Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the HTA programme as project number 08/68/01. The contractual start date was in May 2010. The draft report began editorial review in August 2017 and was accepted for publication in January 2018. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Ibrahim Abubakar is a member of the Health Technology Assessment (HTA) Commissioning Board. Ajit Lalvani is a named inventor on several patents underpinning the T-SPOT.TB test assigned by the University of Oxford to Oxford Immunotec Ltd and has royalty entitlements from the University of Oxford. He was the scientific founder of Oxford Immunotec Ltd and ceased to be a director 10 years ago. He is a member of the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Efficacy and Mechanism Evaluation Board. Charlotte Jackson was funded by NIHR, during the conduct of the study, and reports personal fees from Otsuka Pharmaceutical, outside the submitted work. Chris Griffiths is involved in NIHR-funded clinical trials units. Jonathan J Deeks is Chairperson of the NIHR HTA Efficient Studies Themed Board, Chairperson of the NIHR HTA Multimorbidities in Older People Themed Board, Deputy Chairperson of the NIHR HTA Commissioning Board, Chairperson of the NIHR HTA Monitoring Strategy Group, a member of the NIHR HTA Methods Group for Diagnostic, Technologies & Screening, a member of the NIHR HTA Methods Group for Elective & Emergency Specialist Care, a member of the NIHR HTA Programme Commissioning Strategy Group and a member of the NIHR HTA Strategy and Oversight Group. The other authors have no competing interests to declare.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2018. This work was produced by Abubakar et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2018 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Background, aims and objectives
Background
Tuberculosis (TB) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. In 2015, an estimated 9 million cases occurred globally and > 1.5 million people died of TB. 1 The UK has seen a resurgence of TB since the late 1980s, and there are currently > 7000 new cases each year. 2 Although there has been a decline over the last few years, levels remain higher than in most Western European countries. Most cases in the UK occur in major cities, particularly London, and two-thirds of TB patients were born abroad. There are also high rates among those with social risk factors such as homelessness and/or drug/alcohol misuse. Control measures have traditionally relied on the prompt diagnosis of active TB and ensuring that patients completed their treatment. More recently, the collaborative TB strategy for England has initiated a programme of latent TB screening of migrants entering the UK from countries with a high TB burden. 3
The majority of TB cases in the UK are a result of reactivation of latent infection. 2 Among migrant groups, the infection is likely to have been acquired abroad whereas, among the elderly UK-born population, the infection is likely to represent acquisition several decades ago when TB was highly prevalent in the UK. The policy of targeting active TB cases for treatment alone will therefore not be sufficient to control and eventually eliminate TB in the UK. The identification and treatment of individuals with latent TB infection (LTBI) who are at high risk of developing active TB may therefore be an essential additional measure provided that (1) true LTBI can be identified [and distinguished from prior bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) vaccination], (2) the probability of developing active TB in people with untreated LTBI can be determined and (3) the intervention strategy available (treatment of latent infection) is effective and can be successfully implemented.
Identification of latent tuberculosis infection
It is estimated that between one-quarter and one-third of the world’s population is latently infected with the tubercle bacterium4,5 and it is widely accepted that, among those with LTBI, there is approximately a 10% lifetime chance of progression to active TB. Until recently, the tuberculin skin test (TST) was the only tool for the diagnosis of LTBI. TST assesses the delayed-type hypersensitivity response to a purified protein derivative, which contains antigens shared by several mycobacteria and Mycobacterium bovis BCG, by measuring the size of the skin induration following the injection of the antigen. Limitations to the validity (sensitivity and specificity) of TST as a measure of latent infection have been recognised for many years. These are partly attributable to variability in the quality of the administration and interpretation of the test, as well as the state of host immunity.
Interferon gamma release assays
Interferon gamma release assays (IGRAs) are based on the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex specific region of difference 1 (RD1) antigens such as early secretory antigenic target 6 (ESAT-6), culture filtrate protein 10 (CFP-10) and other TB-specific antigens. Two commercial assays have been developed using these M. tuberculosis antigens: (1) QuantiFERON® TB Gold In-Tube (QFT-GIT; Cellestis International Pty Ltd, Chadstone, VIC, Australia), which uses an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) format; and (2) the T-SPOT®.TB test (Oxford Immunotec Ltd, Oxford, UK), which is an enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT)-based assay.
Predictive value studies of interferon gamma release assays
Early systematic reviews6 of the role of IGRAs in the diagnosis of latent infection with M. tuberculosis concluded that they have several advantages over the TST, including higher specificity (less cross-reactivity with BCG vaccine and environmental mycobacteria) and better correlation with exposure to M. tuberculosis. In the absence of a gold standard for the diagnosis of LTBI, all of the studies in these reviews have used other proxy measures to estimate the sensitivity and specificity of IGRAs for latent infection. These measures include ‘degree of contact with a case of TB’ and the use of ‘active TB disease’ as an indicator of a true positive result and ‘low prevalence of infection in the test population’ to estimate true negative results. 4
The majority of the studies included in these reviews were conducted in high-incidence countries, with a limited number conducted in low-incidence countries. Most of the completed studies either had low power7–9 or used routinely collected data. 10 More recent systematic reviews still conclude that the predictive value of IGRAs is comparable to that of TST. 11,12 We have updated these reviews in Diagnostic performance of interferon gamma release assays for development of active tuberculosis: evidence summary.
National and international guidelines and policy context
National policy
The national policy for the control of TB is currently based on the Collaborative Tuberculosis Strategy for England,3 published in January 2015, which outlines 10 action areas including treatment of LTBI in new entrants to the UK from high-burden countries. Based on this strategy, Public Health England (PHE; formerly the Health Protection Agency) recommends screening using IGRA alone. 13 In contrast, the most recently published (January 2016) National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidance14 recommended that a TST and, where this is not available, an IGRA for migrants (as this was the most cost-effective strategy based on analysis using predictive value data) and a two-step approach using the TST followed by an IGRA if the TST was positive for contacts.
International policy
The World Health Organization (WHO) has published guidelines for the management of LTBI,12 which is targeted at countries with an incidence of TB of < 100 cases per 100,000 people. These guidelines recommend the use of either IGRAs or TST as alternatives based on very low-quality evidence. Internationally, individual country guidelines differ considerably with five broad approaches: (1) an IGRA and TST as alternatives, (2) a two-step process consisting of a TST followed by an IGRA, (3) an IGRA and TST together, (4) an IGRA alone, replacing the TST, and (5) the TST alone.
Diagnostic performance of interferon gamma release assays for development of active tuberculosis: evidence summary
Because of the known limitations of the TST, there is no gold standard against which to compare IGRAs to estimate their sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) or negative predictive value (NPV) for the presence of LTBI. However, for clinical and public health purposes, arguably a more important issue is what a positive or negative IGRA result means for the risk of developing active TB. Several studies have estimated PPV and NPV, sensitivity or specificity of IGRAs for the development of active TB, and two recent systematic reviews15,16 have included meta-analyses of these parameters. A further, more up-to-date, review12 concluded that the two tests were not significantly different in terms of their PPV and NPV.
The two recently published reviews15,16 had slightly different objectives, inclusion criteria and analytical approaches and, for this reason, reached different conclusions. One of them15 estimated a pooled PPV of 2.7% [95% confidence interval (CI) 2.3% to 3.2%] from 17 studies and 6.8% (95% CI 5.6% to 8.3%) from 13 studies that were conducted in high-risk groups. The pooled NPV was considerably higher, at 99.7% (95% CI 99.5% to 99.8%). The included studies were heterogeneous for both PPV and NPV. The other review16 compared rates and risks of TB disease in IGRA-positive and IGRA-negative individuals, as well as estimating sensitivity and specificity of IGRAs for the development of active TB. The pooled rate ratio was 2.10 (95% CI 1.42 to 3.08) and the pooled risk ratio was 3.54 (95% CI 2.23 to 5.60). Sensitivity was estimated as 72% (95% CI 58% to 82%) and specificity as 50% (95% CI 41% to 58%) for the ELISPOT assay; for whole-blood ELISA, only two eligible studies estimated sensitivity and specificity, with values of 79% (95% CI 61% to 91%) and 43% (95% CI 18% to 72%) for sensitivity and 34% (95% CI 32% to 36%) and 59% (95% CI 55% to 62%) for specificity. In the subset of studies that assessed both IGRA and TST, Rangaka et al. 16 reported incidence rate ratios (IRRs) of 2.11 (95% CI 1.29 to 3.46) for IGRA, 1.60 (95% CI 0.94 to 2.72) for TST with a 10-mm cut-off point and 1.43 (95% CI 0.75 to 2.72) for TST with a 5-mm cut-off point. In the review by Diel et al. ,15 PPV appeared higher for IGRA (2.1%, 95% CI 1.7% to 2.5%) than for TST (1.4%, 95% CI 1.2% to 1.8%) in studies that assessed both tests.
The review by Rangaka et al. 16 was updated by Pai et al. ,11 who identified an additional five longitudinal studies that compared the incidence of TB between individuals with positive and negative IGRA results. Three of these studies were conducted in immunocompromised populations: human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-positive patients,17 patients with various immunosuppressive conditions18 and renal transplant recipients19. The remaining two studies assessed the development of active TB among contacts of TB cases in the UK7 and France,20 comparing those with a positive IGRA result at baseline with those with a negative result. In the UK, this generated a rate ratio of 4.9 (95% CI 2.7 to 8.7) over 2 years,7 whereas the French study reported a PPV of 1.96% among contacts who were not given chemoprophylaxis (CPX), over a mean follow-up period of 34 months. 20
PubMed was searched on 19 July 2016 to update the evidence base, using the search strategy of Rangaka et al. 16 (which was itself based on strategies used in previous reviews21) and restricting to publication dates in 2013 or later. We sought to identify primary studies in which individuals underwent IGRA testing at baseline and were followed up for the development of active TB, and which either presented estimates of PPV and NPV or provided sufficient information for these to be estimated. Studies in which no cases of active TB occurred were considered not to be informative for this purpose and were excluded.
The search of PubMed generated 2399 results (Figure 1), of which 597,9,10,22–77 included the required information on PPV and/or NPV (see Appendix 2, Figure 14). In addition, we are aware of a further relevant study78 that was published after we conducted our review. Many of these 59 studies did not have the primary aim of assessing diagnostic accuracy. Many recorded few cases of active TB (often < 10)22,25–27,29–33,35–38,40,42–45,47,48,50,51,56–59,62–65,67–75,77,78 and/or were restricted to groups such as patients infected with HIV,9,28,29,36,49,51,56,60,65,68,75 recipients of haemodialysis or kidney transplants,35,43,44,62–64 patients taking or initiating treatment with biological agents such as tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors,37–40,42,45,47,48,58,71,74 recipients of haematopoietic stem cell transplants,50,57 lung cancer patients30 or patients with combinations of these conditions. 61 Four further studies were conducted among health-care workers. 59,69,73,77 The duration of follow-up ranged from 8 to 10 weeks to 10 years. Consistent with the previous systematic review,15 estimates of PPV were consistently low, ranging from 0% to 24%; NPV was considerably higher (always ≥ 90%).
FIGURE 1.
Flow diagram summarising study selection.
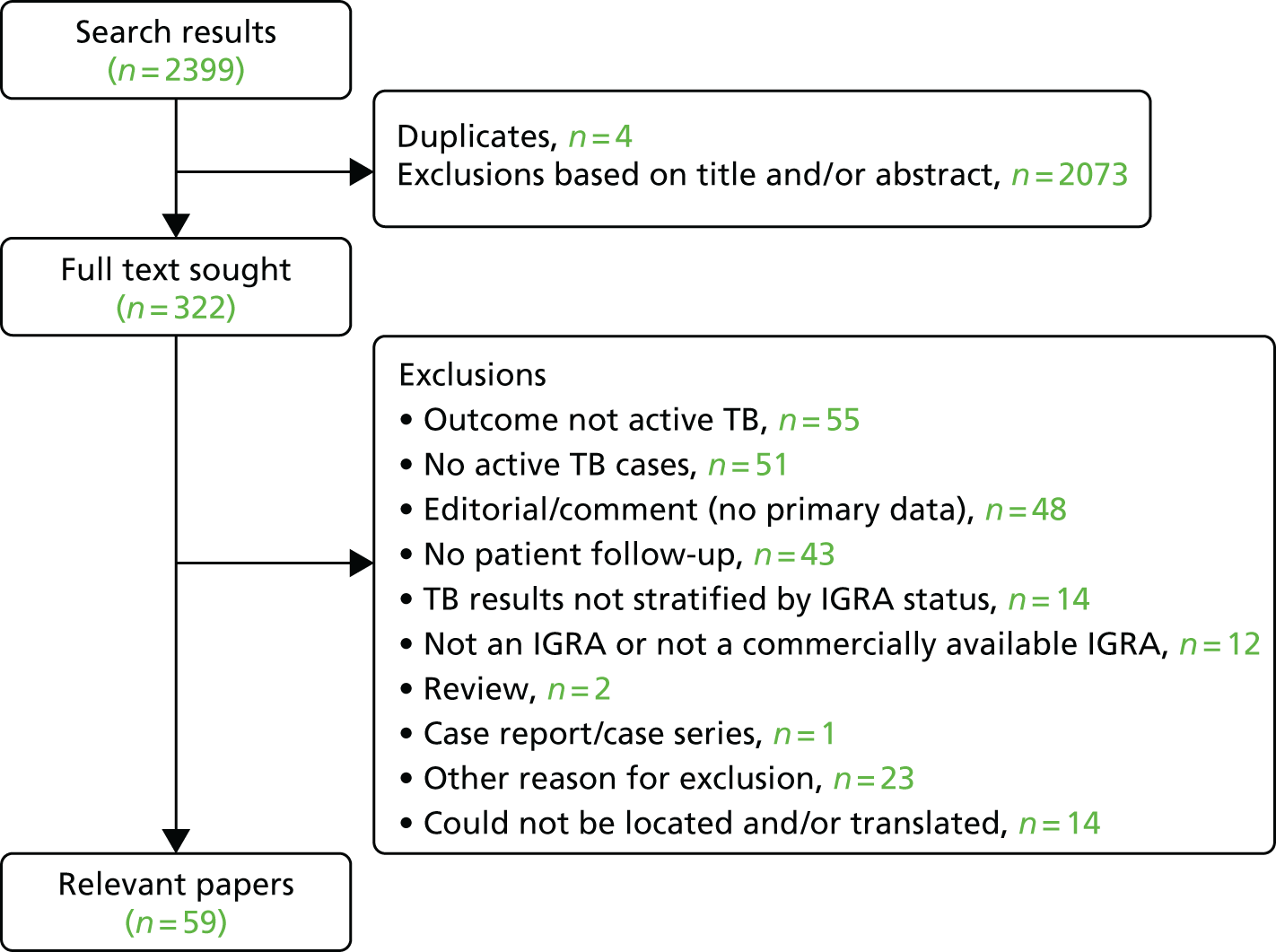
Eighteen studies (including the additional study78) did specifically assess the diagnostic accuracy of IGRAs for future development of active TB (Table 1) or otherwise quantify the association between a positive IGRA and subsequent TB. Of these, five assessed both IGRAs and TST. 23,52,56,62,72 Except when noted, these studies did not include treatment for LTBI. In this subset of studies, estimates of the PPVs ranged from < 1% to 17%, whereas the NPV was ≥ 97%. Sensitivity was reported as 37.5–100.0% and specificity as 27.0–86.0%. Even among these studies, case numbers were sometimes low (see Table 1). In addition, several of the studies29,31,32,35,36,52,56,62,72 did not explicitly state that prevalent cases were excluded, although the extent to which this may have affected their estimates was not always clear.
| Study | Population | Participants, n/N (%) | Number of active TB cases | Follow-up duration | PPV (%) (95% CI) | NPV (%) (95% CI) | Sensitivity (%) (95% CI) | Specificity (%) (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGRA positive at baseline | IGRA negative at baseline | IGRA indeterminate at baseline | IGRA positive at baseline | IGRA negative at baseline | |||||||
| aAltet et al.23 | Contacts (Spain) | 81/453 (18) | 372/453 (82) | 0 | 14 | 0 | 4 years | 17 (9 to 26) | 100 (100 to 100) | 100 (100 to 100) | 85 (81 to 88) |
| bBlount et al.78 | New entrants (USA) | 513/1152 (45) | 639/1152 (55) | 0 (excluded) | 5 | 2 | 10 years | 0.97 (0.32 to 2.3) | 99.7 (98.9 to 100) | 71 (29 to 96) | 56 (53 to 59) |
| cDoyle et al.29 | HIV-positive patients being screened for LTBI at a sexual health centre (Australia) | 29/917 (3) | 884/917 (96) | 4/917 (0.4) | 1 | 1 | Median 26.4 months | 3.4 (0.1 to 17.8) | 99.9 (99.4 to 99.9) | N/A | N/A |
| aGeis et al.31 | IGRA-positive contacts without history of TB disease (Germany) | 207/207 (100) | 0 | 0 | 5 | N/A | ≈1 year | 2.9 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Goebel et al.32 | Contacts (Australia) | 212/643 (33) | 431/643 (67) | 0 | 4 | 2 | Mean 3.7 years | 2 | 99 | N/A | N/A |
| Haldar et al.7 | Contacts not receiving LTBI treatment (UK) | 112/1669 (7) | 1557/1669 (93) | 0 | Unclear | Unclear | 2 years | 13 (7 to 20) | 99 (98 to 100) | 70 (46 to 88) | 86 (83 to 88) |
| Hermansen et al.34 | General population (Denmark) | 1520/15,749 (10) | 13,425/15,749 (85) | 804/15,749 (5) | 20 | 20 | Median 3.36 years | 1.3 | 99.9 | N/A | N/A |
| Jeong et al.35 | Kidney transplant recipients (Republic of Korea) | 42/129 (33) | 87/129 (67) | 0 | 1 | 1 | Median 8.4 months | 2.4 | 98.9 | 50 | 67.7 |
| Jonnalagadda et al.36 | HIV-positive pregnant women tested during pregnancy and followed up for post-partum TB (Kenya) | 125/327 (38) | 157/327 (48) | 45/327 (14) | 7 | 2 | 1 year in primary analysis (2 years in supplementary analysis) | 5.9 (2.4 to 12.2) | N/A | 77.7 (45.7 to 100.0) | 54.6 (49.3 to 60.1) |
| Lee et al.49 | HIV-infected patients (Taiwan) | 90/772 (12) | 651/772 (84) | 31/772 (4) | 6 | 10 | Median 5.2 years | N/A | 98.5 | 37.5 | |
| aLeung et al.52 | Contacts (Hong Kong) | 244/865 (28) | 621/865 (72) | 0 | 15 | 5 | Mean 4.68 years | 6.1 (3.5 to 9.9) | 99.2 (98.1 to 99.9) | 75.0 (50.9 to 91.3) | 72.9 (69.8 to 75.9) |
| Mathad et al.56 | Pregnant women infected with HIV (India) | 71/252 (28) | 173/252 (69) | 8/252 (3) | 5 | 0 | ≈1 year | 7 | N/A | 100 | 27 |
| Seyhan et al.62 | Haemodialysis patients (Turkey) | 39/95 (41) | 56/95 (59) | 0 | 4 | 0 | Mean 4.9 years | 10.3 | 100 | 100 | 62 |
| Shu et al.64 | Haemodialysis patients (Taiwan) | 193/940 (21) | 713/940 (76) | 34/940 (4) | 3 | 1 | Average 3 years | 1.6 | 99.9 | 75.0 | 79.7 |
| Soborg et al.65 | HIV-infected patients (Denmark) | 28/522 (5) | 478/522 (91) | 16/522 (4) | 2 | 0 | 6 years | 7 (1 to 22) | 100 (99 to 100) | ||
| Sun et al.68 | HIV-infected patients (Taiwan) | 64/608 (11) | 534/608 (88) | 10/608 (2) | 1 | 0 | Mean 2.6 years | 1.6 | 100 | ||
| Verhagen et al.72 | Indigenous child contacts (Venezuela) | 56/142 (39) | 76/142 (54) | 10/142 (7) | 2 | 2 | 12 months | 4 (1 to 12) | 97 (91 to 100) | ||
| dZellweger et al.10 (QFT-GIT) | Contacts (multiple European countries) | 1068/3895 (27) | 2803/3895 (72) | 24/3895 (< 1) | 17 | 3 | Median 2.5 years | 1.9 (1.1 to 3.0) | 99.9 (99.7 to 100.0) | 85.0 (62.1 to 96.6) | 74.0 (72.5 to 75.5) |
| dZellweger et al.10 (T-SPOT.TB) | Contacts (multiple European countries) | 299/1125 (27) | 823/1125 (73) | 3/1125 (< 1) | 2 | 2 | Median 2.5 years | 0.7 (0.1 to 2.6) | 99.7 (99.1 to 99.9) | 50.0 (8.3 to 91.7) | 73.6 (70.8 to 76.2) |
Within the subset of 18 studies, several compared the frequency of TB disease between IGRA-positive and IGRA-negative participants, consistently finding that rates, hazards or odds of TB were higher among the former (although CIs sometimes crossed the null value). Unadjusted estimates included a hazard ratio of 4.0 (95% CI 0.8 to 19.3),36 odds ratio of 2.10 (95% CI 0.13 to 34.4)35 and rate ratios of 8.5 (no CI given),34 2.9 (95% CI 2.8 to 21.2)78 and 7.7 (95% CI 2.8 to 21.2). 52 Doyle et al. 29 estimated the hazard ratio as 42.4 (95% CI 2.2 to 827) after adjustment for age, gender, cluster of differentiation 4 (CD4) count, viral load and country of birth. Of the studies that did not specifically aim to assess diagnostic performance, such estimates included unadjusted rate ratios of 2.12,24 3.4650 and 73.9 (95% CI 3.9 to 1397.7);75 odds ratios of 9.26 (95 CI 1.02 to 84.0)30 and 7.9 (95% CI 3.46 to 18.06);66 and hazard ratios were 16.82 (95% CI 5.84 to 48.46), excluding treated individuals, and 2.38 (95% CI 1.15 to 4.91), including treated individuals. 41 Adjusted values included a hazard ratio of 2.0 (95% CI 1.2 to 3.3), after adjustment for BCG vaccination scar, maternal education and current/prior household TB contact,54 and an odds ratio of 14.9 (95% CI 2.77 to 80.3), adjusted for the number of IGRA-positive contacts of the same index case, receipt of treatment and place of contact (household vs. other). 76 These effect estimates varied considerably and were often imprecise. In addition, analyses of data from contacts often did not account for clustering by index case, and logistic regression did not account for differences in time at risk of developing active TB.
Table 2 summarises the studies that compared IGRAs with TST in the same participants and assessed predictive values, combining the results of our literature search with earlier studies identified in previous reviews. 12 Only four of these studies23,79–81 were conducted in low-incidence countries with a PPV range of 3% to 17% for IGRA compared with 2–5% for TST. The estimates of NPV for both IGRA (range 98–100%) and TST (99–100%) were very high. Studies from intermediate- and high-burden settings56,62,72,75,82–84 had a wider range of PPV for both IGRA and TST and, similarly, a high but wider range of NPVs.
| Study | Location | Study population | Follow-up | Mean follow-up duration (months) | Tests done | PPV of (%) | NPV of (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TST | IGRA | TST | IGRA | ||||||
| Altet et al.23 | Spain | Adult and child contacts | Active | 48 | TST (5 mm) and QFT-GIT | 2 | 17 | 100 | 100 |
| Diel et al.79 | Germany | Adult and child contacts | Passive | 43 | TST and QFT-GIT | 5 | 13 | 99 | 100 |
| Harstad et al.80 | Norway | Asylum seekers (adults) | Passive | 23–32 | TST and QFT-GIT | 2 | 3 | 100 | 100 |
| Kik et al.81 | The Netherlands | Adult contacts in migrants | Active | 24 | TST, QFT-GIT and T-SPOT.TB | 3 | 3 | 100 | 98 |
| Lee et al.82 | Taiwan | Adults with end-stage renal disease | Active | 24 | TST and T-SPOT.TB | 5 | 0 | 92 | 88 |
| Leung et al.83 | China | Adult silicosis patients | Passive | 29.9 | TST and T-SPOT.TB | 7 | 8 | 96 | 99 |
| Mahomed et al.84 | South Africa | Adolescents | Active | 27.6 | TST and QFT-GIT | 1 | 1 | 99 | 99 |
| Mathad et al.56 | India | Pregnant women infected with HIV | Active | 12 | TST and QFT-GIT | 7 | 7 | 99 | 100 |
| Seyhan et al.62 | Turkey | Dialysis patients | Unclear | 60 | TST (10 mm/15 mm with BCG) and QFT-IG | 3 | 10 | 95 | 100 |
| Verhagen et al.72 | Venezuela | Child contacts | Active | 12 | TST and QFT-GIT | 3 | 4 | 98 | 97 |
| Yang et al.75 | Taiwan | Adults infected with HIV | Active | 35.6 | TST and T-SPOT.TB | 3 | 5 | 100 | 100 |
Our evidence review, and the previously published systematic reviews and meta-analyses, highlight several important research gaps. There has been relatively little study of the diagnostic performance of IGRAs, compared with TST, for the development of active TB in low-incidence countries and particularly in the UK. The one study in Table 1 that was UK based7 did not include a head-to-head comparison with TST and was focused on contacts of TB cases. Although contacts are an important risk group, current guidance in many low-incidence countries includes testing of new entrants from high-burden countries, in whom there is limited evidence of diagnostic performance. Predictive values, both positive and negative, depend on the prevalence of the condition within the population of interest; consequently, results from high-incidence settings may not be generalisable to the UK. Owing to the low risk of progression from LTBI to active TB disease, the PPV of IGRAs for this outcome will, in general, be low. 11 It is therefore important to identify which individuals, among those with a positive IGRA (or TST) result, are most likely to develop disease and, therefore, benefit from treatment of LTBI. The PREDICT (Prognostic Evaluation of Diagnostic IGRAs ConsorTium) study aimed to address these gaps in the evidence base in order to inform UK and international policy for testing and treating LTBI in contacts of TB cases and in migrants.
Review of cost-effectiveness studies
The NICE guideline on TB, which was published in 2006,85 recommended a two-step testing strategy to diagnose LTBI: TST followed by IGRA for patients with a positive TST result. This recommendation was informed by a cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) based on a simple decision tree model, a systematic review of diagnostic accuracy of TST compared with IGRA, and a series of assumptions about the predictive performance of IGRA in populations at different levels of risk. The impact of transmission was estimated by assuming a fixed number of incident cases in contacts of the modelled cohort. The Guideline Development Group noted the high degree of uncertainty over the estimates of cost-effectiveness of different testing strategies for LTBI.
In 2011, NICE published an updated review86 of diagnostic accuracy of tests for LTBI and economic analysis, reaching rather different conclusions. The revised model suggested that the IGRA-alone strategy (without TST) was optimal, although the estimated differences in costs and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) were small. Given the high level of uncertainty, the 2011 NICE guideline recommended IGRA-alone or TST-IGRA strategies as options. Owing to limitations in the evidence base, the 200685 and 201186 NICE guidelines did not distinguish between the two types of commercially available IGRAs [QuantiFERON TB Gold (QFT-G) and T-SPOT.TB], and compared only three screening strategies (TST alone, IGRA alone and TST followed by IGRA if TST result was positive). Both the 2006 and 2011 guidelines followed policy at the time, recommending two cut-off points for defining a positive TST result: induration of ≥ 15 mm for patients with a prior BCG vaccination or ≥ 6 mm for patients without a BCG vaccination. More recent NICE guidelines,14 published in 2016, based on a new decision model, led to revised recommendations, described further in the following paragraphs.
A series of cost-effectiveness analyses have also been published in the literature. In 2011, Nienhaus et al. 87 published a review of economic studies evaluating TST and/or IGRA as components of screening strategies for groups at high risk of TB, such as migrants, close contacts and health-care workers, mostly in low-incidence countries. 87 Of the 13 papers that met their inclusion criteria, eight88–95 involved CEA, whereas five96–100 were cost analyses.
The published cost-effectiveness studies reviewed by Nienhaus et al. 87 all used Markov modelling to estimate transition of a cohort through different health states, assuming a fixed rate of infection in the cohort. None modelled the dynamics of transmission within a wider population. One CEA study95 presented results in terms of cost per avoided TB case, whereas the remaining studies88–94 used QALYs or life-years gained as treatment outcomes. The time horizon for analysis after initial testing for LTBI ranged from 2 years to lifetime in the different CEA models. Some populations were stratified, for example health-care workers with/without BCG vaccination. Although the CEA studies generally supported the IGRA-alone or IGRA-based strategies, Nienhaus et al. 87 noted that comparison of the different models was hindered by a wide range of assumptions. The models were most sensitive to assumptions about specificity of TST, which varied among non-BCG-vaccinated individuals from as low as 34% in one study to 98% in another. There was also significant uncertainty surrounding the rates of progression to active TB following a positive test, as well as overassumptions for IGRA and TST sensitivities.
In 2011, after the Nienhaus et al. 87 review, Pareek et al. 101 published a UK-based prospective assessment and an economic analysis. They sought to address the limitations of the existing models and to examine how LTBI prevalence varied by TB-incidence thresholds in migrants’ regions of origin. They found that single-step QFT-GIT without port-of-arrival chest radiography could be cost-effective at certain incidence thresholds. The results are, however, limited by the small number of participants and the fact that not all of the participants received all three tests.
The NICE TB clinical guideline was updated again in 2016,14 making the following recommendations for LTBI testing in contacts and new entrants to the UK.
-
Offer TST to diagnose LTBI in adults aged 18–65 years who are close contacts of a person with pulmonary or laryngeal TB:
-
If the TST is inconclusive, refer the person to a TB specialist.
-
If the TST is positive (an induration of ≥ 5 mm, regardless of BCG vaccination history), assess for active TB.
-
If the TST is positive but a diagnosis of active TB is excluded, consider an IGRA if more evidence of infection is needed to decide treatment.
-
If the TST is positive, and if an IGRA was carried out and that is also positive, offer treatment for LTBI.
-
-
Offer TST as the initial diagnostic test for LTBI in people who have recently arrived from high-incidence countries and who present to health-care services. If the TST is positive (an induration of ≥ 5 mm, regardless of BCG vaccination history):
-
assess for active TB
-
and if this assessment is negative, offer treatment for LTBI
-
if TST is unavailable, offer IGRA.
-
These recommendations differ from the previous NICE guidelines85,86 in two key respects. First, they downplay the role of IGRA, recommending it as an option following TST when more evidence is needed before treating contacts, or when TST is not available for new entrants to the UK. Second, they recommend a single cut-off point for a positive TST (an induration of ≥ 5 mm) regardless of BCG vaccination status, rather than two cut-off points, as recommended in previous guidelines (an induration of ≥ 6 mm without prior BCG vaccination or an induration of ≥ 15 mm with prior BCG vaccination).
The 2016 NICE recommendations14 were informed by an evidence review and new economic analysis by Auguste et al. 102 (henceforth referred to as the Warwick Evidence report). Auguste et al.'s model consisted of two stages. In the first stage (illustrated in Figures 2 and 3), a decision tree was used to represent LTBI screening, active TB diagnosis and treatment adherence. They examined four diagnostic strategies:
-
IGRA alone
-
TST alone
-
combined strategies – TST followed by IGRA if TST is positive
-
simultaneous testing – both TST and IGRA are carried out.
FIGURE 2.
Starting decision tree of the Warwick Evidence analysis for new entrants from high-incidence countries. Reproduced from Auguste et al. 102 Contains information licensed under the Non-Commercial Government Licence v2.0.
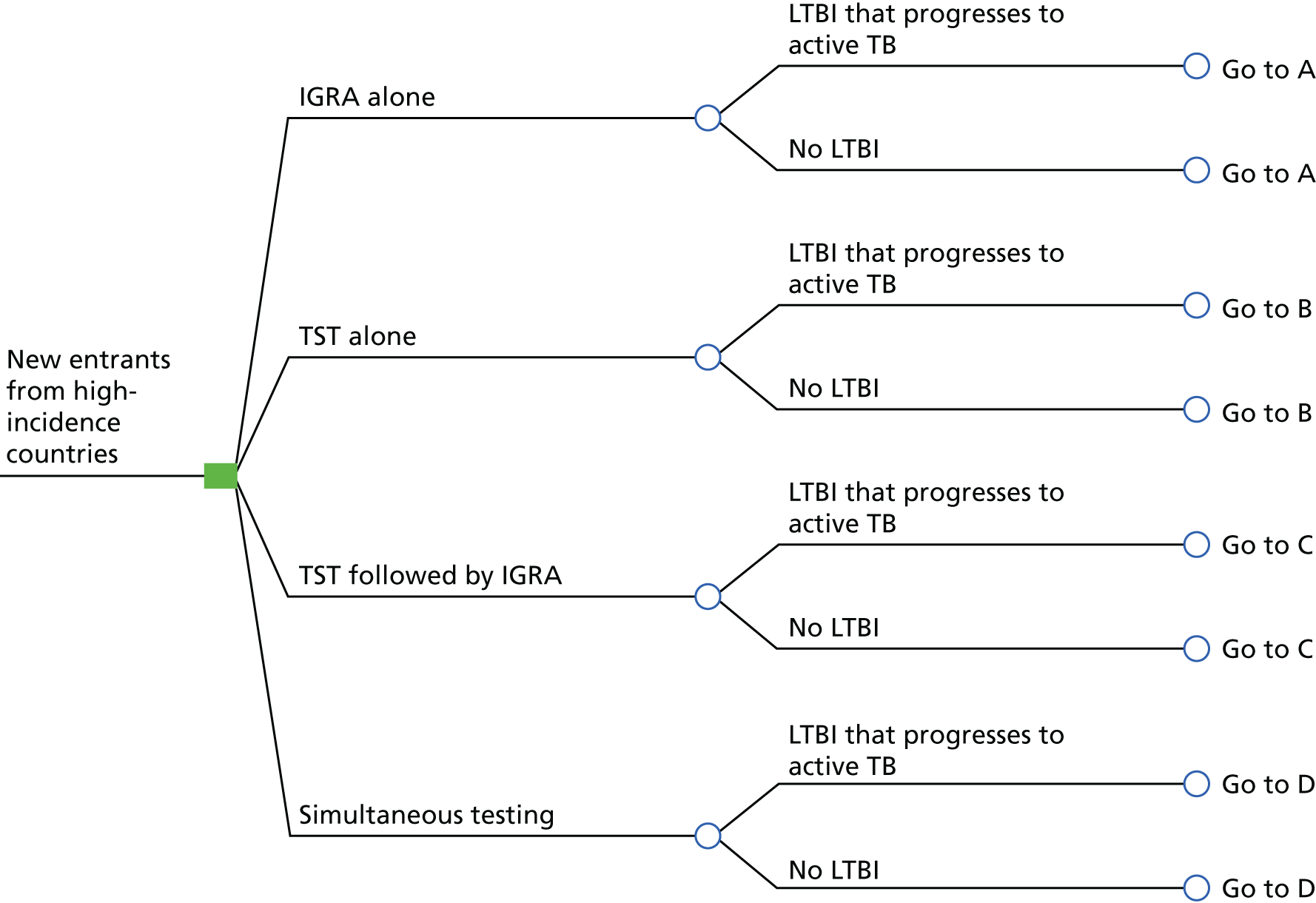
FIGURE 3.
Example decision tree extension from Figure 2, showing only strategy A (i.e. IGRA alone). +ve, positive; –ve, negative. Reproduced from Auguste et al. 102 Contains information licensed under the Non-Commercial Government Licence v2.0.
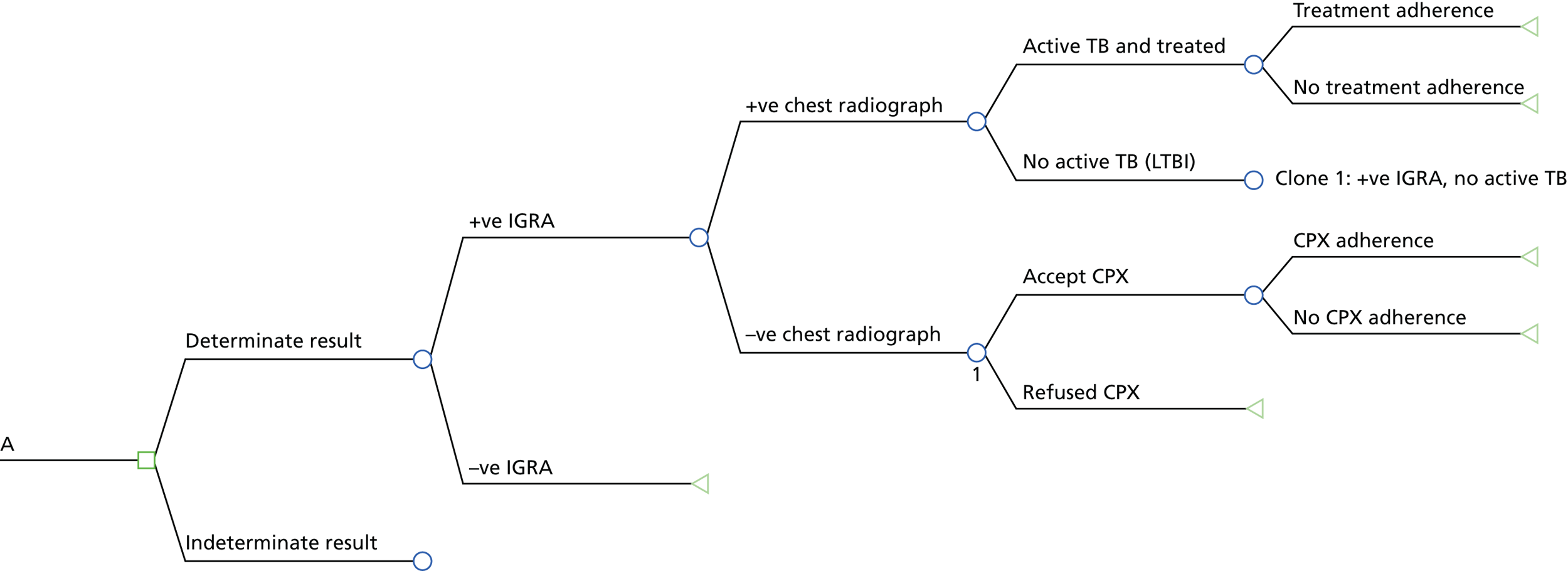
Only the pathway for the IGRA-alone strategy (A) is presented here (see Figure 3). A do-nothing (no test) strategy was not explored. The IGRA strategies A, C and D were evaluated for three types of commercially available IGRAs: QTF-G, QFT-GIT and T-SPOT.TB.
The decision tree was used to estimate the proportion of patients emerging from the initial assessment, diagnosis and treatment stages with different risks of disease progression in the second stage of the model. Three populations were considered: (1) children, (2) immunocompromised individuals and (3) recently arrived individuals from high-incidence countries.
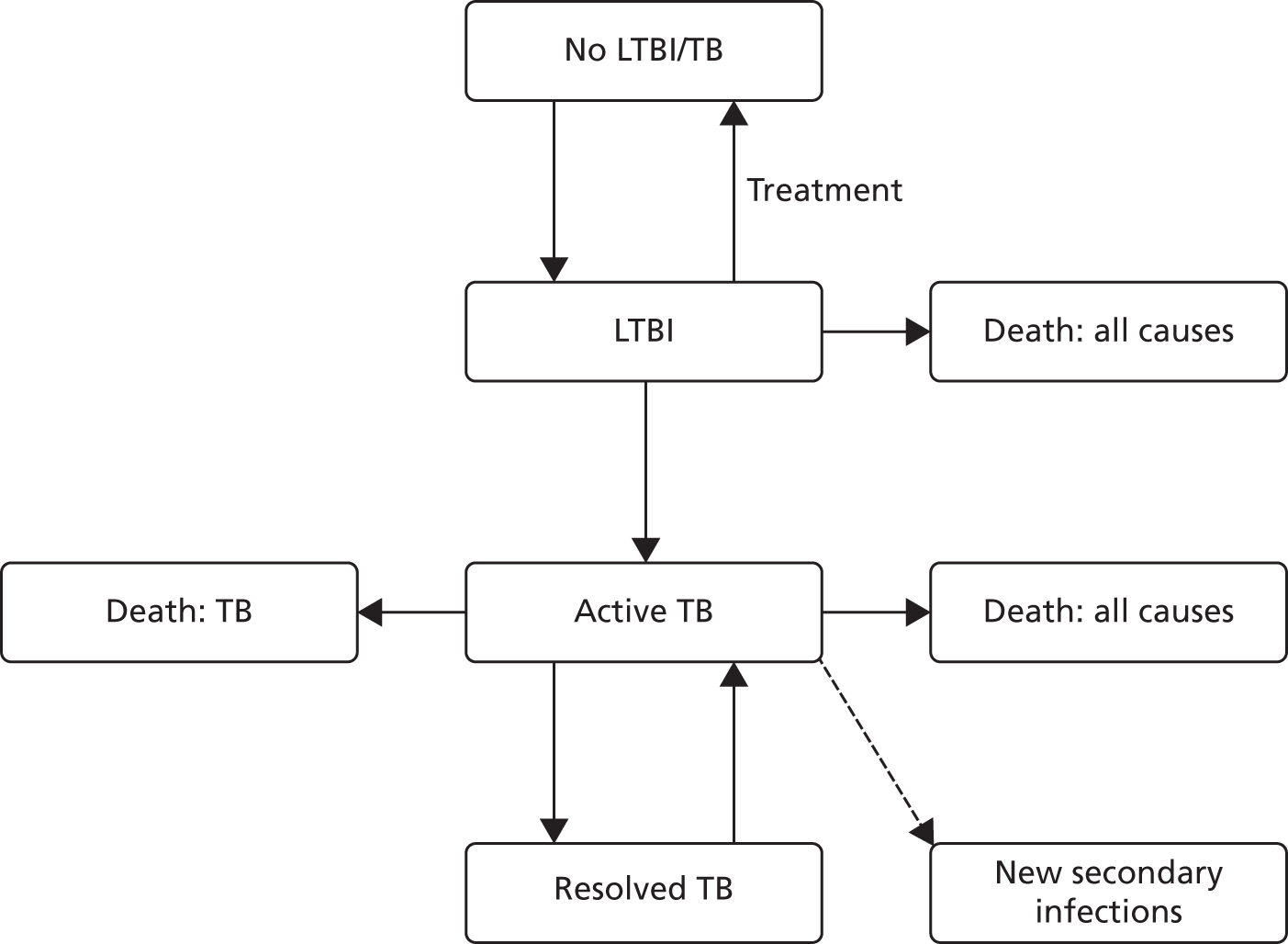
The second stage of the Warwick Evidence model102 (Figure 4) was a transmission model, operationalised using discrete event simulation (DES), programmed using R (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). Individuals arriving from the decision tree were grouped as (1) having active TB, (2) already successfully treated for LTBI and, hence, free of LTBI/TB or (3) untreated for LTBI. The model then tracked disease progression, deaths and cases of new secondary infection. Secondary infection in other individuals was modelled as a proportion of the initial cohort (sampled from a Poisson distribution) who progressed or relapsed to active TB. The analysis assumed that individuals who entered the transmission model with LTBI would ultimately develop active TB if they did not receive treatment, although they might die of other causes before developing TB. In the initial population, as well as in secondary cases, people with LTBI who do not progress to active TB were not simulated in the second part of the model. The risk of an event in the transmission model, such as death or onset of active TB, was dependent on an individual’s age, TB status and current treatment, and was updated when any of these factors changed. Time to activation of TB for individuals entering stage two of the model with LTBI (untreated or unsuccessfully treated LTBI cases) was simulated assuming a constant activation rate over time.
FIGURE 4.
Warwick Evidence analysis (Tuberculosis Clinical Guidance) transition model. Reproduced from Auguste et al. 102 Contains information licensed under the Non-Commercial Government Licence v2.0.
The Warwick Evidence analysis102 presented per-patient costs as well as a breakdown of total costs (including costs of diagnosis, LTBI treatment, active TB and treatment-related hepatitis) for all of the strategies, based on the mean values of all parameters after 250,000 individual patient simulations. The incidence rates (IRs) of active TB in the initial cohort, the number of secondary infections and the mean life-years and QALYs per strategy were also presented. In addition, based on 2000 Monte Carlo simulations, probabilistic estimates of the total cost, incremental costs, diagnostic errors (false-positive results plus false-negative results), incremental diagnostic error, mean QALYs, incremental QALYs and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) were also presented.
The analysis suggested that, for new entrants from high-incidence countries, simultaneous testing strategies were dominated by the equivalent sequential strategies. The QFT-GIT-alone strategy was least costly, but the TST-positive (an induration of ≥ 5 mm) followed by QFT-GIT strategy had the fewest errors. At a willingness-to-pay threshold of £20,000 per QALY gained, the TST-alone (≥ 5 mm) strategy was optimal, with an ICER of £1524 per QALY gained compared with the QFT-GIT strategy. The TST-negative (an induration of < 5 mm) followed by QFT-GIT strategy was ranked as the next most cost-effective strategy, with an ICER of £58,720 per QALY gained compared with TST (an induration of ≥ 5 mm). The other strategies were dominated. Univariate sensitivity analysis suggested that the TST-alone strategy remained cost-effective in most scenarios. However, results were sensitive to LTBI prevalence, sensitivity of QFT-GIT and sensitivity of TST.
A major common limitation of all current CEA of screening strategies for LTBI relates to assumptions surrounding the predictive value of IGRAs and TST, because there is no gold standard against which to establish the sensitivity or specificity of the different tests. Previous CEA studies have based their estimates of LTBI predictive values on various, and often conflicting, sources and assumptions. This leaves considerable uncertainty over the cost-effectiveness of LTBI screening strategies.
We adopted a different approach, basing our economic analysis on the ability of the three tests (TST, QFT-GIT and T-SPOT.TB), individually and in combination, to predict progression to active TB in the PREDICT cohort. This represents a much stronger evidence base for modelling the predictive performance of LTBI test strategies than was available for previous economic evaluations, with three main advantages. First, the cohort provides a coherent source of baseline data, including risk factors and TST, QFT-GIT and T-SPOT.TB test results for large samples of new entrants and contacts being tested for LTBI in the UK. Second, the long-term follow-up and predictive modelling of TB incidence bypasses the problems of conventional diagnostic accuracy in the absence of a reliable reference standard test. Third, this evidence source enables the comparison of two commercially available IGRAs (T-SPOT.TB and QFT-GIT) with TST strategies with a single cut-off point (an induration of ≥ 5 mm) or with different cut-off points for BCG-naive and BCG-experienced patients (indurations of ≥ 5 mm and ≥ 15 mm, respectively).
Objectives
Primary objectives
-
To assess the prognostic value of the two current IGRAs compared with the standard Mantoux test for predicting the development of active TB among untreated individuals at increased risk of LTBI, specifically:
-
contacts of active TB cases
-
new entrants to the UK from high-TB-burden countries.
-
-
To assess the cost-effectiveness of various screening strategies (including the NICE-recommended two-step approach86) using IGRAs and/or TST in defined patient groups (contacts and new entrants to the UK stratified by age and risk).
Secondary objectives
-
To quantify and compare the predictive value of a whole-blood ELISA and an ELISPOT-based assay independently.
-
To develop a collection of specimens (serum and white blood cells), with linked clinical and epidemiological information, to investigate the prognostic value of new biomarkers for TB infection and disease progression.
Structure of the report
In this chapter of the report, we have included a description of the background of the project as well as the primary and secondary objectives. Chapter 2 describes the methods used in the research. In Chapter 3, we present the results of the epidemiological study by describing the cohort and the development of active TB in the cohort. We present the results of the economic analysis examining multiple screening scenarios in Chapter 4 and, in Chapter 5, we discuss the findings, implications for TB testing and treatment guidelines and recommended future research areas.
Chapter 2 Methods
Design
Setting, population and disease burden
This prospective cohort study recruited individuals aged ≥ 16 years who were (1) close contacts of patients with active TB or (2) new entrants to the UK arriving in the last 5 years from high-incidence countries, defined as exceeding 40 cases per 100,000 people, and operationalised by focusing on those from sub-Saharan Africa or Asia.
Participants were recruited in TB clinics from a network of hospitals in London, Leicester and Birmingham, general practices (GPs) in London and several community settings in London (see Appendix 1). All study sites were co-ordinated from the tuberculosis section of PHE.
Recruitment and inclusion criteria
Participants were recruited between May 2010 and July 2015. Contacts of active TB (pulmonary and extrapulmonary) patients and new entrants arriving in the UK in the last 5 years from high-incidence countries (as defined in Setting, population and disease burden) and attending participating TB clinics or primary care centres for screening were invited to take part. Those born in high-incidence countries who entered the UK > 5 years ago, but who had spent > 1 year (cumulative) in the past 5 years in a high-incidence country, as per the study’s defined list, were also invited to participate. Contacts included all individuals with a cumulative duration of exposure of > 8 hours to the relevant index case in a confined space during the period of infectiousness (prior to initiation of treatment).
Eligible persons were identified by study TB specialists or practice nurses, and written informed consent was obtained following the provision of information sheets (translated as appropriate). Baseline assessment questionnaires, including demographic and clinical information, were completed by the research nurse.
In addition, recruitment was undertaken en masse using two methods.
-
New entrants to the UK were recruited from non-NHS community settings, such as places of worship and community centres.
-
Contacts of active cases were recruited through mass screening events organised as part of the public health response to a case of active TB in some situations. For example, clinical teams may attend workplaces or colleges where an exposure had taken place, to facilitate screening of large numbers of contacts.
For recruitment through primary care, study flyers and the contact details of the co-ordinating centre were displayed in general practices so that interested people could contact the study team to book an appiontment. At the appointment, as with all recruitment meetings, a study nurse went through the full patient information leaflet before taking written informed consent to undertake study procedures. We also utilised the primary care trust (PCT)-held Flag 4 data (records held by the local primary care group about international migrants who register with a NHS GP) to invite newly registered patients, recently arrived from the countries of interest, to take part in the study.
At the time of the study, treatment of LTBI was recommended only for individuals aged < 35 years. We therefore prioritised the recruitment of patients aged > 35 years (who were not eligible for CPX) in order to estimate and compare the ability of the TST and IGRAs to predict natural progression to active disease in the absence of treatment. Individuals aged 16–35 years were also eligible, as they may not be offered, or may not accept, CPX.
The general practioners of all participants were informed of their patients’ participation by letter.
Health technologies being assessed
Participants were tested by the Mantoux test and two IGRAs: ELISA (QFT-GIT) and ELISPOT assay (T-SPOT.TB). All tests were conducted using standardised protocols. 17–19 Tests for LTBI were undertaken among contacts at about 6 weeks after last known exposure (consistent with NICE guidelines14), and at ≥ 6 weeks for new entrants after arrival in the UK.
The QFT-GIT and T-SPOT.TB assay samples were transported to a study testing centre (see Statistical analysis).
After IGRA testing, samples were used for repetition of indeterminate assays. Paxgene tubes, plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stored for future research.
Test results and further action
All test results were obtained by clinicians who were blind to other results. Clinicians were informed of all test results by the testing laboratory for tests conducted at the National Mycobacterial Reference Laboratory (NMRL), whereas those results from the Imperial College London laboratory were not reported. Subsequent action after testing followed the version of NICE guidance that was applicable at the time of screening and took place after discussion with participants. Further action followed one of three options:86
-
If the participant had a negative result in the TST and IGRA, follow-up only was conducted.
-
If the participant had a positive result in either the TST or IGRA, and active TB was excluded, follow-up was conducted irrespective of age.
-
If the participant had a positive result in the TST and either one or both IGRA(s), follow-up only was conducted for those aged ≥ 35 years, and, for those aged 16–35 years, CPX was offered within the routine care setting after excluding active TB, with balanced advice about potential benefits and risks.
Follow-up
Participants were followed prospectively after IGRA/TST testing. Follow-up utilised multiple data sources to enable the comprehensive national identification of participants and to minimise loss attributable to transfer of care to other centres by physicians. Data were sourced from (1) telephone calls to the participants at 12 months and at 24 months or at the end of follow-up, (2) a search of national mandatory enhanced TB surveillance (ETS) reports, (3) a search of the national database of culture-proven TB and (4) a search of clinical records. Individuals found to have active TB were excluded from the analysis if they had evidence of active disease at the time of recruitment (see Primary outcome). Follow-up continued until the development of active TB, death or May 2016.
Data collection
Baseline data were collected by trained research nurses using paper questionnaires. Outcome data were collected using the four approaches outlined in Follow-up. Questionnaire data were entered into a purpose-built database [using Microsoft Access® (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA)] that was maintained at the TB section at PHE and linked, as necessary, to data from the other sources. IGRA results were received from laboratories in Microsoft Excel® (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA) spreadsheets and imported into the database.
Data collected from participants included age; gender; country of birth and date of entry to the UK for non-UK-born persons; ethnicity; current employment; the nature and duration (in hours) of contact with the index case (for contacts); the time interval between the most recent suspected exposure date and the date of diagnosis in the index case; details of any previous contact tracing; history of previous TB, including treatment, results of previous TST and chest radiographic findings; BCG vaccination status (assessed based on criteria in the Green Book:103 a scar or reliable recall or vaccination record); associated medical diagnoses; and use of immunosuppressive agents. Self-reported HIV infection status was collected, and further work through record linkage with the national HIV surveillance system will be used to improve the completeness of HIV data. Quality-of-life data were collected using the EuroQol-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) questionnaire. During follow-up, information on the drugs used for the treatment of LTBI and adverse effects of CPX was collected and validated through a review of clinical records.
Index cases (identified through clinical records) of contacts were identified through a web-based ETS system using data provided by the contact and/or clinicians. The characteristics of index cases were summarised descriptively. For contacts who progressed to active TB disease during follow-up, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) fingerprinting data [24-locus mycobacterial interspersed repetitive unit – variable number tandem repeats (MIRU-VNTR)] from the UK national TB strain typing database, hosted by PHE, were utilised to compare strain types between index cases and subsequent diagnoses among contacts. This enabled the assessment of whether any TB disease in secondary cases was likely to have arisen from the initial infection (i.e. that the test result related to the outcome) and not as a result of subsequent exposure to another case.
Sample size
The study size (and associated power) was determined by simulating the study and its analysis 1000 times and observing the proportion of simulations yielding significant results across various scenarios. Conventional methods for sample size calculation would not account for the Poisson nature of the data and the within-patient comparisons of the tests; therefore, simulation was necessary. The simulated data on the disease progression of study participants were created, presuming a LTBI prevalence of 30% and presuming that 5% of participants with LTBI would progress to active TB in 2 years if untreated, as observed in previous studies. 81,104 Test results were simulated for each participant using sensitivities and specificities of IGRA in the range of 65–95%.
The simulations indicated that a cohort of 5000 participants, among whom 90 incident events were observed, would have around 85% power to detect significant (p < 0.05) differences in predictive performance that would arise from differences in sensitivity and specificity of 10% between tests. These differences correspond to increases in predictive performance (expressed as a ratio of relative rates between patients with a positive test result) of 30%, which would be clinically useful.
It was assumed that 50% of TB contacts and new entrants would be aged ≥ 35 years, so a cohort of 10,000 would initially yield at least 5000 participants for the primary analysis of progression without treatment, among whom 90 evaluable events would occur. Given the probable loss to follow-up (which, based on clinic data, was likely to be around 20%) and the possibility that progression to disease may be < 5%, the power of the study would be maintained by including in the cohort all participants aged 16–35 years who did not take CPX (estimated to be an additional 2500 participants). A total of 90 incident events would still be observed should 7500 participants be recruited, 20% be lost to follow-up and the rate of progression to disease be only 4.2%.
Primary outcome
The primary outcome of interest was the development of active TB, with the prognostic values of tests quantified as IRRs, comparing those with positive results and those with negative results, among contacts and new entrants to the UK. Individuals were considered to have progressed to active TB if they had culture-confirmed TB or were clinically diagnosed with radiological or histological evidence of TB and a clinician had decided to treat the individual with a full course of anti-TB disease treatment, the definition used for the TB register. In addition, participants were considered to have progressed to active TB only if:
-
The participant had no evidence of active TB at the time of enrolment, determined through the review of clinical records.
-
The clinical diagnosis of active TB was at least 3 weeks after recruitment/enrolment to the PREDICT study, based on the date of diagnosis (or treatment start date if date of diagnosis was not available).
In the absence of laboratory confirmation of TB, awareness by the clinician of a prior positive IGRA/TST result should not influence the clinical diagnosis of active TB.
Any case that was subsequently denotified was excluded from analyses (i.e. when the clinician reported that the patient did not have TB).
For any cases in which participants were reported to have TB in a follow-up telephone call at 12 or 24 months, the record was searched in the national data set of clinical reports and through the review of case notes at the hospital where the participant was treated. Only cases in which the participant was confirmed to have active TB, meeting the criteria outlined above, were included as a case of TB. The central team ascertaining the diagnosis were blinded to the IGRA and TST status of participants.
Statistical analysis
Primary analysis
The analysis estimated the ability of the tests (TST, T-SPOT.TB and QFT-GIT), individually and in combination, to predict progression to active TB in latently infected individuals, and made comparisons between tests. Estimated rates of progression to active TB were calculated, accounting for the follow-up period for each individual.
The predictive performance of each test (TST, T-SPOT.TB and QFT-GIT) and of each two-step test strategy [using combinations of TST + T-SPOT.TB, TST + QFT-GIT and IGRA (T-SPOT.TB or QFT-GIT) + TST] was summarised by the calculation of IRs of developing active TB in the ‘test-positive’ and ‘test-negative’ groups, expressed with 95% CIs computed using Poisson exact methods. In each combination strategy, the second test result was used if the first was positive, meaning that both tests must be positive for a participant to be positive for the strategy. IRs were calculated using all available follow-up data and also at 1 year and 2 years after study entry. The discriminatory predictive value of the test was based on the relative comparison of these rates (the relative IRs comparing those with positive test results and negative test results), together with the prevalence of positive test results (indicating the number of patients who would be treated should the test be used for recommending CPX).
The primary analyses of the performance of tests used only participants with test result data for all three tests. Participants who were treated for LTBI were excluded.
We made pairwise comparisons of the ability of tests and strategies to identify (1) those participants who progress and (2) those participants who do not progress using generalised estimating equation (GEE) marginal regression models. 105 These models estimate (1) ratios of positive test results and (2) ratios of negative test results in those participants who progress compared with those participants who do not, which are comparable to positive and negative likelihood ratios for diagnostic studies. We compute ratios of these ratios to make pairwise comparisons between tests, accounting for the paired data. A marginal regression GEE model was fitted, with the two test results as outcomes (with a positive test result coded as the event) and with test type and progression status as predictors, and an interaction term between test type and progression. The interaction term assessed whether or not the relationship between progression and test positivity was stronger for one test than the other. A similar second model was fitted with test negative as the outcome, such that the interaction term assessed whether or not the relationship between non-progression and test negativity was stronger for one test than the other. The model accounted for the intra-individual correlation between tests using an unstructured correlation matrix and was configured to give population average estimates. The primary analysis fitted models with a binomial error structure and a log link (as described by Pepe105). In a sensitivity analysis, we adapted the Poisson model to include follow-up using an offset and obtained identical point estimates to two decimal places and confidence limits to one decimal place. We report the binomial model results.
Regression models were fitted in Stata® version 15.0 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA).
Positive predictive values and NPVs were also calculated as the percentage of people with a positive result developing TB across all follow-up (PPV) and as the percentage of people with a negative result who did not develop TB (NPV).
Owing to testing processes, a small number of participants had two T-SPOT.TB and/or QFT-GIT tests performed (T-SPOT.TB, n = 21; QFT-GIT, n = 33). For participants with multiple results for a single test, results from the primary research laboratories were used (Imperial College London and NMRL), with results from Imperial College London being used if the test was carried out at both Imperial College London and NMRL. For some participants, neither T-SPOT.TB result was obtained from Imperial College London or NMRL and, therefore, the result from Oxford Immunotec or SYNLAB (London, UK) was used.
The QuantiFERON TB Gold In-Tube test
The QuantiFERON test results were classified as positive, negative or indeterminate according to the manufacturer’s algorithm. 106 For analysis purposes, indeterminate results were treated as missing.
The T-SPOT.TB test
The T-SPOT.TB test can have positive, borderline positive, negative, borderline negative or indeterminate results. All categories of test results were reported. For the majority of participants, the required test information (spot count) was available and T-SPOT.TB test result classifications were calculated by the study team in accordance with the manufacturer’s algorithm (Figure 5)107 For 660 tests (7.9% of the 8387 participants, or of the 8366 participants with a duplicate test for 21 participants) in which the necessary information (T-SPOT.TB counts and positive and negative control values) was not provided, the classification of results reported from the laboratory was used in all subsequent analyses.
FIGURE 5.
T-SPOT.TB result classification algorithm.
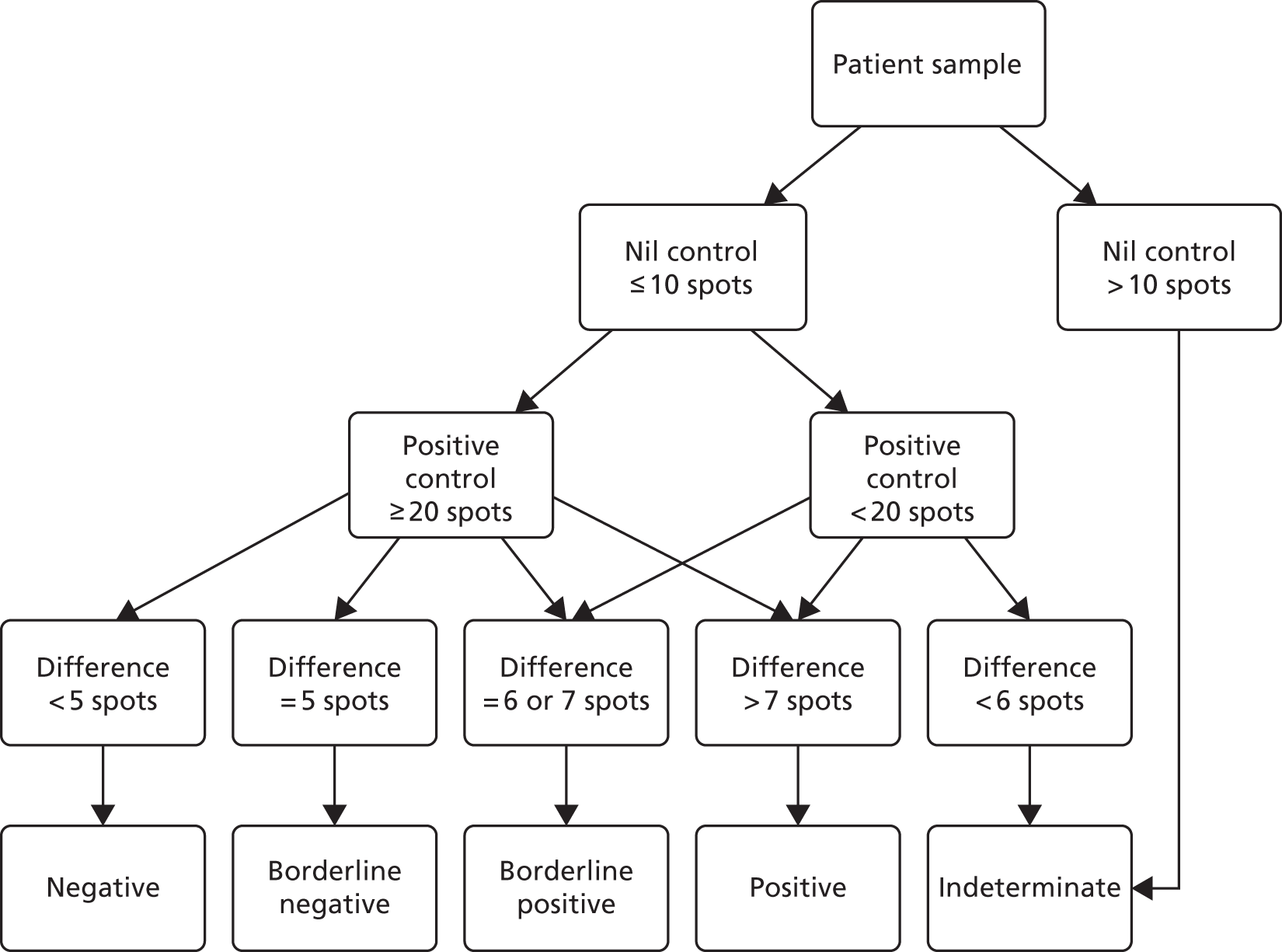
Indeterminate results were treated as missing, borderline positive results were treated as positive and borderline negative results were treated as negative, in line with the interpretation of results in clinical practice. 1
The Mantoux test
The TST was administered in accordance with national guidelines. Different thresholds for TST positivity were considered. In the primary analysis, participants were considered to have a positive result if they had a skin induration of ≥ 5 mm (this will be referred to as TSTa), consistent with the 2016 NICE guidelines. 14 Alternatively considered was the strategy varying with BCG status, in which a skin induration measuring ≥ 6 mm following the standard TST test was considered a positive result if the participant was not known to have had a BCG vaccination, and in which a skin induration of ≥ 15 mm following the standard TST test indicated a positive result for those known to have had a BCG vaccination, the strategy previously recommended by NICE. 86 When BCG vaccination status was unknown, BCG vaccination was assumed for those participants who were born outside the UK and, for UK-born participants with unknown BCG vaccination status, a positive or negative TST result could not be obtained. The secondary definition will be referred to as TSTb.
Sensitivity analyses
Sensitivity analyses were carried out using all available test data rather than using data only from participants with results for all three tests. Analyses were also performed excluding those participants with BCG vaccination status assumed to generate a TSTb result and those participants with an uncertain progression status because of a short period between testing and diagnosis. Additional sensitivity analyses were performed using data from new entrants only and restricted to 2 years of follow-up, and from contacts of pulmonary TB cases only.
Economic analysis
The decision problem
We developed an individual-level DES model to estimate the effect of different test strategies on risk prediction, use of preventative CPX and BCG vaccination, subsequent incidence of TB, and, hence, costs to the health-care system and health outcomes for patients. We considered a DES model to be most suitable as individual simulation and a bootstrapping approach preserved individual patient data and the correlation between baseline risk factors and the test results. The analysis followed the NICE reference case for public health interventions. Health outcomes were quantified using QALYs, including the impact of TB and treatment-related adverse effects on mortality and health-related quality of life (the utility). EuroQol-5 Dimensions, three-level version scores from the PREDICT study were valued using the UK general population tariff. Costs were estimated from a UK public sector perspective, including costs for case finding, prevention (BCG vaccination and CPX) and treatment of active TB and adverse effects. In the base case, we discounted costs and QALYs at 3.5% per annum and simulated outcomes over a lifetime horizon for a cohort of patients undergoing tests for LTBI.
Population
We evaluated the cost-effectiveness of LTBI testing strategies in the PREDICT cohort. The model used an individual patient data set comprising 4162 contacts and 3795 new entrants without active TB at baseline (total of 7957 participants) with sufficient data: age, sex, BCG vaccination status, baseline EQ-5D score (utility) and contact/new entrant status. We excluded participants with active TB at the baseline assessment, but included those with missing values for one or more baseline LTBI tests (TST, QFT-GIT or T-SPOT.TB) in order to model the impact of missing or indeterminate test results.
For our base-case analyses, we evaluated results for the whole cohort, and also for the two subgroups: new entrants to the UK and contacts. We had initially intended to present stratified analysis for other risk factors: age, BCG vaccination status, previous treatment status and baseline risk (defined by level of exposure or duration and nature of contact; or by country or region of birth for new entrants to the UK). However, an analysis of the PREDICT results did not show any important or statistically significant differences in incidence according to these risk factors (see Chapter 4). Instead, we investigated the sensitivity of results for populations at different a priori levels of risk in the absence of preventative treatment (BCG vaccination or CPX). This illustrated the possible effects of changing referral thresholds for LTBI tests, such as the threshold for defining a ‘close’ contact or ‘high-incidence’ country of recent residence.
In our modelling protocol, we stated that we would consider additional exploratory analyses in other subgroups, such as people infected with HIV or who have diabetes mellitus, but the numbers of participants in these groups were too low to support such analysis.
Interventions and comparators
We compare 11 approaches to LTBI testing:
-
0. no test
-
1. T-SPOT.TB
-
2. QFT-GIT
-
3. TSTa: positive if induration is ≥ 5 mm
-
4. TSTb: positive if induration is ≥ 6 mm without prior BCG vaccination or ≥ 15 mm with prior BCG vaccination
-
5. TSTa + T-SPOT.TB: positive if both TSTa and T-SPOT.TB are positive
-
6. TSTa + QFT-GIT: positive if both TSTa and QFT-GIT are positive
-
7. TSTa + IGRA: positive if TSTa is positive and either T-SPOT.TB or QFT-GIT are positive
-
8. TSTb + T-SPOT.TB: positive if both TSTb and T-SPOT.TB are positive
-
9. TSTb + QFT-GIT: positive if both TSTb and QFT-GIT are positive
-
10. TSTb + IGRA: positive if TSTb is positive and either T-SPOT.TB or QFT-GIT are positive.
In the single-test strategies (1–4), participants who tested positive for LTBI were assumed to undergo diagnostic tests to rule out active TB, then to be offered appropriate treatment (CPX if aged ≤ 35 years), whereas those who tested negative for LTBI would be offered BCG vaccination if eligible (no previous BCG vaccination and age ≤ 35 years). Participants with missing test results for a strategy were assumed not to receive any preventative treatment (CPX or BCG vaccination).
In the dual-test strategies (5, 6, 8 and 9), the second test would only be carried out if the first test result was positive. Participants who tested positive in the second test (T-SPOT.TB or QFT-GIT) would be further evaluated to rule out active TB, and offered CPX or BCG vaccination if appropriate. Participants without a TST result, or with a positive TST result but missing T-SPOT.TB or QFT-GIT data, were assumed to not receive any preventative treatment.
In the three-test strategies (7 and 10), we assumed that participants with a positive TST result would have both IGRAs (T-SPOT.TB and QFT-GIT). Then, if either of the IGRAs were positive, they would be tested for active disease and offered treatment or CPX if appropriate. If both IGRAs were negative they would be offered a BCG vaccination if appropriate. Participants with an indeterminate result attributable to one or more missing test results would not receive preventative treatment; this included all participants with a missing TST result, and those with a positive TST result and either both IGRAs missing or one negative IGRA and one missing IGRA.
The ‘no test’ strategy was included as a comparator, which allowed us to investigate changes to the referral thresholds for LTBI testing.
Outcomes
Strategies were evaluated in terms of the health-care costs and health outcomes measured using QALYs. For validation purposes, we also present disaggregated outcomes (numbers of incident TB cases; numbers given a BCG vaccination, CPX and active TB treatment; treatment-related adverse events; deaths from TB; and life-years) and costs [costs of diagnosis, preventative treatment (BCG vaccination and CPX) and active TB treatment (including treatment of adverse effects)].
Modelling methods
Model structure
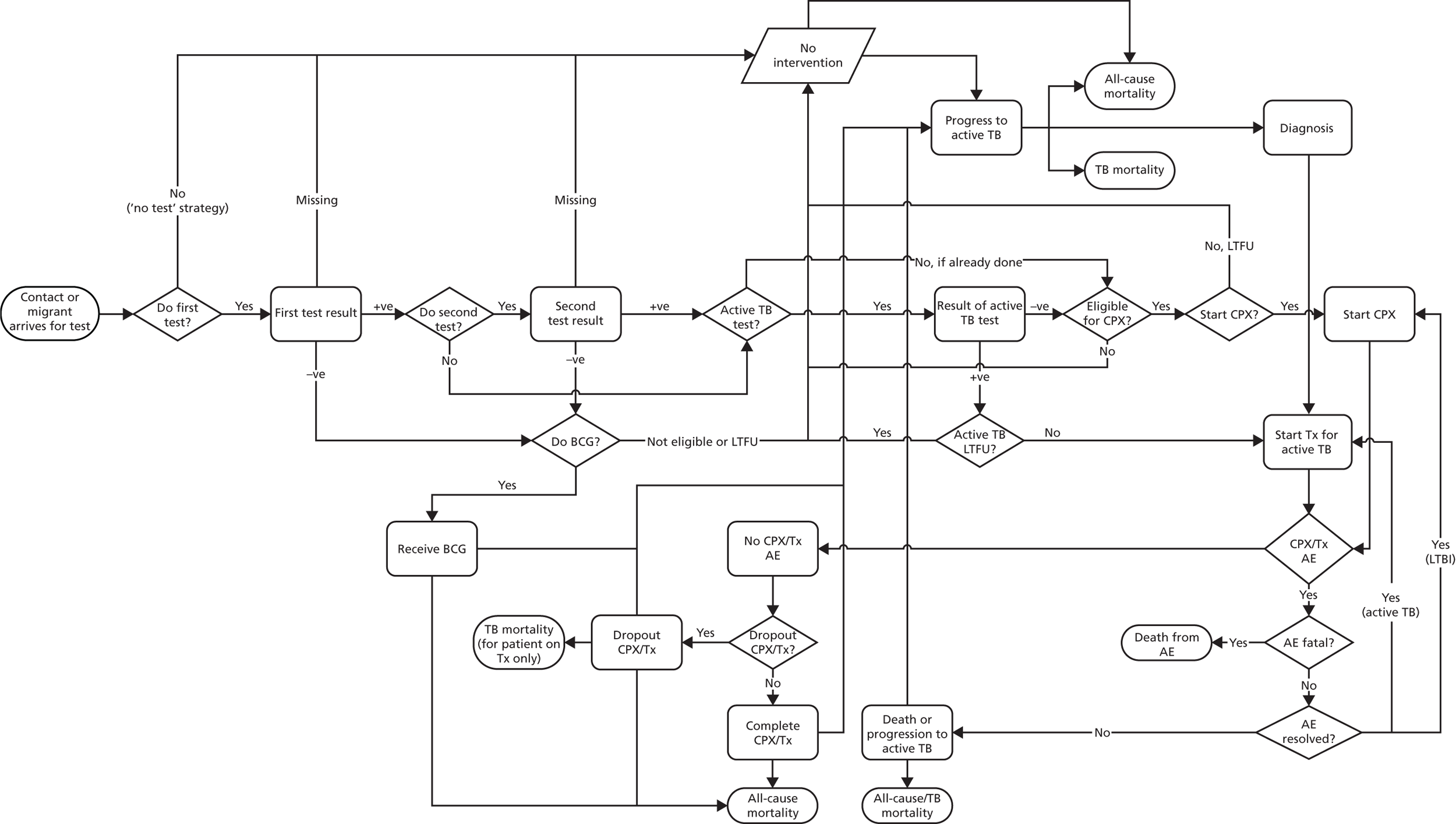
Figure 6 is a process map of our model. The software used to develop the DES model was SIMUL8 Professional 2017 (SIMUL8 Corporation, Boston, MA, USA).
FIGURE 6.
Model process map. –ve, negative; +ve, positive; AE, adverse event; LTFU, lost to follow-up; Tx, treatment for active TB.
Cohort selection
The model was programmed so that a cohort of patients with chosen initial characteristics could be selected to run through the pathway, to allow flexible subgroup analysis. However, for this report we present results only for the whole cohort, and for the ‘new entrant’ and ‘contact’ subgroups.
Individual participants from the PREDICT cohort were randomly sampled (with replacement) from an individual-level data set from the PREDICT cohort. This data set included individuals’ demographic information and baseline characteristics: age, gender, prior BCG vaccination status, utility (EQ-5D scores) and LTBI test results (TST, T-SPOT.TB and QFT-GIT). For the purposes of this analysis, we excluded patients who were diagnosed with active TB at the beginning of the PREDICT study (n = 175). This left a data set of 7957 individuals for inclusion in the economic analysis.
The size of the sampled population in the model can be changed, but for the analysis presented below we used a bootstrapping approach; for each probabilistic iteration of the model, we sampled a simulation cohort (with replacement) of the same size as the individual patient data set (n = 7957). This scales uncertainty over the distribution of baseline characteristics in our probabilistic sensitivity analysis (PSA) to reflect sampling error in the PREDICT cohort.
Screening, diagnosis and treatment initiation
The model can be set to one of the 11 test strategies, and members of the cohort enter to be offered the chosen strategy. Treatment decisions, such as whether a patient is offered BCG vaccination, CPX or treatment for active TB, depend on the patient’s test results and history or demographic data. For example, under strategy 5 (TSTa + T-SPOT.TB), an individual aged ≤ 35 years with no prior BCG vaccination, no active TB, a TST induration of 7 mm and a negative T-SPOT.TB test result would be offered a BCG vaccination. Or, under the same strategy, a patient aged ≤ 35 years, who has had a BCG vaccination, with no TB, a TST induration of 18 mm and a positive T-SPOT.TB result would be offered CPX.
This first section of the model is treated as timeless; patients cannot experience adverse events and their utility is fixed at their baseline EQ-5D value (as observed in PREDICT), but they accrue costs based on choices that are made within the model as per LTBI testing, active TB diagnosis, BCG vaccination and initiation of CPX and treatment of active disease.
Health status
Having received tests and treatments, or having been lost to follow-up, participants flow into the second part of the model, in which time starts to elapse. At any time, each member of the cohort who is alive is in one, and only one, of the following health states:
-
Active TB and on treatment – participants in this state have been diagnosed with active TB and are being treated. From this state, participants might successfully finish treatment, experience an adverse reaction to treatment and/or drop out of treatment, or they may die from TB or other causes.
-
Active TB and not on treatment – this state includes participants with active TB who have not yet been diagnosed, as well as participants who have been diagnosed but have stopped treatment for some reason. From this state, participants might present clinically with symptoms and be diagnosed, or they might die from TB or other causes. Contacts of people with untreated active TB who are at heightened risk enter the model in the ‘no TB and not on CPX’ state.
-
No TB and on CPX – these participants do not have TB but have tested positive for LTBI (according to the defined test strategy) and are taking prophylactic treatment. Future possibilities for this group are to complete CPX, have an adverse event and/or stop CPX, progress to TB or to die from other causes.
-
No TB and not on CPX – this state includes all participants who do not have TB and are not taking CPX. This is a diverse group including participants who have tested positive for LTBI but did not start CPX or defaulted from CPX, those who have tested negative for LTBI and who may or may not have been vaccinated, as well as those who did not complete the LTBI test(s) or who had indeterminate results. All of these people are at risk of progressing to TB or they might die from other causes.
Note that LTBI is not modelled as a ‘disease state’ as such, but rather it means that each person who does not currently have active TB is at risk of developing active TB. Each person’s risk of an event is estimated using observed IRs in the PREDICT cohort, based on their current status, other characteristics and treatment effects. Then, for each possible event, a time to event is sampled.
Events and outcomes
The possible events are:
-
Adverse events from treatment for active TB or CPX – this may result in death, in which case costs and QALYs are calculated. If the individual survives, the adverse event (drug-induced hepatotoxicity) may resolve with the participant continuing treatment, or symptoms may persist, in which case the participant is withdrawn from treatment.
-
Dropout from CPX or treatment for active TB – for simplicity, we assume that dropout from CPX and treatment for active TB will take place halfway through the treatment period (after 1.5 months for CPX or 3 months for treatment for active TB). Possible events following dropout from CPX are death and progression to active TB. The next event after dropout from active TB treatment is either reinitiation of treatment (as patients with active disease are likely to re-present at some time), death from TB or death from other causes.
-
Complete CPX or treatment for active TB – participants who complete CPX (after 3 months) may still progress to active TB, or die from other causes. Individuals who complete treatment for active TB (after 6 months) may be reinfected but we assume that this would be captured as secondary infection in a new incident cohort and is therefore outside the scope of this model. They may also suffer reactivation. The next event after completing treatment for active TB may therefore be death from other causes or active TB diagnosis if reactivation takes place.
-
Progression to active TB – all individuals without current active TB have a risk of progressing to active TB. Those with positive LTBI test results are at higher risk. Once participants progress, they become undiagnosed cases of TB and the next event may be death or active TB diagnosis.
-
Active TB diagnosis – individuals with active TB who are not on treatment will develop symptoms and are likely to present clinically, leading to diagnosis and an offer of treatment. We assume a fixed time to diagnosis for these individuals based on the average time between onset of symptoms and diagnosis (3 months).
-
Death from active TB or other causes – costs and QALYs are calculated at this point.
Model assumptions
The key modelling assumptions are:
-
Only BCG-naive individuals who are aged ≤ 35 years are offered a BCG vaccination, a proportion of whom accept (94% in the base-case model). Any adverse effects of BCG vaccination are assumed to be negligible.
-
Only those individuals aged ≤ 35 years are offered CPX; this reflects UK practice and guidelines86 during the study period. A proportion of patients who are eligible accept and start CPX (94% in the base case), although they may drop out or suffer an adverse event.
-
Death from a CPX-related adverse event (hepatotoxicity) is possible, and is assumed to take place at the start of treatment. Fatal adverse reactions to CPX are very rare; thus, the timing of adverse events during treatment is unlikely to influence the results.
-
If the patient survives and the adverse event resolves, the patient resumes CPX but may drop out later. We assume that if the patient resumes CPX they will not experience a second adverse event. If the adverse event is not resolved, the patient stops CPX and will either develop active TB or die from other causes.
-
Patients who drop out from CPX are assumed to do so in 1.5 months and incur half of the cost of a complete course (3 months) of CPX. Incomplete CPX provides some protection against progression to active TB, but is less effective than complete CPX.
-
After completing CPX patients may still progress to active TB (despite preventative treatment) or die from other causes.
-
All individuals have a risk of developing active TB with a hazard conditional on their baseline test results (based on IRs estimated and sampled probabilistically from the PREDICT study). Hazards are estimated based on patients’ available test results, using the test or combination of tests with the greatest predictive value.
-
Once an individual progresses to active TB they may be diagnosed, die from active TB or die from other causes. For patients who are diagnosed with active TB, the time from TB onset to diagnosis is assumed to be 3 months.
-
All those diagnosed with active TB are assumed to start treatment, although they may drop out or suffer an adverse event.
-
A treatment-related adverse event can only take place once. Death from an adverse event is possible and is assumed to take place at the start of treatment.
-
If the patient survives, and the adverse event resolves, the patient resumes treatment but may drop out later. A second adverse event is not possible.
-
If the patient survives but the adverse event is not resolved, the patient stops treatment and will either die from active TB or die from other causes. For simplicity, we have not modelled second and subsequent lines of treatment for patients who experience adverse reactions or resistance to the standard regimen.
-
Patients who drop out from treatment for active TB are assumed to do so in 3 months and incur half of the cost of a complete course of 6 months. They do not get any treatment benefits from incomplete treatment for active TB and are still at risk of active TB death, as well as death from other causes. However, patients who have dropped out may be identified through opportunistic testing or clinical presentation, and will be offered a repeat course of treatment.
-
Patients who complete treatment for active TB are assumed to be free of TB and will die only from other causes.
-
Individuals come into the model with a utility estimated from their PREDICT EQ-5D data. For simplicity, we have assumed that an individual’s utility score remains constant as they age. As utility tends to fall with increasing age, QALY differences between strategies will be overestimated.
-
Individuals’ utility scores are adjusted when they have active TB. A pre-treatment utility multiplier is applied as soon as the patient develops active TB to reflect the impact of emerging TB symptoms prior to treatment. A lower utility multiplier is applied during the first 3 months of treatment to reflect continuing symptoms, inconvenience and distress caused by isolation and adverse effects of treatment that are tolerated. The utility multiplier applied during the last 3 months of treatment is then higher as most patients will have less-severe symptoms by this time, and the prevalence of adverse effects is likely to be lower. After completion of treatment, patients are assumed to return to their initial utility value. 108
-
It is assumed that CPX has a negligible impact on utility. 108
-
For simplicity, our base-case model does not include transmission from members of the cohort who develop TB to their contacts. This will tend to underestimate the benefits (QALY gain and health-care cost savings) associated with TB prevention. We conducted a scenario analysis with a ‘cascade’ approach to model the impact of secondary transmission.
Model parameters
Tuberculosis incidence
The incidence of TB was modelled using a Weibull distribution to reflect the falling number of cases over time in the PREDICT cohort. This is expected as contacts of people with active TB are most likely to develop TB close to the time of exposure, and, similarly, migrants from high-incidence countries are at most risk shortly after entry to the country they are migrating to. In the PREDICT cohort, 77 participants were diagnosed with active TB over a total of 20,571.4 person-years at risk. This equates to an overall IR of 0.00374 per person-year. We used a calibration approach to fit a Weibull distribution to these data (Table 3). Our best estimate used a scale parameter of 2.5 and a shape parameter of 6. This achieved an IR of 0.00932 in year 1 (matching that in PREDICT), 0.00115 in year 2 (compared with 0.00167 in PREDICT) and 0.00373 averaged over the first 3 years (compared with 0.00375 in PREDICT).
| Parameter | Base-case value | 95% CI | PSA distribution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IR (TB incidence per person-year) | 0.00374 | 0.00296 to 0.00462 | Beta (77, 20,494.4) | PREDICT |
| Hazard multiplier for year 1 | 2.5 | – | – | Fitted Weibull distribution |
| Shape parameter | 6.0 | – | – |
Test performance
Estimates of the predictive performance of the various test strategies were taken from the analysis of PREDICT data presented in Chapter 3. For the PSA, we used a chained approach to generate correlated estimates of the TB IRs for patients testing positive or negative for each of the modelled strategies.
We started by estimating IRs for patients with a negative TSTa result [IR(TSTa–)] from the overall incidence of TB in the population (R), the proportion of person-years in patients with a positive TSTa result (p) and the IRR for TSTa positive compared with TST negative [IRR(TSTa+ vs. TSTb–)]:
The IR for patients with a positive TSTa result is then:
For each strategy, the positive predictive performance statistic compared with TSTa was used to estimate the IR for patients with a positive result. Similarly, the negative predictive performance compared with TSTa was used to generate estimates of IRs for patients with negative results for each strategy.
The overall incidence rate (R) and the proportion of observed person-years in people with a positive baseline TSTa result (p) were sampled from beta distributions. IRRs were sampled using gamma distributions, fitted to the mean and standard error of the multilevel Poisson regression results for each comparison (Table 4). The resulting estimates of IRs (per person-year) and hazards are shown in Table 5.
| Parameter | Base-case value | 95% CI | PSA distribution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person-years TSTa+ (%) | 0.458 | 0.451 to 0.465 | Beta (9416.8, 11,154.6) | PREDICT |
| IRR TSTa+ vs. TSTa– | 5.83 | 2.89 to 9.79 | Gamma (10.805, 0.540) | PREDICT |
| Positive predictive performance: IRR for positive results | ||||
| TSTb vs. TSTa | 1.64 | 1.28 to 2.04 | Gamma (72.087, 0.023) | PREDICT |
| T-SPOT.TB vs. TSTa | 1.99 | 1.43 to 2.63 | Gamma (41.709, 0.048) | PREDICT |
| QFT-GIT vs. TSTa | 1.52 | 1.08 to 2.04 | Gamma (38.285, 0.040) | PREDICT |
| TSTa + T-SPOT.TB vs. TSTa | 2.39 | 1.77 to 3.11 | Gamma (48.637, 0.049) | PREDICT |
| TSTa + QFT-GIT vs. TSTa | 1.97 | 1.45 to 2.57 | Gamma (47.230, 0.042) | PREDICT |
| TSTa + IGRA vs. TSTa | 2.01 | 1.52 to 2.56 | Gamma (57.755, 0.035) | PREDICT |
| TSTb + T-SPOT.TB vs. TSTa | 2.92 | 2.09 to 3.89 | Gamma (40.152, 0.073) | PREDICT |
| TSTb + QFT-GIT vs. TSTa | 2.43 | 1.72 to 3.27 | Gamma (37.737, 0.064) | PREDICT |
| TSTb + IGRA vs. TSTa | 2.58 | 1.88 to 3.40 | Gamma (44.298, 0.058) | PREDICT |
| Negative predictive performance: IRR for negative results | ||||
| TSTb vs. TSTa | 1.35 | 0.84 to 1.98 | Gamma (21.155, 0.064) | PREDICT |
| T-SPOT.TB vs. TSTa | 1.28 | 0.70 to 2.04 | Gamma (13.761, 0.093) | PREDICT |
| QFT-GIT vs. TSTa | 1.60 | 0.88 to 2.55 | Gamma (13.997, 0.115) | PREDICT |
| TSTa + T-SPOT.TB vs. TSTa | 1.41 | 0.82 to 2.16 | Gamma (16.740, 0.084) | PREDICT |
| TSTa + QFT-GIT vs. TSTa | 1.68 | 0.98 to 2.55 | Gamma (17.343, 0.097) | PREDICT |
| TSTa + IGRA vs. TSTa | 1.32 | 0.79 to 1.99 | Gamma (18.313, 0.072) | PREDICT |
| TSTb + T-SPOT.TB vs. TSTa | 1.58 | 0.90 to 2.46 | Gamma (15.503, 0.102) | PREDICT |
| TSTb + QFT-GIT vs. TSTa | 1.83 | 1.04 to 2.83 | Gamma (15.837, 0.115) | PREDICT |
| TSTb + IGRA vs. TSTa | 1.52 | 0.87 to 2.35 | Gamma (16.105, 0.095) | PREDICT |
| Test strategy | Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | |||
| Per person-year | Hazard | Per person-year | Hazard | |
| 1: no test (all results) | 0.00374 | 0.00375 | ||
| 4: TSTa | 0.00680 | 0.00682 | 0.00117 | 0.00117 |
| 5: TSTb | 0.01115 | 0.01121 | 0.00157 | 0.00157 |
| 2: T-SPOT.TB | 0.01350 | 0.01360 | 0.00149 | 0.00149 |
| 3: QFT-GIT | 0.01034 | 0.01039 | 0.00187 | 0.00187 |
| 6: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 0.01628 | 0.01641 | 0.00164 | 0.00164 |
| 7: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 0.01341 | 0.01350 | 0.00195 | 0.00196 |
| 8: TSTa + IGRA | 0.01365 | 0.01374 | 0.00154 | 0.00154 |
| 9: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 0.01984 | 0.02003 | 0.00184 | 0.00185 |
| 10: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 0.01654 | 0.01667 | 0.00213 | 0.00213 |
| 11: TSTb + IGRA | 0.01754 | 0.01770 | 0.00177 | 0.00178 |
Each individual in the PREDICT cohort was allocated a best estimate of their TB hazard, conditional on their baseline test results. Overall, there were 36 different combinations of positive, negative and missing/indeterminate results for the four tests measured at baseline (TSTa, TSTb, QFT-GIT and T-SPOT.TB). For each combination, participants were assigned the hazard for the test strategy for which they had a non-missing/indeterminate result with the greatest predictive power (highest IRR for positive vs. negative results). For example, participants with no missing or discordant results were assigned hazards for the TSTb + T-SPOT.TB strategy (0.00682 if positive or 0.00117 if negative). Participants with discordant QFT-GIT and T-SPOT.TB results (one positive and one negative) were assigned to the TSTb + IGRA hazards. The mean hazard rate estimates for each combination are shown in Table 6.
| Combination | Test | Most predictive strategy | Hazard | Comments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSTa | TSTb | T-SPOT.TB | QFT-GIT | ||||
| 1 | + | + | + | + | TSTb + T-SPOT.TB+ | 0.02003 | All tests available |
| 2 | + | + | + | – | TSTb + IGRA+ | 0.01770 | Discordant IGRA results |
| 3 | + | + | + | ? | TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 0.02003 | No QFT-GIT |
| 4 | + | + | – | + | TSTb + IGRA+ | 0.01770 | Discordant IGRA results |
| 5 | + | + | – | – | TSTb + T-SPOT.TB– | 0.00185 | All tests available |
| 6 | + | + | – | ? | TSTb + T-SPOT.TB– | 0.00185 | No QFT-GIT |
| 7 | + | + | ? | + | TSTb + QFT-GIT+ | 0.01667 | No T-SPOT.TB |
| 8 | + | + | ? | – | TSTb + QFT-GIT– | 0.00213 | No T-SPOT.TB |
| 9 | + | + | ? | ? | TSTb+ | 0.01121 | No T-SPOT.TB or QFT-GIT |
| 10 | + | – | + | + | TSTb + T-SPOT.TB– | 0.00185 | All tests available |
| 11 | + | – | + | – | TSTb + IGRA– | 0.00178 | Discordant IGRA results |
| 12 | + | – | + | ? | TSTb + T-SPOT.TB– | 0.00185 | No QFT-GIT |
| 13 | + | – | – | + | TSTb + IGRA– | 0.00178 | Discordant IGRA results |
| 14 | + | – | – | – | TSTb + T-SPOT.TB– | 0.00185 | All tests available |
| 15 | + | – | – | ? | TSTb + T-SPOT.TB– | 0.00185 | No QFT-GIT |
| 16 | + | – | ? | + | TSTb + QFT-GIT– | 0.00213 | No T-SPOT.TB |
| 17 | + | – | ? | – | TSTb + QFT-GIT– | 0.00213 | No T-SPOT.TB |
| 18 | + | – | ? | ? | TSTb– | 0.00157 | No T-SPOT.TB or QFT-GIT |
| 19 | – | – | + | + | TSTb + T-SPOT.TB– | 0.00185 | All tests available |
| 20 | – | – | + | – | TSTb + IGRA– | 0.00178 | Discordant IGRA results |
| 21 | – | – | + | ? | TSTb + T-SPOT.TB– | 0.00185 | No QFT-GIT |
| 22 | – | – | – | + | TSTb + IGRA– | 0.00178 | Discordant IGRA results |
| 23 | – | – | – | – | TSTb + T-SPOT.TB– | 0.00185 | All tests available |
| 24 | – | – | – | ? | TSTb + T-SPOT.TB– | 0.00185 | No QFT-GIT |
| 25 | – | – | ? | + | TSTb + QFT-GIT– | 0.00213 | No T-SPOT.TB |
| 26 | – | – | ? | – | TSTb + QFT-GIT– | 0.00213 | No T-SPOT.TB |
| 27 | – | – | ? | ? | TSTb– | 0.00157 | No T-SPOT.TB or QFT-GIT |
| 28 | ? | ? | + | + | T-SPOT.TB+ | 0.01360 | No TST |
| 29 | ? | ? | + | – | T-SPOT.TB+ | 0.01360 | No TST |
| 30 | ? | ? | + | ? | T-SPOT.TB+ | 0.01360 | Only T-SPOT.TB |
| 31 | ? | ? | – | + | T-SPOT.TB– | 0.00149 | No TST |
| 32 | ? | ? | – | – | T-SPOT.TB– | 0.00149 | No TST |
| 33 | ? | ? | – | ? | T-SPOT.TB– | 0.00149 | Only T-SPOT.TB |
| 34 | ? | ? | ? | + | QFT-GIT+ | 0.01039 | Only QFT-GIT |
| 35 | ? | ? | ? | – | QFT-GIT– | 0.00187 | Only QFT-GIT |
| 36 | ? | ? | ? | ? | No test | 0.00375 | No tests available |
Chemoprophylaxis
It was assumed that participants aged ≤ 35 years who tested positive for LTBI would be offered CPX. Parameters related to the uptake of CPX in this eligible group, and the incidence and consequences of adverse reactions to CPX, were based on those used in the Warwick Evidence economic analysis by Auguste et al. 102 (Table 7). We assumed that, of those participants who experienced a non-fatal adverse event, 50% would resume CPX. We also assumed that, of those participants who started CPX and did not stop because of an adverse event, 85% would complete a full course of 3 months’ duration. The remaining 15% of participants who dropped out of CPX were assumed to stop after 1.5 months. The effectiveness of CPX was based on results from the International Union Against Tuberculosis trial,110 as used in the Pooran et al. 95 economic model.
| Parameter | Base-case value | 95% CI | PSA distribution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uptake of CPX (%) | 0.94 | 0.90 to 0.97 | Beta (141, 9) | Warwick Evidence102 |
| CPX adverse event (%) | 0.0040 | 0.0007 to 0.0101 | Beta (2.7, 664) | Warwick Evidence102 |
| Death from CPX event (%) | 0.00002 | 0.00000 to 0.00010 | Beta (0.5, 25,125) | Warwick Evidence102 |
| CPX event resolved (%) | 0.50 | 0.30 to 0.70 | Beta (11.51, 11.51) | Assumption |
| Completion for CPX (%) | 0.85 | N/A | N/A | Mears et al.109 |
| Duration of complete CPX (months) | 3 | N/A | N/A | NG3314 |
| Duration of incomplete CPX (months) | 1.5 | N/A | N/A | Assumption |
| TB cases with complete CPX (%) | 0.33 | 0.24 to 0.43 | Beta (32, 65) | IUAT, 1982110 |
| TB cases with incomplete CPX (%) | 0.78 | 0.70 to 0.86 | Beta (76, 21) | IUAT, 1982110 |
| Uptake of BCG vaccination (%) | 0.94 | 0.90 to 0.97 | Beta (164, 10.5) | Warwick Evidence102 |
| TB cases averted with BCG vaccination (%) | 0.49 | 0.34 to 0.7 | Beta (14.03, 14.60) | Colditz et al.111 |
| Treatment for active TB adverse event (%) | 0.0040 | 0.0007 to 0.0101 | Beta (2.7, 664) | Warwick Evidence102 |
| Death from treatment for active TB event (%) | 0.00002 | 0.00000 to 0.00010 | Beta (0.5, 25,125) | Warwick Evidence102 |
| Treatment for active TB event resolved (%) | 0.50 | 0.30 to 0.70 | Beta (11.51, 11.51) | Assumption |
| Completion for treatment for active TB (%) | 0.85 | N/A | N/A | Mears et al.109 |
| Duration of complete treatment for active TB (months) | 6 | N/A | N/A | NG3314 |
| Duration of incomplete treatment for active TB (months) | 3 | N/A | N/A | Assumption |
| Time to diagnosis for active TB (months) | 3 | N/A | N/A | Assumption |
| Time to presentation for treatment for active TB after initial dropout (months) | 3 | N/A | N/A | Assumption |
Bacillus Calmette–Guérin vaccination
Patients with a negative test result for LTBI, who were aged ≤ 35 years and who had not previously been vaccinated were assumed to be offered a BCG vaccination. Uptake in this eligible group was assumed to be 94%, following the assumption in the Warwick Evidence analysis102 for the proportion of patients returning to have a TST result read (see Table 7). The efficacy of BCG vaccination was based on a published meta-analysis. 111
Tuberculosis treatment
Parameters related to the diagnosis and treatment of active disease are shown in Table 7. We assumed that diagnosis would take place 3 months after the onset of active TB, at which time all patients would start treatment. A proportion was assumed to experience adverse effects, with a small mortality risk, as in the Warwick Evidence analysis. 102 We assumed that, of those patients with a non-fatal adverse event, 50% would continue treatment. As with CPX, we assumed that 85% of patients (who started treatment for active disease and did not stop because of an adverse event) would complete a full course of 6 months. Those with an incomplete course were assumed to drop out after 3 months of treatment, but to re-present and start a new course of treatment after 3 months. For patients who completed a complete course, treatment was assumed to be 100% effective with no residual mortality risk or loss of utility.
Health impact of tuberculosis
The model applied a case fatality rate for patients who progressed to active TB, based on estimates reported by Crofts et al. 112 At younger ages, the proportion of participants dying of TB within 12 months of the start of treatment or notification rate was relatively low (1.2% for those aged 15–44 years and 4.8% for those aged 45–54 years), but the risk was much higher for older participants (17.6% for those aged ≥ 65 years) (Table 8). For simplicity, we modelled any TB-related deaths as taking place at the time of diagnosis.
| Parameter | Base-case value | 95% CI | PSA distribution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case fatality for participants, by age group | ||||
| 15–44 years | 0.012 | 0.010 to 0.015 | Beta (88, 7249) | Crofts et al.112 |
| 45–64 years | 0.048 | 0.040 to 0.056 | Beta (125, 2500) | Crofts et al.112 |
| ≥ 65 years | 0.176 | 0.160 to 0.191 | Beta (413, 1940) | Crofts et al.112 |
| Initial utility | N/A | N/A | N/A | PREDICT EQ-5D scores (from this trial) |
| Utility multiplier | ||||
| When active TB progression takes place | 0.900 | N/A | N/A | Assumption |
| An acute treatment period during treatment (the first 3 months) | 0.675 | N/A | N/A | Kruijshaar et al.113 |
| For a post-acute treatment period during treatment for active TB | 0.813 | N/A | N/A | Kruijshaar et al.113 |
Members of the cohort entered the model with an initial utility based on their EQ-5D score at baseline. This value was adjusted on progression to TB to reflect the impact of symptoms on quality of life. For the time between the onset of TB and diagnosis (assumed to be 3 months) in the model, a multiplier of 0.9 was applied to individuals’ utility scores. This multiplier was an assumption as utility scores are not available for this pre-diagnostic phase, when symptoms are developing. Utility multipliers for the first 3 months after diagnosis (the ‘acute’ period), and for the remaining time up to the completion of treatment (the ‘post-acute’ period), were estimated using a EQ-5D survey of 61 participants with active TB113 (see Table 8). Participants who dropped out of treatment retained the lower, acute-period utility until they re-presented and completed the first 3 months of treatment.
General mortality was modelled by simulating a time to death from other causes (not TB) at the time of model entry for all participants. Individual values were sampled using a Gompertz distribution with life expectancy by age from UK life tables114 and assuming a 5-year standard deviation. As TB is a rare cause of death in the UK, we did not adjust all-cause mortality.
Resource use and costs
The costs of treatments and tests are shown in Table 9. We assumed that test strategies involving TST would require two clinic visits, whereas those involving only IGRAs (T-SPOT.TB or QFT-GIT or both) would only require one clinic visit.
| Parameter | Base-case value | 95% CI | PSA distribution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCG vaccination | £4 | £1 to £10 | Gamma (2.46, 1.63) | NICE CG3385 |
| Adverse event (assumed to be the same for treatment for active TB and CPX) | £397 | £161 to £737 | Gamma (7.13, 55.64) | Warwick Evidence102 |
| Active TB diagnosis | £434 | £353 to £523 | Gamma (100, 4.34) | Mears et al.109 |
| Treatment for active TB (6 months) | £1114 | £906 to £1343 | Gamma (100, 11.14) | Mears et al.109 |
| CPX (3 months) | £743 | £605 to £896 | Gamma (100, 7.43) | Mears et al.109 |
| TST | £1.22 | N/A | N/A | NICE CG11786 |
| T-SPOT.TB | £71 | N/A | N/A | Pareek et al.101 |
| QFT-GIT | £41 | N/A | N/A | Pareek et al.101 |
| IGRA | £112 | N/A | N/A | Assumed to be sum of T-SPOT.TB and QFT-GIT |
| Clinic visit: TB specialist nursing, adult, face to face | £62 | N/A | N/A | Department of Health and Social Care’s NHS Reference Costs115 |
| Number of clinic visits for T-SPOT.TB or QFT-GIT | 1 | N/A | N/A | Assumption |
| Number of clinic visits for TST or two-step tests | 2 | N/A | N/A | Assumption |
Ethics and research governance
This study was approved by the Brent Research Ethics Committee (10/H0717/14). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. For community recruitment, formal NHS Research and Development permission was sought from the managers or leaders of the institutions to conduct the study on their premises, and to ensure that appropriate areas to protect individuals’ privacy were available and were clinically appropriate.
Latent TB infection treatment was recommended only to those aged < 35 years, by their general practioner, following NICE guidelines at the time of the study. Any treatment for active TB was offered to participants through the TB clinic after communication of the results, separately from the study procedures.
All study data were held in accordance with NHS data protection principles, including the use of secure password-protected systems.
Although this was not a randomised controlled trial, a formal independent data monitoring committee and a trial steering committee were set up (see Acknowledgements for a full list of members).
The study was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01162265). The full protocol is available at https://njl-admin.nihr.ac.uk/document/download/2006769 (accessed 12 June 2017).
Chapter 3 Results: progression to active tuberculosis
Baseline participant information
The PREDICT study recruited 10,045 participants between May 2010 and July 2015. Of these participants, 175 were identified as having TB at baseline (i.e. diagnosed or treated < 21 days after being recruited) and an additional 260 participants received treatment for latent TB during the study. Removing those with TB at baseline and those receiving latent TB treatment left 9610 evaluable participants (Figure 7).
FIGURE 7.
Study flow chart. *Six participants did not have data allowing follow-up to be calculated, leaving a total of 6380 participants for analysis. Table 16 provides further details of ‘no results’ for each test, Figure 8 provides all details of available data for all test combinations and Tables 25, 27 and 28 provide full results for all test combinations. Note that in accordance with national guidelines, only contacts aged < 35 years were offered treatment.
Participants were recruited from 54 different NHS centres and community settings located in London, Leicester and Birmingham. Participants were recruited from health-care, work and community settings including places of worship, schools, colleges and workplaces.
Owing to the small numbers of participants who were receiving treatment for LTBI and those who were diagnosed with a HIV infection, further analyses of these groups were not performed.
Of the 9610 participants, 4861 individuals (50.6%) had contact with someone with TB and 4749 participants (49.4%) were new entrants to the UK from a high-incidence country. The proportion of participants who reported not being born in the UK was 83.3% (n = 8008), and 57.5% (n = 5526) were aged ≤ 35 years. Full participant demographics are given in Table 10.
| Characteristic | Participants | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Contacts (N = 4861) | New entrants (N = 4749) | All (N = 9610) | |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Female | 2400 (49.4) | 2329 (49.0) | 4729 (49.2) |
| Male | 2433 (50.1) | 2376 (50.0) | 4809 (50.0) |
| Missing | 28 (0.6) | 44 (0.9) | 72 (0.8) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| Bangladeshi | 201 (4.1) | 515 (10.8) | 716 (7.5) |
| Black African | 770 (15.8) | 368 (7.8) | 1138 (11.8) |
| Black Caribbean | 235 (4.8) | 7 (0.2) | 242 (2.5) |
| Indian | 1352 (27.8) | 2629 (55.4) | 3981 (41.4) |
| Mixed | 654 (13.5) | 238 (5.0) | 892 (9.3) |
| Other | 194 (4.0) | 126 (2.7) | 320 (3.3) |
| Pakistani | 398 (8.2) | 508 (10.7) | 906 (9.4) |
| White | 942 (19.4) | 231 (4.9) | 1173 (12.2) |
| Missing | 115 (2.4) | 127 (2.7) | 242 (2.5) |
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 32 (25–44) | 33 (26–51) | 33 (26–47) |
| Missing, n (%) | 7 (0.1) | 15 (0.3) | 22 (0.2) |
| Age (years), n (%) | |||
| ≤ 35 | 2849 (58.6) | 2677 (56.4) | 5526 (57.5) |
| > 35 | 2005 (41.3) | 2057 (43.3) | 4062 (42.3) |
| Missing | 7 (0.1) | 15 (0.3) | 22 (0.2) |
| UK born, n (%) | |||
| No | 3414 (70.2) | 4594 (96.7) | 8008 (83.3) |
| Yes | 1423 (29.3) | 129 (2.7) | 1552 (16.2) |
| Missing | 24 (0.5) | 26 (0.6) | 50 (0.5) |
A BCG vaccination was reported by 6618 participants (68.9%) and previous contact with TB was reported by 1207 participants (12.6%). Only 55 participants (0.6%) reported being HIV positive. Many of the participants had travelled or lived outside the UK (not including Western Europe, the USA, Canada and Australia) in the last 2 years (n = 3563, 37.1%) and before the last 2 years (n = 3033, 31.6%). Full participant risk factors are provided in Table 11.
| Risk factor | Participants | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Contacts (N = 4861) | New entrants (N = 4749) | All (N = 9610) | |
| Previous TB contact prior to the recent exposure, n (%) | 670 (13.8) | 537 (11.3) | 1207 (12.6) |
| Missing | 156 (3.2) | 224 (4.7) | 380 (4.0) |
| Previous TB diagnosis, n (%) | 140 (2.9) | 213 (4.5) | 353 (3.7) |
| Missing | 79 (1.6) | 108 (2.3) | 187 (2.0) |
| BCG vaccination, n (%) | 3685 (75.8) | 2933 (61.8) | 6618 (68.9) |
| Missing | 640 (13.2) | 882 (18.6) | 1522 (15.8) |
| BCG vaccination,a n (%) | 4155 (85.5) | 3791 (79.8) | 7946 (82.7) |
| Missing | 170 (3.5) | 24 (0.5) | 194 (2.0) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 325 (6.7) | 481 (10.1) | 806 (8.4) |
| Missing | 17 (0.4) | 23 (0.5) | 40 (0.4) |
| Haematological malignancy, n (%) | 10 (0.2) | 6 (0.1) | 16 (0.2) |
| Missing | 36 (0.7) | 54 (1.1) | 90 (0.9) |
| HIV positive, n (%) | 43 (0.9) | 12 (0.3) | 55 (0.6) |
| Missing | 182 (3.7) | 498 (10.5) | 680 (7.1) |
| Smoker, n (%) | 1172 (24.1) | 635 (13.4) | 1807 (18.8) |
| Missing | 31 (0.6) | 36 (0.8) | 67 (0.7) |
| Previous transplant, n (%) | 15 (0.3) | 10 (0.2) | 25 (0.3) |
| Missing | 33 (0.7) | 42 (0.9) | 75 (0.8) |
| Anti-TNF-α, n (%) | 17 (0.4) | 15 (0.3) | 32 (0.3) |
| Missing | 180 (3.7) | 620 (13.1) | 800 (8.3) |
| Immunosuppressive drugs, n (%) | 43 (0.9) | 32 (0.7) | 75 (0.8) |
| Missing | 179 (3.7) | 631 (13.3) | 810 (8.4) |
| Problem drug use, n (%) | 166 (3.4) | 32 (0.7) | 198 (2.1) |
| Missing | 23 (0.5) | 40 (0.8) | 63 (0.7) |
| Homeless, n (%) | 111 (2.3) | 73 (1.5) | 184 (1.9) |
| Missing | 22 (0.5) | 34 (0.7) | 56 (0.6) |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean (SD) | 25.3 (4.9) | 25.0 (4.6) | 25.1 (4.8) |
| Missing, n (%) | 368 (7.6) | 307 (6.5) | 675 (7.0) |
| Occupation, n (%) | |||
| Health care | 257 (5.3) | 95 (2.0) | 352 (3.7) |
| Social/prison sector | 33 (0.7) | 9 (0.2) | 42 (0.4) |
| Laboratory/pathology | 11 (0.2) | 4 (0.1) | 15 (0.2) |
| Agriculture/animal care | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Education | 974 (20.0) | 708 (14.9) | 1682 (17.5) |
| None | 1119 (23.0) | 1881 (39.6) | 3000 (31.2) |
| Other | 2257 (46.4) | 1691 (35.6) | 3948 (41.1) |
| Unknown | 210 (4.3) | 361 (7.6) | 571 (5.9) |
| Travelb in the last 2 years, n (%) | 1822 (37.5) | 1741 (36.7) | 3563 (37.1) |
| Missing | 159 (3.3) | 937 (19.7) | 1096 (11.4) |
| Travelb before the last 2 years, n (%) | 1630 (33.5) | 1403 (29.5) | 3033 (31.6) |
| Missing | 414 (8.5) | 1099 (23.1) | 1513 (15.7) |
Information that was collected for the 4861 participants in the study who had a contact with TB indicated that the most common type of contact with someone with TB was ‘household non-sexual’, reported by 2402 participants (49.4%). ‘Household sexual’ contact was reported by 673 contact participants (13.8%). Table 12 provides full details of contact types.
| Contact type | Contact participants (N = 4861), n (%) |
|---|---|
| Household sexual | 673 (13.8) |
| Household non-sexual | 2402 (49.4) |
| Health care | 141 (2.9) |
| Education | 238 (4.9) |
| Detention | 5 (0.1) |
| Homeless | 23 (0.5) |
| Other congregate living | 1 (0.0) |
| Travel | 6 (0.1) |
| Workplace/social | 747 (15.4) |
| Other | 304 (6.3) |
A total of 2211 index cases were identified for the 4861 contacts (i.e. 45.5% of contacts had an identified index case). The number of contacts participating in PREDICT per index case ranged from 1 to 20 (median 2). Most of the index case patients (693/1263, 54.9%) had pulmonary TB, with (n = 138) or without (n = 555) TB disease at extrapulmonary sites. The infecting species was reported in 875 index cases, being identified as M. tuberculosis or M. tuberculosis complex in 858 cases and one case, respectively, as M. bovis in four cases and M. africanum in five cases. Seven index case participants were reported to have mixed infections with members of the M. tuberculosis complex (M. tuberculosis and M. africanum, n = 5; M. tuberculosis and M. bovis, n = 2). A total of 549 out of 1263 index case participants (43.5%) were female and the median age was 35 years [interquartile range (IQR) 26–49 years]. Of 1250 index cases in which the participant’s country of birth was known, 992 participants (79.4%) were born outside the UK.
Test results
The QFT-GIT tests were carried out in four centres (NMRL, Imperial College London, Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust and SYNLAB) and the T-SPOT.TB test was carried out in three centres (NMRL, Imperial College London and Oxford Immunotec Ltd). The results are summarised in Table 13. Positive test results (positive and borderline positive) were seen for participants when using the T-SPOT.TB test (n = 1571, 16.3%), QFT-GIT (n = 1892, 19.7%), TSTa (n = 3513, 36.6%) and TSTb (n = 1729, 18.0%). There were 6520 participants (67.8%) with a non-missing or indeterminate result (positive or negative) for the three tests (T-SPOT.TB, QFT-GIT and TSTa) and 6386 participants (66.5%) had a non-missing or indeterminate result (positive or negative) for all tests including TSTb. An ‘error’ was reported when a result could not be obtained as a result of the testing procedures, for example because there was not enough sample material.
| Result | Test, n (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-SPOT.TB | QFT-GIT | TSTa | TSTb | |
| Positive | 1381 (14.4) | 1892 (19.7) | 3513 (36.6) | 1729 (18.0) |
| Borderline positive | 190 (2.0) | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Borderline negative | 126 (1.3) | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Negative | 6288 (65.4) | 6640 (69.1) | 4320 (45.0) | 5940 (61.8) |
| Indeterminate | 121 (1.3) | 163 (1.7) | N/A | N/A |
| Error | 260 (2.7) | 65 (0.7) | N/A | N/A |
| Missing | 1244 (12.9) | 850 (8.8) | 1777 (18.5) | 1941 (20.2) |
Some participants had multiple tests carried out (21 participants had two T-SPOT.TB tests and 33 participants had two QFT-GIT tests).
In the following discussion, ‘borderline positive’ results are categorised as positive; ‘borderline negative’ results are categorised as negative; and ‘error’ and ‘indeterminate’ results are categorised as missing, as only positive and negative results can be used in decision-making.
Evaluation of the combination of results for the different tests showed that, when considering the results from the three tests, T-SPOT.TB, QFT-GIT and TSTa (6520 participants had available data), the results were positive for all three for 797 participants (12.2%) and were negative for all three for 2995 participants (45.9%), and the three results differed for 2728 participants (41.8%). When comparing the results for T-SPOT.TB and TSTa (6843 participants had available data), the results were both positive for 1020 participants (14.9%), were both negative for 3414 participants (49.9%) and disagreed for 2409 participants (35.2%). Comparing the results for QFT-GIT and TSTa (7041 participants had available data), 1113 participants (15.8%) had positive results for both, 3373 participants (47.9%) had a negative result for both and 2555 participants (36.3%) had discordant results.
A total of 6386 participants had a test result for each of T-SPOT.TB, QFT-GIT and TSTb. Of the 6706 participants with T-SPOT.TB and TSTb results, 743 (11.1%) had positive results for both, 4598 (68.6%) had negative results for both and the results disagreed for 1365 participants (20.4). For the 6897 participants with TSTb and QFT-GIT results, 785 (11.4%) had positive results for both, 4563 (66.2%) had negative results for both and the results for 1549 participants (22.5%) disagreed. Of the 6386 participants with all results, 620 (9.7%) had all positive results, 4026 (63.0%) had all negative results and the results for 1740 participants (27.2%) disagreed.
A comparison of the results for the two IGRAs only (data were available for 7594 participants) showed that 1176 participants (15.5%) had a positive result for both, 5588 participants (73.6%) had a negative result for both, and 830 participants (10.9%) had discordant results. Tables 14 and 15 show the cross-tabulations of test results, and Figure 8 shows the completeness of data for each testing combination. Further cross-tabulations of results showing the full categorisation of results (including missing, indeterminate and error) are presented in Appendix 2, Tables 44 and 45. Cross-tabulations for participants who did and did not progress to active TB are shown in Appendix 2, Tables 46–48.
| QFT-GIT | Test result, n (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSTa positive | TSTa negative | TSTa missing | ||||||||||
| T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | |
| Positive | 797 (22.7) | 249 (7.1) | 67 (1.9) | 1113 (31.7) | 195 (4.5) | 230 (5.3) | 25 (0.6) | 450 (10.4) | 184 (10.4) | 52 (2.9) | 93 (5.2) | 329 (18.5) |
| Negative | 173 (4.9) | 1791 (51.0) | 141 (4.0) | 2105 (59.9) | 90 (2.1) | 2995 (69.3) | 288 (6.7) | 3373 (78.1) | 36 (2.0) | 802 (45.1) | 324 (18.2) | 1162 (65.4) |
| Missing | 50 (1.4) | 57 (1.6) | 188 (5.4) | 295 (8.4) | 27 (0.6) | 189 (4.4) | 281 (6.5) | 497 (11.5) | 19 (1.1) | 49 (2.8) | 218 (12.3) | 286 (16.1) |
| Total | 1020 (29.0) | 2097 (59.7) | 396 (11.3) | 3513 (100.0) | 312 (7.2) | 3414 (79.0) | 594 (13.8) | 4320 (100.0) | 239 (13.4) | 903 (50.8) | 635 (35.7) | 1777 (100.0) |
| QFT-GIT | Test result, n (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSTb positive | TSTb negative | TSTb missing | ||||||||||
| T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | |
| Positive | 620 (35.9) | 124 (7.2) | 41 (2.4) | 785 (45.4) | 356 (6.0) | 345 (5.8) | 48 (0.8) | 749 (12.6) | 200 (10.3) | 62 (3.2) | 96 (4.9) | 358 (18.4) |
| Negative | 89 (5.1) | 655 (37.9) | 56 (3.2) | 800 (46.3) | 171 (2.9) | 4026 (67.8) | 366 (6.2) | 4563 (76.8) | 39 (2.0) | 907 (46.7) | 331 (17.1) | 1277 (65.8) |
| Missing | 34 (2.0) | 16 (0.9) | 94 (5.4) | 144 (8.3) | 43 (0.7) | 227 (3.8) | 358 (6.0) | 628 (10.6) | 19 (1.0) | 52 (2.7) | 235 (12.1) | 306 (15.8) |
| Total | 743 (43.0) | 795 (46.0) | 191 (11.0) | 1729 (100.0) | 570 (9.6) | 4598 (77.4) | 772 (13.0) | 5940 (100.0) | 258 (13.3) | 1021 (52.6) | 662 (34.1) | 1941 (100.0) |
FIGURE 8.
Test result combinations. *T-SPOT.TB, QuantiFERON + TSTa; †T-SPOT.TB, QuantiFERON + TSTb. TSTa was considered positive if participants had a skin induration measuring ≥ 5 mm. TSTb was considered positive if participants without a previous BCG vaccination had a skin induration measuring ≥ 6 mm following the standard TST; for participants with a previous BCG vaccination, a skin induration of ≥ 15 mm following the standard TST indicated a positive result.
Progression to active tuberculosis
Of the total number of participants, 97 (1.0%) developed active TB. Of the participants progressing to active TB, 66 (68.0%) were aged ≤ 35 years and 63 (64.9%) were recruited to the study because of contact with an individual with TB. The follow-up duration for participants in the study ranged from 21 days to 5.9 years (for non-progressing participants: range 0.3–5.9 years, mean 2.9 years, median 3.0 years; for progressing participants: range 21 days–4.1 years, mean 0.8 years, median 0.5 years) (Figure 9).
FIGURE 9.
Histogram of follow-up duration for participants who progressed to active TB and participants who did not progress to active TB.
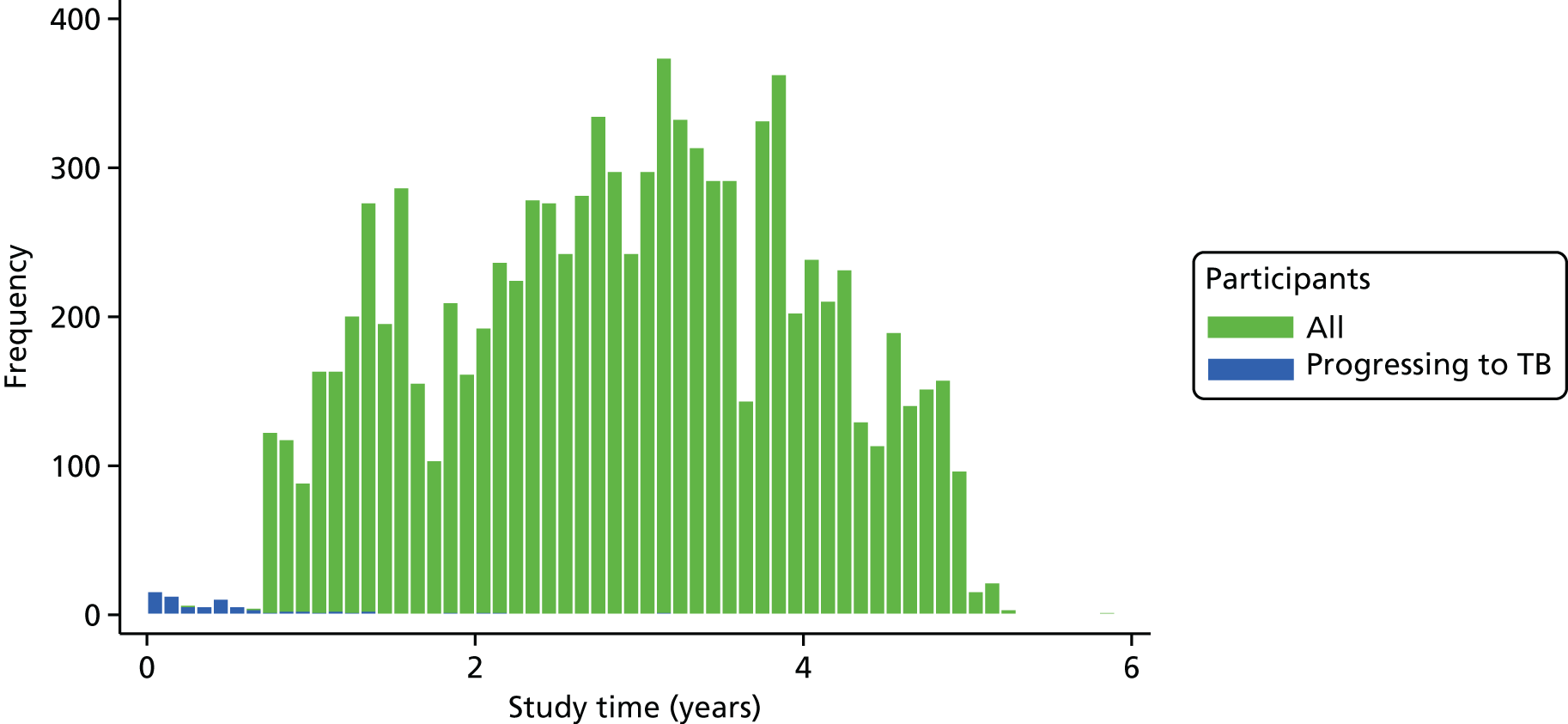
Fifty-two out of the 97 participants (53.6%) who progressed to active TB developed TB within 6 months of follow-up (33 contact participants and 19 new entrant participants), and within 12 months 70 participants (72.2%) had progressed to active TB (46 contact participants and 24 new entrant participants). Twenty-seven participants (27.8%) developed active TB after 1 year of follow-up.
The characteristics of the 97 participants who progressed to active TB are summarised in Table 16. Forty-five of these participants had pulmonary TB, with (n = 7) or without (n = 38) TB disease at an extrapulmonary site; the remaining 52 participants had extrapulmonary TB only. Approximately two-thirds of participants were contacts and 48.5% were female. A total of 81 out of 97 participants (83.5%) were born outside the UK. The majority of participants (74.2%) had received a BCG vaccination. Sixteen participants (16.5%) reported contact with a patient with TB prior to the contact that led to their enrolment in the study. At the time of enrolment, four of the participants (4.1%) who went on to develop active TB reported problem drug use and three (3.1%) were homeless.
| Characteristic | Participants | |
|---|---|---|
| Progressing to active TB (N = 97) | With all test results and progressing to active TB (N = 77) | |
| Contact or migrant, n (%) | ||
| Contact | 63 (65.0) | 51 (66.2) |
| Migrant | 34 (35.1) | 26 (33.8) |
| Sex, n (%) | ||
| Female | 47 (48.5) | 37 (48.1) |
| Male | 50 (51.6) | 40 (52.0) |
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 30 (26–38) | 30 (26–38) |
| Age (years), n (%) | ||
| ≤ 35 | 66 (68.0) | 52 (67.5) |
| > 35 | 31 (32.0) | 25 (32.5) |
| UK born, n (%) | ||
| No | 81 (83.5) | 64 (83.1) |
| Yes | 16 (16.5) | 13 (16.9) |
| BCG vaccination, n (%) | 72 (74.2)a | 57 (74.0)a |
| Smoker, n (%) | 18 (18.6) | 15 (19.5) |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean (SD) | 23.6 (4.5)b | 23.4 (4.5)c |
There were 14 index case/contact pairs with 24-locus MIRU-VNTR data available for both individuals’ infections: 11 of 12 pairs with data on ≥ 22 loci were identical at all available loci and one pair was identical at the 12 loci available.
T-SPOT.TB, QFT-GIT, TSTa and TSTb identified 56 (57.7%), 53 (54.6%), 77 (79.4%) and 60 (61.9%) of the participants developing active TB as positive, respectively. Participants who progressed to active TB accounted for 3.6%, 2.8%, 2.2% and 3.5% of the positive results for T-SPOT.TB, QFT-GIT, TSTa and TSTb (PPVs), respectively, and 0.5%, 0.5%, 0.3% and 0.5% of the negative results for each test, respectively (NPVs of 99.5%, 99.5%, 99.7% and 99.5%) (Table 17).
| Test result | Test, number of progressors/total number (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-SPOT.TB | QFT-GIT | TSTa | TSTb | |
| Positive | 56/1571 (3.6) | 53/1892 (2.8) | 77/3513 (2.2) | 60/1729 (3.5) |
| Negative | 29/6414 (0.5) | 33/6640 (0.5) | 15/4320 (0.3) | 31/5940 (0.5) |
| Missing | 12/1625 (0.7) | 11/1078 (1.0) | 5/1777 (0.3) | 6/1941 (0.3) |
For the participants aged ≤ 35 years, individuals developing active TB accounted for 4.7%, 3.9%, 2.7% and 4.6% of the positive results for T-SPOT.TB, QFT-GIT, TSTa and TSTb, respectively; for participants aged > 35 years, this was 2.4%, 1.8%, 1.6% and 2.2%, respectively. For contact participants, individuals who progressed to active TB accounted for 4.3%, 3.5%, 2.5% and 3.7% of the positive results for T-SPOT.TB, QFT-GIT, TSTa and TSTb, respectively; for the new entrant participants, this was 2.9%, 2.1%, 1.7% and 3.2%, respectively. Tables 17–19 provide further information.
| Test result | Test, number of progessors/total number (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSTa | TSTb | T-SPOT.TB | QFT-GIT | |||||||||
| Age group, n/N (%) | ||||||||||||
| ≤ 35 years | > 35 years | Missing | ≤ 35 years | > 35 years | Missing | ≤ 35 years | > 35 years | Missing | ≤ 35 years | > 35 years | Missing | |
| Positive | 53/1995 (2.7) | 24/1516 (1.6) | 0/2 (0.0) | 42/923 (4.6) | 18/804 (2.2) | 0/2 (0.0) | 38/805 (4.7) | 18/763 (2.4) | 0/3 (0.0) | 36/935 (3.9) | 17/953 (1.8) | 0/4 (0.0) |
| Negative | 8/2804 (0.3) | 7/1514 (0.5) | 0/2 (0.0) | 19/3767 (0.5) | 12/2173 (0.6) | 0/0 (0.0) | 20/4122 (0.5) | 9/2284 (0.4) | 0/8 (0.0) | 22/3991 (0.6) | 11/2641 (0.4) | 0/8 (0.0) |
| Missing | 5/727 (0.7) | 0/1032 (0.0) | 0/18 (0.0) | 5/836 (0.6) | 1/1085 (0.1) | 0/20 (0.0) | 8/599 (1.3) | 4/1015 (0.4) | 0/11 (0.0) | 8/600 (1.3) | 3/468 (0.6) | 0/10 (0.0) |
| Test result | Test, number of progressors/total number (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-SPOT.TB | QFT-GIT | TSTa | TSTb | |||||
| Participant type | ||||||||
| Contacts | New entrants | Contacts | New entrants | Contacts | New entrants | Contacts | New entrants | |
| Positive | 34/800 (4.3) | 22/771 (2.9) | 33/952 (3.5) | 20/940 (2.1) | 51/2019 (2.5) | 26/1494 (1.7) | 38/1036 (3.7) | 22/693 (3.2) |
| Negative | 23/3475 (0.7) | 6/2939 (0.2) | 22/3324 (0.7) | 11/3316 (0.3) | 9/2249 (0.4) | 6/2071 (0.3) | 21/3081 (0.7) | 10/2859 (0.3) |
| Missing | 6/586 (1.0) | 6/1039 (0.6) | 8/585 (1.4) | 3/493 (0.6) | 3/593 (0.5) | 2/1184 (0.2) | 4/744 (0.5) | 2/1197 (0.2) |
Primary analyses
For the primary analyses, the data for the 6386 participants who had all test data were used, which included 77 participants who developed active TB. As six of these participants did not have data enabling time in the study to be calculated, the final sample used for the primary analyses was 6380 participants, and 77 of these participants developed TB.
Incidence rates and incidence rate ratios for individual tests
When utilising all follow-up data, the IR of TB per 1000 participants per annum for those with a positive result for T-SPOT.TB was 13.2 (95% CI 9.9 to 17.4), and it was 1.5 (95% CI 1.0 to 2.2) for those with a negative result. For QFT-GIT, the IRs for participants with positive and negative results were 10.1 (95% CI 7.4 to 13.4) and 1.9 (95% CI 1.3 to 2.7). For TSTa, the IRs for participants with positive and negative results were 6.8 (95% CI 5.2 to 8.7) and 1.2 (95% 0.6 to 2.0), respectively. For TSTb, the IR for participants with positive results was 11.1 (95% CI 8.3 to 14.6), and it was 1.6 (95% CI 1.0 to 2.3) for those with negative results (Table 20).
| Progression measure | Test and result | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-SPOT.TB | QFT-GIT | TSTa | TSTb | |||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| Progression (n/N) | 52/1235 | 25/5145 | 47/1444 | 30/4936 | 64/2957 | 13/3423 | 52/1485 | 25/4895 |
| Total years at risk | 3926.2 | 16,645.3 | 4649.9 | 15,921.6 | 9416.8 | 11,154.6 | 4674.8 | 15,896.6 |
| IR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 13.2 | 1.5 | 10.1 | 1.9 | 6.8 | 1.2 | 11.1 | 1.6 |
| 95% CI | 9.9 to 17.4 | 1.0 to 2.2 | 7.4 to 13.4 | 1.3 to 2.7 | 5.2 to 8.7 | 0.6 to 2.0 | 8.3 to 14.6 | 1.0 to 2.3 |
| IRR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 8.8 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 7.1 | ||||
| 95% CI | 5.5 to 14.2 | 3.4 to 8.5 | 3.2 to 10.6 | 4.4 to 11.4 | ||||
When restricting the follow-up of participants to just 1 year, 59 of the 77 participants (76.6%) who progressed to active TB in the total study duration had progressed at this stage. With the 1-year restricted follow-up, the IR of TB per 1000 participants per annum for participants with a positive T-SPOT.TB result was 34.0 (95% CI 24.4 to 46.2), and it was 3.5 (95% CI 2.1 to 35.1) for participants with a negative T-SPOT.TB result. For participants with a positive QFT-GIT test result, the IR was 25.4 (95% CI 17.8 to 35.1), and it was 4.7 (95% CI 3.0 to 7.0) for those with a negative result. For participants with a positive TSTa result, the IR was 17.1 (95% CI 12.7 to 22.6), and it was 2.6 (95% CI 1.2 to 5.0) for those with a positive result; for TSTb, the IR for participants with a positive result was 28.9 (95% CI 2.08 to 39.1), and it was 3.5 (95% CI 2.0 to 5.6) for those with a negative result (Table 21).
| Progression measure | Test and result | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-SPOT.TB | QFT-GIT | TSTa | TSTb | |||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| 1 year of follow-up | ||||||||
| Progression (n/N) | 41/1235 | 18/5145 | 36/1444 | 23/4936 | 50/2957 | 9/3423 | 42/1485 | 17/4895 |
| Years at risk | 1204.4 | 5125.3 | 1418.7 | 4911.1 | 2918.9 | 3410.8 | 1453.7 | 4876.0 |
| IR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 34.0 | 3.5 | 25.4 | 4.7 | 17.1 | 2.6 | 28.9 | 3.5 |
| 95% CI | 24.4 to 46.2 | 2.1 to 5.6 | 17.8 to 35.1 | 3.0 to 7.0 | 12.7 to 22.6 | 1.2 to 5.0 | 20.8 to 39.1 | 2.0 to 5.6 |
| IRR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 9.7 | 5.4 | 6.5 | 8.3 | ||||
| 95% CI | 5.6 to 16.9 | 3.2 to 9.1 | 3.2 to 13.2 | 4.7 to 14.6 | ||||
| 2 years of follow-up | ||||||||
| Progression (n/N) | 48/1235 | 21/5145 | 43/1444 | 26/4936 | 57/2957 | 12/3423 | 47/1485 | 22/4895 |
| Years at risk | 2340.6 | 9987.7 | 2761.4 | 9566.9 | 5683.5 | 6644.8 | 2824.0 | 9504.3 |
| IR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 20.5 | 2.1 | 15.6 | 2.7 | 10.0 | 1.8 | 16.6 | 2.3 |
| 95% CI | 15.1 to 27.2 | 1.3 to 3.2 | 11.3 to 21.0 | 1.8 to 4.0 | 7.6 to 13.0 | 0.9 to 3.2 | 12.2 to 22.1 | 1.5 to 3.5 |
| IRR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 9.8 | 5.7 | 5.6 | 7.2 | ||||
| 95% CI | 5.8 to 16.3 | 3.5 to 9.3 | 3.0 to 10.3 | 4.3 to 11.9 | ||||
When extending the follow-up period to 2 years, the IR decreased. For participants with a positive T-SPOT.TB result, the IR was 20.5 (95% CI 15.1 to 27.2), and it was 2.1 (95% CI 1.3 to 3.2) for participants with a negative result. For participants who had a positive QFT-GIT result, the IR was 15.6 (95% CI 11.3 to 21.0), and it was 2.7 (95% CI 1.8 to 4.0) for those with a negative result. For TSTa, the IR for participants with a positive result was 10.0 (95% CI 7.6 to 13.0), and for those with a negative result it was 1.8 (95% CI 0.9 to 3.2); for TSTb, the IR for participants with a positive result was 16.6 (95% CI 1.2 to 22.1), and for those with a negative result it was 2.3 (95% CI 1.5 to 3.5).
The IRR (the incidence of TB for those with a positive test result compared with those with a negative test result, with adjustment for person-years) for T-SPOT.TB was 8.8 (95% CI 5.5 to 14.2), for QFT-GIT it was 5.4 (95% CI 3.4 to 8.5), for TSTa it was 5.8 (95% CI 3.2 to 10.6) and for TSTb it was 7.1 (95% CI 4.4 to 11.4). Similar IRRs were produced for each test when restricting the follow-up duration to 1 year and 2 years (see Tables 20 and 21).
Incidence rates and incidence rate ratios for test strategies
For the two-step strategies, the IRs for positive and negative results were 15.9 (95% CI 11.7 to 21.1) and 1.7 (95% CI 1.1 to 2.4) for TSTa + T-SPOT.TB, respectively; 13.2 (95% CI 9.6 to 17.8) and 2.0 (95% CI 1.4 to 2.7) for TSTa + QFT-GIT, respectively; and 13.4 (95% CI 10.0 to 17.6) and 1.6 (95% CI 1.0 to 2.3) for IGRA + TSTa, respectively. For the two-step strategies including TSTb, the IRs for positive and negative results were 19.6 (95% CI 14.2 to 26.4) and 1.9 (95% CI 1.3 to 2.6) for TSTb + T-SPOT.TB, respectively; 16.4 (95% CI 11.6 to 22.6) and 2.1 (95% CI 1.5 to 2.9) for TSTb + QFT-GIT, respectively; and 17.4 (95% CI 12.7 to 23.2) and 1.8 (95% CI 1.2 to 2.5) for TSTb + IGRA, respectively (Tables 22 and 23).
| Progression measure | Test and result | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | TSTa + QFT-GIT | TSTa + IGRA | ||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| Progression (n/N) | 48/954 | 29/5426 | 43/1028 | 34/5352 | 51/1199 | 26/5181 |
| Years at risk | 3017.6 | 17,553.8 | 3256.1 | 17,315.3 | 3813.5 | 16,757.9 |
| IR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 15.9 | 1.7 | 13.2 | 2.0 | 13.4 | 1.6 |
| 95% CI | 11.7 to 21.1 | 1.1 to 2.4 | 9.6 to 17.8 | 1.4 to 2.7 | 10.0 to 17.6 | 1.0 to 2.3 |
| IRR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 9.6 | 6.7 | 8.6 | |||
| 95% CI | 6.1 to 15.3 | 4.3 to 10.5 | 5.4 to 13.8 | |||
| Progression measure | Test and result | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | TSTb + QFT-GIT | TSTb + IGRA | ||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| Progression (n/N) | 43/709 | 34/5671 | 38/744 | 39/5636 | 45/833 | 32/5547 |
| Years at risk | 2198.1 | 18,373.3 | 2311.8 | 18,259.6 | 2590.7 | 17,980.7 |
| IR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 19.6 | 1.9 | 16.4 | 2.1 | 17.4 | 1.8 |
| 95% CI | 14.2 to 26.4 | 1.3 to 2.6 | 11.6 to 22.6 | 1.5 to 2.9 | 12.7 to 23.2 | 1.2 to 2.5 |
| IRR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 10.6 | 7.7 | 9.8 | |||
| 95% CI | 6.7 to 16.6 | 4.9 to 12.0 | 6.2 to 15.4 | |||
For the two-step strategies using results from each IGRA with the TSTa result, the calculated IRRs were 9.6 (95% CI 6.1 to 15.3) for TSTa + T-SPOT.TB, 6.7 (95% CI 4.3 to 10.5) for TSTa + QFT-GIT and 8.6 (95% CI 5.4 to 13.8) for IGRA + TSTa. For the two-step strategies using results from each IGRA with the TSTb result, the calculated IRRs were 10.6 (95% CI 6.7 to 16.6) for TSTb + T-SPOT.TB, 7.7 (95% CI 4.9 to 12.0) for TSTb + QFT-GIT and 9.8 (95% CI 6.2 to 15.4) for IGRA + TSTa (see Tables 22 and 23). See Appendix 2, Figures 12 and 13, for tables showing the results for each step of the investigated two-step strategies.
Comparative performance of tests and test strategies
Positive predictive performance
Formal statistical comparisons of the predictive value of positive and negative results of tests and strategies showed that a positive result for TSTa was a significantly poorer predictor of progression to active TB than positive results for all other tests (TSTb, T-SPOT.TB, QFT-GIT, TSTa + T-SPOT.TB, TSTa + QFT-GIT, TSTa + IGRA, TSTb + T-SPOT.TB, TSTb + QFT-GIT and TSTb + IGRA), with TSTb + T-SPOT.TB yielding the largest difference [ratio of likelihood ratio (RLR) 2.92, 95% CI 2.40 to 3.56; p < 0.001]. Comparing positive results for tests and strategies with positive results for TSTb alone, T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.21, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.45; p = 0.037), the strategies TSTa + T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.46, 95% CI 1.23 to 1.74; p < 0.001), TSTa + IGRA (RLR 1.22, 95% CI 1.04 to 1.43; p = 0.014) and the three combination strategies including TSTb [TSTb + T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.78, 95% CI 1.51 to 2.10; p < 0.001), TSTb + QFT-GIT (RLR 1.48, 95% CI 1.24 to 1.77; p < 0.001) and TSTb + IGRA (RLR 1.57, 95% CI 1.36 to 1.82; p < 0.001)] were significantly superior predictors of progression.
When comparing positive results for tests and test strategies with positive results for T-SPOT.TB alone, TSTa + T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.21, 95% CI 1.04 to 1.40; p = 0.016), TSTb + T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.47, 95% CI 1.27 to 1.70; p < 0.001), TSTb + QFT-GIT (RLR 1.22, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.49; p = 0.041) and TSTb + IGRA (RLR 1.30, 95% CI 1.11 to 1.52; p = 0.001) were significantly superior predictors of progression. Compared with positive results for QFT-GIT alone, positive results for T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.31, 95% CI 1.13 to 1.51; p < 0.001), TSTa + T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.57, 95% CI 1.33 to 1.86; p < 0.001), TSTa + QFT-GIT (RLR 1.30, 95% CI 1.15 to 1.47; p < 0.001), TSTa + IGRA (RLR 1.32, 95% CI 1.16 to 1.51; p < 0.001), and for the three combination strategies including TSTb [TSTb + T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.92, 95% CI 1.59 to 2.32; p < 0.001), TSTb + QFT-GIT (RLR 1.60, 95% CI 1.34 to 1.91; p < 0.001) and TSTb + IGRA (RLR 1.70, 95% CI 1.43 to 2.01; p < 0.001)] were significantly superior predictors of progression.
When comparing positive results for tests and test strategies with positive results for test strategies including TSTa, compared with TSTa + T-SPOT.TB, TSTb + T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.22, 95% CI 1.09 to 1.37; p = 0.001) was a significantly superior predictor of progression; compared with TSTa + QFT-GIT, TSTa + T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.21, 95% CI 1.05 to 1.40; p = 0.007), and the three combination strategies including TSTb [TSTb + T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.48, 95% CI 1.25 to 1.75; p < 0.001), TSTb + QFT-GIT (RLR 1.23, 95% CI 1.03 to 1.48; p = 0.022) and TSTb + IGRA (RLR 1.31, 95% CI 1.14 to 1.50; p < 0.001)] were significantly superior predictors of progression; and, compared with TSTa + IGRA, the strategies TSTa + T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.19, 95% CI 1.09 to 1.31; p < 0.001), TSTb + T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.45, 95% CI 1.26 to 1.68; p = 0.001), TSTb + QFT-GIT (RLR 1.21, 95% CI 1.04 to 1.42; p = 0.016) and TSTb + IGRA (RLR 1.29, 95% CI 1.14 to 1.45; p < 0.001) were significantly superior predictors of progression.
Comparing positive results from tests and test strategies with positive results from test strategies including TSTb showed that when comparing with positive results from TSTb + QFT-GIT, positive results from TSTb + T-SPOT.TB were significantly superior predictors of progression (RLR 1.20, 95% CI 1.05 to 1.37; p = 0.007); and, also, when comparing positive results from TSTb + IGRA, positive results from TSTb + T-SPOT.TB were significantly superior predictors of progression (RLR 1.13, 95% CI 1.04 to 123; p = 0.006). Table 24 provides all results.
| Reference strategy B | Strategy A, ratio of likelihood ratios (95% CI); p-value | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSTa | TSTb | T-SPOT.TB | QFT-GIT | TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | TSTa + QFT-GIT | TSTa + IGRA | TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | TSTb + QFT-GIT | TSTb + IGRA | |
| TSTa | 1.64 (1.44 to 1.87); < 0.001 | 1.99 (1.68 to 2.34); < 0.001 | 1.52 (1.26 to 1.83); < 0.001 | 2.39 (2.03 to 2.83); < 0.001 | 1.97 (1.64 to 2.37); < 0.001 | 2.00 (1.74 to 2.32); < 0.001 | 2.92 (2.40 to 3.56); < 0.001 | 2.43 (1.96 to 3.03); < 0.001 | 2.58 (2.15 to 3.10); < 0.001 | |
| TSTb | 1.21 (1.01 to 1.45); 0.037 | 0.93 (0.76 to 1.13); 0.453 | 1.46 (1.23 to 1.74); < 0.001 | 1.20 (1.00 to 1.45); 0.054 | 1.22 (1.04 to 1.43); 0.014 | 1.78 (1.51 to 2.10); < 0.001 | 1.48 (1.24 to 1.77); < 0.001 | 1.57 (1.36 to 1.82); < 0.001 | ||
| T-SPOT.TB | 0.77 (0.66 to 0.89); < 0.001 | 1.21 (1.04 to 1.40); 0.016 | 0.99 (0.84 to 1.17); 0.935 | 1.01 (0.89 to 1.14); 0.865 | 1.47 (1.27 to 1.70); < 0.001 | 1.22 (1.01 to 1.49); 0.041 | 1.30 (1.11 to 1.52); 0.001 | |||
| QFT-GIT | 1.57 (1.33 to 1.86); < 0.001 | 1.30 (1.15 to 1.47); < 0.001 | 1.32 (1.16 to 1.51); < 0.001 | 1.92 (1.59 to 2.32); < 0.001 | 1.60 (1.34 to 1.91); < 0.001 | 1.70 (1.43 to 2.01); < 0.001 | ||||
| TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 0.82 (0.72 to 0.95); 0.007 | 0.84 (0.77 to 0.92); < 0.001 | 1.22 (1.09 to 1.37); 0.001 | 1.02 (0.86 to 1.21); 0.857 | 1.08 (0.94 to 1.23); 0.274 | |||||
| TSTa + QFT-GIT | 1.02 (0.93 to 1.11); 0.697 | 1.48 (1.25 to 1.75); < 0.001 | 1.23 (1.03 to 1.48); 0.022 | 1.31 (1.14 to 1.50); < 0.001 | ||||||
| TSTa + IGRA | 1.45 (1.26 to 1.68); < 0.001 | 1.21 (1.04 to 1.42); 0.016 | 1.29 (1.14 to 1.45); < 0.001 | |||||||
| TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 0.83 (0.73 to 0.95); 0.007 | 0.88 (0.81 to 0.97); 0.006 | ||||||||
| TSTb + QFT-GIT | 1.06 (0.97 to 1.16); 0.174 | |||||||||
| TSTb + IGRA | ||||||||||
Negative predictive performance
When evaluating the negative predictive performance of tests and strategies, negative results for TSTa + QFT-GIT were significantly poorer predictors of non-progression than negative results for TSTa (RLR 1.68, 95% CI 1.08 to 2.60; p = 0.021), T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.31, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.69; p = 0.040) and TSTa + IGRA (RLR 1.27, 95% CI 1.11 to 1.45; p = 0.001).
Negative results for TSTb + QFT-GIT were significantly poorer predictors of non-progression than negative results for TSTa (RLR 1.83, 95% CI 1.16 to 2.89; p = 0.010), TSTb (RLR 1.36, 95% CI 1.06 to 1.73; p = 0.014), T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.43, 95% CI 1.10 to 1.86; p = 0.008), TSTa + T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.30, 95% CI 1.05 to 1.60; p = 0.015), TSTa + IGRA (RLR 1.38, 95% CI 1.12 to 1.70; p = 0.002), TSTb + T-SPOT.TB (RLR 1.16, 95% CI 1.00 to 1.33; p = 0.043) and TSTb + IGRA (RLR 1.20, 95% CI 1.09 to 1.32; p < 0.001). Table 25 provides all results.
| Reference strategy B | Strategy A, ratio of likelihood ratios (95% CI); p-value | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSTa | TSTb | T-SPOT.TB | QFT-GIT | TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | TSTa + QFT-GIT | TSTa + IGRA | TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | TSTb + QFT-GIT | TSTb + IGRA | |
| TSTa | 1.35 (0.90 to 2.01); 0.147 | 1.28 (0.77 to 2.12); 0.337 | 1.60 (0.97 to 2.65); 0.065 | 1.41 (0.90 to 2.21); 0.134 | 1.68 (1.08 to 2.60); 0.021 | 1.32 (0.86 to 2.03); 0.202 | 1.58 (0.99 to 2.52); 0.053 | 1.83 (1.16 to 2.89); 0.010 | 1.52 (0.96 to 2.40); 0.071 | |
| TSTb | 0.95 (0.67 to 1.36); 0.784 | 1.19 (0.84 to 1.68); 0.319 | 1.05 (0.77 to 1.42); 0.771 | 1.25 (0.93 to 1.67); 0.142 | 0.98 (0.72 to 1.34); 0.912 | 1.17 (0.91 to 1.51); 0.212 | 1.36 (1.06 to 1.73); 0.014 | 1.13 (0.89 to 1.43); 0.305 | ||
| T-SPOT.TB | 1.25 (0.97 to 1.61); 0.081 | 1.10 (0.93 to 1.30); 0.265 | 1.31 (1.01 to 1.69); 0.040 | 1.03 (0.82 to 1.3); 0.787 | 1.24 (0.99 to 1.55); 0.067 | 1.43 (1.10 to 1.86); 0.008 | 1.19 (0.92 to 1.53); 0.186 | |||
| QFT-GIT | 0.88 (0.68 to 1.14); 0.324 | 1.05 (0.88 to 1.24); 0.601 | 0.82 (0.66 to 1.03); 0.091 | 0.99 (0.76 to 1.27); 0.916 | 1.14 (0.92 to 1.41); 0.226 | 0.95 (0.75 to 1.21); 0.668 | ||||
| TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 1.19 (0.98 to 1.44); 0.079 | 0.94 (0.80 to 1.10); 0.426 | 1.12 (0.96 to 1.31); 0.148 | 1.30 (1.05 to 1.60); 0.015 | 1.08 (0.89 to 1.31); 0.438 | |||||
| TSTa + QFT-GIT | 0.79 (0.69 to 0.90); 0.001 | 0.94 (0.77 to 1.15); 0.569 | 1.09 (0.94 to 1.27); 0.258 | 0.91 (0.76 to 1.08); 0.280 | ||||||
| TSTa + IGRA | 1.20 (0.96 to 1.48); 0.104 | 1.38 (1.12 to 1.70); 0.002 | 1.15 (0.95 to 1.39); 0.143 | |||||||
| TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 1.16 (1.00 to 1.33); 0.043 | 0.96 (0.86 to 1.07); 0.492 | ||||||||
| TSTb + QFT-GIT | 0.83 (0.76 to 0.92); < 0.001 | |||||||||
| TSTb + IGRA | ||||||||||
Association of participant risk factors and progression to active tuberculosis
For the 6380 participants included in the main analysis, further analyses to identify associations of participants’ demographic characteristics and risk factors with progression to active TB identified that an increased body mass index (BMI) was associated with a lower IR of progression to active TB (IRR 0.92, 95% CI 0.86 to 0.97; p = 0.003). A borderline significant association was seen with haematological malignancy; however, only one participant with haematological malignancy progressed to active TB (Tables 26 and 27).
| Demographic characteristic | Progression to active TB? | IRR | 95% CI | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | ||||
| Sex (n) | |||||
| Male | 3173 | 40 | – | – | – |
| Female | 3103 | 37 | 0.98 | 0.63 to 1.54 | 0.940 |
| Missing | 27 | 0 | – | – | – |
| Participant type (n) | |||||
| TB contact | 3513 | 51 | – | – | – |
| New entrant | 2790 | 26 | 0.70 | 0.44 to 1.13 | 0.143 |
| Ethnicity (n) | |||||
| Indian | 2257 | 31 | – | – | – |
| White | 817 | 9 | 0.82 | 0.39 to 1.72 | 0.596 |
| Black African | 846 | 7 | 0.57 | 0.25 to 1.30 | 0.184 |
| Mixed | 642 | 7 | 0.78 | 0.34 to 1.76 | 0.545 |
| Pakistani | 644 | 10 | 1.11 | 0.55 to 2.27 | 0.769 |
| Bangladeshi | 555 | 4 | 0.54 | 0.19 to 1.53 | 0.244 |
| Black Caribbean | 156 | 4 | 1.66 | 0.58 to 4.69 | 0.342 |
| Other | 222 | 5 | 1.77 | 0.69 to 4.54 | 0.238 |
| Missing | 164 | 0 | – | – | – |
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 31 (25–42) | 30 (26–38) | 0.99 | 0.97 to 1.01 | 0.202 |
| Age (years) (n) | |||||
| ≤ 35 | 4008 | 52 | – | – | – |
| > 35 | 2294 | 25 | 0.85 | 0.53 to 1.37 | 0.499 |
| Missing | 1 | 0 | – | – | – |
| UK born (n) | |||||
| No | 5277 | 64 | – | – | – |
| Yes | 1011 | 13 | 1.03 | 0.57 to 1.87 | 0.921 |
| Missing | 15 | 0 | – | – | – |
| Risk factor | Progression to active TB? | IRR | 95% CI | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | ||||
| Previous TB contact (n) | 746 | 12 | 1.37 | 0.74 to 2.54 | 0.318 |
| Previous TB diagnosis (n) | 152 | 2 | 1.03 | 0.25 to 4.19 | 0.968 |
| BCG vaccination (n) | 4553 | 57 | 1.17 | 0.60 to 2.29 | 0.650 |
| Diabetes mellitus (n) | 411 | 4 | – | – | – |
| Haematological malignancy (n) | 10 | 1 | 6.76 | 0.94 to 48.61 | 0.058 |
| HIV positive (n) | 40 | 0 | – | – | – |
| Smoker (n) | 1277 | 15 | 0.92 | 0.53 to 1.62 | 0.781 |
| Previous transplant (n) | 12 | 0 | – | – | – |
| Anti-TNF-α (n) | 18 | 0 | – | – | – |
| Immunosuppressive drugs (n) | 40 | 0 | – | – | – |
| Problem drug use (n) | 141 | 4 | 2.23 | 0.82 to 6.10 | 0.118 |
| Homeless (n) | 120 | 3 | 1.80 | 0.57 to 5.70 | 0.320 |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean (SD) | 24.5 (4.7) | 22.8 (4.5) | 0.92 | 0.86 to 0.97 | 0.003 |
| Occupation (n) | |||||
| Education | 1239 | 16 | – | – | – |
| Health care | 254 | 3 | 0.90 | 0.26 to 3.08 | 0.865 |
| Social/prison sector | 32 | 1 | 2.40 | 0.32 to 18.07 | 0.395 |
| Laboratory/pathology | 12 | 0 | – | – | – |
| Agriculture/animal care | 0 | 0 | – | – | – |
| None | 1943 | 22 | 0.93 | 0.49 to 1.77 | 0.820 |
| Other | 2510 | 32 | 1.07 | 0.59 to 1.95 | 0.818 |
| Unknown | 313 | 3 | – | – | – |
| Travela in the last 3 years (n) | 2014 | 18 | 0.66 | 0.38 to 1.13 | 0.128 |
| Travela before the last 3 years (n) | 1738 | 21 | 1.13 | 0.66 to 1.91 | 0.660 |
Test performance in new entrants and contacts
The test performance for new entrants and contacts (separately) is shown in Table 28; CIs for the IRRs among contacts and new entrants overlapped for all tests. Point estimates of IRRs were higher among new entrants than contacts for T-SPOT.TB, QFT-GIT and TSTb, but not for TSTa. The difference was more marked for T-SPOT.TB for new entrants (IRR 15.7, 95% CI 5.9 to 41.6) than for contacts (IRR 7.2, 95% CI 4.1 to 12.7).
| Progression measure | Test and result | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-SPOT.TB | QFT-GIT | TSTa | TSTb | |||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| New entrants only | ||||||||
| Progression (n/N) | 21/587 | 5/2229 | 17/651 | 9/2165 | 21/1253 | 5/1563 | 18/586 | 8/2230 |
| Years at risk | 1826.0 | 6823.5 | 2036.0 | 6613.4 | 3874.5 | 4775.0 | 1812.4 | 6837.0 |
| IR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 11.5 | 0.7 | 8.3 | 1.4 | 5.4 | 1.0 | 9.9 | 1.2 |
| 95% CI | 7.1 to 17.6 | 0.2 to 1.7 | 4.9 to 13.4 | 0.6 to 2.6 | 3.4 to 8.3 | 0.3 to 2.4 | 5.9 to 15.7 | 0.5 to 2.3 |
| IRR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 15.7 | 6.1 | 5.2 | 8.5 | ||||
| 95% CI | 5.9 to 41.6 | 2.7 to 13.8 | 2.0 to 13.7 | 3.7 to 19.5 | ||||
| Contacts only | ||||||||
| Progression (n/N) | 31/648 | 20/2916 | 30/793 | 21/2771 | 43/1704 | 8/1860 | 34/899 | 17/2665 |
| Years at risk | 2100.1 | 9821.8 | 2613.8 | 9308.2 | 5542.3 | 6379.6 | 2862.4 | 9059.6 |
| IR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 14.8 | 2.0 | 11.5 | 2.3 | 7.8 | 1.3 | 11.9 | 1.9 |
| 95% CI | 10.0 to 21.0 | 1.2 to 3.1 | 7.7 to 16.4 | 1.4 to 3.4 | 5.6 to 10.5 | 0.5 to 2.5 | 8.2 to 16.6 | 1.1 to 3.0 |
| IRR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 7.2 | 5.1 | 6.2 | 6.3 | ||||
| 95% CI | 4.1 to 12.7 | 2.9 to 8.9 | 2.9 to 13.2 | 3.5 to 11.3 | ||||
Test performance by demographic group
Table 26 provides further subgroup analysis by age, gender and ethnic group, showing the number of participants progressing to active TB and the IRR for each demographic group. Although there is variation by subgroup, the observed differences were not significant.
Use of Mantoux testing
The difference between the two outcomes of Mantoux testing (TSTa and TSTb) is shown further in Appendix 2, with the combination of results highlighting the additional number of positive results for TSTa compared with TSTb.
Sensitivity analyses
Sensitivity analyses were performed excluding those participants with assumed BCG vaccination status, excluding participants with an unclear progression status, using all available test results rather than only using participants with all test results available, using data from new entrants with 2 years of follow-up only and using data for contacts of pulmonary TB patients only. The results of these analyses are provided in Appendix 2, Tables 50–55.
Chapter 4 Results: economic analysis
Base-case analysis
Stability of results by number of iterations
For the base-case analyses, we performed 5000 PSA iterations for each strategy, using bootstrap samples of 4162 patients for contacts and 3795 for new entrants for each iteration (reflecting the sample sizes available for economic analysis).
Figure 10 shows the incremental effects (mean discounted QALYs per patient for each strategy compared with the ‘no test’ strategy) for contacts and new entrants at increasing numbers of PSA iterations. The estimates and ranking of test strategies by incremental effect stabilise after around 3500 iterations in the contacts subgroup. Results are less stable in the new entrant subgroup, and there is still some swapping of position among strategies at the cut-off point of 5000 runs. Owing to the very small QALY differences between strategies, longer runs are required to rank strategies confidently according to effectiveness alone, but, at a runtime of about 2 hours per strategy for 5000 iterations, additional runs are computationally prohibitive.
FIGURE 10.
Incremental effectiveness (compared with ‘no test’) by number of iterations. (a) Contacts; and (b) migrants.
Figure 11 shows incremental net benefit (INB) estimates for the contacts and new entrant subgroups; these are the mean monetary values per patient for each strategy compared with the ‘no test’ strategy, with QALYs valued at £20,000 (the lower end of the cost-effectiveness threshold range used by NICE). It can be seen that INB is much more stable than QALYs, resolving after about 250 iterations. This suggests that INB differences between strategies are largely driven by cost differences rather than by QALYs.
FIGURE 11.
Incremental net benefit (compared with ‘no test’) by number of iterations. (a) Contacts; and (b) migrants.
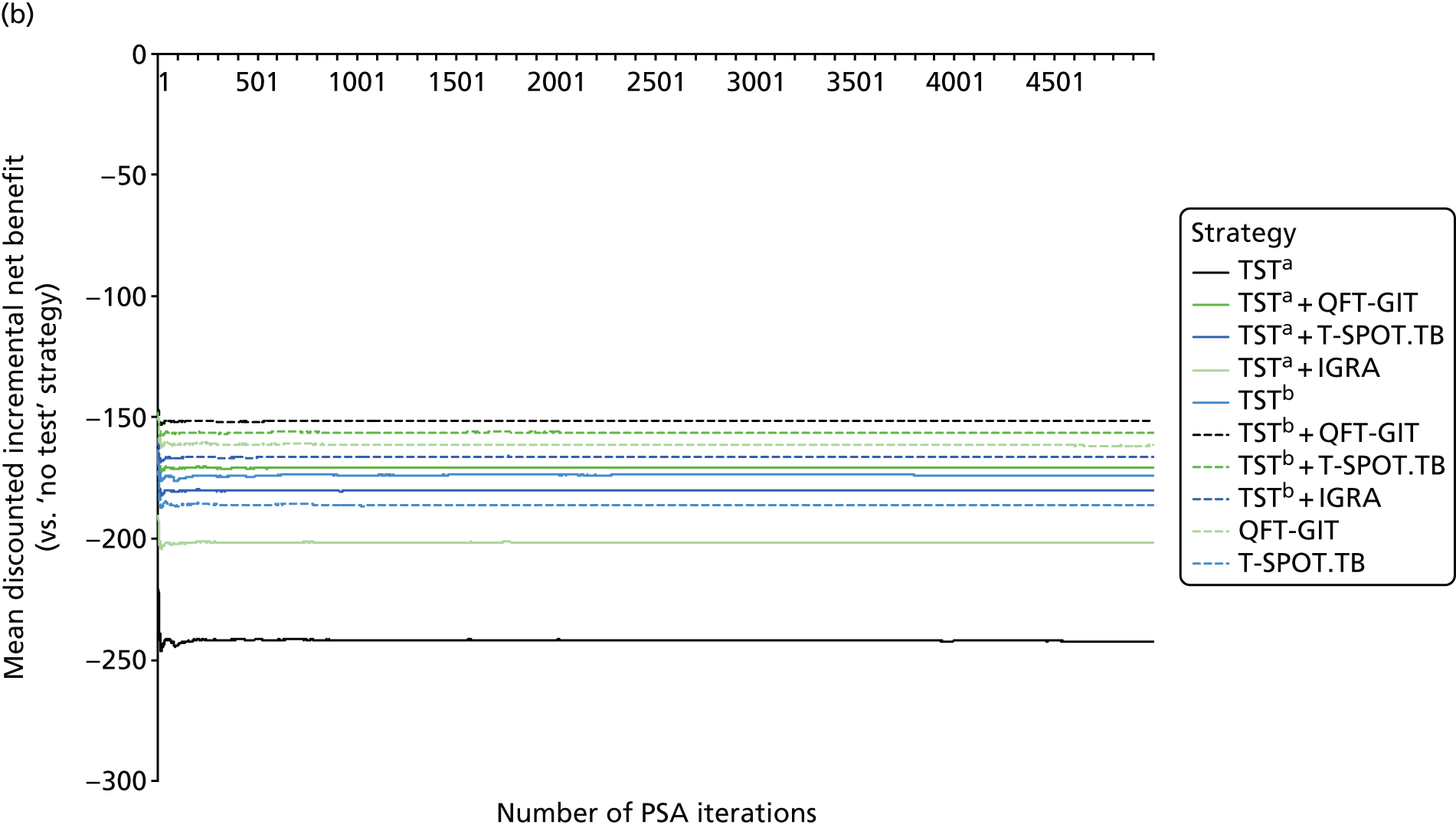
Clinical outcomes
Key health outcomes from the base-case analysis are shown in Tables 29 and 30 for the contacts and new entrant subgroups, respectively. Strategies are ranked by undiscounted QALYs. It can be seen that without testing or preventative treatment (no test), the estimated mean life expectancy was approximately 47 years for contacts and 44 years for new entrants; these estimates reflect the lower mean age of contacts at baseline in the PREDICT cohort. The mean numbers of QALYs per participant in the contacts and new entrant subgroups were 46.01 and 42.96, respectively. The small differences between QALY and life-year estimates can be explained the high baseline EQ-5D scores for PREDICT participants. The simulated number of TB cases (over the lifetime horizon) per 10,000 people without testing was 189 for contacts and 179 for new entrants. This equates to an annual rate of approximately 42 cases per 100,000 people. For comparison, the rate of TB in the non-UK-born population of England in 2015 was 51 cases per 100,000 people. 116 However, the use of a fitted Weibull distribution in our model to estimate the long-term incidence from PREDICT data means that the simulated incidence was much higher in the first year and levelled off over time.
| Strategy | Number of cases (per 10,000 patients offered LTBI test) | Mean per patient (undiscounted) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TB | BCG | Started CPX | CPX AE | Started treatment for active TB | Treatment for active TB AE | Life-years | QALYs | |
| 10: no test | 189 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 189 | 0.8 | 46.91772 | 46.00851 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 162 | 665 | 365 | 1.6 | 162 | 0.6 | 46.91782 | 46.00903 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 160 | 665 | 533 | 2.3 | 160 | 0.6 | 46.91781 | 46.00903 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 161 | 665 | 361 | 1.6 | 161 | 0.6 | 46.91783 | 46.00903 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 161 | 665 | 474 | 2.1 | 161 | 0.6 | 46.91782 | 46.00904 |
| 8: QFT-GIT | 157 | 606 | 858 | 3.7 | 157 | 0.6 | 46.91778 | 46.00906 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 158 | 615 | 668 | 2.9 | 158 | 0.6 | 46.91780 | 46.00907 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 158 | 645 | 438 | 1.9 | 158 | 0.6 | 46.91784 | 46.00910 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 156 | 645 | 648 | 2.8 | 156 | 0.6 | 46.91782 | 46.00910 |
| 4: TSTb | 152 | 531 | 1078 | 4.6 | 152 | 0.5 | 46.91783 | 46.00917 |
| 0: TSTa | 145 | 522 | 2192 | 9.6 | 145 | 0.5 | 46.91775 | 46.00921 |
| Strategy | Number of cases (per 10,000 patients offered LTBI test) | Mean per patient (undiscounted) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TB | BCG | Started CPX | CPX AE | Started treatment for active TB | Treatment for active TB AE | Life-years | QALYs | |
| 10: no test | 179 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 179 | 0.7 | 44.44023 | 42.96137 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 145 | 1132 | 580 | 2.5 | 145 | 0.5 | 44.44031 | 42.96193 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 146 | 1147 | 401 | 1.8 | 146 | 0.5 | 44.44034 | 42.96195 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 145 | 1129 | 578 | 2.5 | 145 | 0.5 | 44.44031 | 42.96195 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 146 | 1144 | 407 | 1.8 | 146 | 0.5 | 44.44033 | 42.96195 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 142 | 1097 | 709 | 3.1 | 142 | 0.5 | 44.44032 | 42.96200 |
| 8: QFT-GIT | 139 | 1040 | 974 | 4.2 | 139 | 0.5 | 44.44028 | 42.96200 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 143 | 1122 | 473 | 2.1 | 143 | 0.5 | 44.44035 | 42.96201 |
| 4: TSTb | 141 | 936 | 832 | 3.7 | 141 | 0.5 | 44.44032 | 42.96202 |
| 0: TSTa | 135 | 884 | 1815 | 8.0 | 135 | 0.4 | 44.44023 | 42.96202 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 138 | 1074 | 905 | 4.0 | 138 | 0.5 | 44.44032 | 42.96205 |
The QALY estimates were higher in all of the LTBI testing strategies than for the ‘no test’ strategy. This was generally because of the lower number of TB cases predicted, attributable to the use of preventative treatments (CPX). It should be noted, however, that QALYs are not always directly related to the number of TB cases because of QALY losses as a result of adverse reactions to CPX; for example, in the new entrant subgroup, although there are three fewer TB cases with TSTa than with T-SPOT.TB, there are also four more CPX-related adverse events, and, hence, mean QALYs are slightly lower with TSTa than with T-SPOT.TB.
A further ranking of strategies by the number of TB cases that were prevented (compared with ‘no test’), cases in which CPX was started and cases in which BCG vaccination was offered is presented in Table 31.
| TB cases prevented* | Cases in which | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategy | n | CPX was started | BCG vaccination was offered | ||
| Strategy | n | Strategy | n | ||
| Contacts | |||||
| 10: no test | 0.0 | 11: no test | 0.0 | 11: no test | 0.0 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 27.3 | 7: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 361.0 | 1: TSTa | 522.4 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 27.4 | 6: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 365.4 | 5: TSTb | 531.4 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 28.2 | 8: TSTb + IGRA | 437.8 | 9: QFT-GIT | 605.8 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 28.5 | 3: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 473.9 | 10: T-SPOT.TB | 615.0 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 31.0 | 2: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 532.7 | 8: TSTb + IGRA | 644.7 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 31.2 | 4: TSTa + IGRA | 647.9 | 4: TSTa + IGRA | 644.7 |
| 8: QFT-GIT | 32.3 | 10: T-SPOT.TB | 668.1 | 6: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 665.0 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 32.5 | 9: QFT-GIT | 858.0 | 2: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 665.0 |
| 4: TSTb | 36.9 | 5: TSTb | 1077.7 | 7: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 665.0 |
| 0: TSTa | 44.3 | 1: TSTa | 2191.7 | 3: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 665.0 |
| New entrants | |||||
| 10: no test | 0.0 | 11: no test | 0.0 | 11: no test | 0.0 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 32.3 | 6: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 401.3 | 1: TSTa | 883.9 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 32.7 | 7: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 406.6 | 5: TSTb | 935.7 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 33.4 | 8: TSTb + IGRA | 473.2 | 9: QFT-GIT | 1039.7 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 33.7 | 3: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 577.9 | 10: T-SPOT.TB | 1074.5 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 35.7 | 2: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 579.7 | 4: TSTa + IGRA | 1097.2 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 37.1 | 4: TSTa + IGRA | 708.6 | 8: TSTb + IGRA | 1121.8 |
| 4: TSTb | 37.7 | 5: TSTb | 832.1 | 3: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 1129.2 |
| 8: QFT-GIT | 40.0 | 10: T-SPOT.TB | 905.3 | 2: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 1132.0 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 40.2 | 9: QFT-GIT | 973.8 | 7: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 1144.0 |
| 0: TSTa | 44.0 | 1: TSTa | 1814.8 | 6: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 1146.7 |
Cost-effectiveness
Tables 32 and 33 show the estimated mean discounted costs and QALYs per participant by strategy under the base-case analysis, for the two subgroups. The ‘no test’ strategy had the lowest costs and QALYs. The incremental costs for the LTBI testing strategies compared with ‘no test’ were between £156 (TSTb + QFT-GIT) and £273 (TSTa) for contacts and between £155 (TSTb + QFT-GIT) and £247 (TSTa) for new entrants. The additional cost yielded few extra QALYs; there was a mean gain of around 0.0002 per patient. Although none of the strategies under this base-case scenario appeared to be cost-effective compared with ‘no test’, the primary objective of this study was to assess the most cost-effective test or combination of tests and not to assess the cost-effectiveness of contact tracing or migrant tracing. Other QALY benefits will accrue from contact tracing and migrant screening through the detection of active TB and from the prevention of subsequent transmission, which we have not accounted for in the base case. Nevertheless, the comparison of strategies remains valid as the probable subsequent benefit was directly proportional to the extent to which each testing strategy prevented incident cases.
| Strategy | Mean per patient (discounted) | Incremental (vs. no test) | INB* (£) | Probability† (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (£) | QALYs | Cost (£) | QALYs | |||
| 0: TSTa | 301.53 | 22.131076 | 272.96 | 0.0002367 | –268.22 | 0.0 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 241.73 | 22.131048 | 213.15 | 0.0002081 | –208.99 | 0.0 |
| 4: TSTb | 224.24 | 22.131074 | 195.67 | 0.0002347 | –190.97 | 0.0 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 212.93 | 22.131021 | 184.36 | 0.0001811 | –180.74 | 0.0 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 205.05 | 22.131047 | 176.48 | 0.0002076 | –172.33 | 0.0 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT | 204.41 | 22.131019 | 175.84 | 0.0001788 | –172.26 | 0.0 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 204.07 | 22.131031 | 175.49 | 0.0001917 | –171.66 | 0.0 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 191.09 | 22.131021 | 162.51 | 0.0001808 | –158.90 | 0.7 |
| 8: QFT | 187.25 | 22.131027 | 158.68 | 0.0001872 | –154.94 | 35.6 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT | 184.73 | 22.131019 | 156.16 | 0.0001795 | –152.57 | 63.7 |
| 10: no test | 28.57 | 22.13084 | 0.00 | 0.0000000 | 0.00 | – |
| Strategy | Mean per patient (discounted) | Incremental (vs. no test) | INB* (£) | Probability† (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (£) | QALYs | Cost (£) | QALYs | |||
| 0: TSTa | 273.62 | 21.042235 | 246.59 | 0.0002179 | –242.23 | 0.0 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 233.06 | 21.042235 | 206.03 | 0.0002178 | –201.67 | 0.0 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 218.03 | 21.042253 | 191.00 | 0.0002359 | –186.28 | 0.0 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 211.15 | 21.042212 | 184.12 | 0.0001949 | –180.22 | 0.0 |
| 4: TSTb | 205.43 | 21.042244 | 178.40 | 0.0002272 | –173.86 | 0.0 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT | 201.63 | 21.042205 | 174.60 | 0.0001881 | –170.84 | 0.0 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 197.80 | 21.042242 | 170.77 | 0.0002249 | –166.27 | 0.0 |
| 8: QFT | 192.88 | 21.042230 | 165.85 | 0.0002134 | –161.58 | 3.8 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 187.27 | 21.042215 | 160.24 | 0.0001983 | –156.27 | 2.4 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT | 182.32 | 21.042213 | 155.29 | 0.0001963 | –151.36 | 93.7 |
| 10: no test | 27.03 | 21.042017 | 0.00 | 0.0000000 | 0.00 | – |
The most cost-effective of the LTBI strategies was TSTb + QFT-GIT because, although the QALY gain was lower than for some of the other strategies (e.g. TSTb alone in both subgroups), it was cheaper. The estimated INB differences between the LTBI test strategies were small. In particular, in both subgroups, very similar INB estimates were obtained for the three most cost-effective test strategies: (1) TSTb + QFT-GIT, (2) TSTb + T-SPOT.TB and (3) QFT-GIT alone. Despite this, the conclusion that TSTb + QFT-GIT was the most cost-effective of the LTBI test strategies was relatively robust in the PSA. In the contacts subgroup, the estimated probability that TSTb + QFT-GIT was the most cost-effective of the LTBI test strategies was 64%, followed by QFT-GIT alone (with 36% probability). Using a higher cost-effectiveness threshold of £30,000 per QALY gained, the estimated probabilities were 59% for TSTb + QFT-GIT and 39% for QFT-GIT alone. In the new entrant subgroup, the estimated probability that TSTb + QFT-GIT was the most cost-effective of the LTBI test strategies was 94% at a cost-effectiveness threshold of £20,000 per QALY and 87% at a cost-effectiveness threshold of £30,000 per QALY.
Sensitivity analyses
We conducted a number of one-way and two-way sensitivity analyses to test the robustness of the base-case results to key uncertainties in model parameters. The results for most sensitivity analyses were estimated from 500 PSA iterations. Although longer model runs are preferred, these analyses offer fairly robust indications of how parameter changes are likely to influence cost-effectiveness.
Doubled baseline incidence of tuberculosis in both subgroups
When the baseline incidence of TB was doubled for contacts (Table 34), compared with the base-case analysis (see Table 32) only the TSTa + QFT and TSTb + IGRA strategies swap positions. In the new entrants’ subgroup, doubling the baseline incidence of TB does not alter the position of strategies and the difference in probability of cost-effectiveness is marginal (Table 35). Although the increasing costs observed with doubling the TB incidence accrues from treating more TB cases, the lowered INBs suggest that the LTBI test strategies become more cost-effective at higher TB incidences.
| Strategy | Mean per patient (discounted) | Incremental (vs. no test) | INB* (£) | Probability† (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (£) | QALYs | Cost (£) | QALYs | |||
| 0: TSTa | 321.64 | 22.112022 | 266.04 | 0.0005891 | –254.26 | 0 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 264.09 | 22.111876 | 208.50 | 0.0004435 | –199.63 | 0 |
| 4: TSTb | 245.71 | 22.111962 | 190.12 | 0.0005292 | –179.53 | 0 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 235.90 | 22.111813 | 180.30 | 0.0003803 | –172.70 | 0 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 227.36 | 22.111821 | 171.76 | 0.0003876 | –164.01 | 0 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 227.56 | 22.111866 | 171.96 | 0.0004335 | –163.29 | 0 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 226.54 | 22.111830 | 170.95 | 0.0003973 | –163.00 | 0 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 214.12 | 22.111801 | 158.53 | 0.0003676 | –151.18 | 1 |
| 8: QFT-GIT | 209.72 | 22.111825 | 154.13 | 0.0003918 | –146.29 | 47 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 207.74 | 22.111815 | 152.15 | 0.0003817 | –144.52 | 52 |
| 10: no test | 55.59 | 22.111433 | 0.00 | 0.0000000 | 0.00 | – |
| Strategy | Mean per patient (discounted) | Incremental (vs. no test) | INB* (£) | Probability† (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (£) | QALYs | Cost (£) | QALYs | |||
| 0: TSTa | 292.83 | 21.025638 | 239.92 | 0.0005958 | –228.00 | 0 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 253.59 | 21.025557 | 200.68 | 0.0005144 | –190.39 | 0 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 237.81 | 21.025593 | 184.90 | 0.0005507 | –173.89 | 0 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 232.12 | 21.025512 | 179.21 | 0.0004695 | –169.82 | 0 |
| 4: TSTb | 225.86 | 21.025552 | 172.95 | 0.0005102 | –162.75 | 0 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 222.65 | 21.025478 | 169.74 | 0.0004361 | –161.01 | 0 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 218.61 | 21.025536 | 165.70 | 0.0004941 | –155.81 | 0 |
| 8: QFT-GIT | 212.66 | 21.025574 | 159.75 | 0.0005312 | –149.12 | 13 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 208.52 | 21.025496 | 155.61 | 0.0004535 | –146.54 | 5 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 203.53 | 21.025463 | 150.62 | 0.0004203 | –142.22 | 82 |
| 10: no test | 52.91 | 21.025042 | 0.00 | 0.0000000 | 0.00 | – |
Decreased cost per patient of T-SPOT.TB to equal that of QuantiFERON TB Gold In Tube
Compared with the base-case cost-effectiveness results, Tables 36 and 37 show that when the costs of T-SPOT.TB and QFT-GIT are equal, at £41, the T-SPOT.TB -based LTBI strategies become optimal. Among contacts, T-SPOT.TB was the most cost-effective strategy, whereas TSTb + T-SPOT.TB was the most cost-effective strategy among new entrants.
| Strategy | Mean per patient (discounted) | Incremental (vs. no test) | INB* (£) | Probability† (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (£) | QALYs | Cost (£) | QALYs | |||
| 0: TSTa | 301.33 | 22.134428 | 272.38 | 0.0002381 | –267.62 | 0 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 229.49 | 22.134375 | 200.54 | 0.0001853 | –196.83 | 0 |
| 4: TSTb | 224.36 | 22.134422 | 195.40 | 0.0002329 | –190.74 | 0 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 204.75 | 22.134354 | 175.79 | 0.0001647 | –172.50 | 0 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 200.70 | 22.134348 | 171.74 | 0.0001586 | –168.57 | 0 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 198.67 | 22.134373 | 169.71 | 0.0001838 | –166.03 | 0 |
| 8: QFT-GIT | 187.69 | 22.134321 | 158.73 | 0.0001318 | –156.10 | 0 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 184.72 | 22.134340 | 155.76 | 0.0001509 | –152.74 | 1 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 184.99 | 22.134356 | 156.03 | 0.0001665 | –152.70 | 0 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 174.38 | 22.134336 | 145.42 | 0.0001467 | –142.49 | 99 |
| 10: no test | 28.96 | 22.134189 | 0.00 | 0.0000000 | 0.00 | – |
| Strategy | Mean per patient (discounted) | Incremental (vs. no test) | INB* (£) | Probability† (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (£) | QALYs | Cost (£) | QALYs | |||
| 0: TSTa | 273.49 | 21.045602 | 246.11 | 0.0002356 | –241.40 | 0 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 223.57 | 21.045583 | 196.19 | 0.0002165 | –191.86 | 0 |
| 4: TSTb | 205.62 | 21.045569 | 178.25 | 0.0002025 | –174.20 | 0 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 201.82 | 21.045546 | 174.44 | 0.0001788 | –170.87 | 0 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 201.63 | 21.045569 | 174.25 | 0.0002023 | –170.20 | 0 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 193.45 | 21.045575 | 166.07 | 0.0002079 | –161.91 | 0 |
| 8: QFT-GIT | 192.83 | 21.045586 | 165.46 | 0.0002190 | –161.08 | 1 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 188.04 | 21.04560 | 160.66 | 0.0002336 | –155.99 | 16 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 182.55 | 21.045539 | 155.17 | 0.0001718 | –151.74 | 46 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 182.94 | 21.045563 | 155.57 | 0.0001959 | –151.65 | 38 |
| 10: no test | 27.38 | 21.045367 | 0.00 | 0.0000000 | 0.00 | – |
Further increased baseline incidence by multiples of 2 for TSTb + QuantiFERON TB Gold In-Tube compared with no test
In Tables 38 and 39, the baseline incidence of TB is increased by multiples of 2 and the comparison is only between TSTb + QFT-GIT and no test. This analysis was carried out to explore a TB incidence threshold or range for cost-effectiveness and for model validation, rather than to explore cost-effectiveness among LTBI test strategies. TSTb + QFT-GIT appeared to become cost-effective at a lower incidence in new entrants than in contacts. However, the high incidences that are required to achieve cost-effectiveness in both subgroups (compared with no test) are probably overestimated, as the analysis did not account for the benefits from LTBI testing, because the number of individuals who were offered CPX or a BCG vaccination was fixed at for all scenarios.
| Incidence | Mean per patient (discounted) | Incremental (vs. no test) | INB* (£) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (£) | QALYs | Cost (£) | QALYs | ||
| Incidence X4 | 250.22 | 22.07031 | 145.25 | 0.000829 | –128.66 |
| Incidence X8 | 329.25 | 21.99264 | 134.06 | 0.00178 | –98.47 |
| Incidence X16 | 457.58 | 21.85984 | 119.08 | 0.003896 | –41.16 |
| Incidence X18 | 490.25 | 21.82729 | 116.49 | 0.004309 | –30.32 |
| Incidence X20 | 515.22 | 21.80021 | 114.38 | 0.004800 | –18.39 |
| Incidence X22 | 533.86 | 21.78072 | 112.94 | 0.005150 | –9.94 |
| Incidence X26 | 582.56 | 21.72964 | 109.58 | 0.006059 | 11.60 |
| Incidence | Mean per patient (discounted) | Incremental (vs. no test) | INB* (£) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (£) | QALYs | Cost (£) | QALYs | ||
| Incidence X4 | 242.89 | 20.98666 | 142.37 | 0.000897 | –124.44 |
| Incidence X8 | 316.03 | 20.91454 | 128.50 | 0.001999 | –88.51 |
| Incidence X16 | 436.56 | 20.79132 | 109.68 | 0.004382 | –22.04 |
| Incidence X18 | 467.96 | 20.76073 | 106.11 | 0.004839 | –9.33 |
| Incidence X20 | 492.26 | 20.73590 | 103.20 | 0.005407 | 4.94 |
| Incidence X22 | 510.24 | 20.71721 | 100.97 | 0.005792 | 14.86 |
| Incidence X26 | 557.77 | 20.66879 | 96.15 | 0.00679 | 39.65 |
Changed chemoprophylaxis uptake to 59.9% and chemoprophylaxis completion rate to 57%, as stated in the Tuberculosis in England 2016 report2
We tested lower proportions of CPX uptake (59.9%) and CPX completion (57%) as reported in the Tuberculosis in England 2016 report. 2 Tables 40 and 41 indicate that, with fewer individuals being offered CPX and completing CPX, QFT-GIT was the most cost-effective LTBI strategy with a probability of cost-effectiveness of 98% for contacts and 84% for new entrants.
| Strategy | Mean per patient (discounted) | Incremental (vs. no test) | INB* (£) | Probability† (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (£) | QALYs | Cost (£) | QALYs | |||
| 0: TSTa | 249.02 | 22.13418 | 220.06 | –0.000005 | –220.15 | 0 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 226.93 | 22.13420 | 197.98 | 0.000014 | –197.69 | 0 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 202.27 | 22.13421 | 173.31 | 0.000016 | –172.99 | 0 |
| 4: TSTb | 198.88 | 22.13422 | 169.92 | 0.000035 | –169.21 | 0 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 195.30 | 22.13421 | 166.34 | 0.000023 | –165.89 | 0 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT | 192.29 | 22.13421 | 163.33 | 0.000018 | –162.96 | 0 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 188.68 | 22.13417 | 159.73 | –0.000016 | –160.04 | 0 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 183.12 | 22.13420 | 154.16 | 0.000013 | –153.90 | 0 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT | 176.61 | 22.13422 | 147.65 | 0.000027 | –147.11 | 2 |
| 8: QFT | 167.34 | 22.13415 | 138.39 | –0.000039 | –139.17 | 98 |
| 10: no test | 28.96 | 22.13419 | 0.00 | 0.0000000 | 0.00 | – |
| Strategy | Mean per patient (discounted) | Incremental (vs. no test) | INB* (£) | Probability† (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (£) | QALYs | Cost (£) | QALYs | |||
| 0: TSTa | 230.28 | 21.04539 | 202.90 | 0.000021 | –202.48 | 0 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 216.77 | 21.04541 | 189.40 | 0.000047 | –188.45 | 0 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 197.92 | 21.04542 | 170.55 | 0.000054 | –169.47 | 0 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 196.84 | 21.04541 | 169.46 | 0.000041 | –168.63 | 0 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT | 188.40 | 21.04540 | 161.02 | 0.000036 | –160.30 | 0 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 187.25 | 21.04541 | 159.88 | 0.000045 | –158.97 | 0 |
| 4: TSTb | 186.12 | 21.04539 | 158.75 | 0.000023 | –158.28 | 0 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 178.26 | 21.04542 | 150.88 | 0.000053 | –149.83 | 0 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT | 173.40 | 21.04540 | 146.03 | 0.000034 | –145.34 | 16 |
| 8: QFT-GIT alone | 170.04 | 21.04540 | 142.66 | 0.000034 | –141.97 | 84 |
| 10: no test | 27.38 | 21.04537 | 0.00 | 0.000000 | 0.00 | – |
Used a 20-year time horizon
Compared with a lifetime horizon in the base case, Tables 42 and 43 show an almost identical ordering of strategies. However, there is a huge drop in QALYs, from about 22.0 to 14.0 in contacts and from about 21.0 to 13.6 in new entrants. Compared with QALYs, the drop in costs from the base case is negligible.
| Strategy | Mean per patient (discounted) | Incremental (vs. no test) | INB* (£) | Probability† (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (£) | QALYs | Cost (£) | QALYs | |||
| 0: TSTa | 298.94 | 13.99950 | 273.40 | 0.000506 | –263.27 | 0 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 239.42 | 13.99937 | 213.88 | 0.000376 | –206.36 | 0 |
| 4: TSTb | 221.80 | 13.99944 | 196.26 | 0.000441 | –187.44 | 0 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 210.54 | 13.99932 | 184.99 | 0.000325 | –178.49 | 0 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 202.00 | 13.99932 | 176.45 | 0.000326 | –169.92 | 0 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 202.66 | 13.99936 | 177.11 | 0.000363 | –169.86 | 0 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 201.71 | 13.99934 | 176.16 | 0.000343 | –169.30 | 0 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 188.63 | 13.99931 | 163.09 | 0.000313 | –156.82 | 0 |
| 8: QFT-GIT | 185.02 | 13.99933 | 159.47 | 0.000338 | –152.72 | 38 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 182.21 | 13.99931 | 156.67 | 0.000318 | –150.30 | 62 |
| 10: no test | 25.55 | 13.99899 | 0.00 | 0.000000 | 0.00 | – |
| Strategy | Mean per patient (discounted) | Incremental (vs. no test) | INB* (£) | Probability† (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (£) | QALYs | Cost (£) | QALYs | |||
| 0: TSTa | 271.35 | 13.62039 | 247.11 | 0.000487 | –237.37 | 0 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 230.96 | 13.62032 | 206.72 | 0.000413 | –198.46 | 0 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 215.81 | 13.62036 | 191.57 | 0.000451 | –182.54 | 0 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 208.95 | 13.62028 | 184.71 | 0.000376 | –177.18 | 0 |
| 4: TSTb | 203.33 | 13.62032 | 179.09 | 0.000412 | –170.85 | 0 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT | 199.44 | 13.62027 | 175.20 | 0.000360 | –168.00 | 0 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 195.73 | 13.62030 | 171.49 | 0.000396 | –163.56 | 0 |
| 8: QFT | 190.61 | 13.62035 | 166.37 | 0.000440 | –157.58 | 5 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 185.16 | 13.62027 | 160.92 | 0.000363 | –153.65 | 2 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT | 180.14 | 13.62025 | 155.90 | 0.000346 | –148.97 | 93 |
| 10: no test | 24.24 | 13.61991 | 0.00 | 0.000000 | 0.00 | – |
Allowing for transmission
The results for a modelled transmission scenario are reported in Appendix 2, Tables 58 and 59. Our approach to modelling transmission was based on the assumption that, for every case of active TB in the original cohorts (4162 in the contacts subgroup and 3795 in the new entrants subgroup), four new secondary contacts were traced. The traced contacts, drawn randomly from the original contacts cohort, were introduced into the model and subsequently followed the same pathway as individuals from the original cohort. For instance, of 4162 participants in the original cohort, 79 developed active TB (i.e. there were 79 index cases, each accounting for four secondary cases randomly drawn into the model) (see Appendix 2, Table 58). The number of secondary cases is slightly higher than the sum of 4 and 79 because some of the secondary contacts also develop active TB, resulting in additional participants being introduced into the model.
Chapter 5 Discussion
Main findings
Diagnostic accuracy
We assessed the ability of 12 screening strategies to predict the development of active TB through latent TB detection that used IRRs comparing those with positive and negative screening results. The point estimate of the IR for active TB per annum was 10-fold or more higher in those with a positive IGRA result or in whom the TSTb strategy was applied. TSTa was less predictive, at about a sevenfold higher IR when comparing those with a positive test result and those with a negative test result. Although T-SPOT.TB and combinations of T-SPOT.TB with various thresholds of TST appeared to perform better, the confidence limits for all strategies overlapped.
The TSTa approach identified more progressors than any other strategy. The IRs in the TSTa-positive and TSTa-negative groups were lower than in the corresponding positive and negative groups identified by the other individual tests, although we did not find evidence that these differences were real rather than chance occurrences. The poorer predictive value of the TSTa approach than of IGRAs was consistent with the greater number of false-positive results because of a previous BCG vaccination; this was expected in this TST strategy that did not take prior vaccination into account. In the secondary analysis, assessing contacts and migrants separately, progression rates were higher among contacts than among migrants, although, again, this may have been attributable to chance.
Although no test was clearly superior to other tests or test strategies in all test dimensions, for PPV, all strategies appeared to be better than TSTa alone. The combination of T-SPOT.TB alone, QFT-GIT alone and TSTb (in that order) appears to be the most favourable option for predicting the development of active TB. Although the effect was more modest, combining TSTb with any of the IGRAs also appeared to be better than TSTb alone. The approaches using T-SPOT.TB or QFT-GIT alone were also not as good in their PPVs as strategies that combine TST with the respective IGRA.
For the NPVs of tests and strategies, all tests appeared to have high predictive values. Compared with TSTa + QFT-GIT, TSTa, T-SPOT.TB and TSTa + IGRA appeared to be the best approaches. Compared with TSTb + QFT-GIT, TSTa, TSTb, T-SPOT.TB, TSTa + T-SPOT.TB, TSTa + IGRA and TSTb + IGRA were better.
Cost-effectiveness
We developed a DES model to estimate the cost-effectiveness of alternative testing strategies for LTBI in two high-risk subgroups: contacts of people with active TB and recent migrants from high-incidence countries. The model used individual data from the PREDICT cohort to characterise baseline risk factors and test results in these subgroups, simulated the LTBI screening process and, when appropriate, preventative treatment with CPX or a BCG vaccination. The model accounted for missing and indeterminate test results, as observed in PREDICT, and simulated imperfect uptake and completion of preventative treatment and related adverse events. TB incidence was simulated over the individuals’ lifetimes, using available information on their actual test results and estimates of the prognostic value of tests from the statistical analyses, with adjustment for the effects of any preventative treatment. Public sector costs were estimated, including LTBI testing, preventative treatment and treatment of adverse events and active TB. Health outcomes were estimated in the form of QALYs, calculated from simulated survival and quality-of-life impact of incident TB and adverse events. The costs and QALYs were both discounted at the current recommended rate of 3.5% per year.
In these populations (contacts of people with active TB and recent migrants from high-incidence countries), although none of the test strategies was cost-effective, our base-case assumptions and parameters limited the application of this analysis to a comparison of strategies with no testing for the following reasons:
-
The model did not reflect transmission of infection, and so would underestimate health gain and cost savings from TB prevention.
-
The model did not account for cases of active TB detected at baseline, which, if asymptomatic, may be detected through further investigation following a positive LTBI test.
Partly attributable to these assumptions, the estimated QALY gains of 0.0002 per person were small, despite LTBI testing and treatment preventing TB cases, for an additional cost of between £150 and £270. The model predicted that LTBI testing and preventative treatment would prevent between 27 and 44 cases of TB in a population of 10,000 people over the lifetime horizon, depending on the test strategy. To achieve this, between 361 and 2192 people would need to start CPX and between 522 and 1146 people would need to have a BCG vaccination. In general, strategies with a higher number of individuals starting CPX had fewer patients developing active TB. However, diminishing returns were observed, with fewer additional cases prevented from successive increases in the number of individuals given CPX.
The most cost-effective LTBI test strategy was QFT-GIT following a positive TSTb result, which had an estimated cost per QALY gained (compared with no testing) of > £790,000 in new entrants or > £870,000 in contacts. The less discriminating strategies (i.e. the strategies that generate the greatest number of LTBI-positive results, such as TSTa), and consequently those in which the greatest numbers of patients received CPX, were generally the least cost-effective, suggesting that CPX costs are the main driver of cost-effectiveness. Although less obvious, the cost of the IGRAs does also influence cost-effectiveness. In particular, we noted that TSTb + QFT-GIT and TSTb + T-SPOT.TB prevented about the same number of TB cases and yielded similar QALY increases, but TSTb + QFT-GIT appeared to be more cost-effective as it was cheaper.
Comparison with previous studies
Head-to-head interferon gamma release assay versus tuberculin skin test comparison studies
This study provides a comprehensive comparison of latent TB testing strategies. Prior comparison studies have largely been in high-incidence countries, where the risk of reinfection limits the applicability of results to the UK. Four head-to-head comparison studies23,80,81,104 have been published in low-incidence countries. Only one of these studies81 compared the TST with each of the commercially available IGRAs; the other three23,80,104 utilised QFT-GIT alone. Sample sizes ranged from 339 to 1335 people, and all four studies included ≤ 15 individuals who progressed to active TB. None directly compared rates of TB development between individuals with positive and negative baseline test results.
Our study is the largest study of the predictive values of IGRAs published to date, in terms of both the number of participants and the number of progressions to active TB in a low-incidence setting. This has allowed us to quantify the prognostic value of IGRAs, in direct comparisons with the TST, with a high degree of precision and taking into account follow-up duration. The results are directly relevant to clinical practice in the UK because the study population comprised individuals who are being targeted for screening in national policies.
Of the four previous studies, two reported point estimates of PPV for IGRA that were higher than those for the TST (17% for IGRA vs. 2% for TST23 and 13% for IGRA vs. 5% for TST104). The other two studies reported a similar PPV for IGRA and TST (3% for IGRA vs. 2% for TST80 and 3% for IGRA vs. 3% for TST81). The TST threshold that was used in these studies differed. We found only limited differences between the PPVs of T-SPOT.TB, QFT-GIT, TSTa and TSTb, which ranged from 2.2% for TSTa to 3.6% for T-SPOT.TB. Our estimates of NPV were high (≥ 99.5%) for all four tests; this was consistent with the four previous studies, all of which reported NPVs of ≥ 98%.
Comparison with previous estimates of interferon gamma release assay predictive value
The pooled IRR (comparing individuals with a positive IGRA result with those with a negative result) from a previous meta-analysis was 2.11 (95% CI 1.29 to 3.46) for IGRA, 1.60 (95% CI 0.94 to 2.72) for TST with a 10-mm cut-off point and 1.43 (95% CI 0.75 to 2.72) for TST with a 5-mm cut-off point. 16 Results for IGRAs published since the systematic review117 included hazard ratios ranging from 2.054 to 42.4,29 odds ratios of 2.10–14.935,76 and rate ratios of 2.12–73.9. 24,75 Our estimates for T-SPOT.TB and QFT-GIT were 8.8 (95% CI 5.5 to 14.2) and 5.4 (95% CI 3.4 to 8.5), respectively; these were higher than the pooled estimate and broadly consistent with the less extreme estimates from the later studies.
Our estimates of PPV were at the lower end of those previously reported (see Table 1), but were fairly similar to the pooled estimate of 2.7% (95% CI 2.3% to 3.2%) from a meta-analysis of risk groups. 15 The PPV for the development of active TB depends in part on the incidence of TB in the study population, being higher when the incidence is higher; consistent with this, the pooled estimate among high-risk groups was 6.8% (95% CI 5.6% to 8.3%). 15 Although our study focused on high-risk groups within the UK, the incidence here is still relatively low compared with the high-burden countries in which many of the previous studies were conducted. Our estimates of NPV were similar to those previously published; for example, the meta-analysis produced a pooled estimate of 99.7% (95% CI 99.5% to 99.8%). 15
The PREDICT study therefore confirmed the relatively low PPV of IGRA for the development of active TB disease. Several factors contributed to this relatively poor performance. First, the test detects an immune response to M. tuberculosis antigens, rather than the presence of the organism itself. A positive result therefore did not necessarily indicate that the bacterium was present in the body and able to reactivate to cause disease. Second, although there were accepted cut-off values to define positive and negative IGRA results, categorical results may vary within the same individual, particularly if they were close to the cut-off value. 118 Further analysis of the PREDICT data will help to determine the utility of quantitative (rather than categorical) IGRA results in predicting active TB.
Strengths and limitations
To our knowledge, this is the largest study that has compared the two commercially available IGRAs with the TST to study their predictive value. Both contacts and migrants were invited to participate in the study based on standardised criteria, limiting selection bias for inclusion in the study. We used four different approaches to identify participants who progressed to active TB, maximising ascertainment of the outcome. Every participant in our primary analysis had all three assays, making the estimates for the tests comparable; in addition, a sensitivity analysis using all available participants generated similar results. The assessment of exposure, outcome and covariates was done using the same standards for all participants, minimising the chance of information bias. We utilised standardised testing methods for both IGRAs in five laboratories, and TST was administered using the Mantoux test by our trained research nurses to decrease measurement error.
We also sought to minimise so-called ‘incorporation bias’, which is likely to arise when IGRA results are incorporated into the reference standard for diagnosis of active TB (i.e. if the IGRA result influences the clinician’s investigation for, or diagnosis of, TB, then those classified as having active TB would be more likely to have been from the IGRA-positive group, consequently favouring IGRAs). Although IGRAs are part of the UK guidance, we limited the analysis to participants who were not treated for latent TB, minimising incorporation bias. Participants were deliberately recruited from the groups that were not eligible for treatment to ensure a higher probability of progression and to decrease incorporation bias.
The assessment for active TB by the central team was completed blind to IGRA results. As those participants who were recruited in primary care were not referred for treatment of latent TB, we further minimised bias in subsequent active TB diagnoses. These measures minimised any bias arising from either TST- or IGRA-positive results, leading to further TB investigations that might be more extensive than they would be for those with a negative TST or IGRA results; this is the so-called ‘work-up bias’.
Despite the large sample size and numerous strengths of our design, our study has some limitations. Although follow-up within the UK was extensive, it is likely that any participants who have left the UK would not have been included in the progression data. We may therefore have underestimated the overall progression rate; however, this effect is likely to be similar for the positive and negative groups as defined by each assay.
High-quality studies of the predictive values of IGRAs require microbiological confirmation of cases. 16 We sought culture confirmation of all cases; however, consistent with variable confirmation rates for TB in the UK, not all cases in this cohort were culture confirmed. Among the cases with culture confirmation and results of MIRU-VNTR typing for both the index case and subsequent progressing case, nearly all had the same fingerprint, with only two cases differing by one locus. This is consistent with the conclusion that, at least for these cases, the observed incident cases are likely to have progressed from recent infection (i.e. as a result of the contact with the index case just prior to recruitment). However, we cannot exclude the possibility that index cases and contacts became infected with the same strain from a shared or different source. Among migrants, we did not have information on the related source cases as transmission might have occurred many years prior to recruitment to this study or overseas. We conducted a sensitivity analysis, removing participants whose diagnosis of active TB was uncertain, and our results remained consistent with the main analysis. Despite our large sample size, the trial may not have been adequately powered to detect differences in subgroup analyses.
A further weakness of our study was the self-reported nature of comorbidities. We did not test participants for a HIV infection or diabetes mellitus. Furthermore, our study protocol included secondary objectives to investigate the prognostic value of IGRAs compared with TST for predicting active disease in HIV-infected individuals, including those from high-burden countries and among those having treatment for LTBI. The small number of participants having LTBI treatment and with self-reported HIV infection prevented us from undertaking such analysis. Future analysis of this cohort should include record linkage to the national HIV database to determine the predictive value of these assays in HIV-infected populations.
The health economic model had several strengths. The PREDICT study represents a much stronger evidence base for modelling the predictive performance of LTBI test strategies than was available for previous economic evaluations, with three main advantages. First, the cohort provides a coherent source of baseline data, including risk factors and TST, QFT-GIT and T-SPOT.TB test results for large samples of new entrants and contacts being tested for LTBI in the UK. These data integrate correlations between test results and between individual characteristics, test results and eligibility for preventative treatment. Second, the long-term follow-up and predictive modelling of TB incidence bypasses the problems of conventional diagnostic accuracy in the absence of a reliable reference standard test. Third, this evidence source enables the comparison of two commercially available IGRAs (T-SPOT.TB and QFT-GIT) and TST strategies with a single cut-off point (an induration of ≥ 5 mm) or with different cut-off points for BCG-naive and BCG-experienced patients (indurations of ≥ 5 mm and ≥ 15 mm, respectively). The model also allows for costs and delays in treatment associated with missing or indeterminate results for each of these tests, as observed in the PREDICT cohort.
However, the model is subject to a number of limitations. Most significantly, in this project we were not able to model the full population effect of better LTBI testing and treatment on the transmission of M. tuberculosis. Thus, our model is likely to underestimate the health benefits and cost savings associated with preventing progression within the cohort, making LTBI testing appear less cost-effective than it is actually likely to be. If the rate of TB transmission in the community is very high, the net benefit per index case prevented might be much higher than our estimate, possibly to the extent that a less discriminating test than TSTb + QFT-GIT would become optimal. Adapting the economic model into a full-population dynamic model is therefore a priority for future research. In a sensitivity analysis, we extended the model to estimate the impact of transmission using a simple cascading approach in which, for every case of active TB (index case), four new secondary contacts entered the model through contact tracing. This demonstrated that the addition of transmission made little difference to the cost-effectiveness results, given the low incidence of TB in the PREDICT cohort. Although more cases of TB were simulated when transmission was considered, the number of additional cases was small: 3–6 secondary cases were generated in the model from contacts of 50–80 cases in the initial cohorts. Further analysis that varies the number of contacts traced per case and TB incidence in the population being screened may be worth exploring.
Quality-adjusted life-years were similar to life-years, which is partly attributable to the high quality of life reported in the cohort: most participants reported a ‘perfect’ health state (an EQ-5D score of 11111). This might reflect the nature of the population, which was mostly made up of young healthy individuals. However, it is also possible that there might have been a degree of reporting bias; for example, new entrants to the UK or people from vulnerable groups who were being tested for TB might not want to report ill health. We also note that the QALY loss attributable to TB symptoms and treatment was relatively modest; this is because of the rarity of progression and assumptions about the duration of symptoms and impact on quality of life. We further note that, for simplicity, we did not introduce a reduction in quality of life associated with ageing in the model. This means that the QALY estimates for all scenarios are likely to be overestimated.
Other potentially important limitations of our analysis relate to the availability and use of data from PREDICT, the paucity of good-quality evidence to inform some input parameter estimates, and our modelling assumptions. First, we note that of the 9610 PREDICT participants included in the total analysis (this excludes 175 participants who were treated for active TB and 260 who were treated for latent TB), 7957 had sufficient data for inclusion in our simulation data set (age, sex, BCG vaccination status, baseline EQ-5D score and contact/migrant status). We did not attempt imputation for these missing data and, therefore, our sample might be subject to selection bias, making the results less generalisable. We did include patients in our data set who had missing or indeterminate results for one or more of the LTBI tests, in order to model the costs and treatment delay associated with incomplete testing. This did, however, necessitate assumptions to estimate TB hazard rates for the individuals within the simulation (see Table 6). In addition, for participants with results for all three LTBI tests (TST, T-SPOT.TB and QFT-GIT), we estimated hazards based only on the pair of tests with the best predictive value (the highest IRR for positive vs. negative results). A more powerful approach might be to estimate hazards from a predictive equation including all three tests and information on other baseline risk factors as covariates. We might also be able to improve on our method for extrapolating incidence beyond the PREDICT follow-up period. We used a simple calibration approach to fit a Weibull distribution to the observed IRs over 1, 2 and 3 years of follow-up. A more thorough approach would be to estimate and compare alternative survival functions, using statistical measures of fit (such as the Akaike information criterion) and also to consider other external data for validation (e.g. considering the long-term incidence projection in relation to national data). Finally, the model included a number of simplifying assumptions and some of the sources for input parameter estimates were weak. In particular, estimates of rates of uptake, completion and duration of treatment, delay from onset of symptoms to TB diagnosis and incidence and resolution of treatment-related adverse events were based on informal estimates and might be improved. Assumptions were also required to estimate the extent of utility loss associated with TB symptoms and treatment.
Clinical implications
Our results have implications for UK, and global, LTBI screening among contacts of TB cases and recent migrants from high-TB-burden countries. In the UK, there are implications for NICE guideline recommendations on contact investigation and for the NHS England/PHE screening programme.
The current recommendation by NICE14 for contacts is to offer the Mantoux test using a 5-mm threshold as the more cost-effective option, and to consider IGRAs if TST is not available. Our results suggest that a two-step process using the more nuanced TSTb strategy, which stratifies the TST by prior BCG vaccination, followed by an IGRA is the most cost-effective approach. Further analysis should examine the best combination of risk factors among contacts that predicts greater cost-effectiveness.
The NHS England/PHE national TB screening programme for migrants from high-TB-burden countries recommends a single IGRA as the optimal screening strategy. Our results suggest that a combination of the TST and IGRA would provide better value for money. Data from this cohort should be used to investigate the cost-effectiveness of the national screening programme, taking into account subsequent transmission and baseline active TB cases detected. As the current analysis focuses primarily on the comparison of the testing strategies using the entire cohort, it would be appropriate to examine various thresholds; this could include limiting CEA to those arriving in the last 2 years or 5 years.
The global effort to expand LTBI screening to high-risk groups should take into account the relative cost-effectiveness of screening in various populations. Low-TB-incidence countries, in which risk-group-based screening is currently recommended by WHO, should examine which groups are most likely to benefit from treatment to inform national testing policy.
Implications for research
Our results suggest that the probability of cases arising as a result of new infection in this low-incidence setting, the absolute risk of progression in IGRA- or TST-positive individuals and the discriminatory power of these tests are all low. Further research to develop new markers with better predictive ability utilising transcriptomics, new antigens and cytokines, metabolomics and proteomics are ongoing.
Our results indicate that the need for tests with improved predictive value remains. Ongoing work with the PREDICT biobank will probably result in better biomarkers for progression and the development of new assays. The cost-effectiveness of these new assays, using progression data from this study, should be assessed.
It is also likely that the future risk of TB and, therefore, the ability of biomarkers to correctly predict who will develop active TB, is influenced by subsequent changes that are not apparent at baseline. For example, exogenous events such as a new HIV infection after the time of the IGRA or TST or the development of other immunocompromising conditions or treatment that suppresses immunity will alter the risk of progression to active TB. The follow-up data collected should inform analysis that takes into account these changing risks in predictive models.
The low probability of progression to active TB, based on IGRAs and the TST, limits the value of latent TB screening and treatment, making the development of an affordable vaccine that will prevent progression to active TB in those already exposed to TB more important. The widespread treatment of populations in which people may have a positive IGRA or TST result is unlikely to be cost-effective if it is not focused on the highest-risk groups.
Acknowledgements
The study involved > 50 NHS sites and numerous community sites.
PREDICT study team: Ibrahim Abubakar, David Adeboyeku, Sarah Anderson, Nabeela Bari, Jack Barker, Helen Booth, Graham Bothamley, Helen Burgess, Felix Chua, Dean Creer, Mathina Darmalingam, Robert N Davidson, Martin Dedicoat, Jonathan J Deeks, Francis Drobniewski, Anne Dunleavy, Jose Figueroa, Chris Griffiths, Pranab Haldar, Mimi Haseldean, Andrew Hayward, Norman Johnson, Onn Min Kon, Heinke Kunst, Ajit Lalvani, Marc Lipman, Stefan Losewicz, Saranya Sridhar, Joanne Lord, William Lynn, Bobby Mann, Heather Milburn, John Moore-Gillon, Geoff Packe, Manish Pareek, Simon Tiberi, Anton Pozniak, Frances Sanderson, Jo Southern and John Watson.
Trial Steering Committee: Professor Bertel S Squire (chairperson) and Dr Sani Aliyu, Dr Stuart Baugh and Aurora Dawson (members).
Data Monitoring Committee: Dr Ann Chapman (chairperson) and Dr Adrian Smith and Dr John Innes (members).
The conduct of the study and supervision of study staff was led by Dr Jo Southern at PHE.
Laboratory tests for the study were led by Imperial College London (Ajit Lalvani, Saranya Sridhar, Melanie Rees-Roberts and Hilary Whitworth), PHE/Queen Mary University of London (Francis Drobniewski, Chuen-Yan Tsou and Vladyslav Nikolayevskyy) and the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust immunology laboratory.
Contributions of others
Other contributors include the research nurses without whom this study would not have succeeded, with particular thanks to the team of study nurses and Beverley Marks (Study Administrator). We are very grateful to Aurora Dawson and the many leads at temples and other community settings for their input into the study including the design and the recruitment of participants.
Patient and public involvement
Input to the design, conduct and analysis of this study was obtained through a lay member of our study advisory group, Aurora Dawson. Furthermore, there was active engagement of multiple stakeholders to facilitate recruitment during the conduct of the study, including numerous temples, churches and mosques and other community organisations in London and Birmingham. We are particularly grateful for the input on Neasden Temple in the design of our community recruitment model and input into the conduct of this research. In Birmingham, we had help from Mango Hoto from the Welcome to Birmingham Project.
Contributions of authors
All authors contributed to writing the report. In addition:
Ibrahim Abubakar (Professor of Infectious Disease Epidemiology) conceptualised the study and oversaw recruitment and the conduct of the study.
Ajit Lalvani (Professor of Medicine) was involved in the conceptualisation of the study and contributed to the oversight of the laboratory analysis.
Jo Southern (Senior Scientist) co-ordinated the study from inception to completion.
Alice Sitch (Lecturer in Medical Statistics) undertook the statistical analysis and wrote the statistical section of the report.
Charlotte Jackson (Research Associate) contributed to the analysis of the data.
Oluchukwu Onyimadu (Senior Research Assistant in Health Economics) conducted the economic analysis.
Marc Lipman (Consultant Physician and Reader in Medicine) contributed to the study design and recruitment.
Jonathan J Deeks (Professor of Biostatistics) contributed to the conceptualisation of the study and supervision of the statistical analysis.
Chris Griffiths (Professor of Primary Care) contributed to the study design and recruitment.
Graham Bothamley (Consultant Physician and Professor) contributed to the study design and recruitment.
Onn Min Kon (Consultant Physician and Professor) contributed to the study design and recruitment.
Andrew Hayward (Professor of Infectious Disease Epidemiology and Inclusion Health Research) contributed to the conceptualisation of the study.
Joanne Lord (Professor of Health Economics) designed and supervised the economic analysis.
Francis Drobniewski (Professor) contributed to the conceptualisation of the study, and laboratory analysis and oversight.
Publications
Jackson C, Southern J, Lalvani A, Drobniewski F, Griffiths CJ, Lipman M, et al. Diabetes mellitus and latent tuberculosis infection: baseline analysis of a large UK cohort [published online ahead of print 15 May 2018]. Thorax 2018.
Abubakar I, Drobniewski F, Southern J, Sitch A, Jackson C, Lipman M, et al. Prognostic value of interferon gamma release assays and tuberculin skin test in predicting the development of active tuberculosis: the UK PREDICT TB cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis 2018;18:1077–87.
MacLellan J, Wallace K, Vacchelli E, Roe J, Davidson R, Abubakar I, Southern J. A multi-perspective service evaluation exploring tuberculosis contact screening attendance among adults at a North London hospital. J Public Health (Oxf) 2016;38:e362–e367.
Abubakar I, Stagg HR, Whitworth H, Lalvani A. How should I interpret an interferon gamma release assay result for tuberculosis infection? Thorax 2013;68:298–301.
Data-sharing statement
All data requested should be submitted to the corresponding author for consideration. Access to anonymised data may be granted following review.
Patient data
This work uses data provided by patients and collected by the NHS as part of their care and support. Using patient data is vital to improve health and care for everyone. There is huge potential to make better use of information from people’s patient records, to understand more about disease, develop new treatments, monitor safety, and plan NHS services. Patient data should be kept safe and secure, to protect everyone’s privacy, and it’s important that there are safeguards to make sure that it is stored and used responsibly. Everyone should be able to find out about how patient data are used. #datasaveslives You can find out more about the background to this citation here: https://understandingpatientdata.org.uk/data-citation.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health and Social Care. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health and Social Care.
References
- Global Tuberculosis Report 2016. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016.
- Tuberculosis in England: Annual Report. London: Public Health England; 2016.
- Collaborative Tuberculosis Strategy for England: 2015 to 2020. London: Public Health England; 2015.
- Houben RM, Dodd PJ. The global burden of latent tuberculosis infection: a re-estimation using mathematical modelling. PLOS Med 2016;13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002152.
- Dye C, Scheele S, Dolin P, Pathania V, Raviglione MC. Consensus statement. Global burden of tuberculosis: estimated incidence, prevalence, and mortality by country. WHO Global Surveillance and Monitoring Project. JAMA 1999;282:677-86. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.282.7.677.
- Pai M, Riley LW, Colford JM. Interferon-gamma assays in the immunodiagnosis of tuberculosis: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis 2004;4:761-76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(04)01206-X.
- Haldar P, Thuraisingam H, Patel H, Pereira N, Free RC, Entwisle J, et al. Single-step QuantiFERON screening of adult contacts: a prospective cohort study of tuberculosis risk. Thorax 2013;68:240-6. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-200956.
- Diel R, Loddenkemper R, Meywald-Walter K, Gottschalk R, Nienhaus A. Comparative performance of tuberculin skin test, QuantiFERON-TB-Gold In Tube assay, and T-SPOT.TB test in contact investigations for tuberculosis. Chest 2009;135:1010-18. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.08-2048.
- Aichelburg MC, Reiberger T, Breitenecker F, Mandorfer M, Makristathis A, Rieger A. Reversion and conversion of interferon-γ release assay results in HIV-1-infected individuals. J Infect Dis 2014;209:729-33. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jit418.
- Zellweger JP, Sotgiu G, Block M, Dore S, Altet N, Blunschi R, et al. Risk assessment of tuberculosis in contacts by IFN-γ release assays. A Tuberculosis Network European Trials Group study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2015;191:1176-84. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201502-0232OC.
- Pai M, Denkinger CM, Kik SV, Rangaka MX, Zwerling A, Oxlade O, et al. Gamma interferon release assays for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Clin Microbiol Rev 2014;27:3-20. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00034-13.
- Guidelines on the Management of Latent Tuberculosis Infection. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015.
- Latent TB Infection (LTBI): Testing and Treatment. London: Public Health England; 2016.
- Tuberculosis: NICE Guidelines. London: NICE; 2016.
- Diel R, Loddenkemper R, Nienhaus A. Predictive value of interferon-γ release assays and tuberculin skin testing for progression from latent TB infection to disease state: a meta-analysis. Chest 2012;142:63-75. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.11-3157.
- Rangaka MX, Wilkinson KA, Glynn JR, Ling D, Menzies D, Mwansa-Kambafwile J, et al. Predictive value of interferon-γ release assays for incident active tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2012;12:45-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70210-9.
- Kim YJ, Kim SI, Kim YR, Wie SH, Park YJ, Kang MW. Predictive value of interferon-γ ELISPOT assay in HIV 1-infected patients in an intermediate tuberculosis-endemic area. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 2012;28:1038-43. https://doi.org/10.1089/AID.2011.0360.
- Lange B, Vavra M, Kern WV, Wagner D. Development of tuberculosis in immunocompromised patients with a positive tuberculosis-specific IGRA. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2012;16:492-5. https://doi.org/10.5588/ijtld.11.0416.
- Kim SH, Lee SO, Park JB, Park IA, Park SJ, Yun SC, et al. A prospective longitudinal study evaluating the usefulness of a T-cell-based assay for latent tuberculosis infection in kidney transplant recipients. Am J Transplant 2011;11:1927-35. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03625.x.
- Bergot E, Haustraete E, Malbruny B, Magnier R, Salaün MA, Zalcman G. Observational study of QuantiFERON®-TB Gold In-Tube assay in tuberculosis contacts in a low incidence area. PLOS ONE 2012;7. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0043520.
- Cattamanchi A, Smith R, Steingart KR, Metcalfe JZ, Date A, Coleman C, et al. Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection in HIV-infected individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2011;56:230-8. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAI.0b013e31820b07ab.
- Adetifa IM, Ota MO, Jeffries DJ, Lugos MD, Hammond AS, Battersby NJ, et al. Interferon-γ ELISPOT as a biomarker of treatment efficacy in latent tuberculosis infection: a clinical trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2013;187:439-45. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201208-1352OC.
- Altet N, Dominguez J, Souza-Galvão ML, Jiménez-Fuentes MÁ, Milà C, Solsona J, et al. Predicting the development of tuberculosis with the tuberculin skin test and QuantiFERON testing. Ann Am Thorac Soc 2015;12:680-8. https://doi.org/10.1513/AnnalsATS.201408-394OC.
- Andrews JR, Hatherill M, Mahomed H, Hanekom WA, Campo M, Hawn TR, et al. The dynamics of QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube conversion and reversion in a cohort of South African adolescents. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2015;191:584-91. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201409-1704OC.
- Arnedo-Pena A, Juan-Cerdán JV, Romeu-García MA, García-Ferrer D, Holguín-Gómez R, Iborra-Millet J, et al. Vitamin D status and incidence of tuberculosis infection conversion in contacts of pulmonary tuberculosis patients: a prospective cohort study. Epidemiol Infect 2015;143:1731-41. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268814002386.
- Balcells ME, Huilcamán M, Peña C, Castillo C, Carvajal C, Scioscia N, et al. M. tuberculosis DNA detection in nasopharyngeal mucosa can precede tuberculosis development in contacts. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2016;20:848-52. https://doi.org/10.5588/ijtld.15.0872.
- Belay M, Legesse M, Dagne D, Mihret A, Bekele Y, Medhin G, et al. QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube test conversions and reversions among tuberculosis patients and their household contacts in Addis Ababa: a one year follow-up study. BMC Infect Dis 2014;14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-014-0654-5.
- Danel C, Kabran M, Inwoley A, Badje A, Herrmann JL, Moh R, et al. QuantiFERON-TB Gold: performance for ruling out active tuberculosis in HIV-infected adults with high CD4 count in Côte d’Ivoire, West Africa. PLOS ONE 2014;9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107245.
- Doyle JS, Bissessor M, Denholm JT, Ryan N, Fairley CK, Leslie DE. Latent tuberculosis screening using interferon-gamma release assays in an Australian HIV-infected cohort: is routine testing worthwhile?. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2014;66:48-54. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAI.0000000000000109.
- Fan WC, Ting WY, Lee MC, Huang SF, Chiu CH, Lai SL, et al. Latent TB infection in newly diagnosed lung cancer patients – a multicenter prospective observational study. Lung Cancer 2014;85:472-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.07.001.
- Geis S, Bettge-Weller G, Goetsch U, Bellinger O, Ballmann G, Hauri AM. How can we achieve better prevention of progression to tuberculosis among contacts?. Eur Respir J 2013;42:1743-6. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00187112.
- Goebel KM, Tay EL, Denholm JT. Supplemental use of an interferon-gamma release assay in a state-wide tuberculosis contact tracing program in Victoria: a six-year review. Commun Dis Intell Q Rep 2015;39:E191-6.
- Gonzślez-Moreno J, García-Gasalla M, Gállego-Lezaun C, Fernández-Baca V, Mir Viladrich I, Cifuentes-Luna C, et al. Role of QuantiFERON(®)-TB Gold In-Tube in tuberculosis contact investigation: experience in a tuberculosis unit. Infect Dis 2015;47:244-51. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365548.2014.987813.
- Hermansen TS, Lillebaek T, Langholz Kristensen K, Andersen PH, Ravn P. Prognostic value of interferon-γ release assays, a population-based study from a TB low-incidence country. Thorax 2016;71:652-8. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2015-208228.
- Jeong JC, Koo TY, Jeon HJ, Park HC, Ryu HJ, Lee JP, et al. Utility of QuantiFERON-TB assay for prediction of tuberculosis development in kidney transplant patients in an intermediate-tuberculosis-burden country: lack of evidence for enhanced prediction for short-term tuberculosis development. Transplant Proc 2014;46:583-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.11.108.
- Jonnalagadda SR, Brown E, Lohman-Payne B, Wamalwa D, Farquhar C, John-Stewart GC. Predictive value of interferon-gamma release assays for postpartum active tuberculosis in HIV-1-infected women. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2013;17:1552-7. https://doi.org/10.5588/ijtld.13.0239.
- Jung YJ, Lee JY, Jo KW, Yoo B, Lee CK, Kim YG, et al. The ‘either test positive’ strategy for latent tuberculous infection before anti-tumour necrosis factor treatment. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2014;18:428-34. https://doi.org/10.5588/ijtld.13.0644.
- Jung YJ, Woo HI, Jeon K, Koh WJ, Jang DK, Cha HS, et al. The significance of sensitive interferon gamma release assays for diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection in patients receiving tumor necrosis factor-α antagonist therapy. PLOS ONE 2015;10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141033.
- Kim ES, Song GA, Cho KB, Park KS, Kim KO, Jang BI, et al. Significant risk and associated factors of active tuberculosis infection in Korean patients with inflammatory bowel disease using anti-TNF agents. World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:3308-16. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i11.3308.
- Kim HC, Jo KW, Jung YJ, Yoo B, Lee CK, Kim YG, et al. Diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection before initiation of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy using both tuberculin skin test and QuantiFERON-TB Gold In Tube assay. Scand J Infect Dis 2014;46:763-9. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365548.2014.938691.
- Kim HJ, Lee GH, Ryoo S, Oh SY, Lee JB, Kim JH, et al. Role of confirmatory interferon-gamma release assays in school outbreaks of tuberculosis in South Korea. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2015;19:576-81. https://doi.org/10.5588/ijtld.14.0636.
- Kim JH, Won S, Choi CB, Sung YK, Song GG, Bae SC. Evaluation of the usefulness of interferon-gamma release assays and the tuberculin skin test for the detection of latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections in Korean rheumatic patients who are candidates for biologic agents. Int J Rheum Dis 2015;18:315-22. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.12515.
- Kim JS, Cho JH, Park GY, Kang YJ, Kwon O, Choi JY, et al. Comparison of QuantiFERON-TB Gold with tuberculin skin test for detection of latent tuberculosis infection before kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc 2013;45:2899-902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.08.059.
- Kim SH, Lee SO, Park IA, Kim SM, Park SJ, Yun SC, et al. Isoniazid treatment to prevent TB in kidney and pancreas transplant recipients based on an interferon-γ-releasing assay: an exploratory randomized controlled trial. J Antimicrob Chemother 2015;70:1567-72. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dku562.
- Klein M, Jarosová K, Forejtová S, Bečvář R, Sedová L, Pavelka K, et al. QuantiFERON TB Gold and tuberculin skin tests for the detection of latent tuberculosis infection in patients treated with tumour necrosis factor alpha blocking agents. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2013;31:111-17.
- Kruczak K, Duplaga M, Sanak M, Cmiel A, Mastalerz L, Sladek K, et al. Comparison of IGRA tests and TST in the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection and predicting tuberculosis in risk groups in Krakow, Poland. Scand J Infect Dis 2014;46:649-55. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365548.2014.927955.
- Lee H, Park HY, Jeon K, Jeong BH, Hwang JW, Lee J, et al. QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube assay for screening arthritis patients for latent tuberculosis infection before starting anti-tumor necrosis factor treatment. PLOS ONE 2015;10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119260.
- Lee SK, Kim SY, Kim EY, Jung JY, Park MS, Kim YS, et al. Mycobacterial infections in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists in South Korea. Lung 2013;191:565-71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-013-9481-5.
- Lee SS, Lin HH, Tsai HC, Su IJ, Yang CH, Sun HY, et al. A clinical algorithm to identify HIV patients at high risk for incident active tuberculosis: a prospective 5-year cohort study. PLOS ONE 2015;10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0135801.
- Lee YM, Lee SO, Choi SH, Kim YS, Woo JH, Kim DY, et al. A prospective longitudinal study evaluating the usefulness of the interferon-gamma releasing assay for predicting active tuberculosis in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. J Infect 2014;69:165-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2014.02.019.
- Leung CC, Chan K, Yam WC, Lee MP, Chan CK, Wong KH, et al. Poor agreement between diagnostic tests for latent tuberculosis infection among HIV-infected persons in Hong Kong. Respirology 2016;21:1322-9. https://doi.org/10.1111/resp.12805.
- Leung CC, Yam WC, Ho PL, Yew WW, Chan CK, Law WS, et al. T-SPOT.TB outperforms tuberculin skin test in predicting development of active tuberculosis among household contacts. Respirology 2015;20:496-503. https://doi.org/10.1111/resp.12483.
- Luabeya KK, Tameris MD, Geldenhuys HD, Mulenga H, Van Schalkwyk A, Hughes EJ, et al. Risk of disease after isoniazid preventive therapy for Mycobacterium tuberculosis exposure in young HIV-uninfected children. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2015;34:1218-22. https://doi.org/10.1097/INF.0000000000000874.
- Mahomed H, Ehrlich R, Hawkridge T, Hatherill M, Geiter L, Kafaar F, et al. TB incidence in an adolescent cohort in South Africa. PLOS ONE 2013;8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059652.
- Mandalakas AM, Kirchner HL, Walzl G, Gie RP, Schaaf HS, Cotton MF, et al. Optimizing the detection of recent tuberculosis infection in children in a high tuberculosis-HIV burden setting. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2015;191:820-30. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201406-1165OC.
- Mathad JS, Bhosale R, Balasubramanian U, Kanade S, Mave V, Suryavanshi N, et al. Quantitative IFN-γ and IL-2 response associated with latent tuberculosis test discordance in HIV-infected pregnant women. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2016;193:1421-8. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201508-1595OC.
- Moon SM, Lee SO, Choi SH, Kim YS, Woo JH, Yoon DH, et al. Comparison of the QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube test with the tuberculin skin test for detecting latent tuberculosis infection prior to hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis 2013;15:104-9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3062.2012.00765.x.
- Muñoz L, Casas S, Juanola X, Bordas X, Martinez C, Santin M. Prevention of anti-TNF – associated Tuberculosis study team of Bellvitge University Hospital. Prevention of anti-tumor necrosis factor-associated tuberculosis: a 10-year longitudinal cohort study. Clin Infect Dis 2015;60:349-56. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciu796.
- Nienhaus A, Costa JT. Screening for tuberculosis and the use of a borderline zone for the interpretation of the interferon-γ release assay (IGRA) in Portuguese healthcare workers. J Occup Med Toxicol 2013;8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6673-8-1.
- Rangaka MX, Wilkinson RJ, Boulle A, Glynn JR, Fielding K, van Cutsem G, et al. Isoniazid plus antiretroviral therapy to prevent tuberculosis: a randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2014;384:682-90. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60162-8.
- Sester M, van Leth F, Bruchfeld J, Bumbacea D, Cirillo DM, Dilektasli AG, et al. Risk assessment of tuberculosis in immunocompromised patients. A TBNET study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2014;190:1168-76. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201405-0967OC.
- Seyhan EC, Gunluoglu G, Gunluoglu MZ, Tural S, Sökücü S. Predictive value of the tuberculin skin test and QuantiFERON-tuberculosis Gold In-Tube test for development of active tuberculosis in hemodialysis patients. Ann Thorac Med 2016;11:114-20. https://doi.org/10.4103/1817-1737.180023.
- Sherkat R, Yaran M, Shoaie P, Mortazavi M, Shahidi S, Hamidi H, et al. Concordance of the tuberculin skin test and T-SPOT(®).TB test results in kidney transplant candidates. J Res Med Sci 2014;19:26-9.
- Shu CC, Hsu CL, Wei YF, Lee CY, Liou HH, Wu VC, et al. Risk of tuberculosis among patients on dialysis: the predictive value of serial interferon-gamma release assay. Medicine 2016;95. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000003813.
- Soborg C, Ruhwald M, Andersen PH, Ravn P. 6-year follow-up of 522 HIV-positive individuals screened for Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in Denmark. Eur Respir J 2014;44:540-3. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00170913.
- Song SE, Yang J, Lee KS, Kim H, Kim YM, Kim S, et al. Comparison of the tuberculin skin test and interferon gamma release assay for the screening of tuberculosis in adolescents in close contact with tuberculosis TB patients. PLOS ONE 2014;9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0100267.
- Stennis NL, Trieu L, Ahuja SD, Harris TG. Estimated prevalence of tuberculosis infection among a New York City clinic population using interferon-gamma release assays. Open Forum Infect Dis 2014;1. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofu047.
- Sun HY, Hsueh PR, Liu WC, Su YC, Chang SY, Hung CC, et al. Risk of active tuberculosis in HIV-infected patients in Taiwan with free access to HIV care and a positive T-SPOT.TB test. PLOS ONE 2015;10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125260.
- Tsang DN, Lai CK, Yam WC, Chan JW, Mok YW, Seto WH, et al. Use of interferon gamma release assay to assess latent tuberculosis infection among healthcare workers in Hong Kong. Hong Kong Med J 2015;21:22-5.
- Tsou PH, Huang WC, Huang CC, Lin CF, Wu KM, Hsu JY, et al. QuantiFERON TB-Gold conversion can predict active tuberculosis development in elderly nursing home residents. Geriatr Gerontol Int 2015;15:1179-84. https://doi.org/10.1111/ggi.12416.
- van der Have M, Belderbos TD, Fidder HH, Leenders M, Dijkstra G, Peters CP, et al. Screening prior to biological therapy in Crohn’s disease: adherence to guidelines and prevalence of infections. Results from a multicentre retrospective study. Dig Liver Dis 2014;46:881-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2014.07.006.
- Verhagen LM, Maes M, Villalba JA, d’Alessandro A, Rodriguez LP, España MF, et al. Agreement between QuantiFERON®-TB Gold In-Tube and the tuberculin skin test and predictors of positive test results in Warao Amerindian pediatric tuberculosis contacts. BMC Infect Dis 2014;14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-14-383.
- Whitaker JA, Mirtskhulava V, Kipiani M, Harris DA, Tabagari N, . Prevalence and incidence of latent tuberculosis infection in Georgian healthcare workers. PLOS ONE 2013;8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0058202.
- Woodfield G, Passey-Heaton B, Chakrabarti A, Pozniak A, Loebinger MR. An evaluation of the use of a negative interferon-γ release assay for tuberculosis screening before TNF antagonist therapy. Eur Respir J 2014;44:1369-72. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00125714.
- Yang CH, Chan PC, Liao ST, Cheng SH, Wong WW, Huang LM, et al. Strategy to better select HIV-infected individuals for latent TB treatment in BCG-vaccinated population. PLOS ONE 2013;8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073069.
- Yoshiyama T, Harada N, Higuchi K, Saitou M, Kato S. Use of the QuantiFERON®-TB Gold In Tube test for screening TB contacts and predictive value for active TB. Infect Dis 2015;47:542-9. https://doi.org/10.3109/23744235.2015.1026935.
- Zhang LF, Liu XQ, Zhang Y, Deng GH, Pareek M, Lalvani A. A prospective longitudinal study evaluating a T-cell-based assay for latent tuberculosis infection in health-care workers in a general hospital in Beijing. Chin Med J 2013;126:2039-44.
- Blount RJ, Tran MC, Everett CK, Cattamanchi A, Metcalfe JZ, Connor D, et al. Tuberculosis progression rates in U.S. Immigrants following screening with interferon-gamma release assays. BMC Public Health 2016;16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-016-3519-6.
- Diel R, Loddenkemper R, Niemann S, Meywald-Walter K, Nienhaus A. Negative and positive predictive value of a whole-blood interferon-γ release assay for developing active tuberculosis: an update. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011;183:88-95. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201006-0974OC.
- Harstad I, Winje BA, Heldal E, Oftung F, Jacobsen GW. Predictive values of QuantiFERON-TB Gold testing in screening for tuberculosis disease in asylum seekers. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2010;14:1209-11.
- Kik SV, Franken WP, Mensen M, Cobelens FG, Kamphorst M, Arend SM, et al. Predictive value for progression to tuberculosis by IGRA and TST in immigrant contacts. Eur Respir J 2010;35:1346-53. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00098509.
- Lee SS, Chou KJ, Su IJ, Chen YS, Fang HC, Huang TS, et al. High prevalence of latent tuberculosis infection in patients in end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis: comparison of QuantiFERON-TB GOLD, ELISPOT, and tuberculin skin test. Infection 2009;37:96-102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-008-8082-3.
- Leung CC, Yam WC, Yew WW, Ho PL, Tam CM, Law WS, et al. T-SPOT.TB outperforms tuberculin skin test in predicting tuberculosis disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010;182:834-40. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200912-1875OC.
- Mahomed H, Hawkridge T, Verver S, Abrahams D, Geiter L, Hatherill M, et al. The tuberculin skin test versus QuantiFERON TB Gold® in predicting tuberculosis disease in an adolescent cohort study in South Africa. PLOS ONE 2011;6. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0017984.
- Tuberculosis: Clinical Diagnosis and Management of Tuberculosis, and Measures for its Prevention and Control. London: Royal College of Physicians; 2006.
- Tuberculosis: Clinical Diagnosis and Management of Tuberculosis, and Measures for its Prevention and Control. NICE; 2011.
- Nienhaus A, Schablon A, Costa JT, Diel R. Systematic review of cost and cost-effectiveness of different TB-screening strategies. BMC Health Serv Res 2011;11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-11-247.
- de Perio MA, Tsevat J, Roselle GA, Kralovic SM, Eckman MH. Cost-effectiveness of interferon gamma release assays vs tuberculin skin tests in health care workers. Arch Intern Med 2009;169:179-87. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2008.524.
- Deuffic-Burban S, Atsou K, Viget N, Melliez H, Bouvet E, Yazdanpanah Y. Cost-effectiveness of QuantiFERON-TB test vs. tuberculin skin test in the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2010;14:471-81.
- Diel R, Nienhaus A, Loddenkemper R. Cost-effectiveness of interferon-gamma release assay screening for latent tuberculosis infection treatment in Germany. Chest 2007;131:1424-34. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.06-2728.
- Diel R, Wrighton-Smith P, Zellweger JP. Cost-effectiveness of interferon-gamma release assay testing for the treatment of latent tuberculosis. Eur Respir J 2007;30:321-32. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00145906.
- Kowada A, Takahashi O, Shimbo T, Ohde S, Tokuda Y, Fukui T. Cost effectiveness of interferon-gamma release assay for tuberculosis contact screening in Japan. Mol Diagn Ther 2008;12:235-51. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03256289.
- Marra F, Marra CA, Sadatsafavi M, Morán-Mendoza O, Cook V, Elwood RK, et al. Cost-effectiveness of a new interferon-based blood assay, QuantiFERON(R)-TB Gold, in screening tuberculosis contacts. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2008;12:1414-24.
- Oxlade O, Schwartzman K, Menzies D. Interferon-gamma release assays and TB screening in high-income countries: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2007;11:16-2.
- Pooran A, Booth H, Miller RF, Scott G, Badri M, Huggett JF, et al. Different screening strategies (single or dual) for the diagnosis of suspected latent tuberculosis: a cost effectiveness analysis. BMC Pulm Med 2010;10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2466-10-7.
- Diel R, Nienhaus A, Lange C, Schaberg T. Cost-optimisation of screening for latent tuberculosis in close contacts. Eur Respir J 2006;28:35-44. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.06.00011806.
- Diel R, Schaberg T, Loddenkemper R, Welte T, Nienhaus A. Enhanced cost–benefit analysis of strategies for LTBI screening and INH chemoprevention in Germany. Respir Med 2009;103:1838-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2009.07.008.
- Fox BD, Kramer MR, Mor Z, Preiss R, Rusanov V, Fuks L, et al. The QuantiFERON-TB-Gold assay for tuberculosis screening in healthcare workers: a cost-comparison analysis. Lung 2009;187:413-19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-009-9182-2.
- Hardy AB, Varma R, Collyns T, Moffitt SJ, Mullarkey C, Watson JP. Cost-effectiveness of the NICE guidelines for screening for latent tuberculosis infection: the QuantiFERON-TB Gold IGRA alone is more cost-effective for immigrants from high burden countries. Thorax 2010;65:178-80. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.2009.119677.
- Wrighton-Smith P, Zellweger JP. Direct costs of three models for the screening of latent tuberculosis infection. Eur Respir J 2006;28:45-50. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.06.00005906.
- Pareek M, Bond M, Shorey J, Seneviratne S, Guy M, White P, et al. Community-based evaluation of immigrant tuberculosis screening using interferon γ release assays and tuberculin skin testing: observational study and economic analysis. Thorax 2012;68:230-9. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-201542.
- Auguste P, Tsertsvadze A, Pink J, Court R, Seedat F, Gurung T, et al. Accurate diagnosis of latent tuberculosis in children, people who are immunocompromised or at risk from immunosuppression and recent arrivals from countries with a high incidence of tuberculosis: systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 2016;20. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta20380.
- Immunisation Against Infectious Disease. London: Public Health England; 2013.
- Diel R, Loddenkemper R, Meywald-Walter K, Niemann S, Nienhaus A. Predictive value of a whole blood IFN-gamma assay for the development of active tuberculosis disease after recent infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008;177:1164-70. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200711-1613OC.
- Pepe M. The Statistical Evaluation of Medical Tests for Classification and Prediction. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2003.
- QuantiFERON®-TB Gold (QFT®) ELISA Package Insert. Hilden: QIAGEN; 2016.
- Interpreting Tuberculosis Test Results with the T-SPOT.TB Test. Oxford: Oxford Immunotec; 2017.
- Bauer M, Ahmed S, Benedetti A, Greenaway C, Lalli M, Leavens A, et al. Health-related quality of life and tuberculosis: a longitudinal cohort study. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2015;13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-015-0250-4.
- Mears J, Vynnycky E, Lord J, Borgdorff MW, Cohen T, Crisp D, et al. The prospective evaluation of the TB strain typing service in England: a mixed methods study. Thorax 2016;71:734-41. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206480.
- International Union Against Tuberculosis Committee on Prophylaxis . Efficacy of various durations of isoniazid preventive therapy for tuberculosis: five years of follow-up in the IUAT trial. Bull World Health Organ 1982;60:555-64.
- Colditz GA, Brewer TF, Berkey CS, Wilson ME, Burdick E, Fineberg HV, et al. Efficacy of BCG vaccine in the prevention of tuberculosis. Meta-analysis of the published literature. JAMA 1994;271:698-702. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1994.03510330076038.
- Crofts JP, Pebody R, Grant A, Watson JM, Abubakar I. Estimating tuberculosis case mortality in England and Wales, 2001–2002. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2008;12:308-13.
- Kruijshaar ME, Lipman M, Essink-Bot ML, Lozewicz S, Creer D, Dart S, et al. Health status of UK patients with active tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2010;14:296-302.
- National Life Tables, United Kingdom: 2012–2014. Newport: ONS; 2015.
- NHS Reference Costs. London: DHSC; 2014.
- Tuberculosis in England: Annual Report. London: Public Health England; 2015.
- Latent TB Infection: Updated and Consolidated Guidelines for Programmatic Management. Geneva: WHO; 2018.
- Metcalfe JZ, Cattamanchi A, McCulloch CE, Lew JD, Ha NP, Graviss EA. Test variability of the QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube assay in clinical practice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2013;187:206-11. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201203-0430OC.
Appendix 1 List of participating sites
-
Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust.
-
Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust.
-
Homerton Hospital.
-
North Middlesex University Hospital NHS Trust.
-
Whittington Hospital.
-
Barnet and Chase Farm NHS Hospitals Trust.
-
Barts Health NHS Trust.
-
Charing Cross Hospital.
-
Northwick Park Hospital.
-
Central Middlesex Hospital.
-
Ealing Hospital.
-
St George’s Hospital.
-
Whipps Cross University Hospital.
-
Newham General Hospital.
-
Tower Hamlets PCT.
-
City and Hackney PCT.
-
University College London Hospital.
-
Newham PCT.
-
Westminster PCT.
-
Lambeth PCT.
-
Hillingdon Hospital NHS Trust.
-
Croydon Health Services NHS Trust.
-
Chelsea and Westminster Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
-
King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
-
South London Healthcare NHS Trust.
-
West Middlesex University Hospital.
-
Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust.
-
Heart of England NHS Foundation Trust.
-
Barking, Havering and Redbridge University Hospitals NHS Trust.
-
NHS Brent (PCT).
-
NHS Harrow (PCT).
-
NHS Hillingdon (PCT).
-
Leicester PCT.
-
Greenwich Teaching PCT.
-
Heart of Birmingham PCT.
-
NHS Hounslow (PCT).
-
NHS Birmingham.
-
South Birmingham PCT.
-
Solihull PCT.
-
Kingston PCT.
-
Croydon PCT.
-
Sutton and Merton PCT.
-
Wandsworth PCT.
-
Sandwell PCT.
-
Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust.
-
Barnet PCT.
-
Camden PCT.
-
Enfield PCT.
-
Haringey Teaching PCT.
-
Hammersmith and Fulham PCT.
-
Ealing PCT.
-
Sandwell and West Birmingham Hospitals.
-
University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust.
-
Coventry and Warwickshire Partnership NHS Trust.
Appendix 2 Supplementary results
| QFT-GIT result | T-SPOT.TB result | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Borderline positive | Borderline negative | Negative | Indeterminate | Error | Missing | ||
| TSTa positive | ||||||||
| Positive | (39) 745 | (2) 52 | 24 | (3) 225 | 11 | 16 | (3) 40 | (47) 1113 |
| Negative | (7) 124 | (1) 49 | 41 | (13) 1750 | (1) 34 | 27 | 80 | (22) 2105 |
| Indeterminate | 18 | 0 | 1 | (1) 30 | 2 | 1 | (1) 20 | (2) 72 |
| Error | 6 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16 |
| Missing | (2) 21 | 5 | 0 | 16 | 0 | 3 | (4) 162 | (6) 207 |
| Total | (48) 914 | (3) 106 | 67 | (17) 2030 | (1) 47 | 47 | (8) 302 | (77) 3513 |
| TSTa negative | ||||||||
| Positive | (2) 170 | (2) 25 | 8 | 222 | 4 | 7 | 14 | (4) 450 |
| Negative | (2) 56 | (7) 34 | 29 | 2966 | 54 | 89 | 145 | (1) 3373 |
| Indeterminate | 0 | (1) 0 | 0 | 33 | 1 | 1 | 19 | (1) 54 |
| Error | 3 | 0 | 1 | 30 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 35 |
| Missing | 20 | 4 | 4 | 121 | 1 | 0 | (1) 258 | (1) 408 |
| Total | (4) 249 | (6) 63 | 42 | 3372 | 60 | 98 | (1) 436 | (15) 4320 |
| TSTa missing | ||||||||
| Positive | (1) 174 | 10 | 6 | 46 | (1) 3 | 27 | 63 | 329 |
| Negative | 26 | 10 | 7 | (2) 795 | 8 | 84 | 232 | 1162 |
| Indeterminate | 5 | 0 | 3 | 10 | 2 | 0 | 17 | 37 |
| Error | 2 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 14 |
| Missing | 11 | 1 | 1 | 27 | 1 | 1 | (1) 193 | 235 |
| Total | (1) 218 | 21 | 17 | (2) 886 | (1) 14 | 115 | (1) 506 | (5) 1777 |
| QFT-GIT result | T-SPOT.TB result | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Borderline positive | Borderline negative | Negative | Indeterminate | Error | Missing | ||
| TSTb positive | ||||||||
| Positive | (36) 585 | 35 | 12 | (2) 112 | 6 | 8 | (3) 27 | (41) 785 |
| Negative | (6) 68 | (1) 21 | 19 | (7) 636 | (1) 16 | 8 | 32 | (15) 800 |
| Indeterminate | 14 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 1 | 0 | (1) 11 | (1) 36 |
| Error | 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Missing | (2) 12 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 2 | (1) 80 | (3) 101 |
| Total | (44) 685 | (1) 58 | 32 | (9) 763 | (1) 23 | 18 | (5) 150 | (60) 1729 |
| TSTb negative | ||||||||
| Positive | (5) 317 | (1) 39 | 20 | (3) 325 | 8 | 15 | 25 | (9) 749 |
| Negative | (3) 111 | 60 | 50 | (13) 3976 | 71 | 107 | 188 | (16) 4563 |
| Indeterminate | 4 | 0 | 1 | (2) 52 | 2 | 2 | 28 | (2) 89 |
| Error | 3 | 0 | 1 | 38 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 43 |
| Missing | 29 | 7 | 4 | 131 | 1 | 1 | (4) 323 | (4) 496 |
| Total | (8) 464 | (1) 106 | 76 | (18) 4522 | 82 | 126 | (4) 564 | (31) 5940 |
| TSTb missing | ||||||||
| Positive | (1) 187 | (1) 13 | 6 | 56 | (1) 4 | 27 | 65 | (3) 358 |
| Negative | 27 | 12 | 8 | (2) 899 | 9 | 85 | 237 | (2) 1277 |
| Indeterminate | 5 | 0 | 3 | 11 | 2 | 0 | 17 | 38 |
| Error | 2 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 15 |
| Missing | 11 | 1 | 1 | 28 | 1 | 1 | (1) 210 | (1) 253 |
| Total | (1) 232 | (1) 26 | 18 | (2) 1003 | (1) 16 | 116 | (1) 530 | (6) 1941 |
| QFT-GIT | Test result, n (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSTa positive | TSTa negative | TSTa missing | ||||||||||
| T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | |
| Positive | 41 (53.2) | 3 (3.9) | 3 (3.9) | 47 (61.0) | 2 (13.3) | 2 (13.3) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (26.7) | 1 (20.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (20.0) | 2 (40.0) |
| Negative | 8 (10.4) | 13 (16.9) | 1 (1.3) | 22 (28.6) | 2 (13.3) | 7 (46.7) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (60.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (40.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (40.0) |
| Missing | 2 (2.6) | 1 (1.3) | 5 (6.5) | 8 (10.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (6.7) | 1 (6.7) | 2 (13.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (20.0) | 1 (20.0) |
| Total | 51 (66.2) | 17 (22.1) | 9 (11.7) | 77 (100.0) | 4 (26.7) | 10 (66.7) | 1 (6.7) | 15 (100.0) | 1 (20.0) | 2 (40.0) | 2 (40.0) | 5 (100.0) |
| QFT-GIT | Test result, n (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSTa positive | TSTa negative | TSTa missing | ||||||||||
| T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | |
| Positive | 756 (22.0) | 246 (7.2) | 64 (1.9) | 1066 (31.0) | 193 (4.5) | 228 (5.3) | 25 (0.6) | 446 (10.4) | 183 (10.3) | 52 (2.9) | 92 (5.2) | 327 (18.5) |
| Negative | 165 (4.8) | 1778 (51.7) | 140 (4.1) | 2083 (60.6) | 88 (2.0) | 2988 (69.4) | 288 (6.7) | 3364 (78.1) | 36 (2.0) | 800 (45.1) | 324 (18.3) | 1160 (65.5) |
| Missing | 48 (1.4) | 56 (1.6) | 183 (5.3) | 287 (8.4) | 27 (0.6) | 188 (4.4) | 280 (6.5) | 495 (11.5) | 19 (1.1) | 49 (2.8) | 217 (12.2) | 285 (16.1) |
| Total | 969 (28.2) | 2080 (60.5) | 387 (11.3) | 3436 (100.0) | 308 (7.2) | 3404 (79.1) | 593 (13.8) | 4305 (100.0) | 238 (13.4) | 901 (50.8) | 633 (35.7) | 1772 (100.0) |
| QFT-GIT | Test result, n (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSTb positive | TSTb negative | TSTb missing | ||||||||||
| T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | |
| Positive | 36 (60.0) | 2 (3.3) | 3 (5.0) | 41 (68.3) | 6 (19.4) | 3 (9.7) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (29.0) | 2 (33.3) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (16.7) | 3 (50.0) |
| Negative | 7 (11.7) | 7 (11.7) | 1 (1.7) | 15 (25.0) | 3 (9.7) | 13 (41.9) | 0 (0.0) | 16 (51.6) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (33.3) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (33.3) |
| Missing | 2 (3.3) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (3.3) | 4 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (6.5) | 4 (12.9) | 6 (19.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) |
| Total | 45 (75.0) | 9 (15.0) | 6 (10.0) | 60 (100.0) | 9 (29.0) | 18 (58.1) | 4 (12.9) | 31 (100.0) | 2 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) | 6 (100.0) |
| QFT-GIT | Test result, n (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSTb positive | TSTb negative | TSTb missing | ||||||||||
| T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | T-SPOT.TB positive | T-SPOT.TB negative | T-SPOT.TB missing | T-SPOT.TB total | |
| Positive | 584 (35.0) | 122 (7.3) | 38 (2.3) | 744 (44.6) | 350 (5.9) | 342 (5.8) | 48 (0.8) | 740 (12.5) | 198 (10.2) | 62 (3.2) | 95 (4.9) | 355 (18.3) |
| Negative | 82 (4.9) | 648 (38.8) | 55 (3.3) | 785 (47.0) | 168 (2.8) | 4013 (67.9) | 366 (6.2) | 4547 (77.0) | 39 (2.0) | 905 (46.8) | 331 (17.1) | 1275 (65.9) |
| Missing | 32 (1.9) | 16 (1.0) | 92 (5.5) | 140 (8.4) | 43 (0.7) | 225 (3.8) | 354 (6.0) | 622 (10.5) | 19 (1.0) | 52 (2.7) | 234 (12.1) | 305 (15.8) |
| Total | 698 (41.8) | 786 (47.1) | 185 (11.1) | 1669 (100.0) | 561 (9.5) | 4580 (77.5) | 768 (13.0) | 5909 (100.0) | 256 (13.2) | 1019 (52.7) | 660 (34.1) | 1935 (100.0) |
FIGURE 12.
Two-step strategies with TSTa as the first test.
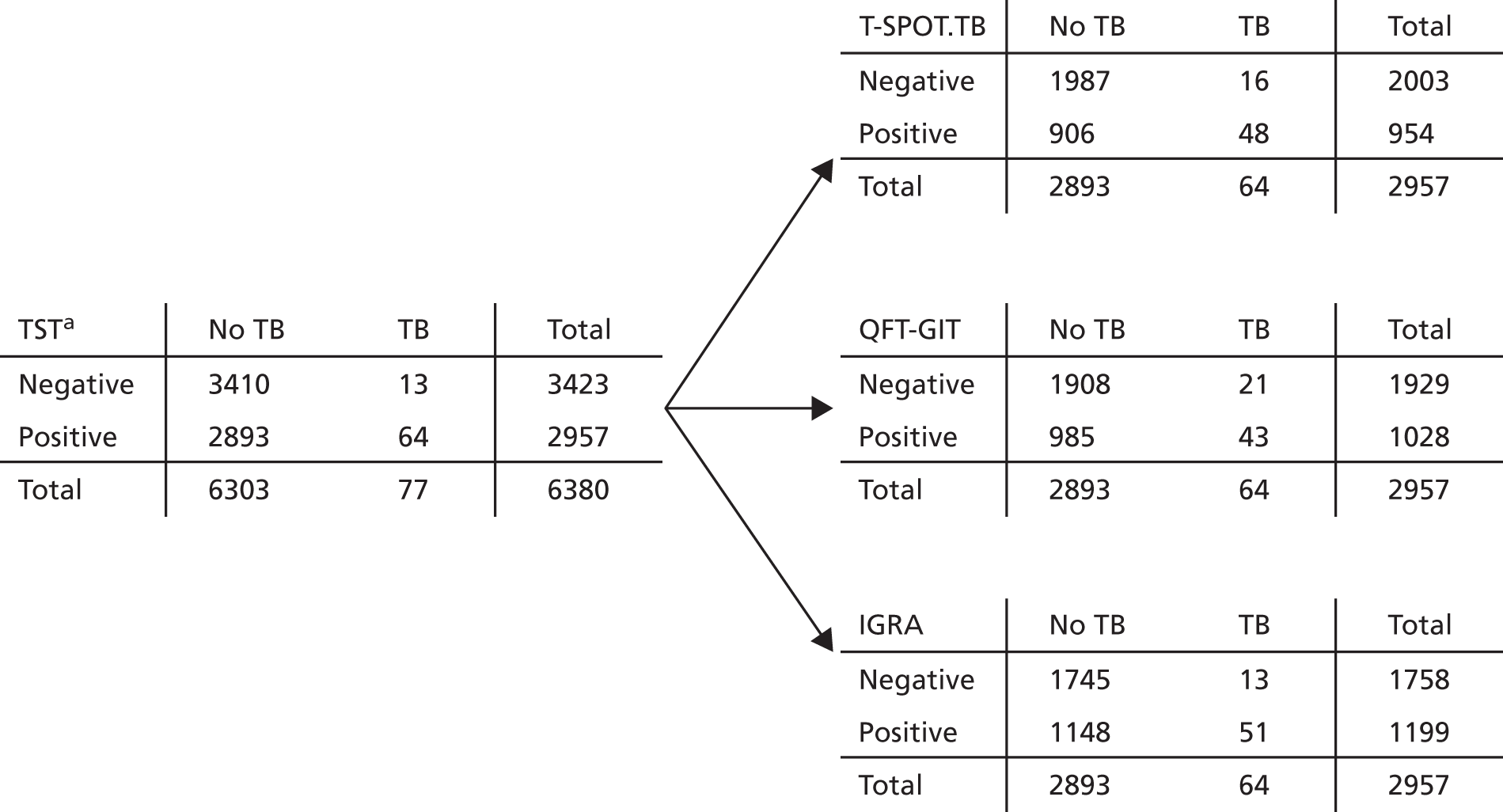
FIGURE 13.
Two-step strategies with TSTb as the first test.
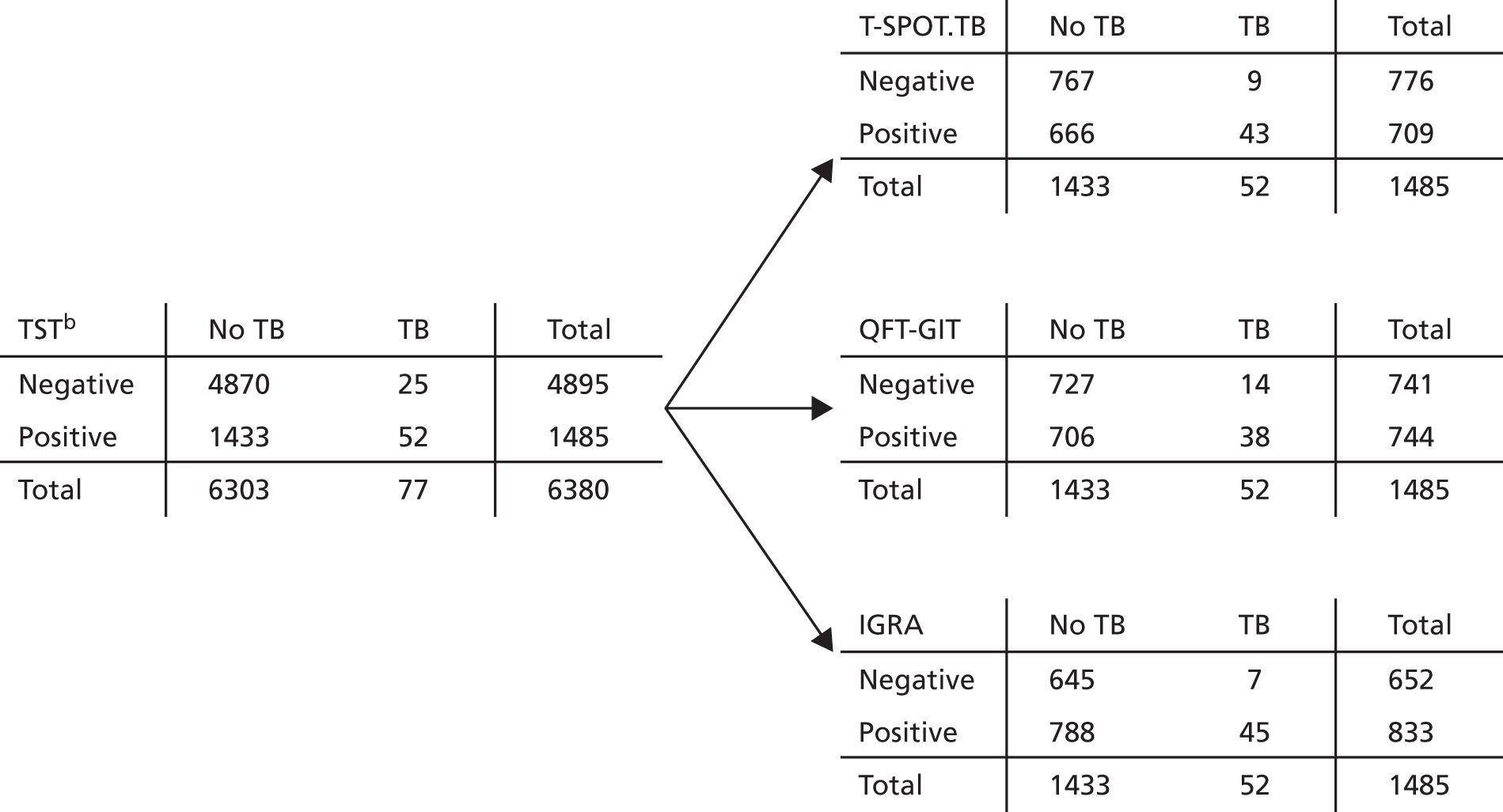
FIGURE 14.
Two-step strategies with T-SPOT.TB as the first test.
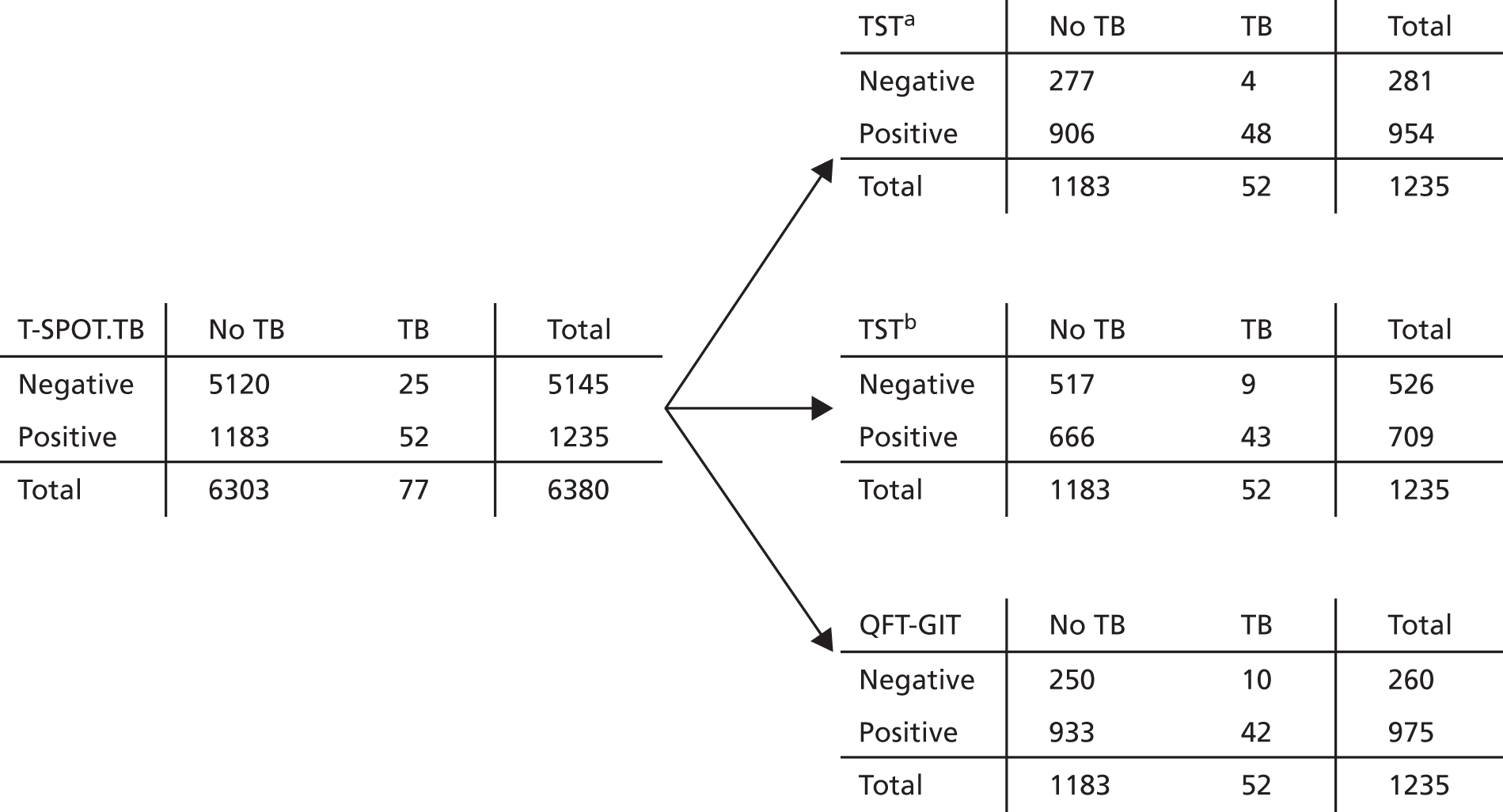
| Progression measure | TSTb result | TSTb result (assumed BCG vaccination status excluded) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| Progression (n/N) | 52/1485 | 25/4895 | 44/1320 | 23/4273 |
| Years at risk | 4674.8 | 15,896.6 | 4173.9 | 13,882.2 |
| IR (per 1000 participants per annum) | 11.1 | 1.6 | 10.5 | 1.7 |
| 95% CI | 8.3 to 14.6 | 1.0 to 2.3 | 7.7 to 14.2 | 1.1 to 2.5 |
| IRR (per 1000 per annum) | 7.1 | 6.4 | ||
| 95% CI | 4.4 to 11.4 | 3.8 to 10.5 | ||
| Progression measure | Test and result | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-SPOT.TB | QFT-GIT | TSTa | TSTb | |||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| No exclusions | ||||||||
| Progression (n/N) | 52/1235 | 25/5145 | 47/1444 | 30/4936 | 64/2957 | 13/3423 | 52/1485 | 25/4895 |
| Years at risk | 3926.2 | 16,645.3 | 4649.9 | 15,921.6 | 9416.8 | 11,154.6 | 4674.8 | 15,896.6 |
| IR (per 1000 per annum) | 13.2 | 1.5 | 10.1 | 1.9 | 6.8 | 1.2 | 11.1 | 1.6 |
| 95% CI | 9.9 to 17.4 | 1.0 to 2.2 | 7.4 to 13.4 | 1.3 to 2.7 | 5.2 to 8.7 | 0.6 to 2.0 | 8.3 to 14.6 | 1.0 to 2.3 |
| IRR (per 1000 per annum) | 8.8 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 7.1 | ||||
| 95% CI | 5.5 to 14.2 | 3.4 to 8.5 | 3.2 to 10.6 | 4.4 to 11.4 | ||||
| Excluding less-certain progressors | ||||||||
| Progression (n/N) | 49/1232 | 23/5143 | 44/1441 | 28/4934 | 60/2953 | 12/3422 | 48/1481 | 24/4894 |
| Years at risk | 3925.5 | 16,644.9 | 4649.2 | 15,921.2 | 9415.9 | 11,154.5 | 4673.9 | 15,896.5 |
| IR (per 1000 per annum) | 12.5 | 1.4 | 9.5 | 1.8 | 6.4 | 1.1 | 10.3 | 1.5 |
| 95% CI | 9.2 to 16.5 | 0.9 to 2.1 | 7.7 to 14.2 | 1.2 to 2.5 | 4.9 to 8.2 | 0.6 to 1.9 | 7.6 to 13.6 | 1.0 to 2.2 |
| IRR (per 1000 per annum) | 9.0 | 5.4 | 5.9 | 6.8 | ||||
| 95% CI | 5.5 to 14.8 | 3.4 to 8.6 | 3.2 to 11.0 | 4.2 to 11.1 | ||||
| Progression measure | Test and result | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-SPOT.TB | QFT-GIT | TSTa | TSTb | |||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| Must have data for all tests (n = 6380) | ||||||||
| Progression (n/N) | 52/1235 | 25/5145 | 47/1444 | 30/4936 | 64/2957 | 13/3423 | 52/1485 | 25/4895 |
| Years at risk | 3926.2 | 16,645.3 | 4649.9 | 15,921.6 | 9416.8 | 11,154.6 | 4674.8 | 15,896.6 |
| IR (per 1000 per annum) | 13.2 | 1.5 | 10.1 | 1.9 | 6.8 | 1.2 | 11.1 | 1.6 |
| 95% CI | 9.9 to 17.4 | 1.0 to 2.2 | 7.4 to 13.4 | 1.3 to 2.7 | 5.2 to 8.7 | 0.6 to 2.0 | 8.3 to 14.6 | 1.0 to 2.3 |
| IRR (per 1000 per annum) | 8.8 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 7.1 | ||||
| 95% CI | 5.5 to 14.2 | 3.4 to 8.5 | 3.2 to 10.6 | 4.4 to 11.4 | ||||
| All available data for each test | ||||||||
| Progression n/N | 56/1566 | 29/6402 | 53/1888 | 33/6624 | 77/3510 | 15/4315 | 60/1726 | 31/5935 |
| Years at risk | 4633.6 | 19,506.8 | 5605.5 | 19,541.2 | 10,831.2 | 13,365.2 | 5285.7 | 18,372.6 |
| IR (per 1000 per annum) | 12.1 | 1.5 | 9.5 | 1.7 | 7.1 | 1.1 | 11.4 | 1.7 |
| 95% CI | 9.1 to 15.7 | 1.0 to 2.1 | 7.1 to 12.4 | 1.2 to 2.4 | 5.6 to 8.9 | 0.6 to 1.9 | 8.7 to 14.6 | 1.1 to 2.4 |
| IRR (per 1000 per annum) | 8.1 | 5.6 | 6.3 | 6.7 | ||||
| 95% CI | 5.2 to 12.7 | 3.6 to 8.6 | 3.6 to 11.0 | 4.4 to 10.4 | ||||
| Progression measure | Test and result | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-SPOT.TB | QFT-GIT | TSTa | TSTb | |||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| Progression (n/N) | 11/280 | 3/994 | 9/318 | 5/956 | 11/588 | 3/686 | 9/283 | 5/991 |
| Years at risk | 940.9 | 3321.8 | 1075.9 | 3186.8 | 1967.9 | 2294.7 | 948.4 | 3314.2 |
| IR (per 1000 per annum) | 11.7 | 0.9 | 8.4 | 1.6 | 5.6 | 1.3 | 9.5 | 1.5 |
| 95% CI | 5.8 to 20.9 | 0.2 to 2.6 | 3.8 to 15.9 | 0.5 to 3.7 | 2.8 to 10.0 | 0.3 to 3.8 | 4.3 to 18.0 | 0.5 to 3.5 |
| IRR (per 1000 per annum) | 12.9 | 5.3 | 4.3 | 6.3 | ||||
| 95% CI | 3.6 to 46.4 | 1.8 to 15.9 | 1.2 to 15.3 | 2.1 to 18.8 | ||||
| Progression measure | Test and result | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-SPOT.TB | QFT-GIT | TSTa | TSTb | |||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| Progression (n/N) | 9/171 | 4/804 | 8/212 | 5/763 | 13/509 | 0/466 | 10/264 | 3/711 |
| Years at risk | 584.5 | 2752.4 | 741.8 | 2595.1 | 1725.2 | 1611.6 | 885.2 | 2451.6 |
| IR (per 1000 per annum) | 15.4 | 1.5 | 10.8 | 1.9 | 7.5 | 0.0 | 11.3 | 1.2 |
| 95% CI | 7.0 to 29.2 | 0.4 to 3.7 | 4.7 to 21.3 | 0.6 to 4.5 | 4.0 to 12.9 | 0.0 to 2.3 | 5.4 to 20.8 | 0.3 to 3.6 |
| IRR (per 1000 per annum) | 10.6 | 5.6 | N/A | 9.2 | ||||
| 95% CI | 3.3 to 34.4 | 1.8 to 17.1 | N/A | 2.5 to 33.5 | ||||
| Progression measure | TSTa/TSTb results | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive/positive | Positive/negative | Negative/negative | |
| Progression (n/N) | 52/1485 | 13/3423 | 12/1472 |
| Years at risk | 4674.8 | 4742.0 | 11,154.6 |
| IR (per 1000 per annum) | 11.1 | 2.5 | 1.2 |
| 95% CI | 8.3 to 14.6 | 1.3 to 4.4 | 0.6 to 2.0 |
Used a 1.5% discount rate for quality-adjusted life-years while retaining a 3.5% discount rate for costs
Maintaining the base-case discount rate of 3.5% for costs, we adjusted the discount rate for effects to 1.5% and, when necessary, we applied an instantaneous rate (the natural log of 1.5%). Compared with the base case, the three most cost-effective strategies maintain their positions in both subgroups, with similar probabilities of cost-effectiveness. There is, however, a notable increase in the number of discounted QALYs in both subgroups.
| Strategy | Mean per patient (discounted) | Incremental (vs. no test) | £20,000 per QALY | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (£) | QALYs | Cost (£) | QALYs | INB* (£) | Probability† (%) | |
| 0: TSTa | 301.33 | 32.43492 | 272.38 | 0.00046 | 263.18 | 0 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 242.07 | 32.43482 | 213.12 | 0.000359 | 205.93 | 0 |
| 4: TSTb | 224.36 | 32.4349 | 195.40 | 0.000441 | 186.58 | 0 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 213.28 | 32.43477 | 184.32 | 0.000315 | 178.01 | 0 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 204.38 | 32.43476 | 175.42 | 0.000302 | 169.39 | 0 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 204.75 | 32.43478 | 175.79 | 0.000323 | 169.34 | 0 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 205.34 | 32.43482 | 176.39 | 0.000356 | 169.27 | 0 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 191.39 | 32.43476 | 162.43 | 0.000303 | 156.37 | 0 |
| 8: QFT-GIT | 187.69 | 32.43474 | 158.73 | 0.000279 | 153.15 | 40 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 184.99 | 32.43478 | 156.03 | 0.000324 | 149.55 | 60 |
| 10: no test | 28.96 | 32.43446 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 |
| Strategy | Mean per patient (discounted) | Incremental (vs. no test) | £20,000 per QALY | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (£) | QALYs | Cost (£) | QALYs | INB* (£) | Probability† (%) | |
| 0: TSTa | 273.49 | 30.55115 | 246.11 | 0.00046 | 236.92 | 0 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 233.27 | 30.55111 | 205.89 | 0.000418 | 197.54 | 0 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 218.04 | 30.55114 | 190.66 | 0.000449 | 181.69 | 0 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 211.33 | 30.55108 | 183.95 | 0.000393 | 176.09 | 0 |
| 4: TSTb | 205.62 | 30.55108 | 178.25 | 0.000394 | 170.37 | 0 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 201.82 | 30.55105 | 174.44 | 0.00036 | 167.25 | 0 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 198.08 | 30.55109 | 170.70 | 0.000401 | 162.68 | 0 |
| 8: QFT-GIT | 192.83 | 30.55112 | 165.46 | 0.000433 | 156.80 | 7 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 187.57 | 30.55107 | 160.19 | 0.00038 | 152.59 | 2 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 182.55 | 30.55103 | 155.17 | 0.000346 | 148.25 | 91 |
| 10: No test | 27.38 | 30.55069 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 |
| Strategy | Original cohort (contacts) | Secondary contacts of index cases | Mean costs (£) combined (discounted) | Mean number of QALYs combined (discounted) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of TB cases | Number in cohort | TB incidence per 10,000 patients | Mean number of discounted QALYs | Number of TB cases | Number of secondary contacts | TB incidence per 10,000 patients | Mean number of discounted QALYs | |||
| 0: TSTa | 60 | 4162 | 145 | 22.13163 | 4 | 250 | 150 | 22.11595 | 302 | 22.13084 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 67 | 4162 | 160 | 22.13151 | 5 | 278 | 166 | 22.11877 | 204 | 22.13082 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 67 | 4162 | 161 | 22.13150 | 5 | 279 | 166 | 22.11905 | 213 | 22.13083 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 65 | 4162 | 156 | 22.13155 | 4 | 271 | 162 | 22.11736 | 242 | 22.13080 |
| 4: TSTb | 63 | 4162 | 152 | 22.13160 | 4 | 263 | 158 | 22.11746 | 224 | 22.13087 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 67 | 4162 | 162 | 22.13151 | 5 | 280 | 167 | 22.11921 | 185 | 22.13084 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 67 | 4162 | 161 | 22.13150 | 5 | 280 | 166 | 22.11915 | 191 | 22.13083 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 66 | 4162 | 158 | 22.13155 | 4 | 274 | 163 | 22.11805 | 205 | 22.13084 |
| 8: QFT-GIT | 65 | 4162 | 157 | 22.13154 | 4 | 271 | 162 | 22.11755 | 187 | 22.13080 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 66 | 4162 | 158 | 22.13152 | 4 | 273 | 162 | 22.11852 | 204 | 22.13085 |
| 10: no test | 79 | 4162 | 189 | 22.13122 | 6 | 330 | 195 | 22.12407 | 29 | 22.13076 |
| Strategy | Original cohort (contacts) | Secondary contacts of index cases | Mean costs (£) combined (discounted) | Mean QALYs combined (discounted) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of TB cases | Number in cohort | TB incidence per 10,000 patients | Mean number of discounted QALYs | Number of TB cases | Number of secondary contacts | TB incidence per 10,000 patients | Mean number of discounted QALYs | |||
| 0: TSTa | 51 | 3795 | 135 | 21.04275 | 3 | 212 | 150 | 22.11809 | 275 | 21.09962 |
| 1: TSTa + QFT-GIT | 55 | 3795 | 145 | 21.04265 | 4 | 230 | 166 | 22.11829 | 202 | 21.10401 |
| 2: TSTa + T-SPOT.TB | 55 | 3795 | 145 | 21.04265 | 4 | 229 | 166 | 22.11728 | 211 | 21.10384 |
| 3: TSTa + IGRA | 54 | 3795 | 142 | 21.04270 | 4 | 224 | 162 | 22.11736 | 234 | 21.10249 |
| 4: TSTb | 54 | 3795 | 141 | 21.04274 | 4 | 223 | 157 | 22.11721 | 206 | 21.10220 |
| 5: TSTb + QFT-GIT | 56 | 3795 | 146 | 21.04266 | 4 | 232 | 167 | 22.11816 | 182 | 21.10445 |
| 6: TSTb + T-SPOT.TB | 55 | 3795 | 146 | 21.04266 | 4 | 231 | 167 | 22.11774 | 187 | 21.10430 |
| 7: TSTb + IGRA | 54 | 3795 | 143 | 21.04271 | 4 | 226 | 163 | 22.11729 | 198 | 21.10307 |
| 8: QFT-GIT | 53 | 3795 | 139 | 21.04269 | 4 | 219 | 162 | 22.11858 | 193 | 21.10139 |
| 9: T-SPOT.TB | 53 | 3795 | 138 | 21.04270 | 4 | 219 | 163 | 22.11843 | 217 | 21.10130 |
| 10: No test | 68 | 3795 | 179 | 21.04237 | 6 | 285 | 194 | 22.12137 | 27 | 21.11764 |
List of abbreviations
- BCG
- bacillus Calmette–Guérin
- BMI
- body mass index
- CEA
- cost-effectiveness analysis
- CI
- confidence interval
- CPX
- chemoprophylaxis
- DES
- discrete event simulation
- ELISA
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- ELISPOT
- enzyme-linked immunospot
- EQ-5D
- EuroQol-5 Dimensions
- ETS
- enhanced tuberculosis surveillance
- GEE
- generalised estimating equation
- GP
- general practice
- HIV
- human immunodeficiency virus
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- IGRA
- interferon gamma release assay
- INB
- incremental net benefit
- IQR
- interquartile range
- IR
- incidence rate
- IRR
- incidence rate ratio
- LTBI
- latent tuberculosis infection
- MIRU-VNTR
- mycobacterial interspersed repetitive units – variable number tandem repeats
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NMRL
- National Mycobacterial Reference Laboratory
- NPV
- negative predictive value
- PBMC
- peripheral blood mononuclear cell
- PCT
- primary care trust
- PHE
- Public Health England
- PPV
- positive predictive value
- PREDICT
- Prognostic Evaluation of Diagnostic IGRAs ConsorTium
- PSA
- probabilistic sensitivity analysis
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- QFT-G
- QuantiFERON TB Gold
- QFT-GIT
- QuantiFERON TB Gold In-Tube
- RLR
- rate of likelihood ratio
- TB
- tuberculosis
- TNF-α
- tumour necrosis factor alpha
- TST
- tuberculin skin test
- WHO
- World Health Organization
