacement: 106 days (range 0–672 days) Freedom from major device malfunction resulting in death (n = 4) or device replacement for all causes (malfunction, thrombosis or infection; nine without deaths) was 96% (95% CI 95% to 99%) at 6 months, 93% (95% CI 90% to 98%) at 1 year, and 92% (95% CI 88% to 97%) at 18 months Fifty-nine per cent of patients (165/281) required 368 operations or procedures after device implantation. The majority of these occurred within 30 days of device implantation (245/368; 67%), and most were required for re-explorations or sternal closures for bleeding complications (177/245; 72%) followed by temporary RVAD insertion or removal (n = 18; 7%), tracheostomy (n = 12; 5%), ICD insertion or replacement (n = 9; 4%), infection (n = 7; 3%), pump replacement (n = 4; 2%), and various other cardiac (n = 15; 6%) and non-cardiac (n = 3; 1%) procedures After 30 days, the most frequent indication for reoperation was for infection complications (49/123; 40%), bleeding (n = 19; 9%), pump replacement (n = 8; 7%), RVAD insertion or removal (n = 3; 2%), ICDs (n = 5; 4%), and various other non-cardiac (n = 24; 20%) and cardiac procedures (n = 14; 11%) Total pump replacements = 4 + 8 = 12 (4.3% of all implants) End-organ function Hepatic (total bilirubin, serum AST, serum ALT) and renal (BUN) function significantly improved from baseline to 6 months, but changes in serum creatinine were not statistically significant Results for patients with paired data at baseline and at 6 monthsParameterBaseline6 monthsnp-valueaBlood chemistry Serum sodium (mmol/l)134.1 ± 5.0139.3 ± 3.1130< 0.001 BUN (mg/dl)28.0 ± 15.220.3 ± 9.0130< 0.001 Serum creatinine (mg/dl)1.4 ± 0.51.3 ± 0.71300.119 ALT (IU/l)108 ± 32728 ± 151280.006 AST (IU/l)93 ± 29534 ± 161280.026 Total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.3 ± 0.90.8 ± 0.4127< 0.001 INR1.3 ± 0.52.1 ± 0.9127< 0.001a Paired t-test. |
Parameter | Baseline | 6 months | n | p-valuea | Blood chemistry | Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 134.1 ± 5.0 | 139.3 ± 3.1 | 130 | < 0.001 | BUN (mg/dl) | 28.0 ± 15.2 | 20.3 ± 9.0 | 130 | < 0.001 | Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.7 | 130 | 0.119 | ALT (IU/l) | 108 ± 327 | 28 ± 15 | 128 | 0.006 | AST (IU/l) | 93 ± 295 | 34 ± 16 | 128 | 0.026 | Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.3 ± 0.9 | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 127 | < 0.001 | INR | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | 127 | < 0.001 | a Paired t-test. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Baseline | 6 months | n | p-valuea | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blood chemistry | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 134.1 ± 5.0 | 139.3 ± 3.1 | 130 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 28.0 ± 15.2 | 20.3 ± 9.0 | 130 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.7 | 130 | 0.119 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT (IU/l) | 108 ± 327 | 28 ± 15 | 128 | 0.006 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST (IU/l) | 93 ± 295 | 34 ± 16 | 128 | 0.026 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.3 ± 0.9 | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 127 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INR | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | 127 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Paired t-test. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reportedAdverse events reportedOverall [cumulative support duration (patient-years) = 182]0–30 days [cumulative support duration (patient-years) = 21.7]> 30 days [cumulative support duration (patient-years) = 160]Patients with event, n (%)No. of eventsRateaPatients with event, n (%)No. of eventsRateaPatients with event, nNo. of eventsRateaBleeding Requiring surgery72 (26)820.4567723.3210100.06 Requiring ≥ 2 units PRBC only148 (53)3031.671281908.76541110.69Ventricular arrhythmiasb56 (20)720.437411.8923310.19Infection Local non-device-related infection84 (30)1550.8564783.5946780.49 Sepsis49 (17)640.3526271.2427370.23 Percutaneous lead infection41 (14)560.31220.0939540.34 Pump pocket infection5 (2)50.03110.05440.02Respiratory failure72 (26)880.4861693.1816190.12Renal failure30 (11)310.1724241.11770.04Right HF Need for RVAD17 (6)170.0916160.74110.01 Need for extended inotropic supportc36 (13)370.228291.34880.05Stroke Ischaemic15 (5)160.098d80.37780.05 Haemorrhagic9 (3)90.05440.18550.03 Spinal cord infarct1 (< 1)10.01000110.01TIA6 (2)70.04330.14440.02Psychological16 (6)180.113130.6350.03Other neurological15 (5)170.09440.1811130.08Peripheral non-neurological thromboembolic event18 (6)250.1416221.02330.02Device replacemente Primary device thrombosisf4 (1)40.02220.09220.01 Complications of surgical implantationg3 (1)30.02220.09110.01 Percutaneous lead wire damage4 (1)40.02000440.03 Lead and pump pocket infection1 (0.4)10.01000110.01Haemolysis11 (4)110.06660.28550.03Hepatic dysfunction7 (2)70.04440.18330.02a Events/patient-year.b Requiring cardioversion or defibrillation.c Longer than 14 days or starting after day 14.d Five events within days 0–2.e Replaced with HMII (n = 9) or other LVADs (n = 3).f Days 0, 24, 56 and 123.g Surgical pledget trapped in pump (day 1), temporary RVAD caused kink in LVAD outflow graft (day 15), or malposition of inflow cannula (day 31). | Adverse events reported | Overall [cumulative support duration (patient-years) = 182] | 0–30 days [cumulative support duration (patient-years) = 21.7] | > 30 days [cumulative support duration (patient-years) = 160] | Patients with event, n (%) | No. of events | Ratea | Patients with event, n (%) | No. of events | Ratea | Patients with event, n | No. of events | Ratea | Bleeding | Requiring surgery | 72 (26) | 82 | 0.45 | 67 | 72 | 3.32 | 10 | 10 | 0.06 | Requiring ≥ 2 units PRBC only | 148 (53) | 303 | 1.67 | 128 | 190 | 8.76 | 54 | 111 | 0.69 | Ventricular arrhythmiasb | 56 (20) | 72 | 0.4 | 37 | 41 | 1.89 | 23 | 31 | 0.19 | Infection | Local non-device-related infection | 84 (30) | 155 | 0.85 | 64 | 78 | 3.59 | 46 | 78 | 0.49 | Sepsis | 49 (17) | 64 | 0.35 | 26 | 27 | 1.24 | 27 | 37 | 0.23 | Percutaneous lead infection | 41 (14) | 56 | 0.31 | 2 | 2 | 0.09 | 39 | 54 | 0.34 | Pump pocket infection | 5 (2) | 5 | 0.03 | 1 | 1 | 0.05 | 4 | 4 | 0.02 | Respiratory failure | 72 (26) | 88 | 0.48 | 61 | 69 | 3.18 | 16 | 19 | 0.12 | Renal failure | 30 (11) | 31 | 0.17 | 24 | 24 | 1.11 | 7 | 7 | 0.04 | Right HF | Need for RVAD | 17 (6) | 17 | 0.09 | 16 | 16 | 0.74 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | Need for extended inotropic supportc | 36 (13) | 37 | 0.2 | 28 | 29 | 1.34 | 8 | 8 | 0.05 | Stroke | Ischaemic | 15 (5) | 16 | 0.09 | 8d | 8 | 0.37 | 7 | 8 | 0.05 | Haemorrhagic | 9 (3) | 9 | 0.05 | 4 | 4 | 0.18 | 5 | 5 | 0.03 | Spinal cord infarct | 1 (< 1) | 1 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | TIA | 6 (2) | 7 | 0.04 | 3 | 3 | 0.14 | 4 | 4 | 0.02 | Psychological | 16 (6) | 18 | 0.1 | 13 | 13 | 0.6 | 3 | 5 | 0.03 | Other neurological | 15 (5) | 17 | 0.09 | 4 | 4 | 0.18 | 11 | 13 | 0.08 | Peripheral non-neurological thromboembolic event | 18 (6) | 25 | 0.14 | 16 | 22 | 1.02 | 3 | 3 | 0.02 | Device replacemente | Primary device thrombosisf | 4 (1) | 4 | 0.02 | 2 | 2 | 0.09 | 2 | 2 | 0.01 | Complications of surgical implantationg | 3 (1) | 3 | 0.02 | 2 | 2 | 0.09 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | Percutaneous lead wire damage | 4 (1) | 4 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 0.03 | Lead and pump pocket infection | 1 (0.4) | 1 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | Haemolysis | 11 (4) | 11 | 0.06 | 6 | 6 | 0.28 | 5 | 5 | 0.03 | Hepatic dysfunction | 7 (2) | 7 | 0.04 | 4 | 4 | 0.18 | 3 | 3 | 0.02 | a Events/patient-year. | b Requiring cardioversion or defibrillation. | c Longer than 14 days or starting after day 14. | d Five events within days 0–2. | e Replaced with HMII (n = 9) or other LVADs (n = 3). | f Days 0, 24, 56 and 123. | g Surgical pledget trapped in pump (day 1), temporary RVAD caused kink in LVAD outflow graft (day 15), or malposition of inflow cannula (day 31). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported | Overall [cumulative support duration (patient-years) = 182] | 0–30 days [cumulative support duration (patient-years) = 21.7] | > 30 days [cumulative support duration (patient-years) = 160] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with event, n (%) | No. of events | Ratea | Patients with event, n (%) | No. of events | Ratea | Patients with event, n | No. of events | Ratea | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Requiring surgery | 72 (26) | 82 | 0.45 | 67 | 72 | 3.32 | 10 | 10 | 0.06 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Requiring ≥ 2 units PRBC only | 148 (53) | 303 | 1.67 | 128 | 190 | 8.76 | 54 | 111 | 0.69 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventricular arrhythmiasb | 56 (20) | 72 | 0.4 | 37 | 41 | 1.89 | 23 | 31 | 0.19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Local non-device-related infection | 84 (30) | 155 | 0.85 | 64 | 78 | 3.59 | 46 | 78 | 0.49 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 49 (17) | 64 | 0.35 | 26 | 27 | 1.24 | 27 | 37 | 0.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Percutaneous lead infection | 41 (14) | 56 | 0.31 | 2 | 2 | 0.09 | 39 | 54 | 0.34 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump pocket infection | 5 (2) | 5 | 0.03 | 1 | 1 | 0.05 | 4 | 4 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory failure | 72 (26) | 88 | 0.48 | 61 | 69 | 3.18 | 16 | 19 | 0.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure | 30 (11) | 31 | 0.17 | 24 | 24 | 1.11 | 7 | 7 | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HF | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Need for RVAD | 17 (6) | 17 | 0.09 | 16 | 16 | 0.74 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Need for extended inotropic supportc | 36 (13) | 37 | 0.2 | 28 | 29 | 1.34 | 8 | 8 | 0.05 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic | 15 (5) | 16 | 0.09 | 8d | 8 | 0.37 | 7 | 8 | 0.05 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic | 9 (3) | 9 | 0.05 | 4 | 4 | 0.18 | 5 | 5 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spinal cord infarct | 1 (< 1) | 1 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TIA | 6 (2) | 7 | 0.04 | 3 | 3 | 0.14 | 4 | 4 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Psychological | 16 (6) | 18 | 0.1 | 13 | 13 | 0.6 | 3 | 5 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other neurological | 15 (5) | 17 | 0.09 | 4 | 4 | 0.18 | 11 | 13 | 0.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Peripheral non-neurological thromboembolic event | 18 (6) | 25 | 0.14 | 16 | 22 | 1.02 | 3 | 3 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device replacemente | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary device thrombosisf | 4 (1) | 4 | 0.02 | 2 | 2 | 0.09 | 2 | 2 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Complications of surgical implantationg | 3 (1) | 3 | 0.02 | 2 | 2 | 0.09 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Percutaneous lead wire damage | 4 (1) | 4 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lead and pump pocket infection | 1 (0.4) | 1 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemolysis | 11 (4) | 11 | 0.06 | 6 | 6 | 0.28 | 5 | 5 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hepatic dysfunction | 7 (2) | 7 | 0.04 | 4 | 4 | 0.18 | 3 | 3 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Events/patient-year. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Requiring cardioversion or defibrillation. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c Longer than 14 days or starting after day 14. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| d Five events within days 0–2. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| e Replaced with HMII (n = 9) or other LVADs (n = 3). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| f Days 0, 24, 56 and 123. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| g Surgical pledget trapped in pump (day 1), temporary RVAD caused kink in LVAD outflow graft (day 15), or malposition of inflow cannula (day 31). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of deaths = 56 Survival analysis for patients continuing on mechanical support was performed with the K–M method. Patients were censored for transplantation, recovery of the natural heart, and withdrawal from the studyCause of deathn (%)Sepsis11 (4)Stroke10 (4)Ischaemic5 (2)Haemorrhagic5 (2)Right HF7 (3)Device related7 (3)Multiorgan failure5 (2)Anoxic brain injury3 (1)Bleeding3 (1)Others: cancer, respiratory failure, hyperthermia, air embolism10 (4) |
Cause of death | n (%) | Sepsis | 11 (4) | Stroke | 10 (4) | Ischaemic | 5 (2) | Haemorrhagic | 5 (2) | Right HF | 7 (3) | Device related | 7 (3) | Multiorgan failure | 5 (2) | Anoxic brain injury | 3 (1) | Bleeding | 3 (1) | Others: cancer, respiratory failure, hyperthermia, air embolism | 10 (4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death | n (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 11 (4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke | 10 (4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic | 5 (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic | 5 (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HF | 7 (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device related | 7 (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Multiorgan failure | 5 (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Anoxic brain injury | 3 (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding | 3 (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others: cancer, respiratory failure, hyperthermia, air embolism | 10 (4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Functional assessment, QoL (see below) Fuller details are reported in Rogers et al.53 Results for patients with paired data at baseline and at 6 monthsParameterBaseline6 monthsnp-valueaFunctional status NYHA functional class (mean ± SD)3.9 ± 0.31.8 ± 0.7110< 0.001 Class I or II (%)0%83%110< 0.001b6-minute walk distance (m) Patients able to walk at baseline (mean ± SD)201 ± 140368 ± 12514< 0.001 Unable to walk at baseline (mean ± SD)0 ± 0326 ± 23295< 0.001 Per cent of patients able to walk1389c109< 0.001bQoL MLWHFd (mean ± SD)69.4 ± 23.340.7 ± 24.692< 0.001 KCCQe (mean ± SD)35.8 ± 21.462.5 ± 22.690< 0.001a Paired t-test.b McNemar's test.c 12 patients were unable to walk at baseline or at 6 months.d Lower values indicate better QoL.e Overall score; greater values indicate better QoL. |
Parameter | Baseline | 6 months | n | p-valuea | Functional status | NYHA functional class (mean ± SD) | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 1.8 ± 0.7 | 110 | < 0.001 | Class I or II (%) | 0% | 83% | 110 | < 0.001b | 6-minute walk distance (m) | Patients able to walk at baseline (mean ± SD) | 201 ± 140 | 368 ± 125 | 14 | < 0.001 | Unable to walk at baseline (mean ± SD) | 0 ± 0 | 326 ± 232 | 95 | < 0.001 | Per cent of patients able to walk | 13 | 89c | 109 | < 0.001b | QoL | MLWHFd (mean ± SD) | 69.4 ± 23.3 | 40.7 ± 24.6 | 92 | < 0.001 | KCCQe (mean ± SD) | 35.8 ± 21.4 | 62.5 ± 22.6 | 90 | < 0.001 | a Paired t-test. | b McNemar's test. | c 12 patients were unable to walk at baseline or at 6 months. | d Lower values indicate better QoL. | e Overall score; greater values indicate better QoL. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Baseline | 6 months | n | p-valuea | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Functional status | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA functional class (mean ± SD) | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 1.8 ± 0.7 | 110 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class I or II (%) | 0% | 83% | 110 | < 0.001b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-minute walk distance (m) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients able to walk at baseline (mean ± SD) | 201 ± 140 | 368 ± 125 | 14 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unable to walk at baseline (mean ± SD) | 0 ± 0 | 326 ± 232 | 95 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Per cent of patients able to walk | 13 | 89c | 109 | < 0.001b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLWHFd (mean ± SD) | 69.4 ± 23.3 | 40.7 ± 24.6 | 92 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KCCQe (mean ± SD) | 35.8 ± 21.4 | 62.5 ± 22.6 | 90 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Paired t-test. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b McNemar's test. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c 12 patients were unable to walk at baseline or at 6 months. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| d Lower values indicate better QoL. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| e Overall score; greater values indicate better QoL. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CF HMII provides effective haemodynamic support for at least 18 months in patients awaiting transplantation, with improved functional status and QoL, and is associated with a very low rate of device malfunction or infection requiring device exchange. CF rotary pumps provide a superior alternative to pumps with a pulsatile design in patients awaiting transplantation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| There was no formal comparison with pulsatile devices and the study was not designed to make a comparison, therefore the authors' conclusion regarding differential performance should be viewed with caution | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pak 201072
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Pak Year of publication: 2010 Country: USA Study design: Retrospective Study setting: Unclear Number of centres: One Duration of study: January 2004 and September 2009: 5-year period Follow-up period: Studies were categorised into post-operative time intervals: 0–1 month, 1–3 months, 3–6 months, 6–12 months, 12–18 months and 18–24 months Funding: One author received consulting fees from Thoratec Inc. and Jarvik (Modest), another author has received consulting fees from Thoratec Inc. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To examine the incidence of new-onset AI in patients supported with long-term LVADs. Present the development of de novo AI during LVAD support in both HMI and HMII patients who underwent implantation at a single institution during a 5-year period | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: HMXVE (n = 67); HMII (n = 63) Sample attrition/dropout: None Inclusion criteria: Not clear, echocardiographic studies with adequate assessments of aortic valve Exclusion criteria: Patients with prior or concurrent surgical manipulation of the aortic valve, with baseline AI, or without baseline echoes, patients who had prosthetic aortic valves, patients with pre-operative AI and patients who underwent aortic valve surgery at the time of device placement Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): HMXVE 53.2 ± 13.9; HMII 55.5 ± 13.0 Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: HMXVE male n = 55 (82.1%); HMII male n = 49 (77.8%) Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Unclear. Patients supported with long-term LVADs |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: 13 HMXVE patients (19.4%) and 10 HMII patients (15.9%) received devices with DT as the initial goal (p = 0.530) Type of device used: HMXVE and HMII Any comparison: HMXVE vs. HMII Duration of treatment: Mean duration of device support was 176.4 ± 142.9 days (range 4–526 days) for HMI patients and 257.2 ± 246.6 days (range 7–1179 days) for HMII patients (p = 0.023). Median time to transplant was 24 days (range 8–474 days) Support durationVariableHMXVE (n = 67)HMII (n = 63)p-valueSupport duration, days Mean ± SD176.4 ± 142.9257.2 ± 246.60.023 Median (range)134 (4–526)204 (7–4170)(n = 4)(n = 9)Time to AI development, days Mean ± SD99.3 ± 119.8115.2 ± 100.20.806 Median (range)48 (23–278)90 (7–364) Percentage of patients using inotropes: Not reported Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
Variable | HMXVE (n = 67) | HMII (n = 63) | p-value | Support duration, days | Mean ± SD | 176.4 ± 142.9 | 257.2 ± 246.6 | 0.023 | Median (range) | 134 (4–526) | 204 (7–4170) | (n = 4) | (n = 9) | Time to AI development, days | Mean ± SD | 99.3 ± 119.8 | 115.2 ± 100.2 | 0.806 | Median (range) | 48 (23–278) | 90 (7–364) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variable | HMXVE (n = 67) | HMII (n = 63) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Support duration, days | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 176.4 ± 142.9 | 257.2 ± 246.6 | 0.023 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median (range) | 134 (4–526) | 204 (7–4170) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (n = 4) | (n = 9) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time to AI development, days | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 99.3 ± 119.8 | 115.2 ± 100.2 | 0.806 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median (range) | 48 (23–278) | 90 (7–364) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Degree of AI Secondary outcomes: Aortic root dimensions Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: No Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: Studies were categorised into post-operative time intervals: 0–1 month, 1–3 months, 3–6 months, 6–12 months, 12–18 months and 18–24 monthsNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedAll clinical echocardiographic reports from consecutive patients who underwent LVAD implantation (n = 93 HMXVE) were retrospectively reviewedAll clinical echocardiographic reports from consecutive patients who underwent LVAD implantation (n = 73 HMII) were retrospectively reviewedRandomised/includedFinal study population included 67 HMXVE patientsFinal study population included 63 HMII patientsExcludedAnalysis excluded six HMXVE patientsAnalysis excluded two HMII patientsMissing participantsWithdrawals |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | All clinical echocardiographic reports from consecutive patients who underwent LVAD implantation (n = 93 HMXVE) were retrospectively reviewed | All clinical echocardiographic reports from consecutive patients who underwent LVAD implantation (n = 73 HMII) were retrospectively reviewed | Randomised/included | Final study population included 67 HMXVE patients | Final study population included 63 HMII patients | Excluded | Analysis excluded six HMXVE patients | Analysis excluded two HMII patients | Missing participants | Withdrawals | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | All clinical echocardiographic reports from consecutive patients who underwent LVAD implantation (n = 93 HMXVE) were retrospectively reviewed | All clinical echocardiographic reports from consecutive patients who underwent LVAD implantation (n = 73 HMII) were retrospectively reviewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | Final study population included 67 HMXVE patients | Final study population included 63 HMII patients | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Analysis excluded six HMXVE patients | Analysis excluded two HMII patients | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VariableHMXVE (n = 67)HMII (n = 63)p-valueAge, (years)53.2 ± 13.955.5 ± 13.00.329Male55 (82.1)49 (77.8)0.539BMI (kg/m2)28.5 ± 5.826.0 ± 5.10.011Ischaemic cardiomyopathy29 (43.3)28 (44.4)0.894Hypertension27 (40.3)31 (49.2)0.307Diabetes mellitus28 (41.8)22 (34.9)0.421COPD4 (6.0)6 (9.5)0.522BTT/DT54/1353/100.530Baseline creatinine (mg/dl)1.53 ± 1.061.49 ± 0.430.745Pre-operative ejection fraction (%)15.5 ± 5.616.0 ± 5.60.608Pre-operative systolic BP (mmHg)103.8 ± 14.1102.8 ± 15.10.698Pre-operative diastolic BP (mmHg)66.4 ± 10.366.8 ± 13.70.865Pre-operative cardiac output, (l/minute)2.38 ± 1.932.72 ± 1.210.231Pre-operative IABP39 (58.2)21 (33.3%)0.004Continuous data are shown as mean ± SD; categorical data are n (%). | Variable | HMXVE (n = 67) | HMII (n = 63) | p-value | Age, (years) | 53.2 ± 13.9 | 55.5 ± 13.0 | 0.329 | Male | 55 (82.1) | 49 (77.8) | 0.539 | BMI (kg/m2) | 28.5 ± 5.8 | 26.0 ± 5.1 | 0.011 | Ischaemic cardiomyopathy | 29 (43.3) | 28 (44.4) | 0.894 | Hypertension | 27 (40.3) | 31 (49.2) | 0.307 | Diabetes mellitus | 28 (41.8) | 22 (34.9) | 0.421 | COPD | 4 (6.0) | 6 (9.5) | 0.522 | BTT/DT | 54/13 | 53/10 | 0.530 | Baseline creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.53 ± 1.06 | 1.49 ± 0.43 | 0.745 | Pre-operative ejection fraction (%) | 15.5 ± 5.6 | 16.0 ± 5.6 | 0.608 | Pre-operative systolic BP (mmHg) | 103.8 ± 14.1 | 102.8 ± 15.1 | 0.698 | Pre-operative diastolic BP (mmHg) | 66.4 ± 10.3 | 66.8 ± 13.7 | 0.865 | Pre-operative cardiac output, (l/minute) | 2.38 ± 1.93 | 2.72 ± 1.21 | 0.231 | Pre-operative IABP | 39 (58.2) | 21 (33.3%) | 0.004 | Continuous data are shown as mean ± SD; categorical data are n (%). | |||
| Variable | HMXVE (n = 67) | HMII (n = 63) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, (years) | 53.2 ± 13.9 | 55.5 ± 13.0 | 0.329 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male | 55 (82.1) | 49 (77.8) | 0.539 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.5 ± 5.8 | 26.0 ± 5.1 | 0.011 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic cardiomyopathy | 29 (43.3) | 28 (44.4) | 0.894 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension | 27 (40.3) | 31 (49.2) | 0.307 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 28 (41.8) | 22 (34.9) | 0.421 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COPD | 4 (6.0) | 6 (9.5) | 0.522 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTT/DT | 54/13 | 53/10 | 0.530 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.53 ± 1.06 | 1.49 ± 0.43 | 0.745 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative ejection fraction (%) | 15.5 ± 5.6 | 16.0 ± 5.6 | 0.608 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative systolic BP (mmHg) | 103.8 ± 14.1 | 102.8 ± 15.1 | 0.698 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative diastolic BP (mmHg) | 66.4 ± 10.3 | 66.8 ± 13.7 | 0.865 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative cardiac output, (l/minute) | 2.38 ± 1.93 | 2.72 ± 1.21 | 0.231 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative IABP | 39 (58.2) | 21 (33.3%) | 0.004 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Continuous data are shown as mean ± SD; categorical data are n (%). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K–M analysis reports the freedom from AI in patients who received the HMXVE and HMII devices K–M analysis showed that patients who remained on device support at 6 and 12 months, freedom from AI was 94.5% and 88.9% in HMI patients and 83.6% and 75.2% in HMII patients (log-rank p = 0.194) Number at riskDeviceDays post implant0100200300400HMXVE, n673922147HMII, n634029159 Aortic root diametersDiameters (cm)HMXVE (n = 20)HMII (n = 22)p-valueAI (n = 13)No AI (n = 29)p-valueBaseline3.15 ± 0.393.31 ± 0.440.2233.43 ± 0.433.15 ± 0.400.067At 31–90 days follow-up3.30 ± 0.523.44 ± 0.530.3903.58 ± 0.543.29 ± 0.500.130 Aortic root circumference from pathology reportsDevice typeAortic insufficiency (n = 7)No aortic insufficiency (n = 70)p-valueHMI, cm (aortic insufficiency = 2/no aortic insufficiency = 42)8.25 ± 1.067.28 ± 1.020.198HMII, cm (aortic insufficiency = 5/no aortic insufficiency = 28)8.44 ± 0.897.36 ± 1.020.034Overall, cm8.39 ± 0.857.31 ± 1.020.009 Aortic root diameters for patients with AI were often larger at baseline (3.43 ± 0.43 vs. 3.15 ± 0.40; p = 0.067) and follow-up (3.58 ± 0.54 vs. 3.29 ± 0.50; p = 0.130) compared with patients with no AI Aortic root circumferences in those patients who underwent transplant were significantly larger in HMII patients who developed AI compared with those patients who did not (8.44 ± 0.89 cm vs. 7.36 ± 1.02 cm; p = 0.034) AI was more common in patients who had aortic valves that did not open (11/26 vs. 1/14; p = 0.03) |
Device | Days post implant | 0 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | HMXVE, n | 67 | 39 | 22 | 14 | 7 | HMII, n | 63 | 40 | 29 | 15 | 9 | Diameters (cm) | HMXVE (n = 20) | HMII (n = 22) | p-value | AI (n = 13) | No AI (n = 29) | p-value | Baseline | 3.15 ± 0.39 | 3.31 ± 0.44 | 0.223 | 3.43 ± 0.43 | 3.15 ± 0.40 | 0.067 | At 31–90 days follow-up | 3.30 ± 0.52 | 3.44 ± 0.53 | 0.390 | 3.58 ± 0.54 | 3.29 ± 0.50 | 0.130 | Device type | Aortic insufficiency (n = 7) | No aortic insufficiency (n = 70) | p-value | HMI, cm (aortic insufficiency = 2/no aortic insufficiency = 42) | 8.25 ± 1.06 | 7.28 ± 1.02 | 0.198 | HMII, cm (aortic insufficiency = 5/no aortic insufficiency = 28) | 8.44 ± 0.89 | 7.36 ± 1.02 | 0.034 | Overall, cm | 8.39 ± 0.85 | 7.31 ± 1.02 | 0.009 | ||||||||
| Device | Days post implant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMXVE, n | 67 | 39 | 22 | 14 | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII, n | 63 | 40 | 29 | 15 | 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diameters (cm) | HMXVE (n = 20) | HMII (n = 22) | p-value | AI (n = 13) | No AI (n = 29) | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | 3.15 ± 0.39 | 3.31 ± 0.44 | 0.223 | 3.43 ± 0.43 | 3.15 ± 0.40 | 0.067 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At 31–90 days follow-up | 3.30 ± 0.52 | 3.44 ± 0.53 | 0.390 | 3.58 ± 0.54 | 3.29 ± 0.50 | 0.130 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type | Aortic insufficiency (n = 7) | No aortic insufficiency (n = 70) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMI, cm (aortic insufficiency = 2/no aortic insufficiency = 42) | 8.25 ± 1.06 | 7.28 ± 1.02 | 0.198 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII, cm (aortic insufficiency = 5/no aortic insufficiency = 28) | 8.44 ± 0.89 | 7.36 ± 1.02 | 0.034 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall, cm | 8.39 ± 0.85 | 7.31 ± 1.02 | 0.009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AI developed in 4 of 67 HMI (6%) and in 9 of 63 HMII patients (14.3%) Median times to AI development were 48 days for HMI patients and 90 days for HMII patients One HMII patient underwent an aortic valve repair One HMXVE and three HMII patients remain on device therapy with AI graded mild/moderate or greater |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| One HMXVE patient died after AI onset of multiorgan system failure not directly related to AI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AI development, mainly during CF with HMII, was common and occurred after a relatively short duration of support. Data demonstrate that AI occurs frequently in patients who receive CF support with a HMII LVAD. The findings require thorough pre-operative patient evaluation and additional studies to investigate factors associated with AI development | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K–M analyses were performed to characterise freedom from AI. Underpowered analysis – too few events. Cox's regression was not performed. Difficulty in ascertaining a causal mechanism for AI development in these LVAD patients owing to retrospective study design. Limited relevance to the current report | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pal 200973
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Pal Year of publication: 2009 Country: USA, multicentres Study design: Unclear, prospective study Study setting: Multicentres in USA Number of centres: 33 clinical sites Duration of study: March 2005 until March 2007 Follow-up period: 180 days Funding: This study was supported in part by an unrestricted educational grant from Thoratec Inc. to one author. Three authors received research support from Thoratec Inc. One author received research support and serves as a clinical consultant for Thoratec Inc. One author is an employee of Thoratec Inc. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To determine impact of concurrent cardiac procedures on patient outcomes after HMII LVAD implantation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 170 patients who underwent isolated HMII implantation with 81 patients with HMII implantation with concurrent cardiac procedures. The initial BTT study included 133 patients enrolled at 26 sites. An additional 148 patients were enrolled resulting in a total of 281 patients included in analysis Sample attrition/dropout: It is noted that 14 patients had non-cardiac procedures and 97 were concurrent cardiac; excluded an additional 16 patients who underwent placement of a RVAD Inclusion criteria: Patients listed for a HT at study centres were eligible for enrolment. Further inclusion criteria were UNOS 1A or 1B status with impaired haemodynamics (PCWP > 20 mmHg, cardiac index < 2.2 l/minute/m2, or systolic BP 90 mmHg). Also refer to Miller et al.70 for more details – included paper Exclusion criteria: Patients with any mechanical circulatory support other than an IABP, BMI > 40 kg/m2, or history of cardiac transplantation. Also presence of severe end-organ dysfunction manifested by INR 2.5 not on anticoagulation therapy, bilirubin > 5 mg/dl, cirrhosis, severe COPD or restrictive lung disease, fixed pulmonary hypertension (PVR > 6 Wood units), unresolved stroke, creatinine 3.5, or dialysis. Also refer to Miller et al.70 for more details – included paper Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): HMII 51 ± 13 years; HMII + CCP 50 ± 14 years Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: HMII 25.9% female; HMII + CCP 18.5% female Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Patients with end-stage HF who were on a WL for a HT |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: HMII vs. HMII + CCP Duration of treatment: Not reported Percentage of patients using inotropes: Not reported Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Mortality at 30 days after the procedure and survival to transplantation, recovery of ventricular function, or ongoing support at 180 days Secondary outcomes: Causes of mortality and frequency of adverse events were recorded for all patients Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: Yes Adverse event: No HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: 180 daysNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreened281 BTT patients who underwent implantation of a HMII pump, 111 had additional procedures performed at time of initial operationRandomised/included170 patients who underwent isolated HMII implantation81 patients with HMII implantation with concurrent cardiac proceduresExcluded14 were non-cardiac procedures and 97 were concurrent cardiac. Excluded an additional 16 patients who underwent placement of a RVADMissing participantsWithdrawals |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | 281 BTT patients who underwent implantation of a HMII pump, 111 had additional procedures performed at time of initial operation | Randomised/included | 170 patients who underwent isolated HMII implantation | 81 patients with HMII implantation with concurrent cardiac procedures | Excluded | 14 were non-cardiac procedures and 97 were concurrent cardiac. Excluded an additional 16 patients who underwent placement of a RVAD | Missing participants | Withdrawals | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | 281 BTT patients who underwent implantation of a HMII pump, 111 had additional procedures performed at time of initial operation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 170 patients who underwent isolated HMII implantation | 81 patients with HMII implantation with concurrent cardiac procedures | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | 14 were non-cardiac procedures and 97 were concurrent cardiac. Excluded an additional 16 patients who underwent placement of a RVAD | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ParameterValue (intervention)Value (comparator)Age, years51 ± 1350 ± 14SexFemale 25.9%Female 18.5%BSA, m2Weight, kg, BMIIschaemic causes of HF41.8%39.5% Baseline characteristics for patients with HMII: implantation alone and those with implantation and CCPParameterHMII (n = 170)HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures (n = 81)p-valueAge, years51 ± 1350 ± 140.578Female, %25.918.50.265Creatinine (mg/dl)1.4 ± 0.51.5 ± 0.60.167CVP (mm/Hg)11.6 ± 6.114.5 ± 6.90.001INR1.30 ± 0.341.34 ± 0.330.380Ischaemic (%)41.839.50.785Mechanical ventilation (%)5.98.60.429 |
Parameter | Value (intervention) | Value (comparator) | Age, years | 51 ± 13 | 50 ± 14 | Sex | Female 25.9% | Female 18.5% | BSA, m2 | Weight, kg, BMI | Ischaemic causes of HF | 41.8% | 39.5% | Parameter | HMII (n = 170) | HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures (n = 81) | p-value | Age, years | 51 ± 13 | 50 ± 14 | 0.578 | Female, % | 25.9 | 18.5 | 0.265 | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 0.167 | CVP (mm/Hg) | 11.6 ± 6.1 | 14.5 ± 6.9 | 0.001 | INR | 1.30 ± 0.34 | 1.34 ± 0.33 | 0.380 | Ischaemic (%) | 41.8 | 39.5 | 0.785 | Mechanical ventilation (%) | 5.9 | 8.6 | 0.429 | ||||
| Parameter | Value (intervention) | Value (comparator) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, years | 51 ± 13 | 50 ± 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex | Female 25.9% | Female 18.5% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA, m2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight, kg, BMI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic causes of HF | 41.8% | 39.5% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | HMII (n = 170) | HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures (n = 81) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, years | 51 ± 13 | 50 ± 14 | 0.578 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Female, % | 25.9 | 18.5 | 0.265 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 0.167 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CVP (mm/Hg) | 11.6 ± 6.1 | 14.5 ± 6.9 | 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INR | 1.30 ± 0.34 | 1.34 ± 0.33 | 0.380 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic (%) | 41.8 | 39.5 | 0.785 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical ventilation (%) | 5.9 | 8.6 | 0.429 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actuarial survival for patients receiving LVAD implantation with and without CCP is presented K–M analysis of survival with device support for patients with and without CCP found at 1, 6 and 12 months the number remaining at risk was HMII 170, 86 and 49 and HMII + CCP indicates CCP 81, 28 and 15, respectively K–M analysis of survival extraction from the curve at 1, 6 and 12 months for HMII was 94% ± 2%, 84% ± 3% and 77% ± 4%, respectively K–M analysis of survival extraction from the curve at 1, 6 and 12 months for HMII + CCP was 89% ± 4%, 77% ± 5% and 66% ± 7%, respectively Differences in overall survival rates were statistically significant between two groups (p = 0.048, log-rank test) The hazard ratio for concurrent procedures adjusted for baseline parameters was 1.82 (95% CI 1.07 to 3.10; p = 0.026) Overall and subgroup 30-day mortality rates and survival to transplantation, recovery of ventricular function, or ongoing device support at 180 daysPatient groupn30-day mortalitySurvival to study outcomes at 180 days, %HMII alone1705.986.5HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures8111.180.3Concurrent cardiac procedures subgroups HMII + patent foramen ovale15093.3 HMII +valve478.580.9 Tricuspid303.386.6 Mitral50100.0 Aortic1225.058.3 HMII + other68.468.468.4 |
Patient group | n | 30-day mortality | Survival to study outcomes at 180 days, % | HMII alone | 170 | 5.9 | 86.5 | HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures | 81 | 11.1 | 80.3 | Concurrent cardiac procedures subgroups | HMII + patent foramen ovale | 15 | 0 | 93.3 | HMII +valve | 47 | 8.5 | 80.9 | Tricuspid | 30 | 3.3 | 86.6 | Mitral | 5 | 0 | 100.0 | Aortic | 12 | 25.0 | 58.3 | HMII + other | 68.4 | 68.4 | 68.4 | |||||||||||||
| Patient group | n | 30-day mortality | Survival to study outcomes at 180 days, % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII alone | 170 | 5.9 | 86.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures | 81 | 11.1 | 80.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concurrent cardiac procedures subgroups | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII + patent foramen ovale | 15 | 0 | 93.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII +valve | 47 | 8.5 | 80.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tricuspid | 30 | 3.3 | 86.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mitral | 5 | 0 | 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aortic | 12 | 25.0 | 58.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII + other | 68.4 | 68.4 | 68.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CCP (n = 81): Valvular procedures (n = 47); tricuspid (n = 30); aortic (n = 12, 8 aortic valve replacement and 4 valve patch); mitral (n = 5); patent foramen ovale closure (n = 15); removal of left ventricular thrombus (n = 3); left ventricular aneurysm resection (n = 3); insert implantable cardioverter-defibrillator/repair implantable cardioverter-defibrillator lead (n = 3); CABG (n = 2); left ventricular laceration repair (n = 2); right atrial ablation; ventricular septal defect repair; right atrial thrombectomy; repair of dissection of ascending aorta; left ventricular remodelling; lysis of intrapericardial adhesions Cardiopulmonary bypass time and length of stay for HMII implantation alone or with CCPProcedureHMII (n = 170)HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures (n = 81)Cardiopulmonary bypass time (minutes) Mean ± SD100 ± 37121 ± 40a Median98.5123.5Length of stay (days) Mean ± SD30 ± 2435 ± 27 Median2326.5a p = 0.001. |
Procedure | HMII (n = 170) | HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures (n = 81) | Cardiopulmonary bypass time (minutes) | Mean ± SD | 100 ± 37 | 121 ± 40a | Median | 98.5 | 123.5 | Length of stay (days) | Mean ± SD | 30 ± 24 | 35 ± 27 | Median | 23 | 26.5 | a p = 0.001. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Procedure | HMII (n = 170) | HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures (n = 81) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiopulmonary bypass time (minutes) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 100 ± 37 | 121 ± 40a | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median | 98.5 | 123.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Length of stay (days) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 30 ± 24 | 35 ± 27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median | 23 | 26.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a p = 0.001. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incidence of adverse eventsIncidence of adverse eventsHMII % (n = 170)HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures, % (n = 81)p-valueBleeding26250.877Sepsis17181.000Driveline infection10180.132Ventricular arrhythmias20220.743Perioperative stroke420.391Renal failure1480.259 No significant differences for the incidence of adverse events |
Incidence of adverse events | HMII % (n = 170) | HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures, % (n = 81) | p-value | Bleeding | 26 | 25 | 0.877 | Sepsis | 17 | 18 | 1.000 | Driveline infection | 10 | 18 | 0.132 | Ventricular arrhythmias | 20 | 22 | 0.743 | Perioperative stroke | 4 | 2 | 0.391 | Renal failure | 14 | 8 | 0.259 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incidence of adverse events | HMII % (n = 170) | HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures, % (n = 81) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding | 26 | 25 | 0.877 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 17 | 18 | 1.000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline infection | 10 | 18 | 0.132 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventricular arrhythmias | 20 | 22 | 0.743 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Perioperative stroke | 4 | 2 | 0.391 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure | 14 | 8 | 0.259 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Causes of deathHMII, % (n = 170)HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures, % (n = 81)p-valueBleeding26250.877Sepsis17181.000Driveline infection10180.132Ventricular arrhythmias20220.743Perioperative stroke420.391Renal failure1480.259 No significant differences in causes of death |
Causes of death | HMII, % (n = 170) | HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures, % (n = 81) | p-value | Bleeding | 26 | 25 | 0.877 | Sepsis | 17 | 18 | 1.000 | Driveline infection | 10 | 18 | 0.132 | Ventricular arrhythmias | 20 | 22 | 0.743 | Perioperative stroke | 4 | 2 | 0.391 | Renal failure | 14 | 8 | 0.259 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Causes of death | HMII, % (n = 170) | HMII + concurrent cardiac procedures, % (n = 81) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding | 26 | 25 | 0.877 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 17 | 18 | 1.000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline infection | 10 | 18 | 0.132 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventricular arrhythmias | 20 | 22 | 0.743 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Perioperative stroke | 4 | 2 | 0.391 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure | 14 | 8 | 0.259 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isolated HMII implants in HMII BTT trial have low procedural mortality. Concurrent procedures such as closure of patent foramen ovale and tricuspid procedures do not appear to add procedural risk, although implants with concurrent aortic procedures had a higher mortality rate. Further investigation of LVAD implant procedures with CCP is needed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unclear when patients were stratified into those with CCP or no such procedures. The evidence supports the author's conclusions that a more complex surgical procedure at implant of HMII may result in poorer survival. However, this appears to be a post-hoc analysis. An unadjusted p-value of 0.048 (adjusted for baseline characteristics p = 0.026) was reported, therefore the conclusions should be treated with some caution. The authors did not appear to test the assumptions for proportional hazards | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Petrucci 200974
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Petrucci Year of publication: 2009 Country: USA Study design: Single-arm trial non-randomised prospective Study setting: Hospital Number of centres: 11 of 35 in the study by Miller et al.70 Duration of study: NC assessments were performed in the same order only at 1, 3 and 6 months after LVAD implantation Follow-up period: Not reported Funding: Not reported |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To document changes in the cognitive performance of patients with the CF HMII LVAD as a BTT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 93 Sample attrition/dropout: Not clear. Missing participants n = 65; patient refusal (43%); examiner not available (36%); patient too ill or intubated (23%) Inclusion criteria: Patients from trial of Miller et al.70 Inclusion criteria for the NC tests consisted of non-intubation, ability to sit and provide verbal responses in English, and oxygen saturation > 90% Exclusion criteria: Centres not selected by first investigator Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): 50 ± 14 years Median age: 54 years Age range: 16–73 years Sex: 81% male Race: Not reported Diagnosis: End-stage HF |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT; ischaemic (41%), idiopathic cardiomyopathies (51%) and other (8%) Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: Paired results of neurocognitive performance at 3 and 6 months vs. 1 month after implant Duration of treatment: Various Percentage of patients using inotropes: 90% Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Neurocognitive tests selected from FDA suggestions in a 2003 report Assessment of neurological/neurocognitive function: guidance for industry.124 Nurse co-ordinators administered tests Secondary outcomes: Not reported Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records or prospective data collection Survival: No Adverse event: No HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: 6 monthsNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreened158 at 11 centresNot reportedRandomised/includedNot reportedNot reportedExcludedNot reportedNot reportedMissing participants65Not reportedWithdrawalsPatient refusal (43%), examiner not available (36%), patient too ill or intubated (23%)Not reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | 158 at 11 centres | Not reported | Randomised/included | Not reported | Not reported | Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | Missing participants | 65 | Not reported | Withdrawals | Patient refusal (43%), examiner not available (36%), patient too ill or intubated (23%) | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | 158 at 11 centres | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | 65 | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Patient refusal (43%), examiner not available (36%), patient too ill or intubated (23%) | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CharacteristicValuen93Male, n (%)75 (81%)Female, n (%)18 (19%)Age (years)50 ± 14; median 54 (range 16–73)Ischaemic aetiology (%)41BSA (m2)2.0 ± 0.3; median 2.0 (range 1.35–2.69)LVEF (%)16 ± 7LVEDD mm)79 ± 12Systolic BP (mmHg)95 ± 14Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)2.1 ± 0.7RA pressure (mmHg)12.3 ± 6.0PA mean pressure (mmHg)36 ± 10PCWP (mmHg)25 ± 8CRT (%)46Intravenous inotropes (%)90IABP (%)34Creatinine (mg/dl)1.4 ± 0.5BUN (mg/dl)30 ± 15Total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.4 ± 0.8 | Characteristic | Value | n | 93 | Male, n (%) | 75 (81%) | Female, n (%) | 18 (19%) | Age (years) | 50 ± 14; median 54 (range 16–73) | Ischaemic aetiology (%) | 41 | BSA (m2) | 2.0 ± 0.3; median 2.0 (range 1.35–2.69) | LVEF (%) | 16 ± 7 | LVEDD mm) | 79 ± 12 | Systolic BP (mmHg) | 95 ± 14 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.1 ± 0.7 | RA pressure (mmHg) | 12.3 ± 6.0 | PA mean pressure (mmHg) | 36 ± 10 | PCWP (mmHg) | 25 ± 8 | CRT (%) | 46 | Intravenous inotropes (%) | 90 | IABP (%) | 34 | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | BUN (mg/dl) | 30 ± 15 | Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristic | Value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | 93 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male, n (%) | 75 (81%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Female, n (%) | 18 (19%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 50 ± 14; median 54 (range 16–73) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic aetiology (%) | 41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 2.0 ± 0.3; median 2.0 (range 1.35–2.69) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF (%) | 16 ± 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEDD mm) | 79 ± 12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 95 ± 14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.1 ± 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RA pressure (mmHg) | 12.3 ± 6.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PA mean pressure (mmHg) | 36 ± 10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 25 ± 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CRT (%) | 46 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intravenous inotropes (%) | 90 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP (%) | 34 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 30 ± 15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neurocognitive tests Of 158 patients 93 had tests. There were 239 tests out of a possible 316 ‘potential’ tests (76%) completion rate Reasons for not obtaining data in the 65 additional patients included patient refusal (43%), examiner not available (36%) and patient too ill or intubated (23%) NC domains were: (1) visual–spatial perception, the CD and the WAIS-111-BD; (2) memory, WATS-HUM (modified), WMS-III-LM and WMS-III-VR; (3) executive functions, TM-B and WAIS-III-DS; (4) language, abbreviated BNT; and (5) processing speed, TM-A Test score ranges were: CD, 1–10; WAIS-III-BD, 0–83; WMS-III-LM and WMS-III-LM Delay, 0–50; WMS-III-VR and WMS-III-VR Delay, 0–104; WAIS-III-DS, 1–133; TMB in seconds, lower is better; BNT, 0–15; processing speed in seconds, lower is better. In all cases (except TMB and processing speed) higher scores represent better performance All neurocognitive test results at 1, 3 and 6 months after implantation (these are mean and SD for all those with a test results at each time pointDomainTest1 month3 months6 monthsnMean ± SDnMean ± SDnMean ± SDVisual spatial perceptionCD928.7 ± 1.5748.9 ± 1.4388.6 ± 1.9WAIS-III-BD9228.2 ± 11.77429.3 ± 11.53831.3 ± 12.3Auditory memoryWMS-III-LMa9219.7 ± 6.67720.7 ± 6.14019.9 ± 8.1WMS-III-LM Delaya8815.3 ± 6.47716.8 ± 6.73916.1 ± 7.8Visual memoryWMS-III-VR9270.8 ± 20.57775.2 ± 18.34271.3 ± 20.7WMS-III-VR Delay8037.3 ± 25.57447.4 ± 26.14047.9 ± 27.1Executive functionWAIS-III-DS8942.9 ± 17.67647.4 ± 15.94143.4 ± 15.6TM-B87137 ± 8174114 ± 6238124 ± 70Confrontational languageBNT9312.5 ± 2.47212.4 ± 2.33812.4 ± 2.5Processing speedTM-A8953.7 ± 42.87743.6 ± 19.94047.1 ± 22.8a Modified administration. Of the completed NC tests, 51–57 pairs (paired test result of a patient) were available for the 1- vs. 3-month analysis and 23–31 pairs for the 1- vs. 6-month analysis, whereas 20–28 patients had test results from all three time points (this depended on the test type) Decreasing numbers of patients available for paired NC performance over the 6 months were mostly due to HT (37%), death (15%) and recovery of the natural heart with device removal (0.4%). By 6 months of support, 47% of patients remained on device support and theoretically would be available for NC testing Paired test results are summarised in the following tables Paired neurocognitive test results between 1 and 3 months after implantDomainTest1–3 monthsn1 month3 monthsp-valueVisual spatial perceptionCD558.8 ± 1.58.8 ± 1.50.936WAIS-III-BD5427.8 ± 11.628.7 ± 11.30.403Auditory memoryWMS-III-LMa5719.6 ± 6.921.4 ± 6.30.005WMS-III-LM Delay5415.2 ± 6.918. ± 6.60.001Visual memoryWMS-III-VR5670.6 ± 19.876.1 ± 18.30.004WMS-III-VR Delay4935.7 ± 25.350.7 ± 27.1< 0.0001Executive functionWAIS-III-DS5442.4 ± 17.248.2 ± 16.30.001TM-B51135 ± 71111 ± 630.0001Confrontational languageBNT5312.4 ± 2.412.3 ± 2.30.478Processing speedTM-A5450.4 ± 22.940.4 ± 17.3< 0.0001a Modified administration. Paired neurocognitive test results between 1 and 6 months after implant and for patients without subsequent paired retesting (mean ± SD)DomainTest1–6 monthsNot retestedn1 month6 monthsp-valuen1 monthVisual spatial perceptionCD298.6 ± 1.68.6 ± 1.90.929358.6 ± 1.5WAIS-III-BD2823.2 ± 9.030 ± 11.3< 0.0013629.6 ± 11.9Auditory memoryWMS-III-LMa3117.1 ± 6.919.5 ± 7.90.1093219.9 ± 6.5WMS-III-LM Delaya2713.6 ± 7.115.8 ± 7.60.1323115.8 ± 5.1Visual memoryWMS-III-VR3063.3 ± 20.973 ± 17.9< 0.0013373.2 ± 21.1WMS-III-VR Delay2527.5 ± 25.347.3 ± 30.0< 0.0012741.4 ± 26.5Executive functionWAIS-III-DS2737.6 ± 14.641.2 ± 16.40.183244.5 ± 18.8TM-B23175 ± 111127 ± 770.00735128 ± 66Confrontational languageBNT2812.3 ± 1.912.2 ± 2.20.8593812.7 ± 2.6Processing speedTM-A2671.8 ± 73.044.7 ± 21.80.0713246.7 ± 15.2a Modified administration. Statistically improved WMS-III-LM and processing speed, and executive function WAIS-III-DS paired results at 3 months (n= 51–57) were not sustained at 6 months (n = 23–31); however, WMS-III-VR and executive function TM-B paired results were statistically significant for improvement at both 3 and 6 months. WAIS-III-BD reached statistical significance at 6 months Results for patients tested at all three time points: 1, 3 and 6 months after implantation (mean ± SD)DomainTestn1 month3 months6 monthsp-valueVisual spatial perceptionCD268.6 ± 1.78.8 ± 1.58.6 ± 2.00.963WAIS-Ill-BD2524.3 ± 8.826.0 ± 9.530.6 ± 11.7< 0.001Auditory memoryWMS-III-LMa2817.0 ± 7.119.4 ± 6.019.8 ± 8.00.065WMS-III-LM Delaya2413.7 ± 7.116.3 ± 5.816.0 ± 7.10.097Visual memoryWMS-III-VR2666.2 ± 20.471.7 ± 19.774.2 ± 18.10.004WMS-III-VR Delay2030.4 ± 27.246.7 ± 31.449.6 ± 31.8< 0.001Executive functionWAIS-III-DS2438.0 ± 15.044.3 ± 17.642.6 ± 16.90.034TM-B22159 ± 80143 ± 79123 ± 760.003Confrontational languageBNT2612.2 ± 2.012.1 ± 1.712.2 ± 2.30.926Processing speedTM-A2356.7 ± 27.747.8 ± 21.345.1 ± 22.80.001a Modified administration. In paired tests at all three time points indicated statistically significant improvement (analysis of variance repeated measures) for WAIS-Ill-BD (n = 25), WMS-III-VR (n = 26) and WMS-III-VR Delay (n = 20), WAIS-III-DS (n = 24), TM-A (n = 23) and TM-B (n = 22) |
Domain | Test | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | n | Mean ± SD | n | Mean ± SD | n | Mean ± SD | Visual spatial perception | CD | 92 | 8.7 ± 1.5 | 74 | 8.9 ± 1.4 | 38 | 8.6 ± 1.9 | WAIS-III-BD | 92 | 28.2 ± 11.7 | 74 | 29.3 ± 11.5 | 38 | 31.3 ± 12.3 | Auditory memory | WMS-III-LMa | 92 | 19.7 ± 6.6 | 77 | 20.7 ± 6.1 | 40 | 19.9 ± 8.1 | WMS-III-LM Delaya | 88 | 15.3 ± 6.4 | 77 | 16.8 ± 6.7 | 39 | 16.1 ± 7.8 | Visual memory | WMS-III-VR | 92 | 70.8 ± 20.5 | 77 | 75.2 ± 18.3 | 42 | 71.3 ± 20.7 | WMS-III-VR Delay | 80 | 37.3 ± 25.5 | 74 | 47.4 ± 26.1 | 40 | 47.9 ± 27.1 | Executive function | WAIS-III-DS | 89 | 42.9 ± 17.6 | 76 | 47.4 ± 15.9 | 41 | 43.4 ± 15.6 | TM-B | 87 | 137 ± 81 | 74 | 114 ± 62 | 38 | 124 ± 70 | Confrontational language | BNT | 93 | 12.5 ± 2.4 | 72 | 12.4 ± 2.3 | 38 | 12.4 ± 2.5 | Processing speed | TM-A | 89 | 53.7 ± 42.8 | 77 | 43.6 ± 19.9 | 40 | 47.1 ± 22.8 | a Modified administration. | Domain | Test | 1–3 months | n | 1 month | 3 months | p-value | Visual spatial perception | CD | 55 | 8.8 ± 1.5 | 8.8 ± 1.5 | 0.936 | WAIS-III-BD | 54 | 27.8 ± 11.6 | 28.7 ± 11.3 | 0.403 | Auditory memory | WMS-III-LMa | 57 | 19.6 ± 6.9 | 21.4 ± 6.3 | 0.005 | WMS-III-LM Delay | 54 | 15.2 ± 6.9 | 18. ± 6.6 | 0.001 | Visual memory | WMS-III-VR | 56 | 70.6 ± 19.8 | 76.1 ± 18.3 | 0.004 | WMS-III-VR Delay | 49 | 35.7 ± 25.3 | 50.7 ± 27.1 | < 0.0001 | Executive function | WAIS-III-DS | 54 | 42.4 ± 17.2 | 48.2 ± 16.3 | 0.001 | TM-B | 51 | 135 ± 71 | 111 ± 63 | 0.0001 | Confrontational language | BNT | 53 | 12.4 ± 2.4 | 12.3 ± 2.3 | 0.478 | Processing speed | TM-A | 54 | 50.4 ± 22.9 | 40.4 ± 17.3 | < 0.0001 | a Modified administration. | Domain | Test | 1–6 months | Not retested | n | 1 month | 6 months | p-value | n | 1 month | Visual spatial perception | CD | 29 | 8.6 ± 1.6 | 8.6 ± 1.9 | 0.929 | 35 | 8.6 ± 1.5 | WAIS-III-BD | 28 | 23.2 ± 9.0 | 30 ± 11.3 | < 0.001 | 36 | 29.6 ± 11.9 | Auditory memory | WMS-III-LMa | 31 | 17.1 ± 6.9 | 19.5 ± 7.9 | 0.109 | 32 | 19.9 ± 6.5 | WMS-III-LM Delaya | 27 | 13.6 ± 7.1 | 15.8 ± 7.6 | 0.132 | 31 | 15.8 ± 5.1 | Visual memory | WMS-III-VR | 30 | 63.3 ± 20.9 | 73 ± 17.9 | < 0.001 | 33 | 73.2 ± 21.1 | WMS-III-VR Delay | 25 | 27.5 ± 25.3 | 47.3 ± 30.0 | < 0.001 | 27 | 41.4 ± 26.5 | Executive function | WAIS-III-DS | 27 | 37.6 ± 14.6 | 41.2 ± 16.4 | 0.18 | 32 | 44.5 ± 18.8 | TM-B | 23 | 175 ± 111 | 127 ± 77 | 0.007 | 35 | 128 ± 66 | Confrontational language | BNT | 28 | 12.3 ± 1.9 | 12.2 ± 2.2 | 0.859 | 38 | 12.7 ± 2.6 | Processing speed | TM-A | 26 | 71.8 ± 73.0 | 44.7 ± 21.8 | 0.071 | 32 | 46.7 ± 15.2 | a Modified administration. | Domain | Test | n | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value | Visual spatial perception | CD | 26 | 8.6 ± 1.7 | 8.8 ± 1.5 | 8.6 ± 2.0 | 0.963 | WAIS-Ill-BD | 25 | 24.3 ± 8.8 | 26.0 ± 9.5 | 30.6 ± 11.7 | < 0.001 | Auditory memory | WMS-III-LMa | 28 | 17.0 ± 7.1 | 19.4 ± 6.0 | 19.8 ± 8.0 | 0.065 | WMS-III-LM Delaya | 24 | 13.7 ± 7.1 | 16.3 ± 5.8 | 16.0 ± 7.1 | 0.097 | Visual memory | WMS-III-VR | 26 | 66.2 ± 20.4 | 71.7 ± 19.7 | 74.2 ± 18.1 | 0.004 | WMS-III-VR Delay | 20 | 30.4 ± 27.2 | 46.7 ± 31.4 | 49.6 ± 31.8 | < 0.001 | Executive function | WAIS-III-DS | 24 | 38.0 ± 15.0 | 44.3 ± 17.6 | 42.6 ± 16.9 | 0.034 | TM-B | 22 | 159 ± 80 | 143 ± 79 | 123 ± 76 | 0.003 | Confrontational language | BNT | 26 | 12.2 ± 2.0 | 12.1 ± 1.7 | 12.2 ± 2.3 | 0.926 | Processing speed | TM-A | 23 | 56.7 ± 27.7 | 47.8 ± 21.3 | 45.1 ± 22.8 | 0.001 | a Modified administration. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Domain | Test | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | Mean ± SD | n | Mean ± SD | n | Mean ± SD | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Visual spatial perception | CD | 92 | 8.7 ± 1.5 | 74 | 8.9 ± 1.4 | 38 | 8.6 ± 1.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WAIS-III-BD | 92 | 28.2 ± 11.7 | 74 | 29.3 ± 11.5 | 38 | 31.3 ± 12.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Auditory memory | WMS-III-LMa | 92 | 19.7 ± 6.6 | 77 | 20.7 ± 6.1 | 40 | 19.9 ± 8.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WMS-III-LM Delaya | 88 | 15.3 ± 6.4 | 77 | 16.8 ± 6.7 | 39 | 16.1 ± 7.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Visual memory | WMS-III-VR | 92 | 70.8 ± 20.5 | 77 | 75.2 ± 18.3 | 42 | 71.3 ± 20.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WMS-III-VR Delay | 80 | 37.3 ± 25.5 | 74 | 47.4 ± 26.1 | 40 | 47.9 ± 27.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive function | WAIS-III-DS | 89 | 42.9 ± 17.6 | 76 | 47.4 ± 15.9 | 41 | 43.4 ± 15.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TM-B | 87 | 137 ± 81 | 74 | 114 ± 62 | 38 | 124 ± 70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Confrontational language | BNT | 93 | 12.5 ± 2.4 | 72 | 12.4 ± 2.3 | 38 | 12.4 ± 2.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Processing speed | TM-A | 89 | 53.7 ± 42.8 | 77 | 43.6 ± 19.9 | 40 | 47.1 ± 22.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Modified administration. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Domain | Test | 1–3 months | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | 1 month | 3 months | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Visual spatial perception | CD | 55 | 8.8 ± 1.5 | 8.8 ± 1.5 | 0.936 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WAIS-III-BD | 54 | 27.8 ± 11.6 | 28.7 ± 11.3 | 0.403 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Auditory memory | WMS-III-LMa | 57 | 19.6 ± 6.9 | 21.4 ± 6.3 | 0.005 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WMS-III-LM Delay | 54 | 15.2 ± 6.9 | 18. ± 6.6 | 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Visual memory | WMS-III-VR | 56 | 70.6 ± 19.8 | 76.1 ± 18.3 | 0.004 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WMS-III-VR Delay | 49 | 35.7 ± 25.3 | 50.7 ± 27.1 | < 0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive function | WAIS-III-DS | 54 | 42.4 ± 17.2 | 48.2 ± 16.3 | 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TM-B | 51 | 135 ± 71 | 111 ± 63 | 0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Confrontational language | BNT | 53 | 12.4 ± 2.4 | 12.3 ± 2.3 | 0.478 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Processing speed | TM-A | 54 | 50.4 ± 22.9 | 40.4 ± 17.3 | < 0.0001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Modified administration. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Domain | Test | 1–6 months | Not retested | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | 1 month | 6 months | p-value | n | 1 month | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Visual spatial perception | CD | 29 | 8.6 ± 1.6 | 8.6 ± 1.9 | 0.929 | 35 | 8.6 ± 1.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WAIS-III-BD | 28 | 23.2 ± 9.0 | 30 ± 11.3 | < 0.001 | 36 | 29.6 ± 11.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Auditory memory | WMS-III-LMa | 31 | 17.1 ± 6.9 | 19.5 ± 7.9 | 0.109 | 32 | 19.9 ± 6.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WMS-III-LM Delaya | 27 | 13.6 ± 7.1 | 15.8 ± 7.6 | 0.132 | 31 | 15.8 ± 5.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Visual memory | WMS-III-VR | 30 | 63.3 ± 20.9 | 73 ± 17.9 | < 0.001 | 33 | 73.2 ± 21.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WMS-III-VR Delay | 25 | 27.5 ± 25.3 | 47.3 ± 30.0 | < 0.001 | 27 | 41.4 ± 26.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive function | WAIS-III-DS | 27 | 37.6 ± 14.6 | 41.2 ± 16.4 | 0.18 | 32 | 44.5 ± 18.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TM-B | 23 | 175 ± 111 | 127 ± 77 | 0.007 | 35 | 128 ± 66 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Confrontational language | BNT | 28 | 12.3 ± 1.9 | 12.2 ± 2.2 | 0.859 | 38 | 12.7 ± 2.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Processing speed | TM-A | 26 | 71.8 ± 73.0 | 44.7 ± 21.8 | 0.071 | 32 | 46.7 ± 15.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Modified administration. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Domain | Test | n | 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Visual spatial perception | CD | 26 | 8.6 ± 1.7 | 8.8 ± 1.5 | 8.6 ± 2.0 | 0.963 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WAIS-Ill-BD | 25 | 24.3 ± 8.8 | 26.0 ± 9.5 | 30.6 ± 11.7 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Auditory memory | WMS-III-LMa | 28 | 17.0 ± 7.1 | 19.4 ± 6.0 | 19.8 ± 8.0 | 0.065 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WMS-III-LM Delaya | 24 | 13.7 ± 7.1 | 16.3 ± 5.8 | 16.0 ± 7.1 | 0.097 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Visual memory | WMS-III-VR | 26 | 66.2 ± 20.4 | 71.7 ± 19.7 | 74.2 ± 18.1 | 0.004 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WMS-III-VR Delay | 20 | 30.4 ± 27.2 | 46.7 ± 31.4 | 49.6 ± 31.8 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive function | WAIS-III-DS | 24 | 38.0 ± 15.0 | 44.3 ± 17.6 | 42.6 ± 16.9 | 0.034 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TM-B | 22 | 159 ± 80 | 143 ± 79 | 123 ± 76 | 0.003 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Confrontational language | BNT | 26 | 12.2 ± 2.0 | 12.1 ± 1.7 | 12.2 ± 2.3 | 0.926 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Processing speed | TM-A | 23 | 56.7 ± 27.7 | 47.8 ± 21.3 | 45.1 ± 22.8 | 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Modified administration. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The cognitive performance of advanced HF patients remained stable or showed slight improvements from month 1 to month 6 of continuous-blood-flow support with the HMII | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Study provides some evidence for small improvements in some aspects of NC; however, results were not all internally consistent and there was a significant amount of missing data. As few patients were able to perform tests prior to implant the ‘baseline’ was taken to be 1 month after implant; there is no assurance of that similar differences would be observed vs. baseline. One interpretation is that the adverse effect of implantation seen at 1 month post operation for some NCV outcome is reversed by 6 months | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rogers 201053
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Rogers Year of publication: 2010 Country: USA Study design: Two single-arm trials conducted in compliance with FDA Study setting: Multicentre Number of centres: 38 Duration of study: 2005–9 Follow-up period: 6 months BTT; 24 months DT Funding: Industry; Thoratec Inc. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To report the impact of a CF LVAD HMII in > 650 patients with advanced HF on QoL and functional capacity for up to 24 months of circulatory support | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 655 Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported Inclusion criteria: NYHA functional class IV HF symptoms and were listed as high priority for transplantation (UNOS status 1A or 1B). Patients with NYHA functional classes IIIB and IV HF who were ineligible for a HT and refractory to optimal MM were considered for enrolment in the DT trial Exclusion criteria: See Miller et al.,70 Pagani et al.71 and Slaughter et al.47 For both the trials included severe renal, pulmonary, or hepatic dysfunction, active uncontrolled infection, a mechanical aortic valve, aortic insufficiency, an aortic aneurysm, other mechanical circulatory support (except an IABP), and technical obstacles thought by the investigator to pose excessive surgical risk Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): BTT 50 years (13); DT 63 years (12) Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: BTT 76% male; DT 73% male Race: Not reported Diagnosis: End-stage HF |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT or DT Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: BTT vs. DTT for a few outcomes Duration of treatment: Not reported Percentage of patients using inotropes: BTT 250 (90%); DT 289 (77%) Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Not specified Secondary outcomes: Changes in NYHA classification, 6-minute walk test, activity level (METs), MLWHF and KCCQ Method of assessing outcomes: Prospective data collection Survival: No Adverse event: No HRQoL: Yes Length of follow-up: 6 months BTT; 24 months DTNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reportedNot reportedRandomised/includedBTT n = 281DT n = 374ExcludedNot reportedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reportedNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported | Not reported | Randomised/included | BTT n = 281 | DT n = 374 | Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | BTT n = 281 | DT n = 374 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ParameterBTTDTp-valueAge (years)50 ± 1363 ± 12< 0.001Female, n (%)67 (24)102 (27)0.322Ischaemic aetiology of HF, n (%)121 (43)217 (58)< 0.001LVEF (%)16.3 ± 6.517.1 ± 5.80.025Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)2.1 ± 0.62.1 ± 0.60.889PCWP (mmHg)25.4 ± 7.923.9 ± 8.30.021Systolic BP (mmHg)98.1 ± 15.0102.1 ± 15.1< 0.001BUN (mg/dl)30.4 ± 17.134.4 ± 21.30.023Creatinine (mg/dl)1.4 ± 0.51.5 ± 0.60.04Total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.3 ± 0.91.3 ± 1.00.603ALT (U/l)106 ± 27844 ± 69< 0.001Serum sodium (mmol/l)134 ± 5135 ± 50.002CRT, n (%)135 (48)268 (72)< 0.001Intravenous inotropes, n (%)252 (90)a289 (77)0.001IABP, n (%)126 (45)78 (21)< 0.001a 10% intolerant due to arrhythmias. | Parameter | BTT | DT | p-value | Age (years) | 50 ± 13 | 63 ± 12 | < 0.001 | Female, n (%) | 67 (24) | 102 (27) | 0.322 | Ischaemic aetiology of HF, n (%) | 121 (43) | 217 (58) | < 0.001 | LVEF (%) | 16.3 ± 6.5 | 17.1 ± 5.8 | 0.025 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 0.889 | PCWP (mmHg) | 25.4 ± 7.9 | 23.9 ± 8.3 | 0.021 | Systolic BP (mmHg) | 98.1 ± 15.0 | 102.1 ± 15.1 | < 0.001 | BUN (mg/dl) | 30.4 ± 17.1 | 34.4 ± 21.3 | 0.023 | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 0.04 | Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.3 ± 0.9 | 1.3 ± 1.0 | 0.603 | ALT (U/l) | 106 ± 278 | 44 ± 69 | < 0.001 | Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 134 ± 5 | 135 ± 5 | 0.002 | CRT, n (%) | 135 (48) | 268 (72) | < 0.001 | Intravenous inotropes, n (%) | 252 (90)a | 289 (77) | 0.001 | IABP, n (%) | 126 (45) | 78 (21) | < 0.001 | a 10% intolerant due to arrhythmias. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | BTT | DT | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 50 ± 13 | 63 ± 12 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Female, n (%) | 67 (24) | 102 (27) | 0.322 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic aetiology of HF, n (%) | 121 (43) | 217 (58) | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF (%) | 16.3 ± 6.5 | 17.1 ± 5.8 | 0.025 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 0.889 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 25.4 ± 7.9 | 23.9 ± 8.3 | 0.021 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 98.1 ± 15.0 | 102.1 ± 15.1 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 30.4 ± 17.1 | 34.4 ± 21.3 | 0.023 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.3 ± 0.9 | 1.3 ± 1.0 | 0.603 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT (U/l) | 106 ± 278 | 44 ± 69 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum sodium (mmol/l) | 134 ± 5 | 135 ± 5 | 0.002 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CRT, n (%) | 135 (48) | 268 (72) | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intravenous inotropes, n (%) | 252 (90)a | 289 (77) | 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP, n (%) | 126 (45) | 78 (21) | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a 10% intolerant due to arrhythmias. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA Changes in NYHA class by month BTT and DT At baseline, most were NYHA class IV At 1 month, 59% (BTT) and 47% (DT) improved to NYHA class I or II At 6 months, 82% (BTT) and 80% (DT) were NYHA class I or II From 6–24 months, 80% of DT patients remained in NYHA functional class I or II Relative to baseline scores highly significant improvement in NYHA functional class were observed at all study intervals for both the study groups (p < 0.001) There was no significant difference in the improvements seen in NYHA class between BTT and DT patients 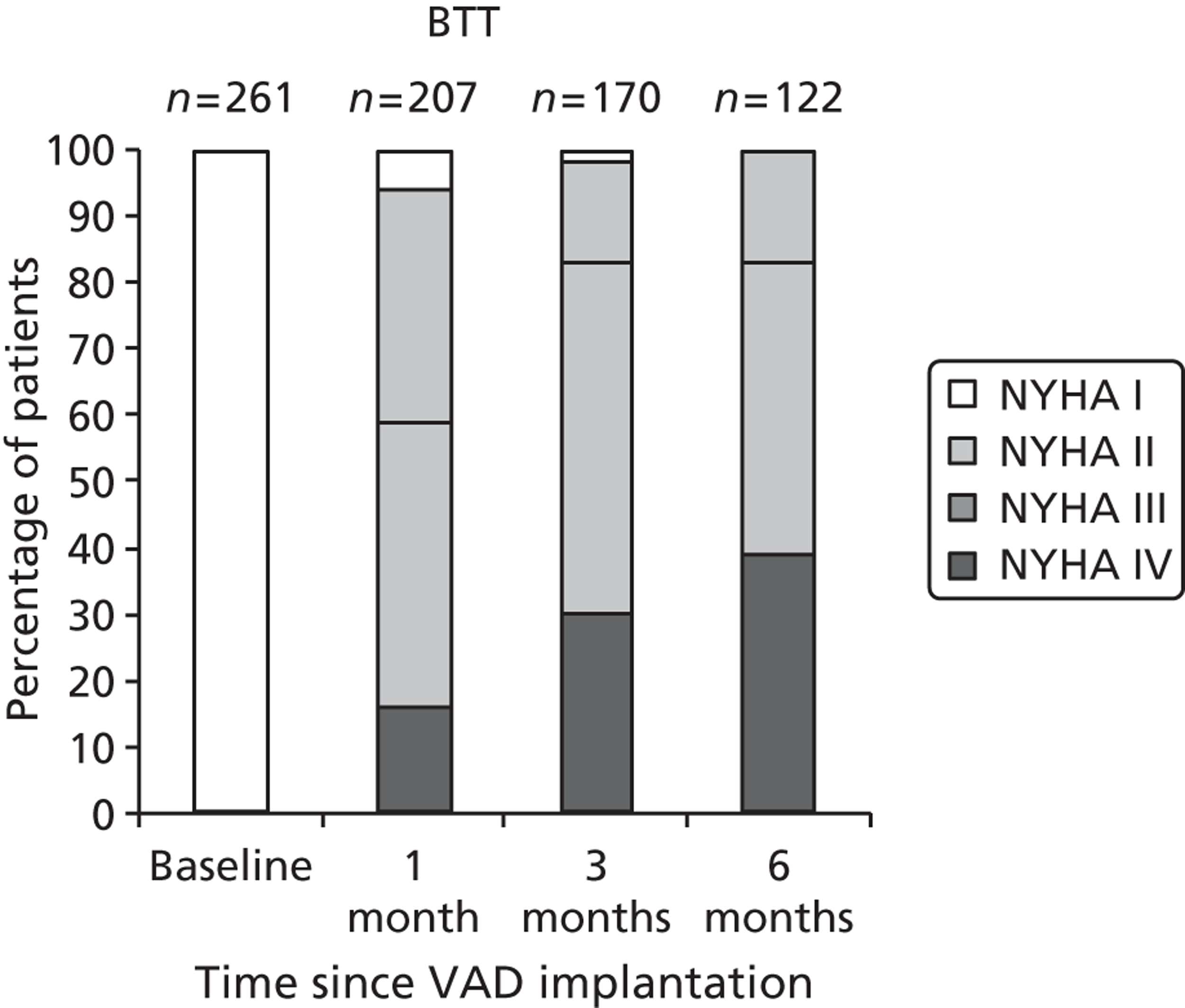 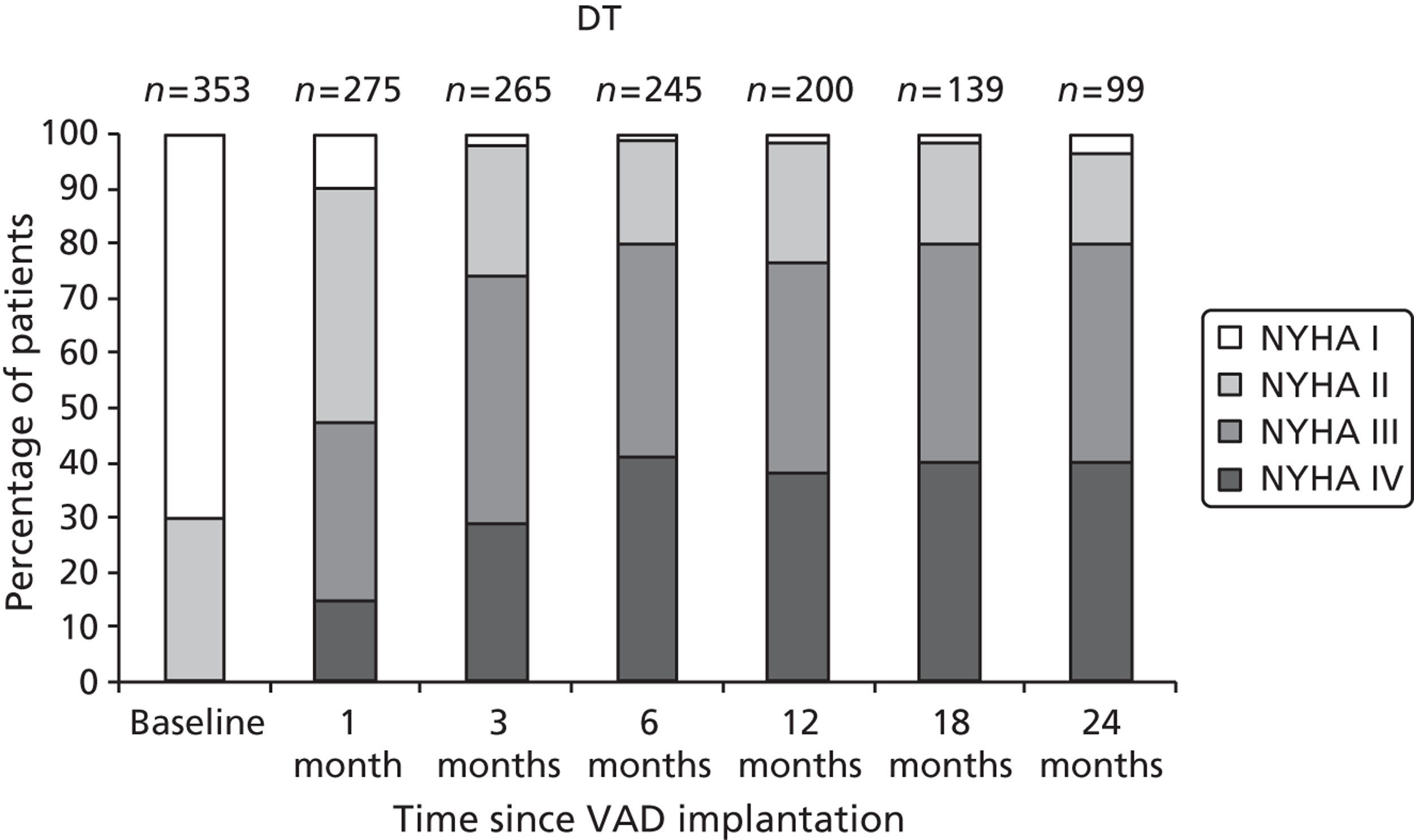 NYHA functional class was determined by an independent clinician at the time points shown in the BTT and DT trials. Study inclusion criteria required NYHA functional class III to IV symptoms at baseline. NYHA functional class improvements were statistically significant in both trials (p < 0.001) 6-minute walk test At baseline, 38 BTT and 129 of DT cohorts (14% and 34%, respectively) were able to perform the 6-minute walk test Baseline distance: 214 ± 125 m (BTT); 204 ± 150 m (DT) At 6 months distance: 372 ± 199 m (BTT), n = 97; 350 ± 198 m (DT), n = 199 At 24 months: 60 ± 210 m (DT), n = 75 Overall there was a statistically significant improvement over time at all test intervals for both study groups 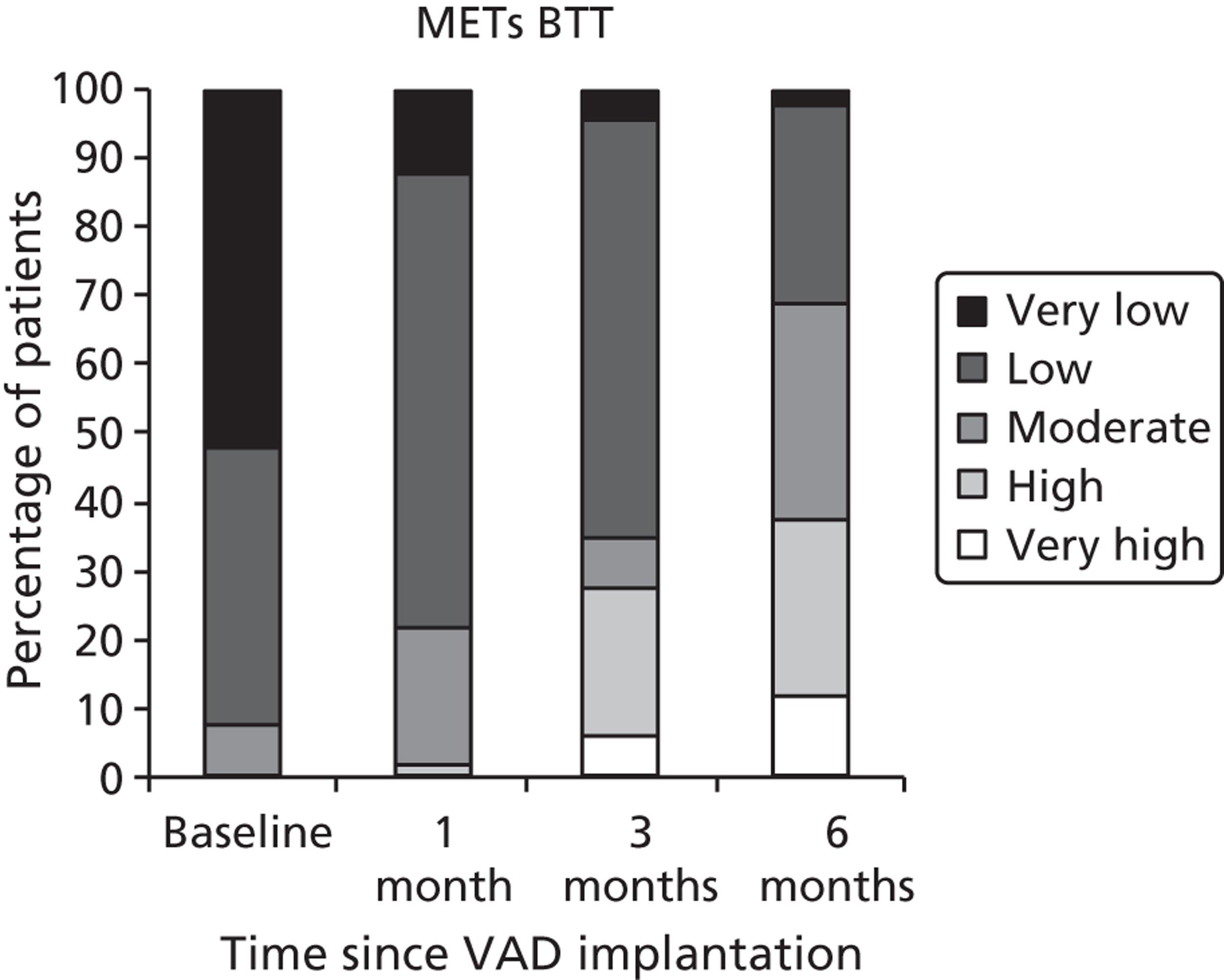 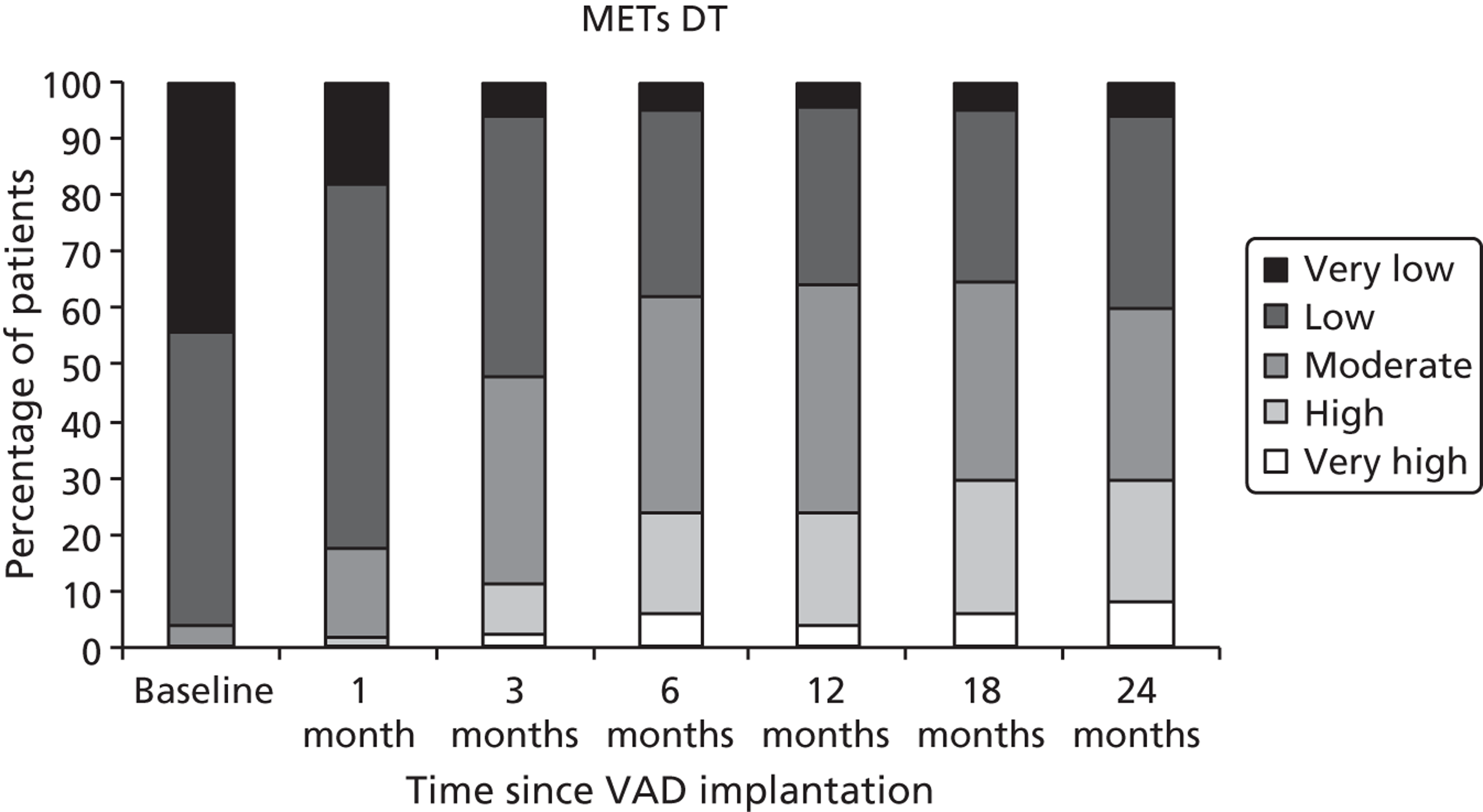 METs Serial assessment of METs. At baseline, > 90% of patients in both trials described their level of function as low or very low. At 6 months, approximately two-thirds of patients described their level of function as moderate to very high (p < 0.001 vs. baseline). QoL measure MLWHF and KCCQ Major resultsBTTDTMonthnMean ± SDMedian [25th, 75th]% improvement of mediannMean ± SDMedian [25th, 75th]% improvement of medianMLWHF 1167−12 ± 27−10 [−28, 4]13241−17 ± 31−13 [−40, 4]17 3126−24 ± 31−30 [−47, −4]39231−35 ± 28−37 [−58, −17]48 687−28 ± 28−29 [−50, −9]38209−39 ± 27−40 [−60, −20]52 120177−39 ± 30−41 [−62, −17]53 180126−39 ± 25−42 [−57, −22]55 24082−41 ± 25−42 [−57, −20]55KCCQ OSS 117213 ± 2514 [−3, 29]0.5424217 ± 2616 [−1, 35]0.70 313222 ± 2620 [9, 42]0.7723235 ± 2434 [19, 53]1.48 69027 ± 2828 [7, 45]1.0821139 ± 2439 [20, 58]1.70 12018140 ± 2542 [24, 61]1.83 18012941 ± 2438 [22, 61]1.65 2408942 ± 2341 [25, 60]1.78KCCQ CSS 117012 ± 2711 [−6, 31]0.324015 ± 2713 [−3, 34]0.41 313221 ± 2821 [4, 42]0.5723132 ± 2532 [14, 50]1.00 69025 ± 3124 [8, 43]0.6521037 ± 2536 [17, 55]1.13 12018136 ± 2839 [18, 57]1.22 18012937 ± 2734 [18, 61]1.06 2408938 ± 2635 [20, 55]1.09Values are the mean ± SD and median [25th, 75th percentiles] of paired changes at each time point compared with baseline. Also shown are the per cent improvements of the median from baseline. MLWHF Scores decreased over time, indicating an improvement in QoL (p < 0.001)Change in median from baselineBTTDTAt 1 month1013 pointsAt 6 months2940 pointsMedian % improvement at 6 months3852Median % improvement at 24 months55 (42 points) KCCQ OSSChange in median from baselineBTTDTAt 1 month1416At 6 months2839Median improvement at 24 months41 points41 pointsAfter 6 months score remained stable. KCCQ CSS Results were similar to KCCQ OSS At 6 months, 79% of BTT patients and 92% of DT patients with paired data had achieved a clinically meaningful improvement of > 5 points in KCCQ OSS compared with baseline. Similar results were found for the KCCQ CSS2 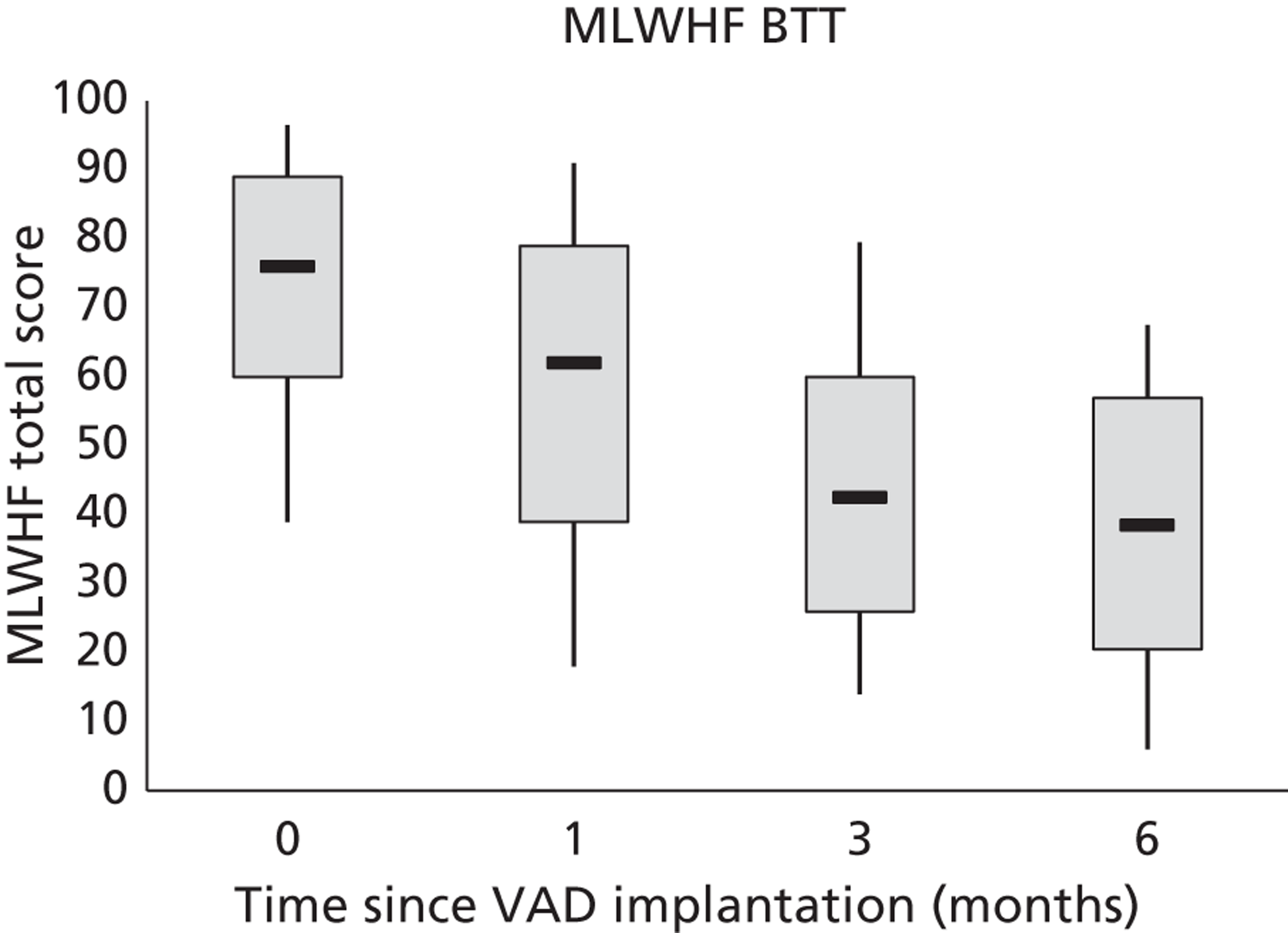 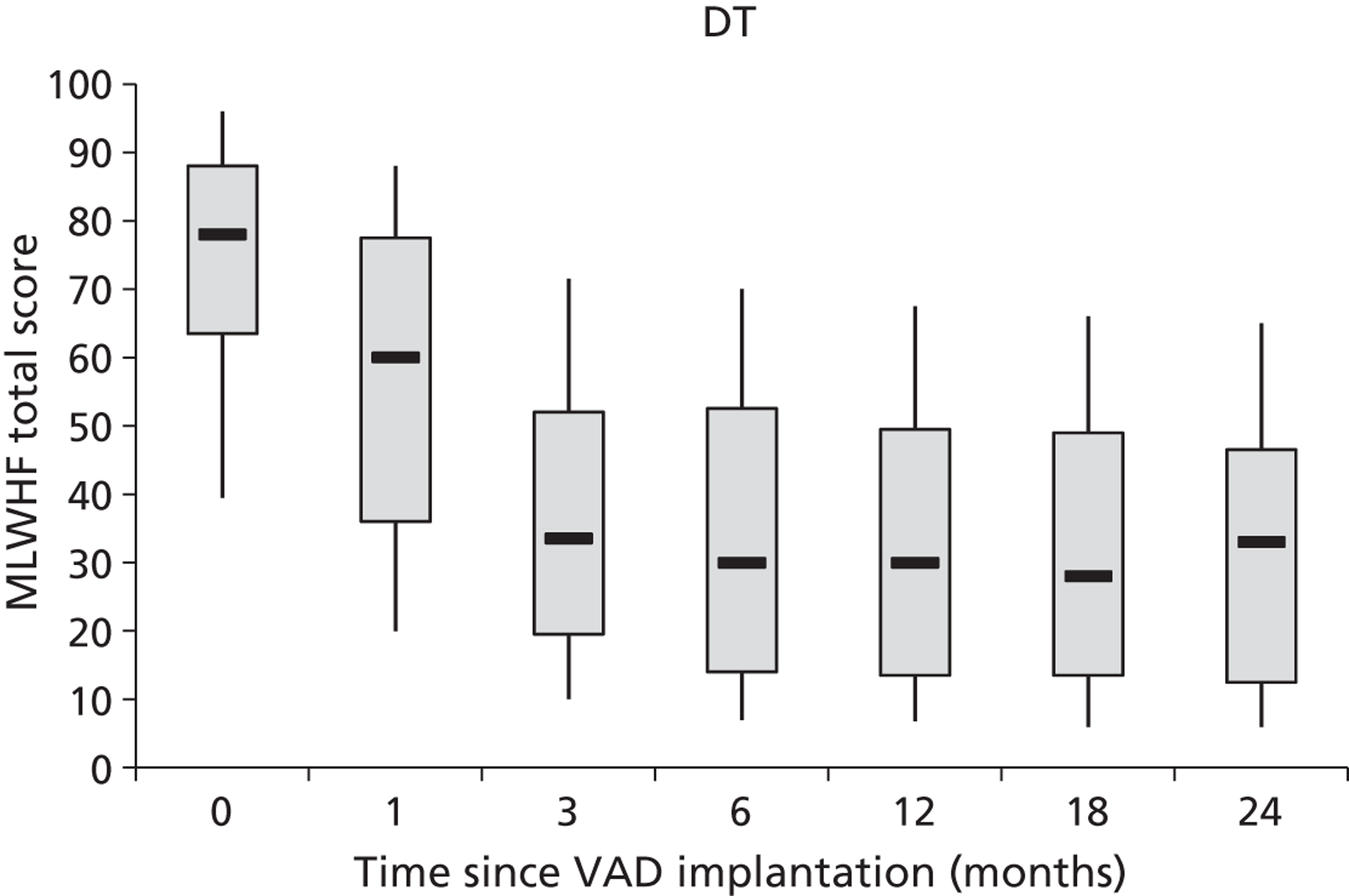 Changes in QoL assessed with the MLWHF are shown. Lower values signify improved QoL. Bars indicate 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles, whiskers indicate fifth and 95th percentiles. p < 0.05 for time points compared with baseline KCCQ BTT Changes in QoL assessed with the MLWHF are shown. Lower values signify improved QoL. Bars indicate 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles, whiskers indicate fifth and 95th percentiles. p < 0.05 for all time points relative to baseline compared with baseline 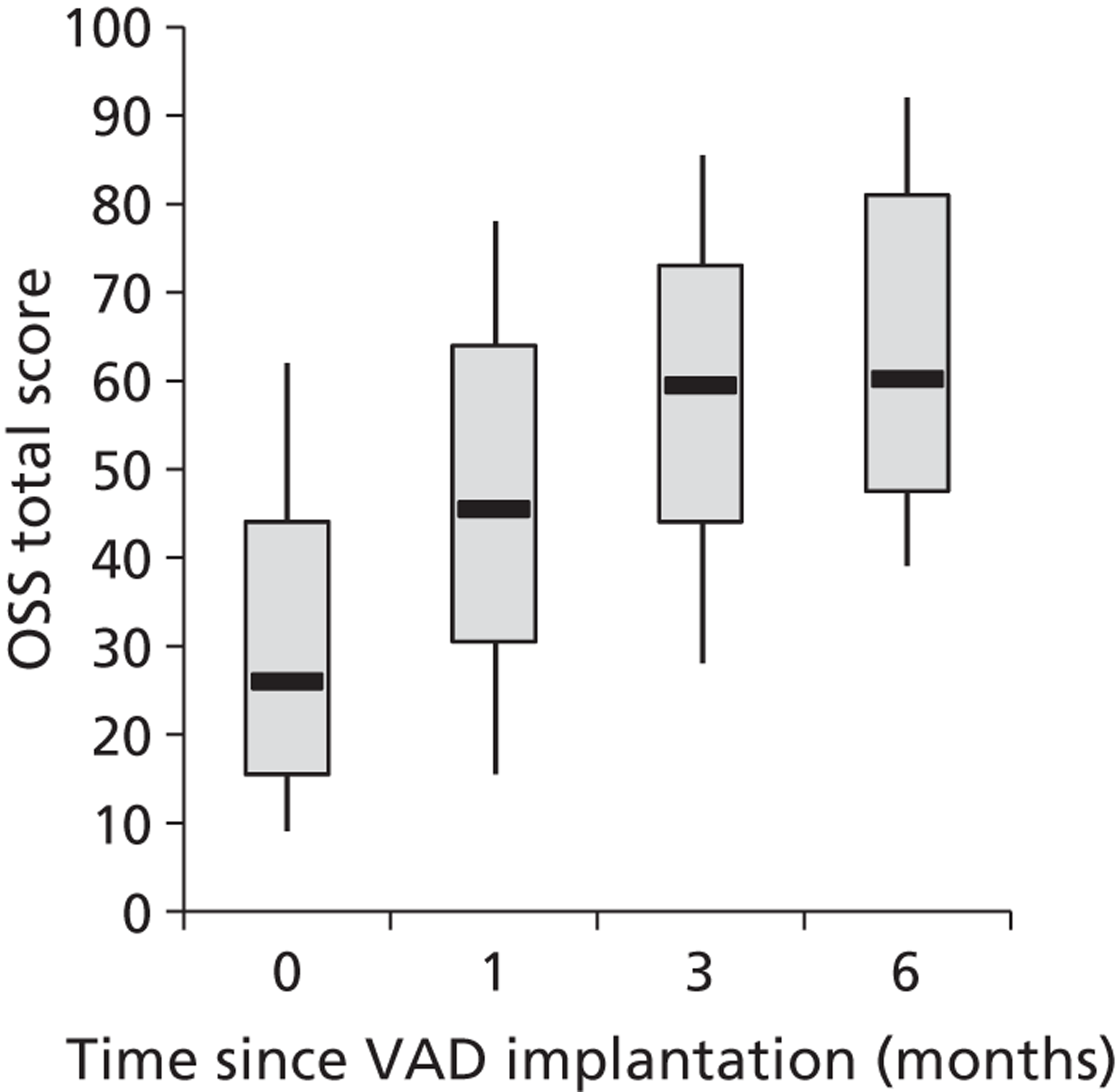 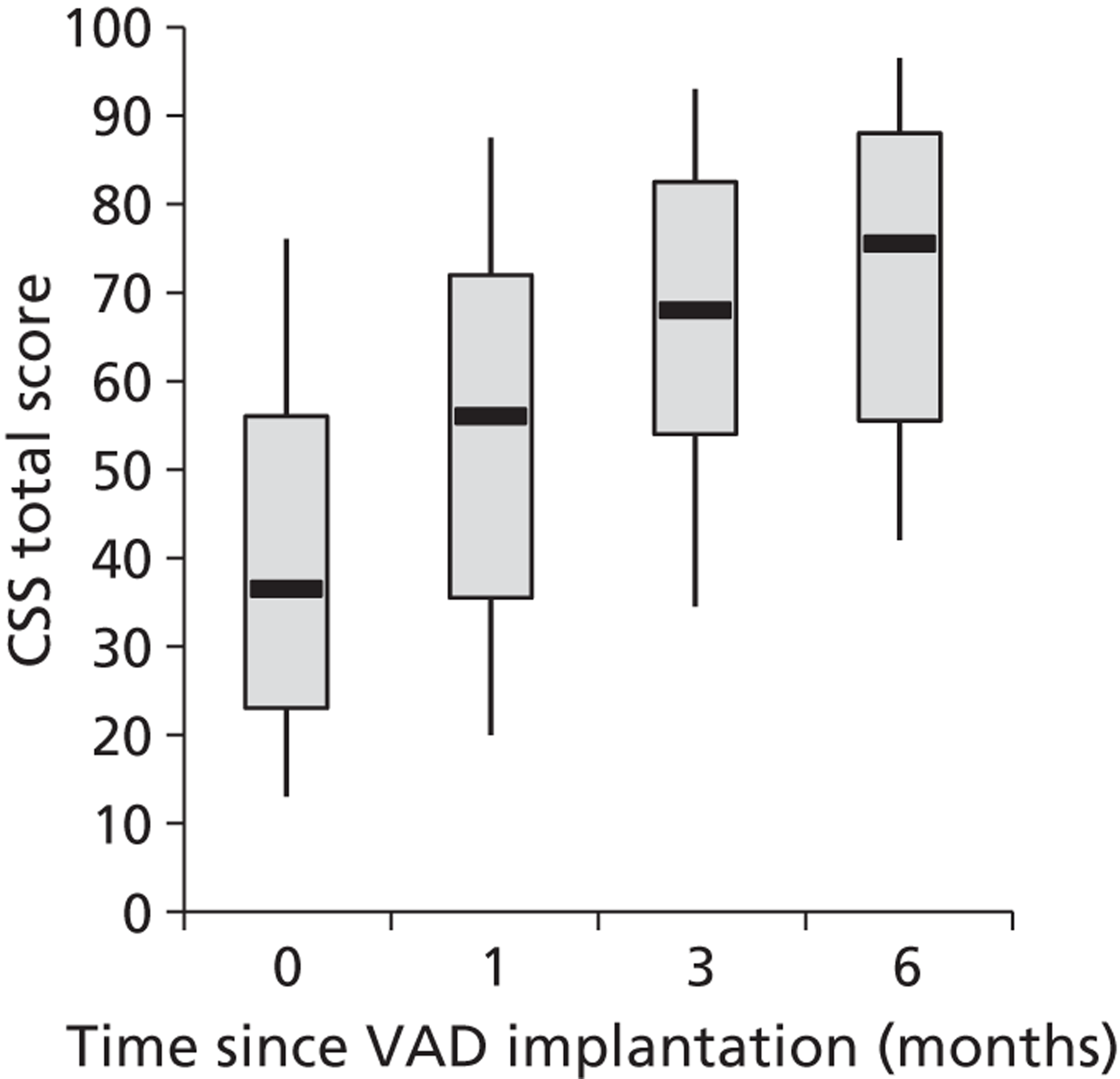 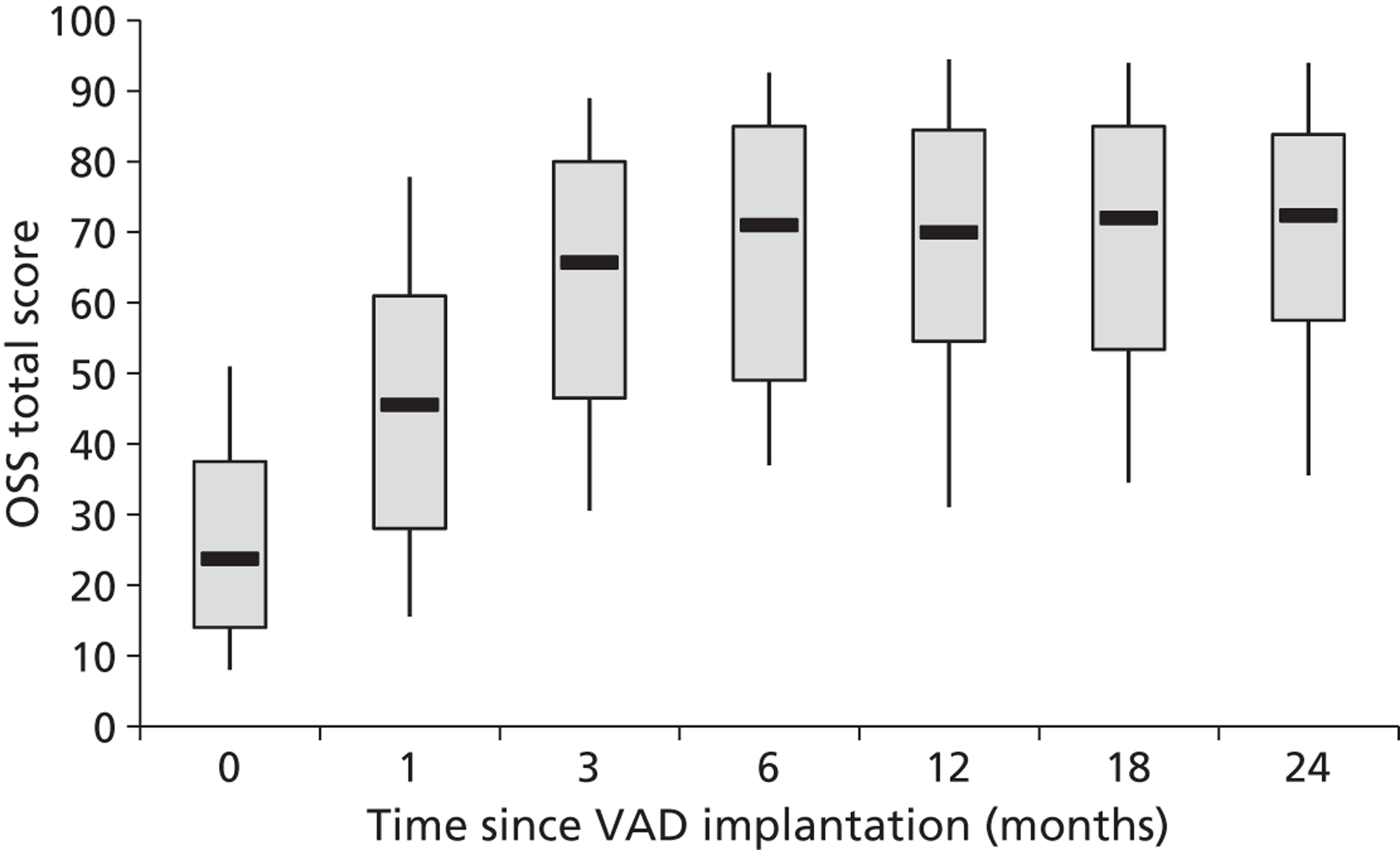 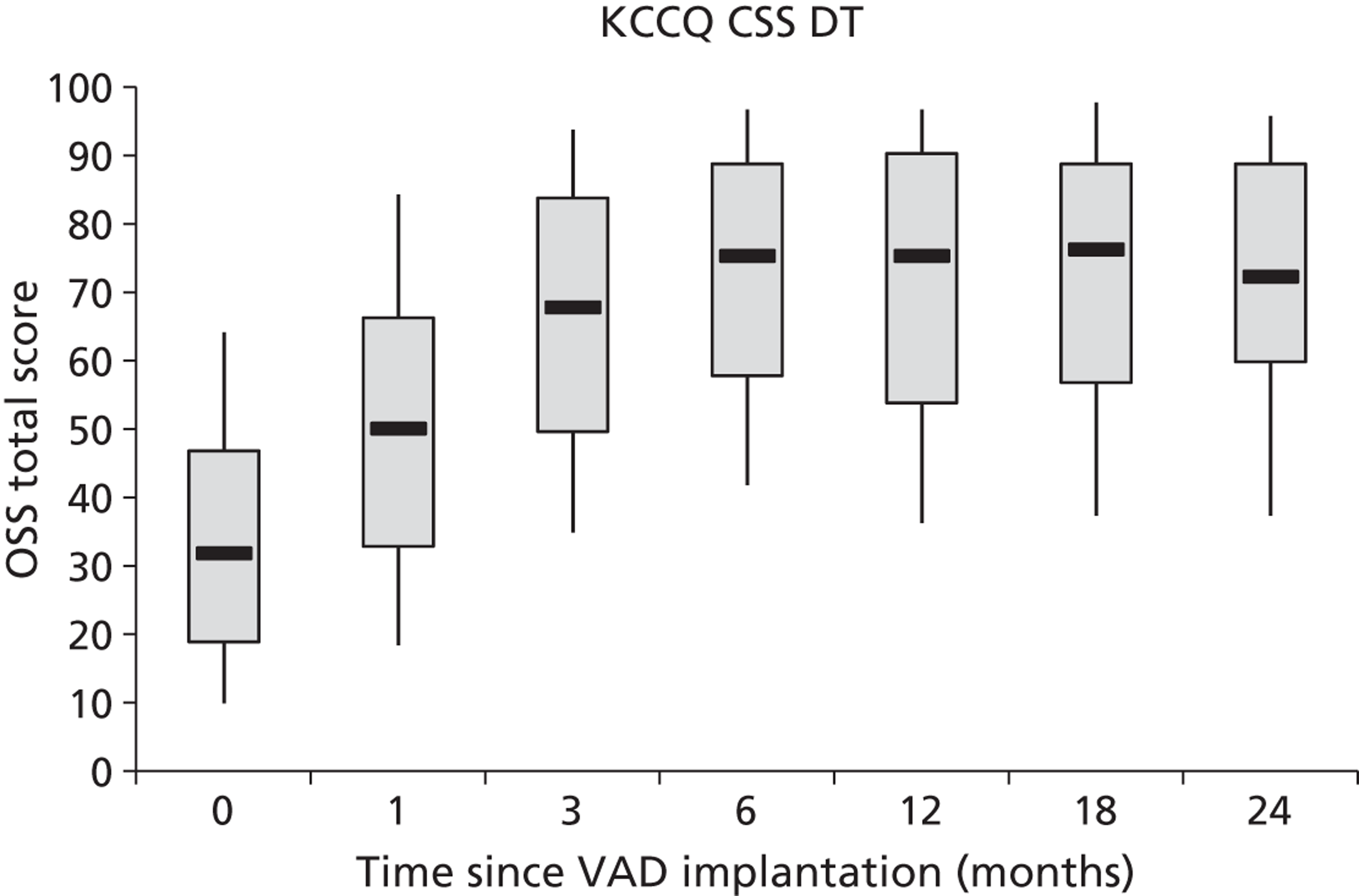 Changes in QoL assessed with the MLWHF are shown. Lower values signify improved QoL. Bars indicate 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles, whiskers indicate fifth and 95th percentiles. p < 0.05 for all time points relative to baseline compared with baseline |
BTT | DT | Month | n | Mean ± SD | Median [25th, 75th] | % improvement of median | n | Mean ± SD | Median [25th, 75th] | % improvement of median | MLWHF | 1 | 167 | −12 ± 27 | −10 [−28, 4] | 13 | 241 | −17 ± 31 | −13 [−40, 4] | 17 | 3 | 126 | −24 ± 31 | −30 [−47, −4] | 39 | 231 | −35 ± 28 | −37 [−58, −17] | 48 | 6 | 87 | −28 ± 28 | −29 [−50, −9] | 38 | 209 | −39 ± 27 | −40 [−60, −20] | 52 | 12 | 0 | 177 | −39 ± 30 | −41 [−62, −17] | 53 | 18 | 0 | 126 | −39 ± 25 | −42 [−57, −22] | 55 | 24 | 0 | 82 | −41 ± 25 | −42 [−57, −20] | 55 | KCCQ OSS | 1 | 172 | 13 ± 25 | 14 [−3, 29] | 0.54 | 242 | 17 ± 26 | 16 [−1, 35] | 0.70 | 3 | 132 | 22 ± 26 | 20 [9, 42] | 0.77 | 232 | 35 ± 24 | 34 [19, 53] | 1.48 | 6 | 90 | 27 ± 28 | 28 [7, 45] | 1.08 | 211 | 39 ± 24 | 39 [20, 58] | 1.70 | 12 | 0 | 181 | 40 ± 25 | 42 [24, 61] | 1.83 | 18 | 0 | 129 | 41 ± 24 | 38 [22, 61] | 1.65 | 24 | 0 | 89 | 42 ± 23 | 41 [25, 60] | 1.78 | KCCQ CSS | 1 | 170 | 12 ± 27 | 11 [−6, 31] | 0.3 | 240 | 15 ± 27 | 13 [−3, 34] | 0.41 | 3 | 132 | 21 ± 28 | 21 [4, 42] | 0.57 | 231 | 32 ± 25 | 32 [14, 50] | 1.00 | 6 | 90 | 25 ± 31 | 24 [8, 43] | 0.65 | 210 | 37 ± 25 | 36 [17, 55] | 1.13 | 12 | 0 | 181 | 36 ± 28 | 39 [18, 57] | 1.22 | 18 | 0 | 129 | 37 ± 27 | 34 [18, 61] | 1.06 | 24 | 0 | 89 | 38 ± 26 | 35 [20, 55] | 1.09 | Values are the mean ± SD and median [25th, 75th percentiles] of paired changes at each time point compared with baseline. Also shown are the per cent improvements of the median from baseline. | Change in median from baseline | BTT | DT | At 1 month | 10 | 13 points | At 6 months | 29 | 40 points | Median % improvement at 6 months | 38 | 52 | Median % improvement at 24 months | 55 (42 points) | Change in median from baseline | BTT | DT | At 1 month | 14 | 16 | At 6 months | 28 | 39 | Median improvement at 24 months | 41 points | 41 points | After 6 months score remained stable. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTT | DT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Month | n | Mean ± SD | Median [25th, 75th] | % improvement of median | n | Mean ± SD | Median [25th, 75th] | % improvement of median | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLWHF | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 167 | −12 ± 27 | −10 [−28, 4] | 13 | 241 | −17 ± 31 | −13 [−40, 4] | 17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 126 | −24 ± 31 | −30 [−47, −4] | 39 | 231 | −35 ± 28 | −37 [−58, −17] | 48 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 87 | −28 ± 28 | −29 [−50, −9] | 38 | 209 | −39 ± 27 | −40 [−60, −20] | 52 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | 0 | 177 | −39 ± 30 | −41 [−62, −17] | 53 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | 0 | 126 | −39 ± 25 | −42 [−57, −22] | 55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | 0 | 82 | −41 ± 25 | −42 [−57, −20] | 55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KCCQ OSS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 172 | 13 ± 25 | 14 [−3, 29] | 0.54 | 242 | 17 ± 26 | 16 [−1, 35] | 0.70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 132 | 22 ± 26 | 20 [9, 42] | 0.77 | 232 | 35 ± 24 | 34 [19, 53] | 1.48 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 90 | 27 ± 28 | 28 [7, 45] | 1.08 | 211 | 39 ± 24 | 39 [20, 58] | 1.70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | 0 | 181 | 40 ± 25 | 42 [24, 61] | 1.83 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | 0 | 129 | 41 ± 24 | 38 [22, 61] | 1.65 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | 0 | 89 | 42 ± 23 | 41 [25, 60] | 1.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KCCQ CSS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 170 | 12 ± 27 | 11 [−6, 31] | 0.3 | 240 | 15 ± 27 | 13 [−3, 34] | 0.41 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 132 | 21 ± 28 | 21 [4, 42] | 0.57 | 231 | 32 ± 25 | 32 [14, 50] | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 90 | 25 ± 31 | 24 [8, 43] | 0.65 | 210 | 37 ± 25 | 36 [17, 55] | 1.13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | 0 | 181 | 36 ± 28 | 39 [18, 57] | 1.22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | 0 | 129 | 37 ± 27 | 34 [18, 61] | 1.06 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | 0 | 89 | 38 ± 26 | 35 [20, 55] | 1.09 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Values are the mean ± SD and median [25th, 75th percentiles] of paired changes at each time point compared with baseline. Also shown are the per cent improvements of the median from baseline. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change in median from baseline | BTT | DT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At 1 month | 10 | 13 points | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At 6 months | 29 | 40 points | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median % improvement at 6 months | 38 | 52 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median % improvement at 24 months | 55 (42 points) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change in median from baseline | BTT | DT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At 1 month | 14 | 16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At 6 months | 28 | 39 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median improvement at 24 months | 41 points | 41 points | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| After 6 months score remained stable. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Use of a CF LVAD in advanced HF patients results in clinically relevant improvements in functional capacity and HF-related QoL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Those patients who survive VAD implant and were available for analysis exhibited improvements in functional performance and QoL. The total number of patients available for analysis at the various time points was not reported. This could be available from Miller et al.,70 Pagani et al.71 and Slaughter et al.47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Russell 200975
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Russell Year of publication: 2009 Country: USA Study design: Uncontrolled single-arm trial Study setting: Hospital Number of centres: 26; based on Miller et al.70 Duration of study: Unclear Follow-up period: 180 days Funding: Industry (Thoratec Inc.) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To determine whether or not patients with impaired renal and hepatic function improve over time with CF LVAD support and whether or not there are any detrimental effects over time in patients with normal organ function during CF support | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 309 Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported Inclusion criteria: Not reported. End-stage HF awaiting transplantation with UNOS status 1a or 1b were eligible for enrolment and underwent implantation of the HMII LVAD Exclusion criteria: Patients were excluded for severe renal (serum creatinine > 3.5 mg/dl or long-term dialysis), hepatic (INR > 2.5, total bilirubin > 5 mg/dl, or transaminases > 2000 U/l), or pulmonary (severe chronic obstructive or restrictive disease) dysfunction. Additionally, patients with uncontrolled infections, strokes, mechanical aortic valves, aortic insufficiency, aortic aneurysm > 5.0 cm, or other mechanical circulatory support devices (except IABPs) were also excluded. See Miller et al.70 for further details Hepatic (INR > 2.5, total bilirubin > 5 mg/dl, or transaminases > 2000 U/l), or pulmonary (severe chronic obstructive or restrictive disease) dysfunction, uncontrolled infections, strokes, mechanical aortic valves, aortic insufficiency, aortic aneurysm > 5.0 cm, or other mechanical circulatory support devices (except IABPs) Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): 50 years (14) Median age: 54 years Age range: 15–73 years Sex: 75% male Race: Not reported Diagnosis: End-stage HF |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: Normal vs. above normal according to renal and liver function Duration of treatment: Unclear Percentage of patients using inotropes: 89% Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Not stated Secondary outcomes: Changes from baseline in indicators of renal and hepatic function Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records or prospective data collection Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: 180 daysNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedRandomised/includedn = 309ExcludedMissing participantsWithdrawals |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Randomised/included | n = 309 | Excluded | Missing participants | Withdrawals | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | n = 309 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CharacteristicValuen309Male sex, n (%)235 (76)Female sex, n (%)74 (24)Age (years)50 ± 14; median 54 (range 15–73)Ischaemic origin (%)43BSA (m2)2.0 ± 0.3; median 2.0 (range 1.33–2.81)LVEF (%)16.5 ± 6.6LVEDD (mm)70 ± 13Systolic BP (mmHg)98 ± 14Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)2.1 ± 0.7RA pressure (mmHg)12.3 ± 6.4PA mean pressure (mmHg)36 ± 9PCW pressure (mmHg)25 ± 8ACE inhibitors/ARBs, n (%)28/5 (–/–)Beta-blockers, n (%)34CRT (%)47Intravenous inotropes (%)89IABP (%)44 Baseline (mean ± SD) renal and hepatic function for all patients, for patients with paired values through 180 days and subgroups of those with abnormal and normal baseline values, and patients who were supported for < 180 daysCharacteristicAll patients (n = 309)Patients with paired values through 180 daysPatients supported for < 180 daysOverall (n = 160)Normal thresholdAbnormal (n)Normal (n)Died < 180 days (n = 34)Transplanted < 180 days (n = 115)BUN (mg/dl)29 ± 1628 ± 152237 ± 14 (99)15 ± 4 (60)33 ± 2029 ± 16Creatinine (mg/dl)1.4 ± 0.51.4 ± 0.51.31.8 ± 0.4 (78)1.0 ± 0.2 (81)1.4 ± 0.61.4 ± 0.5Total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.3 ± 0.91.3 ± 0.91.22.1 ± 0.9 (71)0.7 ± 0.3 (88)1.1 ± 0.81.2 ± 0.8ALT (U/L)95 ± 23085 ± 23440171 ± 348 (70)24 ± 9 (89)126 ± 302101 ± 200AST (U/L)80 ± 21467 ± 14437121 ± 206 (86)25 ± 6 (93)141 ± 47581 ± 180 |
Characteristic | Value | n | 309 | Male sex, n (%) | 235 (76) | Female sex, n (%) | 74 (24) | Age (years) | 50 ± 14; median 54 (range 15–73) | Ischaemic origin (%) | 43 | BSA (m2) | 2.0 ± 0.3; median 2.0 (range 1.33–2.81) | LVEF (%) | 16.5 ± 6.6 | LVEDD (mm) | 70 ± 13 | Systolic BP (mmHg) | 98 ± 14 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.1 ± 0.7 | RA pressure (mmHg) | 12.3 ± 6.4 | PA mean pressure (mmHg) | 36 ± 9 | PCW pressure (mmHg) | 25 ± 8 | ACE inhibitors/ARBs, n (%) | 28/5 (–/–) | Beta-blockers, n (%) | 34 | CRT (%) | 47 | Intravenous inotropes (%) | 89 | IABP (%) | 44 | Characteristic | All patients (n = 309) | Patients with paired values through 180 days | Patients supported for < 180 days | Overall (n = 160) | Normal threshold | Abnormal (n) | Normal (n) | Died < 180 days (n = 34) | Transplanted < 180 days (n = 115) | BUN (mg/dl) | 29 ± 16 | 28 ± 15 | 22 | 37 ± 14 (99) | 15 ± 4 (60) | 33 ± 20 | 29 ± 16 | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.3 | 1.8 ± 0.4 (78) | 1.0 ± 0.2 (81) | 1.4 ± 0.6 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.3 ± 0.9 | 1.3 ± 0.9 | 1.2 | 2.1 ± 0.9 (71) | 0.7 ± 0.3 (88) | 1.1 ± 0.8 | 1.2 ± 0.8 | ALT (U/L) | 95 ± 230 | 85 ± 234 | 40 | 171 ± 348 (70) | 24 ± 9 (89) | 126 ± 302 | 101 ± 200 | AST (U/L) | 80 ± 214 | 67 ± 144 | 37 | 121 ± 206 (86) | 25 ± 6 (93) | 141 ± 475 | 81 ± 180 | ||||
| Characteristic | Value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | 309 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male sex, n (%) | 235 (76) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Female sex, n (%) | 74 (24) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 50 ± 14; median 54 (range 15–73) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic origin (%) | 43 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 2.0 ± 0.3; median 2.0 (range 1.33–2.81) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF (%) | 16.5 ± 6.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEDD (mm) | 70 ± 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 98 ± 14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.1 ± 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RA pressure (mmHg) | 12.3 ± 6.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PA mean pressure (mmHg) | 36 ± 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCW pressure (mmHg) | 25 ± 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACE inhibitors/ARBs, n (%) | 28/5 (–/–) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beta-blockers, n (%) | 34 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CRT (%) | 47 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intravenous inotropes (%) | 89 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP (%) | 44 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristic | All patients (n = 309) | Patients with paired values through 180 days | Patients supported for < 180 days | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall (n = 160) | Normal threshold | Abnormal (n) | Normal (n) | Died < 180 days (n = 34) | Transplanted < 180 days (n = 115) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 29 ± 16 | 28 ± 15 | 22 | 37 ± 14 (99) | 15 ± 4 (60) | 33 ± 20 | 29 ± 16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.3 | 1.8 ± 0.4 (78) | 1.0 ± 0.2 (81) | 1.4 ± 0.6 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.3 ± 0.9 | 1.3 ± 0.9 | 1.2 | 2.1 ± 0.9 (71) | 0.7 ± 0.3 (88) | 1.1 ± 0.8 | 1.2 ± 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT (U/L) | 95 ± 230 | 85 ± 234 | 40 | 171 ± 348 (70) | 24 ± 9 (89) | 126 ± 302 | 101 ± 200 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST (U/L) | 80 ± 214 | 67 ± 144 | 37 | 121 ± 206 (86) | 25 ± 6 (93) | 141 ± 475 | 81 ± 180 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 34 of 309 patients died before 180 days 160 of 309 remained alive on VAD to 180 days after implantation A total of 115 of 309 patients underwent transplantation before 180 days |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Initial rises in immediate post-implant values were followed by trends towards normal values) Linear mixed-effects analysis: revealed that group type (above-normal or normal baseline values) and time had statistically significant impacts on BUN and creatinine levels. There were significant (p < 0.0001) reductions in BUN and creatinine levels over the period of support for the above-normal groups, and no significant changes for the normal groups Paired changes to 6 months, BUN: there was a statistically significant improvement in mean BUN for the overall group (from 28 ± 15 mg/dl to 21 ± 10 mg/dl; p < 0.001) and the above-normal group (from 37 ± 14 mg/dl to 23 ± 10 mg/dl; p < 0.0001), whereas values in the normal group remained in the normal range. Patients who received HTs before 180 days of support showed improvements in BUN whereas there was no change in patients who died before 180 days Paired changes to 6 months, creatinine: the above-normal group experienced significant reductions in creatinine from 1.8 ± 0.4 mg/dl to 1.4 ± 0.8 mg/dl at 6 months (p < 0.001), with the normal group remaining in the normal range. Patients who received HTs before 180 days of support showed improvements in creatinine, whereas there was no change in patients who died before 180 days |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hepatic function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Initial rises in immediate post-implant values were followed by trends towards normal values) Linear mixed-effects analysis: revealed that group type (above-normal or normal) and time had statistically significant impacts on AST, ALT and total bilirubin values (p < 0.0001) All: Baseline AST of 67 ± 144, 1 month 38 ± 23, 6 months 35 ± 17; baseline ALT of 85 ± 234, 1 month 33 ± 32, 6 months 29 ± 16 Abnormal: Baseline AST of 121 ± 206, 1 month 46 ± 27, 6 months sustained; baseline ALT 171 ± 318, 1 month 40 ± 26, 6 months sustained Paired changes in indicators of renal and hepatic function [mean (SD)]. Full data in figure 1 of Russell et al. study75Parameter/groupBaseline6 monthsp-valueBUN All (n = 160)28 (15)21 (10)< 0.001 Above normal37 (14)23 (10)< 0.0001Creatinine All (n = 160)1.4 (0.5)1.2 read from graph Above normal1.8 (0.4)1.4 (0.8)< 0.001Baseline1 month6 monthsAST All (n = 160)67 (144)38 (23)35 (17) Above normal121 (206)46 (27)40 read from graph Normal24 (9)25 (6)ALT All (n = 160)85 (234)33 (32)29 (16) Above normal171 (318)40 (26)30 read from graph Normal27 (11)33 (15)> 0.05 Bilirubin increased by day 7 before improving to baseline in both normal and abnormal groups The above-normal group at baseline experienced the highest increase, to > 5 mg/dl at day 7; however, by 2 months all groups decreased to the normal range and remained there through month 6 |
Parameter/group | Baseline | 6 months | p-value | BUN | All (n = 160) | 28 (15) | 21 (10) | < 0.001 | Above normal | 37 (14) | 23 (10) | < 0.0001 | Creatinine | All (n = 160) | 1.4 (0.5) | 1.2 read from graph | Above normal | 1.8 (0.4) | 1.4 (0.8) | < 0.001 | Baseline | 1 month | 6 months | AST | All (n = 160) | 67 (144) | 38 (23) | 35 (17) | Above normal | 121 (206) | 46 (27) | 40 read from graph | Normal | 24 (9) | 25 (6) | ALT | All (n = 160) | 85 (234) | 33 (32) | 29 (16) | Above normal | 171 (318) | 40 (26) | 30 read from graph | Normal | 27 (11) | 33 (15) | > 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter/group | Baseline | 6 months | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All (n = 160) | 28 (15) | 21 (10) | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Above normal | 37 (14) | 23 (10) | < 0.0001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All (n = 160) | 1.4 (0.5) | 1.2 read from graph | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Above normal | 1.8 (0.4) | 1.4 (0.8) | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | 1 month | 6 months | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All (n = 160) | 67 (144) | 38 (23) | 35 (17) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Above normal | 121 (206) | 46 (27) | 40 read from graph | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal | 24 (9) | 25 (6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All (n = 160) | 85 (234) | 33 (32) | 29 (16) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Above normal | 171 (318) | 40 (26) | 30 read from graph | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal | 27 (11) | 33 (15) | > 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See above for renal and hepatic function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In a BTT patient population with mildly abnormal renal or hepatic function, the use of a CF LVAD improved renal and hepatic function in patients with abnormal baseline parameters and did not worsen function in patients with normal baseline renal and hepatic values. Furthermore, this function was maintained through 6 months | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with considerably impaired renal and liver function were not included in the study, the above-normal patients studied were probably at the mild end of impaired organ function. For those patients who survive VAD implantation to 6 months renal and hepatic function on average appear to improve in those with pre-implant indicators of abnormality, those without abnormality do not deteriorate in these indicators once beyond a few months after implant | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sandner 2009a91
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Sandner Year of publication: 2009 Country: Austria Study design: Retrospective observational analysis Study setting: Hospital Number of centres: One Duration of study: Devices Implanted November 1998 to July 2007 Follow-up period: Patients were followed for at least 180 days or until either transplantation or death Funding: Not reported |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To determine the effect of age on outcomes after CF LVAD implantation as a BTT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 86 patients; please refer to Sandner et al.91 patient characteristics Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported Inclusion criteria: Unclear Exclusion criteria: Not reported Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): Unclear age Median age: Not reported Age range:n = 56 < 60 years; n = 30 > 60 years Sex: Not reported Race: Not reported Diagnosis: End-stage HF |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT for end-stage HF NYHA class IV Type of device used: MicroMed DeBakey VAD (n = 75), HVAD (n = 6) and DuraHeart LVAD (n = 5) Any comparison: Patients aged > 60 years vs. patients aged < 60 years Duration of treatment: Unclear Percentage of patients using inotropes: < 60 years 46.4%% and > 60 years 53.3% Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Survival; composite outcome (HT or supported on VAD for 180 days) Secondary outcomes: Not applicable Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records or prospective data collection Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: Patients were followed for at least 180 days or until either transplantation or deathNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reportedNot reportedRandomised/includedNot reportedNot reportedExcludedNot reportedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reportedNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported | Not reported | Randomised/included | Not reported | Not reported | Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variablea< 60 years (n = 56)> 60 years (n = 30)p-valueMale46 (82.1)27 (90.0)0.332BMI (kg/m2)26.5 ± 3.926.5 ± 3.10.935Hypertension13 (23.2)14 (46.7)0.026Diabetes mellitus10 (17.9)16 (53.3)0.001Ischaemic aetiology18 (32.1)19 (63.3)0.005PCWP (mmHg)26.0 ± 6.626.1 ± 7.70.994Cardiac index, (l/minute/m2)1.8 ± 0.51.7 ± 0.40.45PAP (mmHg)40.0 ± 8.337.8 ± 10.10.39NYHA class IV5630Intravenous inotropic agents26 (46.4)16 (53.3)0.542IABP2 (3.6)00.295Mechanical ventilation3 (5.4)1 (3.3)0.671Previous thoracotomy6 (10.7)5 (16.7)0.431a Categoric data are n (%), continuous data the mean ± SD. Baseline laboratory valuesSerum values< 60 years (n = 56)> 60 years (n = 30)p-valueSodium (mmol/l)135.1 ± 3.9136.6 ± 4.90.179Total protein (g/l)66.5 ± 7.969.5 ± 8.70.135Albumin (g/l)36 ± 5.237.1 ± 5.60.391Creatinine (mg/dl)1.2 ± 0.41.5 ± 0.40.008Urea nitrogen (mg/dl)28.3 ± 17.837.2 ± 18.70.033ALT (U/l)95.9 ± 357.247.6 ± 61.20.481AST (U/l)65.4 ± 236.835.3 ± 35.30.508Total bilirubin (mg/dl)2 ± 2.61.4 ± 0.80.17GFR (ml/minute/1.73 m2)68 ± 20.551.9 ± 15.9< 0.001Haemoglobin (g/dl)12.3 ± 1.712.2 ± 1.70.885White cell count (g/μl)7.6 ± 1.77.1 ± 2.00.245Platelets (g/μl)220.6 ± 88.9203.1 ± 64.30.366CRP (mg/dl)2.9 ± 5.71.6 ± 2.00.264Data are mean ± SD. |
Variablea | < 60 years (n = 56) | > 60 years (n = 30) | p-value | Male | 46 (82.1) | 27 (90.0) | 0.332 | BMI (kg/m2) | 26.5 ± 3.9 | 26.5 ± 3.1 | 0.935 | Hypertension | 13 (23.2) | 14 (46.7) | 0.026 | Diabetes mellitus | 10 (17.9) | 16 (53.3) | 0.001 | Ischaemic aetiology | 18 (32.1) | 19 (63.3) | 0.005 | PCWP (mmHg) | 26.0 ± 6.6 | 26.1 ± 7.7 | 0.994 | Cardiac index, (l/minute/m2) | 1.8 ± 0.5 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 0.45 | PAP (mmHg) | 40.0 ± 8.3 | 37.8 ± 10.1 | 0.39 | NYHA class IV | 56 | 30 | Intravenous inotropic agents | 26 (46.4) | 16 (53.3) | 0.542 | IABP | 2 (3.6) | 0 | 0.295 | Mechanical ventilation | 3 (5.4) | 1 (3.3) | 0.671 | Previous thoracotomy | 6 (10.7) | 5 (16.7) | 0.431 | a Categoric data are n (%), continuous data the mean ± SD. | Serum values | < 60 years (n = 56) | > 60 years (n = 30) | p-value | Sodium (mmol/l) | 135.1 ± 3.9 | 136.6 ± 4.9 | 0.179 | Total protein (g/l) | 66.5 ± 7.9 | 69.5 ± 8.7 | 0.135 | Albumin (g/l) | 36 ± 5.2 | 37.1 ± 5.6 | 0.391 | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 0.008 | Urea nitrogen (mg/dl) | 28.3 ± 17.8 | 37.2 ± 18.7 | 0.033 | ALT (U/l) | 95.9 ± 357.2 | 47.6 ± 61.2 | 0.481 | AST (U/l) | 65.4 ± 236.8 | 35.3 ± 35.3 | 0.508 | Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 2 ± 2.6 | 1.4 ± 0.8 | 0.17 | GFR (ml/minute/1.73 m2) | 68 ± 20.5 | 51.9 ± 15.9 | < 0.001 | Haemoglobin (g/dl) | 12.3 ± 1.7 | 12.2 ± 1.7 | 0.885 | White cell count (g/μl) | 7.6 ± 1.7 | 7.1 ± 2.0 | 0.245 | Platelets (g/μl) | 220.6 ± 88.9 | 203.1 ± 64.3 | 0.366 | CRP (mg/dl) | 2.9 ± 5.7 | 1.6 ± 2.0 | 0.264 | Data are mean ± SD. | |||||||
| Variablea | < 60 years (n = 56) | > 60 years (n = 30) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male | 46 (82.1) | 27 (90.0) | 0.332 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.5 ± 3.9 | 26.5 ± 3.1 | 0.935 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension | 13 (23.2) | 14 (46.7) | 0.026 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 10 (17.9) | 16 (53.3) | 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic aetiology | 18 (32.1) | 19 (63.3) | 0.005 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 26.0 ± 6.6 | 26.1 ± 7.7 | 0.994 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index, (l/minute/m2) | 1.8 ± 0.5 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 0.45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PAP (mmHg) | 40.0 ± 8.3 | 37.8 ± 10.1 | 0.39 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class IV | 56 | 30 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intravenous inotropic agents | 26 (46.4) | 16 (53.3) | 0.542 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP | 2 (3.6) | 0 | 0.295 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 3 (5.4) | 1 (3.3) | 0.671 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Previous thoracotomy | 6 (10.7) | 5 (16.7) | 0.431 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Categoric data are n (%), continuous data the mean ± SD. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum values | < 60 years (n = 56) | > 60 years (n = 30) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sodium (mmol/l) | 135.1 ± 3.9 | 136.6 ± 4.9 | 0.179 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total protein (g/l) | 66.5 ± 7.9 | 69.5 ± 8.7 | 0.135 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albumin (g/l) | 36 ± 5.2 | 37.1 ± 5.6 | 0.391 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 0.008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Urea nitrogen (mg/dl) | 28.3 ± 17.8 | 37.2 ± 18.7 | 0.033 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT (U/l) | 95.9 ± 357.2 | 47.6 ± 61.2 | 0.481 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST (U/l) | 65.4 ± 236.8 | 35.3 ± 35.3 | 0.508 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 2 ± 2.6 | 1.4 ± 0.8 | 0.17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GFR (ml/minute/1.73 m2) | 68 ± 20.5 | 51.9 ± 15.9 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemoglobin (g/dl) | 12.3 ± 1.7 | 12.2 ± 1.7 | 0.885 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| White cell count (g/μl) | 7.6 ± 1.7 | 7.1 ± 2.0 | 0.245 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets (g/μl) | 220.6 ± 88.9 | 203.1 ± 64.3 | 0.366 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CRP (mg/dl) | 2.9 ± 5.7 | 1.6 ± 2.0 | 0.264 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Data are mean ± SD. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| After implantationYearGroup < 60 years (%)Group > 60 years (%)187.890.0282.367.5376.067.5 K–M survival post-VAD implant (2, 4 and 5 months read from graph)Month% alive, < 60 years% alive, > 60 years0100100192.99028272379.962479.9595744667437 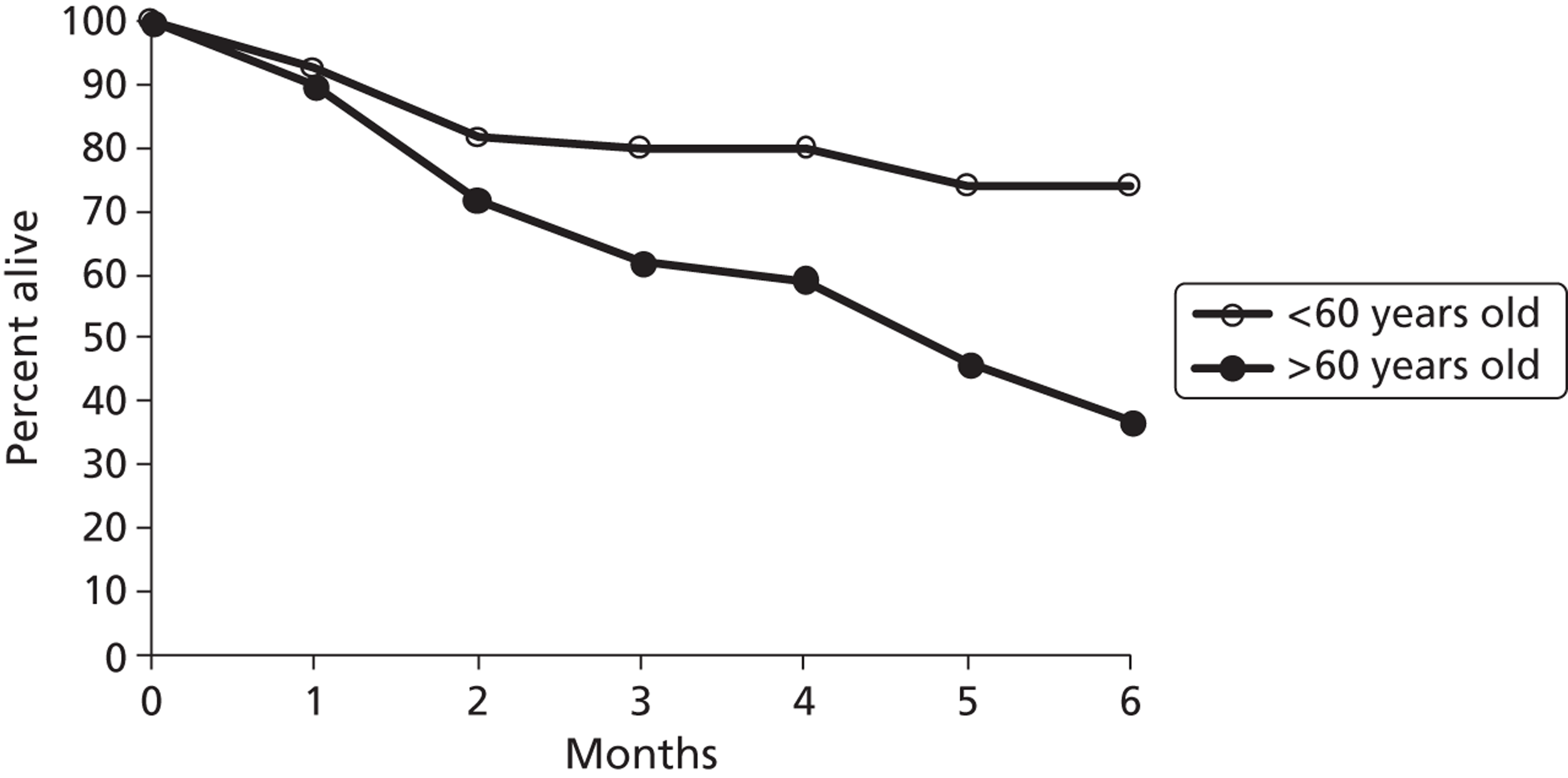 Multivariable Cox model: independent predictors of death after LVAD ImplantationVariableHR95% CIp-valueAgea1.41.1 to 1.80.003Male gender0.70.2 to 1.90.521Inotropic support0.70.3 to 1.60.500Haemoglobin0.80.6 to 1.00.120Serum albumin1.00.7 to 1.50.874GFRb1.10.8 to 1.30.361a Hazard ratio for every 5-year increase in age.b Calculated by Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formula. Multivariable Cox regression analysis: age was the only independent predictor of post-LVAD mortality (HR 1.4, 95% CI 1.1 to 1.8; p = 0.003; table) When the Cox model was calculated to include incidence of IHD, diabetes mellitus and hypertension, all of which had a higher incidence in > 60 years group, age remained the only independent predictor of post-LVAD mortality (HR 1.4, 95% CI 1.1 to 1.8; p = 0.006) Cox regression model: Proportional hazards assumption was verified by means of Schoenfeld residuals Survival after HTYearAge at LVAD < 60 yearsAge at LVAD > 60 years187.890.0382.367.5576.067.5 |
Year | Group < 60 years (%) | Group > 60 years (%) | 1 | 87.8 | 90.0 | 2 | 82.3 | 67.5 | 3 | 76.0 | 67.5 | Month | % alive, < 60 years | % alive, > 60 years | 0 | 100 | 100 | 1 | 92.9 | 90 | 2 | 82 | 72 | 3 | 79.9 | 62 | 4 | 79.9 | 59 | 5 | 74 | 46 | 6 | 74 | 37 | Variable | HR | 95% CI | p-value | Agea | 1.4 | 1.1 to 1.8 | 0.003 | Male gender | 0.7 | 0.2 to 1.9 | 0.521 | Inotropic support | 0.7 | 0.3 to 1.6 | 0.500 | Haemoglobin | 0.8 | 0.6 to 1.0 | 0.120 | Serum albumin | 1.0 | 0.7 to 1.5 | 0.874 | GFRb | 1.1 | 0.8 to 1.3 | 0.361 | a Hazard ratio for every 5-year increase in age. | b Calculated by Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formula. | Year | Age at LVAD < 60 years | Age at LVAD > 60 years | 1 | 87.8 | 90.0 | 3 | 82.3 | 67.5 | 5 | 76.0 | 67.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year | Group < 60 years (%) | Group > 60 years (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 87.8 | 90.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 82.3 | 67.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 76.0 | 67.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Month | % alive, < 60 years | % alive, > 60 years | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 92.9 | 90 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 82 | 72 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 79.9 | 62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 79.9 | 59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 74 | 46 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 74 | 37 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variable | HR | 95% CI | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agea | 1.4 | 1.1 to 1.8 | 0.003 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male gender | 0.7 | 0.2 to 1.9 | 0.521 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inotropic support | 0.7 | 0.3 to 1.6 | 0.500 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemoglobin | 0.8 | 0.6 to 1.0 | 0.120 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum albumin | 1.0 | 0.7 to 1.5 | 0.874 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GFRb | 1.1 | 0.8 to 1.3 | 0.361 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Hazard ratio for every 5-year increase in age. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Calculated by Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formula. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year | Age at LVAD < 60 years | Age at LVAD > 60 years | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 87.8 | 90.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 82.3 | 67.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 76.0 | 67.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OutcomesOutcomeGroup < 60 years (n = 56)Group > 60 years (n = 30)p-valueComposite end point,an (%)43 (76.8)14 (46.7)0.005BTT rate, %62.533.30.010Median/mean (SD) VAD support (days)135/166.0 (± 128.4)97/119.6 (± 100.9)0.090Cumulative follow-up (patient-years)25.49.8Mean (SD) time to transplantation (days)169.3 ± 95.7119.1 ± 47.70.031a HT or survival at 180 days with ongoing VAD support. | Outcome | Group < 60 years (n = 56) | Group > 60 years (n = 30) | p-value | Composite end point,an (%) | 43 (76.8) | 14 (46.7) | 0.005 | BTT rate, % | 62.5 | 33.3 | 0.010 | Median/mean (SD) VAD support (days) | 135/166.0 (± 128.4) | 97/119.6 (± 100.9) | 0.090 | Cumulative follow-up (patient-years) | 25.4 | 9.8 | Mean (SD) time to transplantation (days) | 169.3 ± 95.7 | 119.1 ± 47.7 | 0.031 | a HT or survival at 180 days with ongoing VAD support. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcome | Group < 60 years (n = 56) | Group > 60 years (n = 30) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Composite end point,an (%) | 43 (76.8) | 14 (46.7) | 0.005 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTT rate, % | 62.5 | 33.3 | 0.010 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median/mean (SD) VAD support (days) | 135/166.0 (± 128.4) | 97/119.6 (± 100.9) | 0.090 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cumulative follow-up (patient-years) | 25.4 | 9.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean (SD) time to transplantation (days) | 169.3 ± 95.7 | 119.1 ± 47.7 | 0.031 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a HT or survival at 180 days with ongoing VAD support. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse eventsGroup < 60 years (n = 56)Group > 60 years (n = 30)p-valueDeath < 30 days, n (%)4 (7.1)3 (10.0)0.644Bleeding requiring surgery, n (%)15 (26.8)7 (23.3)0.727Stroke, n (%)11 (19.6)8 (26.7)0.454 Ischaemic, n (%)5 (8.9)4 (13.3)0.525 Haemorrhagic, n (%)6 (10.7)4 (13.3)0.718Renal failure requiring CVVD, n (%)14 (25.0)16 (53.3)0.009Right HF requiring RVAD, n (%)2 (3.6)3 (10.0)0.225 | Adverse events | Group < 60 years (n = 56) | Group > 60 years (n = 30) | p-value | Death < 30 days, n (%) | 4 (7.1) | 3 (10.0) | 0.644 | Bleeding requiring surgery, n (%) | 15 (26.8) | 7 (23.3) | 0.727 | Stroke, n (%) | 11 (19.6) | 8 (26.7) | 0.454 | Ischaemic, n (%) | 5 (8.9) | 4 (13.3) | 0.525 | Haemorrhagic, n (%) | 6 (10.7) | 4 (13.3) | 0.718 | Renal failure requiring CVVD, n (%) | 14 (25.0) | 16 (53.3) | 0.009 | Right HF requiring RVAD, n (%) | 2 (3.6) | 3 (10.0) | 0.225 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events | Group < 60 years (n = 56) | Group > 60 years (n = 30) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Death < 30 days, n (%) | 4 (7.1) | 3 (10.0) | 0.644 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding requiring surgery, n (%) | 15 (26.8) | 7 (23.3) | 0.727 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke, n (%) | 11 (19.6) | 8 (26.7) | 0.454 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic, n (%) | 5 (8.9) | 4 (13.3) | 0.525 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic, n (%) | 6 (10.7) | 4 (13.3) | 0.718 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure requiring CVVD, n (%) | 14 (25.0) | 16 (53.3) | 0.009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HF requiring RVAD, n (%) | 2 (3.6) | 3 (10.0) | 0.225 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incomplete reporting. Most common causes of death in the first 180 days after LVAD implantation included sepsis, multisystem organ failure and haemorrhagic stroke. Incidence of sepsis as cause of death was significantly | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis revealed significantly lower survival in VAD patients aged > 60 years. Given the dismal survival and poor QoL associated with advanced HF, the authors did not consider age alone to be an absolute exclusion criterion for LVAD implantation among BTT candidates. Advocate LVAD placement as BTT therapy only in carefully selected older patients most well suited for transplantation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The findings do not appear to be surprising as one might expect older patients to fair less well. The authors did undertake Cox's regression model. Proportional hazards assumption was verified by means of Schoenfeld residuals | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sandner 2009b92
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Sandner Year of publication: 2009 Country: Austria Study design: Retrospective observational analysis Study setting: Hospital setting Number of centres: One Duration of study: Not reported (devices implanted November 1998 to July 2007) Follow-up period: All 86 patients were followed up for at least 180 days or until transplantation or death. Cumulative follow-up of 20.1 patient-years (GFR > 60) 15.2 patient-years (GFR < 60) Funding: Not reported |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To determine the effect of pre-implant renal function on outcomes after CF LVAD implantation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 86 Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported Inclusion criteria: Consecutive CF LVAD patients implanted November 1998 to July 2007 Exclusion criteria: Not reported Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): GFR > 60 47.3 ± 12.7 years; GFR < 60 58.7 ± 6.0 years Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: GFR > 60 91.3% male; GFR < 60 77.5% male Race: Not reported Diagnosis: End-stage HF |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT for end-stage HF NYHA class IV Type of device used: MicroMed DeBakey VAD (n = 75), HVAD (n = 6) and DuraHeart LVAD (n = 5) Any comparison: GFR < 60 patients vs. GFR > 60 patients (former termed renal dysfunction) Duration of treatment: Median VAD duration of support, GFR > 60 129 days; GFR < 60 113 days Mean duration of VAD support: GFR > 60 159.5 ± 117 days; GFR < 60 138.8 ± 126 days Percentage of patients using inotropes: GFR > 60 50%; GFR < 60 47.5% Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Composite end point of support to 180 days or receipt of HT Secondary outcomes: Survival; renal function Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: Not reportedNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reportedNot reportedRandomised/includedNot reportedNot reportedExcludedNot reportedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reportedNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported | Not reported | Randomised/included | Not reported | Not reported | Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ParameterGFR > 60 (n = 46)GFR < 60 (n = 40)p-valueAge (years)47.3 ± 12.758.7 ± 6.0< 0.001Male (%)42 (91.3)31 (77.5)0.075BMI (kg/m2)26.1 ± 3.726.9 ± 3.60.299Hypertension (%)10 (21.7)17 (42.5)0.039Diabetes mellitus (%)12 (26.1)14 (35.0)0.369Ischaemic aetiology (%)13 (28.3)24 (60.0)0.003PCWP (mmHg)28.1 ± 6.627.1 ± 6.50.548Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)1.7 ± 0.51.8 ± 0.40.742PAP mean (mmHg)42.2 ± 7.143.7 ± 8.00.453PVR (dyne/second/cm5)359.4 ± 156.6371.6 ± 221.60.804NYHA functional classIVIVSerum sodium (mmol/ml)136.1 ± 3.6135.1 ± 4.90.332Serum creatinine (mg/dl)1.0 ± 0.11.6 ± 0.4< 0.001BUN (mg/dl)21.0 ± 7.143.5 ± 20.4< 0.001Serum albumin (g/l)35.4 ± 5.637.5 ± 4.70.066Serum total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.9 ± 2.81.5 ± 1.10.426Intravenous inotropes (%)23 (50.0)19 (47.5)0.817IABP (%)1 (2.2)1 (2.5)0.92Mechanical ventilation (%)2 (4.3)2 (5.0)0.886GFR calculated by Modification of Diet in Renal Disease study calculation (ml/minute/1.73 m2). | Parameter | GFR > 60 (n = 46) | GFR < 60 (n = 40) | p-value | Age (years) | 47.3 ± 12.7 | 58.7 ± 6.0 | < 0.001 | Male (%) | 42 (91.3) | 31 (77.5) | 0.075 | BMI (kg/m2) | 26.1 ± 3.7 | 26.9 ± 3.6 | 0.299 | Hypertension (%) | 10 (21.7) | 17 (42.5) | 0.039 | Diabetes mellitus (%) | 12 (26.1) | 14 (35.0) | 0.369 | Ischaemic aetiology (%) | 13 (28.3) | 24 (60.0) | 0.003 | PCWP (mmHg) | 28.1 ± 6.6 | 27.1 ± 6.5 | 0.548 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 0.742 | PAP mean (mmHg) | 42.2 ± 7.1 | 43.7 ± 8.0 | 0.453 | PVR (dyne/second/cm5) | 359.4 ± 156.6 | 371.6 ± 221.6 | 0.804 | NYHA functional class | IV | IV | Serum sodium (mmol/ml) | 136.1 ± 3.6 | 135.1 ± 4.9 | 0.332 | Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | < 0.001 | BUN (mg/dl) | 21.0 ± 7.1 | 43.5 ± 20.4 | < 0.001 | Serum albumin (g/l) | 35.4 ± 5.6 | 37.5 ± 4.7 | 0.066 | Serum total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.9 ± 2.8 | 1.5 ± 1.1 | 0.426 | Intravenous inotropes (%) | 23 (50.0) | 19 (47.5) | 0.817 | IABP (%) | 1 (2.2) | 1 (2.5) | 0.92 | Mechanical ventilation (%) | 2 (4.3) | 2 (5.0) | 0.886 | GFR calculated by Modification of Diet in Renal Disease study calculation (ml/minute/1.73 m2). | ||||
| Parameter | GFR > 60 (n = 46) | GFR < 60 (n = 40) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 47.3 ± 12.7 | 58.7 ± 6.0 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male (%) | 42 (91.3) | 31 (77.5) | 0.075 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.1 ± 3.7 | 26.9 ± 3.6 | 0.299 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension (%) | 10 (21.7) | 17 (42.5) | 0.039 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 12 (26.1) | 14 (35.0) | 0.369 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic aetiology (%) | 13 (28.3) | 24 (60.0) | 0.003 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 28.1 ± 6.6 | 27.1 ± 6.5 | 0.548 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 0.742 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PAP mean (mmHg) | 42.2 ± 7.1 | 43.7 ± 8.0 | 0.453 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PVR (dyne/second/cm5) | 359.4 ± 156.6 | 371.6 ± 221.6 | 0.804 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA functional class | IV | IV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum sodium (mmol/ml) | 136.1 ± 3.6 | 135.1 ± 4.9 | 0.332 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 21.0 ± 7.1 | 43.5 ± 20.4 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum albumin (g/l) | 35.4 ± 5.6 | 37.5 ± 4.7 | 0.066 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.9 ± 2.8 | 1.5 ± 1.1 | 0.426 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intravenous inotropes (%) | 23 (50.0) | 19 (47.5) | 0.817 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP (%) | 1 (2.2) | 1 (2.5) | 0.92 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical ventilation (%) | 2 (4.3) | 2 (5.0) | 0.886 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GFR calculated by Modification of Diet in Renal Disease study calculation (ml/minute/1.73 m2). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall actuarial survival was 91.3% at 1 month, 79.9% at 3 months and 72.6% at 6 months for patients normal renal function, compared with 92.5%, 66.5% and 47.9% for patients with renal dysfunction, respectively (p = 0.038)Deathn (%)n (%)p-valueAt < 30 days4 (8.7)3 (7.5)0.840At 30–180 days7 (15.2)15 (37.5)0.018 Multivariable Cox regression analysis was adjusted for the following factors (previously identified as risk factors for outcome on LVAD): age, sex, haematological abnormalities (haemoglobin), nutritional status (serum albumin) and inotropic support. Pre-LVAD GFR < 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 was identified as a significant predictor of post-LVAD mortality by univariate analysis (OR 2.0, 95% CI 1.1 to 4.1; p = 0.047); however, GFR was not an independent predictor in the multivariable model (OR 1.2, 95% CI 0.5 to 2.5; p = 0.676)Variablep-valueOR95% CIUnivariate analysis GFR < 600.0472.01.1 to 4.1Multivariate analysis GFR < 600.6761.20.5 to 2.5 K–M analysis of survival p = 0.038 for difference between groups. 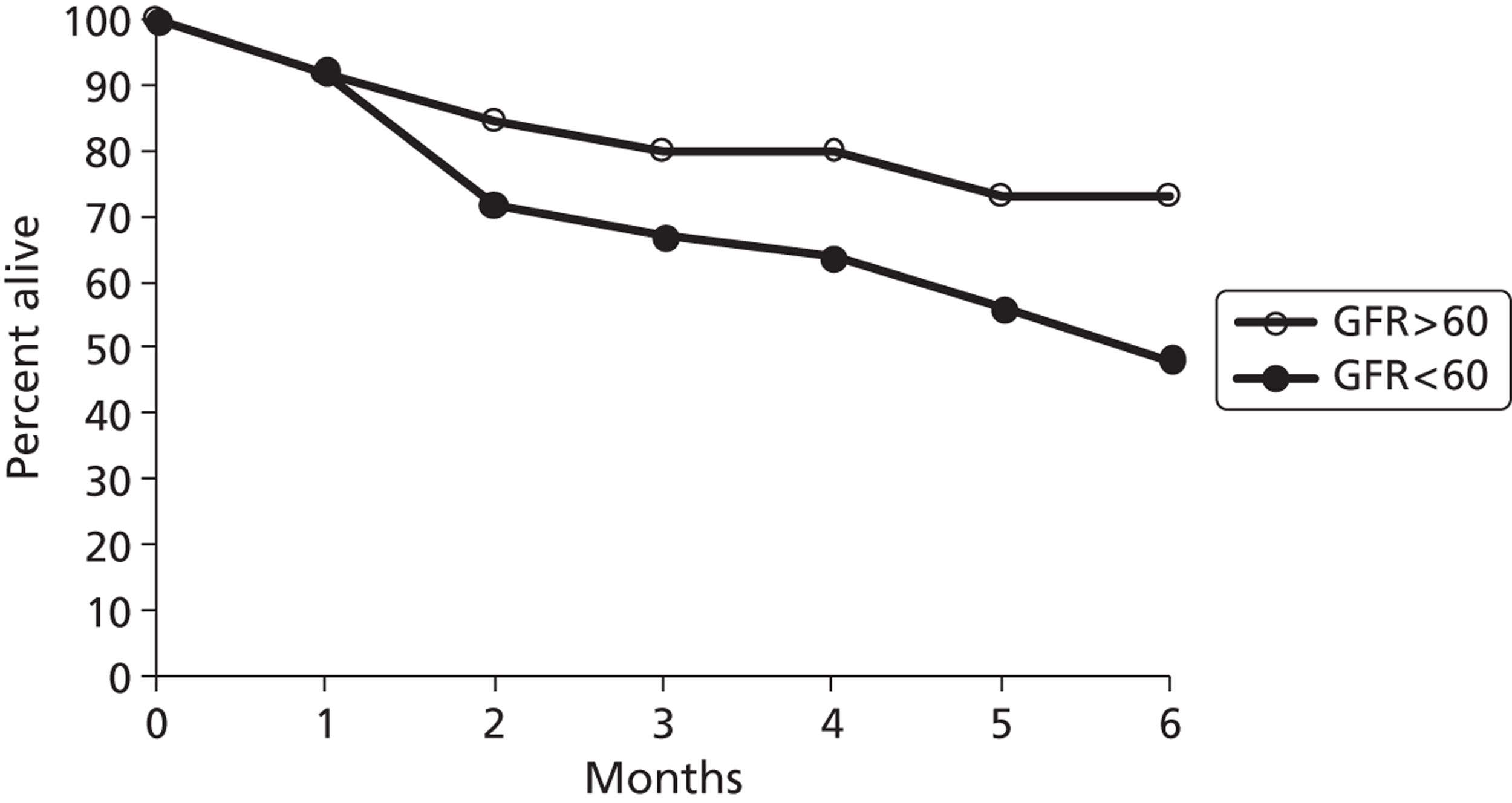 |
Death | n (%) | n (%) | p-value | At < 30 days | 4 (8.7) | 3 (7.5) | 0.840 | At 30–180 days | 7 (15.2) | 15 (37.5) | 0.018 | Variable | p-value | OR | 95% CI | Univariate analysis GFR < 60 | 0.047 | 2.0 | 1.1 to 4.1 | Multivariate analysis GFR < 60 | 0.676 | 1.2 | 0.5 to 2.5 | Month | GFR > 60% alive | GFR < 60% alive | 0 | 100 | 100 | 1 | 91.3 | 92.5 | 2 | 84.5 | 72 | 3 | 79.9 | 66.5 | 4 | 80 | 64 | 5 | 73 | 56 | 6 | 72.6 | 47.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Death | n (%) | n (%) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At < 30 days | 4 (8.7) | 3 (7.5) | 0.840 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At 30–180 days | 7 (15.2) | 15 (37.5) | 0.018 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variable | p-value | OR | 95% CI | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Univariate analysis GFR < 60 | 0.047 | 2.0 | 1.1 to 4.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Multivariate analysis GFR < 60 | 0.676 | 1.2 | 0.5 to 2.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Month | GFR > 60% alive | GFR < 60% alive | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 91.3 | 92.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 84.5 | 72 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 79.9 | 66.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 80 | 64 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 73 | 56 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 72.6 | 47.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recovery of renal function Changes in renal function post-LVAD implantation. Paired samples analysis patients with renal function measurements at consecutive time intervals after LVAD implantation. Among patients with renal dysfunction an overall improvement of GFR (ml/minute/1.73 m2) was observed: Implant to month 1 – 44.6 ± 13.6 to 80.7 ± 32.6 (p < 0.001) Implant to month 3 – 40.8 ± 10.3 to 70.9 ± 21.9 (p < 0.001) Implant to month 6 – 41.7 ± 11.5 to 62.7 ± 25.0 (p = 0.021) Among patients with normal renal function, only an early improvement of GFR was observed: Implant to month 1 – 76.7 ± 12.5 to 93.7 ± 36.5 (p = 0.002) Absence of diabetes mellitus was the only variable that reached statistical significance when predictors of recovery of renal function were analysed in a regression model (OR 0.2, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.8; p = 0.022) Results (n, %) for other outcomes reported are tabulated belowOutcome/adverse eventGFR > 60 (n = 46)GFR < 60 (n = 40)p-valueHT or ongoing support > 180 days,a n (%)35 (76.1)22 (55.0)0.039BTT, n (%)29 (63.0)16 (40.0)0.033Bleeding requiring surgery, n (%)11 (23.9)11 (27.5)0.704Right HF requiring RVAD , n (%)2 (4.3)3 (7.5)0.533Stroke, n (%)6 (13.0)13 (32.5)0.03Ischaemic, n (%)4 (8.7)5 (12.5)0.565Haemorrhagic, n (%)2 (4.3)8 (20.0)0.024Renal failure requiring CVVHD, n (%)13 (28.3)17 (42.5)0.167a The composite primary outcome. |
Outcome/adverse event | GFR > 60 (n = 46) | GFR < 60 (n = 40) | p-value | HT or ongoing support > 180 days,a n (%) | 35 (76.1) | 22 (55.0) | 0.039 | BTT, n (%) | 29 (63.0) | 16 (40.0) | 0.033 | Bleeding requiring surgery, n (%) | 11 (23.9) | 11 (27.5) | 0.704 | Right HF requiring RVAD , n (%) | 2 (4.3) | 3 (7.5) | 0.533 | Stroke, n (%) | 6 (13.0) | 13 (32.5) | 0.03 | Ischaemic, n (%) | 4 (8.7) | 5 (12.5) | 0.565 | Haemorrhagic, n (%) | 2 (4.3) | 8 (20.0) | 0.024 | Renal failure requiring CVVHD, n (%) | 13 (28.3) | 17 (42.5) | 0.167 | a The composite primary outcome. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcome/adverse event | GFR > 60 (n = 46) | GFR < 60 (n = 40) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HT or ongoing support > 180 days,a n (%) | 35 (76.1) | 22 (55.0) | 0.039 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTT, n (%) | 29 (63.0) | 16 (40.0) | 0.033 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding requiring surgery, n (%) | 11 (23.9) | 11 (27.5) | 0.704 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HF requiring RVAD , n (%) | 2 (4.3) | 3 (7.5) | 0.533 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke, n (%) | 6 (13.0) | 13 (32.5) | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic, n (%) | 4 (8.7) | 5 (12.5) | 0.565 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic, n (%) | 2 (4.3) | 8 (20.0) | 0.024 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure requiring CVVHD, n (%) | 13 (28.3) | 17 (42.5) | 0.167 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a The composite primary outcome. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See above | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Causes of death in the first 180 days after LVAD implantation included: Sepsis (GFR > 60, n = 6, GFR < 60, n = 7; p = 0.565) Haemorrhagic stroke (GFR > 60, n = 2, GFR < 60, n = 6; p = 0.090) Multiorgan failure (n = 5) Ischaemic stroke (n = 1) Unknown (n = 1) Total 28/86 (29 deaths listed above to 180 days) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with renal dysfunction have poorer outcomes after CF LVAD implantation. However, renal function improves after LVAD implantation and is associated with improved survival | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post-hoc analyses of a small cohort that may have received different levels of treatment over the 9-year period using several different devices. Poor renal function pre implant may contribute to risk of death, but in this analysis was not found to be a statistically significant independent indicator. Proportional hazards assumption may not have been tested | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Schaffer 201176
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Schaffer Year of publication: 2011 Country: USA Study design: Retrospective observational Study setting: Hospital Number of centres: One Duration of study: June 2000 to May 2009 Follow-up period: Unclear Funding: Charitable trust |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To examine the incidence of infectious complications in patients receiving CF and PF devices | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 133 (86 HMII; 47 HMXVE) Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported Inclusion criteria: All LVADs at single institution Exclusion criteria: Not reported Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): 49.4 years ( ± 13.0) Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: 75.2% male Race: Caucasian n = 67 (50.4%) Diagnosis: HF |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT 93/133, DT 40/133; cannot split Type of device used: HMII and HMXVE Any comparison: HMII vs. HMXVE for infection Duration of treatment: Various Percentage of patients using inotropes: Not reported Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Infections Secondary outcomes: Not applicable Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: UnclearNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reportedNot reportedRandomised/includedn = 133 (HMII n = 86; HMXVE n = 47)Not reportedExcludedNot reportedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reportedNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported | Not reported | Randomised/included | n = 133 (HMII n = 86; HMXVE n = 47) | Not reported | Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | n = 133 (HMII n = 86; HMXVE n = 47) | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ParameterOverall (n = 133) [n (%) or mean (± SD)]CF (n = 86) [n (%) or mean (± SD)]PF (n = 47) [n (%) or mean (± SD)]p-valueBaseline characteristics Age, years49.4 (± 13.0)49.7 (± 13.1)49.0 (± 13.1)0.76 Gender (male)100 (75.2)61 (70.9)39 (83.0)0.12 Race (Caucasian)67 (50.4)38 (44.2)29 (61.7)0.24 BTT93 (69.9)57 (66.3)36 (76.6)0.22 BMI (kg/m2)27.9 (± 6.8)28.3 (± 7.0)27.1 (± 6.6)0.37 BSA (m2)1.99 (± 0.29)2.01 (± 0.27)1.96 (± 0.32)0.36 Ejection fraction13.4 (± 5.8)14.1 (± 6.4)12.1 (± 4.3)0.07 Cardiac index (l/minute)1.96 (± 0.55)1.95 (± 0.50)1.96 (± 0.63)0.88 Cardiogenic shocka77 (57.9)50 (58.1)27 (57.5)0.94 Pre-operative IABP55 (41.4)33 (38.4)22 (46.8)0.35 Previous ICD94 (70.7)69 (80.2)25 (50.2)0.001 Previous MI47 (35.3)27 (31.4)20 (42.6)0.2 Prior heart surgery52 (39.1)32 (37.2)20 (38.5)0.55 NYHA (class IV)129 (97.0)84 (97.7)45 (95.7)0.53 Month/year of implantJuly/2005 (± 2.5 years)January/2007 (± 1.25 years)November/2002 (± 2.0 years)< 0.001Pre-operative risk scores APACHE II16.2 (± 4.7)15.6 (± 4.3)17.4 (± 5.3)0.04 INTERMACS2.47 (± 1.13)2.64 (± 1.01)2.17 (± 1.16)0.02 SHFM3.17 (± 1.35)2.97 (± 1.42)3.53 (± 1.14)0.02a Patients were defined as having cardiogenic shock if they had a mean BP < 90 mmHg, a PCWP > 15 mmHg and a cardiac index < 2.2 l/minute.p-value based on comparison between two groups by either Fisher's exact test or Student's t-test, with p < 0.05 considered significant. | Parameter | Overall (n = 133) [n (%) or mean (± SD)] | CF (n = 86) [n (%) or mean (± SD)] | PF (n = 47) [n (%) or mean (± SD)] | p-value | Baseline characteristics | Age, years | 49.4 (± 13.0) | 49.7 (± 13.1) | 49.0 (± 13.1) | 0.76 | Gender (male) | 100 (75.2) | 61 (70.9) | 39 (83.0) | 0.12 | Race (Caucasian) | 67 (50.4) | 38 (44.2) | 29 (61.7) | 0.24 | BTT | 93 (69.9) | 57 (66.3) | 36 (76.6) | 0.22 | BMI (kg/m2) | 27.9 (± 6.8) | 28.3 (± 7.0) | 27.1 (± 6.6) | 0.37 | BSA (m2) | 1.99 (± 0.29) | 2.01 (± 0.27) | 1.96 (± 0.32) | 0.36 | Ejection fraction | 13.4 (± 5.8) | 14.1 (± 6.4) | 12.1 (± 4.3) | 0.07 | Cardiac index (l/minute) | 1.96 (± 0.55) | 1.95 (± 0.50) | 1.96 (± 0.63) | 0.88 | Cardiogenic shocka | 77 (57.9) | 50 (58.1) | 27 (57.5) | 0.94 | Pre-operative IABP | 55 (41.4) | 33 (38.4) | 22 (46.8) | 0.35 | Previous ICD | 94 (70.7) | 69 (80.2) | 25 (50.2) | 0.001 | Previous MI | 47 (35.3) | 27 (31.4) | 20 (42.6) | 0.2 | Prior heart surgery | 52 (39.1) | 32 (37.2) | 20 (38.5) | 0.55 | NYHA (class IV) | 129 (97.0) | 84 (97.7) | 45 (95.7) | 0.53 | Month/year of implant | July/2005 (± 2.5 years) | January/2007 (± 1.25 years) | November/2002 (± 2.0 years) | < 0.001 | Pre-operative risk scores | APACHE II | 16.2 (± 4.7) | 15.6 (± 4.3) | 17.4 (± 5.3) | 0.04 | INTERMACS | 2.47 (± 1.13) | 2.64 (± 1.01) | 2.17 (± 1.16) | 0.02 | SHFM | 3.17 (± 1.35) | 2.97 (± 1.42) | 3.53 (± 1.14) | 0.02 | a Patients were defined as having cardiogenic shock if they had a mean BP < 90 mmHg, a PCWP > 15 mmHg and a cardiac index < 2.2 l/minute. | p-value based on comparison between two groups by either Fisher's exact test or Student's t-test, with p < 0.05 considered significant. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Overall (n = 133) [n (%) or mean (± SD)] | CF (n = 86) [n (%) or mean (± SD)] | PF (n = 47) [n (%) or mean (± SD)] | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age, years | 49.4 (± 13.0) | 49.7 (± 13.1) | 49.0 (± 13.1) | 0.76 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gender (male) | 100 (75.2) | 61 (70.9) | 39 (83.0) | 0.12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Race (Caucasian) | 67 (50.4) | 38 (44.2) | 29 (61.7) | 0.24 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTT | 93 (69.9) | 57 (66.3) | 36 (76.6) | 0.22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.9 (± 6.8) | 28.3 (± 7.0) | 27.1 (± 6.6) | 0.37 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 1.99 (± 0.29) | 2.01 (± 0.27) | 1.96 (± 0.32) | 0.36 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ejection fraction | 13.4 (± 5.8) | 14.1 (± 6.4) | 12.1 (± 4.3) | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute) | 1.96 (± 0.55) | 1.95 (± 0.50) | 1.96 (± 0.63) | 0.88 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiogenic shocka | 77 (57.9) | 50 (58.1) | 27 (57.5) | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative IABP | 55 (41.4) | 33 (38.4) | 22 (46.8) | 0.35 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Previous ICD | 94 (70.7) | 69 (80.2) | 25 (50.2) | 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Previous MI | 47 (35.3) | 27 (31.4) | 20 (42.6) | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prior heart surgery | 52 (39.1) | 32 (37.2) | 20 (38.5) | 0.55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA (class IV) | 129 (97.0) | 84 (97.7) | 45 (95.7) | 0.53 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Month/year of implant | July/2005 (± 2.5 years) | January/2007 (± 1.25 years) | November/2002 (± 2.0 years) | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative risk scores | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| APACHE II | 16.2 (± 4.7) | 15.6 (± 4.3) | 17.4 (± 5.3) | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INTERMACS | 2.47 (± 1.13) | 2.64 (± 1.01) | 2.17 (± 1.16) | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SHFM | 3.17 (± 1.35) | 2.97 (± 1.42) | 3.53 (± 1.14) | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Patients were defined as having cardiogenic shock if they had a mean BP < 90 mmHg, a PCWP > 15 mmHg and a cardiac index < 2.2 l/minute. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-value based on comparison between two groups by either Fisher's exact test or Student's t-test, with p < 0.05 considered significant. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-year survival HMXVE patients with severe sepsis (19%), those with sepsis (65%) and those without sepsis (81%) HMII patients 6-month mortality 23% |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Intervention type by year |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infections Ninety-one (68%) patients developed sepsis. Of the patients with sepsis, 26 (28%) developed severe sepsis Twenty (77%) patients with severe sepsis developed septic shock, of whom 19 (95%) died Number and incidence of infections by LVAD and time of incidenceEventCF (n = 86)PF (n = 47)p-valuen (%)EPYn (%)EPYSystemic infectionsBacteraemia (all)23 (27)0.4221 (45)0.980.002 0–30 days3 (4)0.4612 (26)4.16< 0.001 31–90 days4 (5)0.383 (6)0.790.33 Beyond 90 days16 (19)0.426 (13)0.410.78Sepsis (all)55 (64)2.1336 (77)5.340.01 0–30 days46 (53)12.134 (72)25.1< 0.01 31–90 days4 (5)0.872 (4)1.840.41 Beyond 90 days5 (6)0.290 (0)0.000.32Severe sepsis (all)14 (16)0.2212 (26)0.550.11 0–30 days9 (10)1.448 (17)2.550.24 31–90 days4 (5)0.393 (6)0.70.42 Beyond 90 days1 (1)0.021 (2)0.070.43Septic shock (all)11 (13)0.179 (19)0.370.19 0–30 days5 (6)0.776 (13)1.870.12 31–90 days6 (7)0.103 (6)0.150.81 Beyond 90 days0 (0)0.000 (0)0.001.00Device-associated infectionsDriveline (all)26 (30)0.5819 (40)1.080.02 0–30 days0 (0)0.002 (4)0.630.04 31–90 days2 (2)0.185 (11)1.22< 0.01 Beyond 90 days24 (28)0.8312 (26)1.070.42LVAD pocket (all)9 (10)0.1516(34)0.88< 0.001 0–30 days2 (2)0.315 (11)1.620.03 31–90 days2 (2)0.165 (11)1.010.01 Beyond 90 days5 (6)0.126 (13)0.530.01Driveline or pocket (all)31 (36)0.7228 (60)2.31< 0.001 0–30 days2 (2)0.316 (13)1.96< 0.010 31–90 days4 (5)0.3910 (21)2.88< 0.001 Beyond 90 days25 (29)0.9512 (26)2.160.04Sternal wound (all)2 (2)0.035 (11)0.210.02 0–30 days1 (1)0.154 (9)1.270.02 31–90 days1 (1)0.090 (0)0.000.53 Beyond 90 days0 (0)0.001 (2)0.060.10Non-device-associated infectionsCRBSI (all)14 (16)0.2520 (43)1.02< 0.001 0–30 days1 (1)0.1513 (28)4.62< 0.001 31–90 days4 (5)0.381 (2)0.270.75 Beyond 90 days9 (10)0.236 (13)0.460.12Pneumonia (all)27 (31)0.5517 (36)1.000.23 0–30 days20 (23)3.5615 (32)6.140.14 31–90 days3 (3)0.352 (4)0.680.50 Beyond 90 days4 (5)0.110 (0)0.000.23Urinary tract (all)31 (36)0.6212 (26)0.680.67 0–30 days16 (19)2.607 (15)2.310.77 31–90 days10 (12)1.194 (9)1.090.89 Beyond 90 days5 (6)0.141 (2)0.090.72p-value based on comparison between two groups by the log-rank test, with p < 0.05 considered significant. |
Event | CF (n = 86) | PF (n = 47) | p-value | n (%) | EPY | n (%) | EPY | Systemic infections | Bacteraemia (all) | 23 (27) | 0.42 | 21 (45) | 0.98 | 0.002 | 0–30 days | 3 (4) | 0.46 | 12 (26) | 4.16 | < 0.001 | 31–90 days | 4 (5) | 0.38 | 3 (6) | 0.79 | 0.33 | Beyond 90 days | 16 (19) | 0.42 | 6 (13) | 0.41 | 0.78 | Sepsis (all) | 55 (64) | 2.13 | 36 (77) | 5.34 | 0.01 | 0–30 days | 46 (53) | 12.1 | 34 (72) | 25.1 | < 0.01 | 31–90 days | 4 (5) | 0.87 | 2 (4) | 1.84 | 0.41 | Beyond 90 days | 5 (6) | 0.29 | 0 (0) | 0.00 | 0.32 | Severe sepsis (all) | 14 (16) | 0.22 | 12 (26) | 0.55 | 0.11 | 0–30 days | 9 (10) | 1.44 | 8 (17) | 2.55 | 0.24 | 31–90 days | 4 (5) | 0.39 | 3 (6) | 0.7 | 0.42 | Beyond 90 days | 1 (1) | 0.02 | 1 (2) | 0.07 | 0.43 | Septic shock (all) | 11 (13) | 0.17 | 9 (19) | 0.37 | 0.19 | 0–30 days | 5 (6) | 0.77 | 6 (13) | 1.87 | 0.12 | 31–90 days | 6 (7) | 0.10 | 3 (6) | 0.15 | 0.81 | Beyond 90 days | 0 (0) | 0.00 | 0 (0) | 0.00 | 1.00 | Device-associated infections | Driveline (all) | 26 (30) | 0.58 | 19 (40) | 1.08 | 0.02 | 0–30 days | 0 (0) | 0.00 | 2 (4) | 0.63 | 0.04 | 31–90 days | 2 (2) | 0.18 | 5 (11) | 1.22 | < 0.01 | Beyond 90 days | 24 (28) | 0.83 | 12 (26) | 1.07 | 0.42 | LVAD pocket (all) | 9 (10) | 0.15 | 16(34) | 0.88 | < 0.001 | 0–30 days | 2 (2) | 0.31 | 5 (11) | 1.62 | 0.03 | 31–90 days | 2 (2) | 0.16 | 5 (11) | 1.01 | 0.01 | Beyond 90 days | 5 (6) | 0.12 | 6 (13) | 0.53 | 0.01 | Driveline or pocket (all) | 31 (36) | 0.72 | 28 (60) | 2.31 | < 0.001 | 0–30 days | 2 (2) | 0.31 | 6 (13) | 1.96 | < 0.010 | 31–90 days | 4 (5) | 0.39 | 10 (21) | 2.88 | < 0.001 | Beyond 90 days | 25 (29) | 0.95 | 12 (26) | 2.16 | 0.04 | Sternal wound (all) | 2 (2) | 0.03 | 5 (11) | 0.21 | 0.02 | 0–30 days | 1 (1) | 0.15 | 4 (9) | 1.27 | 0.02 | 31–90 days | 1 (1) | 0.09 | 0 (0) | 0.00 | 0.53 | Beyond 90 days | 0 (0) | 0.00 | 1 (2) | 0.06 | 0.10 | Non-device-associated infections | CRBSI (all) | 14 (16) | 0.25 | 20 (43) | 1.02 | < 0.001 | 0–30 days | 1 (1) | 0.15 | 13 (28) | 4.62 | < 0.001 | 31–90 days | 4 (5) | 0.38 | 1 (2) | 0.27 | 0.75 | Beyond 90 days | 9 (10) | 0.23 | 6 (13) | 0.46 | 0.12 | Pneumonia (all) | 27 (31) | 0.55 | 17 (36) | 1.00 | 0.23 | 0–30 days | 20 (23) | 3.56 | 15 (32) | 6.14 | 0.14 | 31–90 days | 3 (3) | 0.35 | 2 (4) | 0.68 | 0.50 | Beyond 90 days | 4 (5) | 0.11 | 0 (0) | 0.00 | 0.23 | Urinary tract (all) | 31 (36) | 0.62 | 12 (26) | 0.68 | 0.67 | 0–30 days | 16 (19) | 2.60 | 7 (15) | 2.31 | 0.77 | 31–90 days | 10 (12) | 1.19 | 4 (9) | 1.09 | 0.89 | Beyond 90 days | 5 (6) | 0.14 | 1 (2) | 0.09 | 0.72 | p-value based on comparison between two groups by the log-rank test, with p < 0.05 considered significant. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Event | CF (n = 86) | PF (n = 47) | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n (%) | EPY | n (%) | EPY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systemic infections | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bacteraemia (all) | 23 (27) | 0.42 | 21 (45) | 0.98 | 0.002 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0–30 days | 3 (4) | 0.46 | 12 (26) | 4.16 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31–90 days | 4 (5) | 0.38 | 3 (6) | 0.79 | 0.33 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beyond 90 days | 16 (19) | 0.42 | 6 (13) | 0.41 | 0.78 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis (all) | 55 (64) | 2.13 | 36 (77) | 5.34 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0–30 days | 46 (53) | 12.1 | 34 (72) | 25.1 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31–90 days | 4 (5) | 0.87 | 2 (4) | 1.84 | 0.41 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beyond 90 days | 5 (6) | 0.29 | 0 (0) | 0.00 | 0.32 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Severe sepsis (all) | 14 (16) | 0.22 | 12 (26) | 0.55 | 0.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0–30 days | 9 (10) | 1.44 | 8 (17) | 2.55 | 0.24 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31–90 days | 4 (5) | 0.39 | 3 (6) | 0.7 | 0.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beyond 90 days | 1 (1) | 0.02 | 1 (2) | 0.07 | 0.43 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Septic shock (all) | 11 (13) | 0.17 | 9 (19) | 0.37 | 0.19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0–30 days | 5 (6) | 0.77 | 6 (13) | 1.87 | 0.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31–90 days | 6 (7) | 0.10 | 3 (6) | 0.15 | 0.81 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beyond 90 days | 0 (0) | 0.00 | 0 (0) | 0.00 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device-associated infections | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline (all) | 26 (30) | 0.58 | 19 (40) | 1.08 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0–30 days | 0 (0) | 0.00 | 2 (4) | 0.63 | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31–90 days | 2 (2) | 0.18 | 5 (11) | 1.22 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beyond 90 days | 24 (28) | 0.83 | 12 (26) | 1.07 | 0.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD pocket (all) | 9 (10) | 0.15 | 16(34) | 0.88 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0–30 days | 2 (2) | 0.31 | 5 (11) | 1.62 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31–90 days | 2 (2) | 0.16 | 5 (11) | 1.01 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beyond 90 days | 5 (6) | 0.12 | 6 (13) | 0.53 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline or pocket (all) | 31 (36) | 0.72 | 28 (60) | 2.31 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0–30 days | 2 (2) | 0.31 | 6 (13) | 1.96 | < 0.010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31–90 days | 4 (5) | 0.39 | 10 (21) | 2.88 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beyond 90 days | 25 (29) | 0.95 | 12 (26) | 2.16 | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sternal wound (all) | 2 (2) | 0.03 | 5 (11) | 0.21 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0–30 days | 1 (1) | 0.15 | 4 (9) | 1.27 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31–90 days | 1 (1) | 0.09 | 0 (0) | 0.00 | 0.53 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beyond 90 days | 0 (0) | 0.00 | 1 (2) | 0.06 | 0.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-device-associated infections | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CRBSI (all) | 14 (16) | 0.25 | 20 (43) | 1.02 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0–30 days | 1 (1) | 0.15 | 13 (28) | 4.62 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31–90 days | 4 (5) | 0.38 | 1 (2) | 0.27 | 0.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beyond 90 days | 9 (10) | 0.23 | 6 (13) | 0.46 | 0.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumonia (all) | 27 (31) | 0.55 | 17 (36) | 1.00 | 0.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0–30 days | 20 (23) | 3.56 | 15 (32) | 6.14 | 0.14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31–90 days | 3 (3) | 0.35 | 2 (4) | 0.68 | 0.50 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beyond 90 days | 4 (5) | 0.11 | 0 (0) | 0.00 | 0.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Urinary tract (all) | 31 (36) | 0.62 | 12 (26) | 0.68 | 0.67 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0–30 days | 16 (19) | 2.60 | 7 (15) | 2.31 | 0.77 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31–90 days | 10 (12) | 1.19 | 4 (9) | 1.09 | 0.89 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beyond 90 days | 5 (6) | 0.14 | 1 (2) | 0.09 | 0.72 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-value based on comparison between two groups by the log-rank test, with p < 0.05 considered significant. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cox proportional hazards analysis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Univariate analyses assessed predictive variables for primary outcomes. Bivariate analysis of the variables ‘device type’ and ‘year of implant’ demonstrated that year of implant was a better predictor of all outcomes aside from LVAD pocket infection. Further multivariate analysis demonstrated that year of implant was a significant predictor of all primary outcomes aside from severe sepsis, for which the SHFM score and age were the best predictors. (Results summarised in following tables) Univariate analysisBaseline characteristicsSepsisSevere sepsisDriveline or pocket infectionCRBSIHR95% CIp-valueHR95% CIp-valueHR95% CIp-valueHR95% CIp-valueYear of implant0.880.82 to 0.96< 0.010.880.76 to 1.010.070.780.70 to 0.86< 0.010.720.63 to 0.82< 0.01Device type0.560.37 to 0.86< 0.010.540.25 to 1.170.120.310.19 to 0.52< 0.010.260.13 to 0.51< 0.01Age0.990.97 to 1.010.21.051.01 to 1.09< 0.010.990.97 to 1.010.431.010.98 to 1.030.89Gender1.240.77 to 2.020.352.940.88 to 9.810.081.230.70 to 2.180.461.630.71 to 3.760.25Race1.240.80 to 1.840.382.591.12 to 5.980.031.060.63 to 1.780.821.40.71 to 2.750.33Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)0.840.57 to 1.220.361.360.68 to 2.720.381.681.02 to 2.740.041.330.73 to 2.420.35Pre-operative IABP1.881.22 to 2.86< 0.012.261.04 to 4.940.040.580.33 to 1.040.080.990.50 to 2.000.99Prior heart surgery1.30.86 to 1.980.21.320.61 to 2.860.481.741.03 to 2.940.041.530.78 to 3.010.22APACHE II1.040.99 to 1.090.061.11.03 to 1.17< 0.011.020.97 to 1.080.411.11.04 to 1.17< 0.01INTERMACS0.690.55 to 0.85< 0.010.580.38 to 0.880.011.170.93 to 1.470.180.870.63 to 1.200.39SHFM1.271.09 to 1.49< 0.011.481.11 to 1.98< 0.010.990.83 to 1.190.971.341.04 to 1.710.02 Bivariate Cox proportional hazards analysis of variables ‘year of implant’ and ‘device type’Component variables included in the separate bivariatea models'Univariate analysis hazard ratio (CI)p-valuebBivariate analysis hazard ratio (CI)p-valuecBacteraemia Device type (CF device)0.40 (0.22 to 0.73)< 0.011.34 (0.46 to 3.88)0.54 Year of implant0.78 (0.70 to 0.87)< 0.010.75 (0.61 to 0.91)< 0.01Sepsis Device type (CF device)0.59 (0.39 to 0.91)0.020.94 (0.46 to 1.92)0.86 Year of implant0.88 (0.82 to 0.96)< 0.010.89 (0.78 to 1.02)0.10Severe sepsis Device type (CF device)0.54 (0.25 to 1.17)0.120.83 (0.23 to 3.04)0.78 Year of implant0.88 (0.76 to 1.01)0.080.90 (0.71 to 1.15)0.41Septic shock Device type (CF device)0.56 (0.23 to 1.35)0.201.10 (0.23 to 5.21)0.90 Year of implant0.87 (0.74 to 1.02)0.080.86 (0.64 to 1.14)0.28Driveline Device type (CF device)0.50 (0.27 to 0.90)0.021.16 (0.44 to 3.04)0.76 Year of implant0.81 (0.72 to 0.91)< 0.010.79 (0.66 to 0.96)0.02LVAD pocket Device type (CF device)0.20 (0.09 to 0.46)< 0.010.33 (0.10 to 1.10)0.07 Year of implant0.75 (0.65 to 0.87)< 0.010.88 (0.71 to 1.11)0.29Driveline or LVAD pocket infection Device type (CF device)0.31 (0.19 to 0.52)< 0.010.57 (0.26 to 1.25)0.16 Year of implant0.77 (0.70 to 0.86)< 0.010.85 (0.72 to 0.99)0.04Sternal wound infection Device type (CF device)0.18 (0.03 to 0.92)0.041.08 (0.93 to 1.24)0.32 Year of implant0.73 (0.56 to 0.96)0.030.70 (0.37 to 1.33)0.28CRBSI Device type (CF device)0.26 (0.13 to 0.51)< 0.011.01 (0.98 to 1.04)0.42 Year of implant0.72 (0.63 to 0.82)< 0.010.71 (0.62 to 0.82)< 0.01Pneumonia Device type (CF device)0.69 (0.38 to 1.27)0.242.10 (0.71 to 6.21)0.18 Year of implant0.86 (0.76 to 0.96)< 0.010.76 (0.62 to 0.94)0.01Urinary tract infection Device type (CF device)1.16 (0.59 to 2.26)0.671.55 (0.51 to 4.73)0.44 Year of implant0.99 (0.88 to 1.12)0.940.93 (0.76 to 1.15)0.51a A separate bivariate model was constructed for each of the outcome measures using the variables ‘year of implant’ and ‘device type’.b p-value based on bivariate Cox analysis applying variables ‘year of implant’ and ‘device.c p-value based on univariate Cox analysis. Results of Multivariate Cox proportional hazard analysis of pre-operative variablesComponent variables included in the three separate multivariable modelsaUnivariate analysisMultivariate analysisHR95% CIp-valuebHR95% CIp-valuecSepsis Prior heart surgery1.300.86 to 1.980.2001.330.88 to 2.030.18 Year of implant0.880.82 to 0.960.0030.910.84 to 0.990.04 SHFM score1.271.09 to 1.490.0021.211.03 to 1.430.02Severe sepsis Age1.051.01 to 1.090.0091.051.02 to 1.100.006 Year of implant0.880.76 to 1.010.0800.890.76 to 1.040.15 SHFM score1.481.10 to 1.980.0081.41.04 to 1.880.03Drive or LVAD pocket infection Prior heart surgery1.741.03 to 2.940.041.590.94 to 2.700.09 Cardiac index1.671.03 to 2.740.041.961.22 to 3.140.005 Year of implant0.780.70 to 0.86< 0.0010.760.68 to 0.85< 0.001Catheter-related bloodstream infection Year of implant0.720.63 to 0.82< 0.0010.720.63 to 0.84< 0.001 APACHE II score1.101.04 to 1.170.0011.081.01 to 1.140.02 SHFM score1.341.04 to 1.710.0200.980.73 to 1.320.89a A separate multivariate model was constructed for each of the four outcome measures (see text).b p-value based on univariate Cox analysis.c p-value based on bivariate Cox analysis applying the variables ‘year of implant’ and ‘device type’. Bivariate analysis demonstrated that year of implant significantly predicted bacteraemia, driveline infection and CRBSI, while approaching significance for sepsis (p = 0.10). Device type did not achieve significance for any end point, although it approached significance for LVAD pocket infections On multivariate analysis, year of implant remained significant for all primary outcomes except severe sepsis. After risk adjustment, SHFM score and age at implant better predicted severe sepsis, suggesting that pre-operative acuity plays a role in the likelihood of a patient to progress from sepsis to severe sepsis |
Baseline characteristics | Sepsis | Severe sepsis | Driveline or pocket infection | CRBSI | HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | Year of implant | 0.88 | 0.82 to 0.96 | < 0.01 | 0.88 | 0.76 to 1.01 | 0.07 | 0.78 | 0.70 to 0.86 | < 0.01 | 0.72 | 0.63 to 0.82 | < 0.01 | Device type | 0.56 | 0.37 to 0.86 | < 0.01 | 0.54 | 0.25 to 1.17 | 0.12 | 0.31 | 0.19 to 0.52 | < 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.13 to 0.51 | < 0.01 | Age | 0.99 | 0.97 to 1.01 | 0.2 | 1.05 | 1.01 to 1.09 | < 0.01 | 0.99 | 0.97 to 1.01 | 0.43 | 1.01 | 0.98 to 1.03 | 0.89 | Gender | 1.24 | 0.77 to 2.02 | 0.35 | 2.94 | 0.88 to 9.81 | 0.08 | 1.23 | 0.70 to 2.18 | 0.46 | 1.63 | 0.71 to 3.76 | 0.25 | Race | 1.24 | 0.80 to 1.84 | 0.38 | 2.59 | 1.12 to 5.98 | 0.03 | 1.06 | 0.63 to 1.78 | 0.82 | 1.4 | 0.71 to 2.75 | 0.33 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 0.84 | 0.57 to 1.22 | 0.36 | 1.36 | 0.68 to 2.72 | 0.38 | 1.68 | 1.02 to 2.74 | 0.04 | 1.33 | 0.73 to 2.42 | 0.35 | Pre-operative IABP | 1.88 | 1.22 to 2.86 | < 0.01 | 2.26 | 1.04 to 4.94 | 0.04 | 0.58 | 0.33 to 1.04 | 0.08 | 0.99 | 0.50 to 2.00 | 0.99 | Prior heart surgery | 1.3 | 0.86 to 1.98 | 0.2 | 1.32 | 0.61 to 2.86 | 0.48 | 1.74 | 1.03 to 2.94 | 0.04 | 1.53 | 0.78 to 3.01 | 0.22 | APACHE II | 1.04 | 0.99 to 1.09 | 0.06 | 1.1 | 1.03 to 1.17 | < 0.01 | 1.02 | 0.97 to 1.08 | 0.41 | 1.1 | 1.04 to 1.17 | < 0.01 | INTERMACS | 0.69 | 0.55 to 0.85 | < 0.01 | 0.58 | 0.38 to 0.88 | 0.01 | 1.17 | 0.93 to 1.47 | 0.18 | 0.87 | 0.63 to 1.20 | 0.39 | SHFM | 1.27 | 1.09 to 1.49 | < 0.01 | 1.48 | 1.11 to 1.98 | < 0.01 | 0.99 | 0.83 to 1.19 | 0.97 | 1.34 | 1.04 to 1.71 | 0.02 | Component variables included in the separate bivariatea models' | Univariate analysis hazard ratio (CI) | p-valueb | Bivariate analysis hazard ratio (CI) | p-valuec | Bacteraemia | Device type (CF device) | 0.40 (0.22 to 0.73) | < 0.01 | 1.34 (0.46 to 3.88) | 0.54 | Year of implant | 0.78 (0.70 to 0.87) | < 0.01 | 0.75 (0.61 to 0.91) | < 0.01 | Sepsis | Device type (CF device) | 0.59 (0.39 to 0.91) | 0.02 | 0.94 (0.46 to 1.92) | 0.86 | Year of implant | 0.88 (0.82 to 0.96) | < 0.01 | 0.89 (0.78 to 1.02) | 0.10 | Severe sepsis | Device type (CF device) | 0.54 (0.25 to 1.17) | 0.12 | 0.83 (0.23 to 3.04) | 0.78 | Year of implant | 0.88 (0.76 to 1.01) | 0.08 | 0.90 (0.71 to 1.15) | 0.41 | Septic shock | Device type (CF device) | 0.56 (0.23 to 1.35) | 0.20 | 1.10 (0.23 to 5.21) | 0.90 | Year of implant | 0.87 (0.74 to 1.02) | 0.08 | 0.86 (0.64 to 1.14) | 0.28 | Driveline | Device type (CF device) | 0.50 (0.27 to 0.90) | 0.02 | 1.16 (0.44 to 3.04) | 0.76 | Year of implant | 0.81 (0.72 to 0.91) | < 0.01 | 0.79 (0.66 to 0.96) | 0.02 | LVAD pocket | Device type (CF device) | 0.20 (0.09 to 0.46) | < 0.01 | 0.33 (0.10 to 1.10) | 0.07 | Year of implant | 0.75 (0.65 to 0.87) | < 0.01 | 0.88 (0.71 to 1.11) | 0.29 | Driveline or LVAD pocket infection | Device type (CF device) | 0.31 (0.19 to 0.52) | < 0.01 | 0.57 (0.26 to 1.25) | 0.16 | Year of implant | 0.77 (0.70 to 0.86) | < 0.01 | 0.85 (0.72 to 0.99) | 0.04 | Sternal wound infection | Device type (CF device) | 0.18 (0.03 to 0.92) | 0.04 | 1.08 (0.93 to 1.24) | 0.32 | Year of implant | 0.73 (0.56 to 0.96) | 0.03 | 0.70 (0.37 to 1.33) | 0.28 | CRBSI | Device type (CF device) | 0.26 (0.13 to 0.51) | < 0.01 | 1.01 (0.98 to 1.04) | 0.42 | Year of implant | 0.72 (0.63 to 0.82) | < 0.01 | 0.71 (0.62 to 0.82) | < 0.01 | Pneumonia | Device type (CF device) | 0.69 (0.38 to 1.27) | 0.24 | 2.10 (0.71 to 6.21) | 0.18 | Year of implant | 0.86 (0.76 to 0.96) | < 0.01 | 0.76 (0.62 to 0.94) | 0.01 | Urinary tract infection | Device type (CF device) | 1.16 (0.59 to 2.26) | 0.67 | 1.55 (0.51 to 4.73) | 0.44 | Year of implant | 0.99 (0.88 to 1.12) | 0.94 | 0.93 (0.76 to 1.15) | 0.51 | a A separate bivariate model was constructed for each of the outcome measures using the variables ‘year of implant’ and ‘device type’. | b p-value based on bivariate Cox analysis applying variables ‘year of implant’ and ‘device. | c p-value based on univariate Cox analysis. | Component variables included in the three separate multivariable modelsa | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | HR | 95% CI | p-valueb | HR | 95% CI | p-valuec | Sepsis | Prior heart surgery | 1.30 | 0.86 to 1.98 | 0.200 | 1.33 | 0.88 to 2.03 | 0.18 | Year of implant | 0.88 | 0.82 to 0.96 | 0.003 | 0.91 | 0.84 to 0.99 | 0.04 | SHFM score | 1.27 | 1.09 to 1.49 | 0.002 | 1.21 | 1.03 to 1.43 | 0.02 | Severe sepsis | Age | 1.05 | 1.01 to 1.09 | 0.009 | 1.05 | 1.02 to 1.10 | 0.006 | Year of implant | 0.88 | 0.76 to 1.01 | 0.080 | 0.89 | 0.76 to 1.04 | 0.15 | SHFM score | 1.48 | 1.10 to 1.98 | 0.008 | 1.4 | 1.04 to 1.88 | 0.03 | Drive or LVAD pocket infection | Prior heart surgery | 1.74 | 1.03 to 2.94 | 0.04 | 1.59 | 0.94 to 2.70 | 0.09 | Cardiac index | 1.67 | 1.03 to 2.74 | 0.04 | 1.96 | 1.22 to 3.14 | 0.005 | Year of implant | 0.78 | 0.70 to 0.86 | < 0.001 | 0.76 | 0.68 to 0.85 | < 0.001 | Catheter-related bloodstream infection | Year of implant | 0.72 | 0.63 to 0.82 | < 0.001 | 0.72 | 0.63 to 0.84 | < 0.001 | APACHE II score | 1.10 | 1.04 to 1.17 | 0.001 | 1.08 | 1.01 to 1.14 | 0.02 | SHFM score | 1.34 | 1.04 to 1.71 | 0.020 | 0.98 | 0.73 to 1.32 | 0.89 | a A separate multivariate model was constructed for each of the four outcome measures (see text). | b p-value based on univariate Cox analysis. | c p-value based on bivariate Cox analysis applying the variables ‘year of implant’ and ‘device type’. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline characteristics | Sepsis | Severe sepsis | Driveline or pocket infection | CRBSI | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.88 | 0.82 to 0.96 | < 0.01 | 0.88 | 0.76 to 1.01 | 0.07 | 0.78 | 0.70 to 0.86 | < 0.01 | 0.72 | 0.63 to 0.82 | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type | 0.56 | 0.37 to 0.86 | < 0.01 | 0.54 | 0.25 to 1.17 | 0.12 | 0.31 | 0.19 to 0.52 | < 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.13 to 0.51 | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age | 0.99 | 0.97 to 1.01 | 0.2 | 1.05 | 1.01 to 1.09 | < 0.01 | 0.99 | 0.97 to 1.01 | 0.43 | 1.01 | 0.98 to 1.03 | 0.89 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gender | 1.24 | 0.77 to 2.02 | 0.35 | 2.94 | 0.88 to 9.81 | 0.08 | 1.23 | 0.70 to 2.18 | 0.46 | 1.63 | 0.71 to 3.76 | 0.25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Race | 1.24 | 0.80 to 1.84 | 0.38 | 2.59 | 1.12 to 5.98 | 0.03 | 1.06 | 0.63 to 1.78 | 0.82 | 1.4 | 0.71 to 2.75 | 0.33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 0.84 | 0.57 to 1.22 | 0.36 | 1.36 | 0.68 to 2.72 | 0.38 | 1.68 | 1.02 to 2.74 | 0.04 | 1.33 | 0.73 to 2.42 | 0.35 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative IABP | 1.88 | 1.22 to 2.86 | < 0.01 | 2.26 | 1.04 to 4.94 | 0.04 | 0.58 | 0.33 to 1.04 | 0.08 | 0.99 | 0.50 to 2.00 | 0.99 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prior heart surgery | 1.3 | 0.86 to 1.98 | 0.2 | 1.32 | 0.61 to 2.86 | 0.48 | 1.74 | 1.03 to 2.94 | 0.04 | 1.53 | 0.78 to 3.01 | 0.22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| APACHE II | 1.04 | 0.99 to 1.09 | 0.06 | 1.1 | 1.03 to 1.17 | < 0.01 | 1.02 | 0.97 to 1.08 | 0.41 | 1.1 | 1.04 to 1.17 | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INTERMACS | 0.69 | 0.55 to 0.85 | < 0.01 | 0.58 | 0.38 to 0.88 | 0.01 | 1.17 | 0.93 to 1.47 | 0.18 | 0.87 | 0.63 to 1.20 | 0.39 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SHFM | 1.27 | 1.09 to 1.49 | < 0.01 | 1.48 | 1.11 to 1.98 | < 0.01 | 0.99 | 0.83 to 1.19 | 0.97 | 1.34 | 1.04 to 1.71 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Component variables included in the separate bivariatea models' | Univariate analysis hazard ratio (CI) | p-valueb | Bivariate analysis hazard ratio (CI) | p-valuec | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bacteraemia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type (CF device) | 0.40 (0.22 to 0.73) | < 0.01 | 1.34 (0.46 to 3.88) | 0.54 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.78 (0.70 to 0.87) | < 0.01 | 0.75 (0.61 to 0.91) | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type (CF device) | 0.59 (0.39 to 0.91) | 0.02 | 0.94 (0.46 to 1.92) | 0.86 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.88 (0.82 to 0.96) | < 0.01 | 0.89 (0.78 to 1.02) | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Severe sepsis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type (CF device) | 0.54 (0.25 to 1.17) | 0.12 | 0.83 (0.23 to 3.04) | 0.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.88 (0.76 to 1.01) | 0.08 | 0.90 (0.71 to 1.15) | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Septic shock | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type (CF device) | 0.56 (0.23 to 1.35) | 0.20 | 1.10 (0.23 to 5.21) | 0.90 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.87 (0.74 to 1.02) | 0.08 | 0.86 (0.64 to 1.14) | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type (CF device) | 0.50 (0.27 to 0.90) | 0.02 | 1.16 (0.44 to 3.04) | 0.76 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.81 (0.72 to 0.91) | < 0.01 | 0.79 (0.66 to 0.96) | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD pocket | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type (CF device) | 0.20 (0.09 to 0.46) | < 0.01 | 0.33 (0.10 to 1.10) | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.75 (0.65 to 0.87) | < 0.01 | 0.88 (0.71 to 1.11) | 0.29 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline or LVAD pocket infection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type (CF device) | 0.31 (0.19 to 0.52) | < 0.01 | 0.57 (0.26 to 1.25) | 0.16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.77 (0.70 to 0.86) | < 0.01 | 0.85 (0.72 to 0.99) | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sternal wound infection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type (CF device) | 0.18 (0.03 to 0.92) | 0.04 | 1.08 (0.93 to 1.24) | 0.32 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.73 (0.56 to 0.96) | 0.03 | 0.70 (0.37 to 1.33) | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CRBSI | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type (CF device) | 0.26 (0.13 to 0.51) | < 0.01 | 1.01 (0.98 to 1.04) | 0.42 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.72 (0.63 to 0.82) | < 0.01 | 0.71 (0.62 to 0.82) | < 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumonia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type (CF device) | 0.69 (0.38 to 1.27) | 0.24 | 2.10 (0.71 to 6.21) | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.86 (0.76 to 0.96) | < 0.01 | 0.76 (0.62 to 0.94) | 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Urinary tract infection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device type (CF device) | 1.16 (0.59 to 2.26) | 0.67 | 1.55 (0.51 to 4.73) | 0.44 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.99 (0.88 to 1.12) | 0.94 | 0.93 (0.76 to 1.15) | 0.51 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a A separate bivariate model was constructed for each of the outcome measures using the variables ‘year of implant’ and ‘device type’. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b p-value based on bivariate Cox analysis applying variables ‘year of implant’ and ‘device. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c p-value based on univariate Cox analysis. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Component variables included in the three separate multivariable modelsa | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HR | 95% CI | p-valueb | HR | 95% CI | p-valuec | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prior heart surgery | 1.30 | 0.86 to 1.98 | 0.200 | 1.33 | 0.88 to 2.03 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.88 | 0.82 to 0.96 | 0.003 | 0.91 | 0.84 to 0.99 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SHFM score | 1.27 | 1.09 to 1.49 | 0.002 | 1.21 | 1.03 to 1.43 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Severe sepsis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age | 1.05 | 1.01 to 1.09 | 0.009 | 1.05 | 1.02 to 1.10 | 0.006 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.88 | 0.76 to 1.01 | 0.080 | 0.89 | 0.76 to 1.04 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SHFM score | 1.48 | 1.10 to 1.98 | 0.008 | 1.4 | 1.04 to 1.88 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drive or LVAD pocket infection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prior heart surgery | 1.74 | 1.03 to 2.94 | 0.04 | 1.59 | 0.94 to 2.70 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index | 1.67 | 1.03 to 2.74 | 0.04 | 1.96 | 1.22 to 3.14 | 0.005 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.78 | 0.70 to 0.86 | < 0.001 | 0.76 | 0.68 to 0.85 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Catheter-related bloodstream infection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year of implant | 0.72 | 0.63 to 0.82 | < 0.001 | 0.72 | 0.63 to 0.84 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| APACHE II score | 1.10 | 1.04 to 1.17 | 0.001 | 1.08 | 1.01 to 1.14 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SHFM score | 1.34 | 1.04 to 1.71 | 0.020 | 0.98 | 0.73 to 1.32 | 0.89 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a A separate multivariate model was constructed for each of the four outcome measures (see text). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b p-value based on univariate Cox analysis. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c p-value based on bivariate Cox analysis applying the variables ‘year of implant’ and ‘device type’. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incompletely reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In this institutional review of post-LVAD infections, a decrease in infectious complications in CF patients was likely related to increased provider experience associated with a more recent date of implantation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The data support the author's conclusion. The proportional hazards assumption does not appear to have been tested | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Schaffer 200977
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Schaffer Year of publication: 2009 Country: USA Study design: Retrospective analysis Study setting: Hospital Number of centres: One Duration of study: VAD implants June 2000 to May 2009 Follow-up period: 1 year Funding: Not reported |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To assess the predictive ability of LM, COL, APACHE II, INTERMACS and SHFM prognostic systems for patients in receipt of HMII at a single institution | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 86 Sample attrition/dropout: 0 Inclusion criteria: All HMII recipients to May 2009 Exclusion criteria: NR Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): 49.7 years (13.1) Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: 61/86 (70.9% male) Race: 38/86 (44.2% white) Diagnosis: Various HF NOTE: This is the same population of HMII patients as in Schaffer et al.76 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: 57/86 BTT; 29/86 DT Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: High risk vs. low risk patients Duration of treatment: October 2004 to May 2009 Percentage of patients using inotropes: 54/86 62.8% Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Survival Secondary outcomes: None Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: Yes Adverse event: No HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: 1 yearNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableRandomised/includedn = 86 overallNot reported/not applicableExcludedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableMissing participantsNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableWithdrawalsNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicable |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Randomised/included | n = 86 overall | Not reported/not applicable | Excluded | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Missing participants | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Withdrawals | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | n = 86 overall | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristicsn (%) or mean ± SDBaseline Age (years)49.7 ± 13.1 Gender, male61 (70.9) Race, white38 (44.2) BTT57 (66.3) BMI (kg/m2)28.3 ± 7.0 NYHA class IV84 (97.7) Ischaemic aetiology28 (32.6) Pre-operative ventilation6 (7.0) Pre-operative IABP33 (38.4) Previous open heart operation32 (37.2) Previous LVAD10 (11.6)Composite risk scores COL1.05 ± 1.59 LM11.9 ± 5.4 INTERMACS2.64 ± 1.01 APACHE II15.6 ± 4.3 SHFM2.97 ± 1.42 Eighty-four of 86 patients were NYHA class IV; 50 (58.1%) patients in cardiogenic shock; 54 (62.8%) patients on inotropes; 33 (38.4%) patients on IABPs; 32 (37.2%) patients had previous open heart surgery; 10 (11.6%) patients had a previous VAD; 29 (33.7%) patients were implanted for DT; 28 (32.6%) patients had ischaemic cardiomyopathy Mean pre-operative cardiac index = 1.95 ± 0.50 Mean ejection fraction = 0.14 ± 0.06 |
Characteristics | n (%) or mean ± SD | Baseline | Age (years) | 49.7 ± 13.1 | Gender, male | 61 (70.9) | Race, white | 38 (44.2) | BTT | 57 (66.3) | BMI (kg/m2) | 28.3 ± 7.0 | NYHA class IV | 84 (97.7) | Ischaemic aetiology | 28 (32.6) | Pre-operative ventilation | 6 (7.0) | Pre-operative IABP | 33 (38.4) | Previous open heart operation | 32 (37.2) | Previous LVAD | 10 (11.6) | Composite risk scores | COL | 1.05 ± 1.59 | LM | 11.9 ± 5.4 | INTERMACS | 2.64 ± 1.01 | APACHE II | 15.6 ± 4.3 | SHFM | 2.97 ± 1.42 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristics | n (%) or mean ± SD | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 49.7 ± 13.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gender, male | 61 (70.9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Race, white | 38 (44.2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTT | 57 (66.3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.3 ± 7.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class IV | 84 (97.7) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic aetiology | 28 (32.6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative ventilation | 6 (7.0) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative IABP | 33 (38.4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Previous open heart operation | 32 (37.2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Previous LVAD | 10 (11.6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Composite risk scores | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COL | 1.05 ± 1.59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LM | 11.9 ± 5.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INTERMACS | 2.64 ± 1.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| APACHE II | 15.6 ± 4.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SHFM | 2.97 ± 1.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The 30-day, 90-day, and 1-year mortality were 10.6% (n = 9), 22.7% (n = 19), and 30.3% (n = 24), respectively Each patient was given a risk score according to each of the five predictive models that use pre-operative patient characteristics to arrive at risk assessment. A cut-off was determined for each model so as to divide the 86 patients into high-risk and low-risk groups. The cut-off score for each model was decided according to which of those cut-offs tried gave the best discrimination (by log-rank test the lowest p-value) between the K–M observed survival for the high- and low-risk designated patients. The cut-off score for SHFM was determined according to a survival equation: S(t) = exp (−0.045 × t × exp (SHFM score)). When S = 50% at t = 0.5 years The number of patients in low-risk and high-risk groups, and p-value from K–M plots were:LowHighK–M % alive at 1 yearp-valueLowHighCOL833100640.31LM533374.169.10.33INTERMACS434384.155.50.004APACHE II553182.944.4< 0.001SHFM553183.646.1< 0.001 Univariate and multivariate (including risk scores from all five models) Cox proportional hazard analysis results are shown below:Composite scoresUnivariate analysisMultivariable analysisHR (95% CI)p-valueaHR (95% CI)p-valueb30-day mortality COL1.02 (0.69 to 1.52)0.901.02 (0.58 to 1.77)0.95 LM0.95 (0.83 to 1.08)0.390.92 (0.80 to 1.06)0.25 INTERMACS0.75 (0.38 to 1.44)0.381.15 (0.48 to 2.28)0.75 APACHE II1.13 (0.98 to 1.30)0.091.10 (0.93 to 1.30)0.27 SHFM1.73 (1.06 to 2.85)0.031.75 (0.93 to 3.32)0.0890-day mortality COL1.04 (0.80 to 1.34)0.790.89 (0.62 to 1.28)0.53 LM0.98 (0.90 to 1.07)0.680.96 (0.88 to 1.06)0.43 INTERMACS0.56 (0.35 to 0.92)0.020.70 (0.36 to 1.36)0.3 APACHE II1.10 (1.00 to 1.21)0.051.07 (0.96 to 1.20)0.2 SHFM1.70 (1.21 to 2.37)0.0021.46 (0.94 to 2.28)0.091-year mortality COL1.04 (0.83 to 1.31)0.710.92 (0.67 to 1.26)0.59 LM0.99 (0.92 to 1.06)0.760.96 (0.89 to 1.04)0.37 INTERMACS0.64 (0.42 to 0.98)0.040.86 (0.49 to 1.52)0.61 APACHE II1.12 (1.03 to 1.22)0.0061.10 (1.01 to 1.21)0.04 SHFM1.64 (1.23 to 2.20)0.0011.50 (1.02 to 2.21)0.04a Based on univariate Cox analysis, p < 0.05 statistically significant.b Based on multivariable Cox regression analysis, p < 0.05 statistically significant. On univariate analysis, SHFM predicted mortality at each of the three mortality end points examined, whereas APACHE II and INTERMACS significantly predicted 90-day and 1-year mortality. The LM and COL were not predictive of mortality at any end point studied Multivariable analysis used all five scores as covariates (‘possible due to lack of overlapping variables between scores only age, NYHA, ventilator status, serum sodium level, haematocrit/haemoglobin, prothrombin time/INR, and pre-operative inotropes were used in multiple scores’). In multivariate analysis SHFM (HR 1.50, 95% CI 1.02 to 2.21; p = 0.04) and APACHE II (HR 1.10, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.21; p = 0.04) remained predictive of 1-year mortality. No score achieved significance in predicting 30-day or 90-day mortality on multivariable analysis, although SHFM approached significance for both end points (p = 0.08 and p = 0.09, respectively) Pre-operative variables for the 86 single-centre cohort were also explored using univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards models. The results are tabulated below: Univariate analysisSignificant variablesScore variable30-day mortality90-day mortality1-year mortalityHR (95% CI)p-valueaHR (95% CI)p-valueaHR (95% CI)p-valueaBaseline variables AgeA, S1.07 (0.99 to 1.14)0.071.06 (1.01 to 1.11)0.011.04 (1.01 to 1.18)0.02 Gender, maleSb8.85 (1.18 to 66.4)0.032.65 (0.90 to 7.76)0.08 Race, white2.62 (0.66 to 10.5)0.173.05 (1.16 to 8.02)0.023.03 (1.29 to 7.10)0.01 Pre-operative IABP0.82 (0.20 to 3.26)0.771.93 (0.78 to 4.75)0.152.22 (1.00 to 4.96)0.05 Pre-operative IABP/ventilatorS1.21 (0.32 to 4.49)0.782.22 (0.89 to 5.53)0.092.44 (1.08 to 5.50)0.03Vital signs Ejection fractionS1.02 (0.93 to 1.12)0.671.04 (0.98 to 1.10)0.231.06 (1.01 to 1.11)0.03 Cardiac index0.21 (0.05 to 0.88)0.030.57 (0.23 to 1.43)0.230.73 (0.32 to 1.68)0.46Lab values Serum urea nitrogenLM1.02 (1.00 to 1.05)0.051.03 (1.01 to 1.04)0.0011.03 (1.02 to 1.05)< 0.001 Serum creatinineA1.56 (1.19 to 2.04)< 0.0011.53 (1.19 to 1.97)0.0011.63 (1.27 to 2.09)< 0.001 Serum cholesterolS0.98 (0.97 to 1.00)0.080.98 (0.97 to 0.99)0.010.99 (0.98 to 0.99)0.008 HaemoglobinS0.74 (0.53 to 1.05)0.090.84 (0.68 to 1.05)0.130.81 (0.66 to 0.98)0.04 PlateletsLM1.01 (1.00 to 1.02)0.011.01 (1.00 to 1.02)0.0081.01 (1.00 to 1.01)0.02 LymphocytecS0.89 (0.80 to 1.00)0.050.91 (0.85 to 0.98)0.010.92 (0.87 to 0.98)0.007 Prothrombin timeC1.11 (1.01 to 1.23)0.031.10 (1.00 to 1.20)0.051.10 (1.01 to 1.19)0.03Pre-operative medications ACE inhibitorS0.16 (0.02 to 1.25)0.080.20 (0.06 to 0.70)0.010.27 (0.10 to 0.72)0.009 Beta-blockerS0.25 (0.06 to 0.99)0.050.53 (0.22 to 1.31)0.170.59 (0.26 to 1.31)0.20a Based on univariate Cox proportional hazard analysis; values of p < 0.05 are significant.b Risk of 30-day mortality not possible to calculate for the variable ‘gender’ owing to limited variability in the outcome.c Lymphocyte per cent on complete blood cell count differential. Multivariate analysisComponent variablesScore variableUnivariate analysisMultivariable analysisHR (95% CI)p-valueaHR (95% CI)p-valueb30-day mortality AgeA, S1.07 (0.99 to 1.14)0.071.06 (0.99 to 1.13)0.12 Cardiac index0.21 (0.05 to 0.88)0.030.20 (0.02 to 2.00)0.17 Serum creatinineA1.56 (1.19 to 2.04)< 0.0011.70 (1.20 to 2.41)0.003 PlateletsLM1.01 (1.00 to 1.02)0.011.01 (1.00 to 1.02)0.009 LymphocytescS0.89 (0.80 to 1.00)0.050.91 (0.78 to 1.06)0.21 Prothrombin timeC1.11 (1.01 to 1.23)0.031.03 (0.89 to 1.18)0.74 Pre-operative ACE inhibitorS0.16 (0.02 to 1.25)0.080.49 (0.04 to 5.57)0.56 Pre-operative beta-blockerS0.25 (0.06 to 0.99)0.050.19 (0.03 to 1.11)0.0790-day mortality AgeA, S1.06 (1.01 to 1.11)0.011.03 (0.99 to 1.08)0.12 Sex, maleS8.85 (1.18 to 66.4)0.033.41 (0.40 to 28.8)0.26 Race, white3.05 (1.16 to 8.02)0.021.85 (0.56 to 6.12)0.31 Serum creatinineA1.53 (1.19 to 1.97)0.0011.57 (1.15 to 2.14)0.004 Serum cholesterolS0.98 (0.97 to 0.99)0.010.99 (0.98 to 1.01)0.28 PlateletsLM1.01 (1.00 to 1.02)0.0081.01 (1.00 to 1.02)0.05 LymphocytescS0.20 (0.06 to 0.70)0.010.97 (0.90 to 1.04)0.44 Pre-operative ACE inhibitorS0.20 (0.06 to 0.70)0.010.33 (0.09 to 1.23)0.101-year mortality AgeA, S1.04 (1.01 to 1.18)0.021.05 (1.00 to 1.10)0.04 Race, white3.03 (1.29 to 7.10)0.012.10 (0.80 to 5.56)0.13 Pre-operative IABP/ventilatorS2.44 (1.08 to 5.50)0.032.42 (0.85 to 6.92)0.10 Serum creatinineA1.63 (1.27 to 2.09)< 0.0011.86 (1.40 to 2.48)< 0.001 Serum cholesterolS0.99 (0.98 to 0.99)0.0080.99 (0.98 to 1.01)0.21 PlateletsLM1.01 (1.00 to 1.01)0.021.01 (1.00 to 1.01)0.03 LymphocytescS0.92 (0.87 to 0.98)0.0070.98 (0.92 to 1.47)0.58 Pre-operative ACE inhibitorS0.27 (0.10 to 0.72)0.0090.49 (0.16 to 1.47)0.20a Based on univariate Cox analysis.b Based on multivariate Cox analysis.c Lymphocyte per cent on complete blood cell count differential. On multivariable analysis, older age and serum creatinine level remained significant at predicting 1-year mortality |
Low | High | K–M % alive at 1 year | p-value | Low | High | COL | 83 | 3 | 100 | 64 | 0.31 | LM | 53 | 33 | 74.1 | 69.1 | 0.33 | INTERMACS | 43 | 43 | 84.1 | 55.5 | 0.004 | APACHE II | 55 | 31 | 82.9 | 44.4 | < 0.001 | SHFM | 55 | 31 | 83.6 | 46.1 | < 0.001 | Composite scores | Univariate analysis | Multivariable analysis | HR (95% CI) | p-valuea | HR (95% CI) | p-valueb | 30-day mortality | COL | 1.02 (0.69 to 1.52) | 0.90 | 1.02 (0.58 to 1.77) | 0.95 | LM | 0.95 (0.83 to 1.08) | 0.39 | 0.92 (0.80 to 1.06) | 0.25 | INTERMACS | 0.75 (0.38 to 1.44) | 0.38 | 1.15 (0.48 to 2.28) | 0.75 | APACHE II | 1.13 (0.98 to 1.30) | 0.09 | 1.10 (0.93 to 1.30) | 0.27 | SHFM | 1.73 (1.06 to 2.85) | 0.03 | 1.75 (0.93 to 3.32) | 0.08 | 90-day mortality | COL | 1.04 (0.80 to 1.34) | 0.79 | 0.89 (0.62 to 1.28) | 0.53 | LM | 0.98 (0.90 to 1.07) | 0.68 | 0.96 (0.88 to 1.06) | 0.43 | INTERMACS | 0.56 (0.35 to 0.92) | 0.02 | 0.70 (0.36 to 1.36) | 0.3 | APACHE II | 1.10 (1.00 to 1.21) | 0.05 | 1.07 (0.96 to 1.20) | 0.2 | SHFM | 1.70 (1.21 to 2.37) | 0.002 | 1.46 (0.94 to 2.28) | 0.09 | 1-year mortality | COL | 1.04 (0.83 to 1.31) | 0.71 | 0.92 (0.67 to 1.26) | 0.59 | LM | 0.99 (0.92 to 1.06) | 0.76 | 0.96 (0.89 to 1.04) | 0.37 | INTERMACS | 0.64 (0.42 to 0.98) | 0.04 | 0.86 (0.49 to 1.52) | 0.61 | APACHE II | 1.12 (1.03 to 1.22) | 0.006 | 1.10 (1.01 to 1.21) | 0.04 | SHFM | 1.64 (1.23 to 2.20) | 0.001 | 1.50 (1.02 to 2.21) | 0.04 | a Based on univariate Cox analysis, p < 0.05 statistically significant. | b Based on multivariable Cox regression analysis, p < 0.05 statistically significant. | Significant variables | Score variable | 30-day mortality | 90-day mortality | 1-year mortality | HR (95% CI) | p-valuea | HR (95% CI) | p-valuea | HR (95% CI) | p-valuea | Baseline variables | Age | A, S | 1.07 (0.99 to 1.14) | 0.07 | 1.06 (1.01 to 1.11) | 0.01 | 1.04 (1.01 to 1.18) | 0.02 | Gender, male | S | b | 8.85 (1.18 to 66.4) | 0.03 | 2.65 (0.90 to 7.76) | 0.08 | Race, white | 2.62 (0.66 to 10.5) | 0.17 | 3.05 (1.16 to 8.02) | 0.02 | 3.03 (1.29 to 7.10) | 0.01 | Pre-operative IABP | 0.82 (0.20 to 3.26) | 0.77 | 1.93 (0.78 to 4.75) | 0.15 | 2.22 (1.00 to 4.96) | 0.05 | Pre-operative IABP/ventilator | S | 1.21 (0.32 to 4.49) | 0.78 | 2.22 (0.89 to 5.53) | 0.09 | 2.44 (1.08 to 5.50) | 0.03 | Vital signs | Ejection fraction | S | 1.02 (0.93 to 1.12) | 0.67 | 1.04 (0.98 to 1.10) | 0.23 | 1.06 (1.01 to 1.11) | 0.03 | Cardiac index | 0.21 (0.05 to 0.88) | 0.03 | 0.57 (0.23 to 1.43) | 0.23 | 0.73 (0.32 to 1.68) | 0.46 | Lab values | Serum urea nitrogen | LM | 1.02 (1.00 to 1.05) | 0.05 | 1.03 (1.01 to 1.04) | 0.001 | 1.03 (1.02 to 1.05) | < 0.001 | Serum creatinine | A | 1.56 (1.19 to 2.04) | < 0.001 | 1.53 (1.19 to 1.97) | 0.001 | 1.63 (1.27 to 2.09) | < 0.001 | Serum cholesterol | S | 0.98 (0.97 to 1.00) | 0.08 | 0.98 (0.97 to 0.99) | 0.01 | 0.99 (0.98 to 0.99) | 0.008 | Haemoglobin | S | 0.74 (0.53 to 1.05) | 0.09 | 0.84 (0.68 to 1.05) | 0.13 | 0.81 (0.66 to 0.98) | 0.04 | Platelets | LM | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.02) | 0.01 | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.02) | 0.008 | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.01) | 0.02 | Lymphocytec | S | 0.89 (0.80 to 1.00) | 0.05 | 0.91 (0.85 to 0.98) | 0.01 | 0.92 (0.87 to 0.98) | 0.007 | Prothrombin time | C | 1.11 (1.01 to 1.23) | 0.03 | 1.10 (1.00 to 1.20) | 0.05 | 1.10 (1.01 to 1.19) | 0.03 | Pre-operative medications | ACE inhibitor | S | 0.16 (0.02 to 1.25) | 0.08 | 0.20 (0.06 to 0.70) | 0.01 | 0.27 (0.10 to 0.72) | 0.009 | Beta-blocker | S | 0.25 (0.06 to 0.99) | 0.05 | 0.53 (0.22 to 1.31) | 0.17 | 0.59 (0.26 to 1.31) | 0.20 | a Based on univariate Cox proportional hazard analysis; values of p < 0.05 are significant. | b Risk of 30-day mortality not possible to calculate for the variable ‘gender’ owing to limited variability in the outcome. | c Lymphocyte per cent on complete blood cell count differential. | Component variables | Score variable | Univariate analysis | Multivariable analysis | HR (95% CI) | p-valuea | HR (95% CI) | p-valueb | 30-day mortality | Age | A, S | 1.07 (0.99 to 1.14) | 0.07 | 1.06 (0.99 to 1.13) | 0.12 | Cardiac index | 0.21 (0.05 to 0.88) | 0.03 | 0.20 (0.02 to 2.00) | 0.17 | Serum creatinine | A | 1.56 (1.19 to 2.04) | < 0.001 | 1.70 (1.20 to 2.41) | 0.003 | Platelets | LM | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.02) | 0.01 | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.02) | 0.009 | Lymphocytesc | S | 0.89 (0.80 to 1.00) | 0.05 | 0.91 (0.78 to 1.06) | 0.21 | Prothrombin time | C | 1.11 (1.01 to 1.23) | 0.03 | 1.03 (0.89 to 1.18) | 0.74 | Pre-operative ACE inhibitor | S | 0.16 (0.02 to 1.25) | 0.08 | 0.49 (0.04 to 5.57) | 0.56 | Pre-operative beta-blocker | S | 0.25 (0.06 to 0.99) | 0.05 | 0.19 (0.03 to 1.11) | 0.07 | 90-day mortality | Age | A, S | 1.06 (1.01 to 1.11) | 0.01 | 1.03 (0.99 to 1.08) | 0.12 | Sex, male | S | 8.85 (1.18 to 66.4) | 0.03 | 3.41 (0.40 to 28.8) | 0.26 | Race, white | 3.05 (1.16 to 8.02) | 0.02 | 1.85 (0.56 to 6.12) | 0.31 | Serum creatinine | A | 1.53 (1.19 to 1.97) | 0.001 | 1.57 (1.15 to 2.14) | 0.004 | Serum cholesterol | S | 0.98 (0.97 to 0.99) | 0.01 | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.01) | 0.28 | Platelets | LM | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.02) | 0.008 | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.02) | 0.05 | Lymphocytesc | S | 0.20 (0.06 to 0.70) | 0.01 | 0.97 (0.90 to 1.04) | 0.44 | Pre-operative ACE inhibitor | S | 0.20 (0.06 to 0.70) | 0.01 | 0.33 (0.09 to 1.23) | 0.10 | 1-year mortality | Age | A, S | 1.04 (1.01 to 1.18) | 0.02 | 1.05 (1.00 to 1.10) | 0.04 | Race, white | 3.03 (1.29 to 7.10) | 0.01 | 2.10 (0.80 to 5.56) | 0.13 | Pre-operative IABP/ventilator | S | 2.44 (1.08 to 5.50) | 0.03 | 2.42 (0.85 to 6.92) | 0.10 | Serum creatinine | A | 1.63 (1.27 to 2.09) | < 0.001 | 1.86 (1.40 to 2.48) | < 0.001 | Serum cholesterol | S | 0.99 (0.98 to 0.99) | 0.008 | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.01) | 0.21 | Platelets | LM | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.01) | 0.02 | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.01) | 0.03 | Lymphocytesc | S | 0.92 (0.87 to 0.98) | 0.007 | 0.98 (0.92 to 1.47) | 0.58 | Pre-operative ACE inhibitor | S | 0.27 (0.10 to 0.72) | 0.009 | 0.49 (0.16 to 1.47) | 0.20 | a Based on univariate Cox analysis. | b Based on multivariate Cox analysis. | c Lymphocyte per cent on complete blood cell count differential. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Low | High | K–M % alive at 1 year | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Low | High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COL | 83 | 3 | 100 | 64 | 0.31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LM | 53 | 33 | 74.1 | 69.1 | 0.33 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INTERMACS | 43 | 43 | 84.1 | 55.5 | 0.004 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| APACHE II | 55 | 31 | 82.9 | 44.4 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SHFM | 55 | 31 | 83.6 | 46.1 | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Composite scores | Univariate analysis | Multivariable analysis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HR (95% CI) | p-valuea | HR (95% CI) | p-valueb | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30-day mortality | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COL | 1.02 (0.69 to 1.52) | 0.90 | 1.02 (0.58 to 1.77) | 0.95 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LM | 0.95 (0.83 to 1.08) | 0.39 | 0.92 (0.80 to 1.06) | 0.25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INTERMACS | 0.75 (0.38 to 1.44) | 0.38 | 1.15 (0.48 to 2.28) | 0.75 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| APACHE II | 1.13 (0.98 to 1.30) | 0.09 | 1.10 (0.93 to 1.30) | 0.27 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SHFM | 1.73 (1.06 to 2.85) | 0.03 | 1.75 (0.93 to 3.32) | 0.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 90-day mortality | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COL | 1.04 (0.80 to 1.34) | 0.79 | 0.89 (0.62 to 1.28) | 0.53 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LM | 0.98 (0.90 to 1.07) | 0.68 | 0.96 (0.88 to 1.06) | 0.43 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INTERMACS | 0.56 (0.35 to 0.92) | 0.02 | 0.70 (0.36 to 1.36) | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| APACHE II | 1.10 (1.00 to 1.21) | 0.05 | 1.07 (0.96 to 1.20) | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SHFM | 1.70 (1.21 to 2.37) | 0.002 | 1.46 (0.94 to 2.28) | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-year mortality | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COL | 1.04 (0.83 to 1.31) | 0.71 | 0.92 (0.67 to 1.26) | 0.59 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LM | 0.99 (0.92 to 1.06) | 0.76 | 0.96 (0.89 to 1.04) | 0.37 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INTERMACS | 0.64 (0.42 to 0.98) | 0.04 | 0.86 (0.49 to 1.52) | 0.61 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| APACHE II | 1.12 (1.03 to 1.22) | 0.006 | 1.10 (1.01 to 1.21) | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SHFM | 1.64 (1.23 to 2.20) | 0.001 | 1.50 (1.02 to 2.21) | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Based on univariate Cox analysis, p < 0.05 statistically significant. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Based on multivariable Cox regression analysis, p < 0.05 statistically significant. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Significant variables | Score variable | 30-day mortality | 90-day mortality | 1-year mortality | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HR (95% CI) | p-valuea | HR (95% CI) | p-valuea | HR (95% CI) | p-valuea | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline variables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age | A, S | 1.07 (0.99 to 1.14) | 0.07 | 1.06 (1.01 to 1.11) | 0.01 | 1.04 (1.01 to 1.18) | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gender, male | S | b | 8.85 (1.18 to 66.4) | 0.03 | 2.65 (0.90 to 7.76) | 0.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Race, white | 2.62 (0.66 to 10.5) | 0.17 | 3.05 (1.16 to 8.02) | 0.02 | 3.03 (1.29 to 7.10) | 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative IABP | 0.82 (0.20 to 3.26) | 0.77 | 1.93 (0.78 to 4.75) | 0.15 | 2.22 (1.00 to 4.96) | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative IABP/ventilator | S | 1.21 (0.32 to 4.49) | 0.78 | 2.22 (0.89 to 5.53) | 0.09 | 2.44 (1.08 to 5.50) | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vital signs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ejection fraction | S | 1.02 (0.93 to 1.12) | 0.67 | 1.04 (0.98 to 1.10) | 0.23 | 1.06 (1.01 to 1.11) | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index | 0.21 (0.05 to 0.88) | 0.03 | 0.57 (0.23 to 1.43) | 0.23 | 0.73 (0.32 to 1.68) | 0.46 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lab values | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum urea nitrogen | LM | 1.02 (1.00 to 1.05) | 0.05 | 1.03 (1.01 to 1.04) | 0.001 | 1.03 (1.02 to 1.05) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum creatinine | A | 1.56 (1.19 to 2.04) | < 0.001 | 1.53 (1.19 to 1.97) | 0.001 | 1.63 (1.27 to 2.09) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum cholesterol | S | 0.98 (0.97 to 1.00) | 0.08 | 0.98 (0.97 to 0.99) | 0.01 | 0.99 (0.98 to 0.99) | 0.008 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemoglobin | S | 0.74 (0.53 to 1.05) | 0.09 | 0.84 (0.68 to 1.05) | 0.13 | 0.81 (0.66 to 0.98) | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets | LM | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.02) | 0.01 | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.02) | 0.008 | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.01) | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lymphocytec | S | 0.89 (0.80 to 1.00) | 0.05 | 0.91 (0.85 to 0.98) | 0.01 | 0.92 (0.87 to 0.98) | 0.007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prothrombin time | C | 1.11 (1.01 to 1.23) | 0.03 | 1.10 (1.00 to 1.20) | 0.05 | 1.10 (1.01 to 1.19) | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative medications | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACE inhibitor | S | 0.16 (0.02 to 1.25) | 0.08 | 0.20 (0.06 to 0.70) | 0.01 | 0.27 (0.10 to 0.72) | 0.009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beta-blocker | S | 0.25 (0.06 to 0.99) | 0.05 | 0.53 (0.22 to 1.31) | 0.17 | 0.59 (0.26 to 1.31) | 0.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Based on univariate Cox proportional hazard analysis; values of p < 0.05 are significant. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Risk of 30-day mortality not possible to calculate for the variable ‘gender’ owing to limited variability in the outcome. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c Lymphocyte per cent on complete blood cell count differential. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Component variables | Score variable | Univariate analysis | Multivariable analysis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HR (95% CI) | p-valuea | HR (95% CI) | p-valueb | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30-day mortality | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age | A, S | 1.07 (0.99 to 1.14) | 0.07 | 1.06 (0.99 to 1.13) | 0.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index | 0.21 (0.05 to 0.88) | 0.03 | 0.20 (0.02 to 2.00) | 0.17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum creatinine | A | 1.56 (1.19 to 2.04) | < 0.001 | 1.70 (1.20 to 2.41) | 0.003 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets | LM | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.02) | 0.01 | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.02) | 0.009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lymphocytesc | S | 0.89 (0.80 to 1.00) | 0.05 | 0.91 (0.78 to 1.06) | 0.21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prothrombin time | C | 1.11 (1.01 to 1.23) | 0.03 | 1.03 (0.89 to 1.18) | 0.74 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative ACE inhibitor | S | 0.16 (0.02 to 1.25) | 0.08 | 0.49 (0.04 to 5.57) | 0.56 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative beta-blocker | S | 0.25 (0.06 to 0.99) | 0.05 | 0.19 (0.03 to 1.11) | 0.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 90-day mortality | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age | A, S | 1.06 (1.01 to 1.11) | 0.01 | 1.03 (0.99 to 1.08) | 0.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex, male | S | 8.85 (1.18 to 66.4) | 0.03 | 3.41 (0.40 to 28.8) | 0.26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Race, white | 3.05 (1.16 to 8.02) | 0.02 | 1.85 (0.56 to 6.12) | 0.31 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum creatinine | A | 1.53 (1.19 to 1.97) | 0.001 | 1.57 (1.15 to 2.14) | 0.004 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum cholesterol | S | 0.98 (0.97 to 0.99) | 0.01 | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.01) | 0.28 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets | LM | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.02) | 0.008 | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.02) | 0.05 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lymphocytesc | S | 0.20 (0.06 to 0.70) | 0.01 | 0.97 (0.90 to 1.04) | 0.44 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative ACE inhibitor | S | 0.20 (0.06 to 0.70) | 0.01 | 0.33 (0.09 to 1.23) | 0.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-year mortality | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age | A, S | 1.04 (1.01 to 1.18) | 0.02 | 1.05 (1.00 to 1.10) | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Race, white | 3.03 (1.29 to 7.10) | 0.01 | 2.10 (0.80 to 5.56) | 0.13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative IABP/ventilator | S | 2.44 (1.08 to 5.50) | 0.03 | 2.42 (0.85 to 6.92) | 0.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum creatinine | A | 1.63 (1.27 to 2.09) | < 0.001 | 1.86 (1.40 to 2.48) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serum cholesterol | S | 0.99 (0.98 to 0.99) | 0.008 | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.01) | 0.21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets | LM | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.01) | 0.02 | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.01) | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lymphocytesc | S | 0.92 (0.87 to 0.98) | 0.007 | 0.98 (0.92 to 1.47) | 0.58 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative ACE inhibitor | S | 0.27 (0.10 to 0.72) | 0.009 | 0.49 (0.16 to 1.47) | 0.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Based on univariate Cox analysis. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Based on multivariate Cox analysis. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c Lymphocyte per cent on complete blood cell count differential. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Days on LVAD support = 277 ± 233; n = 27 (31.4%) received more than 1 year of support | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Among the LM, COL, APACHE II, INTERMACS and SHFM scores, the best predictor of mortality in a single institutional cohort of CF LVAD patients was the SHFM score | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SHFM was derived from a large cohort of non-VAD patients but appears to be the better performing prognostic indicator for this small cohort of HMII patients. How generalisable this finding is for other CF devices and populations remains to be researched. 57/86 BTT; 29/86 DT; cannot split (authors stated: our analysis did not stratify patients by therapeutic intent, because therapeutic intent was not a significant covariate for any of our mortality end points) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Schmid 200886
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Schmid Year of publication: 2008 Country: Worldwide Study design: Retrospective observational of Berlin Heart Registry Study setting: Hospital Number of centres: Multicentre Duration of study: 16 June 2002 to 30 June 2006 Follow-up period: 4 years Funding: Unclear |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Investigate the dependence of the neurological adverse event rate on the length of the inflow cannula (short vs. long) of the INCOR; Berlin Heart axial-flow VAD pump | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 216 Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported Inclusion criteria: Consecutive patients in receipt of Berlin Heart Exclusion criteria: Patients undergoing device implantations via a lateral thoracotomy and at centres with only minimal INCOR experience (fewer than five implants) Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): Short: 49.3 years (± 12.6); long years: 53.1 (± 10.9) Median age: Not reported Age range: Short 16–72 years; long 25–70 years Sex: Short n = 119 male (86.2%); long n = 68 male (87.2%) Race: Not reported Diagnosis: HF |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT or DT Type of device used: INCOR (Berlin Heart) Any comparison: Between SC and LC devices Duration of treatment: Various Percentage of patients using inotropes: Not reported Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – INCOR (Berlin Heart) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Cerebrovascular events Secondary outcomes: Deaths, transplants, ongoing support, ‘weaning’ from device (presumably for recovery of ventricular function) Method of assessing outcomes: Retrospective analysis of medical records Survival: Yes Adverse event: HRQoL: No measures reported Length of follow-up: Up to 4 yearsNumber of participantsIntervention short cannulaComparator, if presentScreenedTotal ‘screened’ = 273 not reported by groupNot reportedRandomised/includedThe first four patients received a LC device. From October 2002 until May 2004 the SC device was used. After May 2004 new LC device was progressively introduced, and use of the SC device was limited to patients with an extremely thin left ventricular wall at the insertion siteNot reportedExcluded57 not reported by groupNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reportedNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention short cannula | Comparator, if present | Screened | Total ‘screened’ = 273 not reported by group | Not reported | Randomised/included | The first four patients received a LC device. From October 2002 until May 2004 the SC device was used. After May 2004 new LC device was progressively introduced, and use of the SC device was limited to patients with an extremely thin left ventricular wall at the insertion site | Not reported | Excluded | 57 not reported by group | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention short cannula | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Total ‘screened’ = 273 not reported by group | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | The first four patients received a LC device. From October 2002 until May 2004 the SC device was used. After May 2004 new LC device was progressively introduced, and use of the SC device was limited to patients with an extremely thin left ventricular wall at the insertion site | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | 57 not reported by group | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ParameterSC group (n = 138)LC group (n = 78)p-valueAge (years), mean (range; SD)49.3 (16–72; ± 12.6)53.1 (25–70; ± 10.9)0.025Male gender, n (%)119 (86.2)68 (87.2)0.51Height (cm), mean (range; SD)176.3 (152–221; ± 8.8)176.1 (150–196; ± 9.6)0.887Weight (kg), mean (range; SD)80.2 (45–152; ± 15.3)81.1 (55–132; ± 15.6)0.667BSA (m2), mean (range; SD)1.96 (1.50–2.72; ± 0.20)1.97 (1.58–2.54; ± 0.21)0.777BMI (kg/m2), mean (range; SD)25.8 (15.57–42.55; ± 0.72)26.2 (16.95–37.75; ± 0.51)0.506Aetiology, n (%) Dilative CMP62 (44.9)37 (47.4)0.415 Ischaemic CMP45 (32.6)31 (39.7)0.506 Acute infarction16 (11.6)7 (9.0)0.362 Acute myocarditis9 (6.5)0 (0)0.016 Other6 (4.3)3 (3.8)LVEF (%), mean (range; SD)16.7 (4–40; ± 6.2)17.0 (5–40; ± 7.5)0.755LVEDD (mm), mean (range; SD)71.8 (33a –90; ± 10.7)74.1 (54–110; ± 11.4)0.3Cardiac index (l/minute/m2), mean (range; SD)1.7 (0.7–2.8a; ± 0.4)1.7 (0.8–3; ± 0.5)0.634mPAP (mmHg), mean (range; SD)36.7 (7–90; ± 11.5)37.4 (17–74; ± 13.6)0.744CVP (mmHg), mean (range; SD)14.6 (3–30; ± 5.5)14.1 (1–33; ± 7.0)0.625a One patient presented with severe RCMP. | Parameter | SC group (n = 138) | LC group (n = 78) | p-value | Age (years), mean (range; SD) | 49.3 (16–72; ± 12.6) | 53.1 (25–70; ± 10.9) | 0.025 | Male gender, n (%) | 119 (86.2) | 68 (87.2) | 0.51 | Height (cm), mean (range; SD) | 176.3 (152–221; ± 8.8) | 176.1 (150–196; ± 9.6) | 0.887 | Weight (kg), mean (range; SD) | 80.2 (45–152; ± 15.3) | 81.1 (55–132; ± 15.6) | 0.667 | BSA (m2), mean (range; SD) | 1.96 (1.50–2.72; ± 0.20) | 1.97 (1.58–2.54; ± 0.21) | 0.777 | BMI (kg/m2), mean (range; SD) | 25.8 (15.57–42.55; ± 0.72) | 26.2 (16.95–37.75; ± 0.51) | 0.506 | Aetiology, n (%) | Dilative CMP | 62 (44.9) | 37 (47.4) | 0.415 | Ischaemic CMP | 45 (32.6) | 31 (39.7) | 0.506 | Acute infarction | 16 (11.6) | 7 (9.0) | 0.362 | Acute myocarditis | 9 (6.5) | 0 (0) | 0.016 | Other | 6 (4.3) | 3 (3.8) | LVEF (%), mean (range; SD) | 16.7 (4–40; ± 6.2) | 17.0 (5–40; ± 7.5) | 0.755 | LVEDD (mm), mean (range; SD) | 71.8 (33a –90; ± 10.7) | 74.1 (54–110; ± 11.4) | 0.3 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2), mean (range; SD) | 1.7 (0.7–2.8a; ± 0.4) | 1.7 (0.8–3; ± 0.5) | 0.634 | mPAP (mmHg), mean (range; SD) | 36.7 (7–90; ± 11.5) | 37.4 (17–74; ± 13.6) | 0.744 | CVP (mmHg), mean (range; SD) | 14.6 (3–30; ± 5.5) | 14.1 (1–33; ± 7.0) | 0.625 | a One patient presented with severe RCMP. | |||||||||||||
| Parameter | SC group (n = 138) | LC group (n = 78) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years), mean (range; SD) | 49.3 (16–72; ± 12.6) | 53.1 (25–70; ± 10.9) | 0.025 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male gender, n (%) | 119 (86.2) | 68 (87.2) | 0.51 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Height (cm), mean (range; SD) | 176.3 (152–221; ± 8.8) | 176.1 (150–196; ± 9.6) | 0.887 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight (kg), mean (range; SD) | 80.2 (45–152; ± 15.3) | 81.1 (55–132; ± 15.6) | 0.667 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2), mean (range; SD) | 1.96 (1.50–2.72; ± 0.20) | 1.97 (1.58–2.54; ± 0.21) | 0.777 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2), mean (range; SD) | 25.8 (15.57–42.55; ± 0.72) | 26.2 (16.95–37.75; ± 0.51) | 0.506 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aetiology, n (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dilative CMP | 62 (44.9) | 37 (47.4) | 0.415 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic CMP | 45 (32.6) | 31 (39.7) | 0.506 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acute infarction | 16 (11.6) | 7 (9.0) | 0.362 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acute myocarditis | 9 (6.5) | 0 (0) | 0.016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 6 (4.3) | 3 (3.8) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF (%), mean (range; SD) | 16.7 (4–40; ± 6.2) | 17.0 (5–40; ± 7.5) | 0.755 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEDD (mm), mean (range; SD) | 71.8 (33a –90; ± 10.7) | 74.1 (54–110; ± 11.4) | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2), mean (range; SD) | 1.7 (0.7–2.8a; ± 0.4) | 1.7 (0.8–3; ± 0.5) | 0.634 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| mPAP (mmHg), mean (range; SD) | 36.7 (7–90; ± 11.5) | 37.4 (17–74; ± 13.6) | 0.744 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CVP (mmHg), mean (range; SD) | 14.6 (3–30; ± 5.5) | 14.1 (1–33; ± 7.0) | 0.625 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a One patient presented with severe RCMP. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
K–M survival analysis: Probability of survival % alive vs. time (data read from graph):At risk:t = 0t = 0.5t = 1t = 1.5t = 2t = 3t = 3.57824114321138502453p = 0.27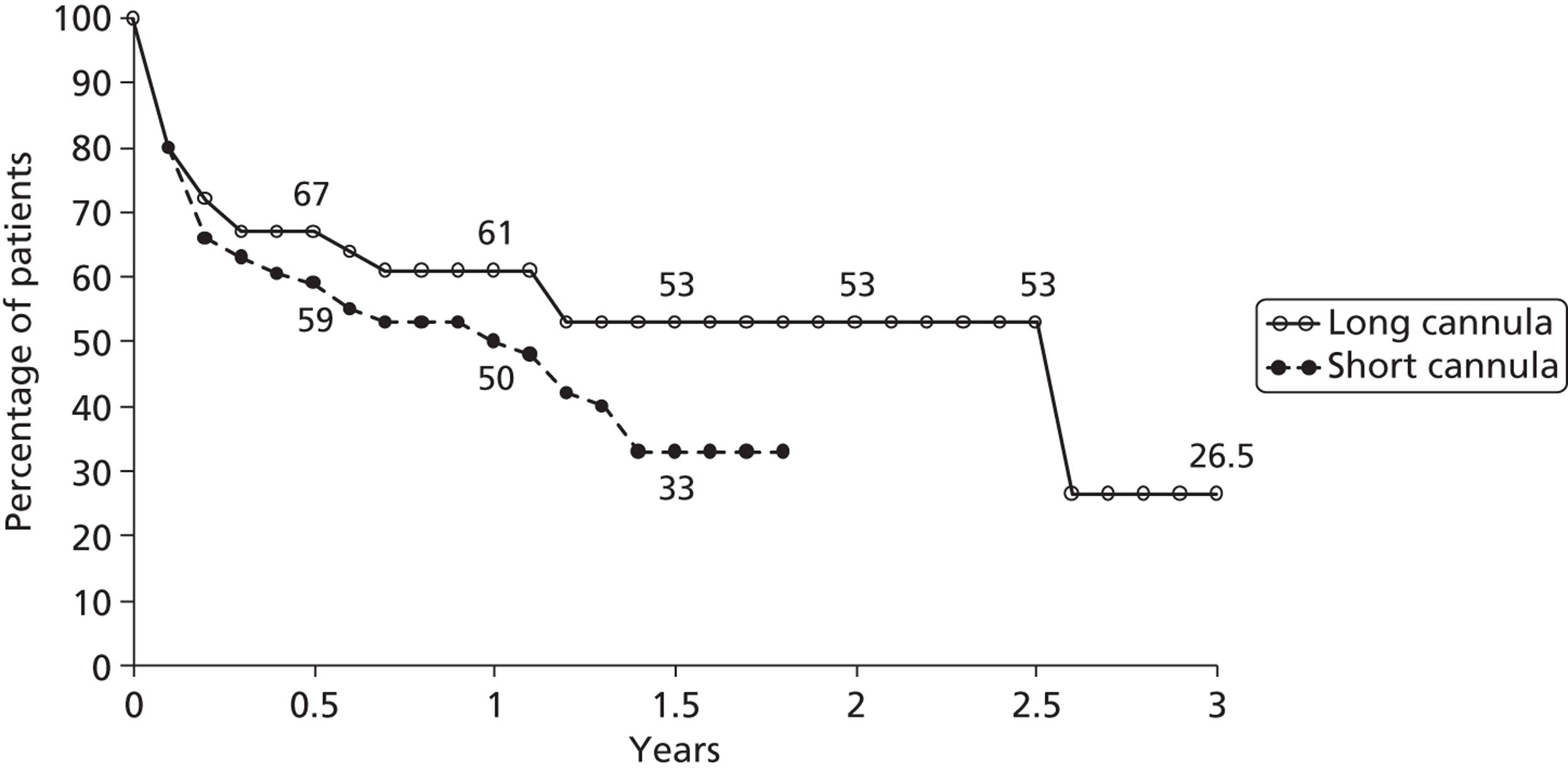 Note: it was not clear if patients were censored on receipt of a HT, and therefore the survival data is difficultr to interpret. In addition, the proportion of DTR vs. BTT patients was different between groups but these proportions were not reported At the end of the observation period, overall survival was better in the LC group as compared with the SC group (SC 52.9%; LC 63.4%; p = 0.05) Survival rates based on the K–M survival curves were (p = 0.27): At l year: SC 53%; LC 61% At 2 years: SC 33%; LC 50% At end of follow-up overall deceased were:ConditionSC group (n = 138)LC group (n = 78)p-valueDeceased, n (%)65 (47.1)27 (34.6)0.05Not deceased, n (%)73 (52.9)51 (65.4) |
At risk: | t = 0 | t = 0.5 | t = 1 | t = 1.5 | t = 2 | t = 3 | t = 3.5 | 78 | 24 | 11 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 138 | 50 | 24 | 5 | 3 | p = 0.27 | Condition | SC group (n = 138) | LC group (n = 78) | p-value | Deceased, n (%) | 65 (47.1) | 27 (34.6) | 0.05 | Not deceased, n (%) | 73 (52.9) | 51 (65.4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At risk: | t = 0 | t = 0.5 | t = 1 | t = 1.5 | t = 2 | t = 3 | t = 3.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 78 | 24 | 11 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 138 | 50 | 24 | 5 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p = 0.27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Condition | SC group (n = 138) | LC group (n = 78) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deceased, n (%) | 65 (47.1) | 27 (34.6) | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not deceased, n (%) | 73 (52.9) | 51 (65.4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Difference in VAD support time (table) was explained by an increased waiting time on the transplant list, a more recent implantation date, and a larger number of DT patients in the LC group. Consequently, fewer patients in the LC groups underwent a HT (table)OutcomeSC group (n = 138)LC group (n = 78)p-valueSupport interval (days), mean (range; SD)186 (1–805; ± 187)171 (0–1128; ± 211)0.603Outcome of all, n (%) Ongoing support7 (5.1)30 (38.5)< 0.001 HT60 (43.5)18 (23.1)< 0.002 Weaned from device6 (4.3)3 (3.8)0.582 Deceased65 (47.1)27 (34.6)0.05 | Outcome | SC group (n = 138) | LC group (n = 78) | p-value | Support interval (days), mean (range; SD) | 186 (1–805; ± 187) | 171 (0–1128; ± 211) | 0.603 | Outcome of all, n (%) | Ongoing support | 7 (5.1) | 30 (38.5) | < 0.001 | HT | 60 (43.5) | 18 (23.1) | < 0.002 | Weaned from device | 6 (4.3) | 3 (3.8) | 0.582 | Deceased | 65 (47.1) | 27 (34.6) | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcome | SC group (n = 138) | LC group (n = 78) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Support interval (days), mean (range; SD) | 186 (1–805; ± 187) | 171 (0–1128; ± 211) | 0.603 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcome of all, n (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ongoing support | 7 (5.1) | 30 (38.5) | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HT | 60 (43.5) | 18 (23.1) | < 0.002 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weaned from device | 6 (4.3) | 3 (3.8) | 0.582 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deceased | 65 (47.1) | 27 (34.6) | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Freedom from strokeEventSC group (n = 138)LC group (n = 78)p-valueStroke, n354 Patients effected, n (%)32 (23.2)3 (3.8)< 0.001 Events per patient-year0.50.11 Time to event (days), mean (range; SD)73 (2–429; ± 86)38 (4–66; ± 31)Intracerebral bleeding, n154 Patients effected, n (%)14 (10.1)4 (5.1)0.152 Events per patient-year0.210.11 Time to event (days), mean (range; SD)118 (18–330; ± 110)271 (15–933; ± 442)Cerebral bleeding confirmed by CT scan. Freedom from stroke K–M analysis (data read from graph):At risk:t = 0t = 0.5t = 1t = 1.5t = 2t = 3t = 3.57824114321138502453 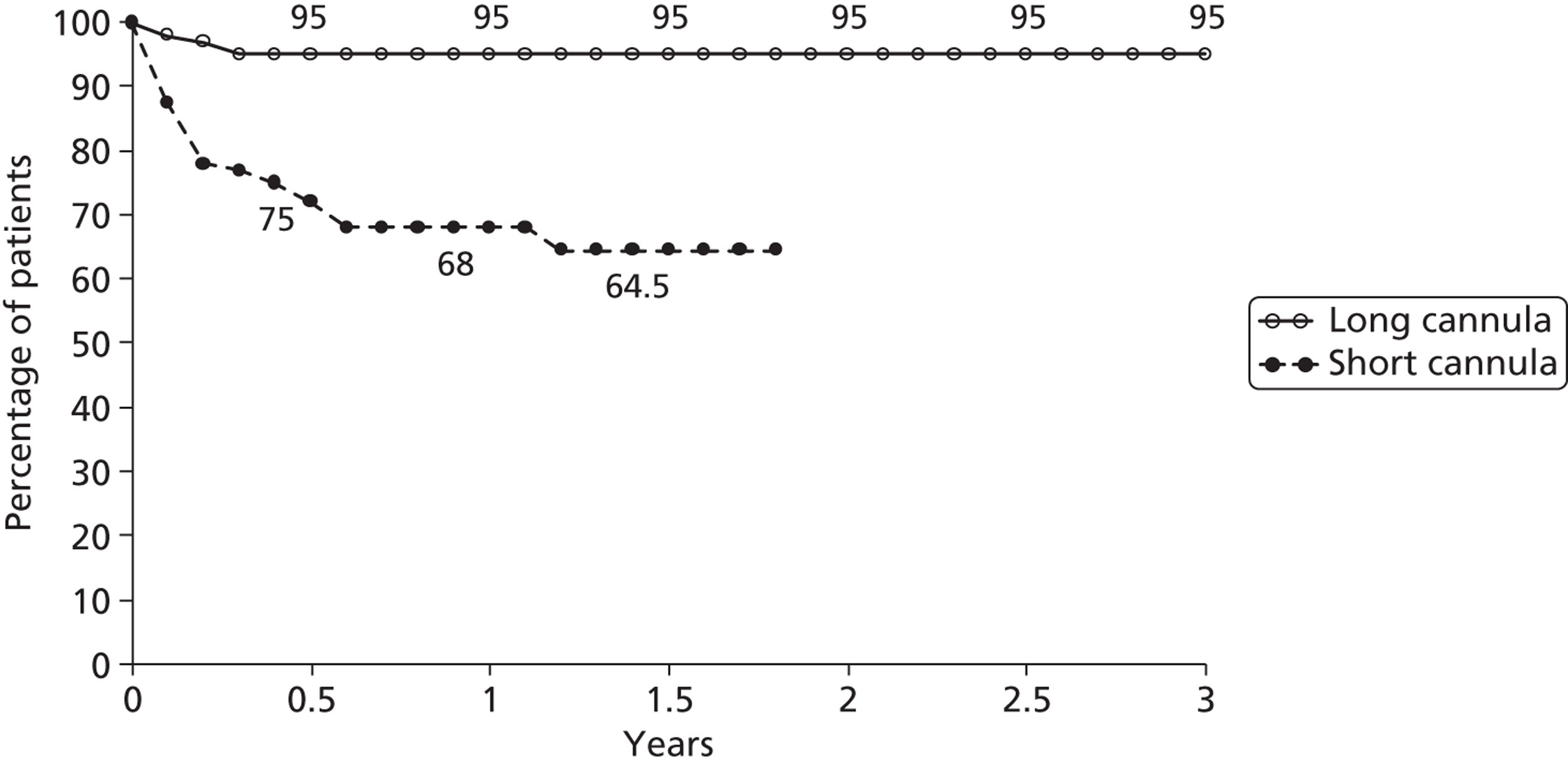 Cox proportional hazards model for freedom from stroke (clinically diagnosed)Variablep-valueInflow cannula0.005Age at implant0.261Height0.320Weight0.605Gender0.607Myocarditis0.936Acute infarction0.937Ischaemic CMP0.944 Note: DT BTT not testede as variable. Proportional hazards assumption not tested or not reported Event rates for cerebral bleeding: SC group 10.1%; LC group 5.1% (p = 0.152) Event per patient-year: SC group 0.11; LC goup 0.21 The RR of intracerebral bleeding was 1.98 times higher in the SC group |
Event | SC group (n = 138) | LC group (n = 78) | p-value | Stroke, n | 35 | 4 | Patients effected, n (%) | 32 (23.2) | 3 (3.8) | < 0.001 | Events per patient-year | 0.5 | 0.11 | Time to event (days), mean (range; SD) | 73 (2–429; ± 86) | 38 (4–66; ± 31) | Intracerebral bleeding, n | 15 | 4 | Patients effected, n (%) | 14 (10.1) | 4 (5.1) | 0.152 | Events per patient-year | 0.21 | 0.11 | Time to event (days), mean (range; SD) | 118 (18–330; ± 110) | 271 (15–933; ± 442) | Cerebral bleeding confirmed by CT scan. | At risk: | t = 0 | t = 0.5 | t = 1 | t = 1.5 | t = 2 | t = 3 | t = 3.5 | 78 | 24 | 11 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 138 | 50 | 24 | 5 | 3 | Variable | p-value | Inflow cannula | 0.005 | Age at implant | 0.261 | Height | 0.320 | Weight | 0.605 | Gender | 0.607 | Myocarditis | 0.936 | Acute infarction | 0.937 | Ischaemic CMP | 0.944 | |||||||||||||
| Event | SC group (n = 138) | LC group (n = 78) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke, n | 35 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients effected, n (%) | 32 (23.2) | 3 (3.8) | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Events per patient-year | 0.5 | 0.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time to event (days), mean (range; SD) | 73 (2–429; ± 86) | 38 (4–66; ± 31) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intracerebral bleeding, n | 15 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients effected, n (%) | 14 (10.1) | 4 (5.1) | 0.152 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Events per patient-year | 0.21 | 0.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time to event (days), mean (range; SD) | 118 (18–330; ± 110) | 271 (15–933; ± 442) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cerebral bleeding confirmed by CT scan. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At risk: | t = 0 | t = 0.5 | t = 1 | t = 1.5 | t = 2 | t = 3 | t = 3.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 78 | 24 | 11 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 138 | 50 | 24 | 5 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variable | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inflow cannula | 0.005 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age at implant | 0.261 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Height | 0.320 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight | 0.605 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gender | 0.607 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myocarditis | 0.936 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acute infarction | 0.937 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic CMP | 0.944 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of deathSC group (n = 138)LC group (n = 78)p-valueTotal, n6527Multiorgan failure, n (%)34 (52.3)14 (51.9)0.167Cerebrovascular event, n (%)9 (13.8)4 (14.8)0.464Cancer, n (%)2 (3.1)0Trauma, n (%)2 (3.1)0Right ventricular failure artery, n (%)4 (6.2)4 (14.8)Pulmonary artery embolus, n (%)1 (1.5)0Bleeding, n (%)1 (1.5)0Other, n (%)10 (15.4)5 (18.5)Unknown, n (%)2 (3.1)0 | Cause of death | SC group (n = 138) | LC group (n = 78) | p-value | Total, n | 65 | 27 | Multiorgan failure, n (%) | 34 (52.3) | 14 (51.9) | 0.167 | Cerebrovascular event, n (%) | 9 (13.8) | 4 (14.8) | 0.464 | Cancer, n (%) | 2 (3.1) | 0 | Trauma, n (%) | 2 (3.1) | 0 | Right ventricular failure artery, n (%) | 4 (6.2) | 4 (14.8) | Pulmonary artery embolus, n (%) | 1 (1.5) | 0 | Bleeding, n (%) | 1 (1.5) | 0 | Other, n (%) | 10 (15.4) | 5 (18.5) | Unknown, n (%) | 2 (3.1) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death | SC group (n = 138) | LC group (n = 78) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total, n | 65 | 27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Multiorgan failure, n (%) | 34 (52.3) | 14 (51.9) | 0.167 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cerebrovascular event, n (%) | 9 (13.8) | 4 (14.8) | 0.464 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cancer, n (%) | 2 (3.1) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trauma, n (%) | 2 (3.1) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right ventricular failure artery, n (%) | 4 (6.2) | 4 (14.8) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary artery embolus, n (%) | 1 (1.5) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding, n (%) | 1 (1.5) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other, n (%) | 10 (15.4) | 5 (18.5) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unknown, n (%) | 2 (3.1) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INCOR patients with a long inflow cannula demonstrated significantly better survival and a significantly lower incidence of cerebrovascular adverse events. The overall rate of cerebrovascular complications has declined to a very acceptable level, rendering the INCOR an excellent tool for long-term mechanical support in cases of acute or chronic HF | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K–M analysis of survival difference was not statistically significant. Groups were not sufficiently comparable for a rigorous comparison (received implant at different times during surgical learning curves) and either as DT or BTT. Proportional hazards assumption not tested. Direction of evidence tends to favour the author's conclusions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Starling 201152
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Starling Year of publication: 2011 Country: USA Study design: Prospective post-approval (FDA) evaluation following a multicentre clinical trial Study setting: Multicentre Number of centres: 77 Duration of study: Patients enrolled from September 2007 to February 2009 Follow-up period: At least 1 year Funding: Unclear |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The aim was to determine whether or not results with the HMII LVAD in a commercial setting are comparable to other available devices for the same indication | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 304 Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported Inclusion criteria: First 169 consecutive HMII patients after FDA approval enrolled in INTERMACS comparator group; 135 (80%) received the electric HMXVE LVAD and 34 (20%) received the pneumatic Thoratec Implantable VAD (Thoratec Inc., Pleasanton, CA, USA). Population eligible or likely to become eligible for HT Exclusion criteria: Unclear Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): Not reported Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: HMII 78% male; comparator 83% male Race: n (%) – Caucasian HMII 125 (74), comparator 113 (67); African American HMII 29 (17), comparator 37 (22); other HMII 15 (9), comparator 19 (11) Diagnosis: HF |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: HF BTT with LVAD Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: HMII vs. other devices Duration of treatment: Average support duration for HMII was 306 ± 173 days (median 386 days), significantly longer than comparator at 207 ± 188 days (median 152 days). Cumulative follow-up duration was 142.0 (HMII) and 96.2 (comparator) patient-years of support Percentage of patients using inotropes: 80% HMII; 89% comparator Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Survival to transplant, recovery of the heart, or ongoing support at 6 months Secondary outcomes: QoL (EQ-5D/VAS), adverse events Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records and prospective data collection Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: Yes Length of follow-up: At least 12 months or to transplant or deathNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reportedNot reportedRandomised/includedHMII (n = 169)Comparator (n = 169)ExcludedNot reportedNot reportedMissing participantsNot reportedNot reportedWithdrawalsNot reportedNot reported |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported | Not reported | Randomised/included | HMII (n = 169) | Comparator (n = 169) | Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | HMII (n = 169) | Comparator (n = 169) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demographic parameterHMII (n = 169)Comparator (n = 169)p-valueMale subjects131 (78)141 (83)0.217Age (years) 0–183 (2)6 (4)0.631 19–3926 (15)22 (13) 40–5981 (48)87 (51) 60–7959 (35)54 (32)Race Caucasian125 (74)113 (67)0.380 African American29 (17)37 (22) Other15 (9)19 (11)BSA (m2)2.03 ± 0.252.06 ± 0.250.182INTERMACS profile< 0.001a 141 (24)66 (39.0) 263 (37)75 (44) 333 (20)8 (5) 421 (12)12 (7) 5, 6, 711 (7)8 (5)Haemodynamic status before implant Heart rate (b.p.m.)88.0 ± 18.4 (167)94.1 ± 20.3 (167)0.005a BP systolic (mmHg)97.8 ± 13.8 (167)99.9 ± 16.0 (168)0.214 BP diastolic (mmHg)60.4 ± 11.1 (165)61.5 ± 12.1 (168)0.404 PAP systolic (mmHg)48.6 ± 14.4 (106)50.0 ± 14.4 (101)0.511 PAP diastolic (mmHg)23.8 ± 7.5 (106)26.7 ± 8.3 (102)0.010a RA pressure (mmHg)12.4 ± 6.7 (92)14.0 ± 7.4 (89)0.131 PCWP (mmHg)24.2 ± 7.5 (68)25.3 ± 9.4 (69)0.451 Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)2.2 ± 0.7 (96)2.1 ± 0.7 (94)0.497Laboratory values BUN (mg/dl)27.6 ± 14.3 (169)31.9 ± 18.8 (167)0.019a Creatinine (mg/dl)1.33 ± 0.5 (169)1.67 ± 0.9 (169)< 0.0001a Total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.57 ± 1.9 (155)1.64 ± 1.7 (145)0.756 Sodium (mg/l)134.6 ± 5.0 (169)134.0 ± 5.4 (169)0.260 INR1.39 ± 0.5 (165)1.46 ± 0.5 (152)0.251 White blood cell (K/sl)9.4 ± 4.3 (169)10.6 ± 5.3 (168)0.018a Platelets (K/sl)212 ± 102 (169)203 ± 96 (169)0.412 AST (s/l)91 ± 213 (155)210 ± 648 (145)0.035a ALT (s/l)126 ± 361 (154)188 ± 539 (145)0.249 Cholesterol (mg/dl)123.7 ± 39.7 (81)120.0 ± 38.9 (68)0.566 Potassium (mEq/l)4.1 ± 0.5 (169)4.1 ± 0.6 (168)0.336 Haemoglobin (mg/dl)11.3 ± 2.0 (168)11.1 ± 2.0 (167)0.277 Albumin (mg/dl)3.4 ± 0.6 (148)3.3 ± 0.7 (140)0.212 BNP (pg/ml)1182 ± 1074 (58)1306 ± 1399 (72)0.568Concomitant therapies Prior mechanical circulatory support10 (6)6 (4)0.443 IABP15 (10)56 (33)0.116 Mechanical ventilation16 (10)27 (16)0.102 ACE inhibitors95 (56)70 (41)0.009 Beta-blockers122 (72)110 (65)0.197 Intravenous inotropic agents136 (80)151 (89)0.033 Two or more inotropic agents58 (34)86 (51)0.003a Fewer HMII patients were in profile 1 (acute cardiogenic shock) compared with the comparison group and more in profiles 3 (stable on inotropes) and 4 (symptomatic on oral medications).Values are n (%) or mean ± SD (n). | Demographic parameter | HMII (n = 169) | Comparator (n = 169) | p-value | Male subjects | 131 (78) | 141 (83) | 0.217 | Age (years) | 0–18 | 3 (2) | 6 (4) | 0.631 | 19–39 | 26 (15) | 22 (13) | 40–59 | 81 (48) | 87 (51) | 60–79 | 59 (35) | 54 (32) | Race | Caucasian | 125 (74) | 113 (67) | 0.380 | African American | 29 (17) | 37 (22) | Other | 15 (9) | 19 (11) | BSA (m2) | 2.03 ± 0.25 | 2.06 ± 0.25 | 0.182 | INTERMACS profile | < 0.001a | 1 | 41 (24) | 66 (39.0) | 2 | 63 (37) | 75 (44) | 3 | 33 (20) | 8 (5) | 4 | 21 (12) | 12 (7) | 5, 6, 7 | 11 (7) | 8 (5) | Haemodynamic status before implant | Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 88.0 ± 18.4 (167) | 94.1 ± 20.3 (167) | 0.005a | BP systolic (mmHg) | 97.8 ± 13.8 (167) | 99.9 ± 16.0 (168) | 0.214 | BP diastolic (mmHg) | 60.4 ± 11.1 (165) | 61.5 ± 12.1 (168) | 0.404 | PAP systolic (mmHg) | 48.6 ± 14.4 (106) | 50.0 ± 14.4 (101) | 0.511 | PAP diastolic (mmHg) | 23.8 ± 7.5 (106) | 26.7 ± 8.3 (102) | 0.010a | RA pressure (mmHg) | 12.4 ± 6.7 (92) | 14.0 ± 7.4 (89) | 0.131 | PCWP (mmHg) | 24.2 ± 7.5 (68) | 25.3 ± 9.4 (69) | 0.451 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.2 ± 0.7 (96) | 2.1 ± 0.7 (94) | 0.497 | Laboratory values | BUN (mg/dl) | 27.6 ± 14.3 (169) | 31.9 ± 18.8 (167) | 0.019a | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.33 ± 0.5 (169) | 1.67 ± 0.9 (169) | < 0.0001a | Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.57 ± 1.9 (155) | 1.64 ± 1.7 (145) | 0.756 | Sodium (mg/l) | 134.6 ± 5.0 (169) | 134.0 ± 5.4 (169) | 0.260 | INR | 1.39 ± 0.5 (165) | 1.46 ± 0.5 (152) | 0.251 | White blood cell (K/sl) | 9.4 ± 4.3 (169) | 10.6 ± 5.3 (168) | 0.018a | Platelets (K/sl) | 212 ± 102 (169) | 203 ± 96 (169) | 0.412 | AST (s/l) | 91 ± 213 (155) | 210 ± 648 (145) | 0.035a | ALT (s/l) | 126 ± 361 (154) | 188 ± 539 (145) | 0.249 | Cholesterol (mg/dl) | 123.7 ± 39.7 (81) | 120.0 ± 38.9 (68) | 0.566 | Potassium (mEq/l) | 4.1 ± 0.5 (169) | 4.1 ± 0.6 (168) | 0.336 | Haemoglobin (mg/dl) | 11.3 ± 2.0 (168) | 11.1 ± 2.0 (167) | 0.277 | Albumin (mg/dl) | 3.4 ± 0.6 (148) | 3.3 ± 0.7 (140) | 0.212 | BNP (pg/ml) | 1182 ± 1074 (58) | 1306 ± 1399 (72) | 0.568 | Concomitant therapies | Prior mechanical circulatory support | 10 (6) | 6 (4) | 0.443 | IABP | 15 (10) | 56 (33) | 0.116 | Mechanical ventilation | 16 (10) | 27 (16) | 0.102 | ACE inhibitors | 95 (56) | 70 (41) | 0.009 | Beta-blockers | 122 (72) | 110 (65) | 0.197 | Intravenous inotropic agents | 136 (80) | 151 (89) | 0.033 | Two or more inotropic agents | 58 (34) | 86 (51) | 0.003 | a Fewer HMII patients were in profile 1 (acute cardiogenic shock) compared with the comparison group and more in profiles 3 (stable on inotropes) and 4 (symptomatic on oral medications). | Values are n (%) or mean ± SD (n). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demographic parameter | HMII (n = 169) | Comparator (n = 169) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male subjects | 131 (78) | 141 (83) | 0.217 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0–18 | 3 (2) | 6 (4) | 0.631 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19–39 | 26 (15) | 22 (13) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40–59 | 81 (48) | 87 (51) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 60–79 | 59 (35) | 54 (32) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Race | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caucasian | 125 (74) | 113 (67) | 0.380 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| African American | 29 (17) | 37 (22) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 15 (9) | 19 (11) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 2.03 ± 0.25 | 2.06 ± 0.25 | 0.182 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INTERMACS profile | < 0.001a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 41 (24) | 66 (39.0) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 63 (37) | 75 (44) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 33 (20) | 8 (5) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 21 (12) | 12 (7) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5, 6, 7 | 11 (7) | 8 (5) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemodynamic status before implant | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 88.0 ± 18.4 (167) | 94.1 ± 20.3 (167) | 0.005a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BP systolic (mmHg) | 97.8 ± 13.8 (167) | 99.9 ± 16.0 (168) | 0.214 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BP diastolic (mmHg) | 60.4 ± 11.1 (165) | 61.5 ± 12.1 (168) | 0.404 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PAP systolic (mmHg) | 48.6 ± 14.4 (106) | 50.0 ± 14.4 (101) | 0.511 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PAP diastolic (mmHg) | 23.8 ± 7.5 (106) | 26.7 ± 8.3 (102) | 0.010a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RA pressure (mmHg) | 12.4 ± 6.7 (92) | 14.0 ± 7.4 (89) | 0.131 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 24.2 ± 7.5 (68) | 25.3 ± 9.4 (69) | 0.451 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 2.2 ± 0.7 (96) | 2.1 ± 0.7 (94) | 0.497 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Laboratory values | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 27.6 ± 14.3 (169) | 31.9 ± 18.8 (167) | 0.019a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.33 ± 0.5 (169) | 1.67 ± 0.9 (169) | < 0.0001a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.57 ± 1.9 (155) | 1.64 ± 1.7 (145) | 0.756 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sodium (mg/l) | 134.6 ± 5.0 (169) | 134.0 ± 5.4 (169) | 0.260 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INR | 1.39 ± 0.5 (165) | 1.46 ± 0.5 (152) | 0.251 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| White blood cell (K/sl) | 9.4 ± 4.3 (169) | 10.6 ± 5.3 (168) | 0.018a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets (K/sl) | 212 ± 102 (169) | 203 ± 96 (169) | 0.412 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST (s/l) | 91 ± 213 (155) | 210 ± 648 (145) | 0.035a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT (s/l) | 126 ± 361 (154) | 188 ± 539 (145) | 0.249 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cholesterol (mg/dl) | 123.7 ± 39.7 (81) | 120.0 ± 38.9 (68) | 0.566 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Potassium (mEq/l) | 4.1 ± 0.5 (169) | 4.1 ± 0.6 (168) | 0.336 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemoglobin (mg/dl) | 11.3 ± 2.0 (168) | 11.1 ± 2.0 (167) | 0.277 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albumin (mg/dl) | 3.4 ± 0.6 (148) | 3.3 ± 0.7 (140) | 0.212 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BNP (pg/ml) | 1182 ± 1074 (58) | 1306 ± 1399 (72) | 0.568 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concomitant therapies | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prior mechanical circulatory support | 10 (6) | 6 (4) | 0.443 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP | 15 (10) | 56 (33) | 0.116 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 16 (10) | 27 (16) | 0.102 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACE inhibitors | 95 (56) | 70 (41) | 0.009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beta-blockers | 122 (72) | 110 (65) | 0.197 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intravenous inotropic agents | 136 (80) | 151 (89) | 0.033 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Two or more inotropic agents | 58 (34) | 86 (51) | 0.003 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Fewer HMII patients were in profile 1 (acute cardiogenic shock) compared with the comparison group and more in profiles 3 (stable on inotropes) and 4 (symptomatic on oral medications). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Values are n (%) or mean ± SD (n). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Competing outcomes (HMII)MonthsTransplanted or recovered or ongoing VAD, nOngoing LVAD, nTransplanted, nDead, nExplanted/recovery, nHMIIComparatorHMIIComparatorHMIIComparatorHMIIComparatorHMIIComparator69080694520349191/11/11286745124344713221/14/2 K–M survival for patients with INTERMACS profiles 1, 2–3 and 4–7GroupProfile6-month survival12-month survivalp-value HMII vs. comparatorp-value between profilesHMII186.9% ± 5.5% (27)86.9% ± 5.5% (22)0.01530.80382–390.0% ± 3.2% (66)83.7% ± 4.2% (48)0.07244–793.0% ± 4.8% (23)83.8% ± 7.6% (17)0.2814Comparator170.9% ± 5.9% (24)64.2% ± 7.0% (16)0.31492–384.7% ± 4.3% (41)75.0% ± 6.6% (18)4–783.1% ± 9.1% (12)74.8% ± 11.4% (3) K–M plot data read from graph 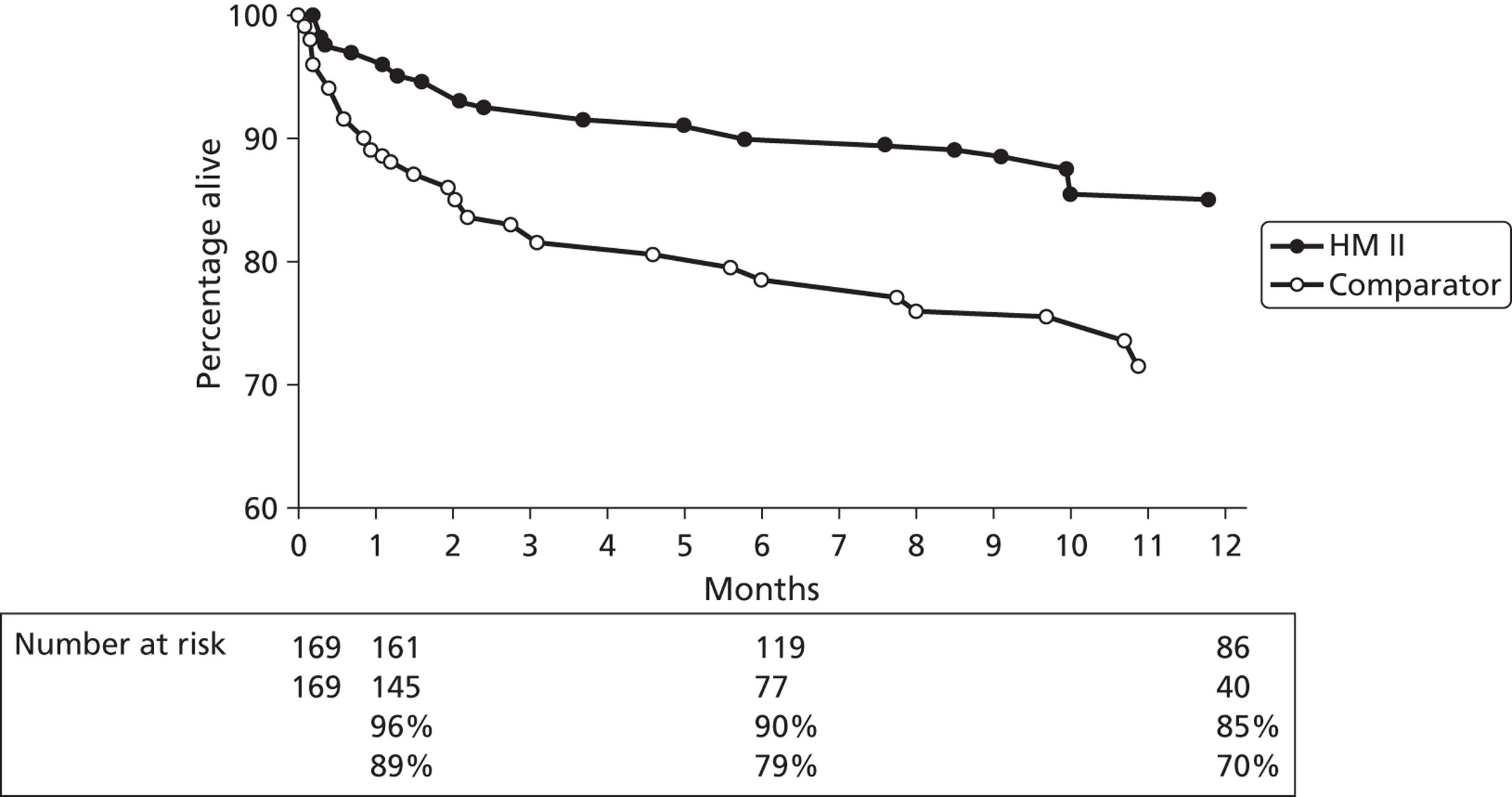 Temporal comparison of BTT outcomes with HMII LVADStudyEnrolment periodn30-day operative mortalityTransplantation recovery or ongoing VADK–M survival at 1 yearHMII pivotal trial Miller et al.70March 2005 to May 20061330.110.790.68HMII pivotal trial Pagani et al.71March 2005 to March 20072810.080.840.74Post-approval INTERMACS registry study (current study)April 2008 to August 20081690.040.910.85 |
Months | Transplanted or recovered or ongoing VAD, n | Ongoing LVAD, n | Transplanted, n | Dead, n | Explanted/recovery, n | HMII | Comparator | HMII | Comparator | HMII | Comparator | HMII | Comparator | HMII | Comparator | 6 | 90 | 80 | 69 | 45 | 20 | 34 | 9 | 19 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 12 | 86 | 74 | 51 | 24 | 34 | 47 | 13 | 22 | 1/1 | 4/2 | Group | Profile | 6-month survival | 12-month survival | p-value HMII vs. comparator | p-value between profiles | HMII | 1 | 86.9% ± 5.5% (27) | 86.9% ± 5.5% (22) | 0.0153 | 0.8038 | 2–3 | 90.0% ± 3.2% (66) | 83.7% ± 4.2% (48) | 0.0724 | 4–7 | 93.0% ± 4.8% (23) | 83.8% ± 7.6% (17) | 0.2814 | Comparator | 1 | 70.9% ± 5.9% (24) | 64.2% ± 7.0% (16) | 0.3149 | 2–3 | 84.7% ± 4.3% (41) | 75.0% ± 6.6% (18) | 4–7 | 83.1% ± 9.1% (12) | 74.8% ± 11.4% (3) | Study | Enrolment period | n | 30-day operative mortality | Transplantation recovery or ongoing VAD | K–M survival at 1 year | HMII pivotal trial Miller et al.70 | March 2005 to May 2006 | 133 | 0.11 | 0.79 | 0.68 | HMII pivotal trial Pagani et al.71 | March 2005 to March 2007 | 281 | 0.08 | 0.84 | 0.74 | Post-approval INTERMACS registry study (current study) | April 2008 to August 2008 | 169 | 0.04 | 0.91 | 0.85 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Months | Transplanted or recovered or ongoing VAD, n | Ongoing LVAD, n | Transplanted, n | Dead, n | Explanted/recovery, n | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII | Comparator | HMII | Comparator | HMII | Comparator | HMII | Comparator | HMII | Comparator | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 90 | 80 | 69 | 45 | 20 | 34 | 9 | 19 | 1/1 | 1/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | 86 | 74 | 51 | 24 | 34 | 47 | 13 | 22 | 1/1 | 4/2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | Profile | 6-month survival | 12-month survival | p-value HMII vs. comparator | p-value between profiles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII | 1 | 86.9% ± 5.5% (27) | 86.9% ± 5.5% (22) | 0.0153 | 0.8038 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2–3 | 90.0% ± 3.2% (66) | 83.7% ± 4.2% (48) | 0.0724 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4–7 | 93.0% ± 4.8% (23) | 83.8% ± 7.6% (17) | 0.2814 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comparator | 1 | 70.9% ± 5.9% (24) | 64.2% ± 7.0% (16) | 0.3149 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2–3 | 84.7% ± 4.3% (41) | 75.0% ± 6.6% (18) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4–7 | 83.1% ± 9.1% (12) | 74.8% ± 11.4% (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Study | Enrolment period | n | 30-day operative mortality | Transplantation recovery or ongoing VAD | K–M survival at 1 year | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII pivotal trial Miller et al.70 | March 2005 to May 2006 | 133 | 0.11 | 0.79 | 0.68 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII pivotal trial Pagani et al.71 | March 2005 to March 2007 | 281 | 0.08 | 0.84 | 0.74 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post-approval INTERMACS registry study (current study) | April 2008 to August 2008 | 169 | 0.04 | 0.91 | 0.85 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-minute walk test: insufficient participants completed test Support duration: HMII mean 306 ± 173 days, median 186 days; comparator mean 207 ± 188 days, median 152 days Cumulative follow-up duration of support: HMII 142 patient-years and comparator 96.2 patient-years |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EventHMII (n = 169) cumulative142.0 patient-years; mean duration 306 ± 173 daysComparator (n = 169) cumulative96.2 patient-years; mean duration207 ± 188 daysRR95% CIp-valuen% patientsEvents (n)Events/patient-yearn% patientsEvents (n)Events/patient-yearBleeding7544.42041.446538.51721.790.800.58 to 1.120.1931Infectiona7846.21421.007242.62042.120.470.34 to 0.66< 0.0001bDriveline3017.8450.322716.0440.460.690.42 to 1.130.1419Pump pocket31.840.03127.1160.170.170.06 to 0.520.0006bPump interior10.620.0100.000.000.2466Blood3218.9470.333621.3710.740.450.29 to 0.700.0004bLine sepsis31.830.0295.3100.100.200.05 to 0.760.0096bOther infectiona4929.0860.615029.61191.240.490.34 to 0.720.0002bStroke116.5110.0895.3110.110.680.28 to 1.630.3821Haemorrhagic21.220.0121.220.020.680.09 to 4.890.6986Embolic84.780.0663.670.070.770.27 to 2.210.6323Unknown10.610.0121.220.020.340.03 to 3.790.3584Other neurological dysfunction74.170.05137.7160.170.300.12 to 0.750.0071bMyocardial infarction31.830.0210.610.012.030.21 to 19.80.5342Pericardial drainage1710.1200.142011.8220.230.620.32 to 1.190.1477Psychiatric episode148.3170.121710.1230.240.500.25 to 0.990.0435bRenal dysfunction1710.1190.132112.4280.290.460.24 to 0.870.0156bHepatic dysfunction116.5120.0895.3110.110.740.31 to 1.740.4899Respiratory failure3420.1410.294325.4530.550.520.32 to 0.850.0084bRight HFc2514.8260.182011.8220.230.800.43 to 1.490.4859Haemolysis53.050.0421.220.021.690.32 to 8.910.5300Hypertension31.840.032615.4350.360.080.03 to 0.23< 0.0001bCardiac arrhythmia4627.2690.494727.8850.880.550.37 to 0.830.0041bArterial non-CNS thromboembolism10.610.0121.230.030.230.02 to 2.200.1637Venous thromboembolism116.5130.09137.7150.160.590.27 to 1.290.1820Wound dehiscence31.830.0231.830.030.680.13 to 3.430.6368Device replacement21.220.01137.7130.140.100.02 to 0.470.0005a Other infections include pneumonia, urinary tract, mediastinum, peripheral wound and unknown.b Statistically significant.c Including 5 (3.0%) HMII patients and 21 (12%) comparator patients requiring RVAD support. | Event | HMII (n = 169) cumulative 142.0 patient-years; mean duration 306 ± 173 days |
Comparator (n = 169) cumulative 96.2 patient-years; mean duration 207 ± 188 days |
RR | 95% CI | p-value | n | % patients | Events (n) | Events/patient-year | n | % patients | Events (n) | Events/patient-year | Bleeding | 75 | 44.4 | 204 | 1.44 | 65 | 38.5 | 172 | 1.79 | 0.80 | 0.58 to 1.12 | 0.1931 | Infectiona | 78 | 46.2 | 142 | 1.00 | 72 | 42.6 | 204 | 2.12 | 0.47 | 0.34 to 0.66 | < 0.0001b | Driveline | 30 | 17.8 | 45 | 0.32 | 27 | 16.0 | 44 | 0.46 | 0.69 | 0.42 to 1.13 | 0.1419 | Pump pocket | 3 | 1.8 | 4 | 0.03 | 12 | 7.1 | 16 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.06 to 0.52 | 0.0006b | Pump interior | 1 | 0.6 | 2 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.2466 | Blood | 32 | 18.9 | 47 | 0.33 | 36 | 21.3 | 71 | 0.74 | 0.45 | 0.29 to 0.70 | 0.0004b | Line sepsis | 3 | 1.8 | 3 | 0.02 | 9 | 5.3 | 10 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.05 to 0.76 | 0.0096b | Other infectiona | 49 | 29.0 | 86 | 0.61 | 50 | 29.6 | 119 | 1.24 | 0.49 | 0.34 to 0.72 | 0.0002b | Stroke | 11 | 6.5 | 11 | 0.08 | 9 | 5.3 | 11 | 0.11 | 0.68 | 0.28 to 1.63 | 0.3821 | Haemorrhagic | 2 | 1.2 | 2 | 0.01 | 2 | 1.2 | 2 | 0.02 | 0.68 | 0.09 to 4.89 | 0.6986 | Embolic | 8 | 4.7 | 8 | 0.06 | 6 | 3.6 | 7 | 0.07 | 0.77 | 0.27 to 2.21 | 0.6323 | Unknown | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.01 | 2 | 1.2 | 2 | 0.02 | 0.34 | 0.03 to 3.79 | 0.3584 | Other neurological dysfunction | 7 | 4.1 | 7 | 0.05 | 13 | 7.7 | 16 | 0.17 | 0.30 | 0.12 to 0.75 | 0.0071b | Myocardial infarction | 3 | 1.8 | 3 | 0.02 | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.01 | 2.03 | 0.21 to 19.8 | 0.5342 | Pericardial drainage | 17 | 10.1 | 20 | 0.14 | 20 | 11.8 | 22 | 0.23 | 0.62 | 0.32 to 1.19 | 0.1477 | Psychiatric episode | 14 | 8.3 | 17 | 0.12 | 17 | 10.1 | 23 | 0.24 | 0.50 | 0.25 to 0.99 | 0.0435b | Renal dysfunction | 17 | 10.1 | 19 | 0.13 | 21 | 12.4 | 28 | 0.29 | 0.46 | 0.24 to 0.87 | 0.0156b | Hepatic dysfunction | 11 | 6.5 | 12 | 0.08 | 9 | 5.3 | 11 | 0.11 | 0.74 | 0.31 to 1.74 | 0.4899 | Respiratory failure | 34 | 20.1 | 41 | 0.29 | 43 | 25.4 | 53 | 0.55 | 0.52 | 0.32 to 0.85 | 0.0084b | Right HFc | 25 | 14.8 | 26 | 0.18 | 20 | 11.8 | 22 | 0.23 | 0.80 | 0.43 to 1.49 | 0.4859 | Haemolysis | 5 | 3.0 | 5 | 0.04 | 2 | 1.2 | 2 | 0.02 | 1.69 | 0.32 to 8.91 | 0.5300 | Hypertension | 3 | 1.8 | 4 | 0.03 | 26 | 15.4 | 35 | 0.36 | 0.08 | 0.03 to 0.23 | < 0.0001b | Cardiac arrhythmia | 46 | 27.2 | 69 | 0.49 | 47 | 27.8 | 85 | 0.88 | 0.55 | 0.37 to 0.83 | 0.0041b | Arterial non-CNS thromboembolism | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.01 | 2 | 1.2 | 3 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.02 to 2.20 | 0.1637 | Venous thromboembolism | 11 | 6.5 | 13 | 0.09 | 13 | 7.7 | 15 | 0.16 | 0.59 | 0.27 to 1.29 | 0.1820 | Wound dehiscence | 3 | 1.8 | 3 | 0.02 | 3 | 1.8 | 3 | 0.03 | 0.68 | 0.13 to 3.43 | 0.6368 | Device replacement | 2 | 1.2 | 2 | 0.01 | 13 | 7.7 | 13 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.02 to 0.47 | 0.0005 | a Other infections include pneumonia, urinary tract, mediastinum, peripheral wound and unknown. | b Statistically significant. | c Including 5 (3.0%) HMII patients and 21 (12%) comparator patients requiring RVAD support. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Event | HMII (n = 169) cumulative 142.0 patient-years; mean duration 306 ± 173 days |
Comparator (n = 169) cumulative 96.2 patient-years; mean duration 207 ± 188 days |
RR | 95% CI | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | % patients | Events (n) | Events/patient-year | n | % patients | Events (n) | Events/patient-year | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding | 75 | 44.4 | 204 | 1.44 | 65 | 38.5 | 172 | 1.79 | 0.80 | 0.58 to 1.12 | 0.1931 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infectiona | 78 | 46.2 | 142 | 1.00 | 72 | 42.6 | 204 | 2.12 | 0.47 | 0.34 to 0.66 | < 0.0001b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline | 30 | 17.8 | 45 | 0.32 | 27 | 16.0 | 44 | 0.46 | 0.69 | 0.42 to 1.13 | 0.1419 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump pocket | 3 | 1.8 | 4 | 0.03 | 12 | 7.1 | 16 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.06 to 0.52 | 0.0006b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump interior | 1 | 0.6 | 2 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.2466 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blood | 32 | 18.9 | 47 | 0.33 | 36 | 21.3 | 71 | 0.74 | 0.45 | 0.29 to 0.70 | 0.0004b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line sepsis | 3 | 1.8 | 3 | 0.02 | 9 | 5.3 | 10 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.05 to 0.76 | 0.0096b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other infectiona | 49 | 29.0 | 86 | 0.61 | 50 | 29.6 | 119 | 1.24 | 0.49 | 0.34 to 0.72 | 0.0002b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stroke | 11 | 6.5 | 11 | 0.08 | 9 | 5.3 | 11 | 0.11 | 0.68 | 0.28 to 1.63 | 0.3821 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic | 2 | 1.2 | 2 | 0.01 | 2 | 1.2 | 2 | 0.02 | 0.68 | 0.09 to 4.89 | 0.6986 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Embolic | 8 | 4.7 | 8 | 0.06 | 6 | 3.6 | 7 | 0.07 | 0.77 | 0.27 to 2.21 | 0.6323 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unknown | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.01 | 2 | 1.2 | 2 | 0.02 | 0.34 | 0.03 to 3.79 | 0.3584 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other neurological dysfunction | 7 | 4.1 | 7 | 0.05 | 13 | 7.7 | 16 | 0.17 | 0.30 | 0.12 to 0.75 | 0.0071b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myocardial infarction | 3 | 1.8 | 3 | 0.02 | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.01 | 2.03 | 0.21 to 19.8 | 0.5342 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pericardial drainage | 17 | 10.1 | 20 | 0.14 | 20 | 11.8 | 22 | 0.23 | 0.62 | 0.32 to 1.19 | 0.1477 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Psychiatric episode | 14 | 8.3 | 17 | 0.12 | 17 | 10.1 | 23 | 0.24 | 0.50 | 0.25 to 0.99 | 0.0435b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal dysfunction | 17 | 10.1 | 19 | 0.13 | 21 | 12.4 | 28 | 0.29 | 0.46 | 0.24 to 0.87 | 0.0156b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hepatic dysfunction | 11 | 6.5 | 12 | 0.08 | 9 | 5.3 | 11 | 0.11 | 0.74 | 0.31 to 1.74 | 0.4899 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory failure | 34 | 20.1 | 41 | 0.29 | 43 | 25.4 | 53 | 0.55 | 0.52 | 0.32 to 0.85 | 0.0084b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HFc | 25 | 14.8 | 26 | 0.18 | 20 | 11.8 | 22 | 0.23 | 0.80 | 0.43 to 1.49 | 0.4859 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemolysis | 5 | 3.0 | 5 | 0.04 | 2 | 1.2 | 2 | 0.02 | 1.69 | 0.32 to 8.91 | 0.5300 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension | 3 | 1.8 | 4 | 0.03 | 26 | 15.4 | 35 | 0.36 | 0.08 | 0.03 to 0.23 | < 0.0001b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac arrhythmia | 46 | 27.2 | 69 | 0.49 | 47 | 27.8 | 85 | 0.88 | 0.55 | 0.37 to 0.83 | 0.0041b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arterial non-CNS thromboembolism | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.01 | 2 | 1.2 | 3 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.02 to 2.20 | 0.1637 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Venous thromboembolism | 11 | 6.5 | 13 | 0.09 | 13 | 7.7 | 15 | 0.16 | 0.59 | 0.27 to 1.29 | 0.1820 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wound dehiscence | 3 | 1.8 | 3 | 0.02 | 3 | 1.8 | 3 | 0.03 | 0.68 | 0.13 to 3.43 | 0.6368 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device replacement | 2 | 1.2 | 2 | 0.01 | 13 | 7.7 | 13 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.02 to 0.47 | 0.0005 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Other infections include pneumonia, urinary tract, mediastinum, peripheral wound and unknown. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Statistically significant. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c Including 5 (3.0%) HMII patients and 21 (12%) comparator patients requiring RVAD support. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Improvements in EQ 5D are mentioned but the text is difficult to interpret. The EQ-5D QoL VAS results are shown below (data read from histograms) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The results in a post-market approval, actual patient care setting BTT population support the original findings from the pivotal clinical trial regarding the efficacy and risk profile of the HMII LVAD. These data suggest that dissemination of this technology after approval has been associated with continued excellent results | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post-HMII implant survival to 1 year was reported. The comparison with other LVADs is likely to be underpowered and caution is needed when interpreting the findings as the patients in each group were not randomised from a common pool | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Strueber 201183
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Strueber Year of publication: 2011 Country: Australia and Europe Study design: Prospective single-arm trial with ‘virtual’ comparison group Study setting: Multicentre Number of centres: Five (three Europe, two Australia) Duration of study: Enrolment March 2006 to December 2008, follow-up (adverse events) June 2009 Follow-up period: Minimum 24 months Funding: Unclear |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Clinical evaluation of the HW LVAD | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 50 Sample attrition/dropout: None Inclusion criteria: All NYHA class IV. All receiving inotropic treatment. See also online appendix83 Exclusion criteria: See online appendix Characteristics of participants: Mean age: 48.5 years (20–75 years) Sex: 86% male Race: Not reported Diagnosis: Idiopathic CMP n = 22 (44%); ischaemic CMP n = 20 (40%); familial or congenital CMP n = 5 (10%); myocarditis n = 3 (6%) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT only. Patients with end-stage HF eligible for cardiac transplantation Type of device used: HW (CF) Any comparison: Virtual comparator group based on the SHFM Percentage of patients using inotropes: 100% Duration of treatment: Indefinite, until death Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HW |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Success rates were composite of survival to transplant, cardiac recovery with device explant, or continuing device support at 180 days Secondary outcomes: Proportion HT; proportion on LVAD; device failures; adverse events; pump flow index Method of assessing outcomes: Prospective data collection Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: Yes Length of follow-up: To death or VAD removal, or end of trialNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedOnline appendix?Not reported/not applicableRandomised/included50Not reported/not applicableExcludedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableMissing participantsNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableWithdrawalsNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicable |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Online appendix? | Not reported/not applicable | Randomised/included | 50 | Not reported/not applicable | Excluded | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Missing participants | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Withdrawals | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Online appendix? | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 50 | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ParameterValueAge (years)48.5 (20–75)Sex, male43 (86)BSA (m2)1.9 (1.4–2.6)BMI (kg/m2)25.6 (16.5–40.8)HF aetiology Idiopathic CMP22 (44) Ischaemic CMP20 (40) Familial or congenital CMP5 (10) Myocarditis3 (6)INTERMACS profile 211 (22) 335 (70) 44 (8)Inotropic support50 (100)IABP4 (8)LVEF (%)18.7 ± 5.9LVEDD (mm)68.6 ± 8.0Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)1.94 ± 0.54PCWP (mmHg)23.7 ± 6.5CVP (mmHg)12.3 ± 5.9Heart rate (b.p.m.)89.1 ± 20.2Arterial BP (mmHg) Systolic101.5 ± 13.9 Diastolic64.2 ± 10.9 Mean76.7 ± 10.6Pulmonary artery pressure (mmHg) Systolic47.6 ± 15.7 Diastolic27.7 ± 9.3Laboratory values BUN (mg/dl)28.9 ± 15.6 Creatinine (mg/dl)1.3 ± 0.5 ALT (IU/l)63.5 ± 127 AST (IU/l)75.8 ± 132 LDH (IU/l)316 ± 159 Total bilirubin (mg/dl)1.5 ± 1.0 Hgb (g/dl)12.5 ± 2.0 HCT (%)36.8 ± 6.0 PFH (mg/dl)10.1 ± 13.8 Platelets (× 109/l)243 ± 101 INR1.6 ± 0.6 APTT (s)39.7 ± 10.6Values are median (range), n (%), or mean ± SD. Pre-operative risk factors (n = 50)ParameternInotropic support50Previous myocardial infarction10Coronary angioplasty13Previous sternotomy6Arrhythmias25ICD32Pacemaker9Moderate–severe right ventricular dysfunction19Hypertension15Diabetes mellitus7 |
Parameter | Value | Age (years) | 48.5 (20–75) | Sex, male | 43 (86) | BSA (m2) | 1.9 (1.4–2.6) | BMI (kg/m2) | 25.6 (16.5–40.8) | HF aetiology | Idiopathic CMP | 22 (44) | Ischaemic CMP | 20 (40) | Familial or congenital CMP | 5 (10) | Myocarditis | 3 (6) | INTERMACS profile | 2 | 11 (22) | 3 | 35 (70) | 4 | 4 (8) | Inotropic support | 50 (100) | IABP | 4 (8) | LVEF (%) | 18.7 ± 5.9 | LVEDD (mm) | 68.6 ± 8.0 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.94 ± 0.54 | PCWP (mmHg) | 23.7 ± 6.5 | CVP (mmHg) | 12.3 ± 5.9 | Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 89.1 ± 20.2 | Arterial BP (mmHg) | Systolic | 101.5 ± 13.9 | Diastolic | 64.2 ± 10.9 | Mean | 76.7 ± 10.6 | Pulmonary artery pressure (mmHg) | Systolic | 47.6 ± 15.7 | Diastolic | 27.7 ± 9.3 | Laboratory values | BUN (mg/dl) | 28.9 ± 15.6 | Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.3 ± 0.5 | ALT (IU/l) | 63.5 ± 127 | AST (IU/l) | 75.8 ± 132 | LDH (IU/l) | 316 ± 159 | Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.5 ± 1.0 | Hgb (g/dl) | 12.5 ± 2.0 | HCT (%) | 36.8 ± 6.0 | PFH (mg/dl) | 10.1 ± 13.8 | Platelets (× 109/l) | 243 ± 101 | INR | 1.6 ± 0.6 | APTT (s) | 39.7 ± 10.6 | Values are median (range), n (%), or mean ± SD. | Parameter | n | Inotropic support | 50 | Previous myocardial infarction | 10 | Coronary angioplasty | 13 | Previous sternotomy | 6 | Arrhythmias | 25 | ICD | 32 | Pacemaker | 9 | Moderate–severe right ventricular dysfunction | 19 | Hypertension | 15 | Diabetes mellitus | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 48.5 (20–75) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex, male | 43 (86) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | 1.9 (1.4–2.6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.6 (16.5–40.8) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HF aetiology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Idiopathic CMP | 22 (44) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic CMP | 20 (40) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Familial or congenital CMP | 5 (10) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myocarditis | 3 (6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INTERMACS profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 11 (22) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 35 (70) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 4 (8) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inotropic support | 50 (100) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP | 4 (8) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF (%) | 18.7 ± 5.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEDD (mm) | 68.6 ± 8.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.94 ± 0.54 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 23.7 ± 6.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CVP (mmHg) | 12.3 ± 5.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 89.1 ± 20.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arterial BP (mmHg) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic | 101.5 ± 13.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic | 64.2 ± 10.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean | 76.7 ± 10.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary artery pressure (mmHg) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic | 47.6 ± 15.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic | 27.7 ± 9.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Laboratory values | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (mg/dl) | 28.9 ± 15.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.3 ± 0.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT (IU/l) | 63.5 ± 127 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST (IU/l) | 75.8 ± 132 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LDH (IU/l) | 316 ± 159 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 1.5 ± 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hgb (g/dl) | 12.5 ± 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HCT (%) | 36.8 ± 6.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PFH (mg/dl) | 10.1 ± 13.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets (× 109/l) | 243 ± 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INR | 1.6 ± 0.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| APTT (s) | 39.7 ± 10.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Values are median (range), n (%), or mean ± SD. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | n | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inotropic support | 50 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Previous myocardial infarction | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coronary angioplasty | 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Previous sternotomy | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arrhythmias | 25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICD | 32 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pacemaker | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Moderate–severe right ventricular dysfunction | 19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension | 15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ParameterHWVirtual MM (estimated with SHFM)Actuarial overall survival, % 6 months9073 12 months8458 18 months8248 24 months8240Proportion received HT by 24 months, %40; median time to HT = 94 days (range 13 –515 days)Proportion alive on VAD at 24 months, %34 (32 in text)Proportion explanted by 24 months, %8Success rate (heart transplanted, recovered, or on LVAD alive at end of follow-up), % 6 months90 12 months85 18 monthsNot reported 24 months79 | Parameter | HW | Virtual MM (estimated with SHFM) | Actuarial overall survival, % | 6 months | 90 | 73 | 12 months | 84 | 58 | 18 months | 82 | 48 | 24 months | 82 | 40 | Proportion received HT by 24 months, % | 40; median time to HT = 94 days (range 13 –515 days) | Proportion alive on VAD at 24 months, % | 34 (32 in text) | Proportion explanted by 24 months, % | 8 | Success rate (heart transplanted, recovered, or on LVAD alive at end of follow-up), % | 6 months | 90 | 12 months | 85 | 18 months | Not reported | 24 months | 79 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | HW | Virtual MM (estimated with SHFM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actuarial overall survival, % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 months | 90 | 73 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 months | 84 | 58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 months | 82 | 48 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 months | 82 | 40 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proportion received HT by 24 months, % | 40; median time to HT = 94 days (range 13 –515 days) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proportion alive on VAD at 24 months, % | 34 (32 in text) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proportion explanted by 24 months, % | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Success rate (heart transplanted, recovered, or on LVAD alive at end of follow-up), % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 months | 90 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 months | 85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 months | Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 months | 79 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median duration of VAD support was 322 days, mean 348 days The mean hospital stay was 45 days; of this time, 13.1 ± 9.3 days were in the ICU, 16.4 ± 12.6 days in step-down unit, and 15.4 ± 10.2 days in a regular floor unit Haemodynamic changes 24 and 48 hours after VAD implantParameterBaseline24 hoursp-value 24 hours vs. baseline48 hoursp-value 48 hours vs. baselineCardiac index (l/minute/m2)1.94 ± 0.542.9 ± 0.760.00012.83 ± 0.630.0001MAP (mmHg)76.7 ± 10.679.8 ± 11.6Not significant82.4 ± 10.50.01PCWP (mmHg)23.7 ± 6.515 ± 3.60.00115.5 ± 3.40.0001HVAD flow index (l/minute/m2)Not applicable3.32 ± 0.60.00013.14 ± 0.540.0001   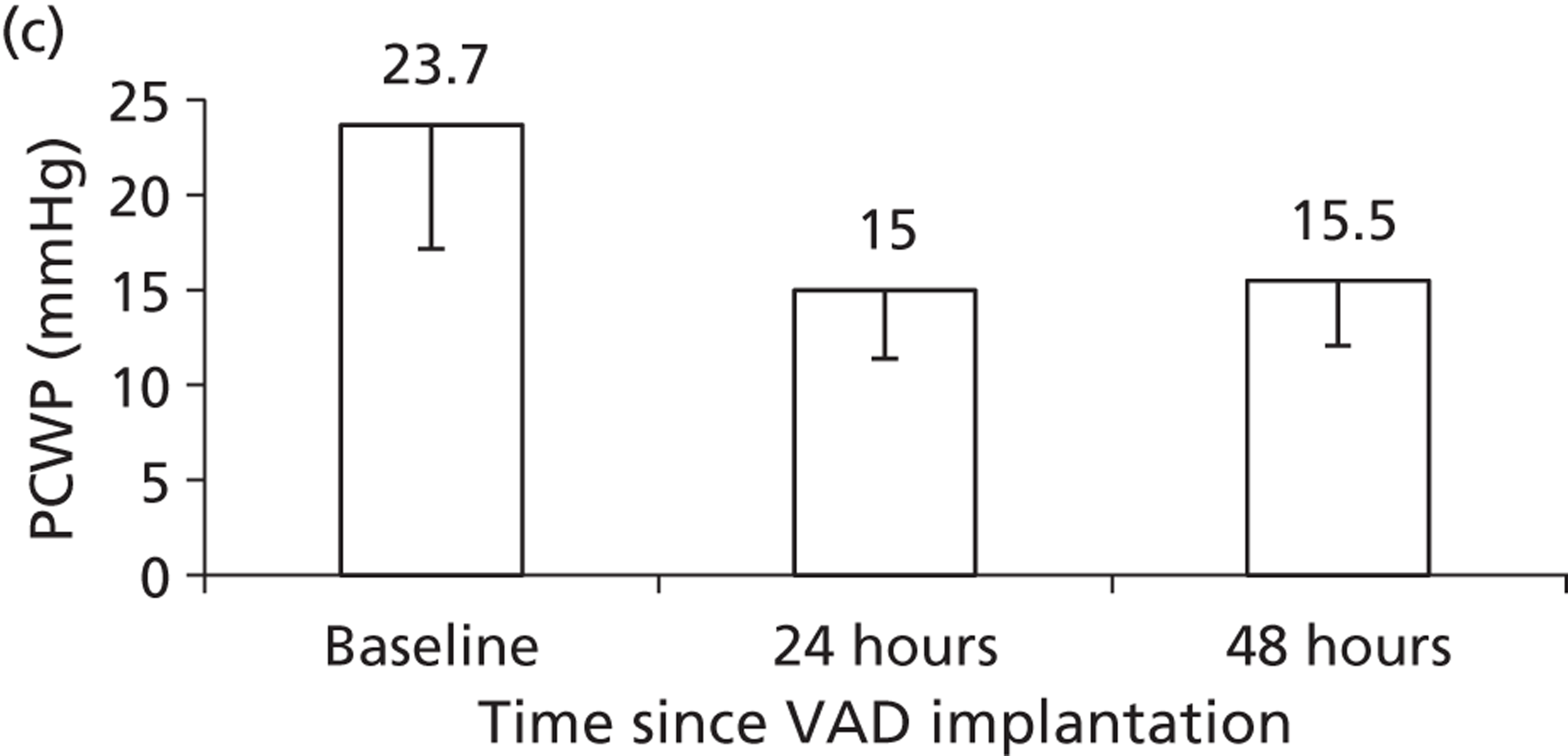 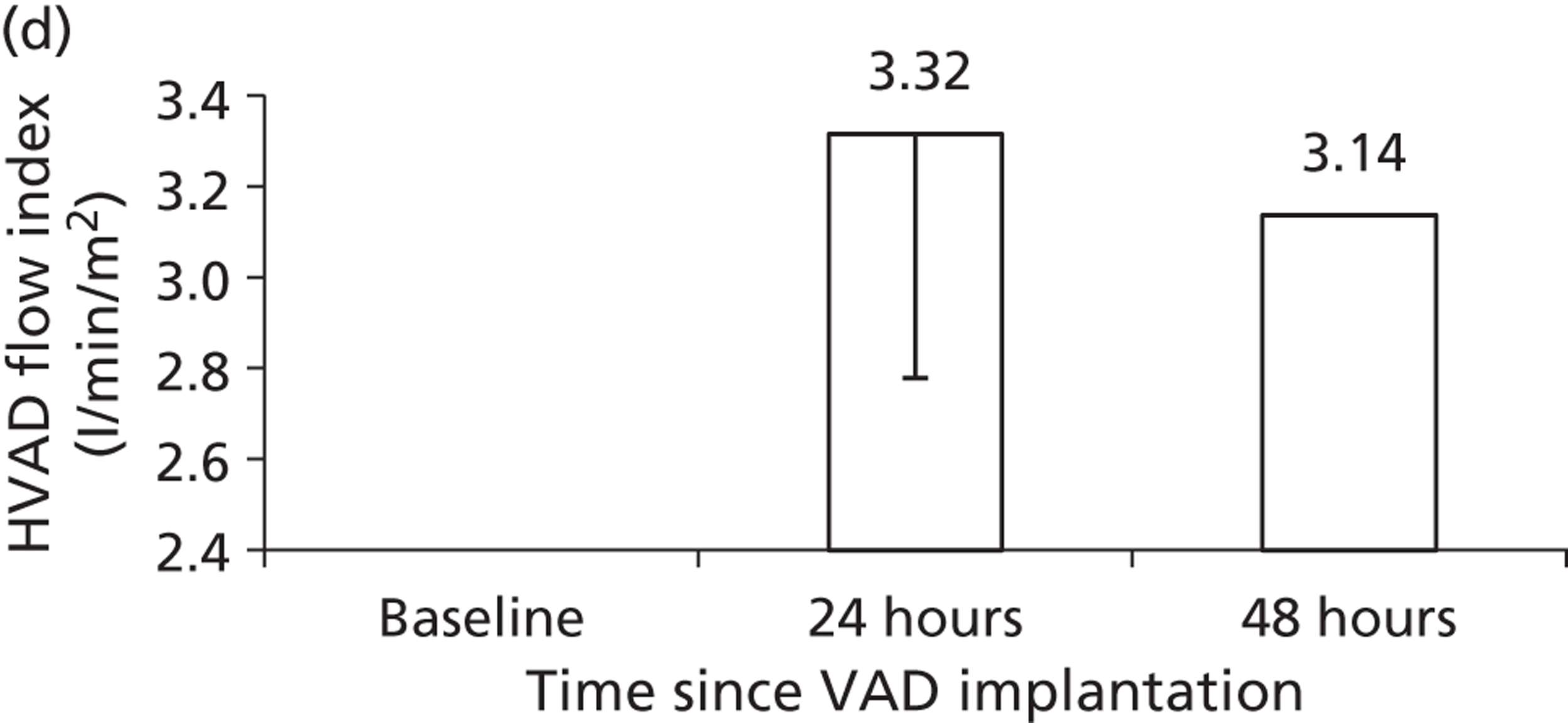 |
Parameter | Baseline | 24 hours | p-value 24 hours vs. baseline | 48 hours | p-value 48 hours vs. baseline | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.94 ± 0.54 | 2.9 ± 0.76 | 0.0001 | 2.83 ± 0.63 | 0.0001 | MAP (mmHg) | 76.7 ± 10.6 | 79.8 ± 11.6 | Not significant | 82.4 ± 10.5 | 0.01 | PCWP (mmHg) | 23.7 ± 6.5 | 15 ± 3.6 | 0.001 | 15.5 ± 3.4 | 0.0001 | HVAD flow index (l/minute/m2) | Not applicable | 3.32 ± 0.6 | 0.0001 | 3.14 ± 0.54 | 0.0001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parameter | Baseline | 24 hours | p-value 24 hours vs. baseline | 48 hours | p-value 48 hours vs. baseline | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.94 ± 0.54 | 2.9 ± 0.76 | 0.0001 | 2.83 ± 0.63 | 0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MAP (mmHg) | 76.7 ± 10.6 | 79.8 ± 11.6 | Not significant | 82.4 ± 10.5 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCWP (mmHg) | 23.7 ± 6.5 | 15 ± 3.6 | 0.001 | 15.5 ± 3.4 | 0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HVAD flow index (l/minute/m2) | Not applicable | 3.32 ± 0.6 | 0.0001 | 3.14 ± 0.54 | 0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse eventOverall (support duration 47.8 patient-years)0–30 days (support duration 4.0 patient-years)> 30 days (support duration 43.8 patient-years)Patients with event, n (%)Number of eventsEvent ratePatients with event, nNumber of eventsEvent ratePatients with event, nNumber of eventsEvent rateInfection Localised non-device related7 (14)70.15220.50550.11 Sepsis5 (10)50.10110.25440.09 Driveline exit site9 (18)100.20000.009100.21Bleeding Surgery10 (20)110.23882.00330.07 Transfusion ≥ 2 units2 (4)20.04110.25110.02 Hospital stay3 (6)30.06110.25220.05Ventricular arrhythmias2 (4)20.04110.25110.02Neurological dysfunction Ischaemic stroke2 (4)20.04220.50000.00 Haemorrhagic stroke4 (8)40.08000.00440.09 TIA2 (4)30.06000.00230.07Pulmonary dysfunction8 (16)90.19782.00110.02 Device replacement7 (14)70.15441.00330.07 Manufacturing defect2 (4)20.04220.50000.00 Left heart embolus4 (8)40.08110.25330.07 Inflow occlusion1 (2)10.02110.25000.00 Pleural effusion6 (12)70.15551.25120.05Right HF RVAD3 (6)30.06220.50110.02 Intravenous inotropes3 (6)30.06110.25220.05Renal dysfunction5 (10)50.10551.25000.00Hepatic dysfunction3 (6)30.06110.25220.05Haemolysis1 (2)10.02110.25000.00HF3 (6)30.06110.25220.05Chest pain1 (2)10.02000.00110.02Femoral embolism2 (4)20.04110.25110.02 | Adverse event | Overall (support duration 47.8 patient-years) | 0–30 days (support duration 4.0 patient-years) | > 30 days (support duration 43.8 patient-years) | Patients with event, n (%) | Number of events | Event rate | Patients with event, n | Number of events | Event rate | Patients with event, n | Number of events | Event rate | Infection | Localised non-device related | 7 (14) | 7 | 0.15 | 2 | 2 | 0.50 | 5 | 5 | 0.11 | Sepsis | 5 (10) | 5 | 0.10 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 4 | 4 | 0.09 | Driveline exit site | 9 (18) | 10 | 0.20 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 9 | 10 | 0.21 | Bleeding | Surgery | 10 (20) | 11 | 0.23 | 8 | 8 | 2.00 | 3 | 3 | 0.07 | Transfusion ≥ 2 units | 2 (4) | 2 | 0.04 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | Hospital stay | 3 (6) | 3 | 0.06 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 2 | 2 | 0.05 | Ventricular arrhythmias | 2 (4) | 2 | 0.04 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | Neurological dysfunction | Ischaemic stroke | 2 (4) | 2 | 0.04 | 2 | 2 | 0.50 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | Haemorrhagic stroke | 4 (8) | 4 | 0.08 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 4 | 4 | 0.09 | TIA | 2 (4) | 3 | 0.06 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 2 | 3 | 0.07 | Pulmonary dysfunction | 8 (16) | 9 | 0.19 | 7 | 8 | 2.00 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | Device replacement | 7 (14) | 7 | 0.15 | 4 | 4 | 1.00 | 3 | 3 | 0.07 | Manufacturing defect | 2 (4) | 2 | 0.04 | 2 | 2 | 0.50 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | Left heart embolus | 4 (8) | 4 | 0.08 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 3 | 3 | 0.07 | Inflow occlusion | 1 (2) | 1 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | Pleural effusion | 6 (12) | 7 | 0.15 | 5 | 5 | 1.25 | 1 | 2 | 0.05 | Right HF | RVAD | 3 (6) | 3 | 0.06 | 2 | 2 | 0.50 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | Intravenous inotropes | 3 (6) | 3 | 0.06 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 2 | 2 | 0.05 | Renal dysfunction | 5 (10) | 5 | 0.10 | 5 | 5 | 1.25 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | Hepatic dysfunction | 3 (6) | 3 | 0.06 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 2 | 2 | 0.05 | Haemolysis | 1 (2) | 1 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | HF | 3 (6) | 3 | 0.06 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 2 | 2 | 0.05 | Chest pain | 1 (2) | 1 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | Femoral embolism | 2 (4) | 2 | 0.04 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse event | Overall (support duration 47.8 patient-years) | 0–30 days (support duration 4.0 patient-years) | > 30 days (support duration 43.8 patient-years) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with event, n (%) | Number of events | Event rate | Patients with event, n | Number of events | Event rate | Patients with event, n | Number of events | Event rate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Localised non-device related | 7 (14) | 7 | 0.15 | 2 | 2 | 0.50 | 5 | 5 | 0.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 5 (10) | 5 | 0.10 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 4 | 4 | 0.09 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline exit site | 9 (18) | 10 | 0.20 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 9 | 10 | 0.21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surgery | 10 (20) | 11 | 0.23 | 8 | 8 | 2.00 | 3 | 3 | 0.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transfusion ≥ 2 units | 2 (4) | 2 | 0.04 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hospital stay | 3 (6) | 3 | 0.06 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 2 | 2 | 0.05 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventricular arrhythmias | 2 (4) | 2 | 0.04 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neurological dysfunction | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic stroke | 2 (4) | 2 | 0.04 | 2 | 2 | 0.50 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhagic stroke | 4 (8) | 4 | 0.08 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 4 | 4 | 0.09 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TIA | 2 (4) | 3 | 0.06 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 2 | 3 | 0.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary dysfunction | 8 (16) | 9 | 0.19 | 7 | 8 | 2.00 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device replacement | 7 (14) | 7 | 0.15 | 4 | 4 | 1.00 | 3 | 3 | 0.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing defect | 2 (4) | 2 | 0.04 | 2 | 2 | 0.50 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left heart embolus | 4 (8) | 4 | 0.08 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 3 | 3 | 0.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inflow occlusion | 1 (2) | 1 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pleural effusion | 6 (12) | 7 | 0.15 | 5 | 5 | 1.25 | 1 | 2 | 0.05 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HF | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVAD | 3 (6) | 3 | 0.06 | 2 | 2 | 0.50 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intravenous inotropes | 3 (6) | 3 | 0.06 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 2 | 2 | 0.05 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal dysfunction | 5 (10) | 5 | 0.10 | 5 | 5 | 1.25 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hepatic dysfunction | 3 (6) | 3 | 0.06 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 2 | 2 | 0.05 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemolysis | 1 (2) | 1 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HF | 3 (6) | 3 | 0.06 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 2 | 2 | 0.05 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chest pain | 1 (2) | 1 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Femoral embolism | 2 (4) | 2 | 0.04 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis n = 3, multiorgan failure n = 3 and haemorrhagic stroke n = 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KCCQ n = 38, n = 37, n = 36, n = 21 at presurgery, 1, 3 and 6 months, respectively Data read from histograms 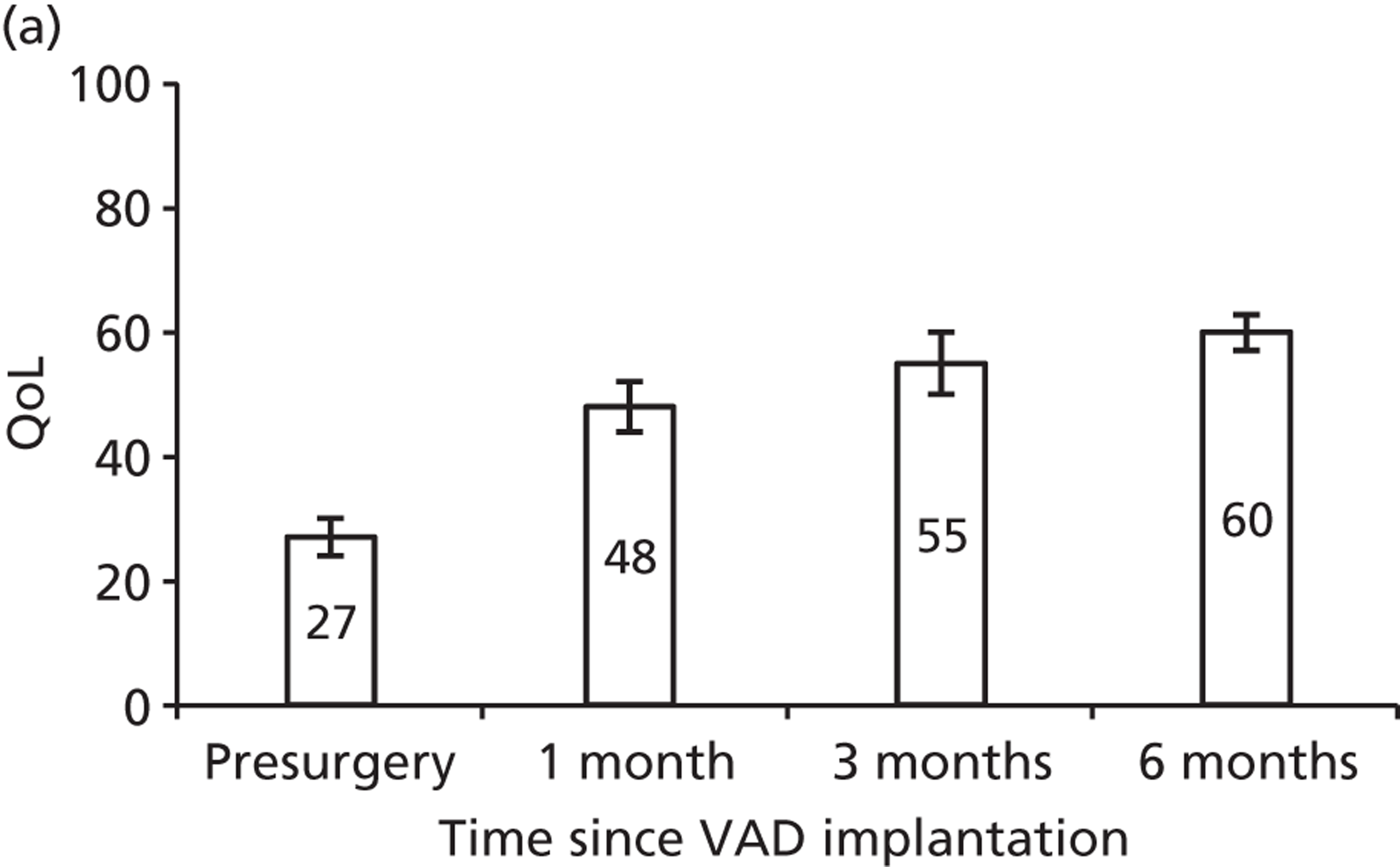 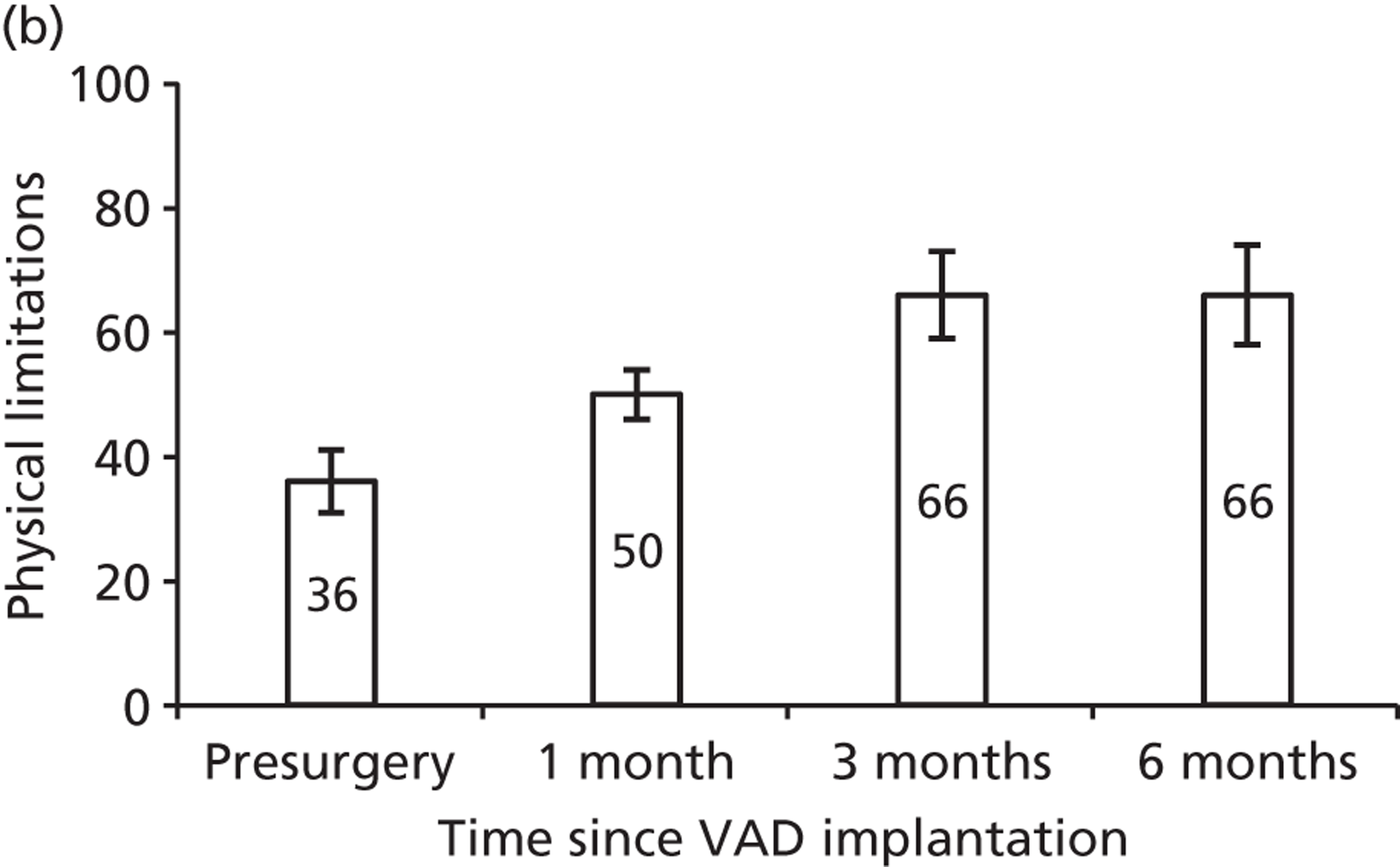 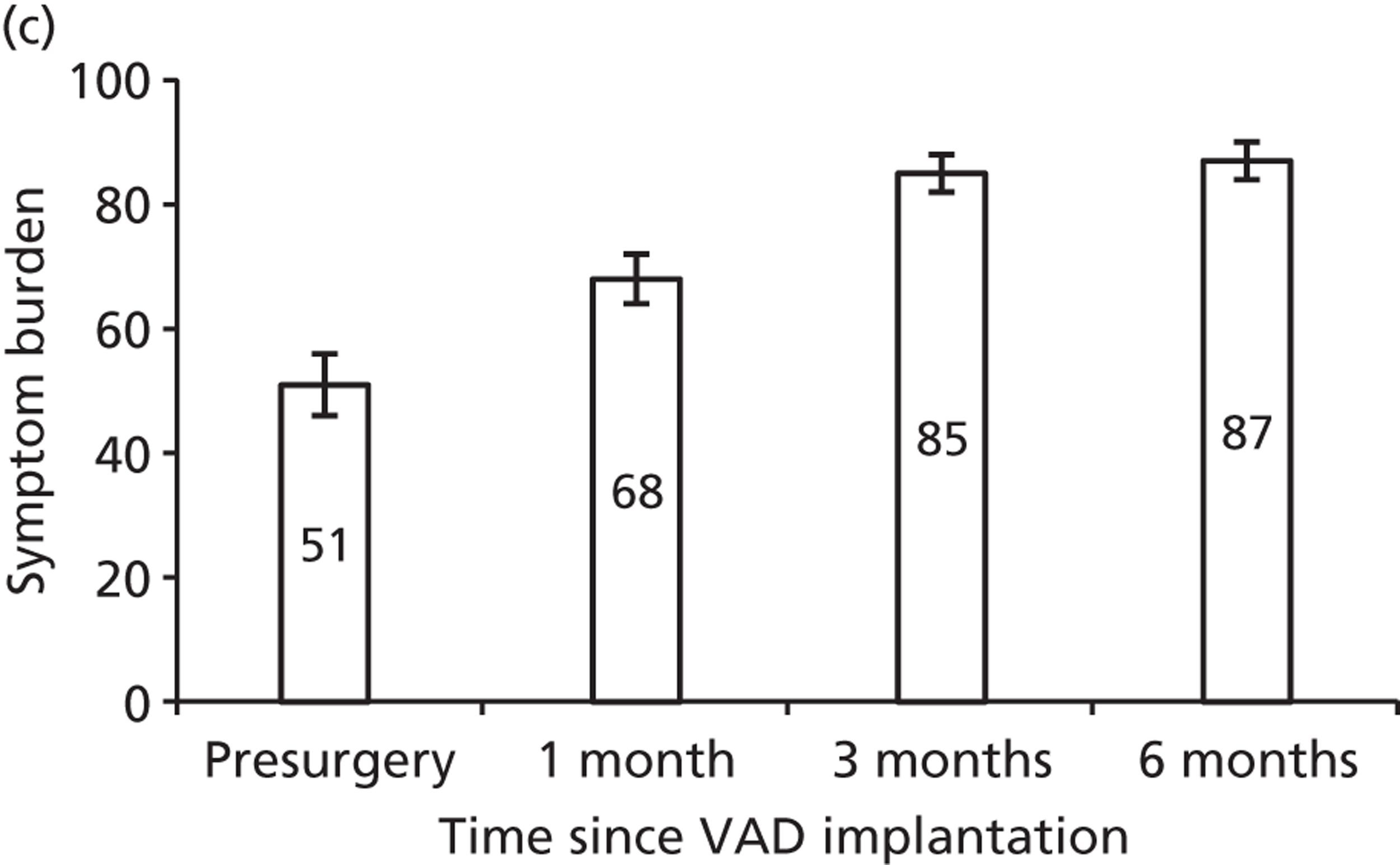 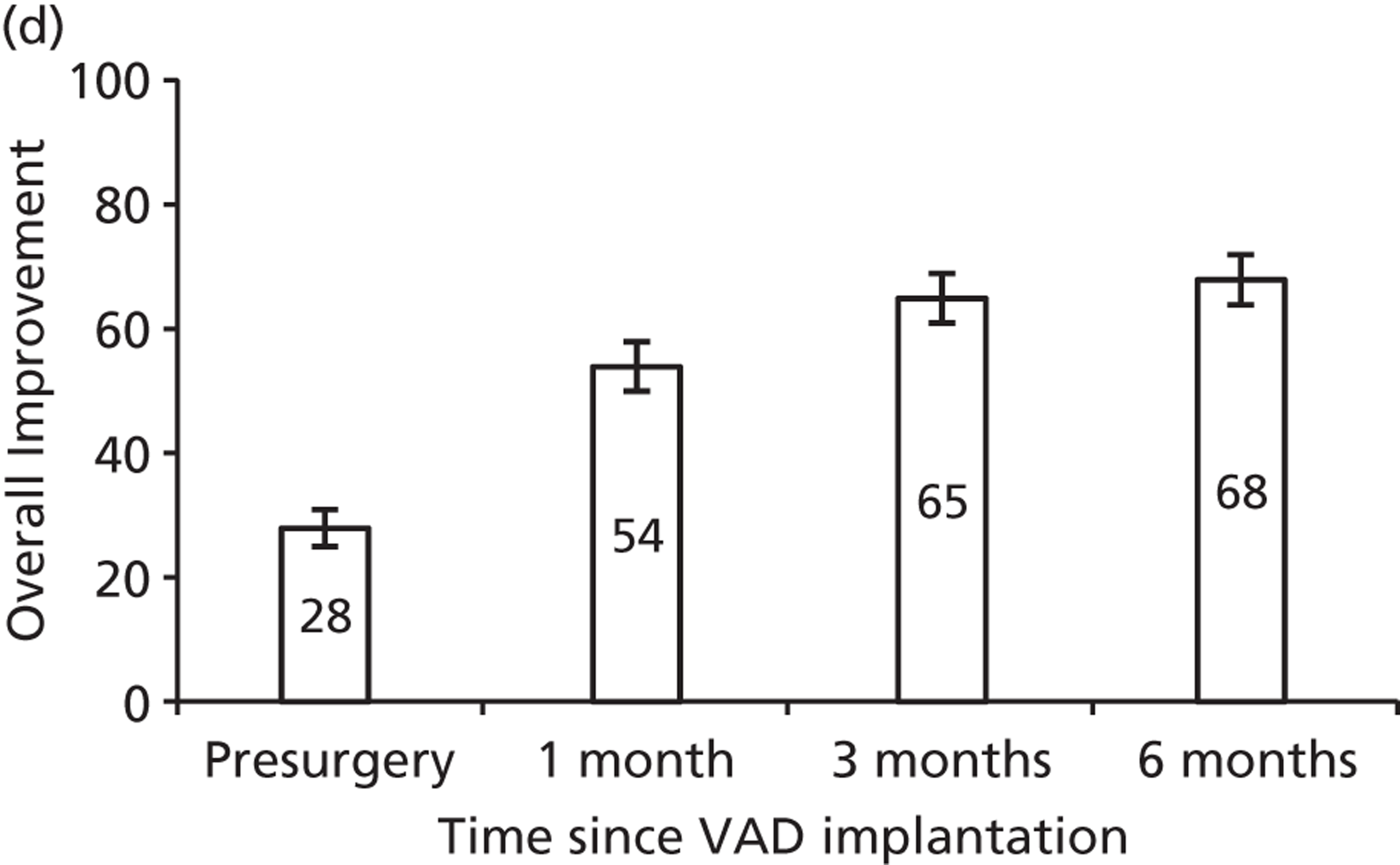 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The HVAD system provided safe and effective circulatory support in a population of end-stage HF patients. During HVAD system support, haemodynamic status, QoL and neurocognitive function improved for the majority of patients. In this first clinical study with a miniaturised LVAD placed in the pericardial space, the 2-year survival rate was similar to that of HT, which suggests that this long-term therapy is promising for the HF population | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The authors' conclusions are reasonably supported by the data presented. Mortality was depicted as 18% by 2 years (figure 2) and it was stated that 9 of 50 patients died during LVAD support, with 40% having received a transplant by 2 years, this implies there was no mortality associated with HT which is difficult to understand | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Strueber 200878
Name of the reviewer: Paul Sutcliffe (agreed with Martin Connock)
| Study details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Strueber Year of publication: 2008 Country: European countries (not UK) Study design: Retrospective survey of medical records Study setting: Multicentres Number of centres: 12 in 7 European countries Duration of study: March 2004 until January 2007 Follow-up period: 166 ± 175 days Funding: Not reported |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To gain an overview of the use and performance of the HMII device in Europe | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 101 Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported Inclusion criteria: First 101 consecutive HMII recipients in Europe Exclusion criteria: Not reported Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): 48 ± 13 years; BTT 44.4 ± 13 years, DT 52.5 ± 14 years Median age: Not reported Age range: 14–72 years Sex: Not reported Race: Not reported Diagnosis: HF. Most patients had ischaemic (n = 61) and dilative (n = 30) cardiomyopathy, 10 patients had other severe HF (e.g. myocarditis, postpartum cardiomyopathy and post-cardiotomy failure) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT + DT (split for survival only) Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: DT vs. BTT – no other devices were compared Duration of treatment: Days on device ranged from 1 to 972 days with a mean follow-up of 166 ± 175 days (total of 16,227 patient days) Percentage of patients using inotropes: Continuous in 75% Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Survival and adverse events Secondary outcomes: Not reported Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: Mean follow-up of 166 ± 175 daysNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableRandomised/included101 consecutive casesNot reported/not applicableExcludedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableMissing participantsNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableWithdrawalsNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicable |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Randomised/included | 101 consecutive cases | Not reported/not applicable | Excluded | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Missing participants | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Withdrawals | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | 101 consecutive cases | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No baseline characteristics table was provided. The following information was extracted from the text Additional baseline characteristicsCharacteristicsn or %Cardiomyopathy Ischaemic61 Dilative30 Other10NYHA class IV89% IIIb6% IIIa3%Continuous inotrope75% |
Characteristics | n or % | Cardiomyopathy | Ischaemic | 61 | Dilative | 30 | Other | 10 | NYHA class | IV | 89% | IIIb | 6% | IIIa | 3% | Continuous inotrope | 75% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristics | n or % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiomyopathy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic | 61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dilative | 30 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IV | 89% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IIIb | 6% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IIIa | 3% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Continuous inotrope | 75% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall survival was 67% at 6 months follow-up (n = 68) During follow-up 17 patients were transplanted, two recovered and the device was successfully removed Hospitalisation status on 69 living patients (1 January 2007): 9 still hospitalised, 60 discharged, and 53 ongoing with device Thirty patients of entire cohort expired: 29 on device and 1 after a HT Mortality was highest in perioperative period: 17 patients expired in first month post implantation and 23 in first 3 months Two deaths after 6 months on device caused by intracerebral bleeding and to an unknown cause (patient was found with a disconnected driveline cable). Three cases of this group had a successful HT. Remaining 28 patients were ongoing with the device. Intention to treat was DT in 33% and BTT in 67% in this subgroup When survival was stratified by intention to treat, a remarkable difference in the initial post-operative mortality was found: in the DT group survival was 93% in the BTT group 80%; however, after 4 months following implant comparable survival was seen in both groups |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In 33 patients a follow-up of > 180 days (198–972 days; mean 350 ± 180 days) was completed. In this subgroup the diagnoses leading to HF were ischaemic cardiomyopathy (55%), dilative cardiomyopathy (33%) and other (12%), including a case with a failing HMI LVAD Of 17, 16 HT procedures were successful in entire patient cohort Main support time on device was 4.6 ± 3 months prior transplant (range 0–12 months) Two patients had device removed after myocardial recovery after 3 and 6 months Infections Isolated driveline infections were present in 21 patients (incidence 0.37/patient year) Recurrent driveline infections were found in six patients. Four of these patients were transplanted 30, 53, 78 and 135 days after onset of infection There was no mortality caused by isolated driveline infection Pocket infections were reported for three cases. One patient was transplanted, in another patient, the device was successfully removed after myocardial recovery, and a third patient was ongoing with an omental wrap and antibiotic therapy |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse eventEarly post operation (≤ 90 days)Mid-term (≤ 6 months)Long term (> 6 months)Missing dataTotalAdverse event, %Bleeding5125321.1Cardiac arrhythmias411244819.1Sepsis21522811.2Site infection681212710.8Local infection1153197.6Renal failure171187.2Pneumonia1011124.8Hepatic dysfunction101114.4Right HF10104Haemolysis22262.4Neurological CVA ischaemic441.6Neurological other3141.6Neurological CVA haematological2131.2Pocket infection331.2Device thrombosis110.4Neurological metabolic110.4Neurological seizures110.4Neurological TIA110.4Thromboembolic event110.4Total192262112251100 | Adverse event | Early post operation (≤ 90 days) | Mid-term (≤ 6 months) | Long term (> 6 months) | Missing data | Total | Adverse event, % | Bleeding | 51 | 2 | 53 | 21.1 | Cardiac arrhythmias | 41 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 48 | 19.1 | Sepsis | 21 | 5 | 2 | 28 | 11.2 | Site infection | 6 | 8 | 12 | 1 | 27 | 10.8 | Local infection | 11 | 5 | 3 | 19 | 7.6 | Renal failure | 17 | 1 | 18 | 7.2 | Pneumonia | 10 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 4.8 | Hepatic dysfunction | 10 | 1 | 11 | 4.4 | Right HF | 10 | 10 | 4 | Haemolysis | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2.4 | Neurological CVA ischaemic | 4 | 4 | 1.6 | Neurological other | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1.6 | Neurological CVA haematological | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1.2 | Pocket infection | 3 | 3 | 1.2 | Device thrombosis | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | Neurological metabolic | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | Neurological seizures | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | Neurological TIA | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | Thromboembolic event | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | Total | 192 | 26 | 21 | 12 | 251 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse event | Early post operation (≤ 90 days) | Mid-term (≤ 6 months) | Long term (> 6 months) | Missing data | Total | Adverse event, % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding | 51 | 2 | 53 | 21.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac arrhythmias | 41 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 48 | 19.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | 21 | 5 | 2 | 28 | 11.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Site infection | 6 | 8 | 12 | 1 | 27 | 10.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Local infection | 11 | 5 | 3 | 19 | 7.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal failure | 17 | 1 | 18 | 7.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumonia | 10 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 4.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hepatic dysfunction | 10 | 1 | 11 | 4.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HF | 10 | 10 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemolysis | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neurological CVA ischaemic | 4 | 4 | 1.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neurological other | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neurological CVA haematological | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pocket infection | 3 | 3 | 1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device thrombosis | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neurological metabolic | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neurological seizures | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neurological TIA | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thromboembolic event | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 192 | 26 | 21 | 12 | 251 | 100 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of deathnMultiorgan failure13Right HF5CVAs5 (3 haemorrhagic, 2 ischaemic)Respiratory failure3Driveline disconnection2Bleeding after ventricular rupture1Suffocation after epistaxis (nose bleed)1 | Cause of death | n | Multiorgan failure | 13 | Right HF | 5 | CVAs | 5 (3 haemorrhagic, 2 ischaemic) | Respiratory failure | 3 | Driveline disconnection | 2 | Bleeding after ventricular rupture | 1 | Suffocation after epistaxis (nose bleed) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death | n | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Multiorgan failure | 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right HF | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CVAs | 5 (3 haemorrhagic, 2 ischaemic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory failure | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driveline disconnection | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding after ventricular rupture | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Suffocation after epistaxis (nose bleed) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Early experience with HMII in Europe was favourable and beyond expectations derived from earlier experiences with pulsatile devices. The absence of adverse events beyond the perioperative period, the rare event of a readmission and the mechanical stability of LVAD seem to indicate the suitability for chronic support. High rates of bleeding events at time of implantation and low rates of both thrombus formation and ischaemic strokes warrant the development of new, safe and less aggressive anticoagulation protocols | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Limited information provided on baseline characteristics of included patients | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Topilsky 2011a79
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Topilsky Year of publication: 2011 Country: USA Study design: Retrospective observational; analysis of prospectively collected data Study setting: Hospital Number of centres: One (Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA) Duration of study: February 2007 to May 2010 Follow-up period: Median 166 days (range 1–1044 days) Funding: Not reported |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To analyse the outcome of LVAD therapy (HMII) in patients with end-stage HF caused by RCM or HCM. These were compared with HMII recipients with D or I | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 75 I/D; 8 RCM/HCM Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported (probably 0) Inclusion criteria: All consecutive HMII recipients at clinic Exclusion criteria: Not reported Characteristics of participants: Mean: 65 years (range 55–70 years). 63 years RCM/HCM; 67 years I/D Median age: Unclear Sex: 80.7% male; 75% male RCM/HCM; 82% male I/D Race: Not reported Diagnosis: NYHA IV and IIIb HF (see above) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: RCM/HCM: 6/8 BTT; I/D: 21/75 BTT; others DT Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: RCM/HCM vs. I/D. (Also VAD RCM/HCM vs. MM RCM/HCM) Duration of treatment: Various Percentage of patients using inotropes: RCM/HCM 5/8; I/D 56/75 Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Operative mortality (within 30 days of implant); need for RVAD or inotropes beyond 168 days; hospital days from operation to discharge; total mortality over follow-up Secondary outcomes: Not distinguished from primary Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: Median 166 days (range 1–1044 days)Number of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableRandomised/includedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableExcludedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableMissing participantsNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableWithdrawalsNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicable |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Randomised/included | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Excluded | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Missing participants | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Withdrawals | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CharacteristicRM or HM (n = 8)BTT only (n = 6)D or I (n = 75)BTT only (n = 21)p-valuep-value (BTT)Age (range)63 (44.5–68)54 (43.5–66.7)67 (59–73)55 (45.5–61.5)0.180.77Sex, n (%)Male 6 (75); female 2 (25)Male 5 (83); female 1 (17)Male 61 (82); female 14 (18)Male 17 (81); female 4 (19)0.631.0NYHA class, n (%)IIIb 3 (38); IV 5 (62)IIIb 3 (50); IV 3 (50)IIIb 26 (35); IV 49 (65)IIIb 8 (40); IV 13 (60)0.420.62Prior sternotomy, n (%)2 (25)1 (16)40 (53)3 (14)0.151.0Pre-operative IABP, n (%)3 (37)3 (50)24 (32)6 (28)1.00.36Pre-operative inotrope use, n (%)5 (62)4 (66)56 (74)16 (76)0.920.60DT, n (%)2 (25)N/A51 (68)N/A0.01Heart rate, b.p.m. (range)75 (70.5–84.5)75 (71.5–82.5)73.5 (68–86)73.5 (66.2–85.5)0.970.62Systolic BP, mmHg (range)100 (87–128)121 (79–134)98 (90–108)97.5 (90–109.5)0.520.30Diastolic BP, mmHg (range)72 (59–77)76 (58.5–88.5)62 (58–69.2)67 (60.5–75)0.080.54Haemoglobin12.1 ± 112.1 ± 111.8 ± 212.1 ± 20.690.91Bilirubin (range)1.6 (0.62–2.4)2.0 (0.7–2.8)1.0 (0.7–1.52)0.95 (0.6–1.6)0.250.077BUN (range)25.5 (13.2–40.5)25.5 (15.7–45.5)26 (20–39)21 (12.5–26)0.580.23Creatinine (range)1.4 (0.97–2.0)1.4 (1.1–2.2)1.3 (1.0–1.7)1.1 (0.9–1.4)0.810.12NT-pro-BNP (range)2178 (1243–8813)1639 (653–7167)4058 (2251–7482)4673 (1352–10,839)0.330.44LM score (range)12 (5–19.5)13 (3.5–20.2)9 (4–13)11 (4–13)0.290.36Platelets < 148 × 103/μl, n (%)5 (62)3 (50)31 (41)8 (38)0.291.0Albumin < 3.3 g/dl, n (%)3 (37)3 (50)18 (24)6 (28)0.420.36INR > 1.1, n (%)7 (87)5 (83)55 (73)17 (81)0.671.0Vasodilator therapy at implantation, n (%)2 (25)2 (33)17 (23)4 (19)0.970.60Mean PA pressure < 25.3 mmHg, n (%)1 (12)1 (17)6 (8)3 (14)0.531.0AST > 45 U/dl, n (%)3 (37)3 (50)20 (27)3 (14)0.680.12Haematocrit < 34, n (%)3 (37)2 (33)34 (45)7 (33)0.721.0BUN > 51 U/dl, n (%)008 (11)00.901.0Left ventricular diastolic diameter (mm)52.5 ± 652.6 ± 768.6 ± 868.8 ± 9< 0.00010.0004Left ventricular systolic diameter (mm)43.1 ± 843.3 ± 861.8 ± 963.6 ± 90.00080.001Septal thickness, mm (range)16 (12–19)16.5 (14.5–20)10 (8.5–11)9.5 (7.7–11)0.00030.0021Posterior wall thickness, mm (range)11 (9.7–13.7)12 (9.5–15.2)10 (8.0–11)10 (9–12)0.08680.23Ejection fraction, % (range)21 (20–36)20.5 (19.7–42.5)17 (15–22)17 (15–20)0.00870.013E/e/ ratioa (range)35 (21.6–55)23.3 (20–35)23.3 (19–33.3)20.0 (16–33.3)0.100.63Deceleration timeb (range)119 (117–158.5)119 (116–144)135 (112–153.5)122.5 (110–144)0.960.84Tricuspid valve lateral annulus velocity, m/s (range)0.07 (0.06–0.08)0.06 (0.06–0.06)0.08 (0.06–0.1)0.08 (0.07–0.12)0.550.074Severe RV dysfunction, n (%)5 (62)4 (66)50 (67)13 (62)0.621.0Severe mitral regurgitation, n (%)1 (12)0 (0)23 (31)1 (6)0.220.1Severe tricuspid regurgitation, n (%)3 (37)3 (50)27 (36)7 (33)0.921.0Mean RA pressure, mmHg (range)17.5 (12–20)15.5 (10.2–22)14.5 (10–19.7)13 (9.5–18.5)0.510.64Mean PA pressure (mmHg)33.3 ± 9.832.6 ± 11.436.3 ± 9.235.2 ± 11.00.430.77PVR, Wood units (range)3.1 (1.1–5.2)2.66 (1.4–4.0)3.5 (2.2–5.4)3.5 (2.1–4.2)0.600.32RV, dP/dt (range)432 (360–720)552 (360–744)432 (336–576)480 (336–732)0.710.86RVSWI (mmHg ml/m2)3.9 ± 3.03.9 ± 3.55.4 ± 2.95.3 ± 3.30.230.46Mean wedge pressure (mmHg)24.1 ± 4.024.8 ± 3.223.4 ± 7.124.0 ± 7.90.780.81Cardiac output (l/minute)3.2 ± 0.83.5 ± 0.83.9 ± 1.24.3 ± 1.10.070.22Cardiac index (l/minute/m2)1.6 ± 0.31.7 ± 0.42.0 ± 0.52.0 ± 0.50.080.36a E/e/ indicates ratio of E velocity of mitral inflow to early diastolic relaxation tissue velocity of medial annulus.b Deceleration time of early mitral inflow. To assess the possibility of a selection bias, data were reanalysed in the BTT patients only by excluding all the DT patients in both groups (see above). There were no significant differences between the groups |
Characteristic | RM or HM (n = 8) | BTT only (n = 6) | D or I (n = 75) | BTT only (n = 21) | p-value | p-value (BTT) | Age (range) | 63 (44.5–68) | 54 (43.5–66.7) | 67 (59–73) | 55 (45.5–61.5) | 0.18 | 0.77 | Sex, n (%) | Male 6 (75); female 2 (25) | Male 5 (83); female 1 (17) | Male 61 (82); female 14 (18) | Male 17 (81); female 4 (19) | 0.63 | 1.0 | NYHA class, n (%) | IIIb 3 (38); IV 5 (62) | IIIb 3 (50); IV 3 (50) | IIIb 26 (35); IV 49 (65) | IIIb 8 (40); IV 13 (60) | 0.42 | 0.62 | Prior sternotomy, n (%) | 2 (25) | 1 (16) | 40 (53) | 3 (14) | 0.15 | 1.0 | Pre-operative IABP, n (%) | 3 (37) | 3 (50) | 24 (32) | 6 (28) | 1.0 | 0.36 | Pre-operative inotrope use, n (%) | 5 (62) | 4 (66) | 56 (74) | 16 (76) | 0.92 | 0.60 | DT, n (%) | 2 (25) | N/A | 51 (68) | N/A | 0.01 | Heart rate, b.p.m. (range) | 75 (70.5–84.5) | 75 (71.5–82.5) | 73.5 (68–86) | 73.5 (66.2–85.5) | 0.97 | 0.62 | Systolic BP, mmHg (range) | 100 (87–128) | 121 (79–134) | 98 (90–108) | 97.5 (90–109.5) | 0.52 | 0.30 | Diastolic BP, mmHg (range) | 72 (59–77) | 76 (58.5–88.5) | 62 (58–69.2) | 67 (60.5–75) | 0.08 | 0.54 | Haemoglobin | 12.1 ± 1 | 12.1 ± 1 | 11.8 ± 2 | 12.1 ± 2 | 0.69 | 0.91 | Bilirubin (range) | 1.6 (0.62–2.4) | 2.0 (0.7–2.8) | 1.0 (0.7–1.52) | 0.95 (0.6–1.6) | 0.25 | 0.077 | BUN (range) | 25.5 (13.2–40.5) | 25.5 (15.7–45.5) | 26 (20–39) | 21 (12.5–26) | 0.58 | 0.23 | Creatinine (range) | 1.4 (0.97–2.0) | 1.4 (1.1–2.2) | 1.3 (1.0–1.7) | 1.1 (0.9–1.4) | 0.81 | 0.12 | NT-pro-BNP (range) | 2178 (1243–8813) | 1639 (653–7167) | 4058 (2251–7482) | 4673 (1352–10,839) | 0.33 | 0.44 | LM score (range) | 12 (5–19.5) | 13 (3.5–20.2) | 9 (4–13) | 11 (4–13) | 0.29 | 0.36 | Platelets < 148 × 103/μl, n (%) | 5 (62) | 3 (50) | 31 (41) | 8 (38) | 0.29 | 1.0 | Albumin < 3.3 g/dl, n (%) | 3 (37) | 3 (50) | 18 (24) | 6 (28) | 0.42 | 0.36 | INR > 1.1, n (%) | 7 (87) | 5 (83) | 55 (73) | 17 (81) | 0.67 | 1.0 | Vasodilator therapy at implantation, n (%) | 2 (25) | 2 (33) | 17 (23) | 4 (19) | 0.97 | 0.60 | Mean PA pressure < 25.3 mmHg, n (%) | 1 (12) | 1 (17) | 6 (8) | 3 (14) | 0.53 | 1.0 | AST > 45 U/dl, n (%) | 3 (37) | 3 (50) | 20 (27) | 3 (14) | 0.68 | 0.12 | Haematocrit < 34, n (%) | 3 (37) | 2 (33) | 34 (45) | 7 (33) | 0.72 | 1.0 | BUN > 51 U/dl, n (%) | 0 | 0 | 8 (11) | 0 | 0.90 | 1.0 | Left ventricular diastolic diameter (mm) | 52.5 ± 6 | 52.6 ± 7 | 68.6 ± 8 | 68.8 ± 9 | < 0.0001 | 0.0004 | Left ventricular systolic diameter (mm) | 43.1 ± 8 | 43.3 ± 8 | 61.8 ± 9 | 63.6 ± 9 | 0.0008 | 0.001 | Septal thickness, mm (range) | 16 (12–19) | 16.5 (14.5–20) | 10 (8.5–11) | 9.5 (7.7–11) | 0.0003 | 0.0021 | Posterior wall thickness, mm (range) | 11 (9.7–13.7) | 12 (9.5–15.2) | 10 (8.0–11) | 10 (9–12) | 0.0868 | 0.23 | Ejection fraction, % (range) | 21 (20–36) | 20.5 (19.7–42.5) | 17 (15–22) | 17 (15–20) | 0.0087 | 0.013 | E/e/ ratioa (range) | 35 (21.6–55) | 23.3 (20–35) | 23.3 (19–33.3) | 20.0 (16–33.3) | 0.10 | 0.63 | Deceleration timeb (range) | 119 (117–158.5) | 119 (116–144) | 135 (112–153.5) | 122.5 (110–144) | 0.96 | 0.84 | Tricuspid valve lateral annulus velocity, m/s (range) | 0.07 (0.06–0.08) | 0.06 (0.06–0.06) | 0.08 (0.06–0.1) | 0.08 (0.07–0.12) | 0.55 | 0.074 | Severe RV dysfunction, n (%) | 5 (62) | 4 (66) | 50 (67) | 13 (62) | 0.62 | 1.0 | Severe mitral regurgitation, n (%) | 1 (12) | 0 (0) | 23 (31) | 1 (6) | 0.22 | 0.1 | Severe tricuspid regurgitation, n (%) | 3 (37) | 3 (50) | 27 (36) | 7 (33) | 0.92 | 1.0 | Mean RA pressure, mmHg (range) | 17.5 (12–20) | 15.5 (10.2–22) | 14.5 (10–19.7) | 13 (9.5–18.5) | 0.51 | 0.64 | Mean PA pressure (mmHg) | 33.3 ± 9.8 | 32.6 ± 11.4 | 36.3 ± 9.2 | 35.2 ± 11.0 | 0.43 | 0.77 | PVR, Wood units (range) | 3.1 (1.1–5.2) | 2.66 (1.4–4.0) | 3.5 (2.2–5.4) | 3.5 (2.1–4.2) | 0.60 | 0.32 | RV, dP/dt (range) | 432 (360–720) | 552 (360–744) | 432 (336–576) | 480 (336–732) | 0.71 | 0.86 | RVSWI (mmHg ml/m2) | 3.9 ± 3.0 | 3.9 ± 3.5 | 5.4 ± 2.9 | 5.3 ± 3.3 | 0.23 | 0.46 | Mean wedge pressure (mmHg) | 24.1 ± 4.0 | 24.8 ± 3.2 | 23.4 ± 7.1 | 24.0 ± 7.9 | 0.78 | 0.81 | Cardiac output (l/minute) | 3.2 ± 0.8 | 3.5 ± 0.8 | 3.9 ± 1.2 | 4.3 ± 1.1 | 0.07 | 0.22 | Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.6 ± 0.3 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 0.08 | 0.36 | a E/e/ indicates ratio of E velocity of mitral inflow to early diastolic relaxation tissue velocity of medial annulus. | b Deceleration time of early mitral inflow. | |||||||||||||
| Characteristic | RM or HM (n = 8) | BTT only (n = 6) | D or I (n = 75) | BTT only (n = 21) | p-value | p-value (BTT) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (range) | 63 (44.5–68) | 54 (43.5–66.7) | 67 (59–73) | 55 (45.5–61.5) | 0.18 | 0.77 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex, n (%) | Male 6 (75); female 2 (25) | Male 5 (83); female 1 (17) | Male 61 (82); female 14 (18) | Male 17 (81); female 4 (19) | 0.63 | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class, n (%) | IIIb 3 (38); IV 5 (62) | IIIb 3 (50); IV 3 (50) | IIIb 26 (35); IV 49 (65) | IIIb 8 (40); IV 13 (60) | 0.42 | 0.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prior sternotomy, n (%) | 2 (25) | 1 (16) | 40 (53) | 3 (14) | 0.15 | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative IABP, n (%) | 3 (37) | 3 (50) | 24 (32) | 6 (28) | 1.0 | 0.36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative inotrope use, n (%) | 5 (62) | 4 (66) | 56 (74) | 16 (76) | 0.92 | 0.60 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DT, n (%) | 2 (25) | N/A | 51 (68) | N/A | 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heart rate, b.p.m. (range) | 75 (70.5–84.5) | 75 (71.5–82.5) | 73.5 (68–86) | 73.5 (66.2–85.5) | 0.97 | 0.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic BP, mmHg (range) | 100 (87–128) | 121 (79–134) | 98 (90–108) | 97.5 (90–109.5) | 0.52 | 0.30 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic BP, mmHg (range) | 72 (59–77) | 76 (58.5–88.5) | 62 (58–69.2) | 67 (60.5–75) | 0.08 | 0.54 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemoglobin | 12.1 ± 1 | 12.1 ± 1 | 11.8 ± 2 | 12.1 ± 2 | 0.69 | 0.91 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilirubin (range) | 1.6 (0.62–2.4) | 2.0 (0.7–2.8) | 1.0 (0.7–1.52) | 0.95 (0.6–1.6) | 0.25 | 0.077 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN (range) | 25.5 (13.2–40.5) | 25.5 (15.7–45.5) | 26 (20–39) | 21 (12.5–26) | 0.58 | 0.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine (range) | 1.4 (0.97–2.0) | 1.4 (1.1–2.2) | 1.3 (1.0–1.7) | 1.1 (0.9–1.4) | 0.81 | 0.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NT-pro-BNP (range) | 2178 (1243–8813) | 1639 (653–7167) | 4058 (2251–7482) | 4673 (1352–10,839) | 0.33 | 0.44 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LM score (range) | 12 (5–19.5) | 13 (3.5–20.2) | 9 (4–13) | 11 (4–13) | 0.29 | 0.36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets < 148 × 103/μl, n (%) | 5 (62) | 3 (50) | 31 (41) | 8 (38) | 0.29 | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albumin < 3.3 g/dl, n (%) | 3 (37) | 3 (50) | 18 (24) | 6 (28) | 0.42 | 0.36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INR > 1.1, n (%) | 7 (87) | 5 (83) | 55 (73) | 17 (81) | 0.67 | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vasodilator therapy at implantation, n (%) | 2 (25) | 2 (33) | 17 (23) | 4 (19) | 0.97 | 0.60 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean PA pressure < 25.3 mmHg, n (%) | 1 (12) | 1 (17) | 6 (8) | 3 (14) | 0.53 | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST > 45 U/dl, n (%) | 3 (37) | 3 (50) | 20 (27) | 3 (14) | 0.68 | 0.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haematocrit < 34, n (%) | 3 (37) | 2 (33) | 34 (45) | 7 (33) | 0.72 | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN > 51 U/dl, n (%) | 0 | 0 | 8 (11) | 0 | 0.90 | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left ventricular diastolic diameter (mm) | 52.5 ± 6 | 52.6 ± 7 | 68.6 ± 8 | 68.8 ± 9 | < 0.0001 | 0.0004 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left ventricular systolic diameter (mm) | 43.1 ± 8 | 43.3 ± 8 | 61.8 ± 9 | 63.6 ± 9 | 0.0008 | 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Septal thickness, mm (range) | 16 (12–19) | 16.5 (14.5–20) | 10 (8.5–11) | 9.5 (7.7–11) | 0.0003 | 0.0021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Posterior wall thickness, mm (range) | 11 (9.7–13.7) | 12 (9.5–15.2) | 10 (8.0–11) | 10 (9–12) | 0.0868 | 0.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ejection fraction, % (range) | 21 (20–36) | 20.5 (19.7–42.5) | 17 (15–22) | 17 (15–20) | 0.0087 | 0.013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E/e/ ratioa (range) | 35 (21.6–55) | 23.3 (20–35) | 23.3 (19–33.3) | 20.0 (16–33.3) | 0.10 | 0.63 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deceleration timeb (range) | 119 (117–158.5) | 119 (116–144) | 135 (112–153.5) | 122.5 (110–144) | 0.96 | 0.84 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tricuspid valve lateral annulus velocity, m/s (range) | 0.07 (0.06–0.08) | 0.06 (0.06–0.06) | 0.08 (0.06–0.1) | 0.08 (0.07–0.12) | 0.55 | 0.074 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Severe RV dysfunction, n (%) | 5 (62) | 4 (66) | 50 (67) | 13 (62) | 0.62 | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Severe mitral regurgitation, n (%) | 1 (12) | 0 (0) | 23 (31) | 1 (6) | 0.22 | 0.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Severe tricuspid regurgitation, n (%) | 3 (37) | 3 (50) | 27 (36) | 7 (33) | 0.92 | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean RA pressure, mmHg (range) | 17.5 (12–20) | 15.5 (10.2–22) | 14.5 (10–19.7) | 13 (9.5–18.5) | 0.51 | 0.64 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean PA pressure (mmHg) | 33.3 ± 9.8 | 32.6 ± 11.4 | 36.3 ± 9.2 | 35.2 ± 11.0 | 0.43 | 0.77 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PVR, Wood units (range) | 3.1 (1.1–5.2) | 2.66 (1.4–4.0) | 3.5 (2.2–5.4) | 3.5 (2.1–4.2) | 0.60 | 0.32 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RV, dP/dt (range) | 432 (360–720) | 552 (360–744) | 432 (336–576) | 480 (336–732) | 0.71 | 0.86 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVSWI (mmHg ml/m2) | 3.9 ± 3.0 | 3.9 ± 3.5 | 5.4 ± 2.9 | 5.3 ± 3.3 | 0.23 | 0.46 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean wedge pressure (mmHg) | 24.1 ± 4.0 | 24.8 ± 3.2 | 23.4 ± 7.1 | 24.0 ± 7.9 | 0.78 | 0.81 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac output (l/minute) | 3.2 ± 0.8 | 3.5 ± 0.8 | 3.9 ± 1.2 | 4.3 ± 1.1 | 0.07 | 0.22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.6 ± 0.3 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 0.08 | 0.36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a E/e/ indicates ratio of E velocity of mitral inflow to early diastolic relaxation tissue velocity of medial annulus. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Deceleration time of early mitral inflow. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MethodRCM/HCMD/IActuarial survivalBTT only1 year: 75% (95% CI 23% to 96.5%)BTT only1 year: 85.7% (95% CI 41.0% to 98.5%); p = 0.16Overall survivalGroups combined 18/83 died. 1 year: 77.4% (± 5.5) 2 years: 62.6% (± 9.2)K–M estimatesFigure 2 of paper: BTT and DT patients combinedFigure 2 of paper: BTT and DT patients combined K–M for D/I group (n = 75; both BTT and DT patients) data read from graph  |
Method | RCM/HCM | D/I | Actuarial survival | BTT only 1 year: 75% (95% CI 23% to 96.5%) |
BTT only 1 year: 85.7% (95% CI 41.0% to 98.5%); p = 0.16 |
Overall survival | Groups combined 18/83 died. 1 year: 77.4% (± 5.5) 2 years: 62.6% (± 9.2) | K–M estimates | Figure 2 of paper: BTT and DT patients combined | Figure 2 of paper: BTT and DT patients combined | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | RCM/HCM | D/I | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actuarial survival | BTT only 1 year: 75% (95% CI 23% to 96.5%) |
BTT only 1 year: 85.7% (95% CI 41.0% to 98.5%); p = 0.16 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall survival | Groups combined 18/83 died. 1 year: 77.4% (± 5.5) 2 years: 62.6% (± 9.2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K–M estimates | Figure 2 of paper: BTT and DT patients combined | Figure 2 of paper: BTT and DT patients combined | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class > III 100% > class III at baseline 12% > class III at 3 months Clinical post-operative (30 days) outcomesOutcomeAll patients (n = 83)RCM or HCM (n = 8)I or D (n = 75)p-valueOperative mortality, n (%)8 (10)1 (12)7 (9)0.57Cardiopulmonary bypass time, minutes (range)96.5 (80.2–121.5)89 (83–120)99 (78–123)0.56Post-operative red blood cell transfusion, units (range)8 (5–13)7 (3.5–14.5)8 (5–13)0.94Need for RVAD, n (%)3 (4)1 (12)2 (2)0.26Infection, n (%)41 (49)7 (88)34 (45)0.03Bleeding, n (%)a56 (68)3 (37)53 (71)0.10Prolonged intubation, (%)b19 (23)3 (37)16 (21)0.37Arrhythmia, n (%)c16 (19)2 (25)14 (19)0.65Acute renal failure, n (%)d13 (16)3 (37)10 (13)0.11Acute cerebral event, n (%)e10 (12)1 (12)9 (12)1.0Hepatic dysfunction, n (%)f15 (18)3 (37)12 (16)0.15Thromboembolic event, n (%)g9 (11)1 (12)8 (11)1.0Dialysis, n (%)8 (10)2 (25)6 (8)0.19Mean RA pressure, mmHg (range)h12 (9–17)18 (15–20)12 (9–15)0.03Mean PA pressure, mmHg (range)h26 (23–30)24 (23–28)26 (23–30.7)0.42Cardiac output, U/minute (range)h5.5 (4.8–6)4.5 (4.4–5.6)5.5 (4.9–6.2)0.07bCardiac index, U/minute/m2 (range)2.7 (2.4–3.1)2.4 (2.1–2.9)2.8 (2.4–3.2)0.08Pump, RPM (range)9400 (9200–9600)9300 (9150–9450)9400 (9200, 9600)0.45Pump flow, l/minute (range)5.2 (4.5–5.5)4.3 (3.8–4.5)5.2 (4.7–5.5)0.0011LOS, days (range)17.5 (11–27.5)11 (8–45)18.5 (12.2–27.7)0.48Duration of inotropic support, hours (range)114 (66.5–166.5)157 (98.2–954)111.5 (66–160)0.078RV failure, n (%)20 (24)4 (50)16 (21)0.16LOS > 30 days, n (%)14 (17)2 (25)12 (16)0.61Death or RV failure, n (%)20 (24)4 (50)16 (21)0.21a Bleeding requiring blood transfusion more than 24 hours after surgery.b Mechanical ventilation for more than 1 week or need for tracheostomy.c Haemodynamically significant arrhythmia or requiring cardioversion.d Renal failure requiring dialysis, increase in creatinine to > 2 or by > 50% from baseline.e Any stroke, brain haemorrhage, or hyperperfusion injury.f Liver enzymes > 300 or bilirubin > 5.0 after surgery.g Any embolic event after surgery.h The haemodynamic data represent the last measurement before taking out the pulmonary artery catheter; pump flow and RPM. |
Outcome | All patients (n = 83) | RCM or HCM (n = 8) | I or D (n = 75) | p-value | Operative mortality, n (%) | 8 (10) | 1 (12) | 7 (9) | 0.57 | Cardiopulmonary bypass time, minutes (range) | 96.5 (80.2–121.5) | 89 (83–120) | 99 (78–123) | 0.56 | Post-operative red blood cell transfusion, units (range) | 8 (5–13) | 7 (3.5–14.5) | 8 (5–13) | 0.94 | Need for RVAD, n (%) | 3 (4) | 1 (12) | 2 (2) | 0.26 | Infection, n (%) | 41 (49) | 7 (88) | 34 (45) | 0.03 | Bleeding, n (%)a | 56 (68) | 3 (37) | 53 (71) | 0.10 | Prolonged intubation, (%)b | 19 (23) | 3 (37) | 16 (21) | 0.37 | Arrhythmia, n (%)c | 16 (19) | 2 (25) | 14 (19) | 0.65 | Acute renal failure, n (%)d | 13 (16) | 3 (37) | 10 (13) | 0.11 | Acute cerebral event, n (%)e | 10 (12) | 1 (12) | 9 (12) | 1.0 | Hepatic dysfunction, n (%)f | 15 (18) | 3 (37) | 12 (16) | 0.15 | Thromboembolic event, n (%)g | 9 (11) | 1 (12) | 8 (11) | 1.0 | Dialysis, n (%) | 8 (10) | 2 (25) | 6 (8) | 0.19 | Mean RA pressure, mmHg (range)h | 12 (9–17) | 18 (15–20) | 12 (9–15) | 0.03 | Mean PA pressure, mmHg (range)h | 26 (23–30) | 24 (23–28) | 26 (23–30.7) | 0.42 | Cardiac output, U/minute (range)h | 5.5 (4.8–6) | 4.5 (4.4–5.6) | 5.5 (4.9–6.2) | 0.07 | bCardiac index, U/minute/m2 (range) | 2.7 (2.4–3.1) | 2.4 (2.1–2.9) | 2.8 (2.4–3.2) | 0.08 | Pump, RPM (range) | 9400 (9200–9600) | 9300 (9150–9450) | 9400 (9200, 9600) | 0.45 | Pump flow, l/minute (range) | 5.2 (4.5–5.5) | 4.3 (3.8–4.5) | 5.2 (4.7–5.5) | 0.0011 | LOS, days (range) | 17.5 (11–27.5) | 11 (8–45) | 18.5 (12.2–27.7) | 0.48 | Duration of inotropic support, hours (range) | 114 (66.5–166.5) | 157 (98.2–954) | 111.5 (66–160) | 0.078 | RV failure, n (%) | 20 (24) | 4 (50) | 16 (21) | 0.16 | LOS > 30 days, n (%) | 14 (17) | 2 (25) | 12 (16) | 0.61 | Death or RV failure, n (%) | 20 (24) | 4 (50) | 16 (21) | 0.21 | a Bleeding requiring blood transfusion more than 24 hours after surgery. | b Mechanical ventilation for more than 1 week or need for tracheostomy. | c Haemodynamically significant arrhythmia or requiring cardioversion. | d Renal failure requiring dialysis, increase in creatinine to > 2 or by > 50% from baseline. | e Any stroke, brain haemorrhage, or hyperperfusion injury. | f Liver enzymes > 300 or bilirubin > 5.0 after surgery. | g Any embolic event after surgery. | h The haemodynamic data represent the last measurement before taking out the pulmonary artery catheter; pump flow and RPM. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcome | All patients (n = 83) | RCM or HCM (n = 8) | I or D (n = 75) | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operative mortality, n (%) | 8 (10) | 1 (12) | 7 (9) | 0.57 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiopulmonary bypass time, minutes (range) | 96.5 (80.2–121.5) | 89 (83–120) | 99 (78–123) | 0.56 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Post-operative red blood cell transfusion, units (range) | 8 (5–13) | 7 (3.5–14.5) | 8 (5–13) | 0.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Need for RVAD, n (%) | 3 (4) | 1 (12) | 2 (2) | 0.26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection, n (%) | 41 (49) | 7 (88) | 34 (45) | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding, n (%)a | 56 (68) | 3 (37) | 53 (71) | 0.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prolonged intubation, (%)b | 19 (23) | 3 (37) | 16 (21) | 0.37 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arrhythmia, n (%)c | 16 (19) | 2 (25) | 14 (19) | 0.65 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acute renal failure, n (%)d | 13 (16) | 3 (37) | 10 (13) | 0.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acute cerebral event, n (%)e | 10 (12) | 1 (12) | 9 (12) | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hepatic dysfunction, n (%)f | 15 (18) | 3 (37) | 12 (16) | 0.15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thromboembolic event, n (%)g | 9 (11) | 1 (12) | 8 (11) | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dialysis, n (%) | 8 (10) | 2 (25) | 6 (8) | 0.19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean RA pressure, mmHg (range)h | 12 (9–17) | 18 (15–20) | 12 (9–15) | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean PA pressure, mmHg (range)h | 26 (23–30) | 24 (23–28) | 26 (23–30.7) | 0.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac output, U/minute (range)h | 5.5 (4.8–6) | 4.5 (4.4–5.6) | 5.5 (4.9–6.2) | 0.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| bCardiac index, U/minute/m2 (range) | 2.7 (2.4–3.1) | 2.4 (2.1–2.9) | 2.8 (2.4–3.2) | 0.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump, RPM (range) | 9400 (9200–9600) | 9300 (9150–9450) | 9400 (9200, 9600) | 0.45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump flow, l/minute (range) | 5.2 (4.5–5.5) | 4.3 (3.8–4.5) | 5.2 (4.7–5.5) | 0.0011 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LOS, days (range) | 17.5 (11–27.5) | 11 (8–45) | 18.5 (12.2–27.7) | 0.48 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Duration of inotropic support, hours (range) | 114 (66.5–166.5) | 157 (98.2–954) | 111.5 (66–160) | 0.078 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RV failure, n (%) | 20 (24) | 4 (50) | 16 (21) | 0.16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LOS > 30 days, n (%) | 14 (17) | 2 (25) | 12 (16) | 0.61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Death or RV failure, n (%) | 20 (24) | 4 (50) | 16 (21) | 0.21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Bleeding requiring blood transfusion more than 24 hours after surgery. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b Mechanical ventilation for more than 1 week or need for tracheostomy. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c Haemodynamically significant arrhythmia or requiring cardioversion. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| d Renal failure requiring dialysis, increase in creatinine to > 2 or by > 50% from baseline. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| e Any stroke, brain haemorrhage, or hyperperfusion injury. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| f Liver enzymes > 300 or bilirubin > 5.0 after surgery. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| g Any embolic event after surgery. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| h The haemodynamic data represent the last measurement before taking out the pulmonary artery catheter; pump flow and RPM. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CMH/HMH: 1/8 perioperative (in 30 days) I/D: 7/75 perioperative (in 30 days) Both groups combined (post 30 days): multiorgan failure n = 2, intractable right HF n = 2, hyperperfusion brain injury n = 2, sepsis n = 1, uncontrollable bleeding n = 1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See above for NYHA class change | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CF axial LVAD therapy may be feasible in patients with end-stage RCM or HCM and may prove to become a useful option to treat these patients who have end-stage HF. However, the present preliminary report lacks the statistical power to make conclusions regarding survival and prospective clinical trials will be required to assess whether LVAD therapy should be used routinely in this challenging group of patients | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Because results for BTT and DT patients in each group were mostly combined within RCM/HCM and I/D groups it is difficult to extract useful data. Most patients received DT rather than BTT. The hospital stays associated with LVAD implantation were relatively short. Please note that it is not possible to split BTT + DT except for actuarial survival; authors state ‘the percentage of patients considered DT was significantly higher in the DCM/ICM group as compared with the RCM/HCM group’. To assess the possibility of a selection bias data were reanalysed in the BTT patients only by excluding all the DT patients in both groups (see above). There were no significant differences between the two analyses | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Topilsky 2011b80
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Topilsky Year of publication: 2011 Country: USA Study design: Retrospective observational Study setting: Hospital Number of centres: One Duration of study: February 2007 to August 2010 Follow-up period: Mean 321 days (range 106–602 days) Funding: Not reported |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To determine if echocardiographic variables 1 month after surgery suggesting appropriate degree of LV unloading and an adequate forward flow are associated with (‘important in determining’) clinical outcomes after the initial successful LVAD implantation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 76 (47 DT, 29 BTT) Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported (probably 0 other than deaths within 30 days) Inclusion criteria: All consecutive HMII recipients at clinic (see comment below) Exclusion criteria: Not reported Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): 63.2 years (12) Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: 80% male Race: Mostly Caucasian Diagnosis: Restrictive CM (11%), ischaemic CM (51%) dilated CM (38%) Note: the population is almost identical to Topilsky et al. (2011a)79 through also described as consecutive HMII recipients over the same period (other than a 3 months longer of June July August) there were fewer (rather than more) patients in this study than in the other (i.e. 76 vs. 83 in Topilsky et al.79). As the emphasis of this study80 was prognostic and outcomes reported were mostly overlapping limited data has been extracted |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: 47 DT; 29 BTT – restrictive CM (11%), ischaemic CM (51%) dilated CM (38%) Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: 30-day results from echocardiography that potentially could be prognostic for 90-day outcomes. Population divided into poor 90-day post-surgery outcomes (PO) n = 30 (persistent NYHA class III+ or readmission for HF between 30 and 90 days, or dead by 90 days) vs. the remainder termed ‘normal’ 90-day post-surgery outcomes (NO), n = 46. (Patients dead within 30 days of surgery were excluded from analyses) Duration of treatment: Variable (to death, explants or HT) Percentage of patients using inotropes: PO 60%; NO 69% Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Association of echocardiography features with 90-day outcomes Secondary outcomes: Not applicable Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: Mean 321 days (range 106–602 days)Number of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableRandomised/includedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableExcludedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableMissing participantsNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableWithdrawalsNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicable |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Randomised/included | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Excluded | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Missing participants | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Withdrawals | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CharacteristicsNormal outcome (NO; n = 46)Adverse outcome (PO; n = 30)p-valueAge (years)61.9 ± 1463.9 ± 110.5Sex, male (%)75900.3Race (%)0.4 Caucasian9694 African American23 Asian20 Native American03Diabetes mellitus (%)20370.1Chronic renal failure (%)44630.1Atrial fibrillation (%)15200.6AICD44370.4Weight (kg)83.7 ± 1988.2 ± 210.4BSA2.0 ± 0.22.0 ± 0.20.6NYHA class IV (%)44760.02Prior sternotomy (%)42500.7Pre-operative IABP (%)25400.2Pre-operative inotropic use60690.5Pre-operative mechanical ventilation030.2DT (%)56700.4Type of cardiomyopathy (%)0.2 Ischaemic5643 Restrictive520 Dilated3937Heart rate (b.p.m.)75.5 ± 1575.5 ± 130.9Systolic BP (mmHg)98.3 ± 1198.3 ± 170.9Diastolic BP (mmHg)66.8 ± 1062.5 ± 100.1Haemoglobina12.5 ± 211.4 ± 120.02Bilirubina1.23 ± 0.61.12 ± 0.80.5AST59 ± 9081 ± 2310.6ALT88 ± 20471 ± 1970.7BUNa28 ± 1330 ± 140.6Creatininea1.5 ± 0.81.6 ± 0.60.5Prothrombin INR1.4 ± 0.41.4 - ± 0.40.9NT-pro-BNPa6567 ± 61235652 ± 60350.6Log-NT-pro-BNP8.4 ± 0.98.1 ± 1.10.4LM scorea7.8 ± 48.4 ± 70.6ACE inhibitors58530.3Beta-blocker77880.9Aldospirone (%)43470.5Digoxin65400.1Diuretics88960.3Statins (%)63430.36-minute walk (m)b322 ± 83308 ± 1170.8VO2 max. (ml/kg/minute)b10.3 ± 2.510.0 ± 3.20.7Left ventricular diastolic diameter (mm)c69.3 ± 864.8 ± 110.06Left ventricular systolic diameter (mm)c63.2 ± 758.2 ± 110.05Ejection fraction (%)c18.8 ± 722.7 ± 110.1cLeft atrial volume index (ml/m2)65.7 ± 2867.2 ± 180.8E/e/ ratioc26.5 ± 1226.3 ± 100.9Tricuspid regurgitation velocity (m/s)c3.1 ± 0.62.8 ± 0.60.05Tricuspid valve lateral annulus velocity (m/s)c0.08 ± 0.030.08 ± 0.030.3RV dysfunction > M0c,d63760.2TRD (m/s)482 ± 66446 ± 720.04RIMPc0.61 ± 0.250.52 ± 0.240.2Mean right atrial pressure (mmHg)c14.4 ± 516.3 ± 80.3Mean pulmonary pressure (mmHg)c36.6 ± 1034.5 ± 80.3PVR (Wood units)e4.6 ± 33.8 ± 30.3RV dP/dtc,e502 ± 208440 ± 1800.2Mean wedge pressure (mmHg)c,e23.1 ± 622.9 ± 60.9Cardiac output (l/minute)c,e3.7 ± 14.1 ± 10.1eCardiac index (l/minute/m2)1.9 ± 0.52.0 ± 0.60.2a Variables measured or calculated before LVAD implantation.b VO2 max. measured in 10 patients in the adverse outcome group and 30 patients in the no adverse outcome group; 6-minute walk assessed in 6 patients in the adverse outcome group and 15 patients in the no adverse outcome group.c Last echocardiographic measurement before LVAD implantation. Variables measured or calculated before LVAD implantation.d RV dysfunction greater than moderate by the qualitative assessment.e Last haemodynamic study before transplant. Note: significant difference between groups in NYHA classification |
Characteristics | Normal outcome (NO; n = 46) | Adverse outcome (PO; n = 30) | p-value | Age (years) | 61.9 ± 14 | 63.9 ± 11 | 0.5 | Sex, male (%) | 75 | 90 | 0.3 | Race (%) | 0.4 | Caucasian | 96 | 94 | African American | 2 | 3 | Asian | 2 | 0 | Native American | 0 | 3 | Diabetes mellitus (%) | 20 | 37 | 0.1 | Chronic renal failure (%) | 44 | 63 | 0.1 | Atrial fibrillation (%) | 15 | 20 | 0.6 | AICD | 44 | 37 | 0.4 | Weight (kg) | 83.7 ± 19 | 88.2 ± 21 | 0.4 | BSA | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 0.6 | NYHA class IV (%) | 44 | 76 | 0.02 | Prior sternotomy (%) | 42 | 50 | 0.7 | Pre-operative IABP (%) | 25 | 40 | 0.2 | Pre-operative inotropic use | 60 | 69 | 0.5 | Pre-operative mechanical ventilation | 0 | 3 | 0.2 | DT (%) | 56 | 70 | 0.4 | Type of cardiomyopathy (%) | 0.2 | Ischaemic | 56 | 43 | Restrictive | 5 | 20 | Dilated | 39 | 37 | Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 75.5 ± 15 | 75.5 ± 13 | 0.9 | Systolic BP (mmHg) | 98.3 ± 11 | 98.3 ± 17 | 0.9 | Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 66.8 ± 10 | 62.5 ± 10 | 0.1 | Haemoglobina | 12.5 ± 2 | 11.4 ± 12 | 0.02 | Bilirubina | 1.23 ± 0.6 | 1.12 ± 0.8 | 0.5 | AST | 59 ± 90 | 81 ± 231 | 0.6 | ALT | 88 ± 204 | 71 ± 197 | 0.7 | BUNa | 28 ± 13 | 30 ± 14 | 0.6 | Creatininea | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 0.5 | Prothrombin INR | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 1.4 - ± 0.4 | 0.9 | NT-pro-BNPa | 6567 ± 6123 | 5652 ± 6035 | 0.6 | Log-NT-pro-BNP | 8.4 ± 0.9 | 8.1 ± 1.1 | 0.4 | LM scorea | 7.8 ± 4 | 8.4 ± 7 | 0.6 | ACE inhibitors | 58 | 53 | 0.3 | Beta-blocker | 77 | 88 | 0.9 | Aldospirone (%) | 43 | 47 | 0.5 | Digoxin | 65 | 40 | 0.1 | Diuretics | 88 | 96 | 0.3 | Statins (%) | 63 | 43 | 0.3 | 6-minute walk (m)b | 322 ± 83 | 308 ± 117 | 0.8 | VO2 max. (ml/kg/minute)b | 10.3 ± 2.5 | 10.0 ± 3.2 | 0.7 | Left ventricular diastolic diameter (mm)c | 69.3 ± 8 | 64.8 ± 11 | 0.06 | Left ventricular systolic diameter (mm)c | 63.2 ± 7 | 58.2 ± 11 | 0.05 | Ejection fraction (%)c | 18.8 ± 7 | 22.7 ± 11 | 0.1 | cLeft atrial volume index (ml/m2) | 65.7 ± 28 | 67.2 ± 18 | 0.8 | E/e/ ratioc | 26.5 ± 12 | 26.3 ± 10 | 0.9 | Tricuspid regurgitation velocity (m/s)c | 3.1 ± 0.6 | 2.8 ± 0.6 | 0.05 | Tricuspid valve lateral annulus velocity (m/s)c | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.3 | RV dysfunction > M0c,d | 63 | 76 | 0.2 | TRD (m/s) | 482 ± 66 | 446 ± 72 | 0.04 | RIMPc | 0.61 ± 0.25 | 0.52 ± 0.24 | 0.2 | Mean right atrial pressure (mmHg)c | 14.4 ± 5 | 16.3 ± 8 | 0.3 | Mean pulmonary pressure (mmHg)c | 36.6 ± 10 | 34.5 ± 8 | 0.3 | PVR (Wood units)e | 4.6 ± 3 | 3.8 ± 3 | 0.3 | RV dP/dtc,e | 502 ± 208 | 440 ± 180 | 0.2 | Mean wedge pressure (mmHg)c,e | 23.1 ± 6 | 22.9 ± 6 | 0.9 | Cardiac output (l/minute)c,e | 3.7 ± 1 | 4.1 ± 1 | 0.1 | eCardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 0.2 | a Variables measured or calculated before LVAD implantation. | b VO2 max. measured in 10 patients in the adverse outcome group and 30 patients in the no adverse outcome group; 6-minute walk assessed in 6 patients in the adverse outcome group and 15 patients in the no adverse outcome group. | c Last echocardiographic measurement before LVAD implantation. Variables measured or calculated before LVAD implantation. | d RV dysfunction greater than moderate by the qualitative assessment. | e Last haemodynamic study before transplant. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristics | Normal outcome (NO; n = 46) | Adverse outcome (PO; n = 30) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 61.9 ± 14 | 63.9 ± 11 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex, male (%) | 75 | 90 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Race (%) | 0.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caucasian | 96 | 94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| African American | 2 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Asian | 2 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Native American | 0 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 20 | 37 | 0.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chronic renal failure (%) | 44 | 63 | 0.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atrial fibrillation (%) | 15 | 20 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AICD | 44 | 37 | 0.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight (kg) | 83.7 ± 19 | 88.2 ± 21 | 0.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class IV (%) | 44 | 76 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prior sternotomy (%) | 42 | 50 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative IABP (%) | 25 | 40 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative inotropic use | 60 | 69 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre-operative mechanical ventilation | 0 | 3 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DT (%) | 56 | 70 | 0.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type of cardiomyopathy (%) | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic | 56 | 43 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restrictive | 5 | 20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dilated | 39 | 37 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 75.5 ± 15 | 75.5 ± 13 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 98.3 ± 11 | 98.3 ± 17 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 66.8 ± 10 | 62.5 ± 10 | 0.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemoglobina | 12.5 ± 2 | 11.4 ± 12 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilirubina | 1.23 ± 0.6 | 1.12 ± 0.8 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AST | 59 ± 90 | 81 ± 231 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALT | 88 ± 204 | 71 ± 197 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUNa | 28 ± 13 | 30 ± 14 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatininea | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prothrombin INR | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 1.4 - ± 0.4 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NT-pro-BNPa | 6567 ± 6123 | 5652 ± 6035 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Log-NT-pro-BNP | 8.4 ± 0.9 | 8.1 ± 1.1 | 0.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LM scorea | 7.8 ± 4 | 8.4 ± 7 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACE inhibitors | 58 | 53 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beta-blocker | 77 | 88 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aldospirone (%) | 43 | 47 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Digoxin | 65 | 40 | 0.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diuretics | 88 | 96 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Statins (%) | 63 | 43 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-minute walk (m)b | 322 ± 83 | 308 ± 117 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VO2 max. (ml/kg/minute)b | 10.3 ± 2.5 | 10.0 ± 3.2 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left ventricular diastolic diameter (mm)c | 69.3 ± 8 | 64.8 ± 11 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left ventricular systolic diameter (mm)c | 63.2 ± 7 | 58.2 ± 11 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ejection fraction (%)c | 18.8 ± 7 | 22.7 ± 11 | 0.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| cLeft atrial volume index (ml/m2) | 65.7 ± 28 | 67.2 ± 18 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E/e/ ratioc | 26.5 ± 12 | 26.3 ± 10 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tricuspid regurgitation velocity (m/s)c | 3.1 ± 0.6 | 2.8 ± 0.6 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tricuspid valve lateral annulus velocity (m/s)c | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RV dysfunction > M0c,d | 63 | 76 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRD (m/s) | 482 ± 66 | 446 ± 72 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RIMPc | 0.61 ± 0.25 | 0.52 ± 0.24 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean right atrial pressure (mmHg)c | 14.4 ± 5 | 16.3 ± 8 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean pulmonary pressure (mmHg)c | 36.6 ± 10 | 34.5 ± 8 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PVR (Wood units)e | 4.6 ± 3 | 3.8 ± 3 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RV dP/dtc,e | 502 ± 208 | 440 ± 180 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean wedge pressure (mmHg)c,e | 23.1 ± 6 | 22.9 ± 6 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiac output (l/minute)c,e | 3.7 ± 1 | 4.1 ± 1 | 0.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| eCardiac index (l/minute/m2) | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Variables measured or calculated before LVAD implantation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b VO2 max. measured in 10 patients in the adverse outcome group and 30 patients in the no adverse outcome group; 6-minute walk assessed in 6 patients in the adverse outcome group and 15 patients in the no adverse outcome group. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c Last echocardiographic measurement before LVAD implantation. Variables measured or calculated before LVAD implantation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| d RV dysfunction greater than moderate by the qualitative assessment. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| e Last haemodynamic study before transplant. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See Topilsky et al. (2011)79 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30-day outcomesCharacteristicNO (n = 46)PO (n = 30)p-valueNative LV and valves Left ventricular diastolic diameter (mm)a58.3 ± 955.0- ± 110.3 Left ventricular systolic diameter (mm)a50.2 ± 1047.4- ± 130.4 Ejection fraction (%)a26.0 ± 1225.6 ± 130.9 Aortic regurgitation > triviala41530.4 Mitral regurgitation > milda9270.4RV function and size Tricuspid regurgitation velocity (m/s)a2.5 ± 0.42.4 ± 0.50.3 TV lateral annulus velocity (m/s)a0.09 ± 0.030.07 ± 0.020.01 RV dysfunction > M0a,b11460.03 aRVEDA (cm2)28.8 ± 729.2 ± 70.8 aRVESA (cm2)18.1 ± 519.8 ± 60.3 RV FAC (%)a38.0 ± 1032.6 ± 130.09 TRDc (m/s)412 ± 60389 ± 550.3 RIMP0.28 ± 0.120.34 ± 0.20.2 TV annulus diametera3.2 ± - 0.43.3 - ± 0.50.7 TR vena contractaa3.6 ± 2.44.4 ± 2.50.3 LV unloading E-wave velocitya0.72 ± 0.10.79 - ± 0.180.2 E/e/ ratioa14.5 ± 422.8 ± 130.3 Aortic valve status (%)aO (29); I (12); C (59)O (18); I (11); C (71)0.5 Atrial septal position (%)aR (3); N (71); L (26)R (24); N (51); L (25)0.01 Atrial septal position to right (%)a3240.004 Ventricular septal position (%)aR (57); N (39); L (4)R (43); N (40); L (17)0.2 Ventricular septal position to left (%)a4170.07 Left ventricular diastolic diameter change (%)a−15.8 ± 11−13.2 ± 190.6 Left ventricular systolic diameter change (%)a−20.5 ± 17−13.7 ± 250.4 ELAPa7.4 ± 414.1 - ± 6< 0.0001 ELAP > 15 mmHg, %a755< 0.0001 Deceleration timea189 ± 51170 ± 630.3 Deceleration time < 150a15420.04 MDI [ms/(cm/s)]a288 ± 137219 ± 1210.09 MDI [< 2 m/(cm/s)]a20560.01LVAD flows by echocardiography Total outputa5.6 ± 25.8 - ± 20.8 LVAD outputa5.3 ± 1.34.7 ± 1.20.3 LVAD output indexa2.7 ± 0.72.4 - ± 0.60.4 Inflow velocitya77.4 ± 4175.5 ± 320.8 Outflow velocitya109.7 ± 3997.3 ± 410.3Controller pump parameters Pump speedc9538 ± 2219542 ± 3010.9 Pump flowc5.5 ± 0.85.3 ± 0.70.5 Pump flow indexc2.6 ± 0.42.6 ± 0.40.8Laboratory and clinical parameters at the day of echocardiography NYHA classI (7); II (68); III (23); IV (2)I (0); II (20); III (43); IV (37)< 0.0001 NYHA class III/IV, %2580< 0.0001 Heart rate (b.p.m.)85.7 ± 1188.7 ± 100.3 Mean BP (mmHg)88.7 ± 787.1 ± 110.6 Atrial fibrillation (%)1116.60.7 NT-pro-BNP2840 ± 14113981 ± 41880.2 Log-NT-pro-BNP7.8 ± 0.58.0 ± 0.70.3 Haemoglobind10.7 ± 210.2 ± 10.2 Albumind3.5 ± 0.73.3 ± 0.60.3 Creatinined0.94 ± 0.31.3 ± 0.70.02 BUNd20.1 ± 927.6 ± 160.05 Bilirubind0.94 ± 0.52.3 ± 6.30.3 ACE inhibitors (%)c30100.03 Beta-blocker (%)c52200.008 Diuretics (%)c83920.390-day post-discharge parameters NYHAdI (36); II (64); III (0); IV (0)I (0); II (4); III (81); IV (15)< 0.0001 NT-pro-BNPd1885 ± 15093125 ± 20670.05 6-minute walk (m)d273 ± 128239 ± 950.0009a Echocardiographic measurement performed 30 days after LVAD implant.b RV dysfunction greater than moderate by quantitative measurement.c Variables measured at the end of 90-day period after LVAD implantation.d Variables measured 30 days after LVAD implantation. Variables potentially associated with poor vs. normal 90-day outcomesVariableOR (95% CI)p-valueLeft ventricular diastolic diameter, mm0.96 (0.89 to 1.03)0.3Left ventricular systolic diameter, mm0.97 (0.92 to 1.03)0.4Mitral regurgitationMi/No 0.48 (0.15 to 1.6); Mo/Mi 2.0 (0.20 to 23.5)0.5Aortic regurgitationMi/No 2.4 (0.48 to 15.4)0.3TR vena contracta1.14 (0.91 to 1.44)0.2Tricuspid regurgitation velocity, m/s0.46 (0.12 to 1.62)0.2Tricuspid lateral annulus velocity, m/s0.7 (0.95 to 9.48)0.02RV dysfunction > moderate1.07 (0.57 to 2.0)0.8RIMP, 0.1 increase1.3 (0.89 to 1.96)0.2RVEDA, cm21.01 (0.93 to 1.09)0.8RVESA, cm21.05 (0.96 to 1.16)0.3RV FAC, %0.96 (0.91 to 1.00)0.07Total output1.07 (0.65 to 1.8)0.8LVAD output0.67 (0.31 to 1.3)0.2LVAD output index0.56 (0.14 to 1.95)0.4Inflow velocity0.99 (0.98 to 1.01)0.8Outflow velocity0.99 (0.98 to 1.01)0.3E/e/ ratio1.15 (0.95 to 1.68)0.2Deceleration time0.99 (0.98 to 1.0)0.3Deceleration time < 150 ms2.04 (1.04 to 4.3)0.04MDI0.99 (0.98 to 1.00)0.07MDI < 2 ms/[cm/s]4.4 (1.22 to 18.0)0.02ELAP1.3 (1.16 to 1.48)< 0.0001ELAP > 15 mmHg15.6 (4.4 to 73.7)< 0.0001Atrial septal positionN/R 0.18 (0.02 to 0.89); L/N 2.02 (0.69 to 6.05)0.07Atrial septal position to the right2.1 (1.02 to 5.6)0.05Ventricular septal positionN/R 2.25 (0.86 to 6.0); L/N 5.9 (1.12 to 119.1)0.01Ventricular septal position to the left3.03 (1.21 to 13.3)0.01Aortic valve statusI/O 1.09 (0.17 to 6.2); C/I 1.46 (0.32 to 7.8)0.7Left ventricular diastolic diameter change, %1.00 (0.96 to 1.06)0.7Left ventricular systolic diameter change, %1.00 (0.98 to 1.04)0.5Laboratory and clinical parameters at the day of echocardiography Haemoglobin0.77 (0.55 to 1.01)0.06 Bilirubin1.09 (0.93 to 1.69)0.3 Albumin0.18 (0.03 to 0.61)0.003 Creatinine3.4 (0.84 to 19.2)0.03 BUN1.04 (1.01 to 1.1)0.04 Platelets0.99 (0.98 to 0.99)0.04 NT-BNP, 100 pg/ml1.18 (0.98 to 1.56)0.08 Log-NT-pro-BNP1.5 (0.71 to 3.6)0.3 NT-pro-BNP change, %0.6 (0.21 to 0.96)0.02 Log-NT-BNP change0.8 (0.4 to 1.6)0.6 NYHA class III or IV12.0 (4.1 to 39.9)< 0.0001 No significant association for the variables related to the valvular function, LV function or size or pump flows, and output. The only variables assessing RV function that were significantly associated with worse 90-day outcome were a lower tricuspid lateral annulus velocity and an interventricular septum deviated to the left, suggesting that the RV flow is not rapid enough to fill the LV. The decrease (%) in NT-pro-BNP from baseline (before LVAD) to 30 days after LVAD implantation was significantly associated with the 90-day adverse outcome (RR 0.6, 95% CI 0.21 to 0.96; p = 0.02 for 1% change) |
Characteristic | NO (n = 46) | PO (n = 30) | p-value | Native LV and valves | Left ventricular diastolic diameter (mm)a | 58.3 ± 9 | 55.0- ± 11 | 0.3 | Left ventricular systolic diameter (mm)a | 50.2 ± 10 | 47.4- ± 13 | 0.4 | Ejection fraction (%)a | 26.0 ± 12 | 25.6 ± 13 | 0.9 | Aortic regurgitation > triviala | 41 | 53 | 0.4 | Mitral regurgitation > milda | 9 | 27 | 0.4 | RV function and size | Tricuspid regurgitation velocity (m/s)a | 2.5 ± 0.4 | 2.4 ± 0.5 | 0.3 | TV lateral annulus velocity (m/s)a | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.01 | RV dysfunction > M0a,b | 11 | 46 | 0.03 | aRVEDA (cm2) | 28.8 ± 7 | 29.2 ± 7 | 0.8 | aRVESA (cm2) | 18.1 ± 5 | 19.8 ± 6 | 0.3 | RV FAC (%)a | 38.0 ± 10 | 32.6 ± 13 | 0.09 | TRDc (m/s) | 412 ± 60 | 389 ± 55 | 0.3 | RIMP | 0.28 ± 0.12 | 0.34 ± 0.2 | 0.2 | TV annulus diametera | 3.2 ± - 0.4 | 3.3 - ± 0.5 | 0.7 | TR vena contractaa | 3.6 ± 2.4 | 4.4 ± 2.5 | 0.3 | LV unloading | E-wave velocitya | 0.72 ± 0.1 | 0.79 - ± 0.18 | 0.2 | E/e/ ratioa | 14.5 ± 4 | 22.8 ± 13 | 0.3 | Aortic valve status (%)a | O (29); I (12); C (59) | O (18); I (11); C (71) | 0.5 | Atrial septal position (%)a | R (3); N (71); L (26) | R (24); N (51); L (25) | 0.01 | Atrial septal position to right (%)a | 3 | 24 | 0.004 | Ventricular septal position (%)a | R (57); N (39); L (4) | R (43); N (40); L (17) | 0.2 | Ventricular septal position to left (%)a | 4 | 17 | 0.07 | Left ventricular diastolic diameter change (%)a | −15.8 ± 11 | −13.2 ± 19 | 0.6 | Left ventricular systolic diameter change (%)a | −20.5 ± 17 | −13.7 ± 25 | 0.4 | ELAPa | 7.4 ± 4 | 14.1 - ± 6 | < 0.0001 | ELAP > 15 mmHg, %a | 7 | 55 | < 0.0001 | Deceleration timea | 189 ± 51 | 170 ± 63 | 0.3 | Deceleration time < 150a | 15 | 42 | 0.04 | MDI [ms/(cm/s)]a | 288 ± 137 | 219 ± 121 | 0.09 | MDI [< 2 m/(cm/s)]a | 20 | 56 | 0.01 | LVAD flows by echocardiography | Total outputa | 5.6 ± 2 | 5.8 - ± 2 | 0.8 | LVAD outputa | 5.3 ± 1.3 | 4.7 ± 1.2 | 0.3 | LVAD output indexa | 2.7 ± 0.7 | 2.4 - ± 0.6 | 0.4 | Inflow velocitya | 77.4 ± 41 | 75.5 ± 32 | 0.8 | Outflow velocitya | 109.7 ± 39 | 97.3 ± 41 | 0.3 | Controller pump parameters | Pump speedc | 9538 ± 221 | 9542 ± 301 | 0.9 | Pump flowc | 5.5 ± 0.8 | 5.3 ± 0.7 | 0.5 | Pump flow indexc | 2.6 ± 0.4 | 2.6 ± 0.4 | 0.8 | Laboratory and clinical parameters at the day of echocardiography | NYHA class | I (7); II (68); III (23); IV (2) | I (0); II (20); III (43); IV (37) | < 0.0001 | NYHA class III/IV, % | 25 | 80 | < 0.0001 | Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 85.7 ± 11 | 88.7 ± 10 | 0.3 | Mean BP (mmHg) | 88.7 ± 7 | 87.1 ± 11 | 0.6 | Atrial fibrillation (%) | 11 | 16.6 | 0.7 | NT-pro-BNP | 2840 ± 1411 | 3981 ± 4188 | 0.2 | Log-NT-pro-BNP | 7.8 ± 0.5 | 8.0 ± 0.7 | 0.3 | Haemoglobind | 10.7 ± 2 | 10.2 ± 1 | 0.2 | Albumind | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 0.3 | Creatinined | 0.94 ± 0.3 | 1.3 ± 0.7 | 0.02 | BUNd | 20.1 ± 9 | 27.6 ± 16 | 0.05 | Bilirubind | 0.94 ± 0.5 | 2.3 ± 6.3 | 0.3 | ACE inhibitors (%)c | 30 | 10 | 0.03 | Beta-blocker (%)c | 52 | 20 | 0.008 | Diuretics (%)c | 83 | 92 | 0.3 | 90-day post-discharge parameters | NYHAd | I (36); II (64); III (0); IV (0) | I (0); II (4); III (81); IV (15) | < 0.0001 | NT-pro-BNPd | 1885 ± 1509 | 3125 ± 2067 | 0.05 | 6-minute walk (m)d | 273 ± 128 | 239 ± 95 | 0.0009 | a Echocardiographic measurement performed 30 days after LVAD implant. | b RV dysfunction greater than moderate by quantitative measurement. | c Variables measured at the end of 90-day period after LVAD implantation. | d Variables measured 30 days after LVAD implantation. | Variable | OR (95% CI) | p-value | Left ventricular diastolic diameter, mm | 0.96 (0.89 to 1.03) | 0.3 | Left ventricular systolic diameter, mm | 0.97 (0.92 to 1.03) | 0.4 | Mitral regurgitation | Mi/No 0.48 (0.15 to 1.6); Mo/Mi 2.0 (0.20 to 23.5) | 0.5 | Aortic regurgitation | Mi/No 2.4 (0.48 to 15.4) | 0.3 | TR vena contracta | 1.14 (0.91 to 1.44) | 0.2 | Tricuspid regurgitation velocity, m/s | 0.46 (0.12 to 1.62) | 0.2 | Tricuspid lateral annulus velocity, m/s | 0.7 (0.95 to 9.48) | 0.02 | RV dysfunction > moderate | 1.07 (0.57 to 2.0) | 0.8 | RIMP, 0.1 increase | 1.3 (0.89 to 1.96) | 0.2 | RVEDA, cm2 | 1.01 (0.93 to 1.09) | 0.8 | RVESA, cm2 | 1.05 (0.96 to 1.16) | 0.3 | RV FAC, % | 0.96 (0.91 to 1.00) | 0.07 | Total output | 1.07 (0.65 to 1.8) | 0.8 | LVAD output | 0.67 (0.31 to 1.3) | 0.2 | LVAD output index | 0.56 (0.14 to 1.95) | 0.4 | Inflow velocity | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.01) | 0.8 | Outflow velocity | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.01) | 0.3 | E/e/ ratio | 1.15 (0.95 to 1.68) | 0.2 | Deceleration time | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.0) | 0.3 | Deceleration time < 150 ms | 2.04 (1.04 to 4.3) | 0.04 | MDI | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.00) | 0.07 | MDI < 2 ms/[cm/s] | 4.4 (1.22 to 18.0) | 0.02 | ELAP | 1.3 (1.16 to 1.48) | < 0.0001 | ELAP > 15 mmHg | 15.6 (4.4 to 73.7) | < 0.0001 | Atrial septal position | N/R 0.18 (0.02 to 0.89); L/N 2.02 (0.69 to 6.05) | 0.07 | Atrial septal position to the right | 2.1 (1.02 to 5.6) | 0.05 | Ventricular septal position | N/R 2.25 (0.86 to 6.0); L/N 5.9 (1.12 to 119.1) | 0.01 | Ventricular septal position to the left | 3.03 (1.21 to 13.3) | 0.01 | Aortic valve status | I/O 1.09 (0.17 to 6.2); C/I 1.46 (0.32 to 7.8) | 0.7 | Left ventricular diastolic diameter change, % | 1.00 (0.96 to 1.06) | 0.7 | Left ventricular systolic diameter change, % | 1.00 (0.98 to 1.04) | 0.5 | Laboratory and clinical parameters at the day of echocardiography | Haemoglobin | 0.77 (0.55 to 1.01) | 0.06 | Bilirubin | 1.09 (0.93 to 1.69) | 0.3 | Albumin | 0.18 (0.03 to 0.61) | 0.003 | Creatinine | 3.4 (0.84 to 19.2) | 0.03 | BUN | 1.04 (1.01 to 1.1) | 0.04 | Platelets | 0.99 (0.98 to 0.99) | 0.04 | NT-BNP, 100 pg/ml | 1.18 (0.98 to 1.56) | 0.08 | Log-NT-pro-BNP | 1.5 (0.71 to 3.6) | 0.3 | NT-pro-BNP change, % | 0.6 (0.21 to 0.96) | 0.02 | Log-NT-BNP change | 0.8 (0.4 to 1.6) | 0.6 | NYHA class III or IV | 12.0 (4.1 to 39.9) | < 0.0001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristic | NO (n = 46) | PO (n = 30) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Native LV and valves | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left ventricular diastolic diameter (mm)a | 58.3 ± 9 | 55.0- ± 11 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left ventricular systolic diameter (mm)a | 50.2 ± 10 | 47.4- ± 13 | 0.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ejection fraction (%)a | 26.0 ± 12 | 25.6 ± 13 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aortic regurgitation > triviala | 41 | 53 | 0.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mitral regurgitation > milda | 9 | 27 | 0.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RV function and size | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tricuspid regurgitation velocity (m/s)a | 2.5 ± 0.4 | 2.4 ± 0.5 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TV lateral annulus velocity (m/s)a | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RV dysfunction > M0a,b | 11 | 46 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| aRVEDA (cm2) | 28.8 ± 7 | 29.2 ± 7 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| aRVESA (cm2) | 18.1 ± 5 | 19.8 ± 6 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RV FAC (%)a | 38.0 ± 10 | 32.6 ± 13 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRDc (m/s) | 412 ± 60 | 389 ± 55 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RIMP | 0.28 ± 0.12 | 0.34 ± 0.2 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TV annulus diametera | 3.2 ± - 0.4 | 3.3 - ± 0.5 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TR vena contractaa | 3.6 ± 2.4 | 4.4 ± 2.5 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LV unloading | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E-wave velocitya | 0.72 ± 0.1 | 0.79 - ± 0.18 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E/e/ ratioa | 14.5 ± 4 | 22.8 ± 13 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aortic valve status (%)a | O (29); I (12); C (59) | O (18); I (11); C (71) | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atrial septal position (%)a | R (3); N (71); L (26) | R (24); N (51); L (25) | 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atrial septal position to right (%)a | 3 | 24 | 0.004 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventricular septal position (%)a | R (57); N (39); L (4) | R (43); N (40); L (17) | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventricular septal position to left (%)a | 4 | 17 | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left ventricular diastolic diameter change (%)a | −15.8 ± 11 | −13.2 ± 19 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left ventricular systolic diameter change (%)a | −20.5 ± 17 | −13.7 ± 25 | 0.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ELAPa | 7.4 ± 4 | 14.1 - ± 6 | < 0.0001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ELAP > 15 mmHg, %a | 7 | 55 | < 0.0001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deceleration timea | 189 ± 51 | 170 ± 63 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deceleration time < 150a | 15 | 42 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MDI [ms/(cm/s)]a | 288 ± 137 | 219 ± 121 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MDI [< 2 m/(cm/s)]a | 20 | 56 | 0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD flows by echocardiography | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total outputa | 5.6 ± 2 | 5.8 - ± 2 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD outputa | 5.3 ± 1.3 | 4.7 ± 1.2 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD output indexa | 2.7 ± 0.7 | 2.4 - ± 0.6 | 0.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inflow velocitya | 77.4 ± 41 | 75.5 ± 32 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outflow velocitya | 109.7 ± 39 | 97.3 ± 41 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Controller pump parameters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump speedc | 9538 ± 221 | 9542 ± 301 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump flowc | 5.5 ± 0.8 | 5.3 ± 0.7 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pump flow indexc | 2.6 ± 0.4 | 2.6 ± 0.4 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Laboratory and clinical parameters at the day of echocardiography | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class | I (7); II (68); III (23); IV (2) | I (0); II (20); III (43); IV (37) | < 0.0001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class III/IV, % | 25 | 80 | < 0.0001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heart rate (b.p.m.) | 85.7 ± 11 | 88.7 ± 10 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean BP (mmHg) | 88.7 ± 7 | 87.1 ± 11 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atrial fibrillation (%) | 11 | 16.6 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NT-pro-BNP | 2840 ± 1411 | 3981 ± 4188 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Log-NT-pro-BNP | 7.8 ± 0.5 | 8.0 ± 0.7 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemoglobind | 10.7 ± 2 | 10.2 ± 1 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albumind | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinined | 0.94 ± 0.3 | 1.3 ± 0.7 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUNd | 20.1 ± 9 | 27.6 ± 16 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilirubind | 0.94 ± 0.5 | 2.3 ± 6.3 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACE inhibitors (%)c | 30 | 10 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beta-blocker (%)c | 52 | 20 | 0.008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diuretics (%)c | 83 | 92 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 90-day post-discharge parameters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHAd | I (36); II (64); III (0); IV (0) | I (0); II (4); III (81); IV (15) | < 0.0001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NT-pro-BNPd | 1885 ± 1509 | 3125 ± 2067 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-minute walk (m)d | 273 ± 128 | 239 ± 95 | 0.0009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Echocardiographic measurement performed 30 days after LVAD implant. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b RV dysfunction greater than moderate by quantitative measurement. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| c Variables measured at the end of 90-day period after LVAD implantation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| d Variables measured 30 days after LVAD implantation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variable | OR (95% CI) | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left ventricular diastolic diameter, mm | 0.96 (0.89 to 1.03) | 0.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left ventricular systolic diameter, mm | 0.97 (0.92 to 1.03) | 0.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mitral regurgitation | Mi/No 0.48 (0.15 to 1.6); Mo/Mi 2.0 (0.20 to 23.5) | 0.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aortic regurgitation | Mi/No 2.4 (0.48 to 15.4) | 0.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TR vena contracta | 1.14 (0.91 to 1.44) | 0.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tricuspid regurgitation velocity, m/s | 0.46 (0.12 to 1.62) | 0.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tricuspid lateral annulus velocity, m/s | 0.7 (0.95 to 9.48) | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RV dysfunction > moderate | 1.07 (0.57 to 2.0) | 0.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RIMP, 0.1 increase | 1.3 (0.89 to 1.96) | 0.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVEDA, cm2 | 1.01 (0.93 to 1.09) | 0.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RVESA, cm2 | 1.05 (0.96 to 1.16) | 0.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RV FAC, % | 0.96 (0.91 to 1.00) | 0.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total output | 1.07 (0.65 to 1.8) | 0.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD output | 0.67 (0.31 to 1.3) | 0.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVAD output index | 0.56 (0.14 to 1.95) | 0.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inflow velocity | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.01) | 0.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outflow velocity | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.01) | 0.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E/e/ ratio | 1.15 (0.95 to 1.68) | 0.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deceleration time | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.0) | 0.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deceleration time < 150 ms | 2.04 (1.04 to 4.3) | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MDI | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.00) | 0.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MDI < 2 ms/[cm/s] | 4.4 (1.22 to 18.0) | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ELAP | 1.3 (1.16 to 1.48) | < 0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ELAP > 15 mmHg | 15.6 (4.4 to 73.7) | < 0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atrial septal position | N/R 0.18 (0.02 to 0.89); L/N 2.02 (0.69 to 6.05) | 0.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atrial septal position to the right | 2.1 (1.02 to 5.6) | 0.05 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventricular septal position | N/R 2.25 (0.86 to 6.0); L/N 5.9 (1.12 to 119.1) | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ventricular septal position to the left | 3.03 (1.21 to 13.3) | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aortic valve status | I/O 1.09 (0.17 to 6.2); C/I 1.46 (0.32 to 7.8) | 0.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left ventricular diastolic diameter change, % | 1.00 (0.96 to 1.06) | 0.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Left ventricular systolic diameter change, % | 1.00 (0.98 to 1.04) | 0.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Laboratory and clinical parameters at the day of echocardiography | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemoglobin | 0.77 (0.55 to 1.01) | 0.06 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilirubin | 1.09 (0.93 to 1.69) | 0.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albumin | 0.18 (0.03 to 0.61) | 0.003 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creatinine | 3.4 (0.84 to 19.2) | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUN | 1.04 (1.01 to 1.1) | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets | 0.99 (0.98 to 0.99) | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NT-BNP, 100 pg/ml | 1.18 (0.98 to 1.56) | 0.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Log-NT-pro-BNP | 1.5 (0.71 to 3.6) | 0.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NT-pro-BNP change, % | 0.6 (0.21 to 0.96) | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Log-NT-BNP change | 0.8 (0.4 to 1.6) | 0.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class III or IV | 12.0 (4.1 to 39.9) | < 0.0001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Used in part to dichotomisation of study participant population | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 deaths recorded as for Topilsky et al.79 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NYHA class changes see tables above | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mortality and HF after LVAD surgery appear to be predominantly determined by echocardiographic evidence of inefficient unloading of the LV and persistence of right ventricular dysfunction. Increased estimated LA pressure and short MDI are associated with worse mid-term outcome. Leftward deviation of the septum is associated with worse outcome as well | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lack of power forced the use of a composite end point. Authors state the results should be viewed as preliminary | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Uriel 201081
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Uriel Year of publication: 2010 Country: France Study design: Retrospective chart review Study setting: Hospital Number of centres: One Duration of study: 1 April 2004 to 1 August 2009 Follow-up period: 370 ± 486 days (range 3–1978 days) Funding: Not reported |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To determine the prevalence of bleeding during CF LVAD support and to identify potential mechanisms for those bleeding events | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: 79 HMII 62 HMXVE Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported Inclusion criteria: All HMII implants between specified dates, 1 April 2004 to 1 August 2009 Exclusion criteria: Not reported Characteristics of participants: Mean age (SD): 56.3 ± 13.7 years Median age: Not reported Age range: Not reported Sex: n = 63 (80%) Race: Not reported Diagnosis: HF |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT and DT, cannot split Type of device used: HMII Any comparison: HMXVE Duration of treatment: Variable 40/63 BTT received HT; 15/79 died Percentage of patients using inotropes: Not reported Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Bleeding. Minor bleeding was defined as observable blood loss without the need for transfusion. Major bleeding was defined as need for blood transfusion > 7 days after device insertion Secondary outcomes: Haemorrhagic stroke; bleeding requiring at least 1 unit of PRBCs; ischaemic stroke; pump thrombosis; systemic embolic events. Stroke was defined as any neurological event lasting > 24 hours and categorised as having a haemorrhagic or thromboembolic aetiology. (Listed but not necessarily reported) Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: 370 ± 486 days (range 3–1978 days)Number of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableRandomised/includedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableExcludedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableMissing participantsNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableWithdrawalsNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicable |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Randomised/included | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Excluded | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Missing participants | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Withdrawals | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII patient characteristics (n = 79)Age (years)56.3 ± 13.7Male sex, n (%)63 (79.8)BMI (kg/m2)25.9 ± 5.0BTT/DT63/14HF aetiology, n (%)ICM33 (45.2)DCM40 (54.8)Previous thoracic surgery, n (%)22 (29.0)Diabetes mellitus, n (%)26 (33.3)Hypertension, n (%)37 (47.4)LVEF16.1 ± 7.2Obstructive lung disease, n (%)6 (7.7)LM score (n = 63)9.1 | HMII patient characteristics (n = 79) | Age (years) | 56.3 ± 13.7 | Male sex, n (%) | 63 (79.8) | BMI (kg/m2) | 25.9 ± 5.0 | BTT/DT | 63/14 | HF aetiology, n (%) | ICM | 33 (45.2) | DCM | 40 (54.8) | Previous thoracic surgery, n (%) | 22 (29.0) | Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 26 (33.3) | Hypertension, n (%) | 37 (47.4) | LVEF | 16.1 ± 7.2 | Obstructive lung disease, n (%) | 6 (7.7) | LM score (n = 63) | 9.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII patient characteristics (n = 79) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 56.3 ± 13.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male sex, n (%) | 63 (79.8) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.9 ± 5.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTT/DT | 63/14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HF aetiology, n (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICM | 33 (45.2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DCM | 40 (54.8) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Previous thoracic surgery, n (%) | 22 (29.0) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 26 (33.3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 37 (47.4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LVEF | 16.1 ± 7.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Obstructive lung disease, n (%) | 6 (7.7) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LM score (n = 63) | 9.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall survival 15 of 79 patients died K–M estimates: Not reported |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bleeding Of 79 patients, 35 had major bleeding events during LVAD support Comparison of those with major bleeding and those withoutCharacteristicBleedNormalp-valueAge (years)60.1 ± 13.553.4 ± 13.20.031Male sex, n (%)30 (85.7)33 (75)0.239Basic metabolic index26.3 ± 5.425.3 ± 4.50.398Ejection fraction (%)16.1 ± 6.016.1 ± 8.30.998BTT, n (%)26/8 (76.5)37/6 (86.1)0.279HF aetiology, n (%) ICM20 (58.8)13 (33.3)0.029 DCM14 (41.2)26 (66.7) Diabetes mellitus12 (35.3)14 (31.8)0.747 Hypertension21 (61.8)16 (46.4)0.026 COPD3 (8.8)3 (6.8)1LM score9.28 ± 4.88.97 ± 5.80.822Anticoagulation, n (%) Warfarin24 (75.0)30 (79.0)0.695 Aspirin19 (59.4)25 (65.8)0.58 Dipyridamole20 (62.5)26 (68.4)0.603 Sites of bleeding events requiring transfusionEvent sitenEventGI24Chest76 pericardial effusion, 1 hemothoraxOther3Dental, LE wound, postmenopausalEpistaxis1Total35 Bleeding frequency per quartile age group Major bleeding events occurred more frequently in older patients, with patients aged > 66 years having twice the risk of bleeding during device support compared with patients aged < 44 years. Age groups: 18–44 years, n = 20; 45–59 years, n = 19 Bleeding was more common in those with ICM as their underlying HF aetiology (58.8% vs. 33.3%; p = 0.03); hypertension was also more common (61.8% vs. 46.4%; p = 0.026)  Eighteen HMII patients with major bleeds were tested and found deficient in HMW forms of vW factor sufficient for diagnosis of acquired vW syndrome |
Characteristic | Bleed | Normal | p-value | Age (years) | 60.1 ± 13.5 | 53.4 ± 13.2 | 0.031 | Male sex, n (%) | 30 (85.7) | 33 (75) | 0.239 | Basic metabolic index | 26.3 ± 5.4 | 25.3 ± 4.5 | 0.398 | Ejection fraction (%) | 16.1 ± 6.0 | 16.1 ± 8.3 | 0.998 | BTT, n (%) | 26/8 (76.5) | 37/6 (86.1) | 0.279 | HF aetiology, n (%) | ICM | 20 (58.8) | 13 (33.3) | 0.029 | DCM | 14 (41.2) | 26 (66.7) | Diabetes mellitus | 12 (35.3) | 14 (31.8) | 0.747 | Hypertension | 21 (61.8) | 16 (46.4) | 0.026 | COPD | 3 (8.8) | 3 (6.8) | 1 | LM score | 9.28 ± 4.8 | 8.97 ± 5.8 | 0.822 | Anticoagulation, n (%) | Warfarin | 24 (75.0) | 30 (79.0) | 0.695 | Aspirin | 19 (59.4) | 25 (65.8) | 0.58 | Dipyridamole | 20 (62.5) | 26 (68.4) | 0.603 | Event site | n | Event | GI | 24 | Chest | 7 | 6 pericardial effusion, 1 hemothorax | Other | 3 | Dental, LE wound, postmenopausal | Epistaxis | 1 | Total | 35 | Transfusion requirement during HT | Intervention HMII | Comparator HMXVE | p-value | PRBCs (U) | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 6.3 ± 0.8 | 0.0055 | Platelets (U) | 8.6 ± 6.4 | 12.5 ± 5.4 | 0.0027 | Fresh frozen plasma (U) | 4.9 ± 3.6 | 9.6 ± 4.9 | 0.0000 | Cryoprecipitate (U) | 2.2 ± 3.5 | 4.3 ± 3.6 | 0.0035 | CellSavera (U) | 3.9 ± 2.3 | 5.0 ± 4.0 | 0.50 | a Haemonetics Corporation Braintree, MA, USA. | |||||||||||||
| Characteristic | Bleed | Normal | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 60.1 ± 13.5 | 53.4 ± 13.2 | 0.031 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male sex, n (%) | 30 (85.7) | 33 (75) | 0.239 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic metabolic index | 26.3 ± 5.4 | 25.3 ± 4.5 | 0.398 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ejection fraction (%) | 16.1 ± 6.0 | 16.1 ± 8.3 | 0.998 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BTT, n (%) | 26/8 (76.5) | 37/6 (86.1) | 0.279 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HF aetiology, n (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ICM | 20 (58.8) | 13 (33.3) | 0.029 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DCM | 14 (41.2) | 26 (66.7) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 12 (35.3) | 14 (31.8) | 0.747 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension | 21 (61.8) | 16 (46.4) | 0.026 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COPD | 3 (8.8) | 3 (6.8) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LM score | 9.28 ± 4.8 | 8.97 ± 5.8 | 0.822 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Anticoagulation, n (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warfarin | 24 (75.0) | 30 (79.0) | 0.695 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aspirin | 19 (59.4) | 25 (65.8) | 0.58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dipyridamole | 20 (62.5) | 26 (68.4) | 0.603 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Event site | n | Event | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GI | 24 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chest | 7 | 6 pericardial effusion, 1 hemothorax | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 3 | Dental, LE wound, postmenopausal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Epistaxis | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 35 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transfusion requirement during HT | Intervention HMII | Comparator HMXVE | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PRBCs (U) | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 6.3 ± 0.8 | 0.0055 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platelets (U) | 8.6 ± 6.4 | 12.5 ± 5.4 | 0.0027 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fresh frozen plasma (U) | 4.9 ± 3.6 | 9.6 ± 4.9 | 0.0000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cryoprecipitate (U) | 2.2 ± 3.5 | 4.3 ± 3.6 | 0.0035 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CellSavera (U) | 3.9 ± 2.3 | 5.0 ± 4.0 | 0.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a Haemonetics Corporation Braintree, MA, USA. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See Bleeding, above | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with the HMII had a high incidence of bleeding events during device support and at HT. All HMII patients had reduced HMW vW factor multimers. The role of these abnormalities in the high incidence of bleeding deserves further investigation. Furthermore, alterations in anticoagulation should be considered during device support and before surgery in patients supported with the HMII | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The conclusions regarding frequency of bleeding appear supported by the evidence. There was a large difference in requirement for blood products associated with HT in HMII supported patients relative to HMXVE supported patients, this may be too large to be explained by the greater use of anticoagulants in the former; however, little other demographic information was provided for the HMXVE group. The measurements of vW factor were not performed systematically and there was missing data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ventura 201182
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock (agreed with Paul Sutcliffe)
| Study details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author surname: Ventura Year of publication: 2011 Country: USA Study design: Comparative retrospective analysis of National Registry data (Organ Procurement and Transplant Network UNOS) Study setting: Not applicable Number of centres: Many, not reported Duration of study: Registry records 2004–9 Follow-up period: Variable Funding: Not reported |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aim of the study | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To compare post-HT patient outcomes for BTT patients with HMII (continuous) and BTT patients with HMXVE (pulsatile) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Participants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total number of participants: HMII 484; HMXVE 673 Sample attrition/dropout: Not reported Inclusion criteria: Any recipient of specified VADs within specified time period in National Registry Exclusion criteria: None stated Characteristics of participants: Mixed population Total number of participants: HMII 484; HMXVE 673 Mean age (SD): HMII 51.27 years (12.6); HM XVE 51.54 years (10.92) Sex: HMII 18.8% female; HM XVE 11.14% female Race: White – HMII 70.25%, HMXVE 69.39%; Hispanic – HMII 5.99%, HMXVE 6.69% Diagnosis: HMII ischaemic 38.8%, idiopathic 39.2%, other 22%; HMXVE ischaemic 41.4%, idiopathic 35.7%, other 22.8% |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication for treatment: BTT alone – HF various pathologies Type of device used: HMII vs. HMXVE Duration of treatment: Variable Percentage of patients using inotropes: HMII 18%; HMXVE 16% Other interventions used: See section Patient's baseline characteristics, below Any FDA or CE approval: Yes – HMII |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcomes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary outcomes: Post-HT survival Secondary outcomes: Post-treatment causes of death; rejection-free survival; HT rejection between transplant and discharge; post-HT hospitalisation for infection Method of assessing outcomes: Medical records Survival: Yes Adverse event: Yes HRQoL: No Length of follow-up: UnclearNumber of participantsInterventionComparator, if presentScreenedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableRandomised/includedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableExcludedNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableMissing participantsNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicableWithdrawalsNot reported/not applicableNot reported/not applicable |
Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | Screened | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Randomised/included | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Excluded | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Missing participants | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | Withdrawals | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of participants | Intervention | Comparator, if present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Screened | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Randomised/included | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excluded | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Missing participants | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Withdrawals | Not reported/not applicable | Not reported/not applicable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient's baseline characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII (n = 484)HMXVE (n = 673)Age (years)51.27 (12.63)51.54 (10.92)SexMale 81.2%Male 88.86%BSA (m2)Weight, kg (BMI kg/m2)83.87 (19.20)90.08 (17.83)Ischaemic causes of HF38.78%41.39% Baseline characteristicsHMII (n = 484)HMXVE (n = 673)p-valueFemale (%)18.8011.14< 0.001Mean (SD) recipient age, years51.27 (12.63)51.54 (10.92)0.707White (%)70.269.390.795Hispanic or Latino (%)5.996.690.715Mean (SD) weight, kg83.87 (19.20)90.08 (17.83)< 0.001Mean (SD) BMI, kg/m227.91 (17.03)28.53 (5.22)0.448Cardiomyopathy (%) Ischaemic38.7841.390.397 Idiopathic39.1835.760.243 Other22.0422.850.776Mean (SD) TRR cardiac output, l/minute4.84 (1.71)4.83 (1.55)0.998Mean (SD) PCW pressure, mmHg18.06 (9.71)19.17 (10.22)0.090Mean (SD) PVR, Wood unit2.39 (1.74)2.29 (2.02)0.402Most recent PRA (%) HLA 1 10%841230.698 HLA 2 10%37640.292 HLA 1 90%10190.452 HLA 2 90%9131.000IABP at transplant (%)2.891.780.231Dialysis before transplant (%)3.725.350.207Inotropes at transplant (%)17.7716.490.580TRR transfusions since listing (%)44.6349.180.136Mean active days on WL Male223.63198.550.187 Female207.37249.610.328Mean Ischaemic time, hours3.383.400.730Mean (STD) serum creatinine at transplant, mg/dl1.3 (0.63)1.3 (0.60)0.490Mean (STD) bilirubin, mg/dl1.3 (2.67)1.0 (1.12)0.032 |
HMII (n = 484) | HMXVE (n = 673) | Age (years) | 51.27 (12.63) | 51.54 (10.92) | Sex | Male 81.2% | Male 88.86% | BSA (m2) | Weight, kg (BMI kg/m2) | 83.87 (19.20) | 90.08 (17.83) | Ischaemic causes of HF | 38.78% | 41.39% | HMII (n = 484) | HMXVE (n = 673) | p-value | Female (%) | 18.80 | 11.14 | < 0.001 | Mean (SD) recipient age, years | 51.27 (12.63) | 51.54 (10.92) | 0.707 | White (%) | 70.2 | 69.39 | 0.795 | Hispanic or Latino (%) | 5.99 | 6.69 | 0.715 | Mean (SD) weight, kg | 83.87 (19.20) | 90.08 (17.83) | < 0.001 | Mean (SD) BMI, kg/m2 | 27.91 (17.03) | 28.53 (5.22) | 0.448 | Cardiomyopathy (%) | Ischaemic | 38.78 | 41.39 | 0.397 | Idiopathic | 39.18 | 35.76 | 0.243 | Other | 22.04 | 22.85 | 0.776 | Mean (SD) TRR cardiac output, l/minute | 4.84 (1.71) | 4.83 (1.55) | 0.998 | Mean (SD) PCW pressure, mmHg | 18.06 (9.71) | 19.17 (10.22) | 0.090 | Mean (SD) PVR, Wood unit | 2.39 (1.74) | 2.29 (2.02) | 0.402 | Most recent PRA (%) | HLA 1 10% | 84 | 123 | 0.698 | HLA 2 10% | 37 | 64 | 0.292 | HLA 1 90% | 10 | 19 | 0.452 | HLA 2 90% | 9 | 13 | 1.000 | IABP at transplant (%) | 2.89 | 1.78 | 0.231 | Dialysis before transplant (%) | 3.72 | 5.35 | 0.207 | Inotropes at transplant (%) | 17.77 | 16.49 | 0.580 | TRR transfusions since listing (%) | 44.63 | 49.18 | 0.136 | Mean active days on WL | Male | 223.63 | 198.55 | 0.187 | Female | 207.37 | 249.61 | 0.328 | Mean Ischaemic time, hours | 3.38 | 3.40 | 0.730 | Mean (STD) serum creatinine at transplant, mg/dl | 1.3 (0.63) | 1.3 (0.60) | 0.490 | Mean (STD) bilirubin, mg/dl | 1.3 (2.67) | 1.0 (1.12) | 0.032 | |||||||||||||||||||
| HMII (n = 484) | HMXVE (n = 673) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | 51.27 (12.63) | 51.54 (10.92) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex | Male 81.2% | Male 88.86% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BSA (m2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight, kg (BMI kg/m2) | 83.87 (19.20) | 90.08 (17.83) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic causes of HF | 38.78% | 41.39% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMII (n = 484) | HMXVE (n = 673) | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Female (%) | 18.80 | 11.14 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean (SD) recipient age, years | 51.27 (12.63) | 51.54 (10.92) | 0.707 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| White (%) | 70.2 | 69.39 | 0.795 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hispanic or Latino (%) | 5.99 | 6.69 | 0.715 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean (SD) weight, kg | 83.87 (19.20) | 90.08 (17.83) | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean (SD) BMI, kg/m2 | 27.91 (17.03) | 28.53 (5.22) | 0.448 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiomyopathy (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic | 38.78 | 41.39 | 0.397 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Idiopathic | 39.18 | 35.76 | 0.243 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 22.04 | 22.85 | 0.776 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean (SD) TRR cardiac output, l/minute | 4.84 (1.71) | 4.83 (1.55) | 0.998 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean (SD) PCW pressure, mmHg | 18.06 (9.71) | 19.17 (10.22) | 0.090 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean (SD) PVR, Wood unit | 2.39 (1.74) | 2.29 (2.02) | 0.402 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Most recent PRA (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HLA 1 10% | 84 | 123 | 0.698 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HLA 2 10% | 37 | 64 | 0.292 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HLA 1 90% | 10 | 19 | 0.452 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HLA 2 90% | 9 | 13 | 1.000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IABP at transplant (%) | 2.89 | 1.78 | 0.231 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dialysis before transplant (%) | 3.72 | 5.35 | 0.207 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inotropes at transplant (%) | 17.77 | 16.49 | 0.580 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRR transfusions since listing (%) | 44.63 | 49.18 | 0.136 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean active days on WL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male | 223.63 | 198.55 | 0.187 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Female | 207.37 | 249.61 | 0.328 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean Ischaemic time, hours | 3.38 | 3.40 | 0.730 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean (STD) serum creatinine at transplant, mg/dl | 1.3 (0.63) | 1.3 (0.60) | 0.490 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean (STD) bilirubin, mg/dl | 1.3 (2.67) | 1.0 (1.12) | 0.032 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actuarial survivalActuarial survivalHMII (n = 484)HMXVE (n = 673)Year 1, %86.4188.68Year 3, %83.3384.07 K–M (data read from graph) Adjusted HR, p = 0.910 HMXVE vs. HMII. Note: about 5% early mortality after HT 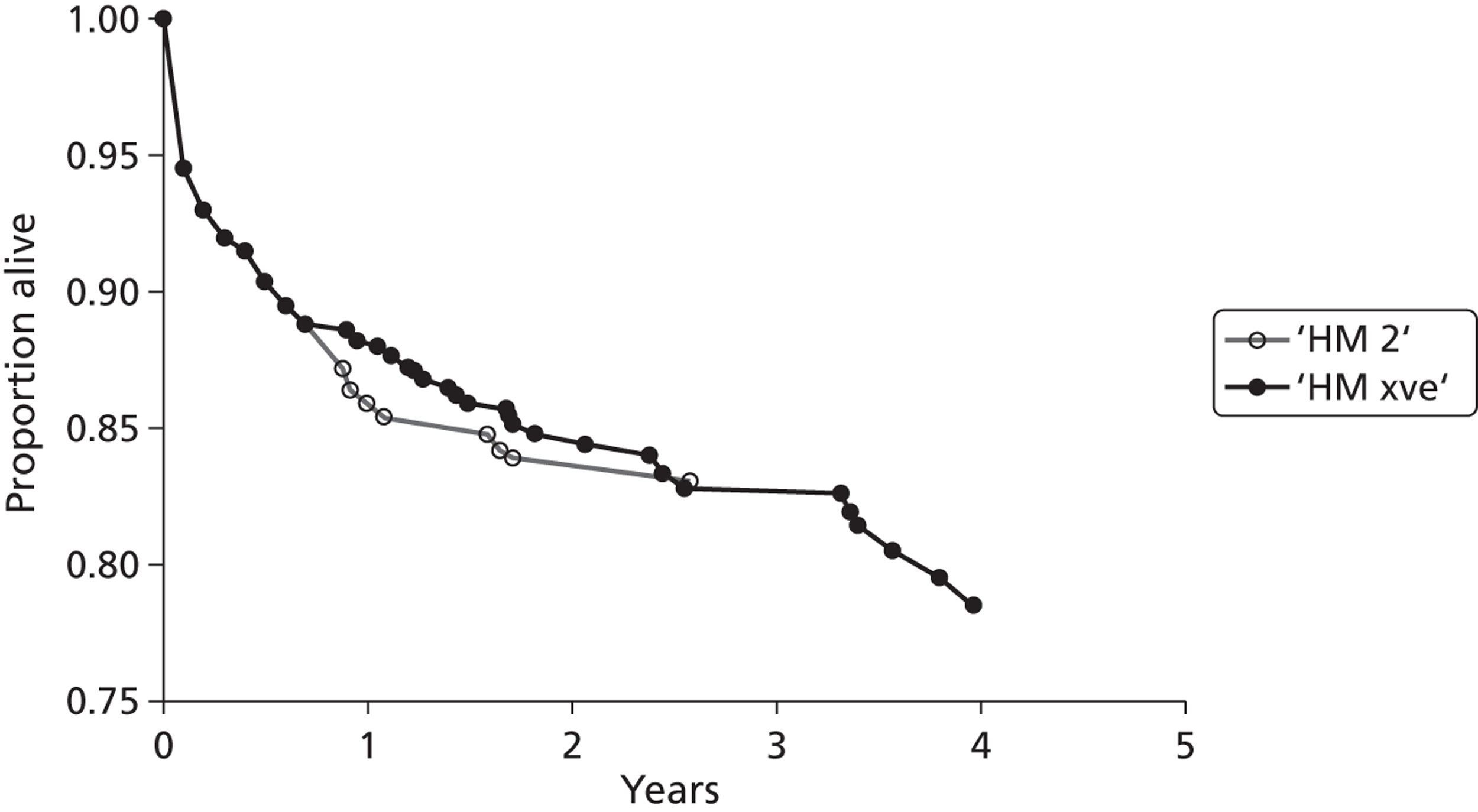 Comparison of post-implant survival after implantation of HMII and HMXVE LVADs for HF. p = 0.91 for difference between devices. |
Actuarial survival | HMII (n = 484) | HMXVE (n = 673) | Year 1, % | 86.41 | 88.68 | Year 3, % | 83.33 | 84.07 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actuarial survival | HMII (n = 484) | HMXVE (n = 673) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year 1, % | 86.41 | 88.68 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year 3, % | 83.33 | 84.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other specified/relevant outcomes reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ComplicationsHMII (n = 484)HMXVE (n = 673)p-valueEarly rejection (HT to discharge (%))27.539.5< 0.001Hospitalised for infection (%)15.329.3< 0.001Length of stay post transplant (days)22.8723.460.749 | Complications | HMII (n = 484) | HMXVE (n = 673) | p-value | Early rejection (HT to discharge (%)) | 27.5 | 39.5 | < 0.001 | Hospitalised for infection (%) | 15.3 | 29.3 | < 0.001 | Length of stay post transplant (days) | 22.87 | 23.46 | 0.749 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Complications | HMII (n = 484) | HMXVE (n = 673) | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Early rejection (HT to discharge (%)) | 27.5 | 39.5 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hospitalised for infection (%) | 15.3 | 29.3 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Length of stay post transplant (days) | 22.87 | 23.46 | 0.749 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse events reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See above | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death post HTHMIIHMXVEGraft failure1525Infection923Cardiovascular717Cerebrovascular32Multiorgan failure813Haemorrhage43Malignancy12Unknown27Other109Total59101 | Cause of death post HT | HMII | HMXVE | Graft failure | 15 | 25 | Infection | 9 | 23 | Cardiovascular | 7 | 17 | Cerebrovascular | 3 | 2 | Multiorgan failure | 8 | 13 | Haemorrhage | 4 | 3 | Malignancy | 1 | 2 | Unknown | 2 | 7 | Other | 10 | 9 | Total | 59 | 101 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause of death post HT | HMII | HMXVE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Graft failure | 15 | 25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infection | 9 | 23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiovascular | 7 | 17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cerebrovascular | 3 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Multiorgan failure | 8 | 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemorrhage | 4 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Malignancy | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unknown | 2 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 10 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 59 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL reported (by group and/or intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not relevant | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Author's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Survival post HT is equally good between different modes of bridging, infections and acute rejection are reduced in HMII recipients relative to HMXVE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reviewer's conclusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The data are generally supportive of authors conclusions. However patients were not randomised to different VADs and balance between groups may have been suboptimal; the proportion of patients who received HMXVE or HMII VADs but who did not later receive a transplant was not reported, and therefore the patients who may have died with VAD were excluded. The mean waiting days before HT was similar in the two groups (male 223 days and female 207 days for HMII, and male 198 days female 250 days for HMXVE) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Appendix 4 Quality assessment forms for primary studies
Adapted from the quality criteria by Thomas et al. 55 and Clegg et al. 4
First author surname: Adamson 201156
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Bogaev 201157
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell b | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes c | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Boyle 200958
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | Not applicable a | |
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell b | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No c | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate to weak |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Brewer 201259
Ret Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Cowger 201060
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No a | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No b | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate to weak |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Demirozu 201161
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate to weak |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Drews 201087
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell a | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Goldstein 200384
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell a | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes c | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes d | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Hasin 201262
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell a | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: John 201063
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell a | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes c | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes d | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No e | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: John 2011a64
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell a | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell b | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes c | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: John 2011b65
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Kato 201266
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Klotz 200688
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate a | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell b | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell c | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate to weak |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Kormos 201067
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Lahpor 201068
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate to weak |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Martin 201069
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell a | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate to weak |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Miller 200770
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | Not applicable a | |
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes c | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Morshuis 200985
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Morshuis 201042
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Nativi 201189
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Oswald 201090
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell a | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell c | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate to weak |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Pagani 200971
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | Not applicable a | |
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes c | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes d | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Pak 201072
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate to weak |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Pal 200973
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | Not applicable | |
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes c | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Petrucci 200974
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | Not applicable a | |
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes c | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes d | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Rogers 201053
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | Not applicable a | |
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Russell 200975
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | Not applicable | |
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate a | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes c | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Strong |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Sandner 2009a91
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Sandner 2009b92
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Schaffer 201176
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Schaffer 200977
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell a | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60%) | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell b | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate to weak |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Schmid 200886
Ret Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias(Methodological strength of study) | Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell b | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Starling 201152
Prospective study Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell a | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No c | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Strueber 201183
Prospective study Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell a | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes b | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes c | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes d | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Strueber 200878
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell a | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell b | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate to weak |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Topilsky 2011a79
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell b | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Topilsky 2011b80
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes a | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Strong to moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Uriel 201081
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Weak |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
First author surname: Ventura 201182
Name of the reviewer: Martin Connock and Paul Sutcliffe (agreed)
| A. Selection bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Are the individuals selected to participate in the study likely to be representative of the target population? | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Not likely | Cannot tell | |
| 2. What percentage of selected individuals agreed to participate? | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | N/A | Cannot tell |
| 3. Summary of selection bias (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| B. Study design | |||||
| 1. What was the study design? |
|
||||
| 2. Was the study described as randomised? If answer to 2 is no, ignore No. 3 and 4 below. If answer yes, answer No. 3 and 4 below |
Yes | No | |||
| 3. If answer was yes, was the method of randomisation described? | Yes | No | |||
| 4. If answer was yes, was the method appropriate? | Yes | No | |||
| Summary of study design (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| C. Confounders | |||||
| 1. Were there important differences between groups prior to the intervention? (e.g. sex, age, health status) |
Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. If yes, indicate the percentage of relevant confounders that were controlled (either in the design (e.g. stratification, matching) or analysis? (80–100%, 60–79%, < 60%) |
80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of confounders (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| D. Blinding | |||||
| 1. Was the outcome assessor aware of the intervention or exposure status of participants? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were the study participants aware of the research question? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of blinding (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| E. Data collection methods | |||||
| 1. Were data collection tools shown to be valid? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Were data collection tools shown to be reliable? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| Summary of data collection (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| F. Withdrawals and dropouts | |||||
| 1. Were withdrawals and dropouts reported in terms of numbers and reasons per group? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 2. Indicate the percentage of participants completing the study (if the percentage differs by groups, record the lowest) | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| Summary of withdrawals and dropouts (Methodological strength of study) |
Strong | Moderate | Weak | ||
| G. Intervention integrity | |||||
| 1. What percentage of participants received the allocated intervention of exposure of interest | 80–100% | 60–79% | < 60% | Cannot tell | |
| 2. Was the consistency of the intervention measured? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 3. Is it likely that subjects received an unintended intervention that may influence the results? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| H. Analysis | |||||
| 1. Indicate the unit of allocation | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 2. Indicate the unit of analysis | Community | Organisation/institution | Practice/office | Provider | Client |
| 3. Are the statistical methods appropriate for the study design? | Yes | No | Cannot tell | ||
| 4. Is the analysis performed by intervention allocation status rather than the actual intervention received? | Yes | No a | Cannot tell | ||
| Global rating for study (overall methodological strength of study – based on section A–F) | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
| Overall rating (to be assessed following discussion by two reviewers) Moderate |
|||||
| Is there any discrepancy between the two reviewers with respect to the different component ratings? | Yes | No | |||
| If yes, indicate the reason for the discrepancy | Oversight | Difference in interpretation of criteria | Difference in interpretation of study | ||
| FINAL DECISION OF REVIEWERS | Strong | Strong to moderate | Moderate | Moderate to weak | Weak |
Appendix 5 List of excluded papers with reasons
| Reference number | Reference | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Benton CR, Sayer G, Ashley K, Flynn R, Nair AP, Domanski MJ, et al. Left ventricular assist devices improve functional class but fail to normalize peak oxygen consumption. J Cardiac Fail 2011;17(Suppl. 1):S40 | Abstract |
| 2 | Healy AH, Mason NO, Hammond ME, Reid BB, Clayson SE, Drakos SG, et al. Allograft rejection in patients supported with continuous flow left ventricular assist devices. Ann Thorac Surg 2011;92:1601–7 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 3 | Swetz KM, Mueller PS, Ottenberg AL, Dib C, Freeman MR, Sulmasy DP. The use of advance directives among patients with left ventricular assist devices. Hosp Prac 2011;39:78–84 | Non-systematic review |
| 4 | Adamson RM, Baradarian S, Chammas J, Norman V, Jaski B, Hoagland P, et al. Can right ventricular failure associated with LVAD insertion be avoided? J Cardiac Fail 2011;17(Suppl. 1):S46 | Abstract |
| 5 | Adamson RM, Jaski B, Hoagland P, Chammas J, Baradarian S, Norman V, et al. Are LVAD support and cardiac transplantation approaching equipoise? J Cardiac Fail 2011;17(Suppl. 1):S38 | Abstract |
| 6 | Adamson RM, Dembitsky WP, Baradarian S, Chammas J, May-Newman K, Chillcott S, et al. Aortic valve closure associated with HeartMate left ventricular device support: technical considerations and long-term results. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:576–82 | Fewer than 50 participants |
| 7 | Aissaoui N, Paluszkiewicz L, Schulte-Eistrup S, Morshuis M, Gummert J. An atypical thrombus in the inflow cannula of the HeartWare left ventricular assist device. Ann Thorac Surg 2011;92:e57 | Case study |
| 8 | Alba AC, Rao V, Ross HJ, Jensen AS, Sander K, Gustafsson F, et al. Impact of fixed pulmonary hypertension on postheart transplant outcomes in bridge-to-transplant patients. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29:1253–8 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 9 | Alba AC, Rao V, Ivanov J, Ross HJ, Delgado DH. Predictors of acute renal dysfunction after ventricular assist device placement. J Cardiac Fail 2009;15:874–81 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 10 | Allen JG, Weiss ES, Schaffer JM, Patel ND, Ullrich SL, Russell SD, et al. Quality of life and functional status in patients surviving 12 months after left ventricular assist device implantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29:278–85 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 11 | Amir O, Radovancevic B, Delgado RM III, Kar B, Radovancevic R, Henderson M, et al. Peripheral vascular reactivity in patients with pulsatile vs axial flow left ventricular assist device support. J Heart Lung Transplant 2006;25:391–4 | Irrelevant outcomes |
| 12 | Anastasiadis K, Antonitsis P, Papakonstantinou C, Westaby S. Use of Jarvik 2000 left ventricular assist device for treating acutely decompensated heart failure. Eur J Cardio Thorac Surg 2009;35:172 | Fewer than 30 participants |
| 13 | Angermayr L, Velasco GM, Busse R. Ventricular assist devices for heart failure. GMS Health Technol Assess 2007;3:1–7. | Written in German |
| 14 | Anyanwu AC. Technique for less invasive implantation of Heartmate II left ventricular assist device without median sternotomy. Sem Thoracic Cardiovasc Surg 2011;23:241–4 | Fewer than 30 participants |
| 15 | Aranda JM, Rogers JG, Aronson KD, Boyle AJ, Russell SD, Edwards B, et al. Quality of life improvements are greater in destination therapy than bridge to transplant patients with a continuous flow left ventricular assist device. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;55(Suppl. 1):A22 | Abstract |
| 16 | Arnaoutakis GJ, George TJ, Kilic A, Weiss ES, Russell SD, Conte JV, et al. Effect of sensitization in US heart transplant recipients bridged with a ventricular assist device: update in a modern cohort. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2011;142:1236–45 | Abstract |
| 17 | Arrieta-Garcia C, Klein LW. Right ventricular assist devices in right ventricular infarction: do they augment right ventricular function sufficiently to improve prognosis? J Invasive Cardiol 2011;23:252–4 | Non-systematic review |
| 18 | Ashrith G, Franzwa J, Mathews E, Goerbig-Campbell J, Suzuki Y, Johnson F. Patients with low socio-economic status undergoing ventricular assist device implant do not have increased occurrence of adverse events. Eur J Heart Fail 2010;9:S193 | Abstract |
| 19 | Aslam S, Hernandez M, Thornby J, Zeluff B, Darouiche RO. Risk factors and outcomes of fungal ventricular-assist device infections. Clin Infect Dis 2010;50:664–71 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 20 | Atluri P, Acker M, Jessup M. The next decade in mechanical assist: advances that will help the patient and the doctor. Curr Opin Cardiol 2011;26:256–60 | Non-systematic review |
| 21 | Baker JN, Ennis SC, Gonczarek KM, Kleinkauf L, Ennis CA, Lam KM, et al. Trend or treason: No increase in thromboembolic events in LVAD patients with atrial fibrillation off coumadin. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28(Suppl. 1):S70 | Abstract |
| 22 | Ball V, Snow AL, Steele AB, Morgan RO, Davila JA, Wilson N, et al. Quality of relationships as a predictor of psychosocial functioning in patients with dementia. J Geriatr Psychiatr Neurol 2010;23:109–14 | Non-VADs intervention |
| 23 | Baumwol J, Macdonald PS, Keogh AM, Kotlyar E, Spratt P, Jansz P, et al. Right heart failure and ‘failure to thrive’ after left ventricular assist device: clinical predictors and outcomes. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:888–95 | Fewer than 50 participants |
| 24 | Bedi M, Kormos R, Winowich S, McNamara DM, Mathier MA, Murali S. Ventricular arrhythmias during left ventricular assist device support. Am J Cardiol 2007;99:1151–3 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 25 | Beiras-Fernandez A, Kur F, Kiefer S, Sodian R, Schmoeckel M, Weis M, et al. Multidrug-resistant gram-positive infections in patients with ventricular assist devices: the role of daptomycin. Transplant Proc 2009;41:2589–91 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 26 | Bentz B, Hupcey JE, Polomano RC, Boehmer JP. A retrospective study of left ventricular assist device-related infections. J Cardiovasc Manag 2004;15:9–16 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 27 | Bhamidipati CM, Ailawadi G, Bergin J, Kern JA. Early thrombus in a HeartMate II left ventricular assist device: a potential cause of hemolysis and diagnostic dilemma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2010;140:e7–8 | Case study |
| 28 | Birks EJ. Current and future status of left ventricular assist devices in the UK. Br J Cardiol 2005;12:333–5 | Non-systematic review |
| 29 | Bomholt T, Moser C, Sander K, Boesgaard S, Kober L, Olsen PS, et al. Driveline infections in patients supported with a HeartMate II: incidence, aetiology and outcome. Scand Cardiovasc J 2011;45:273–8 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 30 | Boyle AJ, Ascheim DD, Russo MJ, Kormos RL, John R, Naka Y, et al. Clinical outcomes for continuous flow left ventricular assist device patients stratified by pre-operative INTERMACS classification. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:402–7 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 31 | Brehm C, Eleuteri K, Wallace S, Soleimani B, Stephenson E, Boehmer J, et al. A. Gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB) following rotary blood pump implantation; Are arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) the culprit lesions? J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30(Suppl. 1):S207–8 | Abstract |
| 32 | Brehm K, Heilmann C, Siepe M, Benk C, Beyersdorf F, Schlensak C. Thoratec paracorporeal biventricular assist device therapy: the Freiburg experience. Eur J Cardio Thorac Surg 2012;41:207–12 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 33 | Brisco MA, Sundareswaran K, Milano CA, Feldman D, Ewald GA, Slaughter MS, et al. Atrial arrhythmias in patients with continuous flow left ventricular assist devices (CF-LVADs): The incidence, the risk, the consequences. Circulation. Conference: American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2011 Orlando, FL United States. Conference Publication 2011;124(Suppl. 1) | Abstract |
| 34 | Brisco MA, Sundareswaran K, Milano CA, Feldman D, Ewald GA, Slaughter MS, et al. Risk and impact of early and late ventricular arrhythmias in patients with continuous flow left ventricular assist devices (CF-LVADs). Circulation Conference: American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2011 Orlando, FL United States. 2011;124(Suppl. 1) | Abstract |
| 35 | Broussard D, Donaldson E, Falterman J, Bates M. Anesthesia for left ventricular assist device insertion: a case series and review. Ochsner J 2011;11:70–7 | Irrelevant outcomes |
| 36 | Brown JB, Hallinan WM, Massey HT, Bankey PE, Cheng JD, Stassen NA, et al. Does the need for noncardiac surgery during ventricular assist device therapy impact clinical outcome? Surgery 2009;146:627–33 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 37 | Bruckner BA, DiBardino DJ, Ning Q, Adeboygeun A, Mahmoud K, Valdes J, et al. High incidence of thromboembolic events in left ventricular assist device patients treated with recombinant activated factor VII. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28:785–90 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 38 | Bull DA, Reid BB, Selzman CH, Mesley R, Drakos S, Clayson S, et al. The impact of bridge-to-transplant ventricular assist device support on survival after cardiac transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2010;140:169–73 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 39 | Bunzel B, Laederach-Hofmann K, Wieselthaler GM, Roethy W, Drees G. Posttraumatic stress disorder after implantation of a mechanical assist device followed by heart transplantation: evaluation of patients and partners. Transplant Proc 2005;37:1365–8 | Irrelevant outcomes |
| 40 | Butler J, Geisberg C, Howser R, Portner PM, Rogers JG, Deng MC, et al. Relationship between renal function and left ventricular assist device use. Ann Thorac Surg 2006;81:1745–51 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 41 | Butler J, Howser R, Portner PM, Pierson RN III. Body mass index and outcomes after left ventricular assist device placement. Ann Thorac Surg 2005;79:66–73 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 42 | Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health (2011) HeartWare® Ventricular Assist System for end stage heart failure: Clinical effectiveness. URL: www.etsad.fr/etsad/afficher_lien.php?id=3890 | Non-systematic review |
| 43 | Camacho M, Baran DA, Martin A, Zucker MJ. Improved survival in High-risk patients with smaller implantable LVAD's: single- center experience over 3 years. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28(Suppl. 1):S274 | Abstract |
| 44 | Cantillon DJ, Tarakji KG, Kumbhani DJ, Smedira NG, Starling RC, Wilkoff BL. Improved survival among ventricular assist device recipients with a concomitant implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm 2010;7:466–71 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 45 | Carrier M, Perrault LP, Bouchard D, Pellerin M, Racine N, White M, et al. Effect of left ventricular assist device bridging to transplantation on donor waiting time and outcomes in Canada. Can J Cardiol 2004;20:501–4 | VADs unclear |
| 46 | Chatterjee S, Williams NN, Ohara ML, Twomey C, Morris JB, Acker MA. Diaphragmatic hernias associated with ventricular assist devices and heart transplantation. Ann Thorac Surg 2004;77:2111–14 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 47 | Cleveland JC Jr, Naftel DC, Reece TB, Murray M, Antaki J, Pagani FD, et al. Survival after biventricular assist device implantation: an analysis of the Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support database. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:862–9 | Not differentiated according to devices |
| 48 | Colacino FM, Arabia M, Danieli GA, Moscato F, Nicosia S, Piedimonte F, et al. Hybrid test bench for evaluation of any device related to mechanical cardiac assistance. Int J Artific Organ 2005;28:817–26 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 49 | Costantini TW, Taylor JH, Beilman GJ. Abdominal complications of ventricular assist device placement. Surg Infect 2005;6:409–18 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 50 | Cowger J, Romano MA, Stulak J, Haft J, Pagani FD, Aaronson KD. Correlates of gastrointestinal bleeding development during LVAD support. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30(Suppl. 1):S155–6 | Abstract |
| 51 | Cowger JA, Sundareswaran K, Rogers JG, Kushwaha SS, Pagani FD, Tatooles A, et al. Patient selection for ventricular assist device therapy in the elderly: Application of the HeartMate II risk score. Circulation Conference: American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2011 Orlando, FL United States. 2011;124(Suppl. 1) | Abstract |
| 52 | Crow S, Chen D, Milano C, Thomas W, Joyce L, Piacentino V, et al. Acquired von Willebrand Syndrome in Continuous flow Ventricular Assist Device Recipients. Ann Thorac Surg 2010;90:1263–9 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 53 | Crow S, John R, Boyle A, Shumway S, Liao K, Colvin-Adams M, et al. Gastrointestinal bleeding rates in recipients of nonpulsatile and pulsatile left ventricular assist devices. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2009;137:208–15 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 54 | Damiano S, Russo F, Campana C, Ghio S, Pellegrini C, Vigano M, et al. Effects of intra-aortic balloon pump on markers of right ventricular dysfunction among end-stage heart failure patients candidates to cardiac transplant or ventricular assist device. Circulation Conference: American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2011 Orlando, FL United States. 2011;124(Suppl. 1) | Abstract |
| 55 | Dandel M, Weng Y, Siniawski H, Potapov E, Lehmkuhl HB, Hetzer R. Long results in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy after weaning from left ventricular assist devices. Circulation 2005;112:1–45 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 56 | Daneshmand MA, Rajagopal K, Lima B, Khorram N, Blue LJ, Lodge AJ, et al. Left ventricular assist device destination therapy versus extended criteria cardiac transplant. Ann Thorac Surg 2010;89:1205–9 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 57 | Dang NC, Topkara VK, Kim BT, Mercando ML, Kay J, Naka Y. Clinical outcomes in patients with chronic congestive heart failure who undergo left ventricular assist device implantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2005;130:1302–9 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 58 | Dang NC, Topkara VK, Leacche M, John R, Byrne JG, Naka Y. Left ventricular assist device implantation after acute anterior wall myocardial infarction and cardiogenic shock: a two- center study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2005;130:693–8 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 59 | Dang NC, Topkara VK, Mercando M, Kay J, Kruger KH, Aboodi MS, et al. Right heart failure after left ventricular assist device implantation in patients with chronic congestive heart failure. J Heart Lung Transplant 2006;25:1–6 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 60 | Delgado R, Bergheim M. HeartMate II left ventricular assist device: a new device for advanced heart failure. Exp Rev Med Devices 2005;2:529–32 | Non-systematic review |
| 61 | Dembitsky WP, Tector AJ, Park S, Moskowitz AJ, Gelijns AC, Ronan NS, et al. Left ventricular assist device performance with long-term circulatory support: lessons from the REMATCH trial. Ann Thorac Surg 78:2123–9 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 62 | Demiro ZT, Radovancevi R, Frazi OH. The effect of continuous, nonpulsatile flow on renal function in patients supported by the heartmate II left ventricular assist device. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29(Suppl. 1):S181 | Abstract |
| 63 | Demirozu ZT, Etheridge WB, Radovancevic R, Frazier OH. Results of HeartMate II left ventricular assist device implantation on renal function in patients requiring post-implant renal replacement therapy. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:182–7 | Fewer than 50 participants |
| 64 | Dewald O, Schmitz C, Diem H, Goehring P, Vetter HO, Roell W, et al. B. Platelet activation markers in patients with heart assist device. Artific Organs 2005;29:292–9 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 65 | Dhruva SS, Redberg RF. Sex-specific outcomes for HeartMate II. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;58:1285–6 | Commentary |
| 66 | Drakos SG, Janicki L, Horne BD, Kfoury AG, Reid BB, Clayson S, et al. Risk factors predictive of right ventricular failure after left ventricular assist device implantation. Am J Cardiol 2010;105:1030–5 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 67 | Drews TNH, Krabatsch T, Potapov E, Stepanenko A, Hubler M, Pasic M, et al. Outpatients on mechanical circulatory support: risk or chance? J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29(Suppl. 1):S89–90 | Abstract |
| 68 | Drews T, Jurmann M, Michael D, Miralem P, Weng Y, Hetzer R. Differences in pulsatile and non-pulsatile mechanical circulatory support in long-term use. J Heart Lung Transplant 2008;27:1096–101 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 69 | Dupont M, Oliveira GH, Naftel DC, Yuan Y, Meyers SL, Schmuhl D, et al. Anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy patients treated with ventricular assist devices frequently need biventricular support: Data from the INTERMACS registry. Circulation Conference: American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2011 Orlando, FL United States. 2011;124(Suppl. 1) | Abstract |
| 70 | Eckman PM, Gonzalez-Stawinski GV, Kendall K, Racicki D, Tang W, Starling RC, et al. Standardized psychosocial evaluation prior to LVAD may predict mortality and length of stay. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29(Suppl. 1):S51–2 | Abstract |
| 71 | El-Banayosy A, Cobaugh D, Zittermann A, Kitzner L, Arusoglu L, Morshuis M, et al. A multidisciplinary network to save the lives of severe, persistent cardiogenic shock patients. Ann Thoracic Surg 2005;80:543–7 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 72 | Elefteriades JA, Botta DM Jr. Avoiding technical pitfalls in left ventricular assist device placement. Cardiol Clin 2011;29:507–14 | Non-systematic review |
| 73 | El-Hamamsy I, Jacques F, Perrault LP, Bouchard D, Demers P, White M, et al. Results following implantation of mechanical circulatory support systems: the Montreal Heart Institute experience. Can J Cardiol 2009;25:107–10 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 74 | Elhenawy AM, Algarni KD, Rodger M, Maciver J, Maganti M, Cusimano RJ, et al. Mechanical circulatory support as a bridge to transplant candidacy. J Cardiac Surg 2011;26:542–7 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 75 | Engin C, Ayik F, Oguz E, Eygi B, Yagdi T, Karakula S, et al. Ventricular assist device as a bridge to heart transplantation in adults. Transplant Proc 2011;43:927–30 | Fewer than 30 participants |
| 76 | Ensor CR, Paciullo CA, Cahoon WD Jr, Nolan PE Jr. Pharmacotherapy for mechanical circulatory support: a comprehensive review. Ann Pharmacother 2011;45:60–77 | Non-systematic review |
| 77 | Etz C, Welp H, Rothenburger M, Tjan TD, Wenzelburger F, Schmidt C, et al. Analysis of platelet function during left ventricular support with the INCOR and EXCOR system. Heart Surg Forum 2004;7:E423–7 | Case reports |
| 78 | Factora FN, Bustamante S, Spiotta A, Avitsian R. Intracranial hemorrhage surgery on patients on mechanical circulatory support: a case series. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 2011;23:30–4 | Case reports |
| 79 | Feller ED, Sorensen EN, Haddad M, Pierson RN III, Johnson FL, Brown JM, et al. Clinical outcomes are similar in pulsatile and nonpulsatile left ventricular assist device recipients. Ann Thorac Surg 2007;83:1082–8 | Not transplant-eligible |
| 80 | Ficke DJ, Lee J, Chaney MA, Bas H, Vidal-Melo MF, Stone ME. Case 6–2010: Noncardiac surgery in patients with a left ventricular assist device. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesthesia 2010;24:1002–9 | Case reports |
| 81 | Fitzpatrick JR III, Frederick JR, Hiesinger W, Hsu VM, McCormick RC, Kozin ED, et al. Early planned institution of biventricular mechanical circulatory support results in improved outcomes compared with delayed conversion of a left ventricular assist device to a biventricular assist device. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2009;137:971–7 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 82 | Fitzpatrick JR III, Frederick JR, Hsu VM, Kozin ED, O'Hara ML, Howell E, et al. Risk score derived from pre-operative data analysis predicts the need for biventricular mechanical circulatory support. J Heart Lung Transplant 2008;27:1286–92 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 83 | Frazier OH, Gemmato C, Myers TJ, Gregoric ID, Radovancevic B, Loyalka P, et al. Initial clinical experience with the HeartMate II axial-flow left ventricular assist device. Texas Heart Inst J 2007;34:275–81 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 84 | Frazier OH, Gregoric ID, Cohn WE. Initial experience with non-thoracic, extraperitoneal, off-pump insertion of the Jarvik 2000 Heart in patients with previous median sternotomy. J Heart Lung Transplant 2006;25:499–503 | Fewer than 30 participants |
| 85 | Garatti A, Bruschi G, Colombo T, Russo C, Lanfranconi M, Milazzo F, et al. Clinical outcome and bridge to transplant rate of left ventricular assist device recipient patients: comparison between continuous flow and pulsatile-flow devices. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2008;34:275–80 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 86 | Garbade J, Langenstroth EM, Barten M, Bittner H, Lhr M, Rastan A, et al. Advanced heart failure managed with new generation of non-pulsatile ventricular assist device. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2011;59 | Abstract |
| 87 | Geens J, Tenson S, Rega F, Droogne W, Vancleemput J, Vanhaecke J, et al. Gender and pre-operative CRP influence survival after LVAD implantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28(Suppl. 1):S84–5 | Abstract |
| 88 | Geisen U, Heilmann C, Beyersdorf F, Benk C, Berchtold-Herz M, Schlensak C, et al. Non-surgical bleeding in patients with ventricular assist devices could be explained by acquired von Willebrand disease. Eur J Cardio Thorac Surg 2008;33:679–84 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 89 | Genovese EA, Dew MA, Teuteberg JJ, Simon MA, Bhama JK, Bermudez CA, et al. Early adverse events as predictors of 1-year mortality during mechanical circulatory support. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29:981–8 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 90 | Genovese EA, Dew MA, Teuteberg JJ, Simon MA, Kay J, Siegenthaler MP, et al. Incidence and patterns of adverse event onset during the first 60 days after ventricular assist device implantation. Ann Thorac Surg 2009;88:1162–70 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 91 | George RS, Yacoub MH, Bowles CT, Hipkin M, Rogers P, Hallas C, et al. Quality of life after removal of left ventricular assist device for myocardial recovery. J Heart Lung Transplant 2008;27:165–72 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 92 | Gerosa G, Di GG, Sani G, Maccherini M, Rinaldi M, De BM, et al. The use of post auricular pedestal is a winning strategy in reducing driveline infections during long-term mechanical support with LVADs. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30(Suppl. 1):S94 | Abstract |
| 93 | Gkouziouta A, Adamopoulos S, Leontiades E, Kostopoulou A, Elivanis MT, Pavlides G, et al. Role of implantable cardioverterdefibrillators in patients with left ventricular assist devices. PACE – Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology: Conference of the World Society of Arrhythmias, ICPES 2011 Athens Greece 2011;34:1336 | Abstract |
| 94 | Goda A, Takayama H, Koeckert M, Pak SW, Sutton EM, Cohen S, et al. Use of ventricular assist devices in patients with mitral valve prostheses. J Cardiac Surg 2011;26:334–7 | Fewer than 30 participants |
| 95 | Goda A, Takayama H, Pak SW, Uriel N, Mancini D, Naka Y, et al. Aortic valve procedures at the time of ventricular assist device placement. Ann Thorac Surg 2011;91:750–4 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 96 | Goldstein DJ, Zucker M, Arroyo L, Baran D, McCarthy PM, Loebe M, et al. Safety and feasibility trial of the MicroMed DeBakey ventricular assist device as a bridge to transplantation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2005;45:962–3 | Research correspondence |
| 97 | Grady KL, Meyer PM, Dressler D, Mattea A, Chillcott S, Loo A, et al. Longitudinal change in quality of life and impact on survival after left ventricular assist device implantation. Ann Thorac Surg 2004;77:1321–7 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 98 | Grady KL, Meyer PM, Dressler D, White-Williams C, Kaan A, Mattea A, et al. Change in quality of life from after left ventricular assist device implantation to after heart transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2003;22:1254–67 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 99 | Grady KL, Meyer PM, Mattea A, Dressler D, Ormaza S, White-Williams C, et al. Change in quality of life from before to after discharge following left ventricular assist device implantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2003;22:322–33 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 100 | Granfeldt H, Koul B, Wiklund L, Peterzen B, Lonn U, Babic A, et al. Risk factor analysis of Swedish Left Ventricular Assist Device (LVAD) patients. Ann Thorac Surg 1999;76:1993–8 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 101 | Gregoric ID, La FS, Myers T, Cohn W, Loyalka P, Kar B, et al. A less invasive approach to axial flow pump insertion. J Heart Lung Transplant 2008;27:423–6 | Fewer than 30 participants |
| 102 | Gregory SD, Timms D, Gaddum N, Mason DG, Fraser JF. Biventricular assist devices: a technical review. Ann Biomed Engin 2011;39:2313–28 | Non-systematic review |
| 103 | Haddad M, Hendry PJ, Masters RG, Mesana T, Haddad H, Davies RA, et al. Ventricular assist devices as a bridge to cardiac transplantation: the Ottawa experience. Artific Organ 2004;28:136–41 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 104 | Haft J, Armstrong W, Dyke DB, Aaronson KD, Koelling TM, Farrar DJ, et al. Hemodynamic and exercise performance with pulsatile and continuous flow left ventricular assist devices. Circulation 2007;116(Suppl. 11):S15 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 105 | Haj-Yahia S, George R, Waligorski S, Dreyfus G, Amrani M, Yacoub M, et al. Limited surgical approaches for LVAD explant following myocardial recovery are associated with low morbidity and improved outcome. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28(Suppl. 1):S130 | Abstract |
| 106 | Hasin T, Topilsky Y, Boilson BA, Schirger JA, Edwards BS, Clavell AL, et al. Impaired exercise tolerance after continuous axial flow pump implantation is associated with reduced survival. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30(Suppl. 1):S156 | Abstract |
| 107 | Healy AH, Mason NO, Hammond ME, Reid BB, Clayson SE, Drakos SG, et al. Allograft rejection in patients supported with continuous flow left ventricular assist devices. Ann Thorac Surg 2011;92:1601–7 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 108 | Heflin LA, Snyder TA, Nelson KE, Long JW, Horstmanshof DA. Time to reconsider VAD therapy? A review of mortality and quality of life in advanced heart failure clinical trials. Journal of Cardiac Failure. Conference: 14th Annual Scientific Meeting Heart Failure Society of America San Diego, CA United States. Conference Start: 20100912 Conference End: 20100915. Conference Publication: (var.pagings). 2010;16(Suppl. 1):S49 | Abstract |
| 109 | Heilmann C, Kuijpers N, Beyersdorf F, Berchtold-Herz M, Trummer G, Stroh AL, et al. Supportive psychotherapy for patients with heart transplantation or ventricular assist devices. Eur J Cardiothoracic Surg 2011;39:e44–50 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 110 | Hennig F, Stepanenko A, Krabatsch T, Potapov EV, Hetzer R. Mechanical circulatory support in restrictive cardiomyopathy. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30(Suppl. 1):S161 | Abstract |
| 111 | Hernandez AF, Grab JD, Gammie JS, O'Brien SM, Hammill BG, Rogers JG, et al. A decade of short-term outcomes in post cardiac surgery ventricular assist device implantation: data from the Society of Thoracic Surgeons' National Cardiac Database. Circulation 2007;116:606–12 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 112 | Hernandez AF, Shea AM, Milano CA, Rogers JG, Hammill BG, O'Connor CM, et al. Long-term outcomes and costs of ventricular assist devices among Medicare beneficiaries. JAMA 2008;300:2398–406 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 113 | Hetzer R, Krabatsch T, Stepanenko A, Hennig E, Potapov EV. Long-term biventricular support with the heartware implantable continuous flow pump. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29:822–4 | Letter |
| 114 | Holman WL, Kormos RL, Naftel DC, Miller MA, Pagani FD, Blume E, et al. Predictors of death and transplant in patients with a mechanical circulatory support device: a multi-institutional study. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28:44–50 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 115 | Holman WL, Pae WE, Teutenberg JJ, Acker MA, Naftel DC, Sun BC, et al. INTERMACS: interval analysis of registry data. J Am Coll Surg 2009;208:755–61 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 116 | Holman WL, Park SJ, Long JW, Weinberg A, Gupta L, Tierney AR, et al. Infection in permanent circulatory support: experience from the REMATCH trial. J Heart Lung Transplant 2004;23:1359–65 | Not transplant-eligible |
| 117 | Hong KN, Iribarne A, Yang J, Ramlawi B, Takayama H, Naka Y, et al. Do posttransplant outcomes differ in heart transplant recipients bridged with continuous and pulsatile flow left ventricular assist devices? Ann Thorac Surg 2011;91:1899–906 | Unable to determine the number of patients with VentrAssist. Cannot conclude if less than 80% of included devices were used in this study |
| 118 | Hoshi H, Shinshi T, Takatani S. Third-generation blood pumps with mechanical noncontact magnetic bearings. Artific Organ 2006;30:324–38 | Non-systematic review |
| 119 | Houghton P. Living with the Jarvik 2000: a five-plus year experience. Artific Organ 2006;30:322–3 | Editorial |
| 120 | Huang R, Deng M, Rogers JG, Howser R, Portner PM, Pierson RN III, et al. Effect of age on outcomes after left ventricular assist device placement. Transplant Proc 2006;38:1496–8 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 121 | Hubler S, Potapov EV, Loebe M, Nasseri BA, Gosmann D, Hoffmann K, et al. Development of a database of patients supported by ventricular assist devices. ASAIO J 2003;49:340–4 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 122 | John R, Kamdar F, Liao K, Colvin-Adams M, Boyle A, Joyce L. Improved survival and decreasing incidence of adverse events with the HeartMate II left ventricular assist device as bridge-to-transplant therapy. Ann Thorac Surg 2008;86:1227–34 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 123 | John R, Kamdar F, Liao K, Colvin-Adams M, Miller L, Joyce L, et al. Low thromboembolic risk for patients with the Heartmate II left ventricular assist device. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2008;136:1318–23 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 124 | Joyce DL, Conte JV, Russell SD, Joyce LD, Chang DC. Disparities in access to left ventricular assist device therapy. J Surg Res 2009;152:111–17 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 125 | Jurmann MJ, Weng Y, Drews T, Pasic M, Hennig E, Hetzer R. Permanent mechanical circulatory support in patients of advanced age. Eur J Cardio Thorac Surg 2004;25:610–18 | Not transplant-eligible |
| 126 | Kalya AV, Tector AJ, Crouch JD, Downey FX, McDonald ML, Anderson AJ, et al. Comparison of Novacor and HeartMate vented electric left ventricular assist devices in a single institution. J Heart Lung Transplant 2005;24:1973–5 | Unclear HM VAD type |
| 127 | Kamdar F, Boyle A, Liao K, Colvin-Adams M, Joyce L, John R. Effects of centrifugal, axial, and pulsatile left ventricular assist device support on end-organ function in heart failure patients. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28:352–9 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 128 | Kashiwa K, Nishimura T, Kubo H, Tamai H, Baba A, Ono M, et al. Study of device malfunctions in patients with implantable ventricular assist devices living at home. J Artific Organ 2010;13:134–8 | Fewer than 30 participants |
| 129 | Kato TS, Farr M, Schulze PC, Maurer M, Shahzad K, Iwata S, et al. Usefulness of two-dimensional echocardiographic parameters of the left side of the heart to predict right ventricular failure after left ventricular assist device implantation. Am J Cardiol 2012;109:246–51 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 130 | Kavarana MN, Sinha P, Naka Y, Oz MC, Edwards NM. Mechanical support for the failing cardiac allograft: a single-centre experience. J Heart Lung Transplant 2003;22:542–7 | Not transplant-eligible |
| 131 | Ketchum ES, Moorman AJ, Fishbein DP, Mokadam NA, Verrier ED, Aldea GS, et al. Predictive value of the Seattle Heart Failure Model in patients undergoing left ventricular assist device placement. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29:1021–5 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 132 | Khot UN, Mishra M, Yamani MH, Smedira NG, Paganini E, Yeager M, et al. Severe renal dysfunction complicating cardiogenic shock is not a contraindication to mechanical support as a bridge to cardiac transplantation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;41:381–5 | Unclear HM VAD type |
| 133 | Kimball PM, Flattery M, McDougan F, Kasirajan V. Cellular immunity impaired among patients on left ventricular assist device for 6 months. Ann Thorac Surg 2008;85:1656–61 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 134 | Kirklin JK, Naftel DC, Kormos RL, Stevenson LW, Pagani FD, Miller MA, et al. Second INTERMACS annual report: more than 1,000 primary left ventricular assist device implants. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29:1–10 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 135 | Komoda T, Drews T, Hetzer R, Lehmkuhl HB. Optimal body surface area for incor left ventricular assist device implantation. Carden Jennings Publishing Co. Ltd. Heart Surgery Forum 2010;13:S148 | Abstract |
| 136 | Komoda T, Drews T, Hetzer R, Lehmkuhl HB. New prioritization of heart transplant candidates on mechanical circulatory support in an era of severe donor shortage. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29:989–96 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 137 | Komoda T, Drews T, Lehmkuhl HB, Hetzer R. Role of ventricular assist devices in the German heart allocation system. J Artific Organ 2006;9:29–33 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 138 | Komoda T, Drews T, Lehmkuhl HB, Hetzer R. Lower body surface area is highly related to mortality due to stroke or systemic bleeding in patients receiving an axial flow blood pump as left ventricular assist device. Circulation Conference: American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2011 Orlando, FL United States. 2011;124(Suppl. 1) | Abstract |
| 139 | Komoda T, Hetzer R, Lehmkuhl HB. Who should be delisted from urgent heart transplantation in Germany? ASAIO J 2009;55:452–5 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 140 | Komoda T, Komoda S, Dandel M, Weng Y, Hetzer R. Explantation of INCOR left ventricular assist device after myocardial recovery. J Cardiac Surg 2008;23:642–7 | Fewer than 30 participants |
| 141 | Krabatsch T. Is bridge to recovery more likely with pulsatile left ventricular assist devices than with nonpulsatile-flow systems? Ann Thorac Surg 2011;91:1335–41 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 142 | Krabatsch T, Schweiger M, Stepanenko A, Kukucka M, Vierecke J, Lehmkuhl HB, et al. Mechanical circulatory support-results, developments and trends. J Cardiovasc Translational Res 2011;4:332–9 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 143 | Krabatsch T, Stepanenko A, Drews T, Schweiger M, Siniawski H, Lehmkuhl H, et al. Mechanical circulatory support with the heart-mate II left ventricular assist device. Heart Surg Forum 2010;13:S147–8 | Abstract |
| 144 | Kugler C, Malehsa D, Tegtbur U, Guetzlaff E, Meyer AL, Bara C, et al. Health-related quality of life and exercise tolerance in recipients of heart transplants and left ventricular assist devices: a prospective, comparative study. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:204–10 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 145 | Kuhne M, Sakumura M, Reich SS, Sarrazin JF, Wells D, Chalfoun N, et al. Simultaneous use of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators and left ventricular assist devices in patients with severe heart failure. Am J Cardiol 2010;105:378–82 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 146 | Kurien S, Hughes KA. Anticoagulation and bleeding in patients with ventricular assist devices: walking the tightrope. AACN Advanced Crit Care 2012;23:91–8 | Non-systematic review |
| 147 | Kwon MH, Moriguchi JD, Ardehali A, Jocson R, Marelli D, Laks H, et al. Use of ventricular assist device as a bridge to cardiac transplantation: impact of age and other determinants on outcomes. Tex Heart Inst J 2009;36:214–19 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 148 | Lahpor JR. State of the art: implantable ventricular assist devices. Curr Opin Organ Transplant 2009;14:554–9 | Non-systematic review |
| 149 | Lainez R, Parrino G, Bates M. Right ventricular function and left ventricular assist device placement: clinical considerations and outcomes. Ochsner J 2010;10:241–4 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 150 | Laoutaris ID, Dritsas A, Vartela V, Manginas A, Adamopoulos S, Gouziouta A, et al. Exercise capacity and quality of life in left ventricular assist device recipients of continuous flow intracorporeal support versus pulsatile-flow extracorporeal support. Heart Surg Forum 2010;13:S93 | Abstract |
| 151 | Lazar RM, Shapiro PA, Jaski BE, Parides MK, Bourge RC, Watson JT, et al. Neurological events during long-term mechanical circulatory support for heart failure: the Randomized Evaluation of Mechanical Assistance for the Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure (REMATCH) experience. Circulation 2004;109:2423–7 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 152 | Lee S, Kamdar F, Madlon-Kay R, Boyle A, Colvin-Adams M, Pritzker M, et al. Effects of the HeartMate II continuous flow left ventricular assist device on right ventricular function. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29:209–15 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 153 | Leshnower BG, Gleason TG, O'Hara ML, Pochettino A, Woo YJ, Morris RJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of left ventricular assist device support in postmyocardial infarction cardiogenic shock. Ann Thoracic Surg 2006;81:1365–70 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 154 | Liden H, Haraldsson A, Ricksten SE, Kjellman U, Wiklund L. Does pretransplant left ventricular assist device therapy improve results after heart transplantation in patients with elevated pulmonary vascular resistance? Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2009;35:1029–34 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 155 | Lietz K, Miller LW. Destination therapy: current results and future promise. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2008;20:225–33 | Non-systematic review |
| 156 | Lietz K, Miller LW. Patient selection for left-ventricular assist devices. Curr Opin Cardiol 2009;24:246–51 | Non-systematic review |
| 157 | Lietz K, Long JW, Kfoury AG, Slaughter MS, Silver MA, Milano CA, et al. Outcomes of left ventricular assist device implantation as destination therapy in the post-REMATCH era: implications for patient selection. Circulation 2007;116:497–505 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 158 | Lima B, Kherani AR, Hata JA, Cheema FH, Casher J, Oz MC, et al. Does a pre-left ventricular assist device screening score predict long-term transplantation success? A 2-center analysis. Heart Surg Forum 2006;9:E783–5 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 159 | Liu M, Lin G, Topilsky Y, Hasin T, Boege MA, Kushwaha SS, et al. Decreased right ventricular strain before left ventricular assist device implantation is associated with adverse early outcome. Circulation Conference: American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2011 Orlando, FL United States. 2011;124(Suppl. 1) | Abstract |
| 160 | Lockard KL, DeGore L, Schwarm P, Winowich S, O'Shea G, Siegenthaler M, et al. Lack of improvement in prealbumin at two weeks predicts a poor outcome after mechanical circulatory support. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28(Suppl. 1):S66 | Abstract |
| 161 | Loebe M, Bruckner B, Reardon MJ, van DE, Estep J, Gregoric I, et al. Initial clinical experience of total cardiac replacement with dual HeartMate-II axial flow pumps for severe biventricular heart failure. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc J 2011;7:40–4 | Fewer than 30 participants |
| 162 | Loforte A, Montalto A, Monica PLD, Contento C, Musumeci F. Biventricular support with the HeartWare implantable continuous flow pump: An additional contribution. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29:1443–4 | Editorial |
| 163 | Loforte A, Montalto A, Ranocchi F, Casali G, Luzi G, Della Monica PL, et al. Long-term mechanical support with the HeartMate II LVAS. Transplant Proc 2009;41:1357–9 | Fewer than 30 participants |
| 164 | Loforte A, Montalto A, Ranocchi F, Casali G, Luzi G, Losasso G, et al. Bridge to heart transplantation with mid to long-term VAD mechanical support. Interactive Cardiovascthorac Surg 2009;8:S87–8 | Abstract |
| 165 | Loforte A, Ranocchi F, Montalto A, Casali G, Luzi G, Lilla Delia MP, Sbaragiia F. Long-term VAD mechanical support as bridge to heart transplantation. Eur J Heart Fail 2009;8(Suppl.):103 | Abstract |
| 166 | Long JW, Kfoury AG, Slaughter MS, Silver M, Milano C, Rogers J, et al. Long-term destination therapy with the HeartMate XVE left ventricular assist device: improved outcomes since the REMATCH study. Congestive Heart Fail 2005;11:133–8 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 167 | Mano A, Fujita K, Uenomachi K, Kazama K, Katabuchi M, Wada K, et al. Body mass index is a useful predictor of prognosis after left ventricular assist system implantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28:428–33 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 168 | Mano A, Nakatani T, Oda N, Kato T, Niwaya K, Tagusari O, et al. Which factors predict the recovery of natural heart function after insertion of a left ventricular assist system? J Heart Lung Transplant 2008;27:869–74 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 169 | Martin S, Wellington L, Stevenson K, Sai-Sudhakar C, Firstenberg M, Blais D, et al. Risk of infection after LVAD placement for long-term support by body-mass index and device type. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28(Suppl. 1):S67 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 170 | Mason NO, Kfoury AG, Janicki L, Stoker S, Clayson SP, Thomsen GE, et al. Impact of illness acuity on blood products usage in patients implanted with left ventricular assist devices (LVAD). J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28(Suppl. 1):S277 | Abstract |
| 171 | Matthews JC, Koelling TM, Pagani FD, Aaronson KD. The right ventricular failure risk score a pre-operative tool for assessing the risk of right ventricular failure in left ventricular assist device candidates. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;51:2163–72 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 172 | Melnitchouk S, Jorde U, Takayama H, Uriel N, Colombo P, Yang J, et al. Continuous flow LVAD Destination Therapy versus orthotopic heart transplantation in patients above 65 years of age. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30(Suppl. 1):S125–6 | Abstract |
| 173 | Meyns B, Rega F, Simon A, Klotz S, Schlensak C, Wittwer T, et al. Less invasive surgery with circulite synergy pocket micro-pump reduces adverse events verses traditional VADs. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29(Suppl. 1):S183–4 | Abstract |
| 174 | Mikus E, Stepanenko A, Krabatsch T, Dandel M, Lehmkuhl HB, Loforte A, et al. Left ventricular assist device or heart transplantation: impact of transpulmonary gradient and pulmonary vascular resistance on decision making. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2011;39:310–16 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 175 | Mikus E, Stepanenko A, Krabatsch T, Loforte A, Dandel M, Lehmkuhl HB, et al. Reversibility of fixed pulmonary hypertension in left ventricular assist device support recipients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2011;40:971–7 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 176 | Mitter N, Sheinberg R. Update on ventricular assist devices. Curr Opin Anesthesiol 2010;23:57–66 | Non-systematic review |
| 177 | Moazami N, Sun B, Milano C, John R, Conte J, Adamson R, et al. Pump replacement for lvad failure can be done safely and is associated with low mortality. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29(Suppl. 1):S53 | Abstract |
| 178 | Monkowski DH, Axelrod P, Fekete T, Hollander T, Furukawa S, Samuel R. Infections associated with ventricular assist devices: epidemiology and effect on prognosis after transplantation. Transplant Infect Dis 2007;9:114–20 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 179 | Mookadam F, Kendall CB, Wong RK, Kalya A, Warsame T, Arabia FA, et al. Left ventricular assist devices: physiologic assessment using echocardiography for management and optimization. Ultrasound Med Biol 2012;38:335–45 | Non-systematic review |
| 180 | Morales DL, Lowry AW, Epstein DJ, Rosenthal DN, Chen JM, Almond CS, et al. Outcomes of children implanted with ventricular assist devices in the united states: Analysis of the interagency registry for mechanical circulatory support (INTERMACS). Circulation Conference: American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2011 Orlando, FL United States 2011;124(Suppl. 1) | Abstract |
| 181 | Morgan JA, Brewer RJ, Nemeh HW, Henry SE, Borgi J, Czerska B, et al. Impact of acute renal failure on survival after HMII LVAD implantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29(Suppl. 1):S178 | Abstract |
| 182 | Morgan JA, Naseem TM, Cheema FH, Scripps TB, Russo MJ, Davies RR, et al. A single-institutional 4-year experience comparing HMII and HM I XVE as a bridge to transplant. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28(Suppl. 1):S164 | Abstract |
| 183 | Morgan JA, John R, Lee BJ, Oz MC, Naka Y. Is severe right ventricular failure in left ventricular assist device recipients a risk factor for unsuccessful bridging to transplant and post-transplant mortality. Ann Thorac Surg 2004;77:859–63 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 184 | Morgan JA, John R, Rao V, Weinberg AD, Lee BJ, Mazzeo PA, et al. Bridging to transplant with the HeartMate left ventricular assist device: The Columbia Presbyterian 12-year experience. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2004;127:1309–16 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 185 | Morgan JA, Park Y, Kherani AR, Vigilance DW, Cheema FH, Oz MC, et al. Does bridging to transplantation with a left ventricular assist device adversely affect posttransplantation survival? A comparative analysis of mechanical versus inotropic support. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2003;126:1188–90 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 186 | Morgan JA, Park Y, Oz MC, Naka Y. Device related infections while on left ventricular assist device support do not adversely impact bridging to transplant or posttransplant survival. ASAIO J 2003;49:748–50 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 187 | Morris RJ, Pochettino A, O'Hara M, Gardner TJ, Acker MA. Emergent mechanical support in the community: improvement with early transplant center referral. J Heart Lung Transplant 2005;24:764–8 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 188 | Mufti HN, Legare JF, Osmond S, Baskett RJ. Long term ventricular assist devices: the maritime experience. Can J Cardiol 2011;27(Suppl. 1):S97 | Abstract |
| 189 | Musci M, Loforte A, Potapov EV, Krabatsch T, Weng Y, Pasic M, et al. Body mass index and outcome after ventricular assist device placement. Ann Thorac Surg 2008;86:1236–42 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 190 | Mushtaq A, Xu J, Elias B, Orrego C, Torre-Amione G, Bruckner B, et al. A comparison of established screening scales to predict survival in patients requiring mechanical circulatory support. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28(Suppl. 1):S301 | Abstract |
| 191 | Mussivand T, Holmes KS. Neurological complications with pulsatile and rotary blood pumps. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28(Suppl. 1):S278 | Abstract |
| 192 | Nakajima I, Kato TS, Komamura K, Takahashi A, Oda N, Sasaoka T, et al. Pre- and post-operative risk factors associated with cerebrovascular accidents in patients supported by left ventricular assist device. Single center's experience in Japan. Circulation 2011;75:1138–46 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 193 | Nawata K, Nishimura T, Kyo S, Hisagi M, Kinoshita O, Saito A, et al. Outcomes of midterm circulatory support by left ventricular assist device implantation with descending aortic anastomosis. J Artific Organ 2010;13:197–201 | Fewer than 30 participants |
| 194 | Noor M, Bowles C, Firouzi A, Simon A, Banner NR. Myocardial recovery after support with HeartMate I and HeartMate II left ventricular assist devices. [Retraction of J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:S75]. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:1423 | Erratum |
| 195 | Nunes AJ, Buchholz H, Sinnadurai S, Mullen JC, Singh G, Meyer SR, et al. Clinical outcomes of long-term mechanical circulatory support at a large Canadian transplant centre. Can J Cardiol 2011;27(Suppl. 1):S216 | Abstract |
| 196 | Osaki S, Edwards NM, Johnson MR, Velez M, Munoz A, Lozonschi L, et al. Improved survival after heart transplantation in patients with bridge to transplant in the recent era: a 17-year single-center experience. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28:591–7 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 197 | Osaki S, Edwards NM, Velez M, Johnson MR, Murray MA, Hoffmann JA, et al. Improved survival in patients with ventricular assist device therapy: the University of Wisconsin experience. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2008;34:281–8 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 198 | Osorio J. Continuous flow LVAD improves quality of life. Nature Rev Cardiol 2010;7:360 | Commentary |
| 199 | Pal JD, Piacentino V, Cuevas AD, Depp T, Daneshmand MA, Hernandez AF, et al. Impact of left ventricular assist device bridging on posttransplant outcomes. Ann Thorac Surg 2009;88:1457–61 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 200 | Palardy M, Nohria A, Rivero J, Lakdawala N, Campbell P, Kato M, et al. Right ventricular dysfunction during intensive pharmacologic unloading persists after mechanical unloading. J Cardiac Fail 2010;16:218–24 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 201 | Pamboukian SV, Tallaj JA, Brown RN, Holman WL, Blood M, George JF, et al. Improvement in 2-year survival for ventricular assist device patients after implementation of an intensive surveillance protocol. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:879–87 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 202 | Pasierski T, Buksinska-Lisik M. Left ventricular assist device – unexpected benefits for the failing heart. Kardiologia Polska 2008;66:678–83 | Non-systematic review |
| 203 | Patel CB, Rogers JG. Durable mechanical circulatory support devices. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 2011;54:132–43 | Non-systematic review |
| 204 | Patel ND, Weiss ES, Schaffer J, Ullrich SL, Rivard DC, Shah AS, et al. Right heart dysfunction after left ventricular assist device implantation: a comparison of the pulsatile HeartMate I and axial-flow HeartMate II devices. Ann Thorac Surg 2008;86:832–40 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 205 | Patel SR, Bhatia V, Edwards P, Nucci C, Goldstein D, Maybaum S. Rate of cardiac recovery with combined pharmacological therapy and continuous flow LVAD support. Circulation Conference: American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2011 Orlando, FL United States. 2011;124(Suppl. 1) | Abstract |
| 206 | Patlolla V, Patten RD, DeNofrio D, Konstam MA, Krishnamani R. The effect of ventricular assist devices on post-transplant mortality an analysis of the United network for organ sharing thoracic registry. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009;53:264–71 | Unable to determine what type of Heartmate VAD |
| 207 | Pawale A, Pinney S, Ashley K, Flynn R, Milla F. Anyanwu AC. Implantable LVADs as initial therapy for refractory post myocardial infarction cardiogenic shock – a challenge to the ‘bridge to bridge’ paradigm. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30(Suppl. 1):S160 | Abstract |
| 208 | Pedrotty DM, Welsby I, Daneshmand MA, Blue L, Lodge AJ, Hernandez AF, et al. Bleeding and thromboembloic complications with pulsatile versus non-pulsatile LVADs. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28(Suppl. 1):S84 | Abstract |
| 209 | Piacentino V III, Williams ML, Depp T, Garcia-Huerta K, Blue L, Lodge AJ, et al. Impact of tricuspid valve regurgitation in patients treated with implantable left ventricular assist devices. Ann Thorac Surg 91:1342–6 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 210 | Piacentino V, Troupes CD, Ganapathi AM, Blue LJ, Mackensen GB, Swaminathan M, et al. Clinical impact of concomitant tricuspid valve procedures during left ventricular assist device implantation. Ann Thorac Surg 2011;92:1414–18 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 211 | Potapov EV, Stepanenko A, Krabatsch T, Hetzer R. Managing long-term complications of left ventricular assist device therapy. Curr Opin Cardiol 2011;26:237–44 | Non-systematic review |
| 212 | Potapov EV, Loforte A, Weng Y, Jurmann M, Pasic M, Drews T, et al. Experience with over 1000 implanted ventricular assist devices. J Cardiac Surg 2008;23:185–94 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 213 | Pruijsten RV, de JN, Kirkels JH, Klopping C, Doevendans PA, Oosterom A, et al. Left ventricular assist device: a functional comparison with heart transplantation. Netherlands Heart J 2008;16:41–6 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 214 | Raasch H, Jensen B, Sheridan B, Bowen A, Gehi A, Chung EH, et al. Ventricular assist devices do not treat ventricular arrhythmias: Significant morbidity persists after implantation. Circulation Conference: American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2011 Orlando, FL United States. 2011;124(Suppl. 1) | Abstract |
| 215 | Radovancevic B, Golino A, Vrtovec B, Thomas CD, Radovancevic R, Odegaard P, et al. Is bridging to transplantation with a left ventricular assist device a risk factor for transplant coronary artery disease? J Heart Lung Transplant 2005;24:703–7 | VADs unclear |
| 216 | Radovancevic B, Vrtovec B, Frazier OH. Left ventricular assist devices: an alternative to medical therapy for end-stage heart failure. Curr Opin Cardiol 2003;18:210–14 | Non-systematic review |
| 217 | Radovancevic B, Vrtovec B, de KE, Radovancevic R, Gregoric ID, Frazier OH. End-organ function in patients on long-term circulatory support with continuous- or pulsatile-flow assist devices. J Heart Lung Transplant 2007;26:815–18 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 218 | Raymond AL, Kfoury AG, Bishop CJ, Davis ES, Goebel KM, Stoker S, et al. Obesity and left ventricular assist device driveline exit site infection. ASAIO J 2010;56:57–60 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 219 | Refaat M, Chemaly E, Lebeche D, Gwathmey JK, Hajjar RJ. Ventricular arrhythmias after left ventricular assist device implantation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2008;31:1246–52 | VADs unclear |
| 220 | Refaat MM, Tanaka T, Kormos RL, McNamara D, Teuteberg J, Winowich S, et al. Survival benefit of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators in left ventricular assist device-supported heart failure patients. J Cardiac Fail 2012;18:140–5 | VADs unclear |
| 221 | Robertson JO, Lober C, Smedira NG, Navia JL, Sopko N, Gonzalez-Stawinski GV. One hundred days or more bridged on a ventricular assist device and effects on outcomes following heart transplantation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2008;34:295–300 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 222 | Russo MJ, Hong KN, Davies RR, Chen JM, Sorabella RA, Ascheim DD, et al. Posttransplant survival is not diminished in heart transplant recipients bridged with implantable left ventricular assist devices. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2009;138:1425–32 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 223 | Saeed D, Kidambi T, Shalli S, Lapin B, Malaisrie SC, Lee R, et al. Tricuspid valve repair with left ventricular assist device implantation: is it warranted? J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:530–5 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 224 | Saito S, Matsumiya G, Sakaguchi T, Miyagawa S, Yoshikawa Y, Yamauchi T, et al. Risk factor analysis of long-term support with left ventricular assist system. Circulation 2010;74:715–22 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 225 | Saito S, Sakaguchi T, Sawa Y. Clinical report of long-term support with dual Jarvik 2000 biventricular assist device. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30:845–7 | Commentary |
| 226 | Sandner SE, Zimpfer D, Zrunek P, Dunkler D, Schima H, Rajek A, et al. Renal function after implantation of continuous versus pulsatile flow left ventricular assist devices. J Heart Lung Transplant 2008;27:469–73 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 227 | Santambrogio L, Bianchi T, Fuardo M, Gazzoli F, Veronesi R, Braschi A, et al. Right ventricular failure after left ventricular assist device insertion: preoperative risk factors. Interactive Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2006;5:379–82 | VADs unclear |
| 228 | Sasaki H, Mitchell JD, Jessen ME, Lavingia B, Kaiser PA, Comeaux A, et al. Bridge to heart transplantation with left ventricular assist device versus inotropic agents in status 1 patients. J Cardiac Surg 2009;24:756–62 | VADs unclear |
| 229 | Schenk S, McCarthy PM, Blackstone EH, Feng J, Starling RC, Navia JL, et al. Duration of inotropic support after left ventricular assist device implantation: risk factors and impact on outcome. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2006;131:447–54 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 230 | Schmid C, Welp H, Klotz S, Baba HA, Wilhelm MJ, Scheld HH. Outcome of patients surviving to heart transplantation after being mechanically bridged for more than 100 days. J Heart Lung Transplant 2003;22:1054–8 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 231 | Schroder JN, Daneshmand MA, Villamizar NR, Petersen RP, Blue LJ, Welsby IJ, et al. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in left ventricular assist device bridge-to-transplant patients. Ann Thorac Surg 2007;84:841–5 | VADs unclear |
| 232 | Schulman AR, Martens TP, Russo MJ, Christos PJ, Gordon RJ, Lowy FD, et al. Effect of left ventricular assist device infection on post-transplant outcomes. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28:237–42 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 233 | Schweiger M, Stepanenko A, Vierecke J, Drews T, Potapov E, Hetzer R, et al. Preexisting mitral valve prosthesis in patients undergoing left ventricular assist device implantation. Artific Organ 2012;36:49–53 | Case study had fewer than 30 participants |
| 234 | Sharples LD, Cafferty F, Demitis N, Freeman C, Dyer M, Banner N, et al. Evaluation of the clinical effectiveness of the Ventricular Assist Device Program in the United Kingdom (EVAD UK). J Heart Lung Transplant 2007;26:9–15 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 235 | Sharples LD, Dyer M, Cafferty F, Demiris N, Freeman C, Banner NR, et al. Cost-effectiveness of ventricular assist device use in the United Kingdom: results from the evaluation of ventricular assist device programme in the UK (EVAD-UK). J Heart Lung Transplant 2006;25:1336–43 | Cost effectiveness paper |
| 236 | Shoham S, Shaffer R, Sweet L, Cooke R, Donegan N, Boyce S. Candidemia in patients with ventricular assist devices. Clin Infect Dis 2007;44:e9–12 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 237 | Shuhaiber J, Hur K, Gibbons R. Does the type of ventricular assisted device influence survival, infection, and rejection rates following heart transplantation? J Cardiac Surg 2009;24:250–5 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 238 | Shuhaiber JH, Hur K, Gibbons R. The influence of preoperative use of ventricular assist devices on survival after heart transplantation: propensity score matched analysis. BMJ 2010;340:c392 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 239 | Siegenthaler MP, Brehm K, Strecker T, Hanke T, Notzold A, Olschewski M, et al. The Impella Recover microaxial left ventricular assist device reduces mortality for postcardiotomy failure: a three-center experience. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2004;127:812–22 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 240 | Siegenthaler MP, Martin J, Pernice K, Doenst T, Sorg S, Trummer G, et al. The Jarvik 2000 is associated with less infections than the HeartMate left ventricular assist device. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2003;23:748–54 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 241 | Simon D, Fischer S, Grossman A, Downer C, Hota B, Heroux A, et al. Left ventricular assist device-related infection: treatment and outcome. Clin Infect Dis 2005;40:1108–15 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 242 | Singh M, Shullo M, Kormos RL, Lockard K, Zomak R, Simon MA, et al. Impact of renal function before mechanical circulatory support on posttransplant renal outcomes. Ann Thorac Surg 2011;91:1348–54 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 243 | Slaughter MS, Aaronson KD, Boyce S, Miller LW, McGee EC, Cotts WG, et al. HVAD BTT pivotal trial and Continued Access Program (ADVANCE): Interim report of the expanded study. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30(Suppl. 1):S84–5 | Abstract |
| 244 | Slaughter MS. Implantation of the HeartWare left ventricular assist device. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2011;23:245–7 | Non-systematic review |
| 245 | Slaughter MS, Pagani FD, Rogers JG, Miller LW, Sun B, Russell SD, et al. Clinical management of continuous flow left ventricular assist devices in advanced heart failure. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29:S1–39 | Ineligible for heart transplant |
| 246 | Slaughter MS, Rogers JG, Milano CA, Russell SD, Conte JV, Feldman D, et al. Advanced heart failure treated with continuous flow left ventricular assist device. N Engl J Med 2009;361:2241–51 | Ineligible for heart transplant |
| 247 | Slaughter MS, Tsui SS, El-Banayosy A, Sun BC, Kormos RL, Mueller DK, et al. Results of a multicenter clinical trial with the Thoratec Implantable Ventricular Assist Device. J Thorac Cardiovas Surg 2007;133;1573–80. [Erratum appears in J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2007;134:A34] | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 248 | Sridhar ARM, Mizrahi I, Najjar SS, Hanny-Gilbert C, Shoham S. Epidemiological and microbiological features of ventricular assist device associated infections. Journal of Cardiac Failure.Conference: 14th Annual Scientific Meeting Heart Failure Society of America San Diego, CA United States 2010;16(Suppl. 1):S115 | Abstract |
| 249 | Stahl MA, Richards NM. CE Update on ventricular assist device technology. AACN Adv Crit Care 2009;20:26–36 | Non-systematic review |
| 250 | Stehlik J, Nelson DM, Kfoury AG, Reid BB, Clayson SE, Nelson KE, et al. Outcome of noncardiac surgery in patients with ventricular assist devices. Am J Cardiol 2009;103:709–12 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 251 | Stepanenko A, Krabatsch T, Hennig E, Kaufmann F, Jurmann B, Dranishnikov N, et al. Retrospective hemolysis comparison between patients with centrifugal biventricular assist and left ventricular assist devices. ASAIO J 2011;57:382–7 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 252 | Stepanenko A, Potapov EV, Jurmann B, Lehmkuhl HB, Dandel M, Siniawski H, et al. Outcomes of elective versus emergent permanent mechanical circulatory support in the elderly: a single-center experience. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29:61–5 | Case study had fewer than 30 participants |
| 253 | Stephenson ER, Wallace SB, El-Banayosy A, Brehm C, Soleimani B, Popjes ED, et al. Obesity is not a contraindication to ventricular assist support. J Heart Lung Transplant 2011;30(Suppl. 1):S162 | Abstract |
| 254 | Stern DR, Kazam J, Edwards P, Maybaum S, Bello RA, D'Alessandro DA, et al. Increased incidence of gastrointestinal bleeding following implantation of the HeartMate II LVAD. J Cardiac Surg 2010;25:352–6 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 255 | Stewart GC, Brooks K, Pratibhu PP, Tsang SW, Semigran MJ, Smith CM, et al. Thresholds of physical activity and life expectancy for patients considering destination ventricular assist devices. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28:863–9 | VADs unclear |
| 256 | Stone ML, LaPar DJ, Benrashid E, Mulloy DP, Ailawadi G, Kron IL, et al. The impact of ventricular assist devices on blood product utilization for cardiac transplantation. Circulation Conference: American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2011 Orlando, FL United States 2011;124(Suppl. 1) | Abstract |
| 257 | Strueber M, Meyer A, Malehsa D, Goerler A, Simon A, Haverich A, et al. Implantation of rotary blood pumps into 100 patients: A single centre experience. Interactive Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2009;9:S98 | Abstract |
| 258 | Thompson K, Dhesi P, Nguyen D, Czer L, Moriguchi J, Schwarz E. Evaluation of the HeartMate IITM left ventricular assist device in obese heart failure patients: effects on weight loss. Ann Transplant 2011;16:63–7 | Ineligible for heart transplant |
| 259 | Thunberg CA, Gaitan BD, Arabia FA, Cole DJ, Grigore AM. Ventricular assist devices today and tomorrow. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesthesia 2010;24:656–80 | Non-systematic review |
| 260 | Timms D. A review of clinical ventricular assist devices. Med Engin Phys 2011;33:1041–7 | Non-systematic review |
| 261 | Toda K, Fujita T, Kobayashi J, Shimahara Y, Kitamura S, Seguchi O, et al. Impact of preoperative percutaneous cardiopulmonary support on outcome following left ventricular assist device implantation. Circulation 2012;76:88–95 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 262 | Topkara VK, Kondareddy S, Wan IW, Mann DL, Ewald GA, Moazami N. Changing trends in mechanical circulatory assistance: A single center experience. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;55(Suppl. 1):A18 | Poster |
| 263 | Topkara VK, Dang NC, Barili F, Cheema FH, Martens TP, George I, et al. Predictors and outcomes of continuous veno-venous hemodialysis use after implantation of a left ventricular assist device. J Heart Lung Transplant 2006;25:404–8 | VADs unclear |
| 264 | Topkara VK, Dang NC, Martens TP, Cheema FH, Liu JF, Liang LM, et al. Effect of diabetes on short- and long-term outcomes after left ventricular assist device implantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2005;24:2048–53 | Ineligible for heart transplant |
| 265 | Topkara VK, Kondareddy S, Malik F, Wang IW, Mann DL, Ewald GA, et al. Infectious complications in patients with left ventricular assist device: etiology and outcomes in the continuous flow era. Ann Thorac Surg 2010;90:1270–7 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 266 | Tsukui H, Abla A, Teuteberg JJ, McNamara DM, Mathier MA, Cadaret LM, et al. Cerebrovascular accidents in patients with a ventricular assist device. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2007;134:114–23 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 267 | Tsukui H, Teuteberg JJ, Murali S, McNamara DM, Buchanan JR, Winowich S, et al. Biventricular assist device utilization for patients with morbid congestive heart failure: a justifiable strategy. Circulation 2005;112(Suppl. 9) | VADs unclear |
| 268 | Uriel N, Pak SW, Colombo P, Song R, Mancini D, Naka Y, et al. Thyroid deficiency is common in advanced heart failure and associated with increased operative mortality after assist device implantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29(Suppl. 1):S25 | Abstract |
| 269 | Uriel N, Sharaiha R, Murray L, Yang J, Devaraj KM, Colombo PC, et al. The incidence and etiology of gi bleeding in patients supported by continuous flow left ventricular assist device. Circulation.Conference: American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2011 Orlando, FL United States 2011;124(Suppl. 1) | Abstract |
| 270 | Vierecke J, Schweiger M, Stepanenko A, Dranishnikow N, Stein J, Drews T, et al. Evaluation of scores used to predict right ventricular failure after lvad implantation. Heart Surg Forum 2011;14:S97 | Abstract |
| 271 | Vitali E, Lanfranconi M, Bruschi G, Ribera E, Garatti A, Colombo T, et al. Mechanical circulatory support in severe heart failure: single-center experience. Transplant Proc 2004;36:620–2 | Less than 80% of included devices |
| 272 | Vitali E, Lanfranconi M, Bruschi G, Russo C, Colombo T, Ribera E. Left ventricular assist devices as bridge to heart transplantation: The Niguarda Experience. J Cardiac Surg 2003;18:107–13 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 273 | Vrtovec B, Radovancevic R, Delgado RM, Radovancevic B, Bracey AW, Gregoric ID, et al. Significance of anaemia in patients with advanced heart failure receiving long-term mechanical circulatory support. Eur J Heart Fail 2009;11:1000–4 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 274 | Wang IW, Guthrie T, Ewald GA, Geltman EM, Joseph S, Moazami N. Gastrointestinal bleeding complications in continuous flow LVAD patients – Is it device specific? J Heart Lung Transplant 2010;29(Suppl. 1):S8 | Abstract |
| 275 | Wang SS, Chou NK, Hsu RB, Ko WJ, Yu HY, Chen YS, et al. Heart transplantation in the patient under ventricular assist complicated with device-related infection. Transplant Proc 2004;36:2377–9 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 276 | Weitkemper HH, El-Banayosy A, Arusoglu L, Sarnowski P, Korfer R. Mechanical circulatory support: reality and dreams experience of a single center. J Extra-Corporeal Technol 2004;36:169–73 | Unclear Heartmate VAD type |
| 277 | Welp H, Rukosujew A, Tjan TD, Hoffmeier A, Kosek V, Scheld HH, et al. Effect of pulsatile and non-pulsatile left ventricular assist devices on the renin-angiotensin system in patients with end-stage heart failure. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2010;58(Suppl. 8) | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 278 | Williams M, Casher J, Joshi N, Hankinson T, Warren M, Oz M, et al. Insertion of a left ventricular assist device in patients without thorough transplant evaluations: a worthwhile risk? J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2003;126:436–41 | VADs unclear |
| 279 | Williams ML, Trivedi JR, McCants KC, Prabhu SD, Birks EJ, Oliver L, et al. Heart transplant vs left ventricular assist device in heart transplant-eligible patients. Ann Thorac Surg 2011;91:1330–3 | Cost effectiveness paper |
| 280 | Wolner E, Wieselthaler G. Vienna exprience with ventricular assist devices. Heart Surg Forum 2010;13:S29 | Abstract |
| 281 | Yamani MH, Chuang HH, Ozduran V, Avery RK, Mawhorter SD, Cook DJ, et al. The impact of hypogammaglobulinemia on infection outcome in patients undergoing ventricular assist device implantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2006;25:820–4 | VADs unclear |
| 282 | Yang N, Deutsch S, Paterson EG, Manning KB. Comparative study of continuous and pulsatile left ventricular assist devices on hemodynamics of a pediatric end-to-side anastomotic graft. Cardiovasc Engin Technol 2010;1:88–103 | Pediatric |
| 283 | Zahr F, Ootaki Y, Starling RC, Smedira NG, Yamani M, Thuita L, et al. Preoperative risk factors for mortality after biventricular assist device implantation. J Cardiac Fail 2008;14:844–9 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 284 | Zierer A, Melby SJ, Voelle, RK, Guthrie TJ, Ewald GA, Shelton K, et al. Late-onset driveline infections: the Achilles' heel of prolonged left ventricular assist device support. Ann Thorac Surg 2007;84:515–20 | Concerns non-included VADs |
| 285 | Zimpfer D, Mahr S, Aliabadi A, Groemmer M, Dunkler D, Sandner S, et al. Post-transplant outcome of elective vs LVAD vs urgent patients undergoing cardiac transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2009;28(Suppl. 1):S264–5 | Abstract |
| 286 | Zimpfer D, Wieselthaler G, Czerny M, Fakin R, Haider D, Zrunek P, et al. Neurocognitive function in patients with ventricular assist devices: a comparison of pulsatile and continuous blood flow devices. ASAIO J 2006;52:24–7 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 287 | Zimpfer D, Zrunek P, Roethy W, Czerny M, Schima H, Huber L, et al. Left ventricular assist devices decrease fixed pulmonary hypertension in cardiac transplant candidates. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2007;133:689–95 | Fewer than 50 participants in included VADs group(s) |
| 288 | Ziv O, Dizon J, Thosani A, Naka Y, Magnano AR, Garan H. Effects of left ventricular assist device therapy on ventricular arrhythmias. J Am Coll Cardiol 2005;45:1428–34 | VADs unclear |
Appendix 6 Eligibility criteria for registration for heart transplant
The National Protocol for Assessment of Cardiothoracic patients lists below the medical indications for patients eligible for a HT.
-
End-stage heart disease with a life expectancy of between 12 to 18 months.
-
NYHA classification III or IV HF.
-
Refractory to medical therapy, including if necessary cardiac resynchronisation therapy. This assessment should be made by a cardiologist with a special interest in heart failure.
-
Usually < 60 years of age as there is an increase in comorbidity with the ageing process. Outcome is less satisfactory; however, consider biologically fit older patients.
Glossary
- Alternative to transplant
- Refers to the use of a ventricular assist device in patients who, although eligible for heart transplant, are given a ventricular assist device as an alternative. Alternative to transplant was a term developed by the authors in order to distinguish this procedure from use of ventricular assist devices in patients ineligible for transplant as destination therapy.
- Bridge to recovery
- Bridge to recovery is used to refer to a situation where a ventricular assist device is implanted temporarily to allow the heart to recover from a condition such as post-myocardial infarction or post-cardiotomy shock. The ventricular assist device is then removed without the need for transplant.
- Bridge to transplant
- Bridge to transplant is used to refer to the use of a ventricular assist device for a short duration of time to increase survival, while waiting for a suitable heart to become available for transplantation.
- Conformité Européenne
- The Conformité Européenne marking is a mandatory conformity mark for products placed on the market in the European Economic Area.
- Destination therapy
- When recovery is impossible and patients are ineligible for heart transplant, then ventricular assist devices are used as destination therapy. This is distinguished from alternative to transplant because patients are ineligible for heart transplant.
- Food and Drug Administration
- This is an agency of the US Department of Health and Human Services responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the regulation and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, dietary supplements, prescription and over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs, vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices and veterinary products.
- Heart failure
- A disease characterised by a decline in the heart's ability to pump blood around a person's body at normal filling pressures so as to meet its metabolic needs.
- Incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- An equation used in health economics to support decision-making regarding health interventions. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio is the ratio of the differences in costs between the intervention and comparator divided by the difference in benefits between intervention and comparator; benefits are often measured in terms of quality-adjusted life-years.
- Medical management
- In this report medical management refers to the range of medical therapies used to treat patients with advanced heart failure in the absence of operative intervention. Examples include angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers and intravenous inotropes for those with severe heart failure.
- New York Heart Association functional classification
- The severity of heart failure is often assessed using the New York Heart Association functional classification which is based on the severity of symptoms patients develop in relation to physical activity. There are four New York Heart Association grades classified according to symptom severity.
- Quality-adjusted life-year
- According to the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, this is ‘a measure of the state of health of a person or group in which the benefits, in terms of length of life, are adjusted to reflect the quality of life. One quality-adjusted life-year is equal to 1 year of life in perfect health. Quality-adjusted life-years are calculated by estimating the years of life remaining for a patient following a particular treatment or intervention and weighting each year with a quality of life score (on a zero to one scale). It is often measured in terms of the person's ability to perform the activities of daily life, freedom from pain and mental disturbance' (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Glossary. URL: www.nice.org.uk/website/glossary/glossary.jsp?alpha=Q).
- Randomized Evaluation of Mechanical Assistance for the Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure (REMATCH)
- This is a published randomised controlled trial of destination therapy with a left ventricular assist device compared with medical management for patients who were not eligible for heart transplant.
- UK Blood and Transplant Database
- Individual patient data set provided by NHS Blood and Transplant from the UK Transplant Registry maintained on behalf of the UK transplant community as part of the NHS National Specialist Commissioning Advisory Group ventricular assist device programme. The data set is known in this report as the UK Blood and Transplant Database.
- Ventricular assist device
- A mechanical circulatory device either used as short- or long-term support in patients awaiting hear transplant. Ventricular assist devices have been classified as (a) first-generation pulsatile volume displacement pumps; (b) second-generation axial continuous flow (CF) pumps; and (c) third-generation bearingless CF pumps.
List of abbreviations
- ACE
- angiotensin-converting enzyme
- AIC
- Akaike information criterion
- AICD
- automatic implantable cardioverter defibrillator
- ARB
- angiotensin receptor blocker
- ATT
- alternative to transplant
- BiVAD
- biventricular assist device
- BMI
- body mass index
- BNP
- B-type natriuretic peptide
- BP
- blood pressure
- BTDB
- UK Blood and Transplant Database
- BTNR
- NHS Blood and Transplant National Registry
- BTR
- bridge to recovery
- BTT
- bridge to transplant
- CCU
- critical care unit
- CDSR
- Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
- CE
- Conformité Européenne
- CEAC
- cost-effectiveness acceptability curve
- CF
- continuous flow
- CHD
- coronary heart disease
- CI
- confidence interval
- COPD
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- CRD
- Centre for Reviews and Dissemination
- CRT
- cardiac resynchronisation treatment
- CSS
- clinical summary score
- CVA
- cerebrovascular accident
- CVP
- central venous pressure
- DARE
- Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects
- DT
- destination therapy
- ECMO
- extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation
- EQ-5D
- European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions
- FDA
- US Food and Drug Administration
- GFR
- glomerular filtration rate
- GJNH
- Golden Jubilee National Hospital
- HF
- heart failure
- HM
- HeartMate
- HRQoL
- health-related quality of life
- HT
- heart transplant
- HTA
- Health Technology Assessment
- HW
- HeartWare
- IABP
- intra-aortic balloon pump
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- ICU
- intensive care unit
- INB
- incremental net benefit
- INTERMACS
- Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support
- IPD
- individual patient data
- ISHLT
- International Society for Heart & Lung Transplantation
- KCCQ
- Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire
- K–M
- Kaplan–Meier
- LV
- left ventricle
- LVAD
- left ventricular assist device
- LVAS
- left ventricular assist system
- LYG
- life-year gain/gained
- MCD
- mechanical circulatory device
- METs
- metabolic equivalent task score
- MLWHF
- Minnesota Living With Heart Failure Questionnaire
- MM
- medical management
- NC
- neurological complication
- NHS EED
- NHS Economic Evaluation Database
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NSCAG
- National Specialist Commissioning Advisory Group
- NSCT
- National Specialist Commissioning Team
- NSRC
- national schedule of reference costs
- NT-pro-BNP
- N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide
- NUT
- Newcastle upon Tyne Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
- NYHA
- New York Heart Association
- OSS
- overall summary score
- PCWP
- pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
- PVAD
- percutaneous ventricular assist device
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- QoL
- quality of life
- RB
- Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- REMATCH
- Randomized Evaluation of Mechanical Assistance for the Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure
- RR
- relative risk
- RV
- right ventricle
- RVAD
- right ventricular assist device
- SD
- standard deviation
- SF-36
- Short Form questionnaire-36 items
- SHFM
- Seattle Heart Failure Model
- TAH
- total artificial heart
- TP
- transition probability
- UHSM
- University Hospital of South Manchester NHS Foundation Trust
- UNB
- University Hospital of Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust
- UNOS
- United Network for Organ Sharing
- VAD
- ventricular assist device
- VAS
- visual analogue scale
- WL
- waiting list