Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was commissioned and funded by the HTA programme on behalf of NICE as project number 16/30/05. The protocol was agreed in March 2018. The assessment report began editorial review in October 2018 and was accepted for publication in January 2019. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Howard Thom reports personal fees from Novartis Pharmaceuticals UK Ltd (Camberley, UK), Pfizer Inc. (New York, NY, USA), F. Hoffman-La Roche AG (Basel, Switzerland), Bayer AG (Leverkusen, Germany) and Janssen (Beerse, Belgium), all unrelated to the submitted work. Tom Marshall was a member of the National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment and Efficacy and Mechanism Evaluation Editorial Board (2009–11).
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2020. This work was produced by Duarte et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2020 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Background
Description of the target condition
Atrial fibrillation (AF) refers to a disturbance in heart rhythm (arrhythmia) that is caused by abnormal electrical activity in the upper chambers of the heart (atria). 1 The arrhythmia reduces the efficiency of the heart to move blood into the ventricles, increasing the risk of blood clots and consequent stroke. 1 AF is associated with conditions such as hypertension, heart failure, coronary artery disease, valvular heart disease, obesity, diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. 2
Types of atrial fibrillation
Three types of AF (based on presentation and duration of the arrhythmia) are described in Table 1.
| Type of AF | Description |
|---|---|
| Paroxysmal (intermittent) | Intermittent episodes that usually last < 7 days and stop without treatment |
| Persistent | Episodes that last > 7 days and do not stop without treatment |
| Permanent | Present all the time |
Atrial fibrillation can be categorised as valvular or non-valvular for the purposes of choosing the most suitable treatment. Categorisation as valvular or non-valvular refers to the underlying condition causing AF (i.e. whether or not there is valve disease present) rather than the duration of AF episodes. Both valvular AF and non-valvular AF can be paroxysmal, persistent or permanent. Patients diagnosed with paroxysmal AF can develop persistent or permanent AF. 2 It is also possible, but most unusual, for patients with persistent AF to revert to normal sinus rhythm. 2
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation
Patients with AF may experience palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath and tiredness. However, AF can be asymptomatic and may be identified only during medical appointments for other conditions. Because the symptoms are intermittent, many cases of paroxysmal AF remain undiagnosed. 2 Cases of paroxysmal AF may be detected only after a prolonged monitoring period, rather than from a single examination. 2
Epidemiology
Atrial fibrillation is the most common type of cardiac arrhythmia. Estimates from 2010 suggest that, worldwide, 20.9 million men and 12.6 million women are living with AF. 2 Higher rates of AF are recorded in developed countries than in undeveloped countries; however, this may be explained by differences in reporting. 2 Higher rates of AF are recorded in people living in Western countries (estimated incidence rate of 9.03 per 1000 patient-years)4 than in people living in Asian countries (estimated incidence rate of 5.38 per 1000 patient-years). 5 Despite a higher exposure to potential AF risk factors, such as hypertension and obesity, African American people were found to have a lower age- and sex-adjusted risk of being diagnosed with AF than white American people. 6
In the 2016 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines,2 the prevalence of AF in the European Union was reported to be 3%.The ESC also notes that one in four middle-aged people in Europe and the USA will develop AF. 2 The prevalence of AF in Europe is projected to increase over time because of the ageing population, an increase in incidence of conditions associated with AF and the improvements in the detection of AF. 2
The overall age-adjusted incidence of AF per 1000 patient-years in the primary care setting in the UK has increased from 1.11 [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.09 to 1.13] in 1998–2001 to 1.33 (95% CI 1.31 to 1.35) in 2007–10, with a constant increase in incidence reported in people aged ≥ 75 years. 7
In the NHS Quality and Outcomes Framework for 2015–16,8 the prevalence of AF in England is estimated to be 1.7%, which equates to 985,000 people. However, as noted, AF can be asymptomatic, which suggests that 1.7% may be an underestimate of the true prevalence. 9 Based on a reference population in a region of Sweden, Public Health England has estimated that the true prevalence of AF in England is likely to be 2.5% and that 1.4 million people in England are living with AF. 10 In the most recent data from the NHS Quality and Outcomes Framework for 2016–17, the prevalence of AF in England is estimated to be 1.8%, equating to 1,066,000 people. 11 An assessment of electronic primary care records identified an increase in the prevalence of AF in the UK from 2.14% in 2000 to 3.29% in 2016 in those aged ≥ 35 years. 12
The prevalence of AF increases with age and a higher proportion of men than women live with the condition (2.9% and 2.0%, respectively). 10 The median age at which people are diagnosed with AF is 75 years. 10 The largest numbers of AF diagnoses in men and women occur between the ages of 75 and 79 years and 80 and 84 years, respectively. 10 Although fewer women than men have AF, women experience higher mortality rates owing to AF-related strokes. 10
Paroxysmal AF is estimated to account for between 25% and 62% of patients with AF treated in hospitals and general practitioner (GP) practices. 13 Patients with paroxysmal AF tend to be younger and have fewer comorbidities (e.g. hypertension or congestive heart failure) than patients with persistent or permanent AF. 13,14
Impact of atrial fibrillation
Untreated AF is a major risk factor for stroke. AF is associated with a fivefold increase in the risk of stroke and a threefold increase in the risk of congestive heart failure. 15 Strokes with AF as the underlying cause may be more severe than strokes unrelated to AF. 16 Furthermore, each year in the UK, 100,000 people have a stroke and one in five of those strokes has AF as the underlying cause. 17
There is evidence to suggest that there are differences in the risk of stroke between patients with paroxysmal, persistent and permanent AF, with patients with paroxysmal AF having a lower risk of stroke than those with persistent or permanent AF. 18,19 The risk of stroke in patients with symptomatic AF is similar to that in patients with asymptomatic AF. 20
The ESC reports that, annually, between 10% and 40% of patients with AF are hospitalised and that patients with AF have impaired health-related quality of life (HRQoL), regardless of co-existing cardiovascular conditions. 2 Cognitive decline and vascular dementia are conditions suggested to develop from the onset of AF. 2
Current diagnostic and treatment pathways
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) clinical guideline CG1803 provides recommendations for the diagnosis and management of AF. An update of CG1803 is in progress.
Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation
In CG180,3 NICE recommends the use of manual pulse palpation (MPP) to detect the presence of an irregular pulse that may indicate underlying AF in people who have symptoms such as breathlessness/dyspnoea, palpitations, syncope/dizziness, chest discomfort, previous stroke or suspected transient ischaemic attack (TIA).
During the scoping stage of this assessment, clinical experts commented that people presenting with a stroke or TIA would undergo electrocardiogram (ECG) testing for AF in secondary care and are, therefore, outside the scope of an assessment that focuses on diagnosis in primary care.
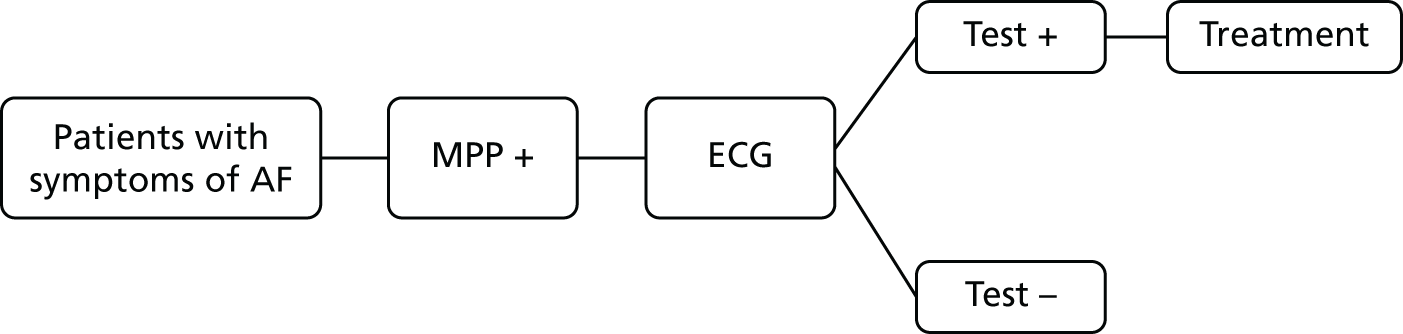
If AF is suspected because of an irregular pulse, NICE3 recommends that the diagnosis should be confirmed based on the results of an ECG. Patients who are suspected of having paroxysmal AF that is not detected by the ECG should be monitored using either a 24-hour ambulatory monitor or an event recorder ECG. Patients with confirmed AF may also undergo echocardiography to further inform the management of their condition. The current diagnostic pathway for people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of the condition and who have an irregular pulse is depicted in Figure 1.
FIGURE 1.
Current diagnostic pathway.
Management of atrial fibrillation
An overview of the treatment pathway described in CG1803 is provided in Figure 2. As shown in Figure 2, the management of AF is subdivided into four algorithms.
FIGURE 2.
Overview of AF algorithms. Source: NICE CG180. 3 © NICE 2014 Atrial fibrillation: management. Available from www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg180. All rights reserved. Subject to notice of rights (www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-of-rights).
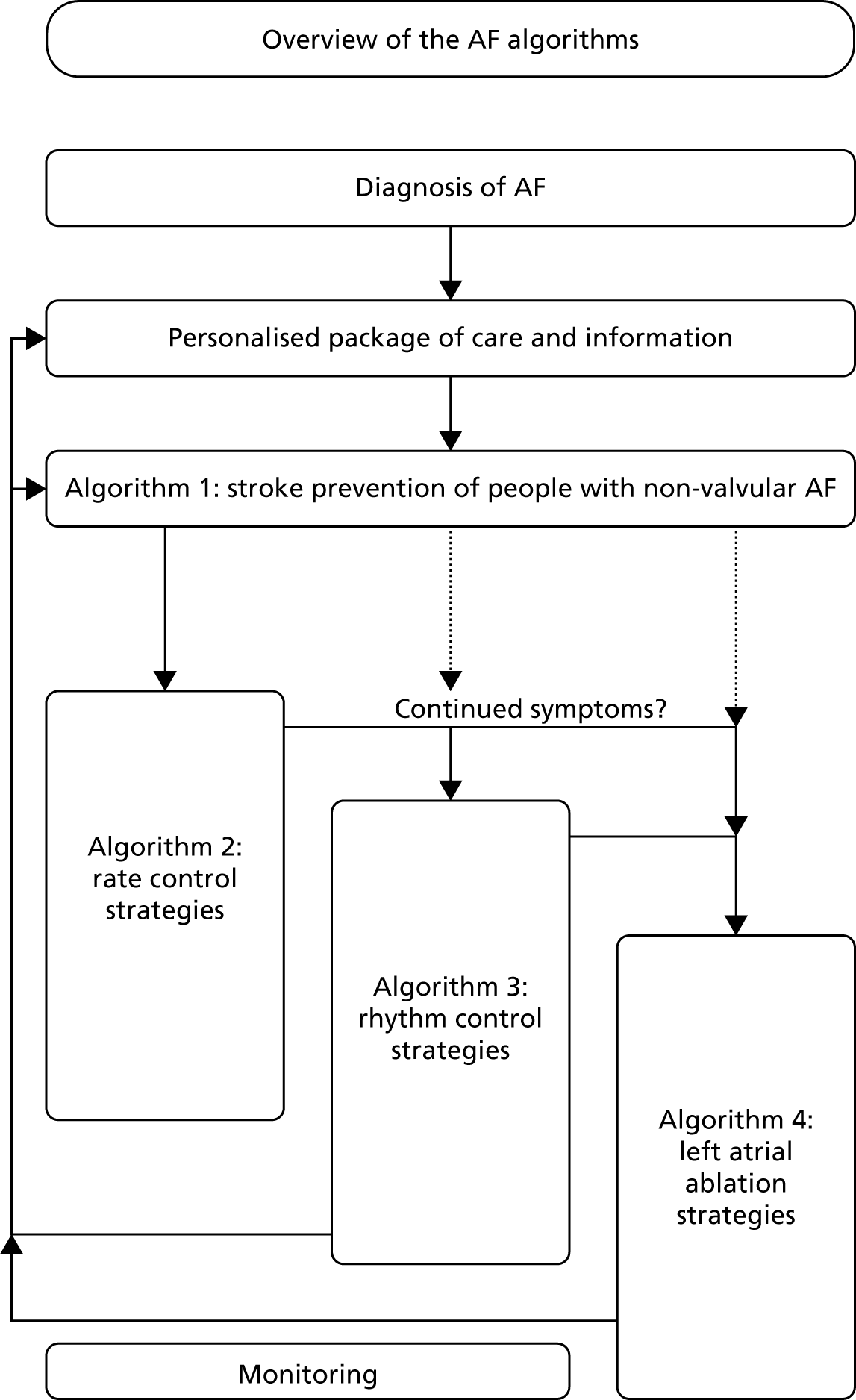
The aim of treatment is to reduce the symptoms of AF and prevent the potential consequences of undiagnosed AF, such as stroke. 3
Reducing stroke risk
In CG180,3 NICE recommends that patients with AF should be assessed for both their risk of stroke and their risk of bleeding. The risk of stroke should be assessed using the CHA2DS2-VASc21 algorithm [history of congestive heart failure, hypertension, age ≥ 75 years (doubled), diabetes mellitus, prior stroke or TIA (doubled), vascular disease, age 65–74 years, female] and the risk of bleeding should be assessed using the HAS-BLED22 algorithm (hypertension, abnormal liver/renal function, stroke history, bleeding predisposition, labile international normalised ratio, age, drug/alcohol use).
Depending on the age of the patient, the results of the CHA2DS2-VASc21 assessment and the results of the HAS-BLED22 assessment, patients with non-valvular AF may be offered stroke prevention treatment with either a vitamin K antagonist (usually warfarin) or a non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulant (NOAC) [i.e. apixaban (Eliquis®; Bristol–Myers Squibb, NY), dabigatran etexilate (Pradaxa®, Prazaxa®, Pradax®; Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH, Germany), rivaroxaban (Xarelto®; Bayer Health Care, Germany) or edoxaban (Lixiana®; Daiichi Sankyo, Japan)].
Rate and rhythm control
In CG180,3 NICE recommends (with some exceptions) that people with AF who need drug treatment as part of their rate-control strategy should be offered either a standard beta-blocker or a rate-limiting calcium-channel blocker. Exceptions include people whose AF has a reversible cause, those who have heart failure thought to be primarily caused by AF, those with new-onset AF, those with an atrial flutter whose condition is considered suitable for an ablation strategy to restore sinus rhythm or for those whom a rhythm control strategy would be more suitable based on clinical judgement. Digoxin may be offered to sedentary people who have non-paroxysmal AF. If monotherapy does not control the AF symptoms, and the symptoms are a result of poor ventricular rate control, dual therapy with any two of a beta-blocker, diltiazem and digoxin is recommended. 3 For rhythm control, NICE3 recommends pharmacological treatment with or without electrical rhythm control (cardioversion).
In CG180,3 NICE also recommends strategies for left atrial ablation to control AF.
Description of technologies under assessment
The technologies assessed (i.e. index tests) were lead-I ECG devices. Lead-I ECG devices are handheld instruments that can be used in primary care to detect AF at a single time point in people who present with relevant signs or symptoms (i.e. palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath and tiredness). Although lead-I ECG devices may also be used for ongoing or repeated testing for AF, and for the diagnosis of non-AF conditions, this use is outside the scope of this assessment.
Lead-I ECG devices feature touch electrodes and internal storage for ECG recordings, as well as software with an algorithm to interpret the ECG trace and indicate the presence of AF. Data from the lead-I ECG device can be uploaded to a computer to allow further analysis if necessary (e.g. in cases of paroxysmal AF).
The manufacturers of lead-I ECG devices all state that the diagnosis of AF should not be made using the algorithm alone, and that the ECG traces measured by the devices should be reviewed by a qualified health-care professional. The use of lead-I ECG devices following the detection of an irregular pulse by MPP may allow people with AF to initiate and benefit from earlier treatment with anticoagulants instead of waiting for the results of a confirmatory 12-lead ECG as per current practice.
Five different lead-I ECG devices are included in the final scope issued by NICE: imPulse (Plessey Semiconductors, Ilford, UK),23 Kardia Mobile (AliveCor Inc., Mountain View, CA, USA),24 MyDiagnostick (MyDiagnostick Medical B.V., Maastricht, the Netherlands),25 RhythmPad GP (Cardiocity, Lancaster, UK)26 and Zenicor ECG (Zenicor Medical Systems AB, Stockholm, Sweden). 27 The features of each device are described in imPulse, Kardia Mobile, MyDiagnostick, RhythmPad GP and Zenicor-ECG, respectively. All devices are CE (Conformité Européenne) marked.
imPulse
The lead-I ECG device is provided with downloadable software for data analysis (imPulse Viewer) and a cable for charging the device. The ECG readings are taken by holding the device in both hands and placing each thumb on a separate sensor on the device for a pre-set length of time (from 30 seconds to 10 minutes). To be operated, the device requires the associated software to be installed on a nearby PC or tablet. Data are transferred to hardware hosting the analytical software using Bluetooth (Bluetooth Special Interest Group, WA, USA), with the recorded ECG trace being displayed in real time.
Once the recording has finished, the generated ECG trace can be saved in the imPulse viewer. Previously recorded readings can also be loaded into this viewer and ECG traces can be saved as a PDF (Portable Document Format). The software has an AF algorithm that analyses the reading and states whether AF is unlikely, possible or probable. In the event of a ‘possible’ or ‘probable’ result, the company recommends that the person should undergo further investigation, and that the algorithm should not be used for a definitive clinical diagnosis of AF.
Kardia Mobile
The Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device works with the Kardia Mobile app to record and interpret ECGs. In addition to the Kardia Mobile device and app [www.alivecor.com/ (accessed January 2018)], a compatible Android (Google Inc., Mountain View, CA, USA) or Apple (Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA, USA) smartphone or tablet is required.
Two fingers from each hand are placed on the Kardia Mobile device to record an ECG that is sent wirelessly to the device hosting the Kardia Mobile app. The default length of recording is 30 seconds; however, this can be extended up to 5 minutes. The measured ECG trace is then automatically transmitted as an anonymous file to a European server for storage as an encrypted file.
The app uses an algorithm to classify measured ECG traces as (1) normal, (2) possible AF detected or (3) unclassified. The instructions for use state that the Kardia Mobile app assesses the patient for AF only, and the device will not detect other cardiac arrhythmias. Any detected non-AF arrhythmias, including sinus tachycardia, are labelled as unclassified. The company states that any ECG labelled as ‘possible AF’ or ‘unclassified’ should be reviewed by a cardiologist or trained health-care professional. ECG traces measured by the device can be sent from a smartphone or tablet by e-mail as a PDF attachment and stored in the patient’s records. The first version of the Kardia app did not have automatic diagnostic functionality. The AF algorithm was added to the app in January 2015. The Kardia Mobile has previously been available as the AliveCor Heart Monitor.
MyDiagnostick
The MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG recording is generated after a patient holds the metal handles at each end of the device for 1 minute. A light on the device will turn green if no AF is detected or turn red if AF is detected. If an error occurs during the reading, the device produces both an audible warning and a visible warning from the light on the device. Up to 140 ECG recordings can be recorded on the device before it starts to overwrite previous recordings. The MyDiagnostick device can be connected to a computer via a USB (universal serial bus) connection to download the generated ECG trace for review and storage using free software that can be downloaded from the MyDiagnostick website [www.mydiagnostick.com (accessed January 2018)].
RhythmPad GP
The RhythmPad GP lead-I ECG readings are taken by placing the palms of both hands on the surface of the device for 30 seconds. Alternative configurations can be used if a person is unable to place their hands flat on the device, for example if they have arthritis. The software needs to be installed on a device running Windows XP (Microsoft, WA, USA) or a later version, and that has a USB port. Data are transferred directly to a computer using the USB connection to be stored on the device’s hard drive in PDF format.
The software includes an algorithm that can determine if a person has AF, and can additionally detect if a person has bradycardia, tachycardia, sinus arrhythmia, premature ventricular contractions or right bundle branch block. The recorded ECG trace is also available for further analysis by a health-care professional. The company recommends that a 12-lead ECG device is used to confirm a case of AF detected by the RhythmPad GP device.
Zenicor-ECG
The Zenicor-ECG is a system with two components: a lead-I ECG device (Zenicor-EKG 2) and an online system for analysis and storage (Zenicor-EKG Backend System version 3.2). The online system is not locally installed; the device transmits data to a remote server that can be accessed using a web browser, without prior installation of software, and requires a user licence. ECG readings are taken by placing both thumbs on the device for 30 seconds. The instructions for use state that the electrodes in the Zenicor EKG-2 should be replaced after every 500 measurements. The device is powered by three alkaline batteries that the company states are expected to last for at least 200 measurements and transmissions.
Once a measurement is made using the Zenicor-EKG 2 device, the ECG measurement can be transferred from the device (using a built-in mobile network modem) to a Zenicor server in Sweden. Here, the ECG trace is analysed using the Zenicor-EKG Backend System, which includes an automated algorithm. The algorithm categorises an ECG into one of 12 groups corresponding to potential arrhythmias, one of which includes AF. The algorithm will also report if the recorded ECG trace cannot be analysed. The company states that a clinician needs to manually interpret the ECG trace generated by the Zenicor-ECG to make a final diagnosis of AF.
The measured ECG trace can be downloaded or printed as a PDF report. The company states that the ECG is available via the web interface approximately 4–5 seconds after the ECG has been transmitted from the device.
The company states that the Zenicor EKG-2 does not store, contain or transmit any patient-identifying information. ECGs are sent via the built-in mobile network modem to the Zenicor server labelled with the device’s identity number. Communication between the Zenicor server and the web browser accessing it is encrypted.
Comparator
To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of lead-I ECG devices, the comparator of interest is other lead-I ECG devices as described above or no comparator (Table 2). To evaluate the clinical impact of lead-I ECG devices, the comparator of interest is MPP followed by a 12-lead ECG in primary or secondary care prior to initiation of anticoagulation therapy.
| Characteristic | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Population | (1) People with signs or symptoms that may indicate underlying AF and who have an irregular pulse; or (2) asymptomatic populationa if no evidence for (1) is available | |
| Setting | Primary care (ideal), secondary or tertiary care | |
| Index tests | Lead-I ECG using one of the following technologies:
|
|
| Clinical impact | DTA | |
| Comparator | Manual pulse palpation followed by a 12-lead ECG in primary or secondary care prior to initiation of anticoagulation therapy or other lead-I ECG devices as specified in Description of technologies under assessment | Other lead-I ECG devices as specified above, or no comparator |
| Reference standard | Not applicable | 12-lead ECG performed and interpreted by a trained health-care professional |
| Outcomes | Intermediate outcomes
|
DTA
|
Clinical outcomes
|
||
Patient-reported outcomes
|
||
| Study design | RCTs, cross-sectional, case–control, cohort and uncontrolled single-arm studies. Qualitative studies were considered to evaluate the ease of use of the devices | Diagnostic cross-sectional and case–control studies |
Reference standard
The index test results are compared with the results of a reference standard for an assessment of DTA. The reference standard is used to verify the presence or absence of the target condition (i.e. AF). The reference standard for this assessment is 12-lead ECG performed and interpreted by a trained health-care professional.
Aim of the assessment
The aim of this assessment was to evaluate whether or not the use of lead-I ECG devices to detect AF in people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of the condition and who have an irregular pulse represents a cost-effective use of NHS resources compared with MPP followed by a 12-lead ECG in primary or secondary care prior to initiation of anticoagulation therapy.
Chapter 2 Methods for assessing diagnostic test accuracy and clinical impact
Two systematic literature reviews were conducted to evaluate (1) the DTA of single-time point lead-I ECG for the diagnosis of AF, using 12-lead ECG as the reference standard, in people with signs or symptoms that may indicate underlying AF and who have an irregular pulse, and (2) the clinical impact of single time point lead-I ECG devices compared with MPP followed by a 12-lead ECG in both primary care and secondary care. The methods for the systematic review followed the general principles outlined in the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination guidance for conducting reviews in health care,28 NICE’s Diagnostics Assessment Programme manual29 and the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy. 30 The systematic review is reported in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines for DTA studies. 31 The PRISMA-DTA checklist and PRISMA-DTA for abstracts checklist are presented in Appendices 1 and 2, respectively.
Search strategy
The search strategies were designed to focus on the specified devices (i.e. imPulse, Kardia Mobile, MyDiagnostick, RhythmPad GP and Zenicor ECG) and the target condition (i.e. AF). No study design filters were applied and all electronic databases were searched from inception to 9 March 2018. The search strategy used for the MEDLINE database is presented in Appendix 3. The MEDLINE search strategy was adapted to enable similar searches of the other relevant electronic databases. The following databases were searched for relevant studies:
-
MEDLINE (via Ovid)
-
MEDLINE Epub Ahead of Print and MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations (via Ovid)
-
EMBASE (via Ovid)
-
PubMed
-
CDSR
-
CENTRAL
-
DARE (via The Cochrane Library)
-
Health Technology Assessment (HTA) database (via The Cochrane Library).
The results of the searches were uploaded to, and managed, using EndNote X8 software [Clarivate Analytics (formerly Thomson Reuters), Philadelphia, PA, USA]. The reference lists of relevant systematic reviews and eligible studies were hand-searched to identify further potentially relevant studies. Data submitted by the manufacturers of the five lead-I ECG devices that are the focus of this assessment were considered for inclusion in the review.
Eligibility criteria
The eligibility criteria for the inclusion of studies assessing the clinical impact or DTA of lead-I ECG devices are presented in Table 2.
Although the index test (i.e. the test being evaluated) should be performed in a primary care setting, studies in which the index tests were performed and interpreted by a cardiologist in a secondary or tertiary care setting were also considered eligible for inclusion. This is because it is plausible that in clinical practice (primary care setting) the test results could be sent for remote interpretation by a cardiologist.
Studies that assessed the DTA or the clinical impact of lead-I ECG devices used at a single time point to detect AF in an asymptomatic population were considered for inclusion if no studies were identified in a symptomatic population. An asymptomatic population was considered to be people not presenting with symptoms of AF, with or without a previous diagnosis of AF. These patients could have other cardiovascular comorbidities, or could be attending a clinic for cardiovascular-related reasons, but not be presenting with signs or symptoms of AF. The use of lead-I ECG devices for ongoing or repeated testing for AF is outside the scope of this assessment.
Studies that did not present original data (i.e. reviews, editorials and opinion papers), case reports and non-English language studies were excluded from the review. Conference proceedings published from 2013 onwards were considered for inclusion.
Study selection
The citations identified were assessed for inclusion in the review using a two-stage process. First, two reviewers independently screened all of the titles and abstracts identified by the electronic searches to distinguish the potentially relevant studies to be retrieved. Second, full-text copies of these studies were obtained and assessed independently by two reviewers for inclusion using the eligibility criteria outlined in Table 2. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion at each stage, and, if necessary, in consultation with a third reviewer.
Data extraction
A data extraction form was designed, piloted and finalised to enable data extraction relating to study authors, year of publication, study design, characteristics of study participants, prevalence of comorbidities, prevalence of AF by type, characteristics of the index, comparator and reference standard tests (including length of monitoring, who performed and interpreted the test), the order in which the index and comparator/reference standard tests were performed, whether or not the person who interpreted the reference standard test was blind to the results of the index test, and the outcome measures as described in Table 2.
Data extraction was performed by one reviewer and checked for accuracy by a second reviewer. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion, and, if necessary, in consultation with a third reviewer. The manufacturers of the index tests and the corresponding authors of the studies selected for assessment of DTA were contacted for missing data or clarification of the data presented.
Quality assessment
The methodological quality of DTA studies was assessed using the QUality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies–2 (QUADAS-2) tool tailored to the review question. 32 The QUADAS-2 tool considers four domains: (1) patient selection, (2) index test(s), (3) reference standard and (4) flow of patients through the study and the timing of the tests.
The methodological quality of cross-sectional and case–controlled studies that evaluated the clinical impact of lead-I ECG devices was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa quality assessment scale. 33,34 We had planned to use the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool35 to assess the methodological quality of randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of clinical impact, but no RCTs were identified. 35 Qualitative studies were assessed using the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) tool. 36
Quality assessment of the included studies was undertaken by one reviewer and checked by a second reviewer. Any disagreements were resolved by discussion, and, if necessary, in consultation with a third reviewer.
Methods of analysis/synthesis of diagnostic test accuracy studies
Statistical analysis and data synthesis
Individual study results
The sensitivity and specificity of each index test from studies of diagnostic accuracy were summarised in forest plots and plotted in receiver operating characteristic (ROC) space.
Meta-analysis
The bivariate model was used to obtain pooled estimates of sensitivity and specificity for lead-I ECG devices. 37 The pooled estimates for sensitivity and specificity were plotted in ROC space with a 95% confidence region around this summary estimate. The 95% confidence region depicts a range of sensitivity and specificity values within which the analyst can be 95% confident that the true sensitivity and specificity values for the index test lie.
The analyses were stratified by whether the diagnosis of AF was made by a trained health-care professional interpreting the lead-I ECG trace, or by the lead-I ECG algorithm. Within these stratified analyses, it was not possible to compare the diagnostic accuracy of different types of lead-I ECG device by adding a covariate for device type owing to the sparsity of the data. We were also unable to perform subgroup analyses to assess the impact of potential sources of heterogeneity on the diagnostic accuracy of lead-I ECG devices owing to the sparsity of the data.
For one study38 that reported data for two types of lead-I ECG device (MyDiagnostick and Kardia Mobile) and for two different interpreters of lead-I and 12-lead ECG traces for the same patient cohort, we performed multiple analyses so that we could investigate the impact of varying both the type of lead-I ECG device and the interpreter on the results of the overall pooled analysis. Therefore, no set of patients was double-counted in any of the meta-analyses performed. The data for the lead-I ECG device (MyDiagnostick defined as device 1 and Kardia Mobile defined as device 2) and the electrophysiologist (EP) (EP1 or EP2) that were included in the main analysis were randomly selected by using the command r(uniform) in Stata version 14 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA) to randomly generate the number 1 or 2 first for device and then for EP. Additional analyses are presented as sensitivity analyses.
One study39 reported data for one lead-I ECG device (Kardia Mobile) and two different interpreters (a cardiologist and a GP with an interest in cardiology) of lead-I and 12-lead ECG traces. The data interpreted by the cardiologist were used in the main analysis because the interpreters in the other included studies were either cardiologists or EPs. The analysis with data interpreted by the GP is presented as a sensitivity analysis.
The bivariate model was fitted using the metandi and xtmelogit commands in Stata version 14 where at least four studies could be included in meta-analysis. Summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) plots were produced using RevMan 5.3 (RevMan; The Cochrane Collaboration, The Nordic Cochrane Centre, Copenhagen, Denmark). When there were fewer than four studies, the bivariate model was reduced to two univariate random-effect logistic regression models by assuming no correlation between sensitivity and specificity across studies. 40 When little or no heterogeneity was observed on forest plots and SROC plots, the models were further simplified into fixed-effect models by eliminating the random-effects parameters for sensitivity and/or specificity. 40 Judgement of heterogeneity was based on the visual appearance of forest plots and SROC plots in addition to clinical judgement regarding potential sources of heterogeneity.
Sensitivity analyses
We had planned to conduct sensitivity analyses by excluding studies judged as having a high risk of bias or studies where the appropriateness of inclusion in the primary meta-analyses was uncertain. Sensitivity analyses stratified by risk of bias were not performed owing to the small number of studies included in the meta-analysis with similar risk-of-bias judgements.
Methods of analysis/synthesis of clinical impact studies
We had planned to perform a meta-analysis of the clinical and intermediate outcomes stated in Table 2. After data extraction, we considered pooling data for the outcome of diagnostic yield; however, on examination of the forest plots displaying diagnostic yield data for the included studies, we judged the data to be too heterogeneous for pooling to give clinically meaningful results. Therefore, we produced forest plots displaying individual study results from all included studies and additional forest plots displaying individual study results stratified by device type and by setting. These forest plots were produced in Stata 14 using the metaprop command.
Other considerations
‘Real-world’ data describing the clinical impact of lead-I ECG devices were received from the Kent Surrey Sussex Academic Health Science Health Network (AHSN) and these are included in Chapter 3, Clinical impact results.
Chapter 3 Results of the assessment of diagnostic test accuracy and clinical impact
Study selection
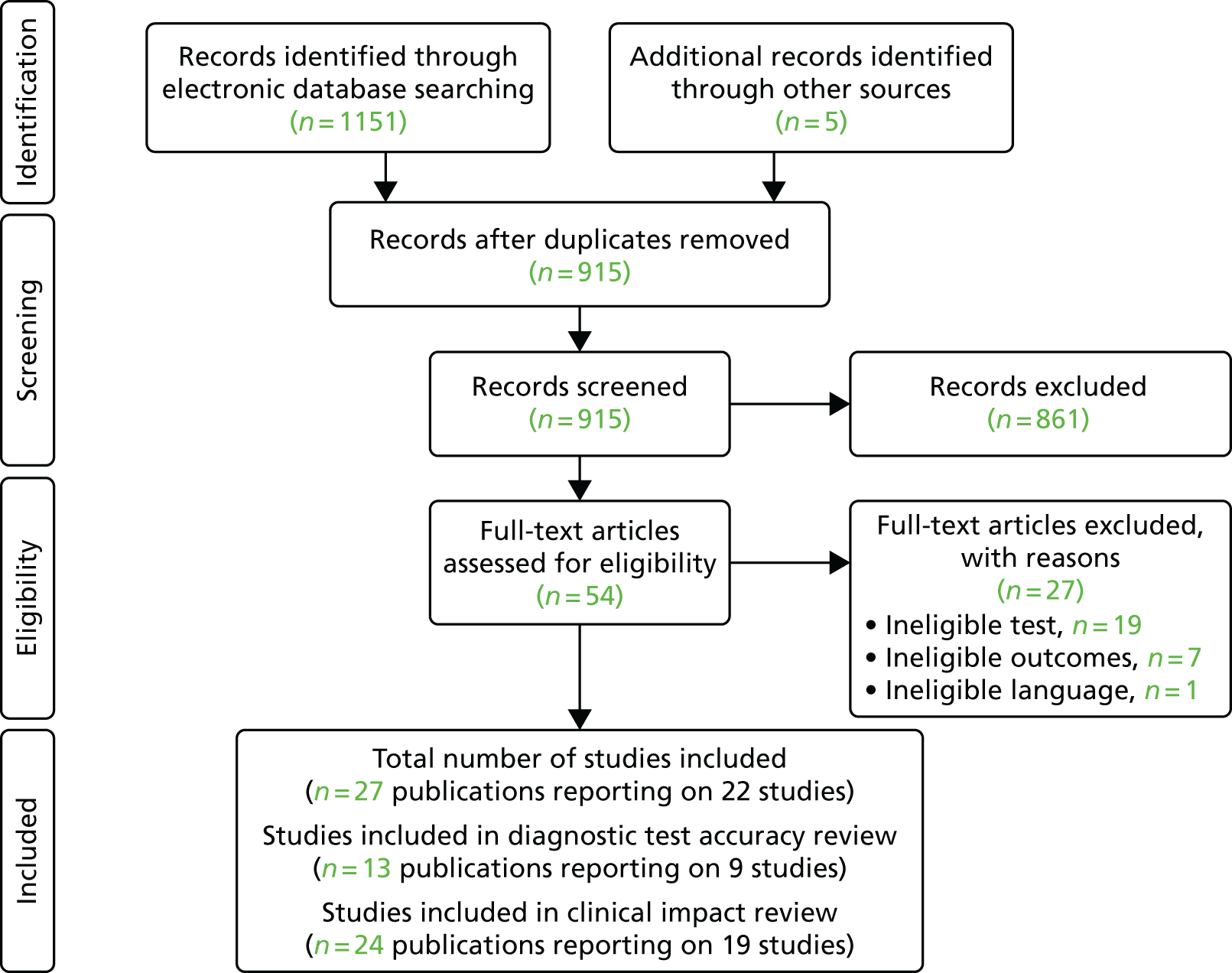
The searches of the electronic databases identified 1151 citations. After the removal of duplicate records, 915 potential citations remained. Following initial screening of titles and abstracts, 54 publications were considered to be potentially relevant and were retrieved to allow assessment of the full-text publication.
No studies were identified for the population of interest (i.e. people with signs or symptoms that may indicate underlying AF and who have an irregular pulse). Therefore, all of the included studies assessed the DTA and clinical impact of lead-I ECG devices used at a single time point to detect AF in an asymptomatic population (see Chapter 2, Eligibility criteria).
After review of the full-text publications, 13 publications38,39,41–51 reporting on nine studies were included in the DTA review and 24 publications38,41–48,51–65 reporting on 19 studies were included in the clinical impact review. Where there were overlaps in data and reporting as a result of studies being reported in several papers and abstracts, we selected the publication with the most complete data and treated it as the main publication. The PRISMA66 flow chart detailing the screening process for the review is shown in Figure 3. Studies excluded at the full-text paper screening stage and the reasons for exclusion are presented in Appendix 4.
FIGURE 3.
The PRISMA flow chart. Reproduced from Duarte et al. 67 © The Authors, 2019. This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt and build upon this work, for commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
We contacted the authors of three studies47,50,51 to obtain additional data on DTA or to clarify the data on DTA reported in the publication. We did not receive a response from one set of authors. 51 One set of authors provided additional information that allowed their study47 to be included in the DTA meta-analysis. One set of authors also provided additional information on their study,50 but stated that the algorithm had been modified since the study was reported. For this reason, the sensitivity and specificity of the lead-I ECG device used are presented but are not included in the meta-analysis.
Assessment of diagnostic test accuracy
Characteristics of the included studies
The characteristics of the nine included DTA studies are summarised in Table 3.
| Study (first author, year) | Study design; country and setting | Population; number in analysis and recruitment details | Mean age and SD (years); sex; risk factors for AF | Lead-I ECG device | Interpreter of lead-I ECG | Test sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crockford, 201350 | Cross-sectional; UK; secondary care | Patients referred to an electrophysiology department; N = 176; NR | NR | RhythmPad GP | Algorithm | 12-lead ECG followed by lead-I ECG |
| Desteghe, 201738 | Case–control; Belgium; tertiary care | Inpatients at cardiology ward; N = 265; NR |
67.9 ± 14.6; female, n = 138 (43.1%); Pacemaker: 4 out of 55 (7.3%) were intermittently paced, and 18 out of 55 (32.7%) were not being paced during the recordings Known AF: 114 out of 320 (35.6%) AF at time of study: 11.9% on 12-lead ECG; 3.4% of all patients admitted because of symptomatic AF Paroxysmal AF: 54.4% |
MyDiagnostick and Kardia Mobile | Algorithm and two EPs (results presented separately for algorithm and two EPs) | 12-lead ECG followed by lead-I ECG (order for the use of the different lead-I ECG tests not specified) |
| Doliwa, 200943 | Case–control; Sweden; secondary care | People with AF, atrial flutter or sinus rhythm; N = 100; patients were recruited from a cardiology outpatient clinic | NR | Zenicor-ECG | Cardiologist | 12-lead ECG followed by lead-I ECG |
| Haberman, 201545 | Case–control; USA; community and secondary care | Healthy young adults, elite athletes and cardiology clinic patients; N = 130; NRa |
59 ± 15; male, n = 73 (56%); NR |
Kardia Mobile | EP | Lead-I ECG followed by 12-lead ECG |
| Koltowski, 201751 | Cross-sectional; Poland; tertiary care | Patients in a tertiary care centre; N = 100; NR | NR | Kardia Mobile | Cardiologist | Lead-I ECG followed by 12-lead ECG |
| Lau, 201347 | Case–control; Australia; secondary care | Patients at cardiology department; N = 204; NR |
NR; Known AF: n = 48 (24%) |
Kardia Mobile | Algorithm | Lead-I ECG followed by 12-lead ECG |
| Tieleman, 201448 | Case–control; Netherlands; secondary care | Patients with known AF and patients without a history of AF attending an outpatient cardiology clinic or a specialised AF outpatient clinic; N = 192; random selection of patients awaiting a 12-lead ECG |
69.4 ± 12.6; male, 48.4%; NR |
MyDiagnostick | Algorithm | Lead-I ECG followed by 12-lead ECG |
| Vaes, 201449 | Case–control; Belgium; primary care | Patients with known AF and patients without a history of AF; N = 181; GP invitation |
74.6 ± 9.7; female, n = 91 (48%); Known AF: n = 151 (83.4%) |
MyDiagnostick | Algorithm | Lead-I ECG followed by 12-lead ECG |
| Williams, 201539 | Case–control; UK; secondary care | Patients with known AF attending an AF clinic and patients with AF status unknown who were attending the clinic for non-AF-related reasons; N = 95; patients attending clinic appointments who were awaiting a 12-lead ECG | NR | Kardia Mobile | Cardiologist and GP with an interest in cardiology | 12-lead and lead-I ECG carried out simultaneously |
The studies included in the DTA review were either case–control studies38,39,43,45,47–49 or cross-sectional studies. 50,51 Two of the studies were based in the UK. 39,50 Only one study was conducted in primary care,49 with the remaining studies being conducted in either secondary39,43,45,47,48,50 or tertiary care. 38,51 All of the studies included either patients with a known history of AF or patients recruited from cardiology clinics. Only one study38 presented the reasons that patients were admitted to a cardiology department. Eleven patients (3.4%) were admitted because of symptomatic AF, all of whom had a known history of AF. The study by Haberman et al. 45 included a community-based population comprising healthy young adults and elite athletes. The results for the healthy young adults and elite athletes were excluded from the analysis because these participants did not meet the population inclusion criteria for this review and do not represent the typical population with AF (i.e. those aged > 75 years). 10 The study by Lau et al. 47 included a ‘learning set’ and data from this group were used to optimise the algorithm. The ‘learning set’ data were excluded from the analysis because, according to the author of the study (Ben Freedman, University of Sydney, 15 June 2018, personal communication), two separate cardiologists interpreted the rhythm strips, and the interpretation by cardiologist A seemed to have a bias towards sensitivity, with a resultant lower specificity, while the interpretation by cardiologist B had a slightly lower sensitivity, with a resulting higher specificity.
Only one study included results based on lead-I ECG interpretation by the device algorithm and a trained health-care professional presenting the results separately. 38 One study39 reported data for a lead-I ECG trace that was interpreted both by a cardiologist and by a GP with an interest in cardiology; the results were presented separately for each interpreter. In four studies,47–50 the lead-I ECG was interpreted by the device algorithm alone.
The lead-I ECG devices used in the included studies were Kardia Mobile,39,45,47,51 MyDiagnostick,48,49 RhythmPad GP50 and Zenicor-ECG. 43 The study by Desteghe et al. 38 used both Kardia Mobile and MyDiagnostick and presented the results separately for each device.
The trained health-care professional interpreting the 12-lead ECG in all of the studies included in the DTA review was a cardiologist,39,43,47–49,51 an EP38,45,50 or a GP with an interest in cardiology. 39
Quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies
All of the included studies were assessed for risk of bias and applicability using the QUADAS-2 tool. 32 A summary of the results that assessed risk of bias and applicability concerns across all studies is presented in Table 4. The full assessment for each included study is presented in Appendix 5.
| Study (first author, year) | Risk of bias | Applicability concerns | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient selection | Index test | Reference standard | Flow and timing | Patient selection | Index test | Reference standard | |
| aCrockford, 201350 | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | High | Unclear | Low |
| Desteghe, 201738 | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| Doliwa, 200943 | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| Haberman, 201545 | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | High | Low | Low |
| bKoltowski, 201751 | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | High | Unclear | Low |
| Lau, 201347 | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | High | High | Low |
| Tieleman, 201448 | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | High | High | Low |
| Vaes, 201449 | Unclear | Low | Low | Unclear | High | High | Low |
| Williams, 201539 | Unclear | Low | Low | Unclear | High | Low | Low |
All of the included studies were judged as being at an unclear risk of bias for the patient selection domain. Only one study48 reported the method used for patient inclusion. There was an overall lack of information regarding patient eligibility for participation in the studies, and whether or not any patients were excluded at the stage of study selection. All of the included studies were judged as having a high applicability concern for patient selection as none of these studies was performed in the population of interest. One study38 included a proportion (3.4%) of patients admitted to a cardiology department because of symptomatic AF; however, all of these patients had a known history of AF.
Three studies45,50,51 were judged as having an unclear risk of bias in the index test domain because there was lack of information regarding whether or not the index tests were interpreted without knowledge of the reference standard test result. The remaining six studies38,39,43,47–49 were judged as having a low risk of bias on the index test domain. Studies in which the index test was interpreted by a trained health-care professional were judged to be more applicable (low concern)38,39,43,45 than those interpreted by the lead-I ECG device algorithm alone. 47–49 Two studies50,51 were judged as having an unclear applicability concern because of a lack of information in the publication.
Three studies45,50,51 were judged as having an unclear risk of bias for the reference standard domain because they did not explicitly report whether or not the interpreters of the reference standard were blinded to the results of the index test. The reference standard for all of the included studies was the results of a 12-lead ECG, which were interpreted by a trained health-care professional; therefore, all of the studies were judged to have a low concern regarding applicability of the reference standard.
Risk of bias was judged as being unclear for three studies39,49,50 for the flow and timing domain because not all patients were included in the study analyses.
Diagnostic test accuracy results
Interpreter of lead-I electrocardiogram: trained health-care professional
All lead-I electrocardiogram devices: main analysis
We investigated the sensitivity and specificity of a lead-I ECG device when the trace was interpreted by a trained health-care professional and the reference standard was a 12-lead ECG interpreted by a trained health-care professional. Data from four studies38,39,43,45 were included in a meta-analysis. Two studies39,45 had data for Kardia Mobile alone, one study43 had data for Zenicor-ECG and one study38 had data for MyDiagnostick and Kardia Mobile. One additional study51 had data for Kardia Mobile but was not included in the pooled analysis because the numbers of true-positive, false-negative, false-positive and true-negative test results were not reported. The sensitivity and specificity values reported in this study51 were 92.8% and 100%, respectively.
Four meta-analyses were conducted to investigate the impact of using data for each combination of type of lead-I ECG device (MyDiagnostick or Kardia Mobile) and interpreter (EP1 or EP2) from the Desteghe et al. study38 from the results of the meta-analysis. Both EPs interpreted the lead-I ECG trace and the 12-lead ECG trace. The data based on the use of Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device and interpretation by EP1 were randomly selected to be included in the main analysis. Additional meta-analyses are presented as sensitivity analyses (see Appendix 6, Figure 13).
One study39 reported data for one lead-I device (Kardia Mobile) and two different interpreters (a cardiologist and a GP with an interest in cardiology) of lead-I and 12-lead ECG traces. The data interpreted by the cardiologist were used in the main analysis because the interpreters in the other included studies were either cardiologists or EPs. The analysis with data interpreted by the GP is presented as a sensitivity analysis (see Appendix 6, Figure 17).
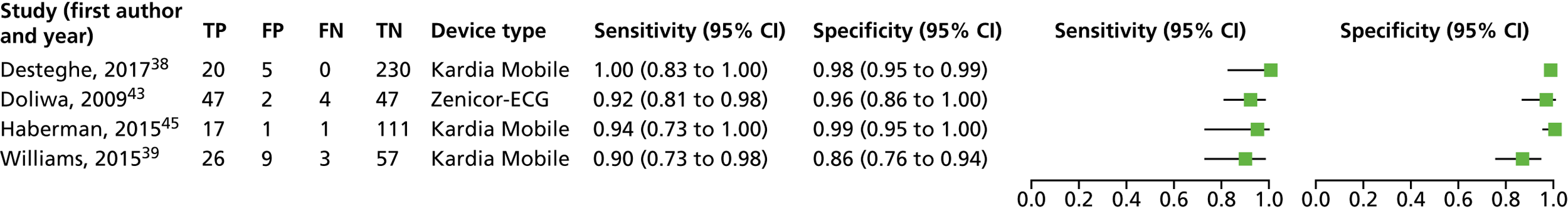
A forest plot displaying the results of the individual studies included in the meta-analysis is presented in Figure 4.
FIGURE 4.
Forest plot of individual studies included in the meta-analysis of all lead-I ECG devices; trace interpreted by a trained health-care professional (Kardia Mobile and EP1 data from the Desteghe study). FN, false negative; FP, false positive; TN, true negative; TP, true positive. Reproduced from Duarte et al. 67 © The Authors, 2019. This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt and build upon this work, for commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
A SROC plot that displays the individual study results as well as the meta-analysis result is presented in Figure 5. A visual inspection of Figure 4 and the individual study results presented in Figure 5 shows that the results were relatively homogeneous across the included studies in this meta-analysis. However, owing to some potential heterogeneity between studies, we adopted a conservative approach and used a bivariate model with random effects in the meta-analysis.
FIGURE 5.
Summary receiver operating characteristic plot for lead-I ECG device as index test with trace interpreted by a trained health-care professional and 12-lead ECG interpreted by a trained health-care professional as reference standard (using Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device and EP1 data from the study by Desteghe et al. 38).
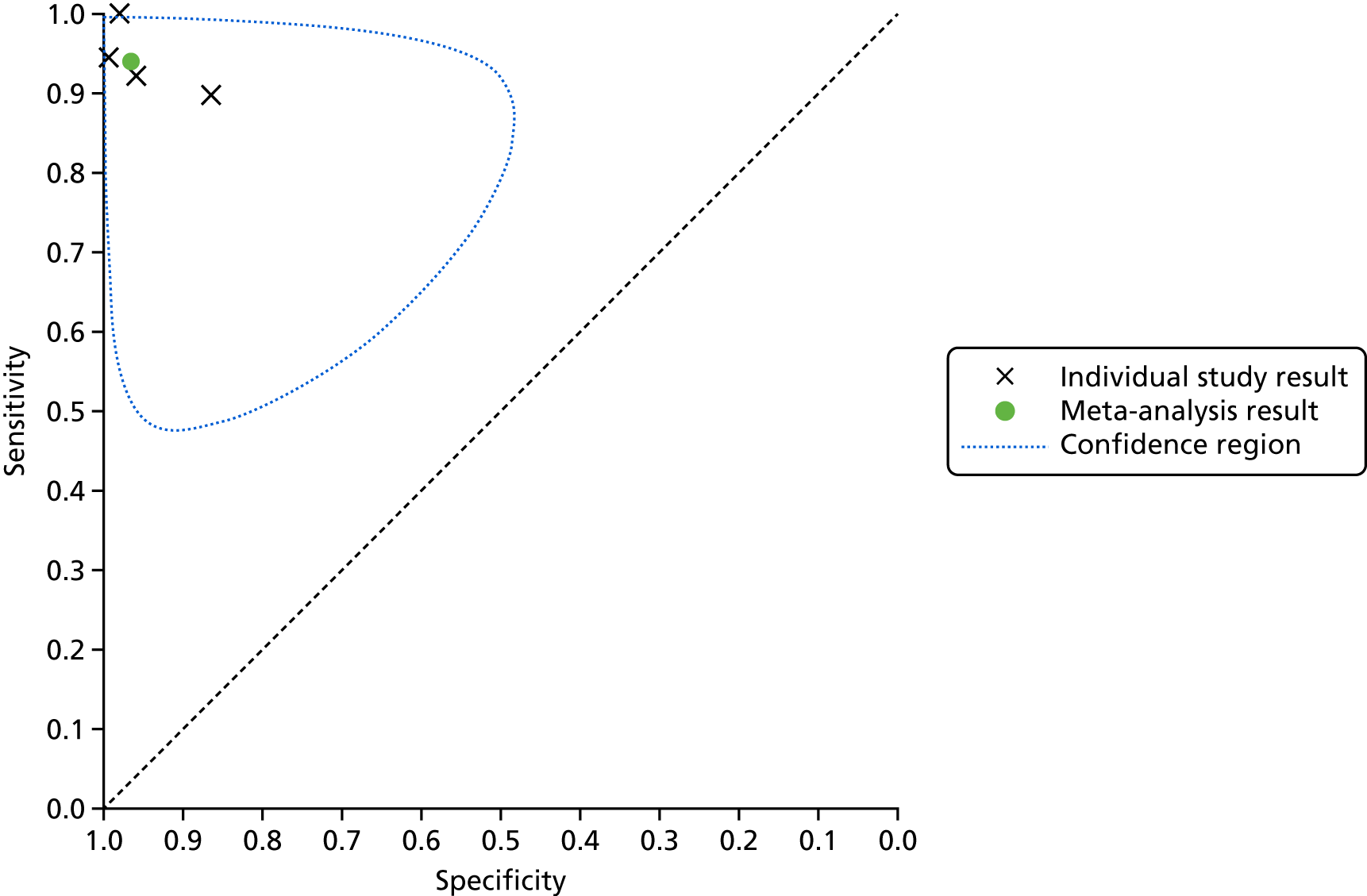
This meta-analysis included 580 participants, of whom 118 had AF. The pooled sensitivity was 93.9% (95% CI 86.2% to 97.4%) and the pooled specificity was 96.5% (95% CI 90.4% to 98.8%).
All lead-I electrocardiogram devices: sensitivity analyses
Forest plots displaying the results of the individual studies included in the meta-analyses are presented in Appendix 6, Figure 13.
Summary receiver operating characteristic plots are presented in Appendix 6, Figure 14. A visual inspection of the forest plots (see Appendix 6, Figure 13) and the individual study results (see Appendix 6, Figure 14) shows that the results were relatively homogeneous across the included studies in these meta-analyses. However, owing to some potential heterogeneity between studies, we adopted a conservative approach and used a bivariate model with random effects in the meta-analysis.
Pooled sensitivity values from these additional meta-analyses ranged from 89.8% to 91.8%, while pooled specificity values ranged from 95.6% to 97.1% (Table 5). Overall, the use of either Kardia Mobile or MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG and an interpretation by different EPs does not seem to make a difference to the pooled results. Considering only the study by Desteghe et al. ,38 specificity is similar across all combinations, whereas the sensitivity of Kardia Mobile seems higher than the sensitivity of MyDiagnostick and EP1 seems to show slightly higher sensitivity than EP2.
| Data input from the study by Desteghe et al.38 | AF cases (n) | Total number of patients (N) | Pooled sensitivity (95% CI) | Pooled specificity (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MyDiagnostick device and EP1 data | 118 | 582 | 90.8% (83.8% to 95.0%) | 95.6% (89.4% to 98.3%) |
| MyDiagnostick device and EP2 data | 118 | 582 | 89.8% (82.7% to 94.1%) | 96.8% (90.6% to 99.0%) |
| Kardia Mobile device and EP2 data | 120 | 584 | 91.8% (85.1% to 95.7%) | 97.1% (90.8% to 99.1%) |
One study39 also presented data for one lead-I device (Kardia Mobile) that were interpreted by a GP with an interest in cardiology, and these data were included in a sensitivity analysis. The forest plot displaying the results of the individual studies included in the meta-analysis is presented in Appendix 6, Figure 17.
The SROC plot that shows the individual study results as well as the meta-analysis result is presented in Appendix 6, Figure 18. When the results presented in Appendix 6, Figure 17, and the individual study results presented in Appendix 6, Figure 18, were studied, they were found to be relatively homogeneous; however, in the study by Williams et al. ,39 specificity was lower when the lead-I ECG trace was interpreted by the GP (76%), than when it was interpreted by a cardiologist (86%) (see Figure 4). Owing to some potential heterogeneity between studies, we adopted a conservative approach and used a bivariate model with random effects in the meta-analysis.
For this meta-analysis (number of AF cases, 118; total number of patients, 580), the sensitivity was 94.3% (95% CI 87.9% to 97.4%) and the specificity was 96.0% (95% CI 85.4% to 99.0%).
Kardia Mobile lead-I electrocardiogram device
Data for the Kardia Mobile device were derived from only three studies. 38,39,45 We conducted two meta-analyses to investigate the impact of using data for each interpreter (EP1 or EP2) from the study by Desteghe et al. 38 on the results of the meta-analysis. Forest plots displaying the results of the individual studies included in each meta-analysis are presented in Appendix 6, Figure 19.
For both meta-analyses, we fitted a univariate random-effects logistic regression model for specificity and a univariate fixed-effects logistic regression model for sensitivity because minimal variability in sensitivity was observed across the studies.
For the meta-analysis that included EP1 data from the study by Desteghe et al. 38 (number of AF cases, 67; total number of patients, 480), sensitivity was 94.0% (95% CI 85.1% to 97.7%) and specificity was 96.8% (95% CI 88.0% to 99.2%). For the meta-analysis that included EP2 results from the study by Desteghe et al. 38 (number of AF cases, 69; total number of patients, 484), sensitivity was lower, at 91.3% (95% CI 82.0% to 96.0%), and specificity was slightly higher, at 97.4% (95% CI 88.3% to 99.5%). As only three studies38,39,45 were included in this analysis, it was not possible to produce confidence regions.
There were insufficient data to generate pooled estimates of sensitivity and specificity for other types of lead-I ECG device based on the interpreter of the lead-I ECG being a trained health-care professional, or to assess differences between types of devices. The sensitivity and specificity estimates for Zenicor-ECG and MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG devices are presented in Appendix 6, Figure 13.
Interpreter of lead-I electrocardiogram: algorithm
All lead-I electrocardiogram devices
We investigated the sensitivity and specificity of the lead-I ECG device when the trace was interpreted by the device algorithm alone. The reference standard used was interpretation of the 12-lead ECG trace by a trained health-care professional. Data from four studies38,47–49 were included in a meta-analysis. Two studies48,49 had data for MyDiagnostick alone,48,49 one study47 had data for Kardia Mobile alone and one study38 had data for MyDiagnostick and Kardia Mobile. One study50 reported sensitivity (67%) and specificity (97%) for RhythmPad GP. Although the authors of this study50 provided the numbers for true-positive, false-negative, false-positive and true-negative test results, these were not included in the pooled analysis because the authors reported that the algorithm had since been modified (Chris Crockford, CardioCity, 3 August 2018, personal communication via NICE). We conducted two meta-analyses in order to investigate the impact of using data for each type of lead-I ECG device (MyDiagnostick or Kardia Mobile) from the study by Desteghe et al. 38 on the results of the initial meta-analysis. In the study by Desteghe et al. ,38 the same patient cohort was tested using both lead-I ECG devices. We performed multiple analyses in order to investigate the impact of varying the type of lead-I ECG device on the results of the overall pooled analysis with no set of patients double-counted. Forest plots displaying the results of the individual studies included in each meta-analysis are presented in Figure 6.
FIGURE 6.
Forest plots of individual studies included in each meta-analysis of all lead-I ECG devices (trace interpreted by the device algorithm). (a) MyDiagnostick data from the Desteghe study; and (b) Kardia Mobile data from the Desteghe study. FN, false negative; FP, false positive; TN, true negative; TP, true positive.
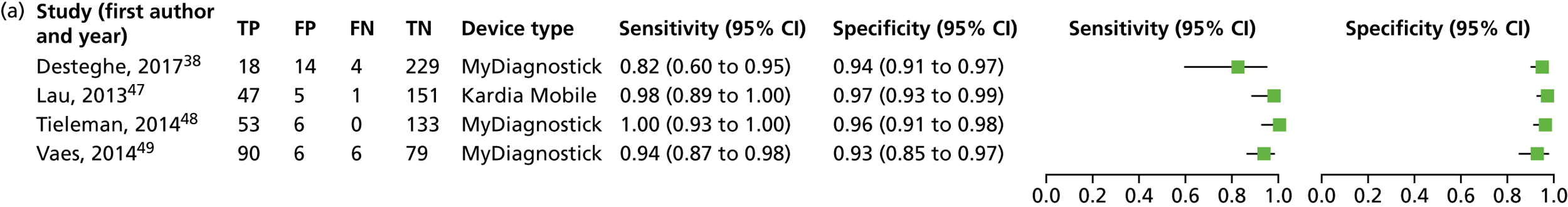
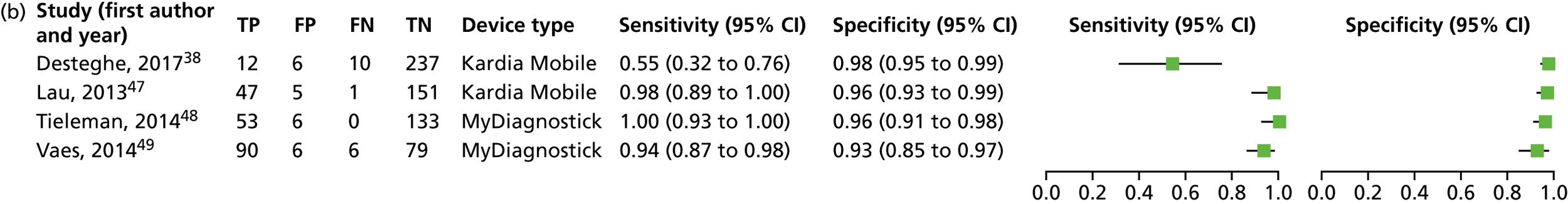
The SROC plots are presented in Appendix 6, Figures 20 and 21. The results were relatively homogeneous across the included studies in both meta-analyses. However, owing to some potential heterogeneity between studies, we adopted a conservative approach and used a bivariate model with random effects in the meta-analysis.
For the meta-analysis that included MyDiagnostick data from the study by Desteghe et al. 38 (number of AF cases, 219; total number of patients, 842), sensitivity was 96.2% (95% CI 86.0% to 99.0%) and specificity was 95.2% (95% CI 92.9% to 96.8%). For the meta-analysis that included Kardia Mobile data from the study by Desteghe et al. 38 (number of AF cases, 219; total number of patients, 842), the pooled estimates for sensitivity were 95.3% (95% CI 70.4% to 99.4%) and for specificity were 96.2% (95% CI 94.2% to 97.6%), which were similar to those obtained from the meta-analysis including MyDiagnostick data from the study by Desteghe et al. 38
MyDiagnostick lead-I electrocardiogram device
A forest plot displaying the results of the individual studies included in this meta-analysis is presented in Appendix 6, Figure 22.
As only three studies38,48,49 were included in this analysis, it was not possible to produce a SROC plot with a confidence region.
For MyDiagnostick, data from three studies38,48,49 (number of AF cases, 171; total number of patients, 638) were included in the meta-analysis; sensitivity was 95.2% (95% CI 79.0% to 99.1%) and specificity was 94.4% (95% CI 91.9% to 96.2%). For this meta-analysis, we fitted a univariate random-effects logistic regression model for sensitivity and a univariate fixed-effect logistic regression model for specificity because minimal variability in specificity was observed across the studies. The results were relatively homogeneous across the three included studies.
Kardia Mobile lead-I electrocardiogram device
We estimated sensitivity and specificity for the Kardia Mobile device, and for the MyDiagnostick device separately. A forest plot displaying the results of the individual studies included in this meta-analysis is presented in Appendix 6, Figure 23. In the study by Desteghe et al. ,38 sensitivity was 55% (95% CI 32% to 76%), much lower than that in the study by Lau et al. ,47 which was 98% (95% CI 89% to 100%).
As only two studies38,47 were included in this analysis, it was not possible to produce a SROC plot with a confidence region.
For Kardia Mobile, data from two studies (number of AF cases, 70; total number of patients, 469) were included in the meta-analysis; sensitivity was 88.0% (95% CI 32.3% to 99.1%), and specificity was 97.2% (95% CI 95.1% to 98.5%). For this meta-analysis, we fitted a univariate random-effects logistic regression model for sensitivity and a univariate fixed-effect logistic regression model for specificity, because minimal variability in specificity was observed across the studies.
Data were not sufficient to pool estimates of sensitivity and specificity for other types of lead-I device based on the interpreter of the lead-I ECG being a trained health-care professional, or to formally assess the differences between types of devices.
Summary of findings: diagnostic test accuracy
No studies were identified that evaluated the DTA of lead-I ECG devices in people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse.
Of the nine included studies, only one study49 was conducted in primary care. The remaining eight studies were conducted in secondary care, tertiary care or community settings.
Of the nine included studies, only one study38 explicitly stated that some patients (n = 11, 3.4%) had signs or symptoms of AF on admission to a cardiology ward. Another study49 included a large proportion of people with known AF (83.4%); however, it is not clear whether or not the patients had signs or symptoms of AF at the time of the assessment and/or if the patients had been previously diagnosed with AF.
As prespecified in the protocol,68 owing to a lack of evidence, we next focused the reviews on an asymptomatic population in any health-care setting. We considered an asymptomatic population to be people not presenting with signs or symptoms of AF, with or without a previous diagnosis of AF. These patients could have had co-existing cardiovascular conditions or could have been attending a cardiovascular clinic but did not present with signs or symptoms of AF. We identified 13 publications38,39,41–51 reporting on nine studies assessing the DTA of lead-I ECG devices in an asymptomatic population. However, all of these studies were judged as having a high applicability concern for patient selection, as none was performed in the population and setting of interest.
We included studies in which the interpreter of the lead-I ECG trace was a trained health-care professional38,39,43,45,51 and studies that included interpretations of the lead-I ECG trace by the lead-I ECG device algorithm only. 38,47–50 The lead-I ECG devices used in the studies were Kardia Mobile,39,45,47 MyDiagnostick48,49 and Zenicor-ECG. 43 The study by Desteghe et al. 38 used both Kardia Mobile and MyDiagnostick.
The results from the meta-analyses are summarised in Table 6. Across all meta-analyses where the interpreter of the lead-I ECG trace was a trained health-care professional, the sensitivity ranged from 89.8% to 94.3% and the specificity ranged from 95.6% to 97.4%. Across all meta-analyses where the interpreter of the lead-I ECG trace was the device algorithm, the sensitivity ranged from 88% to 96.2% and the specificity ranged from 94.4% to 97.2%. Pooled sensitivity and specificity values were similar across the different meta-analyses, irrespective of the interpreter of the lead-I ECG trace or the lead-I ECG device used. However, it should be noted that studies in which the index test was interpreted by the lead-I ECG device algorithm alone were judged as having a high applicability concern for the index test domain. This judgement was based on the consideration made by all manufacturers of the lead-I ECG devices that the diagnosis of AF should not be made using the algorithm alone, and that the ECG traces measured by the devices should be reviewed by a qualified health-care professional.
| Data input from the Desteghea and Williamsb studies | Studies of lead-I ECG devices in the meta-analyses (n) | AF cases (n) | Total number of patients (N) | Pooled sensitivity (95% CI) | Pooled specificity (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-I ECG trace interpreted by a trained health-care professional (main analysis) | |||||
| Kardia Mobile device, EP1a and cardiologistb data | Kardia Mobile (3), Zenicor-ECG (1) | 118 | 580 | 93.9% (86.2% to 97.4%) | 96.5% (90.4% to 98.8%) |
| Lead-I ECG trace interpreted by a trained health-care professional (sensitivity analyses, cardiologist datab) | |||||
| MyDiagnostick device and EP1a data | Kardia Mobile (2), Zenicor-ECG (1), MyDiagnostick (1) | 118 | 582 | 90.8% (83.8% to 95.0%) | 95.6% (89.4% to 98.3%) |
| MyDiagnostick device and EP2 data | Kardia Mobile (2), Zenicor-ECG (1), MyDiagnostick (1) | 118 | 582 | 89.8% (82.7% to 94.1%) | 96.8% (90.6% to 99.0%) |
| Kardia Mobile device and EP2a data | Kardia Mobile (3), Zenicor-ECG (1) | 120 | 584 | 91.8% (85.1% to 95.7%) | 97.1% (90.8% to 99.1%) |
| Lead-I ECG trace interpreted by a trained health-care professional (sensitivity analyses, GP datab) | |||||
| Kardia Mobile device, EP1a and GPb data | Kardia Mobile (3), Zenicor-ECG (1) | 118 | 580 | 94.3% (87.9% to 97.4%) | 96.0% (85.4% to 99.0%) |
| Lead-I ECG trace interpreted by a trained health-care professional (sensitivity analyses, Kardia Mobile) | |||||
| Kardia Mobile device and EP1a data | Kardia Mobile (3) | 67 | 480 | 94.0% (85.1% to 97.7%) | 96.8% (88.0% to 99.2%) |
| Kardia Mobile device and EP2a data | Kardia Mobile (3) | 69 | 484 | 91.3% (82.0% to 96.0%) | 97.4% (88.3% to 99.5%) |
| Lead-I ECG trace interpreted by lead-I ECG device algorithm alone | |||||
| MyDiagnostick devicea data | Kardia Mobile (1), MyDiagnostick (3) | 219 | 842 | 96.2% (86.0% to 99.0%) | 95.2% (92.9% to 96.8%) |
| Kardia Mobile devicea data | Kardia Mobile (2), MyDiagnostick (2) | 219 | 842 | 95.3% (70.4% to 99.4%) | 96.2% (94.2% to 97.6%) |
| MyDiagnostick device only | MyDiagnostick (3) | 171 | 638 | 95.2% (79.0% to 99.1%) | 94.4% (91.9% to 96.2%) |
| Kardia Mobile device only | Kardia Mobile (2) | 70 | 469 | 88.0% (32.3% to 99.1%) | 97.2% (95.1% to 98.5%) |
Details of the excluded studies that report sensitivity and specificity values for the lead-I ECG devices investigated in this assessment, and the reasons for exclusion, are presented in Appendix 7.
Assessment of clinical impact
Characteristics of the included studies
The characteristics of the 18 quantitative studies included in the clinical impact review are summarised in Table 7. One qualitative study53 included in the clinical impact review reported the results of semistructured interviews with patients, receptionists, practice nurses and GPs.
| Study (first author, year) | Study design; country and setting | Population; number in analysis and recruitment details | Mean age and SD (years); sex; risk factors for AF | Lead-I ECG device | Interpreter of lead-I ECG | Test sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Battipaglia, 201652 | Cross-sectional; UK; community | General population without known AF or implanted pacemaker; N = 855; campaign for rhythm awareness in a shopping centre | NR | MyDiagnostick | Cardiologist | NA |
| Chan, 201756 | Cross-sectional; China; community | People aged ≥ 18 years; N = 13,122; screening programme publicised via channels including media promotion and placement of posters in community centres by non-governmental organisations |
64.7 ± 13.4; female, n = 9384 (71.5%) Hypertension: n = 5012 (38.2%) Diabetes: n = 1944 (14.8%) Hyperlipidaemia: n = 2613 (19.9%) Heart failure: n = 97 (0.7%) Stroke: n = 367 (2.8%) Coronary artery disease: n = 295 (2.2%) Valvular heart disease: n = 114 (0.9%) Peripheral vascular disease: n = 66 (0.5%) Obstructive sleep apnoea: n = 146 (1.1%) Thyroid disease: n = 517 (3.9%) COPD: n = 56 (0.4%) Cardiothoracic surgery: n = 354 (2.7%) |
Kardia Mobile | Cardiologist | NA |
| Chan, 201657 | Cross-sectional; China; primary care | People with history of hypertension and/or diabetes mellitus or aged ≥ 65 years; N = 1013; patients recruited from a general outpatient clinic |
68.4 ± 12.2; Sex: 539 (53.2%) female Hypertension: n = 916 (90.4%) Diabetes: n = 371 (36.6%) Coronary artery disease: n = 164 (16.2%) Previous stroke: n = 106 (10.5%) Mean CHA2DS2-VASc ± SD – 3.0 ± 1.5 |
Kardia Mobile | Algorithm and cardiologist | 12-lead ECG performed only when a diagnosis of AF was made by the algorithm (results not presented) |
| Chan, 201754 | Cross-sectional; Hong Kong; primary care | Patients aged ≥ 65 years attending primary care clinics; N = 1041; NR |
Aged ≥ 65 years; NR |
Kardia Mobile | Cardiologist | NA |
| Desteghe, 201738 | Case–control; Belgium; tertiary care | Inpatients at cardiology ward; N = 265; NR |
67.9 ± 14.6; female, n = 138 (43.1%); Pacemaker: 4 out of 55 (7.3%) were intermittently paced, and 18 out of 55 (32.7%) were not being paced during the recordings Known AF: 114 out of 320 (35.6%) AF at time of study: 11.9% (on 12-lead ECG) Paroxysmal AF: 54.4% |
MyDiagnostick and Kardia Mobile | Algorithm and EP | 12-lead ECG followed by lead-I ECG (order for the use of the different lead-I ECG tests not specified) |
| Doliwa, 200943 | Case–control; Sweden; secondary care | People with atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or sinus rhythm; N = 100; patients were recruited from a cardiology outpatient clinic | NR | Zenicor-ECG | Cardiologist | 12-lead ECG followed by lead-I ECG |
| Gibson, 201758 | Cross-sectional; UK; primary care | Patients aged ≥ 65 years without a diagnosis of AF, attending a practice nurse or health-care assistant clinic; N = 445; NR | NR | MyDiagnostick | Algorithm | NA |
| Haberman, 201545 | Case–control; USA; community and secondary care | Healthy young adults, elite athletes and cardiology clinic patients; N = 130; NRa | 59 ± 15; male, n = 73 (56%); NR | Kardia Mobile | EP | Lead-I ECG followed by 12-lead ECG |
| Hussain, 201659 | Cross-sectional; UK; primary care | Patients attending a flu clinic; N = 357; lead-I ECG used while patients waited for flu vaccination |
Aged > 65 years: n = 257; NR |
Kardia Mobile | GP | NA |
| Kaasenbrood, 201660 | Case–control; Netherlands; primary care | Patients aged ≥ 60 years with and without known AF attending for flu vaccination; N = 3269; asked by nurses |
69.4 ± 8.9; male, n = 1602 (49%); NR |
MyDiagnostick | Algorithm and cardiologist | NA |
| Koltowski, 201751 | Cross-sectional; Poland; tertiary care | Patients in a tertiary care centre; N = 100; NR | NR | Kardia Mobile | Cardiologist | Lead-I ECG followed by 12-lead ECG |
| Lau, 201347 | Case–control; Australia; secondary care | Patients at cardiology department; N = 204; NR |
NR; Known AF: n = 48 (24%) |
Kardia Mobile | Algorithm | Lead-I ECG followed by 12-lead ECG |
| Lowres, 201461 | Cross-sectional; Australia; community | People aged ≥ 65 years entering the pharmacy without a severe coexisting medical condition; N = 1000; availability of screening in participating pharmacies was advertised through flyers displayed within each pharmacy, and pharmacists and staff also directly approached potentially eligible clients |
76 ± 7; male, n = 436 (44%); NR |
Kardia Mobile | Algorithm and cardiologist | Pulse palpation followed by lead-I ECG (12-lead ECG used for participants with suspected unknown AF indicated by lead-I device) |
| Orchard, 201662 | Case–control; Australia; primary care | Patients with known AF and patients without a history of AF attending for flu vaccination; N = 972 |
New AF: n = 7; 80 ± 3; male; 3 out of 7 male; Known AF: n = 29; 77.1 ± 1; male; n = 15 (52%) All AF (N = 36); 78 years ± 1; male, n = 18 (50%); NR |
Kardia Mobile | Algorithm and cardiologist | Lead-I ECG followed by 12-lead ECG in cases where AF was detected by lead-I (and was a new diagnosis) |
| Reeves, (NR)63 | Cross-sectional; UK; secondary care | Patients aged ≥ 18 years recovering in the cardiac intensive care unit or a cardiac surgery ward, following cardiac surgery, or who had been admitted to the coronary care unit or a cardiology ward after a cardiac related event; N = 53; research nurses working in one or other of the clinical settings identified and approached eligible patients |
23–90 (range); male, n = 37 (70%); NR |
imPulse | Two cardiology registrars, two cardiac physiologists and two specialist cardiac nurses | Lead-I ECG and 12-lead ECG recorded simultaneously |
| Tieleman, 201448 | Case–control; Netherlands; secondary care | Patients with known AF and patients without a history of AF visiting an outpatient cardiology clinic or a specialised AF outpatient clinic; N = 192; random selection of patients due to have a 12-lead ECG |
69.4 ± 12.6; male, 48.4%; NR |
MyDiagnostick | Algorithm | Lead-I ECG followed by 12-lead ECG |
| Primary care | People with unknown AF status; N = 676; people attending GP for flu vaccination |
74 ± 7.1; NR |
MyDiagnostick | Algorithm and cardiologist | NA | |
| Waring, 201664 | Cross-sectional; UK; community | People aged ≥ 65 years; N = 1153; NR | NR | Kardia Mobile | Cardiologist | NA |
| Yan, 201665 | Cross-sectional; Hong Kong; secondary care | People aged ≥ 65 years without a history of AF; N = 9046; consecutive patients attending clinics |
79 ± 12.1; male, 49.4%; NR |
Kardia Mobile | Cardiologist | NA |
Eleven of the studies included in the clinical impact review were cross-sectional studies,51,52,54,56–59,61,63–65 seven were case–control studies38,43,45,47,48,60,62 and one study was qualitative. 53 Seven studies were conducted in primary care,53,54,57–60,62 five were conducted in secondary care,43,47,48,63,65 two were conducted in tertiary care38,51 and the remaining four were conducted in a community setting. 52,56,61,64 One study45 included participants recruited from secondary care, but also included (as separate groups) elite athletes and healthy young adults. As discussed in Characteristics of the included studies, the results for these populations45 were excluded from the analysis as these participants did not meet our inclusion criterion for population and do not represent the typical population with AF (i.e. those aged ≥ 75 years).
Four studies included only people without known AF. 52,58,61,65 Three studies54,59,64 may have included only people without known AF as either participants were attending a primary care clinic or the study was conducted in a community setting. However, these studies were available only as conference abstracts and did not provide sufficient information to enable us to determine whether or not the population had a history of AF. The remaining 11 studies38,43,45,47,48,51,56,57,60,62,63 recruited people with known AF or cardiovascular comorbidities or who were attending a clinic for cardiovascular-related reasons.
Quality assessment
The methodological quality of the four cross-sectional52,56,57,61 and the two case–control studies60,62 included in the clinical impact review of lead-I ECG devices, was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa quality assessment scale. 33,34 The results of the quality assessment of cross-sectional and case–control studies are presented in Appendix 8, Table 40.
The methodological quality of the diagnostic accuracy studies included in the clinical impact review was assessed using the QUADAS-2 tool. 32 A summary of the results for the risk of bias in the studies38,43,45,47,48,51 that were included in the clinical impact review but had already been assessed as part of the DTA review is presented in Table 4 and a full assessment is reported in Appendix 5. A summary of the risk of bias for one diagnostic accuracy study63 not eligible for inclusion in the DTA review is presented in Appendix 8, Table 41; the full quality assessment for this study63 is presented in Appendix 5.
Five studies54,58,59,64,65 that were available only as conference abstracts and were assessed as meeting the study eligibility criteria for inclusion in the clinical impact review were subjected to data extraction only and not to quality assessment, because there was not enough information to allow a judgement to be made on some of the quality assessment criteria.
Overall, the quality of the four cross-sectional52,56,57,61 and the two case–control studies60,62 was similar across the different domains. None of the included studies was considered to be representative of the target population. Only one study61 included a sample size calculation. In all studies, the test failure rate was low; therefore, the response rate was considered satisfactory. All of the included studies described the intervention. None of the studies accounted for confounding factors in the analyses presented. An assessment of the outcome was described in all of the studies; however, those studies with independent blind assessment or record linkage were judged as being of better quality than the studies without blind assessment or record linkage. The statistical tests used to analyse the data were clearly described and appropriate in all included studies.
The diagnostic accuracy study63 was judged as being at an unclear risk of bias and having a high applicability concern for patient selection. This study63 was judged as being at low risk of bias on the index test domain as the test results were interpreted without knowledge of the reference standard test result and, therefore, there was also low applicability concern for this domain. All of the interpreters of the reference standard test results were blind to the results of the index test; therefore, the study63 was judged as being at low risk of bias for the reference standard domain. However, there were two reference standards: (1) a clinical ECG diagnosis based on additional information not available to the assessors, and (2) consensus (three of the four assessors) that matched this clinical ECG diagnosis. Therefore, this study63 was judged as having a high concern regarding applicability of the reference standard test.
The methodological quality of the qualitative study53 included in the clinical impact review was assessed using the CASP tool36 and the results are presented in Appendix 8, Table 42. In the qualitative study,53 semistructured interviews were conducted with two receptionists, one nurse, three GPs and eight patients across three GP practices. The aim of the study was to investigate the feasibility of using practice nurses and receptionists to systematically screen patients aged ≥ 65 years for AF using a lead-I ECG device (Kardia Mobile) prior to the GP consultation. No details were available about the selection of the interviewees; although the study aim was to investigate the feasibility for practice nurses and receptionists to use the lead-I ECG device, these were the least represented groups in the interviews. The researchers do not discuss their own potential biases, such as relationships with participants or choice of locations for the study. Although the methods are not described in depth, the publication clearly states how the interviews were analysed and how themes were derived from the data and that interviews ceased once information saturation was reached. The duration of the interviews ranged from 5 to 40 minutes. Considering that there were four different groups of participants (i.e. receptionists, nurses, GPs and patients), it is unclear how information saturation was reached, especially for nurses’ views, as only one nurse was interviewed.
Clinical impact results
Intermediate outcomes
The results for the most commonly reported intermediate outcomes (test failure rate, time to complete test and store the ECG trace, number of 12 lead ECGs carried out and diagnostic yield) are provided in Table 8.
| Study (first author, year) | Lead-I ECG device | Test failure rate | Time to complete testing and storage | 12-lead ECGs carried out (n) | Diagnostic yield (% new AF cases) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Battipaglia, 201652 | MyDiagnostick | 60 out of 855 (7%) | 15-second rhythm strips | NA | 7 out of 855 (0.8%) |
| Chan, 201656 | Kardia Mobile | 56 out of 13,122 (0.4%) | 30-second rhythm strips | NA | 101 out of 13122 (0.8%) |
| Chan, 201657 | Kardia Mobile | 13 out of 1026 (1.3%) | 30-second rhythm strips | Unclear | 5 out of 1013 (0.5%) |
| Chan, 201754 | Kardia Mobile | NR | NR | NA | 15 out of 1041 (1.4%) |
| Desteghe, 201738 | MyDiagnostick and Kardia Mobile |
MyDiagnostick 8 out of 265 (3%) for both EP1 and EP2 Kardia Mobile 10 out of 265 (3.8%) for EP1 and 6 out of 265 (2.3%) for EP2 |
MyDiagnostick – 1-minute recording Kardia Mobile – 30-second recording |
265 | 1 out of 265 (0.4%) |
| Doliwa, 200943 | Zenicor-ECG | NR | 10-second rhythm trace. Registration, transfer and evaluation of the information take ≤ 5 minutes | 100 | NR |
| Gibson, 201758 | MyDiagnostick | NR | NR | NA | 26 out of 445 (5.8%) |
| Haberman, 201545 | Kardia Mobile | 1 out of 381 (0.3%) based on overall study population | NR | 130 | NR |
| Hussain, 201659 | Kardia Mobile | NR | 30–45 seconds to apply | NA | 6 out of 357 (1.7%) |
| Kaasenbrood, 201660 | MyDiagnostick | 3 out of 3269 (0.1%) uninterpretable results | 1-minute recording | NA | 37 out of 3269 (1.1%) |
| Koltowski, 201751 | Kardia Mobile | NR | NR | 100 | NR |
| Lau, 201347 | Kardia Mobile | NR | 1 minute | 204 | NR |
| Lowres, 201461 | Kardia Mobile | 4 out of 1000 (0.4%) excluded as a result of excessive movement artefact | ≤ 5 minutes | 35 | 15 out of 1000 (1.5%) |
| Orchard, 201662 | Kardia Mobile | 82 out of 1044 (7.9%) recorded ECGs unclassified of which 20 were as a result of unreadable trace | 5 minutes (range 1.5 to 10 minutes) | 30 | 8 out of 973 (0.8%) |
| Reeves, (NR)63 | imPulse | 5 out of 53 (9%) | 2-minute recording | 53 | NR |
| Tieleman, 201448 | MyDiagnostick | NR | 1-minute recording | 192 (secondary care population) | 11 out of 676 (1.6%) (primary care population) |
| Waring, 201664 | Kardia Mobile | NR | NR | NA | 5 out of 1153 (0.4%) |
| Yan, 201665 | Kardia Mobile | NR | NR | NA | 121 out of 9046 (1.3%) |
Results for failure rate included both failure of the lead-I ECG algorithm to produce a result and poor quality of the lead-I ECG trace (i.e. uninterpretable or illegible trace).
Time to diagnosis of AF was reported in only one study61 [16.6 ± 14.3 days (mean ± standard deviation)]. This was measured as the mean time between the initial diagnostic test with the lead-I ECG device at a pharmacy and the confirmation of result with a 12-lead ECG.
One study48 reported that the participants were able to use the MyDiagnostick device with minimal instructions and another study reported that the Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device was easy to operate. 54 A key barrier was identified relating to the ease of use of the lead-I ECG devices. Specifically, it was difficult for elderly patients to hold the device very still, which was required to take a reading. 62 One study38 reported that 24 out of 344 (7%) patients were excluded because they were not able to hold the devices properly (MyDiagnostick and Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG devices were used in the study and the type of lead-I ECG device, on which this proportion is based, was not provided).
Only the study by Desteghe et al. 38 reported the concordance between lead-I ECG devices (Kardia Mobile and MyDiagnostick) and there were no differences in agreement (based on kappa values) between devices when all patients were included (p = 0.677) and after patients with an implanted device (i.e. pacemaker or implantable cardioverter defibrillator) were excluded (p = 0.411).
Two studies59,61 reported the impact of test results on clinical decision-making. In the study by Hussain and Thakar,59 there was a change in treatment management as a result of using the Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device for five out of six new cases of AF in 357 people tested (one patient was clinically unwell and died as an inpatient following referral to the hospital). In the study by Lowres et al. ,61 oral anticoagulants (OACs) were prescribed in 6 out of 10 new cases of AF as a consequence of using the lead-I ECG device followed by a 12-lead ECG interpreted by a cardiologist. Of five participants with unknown recurrence of AF ≥ 3 years after cardioversion, three were prescribed OACs following review by a cardiologist. 61
Diagnostic yield was reported in 13 studies. 38,48,52,54,56–62,64,65 The proportion of new patients diagnosed with AF ranged from 0.4% to 5.8%. The proportions of new patients diagnosed with AF in all of the included studies are presented in Appendix 9, Figure 24, in Appendix 9, Figure 25 (studies grouped by type of lead-I ECG device) and in Appendix 9, Figure 26 (studies grouped by setting).
Time to initiation of preventative treatment was not reported in any of the identified studies.
Clinical outcomes
Only one study59 reported clinical outcomes. One patient had a normal 12-lead ECG trace and did not receive anticoagulant therapy, but later had a stroke. The authors reported that the Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG trace had been difficult to interpret for this patient, who probably had AF.
Acceptability and patient-reported outcomes
The acceptability of the lead-I ECG devices was reported in four studies. 54,58,59,62 In one of the studies using the Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device, the staff indicated that the patients generally liked the device and the screening process. It was also reported that the GPs liked the lead-I ECG device because it raised awareness of AF and nurses could perform the screening. 62 One study reported that all patients were willing to undergo repeated screening with the Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device in future GP visits, and 86% of the GPs considered that the lead-I ECG device was useful for AF screening and said that they would use it in their daily practice. 54 Although the views were generally positive, one study reported that patients’ suggestions for improvements in the use of the MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG device included having more time to make decisions about taking the test and being given a clearer explanation of the results (it was unclear if this was in the context of patient self-use of the device or the clinician’s explanation of the results). 58 In the same study, interviews with seven staff members suggested that, although the opportunity to detect and treat AF was valued, challenges (e.g. technical problems, documentation and referral, and management of workload) needed to be overcome. 58 In another study,59 the process was found to be acceptable and it was reported that the Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG test was easily administered and that no patients refused to be tested.
Barriers to and enablers of the use of lead-I ECG devices for AF screening in primary care were explored in a qualitative study. 53 This study investigated the feasibility of using practice nurses and receptionists to systematically screen patients aged ≥ 65 years for AF using a lead-I ECG device (Kardia Mobile) prior to a GP consultation. Barriers that were identified by three GPs were having to rely on others to carry out the screening, not having the required software, information technology (IT) being blocked, having to remember to charge the phone and the technology not working. GPs liked the lead-I ECG device and its portability, and they considered that use of the lead-I ECG device could add value, provide reassurance and act as a prompt to look for other health conditions. The eight patients who were interviewed did not understand the reasons for screening and were not interested in whether or not the result was negative. However, they considered that having access to the lead-I ECG device in the surgery was more convenient than having to attend another health-care facility for a 12-lead ECG, and they stated that they were impressed with the technology. One practice nurse mentioned two barriers: (1) the possible lack of availability of the lead-I ECG device when required and (2) that the results needed to be reviewed by a GP. The practice nurse was able to confidently screen patients and explain the process. The nurse considered that the use of the lead-I ECG device raised awareness of AF in the practice and believed that the lead-I ECG device algorithm was an enabler of the screening for AF. Although both receptionists expressed their ease with using the device, they explicitly identified only barriers: they were reluctant to ask patients to use the lead-I ECG device, were uncertain about how to explain the purpose of the AF screening and were unsure how to respond to patients’ questions.
None of the studies identified reported on HRQoL.
‘Real-world’ data
Evidence was submitted on the use of Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG across Eastbourne, Hailsham and Seaford Clinical Commissioning Group (CCG) and Hastings and Rother CCG (Kent Surrey Sussex AHSN and Richard Blakey, AliveCor in East Sussex, unpublished evidence submitted via NICE, 28 March 2018). Over a 2-year period, Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG was used in primary care or during home visits if people were found to have an irregular pulse or symptoms indicative of AF. During this time, 183 lead-I ECG traces were reported, identifying 128 new cases of AF. The percentage of new patients diagnosed with AF during the project was 69.9%, which is considerably higher than the diagnostic yield reported in our included studies (0.4–5.8%). There was also a higher increase in the prevalence of AF in the participating CCGs (2.73–2.96% for Hastings & Rother CCG and 3.01–3.22% for Eastbourne, Hailsham & Seaford CCG) than for other CCGs in the Kent Surrey Sussex AHSN. 11
Summary of findings: clinical impact
As per the DTA review, no studies were identified that evaluated the clinical impact of lead-I ECG devices in people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse, which limits the applicability of the results presented. Therefore, the 24 publications38,41–48,51–65 reporting on the 19 studies that were included in the clinical impact review were focused on an asymptomatic population. Four studies included only people without known AF. 52,58,61,65 Three studies54,59,64 may have included only people without known AF, as either participants were attending a primary care clinic or the study was conducted in a community setting. However, the information describing these studies was limited and the data were available only as conference abstracts.
Test failure rate was reported in nine studies38,45,52,56,57,60–63 and ranged from 0.1% to 9%. Results for test failure rate included both failure of the lead-I ECG algorithm to produce a result and poor quality of the lead-I ECG trace. Diagnostic yield was reported in 13 studies. 38,48,52,54,56–62,64,65 The percentage of new patients diagnosed with AF ranged from 0.38% to 5.84%. Two studies59,61 reported a change in treatment management following the use of the Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG for new patients diagnosed with AF. Acceptability of lead-I ECG devices was reported in four studies,54,58,59,62 with generally positive views. Time to initiation of preventative treatment and HRQoL were not reported in any of the identified studies.
The ‘real-world’ data submitted by Kent Surrey Sussex AHSN reports on the use of Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device for people with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse during a 2-year project. Although the information available was limited [Microsoft PowerPoint presentation (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA) and a one-page summary], we considered it relevant to the population of interest. Data from this 2-year project showed that the percentage of new patients diagnosed with AF during the project was 69.9%, which is considerably higher than the diagnostic yield reported in our included studies (0.4–5.8%).
Chapter 4 Methods for assessing cost-effectiveness
The External Assessment Group’s (EAG’s) economic evaluation assesses the cost-effectiveness of single time point lead-I ECG devices compared with MPP for people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF who have an irregular pulse followed by a 12-lead ECG in primary or secondary care. The economic evaluation includes a systematic review of existing economic evaluations of lead-I ECG devices and the creation of a de novo economic model.
The economic evaluation is applicable to the use of lead-I ECG devices in primary care practices where there is a wait of ≥ 48 hours between initial presentation and follow-up with a 12-lead ECG.
Systematic review of cost-effectiveness evidence
Search strategy
The EAG undertook a systematic review to identify published full economic evaluations of lead-I ECG devices for detecting AF. A search filter to identify economic evaluations was applied to the search strategies and the electronic databases were searched from inception until 24 April 2018. The search strategy used in MEDLINE is presented in Appendix 10. The MEDLINE search was adapted to enable similar searching of the other relevant electronic databases. The following databases were searched for relevant studies:
-
MEDLINE (via Ovid)
-
MEDLINE Epub Ahead of Print and MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations (via Ovid)
-
EMBASE (via Ovid)
-
PubMed
-
EconLit (via EBSCOhost)
-
NHS Economic Evaluation Database.
The results of the searches were uploaded to, and managed using, EndNote X8 software. The reference lists of relevant systematic reviews and eligible studies were hand-searched to identify further potentially relevant studies.
Broader searches were carried out to identify existing economic models of ECG devices when used for the detection of AF. Separate searches were carried out to identify supporting information on costs and health-state utility data.
Eligibility criteria
In stage 1, all titles and abstracts identified via searches of the electronic databases were screened for relevance according to prespecified eligibility criteria (Table 9). Any studies that did not meet the criteria were excluded. The EAG planned to obtain full-text manuscripts for all economic evaluations identified at stage 1 to assess relevance against the prespecified eligibility criteria (stage 2).
| Characteristic | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Intervention or comparator | Single time point lead-I or single lead ECG, MPP | Ambulatory, inserted, multiple assessments |
| Indication | AF | Not AF |
| Study designa | Full economic evaluation | Partial economic evaluation, methodological paper |
| Perspective | UK or European perspective | Non-European perspective |
| Population | Adults with signs or symptoms indicative of AF plus irregular pulse assessed by MPPs presenting at primary care | Screening population, adults with asymptomatic or silent AF |
Data extraction and quality assessment strategy
The EAG planned to extract data relating to bibliographic information [author(s) and year of publication]; general information [country, condition, intervention and comparator(s)]; methodological characteristics (type of economic evaluation, perspective, time horizon, discount rate, key cost categories, year of valuation and key outcomes) and main findings. The EAG planned to assess the quality of all economic evaluations identified for inclusion in the review using the Drummond 10-point checklist. 69
Results of the systematic review of existing cost-effectiveness evidence
The searches of electronic databases identified 40 unique citations after de-duplication. Following screening of titles and abstracts, all 40 records were excluded as they did not include the relevant interventions or comparator, did not consider an eligible study population or were not full economic evaluations.
Conclusions of the systematic review of cost-effectiveness evidence
The EAG did not identify any published papers that met the inclusion criteria for the systematic review.
Development of a de novo economic model
Approach to modelling
The EAG did not identify any studies in a systematic review of the economic literature that evaluated the cost-effectiveness of single time point lead-I ECG devices compared with MPP followed by a 12-lead ECG in primary or secondary care (prior to initiation of anticoagulation therapy) in people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF who have an irregular pulse. The EAG therefore undertook a de novo economic analysis.
The economic analysis follows the diagnostic pathway for patients presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms indicative of AF plus an irregular pulse. The results are presented over a time horizon of 30 years, with patients entering the model at the age of 70 years.
The economic evaluation is relevant only to primary care practices where patients have to wait ≥ 48 hours between an initial consultation with the GP and a 12-lead ECG; this allows the benefit of early anticoagulation and rate-control treatment for those patients who receive a positive lead-I ECG to be considered.
A decision tree and two cohort Markov models were built in Microsoft Excel® (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA). The decision tree describes the pathway that a patient presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse follows in the initial GP consultation. The first Markov model captures the differences in the costs and benefits of treatment (standard diagnostic pathway compared with lead-I ECG pathway) during the first 3 months after the initial appointment. During this period, some patients will have a diagnosis of AF and start treatment for AF, whereas other patients will have further tests to diagnose or to rule out AF (where ‘rule out’ means that no diagnosis of AF is recorded in the patient’s notes and no treatment for AF is started). The second Markov model captures the differences in lifetime costs and benefits after diagnosis of AF or the time when AF is ruled out.
Population
The modelled patient population is adults presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF who have an irregular pulse. The DTA data included in the model are based on the results of a systematic review (see Chapter 3, Study selection). However, no studies included in the systematic review were carried out in the population of interest. All studies included asymptomatic patients who either had a known history of AF or were recruited from cardiology clinics, except for one study49 that was carried out in primary care. It has been recognised that diagnostic accuracy test specificity and sensitivity values may be affected by prevalence; the use of a test in a more severely diseased population is associated with better performance of the test. 70 It is therefore possible that the sensitivity and specificity data from the systematic review do not represent the true DTA of lead-I ECG devices in the population of interest. It is not possible to know how the sensitivity and specificity of lead-I ECG devices would be affected if different populations were tested. The economic evaluation is therefore limited by the lack of DTA data in the population of interest.
The symptomatic population with an irregular pulse is assumed to consist of people with AF and people with atrial or ventricular ectopy. Clinical advice to the EAG is that the only other condition that would produce an irregular pulse similar to that found with AF is atrial or ventricular ectopy. It is assumed that the symptoms of patients with AF, or atrial or ventricular ectopy, are not severe enough to require urgent referral to cardiology. Advice from the NICE Clinical Knowledge Summary71 on managing atrial and ventricular ectopy for patients without underlying heart disease is to reassure patients.
The mean age of patients in the base-case model is 70 years. The proportions of men and women are based on the age-adjusted ratio in the general population. 72
Comparators
Diagnostic test accuracy data were not available for the population of interest (symptomatic patients with suspected AF and an irregular pulse presenting to primary care) for any of the devices listed in the final scope issued by NICE9 (see Chapter 3, Characteristics of the included studies). The EAG therefore searched for DTA data in an asymptomatic population as prespecified in the protocol to use as a proxy for the population of interest. The economic model includes only the diagnostic strategies for which proxy DTA data were available. The diagnostic strategies (following MPP and before 12-lead ECG) included in the economic model are:
-
standard diagnostic pathway (no further testing)
-
any lead-I ECG device (interpreted by trained health-care professional)
-
imPulse (interpreted by trained health-care professional)
-
Kardia Mobile (interpreted by trained health-care professional)
-
MyDiagnostick (interpreted by trained health-care professional)
-
RhythmPad-GP (interpreted by algorithm)
-
Zenicor-ECG (interpreted by trained health-care professional).
Model structure
The model comprises decision trees and two cohort Markov models that describe the patient pathway over a lifetime horizon of 30 years. A decision tree covers the patient pathway in the initial consultation. Patients then feed into a cohort Markov structure with daily cycles for 3 months. This first Markov model includes all testing for AF after the initial GP consultation (12-lead ECG and Holter monitoring for paroxysmal AF). By the end of the first 3-month Markov model, all patients either have an AF diagnosis or have AF ruled out. Patients then move into the second Markov model. All patients in the second Markov model have AF diagnosed or ruled out (either correctly or incorrectly). Patients remain in the second Markov model until death. The cycle length is 3 months in the second Markov model. Costs and benefits are discounted at 3.5% per year.
Diagnostic phase
The diagnostic phase of the model encompasses the initial consultation and the following 3 months. At the end of the first 3-month period in the model, all patients who remain alive have had AF either diagnosed or ruled out (whether correctly or incorrectly; here ‘ruled out’ means that no diagnosis of AF is recorded in the patient’s notes and no treatment for AF has started).
A decision tree structure describes the pathway that a patient presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse follows in the initial GP consultation. Patients then enter a cohort Markov model either in a testing state (while waiting for the results of a 12-lead ECG or paroxysmal test) or in a diagnosed state (AF diagnosed or ruled out). Patients may stay in the testing period for a maximum number of days, depending on the test. Clinical advice to the EAG is that patients who cannot have a 12-lead ECG in the GP practice immediately would have to wait between 2 and 14 days for the test. Patients receiving testing for paroxysmal AF using a Holter monitor will stay in the paroxysmal testing state for 7 days.
At the end of the testing period, patients who received a 12-lead ECG may move to another testing state (paroxysmal test), to a diagnosed state (AF diagnosed or ruled out) or to the death state. At the end of the testing period, patients receiving a paroxysmal test may move to a diagnosed state (AF diagnosed or ruled out) or to the death state.
Patients may move out of a testing state before the end of the testing period by experiencing a cardiovascular event (CVE) or death. Patients who experience a CVE and who have not had AF diagnosed or ruled out are assumed to receive a diagnosis as part of treatment for the CVE. CVEs included in the model are TIA, ischaemic stroke (IS) and haemorrhagic stroke (HS). Patients can experience up to two CVEs. Clinically relevant adverse events (AEs) are included in the model (e.g. non-major bleeds). An AE can be experienced in any state and does not affect the risk of transition to another state.
The schematics for the decision tree element of the diagnostic phase of the model are shown in Figures 7–9. The schematic for the Markov element of the diagnostic phase of the model is shown in Figure 10.
FIGURE 7.
Diagnostic phase: decision tree – standard diagnostic pathway.
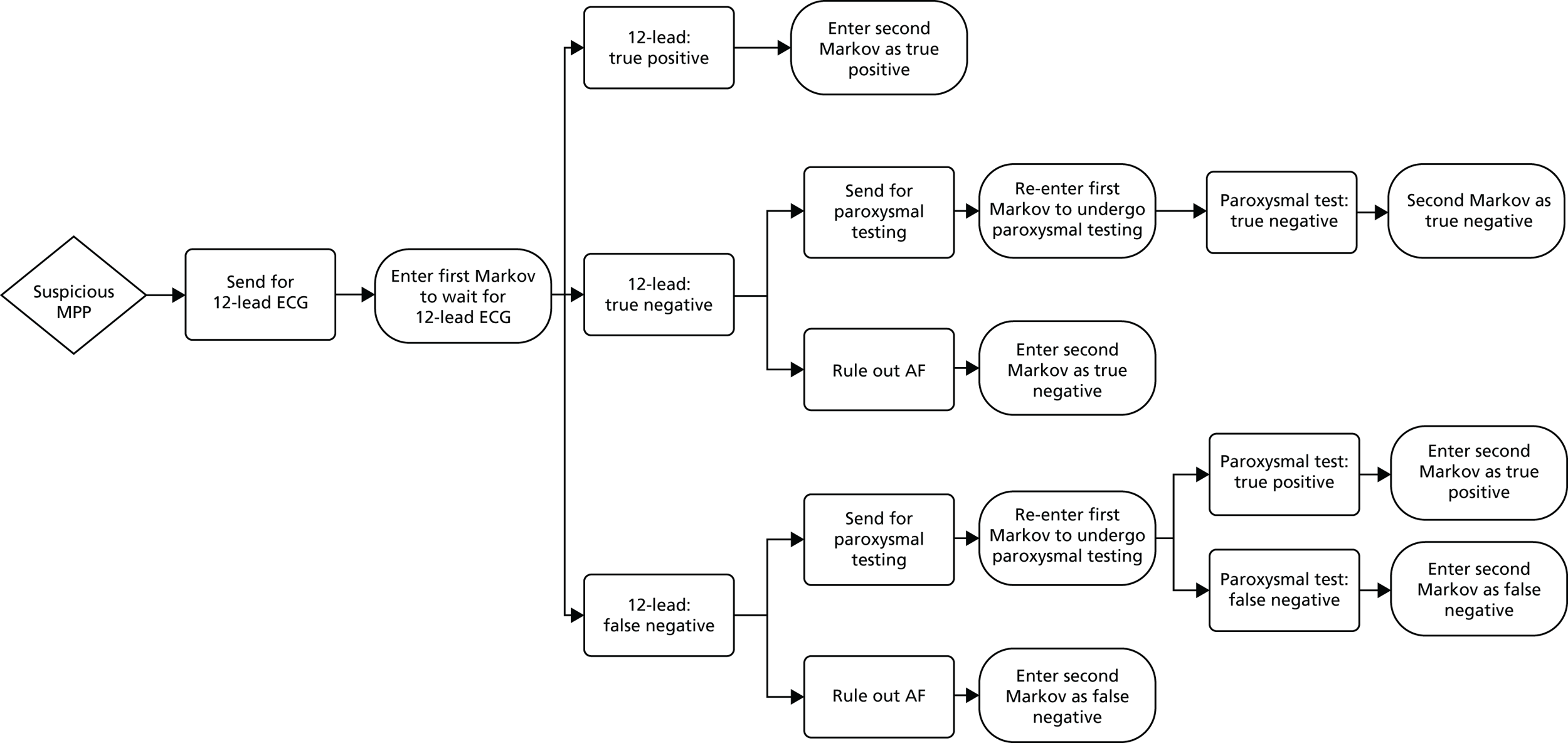
FIGURE 8.
Diagnostic phase: decision tree – lead-I ECG diagnostic pathway (positive result).
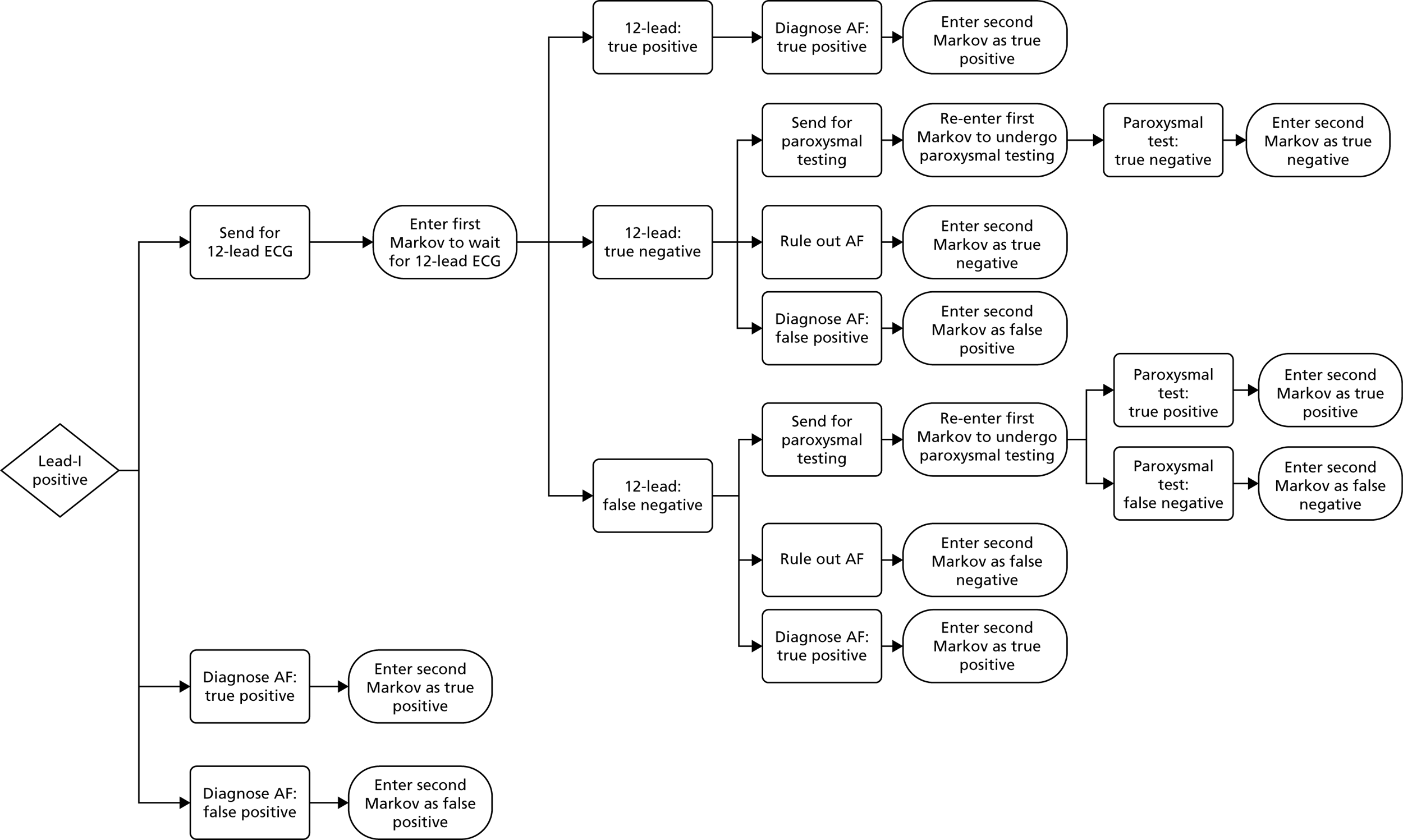
FIGURE 9.
Diagnostic phase: decision tree – lead-I ECG diagnostic pathway (negative result).
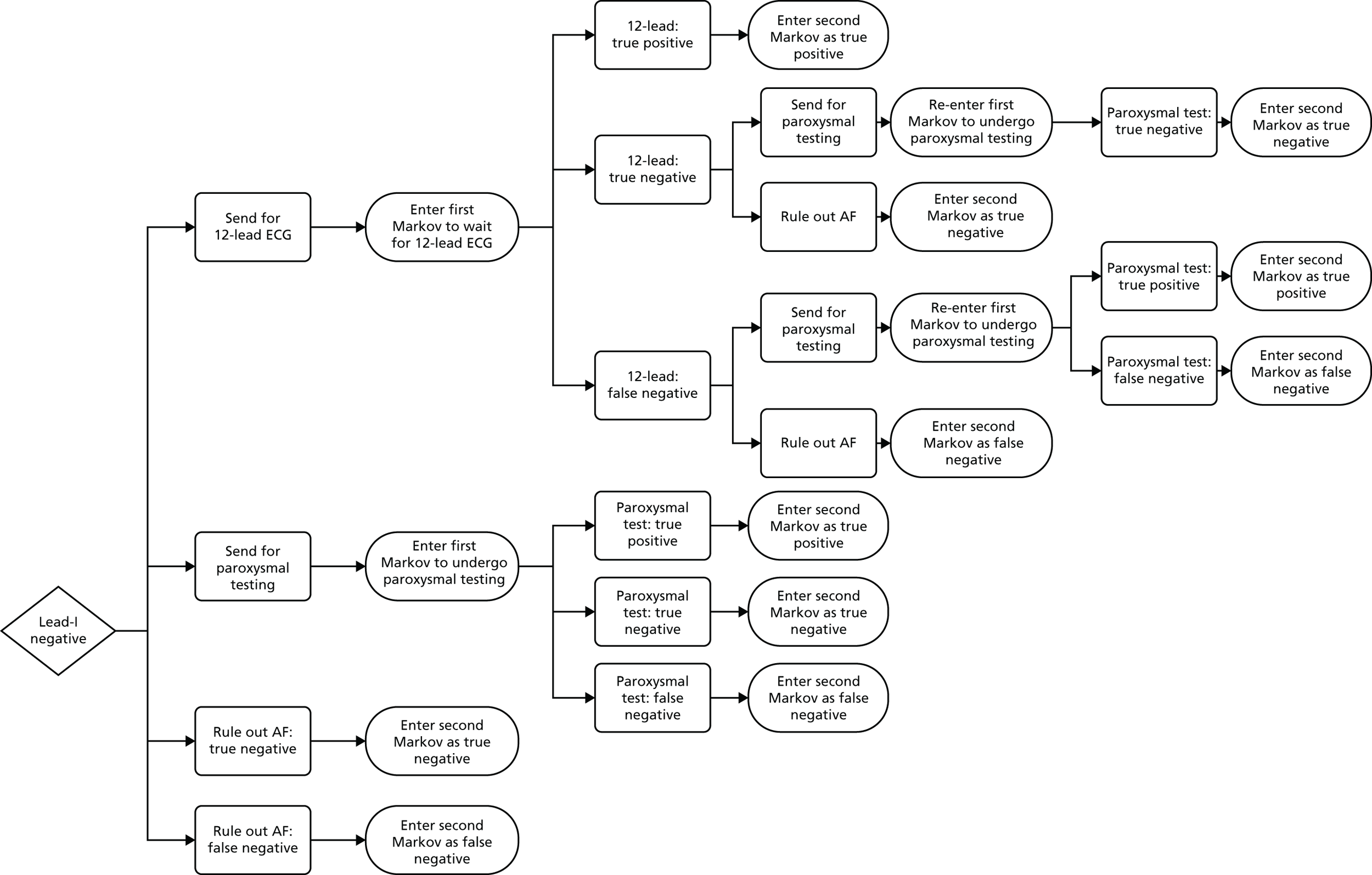
FIGURE 10.
Diagnostic phase: Markov model. Note: transition to the death state is possible from all health states.
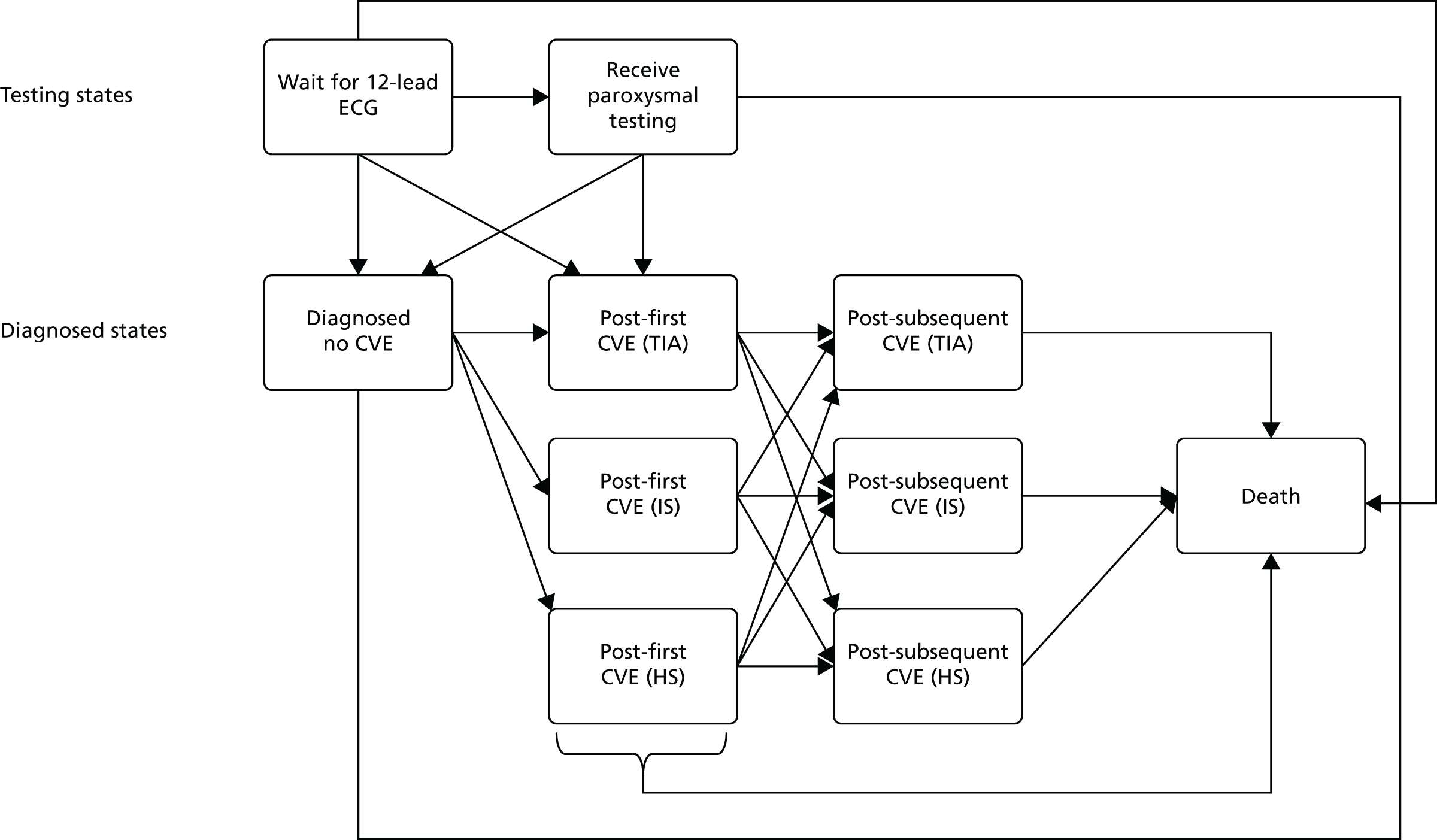
Standard pathway
All patients in the standard pathway are sent for a 12-lead ECG. No patients receive treatment for AF while waiting for the 12-lead ECG test.
All patients with a positive result from a 12-lead ECG are assumed to be correctly diagnosed with AF and begin treatment. A proportion of patients with a negative result from the 12-lead ECG are sent for further testing for paroxysmal AF and a proportion of patients have AF ruled out at this point in the pathway. All patients with a positive result from further testing for paroxysmal AF with a Holter monitor are correctly diagnosed with AF and begin treatment. All patients with a negative result from a paroxysmal test have AF ruled out. A proportion of patients who have AF ruled out after either a 12-lead ECG or a paroxysmal test will have false-negative results owing to patients with paroxysmal AF not being in AF at the time of the 12-lead ECG or paroxysmal test.
Lead-I electrocardiogram pathway: positive result
All patients in the lead-I ECG pathway with a positive result from a lead-I ECG (who are either true positives or false positives for AF) are diagnosed with AF and sent for a 12-lead ECG following the initial consultation. Clinical advice to NICE, as reported in the final scope,9 is that a 12-lead ECG is important so that any additional abnormalities can be identified in people diagnosed with AF, such as left ventricular hypertrophy. All patients in the lead-I ECG pathway with a positive result from a lead-I ECG begin rate-control treatment for AF, but do not receive Holter monitoring to test for paroxysmal AF, before the 12-lead ECG. As per the final scope issued by NICE,9 patients with positive lead-I ECG test results begin rate-control treatment and NOACs after the initial GP consultation unless contraindicated.
Patients with a positive 12-lead ECG result retain the (correct) diagnosis of AF and continue treatment. Patients with a negative 12-lead ECG result are assumed to have paroxysmal AF and continue treatment, have AF ruled out and discontinue treatment for AF or are sent for further testing for paroxysmal AF. The last group of patients remains on treatment during further testing.
All patients with a positive result from a paroxysmal test are correctly diagnosed with AF and stay on treatment. Patients with a negative result from a paroxysmal test either have AF ruled out and discontinue treatment or are assumed to have paroxysmal AF based on the original lead-I ECG diagnosis and continue treatment despite the negative 12-lead ECG and paroxysmal test result. A proportion of patients who have AF ruled out after either a 12-lead ECG or a paroxysmal test will have false-negative results owing to patients with paroxysmal AF not being in AF at the time of the 12-lead ECG or paroxysmal test.
Lead-I electrocardiogram pathway: negative result
No patients begin treatment following a negative result from a lead-I ECG test. Clinical advice to the EAG about whether patients who receive a negative result from a lead-I ECG device would be sent for a 12-lead ECG or for further testing for paroxysmal AF (see Appendix 11) indicated substantial variation in clinical practice. The EAG has assumed in the base case that 80% of patients who receive a negative result from a lead-I ECG device would be sent for a 12-lead ECG, 10% would be sent for ambulatory Holter monitoring and the remaining 10% of patients would have AF ruled out. The EAG acknowledges that this base case may not represent clinical practice anywhere in the UK; however, it considers that these assumptions may represent ‘average’ clinical practice, given the variation in clinical advice received. These assumptions are tested in scenario analyses.
All patients with a positive result from a 12-lead ECG are correctly diagnosed with AF and begin rate-control treatment and NOACs. A proportion of patients with a negative result from the 12-lead ECG are sent for further testing for paroxysmal AF and a proportion of patients have AF ruled out at this point in the pathway. All patients with a positive result from a paroxysmal test are correctly diagnosed with AF and begin treatment. All patients with a negative result from a paroxysmal test have AF ruled out. A proportion of patients who have AF ruled out after either a 12-lead ECG or a paroxysmal test will have false-negative results owing to patients with paroxysmal AF not being in AF at the time of testing.
Post-diagnostic phase
Once AF has been either diagnosed or ruled out, patients move into a second cohort Markov model that tracks the costs and benefits of these decisions over their lifetime (Figure 11). The second Markov model follows the same structure as the first Markov model after AF has been diagnosed or ruled out. Patients enter the second Markov model in a diagnosed state (AF diagnosed or ruled out) having experienced zero, one or two CVEs. In each cycle, patients with zero or one previous CVE can remain in their current state, move to a worse state following a CVE or move to the death state. Patients with two previous CVEs remain in that state until death. Patients who have incorrectly had AF ruled out and experience a CVE are assumed to have their AF diagnosed as part of the treatment for the CVE. These patients then move on to treatment for AF.
FIGURE 11.
Post-diagnostic phase: Markov model. Note: death is possible from all states.
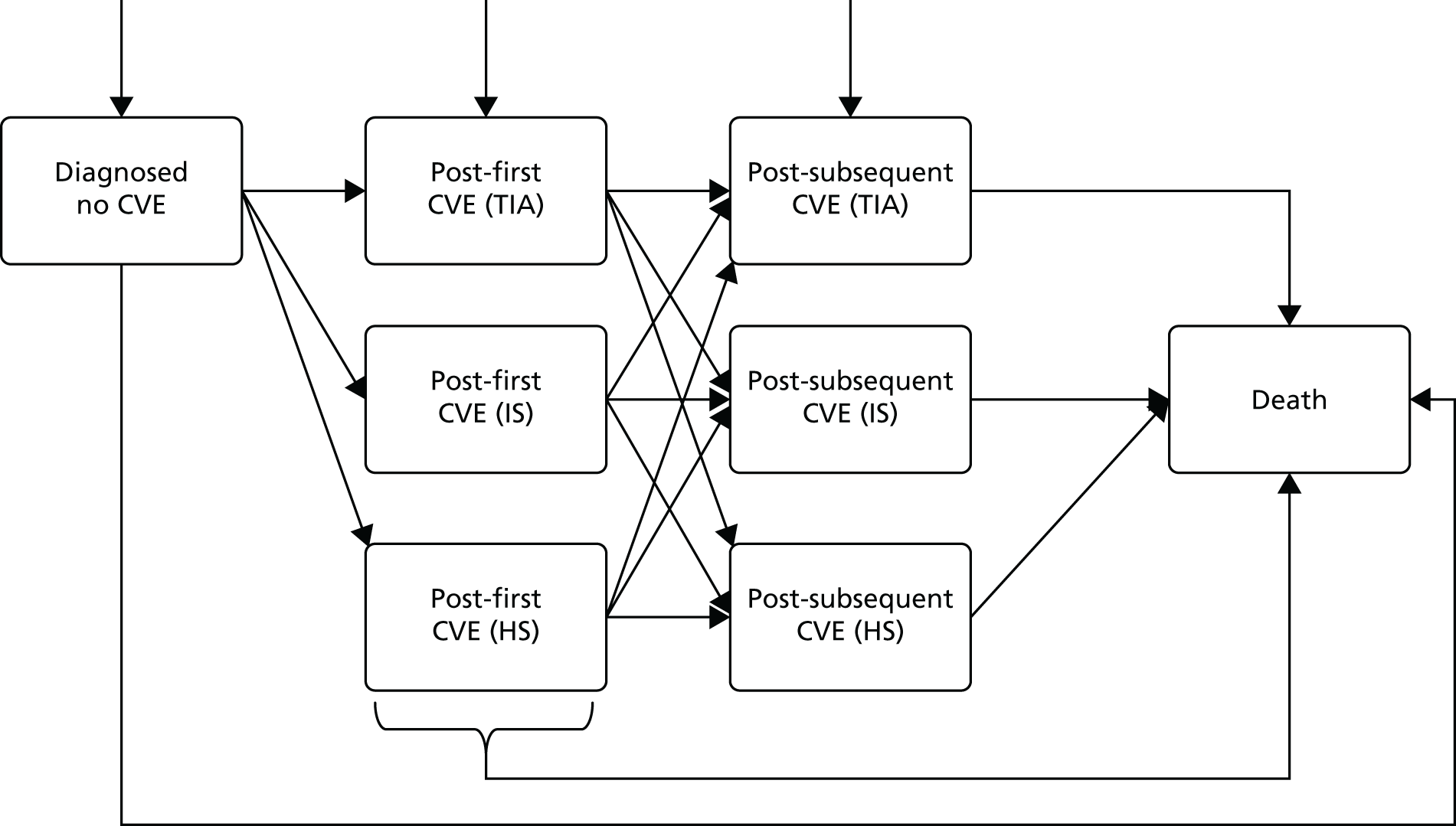
Model parameters
Patient population
Signs or symptoms of atrial fibrillation
The modelled patient population is people with signs or symptoms of AF plus an irregular pulse. This population comprises patients with AF and patients without AF who are similarly symptomatic. Clinical advice to the EAG is that the symptomatic population with an irregular pulse but without AF will consist of people with atrial or ventricular ectopy. Estimates of the proportion of patients with signs or symptoms of AF plus an irregular pulse who have AF compared with those who have atrial or ventricular ectopy were not available in the literature. Clinical advice to the EAG is that around 20% of patients with signs or symptoms of AF plus an irregular pulse will have AF.
Prevalence of atrial fibrillation
Estimates of the prevalence of AF by age and sex were taken from a paper by Adderley et al. 12 The age- and sex-specific prevalence estimates reported by Adderley et al. 12 are based on the results of a study carried out using primary care records from UK general practice in 2016. The prevalence estimates in this paper12 were identified by the EAG as being the most up-to-date estimates available for the UK primary care population. The age- and sex-standardised prevalence rates used in the model are shown in Table 10.
| Age group (years) | Prevalence per 1000 population | |
|---|---|---|
| Men (95% CI)a | Women (95% CI)a | |
| 45–54 | 7.60 (5.90 to 9.30) | 2.55 (2.26 to 2.88) |
| 55–64 | 24.01 (23.18 to 24.86) | 9.28 (8.79 to 9.86) |
| 65–74 | 66.78 (65.85 to 67.70) | 34.25 (33.33 to 35.19) |
| 75–84 | 147.38 (145.20 to 149.60) | 97.56 (95.70 to 99.40) |
| ≥ 85 | 220.94 (218.40 to 223.50) | 165.33 (163.00 to 167.60) |
Proportion of atrial fibrillation population who are symptomatic
The proportion of patients with AF who are symptomatic is taken from an observational cohort study of data from the US Outcomes Registry for Better Informed Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation by Piccini et al. 73 The study reported that women with AF were more likely to be symptomatic than men with AF (67.9% vs. 57.5%). The proportions of women and men with AF who are symptomatic used in the model are 0.679 (95% CI 0.665 to 0.693) and 0.575 (95% CI 0.562 to 0.588), respectively.
Proportion of patients with undiagnosed symptomatic atrial fibrillation who have paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
The proportion of patients with symptomatic undiagnosed AF who have paroxysmal AF could not be found in the literature. A fixed-effects meta-analysis by Welton et al. 74 reported that the proportion of patients with paroxysmal AF (not explicitly symptomatic) varied substantially between the studies75–77 included in the meta-analysis (from 0.059 to 0.835). Given the wide range reported by Welton et al. 74 and the lack of evidence specifically on incidence rates for symptomatic paroxysmal AF, in the base case it was assumed that 50% of patients in the model with AF would have paroxysmal AF; a sensitivity analysis was carried out to explore the impact of changes in the proportions between all patients with AF having paroxysmal AF and no patients having paroxysmal AF.
Proportion of symptoms reported by symptomatic patients
The prevalence of AF symptoms in men and women was taken from a study of sex differences in clinical presentation in AF by Schnabel et al. 78 The prevalence of symptoms was used in the EAG’s model to estimate the disutility associated with having symptoms indicative of AF. The paper by Schnabel et al. 78 does not give associated EQ-5D (EuroQol-5 Dimensions) measures for the symptoms noted in the study, so symptoms were mapped to a set of symptoms given in a HRQoL study by Berg et al. 79 The paper by Berg et al. 79 gives utility decrement estimates for various AF symptoms but does not list the baseline frequency of those symptoms. The prevalence of symptoms from the Schnabel et al. 78 paper is shown in Table 11. The prevalence of symptoms used in the model after mapping to symptoms reported by Berg et al. 79 is shown in Table 12.
| Symptom | Occasional, intermediate or frequent symptoms at baseline by sex in patients with new-onset AF (< 90 days), n (%) (N = 847) | |
|---|---|---|
| Men | Women | |
| Palpitations | 291 (61) | 267 (73) |
| Fatigue | 321 (67) | 270 (75) |
| Dizziness | 156 (33) | 159 (44) |
| Dyspnoea | 282 (58) | 240 (66) |
| Chest pain | 142 (30) | 99 (27) |
| Anxiety | 208 (44) | 218 (61) |
| Symptoms reported | Modelled prevalence (%) |
|---|---|
| Shortness of breath | 62 |
| Fatigue | 70 |
| Other AF symptoms | 52 |
| Congestive heart failure symptoms | 29 |
| Angina pectoris symptoms | 29 |
Eligible population
The modelled cohort (eligible population) is the estimated mean number of people with signs or symptoms of AF plus an irregular pulse that would present to a single GP over the course of a year. The eligible population is calculated using the equation:
where nAF is the number of symptomatic patients with AF estimated to visit a GP in 1 year, nnoAF is the number of symptomatic patients without AF estimated to visit a GP in 1 year and pAF is the estimated proportion of patients with signs or symptoms of AF who have AF and are estimated to visit a GP in 1 year.
The cost of a lead-I ECG device is estimated on a per-patient basis depending on whether a GP practice has one lead-I ECG device per GP or a single lead-I ECG device is shared among all GPs in the same practice. Real-world evidence from a report (Kent Surrey Sussex AHSN and Richard Blakey, AliveCor in East Sussex, unpublished evidence submitted via NICE) indicates that each GP in a practice will use their own device. It is assumed in the EAG base case that each GP in a practice will have access to their own device.
Number of general practitioners per practice
The mean number of GPs per practice in England was taken from the Practice List Size and GP Count report (January 2018) published by NHS Business Services. 80 The mean number of GPs per practice used in the model is 5.90 (95% CI 5.81 to 5.99).
Practice list size
The mean practice list size in England was taken from the Practice List Size and GP Count report (January 2018) published by NHS Business Services. 80 The mean practice list size used in the model is 8187 (95% CI 8068 to 8306). The corresponding average list size per GP is 1388 patients (8187/5.90).
Proportion of patients for whom use of the lead-I electrocardiogram device will be unsuitable
For a proportion of patients, use of the lead-I ECG device will be unsuitable, and this proportion is likely to vary depending on the device owing to the different methods of operation. The manufacturer of the RhythmPad GP device estimates that around 6% of patients would not be able to get a usable reading from the lead-I ECG test owing to low voltage emitted from the patient’s hands or if the patient is deemed to be isoelectric. Therefore, a value of 6% is applied in the model to all index tests to estimate the proportion of people unable to use the lead-I ECG device.
Proportion of lead-l electrocardiogram tests interpreted by algorithm, general practitioner or cardiologist
It is assumed in the EAG base-case analysis that the algorithm will not be used in isolation for making a judgement about whether or not patients have AF. Diagnostic accuracy data according to interpretation by a trained health-care professional were applied for each index test, with the exception of the RhythmPad GP device. Sensitivity and specificity estimates were not available for trained health-care professional interpretation for the RhythmPad GP device. Therefore, sensitivity and specificity estimates for algorithm interpretation for the RhythmPad GP device were used in the model as a proxy for interpretation by a trained health-care professional. The proportion of lead-I ECG test results that require interpretation by a cardiologist is assumed to be 10%, following assumptions in a previous economic evaluation of screening tests for AF. 74
Diagnostic test accuracy
Lead-I electrocardiogram devices
The DTA estimates for each lead-I ECG index test have been taken from the available published evidence (see Chapter 3, Study selection). Sensitivity and specificity values included in the model base case for each index test are presented in Table 13. It is assumed that all patients presenting to a GP who are experiencing symptoms of AF will be in AF at the time of the lead-I ECG test and so the sensitivity and specificity of the lead-I ECG devices are equal for paroxysmal and permanent or persistent AF.
| Index test | Interpreter | Source | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| imPulse | Health-care professional | Reeves (NR)63 | 83.5a | 91.5a |
| Kardia Mobile | Health-care professional | Pooled analysis | 94.0 | 96.8 |
| MyDiagnostick | Health-care professional | Desteghe, 2017 (EP1)38 | 85.0 | 95.0 |
| RhythmPad GP | Algorithm | Crockford, 201350 | 67.0 | 97.0 |
| Zenicor-ECG | Health-care professional | Doliwa, 200943 | 92.0 | 96.0 |
| Generic lead-I device | Health-care professional | Pooled analysis from EAG SR | 93.9 | 96.5 |
Sensitivity and specificity estimates for the MyDiagnostick device varied depending on the interpreter (EP1 and EP2) of the results. Interpreter EP1 produced results with higher sensitivity and lower specificity than interpreter EP2. The EAG has used the diagnostic accuracy estimates for the MyDiagnostick device from EP1 in the base case, as these had the highest sensitivity and might be expected to produce the most benefits in patients receiving early NOAC treatment. Diagnostic accuracy results based on interpretation of MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG trace by EP2 are presented as a scenario analysis. The sensitivity and specificity values used in the scenario analysis are presented in Table 14.
| Index test | Interpreter | Source (first author and year) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MyDiagnostick | Health-care professional | Desteghe 201738 (EP2) | 80.0 | 98.0 |
12-lead electrocardiogram
The EAG has assumed that 12-lead ECG tests have 100% specificity and sensitivity when patients are in AF at the time of the test, as a 12-lead ECG is the gold-standard reference test for lead-I ECG devices.
A proportion of patients with paroxysmal AF will not be in AF at the time of the 12-lead ECG. The estimate of the proportion of patients with paroxysmal AF who are not in AF at the time of the 12-lead ECG is taken from a study by Israel et al. 81 to investigate the long-term risk of recurrence of AF. This trial was conducted in patients with an existing diagnosis of paroxysmal or persistent AF who were receiving anti-arrhythmic therapy. Patients were given an implantable device to record episodes of AF and were also followed up with standard resting ECGs. The EAG acknowledges that the trial population is different from the population in the model and notes that this is a limitation. In the study by Israel et al. ,81 47.5% (46 out of 97) of patients had an episode of AF picked up by the implanted device that was not picked up by resting ECG. The EAG has used this estimate in the model to represent the proportion of patients with paroxysmal AF who are not in AF at the time of a 12-lead ECG.
Holter monitoring
The EAG has assumed that Holter monitor tests have 100% specificity and sensitivity when patients are in AF at the time of the test.
An estimate of the proportion of patients with paroxysmal AF who are not in AF at the time of a 7-day Holter monitor test was taken from a paper reporting the consensus of members of the German Atrial Fibrillation Competence NETwork and the European Heart Rhythm Association on outcome parameters for atrial fibrillation trials. 82 This report suggests that 7-day Holter monitoring will detect around 70% of AF recurrences.
Treatment after diagnosis
According to NICE CG180,3 patients with a positive diagnosis of AF and a CHA2DS2-VASc score of ≥ 2 should be offered anticoagulation treatment (once bleeding risk has been taken into account). It is assumed in the model that a proportion of patients who are AF-positive and have a CHA2DS2-VASc score of ≥ 2 will receive both anticoagulation (NOACs) and rate-control treatment (beta blockers). No patients are modelled to receive anticoagulation without rate-control treatment. The remaining patients will not receive anticoagulation, as a result of either contraindications or patient choice, but a proportion will still receive rate-control treatment. The proportion of patients who have a positive lead-I ECG test who do not receive anticoagulation but do receive rate-control treatment is assumed to be 100% in the base case.
Proportion of atrial fibrillation-positive patients with CHA2DS2-VASc score of ≥ 2
The proportion of AF-positive patients with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of ≥ 2 used in the base-case analysis is 82.4%. This value is calculated as the ratio of the number of patients with AF in England with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of ≥ 2 and the registered number of patients diagnosed with AF in England reported in the NHS Quality and Outcomes Framework 2016/17 indicator AF007. 11
Proportion of atrial fibrillation-positive patients with CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥ 2 treated with anticoagulants
The proportion of AF-positive patients with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of ≥ 2 who are treated with anticoagulants used in the base-case analysis is 81.2%. This value is taken from the NHS Quality and Outcomes Framework 2016/17 indicator AF007. 11
Proportion of patients who receive anticoagulants who receive NOACs
The proportion of patients who receive anticoagulants who receive NOACs used in the base-case model is calculated using data from May 2018, from the openprescribing.net database published by the University of Oxford. 83 The openprescribing.net database brings together raw, GP-level prescribing data published by NHS Digital. 84 Analysis of the data from the openprescribing.net database indicates that NOAC prescriptions (apixaban, rivaroxaban, dabigatran and edoxaban) have increased steadily in England, overtaking warfarin prescriptions in March 2018. The EAG notes that these figures are for anticoagulants prescribed for any condition and are not restricted to prescriptions for AF; however, the EAG considers that the rapid increase in use of NOACs over warfarin suggests that NOACs are becoming the treatment of choice for patients and physicians. To produce a tractable model without unnecessary complexity, the EAG assumed all patients would be prescribed a NOAC rather than warfarin. This assumption also allows the maximum potential benefit from earlier diagnosis with lead-I ECG to be achieved; clinical advice to the EAG is that NOAC could be prescribed immediately but prescribing warfarin would always require an appointment with the anticoagulation clinic first.
The overall proportion of patients diagnosed with AF (false or true positives following testing) who receive NOACs is estimated to be 66.9%. This proportion is based on estimates of the proportion of patients with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of ≥ 2 and the proportion of those patients treated with anticoagulants (assumed to be 100% NOACs) (Table 15).
| Proportion of AF-positive patients | Value used in model (%) | Cumulative proportion of AF population (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Proportion of AF-positive patients with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of ≥ 2 | 82.4 | 82.4 |
| Proportion of AF-positive patients with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of ≥ 2 treated with anticoagulants (assumed to be NOACs) | 81.2 | 66.9 |
The EAG used a single NOAC (apixaban) as the basis for modelling costs and outcomes for patients receiving NOAC therapy. Apixaban has been shown to be the most cost-effective NOAC for patients with AF in England and Wales; however, other NOACs have been found to have similar costs and benefits. 85 Apixaban is also the most commonly prescribed NOAC in England and accounted for almost 50% of all NOAC prescriptions in May 2018. 83 This approach has been taken in previous economic evaluations for AF. 74
Time to initiation of anticoagulation treatment after lead-I electrocardiogram test
Clinical advice to the EAG on how long it would take for a patient to be prescribed NOACs (if indicated) after a positive lead-I ECG test varied substantially depending on local Clinical Commissioning Group guidelines. In some cases, patients would be prescribed NOACs immediately after taking the lead-I ECG test during the initial consultation. In others, patients would need to wait ≥ 2 weeks for an appointment at an anticoagulation clinic. It is assumed in the base-case analysis that treatment with NOACs will be offered immediately to those patients who do not have contraindications. This approach was used to capture the full potential benefit of beginning NOAC treatment earlier than would be the case in the standard diagnostic pathway (when anticoagulation treatment is assumed to begin immediately after the 12-lead ECG test).
Time to 12-lead ECG
An estimate of the time taken to diagnose AF following a lead-I ECG test is reported by Lowres et al. 61 However, the study by Lowres et al. 61 was carried out in pharmacies in Australia. This setting was not considered to be sufficiently similar to the setting of interest in this assessment for the data to be included in the model. The EAG therefore sought clinical advice from primary care physicians in the NHS. Clinical advice given to the EAG on how long it would take for a patient to receive a 12-lead ECG varied substantially. In some cases, the patient would be expected to have a 12-lead ECG within 48 hours. In others, the wait might be up to 2 weeks. The EAG has produced base-case cost-effectiveness estimates for two scenarios (2 days and 14 days) to account for the variation in time to 12-lead ECG in clinical practice.
Mortality rates (no previous cardiovascular events)
Age- and sex-adjusted general mortality rates for England86 were used to estimate deaths in the AF-negative population. Annual mortality rates are interpolated linearly between published annual mortality rates and then converted to daily probabilities using the equation:
Age- and sex-adjusted mortality rates in the AF-positive population were estimated based on published risk (or hazard) ratios or incidence rates. Single incidence rates were adjusted for age according to the proportionate mortality risk for the given age in the general population. Risk ratios were applied to mortality rates in the appropriate comparative population. It was assumed that proportionate risk remains stable over time. Mortality rates and mortality risk ratios for patients with no history of CVEs are given in Table 16.
| State | Source | Value type | Value | Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF: treated – NOAC | Sterne 201785 | HR vs. warfarin (< 80 years) | 0.890 | |
| AF: untreated | Sterne 201785 | HR vs. warfarin | 1.178 | |
| AF: treated – warfarin | Sterne 201785 | Annual rate (70 years) | 0.038 | Reference value |
| No AF: treated – NOAC | ONS86 | Annual rate | Various | |
| No AF: untreated | ||||
Mortality rates (previous cardiovascular events)
The risk of death for people who have had a previous IS, HS or TIA increased compared with that of people who have not had a previous CVE by applying a hazard ratio (HR) to mortality rates for people with no previous CVEs. The HR was taken from a study of stroke survivors in Norway by Mathisen et al. ,87 which reported mortality HRs for stroke survivors (IS, HS or TIA) with a mean age of 67 years compared with those for people without these events aged > 16 years. This study did not report results according to AF status, which is a limitation of the data. The HR after repeated stroke or TIA versus mortality in the general population reported in this study87 was 2.6. The EAG considered it appropriate to apply the HR to all ages in the model because analysis of the Kaplan–Meier data from the study by Mathisen et al. 87 suggested that HR was proportional over time. As the HR reported in the study by Mathisen et al. 87 was pooled for patients with IS, HS and TIA, the EAG assumed that the risk of death after any CVE was 2.6 times greater than the risk of death with no history of CVEs. This increased mortality risk is applied for life once a patient experiences a CVE.
Cardiovascular and adverse event rates (no previous cardiovascular events)
The CVEs included in the model are IS, TIA and HS. Clinically relevant bleeds are considered to be AEs. Rates for AEs are assumed to be independent and do not take account of the history of previous events.
Age- and sex-adjusted CVE rates in the AF-positive population for patients with no history of previous CVEs are estimated based on published risk (or hazard) ratios, incidence rates or probabilities. Incidence rates are adjusted for age according to the proportionate mortality risk for the given age in the general population. Probabilities are adjusted for age by translating the probability into a rate before adjusting by the proportionate mortality risk for the given age in the general population. Risk ratios are applied to CVE in the appropriate comparative population. It is assumed that proportionate risk remains stable over time.
CVE rates in the untreated AF-negative population with no history of previous CVEs are estimated based on published incidence rates. CVE rates in the NOAC- and warfarin-treated AF-negative population (i.e. the false-positive population) are estimated based on the following rule: if the risk ratio for a particular event between the treated and untreated AF-positive populations is > 1, increase the risk for that event in the treated AF-negative population. If the risk ratio for a particular event between the treated and untreated AF-positive populations is ≤ 1, the model uses general population rates86 for that event.
Base-case CVE and AE rates used in the economic model are given in Tables 17–20. Rates for warfarin treatment are given, whereas rates for NOAC and no treatment are calculated using a HR applied to the rate associated with treatment with warfarin.
| State | Source (first author and year) | Value type | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| AF: treated – NOAC | Sterne 201785 | HR vs. warfarin | 0.9000 |
| AF: treated – warfarin | Sterne 201785 | Annual rate (70 years) | 0.0120 |
| AF: untreated | Sterne 201785 | HR vs. warfarin | 1.1780 |
| No AF: treated – NOAC | Equal to ‘No AF: untreated’ | ||
| No AF: untreated | PHE 201888 | Annual rate (female, 50 years) | 0.0007 |
| Annual rate (female, 60 years) | 0.0013 | ||
| Annual rate (female, 70 years) | 0.0030 | ||
| Annual rate (female, 80 years) | 0.0060 | ||
| Annual rate (female, 90 years) | 0.0108 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 50 years) | 0.0012 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 60 years) | 0.0023 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 70 years) | 0.0044 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 80 years) | 0.0064 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 90 years) | 0.0099 |
| State | Source (first author and year) | Value type | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| AF: treated – NOAC | Sterne 201785 | HR vs. warfarin | 0.820 |
| AF: treated – warfarin | Sterne 201785 | Annual rate (70 years) | 0.066 |
| AF: untreated | Sterne 201785 | HR vs. warfarin | 0.543 |
| No AF: treated – NOAC | Calculated | HR vs. untreated | 1.511 |
| No AF: untreated |
2016/17 Reference Costs and Guidance 89 Includes: gastrointestinal bleed (FD03 A:FD03H), unspecified haematuria (LB38C:LB38H), non-malignant GI tract disorders (FD10 A: FD10M) |
Annual rate (assume 70 years) | 0.011a |
| State | Source (first author and year) | Value type | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| AF: treated – NOAC | Sterne 201785 | HR vs. warfarin | 0.7400 |
| AF: treated – Warfarin | Sterne 201785 | Annual rate (70 years) | 0.0250 |
| AF: untreated | Sterne 201785 | HR vs. warfarin | 1.6170 |
| No AF: treated – NOAC | Equal to ‘No AF: untreated’ | ||
| No AF: untreated | aRothwell 200590 | Annual rate (female, 50 years) | 0.0003 |
| Annual rate (female, 60 years) | 0.0011 | ||
| Annual rate (female, 70 years) | 0.0022 | ||
| Annual rate (female, 80 years) | 0.0057 | ||
| Annual rate (female, 90 years) | 0.0093 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 50 years) | 0.0002 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 60 years) | 0.0005 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 70 years) | 0.0014 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 80 years) | 0.0034 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 90 years) | 0.0080 |
| State | Source | Value type | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| AF: treated – NOAC | Sterne 201785 | HR vs. warfarin | 0.46000 |
| AF: treated – warfarin | Sterne 201785 | Annual rate (70 years) | 0.00900 |
| AF: untreated | Sterne 201785 | HR vs. warfarin | 0.54300 |
| No AF: treated – NOAC | Equal to ‘No AF: untreated’ | ||
| No AF: untreated | aRothwell 200590 | Annual rate (female, 50 years) | 0.00002 |
| Annual rate (female, 60 years) | 0.00019 | ||
| Annual rate (female, 70 years) | 0.00034 | ||
| Annual rate (female, 80 years) | 0.00100 | ||
| Annual rate (female, 90 years) | 0.00104 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 50 years) | 0.00002 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 60 years) | 0.00019 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 70 years) | 0.00026 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 80 years) | 0.00171 | ||
| Annual rate (male, 90 years) | 0.00078 |
Cardiovascular and adverse event rates (previous cardiovascular events)
A meta-analysis of stroke recurrence was conducted in 2010 that reported recurrence rates of 6.5% at 1 year and 14.3% at 5 years. 91 These subsequent stroke rates were applied to people in the model after their first TIA, IS or HS. The proportion of subsequent strokes that were TIA, IS or HS was calculated using proportionate incidence rates reported in a study by Rothwell et al. 90 The annual recurrent stroke rate between year 2 and year 5 was calculated by assuming the rate was constant between years 2 and 5. The subsequent stroke rate from year 5 onwards was assumed to be the same as in years 2–5. Having a subsequent stroke after first IS or HS post-discharge did not alter any transition probabilities in the model as the increase in mortality risk was assumed to have been captured after the initial IS or HS. The probability of subsequent stroke and the proportion of subsequent strokes that are TIA, IS or HS are shown in Table 21.
Utilities
State-specific utilities
Utility values have been estimated for symptomatic and asymptomatic populations with and without AF. Utility values are assumed to be the same for all populations except those people with symptomatic (i.e. untreated) AF (Table 22).
| AF (95% CI) | No AF (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| Untreated (symptomatic) | 0.665 (0.537 to 0.881) | 0.744 (0.480 to 0.942) |
| Treated (asymptomatic) | 0.744 (0.480 to 0.942) | 0.744 (0.480 to 0.942) |
Utility values for the symptomatic and asymptomatic AF-positive population are based on a study by Berg et al. 79 Berg et al. provide the coefficients of two regression models fitted to the results of the EQ-5D-3L (EuroQol-5 Dimensions, three-level version)92 questionnaire, completed at baseline and follow-up as part of a large European survey of patients with AF. Mean age-specific utility values for symptomatic patients with AF were calculated using the baseline coefficients from the study by Berg et al. 79 and adjusted for model age, sex ratio and symptom proportions. Mean age-specific utility values for asymptomatic patients with AF were calculated similarly using the coefficients at follow-up.
The HRQoL of people without AF presenting at primary care with symptoms indicative of AF was assumed to be lower than that of the general population, as the former are still ill with symptoms assumed to be caused by atrial or ventricular ectopy. However, HRQoL was assumed not to be as low as that of patients with symptomatic AF, as the recommended action for patients with atrial or ventricular ectopy (who are not showing immediate signs of a serious underlying cardiac cause or complication) is to reassure. 71 Treatment for AF was assumed not to have an impact on the HRQoL of patients without AF, as in the model treatment is associated with a reduction in AF symptoms. Utility values for the AF-negative population (both treated and untreated) were assumed to be equal to the utility values for the treated AF population whose AF is under control.
Cardiovascular and adverse event utility decrements
Lifetime utility decrements were assumed to apply to all ischaemic and HS events (Table 23). Utility decrements for stroke were taken from the study by Berg et al. 79 Utility decrements were applied at the time of the first IS or HS and no further decrements were applied for any subsequent IS or HS. Bleed and TIA events were assumed in the base case to be acute events that fully resolve and have no long-term impact on HRQoL.
| AE | Base case | Sensitivity analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decrement | Source (first author and year) | Decrement or value | Source (first author and year) | |
| IS | –0.272 (95% CI –0.345 to –0.198) | Berg 201079 | –0.590 | Robinson 200193 |
| HS | Assumed equal to IS | Value for ICH: –0.108 (95% CI –0.135 to –0.082) | Berg 201079 | |
Test costs
Annual lead-I electrocardiogram device unit costs
The annual cost of each lead-I ECG device was calculated as the unit cost per device [excluding VAT (value-added tax)] divided across the expected life of the device in years, plus annual licence fee. No companies reported any maintenance costs associated with their devices, so these have not been included in the model. The cost of an accompanying smartphone or tablet for the Kardia Mobile device has not been included in the base case, as it was assumed that GPs would already have access to a smartphone or tablet. An average cost for a generic lead-I ECG device was calculated using the simple mean of the annual cost of individual devices. The annual cost of each index test included in the model is given in Table 24. Lead-I ECG devices are also likely to be used in populations other than the population with signs or symptoms of AF, which would decrease the unit cost per use of each device. The impact on cost-effectiveness of not including the cost of the lead-I ECG device has been investigated in a sensitivity analysis.
| Device | Item | Lifetime cost (£) (excluding VAT) | Life of device (years) | Annual cost (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| imPulse | Device | 175.00 | 2 | 87.50 |
| Kardia Mobile | Device | 82.50 | 5 | 16.50 |
| MyDiagnostick | Device | 450.00 | 5 | 90.00 |
| RhythmPad GP | Device | 1100.00 | 1 | 1100.00 |
| Zenicor ECG | Device and 36-month licence | 1980.00 | 10 | 613.27 |
| Extra 36-month licence | 1780.00 | |||
| Generic lead-I device | 381.45 |
Cost per lead-I electrocardiogram test
The cost per lead-I ECG test in the standard diagnostic pathway was zero, as it was assumed the only resource use in this context was the cost of the GP consultation. The cost of the initial GP consultation is assumed to be equal in both diagnostic pathways and is not included in the model. No extra time is included in the base-case model for administering the lead-I ECG or interpreting the results during the initial consultation. It is assumed that review of the results of a lead-I ECG test by a cardiologist would take 1 minute, in accordance with results from the study by Hobbs et al. 94 Assumptions about the time taken to administer and review a lead-I ECG test are varied in the sensitivity analysis.
The cost per lead-I ECG test was calculated as the annual cost per device divided by the number of patients in the eligible population per year, plus any extra costs associated with each use of the device; the Zenicor-ECG device was the only index test included in the model to incur extra costs with each use, as the manufacturer recommends that the electrodes are replaced after 500 uses.
The costs per index test and cost of interpreting the lead-I ECG test included in the model are given in Table 25 and 26.
| Device | Annual device cost (£) (excluding VAT) | Number of patients tested per year | Peripheral costs per test (£) | Unit cost per testa (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| imPulse | 87.50 | 54 | 0.00 | 1.62 |
| Kardia Mobile | 16.50 | 54 | 0.00 | 0.31 |
| MyDiagnostick | 90.00 | 54 | 0.00 | 1.67 |
| RhythmPad GP | 1100.00 | 54 | 0.00 | 20.42 |
| Zenicor ECG | 613.27 | 54 | 0.02 | 11.40 |
| Generic lead-I device | 381.45 | 54 | 0.02 | 7.10 |
Cost per 12-lead electrocardiogram test
The cost per 12-lead ECG test varies depending on whether the test is carried out in primary or secondary care.
For 12-lead ECG tests carried out in primary care, the unit cost of a 12-lead ECG device is estimated to be £2251, in line with the estimate used in NICE Guideline 45 (NG45),96 inflated to 2017 prices using the Office for National Statistics Consumer Price Index for Medical Services [DKC3]. 97 It is assumed in the model that a 12-lead ECG device may be used 1000 times before being replaced, in line with the assumption in NICE NG45,96 which equates to £2.25 per use. The cost of disposables such as electrodes and gels is estimated to be £1.13 per use, uplifted to 2017 prices from the estimate used in NICE NG45. 96
The cost of administering a 12-lead ECG test in secondary care is estimated using the NHS Reference Costs 2016/1798 for Electrocardiogram Monitoring or Stress Testing [directly accessed diagnostic services HRG (healthcare resource group): EY51Z DADS].
The costs of administering the 12-lead ECG test in primary and secondary care are summarised in Table 27.
| Health-care setting | Unit cost (£) | Source | Activity | Time taken (minutes) | Cost per test (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary care | |||||
| Device | 2.25 per use | Estimate | 2.25 | ||
| Disposables | 1.13 per use | Hobbs et al. (2005)94 | 1.13 | ||
| Nurse | 42 per hour | PSSRU95 | Administration | 7a | 4.90 |
| GP | 137 per hour | PSSRU95 | Interpretation | 1a | 2.28 |
| Cardiologist | 107 per hour | PSSRU95 | Interpretation | 1a | 1.78 |
| Total cost per 12-lead ECG test in primary care | 12.34 | ||||
| Secondary care | |||||
| ECG monitoring or stress testing | 52 per test | NHS Reference Costs 2016/17 (HRG: EY51Z DADS)98 | N/A | 52.00 | |
Cost per paroxysmal test
Further testing for paroxysmal AF is represented by the use of a Holter monitor. The cost of a Holter monitor test is taken from an estimate in a NICE Medtech innovation briefing [MIB101]99 published in March 2017. The list price of a Holter monitor device in the NHS Supply Chain catalogue is given as £1632.14 in NICE MIB101. 99 It assumed that the device will be used 1000 times before it needs to be replaced, giving a marginal cost per use of £1.63. The cost of administering and interpreting a Holter monitor test is estimated in NICE MIB10199 to be £118.60 including overheads. The total cost per each Holter monitor test in the model is £120.23.
Treatment costs
The NOAC drug costs
The cost of treatment with NOACs was assumed to equal the cost of treatment with apixaban. The cost of 1 month’s (28 days) treatment with apixaban was calculated using dosing information from the British National Formulary (BNF)100 and prices from the NHS Drug Tariff (July 2018)101 and adjusted to reflect the number of days of treatment before receiving a 12-lead ECG. It was assumed that the dosage of NOACs would be prescribed in equal proportions. The number of packs used per month for each dosage was calculated based on the least costly combination of pack sizes. The base-case drug cost of apixaban used in the model was £55.10 per 28 days (Table 28).
Rate control drug costs
The cost of treatment with beta blockers was used as a proxy for the cost of all rate-control treatments. The cost of 1 month’s (28 days) treatment with each of three beta blockers (atenolol, metoprolol and propranolol) was calculated using dosing information from the BNF100 and prices from the NHS Drug Tariff (July 2018)101 and adjusted to reflect the number of days of treatment before receiving a 12-lead ECG. It was assumed that the dosage of rate-control drugs would be prescribed in equal proportions. The number of packs used per month for each dosage was calculated based on the least costly combination of pack sizes. The base-case drug cost of rate-control drugs used in the model was £2.59 per 28 days (Table 29).
| Dose (mg) (BNF)100 | Frequency (per day) (BNF)100 | Tablet size (mg) (NHS)101 | Pack size (tablets) (NHS)101 | Packs per 28 days | Pack cost (NHS)101 (£) | Monthly cost per dose (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atenolol | ||||||
| 50 | 1 | 50 | 28 | 1 | 0.47 | 0.47 |
| 100 | 1 | 100 | 28 | 1 | 0.51 | 0.51 |
| Average cost per 28 days | 0.49 | |||||
| Metoprolol | ||||||
| 50 | 2 | 50 | 28 | 2 | 0.78 | 1.56 |
| 50 | 3 | 50 | 28 | 3 | 0.78 | 2.34 |
| Average cost per 28 days | 1.95 | |||||
| Propranolol | ||||||
| 10 | 2.61 | 2.61 | 2.61 | 2.61 | 2.61 | 2.61 |
| 10 | 3.48 | 3.48 | 3.48 | 3.48 | 3.48 | 3.48 |
| 20 | 5.22 | 5.22 | 5.22 | 5.22 | 5.22 | 5.22 |
| 20 | 6.96 | 6.96 | 6.96 | 6.96 | 6.96 | 6.96 |
| 30 | 7.83 | 7.83 | 7.83 | 7.83 | 7.83 | 7.83 |
| 30 | 10.44 | 10.44 | 10.44 | 10.44 | 10.44 | 10.44 |
| 40 | 2.64 | 2.64 | 2.64 | 2.64 | 2.64 | 2.64 |
| 40 | 3.52 | 3.52 | 3.52 | 3.52 | 3.52 | 3.52 |
| Average cost per 28 days | 5.34 | |||||
| All drugs | ||||||
| Average cost per 28 days | 2.59 | |||||
Prescription costs
The EAG model base case includes a prescription cost for each treated patient. The same prescription cost was applied regardless of the number of treatments a patient receives (anticoagulation plus rate control or rate-control treatment alone). The prescription fee included in the model was £1.29 per prescription and was taken from the NHS Drug Tariff (July 2018). 101
The NOAC monitoring costs
No costs were included in the model for monitoring patients taking NOAC or rate-control treatment.
Cardiovascular and adverse event costs
Acute event costs
The cost of each acute bleed and TIA event was calculated as the weighted average of the appropriate HRG codes included in the NHS Reference Costs 2016/17. 98 The full cost of each event was applied. Costs used in the model base case for each event are shown in Table 30.
| AE | HRG codes | Mean cost per event (£) (IQR) |
|---|---|---|
| Bleed |
Gastrointestinal Bleed without Interventions (FD03F:FD03H) Unspecified Haematuria with Interventions (LB38C:LB38E) |
704.05 (592.24–782.48) |
| TIA | Transient Ischaemic Attack (AA29C:AA29F) | 729.62 (570.08–837.65) |
Long-term cardiovascular event costs
Age- and sex-adjusted 1- and 5-year costs for ischaemic and HS were taken from the Sentinel Stroke National Audit Programme (SSNAP) Cost and Cost-effectiveness report 2016 (Tables 31 and 32). 102 One-year costs were applied in the first year after the stroke event. The annual costs between year 2 and year 5 were calculated by assuming that the difference in cost between year 1 and year 5 accrued linearly between years 2 and 5. The cost from year 5 onwards was assumed to be the same as in years 2–5. Costs restart at year 1 for patients who experience a subsequent CVE.
| Sex | Age (years) | 1-year costs (£) | 5-year costs (£) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NHS | Social care | NHS | Social care | ||
| Male | 40–64 | 9779 | 2241 | 16,017 | 8835 |
| Male | 65–74 | 11,495 | 3684 | 16,843 | 14,110 |
| Male | 75–84 | 13,217 | 7620 | 17,816 | 25,148 |
| Male | 85–100 | 14,906 | 13,070 | 18,613 | 38,623 |
| Female | 40–64 | 9627 | 2312 | 15,954 | 9308 |
| Female | 65–74 | 11,705 | 3878 | 16,987 | 14,668 |
| Female | 75–84 | 13,441 | 7923 | 17,995 | 26,370 |
| Female | 85–100 | 15,803 | 13,500 | 18,947 | 38,585 |
| Sex | Age (years) | 1-year costs (£) | 5-year costs (£) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NHS | Social care | NHS | Social care | ||
| Male | 40–64 | 11,465 | 3661 | 17,857 | 15,063 |
| Male | 65–74 | 12,773 | 4862 | 18,188 | 18,960 |
| Male | 75–84 | 14,605 | 10,545 | 19,389 | 36,994 |
| Male | 85–100 | 16,291 | 15,551 | 19,896 | 49,256 |
| Female | 40–64 | 11,260 | 3256 | 17,538 | 13,508 |
| Female | 65–74 | 12,734 | 5285 | 18,143 | 20,476 |
| Female | 75–84 | 14,747 | 11,379 | 19,103 | 37,630 |
| Female | 85–100 | 16,481 | 15,425 | 19,750 | 46,730 |
Summary of base-case assumptions
Parameter assumptions and sources used in the base-case model are summarised in Table 33.
| Parameter | Assumption or source | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| AF status at initial consultation | All patients with AF are in AF at the time of the initial consultation | Population is patients presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse. These symptoms are assumed to be caused by AF if the patient has AF |
| Mean age (years) | 70 | Mean age observed in RCTs used by Sterne et al.85 and to estimate CVE rate parameters |
| Per cent female | 51.6 | Age-adjusted proportion in the general population, assumed to match proportion in GP lists |
| AF prevalence | Adderley et al., 201812 | Recent data from UK primary care |
| Proportion of AF undiagnosed | Turakhia et al., 2018103 | Recent data |
| Proportion of AF with signs or symptoms | Mapped from Schnabel et al.78 to Berg et al.79 | Real-world data (Kent Surrey Sussex AHSN) |
| Proportion of patients with undiagnosed symptomatic AF who have paroxysmal AF (%) | 50 | Assumption owing to wide range reported by Welton et al.,74 and the lack of evidence specifically on incidence rates for symptomatic paroxysmal AF |
| Number of lead-I ECG devices per practice | One per GP | Previous economic evaluation74 |
| Proportion of lead-I ECG tests interpreted by GP and cardiologist (%) | 10 | Data from Hobbs et al.94 estimate 7 minutes for a nurse to administer a 12-lead ECG. Assume < 7 minutes for a lead-I ECG, but some extra time still required to explain and carry out procedure |
| Extra time taken to administer lead-I ECG test (minutes) | 0 | Test is assumed to be administered during standard GP appointment |
| Proportion of patients receiving anticoagulation | Only CHA2DS2-VASc ≥ 2 receive anticoagulation (if not contraindicated) | Scope |
| Proportion of patients receiving anticoagulation who receive NOACs (%) | 100 | Simplifying assumption based on evidence that prescriptions for NOACs overtook prescriptions for warfarin in 2018 |
| Time from diagnosis to anticoagulation | Immediate | Simplifying assumption allowing the maximum potential benefit from earlier diagnosis with lead-I ECG |
| Proportion of patients receiving 12-lead ECG |
100% for standard pathway and lead-I positive 80% for lead-I negative |
Standard pathway: NICE CG1803 Lead-I positive (AF diagnosed): NICE CG1803 Lead-I negative: assumption based on clinical advice (see Appendix 11) and varied in sensitivity analyses |
| Diagnostic accuracy of 12-lead ECG | 100% sensitivity and specificity for those patients in AF at time of test | 12-lead ECG is reference test for lead-I devices, hence must be assumed to be 100% accurate |
| Proportion of patients with paroxysmal AF not in AF at time of 12-lead ECG (%) | 47.5 | Data from Israel et al., 200481 |
| Diagnostic accuracy of Holter monitor | 100% sensitivity and specificity for those patients in AF at time of test | Simplifying assumption |
| Proportion of patients with paroxysmal AF not in AF at time of Holter monitor (%) | 30 | Data from Kirchoff et al., 200682 |
Uncertainty
Uncertainty in parameter values and the impact this could have on results has been explored both through the scenario and through the sensitivity analyses. Parameters have been varied through probability sensitivity analysis parameters, where probability distributions could be derived from, or were provided in, the literature. Probabilistic sensitivity analysis results have been presented as cost-effectiveness acceptability curves (CEACs) where different willingness to pay (WTP) thresholds for a quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) are used to show which strategy is likely to have the largest net benefit for that threshold.
Interpreting results
Incremental cost-effectiveness ratios
The results of the cost-effectiveness analysis are presented as incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) per QALY gained. These are calculated by dividing the difference in costs associated with two alternative strategies by the difference in QALYs:
Where more than two strategies are compared, the ICER is calculated according to the following process:
-
The strategies are ranked in terms of cost, from least to most expensive.
-
If a strategy is more expensive and less effective than the preceding strategy, it is said to be ‘dominated’ and is excluded from further analysis.
-
ICERs are then calculated for each strategy compared with the next most expensive non-dominated option. If the ICER for a strategy is higher than that of the next most effective strategy, then it is ruled out by ‘extended dominance’.
-
ICERs are recalculated excluding any strategy subject to dominance or extended dominance.
-
The non-dominated strategies form an ‘efficiency frontier’ of strategies that are cost-effective and can then be judged against the value of an ICER that is generally considered cost-effective by NICE (i.e. £20,000–30,000 per QALY gained).
Base-case results
The model included a hypothetical cohort of 53.88 patients. This figure equates to the estimated number of patients with signs or symptoms indicative of AF and with an irregular pulse who would visit a single GP annually and be eligible for testing with a lead-I ECG device. Of the total eligible population in the model, 10.78 had AF and 43.11 did not have AF.
Four base-case scenarios were investigated to estimate cost-effectiveness depending on the waiting times for a 12-lead ECG test and the location of the 12-lead ECG test. The base-case scenarios are:
-
base case 1: 12-lead ECG in primary care, 2 days to 12-lead ECG
-
base case 2: 12-lead ECG in primary care, 14 days to 12-lead ECG
-
base case 3: 12-lead ECG in secondary care, 2 days to 12-lead ECG
-
base case 4: 12-lead ECG in secondary care, 14 days to 12-lead ECG.
Results for base cases 2–4 are presented in Appendix 12.
Base case 1: 12-lead ECG in primary care, 2 days to 12-lead electrocardiogram
Costs and QALYs generated in base case 1 are shown in Tables 34 and 35, respectively.
| Strategy | Lead-I ECG test (£) | Treatment (NOACs and rate control) (£) | CVEs and AEs (£) | 12-lead ECG (£) | Paroxysmal testing (Holter monitor) (£) | Total costs (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 0 | 90,630 | 420,279 | 536 | 2743 | 514,187 |
| Kardia Mobile | 26 | 102,952 | 409,881 | 452 | 2240 | 515,551 |
| imPulse | 97 | 116,317 | 411,612 | 454 | 2265 | 530,745 |
| MyDiagnostick | 100 | 107,077 | 411,358 | 451 | 2247 | 521,233 |
| Generic lead-I device | 392 | 103,746 | 409,898 | 452 | 2242 | 516,730 |
| Zenicor-ECG | 624 | 104,938 | 410,210 | 452 | 2244 | 518,468 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 1110 | 100,358 | 414,292 | 446 | 2231 | 518,436 |
| Strategy | IS | HS | TIA | False negatives | False positives | Bleeds | Total QALYs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 11.621 | 2.124 | 8.406 | 1.606 | 0.000 | 23.581 | 447.963 |
| Kardia Mobile | 11.452 | 1.996 | 8.359 | 0.144 | 1.379 | 23.751 | 449.249 |
| imPulse | 11.482 | 2.019 | 8.366 | 0.397 | 3.663 | 23.730 | 448.987 |
| MyDiagnostick | 11.478 | 2.015 | 8.365 | 0.361 | 2.155 | 23.720 | 449.024 |
| Generic lead-I device | 11.452 | 1.996 | 8.359 | 0.147 | 1.508 | 23.752 | 449.246 |
| Zenicor-ECG | 11.457 | 2.000 | 8.360 | 0.193 | 1.724 | 23.746 | 449.199 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 11.530 | 2.054 | 8.377 | 0.794 | 1.293 | 23.630 | 448.573 |
Pairwise cost-effectiveness results from the base case 1 analysis for each index test versus the standard diagnostic pathway are presented in Table 36 and incremental analysis results are shown in Table 37.
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 514,187 | 447.963 | |||
| Kardia Mobile | 515,551 | 449.249 | 1364 | 1.286 | 1060 |
| imPulse | 530,745 | 448.987 | 16,557 | 1.024 | 16,165 |
| MyDiagnostick | 521,233 | 449.024 | 7046 | 1.061 | 6638 |
| Generic lead-I device | 516,730 | 449.246 | 2543 | 1.284 | 1981 |
| Zenicor-ECG | 518,468 | 449.199 | 4281 | 1.236 | 3462 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 518,436 | 448.573 | 4249 | 0.610 | 6962 |
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 514,187 | 447.963 | |||
| Kardia Mobile | 515,551 | 449.249 | 1364 | 1.286 | 1060 |
| Generic lead-I device | 516,730 | 449.246 | 1179 | –0.002 | Dominated |
| RhythmPad GPa | 518,436 | 448.573 | 2885 | –0.676 | Dominated |
| Zenicor-ECG | 518,468 | 449.199 | 2917 | –0.050 | Dominated |
| MyDiagnostick | 521,233 | 449.024 | 5682 | –0.225 | Dominated |
| imPulse | 530,745 | 448.987 | 15,194 | –0.262 | Dominated |
Summary of base-case cost-effectiveness results
The results of the pairwise analysis show that all lead-I ECG tests lie on the efficiency frontier in each of the four base-case analyses, with ICERs below the £20,000–30,000 threshold usually considered to be cost-effective by NICE. Kardia Mobile is the most cost-effective option in a full incremental analysis, with an ICER no higher than £1060 per QALY gained, compared with the standard pathway and dominates the other lead-I ECG devices (costing less and generating more QALYs).
Lead-I ECG devices are more cost-effective when there is a longer wait to 12-lead ECG (as treatment for AF with a lead-I ECG device is assumed in the model to start earlier than in the standard pathway) and if the 12-lead ECG is performed in hospital. The majority of the patient benefit, however, comes after diagnosis, when a greater proportion of patients are correctly diagnosed with AF and treated for AF than in the standard diagnostic pathway, even if this benefit is slightly offset by an increase in patients incorrectly diagnosed with AF with a lead-I ECG device.
Scenario analyses
Scenario analyses were undertaken to investigate the impact on the ICER per QALY gained of varying some of the base-case assumptions. Results for scenario analyses using the least cost-effective base case [base case 1 (12-lead ECG in primary care, 2 days to 12-lead ECG)] are presented; if the conclusions drawn from results remain unchanged from the least cost-effective scenario for lead-I ECG testing, they should also remain unchanged for the more cost-effective scenarios. Scenario analyses are presented in Appendix 13.
The scenario analyses were as follows.
-
Scenario A: the unit cost associated with the lead-I ECG device changed from full cost of the device to no cost. This assumption was varied to take into account other populations that might use a lead-I ECG device in primary care that would share the cost of the device.
-
Scenario B: sensitivity and specificity estimates from interpretation of the MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG trace by EP2.
-
Scenario C: diagnosis and decisions made to refer for paroxysmal testing based only on the lead-I ECG results (i.e. no referral for 12-lead ECG or Holter monitor).
-
Scenario D: the time horizon is limited to 5 years to reflect clinical feedback to the EAG that it is plausible that all patients with paroxysmal AF not correctly diagnosed with AF after lead-I, 12-lead ECG or Holter monitoring will be picked up within 5 years if they do not have a CVE.
-
Scenarios E1 to E40: the proportions of patients sent for further testing for paroxysmal AF depending on the outcomes of the combined lead-I ECG and 12-lead ECG tests are varied. Clinical advice provided to the EAG highlighted the significant difference in clinical practice around how patients with positive or negative lead-I ECG and 12-lead ECG results would continue on the diagnostic pathway so each scenario may represent the true ‘base-case’ scenario for a specific GP or practice depending on the diagnostic pathway they follow.
-
Scenario F: cost of a supplementary smartphone or tablet added to the cost of the Kardia Mobile device. A threshold analysis was performed to determine the minimum unit cost of a smartphone or tablet that would result in Kardia Mobile no longer dominating the other lead-I ECG devices.
-
Scenario G: extending the lifespan of the RhythmPad GP device from 1 year to 3 years.
-
Scenario H: including a QALY decrement for bleeds.
-
Scenario I: using alternative sensitivity and specificity estimates for Kardia Mobile from the pooled analysis with interpretation of the trace from EP2.
-
Scenario J: assuming that rates of HS are the same for people treated with NOACs who do not have AF as the rates of HS for people treated with NOACs who have AF.
Deterministic sensitivity analysis
One-way sensitivity analyses were run to identify the individual parameters with the biggest impact on the model results. Tornado diagrams are presented in Appendix 14, Figures 28–33, for each index test using base case 1 (12-lead ECG in primary care, 2 days to 12-lead ECG).
Probabilistic sensitivity analysis
Probabilistic sensitivity analyses were undertaken for the lead-I ECG pathway with each index test compared with the standard diagnostic pathway. The CEACs in base case 1 for each device are presented in Appendix 15, Figures 34–39. The CEAC for all devices is shown in Figure 12. The parameters for the probability sensitivity analysis are presented in Appendix 16.
FIGURE 12.
CEAC base case 1: all lead-I ECG devices.
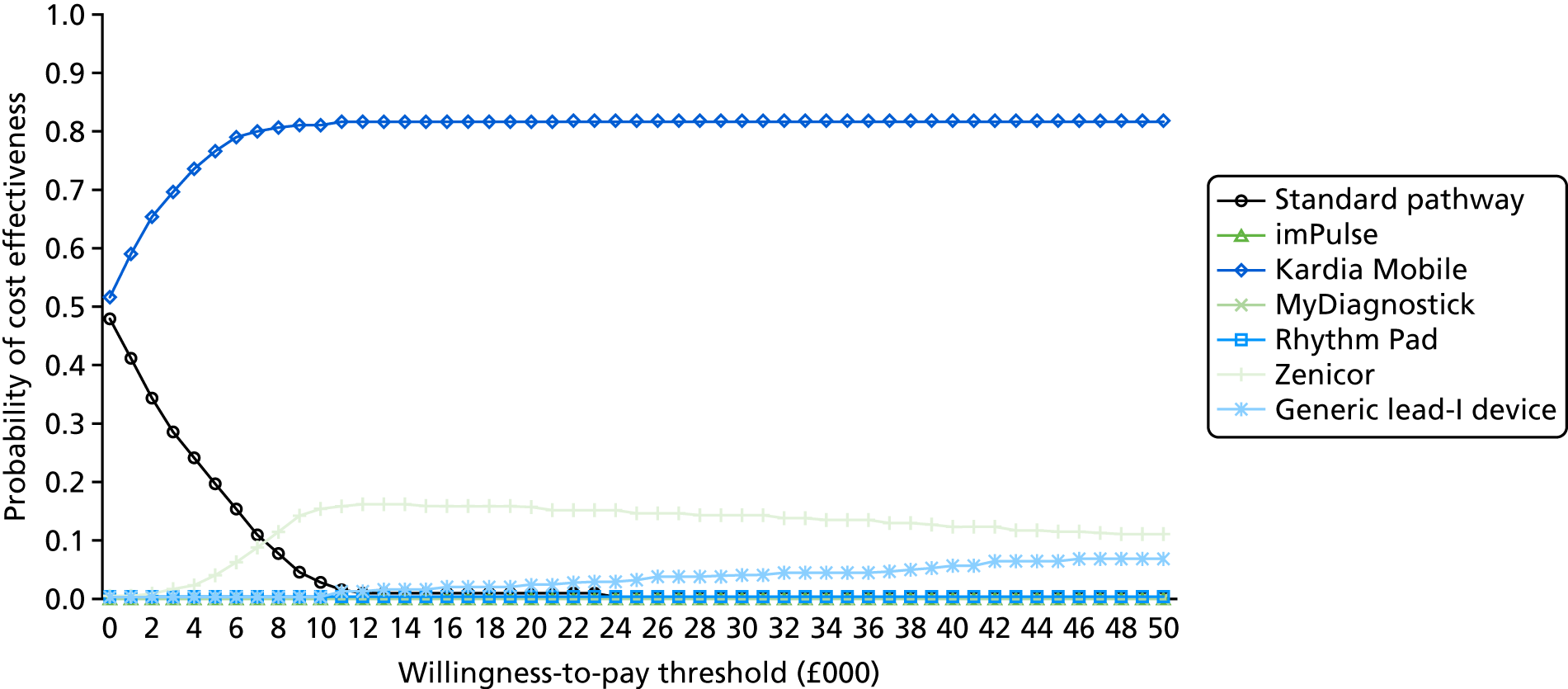
Summary of scenario and sensitivity analyses cost-effectiveness results
The one-way sensitivity analysis showed that the results were sensitive to the assumed prevalence of paroxysmal AF versus persistent and permanent AF. Decreased prevalence of paroxysmal AF increased incremental costs and decreased incremental QALYs for lead-I ECG devices versus the standard pathway. At the extreme, where the prevalence of paroxysmal AF was assumed to be zero, incremental QALYs decreased sufficiently to become negative and resulted in some lead-I ECG devices (imPulse, MyDiagnostick and RhythmPad) being dominated by the standard pathway. The ICERs per QALY gained yielded for other lead-I ECG devices when the prevalence of paroxysmal AF was zero were very large as a result of very small incremental QALYs. When the prevalence of paroxysmal AF was assumed to be 1, incremental costs decreased and incremental QALYs decreased. Increasing the prevalence of paroxysmal AF to 1 resulted in all lead-I ECG devices except imPulse and MyDiagnostick dominating the standard pathway.
The results of the probabilistic sensitivity analysis indicate that, in pairwise comparisons, all lead-I ECG devices included in this assessment were cost-effective in at least 50% of iterations with a WTP threshold of around £15,000 per QALY. When all of the devices were considered together, at a threshold of £20,000 per QALY, just over 80% of iterations showed that Kardia Mobile would be the most cost-effective option, with Zenicor-ECG being the most cost-effective in around 15% of iterations. The standard pathway was found to be the most cost-effective option in zero iterations at a WTP threshold of £20,000 per QALY.
The scenario analysis showed that the results were sensitive to using alternative sensitivity and specificity values for MyDiagnostick. MyDiagnostick yielded the lowest overall costs of all the strategies when sensitivity and specificity estimates from interpretation of the MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG trace by EP2 were used. Kardia Mobile remained the index test with the highest overall QALYs in this scenario, which yielded an ICER per QALY gained of £5503 versus MyDiagnostick (using EP2).
The scenario analysis showed that results were invariant to the following assumptions:
-
removing the cost of the lead-I ECG device from the analysis
-
patients with AF incorrectly ruled out are not diagnosed with AF prior to a CVE
-
removal of 12-lead ECG and Holter monitoring from the lead-I ECG pathway
-
shortening the time horizon to 5 years.
The finding that removal of the 12-lead ECG and Holter monitoring from the lead-I ECG pathway did not affect cost-effectiveness results is unsurprising; if a patient had paroxysmal AF, they were assumed to be in AF at the time of lead-I ECG monitoring and therefore the majority of paroxysmal AF would be detected with a lead-I ECG device without the need for 12-lead ECG or Holter monitoring. However, this result should be interpreted with caution as the potential further benefits of a specific diagnosis of paroxysmal AF or of the more detailed diagnosis from 12-lead ECG testing was not considered in the model. Similarly, the extensive scenario analyses on the use of Holter monitoring following 12-lead ECG tests, with or without lead-I ECG testing, showed that, if Holter monitoring is not routinely used for the majority of patients with a negative 12-lead ECG, Kardia Mobile will always have an ICER below £10,000 per QALY gained compared with the standard pathway and, in some circumstances, will be a dominant strategy.
Effect of sensitivity and specificity
High specificity (i.e. high true-negative rate that results in a low false-positive rate) has a greater impact on the model results than high sensitivity (i.e. high true-positive rate), although the impact of high specificity is eroded the lower the sensitivity estimate becomes. For instance, the estimate of specificity for the RhythmPad GP device in the base-case analysis is higher than that for any other device (97.0%, 95% CI 95.5% to 100.0%). However, the benefit of higher specificity for the RhythmPad GP device is eroded by an estimate of sensitivity (67.0%, 95% CI 50.5% to 100.0%) that is substantially lower than the estimate of sensitivity for any of the other devices. In contrast, the Kardia Mobile device has an estimate of specificity (96.8%, 95% CI 88.0% to 99.2%) similar to that of the RhythmPad GP device but a much higher estimate of sensitivity (94.0%, 95% CI 81.5% to 97.7%).
High specificity is important because it reduces the additional treatment costs associated with an incorrect diagnosis of AF. It is assumed in the model that people incorrectly diagnosed with AF will remain misdiagnosed for the rest of their lives, so those who begin treatment with NOACs and rate-control treatment will remain on treatment for their lifetime. No benefit is assumed from treating people without AF with NOACs and rate-control treatment, and a higher risk of bleeding is assumed as a result of treatment with NOACs. Therefore, the higher the false positive rate (i.e. the lower the specificity), the greater the costs that are accrued from the treatment itself and from treating bleeds associated with NOACs without any associated benefit from treatment.
Sensitivity is important because the earlier people with AF are diagnosed, the sooner they can begin treatment and reduce their risk of having a CVE. Low sensitivity (low true positive rate) means that many people with AF may only be identified later and so do not benefit from early NOACs and rate-control treatment. However, the impact of the sensitivity estimate is mitigated in the model by the assumption that people with undiagnosed AF will later have their AF diagnosed (and begin treatment) if they experience a CVE. This means that people with AF that is initially undiagnosed do not accrue the costs of NOACs and rate-control treatment for some months or years, which offsets some of the costs associated with their higher risk of experiencing a CVE.
Chapter 5 Discussion
Assessment of diagnostic test accuracy
No studies were identified that evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of lead-I ECG devices in people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse. As no studies were identified for the population and setting of interest, the review focused on an asymptomatic population as prespecified in the protocol. 68 We considered an asymptomatic population to comprise people not presenting with symptoms of AF, with or without a previous diagnosis of AF. These patients could have had co-existing cardiovascular conditions or could have been attending a cardiovascular clinic but did not present with signs or symptoms of AF.
We identified 13 publications38,39,41–51 reporting on nine studies assessing the DTA of lead-I ECG devices. In three studies,43,45,51 the lead-I ECG trace was interpreted by one trained health-care professional (i.e. cardiologist or EP). In one study,39 the lead-I ECG trace was interpreted independently by a cardiologist and by a GP with an interest in cardiology. In one study,38 the trace was interpreted independently by two EPs and by the device algorithm. In four studies,47–50 the lead-I ECG trace was interpreted by the device algorithm alone. The reference standard in all of the included studies was a 12-lead ECG interpreted by a trained health-care professional. The trained health-care professional was a cardiologist, an EP or a GP with an interest in cardiology. The analyses were stratified by the interpreter of the lead-I ECG trace.
In the included studies, the sensitivity of lead-I ECG devices ranged from 80% to 100% and specificity ranged from 76% to 99% when the lead-I ECG trace was interpreted by a trained health-care professional. The lowest specificity value (76%) was observed when interpretation of the lead-I ECG trace was performed by a GP with an interest in cardiology; sensitivity was similar to that observed in the other included studies. 39
In the main meta-analysis, when the lead-I ECG trace was interpreted by a trained health-care professional, the pooled sensitivity and specificity values were 93.9% and 96.5%, respectively. In the sensitivity analyses, pooled sensitivity values ranged from 88.0% to 96.2% and pooled specificity values ranged from 94.4% to 97.4%.
Across the meta-analyses, where the lead-I ECG trace was interpreted by the device algorithm, the sensitivity ranged from 88% to 96.2% and the specificity ranged from 94.4% to 97.2%. Pooled sensitivity and specificity values were similar across the different meta-analyses irrespective of the interpreter of the lead-I ECG trace or the lead-I ECG device used.
In one study,38 inter-rater variability between the two EP interpreters was observed. When the lead-I ECG trace was interpreted by EP1, sensitivity values were consistently higher than when the trace was interpreted by EP2, irrespective of the lead-I ECG device being used (i.e. MyDiagnostick or Kardia Mobile). Specificity values were similar irrespective of the interpreter of the lead-I ECG trace (i.e. EP1 or EP2) and lead-I ECG device being used (i.e. MyDiagnostick or Kardia Mobile). The authors suggested that the reason for discordance between the interpretation of the lead-I ECG trace and the 12-lead ECG was the presence of repetitive atrial or ventricular premature beats, which may have misguided the EPs to classify those lead-I ECG traces incorrectly as AF. 38 The same reasons were suggested for the low sensitivity value reported when the lead-I ECG trace was interpreted by the lead-I ECG device algorithm. The sensitivity values reported were lower than those observed in other studies, irrespective of lead-I ECG device algorithm interpretation (i.e. MyDiagnostick or Kardia Mobile).
The sensitivity from the meta-analyses of lead-I ECG traces interpreted by a trained health-care professional or the lead-I ECG device algorithm was 92% (95% CI 85% to 96%),104 which was similar to the sensitivity reported for MPP in systematic reviews (91.6%, 95% CI 75% to 98.6%). 74 The specificity values for lead-I ECG traces interpreted by a trained health-care professional or the lead-I ECG device algorithm were relatively higher, at 82% (95% CI 76% to 88%),104 than those reported for MPP (78.8%, 95% CI 51% to 94.5%). 74
The included studies did not evaluate the presence of paroxysmal AF using prolonged monitoring following a negative 12-lead ECG. It is likely that, in clinical practice, prolonged monitoring will be considered for people presenting with signs or symptoms of AF who have an irregular pulse and a positive lead-I ECG test followed by a negative 12-lead ECG. In the included studies, both the index test and the reference standard were performed within a 6-hour time interval, with the exception of two studies49,50 in which the time interval for use of the index test and reference standard was not specified. A patient correctly identified as having AF could have this diagnosis ruled out if the AF episode had stopped by the time they underwent assessment with a 12-lead ECG. It is not clear if there was an appropriate time interval between assessments in the study by Crockford et al. ;50 therefore, it is possible that paroxysmal AF contributed to a lower sensitivity than that reported in the other studies. The specificity reported in the study by Crockford et al. 50 was, however, similar to the values reported in other studies. In the study by Vaes et al. ,49 the sensitivity and specificity values observed were similar to the values reported in other studies.
In the systematic review of DTA, none of the studies of lead-I ECG devices included people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse. This means that all of the results presented in this systematic review are derived from an asymptomatic population and were mostly conducted in a setting other than primary care. It is plausible that, if the population in the review had been people with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse, the sensitivity of lead-I ECG devices where the trace was interpreted by a trained health-care professional would have been higher. However, it is also plausible that, in such a population, the specificity of lead-I ECG devices where the trace was interpreted by a trained health-care professional would have been lower.
Assessment of clinical impact
No studies were identified that evaluated the clinical impact of lead-I ECG devices in people presenting to primary care with symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse. As no studies were identified for the population and setting of interest, the review focused on an asymptomatic population as prespecified in the protocol. 68
We identified 24 publications reporting on 19 studies: 18 studies with a total of 33,993 participants and one study that conducted semistructured interviews with two receptionists, one nurse, three GPs and eight patients across three GP practices. The index tests evaluated included imPulse (one study63), Kardia Mobile alone (11 studies45,47,51,54,56,57,59,61,62,64,65), MyDiagnostick alone (four studies48,52,58,60), Zenicor ECG (one study43) and MyDiagnostick and Kardia Mobile (one study38). In nine studies,43,45,51,52,54,56,59,64,65 the lead-I ECG trace was interpreted by one trained health-care professional (i.e. a cardiologist, an EP or a GP with an interest in cardiology). In four studies,57,60–62 the lead-I ECG trace was interpreted independently by one trained health-care professional and by the device algorithm. In three studies,47,48,58 the lead-I ECG trace was interpreted by the device algorithm alone. In one study,38 the trace was interpreted independently by two EPs and by the device algorithm. In one study,63 the lead-I ECG trace was interpreted independently by two cardiology registrars, two cardiac physiologists and two specialist cardiac nurses.
Diagnostic yield was the most commonly reported outcome in 13 studies. 38,48,52,54,56–62,64,65 The diagnostic yield reported in these studies ranged from 0.4% to 5.8% and was similar across the studies, taking into account the type of lead-I ECG device used and the setting in which the study was conducted. One study58 conducted in UK primary care reported the greatest diagnostic yield. However, this study58 was available only as a conference abstract and the reason for the high diagnostic yield is unclear because of the limited information available. Data submitted by Kent Surrey Sussex AHSN (Kent Surrey Sussex AHSN and Richard Blakey, AliveCor in East Sussex, unpublished evidence submitted via NICE) on the use of the Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device for people with symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse during a 2-year project reported a diagnostic yield of 69.9%. It is plausible that the diagnostic yield in people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse would be more comparable with the values reported by Kent Surrey Sussex AHSN than those reported in the published evidence available and included in the systematic review of the clinical impact of lead-I ECG devices.
Test failure rate was reported in nine studies38,45,52,56,57,60–63 and ranged from 0.1% to 9%. Test failure rate considered both failure of the lead-I ECG algorithm to produce a result and poor quality of the lead-I ECG trace. Possible reasons suggested for uninterpretable lead-I ECG results were sinus tachycardia or bradycardia (Kardia Mobile),62 that patients suffered from tremor, or that hospitalised patients were too weak to hold the devices firmly enough (not specified if Kardia Mobile or MyDiagnostick). 38
Two studies59,61 reported a change in treatment management following the use of the Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device, with OACs being prescribed for most new patients diagnosed with AF. Acceptability of the lead-I ECG devices was reported in four studies54,58,59,62 with generally positive views. A key barrier that was identified related to the ease of use of the lead-I ECG device; it was difficult for elderly patients to hold the device still for long enough to take a reading. 62 Furthermore, one study38 reported that 7% of patients were excluded because they were not able to hold the devices properly. A qualitative study53 suggested that nurses in GP practices could confidently use a lead-I ECG device (Kardia Mobile) and were well placed to explain the screening process to and conduct AF screening in people aged ≥ 65 years before their GP appointment. However, only one nurse was interviewed as part of this study, so there are concerns about the generalisability of this finding. Moreover, the study was conducted to evaluate the feasibility of screening in an asymptomatic population and so it is unclear if the results would be applicable to the population of interest in this appraisal. Time to initiation of preventative treatment and HRQoL were not reported in any of the identified studies.
Only one study59 reported on clinical outcomes. One patient who did not receive anticoagulant therapy after a lead-I ECG trace that was difficult to interpret, followed by a normal 12-lead ECG result, later had a stroke. The importance of prolonged monitoring in cases of suspected AF that may be paroxysmal is evident. It has been reported that a period of 2-week monitoring using a hand-held device identified 7.4% (30/403) of cases of paroxysmal AF who had screened negative on a 12-lead ECG but who had two or more risk factors based on the CHADS2 risk classification. 75
Assessment of cost-effectiveness
No published studies were identified that evaluated the cost-effectiveness of lead-I ECG devices compared with MPP for people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse. As no published data evaluating the DTA and the clinical impact of lead-I ECG devices were identified for people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse, DTA data in an asymptomatic population were used as a proxy for the population of interest.
The de novo economic model yielded ICERs per QALY gained. The results of the pairwise analysis show that all lead-I ECG tests lie on the efficiency frontier in each of the four base-case analyses, with ICERs per QALY gained below the £20,000–30,000 threshold usually considered to be cost-effective by NICE. Kardia Mobile is the most cost-effective option in a full incremental analysis and dominates the standard pathway and other lead-I ECG devices (costing less and generating more QALYs), with the exception of the generic lead-I ECG device, which generates a very small QALY gain but at a cost that produces an ICER well above £30,000 per QALY gained.
Lead-I ECG devices are more cost-effective when there is a longer wait to a 12-lead ECG (because treatment for AF with a lead-I ECG device is assumed in the lead-I ECG diagnostic pathway to start earlier than in the standard diagnostic pathway) and when the 12-lead ECG is performed in a hospital. The majority of the patient benefit, however, comes after diagnosis owing to a greater proportion of patients being correctly diagnosed with AF and treated for AF when than using the standard diagnostic pathway, even if this benefit is slightly offset by an increase in the number of patients incorrectly diagnosed with AF by a lead-I ECG device.
The one-way sensitivity analysis showed that the results were particularly sensitive to the assumed prevalence of paroxysmal AF versus persistent and permanent AF. Decreasing the prevalence of paroxysmal AF increased incremental costs and decreased incremental QALYs for the lead-I ECG devices versus the standard pathway. In the extreme, decreasing the prevalence of paroxysmal AF to zero either yielded very large, positive ICERs per QALY gained or resulted in lead-I ECG devices being dominated by the standard pathway. The model results were also shown to be sensitive to the rate of ISs in patients with AF. The results should, therefore, be interpreted with caution if it is considered clinically plausible that the prevalence of paroxysmal AF in the symptomatic population may be substantially lower than 50%.
In line with the conclusions of the EAG concerning the use of lead-I ECG devices for people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse, the results of recently published economic evaluations74,105 have suggested that lead-I ECG devices may represent a cost-effective use of resources for systematic, opportunistic screening of people aged ≥ 65 years during a routine GP appointment. Lead-I ECG devices may be cost-effective for an asymptomatic population because only people who have a positive lead-I ECG test will have a subsequent 12-lead ECG test carried out. If a lead-I ECG test or an alternative screening test were not used, people with asymptomatic AF would remain undiagnosed until the time of an event (e.g. stroke). People with asymptomatic AF who are diagnosed early and receive appropriate treatment gain health benefits in comparison with people whose AF remains undiagnosed and who do not receive treatment for AF.
In the current NICE CG1803 it is recommended that an ECG is performed in all people, whether or not symptomatic, in whom AF is suspected owing to detection of an irregular pulse. There is an emergence of novel technologies to assist in the diagnosis of AF, such as lead-I ECG devices. These technologies need to be clearly distinguished from 12-lead ECG devices when NICE CG1803 is updated.
Strengths and limitations
No published data evaluating the diagnostic accuracy, the clinical impact or the cost-effectiveness of lead-I ECG devices were identified for people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse. Therefore, all of the results presented in this assessment need to be interpreted with caution as the results are based on data from an asymptomatic population used as a proxy for the population of interest. Therefore, using data from asymptomatic patients as a proxy, we present the first economic evaluation, to our knowledge, of lead-I ECG devices for people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse.
Diagnostic test accuracy results are reported for all lead-I ECG devices (i.e. imPulse, Kardia Mobile, MyDiagnostick, RhythmPad GP and Zenicor ECG) within the scope of this assessment. However, for RhythmPad GP, results were based on interpretation by the lead-I ECG algorithm only and, according to the manufacturer (Chris Crockford, CardioCity, 3 August 2018, personal communication via NICE), the device algorithm has been modified since the identified study was published,50 and therefore the sensitivity and specificity estimates observed may have been affected. One study63 reporting on the DTA of the imPulse lead-I ECG device was excluded from the DTA review because the reference standard was ineligible. However, the sensitivity and specificity values from this study63 were considered in the economic evaluation.
Since January 2018, Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG devices have been rolled out to primary care practices as part of the NHS England-funded NHS Innovation Accelerator, delivered in partnership with England’s 15 AHSNs. 106 The aim of the initiative is to improve the detection of AF in order to reduce the number of strokes. 106,107 It has been suggested that, with this initiative, the lead-I ECG device can be used at any time, regardless of whether patients have signs or symptoms of AF. 108
No published data were identified that provided estimates of the effect of treatment for AF on cognitive decline and vascular dementia associated with AF. Therefore, any potential benefit of treatment for AF on the incidence or severity of cognitive decline and vascular dementia could not be included in the model.
There is an absence of data, both qualitative and quantitative, describing the effects of nurse assessment rather than medical assessment. If assessments are undertaken in nurse-led-only clinics, there may be significant delays in presentation of the data to the GP, with potential clinical implications.
Conclusions
The results of the systematic reviews of DTA and clinical impact of lead-I ECG devices suggest that these devices are an important addition to the armamentarium of a GP when diagnosing AF. However, only evidence supporting their use in an asymptomatic population was identified from the published literature. In people with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse, it is recommended that a 12-lead-ECG is performed. If a 12-lead ECG is carried out on the day of the initial appointment, there is unlikely to be any diagnostic benefit to using a lead-I ECG device over a 12-lead ECG in the symptomatic population, as patients with AF are in AF at the time of the initial appointment (and, therefore, at the time of the lead-I ECG test and of any 12-lead ECG that takes place soon after the initial appointment). Only if there is a time interval between the use of a lead-I ECG device and a 12-lead ECG would any health benefits from early treatment initiation be obtained by patients. To allow for these benefits to be considered, the economic evaluation considered primary care practices where patients have to wait at least 48 hours between their initial consultation with the GP and a confirmatory 12-lead ECG.
Future research investigating the DTA of lead-I ECG devices in people presenting to primary care with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse should take into consideration the added value that such research would provide. Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG devices are currently being introduced for use in NHS primary care settings for routine screening in people aged ≥ 65 years.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Sophie Beale (Research Associate, LRiG, University of Liverpool) for feedback on a draft version of the report.
Contributions of authors
Rui Duarte (Senior Research Fellow, Health Technology Assessment Lead) managed the project, contributed to the development of the methods for the systematic review, conducted the review of DTA and clinical impact and supervised the statistical analysis and economic modelling work.
Angela Stainthorpe (Research Associate, Health Economics and Modelling) conducted the review of cost-effectiveness evidence, developed the health economic model, identified inputs to the economic model, and conducted the economic evaluation.
Janette Greenhalgh (Senior Research Fellow, Systematic Reviewer) contributed to the systematic review of DTA and clinical impact and acted as the second reviewer in the systematic review.
Marty Richardson (Research Associate, Statistician) contributed to the statistical analysis methods, performed the statistical analysis for the DTA review, acted as the third reviewer in the systematic review to resolve conflicts.
Sarah Nevitt (Research Associate, Statistician) contributed to the statistical analysis for the DTA review.
James Mahon (Director, Health Economics and Modelling) contributed to the development of the health economic model and to the economic evaluation.
Eleanor Kotas (Research Associate, Information Specialist) devised and performed the literature searches.
Angela Boland (Associate Director, Health Economics) provided senior advice to the project.
Howard Thom (Research Fellow, Health Economics and Modelling) provided input to the health economic model.
Tom Marshall (Professor of Public Health and Primary Care) provided input to the report from a primary care perspective.
Mark Hall (Consultant Cardiologist and Electrophysiologist) provided input to the report from a secondary care perspective.
Yemisi Takwoingi (Senior Research Fellow, Statistician) provided input on the systematic review and statistical analysis methods for assessment of DTA and clinical impact.
All authors contributed to the conception and design of the study or the analysis and interpretation of the data, drafting or revising the report, and final approval of the version to be published.
Publication
Duarte R, Stainthorpe A, Mahon J, Greenhalgh J, Richardson M, Nevitt S, et al. Lead-I ECG for detecting atrial fibrillation in patients attending primary care with an irregular pulse using single-time point testing: a systematic review and economic evaluation. PLOS ONE 2019;14:e0226671.
Data-sharing statement
All the available data are included in the report. All queries should be submitted to the corresponding author for consideration.
Patient data
This work uses data provided by patients and collected by the NHS as part of their care and support. Using patient data is vital to improve health and care for everyone. There is huge potential to make better use of information from people’s patient records, to understand more about disease, develop new treatments, monitor safety, and plan NHS services. Patient data should be kept safe and secure, to protect everyone’s privacy, and it’s important that there are safeguards to make sure that it is stored and used responsibly. Everyone should be able to find out about how patient data are used. #datasaveslives You can find out more about the background to this citation here: https://understandingpatientdata.org.uk/data-citation.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health and Social Care. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health and Social Care.
References
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Clinical Knowledge Summaries: Atrial Fibrillation 2015. https://cks.nice.org.uk/atrial-fibrillation#!topicsummary (accessed January 2018).
- Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, Ahlsson A, Atar D, Casadei B, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J 2016;37:2893-962. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehw210.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Atrial Fibrillation: Management. Clinical Guideline CG180 2014. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg180/chapter/Introduction (accessed January 2018).
- Dewland TA, Olgin JE, Vittinghoff E, Marcus GM. Incident atrial fibrillation among Asians, Hispanics, blacks, and whites. Circulation 2013;128:2470-7. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.002449.
- Bai Y, Wang YL, Shantsila A, Lip GYH. The global burden of atrial fibrillation and stroke: a systematic review of the clinical epidemiology of atrial fibrillation in Asia. Chest 2017;152:810-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2017.03.048.
- Alonso A, Agarwal SK, Soliman EZ, Ambrose M, Chamberlain AM, Prineas RJ, et al. Incidence of atrial fibrillation in whites and African–Americans: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Am Heart J 2009;158:111-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2009.05.010.
- Lane DA, Skjøth F, Lip GYH, Larsen TB, Kotecha D. Temporal trends in incidence, prevalence, and mortality of atrial fibrillation in primary care. J Am Heart Assoc 2017;6. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.116.005155.
- NHS Digital . Quality and Outcomes Framework (QOF) – 2015–16 2016. https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/quality-and-outcomes-framework-achievement-prevalence-and-exceptions-data/quality-and-outcomes-framework-qof-2015-16 (accessed January 2018).
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Lead-I Electrocardiogram (ECG) Devices for Detecting Atrial Fibrillation Using Single-Time Point Testing in Primary Care: Final Scope 2018. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/gid-dg10018/documents/final-scope (accessed March 2018).
- Public Health England . Atrial Fibrillation Prevalence Estimates in England: Application of Recent Population Estimates of AF in Sweden 2017. www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/644869/atrial_fibrillation_AF_briefing.pdf (accessed January 2018).
- NHS Digital . Quality and Outcomes Framework (QOF) – 2016–17 2017. https://digital.nhs.uk/catalogue/PUB30124 (accessed January 2018).
- Adderley NJ, Ryan R, Nirantharakumar K, Marshall T. Prevalence and treatment of atrial fibrillation in UK general practice from 2000 to 2016. Heart 2019;105:27-33. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2018-312977.
- Lip GYH, Hee FLLS. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. QJM 2001;94:665-78. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/94.12.665.
- Lown M, Yue A, Lewith G, Little P, Moore M. Screening for Atrial Fibrillation using Economical and accurate TechnologY (SAFETY) – a pilot study. BMJ Open 2017;7. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013535.
- Camm AJ, Lip GY, De Caterina R, Savelieva I, Atar D, Hohnloser SH, et al. 2012 focused update of the ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Eur Heart J 2012;33:2719-47. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehs253.
- Lin HJ, Wolf PA, Kelly-Hayes M, Beiser AS, Kase CS, Benjamin EJ, et al. Stroke severity in atrial fibrillation. The Framingham Study. Stroke 1996;27:1760-4. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.27.10.1760.
- Stroke Association . State of the Nation: Stroke Statistics 2017. www.stroke.org.uk/sites/default/files/state_of_the_nation_2017_final_1.pdf (accessed June 2018).
- Vanassche T, Lauw MN, Eikelboom JW, Healey JS, Hart RG, Alings M, et al. Risk of ischaemic stroke according to pattern of atrial fibrillation: analysis of 6563 aspirin-treated patients in ACTIVE-A and AVERROES. Eur Heart J 2015;36:281-8. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehu307.
- Senoo K, Lip GY, Lane DA, Büller HR, Kotecha D. Residual risk of stroke and death in anticoagulated patients according to the type of atrial fibrillation: AMADEUS Trial. Stroke 2015;46:2523-8. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.009487.
- Flaker GC, Belew K, Beckman K, Vidaillet H, Kron J, Safford R, et al. Asymptomatic atrial fibrillation: demographic features and prognostic information from the Atrial Fibrillation Follow-up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) study. Am Heart J 2005;149:657-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2004.06.032.
- MDCalc . CHA2DS2-VASc Score for Atrial Fibrillation Stroke Risk 2015. www.mdcalc.com/cha2ds2-vasc-score-for-atrial-fibrillation-stroke-risk/ (accessed June 2018).
- MDCalc . HAS-BLED Score for Major Bleeding Risk 2018. www.mdcalc.com/has-bled-score-major-bleeding-risk (accessed January 2018).
- Plessey . ImPULSE 2018. www.plesseysemiconductors.com/products/impulse/ (accessed January 2018).
- Alive Technologies . Kardia Mobile 2018. www.alivetec.com/pages/alivecor-heart-monitor (accessed January 2018).
- Applied Biomedical Systems BV . Mydiagnostick 2018. www.mydiagnostick.com/ (accessed January 2018).
- Cardiocity Ltd . RhythmPadGP 2017. www.cardiocity.com/?portfolio=rhythm-pad-gp (accessed January 2018).
- Zenicor Medical Systems AB . Zenicor-ECG 2018. https://zenicor.com/zenicor-ekg/ (accessed January 2018).
- Centre for Reviews and Dissemination . Systematic Reviews: CRD’s Guidance for Undertaking Systematic Reviews in Health Care 2009. www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd/SysRev/!SSL!/WebHelp/SysRev3.htm (accessed January 2018).
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Diagnostic Assessment Programme Manual 2011. www.nice.org.uk/Media/Default/About/what-we-do/NICE-guidance/NICE-diagnostics-guidance/Diagnostics-assessment-programme-manual.pdf (accessed January 2018).
- Cochrane Methods: Screening and Diagnostic Tests . Handbook for DTA Reviews 2009. http://srdta.cochrane.org/handbook-dta-reviews (accessed January 2018).
- McInnes MDF, Moher D, Thombs BD, McGrath TA, Bossuyt PM, Clifford T, et al. Preferred Reporting Items for a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies: the PRISMA-DTA statement. JAMA 2018;319:388-96. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.19163.
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 2011;155:529-36. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009.
- Herzog R, Álvarez-Pasquin MJ, Díaz C, Del Barrio JL, Estrada JM, Gil Á. Are healthcare workers’ intentions to vaccinate related to their knowledge, beliefs and attitudes? A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2013;13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-13-154.
- Wells G, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. Ottawa, ON: Ottawa Hospital Research Institute; 2012.
- Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011;343. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d5928.
- CASP . Qualitative Research: Appraisal Tool. 10 Questions to Help You Make Sense of Qualitative Research 2006. www.phru.nhs.uk/Doc_Links/Qualitative_Appraisal_Tool.pdf (accessed February 2018).
- Chu H, Cole SR. Bivariate meta-analysis of sensitivity and specificity with sparse data: a generalized linear mixed model approach. J Clin Epidemiol 2006;59:1331-2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.06.011.
- Desteghe L, Raymaekers Z, Lutin M, Vijgen J, Dilling-Boer D, Koopman P, et al. Performance of handheld electrocardiogram devices to detect atrial fibrillation in a cardiology and geriatric ward setting. Europace 2017;19:29-3. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euw025.
- Williams J, Pearce K, Benett I. The effectiveness of a mobile ECG device in identifying AF: sensitivity, specificity and predictive value. Br J Cardiol 2015;22:70-2.
- Takwoingi Y, Guo B, Riley RD, Deeks JJ. Performance of methods for meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy with few studies or sparse data. Stat Methods Med Res 2017;26:1896-911. https://doi.org/10.1177/0962280215592269.
- Desteghe L, Raymaekers Z, Vijgen J, Dilling-Boer D, Koopman P, Schurmans J, et al. Accuracy and cost-effectiveness of two handheld electrocardiogram recorders to screen for atrial fibrillation in a hospital setting. Eur Heart J 2016;37.
- Desteghe L, Raymaekers Z, Vijgen J, Dilling-Boer D, Koopman P, Schurmans J, et al. Accuracy and usability of handheld electrocardiogram recorders to detect atrial fibrillation in hospitalised patients. EP Europace 2016;18. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/18.suppl_1.i177c.
- Doliwa PS, Frykman V, Rosenqvist M. Short-term ECG for out of hospital detection of silent atrial fibrillation episodes. Scand Cardiovasc J 2009;43:163-8. https://doi.org/10.1080/14017430802593435.
- Haberman ZC, Jahn RT, Bose R, Tun H, Shinbane JS, Doshi RN, et al. Wireless smart phone equipped ECG enables large scale screening in diverse populations. Heart Rhythm 2014;1.
- Haberman ZC, Jahn RT, Bose R, Tun H, Shinbane JS, Doshi RN, et al. Wireless smartphone ECG enables large-scale screening in diverse populations. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2015;26:520-6. https://doi.org/10.1111/jce.12634.
- Lau J, Lowres N, Neubeck L, Brieger DB, Sy RW, Galloway C, et al. Validation of an iphone ECG application suitable for community screening for silent atrial fibrillation: a novel way to prevent stroke. Circulation 2012;126.
- Lau JK, Lowres N, Neubeck L, Brieger DB, Sy RW, Galloway CD, et al. iPhone ECG application for community screening to detect silent atrial fibrillation: a novel technology to prevent stroke. Int J Cardiol 2013;165:193-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.01.220.
- Tieleman RG, Plantinga Y, Rinkes D, Bartels GL, Posma JL, Cator R, et al. Validation and clinical use of a novel diagnostic device for screening of atrial fibrillation. Europace 2014;16:1291-5. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euu057.
- Vaes B, Stalpaert S, Tavernier K, Thaels B, Lapeire D, Mullens W, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of the MyDiagnostick to detect atrial fibrillation in primary care. BMC Fam Pract 2014;15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2296-15-113.
- Crockford CJ, Ahmed O, Kaba R, Berry R. An analysis of the applicability of lead1 screening for cardiac arrhythmia in primary care settings using novel sensing technology & multiple commercial algorithms for automating detection to increase PPV of referrals for further investigation. Europace 2013;15.
- Koltowski L, Balsam P, Glowczynska R, Peller M, Maksym J, Blicharz L, et al. Comparison of Kardia Mobile (one lead ECGs records) with 12-lead ECGs in 100 consecutive patients with various cardiovascular disorders. Europace 2017;19. https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/eux158.263.
- Battipaglia I, Gilbert K, Hogarth AJ, Tayebjee MH. Screening for atrial fibrillation in the community using a novel ECG recorder. J Atr Fibrillation 2016;9. https://doi.org/10.4022/jafib.1433.
- Orchard J, Freedman SB, Lowres N, Peiris D, Neubeck L. iPhone ECG screening by practice nurses and receptionists for atrial fibrillation in general practice: the GP-SEARCH qualitative pilot study. Aust Fam Physician 2014;43:315-19.
- Chan LL, Chan SC, Yan BP. Feasibility and acceptability of atrial fibrillation screening using a hand-held ECG device in general practice setting in Hong Kong. Value in Health 2017;20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2017.08.1136.
- Chan NY, Choy CC. Community screening for atrial fibrillation in a Chinese population using a smartphone-based wireless single-lead ECG. J Am Coll Cardiol 2015;65. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0735-1097(15)60467-3.
- Chan NY, Choy CC. Screening for atrial fibrillation in 13 122 Hong Kong citizens with smartphone electrocardiogram. Heart 2017;103:24-31. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2016-309993.
- Chan PH, Wong CK, Poh YC, Pun L, Leung WW, Wong YF, et al. Diagnostic performance of a smartphone-based photoplethysmographic application for atrial fibrillation screening in a primary care setting. J Am Heart Assoc 2016;5. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.116.003428.
- Gibson J, Hanjari M, Chauhan U, Watkins C. Opportunistic Detection of Atrial Fibrillation in Primary Care: A Mixed Methods Evaluation of the Introduction of New Healthcare Technology n.d.
- Hussain W, Thakrar D. The use of a handheld device in identifying atrial fibrillation patients during flu vaccination clinics. Europace 2016;18.
- Kaasenbrood F, Hollander M, Rutten FH, Gerhards LJ, Hoes AW, Tieleman RG. Yield of screening for atrial fibrillation in primary care with a hand-held, single-lead electrocardiogram device during influenza vaccination. Europace 2016;18:1514-20. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euv426.
- Lowres N, Neubeck L, Salkeld G, Krass I, McLachlan AJ, Redfern J, et al. Feasibility and cost-effectiveness of stroke prevention through community screening for atrial fibrillation using iPhone ECG in pharmacies. The SEARCH-AF study. Thromb Haemost 2014;111:1167-76. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH14-03-0231.
- Orchard J, Lowres N, Freedman SB, Ladak L, Lee W, Zwar N, et al. Screening for atrial fibrillation during influenza vaccinations by primary care nurses using a smartphone electrocardiograph (iECG): a feasibility study. Eur J Prev Cardiol 2016;23:13-20. https://doi.org/10.1177/2047487316670255.
- Reeves B. Preliminary Evaluation of the Viewing Function of the ImPulse ECG Monitor n.d.
- Waring O, Davidson NCD, Stout MS, Pearce KP. Detection of atrial fibrillation in community locations using novel technology’s as a method of stroke prevention in the over 65’s asymptomatic population – should it become standard practise?. Europace 2016;18.
- Yan BPY, Chan LLY, Lee VWY, Freedman B. Medical Outpatient Clinics an Ideal Setting for Atrial Fibrillation Screening Using a Handheld Single-Lead ECG With Automated Diagnosis n.d.
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group . Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA Statement. PLOS Med 2009;6. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097.
- Duarte R, Stainthorpe A, Mahon J, Greenhalgh J, Richardson M, Nevitt S, et al. Lead-I ECG for detecting atrial fibrillation in patients attending primary care with an irregular pulse using single-time point testing: a systematic review and economic evaluation. PLOS ONE 2019;14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0226671.
- Duarte R, Stainthorpe A, Greenhalgh J, Richardson M, Marshall T, Hall M, et al. The Clinical and Cost Effectiveness of Lead-I Electrocardiogram (ECG) Devices for Detecting Atrial Fibrillation Using Single-Time Point Testing in Primary Care n.d. www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/display_record.php?ID=CRD42018090375.
- Drummond MF, Jefferson TO. Guidelines for authors and peer reviewers of economic submissions to the BMJ. The BMJ Economic Evaluation Working Party. BMJ 1996;313:275-83. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.313.7052.275.
- Leeflang MM, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Hooft L, Bossuyt PM. Variation of a test’s sensitivity and specificity with disease prevalence. CMAJ 2013;185:E537-44. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.121286.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) . NICE Clinical Knowledge Summary. Palpitations, Scenario: Current Palpitations 2015. https://cks.nice.org.uk/palpitations#!scenario (accessed June 2018).
- Office for National Statistics . National Life Tables: United Kingdom 2017. www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/birthsdeathsandmarriages/lifeexpectancies/datasets/nationallifetablesunitedkingdomreferencetables (accessed 06 July 2018).
- Piccini JP, Simon DN, Steinberg BA, Thomas L, Allen LA, Fonarow GC, et al. Differences in clinical and functional outcomes of atrial fibrillation in women and men: two-year results from the ORBIT-AF Registry. JAMA Cardiol 2016;1:282-91. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2016.0529.
- Welton NJ, McAleenan A, Thom HH, Davies P, Hollingworth W, Higgins JP, et al. Screening strategies for atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess 2017;21. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta21290.
- Engdahl J, Andersson L, Mirskaya M, Rosenqvist M. Stepwise screening of atrial fibrillation in a 75-year-old population: implications for stroke prevention. Circulation 2013;127:930-7. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.126656.
- Aronsson M, Svennberg E, Rosenqvist M, Engdahl J, Al-Khalili F, Friberg L, et al. Cost-effectiveness of mass screening for untreated atrial fibrillation using intermittent ECG recording. Europace 2015;17:1023-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euv083.
- Svennberg E, Engdahl J, Al-Khalili F, Friberg L, Frykman V, Rosenqvist M. Mass screening for untreated atrial fibrillation: The STROKESTOP Study. Circulation 2015;131:2176-84. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.014343.
- Schnabel RB, Pecen L, Ojeda FM, Lucerna M, Rzayeva N, Blankenberg S, et al. Gender differences in clinical presentation and 1-year outcomes in atrial fibrillation. Heart 2017;103:1024-30. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2016-310406.
- Berg J, Lindgren P, Nieuwlaat R, Bouin O, Crijns H. Factors determining utility measured with the EQ-5D in patients with atrial fibrillation. Qual Life Res 2010;19:381-90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-010-9591-y.
- NHS Business Services . Practice List Size and GP Count for Each Practice 2018. www.nhsbsa.nhs.uk/prescription-data/organisation-data/practice-list-size-and-gp-count-each-practice (accessed 4 July 2018).
- Israel CW, Grönefeld G, Ehrlich JR, Li YG, Hohnloser SH. Long-term risk of recurrent atrial fibrillation as documented by an implantable monitoring device: implications for optimal patient care. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004;43:47-52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2003.08.027.
- Kirchhof P, Auricchio A, Bax J, Crijns H, Camm J, Diener HC, et al. Outcome parameters for trials in atrial fibrillation: recommendations from a consensus conference organized by the German Atrial Fibrillation Competence NETwork and the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace 2007;9:1006-23. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/eum191.
- OpenPrescribing beta . Explore England’s Prescribing Data 2018. https://openprescribing.net/ (accessed 6 July 2018).
- NHS Digital . Practice Level Prescribing in England: A Summary 2018. https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/areas-of-interest/prescribing/practice-level-prescribing-in-england-a-summary (accessed 12 August 2018).
- Sterne JA, Bodalia PN, Bryden PA, Davies PA, López-López JA, Okoli GN, et al. Oral anticoagulants for primary prevention, treatment and secondary prevention of venous thromboembolic disease, and for prevention of stroke in atrial fibrillation: systematic review, network meta-analysis and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess 2017;21. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta21090.
- Office for National Statistics . Estimates of the Population for the UK, England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland 2018. www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/populationandmigration/populationestimates/datasets/populationestimatesforukenglandandwalesscotlandandnorthernireland (accessed June 2018).
- Mathisen SM, Dalen I, Larsen JP, Kurz M. Long-term mortality and its risk factors in stroke survivors. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2016;25:635-41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2015.11.039.
- Public Health England . First Stroke Estimates in England: 2007 to 2016 2018. www.gov.uk/government/publications/first-stroke-estimates-in-england-2007-to-2016 (accessed 12 August 2018).
- NHS Improvement . 2016/17/Reference/Costs/and/Guidance./National/Schedule/of/Reference/Costs/2016/17 2017. https://improvement.nhs.uk/resources/reference-costs/ (accessed 12 August 2018).
- Rothwell PM, Coull AJ, Silver LE, Fairhead JF, Giles MF, Lovelock CE, et al. Population-based study of event-rate, incidence, case fatality, and mortality for all acute vascular events in all arterial territories (Oxford Vascular Study). Lancet 2005;366:1773-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67702-1.
- Mohan KM, Wolfe CD, Rudd AG, Heuschmann PU, Kolominsky-Rabas PL, Grieve AP. Risk and cumulative risk of stroke recurrence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 2011;42:1489-94. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.602615.
- The EuroQol Group . EuroQol-a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy 1990;16:199-208. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-8510(90)90421-9.
- Robinson A, Thomson R, Parkin D, Sudlow M, Eccles M. How patients with atrial fibrillation value different health outcomes: a standard gamble study. J Health Serv Res Policy 2001;6:92-8. https://doi.org/10.1258/1355819011927288.
- Hobbs FD, Fitzmaurice DA, Mant J, Murray E, Jowett S, Bryan S, et al. A randomised controlled trial and cost-effectiveness study of systematic screening (targeted and total population screening) versus routine practice for the detection of atrial fibrillation in people aged 65 and over. The SAFE study. Health Technol Assess 2005;9. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta9400.
- Curtis L. Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2017. Canterbury: PSSRU, University of Kent; 2017.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Routine Preoperative Tests for Elective Surgery (NG45) 2016. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng45 (accessed June 2018).
- Office for National Statistics . Inflation and Price Indices 2017. www.ons.gov.uk/economy/inflationandpriceindices (accessed June 2018).
- Department of Health and Social Care . NHS Reference Costs 2016 17 2017. https://improvement.nhs.uk/resources/reference-costs/ (accessed 19 March 2018).
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Zio Service for Detecting Cardiac Arrhythmias: Medtech Innovation Briefing [MIB101] 2017. www.nice.org.uk/advice/mib101 (accessed 19 October 2018).
- Joint Formulary Committee . British National Formulary n.d. www.medicinescomplete.com (accessed June 2018).
- NHS Business Services . NHS Electronic Drug Tariff 2018. www.drugtariff.nhsbsa.nhs.uk/#/00553921-DA/DA00553911/Part%20VIIIA%20-%20Basic%20Prices%20of%20Drugs (accessed June 2018).
- NHS England . Sentinel Stroke National Audit Programme. Cost and Cost-Effectiveness Analysis 2016. www.strokeaudit.org/SupportFiles/Documents/Health-Economics/Health-economic-report-2016.aspx (accessed 12 August 2018).
- Turakhia MP, Shafrin J, Bognar K, Trocio J, Abdulsattar Y, Wiederkehr D, et al. Estimated prevalence of undiagnosed atrial fibrillation in the United States. PLOS ONE 2018;13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0195088.
- Taggar JS, Coleman T, Lewis S, Heneghan C, Jones M. Accuracy of methods for detecting an irregular pulse and suspected atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol 2016;23:1330-8. https://doi.org/10.1177/2047487315611347.
- Jacobs MS, Kaasenbrood F, Postma MJ, van Hulst M, Tieleman RG. Cost-effectiveness of screening for atrial fibrillation in primary care with a handheld, single-lead electrocardiogram device in the Netherlands. Europace 2018;20:12-8. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euw285.
- West of England Academic Heath Science Networks . AliveCor Kardia Mobile: NHS England Mobile ECG Device Project 2018. www.weahsn.net/wp-content/uploads/KardiaAlivecore-Guidance-Document-v-12-BC-DE-UK-15.02.2018.pdf (accessed June 2018).
- NHS England . Atrial Fibrillation 2018. www.england.nhs.uk/mids-east/clinical-networks/east-midlands-clinical-network/our-networks/cardiovascular/atrial-fibrillation/ (accessed August 2018).
- McKee S. NHS rolls out KardiaMobile to accelerate detection of arrhythmia. PharmaTimes 2018. www.pharmatimes.com/news/nhs_rolls_out_kardiamobile_to_accelerate_detection_of_arrhythmia_1222263 (accessed August 2018).
- Gladstone DJ, Spring M, Dorian P, Panzov V, Thorpe KE, Hall J, et al. Atrial fibrillation in patients with cryptogenic stroke. N Engl J Med 2014;370:2467-77. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1311376.
- Sinha AM, Diener HC, Morillo CA, Sanna T, Bernstein RA, Di Lazzaro V, et al. Cryptogenic Stroke and underlying Atrial Fibrillation (CRYSTAL AF): design and rationale. Am Heart J 2010;160:36-41.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2010.03.032.
Appendix 1 The PRISMA-DTA checklist
| Section/topic | # | PRISMA-DTA checklist item | Reported on page # |
|---|---|---|---|
| TITLE/ABSTRACT | |||
| Title | 1 | Identify the report as a systematic review (+/− meta-analysis) of DTA studies | NA |
| Abstract | 2 | Abstract: see PRISMA-DTA for abstracts | Appendix 2 |
| INTRODUCTION | |||
| Rationale | 3 | Describe the rationale for the review in the context of what is already known | pp. 1–4 |
| Clinical role of index test | D1 | State the scientific and clinical background, including the intended use and clinical role of the index test, and if applicable, the rationale for minimally acceptable test accuracy (or minimum difference in accuracy for comparative design) | pp. 4–8 |
| Objectives | 4 | Provide an explicit statement of question(s) being addressed in terms of participants, index test(s), and target condition(s) | p. 8 |
| METHODS | |||
| Protocol and registration | 5 | Indicate if a review protocol exists, if and where it can be accessed (e.g. URL address), and, if available, provide registration information including registration number | p. xxviii |
| Eligibility criteria | 6 | Specify study characteristics (participants, setting, index test(s), reference standard(s), target condition(s), and study design) and report characteristics (e.g. years considered, language, publication status) used as criteria for eligibility, giving rationale | pp. 9–10 and Table 2 |
| Information sources | 7 | Describe all information sources (e.g. databases with dates of coverage, contact with study authors to identify additional studies) in the search and date last searched | p. 9 |
| Search | 8 | Present full search strategies for all electronic databases and other sources searched, including any limits used, such that they could be repeated | Appendix 3 |
| Study selection | 9 | State the process for selecting studies (i.e. screening, eligibility, included in systematic review, and, if applicable, included in the meta-analysis) | p. 10 |
| Data collection process | 10 | Describe method of data extraction from reports (e.g. piloted forms, independently, in duplicate) and any processes for obtaining and confirming data from investigators | p. 10 |
| Definitions for data extraction | 11 | Provide definitions used in data extraction and classifications of target condition(s), index test(s), reference standard(s) and other characteristics (e.g. study design, clinical setting) | p. 10 and Table 2 |
| Risk of bias and applicability | 12 | Describe methods used for assessing risk of bias in individual studies and concerns regarding the applicability to the review question | pp. 10–11 |
| Diagnostic accuracy measures | 13 | State the principal diagnostic accuracy measure(s) reported (e.g. sensitivity, specificity) and state the unit of assessment (e.g. per-patient, per-lesion) | p. 11 |
| Synthesis of results | 14 | Describe methods of handling data, combining results of studies and describing variability between studies. This could include, but is not limited to a) handling of multiple definitions of the target condition, b) handling of multiple thresholds of test positivity, c) handling multiple index test readers, d) handling of indeterminate test results, e) grouping and comparing tests, and f) handling of different reference standards | pp. 11–12 |
| Meta-analysis | D2 | Report the statistical methods used for meta-analyses, if performed | pp. 11–12 |
| Additional analyses | 16 | Describe methods of additional analyses (e.g. sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression), if done, indicating which were prespecified | p. 12 |
| RESULTS | |||
| Study selection | 17 | Provide numbers of studies screened, assessed for eligibility, included in the review (and included in meta-analysis, if applicable) with reasons for exclusions at each stage, ideally with a flow diagram | pp. 13–14 |
| Study characteristics | 18 | For each included study provide citations and present key characteristics including a) participant characteristics (presentation, prior testing), b) clinical setting, c) study design, d) target condition definition, e) index test, f) reference standard, g) sample size, and h) funding sources | Table 3 |
| Risk of bias and applicability | 19 | Present evaluation of risk of bias and concerns regarding applicability for each study | pp. 14, 17 |
| Results of individual studies | 20 | For each analysis in each study (e.g. unique combination of index test, reference standard, and positivity threshold) report 2x2 data (TP, FP, FN, TN) with estimates of diagnostic accuracy and confidence intervals, ideally with a forest or ROC plot | pp. 17–25 |
| Synthesis of results | 21 | Describe test accuracy, including variability; if meta-analysis was done, include results and confidence intervals | pp. 19–25 |
| Additional analysis | 23 | Give results of additional analyses, if done (e.g. sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression; analysis of index test: failure rates, proportion of inconclusive results, adverse events) | pp. 19–25 |
| DISCUSSION | |||
| Summary of evidence | 24 | Summarise the main findings including the strength of evidence | pp. 23–5 and 67–8 |
| Limitations | 25 | Discuss limitations from included studies (e.g. risk of bias and concerns regarding applicability) and from the review process (e.g. incomplete retrieval of identified research | p. 70–1 |
| Conclusions | 26 | Provide a general interpretation of the results in the context of other evidence. Discuss implications for future research and clinical practice (e.g. the intended use and clinical role of the index test) | p. 67–8, 71 |
| FUNDING | |||
| Funding | 27 | For the systematic review, describe the sources of funding and other support and the role of the funders | p. iii |
Appendix 2 The PRISMA-DTA for abstracts checklist
| Section/topic | # | PRISMA-DTA for abstracts checklist item | Reported on page # |
|---|---|---|---|
| TITLE and PURPOSE | |||
| Title | 1 | Identify the report as a systematic review (+/− meta-analysis) of DTA studies | NA |
| Objectives | 2 | Indicate the research question, including components such as participants, index test, and target conditions | pp. xxv |
| METHODS | |||
| Eligibility criteria | 3 | Include study characteristics used as criteria for eligibility | pp. xxv–xxvi |
| Information sources | 4 | List the key databases searched and the search dates | pp. xxv |
| Risk of bias & applicability | 5 | Indicate the methods of assessing risk of bias and applicability | pp. xxvi |
| Synthesis of results | A1 | Indicate the methods for the data synthesis | pp. xxvi |
| RESULTS | |||
| Included studies | 6 | Indicate the number and type of included studies and the participants and relevant characteristics of the studies (including the reference standard) | pp. xxvii |
| Synthesis of results | 7 | Include the results for the analysis of diagnostic accuracy, preferably indicating the number of studies and participants. Describe test accuracy including variability; if meta-analysis was done, include summary results and confidence intervals | pp. xxvii |
| DISCUSSION | |||
| Strengths and limitations | 9 | Provide a brief summary of the strengths and limitations of the evidence | pp. xxviii |
| Interpretation | 10 | Provide a general interpretation of the results and the important implications | pp. xxviii |
| OTHER | |||
| Funding | 11 | Indicate the primary source of funding for the review | pp. xxviii |
| Registration | 12 | Provide the registration number and the registry name | pp. xxviii |
Appendix 3 Search strategy (MEDLINE)
MEDLINE (via OvidSP)
Date range searched: inception to 9 March 2018.
Date searched: 9 March 2018.
Search strategy
-
Lead-I ECG.tw.
-
single lead ECG.tw.
-
(lead I or single lead or automated algorithm).tw.
-
Electrocardiography/
-
(electrocardiog* or ECG).tw.
-
4 or 5
-
3 and 6
-
lead I electrocardiog*.tw.
-
single lead electrocardiog*.tw.
-
1 or 2 or 7 or 8 or 9
-
Atrial Fibrillation/
-
AF.tw.
-
(Atr* adj3 Fibrill*).tw.
-
11 or 12 or 13
-
10 and 14
-
Kardia Mobile.tw.
-
MyDiagnostick.tw.
-
RhythmPad.tw.
-
Zenicor-ECG.tw.
-
imPulse.tw.
-
10 and 20
-
15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 21
-
Animals/not Humans/
-
22 not 23
Appendix 4 Excluded studies
Ineligible intervention (19 studies)
Boyle KO, Morra D, Dorian P, McCrorie A, Haddad P, Taylor L, et al. Atrial fibrillation screening using a handheld ECG device: results from the heart and stroke foundation (HSF) ‘be pulse aware’ campaign. Stroke 2013;44:e184.
Chellappan K, Ab Malek SNH, Jaafar R, Aminuddin A. Self-monitoring technique for stroke prevention among atrial fibrillation patients. Int J Stroke 2016;11:248.
Chen YH, Hung CS, Huang CC, Hung YC, Hwang JJ, Ho YL. Atrial fibrillation screening in nonmetropolitan areas using a telehealth surveillance system with an embedded cloud-computing algorithm: prospective pilot study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2017;5:e135.
Claes N, Van Laethem C, Goethals M, Goethals P, Mairesse G, Schwagten B, et al. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation in adults participating in a large-scale voluntary screening programme in Belgium. Acta Cardiol 2012;67:273–8.
Gilani M, Eklund JM, Makrehchi M. Automated Detection of Atrial Fibrillation Episode Using Novel Heart Rate Variability Features. Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 16–20 Aug 2016, Orlando, FL, pp. 3461–64.
Hobbs FD, Fitzmaurice DA, Mant J, Murray E, Jowett S, Bryan S, et al. A randomised controlled trial and cost-effectiveness study of systematic screening (targeted and total population screening) versus routine practice for the detection of atrial fibrillation in people aged 65 and over. The SAFE study. Health Technol Assess 2005;9(40). URL: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/o/cochrane/clcentral/articles/854/CN-00530854/frame.html
Kaleschke G, Hoffmann B, Drewitz I, Steinbeck G, Naebauer M, Goette A, et al. Prospective, multicentre validation of a simple, patient-operated electrocardiographic system for the detection of arrhythmias and electrocardiographic changes. Europace 2009;11:1362–8.
Kearley K, Selwood M, Van den Bruel A, Thompson M, Mant D, Hobbs FDR, et al. Triage tests for identifying atrial fibrillation in primary care: a diagnostic accuracy study comparing single-lead ECG and modified BP monitors. BMJ Open 2014;4:e004565.
Mant J, Fitzmaurice DA, Hobbs FDR, Jowett S, Murray ET, Holder R, et al. Accuracy of diagnosing atrial fibrillation on electrocardiogram by primary care practitioners and interpretative diagnostic software: analysis of data from screening for atrial fibrillation in the elderly (SAFE) trial. BMJ 2007;335:380.
McManus DD, Lee J, Maitas O, Esa N, Pidikiti R, Carlucci A, et al. A novel application for the detection of an irregular pulse using an iPhone 4s in patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2013;10:315–9.
McManus DD, Chong JW, Soni A, Saczynski JS, Esa N, Napolitano C, et al. PULSE-SMART: pulse-based arrhythmia discrimination using a novel smartphone application. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2016;27:51–7.
Mortelmans C, Van Haelst R, Van Der Auwera J, Grieten L, Vandervoort P, Vaes B. Validation of a new smartphone application for the diagnosis of atrial fibrillation in primary care. Europace 2017;19:iii16.
Newham WG, Tayebjee MH. Excellent symptom rhythm correlation in patients with palpitations using a novel smartphone based event recorder. J Atr Fibrillation 2017;10:1514.
Proietti M, Mairesse GH, Goethals P, Scavee C, Vijgen J, Blankoff I, et al. A population screening programme for atrial fibrillation: a report from the Belgian Heart Rhythm Week screening programme. Europace 2016;18:1779–86.
Rajendram R, Patel S, Kale S, Nangalia V. Ability of clinicians trained in intensive care to interpret rhythm strips. J Intensive Care Soc 2014;15:S70–S71.
Sandhu RK, Deif B, Barake W, Agarwal G, Connolly SJ, Dolovich L, et al. Identification of actionable atrial fibrillation using an integrated cardiovascular screening approach in community pharmacies. Heart Rhythm 2016;13:S415–6.
Somerville S, Somerville J, Croft P, Lewis M. Atrial fibrillation: a comparison of methods to identify cases in general practice. Br J Gen Pract 2000;50:727–9.
Vyas V, Duran J, Ansaripour A, Niedzielko M, Steel A, Bakhai A. Does a 12-lead ECG more reliably detect atrial fibrillation than a rhythm strip only ECG? Value Health 2014;17:A485–A486.
Winkler S, Axmann C, Schannor B, Kim S, Leuthold T, Scherf M, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of a new detection algorithm for atrial fibrillation in cardiac telemonitoring with portable electrocardiogram devices. J Electrocardiol 2011;44:460–4.
Ineligible outcomes (seven studies)
Ara F, Crockford C, John I, Kaba RA. Novel galvanised titanium-based ECG technology can reliably detect arrhythmias. Europace 2015;17:iii53.
Chan PH, Wong CK, Pun L, Wong YF, Wong MM, Chu DW, Siu CW. Diagnostic performance of an automatic blood pressure measurement device, Microlife WatchBP Home A, for atrial fibrillation screening in a real-world primary care setting. BMJ Open 2017;7:e013685.
Chung EH, Guise KD. QTC intervals can be assessed with the AliveCor heart monitor in patients on dofetilide for atrial fibrillation. J Electrocardiol 2015;48:8–9.
Grieten L, Van Der Auwera J, Vandervoort P, Rivero-Ayerza M, Van Herendael H, De Vusser P, et al. Evaluating smartphone based photoplesythmography as a screening solution for atrial fibrillation: a digital tool to detect afib? J Am Coll Cardiol 2017;69:2499.
Jacobs MS, Kaasenbrood F, Postma MJ, Van Hulst M, Tieleman RG. Cost-effectiveness of screening for atrial fibrillation in primary care with a handheld, single-lead electrocardiogram device in the Netherlands. Europace 2018;20:12–18.
Khanbhai ZM, Manning SE, Hussain W. Community pharmacist led atrial fibrillation screening program has the potential to improve atrial fibrillation detection rates and reduce stroke risk. Circulation 2016;134:A19641.
Mehta DD, Nazir NT, Trohman RG, Volgman AS. Single-lead portable ECG devices: perceptions and clinical accuracy compared to conventional cardiac monitoring. J Electrocardiol 2015;48:710–6.
Ineligible language (one study)
Reimert M, Verhoeven A. Screening for atrial fibrillation with single-lead hand-held ECG. Huisarts Wetenschap 2017;60:474.
Appendix 5 The QUADAS-2 quality assessment
Ideal study
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Population | People with signs or symptoms that may indicate underlying AF and who have an irregular pulse |
| Presentation | Presenting to primary care on account of signs or symptoms associated with AF (e.g. palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath and tiredness) |
| Prior tests | No prior testing for AF |
| Index test | Lead-I ECG using one of the following technologies:
|
| Purpose | To detect AF at a single time point in people who present with relevant signs or symptoms to primary care without previously diagnosed AF |
| Target disorder | AF |
| Reference standard | 12-lead ECG performed and interpreted by a trained health-care professional |
QUADAS-2 assessment of studies included in the diagnostic test accuracy review
Crockford 201350
Domain 1: patient selection
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| Method used in the study for patient selection not described | |
| Was a consecutive or random sample of patients enrolled? | Unclear |
| Was a case–control design avoided? | Unclear |
| Did the study avoid inappropriate exclusions? | Unclear |
| Could the selection of patients have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Patients who had been referred to an electrophysiology department. Reason for referral not provided | |
| Are there concerns that the included patients do not match the review question? | Concerns: high |
Domain 2: index test(s)
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| RhythmPad GP. No details provided regarding who performed the tests. Sequence of tests and blinding of interpreters not clear | |
| Were the index test results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard? | Unclear |
| If a threshold was used, was it prespecified? | Unclear |
| Could the conduct or interpretation of the index test have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the index test, its conduct, or interpretation differ from the review question? | Concerns: unclear |
Domain 3: reference standard
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| 12-lead ECG interpreted by a cardiologist. No details provided regarding who performed the tests | |
| Is the reference standard likely to correctly classify the target condition? | Yes |
| Were the reference standard results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test? | Unclear |
| Could the reference standard, its conduct, or its interpretation have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the target condition as defined by the reference standard does not match the review question? | Concerns: low |
Domain 4: flow and timing
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| All patients received the index test and reference standard. Data from 24 patients were excluded owing to data integrity, or to copies of traces of lead-I ECG or 12-lead ECG not being available at the end of the study. The reference standard was performed before the index test but the interval between assessments is not clear | |
| Was there an appropriate interval between the index test and reference standard? | Unclear |
| Did all patients receive a reference standard? | Yes |
| Did patients receive the same reference standard? | Yes |
| For comparative accuracy studies, did all patients receive all index tests? | NA |
| Were all patients included in the analysis? | No |
| Could the patient flow have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
Desteghe 201738
Domain 1: patient selection
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| The method used in the study for patient selection was not described | |
| Was a consecutive or random sample of patients enrolled? | Unclear |
| Was a case–control design avoided? | Unclear |
| Did the study avoid inappropriate exclusions? | Unclear |
| Could the selection of patients have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Hospitalised patients screened for AF at a cardiology ward. A proportion of the screened population (35.6%) had known AF based on chart review. Reasons for admission were coronary angiography/elective revascularisation (n = 100, 31.2%), electrophysiological examination/ablation (n = 64, 20%), heart failure (n = 37, 11.6%), acute coronary syndrome (n = 36, 11.3%), device implantation or replacement (n = 32, 10%), symptomatic AF (n = 11, 3.4%) or other (n = 40, 12.5%) | |
| Are there concerns that the included patients do not match the review question? | Concerns: high |
Domain 2: index tests
| Risk of bias: MyDiagnostick | |
|---|---|
| MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG device. No details were provided regarding who performed the tests. The lead-I ECG was performed immediately after the use of the reference standard and interpreted by the device algorithm and two EPs blind to the diagnosis based on both the algorithm and the reference standard | |
| Were the index test results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard? | Yes |
| If a threshold was used, was it prespecified? | Unclear |
| Could the conduct or interpretation of the index test have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability: MyDiagnostick | |
| Are there concerns that the index test, its conduct, or interpretation differ from the review question? | Concerns: low |
| Risk of bias: Kardia Mobile | |
| Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG. No details were provided regarding who performed the tests. Lead-I ECG performed immediately after the use of the reference standard and interpreted by device algorithm and two EPs blind to the diagnosis based on both the algorithm and the reference standard | |
| Were the index test results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard? | Yes |
| If a threshold was used, was it prespecified? | Unclear |
| Could the conduct or interpretation of the index test have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability: Kardia Mobile | |
| Are there concerns that the index test, its conduct, or interpretation differ from the review question? | Concerns: low |
Domain 3: reference standard
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| A full 10-second 12-lead ECG performed by a trained nurse immediately before the use of lead-I ECG devices. 12-lead ECG interpreted by two EPs blind to the results of the lead-I ECG algorithm | |
| Is the reference standard likely to correctly classify the target condition? | Yes |
| Were the reference standard results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test? | Yes |
| Could the reference standard, its conduct, or its interpretation have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the target condition as defined by the reference standard does not match the review question? | Concerns: low |
Domain 4: flow and timing
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| Twenty-four patients were excluded from the 2x2 table because they were not able to hold the devices properly. The reference standard was performed immediately before the index tests | |
| Was there an appropriate interval between the index test and the reference standard? | Yes |
| Did all patients receive a reference standard? | Yes |
| Did patients receive the same reference standard? | Yes |
| For comparative accuracy studies, did all patients receive all index tests? | Yes |
| Were all patients included in the analysis? | No |
| Could the patient flow have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
Doliwa 200943
Domain 1: patient selection
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| The method used in the study for patient selection was not described | |
| Was a consecutive or random sample of patients enrolled? | Unclear |
| Was a case–control design avoided? | Unclear |
| Did the study avoid inappropriate exclusions? | Unclear |
| Could the selection of patients have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Patients with AF, atrial flutter or sinus rhythm were recruited from a cardiology outpatient clinic to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity with a lead-I ECG device for sinus rhythm and atrial fibrillation detection. The reason for cardiology outpatient appointment was not provided | |
| Are there concerns that the included patients do not match the review question? | Concerns: high |
Domain 2: index test
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| Zenicor-ECG. No details were provided regarding who performed the tests. Lead-I ECG was performed immediately after the use of the reference standard and was interpreted by a cardiologist blind to the 12-lead ECG registration | |
| Were the index test results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard? | Yes |
| If a threshold was used, was it prespecified? | Unclear |
| Could the conduct or interpretation of the index test have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the index test, its conduct, or interpretation differ from the review question? | Concerns: low |
Domain 3: reference standard
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| A 12-lead ECG performed immediately before the use of a lead-I ECG device and interpreted by a cardiologist. No details were provided regarding who performed the tests | |
| Is the reference standard likely to correctly classify the target condition? | Yes |
| Were the reference standard results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test? | Yes |
| Could the reference standard, its conduct, or its interpretation have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the target condition as defined by the reference standard does not match the review question? | Concerns: low |
Domain 4: flow and timing
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| All patients received the index test and reference standard. All patients were included in the 2x2 table. The reference standard was performed immediately before the index test | |
| Was there an appropriate interval between the index test and the reference standard? | Yes |
| Did all patients receive a reference standard? | Yes |
| Did patients receive the same reference standard? | Yes |
| For comparative accuracy studies, did all patients receive all index tests? | NA |
| Were all patients included in the analysis? | Yes |
| Could the patient flow have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
Haberman 201545
Domain 1: patient selection
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| The method used in the study for patient selection was not described | |
| Was a consecutive or random sample of patients enrolled? | Unclear |
| Was a case–control design avoided? | Unclear |
| Did the study avoid inappropriate exclusions? | Unclear |
| Could the selection of patients have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Patients were recruited from a cardiology outpatient clinic to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity with a lead-I ECG device for sinus rhythm and AF detection. It was unclear if any patients had been previously diagnosed with AF. Reason for cardiology outpatient appointment not provided | |
| Are there concerns that the included patients do not match the review question? | Concern: high |
Domain 2: index test
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG. The test acquisitions were performed and supervised by study investigators. The lead-I ECG was performed immediately before the use of the reference standard and was interpreted by two EPs. It was unclear if interpreters of the test were blind to the results of the reference standard | |
| Were the index test results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard? | Unclear |
| If a threshold was used, was it prespecified? | Unclear |
| Could the conduct or interpretation of the index test have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the index test, its conduct, or interpretation differ from the review question? | Concerns: low |
Domain 3: reference standard
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| A 12-lead ECG performed immediately after the use of a lead-I ECG device and interpreted by two EPs. Test acquisitions were performed and supervised by study investigators | |
| Is the reference standard likely to correctly classify the target condition? | Yes |
| Were the reference standard results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test? | Unclear |
| Could the reference standard, its conduct, or its interpretation have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the target condition as defined by the reference standard does not match the review question? | Concerns: low |
Domain 4: flow and timing
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| All patients received the index test and the reference standard. All patients were included in the 2x2 table. The reference standard was performed immediately after the index test | |
| Was there an appropriate interval between the index test and the reference standard? | Yes |
| Did all patients receive a reference standard? | Yes |
| Did patients receive the same reference standard? | Yes |
| For comparative accuracy studies, did all patients receive all index tests? | NA |
| Were all patients included in the analysis? | Yes |
| Could the patient flow have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
Koltowski 201751
Domain 1: patient selection
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| The method used in the study for patient selection was not described | |
| Was a consecutive or random sample of patients enrolled? | Unclear |
| Was a case–control design avoided? | Unclear |
| Did the study avoid inappropriate exclusions? | Unclear |
| Could the selection of patients have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Patients in a tertiary care centre were recruited to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of the Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device. Reasons for patients attending the tertiary care centre not provided | |
| Are there concerns that the included patients do not match the review question? | Concerns: high |
Domain 2: index test
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG. The test acquisitions were performed by one physician. The lead-I ECG was performed before the use of the reference standard and interpreted by three teams comprised of two cardiologists and one internal medicine specialist | |
| Were the index test results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard? | Unclear |
| If a threshold was used, was it prespecified? | Unclear |
| Could the conduct or interpretation of the index test have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the index test, its conduct, or interpretation differ from the review question? | Concerns: unclear |
Domain 3: reference standard
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| The 12-lead ECG was performed after the use of a lead-I ECG device and interpreted by three teams comprised of two cardiologists and one internal medicine specialist. Test acquisitions were performed by one physician | |
| Is the reference standard likely to correctly classify the target condition? | Yes |
| Were the reference standard results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test? | Unclear |
| Could the reference standard, its conduct, or its interpretation have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the target condition as defined by the reference standard does not match the review question? | Concerns: low |
Domain 4: flow and timing
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| All patients received the reference standard. One patient did not receive the index test. The reference standard was performed after the index test | |
| Was there an appropriate interval between the index test and the reference standard? | Yes |
| Did all patients receive a reference standard? | Yes |
| Did patients receive the same reference standard? | Yes |
| For comparative accuracy studies, did all patients receive all index tests? | NA |
| Were all patients included in the analysis? | No |
| Could the patient flow have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
Lau 201347
Domain 1: patient selection
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| The method used in the study for patient selection was not described | |
| Was a consecutive or random sample of patients enrolled? | Unclear |
| Was a case–control design avoided? | Unclear |
| Did the study avoid inappropriate exclusions? | Unclear |
| Could the selection of patients have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Patients were screened for AF at a cardiology department. A proportion of the screened population (24%) had known AF. The reason for patient attendance at the cardiology department was not provided | |
| Are there concerns that the included patients do not match the review question? | Concerns: high |
Domain 2: index test
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG. No details were provided regarding who performed the tests. The lead-I ECG was performed within six hours after the use of the reference standard and interpreted by device algorithm alone | |
| Were the index test results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard? | Yes |
| If a threshold was used, was it prespecified? | Unclear |
| Could the conduct or interpretation of the index test have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the index test, its conduct, or interpretation differ from the review question? | Concerns: high |
Domain 3: reference standard
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| A 12-lead ECG was performed within six hours before the use of a lead-I ECG device and was interpreted by a cardiologist. No details provided regarding who performed the tests | |
| Is the reference standard likely to correctly classify the target condition? | Yes |
| Were the reference standard results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test? | Yes |
| Could the reference standard, its conduct, or its interpretation have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the target condition as defined by the reference standard does not match the review question? | Concerns: low |
Domain 4: flow and timing
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| All patients received the index test and the reference standard. All patients were included in the 2 × 2 table. The index test was performed within six hours after the reference standard | |
| Was there an appropriate interval between index test and reference standard? | Yes |
| Did all patients receive a reference standard? | Yes |
| Did patients receive the same reference standard? | Yes |
| For comparative accuracy studies, did all patients receive all index tests? | NA |
| Were all patients included in the analysis? | Yes |
| Could the patient flow have introduced bias? | Concern: low |
Reeves (NR)63
Domain 1: patient selection
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| Research nurses identified and approached eligible patients | |
| Was a consecutive or random sample of patients enrolled? | Unclear |
| Was a case–control design avoided? | Unclear |
| Did the study avoid inappropriate exclusions? | Unclear |
| Could the selection of patients have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Patients hospitalised after cardiac surgery or a cardiac-related event were recruited from cardiac intensive care unit, coronary care unit and cardiac surgery and cardiology wards in a regional specialist cardiac centre. The aim of the study was to obtain proof-of-principle data that the imPulse lead-I ECG device can capture and display an ECG trace with sufficient detail and viewing quality to allow experienced practitioners to detect AF | |
| Are there concerns that the included patients do not match the review question? | Concerns: high |
Domain 2: index test
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| imPulse lead-I ECG. It is not clear who performed the tests. The lead-I ECG performed at the same time as the 12-lead ECG. The index test was interpreted by two cardiology doctors, two specialist cardiac nurses and two cardiac physiologists, all with expertise in assessing ECGs blind to the 12-lead ECG registration | |
| Were the index test results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard? | Yes |
| If a threshold was used, was it prespecified? | Unclear |
| Could the conduct or interpretation of the index test have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the index test, its conduct, or interpretation differ from the review question? | Concerns: low |
Domain 3: reference standard
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| 12-lead ECG performed at the same time as the lead-I ECG device and interpreted by two cardiology doctors, two specialist cardiac nurses and two cardiac physiologists. There were two reference standards; the first was the clinical ECG diagnosis and the second was the ECG diagnosis for a subgroup of patients for whom there was consensus among the assessors’ 12-lead diagnoses (at least 3 of 4 in agreement) that the diagnosis was sinus rhythm or AF and this consensus diagnosis matched the clinical ECG diagnosis. No details provided regarding who performed the tests | |
| Is the reference standard likely to correctly classify the target condition? | Yes |
| Were the reference standard results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test? | Yes |
| Could the reference standard, its conduct, or its interpretation have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the target condition as defined by the reference standard does not match the review question? | Concerns: high |
Domain 4: flow and timing
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| All patients received the index test and the 12-lead ECG. All patients were included in the 2 × 2 table, however, interpretations by all of the six assessors were not presented. The 12-lead ECG was performed at the same time as the index test | |
| Was there an appropriate interval between index test and reference standard? | Yes |
| Did all patients receive a reference standard? | Yes |
| Did patients receive the same reference standard? | Unclear |
| For comparative accuracy studies, did all patients receive all index tests? | NA |
| Were all patients included in the analysis? | Yes |
| Could the patient flow have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
Tieleman 201448
Domain 1: patient selection
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| Random selection of patients visiting an outpatient cardiology clinic or a specialised AF outpatient clinic | |
| Was a consecutive or random sample of patients enrolled? | Yes |
| Was a case–control design avoided? | Unclear |
| Did the study avoid inappropriate exclusions? | Unclear |
| Could the selection of patients have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Patients with known AF and patients without a history of AF visiting an outpatient cardiology clinic or a specialised AF outpatient clinic. Reasons for patients attending the clinics not presented | |
| Are there concerns that the included patients do not match the review question? | Concerns: high |
Domain 2: index test
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG. No details were provided regarding who performed the tests. The lead-I ECG was performed immediately before the use of the reference standard and trace interpreted by device algorithm alone | |
| Were the index test results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard? | Yes |
| If a threshold was used, was it prespecified? | Unclear |
| Could the conduct or interpretation of the index test have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the index test, its conduct, or interpretation differ from the review question? | Concerns: high |
Domain 3: reference standard
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| A 12-lead ECG performed immediately after the use of a lead-I ECG device and interpreted by a cardiologist blind to the results of the index test. No details provided regarding who performed the tests | |
| Is the reference standard likely to correctly classify the target condition? | Yes |
| Were the reference standard results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test? | Yes |
| Could the reference standard, its conduct, or its interpretation have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the target condition as defined by the reference standard does not match the review question? | Concerns: low |
Domain 4: flow and timing
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| All patients received the index test and the reference standard. All patients were included in the 2 × 2 table. The reference standard was performed immediately after the index test | |
| Was there an appropriate interval between the index test and the reference standard? | Yes |
| Did all patients receive a reference standard? | Yes |
| Did patients receive the same reference standard? | Yes |
| For comparative accuracy studies, did all patients receive all index tests? | NA |
| Were all patients included in the analysis? | Yes |
| Could the patient flow have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
Vaes 201449
Domain 1: patient selection
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| General practitioners invited patients with known, paroxysmal or chronic AF to participate in the study to achieve a prevalence of AF of at least 50%. Subjects without a history of AF were also invited to participate in the study | |
| Was a consecutive or random sample of patients enrolled? | Unclear |
| Was a case–control design avoided? | No |
| Did the study avoid inappropriate exclusions? | Unclear |
| Could the selection of patients have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Patients with known AF (n = 161) and patients without a history of AF (n = 30) presenting to primary care. Reasons for patients attending a primary care appointment not presented | |
| Are there concerns that the included patients do not match the review question? | Concerns: high |
Domain 2: index test
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG device. A researcher who was not blinded to the medical history of the patient performed the tests. A lead-I ECG was performed before the use of the reference standard and trace interpreted by device algorithm alone | |
| Were the index test results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard? | Yes |
| If a threshold was used, was it prespecified? | Unclear |
| Could the conduct or interpretation of the index test have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the index test, its conduct, or interpretation differ from the review question? | Concerns: high |
Domain 3: reference standard
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| A 12-lead ECG was performed after the use of the lead-I ECG device and interpreted by a cardiologist blind to the results of the index test. A researcher who was not blinded to the medical history of the patient performed the tests | |
| Is the reference standard likely to correctly classify the target condition? | Yes |
| Were the reference standard results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test? | Yes |
| Could the reference standard, its conduct, or its interpretation have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the target condition as defined by the reference standard does not match the review question? | Concerns: low |
Domain 4: flow and timing
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| Ten patients were excluded from the 2x2 table as the pacemaker was active at the moment of the ECG recording. The reference standard was performed after the index test, but timing not specified | |
| Was there an appropriate interval between the index test and the reference standard? | Unclear |
| Did all patients receive a reference standard? | No |
| Did patients receive the same reference standard? | Yes |
| For comparative accuracy studies, did all patients receive all index tests? | NA |
| Were all patients included in the analysis? | No |
| Could the patient flow have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
Williams 201539
Domain 1: patient selection
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| The method used in the study for patient selection was not described | |
| Was a consecutive or random sample of patients enrolled? | Unclear |
| Was a case–control design avoided? | Unclear |
| Did the study avoid inappropriate exclusions? | Unclear |
| Could the selection of patients have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Patients with known AF attending an AF clinic and patients with AF status unknown who were attending the clinic for non-AF related reasons | |
|
|
Domain 2: index test
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG. No details were provided regarding who performed the tests. A lead-I ECG was performed at the same time as the reference standard and interpreted by a cardiologist and a GP with an interest in cardiology. Interpreters of the test were blind to the results of the reference standard | |
| Were the index test results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard? | Yes |
| If a threshold was used, was it prespecified? | Unclear |
| Could the conduct or interpretation of the index test have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the index test, its conduct, or interpretation differ from the review question? | Concerns: low |
Domain 3: reference standard
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| A 12-lead ECG was performed at the same time as the index test and was interpreted by a cardiologist and a GP with an interest in cardiology blind to the results of the index test. No details were provided regarding who performed the tests | |
| Is the reference standard likely to correctly classify the target condition? | Yes |
| Were the reference standard results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test? | Yes |
| Could the reference standard, its conduct, or its interpretation have introduced bias? | Risk: low |
| Concerns regarding applicability | |
| Are there concerns that the target condition as defined by the reference standard does not match the review question? | Concerns: low |
Domain 4: flow and timing
| Risk of bias | |
|---|---|
| Four patients were excluded as a result of artefacts in the ECG recordings (not clear whether these artefacts were in the lead-I or 12-lead ECG traces). The reference standard was performed at the same time as the index test | |
| Was there an appropriate interval between the index test and the reference standard? | No |
| Did all patients receive a reference standard? | No |
| Did patients receive the same reference standard? | Yes |
| For comparative accuracy studies, did all patients receive all index tests? | NA |
| Were all patients included in the analysis? | No |
| Could the patient flow have introduced bias? | Risk: unclear |
Appendix 6 Forest plots and summary receiver operating characteristic plots
FIGURE 13.
Forest plots of individual studies included in each meta-analysis of all lead-I ECG devices (trace interpreted by a trained health-care professional). (a) MyDiagnostick and EP1 data from the Desteghe study; (b) MyDiagnostick and EP2 data from the Desteghe study; and (c) Kardia Mobile and EP2 data from the Desteghe study. FN, false negative; FP, false positive; TN, true negative; TP, true positive.
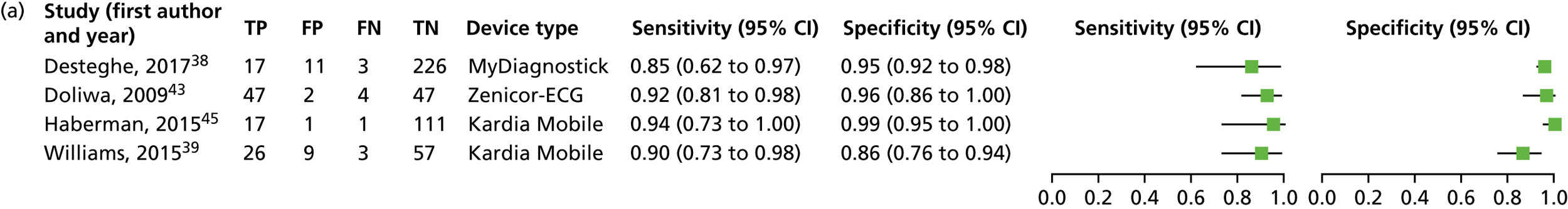
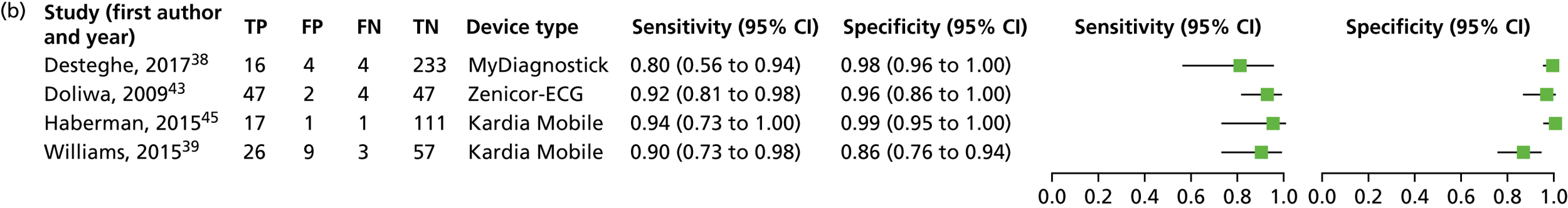
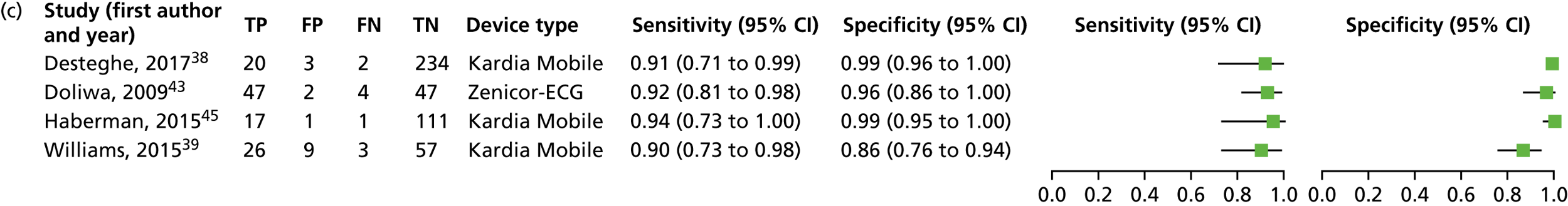
FIGURE 14.
Summary receiver operating characteristic plot for lead-I ECG device as index test with trace interpreted by a trained health-care professional and 12-lead ECG interpreted by a trained health-care professional as a reference standard (using MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG device and EP1 data from the study by Desteghe et al. 38).
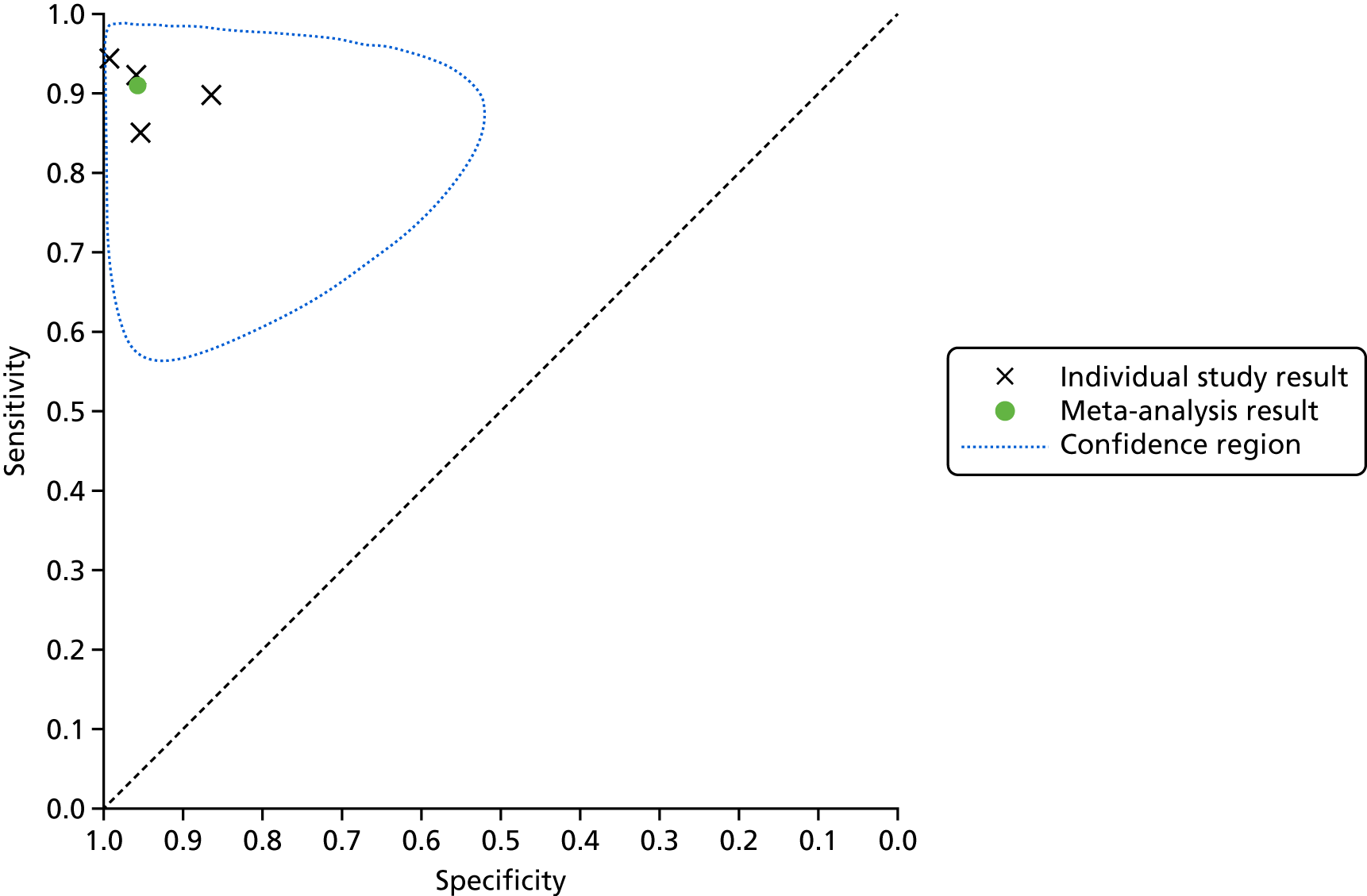
FIGURE 15.
Summary receiver operating characteristic plot for lead-I ECG device as index test with trace interpreted by a trained health-care professional and 12-lead ECG interpreted by a trained health-care professional as a reference standard (using MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG device and EP2 data from the study by Desteghe et al. 38).
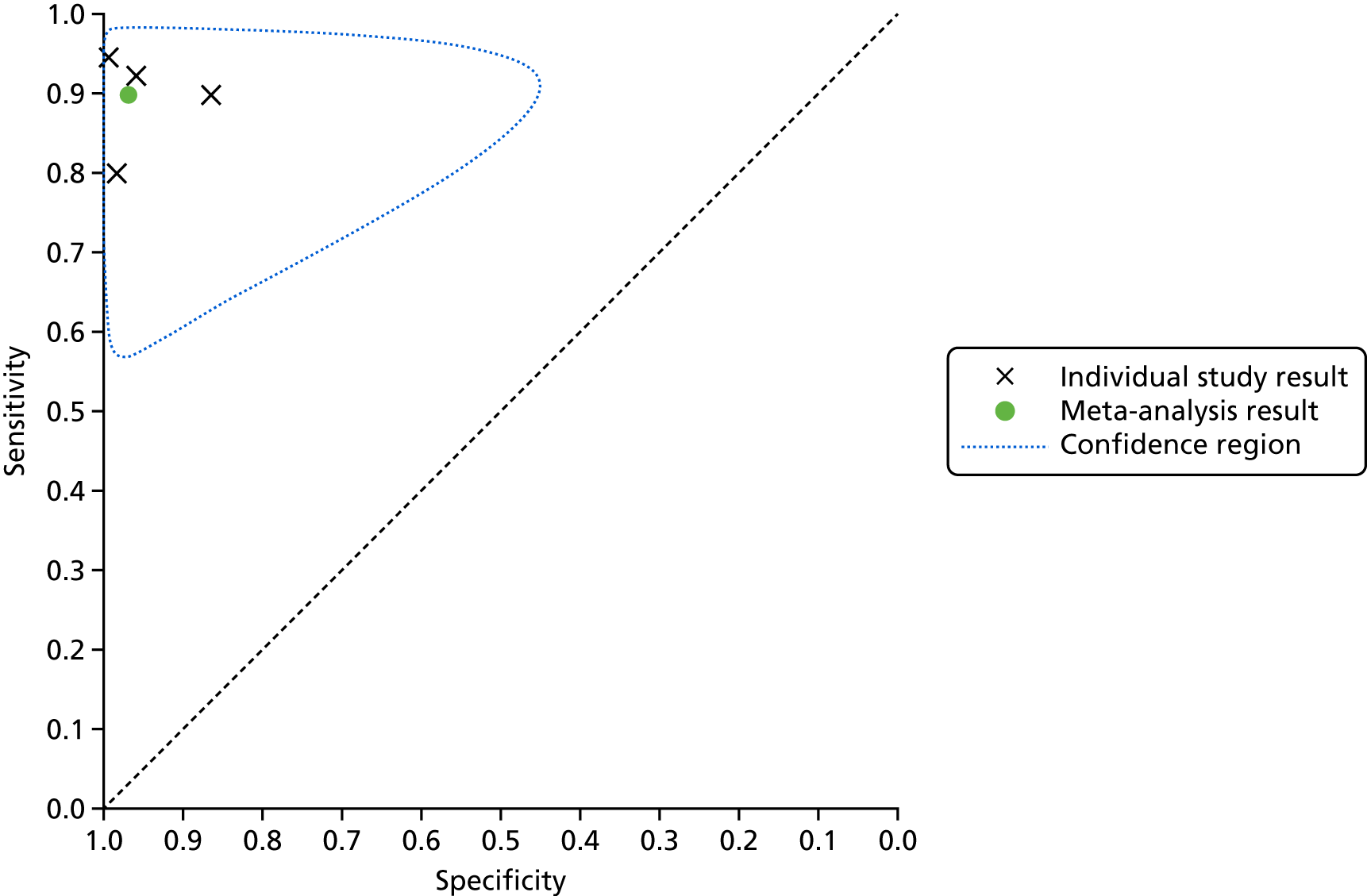
FIGURE 16.
Summary receiver operating characteristic plot for lead-I ECG device as index test with trace interpreted by a trained health-care professional and 12-lead ECG interpreted by a trained health-care professional as a reference standard (using Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device and EP2 data from the study by Desteghe et al. 38).
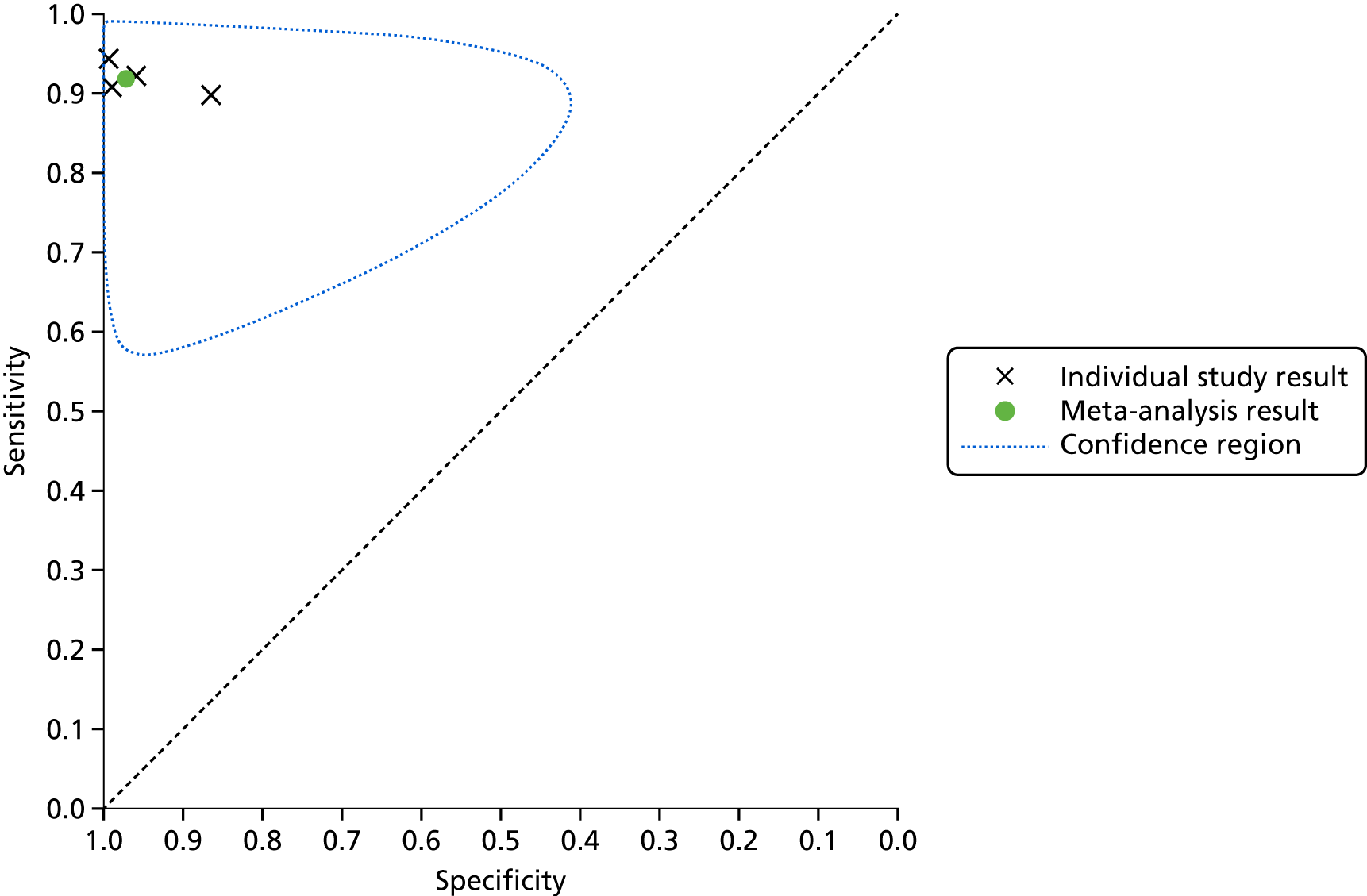
FIGURE 17.
Forest plots of individual studies included in the meta-analysis with trace interpreted by a trained health-care professional (using Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device, EP1 data from the study by Desteghe et al. 38 and trace interpreted by a GP in the study by Williams et al. 39). FN, false negative; FP, false positive; TN, true negative; TP, true positive.
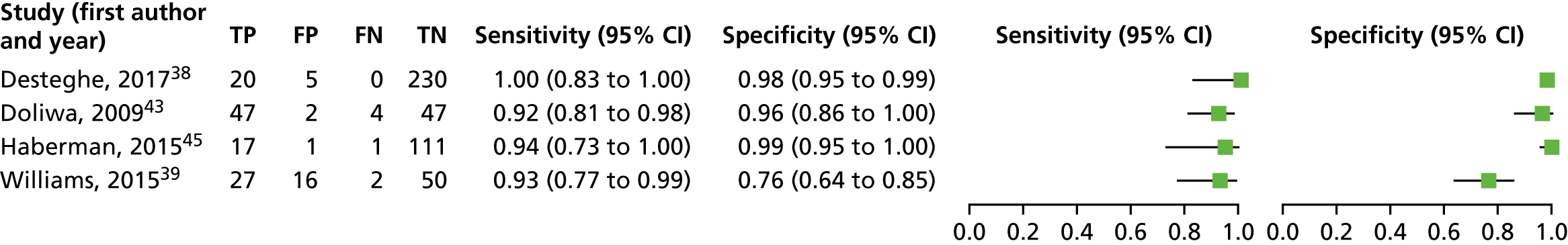
FIGURE 18.
Summary receiver operating characteristic plot for lead-I ECG device as index test with trace interpreted by a trained health-care professional (using Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device, EP 1 data from the study by Desteghe et al. 38 and trace interpreted by a GP in the study by Williams et al. 39).
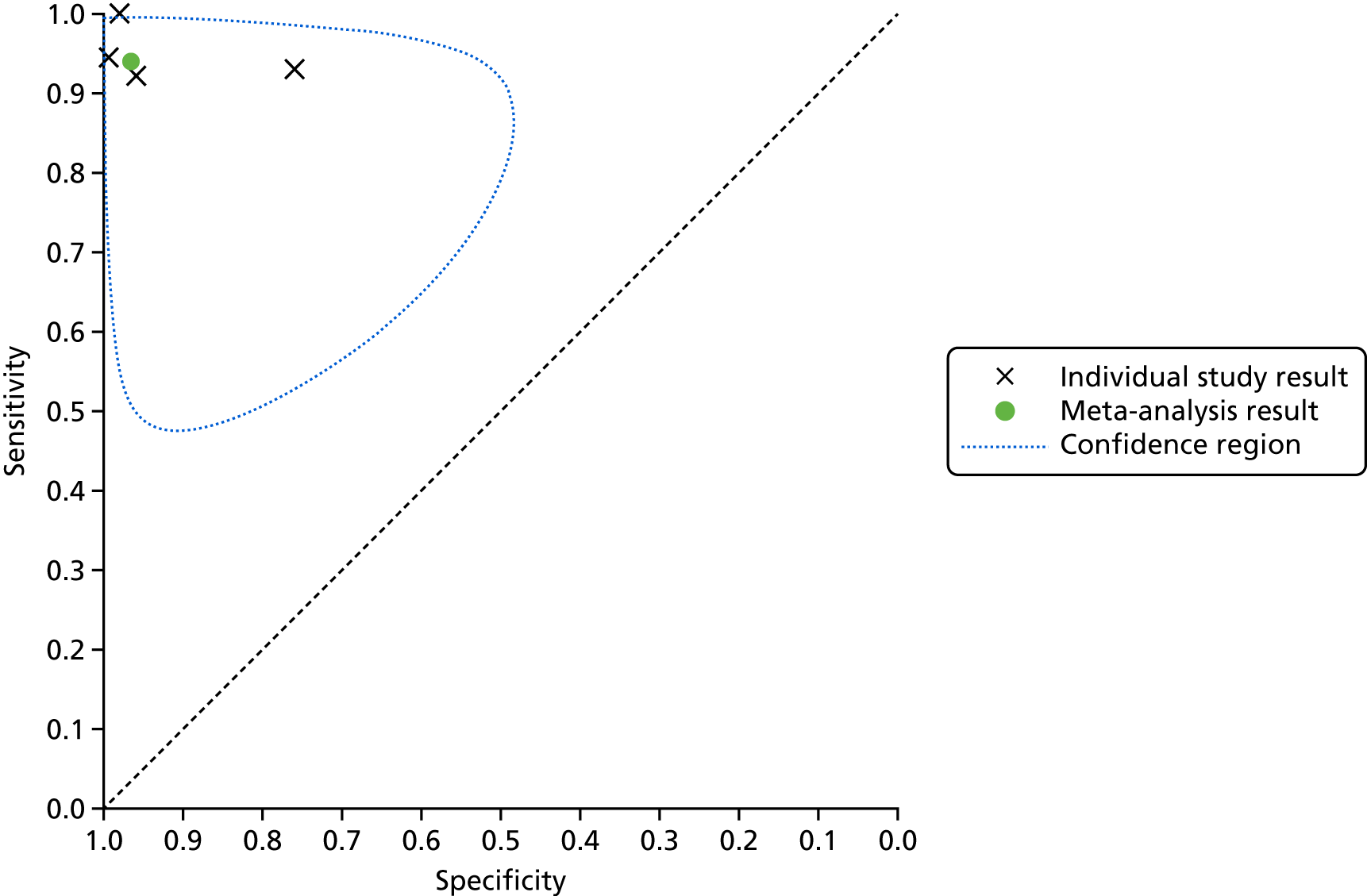
FIGURE 19.
Forest plots of individual studies included in each meta-analysis of the Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device (trace interpreted by a trained health-care professional). (a) EP1 data from the Desteghe study; and (b) EP2 data from the Desteghe study. FN, false negative; FP, false positive; TN, true negative; TP, true positive.
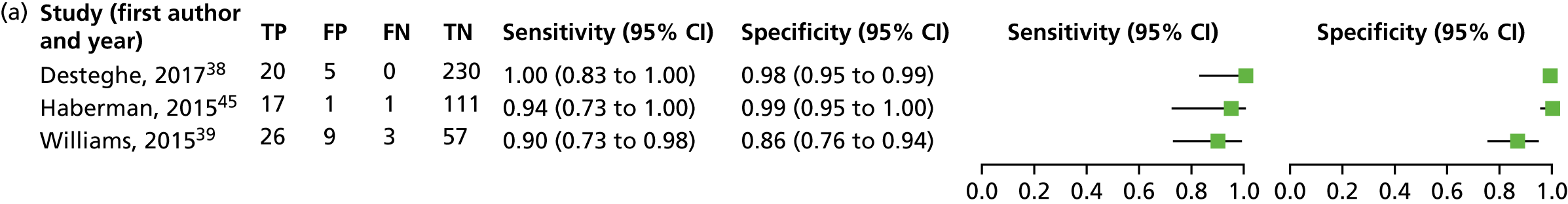
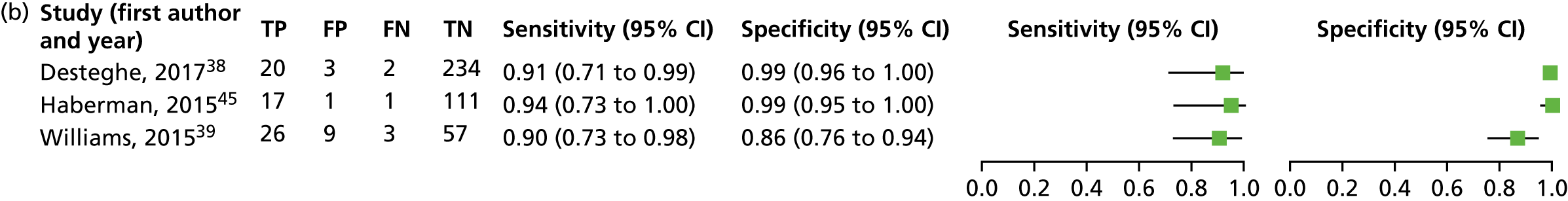
FIGURE 20.
Summary receiver operating characteristic plot for lead-I ECG device as index test with trace interpreted by the device algorithm and 12-lead ECG interpreted by a trained health-care professional as a reference standard (using MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG device data from the study by Desteghe et al. 38).
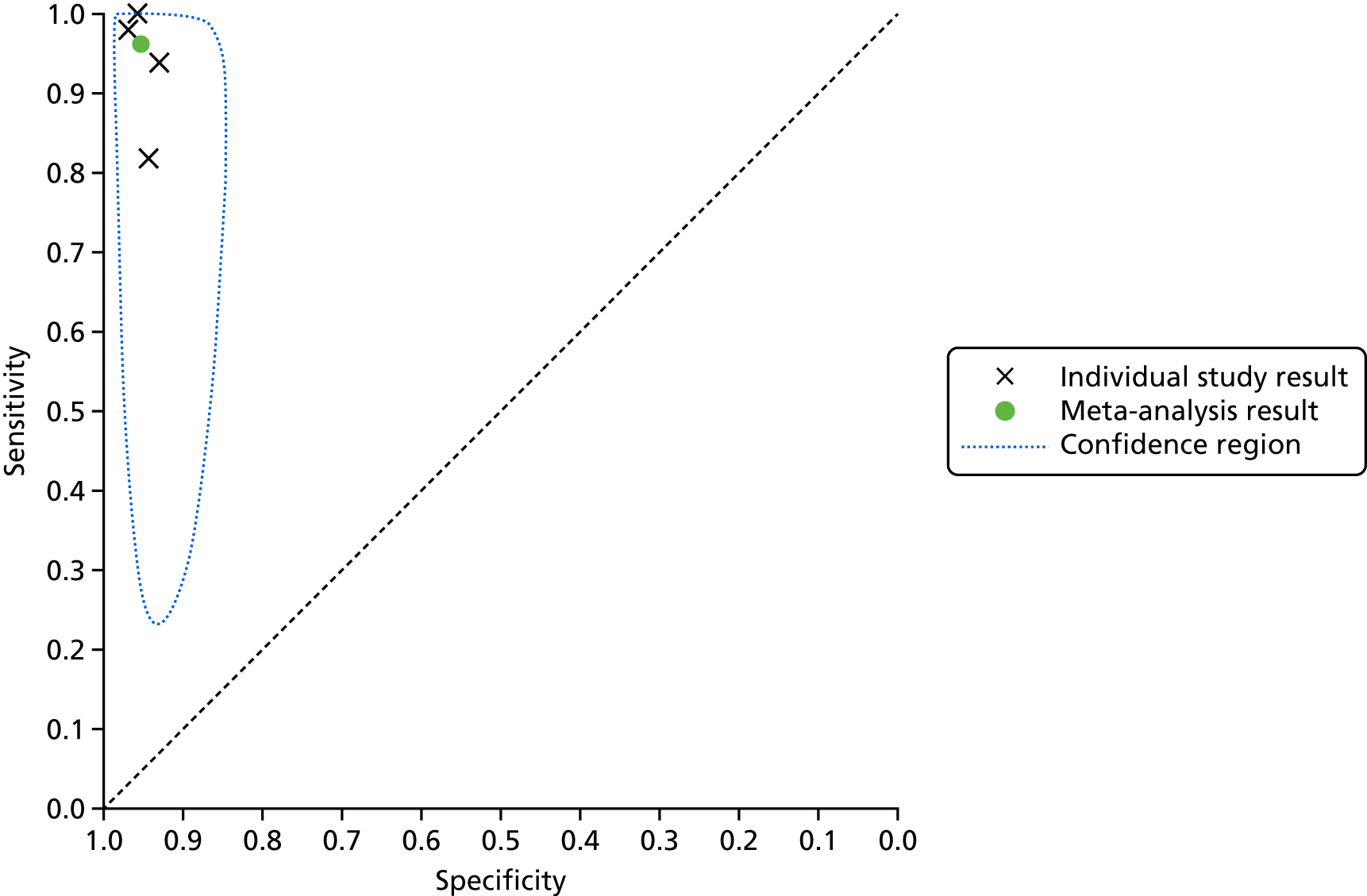
FIGURE 21.
Summary receiver operating characteristic plot for lead-I ECG device as index test with trace interpreted by the device algorithm and 12-lead ECG interpreted by a trained health-care professional as a reference standard (using Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device data from the study by Desteghe et al. 38).
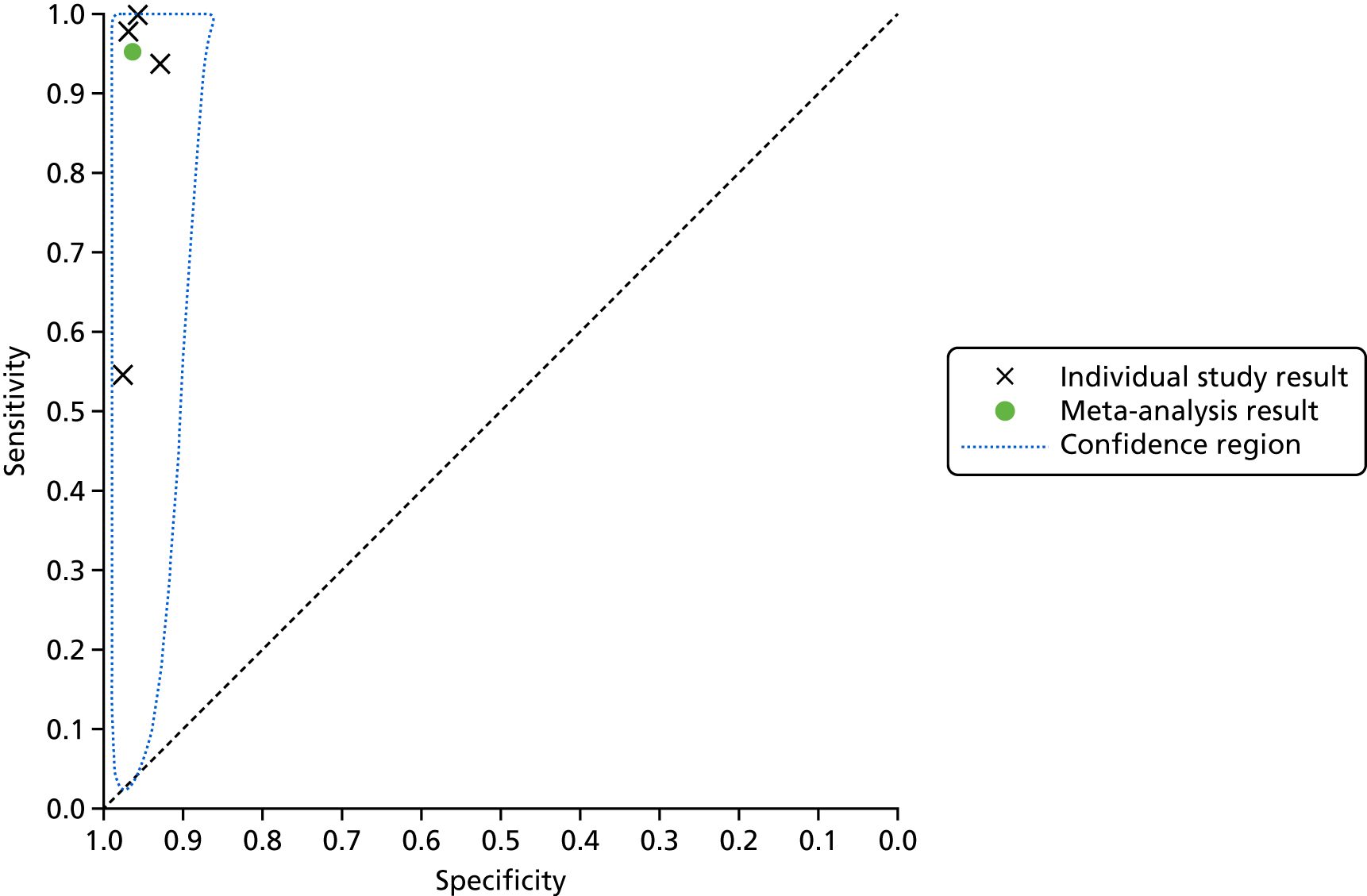
FIGURE 22.
Forest plot displaying the results of individual studies included in the meta-analysis for the MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG device with trace interpreted by the device algorithm.
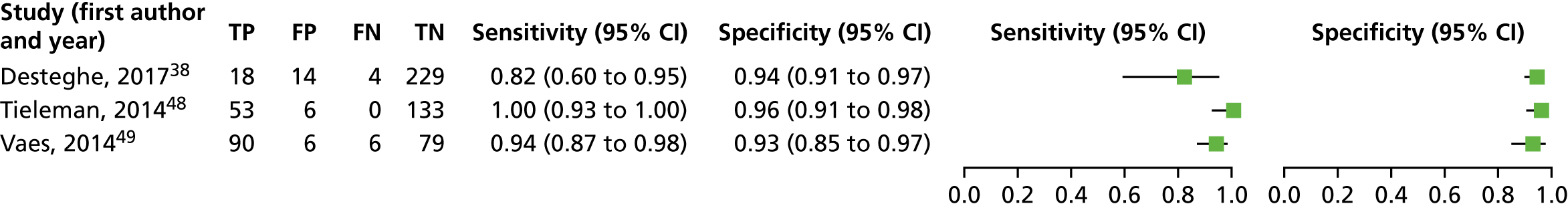
FIGURE 23.
Forest plot displaying the results of individual studies included in the meta-analysis for the Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG device with trace interpreted by the device algorithm.

Appendix 7 Studies reporting on lead-I electrocardiogram diagnostic test accuracy that were excluded from the diagnostic test accuracy review
For the purposes of presenting all available diagnostic accuracy data for lead-I ECG devices, this section reports on studies that were excluded from the DTA review but that provided sensitivity and specificity for the lead-I ECG devices investigated in this assessment. The characteristics of the studies that did not meet all of the eligibility criteria but that presented sensitivity and specificity data of lead-I ECG devices are presented in Table 38.
| Study (first author and year) | Study design; country and setting | Population; number of patients in the analysis; recruitment details | Mean age and SD (years); sex; risk factors for AF | Reason for exclusion from the DTA review |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chan, 201657 | Cross-sectional; China; primary care | People with a history of hypertension and/or diabetes mellitus or aged ≥ 65 years; N = 1013; patients recruited from a general outpatient clinic |
68.4 ± 12.2; female, n = 539 (53.2%) Hypertension: n = 916 (90.4%) Diabetes: n = 371 (36.6%) Coronary artery disease: n = 164 (16.2%) Previous stroke: n = 106 (10.5%) Mean CHA2DS2-VASc ± SD: 3.0 ± 1.5 |
Ineligible reference standard |
| Lowres, 201461 | Cross-sectional; Australia; community | People aged ≥ 65 years entering the pharmacy without a severe coexisting medical condition; N = 1000; availability of screening in participating pharmacies was advertised through flyers displayed within each pharmacy, and pharmacists and staff also directly approached potentially eligible clients |
76 ± 7; male, n = 436 (44%) NR |
Ineligible reference standard |
| Orchard, 201662 | Cross-sectional; Australia; primary care | Patients with known AF and patients without a history of AF attending for flu vaccination; N = 972 |
New AF (N = 7): 80 ± 3; male, 3/7; Known AF (N = 29): 77.1 ± 1; male, n = 15 (52%) All AF (N = 36): 78 ± 1; male, n = 18 (50%); NR |
Ineligible reference standard |
| Reeves63 | Cohort; UK; secondary care | Patients aged ≥ 18 years recovering in the Cardiac Intensive Care Unit or a cardiac surgery ward, following cardiac surgery, or who had been admitted to the Coronary Care Unit or a cardiology ward after a cardiac related event; N = 53; research nurses working in one or other of the clinical settings identified and approached eligible patients | 23–90 years (range); male, n = 37 (70%); NR | Ineligible reference standard |
| Tieleman, 201448 | Cohort; the Netherlands; primary care | People with unknown AF status; N = 676; people attending GP for flu vaccination | 74 ± 7.1 | Ineligible reference standard |
Some studies were excluded from the DTA review because, despite reporting sensitivity and specificity, they did not present data for the true-positive, false-negative, false-positive and true-negative test results50,51 or because the reference standard in the study was not a 12-lead ECG interpreted by a trained health-care professional. 57,61–63 The reference standard used in these studies is presented in Table 39. None of the excluded studies was conducted in people with signs or symptoms of AF. One of the studies was included in the DTA review, but one of its populations was excluded as the reference standard used was not a 12-lead ECG interpreted by a trained health-care professional. 48
| Study (first author and year) | Lead-I ECG device | Interpreter of lead-I ECG | Reference standard | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chan, 201657 | Kardia Mobile | Algorithm and cardiologist | Lead-I ECG trace interpreted by cardiologist | 71.4% (95% CI 51.3% to 86.8%) | 99.4% (95% CI 98.7 to 99.8%) |
| Lowres, 201461 | Kardia Mobile | Algorithm and cardiologist | Lead-I ECG trace interpreted by cardiologist | 98.5% (95% CI 92% to 100%) | 91.4% (95% CI 89% to 93%) |
| Orchard, 201662 | Kardia Mobile | Algorithm and cardiologist | Lead-I ECG trace interpreted by cardiologist | 95% (95% CI 83% to 99%) | 99% (95% CI 98% to 100%) |
| Reeves63 | imPulse | 2 cardiology registrars, 2 cardiac physiologists and 2 specialist cardiac nurses | Clinical ECG diagnosis (may have been made on the basis of additional information available to the assessors) | Range: 67–96% | Range: 58–83% |
| Consensus among the assessors of 12-lead ECG diagnoses (at least 3 of 4 in agreement) and consensus diagnosis matched the clinical ECG diagnosis | Range: 67–100% | Range: 83–100% | |||
| Tieleman, 201448 | MyDiagnostick | Algorithm and cardiologist | Lead-I ECG trace interpreted by cardiologist | 100% | 99% |
Two studies were available only as conference abstracts50,51 and one study was available only as a report submitted by the manufacturer of the lead-I device. 63 Five of the studies50,51,57,61,62 were cross-sectional in design and two were cohort studies. 48,63 Three studies were performed in primary care,48,57,62 two studies in secondary care,50,63 one study in tertiary care51 and one study was performed in a community setting. 61 Only two studies48,61 did not recruit at least a proportion of people with known AF, with known cardiovascular comorbidities57 or attending a clinic for a cardiovascular related condition. 50,51,62,63
The reference standard used in the studies to assess the DTA of lead-I ECG devices was interpretation of the lead-I ECG trace by a trained health-care professional. 48,57,61,62 One study63 used a clinical ECG diagnosis where additional information was available to the assessors and also a consensus among the assessors of 12-lead ECG (at least 3 of 4 in agreement) that matched the clinical ECG diagnosis.
Information on index test used, reference standard and diagnostic accuracy results for the studies that did not meet all of the eligibility criteria but that presented sensitivity and specificity data of lead-I ECG devices is presented in Table 39.
One study,63 although ineligible for inclusion in the DTA review, presented sensitivity and specificity results for the imPulse lead-I ECG device. The sensitivity reported for imPulse lead-I ECG ranged from 67% to 100% and the specificity from 58% to 100%. 63
We did not assess the methodological quality of these studies as they did not meet the eligibility criteria for inclusion in the diagnostic accuracy review.
Appendix 8 Quality assessment clinical impact studies
| Study (first author and year) | Selection | Comparability | Outcome | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Representativeness of the sample | Sample size | Non-respondents | Ascertainment of exposure | Based on design and analysis | Assessment of outcome | Statistical test | |
| Battipaglia, 201652 | – | – | + | + | – | ++ | + |
| Chan, 201656 | – | – | + | + | – | ++ | + |
| Chan, 201657 | – | – | + | + | – | ++ | + |
| Kaasenbrood, 201660 | – | – | + | + | – | + | + |
| Lowres, 201461 | – | + | + | + | – | ++ | + |
| Orchard, 201662 | – | – | + | + | – | ++ | + |
| Study (first author and year) | Risk of bias | Applicability concerns | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient selection | Index test | Reference standard | Flow and timing | Patient selection | Index test | Reference standard | |
| Reeves (NR)63 | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | High | Low | High |
| Question | Possible responses | Response |
|---|---|---|
| Section A: Are the results valid? | ||
| 1. Was there a clear statement of the aims of the research? | Yes | ✗ |
| Cannot tell | ||
| No | ||
| 2. Is a qualitative methodology appropriate? | Yes | ✗ |
| Cannot tell | ||
| No | ||
| 3. Was the research design appropriate to address the aims of the research? | Yes | ✗ |
| Cannot tell | ||
| No | ||
| 4. Was the recruitment strategy appropriate to the aims of the research? | Yes | |
| Cannot tell | ✗ | |
| No | ||
| 5. Was the data collected in a way that addressed the research issue? | Yes | ✗ |
| Cannot tell | ||
| No | ||
| 6. Has the relationship between researcher and participants been adequately considered? | Yes | |
| Cannot tell | ✗ | |
| No | ||
| Section B: What are the results? | ||
| 7. Have ethical issues been taken into consideration? | Yes | ✗ |
| Cannot tell | ||
| No | ||
| 8. Were the data analysis sufficiently rigorous? | Yes | ✗ |
| Cannot tell | ||
| No | ||
| 9. Is there a clear statement of findings? | Yes | ✗ |
| Cannot tell | ||
| No | ||
| Section C: Will the results help locally? | ||
| 10. How valuable is the research? | ||
| The authors discuss the implications of the study for a GP setting. However, the points raised do not necessarily follow from the results of their study | ||
Appendix 9 Forest plots of diagnostic yield
FIGURE 24.
Forest plot displaying the diagnostic yield (percentage of new AF diagnoses) in each study.
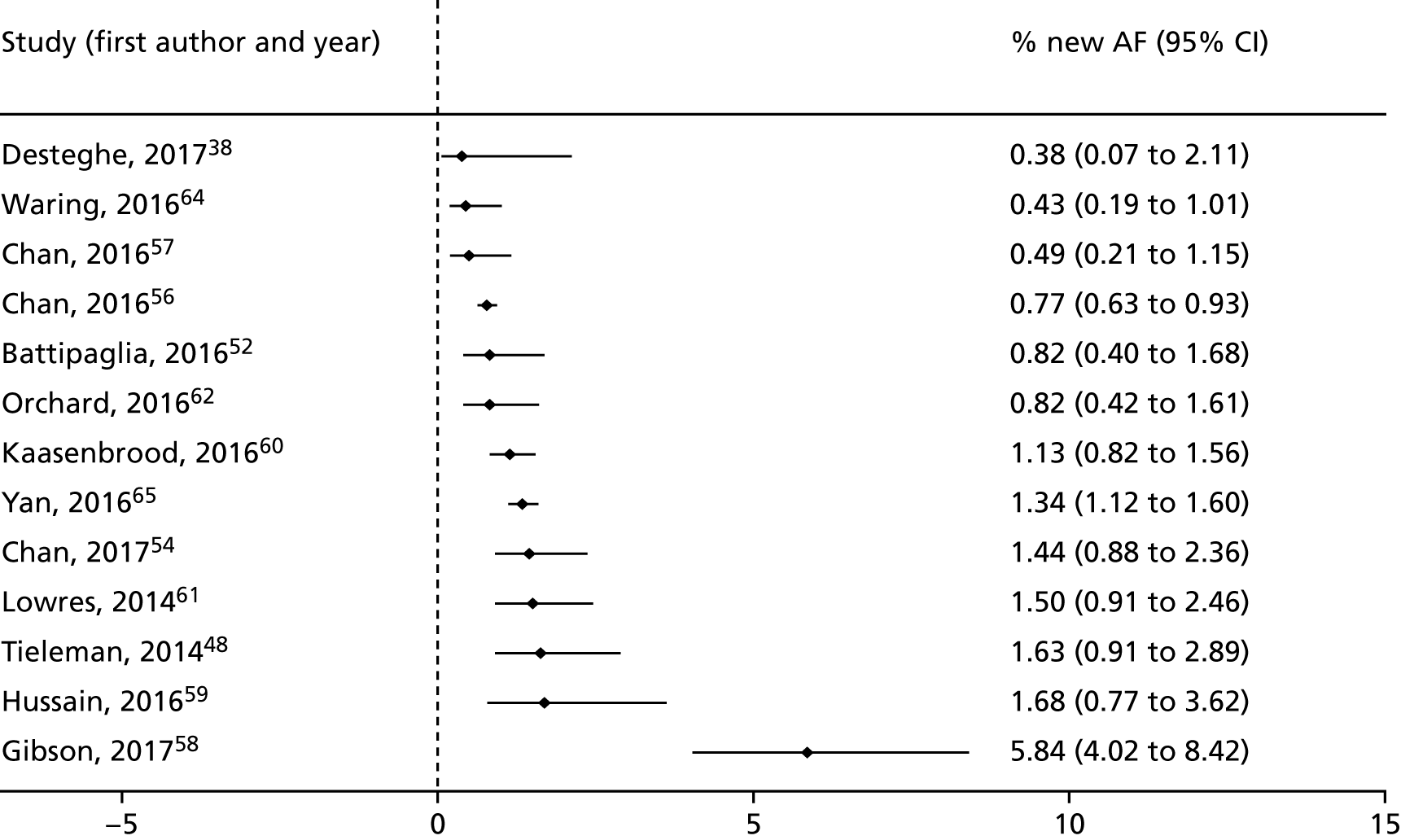
FIGURE 25.
Forest plot displaying the diagnostic yield (percentage of new AF diagnoses) in each study (studies grouped by type of lead-1 ECG device).
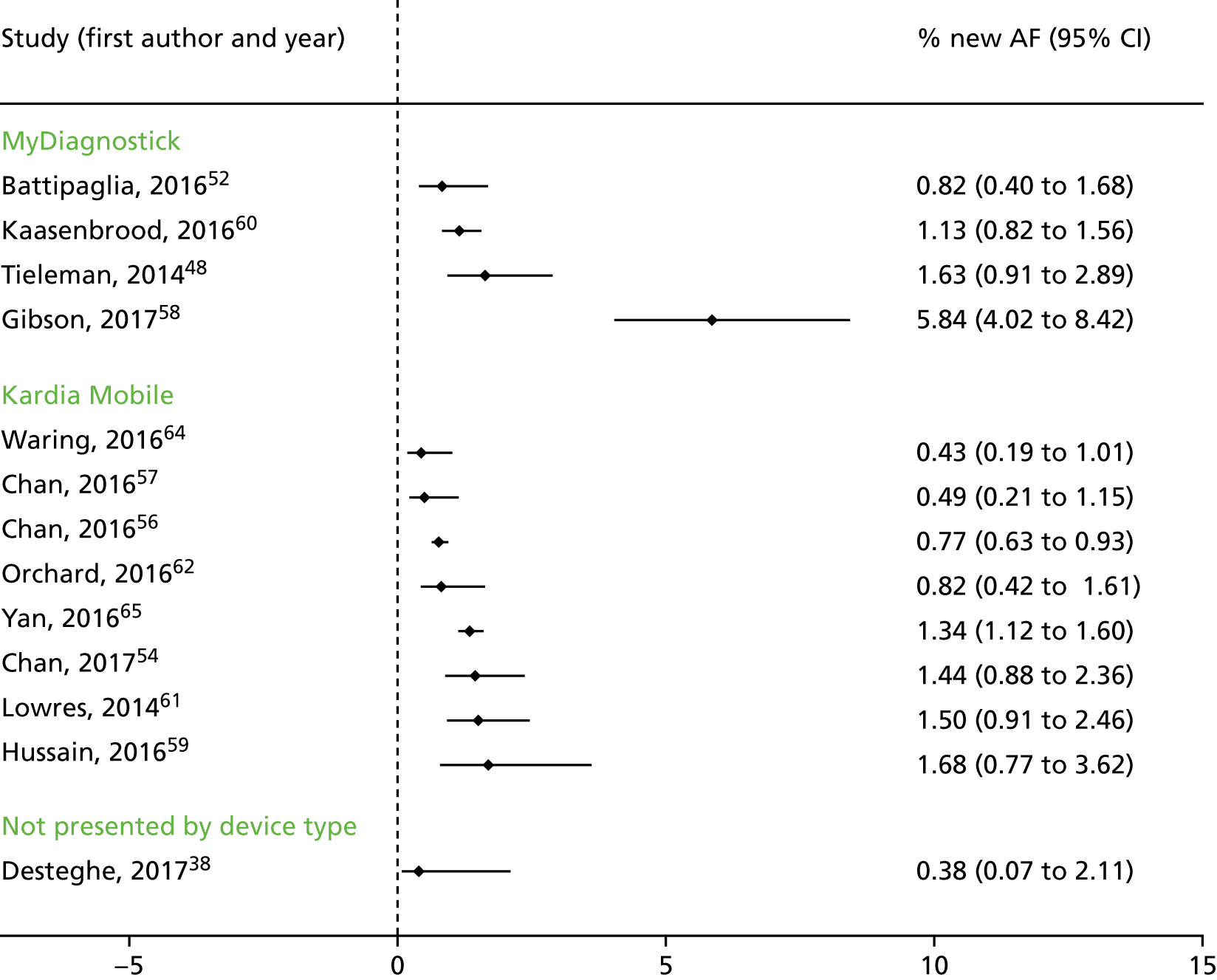
FIGURE 26.
Forest plot displaying the diagnostic yield (percentage of new AF diagnoses) in each study (studies grouped by setting).
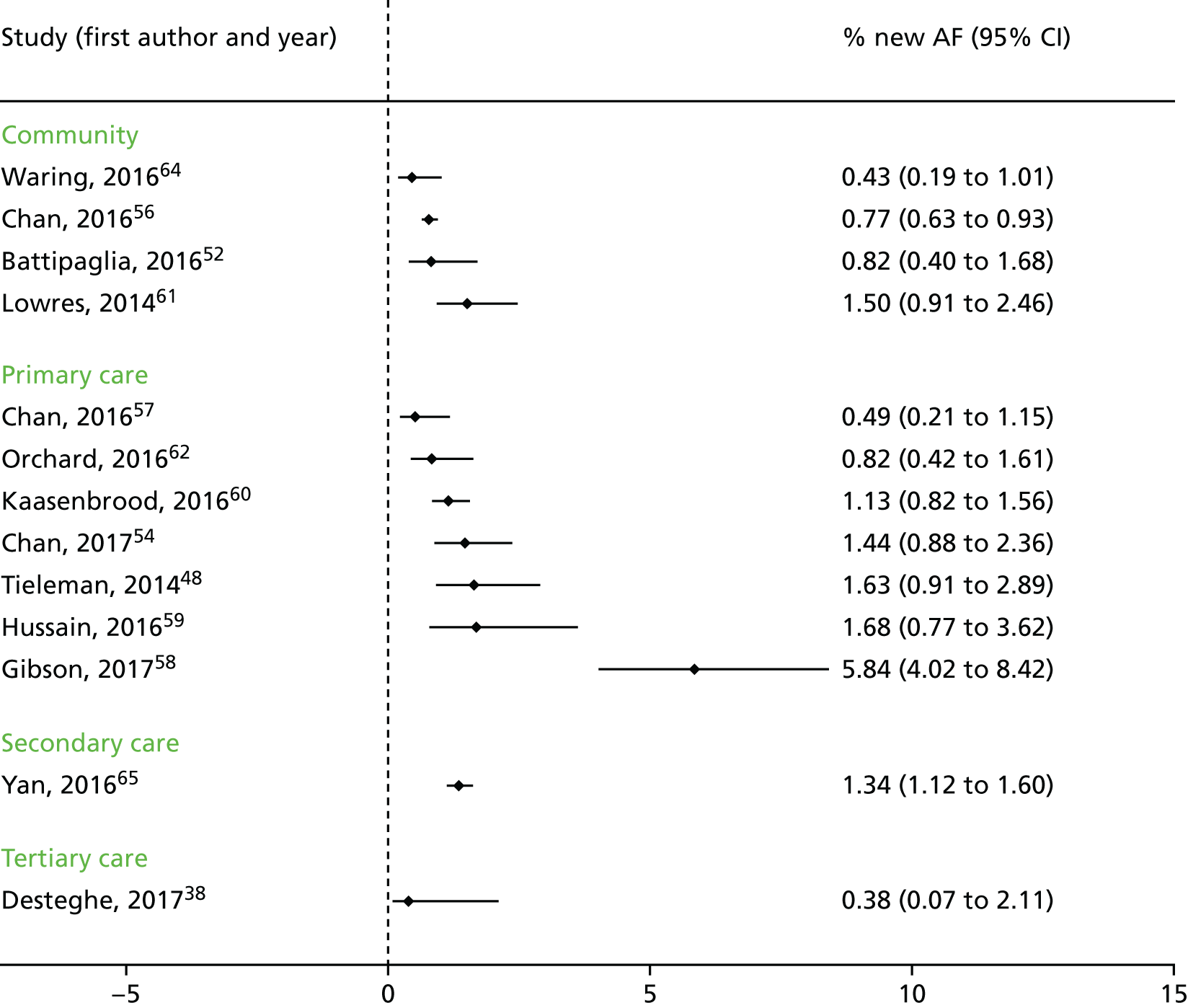
Appendix 10 Search strategy economic evaluations (MEDLINE)
MEDLINE (via OvidSP)
Date range searched: inception to 24 April 2018.
Date searched: 24 April 2018.
Search Strategy
-
Lead-I ECG.tw.
-
single lead ECG.tw.
-
(lead I or single lead or automated algorithm).tw.
-
Electrocardiography/
-
(electrocardiog* or ECG).tw.
-
4 or 5
-
3 and 6
-
lead I electrocardiog*.tw.
-
single lead electrocardiog*.tw.
-
1 or 2 or 7 or 8 or 9
-
Kardia Mobile.tw.
-
MyDiagnostick.tw.
-
RhythmPad.tw.
-
Zenicor-ECG.tw.
-
imPulse.tw.
-
10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14
-
10 and 15
-
16 or 17
-
Economics/
-
‘costs and cost analysis’/
-
Cost allocation/
-
Cost-benefit analysis/
-
Cost control/
-
Cost savings/
-
Cost of illness/
-
Cost sharing/
-
‘deductibles and coinsurance’/
-
Medical savings accounts/
-
Health care costs/
-
Direct service costs/
-
Drug costs/
-
Employer health costs/
-
Hospital costs/
-
Health expenditures/
-
Capital expenditures/
-
Value of life/
-
exp economics, hospital/
-
exp economics, medical/
-
Economics, nursing/
-
Economics, pharmaceutical/
-
exp ‘fees and charges’/
-
exp budgets/
-
(low adj cost).mp.
-
(high adj cost).mp.
-
(health?care adj cost$).mp.
-
(fiscal or funding or financial or finance).tw.
-
(cost adj estimate$).mp.
-
(cost adj variable).mp.
-
(unit adj cost$).mp.
-
(economic$ or pharmacoeconomic$ or price$ or pricing).tw.
-
or/19-50
-
18 and 51
Appendix 11 Questions for clinicians
-
For patients who present at a GP practice with signs or symptoms of AF and in whom MPP suggests AF and who do not have a lead-I ECG before being sent for a 12-lead ECG in either a GP practice or an acute setting:
-
In what proportion of patients who then receive a negative 12-lead ECG would you undertake testing for paroxysmal AF?
-
| Expert | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | This largely depends on whether or not they were having symptoms when they had the 12 lead ECG; if symptomatic and NO AF on the 12 lead ECG then no further AF screening necessary. If asymptomatic during the 12 lead ECG but risk factors for AF (type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, ischaemic heart disease, valvular heart disease, obesity, alcohol, age, past history of cryptogenic stroke) then degree of suspicion is higher and a period of prolonged ambulatory monitoring should be considered |
| 2 | 50% |
| 3 | All |
| 4 | There is no fixed answer to this question. How far I go will depend on patient demographics (age group etc), my own clinical suspicion, and the consequences to the patient if AF is missed. In someone with CHADS-VASc 0 and a wishy-washy history, I will not go any further |
| 5 | Depends, if negative for AF but shows few ectopic may not need testing, but otherwise 100% |
| 6 |
This is a very difficult question as it will depend very much on the individual clinician. If they are aware of the SAFE study, then they will expect at least 8 in 10 people with an irregular pulse not to have AF and they may stop at this point My advice when teaching GP colleagues is that they should undertake a CHADSVASc score (even though they are in sinus rhythm) and if the score is high then this is actually a reasonable determinant as to those where you would expect to find AF and maybe further investigation would be worth while. This is my practice. The problem is the next recording which is often something as unhelpful as a 24hr ECG |
Please note that this section refers to making decisions based on interpreting the trace produced by a lead-I ECG and not on the results of the lead-I ECG algorithm.
-
For patients who present at a GP practice with signs or symptoms of AF and in whom MPP suggests AF and who do have a lead-I ECG before being sent for a 12-lead ECG in either a GP practice or acute setting:
-
Patients with a negative lead-I ECG in a GP practice:
-
Would you expect all patients with a negative lead-I ECG to be sent for a 12-lead ECG?
-
-
| Expert | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | No, see earlier answer, if they were symptomatic at the time of the lead-I ECG and NO AF detected then further 12-lead testing may not be necessary in the context of low clinical suspicion and or the lead-I ECG has detected ectopic; unless there were other reasons to do so, such as risk factors for AF or CVD as listed above, or heart murmur detected on auscultation |
| 2 | No |
| 3 | Yes, unless alternative diagnosis made |
| 4 | Yes |
| 5 | Would ask for a 12-lead ECG if not had one recently. No protocol but probably 6 months |
| 6 | I would not suggest that those who have symptoms and signs of AF at the time of review and then have a negative lead-I ECG should be referred for a 12-lead ECG. This is a sinus rhythm trace correlating to symptoms which excludes AF. Clearly this is dependent on the clarity of the trace. I personally do not rely on the automated interpretation. In the younger cohort who still have physiological sinus arrhythmia the algorithm could easily suggest AF |
-
If not, what proportion of patients with a negative lead-I ECG would you expect to be sent for a 12-lead ECG?
| Expert | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | I would expect the majority of patients to have a 12-lead ECG in this instance |
| 2 | 70% |
| 3 | Not applicable (see response to the previous question) |
| 4 | Not applicable (see response to the previous question) |
| 5 | Probably 75% |
| 6 | Personally none, we have symptom trace correlation and no further ECG is warranted if the lead-I trace is of sufficient quality |
-
In what proportion of patients with a negative lead-I ECG who are not sent for a 12-lead ECG would you undertake testing for paroxysmal AF using a Holter ECG monitor or event recorder?
| Expert | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | Every patient being referred for ambulatory ECG monitoring should have a 12-lead ECG as part of their diagnostic assessment. In this instance if you suspect an underlying arrhythmia a lead-I ECG does not provide enough information to look for other important causes of structural heart disease. i.e. a 12-lead ECG should be a prerequisite for ambulatory Holter recording |
| 2 | 10–20% |
| 3 | All, unless alternative diagnosis made (e.g. you might diagnose ectopic beats on lead I-ECG) |
| 4 | Hypothetical question. I expect everyone to be sent for a 12-lead ECG |
| 5 | Our protocol is if sent for testing for paroxysmal AF, all need a 12-lead ECG |
| 6 | See above. If symptomatic at the time of the trace and this shows sinus rhythm, then we have the wrong diagnosis |
-
Patients with a positive lead-I ECG in a GP practice followed by a negative 12-lead ECG (done at a later time point, i.e. between 48 hours and 14 days after the positive lead-I ECG):
-
In what proportion of these patients would you diagnose AF with no further tests?
-
| Expert | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | A diagnosis of AF can be made securely on a lead-I ECG, but further testing is still usually required with a 12 lead ECG, blood testing and usually an echocardiogram. The majority will require further testing |
| 2 | 80–90% (assuming some will be false positives – if however, we take a positive ECG to be completely accurate then 100% would be diagnosed) |
| 3 | Majority |
| 4 | If I have seen the tracing myself, and concur with the interpretation, then 100% |
| 5 | If lead-I ECG positive, then negative 12-lead ECG is not relevant. Diagnosis is paroxysmal AF |
| 6 | If I have an ECG trace showing AF (reviewed not algorithm driven) then this would be sufficient |
-
In what proportion of these patients would you undertake testing for paroxysmal AF?
| Expert | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | This depends on the quality and confidence of the clinical decision maker with their lead-I ECG device recording |
| 2 | By testing do you mean further ECG evidence or is there an assumption that the diagnosis of AF is confirmed, and ‘testing’ means extra tests linked to AF such as an echocardiogram? |
| 3 | Depends on ongoing symptom burden and/or concerns regarding co-existing bradycardia |
| 4 | Depends on the need for symptom correlation |
| 5 | 100% would get an ambulatory ECG |
| 6 | I have the diagnosis and do not need to work further. They now need working up as AF as per local protocol |
-
Patients with a negative lead-I ECG in a GP practice followed by negative 12-lead ECG (done at a later time point, i.e. between 48 hours and 14 days after the positive lead-I ECG):
-
In what proportion of these patients would you rule out a diagnosis of AF?
-
| Expert | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | See earlier, this depends if they were symptomatic at the time of the recordings |
| 2 | 70–80% |
| 3 | 100% if symptoms/signs present at time of lead I-ECG |
| 4 | 0% |
| 5 | Probably 90–95% rule out |
| 6 | I would accept the patient does not have AF at this time, they may have an atrialopathy but that is a slightly different topic |
-
In what proportion of these patients would you undertake testing for paroxysmal AF?
| Expert | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | In those with a high degree of suspicion of AF and risk factors as outlined earlier |
| 2 | 20–30% |
| 3 | Only if subsequent clinical suspicion |
| 4 | See answer to question 1 |
| 5 | Difficult to answer because either ECG may have given an alternative diagnosis. Possibly 10% have frequent atrial ectopics and therefore I go on to investigate for paroxysmal AF, a further 5% to 10% I feel it was paroxysmal AF but resolves before I can get lead-I ECG trace |
| 6 | Only if symptomatic |
-
For patients who present at a GP practice with signs or symptoms of AF and in whom MPP suggests AF, who do have AF but who have had their AF ruled out after testing (with lead-I ECG and/or 12 lead ECG and/or Holter and event monitoring):
-
What proportion of patients would you expect to have their AF diagnosed, before having a CVE, within 12 months of initially presenting at a GP practice?
-
| Expert | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | Unknown: 20–30% of patients presenting with first stroke will either be known AF and not anticoagulated or will be first presentation of AF (Southport district general hospital stroke admission data 2012–13) |
| 2 | 20% |
| 3 | Difficult to answer but < 50% |
| 4 | I do not understand how anyone can rule out AF just because the tests are negative. Absence of proof is not the same as proof of absence |
| 5 | Really difficult to tell because even with current array of testing we may still be missing paroxysmal AF. Only better way is review of trials of patients with pacemakers or Implantable loop recorders |
| 6 | This is very difficult, you are suggesting the false negatives and I am unaware in a general population if this has been examined. If you look in a high risk population (post embolic stroke of undetermined source) then we can reference STOPSTROKE,77 EMBRACE109 and CRYSTAL.110 But this is a very high risk population |
-
What proportion of patients would you expect to have their AF diagnosed – before having a CVE – within 5 years of initially presenting at a GP practice?
| Expert | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | Unknown: see above |
| 2 | 50% |
| 3 | > 50% |
| 4 | 100% |
| 5 | See response to the previous question |
| 6 | Would be interested to see if anyone has this data |
-
Testing for paroxysmal AF:
-
In the diagnosis of paroxysmal AF, would all patients use both a Holter ECG monitor and an event recorder? If not, what proportion of patients would use (1) Holter ECG monitor or (2) event recorder and what proportion would use both?
-
| Expert | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | This will depend on frequency of symptoms: with daily or near daily symptoms a 24-hour Holter has a greater chance of arrhythmia capture. In patients with less frequent symptoms an event recorder or prolonged period of ambulatory monitoring will have a higher chance of arrhythmia capture |
| 2 | 50/50 split: depending on access to which is available, only 20% we go on to use both |
| 3 | Either/or but not both |
| 4 | Depends on symptoms. I cannot put a number on this |
| 5 | For paroxysmal AF we always use an event recorder for 7 days (R test) unless patient getting symptoms consistent with frequent AF more than once daily |
| 6 | Is this high risk or low risk cohorts? I feel it would be very different in different cohorts |
-
How long would you routinely use (1) Holter ECG monitor (2) event recorder or (3) both to test for paroxysmal AF?
| Expert | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | See above |
| 2 | Depends on duration/frequency of symptoms. Holters are generally 24–48 hrs. Event recorders 5 days to 3 weeks (e.g. hand-held cardio-memo recorder) |
| 3 | 7–14 days |
| 4 | Depends on symptoms. There is no fixed answer |
| 5 | Usually 7 days. Can be up to 30 days with battery change on day 15 but rarely tolerated. We do also loan AliveCor ECGs if patients happy to use them. Loan is up to 2 months |
| 6 | If post stroke the evidence would suggest 2–4 weeks (EMBRACE) but in CRYSTAL 30% were found to develop AF at 3 years |
-
What is the diagnostic and treatment pathway for patients who have paroxysmal AF ruled out by the results of a Holter ECG monitor and/or event recording?
| Expert | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | To seek medical advice as soon as possible when symptomatic if no diagnosis yet made |
| 2 | If there is no diagnosis of AF after a search, then no further routine testing would take place unless the patient re-presents or there is a change in their symptoms to warrant further investigation |
| 3 | Nil else unless ongoing clinical concern |
| 4 | I do not think you can rule out paroxysmal AF just because your Holter or event recorder is negative |
| 5 | Usually discharge back to GP. We are now loaning lead-I ECG devices to patients for up to 2 months. Very high risk e.g. TIA/stroke with high probability owing to AF may be considered for implantable loop recorders |
| 6 | Never seen one |
-
Diagnostic pathway for patients with signs or symptoms of AF and an irregular pulse who do not have AF:
-
Do you think the introduction of lead-I ECGs into the diagnostic pathway for patients, with signs or symptoms of AF and in whom MPP suggests AF but who do not have AF, will affect the diagnosis and treatment of the other conditions causing symptoms in these patients? If yes, how?
-
| Expert | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | Possibly, if the process stops after the Lead-I ECG recording. The clinical context and AF, CVD risk status must be taken into consideration, as other cardiac conditions might be missed |
| 2 | Yes, an irregular pulse may feel like AF but be simple ectopic heart beats. This can mean that these patients are not sent for further routine testing and could be treated with lifestyle advice (reduced caffeine/alcohol) or offered drugs such as beta blockers |
| 3 | Alternative diagnoses might be made e.g. ectopic beats which will allow inform treatment/management decisions |
| 4 | Yes. It may correlate symptoms to another non-AF arrhythmia, which will require treatment in its own right |
| 5 | Yes. Lead-I ECG devices will pick up ectopics and pauses |
| 6 |
This is probably ectopy (atrial or ventricular) as these are the commonest non-sustained dysrhythmias. Questions around how much ectopy would make the diagnosis and what is the significance is hotly debated but unknown This would be investigated as a palpitation and would have a varied pathway depending on local opinion and protocol |
Appendix 12 Results (base cases 2–4)
Base case 2: 12-lead electrocardiogram in primary care, 14 days to 12-lead electrocardiogram
Costs and QALYs generated in base case 2 are shown in Tables 43 and 44, respectively.
| Strategy | Cost of lead-I ECG test (£) | Cost of treatment (NOACs & rate control) (£) | Cost of CVEs and AEs (£) | Cost of 12-lead ECG (£) | Cost of paroxysmal testing (Holter monitor) (£) | Total costs (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 0 | 90,431 | 420,710 | 535 | 2741 | 514,416 |
| Kardia Mobile | 26 | 102,842 | 409,851 | 451 | 2239 | 515,408 |
| imPulse | 97 | 116,189 | 411,588 | 453 | 2263 | 530,590 |
| MyDiagnostick | 100 | 106,951 | 411,334 | 451 | 2245 | 521,080 |
| Generic lead-I device | 392 | 103,636 | 409,868 | 451 | 2240 | 516,587 |
| Zenicor-ECG | 624 | 104,824 | 410,181 | 451 | 2242 | 518,323 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 1110 | 100,198 | 414,279 | 445 | 2229 | 518,261 |
| Strategy | IS | HS | TIA | False negatives | False positives | Bleeds | Total QALYs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 11.620 | 2.123 | 8.407 | 1.606 | 0.000 | 23.572 | 447.895 |
| Kardia Mobile | 11.451 | 1.996 | 8.358 | 0.144 | 1.378 | 23.743 | 449.220 |
| imPulse | 11.482 | 2.018 | 8.365 | 0.396 | 3.660 | 23.721 | 448.956 |
| MyDiagnostick | 11.477 | 2.015 | 8.364 | 0.360 | 2.153 | 23.711 | 448.994 |
| Generic lead-I device | 11.451 | 1.996 | 8.358 | 0.147 | 1.507 | 23.744 | 449.217 |
| Zenicor-ECG | 11.457 | 2.000 | 8.360 | 0.192 | 1.722 | 23.738 | 449.170 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 11.529 | 2.054 | 8.376 | 0.793 | 1.292 | 23.620 | 448.540 |
Pairwise cost-effectiveness results from the base case 2 analysis for each index test compared with the standard diagnostic pathway are presented in Table 45 and the incremental analysis results are shown in Table 46.
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 514,416 | 447.895 | |||
| Kardia Mobile | 515,408 | 449.220 | 1221 | 1.257 | 971 |
| imPulse | 530,590 | 448.956 | 16,403 | 0.994 | 16,506 |
| MyDiagnostick | 521,080 | 448.994 | 6892 | 1.031 | 6684 |
| Generic lead-I device | 516,587 | 449.217 | 2400 | 1.255 | 1912 |
| Zenicor-ECG | 518,323 | 449.170 | 4135 | 1.207 | 3426 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 518,261 | 448.540 | 4073 | 0.577 | 7055 |
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 514,416 | 447.895 | |||
| Kardia Mobile | 515,408 | 449.220 | 992 | 1.324 | £749 |
| Generic lead-I device | 516,587 | 449.217 | 1179 | –0.002 | Dominated |
| RhythmPad GPa | 518,261 | 448.540 | 2853 | –0.680 | Dominated |
| Zenicor-ECG | 518,323 | 449.170 | 2915 | –0.050 | Dominated |
| MyDiagnostick | 521,080 | 448.994 | 5672 | –0.226 | Dominated |
| imPulse | 530,590 | 448.956 | 15,182 | –0.264 | Dominated |
Base case 3: 12-lead electrocardiogram in secondary care, 2 days to 12-lead electrocardiogram
Costs and QALYs generated in base case 3 are shown in Tables 47 and 48, respectively.
| Strategy | Cost of lead-I ECG test (£) | Cost of treatment (NOACs & rate control) (£) | Cost of CVEs and AEs (£) | Cost of 12-lead ECG (£) | Cost of paroxysmal testing (Holter monitor) (£) | Total costs (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 0 | 90,630 | 420,279 | 2801 | 2743 | 516,453 |
| Kardia Mobile | 26 | 102,952 | 409,881 | 2361 | 2240 | 517,460 |
| imPulse | 97 | 116,317 | 411,612 | 2373 | 2265 | 532,663 |
| MyDiagnostick | 100 | 107,077 | 411,358 | 2359 | 2247 | 523,140 |
| Generic lead-I device | 392 | 103,746 | 409,898 | 2362 | 2242 | 518,640 |
| Zenicor-ECG | 624 | 104,938 | 410,210 | 2362 | 2244 | 520,378 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 1110 | 100,358 | 414,292 | 2330 | 2231 | 520,320 |
| Strategy | IS | HS | TIA | False negatives | False positives | Bleeds | Total QALYs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 11.621 | 2.124 | 8.406 | 1.606 | 0.000 | 23.581 | 447.963 |
| Kardia Mobile | 11.452 | 1.996 | 8.359 | 0.144 | 1.379 | 23.751 | 449.249 |
| imPulse | 11.482 | 2.019 | 8.366 | 0.397 | 3.663 | 23.730 | 448.987 |
| MyDiagnostick | 11.478 | 2.015 | 8.365 | 0.361 | 2.155 | 23.720 | 449.024 |
| Generic lead-I device | 11.452 | 1.996 | 8.359 | 0.147 | 1.508 | 23.752 | 449.246 |
| Zenicor-ECG | 11.457 | 2.000 | 8.360 | 0.193 | 1.724 | 23.746 | 449.199 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 11.530 | 2.054 | 8.377 | 0.794 | 1.293 | 23.630 | 448.573 |
Pairwise cost-effectiveness results from the base case 3 analysis for each index test versus the standard diagnostic pathway are presented in Table 49 and the incremental analyses are shown in Table 50.
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 516,453 | 447.963 | |||
| Kardia Mobile | 517,460 | 449.249 | 3273 | 1.286 | 2544 |
| imPulse | 532,663 | 448.987 | 18,476 | 1.024 | 18,038 |
| MyDiagnostick | 523,140 | 449.024 | 8953 | 1.061 | 8435 |
| Generic lead-I device | 518,640 | 449.246 | 4453 | 1.284 | 3468 |
| Zenicor-ECG | 520,378 | 449.199 | 6191 | 1.236 | 5007 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 520,320 | 448.573 | 6133 | 0.610 | 10,048 |
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 516,453 | 447.963 | |||
| Kardia Mobile | 517,460 | 449.249 | 1007 | 1.286 | £783 |
| imPulse | 518,640 | 449.246 | 1180 | –0.002 | Dominated |
| MyDiagnostick | 520,320 | 448.573 | 2860 | –0.676 | Dominated |
| Generic lead-I device | 520,378 | 449.199 | 2918 | –0.050 | Dominated |
| Zenicor-ECG | 523,140 | 449.024 | 5680 | –0.225 | Dominated |
| RhythmPad GPa | 532,663 | 448.987 | 15,203 | –0.262 | Dominated |
Base case 4: 12-lead electrocardiogram in secondary care, 14 days to 12-lead electrocardiogram
Costs and QALYs generated in base case 4 are shown in Tables 51 and 52, respectively.
| Strategy | Cost of lead-I ECG test (£) | Cost of treatment (NOACs & rate control) (£) | Cost of CVEs and AEs (£) | Cost of 12-lead ECG (£) | Paroxysmal testing (Holter monitor) (£) | Total costs (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 0 | 90,431 | 420,710 | 2797 | 2741 | 516,678 |
| Kardia Mobile | 26 | 102,842 | 409,851 | 2358 | 2239 | 517,315 |
| imPulse | 97 | 116,189 | 411,588 | 2370 | 2263 | 532,507 |
| MyDiagnostick | 100 | 106,951 | 411,334 | 2356 | 2245 | 522,985 |
| Generic lead-I device | 392 | 103,636 | 409,868 | 2359 | 2240 | 518,495 |
| Zenicor-ECG | 624 | 104,824 | 410,181 | 2359 | 2242 | 520,231 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 1110 | 100,198 | 414,279 | 2327 | 2229 | 520,142 |
| Strategy | IS | HS | TIA | False negatives | False positives | Bleeds | Total QALYs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 11.620 | 2.123 | 8.407 | 1.606 | 0.000 | 23.572 | 447.895 |
| Kardia Mobile | 11.451 | 1.996 | 8.358 | 0.144 | 1.378 | 23.743 | 449.220 |
| imPulse | 11.482 | 2.018 | 8.365 | 0.396 | 3.660 | 23.721 | 448.956 |
| MyDiagnostick | 11.477 | 2.015 | 8.364 | 0.360 | 2.153 | 23.711 | 448.994 |
| Generic lead-I device | 11.451 | 1.996 | 8.358 | 0.147 | 1.507 | 23.744 | 449.217 |
| Zenicor-ECG | 11.457 | 2.000 | 8.360 | 0.192 | 1.722 | 23.738 | 449.170 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 11.529 | 2.054 | 8.376 | 0.793 | 1.292 | 23.620 | 448.540 |
Pairwise cost-effectiveness results from the base case 4 analysis for each index test compared with the standard diagnostic pathway are presented in Table 53 and the incremental analyses are shown in Table 54.
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 516,678 | 447.895 | |||
| Kardia Mobile | 517,315 | 449.220 | 3127 | 1.257 | 2487 |
| imPulse | 532,507 | 448.956 | 18,319 | 0.994 | 18,435 |
| MyDiagnostick | 522,985 | 448.994 | 8797 | 1.031 | 8532 |
| Generic lead-I device | 518,495 | 449.217 | 4307 | 1.255 | 3433 |
| Zenicor-ECG | 520,231 | 449.170 | 6043 | 1.207 | 5006 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 520,142 | 448.540 | 5955 | 0.577 | 10,314 |
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 516,678 | 447.895 | |||
| Kardia Mobile | 517,315 | 449.220 | 637 | 1.324 | £481 |
| Generic lead-I device | 518,495 | 449.217 | 1180 | –0.002 | Dominated |
| RhythmPad GPa | 520,142 | 448.540 | 2828 | –0.680 | Dominated |
| Zenicor-ECG | 520,231 | 449.170 | 2916 | –0.050 | Dominated |
| MyDiagnostick | 522,985 | 448.994 | 5670 | –0.226 | Dominated |
| imPulse | 532,507 | 448.956 | 15,192 | –0.264 | Dominated |
Appendix 13 Scenario analyses
Scenario A: unit cost associated with the lead-I electrocardiogram device
Incremental cost-effectiveness results from scenario A, which investigates the impact of removing the unit cost of the lead-I ECG device from the analysis (using 12-lead ECG in primary care, 2 days to 12-lead ECG), are presented in Table 55.
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 514,187 | 447.963 | |||
| Kardia Mobile | 515,535 | 449.249 | 1347 | 1.286 | £1047 |
| Generic lead-I device | 516,348 | 449.246 | 813 | –0.002 | Dominated |
| RhythmPad GPa | 517,336 | 448.573 | 1802 | –0.676 | Dominated |
| Zenicor-ECG | 517,854 | 449.199 | 2319 | –0.050 | Dominated |
| MyDiagnostick | 521,143 | 449.024 | 5608 | –0.225 | Dominated |
| imPulse | 530,657 | 448.987 | 15,123 | –0.262 | Dominated |
Scenario B: alternative sensitivity and specificity estimates for MyDiagnostick
Pairwise cost-effectiveness results from scenario B, which investigates the impact of using the sensitivity and specificity estimates based on the interpretation of the MyDiagnostick lead-I ECG trace by EP2 (using 12-lead ECG in primary care, 2 days to 12-lead ECG), are presented in Table 56.
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MyDiagnostick | 513,623 | 448.898 | |||
| Standard pathway | 514,187 | 447.963 | 565 | –0.9359 | Dominated |
| Kardia Mobile | 515,551 | 449.249 | 1928 | 0.3504 | £5503 |
| Generic lead-I device | 516,730 | 449.246 | 1179 | –0.0025 | Dominated |
| RhythmPad GPa | 518,436 | 448.573 | 2885 | –0.6759 | Dominated |
| Zenicor-ECG | 518,468 | 449.199 | 2917 | –0.0499 | Dominated |
| imPulse | 530,745 | 448.987 | 15,194 | –0.2620 | Dominated |
Scenario C: diagnosis without 12-lead electrocardiogram/Holter monitor
Incremental cost-effectiveness results from scenario C, which investigates the impact of removing the 12-lead ECG and Holter monitoring from the lead-I ECG diagnostic pathway (compared to using 12-lead ECG in primary care, 2 days to 12-lead ECG), are presented in Table 57.
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 514,187 | 447.963 | |||
| Kardia Mobile | 515,356 | 448.896 | 1169 | 0.9335 | £1252 |
| Generic lead-I device | 516,575 | 448.888 | 1218 | –0.0085 | Dominated |
| Zenicor-ECG | 519,081 | 448.726 | 3725 | –0.1697 | Dominated |
| MyDiagnostick | 524,667 | 448.131 | 9311 | –0.7647 | Dominated |
| RhythmPad GPa | 529,083 | 446.597 | 13,727 | –2.2991 | Dominated |
| imPulse | 534,767 | 448.004 | 19,411 | –0.8924 | Dominated |
Scenario D: 5-year time horizon
Incremental cost-effectiveness results from scenario D investigating a 5-year time horizon as a proxy for all undiagnosed patients being identified within 5 years (12-lead ECG in primary care, 2 days to 12-lead ECG) are presented in Table 58.
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 101,668 | 173.979 | |||
| Kardia Mobile | 102,543 | 174.550 | 876 | 0.5706 | £1534 |
| Generic lead-I device | 103,234 | 174.549 | 691 | –0.0011 | Dominated |
| Zenicor-ECG | 104,051 | 174.527 | 1508 | –0.0224 | Dominated |
| RhythmPad GPa | 104,073 | 174.247 | 1530 | –0.3028 | Dominated |
| MyDiagnostick | 104,774 | 174.449 | 2231 | –0.1008 | Dominated |
| imPulse | 108,573 | 174.432 | 6030 | –0.1175 | Dominated |
Scenario E1 to E40: varying proportion of patients sent for Holter testing after lead-I electrocardiogram and 12-lead electrocardiogram results
Incremental cost-effectiveness results from scenarios E1 to E40 exploring the uncertainty in the proportion of people sent for paroxysmal testing following a negative 12-lead ECG result are presented in Table 59. Given the complexity of the results, each scenario is shown for only the standard diagnostic pathway compared with Kardia Mobile (the lead-I ECG test was found to be the most cost-effective option in the base-case analyses) with 12-lead ECG undertaken in primary care and a 2-day wait for a 12-lead ECG.
| Scenario | Proportion of patients being referred for Holter monitoring after negative 12-lead ECG (%) | Model results | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-I pathway | Standard pathway | Standard pathway | Lead-I pathway | Incremental | ICER per QALY gained | |||||
| Lead-I ECG negative | Lead-I ECG positive | Costs (£) | QALYs | Costs (£) | QALYs | Costs (£) | QALYs | |||
| E1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 513,532 | 449.215 | –1924 | 1.959 | Dominates |
| E2 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 513,973 | 449.216 | –1482 | 1.959 | Dominates |
| E3 | 0 | 75 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 513,863 | 449.215 | –1593 | 1.959 | Dominates |
| E4 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 513,753 | 449.215 | –1703 | 1.959 | Dominates |
| E5 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 513,642 | 449.215 | –1813 | 1.959 | Dominates |
| E6 | 25 | 100 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 514,873 | 449.232 | –583 | 1.976 | Dominates |
| E7 | 25 | 75 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 514,762 | 449.232 | –693 | 1.976 | Dominates |
| E8 | 25 | 50 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 514,652 | 449.232 | –804 | 1.976 | Dominates |
| E9 | 25 | 25 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 514,541 | 449.232 | –914 | 1.976 | Dominates |
| E10 | 50 | 100 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 515,772 | 449.249 | 316 | 1.993 | £159 |
| E11 | 50 | 75 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 515,661 | 449.249 | 206 | 1.993 | £103 |
| E12 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 515,551 | 449.249 | 96 | 1.992 | £48 |
| E13 | 75 | 100 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 516,671 | 449.266 | 1215 | 2.010 | £605 |
| E14 | 75 | 75 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 516,561 | 449.266 | 1105 | 2.009 | £550 |
| E15 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 515,456 | 447.256 | 517,570 | 449.283 | 2114 | 2.026 | £1043 |
| E16 | 0 | 100 | 25 | 514,824 | 447.610 | 513,973 | 449.216 | –851 | 1.606 | Dominates |
| E17 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 514,824 | 447.610 | 513,863 | 449.215 | –961 | 1.606 | Dominates |
| E18 | 0 | 50 | 25 | 514,824 | 447.610 | 513,753 | 449.215 | –1071 | 1.606 | Dominates |
| E19 | 0 | 25 | 25 | 514,824 | 447.610 | 513,642 | 449.215 | –1182 | 1.606 | Dominates |
| E20 | 0 | 100 | 50 | 514,187 | 447.963 | 513,973 | 449.216 | –214 | 1.253 | Dominates |
| E21 | 0 | 75 | 50 | 514,187 | 447.963 | 513,863 | 449.215 | –324 | 1.253 | Dominates |
| E22 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 514,187 | 447.963 | 513,753 | 449.215 | –435 | 1.253 | Dominates |
| E23 | 0 | 100 | 75 | 513,545 | 448.315 | 513,973 | 449.216 | 428 | 0.901 | £476 |
| E24 | 0 | 75 | 75 | 513,545 | 448.315 | 513,863 | 449.215 | 318 | 0.900 | £353 |
| E25 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 512,895 | 448.667 | 513,973 | 449.216 | 1078 | 0.549 | £1966 |
| E26 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 514,824 | 447.610 | 514,541 | 449.232 | –282 | 1.622 | Dominates |
| E27 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 514,187 | 447.963 | 515,551 | 449.249 | 1364 | 1.286 | £1060 |
| E28 | 50 | 50 | 25 | 514,824 | 447.610 | 515,551 | 449.249 | 727 | 1.639 | £444 |
| E29 | 75 | 75 | 25 | 514,824 | 447.610 | 516,561 | 449.266 | 1737 | 1.656 | £1049 |
| E30 | 75 | 75 | 50 | 514,187 | 447.963 | 516,561 | 449.266 | 2373 | 1.303 | £1821 |
| E31 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 513,545 | 448.315 | 516,561 | 449.266 | 3016 | 0.951 | £3172 |
| E32 | 100 | 100 | 25 | 514,824 | 447.610 | 517,570 | 449.283 | 2746 | 1.673 | £1641 |
| E33 | 100 | 100 | 50 | 514,187 | 447.963 | 517,570 | 449.283 | 3383 | 1.320 | £2562 |
| E34 | 100 | 100 | 75 | 513,545 | 448.315 | 517,570 | 449.283 | 4025 | 0.968 | £4159 |
| E35 | 25 | 50 | 50 | 514,187 | 447.963 | 514,652 | 449.232 | 464 | 1.270 | £366 |
| E36 | 50 | 50 | 75 | 513,545 | 448.315 | 515,551 | 449.249 | 2006 | 0.934 | £2148 |
| E37 | 25 | 75 | 75 | 513,545 | 448.315 | 514,762 | 449.232 | 1217 | 0.917 | £1327 |
| E38 | 25 | 75 | 75 | 513,545 | 448.315 | 514,762 | 449.232 | 1217 | 0.917 | £1327 |
| E39 | 50 | 75 | 75 | 513,545 | 448.315 | 515,661 | 449.249 | 2116 | 0.934 | £2266 |
| E40 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 512,895 | 448.667 | 517,570 | 449.283 | 4675 | 0.616 | £7594 |
Scenario F: cost of a smartphone or tablet added to the cost of the Kardia Mobile device
In order to perform a lead-I ECG with the Kardia Mobile device, it is necessary to connect the device to a smartphone or tablet. The EAG assumed in the base case that a GP would already have access to a smartphone or tablet that could be used alongside the Kardia Mobile device and would incur no extra cost. The cost of a supplementary smartphone or tablet for use alongside the Kardia Mobile device was investigated in a scenario analysis.
The cost of purchasing a smartphone or tablet varies substantially depending on the type of device, meaning that any estimate of the cost of such a device may not reflect reality for some or any GP practices. The EAG considered it would be justified to perform a threshold analysis to estimate the level at which the extra cost of a supplementary smartphone or tablet would result in Kardia Mobile no longer dominating the other lead-I ECG devices or generating an ICER of £20,000 per QALY gained compared with the standard pathway. The estimated minimum cost of a supplementary smartphone or tablet for Kardia Mobile to no longer dominate ranged from £2885 compared with RhythmPad to £15,194 compared with the imPulse device. Provided a supplementary smartphone or tablet costs < £24,362, then the ICER per QALY gained for Kardia Mobile compared with the standard pathway would be < £20,000.
The results of the threshold analysis from scenario F, which calculated the minimum cost of a supplementary smartphone or tablet device that would result in Kardia Mobile no longer being dominant over each of the alternative strategies (using 12-lead ECG in primary care, 2 days to 12-lead ECG) are presented in Table 60.
| Strategy | Minimum cost per supplementary device (£) |
|---|---|
| Kardia Mobile ICER per QALY gained = £20,000 | |
| Standard pathway | 24,362 |
| Kardia Mobile non-dominant ICER per QALY gained | |
| RhythmPad GPa | 2885 |
| Zenicor-ECG | 2917 |
| MyDiagnostick | 5682 |
| imPulse | 15,194 |
Scenario G: extending the lifespan of the RhythmPad GP device from 1 year to 3 years
The manufacturer of the RhythmPad GP device advised that the minimum projected life of the device was 1 year, with the potential for it to last up to 3 years. Changing the lifespan of the RhythmPad GP device from 1 year to 3 years reduces total costs; however, the RhythmPad GP device remains dominated by the Kardia Mobile device.
Incremental cost-effectiveness results from scenario G, which investigates the impact of extending the lifespan of the Rhythmpad GP device from 1 year to 3 years (using 12-lead ECG in primary care, 2 days to 12-lead ECG) are presented in Table 61.
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 514,187 | 447.963 | |||
| Kardia Mobile | 515,551 | 449.249 | 1364 | 1.2863 | £1060 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 517,703 | 448.573 | 2152 | –0.6759 | Dominated |
| Zenicor-ECG | 518,468 | 449.199 | 2917 | –0.0499 | Dominated |
| MyDiagnostick | 521,233 | 449.024 | 5682 | –0.2249 | Dominated |
| imPulse | 530,745 | 448.987 | 15,194 | –0.262 | Dominated |
Scenario H: including a quality-adjusted life-year decrement for bleeds
In the base-case analysis, no disutility value for bleeds was assumed because robust estimates on utility of bleeds could not be identified in the literature. As these are rare events of short duration, the impact on QALYs was expected to be minor. To test the impact of the assumption of no QALY loss for bleeds, a value for utility loss and duration of bleed was taken from the apixaban technology appraisal. Here the company used a disutility value for major bleeds of 0.1070 from a standard gamble exercise of patients with AF, valuing different health outcomes and AEs that could hypothetically occur while taking anticoagulation treatment. The company in the apixaban appraisal assumed that major bleeds would last for 14 days; this was a company assumption and no justification was provided. Applying the duration of the bleed to the utility loss and assuming all bleeds are major, means each bleed results in a 0.004 QALY loss. The impact of introducing a disutility value for bleeds in the model (using 12-lead ECG in primary care, 2 days to 12-lead ECG) are presented in Table 62. As can be seen, although the standard pathway and lead-I devices all lose QALYs as expected, because the total lifetime number of bleeds for the cohort of patients in the model was only 0.017 higher with Kardia Mobile compared with the standard pathway and the QALY loss from bleeds was so small, the impact on incremental QALYs was almost zero; therefore, the introduction of a disutility value for bleeds did not affect the ICER per QALY gained.
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 514,187 | 447.901 | |||
| Kardia Mobile | 515,551 | 449.187 | 1364 | 1.286 | £1060 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 518,436 | 448.511 | 2885 | –0.676 | Dominated |
| Zenicor-ECG | 518,468 | 449.137 | 2917 | –0.050 | Dominated |
| MyDiagnostick | 521,233 | 448.962 | 5682 | –0.225 | Dominated |
| imPulse | 530,745 | 448.925 | 15,194 | –0.262 | Dominated |
Scenario I: using alternative sensitivity and specificity estimates for Kardia Mobile from the pooled analysis with interpretation of the trace by EP2
Incremental deterministic cost-effectiveness results from scenario I, which investigates the impact of using the sensitivity and specificity estimates based on interpretation of the Kardia Mobile lead-I ECG trace by EP2 (using 12-lead ECG in primary care, 2 days to 12-lead ECG) are presented in Table 63. Incremental probabilistic cost-effectiveness results from scenario I are presented in Table 64. The CEAC for scenario I is presented in Figure 27.
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kardia Mobile | 514,177 | 449.181 | |||
| Standard pathway | 514,187 | 447.963 | 10 | –1.219 | Dominated |
| RhythmPad GPa | 518,436 | 448.573 | 4259 | –0.608 | Dominated |
| Zenicor-ECG | 518,468 | 449.199 | 4290 | 0.018 | £242,994 |
| MyDiagnostick | 521,233 | 449.024 | 2765 | –0.175 | Dominated |
| imPulse | 530,745 | 448.987 | 12,277 | –0.212 | Dominated |
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kardia Mobile | 521,903 | 455.16065 | |||
| Standard pathway | 522,204 | 453.96612 | 301 | –1.1945 | Dominated |
| RhythmPad GPa | 526,453 | 454.56963 | 1798 | –0.5910 | Dominated |
| Zenicor | 526,518 | 455.17774 | 1864 | 0.0171 | £109,012 |
| MyDiagnostick | 529,316 | 455.00675 | 4661 | –0.1710 | Dominated |
| imPulse | 538,857 | 454.97117 | 14,203 | –0.2066 | Dominated |
FIGURE 27.
The CEAC for scenario I: all lead-I devices
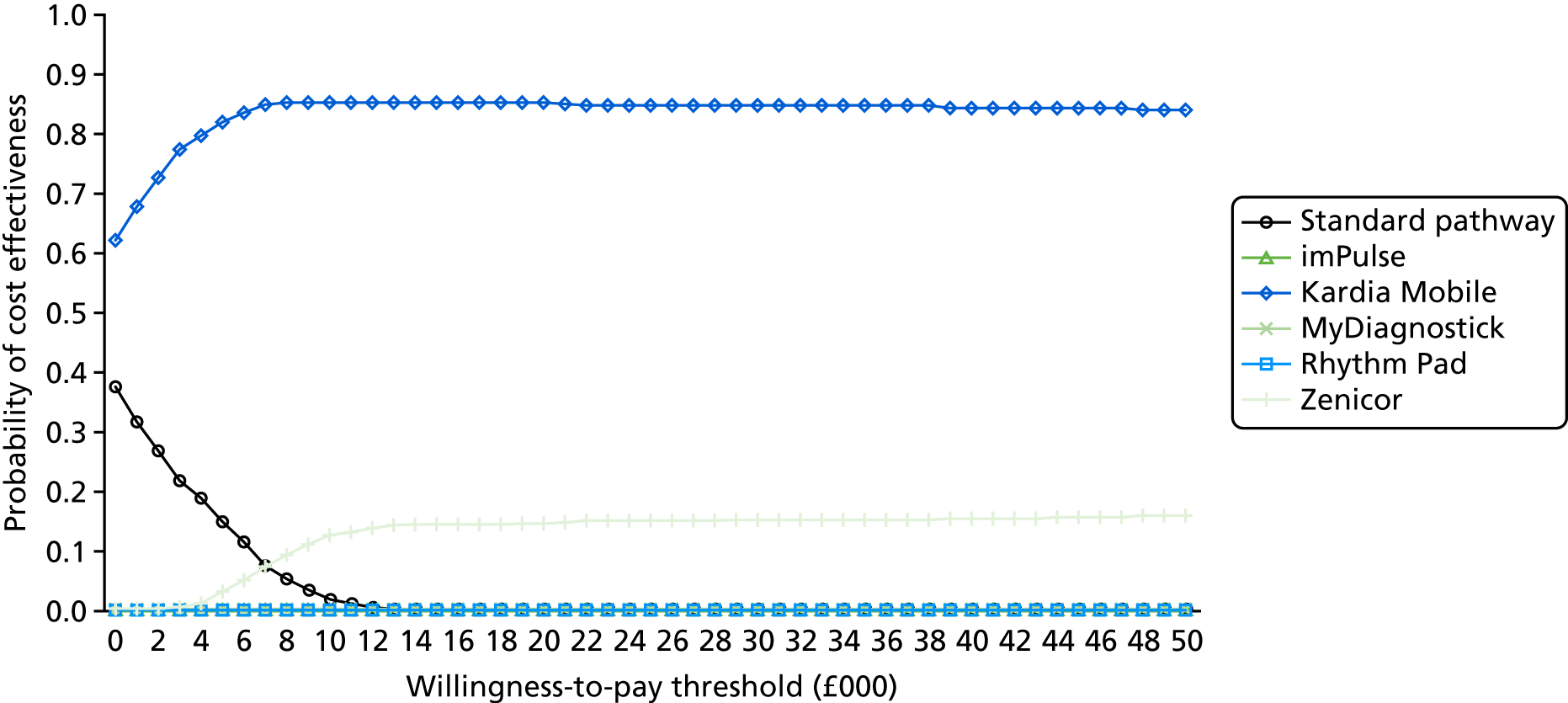
Scenario J: assuming that the rates of haemorrhagic stroke for people treated with NOACs who do not have atrial fibrillation are the same as the rates of haemorrhagic stroke for people treated with NOACs who have atrial fibrillation
Incremental cost-effectiveness results from scenario J, which investigates the impact of assuming that the rates of HS for people treated with NOACs who do not have AF are the same as the rates of HS for people treated with NOACs who have AF (using 12-lead ECG in primary care, 2 days to 12-lead ECG) are presented in Table 65.
| Strategy | Costs (£) | QALYs | Incremental costs (£) | Incremental QALYs | ICER/QALY gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard pathway | 514,187 | 447.963 | |||
| Kardia Mobile | 516,109 | 448.697 | 1922 | 0.734 | £2618 |
| RhythmPad GPa | 518,957 | 448.055 | 2848 | –0.642 | Dominated |
| Zenicor-ECG | 519,177 | 448.511 | 3068 | –0.186 | Dominated |
| MyDiagnostick | 522,133 | 448.166 | 6023 | –0.530 | Dominated |
| imPulse | 532,320 | 447.537 | 16,211 | –1.159 | Dominated |
Appendix 14 Deterministic sensitivity analysis: tornado diagrams
FIGURE 28.
Tornado diagram: base case 1, imPulse.

FIGURE 29.
Tornado diagram: base case 1, Kardia Mobile.

FIGURE 30.
Tornado diagram: base case 1, MyDiagnostick.

FIGURE 31.
Tornado diagram: base case 1, RhythmPad GP.
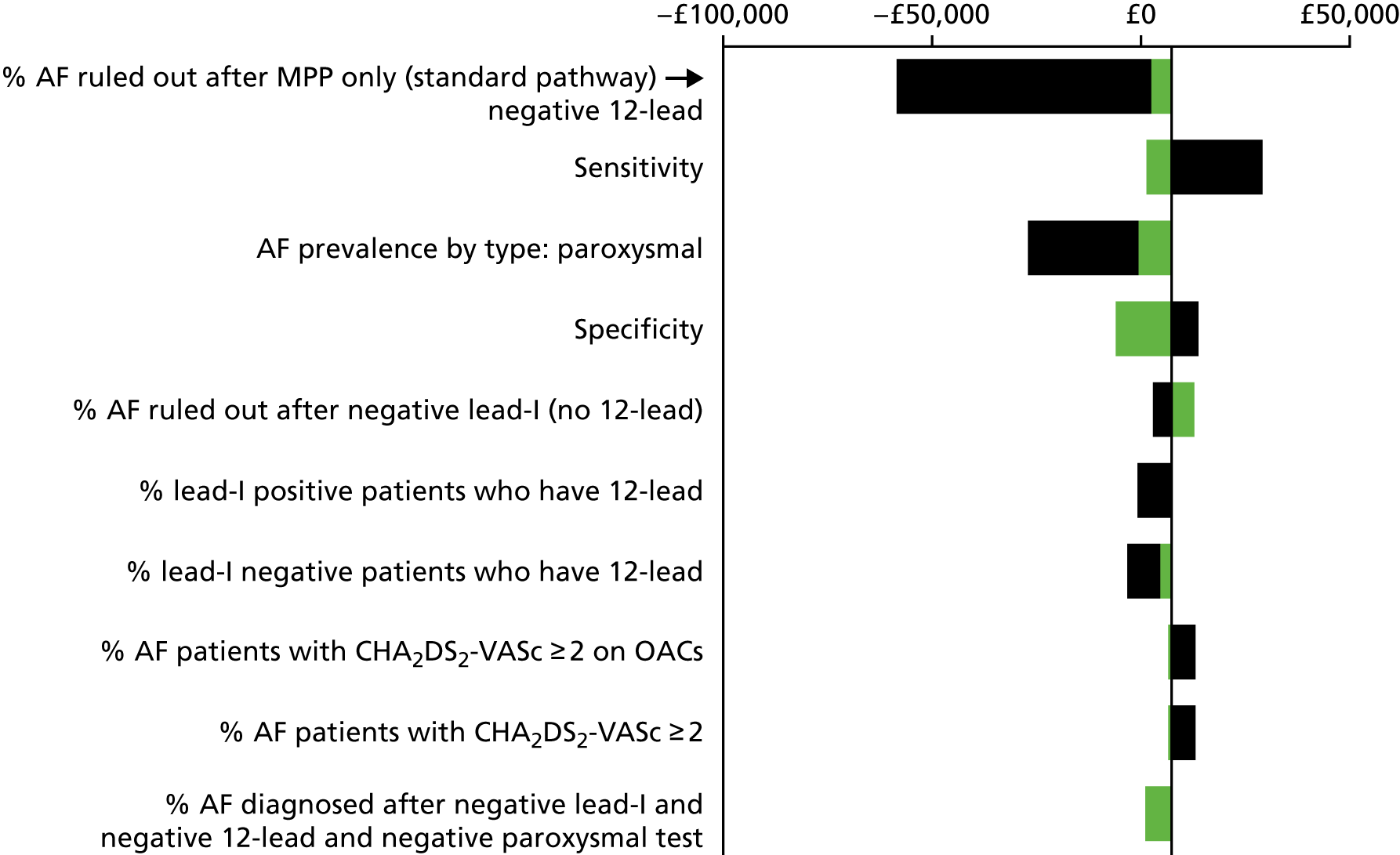
FIGURE 32.
Tornado diagram: base case 1, Zenicor ECG.
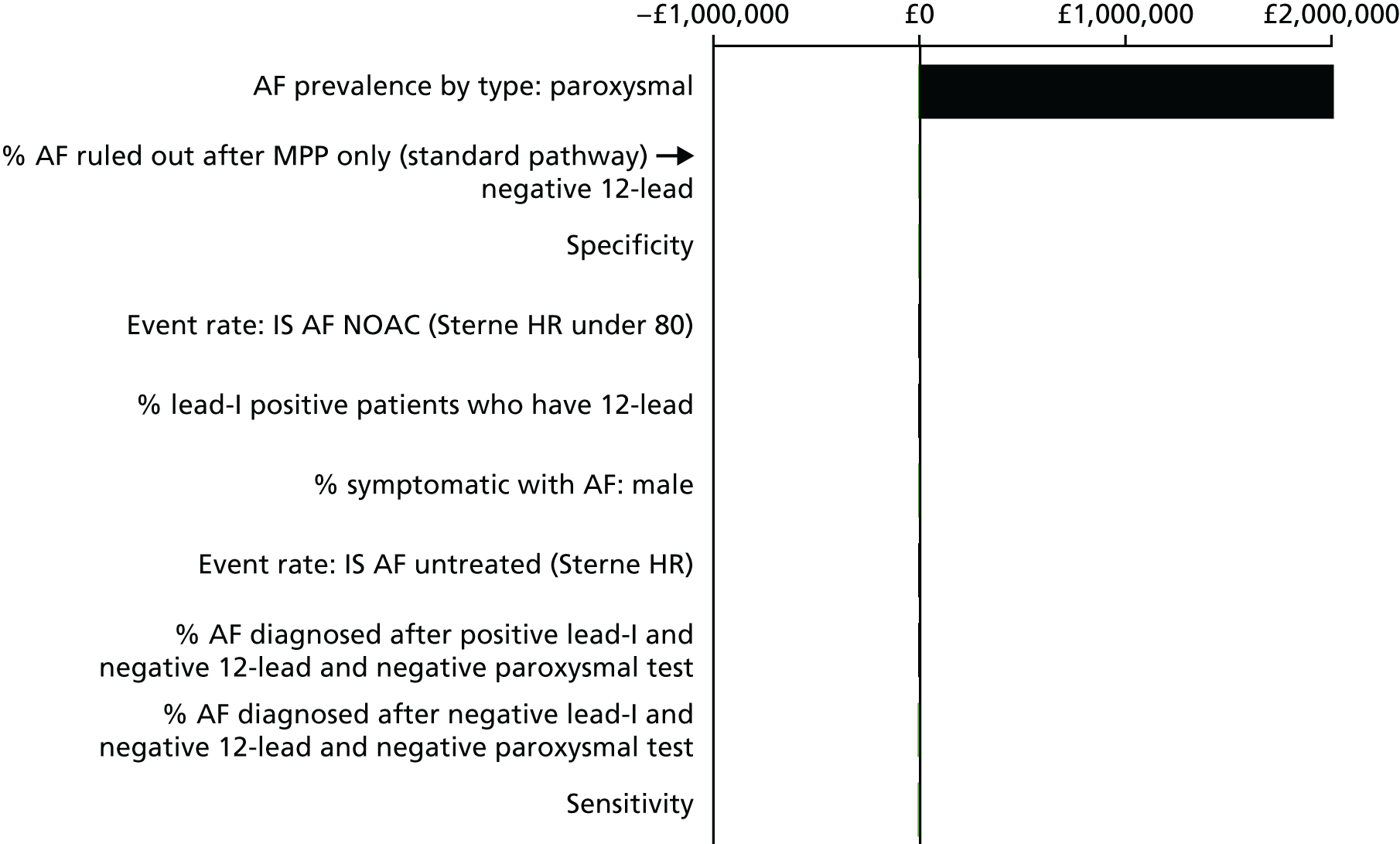
FIGURE 33.
Tornado diagram: base case 1, Generic lead-I device.
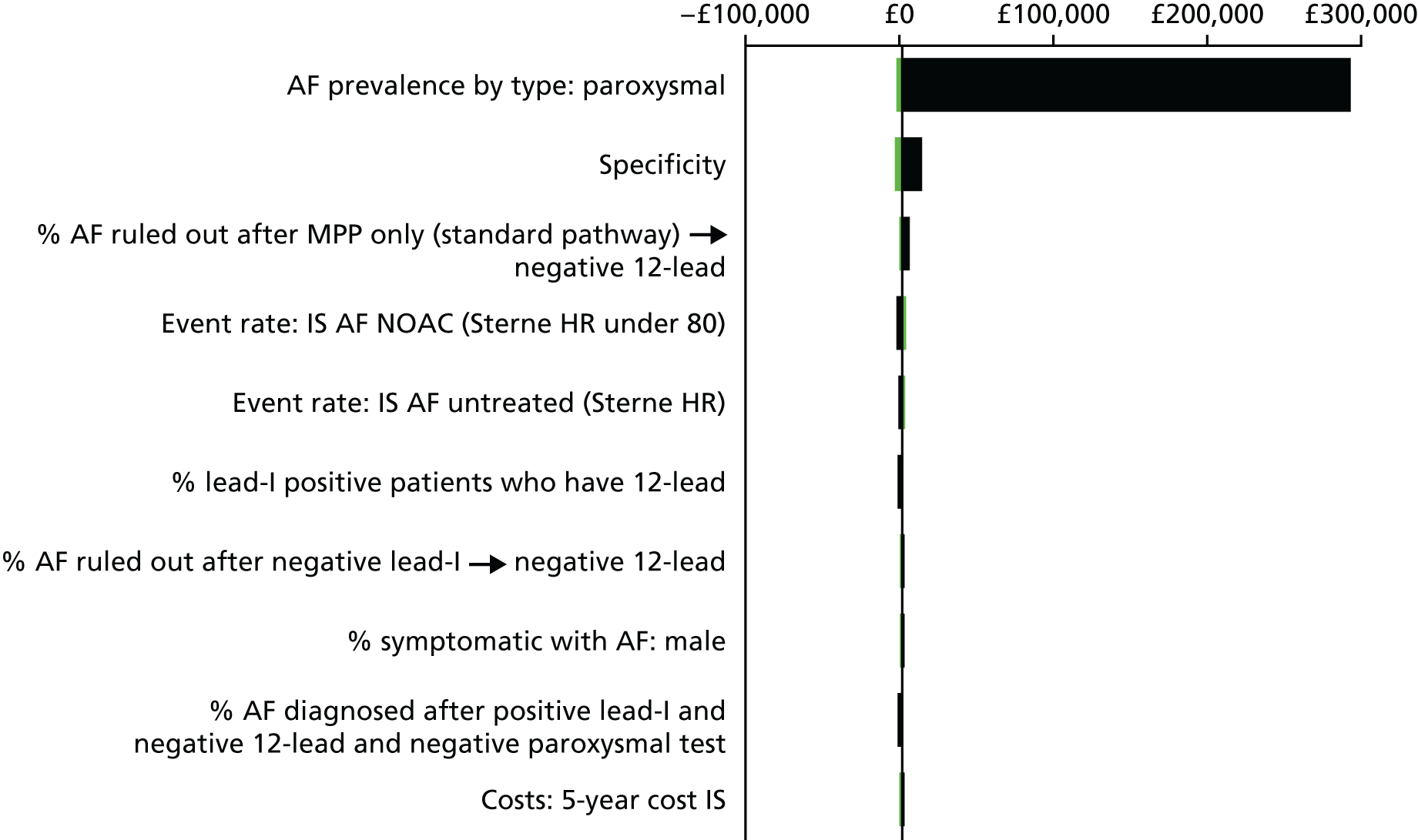
Appendix 15 Probabilistic sensitivity analysis: cost-effectiveness acceptability curves
FIGURE 34.
The CEAC for base case 1: imPulse.
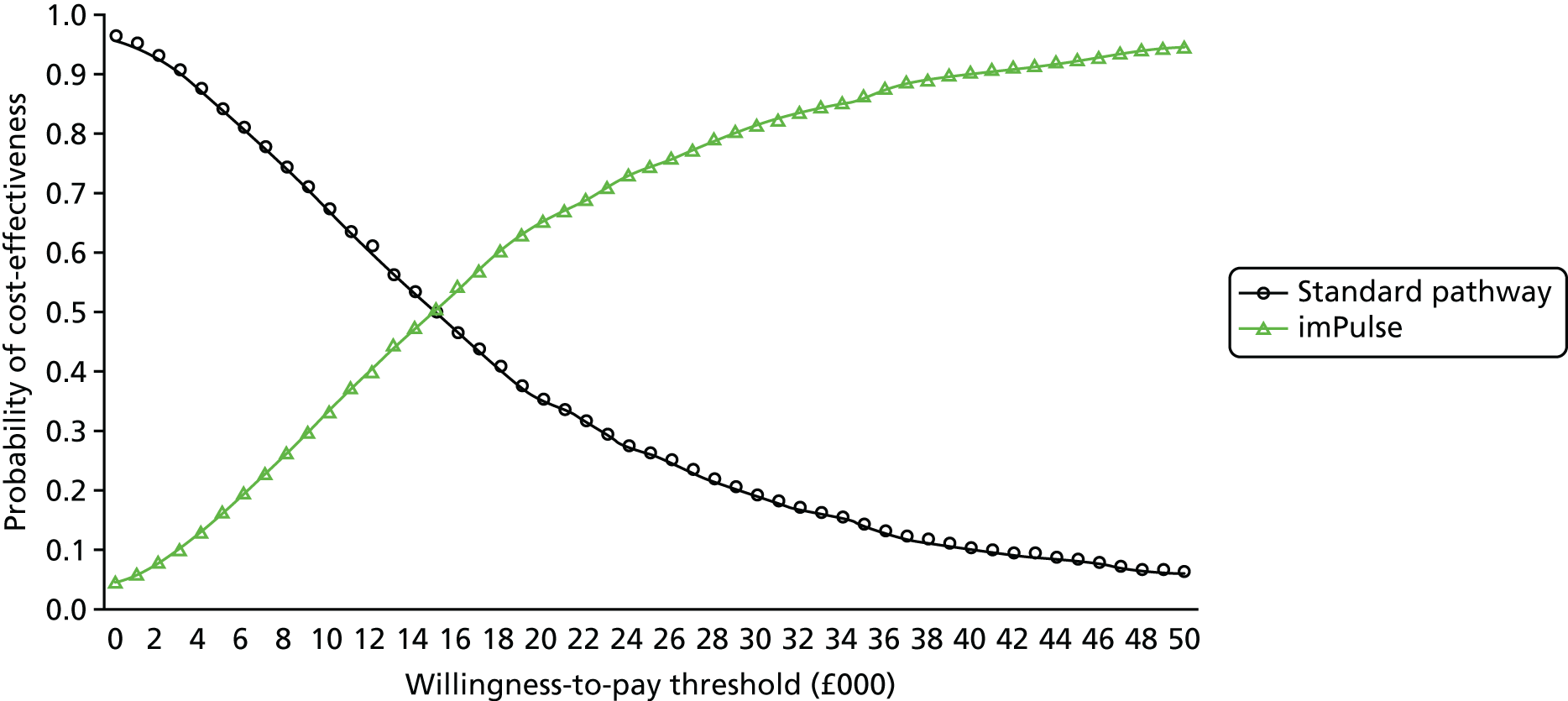
FIGURE 35.
The CEAC for base case 1: Kardia Mobile.
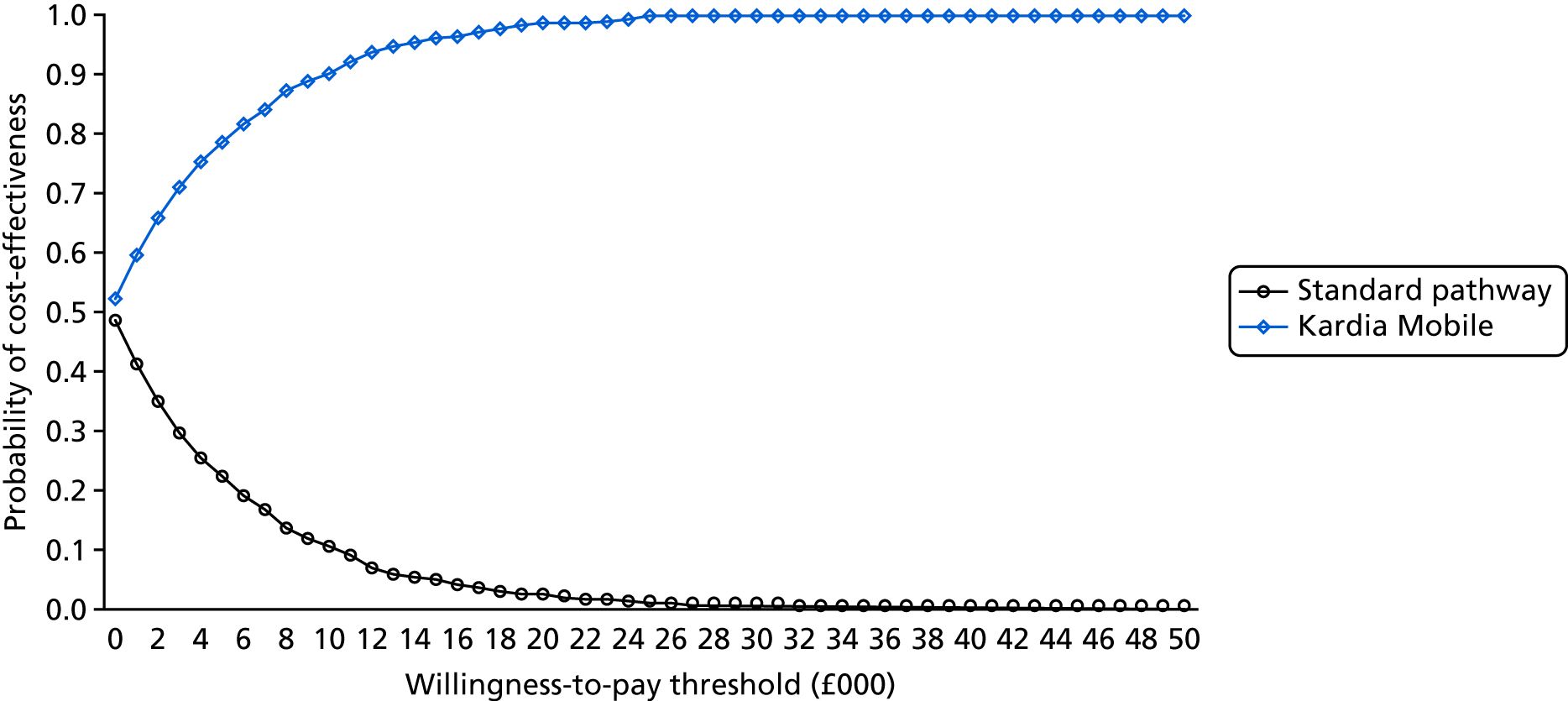
FIGURE 36.
The CEAC for base case 1: MyDiagnostick.
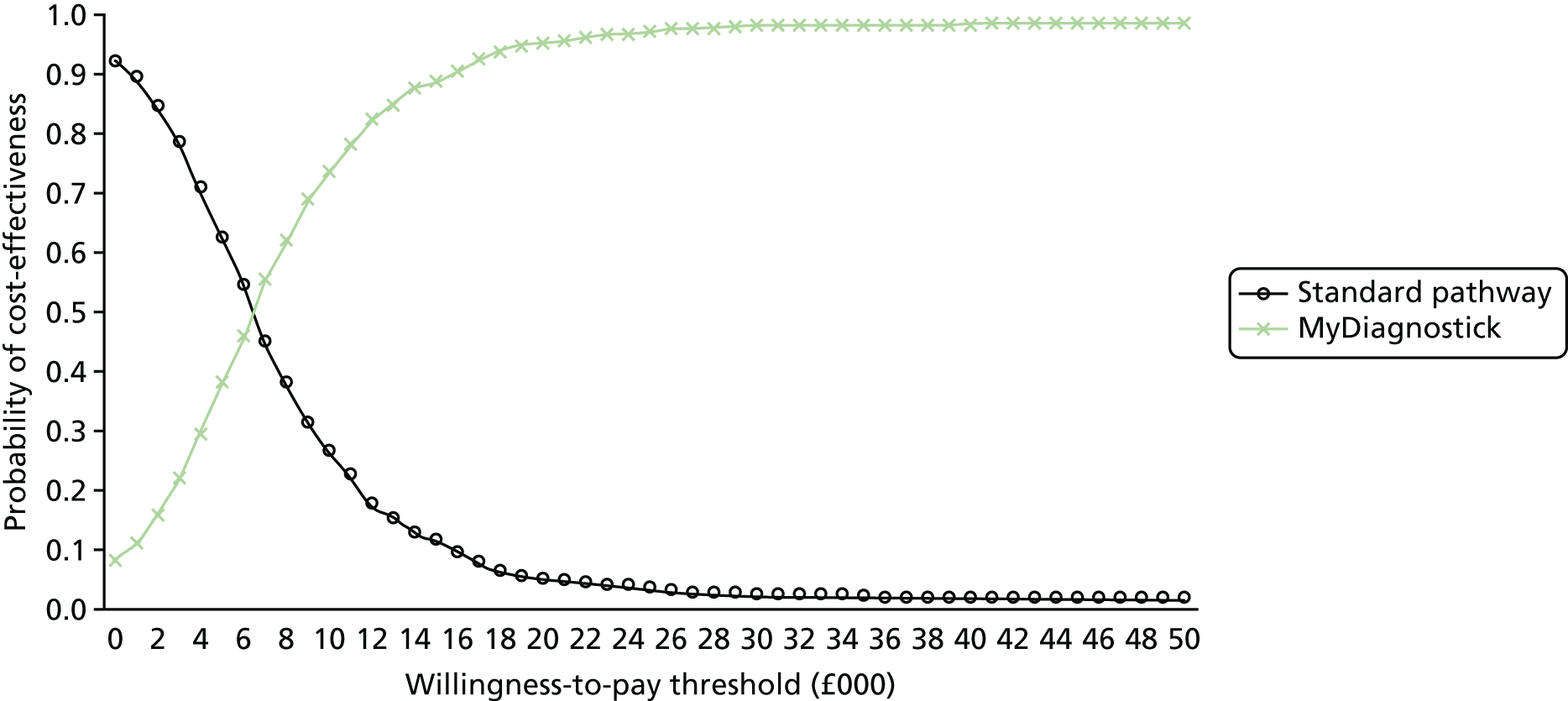
FIGURE 37.
The CEAC for base case 1: RhythmPad GP.
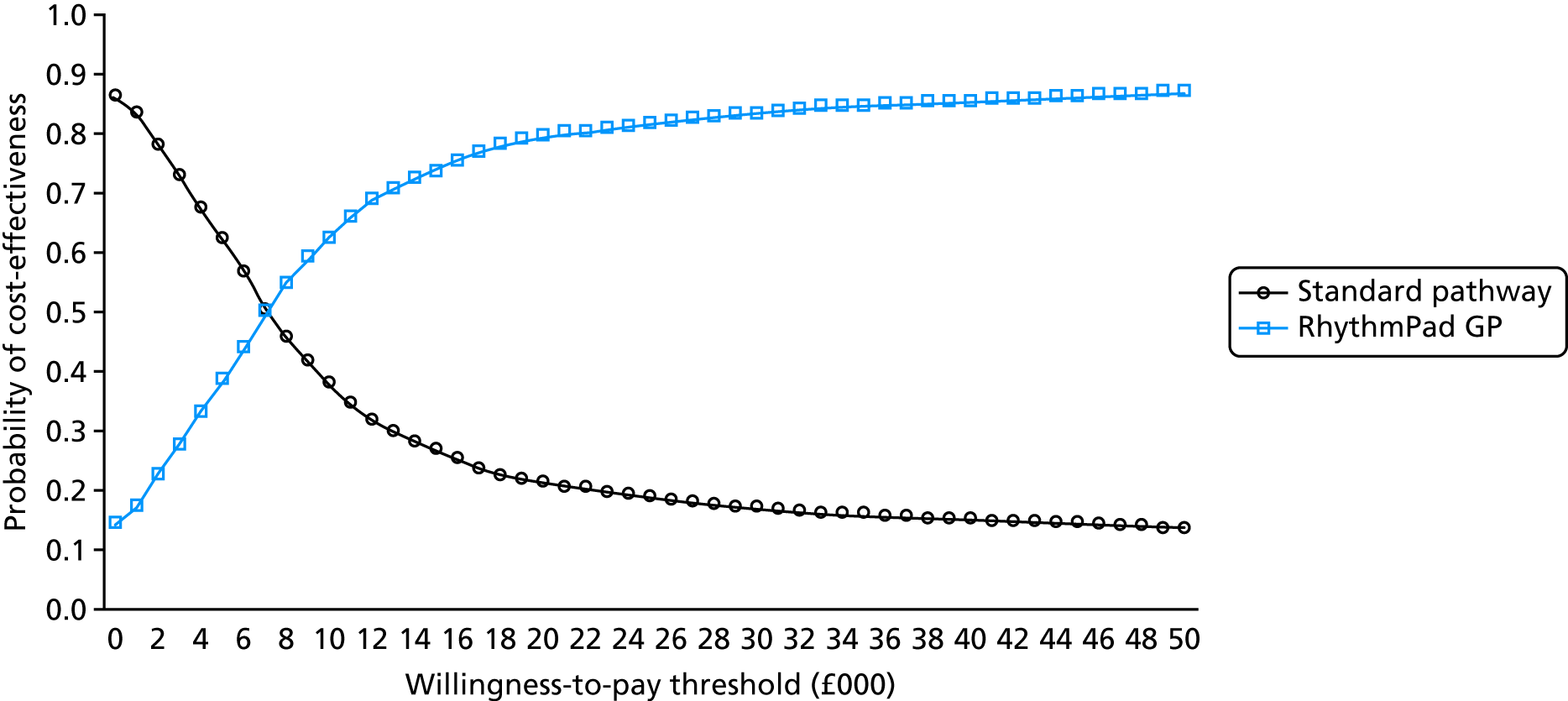
FIGURE 38.
The CEAC for base case 1: Zenicor ECG.
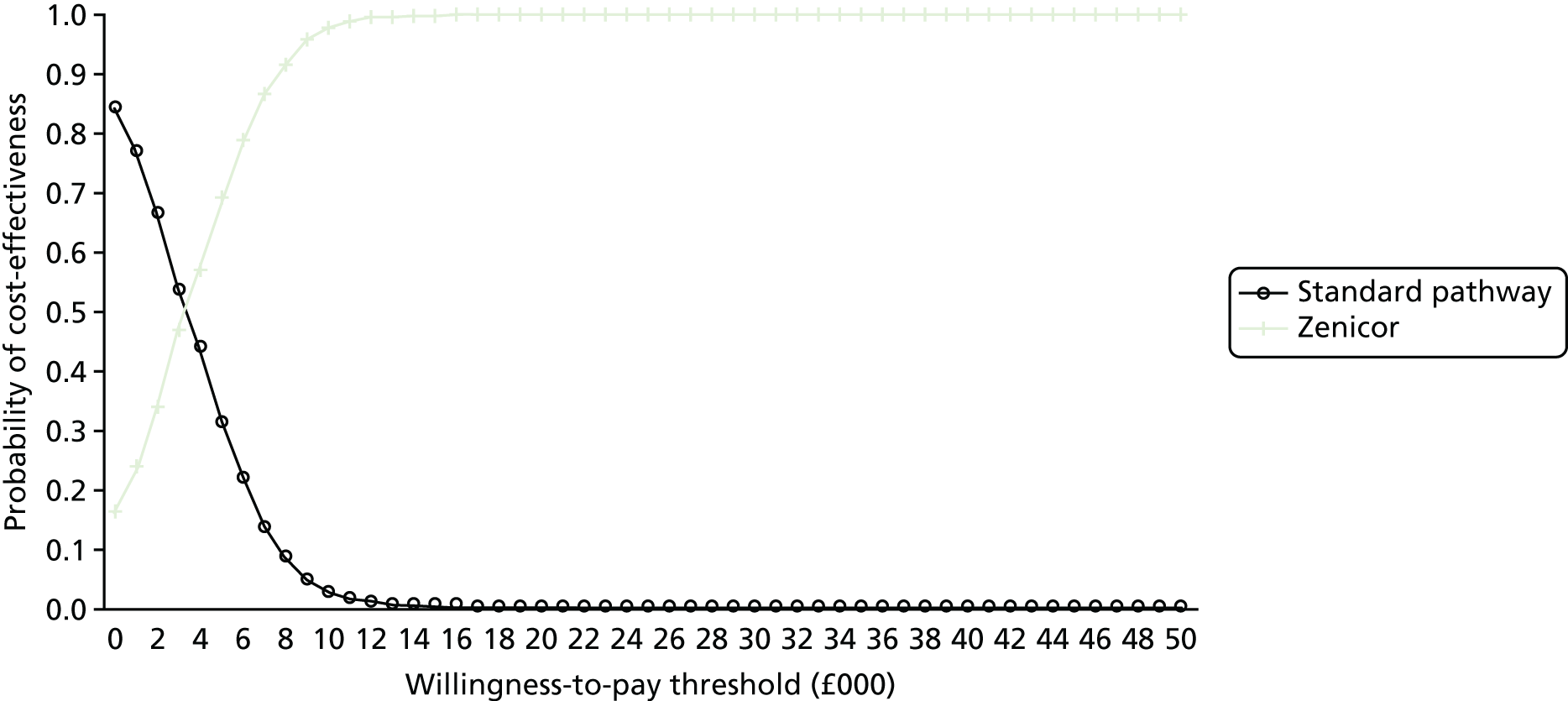
FIGURE 39.
The CEAC for base case 1: generic lead-I ECG device.
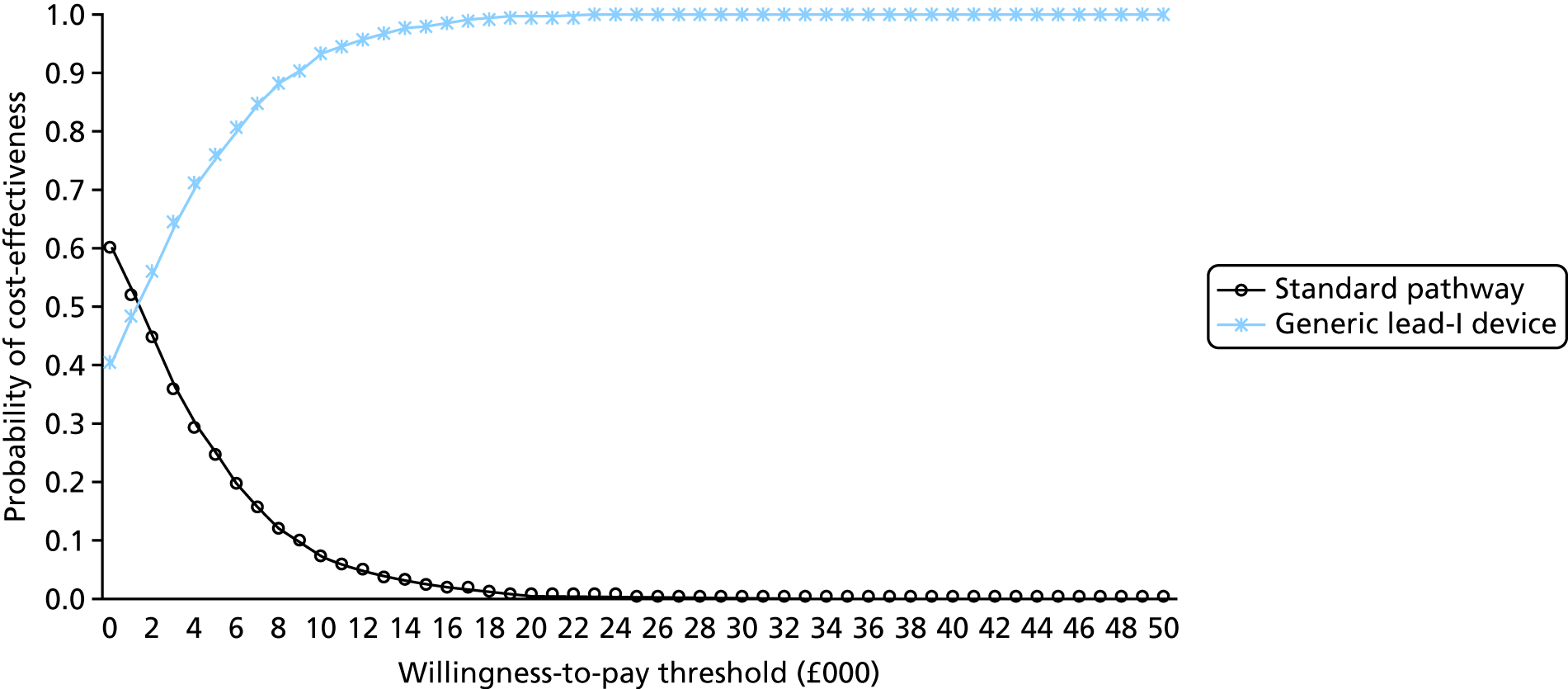
Appendix 16 Parameters for probability sensitivity analysis
| Description | Mean value | LB | UB | SD | Alpha | Beta | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event rate: bleeds | |||||||
| HR compared with Warfarin: AF treated with NOACs > 80 years (Sterne 201785) | 0.630 | 0.473 | 0.788 | 0.155 | Log-normal | ||
| HR compared with Warfarin: AF treated with NOACs ≤ 80 years (Sterne 201785) | 0.820 | 0.615 | 1.025 | 0.155 | Log-normal | ||
| HR compared with Warfarin: AF untreated (Sterne, 201785) | 0.543 | 0.511 | 0.575 | 0.036 | Log-normal | ||
| AF treated with Warfarin (Sterne, 201785) | 0.066 | 0.050 | 0.083 | 0.008 | 59.710 | 844.987 | Beta |
| No AF untreated (NHS Reference Costs98) | 0.011 | 0.008 | 0.014 | 0.001 | 63.270 | 5573.516 | Beta |
| Event rate: ICH | |||||||
| HR compared with Warfarin: AF treated with NOACs > 80 years (Sterne, 201785) | 2.780 | 2.085 | 3.475 | 0.155 | Log-normal | ||
| HR compared with Warfarin: AF treated with NOACs ≤ 80 years (Sterne, 201785) | 0.460 | 0.345 | 0.575 | 0.155 | Log-normal | ||
| AF treated with Warfarin (Sterne, 201785) | 0.009 | 0.007 | 0.012 | 0.001 | 63.389 | 6680.122 | Beta |
| HR compared with Warfarin:AF untreated (Sterne, 201785) | 2.777 | 3.113 | 2.509 | 0.066 | Log-normal | ||
| No AF untreated (NHS Reference Costs98) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 63.979 | 195,185.287 | Beta |
| AF untreated, female 50 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 0.022 | 0.017 | 0.028 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, female 60 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 0.189 | 0.142 | 0.236 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, female 70 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 0.343 | 0.257 | 0.428 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, female 80 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 1.003 | 0.752 | 1.254 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, female 90 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 1.041 | 0.781 | 1.302 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 50 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 0.022 | 0.017 | 0.028 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 60 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 0.189 | 0.142 | 0.236 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 70 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 0.261 | 0.196 | 0.327 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 80 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 1.706 | 1.279 | 2.132 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 90 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 0.778 | 0.583 | 0.972 | Binomial | |||
| Event rate: IS | |||||||
| HR compared with Warfarin:AF treated with NOACs > 80 years (Sterne, 201785) | 0.740 | 0.555 | 0.925 | 0.155 | Log-normal | ||
| HR compared with Warfarin: AF treated with NOACs ≤ 80 years (Sterne, 201785) | 0.900 | 0.675 | 1.125 | 0.155 | Log-normal | ||
| HR compared with Warfarin: AF untreated (Sterne, 201785) | 2.777 | 3.113 | 2.509 | 0.066 | Log-normal | ||
| AF untreated, female 50 years (PHE, 201888) | 0.729 | 0.546 | 0.911 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, female 60 years (PHE, 201888) | 1.347 | 1.010 | 1.683 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, female 70 years (PHE, 201888) | 2.968 | 2.226 | 3.710 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, female 80 years (PHE, 201888) | 6.044 | 4.533 | 7.555 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, female 90 years (PHE, 201888) | 10.770 | 8.077 | 13.462 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 50 years (PHE, 201888) | 1.246 | 0.935 | 1.558 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 60 years (PHE, 201888) | 2.285 | 1.714 | 2.856 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 70 years (PHE, 201888) | 4.423 | 3.317 | 5.529 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 80 years (PHE, 201888) | 6.400 | 4.800 | 8.000 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 90 years (PHE, 201888) | 9.897 | 7.422 | 12.371 | Binomial | |||
| Event rate: TIA | |||||||
| HR compared with Warfarin: AF treated with NOACs > 80 years (Sterne, 201785) | 0.760 | 0.570 | 0.950 | 0.155 | Log-normal | ||
| HR compared with Warfarin: AF treated with NOACs ≤ 80 years (Sterne, 201785) | 0.740 | 0.555 | 0.925 | 0.155 | Log-normal | ||
| HR compared with Warfarin: AF untreated (Sterne, 201785) | 1.617 | 1.935 | 1.434 | 0.091 | Log-normal | ||
| AF untreated, female 50 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 0.287 | 0.215 | 0.359 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, female 60 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 1.098 | 0.824 | 1.373 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, female 70 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 2.213 | 1.660 | 2.766 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, female 80 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 5.706 | 4.279 | 7.132 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, female 90 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 9.321 | 6.991 | 11.651 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 50 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 0.165 | 0.124 | 0.207 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 60 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 0.549 | 0.412 | 0.687 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 70 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 1.359 | 1.019 | 1.699 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 80 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 3.389 | 2.542 | 4.236 | Binomial | |||
| AF untreated, male 90 years (Rothwell, 200590) | 8.041 | 6.031 | 10.051 | Binomial | |||
| Event rate: stroke | |||||||
| AF treated with Warfarin (Sterne, 201785) | 0.012 | 0.009 | 0.015 | 0.002 | 63.220 | 5205.113 | Beta |
| AF untreated, female 65 years (Lowres, 201461) | 0.026 | 0.019 | 0.032 | 0.003 | 62.317 | 2343.726 | Beta |
| AF untreated, female 75 years (Lowres, 201461) | 0.050 | 0.038 | 0.063 | 0.006 | 60.737 | 1149.163 | Beta |
| AF untreated, male 65 years (Lowres, 201461) | 0.019 | 0.014 | 0.024 | 0.002 | 62.746 | 3188.317 | Beta |
| AF untreated, male 75 years (Lowres, 201461) | 0.050 | 0.038 | 0.063 | 0.006 | 60.737 | 1149.163 | Beta |
| Characteristics | |||||||
| Proportion of patients contraindicated for lead-I device use (%) | 0.060 | 0.045 | 0.075 | 0.008 | 60.100 | 941.567 | Beta |
| Cycle length | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | Fixed | |||
| Discount costs | 0.035 | 0.000 | 0.060 | Fixed | |||
| Discount benefits | 0.035 | 0.000 | 0.060 | Fixed | |||
| Include cost of extra anticoagulation discussion? | No | Yes | Yes | Fixed | |||
| Include cost of 12-lead device? | Yes | No | Yes | Fixed | |||
| Include cost of 12-lead test? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Fixed | |||
| Include cost of lead-I device | Yes | No | Yes | Fixed | |||
| Include dispensing cost? | Yes | No | Yes | Fixed | |||
| Use different NOAC dose and event rate for > 80 years? | No | No | Yes | Fixed | |||
| Number of lead-I ECG devices per practice | 1.000 | 0.170 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| Proportion of 12-lead ECGs interpreted by: cardiologist | 0.100 | 0.000 | 0.200 | 0.050 | 3.500 | 31.500 | Beta |
| Proportion of symptoms: angina pectoris symptoms | 0.287 | 0.215 | 0.359 | 0.036 | 45.351 | 112.719 | Beta |
| Proportion of symptoms: shortness of breath | 0.618 | 0.463 | 0.772 | 0.077 | 23.846 | 14.755 | Beta |
| Proportion of symptoms: congestive heart failure | 0.287 | 0.215 | 0.359 | 0.036 | 45.351 | 112.719 | Beta |
| Proportion of symptoms: fatigue | 0.704 | 0.528 | 0.881 | 0.088 | 18.213 | 7.643 | Beta |
| Proportion of lead-I tests interpreted by: cardiologist | 0.100 | 0.000 | 0.200 | 0.050 | 3.500 | 31.500 | Beta |
| AF prevalence by type: paroxysmal | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| Proportion of lead-I negative or standard pathway patients given rate control (%) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | Uniform | |||
| Cost per use: 12-lead | 3.377 | 2.533 | 4.221 | 0.138 | Log-normal | ||
| Sensitivity: algorithm | #N/A | #N/A | #N/A | #N/A | #N/A | #N/A | Beta |
| Sensitivity | 0.939 | 0.862 | 0.974 | 0.028 | 67.664 | 4.396 | Beta |
| Specificity: algorithm | #N/A | #N/A | #N/A | #N/A | #N/A | #N/A | Beta |
| Specificity | 0.965 | 0.904 | 0.988 | 0.021 | 72.942 | 2.646 | Beta |
| Proportion female (%) | 0.516 | 0.258 | 0.775 | 0.129 | 7.221 | 6.761 | Beta |
| Proportion of symptoms: Other symptoms | 0.517 | 0.388 | 0.647 | 0.065 | 30.374 | 28.340 | Beta |
| Mean GPs per practice | 5.898 | 5.805 | 5.991 | Fixed | |||
| Mean GP list size | 8187.121 | 1591.795 | 1630.954 | Fixed | |||
| Proportion of untreated lead-I positive patients given rate control (%) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| Utility: symptom decrements | |||||||
| Bleed | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | Log-normal | |||
| HS | 0.272 | 0.345 | 0.198 | 0.169 | Log-normal | ||
| IS | 0.272 | 0.345 | 0.198 | 0.169 | Log-normal | ||
| TIA | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | Log-normal | |||
| Costs | |||||||
| Bleed | 704.049 | 592.435 | 782.475 | 0.085 | Log-normal | ||
| TIA | 729.616 | 570.081 | 837.648 | 0.117 | Log-normal | ||
| IS: 1-year cost | 15,387.635 | 11,540.727 | 17,695.781 | 0.130 | Log-normal | ||
| IS: 5-year cost | 31,315.530 | 23,486.647 | 36,012.859 | 0.130 | Log-normal | ||
| HS: 1-year cost | 17,833.307 | 13,374.980 | 20,508.303 | 0.130 | Log-normal | ||
| HS: 5-year cost | 37,907.660 | 28,430.745 | 43,593.809 | 0.130 | Log-normal | ||
| AF occurrence | |||||||
| AF prevalence: female (%) | 0.034 | 0.026 | 0.043 | 0.004 | 61.774 | 1741.839 | Beta |
| AF prevalence: male (%) | 0.067 | 0.050 | 0.083 | 0.008 | 59.659 | 833.711 | Beta |
| AF undiagnosed: female (%) | 0.157 | 0.118 | 0.196 | 0.020 | 53.795 | 288.848 | Beta |
| AF undiagnosed: male (%) | 0.120 | 0.090 | 0.150 | 0.015 | 56.200 | 412.133 | Beta |
| AF symptomatic: female (%) | 0.679 | 0.509 | 0.849 | 0.085 | 19.865 | 9.391 | Beta |
| AF symptomatic: male (%) | 0.575 | 0.431 | 0.719 | 0.072 | 26.625 | 19.679 | Beta |
| Symptomatic with AF: female (%) | 0.200 | 0.150 | 0.250 | 0.025 | 51.000 | 204.000 | Beta |
| Symptomatic with AF: male (%) | 0.200 | 0.150 | 0.250 | 0.025 | 51.000 | 204.000 | Beta |
| AF patients with CHA2DS2-VASc ≥ 2 (%) | 0.824 | 0.618 | 1.000 | 0.096 | 12.278 | 2.624 | Beta |
| AF patients with CHA2DS2-VASc ≥ 2 on OACs (%) | 0.812 | 0.609 | 1.000 | 0.098 | 12.157 | 2.821 | Beta |
| Treatment characteristics | |||||||
| OACs that are NOACs (%) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| Time taken to administer lead-I test | 0.000 | 0.000 | 7.000 | Fixed | |||
| Standard pathway patients who have 12-lead (%) | 1.000 | 0.500 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| Patients with paroxysmal AF NOT in AF at 12-lead (%) | 0.475 | 0.356 | 0.594 | 0.059 | 33.125 | 36.612 | Beta |
| Lead-I positive patients who have 12-lead (%) | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| Lead-I negative patients who have 12-lead (%) | 0.800 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF diagnosed after MPP only (standard pathway) -> negative 12-lead (%) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF ruled out after MPP only (standard pathway) -> negative 12-lead (%) | 0.500 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| Patients sent for paroxysmal testing after MPP only (standard pathway) -> negative 12-lead (%) | 0.500 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF diagnosed after MPP only (standard pathway) (no 12-lead) (%) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF ruled out after MPP only (standard pathway) (no 12-lead) (%) | 0.500 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| Patients sent for paroxysmal testing after MPP only (standard pathway) (no 12-lead) (%) | 0.500 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF diagnosed after negative lead-I -> negative 12-lead (%) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF ruled out after negative lead-I -> negative 12-lead (%) | 0.500 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| Patients sent for paroxysmal testing after negative lead-I -> negative 12-lead (%) | 0.500 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF diagnosed after negative lead-I (no 12-lead) (%) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF ruled out after negative lead-I (no 12-lead) (%) | 0.500 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| Patients sent for paroxysmal testing after negative lead-I (no 12-lead) (%) | 0.500 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF diagnosed after positive lead-I -> negative 12-lead (%) | 0.500 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF ruled out after positive lead-I -> negative 12-lead (%) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| Patients sent for paroxysmal testing after positive lead-I -> negative 12-lead (%) | 0.500 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF diagnosed after positive lead-I (no 12-lead) (%) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF ruled out after positive lead-I (no 12-lead) (%) | 0.500 | 0.000 | 0.000 | Fixed | |||
| Patients sent for paroxysmal testing after positive lead-I (no 12-lead) (%) | 0.500 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| Patients with paroxysmal AF NOT in AF at paroxysmal test (%) | 0.300 | 0.225 | 0.375 | 0.038 | 44.500 | 103.833 | Beta |
| AF diagnosed after MPP & negative 12-lead & negative paroxysmal test (%) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF ruled out after MPP & negative 12-lead & negative paroxysmal test (%) | 1.000 | Fixed | |||||
| AF diagnosed after negative lead-I & negative 12-lead & negative paroxysmal test (%) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF ruled out after negative lead-I & negative 12-lead & negative paroxysmal test (%) | 1.000 | Fixed | |||||
| AF diagnosed after positive lead-I & negative 12-lead & negative paroxysmal test (%) | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | Fixed | |||
| AF ruled out after positive lead-I & negative 12-lead & negative paroxysmal test (%) | 0.000 | Fixed | |||||
| Risk ratio for mortality | |||||||
| Previous CVE: AF, NOAC | 2.600 | 2.600 | 2.600 | Fixed | |||
| Previous CVE: AF, Warfarin | 2.600 | 2.600 | 2.600 | Fixed | |||
| Previous CVE: AF, untreated | 2.600 | 2.600 | 2.600 | Fixed | |||
| Previous CVE: no AF | 2.600 | 2.600 | 2.600 | Fixed | |||
| Proportion of subsequent stroke types (%) | |||||||
| HS | 0.057 | 0.042 | 0.071 | 0.007 | 60.324 | 1006.196 | Dirichlet |
| IS | 0.640 | 0.626 | 0.654 | 0.007 | 2949.534 | 1657.159 | Dirichlet |
| TIA | 0.303 | 0.289 | 0.317 | 0.007 | 1280.959 | 2944.294 | Dirichlet |
Glossary
- Cost-effectiveness analysis
- An economic analysis that converts effects into health terms and describes the costs per additional health gain.
- Decision modelling
- A theoretical construct that allows the comparison of the relationship between the costs and outcomes of alternative health-care interventions.
- Decision tree
- A model of a series of related choices and their possible outcomes.
- False negative
- An incorrect negative test result in an affected individual with a negative test result.
- False positive
- An incorrect positive test result in an unaffected individual with a positive test result.
- Incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- The difference in the mean costs of two interventions in the population of interest divided by the difference in the mean outcomes in the population of interest.
- Index test
- The test whose performance is being evaluated.
- Markov model
- An analytical method particularly suited to modelling repeated events or the progression of a chronic disease over time.
- Meta-analysis
- A statistical technique used to combine the results of two or more studies and obtain a combined estimate of effect.
- Negative predictive value
- The probability that people with a negative test result truly do not have the disease.
- Opportunity cost
- The cost of forgone outcomes that could have been achieved through alternative investments.
- Positive predictive value
- The probability that people with a positive test result truly have the disease.
- Probabilistic sensitivity analysis
- A method of quantifying uncertainty in a mathematical model, such as a cost-effectiveness model.
- Receiver operating characteristic curve
- A graph that illustrates the trade-offs between sensitivity and specificity that result from varying the diagnostic threshold.
- Reference standard
- The best currently available diagnostic test against which the index test is compared.
- Sensitivity
- The proportion of people with the target disorder who have a positive test result.
- Specificity
- The proportion of people without the target disorder who have a negative test result.
- True negative
- A correct negative test result in an unaffected individual with a negative test result.
- True positive
- A correct positive test result in an affected individual with a positive test result.
List of abbreviations
- AE
- adverse event
- AF
- atrial fibrillation
- AHSN
- Academic Health Science Health Network
- BNF
- British National Formulary
- CASP
- Critical Appraisal Skills Programme
- CCG
- Clinical Commissioning Group
- CDSR
- Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
- CEAC
- cost-effectiveness acceptability curve
- CENTRAL
- Cochrane Central Database of Controlled Trials
- CHA2DS2-VASc
- history of congestive heart failure, hypertension, age ≥ 75 years [doubled], diabetes mellitus, prior stroke or transient ischaemic attack [doubled], vascular disease, age 65–74 years, female
- CI
- confidence interval
- CVE
- cardiovascular event
- DADS
- directly accessed diagnostic service
- DARE
- Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects
- DTA
- diagnostic test accuracy
- EAG
- External Assessment Group
- ECG
- electrocardiogram
- EP
- electrophysiologist
- EQ-5D
- EuroQol-5 Dimensions
- EQ-5D-3L
- EuroQol-5 Dimensions, three-level version
- ESC
- European Society of Cardiology
- GP
- general practitioner
- HAS-BLED
- hypertension, abnormal liver/renal function, stroke history, bleeding predisposition, labile international normalised ratio, age, drug/alcohol use
- HR
- hazard ratio
- HRG
- Healthcare Resource Group
- HRQoL
- health-related quality of life
- HS
- haemorrhagic stroke
- HTA
- Health Technology Assessment
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- IS
- ischaemic stroke
- IT
- information technology
- MPP
- manual pulse palpation
- NG45
- NICE guideline 45
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NOAC
- non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulant
- OAC
- oral anticoagulant
- PRISMA
- Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- QUADAS
- Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- ROC
- receiver operating characteristic
- SROC
- summary receiver operating characteristic
- SSNAP
- Sentinel Stroke National Audit Programme
- TIA
- transient ischaemic attack
- USB
- universal serial bus
- WTP
- willingness to pay
