Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was commissioned and funded by the HTA programme on behalf of NICE as project number 12/43/01. The protocol was agreed in October 2012. The assessment report began editorial review in February 2013 and was accepted for publication in May 2013. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2014. This work was produced by Llewellyn et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
Chapter 1 Background
The condition
The Eustachian tube is a narrow tube which links the back of the nose to the middle ear. It is normally closed but opens when we swallow, yawn or chew. The Eustachian tube has three main functions: to protect the middle ear from pathogens; to ventilate the middle ear, which can help to keep the air pressure equal on either side of the eardrum, enabling the eardrum to work and vibrate properly; and to help drain secretions from the middle ear cleft.
Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is the inability of the Eustachian tube to adequately perform these functions. However, the precise function and mechanisms of the Eustachian tube and the underlying causes of dysfunction are complex and not fully understood. 1 From a diagnostic perspective, ETD is also poorly defined.
Eustachian tube dysfunction may occur when the mucosal lining of the tube is swollen, or does not open or close properly. 2 If the tube is dysfunctional, symptoms such as muffled hearing, pain, tinnitus, reduced hearing, a feeling of fullness in the ear or problems with balance may occur. Long-term ETD has been associated with damage to the middle ear and the eardrum. 3 Complications include otitis media with effusion (glue ear), middle ear atelectasis (retraction of the eardrum), and chronic otitis media. 1,3 However, the role of the Eustachian tube in the development of other middle ear conditions is not fully understood. 1 Middle ear ventilation is increasingly seen as being associated with other mechanisms, such as those relating to gaseous exchange through the middle ear mucosa. 4,5 Therefore, it may be that problems with middle ear ventilation (and therefore symptoms and signs previously attributed to ETD) may not all be associated with problems with or dysfunction of the Eustachian tube. Abnormal patency (patulous Eustachian tube) is a separate condition, in which the Eustachian tube remains intermittently open, causing an echoing sound of the person’s own heartbeat, breathing, and speech.
Aetiology and prevalence
The lining of the Eustachian tube can become swollen and the Eustachian tube can become dysfunctional following the onset of an infectious or inflammatory condition such as an upper respiratory tract infection, allergic rhinitis or rhinosinusitis, leading to difficulties in pressure equalisation, discomfort and other symptoms. 6,7 Nasal septal deviation has also been associated with symptoms of ETD; this is based on some studies which suggested that, in patients who were unable to equalise pressure during scuba training or submarine service, submucous resection of the nasal septum resolved apparent ETD symptoms. 8–11 Dysfunction of the Eustachian tube may also be related to failure of the muscles associated with Eustachian tube opening. 1 Extrinsic compression of the Eustachian tube potentially due to inflammation or enlargement of the adenoids, tumour or trauma may also result in ETD,2,12 although these conditions and their management are beyond the scope of this review. The incidence of ETD is disproportionately high in patients with cleft palate who may be considered a discrete clinical population. 12 Other potential risk factors include tobacco smoke, reflux and radiation exposure. 13–15 There appears to be no association with sex,1 although it has been suggested that ethnicity and geographical factors (such as proximity to the poles) are associated with increased incidence and prevalence. 1,16
There are limited data on ETD prevalence and incidence, which may reflect the lack of consensus regarding how ETD is defined. A UK national study of hearing17 reported that 0.9% of the 2708 adults assessed (from an initial sampling of 48,313) were considered to have ETD, based on otoscopic examination and audiological assessment. However, this may be an underestimate; a recent study stated that most otolaryngologists encounter a much higher incidence of the condition in their practices. 18
Diagnosis
There are no comprehensive guidelines on diagnosis of ETD. 19 Diagnosis is generally based on medical history and clinical examination to identify potential underlying causes. 19 The UK national survey defined ETD as the presence of a normal or abnormal but intact tympanic membrane with a middle ear pressure of < –100 mmH2O and an air–bone gap of ≥ 15 decibels (dB). 17 The criteria were used for a presumptive diagnosis of ETD. The authors noted that it was a relatively non-specific category, which may include patients in the early or late stages of an episode of otitis media with effusion. However, the presence of either of these signs is not usually considered to be either necessary or sufficient for the diagnosis of ETD in clinical practice; while negative middle ear pressure often indicates ETD, patients with ETD may have normal middle ear pressure and those with negative middle ear pressure may be asymptomatic. Moreover, while an intact eardrum was a requirement of the survey criteria, several investigators include patients with perforated eardrums. 20–25
Although not used in the survey, symptoms of dysfunction are usually a necessary condition for diagnosis in clinical practice. Common diagnostic factors include the inability to ‘clear’ or ‘pop’ the ear with changes in barometric pressure, together with other patient-reported symptoms (e.g. aural fullness, pain, muffled hearing). 19 There are a number of tests that are used to inform diagnosis: otoscopy, tympanometry and nasal endoscopy are initial options in a secondary care setting. Evidence on the predictive value of Eustachian tube function tests is limited, and several tests may be needed for a more reliable and comprehensive assessment of Eustachian tube function. 1 Currently, there is no commonly used patient-reported outcome measure. A scale for the assessment of ETD [the 7-item Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire (ETDQ-7)] was tested for validity; this is a questionnaire addressing a range of symptoms associated with ETD, which is completed by the patient. The data available on reliability were based on a relatively small number of patients (n = 50) and controls (n = 25), but the test discriminated patients and controls and exhibited good test–retest reliability. 26 However, this represents a recent development and it is not yet widely used. Another relevant scale which is also completed by patients, the 22-item Sinonasal Outcome Test (SNOT-22), has been used to assess symptoms of the related condition of rhinosinusitis. 27
The lack of clearly defined diagnostic criteria, together with the uncertainty relating to the aetiology of ETD, presents a key challenge in undertaking a review of interventions for its treatment. Lack of consensus on the necessary features for diagnosis, including clinical history, requires additional awareness of the risk of error and bias in the selection of studies, as well as increasing the probability of clinical heterogeneity in the included studies.
Current research and guidance
Research on treatments for ETD as a distinct condition in adults is limited. A single systematic review was identified in the scoping searches for the current review (see the review protocol). 28 Published in 2002, the previous review had a limited search (MEDLINE and PubMed only) and included a range of interventions and preclinical studies as well as those in both children and adults. It has been recommended that this review be updated. 29 The only guidance relating to ETD treatment which was identified by the scoping searches was issued by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) on balloon dilatation of the Eustachian tube in November 2011. 30 Based on a rapid review of literature,31 three case series were identified,32–34 of which two were published only as conference abstracts. 32,34 The guidance concluded that current evidence on the efficacy and safety of the procedure is inadequate in quantity and quality. NICE recommended that the intervention should only be used in the context of research; future research should address the efficacy of the procedure in the short and longer term, report data on safety outcomes, clearly describe which parts of the Eustachian tube are treated and report subjective measurements of symptom improvement as well as objective measurements of Eustachian tube function.
Other systematic reviews of existing research which were identified assessed treatments for related conditions such as childhood glue ear and otitis media with effusion. 35–37 NICE guidance has also been issued on the treatment of these conditions. 38 There have also been Cochrane reviews in conditions such as tympanic membrane retraction pockets in adults and children. 39
Management
Although ETD symptoms are common, they are often mild and generally resolve after a few days. Simple actions such as swallowing, yawning, chewing or forced exhalation against a closed mouth and nose can help to equalise pressure in the middle ear and resolve symptoms. However, symptoms sometimes persist, in which case treatment may be desirable. There are a number of non-surgical and surgical treatment options aimed at improving Eustachian tube function, but there is limited consensus about management.
Non-surgical
Non-surgical management strategies include:
-
Active observation, which involves monitoring the symptoms to determine whether or not they naturally resolve.
-
Supportive care, which includes advice about self-management such as to swallow, yawn, or chew to help equalise the pressure in the middle ear.
-
Pressure equalisation methods, which is a technique whereby the Eustachian tube is reopened by raising the pressure in the nose. This can be achieved in several ways, including forced exhalation against a closed mouth and nose (Valsalva manoeuvre). Other methods include blowing up a balloon through each nostril, using an anaesthetic mask36 or the use of mechanical devices. 40,41 The aim is to introduce air into the middle ear, via the Eustachian tube, equalising the pressures and allowing better fluid drainage.
-
Nasal douching, in which the nasal cavity is washed with a saline solution to flush out excess mucus and debris from the nose and sinuses. 42
-
Decongestants, antihistamines, nasal or oral corticosteroids which are aimed at reducing nasal congestion and/or inflammation of the lining of the Eustachian tube.
-
Antibiotics, for the treatment of rhinosinusitis.
-
Simethicone, which is currently being investigated in adults to assess whether or not it can help to break up bubbles that may block the opening of the Eustachian tube in the back of the nose during a cold, allowing air to pass between the nose and middle ear. 43 This is not currently a management option used in the UK.
Surgical
We understand that, currently, the main surgical treatment in the UK is a pressure equalising tube (also known as tympanostomy tube, ventilation tube or grommet) which is inserted into the eardrum through a small incision. Pressure equalising tubes typically extrude after 6–9 months. Long-acting tubes are occasionally used, although these may be prone to crusting, infection, obstruction and permanent tympanic membrane perforation. This may be performed under either general or local anaesthesia. Newer surgical methods which are mainly used in the context of research include:
-
Balloon dilatation (dilatation) of the Eustachian tube, a procedure which aims to dilate the Eustachian tube and improve its function. It consists of introducing a balloon catheter into the Eustachian tube through the nose, under transnasal endoscopic vision. The balloon is filled with saline. Pressure is maintained for approximately 2 minutes, following which the balloon is emptied and removed. The procedure has been performed experimentally under local and general anaesthesia.
-
Transtubal application of fluids, an emerging approach for the application of fluids to the middle ear via the Eustachian tube. The transtubal application approach involves placing a nasal microendoscope within the Eustachian tube under local anaesthesia via its nasopharyngeal opening. Subsequently, fluids are applied through an additional working channel after microendoscopic evaluation. 44
-
Eustachian tuboplasty, an emerging treatment in which a laser or rotary cutting tool is used to strip away enlarged mucous membranes and cartilage to clear obstruction to the Eustachian tube. Tuboplasty has been used in patients with chronic ETD as an alternative to pressure equalising tubes which may have extruded on numerous occasions. 23,32 The intervention has also been used for middle ear atelectasis or serous effusion. 45
There is no consensus on indications for treatment, or on the optimal timing of the interventions. Surgical interventions are generally (though not exclusively) used where ETD is resistant to other interventions. A step-up approach is usually adopted, from primary to secondary and tertiary care settings. Treatment choice is based on aetiology, severity and persistence of symptoms, as well as the degree of invasiveness of the treatment and surgical preference.
Decision problem
Although diagnostic and treatment suggestions exist, for example websites such as BMJ (British Medical Journal) Best Practice, there is a lack of comprehensive diagnostic and treatment guidelines and no recent systematic review assessing the effectiveness of interventions for ETD in adults. The National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Health Technology Assessment (HTA) commissioning brief requested a wide systematic review including best available evidence in order to provide primary and secondary care practitioners with evidence about the value of referral, advise surgeons on the effectiveness of surgical interventions and inform recommendations for future research.
As outlined above, key challenges in undertaking a systematic review of treatments for ETD are that ETD is an ill-defined condition and there is a lack of consensus about its diagnostic criteria. In order to provide an informative overview of the evidence, a pragmatic approach was taken regarding how the condition was defined.
The aim of the systematic review was to determine the clinical effectiveness of treatments for adult ETD, and to identify gaps in the evidence in order to inform future research.
Chapter 2 Methods
A systematic review of the evidence on treatments for adult ETD was undertaken following the general principles recommended by the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) guidance for systematic reviews. 46 A protocol was produced and registered on PROSPERO (CRD42012003035). 47
Search strategy
Literature searches were undertaken during September and October 2012. The searches aimed to systematically identify studies of interventions for adults with ETD. The interventions included in the search strategy were steroids, nasal decongestants, antihistamines, simethicone, nasal douching, leukotriene receptor antagonists, xylitol, antibiotics, surgical interventions, active observation or supportive care.
A search strategy was initially developed on MEDLINE (Ovid SP) using terms for the two main concepts: Eustachian tube and the named interventions as listed above. A range of text words, synonyms and subject headings were identified by scanning key papers identified at the beginning of the project, through discussion with the review team, and the use of database thesauri.
Otitis media with effusion can also be a complication of ETD. Therefore, terms such as ‘glue ear’, ‘otitis media with effusion’ and ‘serous otitis media’ were added to the search strategy. This led to a significant increase in the number of retrieved records (from 1196 to 2995 records in MEDLINE). However, screening of a sample of these additional records yielded no new relevant studies, and therefore it was agreed that the initial focus in the search strategy on interventions and the Eustachian tube was the most appropriate balance between sensitivity and specificity.
No language restrictions, date limits or study design filters were applied to the search strategy. The MEDLINE search strategy was adapted for use in each database. The full search strategies and results for each database can be found in Appendix 1 .
The following databases were searched: MEDLINE, MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health (CINAHL), EMBASE, Science Citation Index, Bioscience Information Service (BIOSIS), Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR), Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE), HTA database, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), PASCAL, and Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences (LILACS).
In addition, information on studies in progress, unpublished research or research reported in the grey literature was sought by searching a range of resources: Conference Proceedings Citation Index: Science, Inside Conferences, Dissertation Abstracts, ClinicalTrials.gov, Controlled Clinical Trials, World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform portal, EU Clinical Trials Register, National Research Register Archive, US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency and the European Medicines Agency.
Records were managed within an EndNote library (EndNote version X3, Thomson Reuters, CA, USA). The bibliographies of all included studies and relevant literature reviews were checked for further potentially relevant studies. EPPI-Reviewer 4 was used from the full-text screening stage of the review (Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Co-ordinating Centre, University of London, London, UK).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Abstracts of studies identified by the searches were assessed for inclusion using the criteria outlined below. For abstracts and titles of potential relevance, full papers were also assessed. Both processes were undertaken independently by two reviewers, with disagreements resolved through discussion and, where necessary, by consultation with a third reviewer. Studies were included in the review if they met the following criteria.
Population
Adults (≥ 18 years) with a clinical diagnosis of ETD were included. Given the current lack of consensus on diagnostic criteria for ETD, a strict definition of ETD was not applied and primary study definitions of ETD were accepted, provided that they were based on symptomatology and/or tests such as tympanometry or otoscopy. Studies of patients with known patulous Eustachian tube or nasopharyngeal tumours were excluded as these populations are distinct and are likely to require different management options. Studies with mixed populations of patients with and without ETD were included if separate outcome data were available for the population of interest. The intention was to include only studies of adults or where separate adult data were available.
At the study selection stage, only a single controlled study in adults with ETD was identified. Therefore, to allow a fuller mapping of the literature, the protocol was amended to include controlled studies including adults and children with no separate adult data, as well as controlled studies that did not explicitly state whether or not the whole study population were adults. For all such studies, the authors were contacted to clarify whether or not the population was indeed adults and/or to seek separate data on the adult population. Following this amendment, five additional comparative studies were included. This protocol amendment was not extended to uncontrolled studies of mixed populations, as this would have increased the risk of further uncertainty in the evidence.
Intervention
Interventions explicitly aimed at treating ETD in primary, secondary and tertiary care settings were eligible for inclusion. A list of eligible interventions and examples of specific treatments is provided in Table 1 .
| Treatment | Examples |
|---|---|
| Active observation | Monitoring to determine whether or not the condition resolves naturally |
| Supportive care | Advice on self-management strategies such as advice to swallow, yawn or chew |
| Auto-inflation | Valsalva manoeuvre |
| Nasal douching | Sodium chloride |
| Topical nasal decongestants | Xylomethazoline |
| Antihistamines | Clemastine |
| Intranasal corticosteroids | Fluticasone propionate, budesonide, mometasone |
| Oral corticosteroids | Prednisolone |
| LTRAs | Montelukast, zafirlukast |
| Antibiotics | Doxycycline |
| Simethicone | Gas-X (Novartis) |
| Surgery | Pressure equalisation tubes Balloon dilatation of the Eustachian tube Transtubal application of fluids Laser Eustachian tuboplasty |
Comparator
Any comparator (placebo, no intervention or another eligible treatment) was considered for inclusion.
Outcomes
There is currently no consensus regarding the most appropriate measure of treatment success. Change in severity and/or frequency of symptoms was classified as the primary outcome because of its relevance to patients. Other outcomes of interest included quality of life; improvement in middle ear function based on measurement tools such as tympanometry (reported as a categorical or continuous outcome); improvement in hearing based on audiometry (reported as a categorical or continuous outcome); tympanic membrane mobility; clearance of middle ear effusion; need for additional treatment, for example requirement for surgical procedure (including reintervention); early tube extrusion (for pressure equalising tubes); adverse events of interventions; and complications related to ETD (e.g. atelectasis).
Study design
Experimental trials (randomised and quasirandomised) as well as observational studies with a control group were included. Uncontrolled observational studies (e.g. case series) including at least 10 patients were also considered for interventions where no controlled studies were found.
Only English-language studies were included.
Data extraction
Data relating to study design, population characteristics, inclusion criteria (including method of diagnosing ETD), intervention and comparator, details of outcome measures used and results were extracted by one reviewer and checked by a second, with disagreements resolved through consensus. Where possible, dichotomous outcomes were extracted and calculated as relative risks (RRs) (risk of negative event or risk of no improvement, with values < 1 favouring the intervention) and continuous outcomes as mean differences (MDs) (between-groups difference in change from baseline); 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated. All calculations were made on an intention-to-treat basis, except for middle ear function data, where only participants with abnormal measurements at baseline were included, as the aim was to evaluate change from abnormal to normal middle ear function. Where possible, conversions from normal to abnormal middle ear function were also extracted or calculated. Comparisons were described as statistically significant (at the 5% level) when the CI did not cross 1 for RRs and 0 for the MDs. Where possible, middle ear function data were extracted as normalisation (e.g. change from abnormal tympanogram to type A). It was noted whether outcomes had been measured by participant or by ear. Follow-up duration was reported as time from treatment start.
Authors were contacted for clarification and missing data as necessary. Data from studies with multiple publications were extracted and reported as a single study, with the publication with the largest number of participants treated as the main study.
Study quality
Randomised controlled trials were assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool. 46,48 Tools used by the Technology Assessment Review group in previous reviews were adapted and employed for the assessment of internal and external validity of comparative non-randomised studies49,50 and case series. 49 The assessment was performed independently and in duplicate by two reviewers. Disagreements were resolved through consensus. Items assessed by the quality assessment tools are outlined in Appendix 2 .
Methods for synthesis
A narrative and tabular summary of key study characteristics, quality assessment and results was undertaken. Owing to heterogeneous interventions, outcome measurements and study designs, a quantitative synthesis was not considered feasible or appropriate, and results were reported in a narrative synthesis. Studies were grouped by type of intervention (surgical and non-surgical) and then by outcome. Results were interpreted in the context of the quality of the individual studies and clinical heterogeneity.
The intention was to undertake subgroup analyses. Key characteristics of interest that were identified at the protocol stage were the definition of ETD used by the primary study, duration of ETD, associated conditions and severity of ETD symptoms at baseline. Such analyses were limited by the paucity of data available, but, where possible, these aspects were described in the synthesis.
Chapter 3 Results
Study selection
A total of 3022 records were identified from the searches of databases and other sources including trial registers. There were 196 records identified as potentially relevant and ordered as full papers. Reference checking identified a further 17 records, bringing the total number of ordered papers to 213 ( Figure 1 ). These included seven studies which were reported in languages other than English. Consultation with readers of these languages indicated that they were, at best, small uncontrolled studies. A list of papers excluded is provided in Appendix 3 .
FIGURE 1.
Flow chart of study selection.
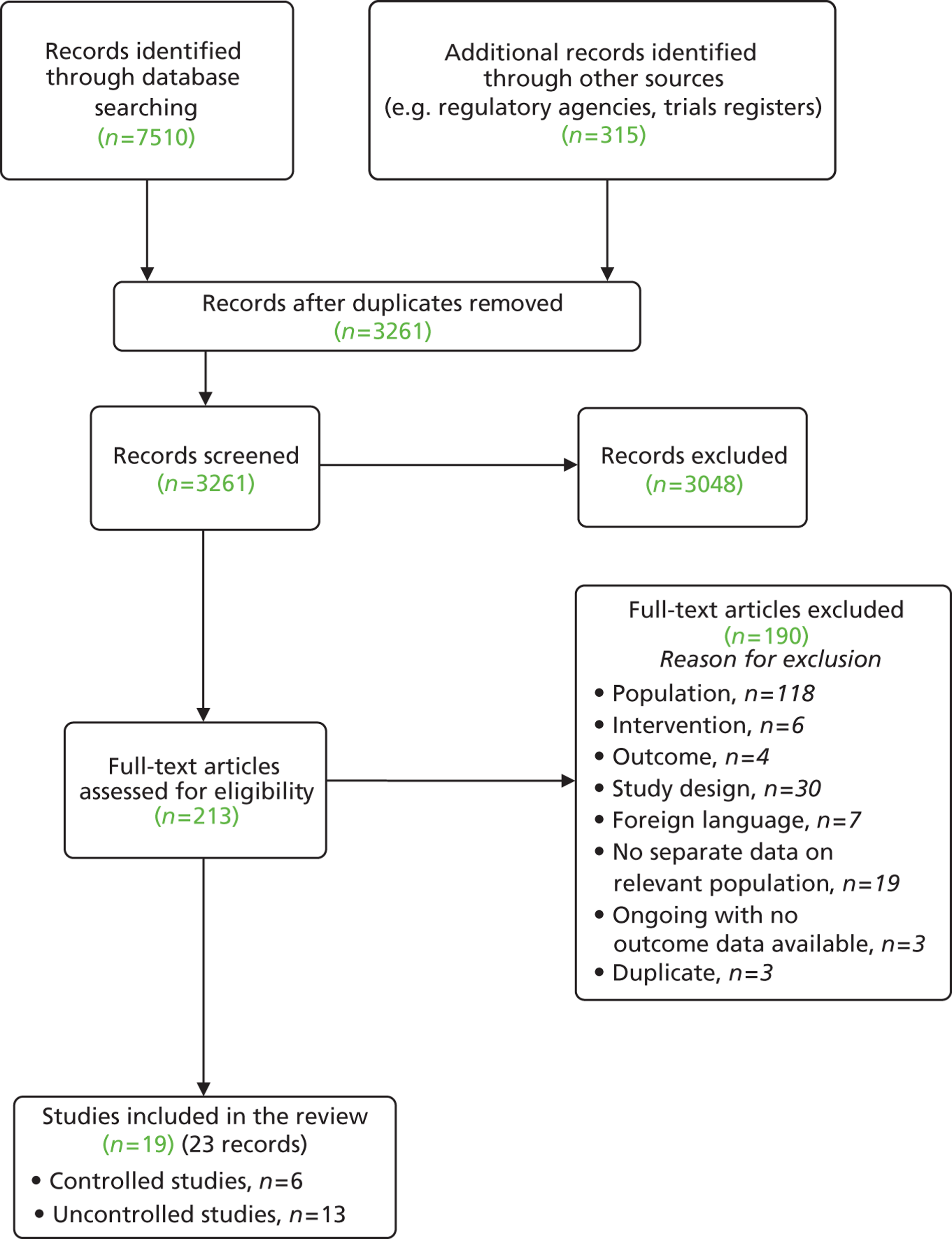
Twenty-three records representing 19 studies met the inclusion criteria (see Figure 1 ). This included seven records related to six comparative studies (three RCTs, two non-RCTs and one retrospective controlled before-and-after study)24,25,40,41,51–53 and 13 case series (reported across 16 records). 18,20–23,34,54–63
Fourteen of the studies were of adults only: all 13 of the case series and one comparative study. Four comparative studies were identified in the searches that included mixed populations of adults and children,24,25,41,52 and one did not specify whether or not the whole population were adults. 40 In each case, it appeared from the information in the publication that a majority of the patients were adults. These were included following a protocol amendment (see Study selection and Chapter 2, Inclusion and exclusion criteria). Attempts to contact the study authors for clarification of whether or not studies were conducted in adults and/or to obtain separate data for adults in a mixed adult/paediatric population were unsuccessful in all except the one surgical comparative study and two of the case series, where author contact established that all patients were adults. 18,51,62
There were a further 19 records representing 15 uncontrolled observational studies (see Appendix 3 ) that met all of the inclusion criteria except that the study was of a mixed adult/child population or a mixed population of patients with ETD and other middle ear problems, but data on adults with ETD were not reported separately. 45,57,64–80 We attempted to contact the authors but were unsuccessful in obtaining separate adult data and/or data on patients identified as having ETD. These studies were, therefore, excluded; a list and further details are provided in Appendix 3 .
Two ongoing RCTs and one ongoing uncontrolled trial were identified; no outcome data were available for these. 43,81,82 Details of the study characteristics of these trials are provided in Appendix 4 .
In Patient characteristics we provide an overview of the characteristics of the included studies. Further details about the included studies, their results and quality assessment of the included studies are reported in Chapter 4 (see Quality of included studies), subgrouped by type of intervention (non-surgical and surgical interventions).
Overview of study characteristics
The included studies were very diverse. The interventions evaluated in the primary studies, the range of outcomes assessed and the measures used varied considerably across the studies. Variation in diagnostic and other inclusion criteria also contributed to substantial heterogeneity in the patient populations (see Patient characteristics).
The interventions evaluated by the comparative studies were, with one exception, pharmacological treatments or mechanical devices ( Table 2 ). Only three RCTs were identified and these were of non-surgical interventions: there were no RCTs of surgical interventions (see Table 2 ). Two of the RCTs assessed different pharmacological interventions25,52 and one evaluated a mechanical device. 40 This was a small study and was reported only as a letter to an editor. 40 All of these studies used a control of either placebo or no active treatment. A single retrospective controlled before-and-after study evaluating a surgical intervention was identified. 51 All other studies assessing surgical treatments were case series.
| Study | Study design | n | Country | Setting | Population | Intervention Comparator | Concomitant treatment | Follow-up (from treatment initiation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmacological interventions | ||||||||
| Gluth (2011)52 | RCT | 91 | USA | NR (recruited in hospital) | Mixed | Intervention: nasal steroid spray Triamcinolone 55 μg, two sprays per nostril s.i.d. for 6 weeks Comparator: placebo spray |
Antibiotics and/or oral decongestants (15%) | 6 weeks |
| Holmquist and Larsson (1976)24 | Non-RCT | 32 | Sweden | NR | Mixed | Intervention: antihistamine + ephedrine N-hydroxiaethylpromethazin chloride 15 mg, ephedrine sulphate 10 mg (tablets), single dose Comparator: placebo (tablet) |
NR | 3 hours |
| Jensen (1990)25 | RCT | 36 | Denmark | NR | Mixed | Intervention: nasal decongestant, sprayed directly towards pharyngeal opening of the ET Xylomethazoline chloride 0.1%, 0.4 ml, sprayed directly towards pharyngeal opening of the ET, single dose Comparator: placebo spray (saline) |
NR | 30 minutes |
| Mechanical devices | ||||||||
| Alpini (2008)40 | RCT | 20 | Italy | NR | Unclear | Intervention: N-300 device applying mild negative pressure to sealed external ear canal Manual device applying mild negative pressure (up to 350–400 mmH2O) to sealed external ear canal. Five minutes t.i.d. for 1 week Comparator: no treatment |
NR | 1 week |
| Silman (1999)41 | Non-RCT | 28 | USA | Private otology practice | Mixed | Intervention: politseration using an automated device twice weekly for 6 weeks Automated manual device delivering continuous air flow through the nose twice weekly for 6 weeks Comparator: no treatment |
NR | 9–10 weeks |
| Surgical interventions (tuboplasty) | ||||||||
| Caffier (2011)20 | Case series | 31 | Germany | Outpatient | Adult | Laser Eustachian tuboplasty; LA | Tympanoplasty type I and myringoplasty for COM patients 10 weeks after laser surgery | 1 year |
| Jumah (2012)54 | Case series | 30 | Germany | University hospital outpatient clinic | Adult | Unilateral minimally invasive laser Eustachian tuboplasty under endoscopic control; GA | NR | 6 weeks |
| Metson (2007)56 | Case series | 20 | USA | NR | Adult | Microdebrider Eustachian tuboplasty; GA | Endoscopic sinus surgery following tuboplasty | Postoperative; 13 months |
| Poe (2007)23 | Case series | 13 | USA | Tertiary medical centre | Adult | Unilateral laser Eustachian tuboplasty; GA and LA | Omeprazole 20 mg/d for 6 weeks postoperatively (where laryngopharyngeal reflux) | 6 months 1 year 2 years |
| Sedlmaier (2009)21 | Case series | 38 | Germany | NR | Adult | Laser ablation of epipharyngeal ET; LA | Nasal decongestant (tetracaine 3% and naphazoline 0.1%) Tympanoplasty 8–10 weeks after (COM group) |
8 weeks |
| bYanez (2008)62 | Case series | 25 | NR | NR | Adult | Laser tuboplasty; anaesthesia: NR | NR | NR (study completion) |
| Yañez (2010)63 | Case series | 25 | Mexico | NR | Adult | Laser Eustachian tuboplasty with cross-hatching technique; GA | NR | Mean 15 months (range 3–37 months) |
| Surgical interventions (balloon dilatation) | ||||||||
| Catalano (2012)18 | Case series | 70 | USA | Clinic (operating theatre used if additional procedures) | Adult | Balloon dilatation; LA unless concomitant procedure required GA | Otologic (five patients/ears) or sinonasal procedure (39 patients, 54 ears) as required. 44 patients (63%) and 59 ears (59%) had a concomitant procedure | Mean 30.3 (SD 3.6) weeks (up to 34 months) |
| McCoul (2012)55 | Case series | 22 | USA | Tertiary referral centre (single surgeon otolaryngological practice) | Adult | Balloon dilatation Eustachian tuboplasty; GA | Partial inferior turbinectomy: all patients Range of other procedures including submucous resection of nasal septum; sphenoethmoidectomy with maxillary sinusotomy; revision ethmoidectomy; revision sphenoidotomy; removal of occluded tympanostomy tube myringoplasty |
3 weeks 6 weeks 12 weeks |
| Poe (2011)22 | Case series | 11 | Finland | Teaching hospital | Adult | Unilateral balloon dilatation at 8–12 atmospheres, reinsertion/repeat dilatation where necessary; GA | Tympanostomy tubes placed/removed | 6–14 (median 7) months |
| Myringotomy | ||||||||
| Potocki (1999)60 | Case series | 13 | USA | NR | Adult | Bilateral thermal myringotomy; LA | NR | 4 months |
| Prokopakis (2005)58 | Case series | 108 | Greece | Academic tertiary referral medical centre | Adult | Laser-assisted tympanostomy without ventilation tubes; LA | NR | 2 months |
| Surgical interventions (others) | ||||||||
| aBoboshko (2005)51 | Retrospective controlled before-and-after | 40 | Russia | NR | Adult | Intervention: point laser coagulation (superior and posterior margin of ET nasopharyngeal opening) unilateral and bilateral; LA Comparator: catheterisation of ET with insufflation, application of medications (not specified) under rhinoscopic control |
NR | 2 weeks; 1 year |
| bSilverstein (2003)61 | Case series | 11 | USA | Tertiary otologic referral centre | Adult | Laser tympanostomy or vertical myringotomy; insertion of ventilation tube and MicroWick (Silverstein MicroWick™, Anthony Products, Indianapolis, IN, USA) through the tube then administration of dexamethasone 4 mg/ml through wick t.i.d. for 4 weeks; LA | Antibiotic solution concurrent with dexamethasone treatment once daily (two drops) | Mean 7.2 months; mean 8 months |
None of the studies was conducted in the UK. Studies of pharmacological agents were carried out in the USA, Denmark and Sweden, studies of mechanical devices in the USA and Italy. Where reported, studies of surgical interventions were conducted in the USA, Germany, Denmark, Finland, Russia and Mexico (see Table 2 ). Publication dates ranged from 1976 to 2011 for studies of pharmacological interventions, were 1999 and 2008 for mechanical devices and ranged from 2005 to 2012 for studies of surgical interventions.
Patient characteristics
Four of the studies of non-surgical interventions reported data on a mixed adult/paediatric population. In the case of Gluth et al. ,52 the proportion of adults in the trial (63%) was reported and some separate data on the primary outcome were reported for the paediatric subgroup (aged 6 to 17 years), allowing results for adult patients to be calculated. 52 In the three other studies, the age ranges indicated that all patients were adolescents or adults, with age ranges of 14–66 years,24 12–75 years25 and 16–76 years. 41 In the fourth study, there was some uncertainty as to whether or not all patients were adults, but the mean age was 39.2 years, suggesting that, unless the range was very wide, the probability was that a majority of individuals were adults. 40
The mean ages of patients undergoing a surgical intervention ranged from 40 to 63 years and age ranges extended from 18 to 90 years where reported. The single controlled before-and-after study evaluating surgery had an age range of 21 to 56 years (mean age not reported). 51 All of the included studies which reported information on patient sex had approximately equal numbers of male and female patients.
There was notable variation in the inclusion criteria used by individual studies, and, consequently, in the characteristics of the patient populations. In particular, there was variation in the length of time patients were required to have had ETD symptoms, the severity of the symptoms and the previous treatments attempted. While two studies of surgical intervention required that patients had a history of 5 years of ETD symptoms,20,23 other studies required merely that patients experienced ongoing ETD symptoms following an aeroplane flight,41,54 while others specified that the symptoms be ‘chronic’18,56,61 or that participants were required to have a long history of symptoms. 21 Although the symptoms considered to be associated with ETD were specified as part of the inclusion criteria in many of the studies, ETD itself was rarely defined. None of the studies of pharmacological agents or mechanical devices specified a minimum duration of symptoms, although one required that symptoms be ‘persistent’. 40 Where symptoms were assessed and reported using a scale to quantify severity, it appeared that patients were in considerable discomfort at baseline. 40,55
Notably, three of the surgical studies included only patients with a diagnosis of otitis media with effusion with an aetiology indicating that ETD was responsible for the condition. 22,23,51 In these and four other studies, including two evaluations of pharmacological treatments, patients with a perforated tympanic membrane or current pressure equalisation tubes were included either as an identified subgroup or together with patients with an intact eardrum. 20,21,24,25
Previous treatment histories also varied widely both among and in some cases within studies. Poor reporting was an issue, particularly in the studies of pharmacological interventions. One study of a mechanical device reported previous therapies of nasal decongestants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antihistamines and antibiotics,40 while the other did not report treatment history. 41 Of the studies of pharmacological interventions, two did not report treatment histories25,52 while the third noted only one previous pressure equalisation tube. 24
Where treatment histories were documented for surgical patients, they indicated considerable variation, with patients in some studies having failed multiple therapies including both medical and surgical interventions, while patients in others had no surgical history or no prior treatment history. In four studies of surgical intervention, failure of conservative or medical management was a criterion for enrolment in the study. 20,23,54,61 In four further surgical studies, repeated courses of medical therapy were documented for all patients. 56,60,63,83 Three studies required prior ventilation tubes. 22,23,61 One surgical study reported no prior treatments. 58 Within some studies, there was variation in the reported treatment histories, with three studies reporting prior surgeries in some but not all of the patients. 56,63,83 Three studies of surgical intervention did not report treatment histories18,21,62 and one noted only that most patients had had previous ETD treatment (Professor Maria Boboshko, St. Petersburg Pavlov State Medical University, 2012, personal communication). 51
There were also differences in the approach to comorbidities such as gastric reflux and rhinosinusitis. In five studies, the incidences of comorbidities were not reported. 18,55,58,62,63 Other studies documented substantial minorities of patients with these and related conditions,22,23,56,60,61 while some used their presence as an exclusion criterion. 20,21,54 One study of tuboplasty included only patients with a diagnosis of rhinosinusitis. 56
Interventions
As can be seen from Table 2 , the interventions represented in the review covered a range of pharmacological, surgical and mechanical devices.
Three studies, including two RCTs and one non-RCT, assessed pharmacological interventions. These were a nasal steroid spray,52 a topical administration of decongestant,25 and oral administration of a combination of antihistamine and ephedrine. 24
Two studies (one small RCT and one non-RCT) assessed pressure equalisation devices. 40,41
Surgical interventions assessed were various techniques for Eustachian tuboplasty, balloon dilatation, thermal or laser-assisted myringotomy, and laser coagulation of the Eustachian tube pharyngeal opening. One case series assessed dexamethasone administered via micro-wick following myringotomy. 61 Seven case series assessed forms of tuboplasty;20,21,23,54,56,62,63 three case series assessed balloon dilatation;18,22,55 and two assessed myringotomy. 58,60 For other interventions, a single retrospective controlled before-and-after study51 or case series were available. 61
Seven of the surgical studies reported that concomitant treatments were administered in addition to the intervention that was the focus of the assessment. These included a range of additional surgical interventions and/or pharmacological treatments. 20–23,55,56,61
The interventions assessed by the included studies did not include several methods which may be used in primary care, including active observation, supportive care, antibiotics, leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs) or nasal douching. There were also no included studies assessing the most common surgical intervention for ETD: insertion of pressure equalisation tubes. For many of the eligible interventions, there was, therefore, no evidence which met the review inclusion criteria. For most interventions where evidence was available, there was no randomised and often no controlled evidence. The number of studies identified for each of the eligible interventions is reported in Table 3 , indicating where gaps in the evidence remain.
| Study design | Intervention | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active observation | Supportive care | PE | Nasal douching | Decongestants | Antihistamines | Corticosteroids | LTRA | Antibiotics | Simethicone | PE tubes | Balloon dilatation | Tuboplasty | Transtubal fluids | Other surgery | |
| RCT | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| Non-RCT | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Controlled before-and-after | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Case series | 3 | 7 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||||
| Ongoing study | 1a | 1a | 1 | 1a | 1 | ||||||||||
Outcomes
Eleven studies, comprising one of the three pharmacological studies,52 one of the two studies of mechanical devices40 and nine studies of 13 studies of surgical interventions,18,20,51,55,56,58,61–63 assessed the primary outcome. Of the studies which did assess symptoms, only four reported using a systematic method to quantify improvement or change in symptomatology. One used scales specific to the condition for which at least some information is available on reliability and validity (the ETDQ-7 and SNOT-22). 55 One used a symptom questionnaire which appeared to be a modified version of the ETDQ-7, and two used a visual analogue scale (VAS). 20,40,52
All other studies which reported symptom change restricted reporting to the number of patients reporting improvement in either global ETD symptoms,55,56,63 specific symptoms such as tinnitus or aural fullness51,58,61 or non-specific ‘improvement’18 or resolution of symptoms. 62
A considerable range of outcomes specified as relevant in the review protocol were assessed ( Table 4 ), although none of the studies reported quality of life, and early tube extrusion was not a relevant outcome as no studies of pressure equalisation tubes were included.
| Study | Study design | Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Clearance of effusion | Need for additional treatment | Adverseevents/complications of ETD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmacological | |||||||
| Gluth (2011)52 | RCT | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Holmquist (1976)24 | Non-RCT | ✓ | |||||
| Jensen (1990)25 | RCT | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Pressure equalisation device | |||||||
| Alpini (2008)40 | RCT | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Silman (1999)41 | Non-RCT | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Surgery: tuboplasty | |||||||
| Caffier (2011)20 | Case series | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Metson (2007)56 | Case series | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Poe (2007)23 | Case series | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Jumah (2012)54 | Case series | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Sedlmaier (2009)21 | Case series | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Yañez (2008)62 | Case series | ✓ | |||||
| Yañez (2010)63 | Case series | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Surgery: balloon dilatation | |||||||
| Catalano (2012)18 | Case series | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| McCoul (2012)55 | Case series | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Poe (2011)22 | Case series | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Surgery: myringotomy | |||||||
| Potocki (1999)60 | Case series | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Prokopakis (2005)58 | Case series | ✓ | |||||
| Surgery: other intervention | |||||||
| aSilverstein (2003)61 | Case series | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| bBoboshko (2005)51 | Controlled before-and-after study | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
Hearing was assessed in seven of the studies of surgical interventions20,23,51,56,60,61,63 and in one of the mechanical device studies. 41 Various audiometry measures were reported, of which the most common was the average pure-tone threshold. 23,56,61,63 Air–bone gap was also commonly reported20,41,51,61 and one study also reported speech discrimination score,61 while another reported bone conduction in addition to air conduction. 20 One study reported only that a patient reported a change in hearing. 60
Most studies reported some measure of middle ear function but the measure used varied considerably. Conversion to a type A tympanogram was reported by one study of a mechanical device,41 one study of a pharmacological intervention52 and eight studies of surgical interventions. 18,20–23,51,54,55,61 Other measures of tympanometry were reported as alternative or additional outcomes. These included ‘improvement to normal or more normal tracing’56 and ‘improvement’. 63
Alternative measures of middle ear function which included outcomes related to pressure equalisation (e.g. tubotympanometry,40 Valsalva manoeuvre,20,21,23,25,84 passive opening pressure20,21,24) and measures based on the appearance of the middle ear on clinical examination22,23,55,57 were used. Multiple outcomes were reported by several studies for both middle ear function and hearing. 20,55,56,84
Two surgical studies reported on clearance of middle ear effusion. 23,51
All three of the pharmacological studies24,25,52 and one of the two studies of mechanical devices41 measured treatment success and provided a definition of successful treatment. Eight of the surgical studies measured treatment success; however, in three of these, the authors did not state how they defined treatment success. 18,51,62 Where provided, the definitions of treatment success varied widely and often included multiple criteria. For example, Gluth et al. defined treatment success as a normal (type A) tympanogram in both ears or as meeting this criterion and not requiring/using additional specified treatments during the study, and reported results according to both criteria. 52 In other studies, different definitions of success were used dependent on patient characteristics; for example, one case series required an improvement in tympanometry or hearing impairment as well as symptoms but an improvement only in symptoms for patients who had normal tympanometry and hearing at baseline. 55
Reporting of safety data was not consistent between studies and for the majority of studies there was insufficient information to establish how systematically the data were collected. Two of the three pharmacological studies reported adverse events information, and 11 of the studies of surgical interventions reported some information.
Finally, there were considerable differences in the length of follow-up, both between studies and within studies for different outcome measures. Where reported, length of follow-up ranged from the extremely short term (30 minutes or up to 3 hours), which may have very limited clinical relevance,24,25 to the more typical short term of between 1 and 8 weeks,40,41,52,54,55,58 and 1 to 2 years or longer in some of the studies assessing surgical interventions. 20,21,23,51 Length of follow-up was not clear in some studies, with assessments being noted as, for example, ‘post-operative’56 or ‘study completion’62 or only a mean duration of follow-up being reported. 18,61
Quality of included studies
Quality of non-surgical studies
Of the three studies reported as being randomised, Gluth et al. 52 was considered to be at low risk of bias. Jensen et al. 25 had an unclear risk of bias primarily due to multiple gaps in reporting. The third RCT, Alpini and Mattei,40 was considered at high risk of bias due to the lack of blinding of outcome assessors, personnel and participants ( Table 5 ). The two non-randomised studies24,41 were considered at high risk of bias due to the lack of randomisation and the lack of clarity around potential differences between groups at baseline (see Table 5 ).
| Study | Random sequence generation | Concealed allocation | Blinding of participants | Blinding of personnel | Blinding of outcome assessors | Incomplete outcome data | Selective outcome reporting | Overall risk of bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpini (2008)40 | ? | ? | – | – | – | + | ? | – |
| Gluth (2011)52 | + | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + |
| Jensen (1990)25 | ? | ? | + | ? | ? | + | ? | ? |
Gluth et al. 52 was the only trial to describe appropriate randomisation methods and adequate allocation concealment methods. Three studies24,25,52 blinded their participants (placebo-controlled studies) but none clearly reported blinding study personnel, and therefore none of the studies were considered to have a low risk of performance bias (i.e. a risk of differences between groups in the care received or in exposure to factors other than the interventions). 48
Detection bias was unclear in all except two studies24,52 which clearly stated blinding outcome assessors. Attrition bias was considered low in all studies. Only Gluth et al. 52 reported sufficient data to rule out selective reporting of outcomes. Two trials25,52 reported a power calculation, but only Jensen et al. 25 reported sufficient power to detect a significant treatment effect. Follow-up duration was considered sufficient to detect a short-term impact in only two studies. 41,52 Further details are reported in Tables 5 and 6 .
| Study | Selection/eligibility criteria adequately reported? | Sample likely to be representative? | Adequate participation (> 80% of eligible)? | At least 80% follow-up from baseline? | Groups balanced at baseline? | Outcome assessors blind to group allocation? | Dropout rates and reasons similar across intervention and control groups? | Statistical analysis appropriate? | Any other important limitations? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Holmquist (1976)24 | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | Unclear | Yes | N/A | Unclear | No |
| Silman (1999)41 | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | N/A | Yes | No |
Quality of surgical studies
The single controlled before-and-after study assessing a surgical intervention had adequately reported eligibility criteria, determined through author contact (Professor Maria Boboshko, St. Petersburg Pavlov State Medical University, 2012, personal communication), and had an adequate length of follow-up. 51 However, details of the intervention received by the control group were limited, and the representativeness of the sample and adequacy of participation rates were unclear ( Table 7 ).
| Study | Selection/eligibility criteria adequately reported?a | Representative sample? | Adequate participation (≥ 80% of eligible)? | At least 80% follow-up from baseline? | Groups balanced at baseline? | Outcome assessors blind to group allocation? | Dropout rates and reasons similar across intervention and control groups? | Statistical analysis appropriate? | Any other important limitations? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boboshko (2005)51 | Yesb | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | N/A | Unclear | Yesc |
The quality of the included case series was variable ( Table 8 ). Nine of the 13 studies were prospective and three reported consecutive recruitment of patients. 22,56,63 All except one study had adequately reported eligibility criteria and there was at least 80% follow-up from baseline in all except one study where this was not clear. 18 It was not clear in any study whether or not the patients assessed constituted a representative sample of those eligible. Even in studies using prospective and consecutive recruitment of patients, the fact that it was unclear whether or not patients were a representative sample meant that these case series, and the controlled before-and-after study, were still at high risk of selection bias, in which patients considered likely to demonstrate a good outcome were preferentially enrolled. This risk is increased for studies in which enrolment was not consecutive and particularly so where recruitment was not prospective. Only six studies used an appropriate statistical analysis with reporting of tests to assess the significance of differences between baseline and follow-up,20–23,54,56 and only four reported appropriate measures of variability such as standard deviations (SDs) for assessments at baseline and follow-up. 20,22,54,55
| Study | Selection/eligibility criteria adequately reported?a | Representative sample? | Prospective recruitment? | Consecutive recruitment? | Adequate participation (≥ 80% of eligible)? | ≥ 80% follow-up from baseline? | Loss to follow-up reported? | Relevant prognostic factors reported (e.g. OME or other baseline comorbidities)? | Other relevant confounding factors reported (e.g. co-interventions)? | Appropriate measure of variability? | Appropriate statistical analysis? | Other important limitation? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caffier (2011)20 | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | N/A | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Catalano (2012)18 | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | No | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| Jumah (2012)54 | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | N/A | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yesb |
| McCoul (2012)55 | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Partially | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yesc |
| Metson (2007)56 | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Poe (2007)23 | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | No | Partially | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Poe (2011)22 | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | N/A | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Potocki (1999)60 | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | N/A | No | Yes | No | Unclear | No |
| Prokopakis (2005)58 | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | N/A | No | No | No | No | Yesd |
| Sedlmaier (2009)21 | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | N/A | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Silverstein (2003)61 | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Yañez (2008)62 | No | Unclear | No | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | N/A | No | No | No | Unclear | No |
| Yañez (2010)63 | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | N/A | No | No | No | Unclear | No |
Six studies also reported both potential confounding and prognostic factors,20–23,55,56 while two reported confounding but not prognostic factors18,60 and one reported prognostic but not confounding factors. 54 Even an ideal case series is subject to the limitation that it is impossible to assess what the outcome would have been for patients had they not been given the intervention assessed. The lack of a control group means that it is unclear how much of the observed benefit(s) may be attributed to this therapy and how much may be a consequence of spontaneous recovery and/or regression to the mean. The natural history of ETD means that this is of particular relevance, as symptoms may be expected to change in intensity and frequency and, in some cases, to resolve without intervention.
In the case series included in this review, an additional consideration is the administration of concomitant therapy. The seven studies reporting confounding factors all documented additional treatments other than the intervention assessed. In some cases, all patients received additional surgical or pharmacological therapies, while in others a proportion of patients were given concomitant treatment according to perceived clinical need resulting from their ETD and/or comorbidity.
Non-surgical studies
Study characteristics
The included studies evaluated a diverse range of interventions. Only single studies were identified for each intervention: there was one randomised placebo-controlled trial for each of a pressure equalisation method,40 nasal steroids52 and a topical decongestant,25 and a non-RCT of a combination of antihistamine and ephedrine24 and a politzerisation method. 41 A description of the interventions is provided in Table 2 . All the studies were small: the number of participants ranged from 20 to 91. Follow-up duration was short, ranging from 30 minutes up to 10 weeks after treatment initiation.
Only one study reported the setting and context in which interventions were delivered (by an ENT specialist in a private otology practice). 41 Antihistamine, ephedrine and topical decongestants were administered as a single dose. 24,25 None of the studies reported on treatment adherence and compliance. One trial reported on the use of concomitant treatments (antibiotics and/or oral decongestants) for 14 (15%) patients. 52 Although the requirement for participants to have ETD was clearly stated in all studies, the condition was not explicitly defined in any of them. Selection criteria varied across the studies. Two studies included patients with a perforated eardrum,24,25 while they were excluded from one. 52 Two studies excluded patients with comorbidities, such as craniofacial syndromes and cleft palate,52 active cholesteatoma, or upper respiratory tract infection. 25 Diagnostic methods of ETD varied. All studies used a combination of at least two diagnostic tools, with tympanometry being the most frequent. Further details on selection criteria are reported in Table 9 .
| Study | n (I/C) | Patient inclusion criteria and relevant characteristics | Patient exclusion criteria | Diagnostic methods | Previous treatments | Related conditions, n/N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmacological treatments | ||||||
| Gluth (2011)52 | 91 (45/46) | OME or negative ME pressure, or OME + negative ME pressure and intact eardrum Dampened or loss of hearing, fullness or pressure in ears, pain, plugged sensation, or popping sensation in ears Abnormal tympanogram (75% ears) |
Perforated eardrum Active cholesteatoma Acute or chronic suppurative OM Craniofacial syndromes Cleft palate Developmental delay Type 4 retraction of tympanic membrane (Dornhoffer’s classification)85 |
Otoscopic examination Tympanometry Nasopharyngoscopy |
NR | Balance problems (22%) Tinnitus (30%) Common cold symptoms (26%) Allergic rhinitis (12%) |
| Holmquist (1976)24 | 32 (19/20 ears) | Opening pressure ≥ 200 mmH2O (perforated eardrum patients) or tympanometric ear pressure between −100 and −400 mmH2O (intact eardrum) Reduced opening pressure or negative ME |
NR | Manometry (opening pressure test) Tympanometry |
Ventilation tube (1 ear) | Perforated eardrum: 14/38 ears (37%) |
| Jensen (1990)25 | 36 (19/17) | Age ≥ 12 years No passage on a Valsalva manoeuvre and/or incomplete pressure equalisation in aspiration/deflation test Dry eardrum perforation Normal ear mucosa Absent or reduced ET patency |
Normal ET function Upper respiratory tract infection Adenoids or other lesions in nasopharynx ME lesions Use of decongestant or antihistamine within 24 hours |
Valsalva manoeuvre, aspiration/deflation test | NR | COM |
| Mechanical devices | ||||||
| Alpini (2008)40 | 20 (10/10) | Persistent ear fullness sensation following OM Abnormal tubotympanometry (95%) Normal pure-tone audiometry and stapedial reflexes |
NR | VAS Tubotympanometry VEMPs |
Nasal decongestants NSAIDs Antihistamines Antibiotics (for OM) |
OM: 20/20 (100%) |
| Silman (1999)41 | 28 (14/14) | Age ≥ 18 years Middle-ear pain, fullness or clogged sensation following aeroplane travel or descent Tympanometric peak pressure < −100 daPa Onset following aeroplane travel/descent Abnormal tympanometric peak pressure |
NR | Otolaryngologic evaluation (including microtoscopy) Audiologic evaluation Tympanometry |
NR | NR |
Where reported, baseline symptoms, related conditions and previous treatments varied between the studies. Three studies reported that the included participants had symptoms associated with ETD, such as fullness, ear pain, plugged sensation, popping sensation, dampened or loss of hearing. 40,41,52 However, only Alpini and Mattei reported an objective measurement of symptom severity at baseline (VAS score for fullness in the ear). 40 Gluth et al. used a non-validated symptoms questionnaire but the baseline results were not reported,52 and patients in Silman and Arick41 all reported ETD symptoms during aeroplane travel but the study did not report measuring their severity. None of the studies reported on the duration or persistence of ETD symptoms before treatment.
Three studies reported using tympanometry at baseline and found results indicating abnormal middle ear function in most evaluated ears. 24,41,52 Participants in Alpini and Mattei were reported to have residual middle ear effusion, although they showed normal audiometric and tympanometric results at baseline. 40 All patients in Jensen et al. 23 and about one-third of participants in Holmquist and Larsson had eardrum perforations. 24,25 Prevalence of eardrum perforations was not reported in the other studies. Two studies did not report any related conditions. 40,41
Only two studies reported on the use of previous treatments. 24,40 All patients in Alpini and Mattei had received pharmacological treatment for otitis media, such as nasal decongestants, NSAIDs, antihistamines and antibiotics. 40 Holmquist and Larsson was the only study to report on the number of patients who had had ventilation tubes placed. 24 Further details on patient characteristics are reported in Table 9 .
Results
The results from individual non-pharmacological studies are reported below, grouped by type of outcome. Given that there was only a single study for each intervention, a quantitative synthesis was not possible. Indeed, due to the poor reporting of results for most outcomes, it was not always possible to extract standard data such as baseline and follow-up values with associated SDs to allow calculation of the 95% CIs for the treatment effect.
Change in severity or frequency of symptoms
Two RCTs reported a measure of symptom frequency or severity ( Table 10 ). 40,52 Gluth et al. 52 used a Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Subject Questionnaire of unknown reliability and validity. The questionnaire assessed frequency and severity of fullness in the ear, pain, plugged sensation, popping sensation, and dampened hearing, all assessed using a five-point Likert scale. The study reported the number of patients who had a positive, a negative or no change in individual symptoms following treatment. Alpini and Mattei used a VAS ranging from 0 to 10 to measure the severity of fullness in the ear of patients. 40
| Study | Intervention | Outcome | Unit of analysis | n of participants in analysis | Intervention, mean (SD) | Control, mean (SD) | Difference between groups at follow-up | Follow-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpini (2008)40 | Pressure equalisation device | Fullness in ear (VAS) Possible score range: 0–10 |
Patient | NR | Baseline: 9.2 (NR) Follow-up: 2 (NR) Difference from baseline: 7.2 (NR) points decrease (p < 0.001) |
Baseline: 8.68 (NR) Follow-up: 6 (NR) Difference from baseline: 2.68 (NR) points decrease (NS) |
MD: 4 pointsa | 1 week |
| Gluth et al. (2011)52 | Nasal steroids | Mean overall symptom scoreb | Patient | NR | NR | NR | NSa | 6 weeks |
The total number of participants for the analysis was unclear in the Alpini and Mattei40 study and the total symptom scores results in Gluth et al. 52 were not reported. Analyses were conducted on a per-patient basis.
Alpini and Mattei38 reported a difference of four points in favour of a pressure equalisation device compared with placebo on a 0–10-point VAS at 1-week follow-up. A measure of variance was not reported and it was not possible to calculate a 95% CI for the between-group difference. The study reported the statistical significance of the change from baseline for each of the groups separately, but not for the difference between groups at follow-up.
Gluth et al. 52 stated there was a non-statistically significant difference between nasal steroids and placebo in overall symptom score at 6 weeks’ follow-up, which favoured the placebo group (p = 0.07), though the actual data were not reported. An additional analysis (analysis of covariance), which adjusted for difference in symptoms at baseline, showed no difference (p = 0.27) between the two groups at follow-up. Analysis of individual symptoms showed a significant between-group difference in plugged sensation in the ear, which was more severe (p = 0.03) and more frequent (p = 0.02) for those receiving nasal steroids. The data underpinning these analyses were not reported.
Quality of life
None of the studies reported quality of life outcomes.
Hearing
One non-RCT reported the effect of treatment on hearing. 41 All patients underwent a complete audiological evaluation (including pure-tone air and bone conduction thresholds, speech recognition thresholds, suprathresholds, speech recognition score for monosyllabic words, and tympanometry) at baseline and follow-up. However, only data on air–bone gap (difference between the threshold for hearing acuity by bone conduction and by air conduction measured by pure-tone audiometry) were reported. Tympanometric data are reported in the following subsection. Mean (SD) air–bone gap results were reported for each group on a per-patient basis. A mean air–bone gap of > 10 dB was considered significant. All 28 patients included in the study were analysed. It was unclear how many ears were evaluated in each patient and in total.
There was a statistically significant difference in air–bone gap favouring modified politzerisation at 3 to 4 weeks following 6 weeks of treatment (MD 12.90 dB; 95% CI 2.85 dB to 22.95 dB). Air–bone gap increased (indicating worsening in hearing) in both arms of the study: in the intervention group (by a mean 0.6 dB, SD 8.7 dB) and in the control group at follow-up (by a mean 13.5 dB, SD 17.1 dB), although the reasons for this deterioration are unclear. Further details are reported in Table 11 .
| Study | n participants in analysis | Intervention | Outcome | Unit of analysis | Intervention, mean dB (SD) | Control, mean dB (SD) | Difference between groups in change from baseline | Follow-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silman (1999)41 | 28 | Politzerisation | Mean air–bone gap | Patient | Baseline: 9.7 (6.3) Follow-up: 10.4 (6.6) Difference from baseline: 0.6a (8.7) increase |
Baseline: 7.6 (5.2) Follow-up: 21.1 (14.9) Difference from baseline: 13.5 (17.1) increase |
MD 12.90 dB (95% CI 2.85 dB to 22.95 dB)b | 9–10 weeksc |
Middle ear function
All five non-surgical studies reported outcome measures of middle ear function. Two assessed outcome based on tympanometry,41,52 and three used other outcome measurement methods. 24,25,40
Middle ear function (tympanogram normalisation)
Two studies assessed resolution of abnormal tympanometric results (from B or C to A) from baseline. 41,52 Follow-up was short, ranging from 6 weeks to 9–10 weeks after treatment initiation.
Silman and Arick41 used an acoustic immitance device, with an air pressure ranging from 200 daPa to –400 daPa, with a 50 daPa/second rate of air-pressure change. Mean (SD) tympanometric peak results were reported for on a per-patient basis. Normalisation was defined as tympanogram peak pressure ≥ –100 daPa at follow-up (9–10 weeks after initiation of a 6-week treatment). All 28 patients included in the study were analysed. It was unclear how many ears were evaluated in each patient and in total. It was also unclear if one or both ears were required to have normal tympanometric peak pressure at follow-up for the treatment to be considered successful, and it was unclear if one or both ears had abnormal tympanometric peak pressure at baseline.
Gluth et al. 52 used tympanograms (with external auditory canal volume measurements) to evaluate middle ear function. Results were reported per patient (primary analysis) and per ear (secondary analysis) for patients with follow-up data. Treatment success was tympanogram normalisation, defined as a change from abnormal tympanogram (type B or C) at baseline to normal tympanogram (type A) at 6 weeks’ follow-up. Seventy-four patients (including 44 adults) were included in the analyses. All patients at baseline had an abnormal tympanogram in at least one ear (47% of patients in the intervention group had both ears with abnormal tympanogram at baseline vs. 54% in the placebo arm).
Silman and Arick41 found that modified politseratisation was associated with a significantly reduced risk of having an abnormal tympanometric peak pressure at follow-up compared with no intervention [risk ratio (RR) 0.36; 95% CI 0.15 to 0.87]. Mean tympanometric peak pressure improved in the treatment group (decrease of 182.9 daPa, SD 153.0) and deteriorated in the control group (increase of 18.1 daPA, SD 182.4). The difference between the two arms significantly favoured patients undergoing modified politzerisation (MD –201.00 daPa; 95% CI –325.71 daPa to –76.29 daPa).
Overall, there was no statistically significant difference in the percentage of patients with tympanogram normalisation between nasal steroids treatment (7 out of 37: 19%) and the placebo group (12 out of 37: 32%), (RR 1.20; 95% CI 0.91 to 1.58) in Gluth et al. 52 When considering patients with treatment failure (those who took an additional treatment such as antibiotics, oral decongestant or nasal spray in the placebo group) as having incomplete resolution, rates of resolution were slightly lower in the intervention group (5 out of 37: 14%) and the placebo arm (9 out of 37: 24%), although the difference between the two group remained non-statistically significant (RR 1.14; 95% CI 0.91 to 1.43).
In Gluth et al. ,52 it was also possible to calculate results on a per-patient basis for the subgroup of adults with follow-up data (22 patients in each arm). No statistically significant differences were found between intervention and placebo in this subgroup, including when accounting for treatment failures. Per-ear analyses were consistent with these findings. Further details are reported in Appendix 5 .
Middle ear function (other outcome measurement methods)
Three additional non-surgical studies measured changes in middle ear function, all significantly favouring treatment. Follow-up duration was short, ranging from 30 minutes to 1 week. 24,25,40
Alpini and Mattei40 used tubotympanometry to assess Eustachian tube function in patients who had recovered from otitis media. The test evaluates the impedance of the eardrum during Valsalva’s manoeuvre and swallowing, by recording the inflow and outflow of air through the tube as a pattern of impedance change which is classified as normal, obstructive, or patent. 86,87 The study used tubotympanometry to assess ‘residual Eustachian dysfunction’, for which no definition was provided. A normal result indicated normal Eustachian tube function, but it was unclear whether abnormal tubotympanometry indicated abnormal Eustachian tube occlusion, patency or both [the test was used in conjunction with vestibular evoked myogenic potential (VEMPs), a neurophysiological assessment technique used to determine the function of nerves and organs (utricle and saccule) within the inner ear. VEMPs results were not reported as they focused on the inner ear and were therefore considered to be beyond the scope of the review]. All 20 patients in the study except one in the control group had abnormal tubotympanometry at baseline. It is unclear whether all patients or only those with abnormal tubotympanometry (n = 19) were included in the analysis.
Holmquist and Larsson24 measured middle ear function using an air pressure equalisation technique (pressure regulator and manometry) in ears with eardrum perforations and tympanometry for ears with intact eardrum. Improvement in middle ear function was evaluated in terms of number of ears with reduction in opening pressure of ≥ 100 mmH2O (patients with perforated eardrums) or pressure change in normalising direction of ≥ 100 mmH2O (patients with intact eardrums). The study reported that Eustachian tube function was measured three or four times within 3 hours of treatment intake. All 39 treated ears (of 32 patients) were analysed, although it is unclear which of these measurements were taken into account to assess treatment success.
Jensen et al. 25 assessed Eustachian tube function using the Valsalva manoeuvre and the aspiration/deflation tests (using an initial pressure of ±200 mmH2O). Valsalva results were considered positive if the test resulted in an audible passage of air at least once in five Valsalva manoeuvres (listening test). Aspiration/deflation tests results were positive if the aspiration test showed a residual pressure of –100 mmH2O or more, or if the deflation test showed a residual pressure of +100 mmH2O or less. Positive treatment effect was defined as a change from pathological to normal measurement in Valsalva, aspiration or deflation tests in at least one occurrence. In addition, results from the three tests (Valsalva, aspiration and deflation tests) were reported separately. Patients were analysed for each test if they had a pathological measurement at baseline (35 patients with negative Valsalva, 35 with pathological aspiration test, 28 with pathological deflation test). All 36 patients had at least one pathological measurement at baseline, and all were analysed for the treatment success outcome.
In Alpini and Mattei,40 tubotympanometry became normal in 9 out of 10 patients using a pressure equalising device, compared with 3 out of 10 patients in the control group after 1 week of treatment. The improvement in the treatment arm was statistically significant compared with control (RR 0.13; 95% CI 0.02 to 0.85).
In Holmquist and Larsson,24 a positive improvement in middle ear function was recorded in 11 out of 19 ears receiving antihistamine–ephedrine combination, compared with 2 out of 20 ears receiving placebo at up to 3 hours after receiving the intervention. The difference between the groups significantly favoured the treatment arm (RR 0.47; 95% CI 0.27 to 0.81).
In Jensen et al. ,25 treatment effect was positive for 12 out of 19 patients undergoing direct application of nasal decongestant, compared with 7 out of 17 patients in the placebo group. The difference was not statistically significant (RR 0.63; 95% CI 0.31 to 1.27). Separate results of each test showed, that compared with placebo, patients receiving topical decongestants had significantly improved Valsalva results 30 minutes following treatment (RR 0.47; 95% CI 0.28 to 0.80). However, no significant effect was demonstrated by the aspiration test (RR 0.94; 95% CI 0.60 to 1.48) or the deflation test (RR 0.80; 95% CI 0.40 to 1.58). The authors concluded that decongestants only had a positive effect on Eustachian tube function at unphysiologically high pressure increases (as with the Valsalva manoeuvre), but not in the case of the smaller and more physiological pressures generated by the aspiration/deflation test.
Clearance of middle ear effusion
No non-surgical study reported clearance of middle ear effusion as a treatment outcome.
Need for additional treatment
Need for additional treatment was assessed in one pharmacological study. 52 Gluth et al. reported that 7 out of 37 patients (19%) receiving nasal steroids required antibiotics or oral decongestants while enrolled in the study. In the placebo group, 7 out of 37 (19%) received antibiotics, oral decongestants and/or nasal spray. There was no statistically significant difference between the groups (RR 1.00; 95% CI 0.39 to 2.57).
Adverse events, discontinuation
Two out of five non-surgical studies stated that they addressed adverse events of treatments, although it was not clear how data on adverse events were elicited. 25,52 Jensen et al. 23 reported no adverse events following treatment with topical decongestant (follow-up duration unclear). Gluth et al. 52 reported that minor events (coughs and nosebleeds) occurred in both arms of the study during a 6-week course of nasal steroids, which did not lead to any treatment discontinuation. However, the number of adverse events was not reported. No discontinuations due to lack of treatment effectiveness were reported.
Key findings of non-surgical studies
There were five studies included that evaluated a variety of non-surgical interventions, namely pharmacological treatments and manual pressure equalisation device. 24,25,40,41,52 None of the interventions was evaluated by more than one study. All of the non-surgical studies included adults, and all except one explicitly reported including a minority of children; therefore, the generalisability of the findings to the broader population of adults with ETD is uncertain. Nearly all patients had a diagnosis of ETD, although the studies were rarely explicit about how they had defined ETD. Diagnostic methods varied, but nearly all studies used a combination of at least two methods, such as tympanometry and audiometry. A single RCT was identified that was assessed as at low risk of bias, though the data available for some outcomes were sparse in this study. 52
One RCT,52 which was the only study with a low risk of bias, showed no evidence that nasal steroids were effective at improving the severity and frequency of ETD symptoms among patients with otitis media with effusion and/or negative middle ear pressure by the end of 6 weeks of treatment. Minor adverse events were reported (coughs and nosebleeds), although there were no significant differences between the two arms of the study.
One RCT25 reported some evidence of improvement in middle ear function for patients with a history of chronic otitis media 30 minutes after receiving direct application of a topical decongestant on the pharyngeal opening of the Eustachian tube. The trial suggested that treatment only improved middle ear function when patients were subject to unphysiologically high pressure changes. The study reported no adverse events. However, the internal validity of this study is unclear, notably due to multiple gaps in reporting of design characteristics and very short-term follow-up. This is also likely to be an unrealistic treatment for primary care; in secondary care, endoscopic guidance would be required.
One non-RCT24 found a significant improvement in middle ear function (significant reduction in opening pressure for patients with eardrum perforation or pressure change in normalising direction for patients with intact eardrums) for patients receiving a single dose of antihistamine and ephedrine compared with placebo. 24 However, the reliability of these findings is uncertain, notably due to a high risk of selection bias and very short follow-up duration (3 hours). All three pharmacological studies included very few patients, and, of the two studies that reported a power calculation,25,52 only one reported sufficient power to detect a significant treatment effect. 24
Two studies40,41 evaluated the use of two different manual pressure equalisation devices, both of which had a high risk of bias. One RCT40 found that self-administration of a manual device applying mild negative pressure to the external ear canal three times a day for 1 week was associated with a significant reduction in severity of fullness in the ear and middle ear function (measured by tubotympanometry) for ETD in patients with residual middle ear effusion by the end of treatment. A non-RCT41 found a statistically significant difference in middle ear function (tympanometric peak pressure) and in hearing (air–bone gap) 9–10 weeks following initiation, which favoured the use of modified politzerisation twice-weekly for 2 weeks. However, the difference in hearing reflected an unexplained deterioration in the control group rather than an improvement in those who received the intervention. Neither study reported data on adverse events of the interventions, making the safety of these interventions uncertain.
Some studies reported some or all data on a per-ear basis, where some patients received bilateral treatment; where this was the case, it was unclear if any statistical analysis undertaken incorporated the within-patient correlation of outcome data.
Overall, the evidence from non-surgical studies is limited due to the small number and size of the studies, poor reporting of study design characteristics, definition of ETD and diagnostic criteria, patient characteristics and outcome data, and limited follow-up duration. The evidence available for any single intervention was extremely sparse. This precludes any definitive conclusions on the effectiveness and safety of non-surgical interventions for ETD in adults.
Surgical studies
Study characteristics
With the exception of Boboshko et al. ,51 all of the studies of surgical interventions were case series. Silverstein et al. (n = 11) used surgery to permit the topical application of steroids (see Table 2 ). 61 The other interventions assessed were procedural variations of laser Eustachian tuboplasty (seven studies, n = 182);20,21,23,54,56,62,63 balloon dilatation of the Eustachian tube (three studies, n = 103);18,22,55 and myringotomy (two studies; n = 121). 58,60 General anaesthesia was used in five studies,22,54–56,63 local in seven studies,18,20,21,51,58,60,61 a combination of the two in one study,23 and one study did not report which method was employed. 62
In most of the studies, all patients were described as having a diagnosis of ETD, although in two these patients were a defined subgroup for whom separate data were reported. 21,60 In three studies, the diagnosis was otitis media with effusion due to ETD;22,23,51 these patients would be expected to have a worse prognosis than those in other studies without otitis media with effusion. Three studies excluded patients with comorbidity such as allergies or reflux disease;20,21,54 conversely, one study required a diagnosis of rhinosinusitis severe enough to warrant surgery. 56 Some studies included patients with a perforated eardrum as a separate subgroup,20,21 while others did not report separate data for these patients, although they were identifiable from their baseline tympanometry. 22,23 Baseline tympanometry data are discussed together with the tympanometric response to therapy in Results, below.
Diagnostic methods varied between studies, but all (except one which did not report these) used more than one method. In all except two studies, the diagnostic process included tympanometry. Although the requirement for participants to have ETD was clearly stated by authors, as with the non-surgical studies, the condition was rarely defined. Most commonly, some of the symptoms characteristic of patients with a diagnosis of ETD such as otalgia during pressure change and aural fullness were cited,18,21,51,54–56,61,63 together with requirements for patients to have an abnormal tympanogram or abnormal appearance on clinical examination. 20,21,23,54–56,61,63 In some cases, ETD was cited as an inclusion criterion with no further information. 62 Full details of the range of criteria used are shown in Table 12 .
| Study | n | Patient inclusion criteria and other relevant characteristics | Patient exclusion criteria | Diagnostic methods | Previous treatment | Related conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuboplasty | ||||||
| Caffier (2011)20 | 31 | Therapy refractory chronic ETD (hyperplastic mucosa at the epipharyngeal dorsal ostium of the ET, abnormal tubal function tests) Other relevant characteristics: ETD symptoms for ≥ 5 years |
History of allergic or reflux disease | Detailed examination and full neuro-otological diagnostics | Previous surgery/treatment with no long-term improvement of tubal function (e.g. tympanoplasty with reperforation in COM, tympanostomy tubes in OME, local decongestants for others): 31/31 (100%) | Chronic/recurrent OME/glue ear: 2/31 (6%) COM (suppurative): 16/31 (52%) (with perforated eardrum) AOM: 4/31 (13%) Atelectasis: 13/31 (42%) (Sadé classification: I: 9; II: 2; III: 2; IV: 0) Dysfunctional pressure equalisation: 9/31 (29%) |
| Jumah (2012)54 | 30 | Chronic obstructive ETD with intact tympanic membrane Otalgia during pressure equalisation while flying/diving, recurrent OME, sensation of fullness in ear Ineffective response to 6–8 weeks’ course conservative treatment (e.g. topical cortisone) Hyperplasia of at least one of the following: adjacent epipharyngeal soft tissue OR dorsal circumference of the ET ostium OR posterior end of the lower turbinate |
Severe allergies or reflux disease | Impedance measurements (ET opening/closing pressures and opening duration) in pressure chamber Valsalva manoeuvre/tympanometry Nasopharyngeal endoscopy Ear microscopy |
Conservative treatment (e.g. topical cortisone): 6–8 weeks’ course: 30/30 (100%) | Severe allergies/reflux disease: 0 |
| Metson (2007)56 | 20 | Chronic rhinosinusitis severe enough to warrant surgery Symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction: [persistent sensation of ear blockage with abnormal tympanogram or recurrent episodes of discomfort with altitude change (flying/diving)] Other relevant characteristics: Baseline medication: PPI 4/20 H2 blocker 1/20 |
NR | Tympanogram Harvard staging and Lund-McKay staging for sinus disease Tissue eosinophil count for sinus disease |
≥ 3 courses antibiotics in previous year (100%) nasal steroid sprays (100%) Patients with sinonasal allergies failed antihistamines and nasal steroids: 16/16 12/20 prior sinus surgery, 8/20 prior ear surgery |
Chronic rhinosinusitis 20/20 (100%) Gastroesophageal reflux disease 5/20 (25%) Sinonasal allergies 16/20 (80%) Sinus ostial obstruction 20/20 (100%) |
| Poe (2007)23 | 13 | Adults with OME for 5 or more years, documented to recur immediately after extrusion/obstruction of most recent tympanostomy tube (2+ recent tube placements required). OME presumed to result from ETD Disease within cartilaginous portion of ET consistent with obstructive disorder Failure to show improvement of OME after medical management |
Cholesteatoma or atalectasis without effusion | Microotoscopy; transnasal endoscopic slow-motion video analysis of ET Endoscopic examination of nasal cavity, nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx and larynx Audiogram Tympanogram Tubal dysfunction score |
≥ 2 tympanostomy tube placements 8 weeks + nasal corticosteroids 8 weeks + oral antihistamines (where allergic disease) 8 weeks + omeprazole (where laryngopharyngeal reflux) |
OME history 13/13 Atalectasis: 4/13 Laryngopharyngeal reflux 9/13 Allergic disease 10/13 |
| Yañez (2008)62 | 25 | Obstructive or non-obstructive (patulous) Eustachian tube disorder | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Yañez (2010)63 | 25 | Obstructive ETD severe enough to warrant ET surgery. ETD defined as persistent sensation of ear blockage with abnormal tympanogram or recurrent episodes of ear discomfort with changes in altitude (flying/diving) Other relevant characteristics: Evidence of tubal dysfunction and valve obstruction on simple endoscopy on slow-motion video-endoscopic analysis |
NR | Simple endoscopy or slow motion video-endoscopic analysis Audiograms Tympanograms Symptom assessment |
≥ 3 previous courses of nasal steroid sprays 25/25 (100%) Previous ear surgery: 18/25 (72%) Multiple pressure equalisation tube placements: 21/25 (84%) Previous myringotomy only: 4/25 (16%) None had previous nasal surgery |
No other medical conditions |
| Sedlmaier (2009)21 | 38 | ME ventilation problems Negative Valsalva, no passive tubal opening, or long history of complaints and symptoms (difficult pressure equalisation, otalgia during pressure change) |
Allergy or reflux disease | Passive tubal opening and Valsalva (COM group) Tympanogram and microscopically controlled Valsalva |
NR | NR |
| Balloon dilatation | ||||||
| Catalano (2012)18 | 70 | Aged at least 18 years Reported chronic sensation of ear fullness, pressure, pain and otitic barotrauma (developed in adulthood) |
Temporomandibular joint disease, early hydrops | Tympanogram Clinical examination Symptomatology |
NR | NR |
| McCoul (2012)55 | 22 | Aged at least 18 years abnormal tympanogram – any non-A curve Abnormal otoscopic examination Unilateral/bilateral ETD symptoms (aural fullness/pressure, clogged/muffled sensation in ears, recurrent/persistent ME effusion, or inability to rapidly self-equilibrate ME pressure following ambient pressure change) |
Head/neck surgery or radiation therapy within 3 months, sinonasal malignancy, acute upper respiratory infection (including acute otitis media), adenoid hypertrophy, nasal polyposis cleft palate or history of repair, craniofacial syndrome, cystic fibrosis, cliliary dismotility syndrome, other systemic immunodeficiency | ETDQ-7 SNOT-22 Physical examination including pneumatic otoscopy Tympanometry Pure-tone audiometry CT scan of paranasal sinuses (Lund–McKay score) |
Medical therapy (oral antihistamine, intranasal corticosteroids, autoinflation exercises) for 2 months: 22/22 Tympanostomy: 3/22 |
NR |
| Poe (2011)22 | 11 | Unilateral or bilateral persistent OME for at least 5 years, broken only by tympanostomy tubes or tympanic membrane perforation (aetiology consistent with ETD) | NR | Valsalva manoeuvre Otomicroscopy Tympanometry Video rigid or fibre-optic endoscopy Mucosal inflammation score CT scans |
Previous tympanostomy tubes: 11/11 (100%) (mean 4.7, range 1–10) Adenoidectomy: 5/11 (45.5%) |
Persistent OME 11/11 (100%) Chronic rhinitis: 5/11 (45.5%) Atelactasis: 1/11 (9%) Chronic rhinosinusitis 1/11 (9%) Polyps: 2/11 (18%) Skull base fracture: 1/11 (9%) Perforated eardrum: 2/11 (18%) |
| Myringotomy | ||||||
| Potocki (1999)60 | 13 | Patients undergoing hyperbaric oxygen therapy who would otherwise have required tympanostomy tubes for ETD | Children | Otoloaryngologic examination Audiologic testing including tympanogram and pure-tone audiometry |
Nasal decongestants: 13/13 Valsalva manoeuvre: 13/13 Prior otologic surgery 0/13 |
Barotrauma: tympanic membrane haemorrhage: 8/13 (62%) |
| Prokopakis (2005)58 | 108 | Adults with serous otitis media, ETD or AOM | Nasopharyngeal tumour | Weekly clinical (including Valsalva-Toynbee and inflation-deflation tests) and audiological examination with tympanogram and audiogram for 8 weeks Nasal endoscopy (all patients negative for tumours) Allergy tests (all ETD patients negative) |
None | NR |
| Other interventions | ||||||
| Boboshko (2005)51 | 40 | Intermittent hearing loss, ear pain, autophony, discomfort in the ears, poor endurance of differences in atmospheric pressure (flying in an aeroplane, diving, etc.), others (NR) (based on author contact)a | NR | Symptomatology; tympanometry (based on author contact)a | Most previously treated for ETD (based on author contact)a | OME: 40/40 (100%) |
| Silverstein (2003)61 | 11 | Chronic ET dysfunction Symptoms consistent with ETD (e.g. hearing loss and aural fullness) Previous medical therapy and at least one ME ventilation tympanometry/clinical examination indicated abnormal ME pressure |
NR | Tympanometry; audiometry; clinical examination | Medical therapy: 11/11 (100%) ≥ 1 ME ventilation procedure: 11/11 (100%) |
Samter’s triad (bronchial asthma, nasal polyps, aspirin sensitivity): 18% |
Patients in most of the studies had extensive histories of previous treatment for ETD and/or related conditions. These included multiple antibiotic and steroid treatments as well as previous aural and nasal surgeries (see Table 2 ). In five studies, failure of one or more medical therapies or previous surgical intervention (e.g. pressure equalisation tubes) was a criterion for inclusion in the study,20,22,23,54,61 while in nine studies, all patients had failed one or more previous treatment. 20,22,23,54–56,60,61,63
Results
Severity and frequency of symptoms
Nine studies assessed change in symptoms of ETD. All reported the number of patients who experienced improvement in symptoms, although the definitions for the outcome varied in terms of symptoms specified; two studies did not specify any symptoms ( Table 13 ). 56,63 In the majority of studies, the methods for outcome assessment were not reported; the authors simply referred to the number of patients who showed improvement or resolution of symptoms. Where this was the case, it appeared that the assessment was based on patient report, although one study included the appearance of the tympanic membrane at examination in the criteria, together with symptomatology. 18 The presence or intensity of subjective symptoms was assessed in some studies but methods of determining whether a patient had improved or resolved symptoms and thresholds for these improvements/resolutions were not always specified. One study specified that the outcome was assessed by ‘patient response’55 and another specified that the assessment was subjective. 56 One study used a VAS but reporting of outcome data was limited. 20 Another study reported mean scores on the ETDQ-7 and the SNOT-22 scales. 55 Length of follow-up ranged from 2 months to 2 years, where reported.
| Study | Intervention | Authors’ criteria for patient reported improvement | Follow-up | Improvement | Unit of analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuboplasty | |||||
| Caffier (2011)20 | Laser Eustachian tuboplasty | Tinnitus (via audiometry) Also assessed by VAS but results NR |
1 year | 13/31 (42%) slight improvement 2/31 (6%) resolved |
Patient |
| Metson (2007)56 | Microdebrider Eustachian tuboplasty | Resolution of subjective symptoms of ETD/ear blockage | 13 months | 14/20 (70%) | Patient |
| Yañez (2008)62 | Laser Eustachian tuboplasty | Symptom free (not further defined) | NR (study completion) | 18/20 (90%) symptom free 1/20 (5%) partial recurrence 1/20 (5%) full recurrence |
Patient |
| Yañez (2010)63 | Laser Eustachian tuboplasty with crosshatching technique | Successful outcome defined as resolution of symptoms (ear blockage, ear pain, hypoacusis, autophony) | Mean 15 months (range 3–37 months) | 23/25 (92%) | Patient |
| Balloon dilatation | |||||
| Catalano (2012)18 | Balloon dilatation | Changes in sensation of ear fullness, pressure, pain and tolerance to air travel; visible alteration in appearance of eardrum | Mean 30.3 (SD 3.6) weeks (up to 34 months) | 71/100 ears (71%) showed improvement; 7/8 (88%) patients reported persistent improvement at 34 months | Ear |
| McCoul (2012)55 | Balloon dilatation | Global improvement (patient response): improved | 3 weeks | 18/29 (62%) | Ear |
| 6 weeks | 23/29 (79%) | ||||
| 12 weeks | 24/26 (92%) | ||||
| Myringotomy | |||||
| Prokopakis (2005)58 | Laser-assisted tympanostomy without ventilation tubes | Symptoms (ear fullness, pain, tinnitus) of ETD resolved | 2 months | 38/48 (79.1%) | Ear |
| Other interventions | |||||
| Boboshko (2005)51 | Point laser coagulation (n = 25, 31 ears) vs. catheterisation of ET with insufflation, application of medications (not specified) under rhinoscopic control (n = 15, 15 ears) | Disappearance or reduction of unpleasant feeling and noise in the ear | 2 weeks | 25/25 (100%) vs. NR | Patient |
| Silverstein (2003)61 | Tympanometry/myringotomy and topical dexamethasone via MicroWick (Silverstein MicroWick™, Anthony Products, Indianapolis, IN, USA) | Improvement in aural fullness or pressure | Mean 7.2 months | 8/11 (72.7%) | Patient |
Four of the studies assessed various techniques for tuboplasty. The study by Caffier et al. only reported the numbers of patients showing improvement for the outcome of tinnitus, but did show patient-reported data using a VAS for overall satisfaction and improvement of ETD, aural fullness and hearing loss. 20 Scores of between 5 and 7 on the VAS were reported for all outcomes at 1 year; these were described by the authors as high, though the possible score range on the scale was not reported. 20 Of the other three studies, two reported success rates of > 90%62,63 and one reported a success rate of 70% based on resolution of symptoms;56 symptoms were specified as ear blockage, ear pain, hypoacusis and autophony in one study but were not specified in the other two.
Two studies assessing balloon dilatation reported symptom resolution. 18,55 One reported improvement in 92% of ears at 6 months’ follow-up;55 the second reported improvement in 71% of ears after a mean of 30 weeks’ follow-up. 18 McCoul et al. assessed symptoms using the ETDQ-7 and the SNOT-22; data were reported for durations of follow-up ranging from 3 weeks to 6 months. 55 ETDQ-7 score improved by a mean of 1.8 points (SD 1.2; 22 ears) at 6-month follow-up from a mean baseline score of 4.5 (SD 1.2; 31 ears) (p = 0.001). The possible score range on the ETDQ-7 is 1.0 to 7.0, with higher scores denoting more severe symptoms. 26 The clinical relevance of changes in ETDQ-7 score was not interpreted in the study, and no data on minimally important clinical difference were found; therefore, the clinical relevance of the change in ETDQ-7 is unclear. The SNOT-22 score improved by a mean of 23.3 (SD 19.6; 21 ears) points at 6-month follow-up from a mean baseline score of 51.4 (SD 21.1; 33 ears) (p = 0.001). The possible score range on the SNOT-22 is 0 to 110. 27 The minimally important difference in SNOT-22 score was estimated to be 8.9;27 therefore, reported changes in SNOT-22 from baseline were likely to be clinically relevant. Both measures showed statistically significant improvements from baseline at all time points.
Studies of laser-assisted tympanostomy (myringotomy) and topical steroid application reported symptom resolution or improvement in 79% and 72% of patients, respectively. 58,61 The controlled before-and-after study found that all 25 patients treated with point laser coagulation reported disappearance or reduction of unpleasant feeling and noise in the ear; results for the 15 patients in the control group were not reported. 51
Across all of the studies, the proportion of patients showing improvement in ETD symptoms, either not further defined by the authors or defined as multiple symptoms (as opposed to a single symptom of tinnitus20 or otitis media with effusion resolution23), was between 70% and 100%. Given the small sample sizes, this suggests some consistency across interventions, despite wide variations in patient characteristics, treatments assessed and use of concomitant therapies.
Quality of life
None of the studies assessed quality of life.
Hearing
Seven studies reported some information on changes in hearing following the intervention ( Table 14 ),20,23,51,56,60,61,63 although one study of myringotomy noted only that 1 out of 13 patients experienced an unspecified change in hearing. 60
| Study | n | Intervention | Outcome assessed | Baseline, mean (SD) | Follow-up, mean (SD) | Difference from baseline | Duration of follow-up | Unit of analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuboplasty | ||||||||
| Caffier (2011)20 | 31 | Laser Eustachian tuboplasty | Air–bone gap (dB) [mean (SD)] | Total: 23.7 (12.2) dBa
Perforated: 29.1 (7.1) dB Intact: 18.0 (14.1) dB |
Total: 11.5 (8.9) dBa
Perforated: 9.1 (3.3) dB Intact: 14.0 (12.1) dB |
Total: –12.3 (14.4) dBa
Perforated: –20 (7.8) dB Intact: –4 (18.5) dB |
1 year | Patient |
| Metson (2007)56 | 20 | Microdebrider Eustachian tuboplasty | Pure-tone average (dB) [mean (SD)] | 18/20 (90%) impaired at baseline Pure-tone average 27 dB |
Number impaired NR 21 dB |
Number improved NR –6 dB (p = 0.013) |
NR: postoperative | Patient |
| Poe (2007)23 | 13 | Laser Eustachian tuboplasty | Pure-tone average (dB) [mean (SD)] | 36.0 dB (12.1) (n = 12)a | 34.6 dB (14.9) (n = 6)a
25.5 dB (17.6) (n = 8)a 25.0 dB (6.5) (n = 8)a |
–4.3 dB (17.1) (n = 6)a
–8.7 dB (20.0) (n = 8)a –9.2 dB (16.6) (n = 8)a |
6 months 1 year 2 years |
Patient |
| Yañez (2010)63 | 25 | Laser Eustachian tuboplasty with crosshatching technique | Pure tone average (dB) [mean (SD)] | 30 dB | 20 dB | –10 dB | Mean 15 (range 3–37 months) | Patient |
| Myringotomy | ||||||||
| Potocki (1999)60 | 13 | Myringotomy | Patient reported change in hearing (change from baseline n/N) | 1/13 (direction unclear) | 4 months | Patient | ||
| Other interventions | ||||||||
| Silverstein (2003)61 | 11 | Tympanometry/myringotomy and topical dexamethasone via MicroWick | Mean pure tone average dB Mean air–bone gap (dB) mean speech discrimination score (%) |
40 dB 11 dB 94% |
34 dB 5 dB 97% |
–6 dB (NS) –6 dB (NS) 3% |
Mean 7.2 months | Patient |
| Boboshko (2005)51 | 40 I: 25 (31 ears) C: 15 |
Point laser coagulation | Air–bone gap (dB) | 26.8 dB (7.2) vs. 26.3 dB (5.5) |
8.8 dB (6.1) vs. 14.9 dB (5.3) |
18.1 dB (5.2) vs. 11.4 dB (5.2) p = 0.0028 |
1 year | Ear |
Length of follow-up ranged from 4 months60 to 2 years23,51 where specified; one study reported only that the assessment was ‘postoperative’. 56 Five studies reported pure-tone averages, measured in DBs across a range of speech frequencies. Other outcomes including the air–bone gap (also measured in DBs) were reported by some studies as additional61 or alternative20,51 measures of hearing.
Change from baseline to follow-up in pure-tone ranged from a mean improvement of 6 dB to 10.7 dB. The change in air–bone gap ranged from a mean improvement of –6 dB to –12.3 dB. The statistical significance of change from baseline to follow-up was not reported in all studies.
Four studies that evaluated a form of tuboplasty assessed changes in hearing. 20,23,56,63 Three of these reported pure-tone averages with improvements of between –6 dB and –10 dB at time points between ‘postoperative’ and 2 years’ follow-up. 23,56,63 The fourth study reported a statistically significant decrease in the air–bone gap of –12.3 dB, although patients with perforated tympanic membranes showed larger improvements than those with intact membranes. 20 This study also reported improvements in both air and bone conduction and found a significant improvement in air–bone gap at 1 year in patients with perforated (p < 0.001) and in patients with intact ear drums at baseline (p < 0.05). 20
None of the studies of balloon dilatation reported data on hearing.
Two studies of other interventions reported a hearing outcome. The study which assessed topical steroid application by MicroWick (Silverstein MicroWick™, Anthony Products, Indianapolis, IN, USA) reported statistically non-significant improvements of 6 dB in the mean pure-tone average, a statistically non-significant change in the air–bone gap of –6 dB at a mean of 7 months’ follow-up, and a slight improvement in mean speech discrimination scores from 94% to 97%. 61
Mean air–bone gap was significantly smaller in patients receiving laser coagulation surgery than in controls at 1-year follow-up [MD –6.70 (95% CI –9.91 to –3.49)]. 51 Twenty-four of the 31 ears (77.4%) that received laser surgery had an air–bone gap of < 10 db at follow-up, compared with 4 out of 15 ears (26.7%) in the control group at 1 year. This difference was statistically significant (RR 0.31; 95% CI 0.15 to 0.63). Data on the numbers of patients with pure-tone average thresholds between 0 dB and 10 dB, 11–20 dB, 21–30 dB and > 30 dB were also reported and indicated greater improvement in the intervention group.
Middle ear function
Nine studies reported on the numbers of patients displaying a type A tympanogram following treatment ( Table 15 ). The proportion of patients with an abnormal (non-type A) tympanogram at baseline ranged from 0% to 66%, although tracings in at least one study, while meeting criteria for type A, were nevertheless considered to be abnormal by the authors. 55 Length of follow-up ranged from 2 weeks to 2 years.
| Study | n | Intervention | Baseline: tympanogram type A, n/N | Follow-up: tympanogram type A, n/N | Conversion to tympanogram type A (n/N) from abnormal B/C | Duration of follow-up | Unit of analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuboplasty | |||||||
| Poe (2007)23 | 13 | Laser Eustachian tuboplasty | 0/13 (0%) | 2/13 (15%) (one type B; one type C, nine NS) | 2/13 (15%) | 2 years | Patient |
| Caffier (2011)20 | 31 | Laser Eustachian tuboplasty | 2/15 (13%) (intact eardrum subgroup)a | 4/15 (26%) (NS)a | NR | 1 year | Patient |
| Jumah (2012)54 | 30 | Minimally invasive laser Eustachian tuboplasty | 20/30 (67%) | 24/30 (80%) | 4/10 (40%) from type B/C to A (p < 0.135) | 6 weeks | Patient |
| Sedlmaier (2009)21 | 38 | Laser ablation of epipharyngeal ET | 3/19 (16%) (intact eardrum subgroup)a | 5/19 (26%)a | NR | 8 weeks | Patient |
| Balloon dilatation | |||||||
| Catalano18 | 70 | Balloon dilatation | 72/100 ears (72%) | 97/100 ears (97%) | 25/28 ears (89%) | NR | Ear |
| McCoul (2012)55 | 22 | Balloon dilatation | 10/35 ears (29%) (all considered abnormal) | 34/35 ears (all considered normal) | 24/25 (96%) | 6 weeks | Ear |
| Poe (2011)22 | 11 | Balloon dilatation | 0/11 (0%) (four type B or C, five tympanostomy tubes, two perforated eardrum) | 4/11(36%) (one type C, four tubes, two perforated) | 4/11 (36%) | 6–14 (median 7) months | Patient |
| Other interventions | |||||||
| Boboshko (2005)51 | 40 Intervention: 25 (31 ears) Comparator: 15 |
Point laser coagulation | Intervention: NR (15 type B, 14 type C, seven type F)b
Comparator: NR |
Intervention: 30/31 (97%) (one type C) Comparator: NR |
NR | 2 weeks | Ear |
| Silverstein (2003)61 | 11 | Tympanometry/myringotomy and topical dexamethasone via MicroWick | 3/11 (27.3%) (six type B, two type C) | 7/11 (63.6%) (four patients with persistent perforations) | 4/8 (50%) | Mean 8 months | Patient |
In Caffier et al. and Sedlmaier et al. , tympanograms were described as normal rather than as type A, with other tympanogram tracings being classified as ‘flat’, ‘flatter’ or ‘negative’. 20,21 These two studies also did not report the number of patients who experienced change from baseline from an abnormal to a type A tympanogram; instead, they reported the number of type A tympanograms at baseline and follow-up. The overall number of patients with type A tympanograms increased in both studies. However, because it is possible for treatment to have a negative impact on tympanogram results in some patients, this does not preclude some individuals having converted from type A to B/C.
Four studies assessed types of tuboplasty. 20,21,23,54 Caffier et al. reported that four patients (26%) had a normal tracing at follow-up compared with two (13%) patients at baseline. 20 Poe et al. 23 reported conversion to type A in 15% of patients. A third study found an increase of 13% in the number of patients with a normal pattern, assessed 8 weeks after surgery. 21 The fourth study assessing tuboplasty which reported change from baseline found normalisation in 36% patients. 54
Three of the studies assessed balloon dilatation. Rates of conversion to type A tympanogram were 36%,22 71%18 and 96%. 55 The lower conversion rate of 36% may be due, at least in part, to the fact that patients in this study had a diagnosis of chronic otitis media with effusion. However, both of the studies reporting higher conversion rates also administered concomitant surgical treatment, either to all or to a majority of patients, meaning that these studies may overestimate the effect of the treatment.
In studies assessing other interventions, Silverstein reported that 50% of the patients with an abnormal baseline tracing had converted to a type A pattern after a mean of 8 months’ follow-up after MicroWick application of dexamethasone. 61 One study of laser coagulation reported no type A tympanograms at baseline and improvement to type A in 97% of affected ears 2 weeks after surgery. 51
Seven studies also reported a range of other measures of middle ear function. These included ability to perform the Valsalva manoeuvre,20–22,54 passive tubal opening,21 response to pressure testing (including Eustachian tube opening and closing pressures)20,54 changes in the waveform of the tympanogram other than a shift from types B or C to type A,56,63 mucosal inflammation score,22 Eustachian tube endoscopy scores,23 and results of clinical examination of the tympanic membrane. 55 Multiple measures were reported by five studies, all of which also reported data on type A tympanograms (see Table 15 ). 20–23,54
Changes in tympanogram other than the presence of a type A pattern were reported in two studies of tuboplasty. One reported that 96% (24 out of 25) of patients with an abnormal tympanogram (defined as non-type A) demonstrated improvement (undefined). 63 Another reported the development of a normal or more normal tracing in 65% (11 out of 17 patients) who showed baseline abnormality (not defined). 56
Changes in the number of patients with a positive Valsalva manoeuvre were reported by three studies of tuboplasty;20,21,54 and one of balloon dilatation in patients with otitis media with effusion. 22 All studies showed an increase in the proportion of patients, ranging from 61% to 100%, with a positive Valsalva manoeuvre (see data extraction tables in Appendix 5 for full details).
Eustachian tube endoscopy scores which assessed valve dilatation, mucosal swelling and function of the levator veli and tensor veli were reported by the tuboplasty study in otitis media with effusion patients and did not show significant changes from baseline,23 while muscosal inflammation scores were reported in the balloon dilatation study in otitis media with effusion patients and did show a statistically significant improvement. 22 The other balloon dilatation study assessed tympanic membrane retraction and found an improvement in all affected patients. 55 Full details are reported in the data extraction tables (see Appendix 5 ).
Measures of response to pressure were reported by one tuboplasty study, which assessed the closing and opening Eustachian tube pressures and the presence of a blocked pattern using a pressure chamber. As with the tympanometry results, this showed a statistically significant improvement. 54 Normal passive tubal opening was assessed by two other studies of tuboplasty. 20,21 Interepretation of graphical data indicated improvement in both studies in the number of patients showing normal response but the statistical significance was unclear. Full details are reported in the data extraction tables (see Appendix 5 ).
Clearance of middle ear effusion
Clearance of middle ear effusion was reported by two studies. 23,51 In one study of patients with chronic otitis media with effusion,23 there was resolution of the symptom in 4 of 11 patients at 6 months following tuboplasty. The method for assessing resolution appeared to be clinical examination. The second study reported that 6% of ears treated with point laser coagulation experienced otitis media with effusion recurrence at 9 to 11 months’ follow-up, compared with 40% of ears in the control group at 1 to 6 months’ follow-up. 51
Need for additional treatment
Eight studies reported data on the need for additional treatment: three of tuboplasty,23,56,63 three of balloon dilatation18,22,55 and one each of myringotomy60 and MicroWick application of steroids. 61 The additional treatment documented was either a repeat of the original procedure18,55,60 or the insertion or removal of pressure equalisation tubes or myringoplasty for persistent perforation. 60,61 One study documented repeated treatments only in those patients with a good response to initial therapy. 18 The duration of follow-up varied from 4 months to 2 years, where reported.
In the three studies assessing forms of tuboplasty, one reported that no additional treatment (pressure equalisation tubes) was required. 63 One study reported that 2 of the 20 patients required pressure equalisation tubes following tuboplasty,56 while the study conducted in patients with chronic otitis media with effusion reported that two of the eight patients on whom follow-up data were available for this outcome required them. 23
One study of balloon dilatation reported repeat procedures in 2 of the 22 patients. 55 The second reported data only for ears which had shown an initial benefit of treatment (71 of 100 ears); seven of these required a repeat dilatation. 18 The third study reported only concomitant treatments of insertion or removal of pressure equalisation tubes. 22
One study of myringtotomy in 13 patients documented one repeat procedure and two myringoplasties for persistent perforation. 60 Myringoplasties were also required in 3 of 11 patients who underwent MicroWick application of dexamethasone. 61
Adverse events and complications of Eustachian tube dysfunction
Information on adverse events was reported in all except three studies. 58,62,63 Duration of follow-up varied from 1 week51 to between 1 and 2 years where it was reported;23 in two of the studies, it was clear that a post-surgical assessment was conducted but no assessment of long-term adverse events was carried out. 21,54 The adverse events documented were generally minor, consisting of discomfort, minor lacerations, formation of adhesions (synechia), and granulomas. Individual cases of bleeding and radiculopathy were documented following balloon dilatations.
Of the tuboplasty studies, one reported that there were no adverse events in the 20 operated patients;56 one reported no acute or long-term complications but no further information was provided;54 one reported two patients with types of synechiae and two with granuloma in the resected area but no significant surgical complications;23 and one reported discomfort which was relieved by additional anaesthesia in three patients and one case of an adhesion. 20 Three other tuboplasty studies did not report data on adverse events. 58,62,63
Of the two studies of balloon dilatation, one reported minor mucosal lacerations to the lumen of the Eustachian tube in 5 of the 11 patients and a contralateral radiculopathy (C6–7 disc space) which showed full recovery; no further complications were reported. 22 The other study reported that one patient (of 22) experienced bleeding, which resolved after myringotomy. 55
The study assessing bilateral thermal myringotomy reported no adverse effects other than persistent bilateral perforations in 2 of 13 patients. 60 A study of laser ablation of the epipharyngeal Eustachian tube reported that one synechia was the only complication. 21 A study of laser point coagulation reported that there were no adverse events.
One study reported complications of ETD: one patient developed profound sensorineural hearing loss as a consequence of severe otitis media following MicroWick application of topical steroids; no negative effects of treatment were documented. 61
Discontinuations of treatment and other losses to follow-up
All of the studies, except that by Silverstein et al. ,61 were of surgical interventions, so discontinuation of therapy was not a relevant outcome for these studies. Silverstein et al. reported one discontinuation of therapy (from 11 patients) as a consequence of the ETD complication described above. 61 Similarly, early tube extrusion was not relevant, as pressure equalising tubes were not the intervention assessed in any of the included studies, although in three studies some patients had them placed before, during or after the assessed therapy. 22,23,55,56
Losses to follow-up were reported by three studies: one of balloon dilatation55 and two of tuboplasty. 21,23 Data from Poe et al. were complicated by missing data from different individual patients at multiple follow-up points,23 while McCoul et al. reported cumulative losses55 and Sedlmaier et al. a single follow-up duration. 21 The fact that other studies did not report losses to follow-up is likely to be due to the fact that in five studies there was no prespecified study duration: these studies reported mean duration of follow-up or range of follow-up duration. 18,22,51,63 In a further two studies, duration of follow-up was reported only as ‘post-surgical assessment’56 or ‘study completion’. 62
Key findings of surgical studies
There were 14 included studies that evaluated a surgical intervention. These were all cases series, with the exception of a controlled before-and-after study. No RCTs were identified. Any interpretation of data from case series is limited by the uncontrolled study design: it is impossible to determine how much improvement in symptoms and other measures would have occurred in the absence of the intervention. The assessment is further limited by the fact that the recruitment of patients to the studies was not well described; although a majority of the studies were prospective, few reported consecutive recruitment of patients, and it was unclear how representative the included patients were in any of the studies. The controlled before-and-after study was also subject to potential sources of bias. 51
A second major limitation was the lack of clear definitions of ETD in the included studies, which was combined with substantial variations in inclusion criteria, baseline patient characteristics and diagnostic methods. Outcome data were poorly reported in some of the studies, although losses to follow-up were generally limited. In many cases, the statistical significance of results was not reported and insufficient data were available to calculate this information. Some studies reported some or all data on a per-ear basis, where some patients received bilateral treatment; where this was the case, it was unclear if any statistical analysis undertaken incorporated the within-patient correlation of outcome data. Follow-up duration also varied substantially, and in some cases was reported only as a mean duration. Where data from multiple follow-up points were reported, these sometimes indicated continuing accrual of benefit with increased length of follow-up; this may be a consequence of the intervention or of a remission of symptoms due to the natural course of the condition of ETD. Finally, many of the studies reported the use of co-interventions for many or all of the patients; these concomitant therapies involved additional surgery as well as some pharmacological therapies. In the absence of control groups, it was not possible to separate the effects of assessed interventions, natural remission or alteration of symptoms, and co-interventions.
The greatest volume of evidence related to various techniques of Eustachian tuboplasty, with seven studies in 182 patients assessing interventions in this category. 20,22,23,54,56,62,63 However, in addition to differences in the techniques used, there were wide variations between the patients in these studies, as well as differences in the outcomes reported and the measures used to assess outcomes. One study also employed sinus surgery in all patients,56 and concomitant interventions for some patients were reported in three of the other studies. 20,22,23
Rates of resolution or improvement were high, at 70–90% in the three studies which assessed symptoms of ETD generally. Unsurprisingly, the study which evaluated the intervention in otitis media with effusion patients and did not systematically use cointerventions reported lower rates of symptom (middle ear effusion) resolution. Improvements in tinnitus reported by another study were also low,20 although improvements in VAS scores for other symptoms were described as significant. Where hearing was assessed, improvements in the pure-tone average were small (6 dB to 10 dB) and, therefore, potentially not clinically significant. Measures of middle ear function indicated low (15% to 40%) rates of conversion to type A tympanogram20,23,54 but higher rates (65% to 96%) of ‘normalisation of the tympanogram’. 56,63 There is insufficient evidence to demonstrate the effectiveness of tuboplasty, or to determine either the details of the surgical technique which should be employed or the patients for whom it should be considered.
Of the three studies of balloon dilatation identified (n = 107), those patients who were not required to have previous surgery as a criterion for inclusion demonstrated high levels of improvement in symptoms of ear fullness, pressure, pain and tolerance to air travel or general ETD symptoms;18,55 the resolution of symptoms was not reported in the study of patients with otitis media with effusion, although tympanometry showed an improvement in 36% of patients. 22 Tympanometric measurement of middle ear function in the other two studies indicated high levels of conversion to type A tracings (89% and 96%, respectively). 18,55 None of the studies reported data on hearing. As with tuboplasty, there is insufficient evidence to demonstrate efficacy or to determine the population in which it should be considered, particularly when the use of cointerventions for some or all of the patients is borne in mind.
Two studies assessed methods of myringotomy. 58,60 The first of these had only 13 patients, of whom 11 had an ETD diagnosis;60 these patients were treated in order to enable hyperbaric oxygen therapy for other indications. A minority of patients in the larger (n = 108) case series had a diagnosis of ETD. 58 In both cases, reporting of outcome data was very limited, as was duration of follow-up. While the data suggested that there may be a benefit to myringotomy, they were too short term and poorly reported to allow any conclusions to be drawn.
The evidence base forotopical application of steroids to the Eustachian tube rests on a single case series of 11 patients. 61 While the limited data available from this series suggested that there may be some benefits to the treatment, they are too limited to allow any conclusions to be drawn.
The single controlled before-and-after study evaluated laser point coagulation and indicated high levels of symptom resolution (100%) and tympanogram normalisation (97%) but did not report comparable data for control subjects. An improvement in hearing did show a statistically significant benefit compared with controls. 51 Therefore, while these studies suggested there may be some benefits to these treatments, the available data were too limited to allow any conclusions to be drawn.
Overall, none of the interventions appeared to be associated with serious adverse effects, although minor complications of surgery were reported in a minority of patients in several studies. It was not clear that adverse events were systematically documented, and several studies did not report any safety data. The evidence pertaining to surgical interventions generally is of limited quantity and quality.
Chapter 4 Discussion
The aims of the project were to undertake a systematic review to determine the clinical effectiveness of interventions for adult ETD and to identify gaps in the evidence. Both surgical and non-surgical treatment options were included in the review. Non-surgical interventions included in this review were classed as pharmacological treatments and manual devices. Pharmacological interventions included nasal steroids, nasal decongestants directly applied to the Eustachian tube and a combination of antihistamine and ephedrine. Two types of manual devices used to equalise middle ear pressure were included: a modified politzerisation device and a self-administered manual tool applying mild negative pressure to the external ear.
Several surgical techniques were identified. These included laser Eustachian tuboplasty, balloon dilatation of the Eustachian tube, laser coagulation, myringotomy, and myringotomy for direct application of topical steroids through a MicroWick tube. Surgical interventions were performed under local or general anaesthesia, on an inpatient or outpatient basis. None of the studies was conducted in a UK NHS setting.
Principal findings
All of the surgical studies and three of the five non-surgical studies were at high risk of bias. One study had a low risk of bias52 and one had an unclear risk. 25 All of the non-surgical studies were comparative (RCT or non-RCT). All non-surgical studies except one explicitly reported including a minority of children or adolescents. Surgical studies only included adults. Only one surgical study used a comparative (controlled before-and-after) design, and all other studies evaluating a surgical intervention were case series. It was inappropriate to statistically pool studies because of their variability and due to limited available data. For this reason, a narrative synthesis was undertaken.
All studies were small, and for all except two it was unclear whether or not they had sufficient power to detect a statistically significant difference between groups; therefore, where there is no evidence of an effect, it cannot be assumed that there is no effect. One study was described as adequately powered, although small,40 while a second trial was known to be underpowered. 52
A key issue was the fact that studies rarely specified how they defined ETD or reported standardised procedures for assessment of symptoms. The presence of related conditions at baseline also varied between studies. This further complicated the extent to which symptoms could be attributed to ETD. Many of the surgical studies reported the use of cointerventions, which often included additional surgery for many or all of the patients. Outcome assessment and duration of follow-up were also sources of substantial heterogeneity. These issues are discussed in detail in Chapter 3 (see Overview of study characteristics).
Non-surgical interventions
Several pharmacological treatments and manual pressure equalisation devices were evaluated, but none of the interventions was evaluated by more than one study. Overall, the evidence from non surgical studies is weak due to the small number and size of the studies, as well as several important limitations, notably poor reporting of study design characteristics, patient characteristics and outcomes data, and limited follow-up duration. In particular, the clinical value of follow-up data at durations measured in minutes or hours is highly uncertain. This paucity of data precludes any definitive conclusions on the clinical effectiveness and safety of pharmacological or manual treatments for adult ETD. Only two of the studies reported measuring adverse events. Minor adverse events were reported in one study,52 and no events in the second. 25
One trial showed no evidence that a 6-week course of nasal steroids was effective at improving the severity and frequency of ETD symptoms among patients with otitis media with effusion and/or negative middle ear pressure by the end of the treatment. 52 This was the only study identified as having a low risk of bias, though even in this study there were limitations in how the outcome data were reported.
There were some data indicating improvement in middle ear function for patients with a history of chronic otitis media 30 minutes after receiving direct application of a topical decongestant on the pharyngeal opening of the Eustachian tube in a single RCT. 25 However, as pointed out by the authors, treatment only improved middle ear function when patients were subject to unphysiologically high pressure changes. The internal and external validity of this study are both unclear, notably due to multiple gaps in reporting of design characteristics and very short-term follow-up. This is also likely to be an unrealistic treatment for primary care; in secondary care, endoscopic guidance would be required.
One non-RCT found a significant improvement in middle ear function for patients receiving a single dose of antihistamine and ephedrine compared with placebo. However, the reliability of these findings is uncertain, notably due to a high risk of selection bias and very short follow-up duration (3 hours). 24
Two studies evaluated the use of two different manual pressure equalisation devices. 40,41 Both studies were small and subject to a high risk of bias. The RCT found that the self-administration of a manual device applying mild negative pressure to the external ear canal three times per day for 1 week was associated with a significant reduction in severity of fullness in the ear and middle ear function. 40 The non-RCT found a statistically significant difference in middle ear function (tympanometric peak pressure) and in hearing at 9 to 10 weeks’ follow-up which favoured the use of modified politzerisation twice-weekly for 6 weeks. 41 However, the difference in hearing reflected an unexplained deterioration in the control group rather than an improvement in those who received the intervention. Neither study reported data on adverse events of the interventions, making the safety of these interventions uncertain. In addition, this may be experienced as being an unpleasant treatment; however, adherence, compliance and patient experience of the treatment were not assessed. Therefore, it is unclear how feasible such a treatment would be in clinical practice.
Surgical interventions
As noted above, a variety of surgical interventions were evaluated. Eustachian tuboplasty and balloon dilatation were evaluated in multiple studies. Myringotomy was assessed in two studies. 58,60 The other surgical interventions, laser coagulation and myringotomy for direct application of topical steroids through a MicroWick tube, were each evaluated by a single study. 51,61 All studies had a high risk of bias. Any interpretation of data from case series is limited by the uncontrolled study designs: it is impossible to determine how much improvement in symptoms and other measures would have occurred in the absence of the intervention, especially in the case of a condition which may resolve naturally. Extensive use of cointerventions contributed to uncertainty.
Eustachian tuboplasty was the most commonly evaluated surgery (seven studies in 182 patients). 20,21,23,54,56,62,63 Where improvement in symptoms was evaluated, it was reported for a substantial proportion of patients at follow-up ranging from 2 to 37 months following surgery, though improvement was defined in a variety of ways. Four studies reported an improvement in hearing, although improvements were generally small with limited clinical significance. 20,23,56,63 Measures of middle ear function indicated low rates of conversion to type A tympanogram in the three studies that reported this outcome. 21,23,54 Tuboplasty may be considered a potentially promising intervention but there is insufficient evidence to demonstrate its effectiveness, or to determine either the details of the surgical technique which should be employed or the patients for whom it should be considered. As well as differences in the techniques used, there were wide variations between the patients in these studies, as well as differences in the outcomes reported and the measures used to assess outcomes. One study also employed sinus surgery in all patients,56 and concomitant interventions for some patients were reported in two other studies. 20,23
Three studies of balloon dilatation were identified (n = 107). 18,22,55 Two reported on symptoms at follow-up (12 weeks and mean 30 weeks); both showed high levels of improvement. 18,55 Tympanometric measurement of middle ear function was reported in all three studies, and all reported conversion to type A tracings, although follow-up duration varied significantly between the studies (from 6 weeks to 1 year). None of the studies reported data on hearing. Two of the studies reported that all or a majority of patients had additional surgery and a minority of patients in the third also had additional treatment. 22 The review findings are, therefore, in line with the NICE guidance which indicated some evidence of effectiveness but uncertainty as to its reliability. 30
Two studies assessing procedures for myringotomy were identified. 58,60 One small study reported efficacy in permitting patients to undergo hyperbaric oxygen therapy, while the other reported symptom alleviation in the subgroup of patients with an ETD diagnosis. The evidence base for topical application of steroids to the Eustachian tube and laser point coagulation each rested on a single study. 51,61
None of the interventions appeared to be associated with serious adverse effects, although minor complications of surgery were reported in a minority of patients in several studies. However, it was not clear that adverse events were systematically documented, and three surgical studies did not report any safety data. 58,62,63 None of the studies reported follow-up beyond a maximum of 10 weeks in non-surgical and 30 months in surgical studies; therefore, the long-term safety profile of the interventions is unknown.
In addition to the limitations arising from study design and use of cointerventions, multiple gaps in the reporting of the studies were identified (notably with regard to patient recruitment, patient characteristics, outcomes and statistical analyses) which limited the extent to which the results could be interpreted. None of the studies was conducted in the UK, which limits the extent to which the results can be interpreted in a NHS context. Therefore, while these studies suggested that there may be some benefits to surgical treatments of ETD, the quality and reliability of the available data are too limited to allow any conclusions to be drawn.
Gaps in the clinical effectiveness evidence
Studies of several relevant surgical and non-surgical interventions were not identified despite extensive searches. No studies were found of active observation (monitoring to determine whether or not the condition resolves naturally) or supportive care (advice on self-management strategies such as advice to swallow, yawn or chew). Participants in the control groups of the two studies evaluating pressure equalisation devices may have effectively been under active observation, although neither of the studies explicitly stated it. No evidence on the effectiveness of nasal douching, oral steroids, antibiotics, LTRAs and simethicone was found. An ongoing RCT of simethicone was identified, though this is not currently used in the UK. 43 No RCTs of surgical interventions were identified in the searches except for an ongoing RCT being conducted in the UK which aims to evaluate the effect of balloon dilatation of the Eustachian tube in adults with long-term ETD. 81
Strengths and limitations of the evidence base
As discussed in Chapter 3 (see Study selection), the review included 19 studies assessing a range of interventions, including pharmacological treatments, mechanical devices for pressure equalisation and several types of surgery. All studies reported relevant outcomes relating to effectiveness and some reported safety data. However, there was a paucity of high-quality research and the informativeness of the evidence base was limited by numerous factors.
Differences in patient characteristics
There is a lack of consensus on how ETD should be defined, as well as on the aetiology of the condition. This lack of consensus was reflected in the considerable variation in inclusion criteria employed in the included studies, and, consequently, in the characteristics of the patients treated in these studies. The included studies, which required patients to have a clinical diagnosis of ETD, exhibited substantial variation in whether or how ETD was defined. Some studies simply reported that patients were required to have ETD, without further details. Even when precise symptoms that were considered necessary for a diagnosis of ETD were reported, the baseline severity and/or frequency of the symptoms were rarely quantified. It was, therefore, often unclear what the precise characteristics of the patient population were in relation to some or all of the criteria which may be considered to form part of the characterisation of ETD.
Studies also varied whether they required patients to have failed previous treatments or to have experienced symptoms for a particular duration. Studies of pharmacological interventions and mechanical devices did not specify duration of symptoms or that patients should have failed previous medical interventions, while several studies of surgical interventions required that patients should have failed multiple attempts at medical management and, in some cases, prior surgical intervention.
Another key difference between the non-surgical and surgical studies was that all except one of the non-surgical studies were conducted in mixed populations of adults and adolescents or children. In the fifth study, it was unclear whether or not this was also the case. 40 Unlike non-surgical interventions, studies of surgical interventions were available in exclusively adult populations.
Despite poor reporting of ETD history, it also appeared that, as might be anticipated, patients in the non-surgical studies might have had less serious or long-lasting ETD than those in the surgical studies. Within-study variation in these characteristics was also seen in several studies assessing surgical interventions. A minority of studies excluded patients with specified comorbidities, while other studies reported that some or all of the patients had these conditions (e.g. rhinosinusitis, allergies or reflux). In three of the surgical studies, it was clear that all patients had chronic otitis media with effusion related to ETD, and that their prognosis was consequently poorer than that of patients in other studies. Finally, there was variance in studies of all types of intervention with regard to whether or not an intact tympanic membrane was required, whether or not patients were required to have an abnormal otological examination, and whether or not an abnormal tympanogram was required. In several studies, poor reporting meant that it was unclear which baseline tests were employed and whether or not test results formed part of the inclusion criteria for the study.
Outcome assessment
Assessment methods were not well defined in most studies. This was a particular issue for the primary review outcome of patient reported symptoms. While a majority of the studies reported some information on this outcome, most of the studies, as with baseline assessment, reported only presence, remission or improvement of symptoms, rather than quantifying them using a validated scale. As with baseline assessment and/or inclusion criteria, some studies reported assessment of specific ETD symptoms, while others reported global improvement or improvement in unspecified symptoms. Owing to the level of symptoms experienced at baseline and follow-up being unclear, it was, therefore, also difficult to ascertain whether or not different studies were assessing comparable symptomatology. Exceptions to this were four studies, which all reported that they measured symptom severity before and after treatment using VASs or a form of the ETDQ-7. 20,40,52,55
Variability in the measure used was an issue for other outcomes, although to a lesser degree. Although data on middle ear function were reported by a majority of studies, a number of different tests were used to assess this, including tympanometry, ability to perform the Valsalva manoeuvre, and appearance on otological examination. Most studies which assessed hearing used a recognised measure such as pure-tone audiometry or air–bone gap.
Follow-up
Even where outcomes were consistently reported, a key issue was the variation between studies in duration of follow-up, which made the meaningful synthesis of data between the studies impossible. An extremely wide range in its duration was found. Two of the three studies of pharmacological agents had extremely short follow-up periods of 30 minutes and 1 to 4 hours. 24,25 These were too short for the data obtained to have any clinical relevance. Therefore, further work with appropriate longer-term assessment of efficacy and safety would be required to adequately assess these interventions. Follow-up in the third pharmacological study was reasonable, although relatively short term (6 weeks). 52 Follow-up in the two studies of mechanical devices was short (1 week)40 or unclear. 41
Follow-up in the studies of surgical interventions also varied considerably, from a few weeks to 2 years or longer. In some cases, mean duration of follow-up was reported, with or without an indication of the range of follow-up time, and data appeared to have been aggregated from patients assessed at different time points.
Conversely, some studies reported follow-up data for all or a majority of patients at multiple time points; in some cases, this appeared to demonstrate continuing improvement over time. This may represent a true accrual of higher levels of benefit from surgery over time, or it may be reflective of remission of symptoms due to the natural course of the condition. As all except one of the studies of surgery were uncontrolled studies, and the single controlled study reported very limited data on outcomes for the control group, it is not possible to determine the cause of the apparent improvement over time. Lack of adequate long-term follow-up is a serious concern in relation to surgical interventions such as tuboplasty, where the procedure may have ongoing implications for middle ear function. For some studies, this uncertainty is additional to the difficulty in determining the effect of the assessed intervention when cointerventions have also been administered.
Interventions and cointerventions
For the small number of interventions where there was more than one study, the details of the interventions varied; there were differences in the surgical technique or pressure applied in studies of tuboplasty and balloon dilatation, respectively. In addition to differences in the primary intervention, many of the studies of surgical interventions reported cointerventions administered concurrently with or subsequent to the intervention being assessed. 18,20–23,55,56,61 As many of these cointerventions were additional sinonasal or otological surgical procedures, it is not possible to determine whether the observed treatment benefits are attributable to the primary intervention or to one or more of the additional treatments. The majority of the surgical evidence base was impacted by the use of cointerventions.
In studies of pharmacological agents and devices, cointervention appeared to be less of an issue, with only the RCT of nasal steroids documenting use of additional pharmacological agents. 52 In this instance, the use of cointerventions was recorded and used to inform a secondary analysis of overall efficacy. The extremely short follow-up and laboratory-based design of the other two pharmacological studies means that use of cointerventions appears unlikely. However, because reporting of the other non-surgical studies was, in some cases, limited, it is difficult to be certain that participants did not use cointerventions in the studies of mechanical devices.
Strengths and limitations of the review
To our knowledge, this is the first systematic review to evaluate interventions for adult ETD. A broad range of interventions were eligible, in particular interventions relevant to the NHS. A total of 12 electronic bibliographic databases were searched as well as multiple potential sources of unpublished data, including trial registers and regulatory websites. Reference checking increased the comprehensiveness of our search. Study validity and risk of bias were assessed systematically and taken into consideration in the synthesis. Rigorous review methods to minimise reviewer bias and error were employed at all stages of the review. Whenever possible, the treatment effect for individual studies was reported with a 95% CI, even when quantitative synthesis was not undertaken.
Only English-language studies were included, leading to the risk of relevant studies being missed. The language restrictions led to the exclusion of seven studies at the full-text selection stage of the review. Consultation with readers of the relevant languages indicated that, at best, all seven studies were small non-controlled studies. 88–94 Although some of these studies might have otherwise met the final selection criteria, it is very unlikely that these would have affected the conclusions of the review in any significant way.
Because of the lack of evidence, the diversity in the interventions and comparators used and the poor reporting of outcome data, a quantitative synthesis was neither possible nor appropriate. This was unfortunate as most of the included studies had a small number of participants and may have been underpowered.
The inclusion criteria specified that only patients with a diagnosis of ETD were included. Ideally, this would be based on an explicit definition as to what constituted ETD. However, there is a lack of clinical consensus on explicit diagnostic criteria for ETD and its relation to broader middle ear ventilation problems. As a result, the inclusion criterion for population was interpreted pragmatically and studies were accepted based on the primary study definition of ETD or description of their included participants as having ETD. The consequence was the inclusion in the review of a probably heterogeneous population. In addition, very few studies assessed the severity and persistence of the condition at baseline with standardised and validated tools. This made it difficult to know whether or not some study populations were homogeneous, and even more difficult to compare the populations across the studies.
Adults were the population of interest for the review. At the outset, only studies of adults or studies where adult data were available separately were eligible for inclusion. At the study selection stage, only a single controlled study evaluating a surgical method in adults with ETD was identified, and no non-surgical studies reporting separate data on an adult ETD population were found. Therefore, to allow a fuller mapping of the literature, the protocol was amended to include controlled studies of mixed populations of adults and children with no separate adult data, as well as controlled studies that did not explicitly state whether or not the whole study population were adults. For all such studies, the authors were contacted to clarify whether or not the population was indeed adults and/or to seek separate data on the adult population. Following this amendment, five additional comparative studies evaluating non-surgical interventions were included. This protocol amendment was not extended to uncontrolled studies of mixed populations, as this would have increased the risk of further uncertainty in the evidence. This was considered justified by the need to minimise the already high levels of confounding and uncertainty in the uncontrolled studies. This means that all non-surgical interventions were evaluated within a population that either explicitly included children or adolescents, or may have done so. This should be taken into account when interpreting the applicability of the non-surgical studies to an adult ETD population, even though all studies appeared to have recruited a majority of adults.
The key limitation of this review was the lack of reliable data available, despite comprehensive searches across a range of sources of studies. Although several studies were identified for interventions such as laser Eustachian tuboplasty and balloon dilatation, they were uncontrolled case series which had multiple factors limiting their internal and external validity. The evidence was of insufficient quality to make robust conclusions about the effectiveness of any of the interventions. However, the review provides a comprehensive and up-to-date synthesis of the gaps in the evidence on adult ETD treatment. This will, hopefully, provide a useful basis for the understanding of future research needs, including the primary need for consensus on the definition and diagnosis of ETD.
Chapter 5 Conclusions
Implications for service provision
The evidence for treatments for adult ETD was limited in quantity and, overall, was of poor quality. Multiple sources of potential bias were identified in the majority of included studies. Additional confounding factors were present in many of the evaluations of surgical interventions, while clinical relevance was limited in two of the three pharmacological studies. Given the limitations of the evidence, it is not possible to make conclusions regarding the effectiveness of any of the interventions for the treatment of patients with a diagnosis of ETD.
A single RCT with a low risk of bias was identified. This RCT found no evidence of benefit with nasal steroids compared with placebo in patients aged > 6 years with ETD of unspecified duration and severity, though it was underpowered to detect an effect. Because of the multiple sources of bias and confounding factors identified in the other studies, it is not possible to form conclusions as to the effectiveness of any of the interventions for the treatment of ‘clinically diagnosed ETD’.
Results of the case series assessing balloon dilatation and laser Eustachian tuboplasty appeared to indicate substantial levels of efficacy in patients who did not have a diagnosis of chronic otitis media or otitis media with effusion in terms of symptom remission, tympanic normalisation and, in the case of tuboplasty, a suggestion of improvement in hearing. However, the lack of a control group in all except one study of surgical interventions made it difficult to determine whether or not improvements were a consequence of the intervention assessed. This is a key issue in assessing treatments for conditions such as ETD, as the natural course of ETD is poorly documented. In related middle ear conditions, the natural course of the disease is known to produce favourable outcomes without interventions, making a control group of critical importance. Additional limitations have also been identified; in particular, the high levels of surgical cointervention in studies of balloon dilatation should be borne in mind. 18,22,55 It may be appropriate to re-evaluate the evidence base for this condition when outcome data from the ongoing RCT are available. 81
Implications for research
One of the principal findings of the review was the variability in inclusion criteria and unclear and variable definitions of ETD used across the included studies. This indicated a lack of consensus as to what the population of interest is and how they should be evaluated for inclusion in any further studies. However, despite the lack of a clear definition, it is nevertheless the case that ETD can be associated with discomfort, pain and reduced hearing. Patients can attend their general practitioner (GP) practice several times with symptoms and it is a frequent reason for referral to secondary care.
Given the extent of the gaps in the evidence and the limitations in the nature of the available evidence, it was difficult to identify which interventions should be prioritised for future research.
A research priority setting exercise is required to identify the most appropriate avenues for further research. In the first instance, this should focus on developing an explicit definition of the population of interest and the diagnostic inclusion criteria that should be used to identify them. The specification of the population of interest should take into consideration the increasing recognition that the signs and symptoms previously attributed to ETD may also be related to other mechanisms; for instance, gaseous exchanges within the middle ear mucosa may play a role in the development of middle ear ventilation problems.
The exercise should also address the question of criteria for consideration of surgical treatment in a patient diagnosed with ETD, the lack of consensus as to what the important clinical outcomes are following treatment, and how these outcomes should be measured. This should include agreement on the duration of follow-up required for an intervention to be adequately assessed for both efficacy and safety. Only when a consensus on these key elements has been arrived at should the question of commissioning further primary research intervention studies be considered.
If this first set of recommendations were implemented and options for further primary research were subsequently considered, then particular attention should be given to designing studies which will not be subject to the same limitations as those identified in this review. Owing to the uncertain natural course of the condition, the use of an appropriate control group would be essential for any study to provide useful and reliable data on efficacy. Where undertaken, trials should use appropriate methods of randomisation and allocation concealment, clear inclusion criteria, full documentation of cointerventions in both intervention and control groups, outcome assessment using validated measures by blinded assessors, and adequate and clearly reported follow-up. Current RCT reporting standards should also be followed. 95
Acknowledgements
Contributions of authors
Mr Alexis Llewellyn (Research Fellow) Involved in all stages of the review from development of the protocol, through screening studies and data extraction to synthesis and production of the final report.
Dr Gill Norman (Research Fellow) Involved in all stages of the review from development of the protocol, through screening studies and data extraction to synthesis and production of the final report.
Ms Melissa Harden (Information Specialist) Devised the search strategy, carried out the literature searches and wrote the search methodology sections of the report.
Dr Andrew Coatesworth (ENT Consultant) Provided clinical advice throughout the review process and commented on the protocol and the draft report.
Dr Daniel Kimberling (GP) Provided clinical advice throughout the review process and commented on the protocol and the draft report.
Professor Anne Schilder (Triallist and ENT Consultant) Provided clinical advice throughout the review process and commented on the protocol and the draft report.
Dr Catriona McDaid (Senior Research Fellow) Led on all stages of the review from development of the protocol, through screening studies and data extraction to synthesis and production of the final report.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Bluestone CD. Eustachian Tube: Structure, Function, Role in Otitis Media. Hamilton, ON: BC Decker Inc.; 2005.
- Monsell EM, Harley RE. Eustachian tube dysfunction. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 1996;29:437-44.
- Tewfik TL, Singh H, Massoud E. Eustachian Tube Function 2011. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/874348-overview (accessed 17 August 2012).
- Doyle WJ, Swarts JD, Banks J, Yuksel S, Alper CM. Transmucosal O2 and CO2 exchange rates for the human middle ear. Auris Nasus Larynx 2011;38:684-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anl.2011.01.006.
- Miura M, Takahashi H, Honjo I, Hasebe S, Tanabe M. Influence of the gas exchange function through the middle ear mucosa on the development of sniff-induced middle ear diseases. Laryngoscope 1998;108:683-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00005537-199805000-00011.
- Lazo-Sáenz JG, Galván-Aguilera AA, Martínez-Ordaz VA, Velasco-Rodríguez VM, Nieves-Rentería A, Rincón-Castañeda C. Eustachian tube dysfunction in allergic rhinitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2005;132:626-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2005.01.029.
- Yeo SG, Park DC, Eun YG, Cha CI. The role of allergic rhinitis in the development of otitis media with effusion: effect on Eustachian tube function. Am J Otolaryngol 2007;28:148-52. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2006.07.011.
- McNicoll WD. Uncomplicated Eustachian tube dysfunction: the site of the nasal septal deformity. J R Nav Med Serv 1982;68:23-9.
- McNicoll WD. Remediable Eustachian tube dysfunction in diving recruits: assessment, investigation, and management. Undersea Biomed Res 1982;9:37-43.
- McNicoll WD, Scanlan SG. Submucous resection: the treatment of choice in the nose-ear distress syndrome. J R Nav Med Serv 1979;65:123-30.
- McNicoll WD, Scanlon SG. The nose ear distress syndrome. J R Nav Med Serv 1975;61:27-9.
- Goldman JL, Martinez SA, Ganzel TM. Eustachian tube dysfunction and its sequelae in patients with cleft palate. South Med J 1993;86:1238-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00007611-199311000-00010.
- Dubin MG, Pollock HW, Ebert CS, Berg E, Buenting JE, Prazma JP. Eustachian tube dysfunction after tobacco smoke exposure. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2002;126:14-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mhn.2002.121320.
- White DR, Heavner SB, Hardy SM, Prazma J. Gastroesophageal reflux and Eustachian tube dysfunction in an animal model. Laryngoscope 2002;112:955-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200206000-00004.
- Young YH, Sheen TS. Preservation of tubal function in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma, post-irradiation. Acta Otolaryngol 1998;118:280-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00016489850155026.
- Coatesworth AP, Addis RJ, Beverley DW. Ear nose and throat diseases in the Bedouin of the South Sinai Desert: a cross-sectional survey and discussion of healthcare needs. J Laryngol Otol 2002;116:83-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1258/0022215021909827.
- Browning GG, Gatehouse S. The prevalence of middle ear disease in the adult British population. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 1992;17:317-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2273.1992.tb01004.x.
- Catalano PJ, Jonnalagadda S, Yu VM. Balloon catheter dilatation of Eustachian tube: a preliminary study. Otol Neurotol 2012;33:1549-52. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0b013e31826a50c3.
- BMJ Publishing Group Ltd . Eustachian Tube Dysfunction 2012. http://bestpractice.bmj.com/best-practice/welcome.html (accessed 17 August 2012).
- Caffier PP, Sedlmaier B, Haupt H, Göktas O, Scherer H, Mazurek B. Impact of laser eustachian tuboplasty on middle ear ventilation, hearing, and tinnitus in chronic tube dysfunction. Ear Hear 2011;32:132-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AUD.0b013e3181e85614.
- Sedlmaier B, Pomorzev A, Haisch A, Halleck P, Scherer H, Göktas O. The improvement of middle ear ventilation by laser ablation of the epipharyngeal Eustachian tube: a prospective study. Lasers Med Sci 2009;24:793-800. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10103-009-0646-7.
- Poe DS, Silvola J, Pyykkö I. Balloon dilation of the cartilaginous Eustachian tube. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2011;144:563-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0194599811399866.
- Poe DS, Grimmer JF, Metson R. Laser Eustachian tuboplasty: two-year results. Laryngoscope 2007;117:231-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.mlg.0000246227.65877.1f.
- Holmquist J, Larsson G. Eustachian tube dysfunction. A preliminary report of medical treatment. Scand Audiol 1976;5:107-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/01050397609043103.
- Jensen JH, Leth N, Bonding P. Topical application of decongestant in dysfunction of the Eustachian tube: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Otolaryngol 1990;15:197-201. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2273.1990.tb00775.x.
- McCoul ED, Anand VK, Christos PJ. Validating the clinical assessment of Eustachian tube dysfunction: the Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire (ETDQ-7). Laryngoscope 2012;122:1137-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/lary.23223.
- Hopkins C, Gillett S, Slack R, Lund VJ, Browne JP. Psychometric validity of the 22-item sinonasal outcome test. Clin Otolaryngol 2009;34:447-54. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-4486.2009.01995.x.
- van Heerbeek N, Ingels KJOA, Rijkers GT, Zielhuis GA. Therapeutic improvement of Eustachian tube function: a review. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 2002;27:50-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.0307-7772.2001.00524.x.
- NHS Evidence: UK Database of Uncertainties about the Effects of Treatments (DUETs) . Therapeutic Improvement of Eustachian Tube Function 2007. www.library.nhs.uk/duets/ViewResource.aspx?resID=302905&tabID=297 (accessed 21 August 2012).
- Balloon Dilatation of the Eustachian Tube. NICE Interventional Procedure Guidance 409. London: NICE; 2011.
- Interventional Procedure Overview of Balloon Dilatation of the Eustachian Tube. London: NICE; 2011.
- Poe D, Silvola J. Balloon dilation of the cartilaginous Eustachian tube. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2010;143. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2010.06.133.
- Ockermann T, Reineke U, Upile T, Ebmeyer J, Sudhoff HH. Balloon dilatation Eustachian tuboplasty: a clinical study. Laryngoscope 2010;120:1411-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/lary.20950.
- Yu V, Jonnalagadda S, Catalano P. Balloon catheter dilation of Eustachian tube: pilot study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2010;143:P86-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2010.06.132.
- Reidpath DD, Glasziou PP, Del Mar C. Systematic review of autoinflation for treatment of glue ear in children. BMJ 1999;318. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.318.7192.1177.
- Perera R, Haynes J, Glasziou PP, Heneghan CJ. Autoinflation for hearing loss associated with otitis media with effusion. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009;4.
- Griffin G, Flynn CA. Antihistamines and/or decongestants for otitis media with effusion (OME) in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011;9.
- Surgical Management of Otitis Media with Effusion in Children. NICE Clinical Guideline 60. London: NICE; 2008.
- Nankivell PC, Pothier DD. Surgery for tympanic membrane retraction pockets. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010;7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007943.pub2.
- Alpini D, Mattei V. A manually operated device for the treatment of residual middle ear effusion and Eustachian tube dysfunction. Audiol Med 2008;6:166-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/16513860701794235.
- Silman S, Arick D. Efficacy of a modified Politzer apparatus in management of Eustachian tube dysfunction in adults. J Am Acad Audiol 1999;10:496-501.
- Hain TC. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) 2007. www.dizziness-and-balance.com/disorders/symptoms/etdysfunction.htm (accessed 8 February 2013).
- Effect of Simethicone on Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; n.d.
- Todt I, Seidl R, Ernst A. A new minimally invasive method for the transtubal, microendoscopic application of fluids to the middle ear. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 2008;17:300-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/13645700802274786.
- Kujawski OB, Poe DS. Laser Eustachian tuboplasty. Otol Neurotol 2004;25:1-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00129492-200401000-00001.
- Systematic Reviews. CRD’s Guidance for Undertaking Reviews in Health Care. York: Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York; 2009.
- Harden M, Llewellyn A, McDaid C, Norman G. Interventions for Adult Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD): A Systematic Review. Centre for Reviews and Dissemination; 2012.
- Higgins J, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration; 2011.
- Maund E, Craig D, Suekarran S, Neilson AR, Wright K, Brealey S, et al. Management of frozen shoulder: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess 2012.
- Systematic Review of the Effects of Interventions for People Bereaved by Suicide. CRD Report 38. York: University of York; 2008.
- Boboshko M, Lopotko A, Karpischenko S. Experiences with Nd:YAG laser interference for correction of Eustachian tube disorders. Rivista Italiana Di Otorinolaringologia Audiologia E Foniatria 2005;25:45-9.
- Gluth MB, McDonald DR, Weaver AL, Bauch CD, Beatty CW, Orvidas LJ. Management of Eustachian tube dysfunction with nasal steroid spray: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2011;137:449-55. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archoto.2011.56.
- Short Term Relief of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction and Serous Otitis Media using Intranasal Steroid Sprays. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; n.d.
- Jumah MD, Jumah M, Pazen D, Sedlmaier B. Laser Eustachian tuboplasty: efficiency evaluation in the pressure chamber. Otol Neurotol 2012;33:406-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0b013e318248edcb.
- McCoul ED, Anand VK. Eustachian tube balloon dilation surgery. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 2012;2:191-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/alr.21007.
- Metson R, Pletcher SD, Poe DS. Microdebrider Eustachian tuboplasty: a preliminary report. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2007;136:422-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2006.10.031.
- Poe DS, Metson RB, Kujawski O. Laser Eustachian tuboplasty: a preliminary report. Laryngoscope 2003;113:583-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200304000-00001.
- Prokopakis EP, Lachanas VA, Christodoulou PN, Bizakis JG, Karatzanis AD, Velegrakis GA. Implications of laser assisted tympanostomy in adults. Otol Neurotol 2005;26:361-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.mao.0000169761.77926.f7.
- Prokopakis EP, Lachanas VA, Helidonis ES, Velegrakis GA, Panchenko VY, Sabotinov NV. Eighth International Conference on Laser and Laser Information Technologies. Bellingham: Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE); 2003.
- Potocki SE, Hoffman DS. Thermal myringotomy for Eustachian tube dysfunction in hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1999;121:185-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0194-5998(99)70169-5.
- Silverstein H, Light JP, Jackson LE, Rosenberg SI, Thompson JHJ. Direct application of dexamethasone for the treatment of chronic eustachian tube dysfunction. Ear Nose Throat J 2003;82:28-32.
- Yanez C, Mora N. Classification system for results in Eustachian tube surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2008;139. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2008.05.238.
- Yañez C. Cross-hatching: a novel technique for Eustachian tuboplasty. Preliminary report. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2010;142:688-93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2009.12.046.
- Kujawski O, Fasel J, Romanowicz R, Oswal V, Remade M. Principles and Practice of Lasers in Otorhinolaryngology and Head Neck Surgery. The Hague: Kugler Publications; 2002.
- Kujawski O. Laser Eustachian tuboplasty (LETP): an overview of four years of experience in endoscopic transnasal laser-assisted cartilaginous Eustachian tube surgery (LETP) for middle ear diseases. Skull Base Surg 2001;11.
- Kujawski O. Laser Eustachian tuboplasty, L.E.T.P. Laryngorhinootologie 2000;79.
- Sajan JA, Hilton CW, Levine SC. Long-term outcomes and reliability of Jahn ventilating tube. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2011;145. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0194599811415823a276.
- Al-Swadi W, Karlsmose B, Gaihede M, Henriksen SD, Rosborg J. Long-term treatment of chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction by subannular ventilation tubes. Otol Neurotol 2005;26.
- Dalchow C, Muenscher A, Knecht R. Endoscopic dilatation of the Eustachian tube. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2011;145. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0194599811416318a164.
- Elluru RG, Dhanda R, Neely JG, Goebel JA. Anterior subannular T-tube for prolonged middle ear ventilation during tympanoplasty: evaluation of efficacy and complications. Otol Neurotol 2001;22:761-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00129492-200111000-00008.
- Gimenez F, Marco-Algarra J, Carbonell R, Morant A, Cano S. Prognostic factors in tympanoplasty: a statistical evaluation. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol 1993;114:335-7.
- Gupta SC, Malhotra M, Singh M. Eustachian tube function after transmyringeal ventilation. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2005;57:39-42. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02907625.
- Jahn AF. Middle ear ventilation with HydroxylVent tube: review of the initial series. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1993;108:701-5.
- Jahnke K, Lieberum B, Tos M, Thomsen J, Balle V. Otitis Media Today. Proceedings of the Third Extraordinary Symposium on Recent Advances in Otitis Media, Copenhagen, Denmark, June 1–5, 1997. The Hague: Kugler Publications; 1999.
- Jensen MG, Jacobsen H, Gaihede ML, Rosborg J, Huber A, Eiber A. Middle Ear Mechanics in Research and Otology. Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium, Zurich, Switzerland, 27–30 July 2006. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Company; 2007.
- O’Hare T, Goebel JA. Anterior subannular T-tube for long-term middle ear ventilation during tympanoplasty. Am J Otol 1999;20:304-8.
- Per-Lee JH. Long-term middle ear ventilation. Laryngoscope 1981;91:1063-73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1288/00005537-198107000-00004.
- Rothera MP, Grant HR. Long-term ventilation of the middle ear using the Goode T-tube. J Laryngol Otol 1985;99:335-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0022215100096791.
- Tos M. Management of tubal function in reconstructive middle ear surgery. J Laryngol Otol 1980;94:25-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0022215100088423.
- Wright JW, Wright JW, Hicks GW. The Eustachian tube prosthesis revisited. Otolaryngology 1978;86:ORL-834.
- Balloon Eustachian Tuboplast (BET). Current Controlled Trials Ltd.; n.d.
- Refractory Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Are the Symptoms Related to Endolymphatic Hydrops. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; n.d.
- McCoul ED, Singh A, Anand VK, Tabaee A. Balloon dilation of the Eustachian tube in a cadaver model: technical considerations, learning curve, and potential barriers. Laryngoscope 2012;122:718-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/lary.23181.
- Jumah MD, Schlachta M, Hoelzl M, Werner A, Sedlmaier B. Pressure regulating ear plug testing in a pressure chamber. Aviat Space Environ Med 2010;81:560-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.3357/ASEM.2717.2010.
- Dornhoffer JL. Surgical management of the atelectatic ear. Am J Otolaryngol 2000;21:315-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0196-0709(00)80038-1.
- Morimitsu T, Enatsu K, Matsumoto I, Ushisako Y. A new test of Eustachian tube function with otoadmittance meter: tubotympanometry. Acta Otolaryngol 1981;91:207-14. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016488109138501.
- Honjo I, Kumazawa T, Honda K. Simple impedance test for Eustachian tube function. Arch Otolaryngol 1981;107:221-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1981.00790400023004.
- Kryukov AI, Garov EV, Antonyan RG, Azarov PV, Gutieva TK. Differential atticoanthrotomy with type 1 tympanoplasty as the method of choice for the treatment of chronic perforating otitis media with expressed mucositis. Vestn Otorinolaringol 2011;5:32-4.
- Lieberum B, Jahnke K. Golden tube wire for temporary or permanent implantation in patients with Eustachian dysfunction. HNO 1996;44:140-2.
- Maeda T. A new method of intratubal spray into the auditory tube. Jibiinkoka 1980;52:1071-5.
- Maier W, Krebs A. Is there an indication for septoplasty and conchotomy before tympanoplasty? Effects of nasal surgery on the Eustachian tube. Laryngorhinootologie 1998;77:682-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-997224.
- Mora AB, Lopez EGZ, Rodriguez JMG. Tympanoplasty in chronic otitis media and its relations to the Eustachian tube. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc 1999;37:127-32.
- Sato Y. Complications of tympanostomy tube insertion for otitis media with effusion. Jibiinkoka 1986;58:79-83.
- Takahashi H, Yamamoto E, Hirono Y, Honjo I. Eustachian tube function in patients with otitis media chronica. Practica Otologica Kyoto 1986;79:37-44. http://dx.doi.org/10.5631/jibirin.79.37.
- Kenneth FS, Douglas GA, David M. CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ 2010;340. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.c332.
Appendix 1 Search strategy
Databases
MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations and MEDLINE via OvidSP: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/
1946 to 4 October 2012.
Searched on 8 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 1345.
-
1. Eustachian Tube/ (2702)
-
2. ((eustachian or auditory or pharyngotympanic) adj3 tub$).ti,ab. (2960)
-
3. (eustachian adj2 (canal or orifice$)).ti,ab. (67)
-
4. (middle ear adj3 dysfunction$).ti,ab. (121)
-
5. (middle ear adj3 pressure$).ti,ab. (823)
-
6. or/1-5 (4399)
Line 6 captures terms for Eustachian tube
-
7. exp Adrenal Cortex Hormones/ (322,423)
-
8. exp Steroids/ (672,905)
-
9. exp Anti-Inflammatory Agents/ (381,776)
-
10. (adrenal cort$ adj2 hormone$).ti,ab. (864)
-
11. (corticosteroid$ or cortico steroid$ or corticoid$).ti,ab. (75,248)
-
12. steroid$.ti,ab. (171,724)
-
13. glucocorticoid$.ti,ab. (48,091)
-
14. (anti inflam$ or antiinflam$).ti,ab. (91,002)
-
15. (fluticason$ or flixonase or flonase or flovent or cultivate or flixotide or atemur or axotide or beconase or cci 18781 or cci18781 or cutivat$ or flixovate or flunase or fluspiral or flutide or flutinase or flutivate or fluxonal or gr 18781 or gr18781 or zoflut).ti,ab,rn. (4575)
-
16. (budeson$ or pulmicort or horacort or rhinocort or bidien or budecort or budicort or CCRIS 5230 or cortivent or entocort or micronyl or noex or preferid or respules or rhinosol or spirocort or symbicort or uceris).ti,ab,rn. (4372)
-
17. (mometason$ or sch 32088 or nasonex or rinelon or elocon or allermax aqueous or asmanex or danitin or dermotasone or dermovel or ecural or elica or elocom or elocone or elocyn or elomet or elosalic or eloson or flumeta or mefurosan or metaspray or momate or mometAid or monovel or morecort or motaderm or nosorex or novasone or propel or rimelon or rivelon or uniclar).ti,ab,rn. (1512)
-
18. (triamcinolone acetonide or tricinolon or cinonide or kenalog or azmacort or kenacort or acetospan or adcortyl A or allerNaze or aristocort or aristoderm or aristogel or CCRIS 5231 or coupe-A or flutex or flutone or kenalone or NSC 21916 or nasacort or omcilon A or oracort or oralone or polcortolon or rineton or solodelf or tramacin or tri-nasal or triacet$ or triacort or triam-Injekt or triamonide or trianex or triatex or triderm or triesence or trivaris or trymex or volon A).ti,ab,rn. (7767)
-
19. (dexameth$ or adrenocot or aflucoson$ or alfalyl or Anaflogistico or Aphtasolon or arcodexan$ or artrosone or Auxiron or Azium or bidexol or Bisu DS or Calonat or CCRIS 7067 or cebedex or cetadexon or colofoam or corsona or Corsone or cortastat or cortidex$ or cortidron$ or Cortisumman or dacortina fuerte or dacortine fuerte or dalalone or danasone or Decacortin or decadeltoson$ or Decaderm or decadion or decadran or decadron$ or decaesadril or Decagel or decaject or Decalix or decameth or Decasone or decaspray or decasterolone or decdan or decilone or decofluor or Dectancyl or Dekacort or delladec or deltafluoren$ or Dergramin or Deronil).ti,ab,rn. (56,163)
-
20. (desacort or desacortone or Desadrene or desalark or desameton$ or Deseronil or desigdron or dexa cortisyl or dexa dabrosan or dexa korti or Dexa Mamallet or dexa scherosan or dexa scherozon$ or Dexacort$ or Dexa-Cort$ or dexadabroson or dexadecadrol or Dexadeltone or dexadrol or Dexafarma or dexagel or dexagen or dexahelvacort or dexakorti or dexalien or dexalocal or Dexalona or dexame$ or Dexametasona or dexan or dexane or dexano or Dexapolcort or Dexapos or dexapot or Dexaprol or dexascheroson or Dexa-Scheroson or dexascherozon$ or Dexa-sine or Dexason$ or Dex-ide or Dexinolon or Dexinoral or dexionil or dexona or Dexone or dexpak or Dextelan).ti,ab,rn. (55,444)
-
21. (dextrasone or Dezone or dibasona or Dinormon or doxamethasone or esacortene or exadion$ or firmalone or fluormethyl prednisolon$ or fluormethylprednisolon$ or Fluormone or Fluorocort or fluorodelta or Fortecortin or Gammacorte$ or grosodexon$ or hexadecadiol or hexadecadrol or hexadiol or hexadrol or Isopto Dex or isopto maxidex or isoptodex or isoptomaxidex or Lokalison F or Loverine or Luxazone or marvidione or maxidex or Mediamethasone or megacortin or mephameson$ or metasolon$ or methazon$ ion or methazonion$ or metisone lafi or mexasone or Mexidex or millicorten$ or Mymethasone or nisomethasona or novocort or NSC 34521 or nsc34521).ti,ab,rn. (74)
-
22. (Ocu-trol or oftan-dexa or opticorten or opticortinol or oradexan or oradexon$ or orgadrone or Ozurdex or pidexon or Policort or Prednisolon F or prodexon$ or sanamethasone or santenson or santeson or sawasone or solurex or spoloven or sterasone or thilodexine or triamcimetil or vexamet or visumetazone or visumethazone or adrecort or Aeroseb or dexacen or isnacort or methylfluorprednisolone or posurdex).ti,ab,rn. (44)
-
23. (beclomet$ or aerobec or afifon or Alanase or Aldecin$ or anceron or apo-beclomethasone or ascocortonyl or asmabec clickhaler or Atomase or atomide or beceze or Beclacin or beclamet or beclate or Beclazone or beclo asma or beclo AZU or beclo rhino or becloasma or beclocort or becloforte or beclojet or beclone or beclorhinol or beclosol or beclotaide or becloturmant or becloturmat or beclovent or becodisk$ or beconase or beconasol or becotide or belax or bemedrex).ti,ab,rn. (3437)
-
24. (Benconase or bronchocort or bronconox or chf 1514 or chf1514 or Clenil or decomit or ecobec or Entyderma or filair or Inalone or junik or Korbutone or Menaderm or miflasone or nasobec aqueous or nexxair or nobec or orbec or prolair or propaderm or qvar or ratioallerg or respocort or rhinivict or Rhino Clenil or Rhinosol or rinaze or rynconox or sanasthmax or sanasthmyl or “sbn 024” or sbn024 or Sch 18020W or Turbinal or vancenase or vanceril or ventolair or viarex or viarin or Viaro or xiten). ti,ab,rn. (141)
-
25. (betamethasone or betamethason or betnesol or bentelan or rinderon$ or celestone phosphate or beta corlan or beta methasone or betam-ophtal or diprospan or durabetason or etnesol or inflacor or linolosal or linosal or NSC 90616 or solucelestan).ti,ab,rn. (6266)
-
26. (apo-flunisolide or inhacort or nasalide or ratio-flunisolide or rhinalar or RS-3999 or syntaris or aeroBid or nasarel or aerospan or bronalide or cyntaris or flunitec or flunisolid$ or gibiflu or locasyn or lokilan or lunibron-a or lunis or nisolid or rs3999 or sanergal or soluzione or synaclyn or val 679 or val679).ti,ab,rn. (355)
-
27. (prednison$ or Adasone or ancortone or Apo-Prednisone or biocortone or Cartancyl or CCRIS 2646 or colisone or Cortan or Cortancyl or cortidelt or cortiprex or Cotone or Cutason or dacorten or Dacortin or de cortisyl or decortancyl or decortin$ or Decortisyl or Dehydrocortisone or dekortin or delitisone or dellacort or delta cortelan or delta Cortisone or delta dome or delta e or delta prenovis or delta-1-Cortisone or delta-1-Dehydrocortisone or deltacort$ or delta-dome or Deltasone or deltison$ or deltra or di adreson or diadreson or drazone or Econosone or Encorton$).ti,ab,rn. (43,824)
-
28. (Enkortolon or enkorton or fernisone or Fiasone or hostacortin or HSDB 3168 or Incocortyl or insone or IN Sone or Juvason or Kortancyl or Liquid Pred or Lisacort or lodotra or Lodtra or me-korti or meprison or metacortandracin or Meticorten or meticortine or NCI-C04897 or nisona or Nizon or Novoprednisone or nsc 10023 or nsc10023 or Nurison or Orasone or orisane or Panafcort or Panasol or paracort or Parmenison or pehacort or precort or precortal).ti,ab,rn. (135)
-
29. (Predni Tablinen or prednicen-m or prednicorm or Prednicort or prednicot or Prednidib or Prednilonga or Predniment or prednitone or Prednizon or Prednovister or Presone or pronison or Pronisone or pronizone or pulmison or Rectodelt or Retrocortine or servisone or SK-Prednisone or steerometz or Sterapred or Supercortil or U 6020 or Ultracorten$ or urtilone or Winpred or Wojtab or Zenadrid).ti,ab,rn. (50)
-
30. (methylprednisolon$ or adlone-40 or adlone-80 or A-Methapred or Artisone-wyeth or Besonia or BRN 2340300 or dep medalone 80 or depmedalone or depoject-80 or Depo-Medrol or depopred or Dopomedrol or esametone or firmacort or HSDB 3127 or Lemod or Medesone or medixon or med-jec-40 or Medlone 21 or mednin or medralone 80 or medrate or Medrol or medrone or meprednisolone or mesopren or Metastab or methacort 40 or methacort 80 or methylcotol or methylcotolone or Methyleneprednisolone or methylpred dp or methylsterolone or metidrol).ti,ab,rn. (19,994)
-
31. (Metilbetasone or Metilprednisolon$ or Metipred or metrisone or Metrocort or metycortin or metypred or metypresol or Metysolon or Moderin or neomedrone or Nirypan or Noretona or nsc 19987 or nsc19987 or Predni N Tablinen or prednol or Promacortine or Reactenol or Sieropresol or solomet or solu decortin or Solu-medrol or Summicort or Suprametil or U 7532 or U-67 590A or Urbason or Urbasone or Wyacort).ti,ab,rn. (195)
-
32. (Prednisolon$ or adelcort or antisolon or antisolone or aprednislon or aprednislone or benisolon or benisolone or berisolon or berisolone or BRN 1354103 or Bubbli-Pred or caberdelta or capsoid or CCRIS 980 or co hydeltra or codelcortone or CO-Hydeltra or compresolon or Cordrol or cortadeltona or cortadeltone or cortalone or cortelinter or cortisolone or Cotogesic or cotolone or dacrotin or ecaprednil or decortril or dehydro cortex or dehydro hydrocortisone or dehydro hydrocortisone or dehydrocortex or dehydrocortisol or dehydrocortisole or dehydrohydrocortison).ti,ab,rn. (36,518)
-
33. (dehydrohydrocortisone or delcortol or delta cortef or delta cortril or delta ef cortelan or delta f or delta hycortol or delta hydrocortisone or delta hydrocortisone or delta ophticor or delta stab or delta1 dehydrocortisol or delta1 dehydrohydrocortisone or delta1 hydrocortisone or deltacortef or delta-cortef or Deltacortenol or deltacortenolo or deltacortil or deltacortoil or deltacortril or deltaderm or delta-Ef-Cortelan or deltaglycortril or deltahycortol or deltahydrocortison or deltahydrocortisone or deltaophticor or deltasolone or deltastab or deltidrosol or deltisilone).ti,ab,rn. (750)
-
34. (deltisolon or deltisolone or deltolasson or deltolassone or deltosona or deltosone or depo-predate or dermosolon or Derpo PD or Dexa-Cortidelt or hostacortin H or dhasolone or diadresone f or DiAdresonF or dicortol or domucortone or Donisolone or Dydeltrone or Eazolin D or encortelon or encortelone or encortolon or Erbacort or Erbasona or Estilsona or Fernisolone or glistelone or hefasolon or HSDB 3385 or hydeltra or hydeltrone or hydrelta or hydrocortancyl or hydrocortidelt or hydrodeltalone or hydrodeltisone or hydroretrocortin or hydroretrocortine or inflanefran).ti,ab,rn. (22)
-
35. (insolone or K 1557 or keteocort or key-pred or lenisolone or Lentosone or leocortol or liquipred or lygal kopftinktur or mediasolone or meprisolon or meprisolone or metacortalon or metacortalone or metacortandralon or metacortandralone or metacortelone or meti derm or meticortelone or metiderm or meti derm or morlone or mydrapred or neo delta or nisolon or nisolone or nsc 9120 or nsc9120 or opredsone or Orapred or panafcortelone or panafort or paracortol or Paracotol or Pediapred or phlogex or PRDL or pre cortisyl).ti,ab,rn. (34)
-
36. (preconin or precortalon or precortancyl or Precortilon or precortisyl or predacort 50 or predaject-50 or predalone 50 or predartrina or predartrine or Predate or predeltilone or predisole or predisyr or pred-ject-50 or predne dome or prednecort or prednedome or Predne-Dome or prednelan or predni coelin or predni h tablinen or Prednicen or prednicoelin or prednicortelone or prednifor drops or predni-helvacort or Predniliderm or predniment or predniretard or prednis or prednisil or prednivet or prednorsolon or prednorsolone or Predonin or Predonine or predorgasolona or predorgasolone).ti,ab,rn. (28,673)
-
37. (prelon or prelone or prenilone or prenin or prenolone or preventan or prezolon or Rolisone or rubycort or scherisolon or scherisolona or serilone or solondo or solone or solupren or soluprene or spiricort or spolotane or Steran or sterane or sterolone or supercortisol or supercortizol or taracortelone or Ulacort or walesolone or wysolone).ti,ab,rn. (64)
-
38. or/7-37 (1,058,233)
Line 38 captures terms for steroids
-
39. 6 and 38 (106)
Line 39 combines terms for Eustachian tube and terms for steroids
-
40. exp Nasal Decongestants/ (15,904)
-
41. Imidazoles/ (38,412)
-
42. Nasal Sprays/ (108)
-
43. (xylometazolin$ or Balkis or Chlorohist-LA or Decongest or espa-rhin or Gelonasal or Idasal or Idril N or Nasan or Imidin or NasenGel or NasenTropfen or NasenSpray or Novorin or Otradrops or Otraspray or Otrivin or Otriven$ or Rapako or schnupfen endrine or Snup or stas or Amidrin or Neo-Synephrine II or Olynth or Otrivine or Rhinactin or ba 11391 or ba11391 or “brn 0180524” or brufasol or otrovin hcl or servilaryn or tixycold or xylometarzoline or xylometazonolin$ or xylomethazoline or xilometazolin$ or zylometazoline or otrix).ti,ab,rn. (464)
-
44. (cirazolin$ or LD 3098).ti,ab,rn. (408)
-
45. (naphazolin$ or Afazol Grin or AK Con or AKCon or Albalon or albasol or All Clear or allersol or alpha-Naphthylmethyl imidazoline or antan or benil or “BRN 0151864” or cefasan or Ciba 2020 or Clear Eyes or Clearine or coldan or Colirio Alfa or comfort eye drops or dazolin or degest 2 or derinox or Idril or imidin or minha or Miraclar or mirafrin or Nafazair or Nafazolin$ or naphacel ofteno or naphasal or Naphcon or naphozoline hydrochloride or naphtears or naphthazoline or naphthizine).ti,ab,rn. (665)
-
46. (naphthyzin or nastizol or nazil ofteno or niazol or ocu-zoline or opcon or Optazine or Privin$ or Proculin or rhinantin or rhinazin or rhinoperd or rimidol or sanorin or sanotin or Siozwo or strictylon or Tele Stulln or TeleStulln or Vasoclear or Vasocon or Vasoconstrictor Pensa or VasoNit or vistalbalon or vistobalon).ti,ab,rn. (15,396)
-
47. (Oxymetazolin$ or afrazine or afrin or atomol or bayfrin or “BRN 0886303” or dristan or drixine or duramist plus or H 990 or Hazol or HSDB 3143 or Iliadin or iliadine or Nafrine or nasivin or Navisin or Nezeril or nostrilla or ocuclear or Oximetazolin$ or Oxylazine or Oxymethazoline or Rhinofrenol or rhinolitan or rhinosan or sch 9384 or Sinerol or sinex long last or sinex or visine).ti,ab,rn. (991)
-
48. (Phenylephrin$ or adrianol or af-taf or Ah-Chew or AI3-02402 or ak-dilate or albalon relief or alconefrin or almefrin or biomidrin or biomydrin or CCRIS 8464 or derizene or despec-sf or disneumon pernasal or dristan nasal mist or drosin or efrin-10 or efrisel or fenylephrine or HSDB 3383 or idrianol or isonefrine or isophrin or isopto frin or isoptofrin or l meta synephrine or lexatol or m synephrine or mesaton$ or meta sympathol or meta synephrine or metaoxedrin$).ti,ab,rn. (19,182)
-
49. (Metasympatol or metasynephrine or Mezaton or m-Methylaminoethanolphenol or m-Oxedrine or m-Sympathol or m-Sympatol or m-Synephrine or mydfrin or nefrin-ofteno or Neo Synephrine or neofrin or neooxedrine or neophryn or neosynephrin or neosynephrine or neosynesin or neosynesine or ocu-phrin or oftan-metaoksedrin or op-isophrin or optistin or phenoptic or phenylefrine or phenylephedrine or prefrin or pupiletto forte or rectasol or rhinall 10 or slv 325 or slv325 or sucraphen or visadron or vistafrin or vistosan).ti,ab,rn. (212)
-
50. (Phenylpropanolamin$ or acutrim or apodrine or apoephedrine or apophedrine or appedrine or BRN 3196918 or descon or Dexatrim or dexatrim or diet gard or dietac premeal or HSDB 6485 or kontexin or monydrin or Mucron or mydriatin or nobese or Norephedrine or NSC 9920 or phenyl propanolamine or phenylpropanolamide or PPA or pressedrine or procol or Prolamine or propadine or propadrine or Propagest or Rhindecon or Super Odrinex or trimolet).ti,ab,rn. (4543)
-
51. (Pseudoephedrin$ or acunaso or afrinol or Besan or dimetapp or d-Isoephedrine or drixora or Ephedrine or HSDB 3177 or Isoephedrine or isofedrine or isophedrine or logicin plus or monofed or nasa-12 or novafed or otrinol or pseudo ephedrine or pseudo-12 or Pseudoefedrina or pseudono or Psi-ephedrin or repedrina or rhinalair or sch 4855 or sch4855 or sinumed or sinutab or subulin or Sudafed or sudomyl or sudosian or symptofed or tiptipot).ti,ab,rn. (5861)
-
52. (Synephrin$ or Sympaethamin$ or Oxedrine or aetaphen or asthma spray spofa or pentedrine or vasoton or Analeptin or DL-Synephrine or Ethaphene or NSC 166285 or NSC 170956 or Parakorper or Parasympatol or S 38537-9 or Simpalon or Simpatol or Sympathol or Sympatol or Synefrin or Synthenate or p-Hydroxyphenylmethylaminoethanol or p-Methylaminoethanolphenol or p-Oxedrine or p-Synephrine).ti,ab,rn. (8094)
-
53. (tetrahydrozolin$ or tetryzoline or Caltheon or Collyrium Fresh or Diabenyl T or Eye-Sine or Eye-Zine or Murine Plus or Murine Sore Eyes or Ophtalmin or Optazine Fresh or Optigene or Rhinopront or Tetra-Ide or Tetraclear or Tetrilin or Tyzine or Vasopos or Visine or Yxin or Vispring or Berberil N or “BRN 0011442” or HSDB 7471 or Tetrizolin$ or Tyzanol or clarine or insto or murine tears or murine-2 or nasan or nazane or nazine or necor tyzine or octilia or ophthalmin-n or opsil-a or optizoline or rhinoprout or stilla drops or visina or visolin).ti,ab,rn. (192)
-
54. (brompheniramine or Bromfed or Lodrane or Dimetapp).ti,ab,rn. (354)
-
55. (decongestant$ or decongestive$).ti,ab. (1474)
-
56. ((nasal or nose) adj2 (spray$ or mist or aerosol$)).ti,ab. (2359)
-
57. or/40-56 (92,301)
Line 57 captures terms for decongestants
-
58. 6 and 57 (71)
Line 58 combines terms for Eustachian tube and terms for decongestants
-
59. exp Histamine Antagonists/ (53989)
-
60. (anti histamin$ or antihistamin$).ti,ab. (10,920)
-
61. (histamine adj3 (antagonist$ or block$)).ti,ab. (5986)
-
62. ((H1 or H2 or H3 or H4) adj2 (antagonist$ or block$)).ti,ab. (10,245)
-
63. (acrivastin$ or semprex or semprex-D or benadryl or prolert or BW 825C or BW825C or BW A825C).ti,ab,rn. (365)
-
64. (bilastine or bilaxten or f 96221 bm1 or f96221 bm1).ti,ab,rn. (35)
-
65. (Cetirizin$ or acidrine or adezio or agelmin or Alercet or Alergex or Alerid or Alerlisin or Alertisin or alertop or alerviden or aletir or alled or Allergy relief or Alleroff or allertec or alltec or alzytec or Apo-Cetirizine or betarhin or cerazine or cerini or cerotec or cesta or Cetalerg or Ceterifug or cethis or Ceti TAD or Cetiderm or Cetidura or Cetil von ct or CetiLich or cetimin or cetin or Ceti-Puren or cetirax or Cetirigamma or cetirin or Cetirlan or cetizin or Cetriler or cetrimed or Cetrine or cetrizet or cetrizin or Cetryn or cetymin or Cetzine or Cezin or cistamine or deallergy or falergi or finallerg or Formistin or histazine or histica or Hitrizin or HSDB 7739).ti,ab,rn. (1453)
-
66. (incidal-od or lergium or nosemin or nosmin or ozen or “P 071” or P071 or prixlae or razene or Reactine or Ressital or rhizin or risima or Riztec or ryvel or Ryzen or Salvalerg or sancotec or selitex or Setir or Setiral or setizin or simtec or Stopaler or Sun mark all day allergy or sutac or symitec or terizin or terzine or Topcare all day allergy or Triz or “UCB-P 071” or vick-zyrt or Virdos or Virlix or Voltric or Xero-sed or zenriz or zensil or zeran or zertine or Zetir or zicet or zinex or Ziptek or zirtec or Zirtek or Zirtin or zyllergy or zymed or zyrac or zyrazine or zyrcon or zyrlex or Zyrtec or Zyrtec-D or zyrtek or Zyrzine).ti,ab,rn. (1556)
-
67. (desloratadine or clarinex or aerius or neoclarityn or azomyr or denosin or SCH 34117 or allex or aviant or claramax or dasselta or decarbethoxyloratadine or desalex or descarboethoxyloratadine or deslor or neoclaritine or sch34117 or supraler).ti,ab,rn. (465)
-
68. (fexofenadine or allegra or telfast or Carboxyterfenadine or MDL 16455A or mdl 16455 or mdl16455).ti,ab,rn. (684)
-
69. (levocetirizine or xusal or xyzal).ti,ab,rn. (251)
-
70. (loratadin$ or aerotina or Alarin or Alavert or alerfast or alernitis or Alerpriv or alertadin or allerta or Allertidin or allertyn or allohex or ambrace or analergal or anhissen or anlos or ardin or Bactimicina allergy or Biloina or bonalerg or caradine or carin or civeran or clalodine or claratyne or clarid or Clarinase or Claritin or claritine or clarityn or clarityne or Clarium or cronitin or cronopen or curyken or demazin anti-allergy or ezasmin or ezede or finska or frenaler or fristamin or genadine or halodin or hislorex or histalor or histaloran or HSDB 3578 or j-tadine or klarihist or klinset or laredine or lergia or Lergy or lertamine or Lesidas or lindine or lisino or lisono or lobeta or lodain or lorabasics or loracert or loraclar or loraderm or loradex).ti,ab,rn. (3041)
-
71. (Loradif or loradin or lorahist or loralerg or lora-lich or lorano or loranox or Loranox or Lorantis or lorastine or lora-tabs or loratadura or loratan or loratazine or loratidin or loratidine or loraton or loratrim or loratyne or Loraver or loreen or lorfast or lorihis or lorin or lorita or Loritine or lotadine or lotarin or lowadina or mosedin or noratin or notamin or Nularef or onemin or optimin or polaratyne or proactin or pylor or restamine or Rhinase or ridamin or rihest or rinityn or Rinomex or rityne or roletra or rotifar or Sanelor or Sch 29851 or Sch29851 or sensibit or Sinhistan Dy or sohotin or Tadine or Talorat Dy or tidilor or tirlor or Topcare or toradine or velodan or versal or voratadine or zeos).ti,ab,rn. (93)
-
72. (mizolastin$ or zolistan or mistamine or mistalin or mizollen or zolim or mizolen or “SL 85 0324” or CCRIS 8410 or mkc 431 or sl 850324).ti,ab,rn. (115)
-
73. (rupatadine or rupafin or UR 12592 or UR12592).ti,ab,rn. (70)
-
74. (Chlorphenamin$ or 4-Chloropheniramine or ahiston or alerfin or alergical or alergidryl or alergitrat or alermine or aller or Aller-Chlor or Allerclor or allerfin or Allergican or Allergin or Allergisan or allergyl or allermin or allerphen or Alunex or analerg or anaphyl or Antagonate or antamin or apomin or barominic or cadistin or Carbinoxamide maleate or CCRIS 1418 or Chlo-Amine or chlometon or chlor trimeton or Chlor-100 or chloramate unicelles or chlorleate or Chlormene or chlorophenamine maleate or Chloropheniramine or Chlorophenylpyridamine or Chloropiril).ti,ab,rn. (4230)
-
75. (Chloroprophenpyridamine or chloroton or Chlorpheniramin$ or chlorpheno or chlorphenon or Chlorpro or Chlorprophenpyridamine or chlorpyrimine or Chlorspan 12 or Chlortab-4 or chlortrimeton or Chlor-Trimeton or chlortripolon or Chlor-Tripolon or Clorfenamina or Clorfeniramina or cloro trimeton or cloroalergan or Cloropiril or clorotrimeton or Cloro-Trimeton or C-Meton or cohistan or com-trimeton or Dehist or dl-Chlorpheniramine maleate or Efidac 24).ti,ab,rn. (13,363)
-
76. (clemastin$ or meclastin$ or neclastine or mecloprodin or tavist or tavegyl or HS 592 or HS592).ti,ab,rn. (463)
-
77. (cyproheptadine or adekin or Antergan or antisemin or apeton 4 or astonin or BRN 1685976 or CCRIS 5232 or ciplactin or cipractin or ciproeptadine or Ciproheptadina or ciproral or ciprovit-a or cryoheptidine or crypoheptadine or cyheptine or cylat or cypraheptidine or cypro h or cyproatin or cyprogin or cyprohaptadi$ or cypromin or cyprono or cyprosian or cytadine or Dihexazin or Dronactin or Eiproheptadine or ennamax or glocyp or heptasan or HSDB 3048 or ifrasal or istam-far or klarivitina or kulinet or MK 141 or nuran or Periact$ or Peritol or petina or pilian or pronicy or sinapdin or trimetabol or Viternum).ti,ab,rn. (2968)
-
78. (ketotifen$ or ketotiphen$ or zaditen or zaditor or BRN 3983897 or HC 20 511 or hc 20511 or HSDB 7283).ti,ab,rn. (1472)
-
79. (Prometh$ or 3277 RP or A-91033 or adgan or Allerfen or allergan or Anergan 25 or Anergan 50 or antiallersin or antinaus 50 or Aprobit or Atosil or Avomine or baymethazine or Bonnox or “BRN 0088554” or Camergan or CCRIS 5873 or CCRIS 7056 or Closin or dimapp or Dimethylamino-isopropyl-phenthiazin or Diphergan or Diprasine or Diprazin$ or diprozin or Dorme or Duplamin or Eusedon Mono or fargan or Farganesse or Fellozine or fenazil or fenazine or Fenergan or Fenetazin$ or Frinova or Ganphen or Hibechin or hiberna or Histantil or Histargan or HL 8700 or HSDB 3173 or insomn-eze or Isophenergan or Isopromethazine or Kinetosin or lercigan or Lergigan or lergigan or “Lilly 01516” or Lilly 1516 or Metaryl or Mymethazine Fortis or NCI-C60673 or NSC 231688).ti,ab,rn. (4507)
-
80. (NSC 30321 or Pelpica or pentazine or phargan or Phenadoz or Phenargan or Phencen or Phenergan or Phenerzine or phenoject-50 or Phensedyl or Pilothia or Pipolfen or Pipolphen$ or Plletia or pm 284 or Primine or Pro-50 or Proazamine or procit or promacot or Promantine or promazinamide or Prome or Promergan or Promesan or Promet or Prometazin or Prometazina or Prometh$ or Promezathine or Promine or Proneurin or Prorex or protazine or Prothazin or Prothiazine or prothazine or provigan or Provigan or Pyrethia or Pyrethiazine or Remsed or Romergan or rp 3277 or rp 3389 or Rumergan or sayomol or SKF 1498 or Soporil or tanidil or thiergan or V GAN or vallergine or WY 509 or Zipan-25 or Zipan-50).ti,ab,rn. (4091)
-
81. or/59-80 (82,509)
Line 81 captures terms for anti-histamines
-
82. 6 and 81 (45)
Line 82 combines terms for Eustachian tube and terms for anti-histamines
-
83. Simethicone/ (270)
-
84. (simethicone or Antifoam A or Antifoam AF or DC antifoam A or Disflatyl or Gas-X or gas relief or HSDB 3906 or Mylanta or mytab gas or Phazyme or Sab Simplex or Simeticone or dimethicone or digel or flatulex or infacol or lefax or minifom or mylicon or silain or Alka-Seltzer Anti-Gas or Colic Drops or Colicon or Degas or Gas Aide or Genasyme or Maalox Anti-Gas or Majorcon or Micon-80 or Mylaval or SonoRx or WindEze or Wind-Eze).ti,ab,rn. (513)
-
85. 83 or 84 (513)
Line 84 captures terms for simethicone
-
86. 6 and 85 (0)
Line 86 combines terms for Eustachian tube and terms for simethicone
-
87. exp Nasal Lavage/ (960)
-
88. Therapeutic Irrigation/ (14,655)
-
89. ((nasal or nose) adj3 (douch$ or irrigat$ or lavage)).ti,ab. (1345)
-
90. (saline adj3 (douch$ or irrigat$ or lavage)).ti,ab. (1689)
-
91. or/87-90 (17,313)
Line 87 captures terms for nasal irrigation
-
92. 6 and 91 (37)
Line 92 combines terms for Eustachian tube and terms for nasal irrigation
-
93. Leukotriene Antagonists/ (2568)
-
94. (leukotriene adj3 (antagonist$ or block$ or inhibitor$)).ti,ab. (2975)
-
95. (montelukast or Singulair or Montelo-10 or montair or montek or montus or romilast or “MK 0476” or mk 476 or mk0476 or mk476 or l 706631 or l706631).ti,ab,rn. (1580)
-
96. (zafirlukast or Accolate or accoleit or Olmoran or Aeronix or respix or vanticon or zafirst or zuvair or ICI 204,219 or ICI 204219).ti,ab,rn. (492)
-
97. (pranlukast or azlaire or ultair or ONO 1078 or SB 205312 or SB205312 or ONO RS 411 or rs411 or rs 411).ti,ab,rn. (404)
-
98. (zileuton$ or A 64077 or A64077 or Abbot 64077 or cgs 23622 or cgs23622 or Zyflo or Leutrol).ti,ab,rn. (518)
-
99. or/93-98 (5395)
Line 99 captures terms for leukotriene antagonists
-
100. 6 and 99 (0)
Line 100 combines terms for Eustachian tube and terms for leukotriene antagonists
-
101. Chewing Gum/ (1895)
-
102. Xylitol/ (1868)
-
103. (Xylitol or BRN 1720523 or Eutrit or HSDB 7967 or Kannit or Klinit or NSC 25283 or Newtol or Xylite or Xylitol or Xyliton or xylit).ti,ab,rn. (2740)
-
104. or/101-103 (4411)
Line 104 captures terms for xylitol
-
105. 6 and 104 (0)
Line 105 combines terms for Eustachian tube and terms for xylitol
-
106. exp Anti-Infective Agents/ (1,191,754)
-
107. (anti bacterial$ or antibacterial$ or anti biotic$ or antibiotic$ or anti mycobacterial$ or antimycobacterial$ or bacteriocid$).ti,ab. (241,072)
-
108. (anti infective$ or antiinfective$ or anti microbial$ or antimicrobial$ or microbicide$).ti,ab. (84764)
-
109. (doxycyclin$ or adoxa or alpha-Doxycycline or amermycin or atrax or azudoxat or bactidox or banndoclin or basedillin or bassado or biocolyn or biodoxi or bmy 28689 or bmy28689 or bronmycin or bu 3839t or bu3839t or cloran or cyclidox or dentistar or deoxycycline or deoxymycin dispersal or deoxymykoin or deoxyoxytetracycline or desoxy oxytetracycline or desoxycycline or doinmycin or doryx or dosil or Dossiciclina or dotur or doxaciclin or doxacycline or doxat or doxatet or doxibiotic or Doxiciclina or doxicycline or doxilin or doximed or doximycin or doxin or doxine or doxi-sergo).ti,ab,rn. (11242)
-
110. (Doxitard or Doxivetin or doxocycline or doxsig or doxy or doxy-1 or doxybiocin or doxy-caps or doxycen or doxychel or doxycin or doxycydine monohydrate or doxylag or doxylin or doxymycin or doxypuren or Doxy-Puren or Doxysol or doxytec or Doxytetracycline or doxytrim or dumoxin or duracycline or esdoxin or etidoxina or gewacyclin or gs 3065 or HSDB 3071 or hydramycin or ibralene or idocyclin or idocyklin or interdoxin or investin or Liviatin or longamycin or lydox or magdrin or medomycin or mespafin or mildox or miraclin or monodox or nordox or novum vibramycin).ti,ab,rn. (7033)
-
111. (nsc 56228 or oracea or paldomycin or pernox gel or radox or remycin or respidox or Ronaxan or roximycin or serodoxy or servidoxine or servidoxyne or siadocin or siclidon or sigadoxin or spanor or supracyclin or supramycina or tenutan or tolexine or torymycin or tsurupioxin or unidox or veemycin or viadoxin or vibra$ or viradoxyl-n or wanmycin or zadorin).ti,ab,rn. (42,398)
-
112. (amoxicil$ or a gram or abdimox or acilina or acimox or actimoxi or adbiotin or agerpen or agram or a-gram or alfamox or alfoxil or almodan or almorsan or alphamox or amagesen solutab or ameclina or amocillin or amoclen or amodex or amo-flamisan or amoflux or amohexal or amolin or amonex or amopen or Amopenixin or amophar ge or amosine or amoval or amoxa or amoxal or amoxapen or amoxaren or amoxcil or amoxcillin or amoxcin or Amoxi or amoxi-basan or Amoxicaps or amoxiclin or amoxicot or amoxidal or Amoxiden or amoxidin or amoxidrops or amoxihexal or amoxil$).ti,ab,rn. (19,750)
-
113. (Amoxi-Mast or amoxipen or amoxipenil or amoxisol or amoxivan or amoxivet or Amoxivet or amoxy or Amoxycillin$ or amoxy-diolan or amoxypen or AMPC or ampliron or Ampy-Penyl or Anemolin or apo-amoxi or ardine or aroxin or Aspenil or azillin or bacihexal or bactamox or bactox ge or beamoxy or betamox or bimox or bintamox or biomox or biotamoxal or bioxidona or bioxyllin or BLP 1410 or bristamox or brl 2333 or brl2333 or broadmetz or cabermox or Cemoxin or cilamox or clamox or clamoxyl or clearamox or clonamox or coamoxin or damoxicil or D-Amoxicillin or Delacillin).ti,ab,rn. (4247)
-
114. (dispermox or doxamil or draximox or edamox or Efpenix or erphamoxy or eupen or farconcil or fisamox or flemoxin or fluamoxina or foxolin or fullcilina or gexcil or gimalxina or glamox or glassatan or gomcillin or grinsul or grunamox or hamoxillin or hiconcil or hidramox or hipen or Histocillin or hosboral or HSDB 3204 or Hydroxyampicillin or ibamox or ibiamox or ikamoxil or imacillin or imaxilin or inamox or infectomycin or intermox or isimoxin or izoltil or julphamox or jutamox or kamoxin or ladoxillin or lamoxy or larocilin or larocin or larotid or macromox or magnimox or maxamox or maxcil).ti,ab,rn. (21)
-
115. (medimox or meixil or Metafarma or metifarma or mopen or morgenxil or moxacin or Moxal$ or moxarin or Moxatag or moxilen or moxilin or moximar or moxitab or moxtid or moxylin or moxypen or moxyvit or neogram or novabritine or novamox or novamoxin or novenzymin or novoxil or NSC 277174 or nuvosyl or optium or ospamox or pamocil or pamoxicillin or pamoxin or panvilon or pasetocin or penamox or penbiosyn or pentyloxycillin or pharmoxyl or p-Hydroxyampicillin or piramox or polymox or pondnoxcill or rancil or ranmoxy or ranoxil or ranoxyl or Ro 10-8756).ti,ab,rn. (1540)
-
116. (robamox or romoxil or ronemox or saltermox or sawacillin or sawamezin or Sawamox PM or servamox or shamoxil or sia-mox or sigamopen or silamox or sil-a-mox or simoxil or solpenox or sumox or superpeni or teramoxyl or tolodina or tormoxin or triafamox or triamoxil or trifamox or trimox or Unicillin or uro clamoxyl or uroclamoxyl or utimox or vastamox or velamox or Vetramox or vistrep or widecillin or winpen or wymox or Wymox or Wymox or xiltrop or zamocillin or zamox or zamoxil or zerrsox or zimox).ti,ab,rn. (14)
-
117. (clarith$ or A 56268 or A56268 or abbotic or abbott 56268 or Adel or aeroxina or Astromen or bactirel or baxin filmtab or Biaxin or biclar or bicrolid or binoklar or bremon or carimycin or c-clarin or CCRIS 8833 or celex or clacin or clacine or clambiotic or clapharma or claribid or Claricide or claridar or clarimac or claripen or claritrol or Claritromicina or claroma or Clathromycin or clormicin).ti,ab,rn. (7366)
-
118. (crixan or cylind or Cyllid or cyllind or dicupal or DRG-0099 or er 36469 or er36469 or gervaken or hecobac or Helas or heliclar or helitic or klacid or klacina or klaciped or klaribac or klaricid or Klarid or klaridex or klaridia or klarin or Klax or klerimed or kofron or lagur or Mabicrol or macladim or macladin or maclar or mavid or monozeclar or naxy or “TE 031” or TE031 or veclam or zeclar).ti,ab,rn. (101)
-
119. (moxif$ or Actira or Avalox or avelon or Avelox or Avolex or BAY 12 8039 or BAY 128039 or bay128039 or CCRIS 8690 or Izilox or megaxin or moxeza or Octegra or Proflox or vigamox).ti,ab,rn. (2639)
-
120. (Telithromycin or Ketek or RU 66647 or HMR 3647 or HMR3647 or levviax or ru 647 or ru 66647 or ru647 or ru66647).ti,ab,rn. (855)
-
121. (azithromycin$ or Aritromicina or aruzilina or atizor or Azadose or azasite or azenil or azimin or azithral or Azitrocin or azitromax or Azitromicine or aziwok or azomyne or aztrin or Azythromycin or BRN 5387583 or CCRIS 1961 or cp 62933 or cp62933 or DRG-0104 or forcin or Goxal or Hemomycin or HSDB 7205 or inedol or isv 401 or isv401 or kromicin or macrozit or mezatrin or Misultina).ti,ab,rn. (5129)
-
122. (Mixoterin or octavax or Setron or Sumamed or sunamed or Tobil or tobyl or Toraseptol or tromix or Trulimax or Ultreon or Vinzam or xithrone or xz 450 or xz450 or zaret or zarom or Zentavion or Zeto or zibramax or zifin or zimericina or zistic or Zithrax or Zithromax or zithrox or zitrim or zitrobifan or Zitromax or Zitrotek or Zmas or zmax or Z-Pak).ti,ab,rn. (401)
-
123. or/106-122 (1,349,743)
Line 123 captures terms for antibiotics
-
124. 6 and 123 (270)
Line 124 combines terms for Eustachian tube and terms for antibiotics
-
125. Balloon Dilation/ (13,893)
-
126. Dilatation/ (7905)
-
127. Dilatation, Pathologic/ (8128)
-
128. Catheterization/ (31,341)
-
129. Catheterization, Peripheral/ (5862)
-
130. catheter$.ti,ab. (142,557)
-
131. dilat$.ti,ab. (101,802)
-
132. (BET or BDET).ti,ab. (4975)
-
133. tuboplast$.ti,ab. (182)
-
134. exp Laser Therapy/ (46,697)
-
135. exp Lasers/ (36,258)
-
136. laser$.ti,ab. (163,455)
-
137. LETP.ti,ab. (5)
-
138. Middle Ear Ventilation/ (1984)
-
139. (tympanostom$ or tympanotom$).ti,ab. (1435)
-
140. grommet$.ti,ab. (453)
-
141. ((ventilat$ or aerat$) adj4 ear$).ti,ab. (1472)
-
142. ((ventilat$ or aerat$) adj4 tub$).ti,ab. (2404)
-
143. (pressur$ adj3 tub$).ti,ab. (1460)
-
144. ear tube$.ti,ab. (67)
-
145. PE tube$.ti,ab. (43)
-
146. T tube$.ti,ab. (2251)
-
147. (transtubal or trans tubal).ti,ab. (60)
-
148. (myringotom$ or myringocentesis).ti,ab. (1163)
-
149. (paracentesis or tympanocentesis).ti,ab. (2556)
-
150. ((eardrum$ or ear drum$ or tympan$) adj3 (punctur$ or tap$)).ti,ab. (23)
-
151. or/125-150 (459,729)
Line 151 captures terms for types of surgery
-
152. 6 and 151 (931)
Line 152 combines terms for Eustachian tube and terms for surgery
-
153. Valsalva Maneuver/ (3361)
-
154. Insufflation/ (1366)
-
155. Yawning/ (533)
-
156. Mastication/ (7711)
-
157. Deglutition/ (6665)
-
158. Watchful Waiting/ (561)
-
159. valsalva$.ti,ab. (6721)
-
160. (autoinflat$ or auto inflat$).ti,ab. (73)
-
161. (insufflat$ or autoinsufflat$ or auto insufflat$).ti,ab. (5159)
-
162. (inflat$ adj4 ear$).ti,ab. (117)
-
163. Politzer$.ti,ab. (124)
-
164. ((equalis$ or equaliz$ or normalis$ or normaliz$) adj5 pressure$).ti,ab. (3810)
-
165. (yawn$ or swallow$ or chew$ or masticat$ or deglutition).ti,ab. (36,922)
-
166. (watch$ adj2 wait$).ti,ab. (1809)
-
167. (wait adj2 see).ti,ab. (873)
-
168. (active$ adj2 observ$).ti,ab. (1012)
-
169. conservative.ti,ab. (68,251)
-
170. (management adj2 (decision$ or option$ or choice$)).ti,ab. (9031)
-
171. (support$ adj4 (care or caring)).ti,ab. (19,380)
-
172. ((standard or usual) adj3 care).ti,ab. (23,669)
-
173. (advice or advis$).ti,ab. (69192)
-
174. or/153-173 (247,702)
Line 174 captures terms for supportive care/advice
-
175. 6 and 174 (603)
Line 175 combines terms for Eustachian tube and terms for supportive care/advice
-
176. 39 or 58 or 82 or 86 or 92 or 100 or 105 or 124 or 152 or 175 (1562)
-
177. exp animals/ not humans/ (3,791,654)
-
178. 176 not 177 (1345)
Line 178 is the final set of records retrieved excluding animal studies
Key
/ = indexing term [medical subject heading (MeSH)]
exp = exploded MeSH heading
$ = truncation
.ti,ab. = terms in either title or abstract fields
adj2 = terms within two words of each other (any order)
Bioscience Information Service Previews via Dialog: www.dialog.com/
1993–2012, September week 5.
Searched on 5 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 139.
| Set | Items | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 844 | (EUSTACHIAN OR AUDITORY OR PHARYNGOTYMPANIC)(3W)TUB?/TI,AB,DE |
| 2 | 21 | EUSTACHIAN(2W)(CANAL OR ORIFICE?)/TI,AB,DE |
| 3 | 36 | MIDDLE(W)EAR(3W)DYSFUNCTION?/TI,AB,DE |
| 4 | 225 | MIDDLE(W)EAR(3W)PRESSURE?/TI,AB,DE |
| 5 | 1046 | S1:S4 |
| 6 | 185 | S5/2008:2012 |
| 7 | 139 | S6/HUMAN |
Key
? = truncation
/TI,AB,DE = terms in title, abstract, or descriptor fields
(W) = terms adjacent to each other (same order)
(2W) = terms within 2 words of each other (same order)
S1:S4 = S1 OR S2 OR S3 OR S4
S5/2008:2012 = limits set 5 to those records published between 1980 and 2012
S6/HUMAN = limits set 6 to human studies
Bioscience Information Service Previews via ISI Web of Knowledge: www.isinet.com/
1969–2008.
Search on 9 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 692.
| # 62 | 692 | #60 not #61 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 61 | 2,676,232 | TI=(rat or rats or mouse or mice or hamster or hamsters or animal or animals or dog or dogs or canine or cat or cats or feline or bovine or sheep or fly or flies or fish or fishes or fisheries or horse or horses or equine or bat or bats or bee or bees or grass or grasses or bird or birds or avian or fossil or fossils or lichen or lichens or mushroom or mushrooms or rabbit or rabbits or moss or mosses or fungus or fungi or cow or cattle or bovine or livestock or swine or poultry or pig or pigs or gerbil or frog or frogs or genera or taxonomy or species or fauna or habitat or marine or ecology or veterinary or “ taxonomic review” or “developmental biology” or “cell biology”) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 60 | 742 | #59 OR #45 OR #37 OR #33 OR #31 OR #27 OR #23 OR #21 OR #15 OR #10 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 59 | 261 | #58 AND #5 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 58 | 114,307 | #57 OR #56 OR #55 OR #54 OR #53 OR #52 OR #51 OR #50 OR #49 OR #48 OR #47 OR #46 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 57 | 24,768 | TS=(advice or advis*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 56 | 5899 | TS=((standard or usual) NEAR/3 care) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 55 | 5655 | TS=(support* NEAR/4 (care or caring)) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 54 | 8151 | TS=(management NEAR/2 (decision* or option* or choice*)) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 53 | 30,689 | TS=conservative Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 52 | 2123 | TS=(active* NEAR/2 observ*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 51 | 282 | TS=(wait NEAR/2 see) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 50 | 776 | TS=(watch* NEAR/2 wait*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 49 | 29,062 | TS=(yawn* or swallow* or chew* or masticat* or deglutition) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 48 | 2502 | TS=((equalis* or equaliz* or normalis* or normaliz*) NEAR/5 pressure*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 47 | 107 | TS=(inflat* NEAR/4 ear*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 46 | 6051 | TS=(valsalva* or autoinflat* or auto-inflat* or insufflat* or autoinsufflat* or auto-insufflat* or politzer*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 45 | 446 | #44 AND #5 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 44 | 286,005 | #43 OR #42 OR #41 OR #40 OR #39 OR #38 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 43 | 19 | TS=((eardrum* or “ear drum*” or tympan*) NEAR/3 (punctur* or tap*)) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 42 | 3392 | TS=(“ear tube*” or “PE tube*” or “T tube*” or transtubal or trans-tubal or myringotom* or myringocentesis or paracentesis or tympanocentesis) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 41 | 1881 | TS=(pressur* NEAR/3 tub*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 40 | 1607 | TS=((ventilat* or aerat*) NEAR/4 tub*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 39 | 932 | TS=((ventilat* or aerat*) NEAR/4 ear*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 38 | 279,543 | TS=(catheter* or dilat* or BET or BDET or tuboplast* or laser* or LETP or tympanostom* or tympanotom* or grommet*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 37 | 100 | #36 AND #5 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 36 | 507,214 | #35 OR #34 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 35 | 60,093 | TS=(doxycyclin* or adoxa or alpha-Doxycycline or amermycin or atrax or azudoxat or bactidox or banndoclin or basedillin or bassado or biocolyn or biodoxi or “bmy 28689” or bmy28689 or bronmycin or “bu 3839t” or bu3839t or cloran or cyclidox or dentistar or deoxycycline or “deoxymycin dispersal” or deoxymykoin or deoxyoxytetracycline or “desoxy oxytetracycline” or desoxycycline or doinmycin or doryx or dosil or Dossiciclina or dotur or doxaciclin or doxacycline or doxat or doxatet or doxibiotic or Doxiciclina or doxicycline or doxilin or doximed or doximycin or doxin or doxine or doxi-sergo or Doxitard or Doxivetin or doxocycline or doxsig or doxy or doxy-1 or doxybiocin or doxy-caps or doxycen or doxychel or doxycin or “doxycydine monohydrate” or doxylag or doxylin or doxymycin or doxypuren or Doxy-Puren or Doxysol or doxytec or Doxytetracycline or doxytrim or dumoxin or duracycline or esdoxin or etidoxina or gewacyclin or “gs 3065” or “HSDB 3071” or hydramycin or ibralene or idocyclin or idocyklin or interdoxin or investin or Liviatin or longamycin or lydox or magdrin or medomycin or mespafin or mildox or miraclin or monodox or nordox or novum vibramycin or “nsc 56228” or oracea or paldomycin or “pernox gel” or radox or remycin or respidox or Ronaxan or roximycin or serodoxy or servidoxine or servidoxyne or siadocin or siclidon or sigadoxin or spanor or supracyclin or supramycina or tenutan or tolexine or torymycin or tsurupioxin or unidox or veemycin or viadoxin or vibra* or viradoxyl-n or wanmycin or zadorin or amoxicil* or “a gram” or abdimox or acilina or acimox or actimoxi or adbiotin or agerpen or agram or a-gram or alfamox or alfoxil or almodan or almorsan or alphamox or “amagesen solutab” or ameclina or amocillin or amoclen or amodex or amo-flamisan or amoflux or amohexal or amolin or amonex or amopen or Amopenixin or “amophar ge” or amosine or amoval or amoxa or amoxal or amoxapen or amoxaren or amoxcil or amoxcillin or amoxcin or Amoxi or amoxi-basan or Amoxicaps or amoxiclin or amoxicot or amoxidal or Amoxiden or amoxidin or amoxidrops or amoxihexal or amoxil* or Amoxi-Mast or amoxipen or amoxipenil or amoxisol or amoxivan or amoxivet or Amoxivet or amoxy or Amoxycillin* or amoxy-diolan or amoxypen or AMPC or ampliron or Ampy-Penyl or Anemolin or apo-amoxi or ardine or aroxin or Aspenil or azillin or bacihexal or bactamox or “bactox ge” or beamoxy or betamox or bimox or bintamox or biomox or biotamoxal or bioxidona or bioxyllin or “BLP 1410” or bristamox or “brl 2333” or brl2333 or broadmetz or cabermox or Cemoxin or cilamox or clamox or clamoxyl or clearamox or clonamox or coamoxin or damoxicil or D-Amoxicillin or Delacillin or dispermox or doxamil or draximox or edamox or Efpenix or erphamoxy or eupen or farconcil or fisamox or flemoxin or fluamoxina or foxolin or fullcilina or gexcil or gimalxina or glamox or glassatan or gomcillin or grinsul or grunamox or hamoxillin or hiconcil or hidramox or hipen or Histocillin or hosboral or “HSDB 3204” or Hydroxyampicillin or ibamox or ibiamox or ikamoxil or imacillin or imaxilin or inamox or infectomycin or intermox or isimoxin or izoltil or julphamox or jutamox or kamoxin or ladoxillin or lamoxy or larocilin or larocin or larotid or macromox or magnimox or maxamox or maxcil or medimox or meixil or Metafarma or metifarma or mopen or morgenxil or moxacin or Moxal* or moxarin or Moxatag or moxilen or moxilin or moximar or moxitab or moxtid or moxylin or moxypen or moxyvit or neogram or novabritine or novamox or novamoxin or novenzymin or novoxil or “NSC 277174” or nuvosyl or optium or ospamox or pamocil or pamoxicillin or pamoxin or panvilon or pasetocin or penamox or penbiosyn or pentyloxycillin or pharmoxyl or p-Hydroxyampicillin or piramox or polymox or pondnoxcill or rancil or ranmoxy or ranoxil or ranoxyl or “Ro 10-8756” or robamox or romoxil or ronemox or saltermox or sawacillin or sawamezin or “Sawamox PM” or servamox or shamoxil or sia-mox or sigamopen or silamox or sil-a-mox or simoxil or solpenox or sumox or superpeni or teramoxyl or tolodina or tormoxin or triafamox or triamoxil or trifamox or trimox or Unicillin or “uro clamoxyl” or uroclamoxyl or utimox or vastamox or velamox or Vetramox or vistrep or widecillin or winpen or wymox or Wymox or Wymox or xiltrop or zamocillin or zamox or zamoxil or zerrsox or zimox or clarith* or “A 56268” or A56268 or abbotic or “abbott 56268” or Adel or aeroxina or Astromen or bactirel or baxin filmtab or Biaxin or biclar or bicrolid or binoklar or bremon or carimycin or c-clarin or “CCRIS 8833” or celex or clacin or clacine or clambiotic or clapharma or claribid or Claricide or claridar or clarimac or claripen or claritrol or Claritromicina or claroma or Clathromycin or clormicin or crixan or cylind or Cyllid or cyllind or dicupal or DRG-0099 or “er 36469” or er36469 or gervaken or hecobac or Helas or heliclar or helitic or klacid or klacina or klaciped or klaribac or klaricid or Klarid or klaridex or klaridia or klarin or Klax or klerimed or kofron or lagur or Mabicrol or macladim or macladin or maclar or mavid or monozeclar or naxy or "TE 031" or TE031 or veclam or zeclar or moxif* or Actira or Avalox or avelon or Avelox or Avolex or “BAY 12 8039” or “BAY 128039” or bay128039 or “CCRIS 8690” or Izilox or megaxin or moxeza or Octegra or Proflox or vigamox or Telithromycin or Ketek or “RU 66647” or “HMR 3647” or HMR3647 or levviax or “ru 647” or “ru 66647” or ru647 or ru66647 or azithromycin* or Aritromicina or aruzilina or atizor or Azadose or azasite or azenil or azimin or azithral or Azitrocin or azitromax or Azitromicine or aziwok or azomyne or aztrin or Azythromycin or “BRN 5387583” or “CCRIS 1961” or “cp 62933” or cp62933 or DRG-0104 or forcin or Goxal or Hemomycin or “HSDB 7205” or inedol or “isv 401” or isv401 or kromicin or macrozit or mezatrin or Misultina or Mixoterin or octavax or Setron or Sumamed or sunamed or Tobil or tobyl or Toraseptol or tromix or Trulimax or Ultreon or Vinzam or xithrone or “xz 450” or xz450 or zaret or zarom or Zentavion or Zeto or zibramax or zifin or zimericina or zistic or Zithrax or Zithromax or zithrox or zitrim or zitrobifan or Zitromax or Zitrotek or Zmas or zmax or Z-Pak) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 34 | 477,047 | TS=(anti-bacterial* or antibacterial* or anti-biotic* or antibiotic* or anti-mycobacterial* or antimycobacterial* or bacteriocid* or anti-infective* or antiinfective* or anti-microbial* or antimicrobial* or microbicide*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 33 | 0 | #32 AND #5 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 32 | 2641 | TS=(Xylitol or “BRN 1720523” or Eutrit or “HSDB 7967” or Kannit or Klinit or “NSC 25283” or Newtol or Xylite or Xylitol or Xyliton or xylit) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 31 | 0 | #30 AND #5 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 30 | 4407 | #29 OR #28 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 29 | 1830 | TS=(montelukast or Singulair or Montelo-10 or montair or montek or montus or romilast or "MK 0476" or “mk 476” or mk0476 or mk476 or “l 706631” or l706631or zafirlukast or Accolate or accoleit or Olmoran or Aeronix or respix or vanticon or zafirst or zuvair or “ICI 204 219” or “ICI 204219” or pranlukast or azlaire or ultair or “ONO 1078” or “SB 205312” or SB205312 or “ONO RS 411” or rs411 or “rs 411” or zileuton* or “A 64077” or A64077 or “Abbot 64077” or “cgs 23622” or cgs23622 or Zyflo or Leutrol) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 28 | 3359 | TS=(leukotriene NEAR/3 (antagonist* or block* or inhibitor*)) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 27 | 1 | #26 AND #5 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 26 | 2706 | #25 OR #24 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 25 | 1846 | TS=(saline NEAR/3 (douch* or irrigat* or lavage)) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 24 | 900 | TS=((nasal or nose) NEAR/3 (douch* or irrigat* or lavage)) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 23 | 0 | #22 AND #5 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 22 | 359 | TS=(simethicone or “Antifoam A” or “Antifoam AF” or “DC antifoam A” or Disflatyl or Gas-X or “gas relief” or “HSDB 3906” or Mylanta or “mytab gas” or Phazyme or “Sab Simplex” or Simeticone or dimethicone or digel or flatulex or infacol or lefax or minifom or mylicon or silain or “Alka-Seltzer Anti-Gas” or “Colic Drops” or Colicon or Degas or “Gas Aide” or Genasyme or “Maalox Anti-Gas” or Majorcon or Micon-80 or Mylaval or SonoRx or WindEze or Wind-Eze) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 21 | 18 | #20 AND #5 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 20 | 35,212 | #19 OR #18 OR #17 OR #16 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 19 | 13,274 | TS=(acrivastin* or semprex or semprex-D or benadryl or prolert or “BW 825C” or BW825C or “BW A825C” or bilastine or bilaxten or “f 96221 bm1” or “f96221 bm1” or Cetirizin* or acidrine or adezio or agelmin or Alercet or Alergex or Alerid or Alerlisin or Alertisin or alertop or alerviden or aletir or alled or “Allergy relief” or Alleroff or allertec or alltec or alzytec or Apo-Cetirizine or betarhin or cerazine or cerini or cerotec or cesta or Cetalerg or Ceterifug or cethis or “Ceti TAD” or Cetiderm or Cetidura or “Cetil von ct” or CetiLich or cetimin or cetin or Ceti-Puren or cetirax or Cetirigamma or cetirin or Cetirlan or cetizin or Cetriler or cetrimed or Cetrine or cetrizet or cetrizin or Cetryn or cetymin or Cetzine or Cezin or cistamine or deallergy or falergi or finallerg or Formistin or histazine or histica or Hitrizin or “HSDB 7739” or incidal-od or lergium or nosemin or nosmin or ozen or "P 071" or P071 or prixlae or razene or Reactine or Ressital or rhizin or risima or Riztec or ryvel or Ryzen or Salvalerg or sancotec or selitex or Setir or Setiral or setizin or simtec or Stopaler or “Sun mark all day allergy” or sutac or symitec or terizin or terzine or “Topcare all day allergy” or Triz or "UCB-P 071" or vick-zyrt or Virdos or Virlix or Voltric or Xero-sed or zenriz or zensil or zeran or zertine or Zetir or zicet or zinex or Ziptek or zirtec or Zirtek or Zirtin or zyllergy or zymed or zyrac or zyrazine or zyrcon or zyrlex or Zyrtec or Zyrtec-D or zyrtek or Zyrzine or desloratadine or clarinex or aerius or neoclarityn or azomyr or denosin or “SCH 34117” or allex or aviant or claramax or dasselta or decarbethoxyloratadine or desalex or descarboethoxyloratadine or deslor or neoclaritine or sch34117 or supraler or fexofenadine or allegra or telfast or Carboxyterfenadine or “MDL 16455A” or “mdl 16455” or mdl16455 or levocetirizine or xusal or xyzal or loratadin* or aerotina or Alarin or Alavert or alerfast or alernitis or Alerpriv or alertadin or allerta or Allertidin or allertyn or allohex or ambrace or analergal or anhissen or anlos or ardin or “Bactimicina allergy” or Biloina or bonalerg or caradine or carin or civeran or clalodine or claratyne or clarid or Clarinase or Claritin or claritine or clarityn or clarityne or Clarium or cronitin or cronopen or curyken or “demazin anti-allergy” or ezasmin or ezede or finska or frenaler or fristamin or genadine or halodin or hislorex or histalor or histaloran or “HSDB 3578” or j-tadine or klarihist or klinset or laredine or lergia or Lergy or lertamine or Lesidas or lindine or lisino or lisono or lobeta or lodain or lorabasics or loracert or loraclar or loraderm or loradex or Loradif or loradin or lorahist or loralerg or lora-lich or lorano or loranox or Loranox or Lorantis or lorastine or lora-tabs or loratadura or loratan or loratazine or loratidin or loratidine or loraton or loratrim or loratyne or Loraver or loreen or lorfast or lorihis or lorin or lorita or Loritine or lotadine or lotarin or lowadina or mosedin or noratin or notamin or Nularef or onemin or optimin or polaratyne or proactin or pylor or restamine or Rhinase or ridamin or rihest or rinityn or Rinomex or rityne or roletra or rotifar or Sanelor or “Sch 29851” or Sch29851 or sensibit or “Sinhistan Dy” or sohotin or Tadine or “Talorat Dy” or tidilor or tirlor or Topcare or toradine or velodan or versal or voratadine or zeos or mizolastin* or zolistan or mistamine or mistalin or mizollen or zolim or mizolen or "SL 85 0324" or “CCRIS 8410” or “mkc 431” or “sl 850324” or rupatadine or rupafin or “UR 12592” or UR12592 or Chlorphenamin* or 4-Chloropheniramine or ahiston or alerfin or alergical or alergidryl or alergitrat or alermine or aller or Aller-Chlor or Allerclor or allerfin or Allergican or Allergin or Allergisan or allergyl or allermin or allerphen or Alunex or analerg or anaphyl or Antagonate or antamin or apomin or barominic or cadistin or “Carbinoxamide maleate” or “CCRIS 1418” or Chlo-Amine or chlometon or “chlor trimeton” or Chlor-100 or “chloramate unicelles” or chlorleate or Chlormene or “chlorophenamine maleate” or Chloropheniramine or Chlorophenylpyridamine or Chloropiril or Chloroprophenpyridamine or chloroton or Chlorpheniramin* or chlorpheno or chlorphenon or Chlorpro or Chlorprophenpyridamine or chlorpyrimine or “Chlorspan 12” or Chlortab-4 or chlortrimeton or Chlor-Trimeton or chlortripolon or Chlor-Tripolon or Clorfenamina or Clorfeniramina or “cloro trimeton” or cloroalergan or Cloropiril or clorotrimeton or Cloro-Trimeton or C-Meton or cohistan or com-trimeton or Dehist or “dl-Chlorpheniramine maleate” or “Efidac 24” or clemastin* or meclastin* or neclastine or mecloprodin or tavist or tavegyl or “HS 592” or HS592 or cyproheptadine or adekin or Antergan or antisemin or “apeton 4” or astonin or “BRN 1685976” or “CCRIS 5232” or ciplactin or cipractin or ciproeptadine or Ciproheptadina or ciproral or ciprovit-a or cryoheptidine or crypoheptadine or cyheptine or cylat or cypraheptidine or “cypro h” or cyproatin or cyprogin or cyprohaptadi* or cypromin or cyprono or cyprosian or cytadine or Dihexazin or Dronactin or Eiproheptadine or ennamax or glocyp or heptasan or “HSDB 3048” or ifrasal or istam-far or klarivitina or kulinet or “MK 141” or nuran or Periact* or Peritol or petina or pilian or pronicy or sinapdin or trimetabol or Viternum or ketotifen* or ketotiphen* or zaditen or zaditor or “BRN 3983897” or “HC 20 511” or “hc 20511” or “HSDB 7283” or Prometh* or “3277 RP” or A-91033 or adgan or Allerfen or allergan or “Anergan 25” or “Anergan 50” or antiallersin or “antinaus 50” or Aprobit or Atosil or Avomine or baymethazine or Bonnox or "BRN 0088554" or Camergan or “CCRIS 5873” or “CCRIS 7056” or Closin or dimapp or Dimethylamino-isopropyl-phenthiazin or Diphergan or Diprasine or Diprazin* or diprozin or Dorme or Duplamin or Eusedon Mono or fargan or Farganesse or Fellozine or fenazil or fenazine or Fenergan or Fenetazin* or Frinova or Ganphen or Hibechin or hiberna or Histantil or Histargan or “HL 8700” or “HSDB 3173” or insomn-eze or Isophenergan or Isopromethazine or Kinetosin or lercigan or Lergigan or lergigan or "Lilly 01516" or “Lilly 1516” or Metaryl or “Mymethazine Fortis” or NCI-C60673 or “NSC 231688” or “NSC 30321” or Pelpica or pentazine or phargan or Phenadoz or Phenargan or Phencen or Phenergan or Phenerzine or phenoject-50 or Phensedyl or Pilothia or Pipolfen or Pipolphen* or Plletia or “pm 284” or Primine or Pro-50 or Proazamine or procit or promacot or Promantine or promazinamide or Prome or Promergan or Promesan or Promet or Prometazin or Prometazina or Promezathine or Promine or Proneurin or Prorex or protazine or Prothazin or Prothiazine or prothazine or provigan or Provigan or Pyrethia or Pyrethiazine or Remsed or Romergan or “rp 3277” or “rp 3389” or Rumergan or sayomol or “SKF 1498” or Soporil or tanidil or thiergan or “V GAN” or vallergine or “WY 509” or Zipan-25 or Zipan-50) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 18 | 11,147 | TS=((“H1” or “H2” or “H3” or “H4”) NEAR/2 (antagonist* or block*)) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 17 | 11,510 | TS=(histamine NEAR/3 (antagonist* or block*)) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 16 | 18,709 | TS=(anti-histamin* or antihistamin*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 15 | 29 | #14 AND #5 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 14 | 30,243 | #13 OR #12 OR #11 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 13 | 1961 | TS=((nasal or nose) NEAR/2 (spray* or mist or aerosol*)) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 12 | 1256 | TS=(decongestant* or decongestive*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 11 | 27,712 | TS=(xylometazolin* or Balkis or Chlorohist-LA or Decongest or espa-rhin or Gelonasal or Idasal or “Idril N” or Nasan or Imidin or NasenGel or NasenTropfen or NasenSpray or Novorin or Otradrops or Otraspray or Otrivin or Otriven* or Rapako or “schnupfen endrine” or Snup or stas or Amidrin or “Neo-Synephrine II” or Olynth or Otrivine or Rhinactin or “ba 11391” or ba11391 or "brn 0180524" or brufasol or “otrovin hcl” or servilaryn or tixycold or xylometarzoline or xylometazonolin* or xylomethazoline or xilometazolin* or zylometazoline or otrix or cirazolin* or “LD 3098” or naphazolin* or “Afazol Grin” or “AK Con” or AKCon or Albalon or albasol or “All Clear” or allersol or “alpha-Naphthylmethyl imidazoline” or antan or benil or "BRN 0151864" or cefasan or “Ciba 2020” or “Clear Eyes” or Clearine or coldan or “Colirio Alfa” or “comfort eye drops” or dazolin or “degest 2” or derinox or Idril or imidin or minha or Miraclar or mirafrin or Nafazair or Nafazolin* or “naphacel ofteno” or naphasal or Naphcon or “naphozoline hydrochloride” or naphtears or naphthazoline or naphthizine or naphthyzin or nastizol or “nazil ofteno” or niazol or ocu-zoline or opcon or Optazine or Privin* or Proculin or rhinantin or rhinazin or rhinoperd or rimidol or sanorin or sanotin or Siozwo or strictylon or “Tele Stulln” or TeleStulln or Vasoclear or Vasocon or “Vasoconstrictor Pensa” or VasoNit or vistalbalon or vistobalon or Oxymetazolin* or afrazine or afrin or atomol or bayfrin or "BRN 0886303" or dristan or drixine or “duramist plus” or “H 990” or Hazol or “HSDB 3143” or Iliadin or iliadine or Nafrine or nasivin or Navisin or Nezeril or nostrilla or ocuclear or Oximetazolin* or Oxylazine or Oxymethazoline or Rhinofrenol or rhinolitan or rhinosan or “sch 9384” or Sinerol or sinex or visine or Phenylephrin* or adrianol or af-taf or Ah-Chew or AI3-02402 or ak-dilate or “albalon relief” or alconefrin or almefrin or biomidrin or biomydrin or “CCRIS 8464” or derizene or despec-sf or “disneumon pernasal” or “dristan nasal mist” or drosin or efrin-10 or efrisel or fenylephrine or “HSDB 3383” or idrianol or isonefrine or isophrin or “isopto frin” or isoptofrin or “l meta synephrine” or lexatol or “m synephrine” or mesaton* or “meta sympathol” or “meta synephrine” or metaoxedrin* or Metasympatol or metasynephrine or Mezaton or m-Methylaminoethanolphenol or m-Oxedrine or m-Sympathol or m-Sympatol or m-Synephrine or mydfrin or nefrin-ofteno or “Neo Synephrine” or neofrin or neooxedrine or neophryn or neosynephrin or neosynephrine or neosynesin or neosynesine or ocu-phrin or oftan-metaoksedrin or op-isophrin or optistin or phenoptic or phenylefrine or phenylephedrine or prefrin or “pupiletto forte” or rectasol or “rhinall 10” or “slv 325” or slv325 or sucraphen or visadron or vistafrin or vistosan or Phenylpropanolamin* or acutrim or apodrine or apoephedrine or apophedrine or appedrine or “BRN 3196918” or descon or Dexatrim or dexatrim or “diet gard” or “dietac premeal” or “HSDB 6485” or kontexin or monydrin or Mucron or mydriatin or nobese or Norephedrine or “NSC 9920” or “phenyl propanolamine” or phenylpropanolamide or PPA or pressedrine or procol or Prolamine or propadine or propadrine or Propagest or Rhindecon or “Super Odrinex” or trimolet or Pseudoephedrin* or acunaso or afrinol or Besan or dimetapp or d-Isoephedrine or drixora or Ephedrine or “HSDB 3177” or Isoephedrine or isofedrine or isophedrine or “logicin plus” or monofed or nasa-12 or novafed or otrinol or “pseudo ephedrine” or pseudo-12 or Pseudoefedrina or pseudono or Psi-ephedrin or repedrina or rhinalair or “sch 4855” or sch4855 or sinumed or sinutab or subulin or Sudafed or sudomyl or sudosian or symptofed or tiptipot or Synephrin* or Sympaethamin* or Oxedrine or aetaphen or “asthma spray spofa” or pentedrine or vasoton or Analeptin or DL-Synephrine or Ethaphene or “NSC 166285” or “NSC 170956” or Parakorper or Parasympatol or “S 38537-9” or Simpalon or Simpatol or Sympathol or Sympatol or Synefrin or Synthenate or p-Hydroxyphenylmethylaminoethanol or p-Methylaminoethanolphenol or p-Oxedrine or p-Synephrine or tetrahydrozolin* or tetryzoline or Caltheon or “Collyrium Fresh” or “Diabenyl T” or Eye-Sine or Eye-Zine or “Murine Plus” or “Murine Sore Eyes” or Ophtalmin or “Optazine Fresh” or Optigene or Rhinopront or Tetra-Ide or Tetraclear or Tetrilin or Tyzine or Vasopos or Visine or Yxin or Vispring or “Berberil N” or "BRN 0011442" or “HSDB 7471” or Tetrizolin* or Tyzanol or clarine or insto or “murine tears” or murine-2 or nasan or nazane or nazine or “necor tyzine” or octilia or ophthalmin-n or opsil-a or optizoline or rhinoprout or “stilla drops” or visina or visolin or brompheniramine or Bromfed or Lodrane or Dimetapp) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 10 | 68 | #9 AND #5 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 9 | 870,116 | #8 OR #7 OR #6 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 8 | 119,071 | TS=(fluticason* or flixonase or flonase or flovent or cultivate or flixotide or atemur or axotide or beconase or “cci 18781” or cci18781 or cutivat* or flixovate or flunase or fluspiral or flutide or flutinase or flutivate or fluxonal or “gr 18781” or “gr18781” or zoflut or budeson* or pulmicort or horacort or rhinocort or bidien or budecort or budicort or “CCRIS 5230” or cortivent or entocort or micronyl or noex or preferid or respules or rhinosol or spirocort or symbicort or uceris or mometason* or “sch 32088” or nasonex or rinelon or elocon or allermax aqueous or asmanex or danitin or dermotasone or dermovel or ecural or elica or elocom or elocone or elocyn or elomet or elosalic or eloson or flumeta or mefurosan or metaspray or momate or mometAid or monovel or morecort or motaderm or nosorex or novasone or propel or rimelon or rivelon or uniclar or “triamcinolone acetonide” or tricinolon or cinonide or kenalog or azmacort or kenacort or acetospan or “adcortyl A” or allerNaze or aristocort or aristoderm or aristogel or “CCRIS 5231” or coupe-A or flutex or flutone or kenalone or “NSC 21916” or nasacort or “omcilon A” or oracort or oralone or polcortolon or rineton or solodelf or tramacin or tri-nasal or triacet* or triacort or triam-Injekt or triamonide or trianex or triatex or triderm or triesence or trivaris or trymex or “volon A2” or dexameth* or adrenocot or aflucoson* or alfalyl or Anaflogistico or Aphtasolon or arcodexan* or artrosone or Auxiron or Azium or bidexol or “Bisu DS” or Calonat or “CCRIS 7067” or cebedex or cetadexon or colofoam or corsona or Corsone or cortastat or cortidex* or cortidron* or Cortisumman or “dacortina fuerte” or “dacortine fuerte” or dalalone or danasone or Decacortin or decadeltoson* or Decaderm or decadion or decadran or decadron* or decaesadril or Decagel or decaject or Decalix or decameth or Decasone or decaspray or decasterolone or decdan or decilone or decofluor or Dectancyl or Dekacort or delladec or deltafluoren* or Dergramin or Deronil or desacort or desacortone or Desadrene or desalark or desameton* or Deseronil or desigdron or “dexa cortisyl” or “dexa dabrosan” or “dexa korti” or “Dexa Mamallet” or “dexa scherosan” or “dexa scherozon*” or Dexacort* or Dexa-Cort* or dexadabroson or dexadecadrol or Dexadeltone or dexadrol or Dexafarma or dexagel or dexagen or dexahelvacort or dexakorti or dexalien or dexalocal or Dexalona or dexame* or Dexametasona or dexan or dexane or dexano or Dexapolcort or Dexapos or dexapot or Dexaprol or dexascheroson or Dexa-Scheroson or dexascherozon* or Dexa-sine or Dexason* or Dex-ide or Dexinolon or Dexinoral or dexionil or dexona or Dexone or dexpak or Dextelan or dextrasone or Dezone or dibasona or Dinormon or doxamethasone or esacortene or exadion* or firmalone or “fluormethyl prednisolon*” or fluormethylprednisolon* or Fluormone or Fluorocort or fluorodelta or Fortecortin or Gammacorte* or grosodexon* or hexadecadiol or hexadecadrol or hexadiol or hexadrol or “Isopto Dex” or “isopto maxidex” or isoptodex or isoptomaxidex or “Lokalison F” or Loverine or Luxazone or marvidione or maxidex or Mediamethasone or megacortin or mephameson* or metasolon* or methazon* ion or methazonion* or “metisone lafi” or mexasone or Mexidex or millicorten* or Mymethasone or nisomethasona or novocort or “NSC 34521” or “nsc34521” or Ocu-trol or oftan-dexa or opticorten or opticortinol or oradexan or oradexon* or orgadrone or Ozurdex or pidexon or Policort or “Prednisolon F” or prodexon* or sanamethasone or santenson or santeson or sawasone or solurex or spoloven or sterasone or thilodexine or triamcimetil or vexamet or visumetazone or visumethazone or adrecort or Aeroseb or dexacen or isnacort or methylfluorprednisolone or posurdex or beclomet* or aerobec or afifon or Alanase or Aldecin* or anceron or apo-beclomethasone or ascocortonyl or “asmabec clickhaler” or Atomase or atomide or beceze or Beclacin or beclamet or beclate or Beclazone or “beclo asma” or “beclo AZU” or “beclo rhino” or becloasma or beclocort or becloforte or beclojet or beclone or beclorhinol or beclosol or beclotaide or becloturmant or becloturmat or beclovent or becodisk* or beconase or beconasol or becotide or belax or bemedrex or Benconase or bronchocort or bronconox or “chf 1514” or “chf1514” or Clenil or decomit or ecobec or Entyderma or filair or Inalone or junik or Korbutone or Menaderm or miflasone or nasobec aqueous or nexxair or nobec or orbec or prolair or propaderm or qvar or ratioallerg or respocort or rhinivict or “Rhino Clenil” or Rhinosol or rinaze or rynconox or sanasthmax or sanasthmyl or "sbn 024" or sbn024 or “Sch 18020W” or Turbinal or vancenase or vanceril or ventolair or viarex or viarin or Viaro or xiten or betamethasone or betamethason or betnesol or bentelan or rinderon* or “celestone phosphate” or “beta corlan” or “beta methasone” or betam-ophtal or diprospan or durabetason or etnesol or inflacor or linolosal or linosal or “NSC 90616” or solucelestan or apo-flunisolide or inhacort or nasalide or ratio-flunisolide or rhinalar or RS-3999 or syntaris or aeroBid or nasarel or aerospan or bronalide or cyntaris or flunitec or flunisolid* or gibiflu or locasyn or lokilan or lunibron-a or lunis or nisolid or rs3999 or sanergal or soluzione or synaclyn or “val 679” or val679 or prednison* or Adasone or ancortone or Apo-Prednisone or biocortone or Cartancyl or “CCRIS 2646” or colisone or Cortan or Cortancyl or cortidelt or cortiprex or Cotone or Cutason or dacorten or Dacortin or “de cortisyl” or decortancyl or decortin* or Decortisyl or Dehydrocortisone or dekortin or delitisone or dellacort or “delta cortelan” or “delta Cortisone” or “delta dome” or “delta e” or “delta prenovis” or delta-1-Cortisone or delta-1-Dehydrocortisone or deltacort* or delta-dome or Deltasone or deltison* or deltra or “di adreson” or diadreson or drazone or Econosone or Encorton* or Enkortolon or enkorton or fernisone or Fiasone or hostacortin or “HSDB 3168” or Incocortyl or insone or “IN Sone” or Juvason or Kortancyl or “Liquid Pred” or Lisacort or lodotra or Lodtra or me-korti or meprison or metacortandracin or Meticorten or meticortine or NCI-C04897 or nisona or Nizon or Novoprednisone or “nsc 10023” or nsc10023 or Nurison or Orasone or orisane or Panafcort or Panasol or paracort or Parmenison or pehacort or precort or precortal or “Predni Tablinen” or prednicen-m or prednicorm or Prednicort or prednicot or Prednidib or Prednilonga or Predniment or prednitone or Prednizon or Prednovister or Presone or pronison or Pronisone or pronizone or pulmison or Rectodelt or Retrocortine or servisone or SK-Prednisone or steerometz or Sterapred or Supercortil or “U 6020” or Ultracorten* or urtilone or Winpred or Wojtab or Zenadrid or methylprednisolon* or adlone-40 or adlone-80 or A-Methapred or Artisone-wyeth or Besonia or “BRN 2340300” or “dep medalone 80” or depmedalone or depoject-80 or Depo-Medrol or depopred or Dopomedrol or esametone or firmacort or “HSDB 3127” or Lemod or Medesone or medixon or med-jec-40 or “Medlone 21” or mednin or “medralone 80” or medrate or Medrol or medrone or meprednisolone or mesopren or Metastab or “methacort 40” or “methacort 80” or methylcotol or methylcotolone or Methyleneprednisolone or “methylpred dp” or methylsterolone or metidrol or Metilbetasone or Metilprednisolon* or Metipred or metrisone or Metrocort or metycortin or metypred or metypresol or Metysolon or Moderin or neomedrone or Nirypan or Noretona or “nsc 19987” or nsc19987 or “Predni N Tablinen” or prednol or Promacortine or Reactenol or Sieropresol or solomet or “solu decortin” or Solu-medrol or Summicort or Suprametil or “U 7532” or “U-67 590A” or Urbason or Urbasone or Wyacort or Prednisolon* or adelcort or antisolon or antisolone or aprednislon or aprednislone or benisolon or benisolone or berisolon or berisolone or “BRN 1354103” or Bubbli-Pred or caberdelta or capsoid or “CCRIS 980” or “co hydeltra” or codelcortone or CO-Hydeltra or compresolon or Cordrol or cortadeltona or cortadeltone or cortalone or cortelinter or cortisolone or Cotogesic or cotolone or dacrotin or ecaprednil or decortril or “dehydro cortex” or “dehydro hydrocortisone” or dehydrocortex or dehydrocortisol or dehydrocortisole or dehydrohydrocortison or dehydrohydrocortisone or delcortol or “delta cortef” or “delta cortril” or “delta ef cortelan” or “delta f” or “delta hycortol” or “delta hydrocortisone” or “delta ophticor” or “delta stab” or “delta1 dehydrocortisol” or “delta1 dehydrohydrocortisone” or “delta1 hydrocortisone” or deltacortef or delta-cortef or Deltacortenol or deltacortenolo or deltacortil or deltacortoil or deltacortril or deltaderm or delta-Ef-Cortelan or deltaglycortril or deltahycortol or deltahydrocortison or deltahydrocortisone or deltaophticor or deltasolone or deltastab or deltidrosol or deltisilone or deltisolon or deltisolone or deltolasson or deltolassone or deltosona or deltosone or depo-predate or dermosolon or “Derpo PD” or Dexa-Cortidelt or “hostacortin H” or dhasolone or “diadresone f” or DiAdresonF or dicortol or domucortone or Donisolone or Dydeltrone or “Eazolin D” or encortelon or encortelone or encortolon or Erbacort or Erbasona or Estilsona or Fernisolone or glistelone or hefasolon or “HSDB 3385” or hydeltra or hydeltrone or hydrelta or hydrocortancyl or hydrocortidelt or hydrodeltalone or hydrodeltisone or hydroretrocortin or hydroretrocortine or inflanefran or insolone or “K 1557” or keteocort or key-pred or lenisolone or Lentosone or leocortol or liquipred or “lygal kopftinktur” or mediasolone or meprisolon or meprisolone or metacortalon or metacortalone or metacortandralon or metacortandralone or metacortelone or “meti derm” or meticortelone or metiderm or morlone or mydrapred or “neo delta” or nisolon or nisolone or “nsc 9120” or nsc9120 or opredsone or Orapred or panafcortelone or panafort or paracortol or Paracotol or Pediapred or phlogex or PRDL or “pre cortisyl” or preconin or precortalon or precortancyl or Precortilon or precortisyl or “predacort 50” or predaject-50 or “predalone 50” or predartrina or predartrine or Predate or predeltilone or predisole or predisyr or pred-ject-50 or “predne dome” or prednecort or prednedome or Predne-Dome or prednelan or “predni coelin” or “predni h tablinen” or Prednicen or prednicoelin or prednicortelone or “prednifor drops” or predni-helvacort or Predniliderm or predniment or predniretard or prednis or prednisil or prednivet or prednorsolon or prednorsolone or Predonin or Predonine or predorgasolona or predorgasolone or prelon or prelone or prenilone or prenin or prenolone or preventan or prezolon or Rolisone or rubycort or scherisolon or scherisolona or serilone or solondo or solone or solupren or soluprene or spiricort or spolotane or Steran or sterane or sterolone or supercortisol or supercortizol or taracortelone or Ulacort or walesolone or wysolone) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 7 | 840,233 | TS=(corticosteroid* or “cortico steroid*” or corticoid* or steroid* or glucocorticoid* or “anti inflam*” or antiinflam*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 6 | 494 | TS=(“adrenal cort*” NEAR/2 hormone*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 5 | 2034 | #1 or #2 or #3 or #4 Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 4 | 527 | TS=(middle-ear NEAR/3 pressure*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 3 | 85 | TS=(middle-ear NEAR/3 dysfunction*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 2 | 73 | TS=(eustachian NEAR/2 (canal or orifice*)) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 1 | 1635 | TS=((eustachian or auditory or pharyngotympanic) NEAR/3 tub*) Databases=BIOSIS Previews Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
Key
TS = topic tag; searches terms in title, abstract, author keywords and keywords plus fields
* = truncation
“ “ = phrase search
NEAR/3 = terms with 3 words of each other
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials via Wiley: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/
Issue 9 of 12, September 2012.
Search date: 8 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 106.
ID Search
#1 MeSH descriptor: [Eustachian Tube] this term only
#2 ((eustachian or auditory or pharyngotympanic) near/3 tub*):ti,ab,kw
#3 (eustachian near/2 (canal or orifice*)):ti,ab,kw
#4 ((middle next ear) near/3 pressure*):ti,ab,kw
#5 ((middle next ear) near/3 dysfunction*):ti,ab,kw
#6 #1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5
Key
MeSH descriptor = indexing term (MeSH heading)
* = truncation
:ti,ab,kw = terms in either title or abstract or keyword fields
NEAR/2 = terms within two words of each other (any order)
NEXT = terms are next to each other
“ “ = phrase search
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews via Wiley: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/
Issue 9 of 12, September 2012.
Search date: 8 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 2.
See above under CENTRAL for search strategy used.
Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Healthcare via EBSCO: www.EBSCO.com/
Inception to 28 September 2012.
Search date: 8 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 369.
| # | Query | Results |
|---|---|---|
| S6 | S1 or S2 or S3 or S4 or S5 | 369 |
| S5 | TI ((“middle ear” or middle-ear) N3 pressure*) OR AB ((“middle ear” or middle-ear) N3 pressure*) | 86 |
| S4 | TI ((“middle ear” or middle-ear) N3 dysfunction*) OR AB ((“middle ear” or middle-ear) N3 dysfunction*) | 24 |
| S3 | TI (eustachian N2 (canal or orifice*)) OR AB (eustachian N2 (canal or orifice*)) | 7 |
| S2 | TI ((eustachian or auditory or pharyngotympanic) N3 tub*) OR AB ((eustachian or auditory or pharyngotympanic) N3 tub*) | 211 |
| S | (MH “Eustachian Tube”) | 222 |
Key
MH = indexing term (CINAHL heading)
* = truncation
TI = words in the title
AB = words in the abstract
“ “ = phrase search
N2 = terms within two words of each other (any order)
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effect via Wiley: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/
Issue 3 of 4, July 2012.
Records retrieved: 0.
See above under CENTRAL for search strategy used.
Dissertation Abstracts via Dialog: www.dialog.com/
1861 to August 2012.
Searched on 5 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 53.
| Set | Items | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 27 | (EUSTACHIAN OR AUDITORY OR PHARYNGOTYMPANIC)(3W)TUB?/TI,AB,DE |
| 2 | 0 | EUSTACHIAN(2W)(CANAL OR ORIFICE?)/TI,AB,DE |
| 3 | 8 | MIDDLE(W)EAR(3W)DYSFUNCTION?/TI,AB,DE |
| 4 | 24 | MIDDLE(W)EAR(3W)PRESSURE?/TI,AB,DE |
| 5 | 53 | S1:S4 |
Key
? = truncation
/TI,AB,DE = terms in title, abstract, or descriptor fields
(W) = terms adjacent to each other (same order)
(2W) = terms within 2 words of each other (same order)
S1:S4 = S1 OR S2 OR S3 OR S4
EMBASE via OvidSP: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/
1974 to week 5, October 2012.
Searched on 8 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 1849.
-
auditory tube/ (3102)
-
auditory tube dysfunction/ (736)
-
middle ear pressure/ (649)
-
((eustachian or auditory or pharyngotympanic) adj3 tub$).ti,ab. (3590)
-
(eustachian adj2 (canal or orifice$)).ti,ab. (77)
-
(middle ear adj3 dysfunction$).ti,ab. (137)
-
(middle ear adj3 pressure$).ti,ab. (992)
-
or/1-7 (5666)
-
exp steroid/ (1,090,248)
-
exp antiinflammatory agent/ (1,120,613)
-
(adrenal cort$ adj2 hormone$).ti,ab. (864)
-
(corticosteroid$ or cortico steroid$ or corticoid$).ti,ab. (101,335)
-
steroid$.ti,ab. (217,679)
-
glucocorticoid$.ti,ab. (58,069)
-
(anti inflam$ or antiinflam$).ti,ab. (122,004)
-
(fluticason$ or flixonase or flonase or flovent or cultivate or flixotide or atemur or axotide or beconase or cci 18781 or cci18781 or cutivat$ or flixovate or flunase or fluspiral or flutide or flutinase or flutivate or fluxonal or gr 18781 or gr18781 or zoflut).ti,ab,rn. (12,301)
-
(budeson$ or pulmicort or horacort or rhinocort or bidien or budecort or budicort or CCRIS 5230 or cortivent or entocort or micronyl or noex or preferid or respules or rhinosol or spirocort or symbicort or uceris).ti,ab,rn. (14,488)
-
(mometason$ or sch 32088 or nasonex or rinelon or elocon or allermax aqueous or asmanex or danitin or dermotasone or dermovel or ecural or elica or elocom or elocone or elocyn or elomet or elosalic or eloson or flumeta or mefurosan or metaspray or momate or mometAid or monovel or morecort or motaderm or nosorex or novasone or propel or rimelon or rivelon or uniclar).ti,ab,rn. (4448)
-
(triamcinolone acetonide or tricinolon or cinonide or kenalog or azmacort or kenacort or acetospan or adcortyl A or allerNaze or aristocort or aristoderm or aristogel or CCRIS 5231 or coupe-A or flutex or flutone or kenalone or NSC 21916 or nasacort or omcilon A or oracort or oralone or polcortolon or rineton or solodelf or tramacin or tri-nasal or triacet$ or triacort or triam-Injekt or triamonide or trianex or triatex or triderm or triesence or trivaris or trymex or volon A).ti,ab,rn. (14,831)
-
(dexameth$ or adrenocot or aflucoson$ or alfalyl or Anaflogistico or Aphtasolon or arcodexan$ or artrosone or Auxiron or Azium or bidexol or Bisu DS or Calonat or CCRIS 7067 or cebedex or cetadexon or colofoam or corsona or Corsone or cortastat or cortidex$ or cortidron$ or Cortisumman or dacortina fuerte or dacortine fuerte or dalalone or danasone or Decacortin or decadeltoson$ or Decaderm or decadion or decadran or decadron$ or decaesadril or Decagel or decaject or Decalix or decameth or Decasone or decaspray or decasterolone or decdan or decilone or decofluor or Dectancyl or Dekacort or delladec or deltafluoren$ or Dergramin or Deronil).ti,ab,rn. (112,780)
-
(desacort or desacortone or Desadrene or desalark or desameton$ or Deseronil or desigdron or dexa cortisyl or dexa dabrosan or dexa korti or Dexa Mamallet or dexa scherosan or dexa scherozon$ or Dexacort$ or Dexa-Cort$ or dexadabroson or dexadecadrol or Dexadeltone or dexadrol or Dexafarma or dexagel or dexagen or dexahelvacort or dexakorti or dexalien or dexalocal or Dexalona or dexame$ or Dexametasona or dexan or dexane or dexano or Dexapolcort or Dexapos or dexapot or Dexaprol or dexascheroson or Dexa-Scheroson or dexascherozon$ or Dexa-sine or Dexason$ or Dex-ide or Dexinolon or Dexinoral or dexionil or dexona or Dexone or dexpak or Dextelan).ti,ab,rn. (112,287)
-
(dextrasone or Dezone or dibasona or Dinormon or doxamethasone or esacortene or exadion$ or firmalone or fluormethyl prednisolon$ or fluormethylprednisolon$ or Fluormone or Fluorocort or fluorodelta or Fortecortin or Gammacorte$ or grosodexon$ or hexadecadiol or hexadecadrol or hexadiol or hexadrol or Isopto Dex or isopto maxidex or isoptodex or isoptomaxidex or Lokalison F or Loverine or Luxazone or marvidione or maxidex or Mediamethasone or megacortin or mephameson$ or metasolon$ or methazon$ ion or methazonion$ or metisone lafi or mexasone or Mexidex or millicorten$ or Mymethasone or nisomethasona or novocort or NSC 34521 or nsc34521).ti,ab,rn. (86)
-
(Ocu-trol or oftan-dexa or opticorten or opticortinol or oradexan or oradexon$ or orgadrone or Ozurdex or pidexon or Policort or Prednisolon F or prodexon$ or sanamethasone or santenson or santeson or sawasone or solurex or spoloven or sterasone or thilodexine or triamcimetil or vexamet or visumetazone or visumethazone or adrecort or Aeroseb or dexacen or isnacort or methylfluorprednisolone or posurdex).ti,ab,rn. (49)
-
(beclomet$ or aerobec or afifon or Alanase or Aldecin$ or anceron or apo-beclomethasone or ascocortonyl or asmabec clickhaler or Atomase or atomide or beceze or Beclacin or beclamet or beclate or Beclazone or beclo asma or beclo AZU or beclo rhino or becloasma or beclocort or becloforte or beclojet or beclone or beclorhinol or beclosol or beclotaide or becloturmant or becloturmat or beclovent or becodisk$ or beconase or beconasol or becotide or belax or bemedrex).ti,ab,rn. (12,486)
-
(Benconase or bronchocort or bronconox or chf 1514 or chf1514 or Clenil or decomit or ecobec or Entyderma or filair or Inalone or junik or Korbutone or Menaderm or miflasone or nasobec aqueous or nexxair or nobec or orbec or prolair or propaderm or qvar or ratioallerg or respocort or rhinivict or Rhino Clenil or Rhinosol or rinaze or rynconox or sanasthmax or sanasthmyl or “sbn 024” or sbn024 or Sch 18020W or Turbinal or vancenase or vanceril or ventolair or viarex or viarin or Viaro or xiten).ti,ab,rn. (208)
-
(betamethasone or betamethason or betnesol or bentelan or rinderon$ or celestone phosphate or beta corlan or beta methasone or betam-ophtal or diprospan or durabetason or etnesol or inflacor or linolosal or linosal or NSC 90616 or solucelestan).ti,ab,rn. (14,841)
-
(apo-flunisolide or inhacort or nasalide or ratio-flunisolide or rhinalar or RS-3999 or syntaris or aeroBid or nasarel or aerospan or bronalide or cyntaris or flunitec or flunisolid$ or gibiflu or locasyn or lokilan or lunibron-a or lunis or nisolid or rs3999 or sanergal or soluzione or synaclyn or val 679 or val679).ti,ab,rn. (2227)
-
(prednison$ or Adasone or ancortone or Apo-Prednisone or biocortone or Cartancyl or CCRIS 2646 or colisone or Cortan or Cortancyl or cortidelt or cortiprex or Cotone or Cutason or dacorten or Dacortin or de cortisyl or decortancyl or decortin$ or Decortisyl or Dehydrocortisone or dekortin or delitisone or dellacort or delta cortelan or delta Cortisone or delta dome or delta e or delta prenovis or delta-1-Cortisone or delta-1-Dehydrocortisone or deltacort$ or delta-dome or Deltasone or deltison$ or deltra or di adreson or diadreson or drazone or Econosone or Encorton$).ti,ab,rn. (128,418)
-
(Enkortolon or enkorton or fernisone or Fiasone or hostacortin or HSDB 3168 or Incocortyl or insone or IN Sone or Juvason or Kortancyl or Liquid Pred or Lisacort or lodotra or Lodtra or me-korti or meprison or metacortandracin or Meticorten or meticortine or NCI-C04897 or nisona or Nizon or Novoprednisone or nsc 10023 or nsc10023 or Nurison or Orasone or orisane or Panafcort or Panasol or paracort or Parmenison or pehacort or precort or precortal).ti,ab,rn. (134)
-
(Predni Tablinen or prednicen-m or prednicorm or Prednicort or prednicot or Prednidib or Prednilonga or Predniment or prednitone or Prednizon or Prednovister or Presone or pronison or Pronisone or pronizone or pulmison or Rectodelt or Retrocortine or servisone or SK-Prednisone or steerometz or Sterapred or Supercortil or U 6020 or Ultracorten$ or urtilone or Winpred or Wojtab or Zenadrid).ti,ab,rn. (66)
-
(methylprednisolon$ or adlone-40 or adlone-80 or A-Methapred or Artisone-wyeth or Besonia or BRN 2340300 or dep medalone 80 or depmedalone or depoject-80 or Depo-Medrol or depopred or Dopomedrol or esametone or firmacort or HSDB 3127 or Lemod or Medesone or medixon or med-jec-40 or Medlone 21 or mednin or medralone 80 or medrate or Medrol or medrone or meprednisolone or mesopren or Metastab or methacort 40 or methacort 80 or methylcotol or methylcotolone or Methyleneprednisolone or methylpred dp or methylsterolone or metidrol).ti,ab,rn. (68,350)
-
(Metilbetasone or Metilprednisolon$ or Metipred or metrisone or Metrocort or metycortin or metypred or metypresol or Metysolon or Moderin or neomedrone or Nirypan or Noretona or nsc 19987 or nsc19987 or Predni N Tablinen or prednol or Promacortine or Reactenol or Sieropresol or solomet or solu decortin or Solu-medrol or Summicort or Suprametil or U 7532 or U-67 590A or Urbason or Urbasone or Wyacort).ti,ab,rn. (347)
-
(Prednisolon$ or adelcort or antisolon or antisolone or aprednislon or aprednislone or benisolon or benisolone or berisolon or berisolone or BRN 1354103 or Bubbli-Pred or caberdelta or capsoid or CCRIS 980 or co hydeltra or codelcortone or CO-Hydeltra or compresolon or Cordrol or cortadeltona or cortadeltone or cortalone or cortelinter or cortisolone or Cotogesic or cotolone or dacrotin or ecaprednil or decortril or dehydro cortex or dehydro hydrocortisone or dehydro hydrocortisone or dehydrocortex or dehydrocortisol or dehydrocortisole or dehydrohydrocortison).ti,ab,rn. (96,870)
-
(dehydrohydrocortisone or delcortol or delta cortef or delta cortril or delta ef cortelan or delta f or delta hycortol or delta hydrocortisone or delta hydrocortisone or delta ophticor or delta stab or delta1 dehydrocortisol or delta1 dehydrohydrocortisone or delta1 hydrocortisone or deltacortef or delta-cortef or Deltacortenol or deltacortenolo or deltacortil or deltacortoil or deltacortril or deltaderm or delta-Ef-Cortelan or deltaglycortril or deltahycortol or deltahydrocortison or deltahydrocortisone or deltaophticor or deltasolone or deltastab or deltidrosol or deltisilone).ti,ab,rn. (179)
-
(deltisolon or deltisolone or deltolasson or deltolassone or deltosona or deltosone or depo-predate or dermosolon or Derpo PD or Dexa-Cortidelt or hostacortin H or dhasolone or diadresone f or DiAdresonF or dicortol or domucortone or Donisolone or Dydeltrone or Eazolin D or encortelon or encortelone or encortolon or Erbacort or Erbasona or Estilsona or Fernisolone or glistelone or hefasolon or HSDB 3385 or hydeltra or hydeltrone or hydrelta or hydrocortancyl or hydrocortidelt or hydrodeltalone or hydrodeltisone or hydroretrocortin or hydroretrocortine or inflanefran).ti,ab,rn. (25)
-
(insolone or K 1557 or keteocort or key-pred or lenisolone or Lentosone or leocortol or liquipred or lygal kopftinktur or mediasolone or meprisolon or meprisolone or metacortalon or metacortalone or metacortandralon or metacortandralone or metacortelone or meti derm or meticortelone or metiderm or meti derm or morlone or mydrapred or neo delta or nisolon or nisolone or nsc 9120 or nsc9120 or opredsone or Orapred or panafcortelone or panafort or paracortol or Paracotol or Pediapred or phlogex or PRDL or pre cortisyl).ti,ab,rn. (62)
-
(preconin or precortalon or precortancyl or Precortilon or precortisyl or predacort 50 or predaject-50 or predalone 50 or predartrina or predartrine or Predate or predeltilone or predisole or predisyr or pred-ject-50 or predne dome or prednecort or prednedome or Predne-Dome or prednelan or predni coelin or predni h tablinen or Prednicen or prednicoelin or prednicortelone or prednifor drops or predni-helvacort or Predniliderm or predniment or predniretard or prednis or prednisil or prednivet or prednorsolon or prednorsolone or Predonin or Predonine or predorgasolona or predorgasolone).ti,ab,rn. (87,742)
-
(prelon or prelone or prenilone or prenin or prenolone or preventan or prezolon or Rolisone or rubycort or scherisolon or scherisolona or serilone or solondo or solone or solupren or soluprene or spiricort or spolotane or Steran or sterane or sterolone or supercortisol or supercortizol or taracortelone or Ulacort or walesolone or wysolone).ti,ab,rn. (89)
-
or/9-38 (1,806,878)
-
8 and 39 (275)
-
exp decongestive agent/ (90,821)
-
cirazoline/ (666)
-
oxedrine/ (663)
-
(xylometazolin$ or Balkis or Chlorohist-LA or Decongest or espa-rhin or Gelonasal or Idasal or Idril N or Nasan or Imidin or NasenGel or NasenTropfen or NasenSpray or Novorin or Otradrops or Otraspray or Otrivin or Otriven$ or Rapako or schnupfen endrine or Snup or stas or Amidrin or Neo-Synephrine II or Olynth or Otrivine or Rhinactin or ba 11391 or ba11391 or “brn 0180524” or brufasol or otrovin hcl or servilaryn or tixycold or xylometarzoline or xylometazonolin$ or xylomethazoline or xilometazolin$ or zylometazoline or otrix).ti,ab,rn. (1340)
-
(cirazolin$ or LD 3098).ti,ab,rn. (728)
-
(naphazolin$ or Afazol Grin or AK Con or AKCon or Albalon or albasol or All Clear or allersol or alpha-Naphthylmethyl imidazoline or antan or benil or “BRN 0151864” or cefasan or Ciba 2020 or Clear Eyes or Clearine or coldan or Colirio Alfa or comfort eye drops or dazolin or degest 2 or derinox or Idril or imidin or minha or Miraclar or mirafrin or Nafazair or Nafazolin$ or naphacel ofteno or naphasal or Naphcon or naphozoline hydrochloride or naphtears or naphthazoline or naphthizine).ti,ab,rn. (1761)
-
(naphthyzin or nastizol or nazil ofteno or niazol or ocu-zoline or opcon or Optazine or Privin$ or Proculin or rhinantin or rhinazin or rhinoperd or rimidol or sanorin or sanotin or Siozwo or strictylon or Tele Stulln or TeleStulln or Vasoclear or Vasocon or Vasoconstrictor Pensa or VasoNit or vistalbalon or vistobalon).ti,ab,rn. (115)
-
(Oxymetazolin$ or afrazine or afrin or atomol or bayfrin or “BRN 0886303” or dristan or drixine or duramist plus or H 990 or Hazol or HSDB 3143 or Iliadin or iliadine or Nafrine or nasivin or Navisin or Nezeril or nostrilla or ocuclear or Oximetazolin$ or Oxylazine or Oxymethazoline or Rhinofrenol or rhinolitan or rhinosan or sch 9384 or Sinerol or sinex long last or sinex or visine).ti,ab,rn. (2646)
-
(Phenylephrin$ or adrianol or af-taf or Ah-Chew or AI3-02402 or ak-dilate or albalon relief or alconefrin or almefrin or biomidrin or biomydrin or CCRIS 8464 or derizene or despec-sf or disneumon pernasal or dristan nasal mist or drosin or efrin-10 or efrisel or fenylephrine or HSDB 3383 or idrianol or isonefrine or isophrin or isopto frin or isoptofrin or l meta synephrine or lexatol or m synephrine or mesaton$ or meta sympathol or meta synephrine or metaoxedrin$).ti,ab,rn. (31,213)
-
(Metasympatol or metasynephrine or Mezaton or m-Methylaminoethanolphenol or m-Oxedrine or m-Sympathol or m-Sympatol or m-Synephrine or mydfrin or nefrin-ofteno or Neo Synephrine or neofrin or neooxedrine or neophryn or neosynephrin or neosynephrine or neosynesin or neosynesine or ocu-phrin or oftan-metaoksedrin or op-isophrin or optistin or phenoptic or phenylefrine or phenylephedrine or prefrin or pupiletto forte or rectasol or rhinall 10 or slv 325 or slv325 or sucraphen or visadron or vistafrin or vistosan).ti,ab,rn. (243)
-
(Phenylpropanolamin$ or acutrim or apodrine or apoephedrine or apophedrine or appedrine or BRN 3196918 or descon or Dexatrim or dexatrim or diet gard or dietac premeal or HSDB 6485 or kontexin or monydrin or Mucron or mydriatin or nobese or Norephedrine or NSC 9920 or phenyl propanolamine or phenylpropanolamide or PPA or pressedrine or procol or Prolamine or propadine or propadrine or Propagest or Rhindecon or Super Odrinex or trimolet).ti,ab,rn. (7117)
-
(Pseudoephedrin$ or acunaso or afrinol or Besan or dimetapp or d-Isoephedrine or drixora or Ephedrine or HSDB 3177 or Isoephedrine or isofedrine or isophedrine or logicin plus or monofed or nasa-12 or novafed or otrinol or pseudo ephedrine or pseudo-12 or Pseudoefedrina or pseudono or Psi-ephedrin or repedrina or rhinalair or sch 4855 or sch4855 or sinumed or sinutab or subulin or Sudafed or sudomyl or sudosian or symptofed or tiptipot).ti,ab,rn. (15,192)
-
(Synephrin$ or Sympaethamin$ or Oxedrine or aetaphen or asthma spray spofa or pentedrine or vasoton or Analeptin or DL-Synephrine or Ethaphene or NSC 166285 or NSC 170956 or Parakorper or Parasympatol or S 38537-9 or Simpalon or Simpatol or Sympathol or Sympatol or Synefrin or Synthenate or p-Hydroxyphenylmethylaminoethanol or p-Methylaminoethanolphenol or p-Oxedrine or p-Synephrine).ti,ab,rn. (814)
-
(tetrahydrozolin$ or tetryzoline or Caltheon or Collyrium Fresh or Diabenyl T or Eye-Sine or Eye-Zine or Murine Plus or Murine Sore Eyes or Ophtalmin or Optazine Fresh or Optigene or Rhinopront or Tetra-Ide or Tetraclear or Tetrilin or Tyzine or Vasopos or Visine or Yxin or Vispring or Berberil N or “BRN 0011442” or HSDB 7471 or Tetrizolin$ or Tyzanol or clarine or insto or murine tears or murine-2 or nasan or nazane or nazine or necor tyzine or octilia or ophthalmin-n or opsil-a or optizoline or rhinoprout or stilla drops or visina or visolin).ti,ab,rn. (553)
-
(brompheniramine or Bromfed or Lodrane or Dimetapp).ti,ab,rn. (1081)
-
(decongestant$ or decongestive$).ti,ab. (1953)
-
((nasal or nose) adj2 (spray$ or mist or aerosol$)).ti,ab. (3331)
-
or/41-57 (102,618)
-
8 and 58 (156)
-
exp antihistaminic agent/ (164,435)
-
(anti histamin$ or antihistamin$).ti,ab. (15,317)
-
(histamine adj3 (antagonist$ or block$)).ti,ab. (8134)
-
((H1 or H2 or H3 or H4) adj2 (antagonist$ or block$)).ti,ab. (15,633)
-
(acrivastin$ or semprex or semprex-D or benadryl or prolert or BW 825C or BW825C or BW A825C).ti,ab,rn. (736)
-
(bilastine or bilaxten or f 96221 bm1 or f96221 bm1).ti,ab,rn. (53)
-
(Cetirizin$ or acidrine or adezio or agelmin or Alercet or Alergex or Alerid or Alerlisin or Alertisin or alertop or alerviden or aletir or alled or Allergy relief or Alleroff or allertec or alltec or alzytec or Apo-Cetirizine or betarhin or cerazine or cerini or cerotec or cesta or Cetalerg or Ceterifug or cethis or Ceti TAD or Cetiderm or Cetidura or Cetil von ct or CetiLich or cetimin or cetin or Ceti-Puren or cetirax or Cetirigamma or cetirin or Cetirlan or cetizin or Cetriler or cetrimed or Cetrine or cetrizet or cetrizin or Cetryn or cetymin or Cetzine or Cezin or cistamine or deallergy or falergi or finallerg or Formistin or histazine or histica or Hitrizin or HSDB 7739).ti,ab,rn. (5508)
-
(incidal-od or lergium or nosemin or nosmin or ozen or “P 071” or P071 or prixlae or razene or Reactine or Ressital or rhizin or risima or Riztec or ryvel or Ryzen or Salvalerg or sancotec or selitex or Setir or Setiral or setizin or simtec or Stopaler or Sun mark all day allergy or sutac or symitec or terizin or terzine or Topcare all day allergy or Triz or “UCB-P 071” or vick-zyrt or Virdos or Virlix or Voltric or Xero-sed or zenriz or zensil or zeran or zertine or Zetir or zicet or zinex or Ziptek or zirtec or Zirtek or Zirtin or zyllergy or zymed or zyrac or zyrazine or zyrcon or zyrlex or Zyrtec or Zyrtec-D or zyrtek or Zyrzine).ti,ab,rn. (2383)
-
(desloratadine or clarinex or aerius or neoclarityn or azomyr or denosin or SCH 34117 or allex or aviant or claramax or dasselta or decarbethoxyloratadine or desalex or descarboethoxyloratadine or deslor or neoclaritine or sch34117 or supraler).ti,ab,rn. (1608)
-
(fexofenadine or allegra or telfast or Carboxyterfenadine or MDL 16455A or mdl 16455 or mdl16455).ti,ab,rn. (3008)
-
(levocetirizine or xusal or xyzal).ti,ab,rn. (1021)
-
(loratadin$ or aerotina or Alarin or Alavert or alerfast or alernitis or Alerpriv or alertadin or allerta or Allertidin or allertyn or allohex or ambrace or analergal or anhissen or anlos or ardin or Bactimicina allergy or Biloina or bonalerg or caradine or carin or civeran or clalodine or claratyne or clarid or Clarinase or Claritin or claritine or clarityn or clarityne or Clarium or cronitin or cronopen or curyken or demazin anti-allergy or ezasmin or ezede or finska or frenaler or fristamin or genadine or halodin or hislorex or histalor or histaloran or HSDB 3578 or j-tadine or klarihist or klinset or laredine or lergia or Lergy or lertamine or Lesidas or lindine or lisino or lisono or lobeta or lodain or lorabasics or loracert or loraclar or loraderm or loradex).ti,ab,rn. (15709)
-
(Loradif or loradin or lorahist or loralerg or lora-lich or lorano or loranox or Loranox or Lorantis or lorastine or lora-tabs or loratadura or loratan or loratazine or loratidin or loratidine or loraton or loratrim or loratyne or Loraver or loreen or lorfast or lorihis or lorin or lorita or Loritine or lotadine or lotarin or lowadina or mosedin or noratin or notamin or Nularef or onemin or optimin or polaratyne or proactin or pylor or restamine or Rhinase or ridamin or rihest or rinityn or Rinomex or rityne or roletra or rotifar or Sanelor or Sch 29851 or Sch29851 or sensibit or Sinhistan Dy or sohotin or Tadine or Talorat Dy or tidilor or tirlor or Topcare or toradine or velodan or versal or voratadine or zeos).ti,ab,rn. (171)
-
(mizolastin$ or zolistan or mistamine or mistalin or mizollen or zolim or mizolen or “SL 85 0324” or CCRIS 8410 or mkc 431 or sl 850324).ti,ab,rn. (666)
-
(rupatadine or rupafin or UR 12592 or UR12592).ti,ab,rn. (197)
-
(Chlorphenamin$ or 4-Chloropheniramine or ahiston or alerfin or alergical or alergidryl or alergitrat or alermine or aller or Aller-Chlor or Allerclor or allerfin or Allergican or Allergin or Allergisan or allergyl or allermin or allerphen or Alunex or analerg or anaphyl or Antagonate or antamin or apomin or barominic or cadistin or Carbinoxamide maleate or CCRIS 1418 or Chlo-Amine or chlometon or chlor trimeton or Chlor-100 or chloramate unicelles or chlorleate or Chlormene or chlorophenamine maleate or Chloropheniramine or Chlorophenylpyridamine or Chloropiril).ti,ab,rn. (238)
-
(Chloroprophenpyridamine or chloroton or Chlorpheniramin$ or chlorpheno or chlorphenon or Chlorpro or Chlorprophenpyridamine or chlorpyrimine or Chlorspan 12 or Chlortab-4 or chlortrimeton or Chlor-Trimeton or chlortripolon or Chlor-Tripolon or Clorfenamina or Clorfeniramina or cloro trimeton or cloroalergan or Cloropiril or clorotrimeton or Cloro-Trimeton or C-Meton or cohistan or com-trimeton or Dehist or dl-Chlorpheniramine maleate or Efidac 24).ti,ab,rn. (20392)
-
(clemastin$ or meclastin$ or neclastine or mecloprodin or tavist or tavegyl or HS 592 or HS592).ti,ab,rn. (2247)
-
(cyproheptadine or adekin or Antergan or antisemin or apeton 4 or astonin or BRN 1685976 or CCRIS 5232 or ciplactin or cipractin or ciproeptadine or Ciproheptadina or ciproral or ciprovit-a or cryoheptidine or crypoheptadine or cyheptine or cylat or cypraheptidine or cypro h or cyproatin or cyprogin or cyprohaptadi$ or cypromin or cyprono or cyprosian or cytadine or Dihexazin or Dronactin or Eiproheptadine or ennamax or glocyp or heptasan or HSDB 3048 or ifrasal or istam-far or klarivitina or kulinet or MK 141 or nuran or Periact$ or Peritol or petina or pilian or pronicy or sinapdin or trimetabol or Viternum).ti,ab,rn. (7695)
-
(ketotifen$ or ketotiphen$ or zaditen or zaditor or BRN 3983897 or HC 20 511 or hc 20511 or HSDB 7283).ti,ab,rn. (4419)
-
(Prometh$ or 3277 RP or A-91033 or adgan or Allerfen or allergan or Anergan 25 or Anergan 50 or antiallersin or antinaus 50 or Aprobit or Atosil or Avomine or baymethazine or Bonnox or “BRN 0088554” or Camergan or CCRIS 5873 or CCRIS 7056 or Closin or dimapp or Dimethylamino-isopropyl-phenthiazin or Diphergan or Diprasine or Diprazin$ or diprozin or Dorme or Duplamin or Eusedon Mono or fargan or Farganesse or Fellozine or fenazil or fenazine or Fenergan or Fenetazin$ or Frinova or Ganphen or Hibechin or hiberna or Histantil or Histargan or HL 8700 or HSDB 3173 or insomn-eze or Isophenergan or Isopromethazine or Kinetosin or lercigan or Lergigan or lergigan or “Lilly 01516” or Lilly 1516 or Metaryl or Mymethazine Fortis or NCI-C60673 or NSC 231688).ti,ab,rn. (13,784)
-
(NSC 30321 or Pelpica or pentazine or phargan or Phenadoz or Phenargan or Phencen or Phenergan or Phenerzine or phenoject-50 or Phensedyl or Pilothia or Pipolfen or Pipolphen$ or Plletia or pm 284 or Primine or Pro-50 or Proazamine or procit or promacot or Promantine or promazinamide or Prome or Promergan or Promesan or Promet or Prometazin or Prometazina or Prometh$ or Promezathine or Promine or Proneurin or Prorex or protazine or Prothazin or Prothiazine or prothazine or provigan or Provigan or Pyrethia or Pyrethiazine or Remsed or Romergan or rp 3277 or rp 3389 or Rumergan or sayomol or SKF 1498 or Soporil or tanidil or thiergan or V GAN or vallergine or WY 509 or Zipan-25 or Zipan-50).ti,ab,rn. (14,656)
-
or/60-81 (198,982)
-
8 and 82 (104)
-
simethicone/ (777)
-
(simethicone or Antifoam A or Antifoam AF or DC antifoam A or Disflatyl or Gas-X or gas relief or HSDB 3906 or Mylanta or mytab gas or Phazyme or Sab Simplex or Simeticone or dimethicone or digel or flatulex or infacol or lefax or minifom or mylicon or silain or Alka-Seltzer Anti-Gas or Colic Drops or Colicon or Degas or Gas Aide or Genasyme or Maalox Anti-Gas or Majorcon or Micon-80 or Mylaval or SonoRx or WindEze or Wind-Eze).ti,ab,rn. (1463)
-
84 or 85 (1463)
-
8 and 86 (0)
-
nasal lavage/ (368)
-
lavage/ (12,033)
-
((nasal or nose) adj3 (douch$ or irrigat$ or lavage)).ti,ab. (1664)
-
(saline adj3 (douch$ or irrigat$ or lavage)).ti,ab. (2156)
-
or/88-91 (15,123)
-
8 and 92 (29)
-
exp leukotriene receptor blocking agent/ (13729)
-
zileuton/ (1886)
-
(leukotriene adj3 (antagonist$ or block$ or inhibitor$)).ti,ab. (3925)
-
(montelukast or Singulair or Montelo-10 or montair or montek or montus or romilast or “MK 0476” or mk 476 or mk0476 or mk476 or l 706631 or l706631).ti,ab,rn. (5838)
-
(zafirlukast or Accolate or accoleit or Olmoran or Aeronix or respix or vanticon or zafirst or zuvair or ICI 204,219 or ICI 204219).ti,ab,rn. (2326)
-
(pranlukast or azlaire or ultair or ONO 1078 or SB 205312 or SB205312 or ONO RS 411 or rs411 or rs 411).ti,ab,rn. (1096)
-
(zileuton$ or A 64077 or A64077 or Abbot 64077 or cgs 23622 or cgs23622 or Zyflo or Leutrol).ti,ab,rn. (1946)
-
or/94-100 (15,465)
-
8 and 101 (6)
-
chewing gum/ (1934)
-
xylitol/ (3087)
-
(Xylitol or BRN 1720523 or Eutrit or HSDB 7967 or Kannit or Klinit or NSC 25283 or Newtol or Xylite or Xylitol or Xyliton or xylit).ti,ab,rn. (3767)
-
or/103-105 (5455)
-
8 and 106 (3)
-
exp antiinfective agent/ (2,031,219)
-
(anti bacterial$ or antibacterial$ or anti biotic$ or antibiotic$ or anti mycobacterial$ or antimycobacterial$ or bacteriocid$).ti,ab. (312,266)
-
(anti infective$ or antiinfective$ or anti microbial$ or antimicrobial$ or microbicide$).ti,ab. (111,188)
-
(doxycyclin$ or adoxa or alpha-Doxycycline or amermycin or atrax or azudoxat or bactidox or banndoclin or basedillin or bassado or biocolyn or biodoxi or bmy 28689 or bmy28689 or bronmycin or bu 3839t or bu3839t or cloran or cyclidox or dentistar or deoxycycline or deoxymycin dispersal or deoxymykoin or deoxyoxytetracycline or desoxy oxytetracycline or desoxycycline or doinmycin or doryx or dosil or Dossiciclina or dotur or doxaciclin or doxacycline or doxat or doxatet or doxibiotic or Doxiciclina or doxicycline or doxilin or doximed or doximycin or doxin or doxine or doxi-sergo).ti,ab,rn. (34,826)
-
(Doxitard or Doxivetin or doxocycline or doxsig or doxy or doxy-1 or doxybiocin or doxy-caps or doxycen or doxychel or doxycin or doxycydine monohydrate or doxylag or doxylin or doxymycin or doxypuren or Doxy-Puren or Doxysol or doxytec or Doxytetracycline or doxytrim or dumoxin or duracycline or esdoxin or etidoxina or gewacyclin or gs 3065 or HSDB 3071 or hydramycin or ibralene or idocyclin or idocyklin or interdoxin or investin or Liviatin or longamycin or lydox or magdrin or medomycin or mespafin or mildox or miraclin or monodox or nordox or novum vibramycin).ti,ab,rn. (31,921)
-
(nsc 56228 or oracea or paldomycin or pernox gel or radox or remycin or respidox or Ronaxan or roximycin or serodoxy or servidoxine or servidoxyne or siadocin or siclidon or sigadoxin or spanor or supracyclin or supramycina or tenutan or tolexine or torymycin or tsurupioxin or unidox or veemycin or viadoxin or vibra$ or viradoxyl-n or wanmycin or zadorin).ti,ab,rn. (38,600)
-
(amoxicil$ or a gram or abdimox or acilina or acimox or actimoxi or adbiotin or agerpen or agram or a-gram or alfamox or alfoxil or almodan or almorsan or alphamox or amagesen solutab or ameclina or amocillin or amoclen or amodex or amo-flamisan or amoflux or amohexal or amolin or amonex or amopen or Amopenixin or amophar ge or amosine or amoval or amoxa or amoxal or amoxapen or amoxaren or amoxcil or amoxcillin or amoxcin or Amoxi or amoxi-basan or Amoxicaps or amoxiclin or amoxicot or amoxidal or Amoxiden or amoxidin or amoxidrops or amoxihexal or amoxil$).ti,ab,rn. (68,789)
-
(Amoxi-Mast or amoxipen or amoxipenil or amoxisol or amoxivan or amoxivet or Amoxivet or amoxy or Amoxycillin$ or amoxy-diolan or amoxypen or AMPC or ampliron or Ampy-Penyl or Anemolin or apo-amoxi or ardine or aroxin or Aspenil or azillin or bacihexal or bactamox or bactox ge or beamoxy or betamox or bimox or bintamox or biomox or biotamoxal or bioxidona or bioxyllin or BLP 1410 or bristamox or brl 2333 or brl2333 or broadmetz or cabermox or Cemoxin or cilamox or clamox or clamoxyl or clearamox or clonamox or coamoxin or damoxicil or D-Amoxicillin or Delacillin).ti,ab,rn. (5713)
-
(dispermox or doxamil or draximox or edamox or Efpenix or erphamoxy or eupen or farconcil or fisamox or flemoxin or fluamoxina or foxolin or fullcilina or gexcil or gimalxina or glamox or glassatan or gomcillin or grinsul or grunamox or hamoxillin or hiconcil or hidramox or hipen or Histocillin or hosboral or HSDB 3204 or Hydroxyampicillin or ibamox or ibiamox or ikamoxil or imacillin or imaxilin or inamox or infectomycin or intermox or isimoxin or izoltil or julphamox or jutamox or kamoxin or ladoxillin or lamoxy or larocilin or larocin or larotid or macromox or magnimox or maxamox or maxcil).ti,ab,rn. (27)
-
(medimox or meixil or Metafarma or metifarma or mopen or morgenxil or moxacin or Moxal$ or moxarin or Moxatag or moxilen or moxilin or moximar or moxitab or moxtid or moxylin or moxypen or moxyvit or neogram or novabritine or novamox or novamoxin or novenzymin or novoxil or NSC 277174 or nuvosyl or optium or ospamox or pamocil or pamoxicillin or pamoxin or panvilon or pasetocin or penamox or penbiosyn or pentyloxycillin or pharmoxyl or p-Hydroxyampicillin or piramox or polymox or pondnoxcill or rancil or ranmoxy or ranoxil or ranoxyl or Ro 10-8756).ti,ab,rn. (1384)
-
(robamox or romoxil or ronemox or saltermox or sawacillin or sawamezin or Sawamox PM or servamox or shamoxil or sia-mox or sigamopen or silamox or sil-a-mox or simoxil or solpenox or sumox or superpeni or teramoxyl or tolodina or tormoxin or triafamox or triamoxil or trifamox or trimox or Unicillin or uro clamoxyl or uroclamoxyl or utimox or vastamox or velamox or Vetramox or vistrep or widecillin or winpen or wymox or Wymox or Wymox or xiltrop or zamocillin or zamox or zamoxil or zerrsox or zimox).ti,ab,rn. (15)
-
(clarith$ or A 56268 or A56268 or abbotic or abbott 56268 or Adel or aeroxina or Astromen or bactirel or baxin filmtab or Biaxin or biclar or bicrolid or binoklar or bremon or carimycin or c-clarin or CCRIS 8833 or celex or clacin or clacine or clambiotic or clapharma or claribid or Claricide or claridar or clarimac or claripen or claritrol or Claritromicina or claroma or Clathromycin or clormicin).ti,ab,rn. (25,489)
-
(crixan or cylind or Cyllid or cyllind or dicupal or DRG-0099 or er 36469 or er36469 or gervaken or hecobac or Helas or heliclar or helitic or klacid or klacina or klaciped or klaribac or klaricid or Klarid or klaridex or klaridia or klarin or Klax or klerimed or kofron or lagur or Mabicrol or macladim or macladin or maclar or mavid or monozeclar or naxy or “TE 031” or TE031 or veclam or zeclar).ti,ab,rn. (453)
-
(moxif$ or Actira or Avalox or avelon or Avelox or Avolex or BAY 12 8039 or BAY 128039 or bay128039 or CCRIS 8690 or Izilox or megaxin or moxeza or Octegra or Proflox or vigamox).ti,ab,rn. (9503)
-
(Telithromycin or Ketek or RU 66647 or HMR 3647 or HMR3647 or levviax or ru 647 or ru 66647 or ru647 or ru66647).ti,ab,rn. (2482)
-
(azithromycin$ or Aritromicina or aruzilina or atizor or Azadose or azasite or azenil or azimin or azithral or Azitrocin or azitromax or Azitromicine or aziwok or azomyne or aztrin or Azythromycin or BRN 5387583 or CCRIS 1961 or cp 62933 or cp62933 or DRG-0104 or forcin or Goxal or Hemomycin or HSDB 7205 or inedol or isv 401 or isv401 or kromicin or macrozit or mezatrin or Misultina).ti,ab,rn. (19,937)
-
(Mixoterin or octavax or Setron or Sumamed or sunamed or Tobil or tobyl or Toraseptol or tromix or Trulimax or Ultreon or Vinzam or xithrone or xz 450 or xz450 or zaret or zarom or Zentavion or Zeto or zibramax or zifin or zimericina or zistic or Zithrax or Zithromax or zithrox or zitrim or zitrobifan or Zitromax or Zitrotek or Zmas or zmax or Z-Pak).ti,ab,rn. (323)
-
or/108-124 (2,169,770)
-
8 and 125 (494)
-
balloon dilatation/ (11,320)
-
dilatation/ (4864)
-
catheterization/ (35,076)
-
catheter$.ti,ab. (187,758)
-
dilat$.ti,ab. (132,494)
-
(BET or BDET).ti,ab. (6346)
-
tuboplast$.ti,ab. (233)
-
low level laser therapy/ (9275)
-
exp laser/ (75,145)
-
laser$.ti,ab. (165,104)
-
LETP.ti,ab. (5)
-
middle ear ventilation/ (790)
-
tympanostomy tube/ (1727)
-
myringotomy/ (2339)
-
t tube/ (1399)
-
(tympanostom$ or tympanotom$).ti,ab. (1764)
-
grommet$.ti,ab. (562)
-
((ventilat$ or aerat$) adj4 ear$).ti,ab. (1944)
-
((ventilat$ or aerat$) adj4 tub$).ti,ab. (2986)
-
(pressur$ adj3 tub$).ti,ab. (1862)
-
ear tube$.ti,ab. (87)
-
PE tube$.ti,ab. (54)
-
T tube$.ti,ab. (2805)
-
(transtubal or trans tubal).ti,ab. (64)
-
(myringotom$ or myringocentesis).ti,ab. (1401)
-
(paracentesis or tympanocentesis).ti,ab. (3287)
-
((eardrum$ or ear drum$ or tympan$) adj3 (punctur$ or tap$)).ti,ab. (30)
-
or/127-153 (528682)
-
8 and 154 (1216)
-
Valsalva maneuver/ (5320)
-
aeration/ (7359)
-
yawning/ (1151)
-
mastication/ (11,913)
-
swallowing/ (11,936)
-
watchful waiting/ (968)
-
conservative treatment/ (36,164)
-
valsalva$.ti,ab. (8682)
-
(autoinflat$ or auto inflat$).ti,ab. (103)
-
(insufflat$ or autoinsufflat$ or auto insufflat$).ti,ab. (6602)
-
(inflat$ adj4 ear$).ti,ab. (126)
-
Politzer$.ti,ab. (157)
-
((equalis$ or equaliz$ or normalis$ or normaliz$) adj5 pressure$).ti,ab. (4936)
-
(yawn$ or swallow$ or chew$ or masticat$ or deglutition).ti,ab. (44,916)
-
(watch$ adj2 wait$).ti,ab. (2449)
-
(wait adj2 see).ti,ab. (1164)
-
(active$ adj2 observ$).ti,ab. (1213)
-
conservative.ti,ab. (87,263)
-
(management adj2 (decision$ or option$ or choice$)).ti,ab. (11,653)
-
(support$ adj4 (care or caring)).ti,ab. (25,573)
-
((standard or usual) adj3 care).ti,ab. (32,634)
-
(advice or advis$).ti,ab. (91,523)
-
or/156-177 (344,713)
-
8 and 178 (763)
-
40 or 59 or 83 or 87 or 93 or 102 or 107 or 126 or 155 or 179 (2115)
-
animal/ (1,804,242)
-
exp animal experiment/ (1,646,534)
-
Nonhuman/ (3,926,525)
-
(rat or rats or mouse or mice or hamster or hamsters or animal or animals or dog or dogs or cat or cats or bovine or sheep).ti,ab,sh. (4,762,757)
-
or/181-184 (6,743,001)
-
exp human/ (13,954,738)
-
human experiment/ (305422)
-
186 or 187 (13,956,174)
-
185 not (185 and 188) (5,304,415)
-
180 not 189 (1849)
Key
/ = indexing term (EMTREE heading)
exp = exploded EMTREE heading
$ = truncation
.ti,ab. = terms in either title or abstract fields
adj2 = terms within two words of each other (any order)
Health Technology Assessment database via Wiley: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/
Issue 3 of 4, July 2012.
Records retrieved: 0.
See above under CENTRAL for search strategy used.
Inside Conferences via Dialog: www.dialog.com/
1993 to October, week 4 2012.
Searched on 5 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 231.
| Set | Items | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 210 | (EUSTACHIAN OR AUDITORY OR PHARYNGOTYMPANIC)(3W)TUB?/TI,AB,DE |
| 2 | 0 | EUSTACHIAN(2W)(CANAL OR ORIFICE?)/TI,AB,DE |
| 3 | 1 | MIDDLE(W)EAR(3W)DYSFUNCTION?/TI,AB,DE |
| 4 | 26 | MIDDLE(W)EAR(3W)PRESSURE?/TI,AB,DE |
| 5 | 231 | S1:S4 |
Key
? = truncation
/TI,AB,DE = terms in title, abstract, or descriptor fields
(W) = terms adjacent to each other (same order)
(2W) = terms within 2 words of each other (same order)
S1:S4 = S1 OR S2 OR S3 OR S4
Latin American and Caribbean Health Science: http://lilacs.bvsalud.org/en/
Search date: 8 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 158.
eustachian AND tub$ 48
auditory AND tub$ 82
pharyngotympanic AND tub$ 0
eustachian AND canal 2
eustachian AND orifice$ 0
middle AND ear AND dysfuntion$ 1
middle AND ear AND pressure$ 25
Key
$ = truncation
PASCAL via Dialog: www.dialog.com/
1973 to September, week 5 2012.
Searched on 5 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 1678.
| Set | Items | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1383 | (EUSTACHIAN OR AUDITORY OR PHARYNGOTYMPANIC)(3W)TUB?/TI,AB,DE |
| 2 | 21 | EUSTACHIAN(2W)(CANAL OR ORIFICE?)/TI,AB,DE |
| 3 | 35 | MIDDLE(W)EAR(3W)DYSFUNCTION?/TI,AB,DE |
| 4 | 377 | MIDDLE(W)EAR(3W)PRESSURE?/TI,AB,DE |
| 5 | 1678 | S1:S4 |
Key
? = truncation
/TI,AB,DE = terms in title, abstract, or descriptor fields
(W) = terms adjacent to each other (same order)
(2W) = terms within 2 words of each other (same order)
S1:S4 = S1 OR S2 OR S3 OR S4
Science Citation Index and Conference Proceedings Citation Index – Science via ISI Web of Knowledge: www.isinet.com/
Search date: 8 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 888.
| # 60 | 888 | #59 OR #45 OR #37 OR #33 OR #31 OR #27 OR #23 OR #21 OR #15 OR #10 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 59 | 255 | #58 AND #5 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 58 | 243,078 | #57 OR #56 OR #55 OR #54 OR #53 OR #52 OR #51 OR #50 OR #49 OR #48 OR #47 OR #46 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 57 | 58,296 | TS=(advice or advis*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 56 | 18,622 | TS=((standard or usual) NEAR/3 care) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 55 | 16,701 | TS=(support* NEAR/4 (care or caring)) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 54 | 21,362 | TS=(management NEAR/2 (decision* or option* or choice*)) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 53 | 73,275 | TS=conservative Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 52 | 4980 | TS=(active* NEAR/2 observ*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 51 | 707 | TS=(wait NEAR/2 see) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 50 | 1595 | TS=(watch* NEAR/2 wait*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 49 | 37,509 | TS=(yawn* or swallow* or chew* or masticat* or deglutition) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 48 | 3424 | TS=((equalis* or equaliz* or normalis* or normaliz*) NEAR/5 pressure*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 47 | 922 | TS=(inflat* NEAR/4 ear*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 46 | 10,233 | TS=(valsalva* or autoinflat* or auto-inflat* or insufflat* or autoinsufflat* or auto-insufflat* or politzer*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 45 | 623 | #44 AND #5 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 44 | 938,093 | #43 OR #42 OR #41 OR #40 OR #39 OR #38 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 43 | 14 | TS=((eardrum* or "ear drum*" or tympan*) NEAR/3 (punctur* or tap*)) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 42 | 4971 | TS=(“ear tube*” or “PE tube*” or “T tube*” or transtubal or trans-tubal or myringotom* or myringocentesis or paracentesis or tympanocentesis) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 41 | 6816 | TS=(pressur* NEAR/3 tub*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 40 | 2529 | TS=((ventilat* or aerat*) NEAR/4 tub*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 39 | 1606 | TS=((ventilat* or aerat*) NEAR/4 ear*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 38 | 924,591 | TS=(catheter* or dilat* or BET or BDET or tuboplast* or laser* or LETP or tympanostom* or tympanotom* or grommet*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 37 | 132 | #36 AND #5 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 36 | 634,941 | #35 OR #34 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 35 | 341,879 | TS=(doxycyclin* or adoxa or alpha-Doxycycline or amermycin or atrax or azudoxat or bactidox or banndoclin or basedillin or bassado or biocolyn or biodoxi or “bmy 28689” or bmy28689 or bronmycin or “bu 3839t” or bu3839t or cloran or cyclidox or dentistar or deoxycycline or “deoxymycin dispersal” or deoxymykoin or deoxyoxytetracycline or “desoxy oxytetracycline” or desoxycycline or doinmycin or doryx or dosil or Dossiciclina or dotur or doxaciclin or doxacycline or doxat or doxatet or doxibiotic or Doxiciclina or doxicycline or doxilin or doximed or doximycin or doxin or doxine or doxi-sergo or Doxitard or Doxivetin or doxocycline or doxsig or doxy or doxy-1 or doxybiocin or doxy-caps or doxycen or doxychel or doxycin or “doxycydine monohydrate” or doxylag or doxylin or doxymycin or doxypuren or Doxy-Puren or Doxysol or doxytec or Doxytetracycline or doxytrim or dumoxin or duracycline or esdoxin or etidoxina or gewacyclin or “gs 3065” or “HSDB 3071” or hydramycin or ibralene or idocyclin or idocyklin or interdoxin or investin or Liviatin or longamycin or lydox or magdrin or medomycin or mespafin or mildox or miraclin or monodox or nordox or novum vibramycin or “nsc 56228” or oracea or paldomycin or “pernox gel” or radox or remycin or respidox or Ronaxan or roximycin or serodoxy or servidoxine or servidoxyne or siadocin or siclidon or sigadoxin or spanor or supracyclin or supramycina or tenutan or tolexine or torymycin or tsurupioxin or unidox or veemycin or viadoxin or vibra* or viradoxyl-n or wanmycin or zadorin or amoxicil* or “a gram” or abdimox or acilina or acimox or actimoxi or adbiotin or agerpen or agram or a-gram or alfamox or alfoxil or almodan or almorsan or alphamox or “amagesen solutab” or ameclina or amocillin or amoclen or amodex or amo-flamisan or amoflux or amohexal or amolin or amonex or amopen or Amopenixin or “amophar ge” or amosine or amoval or amoxa or amoxal or amoxapen or amoxaren or amoxcil or amoxcillin or amoxcin or Amoxi or amoxi-basan or Amoxicaps or amoxiclin or amoxicot or amoxidal or Amoxiden or amoxidin or amoxidrops or amoxihexal or amoxil* or Amoxi-Mast or amoxipen or amoxipenil or amoxisol or amoxivan or amoxivet or Amoxivet or amoxy or Amoxycillin* or amoxy-diolan or amoxypen or AMPC or ampliron or Ampy-Penyl or Anemolin or apo-amoxi or ardine or aroxin or Aspenil or azillin or bacihexal or bactamox or “bactox ge” or beamoxy or betamox or bimox or bintamox or biomox or biotamoxal or bioxidona or bioxyllin or “BLP 1410” or bristamox or “brl 2333” or brl2333 or broadmetz or cabermox or Cemoxin or cilamox or clamox or clamoxyl or clearamox or clonamox or coamoxin or damoxicil or D-Amoxicillin or Delacillin or dispermox or doxamil or draximox or edamox or Efpenix or erphamoxy or eupen or farconcil or fisamox or flemoxin or fluamoxina or foxolin or fullcilina or gexcil or gimalxina or glamox or glassatan or gomcillin or grinsul or grunamox or hamoxillin or hiconcil or hidramox or hipen or Histocillin or hosboral or “HSDB 3204” or Hydroxyampicillin or ibamox or ibiamox or ikamoxil or imacillin or imaxilin or inamox or infectomycin or intermox or isimoxin or izoltil or julphamox or jutamox or kamoxin or ladoxillin or lamoxy or larocilin or larocin or larotid or macromox or magnimox or maxamox or maxcil or medimox or meixil or Metafarma or metifarma or mopen or morgenxil or moxacin or Moxal* or moxarin or Moxatag or moxilen or moxilin or moximar or moxitab or moxtid or moxylin or moxypen or moxyvit or neogram or novabritine or novamox or novamoxin or novenzymin or novoxil or “NSC 277174” or nuvosyl or optium or ospamox or pamocil or pamoxicillin or pamoxin or panvilon or pasetocin or penamox or penbiosyn or pentyloxycillin or pharmoxyl or p-Hydroxyampicillin or piramox or polymox or pondnoxcill or rancil or ranmoxy or ranoxil or ranoxyl or “Ro 10-8756” or robamox or romoxil or ronemox or saltermox or sawacillin or sawamezin or “Sawamox PM” or servamox or shamoxil or sia-mox or sigamopen or silamox or sil-a-mox or simoxil or solpenox or sumox or superpeni or teramoxyl or tolodina or tormoxin or triafamox or triamoxil or trifamox or trimox or Unicillin or “uro clamoxyl” or uroclamoxyl or utimox or vastamox or velamox or Vetramox or vistrep or widecillin or winpen or wymox or Wymox or Wymox or xiltrop or zamocillin or zamox or zamoxil or zerrsox or zimox or clarith* or “A 56268” or A56268 or abbotic or “abbott 56268” or Adel or aeroxina or Astromen or bactirel or baxin filmtab or Biaxin or biclar or bicrolid or binoklar or bremon or carimycin or c-clarin or “CCRIS 8833” or celex or clacin or clacine or clambiotic or clapharma or claribid or Claricide or claridar or clarimac or claripen or claritrol or Claritromicina or claroma or Clathromycin or clormicin or crixan or cylind or Cyllid or cyllind or dicupal or DRG-0099 or “er 36469” or er36469 or gervaken or hecobac or Helas or heliclar or helitic or klacid or klacina or klaciped or klaribac or klaricid or Klarid or klaridex or klaridia or klarin or Klax or klerimed or kofron or lagur or Mabicrol or macladim or macladin or maclar or mavid or monozeclar or naxy or "TE 031" or TE031 or veclam or zeclar or moxif* or Actira or Avalox or avelon or Avelox or Avolex or “BAY 12 8039” or “BAY 128039” or bay128039 or “CCRIS 8690” or Izilox or megaxin or moxeza or Octegra or Proflox or vigamox or Telithromycin or Ketek or “RU 66647” or “HMR 3647” or HMR3647 or levviax or “ru 647” or “ru 66647” or ru647 or ru66647 or azithromycin* or Aritromicina or aruzilina or atizor or Azadose or azasite or azenil or azimin or azithral or Azitrocin or azitromax or Azitromicine or aziwok or azomyne or aztrin or Azythromycin or “BRN 5387583” or “CCRIS 1961” or “cp 62933” or cp62933 or DRG-0104 or forcin or Goxal or Hemomycin or “HSDB 7205” or inedol or “isv 401” or isv401 or kromicin or macrozit or mezatrin or Misultina or Mixoterin or octavax or Setron or Sumamed or sunamed or Tobil or tobyl or Toraseptol or tromix or Trulimax or Ultreon or Vinzam or xithrone or “xz 450” or xz450 or zaret or zarom or Zentavion or Zeto or zibramax or zifin or zimericina or zistic or Zithrax or Zithromax or zithrox or zitrim or zitrobifan or Zitromax or Zitrotek or Zmas or zmax or Z-Pak) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 34 | 310,504 | TS=(anti-bacterial* or antibacterial* or anti-biotic* or antibiotic* or anti-mycobacterial* or antimycobacterial* or bacteriocid* or anti-infective* or antiinfective* or anti-microbial* or antimicrobial* or microbicide*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 33 | 2 | #32 AND #5 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 32 | 3242 | TS=(Xylitol or “BRN 1720523” or Eutrit or “HSDB 7967” or Kannit or Klinit or “NSC 25283” or Newtol or Xylite or Xylitol or Xyliton or xylit) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 31 | 2 | #30 AND #5 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 30 | 5328 | #29 OR #28 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 29 | 2974 | TS=(montelukast or Singulair or Montelo-10 or montair or montek or montus or romilast or "MK 0476" or “mk 476” or mk0476 or mk476 or “l 706631” or l706631or zafirlukast or Accolate or accoleit or Olmoran or Aeronix or respix or vanticon or zafirst or zuvair or “ICI 204 219” or “ICI 204219” or pranlukast or azlaire or ultair or “ONO 1078” or “SB 205312” or SB205312 or “ONO RS 411” or rs411 or “rs 411” or zileuton* or “A 64077” or A64077 or “Abbot 64077” or “cgs 23622” or cgs23622 or Zyflo or Leutrol) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 28 | 3562 | TS=(leukotriene NEAR/3 (antagonist* or block* or inhibitor*)) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 27 | 4 | #26 AND #5 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 26 | 3689 | #25 OR #24 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 25 | 2427 | TS=(saline NEAR/3 (douch* or irrigat* or lavage)) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 24 | 1375 | TS=((nasal or nose) NEAR/3 (douch* or irrigat* or lavage)) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 23 | 0 | #22 AND #5 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 22 | 795 | TS=(simethicone or “Antifoam A” or “Antifoam AF” or “DC antifoam A” or Disflatyl or Gas-X or “gas relief” or “HSDB 3906” or Mylanta or “mytab gas” or Phazyme or “Sab Simplex” or Simeticone or dimethicone or digel or flatulex or infacol or lefax or minifom or mylicon or silain or “Alka-Seltzer Anti-Gas” or “Colic Drops” or Colicon or Degas or “Gas Aide” or Genasyme or “Maalox Anti-Gas” or Majorcon or Micon-80 or Mylaval or SonoRx or WindEze or Wind-Eze) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 21 | 30 | #20 AND #5 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 20 | 27,730 | #19 OR #18 OR #17 OR #16 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 19 | 13,669 | TS=(acrivastin* or semprex or semprex-D or benadryl or prolert or “BW 825C” or BW825C or “BW A825C” or bilastine or bilaxten or “f 96221 bm1” or “f96221 bm1” or Cetirizin* or acidrine or adezio or agelmin or Alercet or Alergex or Alerid or Alerlisin or Alertisin or alertop or alerviden or aletir or alled or “Allergy relief” or Alleroff or allertec or alltec or alzytec or Apo-Cetirizine or betarhin or cerazine or cerini or cerotec or cesta or Cetalerg or Ceterifug or cethis or “Ceti TAD” or Cetiderm or Cetidura or “Cetil von ct” or CetiLich or cetimin or cetin or Ceti-Puren or cetirax or Cetirigamma or cetirin or Cetirlan or cetizin or Cetriler or cetrimed or Cetrine or cetrizet or cetrizin or Cetryn or cetymin or Cetzine or Cezin or cistamine or deallergy or falergi or finallerg or Formistin or histazine or histica or Hitrizin or “HSDB 7739” or incidal-od or lergium or nosemin or nosmin or ozen or "P 071" or P071 or prixlae or razene or Reactine or Ressital or rhizin or risima or Riztec or ryvel or Ryzen or Salvalerg or sancotec or selitex or Setir or Setiral or setizin or simtec or Stopaler or “Sun mark all day allergy” or sutac or symitec or terizin or terzine or “Topcare all day allergy” or Triz or "UCB-P 071" or vick-zyrt or Virdos or Virlix or Voltric or Xero-sed or zenriz or zensil or zeran or zertine or Zetir or zicet or zinex or Ziptek or zirtec or Zirtek or Zirtin or zyllergy or zymed or zyrac or zyrazine or zyrcon or zyrlex or Zyrtec or Zyrtec-D or zyrtek or Zyrzine or desloratadine or clarinex or aerius or neoclarityn or azomyr or denosin or “SCH 34117” or allex or aviant or claramax or dasselta or decarbethoxyloratadine or desalex or descarboethoxyloratadine or deslor or neoclaritine or sch34117 or supraler or fexofenadine or allegra or telfast or Carboxyterfenadine or “MDL 16455A” or “mdl 16455” or mdl16455 or levocetirizine or xusal or xyzal or loratadin* or aerotina or Alarin or Alavert or alerfast or alernitis or Alerpriv or alertadin or allerta or Allertidin or allertyn or allohex or ambrace or analergal or anhissen or anlos or ardin or “Bactimicina allergy” or Biloina or bonalerg or caradine or carin or civeran or clalodine or claratyne or clarid or Clarinase or Claritin or claritine or clarityn or clarityne or Clarium or cronitin or cronopen or curyken or “demazin anti-allergy” or ezasmin or ezede or finska or frenaler or fristamin or genadine or halodin or hislorex or histalor or histaloran or “HSDB 3578” or j-tadine or klarihist or klinset or laredine or lergia or Lergy or lertamine or Lesidas or lindine or lisino or lisono or lobeta or lodain or lorabasics or loracert or loraclar or loraderm or loradex or Loradif or loradin or lorahist or loralerg or lora-lich or lorano or loranox or Loranox or Lorantis or lorastine or lora-tabs or loratadura or loratan or loratazine or loratidin or loratidine or loraton or loratrim or loratyne or Loraver or loreen or lorfast or lorihis or lorin or lorita or Loritine or lotadine or lotarin or lowadina or mosedin or noratin or notamin or Nularef or onemin or optimin or polaratyne or proactin or pylor or restamine or Rhinase or ridamin or rihest or rinityn or Rinomex or rityne or roletra or rotifar or Sanelor or “Sch 29851” or Sch29851 or sensibit or “Sinhistan Dy” or sohotin or Tadine or “Talorat Dy” or tidilor or tirlor or Topcare or toradine or velodan or versal or voratadine or zeos or mizolastin* or zolistan or mistamine or mistalin or mizollen or zolim or mizolen or "SL 85 0324" or “CCRIS 8410” or “mkc 431” or “sl 850324” or rupatadine or rupafin or “UR 12592” or UR12592 or Chlorphenamin* or 4-Chloropheniramine or ahiston or alerfin or alergical or alergidryl or alergitrat or alermine or aller or Aller-Chlor or Allerclor or allerfin or Allergican or Allergin or Allergisan or allergyl or allermin or allerphen or Alunex or analerg or anaphyl or Antagonate or antamin or apomin or barominic or cadistin or “Carbinoxamide maleate” or “CCRIS 1418” or Chlo-Amine or chlometon or “chlor trimeton” or Chlor-100 or “chloramate unicelles” or chlorleate or Chlormene or “chlorophenamine maleate” or Chloropheniramine or Chlorophenylpyridamine or Chloropiril or Chloroprophenpyridamine or chloroton or Chlorpheniramin* or chlorpheno or chlorphenon or Chlorpro or Chlorprophenpyridamine or chlorpyrimine or “Chlorspan 12” or Chlortab-4 or chlortrimeton or Chlor-Trimeton or chlortripolon or Chlor-Tripolon or Clorfenamina or Clorfeniramina or “cloro trimeton” or cloroalergan or Cloropiril or clorotrimeton or Cloro-Trimeton or C-Meton or cohistan or com-trimeton or Dehist or “dl-Chlorpheniramine maleate” or “Efidac 24” or clemastin* or meclastin* or neclastine or mecloprodin or tavist or tavegyl or “HS 592” or HS592 or cyproheptadine or adekin or Antergan or antisemin or “apeton 4” or astonin or “BRN 1685976” or “CCRIS 5232” or ciplactin or cipractin or ciproeptadine or Ciproheptadina or ciproral or ciprovit-a or cryoheptidine or crypoheptadine or cyheptine or cylat or cypraheptidine or “cypro h” or cyproatin or cyprogin or cyprohaptadi* or cypromin or cyprono or cyprosian or cytadine or Dihexazin or Dronactin or Eiproheptadine or ennamax or glocyp or heptasan or “HSDB 3048” or ifrasal or istam-far or klarivitina or kulinet or “MK 141” or nuran or Periact* or Peritol or petina or pilian or pronicy or sinapdin or trimetabol or Viternum or ketotifen* or ketotiphen* or zaditen or zaditor or “BRN 3983897” or “HC 20 511” or “hc 20511” or “HSDB 7283” or Prometh* or “3277 RP” or A-91033 or adgan or Allerfen or allergan or “Anergan 25” or “Anergan 50” or antiallersin or “antinaus 50” or Aprobit or Atosil or Avomine or baymethazine or Bonnox or "BRN 0088554" or Camergan or “CCRIS 5873” or “CCRIS 7056” or Closin or dimapp or Dimethylamino-isopropyl-phenthiazin or Diphergan or Diprasine or Diprazin* or diprozin or Dorme or Duplamin or Eusedon Mono or fargan or Farganesse or Fellozine or fenazil or fenazine or Fenergan or Fenetazin* or Frinova or Ganphen or Hibechin or hiberna or Histantil or Histargan or “HL 8700” or “HSDB 3173” or insomn-eze or Isophenergan or Isopromethazine or Kinetosin or lercigan or Lergigan or lergigan or "Lilly 01516" or “Lilly 1516” or Metaryl or “Mymethazine Fortis” or NCI-C60673 or “NSC 231688” or “NSC 30321” or Pelpica or pentazine or phargan or Phenadoz or Phenargan or Phencen or Phenergan or Phenerzine or phenoject-50 or Phensedyl or Pilothia or Pipolfen or Pipolphen* or Plletia or “pm 284” or Primine or Pro-50 or Proazamine or procit or promacot or Promantine or promazinamide or Prome or Promergan or Promesan or Promet or Prometazin or Prometazina or Promezathine or Promine or Proneurin or Prorex or protazine or Prothazin or Prothiazine or prothazine or provigan or Provigan or Pyrethia or Pyrethiazine or Remsed or Romergan or “rp 3277” or “rp 3389” or Rumergan or sayomol or “SKF 1498” or Soporil or tanidil or thiergan or “V GAN” or vallergine or “WY 509” or Zipan-25 or Zipan-50) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 18 | 3131 | TS=((“H1” or “H2” or “H3” or “H4”) NEAR/2 (antagonist* or block*)) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 17 | 6175 | TS=(histamine NEAR/3 (antagonist* or block*)) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 16 | 9615 | TS=(anti-histamin* or antihistamin*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 15 | 53 | #14 AND #5 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 14 | 27,038 | #13 OR #12 OR #11 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 13 | 3294 | TS=((nasal or nose) NEAR/2 (spray* or mist or aerosol*)) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 12 | 1212 | TS=(decongestant* or decongestive*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 11 | 23,061 | TS=(xylometazolin* or Balkis or Chlorohist-LA or Decongest or espa-rhin or Gelonasal or Idasal or “Idril N” or Nasan or Imidin or NasenGel or NasenTropfen or NasenSpray or Novorin or Otradrops or Otraspray or Otrivin or Otriven* or Rapako or “schnupfen endrine” or Snup or stas or Amidrin or “Neo-Synephrine II” or Olynth or Otrivine or Rhinactin or “ba 11391” or ba11391 or "brn 0180524" or brufasol or “otrovin hcl” or servilaryn or tixycold or xylometarzoline or xylometazonolin* or xylomethazoline or xilometazolin* or zylometazoline or otrix or cirazolin* or “LD 3098” or naphazolin* or “Afazol Grin” or “AK Con” or AKCon or Albalon or albasol or “All Clear” or allersol or “alpha-Naphthylmethyl imidazoline” or antan or benil or "BRN 0151864" or cefasan or “Ciba 2020” or “Clear Eyes” or Clearine or coldan or “Colirio Alfa” or “comfort eye drops” or dazolin or “degest 2” or derinox or Idril or imidin or minha or Miraclar or mirafrin or Nafazair or Nafazolin* or “naphacel ofteno” or naphasal or Naphcon or “naphozoline hydrochloride” or naphtears or naphthazoline or naphthizine or naphthyzin or nastizol or “nazil ofteno” or niazol or ocu-zoline or opcon or Optazine or Privin* or Proculin or rhinantin or rhinazin or rhinoperd or rimidol or sanorin or sanotin or Siozwo or strictylon or “Tele Stulln” or TeleStulln or Vasoclear or Vasocon or “Vasoconstrictor Pensa” or VasoNit or vistalbalon or vistobalon or Oxymetazolin* or afrazine or afrin or atomol or bayfrin or "BRN 0886303" or dristan or drixine or “duramist plus” or “H 990” or Hazol or “HSDB 3143” or Iliadin or iliadine or Nafrine or nasivin or Navisin or Nezeril or nostrilla or ocuclear or Oximetazolin* or Oxylazine or Oxymethazoline or Rhinofrenol or rhinolitan or rhinosan or “sch 9384” or Sinerol or sinex or visine or Phenylephrin* or adrianol or af-taf or Ah-Chew or AI3-02402 or ak-dilate or “albalon relief” or alconefrin or almefrin or biomidrin or biomydrin or “CCRIS 8464” or derizene or despec-sf or “disneumon pernasal” or “dristan nasal mist” or drosin or efrin-10 or efrisel or fenylephrine or “HSDB 3383” or idrianol or isonefrine or isophrin or “isopto frin” or isoptofrin or “l meta synephrine” or lexatol or “m synephrine” or mesaton* or “meta sympathol” or “meta synephrine” or metaoxedrin* or Metasympatol or metasynephrine or Mezaton or m-Methylaminoethanolphenol or m-Oxedrine or m-Sympathol or m-Sympatol or m-Synephrine or mydfrin or nefrin-ofteno or “Neo Synephrine” or neofrin or neooxedrine or neophryn or neosynephrin or neosynephrine or neosynesin or neosynesine or ocu-phrin or oftan-metaoksedrin or op-isophrin or optistin or phenoptic or phenylefrine or phenylephedrine or prefrin or “pupiletto forte” or rectasol or “rhinall 10” or “slv 325” or slv325 or sucraphen or visadron or vistafrin or vistosan or Phenylpropanolamin* or acutrim or apodrine or apoephedrine or apophedrine or appedrine or “BRN 3196918” or descon or Dexatrim or dexatrim or “diet gard” or “dietac premeal” or “HSDB 6485” or kontexin or monydrin or Mucron or mydriatin or nobese or Norephedrine or “NSC 9920” or “phenyl propanolamine” or phenylpropanolamide or PPA or pressedrine or procol or Prolamine or propadine or propadrine or Propagest or Rhindecon or “Super Odrinex” or trimolet or Pseudoephedrin* or acunaso or afrinol or Besan or dimetapp or d-Isoephedrine or drixora or Ephedrine or “HSDB 3177” or Isoephedrine or isofedrine or isophedrine or “logicin plus” or monofed or nasa-12 or novafed or otrinol or “pseudo ephedrine” or pseudo-12 or Pseudoefedrina or pseudono or Psi-ephedrin or repedrina or rhinalair or “sch 4855” or sch4855 or sinumed or sinutab or subulin or Sudafed or sudomyl or sudosian or symptofed or tiptipot or Synephrin* or Sympaethamin* or Oxedrine or aetaphen or “asthma spray spofa” or pentedrine or vasoton or Analeptin or DL-Synephrine or Ethaphene or “NSC 166285” or “NSC 170956” or Parakorper or Parasympatol or “S 38537-9” or Simpalon or Simpatol or Sympathol or Sympatol or Synefrin or Synthenate or p-Hydroxyphenylmethylaminoethanol or p-Methylaminoethanolphenol or p-Oxedrine or p-Synephrine or tetrahydrozolin* or tetryzoline or Caltheon or “Collyrium Fresh” or “Diabenyl T” or Eye-Sine or Eye-Zine or “Murine Plus” or “Murine Sore Eyes” or Ophtalmin or “Optazine Fresh” or Optigene or Rhinopront or Tetra-Ide or Tetraclear or Tetrilin or Tyzine or Vasopos or Visine or Yxin or Vispring or “Berberil N” or "BRN 0011442" or “HSDB 7471” or Tetrizolin* or Tyzanol or clarine or insto or “murine tears” or murine-2 or nasan or nazane or nazine or “necor tyzine” or octilia or ophthalmin-n or opsil-a or optizoline or rhinoprout or “stilla drops” or visina or visolin or brompheniramine or Bromfed or Lodrane or Dimetapp) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 10 | 48 | #9 AND #5 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 9 | 447,713 | #8 OR #7 OR #6 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 8 | 124,731 | TS=(fluticason* or flixonase or flonase or flovent or cultivate or flixotide or atemur or axotide or beconase or “cci 18781” or cci18781 or cutivat* or flixovate or flunase or fluspiral or flutide or flutinase or flutivate or fluxonal or “gr 18781” or “gr18781” or zoflut or budeson* or pulmicort or horacort or rhinocort or bidien or budecort or budicort or “CCRIS 5230” or cortivent or entocort or micronyl or noex or preferid or respules or rhinosol or spirocort or symbicort or uceris or mometason* or “sch 32088” or nasonex or rinelon or elocon or allermax aqueous or asmanex or danitin or dermotasone or dermovel or ecural or elica or elocom or elocone or elocyn or elomet or elosalic or eloson or flumeta or mefurosan or metaspray or momate or mometAid or monovel or morecort or motaderm or nosorex or novasone or propel or rimelon or rivelon or uniclar or “triamcinolone acetonide” or tricinolon or cinonide or kenalog or azmacort or kenacort or acetospan or “adcortyl A” or allerNaze or aristocort or aristoderm or aristogel or “CCRIS 5231” or coupe-A or flutex or flutone or kenalone or “NSC 21916” or nasacort or “omcilon A” or oracort or oralone or polcortolon or rineton or solodelf or tramacin or tri-nasal or triacet* or triacort or triam-Injekt or triamonide or trianex or triatex or triderm or triesence or trivaris or trymex or “volon A2” or dexameth* or adrenocot or aflucoson* or alfalyl or Anaflogistico or Aphtasolon or arcodexan* or artrosone or Auxiron or Azium or bidexol or “Bisu DS” or Calonat or “CCRIS 7067” or cebedex or cetadexon or colofoam or corsona or Corsone or cortastat or cortidex* or cortidron* or Cortisumman or “dacortina fuerte” or “dacortine fuerte” or dalalone or danasone or Decacortin or decadeltoson* or Decaderm or decadion or decadran or decadron* or decaesadril or Decagel or decaject or Decalix or decameth or Decasone or decaspray or decasterolone or decdan or decilone or decofluor or Dectancyl or Dekacort or delladec or deltafluoren* or Dergramin or Deronil or desacort or desacortone or Desadrene or desalark or desameton* or Deseronil or desigdron or “dexa cortisyl” or “dexa dabrosan” or “dexa korti” or “Dexa Mamallet” or “dexa scherosan” or “dexa scherozon*” or Dexacort* or Dexa-Cort* or dexadabroson or dexadecadrol or Dexadeltone or dexadrol or Dexafarma or dexagel or dexagen or dexahelvacort or dexakorti or dexalien or dexalocal or Dexalona or dexame* or Dexametasona or dexan or dexane or dexano or Dexapolcort or Dexapos or dexapot or Dexaprol or dexascheroson or Dexa-Scheroson or dexascherozon* or Dexa-sine or Dexason* or Dex-ide or Dexinolon or Dexinoral or dexionil or dexona or Dexone or dexpak or Dextelan or dextrasone or Dezone or dibasona or Dinormon or doxamethasone or esacortene or exadion* or firmalone or “fluormethyl prednisolon*” or fluormethylprednisolon* or Fluormone or Fluorocort or fluorodelta or Fortecortin or Gammacorte* or grosodexon* or hexadecadiol or hexadecadrol or hexadiol or hexadrol or “Isopto Dex” or “isopto maxidex” or isoptodex or isoptomaxidex or “Lokalison F” or Loverine or Luxazone or marvidione or maxidex or Mediamethasone or megacortin or mephameson* or metasolon* or methazon* ion or methazonion* or “metisone lafi” or mexasone or Mexidex or millicorten* or Mymethasone or nisomethasona or novocort or “NSC 34521” or “nsc34521” or Ocu-trol or oftan-dexa or opticorten or opticortinol or oradexan or oradexon* or orgadrone or Ozurdex or pidexon or Policort or “Prednisolon F” or prodexon* or sanamethasone or santenson or santeson or sawasone or solurex or spoloven or sterasone or thilodexine or triamcimetil or vexamet or visumetazone or visumethazone or adrecort or Aeroseb or dexacen or isnacort or methylfluorprednisolone or posurdex or beclomet* or aerobec or afifon or Alanase or Aldecin* or anceron or apo-beclomethasone or ascocortonyl or “asmabec clickhaler” or Atomase or atomide or beceze or Beclacin or beclamet or beclate or Beclazone or “beclo asma” or “beclo AZU” or “beclo rhino” or becloasma or beclocort or becloforte or beclojet or beclone or beclorhinol or beclosol or beclotaide or becloturmant or becloturmat or beclovent or becodisk* or beconase or beconasol or becotide or belax or bemedrex or Benconase or bronchocort or bronconox or “chf 1514” or “chf1514” or Clenil or decomit or ecobec or Entyderma or filair or Inalone or junik or Korbutone or Menaderm or miflasone or nasobec aqueous or nexxair or nobec or orbec or prolair or propaderm or qvar or ratioallerg or respocort or rhinivict or “Rhino Clenil” or Rhinosol or rinaze or rynconox or sanasthmax or sanasthmyl or "sbn 024" or sbn024 or “Sch 18020W” or Turbinal or vancenase or vanceril or ventolair or viarex or viarin or Viaro or xiten or betamethasone or betamethason or betnesol or bentelan or rinderon* or “celestone phosphate” or “beta corlan” or “beta methasone” or betam-ophtal or diprospan or durabetason or etnesol or inflacor or linolosal or linosal or “NSC 90616” or solucelestan or apo-flunisolide or inhacort or nasalide or ratio-flunisolide or rhinalar or RS-3999 or syntaris or aeroBid or nasarel or aerospan or bronalide or cyntaris or flunitec or flunisolid* or gibiflu or locasyn or lokilan or lunibron-a or lunis or nisolid or rs3999 or sanergal or soluzione or synaclyn or “val 679” or val679 or prednison* or Adasone or ancortone or Apo-Prednisone or biocortone or Cartancyl or “CCRIS 2646” or colisone or Cortan or Cortancyl or cortidelt or cortiprex or Cotone or Cutason or dacorten or Dacortin or “de cortisyl” or decortancyl or decortin* or Decortisyl or Dehydrocortisone or dekortin or delitisone or dellacort or “delta cortelan” or “delta Cortisone” or “delta dome” or “delta e” or “delta prenovis” or delta-1-Cortisone or delta-1-Dehydrocortisone or deltacort* or delta-dome or Deltasone or deltison* or deltra or “di adreson” or diadreson or drazone or Econosone or Encorton* or Enkortolon or enkorton or fernisone or Fiasone or hostacortin or “HSDB 3168” or Incocortyl or insone or “IN Sone” or Juvason or Kortancyl or “Liquid Pred” or Lisacort or lodotra or Lodtra or me-korti or meprison or metacortandracin or Meticorten or meticortine or NCI-C04897 or nisona or Nizon or Novoprednisone or “nsc 10023” or nsc10023 or Nurison or Orasone or orisane or Panafcort or Panasol or paracort or Parmenison or pehacort or precort or precortal or “Predni Tablinen” or prednicen-m or prednicorm or Prednicort or prednicot or Prednidib or Prednilonga or Predniment or prednitone or Prednizon or Prednovister or Presone or pronison or Pronisone or pronizone or pulmison or Rectodelt or Retrocortine or servisone or SK-Prednisone or steerometz or Sterapred or Supercortil or “U 6020” or Ultracorten* or urtilone or Winpred or Wojtab or Zenadrid or methylprednisolon* or adlone-40 or adlone-80 or A-Methapred or Artisone-wyeth or Besonia or “BRN 2340300” or “dep medalone 80” or depmedalone or depoject-80 or Depo-Medrol or depopred or Dopomedrol or esametone or firmacort or “HSDB 3127” or Lemod or Medesone or medixon or med-jec-40 or “Medlone 21” or mednin or “medralone 80” or medrate or Medrol or medrone or meprednisolone or mesopren or Metastab or “methacort 40” or “methacort 80” or methylcotol or methylcotolone or Methyleneprednisolone or “methylpred dp” or methylsterolone or metidrol or Metilbetasone or Metilprednisolon* or Metipred or metrisone or Metrocort or metycortin or metypred or metypresol or Metysolon or Moderin or neomedrone or Nirypan or Noretona or “nsc 19987” or nsc19987 or “Predni N Tablinen” or prednol or Promacortine or Reactenol or Sieropresol or solomet or “solu decortin” or Solu-medrol or Summicort or Suprametil or “U 7532” or “U-67 590A” or Urbason or Urbasone or Wyacort or Prednisolon* or adelcort or antisolon or antisolone or aprednislon or aprednislone or benisolon or benisolone or berisolon or berisolone or “BRN 1354103” or Bubbli-Pred or caberdelta or capsoid or “CCRIS 980” or “co hydeltra” or codelcortone or CO-Hydeltra or compresolon or Cordrol or cortadeltona or cortadeltone or cortalone or cortelinter or cortisolone or Cotogesic or cotolone or dacrotin or ecaprednil or decortril or “dehydro cortex” or “dehydro hydrocortisone” or dehydrocortex or dehydrocortisol or dehydrocortisole or dehydrohydrocortison or dehydrohydrocortisone or delcortol or “delta cortef” or “delta cortril” or “delta ef cortelan” or “delta f” or “delta hycortol” or “delta hydrocortisone” or “delta ophticor” or “delta stab” or “delta1 dehydrocortisol” or “delta1 dehydrohydrocortisone” or “delta1 hydrocortisone” or deltacortef or delta-cortef or Deltacortenol or deltacortenolo or deltacortil or deltacortoil or deltacortril or deltaderm or delta-Ef-Cortelan or deltaglycortril or deltahycortol or deltahydrocortison or deltahydrocortisone or deltaophticor or deltasolone or deltastab or deltidrosol or deltisilone or deltisolon or deltisolone or deltolasson or deltolassone or deltosona or deltosone or depo-predate or dermosolon or “Derpo PD” or Dexa-Cortidelt or “hostacortin H” or dhasolone or “diadresone f” or DiAdresonF or dicortol or domucortone or Donisolone or Dydeltrone or “Eazolin D” or encortelon or encortelone or encortolon or Erbacort or Erbasona or Estilsona or Fernisolone or glistelone or hefasolon or “HSDB 3385” or hydeltra or hydeltrone or hydrelta or hydrocortancyl or hydrocortidelt or hydrodeltalone or hydrodeltisone or hydroretrocortin or hydroretrocortine or inflanefran or insolone or “K 1557” or keteocort or key-pred or lenisolone or Lentosone or leocortol or liquipred or “lygal kopftinktur” or mediasolone or meprisolon or meprisolone or metacortalon or metacortalone or metacortandralon or metacortandralone or metacortelone or “meti derm” or meticortelone or metiderm or morlone or mydrapred or “neo delta” or nisolon or nisolone or “nsc 9120” or nsc9120 or opredsone or Orapred or panafcortelone or panafort or paracortol or Paracotol or Pediapred or phlogex or PRDL or “pre cortisyl” or preconin or precortalon or precortancyl or Precortilon or precortisyl or “predacort 50” or predaject-50 or “predalone 50” or predartrina or predartrine or Predate or predeltilone or predisole or predisyr or pred-ject-50 or “predne dome” or prednecort or prednedome or Predne-Dome or prednelan or “predni coelin” or “predni h tablinen” or Prednicen or prednicoelin or prednicortelone or “prednifor drops” or predni-helvacort or Predniliderm or predniment or predniretard or prednis or prednisil or prednivet or prednorsolon or prednorsolone or Predonin or Predonine or predorgasolona or predorgasolone or prelon or prelone or prenilone or prenin or prenolone or preventan or prezolon or Rolisone or rubycort or scherisolon or scherisolona or serilone or solondo or solone or solupren or soluprene or spiricort or spolotane or Steran or sterane or sterolone or supercortisol or supercortizol or taracortelone or Ulacort or walesolone or wysolone) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 7 | 360,878 | TS=(corticosteroid* or “cortico steroid*” or corticoid* or steroid* or glucocorticoid* or “anti inflam*” or antiinflam*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 6 | 743 | TS=("adrenal cort*" NEAR/2 hormone*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 5 | 2982 | #1 or #2 or #3 or #4 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 4 | 687 | TS=(middle-ear NEAR/3 pressure*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 3 | 108 | TS=(middle-ear NEAR/3 dysfunction*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 2 | 75 | TS=(eustachian NEAR/2 (canal or orifice*)) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
| # 1 | 2442 | TS=((eustachian or auditory or pharyngotympanic) NEAR/3 tub*) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, CPCI-S Timespan=All Years Lemmatization=Off |
Key:
TS = topic tag; searches terms in title, abstract, author keywords and keywords plus fields
* = truncation
“ “ = phrase search
NEAR/3 = terms with 3 words of each other
Trial registers
Clinical Trials.gov: http://clinicaltrials.gov/
Search date: 15 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 40.
Eustachian AND (tube OR tubes OR tubal)
-
15 studies found for: Eustachian AND (tube OR tubes OR tubal)
auditory AND (tube OR tubes OR tubal)
-
3 studies found for: auditory AND (tube OR tubes OR tubal)
pharyngotympanic AND (tube OR tubes OR tubal)
-
no studies found for: pharyngotympanic AND (tube OR tubes OR tubal)
pharyngotympanic
-
no studies found for: pharyngotympanic
eustachian AND (canal OR canals)
-
2 studies found for: eustachian AND (canal OR canals)
Eustachian AND (orifice OR orifices)
-
no studies found for: Eustachian AND (orifice OR orifices)
“middle ear “ AND (dysfunction OR dysfunctional)
-
6 studies found for: “middle ear “ AND (dysfunction OR dysfunctional)
“middle ear “ AND (pressure OR pressures)
-
14 studies found for: “middle ear “ AND (pressure OR pressures)
Current Controlled Trials: www.controlled-trials.com/
Search date: 15 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 88.
Search of all registers via the meta Register of Controlled Trials (mRCT).
Eustachian – 10 results.
auditory AND tube – 12 results.
auditory AND tubes – 7 results.
auditory and tubal – 10 results.
pharyngotympanic – 0 results.
middle ear AND dysfunction – 12 results.
middle ear AND dysfunctional – 0 results.
middle ear AND pressure – 34 results.
middle ear AND pressures – 3 results.
EU Clinical Trials Register: www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/
Search date: 15 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 5.
Eustachian – 0 results.
Auditory AND tube – 3.
Auditory AND tubes – 2.
pharyngotympanic – 0.
“middle ear” AND dysfunction – 0 results.
“middle ear” AND dysfunctional – 0 results.
National Research Register Archive: www.nihr.ac.uk/Pages/NRRArchiveSearch.aspx
Search date: 15 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 0.
Searched using the all fields search option.
Eustachian – 0 results.
auditory AND tube – 0 results.
auditory AND tubes – 0 results.
auditory AND tubal – 0 results.
pharyngotympanic – 0 results.
middle ear – 0 results.
World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform: www.who.int/ictrp/en/
Search date: 15 October 2012.
Records retrieved: 18.
Eustachian – 7 results.
auditory AND tub* – 1 result.
pharyngotympanic – 0 results.
middle ear AND dysfunction* – 2 results.
middlear ear AND pressure* – 8 results.
Websites
European Medicines Agency: www.ema.europa.eu/ema/
Search date: 1 November 2012
Site wide search for:
Eustachian – 1 result
middle ear dysfunction – 0 results
middle ear pressure – 0 results
US Food and Drug Administration: www.fda.gov/
Search date: 1 November 2012
'eustachian AND (tube OR tubes OR tubal OR canal OR orifice OR orifices)' in all of FDA and archived advisory committee and dockets information – 198 results.
“middle ear dysfunction” in all of FDA and archived advisory committee and dockets information – 5 results.
"middle ear pressure" in all of FDA and archived advisory committee and dockets information – 11 results.
Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency: www.mhra.gov.uk/
Search date: 5 November 2012.
Site wide search for:
Eustachian – 5 results.
“middle ear dysfunction” – 0 results.
“middle ear pressure” – 0 results.
Appendix 2 Quality assessment criteria
Randomised controlled trials (Cochrane risk of bias)48
Possible answers for each criterion were ‘yes’ (low risk of bias), ‘no’ or ‘unclear’ (unclear risk of bias). Bias domains corresponding to each item are indicated in brackets.
-
Random sequence generation (selection bias)
-
Are reports of the study free of suggestion of selective outcome reporting?
-
-
Allocation concealment (selection bias)
-
Was allocation adequately concealed?
-
-
Blinding
-
Participant (performance bias)
-
Was participants’ knowledge of the allocated intervention adequately prevented during the study?
-
-
Personnel (performance bias)
-
Was personnel’s knowledge of the allocated intervention adequately prevented during the study?
-
-
Outcome assessors (detection bias)
-
Was assessors’ knowledge of the allocated intervention adequately prevented during the study? (for patient reported outcomes and/or physician reported outcomes)
-
-
-
Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias)
-
Were incomplete outcome data adequately addressed?
-
-
Selective outcome reporting (selective reporting)
-
Are reports of the study free of suggestion of selective outcome reporting?
-
-
Other bias
-
Was the study apparently free of other problems that could put it at a high risk of bias?
-
An overall risk of bias judgement was made for each trial based on the highest risk scored for any single criterion. For example, if a trial was considered at low risk of bias on all criteria except one where the risk was unclear, then the overall risk of bias was recorded as unclear; where the risk was low or unclear on all criteria except one which was scored as high, then the overall risk of bias was recorded as high.
Non-randomised controlled studies
Possible answers for each criterion were ‘yes’, ‘no’, ‘unclear’ or ‘not applicable’.
-
Were the selection/eligibility criteria adequately reported?
-
Is the sample likely to be representative?
-
If yes, was it a random sample?
-
-
Was the participation rate adequate (> 80% of those eligible)
-
Was there at least 80% follow-up from baseline?
-
Were groups balanced at baseline?
-
If no or partial, were baseline differences adequately adjusted for in the design and/or analyses?
-
-
Were outcome assessors blind to group allocation?
-
For patient-reported outcomes?
-
For physician-assessed outcomes?
-
-
Were dropout rates and reasons similar across intervention and control groups?
-
Was there an appropriate statistical analysis?
-
Were there any other important limitations?
Uncontrolled studies
Possible answers for each criterium were ‘yes’, ‘no’, and where relevant, ‘unclear’ or ‘not applicable’.
-
Were the selection/eligibility criteria adequately reported?
-
Is the sample likely to be representative?
-
If yes, was it a random sample?
-
-
Were patients recruited prospectively?
-
Were patients recruited consecutively?
-
Was the participation rate adequate (> 80% of those eligible)
-
Was there at least 80% follow-up from baseline?
-
Was loss to follow-up reported?
-
Were relevant prognostic factors reported? (e.g. otitis media with effusion or other baseline comorbidities)?
-
Were other relevant confounding factors reported? (e.g. use of cointerventions)
-
Was an appropriate measure of variability reported?
-
Was there an appropriate statistical analysis?
-
Were there any other important limitations?
Appendix 3 Excluded references at full-text screening stage
Excluded references: not relevant population
Adkins WY. Long-term middle ear ventilation. Laryngoscope 1977;87:1833–5.
Andreasson L, Reimer A. Tubal function and surgery in chronic otitis media: the predictive value of testing tubal function, Valsalva’s manoeuvre and volume of ear spaces. In Sade J, editor. Basic Aspects of the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases. Selected Papers From a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Geneva, Switzerland, October 26–29, 1989. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 195–200.
Arefyeva NA, Stratieva OV, Salakhova GM, Khafizova FA, Dragunskaia MI, Sharipov RA, et al. [Validation of therapeutical policy choice in exudative otitis media.] Vestn Otorinolaringol 1998;2:24–7.
Avraham S, Goshen S, Luntz M, Sade J. The surgical treatment of atelectatic ears and retraction pockets. In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Clinical Aspects. Selected Papers from a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Geneva, Switzerland, October 26–29, 1989. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 315–20.
Bacciu S, Bortesi G, Magnani M, Pasanisi E, Scandellari R, Zini C. Medium and long-term results of Eustachian tube surgery. In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Clinical Aspects. Selected Papers from a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Geneva, Switzerland, October 26–29, 1989. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 369–73.
Barati B, Omrani MR, Okhovat AR, Kelishadi R, Hashemi M, Hassanzadeh A, et al. Effect of nasal beclomethasone spray in the treatment of otitis media with effusion. J Res Med Sci 2011;16:509–15.
Ben Ami M, Rosen G, Shlezinger T, Konack S. Otitis media with effusion – complications after treatment. J Laryngol Otol 1983;97:1091–4.
Blatnik DS, Millen SJ, Toohill RJ. Ventilating tubes in tympanoplasty. Laryngoscope 1977;87:1847–52.
Bonding P, Lorenzen E. Cicatricial changes of the eardrum after treatment with grommets. Acta Otolaryngol 1973;75:275–6.
Brodsky L, Brookhauser P, Chait D, Reilly J, Deutsch E, Cook S, et al. Office-based insertion of pressure equalization tubes: the role of laser-assisted tympanic membrane fenestration. Laryngoscope 1999;109:2009–14.
Bulkley WJ, Bowes AK, Marlowe JF. Complications following ventilation of the middle ear using Goode T tubes. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1991;117:895–8.
Cantekin EI, Bluestone CD. Membrane ventilating tube for the middle ear. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1976;85(2 Suppl. 25 Pt. 2):270–6.
Cantekin EI, Bluestone CD, Rood SR. Evaluation of the polytetrafluoroethylene-membrane ventilation tube. Laryngoscope 1977;87:1951–60.
Cantekin EI, Doyle WJ, Phillips DC, Reichert TJ, Bluestone CD. Dilation of the Eustachian tube by electrical stimulation of the mandibular nerve. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1979;88:40–51.
Clements KS, Vrabec JT, Mader JT. Complications of tympanostomy tubes inserted for facilitation of hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1998;124:278–80.
Cook SP, Deutsch ES, Reilly JS. Alternative indications for laser-assisted tympanic membrane fenestration. Lasers Surg Med 2001;28:320–3.
Crabtree JA. Permanent tympanic ventilating tube. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 1970;3:61–5.
Damoiseaux RAMJ, Rovers MM. Topical intranasal corticosteroids for otitis media with effusion in primary care. BMJ 2010;340:60–1.
Daudia A, Yelavich S, Dawes PJD. Long-term middle-ear ventilation with subannular tubes. J Laryngol Otol 2010;124:945–9.
Densert B, Densert O, Arlinger S, Sass K, Odkvist L. Immediate effects of middle ear pressure changes on the electrocochleographic recordings in patients with Meniere’s disease. A Clinical Placebo Controlled Study. In Vesterhauge S, Katholm M, Mikines P, editors. 16th Danavox Symposium, Kolding, Denmark, 1995. The Danavox Jubilee Foundation; 1995. pp. 247–54.
Deveze A, Rameh C, Puchol MS, Lafont B, Lavieille JP, Magnan J. Rehabilitation of canal wall down mastoidectomy using a titanium ear canal implant. Otol Neurotol 2010;31:220–4.
Eliachar I, Joachims HZ, Goldsher M, Golz A. Assessment of long-term middle ear ventilation. Acta Otolaryngol 1983;96:105–12.
Elsheikh MN, Elsherief HS, Elsherief SG. Cartilage tympanoplasty for management of tympanic membrane atelectasis: is ventilatory tube necessary? Otol Neurotol 2006;27:859–64.
Foshee WS, Qvarnberg Y. Comparative United States and European trials of loracarbef in the treatment of acute otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1992;11:S12–19.
Gibb AG. Long-term tympanic ventilation by Per-Lee tube. J Laryngol Otol 1986;100:503–8.
Glasscock ME, House WF. Middle fossa Eustachian tuboplasty. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 1970;3:111–18.
Goode RL. T-tube for middle ear ventilation. Arch Otolaryngol 1973;97:402–3.
Goode RL. CO2 laser myringotomy. Laryngoscope 1982;92:420–3.
Gordts F, Clement PAR, Derede M. Lens drain versus Donaldson drain: preliminary results of a prospective study comparing a new with a conventional ventilation tube. In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Clinical Aspects. Selected Papers from a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Geneva, Switzerland, October 26–29, 1989. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 383–88.
Guindi GM. A new concept for auto regulation of endo-tympamic pressure and its application in Eustachian tube dysfunction. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 1980;5:425–6.
Güneren E, Özsoy Z, Ulay M, Eryilmaz E, Özkul H, Geary PM. A comparison of the effects of Veau-Wardill-Kilner palatoplasty and Furlow double-opposing Z-plasty operations on Eustachian tube function. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2000;37:266–70.
Guttenplan MD, Tom LW, DeVito MA, Handler SD, Wetmore RF, Potsic WP. Radial versus circumferential incision in myringotomy and tube placement. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 1991;21:211–15.
Haberkamp TJ, Silverstein HL. Permanent middle ear aeration: long-term follow-up of transosseous ventilating tubes. Laryngoscope 1987;97:1145–8.
Hall LJ. T-tube with tragus cartilage flange in long-term middle ear ventilation. Am J Otol 1990;11:454–7.
Hawthorne MR, Parker AJ. Perforations of the tympanic membrane following the use of Goode-Type ‘long term’ tympanostomy tubes. J Laryngol Otol 1988;102:997–9.
Hayashi M, Sato H, Yamamoto E, Honjo I. [Eustachian tube function in chronic otitis media.] Practica Otologica Kyoto 1987;80:379–84.
Hayashi M, Takahashi H, Sato H, Honjo I. Clearance of the Eustachian tube under negative middle ear pressure. Am J Otolaryngol 1986;7:399–401.
Helms J, Wiedenmann M. Surgery of the atelectatic middle ear. In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Clinical Aspects. Selected Papers from a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Geneva, Switzerland, October 26–29, 1989. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 329–30.
Holmquist J, Lindeman P. Eustachian tube function in ears with cholesteatoma. Am J Otol 1988;9:363–5.
Holmquist J, Renvall U, Svendsen P. Eustachian tube function and retraction of the tympanic membrane. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 1980;89:65–6.
Hurst DS. Allergy management of refractory serous otitis media. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1990;102:664–9.
Iino Y, Nagamine H, Kakizaki K, Komiya T, Katano H, Saruya S, et al. Effectiveness of instillation of triamcinolone acetonide into the middle ear for eosinophilic otitis media associated with bronchial asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2006;97:761–6.
Iliades T, Kiratzidis T, Igoumenidis N. Surgical and medical treatment of secretory otitis media (SOM). In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Clinical Aspects. Selected Papers from a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Geneva, Switzerland, October 26–29, 1989. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 305–11.
Jamal TS. Avoidance of postoperative blockage of ventilation tubes. Laryngoscope 1995;105:833–4.
Jansen C. Results of Eustachian tube surgery in cholesteatoma. In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Clinical Aspects. Selected Papers from a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Geneva, Switzerland, October 26–29, 1989. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 351–2.
Jesic SD, Dimitrijevic MV, Nesic VS, Jotic AD, Slijepcevic NA. Temporalis fascia graft perforation and retraction after tympanoplasty for chronic tubotympanic otitis and attic retraction pockets: factors associated with recurrence. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2011;137:139–43.
Kaylie DM, Miller J. CO(2) Laser myringoplasty. In Kollias N, Choi B, Zeng H, Malek RS, Wong BJF, Ligner JFR, et al. , editors. Photonic Therapeutics and Diagnostics VI. Bellingham: Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE); 2010.
Leek JH. Middle ear ventilation in conjunction with adenotonsillectomy. Laryngoscope 1977;87:1878–83.
Lesinskas E. Factors affecting the results of nonsurgical treatment of secretory otitis media in adults. Auris Nasus Larynx 2003;30:7–14.
Lesinski SG, Fox JM, Seid AB, Bratcher GO, Cotton R. Does the silastic Eustachian tube prosthesis improve Eustachian tube function? Laryngoscope 1980;90:1413–28.
Levinson SR, Gill AJ. Middle ear semipermeable membrane tubes for prolonged retention. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1986;94:438–40.
Lildholdt T. Secretory otitis media. The significance of negative middle ear pressure and the results of a controlled study of ventilation tubes. Dan Med Bull 1983;30:408–15.
Loock JW. A randomised controlled trial of active chronic otitis media comparing courses of eardrops versus one-off topical treatments suitable for primary, secondary and tertiary healthcare settings. Clin Otolaryngol 2012;37:261–70.
Luntz M, Sade J. The value of politzerization in the treatment of atelectatic ears. J Laryngol Otol 1988;102:779–82.
Luntz M, Sade J. The diagnostic and therapeutic value of middle ear inflation. In Sade J, editor. Basic Aspects of the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases. Selected Papers from a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Geneva, Switzerland, October 26–29, 1989. Amsterdam: Kulgler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 183–5.
MacKinnon DM. The sequel to myringotomy for exudative otitis media. J Laryngol Otol 1971;85:773–93.
McNicoll WD. Uncomplicated Eustachian tube dysfunction: the site of the nasal septal deformity. J R Nav Med Serv 1982;68:23–9.
McNicoll WD. Remediable Eustachian tube dysfunction in diving recruits: assessment, investigation, and management. Undersea Biomed Res 1982;9:37–43.
McNicoll WD, Scanlan SG. Submucous resection: the treatment of choice in the nose-ear distress syndrome. J R Nav Med Serv 1979;65:123–30.
Millet D, Talmor D. Follow-up of long-term ventilation of the middle ear using the Goode T-tube. In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Clinical Aspects. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 391–6.
Misurya VK. Tympano-nasopharyngeal shunt operation. A new method of middle ear ventilation. J Laryngol Otol 1975;89:189–97.
Moeller P, Dingsoer G. Secretory otitis media: can erythromycin reduce the need for ventilating tubes? In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Clinical Aspects. Selected Papers from a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, 26–29 October 1989, Geneva, Switzerland. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 67–70.
Mokhtarinejad F, Okhovat SAR, Barzegar F. Surgical and hearing results of the circumferential subannular grafting technique in tympanoplasty: a randomized clinical study. Am J Otolaryngol 2012;33:75–9.
Moore GF. Candidate’s thesis: revision tympanoplasty utilizing fossa triangularis cartilage. Laryngoscope 2002;112:1543–54.
Morita M, Imai T, Kitahara T, Nishiike S, Horii A, Uno A, et al. A novel treatment modality with reference to Eustachian tube function in Meniere’s disease patients. J Vestib Res 2002;11:267.
Murata K, Ohta F. Reconstruction of the Eustachian tube and the anterior tympanum: planned staged tubo-tympanoplasty. Laryngoscope 1985;95:330–4.
Odkvist LM, Arlinger S, Billermark E, Densert B, Lindholm S, Wallqvist J. Effects of middle ear pressure changes on clinical symptoms in patients with Meniere’s disease – a clinical, multicentre, placebo-controlled study. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 1999;543:99–101.
Olaizola F. Tympanoplasties in the AAD technique (antrum exclusion, attic elimination on demand): philosophy and results after seven years. In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Clinical Aspects. Selected Papers from a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, 26–29 October 1989, Geneva, Switzerland,. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 331–4.
Onal K, Uguz MZ, Kazikdas KC, Gursoy ST, Gokce H. A multivariate analysis of otological, surgical and patient-related factors in determining success in myringoplasty. Clin Otolaryngol 2005;30:115–20.
Palva T, Virtanen H. Sonotubometry in chronic ear disease. Arch Otolaryngol 1984;110:596–9.
Park YS, Jung TTK, Choi DJ, Rhee CK, Richmond T, Weeks D. Effect of blockers of leukotriene and/or platelet-activating factor on experimental otitis media with effusion induced by Eustachian tube obstruction. In Mogi G, Honjo I, Ishii T, Takasaka T, editors. Recent Advances in Otitis Media. Proceedings of the Second Extraordinary International Symposium, 31 March–3 April, Oita, Japan. Amsterdam: Kugler Publications; 1994. pp. 671–5.
Parkin JL, Johnson LP, Stringham JC. Transtympanic Eustachian tuboplasty and tolerance of stenting materials. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1983;91:407–11.
Peerless SA, Noiman AH. Etiology of otitis media with effusion: antihistamines – decongestants. Laryngoscope 1980;90:1852–64.
Per-Lee JH. Experiences with a “permanent” wide flange middle ear ventilation tube. Laryngoscope 1969;79:581–91.
Pitman LK. Treatment for chronic suppurative otitis media: report of ninety-six cases treated through the Eustachian tube, with the aid of the catheterizing eustachioscope. AMA Arch Otolaryngol 1954;59:575–8.
Podoshin L, Fradis M, Ben-David Y. The efficacy of oral steroids on persistent otitis media with effusion. In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Clinical Aspects. Selected Papers from a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, 26–29 October 1989, Geneva, Switzerland. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 215–18.
Podoshin L, Fradis M, Malatskey S, Ben-David J. Tympanoplasty in adults: a five-year survey. Ear Nose Throat J 1996;75:149–56.
Qvarnberg Y, Valtonen H. Early treatment with ventilation tube in otitis media: a follow-up study. In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian tube and middle ear diseases, clinical aspects. Selected papers from a conference on the Eustachian tube and middle ear diseases, 26–29 October 1989, Geneva, Switzerland. Amsterdam Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 377–81.
Reimer A, Andreasson L, Harris S, Ivarsson A, Tjernstrom O. Tubal function and surgery in chronic otitis media. A study on the predictive value of testing tubal function, Valsalva’s manoeuvre and volume of ear spaces. Acta Otolaryngol 1988;105(Suppl. 449):127–30.
Renvall U. Tympanometry in secretory otitis media. Scand Audiol 1975;4:83–8.
Renvall U, Holmquist J. Eustachian tube function in secretory otitis media. Scand Audiol 1974;3:87–91.
Renvall U, Nilsson E. Eustachian tube dysfunction. Acta Otolaryngol 1982;94:139–43.
Roberson JB, Mason TP, Stidham KR. Mastoid obliteration: autogenous cranial bone pAte reconstruction. Otol Neurotol 2003;24:132–40.
Robinson PM. Secretory otitis media in the adult. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 1987;12:297–302.
Sade J. Surgical planning of the treatment of cholesteatoma and postoperative follow-up. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2000;109:372–6.
Sade J, Berco E, Fuchs C. Results of preservation of the posterior canal wall in cholesteatoma surgery as related to middle-ear aeration. J Laryngol Otol 1986;100:1351–8.
Saito H, Miyamoto K, Kishimoto S. Burn perforation as a method of middle ear ventilation. Arch Otolaryngol 1978;104:79–81.
Salvinelli F, Casale M, Greco F, D’Ascanio L, Petitti T, Di Peco V. Nasal surgery and Eustachian tube function: effects on middle ear ventilation. Clin Otolaryngol 2005;30:409–13.
Sato H, Nakamura H, Honjo I, Hayashi M. Eustachian tube function in tympanoplasty. Acta Otolaryngol 1990;110:9–12.
Schloegel L, Gottschall JA. SP155 – Balloon dilation of the Eustachian tube: safety and utility. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2009;141(3 suppl. 1):P134.
Sharp M. The manometric investigation of tubal function with reference to myringoplasty results. J Laryngol Otol 1970;84:545–51.
Shinkawa H, Ishidoya M, Okitsu T. Changes in tympanograms after middle ear inflation. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 1990;247:125–8.
Shinnabe A, Hara M, Hasegawa M, Matsuzawa S, Kodama K, Kanazawa H, et al. Relationship between postoperative aeration around the stapes and postoperative hearing outcome after canal wall down tympanoplasty with canal reconstruction for cholesteatoma. Otol Neurotol 2011;32:1230–3.
Silverstein H, Gordon M, Rosenberg SI, Seidman M, Willcox TO, Silverstein J. Middle ear air injection after chronic ear surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1993;109:488–92.
Silverstein H, Kuhn J, Choo D, Krespi YP, Rosenberg SI, Rowan PT. Laser-assisted tympanostomy. Laryngoscope 1996;106:1067–74.
Silverstein H, Wazen J, Silverstein D. Micropuncture of the tympanic membrane after tympanoplasty. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1985;93:224–6.
Skoner DP, Asman B, Fireman P. Effect of chlorpheniramine on airway physiology and symptoms during natural pollen exposure. Am J Rhinol 1994;8:43–8.
Stangerup SE, Tos M. Autoinflation in the treatment of Eustachian tube dysfunction, secretory otitis media and its sequelae. In Mogi G, Honjo I, Ishii T, Takasaka T, editors. Recent Advances in Otitis Media. Proceedings of the Second Extraordinary International Symposium, 31 March–3 April, Otia, Japan. Amsterdam: Kugler Publications; 1994. pp. 759–63.
Sterkers O, Benghalem A, Bowdler DA, Marrakchi A, Sterkers JM. Aeration of Reconstructed Radical Cavities. In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Clinical Aspects. Selected Papers from a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Ddiseases, 26–29 October 1989, Geneva, Switzerland. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 343–46.
Stillwagon PK, Doyle WJ, Fireman P. Effect of an antihistamine/decongestant on nasal and Eustachian tube function. Ann Allergy 1987;58:281.
Stoikes NF, Dutton JM. The effect of endoscopic sinus surgery on symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction. Am J Rhinol 2005;19:199–202.
Stringham JC, Parkin JL. Stent diameter in Eustachian tuboplasty success. Clin Res 1987;35:161A.
Todt I, Seidl R, Ernst A. A new minimally invasive method for the transtubal, microendoscopic application of fluids to the middle ear. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 2008;17:300–2.
Tono T, Morimitsu T, Makino K, Haruta A. Pathogenesis of cholesteatoma inferred from postoperative results of anterior tympanotomy. In McCafferty G, Coman W, Carroll R, editors. Sydney ‘97 – XVI World Congress of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. Bologna: Monduzzi Editore; 1997. pp. 929–32.
Tos M. Tympanoplasty in chronic adhesive otitis media. Acta Otolaryngol 1972;73:53–60.
Tos M. Permanent middle-ear aeration in tympanoplasty. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 1974;36:170–8.
Tos M. Tubal function and tympanoplasty. J Laryngol Otol 1974;88:1113–24.
Tuli BS, Parmar TL, Singh B. Evaluation of tympanostomy tubes in middle ear affections. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2001;53:217–20.
Vartiainen E, Nuutinen J. Success and pitfalls in myringoplasty: follow-up study of 404 cases. Am J Otol 1993;14:301–5.
Virtanen H. The effect of an oral combined preparation (antihistamine and decongestant) on Eustachian tube function in the common cold. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 1982;44:268–76.
Virtanen H, Palva T, Jauhiainen T. The prognostic value of Eustachian tube function measurements in tympanoplastic surgery. Acta Otolaryngol 1980;90:317–23.
Wehrs RE. The Silverstein permanent aeration tube in tympanoplasty. Laryngoscope 1974;84:1369–77.
White P, Malm L, Tjernstrom O. Effect of terbutaline on human Eustachian tube function. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 1989;51:354–9.
Wright PF. Xylitol sugar and acute otitis media. Pediatrics 1998;102:971–2.
Yetiser S, Karapinar U. Middle ear ventilation function in patients with myringoplasty alone and myringoplasty plus mastoidectomy. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg 2011;21:179–83.
Yung MW, Arasaratnam R. Adult-onset otitis media with effusion: results following ventilation tube insertion. J Laryngol Otol 2001;115:874–8.
Excluded references: not relevant interventions
Derebery MJ, Berliner KI. Allergic Eustachian tube dysfunction: diagnosis and treatment. Am J Otol 1997;18:160–5.
El-Sharnouby M, Taha M. Eustachian tube obstruction: new technique for treatment. Am J Otol 1995;16:698–700.
Galletti F, Muscianisi F, Galletti B, Galletti C. [Clinical evaluation of the effect of a new antiphlogistic drug on mucociliary clearance and the surfactant properties of the Eustachian tube mucosa.] Arch Med Interna 1989;41:17–23.
Holmquist J. Middle ear ventilation in chronic otitis media. Arch Otolaryngol 1970;92:617–23.
Rowe-Jones JM, Leighton SE. The value of head dressings for middle ear surgery. J Laryngol Otol 1993;107:17–19.
Salford Royal Hospitals NHS Trust. A Randomised Controlled Trial of the Effects of a Pressure Head Bandage vs. No Pressure Bandage on Discomfort Following Middle Ear Surgery. Current Controlled Trials Ltd. URL: www.controlled-trials.com/mrct/trial/39021 (accessed 9 November 2012).
Excluded references: not relevant outcome
Holmquist J, Bergstrom B. The mastoid air cell system in ear surgery. Arch Otolaryngol 1978;104:127–9.
Misurya V. Physiologic Eustachian tube inflation. Arch Otolaryngol 1975;101:730–2.
Silverstein H. Malleus clip tube for long-term equalization of middle ear pressure. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol 1966;70:640–2.
Wright JW, Wright JW. Preliminary results with use of an Eustachian tube prosthesis. Laryngoscope 1977;87:207–14.
Excluded references: not relevant study design
Armstrong BW. Role of ventilating tubes in tympanoplasty. Arch Otolaryngol 1973;97:13–14.
Butler EC, Burns P. The tympanic ventilating tube: its role in Eustachian tube dysfunction. Tex Med 1972;69:88–9.
Charlett SD, Anari S. Tympanostomy T-tube introducer: a simple technique using a Zoellner suction tube. Laryngoscope 2007;117:563–4.
Crysdale WS. Comparative study of various ventilating tubes. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1976;85(Suppl. 25 Pt. 2):268–9.
Deguine C, Pulec JL. Ventilating tube in an atelectatic ear. Ear Nose Throat J 1999;78:12.
Drettner B, Ekvall L. Tympanomaxillary shunt. A new method of middle ear ventilation. Arch Otolaryngol 1969;90:122–8.
Drettner B, Ekvall L. Tympanomaxillary shunt. Experiences and development. Acta Otolaryngol 1973;75:277–8.
Ekvall L, Drettner B. Tympanomaxillary shunt. Arch Otolaryngol 1973;97:21–3.
Eliachar I. Prolonged ventilation of the middle ear and mastoid cavities: technical considerations. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1985;93:768–72.
Glasscock ME. Middle fossa Eustachian tuboplasty. Arch Otolaryngol 1973;97:15–16.
Gottschalk G. Middle ear inflation: its place in the treatment of otitis media with effusion. In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Clinical Aspects. Selected Papers from a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, 26–29 October 1989, Geneva, Switzerland. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 293–5.
Graham MD, Knight PR. Atelectatic tympanic membrane reversal by nitrous oxide supplemented general anesthesia and polyethylene ventilation tube insertion. A preliminary report. Laryngoscope 1981;91:1469–71.
Hendeles L, Hatton RC. Oral phenylephrine: an ineffective replacement for pseudoephedrine? J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006;118:279–80.
House WF, Glasscock ME, Miles J. Eustachian tuboplasty. Laryngoscope 1969;79:1765–82.
Janeke JB. Pressure-equalizing tubes and middle ear drainage. S Afr Med J 1980;57:521.
Kay NJ Nasal surgery and Eustachian tube function: effects on middle ear ventilation. Clin Otolaryngol 2005;30:409–13.
Kay NJ. Nasal surgery and Eustachian tube function: effects on middle ear ventilation. Clin Otolaryngol 2006;31:80.
Kuschke E. Pressure-equalizing tubes and middle-ear drainage. S Afr Med J 1980;57:1024.
Lapidot A, Rubenstein A. Eustachian tube bypass. IMJ Ill Med J 1984;166:354–5.
LeLiever WC. Eustachian tube dysfunction. JAMA 1993;269:809.
Lutin M. Compositions and Method for Relieving Discomfort in the Ears. US6645532 (Patent) 2003. URL: www.google.com/patents/US6645532 (accessed 17 August 2012).
Magnuson B. How to treat tubal malfunction? In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Clinical Aspects. Selected Papers from a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, 26–29 October 1989, Geneva, Switzerland. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 289–91.
McGee TM. Surgical sequelae of abnormal Eustachian tube function. Am J Otol 1985;6:229–30.
McLaurin JG. Ventilation paracentesis for the relief of stubborn Eustachian tube blockage. Laryngoscope 1949;59:482–501.
Poe D. In reference to balloon dilatation Eustachian tuboplasty: a clinical study. Laryngoscope 2011;121:908.
Scandellari R, Zini C, Bacciu S, Pasanisi E. Presurgical transtympanic catheterism of the Eustachian tube in tympanoplasty. In Sade J, editor. The Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, Clinical Aspects. Selected Papers from a Conference on the Eustachian Tube and Middle Ear Diseases, 26–29 October 1989, Geneva, Switzerland. Amsterdam: Kugler & Ghedini; 1991. pp. 365–68.
Valentino RL. Chronic dysfunction of the Eustachian tube. Clin Advisor 2009;12:21–2.
van Heerbeek N, Ingels KJOA, Rijkers GT, Zielhuis GA. Therapeutic improvement of Eustachian tube function: a review. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 2002;27:50–6.
Yung MW. Permanent mastoid vent: a new treatment for persistent Eustachian tube obstruction. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 1998;23:93–6.
Yung MW, Bowdler D, Swan IRC. The Yung percutaneous mastoid vent: results of a multicenter trial. Otol Neurotol 2004;25:885–90.
Excluded references: not in English
Kryukov AI, Garov EV, Antonyan RG, Azarov PV, Gutieva TK. [Differential atticoanthrotomy with type 1 tympanoplasty as the method of choice for the treatment of chronic perforating otitis media with expressed mucositis.] Vestn Otorinolaringol 2011;5:32–4.
Lieberum B, Jahnke K. [Golden tube wire for temporary or permanent implantation in patients with Eustachian dysfunction.] HNO 1996;44:140–2.
Maeda T. [A new method of intratubal spray into the auditory tube.] Jibiinkoka 1980;52:1071–5.
Maier W, Krebs A. [Is there an indication for septoplasty and conchotomy before tympanoplasty? Effects of nasal surgery on the Eustachian tube.] Laryngorhinootologie 1998;77:682–7.
Mora AB, Lopez EGZ, Rodriguez JMG. [Tympanoplasty in chronic otitis media and its relations to the Eustachian tube.] Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc 1999;37:127–32.
Sato Y. [Complications of tympanostomy tube insertion for otitis media with effusion.] Jibiinkoka 1986;58:79–83.
Takahashi H, Yamamoto E, Hirono Y, Honjo I. [Eustachian tube function in patients with otitis media chronica.] Practica Otologica Kyoto 1986;79:37–44.
Excluded references: uncontrolled studies with mixed or uncertain population
Laser tuboplasty (one case series, five records)
Kujawski O. Laser Eustachian tuboplasty, L.E.T.P. Laryngorhinootologie 2000;79(Suppl.):S162.
Kujawski O. Laser Eustachian tuboplasty (LETP): an overview of four years of experience in endoscopic transnasal laser-assisted cartilaginous Eustachian tube surgery (LETP) for middle ear diseases. Skull Base Surg 2001;11(Suppl. 2):14.
Kujawski O, Fasel J, Romanowicz R. Laser Cartilaginous Eustachian Tuboplasty. In Oswal V, Remade M, editors. Principles and Practice of Lasers in Otorhinolaryngology and Head Neck Surgery. The Hague: Kugler Publications; 2002. pp. 295–9.
Kujawski OB, Poe DS. Laser Eustachian tuboplasty. Otol Neurotol 2004;25:1–8.
Poe D, Kujawaski O. Endoscopic Diagnosis and Surgery of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. In Silverstein H, Rosenberg SI, Poe D, Jackson LE, editors. Minimally Invasive Otological Surgery. New York, NY: Thomson/Delmar Learning; 2003. pp. 51–69.
Balloon dilatation
Dalchow C, Muenscher A, Knecht R. Endoscopic dilatation of the Eustachian tube. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2011;145:P93.
Bouginage
Tos M. Management of tubal function in reconstructive middle ear surgery. J Laryngol Otol 1980;94:25–30.
Eustachian tube prosthesis
Wright JW, Wright JW, Hicks GW. The Eustachian tube prosthesis revisited. Otolaryngology 1978;86:ORL-834–7.
Gold wire
Jahnke K, Lieberum B. A gold wire for temporary or permanent implantation in patients with Eustachian tube dysfunction. In Tos M, Thomsen J, Balle V, editors. Otitis Media Today. Proceedings of the Third Extraordinary Symposium on Recent Advances in Otitis Media, 1–5 June 1997, Copenhagen, Denmark. The Hague: Kugler Publications; 1999. pp. 619–21.
Myringoplasty
Gimenez F, Marco-Algarra J, Carbonell R, Morant A, Cano S. Prognostic factors in tympanoplasty: a statistical evaluation. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol 1993;114:335–7.
Ventilation tubes
Al-Swadi W, Karlsmose B, Gaihede M, Henriksen SD, Rosborg J. Long-term treatment of chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction by subannular ventilation tubes. Otol Neurotol 2005;26:301.
Elluru RG, Dhanda R, Neely JG, Goebel JA. Anterior subannular T-tube for prolonged middle ear ventilation during tympanoplasty: evaluation of efficacy and complications. Otol Neurotol 2001;22:761–5.
Gupta SC, Malhotra M, Singh M. Eustachian tube function after transmyringeal ventilation. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2005;57:39–42.
Jahn AF. Middle ear ventilation with HydroxylVent tube: review of the initial series. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1993;108:701–5.
Jensen MG, Jacobsen H, Gaihede ML, Rosborg J. Subannular ventilation tubes in treatment of chronic tubal dysfunction – results in 85 consecutive cases. In Huber A, Eiber A, editors. Middle Ear Mechanics in Research and Otology. Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium, 27–30 July 2006, Zurich, Switzerland. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Company; 2007. pp. 46–52.
O’Hare T, Goebel JA. Anterior subannular T-tube for long-term middle ear ventilation during tympanoplasty. Am J Otol 1999;20:304–8.
Per-Lee JH. Long-term middle ear ventilation. Laryngoscope 1981;91:1063–73.
Rothera MP, Grant HR. Long-term ventilation of the middle ear using the Goode T-tube. J Laryngol Otol 1985;99:335–7.
Sajan JA, Hilton CW, Levine SC. Long-term outcomes and reliability of Jahn ventilating tube. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2011;145(Suppl. 2):218.
Appendix 4 Ongoing studies
Ongoing relevant studies: summary characteristics
| Study | Design | Estimated enrolment | Country, funding | Anticipated start | Anticipated end |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North Bristol NHS Trust81 | RCT | 200 | UK, North Bristol NHS Trust | 4 January 2012 | 4 January 2015 |
| Vanderbilt University82 | Non-randomised, uncontrolled open-label | 100 | USA, Vanderbilt University | August 2012 | August 2013 |
| Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh43 | RCT | 40 | USA, Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh | March 2011 | December 2013 (final data collection date for primary outcome measure) |
Ongoing relevant studies: interventions, outcomes and intended participants
| Study | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | Interventions | Comparator | Outcome measures | Follow-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North Bristol NHS Trust81 | ≥ 18 years; long-term ETD | Children; active nasal disease, e.g. polyps; deviated septum | Balloon dilatation (randomised to right or left ear) under general anaesthesia | Ventilation tube (contralateral ear) | Primary: ET score (ear popping during swallowing and blowing the ears) Secondary: pure-tone audiometry, tympanostomy |
1 week, 1, 3, 6, 12, 24 months |
| Vanderbilt University82 | 18–70 years; ETD diagnosis (symptomatology and positive ETDQ-7); non-smoker; normotensive or hypertensive; normal renal function; not currently on acetazolamide; not currently on a low-salt diet; no other previous alternative otologic diagnosis | Smoking; kidney disease; hypotension; strong history of vascular disease; Meniere’s disease; allergy or adverse reaction to hydrochlorothiazide/triamterene; concurrent aspirin use; current or planned pregnancy during the course of the study; healthy volunteers | Treatment for endolymphatic hyrdrops:nasal steroids and antihistamine (standard treatment for endolymphatic hydrops); if fails: myringotomy tubes; if fails: low-salt diet and diuretic | None | Improvement in patient ETD symptoms: with nasal steroid and antihistamine alone; with pressure equalisation tubes; with a diuretic and low-salt diet | 2 years |
| Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh43 | 18–50 years; healthy other than current upper respiratory tract infection; Jackson Score of 6; symptom onset within 4 days; unilateral or bilateral middle-ear pressure < –50 mmH2O | Otoscopic diagnosis of unilateral or bilateral otitis media; ventilation tube or eardrum perforations bilaterally; asthma or any chronic medical condition; use of an ‘over-the-counter’ medicine within 24 hours of study or prescription within 4 weeks of the study day (except birth control); use of an experimental drug within 3 months of study; unusual or allergic reaction to simethicone, food dyes, or preservatives; pregnancy or breast feeding; ear surgery other ventilation tube | Simethicone, single 125 mg chewable tablet | Placebo, chewable calcium tablet | Change in Eustachian tube function measures | 30 minutes |
Appendix 5 Data extraction tables of included studies
Pharmacological studies
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gluth (2011)
52
RCT Funding: Sanofi-Aventis US Setting: hospital – department of otorhinolaryngology (recruitment) Number of centres: single centre Number of patients: Total 91 Intervention 45 Comparator 46 Statistical analyses: Tests used: chi-squared test of tympanogram normalisation. 95% CI calculated for difference in proportions between arms. Regression analysis used to evaluate tympanogram normalisation on a per-ear basis, taking into account subject-ear correlation. Wilcoxon rank sum tests for symptom frequency and severity questionnaire. Analysis of covariance model for post-study overall score comparison based on overall follow-up score adjusted for baseline score Unit of analysis: patients (primary analysis), ears (secondary analysis) Population analysed: patients completing treatment (dropouts and loss to follow-up documented but not included) Power calculation: designed to have 80% power to detect difference of 25% (placebo arm) vs. 50% (treatment arm) at 6 weeks, assuming 10% dropout rate. Sample size to achieve this was 146 patients (73 per treatment arm) |
Inclusion criteria: OME, negative middle-ear pressure or both with intact tympanic membrane Exclusion criteria: tympanic membrane perforation on otoscopy active cholesteatoma acute or chronic suppurative otitis media craniofacial syndromes cleft palate developmental delay type 4 retraction of TM (extent of retraction not visualised) Diagnostic methods: otoscopic examination, tympanometry, nasopharyngoscopy (adults only) |
Age (years)
Median: NR Mean: 41.7 (29.5) years Range: 6.1 to 95.8 years (n/N) (%) male: 45/91 (49%) Ethnicity: NR Body weight/BMI: NR Subgroups (1) Adults (aged 18+), n = 57 (2) Children (aged 6–17 years), n = 34 |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: NR ETD diagnosis (n/N; %): 91/91 (100%) High risk (n/N; %): NR Related conditions (n/N; %): Balance problems: 20/91 (22%); tinnitus: 27/91 (30%); common cold symptoms: 24/91 (26%) (all occurred in equal numbers in the study arms) Allergic rhinitis: 12% [17% (placebo) vs. 7% (intervention)] Previous treatment: NR Baseline medication: NR |
|
| Intervention | Comparator | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | |
| Pharmacological: [info] Nasacort AQ nasal spray (Sanofi Aventis) containing triamcinolone 55 μg/spray 2 sprays per nostril once daily) (one spray per nostril for those aged under 12 years) | Placebo spray: identical aqueous solution without triamcinolone. Two sprays per nostril per day (one spray per nostril per day for those aged under 12 years) | Not applicable | Instructed not to use oral or topical decongestants. Antibiotic use was also considered to constitute treatment failure (see secondary outcomes) | |
| Outcomes | ||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up |
| ETDQ-7 (adapted)? Intervention: Pressure [mean (SD)] Change from baseline (N = 38): Frequency Better: 11 (28.9) Same: 17 (44.7) Worse: 10 (26.3) Severity Better: 13 (34.2) Same: 14 (36.8) Worse: 11 (28.9) Pain [mean (SD)] Change from baseline (N = 38): Frequency Better: 11 (28.9) Same: 17 (44.7) Worse: 10 (26.3) Severity Better: 9 (23.7) Same: 19 (50.0) Worse: 10 (26.3) Feeling clogged [mean(SD)] Change from baseline (N = 38): Frequency Better: 10 (26.3) Same: 13 (34.2) Worse: 15 (39.5) Severity Better: 15 (39.5) Same: 8 (21.1) Worse: 15 (39.5) Crackling/popping [mean (SD)] Change from baseline (N = 38): Frequency Better: 11 (28.9) Same: 14 (36.8) Worse: 13 (34.2) Severity Better: 9 (23.7) Same: 17 (44.7) Worse: 12 (31.6) Feeling muffled [mean(SD)] Change from baseline (N = 38): Frequency Better: 16 (42.1) Same: 14 (36.8) Worse: 8 (21.1) Severity Better: 15 (39.5) Same: 13 (34.2) Worse: 10 (26.3) Comparator Crackling/popping [mean (SD)] Feeling muffled [mean (SD)] (N = 40) Frequency Better: NR Same: NR Worse: NR Severity Better: NR Same: NR Worse: NR Pressure [mean (SD)] (N = 40): Frequency Better: 18 (45.0) Same: 17 (42.5) Worse: 5 (12.5) Severity Better: NR Same: NR Worse: NR Pain [mean (SD)] Feeling clogged [mean (SD)] Pressure [mean (SD)] Change from baseline (N = 40): Frequency Better: 18 (45.0) Same: 17 (42.5) Worse: 5 (12.5) Severity Better: 18 (45.0) Same: 13 (32.5) Worse: 9 (22.5) Pain [mean (SD)] Change from baseline (N = 40): Frequency Better: 8 (20.0) Same: 23 (57.5) Worse: 9 (22.5) Severity Better: 6 (15.0) Same: 25 (62.5) Worse: 9 (22.5) Feeling clogged [mean (SD)] Change from baseline (N = 39, 1 missing): Frequency Better: 14 (35.9) Same: 21 (53.8) Worse: 4 (10.3) Severity Better: 14 (35.9) Same: 16 (41.0) Worse: 9 (23.1) Crackling/popping [mean (SD)] Change from baseline (N = 39, 1 missing): Frequency Better: 8 (20.5) Same: 18 (46.2) Worse: 13 (33.3) Severity (N = 38, 2 missing) Better: 6 (15.8) Same: 19 (50.0) Worse: 13 (34.2) Feeling muffled [mean (SD)] Change from baseline (N = 39, 1 missing): Frequency Better: 16 (41.0) Same: 15 (38.5) Worse: 8 (20.5) Severity Better: 14 (35.9) Same: 15 (38.5) Worse: 10 (25.6) Overall [mean (SD)]: Follow up: NS higher for intervention vs. control (p = 0.07) Change from baseline: after adjustment for baseline score, post-study overall score did not differ between groups (p = 0.27). Per cent of subjects with improved symptoms did not differ significantly for any of the five symptoms (chi-square p > 0.05) Pressure [mean (SD)] Follow-up: more moderate severity in intervention group (p = 0.07) Pain [mean (SD)] follow-up: NR Feeling clogged [mean (SD)] Follow-up: more frequent (p = 0.02) and more severe (p = 0.03) in intervention group Crackling/popping [mean (SD)] Follow-up: NR Feeling muffled [mean (SD)] Follow-up: NR Outcome assessed using a reliable tool? Unclear Unclear whether or not this is the ETDQ-7 (if so, two items missing); authors state not validated Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes (6 weeks) |
NR |
Tympanogram type A in both ears (per patient, adult + children)
Intervention Baseline: 0/45 Follow-up: 7/37 normalised Comparator Baseline: 0/46 Follow-up: 12/37 normalised Difference between groups Difference in proportions: 13.5 (95% CI –33.2 to 6.2) p = 0.18 (extracted) RR 1.20 (95% CI 0.91 to 1.58) (calculated) Tympanogram type A in both ears (per patient, adult + children) considering patients who took additional treatment as having incomplete normalisation Intervention Baseline: 0/45 Follow-up: 5/37 normalised Comparator Baseline: 0/46 Follow-up: 9/37 normalised Difference between groups Difference in proportions: 10.8% (95% CI –28.5% to 6.9%) p = 0.24 (extracted) RR 1.14 (95% CI 0.91 to 1.43) (calculated) Tympanogram type A (per ear, adults + children) Intervention Baseline: 24/90 Follow-up: 12/55 normalised Comparator Baseline: 21/92 Follow-up: 20/57 normalised Difference between groups RR 1.20 (95% CI 0.95 to 1.53) (calculated) Tympanogram type A (per ear, adults + children) considering patients who took additional treatment as having incomplete normalisation Intervention Baseline: 24/90 Follow-up: 8/55 normalised Comparator Baseline: 21/92 Follow-up: 16/57 normalised Difference between groups RR 1.19 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.44) (calculated) Subgroup data adult patients subgroup (per patient): 44 adult patients (22 in each arm) had follow-up tympanogram Intervention: 6/22 (27%) normalised (calculated) Comparator: 8/22 (36%) normalised (calculated) Difference between groups: RR 1.14 (95% CI 0.76 to 1.72) (calculated) Adult patients subgroup (per patient), considering patients who took additional treatment as having incomplete normalisation Intervention: 4/22 (18%) normalised (calculated) Comparator: 6/22 (27%) normalised (calculated) Difference between groups: RR 1.13 (95% CI 0.81 to 1.55) (calculated) Paediatric patients subgroup (per patient): 30/34 paediatric patients had follow-up tympanogram Intervention: 1/15 (7%) normalised Comparator: 4/15 (27%) normalised. p = 0.24 (extracted) Difference between groups: RR 5.09 (95% CI 0.50 to 52.29) Paediatric patients subgroup (per patient), considering patients who took additional treatment as having incomplete normalisation: Intervention: 1/15 (7%) Comparator: 3/15 (20%) Difference between groups: p = 0.28 (extracted) RR 3.50 (95% CI 0.32 to 38.23) (calculated) Change from normal to abnormal tympanogram (adult + children, per ear) Intervention: 4/19 with type A at baseline transitioned to type C Comparator: 2/17 with type A at baseline transitioned to type C Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes (6 weeks) |
Quality of life: NR Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment: need for treatment with antibiotics or oral decongestants while enrolled Intervention (n/N): 7/37 (8 NR) Antibiotics: 5/37 Oral decongestants: 2/37 (2/7 had tympanometric normalisation) Comparator (n/N): 7/37 Antibiotics: 4/37 Oral decongestants: 3/37 Nasal spray: 2/37 One patient took both antibiotics/oral decongestants; one took oral decongestants/nasal spray Three had tympanometric normalisation Difference between groups: RR 1.00; 95% CI 0.39 to 2.57 Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Adverse effect of intervention: coughs and nosebleeds reported in both arms of study. No severe events occurred Discontinuation: Intervention (n/N): 7/45 Comparator (n/N): 5/46 Due to lack of effectiveness: NR Due to adverse events: Intervention (n/N): 0/45 Comparator (n/N): 0/45 Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Holmquist (1976)
24
Non-RCT Funding: NR Countries: Sweden Number of centres: NR Number of patients: Total: 32 (39 ears) Intervention: 19 ears Comparator: 20 ears Statistical analyses: Tests used: NR Unit of analysis: ears Population analysed: all treated Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: perforated eardrum patients: opening pressure ≥ 200 mmH2O Intact eardrum patients: tympanometric ear pressure between –100 and –400 mmH2O Exclusion criteria: NR Diagnostic methods: manometry (opening pressure test), tympanometry |
Age (years):
Mean: NR Median: NR Range: 14–66 (n/N) (%) male: 21/32 (66%) Ethnicity: NR Body weight/BMI: NR |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: NR ETD diagnosis, (n/N) (%): 32/32 (100%) High risk (n/N; %): NR Previous treatment: ventilation tube – one ear Related conditions (n/N; %): eardrum perforation: 14/38 ears (37%) Baseline medication: NR |
|
| Intervention | Comparator | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | |
| Antihistamine + ephedrine Two tablets, each with N-hydroxyethyl promethazine chloride 15 mg + ephedrine sulfate 10 mg |
Placebo (tablet) | N/A | NR | |
| Outcomes | ||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up |
| NR | NR |
Tympanogram type A: NR Other measure (1): n ears with reduction in opening pressure of ≥ 100 mmH2O measured by manometry for ears with perforated eardrum; n ears with pressure change in normalising direction of ≥ 100 mmH2O measured by tympanometry for ears with intact eardrum Intervention: Baseline (n/N): 0/19 Follow-up (n/N): 11/19 Change (improvement) (n/N): 11/19 Comparator: Baseline (n/N): 0/20 Follow-up (n/N): 2/20 Change (improvement) (n/N): 2/20 Difference between groups: Baseline (n/N): 0/19 vs. 0/20 Follow-up (n/N): 11/19 (58%) vs. 2/20 (10%) Change (improvement) (n/N): RR 0.47 (95% CI 0.27 to 0.81) Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? No: up to 3 hours |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: NR Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment: NR |
Adverse effect of intervention: NR Complication of ETD: NR Discontinuation: NR |
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Jensen (1990)
25
RCT Funding: NR (equipment and medications supplied free by manufacturers) Countries: Denmark Setting: NR Number of centres: NR Study design: RCT Number of patients: Total: 36 Intervention: 19 Comparator: 17 Statistical analyses: Tests used: one-tailed chi-squared test and Fisher’s exact test Unit of analysis: patients Population analysed: PP Power calculation: yes. 28 patients required for smallest difference in effect (0.6, alpha = 0.05 and beta = 0.05) |
Inclusion criteria: absent or reduced tubal patency; age ≥ 12 years; dry eardrum perforation; normal ear mucosa Exclusion criteria: normal ET function; upper respiratory tract infection; adenoids or other lesions in nasopharynx; middle ear lesions; use of decongestant or antihistamine within 24 hours Diagnostic methods: Valsalva manoeuvre, aspiration/deflation test Definition of ETD: NR Absent or reduced tubal patency: no passage on a Valsalva manoeuvre and/or incomplete pressure equalisation in aspiration/deflation test Pathological aspiration test: residual pressure below –100 mmH2O Pathological deflation test: residual pressure above 100 mmH2O |
Age (years)
Median: 42 Range: 12–75 Patient characteristic n (%) male: 16/36 (44%) Ethnicity: NR Body weight/BMI: NR |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: NR ETD diagnosis (n/N; %) 36/36 (100%) High risk (n/N; %): NR Previoustreatment: NR Related conditions (n/N; %): dry eardrum perforation Baseline medication: NR |
|
| Intervention | Comparator | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | |
| Pharmacological: xylomethazoline chloride 0.1%, 0.4 ml, sprayed directly towards pharyngeal opening of the ET | Placebo (saline) spray | N/A | NR | |
| Outcomes | ||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up |
| NR | NR |
Type A tympanogram: NR Other measure (1): positive Valsalva manoeuvre (audible passage of air) or positive aspiration (residual pressure ≥ –100 mmH2O) or deflation (≤ 100 mmH2O) tests 30 minutes after intervention Intervention: Baseline (n/N): 0/19 Follow-up (n/N): 12/19 Change (improvement) (n/N): 12/19 Comparator: Baseline (n/N): 0/17 Follow-up (n/N): 7/17 Change (improvement) (n/N): 7/17 Difference between groups: Baseline (n/N): 0 Follow-up (n/N): 12/19 (63%) vs. 7/17 (41%) Change (improvement) (n/N): RR 0.63 (95% CI 0.31 to 1.27); p = 0.19 Subgroup data: no difference between age groups or sex Other measure (2): positive Valsalva manoeuvre Intervention: Baseline (n/N): 0/18 Follow-up (n/N): 10/18 Change (improvement) (n/N): 10/18 Comparator: Baseline (n/N): 0/17 Follow-up (n/N): 1/17 Change (improvement) (n/N): 1/17 Difference between groups Baseline (n/N): 0 Follow-up (n/N): 10/18 (56%) vs. 1/17 (6%) Change (improvement) (n/N): RR 0.47 (95% CI 0.28 to 0.80); p < 0.003 Other measure (3): positive aspiration test Intervention: Baseline (n/N): 0/18 Follow up (n/N): 6/18 Change (improvement) (n/N): 6/18 Comparator: Baseline (n/N): 0/17 Follow up (n/N): 5/17 Change (improvement) (n/N): 5/17 Difference between groups Baseline (n/N): 0 Follow-up (n/N): 6/18 (33%) vs. 5/17 (29%) Change (improvement) (n/N): RR 0.94 (95% CI 0.60 to 1.48) Other measure (4): positive deflation test Intervention Baseline (n/N): 0/12 Follow-up (n/N): 6/12 Change (improvement) (n/N): 6/12 Comparator Baseline (n/N): 0/16 Follow-up (n/N): 6/16 Change (improvement) (n/N): 6/16 Difference between groups Baseline (n/N): 0 Follow-up (n/N): 6/12 (50%) vs. 6/16 (38%) Change (improvement) (n/N): RR 0.80 (95% CI 0.40 to 1.58); p = 0.51 Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? No: 30 minutes |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: N/A Early tube extrusion: N/A Need for additional treatment: NR |
Adverse effect of intervention: Intervention 0/19 Comparator 0/17 Complication of ETD: NR Discontinuation: NR |
Mechanical devices
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Alpini (2008)
40
RCT Countries: Italy Funding: NR Setting: NR Number of centres: NR Number of patients: Total: 20 Intervention: 10 Comparator: 10 Statistical analyses: Tests used: NR Unit of analysis: patient Population analysed: ITT Power calculation: NR |
Inclusioncriteria: persistent ear fullness sensation following otitis media Exclusion criteria: NR Diagnostic methods: pure-tone audiometry; tympanometry; stapedial reflexes; VAS for aural fullness tubotympanometry and VEMPs ETD definition: NR |
Age (years)
Median: NR Mean: 39.2 (intervention: 36.9 years; control: 41.5) Range: NR Patient characteristic n (%) male: 13/20 (65%) Ethnicity: NR Body weight/BMI: NR |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: persistent fullness following OM, normal pure-tone audiometry, tympanometry and stapedial reflexes ETD diagnosis (n/N; %): 19/20 (95%) High risk (n/N; %): NR Related conditions (n/N; %): NR Previous treatment: nasal decongestants, NSAIDs, antihistamines, antibiotics Baseline medication: NR |
|
| Intervention | Comparator | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | |
| Non-surgical, non pharmacological: N-300 device applying mild negative pressure to sealed external ear canal three times daily for 5 minutes + each time for 1 week, applied unilaterally | No treatment | NR | NR | |
| Outcomes | ||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up |
|
Visual analogue scale of fullness in ear (mean)
Intervention: Baseline: 9.2 Follow-up: 2 Change from baseline: p < 0.001 Comparator: Baseline: 8.68 Follow-up: 6 Change from baseline: p = NS Difference between groups: Baseline: 0.52 Follow-up: 4 Outcome assessed using a reliable tool? Unclear Length of follow-up sufficient? No: 1 week |
NR |
Tympanogram type A: NR Tympanogram other measure: abnormal tubotympanometry Intervention: Baseline (n/N): 10/10 Follow-up (n/N): 1/10 Change (improvement) (n/N): 9/10 (p < 0.001) Comparator: Baseline (n/N): 9/10 Follow-up (n/N): 7/10 Change (improvement) (n/N): 2/10 (p = NS) Difference between groups: Baseline (n/N): –1 Follow-up (n/N): 6 Change (improvement) (n/N): RR 0.14 (95% CI 0.02 to 0.96) Outcome assessed using a reliable tool? Yes Length of follow-up sufficient? No: 1 week |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: NR Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment: NR |
Adverse effect of intervention: NR Complication of ETD: NR Discontinuations: Intervention (n/N): 0/10 Comparator (n/N): 0/10 Length of follow-up sufficient? No: 1 week |
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Silman (1999)
41
Non-RCT Funding: NR Countries: USA Setting: private otologic practice Number of centres: single centre Number of patients: Total: 28 Intervention: 14 Comparator: 14 Statistical analyses: Tests used: repeated measures t-tests Unit of analysis: patient Population analysed: ITT Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: aged at least 18 years; Eustachian tube dysfunction following air travel (middle-ear pain, fullness or clogged sensation following aeroplane travel or descent); tympanometric peak pressure < –100 daPa Exclusion criteria: NR Diagnostic methods: otolaryngologic evaluation including microtoscopy; audiologic evaluation including pure-tone air and bone-conduction thresholds, and speech recognition thresholds; tympanometry |
Age (years)
Mean: 35 34.6 (experimental) 35.1 (control) Median: NR Range: 16–76 18–76 (experimental) 16–64 (control) n (%) male: NR Body weight/BMI: NR Ethnicity: NR |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: onset following aeroplane travel/descent 100% ETD diagnosis (n/N; %): 28/28 (100%) High risk (n/N; %): NR Related conditions (n/N; %): NR Previous treatment: NR Baseline medication: NR |
||
| Intervention | Comparator | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | ||
| Non-surgical, non-pharmacological Politzeration using an automated device twice-weekly for 6 weeks |
No treatment | None | NR | ||
| Outcomes | |||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up | |
| NR |
Definition and/or criteria for change: mean air–bone gap Difference between groups: Intervention: Baseline, mean (SD): 9.7 (6.3) Follow-up, mean (SD): 10.4 (6.6) Difference from baseline, mean (SD): –0.6 (8.7) Comparator: Baseline, mean (SD): 7.6 (5.2) Follow-up, mean (SD): 21.1 (14.9) Difference from baseline, mean (SD) –13.5 (17.1) Difference between groups: Difference from baseline mean (SD): t = 2.51(p = 0.019) 12.90 (95% CI 2.85 to 22.95) (calculated) Difference between groups: Change (improvement) (n/N): RR 0.36 (95% CI 0.15 to 0.87) Other measure (2): significant air–bone gap Intervention Change (improvement) (n/N): Non-significant to non-significant: 65% Non-significant to significant: 7% Significant to non-significant: 14% Significant to significant: 14% Comparator: Change (improvement) (n/N): Non-significant to non-significant: 43% Non-significant to significant: 43% Significant to non-significant: 7% Significant to significant: 7% Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Unclear: 3–4 weeks (following 6-week treatment) |
Tympanogram type A: NR Other measure (1): normal tympanogram peak pressure Intervention: Baseline (n/N): 0/14 (0%) Follow up (n/N): 10/14 (71%) Change (improvement) (n/N): 10/14 (71%) Comparator: Baseline (n/N): 0/14 (0%) Follow up (n/N): 3/14 (21%) Change (improvement) (n/N): 3/14 (21%) Difference between groups: Baseline: 0/14 Follow-up: 10/14 vs. 3/14 Change (improvement) : 10/14 vs. 3/14 RR 0.36 (95% CI 0.15 to 0.87) Baseline (n/N): 0/14 (0%) Follow up (n/N): 3/14 (21%) Change (improvement) (n/N): 3/14 (21%) Other measure (1): tympanometric peak pressure (mB) Intervention Baseline [mean (SD)]: –282.4 (91.0) Follow-up [mean (SD)]: –99.4 (148.8) Change from baseline [mean (SD)]: –182.9 (153.0) Comparator: Baseline [mean (SD)]: –257.6 (95.8) Follow-up [mean (SD)]: –275.8 (150.8) Change from baseline [mean (SD)] 18.1 (182.4) Difference between groups: Change from baseline [mean (SD)]: –201.00 (95% CI –325.71 to –76.29) (calculated) t = –3.1599 (p = 0.004) (extracted) Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Unclear: 3–4 weeks (following 6-week treatment) |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: NR Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment: NR |
Adverse effect of intervention: NR Complication of ETD: NR Discontinuation: Intervention (n/N): 0/14 Comparator (n/N): 0/14 Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
|
Surgical studies
Tuboplasty
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Caffier (2011)
20
Observational (uncontrolled) Funding: NR Countries: Germany Setting: outpatient Number of centres: NR Number of patients: 31 Statistical analyses: Tests used: chi-squared for frequency data (Valsalva and passive tubal opening); log-linear analysis of frequency tables (tympanometry); Mann–Whitney U-test (VAS, audiometry, tinnitus parameters between subgroups); Wilcoxon test for pair differences (audiometry and tinnitus data before and 1 year after laser surgery) Unit of analysis: patient Population analysed: ITT Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: therapy refractory chronic ETD Exclusion criteria: history of allergic or reflux disease Diagnostic methods: detailed examination and full neuro-otological diagnostics Hyperplastic mucosa at the epipharyngeal dorsal ostium of the ET Abnormal tubal function tests Definition of ETD: NR Chronic ETD definition: duration of at least 5 years. Dysfunctional pressure equalisation: long-lasting history of otalgia during aeroplane landing or scuba-diving descents |
Age (years): Median: NR Mean: 42 Range: 21–72 n (%) male: 14/31 (45%) Body weight/BMI: NR Ethnicity: NR Subgroups:
|
ETD history/baseline symptoms: ETD symptoms for at least 5 years ETD diagnosis (n/N; %): 31/31 (100%) High risk (n/N; %): NR Previous treatment: 100% previous surgery/treatment with no long-term improvement of tubal function (e.g. tympanoplasty with reperforation in COM, tympanostomy tubes in OME, local decongestants for others) Related conditions (n/N; %): chronic/recurrent OME/glue ear: 2/31 (6%) COM (suppurative): 16/31 (52%) (with perforated eardrum) AOM: 4/31 (13%) Atelectasis: 13/31 (42%) (Sadé classification: I: 9; II: 2; III: 2; IV:0) Dysfunctional pressure equalisation: 9/31 (29%) Baseline medication: NR |
||
| Intervention | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | |||
| Surgery: laser Eustachian tuboplasty: Ablation of hyperplastic mucosa at the epipharyngeal dorsal tubal ostium using transnasal fibre-guided videoendoscopic tuboplasty with a semiconductor diode laser |
Local | Tympanolplasty type I and myringoplasty for COM patients 10 weeks after laser surgery Central perforations: 3 to 7 mm diameter Graft used: cartilage perichondrium composite, tragus or concha Removal of tubes at least 8 weeks after placement General anaesthesia |
|||
| Outcomes | |||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up | |
|
Subjective satisfaction and improvement in ETD symptoms at 1 year (VAS scale (0 to 10): median (range)
Overall satisfaction: 7 (1 to 10) Dysfunctional pressure equalisation: 6 (1 to 10) Aural fullness: 6 (1 to 10) Dulled hearing: 5 (0 to 10) Tinnitus: 0 (0 to 4) Subgroup data: Overall satisfaction greater for COM patients than intact eardrum subgroup (p < 0.05) Tinnitus (mode, pitch, loudness) via audiometry Baseline: Tinnitus mode: tone-like (20/31); noise like (11/31) Tinnitus pitch: range 0.125 to 10 kHz Tinnitus loudness: mean 49.9 dB HL Follow-up: Tinnitus mode: NR Tinnitus pitch: NR Tinnitus loudness: mean 43.7 dB HL Change from baseline Tinnitus mode: NR Tinnitus pitch: no significant change Tinnitus loudness: p < 0.05 Subgroup data: Tinnitus No baseline differences between COM vs. intact eardrum patients except for loudness (p < 0.05) Tinnitus loudness (mean dB SL): no significant difference between baseline and 1 year SL in either subgroup Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Hearing
Bone conduction, mean (SD) dB Baseline Total: 17.9 (10.0) Perforated: 19.1 (11.6) Intact: 16.7 (8.2) Follow-up (1 year) Total: 19.5 (10.3) Perforated: 20.3 (11.3) Intact: 18.7 (9.5) Difference from baseline Total: 1.6 (14.4) Perforated: 1.2 (16.2) Intact: 2.0 (12.5) Air conduction, mean (SD) Baseline dB Total: 41.7 (17.8) Perforated: 48.2 (15.8) Intact: 34.7 (17.6) Follow-up (1 year) Total: 31.0 (15.0) Perforated: 29.4 (12.1) Intact: 32.7 (17.8) Difference from baseline Total: –10.7 (23.2) Perforated: –18.8 (19.9) Intact: –2 dB (25.0) Air–bone gap, mean (SD) dB Baseline Total: 23.7 Perforated: 29.1 (7.1) Intact: 18.0 (14.1) Follow-up (1 year) Total: 11.5 (8.9) Perforated: 9.1 (3.3) Intact: 14.0 (12.1) Difference from baseline Total: –12.3 (15.2)a Perforated: –20 (7.8)a Intact: –4 (18.6)a Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Tympanogram type A: intact eardrum subgroup: (normal tympanogram) Baseline: 2/15 Follow-up (1 year): 4/15 (NS) Other measure (1): positive Valsalva manoeuvre For COM patients, positive if investigator heard blow-through noise atpatient’s ear. For all other patients, microscopically controlled, positive if clearly recognisable protrusion of tympanic membrane during active increase of nasopharyngeal air pressure Baseline (n/N): 2/31 Follow up (n/N): 21/31 Change (improvement) (n/N): 19/31 Subgroup data: Subgroup data COM subgroup Baseline: 1/16 (6%) (from graph) 8 weeks: 11/16 (69%) (from graph) 1 year: 12/16 (75%) Intact eardrum subgroup Baseline: 1/15 (7%) (from graph) 8 weeks: 9/15 (60%) (from graph) 1 year: 9/15 (60%) (from graph) Intact eardrum and dysfunctional equalisation pressure subgroup Baseline: 0 8 weeks: 6/9 (67%) 1 year: ‘positive results remained stable’ Intact eardrums and OME or adhesion subgroup Tinnitus mode Baseline: NR 8 weeks: 3/6 (50%) 1 year: ‘positive results remained stable’ ETD in both ears subgroup Baseline: NR – 8 weeks: 50% (5/10), p < 0.01 vs. contralateral side – 1 year: 50% (5/10), p < 0.01 vs. contralateral side Other measure (2): normal passive tubal opening: middle ear inflation with positive pressure up to 300 mmH2O. Abnormal if negative Subgroup data Baseline: 0/16 (from graph) 8 weeks: 8/16 (from graph) 1 year: NR Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: NR Need for additional treatment: NR |
Adverse effect of intervention
Attributed to laser tuboplasty: adhesion between the posterior tubal cushion and the adjacent epipharyngeal tissue without subjective or objective negative consequences in one patient at 2 months No bleeding requiring nasal packing Attributed to tympanoplasty: none Intraoperative pain VAS scale (0 to 10) Overall: median 0, IQR 0 to 2 Three patients with painful laser-induced burning or stinging sensation, resolved by renewing topical anaesthesia Discomfort VAS scale (0 to 10) Complication of ETD: NR Loss to follow-up: NR Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes: 2 months |
|
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Jumah (2012)
54
Observational (uncontrolled) Funding: no external funding Countries: Germany Number of centres: single centre Setting: university hospital outpatient clinic Number of patients: 30 Statistical analyses: Tests used: one-sided Kolmogorov–Smirnov test to confirm normal distribution t-test for dependent random variables to assess differences in means McNemar’s and chi-squared test to compare categorised data Unit of analysis: patient Population analysed: ITT Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: chronic obstructive ETD with intact tympanic membrane otalgia during pressure equalisation while flying/diving, recurrent OME, sensation of fullness in ear. Ineffective response to 6–8 weeks’ course conservative treatment (e.g. topical cortisone) At least one of the following: hyperplasia of adjacent epipharyngeal soft tissue hyperplasia of the dorsal circumference of the ET ostium hyperplasia of the posterior end of the lower turbinate Exclusion criteria: Severe allergies or reflux disease Diagnostic methods: impedance measurements (ET opening/closing pressures and opening duration) in pressure chamber; Valsalva manoeuvre/tympanometry; nasopharyngeal endoscopy; ear microscopy Definition of ETD: NR |
Age (years): Median: 40 Mean: NR Range: 25–57 n (%) male: 19/30 (63%) Body weight/BMI: NR Ethnicity: NR |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: otalgia during pressure equalisation while flying/diving, recurrent OME, sensation of fullness in ear ETD diagnosis (n/N; %): 30/30 (100%) High risk (n/N; %): NR Previous treatment: 6–8 weeks’ course conservative treatment (e.g.) topical cortisone Related conditions (n/N; %): 0 with severe allergies/reflux disease Baseline medication: NR |
|
| Intervention | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | ||
| Unilateral minimally invasive laser Eustachian tuboplasty under endoscopic control | General | None reported | ||
| Outcomes | ||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up |
| NR | NR |
Type A tympanogram
Baseline (n/N): 20/30 (two type B; eight type C) Follow-up (n/N): 24/30 Change to type A (n/N): 4/10 from type B/C to A (p < 0.135 for number with type A) Tympanogram other measure: pressure peaks in type A tympanograms, dePa: mean (SD) Baseline (n/N): N = 20 –21.0 (26.9) Follow-up (n/N): N = 24 1.2 (29.4) Change (improvement) (n/N): p = 0.352 Other measure (1): Valsalva manoeuvre negative Baseline (n/N): 14/30 (46.7%) Follow-up (n/N): 4/30 (13.3%) Change (improvement) (n/N): 10/14 (71% of those affected at baseline) (p < 0.002) Other measure (2): pressure chamber test of ET function (blocked pattern detected) Baseline (n/N): 17/30 Follow up (n/N): 4/30 Change (improvement) (n/N): 13/17 (76.5% of those previously blocked) (p < 0.001) Other measure (3): normal ET opening and closing pressure in pressure test Baseline (n/N): 13/30 (43%) ET closing pressure 6.24 (3.46) mbar; ET opening pressure 26.13 (12.97) mbar Follow-up (n/N): 26/30 (86.7%) ET closing pressure: 3.35 (2.07) mbar; ET opening pressure 25.24 (13.29) mbar Change (improvement) (n/N): In 13 preoperative normal patients the closing pressure was significantly lower postoperatively [4.06 (2.36) mbar (p < 0.013)] Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Unclear |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: NR Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment: NR |
Adverse effect of intervention: no acute complications (e.g. bleeding, infections) No long-term complications (synechia between anterior and posterior ET lining or patulous ET) Complication of ETD: NR Discontinuation Intervention (n/N): 0/30 Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes: 2–4 months |
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Metson (2007)
56
Observational (uncontrolled) Funding: NR Countries: USA Number of centres: NR Setting: NR Number of patients: 20 Statistical analyses: Tests used: Fisher’s exact test and paired t-test Unit of analysis: patient Population analysed: ITT for surgical complications and success of procedure patients without postoperative tube placement or in whom postopertive tympanogram lacking excluded for audiometry/tympanometry (3/20) Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: chronic rhinosinusitis severe enough to warrant surgery Symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction: persistent sensation of ear blockage with abnormal tympanogram or recurrent episodes of discomfort with altitude change (flying/diving) Exclusion criteria: NR Diagnostic methods: tympanogram Harvard staging and Lund-McKay staging for sinus disease Tissue eosinophil count for sinus disease Definition of ETD: NR |
Age (years): Median: NR Mean: 49.1 Range: 23–66 Patient characteristic n (%) male: 8/20 (40%) Body weight/BMI: NR Ethnicity: NR |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: chronic rhinosinusitis severe enough to warrant surgery Symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction: persistent sensation of ear blockage with abnormal tympanogram or recurrent episodes of discomfort with altitude change (flying/diving) [bilateral in 3/20 (15%)] Sinus ostial obstruction on nasal endoscopy or sinus CT scan ETD diagnosis (n/N; %): 20/20 (100%) High risk (n/N; %): NR Previous treatment: ≥ 3 courses of antibiotics in previous year (100%) Nasal steroid sprays (100%) 16 patients with sinonasal allergies all failed treatment with antihistamines and nasal steroids Prior sinus surgery: 12/20 (60%) [6/20 (30%) had 2+ procedures] Prior ear surgery 8/20 (40%) (7/20 (35%) prior pressure equalisation tube placement (four multiple); 1/20 (5%) prior myringotomy only) Related conditions (n/N; %): Chronic rhinosinusitis: 20/20 (100%) Gastroesophageal reflux disease: 5/20 (25%) Sinonasal allergies: 16/20 (80%) Sinus ostial obstruction: 20/20 (100%) Baseline medication PPI: 4/20 H2 blocker: 1/20 |
||
| Intervention | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | |||
| Surgery: microdebrider Eustachian tuboplasty | General | Endoscopic sinus surgery following tuboplasty | |||
| Outcomes | |||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up | |
| Resolution of subjective symptoms of ETD/ear blockage Baseline: 20/20 symptomatic Follow-up (13 months): 14/20 improved Change from baseline : 14/20 Outcome assessed using a reliable tool? Unclear Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Mean improvement across speech frequencies (dB) [mean (SD)]
Baseline impairment: mean (SD): NR Follow-up impairment [mean (SD)] (13 months): NR Difference from baseline [mean (SD)]: decreased 6 dB (p = 0.013) Improvement from baseline (n/N): NR (18 abnormal at baseline) Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Tympanogram type A: NR Other tympnoagram measure: improvement in tympanogram waveform – patients developed a normal or more normal tracing Baseline (n/N): 17/20 abnormal Follow-up (n/N): (mean 13 months): 11/17 patients improved Change (improvement) (n/N): 11/17 Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: unclear Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: NR Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment: postoperative placement of pressure equalisation tubes Intervention (n/N): 2/20 (10%) Length of follow-up sufficient? Unclear |
Adverse effect of intervention: surgical complications 0/20 Complication of ETD: NR Discontinuation: NR Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
|
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Poe (2007)
23
Additional records: Poe (2003) 57 Observational (uncontrolled) Funding: NR Number of patients: 13 Setting: tertiary medical centre Number of centres: single centre Statistical analyses: Tests used: t-test; chi-squared test Unit of analysis: patient Population analysed: ITT Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: adults with AME for 5 or more years, documented to re-occur immediately after extrusion/obstruction of most recent tympanostomy tube (2+ recent tube placements required). OME presumed to result from ETD Disease within cartilaginous portion of ET consistent with obstructive disorder Failure to show improvement of OME after medical management Exclusion criteria: cholesteatoma or atalectasis without effusion Diagnostic methods: micro-otoscopy; transnasal endoscopic slow-motion video analysis of ET; endoscopic examination of nasal cavity, nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx and larynx; audiogram, tympanogram; tubal dysfunction score Definition of ETD: NR |
Age (years): Median: 44 Mean: 44 Range: 29–64 n (%) male: 12/13 (92%) Body weight/BMI: NR Ethnicity: NR Subgroups: (1) Patients with allergic disease, n = 10 (2) Patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux, n = 9 |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: OME related to ETD for at least 5 years (see inclusion criteria) ETD diagnosis (n/N; %): 13/13 (based on OME aetiology) High risk (n/N; %): NR Previous treatment 2+ tympanostomy tube placements 8 weeks + nasal corticosteroids 8 weeks + oral antihistamines (where allergic disease) 8 weeks + omeprazole (where laryngopharyngeal reflux) Related conditions (n/N; %): OME history 13/13 Atalectasis: 4/13 Laryngopharyngeal reflux 9/13 Allergic disease 10/13 Baseline medication: NR |
||
| Intervention | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | |||
| Surgery: unilateral laser Eustachian tuboplasty | General; local lidocaine/adrenaline applied to ET | Omeprazole 20 mg/d for 6 weeks postoperatively (where laryngopharyngeal reflux) | |||
| Outcomes | |||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up | |
| NR See clearance of middle ear effusion |
Pure-tone average (db)
Baseline, mean (SD): 36.0 (12.1) (N = 12)a Follow-up, mean (SD): 6 months: 34.6 (14.9) (N = 6)a 1 year: 25.5 (17.6) (N = 8)a 2 years: 25.0 (6.5) (N = 8)a Difference from baseline mean (SD) dB 6 months: –4.3 (17.1) (N = 6) 1 year: 8.7 (20.0) (N = 8) 2 years: 9.2 (16.6) (N = 8) Subgroup data: Successful patients: Baseline 35.3 1 year: 12.9 2 years: 20.8 (p = 0.028) Unsuccessful patients: no significant difference between baseline and post-treatment tests No statistically significant pre-treatment differences Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Type A tympanogram
Baseline (n/N): 0/13 (eight B, three C, two N/A) Follow-up (n/N): 6 months: 1/13 (five B, three C, four N/A) 1 year: 2/13 (one shallow peak) (five B, one C, five N/A) 2 years: 2/13 (one B, one C, nine N/A) Change from baseline (n/N): 6 months: 1/13 (five B, three C, four N/A) 1 year: 2/13 (one shallow peak) (five B, one C, five N/A) 2 years: 2/13 (one B, one C, nine N/A) Other measure (1): tympanic membrane status (clinical examination) Baseline (n/N): OME: 13/13 Atelactasis: 4/13 Follow-up (n/N): 6 months: OME: 7/13 Atelectasis: 0/13 Retraction: 4/13 of which three slight, two N/A 1 year: OME: 4/13 Atelectasis: 1/13 Retraction: 4/13 of which 3 slight Tympanostomy tube: 1/13, 3 N/A 2 years: OME: 2/13 Atelectasis: 0/13 Retraction: 3/13 of which 3 slight Tympanostomy tube: 2/13 Tiny perforation: 1/13, 5 N/A Other measure (2): success/failure of procedure (failure = OME, perforated TM; unclear if atalectasis and tympanostomy tube included in definition) Baseline: N/A Follow-up (n/N): 6 months: 7/11 (64%) 1 year: 6/10 (60%) 2 years: 5/8 (62%) Other measure (3): Eustachian tube endoscopy scores Baseline [mean (SD)]: n = 10 (from #365) Valve dilatation: 2.7 (0.48) Mucosal swelling: 2.4 (0.52) Levator veli palatini function: 1.2 (0.42) Tensor veli palatini function: 1.4 (0.70) Follow-up [mean (SD)]: Postop (n = 10) (from Poe 2003) Valve dilatation: 2.0 (0.67) Mucosal swelling: 1.7 (0.48) Levator veli palatini function: 1.0 (0) Tensor veli palatini function: 1.2 (0.42) 1 year (n = 5) (from Poe 2003) Valve dilatation: 2.2 (0.84) Mucosal swelling: 2.2 (0.84) Levator veli palatini function: 1.0 (0) Tensor veli palatini function: 1.2 (0.45) Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: OME resolved 6 months: 4/11 (36%) 1 year: 4/10 (40%) 2 years: 3/8 (38%) Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment: tympanostomy tubes required 6 months: 0/11 (2 N/A) 1 year: 1/10 (3 N/A) 2 years: 2/8 (5 N/A) Definition and/or criteria for change Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Adverse effect of intervention: significant surgical complications (including epistaxis, nasal obstruction, intraluminal adhesions/strictures): 0/13 synechia between inferior turbinate and septum: 1/13 synechiae between posterior cushion and nasopharyngeal mucosa: 1/13 granuloma in centre of resected area of mucosa: 2/13 Complication of ETD: see need for additional treatment Discontinuation: 0/13 Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
|
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sedlmaier (2009)
21
Observational (uncontrolled) Countries: Germany Setting: NR Number of centres: NR Number of patients: 38 Statistical analyses: Tests used: McNemar test Unit of analysis: patients Population analysed: all treated patients Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: middle ear ventilation problems; negative Valsalva, no passive tubal opening, or long history of complaints and symptoms (DPE group) Exclusion criteria: allergy or reflux disease Diagnostic methods: passive tubal opening and Valsalva (COM group) Tympanogram and microscopically controlled Valsalva Definition of ETD: NR |
Age (years): Median: 44.7 Mean: NR Range: 21–76 n (%) male: 16/38 (42%) Body weight/BMI: NR Ethnicity: NR Subgroups: (1) COM (perforated eardrum) 19/38 (50%) (2) Intact eardrum 19/38 (50%) of which 14 dysfunctional pressure equalisation |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: COM with perforated eardrum: 19 Intact eardrum: 19 (three persistent OME, two AOM, 14 dysfunctional pressure equalisation) ETD diagnosis (n/N; %) 14/38 High risk (n/N; %): NR Previous treatment: NR Related condition: NR Baseline medication: NR |
|
| Intervention | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | ||
| Laser ablation of epipharyngeal ET | Local (tetracaine 3%) and nasal decongestant (naphazoline 0.1%) | Tympanoplasty 8–10 weeks after (COM group) | ||
| Outcomes | ||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up |
| NR | NR |
Tympanogram improved
COM subgroup Follow-up (n/N): 6/19 (31.5%) Intact eardrum: 12/19 (53%) improvement Other measure (1): Valsalva manoeuvre (perforated eardrum: blow-through noise heard by examiner; Intact eardrum: microscopically observed protrusion of eardrum) Baseline (n/N): 2/38 (5%) Follow-up (n/N): 8 weeks: 28/38 (74%) 1 year: 15/20 (75%) Change (improvement) (n/N): 8 weeks: 26/38 (68%) 1 year: 13/20 (65%) Subgroup data: COM: 14/19 (74%) improvement Intact eardrum: 12/19 (63%) improvement Other measure (2): passive tubal opening COM subgroup Baseline (n/N): 1/19 (5%) Follow-up (n/N) (2 months): 9/19 (47%) Change from baseline (n/N): 8/19 (42%) Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? No: 8 weeks, although 1-year follow-up for Valsalva |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: NR Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment: NR |
Adverse effect of intervention: one synechia between posterior tubal ostium and adjacent epipharynx tissue No other complications Complication of ETD: NR Discontinuation: NR |
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sedlmaier (2009)
21
Observational (uncontrolled) Countries: Germany Setting: NR Number of centres: NR Number of patients: 38 Statistical analyses: Tests used: McNemar test Unit of analysis: patients Population analysed: all treated patients Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: middle ear ventilation problems; negative Valsalva, no passive tubal opening, or long history of complaints and symptoms (DPE group) Exclusion criteria: allergy or reflux disease Diagnostic methods: passive tubal opening and Valsalva (COM group) Tympanogram and microscopically controlled Valsalva Definition of ETD: NR |
Age (years): Median: 44.7 Mean: NR Range: 21–76 n (%) male: 16/38 (42%) Body weight/BMI: NR Ethnicity: NR Subgroups: (1) COM (perforated eardrum) 19/38 (50%) (2) Intact eardrum 19/38 (50%) of which 14 dysfunctional pressure equalisation |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: COM with perforated eardrum: 19 Intact eardrum: 19 (three persistent OME, two AOM, 14 dysfunctional pressure equalisation ETD diagnosis (n/N; %): 14/38 High risk (n/N; %): NR Previous treatment: NR Related condition: NR Baseline medication: NR |
|
| Intervention | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | ||
| Laser ablation of epipharyngeal ET | Local (tetracaine 3%) and nasal decongestant (naphazoline 0.1%) | Tympanoplasty 8–10 weeks after (COM group) | ||
| Outcomes | ||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up |
| NR | NR |
Tympanogram improved
COM subgroup Follow-up (n/N): 6/19 (31.5%) Intact eardrum: 12/19 (53%) improvement Other measure (1): Valsalva manoeuvre (perforated eardrum: blow-through noise heard by examiner; intact eardrum: microscopically observed protrusion of eardrum) Baseline (n/N): 2/38 (5%) Follow up (n/N): 8 weeks: 28/38 (74%) 1 year: 15/20 (75%) Change (improvement) (n/N): 8 weeks: 26/38 (68%) 1 year: 13/20 (65%) Subgroup data: COM: 14/19 (74%) improvement Intact eardrum: 12/19 (63%) improvement Other measure (2): Passive tubal opening COM subgroup Baseline (n/N): 1/19 (5%) Follow-up (n/N) (2 months): 9/19 (47%) Change from baseline (n/N): 8/19 (42%) Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? No: 8 weeks, although 1-year follow-up for Valsalva |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: NR Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment: NR |
Adverse effect of intervention: one synechia between posterior tubal ostium and adjacent epipharynx tissue No other complications Complication of ETD: NR Discontinuation: NR |
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Yanez (2010)
63
Observational (uncontrolled) Funding: none Countries: Mexico Number of centres: NR Setting: NR Number of patients: 25 Statistical analyses: Tests used: NR Unit of analysis: patient Population analysed: ITT Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: obstructive ETD severe enough to warrant ET surgery; persistent sensation of ear blockage with abnormal tympanogram or recurrent episodes of ear discomfort with changes in altitude (flying/diving) Exclusion criteria: NR Diagnostic methods: simple endoscopy or slow-motion video-endoscopic analysis; audiograms; tympanograms Symptom assessment |
Age (years): Median: NR Mean: 48 Range: 27–69 n (%) male: reported as 13/30 (43%) (N = 25) Body weight/BMI: NR Ethnicity: NR |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: evidence of tubal dysfunction and valve obstruction on simple endoscopy on slow-motion video-endoscopic analysis ETD diagnosis (n/N; %): 25/25 (100%) bilateral 10/25 (40%) High risk (n/N; %): NR Previous treatment: At least 3 previous courses of nasal steroid sprays: 25/25 (100%) Previous ear surgery: 18/25 (72%) Multiple pressure equalisation tube placements: 21/25 (84%) Previous myringotomy only: 4/25 (16%) None had previous nasal surgery Related condition (n/N; %): no other medical conditions Baseline medication: NR |
|
| Intervention | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | ||
| Laser Eustachian tuboplasty with cross-hatching technique | General | NR | ||
| Outcomes | ||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up |
| Successful outcome defined as resolution of symptoms (ear blockage, ear pain, hypoacusis, autophony) Baseline: N/A Follow-up [mean 15 months (range 3–37 months)]: 23/25 (92%) Change from baseline: 23/25 Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: unclear Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Pure-tone average: mean impairment (dB) Baseline: 30 dB Follow-up [15 (3–37) months]: 20 dB Difference from baseline: 10 dB (p = 0.015) Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Abnormal tympanogram improved
Baseline (n/N): 25/25 (100%) Follow up (n/N): (15 (3–37) months) 1/25 (4%) Change (improvement) (n/N): 24/25 (96%) Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: unclear Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: NR Early tube extrusion: NR; N/A Need for additional treatment: need for pressure equalisation tubes 0/25 Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Adverse effect of intervention: NR Complication of ETD: NR Discontinuation (n/N): 0/25 Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Balloon dilatation
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Catalano (2012)
18,34
Observational (uncontrolled) Funding: NR Countries: USA Number of centres: NR Setting: clinic (operating theatre used if additional procedures) Number of patients: 70 (100 ears) Statistical analyses: Tests used: NR Unit of analysis: ears Population analysed: all treated Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: aged > 18 years and reported chronic sensation of ear fullness, pressure, pain and otitic barotrauma (developed in adulthood) Exclusion criteria: temporomandibular joint disease, early hydrops Diagnostic methods: tympanogram; clinical examination; symptomatology Definition of ETD: NR |
Age (years): Median: NR Mean: 45 Range: 18–73 n (%) male: 27 (38%) Body weight/BMI: NR Ethnicity: NR Subgroups (1) Patients needing concomintant otologic procedures: 5/70 (five ears) (2) Patients needing concomitant sinonasal procedures: 39/70 (54 ears) |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: NR ETD diagnosis (n/N; %): 70/70 (100%) High risk (n/N; %): NR Previous treatment: NR Related condition: NR Baseline medication: NR |
||
| Intervention | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | |||
| Surgery: bilateral or unilateral balloon catheter dilatation [8 atm for 10 seconds (20 ears) or 30 seconds (75 ears) in revised protocol, previously 6 atm (5 ears)] | Local unless concomitant procedure required general | Otologic (five patients/ears) or sinonasal procedure (39 patients, 54 ears) as required 44 patients (59 ears) (63%) had a concomitant procedure |
|||
| Outcomes | |||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up | |
|
Criteria for improvement: changes in sensation of ear fullness, pressure, pain and tolerance to air travel; visible alteration in appearance of TM 71/100 (71%) showed improvement, of which 30/41 (73%) ears had ET dilatation alone, 36/54 (67%) ears had sinonasal procedures and 3/5 (60%) had otologic procedures 7/8 patients followed for 34 months reported persistent improvement Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: unclear Length of follow-up sufficient? Unclear: mean 30.3 (SD 3.6) weeks (up to 34 months) |
NR |
Type A tympanogram
Baseline (n/N): 72/100 (72%) ears type A; 28/100 (28%) ears abnormal (type B or C) Follow-up (n/N): 97/100 (97%) type A Change to type A (n/N): 25/28 abnormal improved to type A Length of follow-up sufficient? Unclear: NR |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: NR Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment: need for repeat dilatation 7/71 (10%) of ears showing initial improvement required second dilatation to maintain clinical benefit, of which 4/7 were in patients treated with shorter dilatation time Length of follow-up sufficient? Unclear |
Adverse effect of intervention: preauricular emphysema in the ipsilateral parotid region following difficult insertion; resolved within 48 hours: 1/70 Complication of ETD: NR Loss to follow-up: NR Length of follow-up sufficient? Unclear (NR) |
|
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
McCoul (2012)
55
Observational (uncontrolled) Funding: NR Countries: USA Number of centres: single centre Number of patients: 22 Setting: tertiary referral centre (single surgeon otolaryngological practice) Statistical analyses: Tests used: Fisher’s exact test (tympanometry, otoscopy); paired t-test (ETD-Q, SNOT-22) Unit of analysis: ears Population analysed: 29 ears at 3 and 6 weeks; 26 ears at 12 weeks; 22 ears at 6 months Power calculation: yes, based on SNOT-22 score change converted to ETD-Q change of 0.74 with 80% power giving required sample of 15 |
Inclusion criteria: aged at least 18 years; abnormal tympanogram – any non-A curve abnormal otoscopic examination unilateral or bilateral ETD symptoms (aural fullness/pressure, clogged/muffled sensation in ears, recurrent/persistent middle ear effusion, or inability to rapidly self-equilibrate middle ear pressure following ambient pressure change Exclusion criteria: history of head/neck surgery or radiation therapy within 3 months; sinonasal malignancy acute upper respiratory infection (including acute otitis media); adenoid hypertrophy, nasal polyposis, cleft palate or history of repair craniofacial syndrome, cystic fibrosis, cliliary dismotility syndrome, other systemic immunodeficiency Diagnostic methods: ETDQ-7; SNOT-22; physical examination including pneumatic otoscopy, tympanometry pure tone audiometry; CT scan of paranasal sinuses (Lund-McKay score) Definition of ETD: NR |
Age (years): Median: NR Mean 55.1 (8.7) Range: NR n (%) male: NR Body weight/BMI: NR ETD diagnosis (n/N; %): 22/22 (100%) Ethnicity: NR Subgroups (1) Ears with sinus surgery (2) Ears without sinus surgery |
Patient characteristic
ETD history/baseline symptoms: NR High risk: NR Previous treatment: medical therapy (oral antihistamine, intranasal corticosteroids, autoinflation exercises) for 2 months: 22/22 Tympanostomy: 3/22 Related conditions: NR Baseline medication: NR |
||
| Intervention | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | |||
| Surgery: balloon dilatation Eustachian tuboplasty | General and local (4% cocaine solution applied to nasal mucosa; endonasal lidocaine and adrenaline) | Partial inferior turbinectomy: 22/22 patients Submucous resection of nasal septum: 15/35 ears Sphenoethmoidectomy with maxillary sinusotomy: 12/35 ears Revision ethmoidectomy: 2/35 ears Revision sphenoidotomy: 3/35 ears Removal of occluded tympanostomy tube: 1/35 ears Myringoplasty: 1/35 ears |
|||
| Outcomes | |||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up | |
|
ETDQ-7: overall [mean (SD)]
Baseline: 4.5 (1.2) (31 ears) Follow-up: 3 weeks: 2.7 (1.5) (29 ears) 6 weeks 2.6 (1.1) (29 ears) 12 weeks: 2.8 (1.7) (26 ears) 6 months: 2.8 (1.3) (22 ears) Change from baseline: 3 weeks: 1.9 (1.5) (p < 0.001) (29 ears) 6 weeks: 1.9 (1.1) (p < 0.001) (29 ears) 12 weeks: 1.8 (1.3) (p < 0.001) (26 ears) 6 months: 1.8 (1.2) (p < 0.001) (22 ears) Subgroup data: Preoperative with sinus surgery 4.3 (1.4); without sinus surgery 4.7 (1.0); p = 0.34 No significant difference between groups in postoperative scores up to 6 months SNOT-22/SNOT-20 [mean (SD)] Version used SNOT-22 Baseline: 51.4 (21.1) (33 ears) Follow-up: 3 weeks: 39.1 (21.9) (28 ears) 6 weeks: 34.2 (25.3) (30 ears) 12 weeks: 34.2 (21.5) (27 ears) 6 months: 30.0 (23.9) (21 ears) Change from baseline: 3 weeks: 11.9 (17.8) (28 ears) (p = 0.029) 6 weeks: 21.4 (20.9) (30 ears) (p = 0.004) 12 weeks: 21.5 (22.3) (27 ears) (p = 0.003) 6 months: 23.3 (19.6) (21 ears) (p = 0.001) Subgroup data: Preoperative with sinus surgery 50.6 (23.6); without sinus surgery 52.2 (19.0); p = 0.82 No significant difference between groups in postoperative scores at up to 6 months Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
NR |
Type A tympanogram
Baseline (n/N): 10/35 ears (all considered abnormal) (20 type C, five type B) Follow-up (n/N): 6 weeks: 34/35 ears (all considered normal) [1/35 type B (perforation)] Other dichotomous measure (1): tympanic membrane retraction Baseline (n/N): 33/35 Follow-up (n/N): 0/35 Change (improvement) (n/N): 33/33 Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: Yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: NR Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment: symptomatic at 6 months post operation and chose revision procedure (balloon dilatation Eustachian tuboplasty) 2/22 patients Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Adverse effect of intervention: Postoperative complication 1/22: bleeding requiring myringotomy – resolved Complication of ETD: NR Discontinuation: 0/22 Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
|
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Poe (2011)
22
Study design: observational (uncontrolled) Funding: none (equipment supplied free by manufacturer) Countries: Finland Number of centres: single centre Setting: teaching hospital Number of patients: 11 Statistical analyses: Tests used: two–tailed paired sample t-tests Unit of analysis: patient Population analysed: ITT Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: unilateral or bilateral persistent OME for at least 5years, broken only by tympanostomy tubes or tympanic membrane perforation Exclusion criteria: NR Diagnostic methods: Valsalva manoeuvre; otomicroscopy: tympanometry; video rigid or fibre-optic endoscopy; mucosal inflammation score; CT scans Definition of ETD: NR |
Age (years): Median: NR Range: 33–76 Mean: 51.8 Body weight/BMI: NR n (%) male: 5/11 (45%) Ethnicity: NR |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: dilatory dysfunction of the ET on video/fibre-optic endoscopy Negative Valsalva manoeuvre Persistent OME High risk (n/N; %): NR Previous treatment: previous tympanostomy tubes: 11/11 100% (mean 4.7, range 1–10) adenoidectomy: 5/11 (45.5%) Related conditions (n/N; %): OME: 11/11 (100%) Baseline medication: NR |
|
| Intervention | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | ||
| Unilateral balloon dilatation at 8–12 atmospheres, reinsertion/repeat dilatation where necessary | General; topical decongestant applied to nasal cavities | Tympanostomy tubes placed (two patients); tympanostomy tubes removed (three patients) | ||
| Outcomes | ||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up |
| NR | NR | Change to type A (n/N): 4/11 Baseline (n/N): 0/11 (four type B or C, five tympanostomy tubes, two perforated TM) Follow-up (n/N): 4/11 (one type C, four tubes, two perforated) Other dichotomous measure: 1 Definition and/or criteria for change: Valsalva manoeuvre successful Baseline (n/N): 0/11 Follow-up (n/N): 11/11 of which 7/11 consistent at last follow-up, four inconsistent at last follow-up Tympanogram other measure: tympanic membranes appeared normal Follow-up (n/N): 5/11 Baseline (n/N): 0/11 Change (improvement) (n/N): 5/11 (four type A, one type C tympanogram) Other continuous measure (1): mucosal inflammation score Follow-up [mean (SD)]: mean 1.73 (0.79) Baseline [mean (SD)]: mean 2.91 (0.83) Change from baseline [mean (SD)]: p = 0.003 Outcome assessed using a reliable tool? Yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes: 6–14 (median 7) months |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: NR Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment: NR See concomitant treatment |
Adverse effect of intervention: minor mucosal laceration within lumen of ET: 5/11 (4 inflated to 12 atm) All healed without scarring. C6–7 contralateral radiculopathy: one (fully recovered) Injuries, synechial bands, narrowing of lumen, patulous ET, postoperative epistaxis, reflux otitis: 0 Complication of ETD: NR Discontinuation: 0/11 Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Myringotomy
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Potocki (1999)
60
Observational uncontrolled Funding: none reported but devices supplied free by manufacturer Countries: USA Number of centres: NR Setting: NS Number of patients: 13 Statistical analyses: Tests used: NR Unit of analysis: patient Population analysed: ITT Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: patients undergoing hyperbaric oxygen therapy who would otherwise have required tympanostomy tubes for ETD Exclusion criteria: children Diagnostic methods: otoloaryngologic examination; audiologic testing including tympanogram and pure-tone audiometry |
Age (years): Median: 51 Mean: 53 Range: 29–77 n (%) male: 9/13 (69%) Ethnicity: NR Bodyweight/BMI: NR |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: delayed hyperbaric oxygen therapy due to ETD ETD diagnosis (n/N; %): 11/13 (85%) High risk (n/N; %): NR Previous treatment: Nasal decongestants: 13/13 Valsalva manoeuvre: 13/13 Prior otologic surgery: 0/13 Related conditions (n/N; %): barotrauma: tympanic membrane haemorrhage 8/13; hemotympanum 3/13 Baseline medication: NR |
||
| Intervention | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | |||
| Surgery: bilateral thermal myringotomy | Local (canal block 1% lidocaine) | NR | |||
| Outcomes | |||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up | |
| NR | Patient reported change in hearing: Change from baseline (n/N): 1/13 Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: no |
NR |
Quality of life: NR Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment (n/N): need for repeat myringotomy/need for myringoplasty. No patient required second procedure to complete therapy; one required repeat procedure at 4 months; two patients required myringoplasty for perforated TM |
Adverse effect of intervention: Vertigo 0/13 Infection: 0/13 Perforations: 4/26 (2/13 patients) Complication of ETD: NR Loss to follow-up: (n/N) 0/13 |
|
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Prokopakis (2005)
58
Additional records: Prokopakis 2003 59 Observational uncontrolled Funding: Theodore Angelopoulos and Gianna Angelopoulos-Daskalaki Countries: Greece Number of centres: single centre Setting: academic tertiary referral medical centre Number of patients: 108 (142 ears) Statistical analyses: Tests used: none Unit of analysis: ears Population analysed: ITT Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: adults with serous otitis media; ETD; or acute otitis media Exclusion criteria: nasopharyngeal tumour Diagnostic methods: weekly clinical (including Valsalva-Toynbee and inflation-deflation tests) and audiological examination with tympanogram and audiogram for 8 weeks Nasal endoscopy (all patients negative for tumours) Allergy tests (all ETD patients negative) |
Age (years): Median: NR Mean: 53 Range: 17–74 n (%) male: 51/108 (47.2%) Ethnicity: NR Body weight/BMI: NR Subgroups: patients with ETD 36/108 (33%) (48 ears) |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: NR ETD diagnosis (n/N; %): 36/108 (33%) (48 ears) High risk (n/N; %): NR Previous treatment: none Related conditions (n/N; %): NR Baseline medication: NR |
|
| Intervention | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | ||
| Laser-assisted tympanostomy without ventilation tubes | Local | NR | ||
| Outcomes | ||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up |
|
Definition and/or criteria for change: symptoms (ear fullness, pain, tinnitus) of ETD resolved Baseline: 0/48 Follow-up: 38/48 (79.1%) at 2 months Length of follow-up sufficient: unclear (2 months) |
NR | NR |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: NR Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment: NR |
Adverse effect of intervention: NR Complication of ETD: NR Discontinuation Intervention (n/N): 0/36 Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
Other interventions
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Boboshko (2005)
51
Funding: NR Countries: Russia Setting: NR Number of centres: NR Number of patients Total 40 Intervention 25 (31 ears) Comparator 15 (15 ears) Statistical analyses: Tests used: none Unit of analysis: ear Population analysed: ITT Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: intermittent hearing loss; ear pain; autophony; discomfort in the ears; poor endurance of differences in atmospheric pressure (flying in an aeroplane, diving, etc.); others (not reported) (based on author contact) Exclusion criteria: NR Diagnostic methods: symptomatology, tympanometry (based on author contact) Definition of ETD: NR (tympanogram type C is an objective confirmation of ETD) |
Age (years): Median: NR Mean: NR Range: 21–56 n (%) male: 21/40 (52.5%) Ethnicity: NR Body weight/BMI: NR |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: intermittent hearing loss; ear pain; autophony; discomfort in the ears; poor endurance of differences in atmospheric pressure (flying in an aeroplane, diving, etc.); and others (author contact) ETD diagnosis (n/N; %): 40/40 (100%) High risk (n/N; %): NR Related conditions (n/N; %): OME (40/40; 100%) Previous treatment: most previously treated for ETD (author contact) Baseline medication: NR |
||
| Intervention | Control | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | ||
| Surgery: point laser coagulation (superior and posterior margin of ET nasopharyngeal opening) Unilateral and bilateral |
Catheterisation of ET with insufflation, application of medications (not specified) under rhinoscopic control | Local | NR | ||
| Outcomes | |||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up | |
|
Disappearance or reduction of unpleasant feeling and noise in the ear
Intervention: Baseline: 0/25 patients Follow-up: 25/25 (100% patients) Change from baseline: 25/25 (100%) patients Comparator: Baseline: NR Follow-up: NR Change from baseline: NR Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: unclear Length of follow-up sufficient? No: 2 weeks |
Rates of improvement in air–bone gap (dB)
Threshold-audiometry with frequencies of 0.5, 1, 2 and 4 kHz Intervention Baseline (n/N) (%): 0–10 dB: 0/31 (0) 11–20 dB: 5/31 (16.1) 21–30 dB: 16/31 (51.6) > 30 dB: 10/31 (32.3) Follow-up (n/N) (%): 0–10 dB: 24/31 (77.4) 11–20 dB: 5/31 (16.1) 21–30 dB: 2/31 (6.5) > 30 dB: 0 (0) Change from baseline (n/N): NR Comparator Baseline (n/N) (%) 0–10 dB: 0/15 (0) 11–20 dB: 3/15 (20) 21–30 dB: 8/15 (53.3) > 30 dB: 4/15 (26.7) Follow-up (n/N) (%) 0–10 dB: 4/15 (26.7) 11–20 dB: 8/15 (53.3) 21–30 dB: 2/15 (13.3) > 30 dB: 1/15 (6.7) Difference between groups at follow-up Risk of > 10 dB: RR 0.85 (95% CI 0.29 to 2.45) Change from baseline (n/N): NR Other outcome: Number of dB gained, mean air–bone gap Threshold-audiometry with frequencies of 0.5, 1, 2 and 4 kHz Intervention Baseline mean (SD): 26.8 (7.2) Follow-up mean (SD): 8.8 (6.1) Difference from baseline: mean (SD) 18.1 (5.2) Comparator Baseline, mean (SD): 26.3 (5.5) Follow-up, mean (SD): 14.9 (5.3) Difference from baseline, mean (SD) 11.4 (5.2) Difference between groups Baseline, mean (SD): 0.5 (NR) Follow-up, mean (SD): 6.1 (NR) Difference from baseline, mean (SD) p = 0.0028 MD –6.10 (95% –9.69 to –2.51) Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes: 1 year |
Tympanogram type A
Intervention Baseline (n/N): not reported (15 type B; 14 type C; seven type F) (does not sum to total) Follow-up (n/N): 30/31 (97%) (one type C) Change to type A (n/N): NR Comparator Baseline (n/N): NR Follow-up (n/N): NR Change to type A (n/N): NR Difference between groups Baseline (n/N): NR Follow-up (n/N): NR Change to type A (n/N): NR Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? No: 2 weeks |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: recurrence of OME Intervention (n/N): 2/31 ears (9–11 months) Comparator (n/N): 6/15 ears (1–6 months) Difference between groups: RR 0.16 (95% CI 0.04 to 0.71) Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Variable: intervention, 9 to 11 months; control group, 1 to 6 months Need for additional treatment: NR |
Adverse effect of intervention
Intervention: none Complication of ETD: NR Discontinuations: NR Length of follow-up sufficient: unclear (NR) |
|
| Study | Inclusion criteria and diagnosis of ETD | Participant characteristics | ETD characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Silverstein (2003)
61
Funding: NR Countries: USA Number of centres: single centre Setting: tertiary otologic referral centre Number of patients: 11 Statistical analyses: Tests used: none Unit of analysis: patient Population analysed: ITT Power calculation: NR |
Inclusion criteria: chronic ETD symptoms consistent with ETD (e.g. hearing loss and aural fullness); previous medical therapy and at least one middle ear ventilation; tympanometry/clinical examination indicated abnormal middle ear pressure Exclusion criteria: NR Diagnostic methods: tympanometry; audiometry; clinical examination Definition of ETD: NR |
Age (years): Median: NR Mean: 63 Range: 34–90 n (%) male: NR Ethnicity: NR Body weight/BMI: NR Subgroups: (1) Patients with Samter’s triad (2/11) |
ETD history/baseline symptoms: chronic ETD ETD diagnosis (n/N; %) 11/11 (100%) High risk (n/N; %) NR Previous treatment: medical therapy: 11/11 (100%) at least one ME ventilation procedure: 11/11 (100%) Related conditions (n/N; %): Samter’s triad (bronchial asthma, nasal polyps, aspirin sensitivity): 2/11 Baseline medication: NR |
||
| Intervention | Anaesthesia | Concomitant interventions | |||
| Surgery and pharmacological: laser tympanostomy or vertical myringotomy; insertion of ventilation tube and MicroWick through the tube, then administration of dexamethasone 4 mg/ml through wick t.i.d. for 4 weeks | Local | Antibiotic solution Concurrent with dexamethasone Treatment once daily (two drops) |
|||
| Outcomes | |||||
| Symptoms | Hearing | Middle ear function | Other efficacy outcomes | Adverse events, complications, loss to follow-up | |
|
Aural fullness or pressure
Baseline: 11/11 (100%) Follow-up: 8/11 (72.7%) Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: unclear Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes: mean 7.2 months |
Mean pure-tone average
Baseline: 40 dB Follow-up: 34 dB (32 dB postoperative) Difference from baseline: 6 dB Mean air–bone gap (dB) Baseline: 11 dB Follow-up: 5 dB (5 dB postoperative) Difference from baseline: 6 dB Mean speech discrimination score (%) Baseline: 94% Follow-up: 97% Difference from baseline: not statistically significant Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Unclear: 7.2 months |
Tympanogram type A
Intervention Change to type A (n/N): 4/8 (50%) Baseline (n/N): 3/11 (27.3%) (six type B, two type C) Follow-up (n/N): 7/11 (63.6%) (four patients with persistent perforations) (mean follow-up 8 months) Subgroup data: both patients with Samter’s triad converted to type A Outcome assessed using a reliable tool: yes Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes: mean 8 months |
Quality of life: NR Clearance of middle ear effusion: NR Early tube extrusion: NR Need for additional treatment: fat myringoplasty for tympanic perforation Intervention (n/N): 3/11 (fourth patient declined treatment) Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes: at least 3 months |
Adverse effect of intervention: 0/11 sensineural hearing loss attributable to treatment 4/11 persistent perforation for at least 3 months Complication of ETD: 1/11 severe otitis media, developed profound sensorineural hearing loss Discontinuation Total (n/N): 1/11 (otitis media leading to profound sensorineural hearing loss) Due to lack of effectiveness (n/N): 0/11 Length of follow-up sufficient? Yes |
|
Glossary
- Case series
- A study design where observations are made on a series of individuals, usually all receiving the same intervention, before and after an intervention but with no control group.
- Chronic otitis media
- An infected middle ear with eardrum perforation.
- Controlled before-and-after study
- A study in which observations are made before and after the implementation of an intervention, both in a group that receives the intervention and in a control group that does not.
- Intention-to-treat analysis
- Analysis that compares participants in the groups to which they were originally assigned.
- Middle ear atelectasis
- Retraction of the tympanic membrane. A condition in which a part of the eardrum lies deeper within the ear than its normal position. The retracted segment of eardrum is often known as a retraction pocket.
- Non-randomised controlled trial
- A clinical trial with a control group in which patients are not put in the study or control group by chance (randomisation). Instead, they are sorted using other methods.
- Otitis media
- Infection of the middle ear.
- Otitis media with effusion
- A collection of fluid that occurs within the middle ear space. Over weeks and months, middle ear fluid can become very thick and glue-like. Also called serous or secretory otitis media or glue ear.
- PROSPERO
- An international database of prospectively registered systematic reviews in health and social care. Key features from the review protocol are recorded and maintained as a permanent record. This provides a comprehensive listing of systematic reviews registered at inception, and enables comparison of reported review findings with what was planned in the protocol. PROSPERO is managed by Centre for Reviews and Dissemination and funded by the UK National Institute for Health Research.
- Randomised controlled trial
- A trial in which the participants are randomly allocated to the control or treatment groups.
- Retrospective study
- A study that looks backwards and examines exposures to suspected risk or protection factors in relation to an outcome that is established at the start of the study. It differs from a prospective study, which watches for outcomes, such as the development of a disease, during the study period and relates this to other factors such as suspected risk or protection factor(s).
- Tinnitus
- The perception of sound within the human ear in the absence of corresponding external sound.
- Tympanic membrane (or eardrum)
- A thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit sound from the air to the ossicles inside the middle ear, and then to the oval window in the fluid-filled cochlea. It converts and amplifies vibration in air to vibration in fluid.
List of abbreviations
- BIOSIS
- Bioscience Information Service
- CENTRAL
- Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials
- CI
- confidence interval
- CINAHL
- Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature
- CPCI-S
- Conference Proceedings Citation Index – Science
- ETD
- Eustachian tube dysfunction
- ETDQ-7
- 7-item Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire
- FDA
- US Food and Drug Administration
- GP
- general practitioner
- HTA
- Health Technology Assessment
- LILACS
- Latin American and Carribean Health Sciences Literature
- LTRA
- leukotriene receptor antagonist
- MD
- mean difference
- MeSH
- medical subject heading
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NSAID
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- RR
- risk ratio
- SD
- standard deviation
- SNOT-22
- 22-item Sinonasal Outcome Test
- VAS
- visual analogue scale
- VEMP
- vestibular evoked myogenic potential