Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the HTA programme as project number 11/129/187. The contractual start date was in September 2013. The draft report began editorial review in December 2018 and was accepted for publication in September 2019. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Richard Gilson reports grants from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) during the conduct of the study. Lewis J Haddow reports grants from the NIHR Health Technology Assessment programme during the conduct of the study, grants from the British HIV Association‘s Scientific and Research Committee and personal fees from Gilead Sciences, Inc. (London, UK) outside the submitted work.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2020. This work was produced by Gilson et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2020 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Introduction
Background
Genital warts are benign lesions that present as lumps or raised plaques in the skin of the anogenital area. They are usually painless, but can cause irritation or bleeding. More commonly, they cause emotional distress, which is exacerbated by the need for prolonged, time-consuming and uncomfortable treatment. Relapse after apparently successful treatment occurs frequently. Surgery may be required in persistent or severe cases. About 90% of genital warts are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) types 6 or 11, which are sexually transmitted. 1 These viruses are not believed to be associated with a risk of cervical or other genital cancer, and are therefore termed ‘low risk’. Other HPV types, particularly HPV types 16 and 18, are associated with a risk of cancer; indeed, these or one of the other ‘high-risk’ types are found in almost every case of cervical squamous cell carcinoma. However, high-risk types do not cause benign genital warts.
Of the 116,342 episodes of new or recurrent genital warts treated in sexual health services in England in 2017, 49% were recurrent episodes. 2 First-episode genital warts accounted for 15% of new sexually transmitted infections (STIs) diagnosed, making it the second most common STI after chlamydia infection. NHS treatment costs for anogenital warts in 2016 were estimated at £14M, of which about £6M was to treat recurrent episodes. 3
Since 2012, the HPV vaccine programme in 12- to 13-year-old girls has used the quadrivalent human papillomavirus (qHPV) vaccine, which is effective against HPV types 6 and 11, as well as the high-risk HPV types 16 and 18. The incidence of anogenital warts in young adults is beginning to fall, but the current programme is not predicted to result in elimination; therefore, effective treatment for warts will continue to be required.
The best first-line topical treatment for anogenital warts has not been established in clinical trials, so treatment guidelines lack a firm basis for their recommendations. The HPV vaccine is indicated to prevent infection; a therapeutic effect, although suggested, has not been established in a clinical trial.
The most clinically effective, and cost-effective, treatment for anogenital warts remains uncertain, so clinical guidelines lack a secure evidence base. 4–6 Cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen can be used to treat anogenital warts. This treatment may be effective with a single application, but it requires equipment and facilities usually available only in specialist community settings and hospitals, and also requires appropriately trained staff. Repeated clinic attendance is often required for further applications of cryotherapy. Given the inconvenience for patients, and the burden it places on limited health service resources, most cases of warts are now treated with self-administered topical agents, of which podophyllotoxin (PDX) is the most common. 7 The plant extract podophyllin was used in clinics as an unlicensed product for the treatment of warts for many years. The standardised, purified product, PDX, is licensed and can be used safely by patients at home. It is more effective than podophyllin. PDX is a chemotherapeutic agent that probably acts by prevention of tubulin polymerisation required for microtubule assembly and by inhibition of nucleoside transport through the cell membrane. This leads to inhibition of growth of virally infected cells. Licensed forms include a cream and solutions. Efficacy has been demonstrated in randomised trials. 7–15 The cream Warticon® (GlaxoSmithKlein plc, Brentford, UK) contains the active compound at a concentration of 0.15%, whereas the solution is 0.5%. The cream is considered to be easier to apply, at least at some anatomical sites, and may be better tolerated. The consensus has been that the efficacy of the cream and the solution are similar, although a recent systematic review and meta-analysis concluded that the solution is slightly more effective. 16
The main alternative topical treatment is imiquimod (IMIQ). This is more expensive, although the price difference has reduced since the expiry of patent protection. Nonetheless, IMIQ is reserved in many clinics, and in guidelines, as a second-line therapy. IMIQ is available as a 5% cream (Aldara®; Meda Pharmaceutical, Tekely, UK). Some studies have suggested that IMIQ is associated with a lower recurrence rate after complete wart clearance, possibly as a result of its mode of action as an immune response modifier. 17,18 It is a toll-like receptor 7 agonist and stimulates tissue macrophages to release interferon alpha and other cytokines, which trigger a local cell-mediated response. IMIQ has no direct antiviral activity. The response to treatment may be slower than with PDX, and the licensed treatment duration is longer, at up to 16 weeks. Most patients will show a response by 8 weeks.
The efficacy of IMIQ compared with placebo or other treatment modalities has been investigated in a number of trials. 15,19–26 However, the efficacy of PDX and IMIQ as initial therapies for anogenital warts have never been compared in an appropriately powered trial. 5 The only randomised trial that directly compared these two agents was underpowered (n = 51) and did not report recurrence rates. 15 The clearance rates were similar but with wide confidence intervals (CIs): 75% clearance with IMIQ compared with 72% with PDX (95% CI 53% to 89% and 52% to 86%, respectively).
A systematic review of wart treatment undertaken for European guidelines for the treatment of genital warts5 suggested that PDX has a similar rate of initial clearance to IMIQ (43–70% at 4 weeks compared with 55–81% clearance at 16 weeks, respectively), but that recurrence rates may be lower with IMIQ (6–26% at 6 months for IMIQ compared with 6–55% at 8–12 weeks for PDX). The wide variation between reported studies may be related to differences in study design, including the outcome measures and timing. The review5 found no evidence for any single therapy being superior overall, largely owing to the lack of high-quality comparative studies. Those studies reported were heterogeneous in design, and often had high loss to follow-up. Large, well-designed randomised studies are required to make a firm recommendation on treatment. UK national guidelines recommend that the choice of first-line therapy is based on patient preference, morphology and distribution of lesions, with a clinic treatment algorithm to guide treatment. 4
The HPV vaccine is indicated to prevent infection; a therapeutic effect, although suggested, has not been established in a clinical trial. It is not known if the clearance rate of anogenital warts is increased when a HPV types 6 and 11 vaccine is given at the time of initiating either a topical treatment or cryotherapy. Similarly, whether or not recurrence of warts after clearance is reduced by the HPV vaccine has not been established.
Vaccines are currently licensed to prevent only HPV-associated anogenital warts and cancers; the qHPV vaccine Gardasil® (Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA) is the only vaccine that also protects against the low-risk genotypes 6 and 11. This vaccine has been used in the national vaccination programme in the UK since 2012 for girls aged 12–13 years. Whether or not the vaccine has a therapeutic or secondary preventative effect for anogenital warts (or other HPV-associated diseases) has yet to be determined. Although there is no randomised controlled trial (RCT) evidence yet, there are other types of evidence that there may be a therapeutic or secondary preventative effect.
There are case reports that clearance of anogenital warts may have been enhanced by the qHPV vaccine. 27,28 There is some evidence from placebo-controlled vaccine trials that found that women who are HPV seropositive but HPV deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) negative for at least one HPV type at trial entry were protected against subsequent disease related to the HPV type to which they were previously exposed. 29 In addition, women with genital lesions treated surgically while in the vaccine trial were less likely to develop recurrent or progressive disease if they were in the vaccine arm than if they were in the placebo arm of the trial. 30 Patients with anogenital warts or genital intraepithelial neoplasia (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, vulval intraepithelial neoplasia or vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia) have been shown to be at risk of reinfection with the same or different HPV types as well as relapse of existing infection. 31,32 Limited evidence also suggests that the qHPV vaccine (Gardasil) may reduce recurrences of respiratory papillomatosis in children,33 a condition usually caused by low-risk HPV types, principally 6 and 11. Similarly, anal intraepithelial neoplasia,34 caused by high-risk HPV types included in the vaccine, may be less likely to recur in vaccine recipients. Finally, vaccine antibody responses are stronger than those induced by natural infection;35 this means that boosting the immune response with vaccine could reduce the persistence of HPV types 6 and 11 infection and, therefore, the rate of disease recurrence. As an unmet need, the ability of vaccine to reduce the recurrence rate would be of greatest value to patients, given the estimated 30% recurrence seen with all treatments. Recurrence of warts after clearance by topical treatment is also the part of the disease process in which the vaccine is most likely to have activity.
Studies of the treatment cost and quality-of-life impact of genital warts, as well as economic analyses of vaccinating against HPV infection, have been conducted. 3,36,37 These studies have documented significant negative impacts on quality of life and substantial health-care service costs. The cost of IMIQ remains higher than that of PDX. If the effectiveness of IMIQ proves superior, then an economic analysis would allow an assessment of the maximum cost difference that would warrant its use as afirst-line therapy. All available treatments have significant failure and recurrence rates. By maximising initial response rates and reducing recurrence rates using first-line self-administered treatment, a RCT has the capacity to reduce this health and quality-of-life burden for patients and improve cost-effectiveness, now and in the future. Vaccination would add to the cost of treatment of patients with anogenital warts. If efficacy is demonstrated, an economic analysis could determine at which level the increased treatment costs would be justified by reduced future health-care costs and improved quality of life related to persistent or recurrent disease.
Objectives
The trial assessed the comparative efficacy of the two main topical treatments in current use, 0.15% PDX cream (Warticon) and 5% IMIQ cream (Aldara), and investigated the potential therapeutic benefit of a qHPV vaccine (Gardasil) in the management of patients with anogenital warts. The trial also evaluated the relative costs of the two topical treatments, as well as of the novel use of qHPV vaccination for both treatment and secondary prevention. The adoption of a pragmatic trial design with broad entry criteria for the comparison of the two topical therapies means that the results can be generalised to the large number of patients treated each year who present with anogenital warts. The topical therapies assessed and the potential (in the protocol) to use supplementary cryotherapy were closely aligned with current clinical practice.
Chapter 2 Methods
This chapter is adapted from Murray et al. 38 This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Design
The study was a randomised, controlled, partially blinded 2 × 2 factorial-design trial of treatment for anogenital warts with an accompanying economic analysis. All participants received active, topical treatment with either PDX cream or IMIQ cream. They also received a course of qHPV vaccine or saline placebo injections. Participants were allocated in equal numbers to the four combinations of the two topical treatments and the vaccine or placebo: IMIQ cream plus qHPV vaccine, PDX cream plus qHPV vaccine, IMIQ cream plus saline placebo injection and PDX cream plus saline placebo injection. The primary outcome was clearance of warts at 16 weeks and remaining clear until the end of follow-up at 48 weeks. Analysis of the primary outcome was based on logistic regression. In the economic evaluation, we investigated the cost-effectiveness and cost–utility of the two topical treatments and the qHPV vaccine.
Ethics
The trial protocol was reviewed by the Oxfordshire Research Ethics Committee B (reference number 13/SC/0638) and received a favourable opinion on 3 February 2014. Amendments to the protocol were subject to further review, including the decision to reduce the size of the trial, with its attendant impact on the likelihood of reaching a definitive conclusion.
Patient and public involvement
The research proposal was reviewed by a patient representative at the Mortimer Market Centre (Central and North West London NHS Foundation Trust) before funding submission. The design of the study was discussed with a patient user group in the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) clinical service during the development of the protocol. A lay representative was on the Trial Steering Committee (TSC).
Setting
The trial was carried out in 22 sexual health clinics in England and Wales (see Appendix 1 for a list of participating sites). Sexual health clinics in the UK are open-access services, with most patients being self-referred. Approximately 80% of cases of genital warts treated in the NHS are treated in sexual health clinics.
Participants
The eligibility criteria for participants were adults, aged ≥ 18 years, presenting to participating clinics with external anogenital warts that, in the opinion of the investigator, could be appropriately treated with either self-administered IMIQ cream or self-administered PDX cream. Patients with a first episode of warts, and patients for whom this was a repeat episode, were eligible provided that they had not received treatment for warts in the previous 3 months.
Other exclusion criteria included patients who had previously had qHPV vaccine (but having had bivalent HPV vaccine was not an exclusion criterion). Patients with any contraindication to any of the products were excluded, which included previous intolerance to vaccines, pregnancy and lactation. Those with a total wart area of > 4 cm2 were excluded because the 0.15% PDX cream product information advice is to treat more extensive lesions only under medical supervision. Patients requiring topical steroids applied to the affected area, or on systemic immunosuppressive agents, were also excluded.
Initially, participants with known HIV infection were excluded, on the grounds that wart treatment and vaccine responses were reported to be impaired, with implications for the sample size. But, in December 2015, the entry criteria were modified to include patients living with HIV who were stable on antiretroviral treatment and had a cluster of differentiation 4 (CD4) count of > 350 cells/µl and those not on treatment with a CD4 count of > 500 cells/µl. This would exclude only those with more severe immunosuppression. Current evidence indicates that, in the majority of patients with HIV infection with well-preserved or restored immune markers, vaccine and treatment responses are not substantially impaired. 39–41
Interventions
The two topical treatments compared in the trial were 5% IMIQ cream and 0.15% PDX cream, both licensed products for the treatment of anogenital warts.
Participants randomised to IMIQ applied the cream to the warts in accordance with the licence, that is, 3 days of the week (every other day) at bed time, left on overnight, and the area of application washed after 6–10 hours. Duration of treatment was up to 16 weeks.
For participants randomised to PDX, the instruction was to apply the cream twice per day for 3 consecutive days followed by no treatment for 4 days, in weekly cycles. The licensed treatment duration is 4 weeks, but it is common practice to extend this period if there is a response to therapy. In the trial, we therefore allowed continued use of PDX cream for up to 16 weeks. No crossover of the topical treatment was permitted before 16 weeks.
Dose modifications of topical treatment were permitted if required for tolerability. For PDX, the weekly cycle of treatment could be postponed for 3 days, or longer if required, in which case it was restarted once daily. For participants unable to tolerate the standard regimen for IMIQ, the advice was to reduce the frequency of dosing to twice per week, and then to once weekly if tolerability was not improved. Any skin reaction requiring dose modification was reported as an adverse event (AE).
The qHPV vaccine was administered according to the schedule licensed for the prevention of HPV infection, with three doses administered at the time of randomisation and at 8 and 24 weeks. The vaccine volume is 0.5 ml and is presented in a pre-filled syringe. The placebo comparator for the vaccine was 0.5 ml of normal saline.
To retain participants in the trial without crossover of topical treatment before 16 weeks, adjunctive cryotherapy was permitted from week 4 (visit 2) onwards if, in the opinion of the investigator, this was in the best interests of the patient, and after assessment of the response to topical treatment to date.
Randomisation
Participants were randomised to one of four groups:
-
IMIQ cream plus qHPV vaccine
-
PDX cream plus qHPV vaccine
-
IMIQ cream plus saline placebo injection
-
PDX cream plus saline placebo injection.
Allocation to the groups was carried out using minimisation with a random element, with gender, previous occurrence of warts and trial site as stratification factors. HIV status was added as a stratification factor when the eligibility criteria were changed. Participants were randomised 1 : 1 : 1 : 1 to the four groups. Trial participant number and randomisation group allocation were computer-generated and accessed by a secure online facility (Sealed Envelope™; Sealed Envelope Ltd, London, UK), which required entry of participant characteristics to allow the minimisation process to be completed.
Blinding
The differences in posology of the two topical treatments made a blinded comparison impractical. Therefore, the creams were dispensed in unblinded original packs.
The qHPV vaccine and saline placebo were dispensed in blinded packaging comprising an opaque plastic sleeve inside a cardboard box labelled with the trial details and a unique pack code number. Both were in pre-filled syringes, but it was not possible to source matching syringes to produce a fully blinded placebo. Therefore, the vaccine or placebo was administered by a member of staff who was not part of the trial team involved in the assessment of the participant.
Recruitment and consent
Members of the clinical team at participating clinics identified potential trial participants and referred them to the trial team. Participants were provided with the information sheet and gave written informed consent. Most participants were recruited at the same visit, but, if more convenient for the participant, the first visit, and treatment, were delayed for up to a few days.
Baseline visit
The baseline assessment included a record of previous wart episodes and treatments, history of STIs and comorbidities, history of recent sexual contacts, concomitant medication and a quality-of-life questionnaire [EuroQol-5 Dimensions, five-level version (EQ-5D-5L)].
The location of warts present was recorded and the approximate number of warts present was recorded in categories: 1–5, 6–10, 11–20 and > 20. The maximum diameter of the largest wart was recorded, measured against a size gauge. A symptom-directed general physical examination was performed, if appropriate.
A swab from the wart lesions and a blood sample were collected and archived for mechanistic studies, subject to separate review and funding. The details of the baseline and follow-up assessments are tabulated in Appendix 2.
Randomised treatments were then prescribed or administered and participants were supplied with information on their use, risks and side effects. Participants were offered safer-sex advice and access to other sexual and reproductive health services as per routine care. For women of child-bearing potential, a pregnancy test was performed. Diary cards were provided to the participant to remind them when the treatment should be applied and to record its use, if and when warts cleared and any symptoms related to the topical treatment. These were reviewed at follow-up study visits.
Follow-up assessments and treatment
Trial follow-up was for 48 weeks, with scheduled visits at weeks 4, 8, 16, 24 and 48. Presence of warts was determined on examination by a member of the trial clinical team at each of these visits and at any unscheduled visit. Further topical treatment was supplied according to the randomised allocation at weeks 4 and 8 if required. Blinded vaccine or placebo was administered at weeks 8 and 24, regardless of the response to topical treatment.
If warts recurred within the first 16 weeks, the participant was prescribed the treatment to which they were randomised at baseline. Participants were asked to return to the clinic early for an extra visit if they noticed a recurrence of warts after complete clearance so that this could be documented and a swab from the new or recurrent lesion collected.
Cryotherapy was offered at the discretion of the local investigator if this was considered to be in the best interests of the patient and after assessment of response to topical treatment to date. Investigators were encouraged not to give cryotherapy before 4 weeks to allow for assessment of the initial response to topical treatment alone in all cases.
If a participant was unable to tolerate the allocated treatment during the first 16 weeks, and after dose modifications as appropriate, alternative treatment could be administered at the discretion of the investigator. For the purposes of the trial, use of alternative treatments other than additional weeks of PDX or cryotherapy before 16 weeks was considered a topical treatment failure. In the event of treatment failure, participants were still followed up and received vaccine or placebo in accordance with protocol.
After week 16, topical treatment for any persistent or recurrent warts was at the discretion of the investigator, including a switch to the other randomised topical treatment.
The timing of wart clearance was recorded for the secondary outcomes analysis. If there were additional visits for clinical care between weeks 16 and 48, a record was made of whether or not warts were present.
Routine visits included a review of adherence to the treatment regimen, tolerability and health-related quality of life (HRQoL). Participants were also asked about work days lost as a result of clinic visits. Diary cards were collected from participants and reviewed by site staff.
A blood sample was collected at week 48 from all those who attended, and a lesion swab for later HPV DNA detection was collected and stored if warts were present.
To reduce the loss to follow-up rate, a small financial incentive was provided to those participants who attended the week 16 and week 48 visits in the form of Love2shop Gift Cards (highstreetvouchers.com, Birkenhead, UK).
Safety
All AEs and adverse reactions (ARs) were recorded and reported according to procedures specified in the protocol. The severity of AEs and ARs were graded and reported using the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE).
Outcomes
Primary outcome
The primary outcome was a combined end point of wart clearance 16 weeks after starting treatment and remaining wart free between weeks 16 and 48. This captured both the initial clearance efficacy and the impact on relapse or recurrence.
Secondary outcomes
The two components of the combined primary end point were considered as factor-specific, clinically important secondary outcomes:
-
for topical treatment, the proportion that were wart free at week 16
-
for vaccination, the proportion that remained wart free between weeks 16 and 48 in those with wart clearance at week 16.
There were a number of other secondary outcomes specified in the protocol:
-
proportion that were wart free at the end of the assigned treatment course (4 or 16 weeks)
-
proportion that were wart free at the end of the assigned treatment course (4 or 16 weeks) without receiving additional treatment
-
quantity of additional treatment (e.g. number of cryotherapy applications) required to achieve clearance by week 16
-
proportion that were wart free at week 16 without receiving additional treatment
-
proportion that experienced complete wart clearance at any time, up to week 48
-
proportion that experienced wart recurrence or relapse after complete wart clearance
-
time to complete first wart clearance
-
time from complete wart clearance to recurrence or relapse
-
AEs
-
HRQoL as measured by the EQ-5D-5L
-
symptom scores
-
cost of treatment including prescribed agents and clinic visits.
Sample size
The trial was originally designed with a sample size of 1000 participants with equal numbers randomised to each of the two topical treatment arms, and each of the two vaccine or placebo groups, in a 2 × 2 factorial design. After allowing for 20% loss to follow-up, 800 participants would contribute primary outcome data. The anticipated proportion achieving the primary end point in the less favourable topical treatment group was estimated at 35%, assuming a wart clearance rate of 50% within 16 weeks and a subsequent recurrence rate of 30%. This sample size would have provided 80% power (at the 5% significance level) to detect an increase to 45% achieving the primary end point with the better treatment. It would also have provided 80% power to detect an increase from 35% to 45% in the primary end point as a result of an effect of vaccination, as would arise if vaccination reduced the recurrence rate from 30% to 10% while leaving the wart clearance rate unchanged at 50%.
Owing to a lack of feasibility to achieve the proposed recruitment target of 1000 participants, a revised sample size of 500 participants was proposed to the funder in February 2016. With 15% loss to follow-up, this would now provide 52% power (at the 5% significance level) to detect the prespecified difference in the combined primary end point. Even with a reduction in the loss to follow-up rate, which would, in itself, be challenging, the study would be substantially underpowered for its combined primary end point.
The statistical power for the components of the primary end point were therefore also evaluated. It was expected that the main effect of the topical treatment would be on wart clearance and the main effect of vaccination would be on wart recurrence. The power of the study to detect a clinically important difference in each of these secondary outcomes was calculated for the proposed reduced trial size.
The reduced sample size would provide 80% power at the 5% significance level, assuming 15% loss to follow-up, to evaluate each of the two components of the primary outcome: the proportion wart free at week 16 and the proportion of those who were wart free at week 16 remaining wart free at week 48. For the week 16 topical treatment outcome, a difference of 14% in wart clearance (57% wart clearance in the imiquimod group vs. 43% wart clearance in the podophyllotoxin group) could be detected. For the week 48 vaccine outcome, a difference of 16% in recurrence (12% recurrence in the vaccine group vs. 28% recurrence in the placebo group) could be detected. These differences were considered to be clinically important and sufficient to be likely to influence management guidelines. A 5% significance level was still used for these calculations, as there was a different outcome for each of the two factors, to answer two independent questions.
Data collection and management
Data were entered at the Comprehensive Clinical Trials Unit (CCTU) into a MACRO v4.0 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, the Netherlands) database, which incorporated validation checks to improve data quality. Data verification, consistency and range checks were performed during data entry, as were checks for missing data. Data queries were resolved by site staff before database lock and final analysis. Additional data checks were performed when the data sets for analysis were constructed before the final statistical analysis commenced. All variables were examined for unusual, outlying, unlabelled or inconsistent values.
Statistical methods
All analyses were conducted on a modified intention-to-treat (ITT) basis. We included all consented randomised participants for whom at least one follow-up visit was available regardless of their adherence to treatment because the HIPvac [Human papillomavirus infection: a randomised controlled trial of Imiquimod cream (5%) versus Podophyllotoxin cream (0.15%), in combination with quadrivalent human papillomavirus or control vaccination in the treatment and prevention of recurrence of anogenital warts] trial was a pragmatic study concerned with the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topical therapy with or without the addition of qHPV vaccination.
All CIs are 95% and two sided. Statistical tests used a two-sided p-value of 0.05 unless otherwise specified. The analysis for both factors (PDX vs. IMIQ and qHPV vaccine vs. placebo) was based on comparisons at the margins of the 2 × 2 table, such that all participants randomised to PDX were compared with all participants randomised to IMIQ, and all participants randomised to qHPV vaccine were compared with all participants randomised to the placebo injection.
We did not anticipate a substantial interaction between topical treatment and vaccination. However, as a secondary analysis, we performed a prespecified interaction test between the two factors, and present results from a four-arm analysis (in which each of the four treatment combinations is regarded as a separate treatment arm), as recommended for factorial trials.
We adjusted the analyses for the stratification variables HIV status, gender and whether or not the participant had had a previous episode of warts by including them as fixed-effect covariates. Trial site was included in the mixed-effects models as a random effect (random intercept) to account for any possible variation by site. Treatment effects were then estimated, conditional on HIV status, gender and previous occurrence of warts, and account for variation between sites.
In a pragmatic clinical trial over a 48-week time frame, some patients are inevitably lost to follow-up. Outcomes for such patients are, therefore, only partially observed. This can lead to a loss of power, biased estimates and standard errors, and a loss of efficiency. To reduce the potential impact of bias, and to maximise the power to detect a treatment effect, multiple imputation by chained equations42 was used to impute data from missing follow-up visits. Missing data were assumed to be missing at random (MAR), conditional on all variables included in the imputation model, and so independent of the values of the unobserved data themselves. The analyses for all primary and secondary outcomes were performed on fully imputed data sets.
Three separate sets of imputed data were generated; in each case, enough imputed data were generated such that the Monte Carlo error of the treatment effects estimated in the subsequent analyses was minimised. Each of the three multiple imputation sets included the following as (fully observed) explanatory variables in the imputation model: gender, HIV status, previous warts, trial site, allocated treatment, total number of visits attended, number of additional visits attended (over and above scheduled visits), an indicator of non-compliance and an indicator of any additional treatment given. The first set imputed 120 sets of the week 16 wart clearance outcome, the week 48 recurrence outcome and the outcomes wart free by week 4 and wart free by week 16. The primary outcome is a combination of the week 16 wart clearance outcome and the week 48 wart recurrence outcome, and was not directly imputed but determined from the imputed outcomes at weeks 16 and 48. The second set imputed 50 sets of the outcomes wart clearance (at any time) and wart recurrence (at any time). The final set imputed 50 sets of the quality-of-life outcomes [EuroQol-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) health utilities index and visual analogue scale (VAS)] at each time point.
Sensitivity analyses investigated the impact of the MAR assumption and missing data for all participants.
Changes to the protocol
The major change to the protocol was the reduction in the sample size as described in Statistical methods.
Active vaccine comparator
When funding for the trial was awarded, the design included the hepatitis A virus (HAV) vaccine as an active comparator for the qHPV vaccine. This was to be used to ensure effective blinding of the study, because some local reactogenicity would be expected to occur in both arms, whereas the HAV vaccine would have no activity in treating or preventing HPV infection, unless there was any non-specific immune stimulant effect, which was deemed to be unlikely. This design might also have helped recruitment, because the HAV group could also derive benefit from participating, if they were not already immune to the HAV. There is no contraindication to receiving the HAV vaccine in those who are already immune.
This design was predicated on the availability of matching the qHPV and HAV vaccines, as used in a number of HPV vaccine efficacy studies. This methodology had to be changed when the pharmaceutical company support for the HIPvac trial was withdrawn, and it was clear that the additional costs and delays that this immediately imposed on the trial would be exacerbated by trying to source a matching HAV vaccine control.
Blinding
Without pharmaceutical company support for the trial, it was necessary to contract with an independent pharmacy manufacturing facility to make a blinded placebo, using normal saline as the only feasible ‘matching’ placebo. Although syringes identical to the bespoke syringes used for the commercial stock of qHPV vaccine were procured, there were technical difficulties in filling these. To minimise delay to the initiation of the study, an amendment that allowed non-matching placebo syringes to be used for the first 250 participants was submitted and approved. The non-matching syringes were of similar size but not identical in design to the qHPV vaccine. Each syringe (qHPV vaccine or placebo) was therefore packed in an opaque plastic sleeve, and then in a plain cardboard container, labelled with the trial details and a unique vaccine code number. Until the packaging was opened, the allocation would remain blinded. A member of the clinical team who was not involved in any other aspect of the assessment of the participant was instructed to open the package and administer the vaccine, taking care to avoid unblinding any member of the research team.
Although this arrangement was intended to be temporary for the first 6 months of the trial only, further technical problems with the filling of the matching syringes led to the decision to continue the use of non-identical syringes for the remainder of the trial. The protocol was amended accordingly.
Inclusion of participants with HIV infection
Initially, participants known to be living with HIV were excluded on the grounds that wart treatment and vaccine responses were reported to be impaired in this group, with implications for the sample size. But, in December 2015, at the suggestion of the lay member of the TSC, the entry criteria were modified to include participants living with HIV who were stable on antiretroviral treatment with a CD4 count of > 350 cells/µl and those not on antiretroviral treatment with a CD4 count of > 500 cells/µl. This would exclude only those with more severe immunosuppression. Existing evidence indicated that vaccine and treatment responses in the majority of patients living with HIV with a well-preserved or restored CD4 count are not substantially different from those in patients without HIV. 39–41 It was concluded that those living with HIV and fulfilling these criteria should not be excluded. It was estimated that 80% of participants living with HIV with warts would be eligible. It would also be of benefit to observe if the response to the topical wart treatments and the vaccine was comparable in those with and those without HIV, although it was acknowledged that the power to detect any such effect would be limited. As a precaution, HIV status was added as a stratification variable. Finally, given that the accrual to the study was behind schedule and that the prevalence of anogenital warts was higher in those living with HIV, it was hoped that the protocol change would help the trial to meet the overall recruitment target.
Trial oversight
A TSC was established comprising five independent members and the trial chief investigator as the only non-independent member. Membership included a patient and public representative. The day-to-day management of the trial was the responsibility of the University College London CCTU, with oversight by a Trial Management Group responsible for the design, co-ordination and strategic management of the trial and chaired by the chief investigator. An Independent Data Monitoring Committee (IDMC) was appointed with three independent members: a clinician with expertise in HPV, a clinical triallist with experience of HPV trials and a statistician as chairperson. All oversight committees had agreed terms of reference.
During the course of the trial, the TSC and IDMC met together six times; the IDMC met once to review blinded data in connection with a decision to revise the sample size. The TSC and IDMC also made a recommendation to allow inclusion of participants living with HIV.
Chapter 3 Trial results
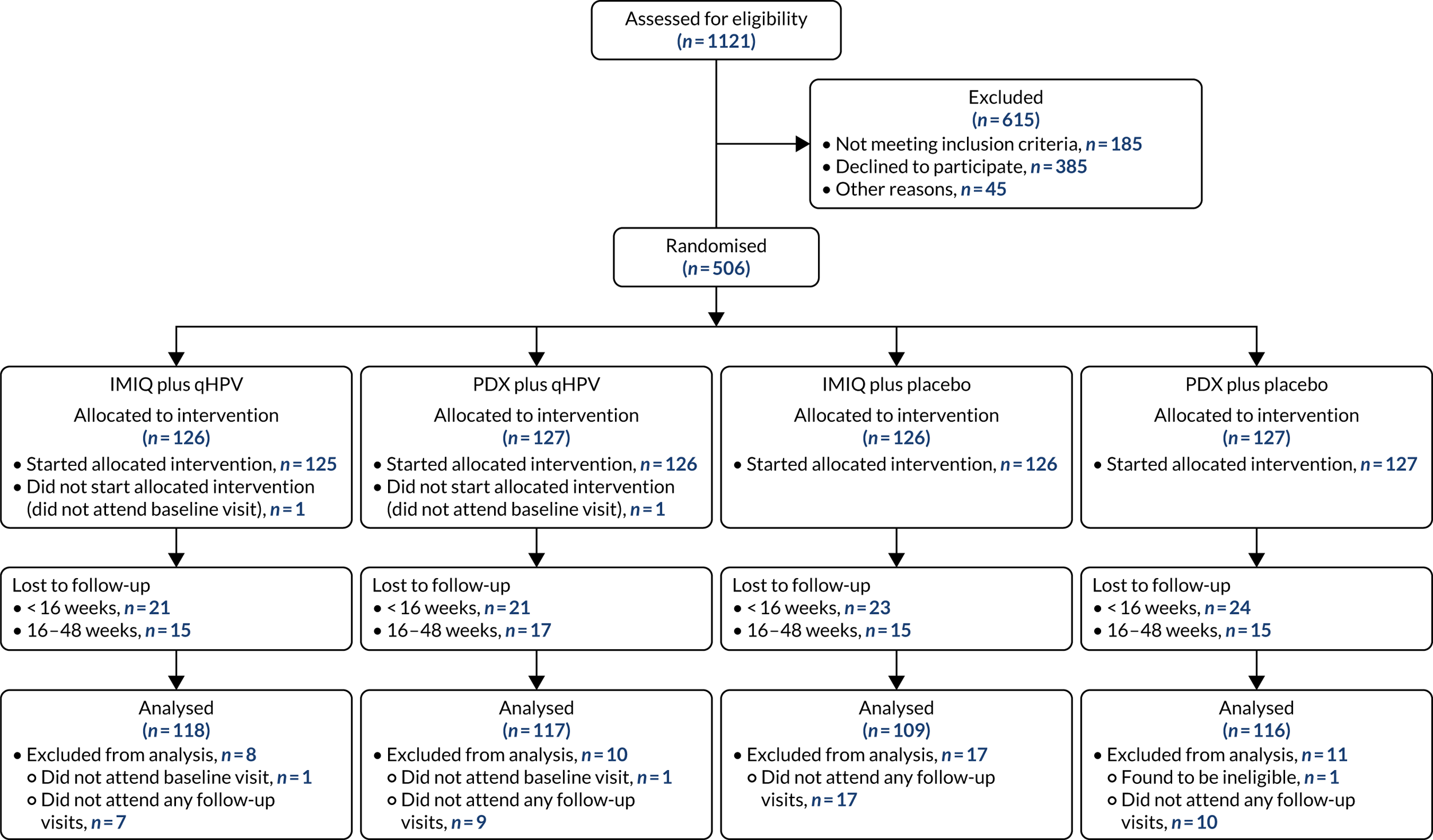
The trial was designed in 2012 and funding was confirmed in 2013. Because of issues with investigational medicinal product manufacture of the blinded vaccine, site activation was delayed; the first site was opened to recruitment on 5 November 2014. Participants were recruited to the trial between November 2014 and December 2016, with the last participant randomised in January 2017 (Figure 1) (see Appendix 1 for recruitment numbers by site). The last scheduled participant follow-up visit was in January 2018. In all, 506 participants consented and were randomised into the trial, of whom 503 are included in the analysis. Three participants did not start the treatment or did not attend any follow-up and are therefore excluded from all analyses. The Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) flow diagram summarising the recruitment and follow-up of participants in each group is shown in Figure 2.
FIGURE 1.
Recruitment graph by date of randomisation.
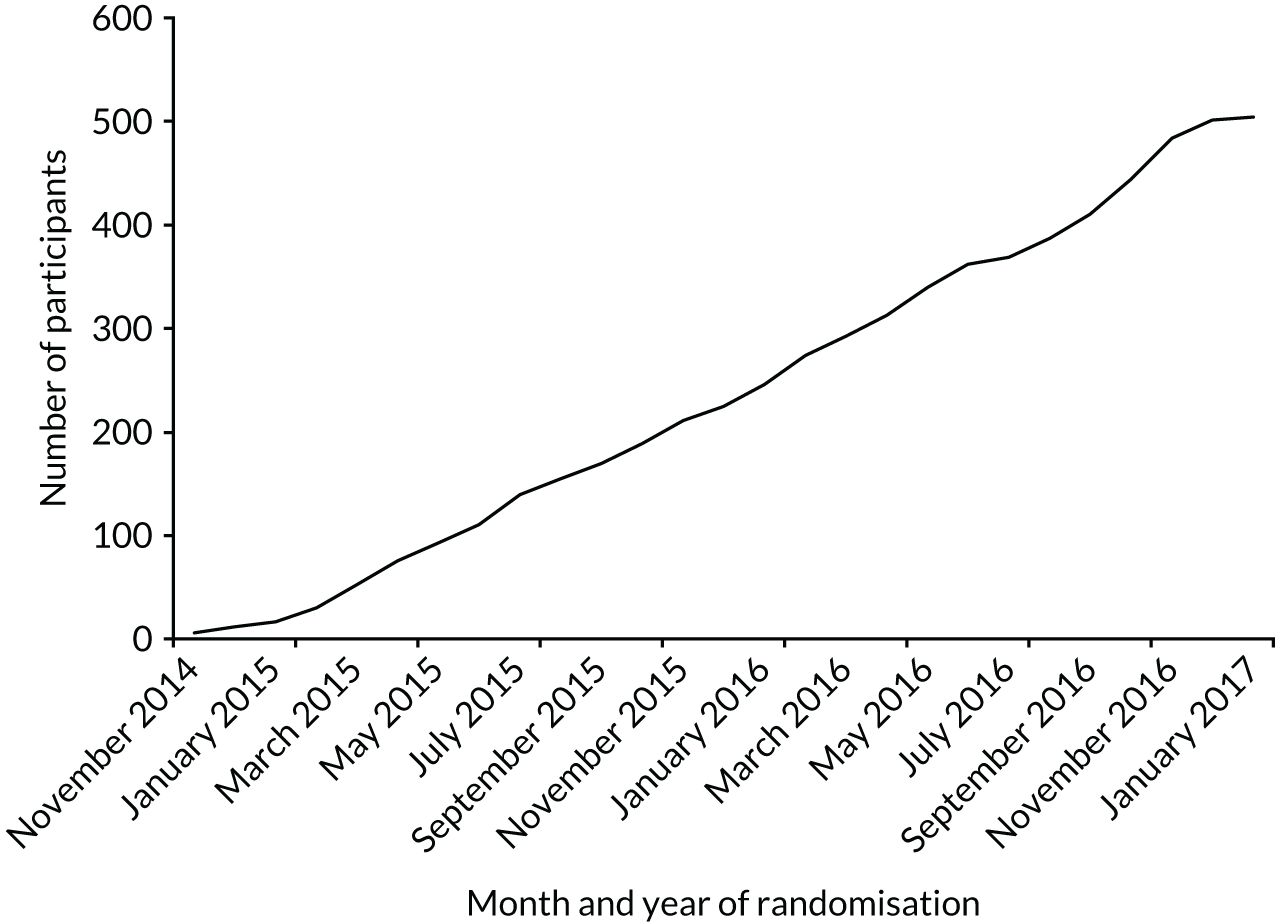
FIGURE 2.
The CONSORT flow diagram showing participant recruitment and the flow of participants in the trial. CONSORT, Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials.
Baseline characteristics of participants
Of the 503 participants included in the analysis, 333 (66%) were male, 170 (34%) were female and the median age was 31 years. A total of 410 (82%) participants were heterosexual, 67 (13%) were homosexual and 25 (5%) were bisexual. Half of the participants (n = 251; 50%) reported one or more previous episodes of warts. A total of 12 participants (2.4%) were HIV positive. Under one-third of participants (n = 151; 30%) were current smokers, reporting cigarette smoking at least daily; 59 (12%) smoked cigarettes less than daily; 118 (23%) were ex-smokers; and 173 (34%) were lifelong non-smokers Information on smoking status was missing for just two participants (0.4%).
The complete data for participant baseline characteristics according to treatment group allocation are shown in Table 1. In general, all baseline characteristics were evenly distributed between the four treatment groups.
| Characteristic | Treatment group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV (N = 125) | PDX plus qHPV (N = 126) | IMIQ plus placebo (N = 126) | PDX plus placebo (N = 126) | |
| Demographics | ||||
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 31 (10) | 31 (10) | 32 (10) | 30 (10) |
| Stratification variables | ||||
| Gender, n (%) | ||||
| Male | 83 (66) | 84 (67) | 83 (66) | 83 (66) |
| Female | 42 (34) | 42 (33) | 43 (34) | 43 (34) |
| Previous occurrence of warts, n (%) | ||||
| No | 63 (50) | 63 (50) | 63 (50) | 63 (50) |
| Yes | 62 (50) | 63 (50) | 63 (50) | 63 (50) |
| HIV positive, n (%) | ||||
| Yes | 2 (2) | 4 (3) | 3 (2) | 3 (2) |
| No | 123 (98) | 122 (97) | 123 (98) | 123 (98) |
| Quantity of warts | ||||
| Diameter of largest wart (mm), median (IQR) | 3 (2–5) | 3 (2–5) | 3 (2–5) | 3 (2–5) |
| Total number of warts, n (%) | ||||
| 1–5 | 63 (50) | 80 (63) | 66 (52) | 57 (45) |
| 6–10 | 26 (21) | 23 (18) | 38 (30) | 32 (25) |
| 11–20 | 24 (19) | 15 (12) | 17 (13) | 21 (17) |
| > 20 | 11 (9) | 8 (6) | 5 (4) | 16 (13) |
| Missing | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Position of warts, n/N (%)a | ||||
| Male | ||||
| Penile, shaft | 48/83 (58) | 45/84 (56) | 41/83 (49) | 52/83 (63) |
| Penile, glans | 9/83 (11) | 6/84 (7) | 10/83 (12) | 3/83 (4) |
| Penile, foreskin | 15/83 (18) | 16/84 (19) | 15/83 (18) | 20/83 (24) |
| Perineum | 3/83 (4) | 3/84 (4) | 5/83 (6) | 0/83 (0) |
| Anal/perianal | 20/83 (24) | 17/84 (20) | 20/83 (24) | 19/83 (23) |
| Other | 22/83 (27) | 25/84 (30) | 28/83 (34) | 20/83 (24) |
| Female | ||||
| External genitalia | 26/42 (62) | 29/42 (69) | 33/43 (77) | 29/43 (67) |
| Perineum | 11/42 (26) | 13/42 (31) | 12/23 (28) | 19/43 (44) |
| Anal/perianal | 9/42 (21) | 11/42 (26) | 9/43 (21) | 9/43 (21) |
| Other | 9/42 (21) | 5/42 (12) | 7/43 (21) | 5/43 (12) |
| Sexual orientation and history | ||||
| Male, n (%) | ||||
| Heterosexual | 65 (78) | 63 (75) | 62 (75) | 62 (75) |
| Homosexual | 15 (18) | 19 (23) | 16 (19) | 16 (19) |
| Bisexual | 3 (4) | 2 (2) | 5 (6) | 5 (6) |
| Other | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Female, n (%) | ||||
| Heterosexual | 39 (93) | 39 (93) | 40 (93) | 40 (93) |
| Homosexual | 0 (0) | 1 (2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Bisexual | 2 (5) | 2 (5) | 3 (7) | 3 (7) |
| Other | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Number of partners in the previous 3 months, median (IQR) | 1 (1, 1) | 1 (1, 2) | 1 (1, 1) | 1 (1, 1) |
| Sexual practices in the previous 3 months, n (%)a | ||||
| Vaginal sex | 91 (73) | 81 (64) | 86 (68) | 92 (73) |
| Passive oral sex | 75 (60) | 73 (58) | 83 (66) | 78 (62) |
| Performed oral sex | 73 (58) | 77 (61) | 82 (65) | 77 (61) |
| Anal-receptive sex | 12 (10) | 21 (17) | 17 (13) | 13 (10) |
| Insertive anal sex | 14 (11) | 22 (18) | 22 (17) | 20 (16) |
| Current contraception (female), n/N (%)a | ||||
| Condoms | 10/43 (24) | 9/42 (21) | 15/43 (35) | 12/42 (29) |
| Hormonal contraception (e.g. pill, IUS, implant, injection) | 20/42 (48) | 21/42 (50) | 16/43 (37) | 22/42 (52) |
| Not sexually active | 4/42 (10) | 4/42 (10) | 5/43 (12) | 2/42 (5) |
| Other | 7/42 (17) | 6/42 (14) | 6/43 (14) | 3/42 (7) |
| None | 1/42 (2) | 2/42 (5) | 0/43 (0) | 1/42 (2) |
| N/A (not of child-bearing potential) | 0/42 (0) | 0/42 (0) | 1/43 (2) | 2/42 (5) |
| Health history | ||||
| Had previous episode(s) of warts, n (%) | 65 (52) | 68 (54) | 63 (50) | 64 (51) |
| Had previous treatment for warts (in those with a previous episode), n/N (%) | 64/65 (98) | 67/68 (99) | 63/63 (100) | 62/64 (97) |
| Wart treatment for most recent episode, n/N (%)a | ||||
| PDX | 18/64 (28) | 16/67 (24) | 14/63 (22) | 17/61 (28) |
| IMIQ | 18/64 (28) | 13/67 (19) | 16/63 (25) | 12/61 (20) |
| Cryotherapy | 48/64 (75) | 47/67 (70) | 43/63 (68) | 42/62 (68) |
| Surgery | 2/64 (3) | 2/67 (3) | 6/63 (3) | 1/62 (2) |
| Other | 1/64 (2) | 3/67 (4) | 1/63 (2) | 4/62 (6) |
| Previous bivalent HPV vaccine, n (%) | ||||
| Yes | 10 (8) | 12 (10) | 8 (6) | 13 (10) |
| No | 115 (92) | 114 (90) | 118 (94) | 110 (87) |
| Number of doses of vaccine in those previously vaccinated, median (IQR) | 3 (3–3) | 3 (2–3) | 3 (3–3) | 3 (3–3) |
| Previous STI excluding anogenital warts, n (%) | ||||
| Yes | 41 (33) | 43 (34) | 40 (32) | 44 (35) |
| No | 82 (67) | 82 (65) | 86 (68) | 82 (65) |
| Type of STI, n/N (%)a | ||||
| Chlamydia | 24/41 (59) | 25/43 (58) | 24/40 (60) | 28/44 (64) |
| Gonorrhoea | 11/41 (27) | 15/43 (36) | 7/40 (18) | 11/44 (25) |
| Syphilis | 2/41 (5) | 2/43 (5) | 2/40 (5) | 1/44 (2) |
| Herpes | 13/41 (32) | 7/43 (16) | 9/40 (23) | 8/44 (18) |
| Other | 7/41 (17) | 8/43 (19) | 7/40 (18) | 9/44 (20) |
| Number of STI episodes, median (IQR) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1) |
| Smoking, n (%) | ||||
| Daily | 42 (34) | 33 (26) | 36 (29) | 40 (32) |
| Less than daily | 13 (10) | 15 (12) | 10 (8) | 21 (17) |
| Ex-smoker | 32 (26) | 27 (21) | 34 (27) | 25 (20) |
| Never smoked | 37 (30) | 50 (40) | 46 (37) | 40 (32) |
| Missing | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Quality of life | ||||
| EQ-5D-5L: health utility | ||||
| n | 110 | 116 | 119 | 112 |
| Mean (SD) | 0.94 (0.11) | 0.92 (0.13) | 0.94 (0.10) | 0.92 (0.10) |
| EQ-5D-5L: VAS | ||||
| n | 111 | 115 | 119 | 110 |
| Mean (SD) | 83 (12) | 82 (13) | 82 (14) | 82 (15) |
Adherence to treatment and receipt of additional treatment
Over the 48-week duration of the study, 34 (15%) participants required a switch in topical treatment from IMIQ and 41 (18%) from PDX. Only four switches in topical treatment occurred before the end of the licensed duration of the allocated treatment (4 weeks for PDX and 16 weeks for IMIQ). A total of 139 out of 227 (61%) participants allocated to IMIQ and 29 out of 233 (12%) participants allocated to PDX completed less than the licensed duration of each topical treatment. A total of 167 out of 233 (72%) participants allocated to PDX extended their topical treatment beyond 4 weeks (the denominator is the number of participants who attended at least one follow-up visit).
Over half of participants (54%) received cryotherapy treatment at any time during the study. The use of cryotherapy was very similar, overall, between the groups: 117 out of 227 (52%) participants in the IMIQ group and 130 out of 233 (56%) in the PDX group; and 118 out of 235 (50%) and 129 out of 225 (57%) in the qHPV and placebo groups, respectively.
Cryotherapy prior to week 16 of the study was administered to 76 out of 460 (17%) participants: 27 out of 227 (12%) in the IMIQ group and 49 out of 233 (21%) in the PDX group. Cryotherapy use occurred earlier in the PDX group, probably owing to the shorter licensed duration of this treatment.
Complete data on participants’ adherence to the allocated treatments, switching of topical treatment and use of additional cryotherapy is shown in Table 2.
| Treatment characteristic | Treatment group | Topical treatment group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | IMIQ | PDX | |
| Number randomised | 125 | 126 | 126 | 126 | 251 | 252 |
| Number analysed (attended at least one follow-up visit) | 118 | 117 | 109 | 116 | 227 | 233 |
| Topical treatment, n (%) | ||||||
| Switched treatment at any time, yes | 15 (13) | 15 (13) | 19 (17) | 26 (22) | 34 (15) | 41 (18) |
| Timing of first treatment switch | ||||||
| Before 4 weeks | 2 (2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (2) | 2 (1) | 2 (1) |
| Between 4 and 16 weeks | 1 (1) | 3 (3) | 4 (4) | 4 (3) | 5 (2) | 7 (3) |
| After 16 weeks | 12 (10) | 12 (10) | 15 (14) | 20 (17) | 27 (12) | 32 (14) |
| Completed less than maximum licensed duration of topical treatment | 71 (60) | 13 (11) | 68 (62) | 16 (14) | 139 (61) | 29 (12) |
| Extended PDX beyond 4 weeks | 87 (74) | 80 (69) | 167 (72) | |||
| Any cryotherapy received | 56 (47) | 62 (53) | 61 (56) | 68 (59) | 117 (52) | 130 (56) |
| Timing of first cryotherapy | ||||||
| Before 4 weeks | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | 1 (0.5) | 3 (1) |
| Between 4 and 16 weeks | 17 (14) | 24 (21) | 9 (8) | 22 (19) | 26 (11) | 46 (20) |
| After 16 weeks | 39 (33) | 37 (32) | 51 (47) | 44 (38) | 90 (40) | 81 (35) |
| Has the patient had any other treatment at their treatment centre other than cryotherapy at any time | 5 (4) | 4 (3) | 4 (4) | 9 (8) | 9 (4) | 13 (6) |
| Has the patient had any treatment from a source outside their treatment centre | 5 (4) | 5 (4) | 5 (5) | 6 (5) | 10 (4) | 11 (5) |
| Vaccine, n (%) | ||||||
| Number of vaccine doses given | ||||||
| 0 | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.4) | 0 (0) |
| 1 | 11 (9) | 13 (11) | 7 (6) | 15 (13) | 18 (8) | 28 (12) |
| 2 | 17 (14) | 15 (11) | 11 (10) | 13 (11) | 28 (12) | 28 (12) |
| 3 | 89 (75) | 89 (76) | 91 (83) | 88 (76) | 180 (79) | 177 (76) |
Primary outcome
The primary outcome of the study was a combination of being wart free at 16 weeks and remaining wart free at 48 weeks from the start of treatment. This was achieved in 35 out of 101 (35%) participants allocated to receive IMIQ plus the qHPV vaccine, 38 out of 99 (38%) of those allocated to receive PDX plus the qHPV vaccine, 25 out of 98 (26%) of those allocated to IMIQ plus the placebo vaccine and 30 out of 99 (30%) of those allocated to PDX plus placebo. The denominator in each group is those participants who provided follow-up data at week 48.
Adjusted odds ratios (aORs) were calculated to estimate the topical treatment and vaccine effects after adjustment for gender, previous wart recurrence and HIV status, and included imputed data for those with missing data. The aOR for the topical treatment effect for IMIQ relative to PDX was 0.81 (95% CI 0.54 to 1.23). The aOR for the effect of vaccine relative to placebo was 1.46 (95% CI 0.97 to 2.20).
The data for the primary outcome are shown in Table 3.
| Outcome | Treatment group, n/N (%) | Treatment effects, aOR (95% CI)a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV (N = 125) | PDX plus qHPV (N = 126) | IMIQ plus placebo (N = 126) | PDX plus placebo (N = 126) | IMIQ vs. PDXb | qHPV vs. placeboc | |
| Wart free at week 16 and remaining wart free between weeks 16 and 48d | 35/101 (35) | 38/99 (38) | 25/98 (26) | 30/99 (30) | 0.81 (0.54 to 1.23) | 1.46 (0.97 to 2.20) |
Secondary outcomes
Clinically important secondary outcomes
Clinically important secondary outcomes were defined as (1) the proportion of participants who were wart free at week 16 (of those not lost to follow-up by this time point) and (2) the proportion of participants remaining wart free at week 48 (of those who had achieved clearance at 16 weeks and were followed up until week 48). To estimate the topical treatment and vaccine effects for each outcome, aORs were calculated and included imputed data for missing follow-up visits.
The proportion of participants who were wart free at week 16 was 58 out of 104 (56%) of those allocated to IMIQ plus qHPV vaccine, 70 out of 105 (67%) of those allocated to PDX plus qHPV vaccine, 56 out of 103 (54%) of those allocated to IMIQ plus placebo vaccine and 57 out of 102 (56%) of those allocated to PDX plus placebo. The aOR for the topical treatment effect for IMIQ relative to PDX was 0.77 (95% CI 0.52 to 1.14). The aOR for the effect of vaccine relative to placebo was 1.30 (95% CI 0.89 to 1.91).
The proportion of participants remaining wart free at week 48 of those with clearance at week 16 was 35 out of 43 (81%) of those allocated to IMIQ plus qHPV vaccine, 38 out of 53 (72%) of those allocated to PDX plus qHPV vaccine, 25 out of 39 (74%) of those allocated to IMIQ plus placebo vaccine and 30 out of 42 (71%) of those allocated to PDX plus placebo. The aOR for the topical treatment effect for IMIQ relative to PDX was 0.98 (95% CI 0.54 to 1.78). The aOR for the effect of vaccine relative to placebo was 1.39 (95% CI 0.73 to 2.63). The data for the clinically important secondary outcomes are shown in Table 4.
| Outcome | Treatment group, n/N (%) | Treatment effects, aOR (95% CI)a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV (N = 125) | PDX plus qHPV (N = 126) | IMIQ plus placebo (N = 126) | PDX plus placebo (N = 126) | IMIQ vs. PDXb | qHPV vs. placeboc | |
| Wart free at week 16d | 58/104 (56) | 70/105 (67) | 56/103 (54) | 57/102 (56) | 0.77 (0.52 to 1.14) | 1.30 (0.89 to 1.91) |
| Remaining wart free at week 48 after clearance at week 16e | 35/43 (81) | 38/53 (72) | 25/39 (74) | 30/42 (71) | 0.98 (0.54 to 1.78) | 1.39 (0.73 to 2.63) |
Other secondary outcomes measuring treatment effectiveness
Other secondary outcomes that measured treatment effectiveness were (1) the proportion of participants who were wart free at the end of the licensed duration of their assigned topical treatment (4 weeks for PDX and 16 weeks for IMIQ), (2) the proportion of participants wart free at any time during the 48-week trial period, (3) the proportion of participants who experienced wart recurrence after achieving complete clearance, (4) the proportion of participants who were wart free at week 16 without additional procedures (cryotherapy or surgery), (5) the proportion of participants who were wart free at the end of the licensed duration of their assigned topical treatment without additional procedures (cryotherapy or surgery), (6) the time to complete wart clearance (days) and (7) the time from complete wart clearance to recurrence (days). To estimate the topical treatment and vaccine effects for binary or ordinal outcomes, aORs were calculated and included imputed data for missing follow-up visits. Hazard ratios were calculated for time to event data (outcomes 6 and 7).
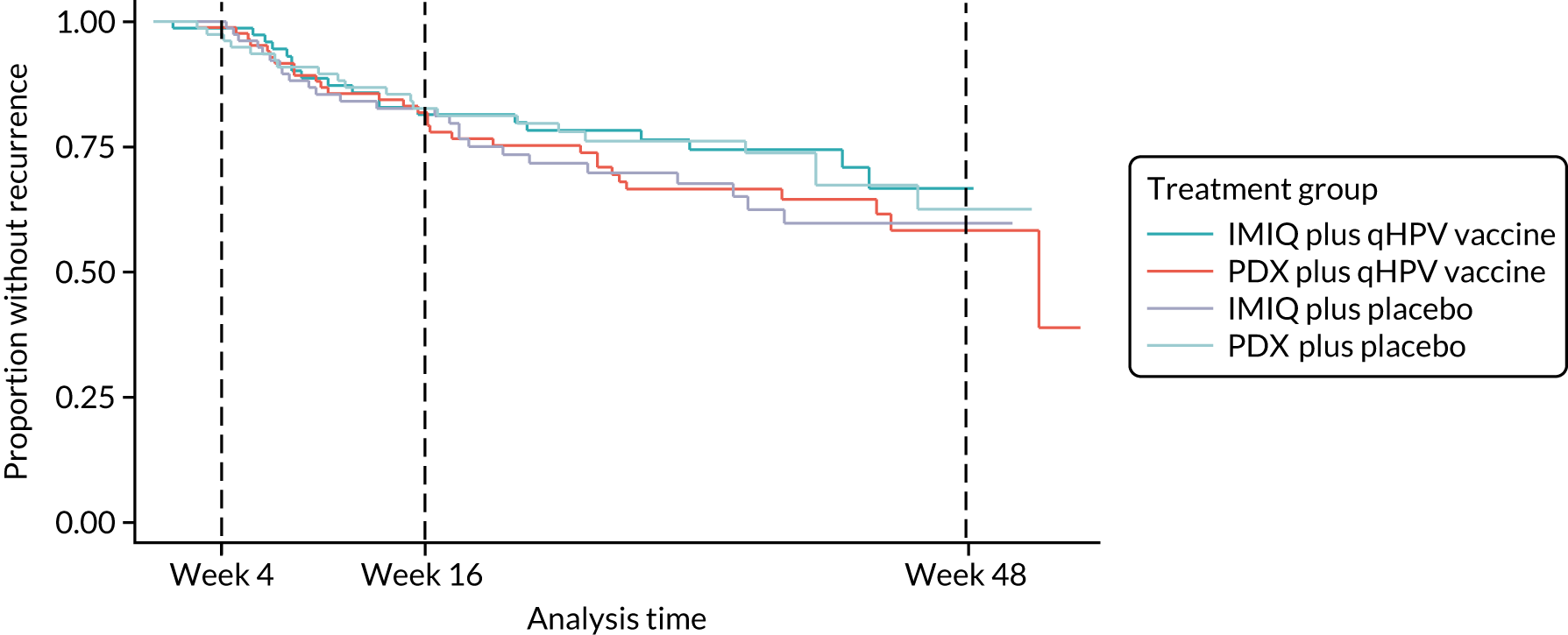
The results for the secondary outcomes measuring treatment effectiveness are shown in Table 5. Kaplan–Meier survival estimates for time to wart clearance and recurrence are shown in Figures 3 and 4.
| Outcome | Treatment group | Treatment effects, aOR (95% CI)a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV (N = 125) | PDX plus qHPV (N = 126) | IMIQ plus placebo (N = 126) | PDX plus placebo (N = 126) | IMIQ vs. PDXb | qHPV vs. placeboc | |
| Wart free at the end of the assigned treatment course (4 or 16 weeks), n/N (%)d | 54/104 (52) | 23/117 (20) | 48/103 (47) | 19/116 (16) | 2.92 (1.75 to 4.87) | 1.13 (0.72 to 1.77) |
| Proportion experiencing complete wart clearance at any time during the 48-week trial period, n/N (%)e | 79/118 (67) | 86/117 (74) | 82/109 (75) | 79/116 (68) | 0.83 (0.52 to 1.34) | 1.13 (0.71 to 1.80) |
| Proportion of patients experiencing wart recurrence/relapse after complete wart clearance, n/N (%)f | 19/79 (24) | 30/86 (35) | 26/82 (32) | 21/79 (27) | 0.84 (0.52 to 1.37) | 1.16 (0.72 to 1.88) |
| Wart free by week 16 without additional treatment, n/N (%)g | 34/104 (33) | 38/105 (36) | 37/103 (36) | 26/102 (25) | 1.11 (0.73 to 1.69) | 1.20 (0.80 to 1.81) |
| Wart free at the end of the assigned treatment period (4 or 16 weeks) without additional treatment, n/N (%)h | 29/104 (28) | 19/117 (16) | 29/103 (28) | 16/116 (14) | 1.63 (0.98 to 2.71) | 1.04 (0.67 to 1.62) |
| Treatment effects, adjusted hazard ratio (95% CI)a | ||||||
| Time to complete wart clearance (days), median (95% CI) | 110 (77 to 120) | 84 (63 to 112) | 114 (91 to 138) | 117 (77 to 144) | 0.77 (0.60 to 0.97) | 1.24 (0.99 to 1.56) |
| Time from complete wart clearance to recurrence/relapse (days), 20th percentile (95% CI) | 149 (61 to 295) | 113 (67 to 183) | 122 (56 to 179) | 150 (76 to 273) | 1.07 (0.66 to 1.73) | 0.72 (0.42 to 1.24) |
FIGURE 3.
Kaplan–Meier survival estimates for time to wart clearance.
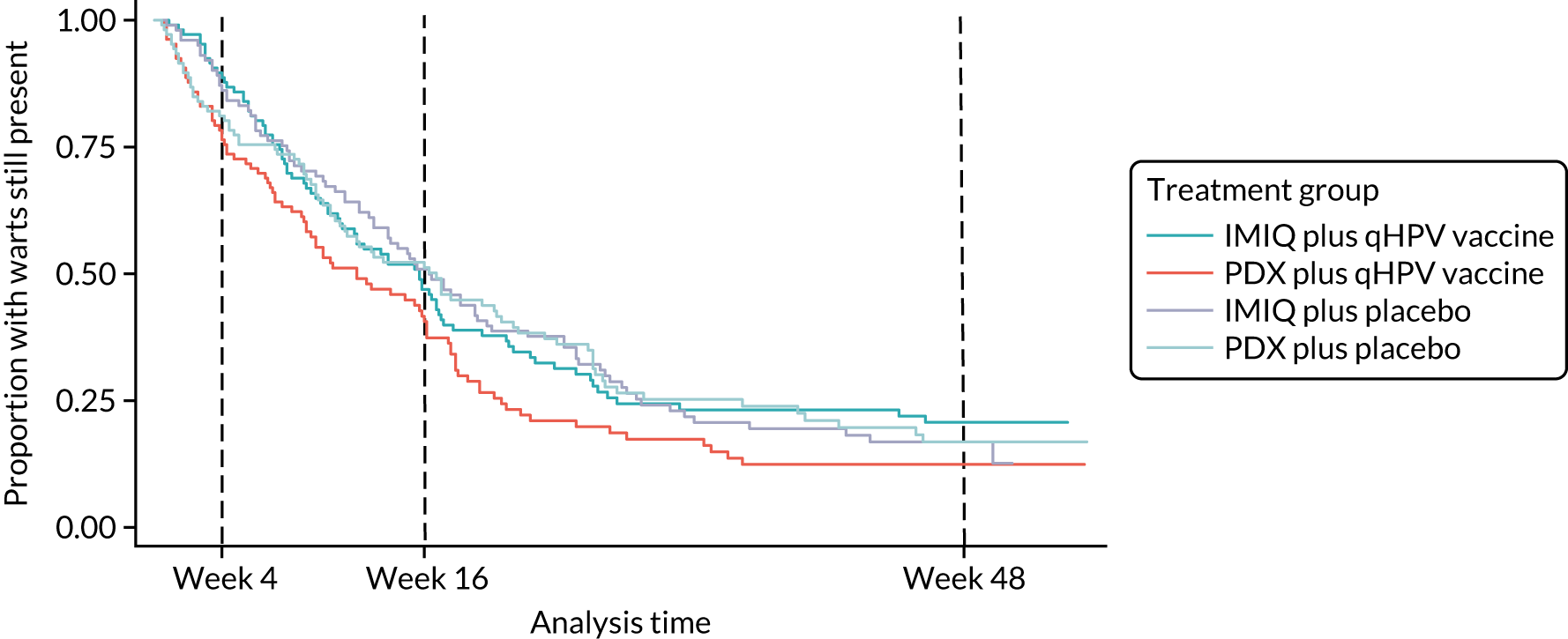
FIGURE 4.
Kaplan–Meier survival estimates for time to wart recurrence in participants who achieved wart clearance.
Adverse events
There were no serious adverse events (SAEs) of grade 4 severity in any of the groups. There were 21 SAEs of grade 3 severity, eight of which occurred in participants allocated to IMIQ plus qHPV vaccine, four in participants allocated to PDX plus qHPV vaccine, three in participants allocated to IMIQ plus placebo vaccine and six in participants allocated to PDX plus placebo vaccine. Of the eight SAEs in the IMIQ plus qHPV vaccine group, six occurred in a single participant and all eight were judged to be unrelated to either the topical treatment or vaccine by the local investigator. Of the four SAEs in the PDX plus qHPV vaccine group, three were judged to be unrelated to either the vaccine or placebo and one was judged unlikely to be related to vaccine and unrelated to topical treatment. Of the three SAEs in the IMIQ plus placebo vaccine group, all three were judged to be unrelated to either topical treatment or vaccine. Of the six SAEs in the PDX plus placebo group, two were in a single participant; four were judged to be unrelated to either topical treatment or vaccine, one was judged unlikely to be related to both topical treatment and vaccine and one was judged unlikely to be related to topical treatment and unrelated to vaccine.
There was one serious adverse reaction to the topical treatment, of grade 3 severity (skin ulceration). This occurred in a patient in the IMIQ plus qHPV vaccine group and was judged to be definitely related to topical treatment.
There was one suspected unexpected serious adverse reaction, which occurred in the PDX plus placebo vaccine group and was judged to be possibly related to vaccine and unrelated to topical treatment.
In addition, two pregnancies were reported (notifiable AEs), one in the PDX plus qHPV vaccine group and one in the PDX plus placebo group.
The number of SAEs by group allocation is shown in Table 6.
| Event | Treatment group (n) | Total (n) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | ||
| SAE | 8 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 21 |
| SAR | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| SUSAR | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 9 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 23 |
For further details of the SAE reports and reasons for withdrawal, see Appendix 3, Tables 17–23.
Symptom scores of adverse effect severity from topical treatment
Participants self-rated the maximum intensity of any adverse effects from their allocated topical treatment since their previous visit as none, mild, moderate or severe. Their symptom scores are shown in Table 7. To estimate the topical treatment and vaccine effects on symptom scores, aORs were calculated from an ordinal logistic regression model and included imputed data for missing follow-up visits. There were no significant differences in symptom scores according to topical treatment or vaccine.
| Time point | Severity of most severe side effects (patient reported) | Treatment group, n/N (%)a | Treatment effects, aOR (95% CI) (calculated from ordinal logistic regression model)b | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV (N = 125) | PDX plus qHPV (N = 126) | IMIQ plus placebo (N = 126) | PDX plus placebo (N = 126) | IMIQ vs. PDXc | qHPV vs. placebod | ||
| Week 4 | None | 33/109 (30) | 36/109 (33) | 44/105 (42) | 39/107 (36) | 0.89 (0.63 to 1.26) | 1.35 (0.95 to 1.91) |
| Mild | 38/76 (50) | 40/73 (55) | 30/61 (49) | 41/68 (60) | |||
| Moderate | 23/76 (30) | 27/73 (37) | 22/61 (36) | 20/68 (29) | |||
| Severe | 15/76 (20) | 6/73 (8) | 9/61 (15) | 7/68 (10) | |||
| Week 8 | None | 37/81 (46) | 44/77 (57) | 42/85 (49) | 29/78 (37) | 0.85 (0.57 to 1.29) | 0.91 (0.60 to 1.38) |
| Mild | 18/44 (41) | 19/33 (58) | 29/43 (67) | 33/49 (67) | |||
| Moderate | 18/44 (41) | 14/33 (42) | 9/43 (21) | 14/49 (29) | |||
| Severe | 8/44 (18) | 0/33 (0) | 5/43 (13) | 2/49 (4) | |||
| Week 16 | None | 21/46 (46) | 32/52 (62) | 25/56 (45) | 16/47 (34) | 0.76 (0.45 to 1.30) | 0.62 (0.36 to 1.06) |
| Mild | 14/25 (56) | 13/20 (65) | 17/31 (65) | 22/31 (71) | |||
| Moderate | 7/25 (28) | 6/20 (30) | 11/31 (35) | 8/31 (26) | |||
| Severe | 4/25 (16) | 1/20 (5) | 3/31 (10) | 1/31 (3) | |||
| Week 24 | None | 18/32 (56) | 15/26 (58) | 15/34 (44) | 20/35 (57) | 0.75 (0.37 to 1.49) | 0.84 (0.42 to 1.68) |
| Mild | 10/14 (71) | 6/11 (55) | 13/19 (68) | 11/15 (73) | |||
| Moderate | 2/14 (14) | 4/11 (36) | 4/19 (21) | 4/15 (27) | |||
| Severe | 2/14 (14) | 1/11 (9) | 2/19 (11) | 0/15 (0) | |||
| Week 48 | None | 13/20 (65) | 8/13 (62) | 6/12 (50) | 12/14 (86) | 0.45 (0.13 to 1.51) | 0.93 (0.29 to 3.03) |
| Mild | 7/7 (100) | 5/5 (100) | 4/6 (67) | 1/2 (50) | |||
| Moderate | 0/7 (0) | 0/5 (0) | 1/6 (17) | 0/2 (0) | |||
| Severe | 0/7 (0) | 0/5 (0) | 1/6 (17) | 1/2 (50) | |||
Health-related quality-of-life outcomes
Heath-related quality-of-life outcome data, as measured by EQ-5D-5L health utility and VAS ratings, are shown in Table 8.
| Measure | Treatment group, mean (SD) | Treatment effects, adjusted coefficient (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV (n = 125) | PDX plus qHPV (n = 126) | IMIQ plus placebo (n = 126) | PDX plus placebo (n = 126) | IMIQ vs. PDX | qHPV vs. placebo | |
| EQ-5D-5L: health utility | ||||||
| Week 4 | 0.95 (0.08) | 0.94 (0.13) | 0.94 (0.09) | 0.93 (0.10) | ||
| Week 8 | 0.95 (0.09) | 0.93 (0.14) | 0.94 (0.09) | 0.94 (0.10) | ||
| Week 16 | 0.95 (0.10) | 0.92 (0.16) | 0.96 (0.06) | 0.95 (0.08) | ||
| Week 24 | 0.94 (0.14) | 0.95 (0.12) | 0.96 (0.08) | 0.93 (0.10) | ||
| Week 48 | 0.94 (0.14) | 0.93 (0.15) | 0.95 (0.09) | 0.95 (0.09) | ||
| Area under the curve: health utility | ||||||
| Multiple imputation analysis | 45.6 (4.71) | 44.5 (6.74) | 45.9 (3.05) | 45.2 (3.77) | 0.14 (–0.63 to 0.91)a | –0.31 (–1.06 to 0.45)a |
| Complete-case analysis | 0.64 (–0.59 to 1.87) | –0.24 (–1.48 to 1.00) | ||||
| EQ-5D-5L: VAS | ||||||
| Week 4 | 85.0 (9.7) | 83.2 (14.2) | 82.2 (14.1) | 81.2 (15.6) | 1.05 (–1.55 to 3.65)a | 2.14 (–0.66 to 4.94)a |
| Week 8 | 85.8 (12.0) | 82.6 (13.9) | 82.4 (13.5) | 84.8 (13.3) | –0.10 (–2.46 to 2.26)a | 0.22 (–2.27 to 2.71)a |
| Week 16 | 86.1 (11.6) | 83.3 (14.2) | 85.6 (13.0) | 85.7 (11.2) | 0.39 (–2.12 to 2.90)a | –0.43 (–2.80 to 1.94)a |
| Week 24 | 87.3 (12.5) | 86.4 (14.5) | 85.0 (15.3) | 85.6 (13.5) | 0.32 (–2.50 to 3.14)a | 1.38 (–1.21 to 3.97)a |
| Week 48 | 88.0 (11.9) | 85.2 (17.1) | 84.5 (14.4) | 87.8 (11.2) | –0.62 (–3.04 to 1.81)a | –0.26 (–2.97 to 2.45)a |
Further analyses
A complete-case analysis (CCA) was performed for the primary outcome and clinically important secondary outcomes without the use of imputed data (see Appendix 3, Table 24, for details of missing data). The results are shown in Table 9 and are consistent with the main results shown in Tables 3 and 4.
| Outcome | Treatment group, n/N (%) | aOR (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV (n = 125) | PDX plus qHPV (n = 126) | IMIQ plus placebo (n = 126) | PDX plus placebo (n = 126) | IMIQ vs. PDXa | qHPV vs. placebob | |
| Wart free at week 16 and remaining wart free between week 16 and 48c | 35/101 (35) | 38/99 (38) | 25/98 (26) | 30/99 (30) | 0.82 (0.53 to 1.27) | 1.55 (1.00 to 2.41) |
| Wart free at week 16d | 58/104 (56) | 70/105 (67) | 56/103 (54) | 57/102 (56) | 0.76 (0.51 to 1.13) | 1.31 (0.88 to 1.95) |
| Remaining wart free at week 48 after clearance at week 16e | 35/43 (81) | 38/53 (72) | 25/39 (74) | 30/42 (71) | 0.97 (0.48 to 1.95) | 1.80 (0.90 to 3.63) |
The results of a four-arm analysis are presented in Table 10. Effectively, this approach considers each treatment combination as a separate treatment arm and is an analysis that is recommended for factorial trials. The reference group was the group allocated to receive PDX plus placebo vaccine, so each of the other three treatment groups were compared with the reference group. The odds of achieving the primary outcome for participants allocated to IMIQ plus qHPV vaccine is 1.18 times (18% higher than) the odds for those allocated to PDX plus placebo (95% CI 0.66 to 2.12); the odds of achieving the primary outcome for the other treatment groups compared with the reference group can be interpreted in a similar way.
| Outcome | Treatment group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV (N = 125) | PDX plus qHPV (N = 126) | IMIQ plus placebo (N = 126) | PDX plus placebo (N = 126) | |
| Participants achieving end point/participants not lost to follow-up at week 48 (%) | 35/100 (35) | 38/99 (38) | 25/98 (26) | 30/99 (30) |
| aOR of remaining wart free at week 16 and remaining wart free between weeks 16 and 48a | 1.18 (0.66 to 2.12) | 1.37 (0.78 to 2.41) | 0.76 (0.42 to 1.38) | Reference |
In addition, we fitted a model for the primary outcome that contained the two main effects (topical treatment and vaccine) and an interaction term (Table 11). The interaction term was not significant (p = 0.76).
| Effect | aOR (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| Topical main effect (IMIQ vs. PDX for participant receiving vaccine placebo) | 0.76 (0.42 to 1.36) | 0.35 |
| Vaccine main effect (qHPV vaccine vs. placebo for participants receiving PDX) | 1.38 (0.78 to 2.41) | 0.27 |
| Interaction effect (IMIQ × qHPV vaccine) | 1.14 (0.51 to 2.53) | 0.76 |
The interpretation of the interaction effect is that the topical treatment effect is no different in the presence or absence of the qHPV vaccine.
Three subgroup analyses were specified a priori: gender (male vs. female), previous occurrence of warts (no previous occurrence vs. one or more previous occurrences) and HIV status (HIV positive vs. HIV negative) and performed by adding interaction terms to the model for the primary outcome for each factor (topical treatment and vaccine). The resulting six interaction terms were tested separately (topical treatment and gender, topical treatment and previous occurrence of warts, topical treatment and HIV status, vaccination and gender, vaccination and previous occurrence of warts, and vaccination and HIV status). There was no evidence of any interaction; all p-values for the interaction terms outlined above were > 0.35. Complete data are shown in Appendix 3, Table 25.
As detailed in the statistical analysis plan, further analyses were undertaken to explore the sensitivity of results to the MAR assumption. As the MAR assumption cannot be tested directly, imputation was undertaken under various scenarios that might occur if the data were not MAR and to see if the results obtained are consistent with the primary analysis. We proceeded as follows: we defined π0 as the proportion of unobserved individuals experiencing the primary outcome (complete wart clearance at week 16 and remaining wart free at week 48); we defined π1 as the corresponding proportion in the observed individuals; we defined θ as the odds ratio for the primary outcome for the observed individuals compared with that for the unobserved individuals, adjusting for covariates in the analysis model.
Under the MAR assumption θ = 1, it may be reasonable to expect that those individuals who have a good outcome (wart clearance) are less likely to attend follow-up visits (π0 > π1; therefore, θ < 1), but π1 > π0 and θ > 1 is also plausible, although perhaps somewhat less so. We therefore generated three sets of imputed data for the sensitivity analysis, with values of θ equal to 0.6, 0.8 and 1.25 using the Stata® version 15 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA) impute command for a logistic model with an offset. Each of the three sets of imputed data for the three scenarios outlined above (θ = 0.6, 0.8 and 1.25) was generated using a logistic imputation model with the offset equal to ln(θ) and combined using Rubin’s rules. The results were compared with those from the multiple imputation analysis performed under the assumption of MAR and with the CCA. No substantive differences were found; the analyses were entirely consistent with the multiple imputation analyses carried out under the MAR assumption and the CCA. Therefore, we are confident that our primary results generated under the MAR assumption are robust to plausible deviations from that assumption.
Chapter 4 Economic evaluation
Introduction
In this chapter, we present the results of an economic evaluation conducted alongside the randomised trial. We investigated the cost-effectiveness and cost–utility of the two topical treatments, as well as the qHPV vaccine, in patients with anogenital warts.
We explored a range of scenarios in the economic evaluation, representing different design choices:
-
factorial design – (1) each of the treatment arms in the 2 × 2 table; (2) qHPV vaccine versus placebo or PDX cream versus IMIQ cream
-
utility values – (1) values based on the EQ-5D-5L instrument used in the trial; (2) values based on mapping values to the EQ-5D-3L
-
trial population – (1) ITT population; (2) a population restricted to those who had never changed from their allocated topical treatment; (3) a complete-case population based on the utility scores
-
data interpolation – (1) interpolating missing data by assuming it is MAR; (2) interpolating missing data by assuming it is missing not at random (MNAR)
-
costs for health-care visits – (1) planned study visits to align with the ITT principle; (2) total number of visits in the trial; (3) number of visits with warts present
-
outcomes – (1) incremental costs per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained; (2) incremental costs per additional patient clearing warts by week 16; (3) incremental costs per avoided recurrence up to 48 weeks after starting treatment.
Methods
We performed a cost-effectiveness analysis (using the trial primary end points) and cost–utility analysis (using QALYs) based on the recommended ITT population. 43 The analysis compared the four randomisation arms, allowing for interaction between the topical treatments and the vaccine. The analysis also compared the topical treatment and vaccine separately, assuming no interaction and mirroring the efficacy analysis. In addition, a per-protocol analysis (PPA) was undertaken, considering patients who had been treated with the allocated topical treatment only (i.e. no change in allocated topical treatment over the course of the trial), and we explored, in a CCA, the impact of missing utility values.
The analysis was defined prior to release of the final data set as an economic evaluation analysis plan. 38 When possible, this economic evaluation followed the reference case of the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) and guidelines for economic evaluations from the Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation,44,45 as well as the recommendations of economic evaluations to be conducted alongside clinical trials. 43
In line with this national guidance,44,45 we adopted the perspective of the NHS. Because the trial follow-up was only 48 weeks, mortality did not occur and there was close similarity of end points in all four treatment arms; therefore, we adopted the time frame of the trial and did not discount future costs or outcomes.
Outcomes
We performed a cost–utility analysis of the incremental costs per QALY gained by each intervention. We performed a full incremental analysis in which both dominated and extendedly dominated interventions were removed. 46 We also calculated the net monetary benefit (NMB), which can be defined as the difference in the value of monetised economic benefits (health outcomes and costs saved) in each arm, where the health outcome is expressed in monetary units using a range of willingness-to-pay (WTP) thresholds. 47,48
An additional threshold analysis was conducted to estimate the threshold price at which the qHPV vaccine would become cost-effective should the vaccine be more effective than placebo.
In scenario analyses, we used both components of the combined primary end point of the trial as the denominators in the cost-effectiveness analysis,43 that is the incremental costs per additional patient clearing warts by week 16 and avoiding recurrence up to week 48 after starting treatment.
Resource use and costs
The total costs per patient consisted of the costs of the study medication (topical treatment and vaccine), the (optional) cryotherapy and the care episodes. For the two topical treatments, we calculated costs based on the number of applications of each treatment. For the qHPV vaccine, we considered the actual number of administered vaccine doses, despite the fact that some patients did not receive all three doses as planned, which is likely to reflect real-world clinical practice. If cryotherapy had been applied, we also used the actual number of applications. The number of care episodes was estimated based on three scenarios: (1) the planned study visits (four within 16 weeks and six within 48 weeks), (2) the actual number of planned and additional visits and (3) the number of visits when warts were reported to be present. We considered these three different cost values because (1) the planned study visits align well with the ITT principle, (2) the total number of observed visits is in line with the other estimated resources based on the trial, but is probably an overestimate of the number of clinic visits seen in clinical practice and (3) the number of visits when warts were present may be regarded as most closely approximating the number of visits seen in clinical practice. Note that the cost scenarios are listed in order of the total number of visits involved (from highest to lowest), rather than in order of which scenario is deemed the most valid or probable.
For the costs of the two topical treatments, we used the NHS Business Services Authority Drug Tariff price [£48.60 for 12 sachets of IMIQ (50 mg/g); £17.83 for 5 g of PDX cream (1.5 mg/g)]. 49 For the qHPV vaccine, we obtained the NHS indicative price for Gardasil of £86.50 per dose from the British National Formulary. 50 For the costs per cryotherapy treatment round (£4.95), we took the costs from the Quality Of Life In patients with GENital warts (QOLIGEN) observational study of anogenital wart treatment in sexual health clinics. 36 For the costs of care episodes (men, £92.80; women, £126.40), we multiplied the number of clinic visits by the sex-specific mean costs per episode of care from the QOLIGEN study. 36 Finally, we assumed that each patient would have had one STI screen, irrespective of treatment randomisation, which is why the costs of STI screens were not included in the costs of our economic analysis.
The base year of the analysis was 2017/18; therefore, we inflated values to Great British pounds (GBP) 2017/18 when appropriate. 51 Similar to the procedure for natural outcomes, we separated costs at weeks 16 and 48 to allow for separate evaluations of wart clearance by week 16 and avoided recurrence up to week 48.
Measurement of health-related quality of life
The HRQoL of patients was measured with the disease-generic EQ-5D-5L questionnaire,52 which measures five dimensions of diseases at five different levels. Measurements of the EQ-5D-5L and the VAS were collected at each study visit at weeks 0 (baseline), 4, 8, 16, 24 and 48. Utility values informed by the EQ-5D-5L scores were calculated based on the English value set, stratified by age. 53 In line with the NICE position statement on use of the EQ-5D-5L valuation set 2017 (last updated in November 2018),54 we also calculated utility values by mapping the EQ-5D-5L data to the EuroQol-5 Dimensions, three-level version (EQ-5D-3L), value set using the preferred mapping function of van Hout et al. 55
The analysis plan suggested extrapolating the data beyond the end of the follow-up period of the clinical trial (week 48) using suitable functions such as piecewise polynomials (also known as splines). Based on the results of the within-trial period of 48 weeks, however, it was decided to not extrapolate the results for HRQoL beyond the trial duration given the considerable overlap of results and convergence of HRQoL across treatment arms (Figure 5).
FIGURE 5.
Box plot of utility scores per treatment at each time point (median and interquartile range with outliers). (a) EQ-5D-5L and (b) mapped EQ-5D-3L.
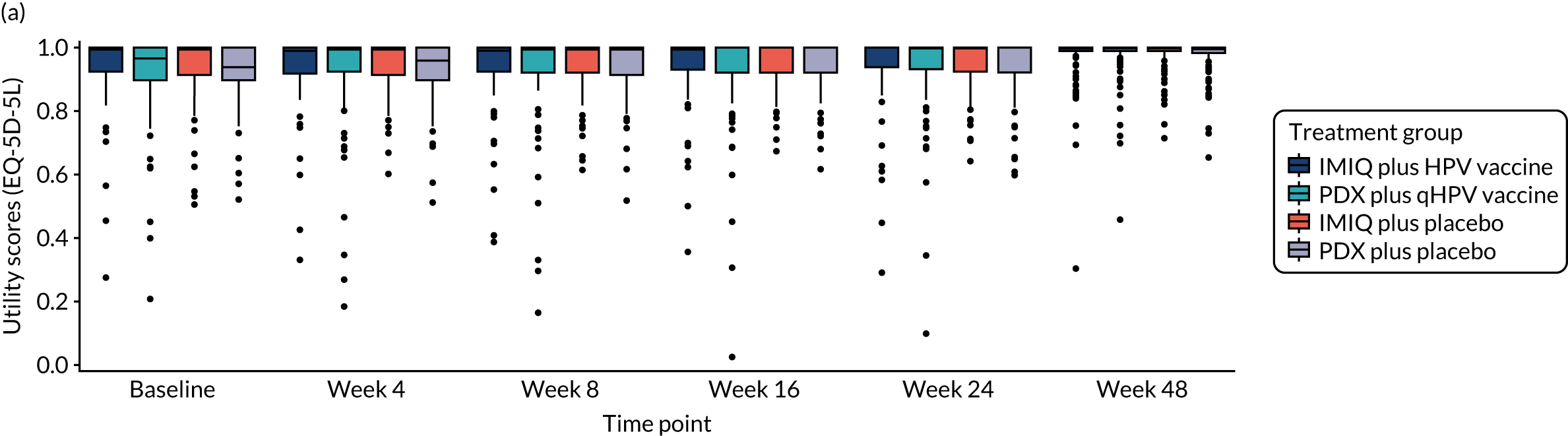
The QALYs gained in each arm were estimated based on the area under the curve as a function of time since recruitment,46 adjusted for the patient-specific baseline HRQoL. 56 In addition to the mapped EQ-5D-3L utility scores used for the base-case analysis, we also explored the EQ-5D-5L utility scores.
Missing data
Multivariate imputations by chained equations were used to impute values for the missing data of EQ-5D utility scores using predictive mean matching and pooling estimates from 50 multiply imputed data sets using Rubin’s rules (see Chapter 2). The data were assumed to be MAR in the base-case analysis, but we also explored an alternative, MNAR, assumption that implied reducing the missing values by 10% and 20%, respectively57 (see Scenario analysis).
Uncertainty analysis
We explored the uncertainty associated with the imputation and the study sample in a combined bootstrapping approach. 43 First, we bootstrapped each treatment group in the original data set that included the missing values. Then, we imputed the missing values before estimating for each patient the total costs and (adjusted) QALYs. Finally, we calculated the mean values for each treatment arm and the expected NMB. We repeated this process for 500 bootstrap replicates.
We visualised the results for all four treatment arms in cost-effectiveness plots, which present the total QALYs gained on the x-axis and the total costs incurred on the y-axis. The plots display outcomes using both the EQ-5D-3L and EQ-5D-5L for measuring the QALY gain as well as the three cost scenarios for care episodes to estimate the total costs per patient. Point estimates are shown in larger size and the uncertainty estimated from the combined bootstrapping approach is shown as scatterplots with contour overlays (see Results).
Furthermore, we used the NMB to visualise the uncertainty of the treatment arms in a cost-effectiveness acceptability curve (CEAC), which presents the joint probability of multiple treatment options being cost-effective in repeated iterations (see Figure 8). Given that the trial dealt with more than two treatment options, we identified the optimal option with the highest mean NMB using the cost-effectiveness acceptability frontier. 58 This is in line with the presumed objective of the NHS of maximising health with limited resources. 44
Scenario analysis
In a scenario analysis, we performed the cost-effectiveness analysis separately for both factors (i.e. PDX vs. IMIQ and qHPV vaccine vs. placebo), corresponding to the primary efficacy analysis, and assuming no interaction. For this analysis, we calculated the incremental QALY gain using a multivariate linear regression model, adjusting for the baseline covariates and HRQoL scores and using the treatment as a dummy variable to estimate the incremental difference. 56
We also performed sensitivity analyses on the MAR assumption in which we reduced the imputed HRQoL scores by 10% and 20% to explore the impact of the imputations on the results. 57
Results
The HIPvac trial recruited a total of 503 participants whose demographic characteristics were similar and well distributed among the four treatment arms, excluding the HIV status of patients receiving IMIQ plus qHPV vaccine (see Table 1). For the PPA, 408 patients who did not switch to the other cream by week 16 were included, as were 382 patients who had not switched by week 48. For the CCA, 454 participants were included for both 16 and 48 weeks given that patients with missing utility values typically missed a value at least once during the first 16 weeks, resulting in no different population between week 16 and week 48. The balance of patient characteristics between treatment arms was preserved in both analyses (see Appendix 4, Tables 26 and 27).
The factor analysis showed lower resource use at week 48 in the qHPV vaccine arms than in the placebo arms in all three analysed populations (except for the vaccine itself; see ITT population in Table 12 and PPA and CCA populations in Appendix 4, Tables 29 and 30).
The factor analysis for the creams is rather inconclusive and indicates slightly lower numbers of cryotherapy sessions in the IMIQ arms, but a higher total number of study visits with warts existent and a lower number of study visits in total (Table 12). Similar results were seen over 16 weeks and for the PPA and CCA populations (see Appendix 4, Tables 28–30).
| Resource | Meana (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | |
| IMIQ courses | 2.14 (0.00 to 6.00) | 0.33 (0.00 to 4.00) | 2.20 (0.00 to 5.00) | 0.55 (0.00 to 4.88) |
| PDX courses | 0.15 (0.00 to 1.90) | 1.55 (0.00 to 3.88) | 0.18 (0.00 to 1.88) | 1.61 (0.00 to 4.00) |
| qHPV vaccines | 2.54 (1.00 to 3.00) | 2.53 (1.00 to 3.00) | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Cryotherapies | 1.06 (0.00 to 6.80) | 1.08 (0.00 to 6.88) | 1.51 (0.00 to 7.00) | 1.56 (0.00 to 7.88) |
| Study visits | 5.30 (1.00 to 11.90) | 5.25 (1.00 to 11.00) | 5.48 (1.00 to 11.00) | 5.69 (1.00 to 12.88) |
| Visits with warts | 3.74 (1.00 to 9.00) | 3.40 (1.00 to 8.88) | 4.03 (1.00 to 10.00) | 3.98 (1.00 to 11.62) |
The costs of the different treatments reflect the pattern seen in the resource consumption. Across the three analysed populations, the costs for the study medications, cryotherapy and vaccine generally increased when moving from ITT to PPA, and they were similar for the ITT and CCA populations (see Appendix 4, Tables 31–33). For the three scenarios of the study visits investigated, the costs for the four or six scheduled visits within 16 or 48 weeks, respectively, did not change. The planned number of study visits was always higher than the observed number of visits and than the number of visits with warts present (Figure 6) because of failure of some participants to attend. The costs for visits when warts were present were about two-thirds the costs of the planned visits.
FIGURE 6.
Breakdown of costs per category and treatment for each analysed population. At (a) 16 weeks and (b) 48 weeks.
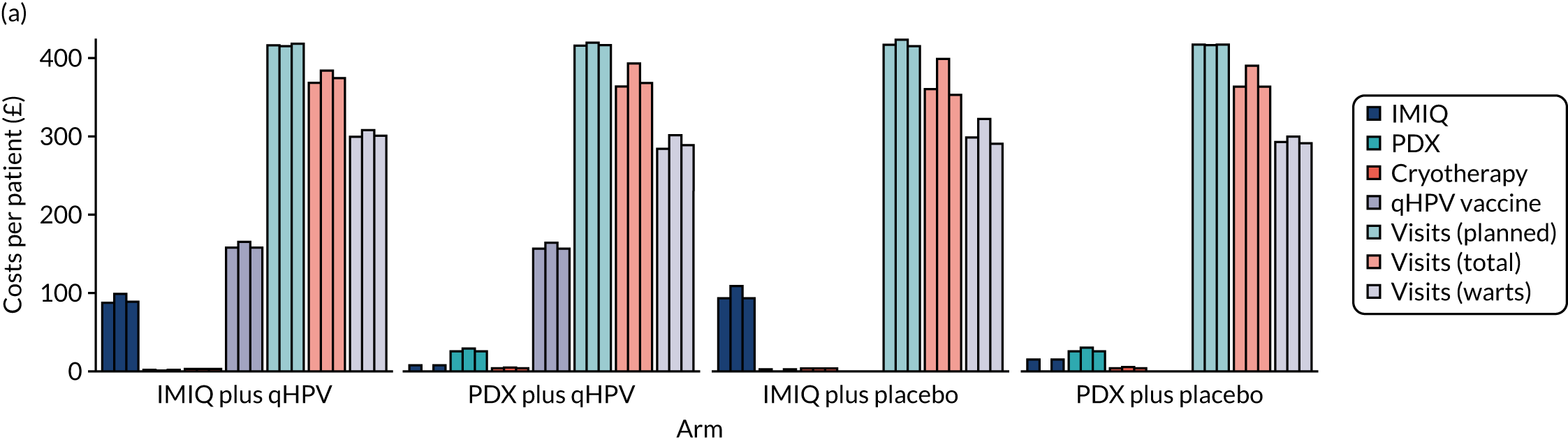

The highest cost category is the cost of clinic visits (driven by the number of visits made), followed by the vaccine costs. The least expensive cost category is cryotherapy.
Mean utility scores (mapped to the EQ-5D-3L) were consistently greater than 0.87 at every time point and across all analysed populations (see Appendix 4, Table 39). The utility values generally seemed to increase over time, although the CIs were wide.
When using the EQ-5D-5L value set to derive utility scores, all mean utility scores were slightly higher and consistently greater than 0.92 at every time point and across all analysed populations (see Appendix 4, Table 40). Similarly, using the EQ-5D-3L utility scores, the values generally increased over time, but with wide CIs.
After adjusting for the different baseline utility values, the mean QALY gain over time was higher for PDX than for IMIQ in all three analysed populations and with both EQ-5D utility scores (Table 13). Likewise, the mean QALY gain over time was always higher for placebo than for the qHPV vaccine (except for PDX in the PPA population). Similar results were seen when looking only at the first 16 weeks (see Appendix 4, Table 41).
| Measure | Adjusted QALY gain (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | |
| ITT analysis | ||||
| EQ-5D-3L | 0.018 (–0.187 to 0.214) | 0.044 (–0.103 to 0.261) | 0.034 (–0.136 to 0.243) | 0.044 (–0.118 to 0.295) |
| EQ-5D-5L | 0.011 (–0.075 to 0.137) | 0.023 (–0.059 to 0.166) | 0.018 (–0.087 to 0.181) | 0.026 (–0.058 to 0.186) |
| PPA without change in allocated topical treatment | ||||
| EQ-5D-3L | 0.016 (–0.177 to 0.188) | 0.056 (–0.144 to 0.238) | 0.029 (–0.091 to 0.275) | 0.044 (–0.102 to 0.284) |
| EQ-5D-5L | 0.009 (–0.062 to 0.090) | 0.030 (–0.091 to 0.174) | 0.016 (–0.052 to 0.177) | 0.026 (–0.060 to 0.182) |
| CCA | ||||
| EQ-5D-3L | 0.017 (–0.180 to 0.217) | 0.038 (–0.105 to 0.263) | 0.037 (–0.132 to 0.276) | 0.043 (–0.116 to 0.292) |
| EQ-5D-5L | 0.011 (–0.082 to 0.143) | 0.021 (–0.060 to 0.165) | 0.019 (–0.081 to 0.184) | 0.026 (–0.056 to 0.189) |
Overall, it is noteworthy that the 95% CIs of the adjusted incremental QALYs were largely overlapping between treatments, and always crossed zero.
The incremental cost-effectiveness results of all three analysed populations (ITT, PPA and CCA) point towards PDX without qHPV vaccine being the most cost-effective intervention among the four treatments considered, at the current list price for qHPV vaccine (£86.50 per dose) and at both week 48 (Table 14) and week 16 (see Appendix 4, Table 34). In addition, treatment with PDX plus qHPV vaccine may be beneficial over treatment with only PDX in the ITT and PPA populations at week 48 as measured with the EQ-5D-3L, but most pronounced in the PPA with incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) between £16,000/QALY and £19,000/QALY (see Table 14). Results were similar at 16 weeks (see Appendix 4, Table 34).
| Treatment | Total cost (£) | Total adjusted QALYs | ICER (£) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six study visits as planned | Total number of visits | Visits with warts existing | EQ-5D-3L | EQ-5D-5L | EQ-5D-3L | EQ-5D-5L | |
| ITT analysis | |||||||
| PDX plus placebo | 689 | 654 | 473 | 0.0437 | 0.0259 | Reference | Reference |
| IMIQ plus placebo | 743 | 696 | 541 | 0.0342 | 0.0176 | Dominated | Dominated |
| PDX plus qHPV vaccine | 892 | 817 | 627 | 0.0443 | 0.0234 | 380,000; 304,000; 288,000a | Dominated |
| IMIQ plus qHPV vaccine | 956 | 875 | 714 | 0.0177 | 0.0106 | Dominated | Dominated |
| PPA without change in allocated topical treatment | |||||||
| PDX plus placebo | 665 | 636 | 417 | 0.0444 | 0.0259 | Reference | Reference |
| IMIQ plus placebo | 766 | 748 | 563 | 0.0294 | 0.0156 | Dominated | Dominated |
| PDX plus qHPV vaccine | 893 | 834 | 612 | 0.0562 | 0.0302 | 19,200; 16,700; 16,500a | 54,100; 46,900; 46,300a |
| IMIQ plus qHPV vaccine | 973 | 902 | 717 | 0.0162 | 0.0093 | Dominated | Dominated |
| CCA | |||||||
| PDX plus placebo | 688 | 648 | 467 | 0.0425 | 0.0256 | Reference | Reference |
| IMIQ plus placebo | 737 | 667 | 512 | 0.0372 | 0.0194 | Dominated | Dominated |
| PDX plus qHPV vaccine | 893 | 814 | 622 | 0.0383 | 0.0212 | Dominated | Dominated |
| IMIQ plus qHPV vaccine | 960 | 886 | 718 | 0.0166 | 0.0111 | Dominated | Dominated |
With the EQ-5D-5L, PDX plus placebo dominates all other options at week 48 in all three analysed populations excluding the PPA, which showed a positive QALY gain with the addition of the qHPV vaccine but at ICERs of > £46,000/QALY. At week 16, PDX plus placebo dominated all other options (see Appendix 4, Table 34).
When considering the uncertainty from both the study sampling itself and from imputation of missing values in the sample, the reduced health gain with IMIQ was most pronounced in the group receiving IMIQ plus the qHPV vaccine (Figure 7). Furthermore, the highest QALY gain at the lowest cost was consistently achievable with PDX plus placebo across all the cost and utility instrument scenarios, even when considering the uncertainty from the combined bootstrap approach (see Figure 7).
FIGURE 7.
Cost-effectiveness planes at week 48 (ITT population) contrasting the three calculated costs per study visits with the EQ-5D-3L and EQ-5D-5L. (a) Six planned visits; (b) actually observed visits; (c) actual visits for warts.
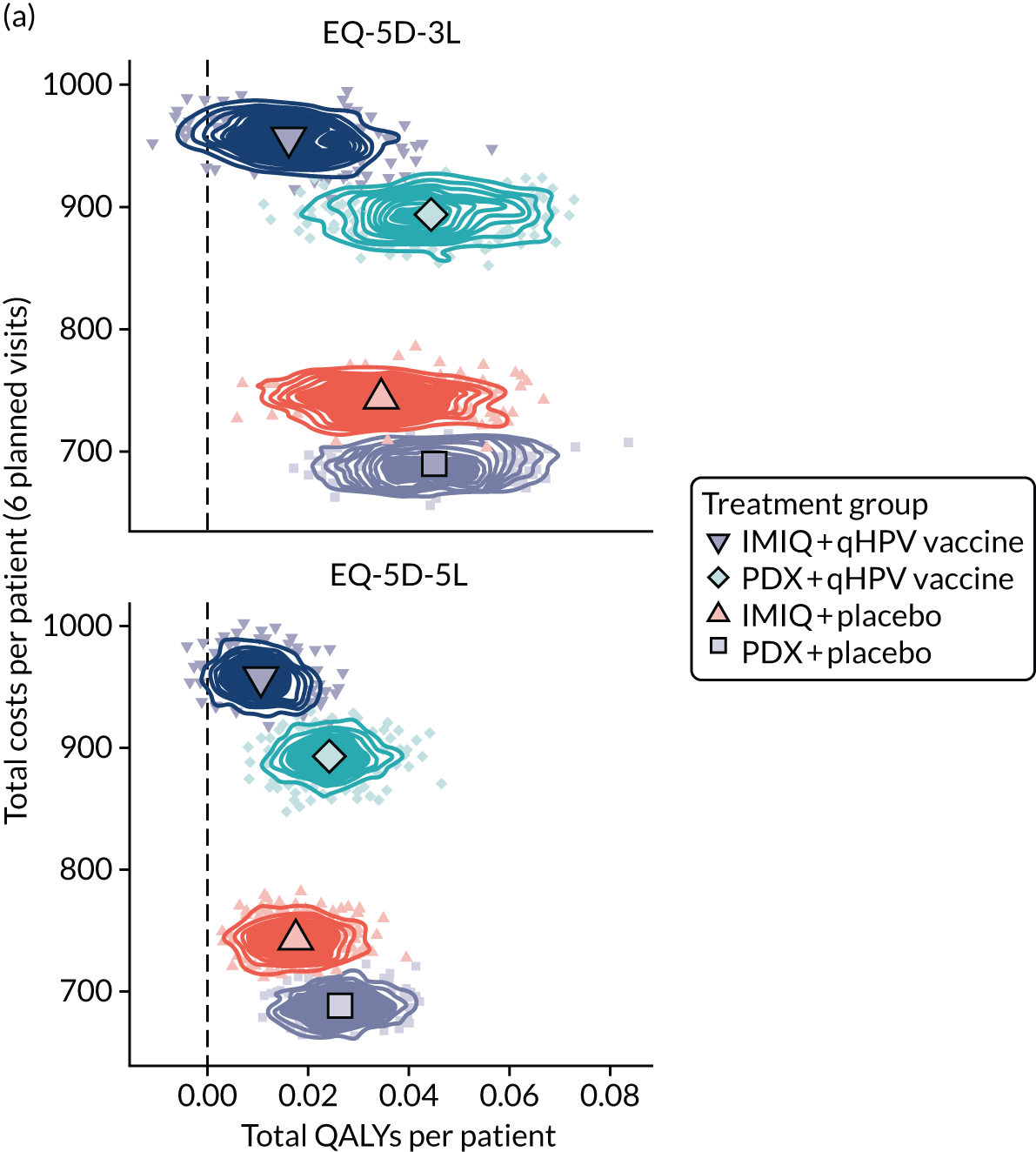
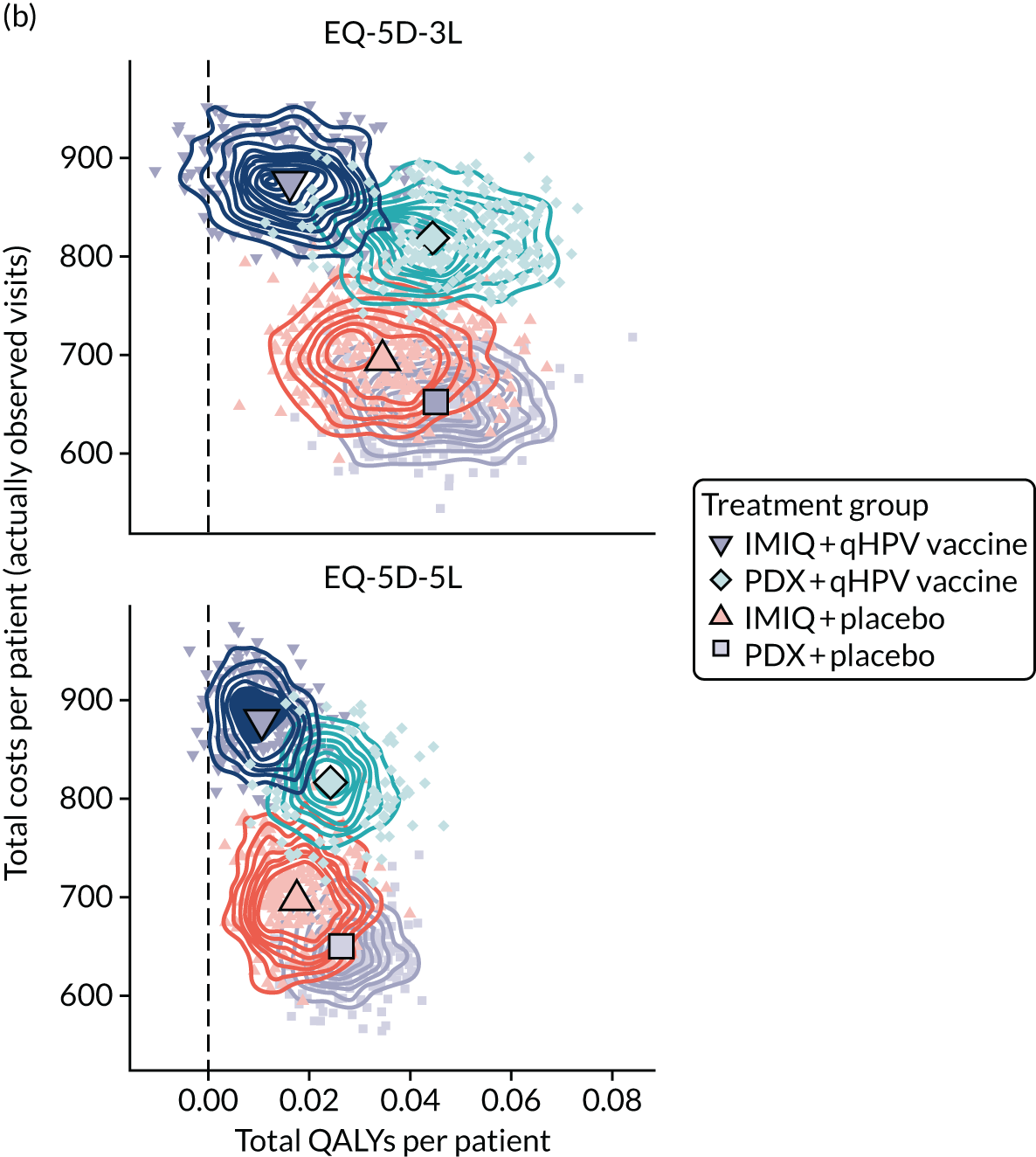
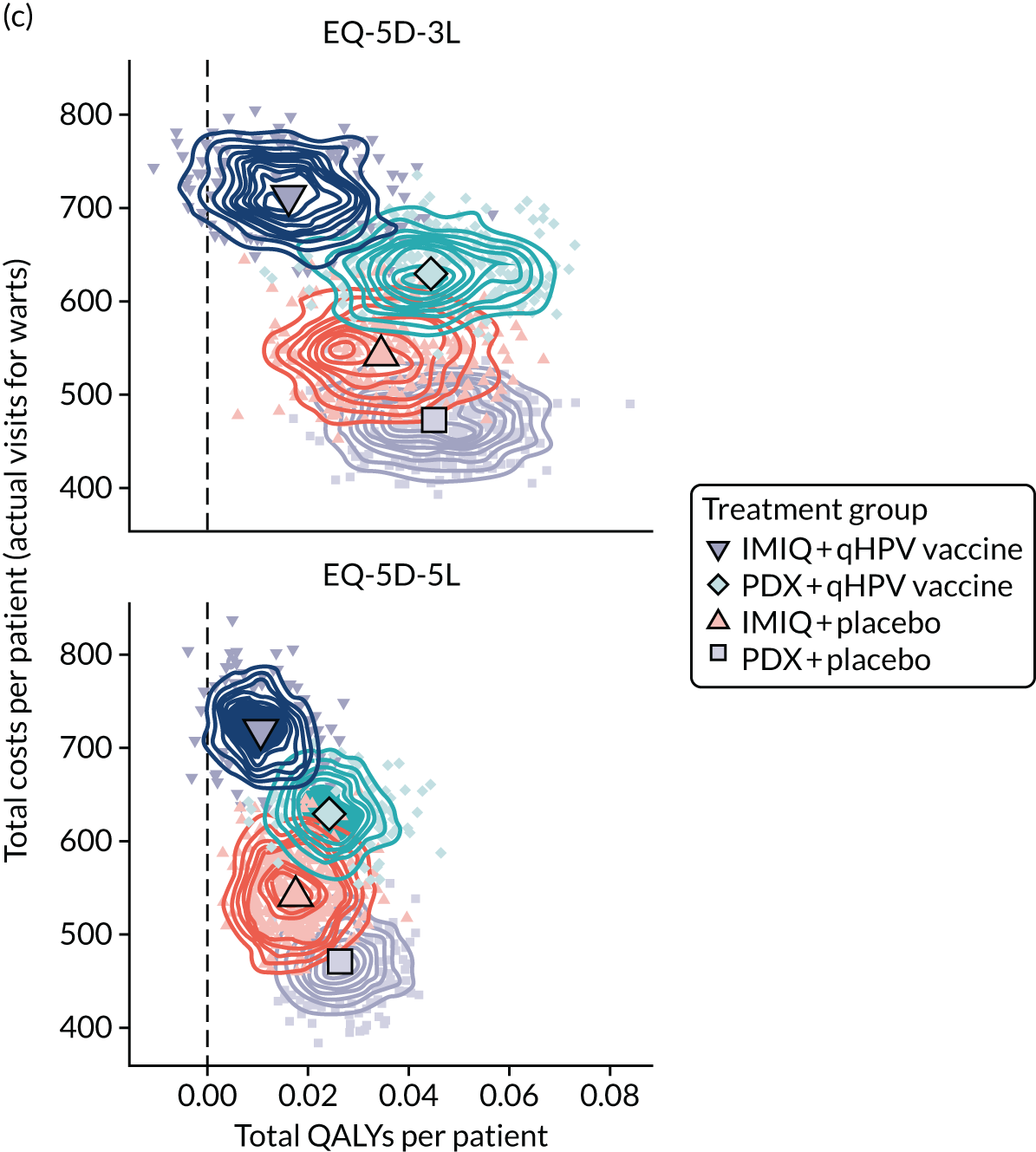
The QALY gains generally increased over time with all treatments, shifting the scatter plots to the right.
With the EQ-5D-3L, across the four treatment options, the probability of being cost-effective is the highest and is ≥ 50% for PDX plus placebo across a range of WTP thresholds, from £0/QALY to £50,000/QALY (Figure 8a). Similarly, the highest net benefit was always achievable with PDX plus placebo over the WTP threshold range investigated here. PDX plus placebo vaccine is thus the economically optimal treatment option to maximise the health gain from a limited budget when looking at the EQ-5D-3L across all three cost scenarios (see Figure 8b). Similar results for week 16 (Figure 9) are shown in Appendix 4.
FIGURE 8.
At week 48, (a) CEACs and (b) CEAFs based on three methods of calculating study visit costs (ITT population, EQ-5D-3L). CEAF, cost-effectiveness acceptability frontier.
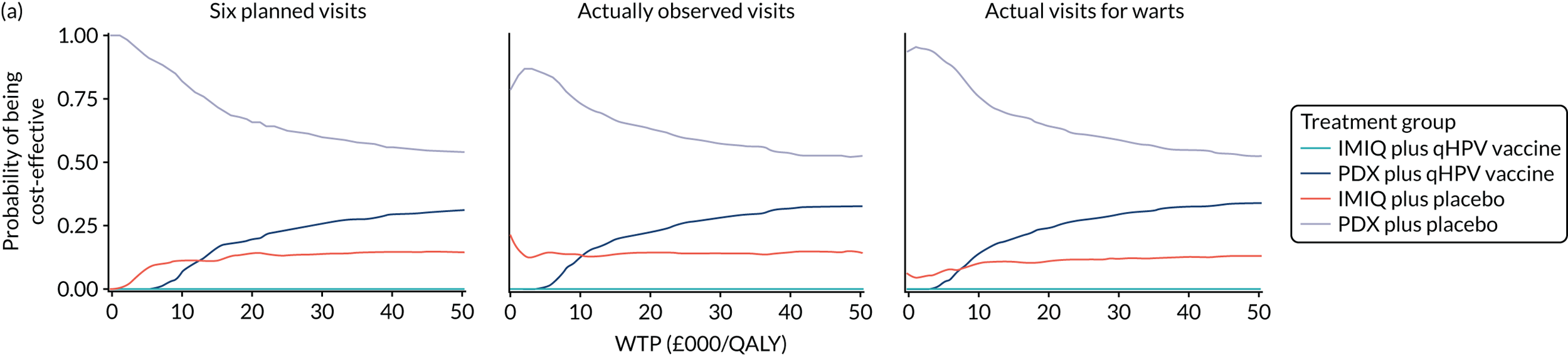
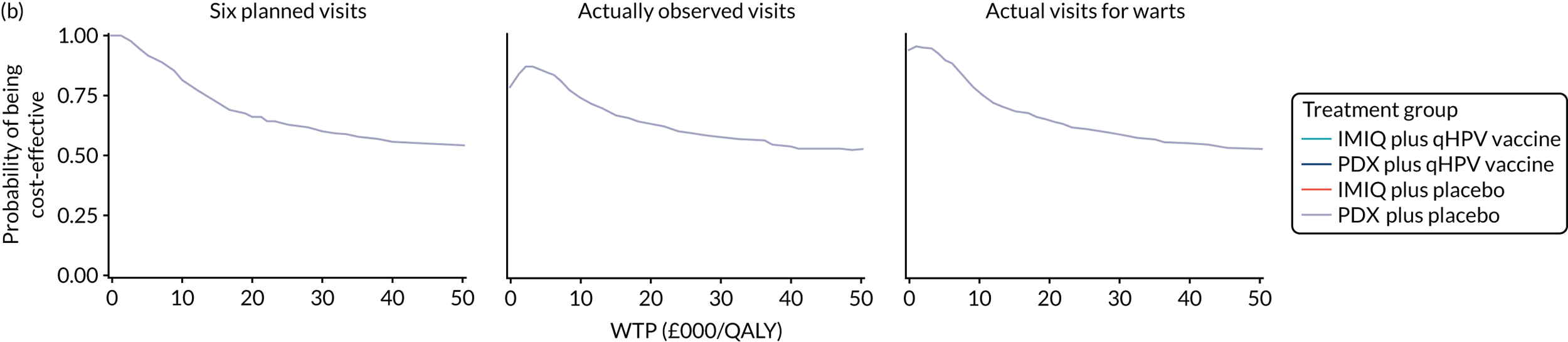
FIGURE 9.
Cost-effectiveness planes at week 16 (ITT population) contrasting the three calculated costs per study visits with the EQ-5D-3L and EQ-5D-5L. (a) Six planned visits; (b) actually observed visits; (c) actual visits for warts.
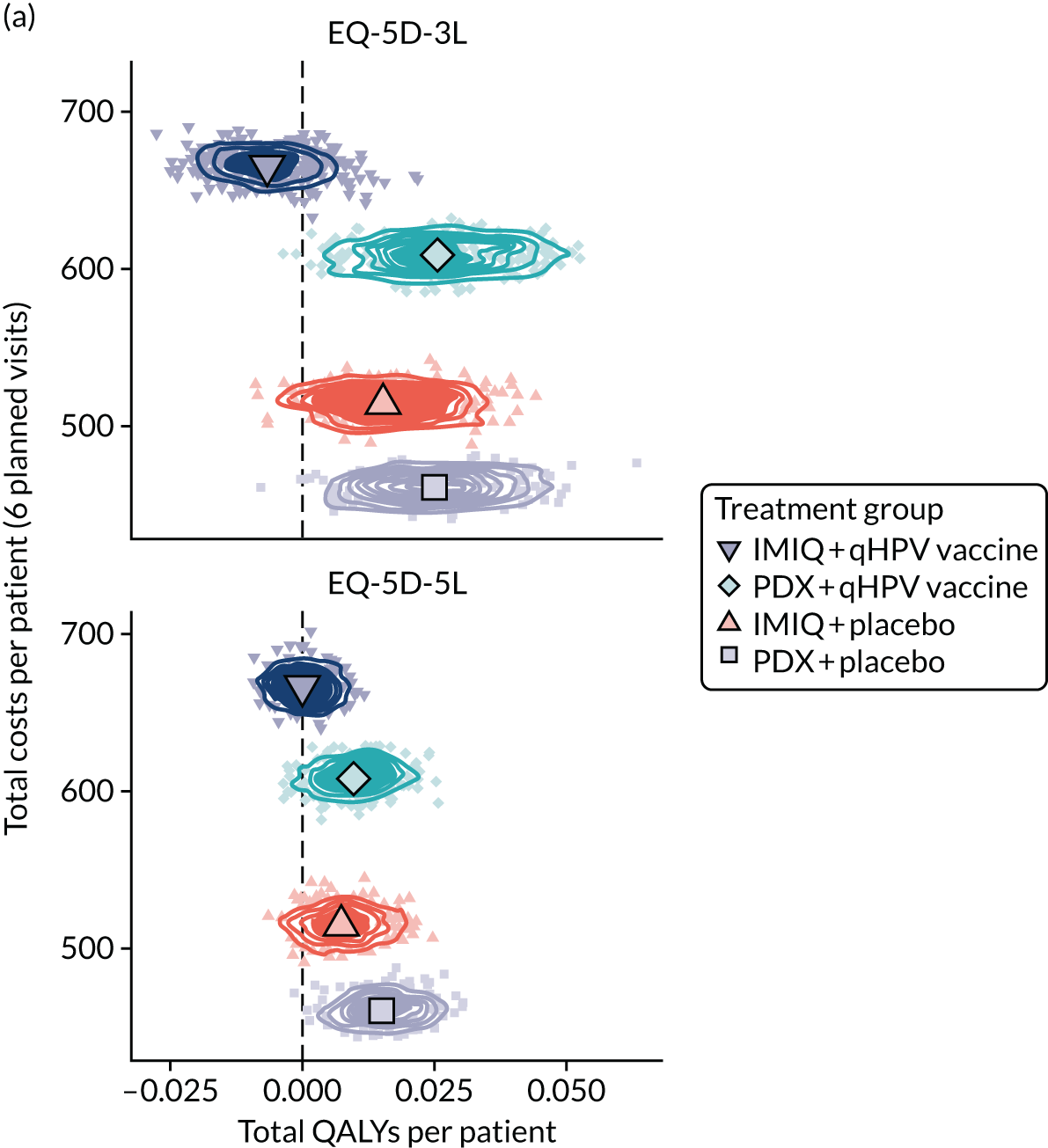
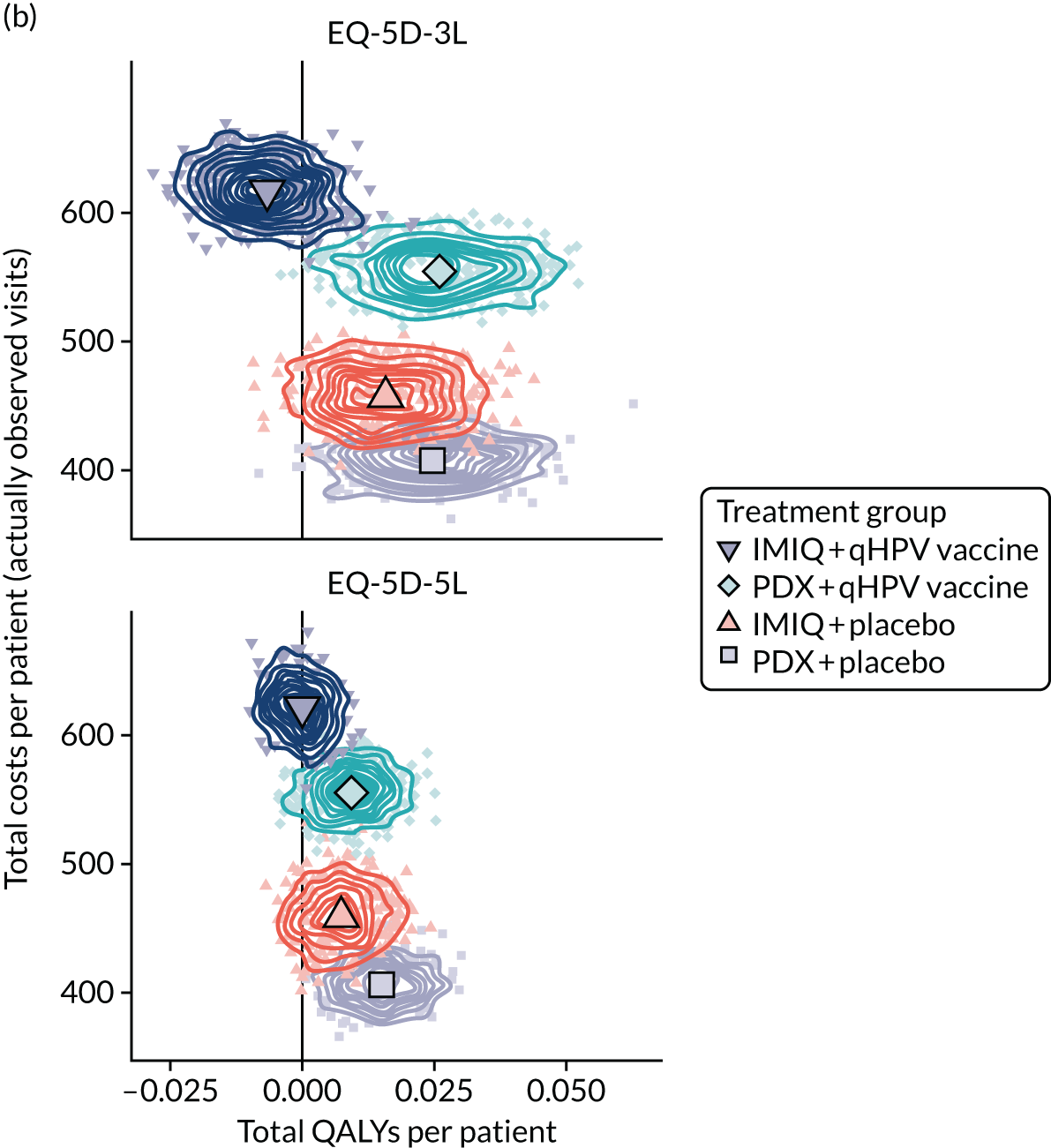
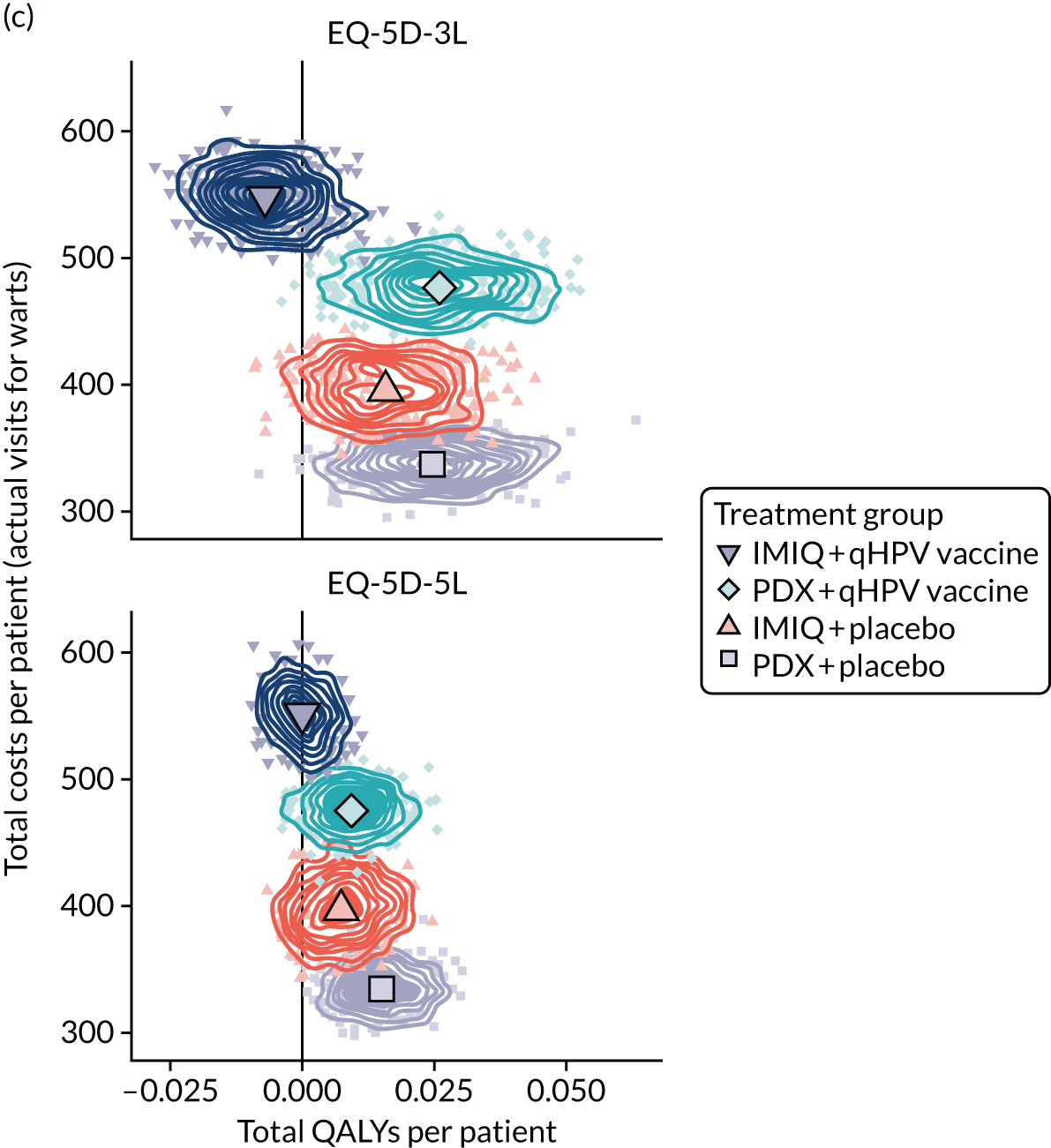
When contrasting these results with the EQ-5D-5L, the probability of PDX plus placebo being cost-effective increased to always > 75% (see Appendix 4, Figure 11a); it also achieves the highest net benefit (see Appendix 4, Figure 12b), again supporting its adoption.
Threshold analysis
Given that the ICERs of the qHPV vaccine failed to be more clinically effective for the IMIQ plus qHPV vaccine arm, no threshold analysis was conducted for it.
For PDX plus qHPV vaccine, positive incremental QALY gains were found ranging between 0.00015 and 0.01180 (Table 15). With incremental costs of PDX plus qHPV vaccine of always > £140 (see Appendix 4, Tables 35 and 36), only three estimates can be rendered as being within that estimate: the values of the EQ-5D-3L in the PPA between a threshold of £20,000/QALY and £30,000/QALY. Results for gains over 16 weeks are shown in Appendix 4, Table 42.
| Measure | Incremental QALYs | WTP threshold (£) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £30,000/QALY | £20,000/QALY | £10,000/QALY | ||
| ITT analysis | ||||
| EQ-5D-3L | 0.0005 | 16.10 | 10.70 | 5.40 |
| EQ-5D-5L | Dominated | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| PPA without change in allocated topical treatment | ||||
| EQ-5D-3L | 0.0118 | 355.00 | 237.00 | 118.00 |
| EQ-5D-5L | 0.0042 | 126.00 | 84.20 | 42.10 |
| CCA | ||||
| EQ-5D-3L | Dominated | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| EQ-5D-5L | Dominated | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Scenario analysis
Factor-specific cost-effectiveness analysis
For the vaccine, at higher incremental costs, the incremental QALYs were always negative (see Appendix 4, Tables 43–46). By contrast, the topical treatment was always associated with positive incremental QALYs and fewer incremental costs for PDX (see Appendix 4, Tables 43–46). Results were the same for weeks 48 and 16. For illustration, the full model is shown for the ITT for both factors in Appendix 4, Table 46). In addition, we also included the results for the EQ-5D-5L utility scores; these were always in the same direction as the EQ-5D-3L scores.
Cost-effectiveness per natural outcomes
Apart from the conventional cost–utility analysis, we also explored the incremental cost-effectiveness of each option in terms of the primary clinical end points of the trial (see Chapter 3).
The most cost-effective option was, again, PDX plus placebo in both primary outcomes. For the patients remaining wart free by week 16, further gains were achievable with PDX plus qHPV vaccine (see Appendix 4, Table 45), with incremental costs per additional patient remaining wart free of between £1280 and £1350 (see Appendix 4, Table 37). For the patients with avoided recurrence by week 48, further gains in reductions were achievable with IMIQ plus placebo and IMIQ plus qHPV (see Appendix 4, Table 38), with the incremental costs per additional patient avoiding recurrence ranging between £1400 and £2300 with IMIQ plus placebo and between £2500 and £3000 with IMIQ plus qHPV vaccine (see Appendix 4, Table 47).
This is the only analysis in which IMIQ achieved higher health gains at higher costs (both with and without vaccine). However, the cost-effectiveness analysis with natural outcomes as the denominator does not allow comparisons with interventions in other disease areas (other than anogenital warts). Thus, from the NHS perspective adopted in this analysis, the cost–utility analysis results (in terms of costs per QALY gained) are of more policy relevance.
Missing-not-at-random assumption of missing values
The scenario analysis of the alternative MNAR assumption (see Chapter 4, Methods, Missing data) resulted in positive mean values for all four treatment groups and for both EQ-5D valuation sets (Table 16) (see Appendix 4, Table 24). The direction of effect is always identical for both factors. The highest QALY gain among the four treatment options would still be seen with PDX plus placebo, except for the EQ-5D-3L utilities over 16 weeks. Compared with the base-case analysis, the improved utility values with the addition of the qHPV vaccine to PDX leads to higher QALY gains over 16 weeks only, not over 48 weeks. The higher values obtained here versus the base case are largely driven by the fact that the majority of missing utility values are missing at the beginning of the study, and reducing them by 10% or 20% thus increases the gain over time.
| Treatment | MNAR missingness assumption (%) | EQ-5D-3L utilities | EQ-5D-5L utilities | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 16 | Week 48 | Week 16 | Week 48 | ||
| PDX plus placebo | –10 | 0.0262 | 0.0486 | 0.0172 | 0.0312 |
| –20 | 0.0291 | 0.0536 | 0.0203 | 0.0365 | |
| IMIQ plus placebo | –10 | 0.0165 | 0.0359 | 0.0093 | 0.0201 |
| –20 | 0.0196 | 0.0398 | 0.0126 | 0.0242 | |
| PDX plus qHPV vaccine | –10 | 0.0277 | 0.0473 | 0.0121 | 0.0271 |
| –20 | 0.0313 | 0.0513 | 0.0159 | 0.0313 | |
| IMIQ plus qHPV vaccine | –10 | 0.0030 | 0.0276 | 0.0078 | 0.0202 |
| –20 | 0.0087 | 0.0347 | 0.0139 | 0.0279 | |
At incremental costs of £203, £163 and £154 over 16 weeks (according to the three cost scenarios; see Appendix 4, Table 36) and incremental QALY gains of 0.0015 (MNAR–10%) and 0.0022 (MNAR–20%), the ICER would still be above conventional thresholds at £135,000, £109,000 and £103,000 per QALY (MNAR–10%) as well as at £92,000, £74,000 £70,000 per QALY (MNAR–20%), respectively.
Chapter 5 Discussion
The trial recruited 503 participants from 22 centres across England and Wales to address two questions that are relevant to the majority of patients with warts presenting to sexual health clinics in the UK: first, the relative efficacy of the two most commonly used topical treatments and, second, a novel question regarding the possible benefit of using the qHPV vaccine to either enhance the clearance of warts or reduce the rate of recurrence.
The combined end point analysis included both the proportion of participants who experienced clearance at 16 weeks after starting their allocated topical treatment and the proportion of participants who remained wart free at the end of 48 weeks. This was chosen as the most meaningful outcome for patients. The analysis used multiple imputation to reduce the possible effect of bias due to incomplete follow-up, and the conclusions were very similar for the CCA. The analysis showed no significant difference between IMIQ and PDX (aOR 0.81 in favour of PDX). The CI is wide (95% CI 0.54 to 1.26) as a consequence of the reduction in the sample size of the trial from 1000 participants, as originally proposed, to a revised target of 500 participants. However, the interval does suggest that IMIQ is not superior to PDX by a clinically important degree (the upper bound is only 1.26). By the same analysis, the qHPV vaccine was compared with placebo: the results favoured the qHPV vaccine (aOR 1.46). The CI was, again, wide, but the lower margin of the interval was very close to 1 (95% CI 0.97 to 2.20). Furthermore, when the individual components were analysed separately, the effect size was similar for both the week 16 clearance (aOR 1.30, 95% CI 0.89 to 1.91) and remaining wart free at week 48 (aOR 1.39, 95% CI 0.73 to 2.63). These results are consistent with an effect of vaccine in both increasing the response to topical treatment and reducing recurrence. However, the results are ultimately inconclusive; the CIs all include 1, indicating uncertainty as to whether or not vaccine has any effect. The separate end point analysis of the topical treatment showed that, although the result favoured PDX for clearance (aOR 0.77), the odds ratio was very close to 1 for remaining wart free at week 48 (aOR 0.98, 95% CI 0.54 to 1.78). This suggests that, with extended use for up to 16 weeks, PDX may be more effective than IMIQ used for a similar period, but this remains uncertain. Prior evidence that IMIQ is associated with a lower recurrence rate than PDX is not supported by this trial.
During the 7 years from the development of the proposal to the completion of this study, no other studies were published that compared the efficacy of IMIQ and PDX, to our knowledge. 59 This remains the largest such study to date, and the first study to compare the recurrence rate in a randomised trial, to our knowledge. There have been no studies published on the effect of vaccine as an adjunct to treatment, or to prevent recurrence, although there are ongoing studies that may provide evidence on recurrence (see Future research).
Trial population
This was a pragmatic trial involving as wide a range of participants as possible to ensure that the results were generalisable to patients attending sexual health services, where 80% of patients with genital warts are treated. Patients with a first presentation of warts, and those with a previous episode, were included, but not those who had only recently been treated (within the previous 3 months); the efficacy of treatment for warts that were resistant to standard treatment was not included in the research question. A history of warts was a stratification variable and was well balanced across groups; 50% of participants had a history of warts, similar to national clinic data.
We excluded patients who had received the qHPV vaccine in the past, but not those who had received the bivalent vaccine because this is specific to HPV types 16 and 18 and is therefore not expected to have a measurable effect against HPV types 6 or 11. Only 9% of participants had received the bivalent vaccine.
Patient and public involvement
Obtaining meaningful patient and public involvement in sexual health studies has proved difficult. In contrast with the related specialty of HIV medicine, sexual health clinic patients are transient and are often seen in a service only once and not under long-term follow-up, although they may be repeat attenders. Therefore, we used a patient support group linked to the HIV outpatient service at the Mortimer Market Centre, which shares facilities with a large sexual health clinic and which was one of the trial sites. Because many of the support group had attended the sexual health clinic as well, their input was useful, even though very few of the study population were living with HIV. The lay representative on the TSC was instrumental in encouraging the change in the protocol to remove the HIV exclusion criterion, which was consistent with a general move not to exclude HIV in clinical trials of other conditions. Since this study was initiated, a public panel has been established by the British Association for Sexual Health and HIV that has the role of commenting on information and guidance produced by the association. The group is available to comment on research proposals.
Interventions
Standard first-line treatment for genital warts is topical therapy or cryotherapy. Our primary interest was the relative efficacy of PDX and IMIQ, so a no-treatment arm was not included. However, the vaccine comparison was against placebo, because use of vaccine in this situation is not currently approved or recommended. A vaccine-only arm would have been of interest, but more difficult to justify: it would have increased the required size of the study, and possibly made it harder to recruit. A cryotherapy arm, without PDX or IMIQ, could also have been included, but this comparison was outside the remit of this study and would also have increased the required sample size.
Trial design
No change of topical treatment before week 16 was allowed, because this was the primary end point for the topical treatment effect, even though the licensed duration of treatment differs for the two products. The addition of cryotherapy after week 4 was permitted because this is consistent with current practice in the UK. A failure of response after 4 weeks of PDX, the licensed duration of treatment, is a prompt to consider an alternative treatment. We wanted to avoid this and to retain participants in their allocated topical treatment arm up to week 16, if at all possible. Use of cryotherapy after week 4 was at the discretion of the investigator and documented. Less than 1% (4/503) of participants used cryotherapy before week 4. Use between weeks 4 and 16 was 14% (72/503 participants), with rather more in the PDX arm than the IMIQ arm (20% vs. 11%, respectively). Previous studies have shown that the time to response for IMIQ is longer than for PDX,7–15,18–25 and this is reflected in the longer licensed treatment course. 60,61 However, current practice is to allow consecutive repeat courses of PDX, provided that there are signs of a continued response, as was observed in this trial. Nonetheless, clinicians may be more likely to seek additional treatment with cryotherapy before 16 weeks. Extending IMIQ beyond 16 weeks, the licensed duration for treatment, is less common; patients are more likely to be switched to an alternative at this point.
We could have set the primary end point for clearance at 4 weeks for PDX and 16 weeks for IMIQ, but considered that a single time point of 16 weeks for the primary analysis was more clinically relevant and closer to standard practice. We included a comparison of the response at the end of the respective licensed treatment durations as a secondary analysis. The results show clearly that 16 weeks of IMIQ is more effective than 4 weeks of PDX (aOR 2.92, CI 1.75 to 4.87), although this analysis is complicated by the difference in cryotherapy use (11% by week 16 in the IMIQ group vs. 1% by week 4 in the PDX group). The results strongly support routine use of longer courses of PDX. If warts were still present at week 16, further treatment was at the discretion of the investigator but this was classed as treatment failure for the primary analysis.
We hypothesised that the qHPV vaccine could affect wart clearance but is more likely to affect recurrence. Nonetheless, we started the vaccine at the same time as topical treatment so that a treatment effect could be observed and because, practically, that would be the easiest way to implement vaccination in this group if it was shown to be beneficial. To detect an effect on recurrence, it was essential to minimise the loss to follow-up. We collected outcome data up to week 48, covering the period when most recurrences are seen, and given the difficulty in keeping participants engaged in such a trial. We allowed wide flexibility in the time of follow-up visits and accepted self-reported outcomes if participants did not attend trial visits after repeated prompting. We achieved 79% follow-up at week 48, which was close to the 80% target in the original proposal, but below the more challenging target of 85% set after reducing the sample size.
Cost-effectiveness
In the economic evaluation, we explored the cost-effectiveness of the two topical treatments as well as the added value of the qHPV vaccine.
Our results showed that the costs and resource use are fairly similar between the topical treatments and there is a non-significant reduction in non-vaccine treatment costs with the qHPV vaccine, compared with placebo. All patients had generally high HRQoL scores at baseline, so the room for improvement in any of the trial arms was minimal, which is reflected in the mixed results between treatment arms in our analysis. Clustering of responses on a few (very high) health states was observed. Overall, however, CIs overlapped between treatments.
When mapping the EQ-5D-5L to the EQ-5D-3L, the slightly lower values obtained for the EQ-5D-3L (see Appendix 4, Tables 39 and 40) are in line with what had been described previously. 62 Based on previous research, the observed smaller QALY gains with the EQ-5D-5L than with the EQ-5D-3L (see Table 13) were to be expected as the interventions considered in HIPvac improve quality of life without extending survival;63 our study thus supports previous findings.
With the EQ-5D-3L, the current preferred measure of the NICE (November 2018), the probability of being cost-effective is highest, at ≥ 50%, for PDX without qHPV vaccine across £0–50,000 per QALY, which increases to > 75% with the EQ-5D-5L. The incremental cost-effectiveness results of all three analyses point towards PDX without the qHPV vaccine being the most cost-effective intervention among the four treatments at current list prices. In addition, the qHPV vaccine may be beneficial over treatment with only PDX as measured with the EQ-5D-3L, which was most pronounced in the PPA with ICERs ≈ £23,000 per QALY (week 16) and £19,000 per QALY (week 48).
With ICERs above or near £100,000 per QALY for all but the PPAs, however, the use of the qHPV vaccine is not cost-effective at the current vaccine price and at conventional thresholds of cost-effectiveness used in England. With incremental costs of PDX plus qHPV vaccine of > £140, again, only three values of the PPA measured with the EQ-5D-3L are between a threshold of £20,000–30,000 per QALY. However, adding the qHPV vaccine to PDX could be cost-effective with the EQ-5D-3L if the price of the qHPV vaccine is substantially reduced below its pharmacy price, which is the case for the national HPV vaccine programmes.
The factorial cost-effectiveness analysis resulted in the vaccine always giving negative incremental QALYs at higher incremental costs. By contrast, the topical treatments were always associated with positive incremental QALYs, with fewer incremental costs for PDX.
Strengths and limitations
Before the trial started, the withdrawal of support by the vaccine manufacturer required a substantial redesign of the study. Without a no-cost supply of qHPV vaccine, and blinded placebo, we had to purchase vaccine, and contract with a pharmacy manufacturing facility to make a placebo, and blind, label and distribute the vaccine and placebo to sites. The sponsor had to take the financial risk of purchasing the vaccine in advance so that it could to be blinded and repackaged. Furthermore, as the syringe design was due to be changed, and we could purchase the current matching syringe only within a limited time or risk having a non-matching placebo, we had to purchase sufficient vaccine for all 1000 participants at the outset.
All this resulted in substantial delays and increased the cost to services to participate. Because the cost of vaccine was now an excess treatment cost to be borne by the sexual health service, we recovered the cost by retaining funds from the site payments. Although the sites were reimbursed for research costs, in practice, the excess treatment cost absorbed most of the payment. This delayed the approval process for sites, and in some cases led to refusal to participate. Identification of potential sites also coincided with an unprecedented period of uncertainty for sexual health services as the introduction of new commissioning arrangements was followed by tendering-out of services and large-scale service configurations. This exacerbated a long-standing lack of research infrastructure in sexual health services. Overall, less than one-quarter of sites approached were confirmed and there were long delays in site initiation and, subsequently, low recruitment rates.
An additional consequence of the loss of vaccine supplier support was that we had to abandon the use of an active comparator. Hepatitis A vaccine has been used in some HPV vaccine studies as a comparator,64,65 with the advantage that the local reactogenicity of the vaccine comparator helps the maintenance of blinding against the qHPV vaccine. Saline injection would be much less likely to be associated with a persistent local reaction, but it was still considered preferable to having no injection in the control group. As the qHPV vaccine is supplied in a bespoke pre-filled syringe, we obtained supplies of the same syringe from the supplier in the USA so that these could be filled and labelled to maintain the blind. Unfortunately, securing the equipment to fill the syringes caused further delay and the available batches of unfilled syringes were found to be faulty and failed the quality assurance assessment after filling. Therefore, a similar but not fully matched syringe had to be used. To minimise the risk of unblinding, the vaccine/placebo was packed in an opaque, sealed pouch contained in an outer carton. The vaccine or placebo was administered by a health-care worker who was not involved in participant recruitment or follow-up assessments and was under instruction to avoid showing the vaccine syringe to either the participant or the trial team.
The study was designed with a sample size of 1000 participants. However, identifying trial sites in the UK with the resources and infrastructure to recruit participants proved to be very difficult. To complete the trial within timelines that could be agreed with the funder, even with two no-cost extensions, a substantially reduced sample size had to be accepted. It was recognised that this would mean that the trial was very likely to be underpowered for the combined primary end point. Although disappointing, it was agreed with the funder that continuing with the trial was still worthwhile, and justifiable on ethical grounds. The trial provided adequate power to detect a meaningful, if substantial, effect on the two secondary end points that made up the combined primary end point, the rate of clearance at week 16 and the rate of recurrence at week 48 in those who have cleared warts by week 16. A proposal to the funder to change the primary end point from the single combined end point to the two components as co-primary end points was not accepted.
There were also a number of strengths and limitations to the economic evaluation. We estimated the resource use based on the actual numbers observed in the trial. To explore different scenarios, we considered cost scenarios based on three different assumptions about the number of care episodes: (1) the planned study visits align with the ITT principle, (2) the total number of observed visits is likely to be an overestimate compared with real-world care46 and (3) the number of visits with warts present approximate the number of care episodes seen in clinical practice. All three cost scenarios explored different assumptions about resource use and their order is not intended to reflect cost scenario validity. Whereas the first scenario, of six planned study visits, explored equalising the differences seen in the number of care visits between patients, the second scenario explored the actual resource use during the trial, which was still protocol driven and therefore may not reflect clinical practice. The third scenario adjusted the number of visits based on the presence of warts, but it may still be affected by the protocol-specified visit schedule. The use of observational data may improve the estimates and could be investigated further.
The CCA may underestimate the costs and overestimate the effects because it is usually the more severe cases that are lost to follow-up. 66 However, the CCA in this trial population showed that, in comparison with the ITT population, the CCA population appeared to have similar costs and HRQoL. This suggests that participants who were lost to follow-up may have been similar to the ITT population.
We did not extrapolate HRQoL outcomes beyond the trial duration given the close similarity of scores in all four arms, which was already very high for all four treatment groups at baseline, and remained at a high level throughout the trial. However, in line with current NICE guidance44,54 we used the EQ-5D-3L utility scores for the economic evaluation and we compared these with the EQ-5D-5L utility scores, as the version of EQ-5D to be used is currently under review in England. 67
Future research
Given the reduction in the size of the trial, we could not reach a definitive conclusion on the efficacy of qHPV vaccine to either enhance wart clearance with a topical agent or prevent recurrence, or both. Evidence to date has been indirect, for example from the vaccine efficacy studies68,69 that were not designed to address this issue. Since this trial commenced, other work has examining this question. A study in Germany,70 commencing in 2014, planned to recruit 200 participants with previous genital warts. All participants were treated by surgical excision, after which they received qHPV vaccine or placebo. The primary end point was recurrence at 6 months after the end of the vaccine course; the trial has been suspended and no results have been reported.
Another double-blind vaccine study in France71 is also investigating qHPV vaccine to prevent recurrence. Vaccine or placebo are started 2–4 weeks after clearance of warts by any standard treatment. The primary outcome is relapse-free survival from the first dose. The study will enrol 300 participants and started in 2017.
Since the HIPvac trial was proposed, a new topical agent has been licensed for the treatment of anogenital warts. Marketed as Veregen® (Fougren Pharmaceuticals Inc, Melville, NY, USA) (in European countries) and as Catephen® (Kora Healthcare, Dublin, Ireland) in the UK, it contains sinecatechins derived from green tea leaves of the species Camellia sinensis. The active ingredient is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). The mechanism of action is uncertain but various immunomodulatory and antiproliferative properties have been proposed. 72,73 EGCG is formulated as a 10% ointment; a 15% ointment preparation is available in the USA only. The ointment is applied three times daily until complete clearance, or for up to 16 weeks. Three double-blind placebo-controlled randomised trials have evaluated the 15% ointment,74–76 of which two also evaluated the 10% ointment; the study by Gross et al. 74 also assessed the efficacy of a 10% cream preparation for which wart clearance was not statistically greater than placebo. The trials found no difference in efficacy between the 10% and 15% ointment preparations. A meta-analysis of the three studies77 concluded that both ointment preparations were efficacious relative to placebo. The reported clearance rates of 47–59% are similar to those observed with IMIQ; however, no head-to-head RCTs have been performed. It is unclear where this product will fit in the algorithm of wart treatment, but comparative efficacy data should be prioritised.
The HIPvac study, and the other vaccine studies referred to above, provide further evidence on the question of wart recurrence. The possible effect of a vaccine as an adjuvant to topical treatment, with or without cryotherapy, will require further investigation. The results of the HIPvac trial provide support for conducting such work, given the potential size of the effect, and the findings of the economic evaluation. Samples collected and archived in the HIPvac trial include wart swabs taken at baseline and at the time of recurrence. These could be used to determine if the HPV type at the time of recurrence is the same, and whether or not the pattern differs between vaccine and placebo groups. Serum samples have also been stored so that the type-specific antibody responses can be correlated. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were due to be stored at selected trial sites but, given all the delays and the over-riding priority to meet the recruitment target, this was not implemented.
Chapter 6 Conclusions
The trial has provided the first high-quality evidence of the comparative efficacy and cost-effectiveness of the two most widely used topical treatments for genital warts, as well as the first randomised trial to investigate the potential therapeutic benefit of a HPV vaccine in the management of patients with anogenital warts. The study does not suggest that IMIQ is superior to PDX in terms of either wart clearance or prevention of recurrence. It does, however, provide evidence that treatment with PDX beyond the 4 weeks‘ licensed treatment duration provides additional benefit in those with warts still present.
No benefit of vaccine when used in combination with either PDX or IMIQ to clear warts or prevent recurrence has been shown. However, given the reduction in the size of the trial, and that the CI includes a clinically meaningful effect, the results suggest that this does warrant further investigation. Some relevant trials are ongoing elsewhere. From the perspective of the NHS, however, the qHPV vaccine seems unlikely to be cost-effective at the current list price of the vaccine.
The challenges of conducting clinical trials to address important questions in sexual health services are great, and need to be addressed if patients attending sexual health services are to benefit from the potential to improve outcomes.
Acknowledgements
This study was sponsored by University College London.
We would like to acknowledge and thank the following for their contribution to the study:
-
the patients in the 22 sexual health clinics who gave their time to take part in the study
-
the clinical staff at all the clinics who worked to recruit and retain participants in the trial: Mohd Abu Bakar, Ade Apoola, Angela Bailey, Andrew de Burgh-Thomas, David Chadwick, Mayur Chauhan, Laura Cunningham, Phillip Hay, Rajesh Hembrom, Elbushra Herieka, Stephen Kegg, Charles Lacey, Mark Lawton, Mayura Nathan, Cecilia Priestley, Daniel Richardson, Karen Rogstad, Mannampallil Itty Samuel, Gabriel Schembri, Anitha Vidhyadharan and David White
-
the members of the TSC – Graham Taylor (chairperson), Simon Collins (lay member), Andrew Freedman, Chris Sonnex, Julie Fox and Richard Gilson
-
the members of the IDMC – Peter Sasieni (chairperson), Alison Fiander and George Kinghorn.
We would like to thank others who were part of the study team at various times: Scott Bevan (data manager), Riona Bowhay (data manager) and Yvonne Sylvestre (statistican).
Contributions of authors
Richard Gilson (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9572-193X) (Associate Professor in Sexual Health and HIV; sexual health) was chief investigator and had overall responsibility for the design and conduct of the study and drafted the report.
Diarmuid Nugent (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7417-8440) (Clinical Fellow; genitourinary medicine) contributed to drafting the report.
Kate Bennett (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2358-4497) (Medical Statistician; statistics) was the trial statistician and conducted the final analysis.
Caroline J Doré (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9796-4970) (Professor of Clinical Trials and Statistics; statistics) was the senior trial statistician.
Macey L Murray (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6418-0854) (Clinical Trial Manager; trial management) managed the study after Jade Meadows left her post.
Jade Meadows (https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0337-5011) (Clinical Trial Manager/Clinical Project Manager; trial management) was the initial trial manager, and then project manager, and co-ordinated the set-up and initial conduct of the trial.
Lewis J Haddow (https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3016-2986) (Senior Clinical Research Fellow; sexual health) contributed to the design and clinical oversight of the study.
Charles Lacey (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9250-2638) (Professor of Infectious Diseases; infectious disease and sexual health) contributed to the conception and design of the study, advised on its conduct and was a site investigator.
Frank Sandmann (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5641-1931) (Health Economist; health economics) carried out the health economic analysis.
Mark Jit (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6658-8255) (Professor of Vaccine Epidemiology; modelling and health economics) oversaw the design and conduct of the health economic analysis.
Kate Soldan (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0361-3174) (Epidemiologist; epidemiology) advised on the design and interpretation of the results.
Michelle Tetlow (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1064-3187) (Clinical Project Manager; trial management) was responsible for oversight of the trial delivery until she left the Clinical Trials Unit.
Emilia Caverly (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4420-713X) (Clinical Project Manager; trial management) took over responsibility for the oversight of the trial delivery after Jade Meadows left her post.
Mayura Nathan (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9123-7657) (Consultant in Sexual Health; genitourinary medicine) provided advice on the clinical aspects of the trial and was a site investigator.
Andrew J Copas (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8968-5963) (Reader in Statistics; statistics) contributed to the original study proposal and funding application and provided statistical advice throughout the trial.
Publication
Murray ML, Meadows L, Doré CJ, Copas AJ, Haddow LJ, Lacey C, et al. Human papillomavirus infection: protocol for a randomised controlled trial of imiquimod cream (5%) versus podophyllotoxin cream (0.15%), in combination with quadrivalent human papillomavirus or control vaccination in the treatment and prevention of recurrence of anogenital warts (HIPvac trial). BMC Med Res Methodol 2018;18:125.
Data-sharing statement
All data requests should be submitted to the corresponding author for consideration. Access to anonymised data may be granted following review.
Patient data
This work uses data provided by patients and collected by the NHS as part of their care and support. Using patient data is vital to improve health and care for everyone. There is huge potential to make better use of information from people’s patient records, to understand more about disease, develop new treatments, monitor safety, and plan NHS services. Patient data should be kept safe and secure, to protect everyone’s privacy, and it’s important that there are safeguards to make sure that it is stored and used responsibly. Everyone should be able to find out about how patient data are used. #datasaveslives You can find out more about the background to this citation here: https://understandingpatientdata.org.uk/data-citation.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health and Social Care. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health and Social Care.
References
- Ball SL, Winder DM, Vaughan K, Hanna N, Levy J, Sterling JC, et al. Analyses of human papillomavirus genotypes and viral loads in anogenital warts. J Med Virol 2011;83:1345-50. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.22111.
- Public Health England (PHE) . Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Annual Data Tables. Table 1: STI Diagnoses and Rates in England by Gender, 2009 to 2018 2019. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/805903/2018_Table_1_STI_diagnoses_and_rates_in_England_by_gender.ods (accessed 26 October 2018).
- Desai S, Wetten S, Woodhall SC, Peters L, Hughes G, Soldan K. Genital warts and cost of care in England. Sex Transm Infect 2011;87:464-8. https://doi.org/10.1136/sti.2010.048421.
- British Association for Sexual Health and HIV (BASHH) . UK National Guidelines on the Management of Anogenital Warts 2015 n.d. www.bashh.org/documents/UK%20national%20guideline%20on%20Warts%202015%20FINAL.pdf (accessed 4 February 2019).
- Lacey CJ, Woodhall SC, Wikstrom A, Ross J. 2012 European guideline for the management of anogenital warts. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2013;27:e263-70. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2012.04493.x.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) . Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines, 2015 n.d. www.cdc.gov/std/tg2015/default.htm (accessed 4 February 2019).
- Edwards A, Atma-Ram A, Thin RN. Podophyllotoxin 0.5% v podophyllin 20% to treat penile warts. Genitourin Med 1988;64:263-5. https://doi.org/10.1136/sti.64.4.263.
- Beutner KR, Conant MA, Friedman-Kien AE, Illeman M, Artman NN, Thisted RA, et al. Patient-applied podofilox for treatment of genital warts. Lancet 1989;1:831-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(89)92282-4.
- Mazurkiewicz W, Jablońska S. Clinical efficacy of Condyline (0.5% podophyllotoxin) solution and cream versus podophyllin in the treatment of external condylomata acuminata. J Dermatolog Treat 1990;1:123-5. https://doi.org/10.3109/09546639009086712.
- Kirby P, Dunne A, King DH, Corey L. Double-blind randomized clinical trial of self-administered podofilox solution versus vehicle in the treatment of genital warts. Am J Med 1990;88:465-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(90)90424-C.
- von Krogh G, Szpak E, Andersson M, Bergelin I. Self-treatment using 0.25%–0.50% podophyllotoxin-ethanol solutions against penile condylomata acuminata: a placebo-controlled comparative study. Genitourin Med 1994;70:105-9. https://doi.org/10.1136/sti.70.2.105.
- Strand A, Brinkeborn RM, Siboulet A. Topical treatment of genital warts in men, an open study of podophyllotoxin cream compared with solution. Genitourin Med 1995;71:387-90. https://doi.org/10.1136/sti.71.6.387.
- Claesson U, Lassus A, Happonen H, Hogström L, Siboulet A. Topical treatment of venereal warts: a comparative open study of podophyllotoxin cream versus solution. Int J STD AIDS 1996;7:429-34. https://doi.org/10.1258/0956462961918400.
- Lacey CJ, Goodall RL, Tennvall GR, Maw R, Kinghorn GR, Fisk PG, et al. Randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of podophyllotoxin solution, podophyllotoxin cream, and podophyllin in the treatment of genital warts. Sex Transm Infect 2003;79:270-5. https://doi.org/10.1136/sti.79.4.270.
- Komericki P, Akkilic-Materna M, Strimitzer T, Aberer W. Efficacy and safety of imiquimod versus podophyllotoxin in the treatment of anogenital warts. Sex Transm Dis 2011;38:216-18. https://doi.org/10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3181f68ebb.
- Werner RN, Westfechtel L, Dressler C, Nast A. Self-administered interventions for anogenital warts in immunocompetent patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sex Transm Infect 2017;93:155-61. https://doi.org/10.1136/sextrans-2016-052768.
- Moore RA, Edwards JE, Hopwood J, Hicks D. Imiquimod for the treatment of genital warts: a quantitative systematic review. BMC Infect Dis 2001;1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-1-3.
- Arany I, Tyring SK, Stanley MA, Tomai MA, Miller RL, Smith MH, et al. Enhancement of the innate and cellular immune response in patients with genital warts treated with topical imiquimod cream 5%. Antiviral Res 1999;43:55-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-3542(99)00033-9.
- Beutner KR, Spruance SL, Hougham AJ, Fox TL, Owens ML, Douglas JM. Treatment of genital warts with an immune-response modifier (imiquimod). J Am Acad Dermatol 1998;38:230-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0190-9622(98)70243-9.
- Beutner KR, Tyring SK, Trofatter KF, Douglas JM, Spruance S, Owens ML, et al. Imiquimod, a patient-applied immune-response modifier for treatment of external genital warts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1998;42:789-94. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.42.4.789.
- Edwards L, Ferenczy A, Eron L, Baker D, Owens ML, Fox TL, et al. Self-administered topical 5% imiquimod cream for external anogenital warts. HPV Study Group. Human PapillomaVirus. Arch Dermatol 1998;134:25-30. https://doi.org/10.1001/archderm.134.1.25.
- Fife KH, Ferenczy A, Douglas JM, Brown DR, Smith M, Owens ML. HPV Study Group . Treatment of external genital warts in men using 5% imiquimod cream applied three times a week, once daily, twice daily, or three times a day. Sex Transm Dis 2001;28:226-31. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007435-200104000-00007.
- Arican O, Guneri F, Bilgic K, Karaoglu A. Topical imiquimod 5% cream in external anogenital warts: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Dermatol 2004;31:627-31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1346-8138.2004.tb00568.x.
- Garland SM, Waddell R, Mindel A, Denham IM, McCloskey JC. An open-label phase II pilot study investigating the optimal duration of imiquimod 5% cream for the treatment of external genital warts in women. Int J STD AIDS 2006;17:448-52. https://doi.org/10.1258/095646206777689161.
- Schöfer H, Van Ophoven A, Henke U, Lenz T, Eul A. Randomized, comparative trial on the sustained efficacy of topical imiquimod 5% cream versus conventional ablative methods in external anogenital warts. Eur J Dermatol 2006;16:642-8.
- Grillo-Ardila CF, Angel-Müller E, Salazar-Díaz LC, Gaitán HG, Ruiz-Parra AI, Lethaby A. Imiquimod for anogenital warts in non-immunocompromised adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;11. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010389.pub2.
- Venugopal SS, Murrell DF. Recalcitrant cutaneous warts treated with recombinant quadrivalent human papillomavirus vaccine (types 6, 11, 16, and 18) in a developmentally delayed, 31-year-old white man. Arch Dermatol 2010;146:475-7. https://doi.org/10.1001/archdermatol.2010.71.
- Lee HJ, Kim JK, Kim DH, Yoon MS. Condyloma accuminatum treated with recombinant quadrivalent human papillomavirus vaccine (types 6, 11, 16, 18). J Am Acad Dermatol 2011;64:e130-2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2010.12.032.
- Olsson SE, Kjaer SK, Sigurdsson K, Iversen OE, Hernandez-Avila M, Wheeler CM, et al. Evaluation of quadrivalent HPV 6/11/16/18 vaccine efficacy against cervical and anogenital disease in subjects with serological evidence of prior vaccine type HPV infection. Hum Vaccin 2009;5:696-704. https://doi.org/10.4161/hv.5.10.9515.
- Joura EA, Garland SM, Paavonen J, Ferris DG, Perez G, Ault KA, et al. Effect of the human papillomavirus (HPV) quadrivalent vaccine in a subgroup of women with cervical and vulvar disease: retrospective pooled analysis of trial data. BMJ 2012;344. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.e1401.
- Hogewoning CJ, Bleeker MC, van den Brule AJ, Voorhorst FJ, Snijders PJ, Berkhof J, et al. Condom use promotes regression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and clearance of human papillomavirus: a randomized clinical trial. Int J Cancer 2003;107:811-16. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.11474.
- Bleeker MC, Berkhof J, Hogewoning CJ, Voorhorst FJ, van den Brule AJ, Starink TM, et al. HPV type concordance in sexual couples determines the effect of condoms on regression of flat penile lesions. Br J Cancer 2005;92:1388-92. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6602524.
- Fromm TSK, Gross M, Schädlich L, Kaufmann AM, Albers AE. Laryngeal Papillomatosis: Immunological and Clinical Responses to HPV and Vaccination n.d.
- Goldstone SE, Vuocolo S. A prophylactic quadrivalent vaccine for the prevention of infection and disease related to HPV-6, -11, -16 and -18. Expert Rev Vaccines 2012;11:395-406. https://doi.org/10.1586/erv.12.20.
- Rose RC, Reichman RC, Bonnez W. Human papillomavirus (HPV) type 11 recombinant virus-like particles induce the formation of neutralizing antibodies and detect HPV-specific antibodies in human sera. J Gen Virol 1994;75:2075-9. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-75-8-2075.
- Woodhall SC, Jit M, Soldan K, Kinghorn G, Gilson R, Nathan M, et al. The impact of genital warts: loss of quality of life and cost of treatment in eight sexual health clinics in the UK. Sex Transm Infect 2011;87:458-63. https://doi.org/10.1136/sextrans-2011-050073.
- Jit M, Chapman R, Hughes O, Choi YH. Comparing bivalent and quadrivalent human papillomavirus vaccines: economic evaluation based on transmission model. BMJ 2011;343. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d5775.
- Murray ML, Meadows J, Doré CJ, Copas AJ, Haddow LJ, Lacey C, et al. Human papillomavirus infection: protocol for a randomised controlled trial of imiquimod cream (5%) versus podophyllotoxin cream (0.15%), in combination with quadrivalent human papillomavirus or control vaccination in the treatment and prevention of recurrence of anogenital warts (HIPvac trial). BMC Med Res Methodol 2018;18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-018-0581-z.
- Geretti AM, Brook G, Cameron C, Chadwick D, French N, Heyderman R, et al. British HIV Association Guidelines on the Use of Vaccines in HIV-Positive Adults 2015. HIV Med 2016;17:s2-s81. https://doi.org/10.1111/hiv.12424.
- Mena G, García-Basteiro AL, Llupià A, Díez C, Costa J, Gatell JM, et al. Factors associated with the immune response to hepatitis A vaccination in HIV-infected patients in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Vaccine 2013;31:3668-74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.06.012.
- Martin TC, Martin NK, Hickman M, Vickerman P, Page EE, Everett R, et al. Hepatitis C virus reinfection incidence and treatment outcome among HIV-positive MSM. AIDS 2013;27:2551-7. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0b013e32836381cc.
- White IR, Royston P, Wood AM. Multiple imputation using chained equations: issues and guidance for practice. Stat Med 2011;30:377-99. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.4067.
- Ramsey SD, Willke RJ, Glick H, Reed SD, Augustovski F, Jonsson B, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis alongside clinical trials II-An ISPOR Good Research Practices Task Force report. Value Health 2015;18:161-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2015.02.001.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) . Guide to the Methods of Technology Appraisal 2013.
- Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation . Code of Practice June 2013 2013.
- Drummond MF, Sculpher MJ, Claxton K, Stoddart GL, Torrance GW. Methods for the Economic Evaluation of Health Care Programmes. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2015.
- Claxton K. The irrelevance of inference: a decision-making approach to the stochastic evaluation of health care technologies. J Health Econ 1999;18:341-64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-6296(98)00039-3.
- Tambour M, Zethraeus N, Johannesson M. A note on confidence intervals in cost-effectiveness analysis. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 1998;14:467-71. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0266462300011442.
- NHS Business Services Authority . Drug Tariff 2018 n.d. www.nhsbsa.nhs.uk/sites/default/files/2018-10/Drug%20Tariff%20November%202018.pdf (accessed 20 November 2018).
- Joint Formulary Committee . British National Formulary 2018.
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) . Consumer Price Indices (CPIs) – Complete Database: Consumer Prices – Annual Inflation, All Items Non-Food Non-Energy n.d. https://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=PRICES_CPI (accessed 20 November 2018).
- Herdman M, Gudex C, Lloyd A, Janssen M, Kind P, Parkin D, et al. Development and preliminary testing of the new five-level version of EQ-5D (EQ-5D-5L). Qual Life Res 2011;20:1727-36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-011-9903-x.
- Devlin NJ, Shah KK, Feng Y, Mulhern B, van Hout B. Valuing health-related quality of life: an EQ-5D-5L value set for England. Health Econ 2018;27:7-22. https://doi.org/10.1002/hec.3564.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Position Statement on Use of the EQ-5D-5L Value Set for England (Updated October 2019) n.d. www.nice.org.uk/Media/Default/About/what-we-do/NICE-guidance/NICE-technology-appraisal-guidance/eq5d5l_nice_position_statement.pdf (accessed 20 November 2018).
- van Hout B, Janssen MF, Feng YS, Kohlmann T, Busschbach J, Golicki D, et al. Interim scoring for the EQ-5D-5L: mapping the EQ-5D-5L to EQ-5D-3L value sets. Value Health 2012;15:708-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2012.02.008.
- Manca A, Hawkins N, Sculpher MJ. Estimating mean QALYs in trial-based cost-effectiveness analysis: the importance of controlling for baseline utility. Health Econ 2005;14:487-96. https://doi.org/10.1002/hec.944.
- Leurent B, Gomes M, Faria R, Morris S, Grieve R, Carpenter JR. Sensitivity analysis for not-at-random missing data in trial-based cost-effectiveness analysis: a tutorial. PharmacoEconomics 2018;36:889-901. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-018-0650-5.
- Barton GR, Briggs AH, Fenwick EA. Optimal cost-effectiveness decisions: the role of the cost-effectiveness acceptability curve (CEAC), the cost-effectiveness acceptability frontier (CEAF), and the expected value of perfection information (EVPI). Value Health 2008;11:886-97. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4733.2008.00358.x.
- Gilson R, Nugent DB, Werner RN, Ballesteros J. 2018 European Guideline for the Management of Anogenital Warts (Draft Version for Consultation) n.d. www.iusti.org/regions/Europe/word_docs/2018/IUSTIguidelinesReview2018_08_07.docx (accessed 7 August 2018).
- Electronic medicines compendium (emc) . Warticon Cream n.d. www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/1507/smpc (accessed 30 November 2018).
- Electronic medicines compendium (emc) . Aldara 5% Cream n.d. www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/823/smpc (accessed 30 November 2018).
- Mulhern B, Feng Y, Shah K, Janssen MF, Herdman M, van Hout B, et al. Comparing the UK EQ-5D-3L and English EQ-5D-5L value sets. PharmacoEconomics 2018;36:699-713. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-018-0628-3.
- Hernandez Alava M, Wailoo A, Grimm S, Pudney S, Gomes M, Sadique Z, et al. EQ-5D-5L versus EQ-5D-3L: the impact on cost effectiveness in the United Kingdom. Value Health 2018;21:49-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2017.09.004.
- Hildesheim A, Wacholder S, Catteau G, Struyf F, Dubin G, Herrero R. CVT Group . Efficacy of the HPV-16/18 vaccine: final according to protocol results from the blinded phase of the randomized Costa Rica HPV-16/18 vaccine trial. Vaccine 2014;32:5087-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.06.038.
- Paavonen J, Jenkins D, Bosch FX, Naud P, Salmerón J, Wheeler CM, et al. Efficacy of a prophylactic adjuvanted bivalent L1 virus-like-particle vaccine against infection with human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 in young women: an interim analysis of a phase III double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2007;369:2161-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60946-5.
- Briggs A, Clark T, Wolstenholme J, Clarke P. Missing . . . presumed at random: cost-analysis of incomplete data. Health Econ 2003;12:377-92. https://doi.org/10.1002/hec.766.
- Devlin N, Brazier J, Pickard AS, Stolk E. 3L, 5L, What the L? A NICE conundrum. PharmacoEconomics 2018;36:637-40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-018-0622-9.
- Garland SM, Hernandez-Avila M, Wheeler CM, Perez G, Harper DM, Leodolter S, et al. Quadrivalent vaccine against human papillomavirus to prevent anogenital diseases. N Engl J Med 2007;356:1928-43. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa061760.
- Future II Study Group . Quadrivalent vaccine against human papillomavirus to prevent high-grade cervical lesions. N Engl J Med 2007;356:1915-27. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa061741.
- EU Clinical Trials Register . A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase IIIb HPV Vaccination Trial With Gardasil® in Patients With Recurrent Condylomata Acuminata n.d. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2012-004007-13/DE (accessed 7 January 2019).
- ClinicalTrials.gov . Efficacy of Quadrivalent HPV Vaccine to Prevent Relapses of Genital Warts After Initial Therapeutic Response (CONDYVAC) n.d. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03296397 (accessed 7 January 2019).
- Lin JK, Liang YC. Cancer chemoprevention by tea polyphenols. Proc Natl Sci Counc Repub China B 2000;24:1-13.
- Kuo CL, Chen TS, Liou SY, Hsieh CC. Immunomodulatory effects of EGCG fraction of green tea extract in innate and adaptive immunity via T regulatory cells in murine model. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 2014;36:364-70. https://doi.org/10.3109/08923973.2014.953637.
- Gross G, Meyer KG, Pres H, Thielert C, Tawfik H, Mescheder A. A randomized, double-blind, four-arm parallel-group, placebo-controlled Phase II/III study to investigate the clinical efficacy of two galenic formulations of Polyphenon E in the treatment of external genital warts. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2007;21:1404-12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2007.02441.x.
- Stockfleth E, Beti H, Orasan R, Grigorian F, Mescheder A, Tawfik H, et al. Topical Polyphenon E in the treatment of external genital and perianal warts: a randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol 2008;158:1329-38. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08520.x.
- Tatti S, Swinehart JM, Thielert C, Tawfik H, Mescheder A, Beutner KR. Sinecatechins, a defined green tea extract, in the treatment of external anogenital warts: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2008;111:1371-9. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181719b60.
- Tzellos TG, Sardeli C, Lallas A, Papazisis G, Chourdakis M, Kouvelas D. Efficacy, safety and tolerability of green tea catechins in the treatment of external anogenital warts: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2011;25:345-53. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03796.x.
Appendix 1 The HIPvac trial: participating sites
| Site name | NHS trust | Principal investigator | Number of recruited participants (n = 506) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mortimer Market Centre | Central and North West London NHS Foundation Trust | Dr Richard Gilson | 108 |
| Yorclinic | York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust | Professor Charles Lacey | 10 |
| Homerton University Hospital | Homerton University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust | Dr Mayura Nathan | 25 |
| Royal Sussex County Hospital | Brighton and Sussex University Hospitals NHS Trust | Dr Daniel Richardson | 30 |
| Birmingham Heartlands Hospital | Heart of England NHS Foundation Trust | Dr David White | 22 |
| Manchester Centre for Sexual Health | Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust | Dr Gabriel Schembri | 37 |
| Southend University Hospital | Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust | Dr Mohd Abu Bakar | 27 |
| Royal Liverpool Hospital | Royal Liverpool and Broadgreen University Hospitals NHS Trust | Dr Mark Lawton | 54 |
| Royal Bournemouth Hospital | Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust | Dr Elbushra Herieka | 13 |
| James Cook University Hospital | South Tees Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust | Dr David Chadwick | 29 |
| Medway Maritime Hospital | Medway NHS Foundation Trust | Dr Rajesh Hembrom | 12 |
| Courtyard Clinic, St George’s University Hospital | St George’s University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust | Dr Phillip Hay | 6 |
| Royal Hallamshire Hospital | Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust | Dr Karen Rogstad | 10 |
| Trafalgar Clinic, Queen Elizabeth Hospital | Lewisham and Greenwich NHS Trust | Dr Stephen Kegg | 12 |
| Caldecot Centre, King’s College Hospital | King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust | Dr Mannampallil Itty Samuel | 19 |
| New Croft Centre | Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust | Dr Mayur Chauhan | 44 |
| Cardiff Royal Infirmary | Cardiff and Vale University Health Board | Dr Laura Cunningham | 3 |
| The Gate Clinic, Kent and Canterbury Hospital | Kent Community Health NHS Foundation Trust | Dr Anitha Vidhyadharan | 10 |
| The Park Centre for Sexual Health, Weymouth Community Hospital | Dorset County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust | Dr Cecilia Priestley | 7 |
| London Road Community Hospital | Derby Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust | Dr Ade Apoola | 12 |
| St Mary’s Hospital | Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust | Dr Angela Bailey | 1 |
| Hope House, Gloucestershire Royal Hospital | Gloucestershire Care Services NHS Trust | Dr Andrew de Burgh-Thomas | 15 |
Appendix 2 Baseline and follow-up assessments and procedures
| Assessment/procedure | Visit | Extra visits if warts recur | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1: 0 weeks (baseline) | 2: 4 (± 1) weeks | 3: 8 (± 2) weeks | 4: 16 (± 3) weeks | 5: 24 (± 3) weeks | 6: 48 (± 5) weeks | ||
| Give participant information sheet and go through trial with participant | ✗ | ||||||
| Check eligibility, complete and sign consent form | ✗ | ||||||
| Randomisation | ✗ | ||||||
| Record wart treatment | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Review and record concomitant medication | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Examine and record approximate number and location of warts/the absence of warts | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Symptom-directed general examination | ✗ | ||||||
| Urine pregnancy test (βhCG) (women of child-bearing potential only) | ✗ | ✗a | ✗a | ✗a | ✗a | ✗a | ✗a |
| Quality-of-life questionnaire | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Assessment of tolerability | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ||
| Assessment of AEs (and pregnancy) | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Assessment of treatment response and need for additional/altered treatment | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | |
| Lesion swab for HPV detection (all participants, samples to be archived) | ✗ | ✗ | |||||
| Blood sample for serum for HPV detection (all participants, samples to be archived) | ✗ | ✗ | |||||
| Blood sample for PBMCs (subset of 120 consenting participants) | ✗b | ✗b | ✗b | ✗b | ✗b | ||
| Supply trial wart treatment | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ||||
| Supply/apply additional/alternative wart treatment if required and as permitted in the protocol | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ (from week 4) | |
| Vaccination | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ||||
| Provide diary card for self-treatment and self-examination record | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ||
| Collect/review diary card | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | |
| Completion/review of electronic trial documentation | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
Appendix 3 Trial results: supplementary data and analyses
| Event | IMIQ plus qHPV, n/N (%) | PDX plus qHPV, n/N (%) | IMIQ plus placebo, n/N (%) | PDX plus placebo, n/N (%) | Difference in proportions between topical treatments (IMIQ and PDX) (95% CI) | Difference in proportions between qHPV and placebo (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AE | 51/125 (41) | 37/126 (29) | 53/126 (42) | 39/126 (31) | 0.11 (0.03 to 0.20) | –0.01 (–0.10 to 0.07) |
| SAE | 4/125 (3)a | 5/126 (4)b | 3/126 (2)b | 5/126 (4) | –0.01 (–0.04 to 0.02) | 0.01 (–0.02 to 0.04) |
| Type of event | Treatment arm | CTCAE term | CTCAE severity grade | Seriousness criterion | Outcome | Causality | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topical treatment | Vaccine | ||||||
| SAR | IMIQ plus qHPV | Skin ulceration | Severe | M | Resolved | Definitely related | Unlikely |
| SAEa | IMIQ plus qHPV | Miscarriage at 20 weeks (fetal death) | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAEa | IMIQ plus qHPV | Uterine infection | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAEa | IMIQ plus qHPV | Uterine infection | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAEa | IMIQ plus qHPV | Uterine infection | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAEa | IMIQ plus qHPV | Rupture of infected uterine fibroid | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAEa | IMIQ plus qHPV | Myomectomy | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAE | IMIQ plus qHPV | Pneumothorax | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAE | IMIQ plus qHPV | Episode of psychosis | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAE | PDX plus qHPV | Pericarditis | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unlikely |
| SAE | PDX plus qHPV | Motorcycle accident | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAE | PDX plus qHPV | Injury to finger and hand then subsequent sepsis | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| NAE | PDX plus qHPV | Pregnancy | N/A | P | Resolved | N/A | N/A |
| SAE | PDX plus qHPV | Occipital headache | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAE | IMIQ plus placebo | Diarrhoea | Severe | M | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAE | IMIQ plus placebo | Thyrotoxicosis | Severe | H | Resolved with sequelae | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAEb | IMIQ plus placebo | Chest infection | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAEb | IMIQ plus placebo | Ear infection | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAE | PDX plus placebo | Anorectal infection leading to anal fistula | Severe | H | Resolved with sequalae | Unlikely | Unrelated |
| SUSAR | PDX plus placebo | Gastrointestinal pain, nausea, non-cardiac chest pain, palpitations | Severe | M | Resolved | Unrelated | Possible |
| SAE | PDX plus placebo | Lymphadenopathy | Severe | H | Resolved with sequelae | Unlikely | Unlikely |
| SAEc | PDX plus placebo | Unclear diagnosis; exacerbation of coeliac disease | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAEc | PDX plus placebo | Abdominal pain | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| SAEc | PDX plus placebo | Urinary retention | Severe | H | Resolved | Unrelated | Unrelated |
| NAE | PDX plus placebo | Pregnancy | N/A | P | Resolved | N/A | N/A |
| System Organ Class | Treatment group (n) | Total (n) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | ||
| Blood and lymphatic system | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| Cardiac | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Ear and labyrinth | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Eye | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Gastrointestinal | 8 | 0 | 11 | 10 | 29 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | 11 | 3 | 10 | 4 | 28 |
| Hepatobiliary | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Infections and infestations | 25 | 25 | 30 | 17 | 97 |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | 2 | 5 | 8 | 4 | 19 |
| Investigations | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4 |
| Metabolism and nutrition | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue | 4 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 13 |
| Neoplasms – benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Nervous system | 5 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 16 |
| Psychiatric | 1 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 13 |
| Renal and urinary | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Reproductive system and breast | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 7 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 14 |
| Skin/subcutaneous tissue | 33 | 5 | 26 | 17 | 81 |
| Vascular | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Total | 100 | 65 | 108 | 70 | 343 |
| System Organ Class | Treatment group (n) | Total (n) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | ||
| Dry skin | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Erythema multiforme | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Pain of skin | 7 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 15 |
| Pruritus | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Rash acneiform | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| Rash maculopapular | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Skin hypopigmentation | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Skin ulceration | 6 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 11 |
| Skin/subcutaneous tissue – other | 15 | 4 | 13 | 10 | 42 |
| Urticaria | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Total | 33 | 5 | 26 | 17 | 81 |
| System Organ Class | Treatment group (n) | Total (n) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | ||
| Anorectal infection | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Eye infection | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Gum infection | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Infections and infestations – other | 0 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 9 |
| Kidney infection | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Lip infection | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Lung infection | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Nail infection | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Otitis media | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Penile infection | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Pharyngitis | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Rash pustular | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Rhinitis infection | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Scrotal infection | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Sinusitis | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| Skin infection | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 11 |
| Tooth infection | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Upper respiratory infection | 5 | 10 | 5 | 1 | 21 |
| Urethral infection | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Urinary tract infection | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 7 |
| Vaginal infection | 1 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 10 |
| Vulval infection | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4 |
| Total | 25 | 25 | 30 | 17 | 97 |
| Reason for withdrawal | Treatment group (n) | Total (n) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | ||
| Non-compliance | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Pregnancy | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| AR | 6 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 14 |
| Lost to follow-up | 19 | 19 | 21 | 19 | 78 |
| Other | 1 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 16 |
| Total | 26 | 24 | 24 | 36 | 110 |
| Reason for withdrawal | Treatment group (n) | Total (n) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | ||
| Pregnancy | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| AR | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Lost to follow-up | 19 | 19 | 22 | 19 | 79 |
| Other | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| Total | 19 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 85 |
| Data | Treatment group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV (n = 125) | PDX plus qHPV (n = 126) | IMIQ plus placebo (n = 126) | PDX plus placebo (n = 126) | |
| Week 4 (n) | ||||
| Visit not attended | 14 | 14 | 19 | 12 |
| Visit attended | 111 | 112 | 107 | 114 |
| Presence of warts | ||||
| Yes | 99 | 91 | 93 | 96 |
| No | 12 | 21 | 14 | 18 |
| Missing | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Warts present, n/N (%) | ||||
| Cream applied | ||||
| Yes | 97/99 | 90/91 | 92/93 | 91/96 |
| No | 2/99 | 1/91 | 1/93 | 4/96 |
| Missing | 0/99 (0) | 0/91 (0) | 0/93 (0) | 1/96 (1) |
| Intensity of side effects, missing | 2/97 (2) | 2/90 (2) | 2/92 (2) | 6/91 (7) |
| EQ-5D, missing | 14/99 (14) | 13/91 (14) | 10/93 (11) | 20/96 (21) |
| Warts not present, n/N (%) | ||||
| Warts seen last, missing | 0/12 (0) | 0/21 (0) | 0/14 (0) | 1/18 (6) |
| EQ-5D, missing | 2/12 (17) | 3/21 (14) | 3/14 (21) | 6/18 (33) |
| Week 8 (n) | ||||
| Visit not attended | 21 | 21 | 25 | 22 |
| Visit attended | 104 | 105 | 101 | 104 |
| Presence of warts | ||||
| Yes | 72 | 74 | 74 | 77 |
| No | 32 | 31 | 27 | 27 |
| Missing | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Warts present, n/N (%) | ||||
| Cream applied | ||||
| Yes | 66/72 | 62/74 | 72/74 | 70/77 |
| No | 6/72 | 12/74 | 2/74 | 2/77 |
| Missing | 0/72 (0) | 0/74 (0) | 0/74 (0) | 0/77 (0) |
| Intensity of side effects, missing | 7/66 (11) | 12/62 (19) | 2/72 (3) | 7/70 (10) |
| EQ-5D, missing | 11/72 (15) | 12/74 (16) | 9/74 (12) | 10/77 (13) |
| Warts not present, n/N (%) | ||||
| Warts seen last, missing | 1/32 (3) | 0/31 (0) | 1/27 (4) | 1/27 (4) |
| EQ-5D, missing | 10/32 (31) | 6/31 (19) | 2/27 (7) | 1/27 (4) |
| Week 16 (n) | ||||
| Visit not attended | 35 | 32 | 37 | 36 |
| Visit attended | 90 | 94 | 89 | 90 |
| Presence of warts | ||||
| Yes | 48 | 48 | 57 | 46 |
| No | 41 | 46 | 32 | 44 |
| Missing | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Warts present, n/N (%) | ||||
| Cream applied | ||||
| Yes | 37/48 | 34/48 | 50/57 | 36/46 |
| No | 11/48 | 14/48 | 7/57 | 10/46 |
| Missing | 0/48 (0) | 0/46 (0) | 0/57 (0) | 0/44 (0) |
| Intensity of side effects, missing | 11/37 (30) | 14/34 (41) | 7/50 (14) | 10/36 (27) |
| EQ-5D, missing | 5/48 (10) | 5/46 (11) | 5/32 (16) | 5/44 (11) |
| Warts not present, n/N (%) | ||||
| Warts seen last, missing | 1/41 (2) | 0/48 (0) | 1/57 (2) | 0/46 (0) |
| EQ-5D, missing | 10/41 (24) | 15/48 (31) | 9/57 (16) | 13/46 (28) |
| Week 24 (n) | ||||
| Visit not attended | 34 | 32 | 33 | 34 |
| Visit attended | 91 | 94 | 93 | 92 |
| Presence of warts | ||||
| Yes | 36 | 25 | 43 | 39 |
| No | 55 | 67 | 50 | 52 |
| Missing | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| Warts present, n/N (%) | ||||
| EQ-5D, missing | 10/36 (27) | 4/32 (13) | 4/33 (12) | 6/34 (18) |
| Warts not present, n/N (%) | ||||
| Warts seen last, missing | 2/55 (4) | 0/67 (0) | 0/50 (0) | 0/52 (0) |
| EQ-5D, missing | 10/55 (18) | 10/67 (15) | 8/50 (16) | 8/52 (15) |
| Week 48 (n) | ||||
| Visit not attended | 46 | 40 | 45 | 44 |
| Visit attended | 79 | 86 | 81 | 58 |
| Presence of warts | ||||
| Yes | 26 | 22 | 29 | 24 |
| No | 53 | 64 | 52 | 58 |
| Missing | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Warts present, n/N (%) | ||||
| Intensity of side effects, missing | 10/26 (38) | 16/22 (72) | 24/29 (83) | 15/24 (63) |
| EQ-5D, missing | 4/26 (15) | 1/22 (5) | 6/29 (21) | 1/24 (4) |
| Warts not present, n/N (%) | ||||
| Warts seen last, missing | 0/53 (0) | 1/64 (2) | 0/52 (0) | 1/58 (2) |
| EQ-5D, missing | 4/53 (8) | 14/64 (22) | 5/52 (10) | 6/58 (10) |
| Subgroup | IMIQ, n/N (%) | PDX, n/N (%) | OR (95% CI) | p-value | qHPV, n/N (%) | Placebo, n/N (%) | OR (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 36/119 (30) | 42/113 (37) | 1.44 (0.63 to 3.27) | 0.389 | 45/119 (38) | 33/113 (29) | 0.88 (0.38 to 2.02) | 0.763 |
| Female | 24/58 (41) | 26/62 (42) | 28/58 (48) | 22/62 (35) | ||||
| Previous warts | 33/89 (37) | 30/82 (37) | 0.81 (0.35 to 1.86) | 0.615 | 36/89 (40) | 27/82 (32) | 0.99 (0.43 to 2.29) | 0.980 |
| No previous warts | 27/88 (31) | 38/93 (41) | 37/88 (42) | 28/86 (33) | ||||
| HIV positive | 58/172 (34) | 65/168 (39) | 0.97 (0.09 to 10.7) | 0.978 | 71/171 (42) | 52/169 (31) | 0.37 (0.03 to 3.99) | 0.411 |
| HIV negative | 2/5 (40) | 3/7 (43) | 2/6 (33) | 3/6 (50) |
Appendix 4 Health economic analysis: additional tables
| Characteristic | Treatment group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | |
| Week 16 | ||||
| n | 107 | 103 | 100 | 98 |
| Age (years), mean (95% CI) | 31.0 (19.5 to 55.5) | 31.6 (20.0 to 59.5) | 32.7 (20.0 to 58.6) | 30.2 (19.1 to 55.9) |
| Gender (female = 1) | 0.327 | 0.359 | 0.390 | 0.334 |
| Previous warts | 0.514 | 0.476 | 0.530 | 0.510 |
| HIV status | 0.019 | 0.039 | 0.020 | 0.020 |
| Week 48 | ||||
| n | 102 | 97 | 95 | 88 |
| Age (years), mean (95% CI) | 31.1 (19.5 to 55.5) | 31.5 (20.0 to 59.5) | 32.7 (20.0 to 58.6) | 30.3 (19.1 to 55.9) |
| Gender (female = 1) | 0.343 | 0.340 | 0.379 | 0.341 |
| Previous warts | 0.520 | 0.485 | 0.537 | 0.500 |
| HIV status | 0.010 | 0.031 | 0.021 | 0.023 |
| Characteristic | Treatment group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | |
| Week 16 | ||||
| n | 112 | 110 | 116 | 116 |
| Age (years), mean (95% CI) | 30.9 (19.5 to 55.5) | 31.6 (20.0 to 59.5) | 31.8 (20.0 to 58.6) | 30.2 (19.1 to 55.9) |
| Gender (female = 1) | 0.348 | 0.336 | 0.328 | 0.345 |
| Previous warts | 0.491 | 0.518 | 0.509 | 0.500 |
| HIV status | 0.018 | 0.036 | 0.026 | 0.026 |
| Week 48 | ||||
| n | 112 | 110 | 116 | 116 |
| Age (years), mean (95% CI) | 30.9 (19.5 to 55.5) | 31.6 (20.0 to 59.5) | 31.8 (20.0 to 58.6) | 30.2 (19.1 to 55.9) |
| Gender (female = 1) | 0.348 | 0.336 | 0.328 | 0.345 |
| Previous warts | 0.491 | 0.518 | 0.509 | 0.500 |
| HIV status | 0.018 | 0.036 | 0.026 | 0.026 |
| Time horizon | Treatment group, mean (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | |
| IMIQ (coursesa) | ||||
| Week 16 | 1.81 (0.00 to 4.00) | 0.14 (0.00 to 2.00) | 1.91 (0.00 to 4.00) | 0.29 (0.00 to 3.88) |
| Week 48 | 2.14 (0.00 to 6.00) | 0.33 (0.00 to 4.00) | 2.20 (0.00 to 5.00) | 0.55 (0.00 to 4.88) |
| PDX (coursesa) | ||||
| Week 16 | 0.05 (0.00 to 1.00) | 1.41 (0.00 to 3.00) | 0.10 (0.00 to 1.00) | 1.42 (0.00 to 3.00) |
| Week 48 | 0.15 (0.00 to 1.90) | 1.55 (0.00 to 3.88) | 0.18 (0.00 to 1.88) | 1.61 (0.00 to 4.00) |
| qHPV vaccine (injections) | ||||
| Week 16 | 1.82 (1.00 to 2.00) | 1.81 (1.00 to 2.00) | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Week 48 | 2.54 (1.00 to 3.00) | 2.53 (1.00 to 3.00) | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Cryotherapy (applications) | ||||
| Week 16 | 0.51 (0.00 to 2.90) | 0.64 (0.00 to 2.90) | 0.52 (0.00 to 3.00) | 0.71 (0.00 to 3.00) |
| Week 48 | 1.06 (0.00 to 6.80) | 1.08 (0.00 to 6.88) | 1.51 (0.00 to 7.00) | 1.56 (0.00 to 7.88) |
| Study visits | ||||
| Week 16 | 3.58 (1.00 to 6.90) | 3.48 (1.00 to 5.00) | 3.42 (1.00 to 6.00) | 3.49 (1.00 to 5.88) |
| Week 48 | 5.30 (1.00 to 11.90) | 5.25 (1.00 to 11.00) | 5.48 (1.00 to 11.00) | 5.69 (1.00 to 12.88) |
| Visits with warts | ||||
| Week 16 | 2.91 (1.00 to 5.90) | 2.71 (1.00 to 5.00) | 2.85 (1.00 to 5.00) | 2.80 (1.00 to 5.00) |
| Week 48 | 3.74 (1.00 to 9.00) | 3.40 (1.00 to 8.88) | 4.03 (1.00 to 10.00) | 3.98 (1.00 to 11.62) |
| Time horizon | Treatment group, mean (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | |
| IMIQ (coursesa) | ||||
| Week 16 | 2.04 (1.0 to 4.0) | 0.00 | 2.24 (1.0 to 4.0) | 0.00 |
| Week 48 | 2.31 (1.0 to 6.0) | 0.00 | 2.58 (1.0 to 5.0) | 0.00 |
| PDX (coursesa) | ||||
| Week 16 | 0.00 | 1.61 (1.0 to 3.0) | 0.00 | 1.66 (1.0 to 3.0) |
| Week 48 | 0.00 | 1.72 (1.0 to 3.0) | 0.00 | 1.86 (1.0 to 4.0) |
| qHPV vaccine (injections) | ||||
| Week 16 | 1.91 (1.0 to 2.0) | 1.89 (1.0 to 2.0) | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Week 48 | 2.66 (1.0 to 3.0) | 2.68 (1.0 to 3.0) | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Cryotherapy (applications) | ||||
| Week 16 | 0.52 (0.0 to 2.3) | 0.73 (0.0 to 3.0) | 0.56 (0.0 to 3.0) | 0.79 (0.0 to 3.0) |
| Week 48 | 0.96 (0.0 to 4.5) | 1.03 (0.0 to 5.0) | 1.39 (0.0 to 7.0) | 1.31 (0.0 to 5.0) |
| Study visits | ||||
| Week 16 | 3.73 (2.0 to 6.3) | 3.77 (2.0 to 5.5) | 3.75 (2.0 to 6.5) | 3.76 (2.0 to 6.0) |
| Week 48 | 5.36 (2.0 to 9.5) | 5.47 (2.0 to 9.2) | 5.82 (2.0 to 11.0) | 5.74 (2.0 to 10.8) |
| Visits with warts | ||||
| Week 16 | 3.00 (1.0 to 5.3) | 2.86 (1.0 to 5.0) | 3.04 (1.0 to 5.5) | 2.88 (1.0 to 5.0) |
| Week 48 | 3.59 (1.0 to 8.0) | 3.31 (1.0 to 6.6) | 4.10 (1.0 to 9.6) | 3.66 (1.0 to 7.8) |
| Time horizon | Treatment group, mean (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | |
| IMIQ (coursesa) | ||||
| Week 16 | 1.82 (0.0 to 4.0) | 0.15 (0.0 to 2.0) | 1.90 (0.0 to 4.0) | 0.30 (0.0 to 3.8) |
| Week 48 | 2.15 (0.0 to 6.1) | 0.33 (0.0 to 3.9) | 2.15 (0.0 to 5.0) | 0.53 (0.0 to 4.7) |
| PDX (coursesa) | ||||
| Week 16 | 0.05 (0.0 to 1.0) | 1.42 (0.0 to 3.0) | 0.09 (0.0 to 1.0) | 1.41 (0.0 to 3.0) |
| Week 48 | 0.17 (0.0 to 1.7) | 1.55 (0.0 to 3.7) | 0.16 (0.0 to 1.7) | 1.58 (0.0 to 4.0) |
| qHPV vaccine (injections) | ||||
| Week 16 | 1.82 (1.0 to 2.0) | 1.81 (1.0 to 2.0) | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Week 48 | 2.55 (1.0 to 3.0) | 2.54 (1.0 to 3.0) | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Cryotherapy (applications) | ||||
| Week 16 | 0.51 (0.0 to 2.7) | 0.65 (0.0 to 3.0) | 0.49 (0.0 to 2.9) | 0.68 (0.0 to 3.0) |
| Week 48 | 1.11 (0.0 to 6.2) | 1.11 (0.0 to 6.5) | 1.41 (0.0 to 7.3) | 1.58 (0.0 to 7.9) |
| Study visits | ||||
| Week 16 | 3.63 (1.0 to 6.9) | 3.53 (1.0 to 5.0) | 3.38 (1.0 to 6.1) | 3.49 (1.0 to 5.8) |
| Week 48 | 5.38 (1.0 to 11.6) | 5.22 (1.0 to 10.8) | 5.29 (1.0 to 11.1) | 5.65 (1.0 to 12.9) |
| Visits with warts | ||||
| Week 16 | 2.93 (1.0 to 5.9) | 2.75 (1.0 to 5.2) | 2.79 (1.0 to 5.2) | 2.79 (1.0 to 5.0) |
| Week 48 | 3.77 (1.0 to 9.2) | 3.35 (1.0 to 8.6) | 3.84 (1.0 to 10.0) | 3.94 (1.0 to 11.3) |
| Time horizon | Treatment group, cost (£) (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | |
| IMIQ | ||||
| Week 16 | 87.90 (0.00 to 194.40) | 6.94 (0.00 to 97.20) | 92.60 (0.00 to 194.40) | 14.30 (0.00 to 188.32) |
| Week 48 | 104.20 (0.00 to 291.60) | 16.20 (0.00 to 194.00) | 106.50 (0.00 to 243.00) | 26.60 (0.00 to 236.90) |
| PDX | ||||
| Week 16 | 0.86 (0.00 to 17.80) | 25.00 (0.00 to 53.50) | 1.70 (0.00 to 17.80) | 25.30 (0.00 to 53.49) |
| Week 48 | 2.71 (0.00 to 33.90) | 27.60 (0.00 to 69.10) | 3.11 (0.00 to 33.40) | 28.70 (0.00 to 71.30) |
| qHPV vaccine | ||||
| Week 16 | 158.00 (86.50 to 173.00) | 157.00 (86.50 to 173.00) | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Week 48 | 219.00 (86.50 to 259.50) | 219.00 (86.50 to 259.50) | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Cryotherapy | ||||
| Week 16 | 2.50 (0.00 to 14.40) | 3.10 (0.00 to 14.90) | 2.60 (0.00 to 14.90) | 3.50 (0.00 to 14.86) |
| Week 48 | 5.30 (0.00 to 33.70) | 5.40 (0.00 to 34.10) | 7.50 (0.00 to 34.70) | 7.70 (0.00 to 39.00) |
| Study visits | ||||
| Week 16 | 368.00 (92.80 to 640.30) | 363.00 (92.80 to 632.20) | 360.00 (92.80 to 742.80) | 364.00 (92.80 to 622.78) |
| Week 48 | 544.00 (126.40 to 1114.00) | 549.00 (92.80 to 1021.00) | 579.00 (92.80 to 1375.00) | 591.00 (92.80 to 1368.00) |
| Visits with warts | ||||
| Week 16 | 299.00 (92.80 to 551.70) | 284.00 (92.80 to 616.40) | 299.00 (92.80 to 632.20) | 292.00 (92.80 to 505.76) |
| Week 48 | 382.00 (92.80 to 999.00) | 359.00 (92.80 to 885.00) | 424.00 (92.80 to 1249.00) | 410.00 (92.80 to 1114.00) |
| Time horizon | Treatment group, cost (£) (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | |
| IMIQ | ||||
| Week 16 | 99.00 (48.60 to 194.40) | 0.00 | 109.00 (48.60 to 194.40) | 0.00 |
| Week 48 | 112.40 (48.60 to 291.60) | 0.00 | 125.00 (48.60 to 243.00) | 0.00 |
| PDX | ||||
| Week 16 | 0.00 | 28.70 (17.80 to 53.50) | 0.00 | 29.70 (17.80 to 53.50) |
| Week 48 | 0.00 | 30.70 (17.80 to 53.50) | 0.00 | 33.20 (17.80 to 71.30) |
| qHPV vaccine | ||||
| Week 16 | 165.00 (86.50 to 1730) | 164.00 (86.50 to 173.00) | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Week 48 | 230.00 (86.50 to 259.50) | 232.00 (86.50 to 259.50) | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Cryotherapy | ||||
| Week 16 | 2.60 (0.00 to 11.60) | 3.60 (0.00 to 14.90) | 2.80 (0.00 to 14.90) | 3.90 (0.00 to 14.90) |
| Week 48 | 4.80 (0.00 to 22.20) | 5.10 (0.00 to 24.80) | 6.90 (0.00 to 34.70) | 6.50 (0.00 to 24.80) |
| Study visits | ||||
| Week 16 | 384.00 (186.00 to 589.00) | 393.00 (186.00 to 632.00) | 400.00 (186.00 to 825.00) | 390.00 (186.00 to 632.00) |
| Week 48 | 555.00 (186.00 to 906.00) | 566.00 (186.00 to 978.00) | 616.00 (186.00 to 1220.00) | 596.00 (186.00 to 1096.00) |
| Visits with warts | ||||
| Week 16 | 308.00 (92.80 to 524.00) | 301.00 (92.80 to 632.20) | 323.00 (92.80 to 699.00) | 300.00 (92.80 to 505.80) |
| Week 48 | 370.00 (92.80 to 795.00) | 345.00 (92.80 to 698.00) | 431.00 (92.80 to 1138.00) | 377.00 (92.80 to 989.00) |
| Time horizon | Treatment group, cost (£) (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | |
| IMIQ | ||||
| Week 16 | 88.50 (0.00 to 194.40) | 7.07 (0.00 to 97.20) | 92.20 (0.00 to 194.40) | 14.70 (0.00 to 182.40) |
| Week 48 | 104.60 (0.00 to 297.80) | 15.90 (0.00 to 189.80) | 104.30 (0.0 to 243.00) | 25.60 (0.00 to 226.70) |
| PDX | ||||
| Week 16 | 0.96 (0.00 to 17.80) | 25.30 (0.00 to 53.50) | 1.54 (0.00 to 17.80) | 25.10 (0.00 to 53.50) |
| Week 48 | 3.03 (0.0 to 30.10) | 27.70 (0.00 to 66.60) | 2.92 (0.00 to 30.90) | 28.10 (0.00 to 71.30) |
| qHPV vaccine | ||||
| Week 16 | 158.00 (86.50 to 173.00) | 157 (86.50 to 173.00) | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Week 48 | 219.00 (86.50 to 259.50) | 219 (86.50 to 259.50) | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Cryotherapy | ||||
| Week 16 | 2.50 (0.00 to 13.30) | 3.20 (0.00 to 14.60) | 2.40 (0.00 to 14.50) | 3.40 (0.00 to 14.90) |
| Week 48 | 5.30 (0.00 to 30.90) | 5.10 (0.00 to 32.10) | 6.70 (0.00 to 36.10) | 7.60 (0.00 to 39.20) |
| Study visits | ||||
| Week 16 | 374.00 (92.80 to 643.20) | 368.00 (92.80 to 632.20) | 353.00 (92.80 to 757.80) | 363.00 (92.80 to 617.30) |
| Week 48 | 553.00 (126.40 to 1113.00) | 546.00 (92.80 to 1032.00) | 553.00 (92.80 to 13630.00) | 587.00 (92.80 to 1342.00) |
| Visits with warts | ||||
| Week 16 | 301.00 (92.80 to 559.00) | 289.00 (92.80 to 590.60) | 290 (92.80 to 640.80) | 291.00 (92.80 to 505.80) |
| Week 48 | 385.00 (92.80 to 961.00) | 354.00 (92.80 to 890.00) | 398 (92.80 to 1226.00) | 406.00 (92.80 to 11150.00) |
| Treatment | Total cost (£) | Total adjusted QALYs | ICER (£) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six study visits as planned | Total number of visits | Visits with warts present | EQ-5D-3L | EQ-5D-5L | EQ-5D-3L | EQ-5D-5L | |
| ITT analysis | |||||||
| PDX plus placebo | 460 | 407 | 335 | 0.0235 | 0.0144 | Reference | Reference |
| IMIQ plus placebo | 514 | 457 | 395 | 0.0151 | 0.0073 | Dominated | Dominated |
| PDX plus qHPV | 608 | 555 | 476 | 0.0251 | 0.0088 | 92,000; 92,000; 88,000a | Dominated |
| IMIQ plus qHPV | 665 | 617 | 548 | –0.0059 | –0.0002 | Dominated | Dominated |
| PPA without change in allocated topical treatment | |||||||
| PDX plus placebo | 450 | 424 | 333 | 0.0225 | 0.0138 | Reference | Reference |
| IMIQ plus placebo | 535 | 511 | 434 | 0.0150 | 0.0068 | Dominated | Dominated |
| PDX plus qHPV | 616 | 589 | 497 | 0.0296 | 0.0097 | 23,200; 23,100; 23,000a | Dominated |
| IMIQ plus qHPV | 682 | 651 | 574 | –0.0084 | –0.0011 | Dominated | Dominated |
| CCA | |||||||
| PDX plus placebo | 461 | 407 | 334 | 0.0202 | 0.0138 | Reference | Reference |
| IMIQ plus placebo | 511 | 449 | 386 | 0.0188 | 0.0093 | Dominated | Dominated |
| PDX plus qHPV | 609 | 560 | 481 | 0.0203 | 0.0065 | 990,000; 1,030,000; 980,000a | Dominated |
| IMIQ plus qHPV | 668 | 624 | 550 | –0.0074 | 0.0004 | Dominated | Dominated |
| Treatment | Incremental cost (£) | Incremental adjusted QALYs | ICER (£) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six study visits as planned | Total number of visits | Visits with warts present | EQ-5D-3L | EQ-5D-5L | EQ-5D-3L | EQ-5D-5L | |
| ITT analysis | |||||||
| PDX plus placebo | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Reference | Reference |
| PDX plus qHPV | 147 | 148 | 141 | 0.0016 | Dominated | 92,000; 92,000; 88,000a | Dominated |
| PPA without change in allocated topical treatment | |||||||
| PDX plus placebo | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Reference | Reference |
| PDX plus qHPV | 166 | 165 | 164 | 0.0072 | Dominated | 23,200; 23,100; 23,000a | Dominated |
| CCA | |||||||
| PDX plus placebo | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Reference | Reference |
| PDX plus qHPV | 148 | 154 | 147 | 0.0001 | Dominated | 990,000; 1,030,000; 980,000a | Dominated |
| Treatment | Incremental cost (£) | Incremental adjusted QALYs | ICER (£) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six study visits as planned | Total number of visits | Visits with warts present | EQ-5D-3L | EQ-5D-5L | EQ-5D-3L | EQ-5D-5L | |
| ITT analysis | |||||||
| PDX plus placebo | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Reference | Reference |
| PDX plus qHPV | 203 | 163 | 154 | 0.0005 | Dominated | 380,000; 304,000; 288,000a | Dominated |
| PPA without change in allocated topical treatment | |||||||
| PDX plus placebo | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Reference | Reference |
| PDX plus qHPV | 228 | 197 | 195 | 0.0118 | 0.0042 | 19,200; 16,700; 16,500a | 54,100; 46,900; 46,300a |
| Treatment | Total cost (£) | Natural outcome: wart free | ICER (£) per person wart free | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six study visits as planned | Total number of visits | Visits with warts existing | |||
| PDX plus placebo | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Reference |
| PDX plus qHPV | 147 | 148 | 141 | 0.11 | 1340; 1350; 1280a |
| Treatment | Total cost (£) | Natural outcomes: no recurrence | ICER (£) per person without recurrence | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six study visits as planned | Total number of visits | Visits with warts existing | |||
| PDX plus placebo | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Reference |
| IMIQ plus placebo | 54 | 42 | 68 | 0.03 | 1800; 1400; 2270a |
| IMIQ plus qHPV | 213 | 179 | 173 | 0.07 | 3040; 2560; 2470a |
| Analysis | Treatment group, score (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | |
| ITT analysis | ||||
| Baseline | 0.911 (0.56 to 1.0) | 0.879 (0.51 to 1.0) | 0.895 (0.59 to 1.0) | 0.877 (0.44 to 1.0) |
| Week 4 | 0.901 (0.52 to 1.0) | 0.906 (0.53 to 1.0) | 0.903 (0.64 to 1.0) | 0.894 (0.58 to 1.0) |
| Week 8 | 0.896 (0.35 to 1.0) | 0.908 (0.56 to 1.0) | 0.912 (0.63 to 1.0) | 0.902 (0.62 to 1.0) |
| Week 16 | 0.919 (0.51 to 1.0) | 0.908 (0.57 to 1.0) | 0.922 (0.69 to 1.0) | 0.917 (0.64 to 1.0) |
| Week 24 | 0.927 (0.52 to 1.0) | 0.915 (0.63 to 1.0) | 0.927 (0.69 to 1.0) | 0.917 (0.53 to 1.0) |
| Week 48 | 0.965 (0.71 to 1.0) | 0.964 (0.69 to 1.0) | 0.960 (0.73 to 1.0) | 0.954 (0.63 to 1.0) |
| PPA without change in allocated topical treatment | ||||
| Baseline | 0.914 (0.61 to 1.0) | 0.879 (0.45 to 1.0) | 0.896 (0.60 to 1.0) | 0.892 (0.60 to 1.0) |
| Week 4 | 0.905 (0.54 to 1.0) | 0.917 (0.54 to 1.0) | 0.908 (0.67 to 1.0) | 0.910 (0.69 to 1.0) |
| Week 8 | 0.899 (0.38 to 1.0) | 0.920 (0.57 to 1.0) | 0.916 (0.65 to 1.0) | 0.920 (0.67 to 1.0) |
| Week 16 | 0.922 (0.51 to 1.0) | 0.916 (0.60 to 1.0) | 0.921 (0.69 to 1.0) | 0.934 (0.70 to 1.0) |
| Week 24 | 0.930 (0.52 to 1.0) | 0.934 (0.70 to 1.0) | 0.918 (0.63 to 1.0) | 0.941 (0.72 to 1.0) |
| Week 48 | 0.962 (0.67 to 1.0) | 0.972 (0.76 to 1.0) | 0.956 (0.74 to 1.0) | 0.958 (0.75 to 1.0) |
| CCA | ||||
| Baseline | 0.905 (0.56 to 1.0) | 0.884 (0.55 to 1.0) | 0.890 (0.49 to 1.0) | 0.877 (0.45 to 1.0) |
| Week 4 | 0.899 (0.53 to 1.0) | 0.906 (0.64 to 1.0) | 0.899 (0.53 to 1.0) | 0.886 (0.59 to 1.0) |
| Week 8 | 0.886 (0.37 to 1.0) | 0.908 (0.64 to 1.0) | 0.908 (0.56 to 1.0) | 0.901 (0.60 to 1.0) |
| Week 16 | 0.912 (0.52 to 1.0) | 0.910 (0.69 to 1.0) | 0.918 (0.56 to 1.0) | 0.917 (0.64 to 1.0) |
| Week 24 | 0.921 (0.54 to 1.0) | 0.913 (0.68 to 1.0) | 0.924 (0.63 to 1.0) | 0.917 (0.54 to 1.0) |
| Week 48 | 0.961 (0.70 to 1.0) | 0.963 (0.73 to 1.0) | 0.956 (0.69 to 1.0) | 0.955 (0.65 to 1.0) |
| Analysis | Treatment group, score (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | |
| ITT analysis | ||||
| Baseline | 0.942 (0.70 to 1.0) | 0.922 (0.62 to 1.0) | 0.938 (0.63 to 1.0) | 0.926 (0.66 to 1.0) |
| Week 4 | 0.939 (0.66 to 1.0) | 0.932 (0.49 to 1.0) | 0.943 (0.75 to 1.0) | 0.935 (0.70 to 1.0) |
| Week 8 | 0.938 (0.64 to 1.0) | 0.930 (0.52 to 1.0) | 0.946 (0.72 to 1.0) | 0.942 (0.75 to 1.0) |
| Week 16 | 0.948 (0.65 to 1.0) | 0.935 (0.61 to 1.0) | 0.950 (0.78 to 1.0) | 0.950 (0.73 to 1.0) |
| Week 24 | 0.948 (0.61 to 1.0) | 0.942 (0.68 to 1.0) | 0.952 (0.76 to 1.0) | 0.948 (0.66 to 1.0) |
| Week 48 | 0.974 (0.84 to 1.0) | 0.974 (0.76 to 1.0) | 0.976 (0.84 to 1.0) | 0.972 (0.74 to 1.0) |
| PPA without change in allocated topical treatment | ||||
| Baseline | 0.945 (0.73 to 1.0) | 0.923 (0.62 to 1.0) | 0.938 (0.63 to 1.0) | 0.935 (0.73 to 1.0) |
| Week 4 | 0.944 (0.75 to 1.0) | 0.938 (0.75 to 1.0) | 0.943 (0.75 to 1.0) | 0.947 (0.74 to 1.0) |
| Week 8 | 0.943 (0.70 to 1.0) | 0.937 (0.73 to 1.0) | 0.948 (0.73 to 1.0) | 0.953 (0.77 to 1.0) |
| Week 16 | 0.953 (0.67 to 1.0) | 0.944 (0.78 to 1.0) | 0.949 (0.78 to 1.0) | 0.962 (0.79 to 1.0) |
| Week 24 | 0.950 (0.61 to 1.0) | 0.953 (0.73 to 1.0) | 0.948 (0.73 to 1.0) | 0.959 (0.76 to 1.0) |
| Week 48 | 0.973 (0.80 to 1.0) | 0.980 (0.84 to 1.0) | 0.973 (0.84 to 1.0) | 0.977 (0.85 to 1.0) |
| CCA | ||||
| Baseline | 0.936 (0.68 to 1.0) | 0.924 (0.62 to 1.0) | 0.935 (0.59 to 1.0) | 0.924 (0.66 to 1.0) |
| Week 4 | 0.936 (0.66 to 1.0) | 0.931 (0.75 to 1.0) | 0.939 (0.46 to 1.0) | 0.932 (0.71 to 1.0) |
| Week 8 | 0.932 (0.64 to 1.0) | 0.931 (0.72 to 1.0) | 0.944 (0.49 to 1.0) | 0.940 (0.74 to 1.0) |
| Week 16 | 0.944 (0.65 to 1.0) | 0.936 (0.78 to 1.0) | 0.949 (0.58 to 1.0) | 0.950 (0.73 to 1.0) |
| Week 24 | 0.943 (0.62 to 1.0) | 0.941 (0.75 to 1.0) | 0.950 (0.67 to 1.0) | 0.946 (0.68 to 1.0) |
| Week 48 | 0.971 (0.82 to 1.0) | 0.974 (0.84 to 1.0) | 0.974 (0.77 to 1.0) | 0.972 (0.75 to 1.0) |
| Analysis | Treatment group, adjusted QALY gain (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIQ plus qHPV | PDX plus qHPV | IMIQ plus placebo | PDX plus placebo | |
| ITT analysis | ||||
| EQ-5D-3L | –0.0059 (–0.159 to 0.155) | 0.0251 (–0.141 to 0.243) | 0.0151 (–0.123 to 0.173) | 0.0235 (–0.148 to 0.258) |
| EQ-5D-5L | –0.0002 (–0.083 to 0.075) | 0.0088 (–0.089 to 0.122) | 0.0073 (–0.083 to 0.120) | 0.0144 (–0.071 to 0.201) |
| PPA without change in allocated topical treatment | ||||
| EQ-5D-3L | –0.0084 (–0.172 to 0.157) | 0.0296 (–0.136 to 0.201) | 0.0150 (–0.137 to 0.271) | 0.0225 (–0.143 to 0.242) |
| EQ-5D-5L | –0.0011 (–0.085 to 0.067) | 0.0097 (–0.087 to 0.153) | 0.0068 (–0.101 to 0.122) | 0.0138 (–0.075 to 0.179) |
| CCA | ||||
| EQ-5D-3L | –0.0074 (–0.163 to 0.153) | 0.0203 (–0.142 to 0.251) | 0.0188 (–0.125 to 0.180) | 0.0202 (–0.148 to 0.256) |
| EQ-5D-5L | 0.0004 (–0.081 to 0.077) | 0.0065 (–0.093 to 0.123) | 0.0093 (–0.084 to 0.127) | 0.0138 (–0.071 to 0.189) |
FIGURE 10.
At week 48, (a) CEACs and (b) CEAFs based on three methods of calculating study visit costs (ITT population, EQ-5D-5L). CEAF, cost-effectiveness acceptability frontier.

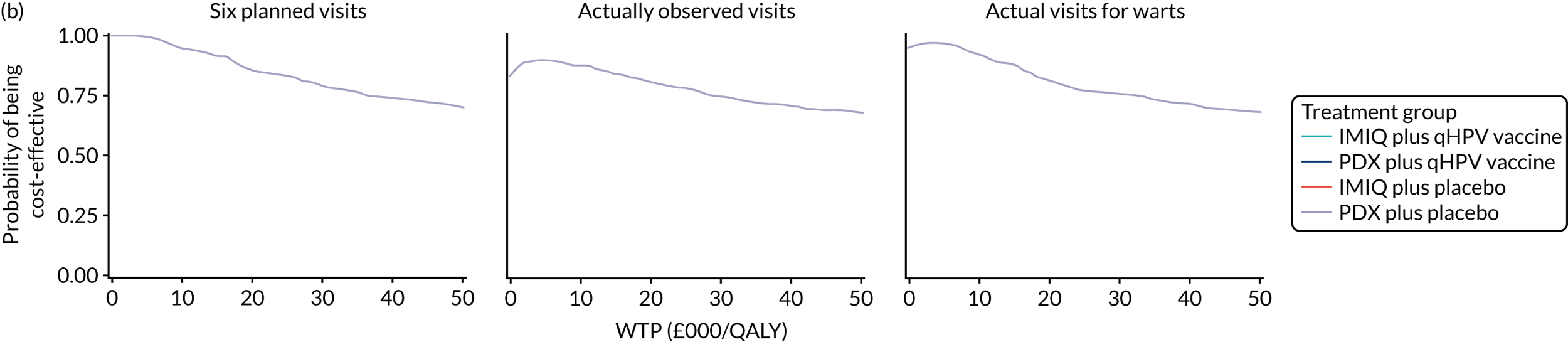
FIGURE 11.
At week 16, (a) CEACs and (b) CEAFs based on three methods of calculating study visit costs (ITT population, EQ-5D-3L). CEAF, cost-effectiveness acceptability frontier.
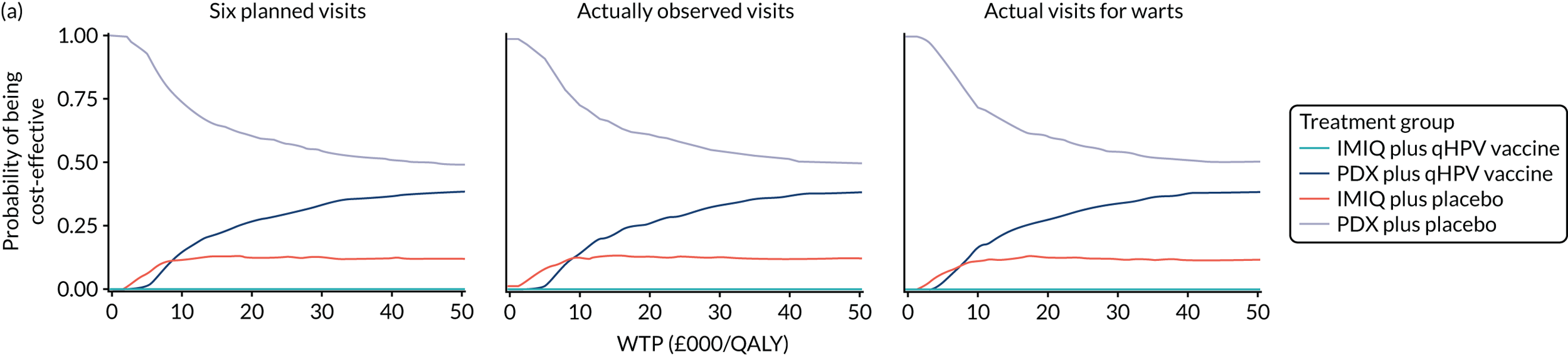
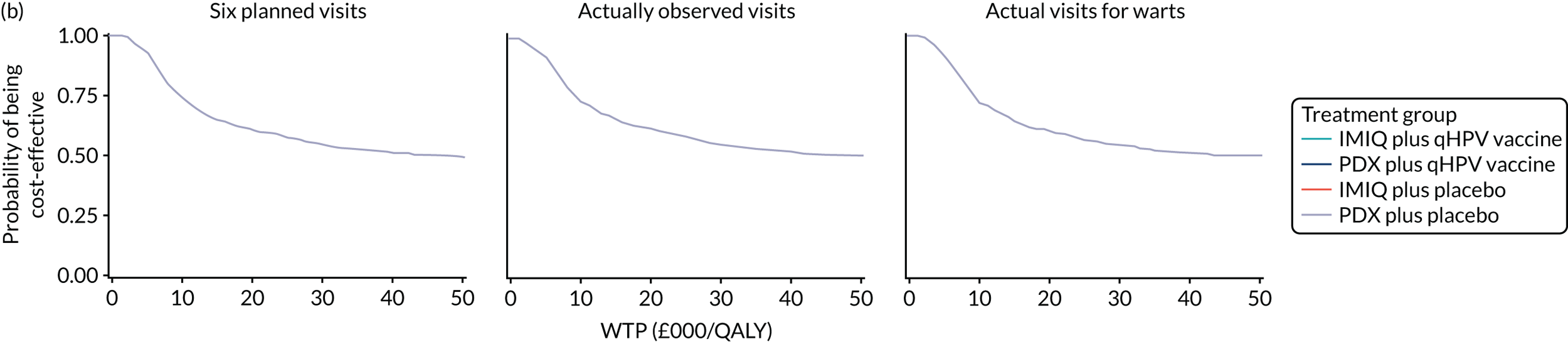
FIGURE 12.
At week 16, (a) CEACs and (b) CEAFs based on three methods of calculating study visit costs (ITT population, EQ-5D-5L). CEAF, cost-effectiveness acceptability frontier.
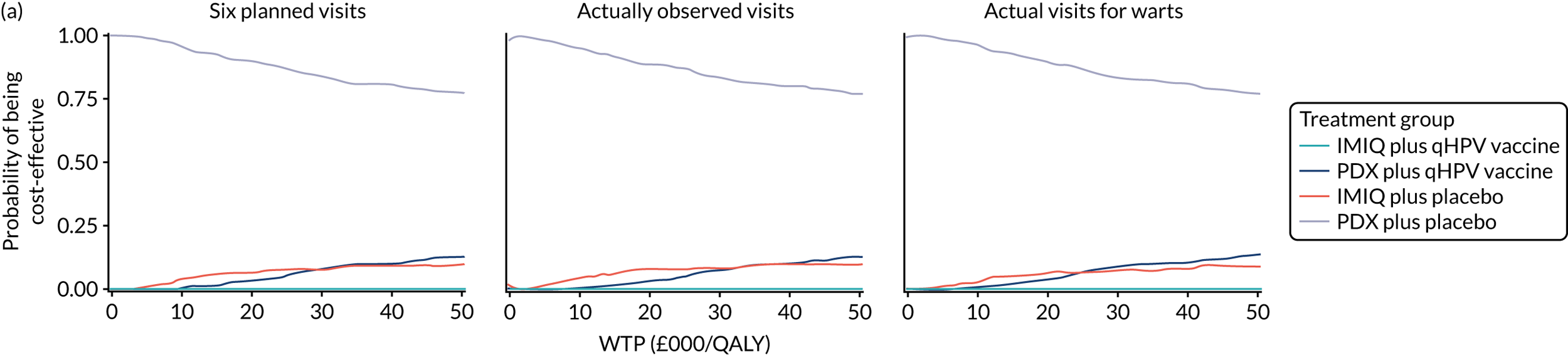
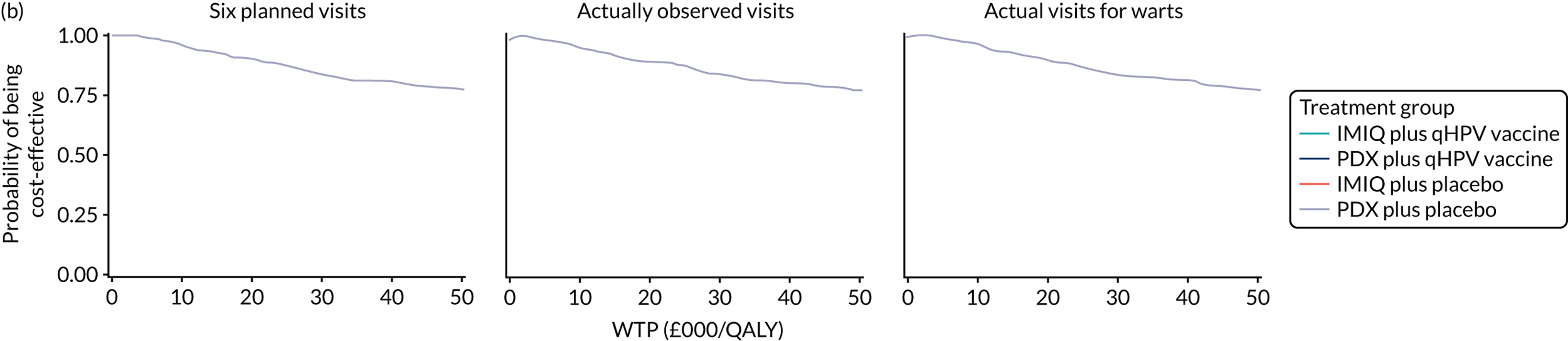
| Measure | Incremental QALYs | £30,000/QALY | £20,000/QALY | £10,000/QALY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITT analysis | ||||
| EQ-5D-3L | 0.0016 | 48.20 | 32.10 | 16.10 |
| EQ-5D-5L | Dominated | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| PPA without change in allocated topical treatment | ||||
| EQ-5D-3L | 0.0072 | 214 | 143 | 71.50 |
| EQ-5D-5L | Dominated | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| CCA | ||||
| EQ-5D-3L | 0.0002 | 4.48 | 2.99 | 1.49 |
| EQ-5D-5L | Dominated | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Treatment | Total cost (£) | Total adjusted QALYs | ICER (£) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six study visits as planned | Total number of visits | Visits with warts present | EQ-5D-3L | EQ-5D-5L | EQ-5D-3L | EQ-5D-5L | |
| Factor at the margins of the vaccine (qHPV vs. placebo) | |||||||
| ITT analysis | |||||||
| Placebo | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| qHPV | 208.00 | 171.00 | 163.00 | –0.0048 | –0.0048 | Dominated | Dominated |
| PPA without change in allocated topical treatment | |||||||
| Placebo | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| qHPV | 217.00 | 175.00 | 173.00 | –0.0003 | –0.0016 | Dominated | Dominated |
| CCA | |||||||
| Placebo | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| qHPV | 215.00 | 193.00 | 181.00 | –0.0061 | –0.0057 | Dominated | Dominated |
| Factor at the margins of the topical creams (PDX vs. IMIQ) | |||||||
| ITT analysis | |||||||
| IMIQ | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| PDX | –58.50 | –50.40 | –77.60 | 0.0046 | 0.0036 | Cost saving | Cost saving |
| PPA without change in allocated topical treatment | |||||||
| IMIQ | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| PDX | –88.20 | –88.10 | –123.20 | 0.0148 | 0.0092 | Cost saving | Cost saving |
| CCA | |||||||
| IMIQ | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| PDX | –59.00 | –45.90 | –70.80 | 0.0048 | 0.0035 | Cost saving | Cost saving |
| Treatment | Total cost (£) | Total adjusted QALYs | ICER (£) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six study visits as planned | Total number of visits | Visits with warts present | EQ-5D-3L | EQ-5D-5L | EQ-5D-3L | EQ-5D-5L | |
| Factor at the margins of the vaccine (qHPV vs. placebo) | |||||||
| ITT analysis | |||||||
| Placebo | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| qHPV | 149.00 | 154.00 | 146.00 | –0.0072 | –0.0063 | Dominated | Dominated |
| PPA without change in allocated topical treatment | |||||||
| Placebo | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| qHPV | 156.00 | 153.00 | 153.00 | –0.0064 | –0.0057 | Dominated | Dominated |
| CCA | |||||||
| Placebo | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| qHPV | 152.00 | 164.00 | 156.00 | –0.0081 | –0.0111 | Dominated | Dominated |
| Factor at the margins of the topical creams (PDX vs. IMIQ) | |||||||
| ITT analysis | |||||||
| IMIQ | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| PDX | –55.40 | –56.30 | –65.80 | 0.0080 | 0.0029 | Cost saving | Cost saving |
| PPA without change in allocated topical treatment | |||||||
| IMIQ | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| PDX | –76.10 | –75.00 | –89.30 | 0.0097 | 0.0030 | Cost saving | Cost saving |
| CCA | |||||||
| IMIQ | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| PDX | –55.50 | –53.80 | –61.10 | 0.0079 | 0.0025 | Cost saving | Cost saving |
| Treatment | Total cost (£) | Natural outcome: wart free | ICER (£) per person wart free | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six study visits as planned | Total number of visits | Visits with warts present | |||
| PDX plus placebo | 460 | 407 | 335 | 0.56 | Reference |
| IMIQ plus placebo | 514 | 457 | 395 | 0.54 | Dominated |
| PDX plus qHPV | 608 | 555 | 476 | 0.67 | 1340; 1350; 1280a |
| IMIQ plus qHPV | 665 | 617 | 548 | 0.56 | Dominated |
| Factor | EQ-5D-3L utilities (mapped) | EQ-5D-5L utilities | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 16 | Week 48 | Week 16 | Week 48 | |||||
| Estimate (SE) | p-value | Estimate (SE) | p-value | Estimate (SE) | p-value | Estimate (SE) | p-value | |
| qHPV vs. placebo | ||||||||
| Intercept | 0.3743 (0.0280) | < 0.0001 | 0.5390 (0.0272) | < 0.0001 | 0.2288 (0.0245) | < 0.0001 | 0.4050 (0.0243) | < 0.0001 |
| Vaccine group (1 if qHPV) | –0.0072 (0.0072) | 0.321 | –0.0048 (0.0070) | 0.492 | –0.0063 (0.0046) | 0.167 | –0.0048 (0.0045) | 0.279 |
| Gender (1 if male) | –0.0010 (0.0077) | 0.893 | –0.0030 (0.0074) | 0.688 | 0.0051 (0.0050) | 0.307 | 0.0031 (0.0048) | 0.519 |
| Age | –0.0005 (0.0004) | 0.177 | –0.0006 (0.0004) | 0.103 | –0.0004 (0.0002) | 0.083 | –0.0006 (0.0002) | 0.018 |
| Previous warts | –0.0050 (0.0075) | 0.504 | –0.0052 (0.0073) | 0.474 | –0.0039 (0.0047) | 0.408 | –0.0017 (0.0047) | 0.721 |
| HIV status | –0.0820 (0.0233) | < 0.001 | –0.1055 (0.0225) | < 0.0001 | –0.0324 (0.0148) | 0.030 | –0.0604 (0.0144) | < 0.0001 |
| Baseline HRQoL score | 0.6231 (0.0262) | < 0.0001 | 0.4642 (0.0251) | < 0.0001 | 0.7810 (0.0235) | < 0.0001 | 0.6085 (0.0231) | < 0.0001 |
| AIC (95% CI) | –1129 (–1151 to –1093) | –1168 (–1195 to –1129) | –1593 (–1617 to –1560) | –1621 (–1648 to –1573) | ||||
| BIC (95% CI) | –1096 (–1117 to –1059) | –1134 (–1162 to –1096) | –1559 (–1583 to –1526) | –1587 (–1615 to –1539) | ||||
| Adjusted R2 (95% CI) | 0.600 (0.538 to 0.657) | 0.487 (0.416 to 0.554) | 0.747 (0.702 to 0.787) | 0.666 (0.610 to 0.716) | ||||
| IMIQ vs. PDX | ||||||||
| Intercept | 0.3649 (0.0286) | < 0.0001 | 0.5333 (0.0278) | < 0.0001 | 0.2230 (0.0249) | < 0.0001 | 0.3993 (0.0248) | < 0.0001 |
| Cream group (1 if PDX) | 0.0080 (0.0074) | 0.280 | 0.0046 (0.0071) | 0.515 | 0.0029 (0.0046) | 0.538 | 0.0036 (0.0045) | 0.421 |
| Gender (1 if male) | –0.0009 (0.0077) | 0.903 | –0.0029 (0.0074) | 0.694 | 0.0051 (0.0050) | 0.301 | 0.0032 (0.0048) | 0.510 |
| Age | –0.0005 (0.0004) | 0.188 | –0.0006 (0.0004) | 0.107 | –0.0004 (0.0002) | 0.087 | –0.0005 (0.0002) | 0.020 |
| Previous warts | –0.0050 (0.0075) | 0.501 | –0.0052 (0.0073) | 0.472 | –0.0039 (0.0048) | 0.409 | –0.0017 (0.0047) | 0.720 |
| HIV status | –0.0827 (0.0233) | < 0.001 | –0.1059 (0.0225) | < 0.0001 | –0.0326 (0.0149) | 0.029 | –0.0607 (0.0144) | < 0.0001 |
| Baseline HRQoL score | 0.6247 (0.0264) | < 0.0001 | 0.4651 (0.0253) | < 0.0001 | 0.7822 (0.0236) | < 0.0001 | 0.6099 (0.0232) | < 0.0001 |
| AIC (95% CI) | –1130 (–1151 to –1094) | –1168 (–1196 to –1129) | –1591 (–1615 to –1559) | –1620 (–1647 to –1572) | ||||
| BIC (95% CI) | –1096 (–1117 to –1061) | –1134 (–1162 to –1096) | –1558 (–1582 to –1525) | –1587 (–1613 to –1538) | ||||
| Adjusted R2 (95% CI) | 0.601 (0.538 to 0.658) | 0.487 (0.416 to 0.554) | 0.747 (0.701 to 0.786) | 0.666 (0.610 to 0.715) | ||||
| Treatment | Total cost (£) | Natural outcomes: no recurrence | ICER (£) per person without recurrence | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six study visits as planned | Total number of visits | Visits with warts existing | |||
| PDX plus placebo | 689 | 654 | 473 | 0.71 | Reference |
| IMIQ plus placebo | 743 | 696 | 541 | 0.74 | 1800; 1400; 2270a |
| PDX plus qHPV | 892 | 817 | 627 | 0.72 | Dominated |
| IMIQ plus qHPV | 956 | 875 | 714 | 0.81 | 3040; 2560; 2470a |
List of abbreviations
- AE
- adverse event
- aOR
- adjusted odds ratio
- AR
- adverse reaction
- CCA
- complete-case analysis
- CCTU
- Comprehensive Clinical Trials Unit
- CD4
- cluster of differentiation 4
- CEAC
- cost-effectiveness acceptability curve
- CI
- confidence interval
- DNA
- deoxyribonucleic acid
- EGCG
- epigallocatechin gallate
- EQ-5D
- EuroQol-5 Dimensions
- EQ-5D-3L
- EuroQol-5 Dimensions, three-level version
- EQ-5D-5L
- EuroQol-5 Dimensions, five-level version
- HAV
- hepatitis A virus
- HIV
- human immunodeficiency virus
- HPV
- human papillomavirus
- HRQoL
- health-related quality of life
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- IDMC
- Independent Data Monitoring Committee
- IMIQ
- imiquimod
- ITT
- intention to treat
- MAR
- missing at random
- MNAR
- missing not at random
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NMB
- net monetary benefit
- PDX
- podophyllotoxin
- PPA
- per-protocol analysis
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- qHPV
- quadrivalent human papillomavirus
- QOLIGEN
- Quality Of Life In patients with GENital warts
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- SAE
- serious adverse event
- STI
- sexually transmitted infection
- TSC
- Trial Steering Committee
- VAS
- visual analogue scale
- WTP
- willingness to pay
