Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was commissioned by the HTA programme as project number 08/72/01. The contractual start date was in September 2009. The draft report began editorial review in December 2010 and was accepted for publication in March 2011. As the funder, by devising a commissioning brief, the HTA programme specified the research question and study design. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the referees for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
JS is Chief Medical Officer of the Fitness Industry Association (FIA). The FIA meets his receipted expenses. The post attracts neither a salary nor fees.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2011. This work was produced by Pavey et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health. This journal is a member of and subscribes to the principles of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) (http://www.publicationethics.org/). This journal may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NETSCC, Health Technology Assessment, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2011 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Background
Physical activity and health
Physical activity (PA) contributes to the prevention and management of over 20 medical conditions and diseases, including coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic back pain, osteoporosis, cancers, falls in the elderly, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), decline in physical and cognitive function, depression and dementia, as summarised in the Chief Medical Officer’s (CMO) report At Least Five a Week: Evidence on the Impact of Physical Activity and its Relationship to Health1 and, more recently, the US guidelines for physical activity. 2 Table 1 lists some of the key conditions in which exercise has been shown to be beneficial. The CMO report estimated the total cost of physical inactivity in England to be £8.2B per year.
| Mental health |
|---|
| Anxietya |
| Depressionb |
| Dementiab |
| Cancer |
| Breasta |
| Lunga |
| Prostatea |
| Colonc |
| Cardiovascular |
| MIa |
| Chronic heart failurea |
| Strokec |
| Peripheral vascular diseaseb |
| Hypertensiona |
| Metabolic |
| Hyperlipidaemiaa |
| Type 1 diabetesa |
| Type 2 diabetesb |
| Musculoskeletal |
| Low back paina |
| Osteoarthritisa |
| Rheumatoid arthritisa |
| Osteoporosisb |
| Other |
| Chronic kidney diseasea |
| Chronic obstructive lung diseasea |
| Chronic fatigue syndromea |
| Falls preventiona |
| Fertilitya |
| Obesitya |
| Parkinson’s diseasea |
| Asthmac |
| Human immunodeficiency virusc |
| Immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)c |
Current recommendations are for adults to aim to be active daily. Over a week, activity should add up to at least 150 minutes (2.5 hours) of moderate-intensity activity in bouts of 10 minutes or more – one way to approach this is to do 30 minutes on at least 5 days a week. Emerging evidence on the effects of time spent in sedentary activities (e.g. television viewing) on obesity, metabolic processes and type 2 diabetes, independent of PA, suggests that reducing time spent in sedentary activities may be an additional useful indicator of the effectiveness of interventions. Worldwide, over 20% of CHD4 has been attributed to physical inactivity, and the most active are at 30% lower risk for developing CHD than the least active,5 with a stepped reduction in risk. The dose for reducing risk in respect of other diseases and for promoting positive well-being is less clear, but the minimum target has been widely recommended as being reasonable for general health benefit at population level. 3
The Health Survey for England (HSE) provides national data on PA prevalence in England. The 2008 HSE report estimated that 39% of men and 29% of women meet the public health target of 5 × 30 minutes per week, with evident variations across age, sex, class and ethnicity. 6 The proportion achieving the targets for PA appears to have increased from 32% in 1997 to 39% in 2008 for men and from 21% to 29% for women. Nevertheless, there is a clear need to promote PA, particularly among the least active, who may have most to gain in terms of health. For adults, efforts in promoting PA have focused on changes in the environment (e.g. walking and cycle paths),7 mass media campaigns, web- and information technology-based communications at population and individual level,8 corporate and workplace initiatives,9 community programmes,10 and provision of individualised professional support11 and new health-care structures. 12
Reviews have also focused on the effectiveness of different PA interventions among specific groups in the population, such as the elderly13 and workers. 14 Systematic reviews suggest that no single approach can be wholly effective8 in helping sedentary people to maintain a physically active lifestyle, and that a wide variety of approaches can each facilitate small increments in behaviour change. The Foresight report on obesity15 reflected determinants of PA with regard to its influence on energy balance, and this is reflected in the cross-governmental policies in transport, health, schools and the built environment to tackle it.
Theories of behaviour change also support the need for multiple-level (e.g. targeting attitudes of both recipients and providers of health promotion messages) and multicomponent approaches (e.g. targeting different belief and attitudinal dimensions, such as the importance or salience of new behaviours, confidence to change, expectancy of benefits and beliefs of others). 16 The past 15 years have seen a growth in the understanding of physically active behaviour and in how to promote it with strategies matched to individual needs. 17 Achieving and maintaining a physically active lifestyle may require numerous and diverse changes in how individuals interact with the environment and with others, as well approaches such as self-monitoring of PA. 18 In evaluating the effectiveness of interventions, it is important to understand precisely what the intervention was and whether this was achieved, and also what process or mediating variables were implicated in changes in primary outcomes (i.e. behavioural and health outcomes). Many reviews and individual studies report the behavioural outcomes or biomedical markers yet very few describe the processes involved in behaviour change. 19
Physical activity promotion in primary care
Primary care has been recognised as a potentially important setting for the promotion of PA. 20 Over 85% of the population in the UK visit their general practitioner (GP) at least once a year, and almost 95% do so over a 3-year period,21 suggesting an opportunity to promote PA. Taylor22 identified, in a review of literature, several barriers that GPs perceived in promoting PA: (1) lack of time in the course of normal clinical interactions in primary care; (2) a lack of desire to pressure patients; (3) a belief that it may not be as beneficial as other therapies or other behavioural targets (e.g. smoking); (4) that patients would not follow advice; and (5) that PA promotion often seemed irrelevant for the needs of patients at the time of consultation. 22
Within the primary-care setting, there are broadly two models of PA promotion – exercise recommendation and EFSs. Although often referred to interchangeably, there are important differences between the two models:
-
Exercise recommendation Within the exercise recommendation framework, primary-care practitioners identify inactive adults and directly offer the advice or counselling regarding exercise, and/or a written prescription of exercise. In its guidance on PA promotion,23 the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) recommended that a validated tool, such as the Department of Health GP Activity Questionnaire (GPPAQ24), be used to identify inactive adults. Boxes 1 and 2 summarise the intervention description from two randomised controlled trials (RCTs) that illustrate the model of exercise recommendation.
-
Exercise referral schemes As in the exercise prescription approach, inactive adults are identified in the primary-care setting. In this case, instead of direct PA advice, the GP or health-care professional refers the patient to a third-party service, with this service taking responsibility for prescribing and monitoring an exercise programme tailored to the individual needs of the patient. NICE defines an exercise referral scheme (ERS) as a process whereby a health professional ‘directs someone to a service offering an assessment of need, development of a tailored PA programme, monitoring of progress and a follow-up. They involve participation by a number of professionals and may require the individual to go to an exercise facility such as a leisure centre’.
‘In a balanced 2 × 2 × 2 factorial design, the three factors were: booklet or no booklet; a counseling session given by a nurse based on attitudes, perceived control of behaviour and techniques for implementing behaviour, or no counseling session; an exercise prescription by the GP or no exercise prescription.’
Exercise prescription‘GPs briefly discussed the benefits of exercise, targets, how to start, and anticipating relapse, and wrote a prescription for 30 minutes, 5 times a week, of brisk walking (or equivalent).’
‘The intervention strategy was similar across the two intervention groups; the only difference was in the focus of the advice given. Patients recruited to the HP (health promotion) intervention group received materials and advice that encouraged them to be more active in order to protect or promote their general health. Patients recruited to the RF (risk factor) intervention group received materials and “medicalised” advice which focused on encouraging them to be more active as an adjunct to managing their hypertension. Physicians were encouraged to discuss the benefits of physical activity, to identify the patient’s preferred types of activity, and to negotiate a program of activity which was then recorded on an “Active Prescription”. The advice and prescription were then supplemented with one of two self-help booklets. The two control groups, HP control and RF control received only usual medical care from their physician. The “Active Prescription” was the same as that used by Smith et al. With the appearance of a clinical prescription; it included a precise prescription of the type, duration and frequency of activity suggested, plus additional space for other comments, a recommended review date and the physician’s signature. Carbon copy duplicates could be kept in the patient’s clinical notes to prompt review during subsequent consultations.’
Within this intervention model, the third-party service may often involve a referral to a local sport or leisure centre. However, the model can also include referral to a practice-based exercise specialist or physiotherapist. The interventions of two recent RCTs evaluating ERS are detailed in Boxes 3 and 4.
‘Patients were given a signed prescription card, with a reason for referral, resting heart rate and blood pressure, intensity of recommended exercise (three levels), and prohibited activity. They were instructed to take it to Hailsham Lagoon Leisure Centre, East Sussex, and arrange an appointment for an introductory session to start a 10 week programme with up to 20 sessions at £1.30 each (that is, half the normal admission price). The introductory session entailed a simple lifestyle assessment, a brief discussion about exercise perceptions and goals, an assessment of blood pressure, weight and height, and advice on use of the cycle ergometers, rowing machines, treadmills, stair climbing machines, and patient record cards. Patients were encouraged to progressively increase the duration and intensity of exercise during the referral period. Supervision was available when requested but patients attended informally between 9 am and 5 pm on weekdays, usually for up to an hour. A mid and end of programme individual assessments were the only formal sessions, though attendance was recorded by leisure centre staff.’
‘After receiving a referral form, the exercise officers telephoned clients to arrange a one-hour consultation at one of three leisure centres. During the consultation, the exercise officer gave person-specific advice and information with the aim of increasing the amount of physical activity clients carried out each week. This included tailored information to meet the needs o each client, taking account of their preferences and abilities, for different types of activity. All clients were offered a subsidized 12 week leisure pass, providing reduced entrance fees to any of the council-run physical activity facilities across the Borough, and were encouraged to attend at least two centre-based sessions a week. Participants were also given information about non-leisure-centre-based activities available across the Borough. At the end of 12 weeks, participants attending the first consultation were invited for an exit interview. This provided an opportunity to review their progress and to identify opportunities to maintain/increase physical activity through the longer term.’
Some trials have been conducted that have evaluated a primary care-based PA promotion including elements of both exercise prescription and ERS. One particular example is The New Zealand ‘green prescription’ (Box 5). In this model, the GP prescribes for the patient an exercise programme, and advises the patient that telephone support is available from the local sports foundation, if required. The failure to differentiate between different models has led to ambiguity within the literature, with different interpretations of these models, particularly in systematic reviews (see Chapter 3, Quality of previous systematic reviews, Scope of previous systematic reviews, and Findings of previous systematic reviews, for further discussion).
-
Primary-care clinicians are offered 4 hours of training in how to use motivational interviewing techniques to give advice on PA and the green prescription.
-
Patients who have been identified as ‘less active’ through screening at the reception desk and who agree to participate receive a prompt card, stating their stage of change, from the researcher, to give to the GP during consultation.
-
In the consultation, the primary care professional discusses increasing PA and decides on appropriate goals with the patient. These goals, usually home-based PA or walking, are written on standard green prescription and given to the patient.
-
A copy of the green prescription is faxed to the local sports foundation with the patient’s consent. Relevant details such as age, weight and particular health conditions are often included.
-
Exercise specialists from the sports foundation make at least three telephone calls (lasting 10–20 minutes) to the patients over the next 3 months to encourage and support them. Motivational interviewing techniques are used. Specific advice about exercise or community groups is provided if appropriate.
-
Quarterly newsletters from the sports foundations about PA initiatives in the community and motivational material are sent to participants. Other mailed materials, such as specific exercise programmes, are sent to interested participants.
-
The staff of the general practice is encouraged to provide feedback to the participant on subsequent visits to the practice.
Development of exercise referral schemes in the UK
Formal links between health care and promoting healthy living through opportunities to exercise are not new. For example, the Peckham Health Centre, in south London, was a bold departure in the medical field in the 1930s, concentrating on a preventative rather than a curative approach to health. To facilitate their grand project, two doctors housed in this purpose-built building engaged with over 900 families as part of ‘the Peckham Experiment’. For one shilling (£0.05 in today’s currency) a week, they relaxed in a club-like atmosphere: physical exercise, games, workshops or even simple relaxation were all encouraged.
The first contemporary ERS was set up around 1990, and over the past two decades there has been a significant and sustained growth in the number with possibly over 600 ERS operating across the UK. This rapid growth in the number of ERS has occurred, in part, in response to new legislation (e.g. compulsory competitive tendering and private management30) of such facilities. Leisure centres with swimming pools and other exercise facilities provide the opportunity to offer diverse options, as well as providing social facilities and became more business orientated, and broadening their clientele base and selling more direct debit-type memberships instead of ‘pay as you go’. The first evaluation of schemes was commissioned by the Health Education Authority in 1994. 31
In the 1990s, several limitations in ERS were indentified:32,33 (1) there were few of them, so they had little potential to impact on public health; (2) staff lacked the training to adapt exercise programmes to the specific health needs of patients; (3) there was little interest in the broader promotion of a more physically active lifestyle, but more interest in building leisure centre membership numbers; (4) GPs were reluctant to refer patients to exercise professionals who had unknown expertise and credentials; (5) there was only limited reference in key NHS policy documents to the promotion of PA; and (6) schemes were inadequately resourced for long-term evaluation. 34 As a result, and after broad consultation with health and exercise professionals, leisure industry operators and exercise scientists, a National Quality Assurance Framework (NQAF) was launched in the UK in 2001 to guide best practice and best value from ERS. 12 The document was aligned with the emerging range of NHS National Service Frameworks (e.g. for CHD, older people) that prioritise PA promotion.
The NQAF12 recommended a service-level agreement to drive the operational links between the primary-care referrer and the exercise or leisure provider, with exercise professionals on the Register for Exercise Professionals (www.exerciseregister.org/) at least at a level compatible with the needs of their clients (level 3: Instructing Physical Activity and Exercise). National Occupational Standards for level 4 (Specialist Exercise Instructor) in Health and Physical Activity were developed in 2007, with core units for CHD, mental health, obesity/diabetes, frailer older adults/falls prevention, after-stroke care and back pain. Despite the publication of the NQAF, capacity and resource constraints have largely dictated the extent to which schemes are meeting these standards. Furthermore, researchers have argued that the NQAF has failed to achieve consistency and comparability of standards, audit and evaluation mechanisms across the country. 33
The most recent survey of ERS programmes was undertaken by the British Heart Foundation National Centre for Physical Activity and Health (BHFNC34), from September 2006 to February 2008. In total, 158 schemes from England and Scotland provided information for the survey. Among these schemes, reported referral rates ranged from 20 to 6500 patients per year. Reported uptake rates (patients attending the initial consultation) ranged from 30% to 98%, with 82.5% of schemes having follow-up system for patients not attending initial consultations (telephone calls, letter/postcard). Scheme completion rates ranged between 20% and 90% depending on the ‘completion’ measure used. Although 95% of schemes reported collecting routine adherence data, adherence levels were not reported as part of the survey.
Fifty per cent of schemes had PA-based inclusion criteria, varying from less than 30 minutes’ activity per week or < 5 × 30 minutes of activity per week, with others using PA questionnaires (e.g. GPPAQ) to determine activity levels. Most schemes received patients with a range of medical conditions, including hypertension, weight problems, diabetes, arthritis, osteoporosis, anxiety and depression (see Appendix 1, Figure 21).
The survey reported further information regarding ERS in the UK that included how long schemes have been running; the aims of the scheme; the scheme characteristics (facilities and activities); the length of referral period (in 47% of schemes this was a 12-week period); and the extent to which the NQAF was used to inform the scheme. However, it was acknowledged that this information provided only a snapshot of operating EFSs, as an estimated 64% provided information.
Current guidance on exercise referral schemes in the UK
In 2006, the NICE Public Health Intervention programme undertook a review of the effectiveness of brief primary care-based intervention for PA promotion that included ERS. 35 NICE determined that there was insufficient evidence to recommend the use of ERS as an intervention to promote PA, other than as part of research studies where their effectiveness could be evaluated. NICE guidance35 recommended that:
Practitioners, policy makers and commissioners should only endorse exercise referral schemes to promote PA that are part of a properly designed and controlled research study to determine effectiveness. Measures should include intermediate outcomes, such as knowledge, attitudes and skills, as well as a measure of PA levels. Individuals should only be referred to schemes that are part of such a study.
Following NICE guidance, and in consultation with exercise referral professionals, commissioners and referring practitioners, the BHFNC published A Toolkit for the Design, Implementation & Evaluation of Exercise Referral Schemes. 34 As noted by its authors, this toolkit is not meant as a replacement for NICE or NQAF guidance, but aims to provide a set of guidance on the implementation and evaluation of ERS for referring health-care professionals, exercise referral professionals and ERS commissioners.
Summary
-
Physical activity contributes to the prevention and management of a number of medical conditions and diseases.
-
Currently, only 25–40% of adults in UK meet the CMO’s target for PA.
-
Primary care is a potentially important setting for the promotion of PA, resulting in the ERS model being developed.
-
Although variations in the model of delivery in ERS across the UK exist, common features include (1) identification of sedentary individuals at risk of lifestyle diseases by a health-care professional operating within a primary health-care setting; (2) referral to an exercise professional who seeks to develop a programme of exercise tailored to the needs of that individual patient; (3) monitoring of progress throughout the programme with appropriate feedback to the referring health-care professional; and (4) auditing to ensure adherence to quality assurance processes (e.g. appropriate staffing, health and safety procedures, ethical and data protection consideration).
-
Despite a NQAF for ERS, capacity and resource constraints have largely dictated the extent to which the majority of schemes are meeting these standards.
-
The NICE guidance in 2006 concluded that there was insufficient evidence to recommend the routine use of ERS to promote PA and called for further clinical effectiveness research.
Chapter 2 Definition of the decision problem
Decision problem
-
Interventions For the purposes of this report, an ERS was defined as comprising the following three core components:
-
– referral by a primary-care health-care professional to a service designed to increase PA or exercise
-
– PA/exercise programme tailored to individual needs
-
– initial assessment and monitoring throughout the programme.
-
-
Population including subgroups The population for this study was defined as people with a diagnosed condition known to benefit from PA. [Although the commissioned scope of this report was to focus on those with a diagnosed condition (known to benefit from PA), given the lack of evidence in this population, we broadened the scope of this report to include individuals without a medical diagnosis.] Subgroups of interest will be identified by diagnosed condition.
-
Relevant comparators All relevant comparators were considered including usual care (e.g. PA advice or leaflets), an alternative form of PA intervention or different forms of ERS.
-
Outcomes All relevant outcomes were sought. Given the nature of the intervention, we were particularly interested in changes in PA. PA can be assessed in number of ways [e.g. self-report or objective measures of PA, proportion of people meeting guideline recommendations, minutes per week of PA (total or moderate intensity), energy expenditure] and we considered all of these approaches. Other outcomes sought were uptake and adherence to ERS, physical fitness, clinical outcomes (e.g. blood pressure, serum lipids), psychological well-being, health-related quality of life (HRQoL), patient satisfaction, and potential adverse events of ERS (e.g. musculoskeletal injuries).
Overall aims and objectives of assessment
The overall aim of this review was to assess the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of ERS in people with a diagnosed condition known to benefit from PA. [Although the commissioned scope of this report was to focus on those with a diagnosed condition (known to benefit from PA), given the lack of evidence in this population, we broadened the scope of this report to include individuals without medical diagnosis.]
This aim is addressed through undertaking:
-
a systematic review of the clinical effectiveness of ERS
-
a systematic review of published economic evaluations of ERS
-
a systematic review to identify predictors of ERS uptake and adherence
-
the development of a decision-analytic model to extend published results and to generate expected values for the health and cost gains/losses associated with ERS.
The specific objectives of the review are to:
-
assess the clinical effectiveness of ERS (see Chapter 3: includes individuals without a medical diagnosis – see note in parentheses above)
-
assess the cost-effectiveness of ERS (see Chapters 4 and 6: includes individuals without a medical diagnosis – see note in parentheses above)2
-
identify predictors of uptake and adherence to ERS (see Chapter 5)
-
explore the factors that might influence the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of ERS (see Chapters 3 and 6: includes individuals without a medical diagnosis – see note in parentheses above)
-
identify priorities for future research in this area (see Chapters 7 and 8).
Chapter 3 Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness of exercise referral schemes
Methods
This clinical effectiveness review was conducted and reported in accordance with the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) statement. 36
Search strategy
An experienced information scientist (TM) conducted an extensive scoping search that resulted in the utilisation of a two-part search strategy. Part 1 searched for ‘exercise referral’ and related synonyms within the title and abstract of articles. Part 2 expanded the terminology for ‘exercise referral’ within the title and abstract, and combined with ‘primary care’ search terms and a controlled trial filter. Limitations were also applied for English language and year of publication where possible (see Appendix 2 for full search strategies).
Both stages of the searches were run in the following databases:
-
Ovid MEDLINE(R) In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations and Ovid
-
MEDLINE(R) 1950 to October 2009
-
Ovid EMBASE 1980 to 2009 week 39
-
Ovid PsycINFO 1967 to September week 4 2009
-
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR), NHS Health Technology Assessment (HTA), NHS Economic Evaluation Database (NHS EED), Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) via The Cochrane Library version 2009 v3
-
SPORTDiscus via Ebsco 1990 to October 2009
-
ISI Web of Knowledge 1900 to October 2009
-
Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE)—1900 to October 2009
-
Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI) – 1898 to October 2009.
Records identified from the part 1 and part 2 searches were combined. The reference lists of included studies were then checked for any additional studies. Given the inception of contemporary ERS in the 1990s, any studies before 1990 were excluded from the search results.
Inclusion criteria
Studies were considered eligible for inclusion if they met the following criteria.
Study design
Systematic reviews, meta-analyses, RCTs (cluster or individual) and non-randomised controlled studies. We excluded studies not published in a peer-reviewed journal (e.g. annual reports of UK ERS programmes), non-systematic reviews, editorials, opinions and reports published as meeting abstracts only (where insufficient methodological details are reported to allow critical appraisal of study quality).
Population
Any individual with or without a medical diagnosis and deemed appropriate for ERS.
Intervention
An ERS (as defined in the decision problem of this report: see Chapter 2).
The ERS exercise/PA programme was required to be more intensive than simple advice and needed to include one or a combination of counselling (face to face or via telephone); written materials; supervised exercise training. Programmes or systems of exercise referral initiated in secondary or tertiary care, such as conventional comprehensive cardiac or pulmonary rehabilitation programmes, were excluded. We excluded trials of exercise programmes for which individuals were recruited from primary care, but there was no clear statement of referral by a member of the primary care team.
Comparator
Any control, for example usual (‘brief’) PA advice, no intervention, attention control or alternative forms of ERS.
Outcomes
Physical activity (self-report or objectively monitored), physical fitness [e.g. maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max)], health outcomes (e.g. blood lipids), adverse events (e.g. musculoskeletal injury) and uptake and adherence to ERS. As we were also interested in patient (e.g. diagnosis, age) and programme factors (e.g. length of and intensity of the exercise programme) that might influence the outcome of ERS, we also extracted these factors from included studies.
Study selection process
Titles and abstracts were screened in a three-stage process. In stage 1, a single reviewer (TP) initially ruled out clearly irrelevant titles and abstracts. At stage 2, two reviewers (TP and RT or KF or MH or AT) then independently screened the remaining titles and abstracts. In stage 3, full papers of abstracts categorised as potentially eligible for inclusion were then screened by a consensus meeting of least two reviewers (TP and RT or KF or MH or AT) and disagreements were resolved in real time by consensus.
Data extraction
Data were extracted by one reviewer (TP) using a standardised data extraction form (see Appendix 3) and checked by another (RT). Discrepancies were resolved by discussion, with involvement of a third reviewer when necessary. Extraction included data on patient characteristics (e.g. age, disease diagnosis), intervention (e.g. duration, location, intensity and mode of the exercise intervention delivered), comparator, study quality, and reported outcomes pertinent to the review. All included study authors were contacted to seek information that was not available in the publication(s).
Risk of bias assessment
Risk of bias criteria were derived from previous quality/risk of bias assessment instruments using published criteria relevant to controlled studies [Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) report 437 and Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions38].
Data analysis and synthesis
Given the heterogeneous nature of outcomes and variable quality of outcome reporting, the primary focus of our data synthesis was descriptive, and detailed tabular summaries are presented. For a small number of outcomes it was possible to consistently extract data across studies to allow quantitative summary using meta-analysis. Dichotomous outcomes were expressed as relative risks (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) calculated for each study. For continuous variables net changes were compared (that is exercise group minus control group to give differences) and a weighted mean difference (WMD) or standardised mean difference (SMD) and 95% CI was calculated for each study. Heterogeneity was explored through consideration of the study populations, methods and interventions, by visualisation of results and, in statistical terms, by the chi-squared test for homogeneity and the I2-statistic. A fixed-effect model meta-analysis was used except where statistical heterogeneity was identified (χ2 p-value ≤ 0.05 or I2 ≥ 50%), in which case a random-effects model was used. Given the small number of studies consistently reporting outcomes in a format to allow meta-analysis, we were not able to undertake a funnel plot and publication-bias analysis. Analyses were conducted using RevMan version 5.0 (Cochrane IMS, London, UK).
Results
Identification and selection of studies
Our bibliographic search yielded 21,563 titles, of which seven primary studies and five systematic reviews were judged to meet the inclusion criteria. Figure 1 summarises the selection and exclusion process.
FIGURE 1.
Study inclusion process for ERS effectiveness systematic review. a, Primary exclusion criteria identified. PHC, primary health care.
Previous systematic reviews of exercise referral scheme effectiveness
A review of previous systematic reviews of the effectiveness of ERS was undertaken to gain an understanding of the evidence for the effectiveness of ERS and information scope and methods of the present systematic review.
Description of included reviews
Four previous systematic reviews of the effectiveness of ERS were identified. 35,39–41 Details of these systematic reviews are summarised in Tables 2–4. 35,39–41 There was considerable variation in the ERS definition applied by these reviews and the type of study design that they included (see Table 2). The systematic reviews by Morgan,39 Sorensen et al. 40 and NICE35 focused on the effectiveness of ERS and included only RCTs. In contrast, Williams et al. 41 included RCTs, non-RCTs, and observational and qualitative studies.
| Authors | Objectives of review (stated by authors) | Databases/end date of searches | ERS definition | Inclusion criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morgan (2005)39 | Review current evidence of the effectiveness for ERS | MEDLINE; EMBASE; CINAHL 2002 | Interventions providing access to exercise activities or facilities and studies based in a primary-care setting | Experimental or quasi-experimental studies, with control groups. Studies including an exercise component with measures of PA or adherence |
| Sorensen et al. (2006)40 |
|
MEDLINE; WinSPIRS; NLM Gateway 2005 | Exercise prescribed by GP or other primary-care staff where EoP included more than just simple advice |
Sedentary adults with signs of lifestyle disease Peer-reviewed studies Reported PA or maximal oxygen uptake Follow-up ≥ 6 months |
| NICE (2006)35 | Examine the evidence for the effectiveness of ERS in increasing PA levels in adults | MEDLINE; PubMed; EMBASE; CINAHL; PsycINFO; SPORTDiscus 2005 | Referral by appropriate professional to a service with formalised process of assessment; development of tailored PA programme; monitoring of progress |
Controlled study design Measurement of PA outcomes or physical fitness at baseline and at least 6 weeks post intervention |
| Williams et al. (2007)41 | Assess whether ERS are effective in improving exercise participation in sedentary adults | MEDLINE; AMED; EMBASE; CINAHL; PsycINFO; SPORTDiscus; The Cochrane Library; SIGLE 2007 | Referred adults from primary care to intervention where encouraged to increase PA; initial assessment; tailored programme; monitoring |
RCT; non-RCT; observational; process evaluation; qualitative Any outcome |
| Studies | Morgan (2005)39 | Sorensen et al. (2006)40 | NICE (2006)35 | Williams et al. (2007)41 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCTs | ||||
| King et al. (1991)45 | ✓ | |||
| Marcus and Stanton (1993)46 | ✓ | |||
| McAuley et al. (1994)47 | ✓ | |||
| Munro et al. (1997)48 | ✓ | |||
| Bull and Jamrozik (1998)49 | ✓ | |||
| Taylor et al. (1998)27 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Stevens and Hillsdon (1998)50 | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Dunn et al. (1998, 1999)51,52 | ✓ | |||
| Goldstein et al. (1999)53 | ✓ | |||
| Harland et al. (1999)43 | ✓ | |||
| Naylor et al. (1999)54 | ✓ | |||
| Halbert et al. (2000)55 | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Writing Group for the Activity Counselling Trial (2001)56 | ✓ | |||
| Dubbert et al. (2002)57 | ✓ | |||
| Lamb et al. (2002)58 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Petrella et al. (2003)59 | ✓ | |||
| Elley et al. (2003)29 | ✓ | |||
| Harrison et al. (2005)28 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Marshall et al. (2005)26 | ✓ | |||
| Jimmy and Martin (2005)60 | ✓ | |||
| Isaacs et al. (2007)61 | ✓ | |||
| Non-randomised trials | ||||
| Robertson et al. (2001)62,63 | ||||
| Fritz et al. (2006)64 | ✓ | |||
| Authors | No. of included studies | Method of data synthesis | Key findings (as reported by author) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morgan (2005)39 |
UK (n = 4) Non-UK (n = 5) |
Narrative |
1. ERS appears to increase PA levels, particularly for those already partially active, older adults and those overweight (not obese) 2. Increases may not be sustained 3. Need strategies to increase long-term adherence |
| Sorensen et al. (2006)40 |
Effectiveness (n = 12) Total (n = 22) |
Narrative, included assessment of quality |
4. Most studies reported moderate improvements in PA or physical fitness for 6–12 months 5. EoP patients displayed 10% improvement in PA compared with control |
| NICE (2006)35 | (n = 4) | Narrative, included, quality appraisal; study type; applicability |
6. Insufficient evidence to make conclusions/recommendations about ERS 7. More research required (e.g. long-term effects) |
| Williams et al. (2007)41 |
Meta-analysis (n = 5) Total (n = 18) |
Narrative and meta-analysis (heterogeneity, quality) |
8. Significant increase in participants doing moderate exercise (number needed to treat: 17 sedentary adults would need referring for one to become moderately active) 9. Poor uptake and adherence to ERS |
Quality of previous systematic reviews
A modified version of the Oxman and Guyatt42 Overview Quality Assessment Questionnaire (OQAQ) assessment tool and scale was used to assess the quality of reviews (see Table 5), with total scores for the reviews ranging from 10 to 18 points. All of the reviews provided a comprehensive search strategy, inclusion/exclusion criteria and risk of bias measure for the included primary studies, with conclusions supporting the data reported in the overview. Three of the reviews35,39,40 were lacking in the application of the quality criteria to inform the review analysis, and the reporting and subsequent application of methods used to combine the findings of included studies. Only the review by Williams et al. 41 fulfilled all of the criteria.
| Quality assessment items | Morgan (2005)39 | NICE (2006)35 | Sorensen et al. (2006)40 | Williams et al. (2007)41 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Were the search methods used to find evidence on the primary question(s) stated? | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points |
| 2. Was the search for evidence reasonably comprehensive? | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points |
| 3. Were the criteria used for deciding which studies to include in the review reported? | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points |
| 4. Was bias in the selection of articles avoided? | No: 0 points | Yes: 2 points | Can’t tell: 1 point | Yes: 2 points |
| 5. Were the criteria used for assessing the validity for the studies (i.e. meeting inclusion criteria) reviewed reported? | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points |
| 6. Were study quality assessment criteria used to inform the review analysis? | No: 0 points | Yes: 2 points | Partially: 1 point | Yes: 2 points |
| 7. Were the methods used to combine the findings of the relevant studies (to reach a conclusion) reported? | No: 0 points | No: 0 points | No: 0 points | Yes: 2 points |
| 8. Were findings of the relevant studies combined appropriately relative to the primary question of the overview? | No: 0 points | No: 0 points | No: 0 points | Yes: 2 points |
| 9. Were the conclusions made by the author(s) supported by the data and/or analysis reported in the overview? | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points | Yes: 2 points |
| Total | 10/18 points | 14/18 points | 12/18 points | 18/18 points |
Scope of previous systematic reviews
Table 3 highlights the lack of consistency in the studies included by these four previous systematic reviews of ERS. Although some of this variation reflects the inclusion of non-randomised studies, the principal reason for this difference is in the scope of inclusion criteria for the interventions. The systematic review by Sorensen et al. 40 assessed what the researchers called ‘exercise on prescription’ (EoP) and included studies that involved physician-delivered PA advice (i.e. exercise recommendation). As discussed in the Background section of this report, such interventions do not meet the standard definition of ERS in the UK.
A number of studies included in these previous systematic reviews did not appear to formally involve a referral from a primary-care health-care practitioner to a third party. For example, the study by Harland et al. 43 took place in primary care and involved an exercise intervention delivered by a third party/service. The methods section of the study publication states:
the researcher (JH) approached all patients aged 40–64 attending routine surgeries. Patients completed a recruitment card, signed by their general practitioner, which they returned to the researcher before leaving
(Harland et al. ,43 p. 828)
Thus, no referral from the GP was made; the researcher recruited subjects opportunistically from the waiting room. Indeed, in response to correspondence following publication of this trial, the authors confirmed that ‘our scheme was not an exercise prescription scheme’ (p. 1470). 44
The study of Lamb et al. 58 has been included in three previous systematic reviews,35,39,41 including the review by NICE. 35 In this study, the participant recruitment process involved several stages: the practice manager initially identified a random sample from computerised records; individuals in this sample were sent a questionnaire and covering letter from GPs to assess inclusion criteria and willingness to participate in a PA promotion trial; eligible patients who returned the questionnaires were sent a second letter explaining the trial in more detail; positive responses were followed up with a telephone call to gain consent and registration. However, there is no actual referral from the GPs, with the researchers using the primary-care setting as a gateway to recruit patients for their PA promotion trial. Finally, Elley29 (included in one of the previous reviews) is an example of an alternative model of PA intervention, i.e. the ‘green prescription’ PA model. In this model, the GP prescribes the patient’s exercise programme and advises the patient that telephone support is available from the local sports foundation, if required, but third-party service provision is not an essential component.
Findings of previous systematic reviews
These previous systematic reviews35,39–41 appear to conclude that ERS have a small effect in increasing PA in the short term, with little or no evidence of long-term sustainability (i.e. 12 months or longer) (Tables 4 and 5). The one review that undertook a meta-analysis (of five UK-based RCTs) reported that participants in the ERS were 20% more likely to be moderately physically active at the threshold of 90–150 minutes/week) than those not participating in ERS [odds ratio (OR) 1.20, 95% CI 1.06 to 1.35]. 41 These reviews provide limited consideration of either the impact of ERS on disease-specific groups or outcomes other than PA.
Primary exercise referral scheme studies
As shown in Figure 1, the most frequent reason for exclusion from the present review was that studies used primary care as means of recruiting individuals into exercise programmes, but there was no clear statement of a referral by a member of the primary-care team to a third-party exercise provider. Examples of three such studies are presented in Boxes 6–8. A full list of excluded papers is provided in Appendix 3.
‘Participants were drawn from a patient electronic database at a local health centre.’
‘A total of 1439 patients were contacted by mail with an invitation letter and information sheet telling them about the study. Three hundred and fifty-eight (28%) accepted the invitation to enter the study by completing a form and returning it in a stamped addressed envelope.’
‘General practitioners at participating practices were asked to identify women in the age group from their practice register, excluding patients deemed inappropriate for participation in a physical activity trial. The general practitioners sent letters to those identified as suitable, inviting them to participate in a lifestyle study. The invitation letter requested that women contact the research team if they were interested in learning more about the study using the reply slip and prepaid envelope supplied.’
‘Two research assistants recruited patients through three primary care practices from different socioeconomic regions of Auckland, New Zealand, from June 2003 to March 2004. The primary care physicians identified and screened all those aged 65 and older on the practice databases (from their files). Those for whom physical activity was not contraindicated and were contactable at the address and telephone number on the practice database (N = 831) were invited to participate in the study via a letter from their primary care physician and follow-up telephone call from the practice where necessary.’
Characteristics of included primary studies
The characteristics of the seven included ERS studies are summarised in Table 6. 26,27,49,60,67–69 These studies included a total of 3030 participants. All studies were RCTs: five undertaken in the UK,27,28,50,61,68 one in Denmark69 and one in Spain. 70 The studies of Jolly et al. 68 and Gusi et al. 70 used cluster allocation (i.e. allocating participants to ERS and control at the ERS provider and general practice level, respectively). The other included studies undertook participant level randomisation. Studies had a median sample size of 347 (range 54–943) and follow-up duration ranged from 2 to 12 months. The GP was the main referrer, usually using a bespoke referral form to a fitness or exercise instructor/officer.
| Study | No. of GP practices | Date study conducted | RCT design | Overall n | Randomised (n) (ERS/control) | Comparator group description | Follow-up periods |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
UK |
3 | January to December 1994 | Individual | 142 | 97/45 |
Initial screen No exercise programme |
8, 16, 26 and 37 weeks |
|
Stevens et al. 50 UK |
1 | Not stated | 714 | 363/351 | No exercise programme; sent exercise promotion materials | 8 months | |
|
Harrison et al. 28 UK |
46 | March 2000 to December 2001 | 545 | 275/270 | No exercise programme; sent a written information pack | 6, 9 and 12 months | |
|
Isaacs et al. 61 UK |
88 | October 1998 to April 2002 | 943 | 317/315/311 |
Initial assessment No exercise programme, advice only or 10-week walking scheme, 2 × 45 minutes/week, 60–80% of heart rate max., group setting |
10 weeks, 6 and 12 months | |
|
Denmark |
14 | 2005–6 | Individual | 52 | 28/24 |
Initial health profile and motivational counselling (45–60 min/session) No exercise programme |
4 and 10 months |
|
Gusi et al. 70 Spain |
Four | Not stated | Cluster | 287 | 127/160 | Best care in general practice, which consisted of routine care and a recommendation of PA | 6 months |
|
Jolly et al. 68 UK |
Not reported (13 leisure centre sites) | November 2007 to July 2008 | 347 | 184/163 | ERS plus SDT programme | 3 and 6 months |
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Most studies determined their inclusion and exclusion of participants based on criteria of the ERS they were evaluating (Table 7). Four studies27,50,68,70 excluded patients with any form of heart condition. Gusi et al. 70 excluded patients with severe obesity or major depression and Taylor et al. 27 excluded patients with diabetes. All excluded individuals were considered to be at especially high risk [e.g. systolic blood pressure (SBP) of > 200 mmHg, insulin-dependent diabetes].
| Study | Age range of patients (years) | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | Inclusion/exclusion criteria determined/evaluated by | No. of participants excluded |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Taylor et al. 27 UK |
40–70 | Smokers, hypertension (140/90 mmHg), overweight (BMI > 25) | SBP > 200 mmHg, history of MI or angina pectoris, diabetes mellitus, musculoskeletal condition preventing PA, previous ERS referral | Research team and GP determined and evaluated | 44 |
|
Stevens et al. 50 UK |
18+ | Sedentary–less than 20 × 30 minutes of moderate-intensity PA or less than 12 × 20 vigorous-intensity PA in the last 4 weeks | Medical reasons for exclusion, e.g. registered disabled, diagnosis of heart disease | Research team determined and evaluated | 113 |
|
Harrison et al. 28 UK |
18+ | Sedentary, participating in < 90 minutes of moderate/vigorous PA a week, additional CHD risk factors; obesity, previous MI, on practice CHD risk management register, diabetes | GP identified contradiction to PA, SBP > 200 mmHg, not sedentary, only one family member (to avoid contamination–research team criterion) | GP evaluation using the trial’s ERS-determined criteria | 285 |
|
Isaacs et al. 61 UK |
40–74 | Not active (no definition reported), raised cholesterol, controlled mild/moderate hypertension, obesity, smoking, diabetes, family history of MI at early age | Pre-existing overt CVD, uncontrolled hypertension, uncontrolled insulin-dependent diabetes, psychiatric or physical conditions preventing PA, conditions requiring specialist programme | GP evaluation using criteria determined by an existing ERS | Not reported |
|
Sorensen et al. 69 Denmark |
18+ | Patients must meet all criteria: (1) having medically controlled lifestyle diseases or at risk of developing lifestyle diseases; (2) motivated to change lifestyle; (3) believed by the GP to be able to improve health from an increased PA level; and (4) willing to pay 750 Danish krone (€100) for the intervention | Not meeting the inclusion criteria | GP evaluation using the trial’s ERS-determined criteria | Not reported |
|
Gusi et al. 70 Spain |
60+ | Moderately depressed (6–9 points on the Geriatric Depression Scale), overweight (BMI 25–39.9), capable of walking for more than 25 minutes | Severe obesity, major depression, debilitating medical condition, known unstable cardiac condition, attention or comprehension problems | Research team determined, GP evaluation | 32 |
|
Jolly et al. 68 UK |
18+ | People with two or more major risk factors of coronary heart disease:
|
Angina pectoris, moderate-to-high (or unstable) hypertension ≥ 160/102 mmHg Poorly controlled insulin-dependent diabetes, history of MI within the last 6 months – unless the patient has completed stage III cardiac rehabilitation, established cerebrovascular disease, severe chronic obstructive airways disease, uncontrolled asthma |
GP evaluation using the trial’s ERS-determined criteria | Not reported |
Trial participants
Studies mainly recruited sedentary, middle-aged white adults who had no medical diagnosis and evidence of at least one lifestyle risk factor, i.e. high blood pressure, raised serum cholesterol, smoking or being overweight (Tables 7 and 8). Studies also included a number of individuals with a medical diagnosis that included diabetes, hypertension, depression, CHD and obesity. However, all included studies reported outcomes aggregated across all participants (see Findings, below). Only Gusi et al. 70 reported a rural population with 66% of participants living in a rural area.
| Study | Age (mean, years) | Gender (% male) | Ethnicity (%) | Reported diagnosed conditions or risk factors (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention | Control | Intervention | Control | Intervention | Control | Intervention | Comparator | |
|
Taylor et al. 27 UK |
54.1 | 54.4 | 37 | 38 | Not reported | Not reported |
Smokers: 43% Overweight: 77% Hypertensive: 46% |
Smokers: 40% Overweight: 71% Hypertensive: 58% |
|
Stevens et al. 50 UK |
59.1 | 59.2 | 40 | 44 |
White: 87 Black: 5 Asian: 4 Other: 4 |
White: 83 Black: 4 Asian: 6 Other: 5 |
BMI > 25: 46 Smoker: 18 |
BMI > 25: 42 Smoker: 17 |
|
Harrison et al. 28 UK |
18–44 = 111 45–59 = 101 > 60 = 63 |
18–44 = 107 45–59 = 98 > 60 = 65 |
33 | 34 | White: 71.9 | White: 74.1 |
Smoker: 24.4 At least one CHD risk factor: 75.3 |
Smoker: 20.7 At least one CHD risk factor: 75.2 |
|
Isaacs et al. 61 UK |
57.1 |
Usual care: 57 Walk: 56.9 |
ERS: 35 |
32 Walk: 31 |
White: 75.7 Asian:16.7 |
(Control/walking) White: 76.5/75.9 Asian: 14/12.2 |
(Exercise/walking) Raised cholesterol: 24.0 Hypertension: 44.5 Obesity: 65.9 Smoking: 10.4 Type 2 diabetes: 12.3/11.3 Family history of MI: 13.9 |
(Control/walking) Raised cholesterol: 17.1/21.5 Hypertension: 43.5/46.3 Obesity: 63.5/58.5 Smoking: 8.3/12.2 Diabetes: 15.6/11.3 Family history of MI: 16.2/12.9 |
|
Sorensen et al. 69 Denmark |
53.9 | 52.9 | 43 | 37 | Not reported | Not reported |
Metabolic syndrome: 36 Type 2 diabetes: 18 CVD: 32 Other diseases: 14 |
Metabolic syndrome: 25 Diabetes: 21 Heart disease: 42 Other diseases: 13 |
|
Gusi et al. 70 Spain |
71 | 74 | 0 | 0 | Not reported | Not reported |
Overweight (BMI>25): 80 Type 2 diabetes: 39 Moderate depression: 34 |
Overweight: 86 Type 2 diabetes: 37 Moderate depression: 38 |
|
Jolly et al. 68 UK |
< 30: 19 30–49: 76 50–64: 64 65+: 25 |
< 30: 11 30–49: 77 50–64: 50 65+: 25 |
24 | 30 |
White: 74.9 Black: 10.6 Asian: 9.5 Other: 5 |
White: 67.5 Black: 14.9 Asian: 14.9 Other: 2.6 |
Smoker: 22.1 Hypertension: 38 Overweight (BMI > 25): 25.3 Obese (BMI > 30): 52.3 Morbidly obese (BMI>40): 12.1 Probable anxiety: 34.2 Probable depression: 21.9 |
Smoker: 23.1 Hypertensive: 37.5 Overweight: 26.3 Obese: 51.9 Morbidly obese: 13.5 Probable anxiety: 31.9 Probable depression: 15.3 |
Exercise referral scheme intervention
The ERS intervention of all studies, except that of Gusi et al. ,70 undertook an initial consultation by the third-party provider, such as an exercise professional (Table 9). The consultations varied in content, but all contained information and advice about being physically active. Other components of the screen (dependent on study outcomes) included lifestyle and health questionnaires and physical fitness measures. Scheme length was typically 10–12 weeks, and took place in a leisure centre,27,28,50,61,68 a clinic, public parks or forest tracks (Table 10). Exercise sessions were usually twice per week, lasted between 30 and 60 minutes per session, and were conducted at either a moderate or individually tailored intensity. Two studies69,70 provided group-based exercise sessions, and four27,28,61,68 provided a combination of group and individual exercise sessions. Only three studies28,50,68 reported an assessment at the end of the ERS programme.
| Study | Referrer | Format of referral | Referred to where | Participant cost | Referred to who |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Taylor et al. 27 UK |
GP | Signed prescription card | Leisure centre | Half-price admission | Fitness instructor |
|
Stevens et al. 50 UK |
GP | Letter | Leisure centre | Not reported | Exercise development officer |
|
Harrison et al. 28 UK |
GP | Faxed referral form | Leisure centre | ‘Subsidised ’ | Exercise officer |
|
Isaacs et al. 61 UK |
GP or practice nurse | Specially prepared ‘prescription pad’ – referral form | Leisure centre | Free | Fitness instructor |
|
Sorensen et al. 69 Denmark |
GP | Not reported | Clinic | Pay €100 | Physiotherapist |
|
Gusi et al. 70 Spain |
GP | Not reported | Supervised walks in a public park or forest tracks | Not reported | Qualified exercise leaders |
|
Jolly et al. 68 UK |
Member of the primary-care team | Not reported | Leisure centre | Not reported | Health and fitness adviser |
| Study | Initial screen/assessment | Scheme duration | Exercise programme | Exit assessment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provider | Exercise sessions per week | Exercise session intensity | Group or individual | ||||
|
Taylor et al. 27 UK |
Yes | 10 weeks | Leisure centre | 2 × 30–40 minutes | Moderate intensity | Group and/or individual | Not reported |
|
Stevens et al. 50 UK |
Yes | 10 weeks | Leisure centre | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Yes |
|
Harrison et al. 28 UK |
Yes | 12 weeks | Leisure centre | 2 × 1 hour | Individually based | Group and/or individual | Yes |
|
Isaacs et al. 61 UK |
Yes | 10 weeks | Leisure centre | 2 × 45 minutes | Not reported | Group and/or Individual | |
|
Sorensen et al. 69 Denmark |
Yes (and motivational counselling) | 4 months | Clinic |
First 2 months 2 sessions × 1 hour Second 2 months 1 session × 1 hour |
More than 50% of heart rate reserve for a minimum of 20 minutes | Group | |
|
Gusi et al. 70 Spain |
Not reported | 6 months | Walking scheme | 3 × 50 minutes | Not reported | Group | |
|
Jolly et al. 68 UK |
Yes | 12 weeks | Leisure centre | Individually based | Individually based | Group and/or Individual | |
Control/comparator group
Five studies27,28,50,61,70 compared ERS with a ‘usual care’ control group, which consisted of no exercise intervention or simple advice on PA (see Table 6). Sorensen et al. 69 compared ERS with motivational counselling aimed at increasing daily PA. In addition to a no-exercise group, the Isaacs et al. study61 also included an instructor-led walking programme. The Jolly et al. study68 compared two forms of ERS, i.e. standard ERS versus a combined ERS plus self-determination theory (SDT)-based intervention.
Risk of bias
Table 11 summarises the risk of bias for each of the included studies. Most included a power calculation and allocated participants using an appropriately generated random number sequence. However, the reporting of concealment of trial group allocation was poor, although there was good evidence of participant characteristics of intervention and control groups at baseline. Although blinding of participants and intervention providers in these studies was not feasible, blinding of outcome assessment was possible. Outcome blinding is particularly important in preventing assessment bias in the case of outcomes that require observer judgement or involvement (e.g. blood pressure measurement or exercise testing). However, only the study of Jolly et al. 68 reported outcome blinding, i.e. self-reported PA using the 7-Day Physical Activity Recall Questionnaire was assessed via telephone to maintain blinding. The reporting and handling of missing data was detailed for most studies, and all studies, except one,27 reported the use of intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis. The level of missing data at follow-up ranged across studies from 16.5% to 50%. Most studies used imputation methods (last observation carried forward or complete case average values) to replace missing data values at follow-up. Overall, three studies were judged to be at moderate overall risk of bias27,28,50 and four to be at low overall risk of bias. 61,68–70
| Risk of bias criterion | Taylor et al.27 UK |
Stevens et al.50 UK |
Harrison et al.28 UK |
Isaacs et al.61 UK |
Sorensen et al.69 Denmark |
Gusi et al.70 Spain |
Jolly et al.68 UK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power calculation reported? | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Method of random sequence generation described? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes+ |
| Method of allocation concealment described? | Yes+ | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Unclear |
| Method of outcome (assessment) blinding described? | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | No | Unclear | Unclear | Yes |
| Were groups similar at baseline? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Was ITT analysis used? | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Was there any statistical handling of missing data? | Unclear | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Were missing data (dropout and loss to follow-up) reported? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Exercise referral scheme eligibility, uptake and adherence
There was a considerable range in the proportion of individuals randomised compared with those deemed eligible (Table 12). In both the Sorensen et al. 69 and Jolly et al. 68 studies, of those deemed eligible for ERS, a substantial number refused participation in the trial. For Sorensen et al. 69 this low number maybe reflective of the €100 payment by patients as part of a standard Danish EoP.
| Study | No. deemed eligible (n) | Total n randomised | ERS (n) | Control (n) | ERS uptake |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Taylor et al. 27 UK |
345 | 142 (41%)+ | 97 | 45 | 85 (88%) |
|
Stevens et al. 50 UK |
827 | 714 (86%)+ | 363 | 351 | 126 (35%) |
|
Harrison et al. 28 UK |
830 | 545 (66%)+ | 275 | 270 | 232 (84%) |
|
Isaacs et al. 61 UK |
1305 | 949 (73%)+ | 317 | 315 + 311 | 293 (92%) |
|
Sorensen et al. 69 Denmark |
327 | 52 (16%)+ | 28 | 24 | 28 (100%) |
|
Gusi et al. 70 Spain |
160 | 127 (79%)+ | 64 | 63 | Not reported |
|
Jolly et al. 68 UK |
1683 | 347 (21%)+ | 184 | 163 | Not reported |
Uptake was defined as the proportion of those individuals offered entry to ERS who attended an initial consultation with an ‘exercise professional’ or attended a first exercise session. Although Taylor et al. ,27 Issacs et al. 61 and Sorensen et al. 69 reported uptake rates in excess of 85%, in the Stevens et al. 50 study only 126 (35%) of the 233 randomised to ERS attended the first consultation. Stevens et al. 50 discussed how the low uptake they experienced may have been reflective of the nature of the invitation letter sent to participants and the point of randomisation (pre-invitation letter). Furthermore, they hypothesise that a change in the format of the letter (e.g. including a specific appointment date for the first ERS appointment) would have improved participation. Uptake was not reported by Jolly et al. 68 or Gusi et al. 70
Harrison et al. 28 and Jolly et al. 68 failed to provide information on participants’ adherence to the ERS intervention. Stevens et al. 50 and Gusi et al. 70 reported ERS programme completion rates of 25% and 86%, respectively. However, these rates do not reflect the number of sessions attended, only those who attended a second consultation50 or follow-up assessment. 70
Sorensen et al. 69 reported that an average 18 of a total of 24 ERS exercise sessions were attended and 68% and 75% of participants attended the counselling sessions at 4 and 10 months, respectively. Both Taylor et al. 27 and Isaacs et al. 61 provide a detailed description of ERS programme adherence. Taylor27 reported 13% attending no exercise sessions and 28% attending 75–100% of exercise sessions, with an average of 9.1 out of 20 prescribed exercise sessions attended. Isaacs et al. 61 reported 7.6% attending no exercise sessions and 42% attending 75–100% of exercise sessions in the leisure centre group. In the walking group, 23.5% attended no exercise sessions, with 21.5% attending 75–100% of exercise sessions. As shown in Table 13, there was no consistent difference in attendance rates between those in at-risk groups and the overall study population in the studies of Taylor et al. 27 and Isaacs et al. 61 In the Isaacs et al. 61 study, the 60- to 69-year age group had the highest adherence in both the ERS (53.3%) and the walking (24.2%) groups. There were no significant differences in attendance rate with employment status, educational level, socioeconomic status, ethnicity or relationship status. Adherence was lower for those without access to private transport in both the ERS and walking groups.
Findings
Only Isaacs et al. 61 reported all outcome domains applicable to this systematic review (Table 14). Outcome results are reported according to the three categories of comparator, i.e. ERS versus usual care; ERS versus alternative exercise intervention and ERS versus alternative form of ERS.
| Study | PA | PA measure | Physical fitness | Clinical outcomes | Psychological well-being | HRQoL | Patient satisfaction | Adverse events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Taylor et al. 27 UK |
Yes |
Self-report 7-day PAR |
Yes Sub-max HR |
Yes BP, BMI, BF%, waist to hip |
Yes PSW |
No | No | No |
|
Stevens et al. 50 UK |
Yes |
Self-report 7-day PAR |
No | No | No | No | No | No |
|
Harrison et al. 28 UK |
Yes |
Self-report 7-day PAR |
No | No | No | No | Yes | No |
|
Isaacs et al. 61 UK |
Yes |
Self-report Minnesota LTPAQ |
Yes Sub-max bike test Sub-max walking test |
Yes BP, cholesterol, lipoproteins, triglycerides, weight, BMI, BF%, waist-to-hip ratio, FEV, PEF |
Yes Anxiety, depression |
Yes SF-36 mental |
Yes |
Yes GP records |
| Sorensen et al.69 Denmark | Yes |
Self-report Unspecified |
Yes Sub-max bike test |
Yes Weight, BMI |
No |
Yes SF-12 mental, physical |
No | No |
|
Gusi et al. 70 Spain |
Not reported | N/A | No |
Yes BMI |
Yes Anxiety, depression |
Yes EQ-5D |
No | No |
|
Jolly et al. 68 UK |
Yes |
Self-report 7-day PAR |
No |
Yes BMI |
Yes Anxiety, depression |
Yes Dartmouth QoL |
No | No |
Physical activity
All studies, with the exception of Gusi et al. ,70 provided a measure of self-reported PA. Self-reported measures included the validated 7-Day Physical Activity Recall Questionnaire,27,28,50,68 a modified version of the validated Minnesota Leisure Time Activity Questionnaire61 and an invalidated questionnaire designed by the research team. 63 No studies reported assessed PA using objective methods. A summary of the main PA outcomes at follow-up is provided in Table 15.
| Study and time of follow-up | Patients achieving PA guidance (90–150 minutes/at least moderate-intensity per week) | Minutes per week at least moderate intensity | Total PA (minutes per week) | Energy expenditure (kcal/kg/day)a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERS, n/N | Usual care, n/N | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | |||
| ERS vs usual care | ||||||||||
| Taylor et al.27 | ||||||||||
| (Moderate) | (Vigorous) | (Moderate) | (Vigorous) | |||||||
| 8 weeksb | 51/63 | 20/31c,d | 247 (174) | 49 (60) | 145 (178)e | 21 (61)e | Not reported | Not reported | 34.6 (1.2) | 33.7 (1.7)e |
| 16 weeksb | 51/57 | 18/31d,e | 226 (252) | 59 (72) | 160 (262)c | 21 (72)e | Not reported | Not reported | 34.6 (1.2) | 33.9 (1.7)e |
| 26 weeksb | 39/47 | 18/31d,e | 183 (234) | 56 (108) | 206 (251)c | 34 (111)c | Not reported | Not reported | 34.4 (1.8) | 34.3 (1.2)c |
| 37 weeksb | 39/57 | 19/c,d | 158 (228) | 42 (96) | 162 (245)c | 23 (106)c | Not reported | Not reported | 34.1 (2.4) | 33.9 (2.2)c |
| Stevens et al.50 | ||||||||||
| 8 monthsf | 204/363 | 174/351c,d | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | ||
| Harrison et al.28 | ||||||||||
| 6 monthsb | 38/168 | 22/162d,e | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | ||
| 9 monthsb | 36/149 | 31/140c | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | ||
| 12 monthsb | 40/155 | 32/157c | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | ||
| Isaacs et al.61 | ||||||||||
| 10 weeksg | 48/164 | 29/157d,e | 93 (115) | 79 (114)c | 584 (479) | 668 (555)c | 34 (26) | 36 (32)c | ||
| 6 monthsg | 70/179 | 66/200c,d | 65 (106) | 58 (98)c | 692 (496) | 647 (463)c | 38 (27) | 35 (27)c | ||
| Gusi et al.70 | ||||||||||
| Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | |||
| Study and time of follow-up | Patients achieving PA guidance (90–150 minutes/at least moderate-intensity per week) | Minutes per week at least moderate intensity | Total PA (minutes per week) | Energy expenditure (kcal/kg/day)a | ||||||
| ERS, n/N | Alternative PA, n/N | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | |||
| ERS vs alternative PA intervention | ||||||||||
| hSorensen et al.69 | ||||||||||
| 4 monthsb | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | 63 (114) | 23 (107)c | 43 (2.4) | 41 (4.8) | ||
| 10 monthsb | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | 20 (124) | 20 (152)c | 41 (2.1) | 40 (5) | ||
| Isaacs et al.61 | ||||||||||
| 10 weeksg | 48/164 | 53/92d,e | 93 (115) | 113 (291)c | 584 (479) | 863 (1026)e | 34 (26) | 43 (38)e | ||
| 6 monthsg | 70/179 | 62//141c,d | 65 (106) | 89 (150)e | 692 (496) | 759 (539)c | 38 (27) | 42 (27)c | ||
| ERS, n/N | ERS plus SDT, n/N | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | |||
| ERS vs ERS plus SDT | ||||||||||
| Jolly et al.68 | ||||||||||
| 3 monthsg | Not reported | Not reported | 319 (338)c | 331 (336)c | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | ||
| 6 monthsg | 66/156 | 83/169c,d | 249 (356)c | 246 (343)c | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | ||
The most consistently reported PA outcome across studies was the proportion of individuals achieving 90–150 minutes of at least moderate-intensity activity per week. (The use of 90–150 minutes of at least moderate-intensity PA/week is pragmatic with the included studies.) When pooled across studies there was a 16% (95% CI 3% to 30%) increase in the RR of achieving this outcome with ERS compared with usual care at 6–12 months’ follow-up (Figure 2).
FIGURE 2.
Meta-analysis of the number of patients achieving 90–150 minutes of at least moderate-intensity PA per week at 6–12 months’ follow-up (denominators as reported by authors).
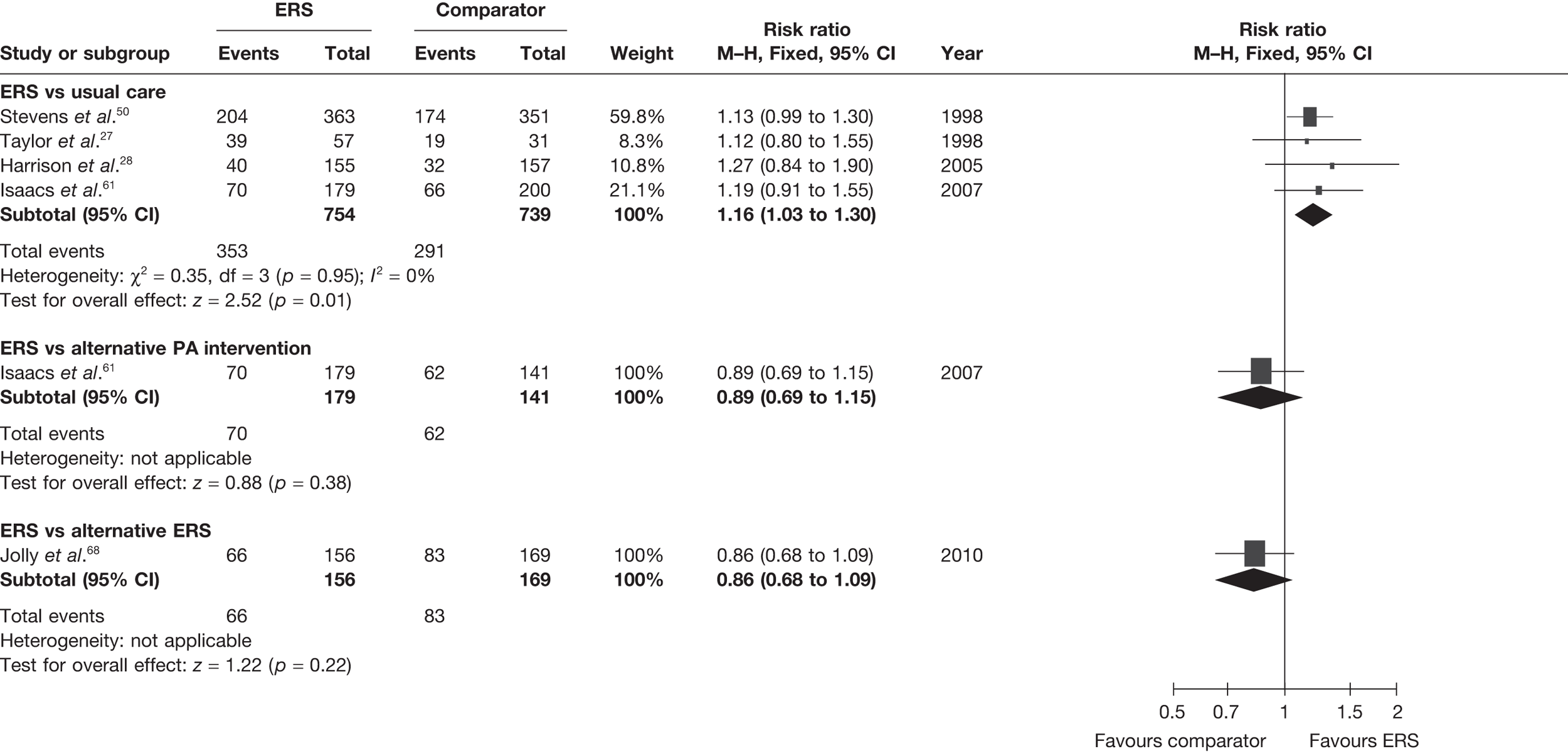
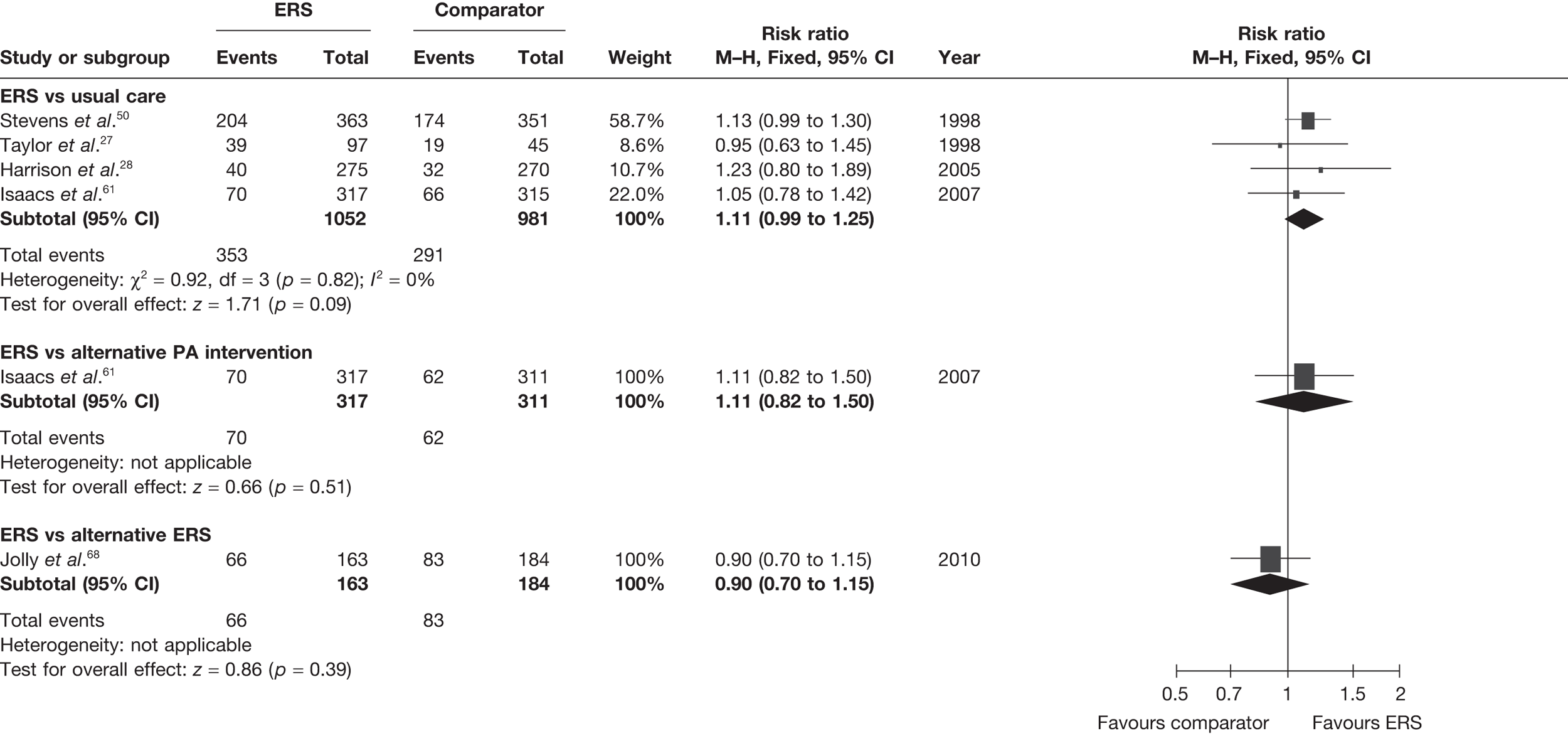
The studies of Taylor et al. 27 and Harrison et al. 28 reported this outcome based on the number of individuals who were available at follow-up. In order to assess the potential (attrition) bias in using completers, we adjusted the denominators of these two studies to all individuals randomised – an ITT analysis (Figure 3). We assumed that all missing cases did not meet the PA threshold. In the pooled ITT analysis, the proportion achieving the PA threshold with ERS than usual care (11%, 95% CI –1% to 45%) this effect was no longer statistically significant.
FIGURE 3.
Meta-analysis of the number of patients achieving 90–150 minutes of at least moderate-intensity PA per week at 6–12 months’ follow-up (denominators adjusted to all randomised – ITT analysis).
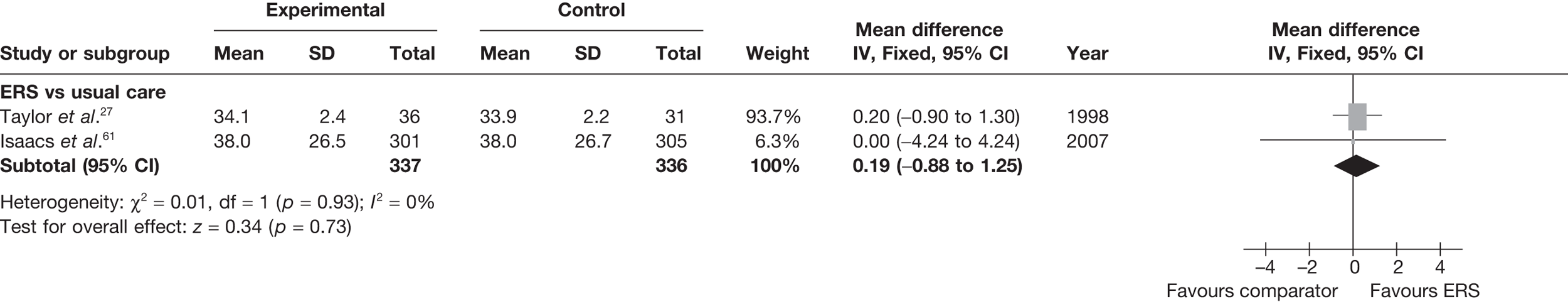
There was no difference between ERS and usual care in either the minutes spent in at least moderate-intensity PA/week or estimated PA-induced energy expenditure (Figures 4 and 5).
FIGURE 4.
Meta-analysis of patient’s minutes spent in at least moderate-intensity PA per week at 6–12 months’ follow-up. SD, standard deviation.
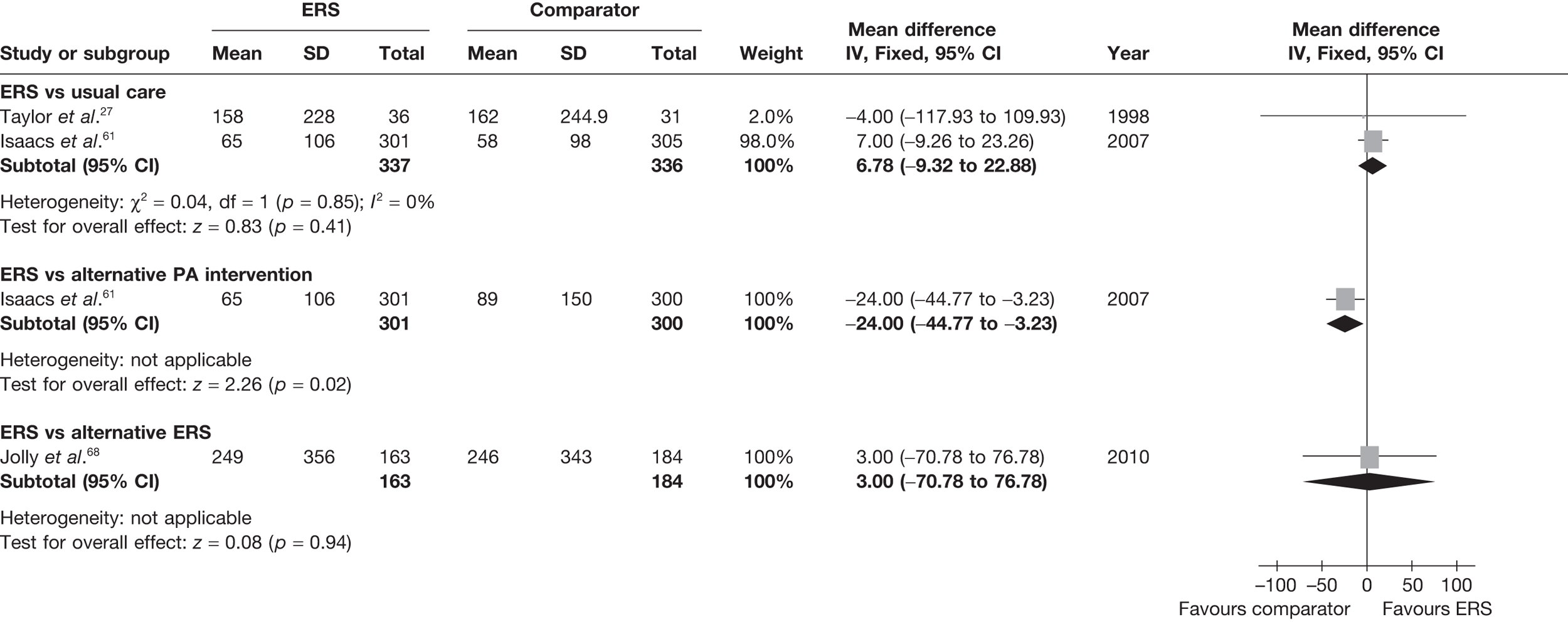
FIGURE 5.
Meta-analysis of energy expenditure (kcal/kg/day) ERS vs usual care at 6–12 months’ follow-up. SD, standard deviation.
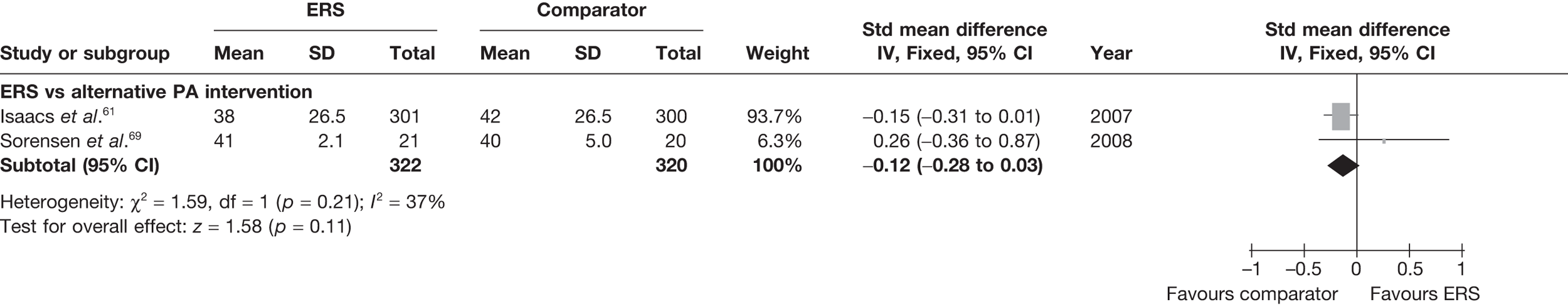
Sorensen et al. 69 reported a higher level of energy expenditure with ERS than with PA counselling. In contrast, the study by Isaacs et al. 61 observed a higher level of PA (minutes of total and moderate-intensity activity, and energy expenditure) in those in the walking programme than in the ERS group. When pooled across studies, there was no significant difference in the total amount of physical or energy expenditure between ERS and alternative PA interventions (Figures 6 and 7).
FIGURE 6.
Meta-analysis of patient’s minutes of total PA/week at 6–12 months’ follow-up. SD, standard deviation.
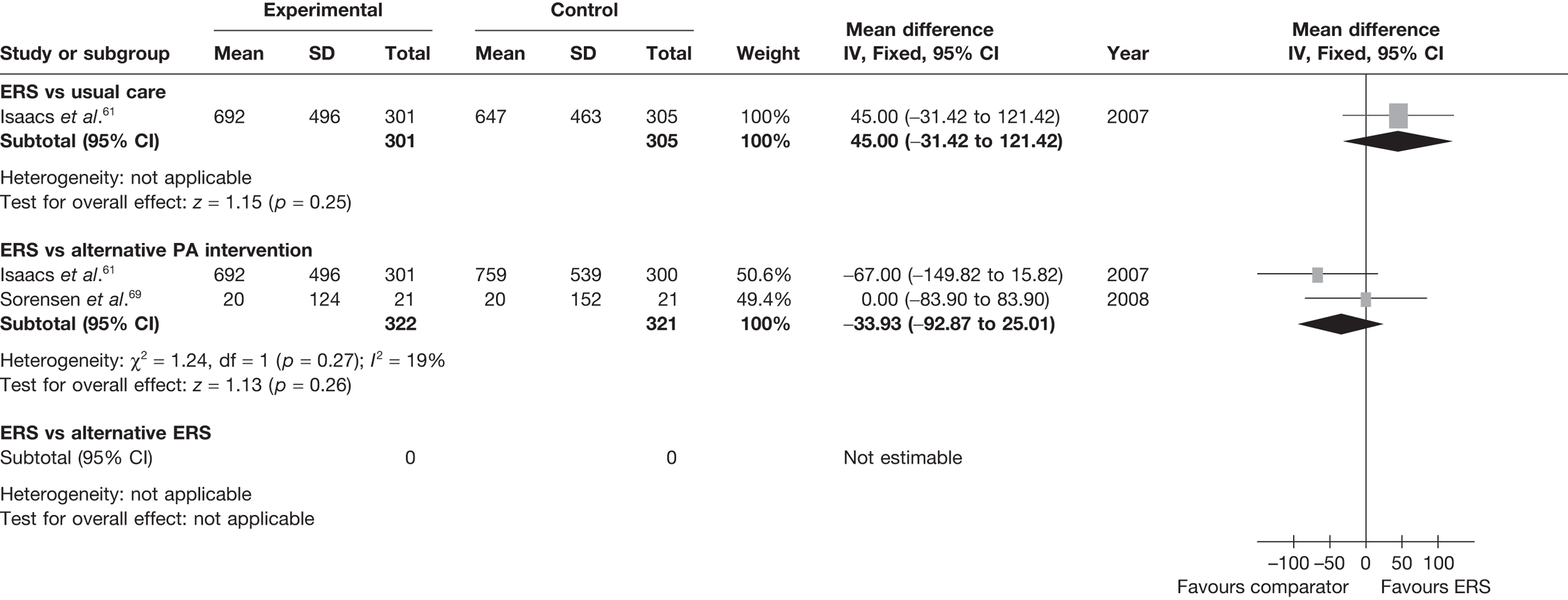
FIGURE 7.
Meta-analysis of energy expenditure ERS vs alternative PA intervention at 6–12 months’ follow-up. SD, standard deviation.
In the Jolly et al. study,68 the proportion of patients achieving at least 150 minutes of moderate PA per week increased in the standard ERS group from 27% at baseline to 63% at 3 months and 46% at 6 months. There were no significant differences in these proportions between the standard ERS and ERS-plus-SDT groups (Table 15).
Harrison et al. 28 reported no statistically significant interaction effects between the ERS effect and pre-specified baseline variables (i.e. CHD risk factors, sex and age). Comparing high adherers (≥ 75% attendance at ERS) with low adherers (< 75% attendance at ERS) in the Isaacs et al. study,61 32 high adherers and 16 low adherers were achieving ≥ 150 minutes of moderate PA per week at 10 weeks. At 6 months, 41 high adherers and 29 low adherers were achieving ≥ 150 minutes of moderate PA per week. However, these proportions were not significantly different. In the Jolly et al. study,68 age, gender, deprivation (Index of Multiple Deprivation score), ethnicity, depression at baseline and level of PA at baseline were assessed by regression methods as predictors of PA at 6 months. Only PA at baseline was associated with PA at the 6-month follow-up (p < 0.001).
Physical fitness
The studies by Taylor et al. ,27 Isaacs et al. 61 and Sorensen et al. 69 reported physical fitness outcomes (Table 16).
| Study and time of follow-up | Mean predicted heart rate at a workload of 150 W | VO2max (ml/kg/minute) | Submaximal bike ergometer (minutes) | Submaximal shuttle walk (m) | Isometric knee strength (N) | Leg extension power (W) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs usual care | ||||||||||||
| Taylor et al.27 | ||||||||||||
| 16 weeksa | 138.6 (23.0) | 147.2 (29.7)b | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| 26 weeksa | 136.3 (22.6) | 142.3 (28.5)b | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| 37 weeksa | 134.2 (19.0) | 146.0 (24.2)c | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Isaacs et al.61 | ||||||||||||
| 10 weeksa | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | 9.65 (1.5) | 8.87 (1.5)c | 456 (102) | 434 (104)b | 277 (54) | 265 (56)b | 174 (31) | 165 (31)b |
| 6 monthsa | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | 8.86 (1.7) | 9.08 (1.7)b | 445 (96) | 434 (97)b | 265 (58) | 267 (66)b | 173 (66) | 167 (68)b |
| ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs alternative: PA intervention | ||||||||||||
| Sorensen et al.69 | ||||||||||||
| 4 monthsa | Not reported | Not reported | 23.8 (7.1) | 21.7 (11.0)b | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| 10 monthsa | Not reported | Not reported | 23.0 (8.2) | 22.4 (12.7)b | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Isaacs et al.61 | ||||||||||||
| 10 weeksa | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | 9.65 (1.5) | 8.92 (1.7)b | 456 (102) | 437 (100)b | 277 (54) | 275 (58)b | 174 (31) | 166 (32)b |
| 6 monthsa | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | 8.86 (1.7) | 8.92 (1.8)b | 445 (96) | 448 (95)b | 265 (58) | 264 (66)b | 173 (66) | 164 (68)b |
Taylor et al. 27 reported a lower (more favourable) submaximal heart rate (at 150 W) for ERS compared with usual care. Isaacs et al. 61 reported no significant differences in any of the physical fitness measures (submaximal bike and shuttle walk, isometric knee strength, leg extension power) between the ERS and usual care groups at follow-up except at 10 weeks for the submaximal bike ergometer test. Pooling of the cardiorespiratory measures (mode: cycle ergometer or cycle/walking) showed no difference between ERS and usual care (Figure 8). There was considerable evidence of statistical heterogeneity.
FIGURE 8.
Meta-analysis of patient’s physical fitness, at 6–12 months’ follow-up. SD, standard deviation.
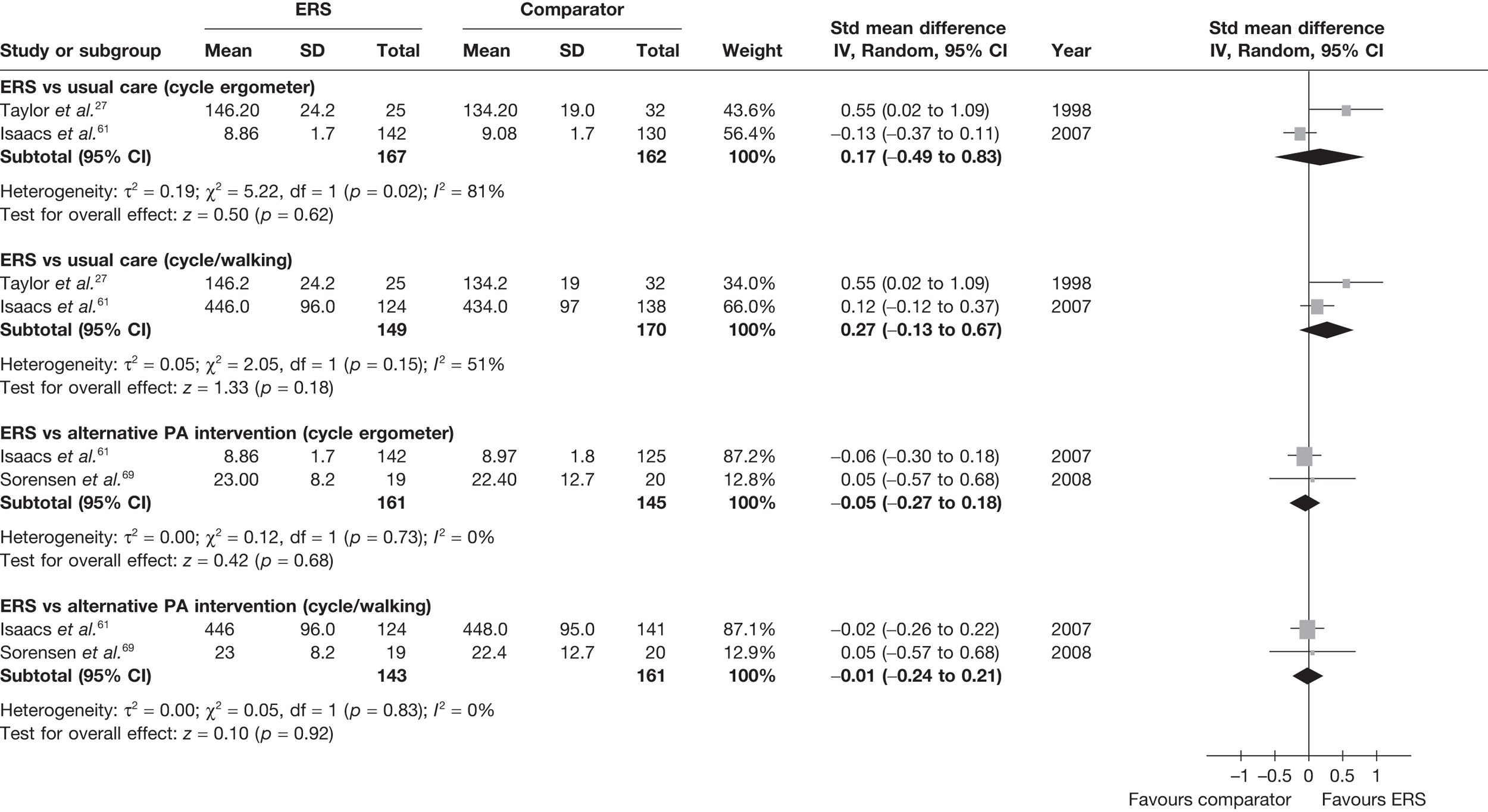
Isaacs et al. 61 and Sorensen et al. 69 reported no significant differences in any of the physical fitness measures between the ERS and the alternative PA intervention groups at follow-up (see Figure 8).
The study of Jolly et al. 68 did not assess physical fitness.
Clinical factors
Five studies27,61,68–70 provided information on clinical outcomes, i.e. CHD risk factors (Table 17), weight and obesity measures (Table 18) and respiratory function (Table 19).
| Study and time of follow-up | SBP (mmHg) | DBP (mmHg) | Cholesterol (mmol/l) | High-density lipoproteins (mmol/l) | Low-density lipoproteins (mmol/l) | Triglycerides (mmol/l) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs usual care | ||||||||||||
| Taylor et al.27 | ||||||||||||
| 16 weeksa | 130 (14.5) | 130 (14)b | 84 (8) | 84 (8)b | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| 26 weeksa | 130 (14) | 131 (14)b | 84 (8) | 84 (8)b | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| 37 weeksa | 130 (17) | 131 (18)b | 85 (9) | 83 (9)b | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Isaacs et al.61 | ||||||||||||
| 10 weeks | 133 (10) | 132 (10)b | 82 (6) | 83 (6)b | 5.68 (0.53) | 5.71 (0.42)b | 1.35 (0.18) | 1.35 (0.18)b | 3.41 (0.46) | 3.44 (0.47)b | 2.12 (0.71) | 2.14 (0.71)b |
| 6 months | 133 (12) | 133 (12)b | 82 (6) | 82 (7)b | 5.65 (0.50) | 5.60 (0.50)b | 1.37 (0.25) | 1.38 (0.17)b | 3.40 (0.48) | 3.37 (0.50)b | 2.04 (0.74) | 2.00 (0.84)b |
| ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs alternative PA intervention | ||||||||||||
| Isaacs et al.61 | ||||||||||||
| 10 weeks | 133 (10) | 134 (10)b | 82 (6) | 84 (6)b | 5.68 (0.53) | 5.69 (0.53)b | 1.35 (0.18) | 1.33 (0.17)b | 3.41 (0.46) | 3.45 (0.46)b | 2.12 (0.71) | 2.05 (0.76)b |
| 6 months | 133 (12) | 134 (12)b | 82 (6) | 83 (6)b | 5.65 (0.50) | 5.56 (0.57)b | 1.37 (0.25) | 1.37 (0.16)b | 3.40 (0.48) | 3.36 (0.48)b | 2.04 (0.74) | 1.95 (0.74)b |
| ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs ERS plus SDT | ||||||||||||
| Jolly et al.68 | ||||||||||||
| 6 monthsa | 130 (17) | 127 (16)b | 82 (11) | 79 (11)b | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Study and time of follow-up | Weight (kg) | BMI (kg/m2) | Body fat (%)a | Waist–hip ratio (cm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERS, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs usual care | ||||||||
| Taylor et al.27 | ||||||||
| 16 weeksb | Not reported | Not reported | 27.5 (0.6) | 27.6 (0.6)c | 70 (8) | 76 (8)d | 0.87 (0.08) | 0.83 (0.09)c |
| 26 weeksb | Not reported | Not reported | 27.3 (1.3) | 27.5 (1.1)c | 70 (11) | 75 (11)d | 0.87 (0.08) | 0.83 (0.09)c |
| 37 weeksb | Not reported | Not reported | 27.5 (1.3) | 27.6 (1.1)c | 71 (13) | 76 (13)d | 0.87 (0.08) | 0.84 (0.09)c |
| Isaacs et al.61 | ||||||||
| 10 weekse | 81 (3) | 81 (3)c | 30.2 (0.8) | 30.1 (1.5)c | 37.4 (1.9) | 37.5 (1.9)c | 0.88 (0.06) | 0.89 (0)c |
| 6 monthse | 82 (3) | 82 (3)c | 30.5 (1.1) | 30.4 (1.1)c | 37.8 (2.4) | 37.8 (2.4)c | 0.88 (0) | 0.88 (0)c |
| Gusi et al.70 | ||||||||
| 6 monthsb | Not reported | Not reported | 29.7 (4.2) | 30.6 (4.3)d | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Study and time of follow-up | Weight (kg) | BMI (kg/m2) | Body fat (%)a | Waist–hip ratio (cm) | ||||
| ERS, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs alternative PA intervention | ||||||||
| fSorensen et al.69 | ||||||||
| 4 monthsb | –1.1 (4) | –1.1 (4)c | –0.3 (1.3) | –0.04 (1.6)c | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| 10 monthsb | –0.3 (4.4) | –0.3 (4.4)c | –0.1 (1.9) | –0.6 (2.8)c | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Isaacs et al.61 | ||||||||
| 10 weekse | 81 (3) | 81 (3)c | 30.2 (0.8) | 30.2 (1.6)c | 37.4 (1.9) | 37.1 (1.9)c | 0.88 (0.06) | 0.88 (0.06)c |
| 6 monthse | 82 (3) | 82 (3)c | 30.5 (1.1) | 30.5 (1.1)c | 37.8 (2.4) | 37.8 (1.1)c | 0.88 (0) | 0.88 (0)c |
| ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs ERS plus SDT | ||||||||
| Jolly et al.68 | ||||||||
| 6 monthse | Not reported | Not reported | 32.8 (6.9) | 32.8 (6.4)c | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Study and time of follow-up | FEV/FVC ratio | PEF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs usual care | ||||
| Isaacs et al.61 | ||||
| 10 weeksa | 0.86 (0.0) | 0.86 (0.06)b | 417 (58) | 409 (58)b |
| 6 monthsa | 0.86 (0.09) | 0.86 (0.09)b | 407 (115) | 411 (117)b |
| ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs alternative PA intervention | ||||
| Isaacs et al.61 | ||||
| 10 weeksa | 0.86 (0.0) | 0.85 (0.06)b | 417 (58) | 407 (61)b |
| 6 monthsa | 0.86 (0.09) | 0.85 (0.09)b | 407 (115) | 416 (117)b |
Taylor et al. 27 reported percentage of body fat in ERS participants compared with usual care at follow-up. Gusi et al. 70 reported a lower BMI, with no other between-group differences in weight and body fat outcomes for the other measured clinical factors (Figures 9 and 10). There was no significant difference in resting blood pressure, serum lipids or respiratory function between ERS and usual care at follow-up (Figures 11 and 12).
FIGURE 9.
Meta-analysis of SBP at 6–12 months’ follow-up. SD, standard deviation.
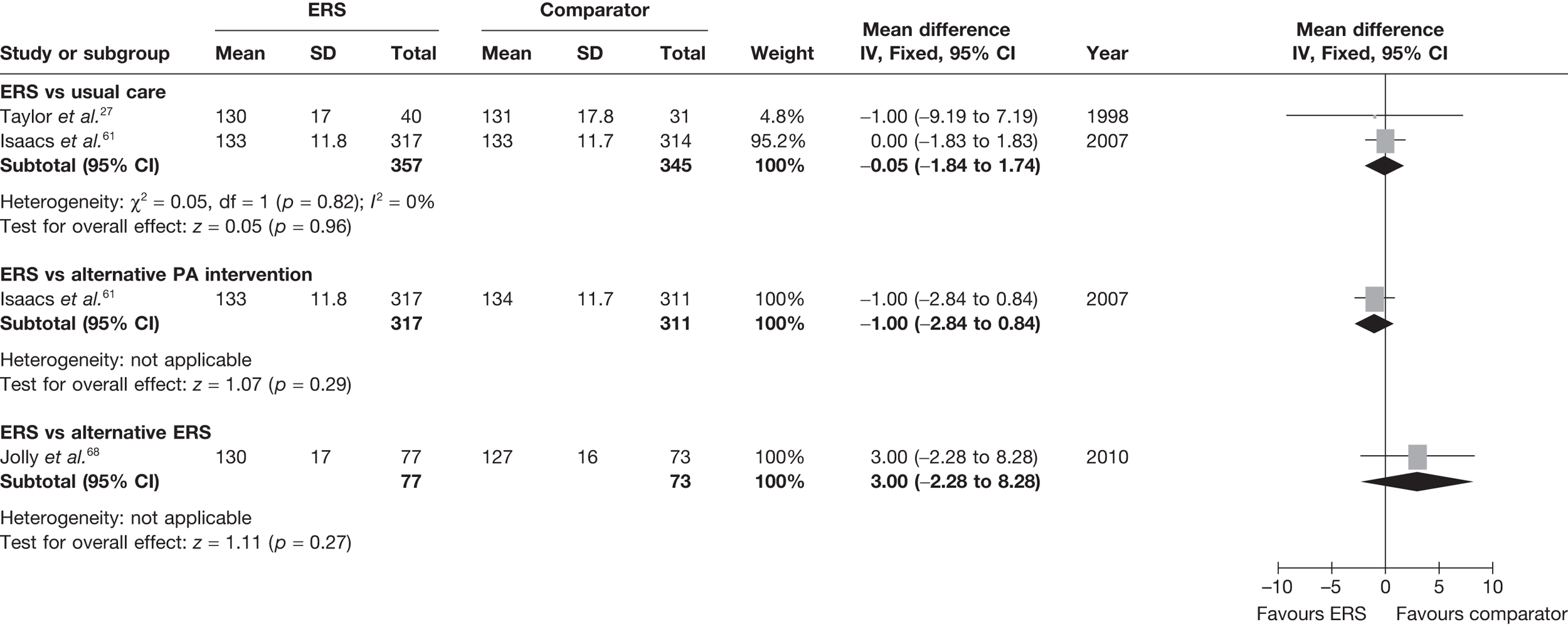
FIGURE 10.
Meta-analysis of diastolic blood pressure at 6–12 months’ follow-up. SD, standard deviation.
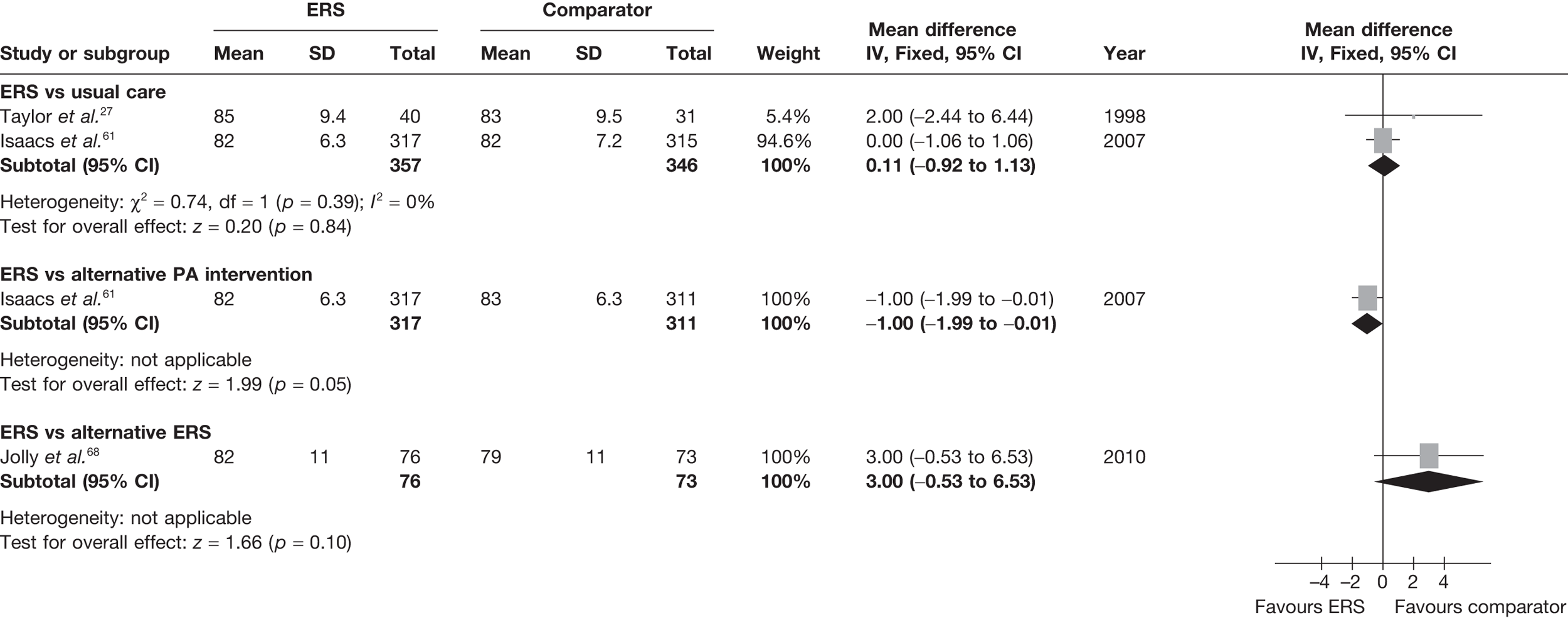
FIGURE 11.
Meta-analysis of BMI at 6–12 months’ follow-up. SD, standard deviation.
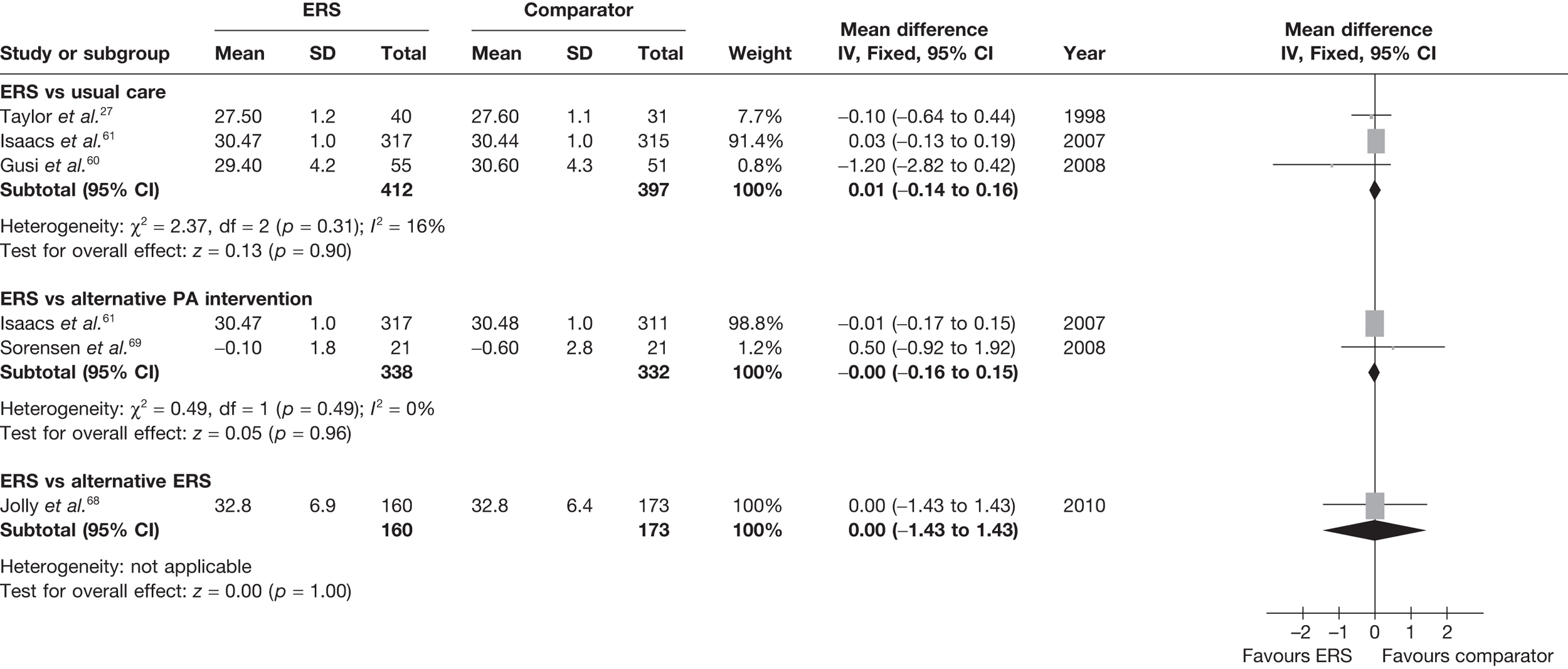
FIGURE 12.
Meta-analysis of body fat at 6–12 months’ follow-up. SD, standard deviation.

In both the studies by Isaacs et al. 61 and Sorensen et al. 69 there were no significant between-group differences at follow-up in resting blood pressure (Figures 9 and 10), BMI (Figure 9), body fat outcomes, serum lipids and respiratory function. The Sorensen et al. 69 trial reported reduced levels of glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) in both the ERS group (mean –0.26%, 95% CI –0.79% to 0.27%) and the PA counselling group (mean –0.23, 95% CI –0.47 to 0.02) at 4-month follow-up, although there was no difference between groups.
Jolly et al. 68 reported no significant difference between standard ERS and ERS plus SDT in body mass index (BMI) or resting blood pressure.
Psychological well-being
Four studies61,68,70,71 reported psychological well-being outcomes and are summarised in Table 20.
| Study | PSW | Anxiety | Depression | Anxiety/depression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs usual care | ||||||||
| aTaylor and Fox71 | ||||||||
| 16 weeksb | 2.31 (0.79) | 2.31 (0.67)c | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| 37 weeksb | 2.41 (0.79) | 2.42 (0.54)c | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| dIsaacs et al.61 | ||||||||
| 6 monthse | Not reported | Not reported | 6.9 | 7.1f | 4.8 | 4.9f | Not reported | Not reported |
| Gusi et al.70 | ||||||||
| 6 monthse | Not reported | Not reported | 14.1 (9) | 22.2 (9.8)c | 1.8 (2.3) | 2.9 (2.5)c | 1.2 (0.4) | 1.5 (0.7)c |
| ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs alternative PA intervention | ||||||||
| dIsaacs et al.61 | ||||||||
| 6 monthse | Not reported | Not reported | 6.9 | 7.5f | 4.8 | 5.1f | Not reported | Not reported |
| ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs ERS plus SDT | ||||||||
| Jolly et al.68 | ||||||||
| 3 monthsb | Not reported | Not reported | 7.7 (4.4)f | 8.89 (4.3) | 5.9 (4.2)f | 6.68 (4.1) | Not reported | Not reported |
| 6 monthsb | Not reported | Not reported | 7.9 (4.8)f | 8.86 (4.7) | 6.1 (4.4)f | 6.65 (4.3) | Not reported | Not reported |
Taylor and Fox71 reported physical self-perceptions measures, with improvements shown in physical self-worth (PSW), and perceptions of physical condition and physical health collected physical self-perceptions data, and reported significant in the ERS group compared with usual-care group at 16 and 37 weeks. Isaacs et al. 61 reported no differences between the ERS and usual-care groups in the anxiety and depression scores using the Hospital Anxiety Depression Scale (HADS) at 6 months. In the Gusi et al. 70 study, all measures [Geriatric Depression Scale, State Trait Anxiety Inventory and the anxiety/depression subscale of the European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D)] at 6 months were found to favour ERS participants compared with those receiving the usual care.
Isaacs et al. 61 reported no differences between the ERS and walking programme in anxiety or depression outcomes at 6 months’ follow-up.
Jolly et al. 68 reported no difference between groups in anxiety or depression outcomes at either 3 or 6 months’ follow-up.
Health-related quality of life
Four studies61,68–70 reported HRQoL, as summarised in Table 21.
| Study and time of follow-up | SF-36 mental | SF-12 mental | SF-12 physical | EQ-5D | Dartmouth QoL (overall QoL scale) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Usual care, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs usual care | ||||||||||
| aIsaacs et al.61 | ||||||||||
| 6 monthsb | 54.2 | 54.3c | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Gusi et al.70 | ||||||||||
| 6 monthsd | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | 0.89 (0.18) | 0.51 (0.2)e | Not reported | Not reported |
| ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | Alternative PA, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs alternative PA intervention | ||||||||||
| Sorensen et al.69 | ||||||||||
| 4 monthsb | Not reported | Not reported | 40 (10.7) | 37 (11.9)c | 49 (1017.6) | 46 (13.1)c | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| 10 monthsb | Not reported | Not reported | 41 (10.8) | 39 (10.9)c | 51 (11.6) | 45 (15.4)c | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| aIsaacs et al.61 | ||||||||||
| 6 monthsb | 54.3 | 53c | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | ERS, mean (SD) | ERS plus SDT, mean (SD) | |
| ERS vs ERS plus SDT | ||||||||||
| Jolly et al.68 | ||||||||||
| 3 months | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | 3.16 (0.8)c | 3.25 (0.7)c |
| 6 months | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | 3.15 (0.8)c | 3.24 (0.8)c |
Isaacs et al. 61 reported no differences between the ERS and usual-care groups at follow-up on the Short Form questionnaire-36 items (SF-36) mental health scale. Gusi et al. 70 observed higher EQ-5D scores in the ERS group than in the usual care group at 6 months.
Isaacs61 reported no differences between the ERS and walking groups at follow-up on the SF-36 mental health scale score. Similarly, Sorensen69 found no differences between the groups at follow-up on the Short Form questionnaire-12 items (SF-12) mental and physical scales.
Jolly et al. 68 reported no difference between groups in overall Dartmouth CO-OP chart score although there was a difference for the feelings subscale at 6 months in favour of the alternative ERS group (not tabularised).
Patient satisfaction
Three studies27,28,61 reported patient satisfaction and results are summarised in Table 22.
| Study | Satisfied with received information (%) | Needed further information (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERS | Usual care | ERS | Usual care | |
| ERS vs usual care | ||||
| Harrison et al.28 | ||||
| 3 months | 92 | 69a | 43 | 54a |
| ERS | Alternative PA | ERS | Alternative PA | |
| ERS vs alternative PA intervention | ||||
| Isaacs et al.61 | ||||
| 10 weeks | 97 | 96b | 15 | 17b |
The Harrison et al. study28 reported that the ERS group were significantly more satisfied with the information they received and felt they needed less information about PA, compared with usual care group. In the Taylor et al. 27 study, comments about the concept of ERS (measured at 8 weeks) identified that 50% of patients were positive, 35% had mixed feelings and 15% had only negative comments. Negative comments included a long waiting time before introductory session, lack of staff support, crowded facilities and inconvenient facility times.
In the Isaacs et al. 61 study there was no between-group difference in participant satisfaction with received information or the need for additional information. In the ERS group, 97.8% felt better for taking part and enjoyed the programme compared with 93.8% feeling better for taking part and 95.2% enjoying the programme for the walking group.
Jolly et al. 68 did not assess participant satisfaction.
Adverse events
Although participation in ERS has the potential to lead to negative events (e.g. an increase in exercise-related musculoskeletal injuries or exercise-related cardiac complications), only the Isaacs et al. 61 study assessed such events. Using GP records, the authors assessed the change in consultations before and after ERS. There was evidence of a small increase in GP visits for falls and fractures in the ERS and walking groups compared with usual care control after the start of the study (Table 23).
| Adverse events | Leisure centre | Walking control | Advice-only control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visits for chest pain | |||
| 12–6 months before start of study | 1 (%) | 3 | 7 |
| 6 months before start of study | 3 (%) | 4 | 7 |
| Start of study to 6 months | 2 (%) | 9 | 7 |
| 6–12 months after start of study | 10 (%) | 4 | – |
| Visits for aches/pains | |||
| 12–6 months before start of study | 54 | 48 | 56 |
| 6 months before start of study | 62 | 53 | 55 |
| Start of study to 6 months | 52 | 42 | 44 |
| 6–12 months after start of study | 63 | 44 | – |
| Visits for sprains | |||
| 12–6 months before start of study | 2 | 2 | 7 |
| 6 months before start of study | 3 | 6 | 2 |
| Start of study to 6 months | 1 | 4 | 6 |
| 6–12 months after start of study | 2 | 0 | – |
| Visits for falls | |||
| 12–6 months before start of study | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 6 months before start of study | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Start of study to 6 months | 9 | 2 | 0 |
| 6–12 months after start of study | 3 | 6 | – |
| Visits for fractures | |||
| 12–6 months before start of study | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 6 months before start of study | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Start of study to 6 months | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 6–12 months after start of study | 0 | 4 | – |
Health-care utilisation
No studies reported hospitalisations, primary care visits or use of medication.
Summary
-
Given the lack of standardisation of the ERS definition used by previous systematic reviews and the publication of further recent evidence, we undertook a de novo systematic review of the effectiveness of ERS.
-
We undertook a search of electronic databases – MEDLINE (Ovid) 1990 to October 2009; EMBASE (Ovid) 1990 to October 2009; PsycINFO; The Cochrane Library (Wiley) 2009 v3 (CENTRAL, DARE, NHS HTA, NHS EED, HTA database), ISI Web of Knowledge (WOK); and SPORTDiscus; ongoing trials registry – and contacted experts in the field to identify unpublished studies. We limited our inclusion criteria to controlled studies (randomised or non-randomised) that met our ERS definition, i.e. (1) referral by a primary-care health-care professional to a third party, (2) that provided a PA programme tailored to individual needs and (3) an initial assessment and monitoring throughout the programme.
-
Our systematic review identified seven RCTs (3030 participants: UK, n = 5; non-UK, n = 2). These studies and were heterogeneous in their population, interventions and comparators. Five studies compared ERS to usual care (e.g. PA advice), two compared ERS with an alternative PA-promoting strategy (i.e. walking programme or PA counselling) and one study compared traditional ERS with combined ERS plus SDT intervention. Although all studies recruited predominantly sedentary middle-aged adults who had at least one lifestyle risk factor (i.e. hypertension, raised serum cholesterol, smoking or being overweight), a number of the studies also included a proportion of specific medical diagnoses [i.e. myocardial infarction (MI), type 2 diabetes, obesity (BMI > 35 kg/m2), hypertension and depression]. ERS mainly took place at a leisure centre and typically involved 10–12 weeks of exercise intervention, with the longest study reporting outcomes up to 6–12 months post baseline measures. Uptake (proportion of individuals randomised to ERS who attended the first exercise session) varied widely across studies (35–85%), as did adherence to the ERS intervention (programme completion rates of 25–86%).
-
Studies were judged to have a low to moderate overall risk of bias. Outcome blinding for PA interventions of this nature is difficult to implement, with other quality issues generally poorly reported as opposed to not being implemented.
-
The most consistently reported outcome was self-reported PA. Pooling across four studies, compared with usual care, 11% (95% CI –2% to 26%) more ERS participants achieved 90–150 minutes of at least moderate-intensity PA per week at 6–12 months’ follow-up (ITT analysis). There was no significant difference in PA between ERS versus alternative PA promotion intervention or ERS versus ERS plus SDT at 6–12 months’ follow-up. Other reported measures of PA (i.e. amount of total and moderate PA and energy expenditure) did not show a difference between ERS and usual care.
-
No studies reported assessment of objective PA using, for example accelerometers. Validated self-report questionnaires were predominantly used.
-
There was no consistent evidence of a difference at follow-up between ERS and comparator groups in respect of other outcomes, i.e. physical fitness, blood pressure, serum lipids, glycaemic control, obesity indices, respiratory function, psychological well-being and HRQoL. Only one study assessed adverse events, reporting a small increase in the rate of falls among those in both the ERS and walking programme compared with usual care.
-
Although some studies reported within-group improvements (compared with baseline) in primary and secondary outcomes with ERS, these differences need to be interpreted with caution as they are subject to regression to the mean and/or a placebo/Hawthorne effect (therefore not tabularised/reported in Results section).
-
None of the studies reported outcomes of ERS by disease-specific subpopulations.
Chapter 4 Systematic review of the cost-effectiveness of exercise referral schemes
Introduction
A systematic review of the literature was conducted to identify economic evidence on ERS as defined in the earlier stages of this report, i.e. schemes that involved referral from a primary health-care professional due to an underlying condition and access to a structured programme of exercise. Both economic evaluations and existing systematic reviews of economic evidence on exercise referral were considered for inclusion. By adhering to a relatively narrow definition of what constitutes ERS, a number of studies exploring the cost-effectiveness of PA were excluded on the basis that (1) they did not include a referral from a health-care professional; (2) they did not consider a population with an underlying health condition; or (3) they did not comprise a structured programme of exercise. In this respect, the findings of this economic review are intended to mirror those of the effectiveness review presented in Chapter 3 of this report.
Methods
This review was conducted and reported in accordance with the PRISMA statement. 36
Search strategy
Studies were identified using the methods described in Chapter 3. For inclusion in this economic systematic review, studies had to satisfy all the inclusion criteria outlined in Chapter 3 and also include cost and/or cost-effectiveness data. Studies for possible inclusion were initially identified by reviewing titles.
Study selection
As described in Chapter 3.
Data extraction and critical appraisal methods
A data extraction framework was established to abstract information from economic evaluations identified for inclusion. For each study, data were extracted on the following: study objective, population characteristics, nature of the intervention and comparator, cost and cost-effectiveness findings and methodological strengths and weaknesses. Primary economic studies considered for review were formally appraised against recognised appraisal criteria for economic evaluations74 and, where appropriate, decision-analytic models. 75 Data extraction was conducted independently by one reviewer (NA) and checked by a second (PT). Discrepancies were resolved by discussion within the research team. Systematic reviews identified as part of the literature search were also considered for inclusion.
Data synthesis
The findings of both the economic evaluations and systematic reviews identified are presented descriptively in the form of detailed tabular summaries. Given that only a small number of primary studies were included in the review, a summary of each study, along with a commentary on the methods used, is provided below.
Results
Identification and selection of studies
The bibliographic searches identified three economic evaluations50,61,70 of ERS that met our inclusion criteria (UK, n = 2; non-UK, n = 1). In addition, we included a model-based economic evaluation of brief interventions designed to promote PA developed to inform public health guidance issued by NICE. 76 This NICE evaluation considered ERS as one method of promoting PA in primary care. Although not published in a peer-reviewed journal, the full report of the study was available in the public domain (available at www.matrixknowledge.com/.%20.%20./physical_activity_economic_modelling_report_april2006.pdf).
In addition to the primary economic evaluations, three systematic reviews of ERS were identified,40,41,77 which included consideration of cost-effectiveness. Findings from the reviews and primary studies are reported separately below. See Figure 13 for details.
FIGURE 13.
Study inclusion process for ERS cost-effectiveness systematic review. PHC, primary health care.
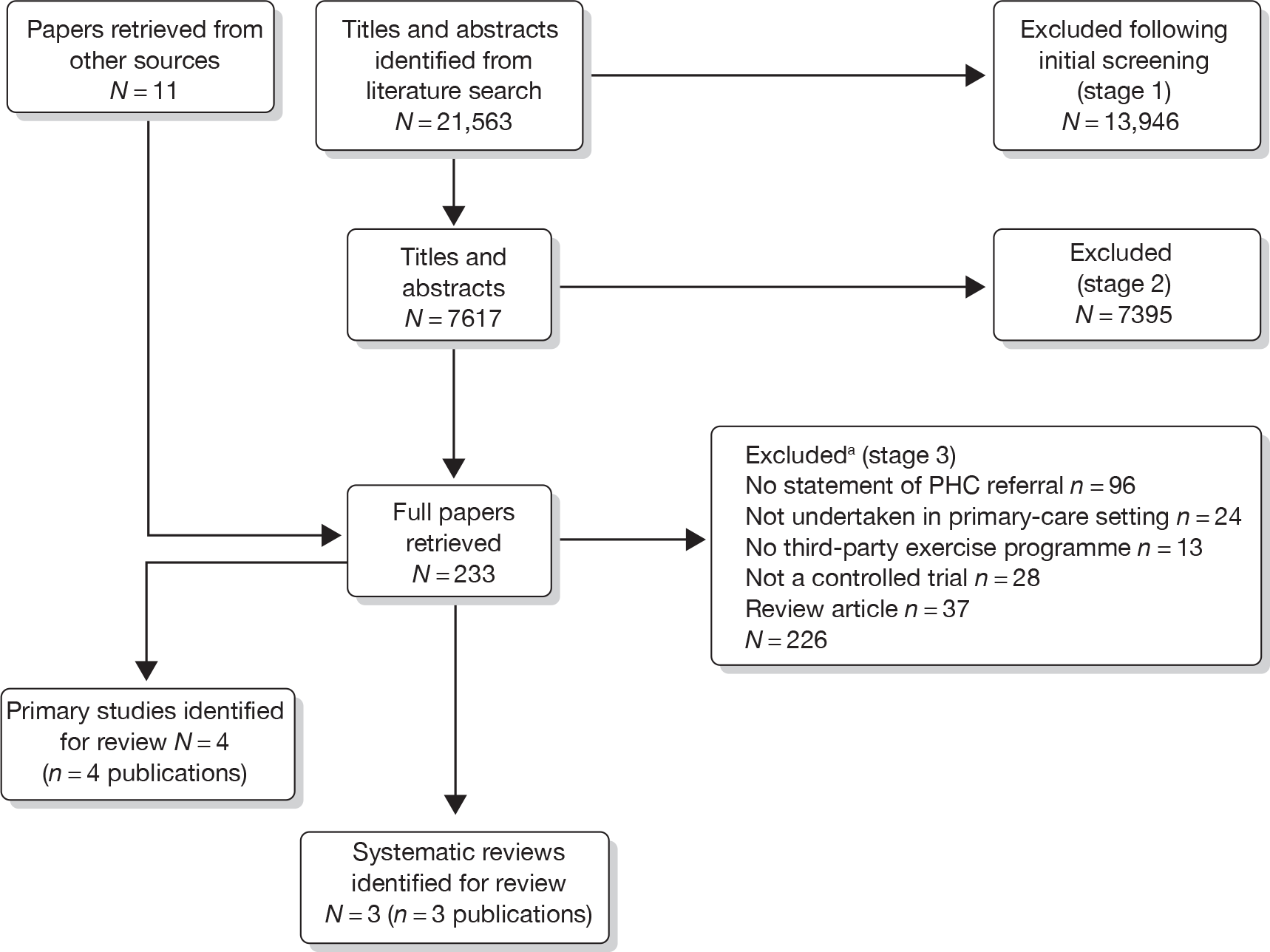
Findings of previous systematic reviews
Two systematic reviews of the effectiveness of ERS included consideration of the cost-effectiveness evidence on ERS. 40,41 A quality appraisal of these systematic reviews is presented in Chapter 3. A third systematic review,77 conducted to inform the development of NICE guidance, specifically considered evidence on the cost-effectiveness of ERS.
Table 24 summarises the objectives, methods and findings of the systematic reviews and highlights notable differences in the definition of ERS and the inclusion criteria applied. All three studies considered referral to exercise by a health-care professional in primary care. However, the review conducted to inform the development of NICE guidance adopted a broader definition of interventions, including the use of pedometers and community-based interventions as well as exercise referral. Although the NICE review focused specifically on economic evidence, the other reviews considered economic evidence alongside the evidence on clinical effectiveness, including uptake levels of PA and other effectiveness outcomes.
| Author | Objectives of review (stated by authors) | Databases/dates covered by search | ERS definition | Inclusion criteria | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NICE (2006)77 | Identify economic studies of brief interventions in primary care aimed at improving PA: pedometers, exercise referral, and walking and cycling programmes in the community |
NHS EED (1994 to August 2005); HEED (1958 to August 2008) |
Referral by a member of the primary-care team to facilities such as leisure centres or gyms for supervised exercise programmes | Studies that assessed the cost-effectiveness of one of the four interventions to increase PA in the adult population | The evidence relating to exercise referral was equivocal with one study reporting that intervention was less costly and more effective (dominant strategy) than the comparator, three studies reporting it to be more costly and more effective, and one study reporting it to be more costly and equally effective |
| Sorensen et al. (2006)40 |
|
MEDLINE; WinSPIRS; NLM Gateway 2005 | Exercise prescribed by GP or other primary-care staff where EoP included more than just simple advice |
Sedentary adults with signs of lifestyle disease Peer-reviewed studies Reported PA or VO2max Follow-up ≥ 6 months |
ERS is a cost-effective intervention compared with usual care |
| Williams et al. (2007)41 | Assess whether ERS is cost-effective in improving exercise participation in sedentary adults | MEDLINE; AMED; EMBASE; CINAHL; PsycINFO; SPORTDiscus; The Cochrane Library; SIGLE 2007 | Referred adults from primary care to intervention where encouraged to increase PA; initial assessment; tailored programme; monitoring |
RCT; non-RCT; observational; process evaluation; qualitative Any outcome |
ERS is marginally more costly than a ‘do-nothing’ approach, but that inadequacies in the evidence of effectiveness mean that it is not possible to determine whether or not it is a cost-effective use of resources |
The findings of the three reviews differ somewhat. The review conducted for NICE77 concluded that most brief interventions to promote PA are marginally more costly than a ‘do-nothing’ alternative, but generate improved long-term outcomes. The evidence relating to exercise referral was equivocal, with one study reporting that intervention was less costly and more effective (i.e. a dominant strategy) than the comparator, three studies reporting it to be more costly and more effective, and one study reporting it to be more costly and equally effective. On balance the authors indicate that the economic case for brief PA promotion interventions is largely positive, although the authors highlight concerns about the applicability of some of the evidence considered to the NHS.
The review by Sorensen et al. 40 indicated ERS to be a cost-effective intervention compared with usual care. This finding appears to be based on a single economic study. 78 Williams et al. 41 examined three UK-based studies and concluded that there is little evidence to suggest that ERS improves outcomes. On this basis, they conclude that an ERS is marginally more costly than usual care, but that inadequacies in the evidence of effectiveness mean that it is not possible to determine whether or not it is a cost-effective use of resources.
The degree to which the conclusions of the reviews differ is, at least in part, due to differences in the inclusion criteria adopted by the reviews. Table 25 shows the lack of consistency in the studies included in the reviews.
| Primary studies | Systematic reviews | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| NICE (2006)77 | Sorensen et al. (2006)40 | Williams et al. (2007)41 | |
| Stevens et al. (1998)50 | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Lowensteyn et al. (2000)79 | ✓ | ||
| Sevick et al. (2000)80 | ✓ | ||
| Sevick et al. (2000)81 | ✓ | ||
| Elley et al. (2004)78 | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Munro et al. (2004)82 | ✓ | ||
| Isaacs et al. (2007)61 | ✓ | ||
Given the variation in the definition of ERS used, it is unsurprising that there were inconsistencies in the number of primary studies identified for inclusion in each of the reviews. This, together with the publication of recent trials of ERS, underscored the need for a de novo systematic review that used a standardised definition of ERS. The findings of this de novo review are presented in the following sections.
Findings of primary economic evaluations
Four economic evaluations were identified for inclusion in this systematic review. These comprised three trial-based economic evaluations of ERS50,61,70 and one model-based evaluation76 of the cost-effectiveness of brief interventions in primary care to promote PA, including ERS. Three of the studies were based on UK populations,50,61,76 whereas one trial-based analysis was conducted in Spain. 70 Given the number of studies identified, a summary of each study is presented below along with a commentary on the quality of the study and the implications of the findings (detailed data extraction in Appendix 5).
Trial-based economic evaluations
Stevens et al. 50 assessed the cost-effectiveness of a primary care-based intervention aimed at increasing levels of PA in inactive people aged 45–74 years (further details of the study design, population and interventions are available in Chapter 3). The study comprised an economic evaluation conducted alongside an RCT. A within-trial analysis was undertaken and no attempt was made to extrapolate the findings beyond the duration of the study (8 months). Although not explicitly stated, the perspective of the analysis appears to be that of the health service. Costs were derived in a top-down manner, i.e. the total costs of administering the ERS scheme were divided by the number of participants to generate a mean cost per participant. Some adjustment was made to exclude costs associated with the research, as differentiated from administration of the intervention. As a result, it was not possible to report disaggregated estimates of resource use and costs.
Evidence on costs was synthesised with evidence on effectiveness to generate cost-effectiveness estimates. A number of outcomes were considered in this process. The primary outcome in the analysis was the cost of promoting one sedentary person to undertake more PA. The cost of doing so was £623. A second analysis considered the cost involved in moving a moderately active individual to the minimum recommended level of PA. This was achieved at a cost of £2498. Finally, the cost of moving an individual to the next level of PA (defined as sedentary, low intermediate, high intermediate and active) was reported as £327.
One-way sensitivity analyses were conducted to explore parameter uncertainty. The findings were found to be sensitive to changes in the response rate, leading the authors to conclude that particular attention should be paid to recruitment strategies in setting up ERS. Furthermore, given the top-down approach to costing, the cost of the intervention is dependent on the number of recipients, and the authors point out that the marginal cost of the intervention is expected to fall if the number of recipients can be increased.
Isaacs et al. 61 conducted an economic evaluation alongside the UK Exercise Evaluation Randomised Trial (EXERT), which compared the effectiveness of a leisure centre-based (ERS) programme, an instructor-led walking programme and advice only in patients referred for exercise by their GPs. (Further details of the trial design, study population and interventions can be found in the effectiveness review in Chapter 3.) A cost-effectiveness analysis was conducted alongside the trial. Outcomes were reported at 6 months and 12 months post intervention (determined by the trial duration) and a partial societal perspective to costing was adopted, capturing costs incurred by the NHS, local government and participants. Attempts were made to provide a detailed assessment of the costs involved in the provision of the interventions. Intervention costs included costs to the provider and the participant, as well as any equipment costs that might be incurred. In addition to this, the study also captured information on GP and hospital consultations and pharmaceutical use prior to the intervention and over the course of the study through a case note review, to determine whether or not PA had any influence on general health-care resource consumption. Detailed costs for the control group and both intervention groups derived from the study are presented in Table 26.
| Cost components | Observations | Mean (£) | SD (£) | Median (£) | Minimum (£) | Maximum (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control groupa | ||||||
| GP costs 12 months pre-randomisation | 123 | 118.86 | 77.68 | 109 | 0 | 411.00 |
| GP costs 6 months post-randomisation | 123 | 46.57 | 46.17 | 34.00 | 0 | 284.00 |
| Pharmaceutical costs 12 months pre-randomisation | 123 | 81.85 | 136.18 | 10.95 | 0 | 697.15 |
| Pharmaceutical costs 6 months post-randomisation | 123 | 53.76 | 89.80 | 12.98 | 0 | 541.07 |
| Hospital costs 12 months pre-randomisation | 310 | 119.13 | 479.95 | 0 | 0 | 4356.42 |
| Hospital costs 6 months post-randomisation | 310 | 46.58 | 206.98 | 0 | 0 | 1995.73 |
| Cost of the intervention to the providers | 316 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cost of the intervention to the participantsb | 316 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Equipment costs (a component of participants costs)b | 316 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Leisure centre group | ||||||
| GP costs pre-intervention | 149 | 125.49 | 93.99 | 110.00 | 0 | 714.00 |
| GP costs 6 months post-intervention | 149 | 57.60 | 49.88 | 51.00 | 0 | 255.00 |
| GP costs 12 months post-intervention | 149 | 107.28 | 82.47 | 85.00 | 0 | 476.00 |
| Pharmaceutical costs 12 months pre-intervention | 149 | 109.08 | 293.01 | 16.7 | 0 | 2764.15 |
| Pharmaceutical costs 6 months post-intervention | 149 | 74.25 | 168.91 | 23.73 | 0 | 1585.92 |
| Pharmaceutical costs 12 months post-intervention | 149 | 136.82 | 329.55 | 47.45 | 0 | 3184.25 |
| Hospital costs 12 months pre-intervention | 312 | 134.32 | 662.31 | 0 | 0 | 7901.25 |
| Hospital costs 6 months post-intervention | 312 | 61.64 | 283.83 | 0 | 0 | 2938.36 |
| Hospital costs 12 months post-intervention | 312 | 127.02 | 441.40 | 0 | 0 | 3360.43 |
| Cost of the intervention to the providers | 317 | 185.66 | 33.23 | 168.96 | 88.76 | 249.16 |
| Cost of the intervention to the participants | 88 | 100.60 | 103.50 | 70.45 | 4.73 | 771.89 |
| Equipment costs (a component of participants costs) | 88 | 6.68 | 15.16 | 0 | 0 | 60.00 |
| Walking group | ||||||
| GP costs pre-intervention | 134 | 125.36 | 82.45 | 110 | 0 | 374.00 |
| GP costs 6 months post-intervention | 134 | 52.30 | 43.10 | 42 | 0 | 187.00 |
| GP costs 12 months post-intervention | 134 | 103.49 | 71.14 | 84.5 | 0 | 323.00 |
| Pharmaceutical costs 12 months pre-intervention | 134 | 148.51 | 294.78 | 25.18 | 0 | 1788.50 |
| Pharmaceutical costs 6 months post-intervention | 134 | 94.38 | 161.01 | 24.26 | 0 | 894.25 |
| Pharmaceutical costs 12 months post-intervention | 134 | 169.25 | 295.62 | 37.59 | 0 | 1609.65 |
| Hospital costs 12 months pre-intervention | 308 | 178.79 | 761.96 | 0 | 0 | 7610.88 |
| Hospital costs 6 months post-intervention | 308 | 46.16 | 219.54 | 0 | 0 | 1682.59 |
| Hospital costs 12 months post-intervention | 308 | 162.07 | 509.17 | 0 | 0 | 4530.51 |
| Cost of the intervention to the providers | 310 | 92.02 | 11.33 | 89.16 | 48.86 | 129.46 |
| Cost of the intervention to the participants | 75 | 84.40 | 170.54 | 35.55 | 0.76 | 1460.01 |
| Equipment costs (a component of participants costs) | 75 | 7.78 | 26.56 | 0 | 0 | 155.00 |
The study was reported to be based on the largest RCT trial of PA promotion conducted in the UK and, as such, provides a valuable source of economic evidence on ERS. Methodologically, the study is a reasonable attempt to estimate the cost-effectiveness of an intervention alongside a trial (see Table 28). However, there are some methodological weaknesses, some of which are acknowledged by the authors. The use of a top-down costing methodology is a limitation and raised challenges for the authors in deriving an accurate estimate of the cost per participant. In particular, there are challenges about whether or not recruitment can be increased at a modest additional cost once the programme is up and running. If this were possible, then it would be possible to reduce the cost per participant significantly by increasing the number of participants. A further challenge relates to the outcome measures considered in the analysis. Although these are perfectly legitimate and translate into meaningful measures of effectiveness, it would have been desirable to present the findings in the form of a cost–utility analysis, reporting an incremental cost per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) or similar outcome. Best practice recommendations for cost-effectiveness analysis developed by NICE in England and Wales identify the use of cost–utility analysis based on preference-based outcome measures as the preferred end point for economic evaluations, as they allow for comparison between different interventions and populations. The absence of this makes interpretation of the findings somewhat challenging for a health-care policy audience. Finally, the economic evaluation is essentially a within-trial analysis and, as such, adopts a relatively short time horizon. Previous research has indicated that the cost-effectiveness of public-health interventions is likely to be dependent not just on their short-term effect, but also on the degree to which any behaviour change is lasting. As such, an attempt to model the benefits over a longer time horizon may provide a richer source of information for health-care planners, acknowledging that this would introduce a greater degree of uncertainty.
The mean cost of the leisure centre ERS intervention over 12 months was estimated to be £186 to the providers, with a further £101 being incurred by participants.
Outcomes were measured using the SF-36. The authors’ state that their intention was to convert SF-36 score into quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs); however, this was not possible owing to instability in the findings. Incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) were generated in the form of the incremental cost per unit change in SF-36 score. A comparison of leisure centre-based interventions with controls resulted in an incremental cost of £19,500 per unit change in SF-36 score at 6-month follow-up.
Parameter uncertainty was explored through probabilistic sensitivity analysis (PSA). The findings suggest that there is a low probability of the leisure centre intervention being dominated by the control group.
The objective of Gusi et al. ,70 the only non-UK-based study considered herein, was to examine the cost/utility of adding a supervised walking programme to standard ‘best care’ in individuals who are obese or depressed. The economic study was conducted alongside a study of the effectiveness of this intervention in four general practices in Spain. Although non-UK, the Gusi et al. 70 paper highlights the ERS model and references other ERS studies for comparison.
A cost–utility analysis was undertaken adopting a health-care provider’s perspective and a time horizon of 6 months. Costs considered included the costs of staffing the intervention, as well as the costs of medication and consultations. However, no difference was seen between the intervention group and the controls in the latter, so the incremental cost of the intervention group comprised only the staff costs involved in delivery. Outcomes were measured using the EQ-5D utility scale.
The findings show that the exercise programme led to an incremental QALY gain of 0.132 over a 6-month period, at an incremental cost of €41 per participant, generating an ICER of €311/QALY. Sensitivity analyses, including PSAs, were presented. One-way sensitivity analysis showed the findings to be relatively robust to changes in parameter estimates, with the worst-case scenario ICER increasing to €811/QALY. PSA showed a high probability of the intervention remaining cost-effective when extreme parameter values were considered.
The study is a useful complement to the existing evidence base on the cost-effectiveness of ERS. Particular mention should go to the effort put into generating detailed estimates of the cost of the intervention to providers and participants. (These estimates have been used in the modelling work presented in the later parts of this report.) The main limitation of the study appears to be the inability to convert the findings presented in the form of SF-36 scores into utility scores that might allow for the derivation of QALYs. The authors acknowledge this as a limitation, although there is relatively little explanation given for why this was not possible (e.g. this could be due to missing data in responses). The other major limitation of the study is the relatively short time horizon that was dictated by the trial design. However, this is true of many of the studies considered in this review and reflects the difficulties that are inherent in conducting long-term RCTs of interventions designed to change behaviour. Estimation of long-term outcomes is important as it allows us to verify the main differences among the alternative options with respect to costs and benefits. 83 However, it is important to note that it is often difficult to extrapolate beyond the observed data on health gains because there is lack of evidence surrounding (1) post-intervention effects on PA behaviour (do participation levels stay constant, decline or increase?) and (2) the nature of the relationship between PA and health gains over time. 84
This study performs well when considered in relation to critical appraisal checklists for economic evaluation and best-practice principles (see Table 5). Estimates of cost and outcomes are presented clearly and the study benefits from the use of the EQ-5D, allowing the authors to generate ICERs in the form of cost/QALY. This allows for comparison with other interventions both in the field of public health and beyond, with the findings suggesting the intervention is likely to be highly cost-effective when compared with accepted thresholds. For our own purposes, the main limitation appears to be the degree to which the intervention and the findings are relevant to a UK population. Given the relatively limited information available, it is difficult to determine whether or not this intervention could be easily reproduced in the NHS at a similar cost and effectiveness.
Economic modelling studies
Only one economic modelling study that attempted to estimate the longer-term costs and benefits of exercise referral was identified as part of this search. This NICE76 study comprised an evaluation of primary care-based interventions designed to promote PA, including exercise referral. The study was commissioned to help inform the development of NICE public health guidance on PA.
A cost–utility analysis was conducted using a decision-analytic model to examine the cost-effectiveness of four interventions. The model considers a cohort of individuals who enter the model in a sedentary state. The individuals are exposed to an intervention (exercise referral) which is assumed to affect their likelihood of becoming physically active.
Physical activity is assumed to have a long-term effect on an individual’s likelihood of developing a number of chronic conditions. Conditions included in the model were selected on the basis that there was evidence of a strong causal relationship between PA and evidence on the magnitude of effect of PA on the incidence of these conditions. Conditions included in the analysis were CHD, stroke, type 2 diabetes mellitus and colon cancer.
Estimates of the RR of developing each of these conditions, depending on PA status, were derived from published sources. The conditions are assumed to be independent of one another and individuals are permitted to experience only one condition within the confines of the model. Estimates of mortality rates and life-years lost associated with each condition were derived from published sources and derived by assuming an average age at onset for each condition, dependent on the age of the population under consideration. Utilities and unit costs associated with each condition were synthesised from multiple published sources.
Outcomes are reported both as cost per person who moves from a sedentary state to a physically active state as well as in the form of cost per QALY. The cost of moving an individual from a sedentary state to a physically active state ranged from £90 to £4500, dependent on the cost of the intervention. The incremental cost per QALY ranged from around £20 to approximately £670, dependent on the cost of the intervention.
Further analyses considered the potential savings that may accrue from reductions in future health-care resource consumption as a result of being physically active. This analysis generated even more favourable cost-effectiveness ratios, which, in most cases, were dominant (that is ERS is cheaper and more effective than the control).
One-way sensitivity analysis explored changes in persistence with exercise (i.e. dropouts), intervention costs and effectiveness. The authors report that the intervention remains cost-effective under most scenarios considered in the analysis.
Unlike the primary studies conducted alongside trials presented above, this modelling study attempts to estimate the longer-term impacts of PA. Any model should be considered a simplification of the real world and the authors acknowledge many of the weaknesses inherent in their analysis. For example, the model considers only a small number of conditions that have been associated with physical inactivity, while excluding many others, such as musculoskeletal disease and respiratory illness. However, this can be justified on the basis of the available evidence on the relationship between PA and these conditions.
In addition to this, the model adopts a fairly simplistic approach to the long-term effectiveness of interventions designed to promote PA, assuming that around 50% of individuals fail to adhere to any intervention for a long enough period to experience reductions in the risk of future events. This rate is not explored in any depth and further attempts are warranted to estimate the degree to which behaviour change is lasting as this is likely to have a significant effect on the cost-effectiveness of interventions.
Other simplifications in the model include the approach to estimating life-years lost, the assumption of independence of the conditions considered and the assumption that individuals experience only one of the conditions. Clearly, these assumptions are unlikely to apply in real life, particularly the assumption that the incidence of CHD, stroke and diabetes are unrelated. However, as with any model, it is relatively easy to take issue with simplifications and assumptions which have been adopted due to the absence of data. In many of these instances, there are relatively few options for improving the model until further long-term evidence becomes available.
One consideration for future research might be whether or not the simple decision-analytic approach to modelling is warranted in this indication. Given that individuals’ behaviours may change over time, it may be that a more dynamic approach to modelling the cost-effectiveness of PA is warranted, although once again this may be limited by the available evidence. In light of this, the model described above provides a useful contribution to the primary evidence on cost-effectiveness presented earlier in this section. The model has also provided a basis for the economic modelling presented in the later stages of this report, although some modifications have been made while further consideration has been given to issues such as uptake and adherence with interventions.
Quality assessment
Studies were reviewed against criteria laid out in critical appraisal checklists for economic evaluations. In general, the studies performed well, particularly with regard to clarity of presentation of the results. There were some deficiencies in relation to the reporting of input parameters, although in many cases these were identified as limitations by the authors. A summary of the characteristics of the economic evaluations is presented in Table 27.
| Quality criteria (adapted from ref. 72) | Stevens et al. (1998)50 UK |
Isaacs et al. (2007)61 UK |
Gusi et al. (2008)70 Spain |
NICE (2006)76 UK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The economic importance of the research question is stated | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| The viewpoint(s) of the analysis are clearly stated and justified | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| The rationale for choosing the alternative programmes or interventions compared is stated | ✗ | ? | ✓ | ✓ |
| The choice of form of economic evaluation is justified in relation to the questions addressed | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Quantities of resources are reported separately from their unit costs | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| Methods for the estimation of quantities and unit costs are described | ? | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| An explanation is given if costs or benefits are not discounted | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Summary of the economic evidence and critical appraisal
A summary of the findings of the economic evidence considered above is presented in Table 28. All studies found the ERS interventions to be cost-effective compared with the controls. However, one study61 attempted to compare an alternative PA intervention with ERS and found that a walking-based intervention is likely to be relatively more cost-effective than leisure centre ERS intervention, with the former leading to a cost saving of £8750 per unit increase in HRQoL scores as measured by SF-36. It would be reasonable to surmise that the available economic evidence on ERS suggests that it appears to be a cost-effective use of health-care resources.
| Parameter | Stevens et al. (1998)50 UK |
Isaacs et al. (2007)61 UK |
Gusi et al. (2008)70 Spain |
NICE (2006)76 UK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICER |
|
|
Cost per QALY gained from intervention compared with control group was €311 |
|
| Currency base | UK £ (year not reported) | 2002 UK £ | 2005 € | 2005 UK £ |
Only one of the economic studies adopted a decision-analytic approach that was suitable for review against best-practice principles for economic modelling. Table 29 highlights the aspects of the guidelines for decision-analytic modelling that were found not to have been addressed by the study. 76 The problems mainly related to the lack of information on validation of the model against existing evidence and incomplete assessment of uncertainties. Regarding the latter, the study focused on parameter uncertainty tending to ignore the other types of uncertainty such as methodological and structural uncertainty.
| Quality criteria (adapted from ref. 74) | NICE (2006)76 UK |
|---|---|
| Is the cycle length defined and justified in terms of natural history of disease? | ✗ |
| Have the four principal types of uncertainty been addressed? | ✗ |
| If not (referring to previous question – our words), has the omission of particular forms of uncertainty been justified? | ✗ |
| Have methodological uncertainties been addressed by running alternative versions of the model with different methodological assumptions? | ✗ |
| Is there evidence that structural uncertainties have been addressed via sensitivity analysis? | ✗ |
| Is there evidence that the mathematical logic of the model has been tested thoroughly before use? | ? |
| Have the results of the model been compared with those of previous models and any differences in results explained? | ✗ |
Summary
-
Given the lack of standardisation of the ERS definition used by previous systematic reviews and the publication of further recent evidence, we undertook a de novo systematic review of cost-effectiveness of ERS.
-
Our systematic review identified only four primary economic evaluations that assessed the cost-effectiveness of ERS – three trial-based economic evaluations and a model-based analysis (commissioned by NICE as part of the development of guidance on brief interventions in primary care for the promotion of PA).
-
Broadly, the previous evidence base suggests that ERS is a cost-effective intervention in sedentary, but otherwise healthy populations. However, there is some significant uncertainty around the estimates of cost-effectiveness because of an absence of evidence on the long-term effectiveness of these interventions. Although modelling studies can go some way to exploring this, ultimately these issues can only be resolved through better evidence of effectiveness derived from RCTs or other well-designed observational studies. As such, any criticism of the economic evidence should be considered in light of the evidence on effectiveness available at the time of the analysis.
-
Each of the previous economic evaluations has its merits and makes a valuable contribution to the limited evidence base on the cost-effectiveness of ERS. The trial-based studies benefit from a high degree of internal consistency, deriving their estimates of effectiveness from the trial and, in some cases, detailed estimates of the cost of the interventions. Any weaknesses inherent in these analyses are also largely as a result of the limitations of the trials, particularly the degree to which the findings can be considered to be externally valid and the relatively short follow-up that was achievable in a trial setting.
-
The NICE economic modelling study overcomes the issue of the short-time horizon inherent in the trial-based analyses. This study allowed for an estimate of the longer-term costs and benefits of PA, taking into account the effects on a number of long-term conditions that are known to be associated with physical inactivity. There are many weaknesses associated with the model although many of these result from an absence of evidence on the effectiveness of ERS (e.g. on the relationship between physical inactivity and long-term conditions, long-term effectiveness of interventions, adherence to interventions etc.). It should also be remembered that any economic model can only ever be a simplification of reality. In an area as complex as PA and behaviour change, and an area characterised by limitations in the evidence base, the need for simplification may be great, leading to a model that fails to meet many of the best-practice criteria.
-
A further limitation of previous economic evaluations is their focus on a sedentary, but otherwise healthy population. Few of the studies explicitly consider whether or not ERS can contribute to improved outcomes in populations with underlying conditions (with the exception of Gusi et al. ,70 which was conducted outside the UK).
-
In light of these findings, we decided to develop a de novo economic model to assess the cost-effectiveness of ERS. Our model builds on the principles of the NICE decision-analytic model, which includes some important further development of the methods and a more robust approach to the incorporation of ERS effectiveness evidence. The findings of this analysis are presented in Chapter 6.
Chapter 5 Systematic review of the predictors of exercise referral scheme uptake and adherence
Background
Chapter 3 provides an overview of the effectiveness of ERS. However, if patients do not initially take up an exercise referral then the beneficial effects of increased PA will not occur, or, conversely, greater adherence to ERS will increase the probability of being physically active. Public health impact depends on ‘real-world’ effectiveness information and is therefore dependent not only on RCT evidence, but also on the external validity of this evidence. With widening health inequalities, those most at need may also be those most likely to have lower uptake and adherence to ERS. Further, the costs related to ERS are ‘front loaded’, so where patients fail to attend or drop out, this will reduce the cost-effectiveness of ERS. Therefore, it is important to understand the patient-level factors and programme-level factors that might influence uptake and adherence to ERS.
The objectives of this systematic review are to (1) quantify the levels of uptake and adherence to ERS; (2) identify demographic and medical diagnosis variables, programme factors and psychosocial factors (e.g. self-determination) that predict uptake and adherence to ERS; and (3) identify from qualitative studies patient perceptions about recruitment, referral and ERS engagement processes, and associated benefits.
Variation in individual ERS programmes and the variable reporting and monitoring of patients characteristics related to uptake and adherence85 may explain the lack of standard definitions for ERS uptake and adherence in the literature. For the purposes of this systematic review, the following definitions were used:
-
Uptake The proportion of those individuals offered entry to ERS who attend an initial consultation with an ‘exercise professional’ or attend a first exercise session.
-
Adherence Of those individuals who take up ERS, what proportion experience at least 75% of the programme.
Methods
This review was conducted and reported in accordance with the PRISMA statement. 36
Search strategy
As described in Chapter 3.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
For inclusion, studies had to meet the population and ERS intervention criteria as described in Chapter 3. For this particular review, we broadened the study design criteria to include uncontrolled studies. Included studies were required to report at least one the following:
-
quantitative estimate (or data to allow calculation) of participant uptake and adherence to ERS
-
quantitative estimate of the statistical association/relationship (e.g. correlation or regression coefficient) between participant demographic (e.g. age, medical diagnosis), participant psychosocial factors (e.g. level of motivation, self-efficacy) and programme factors (e.g. centre vs home-based delivery, group vs individual sessions, dose of exercise) and uptake or adherence to ERS
-
qualitative data (e.g. focus groups and interviews with ERS participants) about the factors uptake and adherence to ERS.
Study selection process
Quantitative studies
As described in Chapter 3.
Qualitative studies
Potential identified studies were screened for inclusion by two reviewers (AT and Brian O’Regan).
Data extraction
Quantitative studies
Data were extracted by one reviewer (TP) using a standardised data extraction form and checked by another (RT). Discrepancies were resolved by discussion, with involvement of a third reviewer when necessary. Extraction included data on patient-level characteristics (e.g. age, disease diagnosis), intervention (e.g. duration, location, intensity and mode of the exercise intervention delivered), study quality, and reported estimates and qualitative data on the association and mediators of uptake and adherence to ERS.
Qualitative studies
A single reviewer (Brian O’Regan) extracted relevant information from included studies and this was checked by a second reviewer (AT).
Data analysis and synthesis
Quantitative studies
Levels of uptake and adherence across studies were pooled using a random-effects model to take into account the clinical and statistical heterogeneity in studies and the various definitions of uptake and adherence across studies. Given the range of methods of reporting predictors of ERS uptake and adherence, it was not possible to quantitatively pool these data across studies. Instead, we undertook categorised findings in each study based on the strength and direction of association. 86
Qualitative studies
Qualitative information on the factors influencing ERS uptake and adherence is presented narratively and summarised in a tabularised format.
Results
Identification and selection of studies
Of the 233 full papers retrieved from the Chapter 3 search and identification through other means (reference list check, author and expert knowledge), five RCTs, 14 observational studies and 10 qualitative studies (28 primary studies in total) and two systematic reviews were judged to meet the inclusion criteria. Figure 14 summarises the selection process.
FIGURE 14.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses flow diagram of study inclusion process for predictors of uptake and adherence to ERS systematic review. PHC, primary health care.
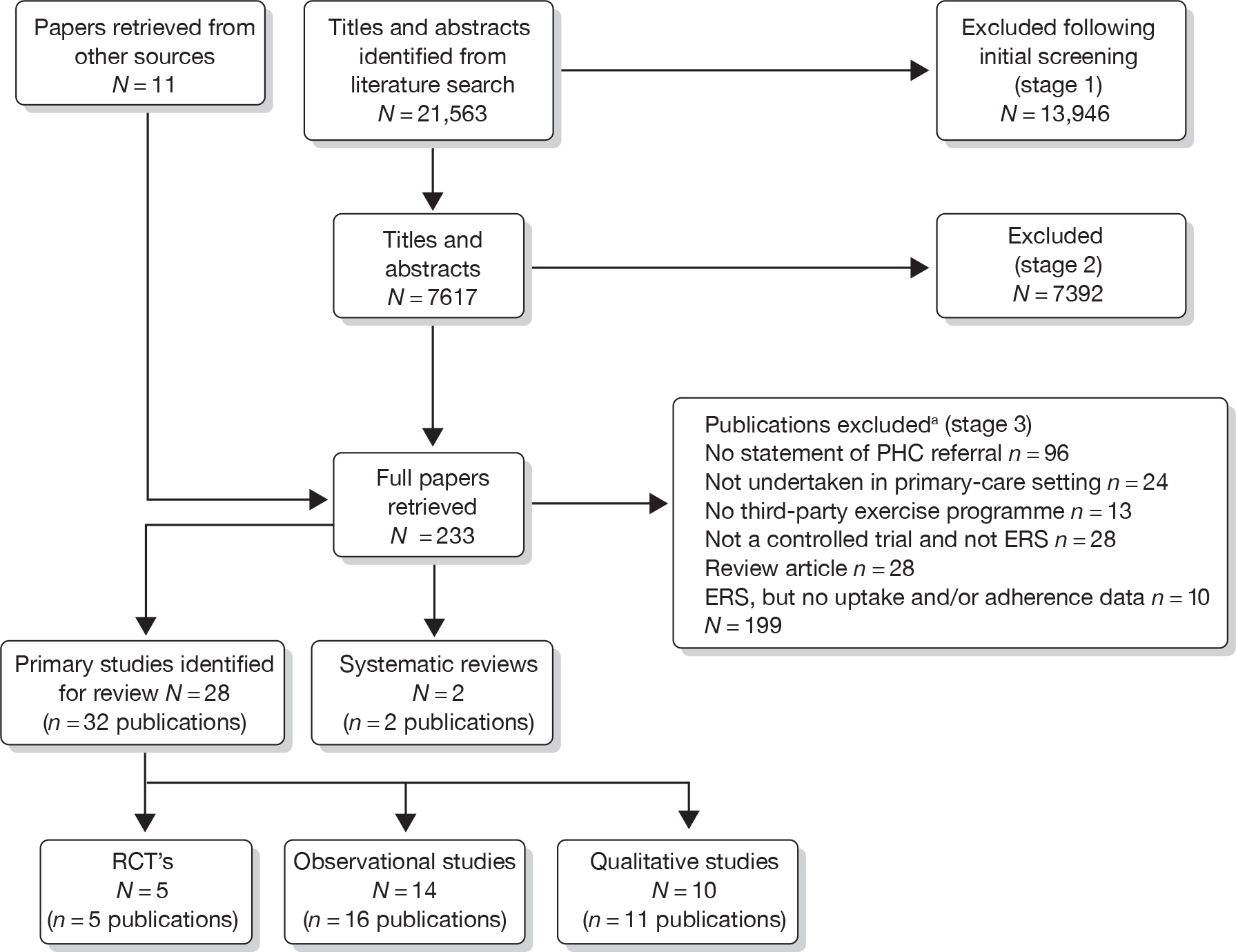
Findings of previous systematic reviews
A review of previous systematic reviews of reporting uptake and adherence to ERS was undertaken to gain an initial understanding of the evidence and inform the approach of the systematic review of primary studies.
Two previous systematic reviews addressed the issue of uptake and adherence to ERS41,87 (Table 30). The quality of these systematic reviews is appraised in Chapter 3. Williams et al. 41 included a small section of their report where the uptake and adherences levels from eight ERS observational studies were presented and discussed. The Gidlow et al. 87 review included uptake and adherence data from five observational studies and four RCTs of ERS (Table 31). Table 31 illustrates the lack of consistency in the studies included by these two reviews, reflecting differences in the definition of ERS.
| Authors | Objectives of review (stated by authors) | Databases/end date of searches | ERS definition | Inclusion criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gidlow et al. (2005)87 | Explore attendance of UK ERS, who attends them, why participants drop out of schemes | PubMed; EMBASE; PsycINFO; SPORTDiscus 2003 | Interventions based in primary care; interventions involved referral to an exercise professional | Studies were based in the UK; interventions were based in primary care; interventions involved referral to an exercise professional; attendance-related outcomes were measured; studies were published in peer-reviewed journals |
| Williams et al. (2007)41 | Assess whether ERS are effective in improving exercise participation in sedentary adults, including reference to uptake and adherence of included studies | MEDLINE; AMED; EMBASE; CINAHL; PsycINFO; SPORTDiscus; The Cochrane Library; SIGLE 2007 | Referred adults from primary care to intervention where encouraged to increase PA; initial assessment; tailored programme; monitoring |
RCT; non-RCT; observational; process evaluation; qualitative Any outcome |
| Studies | Gidlow et al. (2005)87 | Williams et al. (2007)41 |
|---|---|---|
| Observational studies | ||
| Lord and Green (1995)88 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Hammond et al. (1997)89 | ||
| Cochrane and Davey (1998)90 | ✓ | |
| Jackson et al. (1998)91 | ✓ | |
| Martin and Woolf-May (1999)92 | ✓ | |
| Damush et al. (2001)93 | ✓ | |
| Greater Glasgow Health Board (2004)94 | ✓ | |
| Dugdill et al. (2005)95 | ✓ | |
| Dugdill and Graham (2005)96 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Dinan et al. (2006)97 | ✓ | |
| RCTs | ||
| Munro et al. (1997)48 | ✓ | |
| Taylor et al. (1998)27 | ✓ | |
| Stevens et al. (1998)50 | ✓ | |
| Harland et al. (1999)43 | ✓ | |
The review by Williams et al. 41 concluded that uptake and adherence were low, with 33% of patients not participating in the ERS and between 12% and 42% completing a 10- to 12-week period of ERS (Table 32). The Gidlow et al. 87 review concluded that uptake and adherence rates were variable and comparable between observational studies and RCTs. Uptake rates varied between 23% and 60%, and around 80% of patients dropped out before the end of the scheme.
| Authors | No. of included studies | Method of data synthesis | Key findings as stated by author |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gidlow et al. (2005)87 |
n = 9 All UK based |
Narrative |
|
| Williams et al. (2007)41 |
n = 6 UK |
Narrative |
|
Findings of quantitative primary studies
Sample sizes ranged across studies from 30 to 6610 participants in the observational studies, and from 97 to 363 participants in the RCTs. Mean age ranged from 44.9 to 51.9 years across the observational studies and from 53.9 to 59.1 years for RCTs. Across the 19 studies,27,28,50,61,69,88,91,93,95,97–100,102–107 12 provided a definition of uptake (Table 33). 88,89,93,95,97–100,102–107 Uptake was defined in one of two ways: attendance at the initial consultation with the ‘exercise professional’ or attendance at at least one exercise session. Thirteen studies26,60,87,90,91,96,97,99–106 provided a definition of adherence – completion of a set number of exercise sessions, either numerically (e.g. completed 20 sessions92) or as a percentage (e.g. > 80% attendance104). For four studies,88,91,92,103 attendance at a post-ERS consultation was also required to meet the definition of adherence.
| Study | Population characteristics: mean age (years), gender (% male), medical diagnoses or risk factors (%) | Inclusion/exclusion criteria of study | Sample size | ERS setting | Uptake definition | Adherence definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCTs | ||||||
|
Taylor et al. (1998)27 UK |
Mean age: 54.1 Male: 37 Smokers: 43 Overweight: 77 Hypertensive: 46 |
Smokers, hypertension (at least 140/90 mmHg), overweight (BMI > 25) | 97 | Three practices | Attended at least one session | Patients who attended at least 15 sessions |
|
Stevens et al. (1998)50 UK |
Mean age: 59.1 Male: 40 Smoker: 18 |
Sedentary: < 20 × 30 minutes of moderate-intensity PA or less than 12 × 20 vigorous-intensity PA in the last 4 weeks | 363 | One practice | ‘Attended initial consultation with exercise development officer’ | Not reported |
|
Harrison et al. (2005)28 UK |
Mean age: not reported Male: 33 Smoker: 24.4 At least one CHD risk factor: 75.3 |
Scheme related | 275 | 46 practices | ‘Attended the first exercise consultation’ | Not reported |
|
Isaacs et al. (2007)61 UK |
Mean age: 57.1 Male: 35 Raised cholesterol: 24.0 Hypertension: 44.5 Obesity: 65.9 Smoking: 10.4 Type 2 diabetes: 12.3/11.3 Family history of MI: 13.9 |
Not active (no definition reported), raised cholesterol, controlled mild/moderate hypertension, obesity, smoking, diabetes, family history of MI at early age | 317 | 88 practices | Attended at least one session | The adherence of subjects to the active intervention arms was assessed by the use of handheld diaries and class registers (75–100% adherence) |
|
Sorensen et al. (2008)69 Denmark |
Mean age: 53.9 Male: 43 Metabolic syndrome: 36 Type 2 diabetes: 18 CVD: 32 Other diseases: 14 |
Scheme related | 28 | 14 practices | Correspondence with author | Not reported |
| Observational studies | ||||||
|
Damush et al. (2001)93 (prospective) USA |
Mean age: 64.1 (9.1) Male: 0 COPD: 13.1 Congestive heart failure: 14.9 Coronary artery disease: 17.5 Hypertension: 90.5 Type 2 diabetes: 38.9 History of stroke: 13.1 |
Female, age ≥ 50 years, not terminally ill, visited health centre in previous 12 months and had a scheduled or walk-in visit during the 6-month enrolment period | 404 | Two health centres | ‘Participation in at least one exercise class’ | Not reported |
|
Dinan et al. (2006)97 (prospective) UK |
Aged 75 years and over | Scheme related | 242 | 14 practices | ‘Took up the referral’ | ‘Completed the cycle of exercise classes’ |
|
(prospective) UK |
Mean age: not reported A – male: 36 B – male: 41 A – overweight: 37 A – hypertension: 13 A – mental illness: 9 B – arthritis: 28 B – back pain: 26 B – overweight: 23 |
Scheme related |
A: 980 B: 1825 |
Two schemes | Attended first consultation with exercise officer | Not reported |
|
Edmunds et al. (2007)98 (prospective) UK |
Mean age: 44.98 (14.61) Male: 16 Medical diagnoses: not reported |
Overweight or obese | 49 | One scheme | Not reported | 1–5 scale, an individual was defined as having ‘dropped out’ if he/she had stopped participating in their prescribed activities at their exercise referral site/facility |
|
Harrison et al. (2005)99 (prospective) UK |
Mean age: 51.3 (12.6) Male: 39.2 Musculoskeletal problems: 32.8 CVD: 29.9 Overweight: 10.4 Fitness: 5.8 Mental-health problems: 5.1 Respiratory: 4.1 Other: 0.7 |
Scheme related | 6610 | One scheme | Attended first consultation with exercise officer | Not reported |
|
Jackson et al. (1998)91 (retrospective) UK |
Mean age: not reported Gender: not reported Medical diagnoses: not reported |
Not reported | 686 | One scheme | Not reported |
Adherers: exercised at the leisure centre over a 10-week period and attended a 10-week consultation Non-adherers: discontinued exercise at the leisure centre within the 10-week period and did not attend a 10-week consultation |
|
Jones et al. (2005)100 (prospective) UK |
Mean age: not reported Male: 42.1 Medical diagnoses: not reported |
High blood pressure, weight or stress-related problems (or combinations of these) | 152 | One scheme, seven leisure centres | ‘Attended their local gym for an initial assessment’ | Those who completed 24 sessions in total were considered to be successful |
|
Lord and Green (1995)88 (prospective) UK |
Mean age: not reported Male: 25 Overweight: 32.2 Stress/anxiety: 15 Other: 11 Lipids/cholesterol: 6.4 Keep fit: 4.8 Lack of exercise: 4.8 Depression: 4.8 Arthritis: 2.9 Back pain: 2.9 Family history of IHD: 2.4 |
Scheme related | 419 | One scheme | ‘Attended an initial consultation with the community health and fitness officer’ | Compliance: ‘those participants who returned to attend a 10-week consultation and who were still exercising’ |
| Martin and Woolf-May (1999)92 (retrospective) UK |
Mean age (F): 51.1 (12.3) Mean age (NF): 54.7 (14.4) Male: 35 BMI > 25 (F): 50 Cholesterol > 5.2 mmol/l (F): 16.7 Family history of CVD/CHD (F): 23.8 BMI > 25 (NF): 51.4 Cholesterol > 5.2 mmol/l (NF): 2.9 Family history of CVD/CHD (NF): 17.1 |
Scheme related, 60 NFs randomly selected to match F’s number | 490 | One leisure centre | Not reported |
Finishers: completed 20 sessions over the 10-week period and/or completed the final assessment Non-finishers: completed less than 20 sessions over the 10-week period |
|
Morton et al. (2008)101 (prospective) UK |
Mean age: 51.9 (15.7) Male: 26.7 Medical diagnoses: not reported |
Not reported | 30 | One leisure centre | Not reported |
Adherers: ‘attended at least one session per week for the duration of the study’ Partial adherers: ‘attended intermittent sessions, but specifically stated that they had not dropped out of the scheme’ Dropped out: ‘attended’ no sessions or made personal contact with the leisure centre to terminate their involvement with the scheme |
|
Roessler and Ibsen (2009)102 (prospective) Denmark |
Mean age: not reported Male 33 BMI > 25: 35 BMI > 30: 37 BMI > 35: 28 |
Scheme related | 1156 | One scheme | Not reported | Completed intervention (not defined) |
|
Sowden et al. (2008)103 (retrospective) UK |
Mean age: 51 Male: 35 CVD risk: 44.3 Overweight/obese: 30 Musculoskleletal:25.2 Mental health: 19.8 Diabetes: 17.7 Respiratory: 8.1 |
Scheme related | 6101 | Six schemes, 317 practices | ‘Attendance at initial appointment’ | ‘Attends final ERS appointment’ |
|
James et al. (2009)104 (prospective) UK |
Mean age: not reported Male: 34.6 Metabolic diseases: 36.3 Orthopaedic diseases: 24.7 CHD: 17.5 Pulmonary diseases: 9.9 Mental health: 9.4 Neuromuscular diseases: 1.1 Others: 1.1 |
Scheme related | 1315 | One scheme, five leisure centres | Not reported | Completers: ‘attended > 80% of scheduled sessions’ |
|
bGidlow et al. (2007),105 Crone et al. (2008),106 James et al. (2008)107 (prospective) UK |
Mean age: 50.8 (14.4) Male: 39.9 Obesity: 30.3 Musculoskleletal:26.3 CVD: 16 Mental health: 4.6 |
Scheme related | 2864–2958 | One scheme | ‘Attendance of at least one session’ | Completers: ‘attended > 80% of scheduled sessions’ |
Exercise referral schemes uptake and adherence levels
The pooled level of ERS uptake across the observational studies was 66.% (95% CI 57% to 75%) compared with 80% (95% CI 61% to 98%) across the RCT (Figure 15). There was a high level of statistical heterogeneity for both observational studies (I2 = 99.4%, p < 0.0001) and RCTs (I2 = 99.3%, p < 0.0001). The studies of Stevens et al. 50 and Damush et al. 93 reported particularly low levels of uptake, i.e. < 35%. Stevens et al. 50 hypothesise that the low uptake they experienced may have been reflective of the nature of the invitation letter sent to participants and the point of randomisation (pre-invitation letter). They also hypothesise that a change in the format of the letter (e.g. including a specific date offered for the first ERS appointment) would have improved participation. Similarly, Damush et al. 93 used a letter-based recruitment because studies conducted in the USA require a pre-exercise test before the exercise intervention commences, and potentially this could have deterred eligible patients from consenting to the study.
FIGURE 15.
Meta-analysis of ERS uptake levels stratified by study design. Overall test for heterogeneity between subgroups: 691.58 [degrees of freedom (df) 1], p = 0.28. Note: weights are from random-effects analysis.
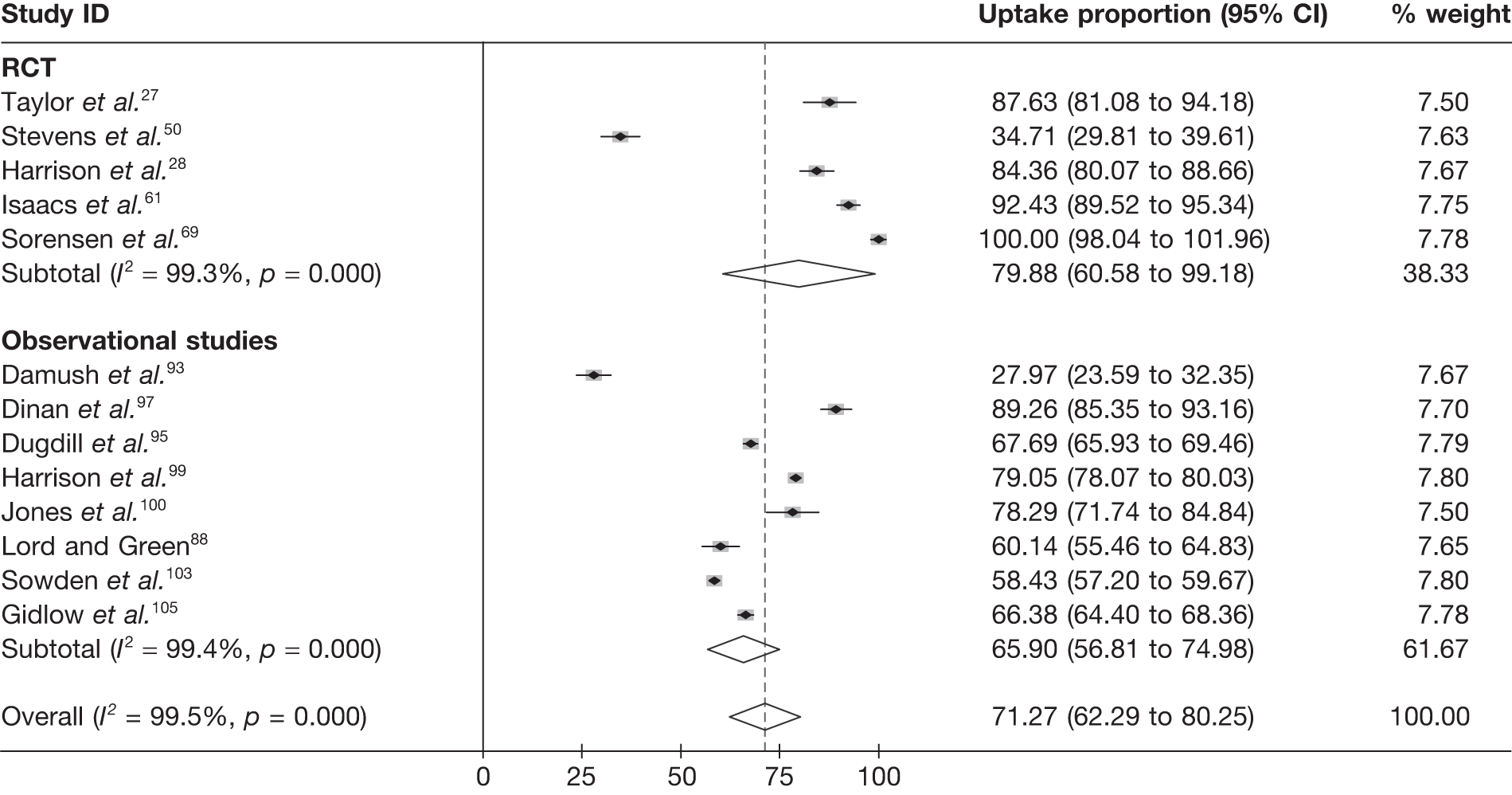
Levels of adherence to ERS were variable across all study types (range 12–93%) (Table 34). The pooled level of ERS adherence was 49% (95% CI 40% to 59%) for observational studies and 37% (95% CI 20% to 54%) for the RCTs (Figure 16). Again, there was a high level of statistical heterogeneity for both observational studies (I2 = 99.1%, p < 0.0001) and RCTs (I2 = 89.0%, p <0.003). The observational study by Martin and Woolf-May92 reported particularly low levels of adherence (12%). Unfortunately, the study publication does not provide sufficient information on the ERS process to allow an appraisal of its contribution to the low adherence rate. The authors stated that ‘of the available 490 subjects there were only 60 known finishers’, suggesting that some individuals who may have adhered may have been missed.
| Study | Uptake | Adherence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| % (n/N) | % (n/N) of patients who took up ERS | % (n/N) of patients who were referred to ERS | |
| RCTs | |||
|
Taylor et al. 27 UK |
88% (85/97) | 28% (24/85) | 25% (24/97) |
|
Stevens et al. 50 UK |
35% (126/363) | Not reported | Not reported |
|
Harrison et al. 28 UK |
84% (232/275) | Not reported | Not reported |
|
Isaacs et al. 61 UK |
92% (293/317) | 45% (133/293) | 42% (133/317) |
|
Sorensen et al. 69 UK |
100% (28/28) | Not reported | Not reported |
| Observational studies | |||
|
Damush et al. 93 USA |
28% (113/404) | Not reported | Not reported |
|
Dinan et al. 97 UK |
89% (216/242) | 82% (178/216) | 74% (178/242) |
|
UK |
B: 68% (1825/2696) |
A: 34% (336/958) B: 46% (849/1829) |
B: 32% (849/2698) |
|
Edmunds et al. 98 UK |
Not reported | 51% (25/49) | Not reported |
|
Harrison et al. 99 UK |
79% (5225/6610) | Not reported | Not reported |
|
Jackson et al. 91 UK |
Not reported | 70% (466/686) | Not reported |
|
Jones et al. 100 UK |
78% (119/152) | 65% (77/119) | 51% (77/152) |
|
Lord and Green88 UK |
60% (252/419) | 31% (77/252) | 18% (77/419) |
|
Martin and Woolf-May92 UK |
Not reported | 12% (60/490) | Not reported |
|
Morton et al. 101 UK |
Not reported | 40% (12/30) | Not reported |
|
Roessler and Ibsen102 Denmark |
Not reported | 70% (811/1156) | Not reported |
|
Sowden et al. 103 UK |
58% (3565/6101) | 39% (1404/3565) | 23% (1404/6101) |
|
James et al. 104 UK |
Not reported | 57% (750/1315) | Not reported |
|
bGidlow et al. ,105 Crone et al. ,106 James et al. 107 UK |
66% (1930/2908) | 48% (931/1930) | 32% (931/2908) |
FIGURE 16.
Meta-analysis of ERS adherence levels stratified by study design. Overall test for heterogeneity between subgroups: 4.57 (df 1), p = 0.397. Note: weights are from random-effects analysis.
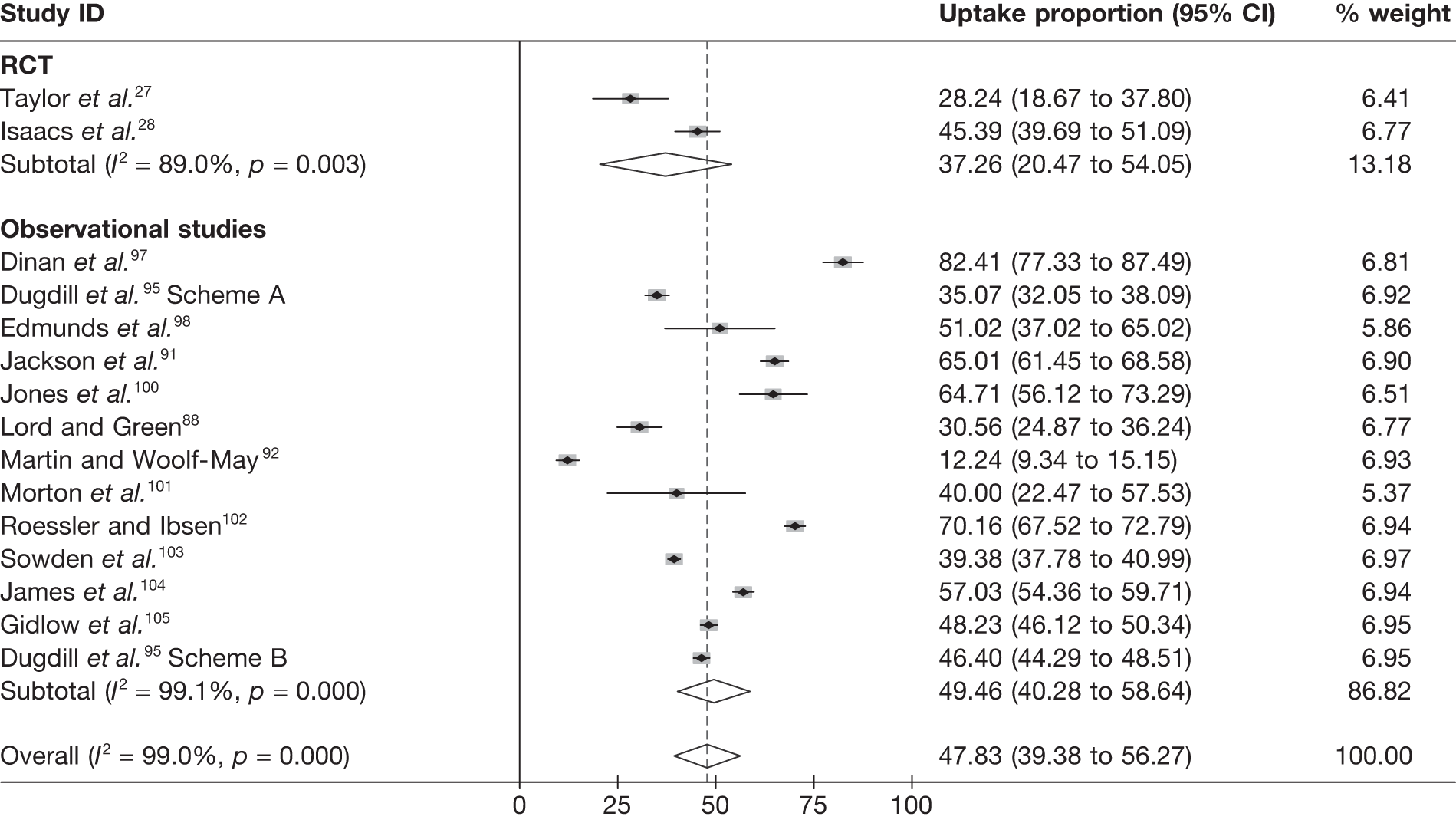
Predictors of participant uptake
Six observational88,93,95,99,103,105 and two RCTs27,61 reported predictors of uptake, with five studies providing bivariate analysis27,61,88,95,105 and four studies multivariate analysis93,99,103,105 in which associations among predictor variables were adjusted for other factors such as age.
Demographic
The findings of studies that assessed demographic predictors of ERS uptake are summarised in Table 35. Two studies88,103 reported that females were more likely to take up ERS than men, whereas two studies99,105 showed no association of gender with uptake. Increasing age was positively associated with increased levels of ERS uptake in three studies,95,103,105 whereas three studies61,88,93 found no such association. Gidlow et al. 105 found that those who were the most deprived were less likely to uptake. Gidlow et al. 105 also found that those individuals living in a more rural location were less likely to take up ERS. Damush et al. 93 found no association between ethnicity and uptake.
| Study | Multivariate analysis | Bivariate analysis | Overall summary | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Harrison et al.99 UK | Sowden et al.103 UK | Gidlow et al.105 UK | Damush et al.93 USA | Lord and Green 88 UK | Dugdill et al.95 UK | Isaacs et al.61 UK | No. of studies on this factor | Any significant association | No significant association | |
| Sample size | n = 6610 | n = 6101 | n = 2958 | n = 404 | n = 419 | n = 2696 | n = 317 | ||||
| + | – | ||||||||||
| Demographic factors | |||||||||||
| Gender (male vs female) | 0 | + | 0 | + | 4 | 2 | 0 | 2 | |||
| Increasing age | + | + | 0 | 0 | + | 0 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 3 | |
| Deprivation | 0 | 0 | – | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| Rurality (urban vs rural) | – | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||
| Ethnicity (African American vs all other racial groups) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||
| Programme factors | |||||||||||
| Scheme locationa | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||
| Clinic locationb | 0 | ||||||||||
| Referrer (GP vs ‘other’) | – | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||
Medical diagnosis
Given the variable way in which referral reason (medical history) was analysed and reported, it was not possible to tabularise this in a summary way. Harrison et al. 99 showed found that those with mental health problems (OR 1.79, 95% CI 1.24 to 2.39, p < 0.01) or fitness needs (OR 10.33, 95% CI 1.44 to 74.3, p < 0.05) were more likely to take up ERS than those with no specified referral reason. Harrison et al. 99 also reported that those with respiratory problems and most deprived were more likely to take up ERS than those with respiratory problems and least deprived (OR 1.45, 95% CI 1.06 to 1.99, p < 0.05). Gidlow et al. 105 showed those patients referred with mental-health (OR 0.33, 95% CI 0.27 to 0.57, p < 0.01), musculoskeletal (OR 0.75 95% CI 0.58 to 0.99, p < 0.05), overweight/obesity (OR 0.63, 95% CI 0.50 to 0.81, p < 0.01) or ‘other’ (not defined) (OR 0.63, 95% CI 0.46 to 0.85, p < 0.01) problems were less likely to take up ERS than patients with cardiovascular disease. In contrast, Sowden et al. 103 found that those referred with a musculoskeletal (OR 1.18, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.38, p < 0.05) problem were more likely to take up ERS. This was not the case for those with diabetes or CVD. Gidlow et al. 105 reported that more patients referred for mental-health problems took up ERS than those referred for physical-health problems (60% vs 69%; p < 0.001). Taylor27 found that more individuals referred for obesity took up ERS than those referred for smoking (p < 0.01).
Predictors of exercise referral scheme adherence
Eight observational88,95,98,100,101,103–105 and two RCTs27,61 reported predictors of adherence. Seven studies undertook bivariate statistical analysis27,61,88,95,100,101,105 and four studies undertook multivariate statistical analysis. 98,103–105
Demographic
The findings of studies that assessed demographic predictors of ERS adherence are summarised in Table 36. Two studies95,105 reported that men are more likely to adhere than women, while three studies88,103,104 found no such association. Increasing age was a predictor of increased ERS adherence in five studies,88,95,103–105 although two studies showed no association with age. 61,88 Deprivation, rurality, referrer, leisure provider105 and occupation104 were all found not to be significant predictors of ERS adherence. Dugdill et al. 95 found that fewer patients adhered to ERS (p < 0.01) when referred by the GP (32%) compared with a practice nurse (45%) or a cardiac nurse (57%). James et al. 104 reported that those of mixed ethnicity were more likely to adhere to an ERS.
| Study | Multivariate analysis | Bivariate analysis | Overall summary | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gidlow et al.105 UK | |||||||||||||
| Variables | Sowden et al.103 UK | James et al.107 UK | James et al.104 UK | Edmunds et al.98 UK | Lord and Green88 UK | Dugdill et al.95 UK | Isaacs et al.61 UK | Jones et al.100 UK | Morton et al.101 UK | No. of studies on this factor | Any significant association | No significant association | |
| Sample size | n = 3565 | n = 1996 | n = 1315 | n = 49 | n = 419 | n = 2696 | n = 317 | n = 119 | n = 30 | ||||
| + | – | ||||||||||||
| Demographic factors | |||||||||||||
| Gender (male vs female) | 0 | – | 0 | 0 | – | 5 | 0 | 2 | 2 | ||||
| Increasing age | + | + | + | 0/+a | + | 0 | 6 | 4/5 | 0 | 1/2 | |||
| Deprivation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | ||||||
| Rurality (urban vs rural) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||
| Occupation | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | ||||||||
| Leisure provider | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||
| Referrer (GP vs other health-care professionals) | 0 | + | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Ethnicity (white vs mixed) | + | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Psychosocial factors | |||||||||||||
| Stage of change | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||
| Self-efficacy | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||
| Expectations of change (health and fitness) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||
| Expectations of change (personal development) | + | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Psychological well-being | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||
| Need satisfaction | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||
| Perceived autonomy | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||
| Support | |||||||||||||
| Self-determination | 0 | + | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||||||
Programme factors
Sowden et al. 103 reported variable levels of patient adherence across six different ERS areas in the London area. This finding illustrates the potential influence of programme-level factors on adherence.
Medical diagnosis
In the James et al. study,104 patients with pulmonary problems were less likely to adhere than those with CVD. Sowden et al. 103 reported that patients with diabetes were less likely to adhere to an ERS (OR 0.76, 95% CI 0.63 to 0.93, p < 0.01) than those with CVD (OR 1.22, 95% CI 1.03 to 1.45, p < 0.05) when both compared with those without either condition.
Gidlow et al. 105 found that those referred for mental health problems were less likely to adhere to ERS than those referred for physical health problems (22% vs 34%, p < 0.001). Taylor et al. 27 reported no difference in adherence between those individuals who were referred because they were a smoker, overweight, obese or hypertensive.
Psychosocial
Three studies98,100,101 assessed the psychosocial predictors of adherence (Table 36). Morton et al. 101 found participant self-determination to positively predict ERS adherence, whereas Edmunds et al. 98 found no such association. An expectation for change in personal development was also found to be positively predictive of ERS adherence. 100
Programme factors
No programme factors were reported in studies examining associations of ERS adherence.
Qualitative studies of exercise referral scheme uptake and adherence
Our searches identified 10 studies that collected qualitative data from participants who were involved in ERS (Table 37). 92,108–117 These studies ranged substantively in their methodological quality. In some studies there was a clear absence of methodological rigour,11,92,115 for example little or no reference to epistemological issues, single researchers coding transcripts, no clear process described for creating categories, and themes largely emerging from the choice of questions. Other studies had well-described processes for data collection and analysis (e.g. demonstration of trustworthiness, verification and multiple layers of data analysis). 108–114,117 Only a few studies involved repeated interviews with the same participants as they passed through schemes;110,111 instead most involved retrospective reflection. Both individual and small-group interviews were conducted to collect data.
| Study | Participant characteristics | ERS characteristics | Qualitative methods | Focus | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Stathi et al. (2004)108 UK |
13 community-dwelling older adults (eight male and five female; age 63–79 years), with physical health conditions | Standard structured exercise | Individual or group semistructured interviews (< 60 minutes), at various stages of referral (but nine at mid-end) |
Successful ageing Contribution of ERS Experience of ERS |
ERS increases sense of purpose and social interaction, with better physical and mental function and feelings of accomplishment and success. Success was contingent on the GP recommendations, exercise professional help and support, and attractiveness of the exercise content |
|
Wormald et al. (2006)109 UK |
16 white adults (five male and 11 female; age 15–73 years), with wide variety of physical and/or mental health conditions | Up to six monthly consultations with active living advisor. Information and signposting service | Focus groups (one to seven participants; 45–60 minutes), after attending at least one consultation |
Referral process Operational aspects of ERS Benefits of the service |
Referrer and public had limited awareness of the scheme, leading to anxiety at the first session. Success appeared dependent on qualities and approach of the ERS advisor. Participants began a range of PA options and enjoyed the lack of pressure to exercise, and gentle progression. Range of physical and mental-health benefits reported, and change in other health behaviours |
|
Hardcastle and Taylor (2001)110 UK |
15 women (age 50–80 years) with a range of physical and psychological conditions | Standard structured 10-week ERS | Repeated unstructured interviews throughout ERS and life story technique | The psychological and social meaning and relevance of an ERS for inexperienced gym users, from start to finish | Highlights the importance of a complex interplay of physical, psychological and social factors in the process of experiencing an ERS, and becoming more physically active among older women |
|
Hardcastle and Taylor (2005)111 UK |
15 women (age 43–77 years, with a range of physical and psychological conditions | Standard structured 10-week ERS | Repeated unstructured interviews throughout ERS and life-story technique | Changes in physical self-perceptions and exercise identity in older women | ERS appeared to enhance physical self-perceptions, which in turn contributed to feelings of control, autonomy and the development of an identity as an exerciser over the course of the scheme |
|
Carroll et al. (2002)112 UK |
South Asian Muslim women |
Standard ERS (10–12 weeks) at a range of times up to 6 weeks |
Informal discussion and semistructured individual or small group interviews | Structural and attitudinal barriers to ERS | Highlighted issues of access, cost, religious, parental and ethnic barriers. Additional notes provided on a range of other schemes involving Muslim women |
|
Crone et al. (2005)113 UK |
18 adults (5 male and 13 female; mean age 55.5 years) with only physical health condition | Standard ERS | Focus groups and individual interviews, some before and after completion of one of three schemes, others just near completion |
Individual experiences Important elements Pros and cons Factors influencing experience Role of exercise leader |
Highlights emotional and social benefits, within themes of experiencing the ERS, structure and conditions of ERS, actions and interactions, and consequences |
|
Martin and Woolf-May (1999)92 UK |
42 Fs (16 male and 26 female) and 35 NFs (12 males and 23 females), with physical health condition | Standard 10-week ERS | Semistructured telephone interviews. Not in-depth interviews with all | Attitude to gym, perceptions of ERS, reasons for non completion (NFs only) | Few apparent differences between Fs and NFs. No clear reason for not finishing, other than time, illness, and need for more support |
|
Wormald and Ingle (2004)114 UK |
30 white adults (10 male and 20 female; age 25–84 years, mostly over 55 years) | Standard 10-week ERS | Six focus groups. Completers and non-completers |
Role of the referee ERS environment/staff Perceived effects of ERS |
ERS provided support, supervision, structure and social opportunities, thereby enhancing motivation. Range of perceived physical and psychological benefits |
|
Singh (1997)115 UK |
13 (11 female, aged 30–61 years). Conditions not defined but results suggest mainly physical | 20 sessions of free ERS | Individual interviews | Not defined | Brief reference to a range of physical and psychological perceived benefits, and motivation. Very limited depth of analysis |
|
Schmidt et al. (2008)116 Netherlands |
38 inactive and almost all obese females (age 31–60 years), from broad range of ethnic backgrounds | 20-week Dutch ERS, subsidised | Individual interviews | Social, ethnic, personal and environmental factors influencing participation | Support by referee, the exercise environment and fitness instructors were important. Access to ERS in ‘unsafe’ environment was an issue. Limited depth of analysis |
|
Wiles et al. (2008)117 UK |
Nine (of 30 approached) stroke patients (eight males, age 18–78 years | Leisure centre-based fitness instructor-led ERS (post hospital-based stroke rehabilitation) | Individual 30- to 60-minute interviews | Experience of ERS and of having a stroke | ERS was perceived as second best to physiotherapy, but better than nothing, and useful for becoming less dependent on NHS services. More personal and social support was needed in this ERS |
The participants included in the study were mainly female in all but two studies. 108,117 Some studies were designed to specifically compare particular groups of ERS participants, for example those who adhered to the ERS versus those who dropped out. Others studies involved taking a convenience sample from the whole ERS population. The participants in these studies appeared to reflect the typical age range and medical conditions of those involved in ERS studies described in Chapters 3–5 of this report. Some studies focused specifically on capturing the voices of ethnic groups,112 those with specific medical conditions (although most were concerned with patients referred with physical health problems),116,117 and a specific age band108,110,111 or gender. 110–112,116,117 All studies were conducted in the UK with the exception of one study, which was based in the Netherlands. 116
Most studies attempted to maximise the utility of qualitative methods to explore process focused on themes such as:
-
experience of the referral process (from GP to exercise practitioner)92,108–110,112,113
-
experiences within the exercise facility and programme (including interactions with fitness instructor/exercise practitioner and support offered)92,109–114,117
The results of studies are summarised in Table 37. The key findings were:
-
Referral process good practice was seen to involve a referrer who explained the process of referral and prepared patients for what to expect, limited delay in the first appointment after referral, and support from the exercise practitioner to reduce anxiety upon arrival. Participants also appreciated a GP who would show an interest in progress, based on feedback from the exercise facility. Reduced-cost or free access to the exercise facilities was often stated as very important, especially in those studies in which there was a focus on deprived communities. Similarly, availability of child care was mentioned as an important in being to take up, and adhere to, ERS.
-
Ethnicity and social–cultural factors appeared to impact on how participants experienced the exercise setting. Mixing ERS participants with regular gym users was identified as an issue and added to anxiety and a feeling of being out of place. For some, single-sex sessions were an essential for any engagement. Good practice seemed to involve patient-centred exercise programming (to maximise a sense of competence and choice) and an opportunity for developing social networks.
-
Participants reported a range of physical, psychological and social benefits from the ERS, together with impact on other positive health behaviours. Few studies considered the impact of the ERS on a sustainable physically active lifestyle when the programme ended, or taking up other PA options outside the gym.
Summary
There has been little consideration of uptake and adherence in previous systematic reviews of ERS.
-
Fourteen observational studies and five RCTs reported their level of ERS uptake (the proportion of those individuals offered entry to ERS who attend an initial consultation with an ‘exercise professional’ or attend a first exercise session) and/or adherence (of those that uptake ERS, what proportion undertake 75–100% of the programme) (UK, n = 16; non-UK, n = 3).
-
The pooled estimate for ERS uptake across the observational studies (66%) appeared to be lower than the pooled estimate for RCTs (80%). The pooled estimate for ERS adherence in the observational studies (50%) appeared to be higher than the pooled estimate for RCTs (37%). However, it is important to note that there was a high degree of statistical heterogeneity in the levels of uptake and adherence across studies.
-
Only 6 of 13 included studies undertook multivariate analysis to assess the association between potential predictors and levels of uptake or adherence, i.e. adjusted for potential confounders. The remaining seven studies undertook bivariate association analysis.
-
Although a number of studies reported an association between participant gender or age and ERS uptake and adherence, very few studies reported associations for psychosocial and programme-level factors, for example the time of day ERS is available at the delivery site.
-
Women and older people were more likely to take up ERS. Although older people were also more likely to adhere, women were less likely to adhere than men.
-
Eleven qualitative studies highlighted the complexity of personal experiences with ERS that might influence uptake and adherence. Several critical factors reflected the importance of individualised support that takes account of low levels of confidence. However, logistic factors such as cost, convenience and child support were also important to some population sectors.
Chapter 6 Economic modelling of cost-effectiveness
Introduction
There is limited evidence on the cost-effectiveness of ERS. The available evidence highlights significant uncertainty, particularly around the effectiveness of ERS. The result is that decision-makers are currently making decisions on the availability of ERS with only limited evidence on its cost-effectiveness.
In light of this, a de novo analysis has been developed to further explore the cost-effectiveness of ERS. The analysis considers a target population of sedentary adults, with further analysis presented to explore the impact of ERS on those with specific pre-existing conditions, where evidence suggests that ERS might improve outcomes. The approach taken uses previous research as a point of departure, and builds on this through use of evidence synthesis (see Chapter 3) and through further analysis of the impact of PA on HRQoL.
The approach here comprises three main activities:
-
The development of a cost–utility analysis, similar to earlier analyses, to estimate the impact of ERS on long-term outcomes based on the effectiveness evidence identified herein, including subgroup analysis, to explore the cost-effectiveness of ERS in individuals with pre-existing conditions.
-
The development of methods to quantify and incorporate short-term benefits of PA into this cost–utility framework.
-
A cost–consequence framework that summarises the costs and benefits associated with ERS in a disaggregated fashion.
Cost–utility analysis
Cost–utility analysis is widely considered to be the prevailing approach to economic evaluation in the UK, mainly as a result of the guidance laid out in the NICE reference case for economic evaluations. 118 There are known to be challenges that are inherent in applying cost–utility analyses to public-health interventions,119 although it has been used previously to estimate the benefits of PA, notably as part of the development of guidance on PA issued by NICE. 120
In order to generate generalisable findings in the form of an incremental cost per QALY and also allow for comparison of our findings with earlier analyses, we sought to develop a cost–utility analysis of ERS based on the evidence reported in Chapter 3 of this report.
Methods for cost–utility modelling approach
Modelling approach
Figure 17 illustrates our modelling approach, which is a based on the structure of the model developed by NICE. 76 A decision-analytic model was developed, which followed a cohort of individuals over time to examine the impact of PA on their health. Specifically, the model considered the lifetime risk of developing a series of conditions that are known to be associated with being physically active. The model considered the impact of ERS on coronary heart disease, stroke and type 2 diabetes, because these are considered to be the conditions for which the most robust quantifiable evidence is available on the relationship between PA and incidence of disease. Furthermore, evidence on the QALY losses associated with the development of these conditions is also available from previous research. 84 PA has been associated with a wide range of conditions. Owing to data limitations, no attempt was made to incorporate the effect of PA on other conditions, such as musculoskeletal or respiratory diseases.
FIGURE 17.
Model structure.
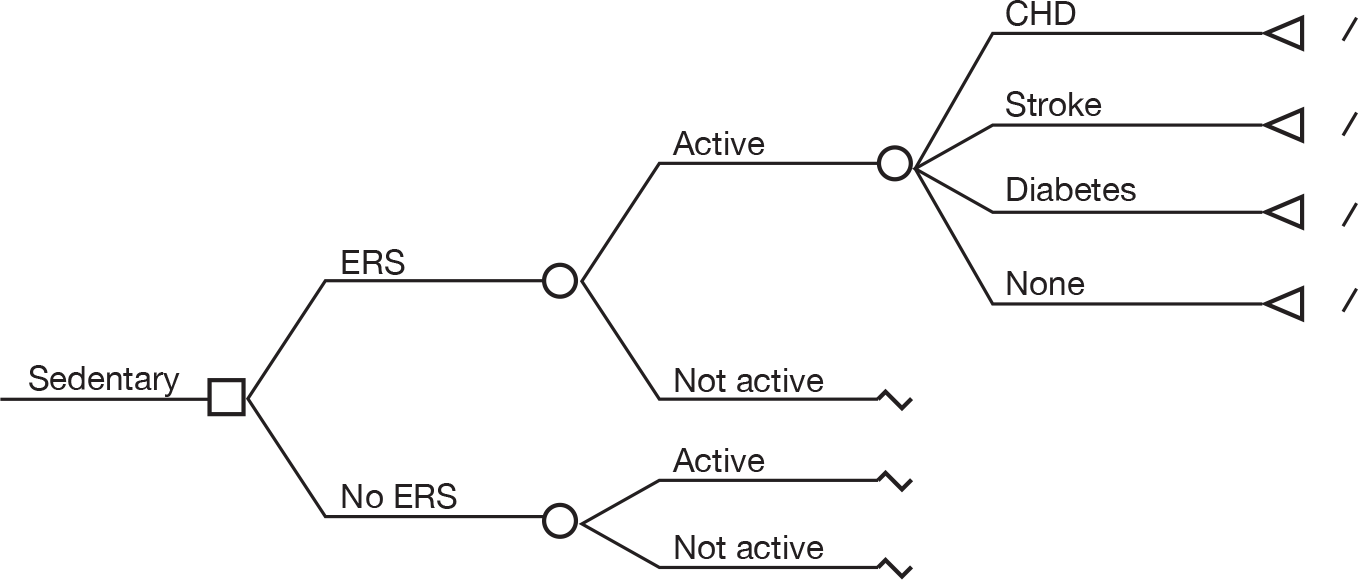
The model considers a cohort of individuals, aged between 40 and 60 years, who present in a sedentary state. The age of the population was selected to reflect the evidence on the clinical effectiveness of ERS reported in Chapter 3. Individuals enter the model as either exposed to an ERS intervention or not; modelling considers two hypothetical cohorts, comparing costs and outcomes of a cohort exposed to ERS with a control cohort not exposed to ERS. Those exposed to ERS are assumed to have a greater probability of becoming active. A physically active individual is assumed to have both improved life expectancy and quality of life (QoL), as a result of a reduced risk of developing each of the morbidities considered in the model. The primary end point for the analysis was QALYs.
The intervention
The ERS intervention in the model is consistent with the definition used throughout this report (see Chapter 1, Physical activity promotion in primary care). Effectiveness data for ERS are derived from the meta-analysis presented herein (Figure 3). For the purposes of our analysis, we assume that the ERS is leisure centre based, as is the case for the majority of studies considered in Chapter 3. Estimates of the cost of the intervention are derived on this basis.
Comparator
The comparator for the analysis is ‘usual care’, which is specified as no active intervention and as the recognised alternative in a sedentary population. This acknowledges that some sedentary individuals may choose to participate in PA without an intervention, although the probability of doing so is assumed to increase as a result of exposure to an intervention.
Perspective
The model adopts a NHS/Personal Social Services perspective, in line with the NICE reference case for cost-effectiveness analysis. 121 Although it is acknowledged that PA may have important effects on non-health-care costs and benefits, these are excluded from the primary/base-case cost–utility analysis, although these broader considerations are addressed in sensitivity analysis and through the presentation of cost–consequence analyses.
Time horizon
A lifetime horizon is adopted to acknowledge the long-term benefits of PA, with alternative time horizons considered in sensitivity analysis.
Model inputs
Data on costs and effects were synthesised to populate the model. Data were primarily derived from the systematic reviews undertaken in Chapters 3 and 4. Further details are provided below.
Effectiveness of exercise referral scheme comparator
Evidence of the effectiveness of ERS/comparator, measured in terms of the probability of moving from a sedentary state to an active state, was derived from the meta-analysis conducted as part of clinical effectiveness review in Chapter 3. This was based on ITT analyses, which adjusted for adherence and uptake and showed ERS to be associated with a higher probability (RR 1.11, 95% CI 0.99 to 1.25) of being active compared with usual care (Figure 3). The active state is defined in line with the effectiveness literature, i.e. doing 90–150 minutes of at least moderate-intensity PA per week. Thus, a sedentary lifestyle corresponds not only to non-participation in PA but also to participation below the requisite amount. The active state is assumed to last long enough to enable health benefits to be obtained, although this remains undefined given the inadequate evidence on the dose–response relationship between PA and the incidence of long-term outcomes. Previous analyses of behaviour change have referred to this scenario as ‘fully engaged’122 to describe an individual who makes lasting changes to his or her lifestyle following an intervention.
Risks of developing health states associated with inactivity
Evidence of the effect of PA on the development of the outcomes considered in the model (CHD, stroke and type 2 diabetes) is derived from a systematic review of economic evaluations in Chapter 4 and HSE – 2006. 123 The derivation of the estimates involved a number of steps. First, the probability of developing these conditions among sedentary individuals was generated from the prevalence of these conditions in that population using the HSE – 2006123 data. Although it is acknowledged that a potential limitation of such univariate analyses is that it does not adjust for confounders, data constraints precluded the inclusion of those confounders. The second step involved estimating the probability of developing the health states among active individuals using RR estimates identified from NICE76 to adjust the estimates derived from the first step. It must be emphasised that the PA levels and study population used to measure the RR estimates match those identified in our clinical effectiveness review. A number of assumptions were made in generating these estimates. First, the risk estimates were assumed to be equivalent to the risk of developing those conditions over a lifetime. Second, the risk of experiencing any of these health states was assumed to be independent of the risk of experiencing other health states. Third, individuals were assumed to experience only one health state within the model.
Exercise referral scheme intervention costs
The cost of the ERS intervention was derived from previously published research identified as part of the review conducted for this study. The study by Isaacs et al. ,61 presenting a detailed bottom-up costing exercise, was identified via a systematic review of the literature, and is regarded here as the best available evidence/estimate for costing of ERS. The estimated cost of the intervention was based on resource use in a health service and/or local authority setting, consistent with the primary perspective taken for analyses here. See Table 26 for further details (information of the calculation of these costs can be found in Isaacs et al. 61 The validity of the costs estimates was assessed by the expert advisory group on this project and judged to be representative of ERS schemes currently in operation. The cost estimates were adjusted for inflation into 2010 prices using the Consumer Price Index. Discounting of the intervention costs was not undertaken as intervention costs were assumed to be wholly incurred in the first year. No attempt was made to estimate a net cost of the intervention, which subtracts any cost savings that might result from ERS from the cost of the intervention. Where this was explored in the systematic review in Chapter 4 (Isaacs et al. ,61 Gusi et al. 70), there was no clear evidence of a change in health-care utilisation (e.g. medications, hospital or primary care) as a result of the intervention.
Treatment costs and quality-adjusted life-years associated with coronary heart disease, stroke and type 2 diabetes
The model considers three outcomes associated with PA, CHD, stroke and type 2 diabetes. The total lifetime treatment costs and QALYs associated with each condition were estimated based on assumptions relating to the age at onset and the likely life expectancy combined with estimates of the annual cost of treating an individual with the condition. This approach was in line with the earlier analysis conducted by NICE. 76
It was assumed that the treatment cost of stroke, unlike the other health states was an event cost that occurs once, rather than a recurring cost. This is acknowledged as a simplification in the model, as in reality there are likely to be acute and ongoing costs associated with stroke. Treatment costs were discounted using the prevailing discount rates as determined by the Treasury and/or NICE guidelines (i.e. 3.5% discounting rate).
Primary outcome measure (quality-adjusted life-years)
The primary outcome of the economic evaluation is expressed in terms of QALYs. QALY losses associated with each of the conditions considered in the model are calculated. QALYs were discounted at 3.5% discount rate. The formula for calculating the QALYs is:
where Q1 = mean QoL associated with being in a non-disease health state; Q2 = mean QoL associated with a particular disease health state; ts = number of years before onset of the disease health state (average age minus 55 years); t3 = age at disease health state onset and t4 = mean age of mortality associated with health state (average age of mortality minus loss of life-years associated with the particular condition). Loss of life-years was calculated by subtracting life-years remaining after onset of the disease health state from the average life-years remaining for the non-disease health state.
Assessment of uncertainty
Uncertainty in parameter estimates was explored through the use of deterministic and probability sensitivity analyses. The deterministic sensitivity analysis, which covered one-way and scenario analysis, explored a number of uncertainties that were recognised at the outset of the analysis. These included uncertainties around the effectiveness of ERS and changes in the cost of ERS to take into account costs incurred by participants as well as providers. The effectiveness of ERS was varied according to estimates of uncertainty reflected in the upper and lower limits of the 95% CI of the RR estimate. Sensitivity analysis also considered how a less intensive form of ERS might look, using evidence on a walking-based intervention (as opposed to a structured leisure centre-based intervention) from Isaacs et al. 61 Further sensitivity analyses considered ‘best-case’ and ‘worst-case’ scenarios that considered the combined effect of extreme values of effectiveness and cost.
In addition, uncertainties around parameters considered to be key drivers of the cost-effectiveness of ERS were addressed simultaneously using PSAs. The parameters that had different unit values in the two arms of the model (i.e. probability to be active and probability to get the disease conditions) were specified as incremental differences between the two arms and not absolute values. The intuition is that the distributions of these parameters may be correlated and, hence, representing them as absolute values may overestimate the uncertainty. The distributions and the calculation of alpha and beta calculations were based on Briggs et al. 124 In cases where there were no data on standard errors (SEs), the standard approach of using 10% of mean estimates as SE was followed. A total of 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations were generated from the PSA.
Model validation
The following procedures were employed to check the validity of the model (Chilcott et al. 125):
-
Internal validation Simulate a series of changes in the input values that are likely to vary the results of the model with checks to see that the impacts on the results are expected. For example, setting all QALY parameters to zero, and checking if the output of the QALYs in each arm is zero. In addition to this, the model was reviewed by an experienced health economist who was not part of the research team.
-
Peer review A peer-review process that involved a modeller, who understands the complexities of the model, scrutinising the spreadsheet of the model and the formulae behind it.
Results
Costs of exercise referral schemes
Estimates of the cost of ERS were derived from a detailed, bottom-up costing exercise conducted as part of a previous health technology assessment (Isaacs et al. 61) and inflated to current prices. Estimates of the intervention costs are presented in Table 38 (see Table 26 for details).
Effectiveness of exercise referral schemes
Estimates of the effectiveness of ERS on PA levels were derived from the meta-analyses conducted in Chapter 3. These are reported in Table 39.
Estimates of the outcomes associated with physical activity
Tables 40–42 summarise the derivation of the outcomes associated with PA. Firstly, the probability of experiencing an outcome (CHD, stroke or type 2 diabetes) considered in the model is generated based on the earlier analysis conducted by NICE. 76 This is reported in Table 40.
| Inputs | Value | Data source |
|---|---|---|
| Probability of experiencing CHD when active | 0.014 | HSE (2006);123 NICE (2006)76 |
| Probability of experiencing CHD when sedentary | 0.027 | HSE (2006);123 NICE (2006)76 |
| Probability of experiencing stroke when active | 0.011 | HSE (2006);123 NICE (2006)76 |
| Probability of experiencing stroke when sedentary | 0.015 | HSE (2006);123 NICE (2006)76 |
| Probability of experiencing type 2 diabetes when active | 0.022 | HSE (2006);123 NICE (2006)76 |
| Probability of experiencing type 2 diabetes when sedentary | 0.044 | HSE (2006);123 NICE (2006)76 |
| Input | Value | Data source |
|---|---|---|
| Utility value of being in CHD state | 0.55 | NICE (2006)76 |
| Utility value of being in stroke state | 0.52 | NICE (2006)76 |
| Utility value of being in type 2 diabetes state | 0.7 | NICE (2006)76 |
| Utility value of being in a non-disease health state | 0.83 | NICE (2006)76 |
| Average age of cohort (in years) | 50 | HSE (2008)6 |
| Average age of mortality (in years) | 84 | ONS (2006–8)126 |
| Assumed average age at onset of a disease health state (in years) | 55 | NICE76 |
| Life-years remaining after onset of CHD | 18.41 | NICE (2006)76 |
| Life-years remaining after onset of stroke | 5.12 | NICE (2006)76 |
| Life-years remaining after onset of type 2 diabetes | 28.13 | NICE (2006)76 |
| Health state | Costs per person [2010 prices (£)] | QALYs per person |
|---|---|---|
| CHD | 17,728 | 9.94 |
| Stroke | 1965 | 5.15 |
| Type 2 diabetes | 50,309 | 14.18 |
| Sedentary (no CHD, stroke or type 2 diabetes) | – | 17.18 |
Estimates of the QALYs associated with each outcome in the model are derived by multiplying the utility of being in a particular health state with the life expectancy in that health state. Life expectancy is derived by assuming an average age at onset. Assumptions about the average age at onset of a health state and the utility of health states were derived from the model developed by NICE. 76 These are reported in Table 41.
The lifetime treatment costs/QALYs for an individual in each health state are summarised in Table 42. Among the conditions included in the model, type 2 diabetes incurred the largest treatment cost and stroke the least, although it should be noted that stroke was considered as an event, whereas other chronic outcomes were associated with ongoing treatment costs.
Estimating the cost-effectiveness of exercise referral schemes
Table 43 shows the estimated ICER of the base-case analyses using a cohort of 1000 individuals and a lifetime horizon. Total costs and outcomes are divided by the cohort size (1000) to generate per-person estimates of costs and benefits. The ICER was calculated with respect to the standard comparator ‘usual care’. Compared with usual care, ERS is marginally more expensive, with additional costs of £169.54, with an incremental QALY gain of 0.008 (i.e. eight QALYs gained in the total cohort). The base-case cost per QALY of ERS compared with usual care is £20,876. If adopting a willingness-to-pay threshold of £30,000, as used by NICE, these findings indicate a net health gain, and suggest that ERS is a cost-effective use of resources.
| Parameter | ERS | Usual care | Difference | Incremental cost (£) per QALY (ICER) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lifetime total health-care costs (£) per persona | 2491.78 | 2322.24 | 169.54 | 20,876.27 |
| Total QALYs per person | 16.743 | 16.735 | 0.008 |
Deterministic sensitivity analysis
Deterministic sensitivity analysis was carried out around parameters with known uncertainty. Sensitivity analyses conducted are summarised in Table 44. Table 45 shows the impact of the variation in parameter estimates (one-way analysis) on the cost-effectiveness of ERS. Assuming a less intensive ERS or more effective ERS resulted in an ICER below £30,000 and lower than the base case. On the other hand, including intervention costs to participants led to an ICER above £30,000, although a less effective ERS resulted in ERS being dominated by usual care (negative ICER) – i.e. ERS is more expensive and leads to loss of health gains.
| Parameters | Value | Data source | How data was adjusted for in the model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention costs to participants | £120a | Isaacs et al. (2007)61 | Costs of intervention varied from £222 to £342 (including costs to providers and participants) |
| Less intensive ERS | £110a | Isaacs et al. (2007)61 | Costs of intervention was varied from £222 to £110 |
| Effectiveness of ERS (based on lower limit of 95% CI) | 0.294 | Meta-analysis in Chapter 3 | Probability of becoming active after exposure to ERS was varied from 0.336 to 0.294 |
| Effectiveness of ERS (based on upper limit of 95% CI) | 0.371 | Meta-analysis in Chapter 3 | Probability of becoming active after exposure to ERS was varied from 0.336 to 0.371 |
| Parameter | Incremental cost per person (£) | Incremental effect per person (QALY) | ICER (£) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base-case assumptions | 169.54 | 0.008 | 20,876.27 |
| Intervention costs to participants | 289.54 | 0.008 | 35,652.46 |
| Less intensive ERS | 57.54 | 0.008 | 7085.16 |
| Effectiveness of ERS (based lower limit of 95% CI) | 226.04 | –0.001 | Dominateda |
| Effectiveness of ERS (based upper limit of 95% CI) | 122.46 | 0.015 | 7947.11 |
Further analyses were conducted which considered ‘best-case’ and ‘worst-case’ scenarios for ERS. These scenarios are summarised in Table 46. The findings of the analysis are presented in Table 47. In the worst-case scenario, ERS was dominated by the comparator. In the best-case scenario, the ICER fell to under £700 per QALY. These findings of the deterministic sensitivity analysis (excluding the dominated cases) are presented in the form of a tornado diagram (Figure 18) to illustrate the relative magnitude of effect of changing each of the parameter values or scenarios. Overall, the cost-effectiveness was found to be most sensitive to changes in the scenarios (best cases of cost and effectiveness).
| Scenarios | Description |
|---|---|
| Worst case | Worst-case cost (£342) and worst-case effectiveness (0.294) |
| Best case | Best-case cost (£110) and best-case effectiveness (0.371) |
| Interaction between worst and best cases |
(1) Best-case cost (£110) and worst-case effectiveness (0.294) (2) Worst-case cost (£342) and best-case effectiveness (0.371) |
| Scenarios | Incremental cost per person (£) | Incremental effect per person (QALY) | ICER (£) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base-case assumptions | 169.54 | 0.008 | 20,876.27 |
| Worst cases of cost and effectiveness | 346.04 | –0.001 | Dominateda |
| Best cases of cost and effectiveness | 10.46 | 0.015 | 678.82 |
| Worst-case cost and best-case effectiveness | 242.46 | 0.015 | 15,734.56 |
| Best-case cost and worst-case effectiveness | 114.04 | –0.001 | Dominateda |
FIGURE 18.
Impact of deterministic sensitivity analysis on base case ICER (£20,876.27).
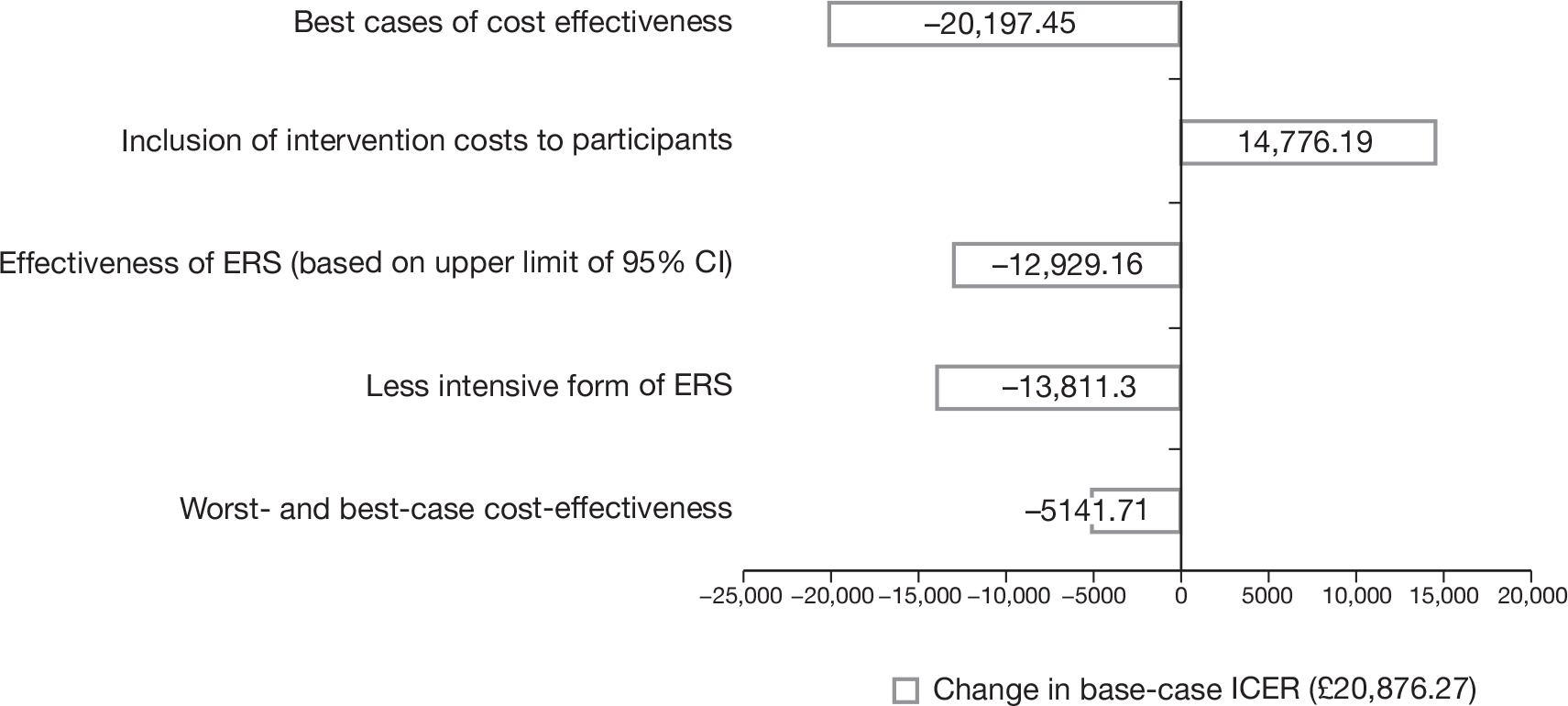
Probabilistic sensitivity analysis
Probabilistic sensitivity analysis, based on 10,000 simulations, was also conducted. A summary of the distributions adopted in the PSA is presented below in Table 48.
| Parameters | Mean | SE | Distribution | Alpha | Beta |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incremental probability to be active | 0.039 | 0.0039 | Beta | 96.061 | 2367.042 |
| Incremental probability to experience CHD | 0.013 | 0.0013 | Beta | 98.687 | 7492.621 |
| Incremental probability to experience stroke | 0.004 | 0.0004 | Beta | 99.596 | 24,799.4 |
| Incremental probability to experience diabetes | 0.022 | 0.0022 | Beta | 97.778 | 4346.677 |
| Treatment discounted cost of CHD | £17,728.03 | £1772.803 | Gamma | 100 | 177.2803 |
| Treatment discounted cost of stroke | £1965.165 | £196.5165 | Gamma | 100 | 19.65165 |
| Treatment discounted cost of diabetes | £50,309.43 | £5030.943 | Gamma | 100 | 503.0943 |
| Discounted QALY for CHD health state | 9.942348 | 0.994235 | Gamma | 100 | 0.099423 |
| Discounted QALY for stroke health state | 5.148217 | 0.514822 | Gamma | 100 | 0.051482 |
| Discounted QALY for type 2 diabetes health state | 14.18193 | 1.418193 | Gamma | 100 | 0.141819 |
| Cost of intervention | £222 | £37.9 | Gamma | 34.31054 | 6.470315 |
A scatterplot of the probabilistic findings, showing simulated estimates of cost difference against QALY difference between ERS and usual care, is provided in Figure 19. The scatterplot shows that all the simulations generated an improved effectiveness of ERS, but also a higher cost than usual care (i.e. all points were in the north-east quadrant of the cost-effectiveness plane). This reflects the relatively modest uncertainty around the cost of the intervention and assumptions about the distribution of uncertainty around the estimates of effect size.
FIGURE 19.
Cost-effectiveness plane showing the scatter plot of 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations for ERS compared with usual care.
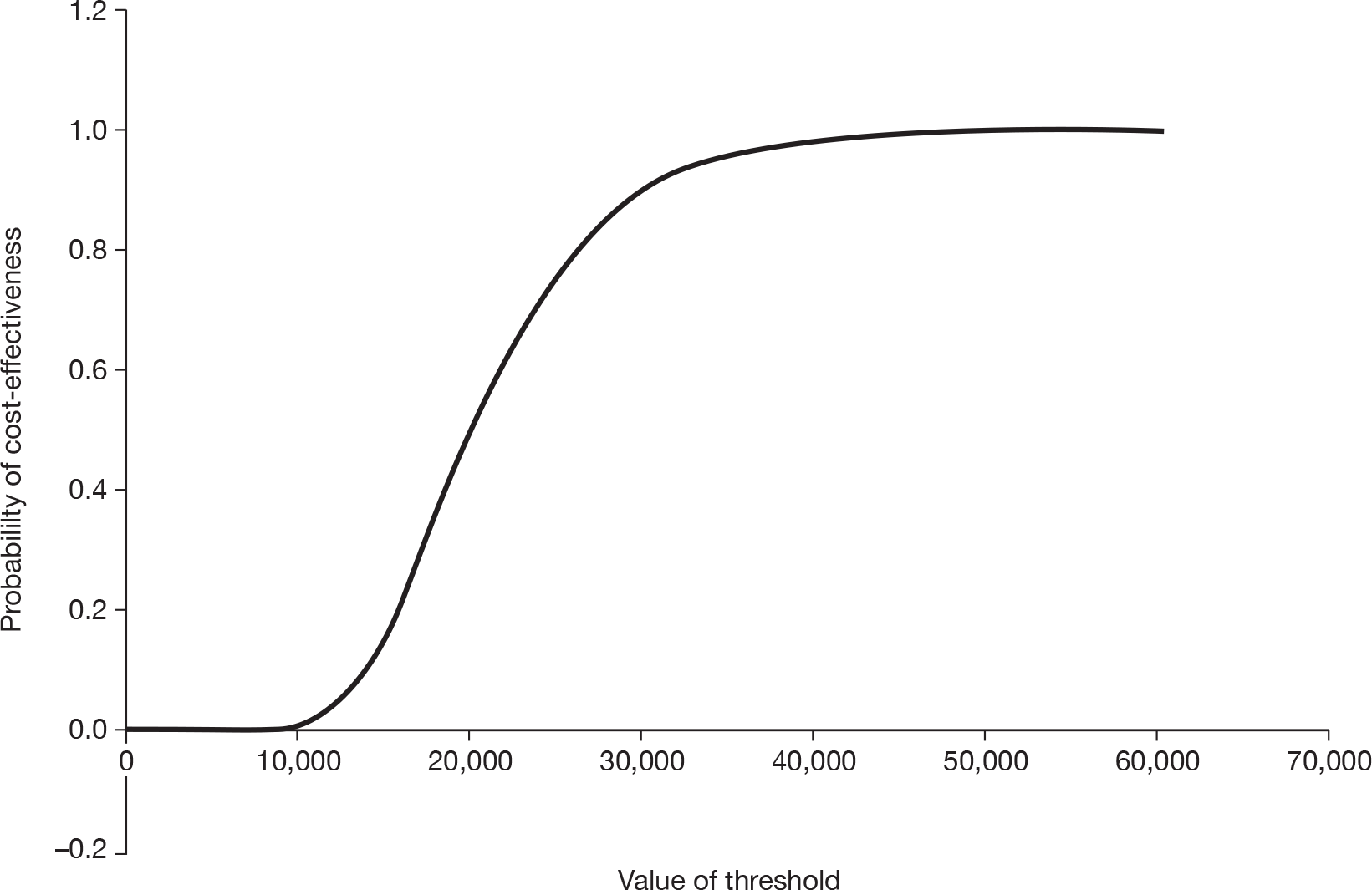
The decision as to whether or not these findings can be considered cost-effective depends on the maximum amount decision-makers are willing to spend to obtain an additional unit of effectiveness (in this case, a QALY). This can be best presented in the form of a cost-effectiveness acceptability curve, as presented in Figure 20. At a threshold of £20,000 there is a 0.508 probability that ERS is cost-effective. This increases to 0.879 when a threshold of £30,000 is considered.
FIGURE 20.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve showing the probability of cost-effectiveness for ERS at varying levels of threshold.
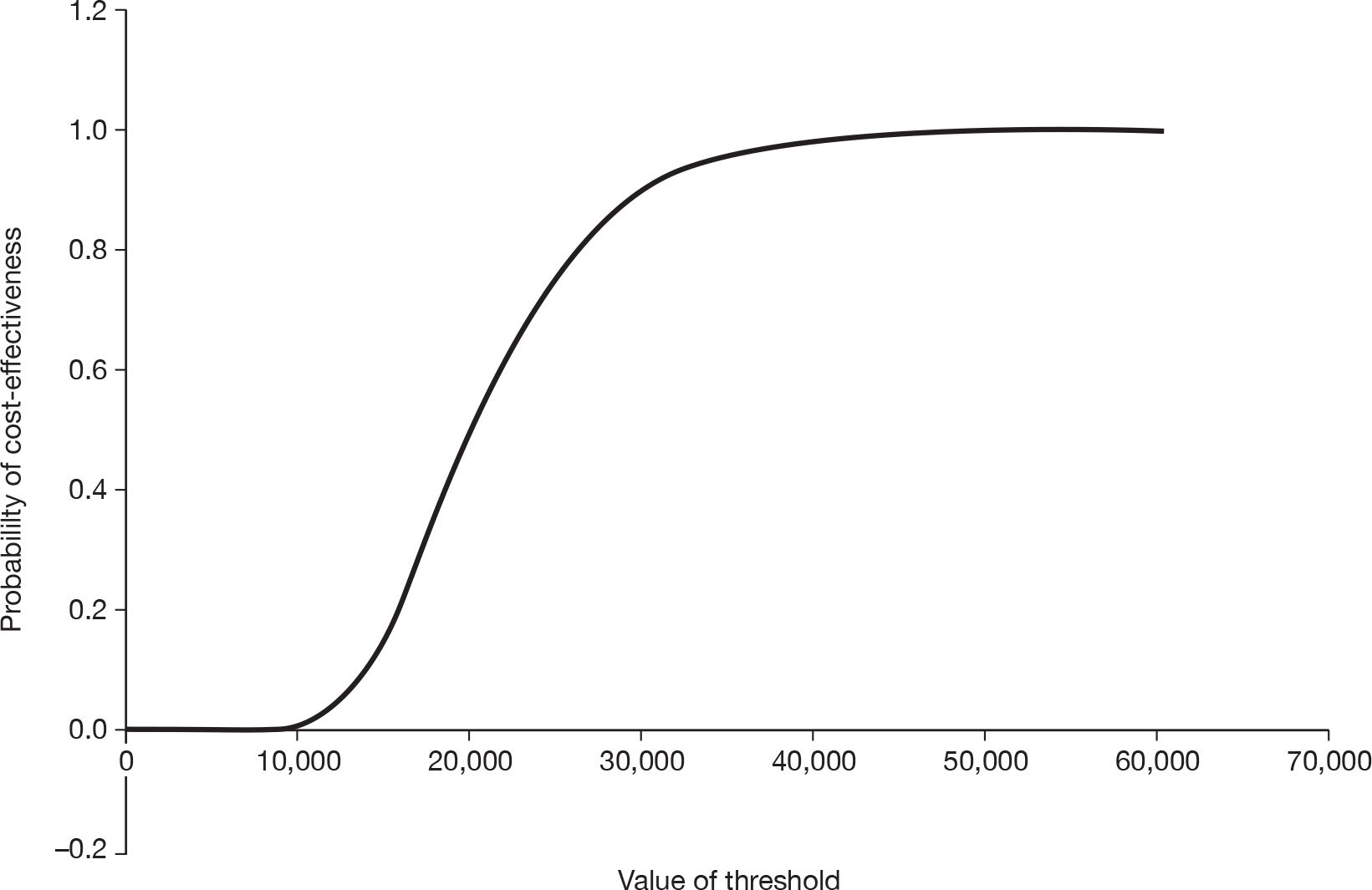
Subgroup analysis of exercise referral schemes in individuals with pre-existing conditions
The remit of this HTA report was to examine the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of ERS in individuals with a pre-existing condition. The cost-effectiveness evidence reviewed in Chapter 4 captured relatively little existing evidence on such individuals. Rather, ERS was used to mitigate against unhealthy behaviours or risk factors for future conditions.
The aim of this section is to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of ERS in people with a diagnosed condition known to benefit from PA. We focused on the top three conditions (Table 49) that have been found to benefit most from increases in PA (BHFNC34); obesity, hypertension and depression (see Appendix 1, Figure 21, for full list).
| Cohort | Inputs | Value | Data source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obese | Probability of experiencing CHD when active | 0.0259 | HSE (2006);123 Hu et al. (2005)127 |
| Probability of experiencing CHD when sedentary | 0.0376 | HSE (2006);123 Hu et al. (2005)127 | |
| Probability of experiencing stroke when active | 0.0259 | HSE (2006);123 Hu et al. (2005)127 | |
| Probability of experiencing stroke when sedentary | 0.0376 | HSE (2006);123 Hu et al. (2005)127 | |
| Probability of experiencing type 2 diabetes when active | 0.0756 | HSE (2006);123 Hu et al. (2004)128 | |
| Probability of experiencing type 2 diabetes when sedentary | 0.0986 | HSE (2006);123 Hu et al. (2004)128 | |
| Hypertensive | Probability of experiencing CHD when active | 0.060 | HSE (2006);123 Hu et al. (2007)129 |
| Probability of experiencing CHD when sedentary | 0.074 | HSE (2006);123 Hu et al. (2007)129 | |
| Probability of experiencing stroke when active | 0.060 | HSE (2006);123 Hu et al. (2007)129 | |
| Probability of experiencing stroke when sedentary | 0.074 | HSE (2006);123 Hu et al. (2007)129 | |
| Depressive | Probability of experiencing CHD when active | 0.0336 | HSE (2006);123 Surtees et al. (2008)130 |
| Probability of experiencing CHD when sedentary | 0.0801 | HSE (2006);123 Surtees et al. (2008)130 |
Methods for subgroup analysis in individuals with pre-existing conditions
The subgroup analysis is based on the use of the same framework for cost–utility analysis reported above. The model was adjusted to reflect differences in the underlying risk of developing each of the morbidities in the model (CHD, diabetes and stroke), according to the existence of a pre-existing condition. The values (Tables 38–42) of other parameters (i.e. efficacy of ERS/control, costs and utilities associated with health events) from the base-case model are assumed to hold for these cohorts. Analysis was run separately for each of the disease specific cohorts. Table 49 shows the data inputs and the data sources used for the probabilities of experiencing the health states in the respective cohorts. The sources for data were selected based on their relevance to our methodology (e.g. age and gender characteristics) given their methodological rigour. Calculation of these probabilities follows the approach in the base case. Data insufficiency precluded the fitting of different probabilities for all health states in all cohorts. In the absence of incidence data to generate the probabilities (e.g. CHD in the obese cohort), we used mortality data with the caveat that the probability of experiencing that health state was similar to the probability of death related to that condition. Also, in cases where data was observed for cardiovascular disease (in the obese and hypertensive cohorts) it was assumed that those probabilities hold for both stroke, and CHD.
Results
Table 50 presents the estimated ICER for the disease-specific cohorts. For each of the conditions considered, the ICER is lower than the base case, reflecting the increased likelihood of developing one of the morbidities considered in the model if the individual has a pre-existing condition. Compared with usual care, ERS in these cohorts remains more costly (albeit less so than in a general population cohort). In terms of effectiveness, ERS (compared with usual care) is more effective, leading to improved QALY gains that are higher than in the base case (ranging from 0.011 to 0.017). The cost per QALY of ERS compared with usual care is between £8414 and £14,618, and thus ERS can be considered cost-effective at the NICE threshold.
| Cohort | Incremental cost per person (£) | Incremental effect per person (QALY) | ICER (£) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obese | 167.89 | 0.011 | 14,618.21 |
| Hypertensive | 168.08 | 0.013 | 12,834.11 |
| Depressive | 146.72 | 0.017 | 8414.01 |
Summary of the cost–utility analysis
Our analysis attempts to estimate the cost-effectiveness of ERS using a cost–utility analysis framework similar to that used in previous analyses (NICE 200676). Our base-case assumptions result in a favourable cost-effectiveness ratio of £20,876 per QALY gained from ERS compared with usual care. It should be acknowledged that our base-case estimate includes some optimistic assumptions with respect to cost and effectiveness. However, our deterministic and PSAs suggest that there is a low possibility of the ICER increasing above £30,000 when these assumptions are relaxed.
Analysis of ERS in groups of individuals with pre-existing conditions suggests that it may be more cost-effective in these groups, than in a sedentary population. ERS is frequently prescribed to individuals with risk factors for CVD. Our subgroup analysis includes populations with obesity and hypertension to reflect these individuals. In these groups, the cost-effectiveness of ERS falls to around £11,000 per QALY. In a population with depression, ERS cost-effectiveness is more favourable, generating an ICER of approximately £8000. Given the higher risk of developing the long-term illnesses considered in the model in these groups, it is not surprising that the subgroup analyses produce more favourable ICERs. This is an encouraging finding and suggests that it might be possible to target ERS to individuals with pre-existing conditions in which the pay-offs/impact may be higher. However, there remain some major uncertainties over whether or not the evidence used to populate the model, derived from the meta-analysis, is applicable to these groups. There may be good reason to believe that uptake, adherence and effectiveness might differ according to the characteristics of the recipients. Although we have attempted to adjust the model to take into account differences in the rate of long-term illnesses, no data were identified as part of the effectiveness review to allow for adjustment of the effect of ERS in different populations. There is a pressing need for better primary evidence to inform these uncertainties.
Although our cost-effectiveness estimates suggest that ERS is a cost-effective use of NHS resources, it should be noted that the individual-level lifetime QALY gains are relatively modest (< 0.01 in our base-case analysis). This estimate is predicated on the evidence of effectiveness derived from the meta-analysis presented earlier in this report. We believe that the meta-analysis has provided the most robust estimate to date of the effectiveness of ERS compared with usual care. However, it should be acknowledged that the cost-effectiveness analysis is attempting to capture lifetime benefits based on evidence of relatively modest effect sizes derived from short-term studies. Any such analysis inevitably involves some assumptions about the degree to which behaviour change is lasting and fails to consider other health behaviours that may impact on long-term outcomes. The result is that the cost-effectiveness analysis estimates that ERS has a modest lifetime cost and a marginal lifetime QALY gain. Even small changes in the source data used to populate the model, particularly evidence of effect size and cost, may lead to significant changes in the resulting ICER. This can best be illustrated through consideration of the net benefit calculation. If we value each QALY gained at £30,000 and accept that our analysis is generating a lifetime QALY gain of approximately 0.008 in most cases, then the value of the benefits generated in monetary terms is approximately £240, which exceeds the cost of the intervention. However, even a modest change in the lifetime QALY gain, to 0.07, would result in the costs exceeding the benefits, making the cost-effectiveness of ERS questionable.
Although sensitivity analysis has sought to address this point, it should be acknowledged that, in many cases, source data were derived from a single study (e.g. cost data from Isaacs et al. 61) and it was necessary to fit distributions to parameters to allow for PSA. Although every effort has been made to explore uncertainty, there is a possibility that the uncertainty around parameter estimates may be greater than predicted within our analysis, which would have a material impact on the ICER.
Although some caution should be taken in interpreting the findings, the authors would wish to emphasise that the estimates of cost-effectiveness generated are believed to be conservative. Our approach generates a partial analysis that considers only the impact of ERS on a number of morbidities known to be associated with PA. The impact on other morbidities was excluded owing to limitations in the available evidence. On this basis, our estimates of cost-effectiveness should be regarded as conservative, as we have made no attempt to quantify these benefits within our analysis.
Limitations of the analysis
The analysis had a number of limitations which should be acknowledged. First, we examine only the long-term impact of PA on selected morbidities. It was not possible to include other morbidities that may be affected by PA owing to uncertainty over the relationship between PA, incidence and quality-adjusted life expectancy. Nor does our model account for potential negative outcomes of PA, such as injuries. Although this may be an important determinant in taking up PA, particularly in the elderly, the evidence on injuries suggests that they are rare (Munro et al. 48), and they are not expected to significantly affect results when considered at a population level. Another set of limitations include assumptions relating to constant and independent risk of experiencing disease health states and age at onset of disease. These assumptions were derived from the NICE 2006 report76 and were meant to allow our analysis to be comparable with previous research. Although we recognised that these assumptions are limiting, their impact on the ICER, when investigated through sensitivity analysis, was considered minimal.
A number of other weaknesses in the model design were identified which were prioritised for further analysis. These include:
-
the potential to capture the short-term improvements in QoL associated with PA (process benefits), which may be particularly important in certain groups, such as those who are prescribed PA for mental-health problems, such as depression
-
the wide range of health benefits associated with increases in PA, including mental health, cancer and musculoskeletal conditions, which are currently excluded from the analysis.
These points are addressed in the remaining sections of this chapter, first through further development of the cost–utility analysis and subsequently through the development of a cost–consequence framework that allows for consideration of other health and non-health costs and benefits that might be associated with ERS.
Further development of the cost–utility analysis to include short-term quality-adjusted life-year gains resulting from physical activity
The previous section highlighted the need to consider the short-term improvements in QoL (e.g. improved mental health) that might result from increased PA, as well as longer-term impacts on common conditions. A key step in achieving this is to estimate the HRQoL gain associated with increases in PA. This section seeks to address this point by first estimating the short-term QoL gain associated with PA using econometric models, and, second, incorporating the estimated QoL gains into the base-case model, reported above, to generate a revised ICER.
Participation in PA has been found to lead to enhanced QoL, an effect that is consistent across socioeconomic details. 131 Nonetheless, to date, economic evaluation of exercise interventions have rarely accounted for these QoL gains. A notable exception is Beale et al. ,84 who included QoL gains associated with a unit increase in PA and found a favourable impact on ICERS generated for environmental interventions to promote PA. Therefore, this section attempts to build on previous analyses by demonstrating the impact of the inclusion of QoL gains associated with an active state (via say ERS) on the cost-effectiveness of ERS.
Methods for further development of the cost–utility analysis to include short-term quality-adjusted life-year gains resulting from physical activity
Data
Data from HSE – 20086 have been used to conduct econometric analyses to explore and estimate the impact of PA on HRQoL. The HSE is a routine cross-sectional survey that draws a nationally representative sample of persons residing in private households in England. The sample and focus of the survey vary each year. Data from the 2008 survey were used in this study and included a sample of 9191 households with 15,102 adults aged 16 years or over, and a total child sample of 7521. This study draws on data for 5537 observations of 40- to 60-year-olds among the adult sample. Sampling was based on a multistage stratified random sampling design that uses the Postcode Address File as a sampling frame. The primary focus of HSE – 20086 was PA and fitness. The method of data collection involved the use of face-to-face interviews, self-completion questionnaires, clinical measurements and physical measurements (including objective measurements of PA via accelerometers). To compensate for seasonal variation in responses, the time period for interviews covered January to December 2008, with the fieldwork spanning from January 2008 to April 2009.
Health-related quality of life
Health-related quality of life is measured in the HSE survey using the EQ-5D, and the summary measure of HRQoL (or health–state utility value) derived from the EQ-5D. 132 These utility scores were generated using the descriptive system of the EQ-5D questionnaire (UK version), a standard HRQoL instrument with preference weights which are attached to combinations of responses. The EQ-5D descriptive system describes HRQoL in five dimensions (i.e. mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort and anxiety/depression), with each dimension including three levels: no problems, some/moderate problems, and severe/extreme problems. Different health states are created from the responses to the descriptive system of the EQ-5D by combining one level from each of the dimensions. A tariff is then applied to these health states to generate utility scores. 132 The utility scores usually range from ‘1’ (perfect health) to ‘0’ (death, with states that are perceived to be worse than death having a negative utility score).
Physical activity
As shown in Table 51, PA in the HSE – 20086 is measured/assessed via (1) specific activities – including walking and sports – and (2) a composite indicator – a combination of different types of PA (i.e. walking, housework, occupational activity and sports/exercise). The composite indicator was captured through either subjective (self-reports) or objective (accelerometers) measurements. Each of these activities is operationalised as a binary variable indicating being ‘physically active’ or not. The variable takes the value of 1 if PA (defined as a minimum of 90 minutes of at least moderate-intensive PA) was done per week, or defined as zero otherwise (not PA). This definition of ‘physically active’ is consistent with the approach in the literature on ERS (see Chapter 3), and was adopted to allow future modelling of the cost-effectiveness of ERS.
| Variable | Specification of variable |
|---|---|
| Walking |
1 = a minimum of 90 minutes of brisk walking per weeka 0 = otherwise |
| Sports and exercise |
1 = a minimum of 90 minutes of at least moderate-intensive sports and exercise activities per week 0 = otherwise |
| Objective measurement |
1 = a minimum of 90 minutes of at least moderate-intensive PA per week 0 = otherwise |
| Subjective measurement |
1 = a minimum of 90 minutes of at least moderate-intensive PA per week 0 = otherwise |
Control variables
A set of sociodemographic, economic, health and other variables that have been found in the literature to be correlates of HRQoL were considered as covariates. Table 52 lists these variables and a priori expectations about the direction of their correlation with HRQoL (see Appendix 7, Table 62, for references). In developing the expected signs, consideration was given to the methodology (e.g. the specification of the dependent variable and the control variable; the origin and characteristics of the sample) used by the studies reporting those findings.
| Variables | Expected sign |
|---|---|
| Age | – |
| Gender (female) | |
| Social class (high) | + |
| Education (high) | |
| Ethnicity (white) | – |
| Marital status (married) | ? |
| Income (high) | + |
| Employment status (employed) | |
| BMI (high) | – |
| House tenure (house owners) | + |
| Smokers (yes) | – |
| Drink alcohol (yes) | + |
| Morbidities (yes)a | – |
| Region of residence | ? |
| Psychosocial well-being (high) | – |
| Height (increased) | + |
| General health (favourable) | |
| Weight (increased) | – |
| Urbanisation (urban) | ? |
Methods of statistical analysis
Means [(standard deviation (SD)] and proportions were calculated for continuous and categorical data, respectively. The chi-squared and Fischer’s exact tests were used to check the association between the HRQoL (dependent variable) and dummy variables representing item non-response for independent variables in order to examine the mechanisms under which the missingness occurred (i.e. missing completely at random or not). 124 If the pattern of missingness did not occur completely at random, a regression-based imputation method was used to replace missing values of continuous variables and a dummy variable specifying item non-response added. For the categorical variables, item non-response was included in the omitted category and a dummy variable for item non-response created. 133
Tobit regression with upper censoring at 1.0 and robust SEs were used to model the relationship between HRQoL and indicators of PA controlling for potential confounders (covariates). Separate Tobit regressions were fitted for each of the indicators of PA to avoid unstable estimates resulting from the collinearity among those indicators. In each case, two models were used: (1) a model that excludes missing observations and (2) a model that includes missing observations. The models were estimated with sampling weights that were calculated as the inverse of the probability of being a respondent in a household multiplied by the household weight, which accounts for non-responding households. 134 Reduced models were derived for each of the regression models by identifying and removing independent variables that were not statistically significant via stepwise regression. Categories of significant categorical variables that were dropped by the stepwise regression were added back into the model, after which variables with the largest p-value (average p-value for categorical variables) were removed one by one, until the reduced model had only significant variables. The Wald test was used to test significance of variable/variables before their removal. 135
Specification errors and goodness-of-fit of regression models were examined using the linktest5,136 and penalised log-likelihood values via Akaike information criterion (AIC) and Bayesian information criteria (BIC),137 respectively. [The idea behind the linktest is that if a regression model is well specified, extra independent variables that are significant should be found by only chance. The linktest works by creating two variables (i.e. the variable of prediction and the variable of squared prediction), after which the model is fitted with these two variables. The null hypothesis is that there is no specification error. This is checked by looking at the statistical significance of the variable of squared prediction, which should not be a statistically significant predictor (at 5%) if the null hypothesis is to be accepted.] In addition, pseudo-R2 was computed by calculating the R2 between the predicted and observed values. 138 The existence of multicollinearity among independent variables was assessed to ascertain whether or not they lie within tolerance ranges. 139,140 [This was measured by indicators of variable inflated factor (VIF) (i.e. measures the amount of inflation of the SE that is caused by collinearity) and ‘tolerance’, which shows the amount of collinearity a regression model can tolerate. A tolerance value of 0.1 or less, and a VIF of 10 or more, shows a variable to be highly collinear and, hence, likely to provide imprecise estimates.] The threshold for statistical significance was set at ≤ 10% in all analyses. All analyses were undertaken using Stata version 10 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA).
Incorporation in the cost–utility analysis
To generate the ICER, the estimated QoL gain associated with PA is then included in the cost–utility model reported above. Where an individual becomes physically active (with or without ERS) they accrue an additional QALY gain. Given the absence of evidence on the duration of this QALY gain we take a conservative approach by assuming that it is a one-off gain that lasts for 1 year. Sensitivity analysis addresses the impact of this assumption on the cost-effectiveness of ERS by generating ICERs at varying levels of duration, which included 1 day, 1 week, 1 month, 6 months and lifetime.
Results
Description of sample
The mean EQ-5D for the sample was 0.86 (SD 0.23) and few had limiting illness (23.4%). The proportion of the sample that was ‘physically active’ ranged from 11.5% (via objective measurement) to 44.4% (via subjective measurement). The sample was predominantly white (90.8%), with the remaining 9% comprising those of mixed race, Asians, Chinese, Black people and those of other race, and had a mean (SD) age of 50 (6.2) years. Of the sample, 54.5% were female and most were married and living with their partners (66.3%), most had an educational qualification (80.8%) and most were in employment (76.1%). Few (25.6%) were classified as obese and smokers (21.8%), although the majority were ‘drinkers’ (84.9%). Further details are available in Appendix 7, Table 63.
Missing observations
The dependent variable (EQ-5D) had 84 missing observations (1.5%). All of the independent variables (except walking; sports and exercise; age; marital status; and region of residence and urbanisation) had missing observations (see Appendix 7, Table 63). Most variables had around 1% of data missing and PA (via objective measurement) had the highest proportion of missing observations (84%). The mean EQ-5D utility scores for individuals who had missing values for the following independent variables were statistically significantly different from those who did not: social class, BMI or smokers. The mean EQ-5D utility scores for proportion of individuals who had missing values for the indicators of PA were not, however, statistically different from those who did not.
Regression models
Table 53 shows the reduced regression models estimating the correlation between indicators of PA and HRQoL, controlling for covariates. Emphasis is placed on the models that exclude missing observations because they provide better fit and specification. Notably, results were similar across models with or without missing observations. Recall that separate models were fitted for each indicator of PA: model 1 (walking); model 2 (sports and exercises); model 3 (objective measurement); and model 4 (subjective measurement). Hereafter, the models will be referred to by these names.
| Independent variables | Dependent variable (HRQoL) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | |||||
| Coefficient | SEa | Coefficient | SEa | Coefficient | SEa | Coefficient | SEa | |
| Walking | ||||||||
| Active | 0.026* | 0.014 | ||||||
| Inactive (reference) | ||||||||
| Sports and exercise | ||||||||
| Active | 0.034** | 0.018 | ||||||
| Inactive (reference) | ||||||||
| Objective measurement | ||||||||
| Active | 0.072* | 0.044 | ||||||
| Inactive (reference) | ||||||||
| Subjective measurement | ||||||||
| Active | 0.047*** | 0.013 | ||||||
| Inactive (reference) | ||||||||
| Age | –0.004*** | 0.001 | –0.004*** | 0.001 | –0.004* | 0.002 | –0.004*** | 0.001 |
| Income | 1.03e-06*** | 2.12E-07 | 1.03e-06*** | 2.13E-07 | 9.41e-07*** | 2.52E-07 | ||
| Employment status | ||||||||
| Unemployed | –0.020 | 0.036 | 0.015 | 0.033 | –0.036 | 0.083 | –0.011 | 0.041 |
| Retired | 0.004 | 0.026 | 0.019 | 0.027 | –0.090 | 0.061 | 0.019 | 0.029 |
| Other economically inactive | –0.176*** | 0.016 | –0.133*** | 0.016 | –0.313*** | 0.043 | –0.180*** | 0.019 |
| Employed (reference) | ||||||||
| Education | ||||||||
| Higher education < degree | –0.049** | 0.022 | ||||||
| NVQ3/GCE ‘A’ level | –0.041* | 0.021 | ||||||
| NVQ2/GCE ‘O’ level | –0.031 | 0.019 | ||||||
| NVQ1/CSE other grade | 0.006 | 0.033 | ||||||
| Foreign/other | –0.149** | 0.061 | ||||||
| No qualification | –0.055** | 0.021 | ||||||
| NVQ4/NVQ5/degree (reference) | ||||||||
| Drink alcohol | ||||||||
| No | –0.077*** | 0.016 | –0.056*** | 0.016 | ||||
| Yes (reference) | ||||||||
| Musculoskeletal problems | ||||||||
| Yes | –0.322*** | 0.013 | –0.342*** | 0.015 | ||||
| No (reference) | ||||||||
| Psychosocial well-being | ||||||||
| Score 1–3 | –0.167*** | 0.013 | –0.149*** | 0.013 | –0.153*** | 0.016 | ||
| Score 4+ | –0.357*** | 0.015 | –0.324*** | 0.015 | –0.350*** | 0.018 | ||
| Score 0 (reference) | ||||||||
| Heart problems | ||||||||
| Yes | –0.041** | |||||||
| No (reference) | ||||||||
| BMI | ||||||||
| Normal (18.5–25) | –0.062 | 0.074 | –0.083 | 0.078 | ||||
| Overweight (25–30) | –0.103 | 0.074 | –0.118 | 0.078 | ||||
| Obese (30+) | –0.126* | 0.074 | –0.149* | 0.078 | ||||
| Underweight (< 18.5) (reference) | ||||||||
| Limiting illness | ||||||||
| Non-limiting | 0.226*** | 0.016 | ||||||
| No illness | 0.333*** | 0.013 | ||||||
| Limiting (reference) | ||||||||
| Urinary problems | ||||||||
| Yes | –0.256** | 0.109 | ||||||
| No (reference) | ||||||||
| Hypertensive | ||||||||
| Yes | –0.054*** | 0.016 | ||||||
| No (reference) | ||||||||
| Mental disorder | ||||||||
| Yes | –0.147*** | 0.029 | ||||||
| No (reference) | ||||||||
| Urbanisation | ||||||||
| Town/fringe | 0.100** | 0.053 | ||||||
| Village/hamlet/isolated dwelling | 0.120** | 0.048 | ||||||
| Urban (reference) | ||||||||
| Constant | 1.456*** | 0.09 | 1.159*** | 0.091 | 1.252*** | 0.12 | 1.393*** | 0.059 |
| No. of observations | 3957 | 3957 | 873 | 2859 | ||||
The results indicate that being ‘physically active’ through walking was statistically significantly associated with better HRQoL (0.026; p-value at 10%) compared with being inactive. Similarly, those who were reported to be ‘physically active’, defined as participation in sports and exercise (0.034), overall PA measured via objective indicators (0.072) or subjective indicators (0.047) were all found to have a statistically significant better HRQoL (p-value at 5–10%) than inactive individuals.
Other factors statistically significantly correlated with better HRQoL included high-income earners, having no/non-limiting illness, and residing in town/fringe or village/hamlet/isolated dwelling. Conversely, people with heart problems, musculoskeletal/mental/urinary/blood pressure problems and psychosocial well-being were likely to have worse HRQoL. Being relatively older, a ‘non-drinker’ of alcohol, economically inactive or obese also had a statistically significant association with worse HRQoL.
Model diagnostics
The specification error tests show that the models had good specification and that additional statistically significant regressors could be found only by chance (see Appendix 7, Table 64). The models’ estimates could be considered stable, as no sign of multicollinearity was found, with average variance inflation factors and tolerance levels at 1.2 and 0.8, respectively. A reasonable proportion (between 10% and 40%) of variation in HRQoL was explained by the models as indicated by the pseudo-R2-value. Model 3 seems to have the best fit, as it had the lowest AIC and BIC values.
Impact of short-term health gains on the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
Table 54 shows the estimated ICER following the inclusion of the short-term QALY gains in the base-case model. As expected, the inclusion of short-term QALY gains leads to lower ICERs for ERS. Compared with usual care, ERS is still more expensive, as it incurs additional costs of £169.54, but it is more effective, leading to QALY gains ranging from 0.009 to 0.011 per person. The cost per QALY of ERS compared with usual care is estimated to be between £15,513 and £18,559. This compares with the estimate from our base-case analysis, which excluded consideration of short-term benefits, of about £20,000. The results are, however, sensitive to the duration that the short-term QALY gains last (Table 55). Assuming they last for between 1 day and 1 month leads to insignificant improvements in the ICER, albeit at 6 months and lifetime durations there is a significant improvement in the ICER to < £6000 per QALY.
| Type of PA | Incremental cost per person (£) | Incremental effect per person (QALY) | ICER (£) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Walking | 169.54 | 0.009 | 18,559.01 |
| Sports and exercise | 169.54 | 0.009 | 17,946.10 |
| Objective measurement | 169.54 | 0.011 | 15,512.60 |
| Subjective measurement | 169.54 | 0.010 | 17,032.00 |
| Type of PA | ICER (£) (1 day) | ICER (£) (1 week) | ICER (£) (1 month) | ICER (£) (6 months) | ICER (£) (lifetime) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Walking | 20,869.13 | 20,826.26 | 20,661.29 | 19,649.56 | 5872.12 |
| Sports and exercise | 20,866.94 | 20,810.92 | 20,596.03 | 19,300.60 | 4084.56 |
| Objective measurement | 20,856.51 | 20,738.37 | 20,291.60 | 17,799.13 | 2157.26 |
| Subjective measurement | 20,863.37 | 20,786.05 | 20,490.86 | 18,759.23 | 3716.96 |
Summary
Results from our econometric analysis support the hypothesis that PA is associated with improved QoL, as measured by the EQ-5D. It is important to note, however, that the analysis in this chapter does not prove causality. In the case of the covariates, a priori expectations formulated, based on the literature with respect to their association with the HRQoL, were all met, hence, providing validity to the models. Further confidence can be drawn from the findings because all regression models had good specification and fit.
The inclusion of short-term QALY gains for individuals who are physically active resulted in reductions in the ICER for ERS, as expected. Assuming that the health gain associated with ERS lasts for 1 year, the base-case ICER is reduced by approximately £1500–4000. If we assume that these ‘feel-good’ benefits resulting from PA are sustained if an individual remains active over the course of his or her lifetime then the ICER falls significantly to < £5000. These benefits have been referred to as short-term benefits in the current analysis to distinguish them from the longer-term impacts of PA on the development of ill-health. However, they might better be regarded as process benefits that arise from the process of engaging in PA. The degree to which the process benefits resulting from PA are lasting is an issue that warrants further exploration. ERS based on composite measure of PA appears to be associated with the greatest short-term health gain and thus the lowest ICER and walking-based ERS the highest. Further studies are needed to examine how long these short-term QALY gains last, as that is critical to its impact on ICER.
Cost–consequence analysis
In addition to the development of the cost–utility analysis, we also sought to develop a cost–consequence analysis of ERS. This was an attempt to acknowledge that ERS and PA more generally might impact on a number of conditions not considered within the cost–utility analysis because of data constraints. In many cases, these impacts relate to an association between PA and an outcome that has not been shown to be causal or has not been adequately quantified to allow for it to be included in the cost–utility analysis. An attempt was made to capture both positive and negative outcomes of ERS that were excluded from the cost–utility analysis. A cost–consequence approach allows these issues to be explored although acknowledges that in many cases the effect cannot be quantified and no attempt is made to generate a single composite end point (such as a QALY or a cost–benefit ratio).
Methods for cost–consequence analysis
The analysis was conducted from a partial societal perspective, including health- and non-health-care costs and benefits. The intervention and its cost remain unchanged from the cost–utility analysis. However, attempts were made to identify a broader range of benefits and disbenefits that might be associated with ERS and PA more generally. The evidence incorporated into the cost–consequence analysis was derived from the base-case model and the literature reviews conducted as part of this assessment.
Outcomes are presented as a synthesis of the available evidence. Wherever possible, attempts are made to quantify the effects of ERS on the outcome under consideration. For example, based on our cost–utility analysis, it is possible to provide an indication of how many strokes might be avoided as a result of increased participation in ERS. Where quantified outcomes are possible, these are expressed as the number of events per 100,000 population.
However, in many cases it is only possible to indicate the direction of change that might be achieved through increased PA, not the magnitude of effect. As such, outcomes are ultimately presented in a disaggregated fashion.
Results
Impacts of exercise referral schemes/physical activity
Table 56 presents the costs and benefits identified in the cost–consequence analysis and their sources of data. The identification of the benefits of ERS was primarily based on the key conditions where PA has been shown to be beneficial (see Table 1).
| Measures in analysis | Data source | Methodology of studya |
|---|---|---|
| Costs | ||
| Intervention cost to providers | Base-case model | – |
| Intervention cost to participants | Base-case model | – |
| Benefits | ||
| Physically active state | Base-case model | – |
| Full health state | Base-case model | – |
| Mental health | ||
| Anxiety | Conn141 | A meta-analysis that used data synthesised across 3289 adult participants (mean age ranged from 21 to 71 years) from 15 studies based on interventions designed to increase PA delivered to healthy adults without anxiety disorders |
| Depression | Craft and Perna142 | A meta-analysis that converted the overall effect sizes of three meta-analyses (which included 37 studies investigating the effect of PA on depression) to a binomial effect size |
| Metabolic | ||
| Diabetes | Boule et al.143 base-case model | A meta-analysis of 14 controlled studies (11 RCT; findings did not differ according to study design) with synthesised data from 504 type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with mean age of 55.0 (7.2) years; 50% of participants were women. Studies, which examined the impact of PA on diabetes, covered different ethnicities (Northern Europeans, Southern Europeans, black people, Asian, Middle Easterners), age groups and medication status (no medication, oral hypoglycaemic agents, insulin therapy) |
| Cancer | ||
| Colon cancer | Lee144 | A narrative systematic review using data sourced from 50 published epidemiological studies that had investigated the relationship between PA and the risk of developing cancer. Studies were conducted in North America, Europe, Asia, Australia and New Zealand |
| Breast cancer | Lee144 | Same as previous |
| Lung cancer | ||
| Cardiovascular | ||
| Hypertension | Whelton et al.145 | A meta-analysis of 54 RCTs (covering 2419 participants) that examined the impact of PA on hypertension. Studies were mainly Europe based. Sample covered both hypertensives and normotensives, diverse ethnic groups, and had a mean age of between 21 and 79 years |
| CHD | Taylor et al.146 base-case model | A meta-analysis of 48 trials (covering 8940 participants who had CHD) that had observed the impact of PA on CHD. Mean age of participants was 48–71 years. Studies originated from Europe, North American and Asia/Australia |
| Stroke | Base-case model | – |
| Musculoskeletal | ||
| Osteoporosis | Moayyeri147 | A meta-analysis of 13 prospective cohort studies showing association between PA and hip fracture is presented. The cohort was aged between 40 and 93 years |
| Osteoarthritis | Roddy et al.148 | A systematic review of 13 RCTs showing the impact of PA on pain and disability among patients with knee osteoarthritis. Patients in the aerobic walking trials had mean age of 62 and 74 years |
| Low back pain | Hayden et al.149 | A meta-analysis of 61 RCTs (6390 participants) evaluating exercise therapy for adult non-specific low back pain. Mean age of participants was 41 years |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Baillet et al.150 | A meta analysis of 14 RCTs (including 1040 patients). Patients were between 44 and 68 years. Age, disease duration, sex ratio, proportion of completers was same among the two groups. Studies originated from Europe, USA and Canada |
| Falls prevention | Chang et al.151 | A meta-analysis of 13 RCTs of participants who were 60 years and over |
| Absenteeism at work | Conn et al.152 | A meta-analysis of worksite PA interventions with 38,231 participants (138 reports) |
| Disbenefits | ||
| Injury | Hootman et al.153 | A study that investigated the relationship between PA and musculoskeletal injury using longitudinal data for those ≥ 20 years old |
| Disability | Lamb et al.154 | A cross-sectional analysis of 769 older women (mean age 77.8, range 65–101 years) with physical disability but no severe cognitive impairment |
The majority of the evidence identified suggested that PA could have a positive impact on health outcomes. Excluding the three health outcomes already considered in the cost–utility analysis, our searches identified evidence of an association between PA and improved outcomes in musculoskeletal disease, cancers and mental health. Non-health benefits and disbenefits were also identified. These suggest that ERS might have a positive impact on absenteeism, although it might also induce some injuries that have a countering effect. Relatively few disbenefits were identified within our searches.
Cost–consequence analysis
Table 57 shows the outcomes for ERS. The results are presented as incremental costs and outcomes attributable to ERS (compared with usual care).
| Measures in analysis | Potential impact of ERS on measures |
|---|---|
| Costs | |
| Intervention cost to providers | £22,200,000 (2010 prices) |
| Intervention cost to participants | £12,000,000 (2010 prices) |
| Benefits | |
| Physically active state | 3900 additional physically active people |
| Non-disease health state | 152 extra people in non-disease health state |
| Mental health | |
| Anxiety | Reduced anxiety in participants with the magnitude of the effect size being 0.219 |
| Depression | Increased the success rate to 67–74% reduction in depressive symptoms |
| Metabolic | |
| Diabetes |
Avoided 86 extra cases of type 2 diabetes Led to small but significant reduction in HbA1c (0.7%). This amount is likely to reduce diabetes complications |
| Cancer | |
| Colon cancer | A 30–40% reduction in the risk of developing colon cancer |
| Breast cancer | A 20–30% reduction in the risk of developing breast cancer |
| Lung cancer | A 20% reduction in the risk of developing lung cancer |
| Cardiovascular | |
| Hypertension |
Decreased SBP by 3.8 mmHg and DBP by 2.6 mmHg in sample of both hypertensives and normotensives In hypertensives, SBP was reduced by 4.94 mmHg and DBP by 3.73 mmHg In normotensives, SBP was reduced by 4.04 mmHg and DBP by 2.33 mmHg |
| CHD |
Avoided 51 extra cases of CHD Reduced all-cause mortality (OR 0.80; 95% CI 0.68 to 0.93) and cardiac mortality (OR 0.74; 95% CI 0.61 to 0.96) |
| Stroke | Avoided 16 extra cases of stroke |
| Musculoskeletal | |
| Osteoporosis | A hip fracture risk reduction of 45% (95% CI 31% to 56%) and 38% (95% CI 31% to 44%), respectively, among men and women |
| Osteoarthritis |
Pooled effect sizes for pain were between 0.39 and 0.52 For self-reported disability, pooled effect sizes ranged from 0.32 and 0.46 |
| Low back pain | Pooled mean improvement (measured on a scale of 100 points) was 7.3 points (95% CI 3.7 to 10.9 points) for pain and 2.5 points (95% CI 1.0 to 3.9 points) for function |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Improved function by 0.24 and pain by 0.31 |
| Falls prevention | Beneficial effect on the risk of falls (adjusted risk ratio 0.86, 0.75 to 0.99) |
| Absenteeism at work | Lower absenteeism at work (effect size = 0.19) |
| Disbenefits | |
| Injury | Increased the risk of musculoskeletal injury by about four times |
| Disability | Walking (more than three city blocks) increased the risk of walking disability because of severe pain (OR = 4.1–5.0) |
In an attempt to present meaningful, population-level outcomes, the analysis considers a cohort of 100,000 individuals who might be eligible for ERS. The cost of ERS for this cohort is estimated to be £22M (2010 prices) to the health-care provider and £12M (2010 prices) to the participants, generating a total cost of £33M. This is based on a leisure centre-based intervention as defined in the cost–utility analysis.
The benefits of ERS, compared with a no active intervention comparator, are summarised below. These include an additional 3900 (3.9%) people becoming physically active, 51 cases of CHD avoided, 16 cases of stroke avoided, 86 cases of diabetes avoided, 152 additional people in health states devoid of illnesses (CHD, stroke and diabetes) and resulting in an expected gain of approximately 800 QALYs. If we assume that each QALY is valued at £30,000 then this generates a positive net benefit of approximately £2M (£24–22M) from a health service perspective and a negative net benefit of approximately £9M from a societal perspective (£24–33M).
In addition to the quantifiable benefits, ERS is also expected to have a positive effect on the prevention or/and management of mental health, metabolic disease, cancer and musculoskeletal conditions. It also had an impact on non-health benefits, leading to an improvement in productivity through a reduction in absenteeism at work. There are potential adverse affects in terms of injuries and pain which are considered rare,48,61 but could still negate some of the positive impacts of ERS.
Summary of cost–consequence analysis
Our cost–utility analysis found ERS to be a cost-effective intervention. The cost-effectiveness was further improved when short-term benefits in QoL were considered and ERS was targeted at individuals with pre-existing conditions. However, it is recognised that the cost–utility analysis failed to take into account a range of costs, benefits and disbenefits associated with ERS.
The cost–consequence analysis presented above attempts to take into account some of the broader impacts of ERS. In addition to reducing rates of CHD, stroke and diabetes, the evidence also suggests that ERS has the potential to reduce the incidence or severity of a number of other conditions. Although it has not proven possible to estimate the costs and benefits (in terms of QALYs) associated with these conditions, the majority of the evidence reviewed suggests that ERS may have a favourable effect on a number of other health outcomes. In addition to this, there is evidence that ERS may lead to non-health benefits, notably an improvement in productivity.
The only major disbenefit associated with ERS is an increased risk of injury, although this is relatively modest and likely to have only a marginal effect on its cost-effectiveness. However, it could be that there is some degree of publication bias in the evidence identified as the majority indicated positive effects of ERS with relatively few, suggesting that there were any negative effects for participants.
The cost–consequence analysis was conducted as a means of presenting the economic findings generated herein in a manner that might be more easily digested by a broader group of stakeholders. By providing disaggregated benefits, for example in the form of the number of cases strokes avoided per 100,000 population, it is hoped that this makes the outcomes of ERS more easily understood. However, it should be noted that the cost–consequence analysis was entirely based on the cost–utility analysis and literature reviews presented herein. No attempt was made to undertake a systematic review of the literature to identify further evidence on the impacts of ERS and it might be that some evidence has been overlooked.
The findings of the cost–consequence analysis support our hypothesis that the cost-effectiveness estimates generated by our cost–utility analysis are conservative. A more holistic analysis, taking into account the broader range of benefits associated with ERS, is likely to lead to much improved cost-effectiveness ratios compared with those presented earlier in this report. However, there is a pressing need to generate further evidence on both the short- and longer-term impacts of ERS to better determine whether or not it is a cost-effective use of health-care resources.
Comparisons with previous research findings
Previous studies have tended to conclude that ERS is a cost-effective use of resources, although they too have highlighted the uncertainty around many of the estimates of effect and cost-effectiveness. Isaacs et al. 61 generated an ICER in the form of the incremental cost per unit change in SF-36 score and concluded that, in comparison with controls, ERS led to an incremental cost of £19,500 per unit change in SF-36 score at 6-month follow-up. Given the outcome measure adopted in the study comparison with our own findings is impossible, although it should be noted that this study also found only a modest change in health status.
In contrast, the study by Gusi et al. 70 showed that ERS resulted in an incremental QALY gain of 0.132 over a 6-month period as measured by change in the EQ-5D, at an incremental cost of €41 per participant, generating an ICER of €311/QALY. The individuals in this study were obese and/or depressed and the findings may provide further evidence to suggest that PA can have process benefits far greater than those suggested by our own analysis. However, no attempt was made to ascertain whether or not the benefits might be sustained beyond the study period.
The findings in NICE76 showed that ERS compared with controls led to an incremental cost per person of £25.10 and a lifetime QALY gain of 0.31 per person, equating to an incremental cost per QALY of £80.96. We are inclined to relate our findings more directly to NICE76 because of similarities in the methods used in both studies. For example, the model used in our study was based on NICE. 76
The analysis conducted for NICE showed a greater QALY gain than our own findings. This might be partially explained by the inclusion of colon cancer as an additional outcome in the NICE model. In addition to this, the NICE model adopted higher estimates of the effectiveness of ERS than our analysis (RR of becoming active of 1.60 vs 1.11 herein) and there are differences in the handling of uptake and adherence between the two analyses. Coupled with a lower estimated cost of ERS, this resulted in the NICE analysis generating improved ICERs compared with our own findings. In testing our own model we sought to reproduce the findings of the NICE model by incorporating the improved effectiveness of ERS. Despite slight differences in the modelling approach, it produced relatively consistent findings. Although we have based our approach to modelling the cost-effectiveness of ERS on the original NICE work, we believe that our meta-analysis of effectiveness has resulted in more robust input data and ultimately more accurate estimates of the cost-effectiveness of ERS.
Summary
-
The cost–utility analysis presented herein was an attempt to adhere to best practice principles in economic evaluation119 and also replicate the methods adopted in previous research. 76
-
Using this method our base-case analysis in a sedentary individuals aged 40–60 years shows an indicative ICER for ERS versus usual care of £20,876/QALY. This result was sensitive to changes in key input parameters, particularly the estimate of effectiveness of ERS (change in PA) sourced from our systematic review. There was a 51% probability that ERS was cost-effective at £20,000/QALY and 88% probability that ERS was cost-effective at £30,000/QALY.
-
Further developments of this model to incorporate short-term benefits in HRQoL associated with ERS reduced the base-case ICER somewhat to £17,032 to £18,559/QALY.
-
The cost-effectiveness of ERS appeared to be improved in disease-specific subgroups compared with base case, i.e. obesity £14,618/QALY, hypertension £12,834/QALY, and depression £8414/QALY.
-
The cost–consequence analysis presented above is an attempt to support this hypothesis and reports further benefits of ERS that could not be incorporated into the cost–utility analysis, although, had they been included, they would almost certainly have further improved the cost-effectiveness of ERS.
-
The previous sections include some lengthy discussion about the limitations of the approaches adopted, in particular the use of decision-analytic modelling and cost–utility analysis to model ERS. ERS involves a complex process, from the point at which an individual is ‘prescribed’ ERS, to the point at which he or she accesses the service and then the degree to which he or she adheres in the programme and beyond. Interventions of this sort, which comprise behaviour change, are difficult to simplify into standard economic evaluation frameworks, and this is exemplified by the analyses presented herein, which include a significant number of assumptions (some of which could fairly be described as heroic) and are partial, capturing only some of the costs and benefits of ERS.
-
Consideration needs to be given to the trade-off between developing a simple model (as we have done here) which can be populated and acknowledges its limitations versus a more complex model which may be a better representation of reality but can only be partially populated, which might result in even greater uncertainty. In both cases, the fundamental issue that needs to be addressed is improvements in the source data on the effectiveness of ERS, including evidence on long-term outcomes.
Chapter 7 Discussion
Statement of principal findings
Systematic review of exercise referral scheme effectiveness
In total seven27,28,50,61,68–70 RCTs (3030 participants) met the review inclusion criteria. Five RCTs compared ERS with usual care (e.g. PA advice),27,28,50,61,70 two RCTS compared an alternative PA-promoting strategy (i.e. walking programme or PA counselling)61,69 with usual care and one RCT compared an alternative form of ERS (i.e. ERS plus SDT intervention) with usual care. 68 Although these trials were all judged to meet our definition of ERS (i.e. a referral from a primary health-care professional to an individualised exercise programme designed to meet the needs of the participant) there was considerable heterogeneity in the nature of the exercise/PA intervention across studies. Studies recruited predominantly sedentary middle-aged adults who had evidence of at least one lifestyle risk factor and five of the studies also included individuals with a medical diagnosis (e.g. hypertension, depression). ERS usually took place at a leisure centre and involved 10–12 weeks of exercise intervention and where there was follow-up it took place at 6 and/or 12 months post randomisation. Studies were judged to have a moderate or low overall risk of bias.
The most consistently reported outcome was self-reported PA. In ITT analysis, compared with usual care, there was weak evidence of an increase in the number of ERS participants who achieved 90–150 minutes of at least moderate-intensity PA per week at 6–12 months’ follow-up (pooled RR 1.11, 95% CI 0.99 to 1.25). There was no difference in PA between ERS versus alternative PA promotion interventions or ERS versus ERS plus SDT at 6–12 months’ follow-up. We found no evidence to support differences across subgroups (e.g. age, gender) in terms of the impact of ERS on PA. There was no consistent evidence for a difference between ERS and any of the comparator groups in the duration of moderate/vigorous intensity and total PA, physical fitness, blood pressure, serum lipids, glycaemic control, obesity indices (body weight, BMI, percentage fat), respiratory function, psychological well-being (perception of self-worth, or symptoms of depression or anxiety) or HRQoL. None of the included trials separately reported outcomes in individuals with medical diagnoses.
Systematic review of predictors of uptake and adherence to exercise referral schemes
We found considerable variation across studies in the level of uptake (i.e. attendance at the first induction visit) and adherence to ERS (i.e. completion of the programme) across the 19 included studies (14 observational studies and five RCTs).Uptake levels were higher, on average, in RCTs than in observational studies, although there was no clear difference in adherence between the two. In bivariate and multivariate analyses, women and older people were more likely to take up ERS. In addition, although older people were also more likely to adhere, women were less likely to adhere than men. Very few studies reported associations between ERS uptake or adherence and participant psychosocial factors or programme-level predictors. However, most qualitative studies found a perception of a range of several short-term physical and psychosocial benefits associated with ERS. As the interviews largely involved females, less is known about these perceptions in males. Less favourable aspects of ERS involved limited involvement from the referrer (e.g. GP), and selected experiences at the exercise facility. However, there were also many positive comments on how the ERS served to initiate an exercise programme. Few qualitative studies attempted to identify if and how an ERS contributes to a sustainable physically active lifestyle beyond the usual 10- to 12-week facility-based programme.
Systematic review of exercise referral scheme cost-effectiveness
Four economic evaluations that assessed the cost-effectiveness of ERS were identified: three trial-based economic evaluations50,61,70 and a model-based analysis. 76 Given the limitations (inclusion of studies providing an effectiveness estimate not meeting our definition of ERS; non-UK; lack of cost per QALY estimates) in these previous analyses we undertook a de novo model-based economic evaluation. Indicative incremental cost per QALY estimates for ERS for various scenarios have been provided. Compared with usual care, the base-case ICER for ERS was £20,876/QALY in sedentary individuals with at least one lifestyle risk factor and £14,618/QALY in sedentary obese individuals, £12,834/QALY in sedentary hypertensives and £8414/QALY for sedentary individuals with depression. These ICERs were highly sensitive to plausible variations in the RR for change in PA and cost of ERS. Allowing for short-term gains in QoL associated with ERS resulted in small reductions (£1500–£3000/QALY) in the ICER compared with the base case, although these findings were sensitive to the duration of any short-term benefits.
Strengths and limitations of the assessment
Exercise referral scheme clinical effectiveness
We undertook a comprehensive and systematic review of the literature for the clinical effectiveness of ERS. This systematic review was restricted to controlled trials, to provide a high level of evidence for ERS clinical effectiveness. Unlike some previous systematic reviews in this field,35,39,41 we carefully selected ERS studies on the basis that there was clear evidence of referral by a primary-care health professional to third-party exercise provider. A central tenet of the ERS intervention is the referral process itself and that is potentially a key motivator and driver for individuals to take up and adhere to exercise interventions. 22 Qualitative studies in the present review also highlighted the importance of the GP in promoting a more active lifestyle. Although this resulted in the exclusion of a number of primary care-based exercise intervention studies [e.g. Elley (‘green prescription’),29,78 Lamb et al. ,58 Harland et al. ,43 Munro et al. 82], we believe this focus to be consistent with the decision problem of this report.
Predictors of exercise referral scheme uptake and adherence
We extended the scope of this report to undertake a review of quantitative and qualitative literature so as to better understand the potential predictors and drivers of ERS uptake and adherence. Although this review incorporated trial, observational and qualitative evidence, it was not fully systematic in that it was limited to studies primarily identified by our electronic searches for effectiveness studies. Furthermore, we did not incorporate formal methods of qualitative synthesis such as meta-ethnography.
Exercise referral scheme cost-effectiveness
A particular strength of our cost-effectiveness analysis was the further development of the economic model used in the NICE evaluation of primary care-based exercise interventions. 76 These further developments included the incorporation of epidemiological data linking PA and the future risk of clinical outcomes (i.e. CHD, stroke, diabetes) in specific medical diagnoses groups (i.e. obesity, hypertension, depression), consideration of short-term gains in HRQoL associated with increased PA, and PSA. Additionally, model effectiveness estimates were based on meta-analysis, in contrast to the previous NICE modelling analysis, which selected effectiveness estimates from specific individual trials.
Two principal limitations of our economic analysis were the dearth of information for a number of key model inputs (detailed in the next section) and the fact that differences in QALYs were often very small, leading to instability of the ICERs. Furthermore, for the purposes of generating a cost per QALY for medical diagnostic groups, we assumed the same benefit in terms of PA gains in those populations as sedentary ‘at-risk’ individuals.
Uncertainties
Exercise referral scheme clinical effectiveness
Although we have identified seven RCTs that recruited some 1400 ERS participants, because of limitations and gaps in this evidence base there remain at least four key uncertainties regarding the clinical effectiveness of ERS. These include (1) the impact of ERS in people with a medical diagnosis; (2) whether ERS consistently affects prognostic outcomes such as blood pressure and serum lipids; (3) whether the small increases in self-reported PA are clinically significant; and (4) whether these small short-term gains in activity are maintained in the longer term.
Exercise referral scheme cost-effectiveness
Evidence on the cost-effectiveness of ERS needs to be interpreted with some caution. Although the ICERs are relatively favourable, these are derived from findings that show small differences in costs and effects, with effectiveness data that suggest that ERS has a modest effect on QALY gains (typically < 0.01 in our analyses). Sensitivity analyses show that the cost per QALY associated with ERS can change markedly with plausible changes in model input values, which means that robust evidence on whether or not ERS are likely to be cost-effective cannot currently be provided. The cost-effective ratios reported should be treated with caution until more robust effectiveness data become available.
Interventions which involve complex behaviour change components are not well suited to decision-analytic models. Individual-level simulation models that can detect changes in individual behaviours over time may better address questions over the cost-effectiveness of ERS interventions. However, there will be a trade-off between developing a simple model (as in this review) which can be populated and acknowledges its limitations versus a more complex model that may be a better representation of reality but can be only partially populated and may result in greater uncertainty. In both cases, the fundamental issue that needs to be addressed is improvements in the source data on the effectiveness of ERS.
Chapter 8 Conclusions
Implications for service provisions
In 2006, NICE commented that there is insufficient evidence for ERS and recommended that the NHS should make ERS available only as part of a controlled trial. Although we have identified four additional trials since the NICE review, there remains very limited support for the potential role of ERS for impacting on PA and, consequently, public health. Arguably, such an uncertain impact provides a case for the disinvestment in ERS. However, we found little evidence of how the ERS intervention sought to develop a sustainable active lifestyle in participants, as recommended in the NHS NQAF. Although ERS programmes in our review aimed to increase medium- to long-term PA, they were typically based on only a 10- to 12-week leisure centre-based period intervention. With the exception of one trial (by Jolly et al. 68), there was minimal reference to health behaviour change techniques and theories that typically underpin interventions to promote an increase in daily PA.
Suggested research priorities*
In 2006, NICE35 recommended that ERS should only be part of controlled research studies in order to better determine its clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness. Sowden and Raine33 argue that (formal) evaluation of ERS is no longer a realistic possibility, due to the comprehensive coverage of schemes, widespread assumptions of effectiveness, likely difficulties in obtaining research funding, and indirect adverse consequences of dismantling schemes. Although this may potentially be the case for sedentary populations, there is still scope for an evidence base in diagnostic populations.
Although we have shown that additional RCT evidence has been produced since NICE made its recommendations, we have identified a number of gaps in the evidence base for ERS, some of which may require further trial-based evaluations:
-
RCTs assessing the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of ERS in disease groups that might benefit from PA. In addition, RCTs should seek to incorporate hard-to-reach populations (e.g. ethnic minorities) that are traditionally not represented in trials.
-
Such RCTs should be better reported, include long-term data on the effectiveness of ERS and the sustainability of PA change, incorporate objective measures of PA (e.g. accelerometers) and health outcomes (e.g. blood pressure, serum lipids) and incorporate parallel process evaluations to better understand the mediators and barriers to behaviour change.
-
Exercise referral scheme programmes vary in their procedures and this may impact on uptake and adherence. Future trials should therefore be designed to better understand the contribution of different programme components (e.g. level of staff training) to the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of ERS.
-
Head-to-head RCTs comparing the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of different models of primary-care interventions aimed at promoting PA.
-
Further quantitative and qualitative studies are needed to determine the moderators of uptake and adherence to ERS.
-
Theory-driven interventions should be developed to complement ERS to foster long-term change in PA, and evaluated to enhance our understanding of mediators and processes of behaviour change (e.g. SDT, motivational interviewing).
-
The development of improved approaches to modelling the cost-effectiveness of ERS, capturing the potential impact on a wide range of health outcomes.
*Note: While undertaking this report we became aware of a large ongoing cluster randomised trial of ERS funded by the Welsh Assembly Government. 155 A total of 2160 sedentary adult men and women with CHD risk factors and/or mild-to-moderate depression, anxiety or stress from 12 local health boards in Wales, referred directly by health professionals working in a range of health-care settings, were randomised either to a 16-week tailored exercise programme run by qualified exercise professionals at community sports centres (intervention) or to receive an information booklet on PA (usual care control). Despite contacting the authors, we were unable to obtain outcome data from this study to allow its incorporation into our analyses. This trial has now been completed and a brief report has recently been made publicly available. 156 The trial findings appear to be very consistent with those of this report. Compared with control, a small increase in the primary outcome of PA (7-Day Physical Activity Recall Questionnaire) with ERS at 12 months’ follow-up (OR 1.19, 95% CI 0.99 to 1.43) was seen. Based on a trial-based economic evaluation and using EQ-5D and cost data collected in the trial, an ICER of £12,111/QALY was reported.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the contribution from authors who contributed additional information regarding studies. Our thanks to Brian O’Regan, an MSc student in Sport and Health Sciences, University of Exeter, who performed preliminary searches and analysis of qualitative data reported in Chapter 5 on predictors of uptake and adherence.
Contribution of authors
Toby Pavey, Rod Taylor and Adrian Taylor co-ordinated the review.
Tiffany Moxham, information specialist, developed the search strategy in consultation with Rod Taylor, Adrian Taylor, Ken Fox and Melvyn Hillsdon and undertook the searches. Toby Pavey, Rod Taylor, Adrian Taylor, Ken Fox and Melvyn Hillsdon screened abstracts and retrieved papers against the inclusion criteria. Toby Pavey appraised the quality of the papers and abstracted data from them for the effectiveness and predictors of uptake and adherence chapters. Dr Nana Anokye appraised the quality of the papers and abstracted data from them for the cost-effectiveness chapter.
Toby Pavey and Rod Taylor analysed the data for the effectiveness, and uptake and adherence chapters, with Nana Anokye and Paul Trueman analysing the data for the cost-effectiveness and economic modelling chapters. Toby Pavey, Rod Taylor and Adrian Taylor wrote the drafted background and discussion chapters. Toby Pavey and Rod Taylor drafted the clinical effectiveness review chapter. Nana Anokye and Paul Trueman drafted the cost-effectiveness review and economic modelling chapters, with Colin Green reviewing and supporting the economic analysis. Toby Pavey and Adrian Taylor drafted the uptake and adherence chapter.
All authors (including John Campbell, Charlie Foster, Nanette Mutrie and John Searle) provided input to interpretation of findings, commented on various drafts of the chapters and contributed to their editing.
Disclaimers
The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Department of Health (DoH) . At Least Five a Week. Evidence on the Impact of Physical Activity and Its Relationship to Health 2004.
- US Department of Health and Human Services . Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans 2008. www.health.gov/paguidelines/pdf/paguide.pdf (accessed 1 May 2010).
- Department of Health (DoH) . Start Active Stay Active: A Report on Physical Activity for Health from the Four Home Countries. A Report from The Chief Medical Officers 2011.
- World Health Organization (WHO) . World Health Report 2002.
- Williams PT. Health effects resulting from exercise versus those from body fat loss. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2001;33:S611-21.
- Health and Safety Executive . Health Survey for England – 2008. Physical Activity and Fitness. Summary of Key Findings 2009.
- National Institute of Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) . Promoting and Creating Built or Natural Environments That Encourage and Support Physical Activity 2008.
- Marcus BH, Williams DM, Dubbert PM, Sallis JF, King AC, Yancey AK, et al. Physical activity intervention studies: what we know and what we need to know: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism (Subcommittee on Physical Activity); Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; and the Interdisciplinary Working Group on Quality of Care and Outcomes Research. Circulation 2006;114:2739-52.
- National Institute of Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) . Promoting Physical Activity in the Workplace 2008.
- Kahn EB, Ramsey LT, Brownson RC, Heath GW, Howze EH, Powell KE, et al. The effectiveness of interventions to increase physical activity. A systematic review. Am J Prev Med 2002;22:73-107.
- Eden KB, Orleans CT, Mulrow CD, Pender NJ, Teutsch SM. Does counseling by clinicians improve physical activity? A summary of the evidence for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med 2002;137:208-15.
- Department of Health (DoH) . Exercise Referral Systems: A National Quality Assurance Framework 2001.
- van der Bij AK, Laurant MGH, Wensing M. Effectiveness of physical activity interventions for older adults: a review. Am J Prev Med 2002;22:120-33.
- Proper KI, Koning M, van der Beek AJ, Hildebrandt VH, Bosscher RJ, van Mechelen W. The effectiveness of worksite physical activity programs on physical activity, physical fitness, and health. Clin J Sport Med 2003;13:106-17.
- Department of Health (DoH) . Foresight Report. Tackling Obesity: Future Choices 2007.
- Biddle S, Mutrie N. Psychology of physical activity: determinants, well-being, and interventions. London: Routledge; 2008.
- Spencer L, Adams TB, Malone S, Roy L, Yost E. Applying the transtheoretical model to exercise: a systematic and comprehensive review of the literature. Health Promot Pract 2006;7:428-43.
- Michie S, Abraham C, Whittington C, McAteer J, Gupta S. Effective techniques in healthy eating and physical activity interventions: a meta-regression. Health Psychol 2009;28:690-701.
- Hillsdon M, Foster C, Thorogood M. Interventions for promoting physical activity. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005;1.
- Fox K, Biddle S, Edmunds L, Bowler I, Killoran A. Physical activity promotion through primary health care in England. Br J Gen Pract 1997;47:367-9.
- Picker Institute . National Survey of Local Health Services 2006. Summary Report of Key Findings from the Study 2007.
- Taylor AH, Riddoch C, McKenna J. Perspectives on health and exercise. London: Macmillan Press; 2003.
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) . Four Commonly Used Methods to Increase Physical Activity: Brief Interventions in Primary Care, Exercise Referral Schemes, Pedometers and Community-Based Exercise Programmes for Walking and Cycling 2006.
- The General Practice Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPPAQ) . A Screening Toll to Assess Adult Physical Activity Levels Within Primary Care 2009.
- Little P, Dorward M, Gralton S, Hammerton L, Pillinger J, White P, et al. A randomised controlled trial of three pragmatic approaches to initiate increased physical activity in sedentary patients with risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Br J Gen Pract 2004;54:189-95.
- Marshall AL, Booth ML, Bauman AE. Promoting physical activity in Australian general practices: a randomised trial of health promotion advice versus hypertension management. Patient Educ Couns 2005;56:283-90.
- Taylor AH, Doust J, Webborn N. Randomised controlled trial to examine the effects of a GP exercise referral programme in Hailsham, East Sussex, on modifiable coronary heart disease risk factors. J Epidemiol Community Health 1998;52:595-601.
- Harrison RA, Roberts C, Elton PJ. Does primary care referral to an exercise programme increase physical activity one year later? A randomized controlled trial. J Public Health 2005;27:25-32.
- Elley CR, Kerse N, Arroll B, Robinson E. Effectiveness of counselling patients on physical activity in general practice: cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2003;326.
- Nichol G. The impact of compulsory competitive tendering on planning in leisure departments. Manag Leisure 2008;1:105-14.
- Biddle S, Fox K, Edmunds L. Physical activity promotion in primary health care in England. London: Health Education Authority; 1994.
- Smith P, Iliffe S, Gould M, See Tai S. Prescription for exercise in primary care: is it worth it?. Br J Health Care Manag 1996;2:324-7.
- Sowden SL, Raine R. Running along parallel lines: how political reality impedes the evaluation of public health interventions. A case study of exercise referral schemes in England. J Epidemiol Community Health 2008;62:835-41.
- British Heart Foundation National Centre . A Toolkit for the Design, Implementation and Evaluation of Exercise Referral Schemes. Guidance for Referring Health Professionals, Exercise Referral Professionals and Exercise Referral Scheme Commissioners 2010. www.bhfactive.org.uk/primary-care/exercisereferral (accessed 1 April 2010).
- National Institute of Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) . A Rapid Review of the Effectiveness of ERS to Promote Physical Activity in Adults 2006.
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. The PRISMA Group . Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol 2009;62:1006-12.
- Khan K, ter Riet G, Glanville J, Sowden A, Kleijen J. Undertaking systematic reviews of research on effectiveness: CRD’s guidance for those carrying out or commissioning reviews. York: NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York; 2001.
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions n.d. www.cochrane-handbook.org (accessed 1 September 2009).
- Morgan O. Approaches to increase physical activity: reviewing the evidence for exercise-referral schemes. Public Health 2005;119:361-70.
- Sorensen JB, Skovgaard T, Puggaard L. Exercise on prescription in general practice: a systematic review. Scand J Prim Health Care 2006;24:69-74.
- Williams NH, Hendry M, France B, Lewis R, Wilkinson C. Effectiveness of exercise-referral schemes to promote physical activity in adults: systematic review. Br J Gen Pract 2007;57:979-86.
- Oxman AD, Guyatt GH. Validation of an index of the quality of review articles. J Clin Epidemiol 1991;44:1271-8.
- Harland J, White M, Drinkwater C, Chinn D, Farr L, Howel D. The Newcastle exercise project: a randomised controlled trial of methods to promote physical activity in primary care. BMJ 1999;319:828-32.
- Kerse N, Walker S. The Newcastle exercise project. Conclusions are misleading. BMJ 2000;320.
- King AC, Haskell WL, Taylor CB, Kraemer HC, DeBusk RF. Group- vs home-based exercise training in healthy older men and women. A community-based clinical trial. JAMA 1991;266:1535-42.
- Marcus BH, Stanton AL. Evaluation of relapse prevention and reinforcement interventions to promote exercise adherence in sedentary females. Res Q Exerc Sport 1993;64:447-52.
- McAuley E, Courneya KS, Rudolph DL, Lox CL. Enhancing exercise adherence in middle-aged males and females. Prev Med 1994;23:498-506.
- Munro J, Brazier J, Davey R, Nicholl J. Physical activity for the over-65s: could it be a cost-effective exercise for the NHS?. J Public Health Med 1997;19:397-402.
- Bull FC, Jamrozik K. Advice on exercise from a family physician can help sedentary patients to become active. Am J Prev Med 1998;15:85-94.
- Stevens W, Hillsdon M, Thorogood M, McArdle D. Cost-effectiveness of a primary care based physical activity intervention in 45–74 year old men and women: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Sports Med 1998;32:236-41.
- Dunn AL, Marcus BH, Kampert JB, Garcia ME, Kohl HW, Blair SN. Comparison of lifestyle and structured interventions to increase physical activity and cardiorespiratory fitness: a randomized trial. JAMA 1999;281:327-34.
- Dunn AL, Garcia ME, Marcus BH, Kampert JB, Kohl HW, Blair SN. Six-month physical activity and fitness changes in Project Active, a randomized trial. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1998;30:1076-83.
- Goldstein MG, Pinto BM, Marcus BH, Lynn H, Jette AM, McDermott S, et al. Physician-based physical activity counseling for middle-aged and older adults: a randomized trial. Ann Behav Med 1999;21:40-7.
- Naylor PJ, Simmonds G, Riddoch C, Velleman G, Turton P. Comparison of stage-matched and unmatched interventions to promote exercise behaviour in the primary care setting. Health Educ Res 1999;14:653-66.
- Halbert JA, Silagy CA, Finucane PM, Withers RT, Hamdorf PA. Physical activity and cardiovascular risk factors: effect of advice from an exercise specialist in Australian general practice. Med J Aust 2000;173:84-7.
- Writing Group for the Activity Counseling Trial Research . Effects of physical activity counseling in primary care: the Activity Counseling Trial: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2001;286:677-87.
- Dubbert PM, Cooper KM, Kirchner KA, Meydrech EF, Bilbrew D. Effects of nurse counseling on walking for exercise in elderly primary care patients. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2002;57A:M733-40.
- Lamb S, Bartlett H, Ashley A, Bird W. Can lay-led walking programmes increase physical activity in middle aged adults? A randomised controlled trial. J Epidemiol Community Health 2002;56:246-52.
- Petrella RJ, Koval JJ, Cunningham DA, Paterson DH. Can primary care doctors prescribe exercise to improve fitness? The Step Test Exercise Prescription (STEP) Project. Am J Prev Med 2003;24:316-22.
- Jimmy G, Martin BW. Implementation and effectiveness of a primary care based physical activity counselling scheme. Patient Educ Couns 2005;56:323-31.
- Isaacs AJ, Critchley JA, Tai SS, Buckingham K, Westley D, Harridge SDR, et al. Exercise Evaluation Randomised Trial (EXERT): a randomised trial comparing GP referral for leisure centre-based exercise, community-based walking and advice only. Health Technol Assess 2007;11.
- Robertson MC, Devlin N, Gardner MM, Campbell AJ. Effectiveness and economic evaluation of a nurse delivered home exercise programme to prevent falls. 1: Randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2001;322:697-701.
- Robertson MC, Devlin N, Scuffham P, Gardner MM, Buchner DM, Campbell AJ. Economic evaluation of a community based exercise programme to prevent falls. J Epidemiol Community Health 2001;55:600-6.
- Fritz T, Wandell P, Aberg H, Engfeldt P. Walking for exercise: does three times per week influence risk factors in type 2 diabetes?. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2006;71:21-7.
- Hardcastle S, Taylor A, Bailey M, Castle R. A randomized controlled trial on the effectiveness of a primary health care based counseling intervention on physical activity, diet and CHD risk. Patient Educ Couns 2008;70:31-9.
- Lawton BA, Rose SB, Elley CR, Dowell AC, Fenton A, Moyes SA. Exercise on prescription for women aged 40–74 recruited through primary care: two year randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2008;337.
- Kolt GS, Schofield GM, Kerse N, Garrett N, Oliver M. Effect of telephone counseling on physical activity for low-active older people in primary care: a randomized, controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc 2007;55:986-92.
- Jolly K, Duda JL, Daley A, Ntoumanis N, Eves F, Rouse P, et al. An Evaluation of the Birmingham Exercise on Prescription Service: Standard Provision and a Self-Determination Focused Arm 2009.
- Sorensen JB, Kragstrup J, Skovgaard T, Puggaard L. Exercise on prescription: a randomized study on the effect of counseling vs counseling and supervised exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2008;18:288-97.
- Gusi N, Reyes MC, Gonzalez-Guerrero JL, Herrera E, Garcia JM. Cost-utility of a walking programme for moderately depressed, obese, or overweight elderly women in primary care: a randomised controlled trial. BMC Public Health 2008;8.
- Taylor AH, Fox KR. Effectiveness of a primary care exercise referral intervention for changing physical self-perceptions over 9 months. Health Psychol 2005;24:11-2.
- Taylor AH. Evaluating GP exercise referral schemes. Findings from a randomised control study. Brighton: University of Brighton; 1996.
- Sorensen JB, Kragstrup J, Kjaer K, Puggaard L. Exercise on prescription: trial protocol and evaluation of outcomes. BMC Health Serv Res 2007;7.
- Drummond MF, Jefferson TO. Guidelines for authors and peer reviewers of economic submissions to the BMJ. BMJ 1996;313:275-83.
- Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Claxton K, Golder S, Riemsma R, et al. Review of guidelines for good practice in decision-analytic modelling in health technology assessment. Health Technol Assess 2004;8.
- National Institute of Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) . Modelling the Cost Effectiveness of Physical Activity Interventions 2006.
- National Institute of Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) . Rapid Review of the Economic Evidence of Physical Activity Interventions 2006.
- Elley R, Kerse N, Arroll B, Swinburn B, Ashton T, Robinson E. Cost-effectiveness of physical activity counselling in general practice. NZ Med J 2004;117.
- Lowensteyn I, Coupal L, Zowall H, Grover SA. The cost-effectiveness of exercise training for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. J Cardiopulm Rehabil 2000;20:147-55.
- Sevick MA, Dunn AL, Morrow MS, Marcus BH, Chen G, Blair SN. Cost-effectiveness of lifestyle and structured exercise interventions in sedentary adults: results of Project ACTIVE. Am J Prev Med 2000;19:1-8.
- Sevick MA, Bradham DD, Muender M, Chen GJ, Enarson C, Dailey M, et al. Cost-effectiveness of aerobic and resistance exercise in seniors with knee osteoarthritis. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2000;32:1534-40.
- Munro JF, Nicholl JP, Brazier JE, Davey R, Cochrane T. Cost effectiveness of a community based exercise programme in over 65 year olds: cluster randomised trial. J Epidemiol Community Health 2004;58:1004-10.
- Briggs A, Sculpher M, Claxton K. Decision modelling for health economic evaluation. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2006.
- Beale S, Bending M, Trueman P. An economic analysis of environmental interventions that promote physical activity. York: York Health Economics Consortium; 2007.
- Gidlow C, Murphy R, Dugdill L, Crone D, Murphy R. Physical activity and health promotion: evidence-based approaches to practice. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell; 2009.
- Ip HYV, Abrishami A, Peng PWH, Wong J, Chung F. Predictors of postoperative pain and analgesic consumption: a qualitative systematic review. Anesthesiology 2009;111:657-77.
- Gidlow C, Johnston LH, Crone D, James D. Attendance of exercise referral schemes in the UK: a systematic review. Health Educ J 2005;64:168-86.
- Lord JC, Green F. Exercise on prescription: does it work?. Health Educ J 1995;54:453-64.
- Hammond JM, Brodie DA, Bundred PE. Exercise on prescription: guidelines for health professionals. Health Promot Int 1997;12:33-41.
- Cochrane T, Davey R. Evaluation of exercise prescription for 25 general practices and a large leisure complex in Sheffield. J Sports Sci 1998;16:17-8.
- Jackson C, Bell F, Smith RA, Dixey R. Do adherers and non-adherers to a GP exercise referral scheme differ in their long-term physical activity levels?. J Sports Sci 1998;16.
- Martin C, Woolf-May K. The retrospective evaluation of a general practitioner exercise prescription programme. J Hum Nutri Diet 1999;12.
- Damush TM, Stump TE, Saporito A, Clark DO. Predictors of older primary care patients’ participation in a submaximal exercise test and a supervised, low-impact exercise Class. Prev Med 2001;33:485-94.
- Greater Glasgow Health Board . An Evaluation Report of the Glasgow Exercise Referral Scheme 2004. www.glasgowcitycouncil.co.uk/healthycities/pdf/exercise_es.pdf (accessed 1 April 2010).
- Dugdill L, Graham RC, McNair F. Exercise referral: the public health panacea for physical activity promotion? A critical perspective of exercise referral schemes; their development and evaluation. Ergonomics 2005;48:1390-410.
- Dugdill L, Graham R, Gormly JH. Exercise in the prevention of treatment and disease. Oxford: Blackwell; 2005.
- Dinan S, Lenihan P, Tenn T, Iliffe S. Is the promotion of physical activity in vulnerable older people feasible and effective in general practice?. Br J Gen Pract 2006;56:791-3.
- Edmunds J, Ntoumanis N, Duda JL. Adherence and well-being in overweight and obese patients referred to an exercise on prescription scheme: a self-determination theory perspective. Psychol Sport Exerc 2007;8:722-40.
- Harrison RA, McNair F, Dugdill L. Access to exercise referral schemes: a population based analysis. J Public Health 2005;27:326-30.
- Jones F, Harris P, Waller H, Coggins A. Adherence to an exercise prescription scheme: the role of expectations, self-efficacy, stage of change and psychological well-being. Br J Health Psychol 2005;10:359-78.
- Morton KL, Biddle SJH, Beauchamp MR. Changes in self-determination during an exercise referral scheme. Public Health 2008;122:1257-60.
- Roessler KK, Ibsen B. Promoting exercise on prescription: recruitment, motivation, barriers and adherence in a Danish community intervention study to reduce type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia and hypertension. J Public Health 2009;17:187-93.
- Sowden SL, Breeze E, Barber J, Raine R. Do general practices provide equitable access to physical activity interventions?. Br J Gen Pract 2008;58:699-702.
- James D, Mills H, Crone D, Johnston LH, Morris C, Gidlow CJ. Factors associated with physical activity referral completion and health outcomes. J Sports Sci 2009;27:1007-17.
- Gidlow C, Johnston LH, Crone D, Morris C, Smith A, Foster C, et al. Socio-demographic patterning of referral, uptake and attendance in physical activity referral schemes. J Public Health 2007;29:107-13.
- Crone D, Johnston LH, Gidlow C, Henley C, James DV. Uptake and participation in physical activity referral schemes in the UK: an investigation of patients referred with mental health problems. Issues Ment Health Nurs 2008;29:1088-97.
- James DVB, Johnston LH, Crone D, Sidford AH, Gidlow C, Morris C, et al. Factors associated with physical activity referral uptake and participation. J Sports Sci 2008;26:217-24.
- Stathi A, McKenna J, Fox KR. The experiences of older people participating in exercise referral schemes. J R Soc Promot Health 2004;124:18-23.
- Wormald H, Waters H, Sleap M, Ingle L. Participants’ perceptions of a lifestyle approach to promoting physical activity: targeting deprived communities in Kingston-Upon-Hull. BMC Public Health 2006;6.
- Hardcastle S, Taylor A. Looking for more that weight loss and fitness gain: psycho-social dimensions among older women in a primary health care exercise referral scheme. J Aging Phys Act 2001;9:313-29.
- Hardcastle S, Taylor AH. Finding an exercise identity in an older body: ‘It’s redefining yourself and working out who you are’. Psychol Sport Exerc 2005;6:173-88.
- Carroll R, Ali N, Azam N. Promoting physical activity in South Asian Muslim women through ‘exercise on prescription’. Health Technol Assess 2002;6.
- Crone D, Smith A, Gough B. ‘I feel totally at one, totally alive and totally happy’: a psycho-social explanation of the physical activity and mental health relationship. Health Educ Res 2005;20:600-11.
- Wormald H, Ingle L. GP exercise referral schemes: improving the patient’s experience. Health Educ J 2004;63:362-73.
- Singh S. Why are GP exercise schemes so successful (for those who attend)?: results from a pilot study. J Manag Med 1997;11:233-7.
- Schmidt M, Absalah S, Nierkens V, Stronks K. Which factors engage women in deprived neighbourhoods to participate in exercise referral schemes?. BMC Public Health 2008;8.
- Wiles R, Demain S, Robison J, Kileff J, Ellis-Hill C, McPherson K. Exercise on prescription schemes for stroke patients post-discharge from physiotherapy. Disabil Rehabil 2008;30:1966-75.
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence . Guide to Methods of Technology Appraisal 2008. www.nice.org.uk/media/B52/A7/TAMethodsGuideUpdatedJune2008.pdf (accessed 5 April 2010).
- Drummond M, Sculpher M, Torrance G, O’Brien B, Stoddart G. Methods for the economic evaluation of health care programmes. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2005.
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) . Promoting Physical Activity, Active Play and Sport for Pre-School and School-Age Children and Young People in Family, Pre-School, School and Community Settings 2009.
- Department of Health (DoH) . NHS Reference Costs 2008 2008.
- Wanless D. Securing good health for the whole population. Norwich: HMSO; 2004.
- Health and Safety Executive . Health Survey for England – 2006 2007.
- Briggs A, Clark T, Wolstenholme J, Clarke P. Missing … presumed at random: cost-analysis of incomplete data. Health Econ 2003;12:377-92.
- Chilcott J, Tappenden P, Rawdin A, Johnson M, Kaltenthaler E, Paisley S, et al. Avoiding and identifying errors in health technology assessment models: qualitative study and methodological review. Health Technol Assess 2010;14.
- Office for National Statistics (ONS) . United Kingdom Interim Life Tables 2009.
- Hu G, Tuomilehto J, Silventoinen K, Barengo NC, Peltonen M, Jousilahti P. The effects of physical activity and body mass index on cardiovascular, cancer and all-cause mortality among 47212 middle-aged Finnish men and women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2005;29:894-902.
- Hu G, Lindstrom J, Valle TT, Eriksson JG, Jousilahti P, Silventoinen K, et al. Physical activity, body mass index, and risk of type 2 diabetes in patients with normal or impaired glucose regulation. Arch Intern Med 2004;164:892-6.
- Hu G, Jousilahti P, Antikainen R, Tuomilehto J. Occupational, commuting, and leisure-time physical activity in relation to cardiovascular mortality among Finnish subjects with hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2007;20:1242-50.
- Surtees PG, Wainwright NWJ, Luben RN, Wareham NJ, Bingham SA, Khaw K-T. Depression and ischemic heart disease mortality: evidence from the EPIC-Norfolk United Kingdom Prospective Cohort Study. Am J Psychiatry 2008;165:515-23.
- Rejeski WJ, Mihalko SL. Physical activity and quality of life in older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2001;56A:23-35.
- Dolan P, Gudex C, Kind P. A social tariff for EuroQol: results from a UK general population survey. Discussion Paper Centre for Health Economics. York: University of York; 1995.
- Morris S, Sutton M, Gravelle H. Inequity and inequality in the use of health care in England: an empirical investigation. Soc Sci Med 2005;60:1251-66.
- Craig R, Mindell J, Hirani V. Health Survey for England 2008. Volume 1: Physical Activity and Fitness Report 2009.
- Baum CF. An introduction to modern econometrics using Stata. College Station, TX: Stata Press; 2006.
- Cameron AC, Trivedi PK. Microeconometrics using Stata. College Station, TX: Stata Press; 2009.
- Greene W. Econometric analysis. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall; 2008.
- StataCorp . Tobit Analysis n.d.
- Chatterjee S, Hadi AS, Price B. Regression analysis by example. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons Inc.; 2000.
- Gujarati D. Basic econometrics. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 1995.
- Conn VS. Anxiety outcomes after physical activity interventions: meta-analysis findings. Nurs Res 2010;59:224-31.
- Craft LL, Perna FM. The benefits of exercise for the clinically depressed. Prim Care Comp J Clin Psychiatry 2004;6:104-11.
- Boule NG, Haddad E, Kenny GP, Wells GA, Sigal RJ. Effects of exercise on glycemic control and body mass in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. JAMA 2001;286:1218-27.
- Lee IM. Physical activity and cancer prevention: data from epidemiologic studies. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2003;35:1823-7.
- Whelton SP, Chin A, Xin X, He J. Effect of aerobic exercise on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Ann Intern Med 2002;136:493-50.
- Taylor RS, Brown A, Ebrahim S, Jolliffe J, Noorani H, Rees K, et al. Exercise-based rehabilitation for patients with coronary heart disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Med 2004;116:682-92.
- Moayyeri A. The association between physical activity and osteoporotic fractures: a review of the evidence and implications for future research. Ann Epidemiol 2008;18:827-35.
- Roddy E, Zhang W, Doherty M. Aerobic walking or strengthening exercise for osteoarthritis of the knee? A systematic review. Ann Rheum Dis 2005;64:544-8.
- Hayden JA, van Tulder MW, Malmivaara AV, Koes BW. Meta-analysis: exercise therapy for nonspecific low back pain. Ann Intern Med 2005;142:765-75.
- Baillet A, Zeboulon N, Gossec L, Combescure C, Bodin LA, Juvin R, et al. Efficacy of cardiorespiratory aerobic exercise in rheumatoid arthritis: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Care Res 2010;62:984-92.
- Chang JT, Morton SC, Rubenstein LZ, Mojica WA, Maglione M, Suttorp MJ, et al. Interventions for the prevention of falls in older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. BMJ 2004;328.
- Conn VS, Hafdahl AR, Cooper PS, Brown LM, Lusk SL. Meta-analysis of workplace physical activity interventions. Am J Prev Med 2009;37:330-9.
- Hootman JM, Macera CA, Ainsworth BE, Martin M, Addy CL, Blair SN. Association among physical activity level, cardiorespiratory fitness, and risk of musculoskeletal injury. Am J Epidemiol 2001;154:251-8.
- Lamb SE, Guralnik JM, Buchner DM, Ferrucci LM, Hochberg MC, Simonsick EM, et al. Factors that modify the association between knee pain and mobility limitation in older women: the Women’s Health and Aging Study. Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59:331-7.
- Murphy S, Raisanen L, Moore G, Edwards R, Linck P, Williams N, et al. A pragmatic randomised controlled trial of the Welsh National Exercise Referral Scheme: protocol for trial and integrated economic and process evaluation. BMC Public Health 2010;10.
- Murphy S, Raisanen L, Moore G, Edwards R, Linck P, Hounsome N, et al. The Evaluation of the National Exercise Referral in Wales 2010. http://wales.gov.uk/docs/caecd/research/101104nationalexerciseschemeen.pdf (accessed 6 November 2010).
- Prochaska JO, DiClemente CC. Stages and processes of self-change of smoking: Toward an integrative model of change. J Consult Clin Psychol 1983;51:390-5.
- Fox KR, Corbin CB. The physical self-perception profile: development and preliminary validation. J Sport Exerc Psychol 1989;11:408-30.
- Fox KR. The Physical Self-Perception Profile Manual. Office for Health Promotion, Northern Illinois University; 1990.
Appendix 1 Common included conditions in exercise referral schemes
FIGURE 21.
The most commonly included conditions in ERS (adapted from British Heart Foundation toolkit34).
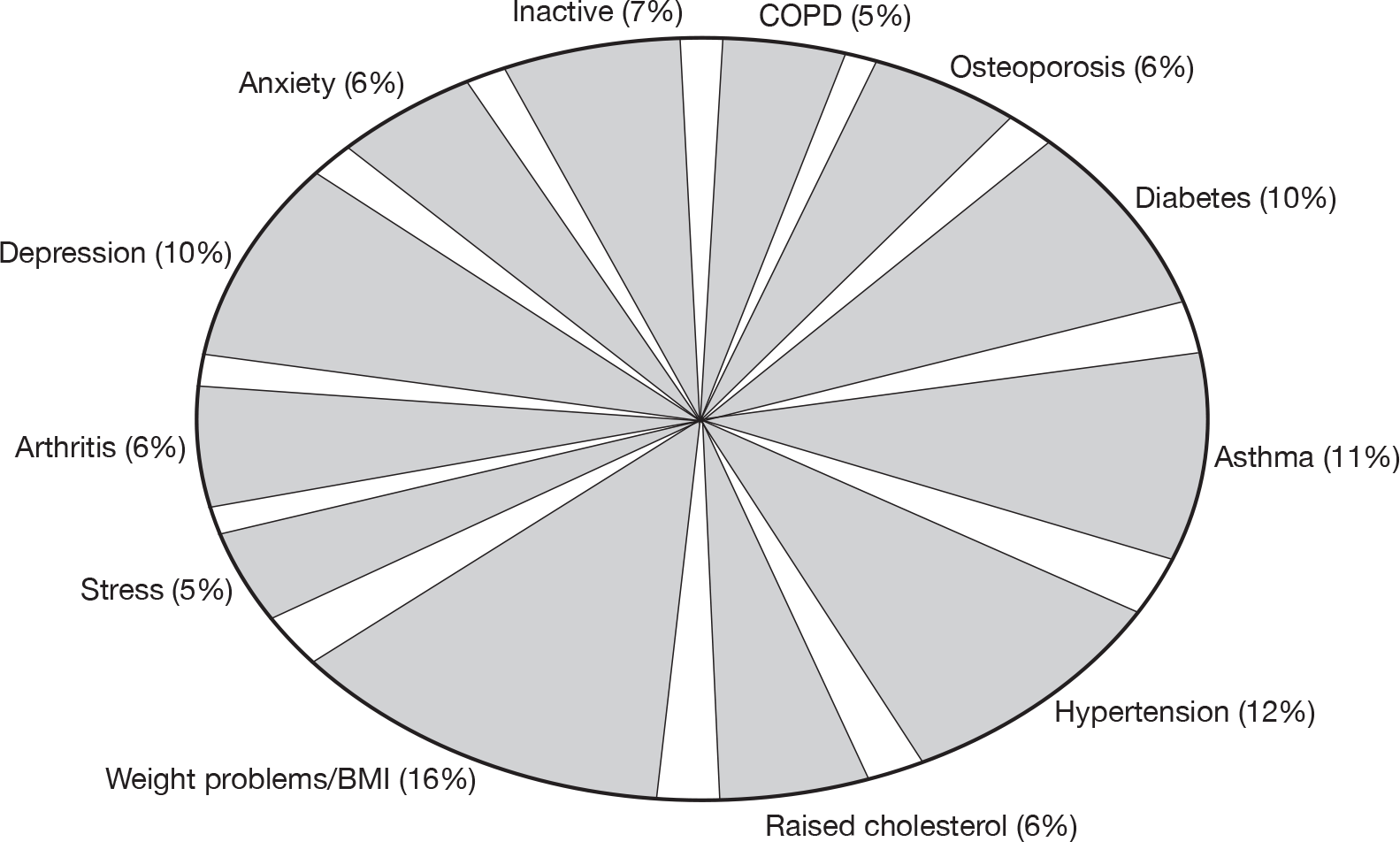
Appendix 2 Literature search strategies
Note: the ERS search strategy was undertaken in two stages. The first stage used text word terms related to ERS, limited to the title and abstract of articles. The second stage utilised a larger set of terms, but incorporated limits included the type of trial and primary-care terms. The search strategy for the primary care terms was developed by Julie Glanville at the York Health Economics Consortium as part of a project specifically aimed at determining the terminology used within the literature for work about and by primary care practice. This two-stage search strategy was utilised after an extensive scoping study found that utilising all ERS terms without limits produced extremely low specificity in the search results.
Stage 1 Exercise referral terms
Search date for all stage 1 databases: 2 October 2009.
Ovid MEDLINE(R) In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations and Ovid MEDLINE(R)
1950 to present.
Ovid EMBASE
1980 to 2009 Week 39.
OVID PsycINFO
1967 to September Week 4 2009:
-
physical activity referral*.ti.
-
physical activity referral*.ab.
-
exercise on prescription.ti.
-
exercise on prescription.ab.
-
exercise referral*.ti.
-
exercise referral*.ab.
-
or/1–6
-
supervised exercise.ti.
Note: lines 7 and 8 downloaded in all databases.
Cochrane CENTRAL and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, HTA, NHS EED, DARE via The Cochrane Library version 2009 v3
-
“supervised exercise”:ti
-
“physical activity referral*”:ti or “physical activity referral*”:ab
-
“exercise referral*”:ti or “exercise referral*”:ab
-
“exercise on prescription*”:ti or “exercise on prescription*”:ab
-
(#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4)
SPORTDiscus via Ebsco
-
S1 TI physical activity referral* or AB physical activity referral* Search modes – Boolean/Phrase
-
S2 TI physical activity referral* or AB physical activity referral* Search modes – Boolean/Phrase
-
S3 TI exercise on prescription or AB exercise on prescription Search modes – Boolean/Phrase
-
S4 TI exercise referral* or AB exercise referral* Search modes – Boolean/Phrase
-
S5 S1 or S2 or S3 or S4 Search modes – Boolean/Phrase
-
S6 TI supervised exercise Search modes – Boolean/Phrase
ISI Web Of Knowledge: SCIE
1900 to present.
Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI)
1898 to present.
-
S1 Title=(supervised exercise) Databases=SCI-EXPANDED Timespan=All Years
-
S2 TI=TI physical activity referral* or TS= physical activity referral* Databases=SCI-EXPANDED Timespan=All Years
-
S3 TI=physical activity referral* or TS=physical activity referral* Databases=SCI-EXPANDED Timespan=All Years
-
S4 TI=exercise on prescription or TS=exercise on prescription Databases=SCI-EXPANDED Timespan=All Years
-
S5 TI=exercise referral* or TS=exercise referral* Databases=SCI-EXPANDED Timespan=All Years
-
S6 #5 OR #4 OR #3 OR #2 Databases=SCI-EXPANDED Timespan=All Years
Note: #1 and #6 downloaded.
Stage 2 Expanded term search
Developed from the background and stage 2 searches.
Ovid MEDLINE(R) In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations and Ovid MEDLINE(R)
1950 to present.
Search date: 19 October 2009.
-
“Referral and Consultation”/
-
(exercise* or physical*).ti,ab.
-
1 and 2
-
((physical* or exercise*) adj2 (superv* or subsid* or prescrib*)).ti.
-
((physical* or exercise*) adj2 (superv* or subsid* or prescrib*)).ab.
-
(exercise* adj2 (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)).ti.
-
(exercise* adj2 (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)).ab.
-
(physical* adj2 (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)).ti.
-
(physical* adj2 (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)).ab.
-
((physical* or exercise*) and referral*).ti.
-
((physical* or exercise*) and referral*).ab.
-
or/4–11
-
Randomized controlled trial.pt.
-
randomized controlled trial/
-
(random$or placebo$).ti,ab,sh.
-
((singl$or double$or triple$or treble$) and (blind$or mask$)).tw,sh.
-
or/13–16
-
“controlled clinical trial”.pt.
-
(retraction of publication or retracted publication).pt.
-
18 or 19 or 17
-
family medicine$.ti,ab.
-
family practice$.ti,ab.
-
general practice$.ti,ab.
-
primary care.ti,ab.
-
primary health care.ti,ab.
-
primary health service$.ti,ab.
-
primary healthcare.ti,ab.
-
primary medical care.ti,ab.
-
family medical practice$.ti,ab.
-
family doctor$.ti,ab.
-
family physician$.ti,ab.
-
family practitioner$.ti,ab.
-
general medical practitioner$.ti,ab.
-
general practitioner$.ti,ab.
-
local doctor$.ti,ab.
-
family practice/
-
Primary Health Care/
-
Physicians, Family/
-
Community Health Centers/
-
(community healthcare or community health care).ti,ab.
-
(GP or GPs).ti,ab.
-
general practic*.ti,ab.
-
or/21–42
-
(referral* or promot* or program* or intervent*).ti,ab.
-
43 or 44
-
Exercise/
-
Exercise Therapy/
-
46 or 47
-
45 and 48
-
49 or 3 or 12
-
(child* or adolescent* or school* or pediatric* or paediatric*).ti.
-
50 not 51
-
52 and 20
-
(animals not humans).sh.
-
53 not 54
-
limit 55 to (english language and yr=“1985 -Current”)
Cochrane CENTRAL and CDSR, HTA, NHS EED, DARE via The Cochrane Library version 2009 v4
Search date: 22 October 2009.
-
MeSH descriptor Referral and Consultation, this term only
-
(exercise* or physical*):ti,ab
-
(#1 AND #2)
-
((physical* or exercise*) and (superv* or subsid* or prescrib*)):ti
-
((physical* or exercise*) and (superv* or subsid* or prescrib*)):ab
-
(exercise* and (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)):ti
-
(exercise* and (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)):ab
-
(physical* and (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)):ti
-
(physical* and (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)):ab
-
((physical* or exercise*) and referral*):ti
-
((physical* or exercise*) and referral*):ab
-
(#4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11)
-
randomized controlled trial:pt
-
((singl* or double* or triple* or treble*) and (blind* or mask*)):ti,ab
-
(random* or placebo*):ti,ab
-
controlled clinical trial:pt.
-
(retraction of publication or retracted publication):pt
-
(#13 OR #14 OR #15 OR #16 OR #17)
-
family medicine*:ti,ab
-
(family practice*):ti,ab
-
(general practice*):ti,ab
-
(primary care):ti,ab
-
(primary health care):ti,ab
-
(primary health service*):ti,ab
-
(primary healthcare):ti,ab
-
(primary medical care):ti,ab
-
(family medical practice*):ti,ab
-
(family doctor*):ti,ab
-
(family physician*):ti,ab
-
(family practitioner*):ti,ab
-
(general medical practitioner*):ti,ab
-
(general practitioner*):ti,ab
-
(local doctor*):ti,ab
-
MeSH descriptor Family Practice, this term only
-
MeSH descriptor Primary Health Care, this term only
-
MeSH descriptor Physicians, Family, this term only
-
MeSH descriptor Community Health Centers, this term only
-
(community healthcare or community health care):ti,ab
-
(GP or GPs):ti,ab
-
(general practic*):ti,ab
-
(#19 OR #20 OR #21 OR #22 OR #23 OR #24 OR #25 OR (#26 AND ro AND #27) OR #28 OR #29 OR #30 OR #31 OR #32 OR #33 OR #34 OR #35 OR #36 OR #37 OR #38 OR #39 OR #40)
-
(referral* or promot* or program* or intervent*):ti,ab
-
(#41 OR #42)
-
MeSH descriptor Exercise, this term only
-
MeSH descriptor Exercise Therapy, this term only
-
(#44 OR #45)
-
(#43 AND #46)
-
(#47 OR #3 OR #12)
-
(child* or adolescent* or school* or pediatric* or paediatric*):ti
-
(#48 AND NOT #49)
-
(#50 AND #18)
-
(#51), from 1985 to 2009
-
“accession number” NEAR pubmed
-
“accession number” near2 embase
-
(#53 OR #54)
-
(#52 AND NOT #55)
PsycINFO 1806 to October Week 3 2009 via Ovid
Search date: 22 October 2009.
-
(exercise* or physical*).ti,ab.
-
(referral* or scheme*).ti,ab.
-
1 and 2
-
((physical* or exercise*) adj2 (superv* or subsid* or prescrib*)).ti.
-
((physical* or exercise*) adj2 (superv* or subsid* or prescrib*)).ab.
-
(exercise* adj2 (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)).ti.
-
(exercise* adj2 (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)).ab.
-
(physical* adj2 (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)).ti.
-
(physical* adj2 (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)).ab.
-
((physical* or exercise*) and referral*).ti.
-
((physical* or exercise*) adj3 referral*).ab.
-
((physical* or exercise*) adj4 prescription program*).ti,ab.
-
((physical* or exercise*) adj2 scheme*).ti,ab.
-
or/4–13
-
clinical trials/
-
treatment outcome clinical trial.md.
-
(random$or placebo$).ti,ab,sh.
-
((singl$or double$or triple$or treble$) and (blind$or mask$)).tw,sh.
-
quantitative study.md.
-
or/15–19
-
“Erratum/correction”.dt.
-
((retract* or withdraw*) adj (public* or artcle*)).ti,ab.
-
21 or 22 or 20
-
family medicine$.ti,ab.
-
family practice$.ti,ab.
-
general practice$.ti,ab.
-
primary care.ti,ab.
-
primary health care.ti,ab.
-
primary health service$.ti,ab.
-
primary healthcare.ti,ab.
-
primary medical care.ti,ab.
-
family medical practice$.ti,ab.
-
family doctor$.ti,ab.
-
family physician$.ti,ab.
-
family practitioner$.ti,ab.
-
general medical practitioner$.ti,ab.
-
general practitioner$.ti,ab.
-
local doctor$.ti,ab.
-
Primary Health Care/
-
(community healthcare or community health care).ti,ab.
-
(GP or GPs).ti,ab.
-
general practic*.ti,ab.
-
or/24–42
-
(referral* or promot* or program*).ti,ab.
-
43 or 44
-
Exercise/
-
physical treatment methods/
-
intervention/
-
46 and (47 or 48)
-
45 and 46
-
49 or 50 or 14 or 3
-
(child* or adolescent* or school* or pediatric* or paediatric*).ti.
-
51 not 52
-
53 and 23
-
limit 54 to (english language and yr=“1985 -Current”)
-
limit 55 to human
SPORTDiscus via Ebsco
Search date: 23 October 2009.
-
S1 exercise* n5 referral* or physical* n5 referral* or exercise* n5 scheme* or physical* n5 scheme*
-
S2 physical* n2 superv* or physical* n2 subsid* or physical* n2 prescrib*
-
S3 exercise* n2 supervis* or exercise* n2 subsid* or exercise* n2 prescrib*
-
S4 physical* n2 prescription*
-
S5 exercise* n2 prescription*
-
S6 s1 or s2 or s3 or s4 or s5
ISI Web Of Knowledge: SCI-EXPANDED
1900 to present.
Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI)
1898 to present.
Search date: 26 October 2009.
TI=(exercise* same referral*) or TI=(physical* same referral*) or TI=(exercise*same scheme*) or TI=(physical* same scheme*) AND Language=(English)
Databases=SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI Timespan=1985–2009
EMBASE 1980 to 2009 Week 49 via Ovid
Search date: 8 December 2009.
-
patient referral/(28808)
-
(exercise* or physical*).ti,ab,sh. (473426)
-
1 and 2 (3083)
-
((physical* or exercise*) adj2 (superv* or subsid* or prescrib*)).ti. (222)
-
((physical* or exercise*) adj2 (superv* or subsid* or prescrib*)).ab. (1357)
-
(exercise* adj2 (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)).ti. (4427)
-
(exercise* adj2 (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)).ab. (13487)
-
(physical* adj2 (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)).ti. (10978)
-
(physical* adj2 (fit* or train* or activit* or promot* or program* or intervention*)).ab. (33058)
-
((physical* or exercise*) and referral*).ti. (51)
-
((physical* or exercise*) and referral*).ab. (2831)
-
or/4–11 (50545)
-
exp controlled clinical trial/(189887)
-
(random$or placebo$).ti,ab,sh. (562901)
-
((singl$or double$or triple$or treble$) and (blind$or mask$)).tw,sh. (107112)
-
or/13–15 (588257)
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE/(3212)
-
16 or 17 (591386)
-
family medicine$.ti,ab. (3531)
-
family practice$.ti,ab. (3856)
-
general practice$.ti,ab. (18378)
-
primary care.ti,ab. (37769)
-
primary health care.ti,ab. (6779)
-
primary health service$.ti,ab. (150)
-
primary healthcare.ti,ab. (914)
-
primary medical care.ti,ab. (447)
-
family medical practice$.ti,ab. (15)
-
family doctor$.ti,ab. (1947)
-
family physician$.ti,ab. (6671)
-
family practitioner$.ti,ab. (950)
-
general medical practitioner$.ti,ab. (161)
-
general practitioner$.ti,ab. (22757)
-
local doctor$.ti,ab. (130)
-
general practice/(23658)
-
exp primary Health Care/(46053)
-
general practitioner/(32101)
-
health center/(9725)
-
(community healthcare or community health care).ti,ab. (352)
-
(GP or GPs).ti,ab. (23498)
-
general practic*.ti,ab. (18469)
-
or/19–40 (137654)
-
(referral* or promot* or program* or intervent*).ti,ab. (890143)
-
41 or 42 (996006)
-
Exercise/(79613)
-
aerobic exercise/(2106)
-
physical activity/(41024)
-
lifestyle modification/(5486)
-
behavior change/(3709)
-
or/44–48 (120743)
-
43 and 49 (28109)
-
50 or 3 or 12 (66466)
-
(child* or adolescent* or school* or pediatric* or paediatric*).ti. (367903)
-
51 not 52 (60457)
-
53 and 18 (11024)
-
(animal$not human$).sh,hw. (2056248)
-
54 not 55 (10612)
-
limit 56 to (english language and yr=“1985 -Current”) (9901)
Appendix 3 Summary of excluded studies
| Paper | Comment |
|---|---|
| Ackermann RT, Deyo RA, LoGerfo JP. Prompting primary providers to increase community exercise referrals for older adults: a randomized trial. J Am Geriatr Soc 2005;53:283–9. | No third-party exercise provider |
| Adachi H, Koike A, Obayashi T, Umezawa S, Aonuma K, Inada M, et al. Does appropriate endurance exercise training improve cardiac function in patients with prior myocardial infarction? Eur Heart J 1996;17:1511–21. | Not primary care based |
| Agurs-Collins TD, Kumanyika SK, Ten Have TR, Adams-Campbell LL. A randomized controlled trial of weight reduction and exercise for diabetes management in older African-American subjects. Diabetes Care 1997;20:1503–11. | No primary care referral |
| Aittasalo M, Miilunpalo S, Kukkonen-Harjula K, Pasanen M. A randomized intervention of physical activity promotion and patient self-monitoring in primary health care. Prev Med 2006;42:40–6. | No third-party exercise provider |
| Aittasalo M, Miilunpalo S, Stahl T, Kukkonen-Harjula K. From innovation to practice: Initiation, implementation and evaluation of a physician-based physical activity promotion programme in Finland. Health Promot Int 2007;22:19–27. | No third-party exercise provider |
| Aittasalo M, Pasanen M, Fogelholm M, Kinnunen TI, Ojala K, Luoto R. Physical activity counseling in maternity and child health care: a controlled trial. BMC Womens Health 2008;8:14. | No primary care referral |
| Albright CL, Cohen S, Gibbons L, Miller S, Marcus B, Sallis J, et al. Incorporating physical activity advice into primary care: physician-delivered advice within the activity counseling trial. Am J Prev Med 2000;18:225–34. | No primary care referral |
| Albright C, Pruitt L, Castro C, Gonzalez A, Woo S, King AC. Modifying physical activity in a multiethnic sample of low-income women: One-year results from the IMPACT (increasing motivation for physical activity) project. Ann Behav Med 2005;30:191–200. | No primary care referral |
| Aldarondo F. Adherence among individuals in an exercise, nutrition, and weight loss program. Dissertation Abstracts International, Section B: The Sciences and Engineering; 1999. | Not controlled trial |
| Allen B. ‘Working out’ health issues in your local community! Austr Aquat Recreation 2004;57:20–2. | Not controlled trial |
| Allen A, Simpson JM. A primary care based fall prevention programme. Physiother Theory Pract 1999;15:121–33. | |
| Allen DH, Puddey IB, Morton AR, Beilin LJ. A controlled study of the effects of aerobic exercise on antihypertensive drug requirements of essential hypertensive patients in the general practice setting. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 1991 May;18:279–82. | No primary care referral |
| Almeida FA, Smith-Ray RL, Van Den Berg R, Schriener P, Gonzales M, Onda P, et al. Utilizing a simple stimulus control strategy to increase physician referrals for physical activity promotion. J Sport Exerc Psychol 2005;27:505–14. | Not controlled trial |
| Alves JoG, Gale CR, Mutrie N, Correia JB, Batty GD. A 6-month exercise intervention among inactive and overweight favela-residing women in Brazil: The Caranguejo Exercise Trial. Am J Publ Health 2009;99:76–80. | No primary care referral |
| Amigo I, Gonzalez A, Herrera J. Comparison of physical exercise and muscle relaxation training in the treatment of mild essential hypertension. Stress Med 1997;13:59–65. | No primary care referral |
| Andersen RE. Exercise, an active lifestyle, and obesity: making the exercise prescription work. Physician Sports Med 1999;27:41–2;4;7–8;50. | Review article |
| Anderson D, Mizzari K, Kain V, Webster J. The effects of a multimodal intervention trial to promote lifestyle factors associated with the prevention of cardiovascular disease in menopausal and postmenopausal Australian women. Health Care Women Int 2006;27:238–53. | No primary care referral |
| Anderson RT, King A, Stewart AL, Camacho F, Rejeski W. Physical activity counseling in primary care and patient well-being: Do patients benefit? Ann Behav Med 2005,30:146–54. | No primary care referral |
| Annesi JJ, Otto LM. Relationship between number of exercise counseling sessions attended and adherence to a new exercise program. Psychol Rep 2004;94:907–8. | No primary care referral |
| Appel LJ, Champagne CM, Harsha DW, Cooper LS, Obarzanek E, Elmer PJ, et al. Effects of comprehensive lifestyle modification on blood pressure control: main results of the PREMIER clinical trial. JAMA 2003;289:2083–9 | No primary care referral |
| Araiza P, Hewes H, Gashetewa C, Vella CA, Burge MR. Efficacy of a pedometer-based physical activity program on parameters of diabetes control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metab Clin Exp 2006;55:1382–7. | No third-party exercise provider |
| Arbour KP, Ginis KA. Helping middle-aged women translate physical activity intentions into action: combining the theory of planned behavior and implementation intentions. J Appl Biobehav Res 2004;9:172–87. | No primary care referral |
| Arbour KP, Ginis KA. A randomised controlled trial of the effects of implementation intentions on women’s walking behaviour. Psychol Health 2009;24:49–65. | Not primary care based |
| Armit CM, Brown WJ, Marshall AL, Ritchie CB, Trost SG, Green A, et al. Randomized trial of three strategies to promote physical activity in general practice. Prev Med 2009;48:156–63. | No primary care referral |
| Armit CM, Brown WJ, Ritchie CB, Trost SG. Promoting physical activity to older adults: a preliminary evaluation of three general practice-based strategies. J Science Med Sport 2005;8:446–50. | No primary care referral |
| Ashworth NL, Chad KE, Harrison EL, Reeder BA, Marshall SC. Home versus center based physical activity programs in older adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005;1:CD004017. | Review article |
| Ayres R, Pocock E. Exercise on prescription. Br J Gen Pract 1995;45:325–6. | Not controlled trial |
| Balde A, Figueras J, Hawking DA, Miller JR. Physician advice to the elderly about physical activity. J Aging Phys Act 2003;11:90–7. | Not controlled trial |
| Bandinelli S, Lauretani F, Boscherini V, Gandi F, Pozzi M, Corsi AM, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of disability prevention in frail older patients screened in primary care: the FRASI study. Design and baseline evaluation. Aging Clin Exp Res 2006;18:359–66. | No primary care referral |
| Barclay C, Procter KL, Glendenning R, Marsh P, Freeman J, Mathers N. Can type 2 diabetes be prevented in UK general practice? A lifestyle-change feasibility study (ISAIAH). Br J Gen Pract 2008;58:541–7. | No primary care referral |
| Batik O, Phelan EA, Walwick JA, Wang G, LoGerfo JP. Translating a community-based motivational support program to increase physical activity among older adults with diabetes at community clinics: a pilot study of Physical Activity for a Lifetime of Success (PALS). Prev Chronic Dis 2008;5:A18. | No primary care referral |
| Bauman A. The role of community programmes and mass events in promoting physical activity to patients. Br J Sports Med 2009;43:44–6. | Review article |
| Berlant NE. Increasing adherence to an exercise intervention. Dissertation Abstracts International, Section B: The Sciences and Engineering; 2004. | No primary care referral |
| Binks M, O’Neil PM. Referral sources to a weight management program. Relation to outcome. J Gen Int Med 2002;17:596–603. | Not controlled trial |
| Blair SN, Applegate WB, Dunn AL, Ettinger WH, Haskell WL, King AC, et al. Activity Counseling Trial (ACT): Rationale, design, and methods. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1998;30:1097–106. | No primary care referral |
| Blanchard CM, Fortier M, Sweet S, O’Sullivan T, Hogg W, Reid R, et al. Explaining physical activity levels from a self-efficacy perspective: the physical activity counseling trial. Ann Behav Med 2007; 34:323–8. | No primary care referral |
| Bolognesi M, Nigg CR, Massarini M, Lippke S. Reducing obesity indicators through brief physical activity counseling (PACE) in Italian primary care settings. Ann Behav Med 2006;31:179–85. | No third-party exercise provider |
| Bonet J, Coll R, Rocha E, Romero R. Supervised versus recommended physical exercise in hypertensive women. Is its recommendation enough? Blood Press 2003;12:139–44. | Not primary care based |
| Boutelle KN, Dubbert P, Vander Weg M. A pilot study evaluating a minimal contact telephone and mail weight management intervention for primary care patients. Eat Weight Disord 2005;10:e1–5. | Not primary care based |
| Bravata DM, Smith-Spangler C, Sundaram V, Gienger AL, Lin N, Lewis R, et al. Using pedometers to increase physical activity and improve health: a systematic review. JAMA 2007;298:2296–304. | Review article |
| Brawley LR, Rejeski W, Lutes L. A group-mediated cognitive-behavioral intervention for increasing adherence to physical activity in older adults. J Appl Biobehav Res 2000;5:47–65. | Not primary care based |
| Bredahl TVG, Puggaard L, Roessler KK. Exercise on Prescription. Effect of attendance on participants’ psychological factors in a Danish version of Exercise on Prescription: a study protocol. BMC Health Serv Res 2008;8. | Not controlled trial |
| Brodie DA, Inoue A. Motivational interviewing to promote physical activity for people with chronic heart failure. J Adv Nurs 2005;50:518–27. | No primary care referral |
| Brodie DA, Inoue A, Shaw DG. Motivational interviewing to change quality of life for people with chronic heart failure: A randomised controlled trial. Int J Nurs Stud 2008;45:489–500. | No primary care referral |
| Brubaker PH, Moore JB, Stewart KP, Wesley DJ, Kitzman DW. Endurance exercise training in older patients with heart failure: results from a randomized, controlled, single-blind trial. J Am Geriatr Soc 2009;57:1982–9. | Not primary care based |
| Bull FC, Jamrozik K. Advice on exercise from a family physician can help sedentary patients to become active. Am J Prev Med 1998;15:85–94. | No third-party exercise provider |
| Bull FC, Jamrozik K, Blanksby BA. Tailored advice on exercise: does it make a difference? Am J Prev Med 1999;16:230–9. | No third-party exercise provider |
| Bull FC, Kreuter MW, Scharff DP. Effects of tailored, personalized and general health messages on physical activity. Patient Educ Couns 1999;36:181–92. | No primary care referral |
| Burtscher M, Gatterer H, Kunczicky H, Brandstatter E, Ulmer H. Supervised exercise in patients with impaired fasting glucose: impact on exercise capacity. Clin J Sport Med 2009;19:394–8. | No primary care referral |
| Calfas KJ, Long BJ, Sallis JF, Wooten WJ, et al. A controlled trial of physician counseling to promote the adoption of physical activity. Prev Med 1996;25:225–33. | No primary care referral |
| Calfas KJ, Sallis JF, Oldenburg B, Ffrench M. Mediators of change in physical activity following an intervention in primary care: PACE. Prev Med 1997;26:297–304. | No primary care referral |
| Campbell AJ, Robertson MC, Gardner MM, Norton RN, Buchner DM. Falls prevention over 2 years: a randomized controlled trial in women 80 years and older. Age Aging 1999; 28:513–8. | No primary care referral |
| Carnegie Research Institute. The national evaluation of LEAP: final report on the national evaluation of the Local Exercise Action Pilots. Leeds: Leeds Metropolitan University; 2007. | Not controlled trial |
| Carver D. GP exercise referral: improving effectiveness in populations that might benefit most. The number of exercise referral schemes is growing. Bases World 2003;10–11. | Review article |
| Chinn DJ, White M, Howel D, Harland JOE, Drinkwater CK. Factors associated with non-participation in a physical activity promotion trial. Publ Health 2006;120:309–19. | No primary care referral |
| Chown M, Whittamore L, Rush M, Allan S, Stott D, Archer M. A prospective study of patients with chronic back pain randomised to group exercise, Physiotherapy or osteopathy. Physiotherapy 2008 Mar;94:21–8. | No primary care referral |
| Clarke P, Eves F. Applying the Transtheoretical Model to the Study of Exercise on Prescription. J Health Psychol 1997;2:195–207. | Not controlled trial |
| Cochrane T, Davey R. Evaluation of exercise prescription for 25 general practices and a large leisure complex in Sheffield. J Sport Sci 1998;16:17–8. | Not controlled trial |
| Cochrane T, Davey RC, Matthes Edwards SM. Randomised controlled trial of the cost-effectiveness of water-based therapy for lower limb osteoarthritis. Health Technol Assess 2005;9:(31). | No primary care referral |
| Cock D, Adams IC, Ibbetson AB, Baugh P. REFERQUAL: a pilot study of a new service quality assessment instrument in the GP exercise referral scheme setting. BMC Health Serv Res 2006;6:61. | Not controlled trial |
| Corbett C, Woodiwiss B. Exercise on prescription. Prof Nurse 2003;18:666–7 | Review article |
| Craig A, Dinan S, Smith A, Taylor A, Webborn N. The Newcastle exercise project. National quality assurance framework will guide best value and practice in GP exercise referral schemes. BMJ 2000; 320:1474 | Review article |
| Cresswell J. Sand, sea and schemes. SportEX Health 2002;13:20. | Review article |
| Crone D, Johnston L, Grant T. Maintaining quality in exercise referral schemes: A case study of professional practice. Primary Health Care Research and Development 2004;5:96–103. | Not controlled trial |
| Daley AJ, Crank H, Mutrie N, Saxton JM, Coleman R. Patient recruitment into a randomised controlled trial of supervised exercise therapy in sedentary women treated for breast cancer. Contemp Clin Trial 2007; 28:603–13. | No third-party exercise provider |
| Daley A, Winter H, Grimmett C, McGuinness M, McManus R, MacArthur C. Feasibility of an exercise intervention for women with postnatal depression: a pilot randomised controlled trial. Br J Gen Pract 2008;58:178–83. | Not primary care based |
| Damush TM, Stump TE, Clark DO, editors. Primary care providers’ perceptions of physical activity referrals for inner-city patients. Society of General Internal Medicine, 26th Annual Meeting, Vancouver BC, 30 April to 3 May 2003 | Not controlled trial |
| Danish Centre for Health Technology A. Exercise on prescription: development and evaluation (brief record). Copenhagen: Danish Centre for Evaluation and Health Technol Assess; 2007. | Review article |
| Davies T. National quality assurance framework: medico-legal considerations. SportEX Health 2001;8:27–8. | Review article |
| Davies T, Craig A. Developments & opportunities for exercise prescription. SportEX Med 1999;1:20–2. | Review article |
| Day F, Nettleton B. The Scottish Borders general practitioners exercise referral scheme (GPERS). Health Bull 2001; 59:343–6. | Not controlled trial |
| Day R, Mills B, Fairbairn F. Exercise prescription: are practice nurses adequately prepared for this? NZ J Sports Med 2001;29:32–6. | No primary care referral |
| Di Loreto C, Fanelli C, Lucidi P, Murdolo G, De Cicco A, Parlanti N, et al. Validation of a counseling strategy to promote the adoption and the maintenance of physical activity by type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 2003;26:404–8. | Not primary care based |
| Drenthen AJM, Assendelft WJJ, Van Der Velden J. Prevention in the general practice: get moving! Huisarts Wet 2008;51:38–41. | Review article |
| Duda JL, Jolly K, Ntoumanis N, Eves F, Daley A, Mutrie N, et al. A 3-month evaluation of the standard provision and a self-determination theory-based exercise on referral program. J Sport Exerc Psychol 2009;31:S117. |
Not controlled trial (insufficient data) |
| Dutton GR. Effects of a primary care weight management intervention on physical activity in low-income African American women. Dissertation Abstracts International, Section B: The Sciences and Engineering; 2006. | No primary care referral |
| Dutton GR, Martin PD, Welsch MA, Brantley PJ. Promoting physical activity for low-income minority women in primary care. Am J Health Behav 2007;31:622–31. | No primary care referral |
| Eakin EG, Glasgow RE, Riley KM. Review of primary care-based physical activity intervention studies: effectiveness and implications for practice and future research. J Fam Pract 2000;49:158–68. | No primary care referral |
| Eakin E, Brown W, Schofield G, Mummery K, Reeves M. General practitioner advice on physical activity: who gets it? Am J Health Promot 2007;21:225–8. | No primary care referral |
| Eakin E, Reeves M, Lawler S, Graves N, Oldenburg B, Del Mar C, et al. Telephone counseling for physical activity and diet in primary care patients. Am J Prev Med 2009;36:142 | |
| Eakin EG, Brown WJ, Marshall AL, Mummery K, Larsen E. Physical activity promotion in primary care: bridging the gap between research and practice. Am J Prev Med 2004;27:297–303. | |
| Eakin EG, Bull SS, Riley K, Reeves MM, Gutierrez S, McLaughlin P. Recruitment and retention of Latinos in a primary care-based physical activity and diet trial: The Resources for Health study. Health Educ Res 2007;22:361–71. | No primary care referral |
| Eakin EG, Bull SS, Riley KM, Reeves MM, McLaughlin P, Gutierrez S. Resources for health: A primary-care-based diet and physical activity intervention targeting urban Latinos with multiple chronic conditions. Health Psychol 2007;26:392–400. | No primary care referral |
| Eakin EG, Reeves MM, Lawler SP, Oldenburg B, Del Mar C, Wilkie K, et al. The Logan Healthy Living Program: A cluster randomized trial of a telephone-delivered physical activity and dietary behavior intervention for primary care patients with type 2 diabetes or hypertension from a socially disadvantaged community: rationale, design and recruitment. Contemp Clin Trial 2008; 29:439–54. | Review article |
| Eaton CB, Menard LM. A systematic review of physical activity promotion in primary care office settings. Br J Sports Med 1998;32:11–16. | Review article |
| Elley CR, Kerse N, Arroll B, Robinson E. Effectiveness of counselling patients on physical activity in general practice: cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2003;326:793. | No primary care referral |
| Elley R, Kerse N, Arroll B, Swinburn B, Ashton T, Robinson E. Cost-effectiveness of physical activity counselling in general practice. NZ Med J 2004;117:U1216. | No primary care referral |
| Eriksson MK, Westborg CJ, Eliasson MCE. A randomized trial of lifestyle intervention in primary healthcare for the modification of cardiovascular risk factors. The Bjorknas study. Scand J Publ Health 2006;34:453 | |
| Eriksson MK, Franks PW, Eliasson M. A 3-year randomized trial of lifestyle intervention for cardiovascular risk reduction in the primary care setting: the Swedish Bjorknas study. PLoS ONE 2009;4:e5195. | No primary care referral |
| Fisher KJ, Li F. A community-based walking trial to improve neighborhood quality of life in older adults: a multilevel analysis. Ann Behav Med 2004;28:186–94. | Not primary care based |
| Fleming P, Godwin M. Lifestyle interventions in primary care: systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Can Fam Physician 2008;54:1706–13. | Review article |
| Fortier MS, Hogg W, O’Sullivan TL, Blanchard C, Reid RD, Sigal RJ, et al. The physical activity counselling (PAC) randomized controlled trial: rationale, methods, and interventions. Applied Physiol Nutr Metab 2007;32:1170–85. | No primary care referral |
| Foster NE, Thomas E, Barlas P, Hill JC, Young J, Mason E, et al. Acupuncture as an adjunct to exercise based Physiotherapy for osteoarthritis of the knee: randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2007;335:436. | No third-party exercise provider |
| Fritz T, Wandell P, Aberg H, Engfeldt P. Walking for exercise: does three times per week influence risk factors in type 2 diabetes? Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2006;71:21–7. | No primary care referral |
| Gidlow C, Murphy R. Physical activity promotion in primary health care. In Dugdilll L, Crone D, Murphy R, editors. Physical activity and health promotion: evidence-based approaches to practice; 2009. pp. 87–109. | Review article |
| Gine-Garriga M, Martin C, Martin C, Puig-Ribera A, Anton JJ, Guiu A, et al. Referral from primary care to a physical activity programme: establishing long-term adherence? A randomized controlled trial. Rationale and study design. BMC Publ Health 2009;9:31. | No primary care referral |
| Graham RC, Dugdill L, Cable NT. Health professionals’ perspectives in exercise referral: Implications for the referral process. BMC Publ Health 2005;48:1411–22. | Not controlled trial |
| Greater Glasgow Health Board. An evaluation report of the Glasgow Exercise Referral Scheme. Glasgow: Greater Glasgow Health Board Health Promotion Department; 2004. | Not controlled trial |
| Greaves CJ, Middlebrooke A, O’Loughlin L, Holland S, Piper J, Steele A, et al. Motivational interviewing for modifying diabetes risk: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Gen Pract 2008;58:535–40. | No primary care referral |
| Green F, Lord J. Prescribing exercise in general practice. Evaluation of scheme exists in Stockport. BMJ 1994;309:872–3. | Not controlled trial |
| Halbert J, Crotty M, Weller D, Ahern M, Silagy C. Primary care-based physical activity programs: effectiveness in sedentary older patients with osteoarthritis symptoms. Arthritis Rheum 2001;45:228–34. | No primary care referral |
| Halbert JA, Silagy CA, Finucane P, Withers RT, Hamdorf PA. Recruitment of older adults for a randomized, controlled trial of exercise advice in a general practice setting. J Am Geriatr Soc 1999;47:477–81. | No primary care referral |
| Hammond JM, Brodie DA, Bundred PE. Exercise on prescription: Guidelines for health professionals. Health Promot Int 1997;12:33–41. | Not controlled trial |
| Hardcastle S, Taylor A, Bailey M, Castle R. A randomized controlled trial on the effectiveness of a primary health care based counseling intervention on physical activity, diet and CHD risk. Patient Educ Couns 2008;70:31–9. | No primary care referral |
| Harland J, White M, Drinkwater C, Chinn D, Farr L, Howel D. The Newcastle exercise project: a randomised controlled trial of methods to promote physical activity in primary care. BMJ 1999;319:828–32. | No primary care referral |
| Hillsdon M. Promoting physical activity: issues in primary health care. Int J Obes RelatMetab Disord 1998;22(Suppl. 2):S52–4. | Review article |
| Hillsdon M. Recruitment strategies for exercise prescription. SportEX Med 2000;4:20–3. | Review article |
| Hillsdon M, Thorogood M, White I, Foster C. Advising people to take more exercise is ineffective: a randomized controlled trial of physical activity promotion in primary care. Int J Epidemiol 2002;31:808–15. | No primary care referral |
| Hinrichs T, Bucchi C, Brach M, Wilm S, Endres HG, Burghaus I, et al. Feasibility of a multidimensional home-based exercise programme for the elderly with structured support given by the general practitioner’s surgery: study protocol of a single arm trial preparing an RCT. BMC Geriatr 2009;9:37. | Not controlled trial, study protocol |
| Holtrop JS, Dosh SA, Torres T, Thum YM. The community health educator referral liaison (CHERL): a primary care practice role for promoting healthy behaviors. Am J Prev Med 2008;35:S365–72. | No third-party exercise provider |
| Hosper K, Deutekom M, Stronks K. The effectiveness of ‘Exercise on Prescription’ in stimulating physical activity among women in ethnic minority groups in the Netherlands: protocol for a randomized controlled trial. BMC Publ Health 2008;8:406. | Not controlled trial |
| Hughes SL, Seymour RB, Campbell RT, Whitelaw N, Bazzarre T. Best-practice physical activity programs for older adults: findings from the national impact study. Am J Publ Health 2009;99:362–8. | No primary care referral |
| Hung DY, Rundall TG, Tallia AF, Cohen DJ, Halpin HA, Crabtree BF. Rethinking prevention in primary care: applying the chronic care model to address health risk behaviors. Milbank Q 2007;85:69–91. | No third-party exercise provider |
| Jimmy G, Martin BW. Implementation and effectiveness of a primary care based physical activity counselling scheme. Patient Educ Couns 2005; 56:323–31. | No primary care referral |
| Johnston LH, Warwick J, De Ste Croix M, Crone D, Sidford A. The nature of all ‘inappropriate referrals’ made to a countywide physical activity referral scheme: Implications for practice. Health Educ J 2005; 64:58–69. | Not controlled trial |
| Jolly K, Duda JL, Daley A, Eves FF, Mutrie N, Ntoumanis N, et al. Evaluation of a standard provision versus an autonomy promotive exercise referral programme: rationale and study design. BMC Publ Health 2009;9:176. | Not controlled trial |
| Jones LW, Courneya KS, Fairey AS, Mackey JR. Effects of an oncologist’s recommendation to exercise on self-reported exercise behavior in newly diagnosed breast cancer survivors: a single-blind, randomized controlled trial. Ann Behav Med 2004;28:105–13. | Not primary care based |
| Jones LW, Courneya KS, Fairey AS, Mackey JR. Does the theory of planned behavior mediate the effects of an oncologist’s recommendation to exercise in newly diagnosed breast cancer survivors? Results From a randomized controlled trial. Health Psychol 2005;24:189–97. | Not primary care based |
| Kallings L, Leijon M, Hellenius M, Stahle A. Physical activity on prescription in primary health care: a follow-up of physical activity level and quality of life. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2008;18:154–61. | No primary care referral |
| Kallings LV, Leijon ME, Kowalski J, Hellenius M-L, Stahle A. Self-reported adherence: a method for evaluating prescribed physical activity in primary health care patients. J Phys Act Health 2009;6:483–92. | No primary care referral |
| Kallings LV, Sierra Johnson J, Fisher RM, Faire Ud, Stahle A, Hemmingsson E, et al. Beneficial effects of individualized physical activity on prescription on body composition and cardiometabolic risk factors: results from a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 2009;16:80–4. | No primary care referral |
| Kerr J, Calfas KJ, Caparosa S, Stein MB, Sieber W, Abascal LB, et al. A pilot study to assess the feasibility and acceptability of a community based physical activity intervention (involving internet, telephone, and pedometer support), integrated with medication and mood management for depressed patients. Ment Health Phys Act 2008;1:40–5. | No primary care referral |
| Kinmonth A-L, Wareham NJ, Hardeman W, Sutton S, Prevost A, Fanshawe T, et al. Efficacy of a theory-based behavioural intervention to increase physical activity in an at-risk group in primary care (ProActive UK): A randomised trial. Lancet 2008;371:41–8. | No primary care referral |
| Klemenc-Ketis Z. Analysis of referrals to Phys Ther at the Topolsica health resort. Zdravstveno Varstvo 2009;48:33–9. | Not primary care based |
| Kohl HW, 3rd, Dunn AL, Marcus BH, Blair SN. A randomized trial of physical activity interventions: design and baseline data from project active. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1998;30:275–83. | No primary care referral |
| Kolt GS, Oliver M, Schofield GM, Kerse N, Garrett N, Latham NK. An overview and process evaluation of Tele Walk: A telephone-based counseling intervention to encourage walking in older adults. Health Promot Int 2006;21:201–8. | No primary care referral |
| Kolt GS, Schofield GM, Kerse N, Garrett N, Oliver M. Effect of telephone counseling on physical activity for low-active older people in primary care: A randomized, controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc 2007;55:986–92. | No primary care referral |
| Krogh J, Saltin B, Gluud C, Nordentoft M. The DEMO trial: A randomized, parallel-group, observer-blinded clinical trial of strength versus aerobic versus relaxation training for patients with mild to moderate depression. J Clin Psychiatry 2009;70:790–800. | No primary care referral |
| Kruidenier LM, Nicolai SP, Hendriks EJ, Bollen EC, Prins MH, Teijink JAW. Supervised exercise therapy for intermittent claudication in daily practice. J Vasc Surg 2009;49:363–70. | No primary care referral |
| Lamb S, Bartlett H, Ashley A, Bird W. Can lay-led walking programmes increase physical activity in middle aged adults? A randomised controlled trial. J Epidemiol Community Health 2002;56:246–52. | No primary care referral |
| Lawton BA, Rose SB, Elley CR, Dowell AC, Fenton A, Moyes SA. Exercise on prescription for women aged 40–74 recruited through primary care: two year randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2008;337. | No primary care referral |
| Leijon ME, Bendtsen P, Nilsen P, Ekberg K, Stahle A. Physical activity referrals in Swedish primary health care: prescriber and patient characteristics, reasons for prescriptions, and prescribed activities. BMC Health Serv Res 2008;8. | No primary care referral |
| Leijon ME, Bendtsen P, Nilsen P, Festin K, Stahle A. Does a physical activity referral scheme improve the physical activity among routine primary health care patients? Scand J Med Sci Sports 2009;19:627–36. | No primary care referral |
| Lister CL, Rae S, Van Blerk C, editors. The effects of a community based exercise referral scheme on the health and wellbeing of people with chronic low back pain. Annual European Congress of Rheumatology, Berlin, Germany, 9–12 June 2004. | Not controlled trial |
| Litterini AJ, Fieler VK. The change in fatigue, strength, and quality of life following a physical therapist prescribed exercise program for cancer survivors. Rehabil Oncol;26:11–17. | Not primary care based |
| Little P, Dorward M, Gralton S, Hammerton L, Pillinger J, White P, et al. A randomised controlled trial of three pragmatic approaches to initiate increased physical activity in sedentary patients with risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Br J Gen Pract 2004;54:189–95. | No third-party exercise provider |
| Luxmore J, Symons LM. The benefits of an exercise on prescription programme for overweight patients J Sport Sci 1998;16:24–5. | Not controlled trial |
| MacEra CA. Weight loss, physical activity, and weight regain in postmenopausal women (commentary). Clin J Sport Med 2009;19:337–8. | Review article |
| Markland D, Tobin VJ. Need support and behavioural regulations for exercise among exercise referral scheme clients: The mediating role of psychological need satisfaction. Psychol Sport Exerc 2009;11:91–99. | Not controlled trial |
| McKay J, Wright A, Lowry R, Steele K, Ryde G, Mutrie N. Walking on prescription: The utility of a pedometer pack for increasing physical activity in primary care. Patient Educ Couns 2009;76:71–6. | No primary care referral |
| Morey MC, Peterson MJ, Pieper CF, Sloane R, Crowley GM, Cowper P, et al. Project LIFE; Learning to Improve Fitness and Function in Elders: methods, design, and baseline characteristics of randomized trial. J Rehabil Res Dev 2008;45:31–42. | No primary care referral |
| Morey MC, Peterson MJ, Pieper CF, Sloane R, Crowley GM, Cowper PA, et al. The Veterans Learning to Improve Fitness and Function in Elders Study: a randomized trial of primary care-based physical activity counseling for older men. J Am Geriatr Soc 2009;57:1166–74. | No primary care referral |
| Munro J, Brazier J, Davey R, Nicholl J. Physical activity for the over-65s: could it be a cost-effective exercise for the NHS? J Publ Health Med 1997;19:397–402. | No primary care referral |
| Munro JF, Nicholl JP, Brazier JE, Davey R, Cochrane T. Cost effectiveness of a community based exercise programme in over 65 year olds: cluster randomised trial. J Epidemiol Community Health 2004; 58:1004–10. | No primary care referral |
| Nanchahal K, Townsend J, Letley L, Haslam D, Wellings K, Haines A. Weight-management interventions in primary care: a pilot randomised controlled trial. Br J Gen Pract 2009;59:349–55. | No primary care referral |
| O’Toole ML, Sawicki MA, Artal R. Structured diet and physical activity prevent postpartum weight retention. J Women’s Health 2003;12:991–8. | No primary care referral |
| Ouellette MM, LeBrasseur NK, Bean JF, Phillips E, Stein J, Frontera WR, et al. High-intensity resistance training improves muscle strength, self-reported function, and disability in long-term stroke survivors. Stroke 2004;35:1404–9. | No primary care referral |
| Pakkala I, Read S, Leinonen R, Hirvensalo M, Lintunen T, Rantanen T. The effects of physical activity counseling on mood among 75- to 81-year-old people: A randomized controlled trial. Prev Med 2008;46:412–18. | No primary care referral |
| Peek ME, Tang H, Alexander G, Chin MH. National prevalence of lifestyle counseling or referral among African-Americans and whites with diabetes. J Gen Int Med 2008;23:1858–64. | Not controlled trial |
| Peters S, Stanley I, Rose M, Kaney S, Salmon P. A randomized controlled trial of group aerobic exercise in primary care patients with persistent, unexplained physical symptoms. Fam Pract 2002;19:665–74. | No primary care referral |
| Petrella R. Cost-effectiveness of a community-based exercise program for older adults (commentary). Clin J Sport Med 2006;16:191–3. | Review article |
| Pinto BM, Goldstein MG, Ashba J, Sciamanna CN, Jette A. Randomized controlled trial of physical activity counseling for older primary care patients. Am J Prev Med 2005;29:247–55 | No primary care referral |
| Raine P, Truman C, Southerst A. The development of a community gym for people with mental health problems: influences of psychological accessibility. J Ment Health 2002;11: 43–53. | Not primary care based |
| Rejeski W, Shelton B, Miller M, Dunn AL, King AC, Sallis JF. Mediators of increased physical activity and change in subjective well-being: results from the activity counseling trial (ACT). J Health Psychol 2001;6:159–68. | No primary care referral |
| Ridsdale L, Darbishire L, Seed P. Is graded exercise better than cognitive behaviour therapy for fatigue? A UK randomized trial in primary care. Psychol Med 2004;34:37–49. | No primary care referral |
| Rimmer JH, Rauworth A, Wang E, Heckerling PS, Gerber BS. A randomized controlled trial to increase physical activity and reduce obesity in a predominantly African American group of women with mobility disabilities and severe obesity. Prev Med 2009;48:473–9. | No third-party exercise provider |
| Robertson MC, Devlin N, Gardner MM, Campbell AJ. Effectiveness and economic evaluation of a nurse delivered home exercise programme to prevent falls. 1: Randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2001;322:697–701. | No primary care referral |
| Robertson MC, Devlin N, Scuffham P, Gardner MM, Buchner DM, Campbell AJ. Economic evaluation of a community based exercise programme to prevent falls. J Epidemiol Community Health 2001;55:600–6. | No primary care referral |
| Ross R, Blair SN, Godwin M, Hotz S, Katzmarzyk PT, Lam M, et al. Prevention and Reduction of Obesity through Active Living (PROACTIVE): rationale, design and methods. Br J Sports Med 2009;43:57–63. | No primary care referral |
| Roux L, Pratt M, Tengs TO, Yore MM, Yanagawa TL, Van Den Bos J, et al. Cost-effectiveness of community-based physical activity interventions. Am J Prev Med 2008;35:578–88. | Review article |
| Schnirring L. Referring patients to personal trainers: Benefits and pitfalls. Physician Sports Med 2000;28:16. | Review article |
| Sevick MA, Bradham DD, Muender M, Chen GJ, Enarson C, Dailey M, et al. Cost-effectiveness of aerobic and resistance exercise in seniors with knee osteoarthritis. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2000;32:1534–40. | Not primary care based |
| Sevick MA, Dunn AL, Morrow MS, Marcus BH, Chen G, Blair SN. Cost-effectiveness of lifestyle and structured exercise interventions in sedentary adults: Results of Project ACTIVE. Am J Prev Med 2000;19:1–8. | Not primary care based |
| Sevick MA, Miller GD, Loeser RF, Williamson JD, Messier SP. Cost-effectiveness of exercise and diet in overweight and obese adults with knee osteoarthritis. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2009;41:1167–74. | Not primary care based |
| Seymour RB, Hughes SL, Campbell RT, Huber GM, Desai P. Comparison of two methods of conducting the fit and strong! program. Arthritis Care Res 2009;61:876–84. | No primary care referral |
| Shepich J, Slowiak JM, Keniston A. Do subsidization and monitoring enhance adherence to prescribed exercise? Am J Health Promot 2007;22:2–5. | Not controlled trial |
| Sherman BJ, Gilliland G, Speckman JL, Freund KM. The effect of a primary care exercise intervention for rural women. Prev Med 2007;44:198–201. | No primary care referral |
| Simons-Morton DG, Blair SN, King AC, Morgan TM, Applegate WB, O’Toole M, et al. Effects of physical activity counseling in primary care: The Activity Counseling Trial: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2001;286:677–87. | No primary care referral |
| Smale B. Leisure links. The publication of the National Quality Assurance Framework for Exercise Referral Systems highlights the important role that leisure can play in health partnerships but what impact will this guidance have on training for leisure professionals? Leisure Manager 2001;19:12–13. | Review article |
| Smeets RJ, Severens JL, Beelen S, Vlaeyen JW, Knottnerus J. More is not always better: Cost-effectiveness analysis of combined, single behavioral and single physical rehabilitation programs for chronic low back pain. Eur J Pain 2009;13:71–81. | Not primary care based |
| Smith BJ, Bauman AE, Bull FC, Booth ML, Harris MF. Promoting physical activity in general practice: a controlled trial of written advice and information materials. Br J Sports Med 2000;34:262–7. | No primary care referral |
| Sogaard R, Bunger CE, Laurberg I, Christensen FB. Cost-effectiveness evaluation of an RCT in rehabilitation after lumbar spinal fusion: a low-cost, behavioural approach is cost-effective over individual exercise therapy. Eur Spine J 2008;17:262–71. | Not primary care based |
| Sowden S, Raine R. Running along parallel lines: How political reality impedes the evaluation of public health interventions. A case study of exercise referral schemes in England. J Epidemiol Community Health 2008;62:835–41. | Review article |
| Steptoe A, Doherty S, Rink E, Kerry S, Kendrick T, Hilton S. Behavioural counselling in general practice for the promotion of healthy behaviour among adults at increased risk of coronary heart disease: randomised trial. BMJ 1999;319:943–7. | No primary care referral |
| Steptoe A, Rink E, Kerry S. Psychosocial predictors of changes in physical activity in overweight sedentary adults following counseling in primary care. Prev Med 2000;31:183–94. | |
| Steptoe A, Kerry S, Rink E, Hilton S. The impact of behavioral counseling on stage of change in fat intake, physical activity, and cigarette smoking in adults at increased risk of coronary heart disease. Am J Publ Health 2001;91:265–9. | No primary care referral |
| Stovitz SD, VanWormer JJ, Center BA, Bremer KL. Pedometers as a means to increase ambulatory activity for patients seen at a family medicine clinic. Journal of the American Board of Fam Pract 2005;18:335–43. | No primary care referral |
| Stuart M, Benvenuti F, Macko R, Taviani A, Segenni L, Mayer F, et al. Community-based adaptive physical activity program for chronic stroke: feasibility, safety, and efficacy of the Empoli model. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 2009;27:726–34. | No primary care referral |
| Sugden JA, Sniehotta FF, Donnan PT, Boyle P, Johnston DW, McMurdo MET. The feasibility of using pedometers and brief advice to increase activity in sedentary older women: a pilot study. BMC Health Serv Res 2008;8:169. | No primary care referral |
| Tanne D, Tsabari R, Chechk O, Toledano A, Orion D, Schwammenthal Y, et al. Improved exercise capacity in patients after minor ischemic stroke undergoing a supervised exercise training program. Israel Med Assoc J 200;10:113. | Not primary care based |
| Taylor JD, Fletcher JP, Tiarks J. Impact of physical therapist-directed exercise counseling combined with fitness center-based exercise training on muscular strength and exercise capacity in people with type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. Phys Ther 2009;89:884–92. | Not primary care based |
| Taylor KI, Oberle KM, Crutcher RA, Norton PG. Promoting health in type 2 diabetes: nurse-physician collaboration in primary care. Biol Res Nurs 2005;6:207–15. | No primary care referral |
| Thurston M, Green K. Adherence to exercise in later life: How can exercise on prescription programmes be made more effective? Health Promot Int 2004;19:379–87. | Review article |
| Tulloch H, Fortier M, Hogg W. Physical activity counseling in primary care: who has and who should be counseling? Patient Educ Couns 2006 Dec;64:6–20. | Review article |
| Tumiati R, Mazzoni G, Crisafulli E, Serri B, Beneventi C, Lorenzi CM, et al. Home-centred physical fitness programme in morbidly obese individuals: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil 2008;22:940–50. | Not primary care based |
| Voutselas V, Sellens MH, Paschali C. Exercise prescribed in general practitioner referral schemes: A case study. J Hum Mov Stud 2006;50:79–90. | Not controlled trial |
| Ward M. The science link. SportEX Health 2003;16:21. | Review article |
| Williams NH. ‘The wise, for cure, on exercise depend’: physical activity interventions in primary care in Wales. Br J Sports Med 2009;43:106–8. | Review article |
| Paper | Comment |
|---|---|
| Carroll R, Ali N, Azam N. Promoting physical activity in South Asian Muslim women through ‘exercise on prescription’. Health Technol Assess 2002;6(8). | Not controlled |
| Crone D, Smith A, Gough B. ‘I feel totally at one, totally alive and totally happy’: a psycho-social explanation of the physical activity and mental health relationship. Health Educ Res 2005;20:600–11. | |
| Crone D, Johnston LH, Gidlow C, Henley C, James DV. Uptake and participation in physical activity referral schemes in the UK: an investigation of patients referred with mental health problems. Issues Ment Health Nurs 2008;29:1088–97. | Not controlled |
| Damush TM, Stump TE, Saporito A, Clark DO. Predictors of older primary care patients’ participation in a submaximal exercise test and a supervised, low-impact exercise class. Prev Med 2001;33:485–94. | Not controlled |
| Dinan S, Lenihan P, Tenn T, Iliffe S. Is the promotion of physical activity in vulnerable older people feasible and effective in general practice? Br J Gen Pract 2006;56:791–3. | Not controlled |
| Dugdill L, Graham RC, McNair F. Exercise referral: The Publ Health panacea for physical activity promotion? A critical perspective of exercise referral schemes; their development and evaluation. BMC Publ Health 2005;48:1390–410. | Not controlled |
| Edmunds J, Ntoumanis N, Duda JL. Adherence and well-being in overweight and obese patients referred to an exercise on prescription scheme: a self-determination theory perspective. Psychol Sport Exerc 2007;8:722–40 | Not controlled |
| Gidlow C, Johnston LH, Crone D, James D. Attendance of exercise referral schemes in the UK: a systematic review. Health Educ J 2005;64:168–86. | Not effectiveness systematic review |
| Gidlow C, Johnston LH, Crone D, Morris C, Smith A, Foster C, et al. Socio-demographic patterning of referral, uptake and attendance in physical activity referral schemes. J Publ Health 2007;29:107–13. | Not controlled |
| Hardcastle S, Taylor AH. Looking for more than weight loss and fitness gain: psychosocial dimensions among older women in a primary-care exercise-referral program. J Aging Phys Act 2001;9:313–28. | Not controlled |
| Hardcastle S, Taylor AH. Finding an exercise identity in an older body: it’s redefining yourself and working out who you are. Psychol Sport Exerc 2005; 6:173–188 | Not controlled |
| Harrison RA, McNair F, Dugdill L. Access to exercise referral schemes: a population based analysis. J Publ Health 2005;27:326–30. | Not controlled |
| Jackson C, Bell F, Smith RA, Dixey R. Do adherers and non-adherers to a GP exercise referral scheme differ in their long-term physical activity levels? J Sport Sci 1998;16:84. | Not controlled |
| James D, Mills H, Crone D, Johnston LH, Morris C, Gidlow CJ. Factors associated with physical activity referral completion and health outcomes. J Sport Sci 2009;27:1007–17. | Not controlled |
| James DVB, Johnston LH, Crone D, Sidford AH, Gidlow C, Morris C, et al. Factors associated with physical activity referral uptake and participation. J Sport Sci 2008;26:217–24. | Not controlled |
| Jones F, Harris P, Waller H, Coggins A. Adherence to an exercise prescription scheme: the role of expectations, self-efficacy, stage of change and psychological well-being. British J Health Psychol 2005;10:359–78. | Not controlled |
| Lord JC, Green F. Exercise on prescription: does it work? Health Educ J 1995;54:453–64. | Not controlled |
| Martin C, Woolf-May K. The retrospective evaluation of a general practitioner exercise prescription programme. J Hum Nutr Diet 1999;12:32. | Not controlled |
| Morton KL, Biddle SJH, Beauchamp MR. Changes in self-determination during an exercise referral scheme. Publ Health 2008;122:1257–60. | Not controlled |
| National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). Modelling the cost-effectiveness of physical activity interventions. London: NICE; 2006. | |
| National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). Rapid review of the economic evidence of physical activity interventions. London: NICE; 2006. | Not controlled |
| Roessler KK, Ibsen B. Promoting exercise on prescription: Recruitment, motivation, barriers and adherence in a Danish community intervention study to reduce type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia and hypertension. J Publ Health 2009;17:187–93. | Not controlled |
| Schmidt M, Absalah S, Nierkens V, Stronks K. Which factors engage women in deprived neighbourhoods to participate in exercise referral schemes? BMC Publ Health 2008;8:371. | Not controlled |
| Singh S. Why are GP exercise schemes so successful (for those who attend)? Results from a pilot study. J Manag Med 1997;11: 233–237 | Not controlled |
| Sowden SL, Raine R. Running along parallel lines: how political reality impedes the evaluation of Publ Health interventions. A case study of exercise referral schemes in England. J Epidemiol Community Health 2008;62:835–41. | Not controlled |
| Stathi A, McKenna J, Fox KR. The experiences of older people participating in exercise referral schemes. J R Soc Promot Health 2004;124:18–23. | Not controlled |
| Wiles R, Demain S, Robison J, Killeff J, Ellis-Hill C, McPherson K. Managing alone: exercise on prescription schemes for stroke patients post-discharge from physiotherapy. Disabil Rehabil 2007;29:25. | Not controlled |
| Wormald H, Ingle L. GP exercise referral schemes: Improving the patient’s experience. Health Educ J 2004;63:362–73. | Not controlled |
| Wormald H, Waters H, Sleap M, Ingle L. Participants’ perceptions of a lifestyle approach to promoting physical activity: targeting deprived communities in Kingston-Upon-Hull. BMC Publ Health 2006;6:202. | Not controlled |
| Paper | Comment |
|---|---|
| Carroll R, Ali N, Azam N. Promoting physical activity in South Asian Muslim women through ‘exercise on prescription’. Health Technol Assess 2002;6(8). | No cost data |
| Crone D, Smith A, Gough B. ‘I feel totally at one, totally alive and totally happy’: a psycho-social explanation of the physical activity and mental health relationship. Health Educ Res 2005;20:600–11. | |
| Crone D, Johnston LH, Gidlow C, Henley C, James DV. Uptake and participation in physical activity referral schemes in the UK: an investigation of patients referred with mental health problems. Issues Ment Health Nurs 2008;29:1088–97. | No cost data |
| Damush TM, Stump TE, Saporito A, Clark DO. Predictors of older primary care patients’ participation in a submaximal exercise test and a supervised, low-impact exercise class. Prev Med 2001;33:485–94. | No cost data |
| Dinan S, Lenihan P, Tenn T, Iliffe S. Is the promotion of physical activity in vulnerable older people feasible and effective in general practice? Br J Gen Pract 2006;56:791–3. | No cost data |
| Dugdill L, Graham RC, McNair F. Exercise referral: The Publ Health panacea for physical activity promotion? A critical perspective of exercise referral schemes; their development and evaluation. BMC Publ Health 2005;48:1390–410. | No cost data |
| Edmunds J, Ntoumanis N, Duda JL. Adherence and well-being in overweight and obese patients referred to an exercise on prescription scheme: a self-determination theory perspective. Psychol Sport Exerc 2007;8:722–40 | No cost data |
| Gidlow C, Johnston LH, Crone D, James D. Attendance of exercise referral schemes in the UK: A systematic review. Health Educ J 2005;64:168–86. | No cost data |
| Gidlow C, Johnston LH, Crone D, Morris C, Smith A, Foster C, et al. Socio-demographic patterning of referral, uptake and attendance in physical activity referral schemes. J Publ Health 2007;29:107–13. | No cost data |
| Hardcastle S, Taylor AH. Looking for more than weight loss and fitness gain: psychosocial dimensions among older women in a primary-care exercise-referral program. J Aging Phys Act 2001;9:313–28. | No cost data |
| Hardcastle S, Taylor AH. Finding an exercise identity in an older body: it’s redefining yourself and working out who you are. Psychol Sport Exerc 2005; 6:173–88. | No cost data |
| Harrison RA, McNair F, Dugdill L. Access to exercise referral schemes: a population based analysis. J Publ Health 2005;27:326–30. | No cost data |
| Jackson C, Bell F, Smith RA, Dixey R. Do adherers and non-adherers to a GP exercise referral scheme differ in their long-term physical activity levels? J Sport Sci 1998;16:84. | No cost data |
| James DVB, Johnston LH, Crone D, Sidford AH, Gidlow C, Morris C, et al. Factors associated with physical activity referral uptake and participation. J Sport Sci 2008;26:217–24. | No cost data |
| James D, Mills H, Crone D, Johnston LH, Morris C, Gidlow CJ. Factors associated with physical activity referral completion and health outcomes. J Sport Sci 2009;27:1007–17. | No cost data |
| Jolly K, Duda JL, Daley A, Ntoumanis N, Eves F, Rouse P, et al. An Evaluation of the Birmingham exercise on prescription service: standard provision and a self-determination focused arm. Final Report; 2009. | No cost data |
| Jones F, Harris P, Waller H, Coggins A. Adherence to an exercise prescription scheme: The role of expectations, self-efficacy, stage of change and psychological well-being. British J Health Psychol 2005;10:359–78. | No cost data |
| Lord JC, Green F. Exercise on prescription: does it work? Health Educ J 1995;54:453–64. | No cost data |
| Martin C, Woolf-May K. The retrospective evaluation of a general practitioner exercise prescription programme. J Hum Nutr Diet 1999;12:32. | No cost data |
| Morgan O. Approaches to increase physical activity: reviewing the evidence for exercise-referral schemes. Publ Health 2005;119:361–70. | No cost data |
| Morton KL, Biddle SJH, Beauchamp MR. Changes in self-determination during an exercise referral scheme. Publ Health 2008;122:1257–60. | No cost data |
| National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). A rapid review of the effectiveness of ERS to promote physical activity in adults. London: NICE; 2006. | No cost data |
| Roessler KK, Ibsen B. Promoting exercise on prescription: Recruitment, motivation, barriers and adherence in a Danish community intervention study to reduce type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia and hypertension. J Publ Health 2009;17:187–93. | No cost data |
| Schmidt M, Absalah S, Nierkens V, Stronks K. Which factors engage women in deprived neighbourhoods to participate in exercise referral schemes? BMC Publ Health 2008;8:371. | No cost data |
| Singh S. Why are GP exercise schemes so successful (for those who attend)? Results from a pilot study. J Manag Med 1997;11:233–37. | No cost data |
| Sorensen JB, Kragstrup J, Kjaer K, Puggaard L. Exercise on prescription: trial protocol and evaluation of outcomes. BMC Health Serv Res 2007;7:36 | No cost data |
| Sorensen JB, Kragstrup J, Skovgaard T, Puggaard L. Exercise on prescription: a randomized study on the effect of counseling vs counseling and supervised exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2008;18:288–97. | No cost data |
| Sowden SL, Raine R. Running along parallel lines: how political reality impedes the evaluation of Publ Health interventions. A case study of exercise referral schemes in England. J Epidemiol Community Health 2008;62:835–41. | No cost data |
| Stathi A, McKenna J, Fox KR. The experiences of older people participating in exercise referral schemes. J R Soc Promot Health 2004;124:18–23. | No cost data |
| Stevens W, Hillsdon M, Thorogood M, McArdle D. Cost-effectiveness of a primary care based physical activity intervention in 45–74 year old men and women: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Sports Med 1998;32:236–41. | No cost data |
| Taylor AH. Evaluating GP exercise referral schemes. Findings from a randomised control study. Brighton: University of Brighton; 1996. | No cost data |
| Taylor AH, Fox KR. Effectiveness of a primary care exercise referral intervention for changing physical self-perceptions over 9 months. Health Psychol 2005;24:11–21. | |
| Taylor AH, Doust J, Webborn N. Randomised controlled trial to examine the effects of a GP exercise referral programme in Hailsham, East Sussex, on modifiable coronary heart disease risk factors. J Epidemiol Community Health 1998;52:595–601. | |
| Wiles R, Demain S, Robison J, Killeff J, Ellis-Hill C, McPherson K. Managing alone: Exercise on prescription schemes for stroke patients post-discharge from physiotherapy. Disabil Rehabil 2007;29:25. | No cost data |
| Wormald H, Ingle L. GP exercise referral schemes: Improving the patient’s experience. Health Educ J 2004;63:362–73. | No cost data |
| Wormald H, Waters H, Sleap M, Ingle L. Participants’ perceptions of a lifestyle approach to promoting physical activity: targeting deprived communities in Kingston-Upon-Hull. BMC Publ Health 2006;6:202. | No cost data |
| Paper | Comment |
|---|---|
| Gusi N, Reyes MC, Gonzalez-Guerrero JL, Herrera E, Garcia JM. Cost-utility of a walking programme for moderately depressed, obese, or overweight elderly women in primary care: a randomised controlled trial. BMC Publ Health 2008;8:231. | No uptake and/or adherence data |
| Morgan O. Approaches to increase physical activity: reviewing the evidence for exercise-referral schemes. Publ Health 2005;119:361–70. | No uptake and/or adherence data |
| Jolly K, Duda JL, Daley A, Ntoumanis N, Eves F, Rouse P, et al. An Evaluation of the Birmingham exercise on prescription service: standard provision and a self-determination focused arm. Final Report 2009. | No uptake and/or adherence data |
| National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). A rapid review of the effectiveness of ERS to promote physical activity in adults. London: NICE; 2006. | No uptake and/or adherence data |
| National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). Modelling the cost-effectiveness of physical activity interventions. London: NICE; 2006. | |
| National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). Rapid review of the economic evidence of physical activity interventions. London: NICE; 2006. | No uptake and/or adherence data |
| Sorensen JB, Skovgaard T, Puggaard L. Exercise on prescription in general practice: A systematic review. Scand J Primary Health Care 2006;24:69–74. | No uptake and/or adherence data |
| Sorensen JB, Kragstrup J, Kjaer K, Puggaard L. Exercise on prescription: trial protocol and evaluation of outcomes. BMC Health Serv Res 2007;7:36 | No uptake and/or adherence data |
| Taylor AH. Evaluating GP exercise referral schemes. Findings from a randomised control study. Brighton: University of Brighton; 1996. | Uptake and/or adherence data taken from Taylor et al. (1998) |
| Taylor AH, Fox KR. Effectiveness of a primary care exercise referral intervention for changing physical self-perceptions over 9 months. Health Psychol 2005;24:11–21. | Uptake and/or adherence data taken from Taylor et al. (1998) |
Appendix 4 Detailed data extraction: effectiveness systematic review
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | 005 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | March 2010 |
| Title of report | Cost-utility of a walking programme for moderately depressed, obese, or overweight elderly women in primary care: a randomized controlled trial |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | BMC Public Health 2008;8:231 |
| Authors | Gusi N, Reyes M C, Gonzalez-Guerrero J L, Herrera E and Garcia J M |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | Spain |
| Funders of the trial | The study was supported by European Social Funds and the Government of Extremadura, Spain |
| Date trial was conducted | Not stated |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Parallel |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | Yes – four general practices |
| Follow-up | Six months post randomisation |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | Medical practitioner |
| Reason for referral | Either moderate depression or were overweight |
| Format of referral | Not stated |
| Referred to who | Qualified exercise leaders |
| Referred to where | Supervised walks with a group in a public park or forest tracks |
| Single or group sessions | Group |
| Referral quote from paper |
‘Medical practitioners spent 2 weeks at each practice referring patients’ ‘Medical practitioners did not know which group patients were randomised to prior to their exercise referral’ |
| Characteristics of the intervention | |
|---|---|
| Components of the intervention | Exercise programme |
| Total duration | Six months |
| No. of sessions per week | Three |
| Duration of sessions | 50 minutes |
| Session intensity | Each session consisted of walking alternating with specific exercises, as follows: 5 minutes of joint mobility (eight to 12 easy rotations at the neck, shoulder, hip and ankle and eight to 12 easy flexions/extensions of the knee, wrist and elbow); 15 minutes of brisk walking; 5 minutes of strengthening (eight to 12 flexions/extensions of arms against a wall, eight to 12 spine flexions with elevation of alternating knees, in a standing position) and stretching [hamstrings and shoulders (trying to touch the fingers on the upper-back)]; 20 minutes of brisk walking including 20 footsteps and 50 hand-claps to provide additional mechanical impact |
| Session mode | See above |
| Control group | ‘Best care in general practice, which consisted of routine care and a recommendation of physical activity’ |
| Other information | |
| Characteristics of the participants | ||
|---|---|---|
| Experimental group | Control group | |
| Inclusion criteria |
Aged ≥ 60 years and old Moderate depression scored 6–9 points in the 15-item Geriatric Depression Scale Overweight (BMI of 25–39.9 kg/m2) Capable of walking for > 25 minutes |
|
| Exclusion criteria |
Poor health (severe obesity or major depression) A debilitating medical condition or a known unstable cardiac condition Attention or comprehension problems (e.g. Alzheimer’s disease, apraxia, global aphasia and other types of dementia or psychopathology) The intention of leaving the region |
|
| Total number of randomised participants | 64 | 63 |
| Information on the age of the participants (mean and SD) | 71 (5) | 74 (6) |
| Information on the sex of the participants (%) | 100% female | 100% female |
| Information on the ethnicity of the participants (%) | Not reported | Not reported |
| Specifics of the population (i.e. disease %) |
Overweight: 80 Type 2 diabetes: 40 Moderately depressed: 33 |
Overweight: 86 Type 2 diabetes: 39 Moderately depressed: 39 |
| Type of outcomes (What outcomes were assessed in this trial? Which of these outcomes have reported information about the result?) | |
|---|---|
| Outcome (domain) | Assessed (measure) |
| Effectiveness | |
| PA | Not reported |
| Fitness (e.g. V O2max) | Not reported |
| Clinical factors (e.g. blood lipids) | BMI (kg/m2) |
| Psychological well-being |
Depression by Geriatric Depression Scale Anxiety by State Trait Anxiety Inventory |
| QoL | EQ-5D |
| Patient satisfaction | Not reported |
| Adverse events | Not reported |
| Patient factors | |
| Uptake | Not reported |
| Adherence | Not reported |
Part 3: extracted results
| ERS (baseline) | Usual care (baseline) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | |
| BMI | 29.7 | 64 | 4.2 | 30.6 | 63 | 4.3 |
| Depression: Geriatric Depression Scale | 2.3 | 64 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 63 | 2.5 |
| Anxiety: State Trait Anxiety Inventory | 19.2 | 64 | 11.2 | 21.2 | 63 | 10.4 |
| Anxiety/depression EQ-5D | 1.4 | 64 | 0.6 | 1.4 | 63 | 0.6 |
| ERS (6 months) | Usual care (6 months) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | |
| BMI | 29.4 | 55 | 4.2 | 30.8 | 51 | 4.3 |
| Depression: Geriatric Depression Scale | 1.8 | 55 | 2.3 | 2.9 | 51 | 2.5 |
| Anxiety: State Trait Anxiety Inventory | 14.1 | 55 | 9 | 22.2 | 51 | 9.8 |
| Anxiety/depression EQ-5D | 1.2 | 55 | 0.4 | 1.5 | 51 | 0.7 |
Part 4: study quality (provide comments and quotes where appropriate)
| Quality | Yes | Unclear | No |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power calculation reported | ‘The primary outcome was the EQ-5D utility. The required sample size was calculated with the Spanish EQ-5D data set for a hypothetical study comparing two groups with a significance level alpha (0.05) and 80% of the power needed for a minimal clinically relevant difference of 0.1’ | ||
| Method of random sequence generation described? | ‘A research assistant, who did not participate in the current investigation, randomized participants to either an intervention group or control group, according to a random numbers table’ | ||
| Method of allocation concealment described? | See above | ||
| Method of outcome (assessment) blinding described? | Not reported | ||
| Are groups similar at baseline? | ‘At baseline, the intervention group was slightly less depressed, less overweight and younger than the control group, but these differences were not statistically significant (p > 0.05) (Table 1)’ | ||
| Was ITT analysis used? | Yes for health outcomes, but not for cost–utility | ||
| Was there any statistical handling of missing data? | ‘The participants who were lost to follow-up (mainly because they had to care for a relative) were similar to those who completed the trial but a slightly higher percentage of them were moderately depressed. The participants in the control group who dropped out were similar to those who followed the trial but they were mainly living in an urban area’ | ||
| Were missing data (dropout and loss to follow-up) reported? | Yes – figure 1 |
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Physical activity data
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | 002 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | March 2010 |
| Title of report | Does primary care referral to an exercise programme increase PA 1 year later? A randomised controlled trial |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | Journal of Public Health |
| Authors | Harrison RA, Roberts C and Elton PJ |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial |
Bolton Metropolitan Borough Council and Wigan and Bolton Health Authority |
| Date trial was conducted | March 2000 to December 2001 |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Parallel RCT |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | Borough in the north-west of England, 52 general practices and diabetes centres |
| Follow-up | Six, 9 and 12 months post randomisation |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | GP |
| Reason for referral |
Sedentary adults with additional CHD risk factors. These were obesity (as determined by the referrer); previous MI; on the practice CHD risk-management register; or diabetes. |
| Format of referral | A faxed referral form |
| Referred to who | Exercise officer |
| Referred to where | Leisure centre for initial consultation, then any of the council-run PA facilities for the duration of the scheme |
| Single or group sessions | Not reported |
| Referral quote from paper |
‘During the period of the study, all referral forms were faxed by the referring practitioner …’ ‘After receiving a referral form, the exercise officers telephoned clients …’ |
| Characteristics of the intervention | |
|---|---|
| Components of the intervention | One-hour consultation, person-specific advice and information taking into account patients’ preferences and abilities for different types of activities. All clients offered a 12-week subsidised leisure pass, encouraged to attend at least two sessions a week. Information on non-leisure centre-based activities available. Exit interview to review progress and identify further PA opportunities |
| Total duration | 12 weeks |
| No. of sessions per week | ≥ 2 sessions/week |
| Duration of sessions | Not reported |
| Session intensity | Not reported |
| Session mode | Not reported |
| Control group | Sent a written information pack |
| Other information | One primary care locality also funded the scheme to accept sedentary patients, regardless of other risk factors |
| Characteristics of the participants | ||
|---|---|---|
| Experimental group | Control group | |
| Inclusion criteria | Sedentary adults with additional CHD risk factors, obesity (as determined by the referrer); previous MI; on the practice CHD risk-management register; or diabetes | |
| Exclusion criteria |
Patients identified by the clinician as having contraindications to PA Hypertension (SBP ≥ 200 mmHg) Aged < 18 years old Not sedentary Not providing consent Additional criteria, imposed for the trial, were that more than one family member could not be knowingly recruited, to minimise contamination, and that the referring practitioner and patient had to give written informed consent |
|
| Total number of randomised participants | 275 | 270 |
| Information on the age (years) of the participants (mean and SD) |
18–44 = 111 45–59 = 101 > 60 = 63 |
18–44 = 107 45–59 = 98 > 60 = 65 |
| Information on the sex of the participants (%) | 32.7% male | 34.1% male |
| Information on the ethnicity of the participants (%) | 71.9% white | 74.1% white |
| Specifics of the population (i.e. disease, %) |
24.4% smoker 75.3% ≥ 1 CHD risk factor |
20.7% smoker 75.2% ≥ 1 CHD risk factor |
| Type of outcomes (What outcomes were assessed in this trial? Which of these outcomes have reported information about the result?) | |
|---|---|
| Outcome (domain) | Assessed (measure) |
| Effectiveness | |
| PA | Percentage of people (at 1 year, 9 months and 6 months since randomisation) who were participating in at least 90 minutes per week of moderate/vigorous PA. 7-Day Physical Activity Recall |
| Fitness (e.g. VO2max) | Not reported |
| Clinical factors (e.g. blood lipids) | Not reported |
| Psychological well-being | Not reported |
| QoL | Not reported |
| Patient satisfaction | Not reported |
| Adverse events | Yes and ‘demand for information’, measure not stated |
| Patient factors | |
| Uptake | 84% (232/275) |
| Adherence | Not reported |
Part 3: extracted results
| ERS (baseline) | Usual care (baseline) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | N | n | N | |
| At least 90 minutes of moderate-intensity PA | 38 | 275 | 22 | 270 |
| ERS (9 months) | Usual care (9 months) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | N | n | N | |
| At least 90 minutes of moderate-intensity PA | 36 | 275 | 31 | 270 |
| ERS (12 months) | Usual care (12 months) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | N | n | N | |
| At least 90 minutes of moderate-intensity PA | 40 | 275 | 32 | 270 |
Part 4: study quality (provide comments and quotes where appropriate)
| Quality | Yes | Unclear | No |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power calculation reported | To identify this with 90% power and two-sided 5% statistical significance required 264 participants. | ||
| Method of random sequence generation described? | Individual patients were randomised by computer using minimisation software and stratified by sex, age group (18–44 years, 45–59 years, ≥ 60 years old) and CHD risk (yes or no to: post MI/on CHD register) | ||
| Method of allocation concealment described? | Not reported | ||
| Method of outcome (assessment) blinding described? | Not reported | ||
| Are groups similar at baseline? | ‘The baseline characteristics of the 275 allocated to the intervention group and 270 to the control group were comparable (Table 1)’ | ||
| Was ITT analysis used? | The analysis was on the basis of ITT subject to the availability of follow-up data | ||
| Was there any statistical handling of missing data? | ‘All analyses assumed that levels of physical activity in non-responders to the follow-up questionnaires would be similar in the two allocation groups. Not all participants returned questionnaires at follow-up and some responded to different assessment points. Therefore, to increase statistical power and to make use of all available data, a post-hoc analysis merged data across the 9 and 12 month assessments using robust SEs that adjust for multiple observations’ | ||
| Were missing data (dropout and loss to follow-up) reported? | Reported in flow diagram – figure 1 |
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | 006 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | March 2010 |
| Title of report | Exercise Evaluation Randomised Trial (EXERT): a Randomised Trial Comparing GP Referral for Leisure Centre-based Exercise, Community-based Walking and Advice Only |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | Health Technol Assess 2007;11(10) |
| Authors | Isaacs AJ, Critchley JA, See Tai S, Buckingham K, Westley D, Harridge SDR, Smith C and Gottlieb JM |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full publication |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | UK HTA programme |
| Date trial was conducted | October 1998 to April 2002 |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Parallel-group RCT 3-group design: 1. Exercise referral scheme; 2. Walking Programme; 3. No exercise (control) |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? |
No Copthall Leisure Centre, Barnet, outer London |
| Follow-up | 10 weeks, 6 months and 12 months post randomisation |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral |
GP or practice nurse Referrals were also accepted in some instances (with approval from the patient’s GP) from other primary and secondary care professionals, such as dieticians and diabetes nurses |
| Reason for referral |
Any patient meeting the inclusion criteria Patients whom the GP considered would improve with regular exercise, who were not already participating in regular exercise and were considered to be at risk from CHD (e.g. with mild or moderate hypertension, overweight, with raised cholesterol levels, or a family history of CHD) |
| Format of referral | Specially prepared ‘prescription pad’ – referral form |
| Referred to who |
ERS group: instructor-led exercise classes in a leisure centre Walking group: instructor-led community-based walking programmes All instructors were qualified to National Vocational Qualification (NVQ) Level 3 standard, consistent with the recommendations of the National Quality Assurance Framework |
| Referred to where |
ERS group: four different leisure centres at different sites in the district Walking group: walking – 12 different locations around the borough parks and open spaces |
| Single or group sessions |
ERS: individual and/or group Walking: group |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘To make a referral, the [primary-care health] professional had to complete and sign the prescription, providing contact information for the patient and information on their cardiovascular risk factors’ |
| Characteristics of the intervention | |
|---|---|
| Components of the intervention |
ERS group: instructor-led exercise classes in a leisure centre setting Walking group: instructor-led walks Both were designed to increase the participants’ general fitness, taking them through a range of exercises and routines. Every class consisted of at least 45 minutes of exercises aimed to increase stamina, strength and flexibility, preceded and followed by a warm-up and warm-down period |
| Total duration | All groups: 10 weeks |
| No. of sessions per week |
ERS group: 2–3 Walking group: ≥ 2 |
| Duration of sessions |
ERS group: ≥ 45 minutes Walking group: 45 minutes |
| Session intensity |
ERS group: not stated Walking group: All participants were encouraged 60% and 80% of their maximum (slightly breathless, but able to carry on a conversation) |
| Session mode |
ERS group: aerobics, body conditioning, aqua aerobics, gymnasium and an optional swimming class Walking group: walking, strengthening (resistance bands), stretching |
| Control group |
Tailored advice and information on PA, including local exercise facilities Put on a waiting list for potential re-randomisation to one of the two active intervention groups after approximately 6–9 months |
| Other information | |
| Characteristics of the participants | ||
|---|---|---|
| Experimental group | Control group | |
| Inclusion criteria | Aged between 40 and 74 years, not currently physically active and with at least one of the following cardiovascular risk factors: raised cholesterol; controlled mild-to-moderate hypertension; obesity; current smoking; diabetes; a family history of MI at an early age | |
| Exclusion criteria |
Major exclusion criterion: pre-existing overt CVD Other exclusion criteria: uncontrolled hypertension, uncontrolled insulin-dependent diabetes, psychiatric conditions, physical disabilities that would prevent participation in an exercise class, conditions requiring a specialist programme (e.g. uncontrolled epilepsy) |
|
| Total number of randomised participants |
ERS: n = 317 Walking: n = 311 |
n = 315 |
| Information on the age of the participants (mean and SD) |
Exercise: 57.1 (8.7) Walking: 56.9 (8.5) |
57.0 (9.0) |
| Information on the sex of the participants (%) |
Exercise: 35 male Walking: 31.2 male |
31.7 male |
| Information on the ethnicity of the participants (%) |
Exercise: 75.7 white, 16.7 Asian Walking: 75.9 white, 12.2 Asian |
76.5 white 14.0 Asian |
| Specifics of the population (i.e. disease, %): | ||
| Raised cholesterol | ERS 24.0, Walking 21.5 | 17.1 |
| Hypertension | ERS 44.5, Walking 46.3 | 43.5 |
| Obesity | ERS 65.9, Walking 58.5 | 63.5 |
| Smoking | ERS 10.4, Walking 12.2 | 8.3 |
| Diabetes | ERS 12.3, Walking 11.3 | 15.6 |
| Family history of MI | ERS 13.9, Walking 12.9 | 16.2 |
| Type of outcomes (What outcomes were assessed in this trial? Which of these outcomes have reported information about the result?) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Outcome (domain) | Assessed (measure) | |
| Effectiveness | ||
| PA | 7-day recall questionnaires (minutes of light, moderate and vigorous category activity) | |
| Fitness (e.g. V O2max) |
Aerobic fitness: submaximal bicycle ergometer exercise test and submaximal shuttle walking test Isometric strength and power of the knee extensor muscles Flexibility – sit and reach, and shoulder abduction |
|
| Clinical factors (e.g. blood lipids) |
SBP, DBP (mmHg) and resting pulse rate (b.p.m.) Anthropometry: weight (kg); waist and hip measurements (cm); ankle body fat (%) was estimated by bioimpedance BMI Respiratory function: PEF (l/minute), FEV1 (l/minute) and FVC (l) Lipids: total cholesterol, HDL, triglycerides, LDL cholesterol |
|
| Psychological well-being: | HADS | |
| QoL | SF-36 | |
| Adverse events (e.g. injury) | Attendance at the GP surgery, presenting conditions and any medication prescribed | |
| Patient satisfaction | Participants allocated to ERS and walking groups, were asked to evaluate their exercise programmes at 10 weeks. | |
| Patient factors | ||
| Uptake | ERS: 92% (293/317) | Walking: 76% (238/311) |
| Adherence | ERS: 42% (133/317) | Walking: 22% (67/311) |
Part 3: extracted results
| ERS group baseline | Advice group baseline | Walking group baseline | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | |
| Minutes of moderate- and/or vigorous-intensity PA | 301 | 0 | 305 | 0 | 305 | 0 | |||
| Total activity (minutes) | 317 | 0 | 153 | 0 | 153 | 0 | |||
| Energy expenditure (kcal/kg/week) | 317 | 0 | 153 | 0 | 153 | 0 | |||
| Weight (kg) | 83 | 317 | 17.80449 | 81.8 | 315 | 10.64894 | 82.4 | 311 | 17.63519 |
| BMI | 30.7 | 317 | 5.341348 | 30.3 | 315 | 5.324472 | 30.6 | 311 | 5.290558 |
| Percentage body fat | 37.6 | 317 | 8.902247 | 37.8 | 315 | 8.87412 | 37.7 | 311 | 8.817596 |
| Waist to hip | 0.88 | 317 | 0.089022 | 0.87 | 315 | 0.088741 | 0.87 | 311 | 0.105811 |
| Resting heart rate | 65.7 | 316 | 10.66583 | 65.8 | 314 | 10.63203 | 64.7 | 311 | 10.58112 |
| SBP | 136.3 | 317 | 19.94103 | 135.4 | 314 | 21.08685 | 136.1 | 311 | 21.51493 |
| DBP | 84.2 | 317 | 9.792472 | 84.4 | 314 | 10.98643 | 84.3 | 311 | 10.05206 |
| FEV | 2.37 | 313 | 0.707672 | 2.33 | 310 | 0.704273 | 2.33 | 306 | 0.699714 |
| FVC | 2.8 | 313 | 0.707672 | 2.74 | 310 | 0.704273 | 2.76 | 306 | 0.699714 |
| FEV/FVC | 0.85 | 313 | 0.070767 | 0.86 | 310 | 0.070427 | 0.85 | 306 | 0.087464 |
| PEF | 410.8 | 285 | 128.1339 | 402.7 | 280 | 126.8377 | 399.9 | 278 | 112.8785 |
| Cycle ergometer (minutes) | 8.5 | 142 | 2.383275 | 8.9 | 130 | 2.280351 | 9 | 125 | 2.236068 |
| Shuttle walk (m) | 416.8 | 127 | 155.5181 | 415 | 139 | 126.1511 | 424.8 | 141 | 143.6795 |
| IKES (N) | 252.7 | 274 | 107.5941 | 263.8 | 267 | 107.8449 | 263.6 | 265 | 109.0681 |
| LEP (W) | 153.2 | 310 | 77.46999 | 157.9 | 309 | 82.61846 | 157.7 | 309 | 75.5871 |
| LEP (W/kg) | 1.8 | 310 | 0.704273 | 1.9 | 309 | 0.87892 | 1.9 | 309 | 0.703136 |
| Shoulder abduction | 143.9 | 315 | 15.97342 | 143.3 | 312 | 15.89717 | 144.2 | 311 | 15.87167 |
| Cholesterol | 5.76 | 262 | 0.971185 | 5.65 | 272 | 0.989545 | 5.76 | 258 | 1.124366 |
| HDL | 1.32 | 258 | 0.321248 | 1.37 | 272 | 0.329848 | 1.41 | 256 | 0.48 |
| Cholesterol/HDL | 4.56 | 258 | 1.124366 | 4.37 | 271 | 1.152345 | 4.37 | 256 | 1.44 |
| LDL | 3.52 | 251 | 0.950579 | 3.47 | 264 | 0.812404 | 3.44 | 250 | 0.948683 |
| Triglycerides | 2.17 | 263 | 1.297382 | 1.9 | 272 | 0.989545 | 2.04 | 258 | 1.28499 |
| ERS group (10 weeks) | Advice group (10 weeks) | Walking group (10 weeks) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | |
| Minutes of moderate- and/or vigorous-intensity PA | 93 | 157 | –115.071 | 79 | 153 | 113.5958 | 113 | 154 | 291.2474 |
| Total activity (minutes) | 584 | 157 | 479.4629 | 668 | 153 | 555.3571 | 863 | 154 | 1025.698 |
| Energy expenditure (kcal/kg/week) | 34 | 157 | 25.57136 | 36 | 153 | 31.55438 | 49 | 154 | 56.9832 |
| Weight (kg) | 80.53 | 164 | 3.2669 | 80.73 | 156 | 3.759744 | 80.38 | 160 | 7.163527 |
| BMI | 30.22 | 164 | 0.849394 | 30.11 | 156 | 1.465663 | 30.22 | 160 | 1.613407 |
| Percentage body fat | 37.41 | 164 | 1.894802 | 37.58 | 156 | 1.911734 | 37.06 | 160 | 1.936088 |
| Waist to hip | 0.88 | 164 | 0.065338 | 0.89 | 156 | 0 | 0.88 | 160 | 0.064536 |
| Resting HR | 64.7 | 164 | 5.22704 | 64.7 | 156 | 12.10765 | 65 | 160 | 5.808265 |
| SBP | 132.9 | 164 | 9.8007 | 132 | 156 | 10.19592 | 134.4 | 160 | 10.3258 |
| DBP | 82 | 164 | 5.88042 | 82.5 | 156 | 6.372447 | 84 | 160 | 6.453628 |
| FEV | 2.38 | 163 | 0.130277 | 2.36 | 152 | 0.188707 | 2.38 | 156 | 0.127449 |
| FVC | 2.78 | 163 | 0.195415 | 2.76 | 152 | 0.188707 | 2.81 | 156 | 0.191173 |
| FEV/FVC | 0.86 | 163 | 0 | 0.86 | 152 | 0.062902 | 0.85 | 156 | 0.063724 |
| PEF | 417.6 | 148 | 57.72418 | 409.1 | 138 | 57.53799 | 407.2 | 144 | 60.61224 |
| Cycle ergometer (minutes) | 9.65 | 77 | 1.522188 | 8.87 | 63 | 1.538855 | 8.92 | 69 | 1.652849 |
| Shuttle walk (m) | 456.7 | 62 | 102.0407 | 434.2 | 68 | 104.3398 | 436.6 | 74 | 99.62897 |
| IKES (N) | 277.9 | 140 | 53.72766 | 265.1 | 134 | 56.10737 | 275 | 142 | 58.36592 |
| LEP (W) | 173.6 | 162 | 30.52104 | 164.6 | 154 | 31.02418 | 165.6 | 160 | 31.62278 |
| LEP (W/kg) | 2.1 | 162 | 0.38963 | 1.98 | 154 | 0.379888 | 1.99 | 160 | 0.387218 |
| Shoulder abduction | 144.7 | 162 | 11.68891 | 143.6 | 154 | 11.39664 | 146.2 | 160 | 12.26189 |
| Cholesterol | 5.68 | 133 | 0.529556 | 5.71 | 136 | 0.416497 | 5.69 | 131 | 0.52556 |
| HDL | 1.35 | 131 | 0.175187 | 1.35 | 135 | 0.177841 | 1.33 | 129 | 0.173844 |
| Cholesterol/HDL | 4.48 | 131 | 0.583955 | 4.46 | 135 | 0.592804 | 4.52 | 129 | 0.57948 |
| LDL | 3.41 | 127 | 0.459977 | 3.44 | 133 | 0.470717 | 3.45 | 126 | 0.458162 |
| Triglycerides | 2.12 | 134 | 0.708725 | 2.14 | 136 | 0.713994 | 2.05 | 131 | 0.759142 |
| ERS group (6 months) | Advice group (6 months) | Walking group (6 months) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | |
| Minutes of moderate- and/or vigorous-intensity PA | 65 | 301 | 106.2205 | 58 | 305 | 98.01364 | 89 | 300 | 150.2289 |
| Total activity (minutes) | 692 | 301 | 495.6958 | 647 | 305 | 463.3372 | 759 | 300 | 539.0566 |
| Energy expenditure (kcal/kg/week) | 38 | 301 | 26.55513 | 35 | 305 | 26.73099 | 42 | 300 | 26.51098 |
| Weight (kg) | 82.28 | 317 | 2.997695 | 82.17 | 315 | 3.078776 | 82.29 | 311 | 3.059166 |
| BMI | 30.47 | 317 | 1.090071 | 30.44 | 315 | 1.086627 | 30.48 | 311 | 1.079706 |
| Percentage body fat | 37.78 | 317 | 2.361821 | 37.83 | 315 | 2.354358 | 37.79 | 311 | 2.339362 |
| Waist to hip | 0.88 | 317 | 0 | 0.88 | 315 | 0 | 0.88 | 311 | 0 |
| Resting HR | 65.3 | 316 | 6.34871 | 65.7 | 314 | 6.328588 | 65.2 | 311 | 6.298283 |
| SBP | 132.5 | 317 | 11.8091 | 133.3 | 314 | 11.75309 | 134.1 | 311 | 11.69681 |
| DBP | 81.6 | 317 | 6.358748 | 82.3 | 314 | 7.232671 | 82.7 | 311 | 6.298283 |
| FEV | 2.35 | 313 | 0.180529 | 2.33 | 310 | 0.179661 | 2.35 | 306 | 0.178499 |
| FVC | 2.74 | 313 | 0.270793 | 2.72 | 310 | 0.179661 | 2.76 | 306 | 0.178499 |
| FEV/FVC | 0.86 | 313 | 0.090264 | 0.86 | 310 | 0.089831 | 0.85 | 306 | 0.089249 |
| PEF | 407.3 | 285 | 115.4174 | 410.6 | 280 | 116.9617 | 415.6 | 278 | 116.5432 |
| Cycle ergometer (minutes) | 8.86 | 142 | 1.702339 | 9.08 | 130 | 1.745166 | 8.97 | 125 | 1.825362 |
| Shuttle walk (m) | 445.8 | 124 | 96.01553 | 434.1 | 138 | 97.09536 | 448.4 | 141 | 95.1159 |
| IKES (N) | 264.5 | 274 | 58.27312 | 267.1 | 267 | 65.86075 | 263.8 | 265 | 65.61361 |
| LEP (W) | 172.7 | 315 | 66.10314 | 167.3 | 312 | 68.49121 | 163.8 | 311 | 68.38136 |
| LEP (W/kg) | 2.08 | 315 | 0.905522 | 2.03 | 312 | 0.9012 | 1.98 | 311 | 0.899755 |
| Shoulder abduction | 145.5 | 315 | 14.48836 | 143.4 | 312 | 14.4192 | 145.4 | 311 | 14.39608 |
| Cholesterol | 5.65 | 262 | 0.495502 | 5.6 | 272 | 0.50487 | 5.56 | 258 | 0.573656 |
| HDL | 1.37 | 258 | 0.245853 | 1.38 | 272 | 0.16829 | 1.37 | 256 | 0.163265 |
| Cholesterol/HDL | 4.36 | 258 | 0.573656 | 4.33 | 271 | 0.587931 | 4.31 | 256 | 0.653061 |
| LDL | 3.4 | 251 | 0.484989 | 3.37 | 264 | 0.49739 | 3.36 | 250 | 0.484022 |
| Triglycerides | 2.04 | 263 | 0.744671 | 2 | 272 | 0.84145 | 1.95 | 258 | 0.737558 |
Part 4: study quality (provide comments and quotes where appropriate)
| Quality | Yes | Unclear | No |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power calculation reported | ‘To detect a difference of 5 mmHg in systolic blood pressure, with 90% power and a two sided p-value of 0.05. A similar number (n = 300) would provide over 90% power to detect a difference of 0.3 mmol / l in total cholesterol’ | ||
| Method of random sequence generation described? | ‘The unit of randomisation was the individual patient. The schedule was designed using the statistical package Stata’ | ||
| Method of allocation concealment described? | ‘The randomisation schedule was concealed from staff carrying out the assessments at all times’ | ||
| Method of outcome (assessment) blinding described? | ‘Ideally, assessors carrying out the postexercise assessments should be blinded to the patient’s allocation. However, this was not practicable’ | ||
| Are groups similar at baseline? | ‘The three trial arms were well matched in terms of referral criteria and sociodemographic characteristics, as shown in Tables 13 and 14. The groups were also well matched by clinical characteristics (Table 15)’ | ||
| Was ITT analysis used? | ‘Data were analysed both for trial completers (where data were available both at baseline and at one or more subsequent assessments) and on an ITT basis’ | ||
| Was there any statistical handling of missing data? |
PA outcome: ‘the median of available data at each assessment point for the control group grouped by gender within each age group was used for imputation of missing data’ Anthropometry and other outcomes when 10-week data were unavailable, baseline data were used for imputation of missing data |
||
| Were missing data (dropout and loss to follow-up) reported? | Yes – figure 3 (p. 19) |
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Three groups: ERS, walking group and advice-only group.
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | 007 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | March 2010 |
| Title of report | An evaluation of the Birmingham Exercise on Prescription service: Standard provision and a self-determination focused arm |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | Final report for funders |
| Authors | Jolly K, Duda J, Daley A, Ntoumanis N, Eves F, Rouse P, Blamey R, Lodhia R, Mutrie N and Williams G |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full report |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | Birmingham Wellbeing Partnership and the three Birmingham PCTS (South Birmingham, Birmingham East and North and Heart of Birmingham). |
| Date trial was conducted | November 2007 to July 2008 |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Cluster RCT |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | 13 EoP sites in Birmingham |
| Follow-up | 3 and 6 months post randomisation |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | Member of the primary care team |
| Reason for referral | For sedentary patients (< 30 minutes/week of moderate-intensity PA) in order to increase:
|
| Format of referral | Not stated |
| Referred to who | Health and fitness advisor |
| Referred to where | Leisure centre |
| Single or group sessions | Not stated |
| Referral quote from paper |
‘Patients are referred from a member of the primary care team according to eligibility criteria (see methods section) and receive an initial consultation and support over a 10-week period with an exit interview’ ‘People referred to the EoP scheme received the intervention consistent with their HFA [health & fitness advisor]’ |
| Characteristics of the intervention | |
|---|---|
| Components of the intervention | ERS group:
|
| Total duration | 10 weeks |
| No. of sessions per week | Negotiated by patients and advisor |
| Duration of sessions | Negotiated by patients and advisor |
| Session intensity | Negotiated by patients and advisor |
| Session mode | Group and/or Individual |
| Control group | Usual ERS programme |
| Other information | |
| Characteristics of the participants | ||
|---|---|---|
| Experimental group | Control group | |
| Inclusion criteria |
Two or more major risk factors of coronary heart People suffering from well-controlled chronic medical condition [mild or controlled asthma; chronic bronchitis; controlled diabetes mellitus; mild-to-moderate depression and/or anxiety; onset of osteoporosis may be delayed through regular exercise (i.e. post-menopausal women); borderline for hypertensive drugs: blood pressure ≤ 160/102 mmHg, prior to medication] People exhibiting motivation to change |
|
| Exclusion criteria |
Angina pectoris Moderate to high (or unstable) hypertension – 160/102 mmHg or above Poorly controlled insulin-dependent diabetes History of MI within the last 6 months – unless the patient has completed stage III cardiac rehabilitation Established cerebrovascular disease Severe chronic obstructive airways disease Uncontrolled asthma |
|
| Total number of randomised participants | n = 184 | n = 163 |
| Information on the age (years) of the participants (mean and SD) |
< 30: 10 30–49: 42 50–64: 34 65+: 14 |
< 30: 7 30–49: 47 50–64: 31 65+: 15 |
| Information on the sex of the participants (%) | Male 24.4 | Male 30.1 |
| Information on the ethnicity of the participants (%) |
White British/Irish 74.9 Black Caribbean/African 10.6 South Asian 9.5 Mixed race/others 5 |
White British/Irish 67.5 Black Caribbean/African 14.9 South Asian 14.9 Mixed race/others 2.6 |
| Specifics of the population (i.e. disease %) |
Smoker: 22.1 Hypertensive: 38 Overweight: 25.3 Obese: 52.3 Morbidly obese: 12.1 Probable anxiety: 34.2 Probable depression: 21.9 |
Smoker: 23.1 Hypertensive: 37.5 Overweight: 26.3 Obese: 51.9 Morbidly obese: 13.5 Probable anxiety: 31.9 Probable depression: 15.3 |
| Type of outcomes (What outcomes were assessed in this trial? Which of these outcomes have reported information about the result?) | |
|---|---|
| Outcome (domain) | Assessed (measure) |
| Effectiveness | |
| PA |
Self-reported PA (7-Day Physical Activity Recall) (primary outcome) Time spent in moderate and vigorous PA (excluding walking) |
| Fitness (e.g. V O2max) | Not reported |
| Clinical factors (e.g. blood lipids) | BMI, blood pressure |
| Psychological well-being |
Anxiety and depression (HADS) Vitality (subjective vitality scale) (Other scales embedded in the Dartmouth CO-OP) |
| QoL | Overall HRQoL (Dartmouth CO-OP charts) |
| Patient satisfaction | Not reported |
| Adverse events | Not reported |
| Patient factors | |
| Uptake | Not reported |
| Adherence | Not reported |
Part 3: extracted results
| ERS group (baseline) | ERS + SDT group (baseline) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean | SD | n | Mean | SD | |
| Minutes PA/week at least moderate intensity | 156 | 134 | 240 | 170 | 132 | 237 |
| Minutes PA/week walking | 156 | 88 | 209 | 169 | 81 | 192 |
| Vitality | 163 | 3.63 | 1.5 | 178 | 3.34 | 1.6 |
| HADS anxiety | 163 | 8.14 | 4.5 | 183 | 9.3 | 4.4 |
| HADS depression | 163 | 6.58 | 4 | 183 | 7.38 | 3.91 |
| Dartmouth QoL domains | ||||||
| Physical fitness | 161 | 2.91 | 1.2 | 168 | 2.68 | 1.1 |
| Feelings | 162 | 3.19 | 1.2 | 176 | 2.96 | 1.2 |
| Daily activities | 161 | 3.45 | 1 | 177 | 3.18 | 1 |
| Change in health | 163 | 3.27 | 0.7 | 176 | 3.1 | 0.8 |
| Overall health | 163 | 2.58 | 0.9 | 177 | 2.29 | 0.9 |
| QoL | 163 | 3.25 | 0.8 | 178 | 3.02 | 0.8 |
| Weight | 157 | 91.9 | 22.4 | 173 | 89.3 | 18.8 |
| BMI | 160 | 33.1 | 6.9 | 173 | 32.8 | 6.3 |
| SDP | 77 | 133.6 | 14.8 | 73 | 129.3 | 13.9 |
| DBP | 76 | 80.5 | 9.3 | 73 | 78.6 | 10 |
| ERS group (3 months) | ERS + SDT group (3 months) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean | SD | n | Mean | SD | |
| Minutes PA/week at least moderate intensity | 156 | 321 | 383 | 170 | 329 | 333 |
| Minutes PA/week walking | 156 | 200 | 312 | 169 | 191 | 258 |
| Vitality | 163 | 3.94 | 1.5 | 178 | 3.71 | 1.5 |
| HADS anxiety | 163 | 7.72 | 4.4 | 183 | 8.89 | 4.3 |
| HADS depression | 163 | 5.94 | 4.2 | 183 | 6.68 | 4.1 |
| Dartmouth QoL domains | ||||||
| Physical fitness | 161 | 3.01 | 1.2 | 168 | 2.88 | 1.2 |
| Feelings | 162 | 3.19 | 1.3 | 176 | 3.13 | 1.1 |
| Daily activities | 161 | 3.49 | 1.1 | 177 | 3.32 | 1.1 |
| Change in health | 163 | 3.38 | 0.7 | 176 | 3.23 | 0.9 |
| Overall health | 163 | 2.7 | 0.9 | 177 | 2.48 | 1.1 |
| QoL | 163 | 3.25 | 0.7 | 178 | 3.16 | 0.8 |
| Weight | N/A | N/A | ||||
| BMI | N/A | N/A | ||||
| SDP | N/A | N/A | ||||
| DBP | N/A | N/A | ||||
| ERS (6 months) | ERS (6 months) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean | SD | n | Mean | SD | |
| Minutes PA/week at least moderate intensity | 156 | 254 | 362 | 170 | 246 | 346 |
| Minutes PA/week walking | 156 | 161 | 317 | 169 | 142 | 297 |
| Vitality | 163 | 3.97 | 1.5 | 178 | 3.68 | 1.6 |
| HADS anxiety | 163 | 7.9 | 4.8 | 183 | 8.86 | 4.7 |
| HADS depression | 163 | 6.1 | 4.4 | 183 | 6.65 | 4.3 |
| Dartmouth QoL domains | ||||||
| Physical fitness | 161 | 2.93 | 1.2 | 168 | 2.83 | 1.1 |
| Feelings | 162 | 3.12 | 1.3 | 176 | 2.15 | 1.3 |
| Daily activities | 161 | 3.5 | 1.1 | 177 | 3.38 | 1.1 |
| Change in health | 163 | 3.27 | 0.9 | 176 | 3.16 | 0.8 |
| Overall health | 163 | 2.64 | 0.9 | 177 | 2.5 | 1 |
| QoL | 163 | 3.24 | 0.9 | 178 | 3.14 | 0.8 |
| Weight | 157 | 91.1 | 21.9 | 173 | 89.2 | 19.1 |
| BMI | 160 | 32.8 | 6.9 | 173 | 32.8 | 6.4 |
| SDP | 77 | 130 | 17.3 | 73 | 126.5 | 15.6 |
| DBP | 76 | 82 | 10.7 | 73 | 79.4 | 11.4 |
Part 4: study quality (provide comments and quotes where appropriate)
| Quality | Yes | Unclear | No |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power calculation reported | ‘This sample size would be more than adequate to achieve 90% power and 5% significance to detect a within group change in minutes of self-reported physical activity from 108 to 266 minutes. To take account of the cluster effect, the sample size was doubled to 500 participants, but this number was not achieved due to low recruitment rates and despite an extended recruitment duration from 26th November 2007 until 12th July 2008’ | ||
| Method of random sequence generation described? | ‘Cluster RCT – an independent statistician undertook the allocation with stratification by PCT’ | ||
| Method of allocation concealment described? | As both intervention and usual care arms were given an active treatment, participants didn’t know which arm they were in | ||
| Method of outcome (assessment) blinding described? | ‘The primary outcome was self-reported physical activity using the 7-Day Physical Activity Recall assessed via telephone to maintain blinding’ | ||
| Are groups similar at baseline? | Table 1 shows the baseline characteristics appear to balanced across groups | ||
| Was ITT analysis used? | ‘When the missing data were replaced with last value carried forward (i.e. ITT analysis)’ | ||
| Was there any statistical handling of missing data? | ‘Baseline values of missing process or outcomes variables were carried forward and a secondary analysis undertaken using these imputed data’ | ||
| Were missing data (dropout and loss to follow-up) reported? |
Figure 2 (p. 26) flow of participants No follow-up data 3 months ERS: 36/163 (82%) ERS + SDT: etc. |
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
ERS versus ERS plus SDT: the aim of the study was to compare standard provision of ERS with a SDT ERS intervention
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Details of the EoP exercise programme.
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | 001 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | March 2010 |
| Title of report | EoP: a randomized study on the effect of counseling vs counseling and supervised exercise |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | Scand J of Med Sci 2008;18:288–97 |
| Authors | Sorensen JB, Kragstrup J, Skovgaard T and Puggaard L |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | Denmark |
| Funders of the trial | Danish Medical Research Council, The Ministry of the Interior and Health, The National Board of Health, the counties of Ribe and Vejle |
| Date trial was conducted | 2005–6 |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | RCT-parallel |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | 14 clinics, two regions – Ribe and Vejle |
| Follow-up | 4 and 10 months post randomisation |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | GP |
| Reason for referral | ‘Having medically controlled lifestyle diseases or at risk of developing lifestyle diseases’ |
| Format of referral | Not stated |
| Referred to who | Physiotherapist – trained prior to evaluation and each clinic received several visits during the study |
| Referred to where | Counselling sessions and group-based activities – not stated where these took place |
| Single or group sessions | Group |
| Referral quote from paper |
‘The eligibility of the patients with regard to the EoP scheme was evaluated by the GPs, who could refer patients’ ‘All patients referred to the EoP scheme were eligible for the study and were offered participation in the randomized study’ |
| Characteristics of the intervention | |
|---|---|
| Components of the intervention |
ERS: aerobic conditioning (e.g. Nordic walking and aerobics), light strength conditioning (primarily using light weights and a high number of repetitions), stretching and games Motivational counselling: motivational counselling [based on the Transtheoretical Model (Prochaska and DiClemente 1983157)] aimed at increasing daily PA at baseline and after 4 and 10 months (45- to 60-min session) |
| Total duration | 4 months – 24 sessions |
| No. of sessions per week |
First 2 months, two sessions Second 2 months, one session |
| Duration of sessions | 1 hour |
| Session intensity | > 50% of heart rate reserve for a minimum of 20 minutes |
| Session mode | Group and/or individual |
| Control group | Motivational counselling |
| Other information | |
| Characteristics of the participants | ||
|---|---|---|
| Experimental group | Control group | |
| Inclusion criteria |
|
|
| Exclusion criteria | None stated | |
| Total number of randomised participants | n = 28 | n = 24 |
| Information on the age of the participants (mean and SD) | 53.9 | 52.9 |
| Information on the sex of the participants (%) | Male 43% | Male 47% |
| Information on the ethnicity of the participants (%) | Not stated | Not stated |
| Specifics of the population (i.e. disease, %) |
Metabolic syndrome: 36% Diabetes: 18% Heart disease: 32% Other diseases: 14% |
Metabolic syndrome: 25% Diabetes: 21% Heart disease: 42% Other diseases: 13% |
| Type of outcomes (What outcomes were assessed in this trial? Which of these outcomes have reported information about the result?) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Outcome (domain) | Assessed (measure) | |
| Effectiveness | ||
| PA |
METs/hour/day – self-report Amount, intensity, 30-minute guidelines – self-report |
|
| Fitness (e.g. V O2max) | V O2max, physical fitness – self-report | |
| Clinical factors (e.g. blood lipids) |
HbA1c Body weight BMI |
|
| Psychological well-being | Not reported | |
| QoL |
SF-12 physical SF-12 mental |
|
| Adverse events (e.g. injury) | Not reported | |
| Patient satisfaction | Not reported | |
| Patient factors | ||
| Uptake | ERS: 28/28 (100%) started exercise training | Control: 24/24 (100%) started motivational counselling |
| Adherence |
Participants attended an average of 18 of the 24 supervised group-based training sessions (25% percentile 14.8 and 75% percentile 21.3) Participation rate in counselling sessions 76% 8/28 (29%) discontinued intervention |
Participation rate in counselling sessions: 91% 4/24 (17%) discontinued control group |
Part 3: extracted results
| ERS (baseline) | Alternative PA intervention (baseline) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | |
| PA minutes/week | 124 | 28 | 113.3893 | 109 | 24 | 104.9781 |
| PA intensity | 2.2 | 28 | 0.809924 | 2.4 | 24 | 0.749844 |
| PA 30 minutes/day/week | 4.6 | 28 | 2.699746 | 4.2 | 24 | 2.749427 |
| Self-reported present physical fitness | 3.4 | 28 | 0.809924 | 3.9 | 24 | 0.749844 |
| Self-reported physical fitness compared with 4 months ago | 3 | 28 | 1.349873 | 3.2 | 24 | 0.499896 |
| Self-reported physical fitness compared with people of own age | 3.6 | 28 | 1.079898 | 3.8 | 24 | 0.999792 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.2 | 15 | 1.383208 | 5.8 | 11 | 0.846078 |
| Body weight (kg) | 94.3 | 28 | 19.43817 | 88.7 | 24 | 18.49615 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 32.3 | 28 | 5.399492 | 30.3 | 24 | 4.749011 |
| V O2max | 21.5 | 28 | 5.669467 | 21.1 | 24 | 7.998334 |
| PA METs/hour/day | 40.5 | 28 | 5.399492 | 38.7 | 24 | 3.999167 |
| SF-12 physical | 47 | 28 | 10.25904 | 42.6 | 24 | 11.24766 |
| SF-12 mental | 39 | 28 | 9.989061 | 36.4 | 24 | 10.24787 |
| ERS (4 months) | Alternative PA intervention (4 months) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | |
| PA minutes/week | 63 | 19 | 113.4203 | 23 | 19 | 106.7485 |
| PA intensity | –0.5 | 19 | 0.667178 | –0.3 | 19 | 0.889571 |
| PA 30 minutes/day/week | 0.7 | 19 | 1.334357 | 0.7 | 19 | 3.113499 |
| Self-reported present physical fitness | –0.7 | 19 | 0.889571 | –0.8 | 19 | 1.111964 |
| Self-reported physical fitness compared with 4 months ago | –0.6 | 19 | 1.55675 | –0.5 | 19 | 0.889571 |
| Self-reported physical fitness compared with people of own age | –0.7 | 19 | 1.334357 | –0.7 | 19 | 0.889571 |
| HbA1c (%) | –0.26 | 10 | 0.855106 | –0.23 | 8 | 0.360769 |
| Body weight (kg) | –1.1 | 19 | 4.00307 | –1.1 | 19 | 3.558285 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | –0.3 | 19 | 1.334357 | –0.4 | 19 | 1.55675 |
| V O2max | 23.8 | 19 | 7.11657 | 21.7 | 18 | 11.03952 |
| PA METs/hour/day | 42.6 | 19 | 2.446321 | 41.1 | 18 | 4.762148 |
| SF-12 physical | 48.97 | 19 | 17.63575 | 46.01 | 18 | 13.18249 |
| SF-12 mental | 40.29 | 19 | 10.69709 | 36.62 | 18 | 11.86208 |
| ERS (10 months) | Alternative PA intervention (10 months) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | |
| PA minutes/week | 20 | 21 | 123.9166 | 20 | 21 | 151.9732 |
| PA intensity | –0.3 | 21 | 0.724795 | –0.4 | 21 | 0.701415 |
| PA 30 minutes/day/week | 0.7 | 21 | 1.870439 | 0 | 21 | 3.039463 |
| Self-reported present physical fitness | –0.6 | 21 | 0.701415 | –0.5 | 21 | 1.145644 |
| Self-reported physical fitness compared with 4 months ago | –0.2 | 21 | 1.169024 | –0.4 | 21 | 1.169024 |
| Self-reported physical fitness compared with people of own age | –0.6 | 21 | 0.93522 | –0.3 | 21 | 0.818317 |
| HbA1c (%) | –0.27 | 10 | 0.87124 | 0.28 | 8 | 0.750399 |
| Body weight (kg) | –0.3 | 21 | 4.442293 | –2 | 21 | 9.11839 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | –0.1 | 21 | 1.870439 | –0.6 | 21 | 2.805659 |
| V O2max | 23 | 19 | 8.228534 | 22.4 | 20 | 12.77753 |
| PA METs/hour/day | 40.91 | 21 | 2.080863 | 40.1 | 20 | 5.019744 |
| SF-12 physical | 50.71 | 21 | 11.66686 | 44.5 | 21 | 15.43112 |
| SF-12 mental | 40.76 | 21 | 10.84855 | 39.49 | 21 | 12.88265 |
Part 4: study quality (provide comments and quotes where appropriate)
| Quality | Yes | Unclear | No |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power calculation reported | ‘Sample size calculations were performed for expected changes and variations in V O2max’ | ||
| Method of random sequence generation described? | ‘Randomization was carried out by the first author by means of concealed envelopes containing the name of the group’ | ||
| Method of allocation concealment described? | ‘Randomization was carried out by the first author by means of concealed envelopes containing the name of the group’ | ||
| Method of outcome (assessment) blinding described? | Not reported | ||
| Are groups similar at baseline? | Yes, the baseline characteristics reported for the two groups in table 1 look balanced between groups | ||
| Was ITT analysis used? | ‘The analyses were performed according to the ITT principle’ | ||
| Was there any statistical handling of missing data? | ‘Missing data were replaced in the physical activity questionnaire and in the two SF-12 component scores’. Missing data section in methods | ||
| Were missing data (dropout and loss to follow-up) reported? |
Yes, flow chart – figure 1 Intervention group 2–4 months: loss to follow-up, n = 1 Discontinued intervention, n = 8 7–10 months: loss to follow-up, n = 0 Discontinued intervention, n = 0 Control group 2–4 months: loss to follow-up, n = 0 Discontinued control, n = 4 7–10 months: loss to follow-up, n = 1 Discontinued control, n = 0 |
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Both groups received counselling, not a ‘no-intervention’ model.
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | 003 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | March 2010 |
| Title of report | Cost-effectiveness of a primary care based physical activity intervention in 45–74 year old men and women: a randomised controlled trial |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | Br J Sports Med 1998;32:236–41 |
| Authors | Stevens W, Hillsdon M, Thorogood M and McArdle D |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | This trial was supported by West London Health Promotion Agency through a grant awarded by North Thames NHS Executive Responsive Funding Programme |
| Date trial was conducted | Not reported |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Parallel |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | Yes, two practices |
| Follow-up | 8 months post randomisation |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | GP |
| Reason for referral | Inactive |
| Format of referral | letter |
| Referred to who | Exercise development officer |
| Referred to where | Local leisure centre |
| Single or group sessions | Not stated |
| Referral quote from paper |
‘The intervention subjects were sent a letter from their GP inviting them to attend a consultation with an exercise development officer at a local leisure centre’ Letter states: ‘I have arranged a consultation with an exercise specialist for you’ (see appendix, letter) |
| Characteristics of the intervention | |
|---|---|
| Components of the intervention |
Initial consultation: (a) full explanation of the scheme (b) a medical/lifestyle questionnaire/consent form(c) physical measurements (height/weight/body mass index)(d) assessment of present activity level (e) options available to be more physically active (f) introduction to the PA diary. ‘Exercise Programme’: At the end of the exercise programme, patients are invited back for a second consultation |
| Total duration | 10 weeks |
| No. of sessions per week | Not reported |
| Duration of sessions | Not reported |
| Session intensity | Not reported |
| Session mode | Not reported |
| Control group | Sent exercise promotion materials |
| Other information | |
| Characteristics of the participants | ||
|---|---|---|
| Experimental group | Control group | |
| Inclusion criteria | Not reported | |
| Exclusion criteria |
Active: a minimum of either 20- to 30-minute episodes of moderate intensity exercise or 12- to 20-minute episodes of vigorous intensity exercise. medical reason for excluding them |
|
| Total number of randomised participants | 363 | 351 |
| Information on the age of the participants (mean and SD) | 59.1 | 59.2 |
| Information on the sex of the participants (%) | 40% (male) | 44% (male) |
| Information on the ethnicity of the participants (%) |
White: 87 Black: 5 Asian: 4 Other: 4 |
White: 83 Black: 4 Asian: 8 Other: 5 |
| Specifics of the population (i.e. disease, %) |
BMI > 25: 46% Smoker: 18% |
BMI > 25: 42% Smoker: 17% |
| Type of outcomes (What outcomes were assessed in this trial? Which of these outcomes have reported information about the result) | |
|---|---|
| Outcome (domain) | Assessed (measure) |
| Effectiveness | |
| PA | PA levels, self-report (type not stated) |
| Fitness (e.g. V O2max) | Not reported |
| Clinical factors (e.g. blood lipids) | Not reported |
| Psychological well-being | Not reported |
| QoL | Not reported |
| Patient satisfaction | Not reported |
| Adverse events | Not reported |
| Patient factors | |
| Uptake | 35% (126/363) |
| Adherence | Not reported |
Part 3: extracted results
| ERS (8 months) | Control (8 months) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | N | n | N | |
| 150 minutes moderate/vigorous PA/week | 204 | 363 | 174 | 351 |
Part 4: study quality (provide comments and quotes where appropriate)
| Quality | Yes | Unclear | No |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power calculation reported | Not reported | ||
| Method of random sequence generation described? | ‘Eligible subjects were randomised using a random number generator’ | ||
| Method of allocation concealment described? | Not reported | ||
| Method of outcome (assessment) blinding described? | Not reported | ||
| Are groups similar at baseline? |
See table 2: ‘the groups were broadly similar, with no significant difference’ |
||
| Was ITT analysis used? |
‘Unless otherwise stated, results are described on an “ITT” ’ basis’ |
||
| Was there any statistical handling of missing data? | ‘those subjects for whom there was no outcome measure, being assigned to the activity level they reported at the start of the study’ | ||
| Were missing data (dropout and loss to follow-up) reported? | Figure 1 – study design diagram |
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
More details of the exercise programme.
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | 004 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | March 2010 |
| Title of report |
Randomised controlled trial to examine the effects of a GP exercise referral programme in Hailsham, East Sussex, on modifiable coronary heart disease risk factors Effectiveness of a Primary Care Exercise Referral Intervention for Changing Physical Self-Perceptions Over 9 Months |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) |
J Epidemiol Community Health 1998;52:595–601 Health Psychol 2005;24:11–21 |
| Authors |
Taylor AH, Doust J and Webborn N Taylor AH and Fox K |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | The South Thames Regional Health Authority Primary Care Development Fund |
| Date trial was conducted | Not stated |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Parallel RCT |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | Yes, two primary health-care centres |
| Follow-up | 8, 16, 26 and 37 weeks post randomisation |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | GP |
| Reason for referral | Smokers, hypertensive (that is, SBP/DBP at least 140/90 mmHg) or overweight (BMI > 25) |
| Format of referral | Signed prescription card |
| Referred to who | Trained assessor initial assessment |
| Referred to where |
Health centre initial assessment Leisure centre for ERS |
| Single or group sessions | Not stated |
| Referral quote from paper |
‘Patients were given a signed prescription card, with a reason for referral’ ‘Up to 30 new patients per week were being referred to the scheme by over 70 GPs during the study’ |
| Characteristics of the intervention | |
|---|---|
| Components of the intervention |
Initial assessment: blood pressure and anthropometric measures, a questionnaire was used to assess smoking behaviour, PA, and medication use, and open-ended perceptions of the exercise programme (only at 8 weeks) Exercise programme |
| Total duration | 10 weeks – 20 sessions |
| No. of sessions per week | Two |
| Duration of sessions | 30–40 minutes |
| Session intensity | ‘Moderate intensity’ |
| Session mode | ‘Usual gym equipment’ |
| Control group | All assessments (see above, but no exercise programme) |
| Other information | Both exercise and control group subjects were given Health Education Authority leaflets on preventing CHD but were given assessments at mid-intervention, and post intervention, and 3 and 6 months later |
| Characteristics of the participants | ||
|---|---|---|
| Experimental group | Control group | |
| Inclusion criteria |
Smokers Hypertensive (i.e. SBP/DBP at least 140/90 mmHg) Overweight (BMI > 25) on medical records |
|
| Exclusion criteria |
SBP > 200 mmHg A history of MI or angina pectoris Diabetes mellitus A musculoskeletal condition that restricted PA Anyone who had previously been referred on the exercise prescription scheme |
|
| Total number of randomised participants | 97 | 45 |
| Information on the age of the participants (mean and SD) | 54.1 (0.8) SEM | 54.4 (1.3) |
| Information on the sex of the participants (%) | 35% men | 17 men |
| Information on the ethnicity of the participants (%) | Not stated | Not stated |
| Specifics of the population (i.e. disease %) |
Smokers: 43 Overweight: 77 Hypertensive: 46 |
Smokers: 40 Overweight: 71 Hypertensive: 58 |
| Type of outcomes (What outcomes were assessed in this trial? Which of these outcomes have reported information about the result?) | |
|---|---|
| Outcome (domain) | Assessed (measure) |
| Effectiveness | |
| PA | Blair’s 7-day recall method, energy expenditure was determined from minutes spent in light, moderate and vigorous activity |
| Fitness (e.g. V O2max) | Mean predicted heart rate at a workload of 150 W |
| Clinical factors (e.g. blood lipids) | SBP and DBP, body weight, BMI, sum of four skinfolds |
| Psychological well-being | Physical self-perceptions, PSPP (Fox and Corbin 1989,158 Fox 1990159) |
| QoL | Not reported |
| Patient satisfaction | Satisfaction with characteristics of the scheme, comments from participants |
| Adverse events | Not reported |
| Patient factors | |
| Uptake | 88% (85/97) |
| Adherence | 28% (24/85) |
| DBP | |
Part 3: extracted results
| ERS baseline | Control baseline | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | |
| Moderate (minutes/week) | 231.3 | 40 | 282.7076 | 116.8 | 31 | 203.2234 |
| Vigorous (minutes/week) | 7.8 | 40 | 28.4605 | 4.6 | 31 | 15.03296 |
| Energy (kcal/kg/day) | 34.3 | 40 | 1.897367 | 33.5 | 31 | 1.670329 |
| SBP | 136.7 | 40 | 14.54648 | 136.9 | 31 | 19.48718 |
| DBP | 86.8 | 40 | 10.11929 | 88.4 | 31 | 12.24908 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.7 | 40 | 3.794733 | 26.7 | 31 | 3.340659 |
| Sum of skinfolds | 85.1 | 40 | 29.72541 | 66.9 | 31 | 18.9304 |
| PSW | 2.1 | 97 | 0.984886 | 2.4 | 45 | 0.67082 |
| Physical condition | 2 | 97 | 0.984886 | 2.5 | 45 | 0.67082 |
| Physical appearance | 2.2 | 97 | 0.984886 | 2.3 | 45 | 0.67082 |
| Physical health | 2.4 | 97 | 0.984886 | 2.7 | 45 | 0.67082 |
| Exercise (8 weeks) | Control (8 weeks) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | |
| Moderate (minutes/week) | 247 | 36 | 282.7076 | 145 | 31 | 178.1685 |
| Vigorous (minutes/week) | 49 | 36 | 28.4605 | 21 | 31 | 61.24541 |
| Energy (kcal/kg/day) | 34.6 | 36 | 1.897367 | 33.7 | 31 | 1.670329 |
| SBP (mmHg) | N/A | 40 | 14.54648 | N/A | 31 | 0 |
| DBP | N/A | 40 | 10.11929 | N/A | 31 | 0 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | N/A | 40 | 3.794733 | N/A | 31 | 0 |
| Sum of skinfolds | N/A | 40 | 29.72541 | N/A | 31 | 0 |
| ERS (16 weeks) | Control (16 weeks) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | |
| Moderate (minutes/week) | 226 | 36 | 252 | 160 | 31 | 261.6849 |
| Vigorous (minutes/week) | 59 | 36 | 72 | 21 | 31 | 72.38094 |
| Energy (kcal/kg/day) | 34.6 | 36 | 1.2 | 33.9 | 31 | 1.670329 |
| SBP | 130 | 40 | 14.54648 | 129.6 | 31 | 14.47619 |
| DBP | 83.9 | 40 | 7.589466 | 83.8 | 31 | 8.351647 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.5 | 40 | 0.632456 | 27.6 | 31 | 0.556776 |
| Sum of skinfolds | 70.3 | 40 | 8.221922 | 75.7 | 31 | 7.79487 |
| PSW | 2.31 | 97 | 0.787909 | 2.31 | 45 | 0.67082 |
| Physical condition | 2.34 | 97 | 0.787909 | 2.49 | 45 | 0.603738 |
| Physical appearance | 2.37 | 97 | 0.787909 | 2.36 | 45 | 0.737902 |
| Physical health | 2.55 | 97 | 0.68942 | 2.69 | 45 | 0.603738 |
| Exercise (26 weeks) | Control (26 weeks) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | |
| Moderate (minutes/week) | 183 | 36 | 234 | 206 | 31 | 250.5494 |
| Vigorous (minutes/week) | 56 | 36 | 108 | 34 | 31 | 111.3553 |
| Energy (kcal/kg/day) | 34.4 | 36 | 1.8 | 34.3 | 31 | 2.227106 |
| SBP | 129.7 | 40 | 13.91402 | 130.6 | 31 | 14.47619 |
| DBP | 83.6 | 40 | 8.221922 | 83.5 | 31 | 8.351647 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.3 | 40 | 1.264911 | 27.5 | 31 | 1.113553 |
| Sum of skinfolds | 69.9 | 40 | 11.3842 | 74.9 | 31 | 11.13553 |
| Exercise (37 weeks) | Control (37 weeks) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | n | SD | Mean | n | SD | |
| Moderate (minutes/week) | 158 | 36 | 228 | 162 | 31 | 244.9816 |
| Vigorous (minutes/week) | 42 | 36 | 96 | 23 | 31 | 105.7875 |
| Energy (kcal/kg/day) | 34.1 | 36 | 2.4 | 33.9 | 31 | 2.227106 |
| SBP | 129.7 | 40 | 17.0763 | 131.3 | 31 | 17.81685 |
| DBP | 84.7 | 40 | 9.486833 | 83.3 | 31 | 9.465199 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.5 | 40 | 1.264911 | 27.6 | 31 | 1.113553 |
| Sum of skinfolds | 71 | 40 | 13.28157 | 76.3 | 31 | 12.80586 |
| PSW | 2.41 | 97 | 0.787909 | 2.42 | 45 | 0.536656 |
| Physical condition | 2.45 | 97 | 0.787909 | 2.52 | 45 | 0.603738 |
| Physical appearance | 2.39 | 97 | 0.787909 | 2.42 | 45 | 0.67082 |
| Physical health | 2.57 | 97 | 0.68942 | 2.58 | 45 | 0.536656 |
Part 4: study quality (provide comments and quotes where appropriate)
| Quality | Yes | Unclear | No |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power calculation reported | The study sample was large enough to detect a difference in blood pressure of 4 mmHg systolic with a power of 0.90 and a two-sided p-value of 0.05 | ||
| Method of random sequence generation described? | Randomisation, using a random numbers table, took place at the end of the first assessment | ||
| Method of allocation concealment described? | Correspondence with author | ||
| Method of outcome (assessment) blinding described? | Not reported | ||
| Are groups similar at baseline? | Randomisation of 142 subjects to the exercise (n = 97) and control (n = 45) groups established comparable baseline measures (see table 2) | ||
| Was ITT analysis used? | No | ||
| Was there any statistical handling of missing data? | Not stated | ||
| Were missing data (dropout and loss to follow-up) reported? | Throughout results section |
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
Taylor AH. Evaluating GP exercise referral schemes Findings from a randomised controlled study. Chelsea School Research Centre, Brighton, UK.
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Appendix 5 Detailed data extraction: cost-effectiveness systematic review
Part 1: background information of study
| Reference number | 01 |
| Reviewed by | N/A |
| Date of review | 11 February 2010 |
| Title | Cost-effectiveness of a primary care based physical activity intervention in 45–74 year old men and women: a randomised controlled trial |
| Author(s) | Stevens et al. |
| Aim | To assess the cost-effectiveness of a primary care-based intervention aimed at increasing levels of PA in inactive people aged 45–74 years |
| Year of publication | 1998 |
| Origin of study | England |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of patients | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosed condition | N/A |
| Definition of ‘sedentariness’ |
Fewer than four 20-minute sessions of moderate or vigorous activity during the last 4 weeks Between 4 and 11 20-minute sessions of moderate or vigorous activity during the last 4 weeks Twelve or more 20-minute sessions of moderate or vigorous activity during the last 4 weeks, but less than either of the current recommendations |
| Gender | Males and females |
| Age | 45–74 years |
| Ethnicity | White, Black, Asian, other |
| Sample size | 714 |
| Description of intervention | |
| Design | RCT |
| Setting | Local leisure centre located within the ward (primary care) |
| Country | England |
| Duration | 10 weeks |
| Exercise program | It consisted of:
|
| Type of supervision delivered | The EDO discussed the progress of participants in terms of doing exercise |
| Comparator | The control group were sent information through the post about local leisure centres and health clubs as well information on PA and health |
Part 3: extracted results
| Scope | |
|---|---|
| Form of economic evaluation | Cost-effectiveness |
| Perspective of analysis | Not explicitly stated though a health-care provide perspective could be inferred given analysis |
| Time horizon of analysis | 8 months |
| Outcomes | |
| What outcomes were reported? (i.e. measures of effectiveness/efficacy, patient/programme factors that may moderate behavioural outcomes) | Change in reported levels of PA (i.e. number of occasions of physical done in last 4 weeks), which was operationalised as:
|
| Data sources for outcome measures | Questionnaire that elicited self-reports of PA levels |
| Discount rate | N/A |
| Costs | |
| What costs were reported? | Costs of recruitment covering cost of questionnaire design and production, mailing, processing of data, labour (include both institution and wage costs), equipment, and follow-up of people who did not reply initially |
| Data sources for costs measures | Records of the scheme, salary records of exercise development officer |
| Discount rate? | N/A |
| Year of costing | N/A |
| Currency | UK pounds sterling |
|
How was cost reported? (average cost/marginal cost/incremental cost/total cost/other – describe) |
Total costs, average cost |
| Sensitivity analysis | |
| Type of sensitivity analysis | It involved gauging the cost impact of variations in the response rates to recruitment at the main stages of the scheme. These stages were: stage 1 – initial recruitment to the scheme; stage 2 – invitation to the exercise consultation; and stage 3 – intervention itself |
| What variables were used in sensitivity analysis? | Response rates to recruitment of participants at different stages (multiway analysis/one way) |
| Findings from sensitivity analysis | Recruitment strategy is an important aspect of cost-effectiveness of exercise promotion programmes as a high uptake rate maximises the cost-effectiveness of the intervention. It indicates that unit costs could be reduced by 50% if there is better recruitment strategy |
| Main results | |
| Findings on the cost-effectiveness |
Cost of inducing one sedentary person to do more PA was £623 Cost of moving a person who is active but below the recommended level of PA to that recommended level was £2500 Cost of achieving any increase in a person’s level of PA was £327 for movement into a higher activity group and < £200 for an absolute increase |
Part 4: study quality
| Challenges | |
|---|---|
| Author-stated limitations | The lack of objective measures for PA |
| Author-stated strengths | N/A |
| Useful ideas from this study | N/A |
| Quality assessment for economic evaluation (checklist from Drummond and Jefferson, 1996)74 | Yes | No | Not clear | Not appropriate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study design | ||||
| 1. The research question is stated | ✓ | |||
| 2. The economic importance of the research question is stated | ✓ | |||
| 3. The viewpoint(s) of the analysis are clearly stated and justified | ✓ | |||
| 4. The rationale for choosing the alternative programmes or interventions compared is stated | ✓ | |||
| 5. The alternatives being compared are clearly described | ✓ | |||
| 6. The form of economic evaluation used is stated | ✓ | |||
| 7. The choice of form of economic evaluation is justified in relation to the questions addressed | ✓ | |||
| Data collection | ||||
| 8. The source(s) of effectiveness estimates used are stated | ✓ | |||
| 9. Details of the design and results of effectiveness study are given (if based on a single study) | ✓ | |||
| 10. Details of the method of synthesis or meta-analysis of estimates are given (if based on an overview of a number of effectiveness studies) | ✓ | |||
| 11. The primary outcome measure(s) for the economic evaluation are clearly stated | ✓ | |||
| 12. Methods to value health states and other benefits are stated | ||||
| 13. Details of the subjects from whom valuations were obtained are given | ||||
| 14. Productivity changes (if included) are reported separately | ✓ | |||
| 15. The relevance of productivity changes to the study question is discussed | ✓ | |||
| 16. Quantities of resources are reported separately from their unit costs | ✓ | |||
| 17. Methods for the estimation of quantities and unit costs are described | ||||
| 18. Currency and price data are recorded | ✓ | |||
| 19. Details of currency of price adjustments for inflation or currency conversion are given | ✓ | |||
| 20. Details of any model used are given | ✓ | |||
| 21. The choice of model used and the key parameters on which it is based are justified | ✓ | |||
| Analysis and interpretation of results | ||||
| 22. Time horizon of costs and benefits is stated | ✓ | |||
| 23. The discount rate(s) is stated | ✓ | |||
| 24. The choice of rate(s) is justified | ✓ | |||
| 25. An explanation is given if costs or benefits are not discounted | ✓ | |||
| 26. Details of statistical tests and CIs are given for stochastic data | ||||
| 27. The approach to sensitivity analysis is given | ✓ | |||
| 28. The choice of variables for sensitivity analysis is justified | ✓ | |||
| 29. The ranges over which the variables are varied are stated | ✓ | |||
| 30. Relevant alternatives are compared | ✓ | |||
| 31. Incremental analysis is reported | ✓ | |||
| 32. Major outcomes are presented in a disaggregated as well as aggregated form | ✓ | |||
| 33. The answer to the study question is given | ✓ | |||
| 34. Conclusions follow from the data reported | ✓ | |||
| 35. Conclusions are accompanied by the appropriate caveats | ✓ | |||
| Did the economic evaluation use a decision-analytic modelling framework? |
Response: yes (✓), no (×), not applicable (N/A) Instruction: if ‘no’, end |
Part 1: background information of study
| Reference number | 02 |
| Reviewed by | N/A |
| Date of review | 13 February 2010 |
| Title | Exercise evaluation randomised trial: a randomised trial company GP referral for leisure centre-based exercise, community-based walking and advice only |
| Author(s) | Isaacs et al. |
| Aim | To evaluate and compare the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of a leisure centre-based exercise programme, an instructor-led walking programme and advice only in patients referred for exercise by their GPs |
| Year of publication | 2007 |
| Origin of study | UK |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of patients | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosed condition | Cardiovascular risk factor (at least one of these: high cholesterol, controlled mild-to-moderate hypertension, obesity, current smoking, diabetes, a family history of MI at an early age) |
| Definition of ‘sedentariness’ | Not physically active (but could not see explicit definition on this) |
| Gender | Males and females |
| Age | 40–75 years |
| Ethnicity | White, Asian |
| Sample size | 932 |
| Description of intervention | |
| Design | RCT |
| Setting | Leisure centres |
| Country | UK |
| Duration | 10 weeks |
| Exercise programme |
|
| Type of supervision delivered | Exercise programmes were instructor led |
| Comparator | Advice-only control group who received tailored advice and information on PA including on local exercise facilities |
Part 3: extracted results
| Scope | |
|---|---|
| Form of economic evaluation | Cost-effectiveness analysis |
| Perspective of analysis | Societal view point |
| Time horizon of analysis | 12 months |
| Outcomes | |
| What outcomes were reported? (i.e. measures of effectiveness/efficacy, patient/programme factors that may moderate behavioural outcomes) | Health outcomes (via SF-36 scores) |
| Data sources for outcome measures | Data from participants |
| Discount rate | N/A |
| Costs | |
| What costs were reported? |
Costs to public sector: cost incurred by health service and local authority in terms of provision of facilities, exercise trainers, and administrative support) Costs to the participants: time costs, travel costs, money costs (i.e. child-care fees, purchase of equipment) Costs averted: reduced use of health services (pharmaceutical costs, health admissions, visits to the GP) |
| Data sources for costs measures |
Department of Transport (for time cost) AA database (for cost per mile of travel using cars) Local district health authority NHS database British National Formulary PSSRU |
| Discount rate? | N/A |
| Year of costing | 2002 |
| Currency | UK pounds sterling |
|
How was cost reported? (average cost/marginal cost/incremental cost/total cost/other- describe) |
Average cost, incremental cost, total cost |
| Sensitivity analysis | |
| Type of sensitivity analysis | Bootstrapping was used to account for uncertainty around cost-effectiveness ratios. |
| What variables were used in sensitivity analysis? | Costs, health outcomes |
| Findings from sensitivity analysis | The findings were consistent with original findings |
| Main results | |
| Findings on the cost-effectiveness |
Cost per unit increase in SF-36 score was £19,500 for leisure centre intervention group compared with control (at 6 months) At 12 months, walking compared with leisure centre group could lead to a cost saving of £8750 per unit improvement in SF-36 score. Walking intervention seemed as effective as leisure centre-based intervention but less costly |
Part 4: study quality
| Challenges | |
|---|---|
| Author-stated limitations |
The information from the SF-36 was not sufficiently stable to afford a specification of outcomes in terms of QALYs Potential contamination of control group Study may not be generalisable to other populations |
| Author-stated strengths | |
| Useful ideas from this study | Data sources for costing particularly time and travel costs |
| Quality assessment for economic evaluation (checklist from Drummond and Jefferson, 1996)74 | Yes | No | Not clear | Not appropriate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study design | ||||
| 1. The research question is stated | ✓ | |||
| 2. The economic importance of the research question is stated | ✓ | |||
| 3. The viewpoint(s) of the analysis are clearly stated and justified | ✓ | |||
| 4. The rationale for choosing the alternative programmes or interventions compared is stated | ✓ | |||
| 5. The alternatives being compared are clearly described | ✓ | |||
| 6. The form of economic evaluation used is stated | ✓ | |||
| 7. The choice of form of economic evaluation is justified in relation to the questions addressed | ✓ | |||
| Data collection | ||||
| 8. The source(s) of effectiveness estimates used are stated | ✓ | |||
| 9. Details of the design and results of effectiveness study are given (if based on a single study) | ✓ | |||
| 10. Details of the method of synthesis or meta-analysis of estimates are given (if based on an overview of a number of effectiveness studies) | ✓ | |||
| 11. The primary outcome measure(s) for the economic evaluation are clearly stated | ✓ | |||
| 12. Methods to value health states and other benefits are stated | ✓ | |||
| 13. Details of the subjects from whom valuations were obtained are given | ✓ | |||
| 14. Productivity changes (if included) are reported separately | ✓ | |||
| 15. The relevance of productivity changes to the study question is discussed | ✓ | |||
| 16. Quantities of resources are reported separately from their unit costs | ✓ | |||
| 17. Methods for the estimation of quantities and unit costs are described | ✓ | |||
| 18. Currency and price data are recorded | ✓ | |||
| 19. Details of currency of price adjustments for inflation or currency conversion are given | ✓ | |||
| 20. Details of any model used are given | ✓ | |||
| 21. The choice of model used and the key parameters on which it is based are justified | ✓ | |||
| Analysis and interpretation of results | ||||
| 22. Time horizon of costs and benefits is stated | ✓ | |||
| 23. The discount rate(s) is stated | ✓ | |||
| 24. The choice of rate(s) is justified | ✓ | |||
| 25. An explanation is given if costs or benefits are not discounted | ✓ | |||
| 26. Details of statistical tests and CIs are given for stochastic data | ||||
| 27. The approach to sensitivity analysis is given | ✓ | |||
| 28. The choice of variables for sensitivity analysis is justified | ✓ | |||
| 29. The ranges over which the variables are varied are stated | ✓ | |||
| 30. Relevant alternatives are compared | ✓ | |||
| 31. Incremental analysis is reported | ✓ | |||
| 32. Major outcomes are presented in a disaggregated as well as aggregated form | ✓ | |||
| 33. The answer to the study question is given | ✓ | |||
| 34. Conclusions follow from the data reported | ✓ | |||
| 35. Conclusions are accompanied by the appropriate caveats | ✓ | |||
| Did the economic evaluation use a decision-analytic modelling framework? |
Response: yes (✓), no (×), not applicable (N/A) Instruction: if ‘no’, end |
Part 1: background information of study
| Reference number | 03 |
| Reviewed by | N/A |
| Date of review | 15 February 2010 |
| Title | Cost–utility of a walking programme for moderately depressed, obese or overweight elderly women in primary care: a randomised controlled trial |
| Author(s) | Gusi et al. |
| Aim | To assess the cost–utility of adding to the standard ‘best care’ of a supervised walking programme that also included strengthening and stretching |
| Year of publication | 2008 |
| Origin of study | Spain |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of patients | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosed condition | Obesity (obese type I or II that was expressed as BMI between 25 and 39.9 kg/m2); depression (moderate depression that was expressed as a score of 6–9 in a 15-item Geriatric Depression Scale) |
| Definition of ‘sedentariness’ | N/A |
| Gender | Females |
| Age | 60 years and older |
| Ethnicity | N/A |
| Sample size | 106 |
| Description of intervention | |
| Design | RCT |
| Setting | Primary care |
| Country | Spain |
| Duration | 6 months |
| Exercise programme | Walking in public park or forest tracks. The walks were interspersed with stretching and strengthening exercise. Each session lasted for 50 minutes and occurred three times per week |
| Type of supervision delivered | Walks were supervised and led by an exercise instructor |
| Comparator | Best care in general practice: consisted of routine care and recommendation of PA |
Part 3: extracted results
| Scope | |
|---|---|
| Form of economic evaluation | Cost–utility analysis |
| Perspective of analysis | Health service |
| Time horizon of analysis | 6 months |
| Outcomes | |
| What outcomes were reported? (i.e. measures of effectiveness/efficacy, patient/programme factors that may moderate behavioural outcomes) | QALY (vía EQ-5D scores) |
| Data sources for outcome measures | Questionnaires (see above) |
| Discount rate | N/A |
| Costs | |
| What costs were reported? | Salary of exercise instructor |
| Data sources for costs measures | 2005 bulletin of regional government |
| Discount rate? | N/A |
| Year of costing | 2005 |
| Currency | Euros |
|
How was cost reported? (average cost/marginal cost/incremental cost/total cost/other – describe) |
Incremental cost |
| Sensitivity analysis | |
| Type of sensitivity analysis | Scenario analysis; one-way analysis |
| What variables were used in sensitivity analysis? | Rate of participation in the programme; cost of a permanent timetable for consultation, assessment and recruitment; salary of technician; effectiveness of programme; sampling variation |
| Findings from sensitivity analysis | Results were consistent with original results on cost-effectiveness |
| Main results | |
| Findings on the cost-effectiveness | Cost per QALY gained from intervention compared with control group was €311 (95% CI €143 to €394). The addition of walking programme to best primary care was cost-effective |
Part 4: study quality
| Challenges | |
|---|---|
| Author-stated limitations |
Small sample size Results cannot be generalised to private care or more widespread services Potential selection bias in favour of low-income, less-educated people |
| Author-stated strengths | First study to conduct cost–utility analysis of walking exercise intervention with elderly females |
| Useful ideas from this study | |
| Quality assessment for economic evaluation (checklist from Drummond and Jefferson, 1996)74 | Yes | No | Not clear | Not appropriate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study design | ||||
| 1. The research question is stated | ✓ | |||
| 2. The economic importance of the research question is stated | ✓ | |||
| 3. The viewpoint(s) of the analysis are clearly stated and justified | ✓ | |||
| 4. The rationale for choosing the alternative programmes orb interventions compared is stated | ✓ | |||
| 5. The alternatives being compared are clearly described | ✓ | |||
| 6. The form of economic evaluation used is stated | ✓ | |||
| 7. The choice of form of economic evaluation is justified in relation to the questions addressed | ✓ | |||
| Data collection | ||||
| 8. The source(s) of effectiveness estimates used are stated | ✓ | |||
| 9. Details of the design and results of effectiveness study are given (if based on a single study) | ✓ | |||
| 10. Details of the method of synthesis or meta-analysis of estimates are given (if based on an overview of a number of effectiveness studies) | ✓ | |||
| 11. The primary outcome measure(s) for the economic evaluation are clearly stated | ✓ | |||
| 12. Methods to value health states and other benefits are stated | ✓ | |||
| 13. Details of the subjects from whom valuations were obtained are given | ✓ | |||
| 14. Productivity changes (if included) are reported separately | ✓ | |||
| 15. The relevance of productivity changes to the study question is discussed | ✓ | |||
| 16. Quantities of resources are reported separately from their unit costs | ✓ | |||
| 17. Methods for the estimation of quantities and unit costs are described | ✓ | |||
| 18. Currency and price data are recorded | ✓ | |||
| 19. Details of currency of price adjustments for inflation or currency conversion are given | ✓ | |||
| 20. Details of any model used are given | ✓ | |||
| 21. The choice of model used and the key parameters on which it is based are justified | ✓ | |||
| Analysis and interpretation of results | ||||
| 22. Time horizon of costs and benefits is stated | ✓ | |||
| 23. The discount rate(s. is stated | ✓ | |||
| 24. The choice of rate(s) is justified | ✓ | |||
| 25. An explanation is given if costs or benefits are not discounted | ✓ | |||
| 26. Details of statistical tests and CIs are given for stochastic data | ||||
| 27. The approach to sensitivity analysis is given | ✓ | |||
| 28. The choice of variables for sensitivity analysis is justified | ✓ | |||
| 29. The ranges over which the variables are varied are stated | ✓ | |||
| 30. Relevant alternatives are compared | ✓ | |||
| 31. Incremental analysis is reported | ✓ | |||
| 32. Major outcomes are presented in a disaggregated as well as aggregated form | ✓ | |||
| 33. The answer to the study question is given | ✓ | |||
| 34. Conclusions follow from the data reported | ✓ | |||
| 35. Conclusions are accompanied by the appropriate caveats | ✓ | |||
| Did the economic evaluation use a decision-analytic modelling framework? |
Response: Yes (✓), no (×), not applicable (N/A) Instruction: if ‘no’, end |
Part 1: background information of study
| Reference number | 04 |
| Reviewed by | N/A |
| Date of review | 12 July 2010 |
| Title | Modelling the cost-effectiveness of physical activity interventions |
| Author(s) | NICE (we focused on the aspect on ERS intervention) |
| Aim | To determine the cost-effectiveness of four types of intervention aimed at increasing PA levels |
| Year of publication | 2006 |
| Origin of study | England |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of patients | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosed condition | Sedentary |
| Definition of ‘sedentariness’ | Doing < 120 minutes (4–30 minutes) of moderate-intensity exercise per week |
| Gender | Male and female |
| Age | 40–60 years |
| Ethnicity | N/A |
| Sample size | 206 |
| Description of intervention | |
| Design | RCT |
| Setting | Primary care |
| Country | England |
| Duration | 12 months |
| Exercise programme | Advice seminar supplemented with general written guidance about exercise, and verbal and written information about health walk programmes. Participation in local health walks, community-based led walking programme |
| Type of supervision delivered | Led walking programmes |
| Comparator | Advice and written guidance about the benefits, recommended levels of PA |
Part 3: extracted results
| Scope | |
|---|---|
| Form of economic evaluation | Cost–utility analysis |
| Perspective of analysis | Public sector perspective in addition to NHS and personal social services perspective |
| Time horizon of analysis | Lifetime |
| Outcomes | |
|
What outcomes were reported? (i.e. measures of effectiveness/efficacy, patient/programme factors that may moderate behavioural outcomes |
Physically active: doing at least 120 minutes (4–30 minutes) of moderate-intensity exercise per week QALYs (via EQ-5D scores to determine the loss in QoL avoided by avoiding health states, i.e. CHD, stroke, type 2 diabetes and colon cancer) |
| Data sources for outcome measures |
National dataset (i.e. HSE – 1996) Harvard cost-effectiveness analysis registry Literature reviews ONS database British Heart Foundation database Diabetes UK database |
| Discount rate | 3.5% |
| Costs | |
| What costs were reported? | Cost of treating health states:
|
| Data sources for costs measures |
Literature review British Heart Foundation database Diabetes UK database |
| Discount rate? | 3.5% |
| Year of costing | 2005 |
| Currency | UK pounds sterling |
| Sensitivity analysis | |
|
How was cost reported? (average cost/marginal cost/incremental cost/total cost/other- describe) |
Average cost/incremental cost |
| Type of sensitivity analysis | One-way sensitivity analysis |
| What variables were used in sensitivity analysis? | Values of RRs, cost of intervention, adherence rates of PA |
| Findings from sensitivity analysis | The conclusion that intervention is cost-effective is not altered |
| Main results | |
| Findings on the cost-effectiveness |
Cost per person being active: £440.35 Cost per QALY gained: £80.96 Cost saving per QALY gained: £2388.41 |
Part 4: study quality
| Challenges | |
|---|---|
| Author-stated limitations | The assumptions surrounding the parameters for the model may have underestimated or overestimated the cost per QALY gained estimates |
| Author-stated strengths | N/A |
| Useful ideas from this study |
|
| Quality assessment for economic evaluation (checklist from Drummond and Jefferson, 1996)74 | Yes | No | Not clear | Not appropriate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study design | ||||
| 1. The research question is stated | ✓ | |||
| 2. The economic importance of the research question is stated | ✓ | |||
| 3. The viewpoint(s) of the analysis are clearly stated and justified | ✓ | |||
| 4. The rationale for choosing the alternative programmes or interventions compared is stated | ✓ | |||
| 5. The alternatives being compared are clearly described | ✓ | |||
| 6. The form of economic evaluation used is stated | ✓ | |||
| 7. The choice of form of economic evaluation is justified in relation to the questions addressed | ✓ | |||
| Data collection | ||||
| 8. The source(s) of effectiveness estimates used are stated | ✓ | |||
| 9. Details of the design and results of effectiveness study are given (if based on a single study) | ✓ | |||
| 10. Details of the method of synthesis or meta-analysis of estimates are given (if based on an overview of a number of effectiveness studies) | ✓ | |||
| 11. The primary outcome measure(s) for the economic evaluation are clearly stated | ✓ | |||
| 12. Methods to value health states and other benefits are stated | ✓ | |||
| 13. Details of the subjects from whom valuations were obtained are given | ✓ | |||
| 14. Productivity changes (if included) are reported separately | ||||
| 15. The relevance of productivity changes to the study question is discussed | ✓ | |||
| 16. Quantities of resources are reported separately from their unit costs | ||||
| 17. Methods for the estimation of quantities and unit costs are described | ✓ | |||
| 18. Currency and price data are recorded | ✓ | |||
| 19. Details of currency of price adjustments for inflation or currency conversion are given | ✓ | |||
| 20. Details of any model used are given | ✓ | |||
| 21. The choice of model used and the key parameters on which it is based are justified | ✓ | |||
| Analysis and interpretation of results | ||||
| 22. Time horizon of costs and benefits is stated | ✓ | |||
| 23. The discount rate(s) is stated | ✓ | |||
| 24. The choice of rate(s) is justified | ✓ | |||
| 25. An explanation is given if costs or benefits are not discounted | ✓ | |||
| 26. Details of statistical tests and CIs are given for stochastic data | ||||
| 27. The approach to sensitivity analysis is given | ✓ | |||
| 28. The choice of variables for sensitivity analysis is justified | ✓ | |||
| 29. The ranges over which the variables are varied are stated | ✓ | |||
| 30. Relevant alternatives are compared | ✓ | |||
| 31. Incremental analysis is reported | ✓ | |||
| 32. Major outcomes are presented in a disaggregated as well as aggregated form | ✓ | |||
| 33. The answer to the study question is given | ✓ | |||
| 34. Conclusions follow from the data reported | ✓ | |||
| 35. Conclusions are accompanied by the appropriate caveats | ✓ | |||
| Did the economic evaluation use a decision-analytic modelling framework? |
Response: yes (✓), no (×), not applicable (N/A) Instruction: if ‘yes’, assess paper using the questions in block 6 |
| Quality assessment for decision-analytic models (checklist from Philips et al., 2004)75 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality criterion | Question(s) | Response (✓, ×, N/A) | Comments |
| S1 | Is there a clear statement of the decision problem? | ✓ | |
| Is the objective of the evaluation and model specified and consistent with the stated decision problem? | ✓ | ||
| Is the primary decision-maker specified? | ✓ | ||
| S2 | Is the perspective of the model stated clearly? | ✓ | |
| Are the model inputs consistent with the stated perspective? | ✓ | ||
| Has the scope of the model been stated and justified? | ✓ | ||
| Are the outcomes of the model consistent with the perspective, scope and overall objective of the model? | ✓ | ||
| S3 | Is the structure of the model consistent with a coherent theory of the health condition under evaluation? | ✓ | |
| Are the sources of data used to develop the structure of the model specified? | ✓ | ||
| Are the causal relationships described by the model structure justified appropriately? | ✓ | ||
| S4 | Are the structural assumptions transparent and justified? | ✓ | |
| Are the structural assumptions reasonable given the overall objective, perspective and scope of the model? | ✓ | ||
| S5 | Is there a clear definition of the options under evaluation? | ✓ | |
| Have all feasible and practical options been evaluated? | ✓ | ||
| Is there justification for the exclusion for the exclusion of feasible options? | ✓ | ||
| S6 | Is the chosen model type appropriate given the decision problem and specified causal relationships within the model? | ✓ | |
| S7 | Is the time horizon of the model sufficient to reflect all important differences between options? | ||
| Are the time horizon of the model, the duration of treatment and the duration of treatment effect described and justified? | ✓ | ||
| S8 | Do the disease states (state-transition model) or the pathways (decision-tree model) reflect the underlying biological process of the disease in question and the impact of interventions? | ✓ | |
| S9 | Is the cycle length defined and justified in terms of natural history of disease? | N/A | |
| D1 | Are the data identification methods transparent and appropriate given the objectives of the model? | ✓ | |
| Where choices have been made between data sources, are these justified appropriately? | ✓ | ||
| Has particular attention been paid to identifying data for the important parameters in the model? | ✓ | ||
| Has the quality of the data been assessed appropriately? | ✓ | ||
| Where expert opinion has been used, are the methods described and justified? | N/A | ||
| D2 | Is the data modelling methodology based on justifiable statistical and epidemiological techniques? | ||
| D2a | Is the choice of baseline data described and justified? | ✓ | |
| Are transition probabilities calculated appropriately? | ✓ | ||
| Has a half-cycle correction been applied to both cost and outcome? | N/A | ||
| If not, has this omission been justified? | N/A | ||
| D2b | If relative treatment effects have been derived from trial data, have they been synthesised using appropriate techniques? | ✓ | |
| Have the methods and assumptions used to extrapolate short-term results to final outcomes been documented and justified? | ✓ | ||
| Have alternative extrapolation assumptions been explored through sensitivity analysis? | ✓ | ||
| Have assumptions regarding the continuing effect of treatment once treatment is complete been documented and justified? | ✓ | ||
| Have alternative assumptions regarding the continuing effect of treatment been explored through sensitivity analysis? | ✓ | ||
| D2c | Are the costs incorporated into the model justified? | ✓ | |
| Has the source for all costs been described? | ✓ | ||
| Have discount rates been described and justified given the target decision-maker? | ✓ | ||
| D2d | Are the utilities incorporated into the model appropriate? | ✓ | |
| Is the source for the utility weights referenced? | ✓ | ||
| Are the methods of derivation for the utility weights justified? | ✓ | ||
| D3 | Have all data incorporated into the model been described and referenced in sufficient detail? | ✓ | |
| Has the use of mutually inconsistent data been justified (i.e. are assumptions and choices appropriate)? | ✓ | ||
| Is the process of data incorporation transparent? | ✓ | ||
| If data have been incorporated as distributions, has the choice of distribution for each parameter been described and justified? | N/A | ||
| If data have been incorporated as distributions, is it clear that second order uncertainty is reflected? | N/A | ||
| D4 | Have the four principal types of uncertainty been addressed? | × | Only parameter uncertainty was addressed |
| If not, has the omission of particular forms of uncertainty been justified? | × | ||
| D4a | Have methodological uncertainties been addressed by running alternative versions of the model with different methodological assumptions? | × | |
| D4b | Is there evidence that structural uncertainties have been addressed via sensitivity analysis? | × | |
| D4c | Has heterogeneity been dealt with by running the model separately for different subgroups? | × | |
| D4d | Are the methods of assessment of parameter uncertainty appropriate? | ✓ | |
| If data are incorporated at point estimates, are the ranges used for sensitivity analysis stated clearly and justified? | ✓ | ||
| C1 | Is there evidence that the mathematical logic of the model has been tested thoroughly before use? | ? | Not mentioned |
| C2 | Are any counterintuitive results from the model explained and justified? | N/A | |
| If the model has been calibrated against independent data, has any differences been explained and justified? | N/A | ||
| Have the results of the model been compared with those of previous models and any differences in results explained? | × | ||
Appendix 6 Detailed data extraction: predictors of uptake and adherence systematic review
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U013 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | Access to ERSs – a population based analysis |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | J Publ Health 2005;27:326–30 |
| Authors | Harrison RA, McNair F and Dugdill L |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | Not reported |
| Date trial was conducted | January 1998 to December 2002 |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Population-based analysis |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | For example, one scheme (name) and x practices or x leisure providers |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | GPs and their staff |
| Reason for referral | Participating in no or only a little PA a week and had no clinical contraindications to PA, as determined by the clinician |
| Format of referral | Referral form |
| Referred to who | Exercise officer |
| Referred to where | Leisure centre |
| Single or group sessions | Both |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘One hundred and twenty-five GPs and their staff were able to refer sedentary patients to the exercise scheme’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | 79% (5225/6610) |
| Adherence rates | Not reported |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
Part 3: extracted results
| Sociodemographics/medical history prediction analysis of uptake and adherence | ||
|---|---|---|
| Uptake (multivariate: ORs) | ||
| Gender: (male vs female) |
(adjusted for age) 0.91, p = 0.64 (adjusted for age and sex) 1.37, (1.15 to 1.64) |
|
| Referral reason | Adjusted for age and sex | Adjusted for age, sex and IMD |
| None specified | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.00 (ref.) |
| Mental health | 1.72 (1.24 to 2.39) 0.001 | 2.36 (1.48 to 3.82) 0.001 |
| Other | 1.73 (0.79 to 3.78) 0.170 | 1.29 (0.89 to 1.86) 0.174 |
| CVD | 1.55 (1.26 to 1.90) 0.001 | 1.03 (0.77 to 1.38) 0.828 |
| Fitness | 1.55 (1.14 to 2.10) 0.005 | 10.33 (1.44 to 74.3) 0.020 |
| Overweight | 1.37 (1.07 to 1.75) 0.014 | 1.22 (0.86 to 1.74) 0.257 |
| Musculoskeletal | 1.21 (1.00 to 1.47) 0.053 | 1.22 (0.95 to 1.55) 0.115 |
| Respiratory | 1.07 (0.78 to 1.48) 0.664 | 0.91 (0.73 to 1.15) 0.428 |
| Socioeconomic status (IMD) | All patients (IMD) (adjusted for age and sex) 1.02 (0.97 to 1.06) | |
| Least deprived (IMD 1) vs most deprived (IMD 5) (age/sex adjusted) | ||
| None specified | 1.08 (0.92 to 1.27) | |
| Mental health | 1.20 (0.94 to 1.54) | |
| Other | Not calculated | |
| CVD | 1.03 (0.94 to 1.14) | |
| Fitness | 0.81 (0.60 to 1.09) | |
| Overweight | 1.11 (0.94 to 1.30) | |
| Musculoskeletal | 0.99 (0.92 to 1.08) | |
| Respiratory | 1.45 (1.06 to 1.99) p = 0.021 | |
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? Yes
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U010 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | Uptake and participation in physical activity referral schemes in the UK: An investigation of patients referred with mental health problems |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | Issues Ment Health Nurs 2008;29:1088–97 |
| Authors | Crone D, Johnston L, Gidlow C, Henley C and James D |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | Not reported |
| Date trial was conducted | 2000–3 |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Observational |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | One county-wide scheme |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | Primary-care health professional: GP, practice nurse, physiotherapist, ‘other’ |
| Reason for referral | Cardiovascular, overweight/obese, diabetes, musculoskeletal, mental health, unfit/sedentary, other |
| Format of referral | Not reported |
| Referred to who | PARS co-ordinator |
| Referred to where | Local authority, local education authority, private or individual provider |
| Single or group sessions | Both |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘Participants are referred by a health professional to the PARS and are offered eight to twelve weeks of either weekly or biweekly supervised exercise sessions at local leisure facilities’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | 68.7% (1996/2901) |
| Adherence rates | 48.3% (964) |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
|
Uptake: • physical health – 1917 (96%) • mental health – 79 (4%) |
Adherence: • physical health – 935 (49%) • mental health – 29 (37%) |
Part 3: extracted results
| Sociodemographics/medical history prediction analysis of uptake and adherence | |
|---|---|
| Adherence (univariate – chi-squared test) | |
| Scheme completion (> 80% attendance): |
Mental health vs physical health 22% vs 34%; p < 0.001 |
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? No
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U011 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | Is the promotion of physical activity in vulnerable older people feasible and effective in general practice? |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | B J Gen Pract 2006;56:791–3 |
| Authors | Dinan S, Lenihan P, Tenn T and Iliffe S |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Brief report |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | Camden & Islington Health Action Zone |
| Date trial was conducted | Not reported |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Evaluation |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | 14 practices |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | GP or practice nurse |
| Reason for referral | Frailty based on ‘Timed Up and Go’ test |
| Format of referral | Not stated |
| Referred to who | Class instructor |
| Referred to where | General practices |
| Single or group sessions | Group |
| Referral quote from paper |
‘GPs had access to exercise prescription schemes, delivered in community-based classes in local leisure centres’ ‘Patients were referred for exercise by the GPs and practice nurses’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | 89% (216/242) |
| Adherence rates | 82% (178/216) |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
Part 3: extracted results
Not reported.
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? No
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U003 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | Socio-demographic patterning of referral, uptake and attendance in Physical Activity Referral Schemes |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | J Publ Health 2007;29:107–13 |
| Authors | Gidlow C, Johnston LH, Crone D, Morris C, Smith A, Foster C and James DVB |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | University of Gloucestershire, Sheffield Hallam University and Taunton Deane PCT |
| Date trial was conducted | 2000–3 |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Evaluation |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | One county-wide scheme |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | Primary-care health professional: GP, practice nurse, physiotherapist, ‘other’ |
| Reason for referral | Cardiovascular, overweight/obese, diabetes, musculoskeletal, mental health, unfit/sedentary, other |
| Format of referral | Not reported |
| Referred to who | PARS co-ordinator |
| Referred to where | Local authority, local education authority, private or individual provider |
| Single or group sessions | Both |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘Details of all referred participants were sent by referring health professionals to the PARS coordinator’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | 65% (1861/2864) |
| Adherence rates | 50.3% (936/1861) |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
Part 3: extracted results
| Sociodemographics/medical history prediction analysis of uptake and adherence | ||
|---|---|---|
| Uptake (multivariate: ORs) | Adherence (multivariate: ORs) | |
| Gender | ||
| (male vs female) | 0.94 (0.79 to 1.12), p = 0.496 | 0.82 (0.68 to 0.99), p = 0.046 |
| Age | ||
| Continuous | 1.01 (1.01 to 1.02), p < 0.001 | 1.02 (1.01 to 1.02), p < 0.001 |
| Age group (years) | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| ≤ 29 | 1 (ref.) | 1 (ref.) |
| 30–39 | 1.35 (0.96 to 1.90), p = 0.085 | 2.02 (1.28 to 3.20), p = 0.003 |
| 40–49 | 1.48 (1.06 to 2.07), p = 0.021 | 1.46 (0.93 to 2.28), p = 0.100 |
| 50–59 | 2.00 (1.35 to 2.78), p < 0.001 | 1.90 (1.24 to 2.91), p = 0.001 |
| 60–69 | 2.41 (1.70 to 3.42), p < 0.001 | 2.44 (1.57 to 3.79), p < 0.001 |
| ≥ 70 | 1.57 (1.05 to 2.36), p = 0.029 | 3.22 (1.93 to 5.39), p < 0.001 |
| Deprivation | ||
| Townsend (continuous) | 0.94 (0.91 to 0.96), p < 0.001 | 0.98 (0.95 to 1.01), p = 0.116 |
| Townsend (quartiles) | p < 0.001 | p = 0.194 |
| Q4 (least) | 1 (ref.) | 1 (ref.) |
| Q3 | 0.85 (0.66 to 1.10), p = 0.211 | 1.10 (0.85 to 1.42), p = 0.478 |
| Q2 | 0.75 (0.59 to 0.97), p = 0.026 | 0.88 (0.68 to 1.15), p = 0.346 |
| Q1 (most) | 0.57 (0.45 to 0.74), p < 0.001 | 0.83 (0.63 to 1.09), p = 0.186 |
| IMD 2004 | 0.97 (0,96 to 0.99), p < 0.001 | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.01), p = 0.441 |
| Rurality | ||
| Rural vs urban | 1.30 (1.09 to 1.55), p = 0.004 | 1.00 (0.83 to 1.22), p = 0.984 |
| Settlement type | p < 0.01 | p = 0.939 |
| Urban | 1 (ref.) | 1 (ref.) |
| Hamlet/isolated | 0.84 (0.60 to 1.18), p = 0.323 | 0.95 (0.67 to 1.37), p = 0.794 |
| Village | 0.67 (0.53 to 0.85), p = 0.001 | 1.06 (0.82 to 1.38), p = 0.655 |
| Small town/fringe | 0.81 (0.65 to 1.01), p = 0.060 | 0.98 (0.77 to 1.25), p = 0.852 |
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? Yes
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U014 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | Do adherers and non-adherers to a GP ERS differ in their long-term physical activity levels? |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | J Sports Sci 1991;16:84 |
| Authors | Jackson C, Bell F, Smith RA and Dixey R |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Conference abstract |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | Not reported |
| Date trial was conducted | January 1993 to March 1996 |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Cross-sectional |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | One scheme: exercise by prescription GP referral scheme in North Yorkshire |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | Not reported |
| Reason for referral | Not reported |
| Format of referral | Not reported |
| Referred to who | Not reported |
| Referred to where | Leisure centre |
| Single or group sessions | Not reported |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘A questionnaire was mailed to 1254 individuals who had attended a gym-based exercise programme on the Exercise by Prescription GP referral scheme in North Yorkshire’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | Not reported |
| Adherence rates | 70% (466/686) |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
Part 3: extracted results
Not reported.
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? No
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U001 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | Factors associated with physical activity referral uptake and participation |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | J Sports Sci 2008;26:217–24 |
| Authors | James DVB, Johnston LH, Crone D, Sidford AH, Gidlow C, Morris C and Foster C |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | Not reported |
| Date trial was conducted | 2000–3 |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Observational prospective cross-sectional survey |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | Not reported |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | Primary-care health professional: GP, practice nurse, physiotherapist, ‘other’ |
| Reason for referral | Cardiovascular, overweight/obese, diabetes, musculoskeletal, mental health, unfit/sedentary, other |
| Format of referral | Not reported |
| Referred to who | PARS co-ordinator |
| Referred to where | Local authority, local education authority, private or individual provider |
| Single or group sessions | Both |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘Details of all referred participants were sent by referring health professionals to the PARS coordinator’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | 65.4% (1934/2958) |
| Adherence rates | 48.4% (936/1934) |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
Part 3: extracted results
| Sociodemographics/medical history prediction analysis of uptake and adherence | ||
|---|---|---|
| Uptake (multivariate: ORs) | Adherence (multivariate: ORs) | |
| Gender | Not significant | |
| Male | 1.00 (ref.) | |
| Female | 0.823 (0.681 to 0.994), p = 0.043 | |
| Age | Not available | 1.016 (1.010 to 1.023), p < 0.001 |
| Referral reason | p <.001 | Not significant |
| CVD | 1.00 (ref.) | |
| Over/obese | 0.639 (0.501 to 0.814), p < 0.001 | |
| Diabetes | 1.003 (0.659 to 1.525), p = 0.990 | |
| Musculoskeletal | 0.759 (0.582 to 0.990), p = 0.042 | |
| Mental health | 0.339 (0.275 to 0.579), p < 0.001 | |
| Unfit/sedentary | 0.758 (0.533 to 1.079), p = 0.124 | |
| Other | 0.630 (0.462 to 0.858), p = 0.003 | |
| Referrer | p = 0.006 | Not significant |
| GP | 1.00 (ref.) | |
| Practice nurse | 1.032 (0.817 to 1.304), p = 0.790 | |
| Physiotherapist | 1.218 (0.919 to 1.615), p = 0.170 | |
| Other | 0.540 (0.369 to 0.792), p = 0.002 | |
| Leisure provider | Not available | |
| Local authority | Not significant | |
| Local education | ||
| Private | ||
| Individual | ||
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? Yes
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
Herman S, Blumenthal JA, Babyak M, Khatri P, Craighead WE, Krishnan KR, et al. Exercise therapy for depression in middle-aged and older adults: predictors of early dropout and treatment failure. Health Psychol 2002;21,553–63.
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U0015 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | Factors associated with physical activity referral completion and health outcomes |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | J Sports Sci 2009;27:1007–17 |
| Authors | James D, Mills H, Crone D, Johnston L, Morris C and Gidlow C |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | Healthwise consortium, which included: Greenwich Leisure Limited (GLL); Greenwich Teaching Primary Care Trust (GTPCT) and Greenwich Council |
| Date trial was conducted | April 2005 to March 2007 |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Cross-sectional |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | One scheme: metropolitan PARS, five leisure centres |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | Primary-care health professional |
| Reason for referral |
|
| Format of referral | Not reported |
| Referred to who | Exercise professional |
| Referred to where | Leisure centre |
| Single or group sessions | Both |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘All participants were referred by a primary-care health professional to one of five leisure centres’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | Not reported |
| Adherence rates | 57% (750/1315) |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
Part 3: extracted results
| Sociodemographics/medical history prediction analysis of uptake and adherence | |
|---|---|
| Adherence (multivariate: ORs) | |
| Gender | |
| Male | 1.000 (ref.) |
| Female | 0.923 (0.72 to 1.18), p = 0.526 |
| Age | |
| Continuous | 1.019 (1.00 to 1.03), p = 0.001 |
| Ethnicity | p = 0.038 |
| White | 1.000 (ref.) |
| Asian | 1.383 (0.94 to 2.20), p = 0.094 |
| Black | 0.866 (0.64 to 1.17), p = 0.352 |
| Chinese | 0.795 (0.224 to 2.82), p = 0.723 |
| Mixed | 6.310 (1.388 to 28.69), p = 0.017 |
| Occupation | p = 0.408 |
| Unemployed | 1.000 (ref.) |
| Retired | 1.300 (0.88 to 1.90), p = 0.176 |
| Unskilled | 0.874 (0.52 to 1.44), p = 0.600 |
| Partly skilled | 1.238 (0.78 to 1.95), p = 0.375 |
| Skilled manual | 1.018 (0.591 to 1.72), p = 0.950 |
| Skilled non-manual | 1.324 (0.93 to 1.87), p = 0.114 |
| Managerial | 1.610 (0.95 to 2.72), p = 0.077 |
| Professional | 1.328 (0.76 to 2.31), p = 0.317 |
| Referral reason | p = 0.065 |
| Cardiovascular | 1.000 (ref.) |
| Pulmonary | 0.546 (0.346 to 0.86),p = 0.009 |
| Metabolic | 0.755 (0.53 to 1.06), p = 0.106 |
| Orthopaedic | 0.724 (0.50 to 1.04), p = 0.081 |
| Neuromuscular | 2.670 (0.70 to 10.05), p = 0.147 |
| Mental | 0.919 (0.57 to 1.47), p = 0.728 |
| Miscellaneous | 0.635 (0.21 to 1.85), p = 0.406 |
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? Yes
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U007 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | Adherence to an exercise prescription scheme: The role of expectations, self-efficacy, stage of change and psychological well-being |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | Br J Health Psychol 2005;10:359–78 |
| Authors | Jones F, Harris P, Waller H and Coggins A |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | Hertfordshire Health Agency |
| Date trial was conducted | Not reported |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Cross-sectional |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | One scheme, Hertfordshire GP ERS, seven leisure centres |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | Medical practitioner or practice nurse |
| Reason for referral | High blood pressure, weight or stress-related problems (or combinations of these) |
| Format of referral | Not reported |
| Referred to who | Gym staff |
| Referred to where | Leisure centre |
| Single or group sessions | Both |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘Referred by either their medical practitioner or practice nurse for a course of 24 exercise sessions. These were to be spread over a 12-week period and provided at a standard reduced rate’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | 78% (119/152) |
| Adherence rates | 65% (77/119) |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
Part 3: extracted results
| Psychosocial prediction analysis of uptake and adherence | |
|---|---|
| Completers vs dropouts | Adherence (ANOVA) |
| GHQ | F = 3.33, p = 0.07 |
| Self-efficacy | F = 0.49, p = 0.48 |
| Expectations of change (health and fitness) | F = 1.81, p = 0.18 |
| Expectations of change (personnel development) | F = 4.20, p = 0.04 |
| Stage of change (chi-squared test) | Not significant |
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? No
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U004 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | Exercise on prescription: does it work? |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | Health Educ J 1995;54:453–64 |
| Authors | Lord JC and Green F |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial |
North Western Regional Health Authority Look After Your Heart grant, a joint finance allocation and contributions from Leisure Services and Stockport Health Commission. |
| Date trial was conducted | 1992 |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Evaluation |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | One scheme (Stockport) |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | GP |
| Reason for referral | CHD prevention programme |
| Format of referral | Not reported |
| Referred to who | Community health and fitness officer |
| Referred to where | Differing local leisure and recreational facilities |
| Single or group sessions | Both |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘This evaluation of Stockport’s Exercise on Prescription Scheme’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | 60% (252/419) |
| Adherence rates | 31% (77/252) |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
|
Uptake: • Male: 53/105 (50.5%) • Female: 198/287 (69%): > 35 years 68/115 (59.1%), 35–54 years 108/205 (52.7%), 55+ years 41/63 (65.1%) • Overweight: 77/135 (57%) • Stress/anxiety: 33/63 (52.4%) • Other: 23/46 (50%) • Lipids/cholesterol: 12/27 (44.4%) • Keep fit: 10/20 (50%) • Lack of exercise: 11/20 (55%) • Depression: 11/20 (55%) • Arthritis: 7/12 (58.3%) • Back pain: 7/12 (58.3%) • Family history IHD: 3/10 (30%) |
Adherence: • Male: 14/53 (26.4%) • Female: 61/198 (30.8%): > 35 years 10/68 (14.7%), 35–54 years 35/108 (32.4%), 55+ years 18/63 (28.5%) • Overweight: 20/77 (25.9%) • Stress/anxiety: 11/33 (33.3%) • Other: 8/23 (34.7%) • Lipids/cholesterol: 3/12 (25%) • Keep fit: 6/10 (60%) • Lack of exercise: 4/11 (36.3%) • Depression: 4/11 (36.3%) • Arthritis: 2/7 (28.5%) • Back pain: 0/7 (0%) • Family history IHD: 0/3 (0%) |
Part 3: extracted results
Not reported.
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? No
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U016 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | The retrospective evaluation of a GPs exercise prescription programme |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | J Hum Nutr Diet 1999;12:S32–42 |
| Authors | Martin C and Woolf-May K |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | Not reported |
| Date trial was conducted | Not reported |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Retrospective evaluation |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | One leisure centre |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | GP, practice nurse, self |
| Reason for referral | Not reported |
| Format of referral | Not reported |
| Referred to who | Exercise advisor |
| Referred to where | Leisure centre |
| Single or group sessions | Not reported |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘This study aimed to evaluate a GP exercise prescription programme that had been running in Margate, Kent, for 3 years’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | Not reported |
| Adherence rates | 12% (60/490) |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
Part 3: extracted results
Not reported.
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? No
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U005 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | Changes in self-determination during an ERS |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | Publ Health 2008;122:1257–60 |
| Authors | Morton KL, Biddle SJH and Beauchamp MR |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Short communication |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | None declared |
| Date trial was conducted | Not reported |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Observational |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | One leisure centre |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | Not reported |
| Reason for referral | Not reported |
| Format of referral | Not reported |
| Referred to who | Not reported |
| Referred to where | Not reported |
| Single or group sessions | Not reported |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘This study involved 30 patients enrolled in an ERS at a leisure centre in the UK’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | Not reported |
| Adherence rates | 40% (12/30) |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
Part 3: extracted results
| Psychosocial prediction analysis of uptake and adherence | |
|---|---|
| Adherence (ANOVA/t-tests) | |
| Self-determination |
F(2, 3) = 9.19, p = 0.001 Post hoc adherers significantly higher self-determination (p < 0.05) than non-adherers and partial adherers |
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? No
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U008 |
| Reviewer ID and name | July 2010 |
| Date of completion of this form | Promoting exercise on prescription: recruitment, motivation, barriers and adherence in a Danish community intervention study to reduce type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia and hypertension |
| Title of report | J Publ Health 2009:17:187–93 |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | Roessler KK and Ibsen B |
| Authors | English |
| Language of publication | Full paper |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | July 2010 |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | Denmark |
| Funders of the trial | Ministry of Social Affairs and Administration of Public Health of the City of Copenhagen |
| Date trial was conducted | 2004–7 |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Evaluation |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | One scheme, Copenhagen |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | GP |
| Reason for referral | Physically inactive, have a BMI < 35, be mobile enough to participate in supervised physical training and have at least one of the following diagnoses: type 2 diabetes, above-normal cholesterol level (dyslipidaemia) or above-normal blood pressure (hypertension) |
| Format of referral | Not stated |
| Referred to who | Physiotherapist |
| Referred to where | Not stated |
| Single or group sessions | Group |
| Referral quote from paper |
‘There are data from the GP who referred the patient to the Exercise and Diet on prescription programme’ ‘Patients received 4 months of supervised physical training in groups’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | Not reported |
| Adherence rates | 70% (811/1156) |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
Part 3: extracted results
Not reported.
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? No
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U002 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | Do general practices provide equitable access to physical activity interventions? |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | British Journal of General Practice 2008 October;58:699–702 |
| Authors | Sowden SL, Breeze E, Barber J and Raine R |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | ESRC/MRC PhD studentship |
| Date trial was conducted | April 2004 to March 2006 |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Cross-sectional |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | Six schemes (Greater London) 317 practices |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | Health professionals |
| Reason for referral | Not reported |
| Format of referral | Not reported |
| Referred to who | Not reported |
| Referred to where | Not reported |
| Single or group sessions | Not reported |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘Each exercise referral scheme was located within a primary care trust (PCT) and every general practice within each of these PCTs was able to refer patients to the scheme’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | 58% (3565/6101) |
| Adherence rates | 39% (1404/3565) |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
Part 3: extracted results
| Sociodemographics/medical history prediction analysis of uptake and adherence | ||
|---|---|---|
| Uptake (multivariate: ORs) | Adherence (multivariate: ORs) | |
| IMD quintiles | p = 0.85 | p = 0.06 |
| 1 (most deprived) | 1 (ref.) | 1 (ref.) |
| 2 | 1.05 (0.93 to 1.21) | 0.89 (0.71 to 1.11) |
| 3 | 0.94 (0.77 to 1.15) | 0.92 (0.63 to 1.34) |
| 4 | 0.99 (0.78 to 1.25) | 1.47 (0.96 to 2.24) |
| 5 (least deprived) | 1.05 (0.83 to 1.33) | 1.23 (0.84 to 1.79) |
| Age (years) | p > 0.001 | p > 0.001 |
| 16–29 | 1 (ref.) | 1 (ref.) |
| 30–44 | 1.67 (1.34 to 2.08) | 1.30 (0.96 to 1.77) |
| 45–59 | 2.09 (1.68 to 2.61) | 1.77 (1.27 to 2.46) |
| 60–74 | 2.67 (2.14 to 3.33) | 2.91 (2.04 to 4.16) |
| ≥ 75 | 2.43 (1.70 to 3.46) | 2.71 (1.65 to 4.46) |
| Gender | p < 0.001 | Did not improve model |
| Male | 1 (ref.) | |
| Female | 1.33 (1.18 to 1.49) | |
| Scheme area | Did not improve model | p > 0.001 |
| 1 | 1 (ref.) | |
| 2 | 0.43 (0.32 to 0.58 | |
| 3 | 4.45 (3.28 to 6.03) | |
| 4 | NI | |
| 5 | 13.49 (8.78 to 20.72) | |
| 6 | 0.45 (0.29 to 0.70) | |
| Referred for musculoskeletal reasons | p = 0.036 | Did not improve model |
| No | 1 (ref.) | |
| Yes | 1.18 (1.01 to 1.38) | |
| Referred for diabetes reasons | Did not improve model | p < 0.007 |
| No | 1 (ref.) | |
| Yes | 0.76 (0.63 to 0.93) | |
| Referred for CVD reasons | Did not improve model | p = 0.020 |
| No | 1 (ref.) | |
| Yes | 1.22 (1.03 to 1.45) | |
Part four: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? Yes
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Uptake and adherence subgroup rates available from PhD thesis.
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U012 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | Exercise referral: the public health panacea for physical activity promotion? A critical perspective of exercise refferral schemes; their development and evaluation |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | Ergonomics 2004:48:1390–410 |
| Authors | Dugdill L, Graham R and McNair F |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | Not reported |
| Date trial was conducted | 2000–3 |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Case study |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | Two schemes |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | Health professional |
| Reason for referral | Not reported |
| Format of referral | Not reported |
| Referred to who | Exercise referral officer |
| Referred to where | Leisure setting |
| Single or group sessions | Not reported |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘The opportunity to become involved in the evaluation of two ERS’s presented itself to the authors in 2000’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | ||
|---|---|---|
| Uptake rates | Scheme B: 68% (1825/2696) | |
| Adherence rates | Scheme A: 34% (336/958) | |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | ||
| Uptake: not reported | Adherence – Scheme A:
|
|
Part 3: extracted results
Not reported.
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? No
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U009 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | Predictors of Older Primary Care Patients’ Participation in a Submaximal Exercise Test and a Supervised, Low-Impact Exercise Class |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | Prev Med 2001;33:485–94 |
| Authors | Damush TM, Stump TE, Saporito A and Clark DO |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | USA |
| Funders of the trial | National Institute on Ageing |
| Date trial was conducted | Not reported |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Cross-sectional |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | Two community health centres |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | Health-care provider |
| Reason for referral | Not reported |
| Format of referral | Not reported |
| Referred to who | Exercise physiologist |
| Referred to where | Local community buildings |
| Single or group sessions | Group |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘Providers screened and referred eligible patients to complete a submaximal exercise test and participate in a group-based community exercise program’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | 28% (113/404) |
| Adherence rates | Not reported |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
Part 3: extracted results
| Sociodemographics/medical history prediction analysis of uptake and adherence | |
|---|---|
| Uptake (multivariate: ORs) | |
| Age | 0.98 (0.95 to 1.01) |
| Ethnicity (African American vs all other racial groups) | 0.88 (0.44 to 1.79) |
| Clinic location | 0.68 (0.34 to 1.38) |
| Current smoker | 0.38 (0.19 to 0.76) |
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? Yes
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Part 1: background information of study
| Study ID | U016 |
| Reviewer ID and name | TP |
| Date of completion of this form | July 2010 |
| Title of report | Adherence and well-being in overweight and obese patients referred to an EoP scheme: a SDT perspective |
| Source (journal year;volume:pages) | Psychol Sport Exerc 2007;8:722–40 |
| Authors | Edmunds J, Ntoumanis N and Duda JL |
| Language of publication | English |
| Type of report (e.g. full paper/abstract/unpublished) | Full paper |
Part 2: information about the study
| Characteristics of the trial | |
|---|---|
| Country of the principal investigators, where the trial was conducted | UK |
| Funders of the trial | Not reported |
| Date trial was conducted | Not reported |
| Type of trial design (e.g. parallel or cluster trial) | Cross-sectional |
| Was the trial multicentre? If so, how many centres were there? | One scheme (West Midlands) |
| Characteristics of the referral | |
|---|---|
| Who made the referral | GP |
| Reason for referral | CHD risk factors |
| Format of referral | Prescription card |
| Referred to who | EoP advisor |
| Referred to where | Leisure centre |
| Single or group sessions | Both |
| Referral quote from paper | ‘EoP schemes are designed for individuals between 15 and 74 years of age who display specific Coronary Heart Disease risk factors. Upon referral to the scheme, an EoP advisor (i.e., a health and fitness instructor who has received specialized training to deliver exercise prescriptions) develops a 3-month exercise routine to suit each patient’s/client’s condition’ |
| Reported uptake and adherence rates | |
|---|---|
| Uptake rates | Not reported |
| Adherence rates | 51% (25/49) |
| Was uptake and/or adherence reported in subgroups? If YES then detail: | |
Part 3: extracted results
Quote from paper (p. 732): ‘Participants who adhered more to their 3-month prescriptions did not report significantly different baseline levels of any of the study variables, compared with those who adhered less’.
Part 4: study quality
Statement of inclusion/exclusion of participants: Yes
Power calculation: No
Was the analysis multivariate? Yes
Do you have any additional comments to make about this study?
Does the reference list of this paper contain additional studies that should be considered for inclusion?
| Is further information required from the authors? | YES | NO |
If YES, give details:
Appendix 7 Economic modelling: supplementary information
| Variables | Evidence base | Expected sign |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Solli et al. (2010), Winter et al. (2010), Muller-Vahl et al. (2010), Berg et al. (2010), Soltoft et al. (2009), Lou et al. (2009), Heyworth et al. (2009), Sorensen et al. (2009), Iglesias et al. (2009), Winter et al. (2009), Konig et al. (2009), Petrous and Kupek (2008), Shimizu et al. (2008), Jerant et al. (2008), Pettersen et al. (2008), Wang et al. (2008), Kralove (2007), Christensen et al. (2007), Boye et al. (2007), Masunari et al. (2007), Dodel et al. (2007), Monz et al. (2007), Sullivan et al. (2007), Saarni et al. (2006), Jia and Lubetkin (2005), Andersen et al. (2004), Hazel et al. (2003), Koopmanschap (2002), Burstrom et al. (2001) and Kind et al. (1998) | – |
| Gender (female) | Muller-Vahl et al. (2010), Gordeev et al. (2010), Berg et al. (2010), Solli et al. (2010), Winter et al. (2010), Lou et al. (2009), Heyworth et al. (2009), Sorensen et al. (2009), Reed et al. (2009), Winter et al. (2009), Konig et al. (2009), Jerant et al. (2008), Pettersen et al. (2008), Petrous and Kupek (2008), Wang et al. (2008), Imai et al. (2008), Christensen et al. (2007), Boye et al. (2007), Masunari et al. (2007), Dodel et al. (2007), Sullivan et al. (2007), Saarni et al. (2006), Lubetkin et al. (2005), Sendi et al. (2005), Jia and Lubetkin (2005), Andersen et al. (2004), Hazel et al. (2003), Koopmanschap (2002) and Burstrom et al. (2001) | – |
| Social class (high) | Soltoft et al. (2009), Petrous and Kupek (2008), Christensen et al. (2007), Genazzani et al. (2002), Guest and Gupta (2002), Burstrom et al. (2001) and Kind et al. (1998) | + |
| Education (high) | Soltoft et al. (2009), Lou et al. (2009), Heyworth et al. (2009), Sorensen et al. (2009), Konig et al. (2009), Ariza-Ariza et al. (2009), Reed et al. (2009), Petrous and Kupek (2008), Jerant et al. (2008), Pettersen et al. (2008), Wang et al. (2008), Kralove (2007), Boye et al. (2007), Sullivan et al. (2007), Saarni et al. (2006), Lubetkin et al. (2005), Sendi et al. (2005) and Kind et al. (1998) | + |
| Ethnicity (white) | Lou et al. (2009), Petrous and Kupek (2008), Lubetkin et al. (2005), Jia and Lubetkin (2005) and Sullivan et al. (2007) | – |
| Marital status (married) | Gordeev et al. (2010), Lou et al. (2009), Konig et al. (2009), Petrous and Kupek (2008), Wang et al. (2008), Dodel et al. (2007), Saarni et al. (2006) and Kind et al. (1998) | ? |
| Income (high) | Muller-Vahl et al. (2010), Winter et al. (2010), Lou et al. (2009), Winter et al. (2009), Konig et al. (2009), Petrous and Kupek (2008), Sullivan et al. (2007), Saarni et al. (2006), Lubetkin et al. (2005), Jia and Lubetkin (2005) and Haacke et al. (2005) | + |
| Employment status (employed) | Muller-Vahl et al. (2010), Winter et al. (2010), Reed et al. (2009), Konig et al. (2009), Petrous and Kupek (2008), Wang et al. (2008), Leslie et al. (2007), Dodel et al. (2007), Monz et al. (2007), Haacke et al. (2005) and Kind et al. (1998) | + |
| BMI (high) | Solli et al. (2010), Soltoft et al. (2009), Reed et al. (2009), Petrous and Kupek (2008), Wee et al. (2008), Sach et al. (2007), Monz et al. (2007), Sendi et al. (2005), Jia and Lubetkin (2005), Hickson and Frost (2004) and Koopmanschap (2002) | – |
| House tenure (house owners) | Petrous and Kupek (2008) and Kind et al. (1998) | + |
| Smokers (yes) | Lou et al. (2009), Heyworth et al. (2009), Iglesias et al. (2009), Petrous and Kupek (2008), Wang et al. (2008), Kralove (2007), Sullivan et al. (2007), Sendi et al. (2005), Jia and Lubetkin (2005), Haacke et al. (2005), Guest and Gupta (2002) and Kind et al. (1998) | – |
| Drink alcohol (yes) | Petrous and kupek(2008), Saarni et al. (2008) and Lou et al. (2009) | + |
| Morbidities (yes)* | Muller-Vahl et al. (2010), Winter et al. (2010), Gordeev et al. (2010), Unsar and Sut (2010), Berg et al. (2010), Solli et al. (2010), Soltoft et al. (2009), Lou et al. (2009), Heyworth et al. (2009), Reed et al. (2009), Cho et al. (2009), Moberg et al. (2009), Winter et al. (2009), Ariza-Ariza et al. (2009), Shimizu et al. (2008), Jerant et al. (2008), Wang et al. (2008), Xie et al. (2008), Saarni et al. (2007), Christensen et al. (2007), Boye et al. (2007), Masunari et al. (2007), Dodel et al. (2007), Monz et al. (2007), Sobocki et al. (2007), Sullivan et al. (2007), Saarni et al. (2006), Xie et al. (2006), Sendi et al. (2005), Jia and Lubetkin (2005), Lubetkin et al. (2005), Andersen et al. (2004), Haacke et al. (2005), Hickson and Frost (2004), Andersen et al. (2004), Hazel et al. (2003), Genazzani et al. (2002), Guest and Gupta (2002), Koopmanschap (2002) and Burstrom et al. (2001) | – |
| Region of residence | Genazzani et al. (2002) | ? |
| Psychosocial well-being (GHQ scores) (high) | Soltoft et al. (2009) | – |
| Height (increased) | Christensen et al. (2007) and Masunari et al. (2007) | + |
| General health (favourable) | Solli et al. (2010) and Burstrom et al. (2001) | + |
| Weight (increased) | Christensen et al. (2007) and Iglesias et al. (2009) | – |
| Urbanisation (urban) | Jelsma et al. (2007) | ? |
| Variables | Observations | Mean (SD)/% |
|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable (HRQoL) | ||
| EQ-5D | 5453 | 0.86 (0.23) |
| Missing | 84 | 1.5 |
| Independent variables (PA) | ||
| Walking | ||
| Active | 873 | 15.8 |
| Inactive | 4664 | 84.2 |
| Sports and exercise | ||
| Active | 660 | 11.9 |
| Inactive | 4877 | 88.1 |
| Objective measurementa | ||
| Active | 102 | 11.5 |
| Inactive | 783 | 88.5 |
| Missing | 4652 | 84 |
| Subjective measurementb | ||
| Active | 2452 | 44.4 |
| Inactive | 3067 | 55.6 |
| Missing | 18 | 0.3 |
| Independent variables (covariates) | ||
| Age | 5537 | 50(6.2) |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 2519 | 45.5 |
| Female | 3018 | 54.5 |
| House tenure | ||
| Own it outright | 1467 | 26.5 |
| Mortgage | 2864 | 51.7 |
| Renters | 1123 | 20.3 |
| Part rent/mortgage | 24 | 0.4 |
| Rent free | 38 | 0.7 |
| Missing | 21 | 0.4 |
| Marital status | ||
| Other | 30 | 0.5 |
| Married (living with partner) | 3618 | 65.3 |
| Single | 735 | 13.3 |
| Separated | 208 | 3.8 |
| Divorced | 816 | 14.7 |
| Widowed | 135 | 2.4 |
| Income | 4535 | 35591.2 (29210) |
| Missing | 1002 | 18.1 |
| Income (missing observations imputed for) | 5537 | 35008.3 (26987.7) |
| Weight | 4867 | 79.1 (17) |
| Missing | 670 | 12.1 |
| Weight (missing observations imputed for) | 5537 | 78.1 (16.3) |
| Height | 4948 | 168 (9.3) |
| Missing | 589 | 10.6 |
| Height (missing observations imputed for) | 5537 | 168(9.2) |
| Drink alcohol | ||
| Yes | 4702 | 84.9 |
| No | 823 | 14.9 |
| Missing | 12 | 0.2 |
| Smokers | ||
| Yes | 1206 | 21.8 |
| No | 1926 | 34.8 |
| Missing | 2405 | 43.4 |
| BMI | ||
| Underweight (< 18.5) | 30 | 0.5 |
| Normal (18.5–25) | 1487 | 26.9 |
| Overweight (25–30) | 1885 | 34 |
| Obese (30+) | 1418 | 25.6 |
| Missing | 717 | 13 |
| General health | ||
| Very good | 1859 | 33.6 |
| Good | 2338 | 42.2 |
| Fair | 959 | 17.3 |
| Bad | 287 | 5.2 |
| Very bad | 90 | 1.6 |
| Missing | 4 | 0.1 |
| Limiting illness | ||
| Limiting | 1293 | 23.4 |
| Non limiting | 1158 | 20.9 |
| No illness | 3084 | 55.7 |
| Missing | 2 | 0.04 |
| Psychosocial well-being | ||
| Score 0 | 3639 | 65.7 |
| Score 1–3 | 1078 | 19.5 |
| Score 4+ | 771 | 13.9 |
| Missing | 49 | 0.9 |
| Hypertensive | ||
| No | 2717 | 49.1 |
| Yes | 704 | 12.7 |
| Missing | 2116 | 38.2 |
| Mental disorder | ||
| No | 5263 | 95.1 |
| Yes | 272 | 4.9 |
| Missing | 2 | 0.04 |
| Vision problems | ||
| No | 5252 | 98.5 |
| Yes | 83 | 1.5 |
| Missing | 2 | 0.04 |
| Ear problems | ||
| No | 5443 | 98.3 |
| Yes | 92 | 1.7 |
| Missing | 2 | 0.04 |
| Musculoskeletal problems | ||
| No | 4558 | 82.3 |
| Yes | 977 | 17.6 |
| Missing | 2 | 0.04 |
| Heart problems | ||
| No | 4911 | 88.7 |
| Yes | 624 | 11.3 |
| Missing | 2 | 0.04 |
| Respiratory problems | ||
| No | 5083 | 91.8 |
| Yes | 452 | 8.2 |
| Missing | 2 | 0.04 |
| Urinary problems | ||
| No | 5437 | 98.2 |
| Yes | 98 | 1.8 |
| Missing | 2 | 0.04 |
| Ethnicity | ||
| White | 5029 | 90.8 |
| Mixed | 44 | 0.8 |
| Asian | 260 | 4.7 |
| Black | 140 | 2.5 |
| Chinese | 28 | 0.5 |
| Other | 17 | 0.3 |
| Missing | 19 | 0.3 |
| Education | ||
| NVQ4/NVQ5/degree or equivalent | 1228 | 22.2 |
| Higher education below degree | 746 | 13.5 |
| NVQ3/GCE ‘A’ level equivalent | 749 | 13.5 |
| NVQ2/GCE ‘O’ level equivalent | 1404 | 25.4 |
| NVQ1/CSE other grade equivalent | 239 | 4.5 |
| Foreign/other | 53 | 1.0 |
| No qualification | 1102 | 19.9 |
| Missing | 16 | 0.3 |
| Employment status | ||
| Employed | 4215 | 76.1 |
| Unemployed | 163 | 2.9 |
| Retired | 259 | 4.7 |
| Other economically inactive | 884 | 16 |
| Missing | 16 | 0.3 |
| Social class | ||
| Professional | 284 | 5.1 |
| Managerial/technical | 1975 | 35.7 |
| Skilled non-manual | 1098 | 19.8 |
| Skilled manual | 915 | 16.5 |
| Semi-skilled manual | 828 | 15.0 |
| Unskilled manual | 285 | 5.2 |
| Other | 15 | 0.3 |
| Missing | 137 | 2.5 |
| Region of residence | ||
| North-east | 370 | 6.7 |
| North-west | 751 | 13.6 |
| Yorkshire | 602 | 10.9 |
| East Midlands | 513 | 9.3 |
| West Midlands | 610 | 11 |
| East | 653 | 11.8 |
| London | 594 | 10.7 |
| South-east | 450 | 8.1 |
| South Central | 422 | 7.6 |
| South-west | 572 | 10.3 |
| Urbanisation | ||
| Urban | 4309 | 77.8 |
| Town/fringe | 542 | 9.8 |
| Village, hamlet and isolated dwellings | 686 | 12.4 |
| Models | Multicollinearity tests | Specification test | Pseudo-R2-value | AIC | BIC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIF | Tolerance | p > |t| | ||||
| 1 | 1.05 to 1.45 | 0.68 to 0.97 | 0.063 | 0.429 | 3247.5 | 3360.6 |
| 2 | 1.04 to 1.55 | 0.65 to 0.95 | 0.084 | 0.430 | 2697.7 | 2798.3 |
| 3 | 1.00 to 1.22 | 0.82 to 0.99 | 0.845 | 0.092 | 841.7 | 889.5 |
| 4 | 1.06 to 1.23 | 0.81 to 0.94 | 0.205 | 0.446 | 1936.9 | 2050.1 |
Appendix 8 Protocol
The following text is extracted from the original application proposal. In addition to our original proposal of undertaking systematic reviews of both the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of ERS and an economic model-based economic analysis, we also undertook a systematic review of ERS uptake and adherence.
Title
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of exercise refferal schemes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
Investigation plan
Research objectives
-
To assess the effectiveness of exercise referral schemes (ERSs) in people with a diagnosed condition known to benefit from physical activity (PA).
-
To assess the cost-effectiveness of ERSs in people with a diagnosed condition known to benefit from PA.
-
To explore the factors that might influence the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of ERSs in people with a diagnosed condition known to benefit from PA.
-
To formulate guidance for the future use of ERSs in the NHS and to identify priorities for future primary research in this area.
Background
Health benefits
Physical activity contributes to the prevention and management of over 20 medical conditions and diseases, including coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic back pain, osteoporosis, cancer, falls in the elderly, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and depression, as summarised in the Chief Medical Officer’s report ‘At Least Five a Week’. 1 The efficacy evidence varies in quality across conditions, but the contribution of physical inactivity to ill health and different disease processes has become clearer each year over the past 50 years.
Current recommendations are for adults to achieve at least 30 minutes of at least moderate-intensity (5.0–7.5 kcal/minute) PA on at least 5 days of the week for health benefit, particularly for reducing risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). 2 Emerging evidence on the effects of time spent in sedentary activities (e.g. TV viewing) on obesity, metabolic processes and type 2 diabetes, independent of PA, suggests that reducing time spent in sedentary activities may be an additional useful indicator of the effectiveness of interventions. Over 20% of worldwide ischaemic heart disease (IHD)3 has been attributed to physical inactivity, and the most active are at 30% lower risk for developing CHD than the least active,4 with a stepped reduction. The dose for reducing risk for other diseases, and promoting positive well-being are less clear, but the minimum target has been recommended widely for general health benefit. 2
Promoting physical activity
The 2006 Health and Safety Executive (HSE) report5 revealed that 40% of men and 28% of women meet the 5 × 30 minutes per week public health target with variations across age, sex, class and ethnicity. The proportion achieving the targets for PA has increased from 32% in 1997 to 40% in 2006 for men, and from 21% to 28% for women. Nevertheless, there is a clear need to promote PA, particularly among the least active who may have most to gain in terms of health. For adults, efforts have focused on changes in the environment,6 mass media campaigns, web- and IT-based communications at population and individual level,7 corporate and workplace initiatives,8 community programmes,9 and provision of individualised professional support10 and new health-care structures. 11 Reviews have also focused on the effectiveness of different interventions among specific groups in the population, such has the elderly and12 workers. 13 Systematic reviews suggest that no single approach can be wholly effective7 in helping sedentary people to maintain a physically active lifestyle, and that a wide variety of approaches can each facilitate small behaviour change. The Foresight report on obesity14 reflected the multiple influences on expenditure and intake and government policy reflects this in its investment and initiatives across different departments and cross-departmental efforts.
Theories of behaviour change also support the need for multiple-level (e.g. targeting attitudes of both recipients and providers of health-promotion messages) and multicomponent approaches (e.g. targeting different belief and attitudinal dimensions such as importance or salience of new behaviours, confidence to change, expectancy of benefits, and beliefs of others. 15 Interventions that fail to provide appropriate support and create barriers for the intended recipients to initiate and maintain target behaviours are unlikely to succeed in the long term. The past 15 years has seen a growth in understanding of physically active behaviour and how to promote it with strategies matched to individual needs. 16 Achieving and maintaining a physically active lifestyle may require numerous and diverse changes in how individuals interact with the environment and others. In terms of evaluating the effectiveness of interventions it is important to understand both what the intervention was intended to involve and whether this was achieved (i.e. treatment fidelity) and also what process or mediating variables were implicated in changes in primary outcomes (i.e. behavioural and health outcomes). Many reviews and individual studies report the behavioural outcomes; virtually none describe the intervention or processes involved in behaviour change. 17
Development and current practice of exercise referral schemes
One setting where increases in PA may be facilitated is in primary health care. 18 Over 85% of the population in the UK visit their general practitioner (GP) at least once a year and almost 95% do so over a 3-year period,19 suggesting an opportunity to promote PA. Taylor and Fox (2005)20 identified, in a review of literature, several barriers that GPs perceived in promoting PA: (1) lack of time; (2) a lack of desire to pressure patients; (3) a belief that it may not be as beneficial as other therapies or other behaviour changes (e.g. smoking); (4) that patients would not follow advice; and (5) that PA promotion often seemed irrelevant for the needs of patients at the time of consultation. To maximise opportunities, practice nurses have been central to many primary care initiatives to promote PA and several qualitative systematic reviews have focused on office-based PA interventions in primary care. 21 The intensity of the intervention can be described along a continuum from ‘Ask’, ‘Assess’, ‘Advise’ and more prolonged counselling. The reviews highlighted the limited effect of advice giving and the lack of research in the UK primary care setting. In contrast, patients may be referred to a specialist with a role to promote PA, for prevention or treatment.
Fox et al. (1997)18 identified only a few schemes in the UK in which exercise sessions took place within GP practices, delivered by health and exercise professionals, to meet the needs of patients with specific needs (e.g. weight loss, chronic low back pain). In contrast, new opportunities began to emerge in the late 1980s to mid-1990s when patients were referred to leisure centres for individual or group ‘exercise on prescription’ (EoP) (now referred to as ERSs). Growth in the number of ERSs was rapid in response to new legislation (i.e. Compulsory Competitive Tendering22) in the operation of such facilities the first evaluation was commissioned by the Health Education Authority in 1994. 24 Leisure centres with swimming pools and other exercise facilities have the opportunity to offer diverse options, as well as social facilities. In the 1990s, however, GP ERSs had a number of limitations:25 (1) there were few of them so they had little potential to impact on public health; (2) staff lacked the training to adapt exercise programmes to the specific health needs of patients; (3) there was little interest in the broader promotion of a more physically active lifestyle, but more interest in creating new leisure centre members; (4) GPs were reluctant to refer patients to exercise professionals who had unknown expertise and credentials; and (5) there was only limited reference in key NHS policy documents to the promotion of PA. These limitations probably limited the effectiveness of such schemes for impacting on long-term sustainable change in PA. As a result, after broad consultation with health and exercise professionals, leisure industry operators, and exercise scientists, a National Quality Assurance Framework (NQAF) was launched in the UK to guide best practice and best value from ERSs. 11 The document was aligned with the emerging range of NHS National Service Frameworks (e.g. for CHD, older people) that prioritise PA promotion.
A report26 identified a huge growth in ERS from 157 in 199424 to 816 in 2004, with probably over 100,000 patients passing through them each year. Referral is largely for CVD prevention (e.g. weight management), but patients with a wide variety of conditions are offered specialist support to increase PA. Some schemes identify specific medical conditions and work closely with exercise therapist to maximise the benefits for referred patients. A survey of 200 GPs found that 22% of GPs now prescribe exercise therapy as one of their three most common treatments for depression compared with only 5% 3 years ago (Mental Health Foundation 2008: see: www.mentalhealth.org.uk), with an increase from 41% to 61% now believing that a supervised programme of exercise would be ‘very effective’ or ‘quite effective’ in treating mild to moderate depression. However, barriers do remain among GPs for the general referral of patients. 27
Exercise referral schemes clearly operate in diverse ways, although the most common approach involves a 10- to 12-week ‘prescription’ with subsidised attendance costs for two visits per week, at specific times in the week. Other approaches involve referral to a PA facilitator, who may act as gatekeeper, to prevent inappropriate referrals and engage with patients to identify the preferred options for increasing PA (e.g. centre- or home-based, group or individual sessions, active commuting, other community-based options such as walking groups). Alternatively, referral may be directly to one of these options. The NQAF11 recommended a service level agreement to drive the operational links between the primary care referrer and the exercise or leisure provider, with exercise professionals on the Register for Exercise Professionals (www.exerciseregister.org/) at least at a level (Level 3 – Instructing Physical Activity and Exercise; Level 4, Specialist Exercise Instructor) compatible with the needs of their clients. National Occupational Standards for level 4 in Health and Physical Activity were developed in 2007, with core units for CHD, mental health, obesity/diabetes, frailer older adults/falls prevention, after-stroke care, back pain. Many of the 800+ schemes in the UK do not meet the NQAF guidelines28 due to a lack of investment in staff and a focus on short-term patient adherence to centre-based exercise rather than sustained lifestyle PA.
In summary, ERSs have evolved in different ways, involve a variety of exercise and health professionals, and a wide range of clients with different needs. Although variation in the ERS model of delivery exist, common features include: (1) referral of sedentary individuals at risk of lifestyle diseases by a health-care professional within primary health care setting; (2) referral to an exercise professional who seeks to develop a programme of exercise that meets the needs of that patient; (3) monitoring of progress throughout the programme with appropriate feedback to the referring health-care professional; (4) auditing to ensure adherence to quality assurance processes (e.g. appropriate staffing, health and safety procedures, ethical and data protection consideration). The NQAF recommended that ERSs should formally involve referral from primary care and should have a service level agreement between referrer and service provider. ERS (or equivalent) interventions have been used in general practice in several other countries in an attempt to promote PA. 29
Effectiveness of exercise referral schemes
The first review of the effectiveness of ERSs included a range of study designs and sources of information. 30 Stakeholders were also interviewed in several case studies. The general view was that ERSs were popular among clients and practitioners but that there was only limited evidence for any lasting effects on PA and health. Recent systematic reviews identify variation in respect of the range of evidence reviewed, the definition of what constitutes an ERS, and the scope of studies reviewed (geographical location, outcomes measures and study design29,31–34). These systematic reviews have consistently concluded that ERSs have a small effect in enhancing short-term PA and with little or no evidence of long-term sustainability. One review undertook a meta-analysis of five UK-based RCTs and reported an overall RR of 1.20 (95% CI 1.06 to 1.35) in favour of ERS versus a control group. 34 Those in the ERS were more likely to be moderately physically active per week (i.e. doing 90–150 minutes). The reviewers did not state at which time point in the trials the effects were derived, but it is likely that these were short-term effects (i.e. < 6 months). As an example, the recent study of Isaacs et al. 35 reported a 6% net effect (13.8% vs 7.5%) meeting the public health guidelines of 5 × 30 minutes per week in favour of the leisure centre group (compared with an advice-only group) at 6 months. 35
The NICE review of ERS undertook a qualitative assessment of the effects of different moderating and mediating factors on PA outcomes among the four included RCTs. 33 This assessment produced a rather limited analysis and answers to many of the questions concerning the additional effects of the characteristics of the intervention, the professionals involved, the setting, and participant characteristics could be better answered by searching for and reviewing a more diverse literature. For example, Harrison et al. 36 and Gidlow et al. 37 have reported how some of these factors prospectively influence uptake and participation in schemes involving 6610 and 3711 patients referred over 5 and 3 years, respectively. Other factors were identified among the Gidlow cohort by James et al. 38 An analysis of which factors moderate PA outcomes is important as the few RCTs conducted have not been powered to investigate moderator effects of patient characteristics for example. Also, data from other studies, albeit in other countries, may be useful in the absence of UK data. For example, Ashworth et al. 39 reviewed evidence on the effects of home-based versus centre-based exercise interventions.
Cost effectiveness of exercise referral schemes
Three systematic reviews29,32,34 considered the economic outcomes of ERS, identifying three UK-based randomised controlled trial (RCT) economic analyses. Two of these analyses were limited to reporting of the costs. 36,40,41 The most detailed economic analysis to date is the RCT of Isaacs. 35 The authors attributed a £100 cost to the patient and £186 cost to the leisure centre, and noted no additional health gain [in terms of quality of life (QoL)] for the ERS, compared with a walking and passive control group. Non-RCTs may provide valuable evidence on the economics of ERS. For example, Project Active, in the USA, reported that at both 6 months and 24 months, the lifestyle intervention42 was more cost-effective than the structured intervention for most outcome measures. 43 Other evidence (e.g. Cochrane 2005 – trial on the effectiveness of water-based therapy for lower limb osteoarthritis) from the UK may also be useful to estimate the potential cost benefits should such a programme be part of an ERS.
Summary
-
Physical activity contributes to the prevention and management of a numerous medical conditions and diseases. UK data suggest that < 40% of men and 30% of women meet the 5 × 30 minutes per week public health target, with variations across age, sex, class and ethnicity.
-
In UK since the early 1990s there has been a rapid development of ERSs, where individuals at risk of lifestyle diseases are referred in the primary care setting to an exercise professional who then prescribes a programme of exercise delivered in a public leisure facility with follow-up checks of adherence and progression. A NQAF for ERS has been published.
-
A number of recent systematic reviews have concluded that ERS has small effect on enhancing short-term PA with little or no evidence of long-term sustainability.
-
These previous reviews have a number of limitations in the terms of addressing the current UK policy question of effectiveness and clinical effectiveness of ERS in people with diagnosed conditions, i.e. lack consistency in definition of ERS, limited consideration of diseased population and outcomes outside of PA and programme attendance, little exploration of the factors that might influence the effectiveness of ERS and limited cost-effectiveness analysis.
Decision problem
Based on our knowledge of the area, and our review of current practice of the ERS in the UK (Section 2) we propose to address the decision problem set out below, which covers the scope of the proposed research. We use the definitions for exercise referral as set out in the recent National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) guidance. 33
Population
Sedentary adults who present in primary care with a diagnosed condition known to benefit from any combination of supervised and unsupervised PA. Conditions that will be specifically considered include CHD, stroke, peripheral vascular disease, cancer, obesity, type 2 diabetes, osteoporosis, low back pain and clinical depression. Where evidence is identified for ERSs associated with other conditions this will be included in the review. Currently active adults are less likely to benefit from exercise and will therefore not be considered [consistent with the Health Technology Assessment (HTA) commissioning brief].
Exercise referral schemes
An ERS should comprise three core components:
-
referral by a primary care health-care professional to a service designed to increased PA or exercise.
-
physical activity programme tailored to individual needs.
-
initial assessment and monitoring throughout the programme.
An ERS is more intensive than simple advice and could include additional counselling, written material, telephone phone-up and supervised training. Programmes or systems of exercise referral initiated in secondary or tertiary care, such as conventional comprehensive cardiac or pulmonary rehabilitation programmes, will not be considered here.
Although primary consideration will made as to the evidence base for ERS, we will also include a secondary review of the evidence of secondary prevention programmes (e.g. smoking cessation, obesity management), where PA/exercise promotion is an stated component of a multicomponent programme. Given the time and resource constraints of this project, we anticipate that we have to limit this secondary review to published literature on UK-based secondary prevention programmes initiated in primary care.
Comparator
Usual (‘brief’) advice, no intervention, attention control or alternative forms of ERSs.
Outcomes
Four outcome domains will be considered:
-
Efficacy/effectiveness – primary outcome: PA (self report or monitored); secondary outcomes: physical fitness (e.g. VO2max), health outcomes (e.g. blood lipids, blood lipids), patient satisfaction, psychological well-being, health-related quality of life (HRQoL); adverse events (e.g. skeletomuscular injury).
-
Patient factors that may moderate behavioural outcomes (e.g. uptake and adherence to programme).
-
Programme factors that may moderate behavioural outcomes (e.g. programme length and intensity).
-
Economics – resource use, costs and cost-effectiveness.
Report methods for identification and synthesis of evidence of effectiveness and cost-effectiveness
A review of the evidence for effectiveness of ERSs will be undertaken systematically following the general principles recommended in Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) Report 444 and the Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses (QUOROM) statement. 45 The systematic review will be registered with the newly formed Cochrane Public Health Collaborative Group. A review of the cost-effectiveness evidence will be undertaken, drawing on CRD Report 6,46 and using accepted formats for the review of economic evaluations. 47,48
Search strategy
The search strategy will comprise the following main elements.
Searching of electronic databases
An experienced information specialist (TM) based at Peninsula Technology Assessment Group (PenTAG) will undertake searches of the following databases: Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), EMBASE, MEDLINE, MEDLINE In-Process, PsycINFO, SPORTDiscus and Science Citation Index (SCI). Economic studies will be identified from EconLit, IDEAS and NHS Economic Evaluation Database (NHS EED). In addition, systematic reviews will be identified using clinical evidence, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR), Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE), HTA Database, NICE website, National Library for Health (NLH) Guidelines Finder, and SIGN Guidelines. These reviews will be used to identify primary studies. No country or language restrictions will be placed on the search. The search will combine topic-specific indexed terms and text words – exercise, physical activity, physical fitness, primary health care, referral, prescription [and synonyms] – and a controlled study design and human filter. An example search strategy is shown in Section 11.
Contact with experts in the field
The topic specific expert co-applicants and two external experts will provide input on the existing research in this field.
Scrutiny of bibliographies of reviews and retrieved papers
The bibliographies of all relevant reviews and guidelines and all included studies will be checked for further potentially relevant studies. In addition, citation searching will be undertaken for selected papers.
Study selection
Studies reporting effectiveness and cost-effectiveness will be considered for inclusion based on the previously defined decision problem (Section 3). Individual or cluster randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and non-randomised controlled studies will be sought. ERS publications (e.g. annual reports) not published in a peer review journal, non-systematic reviews, editorials, opinions and reports published as meeting abstracts only (where insufficient methodological details are reported to allow critical appraisal of study quality) will be excluded. For cost-effectiveness, full economic evaluations will be included (as defined in CRD Report 646) and the review will include economic evaluations presented in reports of HTA agencies (e.g. NICE, Health Technology Board Scotland). Where abstracts are identified that report on cost-effectiveness, these will be identified in the review, but critical appraisal will be dependent on the level of detail available.
Titles and abstracts will be examined for relevance by two reviewers independently; all potentially relevant papers will be ordered. All full papers will be screened by two reviewers independently, relevance to the review and the decision to include studies or not will be made according to the decision problem detailed above. Disagreement will be resolved by consensus.
Data extraction strategy
Data will be extracted independently by one reviewer using a standardised data extraction form and checked by another. Discrepancies will be resolved by discussion, with involvement of a third reviewer when necessary. Extraction will include data on: patient characteristics (e.g. age, disease diagnosis), intervention (e.g. duration, location and level of supervision of exercise intervention delivered), comparison (e.g. brief advice), study quality and reported outcomes pertinent to the review (see Section 3.4).
Quality assessment strategy
Quality assessment instruments will be derived from published criteria, relevant to controlled studies (CRD Report 443). These will be adapted to incorporate topic-specific quality issues (e.g. PA outcome assessed in a standard, valid and reliable way, the results were adjusted baseline PA). If appropriate, an overall quality rating will be developed and incorporated into the synthesis. An assessment of applicability will also be made based on the nature of intervention and population studied. As above, economic evaluations will be assessed using accepted critical appraisal methods. Where economic evaluations have used a decision-analytic modelling framework, these will be critically appraised using published guidance on good practice in decision-analytic modelling in HTA. 49
Methods of analysis/synthesis
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness data will be tabulated and discussed in a narrative review. The heterogeneity of the form and delivery of interventions, their settings and the study population will be assessed in a detailed qualitative way.
Where appropriate, meta-analysis (e.g. RCTs reporting change in PA levels) will be employed to estimate a summary measure of effect on relevant outcomes based on intention-to-treat analyses. Meta-analysis will be carried out using fixed or random effects models, using appropriate software. Heterogeneity will be explored through consideration of the study populations, methods and interventions, by visualisation of results and, in statistical terms, by the chi-squared test for homogeneity and the I2-statistic. Evidence of publication bias will examined using funnel plots.
We will explore specific characteristics of ERS and how these relate to effectiveness and cost effectiveness, for example duration and ‘dose’ of exercise programme, and, where possible, the quality of supervision and assessment, setting, timing of programme relative to diagnosis of index condition.
Decision-analytic modelling
A decision-analytic modelling framework will be developed to explore the cost-effectiveness of ERS. The modelling framework will synthesise research findings on the effectiveness of ERS, consistent with the scope of the research proposed, and data from other sources (e.g. resource use, cost, HRQoL and epidemiological data).
The modelling framework, will extrapolate findings from controlled trials on ERSs, using trial outcomes, to predict longer-term outcomes (i.e. costs and consequences) associated with the impact of ERSs.
Members of the research team have contributed to the development of NICE public health guidelines on PA, environmental interventions to promote PA, workplace interventions to promote PA and PA in children. 6,8 The economic modelling undertaken as part of this prior research has included development of an economic model to estimate the cost-effectiveness of ERSs. The model used to inform the NICE public health guidance33 has been developed and extended by members of the research team (Trueman and colleagues, in York Health Economics Consortium (YHEC)], and it will form the foundation for the modelling of cost-effectiveness proposed here.
The specific objectives of the cost-effectiveness analyses are:
-
To provide policy relevant estimates of the cost-effectiveness of ERSs.
-
To develop the existing models on PA and populate the models using the most appropriate data identified from the clinical effectiveness systematic review, related literature searching and routine data sources.
-
To relate intermediate PA outcomes (i.e. participation rates, duration of activity) to final health outcomes, expressed in terms of events avoided, and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). This is necessary to provide decision-makers with an indication of the health gain achieved by an ERS, relative to its additional cost, in units that permit comparison with other uses of health service resources.
-
To use the modelling framework to explore areas of uncertainty in the data used to populate the model, and the subsequent results. Uncertainty in results will be characterised, and summarised in a manner useful to decision-makers. Assuming the quality and appropriate form of data are available, a probabilistic model will be developed, which will consider simultaneously uncertainty in a range of parameter inputs
-
To inform future research priorities in the NHS. Assuming the quality and appropriate form or data are available, the model will be used to undertake analyses of the expected value of information. These take the decision uncertainty associated with analysis and quantify the cost of this uncertainty in terms of health gain forgone and resources wasted by making the wrong decision. This cost of uncertainty represents the value of perfect information, and this can be estimated for the model overall and for individual parameters.
The model is expected to adopt a lifetime time horizon, to reflect the potential long-term benefits of sustained PA. Results will also be reported at an intermediate time horizon(s) that more directly reflect(s) the data sources. The perspective will be that of the National Health Services and Personal Social Services, although there may be scope for exploring other broader perspectives (e.g. inclusion of indirect costs and benefits), depending on the findings of the literature review. Future costs and outcomes will be discounted at 3.5% in line with accepted practice in the UK.
The modelling of cost-effectiveness, consistent with the model currently available, will quantify the impact of PA on a number of health conditions (e.g. diabetes, CVD, colon cancer). Effectiveness data, to populate the model, will be derived from the literature review undertaken as part of the proposed research. Other data on resource use, costs, and on the prediction of health outcomes from effectiveness data on exercise referral, will be from systematic searching of the relevant literature, and from other sources where appropriate. All data sources will be explicitly stated, model structure will be clearly described and a rationale/justification for the model structure will be presented. Modelling will be undertaken in accordance with guidelines on good practice for decision modelling within HTA,49 and all modelling methods and data will be fully transparent.
Results from the modelling of cost-effectiveness will be presented in a disaggregated format (outcomes, resource use, costs), and also in the form of a cost-effectiveness ratio. Results will include estimation of incremental cost per life-year gained, and cost per QALY (cost per QALY). Where appropriate, results will include presentation of cost-effectiveness consistent with the reference case used by NICE. 50 Where probabilistic modelling is undertaken, probabilistic sensitivity analysis will be presented. Results will include presentation of cost-effectiveness planes, and cost-effectiveness acceptability curves. Sensitivity analysis will also explore structural uncertainty, and further parameter uncertainty, through extensive one-way and multiway sensitivity analyses.
References
- Department of Health (DoH) . At Least Five a Week. Evidence on the Impact of Physical Activity and Its Relationship to Health 2004.
- Haskell WL, Lee IM, Pate RR, Powell KE, Blair SN, Franklin BA, et al. American College of Sports Medicine; American Heart Association . Physical activity and public health: updated recommendation for adults from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Circulation 2007;116:1081-93.
- World Health Organization (WHO) . World Health Report 2002.
- Williams PT. Health effects resulting from exercise versus those from body fat loss. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2001;33:S611-21.
- Health and Safety Executive . Health Survey for England 2006: CVD and Risk Factors Adults, Obesity and Risk Factors Children 2008.
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) . Promoting and Creating Built or Natural Environments That Encourage and Support Physical Activity 2008.
- Marcus BH, Williams DM, Dubbert PM, Sallis JF, King AC, Yancey AK, et al. Physical activity intervention studies: what we know and what we need to know: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism (Subcommittee on Physical Activity); Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; and the Interdisciplinary Working Group on Quality of Care and Outcomes Research. Circulation 2006;114:2739-52.
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) . Promoting Physical Activity in the Workplace 2008.
- Kahn EB, Ramsey LT, Brownson RC, Heath GW, Howze EH, Powell KE, et al. The effectiveness of interventions to increase physical activity: a systematic review. Am J Prev Med 2002;22:73-107.
- Eden KB, Orleans CT, Mulrow CD, Pender NJ, Teutsch SM. Does Counseling by Clinicians Improve Physical Activity? A Summary of the Evidence for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med 2002;137:208-15.
- Department of Health . NHS Exercise Referral Systems: A National Quality Assurance Framework 2001.
- van der Bij AK, Laurant MG, Wensing M. Effectiveness of physical activity interventions for older adults: a review. Am J Prev Med 2002;22:120-33.
- Proper KI, Koning M, van der Beek AJ, Hildebrandt VH, Bosscher RJ, van Mechelen W. The effectiveness of worksite physical activity programs on physical activity, physical fitness, and health. Clin J Sport Med 2003;13:106-17.
- Department of Health (DoH) . Tackling Obesities: Future Choices 2007.
- Biddle SJH, Mutrie N. Psychology of physical activity: determinants, well-being, and interventions. London: Routledge; 2008.
- Spencer L, Adams TB, Malone S, Roy L, Yost E. Applying the transtheoretical model to exercise: a systematic and comprehensive review of the literature. Health Promot Pract 2006;7:428-43.
- Hillsdon M, Foster C, Thorogood M. Interventions for promoting physical activity. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005;1.
- Fox K, Biddle S, Edmunds L, Bowler I. Physical activity promotion through primary health care in England. Br J Gen Pract 1997;47:367-9.
- Picker Institute . National Survey of Local Health Services 2006: Summary Report of Key Findings from the Study 2007.
- Taylor AH, Fox K. Changes in physical self-perceptions: findings from a randomised controlled study of a GP exercise referral scheme. Health Psychol 2005;24:11-2.
- Lawlor DA, Hanratty B. The effect of physical activity advice given in routine primary care consultations: a systematic review. J Pub Health Med 2001;23:219-26.
- Nichol G. The impact of compulsory competitive tendering on planning in leisure departments. Manag Leisure 2008:1-14.
- Biddle S, Fox K, Edmunds L. Physical activity promotion in primary health care in England. London: Health Education Authority; 1994.
- Smith P, Iliffe S, Gould M, See Tai S. Prescription for exercise in primary care: is it worth it?. Br J Health Care Manag 1996;2:324-7.
- Chartered Society of Physiotherapists (CSP) . Exercise on Prescription: A Report for the Chartered Society of Physiotherapy by the Labour Research Department 2004.
- Graham RC, Dugdill L, Cable NT. Health professionals’ perspectives in exercise referral: implications for the referral process. Ergonomics 2005;48:1411-22.
- Dugdill L, Graham RC, McNair F. Exercise referral: the public health panacea for physical activity promotion? A critical perspective of exercise referral schemes; their development and evaluation. Ergonomics 2005;48:1390-410.
- Sorensen JB, Skovgaard T, Puggaard L. Exercise on prescription in general practice: a systematic review. Scand J Prim Health Care 2006;24:69-74.
- Riddoch C, Puig-Ribera A, Cooper A. Effectiveness of physical activity promotion schemes in primary care: a review. London: HEA; 1998.
- Morgan O. Approaches to increase physical activity: reviewing the evidence for exercisereferral schemes. Public Health 2005;119:361-70.
- Gidlow C, Johnston L, Crone D, James D. Attendance of exercise referral schemes in the UK: a systematic review. Health Education J 2005;64:168-86.
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) . Four Commonly Used Methods to Increase Physical Activity: Brief Interventions in Primary Care, Exercise Referral Schemes, Pedometers and Community-Based Exercise Programmes for Walking and Cycling 2006.
- Williams NH, Hendry M, France B, Lewis R, Wilkinson C. Effectiveness of exercisereferral schemes to promote physical activity in adults: systematic review. Br J Gen Pract 2007;57:979-86.
- Isaacs AJ, Critchley JA, See Tai S, Buckingham K, Westley D, Harridge SDR, et al. Exercise Evaluation Randomised Trial (EXERT): a randomised trial comparing GP referral for leisure centre-based exercise, community-based walking and advice only. Health Technol Assess 2007;11.
- Harrison RA, Roberts C, Elton PJ. Does primary care referral to an exercise programme increase physical activity one year later? A randomized controlled trial. J Public Health 2005;27:25-32.
- Gidlow C, Johnston LH, Crone D, Morris C, Smith A, Foster C, et al. Socio-demographic patterning of referral, uptake and attendance in Physical Activity Referral Schemes. J Public Health 2007;29:107-13.
- James DV, Johnston LH, Crone D, Sidford AH, Gidlow C, Morris C, et al. Factors associated with physical activity referral uptake and participation. J Sports Sci 2000;26:217-24.
- Ashworth NL, Chad KE, Harrison EL, Reeder BA, Marshall SC. Home versus center based physical activity programs in older adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005;1.
- Harrison RA, McNair F, Dugdill L. Access to exercise referral schemes: a population based analysis. J Public Health 2005;27:326-30.
- Stevens W, Hillsdon M, Thorogood M, McArdle D. The cost of a primary care-based physical activity intervention in 45–74 year old men and women: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Sports Med 2008;32:236-41.
- Dunn AL, Marcus BH, Kampert JB, Garcia ME, Kohl HW, Blair SN. Comparison of lifestyle and structured interventions to increase physical activity and cardiorespiratory fitness: a randomized trial. JAMA 1999:281-34.
- Sevick MA, Dunn AL, Morrow MS, Marcus BH, Chen GJ, Blair SN. Cost-effectiveness of lifestyle and structured exercise interventions in sedentary adults: results of project ACTIVE. Am J Prev Med 2008;19:1-8.
- Khan K, ter Riet G, Glanville J, Sowden A, Kleijnen J. Undertaking systematic reviews of research on effectiveness: CRD’s guidance for those carrying out or commissioning reviews. York: NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York; 2001.
- Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, Stroup DF. Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Quality of reporting of meta-analyses. Lancet 1999;354:1896-900.
- Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) . Improving Access to Cost-Effectiveness Information for Health Care Decision-Making: The NHS Economic Evaluation Database 2001.
- Drummond MF, Jefferson TO. Guidelines for authors and peer reviewers of economic submissions to the BMJ. The BMJ Economic Evaluation Working Party. BMJ 1996;313:275-83.
- Drummond M, O’Brien B, Stoddart G, Torrance G. Methods for the economic evaluation of health care programmes. Oxford: Oxford Medical Publications; 1997.
- Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Claxton K, Golder S, Riemsma R, et al. Review of guidelines for good practice in decision analytic modelling in health technology assessment. Health Technol Assess 2004;8.
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) . Guide to the Methods of Technology Appraisal 2008.
List of abbreviations
- AIC
- Akaike information criterion
- BHFNC
- British Heart Foundation National Centre
- BIC
- Bayesian information criterion
- BMI
- body mass index
- CENTRAL
- Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials
- CHD
- coronary heart disease
- CI
- confidence interval
- CMO
- Chief Medical Officer
- COPD
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- CRD
- Centre for Reviews and Dissemination
- CVD
- cardiovascular disease
- DARE
- Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects
- EoP
- exercise on prescription
- EQ-5D
- European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions
- ERS
- exercise referral scheme
- FVC
- forced vital capacity
- GP
- general practitioner
- GPPAQ
- General Practitioner Activity Questionnaire
- HADS
- Hospital Anxiety Depression Scale
- HbA1c
- glycosylated haemoglobin
- HRQoL
- health-related quality of life
- HSE
- Health Survey for England
- HTA
- Health Technology Assessment
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- ITT
- intention to treat
- MI
- myocardial infarction
- NHS EED
- NHS Economic Evaluation Database
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
- NQAF
- National Quality Assurance Framework
- OQAQ
- Overview Quality Assessment Questionnaire
- ONS
- Office for National Statistics
- OR
- odds ratio
- PA
- physical activity
- PRISMA
- Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- PSA
- probabilistic sensitivity analysis
- PSW
- physical self-worth
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- QoL
- quality of life
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- RR
- relative risk
- SBP
- systolic blood pressure
- SD
- standard deviation
- SDT
- self-determination theory
- SE
- standard error
- SF-12
- Short Form questionnaire-12 items
- SF-36
- Short Form questionnaire-36 items
- SMD
- standardised mean difference
- VIF
- variable inflated factor
- VO2max
- maximal oxygen uptake
- WMD
- weighted mean difference
All abbreviations that have been used in this report are listed here unless the abbreviation is well known (e.g. NHS), or it has been used only once, or it is a non-standard abbreviation used only in figures/tables/appendices, in which case the abbreviation is defined in the figure legend or in the notes at the end of the table.
Notes
Health Technology Assessment programme
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Professor of Dermato-Epidemiology, Centre of Evidence-Based Dermatology, University of Nottingham
Prioritisation Group
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Professor Imti Choonara, Professor in Child Health, Academic Division of Child Health, University of Nottingham
Chair – Pharmaceuticals Panel
-
Dr Bob Coates, Consultant Advisor – Disease Prevention Panel
-
Dr Andrew Cook, Consultant Advisor – Intervention Procedures Panel
-
Dr Peter Davidson, Director of NETSCC, Health Technology Assessment
-
Dr Nick Hicks, Consultant Adviser – Diagnostic Technologies and Screening Panel, Consultant Advisor–Psychological and Community Therapies Panel
-
Ms Susan Hird, Consultant Advisor, External Devices and Physical Therapies Panel
-
Professor Sallie Lamb, Director, Warwick Clinical Trials Unit, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick
Chair – HTA Clinical Evaluation and Trials Board
-
Professor Jonathan Michaels, Professor of Vascular Surgery, Sheffield Vascular Institute, University of Sheffield
Chair – Interventional Procedures Panel
-
Professor Ruairidh Milne, Director – External Relations
-
Dr John Pounsford, Consultant Physician, Directorate of Medical Services, North Bristol NHS Trust
Chair – External Devices and Physical Therapies Panel
-
Dr Vaughan Thomas, Consultant Advisor – Pharmaceuticals Panel, Clinical
Lead – Clinical Evaluation Trials Prioritisation Group
-
Professor Margaret Thorogood, Professor of Epidemiology, Health Sciences Research Institute, University of Warwick
Chair – Disease Prevention Panel
-
Professor Lindsay Turnbull, Professor of Radiology, Centre for the MR Investigations, University of Hull
Chair – Diagnostic Technologies and Screening Panel
-
Professor Scott Weich, Professor of Psychiatry, Health Sciences Research Institute, University of Warwick
Chair – Psychological and Community Therapies Panel
-
Professor Hywel Williams, Director of Nottingham Clinical Trials Unit, Centre of Evidence-Based Dermatology, University of Nottingham
Chair – HTA Commissioning Board
Deputy HTA Programme Director
HTA Commissioning Board
-
Professor of Dermato-Epidemiology, Centre of Evidence-Based Dermatology, University of Nottingham
-
Department of Public Health and Epidemiology, University of Birmingham
-
Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, Director, NIHR HTA programme, University of Liverpool
-
Professor Ann Ashburn, Professor of Rehabilitation and Head of Research, Southampton General Hospital
-
Professor Peter Brocklehurst, Professor of Women’s Health, Institute for Women’s Health, University College London
-
Professor Jenny Donovan, Professor of Social Medicine, University of Bristol
-
Professor Jonathan Green, Professor and Acting Head of Department, Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, University of Manchester Medical School
-
Professor John W Gregory, Professor in Paediatric Endocrinology, Department of Child Health, Wales School of Medicine, Cardiff University
-
Professor Steve Halligan, Professor of Gastrointestinal Radiology, University College Hospital, London
-
Professor Freddie Hamdy, Professor of Urology, Head of Nuffield Department of Surgery, University of Oxford
-
Professor Allan House, Professor of Liaison Psychiatry, University of Leeds
-
Dr Martin J Landray, Reader in Epidemiology, Honorary Consultant Physician, Clinical Trial Service Unit, University of Oxford
-
Professor Stephen Morris, Professor of Health Economics, University College London, Research Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, University College London
-
Professor Irwin Nazareth, Professor of Primary Care and Head of Department, Department of Primary Care and Population Sciences, University College London
-
Professor E Andrea Nelson, Professor of Wound Healing and Director of Research, School of Healthcare, University of Leeds
-
Professor John David Norrie, Chair in Clinical Trials and Biostatistics, Robertson Centre for Biostatistics, University of Glasgow
-
Dr Rafael Perera, Lecturer in Medical Statisitics, Department of Primary Health Care, University of Oxford
-
Professor Barney Reeves, Professorial Research Fellow in Health Services Research, Department of Clinical Science, University of Bristol
-
Professor Martin Underwood, Professor of Primary Care Research, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick
-
Professor Marion Walker, Professor in Stroke Rehabilitation, Associate Director UK Stroke Research Network, University of Nottingham
-
Dr Duncan Young, Senior Clinical Lecturer and Consultant, Nuffield Department of Anaesthetics, University of Oxford
-
Dr Tom Foulks, Medical Research Council
-
Dr Kay Pattison, Senior NIHR Programme Manager, Department of Health
HTA Clinical Evaluation and Trials Board
-
Director, Warwick Clinical Trials Unit, Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick and Professor of Rehabilitation, Nuffield Department of Orthopaedic, Rheumatology and Musculoskeletal Sciences, University of Oxford
-
Professor of the Psychology of Health Care, Leeds Institute of Health Sciences, University of Leeds
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Professor Keith Abrams, Professor of Medical Statistics, Department of Health Sciences, University of Leicester
-
Professor Martin Bland, Professor of Health Statistics, Department of Health Sciences, University of York
-
Professor Jane Blazeby, Professor of Surgery and Consultant Upper GI Surgeon, Department of Social Medicine, University of Bristol
-
Professor Julia M Brown, Director, Clinical Trials Research Unit, University of Leeds
-
Professor Alistair Burns, Professor of Old Age Psychiatry, Psychiatry Research Group, School of Community-Based Medicine, The University of Manchester & National Clinical Director for Dementia, Department of Health
-
Dr Jennifer Burr, Director, Centre for Healthcare Randomised trials (CHART), University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Linda Davies, Professor of Health Economics, Health Sciences Research Group, University of Manchester
-
Professor Simon Gilbody, Prof of Psych Medicine and Health Services Research, Department of Health Sciences, University of York
-
Professor Steven Goodacre, Professor and Consultant in Emergency Medicine, School of Health and Related Research, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Dyfrig Hughes, Professor of Pharmacoeconomics, Centre for Economics and Policy in Health, Institute of Medical and Social Care Research, Bangor University
-
Professor Paul Jones, Professor of Respiratory Medicine, Department of Cardiac and Vascular Science, St George‘s Hospital Medical School, University of London
-
Professor Khalid Khan, Professor of Women’s Health and Clinical Epidemiology, Barts and the London School of Medicine, Queen Mary, University of London
-
Professor Richard J McManus, Professor of Primary Care Cardiovascular Research, Primary Care Clinical Sciences Building, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Helen Rodgers, Professor of Stroke Care, Institute for Ageing and Health, Newcastle University
-
Professor Ken Stein, Professor of Public Health, Peninsula Technology Assessment Group, Peninsula College of Medicine and Dentistry, Universities of Exeter and Plymouth
-
Professor Jonathan Sterne, Professor of Medical Statistics and Epidemiology, Department of Social Medicine, University of Bristol
-
Mr Andy Vail, Senior Lecturer, Health Sciences Research Group, University of Manchester
-
Professor Clare Wilkinson, Professor of General Practice and Director of Research North Wales Clinical School, Department of Primary Care and Public Health, Cardiff University
-
Dr Ian B Wilkinson, Senior Lecturer and Honorary Consultant, Clinical Pharmacology Unit, Department of Medicine, University of Cambridge
-
Ms Kate Law, Director of Clinical Trials, Cancer Research UK
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Health Services and Public Health Services Board, Medical Research Council
Diagnostic Technologies and Screening Panel
-
Scientific Director of the Centre for Magnetic Resonance Investigations and YCR Professor of Radiology, Hull Royal Infirmary
-
Professor Judith E Adams, Consultant Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Central Manchester & Manchester Children’s University Hospitals NHS Trust, and Professor of Diagnostic Radiology, University of Manchester
-
Mr Angus S Arunkalaivanan, Honorary Senior Lecturer, University of Birmingham and Consultant Urogynaecologist and Obstetrician, City Hospital, Birmingham
-
Dr Diana Baralle, Consultant and Senior Lecturer in Clinical Genetics, University of Southampton
-
Dr Stephanie Dancer, Consultant Microbiologist, Hairmyres Hospital, East Kilbride
-
Dr Diane Eccles, Professor of Cancer Genetics, Wessex Clinical Genetics Service, Princess Anne Hospital
-
Dr Trevor Friedman, Consultant Liason Psychiatrist, Brandon Unit, Leicester General Hospital
-
Dr Ron Gray, Consultant, National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, Institute of Health Sciences, University of Oxford
-
Professor Paul D Griffiths, Professor of Radiology, Academic Unit of Radiology, University of Sheffield
-
Mr Martin Hooper, Public contributor
-
Professor Anthony Robert Kendrick, Associate Dean for Clinical Research and Professor of Primary Medical Care, University of Southampton
-
Dr Nicola Lennard, Senior Medical Officer, MHRA
-
Dr Anne Mackie, Director of Programmes, UK National Screening Committee, London
-
Mr David Mathew, Public contributor
-
Dr Michael Millar, Consultant Senior Lecturer in Microbiology, Department of Pathology & Microbiology, Barts and The London NHS Trust, Royal London Hospital
-
Mrs Una Rennard, Public contributor
-
Dr Stuart Smellie, Consultant in Clinical Pathology, Bishop Auckland General Hospital
-
Ms Jane Smith, Consultant Ultrasound Practitioner, Leeds Teaching Hospital NHS Trust, Leeds
-
Dr Allison Streetly, Programme Director, NHS Sickle Cell and Thalassaemia Screening Programme, King’s College School of Medicine
-
Dr Matthew Thompson, Senior Clinical Scientist and GP, Department of Primary Health Care, University of Oxford
-
Dr Alan J Williams, Consultant Physician, General and Respiratory Medicine, The Royal Bournemouth Hospital
-
Dr Tim Elliott, Team Leader, Cancer Screening, Department of Health
-
Dr Joanna Jenkinson, Board Secretary, Neurosciences and Mental Health Board (NMHB), Medical Research Council
-
Professor Julietta Patrick, Director, NHS Cancer Screening Programme, Sheffield
-
Dr Kay Pattison, Senior NIHR Programme Manager, Department of Health
-
Professor Tom Walley, CBE, Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Policy Research Programme, Department of Health
Disease Prevention Panel
-
Professor of Epidemiology, University of Warwick Medical School, Coventry
-
Dr Robert Cook, Clinical Programmes Director, Bazian Ltd, London
-
Dr Colin Greaves, Senior Research Fellow, Peninsula Medical School (Primary Care)
-
Mr Michael Head, Public contributor
-
Professor Cathy Jackson, Professor of Primary Care Medicine, Bute Medical School, University of St Andrews
-
Dr Russell Jago, Senior Lecturer in Exercise, Nutrition and Health, Centre for Sport, Exercise and Health, University of Bristol
-
Dr Julie Mytton, Consultant in Child Public Health, NHS Bristol
-
Professor Irwin Nazareth, Professor of Primary Care and Director, Department of Primary Care and Population Sciences, University College London
-
Dr Richard Richards, Assistant Director of Public Health, Derbyshire County Primary Care Trust
-
Professor Ian Roberts, Professor of Epidemiology and Public Health, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
-
Dr Kenneth Robertson, Consultant Paediatrician, Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Glasgow
-
Dr Catherine Swann, Associate Director, Centre for Public Health Excellence, NICE
-
Mrs Jean Thurston, Public contributor
-
Professor David Weller, Head, School of Clinical Science and Community Health, University of Edinburgh
-
Ms Christine McGuire, Research & Development, Department of Health
-
Dr Kay Pattison, Senior NIHR Programme Manager, Department of Health
-
Professor Tom Walley, CBE, Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
External Devices and Physical Therapies Panel
-
Consultant Physician North Bristol NHS Trust
-
Reader in Wound Healing and Director of Research, University of Leeds
-
Professor Bipin Bhakta, Charterhouse Professor in Rehabilitation Medicine, University of Leeds
-
Mrs Penny Calder, Public contributor
-
Dr Dawn Carnes, Senior Research Fellow, Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Dr Emma Clark, Clinician Scientist Fellow & Cons. Rheumatologist, University of Bristol
-
Mrs Anthea De Barton-Watson, Public contributor
-
Professor Nadine Foster, Professor of Musculoskeletal Health in Primary Care Arthritis Research, Keele University
-
Dr Shaheen Hamdy, Clinical Senior Lecturer and Consultant Physician, University of Manchester
-
Professor Christine Norton, Professor of Clinical Nursing Innovation, Bucks New University and Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust
-
Dr Lorraine Pinnigton, Associate Professor in Rehabilitation, University of Nottingham
-
Dr Kate Radford, Senior Lecturer (Research), University of Central Lancashire
-
Mr Jim Reece, Public contributor
-
Professor Maria Stokes, Professor of Neuromusculoskeletal Rehabilitation, University of Southampton
-
Dr Pippa Tyrrell, Senior Lecturer/Consultant, Salford Royal Foundation Hospitals’ Trust and University of Manchester
-
Dr Nefyn Williams, Clinical Senior Lecturer, Cardiff University
-
Dr Kay Pattison, Senior NIHR Programme Manager, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Health Services and Public Health Services Board, Medical Research Council
-
Professor Tom Walley, CBE, Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Policy Research Programme, Department of Health
Interventional Procedures Panel
-
Professor of Vascular Surgery, University of Sheffield
-
Consultant Colorectal Surgeon, Bristol Royal Infirmary
-
Mrs Isabel Boyer, Public contributor
-
Mr Sankaran Chandra Sekharan, Consultant Surgeon, Breast Surgery, Colchester Hospital University NHS Foundation Trust
-
Professor Nicholas Clarke, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust
-
Ms Leonie Cooke, Public contributor
-
Mr Seumas Eckford, Consultant in Obstetrics & Gynaecology, North Devon District Hospital
-
Professor Sam Eljamel, Consultant Neurosurgeon, Ninewells Hospital and Medical School, Dundee
-
Dr Adele Fielding, Senior Lecturer and Honorary Consultant in Haematology, University College London Medical School
-
Dr Matthew Hatton, Consultant in Clinical Oncology, Sheffield Teaching Hospital Foundation Trust
-
Dr John Holden, General Practitioner, Garswood Surgery, Wigan
-
Dr Fiona Lecky, Senior Lecturer/Honorary Consultant in Emergency Medicine, University of Manchester/Salford Royal Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
-
Dr Nadim Malik, Consultant Cardiologist/Honorary Lecturer, University of Manchester
-
Mr Hisham Mehanna, Consultant & Honorary Associate Professor, University Hospitals Coventry & Warwickshire NHS Trust
-
Dr Jane Montgomery, Consultant in Anaesthetics and Critical Care, South Devon Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust
-
Professor Jon Moss, Consultant Interventional Radiologist, North Glasgow Hospitals University NHS Trust
-
Dr Simon Padley, Consultant Radiologist, Chelsea & Westminster Hospital
-
Dr Ashish Paul, Medical Director, Bedfordshire PCT
-
Dr Sarah Purdy, Consultant Senior Lecturer, University of Bristol
-
Dr Matthew Wilson, Consultant Anaesthetist, Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
-
Professor Yit Chiun Yang, Consultant Ophthalmologist, Royal Wolverhampton Hospitals NHS Trust
-
Dr Kay Pattison, Senior NIHR Programme Manager, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Health Services and Public Health Services Board, Medical Research Council
-
Professor Tom Walley, CBE, Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Policy Research Programme, Department of Health
Pharmaceuticals Panel
-
Professor in Child Health, University of Nottingham
-
Senior Lecturer in Clinical Pharmacology, University of East Anglia
-
Dr Martin Ashton-Key, Medical Advisor, National Commissioning Group, NHS London
-
Dr Peter Elton, Director of Public Health, Bury Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Ben Goldacre, Research Fellow, Division of Psychological Medicine and Psychiatry, King’s College London
-
Dr James Gray, Consultant Microbiologist, Department of Microbiology, Birmingham Children’s Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
-
Dr Jurjees Hasan, Consultant in Medical Oncology, The Christie, Manchester
-
Dr Carl Heneghan, Deputy Director Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine and Clinical Lecturer, Department of Primary Health Care, University of Oxford
-
Dr Dyfrig Hughes, Reader in Pharmacoeconomics and Deputy Director, Centre for Economics and Policy in Health, IMSCaR, Bangor University
-
Dr Maria Kouimtzi, Pharmacy and Informatics Director, Global Clinical Solutions, Wiley-Blackwell
-
Professor Femi Oyebode, Consultant Psychiatrist and Head of Department, University of Birmingham
-
Dr Andrew Prentice, Senior Lecturer and Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, The Rosie Hospital, University of Cambridge
-
Ms Amanda Roberts, Public contributor
-
Dr Gillian Shepherd, Director, Health and Clinical Excellence, Merck Serono Ltd
-
Mrs Katrina Simister, Assistant Director New Medicines, National Prescribing Centre, Liverpool
-
Professor Donald Singer, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Clinical Sciences Research Institute, CSB, University of Warwick Medical School
-
Mr David Symes, Public contributor
-
Dr Arnold Zermansky, General Practitioner, Senior Research Fellow, Pharmacy Practice and Medicines Management Group, Leeds University
-
Dr Kay Pattison, Senior NIHR Programme Manager, Department of Health
-
Mr Simon Reeve, Head of Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness, Medicines, Pharmacy and Industry Group, Department of Health
-
Dr Heike Weber, Programme Manager, Medical Research Council
-
Professor Tom Walley, CBE, Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Policy Research Programme, Department of Health
Psychological and Community Therapies Panel
-
Professor of Psychiatry, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Consultant & University Lecturer in Psychiatry, University of Cambridge
-
Professor Jane Barlow, Professor of Public Health in the Early Years, Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School
-
Dr Sabyasachi Bhaumik, Consultant Psychiatrist, Leicestershire Partnership NHS Trust
-
Mrs Val Carlill, Public contributor
-
Dr Steve Cunningham, Consultant Respiratory Paediatrician, Lothian Health Board
-
Dr Anne Hesketh, Senior Clinical Lecturer in Speech and Language Therapy, University of Manchester
-
Dr Peter Langdon, Senior Clinical Lecturer, School of Medicine, Health Policy and Practice, University of East Anglia
-
Dr Yann Lefeuvre, GP Partner, Burrage Road Surgery, London
-
Dr Jeremy J Murphy, Consultant Physician and Cardiologist, County Durham and Darlington Foundation Trust
-
Dr Richard Neal, Clinical Senior Lecturer in General Practice, Cardiff University
-
Mr John Needham, Public contributor
-
Ms Mary Nettle, Mental Health User Consultant
-
Professor John Potter, Professor of Ageing and Stroke Medicine, University of East Anglia
-
Dr Greta Rait, Senior Clinical Lecturer and General Practitioner, University College London
-
Dr Paul Ramchandani, Senior Research Fellow/Cons. Child Psychiatrist, University of Oxford
-
Dr Karen Roberts, Nurse/Consultant, Dunston Hill Hospital, Tyne and Wear
-
Dr Karim Saad, Consultant in Old Age Psychiatry, Coventry and Warwickshire Partnership Trust
-
Dr Lesley Stockton, Lecturer, School of Health Sciences, University of Liverpool
-
Dr Simon Wright, GP Partner, Walkden Medical Centre, Manchester
-
Dr Kay Pattison, Senior NIHR Programme Manager, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Health Services and Public Health Services Board, Medical Research Council
-
Professor Tom Walley, CBE, Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Policy Research Programme, Department of Health
Expert Advisory Network
-
Professor Douglas Altman, Professor of Statistics in Medicine, Centre for Statistics in Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Professor John Bond, Professor of Social Gerontology & Health Services Research, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Andrew Bradbury, Professor of Vascular Surgery, Solihull Hospital, Birmingham
-
Mr Shaun Brogan, Chief Executive, Ridgeway Primary Care Group, Aylesbury
-
Mrs Stella Burnside OBE, Chief Executive, Regulation and Improvement Authority, Belfast
-
Ms Tracy Bury, Project Manager, World Confederation of Physical Therapy, London
-
Professor Iain T Cameron, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology and Head of the School of Medicine, University of Southampton
-
Professor Bruce Campbell, Consultant Vascular & General Surgeon, Royal Devon & Exeter Hospital, Wonford
-
Dr Christine Clark, Medical Writer and Consultant Pharmacist, Rossendale
-
Professor Collette Clifford, Professor of Nursing and Head of Research, The Medical School, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Barry Cookson, Director, Laboratory of Hospital Infection, Public Health Laboratory Service, London
-
Dr Carl Counsell, Clinical Senior Lecturer in Neurology, University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Howard Cuckle, Professor of Reproductive Epidemiology, Department of Paediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynaecology, University of Leeds
-
Professor Carol Dezateux, Professor of Paediatric Epidemiology, Institute of Child Health, London
-
Mr John Dunning, Consultant Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Papworth Hospital NHS Trust, Cambridge
-
Mr Jonothan Earnshaw, Consultant Vascular Surgeon, Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Gloucester
-
Professor Martin Eccles, Professor of Clinical Effectiveness, Centre for Health Services Research, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Pam Enderby, Dean of Faculty of Medicine, Institute of General Practice and Primary Care, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Gene Feder, Professor of Primary Care Research & Development, Centre for Health Sciences, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Mr Leonard R Fenwick, Chief Executive, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Mrs Gillian Fletcher, Antenatal Teacher and Tutor and President, National Childbirth Trust, Henfield
-
Professor Jayne Franklyn, Professor of Medicine, University of Birmingham
-
Mr Tam Fry, Honorary Chairman, Child Growth Foundation, London
-
Professor Fiona Gilbert, Consultant Radiologist and NCRN Member, University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Paul Gregg, Professor of Orthopaedic Surgical Science, South Tees Hospital NHS Trust
-
Bec Hanley, Co-director, TwoCan Associates, West Sussex
-
Dr Maryann L Hardy, Senior Lecturer, University of Bradford
-
Mrs Sharon Hart, Healthcare Management Consultant, Reading
-
Professor Robert E Hawkins, CRC Professor and Director of Medical Oncology, Christie CRC Research Centre, Christie Hospital NHS Trust, Manchester
-
Professor Richard Hobbs, Head of Department of Primary Care & General Practice, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Alan Horwich, Dean and Section Chairman, The Institute of Cancer Research, London
-
Professor Allen Hutchinson, Director of Public Health and Deputy Dean of ScHARR, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Peter Jones, Professor of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge
-
Professor Stan Kaye, Cancer Research UK Professor of Medical Oncology, Royal Marsden Hospital and Institute of Cancer Research, Surrey
-
Dr Duncan Keeley, General Practitioner (Dr Burch & Ptnrs), The Health Centre, Thame
-
Dr Donna Lamping, Research Degrees Programme Director and Reader in Psychology, Health Services Research Unit, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London
-
Professor James Lindesay, Professor of Psychiatry for the Elderly, University of Leicester
-
Professor Julian Little, Professor of Human Genome Epidemiology, University of Ottawa
-
Professor Alistaire McGuire, Professor of Health Economics, London School of Economics
-
Professor Neill McIntosh, Edward Clark Professor of Child Life and Health, University of Edinburgh
-
Professor Rajan Madhok, Consultant in Public Health, South Manchester Primary Care Trust
-
Professor Sir Alexander Markham, Director, Molecular Medicine Unit, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Dr Peter Moore, Freelance Science Writer, Ashtead
-
Dr Andrew Mortimore, Public Health Director, Southampton City Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Sue Moss, Associate Director, Cancer Screening Evaluation Unit, Institute of Cancer Research, Sutton
-
Professor Miranda Mugford, Professor of Health Economics and Group Co-ordinator, University of East Anglia
-
Professor Jim Neilson, Head of School of Reproductive & Developmental Medicine and Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, University of Liverpool
-
Mrs Julietta Patnick, Director, NHS Cancer Screening Programmes, Sheffield
-
Professor Robert Peveler, Professor of Liaison Psychiatry, Royal South Hants Hospital, Southampton
-
Professor Chris Price, Director of Clinical Research, Bayer Diagnostics Europe, Stoke Poges
-
Professor William Rosenberg, Professor of Hepatology and Consultant Physician, University of Southampton
-
Professor Peter Sandercock, Professor of Medical Neurology, Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Edinburgh
-
Dr Philip Shackley, Senior Lecturer in Health Economics, Sheffield Vascular Institute, University of Sheffield
-
Dr Eamonn Sheridan, Consultant in Clinical Genetics, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Dr Margaret Somerville, Director of Public Health Learning, Peninsula Medical School, University of Plymouth
-
Professor Sarah Stewart-Brown, Professor of Public Health, Division of Health in the Community, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Dr Nick Summerton, GP Appraiser and Codirector, Research Network, Yorkshire Clinical Consultant, Primary Care and Public Health, University of Oxford
-
Professor Ala Szczepura, Professor of Health Service Research, Centre for Health Services Studies, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Dr Ross Taylor, Senior Lecturer, University of Aberdeen
-
Dr Richard Tiner, Medical Director, Medical Department, Association of the British Pharmaceutical Industry
-
Mrs Joan Webster, Consumer Member, Southern Derbyshire Community Health Council
-
Professor Martin Whittle, Clinical Co-director, National Co-ordinating Centre for Women’s and Children’s Health, Lymington