Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the HTA programme as project number 10/82/01. The contractual start date was in January 2012. The draft report began editorial review in February 2016 and was accepted for publication in May 2016. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Andrew Fisher is deputy director of the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Blood and Transplant Research Unit in Organ Donation and Transplantation, has received grants from the NIHR Health Technology Assessment (HTA) programme and Cystic Fibrosis Trust, and received non-financial support in the form of a loan of perfusion machines to study centres from Vivoline Medical. Catherine Exley is a member of the NIHR Programme Grants for Applied Research (PGfAR) panel and acknowledges the contribution of the NIHR HTA programme. Elaine McColl is a member of the NIHR PGfAR panel and was previously an editor for the NIHR PGfAR journals series. Luke Vale is a member of the NIHR PGfAR panel and the NIHR HTA panel. He is also the Director of the NIHR Research Design Service in the North East. Andreas Andreasson, Thomas Chadwick, Steven Tsui, Nizar Yonan, Andre Simon, Nandor Marczin, Jorge Mascaro and John Dark acknowledge the contribution of the NIHR HTA programme, the Cystic Fibrosis Trust and Vivoline Medical. Mark Pearce acknowledges the contribution of the NIHR HTA programme and also leads the radiation epidemiology theme of the NIHR-funded Health Protection Research Unit on radiation and chemicals in Newcastle.
Disclaimer
This report contains transcripts of interviews conducted in the course of research and contains language that may offend some readers.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2016. This work was produced by Fisher et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
Chapter 1 Introduction and background
Introduction
Respiratory diseases account for one in five deaths in the UK. 1 Lung transplantation is the only realistic therapeutic option for selected patients with end-stage chronic lung disease and provides dramatic improvements in both survival and quality of life. In younger patients with life-threatening cystic fibrosis (CF) lung disease, median survival after lung transplant now exceeds 10 years. However, 20–30% of patients waiting for lung transplantation will die before a donor organ becomes available. Although a shortage of multiorgan donors contributes, the main problem is that in multiorgan donors lungs are very susceptible to dysfunction, and about 80% of potential donor lungs in the UK are deemed unusable for clinical lung transplantation. It has previously been suggested that, in addition to promoting more organ donation, better use of existing organ donors is an important way to increase the numbers of lung transplants performed,2 and many centres worldwide have increased donor lung use by accepting more ‘marginal’ or ‘extended criteria’ donors. This, however, is not without risks to early post-transplantation outcomes. 3 The major early cause of death after lung transplantation is primary graft dysfunction (PGD), a severe lung injury akin to acute respiratory distress syndrome. Evidence that PGD has a major impact on survival comes from experience in several centres worldwide,4 and from the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT); the reported incidences of PGD are up to 25%, and PGD is associated with 30-day mortality of 50%, compared with < 10% among those without PGD. 5 There is, therefore, an urgent clinical need to safely increase the utilisation of donor lungs from the existing donor pool without negatively impacting on early survival after lung transplant.
Background
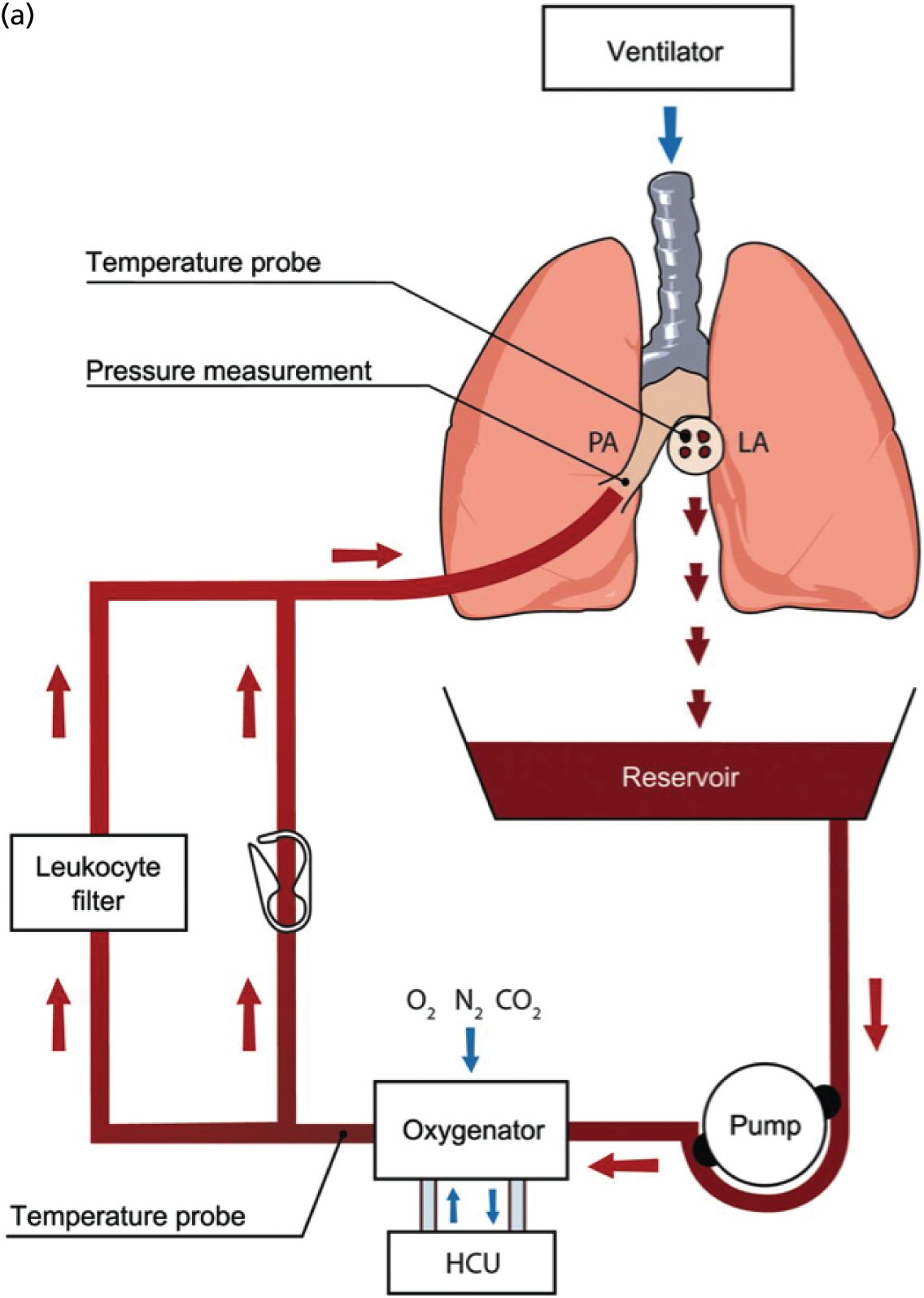
Ex vivo lung perfusion (EVLP) is a novel technique in which donor lungs that are unusable because of poor or uncertain function can be assessed objectively and potentially reconditioned for safe use in clinical lung transplantation, thereby increasing the donor pool. Evaluation of human donor lungs in isolated perfusion circuits, as seen in Figure 1, offers unique advantages, as isolation of the lung may alleviate injurious factors associated with the donor or recipient haemodynamics, hormonal derangements and their pro-inflammatory milieu. This allows time for optimisation of the donor lung without the immediate risk associated with fully supporting the recipient. EVLP can also objectively identify lungs that are not suitable for transplantation either because poor function is a result of irreversible damage, or because pre-existing lung disease is identified in the donor lung. In this respect, EVLP may provide reassurance to potential recipients that ‘marginal’ or ‘extended criteria’ donor lungs that might previously have been considered unusable are now acceptable for lung transplantation.
FIGURE 1.
Schematic diagram of an EVLP circuit. HCU, heater cooler unit; LA, left atrium; PA, pulmonary artery. (a) A line diagram of an EVLP circuit; and (b) a donor lung undergoing EVLP on the Vivoline LS1 system (Vivoline Medical AB, Lund, Sweden). Reproduced from Wallinder et al. , Early results in transplantation of initially rejected donor lungs after ex vivo lung perfusion: a case-control study. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2014;45:40–4, by permission of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. 6

As of June 2011, approximately 25% of the world’s early experience with EVLP, 17 out of 65 cases, had been gained in the UK. Although initial experience has been very promising, a large-scale trial of the procedure was required to demonstrate its effectiveness in increasing lung transplant activity in a safe and cost-effective way.
The Donor Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion in UK lung transplantation (DEVELOP-UK) study was therefore designed to address this urgent clinical need by assessing how effective EVLP assessment and reconditioning of donor lungs is at safely increasing UK lung transplant activity. The overall objective of this study was to evaluate the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the novel technique of donor EVLP in increasing UK lung transplant activity by allowing previously unusable donor lungs to be safely used in clinical lung transplantation. Furthermore, the DEVELOP-UK study would allow the applicability of EVLP to lung transplant services in the NHS to be determined.
Impact of donor lung injury
The lung is very susceptible to injury in the critical care environment, and the vast majority of donor lungs become unusable because of the dysfunction that develops in the hours or days leading up to the donor’s death. Korovesi et al. 7 observed that pulmonary and systemic inflammation occurred in patients who required mechanical ventilation for severe head injury. Characteristic changes in lung mechanics, suggesting subclinical pulmonary inflammation, also developed before the patients became eligible to be organ donors. 7 Fisher et al. 8 have shown that acute inflammation in the donor lung with elevated levels of interleukin 8 in donor bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) is important in determining early outcomes after human lung transplantation. 9 These observations have subsequently been reproduced elsewhere in the world. 10 In addition, an imbalance between inflammatory interleukin 6 and anti-inflammatory interleukin 10 (IL-10) gene expression in the donor lung predicts adverse early outcomes after human lung transplantation. 11 These clinical observations have been modelled by Avlonitis et al. 12 using a rat model of brain death-induced donor lung injury and subsequent rat lung transplantation. Brain death, together with trauma, infection, aspiration or transfusions, is now considered an important cause of donor lung inflammation and significant progress in understanding its pathophysiology has been made. 13 Other animal models of lung transplantation have demonstrated that adenoviral gene therapy to upregulate expression of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in the donor lung downregulates inflammation and improves function in the recipient animal after transplant. 14–17 These observations suggest that attenuating the donor lungs’ inflammatory response before implantation may improve early outcome after lung transplantation, and help to safely maximise lung use from the existing donor pool.
Assessment of donor lung usability
Assessing whether or not potential donor lungs are usable for transplantation is a process that takes into consideration available donor history, subjective evaluation of chest radiograph appearance, bronchoscopy and more exact physiological data such as arterial blood gases (ABGs) following high-concentration oxygen challenge. Despite improvements in donor management practices, currently < 20% of lungs from multiorgan donors in the UK are accepted for transplantation. The internationally accepted selection criteria of the ‘optimal donor’ are primarily opinion based rather than evidence based, and their accuracy in determining the physiological status of the donor lung and predicting post-operative lung function is not optimal. 18 Fisher et al. 19 have shown that current clinical donor lung assessment criteria are poor predictors of existing inflammation or infection in the donor lung, suggesting that many donor lungs deemed unusable may be unnecessarily excluded. Ware et al. 20 evaluated 29 pairs of unusable lungs by physiological, microbiological and histological methods, and concluded that as many as 40% of these lungs would have been potentially suitable for transplantation. Thus, there is urgent need to improve the donor lung selection process through more objective physiological assessment; EVLP can provide a platform to achieve this. In practice, not all of the unused donor cohort will be suitable donors, as some will have absolute contraindications to lung donation, while for others there will not be a suitable matching recipient on the waiting list. It is nonetheless suggested that EVLP could have the potential to increase availability of donor lungs for transplant by 50–100%. However, the current clinical transplantation infrastructures would not cope with a near doubling in activity, therefore, in this study, we were aiming for a 30% overall increase in lung transplant activity.
Early pathway development
Ex vivo lung perfusion was first reported in a canine model in 1970 as a technique to assess the quality of the donor organ in animal models of lung transplantation. 21 Subsequently, porcine studies showed that maintenance of intact vascular function was achievable for up to 24 hours using EVLP, and that functioning lungs could be obtained from donors after circulatory arrest in a porcine model. The clinical EVLP technique was initially developed by Steen et al. 22 in Sweden to assess lungs from donation after circulatory death (DCD) before transplantation. Their initial work in animal models was subsequently translated into the world’s first successful clinical report in 2001 of a lung transplant performed using lungs from a human DCD donor assessed by EVLP prior to successful transplantation. 22 Further experimental work in human donor lungs demonstrated that assessment and reconditioning of unusable organs using EVLP could result in significant improvements in arterial oxygenation and pulmonary vascular resistance. 23 This led to the first clinical report in 2007 of actual reconditioning of an unusable donor lung prior to successful lung transplantation. 24
Clinical ex vivo lung perfusion experience worldwide
Publication of the first successful lung transplantation using a reconditioned donor lung led to a rapid growth in interest in the EVLP technique. 22 The Steen group described successful reconditioning and transplantation of six out of nine donor lungs previously deemed unusable for transplant. 24 All six survived the first 3 months and four of the six were alive and well 12 months after transplant. 25 Subsequently, Cypel et al. 26 in Toronto modified the EVLP protocol significantly to include an acellular perfusate, a closed perfusion circuit and low perfusion pressures of no more than 40% of calculated cardiac output, and demonstrated that lungs can be maintained on EVLP for more prolonged periods with this approach. 26 This group have published their experience of the Human Ex-vivo Lung Perfusion study27 performing EVLP on 23 donor lungs unacceptable for transplant that translated into 20 clinical lung transplants. Outcomes in this group were comparable to that achieved with standard transplants performed over the same time period, with a 15% incidence of PGD in the EVLP group and of 30% in the standard transplant group (p = 0.11).
The UK was the third country worldwide to perform a lung transplantation using EVLP-assessed and -reconditioned donor lungs. The first case was performed by the Manchester group, followed rapidly by the programmes in Harefield,28 Newcastle and Cambridge. By June 2011, UK activity had totalled 17 transplants performed with lungs that would not have been used without EVLP assessment and reconditioning. The 90-day survival in these 17 cases was 100%, with one subsequent death from pneumonia at 9 months, and one further death at 18 months due to rejection. When the Swedish and UK experience was added to the Toronto experience, the findings suggested that early survival is very good, with only two deaths within 90 days among over 65 EVLP transplants. The UK experience revealed that the successful conversion rate during EVLP from unusable to usable donor organs was approximately 50%, which was lower than that reported in the Toronto experience. This may represent the high proportion of DCD donors in Toronto, where EVLP was being used primarily for assessment rather than for reconditioning.
International experience has since grown, with case series now reported by multiple groups internationally, including in Paris, Madrid, Vienna, Milan and Gothenburg, with patients successfully transplanted with EVLP lungs recovered from uncontrolled and controlled DCD donors. 29,30
In 2010–11, the UK was in a unique position, with four of its five adult lung transplant centres having already developed clinical experience in EVLP. At that time, there had been no systematic studies powered to evaluate the clinical effectiveness, safety and cost-effectiveness of EVLP performed anywhere in the world, and this was the impetus for the UK lung transplant community to come together in a collaborative effort in the DEVELOP-UK study.
Keshavjee et al. , in Toronto, have, with their extensive contributions, changed the landscape of EVLP into a technique to significantly expand the limited donor pool currently used in transplant centres all around the world. 27,30–32 The focus of Keshavjee and Cypel’s studies in Toronto has not been just to evaluate whether a graft is usable or not, but also to prolong the perfusion times to be able to potentially treat and better recondition injured lungs before transplantation. They have most notably revised the Lund protocol to potentially increase the option of longer-term perfusion with an acellular perfusate to avoid potential detrimental haemolysis. This is combined with a low-flow strategy with only 40% of estimated cardiac output to reduce pulmonary vascular shear stress and oedema formation, and closed circuit with both the pulmonary artery and left atrium cannulated, creating a positive left atrium pressure. The prospective, non-randomised, multicentre study NOVEL (NOrmothermic ex Vivo lung perfusion as an assessment of Extended/marginal donor Lungs) has recently been completed in the USA with the Toronto EVLP protocol and the XPSTM system (XVIVO Perfusion AB, Gothenburg, Sweden) to approve its clinical use.
Warnecke et al. ,33 in 2012, investigated the effect of normothermic preservation and transportation of standard criteria human donor lungs on a portable EVLP system. Twelve pairs of standard donor lungs were, instead of being brought to their centres by means of cold preservation on ice, preserved by normothermic perfusion and ventilation on the transportable Organ Care SystemTM (OCS) lung (TransMedics Inc., Andover, MA, USA). This was the first report of a portable EVLP system used in clinical transplantation, with short-term outcomes shown to be non-inferior to controls. 33
The OCS protocol used in this pilot study was a hybrid of the Lund and Toronto EVLP protocols. A cellular perfusate based on Steen Solution™ (XVIVO Perfusion AB, Gothenburg, Sweden) supplemented with erythrocytes and an open left atrium was combined with a perfusate flow limited to 2.5 l/minute, resembling the protective approach developed by the Toronto group. The OCS protocol is currently being evaluated on a larger scale in a prospective, randomised multicentre pivotal trial, OCS International Randomized Study of the TransMedics Organ Care System for Lung Preservation and Transplantation (INSPIRE), comparing transplant outcomes of standard criteria lungs preserved and transported by either normothermic EVLP or standard cold preservation. 34 Moreover, the international EXPAND (Evaluate the Safety and Effectiveness of The Portable OCS Lung For Recruiting, Preserving and Assessing Expanded Criteria Donor Lungs for Transplantation) trial was recently launched as a clinical pilot to evaluate the more traditional use of assessing and, possibly, reconditioning lungs deemed unusable for standard transplantation on the OCS lung portable system. 35
The development of semiautomated systems with disposable kits has made conducting EVLP more standardised, and has allowed protocols to be developed, as seen in the Vivoline LS1 (Vivoline Medical AB, Lund, Sweden) in Figure 2. The LS1 is a semiautomated EVLP system that was used at all sites in the DEVELOP-UK study.
FIGURE 2.
Photograph of (a) the Vivoline LS1 EVLP machine and (b) the disposable lung kit.
Ex vivo lung perfusion biological mechanisms of action
There are a number of mechanisms by which the reconditoning effects of EVLP are believed to occur. These are outlined in the following sections.
Haemodynamic factors
Controlling the speed and pressure of initial reperfusion of the transplanted lung in animal models reduces the risk of developing PGD. 28 The EVLP protocol allows initiation of controlled reperfusion after ischaemia, and preservation and controlled perfusion throughout EVLP, which is rarely available in routine clinical transplantation. This allows slow rewarming of the lung tissue and incremental perfusion of pulmonary vasculature over a prolonged period of time with continuous limitation of pulmonary artery pressures and, thereby, arterial and capillary hydrostatic forces to prevent further pulmonary oedema. Conducting EVLP at equivalent to very low left atrial pressures helps further by limiting hydrostatic forces in post-capillary venules and capillaries.
Protective lung ventilation
Protective lung ventilation strategies are the standard of care for intensive therapy unit (ITU) management of injured lungs. However, the need for hyperventilation in the management of head injury generally overrides this principle in potential lung donors, and avoidance of hypercapnia may limit the use of these strategies in transplant recipients. EVLP, therefore, provides a unique opportunity to adopt ventilation strategies that reduce excessive mechanical stretch (low tidal volume) and oxidative stress [low fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2)] and to employ sustained positive end expiratory pressures to overcome atelectasis without deleterious effects on systemic haemodynamics. Bronchial toilet with site-directed BAL limits ventilation–perfusion mismatch, thus avoiding regional hypoxia with high pulmonary vascular resistance and parenchymal damage. Immediate results from Gram stains of BAL directs antibotic therapy, with perfusion itself reducing microbacterial load. 36
Perfusate-related factors
One of the major mechanistic benefits of EVLP is the use of Steen Solution, an albumin- and dextran-rich perfusate solution with a high oncotic pressure. The solution can alter filtration forces to remove interstitial lung water and reduce pulmonary oedema. This may be responsible for the improved oxygenation observed between assessment in the donor and assessments during EVLP. In addition, albumin may act as an antioxidant, and dextran limits cell aggregation and microthrombi formation. The retrograde and antegrade perfusion during EVLP with use of a leucocyte filter in the circuit will also facilitate removal and prevent recirculation of intravascularly primed or activated leucocytes. Indeed, experimental models indicate reduced myeloperoxidase content of EVLP lungs, which are a biomarker of neutrophil-mediated responses.
Removal from the inflammatory donor environment
Another potential mechanism of lung reconditioning using EVLP may simply be the relocation of the donor organ from the suboptimal brain death environment in the donor. Eliminating the ongoing triggers of donor lung inflammation, including the endogenous toll-like receptor ligands and activated donor leucocytes, in a normothermic perfusion state may allow reduced inflammatory gene expression and restore protective anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
Opportunities for pharmacological-, genetic- and cell-based therapies
Along with steroids, heparin and antibiotics, a potential future option may be supplementation of perfusate with cytoprotective pharmacological substances including vasodilators, antioxidants, cytokine blockers, established inhibitors of inflammatory pathways, fibrinolytics and immunomodulators. Such strategies may facilitate better reconditioning of the lungs to increase conversion rates to successful transplantation and long-term survival. A genetic approach to improve cytokine balance has been shown to be beneficial in a large animal model of EVLP and transplantation, and IL-10 gene therapy has been applied to human EVLP lungs. 37 Similarly, a stem cell therapy approach via EVLP has been shown to improve acute lung injury in human lungs. 38
Chapter 2 Study rationale and design
Study design
The DEVELOP-UK study was designed as a multicentre, unblinded, non-randomised, non-inferiority observational study with an adaptive design, to evaluate the clinical and economic effectiveness of EVLP in assessing and reconditioning donor lungs for transplantation compared with standard lung transplantation. The study also includes an embedded qualitative substudy.
Primary outcome measure
Survival during the first 12 months following lung transplantation was chosen as the primary outcome measure in the study. It is a robust, well-recognised, clinically relevant outcome that is used in the Royal College of Surgeons national audit of UK cardiothoracic transplant activity and in the ISHLT lung transplant registry. A dichotomous outcome such as survival ‘yes/no’ at 30 or 90 days would be less informative, and would omit valuable information about potentially differing survival patterns between the two study groups.
Secondary outcome measures
The secondary outcome measures in this study were all deemed to be important, clinically relevant, patient-centred outcomes that are influenced by the effectiveness of lung transplantation, contribute to the health-care costs and impact on health-related quality of life (HRQoL).
Primary graft dysfunction is a clinical entity that reflects the development of early acute lung injury after lung transplantation. PGD was first defined by a working group (which included a number of the study investigators) of the ISHLT in 2005. 39 Its severity is graded between 0 and 3 and it is measured at 0–6, 24, 48 and 72 hours after lung transplantation. The grade is determined by the degree of gas exchange impairment, and by the presence of infiltrate on the post-operative chest radiograph. The PGD grade has been validated in both retrospective and prospective studies, and presence of PGD grade 3 at 72 hours is associated with a reduced early survival. A full PGD score was requested to be determined for all patients in the study.
The durations of invasive ventilation and ITU stay after lung transplantation were collected for all study participants, and provide a valuable source of a range of complications in early post-operative course. In addition, the duration of hospital stay before first discharge home gives a good indication of how effectively the patient is rehabilitating after their lung transplant. These measurements also provided useful information on health resource utilisation for economic evaluation.
The presence of specific post-operative complications was also collected as a secondary outcome measure. These complications included anastomotic complications scored using the recognised and validated Couraud Classification (see Appendix 1),40 which scores airway complications including dehiscence or stricture requiring dilatation or stent placement. Episodes of infection requiring treatment with or without associated hospital admission during the first year, and episodes of acute rejection of ISHLT grade A2 or higher, B1 or higher, or clinically diagnosed acute rejection requiring treatment during the first year, were also collected.
Details of lung function measurements by forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and vital capacity at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months post transplant were collected to demonstrate changes in lung allograft function in the first year. Data on chest radiograph appearance at the same time points as lung function were collected to look for any persistent abnormalities such as effusions, cavitation or chronic scarring from the time of transplantation.
Patient survival rate at 90 days post transplantation was collected as an internationally recognised outcome measure in lung transplantation that can be benchmarked against outcomes reported in both the UK and international (ISHLT) registries.
An assessment of HRQoL using the Short Form questionnaire-36 items (SF-36) was collected at three time points in the study (while participants were waiting for transplant and again at 90 days and 1 year post lung transplantation) allowing comparison of HRQoL measured while on the waiting list with that measured post transplant. The HRQoL scores have allowed health state utility scores to be determined using the Short Form questionnaire-6 Dimensions (SF-6D) as part of the economic evaluation.
Health economic assessment
In addition, the full economic impact of using EVLP-reconditioned lungs was assessed, allowing policy-makers to consider these costs in comparison with benefits of increased donor utilisation and reduced waiting list mortality. We aimed to determine whether or not EVLP is a cost-effective intervention for the NHS to support as standard care within UK lung transplant centres in the future.
Patients’ attitudes and experiences
To gain an understanding of the potential impact of EVLP provision to service users, we explored attitudes towards EVLP in patients awaiting lung transplantation, and the experiences of patients receiving EVLP-reconditioned lungs, in a qualitative interview substudy.
Predicting ex vivo lung perfusion success or failure
The DEVELOP-UK study provided a unique opportunity to better understand the donor- and procedure-related clinical determinants of successful or failed EVLP donor lung reconditioning. Objective clinical and physiological indices in the donor lungs before and during EVLP can therefore be correlated with the decision of whether or not to accept the donor lungs for transplant and with clinical outcomes in recipients of EVLP donor lungs.
Sample collection and storage
To add significant value to the DEVELOP-UK study, standardised protocols for BAL, perfusate and lung tissue sampling during EVLP and subsequent storage have been developed. The collection and storage of samples during EVLP was part of the DEVELOP-UK study, and allowed complementary mechanistic studies of EVLP to be performed from the data set. Details of the laboratory-based mechanistic work are, however, not included in this report, as this element of the study was funded from sources other than the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Health Technology Assessment (HTA) programme.
Justification for non-randomised design
This is a non-randomised study, as randomisation between EVLP and standard lung transplantation was not considered a viable option. The matching of potential donor lungs to potential recipients is dictated by a number of independent factors, including donor and recipient size, blood group and, if applicable, human leucocyte antigen (HLA) tissue matching to avoid any pre-formed HLA antibodies in the recipient. It was, therefore, not logistically possible to randomise recipients to receive either standard or EVLP donor lungs as part of the study. Furthermore, any attempt to randomly pre-allocate patients on the waiting list to an EVLP or standard group could give rise to a situation where a recipient may not be able to access a well-matched donor organ because it did not fall into his or her pre-allocated group, which would not be ethically acceptable. Randomisation would be possible only if all donor organs were being randomly allocated to EVLP or control, but this is a different research question and was not an objective of this study.
Lung donations from donors with brain death and DCD donors were considered in both arms of this study. The number of DCD donors is increasing year on year in the UK. 41 Evidence has emerged that, when lungs from these donors are transplanted, outcomes in recipients are comparable to those achieved with lungs from donation after brain death (DBD) donors. 42 However, only a fraction of the UK DCD donors, currently about 5%, have their lungs used for standard transplantation. 41 Frequently, there are insufficient data available to be able to objectively assess the function of the lungs from DCD donors, or there is a prolonged warm ischaemic phase after withdrawal of life support that renders the lungs unusable for standard transplantation. EVLP does, however, provide the potential to assess and potentially recondition lungs from DCD donors that cannot be used for standard transplantation.
It was anticipated that a direct result of the DEVELOP-UK study would be an increase in the proportion of DCD donor lungs being used, as DCD donor lungs are often deemed unusable because functional information about the organs is unavailable, which is an indication for use of EVLP assessment. It was considered likely that as the number of DCD donors increases, more lungs from this cohort of donors would be transplanted in the EVLP arm of the study than in the standard arm. This reflects the potential for EVLP to significantly increase the use of lungs from DCD donors. To ensure that the possible higher proportion of DCD donor lungs in the EVLP arm of the study did not bias the results, we planned to use the donor type (DCD or DBD) as a covariate in the multiple regression analysis of the primary and secondary outcome measures to determine their influence.
Justification for adaptive study design
The study statistics and trial methodology teams, in consultation with the clinical investigators, made the decision to use an adaptive design for the DEVELOP-UK study, to allow for the possibility of stopping the trial early should non-inferiority in our primary outcome be determined at an interim analysis, and to allow for re-evaluation of the sample size requirements on the basis of a potentially improved standard of care. It was felt that a total of three analyses, two interim and one final, would achieve a suitable balance between allowing for early stopping and ensuring that sufficient data were collected on secondary outcome variables to make these meaningful. The plan was for the interim analyses to be carried out once a prespecified number of patients had been recruited to each arm (see Power calculation and definition of non-inferiority). The O’Brien–Fleming critical values for the analyses during our study were chosen so that the overall study would have sufficient power to detect our target differences at a significance level of 0.05 once allowance had been made for the interim analyses.
Power calculation and definition of non-inferiority
In the standard arm, the initial best available estimate for survival to 30 days was 94.2%, for survival to 90 days was 91.2% and for survival to 1 year was 78.7%. These data were determined from the Royal College of Surgeons’ UK national audit of lung transplant outcomes. Our aim was to demonstrate that using reconditioned EVLP lungs does not increase the hazard rate of death during the first year by a factor of > 2. A doubling of the hazard rate would imply that survival rates on EVLP would be 88.7% for 30 days, 83.2% for 90 days and 61.9% for 1 year. It was considered that such a difference is not clinically significant and still represents an advantage over waiting longer for a transplant.
It was anticipated that over the predicted 3 years of the study, about 100 EVLP lungs would be transplanted and ≥ 300 normal lung transplants would take place. If both treatment arms matched the standard 78.7% rate of survival over 12 months, then approximately 85 deaths would occur within 1 year of transplantation. Using a fixed sample design, this would be sufficient to ensure 80% power of claiming a significant finding of non-inferiority (at a one-sided 5% level) if both treatment groups actually have the same survival pattern. 31 The study was therefore powered to detect a difference of 2, meaning that non-inferiority is assumed to have been achieved if the hazard rate of 12-month survival is not doubled by the use of EVLP.
To obtain sample sizes for an adaptive design, we took the standard sample size and multiplied it by the appropriate inflation factor (which depends on the choices of critical values, number of analyses, significance level and power). For our choices, the inflation factor was 1.0128, resulting in a sample size of 304 in the standard arm and 102 in the EVLP arm. We increased the sample size to 306 in the standard arm while keeping it at 102 in the EVLP arm so that the sample size in both arms would be divisible by 3, to allow for equally spaced interim analyses. This resulted in a required minimum total sample size of 408 with interim analyses after 12-month survival data were available from 102 and 204 patients in the standard arm (34 and 68 in the EVLP arm).
Risks and anticipated benefits for study participants, NHS and society
There is a huge discrepancy between the supply of usable donor lungs and the number of patients with end-stage lung disease who could potentially benefit from lung transplantation surgery in terms of extended longevity and improved quality of life. As a result, many patients die on the waiting list before suitable donor lungs become available. EVLP allows otherwise unusable donor lungs to be meticulously assessed and potentially reconditioned for successful transplantation. The study would also help to understand better how to optimise the use of lungs procured from DCD donors. This technology, therefore, has the potential to expand the donor pool and increase UK lung transplant activity, thereby shortening time spent on the waiting list and reducing waiting list deaths.
The primary risk for the individual participant awaiting lung transplantation is that if they are enrolled in the EVLP arm they may receive a lung or lungs that do not function well, but that risk also exists for standard donor lungs accepted by the current assessment methods. Compared with standard criteria organs, it was not anticipated that EVLP should expose recipients to any different risk profile in terms of microbiological exposure, intensity of induction and maintenance immunosuppression or early post-transplant complications. This was based on reported worldwide experience with EVLP at the time (2010–11) the study was designed and launched. Patients awaiting lung transplantation have severe, often complex, morbidity and place a heavy resource burden on both health and social services. Data from the ISHLT registry clearly demonstrate that nearly 80% of successful lung transplant recipients have no or little functional limitation and around 40% return to either full- or part-time employment, the rest being close to or over retirement age. 43 Fewer than 20% of transplant recipients require inpatient treatment related to their lung disease post hospital discharge following the transplant procedure. Thus, by increasing the numbers of successful transplants, EVLP may help to reduce the UK health- and social-care costs of patients awaiting lung transplantation. Furthermore, by assessing the economic impact of using EVLP-reconditioned lungs, the study results should allow policy-makers to balance these costs against the benefits of increased donor utilisation and reduced waiting time mortality. The study aimed to help determine if EVLP is a cost-effective use of tax-payers’ money and an intervention applicable to NHS lung transplant services.
Study population
The DEVELOP-UK study was a UK national multicentre study involving all five officially designated NHS lung transplant centres: Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne; Harefield Hospital, London; Papworth Hospital, Cambridge; Wythenshawe Hospital, Manchester; and Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham. These five centres provide all adult lung transplant activity to potential recipients with end-stage chronic lung disease in England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
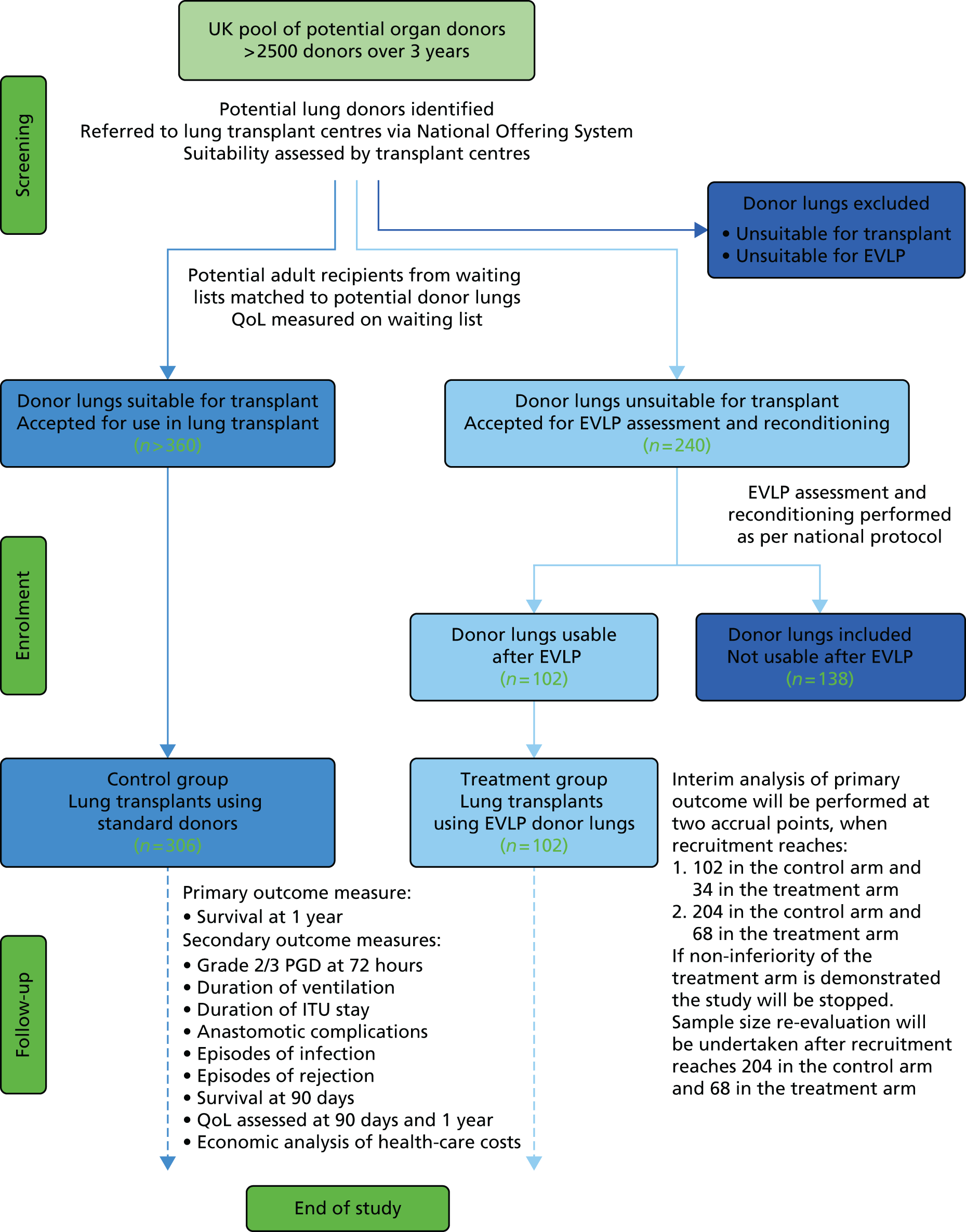
The target population for the study was adult patients aged ≥ 18 years with advanced lung disease, who had already been accepted (at study inception) onto an active lung transplant waiting list in one of the five UK centres, plus any new adult patients who were added to the active waiting list during the study recruitment period of April 2012 to June 2014. The full network coverage means all patients awaiting lung transplantation in the UK, at any one time approximately 250, had the opportunity to take part in the study, and our previous pilot experience suggested that > 90% would consent to take part. The study was designed to have no effect on how potential lung transplant recipients were assessed or selected, or the timing of when they were added to the active transplant waiting list. The flow chart in Figure 3 shows the planned recruitment targets and summary of data collection for the DEVELOP-UK study.
FIGURE 3.
Diagram to explain planned recruitment targets, study end points and planned analysis. QoL, quality of life.
Study inclusion criteria
Male or female adult patients (aged ≥ 18 years) who were either already on or added to the active waiting list for their first lung transplant while the DEVELOP-UK study was in its recruitment phase were eligible to participate; patients provided informed consent for participation in the DEVELOP-UK study at the time of study commencement or time of listing for transplant and reconfirmed informed consent for the DEVELOP-UK study on the day of lung transplant.
Study exclusion criteria
Patients aged < 18 years and adult patients listed for lung retransplantation, heart–lung transplantation, multiorgan transplantation including lung or live donor lobar transplantation were excluded. Patients not in possession of the patient information sheets for the DEVELOP-UK study prior to the day of lung transplantation or those not reconfirming consent for the DEVELOP-UK study on the day of lung transplant were excluded. Patients in the ITU requiring invasive ventilation, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) or interventional lung assist (iLA) support when a donor lung became available were excluded. Patients enrolled in other trials within the preceding 12 months of signing an expression of interest (EOI) or giving full consent had to be discussed with the principal investigator (PI) and chief investigators before being excluded on this basis.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria for interview substudy
All patients who were eligible for the DEVELOP-UK study at The Newcastle Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust and the Royal Brompton and Harefield NHS Foundation Trust were eligible for the interview study. All patients who consented to the DEVELOP-UK study, as a whole, at the above centres were eligible to take part in the interview substudy regardless of whether or not they received a transplant. All patients who consented to the DEVELOP-UK study from Manchester, Papworth and Birmingham sites were excluded from the qualitative study.
Concomitant medications
All standard prescribed medications taken by patients on the waiting list for lung transplantation were permitted in the study. Some medications are stopped at the time of transplant or in the perioperative period. These changes are in line with standard clinical processes and were felt to be equally likely to occur in lung transplant recipients in both arms of the study.
Peri- and post-transplant immunosuppression, including any induction therapy and maintenance immunosuppression, may vary slightly between centres, but continued as per usual practice during the study. In any of the centres, patients in both the EVLP and standard arms of the study got the same standard routine immunosuppressive approach normally used in that centre. The immunosuppressive regimes could, however, be changed, intensified or reduced in line with standard transplant clinical management of the individual patient and his or her circumstances. It was possible that patients awaiting lung transplantation might already be enrolled in a clinical trial of investigational medicinal product (CTIMP) for their underlying disease. Such medications were stopped at the time of transplant and participation in the CTIMP was censored as an event and, therefore, the participation of these patients in the DEVELOP-UK study was not affected.
Patients enrolled in the DEVELOP-UK study who underwent lung transplant in either the standard or EVLP arm should not have been enrolled in any other interventional study in their first 12 months post transplant that might have an effect on 12-month survival. If there was any question of this, then the local PI discussed this with the DEVELOP-UK study chief investigator, who then liaised with the chief investigator of the other study and reported back to the trial steering committee. Observational non-interventional studies were allowable but, again, the local PI had to check with the chief investigator to make sure that there was no interference between the studies. Participants were free to be entered in interventional studies started after their first 12 months post lung transplantation.
Limiting the potential for bias
As a non-randomised, non-blinded study, it was important that the potential for bias in the selection of recipients to receive donor lungs from the EVLP or standard arms was considered and carefully monitored. There was, however, no a priori reason to expect a systematic difference to exist in characteristics between the recipients in the two arms of the study. This is because the donor–recipient match was established before the clinical decision on the usability of the donor lungs was made, meaning that recipient selection should not be influenced by whether EVLP-conditioned or standard lung donation occurs. In particular, there was no evidence to suggest that sicker recipients, whose transplant might be seen as more urgent, would be more likely to receive EVLP-reconditioned lungs than standard donor lungs.
Only when donor lungs were available that had more than one potentially matching recipient was urgency taken into account by the transplant centre. This scenario would be likely to happen as frequently in the standard transplant arm as in the EVLP arm. The two arms of the study were monitored carefully to ensure that no systematic differences occurred in the recipient characteristics. Additionally, it was planned that recognised covariates that are known from the international registry to influence outcomes after lung transplantation would be adjusted for in the statistical analysis. Our pilot experience of transplants performed using EVLP-reconditioned lungs across the UK centres indicated that patients with a range of disease indications, ages, disease severity and both single and bilateral transplants have been included, reflecting the variability that exists on the lung transplant waiting list.
Interventions common to experimental (ex vivo lung perfusion) and control (standard) groups
Donor pathway
Any potential offer of donor lungs was communicated to the transplant centres by standard procedures via the specialist nurses for organ donation (SNODs). Each of the five centres was then responsible for making an initial assessment of the suitability of the donor lungs for transplant, and for determining if they had an appropriately matched potential recipient on their waiting list. If a centre did not have a suitably matched recipient, then the donor lungs were offered to another centre in a controlled rotational manner as part of the standard donor organ placement protocol by NHS Blood and Transplant (NHSBT). The donor lung indices were compared against the donor lung selection criteria for the study and, if suitable for potential transplantation, then the NHSBT zonal organ retrieval team were dispatched to the donor hospital to further assess the donor lungs. After careful assessment, a decision was made using the donor lung acceptance criteria whether the lungs could be used immediately for standard transplantation, should undergo EVLP assessment and reconditioning or were contraindicated completely for transplantation. If appropriate for transplant, the donor lungs were then transported back to the transplant centres in accordance with standard practice.
Donor lung procurement for all lungs in the DEVELOP-UK study
A standard lung procurement procedure was followed for donor lungs used for EVLP in the study. In brief, the organs were antegradely flushed with supplemented PERFADEX® (XVIVO Perfusion AB, Gothenburg, Sweden) [3.3 ml of 3.6% trometamol (THAM), 0.6 ml of calcium chloride (CaCl2) ± 2.5 ml of prostacyclin/l], initially at room temperature and then the remainder at 4 °C. A minimum volume of 60 ml/kg was given. After the antegrade dose, 200 ml was given down each pulmonary vein as a final retrograde flush. An adequate portion of main pulmonary artery, left atrial cuff and, particularly, at least 4 cm of trachea was taken by the retrieval surgeon.
Donor and next of kin consent
Consent for potential donor lungs to be used for lung transplantation was obtained from the donor’s next of kin at the donor hospital by the SNODs, who were employed by NHSBT. This process is standardised nationally and was performed completely independently of the DEVELOP-UK study.
If standard consent for lung donation was granted, the SNODs also asked the next of kin for generic research consent, which is a standard part of the donor consent process. This allowed the study team to collect and store samples from the donor lung before and after EVLP, as described in Appendix 2, for parallel mechanistic studies even if the donor lungs were not deemed transplantable after EVLP. If the donor’s next of kin did not provide generic research consent, then only clinical data measured during the EVLP process were collected and used in the study, and no lung tissue samples were taken for mechanistic work. This did not compromise the delivery of the primary and secondary end points of the study.
Lung recipient pathway pre and post transplantation
Patients referred to any of the five participating sites for consideration of lung transplantation over the course of the study recruitment phase underwent a standard clinical assessment. Those deemed eligible for, and who consented to, lung transplantation were added to the active lung transplant waiting list. Those on the transplant list at the time of study inception would already have been through the same assessment process.
At the time of listing for transplant, patients were offered the opportunity to take part in the DEVELOP-UK study. In addition, at the time of study inception, any patient who was already on the active lung transplant list was also offered the opportunity to take part in the DEVELOP-UK study. The consent process was performed in accordance with National Research Ethics Service guidance, as described in Lung recipient consent. As the period of waiting for lung transplantation can vary widely and commonly exceeds 12 months, it was necessary to reconfirm consent for the study at the time when a potential donor lung(s) became available and the study participant was called in for possible transplantation. However, if the original consent form had been signed on the day of transplant, reconfirmation of consent was not required.
Patients were told on the day of transplant whether they were to receive a donor lung that had undergone EVLP assessment and reconditioning or a standard donor lung. Patients received either standard donor lungs direct from a donor (standard transplant, control arm) or donor lungs after EVLP assessment and reconditioning (intervention arm) in accordance with donor organ–recipient matching. Transplanted lungs, whether ‘standard’ or EVLP reconditioned, always remain vulnerable to the possibility of rejection and one of the main risk factors is low immunosuppression levels. For this reason, patients were thoroughly counselled prior to being accepted onto the transplant list about the need for absolute concordance with their treatment and to attend all arranged post-transplant follow-up visits. As a result, during the multidisciplinary pre-transplant assessment, a considerable amount of time was spent explaining this aspect of care to the patients. If, despite these attempts, there remained evidence of likely non-compliance with treatment, these individuals were not usually offered the option of transplantation.
Lung recipient consent
Informed and voluntary consent was obtained via an iterative process, first at the initial discussion of the clinical and research aspects of the study, and then again, provided this occurred not less than 24 hours later, on the day of possible transplant. If, however, the consent form was signed on the day of transplant, reconsent was not required. Consent for the DEVELOP-UK study participation was sought separately from the standard consent for lung transplant surgery. No additional screening procedures, over and above those necessary to determine eligibility and suitability for lung transplant, were required to determine eligibility for the trial element of the DEVELOP-UK study. Therefore, all adult patients being considered for lung transplant who satisfied the inclusion criteria were approached to take part in the DEVELOP-UK study. Patients waiting for transplantation are desperately sick, very vulnerable and grasping at any lifeline. Securing genuinely informed consent was therefore an important consideration. The initial consent process took place well ahead of the time of transplant and the stressful environment that this generates. Consent was taken either at inception of the study for those already on the transplant waiting list or at the time of listing for transplant for those added to the active transplant list during the course of the study. A copy of the consent documentation is included in Appendices 3 and 4.
Consent was taken by the site PI or a member of the study team with appropriate designated responsibility on behalf of the local PI. In the consent process, care was taken not to unjustifiably inflate hope of a shorter waiting time for transplantation as a result of EVLP being available. A clear definition of what constitutes an unusable donor lung in the study was explained; definitions of acceptability of lungs for standard transplantation and for transplantation after EVLP were agreed and standardised across all centres. Patients were offered firm reassurance that if donor lungs did not improve sufficiently after EVLP reconditioning to satisfy acceptability criteria, they would not be used. Any potential recipient who decided not to participate in the DEVELOP-UK study continued to have equal access to donor lungs for standard transplant. Those choosing not to give consent were not obliged to give a reason, but if they provided a reason this was recorded in an anonymised way to inform the Trial Steering Committee.
Additional informed consent, using a separate participant information sheet and consent form, was sought from the subset of patients approached to take part in the qualitative interviews. Lack of consent to take part in this element of the study did not preclude participation in the trial.
For both the trial and the qualitative substudy, if a potential participant had the capacity to consent for him/herself, but was unable to provide written consent because of visual or motor impairments, or literacy problems, oral informed consent was taken in the presence of an independent witness, who initialled, signed and dated the consent form on the participant’s behalf.
We did not anticipate that any potential study participants would lack capacity to consent on initial recruitment to the study or at the point of reconfirming consent at the time a donor lung became available. It was, however, possible, although unlikely, that they could lose capacity over the follow-up period. For example, if as a result of transplant surgery, any participant were to lose capacity temporarily or permanently, such as by requiring prolonged ventilation in the ITU or by suffering a stroke, we planned to continue to collect outcome measures in relation to such patients, working with personal or nominated consultees and in line with the requirements of the Mental Capacity Act. 44
We did not seek separate written consent from nominated consultees in the event of loss of capacity, as this scenario was included in the initial participant consent form and patients were specifically asked to give consent for continued collection of observational data as part of the study if they lost capacity after transplantation. As many of the data in the follow-up period were observational, their collection did not impact on the standard care that any participant who has lost capacity would expect to receive.
The original signed consent form and reconsent form were retained in the investigator site file, with a copy in the clinical notes and a copy provided to the participant. Participants were asked to consent explicitly to their general practitioner (GP) being informed of their participation in the trial element of the DEVELOP-UK study.
The right to refuse to participate without giving reasons was respected. Owing to the small subject population, the information sheet and consent form for the study were available only in English. Interpreters were available for all visits of patients who required them either for verbal translation to another language or for deaf subjects wishing to take part in the study, via local NHS arrangements.
Protocol compliance
The protocols determining the selection of donor lungs to undergo EVLP and indices that determine whether or not the lungs were suitable for transplant after EVLP were clearly described in the study protocol and are presented in an appendix to this report (see Appendix 2). To ensure compliance with the protocol, data were collected about the donor assessment and EVLP procedure. This allowed confirmation that the donor lung was appropriately allocated to undergo EVLP and that the decision on its suitability was correctly determined. If any instances were identified when the protocol was not followed, this was recorded as a protocol deviation and the site PI was asked to document why the protocol deviation occurred.
Ethics and regulatory issues
The conduct of this study was in accordance with the recommendations for physicians involved in research on human subjects adopted by the 18th World Medical Assembly, Helsinki, 1964, and later revisions. 45 All members of the research team, the investigators and supporting staff at each of the participating sites received training in those aspects of good clinical practice appropriate to their role in the trial, in particular the processes for obtaining informed consent, including the requirements of the Mental Capacity Act,44 and were expected to operate to principles of good clinical practice.
A favourable ethical opinion from the National Research Ethics Service (reference number 11/NE/0342) and NHS research and development (R&D) approval was secured prior to commencement of the study. Local NHS approvals were secured before recruitment commenced at each site. The Newcastle Clinical Trials Unit, in its capacity as study co-ordination centre, obtained a written copy of local approval documentation before initiating each centre and accepting participants into the study.
Information sheets were provided to all eligible subjects, and written informed consent was obtained prior to any study procedures. Patients on the transplant waiting list who lived a significant distance from the transplant centre were given the opportunity to sign an EOI form that allowed them to subsequently consent when next attending the transplant centre (which might be on the day of transplant). Signing of the EOI form permitted completion of the first SF-36 questionnaire and collection of waiting list survival data. Copies of the patient information sheet and consent forms are included in Appendix 4.
We obtained informed and voluntary consent via an iterative process, providing adequate time (i.e. a period of not < 24 hours) for consideration and discussion of the clinical and research aspects of the study. For incident cases, initial consent was taken at the time a patient was listed for lung transplant. For those patients already on the transplant list at the time of study initiation, consent was sought when the study opened at their transplant centre. Reconsent on the day of transplant was sought only from patients initially consenting to the study prior to the day of lung transplant.
Assessments and data collection
All study-specific follow-up data were collected during the time of the clinical admission to hospital for the lung transplantation procedure and, subsequently, at study visits that were co-ordinated to coincide with routine post-lung transplantation clinic visits. The study research nurse ensured that routine clinic visits were mapped to the study visit requirements by liaison with study participants and the transplant outpatient facilities in each centre.
The scheduled outpatient study visits were at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months post transplant. A window of ± 10 days around each timetabled study visit was allowed. If a participant was unable to attend a study visit within the allowable window, for example because he or she was an inpatient at an external hospital that was not the study centre, then every effort was made to acquire the same study-specific information from the non-study hospital. The HRQoL questionnaire (SF-36) was self-completed by each study participant (or in conjunction with their nominated proxy).
Patients’ views and perceptions of EVLP were explored through qualitative interviews conducted by a trained researcher. When possible, these interviews were performed face to face at study visits after transplantation. Those interviewed prior to transplant were interviewed either in their own home or, more usually because of the large geographic spread of individuals, by telephone.
All clinical tests required to determine the success of EVLP assessment and reconditioning of donor lungs, including ABG analysis, glucose and lactate concentration measurement, and microbiological cultures, were performed in each study centre using local laboratories and equipment.
Standard blood profiles during follow-up were performed as part of the recipients’ routine clinic care in each participating centre’s certified NHS laboratories, and results were obtained from hospital data systems.
Data were collected by direct clinical observation, by clinical interpretation and from source patient records or NHS documentation by the study clinical research fellow and the study research nurse, and the required data fields were completed on the case report form (CRF) by the research nurse or a designated data manager in each centre under the supervision of the local PI. A paper CRF was initially used in the study, but in early 2014 an electronic CRF (MACRO; InferMed, Elsevier, London, UK) began to be used, in line with regulations at the sponsoring trust. The donor data required for the study (such as age, comorbidities and oxygenation, among others) were collected routinely by the SNODs, and were then captured electronically by linking to the core data data set collected by NHSBT centrally.
Serious adverse event reporting
Guidance on adverse event (AE) and serious adverse event (SAE) reporting, as well as determining the degree of relatedness and assessment of causality for SAEs that may be related to study participation, was provided in the study protocol.
As lung transplant recipients experience a significant number of AEs as part of their normal recovery from transplant surgery, the study protocol provided clear guidance on what constituted a SAE that required expedited reporting. This was to avoid a huge burden of reporting that had no relevance to this observational study (no CTIMP involved to monitor). Hospitalisations for elective treatment of a pre-existing condition, and hospitalisations as part of routine post-transplant surveillance did not need reporting as SAEs. Unrelated hospitalisations were elicited at the scheduled follow-up appointments and at all emergency appointments.
Serious adverse events requiring expedited reporting included death within 90 days of lung transplantation, severe PGD requiring ECMO/iLA support, bronchial anastomotic dehiscence or any unexpected SAE felt to be probably or definitely causally related to EVLP.
Some SAEs were excluded from expedited reporting to reduce the burden of reporting of events that are common in the transplant journey. These were death on the waiting list prior to transplant or later than 90 days after lung transplantation; PGD grades 1–3 not requiring ECMO/iLA support or severe sepsis associated with consolidation, necrosis or cavitation of lung tissue within 30 days of transplant; renal failure necessitating renal replacement therapy, gastrointestinal complications, central nervous system complications; and infections requiring an addition or change in antimicrobial therapy.
Medium- and longer-term outcomes that did not require reporting as urgent SAEs were bronchial strictures (whether or not they required bronchial stenting), acute rejection requiring augmented immunosuppression, development of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease or obliterative bronchiolitis. Finally, deterioration of any pre-existing medical conditions both before and after transplantation did not require urgent reporting.
Public and patient involvement and engagement
The DEVELOP-UK investigators were committed to ensuring appropriate public and patient engagement throughout the study.
The CF Trust was approached to provide patient and service user expertise in the design of the study. Oli Lewington, who has previously undergone lung transplantation, agreed to join the study team in order to help prepare the application for funding, and to contribute to the study design and to the writing of the Plain English summary. The chief investigator presented the study proposal to the board of directors of the trust, and the concept of the study to the annual public meeting of the CF Trust. Following award of the funding, Mr Lewington assisted in producing the participant documentation and the final study report.
Lay members were appointed to the Trial Steering Committee to regularly review study progress and to provide valuable public input into key decision-making during the study.
Chapter 3 Main study objectives
Study objectives
The DEVELOP-UK study is the first prospective multicentre study to be performed involving all of the adult cardiopulmonary transplant units across the UK. The objective was to assess the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of EVLP, a technology allowing objective assessment and reconditioning of unusable donor lungs, in increasing UK lung transplantation activity. Its strategic importance was recognised by the British Transplantation Society, the NHSBT, NHS specialist commissioners and by patient groups during the study design and funding application process.
The DEVELOP-UK study was designed as a non-randomised, non-inferiority observational study with an adaptive design, with two interim analyses planned for when one-third and two-thirds of total enrolment was reached. The planned interim analyses provided the opportunity to determine if the primary end point had been achieved, but also to calculate if any change in sample size was required. The original primary objective was to determine if the 12-month survival of recipients of ex vivo assessed and reconditioned donor lungs (EVLP intervention group) is non-inferior to 12-month survival in recipients of standard donor lungs (control group). The secondary objective was to measure key early clinical outcomes in recipients and changes in their HRQoL in the treatment and control groups in their first post-transplant year. These data were planned to be used in a within-study cost–utility analysis and a Markov model-based evaluation. The former comparison was to be a direct head-to-head comparison of outcomes over 12 months, and the latter was to model the change in availability of lungs as well as extrapolating over the expected lifetime of those needing a lung transplant. In addition, patients’ perceptions and understandings of EVLP-reconditioned donor lungs were evaluated in a qualitative substudy.
Timelines and targets
The official start date for the study was 1 January 2012 based on release of NIHR funds to the study team. To allow for local R&D approvals, research staff recruitment and subcontractor contracts with sites to be secured, a 3-month run-in period was proposed, anticipating that recruitment would have started in all sites by 1 April 2012. The actual start date of the study was therefore 1 April 2012. Study recruitment and enrolment was scheduled to run for 36 months, with data collection ending by 42 months, and the final study report was scheduled at 45 months in October 2015. The recruitment targets for the study were set based on official waiting list numbers across the UK in the five adult lung transplant centres. The aim was for a total of 600 patients from the lung transplant waiting list to consent to participate. As this was a non-randomised study, enrolment into the two arms of the study, as defined by undergoing lung transplantation (standard and EVLP transplant), occurred independently, and the study was powered on a predicted 3 : 1 (standard arm to EVLP arm) enrolment ratio. The target for enrolment as lung transplant recipients was 408 patients (306 in standard arm and 102 in EVLP arm).
Trial hypothesis
Had the study run to its planned duration in terms of recruitment, the tested hypothesis was to have been that survival during the first 12 months after transplantation in recipients of EVLP-assessed and -reconditioned donor lungs is non-inferior to that in recipients of standard donor lungs. The primary outcome measure was survival during the first 12 months after lung transplantation.
Consequences for the study analyses of the early closure of the study
The study was powered on survival during the first year post transplant and the target recruitment as 306 patients in the standard transplant arm and 102 in the EVLP transplant arm. This chapter reflects the analysis possible following the early closure of the study, with recruitment of patients stopping in early July 2014 on the advice of the Trial Steering Committee because of a combination of poor recruitment rates into the EVLP arm of the study, and also a safety signal from a higher than expected SAE rate resulting from the need for ECMO support in the EVLP arm. The analyses described below are appropriate to the achieved sample size and differ from that intended and described in the original protocol. The analysis to compare standard with EVLP transplant groups, as well as the analysis of overall survival of patients awaiting transplantation, are descriptive in nature and, as such, do not reflect the initial intention of testing for non-inferiority of EVLP to standard transplants. The originally planned interim analyses, intended to test for the possibility of stoping the study early if non-inferiority was achieved and to re-examine the sample size, did not take place, as the recruitment threshold to trigger the first of these (34 EVLP transplants) was never reached.
Planned timelines for study analysis
In light of the change of circumstances of the analysis, the intent has changed from one of conducting interim analyses to inform the continuation of the study while it was in progress, to one of a single main report of outcome data to the funder. The plan was that data should be available for this analysis from the end of May 2015. In practice, the collection and validation of data were delayed because of the large number of missing data and data queries to sites, meaning that the analysis started in October 2015 and continued into early 2016.
Longer-term analysis plans
It is important to recognise that, despite the early closure of the study, there remains a rich data set, particularly in respect of information on standard transplants and on the total cohort of donor lungs exposed to EVLP. Consideration of this alone was not part of the original comparative analysis plans and, as a result, this is outside the scope of the main study analysis.
Following completion of the main study analyses, and outside the scope of the report to the funder, it will be possible to consider further analysis of the data from the standard transplant arm. This did not form part of the trial statistical analysis plan, as it was not in scope of the originally planned study, but the information from this large contemporary cohort of 200 transplants, including extensive follow-up data, is likely to be useful to future study. Possible approaches include modelling of outcome variables using baseline clinical covariates to identify possible predictors of successful outcome at baseline.
In addition, a comprehensive sampling protocol was in place to collect perfusate, lung tissue and BAL from the donor lungs undergoing EVLP. This will provide a valuable assessment of events at a cellular and molecular level that can be correlated with clinical information within the main study data set. The work on the mechanistic understanding of EVLP falls outside this report (as it is not the subject of the NIHR HTA programme funding), but the tissue sample data will contribute to this subsequent analysis.
Recruitment
The study officially commenced on 1 January 2012, opened to recruitment on 1 April 2012, and closed to recruitment on 9 July 2014. There was a temporary halt in recruitment into the EVLP arm from 6 April 2013 until mid-July 2013, when the study activity in the EVLP arm recommenced with a modified protocol.
The timings for study recruitment in each individual site are shown in Table 1. The data analysed and presented in this report were downloaded from the MACRO database in October 2015. Additional data were assembled in Microsoft Excel® 2010 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA) files for some of the outcome measures (e.g. SF-36 and some lung function measurements) not recorded on CRFs, and for the donor characteristics, which were imported from the NHSBT database.
| Site | R&D approval | Delay from 1 January 2012 (official start date) | Date of first EOI/consent | Delay from 1 April 2012 (actual start date) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Newcastle | 1 February 2012 | 1 month | 13 April 2012 | 13 days |
| Manchester | 15 May 2012 | 5 months 15 days | 24 May 2012 | 1 month 24 days |
| Cambridge (Papworth) | 11 June 2012 | 6 months 11 days | 21 September 2012 | 6 months 21 days |
| Birmingham | 30 August 2012 | 8 months | 19 September 2012 | 6 months 19 days |
| London (Harefield) | 9 October 2012 | 10 months 9 days | 26 October 2012 | 7 months 26 days |
| Lost recruitment time | 31 centre-months | 23 centre-months |
A total of 593 patients were screened (from records) for eligibility, of whom 98 did not meet eligibility criteria and a further eight declined to participate. Reasons for not meeting the eligibility criteria included age, need for pre-transplant cardiorespiratory support, and listed for heart–lung transplantation or transplantion of lungs and another organ. The screening failure rate was, therefore, only 16.1%, and the refusal rate for participation was just 1.3%.
A total of 487 patients consented to participate or completed an EOI form while on the transplant waiting list, of whom 19 were subsequently removed from the waiting list because of a change in their transplant eligibility, leaving 468 participants eligible to be included in the study. The breakdown of patients consented per participating site is shown in Table 2, and the rate at which patient consents were accrued is shown in Figure 4.
| Site | Date opened | Number of signed EOI/consent forms |
|---|---|---|
| Birmingham | 30 August 2012 | 50 |
| Cambridge (Papworth) | 11 June 2012 | 69 |
| London (Harefield) | 9 October 2012 | 104 |
| Manchester | 15 May 2012 | 84 |
| Newcastle | 1 February 2012 | 180 |
| Total | 487 |
FIGURE 4.
Cumulative recruitment numbers across all five centres defined as signing EOI or consent forms.
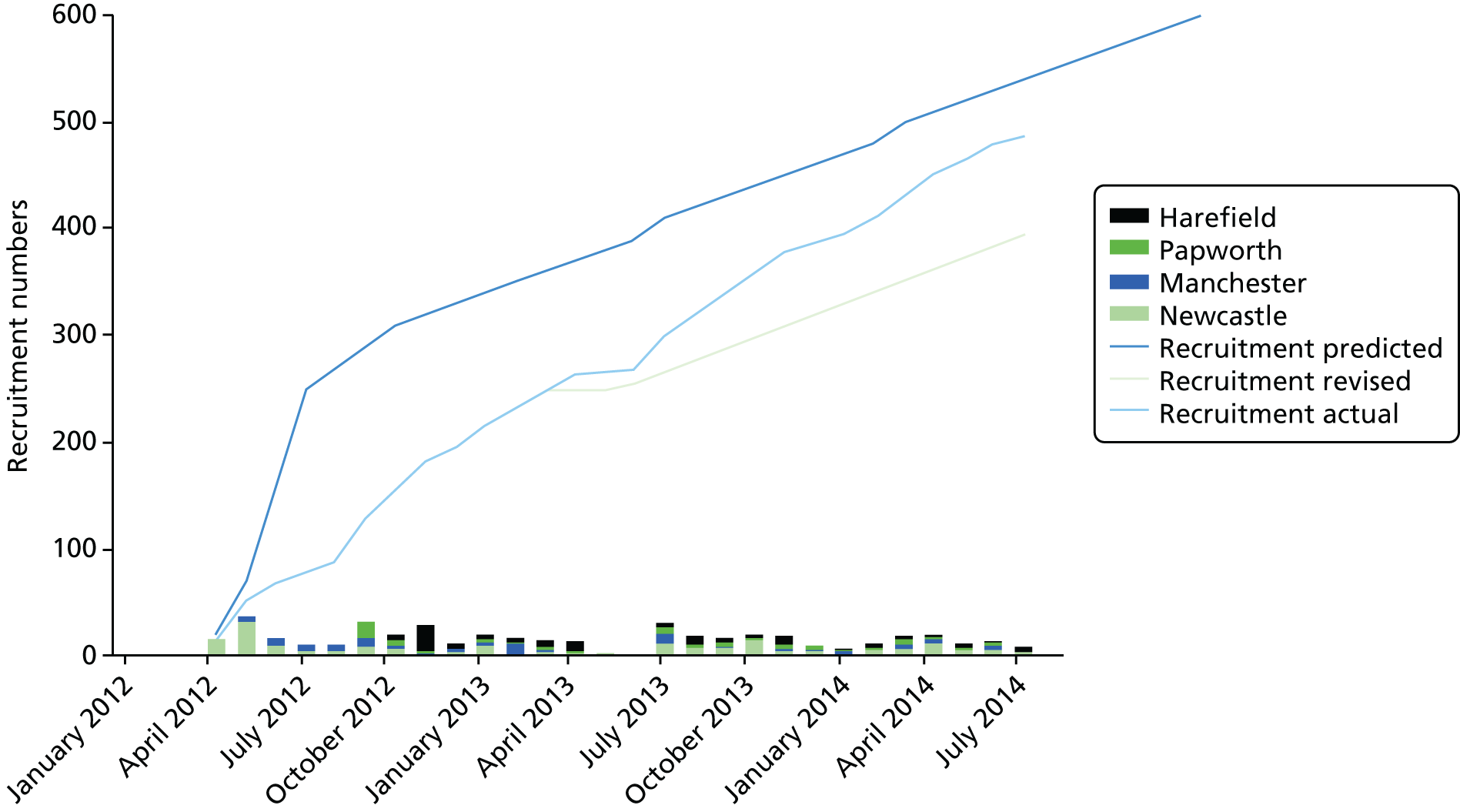
By the end of the study, 158 participants remained on the waiting list for transplant; 74 had died while waiting, before transplant had occurred, and 34 were excluded after transplant as they did not reconfirm their consent, died before giving consent or were erroneously included after the recruitment cut-off date.
A total of 202 participants were included in the two transplant arms of the study, 184 in the standard transplant arm [60.1% of the target recruitment of 306, 95% confidence interval (CI) 55.4% to 65.7%] and 18 in the EVLP transplant arm (17.6% of target recruitment of 102, 95% CI 10.8% to 26.4%). A total of 53 EVLP assessments were performed, leading to the 18 transplants, giving a conversion rate of 34.0% (95% CI 26.6% to 42.0%). The transplant activity in the participating sites is shown in Table 3. It is the small number in the EVLP transplant arm that drives the need to restrict the comparative analysis to the use of descriptive statistics. A Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) diagram showing study activity is shown in Figure 5.
| Centre | Number of transplants (% of total for type) | Number of EVLP assessments (% of total) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study group | Total | |||
| Standard | EVLP | |||
| Birmingham | 16 (8.7) | 1 (5.6) | 17 (8.4) | 6 (11.3) |
| Cambridge (Papworth) | 27 (14.7) | 2 (11.1) | 29 (14.4) | 4 (7.5) |
| London (Harefield) | 37 (20.0) | 2 (11.1) | 39 (19.3) | 9 (17.0) |
| Manchester | 22 (12.0) | 4 (22.2) | 26 (12.9) | 7 (13.2) |
| Newcastle | 82 (44.6) | 9 (50.0) | 91 (45.0) | 27 (60.0) |
| Total | 184 | 18 | 202 | 53 |
FIGURE 5.
The CONSORT diagram: withdrawals.
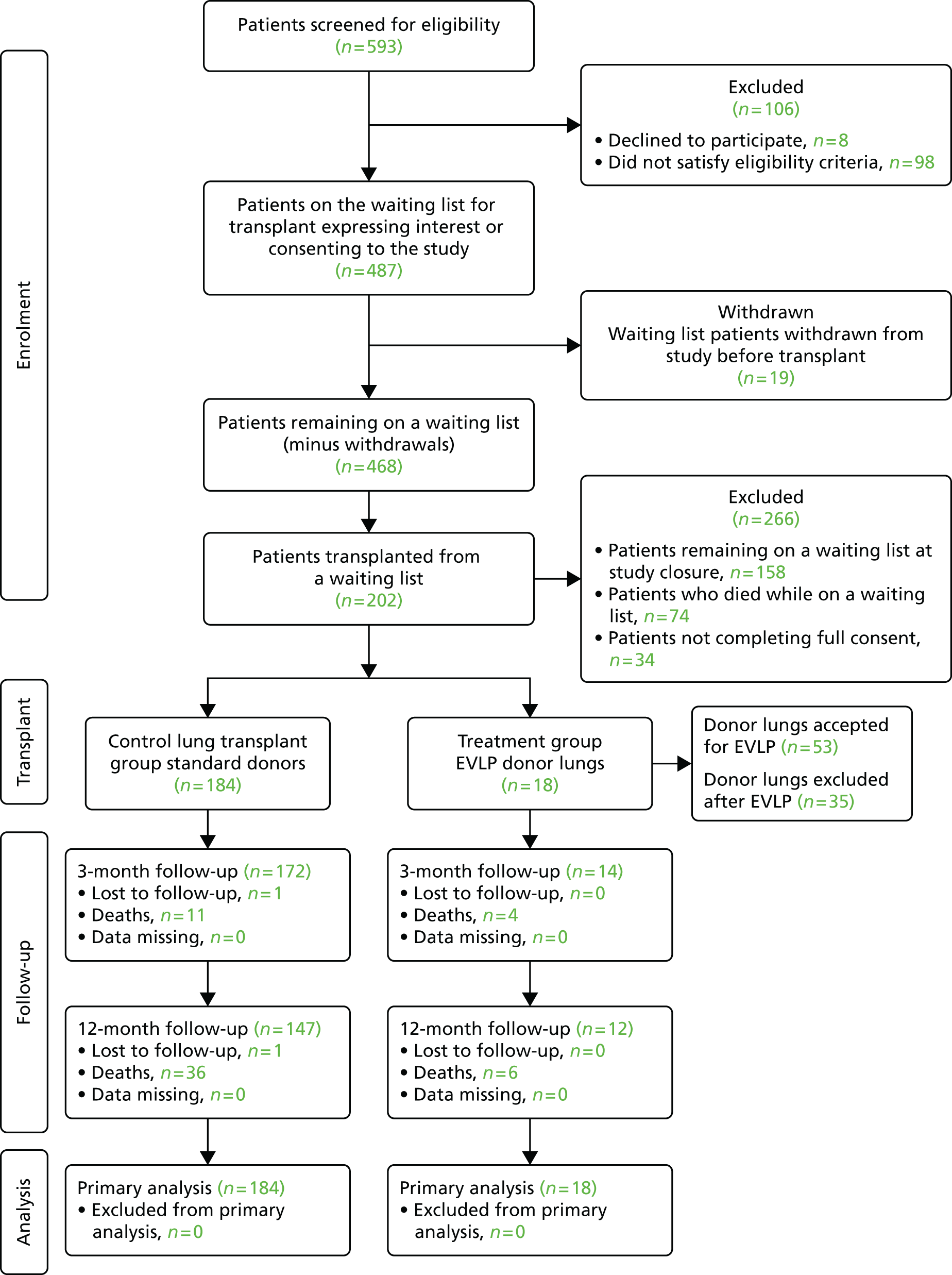
The main delay to commencing recruitment to the study resulted from obtaining NHS R&D approvals across the study sites, which equated to 31 centre-months lost.
Two groups of patients were approached: patients already on a transplant waiting list and patients added to the waiting list during the study. As a result, some patients signed an EOI form only, some signed both (an EOI form followed by a consent form during a subsequent routine visit to the transplant centre or on the day of transplant), and some signed only a consent form on the day of transplant, having received study information previously.
No patients requested to be withdrawn from the study after transplantation, and none was withdrawn by study staff on safety grounds. All withdrawals were due to changes in patients’ eligibility for lung transplantation or to issues with completion of all necessary consent documents.
Analysis groups
Patients were analysed in groups defined by the type of transplant received [i.e. standard (control) or EVLP (intervention)]. Allocation was not random, and it was not possible to switch between groups. All donors who provided lungs assessed by EVLP (n = 53) were included in the descriptive analyses described in Identifying clinical predictors of successful ex vivo lung perfusion reconditioning. Table 4 summarises the times at which the various data were collected for each patient.
| Study events and data collection | Time on waiting list | Day of transplant | Post-operation ITU stay | Post-operation inpatient stay | 1 month (visit 1) | 3 months (visit 2) | 6 months (visit 3) | 12 months (visit 4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Informed consent or EOI form | ✗ | |||||||
| Consent to continuea | ✗ | |||||||
| Donor data | ✗ | |||||||
| Recipient data | ✗ | ✗ | ||||||
| EVLP data (if applicable) | ✗ | |||||||
| ITU data/PGD scores | ✗ | ✗ | ||||||
| Chest radiographic data | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | |
| Blood profile | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ||
| Length of stay | ✗ | ✗ | ||||||
| Airway healing | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | |||
| Lung function | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | |||
| Rejection episodes data | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ||
| Infection episodes data | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ||||
| Hospital admissions data | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ||||
| Use of health services | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ||||
| Patient perceptions (qualitative interviews) | ✗ | ✗ | ||||||
| Quality of life (SF-36) | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | |||||
| Survival/cause of death | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | |||||
| AEs | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
Study population
Baseline patient characteristics
There are a number of donor-, recipient- and procedure-related variables that mean that lung transplant recipients constitute a heterogeneous group. The recipient or donor characteristics listed in Tables 5 and 6 have been identified from the ISHLT registry as those potentially influencing outcomes. Table 5 summarises characteristics of the lung transplant recipients, split according to the type of transplant. The percentage of recipients who were male and the median age were higher in the EVLP group {72.2% and 56 years [interquartile range (IQR) 46–59 years], respectively} than in the standard transplant group [57.6% and 51 years (IQR 38–58 years), respectively]. About half of the patients in each group had been diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or CF; interstitial lung disease (in the EVLP group) or a combination of interstitial lung disease and emphysema (in the standard group) constituted a further 40% of the diagnoses. The 18 EVLP recipients did possess indicators to suggest that they may have been a higher-risk group, such as significant secondary pulmonary hypertension and requirement for non-invasive ventilation prior to transplant. No lung allocation score is used in the UK and so Lung Allocation Scores or other indicators of clinical urgency were not routinely recorded and cannot be reported.
| Recipient characteristic | Study group | Total (N = 202) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EVLP (N = 18) | Standard (N = 184) | ||
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 13 (72.2) | 106 (57.6) | 119 (58.9) |
| Female | 5 (27.8) | 78 (42.4) | 83 (41.1) |
| Age (years) | |||
| n | 18 | 183 | 201 |
| Missing | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Median | 56 | 51 | 52 |
| IQR | 46–59 | 38–58 | 38–58 |
| Rangea | 20–64 | 18–70 | 18–70 |
| Diagnosis, n (%) | |||
| COPD | 5 (27.8) | 40 (21.7) | 45 (22.3) |
| CF | 4 (22.2) | 47 (25.5) | 51 (25.2) |
| Interstitial lung disease | 7 (38.9) | 47 (25.5) | 54 (26.7) |
| Emphysema | 0 (0) | 26 (14.1) | 26 (12.8) |
| Non-CF bronchiectasis | 1 (5.6) | 8 (4.3) | 9 (4.5) |
| Obliterative bronchiolitis | 0 (0) | 2 (1.1) | 2 (1.0) |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 1 (5.6) | 3 (1.6) | 4 (2.0) |
| Other | 0 (0) | 9 (4.9) | 9 (4.5) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 2 (1.1) | 2 (1.0) |
| Diabetes, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 4 (22.2) | 33 (18.1) | 37 (18.3) |
| No | 13 (72.2) | 142 (78.0) | 155 (76.7) |
| Missing | 1 (5.6) | 9 (3.9) | 10 (5.0) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||
| n | 17 | 182 | 199 |
| Missing | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Median | 21.6 | 23.8 | 23.7 |
| IQR | 18.4–26.3 | 20.5–26.5 | 20.4–26.5 |
| Rangea | 17.6–32.5 | 15.4–34.2 | 15.4–34.2 |
| FEV1 (l) | |||
| n | 15 | 176 | 191 |
| Missing | 3 | 8 | 11 |
| Median | 1.2 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| IQR | 0.7–1.9 | 0.6–1.4 | 0.6–1.5 |
| Rangea | 0.5–2.5 | 0.3–3.6 | 0.3–3.6 |
| FEV1 (%) | |||
| n | 15 | 171 | 186 |
| Missing | 3 | 13 | 16 |
| Median | 29 | 26 | 27 |
| IQR | 22–50 | 20–45 | 20–45 |
| Rangea | 15–67 | 11–105 | 11–105 |
| Type of transplant, n (%) | |||
| Single | 2 (11.1)b | 24 (13.0)c | 26 (13) |
| Bilateral | 16 (88.9) | 152 (82.6) | 168 (83) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 8 (4.4) | 8 (4) |
| Cardiopulmonary bypass use, n (%) | |||
| No | 2 (11.1) | 46 (25.0) | 48 (24) |
| Yes | 16 (88.9) | 116 (63.0) | 132 (65) |
| Not known | 0 (0) | 22 (12.0) | 22 (11) |
| Donor characteristics | Study group | Total (N = 202) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EVLP (N = 18) | Standard (N = 184) | ||
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 10 (55.6) | 86 (46.7) | 96 (47) |
| Female | 8 (44.4) | 96 (52.2) | 104 (52) |
| Missing | 0 | 2 (1.1) | 2 (1) |
| Age | |||
| n | 18 | 181 | 199 |
| Missing, n | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| Median (years) | 50.5 | 44 | 46 |
| IQR (years) | 47–54 | 35–54 | 35–54 |
| Rangea (years) | 22–61 | 10–68 | 10–68 |
| Donor type | |||
| n | 18 | 183 | 201 |
| DBD, n (%) | 13 (72.2) | 152 (82.6) | 165 (81) |
| DCD, n (%) | 5 (27.8) | 31 (16.9) | 36 (18) |
| Missing, n (%) | 0 | 1 (0.5) | 1 (1) |
| Side transplanted (n) | |||
| Left | 17 | 161 | 178 |
| Right | 17 | 165 | 182 |
| Total ischaemic time | |||
| n | |||
| Left | 11 | 136 | 147 |
| Right | 12 | 141 | 153 |
| Median (hours) | |||
| Left | 12.98 | 5.8 | 5.93 |
| Right | 13.26 | 5.45 | 5.6 |
| IQR (hours) | |||
| Left | 10.85–14.35 | 4.56–6.89 | 4.65–7.15 |
| Right | 10.35–14.49 | 4.43–6.62 | 4.5–6.95 |
| Rangea (hours) | |||
| Left | 7.92–19.13 | 1.12–14.22 | 1.12–19.13 |
| Right | 8.58–17.12 | 0.82–14.22 | 0.82–17.12 |
The percentage of recipients who were diabetic was similar in the EVLP (22.1%) and standard groups (18.1%), as were the median body mass index values, namely 21.6 kg/m2 (IQR 18.4–26.3 kg/m2) and 23.8 kg/m2 (IQR 20.5–26.5 kg/m2), respectively. The median FEV1 at baseline was 1.2 l (IQR 0.7–1.9 l) for the EVLP group and 0.9 l (IQR 0.6–1.4 l) for the standard group; the corresponding FEV1 percentage predicted was 29% (IQR 22–50%) in the EVLP group and 26% (IQR 20–44%) in the standard group. In both groups, > 80% of the lung transplants performed were bilateral. However, the observed percentage of transplants performed with the use of cardiopulmonary bypass was higher in the EVLP group than in the standard group (88.9% vs. 63.0%), although cardiopulmonary bypass status was missing for 12% of patients in the standard group.
The characteristics of the donors, again split between the EVLP and standard transplant groups, are shown in Table 6. The percentage of donors who were male was slightly higher in the EVLP group than in the standard group (55.6% vs. 46.7%) and donors in the former group were slightly older (median age 50.5 years and 44 years, respectively). DCD donor type was more common in the EVLP group (27.8% of donors) than in the standard group (16.9%). The numbers of left and right lungs were similar, reflecting – as indicated earlier – the high proportion of transplants that were bilateral. Within each transplant group, ischaemic times were similar for left and right donor lungs. However, total ischaemic times were much higher for EVLP transplants than for standard transplants, which reflects the nature of the procedure.
Compliance
Seventeen protocol violations were reported in 15 separate patients (7.4% of the total of 202 patients consented and transplanted). Five were major and were due to patients being transplanted with donor lungs that did not fully meet protocol criteria for transplant after EVLP assessment and reconditioning. In all these cases the decision to proceed to transplant was made by the supervising transplant surgeon on the basis of the balance of risks to the patient.
Twelve violations were minor, including approaching patients to give consent for retrospective data collection post standard transplant even though they had not returned an EOI form; failure to obtain full informed consent as the wrong consent form was signed; failure to obtain reconsent to continue on the night of transplant; and, on nine occasions, a > 24-hour delay in the submission of a SAE to the clinical trials unit. Seven of the protocol violations (all minor) were in standard transplant patients, whereas 10 (five major and five minor) were in EVLP transplant patients.
Serious adverse events
There were 42 SAEs affecting 38 patients (16 patients in Newcastle, four patients in London, four patients in Manchester, 11 patients in Cambridge and three patients in Birmingham). Fifteen (35.7%) of these SAEs (affecting 12 patients) occurred in EVLP transplant patients. Details of the SAEs reported are shown in Table 7.
| Participant ID | SAE details (in medical terms, diagnosis if possible) | Seriousness | Outcome | Type of donor organ (standard/EVLP) | Causality | Expectedness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAE001 | Primary diagnosis: interstitial lung disease | Serious | Death | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE002 | Readmission to ITU resulting from severe pneumonia. Rising PCO2 leading to the insertion of a Novalung® (Xenios, Heilbronn, Germany) | Serious, life-threatening | Condition deteriorating | EVLP | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE003 | Novalung® circuit thrombosed, so device removed | Serious, life-threatening | Death | EVLP | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE004 | Bilateral lung transplant for Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis. Poor oxygenation post-operatively requiring ECMO | Serious, life-threatening | Completely recovered | EVLP | Reasonable possibility that the event may have been caused by inclusion in the study | Expected |
| SAE005 | Multiorgan failure resulting from infection and septicaemia | Life-threatening | Death | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE006 | PGD | Serious, life-threatening | Death | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE007 | Bilateral lung transplant for CF. Severe hypotension and hypoxia post-cardiopulmonary bypass requiring ECMO | Life-threatening | Condition improving | EVLP | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE008 | Bilateral lung transplant for CF. Severe hypotension and hypoxia post bypass requiring ECMO support | Life-threatening. Prolonged inpatient hospitalisation | Completely recovered | EVLP | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE009 | Cardiac arrest resulting from air embolism after patient removed own central line | Life-threatening | Death | EVLP | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE010 | PGD requiring ECMO as a result of poor oxygenation | Involved or prolonged inpatient hospitalisation | Recovered with sequelae | EVLP | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE011 | Bleeding right pulmonary artery anastomosis | Not completed | Recovered with sequelae | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE012 | PGD requiring ECMO | Life-threatening | Condition improving | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE013 | Persistent air leak due to right main bronchus anastomotic dehiscence. Returned to theatre for refashioning of anastomosis on two occasions. Right pneumonectomy performed | Not completed | Condition improving | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE014 | Bilateral lung transplantation for pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in association with severe PH. Unable to wean from cardiopulmonary bypass; therefore, VA ECMO started | Life-threatening | Condition improving | EVLP | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE015 | VA ECMO commenced electively in view of patient underlying diagnosis | Not completed | Not completed | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE016 | Bilateral pulmonary emboli confirmed on CTPA | Life-threatening, prolonged inpatient hospitalisation | Condition improving | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE017 | Death: 1 day post standard lung transplant | Not completed | Death | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE018 | Right leg necrotising fasciitis. Caecal volvulus requiring right hemicolectomy | Not completed | Death | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE019 | Severe respiratory failure with hypercapnia requiring Novalung® support and retransplantation | Life-threatening, prolonged inpatient hospitalisation | Not completed | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE020 | Right pleural cavity infection ± air leak in the right pneumonectomy stump. Aspergillus spp. grown in pleural fluid | Not completed | Death | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE021 | Left bronchial anastomosis dehiscence | Prolonged inpatient hospitalisation | Condition still present and unchanged | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE022 | Multiorgan failure due to Pseudomonas spp. Pneumonia | Not completed | Death | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE023 | Severe RV failure post transplant, commenced ECMO. Returned to theatre and ECMO discontinued | Life-threatening | Condition improving | EVLP | Reasonable possibility that the event may have been caused by inclusion in the study | Expected |
| SAE024 | Commenced on ECMO because of severe graft dysfunction secondary to possible rejection | Not completed | Condition still present and unchanged | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE025 | VA ECMO switched to VV ECMO. Continued to deteriorate | Death | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A | |
| SAE026 | VA ECMO for early PGD | Life-threatening, prolonged inpatient hospitalisation | Condition still present and unchanged | EVLP | Reasonable possibility that the event may have been caused by inclusion in the study | Expected |
| SAE027 | Readmission to ITU because of increasing oxygen requirements | Recovered | Discharged from ITU on 17 December 2013 | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE028 | Readmitted to ITU because of respiratory failure | Recovered | Not completed | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE029 | Readmitted to ITU because of increase in respiratory support requirements | Recovered | Condition improving | EVLP | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE030 | Patient died due to persistent pneumonia and sepsis < 90 days following transplant after EVLP | Life-threatening | Death | EVLP | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE031 | Death following chest sepsis and respiratory arrest | Not completed | Death | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE032 | Cardiac arrest and severe PGD requiring VV ECMO | Prolonged inpatient hospitalisation | Condition improving | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE033 | Severe PGD commenced on ECMO | Life-threatening | Condition still present and unchanged | EVLP | Reasonable possibility that the event may have been caused by inclusion in the study | Expected |
| SAE034 | VV ECMO support started in theatre, now on 30 p.p.m. of nitric oxide | Life-threatening | Condition still present and unchanged | EVLP | Reasonable possibility that the event may have been caused by inclusion in the study | Expected |
| SAE035 | Right pneumonectomy because of lung necrosis, following bilateral lung transplantation | A prolonged inpatient hospitalisation; persistent or significant disability or incapacity; other significant medical event | Condition improving | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE036 | Death within 90 days of transplant; date of death, 3 April 2014 | Not completed | Death | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE037 | Mortality secondary to respiratory arrest following right lung (EVLP) transplantation | Not completed | Death | EVLP | Reasonable possibility that the event may have been caused by inclusion in the study | Expected |
| SAE038 | ECMO on 23 April 2014 following bilateral lung transplant | Not completed | Condition improving | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE039 | Interstitial lung disease; received single lung transplant on 10 June 2014 | Not completed | Death | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE040 | Gastrointestinal complications. Multiorgan failure. Death | Not completed | Death | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE041 | Persistent hypotension, distended abdomen, significant bowel management drainage, decreased white cell count, decreased platelets, heart rate irregular with runs of VT unresponsive to treatment. On CVVH | Not completed | Death | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
| SAE042 | Bilateral lung transplant for CF. Death within 90 days post transplant | Not completed | Death | Standard | No causality with inclusion in the study | N/A |
Of the 42 SAEs, 18 (42.9%) were a result of death within 90 days of transplant; 14 (77.8% of all fatal SAEs) of these were in standard transplant patients and four (22.2%) were in EVLP patients. Of the total of 42 SAEs, four of these events (9.5%) arising in four patients were judged to be possibly causally related to study procedures; all of these serious adverse reactions were initially considered by the site PI to be possibly unexpected AEs. However, after review by the chief investigator, it was decided that all were in fact events that could be expected to occur after lung transplantation, such as PGD or infection.
Activity in the EVLP arm was halted temporarily on 9 April 2013 for just over 3 months to allow an independent review of the early study outcomes as part of a due diligence process. Before this point, four out of eight transplant recipients in the EVLP arm required ECMO support post-operatively; following resumption of EVLP transplants with a revised protocol, 3 out of 10 transplant recipients required ECMO, but in all cases ECMO duration was limited, all patients were successfully weaned from ECMO, and all except one were successfully discharged from the ITU.
Outcomes analyses
The original intention was that the statistical analysis be conducted in a number of parts: first, a comparison of outcomes between recipients of standard and EVLP transplants to establish non-inferiority; and, second, modelling of the effect of EVLP transplants on the overall survival of patients accepted for lung transplantation in the UK, in order to assess the impact on the service. Furthermore, additional analyses were also to be undertaken to identify clinical predictors with respect to donor characteristics of successful EVLP reconditioning.
The early closure of the study and low numbers in the EVLP arm mean that the analysis methods originally described in the protocol are no longer appropriate. Consequently, the comparative analysis of standard and EVLP transplant groups, as well as the analysis of overall survival of patients awaiting transplantation, reported in Primary outcome analysis, are descriptive in nature and, as such, do not reflect the initial intention of testing for non-inferiority of EVLP to standard transplants.
Missing data
From clinical experience of this patient group, it had not been anticipated that there would be significant numbers of dropouts or loss to follow-up of patients with respect to the primary outcome measure. Loss to follow-up or missing data on the secondary outcome measures was assessed but, because of the low numbers in the EVLP group, no imputation was performed for any outcome data. However, a significant number of data were missing because they were not collected at the study sites. Most sites worked very hard to keep data collection as complete as possible, but in one site the proportion of missing data was > 20%. The missing data included, but were not limited to, SF-36 questionnaires, detail from outpatient follow-up visits and some information collected during the EVLP procedure.
Primary outcome analysis
Survival in the 12 months following transplantation
The primary outcome of survival in the first 12 months post transplantation was compared in the EVLP and standard transplant groups. Figure 6 shows the Kaplan–Meier plot of the survival (in days) during the first 12 months post transplantation, split by study group. This analysis takes account of censoring; specifically, one patient (in the standard arm) emigrated during the follow-up, and has been included in the analysis up to the time of the last visit (at 30 days post transplantation).
FIGURE 6.
Kaplan–Meier survival estimates post transplantation, by study group.
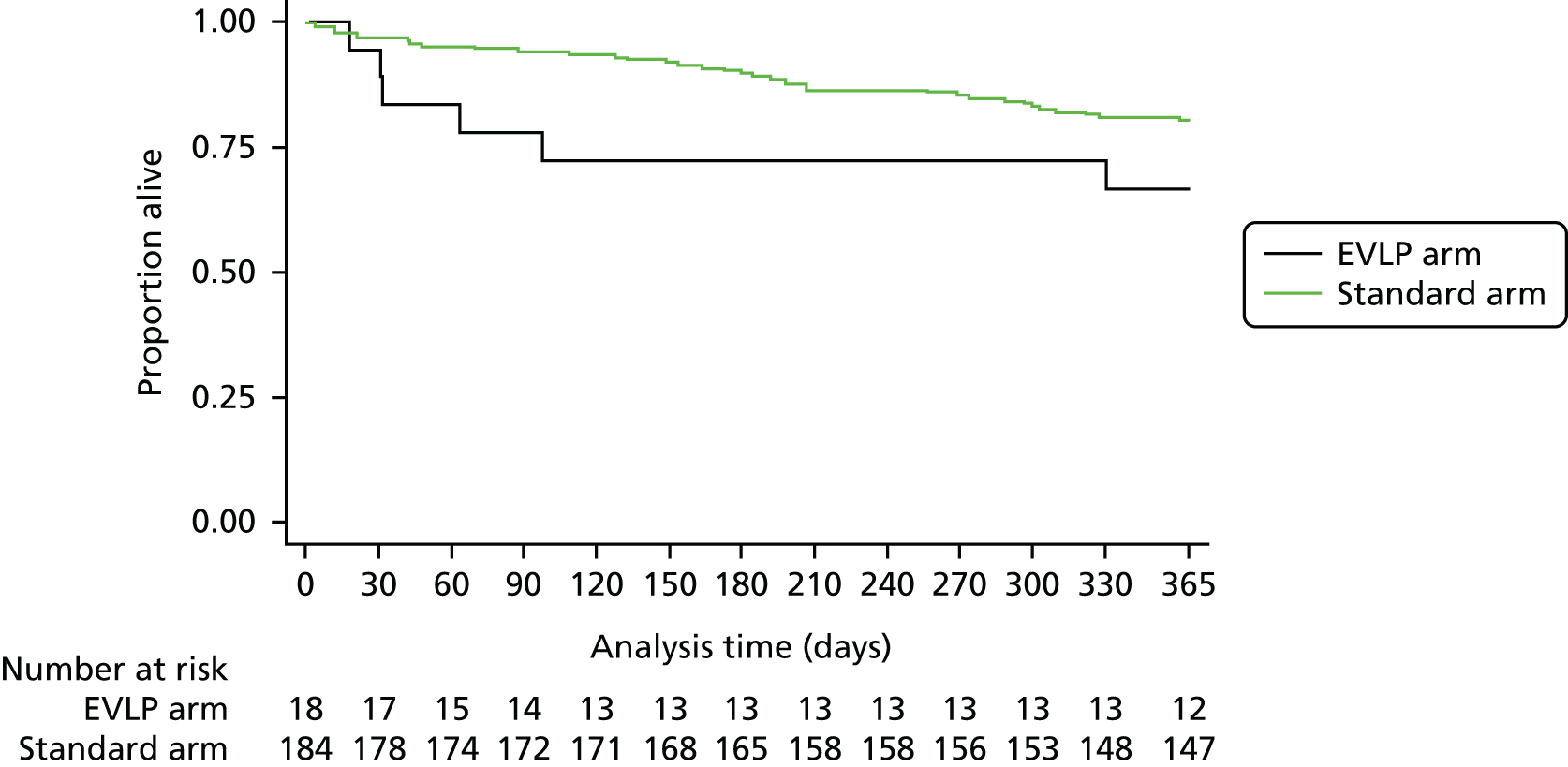
The numbers of patients who died, survived or were censored during the 12-month follow-up are shown in Table 8. The median follow-up was 365 days for both the EVLP and standard transplant groups.
| Study group | Died | Survived | Censored | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVLP | 6 | 12 | 0 | 18 |
| Hybrid protocol | 4 | 4 | 0 | 8 |
| Lund protocol | 2 | 8 | 0 | 10 |
| Standard | 36 | 147 | 1 | 184 |
| Total of standard and EVLP groups | 42 | 159 | 1 | 202 |
The Kaplan–Meier estimate of survival at 12 months was 0.67 (95% CI 0.40 to 0.83) for the EVLP arm and 0.80 (95% CI 0.74 to 0.85) for the standard arm. Based on Cox regression, the hazard ratio for all-cause mortality in the EVLP arm relative to the standard arm over the 12-month follow-up was 1.96 (95% CI 0.83 to 4.67). This equates to roughly a doubling of the risk of death in the EVLP arm relative to the standard arm, although with a wide CI that encompasses the possibility that mortality might be lower in the EVLP arm than in the standard arm. The width of this CI is influenced greatly by the small number of patients who received an EVLP transplant.
Of the 18 patients who received an EVLP transplant, eight received a transplant based on the hybrid protocol, and 10 received a transplant based on the Lund protocol (see Table 8). Survival was then assessed by considering the EVLP protocol groups separately, and Figure 7 shows the Kaplan–Meier plot of survival separately for patients in the standard, EVLP-Lund and EVLP-hybrid groups.
FIGURE 7.
Kaplan–Meier survival estimates post transplantation for the standard, EVLP-hybrid and EVLP-Lund study groups.
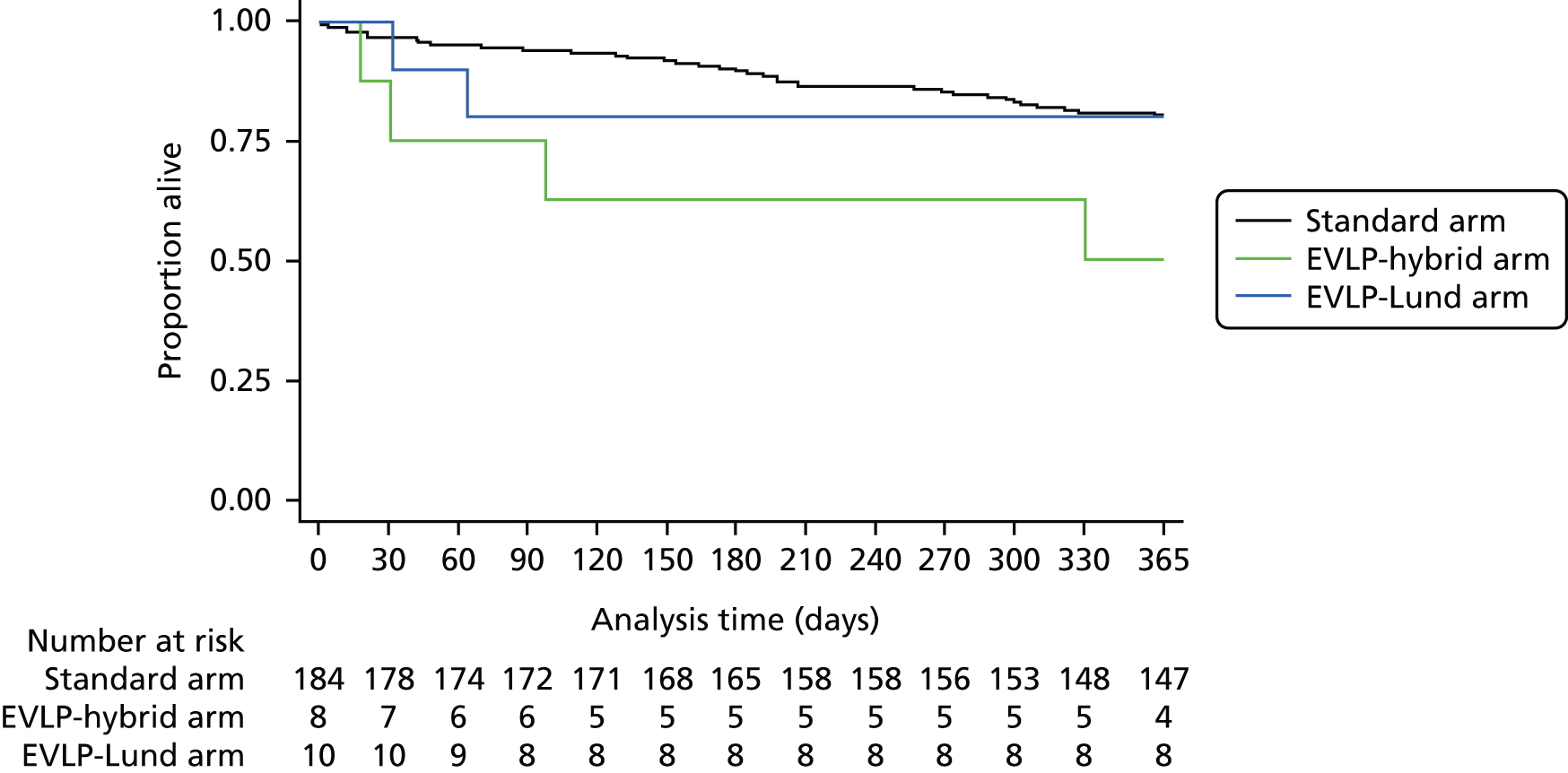
The Kaplan–Meier estimate of survival at 12 months was 0.80 (95% CI 0.41 to 0.95) for the Lund protocol patients and 0.50 (85% CI 0.15 to 0.77) for the hybrid protocol patients. Based on Cox regression, the hazard ratio for all-cause mortality in the EVLP-hybrid group relative to the EVLP-Lund group over the 12-month follow-up was 2.92 (95% CI 0.53 to 15.95). This wide CI reflects the small numbers of patients in these two EVLP protocol groups.
Secondary outcome measures
Survival at 30 and 90 days
Survival in the early post-operative period after lung transplantation is an important indicator of early complications and is widely used in audit and national and international registries of outcomes. The 30-day survival rates for the EVLP and standard transplant groups are shown in Table 9 and the 90-day survival rates in Table 10.
| Study group | Died | Survived | Censored | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVLP | 1 | 17 | 0 | 18 |
| Standard | 6 | 178 | 0 | 184 |
| Total | 7 | 195 | 0 | 202 |
| Study group | Died | Survived | Censored | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVLP | 4 | 14 | 0 | 18 |
| Standard | 11 | 172 | 1 | 184 |
| Total | 15 | 186 | 1 | 202 |
The Kaplan–Meier estimate of survival at 30 days is 0.94 (95% CI 0.67 to 0.99) for the EVLP arm and 0.97 (95% CI 0.93 to 0.98) for the standard arm. In other words, survival at 30 days was similar for the two transplant groups. The Kaplan–Meier estimate of survival at 90 days was 0.78 (95% CI 0.51 to 0.91) for the EVLP arm and 0.94 (95% CI 0.89 to 0.97) for the standard arm.
Primary graft dysfunction
Primary graft dysfunction is the clinical syndrome of chest radiographic changes and poor oxygenation that represents early acute injury to the transplanted lung. The PGD scores used in the study were as defined in the ISHLT consensus definition. 39 The distribution of the PGD score by study group, measured at baseline and 24, 48 and 72 hours after the transplant, is shown in Table 11. A score of 0 represents no evidence of PGD and a score of 3 represents the most severe form of PGD.
| Score | Time point | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 24 hours | 48 hours | 72 hours | |||||
| EVLP, n (%) | Standard, n (%) | EVLP, n (%) | Standard, n (%) | EVLP, n (%) | Standard, n (%) | EVLP, n (%) | Standard, n (%) | |
| Grade 0 | 1 (5.6) | 42 (26.4) | 1 (5.6) | 43 (27.4) | 1 (5.6) | 34 (22.5) | 1 (5.6) | 34 (23.9) |
| Grade 1 | 0 (0) | 27 (17.0) | 3 (16.7) | 43 (27.4) | 7 (38.9) | 51 (33.8) | 7 (38.9) | 52 (36.6) |
| Grade 2 | 1 (5.6) | 42 (26.4) | 6 (33.3) | 43 (27.4) | 3 (16.7) | 33 (21.9) | 5 (27.8) | 24 (16.9) |
| Grade 3 | 16 (88.9) | 48 (30.2) | 8 (44.4) | 28 (17.8) | 7 (38.9) | 33 (21.9) | 5 (27.8) | 32 (22.5) |
| Total | 18 | 159 | 18 | 157 | 18 | 151 | 18 | 142 |
The same information, but with the results for grades 0 and 1 combined, is shown in graph format in Figure 8. The percentage of patients with PGD grade 3 at baseline was much higher in the EVLP group than in the standard group (88.9% vs. 30.2%). However, this difference narrowed as time passed, with 27.8% of patients in the EVLP group and 22.5% of those receiving a standard transplant having PGD grade 3 at 72 hours after transplant. Nevertheless, the percentages of patients with grade 0 remained fairly static over time and were higher in the standard group than in the EVLP group (22.5–27.4% and 5.6%, respectively).
FIGURE 8.
Primary graft dysfunction score by trial arm and time since transplant.
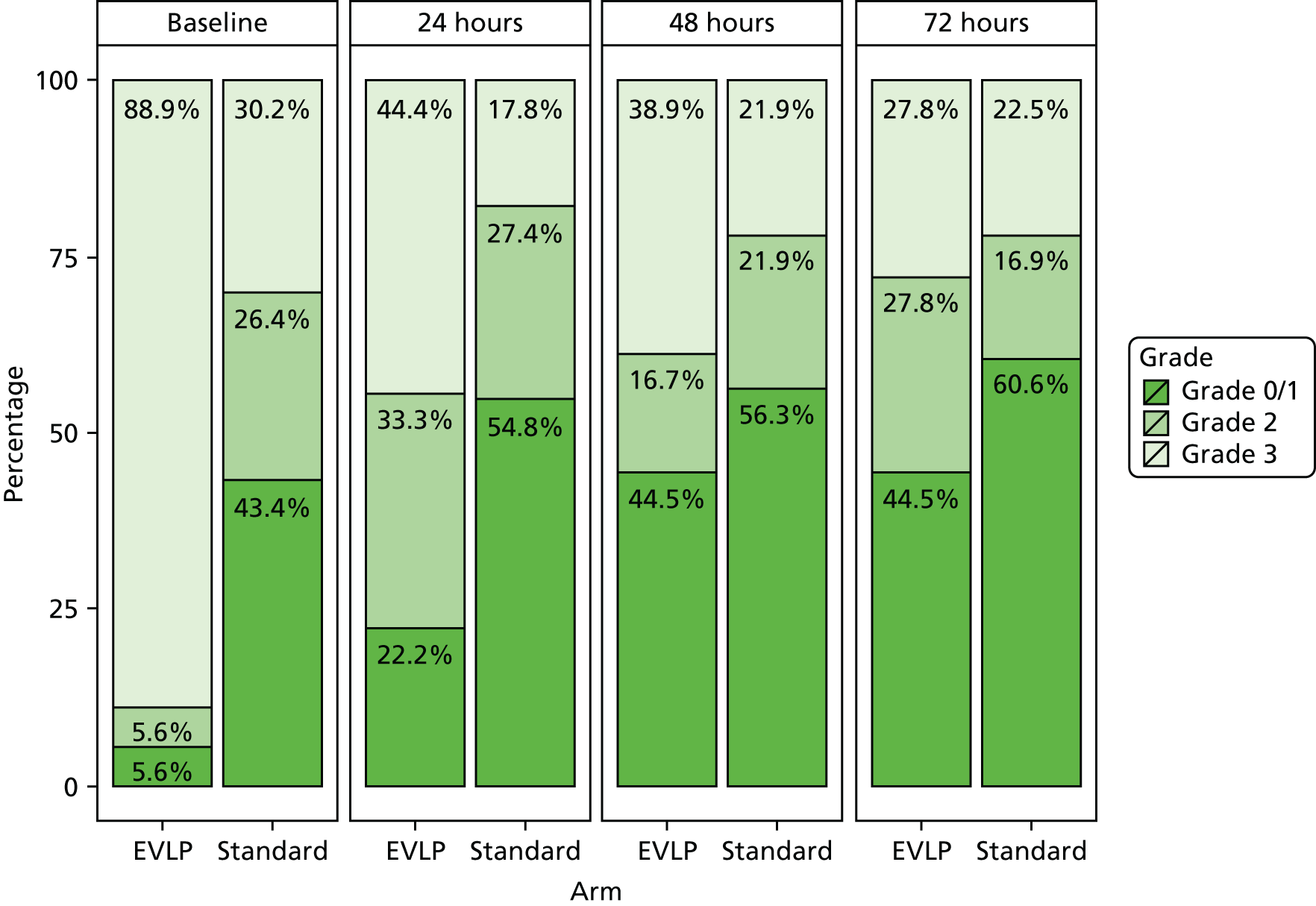
Early intensive therapy unit management and duration of hospital stay
Data on several key aspects of the ITU management and hospital stay were collected for all patients transplanted and are presented in Table 12. The duration of invasive ventilation tended to be longer for patients receiving an EVLP transplant (median 72 hours, IQR 38–624 hours) than for those receiving a standard transplant (median 38 hours, IQR 19–140 hours). Similarly, ITU stay was longer for EVLP patients (median 14.5 days, IQR 5.4–20.6 days) than for patients with a standard transplant (median 4.3 days, IQR 2.1–10.8 days). However, the overall length of hospital stay was similar for both groups of patients (median of 28 days in both groups) and, among those patients readmitted to ITU, length of stay in ITU was similar in both groups [median 6 days (IQR 3–6 days) in the EVLP arm and 8 days (IQR 3–20.5 days) in the standard arm].
| ITU management and hospital stay | Study group | Total (N = 202) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EVLP (N = 18) | Standard (N = 184) | ||
| Invasive ventilation | |||
| n | 18 | 174 | 192 |
| Median (hours) | 72 | 38 | 43 |
| IQR (hours) | 38–624 | 19–140 | 20–180.5 |
| Rangea (hours) | 8–2400 | 0–2208 | 0–2400 |
| ITU stay | |||
| n | 18 | 160 | 178 |
| Median (days) | 14.5 | 4.3 | 4.8 |
| IQR (days) | 5.4–20.6 | 2.1–10.8 | 2.6–15 |
| Rangea (days) | 1.7–98 | 0.4–100.6 | 0.4–100.6 |
| Hospital stay | |||
| n | 18 | 163 | 181 |
| Median (days) | 28 | 28 | 28 |
| IQR (days) | 21–46 | 18–43 | 18–44 |
| Rangea (days) | 16–100 | 2–99 | 2–100 |
| ITU readmission | |||
| n | 3 | 28 | 31 |
| Median (days) | 6 | 8 | 6 |
| IQR (days) | 3–6 | 3–20.5 | 3–18 |
| Rangea (days) | 3–6 | 1–80 | 1–80 |
Post-operative infection
The number of patients with at least one post-operative infection, both at baseline and during subsequent follow-up periods, is shown in Table 13. The associated percentages are displayed graphically in Figure 9. At baseline, just under half of patients in both the EVLP group and the standard group had at least one post-operative infection. In both groups, the percentage of patients with at least one post-operative infection dropped subsequently, as shown in Figure 6. This percentage tended to be lower in the EVLP group than in the standard group. However, inferences are limited by the small numbers of patients with infections in the EVLP group.
| Category | Time period | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline, n (%) | Baseline–1 month, n (%) | 1–3 months, n (%) | 3–6 months, n (%) | 6–12 months, n (%) | ||||||
| EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | |
| Number of patients with at least one episode | 7 (46.7) | 81 (45.5) | 2 (15.4) | 37 (23.9) | 2 (15.4) | 38 (21.5) | 3 (23.1) | 38 (24.5) | 2 (18.2) | 39 (29.1) |
| Number at risk | 18 | 184 | 18 | 184 | 17 | 178 | 14 | 172 | 13 | 165 |
FIGURE 9.
Percentage of patients with at least one post-operative infection, at baseline and during subsequent periods, by study group. Note that the number at risk is based on those at risk at the start of the relevant period.

The number of episodes and number of organisms involved in specific post-operative infections are detailed in Table 14. The most common organisms involved were Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus, Escherichia coli and Candida species. Owing to small numbers, it is difficult to compare any differences in the spectra of infections in the EVLP and standard groups.
| Organism | Time period | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline, n (%) | Baseline–1 month, n (%) | 1–3 months, n (%) | 3–6 months, n (%) | 6–12 months, n (%) | ||||||
| EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | |
| Pseudomonas | 5 (29.4) | 19 (12.8) | 1 (33.3) | 6 (15.0) | 1 (50.0) | 4 (7.7) | 0 (0) | 5 (12.2) | 0 (0) | 5 (11.1) |
| Staphylococcus | 4 (23.5) | 27 (18.1) | 0 (0) | 6 (15.0) | 0 (0) | 3 (5.8) | 0 (0) | 2 (4.9) | 0 (0) | 2 (4.4) |
| Coliforms | 0 (0) | 7 (4.7) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Escherichia coli | 1 (5.9) | 11 (7.4) | 1 (33.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.9) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.4) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.2) |
| Clostridium difficile | 0 (0) | 4 (2.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Klebsiella | 0 (0) | 5 (3.4) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.5) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.9) | 2 (50.0) | 2 (4.9) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.2) |
| Haemophilus | 1 (5.9) | 5 (3.4) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Aspergillus | 0 (0) | 5 (3.4) | 0 (0) | 2 (5.0) | 0 (0) | 3 (5.8) | 0 (0) | 2 (4.9) | 1 (25.0) | 5 (11.1) |
| Candida | 1 (5.9) | 14 (9.4) | 0 (0) | 2 (5.0) | 0 (0) | 3 (5.8) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.2) |
| Influenza virus | 1 (5.9) | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (4.4) |
| Adenovirus | 0 (0) | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Rhinovirus | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (5.8) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (25.0) | 0 (0) |
| Herpesvirus | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.4) | 0 (0) | 3 (6.7) |
| Streptococcus | 0 (0) | 2 (1.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Mycobacterium | 0 (0) | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Scedosporium | 0 (0) | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Stenotrophomonas | 1 (5.9) | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (4.4) |
| Other specified | 3 (17.6) | 34 (22.8) | 1 (33.3) | 12 (30.0) | 0 (0) | 21 (40.4) | 1 (25.0) | 14 (34.1) | 1 (25.0) | 10 (22.2) |
| Organism not specified | 0 (0) | 11 (7.4) | 0 (0) | 8 (20.0) | 1 (50.0) | 13 (25.0) | 1 (25.0) | 14 (34.1) | 1 (25.0) | 13 (28.9) |
| Total number of organisms | 17 | 149 | 3 | 40 | 2 | 52 | 4 | 41 | 4 | 45 |
| Total number of episodes | 16 | 144 | 3 | 38 | 2 | 52 | 4 | 41 | 4 | 44 |
It is recognised that ischaemic injury to the donor lung could adversely affect the bronchus and lead to bronchial complications. It was therefore important to consider if there was any difference in rates of anastomotic complications between the study groups. In Table 15, the numbers of patients with anastomotic complications are presented by study group and time since transplant. None of the patients in the EVLP group had such complications at any of the follow-up times. In the standard group, the percentage of patients with these complications varied between 4.4% and 9.6% over the follow-up period.
| Category | Time period | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline–1 month, n (%) | 1–3 months, n (%) | 3–6 months, n (%) | 6–12 months, n (%) | |||||
| EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | |
| Number of patients with anastomotic complications | 0 (0) | 12 (6.7) | 0 (0) | 7 (4.4) | 0 (0) | 12 (8.0) | 0 (0) | 14 (9.6) |
| Total | 18 | 179 | 14 | 160 | 13 | 150 | 12 | 146 |
| Number at risk | 18 | 184 | 17 | 178 | 14 | 172 | 13 | 165 |
The Couraud Classification of anastomotic healing provides a means to quantify the degree of healing that may be an indicator of low-level ischaemic injury. 40 These scores are presented numerically by study group and time since transplant in Table 16, and as percentages in graphical format in Figure 10. Among both EVLP and standard transplant patients, the percentage with grade 1 healing tended to increase over the period of the follow-up, from around 40% between baseline and 1 month to just over 80% between 6 and 12 months. Over the same period, the percentage of patients with grade 2 healing decreased, from around 50% between baseline and 1 month to roughly 16% between 6 and 12 months.
| Score | Time period | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline–1 month, n (%) | 1–3 months, n (%) | 3–6 months, n (%) | 6–12 months, n (%) | |||||
| EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | |
| Grade 1 | 4 (36.4) | 38 (41.3) | 2 (25.0) | 51 (47.2) | 6 (85.7) | 68 (68.7) | 5 (83.3) | 67 (82.7) |
| Grade 2A | 5 (45.5) | 30 (32.6) | 6 (75.0) | 39 (36.1) | 1 (14.3) | 24 (24.2) | 1 (16.7) | 12 (14.8) |
| Grade 2B | 1 (9.1) | 17 (18.5) | 0 (0) | 13 (12.0) | 0 (0) | 2 (2.0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.2) |
| Grade 3A | 1 (9.1) | 4 (4.3) | 0 (0) | 4 (3.7) | 0 (0) | 5 (5.1) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.2) |
| Grade 3B | 0 (0) | 3 (3.3) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.9) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Total | 11 | 92 | 8 | 108 | 7 | 99 | 6 | 81 |
| Number at risk | 18 | 184 | 17 | 178 | 14 | 172 | 13 | 165 |
FIGURE 10.
Anastomotic healing among patients (based on the Couraud Classification), by study group and time since transplant.
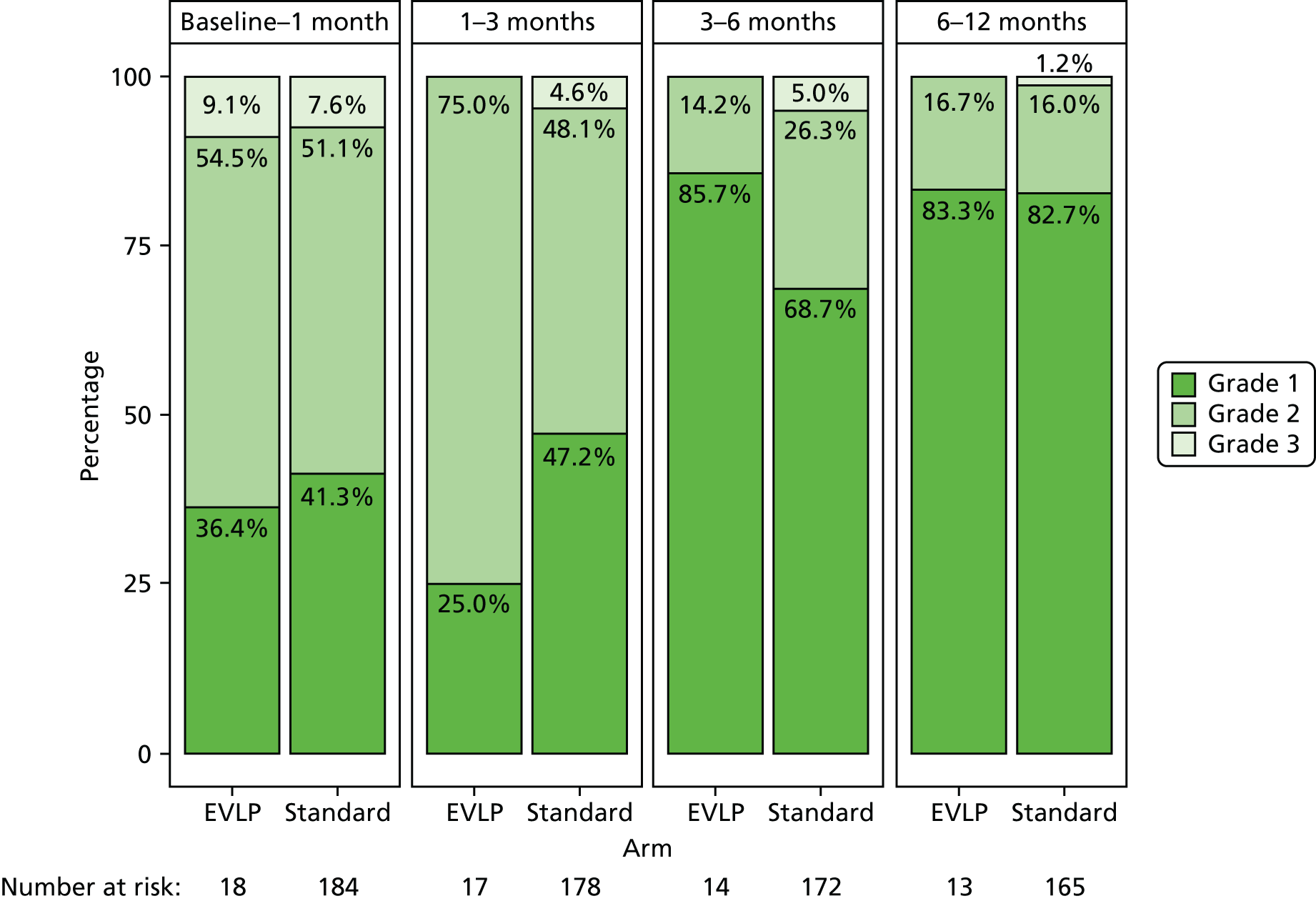
Lung function measurements
Measurement of FEV1 in both absolute volume in litres and as a percentage of the patient’s predicted values based on age, sex, height and measurement of forced vital capacity (FVC) in litres is routinely performed as part of post-lung transplant follow-up. This information is presented in Table 17 and also displayed in box plots in Figures 11–13. Each of these measures tended to increase with increasing length of follow-up. In addition, median values for the EVLP and standard transplant groups were generally similar.
| Lung function parameter | Time point | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 month | 3 months | 6 months | 12 months | |||||
| EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | |
| Number at risk | 17 | 178 | 14 | 172 | 13 | 165 | 12 | 147 |
| FEV1 | ||||||||
| na | 10 | 124 | 13 | 150 | 13 | 149 | 11 | 129 |
| Median (l) | 2.26 | 2.07 | 2.26 | 2.29 | 2.53 | 2.38 | 2.82 | 2.44 |
| IQR (l) | 1.87–3.15 | 1.68–2.60 | 1.89–2.68 | 1.79–2.70 | 2.23–3.65 | 1.85–2.83 | 2.12–3.37 | 1.95–2.93 |
| Rangeb (l) | 1.54–3.89 | 0.77–3.85 | 1.17–4.46 | 0.80–4.53 | 1.53–4.83 | 0.74–4.75 | 1.88–4.30 | 0.78–4.90 |
| FEV1 | ||||||||
| na | 9 | 111 | 12 | 138 | 13 | 129 | 9 | 116 |
| Median (% predicted) | 58 | 69 | 71 | 71 | 85 | 78 | 93 | 77.5 |
| IQR (% predicted) | 45–74 | 55–81 | 51–84 | 57–87 | 65–106 | 63–91 | 62–97 | 65.5–91.5 |
| Rangeb (% predicted) | 44–97 | 25–100 | 34–131 | 29–135 | 44–142 | 23–143 | 51–99 | 30–143 |
| FVC | ||||||||
| na | 10 | 123 | 13 | 150 | 12 | 149 | 11 | 128 |
| Median (l) | 2.70 | 2.49 | 2.80 | 2.70 | 3.23 | 3.03 | 3.35 | 3.53 |
| IQR (l) | 2.60–3.15 | 1.91–3.08 | 2.48–3.71 | 2.25–3.27 | 2.67–4.28 | 2.41–3.60 | 2.66–3.89 | 2.75–4.34 |
| Rangeb (l) | 1.90–4.10 | 1.16–4.80 | 1.82–4.53 | 0.92–5.35 | 1.82–5.88 | 0.85–5.84 | 1.98–5.56 | 1.14–5.96 |
FIGURE 11.
Box plot of FEV1 by time since transplant.
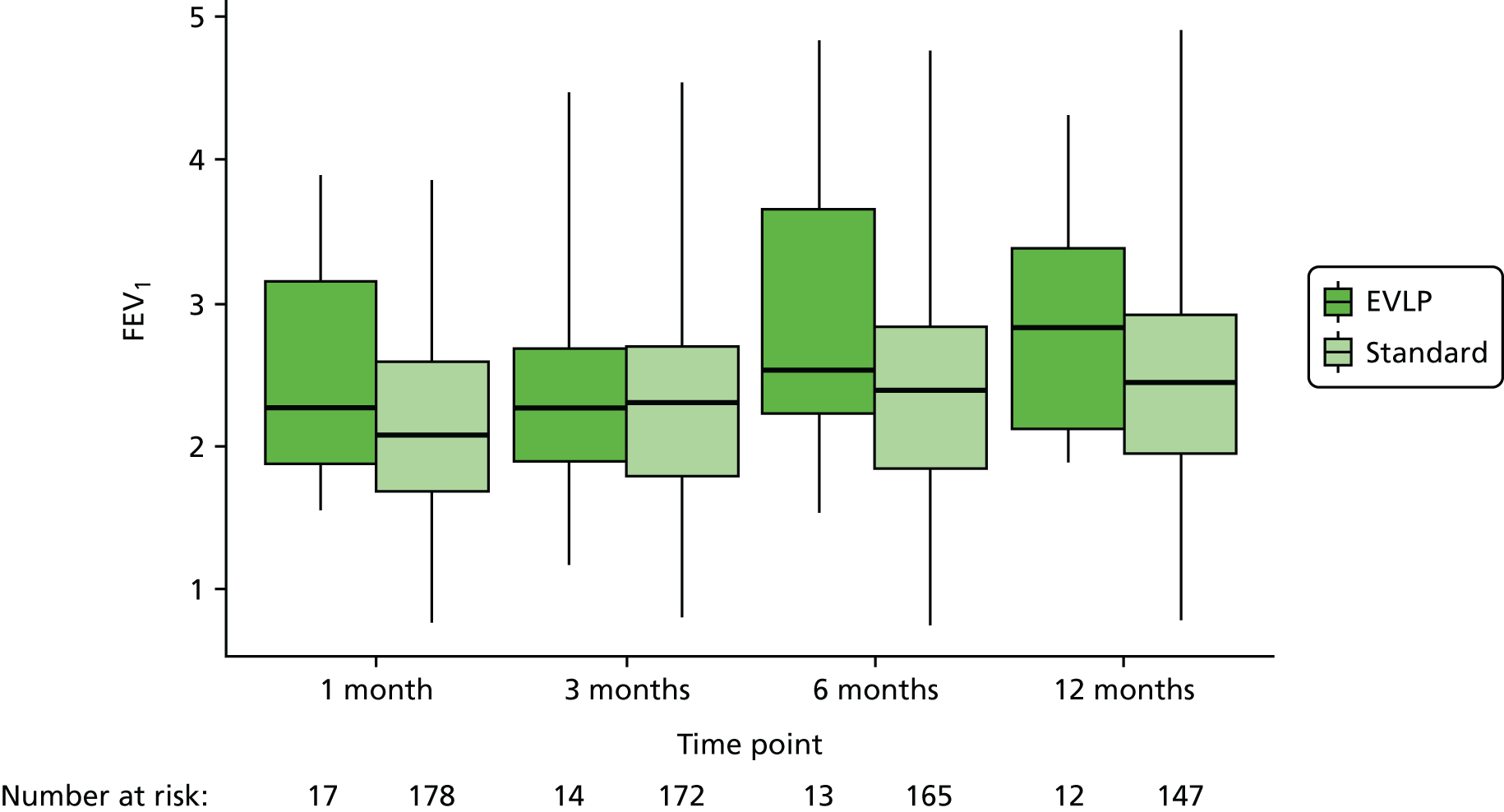
FIGURE 12.
Box plot of FEV1% by time since transplant.
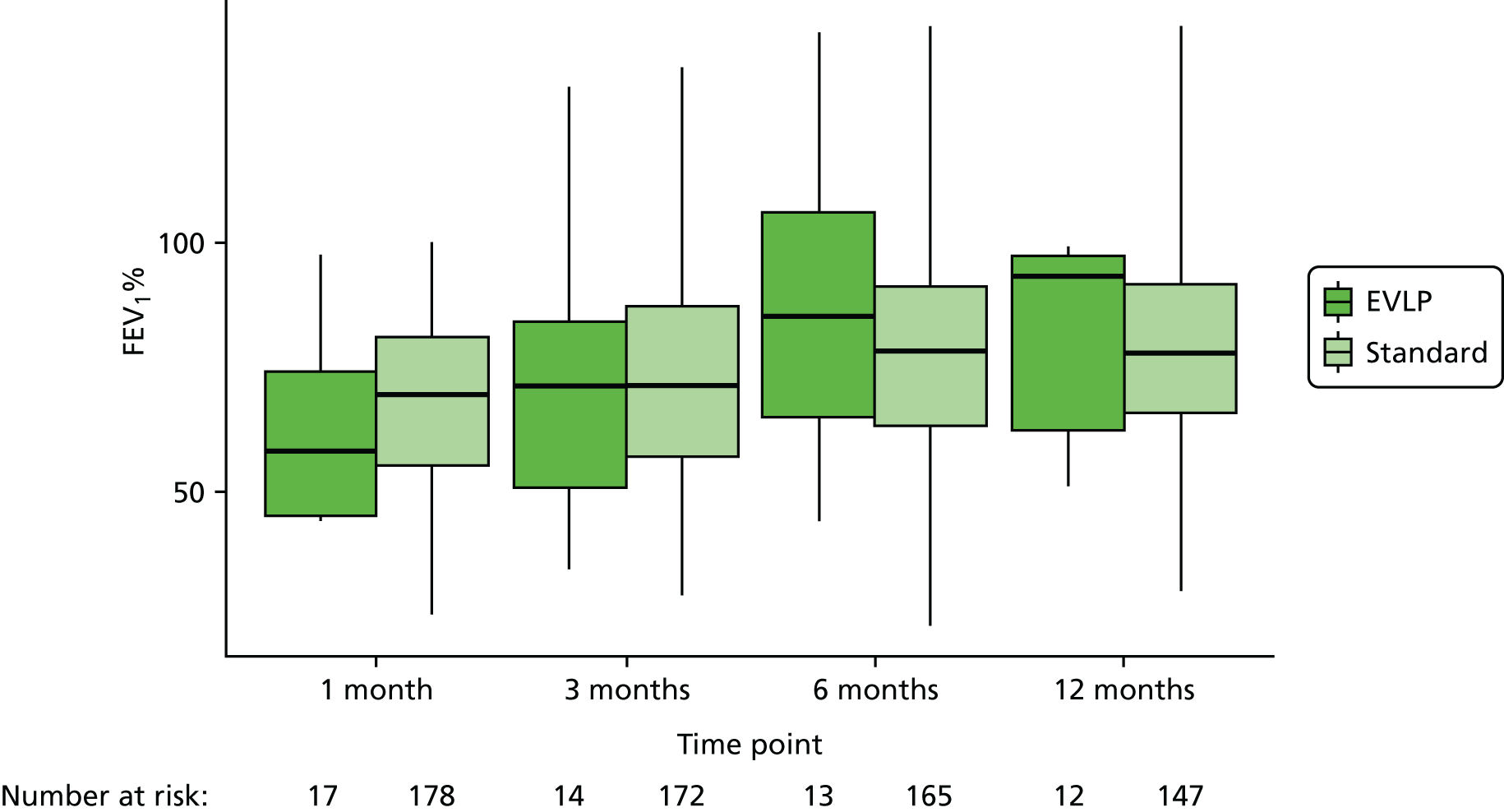
FIGURE 13.
Box plot of FVC by time since transplant.
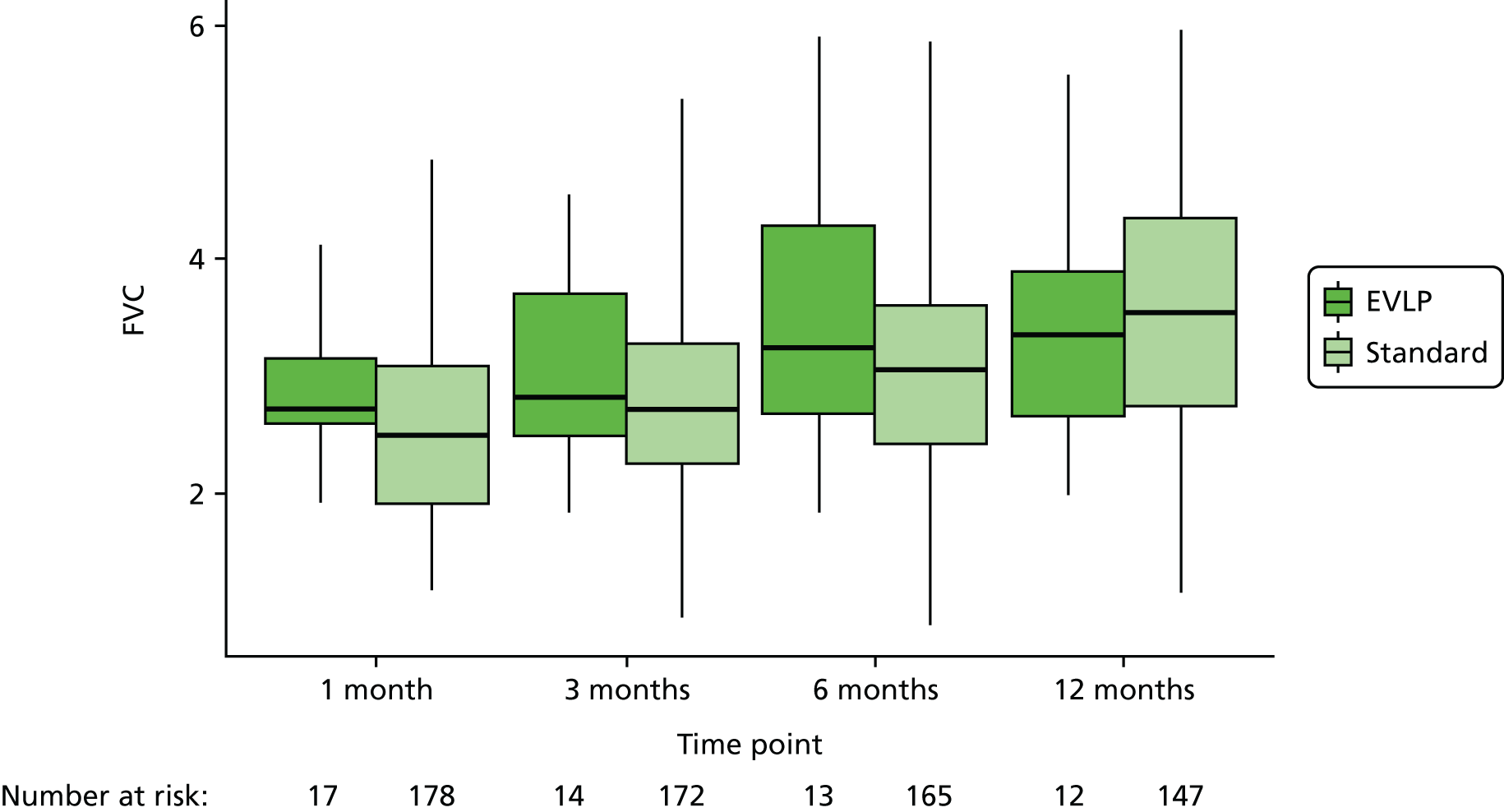
Abnormalities on chest radiographs
The number of patients with abnormalities on chest radiographs, both at baseline and at subsequent follow-up visits over the 12 months after transplant, is shown in Table 18. The associated percentages are also displayed graphically in Figure 14. These percentages were lower at 6 and 12 months than at earlier times. There is also some suggestion that abnormalities were slightly less common in the EVLP group than in the standard group, although inferences are limited because of the small numbers of EVLP patients with abnormalities.
| Category | Time point | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline, n (%) | 1 month, n (%) | 3 months, n (%) | 6 months, n (%) | 12 months, n (%) | ||||||
| EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | |
| Number of patients with abnormality on chest radiographs | 7 (46.7) | 105 (61.8) | 7 (53.8) | 96 (60.0) | 7 (58.3) | 66 (42.9) | 2 (18.2) | 48 (33.3) | 2 (22.2) | 28 (24.6) |
| Total | 15 | 170 | 13 | 160 | 12 | 154 | 11 | 144 | 9 | 114 |
| Number at risk | 18 | 184 | 17 | 178 | 14 | 172 | 13 | 165 | 12 | 147 |
FIGURE 14.
Percentage of patients with abnormalities on chest radiographs, by study group and time since transplant.
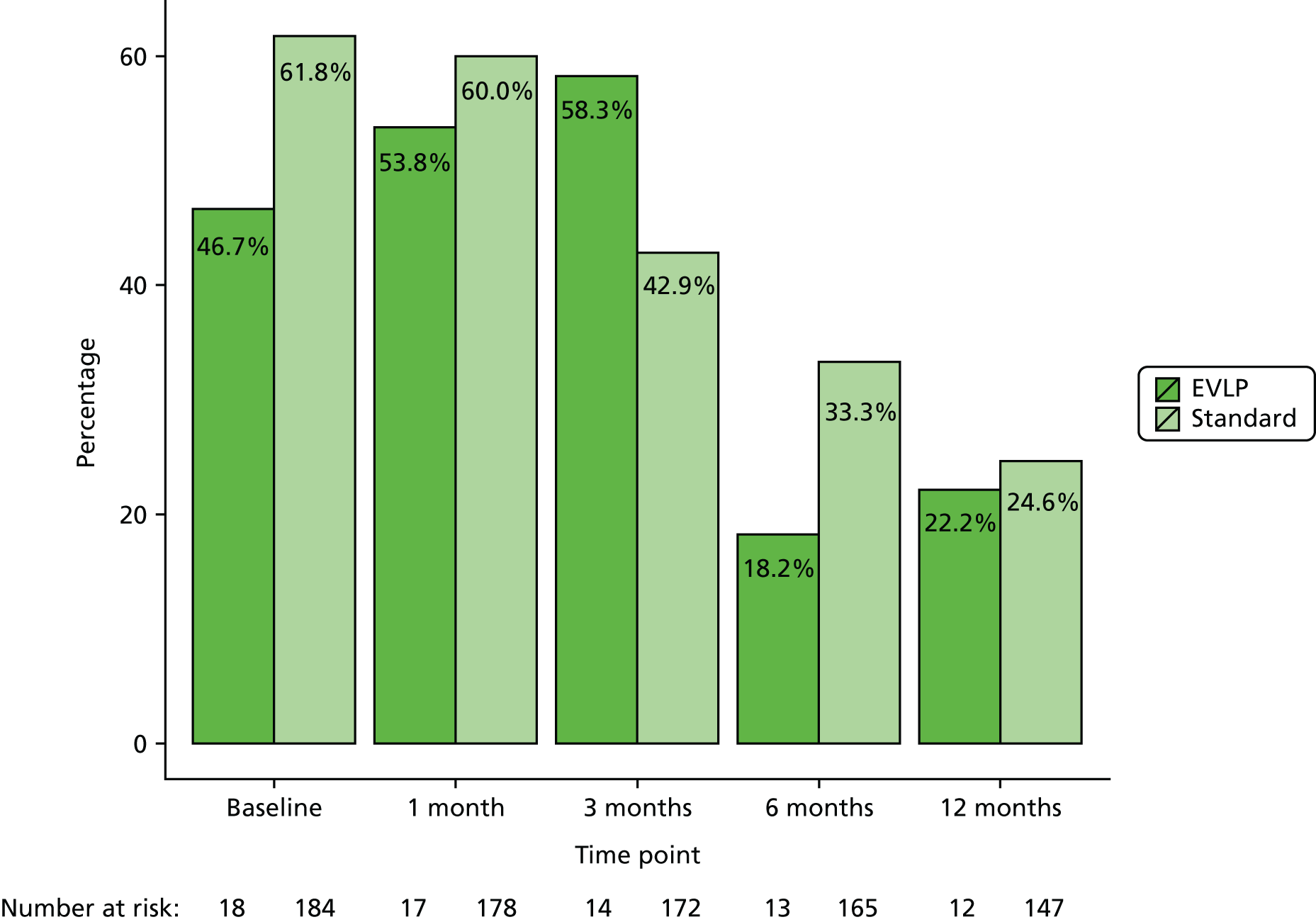
The nature of the specific abnormalities on chest radiographs is shown in Table 19. Overall, effusion was the most common abnormality, followed by pneumothorax, consolidation, atelectasis and shadowing. Owing to the small numbers in EVLP group, it is not possible to compare the spectra of abnormalities between the EVLP and standard groups.
| Type of abnormality | Time point | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline, n (%) | 1 month, n (%) | 3 months, n (%) | 6 months, n (%) | 12 months, n (%) | ||||||
| EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | |
| Pneumothorax | 0 (0) | 21 (15.9) | 1 (8.3) | 12 (9.3) | 0 (0) | 6 (9.0) | 0 (0) | 3 (6.7) | 0 (0) | 2 (6.9) |
| Effusion | 3 (37.5) | 55 (41.7) | 4 (33.3) | 57 (44.2) | 4 (50.0) | 29 (43.3) | 1 (100.0) | 15 (33.3) | 1 (50.0) | 7 (24.1) |
| Consolidation | 3 (37.5) | 20 (15.2) | 3 (25.0) | 22 (17.1) | 0 (0) | 3 (4.5) | 0 (0) | 4 (8.9) | 0 (0) | 3 (10.3) |
| Atelectasis | 1 (12.5) | 16 (12.1) | 2 (16.7) | 17 (13.2) | 3 (37.5) | 9 (13.4) | 0 (0) | 8 (17.8) | 1 (50.0) | 7 (24.1) |
| Collection | 0 (0) | 5 (3.8) | 1 (8.3) | 4 (3.1) | 0 (0) | 2 (3.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Shadowing | 0 (0) | 13 (9.8) | 1 (8.3) | 16 (12.4) | 1 (12.5) | 12 (17.9) | 0 (0) | 11 (24.4) | 0 (0) | 5 (17.2) |
| Elevated hemidiaphragm | 1 (12.5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4 (6.0) | 0 (0) | 3 (6.7) | 0 (0) | 1 (3.4) |
| No valid description | 0 (0) | 2 (1.5) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.8) | 0 (0) | 2 (3.0) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.2) | 0 (0) | 4 (13.8) |
| Total number of abnormalities | 8 | 132 | 12 | 129 | 8 | 67 | 1 | 45 | 2 | 29 |
The number of episodes of allograft alloimmune injury was collected in both study groups. Data on acute vascular rejection by ISHLT score, presence of antibody-mediated rejection and lymphocytic bronchiolitis are presented in Table 20 as numbers of rejection episodes by rejection type, study group and time period. Overall, these episodes were less frequent > 3 months after transplant than at earlier times. This decrease was particularly notable for A2+ episodes. The percentage of patients with at least one rejection episode was generally similar for the EVLP and standard groups.
| Category | Time period | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline–1 month, n (%) | 1–3 months, n (%) | 3–6 months, n (%) | 6–12 months, n (%) | |||||
| EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | EVLP | Standard | |
| A1 | 0 (0) | 11 (22.9) | 1 (16.7) | 13 (26.5) | 0 (0) | 5 (19.2) | 0 (0) | 12 (57.1) |
| A2+ | 4 (100.0) | 30 (62.5) | 4 (66.7) | 25 (51.0) | 1 (50.0) | 11 (42.3) | 1 (50.0) | 8 (38.1) |
| Antibody-mediated rejection | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Clinical rejection without biopsy | 0 (0) | 1 (2.1) | 0 (0) | 2 (4.1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Lymphocytic bronchiolitis | 0 (0) | 1 (2.1) | 0 (0) | 2 (4.1) | 0 (0) | 1 (3.8) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Not classified | 0 (0) | 5 (10.4) | 1 (16.7) | 6 (12.2) | 1 (50.0) | 9 (34.6) | 1 (50.0) | 1 (4.8) |
| Total number of episodes | 4 | 48 | 6 | 49 | 2 | 26 | 2 | 21 |
| Number of patients with at least one rejection episodea | 4 (22.2) | 48 (26.1) | 6 (35.3) | 46 (27.0) | 2 (14.3) | 26 (15.1) | 2 (15.4) | 20 (12.1) |
| Number of patients at riskb | 18 | 184 | 17 | 178 | 14 | 172 | 13 | 165 |
Short Form questionnaire-36 items health-related quality-of-life measure
The assessment of HRQoL in the DEVELOP-UK study was done using a well-validated questionnaire, the SF-36. The SF-36 is a measure of general health that generates eight dimensions and two summary scores from 36 different questions. 46 In order to do so, each one of the 36 questions of the survey relates to a different pre-coded numeric value. In order to interpret the SF-36 data, the raw scores should be translated into a value from 0 (lowest or worst possible level of HRQoL) to 100 (highest or best possible level of HRQoL). These translated scores are then used to calculate the mean for each one of the following eight domains: physical functioning, role limitations due to physical health, bodily pain, general health perceptions, vitality, social functioning, role limitations due to emotional problems and general mental health. From these eight concepts, two summary measures of norm-based mental component score (MCS) and physical component score (PCS), with a mean of 50 and a standard deviation (SD) of 10 in a general population, can be constructed from all the emotionally and physically relevant items, respectively. 47 The higher the value of the summary scores the higher the level of functionality of the patient.
Short Form questionnaire-36 items data analysis
The SF-36 questionnaires were completed while the recipients were still on the waiting list, as well as at 3 and 12 months post transplant, and their mean scores were converted into health-state utilities using the SF-6D algorithm48 described in Chapter 4. In the SF-36 data analysis, the mean (SD) and median (IQR) score for each of the eight domain scores were estimated for each one of the two study groups and for each time point. The SF-36 data were also used to estimate the mean, SD, median and IQR for MCS and PCS scores by study group. No hypothesis testing or modelling was undertaken and no imputation was performed other than that which forms part of the standard scoring system for the SF-36.
The SF-36 data, available at each time point of the study, as well as the number of participants with missing data for both the standard and EVLP trial arms, are summarised in Table 21. A significant number of participants did not complete the SF-36 at each of the three time points identified in the study protocol. The absolute number of patients for whom SF-36 data were collected at different stages of the study is shown in Table 22.
| Time point | Study group | Total, n (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EVLP, n (%)a | Standard, n (%) | ||
| Waiting list | 8 (38.1) | 67 (40.1) | 75 (39.9) |
| 3 months post transplant | 7 (33.3) | 52 (31.1) | 59 (31.4) |
| 12 months post transplant | 6 (28.6) | 48 (28.7) | 54 (28.7) |
| Total number of measurements | 21 | 167 | 188 |
| Number of patients with no SF-36 data | 6 | 83 | 89 |
| Category | Time point | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 3 months | 12 months | Baseline and 3 months | Baseline and 12 months | 3 and 12 months | Baseline, 3 and 12 months | |
| EVLP | |||||||
| Number of patients (%)a | 8 (44.4) | 7 (50.0) | 6 (50.0) | 4 (28.6) | 2 (16.7) | 4 (33.3) | 1 (8.3) |
| Number at risk | 18 | 14 | 12 | 14 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Standard | |||||||
| Number of patients (%) | 67 (36.4) | 52 (30.2) | 48 (32.7) | 31 (18.0) | 27 (18.4) | 26 (17.7) | 18 (12.2) |
| Number at risk | 184 | 172 | 147 | 172 | 147 | 147 | 147 |
| Total | |||||||
| Number of patients (%) | 75 (37.1) | 59 (31.7) | 54 (34.0) | 35 (18.8) | 29 (18.2) | 30 (18.9) | 19 (11.9) |
| Number at risk | 202 | 186 | 159 | 186 | 159 | 159 | 159 |
The detailed scores of the SF-36 questionnaires are presented in Tables 23 and 24. The mean, SD, median, IQR and range of the eight domain scores and the two summary scores, respectively, at each data collection point for each of the two transplant procedures are presented. These two tables also report the number of responses at each time point, together with the number of patients at risk (i.e. the number that would have been eligible to complete the SF-36).
| Domain | Study group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | EVLP | |||||
| Baseline (n = 67) | 3 months (n = 52) | 12 months (n = 48) | Baseline (n = 8) | 3 months (n = 7) | 12 months (n = 6) | |
| Number at risk | 184 | 172 | 147 | 18 | 14 | 12 |
| Bodily pain | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 46.68 (38.21–55.55) | 49.10 (40.63–55.55) | 55.55 (46.68–62.00) | 53.53 (46.68–62.00) | 51.51 (51.51–62.00) | 62.00 (55.55–62.00) |
| 95% CI | 42.61 to 48.36 | 45.35 to 51.00 | 48.55 to 54.85 | 43.02 to 61.22 | 42.29 to 61.89 | 56.36 to 63.35 |
| General health | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 23.71 (21.33–30.84) | 48.43 (38.92–55.56) | 48.43 (42.02–55.56) | 28.46 (22.52–29.65) | 57.94 (50.81–62.70) | 55.56 (54.61–55.56) |
| 95% CI | 24.41 to 28.25 | 43.87 to 49.67 | 45.19 to 51.28 | 22.95 to 32.19 | 52.62 to 62.60 | 50.53 to 62.02 |
| General mental health | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 45.64 (37.79–53.48) | 53.48 (44.33–58.72) | 53.48 (45.64–58.72) | 44.33 (41.71–49.56) | 58.72 (53.48–61.33) | 60.03 (53.48–63.95) |
| 95% CI | 42.06 to 47.33 | 48.38 to 54.07 | 50.81 to 55.40 | 39.18 to 50.13 | 54.35 to 61.59 | 48.95 to 65.87 |
| Physical functioning | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 23.09 (19.26–26.92) | 46.06 (37.45–51.80) | 46.06 (34.58–53.71) | 24.05 (22.14–31.71) | 53.71 (46.06–57.54) | 48.93 (46.06–55.63) |
| 95% CI | 23.57 to 27.18 | 40.55 to 46.71 | 40.65 to 47.25 | 20.91 to 31.97 | 46.72 to 57.42 | 31.41 to 60.71 |
| Role limitations owing to emotional health | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 38.76 (28.31–56.17) | 56.17 (35.28–56.17) | 56.17 (43.98–56.17) | 40.50 (35.28–54.43) | 56.17 (49.20–56.17) | 54.43 (49.20–56.17) |
| 95% CI | 36.46 to 43.66 | 42.30 to 49.82 | 45.66 to 52.02 | 30.87 to 52.75 | 49.64 to 57.72 | 36.34 to 62.07 |
| Role limitations owing to physical health | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 25.72 (21.23–32.46) | 43.68 (33.58–52.66) | 47.05 (35.83–54.91) | 30.21 (25.72–39.20) | 57.16 (41.44–57.16) | 49.30 (41.44–57.16) |
| 95% CI | 25.87 to 29.79 | 39.06 to 45.37 | 41.79 to 48.01 | 24.62 to 40.29 | 42.65 to 58.19 | 31.79 to 60.07 |
| Social functioning | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 27.26 (22.25–37.29) | 52.33 (37.29–57.34) | 47.31 (39.80–57.34) | 37.29 (24.76–39.80) | 57.34 (52.33–57.34) | 52.33 (47.31–57.34) |
| 95% CI | 27.83 to 33.73 | 43.24 to 50.04 | 44.77 to 50.48 | 25.00 to 40.80 | 50.83 to 58.12 | 33.87 to 62.43 |
| Vitality | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 31.80 (28.83–40.72) | 55.57 (40.72–61.51) | 52.60 (46.66–58.54) | 36.26 (34.77–42.20) | 55.57 (46.66–61.51) | 60.03 (55.57–70.42) |
| 95% CI | 32.29 to 36.37 | 48.25 to 55.23 | 49.67 to 55.28 | 31.29 to 44.94 | 48.16 to 63.83 | 41.45 to 73.65 |
| Time and category | Number at risk | Number of patients measured in group | Minimum | Maximum | Median | IQR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | |||||||
| EVLP | 18 | ||||||
| SF-36 MCS | 8 | 31.49 | 57.42 | 43.46 | 41.49–47.31 | 37.96 to 50.40 | |
| SF-36 PCS | 8 | 22.70 | 45.68 | 29.50 | 24.98–37.19 | 24.55 to 38.38 | |
| Standard | 184 | ||||||
| SF-36 MCS | 67 | 18.93 | 69.36 | 40.96 | 33.73–54.05 | 40.52 to 46.40 | |
| SF-36 PCS | 67 | 13.19 | 51.12 | 27.61 | 22.30–30.94 | 25.39 to 29.02 | |
| 3 months | |||||||
| EVLP | 14 | ||||||
| SF-36 MCS | 7 | 50.05 | 59.45 | 58.18 | 57.30–59.43 | 54.21 to 60.25 | |
| SF-36 PCS | 7 | 41.16 | 59.50 | 48.68 | 47.17–59.19 | 44.92 to 57.60 | |
| Standard | 172 | ||||||
| SF-36 MCS | 52 | 23.58 | 65.62 | 55.70 | 42.4–60.08 | 47.73 to 54.35 | |
| SF-36 PCS | 52 | 25.82 | 59.45 | 45.47 | 38.36–50.07 | 41.22 to 46.26 | |
| 12 months | |||||||
| EVLP | 12 | ||||||
| SF-36 MCS | 6 | 33.32 | 62.80 | 58.96 | 53.06–62.19 | 43.19 to 66.57 | |
| SF-36 PCS | 6 | 34.56 | 59.91 | 52.41 | 46.39–56.37 | 40.94 to 59.74 | |
| Standard | 147 | ||||||
| SF-36 MCS | 48 | 33.79 | 68.47 | 54.92 | 45.79–59.51 | 50.24 to 55.42 | |
| SF-36 PCS | 48 | 24.22 | 60.40 | 47.69 | 36.18–54.08 | 42.47 to 48.27 | |
The results show a general increase in the mean scores of the eight SF-36 domains from baseline to 12 months post transplant (see Table 23). The two domains that show the biggest increase in their scores are general health and vitality. Furthermore, although the physical functioning, role limitations owing to physical health and social functioning domains appear to show the same increase after 3 and 12 months from the day of the surgery in the standard arm of the study, they appear to increase at 3 months and then decrease at 12 months for the EVLP arm. The data are, however, too few for the relevance of this change to be sensibly interpreted. Similarly, the same pattern is seen for the general mental health and role limitations owing to emotional health dimensions. For the bodily pain domain there was a slight drop, on average, at 3 months and then an increase at 12 months for the EVLP arm. Nevertheless, the fact that few data are available for these three domains means that further interpretation must be done with caution.
The values of both the SF-36 summary measures, namely MCS and PCS, increase after transplant no matter which transplant procedure was performed. These data are presented in Table 24, and graphically in the box plots in Figures 15 and 16. In other words, the HRQoL of the patients improves throughout the follow-up of the lung recipients. In the standard procedure, the mean MCS score of the lung recipients increases from 43.5 at baseline to 51.0 at 3 months post transplant and 52.8 at 12 months post transplant, whereas the mean PCS score increases from 27.2 at baseline to 43.7 and 45.4 at 3 and 12 months, respectively. As far as the EVLP group is concerned, the mean MCS score changes from 44.2 at baseline to 57.2 at 3 months post transplant and 54.9 at 12 months post transplant, whereas the mean PCS score increases from 31.5 to 51.3 at 3 months after the transplant and drops slightly to 50.3 at 12 months’ follow-up. This slight decrease in the mean 12-month MCS and PCS scores in the EVLP arm of the study is consistent with the decrease in the scores for most of the eight domains at this time point. As mentioned above, any results regarding the effectiveness of the EVLP based on these scores given would not be reliable because of the very limited number of data available.
FIGURE 15.
Box plot of SF-36 MCS scores, by study group and time point.
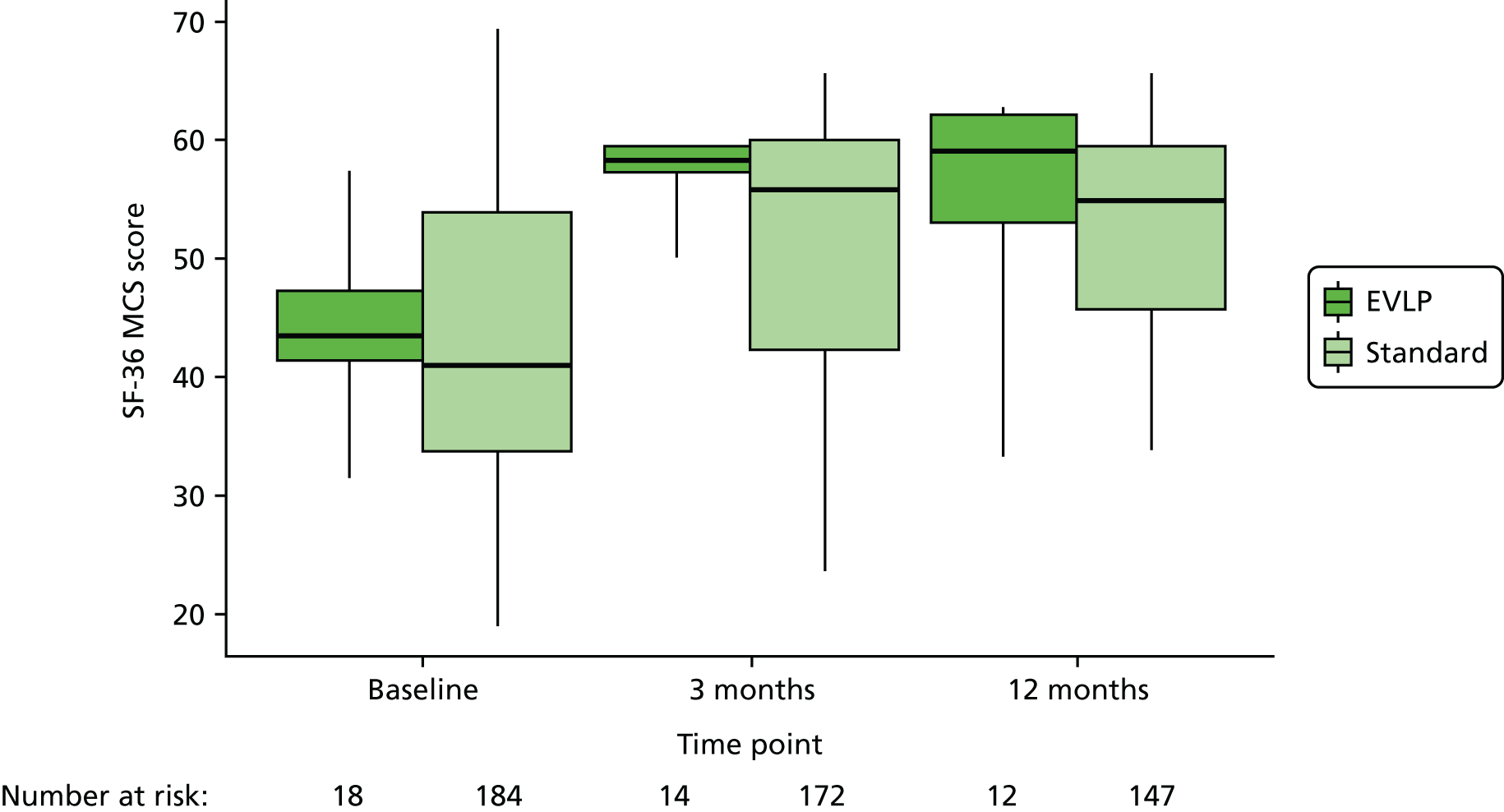
FIGURE 16.
Box plot of SF-36 PCS scores, by study group and time point.
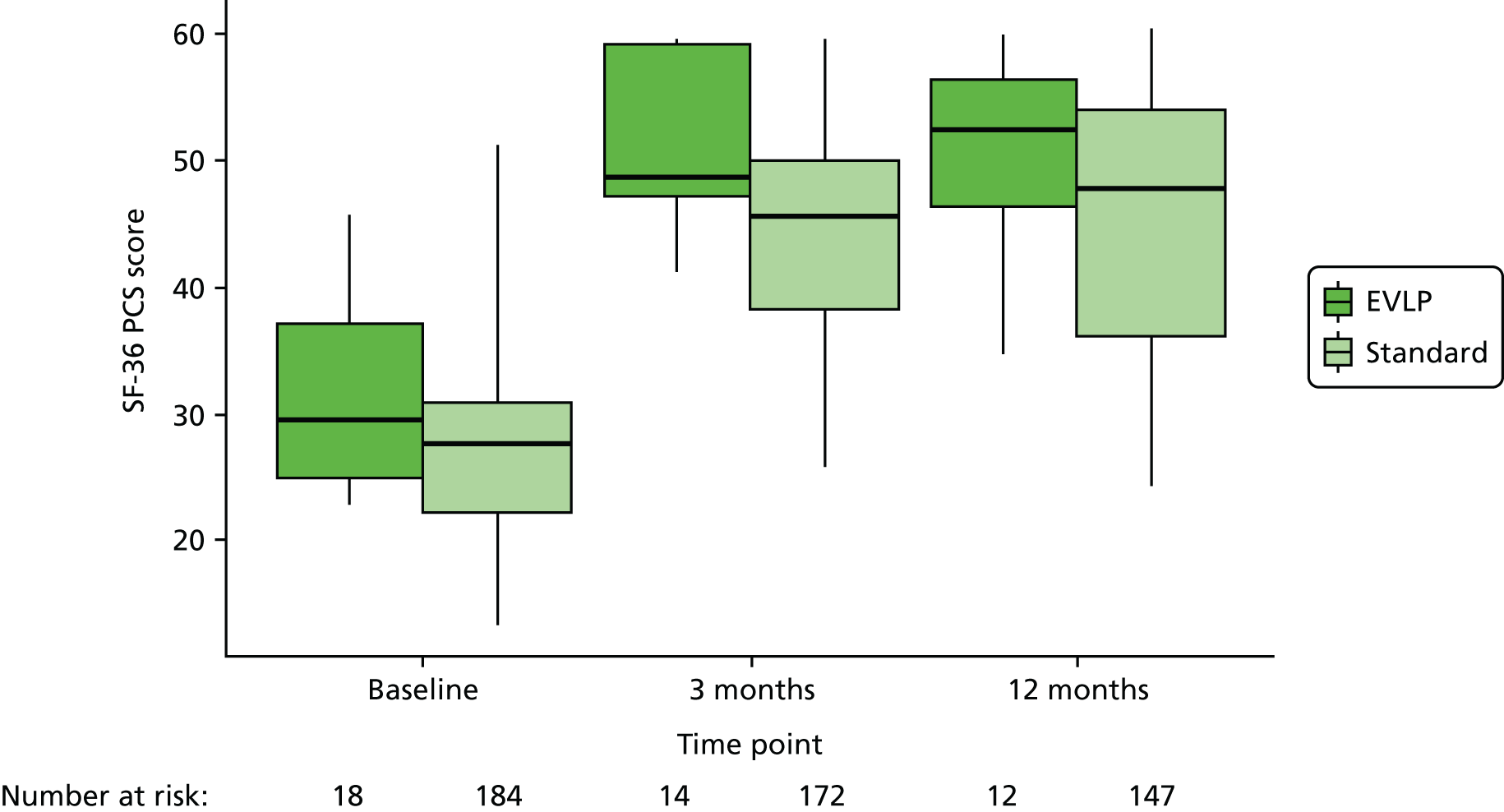
Examining the effect of ex vivo lung perfusion on the overall survival of patients awaiting transplantation
To capture the effects that an increased availability of donor organs due to EVLP might have on the survival of patients awaiting lung transplantation, waiting time in each of the two treatment groups was compared, and then waiting time in each group was compared with survival of those remaining on the waiting list. Waiting time is defined as the time from the date the participant is placed on the waiting list until the date transplant is performed. The waiting times until transplantation in the two study groups is shown in Table 25.
| Transplant type | Waiting time (days) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Minimum | Maximum | |
| Standard (n = 184) | 307 | 348 | 197 | 95–373 | 6 | 2143 |
| EVLP (n = 18) | 178 | 156 | 142 | 60–199 | 9 | 551 |
| Total (N = 202) | 296 | 337 | 184 | 93–367 | 6 | 2143 |
The median waiting time for standard transplant was 197 days (IQR 95–373 days), whereas the median waiting time for a transplant using an EVLP donor was 142 days (IQR 60–199 days), as shown in Table 25. There was a median difference of 55 days between transplant groups, showing a reduction in waiting time if having a transplant using an EVLP-assessed donor organ. This is also illustrated by Figure 17, which shows a maximum waiting time of 551 days for transplant using a EVLP donor compared with a maximum waiting time of 2143 days for a standard transplant. A log-rank test for difference in waiting times between transplant type using the Kaplan–Meier estimates gave a p-value of 0.042, which shows a significant difference in waiting times between the two groups. However, these findings should be interpreted with caution, in view of the small numbers of patients in the EVLP group.
FIGURE 17.
Kaplan–Meier graph of waiting time until transplant by transplant type (each event in this graph indicates a transplant performed).

Survival from listing
To assess overall survival between transplant groups and those remaining on the waiting list, the time from being placed on the waiting list until 12 months post transplant or 1 May 2015, with censoring for death or loss to follow-up, is presented in Table 26. Waiting list dates were collated for all participants during recruitment to the study; however, for those remaining on the waiting list, some of this information was not collated. For these participants, waiting list dates were obtained from the NHSBT registry.
| Group | Survival time (days) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Media | IQR | Minimum | Maximum | |
| Standard (n = 184) | 631 | 362 | 536 | 429–703 | 46 | 2508 |
| EVLP (n = 18) | 453 | 197 | 479 | 412–543 | 73 | 916 |
| No transplant (n = 212) | 621 | 438 | 543 | 324–830 | 18 | 2867 |
| Total (N = 414) | 618 | 399 | 535 | 394–741 | 18 | 2867 |
For the purpose of this analysis, 1 May 2015 was chosen as the end date for those who did not have a transplant, since this is approximately 12 months after the last transplant was performed. Of the 232 participants remaining on the waiting list, 20 have been excluded from the analysis. Thirteen were excluded because they were recruited to another study in which they had a transplant, four were excluded because they no longer wanted to be part of the study and three were excluded because there is no record of the date they were removed from the waiting list. Thirty-nine participants who were included in the analysis have been censored: 11 of these were censored by the date they were removed from the waiting list or were lost to follow-up and 28 were censored by the date on which they had a transplant outside of this trial. There were 41 participants for whom we had been unable to confirm their status as of 1 May 2015. Since we have not received information regarding their death (which we would have expected), we have assumed these participants remained on the waiting list on 1 May 2015.
The Kaplan–Meier estimates of survival from being placed on the transplant list to transplant or death/censoring are shown in Figure 18 for the three study groups. The median survival time from listing was 536 days (IQR 429–703 days), 479 days (IQR 412–543 days) and 543 days (IQR 324–830 days) for standard transplant, EVLP transplant and waiting list groups, respectively (see Table 26). The log-rank test of difference in survival times was significant (p = 0.007), implying that those having a standard lung transplant had better survival than those who remained on the waiting list and those having an EVLP transplant. However, these findings should be interpreted with caution in view of possible selection bias and the small number of patients in the EVLP group.
FIGURE 18.
Kaplan–Meier graph of survival time from being placed on the transplant waiting list.
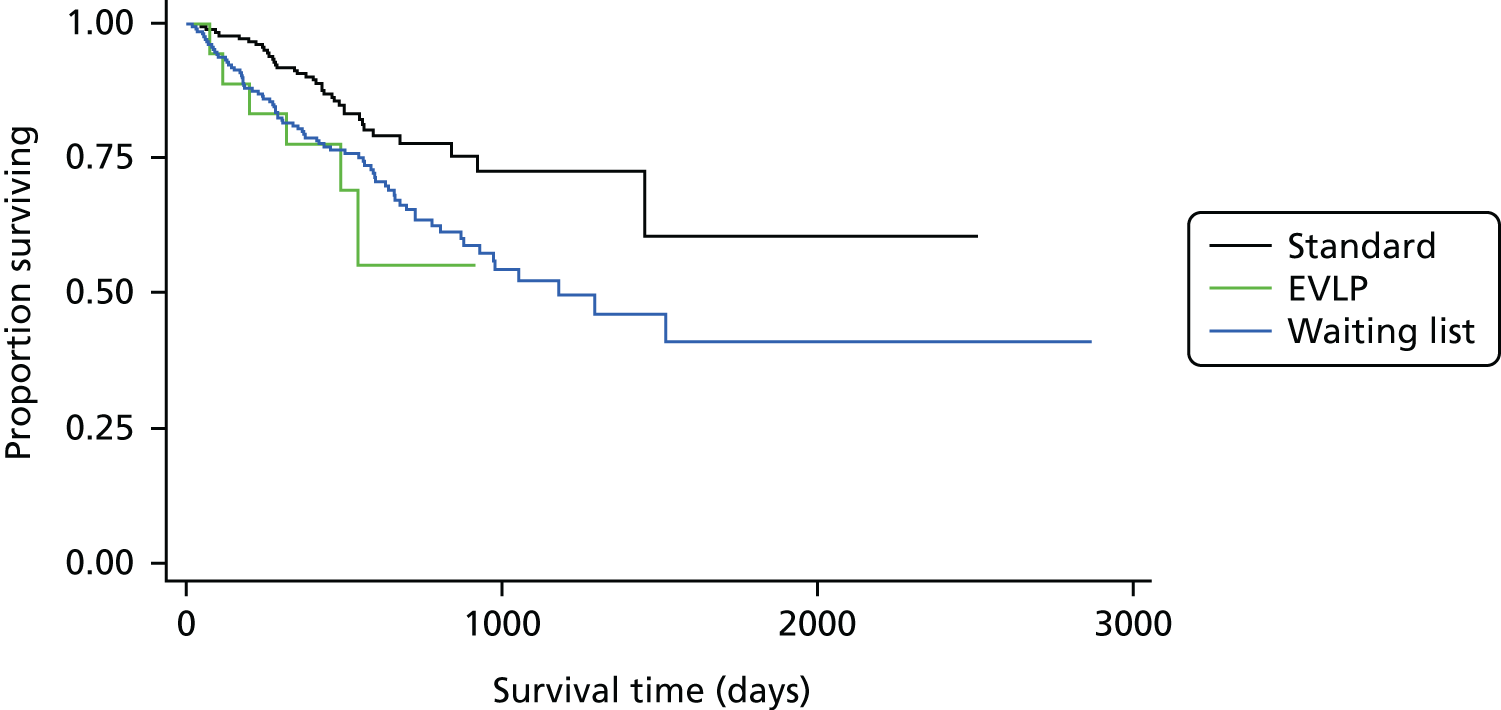
Identifying clinical predictors of successful ex vivo lung perfusion reconditioning
Between 1 April 2012 and 9 July 2014, lungs from 53 UK multiorgan donors were identified as unsuitable for immediate standard transplantation despite extensive donor management. These donors all satisfied the strict entry criteria for inclusion in the EVLP arm of the study (Boxes 1 and 2).
-
Warm ischaemic time > 30 minutes for DCD donors.
-
Withdrawal of life support between 60 and 90 minutes for DCD donors.
-
Chest radiograph findings prohibitive of standard transplantation.
-
Systemic arterial PaO2 < 300 mmHg and/or selective pulmonary vein gas < 225 mmHg on 100% FiO2 and 8 cmH2O PEEP.
-
History of aspiration with bronchoscopic inflammation/soiling of the airway, or recurrent but not prohibitive secretions in the distal airway after adequate bronchial toilet.
-
Difficult to recruit atelectasis.
-
Sustained peak airway pressure > 30 cmH2O.
-
Unsatisfactory deflation test on disconnecting endotracheal tube.
-
Unsatisfactory palpation of the lungs identifying undetermined masses, nodules or gross oedema.
-
Deterioration or cardiac arrest in the donor prior to retrieval such that uncertainty over assessment remains.
-
Unsatisfactory inspection of the lung after administration of the preservation flush and procurement.
-
Logistical reasons that will extend donor lung ischaemic time > 10–12 hours and prevent donor organ use, such as:
-
viral studies awaited
-
HLA compatibility studies
-
pathology assessment of indeterminate mass in any donor
-
awaiting recipient admission.
-
PaO2, partial pressure of oxygen; PEEP, positive end-expiratory pressure.
-
Donor aged > 65 years.
-
Donor HIV positive or other contraindicated infection risk (e.g. hepatitis B or C unless being used for a HIV-, hepatitis B- or C-positive recipient).
-
Chest trauma with extensive bilateral lung contusions.
-
Convincing evidence of bilateral pneumonic consolidation on inspection.
-
Pre-existing structural lung changes (e.g. emphysematous or multiple large bullae).
-
Previous complex intrapleural thoracic surgery or dense adhesions prohibiting safe lung procurement.
-
Confirmation of malignancy within 5 years (excluding central nervous system malignancies).
HIV, human immunodeficiency virus.
Of these 53 donors, 35 died from spontaneous intracranial haemorrhage (66%), eight from hypoxic brain injury (15%), five from traumatic brain injury (9%), three from thrombotic stroke (6%), one from an expansive brain tumour (2%) and one from meningitis (2%). The donor lungs were procured in a routine fashion and transported on ice to the accepting institution. A total of 27 (51%) were assessed in Newcastle, nine in Harefield (17%), seven in Manchester (13%), six in Birmingham (11%) and four in Papworth (8%). Fourteen donor lungs were from donors without a circulation (DCD) (Maastricht category III, 26%) and 39 were from brain-dead donors (DBD) (Maastricht category IV, 74%). The EVLP assessments were evenly distributed between donor sexes [26 female (49%) and 27 male (51%)] and the median donor age was 50 years (range 16–65 years). If one lung did not meet entry criteria and was deemed unusable because of severe consolidation or extensive contusion on inspection, or if the intended recipient was for a specific side (i.e. single-lung transplant), only one lung was procured. Fifty lungs (94%) were perfused as double lungs and three (6%) as singles (two right lungs and one left lung). They were assessed for a median time of 175 minutes (range 73–383 minutes) while being normothermically perfused on the Vivoline LS1 EVLP circuit.
The study protocol allowed for lungs that satisfied certain criteria, as outlined in Box 1, to be assessed using EVLP. The primary indications for EVLP assessment were grouped into three general categories: 35 donor lungs (66%) were found unsuitable for standard transplantation because of poor lung function with an optimised donor ratio of arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) – shown throughout the report as kPa (mmHg) – to FiO2 < 40 (300) and/or a selective pulmonary vein gas < 30 (225) with a FiO2 of 1.0 (100%) at procurement; 13 lungs (25%) were turned down as a result of abnormalities during inspection (pulmonary oedema, abnormal bronchoscopy, extensive atelectasis, etc.); and three lungs (6%) were turned down for standard transplantation for logistical reasons. Some lungs were excluded from EVLP as they had absolute contraindications to transplant (see Box 2).
Of the donor lungs turned down for logistic purposes, two had a suspicious mass in need of urgent histological evaluation before a decision on transplant was made. One was revealed to be cancerous and the lungs were discarded after an otherwise successful EVLP perfusion, and the other was confirmed benign and the lungs were transplanted. In one case, no theatre team was available as they had just started another transplantation. In this case, the lungs also remained stable or improved measurable physiological parameters during preservation on the EVLP circuit, but were in the end turned down for transplantation because of deteriorating oedema formation on inspection.
Of the 53 donors, 24 (45%) were current smokers, 18 (34%) had abnormal chest radiographs at the time of procurement and 22 (42%) had airway secretions deemed prohibitive of standard transplantation, predominantly purulent secretions. The median ventilation time for the EVLP donors before procurement was 2 days (range < 1–10.3 days) and 27 donors (51%) had positive microbiology cultures from sputum, BAL fluid or cerebrospinal fluid. The median optimised PaO2 : FiO2 ratio for the 53 EVLP donors at the time of procurement was 39.9 [299 (range 95–535 mmHg)] and after EVLP was 50.9 [381.5 (range 74–638 mmHg)]. The EVLP assessments followed one of two standardised perfusion protocols depending on when the lungs were entered into the study. Initially, between 1 April 2012 and 31 March 2013, a hybrid protocol combining elements of the Toronto and Lund protocols was used with an open left atrium, an acellular perfusate and a reduced perfusate flow to 40–60% of the donor’s calculated cardiac output. After a pause midway through the study because of concerns over the rate of ECMO use in transplants performed after assessment using the hybrid EVLP protocol, the perfusion strategy was altered and the study was restarted in August 2013 and the hybrid protocol replaced by the Lund protocol.
The Lund protocol uses a cellular perfusate (haematocrit 10–15%) and a full-flow perfusion strategy (100% of cardiac output), but is otherwise identical to the hybrid protocol. The assessment and ventilation strategies, airway and vascular pressure limits, and perfusate composition was otherwise unaltered (Table 27).
| Parameter | Protocol | |
|---|---|---|
| Hybrid (1 April 2012–31 March 2013) | Lund (1 August 2013–9 July 2014) | |
| Perfusion | ||
| Target flow | 40–60% of cardiac output | 100% of cardiac output (70 ml/kg/minute) |
| Pulmonary arterial pressure | < 20 mmHg | < 20 mmHg |
| Left atrial pressure | 0 mmHg (open left atrium) | 0 mmHg (open left atrium) |
| Pump | Roller | Roller |
| Perfusate | 2 l of Steen Solution | 2 l of Steen Solution with red cell concentrates (haematocrit 10–15%) |
| Ventilation | ||
| Mode | Volume controlled | Volume controlled |
| Tidal volume | 6–8 ml/kg | 6–8 ml/kg |
| Frequency | 10–15 b.p.m. | 10–15 b.p.m. |
| Positive end-expiratory pressure | 5 cmH2O | 5 cmH2O |
| FiO2 | 50% | 50% |
| Temperature | ||
| Start of ventilation | 32 °C | 32 °C |
| Start of perfusion | 15 °C | 15 °C |
| Start of evaluation | 37 °C | 37 °C |
Lung performance during ex vivo lung perfusion assessment
Transplant suitability was assessed as soon as the lungs had stabilised, at 37 °C and perfusing at full flow, and thereafter hourly until the end of perfusion. Lungs meeting transplant suitability at any time point were cooled and transplanted (Boxes 3 and 4). Lungs deemed to have futile prospects for improvement were taken off the circuit and discarded.
-
Any DBD or DCD donor lungs meeting previously stated criteria for standard transplant.
-
Pulmonary artery pressure < 20 mmHg, while achieving target perfusate flow.
-
Oxygen capacity shown by ΔPaO2 of > 300 mmHg (perfusate left atrium PaO2 – perfusate pulmonary artery PaO2)/FiO2.
-
Selective pulmonary vein gas > 225 mmHg on 100% FiO2 and 5 cmH2O PEEP.
-
Stable or improving lung compliance and stable or falling lung resistance.
-
No pulmonary oedema build-up in the endotracheal tube.
-
Satisfactory assessment on inspection and palpation.
-
Confirmed reconsent of potential matched recipient to receive an EVLP-reconditioned lung.
-
Any DBD or DCD donor lungs not meeting stated criteria for standard transplant.
-
Not satisfying criteria for transplant after successful EVLP assessment and reconditioning.
The performance of the 53 donor lungs undergoing EVLP assessment in the study is reported in two different ways to give as robust a description as possible of this cohort.
First, clinical EVLP success was defined as any EVLP-assessed donor lung deemed clinically suitable for transplantation at the end of perfusion by the surgical team performing the assessment (n = 22). This included all EVLP lungs that were transplanted within the study (n = 18) and all lungs that were accepted for transplantation on the basis of EVLP performance, but had to be turned down due to unforeseen logistical reasons (n = 4) (Figure 19).
FIGURE 19.
Flow chart for clinical EVLP success (n = 22).
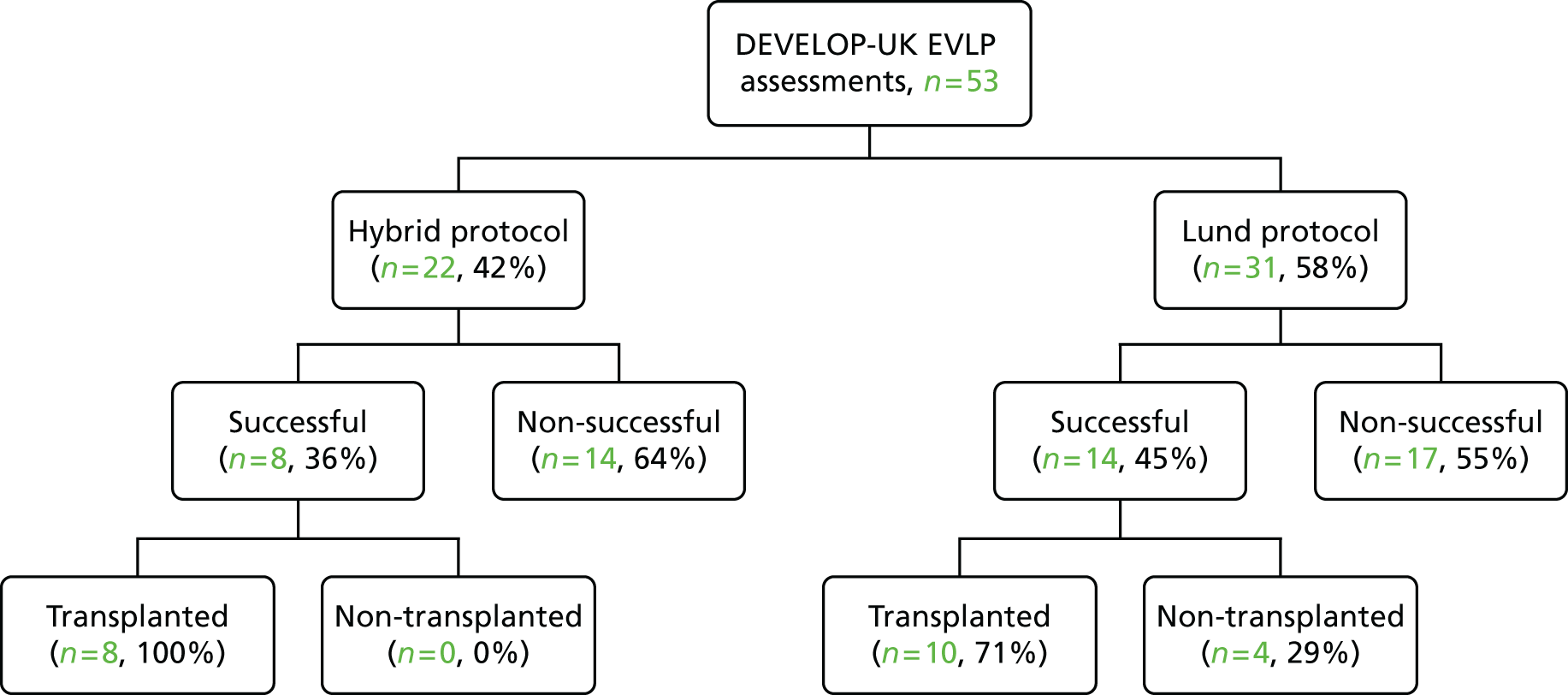
Of these four cases, one pair of lungs accepted for double lung transplant had to be discarded as the recipient presented with an active airway infection and was found to be at too high risk for the operation on arrival at the hospital. The lungs were offered on urgently, but turned down by all UK centres owing to logistics. One lung had an unreported irreparable left pulmonary artery laceration with haematoma formation from the retrieval surgery. The right lung was selectively perfused and deemed suitable for transplantation. There was, at this point, no available matching single lung recipient and the lung had to be discarded after having been offered on to all other UK centres. One left single lung accepted for transplantation for a matched recipient had to be aborted due to an emergency in theatres and lack of additional surgical capacity at the site. One lung was put on EVLP for logistical reasons while awaiting histology of suspicious masses found during the organ procurement. Evaluation of a liver nodule showed chronic lymphatic lymphoma. Although the lung biopsy was found benign, the transplant was aborted because of the elevated risk of tumour transmission to the recipient. The lungs were meanwhile successfully reconditioned on the circuit and deemed to be in a suitable condition for transplant had it not been for the histological liver findings.
Second, per-protocol success was defined as all perfused donor lungs meeting the complete set of predefined study criteria for EVLP success, regardless of clinical transplant result (n = 17). This included all EVLP lungs that were transplanted in the study while meeting all predefined transplant criteria (n = 13) and all non-transplanted EVLP lungs that met all transplant criteria but were discarded purely on logistical grounds (n = 4) (Figure 20).
FIGURE 20.
The flow chart for per-protocol EVLP success (n = 17).
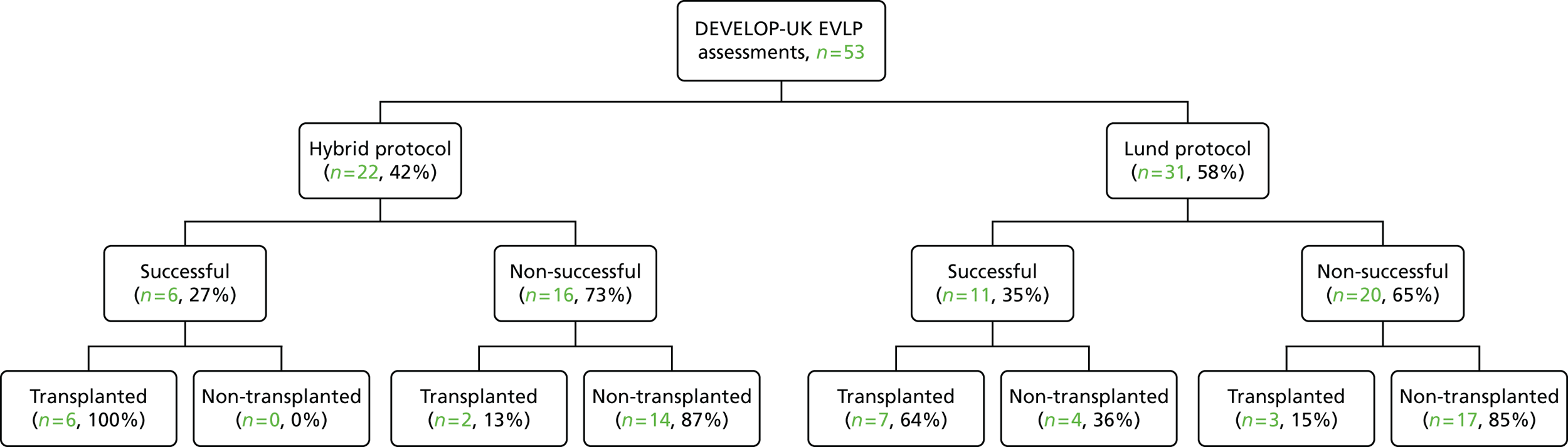
Of the 18 EVLP lungs that were transplanted in the study, five had to be defined as per-protocol non-successful perfusions as, although deemed clinically suitable for transplantation, they failed to meet all predefined transplant criteria and were transplanted as a result of a protocol violation.
Two of these five lungs were transplanted even though their mixed pulmonary vein PaO2 : FiO2 ratio was 40.0 (< 300) during the assessment. One of these almost doubled its optimised retrieval PaO2 : FiO2 ratio during the perfusion, increasing from 22.0 (166) to 38.6 (290), and the other had a recorded mixed pulmonary vein PaO2 : FiO2 ratio of 35 (262), while all selective pulmonary vein gases were well above the study cut-off point [range 46.0–72.0 (345–540)]. Three EVLP lungs were transplanted while having one or two selective lower lobe pulmonary vein gases < 30 (225); however, their mixed pulmonary vein PaO2 : FiO2 met the study transplant criterion of > 40 (300). All five of these lungs were subsequently transplanted into recipients with satisfying post-transplant outcomes and a 100% 1-year survival. Of the 13 recipients receiving lungs that met all study criteria for transplantation, only seven (54%) remained alive 12 months post transplant.
Logistic regression analyses
A logistic regression approach was used to examine the association between successful reconditioning (defined on either of the bases explained above) and a number of potential predictors based on donor characteristics and indices measured during EVLP. As a result of the lower than planned numbers in the EVLP arm, the work here must be regarded as exploratory in nature rather than definitive.
In terms of the variables to be considered for the examination of potential predictors of successful EVLP, univariate exact logistic regression models were fitted with successful EVLP as the dependent variable, and each of the following in turn as the independent variable. These models were fitted using the exlogistic option in Stata® 13.1 (StataCorp LP, TX, USA):
-
donor {age, sex, cause of death, smoking history, ischaemic time, duration of ventilation, oxygenation, donor type [after brain death (DBD) or after circulatory death (DCD)]}
-
EVLP physiology (oxygenation, lung compliance and resistance, airway pressure, perfusion time).
The original intent was also to use similar approaches to examine EVLP donor lungs used in transplantation and the association between early clinical outcome measures in recipients and physiological indices measured during EVLP. However, having only 18 patients in the EVLP transplant group meant that such an analysis would not be statistically meaningful.
Table 28 gives the results of the univariate analyses of predictors of clinical EVLP success. Here odds ratios are presented for different categories or, in the case of continuous variables, based on a unit increase in the variable. Although some of the point estimates for odds ratios varied somewhat from one, in all instances the associated 95% CI included one.
| Variable | Category or units | Number of patients in category | Number of successes | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVLP protocol | Lund | 31 | 14 | 1 |
| Hybrid | 22 | 8 | 0.70 (0.19 to 2.43) | |
| Donor age (years) | Based on a 10-year increase | 53 | 22 | 1.46 (0.90 to 2.50) |
| Sex (reference category: males) | Females | 26 | 9 | 0.58 (0.16 to 1.97) |
| Males | 27 | 13 | 1 | |
| Smoking (reference category: non-smokers) | Non-smokers | 29 | 13 | 1 |
| Smokers | 24 | 9 | 0.74 (0.21 to 2.54) | |
| Ischaemic time (hours) | Based on a 1-hour increase | 48 | 21 | 1.00 (0.61 to 1.64) |
| Duration of ventilation (days) | Based on a 1-day increase | 53 | 22 | 1.17 (0.87 to 1.63) |
| Optimised donor PaO2 : FiO2 ratio before EVLP | Based on a 100-mmHg increase | 53 | 22 | 0.81 (0.50 to 1.27) |
| Donor type (reference category: DBD) | DBD | 39 | 17 | 1 |
| DCD | 14 | 5 | 0.72 (0.16 to 2.96) | |
| PaO2 : FiO2 after EVLP | Based on a 100-mmHg increase | 48 | 22 | 1.34 (0.86 to 2.15) |
| Compliance start (ml/mbar) | Based on a 10 ml/mbar increase | 28 | 15 | 1.25 (0.94 to 1.72) |
| Change in compliance (ml/mbar)a | Based on a 10 ml/mbar increase | 15 | 7 | 0.98 (0.52 to 1.88) |
| Airway resistance start | Based on a 1 mbar/l/second increase | 24 | 11 | 0.93 (0.77 to 1.00) |
| Change in airway resistancea | Based on a 1 mbar/l/second increase | 12 | 4 | 2.11 (0.95 to 19.99) |
| Peak airway pressure start | Based on a 1-cmH2O increase | 41 | 18 | 0.88 (0.73 to 1.05) |
| Change in peak airway pressurea | Based on a 1-cmH2O increase | 24 | 9 | 1.06 (0.85 to 1.35) |
| EVLP time | Based on a 1-hour increase | 49 | 20 | 0.95 (0.54 to 1.65) |
Table 29 shows the results from the corresponding analyses, based on per-protocol success. The odds ratios and CIs are very similar to those based on clinical EVLP success.
| Variable | Category or units | Number of patients in category | Number of successes | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVLP type | Lund | 31 | 6 | 1 |
| Hybrid | 22 | 11 | 0.69 (0.17 to 2.58) | |
| Donor age (years) | Based on a 10-year increase | 53 | 17 | 1.58 (0.92 to 2.93) |
| Sex (reference category: males) | Females | 26 | 8 | 0.89 (0.24 to 3.28) |
| Males | 27 | 9 | 1 | |
| Smoking (reference category: non-smokers) | Non-smokers | 29 | 10 | 1 |
| Smokers | 24 | 7 | 0.79 (0.20 to 2.90) | |
| Ischaemic time (hours) | Based on a 1-hour increase | 48 | 17 | 0.80 (0.45 to 1.33) |
| Duration of ventilation (days) | Based on a 1-day increase | 53 | 17 | 0.97 (0.68 to 1.32) |
| Optimised donor P/F before EVLP | Based on a 100-mmHg increase | 53 | 17 | 0.86 (0.52 to 1.39) |
| Donor type (reference category: DBD) | DBD | 39 | 14 | 1 |
| DCD | 14 | 3 | 0.49 (0.08 to 2.32) | |
| PF after EVLP | Based on a 100-mmHg increase | 48 | 17 | 1.59 (0.97 to 2.77) |
| Compliance start (ml/mbar) | Based on a 10 ml/mbar increase | 28 | 13 | 1.10 (0.84 to 1.47) |
| Change in compliance (ml/mbar)a | Based on a 10 ml/mbar increase | 15 | 6 | 1.02 (0.54 to 2.00) |
| Airway resistance start | Based on a 1 mbar/l/second increase | 24 | 9 | 0.98 (0.82 to 1.01) |
| Change in airway resistancea | Based on a 1 mbar/l/second increase | 12 | 3 | 2.70 (0.95 to 58.58) |
| Peak airway pressure start | Based on a 1-cmH2O increase | 41 | 14 | 0.83 (0.66 to 1.01) |
| Change in peak airway pressurea | Based on a 1-cmH2O increase | 24 | 7 | 1.07 (0.84 to 1.36) |
| EVLP time (hours) | Based on a 1-hour increase | 49 | 17 | 0.93 (0.51 to 1.65) |
In conclusion, there was no strong evidence to indicate specific predictors of successful EVLP reconditioning. However, the analyses were restricted by the relatively small numbers.
Archiving
The trial data were stored on the Newcastle Clinical Trials Unit’s MACRO database system, provided by Infermed’s MACRO software as a service system. The hardware was located at their hosting partner Rackspace’s secure premises in London, UK, and is managed and supported by the Rackspace team. All data were stored and transmitted securely. Data were hosted and backed up only in the UK and were never transferred overseas. Only authorised staff can grant and have control of access. Any snapshots of the database taken will be kept on the Newcastle University server, which is backed up daily.
Once all trial-related analysis and activities are completed, the database will remain on MACRO, with permissions removed. The data will be archived onto disk for each site file and also centrally in accordance with the Newcastle Clinical Trials Unit’s standard operating procedures (SOPs).
Chapter 4 Economic evaluation
Overall aims of the economic evaluation
The original aim of the economic analysis of the DEVELOP-UK study was to estimate the cost-effectiveness of EVLP compared with standard donor lung transplantation. Cost-effectiveness was to be estimated in terms of the incremental cost per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained and compared with the current National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) cost-effectiveness threshold (£20,000 per QALY). This analysis was to take the form of a within-study economic evaluation and a model to extrapolate findings over patients’ lifetime. As previously described, the DEVELOP-UK study was terminated before the target participant recruitment was reached. Therefore, the originally planned economic evaluation of the study was conducted with a few changes within its initial design.
Given the smaller than planned recruitment numbers in the EVLP arm of the study, the aims of the economic section were recast to:
-
provide a descriptive ‘within-study’ analysis of the available data in terms of costs and QALYs for both EVLP and standard donor lung transplantation, without directly comparing the two procedures
-
estimate a regression model to explore predictors of NHS costs for transplants that may aid future modelling studies involving a lung transplant as one of the events of interest
-
report an exploratory economic model populated for both types of lung transplantation (standard and EVLP) with data obtained from the relevant literature and from the DEVELOP-UK study.
Within-study descriptive analysis of costs and quality-adjusted life-years
There are five parts of analysis that were proposed to be presented in this element of the study. First, the unit costs and the sources of these costs for standard donor and EVLP lung transplantation were to be described. Second, an analysis of the resource use was to be conducted to estimate the mean (SD) and the median (IQR) use of each type of resource. In the third part of the analysis, resource use and unit cost data were to be combined in order to estimate the average cost for each area of resource use and in total for each one of the two types of transplantation. The fourth part of the analysis that gives information on HRQoL was to be used to estimate QALYs for each type of transplantation based on the responses of the participants to the SF-36. Fifth, and finally, the net benefits of standard and EVLP lung transplantation were to be calculated based on the costs and QALYs of the two different approaches to achieving a lung transplant.
As the study was terminated early because of a lack of patient recruitment in one of its two arms, it was agreed that no direct within-study comparison would be drawn in terms of cost-effectiveness, and that the presentation of results would be limited to descriptive data. These descriptive data were, however, used to populate an exploratory economic model.
Methods
Outline of the lung transplant procedure
First of all, one of the most important parts of any economic evaluation is to understand the process of care, so as to fully understand what costs and outcomes should be included in the analysis. The first stage of the process is the notification of potential organ donors. In other words, it is necessary for every NHS hospital to identify any potential donors that might exist within its patient population. In this case, the donation of a lung might be after circulatory death (DCD) or brain death (DBD) of the donor. The donor’s hospital is also responsible for informing its local SNOD from NHSBT about the existence of a single- or a multiple-organ donor on its premises. NHSBT would then assess the donor and contact the local transplant centre for them to check its waiting list records in order to find the most suitable organ recipients for that donor. Once a transplant centre is contacted by NHSBT about a possible donor, it should investigate whether or not there are any patients on its lung transplant waiting list that have the necessary size and tissue characteristics that match those of the donor. Here, it is important to mention that the patients who are included in a hospital’s waiting list are frequently monitored in order to ensure that the most appropriate patient will be chosen in case a lung transplant becomes available in the future.
After contacting the SNOD in order to receive more information regarding the condition and the characteristics of the donor, the transplant centre may send a scout – if the donor hospital is less than 2 hours away – and, subsequently, a retrieval team to potentially collect the donor lung(s). Following the initial assessment of the lung by the retrieval team, and assuming that it is in a suitable condition to proceed to transplant, the retrieval team sends the organ back to the transplant site. For the purposes of the study, during the period of time that the study was under way, the retrieval team should have also considered whether or not an unusable lung (i.e. a lung that would not be retrieved otherwise based on standard tests and the subjective assessment of the retrieval surgeon) could be assessed and reconditioned by EVLP in order to be used as a transplant in the EVLP arm of the study. If so, retrieval was performed with the intention that this lung would be transplanted using EVLP. In addition, during the same period of time, more retrieval teams were sent out than normal because there was a higher probability that a lung would be accepted for a transplant.
Here, it should be mentioned that during a usual retrieval, several organs might be retrieved (e.g. heart, kidney, pancreas and liver). It should also be noted that at times no retrieval might be performed if the team decides differently. During this study, 53 lungs were retrieved in order to undergo an EVLP procedure. Of these lungs, only 18 were reconditioned successfully and transplanted at the end. The remainder were not considered appropriate for transplantation at the transplant site. Therefore, in the analysis of this study, the ratio of EVLP transplant per retrieval was considered to be equal to 18 EVLP lungs out of 53 attempts. On the other hand, for the standard arm of the study, it was difficult to calculate the number of lungs assessed but not retrieved given the parameters described above. However, expert opinion from the study team advised that each time a lung is assessed as suitable for transplant, this lung is always transplanted. Consequently, it was assumed that each time a retrieval team was sent to a donor’s hospital a lung was retrieved and sent back to the transplant site in order to be assessed and transplanted.
At the same time as a retrieval team has been dispatched to the donor hospital, the transplant centre should contact the potential recipient in order to inform them about the possibility of a transplant happening. Sometimes, more than one patient is contacted in order to ensure that the lung will be transplanted in the event that one of them has a current infection and cannot be transplanted. Once the intended recipient(s) arrives at the transplant site, the recipient meets with the transplant co-ordinator to receive more information about the transplant, and is prepared for the transplant. In the case of an EVLP lung transplant, the EVLP procedure may be started before the recipient arrives at the hospital and continue while the patient is being prepared for the surgery.
Afterwards, the lung transplant operation is under way, where exactly the same procedure for both standard and EVLP transplants is followed. After the operation, the lung recipient is admitted to the ITU and then onto the transplant ward in order to receive the necessary post-operative care and manage any complications that might occur. Following hospital discharge, and assuming there are no complications, infections or rejection episodes necessitating readmission, the recipient returns to the hospital every month (or less depending on the clinicians’ recommendations) for routine tests (i.e. blood test, bronchoscopy, etc.) and in order to report any complications. In between, the lung recipient might also visit a GP to report any new symptoms or AEs from the medications given.
Study perspective
The perspective of the study (i.e. which costs and outcomes were considered in the analysis) was the national health-care provider (the UK NHS). The duration of follow-up was 12 months following transplant, with outpatient visits planned at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months post transplant.
Cost and use of resources
The data collected on costs were categorised into the following areas based on when the resources were used during the study: donor’s hospital, lung retrieval, transplant preparation, EVLP procedure, lung transplant, post-operative care, outpatient care and concomitant medications.
Donor’s hospital
As mentioned above, the donor’s hospital is responsible for contacting the NHSBT to report any potential lung donors. Before the retrieval team arrives, the SNOD should have performed an initial assessment to provide the patient’s history to the transplant team. This assessment consists of several routine tests, such as a full blood count (FBC) and chest radiography, as well as, sometimes, a bronchoscopy procedure. The cost of the initial assessment was derived from the costing tool of Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals (NuTH; obtained from: www.newcastlejro.org.uk) or the NHS Reference Costs 2013/2014,49 while the information regarding the use of each test was obtained from the CRFs of the study or the hospital staff (personal communications: Mr Tanveer Butt, NuTH, June 2015; Ms Alison Davison, NuTH, June 2015; Mr Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014; and Ms Katie Morley, NuTH, October 2014). The hospital staff should also administer a single dose of methylprednisolone (500 mg, 1 g or 2 g, with the dose decided based on the donor’s weight) to modulate the pulmonary inflammatory activity of the donor. The use of methylprednisolone was reported on the CRF, while its cost was collected from the British National Formulary (BNF) for each dose that was administered. 50
Lung retrieval
Lung retrieval begins when the scout team and/or the retrieval team arrives at the donor’s hospital. Normally, a scout team is sent out if the donor’s hospital is within a 2-hour range from the transplant site in order to make an initial examination of the organ. According to the retrieval team of NuTH (Mr Tanveer Butt, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication), around one-fifth of lung retrievals are scouted first. The scout team consists of a retrieval surgeon (clinical fellow) and a scrub nurse (band 7), while in the retrieval team a perfusionist (band 7) is also included. The retrieval process was estimated, based on clinical advice, to last for approximately 9 hours, with a further 4 hours added if a scouting is performed (one in five cases). All the costs of the staff were obtained from the Personal Social Services Research Unit (PSSRU)’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2014,51 while the resource information came from the NuTH retrieval team (personal communications: Mr Tanveer Butt, NuTH, September 2014; and Mr Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014).
As far as the travelling of the two teams is concerned, this is variable and depends on the distance of the donor’s hospital from the transplant site. According to the NuTH NHS staff (Mr Brian Leadbitter, NuTH NHS, June 2015, personal communication), a scout team always travels by road while a retrieval team travels by road in 74% of the cases, and by road and air in 26% of the cases. Once the lung is retrieved, it might be returned to the transplant centre either by road (50%), or by road and air (50%). The usage and costs of travel were based on the cardiothoracic organ retrieval invoices given by the NHS staff of NuTH.
During the lung retrieval, the team requests the donor’s medical history and the screening tests provided by the hospital staff [i.e. ABG, electrocardiography (ECG), etc.]. Then the team performs an initial assessment of the patient in order to examine whether or not the lung can be transplanted. There are three diagnostic tests that are normally performed by the retrieval team: chest radiography, an ABG test and a bronchoscopy. Here, it should be mentioned that an ABG test is provided only when the lung comes from a DBD donor; in cases of a DCD this test cannot be performed as the heart has already stopped (Mr Tanveer Butt, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication).
Chest radiography is performed with the donor hospital’s equipment and, for the purposes of the analysis, its cost was derived from the NuTH costing tool (obtained from: www.newcastlejro.org.uk) while its use was reported on the CRF. For the ABG test and the bronchoscopy procedure, the retrieval team takes the necessary equipment with them. According to the NuTH retrieval team’s checklist (personal communications: Mr Tanveer Butt, NuTH, September 2014; and Mr Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014), the team always brings a bronchoscope, strapple tape and 0.5% chlorhexidine spray to the donor’s hospital. In addition to these pieces of equipment, a different number of 0.9% sodium chloride solutions might be needed during the retrieval, and these are usually provided by the donor’s hospital. In the case of a DBD donor, the donor’s hospital also provides the necessary equipment for the ABG test (i.e. vacutainers, syringes, portable clinical analyser, etc.).
The costs of most of this equipment used by the retrieval team were obtained from the official websites of the resective medical suppliers. In the case of the bronchoscope and the clinical analyser for blood analysis (i-STAT® device, Abbott Laboratories, Dallas, TX, USA), their equivalent annual costs were estimated based on the life expectancy of the equipment, assuming a 3.5% discount rate. 52 The equivalent annual cost was then divided by the expected annual usage to get a cost per recipient. The cost of the i-STAT test cartridges, which are the testing cartridges used during a diagnostic test with an i-STAT clinical analyser, was obtained from the retrieval team, and the cost of sodium bicarbonate was obtained from the BNF 2014. 50
The perfusionist member of the team is responsible for measuring the breathing (ventilation) and circulation (perfusion) in all areas of the lung retrieved, as well as ensuring the proper maintenance of the organ. In order to increase the cooling, preservation and storage of the lungs, a colloid preservation solution (PERFADEX) is needed. To be more precise, 2.8 l of PERFADEX solution is needed antegrade for lung preservation, whereas 1 l is given retrograde on the back table just after the harvest procedure (250 ml into each of the four veins of the lung). To each litre of this solution, a sterile sodium salt, epoprostenol sodium (FLOLAN®, GlaxoSmithKline), THAM, CaCl2 and heparin sodium are added. The use of the first three was reported by the retrieval team (personal communications: Mr Tanveer Butt, NuTH, September 2014; and Mr Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014), whereas for heparin sodium and CaCl2 it was collected from the BNF 2014. 50 The costs of FLOLAN, THAM, heparin sodium and CaCl2 were obtained from the BNF 2014,50 whereas the price of the different dosages of PERFADEX solutions was given by its producer company, XVIVO Perfusion AB.
Transplant preparation
After the retrieval, the lung is delivered back to the transplant site in order to be prepared for the transplant. In case the lung needs to be reconditioned before the transplant, the EVLP procedure is also followed in parallel (see Ex vivo lung perfusion procedure). Meanwhile, the transplant co-ordinator is responsible for contacting the potential recipient(s) – this normally lasts for 1 hour. The potential recipient is selected from the transplant waiting list by the transplant surgeon on duty. The transplant surgeon on duty is ultimately responsible for deciding which patient meets the necessary criteria and has the appropriate characteristics that match with the donor’s tissue in order to be transplanted (Professor Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication). It should also be noted that each patient on the waiting list receives frequent diagnostic tests, such as FBC and ECG, to monitor their condition. For the purposes of this study, the costs of these tests were not considered as part of the transplant cost.
Once the appropriate patient(s) are selected, they are transferred to the transplant centre by road or air depending on the accessibility to, and the distance from, the site. There are different ways that a patient might be transferred to the hospital, including ambulance, aeroplane (air ambulance) or private car. Nevertheless, during the analysis of the study, it was difficult to obtain more details regarding the resources used for the patient travelling to the transplant centres. As a result, this information was omitted from the estimation of costs.
At the transplant centre, the potential recipient(s) meets with the transplant co-ordinator for approximately 2 hours in order to receive more information regarding the transplant. Following this, a tissue typing procedure is performed by NHSBT in order to test the compatibility between the tissue of the prospective donor and that of the potential recipient. The potential recipients will also receive the following tests to monitor their health status: ABG test, chest radiography and ECG. After these tests, the patient stays in the transplant centre ward until the operation (usually for 1 hour) or until sent home because the transplant has not progressed. During this time, medications tailored to the patient’s health state are administered (e.g. specific antibiotic cocktail). Azathioprine (200 mg) is also given orally before the beginning of the transplant as part of the standard procedure (Professor Andrew Fisher, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication).
The time needed for the contact and meeting with the potential recipients(s), as well as the average waiting time, was sourced by the NuTH staff (personal communications: Ms Alison Davison, NuTH, June 2015; and Ms Katie Morley, NuTH, October 2014). The hospital staff also reported that a tissue typing test is performed after the meeting with the transplant co-ordinator, while an ECG is also provided before the transplant. The CRF reported that an ABG, a FBC and chest radiography are conducted as well. The PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 gave the costs per hour for the transplant co-ordinator, while the cost of the hospital ward time was derived from the NHS Reference Costs 2013/2014. 49 The unit costs of all the diagnostic tests were obtained from the NuTH costing tool (obtained from www.newcastlejro.org.uk), apart from the cost of the tissue typing test that is provided by the Information Services Division (ISD)’s ISD Scotland Theatre Services. 53 In addition, the cost of azathioprine was collected from the BNF 2014. 50
Ex vivo lung perfusion procedure
The EVLP is a procedure that needs, on average, 6 hours in order to be completed. For the EVLP, an operating theatre is required in which the whole procedure takes place. The cost per hour of an operating theatre came from ISD’s ISD Scotland Theatre Services. 53 As far as the staff is concerned, a consultant surgeon, a surgical fellow, a scrub nurse (band 5), a perfusionist (band 7) and an anaesthetic registrar are needed for various amounts of time during the EVLP. The salary calculations for all the members of the staff were based on the PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2014,51 whereas the information regarding the staff time was given by the hospital staff and Vivoline Medical AB company (personal communications: Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014; Anna Söderlund, Vivoline Medical AB, July 2014; Mr Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014; and Ms Katie Morley, NuTH, October 2014).
According to Vivoline Medical AB and the NuTH hospital staff (personal communications: Mr Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014; Ms Anna Söderlund, Vivoline Medical AB, July 2014; and Mr Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014), there are several pieces of equipment and consumables needed during the EVLP procedure. The main equipment needed is a Vivoline system, which is the ‘rig’ unit, and a Vivoline disposable lung set, in which the lung is inserted in order to be reconditioned before the transplant. Other surgical equipment is also needed for the procedure (e.g. tissue forceps, surgical tape and sutures), while equipment for blood gases tests (e.g. syringes for blood gases and blood gases samples) and a bronchoscope are necessary for the screening of the lung. The costs of all the equipment and consumables used during an EVLP run were collected from the official websites of the respective suppliers and the hospital or Vivoline Medical staff. Where equipment is reusable, its equivalent annual costs were estimated based on its expected life expectancy, assuming a 3.5% discount rate. 52 The equivalent annual cost was then divided by the expected annual usage to get a cost per recipient.
There are several drugs that are also administered to the lung during the EVLP procedure. These include heparin sodium and methylprednisolone, as well as insulin and THAM. The CRF (p. 34) and the NuTH clinical staff (Mr Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication) provided the details of the medications used. The unit costs of the medications were obtained from the BNF 2014 based on the doses recorded on the patients’ data set. 50
Lung transplant
The procedure followed during the lung transplant is identical for both standard donor and EVLP lung transplantation. Before lung transplant, the patient is transferred in the anaesthetic room of the operating theatre in order to receive the necessary anaesthesia. In this room, a consultant anaesthetist and an anaesthetic nurse (band 5) are required in order to provide the anaesthetic management of the patient. As described in Post-operative care, the anaesthetic staff move to the surgical room afterwards in order to oversee the level of anaesthesia of the patient during the operation. The anaesthetic preparation needs 45 minutes, on average, in order to be completed based on the NuTH transplant co-ordinators (Ms Alison Davison, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication). As before, the cost of the anaesthetic room, as well as the operating theatre in general, was obtained from ISD Scotland Theatre Services,53 while the costs of the staff were collected from the PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2014. 51
Once the anaesthetic preparation is finished, the patient is moved from the anaesthetic room into the operating theatre. In addition to the anaesthetic staff (with the addition of an anaesthetic fellow), a consultant surgeon, a surgical fellow, two scrub nurses (bands 5 and 7) and a perfusionist (band 7) are required for the surgery (personal communications: A Fisher, NuTH, November 2015; and Mr Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014). Depending on whether a single or a double lung is transplanted, the surgery might last, on average, 4–7 hours. More information regarding the staff members needed was provided by the hospital staff that took part in the study [Qualtrics® survey, 2014 (Qualtrics, Provo, UT, USA); see Appendix 5], while their costs per hour were calculated from the PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2014. 51
As far as the equipment and consumables used during lung transplant are concerned, during the analysis of this study, it was difficult to obtain more details from the different members of the hospital staff and conduct the relevant microcosting. As a result, this information was omitted from the estimation of costs.
Post-operative care
After the operation is completed, the lung recipient is initially transferred to the ITU in order to be closely observed by the anaesthetic team and the transplant physicians. On average, the patient stays for 10 days in the ITU/high-dependency unit (HDU) before being discharged to the transplant ward. After being discharged from the ITU/HDU, some recipients might require to stay for longer (> 1 month, on average) in the hospital so they remain at the level 1 ward. Others might experience complications and may need to be readmitted to ITU/HDU. The time spent in the different hospital wards after the operation was reported on the CRF of the study. The unit costs of the wards were measured per bed-day and were calculated in accordance with the NHS Reference Costs 2013/2014. 49 The costs of the wards included the costs of the ward, equipment and nursing needed during the patient’s hospital stay.
In the ITU/HDU, the patient is observed daily by a consultant surgeon (15 minutes), a surgical fellow (15 minutes), a consultant physician (10 minutes), a consultant anaesthetist (30 minutes) and an anaesthetic fellow (90 minutes). In the hospital ward, there are no visits from the consultant surgeon, the consultant anaesthetist and the anaesthetic fellow, but the consultant physician time increases to 20 minutes, and a transplant specialist registrar is now needed, who will spend approximately 30–40 minutes with each patient every day. During their visits, the clinicians perform several diagnostic tests in order to monitor the progress of the patient’s health (e.g. ABG, FBC, lung function test, etc.). Depending on the patient’s condition, a tracheostomy and a bronchoscopy may be required. The CRF gave more details regarding the use of these tests and procedures, while the staff time needed per day was estimated based on the responses of the clinicians on the Qualtrics survey (see Appendix 5). The costs per hour for all the members of the staff were collected from the PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2014,51 while the unit costs of the tests and procedures performed were calculated using the NuTH costing tool (obtained from www.newcastlejro.org.uk) or NHS Reference Costs 2013/2014. 49
During post-operative care, some patients might require both cardiac and respiratory support if their heart and/or lungs are unable to provide adequate amount of gas exchange to sustain life. This can be solved by using either an ECMO machine, which artificially removes carbon dioxide from the person’s blood and oxygenates red blood cells, or an iLA device, which is an artificial membrane that replaces the lung and its functions. In addition, normally haemodynamic support is provided to the patient by using inotrope drugs (e.g. adrenaline hydrochloride, vasopressin, dobutamine, etc.). In some cases, some plasma volume expanders, such as colloid (e.g. normal saline solution) and crystalloid (e.g. albumin, dextran, etc.) fluids, might be required in order to restore the vascular volume and stabilise the circulatory haemodynamics. When needed, red blood cells, plasma and platelets might also be given in order to change the levels of the main blood components.
The use and amount of all the equipment and consumables described above were recorded on the patient’s CRF (p. 45), while their costs were retrieved from different sources. The costs of ECMO and the blood components were given by the hospital staff (personal communications: Mr Tanveer Butt, NuTH, September 2014; and, Mr Paul Henderson and Ms Yvonne Scott, NuTH, July 2015) or the NHSBT. Using the same methods as described before for reusable equipment (e.g. ECMO machine) a cost per recipient was calculated. 52 The unit costs of colloid and crystalloid fluids, as well as that of the inotrope drugs used, were collected from the BNF. 50
As mentioned above, the patient might be readmitted to ITU/HDU or hospital if any serious complications develop after the operation. The type of management provided is linked to the type of complication experienced. The CRF (pp. 52–58) gave all the information on the type of complications and management received. The unit costs of the procedures came from the NHS Reference Costs 2013/2014,49 whereas all the medications given as a result of rejection or infection episodes were obtained from the BNF. 50
Outpatient care
According to the recommendations of the hospital staff, a lung recipient will need to visit the transplant clinic every few weeks or months in the first year after the operation. During every outpatient visit, the patient is seen for half an hour by a consultant physician and a clinic nurse (band 5). The clinic staff also arrange a FBC, a urea and electrolytes and a liver function test, chest radiography, a pulmonary function test and a bronchoscopy at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months, routinely or at other times if indicated by the recipients’ condition. The information about the use of the tests provided was reported on the CRF, while the outpatient hospital staff gave more information regarding the time spent with the patient (Ms Lyndsey Forrest, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication). The costs of the tests were calculated using the NuTH costing tool (obtained from: www.newcastlejro.org.uk) or the NHS Reference Costs 2013/2014,49 whereas the cost of the staff was measured per hour based on the PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2014. 51
Immunosuppressive medications are prescribed from immediately after the transplant operation and are dispensed when a lung recipient is discharged from the hospital in order to reduce the risk of rejection of the donor lungs. If the patient shows any AEs, rejection or infection episodes, these can be reported either at an outpatient hospital and GP visit, where a clinical diagnosis/biopsy is performed, or the patient can call the transplant centre for further advice. Depending on the complications reported, there might be some new medications or current treatment may be changed. In some cases, a readmission to the ITU/HDU or the level 1 hospital ward might be required. Information on changes in medications was included on the CRF for every outpatient visit. The costs of the diagnostic and treatment procedures provided by the hospital were collected from the NHS Reference Costs 2013/2014,49 whereas the unit costs of the medications were obtained from the BNF. 50 For the GP visits, the costs were calculated per hour based on the costs of the GP per hour from the PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2014. 51
Concomitant medications
There were some additional medications given to the lung recipients depending on their health condition while the study was under way. As it is always difficult to define whether these drugs are required as a result of the transplant or because of other medical conditions, they were reported and costed separately. The doses and duration of treatment for these medications were defined by the CRF of the study or the BNF50 in case the information was missing. The BNF50 was also used in order to provide the unit costs of the concomitant medications used throughout the study.
Cost data analysis
As described previously, the cost analysis of the study data was divided in eight different stages (e.g. donor’s hospital, lung retrieval, etc.) based on the sequence of events of each one of the two transplant procedures that were examined. Each stage was also subdivided into groups in accordance with the point of time that the respective resources were used (e.g. initial assessment, tests, staff time, etc.). The unit costs of each resource were obtained from different sources (e.g. BNF,50 PSSRU51) and they were then multiplied by the mean usage of each resource as reported on the CRF or from the hospital staff (see Appendices 6 and 7). The total costs of each resource were added in order to give the total cost of each group of resources, which were further added in order to provide the total cost of each stage of the transplant process. At the end, the total cost of the transplant was calculated for each lung recipient, and the average cost per recipient was estimated. As noted above, in order to cost the two transplant procedures, a bottom-up methodology was used instead of using the Reference Costs 2013/201449 for lung transplantation. This is because the EVLP procedure is a new procedure and so not adequately captured in routine data sources. It is also essential to mention that for the EVLP arm of the study, the resource costs of the first four stages (i.e. donor’s hospital, lung retrieval, transplant preparation and EVLP procedure) were multiplied by 53/18 in order to consider the additional costs of the lungs that were retrieved and not transplanted for each EVLP recipient. In other words, for every 2.9 set of lungs retrieved only one transplant was performed. Therefore, the cost of a transplant included the cost of the 2.9 retrievals.
The mean and median costs per recipient for each stage of each one of the two transplant procedures are presented together with the relevant SD and IQR (see Tables 30–37). All costs are rounded to their nearest pound sterling. Although this is a descriptive analysis with no intention to directly compare the two transplant procedures in terms of their costs, the mean difference in cost per recipient – with its standard error – is indicated in each table (the minus symbol in the mean difference in cost per recipient between the two arms of the study indicates that the mean cost of the respective resources is lower in the standard donor arm than in the EVLP lung transplant arm). A 95% CI of the mean difference in the cost of the two procedures per recipient is also estimated based on statistical bootstrapping of the available data, which is used to simulate a CI and is useful when data are not parametrically distributed and conventional (parametric) statistical approaches may be inappropriate. Both mean cost differences and 95% CIs are presented for descriptive purposes, with no intention to directly compare the two transplant procedures. The analysis of the costs of the study was conducted using the statistical and decision analysis software Stata 13.1.
Quality of life
In order to examine the changes in HRQoL for each patient, QALYs were measured using the participant responses on the SF-3654 questionnaire administered at the start of the study (baseline), when the participant was added into the waiting list, 90 days and 12 months after lung transplant. In order to measure QALYs, participant responses were then mapped onto the SF-6D using a validated algorithm48 to determine utility values. These utility values had a range from 0 (death) to 1 (perfect health), with the utility value of lung transplant ranking within these two boundaries. The SF-6D score was taken as 0 from the date of death to the end of follow-up, the date of death was recorded as part of the data collection. QALYs were then to be estimated for each study participant using the trapezoid rule. The SF-36 was preferred in this context, as it was felt to be more sensitive over the range of likely health states experienced by an individual than alternative preference-based quality-of-life tools.
Health outcome data analysis
The low rate of questionnaire completion at each stage of the study (see Table 22) meant that assumptions needed to be made in order to follow the procedure described in Cost and use of resources, and this would limit the robustness and increase the bias of the results. Methods, such as multiple imputation, would be useful in these cases; however, given the limited overall sample size and the quality of missing data, it was felt that imputed data might be potentially misleading. For this reason, it was decided that the mean (SD) and median (IQR) SF-6D scores would be calculated for each data collection time point (i.e. baseline, 3 and 12 months post transplant) based on the number of observations (n) available at those time points. The means were then used as point estimates in order to measure the area under the curve, using the trapezoid rule, to give the mean QALYs per transplant type. As in the analysis of costs, no direct comparison between the total numbers of QALYs for each transplant procedure was conducted. This was, again, because of the limited number of data available. The analysis of the SF-36 data of the study was conducted using Stata 13.1.
Net benefits
Based on the values of total costs and QALYs that were measured from the standard donor and EVLP lung transplants, the net benefit of each one of the two procedures was proposed to be calculated using the following equation:
where λ is the current NHS cost-effectiveness threshold (£20,000 per QALY). 52 However, owing to the limitations of the quality-of-life data, which were mentioned above, the calculation of the study net benefits was not performed, as it would not produce any accurate or meaningful results.
Missing data
As already mentioned, the data available for comparative purposes were very limited, and there were missing data for study participants. Therefore, the nature and extent of missing data were reported, and no imputation was attempted. The exceptions to this were that if the missing data were related to standard resources that are normally used during the treatment pathway, it was assumed that these resources were used and, therefore, costs were added.
Results
Cost analysis
The total average cost per recipient, by each area of resource use for each one of the eight stages of the study, is listed in Economic evaluation methods (see Tables 30–37).
Table 30 shows that there were no large variations in the costs of the screening and testing of the donor before the lung retrieval in either of the two types of transplantation. This is because the hospital staff always perform the same type and number of tests in order to examine the person’s health condition before requesting a retrieval team to arrive at the hospital. Any small variations observed in the donor’s initial assessment costs (standard transplant, SD £6; EVLP transplant, SD £18) might be caused by the fact that some of the tests might not be needed in some cases or had been provided recently to the donor. In this stage, medication costs constitute a small component of the total costs, as only methylprednisolone was given as a single dose, whereas the main component of costs for both standard and EVLP lung transplants are the diagnostic tests. In addition, the large differences in mean costs between the two transplant procedures (CostSTD = £403; CostEVLP = £1182) are because in the EVLP arm only 18 lungs were transplanted out of 53 that were retrieved, while in the standard arm all retrieved lungs were transplanted.
| Resource use | Patient details | Study group | Mean (SE) difference in cost per recipient | 95% CI based on bootstrapping | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (n = 184) | EVLP (n = 18) | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | ||||
| Total initial assessment costs | Donor | £392 (£6) | £393 (£391–395) | £1156 (£18) | £1163 (£1151–1163) | –£765 (£2) | |
| Total drug costs | Donor | £11 (£10) | £17 (£0–17) | £26 (£26) | £26 (£0–51) | –£14 (£3) | |
| Total donor’s hospital costs | Donor | £403 (£12) | £408 (£395–412) | £1182 (£35) | £1182 (£1163–1214) | –£779 (£4) | –£786 to –£771 |
The retrieval of the lung involves very similar resources regardless of the subsequent procedure. As can be seen from Table 31, there is some variability in the costs of the equipment used for a DCD and a DBD donor. This is because, during a DBD, the heart is still working and, therefore, an ABG test can also be performed. This also explains the small differences observed in the cost of the tests provided by the retrieval team (standard, SD £9; EVLP, SD £36). Moreover, some variation is observed in the cost of the lung perfusion. This might mean that some of the medications that are normally used during the perfusion of the organ were not needed in practice or that there were several missing patient data items that caused these differences in costs. In this stage, the main components of costs are the staff time and the team’s travelling costs, which would be expected given the potential distances that the scout and retrieval teams have to travel and the time needed to complete the organ retrieval. As mentioned before, the large increase in the costs of the EVLP compared with the standard transplant was mainly caused by the different retrieval-to-transplant ratio of the two transplant procedures.
| Resource use | Patient details | Study group | Mean (SE) difference in cost per recipient | 95% CI based on bootstrapping | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (n = 184) | EVLP (n = 18) | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | ||||
| Total DCD donor equipment costs | Donor | £25 (£4) | £21 (£21–29) | £63 (£0) | £63 (£63–63) | –£38 (£2) | |
| n = 30 | n = 4 | ||||||
| Total DBD donor equipment costs | Donor | £273 (£3) | £274 (£274–274) | £799 (£11) | £806 (£782–806) | –£527 (£1) | |
| n = 154 | n = 14 | ||||||
| Total staff time costs | Donor | £1005 (£0) | £1005 (£1005–1005) | £2958 (£0) | £2958 (£2958–2958) | –£1954 (£0) | |
| Total test costs | Donor | £21 (£9) | £25 (£25–25) | £49 (£36) | £74 (£0–74) | –£28 (£3) | |
| Total perfusion costs | Donor | £623 (£142) | £655 (£655–655) | £1822 (£455) | £1929 (£1929–1929) | –£1199 (£47) | |
| Total travelling costs | Donor | £6770 (£0) | £6770 (£6770–6770) | £19,934 (£0) | £19,934 (£19,934–19,934) | –£13,164 (£0) | |
| Total lung retrieval costs | Donor | £8651 (£170) | £8729 (£8695–8729) | £25,398 (£524) | £25,688 (£24,957–25,700) | –£16,747 (£55) | –£16,856 to –£16,639 |
Table 32 describes the costs of the preparation of the patient before lung transplant. As with the previous two stages of the analysis, there is some variation in the use of the screening tests performed, which might mean either that the test was performed but these data were missing, or that or no test was required during the preparation of the patient. The table also indicates that the most costly resource used during this stage of the transplant process was the time spent in the hospital ward before surgery (£265 per hour). Obviously, the retrieval-to-transplant EVLP ratio (53/18) results in the higher costs for the EVLP arm of the study. Furthermore, as mentioned above in the description of the lung transplant procedure, in this study it was difficult to obtain detailed information about the resources used for the patient transportation to the transplant site. As a result, these costs are missing from Table 31. Given the difference in retrieval-to-transplant ratios between the two arms of the study and the nature of these costs, it might be expected that the costs of travelling would increase the cost of the patient preparation and, subsequently, the cost of the total transplant procedure.
| Resource use | Patient details | Study group | Mean (SE) difference in cost per recipient | 95% CI based on bootstrapping | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (n = 184) | EVLP (n = 18) | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | ||||
| Total potential recipient contacting costs | Recipient | £30 (£0) | £30 (£30–30) | £90 (£0) | £90 (£90–90) | –£59 (£0) | |
| Total potential recipient meeting costs | Recipient | £61 (£0) | £61 (£61–61) | £179 (£0) | £179 (£179–179) | –£118 (£0) | |
| Total tissue typing costs | Recipient | £60 (£0) | £60 (£60–60) | £176 (£0) | £176 (£176–176) | –£116 (0) | |
| Total test costs | Recipient | £50 (£8) | £51 (£51–55) | £140 (£28) | £149 (£149–149) | –£90 (£3) | |
| Total ward time costs | Recipient | £265 (£0) | £265 (£265–265) | £780 (£0) | £780 (£780–780) | –£515 (£0) | |
| Total drug costs | Recipient | £0 (£0) | £0 (£0) | £0 (£0) | £0 (£0) | £0 (£0) | |
| Total transfer to ward costs | Recipient | Missing | Missing | Missing | Missing | Missing | |
| Total transplant preparation costs | Recipient | £466 (£8) | £467 (£467–471) | £1365 (£28) | £1375 (£1375–1375) | –£899 (£3) | –£905 to –£894 |
Table 33 describes the costs for the EVLP procedure. Obviously, because the EVLP procedure is performed only during EVLP lung transplant, no costs are presented for the standard arm of the study. This process includes the assessment and reconditioning of the lung in order to make it suitable for transplant, and it is a stage that occurs between the transplant preparation and the transplant surgery. As expected, the most costly resources used in this stage are the consumables needed for the procedure. These include the lung set in which the lung is reconditioned (Vivoline disposable lung set, £6963). The medications used for the reconditioning of the organ add to the costs of the procedure, as do the cost of staff time and theatre time, because the EVLP procedure lasts for approximately 6 hours. As described in the stages above, the retrieval-to-transplant ratio causes an additional increase in the costs of the EVLP procedure by 53/18.
| Resource use | Patient details | Study group | Mean (SE) difference in cost per recipient | 95% CI based on bootstrapping | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (n = 184) | EVLP (n = 18) | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | ||||
| Total staff time costs | EVLP recipient | – | – | £1533 (£0) | £1533 (£1533–1533) | ||
| Total equipment costs | EVLP recipient | – | – | £59 (£0) | £59 (£59–59) | ||
| Total consumable costs | EVLP recipient | – | – | £22,958 (£606) | £23,017 (£22,487–23,193) | ||
| Total miscellaneous equipment costs | EVLP recipient | – | – | £220 (£0) | £220 (£220–220) | ||
| Total theatre usage costs | EVLP recipient | – | – | £10,382 (£0) | £10,382 (£10,382–10,382) | ||
| Total drug costs | EVLP recipient | – | – | £7482 (£1965) | £7991 (£6362–8057) | ||
| Total EVLP procedure costs | EVLP recipient | – | – | £42,633 (£2172) | £42,675 (£41,167–43,414) | – | – |
The cost of the single lung transplant procedure or a double lung transplant procedure does not vary according to whether it is a standard or EVLP lung transplantation. In this study, only 26 transplants were reported as single, of which two were in the EVLP arm. The rest of the transplants were either reported as double or assumed to be double in this analysis given that more double transplants were performed. A double lung transplant increases the time needed for the surgery by approximately 3 hours, which leads to a significant increase in the mean transplant costs (single transplant cost £4177; double transplant cost £6934), because of increased theatre usage and staff time costs. The variability within the total costs of the transplant (standard, SD £931; EVLP, SD £892) is mainly caused by the difference in the proportion of single or double lung transplants performed in the standard and EVLP arms of the study. As indicated in Table 34, the total cost of the equipment/consumables used during the operation is missing. This is because every surgeon and clinic may differ in how the surgery is performed and, hence, may use different equipment. In this study it was difficult to collect more details about the resources used in order to retrieve their respective costs.
| Resource use | Patient details | Study group | Mean (SE) difference in cost per recipient | 95% CI based on bootstrapping | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (n = 184) | EVLP (n = 18) | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | ||||
| Total anaesthetic preparation costs | Recipient | £501 (£0) | £501 (£501–501) | £501 (£0) | £501 (£501–501) | £0 (£0) | |
| Total single lung surgery staff time costs | Recipient | £1325 (£0) | £1325 (£1325–1325) | £1325 (£0) | £1325 (£1325–1325) | £0 (£0) | |
| n = 24 | n = 2 | ||||||
| Total double lung surgery staff time costs | Recipient | £2320 (£0) | £2320 (£2320–2320) | £2320 (£0) | £2320 (£2320–2320) | £0 (£0) | |
| n = 160 | n = 16 | ||||||
| Total single lung surgery theatre usage costs | Recipient | £2351 (£0) | £2351 (£2351–2351) | £2351 (£0) | £2351 (£2351–2351) | £0 (£0) | |
| n = 24 | n = 2 | ||||||
| Total double lung surgery theatre usage costs | Recipient | £4114 (£0) | £4114 (£4114–4114) | £4114 (£0) | £4114 (£4114–4114) | £0 (£0) | |
| n = 160 | n = 16 | ||||||
| Total equipment/consumable costs | Recipient | Missing | Missing | Missing | Missing | Missing | |
| Total single transplant costs | Recipient | £4177 (£0) | £4177 (£4177–4177) | £4177 (£0) | £4177 (£4177–4177) | £0 (£0) | |
| n = 24 | n = 2 | ||||||
| Total double transplant costs | Recipient | £6934 (£0) | £6934 (£6934–6934) | £6934 (£0) | £6934 (£6934–6934) | £0 (£0) | |
| n = 160 | n = 16 | ||||||
| Total lung transplant costs | Recipient | £6574 (£931) | £6934 (£6934–6934) | £6627 (£892) | £6934 (£6934–6934) | –£53 (£229) | –£505 to £399 |
The post-operative and outpatient care of the patients shows the largest variability in total costs (see Tables 35 and 36) because it is dictated by the nature and severity of any complications and AEs that might occur, which vary markedly between patients. Given the nature of events that might occur and the cost of their management, it would be expected that these costs would be highly skewed, and the mean cost, especially for the EVLP arm, would be greatly affected by the very high costs incurred by a small number of patients. As indicated in Table 35, the highest costs in this stage are the ward use (standard arm, £20,064; EVLP arm, £21,276) and staff time costs (standard arm, £4828; EVLP arm, £5265). This is because the length of hospital stay (especially in the ITU/HDU) varies between different patients and, consequently, different amounts of staff time are required. Table 35 also shows a large variation in the costs of the equipment used. In this case, the variation is mainly caused by the use of the ECMO machine (ECMO cost, £34,000). In addition, variation is also observed in the costs caused by complications and infection episodes. This is to be expected given the fact that each recipient responds differently to their transplanted organ, and thus some patients become more prone to infections than others. (It should be mentioned that the infection episodes and airway complication costs presented in Table 35 include the costs from infections that occur either straight after the transplant or during the subsequent outpatient care of the patient.)
| Resource use | Patient details | Study group | Mean (SE) difference in cost per recipient | 95% CI based on bootstrapping | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (n = 184) | EVLP (n = 18) | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | ||||
| Total staff time costs | Recipient | £4828 (£5331) | £2895 (£1721–6059) | £5265 (£5065) | £2741 (£1996–7795) | –£436 (£1311) | |
| Total test costs | Recipient | £135 (£77) | £183 (£14–183) | £115 (£87) | £183 (£14–183) | £19 (£19) | |
| Total ward usage costs | Recipient | £20,064 (£20,582) | £12,143 (£7459–25,453) | £21,276 (£23,651) | £11,605 (£5944–28,700) | –£1212 (£5152) | |
| Total procedure costs | Recipient | £158 (£167) | £135 (£0–340) | £336 (£150) | £340 (£340–475) | –£178 (£41) | |
| Total equipment costs | Recipient | £3696 (£13,726) | £0 (£0–0) | £22,667 (£30,855) | £0 (£0–68,000) | –£18,971 (£3931) | |
| Total consumable costs | Recipient | £826 (£1711) | £453 (£164–791) | £1469 (£3009) | £708 (£360–1320) | –£644 (£459) | |
| Total inotrope costs | Recipient | £16 (£15) | £10 (£4–27) | £22 (£17) | £23 (£4–34) | –£6 (£4) | |
| Total post-implantation haemodynamic support costs | Recipient | £43 (£160) | £2 (0–14) | £278 (£437) | £120 (£8–224) | –£235 (£49) | |
| Total complication costs | Recipient | £699 (£1799) | £0 (0–70) | £2246 (£2973) | £0 (£0–4580) | –£1547 (£476) | |
| Total airway complication costs | Recipient | £622 (£2020) | £0 (£0–0) | £0 (£0–0) | £0 (£0–0) | £622 (£477) | |
| Total ITU rejection episode costs | Recipient | £59 (£224) | £0 (£0–0) | 95 (275) | £0 (£0–0) | –£36 (£57) | |
| Total ward rejection episode costs | Recipient | £242 (£452) | £0 (£0–851) | 198 (381) | £0 (£0–0) | £45 (£110) | |
| Total infection episode costs | Recipient | £3925 (£14,046) | £286 (£0–1755) | £3518 (£7830) | £39 (£0–1738) | £407 (£3366) | |
| Total post-operative care costs | Recipient | £34,109 (£39,561) | £20,112 (£11,639–42,340) | £56,136 (£57,345) | £21,931 (£12,713–86,464) | –£22,027 (£10,217) | –£42,174 to –£1879 |
The data in Table 36 demonstrate that the outpatient care of a lung recipient varies markedly between participants. Some patients might require more outpatient or GP visits, whereas others might need several unplanned hospital admissions and longer duration of treatment with immunosuppressive medications. The last two resources constitute almost the 70% of the outpatient care costs. As expected, the unplanned hospital admissions of the recipients show a large variation, as their occurrence varies between different patients.
| Resource use | Patient details | Study group | Mean (SE) difference in cost per recipient | 95% CI based on bootstrapping | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (n = 184) | EVLP (n = 18) | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | ||||
| Total outpatient review costs | Recipient | £1420 (£699) | £1515 (£895–2170) | £994 (£842) | £766 (£209–1855) | £426 (£176) | |
| Total staff time costs | Recipient | £130 (£50) | £159 (£120–159) | £100 (£70) | £139 (£40–159) | £31 (£13) | |
| Total rejection episode costs | Recipient | £750 (£3443) | £0 (0–653) | £290 (£463) | £0 (£0–379) | £460 (£814) | |
| Total GP visit costs | Recipient | £9 (£22) | £0 (£0–0) | £18 (£29) | £0 (£0–34) | –£9 (£6) | |
| Total unplanned hospital admission costs | Recipient | £2748 (£10,864) | £0 (£0–559) | £689 (£2395) | £0 (£0–392) | £2059 (£2572) | |
| Total immunosuppressive medication costs | Recipient | £2923 (£1049) | £3187 (£2680–3522) | £2475 (£1522) | £3222 (£1003–3475) | £447 (£271) | |
| Total outpatient care costs | Recipient | £7981 (£12,263) | £5746 (£4552–7025) | £4567 (£3931) | £4969 (£1423–5805) | £3414 (£2911) | –£2326 to £9153 |
Concomitant medications can be considered as an additional part of the analysis of this study. A recipient might need an additional treatment or a change in the current treatment as a result of complications. The duration of treatment is also variable and depends on the condition of the patient. Therefore, the medications given vary between patients, and this explains why such a large variation in the total cost of concomitant medications exists (standard, SD £4505; EVLP, SD £3614) in Table 37.
| Resource use | Patient details | Study group | Mean (SE) difference in cost per recipient | 95% CI based on bootstrapping | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (n = 184) | EVLP (n = 18) | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | ||||
| Total concomitant medication costs | Recipient | £1424 (£4505) | £0 (£0–328) | £1172 (£3614) | £0 (£0–0) | £252 (£1096) | –£1908 to £2412 |
Table 38 presents the total average cost per recipient for the standard donor and the EVLP lung transplantation. These costs were calculated by adding the total costs of each stage of the transplant procedure for each patient and calculating the average cost for each lung recipient. As can be seen from Table 38, the mean and median cost of EVLP per recipient is substantially greater than for standard lung transplant. This is partially because of the different retrieval-to-transplant ratio between the two lung transplants, which leads to higher costs in the early stages of the analysis and, partially, as a result of the actual cost of the EVLP procedure (£14,479 per lung assessed). Also presented in Table 38 is the mean difference and bootstrapped 95% CI. The CI suggests that EVLP recipients are, on average, at least £57,910 more costly and may be as much as £101,036. These data are only suggestive given the very small number of participants in the EVLP arm (n = 18).
| Resource use | Patient details | Study group | Mean (SE) difference in cost per recipient | 95% CI based on bootstrapping | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (n = 184) | EVLP (n = 18) | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | ||||
| Total donor’s hospital costs | Donor | £403 (£12) | £408 (£395–412) | £1182 (£35) | £1182 (£1163–1214) | –£779 (£4) | –£786 to –£771 |
| Total lung retrieval costs | Donor | £8651 (£170) | £8729 (£8695–8729) | £25,398 (£524) | £25,688 (£24,957–25,700) | –£16,747 (£55) | –£16,856 to –£16,639 |
| Total transplant preparation costs | Recipient | £466 (£8) | £467 (£467–471) | £1365 (£28) | £1375 (£1375–1375) | –£899 (£3) | –£905 to –£894 |
| Total EVLP procedure costs | EVLP recipient | – | – | £42,633 (£2172) | £42,675 (£41,167–43,414) | – | – |
| Total lung transplant costs | Recipient | £6574 (£931) | £6934 (£6934–6934) | £6627 (£892) | £6934 (£6934–6934) | –£53 (£229) | –£505 to £399 |
| Total post-operative care costs | Recipient | £34,109 (£39,561) | £20,112 (£11,639–42,340) | £56,136 (£57,345) | £21,931 (£12,713–86,464) | –£22,027 (£10,217) | –£42,174 to –£1879 |
| Total outpatient care costs | Recipient | £7981 (£12,263) | £5746 (£4552–7025) | £4567 (£3931) | £4969 (£1423–5805) | £3414 (£2911) | –£2326 to £9153 |
| Total concomitant medication costs | Recipient | £1424 (£4505) | £0 (£0–328) | £1172 (£3614) | £0 (£0–0) | £252 (£1096) | –£1908 to £2412 |
| Total cost per procedure | – | £59,608 (£42,664) | £43,630 (£33,833–68,748) | £139,081 (£58,916) | £108,255 (£93,492–171,768) | –£79,473 (£10,935) | –£101,036 to –£57,910 |
In Figure 21, the costs of each stage of both standard and EVLP lung transplant procedures are presented as a bar chart. This reveals the significant difference in costs for certain parts of the procedure pathways between standard and EVLP transplants.
FIGURE 21.
Total average cost per recipient per procedure.
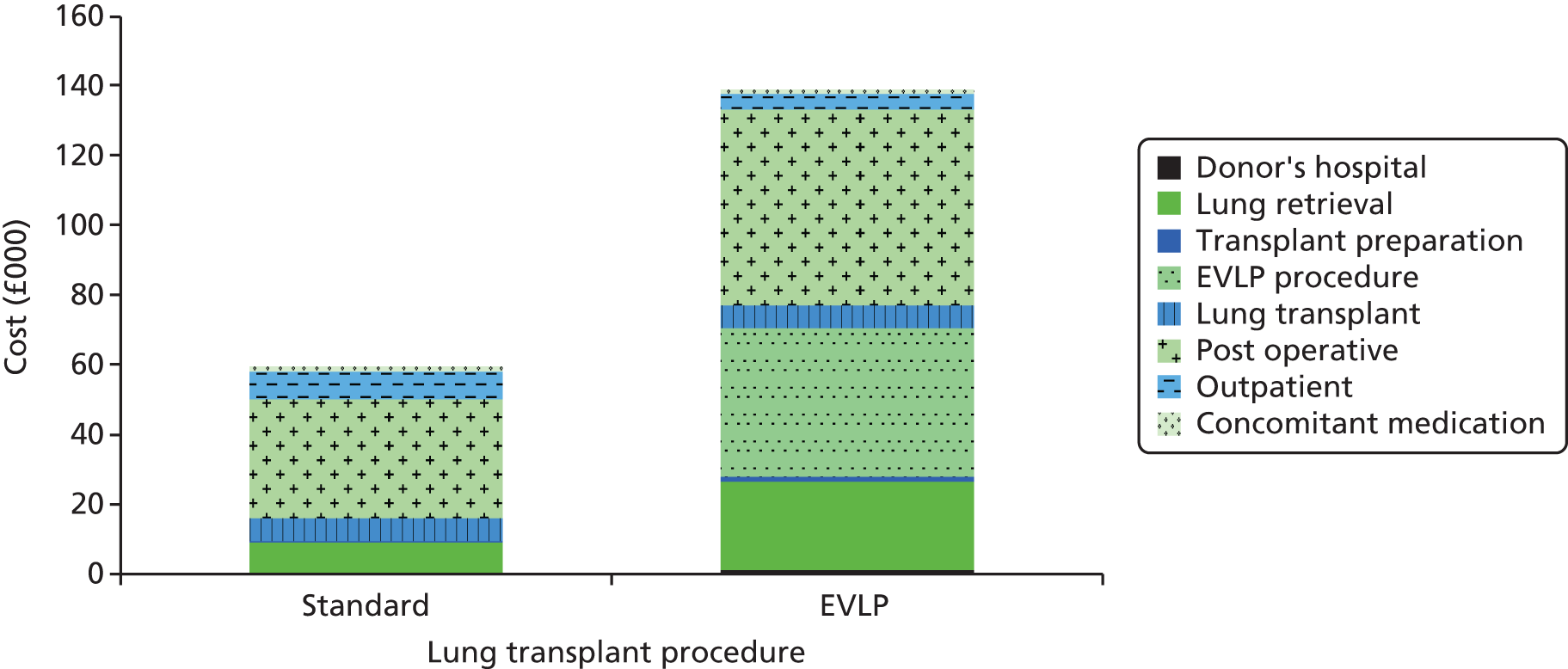
Analysis of the quality of life
As indicated in Table 39, there were only a small number of lung recipients who contributed SF-6D data (22/202) at all expected time points. These patients were those who completed the SF-36 questionnaire at all three time points, or were known to have died by a given time point, in which case SF-6D scores for that and any subsequent time points were given as zero. As a result, Table 40 presents the mean and median SF-6D utility scores for each stage that a questionnaire was completed or a patient was reported as being dead (i.e. at baseline, 3 and 12 months post transplant). It also presents the number of observations (n) based on which the means and the medians were calculated at each time point. At the bottom of the table, the total mean QALYs of each transplant type are shown, which were estimated by measuring the area under the curve created from the mean utility scores of each one of the three time points.
| Study group | Time point | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline only, % (n) | 3 months only, % (n) | 12 months only | Baseline and 3 months, % (n) | Baseline and 12 months, % (n) | 3 and 12 months, % (n) | Baseline, 3 and 12 months, % (n) | |
| Standard (N = 184) | 36.41 (67) | 33.15 (61) | 41.30 (76) | 17.94 (33) | 18.48 (34) | 23.37 (43) | 11.41 (21) |
| EVLP (N = 18) | 44.44 (8) | 55.56 (10) | 55.56 (10) | 22.22 (4) | 16.67 (3) | 38.89 (7) | 5.56 (1) |
| Total (N = 202) | 37.13 (75) | 35.15 (71) | 42.57 (86) | 18.32 (37) | 18.32 (37) | 24.75 (50) | 10.89 (22) |
| Questionnaires | Study group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (n = 184) | EVLP (n = 18) | |||
| Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | |
| At baseline | 0.5510 (0.0846) | 0.5450 (0.5010–0.5970) | 0.5880 (0.0382) | 0.6000 (0.5590–0.6125) |
| Number of observations | 67 | 8 | ||
| 3 months post-transplant | 0.5884 (0.2766) | 0.6660 (0.5540–0.7570) | 0.5551 (0.3942) | 0.7345 (0.0000–0.7990) |
| Number of observations | 61 | 10 | ||
| 12 months post-transplant | 0.4527 (0.3709) | 0.6125 (0.0000–0.7550) | 0.4689 (0.4267) | 0.6010 (0.0000–0.8410) |
| Number of observations | 76 | 10 | ||
| QALYs (from SF-6D mean scores)a | 0.5328 | 0.5269 | ||
Figure 22 presents the differences between the mean SF-6D scores between the two lung transplant procedures. As was expected from the numbers provided in Table 40, the differences are negligible. However, because these are the mean SF-6D scores reported, a comparison between the numbers of QALYs gained from each one of the two procedures would be meaningless.
FIGURE 22.
Health-related quality of life (QALY).

Predicting NHS expenditure costs for UK patients receiving a lung transplant: a regression-based analysis
Rationale
The aim of this part of the economic analysis was to identify the key determinants of costs to the NHS of a lung transplant. This aim was met by using information and data collected from the DEVELOP-UK study in a regression model, where the dependent variable was the NHS costs for a lung transplant and the independent (explanatory) variables were potential determinants of these costs. The purpose of the analysis was to help policy-makers understand what the main determinants of costs are, and also to provide a resource for future modelling where lung transplant is a component of the care pathway modelled.
Methods
Planning the analysis
The first step was to examine the distribution of total transplant costs estimated in order to help decide which type of statistical model would best suit the observed distribution of the data. For example, if the costs were normally distributed, then a linear regression model (ordinary least squares) could be used. On the other hand, if the costs were highly skewed, as was anticipated, a log-linear or a log-gamma generalised linear model would be needed, with the choice between the two dependent on the explanatory variables that would be selected for the model. Based on the observed distribution, the log-transformation of the total NHS costs was considered to be the most appropriate approach to handle the impact of any outlier observations on the predictions of the total expenditure.
The next step in this analysis was to identify all the explanatory variables that could potentially be included in a regression model and define a cogent reason of their selection. From this long list of variables, the most useful variables (i.e. the ones that were thought to make the most significant contribution to the total NHS costs) were selected for the model, while the rest were removed as not being adequate to explain the magnitude or direction of costs. It was expected that there would be some variables that are strongly correlated with other variables selected for the model. These variables were omitted if they provided little additional explanatory power.
After the selection of the most important likely parameters, a preliminary analysis of the relationship between each variable and the total transplant costs was conducted, and this was further illustrated by developing the corresponding scatterplots for each regressor. Once the relationship was understood, the selected variables were introduced in the model in the most appropriate form using the step-wise regression (forward selection) technique. More precisely, the most commonly used variables in this type of economic regression analysis (e.g. demographic characteristics, such as age and sex) were used in order to build a basic econometric model. Once this was done, a new potential variable was added each time in order to check if it would be statistically significant and provide a more accurate prediction of costs. In addition, this model contained a dummy variable that took values 0 or 1 depending on whether or not an EVLP procedure was performed.
Possible explanatory variables and model structure
Table 41 presents the explanatory variables that were tested in order to build the regression model, as well as the reason for their selection. These variables were based on initial assumptions about the factors that might have an impact on the total NHS cost of lung transplant and were divided into three main categories based on the information that they provided: (1) recipient characteristics, (2) donor characteristics and (3) resource use.
| Variable number | Explanatory variable | Reason of selection |
|---|---|---|
| Recipient characteristics | ||
| 1 | Age (> 18 years) | The age of the recipient can affect the health-care services needed. It is common that older people are more susceptible to diseases, especially chronic diseases, and might not respond well to several treatments. Apart from the fact that there might be some compatibility issues, which might be related to age, age might lead easier to GVHD. Age is always included as a variable in this type of analysis |
| 2 | Sex | There might be differences in the resources needed depending on the sex of the recipient. This is because there are several biological differences between men and women that normally lead to different health outcomes. Sex is always included as a variable in this type of analysis |
| 3 | Time on the waiting list (i.e. time between the date added on the waiting list and the date of transplant) | The time from diagnosis and inclusion in the waiting list until lung transplantation might affect the condition of the potential recipient. Obviously here, the time that is needed to find a perfect organ match for the recipient plays the most important role. However, normally the longer the patient stays on the waiting list, the worse their condition will get and, therefore, they might be more susceptible to diseases after the operation |
| 4 | Transplant indication (reason of transplant) | The reason why a lung transplant is needed is important, as this might affect the total condition of the patient as well as the body response of the recipient to the transplant. If possible, different conditions should be grouped in wider categories in order to have more robust results at the end |
| 5 | Number of other diseases (comorbidities) and medications while on the waiting list | Other diseases might have an impact on the overall health of the potential recipient, which might mean additional costs for the NHS. If possible, these conditions should be grouped in bigger categories (e.g. cardiovascular diseases) in order to generalise the values of the variable |
| 6 | SF-6D baseline scores (i.e. on entry on to the waiting list) | These scores can provide information on the HRQoL of the potential recipient while they are on the waiting list. This information could possibly capture the condition of the patient while on the waiting list, which might affect the need for additional health-care services post transplant. The only problem with the SF-6D scores in this study was that there was only a limited number of SF-36 questionnaires completed (73/202 at baseline), which might affect the accuracy of the results. In other words, the result of the analysis would be restricted to a smaller number of observations that could lead to a systematic error in the final results |
| Donor characteristics | ||
| 7 | Cause of death or donor type (i.e. after brain or circulatory death) | The cause of the donor’s death could affect the type of the transplant and may lead to a higher possibility for GVHD. A case might be that a transplant after circulatory death might be more likely to need reconditioning before being used in a surgery (i.e. EVLP). The donor’s previous condition might also affect the quality of the organ donated. However, this might be difficult to capture from the available data set |
| 8 | Donor–patient compatibility test | Instead of including all the different characteristics of the donor (e.g. age, sex, tissue characteristics), which might not have a meaningful relationship to the total transplant costs, the data from the donor–patient compatibility test (perhaps tissue typing test) could be used. In other words, there might be a scale and score with how well the tissues match that may predict any AEs or GVHD |
| Resource use | ||
| 9 | Distance between the donor’s hospital and the transplant site | The distance between the donor’s hospital and the transplant site can have an impact on the cost of the retrieval/scout team. In other words, a longer distance means a higher travelling cost for the retrieval team and, consequently, higher costs for the retrieval of the lung |
| 10 | Type of transplant (i.e. standard vs. EVLP) | One of the main differences between standard and EVLP lung transplant is the occurrence of the EVLP procedure before the operation. This includes several costs, such as the cost of the disposable lung set, the Steen Solution and the operating theatre usage, which increase the cost of the transplant by almost £43,000, on average. In addition, the fact that only 18 EVLP transplants were performed compared with 53 lungs that were retrieved means that there is an extra cost associated with the reconditioning of the lung in different stages of the lung transplant procedure (i.e. donor’s hospital, lung retrieval, transplant preparation). The type of the transplant might also affect the post-operative and outpatient care needed. It would, therefore, be reasonable to introduce the type of the transplant in the form of a dummy variable with value 0 if standard is performed and 1 if EVLP is followed |
| 11 | Number of lungs transplanted (i.e. single or double lung surgery) | The number of lungs that are transplanted is associated with different costs during the operation. This is because the time needed for the surgery changes and as a result, the staff time and usage time of the operating theatre changes. The number of lungs needed might also affect the post-operative and outpatient care. This variable could also take the form of a dummy variable depending on whether a single or a double lung transplant is performed |
According to the assumptions made above, the cost model was expected to have the following form at the beginning of the analysis, but its precise form would depend on which model fitted the data and provided robust predictions of costs (i.e. would be calibrated with the observed data):
where COSTS is NHS expenditure costs; AGE is the recipient age; SEX is the recipient sex; TIME is the potential recipient’s time on the waiting list; IND is the transplant indication; COM is the patient’s comorbidities and medications while on the waiting list; SF-6D is the SF-6D score of the patient while on the waiting list based on their response to the SF-36 questionnaire; COD is the donor’s cause of death; TEST is the donor–patient tissue compatibility test; DIST is the distance between the donor’s hospital and the transplant site; PROC is the type of transplant (standard or EVLP); and LUN is the number of lungs transplanted.
This regression was planned to generate a β0 value and beta values for all of the independent variables in the equation. β0 would be the intersection of the regression line with the y-axis (intercept). This value was not expected to have a meaningful interpretation, especially if this was a negative value, because β0 would be anticipated to represent the minimum or average cost for the NHS. The rest of the beta values would describe the direction and magnitude of the relationship between each variable and the NHS cost of transplant. A p-value of < 0.05 was taken as evidence of a real difference between the expected and actual impact of each variable on the total costs.
The analysis of costs was conducted using the statistical software Stata 13.1.
Results
Base-case analysis
Figure 23 shows the distribution of costs based on the DEVELOP-UK study data. As expected, the costs were highly skewed (i.e. several patients needed additional or more expensive health-care resources), which meant that a simple linear model would not give robust results. As a consequence, the total cost variable was log-transformed. This transformation had the effect of diminishing the impact of the outlier observations on the total lung transplant costs per recipient.
FIGURE 23.
Distribution of total transplant costs based on the DEVELOP-UK study data.
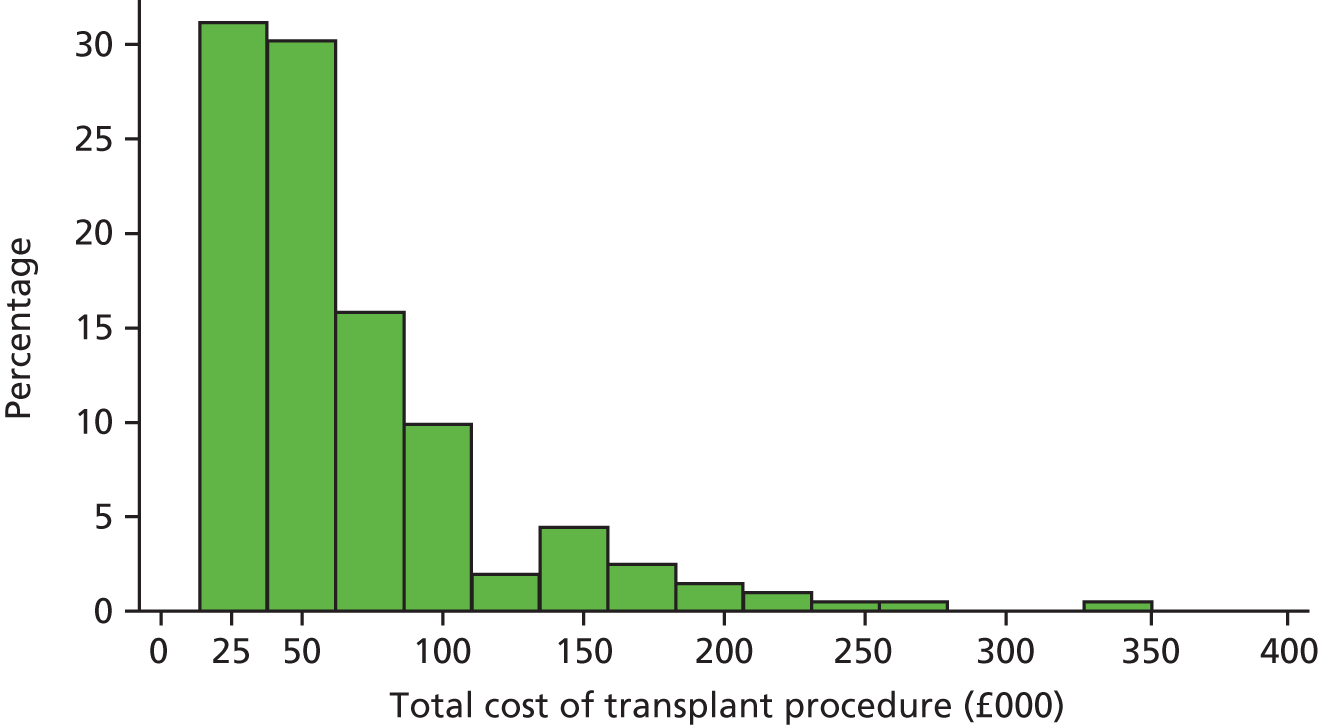
Table 42 presents the variables that were finally selected for the model as well as their marginal effect on arithmetic costs. As shown in Table 42, the regression model was a log-linear model. In other words, there was a linear (additive) relationship between each one of the explanatory variables and the log-form of the total lung transplant costs, which is reasonable when considering that the explanatory variables were mainly qualitative (e.g. age, sex) or categorical (e.g. type of transplant procedure, number of lungs transplanted). Obviously, Table 42 presents the exponential results of this regression model (i.e. the results of the analysis in a normal arithmetic scale).
| Explanatory variables | dy/dx (£)a | SE | z-score | p > zb | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recipient age (years) | 246 | 274 | 0.900 | 0.368 | –290 to 782 |
| Recipient sex (male as reference sex) | |||||
| Female | 4214 | 5945 | 0.710 | 0.478 | –7437 to 15,866 |
| Time on the waiting list (days) | –1 | 9 | –0.100 | 0.924 | –19 to 17 |
| Transplant indication (CF as reference indication) | |||||
| Non-CF bronchiectasis | 36,051 | 24,816 | 1.450 | 0.146 | –12,587 to 84,690 |
| Interstitial lung disease | 11,415 | 9447 | 1.210 | 0.227 | –7101 to 29,931 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 559 | 7459 | 0.070 | 0.940 | –14,061 to 15,179 |
| Emphysema | –9506 | 7777 | –1.220 | 0.222 | –24,748 to 5736 |
| Obliterative bronchiolitis | –11,629 | 9578 | –1.210 | 0.225 | –30,402 to 7144 |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 19,404 | 6380 | 3.040 | 0.002 | 6899 to 31,910 |
| Other and missing indication | 24,850 | 15,737 | 1.580 | 0.114 | –5995 to 55,695 |
| SF-36 score (MCS) while on the waiting list (score units, i.e. 0–100) | 656 | 277 | 2.370 | 0.018 | 112 to 1199 |
| SF-36 score (PCS) while on the waiting list (score units, i.e. 0–100) | 784 | 372 | 2.110 | 0.035 | 56 to 1513 |
| Donor type (DBD as reference type) | |||||
| DCD | 5078 | 7639 | 0.660 | 0.506 | –9894 to 20,050 |
| Transplant procedure (standard transplant as reference procedure) | |||||
| EVLP | 58,097 | 13,041 | 4.450 | 0.000 | 32,537 to 83,658 |
| Number of lungs transplanted | 30,401 | 10,205 | 2.980 | 0.003 | 10,400 to 50,403 |
As indicated in Table 42, there were nine variables that were included in the model instead of the 11 that were initially considered. The reasons for this reduction are listed below. First, the condition of the patient due to comorbidities or medications taken was found to be captured by the SF-6D score of the patient while on the waiting list. Second, the data for the donor–patient compatibility test were difficult to identify, and were possibly not recorded by the transplant sites. Third, the distance between the donor’s hospital and the transplant site was difficult to calculate based on the available data, and the total costs calculated in the descriptive analysis of the study were based on estimates given by the NHS staff. Finally, it was decided that rather than using the SF-6D, the SF-36 should be used with the scores reported as the two main SF-36 summary components (i.e. MCS and PCS), where MCS and PCS are reported on a 0–100 scale, with higher scores indicating better health, in order to have a more accurate understanding of the factors that affect the patient.
In Table 42, four variables are shown to be significant (p < 0.05) when predicting the total cost of a lung transplant for the NHS. These are the two subcomponents of the SF-36 scores (p = 0.018 and p = 0.035 for the MCS and the PCS scores, respectively), the type of the transplant procedure (p < 0.001) and the number of lungs transplanted (p = 0.003). The final two parameters were expected to be statistically significant because an EVLP transplant leads to higher costs because of the addition of the EVLP procedure before the operation (βPROC = 58,097, which means that moving from a standard to an EVLP transplant will cost at least £58,097 more to the NHS), whereas if a double lung surgery is conducted, then more time is needed for the operation, resulting in higher staff and theatre costs. As far as the two subcomponents of the SF-36 scores are concerned, both were significant and both had a coefficient of similar magnitude (βMCS = 656 and βPCS = 784). This suggests that, in addition to the physical health driving lung transplant cost, the mental health of the recipient also increases the cost. Nevertheless, these effects were relatively small when compared with the total cost of transplant.
One interesting issue when looking at the impact of the SF-36 scores on the total transplant costs is the positive symbol of their coefficients. That is, the healthier a person is, the higher the costs are. There are a number of potential explanations for this. First, it could reflect the limited numbers of the SF-36 questionnaire completed at baseline (73/202 participants). This may mean that estimates derived were not very robust and were biased due to missing data, especially if those who did not complete the SF-36 were less well at baseline. Second, and related to the first reason, recipients that had lower scores were more likely to die or had a shorter time to death between the 12-month follow-up of the study than patients with higher scores, which therefore means they had less time to accrue costs. It is also interesting to mention that when the two scores were excluded from the regression model, the impact of EVLP on the total costs was higher (see Sensitivity Analysis).
Regarding the reason for the transplant, Table 42 indicates that pulmonary hypertension is a predictor of cost (p = 0.002), whereas the rest of the indications are not. In order to examine further the significance of the indication variable and compare the different indications, an F-test was performed. The F-test is normally used when comparing two different populations of different sizes in order to examine if the variance between the two groups is bigger than the variance within each group. If the groups are significantly different, the variation in group will be bigger than the variation because of differences among individuals in each group. This test proved that the reason of transplant is a significant predictor for the model as a total (p = 0.006), so it would be wrong to remove it from the model, as this would lead to inaccurate coefficients for the rest of the variables of the model. Based on this test, it was also understood that there is a big difference in costs when the reason for transplant is pulmonary hypertension instead of CF, which was the reference indication during the analysis.
The demographic characteristics of the potential recipient (i.e. age and sex) seem to have a limited effect, that is, almost entirely captured by the two SF-36 subcomponent scores. This was expected since the condition of the patient, as well as the tissue compatibility between the donor and the recipient, would be the main reasons for any complications or AEs. However, age and sex should always be in this type of regression model to represent the characteristics of the patient. The same argument can be also used when examining the low impact of the donor type on the total costs. Perhaps the donor’s cause of death does not influence the cost of the transplant directly, and it is the tissue compatibility that plays the most important role here. Additionally, the time on the waiting list has the smallest impact (βTIME = –1) of all variables. In other words, for every additional day on the waiting list, transplant costs reduce by £1. Again, the longer the time on the waiting list the worse the condition of the patient gets and potentially the less likely they will survive to accrue costs. However, it is worth noting that the impact is very small and, although statistically significant, may not be of any practical significance.
Finally, based on the analysis of the DEVELOP-UK study data, it was calculated that the constant (β0) of the regression model is equal to 3898. In this regression, this number is the minimum or average cost for a lung transplant for a reference participant who is male, was referred for transplant as a result of CF, received a standard single lung transplant, where the organ retrieved was from DBD. The intercept was also calculated by controlling for age, time on the waiting list and SF-36 subcomponent summary scores.
Sensitivity analysis
Given the limited number of responses to the SF-36 questionnaire, a sensitivity analysis was performed where both subscores were omitted from the model and all the observations were tested. This approach would reduce the fit of the statistical model, but would allow more of the sample available for the analysis.
The new model contained seven variables, but did not fit the data as well as the base-case analysis (R2 was equal to 0.338 compared with 0.539 before). This suggests that the loss of model fit when using the larger data set makes the result unreliable. The transplant procedure, as well as the number of lungs that were transplanted, remained significant (p < 0.001 and p = 0.004, respectively), as was the reason for the transplant (probability > F = 0.002), but this time other and/or missing indications were the predictors of cost instead of the pulmonary hypertension that was in the base-case analysis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the base-case regression model described above was the best possible model that could fit the data that were available from the DEVELOP-UK study. Based on this model, there were four variables that were significant when predicting the cost of a lung transplant for the NHS: the two components of the SF-36 scores (i.e. mental and physical component summary), the type of the transplant procedure and the number of lungs that are transplanted. Although this model can be used in further research in this area, it should be considered that it was constrained by the limited number of data from the study. Of course, the fact that this model was based on only 73 observations (owing to the small number of SF-36 questionnaires completed) further limits its robustness and estimation power. However, given the results of the sensitivity analysis that was performed where the two SF-36 summary components were omitted and where all the observations were tested, it was confirmed that the type of transplant and the number of lungs remain significant when trying to predict the total transplant costs for the NHS. Furthermore, the fact that it was not possible to collect the data from the donor–patient tissue compatibility test and the distance between the donor’s hospital and the transplant site is an issue that should be considered when conducting a future analysis. It is anticipated that these two parameters would have an impact on the total lung transplant costs for the NHS.
Exploratory model-based economic evaluation
Aim
The aim of this element of the analysis was to conduct an exploratory model-based economic evaluation of a UK adult lung transplant service that includes both EVLP and standard lung transplant compared with a service that only includes standard lung transplant. As was noted before, the data for this model came from the descriptive analysis described above and the available literature on lung transplantation.
Objectives
The objectives of this work were to:
-
construct a decision-analytic model
-
populate the model, as much as possible, with the DEVELOP-UK study data
-
estimate the incremental costs per additional life-year gained (cost-effectiveness analysis) and per QALY gained (cost–utility analysis) comparing a lung transplant service including both EVLP and standard lung transplants with a service including only standard lung transplants.
Model structure
A decision-analytic model (Figure 24) was built in Microsoft Excel following the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research (ISPOR) guidelines on conceptualising models. 55 The model represents the UK adult lung transplant service care pathway; beginning on the waiting list (state A) and progressing to being removed from the waiting list (state G); dying (state F); or receiving a standard (state B), or EVLP lung transplant (state D). From the lung transplant state, recipients progress either to death or, if they survive 1 year post lung transplant, to a post-lung transplant state; either states C or E depending on the type of lung transplant received.
FIGURE 24.
Model structure.
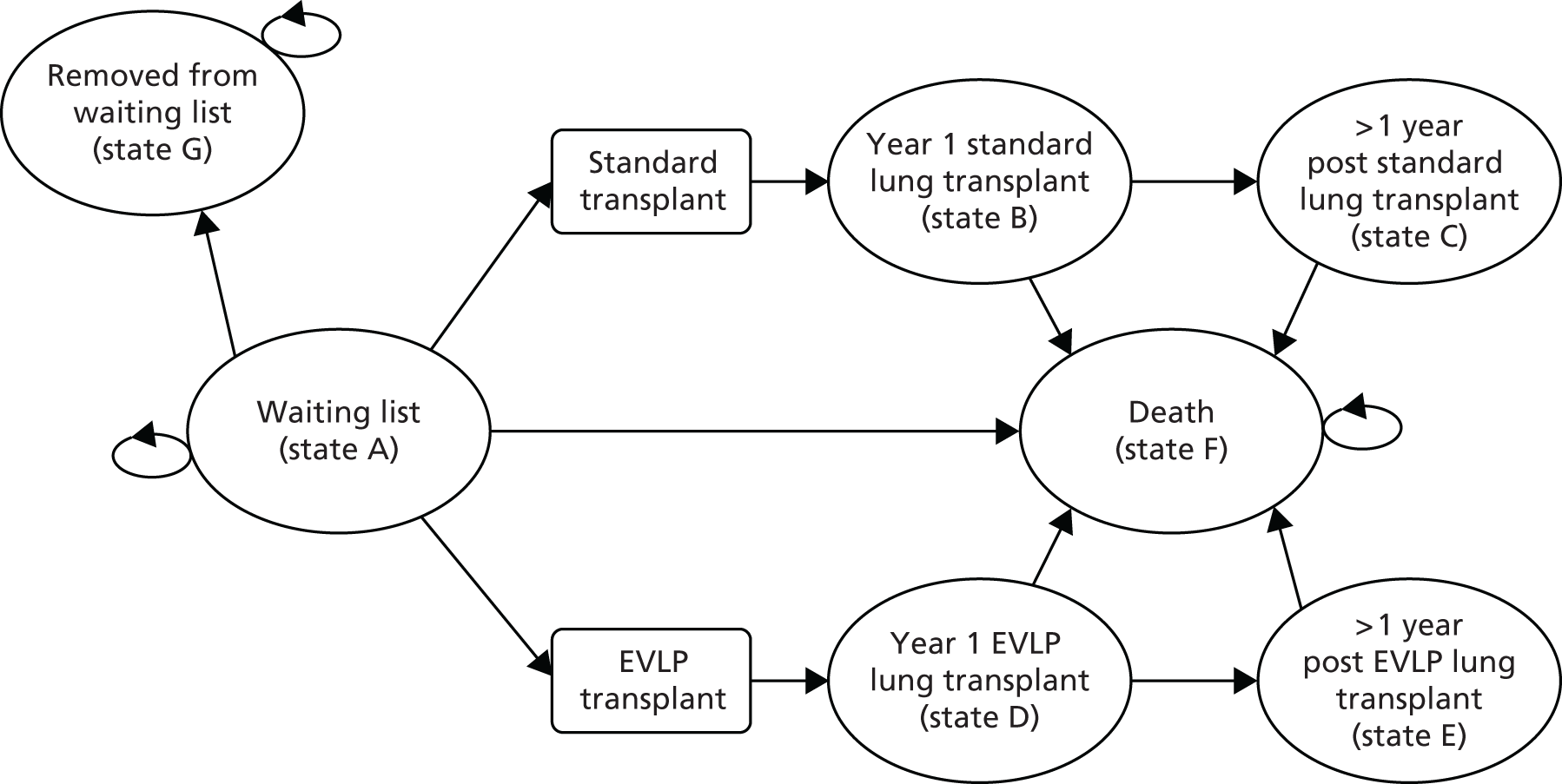
The post-lung transplant states were split into first year post lung transplant (including the cost of the lung transplant), and from year 2 onwards. This method was chosen as existing evidence suggested that the first year post lung transplant is key and should be modelled separately. 56,57
An area-under-the-curve Markov-type model was developed for post-lung transplant progression, where the length of time a lung transplant recipient survived from year 2 post lung transplant onwards was determined from a survival curve and allocated (as a fixed number of years) to each recipient in states C and E. To calculate the area under the curve, UK Cardiothoracic Transplant Audit survival data for 1, 3, 5 and 10 years post lung transplant were used and information on maximum life expectancy was sought. 58 More precisely, the ISHLT data for adults receiving a lung transplant between January 1990 and June 2012 report that survival of 19 years post lung transplant is 12%.
Half-cycle corrections were used for life-years gained in line with ISPOR guidelines,59 which are useful when the timing of the transition within the cycle is not known. On the other hand, no adjustment was made for QALY and cost calculations and, therefore, the QALY incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) would not be affected by the adjustment. A cohort of 1000 patients start in the waiting list state in the same year, and their progression was modelled over a lifetime horizon. The cycle length was 1 year, reflecting waiting list transitions and survival data.
Target population/location
The target population was adults on the UK lung transplant waiting list.
Study perspective
The perspective was the UK NHS using direct health-care costs only.
Comparators
The comparators are a UK adult lung transplant service that includes the use of both EVLP and standard lung transplants as the intervention (EVLP service) and a UK adult lung transplant service that includes only standard lung transplant as the control (standard service).
Time horizon
The time horizon used was lifetime, enabling consideration of costs and effects over the cohort’s lifetime.
Discount rate
The base-case analysis used a 3.5% discount rate for both costs and effects following NICE guidelines. 52,60
Outcomes
The principal outcome measure used was the QALY. Life-years gained was also measured, for the cost-effectiveness analysis, along with the number of lung transplants carried out.
Measurement of effectiveness/transitions
Lung transplant activity witnessed at the Newcastle centre during the study was used to inform the transition from waiting list to lung transplant in order to replicate within trial transitions. The Newcastle centre was chosen as it was the largest study centre. During the trial, standard lung transplants increased by 25% at the Newcastle centre, and this increase was applied to the pre-study transition from waiting list to lung transplant to calculate a within-study transition. A 10% increase in lung transplant activity because of EVLP lung transplant, also witnessed during the study overall by all centres, was used to calculate the transition to EVLP lung transplant. The pre-trial transition was taken from NHSBT data. 61 For transitions from waiting list to removal from waiting list and to death, NHSBT transitions were used from a cohort added to the waiting list in 2010/11 and followed for 3 years (to 2013/14), 2 of which were during the DEVELOP-UK study, reflecting in-trial waiting list transitions. 62
Post-transplant survival during the DEVELOP-UK study was not used to inform the model because of the small number of EVLP transplants carried out during the trial. In the absence of conclusive data from the literature, survival following EVLP and standard lung transplant were taken to be the same. Survival data were taken from the UK Cardiothoracic Transplant Audit, 1-year survival includes surgical mortality. 58 Area-under-the-curve methods were used to calculate a survival estimate that was applied to all recipients of a lung transplant who survived 1 year post transplant. The transitions used in the model are presented in Table 43.
| Parameters | Base case | Source | NHSBT 2013/14 transitions | Source | Pre-trial transitions | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waiting list transitions | ||||||
| Removal from waiting list | ||||||
| Year 1 | 0.04 | NHSBT 2013/1462 | 0.04 | NHSBT’s Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–1462 | 0.08 | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Year 2 | 0.04 | NHSBT 2013/1462 | 0.04 | NHSBT’s Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–1462 | 0.03 | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Year 3 onwards | 0.25 | NHSBT 2013/1462 | 0.25 | NHSBT’s Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–1462 | 0.11 | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Transition to death | ||||||
| Year 1 | 0.17 | NHSBT 2013/1462 | 0.17 | NHSBT’s Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–1462 | 0.17 | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Year 2 | 0.08 | NHSBT 2013/1462 | 0.08 | NHSBT’s Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–1462 | 0.09 | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Year 3 onwards | 0.02 | NHSBT 2013/1462 | 0.02 | NHSBT’s Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–1462 | 0.17 | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Transition to standard lung transplant | ||||||
| Year 1 | 0.5 | Freeman Hospital | 0.5 | NHSBT’s Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–1462 | 0.4 | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Year 2 | 0.56 | Freeman Hospital | 0.4 | NHSBT’s Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–1462 | 0.38 | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Year 3 onwards | 0.58 | Freeman Hospital | 0.069 | NHSBT’s Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–1462 | 0.28 | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Transition to EVLP lung transplant | ||||||
| Year 1 | 0.050 | Freeman Hospital | 0.1 | |||
| Year 2 | 0.056 | Freeman Hospital | 0.08 | |||
| Year 3 onwards | 0.058 | Freeman Hospital | 0.0138 | |||
| Increase in transplants | 0.1 | Freeman Hospital | 0.2 | Boffini et al.;63 Cypel et al.;30 and Henriksen et al.64 | ||
| Post lung transplant survival | ||||||
| 1 year survival (standard and EVLP) | 0.766 | UK cardiothoracic audit62 | ||||
| Area under the curve | ||||||
| 1 year survival | 0.766 | UK cardiothoracic audit62 | ||||
Health state utilities
During the DEVELOP-UK study, SF-36 questionnaires were administered to participants while on the waiting list, and again at 3 and 12 months post surgery. The conversion of SF-36 data to utilities is described in Analysis of quality of life. For this exploratory analysis, average utility means were calculated for baseline/waiting list, 3 and 12 months post transplant. Post-transplant, separate utilities were allocated to the standard and EVLP transplant groups, and only survivor’s utilities were included. Separate utilities for standard and EVLP were not allocated in the waiting list state, as some of the cohort patients will die or be removed from the waiting list, and it is important to capture these utilities as well as the transplant recipient utilities. The utilities used in the model are presented in Table 44.
| Parameters | Base case | Source | Joint utilities | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Utilities | ||||
| Waiting list | 0.563 | DEVELOP-UK study data | 0.563 | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| Standard lung transplant | 0.702 | DEVELOP-UK study data | ||
| 1 year post lung transplant | 0.690 | DEVELOP-UK study data | 0.734 | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| Year 2 onwards post lung transplant | 0.728 | DEVELOP-UK study data | ||
| EVLP lung transplant | ||||
| 1 year post lung transplant | 0.793 | DEVELOP-UK study data | ||
| Year 2 onwards post lung transplant | 0.782 | DEVELOP-UK study data | ||
| Costs | ||||
| Waiting list cost per year | £23,104 | Anyanwu et al.65 | ||
| Transplantation costs: standard | £50,203 | DEVELOP-UK study data | ||
| Transplantation costs: EVLP | £133,342 | DEVELOP-UK study data | ||
| Post transplantation | ||||
| Standard lung transplant | ||||
| Year 1 | £9405 | DEVELOP-UK study data | ||
| Year 2 | £3696 | DEVELOP-UK study data | ||
| Year 3 onwards | £3400 | DEVELOP-UK study data | ||
| Area-under-the-curve cost: year 2 onwards | £24,693 | DEVELOP-UK study data | ||
| EVLP lung transplant | ||||
| Year 1 | £5739 | DEVELOP-UK study data | ||
| Year 2 | £2255 | DEVELOP-UK study data | ||
| Year 3 onwards | £2075 | DEVELOP-UK study data | ||
| Area-under-the-curve cost: year 2 onwards | £15,068 | DEVELOP-UK study data | ||
| Discount rate | 0.035 | NICE60 | ||
Resources and costs
Costs were derived as described earlier in this chapter (see Within-study descriptive analysis of costs and quality-adjusted life-years) and used to populate the model with the exception of waiting list costs that were not available using the DEVELOP-UK study data. In this case, waiting list costs from Anyanwu et al. 65 were used to populate the model. These costs were the results of a published economic evaluation of adult lung transplantation in the UK. The costs for double lung transplantation waiting list were assigned to the model and inflated to 2013/2014 prices using the Hospital and Community Health Services’s 2007/2008 and Index 2013/14. 51
Costs in the transplant states B and D (year 1 standard/EVLP lung transplant) include the costs of donor hospital tests, lung retrieval, recipient preparation, EVLP procedure (if appropriate), lung transplant, inpatient post-operative care, and medication and outpatient costs for 1 year following transplant. Costs in states C and E (> 1 year post standard/EVLP lung transplant) are year 1 annual costs from the DEVELOP-UK study data, extrapolated forward using the data annual costs reported in Anyanwu et al. 65 The costs used in the model are presented in Table 44.
Assumptions
-
It was assumed that patients removed from the waiting list no longer accrue costs or utilities, and so do not contribute further to model outcomes following removal.
-
In line with survival rates reported by the ISHLT, it was assumed that no lung transplant recipients survive beyond 25 years.
-
Waiting list transitions were available for only 3 years post registration and, as only 6% of the cohort was still on the waiting list after 3 years, it was assumed that all transitions remain linear from year 3 onwards, and would have little effect on the overall results of the model after year 3. For example, mortality for year 1 is 17% of the cohort, in year 2 it was 18%, and by year 3 it had only increased to 19% of the original cohort. The year 3 onwards transition to death is 0.02, and the remaining cohort is also small.
-
As no evidence of a difference in survival outcomes was found from a search of clinical trials comparing standard and EVLP lung transplants, it was assumed that survival post lung transplant is the same for standard lung transplant and EVLP lung transplant recipients.
Uncertainty in model parameters
The assumptions used in identifying and calculating parameters can introduce uncertainty into the model; this uncertainty can be explored using sensitivity analysis. In this analysis, two types of sensitivity analysis were used: scenario analysis and probabilistic sensitivity analysis.
Scenario analysis
Scenario analysis explores uncertainty in parameters by analysing results using plausible alternative parameters. Four scenario analyses were carried out, variations in parameter values from the base case are presented in Tables 43 and 44.
NHS Blood and Transplant 2013/14 transitions
In order to explore the choice of transition from waiting list to transplant, the transitions from the waiting list witnessed by all trial centres during the DEVELOP-UK study were used in a scenario analysis. The waiting list transition to lung transplant used in the scenario analysis was the waiting list transition published by NHSBT, plus an EVLP activity increase. To adjust for EVLP lung transplants carried out during the DEVELOP-UK study and included in the NHSBT figures, the transition to lung transplant was decreased by 5%. Leaving an estimated transition to standard lung transplant, an EVLP increase of 20% was used, reflecting levels reported in the literature. 30,63,64
Joint utilities
The utilities used post transplant are separate for EVLP and standard lung transplant. However, the number of SF-36 questionnaires completed by EVLP recipients was low (seven at 3 months compared with 52 standard recipients, and six at 12 months compared with 48 standard recipients). An analysis was run using a joint mean utility for both EVLP and standard lung transplant recipients at 3 and 12 months post transplant calculated from the DEVELOP-UK study data.
NHS Blood and Transplant 2013/14 transitions and joint utilities
A separate scenario analysis was run, combining both of the above scenarios to reflect transitions witnessed by all trial centres, and using the more robust joint utilities.
Increase in standard lung transplant activity
This scenario analysis compared pre-trial NHSBT standard lung transplant transitions61 to the within-trial Newcastle transitions without any EVLP procedures. In other words, it purely compared a standard lung transplant service using pre-trial transitions with a standard lung transplant service using the transitions witnessed at Newcastle during the trial.
Probabilistic sensitivity analysis
Point estimates were used in the model, which do not represent the statistical variability surrounding estimates of costs, effects and cost-effectiveness. For this reason, a probabilistic sensitivity analysis was conducted. Probabilistic sensitivity analysis assigns suitable distributions to each parameter and simulations are carried out, each of which select a possible value across all parameters at once. In this analysis, 1000 simulations were carried out, and results are presented as a cost-effectiveness plane, an incremental cost-effectiveness plane and a cost-effectiveness acceptability curve. Parameters used in the probabilistic sensitivity analysis are presented in Table 45 and distributions used are described below.
-
Waiting list transitions: a beta distribution was chosen to fit to binomial data from the NHSBT service for waiting list removal and death. For transition to lung transplant, a beta distribution was chosen using figures reported by the DEVELOP-UK study.
-
Survival rates post lung transplant: a beta distribution was fitted using the ‘methods of moments’ technique described by Briggs et al. 66
-
Costs: a gamma distribution was fitted to costs using the methods of moments technique. Briggs et al. 66 report that a gamma distribution is constrained by zero and positive infinity, as are costs, making a gamma distribution a good representation for uncertainty of costs.
-
Utilities: a beta distribution was chosen for utility values using the methods of moments technique as described above. Using a beta distribution is a practical approach when utilities are not near zero.
| Parameters | Alpha, beta | Distribution | Source/reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waiting list transitions | |||
| Removal from waiting list | |||
| Year 1 | 38, 184 | Beta | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Year 2 | 3, 50 | Beta | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Year 3 onwards | 1, 19 | Beta | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Transition to death | |||
| Year 1 | 9, 213 | Beta | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Year 2 | 2, 51 | Beta | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Year 3 onwards | 5, 15 | Beta | NHSBT’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–201261 |
| Transition to standard lung transplant | |||
| Year 1 | 111, 111 | Beta | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| Year 2 | 30, 23 | Beta | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| Year 3 onwards | 12, 8 | Beta | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| Increase in lung transplant activity because of EVLP | 4.3, 39 | Beta | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| Post-lung transplant survival | |||
| 1-year survival standard and EVLP | 1694.3, 517.6 | Beta | NHSBT’s Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–1462 |
| Area under the curve | |||
| 1-year survival | 1694.3, 517.6 | Beta | NHSBT’s Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–1462 |
| 3-year survival | 1278.1, 770,2 | Beta | NHSBT’s Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–1462 |
| 5-year survival | 947.0, 863.7 | Beta | NHSBT’s Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–1462 |
| 10-year survival | 388.1, 777.3 | Beta | NHSBT’s Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–1462 |
| Utilities | |||
| Waiting list | 2292.2, 1782.4 | Beta | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| 1 year post standard lung transplant | 418.2, 187.6 | Beta | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| 2 years onwards post standard lung transplant | 436.9, 163.2 | Beta | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| 1 year post EVLP lung transplant | 69.6, 18.2 | Beta | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| 2 years onwards post EVLP lung transplant | 22.4, 6.3 | Beta | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| Costs | |||
| Waiting list cost per year | 100.0, 232.0 | Gamma | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| Standard lung transplant | 294.89, 170.24 | Gamma | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| EVLP lung transplant | 95.43, 1397.21 | Gamma | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| Post-lung transplant costs – standard | |||
| Year 1 | 90.61, 103.8 | Gamma | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| Year 2 | 90.61, 40.79 | Gamma | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| Year 3 onwards | 90.61, 37.53 | Gamma | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| Post-lung transplant costs – EVLP | |||
| Year 1 | 19.55, 293.48 | Gamma | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| Year 2 | 19.55, 115.34 | Gamma | DEVELOP-UK study data |
| Year 3 onwards | 19.55, 106.11 | Gamma | DEVELOP-UK study data |
Model results
Cost-effectiveness results
The base-case cost-effectiveness results are presented in Table 46. The mean undiscounted lifetime cost of a lung transplant in the standard service was £66,208, whereas the discounted lifetime cost was £64,861. The mean undiscounted lifetime cost of a lung transplant in the EVLP service was £70,562, whereas the discounted cost was £69,358. In both services, the largest proportion of cost was the year in which the transplant took place, accounting for 65% of total lifetime cost in the standard service and 71% of total lifetime costs in the EVLP service. The incremental cost of the EVLP service was £4496, while the number of incremental life-years gained and number of QALYs gained was 0.03 and 0.06, respectively. The life-year ICER was £147,000, and the QALY ICER was £73,000.
| Without EVLP | With EVLP | |
|---|---|---|
| Costs (%) | ||
| Waiting list | £9223 (14) | £7157 (10) |
| Year 1 post lung transplant | £43,259 (65) | £49,861 (71) |
| Year 2 onwards post lung transplant | £13,727 (21) | £13,544 (19) |
| Total | ||
| Undiscounted | £66,208 | £70,562 |
| Discounted | £64,861 | £69,358 |
| Outcomes | ||
| Life-years gained | ||
| Undiscounted | 5.61 | 5.63 |
| Discounted | 5.38 | 5.41 |
| QALYs | ||
| Undiscounted | 3.63 | 3.68 |
| Discounted | 3.48 | 3.54 |
| Incremental | ||
| Costs | £4496 | |
| Life-years gained | 0.03 | |
| QALY | 0.06 | |
| ICER | ||
| Life-years gained | £147,000 | |
| QALY | £73,000 | |
| Number of lung transplants | ||
| Standard lung transplant | 726 | 675 |
| EVLP lung transplant | 67 | |
In the standard service, the number of standard lung transplants carried out from a cohort of 1000 was 726. In the EVLP service, the number of standard lung transplants was 675 and the number of EVLP lung transplants 67, a total of 742; 16 (2%) more than the standard service.
Scenario analysis results
The scenario results are presented in Table 47.
| Without EVLP | With EVLP | ICER | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transplant cost | Adjusted total life-years | QALYs | Number of standard lung transplants | Transplant cost | Adjusted total life-years | QALYs | Number of standard lung transplants | Number of EVLP lung transplants | Life-years | QALYs | |
| NHSBT transplant transitions | £64,902 | 5.15 | 3.27 | 644 | £72,638 | 5.30 | 3.47 | 591 | 118 | £52,000 | £40,000 |
| Joint post-transplant utilities | £64,861 | 5.38 | 3.51 | 726 | £69,358 | 5.41 | 3.55 | 675 | 67 | £147,000 | £124,000 |
| Combining both scenarios | £64,902 | 5.15 | 3.30 | 644 | 5.30 | 3.45 | 591 | 118 | £52,000 | £51,000 | |
| Standard lung transplant only | £62,240 | 4.95 | 3.13 | 620 | 5.38 | 3.48 | 726 | 0 | £6000 | £7000 | |
2013/2014 NHS Blood and Transplant transitions
This scenario resulted in an incremental cost per QALY gained of £40,000. The number of lung transplants carried out was 644 in the standard service, and 709 in the EVLP service; thus, there was an increase of 65 lung transplants (10%).
Joint utilities
This scenario resulted in a QALY ICER of £124,000. The number of lung transplants carried out was 726 in the standard service and 742 in the EVLP service, as in the base-case analysis.
Combining NHS Blood and Transplant 2013/14 transitions and joint utilities
This joint scenario resulted in a QALY ICER of £51,000. The number of lung transplants carried out was 644 in the standard service and 709 in the EVLP service, as in the NHSBT 2013/14 transitions scenario.
Standard lung transplant only
This scenario resulted in a QALY ICER of £7000. The number of lung transplants carried out was 620 in the pre-trial standard service and 726 in the ‘Newcastle experience’ service, an increase of 106 lung transplants (17%).
Probabilistic sensitivity analysis results
The results of this analysis are presented for the cost–utility analysis only. The ICER was £72,000, similar to the base case. Figure 25 shows the predicted cost and QALY plots for each intervention, whereas Figure 26 shows the predicted plots for the difference in costs and QALYs between the two interventions, with a threshold of £30,000 per QALY. Figure 25 indicates that the EVLP service is marginally more effective and costly than the standard lung transplant service. Figure 26 indicates that the majority of the simulations fall in the north-east quadrant, where the EVLP service is more costly and more effective than the standard service, but several simulations fall into the north-west quadrant of the figure, where the EVLP service is less effective and more costly than standard service. The incremental effectiveness in QALYs varies between –0.05 and 0.3, with a mean of 0.061 (95% CI –0.006 to 0.152), and the incremental costs vary between £680 and £16,180 with a mean of £4349 (95% CI £1167 to £9742).
FIGURE 25.
Cost-effectiveness plane.

FIGURE 26.
Incremental cost-effectiveness plane.

The data from the Monte Carlo simulation were used to plot a cost-effectiveness acceptability curve (Figure 27). The results indicate that at the typical ceiling ratio adopted by NICE of £20,000, the standard service has a 99.9% chance of being considered cost-effective compared with the EVLP service.
FIGURE 27.
Post-trial cost-effectiveness acceptability curve.
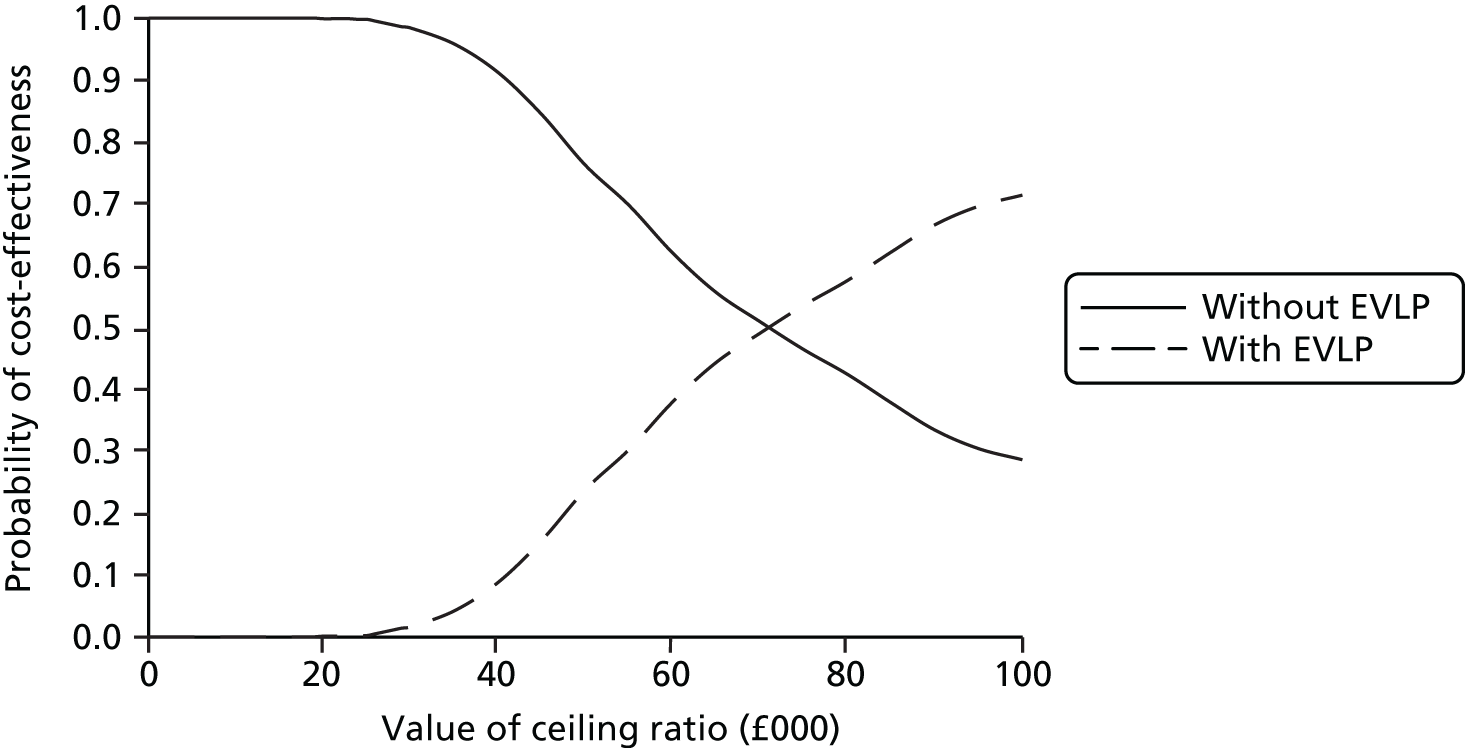
The conclusions of the economic evaluation are discussed in Chapter 6.
Chapter 5 Qualitative study results
Introduction
There is currently no published literature examining patients’ views of EVLP, and research related to people’s experiences of receiving donor organs is also limited. 67–72 It is imperative that if new heath-care technologies, such as EVLP, are to be implemented successfully and achieve real benefits for patients, the views of those receiving them are taken into account. This substudy critically examined patients’ attitudes towards, and understanding of, EVLP; their reasons for participation in the DEVELOP-UK study; and their experiences of waiting for and receiving a transplant.
Research objectives
The aim of this 24-month qualitative substudy was to identify, describe and understand patients’ pre- and post-operative perceptions of EVLP, and to explore how these are mediated by individual, social, physical and clinical factors.
Methods
This qualitative study used focused interviews to explore patients’ views and experiences of consenting to be part of DEVELOP-UK study and their views of EVLP both before and after transplantation. Focused interviews are particularly useful when researching a new area about which relatively little is known. 73 This substudy was conducted with patients from two study sites: the Freeman Hospital, Newcastle, and Harefield Hospital, London. These two sites were chosen as they both provide care to diverse populations across large geographical areas, and they were expected to recruit the largest number of patients to the DEVELOP-UK study.
Prior to commencing data collection, an outline interview topic guide was developed that covered the following key areas:
-
pre transplantation
-
patients’ understandings of EVLP and the perceived acceptability of this procedure in comparison with other donor lungs
-
patients’ hopes and expectations for EVLP
-
patients’ accounts of their own health and experience of living with their condition
-
patients’ experiences of waiting for lung transplantation
-
-
post transplantation
-
patients’ retrospective accounts of their pre-operative health and experiences
-
patients’ accounts of waiting for a transplant
-
patients’ views and experiences of receiving and living with an EVLP or standard transplant.
-
Sampling
The aim of this substudy was to sample a smaller group of patients from the DEVELOP-UK study to explore their views and experiences in more detail. Initially the plan was to recruit between 20 and 30 adult patients waiting for lung transplantation and between 20 and 30 patients 3–6 months post-operatively from across both sites. Maximum variation purposive sampling74 was used to ensure that a range of different experiences was included; specifically, we sampled for: sex, age, location (distance from hospital), diagnosis and length of time on the transplant list.
On consenting to take part in the DEVELOP-UK study, pre transplantation patients were given some brief information about the qualitative substudy and, if they were willing to consider taking part, they were asked to sign an EOI form. On completing an EOI form, patients were then given further detailed information about the qualitative substudy by a research nurse. After this, if patients were still willing to take part, they completed a consent to contact form, which was passed to the qualitative research team. The patients were subsequently contacted by a qualitative researcher and were again given another opportunity to ask further questions. If they were still interested in taking part, a date for interview was organised and a consent form was mailed out for the patient to complete and return. It was made clear to patients at all times that participation in any interviews was optional. During recruitment the team used purposive sampling, as outlined above, and reviewed the sample regularly to ensure that a range of different views and experiences was included, and actively targeted under-represented groups (e.g. patients with CF, younger patients, etc.). At the end of their first interview, patients were asked if they were willing to be interviewed again and all agreed, although only seven of the 26 patients interviewed pre transplantation were able to be interviewed again, as the remainder either had not received a transplant within the timescale for the fieldwork or were not well enough to be interviewed again.
Owing to the nature of the sampling for the study, not everyone who returned a consent to contact form was actually invited to interview before their transplantation. However, following transplantation, a number of patients who had previously returned consent to contact forms to the team but had not already been interviewed were contacted again 3 months post transplantation by a researcher and invited to take part in an interview at this stage. Upon receipt of consent to contact forms, an additional 11 individuals were invited to take part in an interview 3–6 months post-operatively.
As only a small number of EVLP transplantations were undertaken there were only a few people who could be interviewed about this experience. A targeted effort was made to identify and recruit all EVLP patients to the qualitative substudy. However, some patients, although they had expressed an initial interest in being interviewed, did not return a consent to contact form.
Interviews
Individual interviews were conducted either face to face or by telephone by JL. The first three pre-transplantation interviews were carried out in participants’ homes. Subsequent interviews were conducted either face to face in a room at the hospital when the patient attended for outpatient review or by telephone at a time that was convenient to the participant. All except two post-transplantation interviews were conducted by telephone. Telephone interviews were particularly useful in this study as they allowed the team to interview people who lived across a wide geographic area. Transcripts of early face-to-face interviews were carefully compared with initial telephone interviews and there appeared to be little difference in the quality or detail of the data collected.
Data analysis
Following a long tradition in qualitative research,75,76 data collection and analysis occurred concurrently to allow for issues or themes that were identified in earlier interviews to be explored in more depth in subsequent interviews. All interviews were digitally audio-recorded and transcribed verbatim. Initially, interview transcripts were checked against the audio-recording and, in line with Data Protection Legislation and Research Governance stipulations,77 all potentially identifiable information pertaining to individuals was anonymised. After this, transcripts were read; open, then focused, coding was undertaken; and emergent codes from the analysis of this stage were presented to the wider research team for checking and validity. The validity of data interpretation was ensured by independent coding and cross-checking by the qualitative research team (JL and CE). Data collection stopped when no new themes were being identified in the data. NVivo version 10 (QSR International, Warrington, UK) was used to facilitate data analysis management. 78
Results
In total, interviews were conducted with 44 participants (24 men and 20 women) aged 21–69 years. Of these, only 19 were interviewed before transplantation, seven both before and after transplantation and 11 after transplantation.
Patients were located across a wide geographic area across the UK, Ireland and the Channel Islands. The patients interviewed had been diagnosed with a range of conditions: pulmonary fibrosis (n = 7), emphysema (n = 9), CF (n = 8), α1-antitrypsin deficiency (n = 5), idiopathic fibrosis (n = 2) and others (n = 6). Twenty-six interviews (14 Newcastle; 12 Harefield) were conducted before transplantation with 12 women (aged 23–61 years) and 14 were with men (aged 25–69 years). Eighteen interviews were conducted post transplantation (13 Newcastle; 5 Harefield) with eight women (aged 21–62 years) and 10 men (aged 25–69 years). Two patients interviewed had received an EVLP transplantation, the rest a standard transplantation. Seven people (two women and five men) were interviewed both before and after transplantation, and, as outlined above, a further 11 (six women and five men) were interviewed only after transplantation.
Patients’ views and understandings of ex vivo lung perfusion
One of the main foci of the qualitative substudy was to explore patients’ views and understandings of EVLP and their expectations and hopes regarding the use of this new transplantation technology. Patients were asked to explain their understandings of EVLP. When asked specifically to explain EVLP, most people identified the perfusion process and the effect it had on the lungs as the major difference between an EVLP transplant and a standard transplant. Reference to a ‘cleaning out’, ‘improving’ the quality of the lungs was frequently mentioned, and some patients demonstrated a good understanding of the processes involved in EVLP:
I understand to be the sort of passing of some magic liquid through the lungs while they are ex vivo, i.e. after they have been removed from the donor to (a) deal with any bugs and whatever but also as I understand it to potentially improve their quality or bring them up to what they, you know for reasons of bugs.
Dominic, pre transplant, centre 1
They are pumped through with various different gases and a fluid to clean out and sort of recondition these lungs into a better condition so that they are suitable for transplantation.
Mark, pre transplant, centre 2
When describing EVLP, participants tended not to use technical language or give detailed information about the perfusion process. Rather, their explanations focused on what they appeared to regard as the essential information, that EVLP can enhance the quality of lungs, which previously would not have been suitable for transplantation so they could now be used:
They take somebody’s lungs that may have been a smoker and they basically recondition them. Clean them on the machine and then pass them onto the patient that’s needing them.
Adrian, pre transplant, centre 2
It’s retrieving a pair of donor’s lungs that you’re not sure if they’re 100%, so they’re put on like a heart lung by-pass machine and cleansed out given fluids and taken all the muck out, and replenishing as soon as they then can be used as a donors [and] transferred to somebody waiting for them.
Amanda, pre transplant, centre 1
Patients were asked how they would explain the process of EVLP to family and friends, and some used analogies to help explain EVLP to their families in everyday terms:
Well, I think I explained it as being like a washing machine where they take, put the lungs in, give them a clean, give them, fix them up and then just let them dry out a little bit.
Angela, pre transplant, centre 2
A service that’s basically what is was, you’re putting them in basically, donor lungs going for a service or an MOT [Ministry of Transport test] you know just like your car.
Tom, post transplant, centre 2
Although most patients were able to articulate a clear and accurate explanation of EVLP, a small number of people at both sites gave less accurate or confused explanations of EVLP:
My understanding of it is that it’s organs taken from long-term ill patients that perhaps have been on a life-support machine for several months and died very slowly and as the organs, you know as the body dies so the organs you know they lose their selves and they just get weaker and sort of die along with the patient and you know they’ve found that they’re able to revive these lungs and bring them back into working order.
Christine, pre transplant, centre 1
Pickled lungs, pickled lungs. I keep saying to everybody that they pickle the lungs. A set of lungs out of a donor; something wrong with them; they put them in whatever, hoover them out, give them antibiotics, clean them and everything, and hopefully get them up to a standard where they can be transplanted.
Sarah, pre transplant, centre 2
When patients consented to take part in the DEVELOP-UK study they were given a lot of information about the study, and were given several opportunities to ask questions and to clarify anything that was unclear to them. However, some patients still felt the need to seek out additional information about EVLP, often from the internet to supplement their knowledge. Patients in the DEVELOP-UK study also referred to having also consented to participate in other studies. They were willing to do this, however, consenting to several studies with large amounts of complex information sometimes led to some confusion about the details of individual studies:
Oh basically a pair of live lungs isn’t it, they’re not put on ice as it were. They’re kept pumping using the donor’s blood, yeah? I think I’ve got the gist of it.
Joseph, pre transplant, centre 1
Consenting to be part of the DEVELOP-UK study
During the interviews, participants were asked why they had made the decision to take part in the DEVELOP-UK study to explore the motivations of people consenting to be part of a trial of a new technology. Unsurprisingly, the most common reasons patients gave for consenting were the hope of receiving a transplant quicker and the possibility of helping others in the future:
Well my mum like said to me right ‘You would have a better chance of getting a transplant if you go with that’. But I had already made my mind up that it is something that – you’ve got to really give it a go because you can double your chances really, can’t you?
Jack, pre transplant, centre 2
I’m interested in the greater good not just my own good [OK] and I think you know I don’t see how we’ll ever make leaps forward in this stuff unless people are prepared to take a few chances.
Ali, pre transplant, centre 1
For a few, consenting to be part of a trial involving a new intervention was a difficult decision and required considerable time and thought:
No like at first I, I’m sort of thinking oh, oh my goodness, know what I mean? What about I mean what, who it was, he’s [donor] got AIDS [acquired immunodeficiency syndrome], somebody’s got this. Know what I mean, and somebody that like smokes you know a 100 fags a day sort of thing and that so I was initially, I thought at first until I read into, looked into it I thought I was getting the rough end of the deal to be honest. You know whereas now, you know I’ve spoke to Karen [transplant co-ordinator] about it and she just says . . . we wouldn’t go with them unless we’re 100% sure, they’ve got to be as good as the other ones they would have used in the first place.
Connie, pre transplant, centre 2
Others expressed some reservations about the technology or limited understanding, but were willing to put their trust in the medical team who they believed would make the best decisions for them:
I wasn’t really sure at first but then the more I was thinking about it, basically the doctors are always going to do their best for you so they are not going to give you something they think isn’t going to work or anything like that so I wasn’t really phased. To be honest I wasn’t going to really think too much into it. Like even the [standard] transplant I didn’t want to think too much into it I just wanted the doctors to do their job and just not really think about it.
Brenda, post transplant, centre 1
I put my faith in the people that are doing the operation. And, I mean, if they decide that lung’s good enough for me, that’s basically, good enough for me.
Adam, pre transplant, centre 2
However, patients’ accounts demonstrate that, regardless of any fears, concerns or limited understanding of receiving EVLP lungs, they were aware that the lungs they received would function better than the ones they currently had.
What are my, well I’m hoping that the lungs will just be good enough, I get called up, get transplanted, and that even if its 80% better than what I’ve got now you know, I just know I’ve got faith in the system that you just wouldn’t give me a crap pair of lungs really.
Amanda, pre transplant, centre 1
Going on the transplant list
Understanding of EVLP and motivation to take part in the DEVELOP-UK study were of interest to the research team. For patients themselves, being asked to take part in a study employing a new technique to increase the number of lungs available for transplantation appeared to be less significant than actually accepting the need to be placed on the transplant list in the first place. During the interviews, patients spoke in detail about what happened when they were accepted onto the transplant list, what they expected the transplant process to be like and what they were fearful of. Many of the views in this following section relate to transplant generally rather than EVLP specifically, but provide an insight into patients’ broader experiences of waiting for a transplant.
During interviews, patients spoke about their condition needing to deteriorate to a point where the transplant team would consider them to be at a stage where a transplant would be the best option:
I was too fit to go on the transplant list then I think. So it well I wasn’t overly disappointed, I was disappointed slightly but I wasn’t overly disappointed if you know what I mean because I knew that I was still fit enough I was still breathing not too badly I am saying not too bad I was absolutely atrocious but you know what I mean compared to near the end.
Paul, post transplant, centre 2
On being accepted on to transplant waiting list all patients interviewed expressed feelings of hope, relief or joy:
[I] absolutely burst into tears when they told me that I was going on the transplant register, it was like you were getting some form of a lifeline.
Mark, post transplant, centre 2
However, they were aware that if their health deteriorated too much they might be removed from the transplant list:
Well what it is you see it’s like a window, it’s you’ve not got to be too ill but you’ve not got to be too well, you can’t be either side of it you’ve got to be right.
Connie, pre transplant, centre 2
The only thing that I’m really scared of is because each time I get a chest infection now it comes worse each time and the last time I had one well I thought, either, you know, I think I should have been in hospital really but I couldn’t even walk to the toilet but we just got another load of antibiotics so I’ve learnt by that mistake or experience and next time I’ll get the doctor in or get my husband to take me to hospital but and so the only thing that worries me is that I’ll die of a chest infection so that’s the scary bit.
Amanda, pre transplant, centre 1
Several patients spoke about their fear regarding the transplant operation, but acknowledged this had to be balanced by the fact that transplantation was their only hope of survival:
I’d be lying if I said I wasn’t frightened, because I think everybody who’s facing any kind of surgery is worried, apprehensive about it. But it was a choice of sitting in a chair, or having a chance. And I chose the chance. I don’t want to be sitting in this chair.
Sarah, pre transplant, centre 1
Well dying more than owt [anything]. It’s just all going wrong and the first thing you hear like the first thing you hear is like the rates that’s successful and then not successful and it were just like – I think it was an 80% chance of it being successful and 20% that it been not be successful. That is all you can think about really, is that 20% really if its. That’s all I kept thinking about. But now I’ve like kind of thought if you don’t have it done you are going to be that 20% anyway, if so I could as well just take risk.
Jack, pre transplant, centre 2
Being on the list
One of the main topics discussed in detail by patients during their interviews was their experience of living their life while waiting on the transplant list. Although not specifically related to EVLP, it demonstrates the ways in which people adapt to a life waiting for a transplant. However, some of the everyday difficulties encountered may offer some insight into why people were willing to consent to be part of a study involving a new technology that could increase their chances of receiving a transplant sooner. Although patients’ experiences varied, the data suggest that waiting for a transplant had a significant impact on all of their lives. Some people continued to try to do many of their normal activities, whereas others worked hard to become fitter and more active to enhance their chances of a successful transplant:
As I got put on transplant list like I just knew I’d got to make sure I was fit enough and healthy enough to get through this operation if and when it happened. Well just tried to, well I went on exercise bike, you know do as much as I could on exercise bike, walking up and down us [our] drive and obviously not in bad weather but I just do a bit more walking around the house and just doing general housework you know what I mean trying to keep on top of everything.
Adrian, pre transplant, centre 2
Once accepted onto the transplant waiting list patients must adjust to a different way of living; many patients referred to feeling constantly on the alert waiting for a telephone call about a potential donor and needing to be ready to leave for the hospital when the call came:
I can’t go here, I can’t go there without thinking am I going to get a call. I always have my phone with me, my phone is always on loud, it’s always in my hand. I’m constantly staring at it, every time it goes, makes a noise, my heart stops and it’s just crazy and it’s really annoying cos I can’t go on holiday . . . I can’t even leave the county . . . so I basically I am trapped, it’s literally like being in a cage.
Angela, pre transplant, centre 2
As well as affecting their lives, participants also spoke of the impact of waiting on the lives of their families and significant others:
Yeah it’s horrible, because you can’t relax, no you, I know it sounds, phone rings and your hearts in your mouth you know, is it that, is it this? My husband I mean he, he doesn’t want much but now and again he goes out. He can’t go out, all over Christmas week we couldn’t make arrangements to go anywhere or, you know you can’t go out and have a drink . . . You know so it, it’s like you’re sort of waiting with bated breath sort of thing.
Connie, pre transplant, centre 2
On being accepted onto the waiting list after their assessment, all participants spoke of going home to pack their bags in preparation for being called in for a transplant. For many their initial feeling of anxiety and/or expectation of a rapid transplant was replaced by the reality of being on the waiting list and sometimes despondency:
I packed a suitcase. Bought new pyjamas and everything, and it’s been packed for a year. Packed and unpacked and washed and put there. But it’s there.
Sarah, pre transplant, centre 2
Some participants spoke of being called into the hospital several times for potential transplants that failed to progress. These ‘false alarms’, as the patients called them, raise expectations and can be very disruptive, particularly for those travelling long distances to the hospital. However, false alarms could also be reassuring, either because this appeared to convey that they were at the ‘top’ of the list, or because it helped to orientate them towards the process:
I got the stockings on this time. Got the shower, got the gown on . . . Got the white stockings on. Had the heart trace and the X-ray and all the bloods taken. So this was the farthest we’ve getting this this time. I have actually been in the gown the last time, but that’s as far as it’s gone. But this time was a little bit further, and I keep thinking, ‘Getting a little bit. She’s putting stockings on; I’ve never had them on before’. You know, ‘Yes!’ A step closer, but it wasn’t to be. It just wasn’t to be.
Sarah, pre transplant, centre 2
Sarah saw the fact that she had different things done each time as a sign that she was getting further along the line, nearer to her transplant: these may not have the significance that patients assigned to them.
Waiting for a suitable donor organ to become available could take many months or years, and, although patients were waiting, they were conscious that their condition was deteriorating and that they could die while waiting for a transplant. Connie spoke about treating each significant life event such as Christmas and birthdays as her last, although she did not share this with her family:
I don’t know you see it’s like having like, how do I explain it? . . . this Christmas well I’ve seen that as my last Christmas that’s on your mind all of the time. Do you understand what I mean? And that’s there every day. It’s the only thing I haven’t said [to my family] . . . you just feel that everything’s your last Christmas, your last New Year, it’s your last, every hurdle you can’t see beyond it and I still can’t. You can’t dwell on it but it’s there, it’s like a dark shadow on you all the time, that’s the best way, it’s so hard to explain.
Connie, pre transplant, centre 2
Waiting for a transplant means waiting for someone else to die for their chance of survival, something that was not discussed in detail by many people. One exception was Annie who spoke about it being a circle, a link between the patient, the donor and the donor’s family:
And it’s not just a donor’s lung; you know, somebody’s got to die for you to have their lungs. And I mean, that must be horrendous for their family as well, so it’s not just you; it’s a proper little circle. It’s just amazing.
Annie, pre transplant, centre 2
Perhaps to counter or cope with the anxiety and stresses of being on the transplant list, many of those interviewed made extensive plans for their lives post transplantation. These hopes ranged from the mundane to new challenges. Some patients saw their goal as undertaking new physical challenges, others just want to get back to ‘normal’, look after their grandchildren, go on holiday; the majority were happy to be able to do the mundane everyday activities they have missed:
I’ve got a walk planned with a friend and a dog on a beach! And then I just hope to get back to riding again.
Christine, pre transplant, centre 1
I look after my 4-year-old granddaughter quite a lot and sort of, although I’m fine with her because we do a lot of sitting down things, it would be nice to go back to sort of going out with her and things you know and just generally getting back to normal.
Julia, pre transplant, centre 1
Post-transplant experiences and hopes
Of the 18 patients interviewed post transplantation, seven had been interviewed before their transplantation as well, and 11 were interviewed only after receiving their transplant. Two people had received an EVLP transplantation. All the data from post-transplantation interviews are presented together for two reasons: first, to protect the anonymity of the small number of EVLP patients; and, second, from these two interviews it is not possible to ascertain any obvious differences in the reported experiences.
When participants described the events leading up to their transplant, they were often very specific about events, timings and how they felt. Some details they could recall themselves, and other aspects they had been told by relatives after the operation:
It was 1.30 in the morning, no sorry it was 9.30 on the Thursday night the phone rang again, it was Karen [transplant co-ordinator] and she said guess what I’ve been made an offer she said but someone else has also been offered the organs so start making your way to the hospital. I started getting prepped yet again and about quarter to five in the morning Karen got a call from the retrieval team to say, the organs are good it’s a go ahead. So I was then wheeled down to theatre at about 5.30 that was the last time I saw my wife then. Surgery commenced around 5.30 in the morning, 5.30/6.00 in the morning and I believe it took about 10/10.5 hours.
Mark, post transplant, centre 1
A key factor in the transplant process is the need for a donor. Those patients who mentioned the donor referred to the emotion and grief that they felt for the donor’s family and the effect it had on them, which varied between individuals:
Yeah it was definitely emotional time, there’s no doubt about that, thinking about the donor, donor family all the time. Quite a lot of tears, emotional having to you know, them to pass away for me to live like you know. And it’s not an easy thing to digest you know . . . I suppose the whole emotional thing was that I was alive and that someone had lost a brother, a dad, a husband you know a friend it was very raw for a long time and I just couldn’t, I’d be walking down the corridor and just fall out crying you know any little small thing at all emotionally would set me off so actually recently we sent a letter to the donor’s family which helped a lot like and hope to God helps them as well, like you know I wanted to show that I was up and about and achieving stuff before I sent the letter rather than send it at the saying thanks kind of gave them hope what I was beforehand and what my life is today yeah, so it was mentally tough and anything at all, even a song or something on the telly would set you off like you know you ended up watching cookery programmes.
Barry, post transplant, centre 2
Several participants spoke of wanting to make contact with the donor family to thank them and show how well they were doing, but were uncertain as to how this would be received:
What can you do that has any impact on anyone to say thank you? I mean you can write a letter and say thank you and if they get it, even better, but it’s . . . might be a crumb comfort I suppose. If you say who you are in terms of middle-aged or you know, whatever – do they say ‘Christ, what a waste, why didn’t it go to a younger patient?’ – All those conflicts, you know.
Tim, post transplant, centre 1
In addition to talking about their donors, participants spoke of their physical recovery post transplantation and their plans for the future. For all patients the first thing they recalled was the sensation of being able to breathe without struggling. For some this new way of breathing took a while to get used to:
I found the breathing quite hard because I didn’t understand what was going on and I had to kind of make myself do it [right] I didn’t trust it to do it on its own. It was a very strange experience [right] especially at night I was frightened to go to sleep in case it stopped because it felt so different. It’s very eh and the fact that the even now the breath is such a long breath in I think I’m going to stop breathing because it’s such a long time. Yeah I think it is you think oh god it can’t really be that slow a breath surely but then you think well it’s 3 litres instead of 0.5.
Beth, post transplant, centre 2
Some participants also experienced new health problems that they believed were in some way related to the transplant or post-transplant medication. However, the majority felt that living with their new health problem was not a significant issue compared with their condition pre transplant.
After receiving a transplant many patients expected to return to ‘normal’ life, restart work, go on holiday, start running. However, this was not always straightforward or at the rate hoped for, leaving some feeling disappointed:
It’s been ok since I’ll still be out, I’ll still be out of breath, I’m not, I’m not 100% there’s a lot of things I still can’t do I can’t like, I can walk into town but there, I got, I got to rest and I get out of breath very quickly there’re certain jobs I do I get dizzy quickly but other than that, no, I’m fine it’s good.
Keith, post transplant, centre 2
Chapter 6 Summary of study findings and discussion
Lung transplantation is the only therapeutic option for many patients with life-threatening chronic lung disease. The main factor limiting access to this life-saving therapy is the availability of suitable donor lungs. The consequences of this are a significant risk of death while on the waiting list for lung transplantation that, in the UK, for some disease categories, reaches > 30%. The development of EVLP to allow more objective assessment of organ suitability and potentially for reconditioning them has been heralded as a major breakthrough and represents the current frontier in advancing the impact of solid organ transplantation.
In the DEVELOP-UK study, all five UK adult lung transplant centres came together to investigate the possible impact that access to EVLP assessment and reconditioning of donor lungs might have on lung transplantation activity in the UK. Our hope was that EVLP would safely increase lung transplant activity by using more of the donor lungs that are already available, but that are currently felt to be unsuitable. The original hypothesis under investigation was that EVLP assessment and reconditioning of unsuitable donor lungs would produce survival in the first year after lung transplant that was non-inferior to that after standard lung transplantation.
The trial aimed to evaluate the clinical effectiveness of EVLP in increasing UK lung transplantation activity and, specifically, to demonstrate comparable outcomes for patients who received donor lungs exposed to EVLP compared with patients who received standard donor lungs. A within-study economic assessment aimed to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of generating more lung transplants by using EVLP, including modelling what sort of activity levels and costs would make it an intervention that could be adopted into standard use. Finally, the investigators were keen to know how patients waiting for lung transplantation felt about EVLP and use of donor lungs that might not otherwise have been deemed suitable.
The primary outcome measure of survival in the first year after transplant was chosen as a clinically meaningful unequivocal end point. The known historical frequency of mortality events in the first year after standard transplant from the Royal College of Surgeons UK audit58 meant that there were solid data that could be used to calculate a sample size for the study to ensure that it was adequately powered.
Our main finding showed that survival in patients receiving a lung transplant after EVLP was not as good as in those who received a standard lung transplant. The Kaplan–Meier estimate of survival at 12 months was 0.67 (95% CI 0.40 to 0.83) for the EVLP arm and 0.80 (95% CI 0.74 to 0.85) for the standard arm, and the Cox hazard ratio of 1.96 (95% CI 0.83 to 4.67) equated to just less than twice the risk of death in first year in the EVLP arm.
The study was, however, terminated early because of slow recruitment and a concern about high levels of ECMO use, and the sample size of 18 in the EVLP arm is too small to allow firm conclusions to be drawn. There are a number of small studies published that include data on 1-year survival rates after lung transplantation with EVLP-assessed donor lungs, these ranged from 67% to 95%. 24,79 In the only larger study looking at longer-term outcomes including the risk of developing chronic lung allograft dysfunction, the group in Toronto showed 1-year survival of 79% in their EVLP group (n = 63) and 85% in their standard group (n = 408) with no statistical difference. 80 These data come from a single-centre experience performed outside a clinical trial and, therefore, are not directly comparable with the results of the DEVELOP-UK study.
When mortality events were compared by the EVLP protocol used, the hazard ratio for the hybrid protocol relative to the Lund protocol was 2.92 (95% CI 0.53 to 15.95). The outcomes for the 10 EVLP patients in the Lund protocol group were actually very similar to those in the standard transplant group with a Kaplan–Meier estimate of survival at 12 months of 0.80 (95% CI 0.41 to 0.95). This raises the possibility that, had the study continued longer using the Lund protocol, robust conclusions could have been achieved. When examining the causes of death in the SAE reports, it became clear that they were not causally related to EVLP but as result of other complications that can occur after any lung transplantation. It is therefore possible that the higher risk of death seen with the hybrid protocol was as a consequence of small numbers in the study at that time rather than the protocol itself. There is a risk in overinterpreting the higher death rate in the EVLP arm as a whole because of the small numbers and the change in the EVLP protocol used.
The secondary outcomes used in the study were all key clinically relevant measures that indicate success of lung transplantation. Several of these, such as duration of ventilation or length of ITU stay, can be subject to variation that may not be due directly to the effectiveness of lung transplantation, as they can be influenced by factors outside the lungs. We showed that those in the EVLP arm of the study spent longer intubated (median 72 hours vs. 38 hours) and longer in the ITU, by a median of 10 days, than recipients of standard lung transplants. However, the time to discharge from hospital after the transplant was very similar.
These observations fit well with our cautious finding (given the limited sample size) that there was more severe early PGD in the EVLP group and a much higher rate of ECMO use for severe graft dysfunction, but that once the patients recovered from this early graft dysfunction, they made a good recovery to match the time to hospital discharge of the standard group. The largest difference in rates of severe PGD grade 3 was seen at baseline, which relates to that recorded on immediate return from theatre to the ITU, where 88.9% of the EVLP group had PGD grade 3. However, over the next 72 hours the rates of PGD grade 3 equalised between the EVLP and standard transplant group (27.8% vs. 22.5%, respectively). It is worthy of note that the rate of PGD grade 3 at 72 hours was higher than expected in the standard group at > 20%.
The PGD grade 3 rates in published studies in the first 72 hours after transplant range from 0% to 14%. 29,81 In a smaller recent study of eight EVLP transplants, the PGD grade 3 rate at baseline was 37%, but this dropped to 0% at 72 hours; two of these eight (25%) EVLP patients required ECMO support. 82
There was a 10-fold increased use of ECMO in the EVLP arm, with 7 of the 18 patients requiring ECMO. Interestingly, there was no association between use of ECMO and early death as a result of graft failure, as six of the seven patients needing ECMO were successfully discharged from ITU. The duration of ECMO support was short, with the majority weaned off within 72 hours. The exact reason for very high levels of early severe PGD and ECMO use in the EVLP group is not clear, but one possibility is that the use of cardiopulmonary bypass during the transplant surgery might have caused a second hit to donor lungs that already had some degree of vascular endothelial injury after undergoing EVLP. Participants in the EVLP group had an 88.9% rate of cardiopulmonary bypass use during surgery compared with 63% in the standard transplant arm. The use of ECMO to support patients after EVLP transplant in published studies ranges from 0% to 33%. 29
The medium-term outcomes – such as number of clinical infections, lung function as measured by FEV1 and FVC, chest radiograph appearance and numbers of rejection episodes – were comparable between the two groups. This suggests that, despite a higher rate of early PGD in the EVLP group and high rates of ECMO use, there do not appear to be other consequences of lung allograft health during the first year.
Strengths and weaknesses of the main DEVELOP-UK study
The DEVELOP-UK study has a number of strengths. It was the first study that brought together all five lung transplant centres in the UK to investigate a new technology for the benefit of patients waiting for lung transplantation. By involving all centres, the opportunity to demonstrate impact was maximised, and UK-wide policies could take account of the study. All centres were following the same protocols and using the same EVLP system to perform their assessments; this ensured the highest possible level of standardisation of the use of the technology across the study. The level of engagement of the population of patients waiting for lung transplant surgery was an additional strength, as this enabled the opportunities to perform EVLP assessments to be maximised.
Nonetheless, there are a number of weaknesses in the study that affect our ability to draw robust conclusions. The major limitation is the fact that – due to early study termination – the small sample size in the EVLP arm limited the analyses to descriptive statistics and exploratory modelling. The other significant limitation is that the EVLP protocol used changed mid-way through the study from a hybrid protocol to the Lund protocol. This change came about following an analysis of the early safety data by the Data Monitoring Committee and based on advice received after independent safety reviews.
Challenges to study enrolment activity
As each donor lungs offer was made to a transplant centre, the lungs were assessed for suitability for standard transplantation. If they failed to satisfy criteria for standard transplantation, they were considered for EVLP assessment and reconditioning. This was possible only if there was an appropriate potential recipient for that donor organ (based on blood group, tissue typing and size matching) who had signed at least an EOI form for the study. The criteria by which the decisions to perform EVLP were made were clearly defined in the study protocol. If there was no matching recipient or no consented recipient available, then the opportunity to perform an EVLP assessment was lost to the study.
The predicted activity for EVLP assessments of 240 over the 3.5 years of the study was based on the need to enrol 102 EVLP transplants and the expected conversion rate of EVLP assessment to transplantation of approximately 40–50%. The predicted EVLP assessment rate across the study was 6.6 per month. The actual number of EVLP assessments performed in the study was, however, lower across the study sites at < 3 per month, even when allowing for R&D delays to sites opening.
There were five potential reasons for the lower level of EVLP assessment activity seen in the study. There was a learning curve for the teams in each site both with the EVLP technique and with confidence in decision-making in the first few months of performing EVLP assessments. The delays in securing R&D approvals impacted on this during the first 11 months of the study, meaning that many centres did not hit the ground running. Difficulty in recruiting appropriately skilled clinical fellows to support the study in sites meant that no dedicated clinical fellow time was available to support study activities initially. Overcautious interpretation of EVLP inclusion/exclusion criteria by on-call transplant surgeons in sites led to missed opportunities to perform EVLP on donor lungs offered but not accepted for transplant. At one centre, technical issues with the EVLP system led to a delay in recruitment because of a change of equipment and a lack of confidence by the local team, which needed to be overcome. Finally, on numerous occasions, the organ retrieval team were sent out to evaluate donor lungs for EVLP that were not initially suitable for standard transplant to discover that with some simple management the donor lungs improved to satisfy criteria for standard transplant. These were then used in the standard arm of the study. Although a limitation of the study, this does suggest that consideration could be given in future to optimising methods of retrieval of lungs for standard transplantation.
All sites performed audits of donor offer suitability for EVLP over a 1- to 2-month period in November and December 2012 and this revealed at least three missed opportunities for EVLP assessment at each site. This suggested that donor lungs suitable for EVLP were regularly available, but that the opportunities to perform EVLP were not always taken.
Low conversion rate from ex vivo lung perfusion assessment to transplant
Once EVLP assessment and reconditioning of a donor lung was performed, the decision of whether or not the lungs were used in transplantation was determined by the criteria outlined in the study protocol and listed in Appendix 2. The conversion rate in moving from EVLP assessment and reconditioning to EVLP transplant was below our predicted rate of 40–50%, with 18 EVLP transplants performed from 53 EVLP assessments (34%). The number of EVLP transplants in the treatment arm of the study therefore fell behind predicted targets. The lower conversion rate was compounded by the lower than expected numbers of EVLP assessment activity. Previous single-centre publications have suggested that much higher conversion rates can be achieved, with levels of 82% reported in one large series. 32
However, these single-centre reports can be very selective as to which donor lungs are placed on EVLP and were not driven by a study protocol that defined the lungs that should be exposed to EVLP. It is interesting that in the multicentre NOVEL study, in which selection of lungs to undergo EVLP is protocol driven, a conversion rate of 55% was reported. Furthermore, in the NOVEL study the rate of PGD grade 3 was 21% in the 42 EVLP transplants. 83
Actions performed to increase study enrolment activity
Amendment of consent procedures
In order to reduce missed opportunities to enrol patients receiving standard lung transplants into the control group, the consent requirements of the study were changed. The investigators believed that, as the study was simply collecting clinical outcome data in this group and there were no study interventions or changes to routine care, reconsent on the day of transplant was unnecessary and dispensable. In addition, it was felt that patients who had signed the EOI form but did not sign either a consent form or consent to continue form on the night of standard transplant could be approached when conscious and fully competent post transplant to sign their consent form retrospectively and be included in the study. A substantial amendment to the study protocol was approved by the sponsor and the Research Ethics Committee to make this change to the consent arrangements.
Communication
In an attempt to increase communication between the study management team, PIs and staff in the participating sites, the following changes were made:
-
The monthly investigators’ teleconference was also attended by the research nurse/study co-ordinators and clinical fellows from each site, in addition to the site PIs. This allowed the wider study team to contribute to discussions on study performance, and to highlight any specific difficulties at sites to the study management team.
-
The study newsletter was sent out monthly (previously was every 2 months) to update on study progress against targets. The trial managers ensured that the newsletter was passed to the wider transplant team in each site and to the donor management teams to improve engagement and also use it as a means of reminding them of communal responsibility to the study through increasing EVLP assessments of donor lungs.
Research nurses and fellows workshop
In order to support the research nurses/study co-ordinators and clinical fellows in each site, the trial management team organised a face-to-face meeting in Newcastle in March 2013 to review the study protocol, consent process, EVLP protocol and data collection. The fellows and nurses also set up a web-based discussion group to support each other with queries and comments about study-related activities.
Missed ex vivo lung perfusion opportunity audit
Initial audits of donor lung offers in the study sites after 6 months of study activity identified a number of missed opportunities to perform EVLP assessment and reconditioning of donor lungs that were not suitable for standard transplantation. The failure to perform sufficient EVLP assessments represented the greatest threat to the successful completion of the study in an acceptable time frame. The audit results provided evidence that there was a clear potential to increase EVLP assessment activity if the study EVLP inclusion criteria were followed more carefully. A laminated, easy-to-follow sheet outlining the EVLP criteria and a flow chart for decision-making was circulated to the on-call transplant surgeons and co-ordinators. Each site was asked to prospectively audit donor offers on a regular basis and report the results of the audit back to the investigator meeting to show improvement by reducing missed opportunities.
Study site visits
Although all sites were visited by the chief investigator and trial managers as part of site initiation, another round of site visits was arranged by the chief investigator and trial manager prior to recommencement of the study with the Lund protocol to provide support to local PIs, and to allow a meeting for questions and answers about the study. This provided the opportunity to inform the wider transplant team (surgeons, physicians, co-ordinators and perfusionists) at each site about the study progress and the importance of their role in the process, as well as to address any misconceptions or misinterpretations in study criteria for EVLP assessment and reconditioning.
The role of external agency support
The DEVELOP-UK study was fortunate to receive support from a number of groups who believed this to be a very important study. The NHS commissioners provided NHS excess treatment costs and took a keen interest in the progress of the study. The study management team ensured that the commissioners were kept informed of progress in the study through newsletters, and they did get involved to stress the importance of the study to NHS trusts from whom they commission lung transplant services. In addition, NHSBT also provided support with donor data and highlighted the importance of the study in official documents. The support offered by these agencies is testimony to the importance placed on the work by the professional NHS community.
Modifications to the ex vivo lung perfusion standard operating procedure
The DEVELOP-UK study investigators recognised that the conversion rate from EVLP assessment to EVLP transplantation of just 36% was significantly lower than that reported in other small series in single centres worldwide. 29 This might reflect the nature of the donor organs being used in the DEVELOP-UK study, but could also reflect the SOP for EVLP used in the study initially. When the study protocol was first designed, the decision of the investigators was to adopt a hybrid approach containing elements of both the Toronto and Lund approaches. The use of the Vivoline system at all sites in the study did mean fixing some aspects of the SOP, such as having an open left atrium, but the consensus among the investigators was to adopt some aspects of the Toronto protocol as well with a limited flow and acellular perfusate. At the time the initial SOP was agreed, worldwide experience was substantially higher with the acellular and limited-flow approach than with a blood-based perfusion and full-flow approach.
However, after the study commenced, experience with the Vivoline EVLP system had grown worldwide and several groups (Gothenburg, Copenhagen and Brisbane) generated single-centre series with the Lund approach of full flow and red blood cell-supplemented perfusate and an open left atrium. The conversion rate from EVLP assessments to EVLP transplants using the full Lund protocol and the Vivoline system has been reported as being significantly higher, at > 80% than that which was experienced in the first stage of the DEVELOP-UK study.
In an attempt to increase EVLP transplant activity in the DEVELOP-UK study, and following advice from the independent expert review, the investigators agreed to amend the EVLP SOP to follow the Lund approach in its entirety. This was hoped to have a significant impact in converting EVLP assessments to transplants and boosting enrolment to the treatment arm of the study. The impact of such a change on patients already enrolled into the EVLP arm was discussed with the Trial Steering Committee independent statisticians. It was felt that any effect of change of SOP could be considered at the end of the study in an appropriate subanalysis. This subanalysis was performed and the findings were discussed earlier in this chapter.
Health economic analysis
The study included both a within-study assessment of costs and HRQoL, and an exploratory economic model. For the within-study data, it is obvious from the large SDs of Tables 30–37 that there is significant variation in the cost associated with the transplant of each individual, no matter which one of the two procedures was followed. This means that there is a large variability between the lung recipients regarding the resources required in each stage of the study.
Based on the calculations made, the average total cost per recipient for the standard donor lung transplantation is equal to £59,608 (SD £42,664). Almost half of this cost (£34,109) consists of the cost of the post-operative care, which also shows the biggest variability between the patients (SD £39,561). This large difference mainly lies on the need for ECMO and the length of stay in the ITU. In the standard arm, the mean total QALYs gained per recipient were estimated to be 0.533.
As far as the EVLP lung transplant is concerned, the total cost of the transplant was estimated to be around £139,081 (SD £58,916). This high cost is partially a result of the cost of the EVLP procedure (mean cost £42,633) and partly because of the cost of the post-operative care (mean cost £56,136). The variability in the total EVLP cost is similarly high, showing that the cost of the EVLP transplant might vary up to £58,916 from the average cost per recipient. This variability is, again, because of the use of ECMO and the length of hospital stay that the recipient might require after the transplant. Finally, the total QALYs gained per EVLP recipient were estimated to be 0.527.
A regression model on cost identified three statistically significant predictors of increased total cost: higher quality of life when the person joined the waiting list; use of EVLP procedure; and transplanting two lungs rather than one lung. A sensitivity analysis excluding quality of life on joining the waiting list (because relatively few respondents completed the SF-36 at this point) gave broadly similar results, but was a much poorer fit for the model data. One value of the regression model results is that information is now available to assist researchers involved in modelling events that include lung transplantation. They now have an additional data source that can be used and tailored to the characteristics of the patients modelled.
The exploratory model-based analysis estimated an incremental cost per QALY was £73,000, well over the typical ceiling ratio adopted by NICE.
The average discounted lifetime cost for a standard lung transplant was £64,861 and £69,358 for when EVLP available. The number of discounted life-years was 5.38 for standard transplant and 5.41 in the EVLP service, the increased life-years in the EVLP service reflect the increased number of lung transplants in the EVLP service: 726 transplants in the standard service and 742 in the EVLP service. The discounted QALYs are 3.48 and 3.54 in the standard and EVLP services, respectively. The higher level of QALYs in the EVLP service reflected both the increased life-years in this service and the higher utilities in the EVLP recipients. The conclusion was broadly consistent across the range of scenarios considered. Given the novel nature of the therapy, it is not possible to put these findings into the context of other research. A comprehensive literature review identified no other cost-effectiveness studies comparing EVLP lung transplantation with standard lung transplantation.
As far as the exploratory model-based analysis is concerned, the analysis suggests that non-technical solutions to increasing the availability of lungs for transplant may be worthwhile investigating. At present, the Newcastle and Birmingham lung transplant teams are carrying out EVLP lung transplant again as part of a service evaluation. This will provide a valuable opportunity to assess whether or not the increase in standard lung transplant witnessed during the DEVELOP-UK study is replicated when EVLP is again available as a back-up for substandard lungs.
Strengths and limitations of the within-trial descriptive analysis
The economic evaluation and regression model within the DEVELOP-UK study draws upon the strengths described above. It also suffers many of the same limitations; primarily caused by the limited number of data available on EVLP. Therefore, the within-study economic component was limited to a descriptive analysis of the available data; any comparative data are presented primarily for illustrative purposes, and thus should be treated cautiously.
In addition to the limited sample size, there was also a considerable degree of missing data in some parts of the CRF sent by certain sites, which meant that assumptions based on the data collected from the rest of the sites needed to be made. Similarly, responses were sought on the SF-36 for all participants while they were still on the waiting list, as well as after 90 days and 12 months from the date of the transplant. However, there were a considerable number of missing responses from the SF-36, which meant that robust estimates of QALYs could not be made. This same issue limited the regression model on costs. However, a model excluding quality of life that therefore included data from more study participants was a much poorer fit for the data, although it did provide similar results.
Although considerable efforts were made to capture costs over the entire patient pathway, the different administration and organisation systems between the transplant sites meant that data were not readily available to estimate the patient’s travelling to the transplant centre before surgery. Consequently, these costs were considered as missing. This means that total costs were underestimated, although it was believed that these costs would make up only a small proportion of total costs.
Strengths and limitations of the exploratory analysis model
Model strengths include the following: the parameters used in the model were all based on the UK adult lung transplant population, so were generalisable to this population; ISPOR guidelines55 were followed when designing the model, so as to reflect best practice; and uncertainty was evaluated using sensitivity analysis. Nevertheless, the limited number of data available from the DEVELOP-UK study imposes limitations on the model.
In addition to the generally limited data, a further key model limitation is that, in the model, it was assumed that when a patient in the waiting list state was removed from that state to a state ‘removed from waiting list’ (state G), they no longer accrued any costs or utilities. This assumption is in line with assumptions made in a Dutch economic evaluation of a lung transplant service. 84 Although the reason for removal from the waiting list is unknown, it is reasonable to assume that most patients will be removed as a result of worsening health. The impact of this is to increase average total QALYs and reduce average total costs. This in turn would improve the cost-effectiveness of the standard service relative to the service including EVLP, because for the standard service people are less likely to be transplanted in any given time period and hence are more likely to be removed from the list before a transplant.
The qualitative interview substudy
Patients’ understanding and information needs regarding ex vivo lung perfusion
Generally, patients had a good understanding of what was involved in EVLP and were able to give clear explanations of what was involved. However, some patients gave confused explanations or appeared to have a limited understanding of EVLP. This may be explained by conclusions from other research, which suggests that the severity of someone’s illness may affect the amount of information that they are able to retain. 85,86 Alternatively, it could be, as Lowton has argued,69 that simple definitions such as those offered by the participants in this study may illustrate a limited understanding and lack of information. All patients were provided with the same information when taking part in a study. Long et al. 87 suggest that when information is being given at a very emotional time, it is difficult for patients and their families to take in all the detail, and thus that there is a need for better methods of communication to be employed. Information giving in any study is always challenging and it may be, as Entwistle et al. 88 have argued, that to improve everyone’s understanding, key facts about the research should be given to everyone, with supplementary information available for those who request it, including links to online resources.
Reasons for participating in the DEVELOP-UK study
This qualitative substudy suggests a number of reasons why people consented to take part in the DEVELOP-UK study. First, many people interviewed appeared to think that participating in the DEVELOP-UK study might increase the likelihood of them receiving a transplantation sooner. Echoing the research of Bjørk et al. ,89 one of the concerns expressed by several patients was the increasing possibility that that the longer they waited the greater their chance of dying while on the transplant list. Second, people gave altruistic reasons for taking part, such as wanting to help other patients or the clinical team, in whom they had a great deal of trust. Other studies have found that trust in the clinician90 or the notion for some that they will be the ‘first to [have a] go’ may be enough to override any uncertainties patients may have about a treatment. 86 As noted earlier, it is important to emphasise that, for many people, consenting to take part in the DEVELOP-UK study was not considered as significant a decision or event as actually being placed on the transplant waiting list in the first place. The emphasis placed by patients on decision to go on the transplant register ought to be reflected in the information we give patients.
Impact on everyday life of waiting for a transplant
It is recognised that any chronic condition can have a potentially ‘disruptive’ effect on people’s lives and their own biographies,91 and this would seem to be true for patients in this study. Waiting for a transplant involves multiple ongoing disruptions to everyday life, and has an impact not just on patients themselves, but also on others, usually their family. 92,93 Patients have to continually adjust to new routines, restrictions and, sometimes, new treatment regimes. When a patient experiences false alarms or hospital stays as a result of deterioration of their condition, their lives are further disrupted. 91 This waiting, for some, disrupts life to the extent that life is on hold, in limbo; as Naef et al. 93 have argued, the waiting rules their life.
Waiting for a transplant involves experiencing and balancing hope and despair, illness and good health, survival and function. For example, patients need to be sick enough to be put on the list but stay well enough for a transplant should this be offered. Initially, when they are placed on the transplant list they are filled with hope,94 but this can often be replaced by feelings of disappointment as the wait continues and they realise that they may not get a transplant in time. 95 Patients must also manage being on the waiting list and waiting for a transplant with continuing to try to live their everyday lives and function within their families (and for some at work), all of which must be balanced alongside the deterioration of their condition and the further limitations this imposes on them. 96 The impact of deteriorating health, the experience of waiting and the possibility of dying before a transplantation may provide some insight into why people wanted to take part in the DEVELOP-UK study.
Strengths and weaknesses of interview substudy
One of the strengths of this qualitative study is that it gives a unique, detailed insight into patient views, expectations and experiences regarding EVLP specifically, and lung transplantation more generally. The use of telephone interviews in this study enabled us to interview a diverse group of patients spread over a large geographical area. This approach to interviewing in this study appeared to be particularly successful as, given the need for patients to avoid infection and remain well enough to be able to receive a transplant, telephone interviews bore no additional risk to patients in terms of infection. Recruitment to interviews may not have been as successful if patients were required to take part in face-to-face interviews. This is something that may be of use when considering recruiting to future research with vulnerable and/or very sick patient groups.
The weaknesses of this qualitative research are twofold. First, because of the limited number of patients who underwent an EVLP transplant, there were few patients with this experience to recruit. This means that it is difficult to infer anything from the findings specifically about EVLP post-transplantation experiences. Second, the only patients available to be invited to participate in the qualitative study were those who had agreed to be part of the main trial, thus we know nothing of the reasons why people did not want to take part in the trial.
The data from this qualitative substudy provide some insights into patients’ experiences, which can be used to improve future practice development in the area of transplant research and EVLP research in particular. This substudy suggests that patients had a good understanding of the need for, and processes of, EVLP, although in the future clinicians may want to consider exploring different ways and modes of providing information depending on patient preferences. Finally, this work appears to suggest that if EVLP can increase the number of suitable donor lungs available, then it is likely to be regarded as an acceptable technology to patients waiting for a lung transplant.
The DEVELOP-UK study implications for practice
The DEVELOP-UK study is the first to report poorer outcomes in a group of EVLP transplants than a contemporaneous standard lung transplant group. It is, however, the first non-commercial multicentre EVLP study performed and relied on a small number of centres (five) in a single country to aim to deliver a substantial number of EVLP assessments and subsequent transplants. To date, two commercially funded multicentre EVLP studies have been performed, but have not yet published their results other than in abstract format. 97,98
The slow enrolment into the EVLP arm of the study was because of a combination of the low number of EVLP assessments performed, and the low conversion rate from EVLP assessment to transplant. This demonstrates the challenge of running an EVLP assessment service alongside an active clinical transplant programme, when logistics and staff availability because of competing transplant activity can significantly affect units’ ability to perform EVLP assessments, even if resourced.
The higher rate of early PGD grade 3 and need for ECMO support in the EVLP arm has raised issues about the selection of the best lungs on which to perform EVLP. Although there was a much higher ECMO rate in the EVLP arm, it was not associated with a higher mortality risk in the recipients undergoing ECMO, which in most cases was limited to a few days’ support. The almost uniform use of cardiopulmonary bypass in recipients of EVLP donor lungs (89%) may have also contributed to the high early PGD 3 rates and the frequent use of ECMO as a second hit to donor lungs, which already have a disrupted vascular integrity.
Finally, it appears that use of our hybrid EVLP protocol was not as effective in terms of conversion rate and possibly 1-year survival after transplant as the Lund protocol, suggesting that mixing elements of established protocols is not advisable and that matching the appropriate protocol to the appropriate EVLP circuit is an important consideration.
Overall, our main conclusion is that EVLP using a Lund protocol has the potential to offer an increased chance of achieving effective lung transplant in patients at high risk of death on the waiting list.
The DEVELOP-UK study implications for future research
After completing a study of the complexity of DEVELOP-UK, it is important that time is taken to reflect on what lessons can be learnt and how these should guide future research in this area. Although the overall findings of the DEVELOP-UK study were not what was hoped for, and did not allow the original research question to be definitively answered, there are still a significant number of factors to consider that will help to direct further research in the area of EVLP.
Study design
The decision to conduct an open, observational, non-inferiority study was made after careful consideration by the investigator group, in consultation with the HTA programme commissioning brief. However, this approach brought with it some significant challenges. The open nature of the study meant that bias was introduced to the wider clinical teams when early complications occurred. This is likely to have contributed to poor recruitment of lungs for EVLP. It is unlikely to be possible in the future to blind investigators to which organs have been exposed to EVLP assessment and reconditioning if EVLP is conducted at all investigating sites. However, in the future, if EVLP activity was concentrated in a smaller number of more experienced sites and then organs were transported after EVLP to remote sites, this could reduce the risk of bias.
There is also the issue of what is the best research question to evaluate in a future EVLP study. It has been suggested that a better question than comparing EVLP with standard lung transplant outcomes is to compare EVLP outcomes with the risk of waiting list mortality. The difficulty with this question is that not everyone on the waiting list has access to organs in an equal way. Size, blood group and presence of pre-formed HLA antibodies can limit access to transplant opportunity in some patients, and there is also the issue that EVLP might be offered more readily to the more severely ill patients on the list to reduce their waiting time on the transplant list. To compensate for these potential confounders, it might be possible to consider a cluster-type study, with some sites acting as control centres, and others with specific experience offering EVLP.
Study logistics
The model of having dedicated EVLP centres may also be important to consider if future multicentre EVLP studies are to be successfully performed. Our experience was that one centre (Newcastle) did 50% of the EVLP assessments and 50% of the EVLP transplants, and the other four centres did not achieve their targets for recruitment of donor lungs to undergo EVLP. This suggests that expecting every transplant centre to be able to provide an EVLP service is probably unrealistic, even if appropriate resource is provided. EVLP makes an already challenging clinical situation with an emergency surgical procedure requiring huge manpower resources even more complicated. Centres enrolled in EVLP studies in the future should have previously demonstrated an ability to deliver a clinical EVLP service effectively and have performed at least 15–20 EVLP procedures before being invited to enrol in an EVLP study.
Choice of ex vivo lung perfusion protocol
There is evidence that both the Toronto and the Lund protocols can be effective at assessing and reconditioning donor lungs for transplantation. There is a different philosophy behind each protocol with real physiological differences. In the future, work should be done to help determine which elements of the protocols are critical. Our use of a hybrid approach at the start of the DEVELOP-UK study was associated with a high rate of early severe PGD and need for ECMO. The reason for this requires further investigation, particularly whether or not a combination of EVLP followed by performing transplant surgery on cardiopulmonary bypass causes a second hit, which increases vascular leak and early reperfusion injury. In addition, as all but one of the recipients who required ECMO was weaned from this support rapidly, it raises the question if this should be considered a prophylactic intervention to any recipient receiving a higher-risk donor lung after EVLP. The use of ECMO routinely intraoperatively in higher-risk recipients is increasing internationally and maybe this approach should be considered for higher-risk donor organs as well.
Identifying which donor lungs should undergo ex vivo lung perfusion
The conversion rate from EVLP assessment to transplant varies significantly in the published case series from > 90% to 40%. In the DEVELOP-UK study, only 30–40% of the donor lungs perfused satisfied transplant criteria. It is unclear if this was a problem with donor organ selection for EVLP or a result of the rigidity of following a multicentre prospective study protocol, which imposes stricter decision-making than would happen in a single centre outside a formal study setting. The conversion rate has a significant effect on overall costs of offering an EVLP service, and a target conversion rate of > 50% would seem reasonable to aim for. More work needs to be done to help identify which donor lungs can be effectively reconditioned and for which EVLP should not be considered.
In conclusion, many lessons were learnt in conducting the DEVELOP-UK study, and a future study would need to be designed differently, in order to have a better chance of hitting its recruitment targets, and of fully addressing the research question.
Acknowledgements
The DEVELOP-UK study was possible only because of the generous support and enthusiasm of a large number of individuals. The study was funded by the NIHR HTA programme; however, the investigators would also like to acknowledge additional funding support without which the study would not have been possible.
The UK CF Trust provided support for part-funding of clinical research fellows at each participating site to help conduct EVLP. The NHS England Commissioning Group provided support for NHS excess treatment costs associated with additional lung transplants performed as a result of the study and the cost of consumables for each donor lung perfusion.
Vivoline Medical (Sweden) loaned their LS1 EVLP system to each participating centre and provided access to discounted consumables, together with providing all training requirements and technical support for the equipment at each site. Special thanks goes to Anna Soderlund, from Vivoline, whose help and support throughout the study was invaluable.
We would like to thank the biostatistics team from NHSBT, which was very supportive of the study and provided the donor data sets. In particular, we would like to thank David Collett for his advice and support.
The investigators would also like to acknowledge the NIHR Clinical Research Network, which provided NHS research support to the study.
Special thanks goes to Karen Redmond for playing a key role in the design of the study protocol and acting as a co-applicant for funding. Karen moved to another centre outside the UK before study commencement, but her input in helping to make the DEVELOP-UK study a reality was invaluable.
We would like to extend sincere thanks to the clinical research fellows, Marius Roman (Papworth), Rosalba Romano (Harefield) and Jamal Salaie (Manchester), who played a key role in supporting provision of EVLP including out of hours and at weekends. The co-ordination of study activity at each site was supported by the research nurses, and special thanks goes to Jo Hardy (Harefield), Debbie Smith (Manchester), Katie Morley and Alison Davison (Newcastle), Rebecca Maclean (Papworth) and Helen Hunt (Birmingham), for all their support in managing study activity and responding promptly to the data queries.
A significant number of clinicians from across the UK lung transplant teams contributed to the study at individual sites, and we express our gratitude to all the lung transplant surgeons, physicians and cardiothoracic anaesthetists in the UK for their support of study recruitment and data collection. In particular, we would like to thank Stephen Clark and Mahesh Prabhu (Newcastle), and Aaron Ranasinghe and Majid Mukadam (Birmingham).
We would like to thank the cardiothoracic perfusionists from across the UK for their supervision and management of the EVLP process and, in particular, Paul Henderson (Newcastle) for all his input into the protocols.
We would like to thank the Newcastle Clinical Trials Unit staff, in particular the data managers Ruth Wood and Jonathan Pritchard, assistant trial manager Iryna Ziabreva and statistician Colin Muirhead.
We would like to thank the members of the Trial Steering Committee, especially its chairperson Duncan Young for all his support, and the members of the Data Monitoring and Ethics Committee for all their valuable guidance.
We would like to thank Annabel Haynes for her invaluable assistance with the formatting and multiple corrections of the report.
Finally, but most importantly, we would like to thank all our patients and their families for agreeing to participate in the DEVELOP-UK study and for putting their trust in the study team. Thanks must also go to the donor families whose generosity in gifting the organs of their loved ones allows lung transplantation in the UK to be a reality.
Contributions of authors
Andrew Fisher (Professor of Respiratory Transplant Medicine) was the study chief investigator, designed the study, was principal applicant for funding, wrote the study protocol, supervised the overall conduct of the study, interpreted study data, and co-wrote and edited the final report.
Anders Andreasson (Clinical Research Associate in Cardiothoracic Surgery) conducted the Newcastle EVLP assessments, collected and interpreted study-wide data, and co-wrote and edited the final report.
Alexandros Chrysos (Research Associate in Health Economics) collected and interpreted study data, and co-wrote and edited the final report.
Joanne Lally (Research Associate in Qualitative Research) designed the interview study protocol, conducted participant interviews, collected and interpreted study data and co-wrote part of the final report.
Chrysovalanto Mamasoula (Research Associate in Medical Statistics) conducted the main study analysis and co-wrote part of the final report
Catherine Exley (Professor of Qualitative Health Research) was a co-applicant, secured funding, co-wrote the study protocol, interpreted study data, and co-wrote and edited the final report.
Jennifer Wilkinson (Senior Clinical Trial Manager) led the clinical trials unit teams involvement the study, co-wrote the study protocol, interpreted study data and co-wrote the final report.
Jessica Qian (Trial Manager) was responsible for day-to-day running of the study, co-ordinated communications across sites and managed study governance, and provided editorial input into the final report.
Gillian Watson (Trial Manager) was responsible for day-to-day running of the study, co-ordinated communications across sites and managed study governance, and provided editorial input into the final report.
Oli Lewington (Patient and Service User Representative) represented the views of patients in the design of the study, reviewed and edited all participant documentation, and reviewed the final report and our dissemination strategy.
Thomas Chadwick (Clinical Trials Statistician) designed the statistical plan in the study protocol, was a co-applicant for funding and led the final study statistical analysis.
Elaine McColl (Director of Newcastle Clinical Trials Unit) designed the protocol, was a co-applicant for funding, reviewed study results and edited the final report.
Mark Pearce (Professor of Applied Epidemiology) designed the protocol, was a co-applicant for funding, led the survival modelling analysis, reviewed study data and contributed to the final report.
Kay Mann (Research Associate in Clinical Epidemiology) conducted the survival modelling analysis, reviewed study results and contributed to the final report.
Nicola McMeekin (Research Assistant in Health Economics) performed part of the health economic assessment study, interpreted results and contributed to the final report.
Luke Vale (Professor of Health Economics) supervised the health economic assessment part of the study, assessed and interpreted data, and co-wrote and edited the final report.
Steven Tsui (Consultant Cardiothoracic Transplant Surgeon) designed the protocol, was a co-applicant for funding, led study activity at his site, reviewed study results and contributed to the final report.
Nizar Yonan (Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery) designed the protocol, was a co-applicant for funding, led study activity at his site, reviewed study results and contributed to the final report.
Andre Simon (Consultant Cardiothoracic and Transplant Surgeon) designed the protocol, was a co-applicant for funding, led study activity at his site, reviewed study results and contributed to the final report.
Nandor Marczin (Senior Lecturer in Intensive Care Medicine) designed the protocol, was a co-applicant for funding, assisted study activity at his site, reviewed study results and contributed to the final report.
Jorge Mascaro (Consultant Cardiothoracic and Transplant Surgeon) designed the protocol, was a co-applicant for funding, led study activity at his site, reviewed study results and contributed to the final report.
John Dark (Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery) designed the protocol, was a co-applicant for funding, led study activity at his site, reviewed study results and contributed to the final report.
Data sharing statement
We shall make the study data available to the scientific community with as few restrictions as feasible, while retaining exclusive use until the publication of our major outputs. The data will be made available by contacting the corresponding author.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Office for National Statistics . Statistical Bulletin: Deaths Registered in England and Wales (Series DR): 2012 2013. www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/birthsdeathsandmarriages/deaths/bulletins/deathsregisteredinenglandandwalesseriesdr/2013-10-22#leading-causes-of-mortality-in-2012 (accessed 29 January 2016).
- Fisher AJ, Dark JH, Corris PA. Improving donor lung evaluation: a new approach to increase organ supply for lung transplantation. Thorax 1998;53:818-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thx.53.10.818.
- Botha P, Fisher AJ, Dark JH. Marginal lung donors: a diminishing margin of safety?. Transplantation 2006;82:1273-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.tp.0000236099.52382.74.
- Fisher AJ, Wardle J, Dark JH, Corris PA. Non-immune acute graft injury after lung transplantation and the risk of subsequent bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS). J Heart Lung Transplant 2002;21:1206-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1053-2498(02)00450-3.
- Arcasoy SM, Fisher A, Hachem RR, Scavuzzo M, Ware LB. ISHLT Working Group on Primary Lung Graft Dysfunction . Report of the ISHLT Working Group on Primary Lung Graft Dysfunction part V: predictors and outcomes. J Heart Lung Transplant 2005;24:1483-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2004.11.314.
- Wallinder A, Ricksten SE, Silverborn M, Hansson C, Riise GC, Liden H, et al. Early results in transplantation of initially rejected donor lungs after ex vivo lung perfusion: a case-control study. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2014;45:40-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ejcts/ezt250.
- Korovesi I, Papadomichelakis E, Orfanos SE, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Livaditi O, Pelekanou A, et al. Exhaled breath condensate in mechanically ventilated brain-injured patients with no lung injury or sepsis. Anesthesiology 2011;114:1118-29. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e31820d84db.
- Fisher AJ, Donnelly SC, Hirani N, Burdick MD, Strieter RM, Dark JH, et al. Enhanced pulmonary inflammation in organ donors following fatal non-traumatic brain injury. Lancet 1999;353:1412-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(99)00494-8.
- Fisher AJ, Donnelly SC, Hirani N, Haslett C, Strieter RM, Dark JH, et al. Elevated levels of interleukin-8 in donor lungs is associated with early graft failure after lung transplantation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001;163:259-65. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.163.1.2005093.
- De Perrot M, Sekine Y, Fischer S, Waddell TK, McRae K, Liu M, et al. Interleukin-8 release during early reperfusion predicts graft function in human lung transplantation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;165:211-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.165.2.2011151.
- Kaneda H, Waddell TK, de Perrot M, Bai XH, Gutierrez C, Arenovich T, et al. Pre-implantation multiple cytokine mRNA expression analysis of donor lung grafts predicts survival after lung transplantation in humans. Am J Transplant 2006;6:544-51. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2005.01204.x.
- Avlonitis VS, Wigfield CH, Golledge HD, Kirby JA, Dark JH. Early hemodynamic injury during donor brain death determines the severity of primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation. Am J Transplant 2007;7:83-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2006.01593.x.
- Avlonitis VS, Fisher AJ, Kirby JA, Dark JH. Pulmonary transplantation: the role of brain death in donor lung injury. Transplantation 2003;75:1928-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.TP.0000066351.87480.9E.
- Okada Y, Zuo XJ, Toyoda M, Marchevsky A, Matloff JM, Oishi H, et al. Adenovirus mediated IL-10 gene transfer to the airway of the rat lung for prevention of lung allograft rejection. Transpl Immunol 2006;16:95-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.trim.2006.03.012.
- Martins S, de Perrot M, Imai Y, Yamane M, Quadri SM, Segall L, et al. Transbronchial administration of adenoviral-mediated interleukin-10 gene to the donor improves function in a pig lung transplant model. Gene Ther 2004;11:1786-96. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302357.
- Fischer S, Liu M, MacLean AA, de Perrot M, Ho M, Cardella JA, et al. In vivo transtracheal adenovirus-mediated transfer of human interleukin-10 gene to donor lungs ameliorates ischemia–reperfusion injury and improves early post-transplant graft function in the rat. Hum Gene Ther 2001;12:1513-26. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/10430340152480249.
- Itano H, Mora BN, Zhang W, Ritter JH, McCarthy TJ, Yew NS, et al. Lipid-mediated ex vivo gene transfer of viral interleukin 10 in rat lung allotransplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2001;122:29-38. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mtc.2001.114636.
- Orens JB, Boehler A, de Perrot M, Estenne M, Glanville AR, Keshavjee S, et al. A review of lung transplant donor acceptability criteria. J Heart Lung Transplant 2003;22:1183-200. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1053-2498(03)00096-2.
- Fisher AJ, Donnelly SC, Pritchard G, Dark JH, Corris PA. Objective assessment of criteria for selection of donor lungs suitable for transplantation. Thorax 2004;59:434-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thx.2003.007542.
- Ware LB, Wang Y, Fang X, Warnock M, Sakuma T, Hall TS, et al. Assessment of lungs rejected for transplantation and implications for donor selection. Lancet 2002;360:619-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09774-X.
- Jirsch DW, Fisk RL, Couves CM. Ex vivo evaluation of stored lungs. Ann Thorac Surg 1970;10:163-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0003-4975(10)65582-8.
- Steen S, Sjöberg T, Pierre L, Liao Q, Eriksson L, Algotsson L. Transplantation of lungs from a non-heart-beating donor. Lancet 2001;357:825-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04195-7.
- Wierup P, Haraldsson A, Nilsson F, Pierre L, Scherstén H, Silverborn M, et al. Ex vivo evaluation of nonacceptable donor lungs. Ann Thorac Surg 2006;81:460-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.08.015.
- Steen S, Ingemansson R, Eriksson L, Pierre L, Algotsson L, Wierup P, et al. First human transplantation of a nonacceptable donor lung after reconditioning ex vivo. Ann Thorac Surg 2007;83:2191-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2007.01.033.
- Ingemansson R, Eyjolfsson A, Mared L, Pierre L, Algotsson L, Ekmehag B, et al. Clinical transplantation of initially rejected donor lungs after reconditioning ex vivo. Ann Thorac Surg 2009;87:255-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2008.09.049.
- Cypel M, Rubacha M, Yeung J, Hirayama S, Torbicki K, Madonik M, et al. Normothermic ex vivo perfusion prevents lung injury compared to extended cold preservation for transplantation. Am J Transplant 2009;9:2262-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.02775.x.
- Cypel M, Yeung JC, Liu M, Anraku M, Chen F, Karolak W, et al. Normothermic ex vivo lung perfusion in clinical lung transplantation. N Engl J Med 2011;364:1431-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1014597.
- Zych B, Popov AF, Stavri G, Bashford A, Bahrami T, Amrani M, et al. Early outcomes of bilateral sequential single lung transplantation after ex-vivo lung evaluation and reconditioning. J Heart Lung Transplant 2012;31:274-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2011.10.008.
- Andreasson AS, Dark JH, Fisher AJ. Ex vivo lung perfusion in clinical lung transplantation – state of the art. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2014;46:779-88. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ejcts/ezu228.
- Cypel M, Yeung JC, Machuca T, Chen M, Singer LG, Yasufuku K, et al. Experience with the first 50 ex vivo lung perfusions in clinical transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2012;144:1200-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2012.08.009.
- Cypel M, Yeung JC, Hirayama S, Rubacha M, Fischer S, Anraku M, et al. Technique for prolonged normothermic ex vivo lung perfusion. J Heart Lung Transplant 2008;27:1319-25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2008.09.003.
- Cypel M, Aigner C, Sage E, Manchuca T, Slama A, Stern M, et al. Three center experience with clinical normothermic ex vivo lung perfusion. J Heart Lung Transplant 2013;32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2013.01.021.
- Warnecke G, Moradiellos J, Tudorache I, Kühn C, Avsar M, Wiegmann B, et al. Normothermic perfusion of donor lungs for preservation and assessment with the Organ Care System Lung before bilateral transplantation: a pilot study of 12 patients. Lancet 2012;380:1851-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61344-0.
- TransMedics . International Randomized Study of the TransMedics Organ Care System (OCS Lung) for Lung Preservation and Transplantation (INSPIRE) 2011. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01630434 (accessed 20 April 2015).
- TransMedics . International EXPAND Lung Pivotal Trial (EXPANDLung). 2013. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01963780 (accessed 20 April 2015).
- Andreasson A, Karamanou DM, Perry JD, Perry A, Özalp F, Butt T, et al. The effect of ex vivo lung perfusion on microbial load in human donor lungs. J Heart Lung Transplant 2014;33:910-16. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2013.12.023.
- Cypel M, Liu M, Rubacha M, Yeung JC, Hirayama S, Anraku M, et al. Functional repair of human donor lungs by IL-10 gene therapy. Sci Transl Med 2009;1:4-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3000266.
- Lee JW, Fang X, Gupta N, Serikov V, Matthay MA. Allogeneic human mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of E. coli endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in the ex vivo perfused human lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009;106:16357-62. http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0907996106.
- Christie JD, Carby M, Bag R, Corris P, Hertz M, Weill D. ISHLT Working Group on Primary Lung Graft Dysfunction . Report of the ISHLT Working Group on Primary Lung Graft Dysfunction part II: definition. A consensus statement of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2005;24:1454-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2004.11.049.
- Couraud L, Nashef SA, Nicolini P, Jougon J. Classification of airway anastomotic healing. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 1992;6:496-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/1010-7940(92)90247-U.
- National Health Service . Blood and Transplant Data on Organ Donation and Transplantation n.d. www.odt.nhs.uk/donation/deceased-donation/donation-after-circulatory-death/ (accessed December 2015).
- Krutsinger D, Reed RM, Blevins A, Puri V, De Oliveira NC, Zych B, et al. Lung transplantation from donation after cardiocirculatory death: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Heart Lung Transplant 2015;34:675-84. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2014.11.009.
- Benden C, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, Christie JD, Dipchand AI, Dobbels F, et al. The registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: sixteenth official pediatric lung and heart-lung transplantation report – 2013. International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2013;32:989-97. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2013.08.008.
- UK Government Department of Constitutional Affairs . Mental Capacity Act 2005 Code of Practice 2007. www.opsi.gov.uk/acts/acts2005/related/ukpgacop_20050009_en.pdf (accessed 29 January 2016).
- World Medical Organization . Declaration of Helsinki. BMJ 1996;313:1448-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.313.7070.1448a.
- RAND Health Corporation . The 36-Item Short Form Survey from the RAND Medical Outcomes Study n.d. www.rand.org/health/surveys_tools/mos/mos_core_36item.html (accessed 5 November 2015).
- OPTUM . A Community for Measuring Health Outcomes Using SF Tools n.d. www.sf-36.org/tools/sf36.shtml (accessed 5 November 2015).
- Brazier J, Roberts J, Deverill M. The estimation of a preference-based measure of health from the SF-36. J Health Econ 2002;21:271-92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0167-6296(01)00130-8.
- Department of Health . NHS Reference Costs 2013 2014 2014. www.gov.uk/government/publications/nhs-reference-costs-2013-to-2014 (accessed 27 August 2015).
- British National Formulary (Online). London: BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press; 2014.
- Curtis L. Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2014. Canterbury: Personal Services Research Unit, University of Kent; 2014.
- Guide to the Methods of Technology Appraisal 2013. Foreword. Guidance and Guidelines. London: NICE; 2013.
- Information Services Division . ISD Scotland Theatre Services 2014. www.isdscotland.org/Health-Topics/Finance/Costs/Detailed-Tables/Theatres.asp (accessed 27 August 2015).
- RAND Health . 36-Item Short Form Survey from the RAND Medical Outcomes Study 2015 n.d. www.rand.org/health/surveys_tools/mos/mos_core_36item.html (accessed 14 October 2015).
- Roberts M, Russell LB, Paltiel AD, Chambers M, McEwan P, Krahn M, et al. Conceptualizing a model: a report of the ISPOR-SMDM modeling good research practices task force-2. Med Decis Making 2012;32:678-89. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0272989X12454941.
- National Heart Lung and Blood Institute . What Are the Risks of Lung Transplant? 2011. www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/lungtxp/risks (accessed 20 June 2015).
- International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation . Adult Lung Transplantation Statistics 2014. www.ishlt.org/registries/slides.asp?slides=heartLungRegistry (accessed 21 May 2015).
- Royal College of Surgeons . Cardiothoracic Transplantation Audit 2011. http://webtest.rcseng.ac.uk/surgeons/research/surgical-research/docs/uk-cardiothoracic-transplant-audit-report-2011/view (accessed 20 January 2016).
- Siebert U, Alagoz O, Bayoumi AM, Jahn B, Owens DK, Cohen DJ, et al. State-transition modeling: a report of the ISPOR-SMDM modeling good research practices task force-3. Med Decis Making 2012;32:690-70. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0272989X12455463.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Developing NICE Guidelines: The Manual. 7 – Incorporating Economic Evaluation 2014. www.nice.org.uk/article/PMG20/chapter/7-Incorporating-economic-evaluation (accessed 31 May 2015).
- NHS Blood and Transplant . Organ Donation and Transplantation Activity Report 2011–2012 2013. https://nhsbtmediaservices.blob.core.windows.net/organ-donation-assets/pdfs/activity_report_2011_12.pdf (accessed 21 May 2015).
- NHS Blood and Transplant . Annual Report on Cardiothoracic Transplantation 2013–14 2014. www.odt.nhs.uk/pdf/organ_specific_report_cardiothoracic_2014.pdf (accessed 21 May 2015).
- Boffini M, Ricci D, Barbero C, Bonato R, Ribezzo M, Mancuso E, et al. Ex vivo lung perfusion increases the pool of lung grafts: analysis of its potential and real impact on a lung transplant program. Transplant Proc 2013;45:2624-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.08.004.
- Henriksen IS, Møller-Sørensen H, Møller CH, Zemtsovski M, Nilsson JC, Seidelin CT, et al. First Danish experience with ex vivo lung perfusion of donor lungs before transplantation. Dan Med J 2014;61.
- Anyanwu AC, McGuire A, Rogers CA, Murday AJ. An economic evaluation of lung transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2002;123:411-18. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mtc.2002.120342.
- Briggs A, Claxton K, Sculpher M. Decision Modelling for Health Economic Evaluation. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2006.
- Kaba E, Thompson DR, Burnard P, Edwards D, Theodosopoulou E. Somebody else’s heart inside me: a descriptive study of psychological problems after a heart transplantation. Issues Ment Health Nurs 2005;26:611-25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01612840590959452.
- Kierans C. Narrating kidney disease: the significance of sensation and time in the employment of patient experience. Cult Med Psychiatry 2005;29:341-59. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11013-005-9171-8.
- Lowton K. ‘Double or quits’: perceptions and management of organ transplantation by adults with cystic fibrosis. Soc Sci Med 2003;56:1355-67. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0277-9536(02)00134-X.
- Lowton K, Gabe J. Life on a slippery slope: perceptions of health in adults with cystic fibrosis. Sociol Health Illn 2003;25:289-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1467-9566.00348.
- O’Grady JG, Asderakis A, Bradley R, Burnapp L, McPake DM, Perrin M, et al. Multidisciplinary insights into optimizing adherence after solid organ transplantation. Transplantation 2010;89:627-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e3181ca87b0.
- Taylor RM, Franck LS, Dhawan A, Gibson F. The stories of young people living with a liver transplant. Qual Health Res 2010;20:1076-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1049732310368405.
- Fielding N, Thomas H, Gilbert N. Researching Social Life. London: Sage; 2008.
- Mays N, Pope C. Rigour and qualitative research. BMJ 1995;311:109-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.311.6997.109.
- Glaser BG. The constant comparative method of qualitative analysis. Soc Probl 1965;12:436-45. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/798843.
- Charmaz K. Constructing Grounded Theory. A Practical Guide through Qualitative Analysis. London: Sage; 2006.
- Great Britain . Data Protection Act 1998 n.d. www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1998/29/contents (accessed 29 January 2016).
- Gibbs G. Qualitative Data Analysis: Explorations with NVivo. Buckingham: Open University Press; 2002.
- Sage E, Mussot S, Trebbia G, Puyo P, Stern M, Dartevelle P, et al. Lung transplantation from initially rejected donors after ex vivo lung reconditioning: the French experience. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2014;46:794-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ejcts/ezu245.
- Tikkanen JM, Cypel M, Machuca TN, Azad S, Binnie M, Chow CW, et al. Functional outcomes and quality of life after normothermic ex vivo lung perfusion lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2015;34:547-56. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2014.09.044.
- Machuca TN, Cypel M, Yeung JC, Bonato R, Zamel R, Chen M, et al. Protein expression profiling predicts graft performance in clinical ex vivo lung perfusion. Ann Surg 2015;261:591-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000000974.
- Boffini M, Ricci D, Bonato R, Fanelli V, Attisani M, Ribezzo M, et al. Incidence and severity of primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation using rejected grafts reconditioned with ex vivo lung perfusion. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2014;46:789-93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ejcts/ezu239.
- Sanchez PG, Davis RD, D’Ovidio F, Cantu E, Weyant M, Camp P, et al. The NOVEL lung trial one-year outcomes. J Heart Lung Transplant 2014;33:71-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2014.01.226.
- van Enckevort PJ, TenVergert EM, Bonsel GJ, Geertsma A, van der Bij W, de Boer WJ, et al. Technology assessment of the Dutch Lung Transplantation Program. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 1998;14:344-56. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0266462300012307.
- Schaeffer MH, Krantz DS, Wichman A, Masur H, Reed E, Vinicky JK. The impact of disease severity on the informed consent process in clinical research. Am J Med 1996;100:261-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9343(97)89483-1.
- Renshaw A, Clarke A, Diver AJ, Ashcroft RE, Butler PE. Informed consent for facial transplantation. Transpl Int 2006;19:861-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-2277.2006.00358.x.
- Long T, Sque M, Payne S. Information sharing: its impact on donor and nondonor families’ experiences in the hospital. Prog Transplant 2006;16:144-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.7182/prtr.16.2.l715846273q1h784.
- Entwistle VA, Carter SM, Trevena L, Flitcroft K, Irwig L, McCaffery K, et al. Communicating about screening. BMJ 2008;337.
- Bjørk IT, Nåden D. Patients’ experiences of waiting for a liver transplantation. Nurs Inq 2008;15:289-98. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1800.2008.00418.x.
- Behrendt C, Gölz T, Roesler C, Bertz H, Wünsch A. What do our patients understand about their trial participation? Assessing patients’ understanding of their informed consent consultation about randomised clinical trials. J Med Ethics 2011;37:74-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/jme.2010.035485.
- Bury M. Chronic illness as biographical disruption. Sociol Health Illn 1982;4:167-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1467-9566.ep11339939.
- Brown J, Sorrell JH, McClaren J, Creswell JW. Waiting for a liver transplant. Qual Health Res 2006;16:119-36. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1049732305284011.
- Naef R, Bournes DA. The lived experience of waiting: a Parse method study. Nurs Sci Q 2009;22:141-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0894318409331932.
- Haugh KH, Salyer J. Needs of patients and families during the wait for a donor heart. Heart Lung 2007;36:319-29. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hrtlng.2006.11.003.
- Moran A, Scott A, Darbyshire P. Waiting for a kidney transplant: patients’ experiences of haemodialysis therapy. J Adv Nurs 2011;67:501-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2010.05460.x.
- Littlefield C, Abbey S, Fiducia D, Cardella C, Greig P, Levy G, et al. Quality of life following transplantation of the heart, liver, and lungs. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 1996;18:36-47. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0163-8343(96)00082-5.
- Sanchez PG, Davis RD, D’ovidio F, Weyan MJ, Camp PC, Cantu E, et al. Normothermic ex vivo lung perfusion as an assessment of marginal donor lungs – the NOVEL Lung Trial. J Heart Lung Transplant 2013;32:S16-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2013.01.022.
- Warnecke G, Van Raemdonck D, Kukreja J, Smith M, Loor G, Rea F, et al. Mid and long-term clinical results of OCS lung INSPIRE international trial. J Heart Lung Transplant 2016;35:S15-16. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2016.01.042.
- The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust . Annual Report &Amp; Accounts 2012 13 n.d. www.newcastle-hospitals.org.uk/downloads/Performance%20information/2012-13_NuTH_Statutory_Report_part7.pdf (accessed 6 September 2016).
- NHS Business Service Authority . Amendments to the Drug Tariff 2015. www.nhsbsa.nhs.uk/PrescriptionServices/Documents/PPD%20Drug%20Tariff/June_2015.pdf (accessed 6 September 2016).
- XVIVO Perfusion . Homepage n.d. www.xvivoperfusion.com/ (accessed 6 September 2016).
- ISD Scotland . About ISD n.d. www.isdscotland.org/ (accessed 6 September 2016).
- Fisher AJ. A Study of Donor Ex-Vivo Lung Perfusion in UK Lung Transplantation. 2013.
Appendix 1 Couraud et al.’s classification of anastomotic healing
The grades corresponding to Couraud et al. ’s classification40 of anastomotic healing are:
-
grade 1 – complete circumferential primary mucosal healing
-
grade 2A – complete circumferential primary healing of the airway wall without necrosis and partial mucosal healing
-
grade 2B – complete circumferential primary healing of the airway wall without necrosis but no primary mucosal healing
-
grade 3A – limited necrosis
-
grade 3B – extensive necrosis.
Appendix 2 Standard operating procedures
Appendix 3 Expression of interest form version 3.0, 20 February 2013
Appendix 4 Informed consent forms
Appendix 5 Hospital staff resource use survey
Qualtrics survey
In September 2014, a survey was conducted in order to determine the hospital resource use and staff time after lung transplant. In this survey, most of the hospital staff who took part in the DEVELOP-UK study were involved. The survey was conducted using the online Qualtrics software.
Questions
The questions asked to each member of the hospital staff are presented below.
Consultant surgeon/surgical fellow/consultant physician
Question 1
On the day/night of lung transplantation how much time do you spend preparing for the surgery (i.e. on the telephone or in discussion with other team members)?
Question 2
How long do you spend in theatre undertaking the lung transplant procedure?
Question 3
Post operation, how long is it before you leave the hospital/are ready to see another patient?
Question 4
How much time do you spend in ITU on a daily basis with a straightforward, uncomplicated lung transplant patient who requires single organ support or remains in single organ failure?
Question 5
How much time do you spend in ITU on a daily basis with a lung transplant patient experiencing more severe complications with multiorgan failure?
Question 6
In a more specific example, how much time do you spend each day with lung transplant patients on ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation)?
Question 7
How much time do you spend on a daily basis with a lung transplant patient in level 1 ward-based care?
Additional comments
Any additional comments you have regarding the time you input into the care of lung transplant patients would be greatly appreciated.
Consultant anaesthetist/anaesthetic fellow
Question 1
On the day/night of lung transplantation how much time do you spend preparing the patient for anaesthesia?
Question 2
How much time do you spend preparing for the surgery (i.e. discussing with colleagues and transplant co-ordinators)?
Question 3
How much time do you spend in theatre supervising the patient during anaesthesia?
Question 4
How much time do you spend bringing the patient back to ITU to stabilise them?
Question 5
How much time do you spend in ITU on a daily basis with a straightforward, uncomplicated lung transplant patient who requires single organ support or remains in single organ failure?
Question 6
How much time do you spend in ITU on a daily basis with a lung transplant patient experiencing more severe complications with multiorgan failure?
Question 7
In a more specific example, how much time do you spend each day with lung transplant patients on ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation)?
Question 9
How much time do you spend on a daily basis with a lung transplant patient in level 1 ward-based care?
Additional comments
Any additional comments you have regarding the time you input into the care of lung transplant patients would be greatly appreciated.
Transplant co-ordinator
Question 1
How long do you spend in hospital once organs have arrived?
Question 2
How long do you spend in theatre on day/night of transplant?
Question 3
Do you spend time with the relatives of the patient post transplant?
Question 4
How long do you spend with the relatives of the patient post transplant (e.g. comforting them, helping to sort out accommodation for the night if needed)?
Additional comments
Any additional comments you have regarding the time you input into the care of lung transplant patients would be greatly appreciated.
Responses
Table 48 shows the number of responses from the hospital staff resource use survey.
| Response details | First draft | New survey | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total number of responses | 24 | 89 | 113 |
| Completed responses | 2 | 41 | 43 |
| Blank responses: initial question not displayed | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| Blank responses: initial question not answered | 2 | 9 | 11 |
| Job role only: no questions displayed | 6 | 8 | 14 |
| Job role only: no questions answered | 8 | 13 | 21 |
| Job role only: mix of questions not displayed or answered | 6 | 12 | 18 |
Table 49 shows the number of complete responses per each member of the staff.
| Member of staff | Completed responses |
|---|---|
| Consultant surgeon | 7 |
| Surgical fellow | 4 |
| Consultant physician | 8 |
| Physician fellow | 0 |
| Consultant anaesthetist | 8 |
| Anaesthetic fellow | 3 |
| Transplant co-ordinator | 13 |
| Total | 43 |
Appendix 6 Unit costs of resources and interventions
| Resource or intervention | Unit | Patient details | Standard donor lung transplantation (£) | EVLP transplantation (£) | Cost source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donor’s hospital | |||||
| Fixed costs | |||||
| Initial assessment | |||||
| ABG | Test | Donor | 4.37 | 4.37 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| Bronchoscopy | Procedure | Donor | 340.00 | 340.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Chest X-ray (radiography) | Test | Donor | 24.97 | 24.97 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| ECG | Test | Donor | 20.81 | 20.81 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| FBC | Test | Donor | 4.94 | 4.94 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| Drugs | |||||
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 500-mg vial | Donor | 9.60 | 9.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Donor | 17.30 | 17.30 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 2-g vial | Donor | 32.66 | 32.66 | BNF 201450 |
| Lung retrieval | |||||
| Fixed costs | |||||
| Equipment | |||||
| DCD donor | |||||
| Bronchoscope | Instrument | Donor | 8.18 | 8.18 | EAC |
| Pink spray 0.5% chlorhexidine | Spray | Donor | 3.69 | 3.69 | Medical supplies |
| 2 l of 0.9% sodium chloride solution | 1-l solution | Donor | 0.97 | 0.97 | NHSBSA’s Amendments to the Drug Tariff100 |
| Strapple tape | Roll | Donor | 2.00 | 2.00 | Medical supplies |
| DBD donor | |||||
| Blue 23-gauge 25-mm (1-inch) needles | 1-inch needle | Donor | 0.05 | 0.05 | Medical supplies |
| Bronchoscope | Instrument | Donor | 8.18 | 8.18 | EAC |
| 1-l cardioplegia bag (green PLEGIVEX, Ivex Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Larne, UK) | 1-l bag | Donor | 35.92 | 35.92 | Medical supplies |
| Green vacutainers | Vacutainer | Donor | 0.13 | 0.13 | Medical supplies |
| i-STAT portable clinical analyser | Device | Donor | 3.13 | 3.13 | EAC |
| i-STAT cartridges | Cartridge | Donor | 8.00 | 8.00 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Pink spray 0.5% chlorhexidine | Spray | Donor | 3.69 | 3.69 | Medical supplies |
| 1-l pressure infusion bag | 1-l bag | Donor | 49.99 | 49.99 | Medical supplies |
| Red vacutainers | Vacutainer | Donor | 0.12 | 0.12 | Medical supplies |
| 10 ml of 8.4% sodium bicarbonate | 10-ml ampoule | Donor | 11.03 | 11.03 | BNF 201450 |
| 2 l of 0.9% sodium chloride solution | 1-l solution | Donor | 0.97 | 0.97 | NHSBSA’s Amendments to the Drug Tariff100 |
| Spleen pots | Pot | Donor | 0.41 | 0.41 | Medical supplies |
| Strapple tape | Roll | Donor | 2.00 | 2.00 | Medical supplies |
| 1-ml syringes | 1-ml syringe | Donor | 0.08 | 0.08 | Medical supplies |
| Staff time | |||||
| Scout team | |||||
| Retrieval surgeon (fellow) | Hour | Donor | 56.41 | 56.41 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Scrub nurse (band 5) | Hour | Donor | 20.31 | 20.31 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Retrieval team | |||||
| Perfusionist (band 7) | Hour | Donor | 28.09 | 28.09 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Retrieval surgeon (fellow) | Hour | Donor | 56.41 | 56.41 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Scrub nurse (band 5) | Hour | Donor | 20.31 | 20.31 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Tests | |||||
| Chest X-ray (radiography) | Test | Donor | 24.97 | 24.97 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| Perfusion (dosage) | |||||
| 2.8 l of PERFADEX solution | 2.8-l solution | Donor | 376.00 | 376.00 | XVIVO101 |
| 1 l of PERFADEX solution | 1-l solution | Donor | 134.24 | 134.24 | XVIVO101 |
| CaCl2 1 mmol/ml (1.7 ml/2.8 l PERFADEX and 0.6 ml/1 l PERFADEX) | 10-ml ampoule | Donor | 14.94 | 14.94 | BNF 201450 |
| FLOLAN 0.5-mg vial (7 ml/2.8 l PERFADEX) | 0.5-mg vial | Donor | 22.22 | 22.22 | BNF 201450 |
| FLOLAN 0.5-mg vial (2.5 ml/1 l PERFADEX) | 0.5-mg vial | Donor | 22.22 | 22.22 | BNF 201450 |
| Heparin sodium 5000 units/5 ml (15,000 units/2.8 l PERFADEX) | 5-ml ampoule | Donor | 7.58 | 7.58 | BNF 201450 |
| Heparin sodium 5000 units/5 ml (5000 units/1 l PERFADEX) | 5-ml ampoule | Donor | 7.58 | 7.58 | BNF 201450 |
| THAM 1-ml ampoule (7 ml/2.8 l PERFADEX) | 1-ml ampoule | Donor | 1.07 | 1.07 | BNF 201450 |
| THAM 1-ml ampoule (2.5 ml/1 l PERFADEX) | 1-ml ampoule | Donor | 1.07 | 1.07 | BNF 201450 |
| Variable costs | |||||
| Travelling | |||||
| Scout team | |||||
| Road | Transport type | Donor | 225.00 | 225.00 | Brian Leadbitter, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Retrieval team | |||||
| Road | Transport type | Donor | 297.00 | 297.00 | Brian Leadbitter, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Road and air | Transport type | Donor | 9791.00 | 9791.00 | Brian Leadbitter, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Organ (lung) | |||||
| Road | Transport type | Donor | 392.00 | 392.00 | Brian Leadbitter, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Road and air | Transport type | Donor | 7527.00 | 7527.00 | Brian Leadbitter, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Transplant preparation | |||||
| Fixed costs | |||||
| Contacting potential recipients | |||||
| Transplant co-ordinator | Hour | Recipient | 30.41 | 30.41 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Meeting potential recipients | |||||
| Transplant co-ordinator | Hour | Recipient | 30.41 | 30.41 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Tissue typing | |||||
| Tissue typing test | Test | Recipient | 59.87 | 59.87 | ISD Scotland’s About ISD102 |
| Tests | |||||
| ABG | Test | Recipient | 4.37 | 4.37 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| Chest X-ray (radiography) | Test | Recipient | 24.97 | 24.97 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| ECG | Test | Recipient | 20.81 | 20.81 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| FBC | Test | Recipient | 4.94 | 4.94 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| Ward time | |||||
| Transplant centre ward | Bed-day | Recipient | 265.00 | 265.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Drugs | |||||
| Azathioprine, 50 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.48 | 3.48 | BNF 201450 |
| Variable costs | |||||
| Transfer to ward | |||||
| Air | Transport type | Recipient | Missing | Missing | Missing |
| Road | Transport type | Recipient | Missing | Missing | Missing |
| EVLP procedure | |||||
| Fixed costs | |||||
| Staff time | |||||
| Anaesthetic registrar | Hour | EVLP recipient | – | 22.84 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Consultant surgeon | Hour | EVLP recipient | – | 60.11 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Perfusionist (band 7) | Hour | EVLP recipient | – | 28.09 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Scrub nurse/ODA (band 5) | Hour | EVLP recipient | – | 20.31 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Surgical fellow | Hour | EVLP recipient | – | 56.41 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Equipment | |||||
| Bronchoscope | Instrument | EVLP recipient | – | 8.18 | EAC |
| DeBakey tissue forceps | Forceps | EVLP recipient | – | 0.08 | EAC |
| McIndoe scissors | Scissors | EVLP recipient | – | 1.65 | Medical supplies |
| Nebuliser circuit | Item | EVLP recipient | – | 1.32 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| 4–0 Prolene (No. 8935) suture pack (Ethicon Inc., Somerville, NJ, USA) | Pack | EVLP recipient | – | 2.87 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| 10-fg suction catheter (SHODS) | Catheter | EVLP recipient | – | 0.45 | Medical supplies |
| Suction connecting tubing | Tubing | EVLP recipient | – | 2.36 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Consumables | |||||
| Nylon surgical tape | Roll | EVLP recipient | – | 1.56 | Medical supplies |
| Gas (2000 l of N2/CO2) | Cylinder | EVLP recipient | – | 400.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| PERFADEX solution | 1-l solution | EVLP recipient | – | 134.24 | XVIVO101 |
| Packed red blood cells | 274-ml bag | EVLP recipient | – | 120.00 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Yvonne Scott, NuTH, July 2015, personal communication |
| Syringes for blood gases | Syringe | EVLP recipient | – | 0.36 | Medical supplies |
| Syringes (other) | Syringe | EVLP recipient | – | 0.08 | Medical supplies |
| Vivoline disposable lung set | Set | EVLP recipient | – | 6962.87 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| Miscellaneous equipment | |||||
| Blood gases samples | Sample | EVLP recipient | – | 1.77 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Vivoline system | System | EVLP recipient | – | 39.40 | EAC |
| Theatre usage | |||||
| Operating theatre | Hour | EVLP recipient | – | 587.66 | ISD Scotland’s About ISD102 |
| Drugs | |||||
| 2 l of Steen Solution | 500-ml solution | EVLP recipient | – | 528.36 | XVIVO101 |
| Heparin sodium, 1000 units/ml | 1-ml ampoule | EVLP recipient | – | 1.49 | BNF 201450 |
| Heparin sodium, 5000 units/ml | 1-ml ampoule | EVLP recipient | – | 7.58 | BNF 201450 |
| Insulin human [ACTRAPID® HM (Novo Nordisk, Bagsværd, Denmark)], 100 IU/ml | 10-ml vial | EVLP recipient | – | 7.48 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 500-mg vial | EVLP recipient | – | 9.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | EVLP recipient | – | 17.30 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 2-g vial | EVLP recipient | – | 32.66 | BNF 201450 |
| THAM, 30 mg/ml (3.0 mmol/ml) | 1-ml ampoule | EVLP recipient | – | 1.07 | BNF 201450 |
| Antibiotics | |||||
| Meropenem (as trihydrate) | 500-mg vial | EVLP recipient | – | 8.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Moxifloxacin (as hydrochloride), 1.6 mg/ml | 250-ml solution for infusion bottle (400 mg) | EVLP recipient | – | 12.43 | BNF 201450 |
| Antifungal | |||||
| Amphotericin B | 50-mg vial | EVLP recipient | – | 3.88 | BNF 201450 |
| Lung transplant | |||||
| Fixed costs | |||||
| Anaesthetic preparation | |||||
| Anaesthetic room | Hour | Recipient | 587.66 | 587.66 | ISD Scotland’s About ISD102 |
| Anaesthetic nurse (band 5) | Hour | Recipient | 20.31 | 20.31 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Consultant anaesthetist | Hour | Recipient | 59.37 | 59.37 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Staff time | |||||
| Single lung surgery | |||||
| Anaesthetic fellow | Hour | Recipient | 56.41 | 56.41 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Anaesthetic nurse (band 5) | Hour | Recipient | 20.31 | 20.31 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Consultant anaesthetist | Hour | Recipient | 59.37 | 59.37 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Consultant surgeon | Hour | Recipient | 60.11 | 60.11 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Perfusionist (band 7) | Hour | Recipient | 28.09 | 28.09 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Scrub nurse (band 7) | Hour | Recipient | 30.34 | 30.34 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Scrub nurse (band 5) | Hour | Recipient | 20.31 | 20.31 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Surgical fellow | Hour | Recipient | 56.41 | 56.41 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Double lung surgery | |||||
| Anaesthetic fellow | Hour | Recipient | 56.41 | 56.41 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Anaesthetic nurse (band 5) | Hour | Recipient | 20.31 | 20.31 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Consultant anaesthetist | Hour | Recipient | 59.37 | 59.37 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Consultant surgeon | Hour | Recipient | 60.11 | 60.11 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Perfusionist (band 7) | Hour | Recipient | 28.09 | 28.09 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Scrub nurse (band 7) | Hour | Recipient | 30.34 | 30.34 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Scrub nurse (band 5) | Hour | Recipient | 20.31 | 20.31 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Surgical fellow | Hour | Recipient | 56.41 | 56.41 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Theatre usage | |||||
| Single lung surgery | |||||
| Operating theatre | Hour | Recipient | 587.66 | 587.66 | ISD Scotland’s About ISD102 |
| Double lung surgery | |||||
| Operating theatre | Hour | Recipient | 587.66 | 587.66 | ISD Scotland’s About ISD102 |
| Equipment/consumables | |||||
| Usual surgical set | Set | Recipient | Missing | Missing | Missing |
| Post-operative care | |||||
| Fixed costs | |||||
| Staff time in ITU/HDU | |||||
| Anaesthetic fellow | Hour | Recipient | 56.41 | 56.41 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Consultant anaesthetist | Hour | Recipient | 59.37 | 59.37 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Consultant physician | Hour | Recipient | 59.37 | 59.37 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Consultant surgeon | Hour | Recipient | 60.11 | 60.11 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Surgical fellow | Hour | Recipient | 56.41 | 56.41 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Staff time in hospital | |||||
| Consultant physician | Hour | Recipient | 59.37 | 59.37 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Surgical fellow | Hour | Recipient | 56.41 | 56.41 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Transplant specialist registrar | Hour | Recipient | 40.00 | 40.00 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Tests | |||||
| ABG | Test | Recipient | 4.37 | 4.37 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| Chest X-ray (radiography) | Test | Recipient | 24.97 | 24.97 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| FBC | Test | Recipient | 4.94 | 4.94 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| Pulmonary/lung function test | Test | Recipient | 169.00 | 169.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Variable costs | |||||
| Ward usage (if needed) | |||||
| HDU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 852.00 | 852.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| ITU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 852.00 | 852.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| ITU/HDU readmission | Bed-day | Recipient | 852.00 | 852.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Level 1 ward care (hospital stay) | Bed-day | Recipient | 265.00 | 265.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Procedures (if needed) | |||||
| Bronchoscopy | Procedure | Recipient | 340.00 | 340.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Tracheostomy | Procedure | Recipient | 135.00 | 135.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Equipment (if needed) | |||||
| ECMO | Machine | Recipient | 34,000.00 | 34,000.00 | Tanveer Butt, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| iLA membrane ventilator | Device | Recipient | 4.28 | 4.28 | EAC |
| Consumables (if needed) | |||||
| 2 l colloid (plasma and plasma substitutes) | 500 ml | Recipient | 8.00 | 8.00 | BNF 201450 |
| 1 l crystalloid (fluids containing electrolytes) | 500 ml | Recipient | 8.00 | 8.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Fresh-frozen plasma | 271-ml bag | Recipient | 28.46 | 28.46 | NHSBT |
| Packed red blood cells | 274-ml bag | Recipient | 120.00 | 120.00 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Yvonne Scott, NuTH, July 2015, personal communication |
| Platelets | 250-ml bag | Recipient | 196.96 | 196.96 | NHSBT |
| Inotropes (if needed) | |||||
| Adrenaline (base), 1 mg/10 ml (1 in 10,000) | 10-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 6.99 | 6.99 | BNF 201450 |
| Dobutamine (as hydrochloride), 12.5 mg/ml | 20-ml ampoule | Recipient | 5.20 | 5.20 | BNF 201450 |
| Glyceryl trinitrate, 1 mg/ml | 50-ml vial | Recipient | 15.90 | 15.90 | BNF 201450 |
| Milrinone, 1 mg/ml | 10-ml ampoule | Recipient | 19.91 | 19.91 | BNF 201450 |
| Noradrenaline (as acid tartrate), 1 mg/ml | 4-ml ampoule | Recipient | 4.40 | 4.40 | BNF 201450 |
| Pitressin (argipressin – synthetic vasopressin), 20 units/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 22.50 | 22.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Other | |||||
| Dopamine hydrochloride, 40 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 3.88 | 3.88 | BNF 201450 |
| Enoximone, 5 mg/ml | 20-ml ampoule | Recipient | 15.02 | 15.02 | BNF 201450 |
| Isoprenaline | – | Recipient | 5.20 | 5.20 | – |
| Metaraminol | – | Recipient | 4.40 | 4.40 | – |
| Post-implantation haemodynamic support (if needed) | |||||
| Adrenaline (base), 1 mg/10 ml (1 in 10,000) | 10-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 6.99 | 6.99 | BNF 201450 |
| Dobutamine (as hydrochloride), 12.5 mg/ml | 20-ml ampoule | Recipient | 5.20 | 5.20 | BNF 201450 |
| Glyceryl trinitrate, 1 mg/ml | 50-ml vial | Recipient | 15.90 | 15.90 | BNF 201450 |
| Milrinone, 1 mg/ml | 10-ml ampoule | Recipient | 19.91 | 19.91 | BNF 201450 |
| Noradrenaline (as acid tartrate), 1 mg/ml | 4-ml ampoule | Recipient | 4.40 | 4.40 | BNF 201450 |
| Pitressin (argipressin – synthetic vasopressin), 20 units/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 22.50 | 22.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Complications (if reported) | |||||
| Cerebrovascular accident | Treatment | Recipient | 840.65 | 840.65 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Haemofiltration | Procedure | Recipient | 139.00 | 139.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Haemodialysis | Procedure (days) | Recipient | 139.00 | 139.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Re-exploration | Procedure | Recipient | 4580.36 | 4580.36 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Airway complications (if reported) | |||||
| Balloon dilatation | Procedure | Recipient | 4580.36 | 4580.36 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Cryotherapy | Procedure | Recipient | 4580.36 | 4580.36 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Diathermy | Procedure | Recipient | 4580.36 | 4580.36 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Stenting | Procedure | Recipient | 4580.36 | 4580.36 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Surgical intervention | Procedure | Recipient | 4580.36 | 4580.36 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| ITU rejection episodes (if reported) | |||||
| Ward usage | |||||
| HDU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 852.00 | 852.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| ITU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 852.00 | 852.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Procedures | |||||
| Clinical diagnosis/biopsy | Procedure | Recipient | 851.00 | 851.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Treatment | |||||
| Cefuroxime (as sodium) | 750-mg vial | Recipient | 2.52 | 2.52 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 17.30 | 17.30 | BNF 201450 |
| Piperacillin (as sodium), 2 g; and tazobactam (as sodium), 250 mg (Tazocin®, Pfizer Ltd, New York City, NY, USA) | 2.25-g vial | Recipient | 7.65 | 7.65 | BNF 201450 |
| Changes in maintenance therapy | |||||
| Methylprednisolone, 100 mg | 20-tablet pack | Recipient | 48.32 | 48.32 | BNF 201450 |
| Tacrolimus, 5 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 58.45 | 58.45 | BNF 201450 |
| Ward rejection episodes (if reported) | |||||
| Procedures | |||||
| Clinical diagnosis/biopsy | Procedure | Recipient | 851.00 | 851.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Treatment | |||||
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 9.60 | 9.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 17.30 | 17.30 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone, 100 mg | 20-tablet pack | Recipient | 48.32 | 48.32 | BNF 201450 |
| Prednisolone acetate, 25 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 6.87 | 6.87 | BNF 201450 |
| Prednisolone, 25 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 50.00 | 50.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Sulfamethoxazole, 400 mg; and trimethoprim, 80 mg (co-trimoxazole) 480 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.34 | 3.34 | BNF 201450 |
| Tacrolimus, 5 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 58.45 | 58.45 | BNF 201450 |
| Infection episodes (if reported) | |||||
| Treatment | |||||
| Aciclovir (as sodium), 25 mg/ml | 20-ml vial (500 mg) | Recipient | 19.61 | 19.61 | BNF 201450 |
| Adefovir dipivoxil, 10 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 252.22 | 252.22 | BNF 201450 |
| Amikacin (as sulfate), 250 mg/ml | 2-ml vial | Recipient | 9.64 | 9.64 | BNF 201450 |
| Amoxicillin (as trihydrate), 500 mg | 21-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.62 | 1.62 | BNF 201450 |
| Amoxicillin (as trihydrate), 500 mg; and clavulanic acid (as potassium), 125 mg (co-amoxiclav) | 21-tablet pack | Recipient | 4.23 | 4.23 | BNF 201450 |
| Amphotericin B liposomal (AmBisome®) | 50-mg vial | Recipient | 82.19 | 82.19 | BNF 201450 |
| Amphotericin B (as sodium deoxycholate complex) | 50-mg vial | Recipient | 3.88 | 3.88 | BNF 201450 |
| Anidulafungin | 100-mg vial | Recipient | 299.99 | 299.99 | BNF 201450 |
| Azithromycin (as dihydrate), 250 mg | 4-capsule pack | Recipient | 10.06 | 10.06 | BNF 201450 |
| Aztreonam | 1-g vial | Recipient | 9.40 | 9.40 | BNF 201450 |
| BAL | Procedure | Recipient | 340.00 | 340.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Budesonide, 100 µg; and formoterol fumarate, 6 µg [Symbicort Turbohaler® (AstraZeneca, London, UK)] | 120-dose inhaler | Recipient | 33.00 | 33.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Caspofungin (as acetate) | 70-mg vial | Recipient | 416.78 | 416.78 | BNF 201450 |
| Ceftazidime (as pentahydrate) | 2-g vial | Recipient | 17.90 | 17.90 | BNF 201450 |
| Cefuroxime (as sodium) | 750-mg vial | Recipient | 2.52 | 2.52 | BNF 201450 |
| Chloramphenicol (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 1.39 | 1.39 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciprofloxacin (as lactate) 2 mg/ml | 200-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 19.79 | 19.79 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciprofloxacin (as hydrochloride), 500 mg | 20-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.47 | 1.47 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciprofloxacin (as hydrochloride), 3 mg/ml | 5-ml 0.3% eye drops | Recipient | 4.70 | 4.70 | BNF 201450 |
| Clarithromycin | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 9.45 | 9.45 | BNF 201450 |
| Clindamycin (as phosphate), 150 mg/ml | 4-ml ampoule | Recipient | 11.80 | 11.80 | BNF 201450 |
| Colistimethate sodium | 2-million-unit vial | Recipient | 3.24 | 3.24 | BNF 201450 |
| Domperidone (as maleate), 10 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 5.83 | 5.83 | BNF 201450 |
| Doxycycline (as hyclate), 100 mg | 8-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.13 | 1.13 | BNF 201450 |
| Eradication therapy for Helicobacter pylori | 7-day course | Recipient | 4.30 | 4.30 | BNF 201450 |
| Ertapenem (as sodium) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 31.65 | 31.65 | BNF 201450 |
| Ethambutol hydrochloride, 100 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 11.52 | 11.52 | BNF 201450 |
| Flucloxacillin (as sodium), 500 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.60 | 2.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Flucloxacillin (as sodium) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 4.90 | 4.90 | BNF 201450 |
| Fluconazole, 50 mg | 7-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.02 | 1.02 | BNF 201450 |
| Fluconazole, 2 mg/ml | 100-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 27.45 | 27.45 | BNF 201450 |
| Fluconazole, 50 mg | 7-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.02 | 1.02 | BNF 201450 |
| Foscarnet sodium, 24 mg/ml | 250-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 119.85 | 119.85 | BNF 201450 |
| Fosfomycin (as sodium) | 2-g vial | Recipient | 15.00 | 15.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Furosemide, 10 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 0.32 | 0.32 | BNF 201450 |
| Ganciclovir (as sodium) | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 29.77 | 29.77 | BNF 201450 |
| Gentamicin (as sulfate), 40 mg/ml | 2-ml vial | Recipient | 1.40 | 1.40 | BNF 201450 |
| Immunoglobulin | 10-g vial | Recipient | 401.00 | 401.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Itraconazole, 10 mg/ml | 25-ml ampoule | Recipient | 79.71 | 79.71 | BNF 201450 |
| Lamivudine, 150 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 121.82 | 121.82 | BNF 201450 |
| Lesion excision | Day case | Recipient | 2488.00 | 2488.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Linezolid, 2 mg/ml | 300-ml infusion bag | Recipient | 44.50 | 44.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Meropenem (as trihydrate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 16.00 | 16.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 17.30 | 17.30 | BNF 201450 |
| Metoclopramide hydrochloride, 5 mg/ml | 2-ml ampoule | Recipient | 0.32 | 0.32 | BNF 201450 |
| Metronidazole, 200 mg | 21-tablet pack | Recipient | 6.46 | 6.46 | BNF 201450 |
| Micafungin (as sodium) | 100-mg vial | Recipient | 341.00 | 341.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Moxifloxacin (as hydrochloride), 1.6 mg/ml | 250-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 39.95 | 39.95 | BNF 201450 |
| Oseltamivir (as phosphate), 75 mg | 10-capsule pack | Recipient | 15.41 | 15.41 | BNF 201450 |
| Packed red blood cells | 274-ml bag | Recipient | 120.00 | 120.00 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Yvonne Scott, NuTH, July 2015, personal communication |
| Piperacillin (as sodium), 4 g; and tazobactam (as sodium), 500 mg (Tazocin) | 4.5-g vial | Recipient | 12.90 | 12.90 | BNF 201450 |
| Posaconazole, 100 mg | 96-tablet pack | Recipient | 2387.85 | 2387.85 | BNF 201450 |
| Prednisolone, 25 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 50.00 | 50.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Respiratory failure (inpatient) | Treatment | Recipient | 3445.00 | 3445.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Sirolimus, 2 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 172.98 | 172.98 | BNF 201450 |
| Streptokinase | 250,000-unit powder vial | Recipient | 13.52 | 13.52 | BNF 201450 |
| Sulfamethoxazole, 80 mg; and trimethoprim, 16 mg [Septrin® (Aspen Pharmcare Holding Ltd, Durban, South Africa)] | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.78 | 1.78 | BNF 201450 |
| Surgical intervention or VATS | Procedure | Recipient | 4580.36 | 4580.36 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Teicoplanin | 200-mg vial | Recipient | 3.93 | 3.93 | BNF 201450 |
| Trimethoprim, 100 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 7.55 | 7.55 | BNF 201450 |
| Tobramycin (as sulfate), 40 mg/ml | 1-ml vial | Recipient | 3.70 | 3.70 | BNF 201450 |
| Tigecycline | 50-mg vial | Recipient | 32.31 | 32.31 | BNF 201450 |
| Valaciclovir (as hydrochloride), 500 mg | 42-tablet pack | Recipient | 8.50 | 8.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Valganciclovir (as hydrochloride), 450 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 1081.46 | 1081.46 | BNF 201450 |
| Vancomycin (as hydrochloride) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 12.99 | 12.99 | BNF 201450 |
| Voriconazole | 200-mg vial | Recipient | 77.14 | 77.14 | BNF 201450 |
| Ward usage | |||||
| HDU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 852.00 | 852.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| ITU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 852.00 | 852.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Outpatient care | |||||
| Fixed costs | |||||
| Outpatient reviews | |||||
| Bronchoscopy | Procedure/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 340.00 | 340.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Chest X-ray (radiography) | Test/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 24.97 | 24.97 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| FBC | Test/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 4.94 | 4.94 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| Liver function test | Test/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 6.80 | 6.80 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| Pulmonary/lung function test | Test/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 169.00 | 169.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Urea and electrolytes test | Test/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 2.96 | 2.96 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| Staff time | |||||
| Consultant physician | Hour/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 59.37 | 59.37 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Scrub nurse (band 5) | Hour/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 20.31 | 20.31 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Variable costs | |||||
| Rejection episodes (if reported) | |||||
| Procedures | |||||
| Clinical diagnosis/biopsy | Procedure | Recipient | 295.00 | 295.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Ventilation–perfusion scan | Test | Recipient | 203.00 | 203.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Treatment | |||||
| Anti-thymocyte immunoglobulin (rabbit), 25 mg | 25-mg vial | Recipient | 158.77 | 158.77 | BNF 201450 |
| Azathioprine, 25 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.24 | 3.24 | BNF 201450 |
| Azathioprine, 50 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.48 | 3.48 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin, 25 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 13.05 | 13.05 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin, 50 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 25.50 | 25.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin, 100 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 48.50 | 48.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin [NEORAL® (Novartis International AG, Basel, Switzerland)], 10 mg | 60-capsule pack | Recipient | 16.68 | 16.68 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 25 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 16.79 | 16.79 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 50 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 32.88 | 32.88 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 100 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 62.41 | 62.41 | BNF 201450 |
| Immunoglobulin | 10-g vial | Recipient | 401.00 | 401.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Meropenem (as trihydrate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 16.00 | 16.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 125-mg vial | Recipient | 4.75 | 4.75 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 9.60 | 9.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 17.30 | 17.30 | BNF 201450 |
| Mycophenolate mofetil, 500 mg | 50-tablet pack | Recipient | 10.15 | 10.15 | BNF 201450 |
| Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), 250 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 82.26 | 82.26 | BNF 201450 |
| Prednisolone, 1 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.08 | 1.08 | BNF 201450 |
| Prednisolone, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.29 | 1.29 | BNF 201450 |
| Prednisolone, 25 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 50.00 | 50.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Rituximab, 100 mg/ml | 10-ml vial | Recipient | 174.63 | 174.63 | BNF 201450 |
| Tacrolimus [Prograf® (Astellas Pharma Inc., Tokyo, Japan)], 500 µg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 61.88 | 61.88 | BNF 201450 |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 1 mg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 80.28 | 80.28 | BNF 201450 |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 1 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 160.54 | 160.54 | BNF 201450 |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 5 mg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 296.58 | 296.58 | BNF 201450 |
| Valganciclovir (as hydrochloride), 450 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 1081.46 | 1081.46 | BNF 201450 |
| Ward usage | |||||
| HDU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 852.00 | 852.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| ITU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 852.00 | 852.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| GP visits (if needed) | |||||
| Out-of-surgery visit | Visit | Recipient | 85.00 | 85.00 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Surgery visit | Visit | Recipient | 34.00 | 34.00 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Transplant centre advice | Call | Recipient | 34.00 | 34.00 | PSSRU’s Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201451 |
| Unplanned hospital admission (if needed) | |||||
| Treatment | |||||
| Aciclovir (as sodium), 25 mg/ml | 20-ml vial | Recipient | 19.61 | 19.61 | BNF 201450 |
| Aciclovir, 400 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 4.05 | 4.05 | BNF 201450 |
| Adrenaline (base), 100 µg/ml (1 in 10,000) | 10-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 6.99 | 6.99 | BNF 201450 |
| Amiodarone hydrochloride, 30 mg/ml | 10-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 13.50 | 13.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Amoxicillin (as sodium), 500 mg; and clavulanic acid (as potassium), 125 mg (co-amoxiclav) | 500-/100-mg vial | Recipient | 1.21 | 1.21 | BNF 201450 |
| Amphotericin B | 50-mg vial | Recipient | 3.80 | 3.80 | BNF 201450 |
| Aspirin, 300 mg | 32-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.35 | 3.35 | BNF 201450 |
| Azathioprine, 25 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.24 | 3.24 | BNF 201450 |
| Azithromycin (as dihydrate), 250 mg | 4-capsule pack | Recipient | 10.06 | 10.06 | BNF 201450 |
| Aztreonam | 1-g vial | Recipient | 9.40 | 9.40 | BNF 201450 |
| Balloon dilatation | Procedure | Recipient | 4580.36 | 4580.36 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Basiliximab | 20-mg vial | Recipient | 842.38 | 842.38 | BNF 201450 |
| Bisoprolol fumarate, 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.02 | 1.02 | BNF 201450 |
| Bortezomib | 3.5-mg vial | Recipient | 762.38 | 762.38 | BNF 201450 |
| Bronchoscopy | Procedure | Recipient | 340.00 | 340.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Budesonide, 100 µg; and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, 6 µg (Symbicort 100/6 Turbohaler) | 120-dose unit inhaler | Recipient | 33.00 | 33.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Calcium gluconate, 1g | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 15.68 | 15.68 | BNF 201450 |
| Calcium polystyrene sulfonate [Calcium Resonium® (Aventis Pharma Ltd, Mumbai, India)] | 300-g powder | Recipient | 68.47 | 68.47 | BNF 201450 |
| Candesartan cilexetil, 4 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.10 | 1.10 | BNF 201450 |
| Caspofungin (as acetate) | 70-mg vial | Recipient | 416.78 | 416.78 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin, 100 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 48.50 | 48.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin, 50 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 9.16 | 9.16 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciprofloxacin (as hydrochloride), 500 mg | 20-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.47 | 1.47 | BNF 201450 |
| Clarithromycin | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 9.45 | 9.45 | BNF 201450 |
| Clinical diagnosis/biopsy | Procedure | Recipient | 295.00 | 295.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Colistimethate sodium | 1-million-unit vial | Recipient | 5.60 | 5.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Colistimethate sodium | 2-million-unit vial | Recipient | 3.24 | 3.24 | BNF 201450 |
| Computerised tomography | Procedure | Recipient | 91.00 | 91.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| DeBakey tissue forceps | Forceps | Recipient | 0.08 | 0.08 | EAC |
| Docusate sodium, 100 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.09 | 2.09 | BNF 201450 |
| Doxazosin (as mesilate), 4 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.04 | 1.04 | BNF 201450 |
| Doxycycline (as hyclate), 100 mg | 8-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.13 | 1.13 | BNF 201450 |
| ECG | 24-hour test | Recipient | 20.81 | 20.81 | NuTH’s costing tool99 |
| Enoxaparin sodium [Clexane® Forte (Sanofi SA, Gentilly, France)], 150 mg | 1-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 9.99 | 9.99 | BNF 201450 |
| ECMO | Machine | Recipient | 34,000.00 | 34,000.00 | Tanveer Butt, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Filgrastim, 30 million units (300 µg /ml) | 1-ml vial | Recipient | 52.70 | 52.70 | BNF 201450 |
| Flucloxacillin (as sodium) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 4.90 | 4.90 | BNF 201450 |
| Fluticasone propionate, 250 µg; and salmeterol xinafoate, 50 µg [Seretide® 250 Accuhaler® (GlaxoSmithKline, Brentford, London, UK)] | 120-unit dose inhaler | Recipient | 35.00 | 35.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Foscarnet sodium, 24 mg/ml | 250-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 119.85 | 119.85 | BNF 201450 |
| Furosemide, 10 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 0.32 | 0.32 | BNF 201450 |
| Ganciclovir (as sodium) | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 29.77 | 29.77 | BNF 201450 |
| Gastrograffin | Solution | Recipient | 3.42 | 3.42 | Medical supplies |
| Glucose anhydrous, 50 mg/ml | 1000-ml bag | Recipient | 1.38 | 1.38 | BNF 201450 |
| iLA | Device | Recipient | 4.28 | 4.28 | EAC |
| Immunoglobulin | 10-g vial | Recipient | 408.00 | 408.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Insulin, 3 ml | 5 × 3-ml pre-filled disposable injection devices | Recipient | 44.85 | 44.85 | BNF 201450 |
| Intubation | Procedure | Recipient | 235.00 | 235.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Hydralazine hydrochloride, 50 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 18.30 | 18.30 | BNF 201450 |
| Hydrocortisone (as sodium succinate) | 100-mg vial | Recipient | 1.16 | 1.16 | BNF 201450 |
| Lansoprazole, 30 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.52 | 1.52 | BNF 201450 |
| Level 1 ward care (hospital stay) | Bed-day | Recipient | 265.00 | 265.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Macrogol compound oral powder | 50-sachet pack | Recipient | 11.13 | 11.13 | BNF 201450 |
| Magnesium hydroxide with liquid paraffin | 150-ml bottle | Recipient | 11.50 | 11.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 100 mg | 10-ml ampoule | Recipient | 51.93 | 51.93 | BNF 201450 |
| Magnetic resonance imaging scan | Test | Recipient | 412.00 | 412.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Meropenem (as trihydrate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 16.00 | 16.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 9.60 | 9.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 17.30 | 17.30 | BNF 201450 |
| Metoclopramide hydrochloride, 5 mg/ml | 2-ml ampoule | Recipient | 0.32 | 0.32 | BNF 201450 |
| Midazolam (as hydrochloride), 1 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 0.65 | 0.65 | BNF 201450 |
| Minocycline (as hydrochloride), 100 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 13.09 | 13.09 | BNF 201450 |
| Moxifloxacin (as hydrochloride), 1.6 mg/ml | 250-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 39.95 | 39.95 | BNF 201450 |
| Nefopam hydrochloride, 30 mg | 90-tablet pack | Recipient | 10.59 | 10.59 | BNF 201450 |
| Non-invasive ventilation | Procedure | Recipient | 166.00 | 166.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Normal immunoglobulin, 10 g | 200-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 408.00 | 408.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Oxycodone hydrochloride, 10 mg/ml | 120-ml oral solution | Recipient | 46.63 | 46.63 | BNF 201450 |
| Packed red blood cells | 274-ml bag | Recipient | 120.00 | 120.00 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Yvonne Scott, NuTH, July 2015, personal communication |
| Phosphate enema | 133-ml enema pack | Recipient | 0.68 | 0.68 | BNF 201450 |
| Piperacillin (as sodium), 4 g; and tazobactam (as sodium), 500 mg (Tazocin) | 4.5-g vial | Recipient | 15.17 | 15.17 | BNF 201450 |
| Posaconazole, 100 mg | 96-tablet pack | Recipient | 2387.85 | 2387.85 | BNF 201450 |
| Prednisolone, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.29 | 1.29 | BNF 201450 |
| Pregabalin, 150 mg | 56-capsule pack | Recipient | 65.40 | 65.40 | BNF 201450 |
| Redo lung transplantation | Procedure | Recipient | 2702.00 | 2702.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Renal support | Treatment | Recipient | 755.04 | 755.04 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Ribavirin, 200 mg | 42-tablet pack | Recipient | 92.50 | 92.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Ribavirin, 400 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 246.65 | 246.65 | BNF 201450 |
| Salbutamol (as sulfate), 5 mg/2.5 ml | 20-unit dose nebuliser liquid vial | Recipient | 3.82 | 3.82 | BNF 201450 |
| Sirolimus, 2 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 172.98 | 172.98 | BNF 201450 |
| Sodium bicarbonate, 42 mg/ml | 500-ml intravenous infusion bottle | Recipient | 9.39 | 9.39 | BNF 201450 |
| 2 l of 0.9% sodium chloride solution | 1-l solution | Recipient | 0.97 | 0.97 | BNF 201450 |
| Stenting | Procedure | Recipient | 4580.36 | 4580.36 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Sulfamethoxazole, 80 mg; and trimethoprim, 16 mg (Septrin) | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.78 | 1.78 | BNF 201450 |
| Sulfamethoxazole, 400 mg; and trimethoprim, 80 mg (co-trimoxazole) | 5 ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.78 | 1.78 | BNF 201450 |
| Surgical intervention | Procedure | Recipient | 4580.36 | 4580.36 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 1 mg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 80.28 | 80.28 | BNF 201450 |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 1 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 160.54 | 160.54 | BNF 201450 |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 5 mg/ml | 10 × 1-ml ampoules | Recipient | 58.45 | 58.45 | BNF 201450 |
| Tinzaparin sodium, 20,000 units/ml [Innohep® (Leo Pharma A/S, Copenhagen, Denmark) | 0.5-ml vial | Recipient | 5.95 | 5.95 | BNF 201450 |
| Tracheostomy | Procedure | Recipient | 135.00 | 135.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Tramadol hydrochloride, 150 mg | 60-capsule pack | Recipient | 22.92 | 22.92 | BNF 201450 |
| Ultrasound scan | Test | Recipient | 59.00 | 59.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Valganciclovir (as hydrochloride), 450 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 1081.46 | 1081.46 | BNF 201450 |
| Vancomycin (as hydrochloride), 125 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 140.08 | 140.08 | BNF 201450 |
| Voriconazole | 200-mg vial | Recipient | 77.14 | 77.14 | BNF 201450 |
| Warfarin sodium, 3 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.07 | 1.07 | BNF 201450 |
| Warfarin sodium, 1 mg/ml | 150-ml oral suspension | Recipient | 107.98 | 107.98 | BNF 201450 |
| Ward usage | |||||
| HDU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 852.00 | 852.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| ITU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 852.00 | 852.00 | Reference Costs 2013/2014 49 |
| Immunosuppressive medications (if needed) | |||||
| Azathioprine, 25 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.24 | 3.24 | BNF 201450 |
| Azathioprine, 50 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.48 | 3.48 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin, 25 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 13.05 | 13.05 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin, 50 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 25.50 | 25.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin, 100 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 48.50 | 48.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Mycophenolate mofetil, 500 mg | 50-tablet pack | Recipient | 10.15 | 10.15 | BNF 201450 |
| Prednisolone, 1 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.08 | 1.08 | BNF 201450 |
| Prednisolone, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.29 | 1.29 | BNF 201450 |
| Prednisolone, 25 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 50.00 | 50.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Prednisolone acetate, 25 mg/ml | 1 ml ampoule | Recipient | 6.87 | 6.87 | BNF 201450 |
| Sirolimus, 500 µg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 69.00 | 69.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Sirolimus, 1 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 86.49 | 86.49 | BNF 201450 |
| Sirolimus, 2 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 172.98 | 172.98 | BNF 201450 |
| Tacrolimus, 500 µg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 61.88 | 61.88 | BNF 201450 |
| Tacrolimus, 1 mg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 80.28 | 80.28 | BNF 201450 |
| Tacrolimus, 1 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 160.54 | 160.54 | BNF 201450 |
| Tacrolimus, 5 mg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 296.58 | 296.58 | BNF 201450 |
| Other | |||||
| Aciclovir, 200 mg | 25-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.77 | 1.77 | BNF 201450 |
| Amoxicillin (as trihydrate), 500 mg | 21-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.62 | 1.62 | BNF 201450 |
| Azithromycin (as dihydrate), 250 mg | 4-capsule pack | Recipient | 10.06 | 10.06 | BNF 201450 |
| Beclomethasone dipropionate, 400 µg/dose | 100-dose unit | Recipient | 19.61 | 19.61 | BNF 201450 |
| Calcium carbonate (Adcal), 1.5 g | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 8.70 | 8.70 | BNF 201450 |
| Cetirizine hydrochloride, 10 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.07 | 1.07 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 10 mg | 60-capsule pack | Recipient | 16.68 | 16.68 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 25 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 16.79 | 16.79 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 50 mg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 32.88 | 32.88 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin, 100 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 62.41 | 62.41 | BNF 201450 |
| Citalopram (as hydrobromide), 20 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.09 | 1.09 | BNF 201450 |
| Dapsone, 100 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 92.51 | 92.51 | BNF 201450 |
| Dexamethasone, 2 mg | 50-tablet pack | Recipient | 52.41 | 52.41 | BNF 201450 |
| Doxycycline (as hyclate), 100 mg | 8-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.13 | 1.13 | BNF 201450 |
| Furosemide, 40 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 0.88 | 0.88 | BNF 201450 |
| Hydrocortisone, 10 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 65.78 | 65.78 | BNF 201450 |
| Hydrocortisone, 20 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 86.63 | 86.63 | BNF 201450 |
| Lisinopril dihydrate, 2.5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 0.96 | 0.96 | BNF 201450 |
| Lisinopril dihydrate, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 0.98 | 0.98 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone, 2 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.88 | 3.88 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 40-mg vial | Recipient | 1.58 | 1.58 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 17.3 | 17.3 | BNF 201450 |
| Mycophenolic acid (as sodium), 180 mg | 120-tablet pack | Recipient | 96.72 | 96.72 | BNF 201450 |
| Mycophenolic acid (as sodium), 360 mg | 120-tablet pack | Recipient | 193.43 | 193.43 | BNF 201450 |
| N-acetylcysteine, 200 mg/ml | 10-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.96 | 1.96 | BNF 201450 |
| Perindopril erbumine, 2 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.15 | 1.15 | BNF 201450 |
| Perindopril erbumine, 4 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.56 | 1.56 | BNF 201450 |
| Sulfamethoxazole, 400 mg; and trimethoprim, 80 mg (co-trimoxazole) | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.34 | 3.34 | BNF 201450 |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 1 mg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 80.28 | 80.28 | BNF 201450 |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 1 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 160.54 | 160.54 | BNF 201450 |
| Tinzaparin sodium, 3500 units | 0.35-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 2.77 | 2.77 | BNF 201450 |
| Concomitant medications | |||||
| Variable costs | |||||
| Treatment | |||||
| Aciclovir, 200 mg | 25-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.77 | 1.77 | BNF 201450 |
| Adrenaline (base), 100 µg/ml (1 in 10,000) | 10-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 6.99 | 6.99 | BNF 201450 |
| Alendronic acid (as sodium), 70 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.03 | 1.03 | BNF 201450 |
| Alfentanil (as hydrochloride), 500 µg/ml | 2-ml ampoule | Recipient | 0.7 | 0.7 | BNF 201450 |
| Alfentanil (as hydrochloride), 5 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 2.5 | 2.5 | BNF 201450 |
| Allopurinol, 300 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.18 | 1.18 | BNF 201450 |
| Amiloride hydrochloride, 5 mg; and furosemide, 40 mg (co-amilofruse) | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.50 | 2.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Amiodarone hydrochloride, 30 mg/ml | 10-ml pre-filled disposable syringe | Recipient | 13.5 | 13.5 | BNF 201450 |
| Amiodarone hydrochloride, 100 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.08 | 1.08 | BNF 201450 |
| Amiodarone hydrochloride, 200 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.04 | 2.04 | BNF 201450 |
| Amitriptyline hydrochloride, 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.19 | 1.19 | BNF 201450 |
| Amlodipine, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 0.98 | 0.98 | BNF 201450 |
| Amlodipine, 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Amoxicillin (as trihydrate), 500 mg | 21-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.62 | 1.62 | BNF 201450 |
| Amoxicillin (as amoxicillin trihydrate), 500 mg; and clavulanic acid (as potassium), 125 mg | 21-tablet pack | Recipient | 9.60 | 9.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Amphotericin B, 5 mg/ml | 20-lozenge pack | Recipient | 7.84 | 7.84 | BNF 201450 |
| Amphotericin B (as phospholipid complex), 5 mg/ml | 20-ml vial | Recipient | 77.50 | 77.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Antiembolism socks | Socks pack | Recipient | 12.99 | 12.99 | Medical supplies |
| Anti-thymocyte immunoglobulin (rabbit) | 25-mg vial | Recipient | 158.77 | 158.77 | BNF 201450 |
| Aspirin, 75 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 0.94 | 0.94 | BNF 201450 |
| Atracurium besilate, 10 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Azathioprine, 25 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.24 | 3.24 | BNF 201450 |
| Azathioprine, 50 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.48 | 3.48 | BNF 201450 |
| Azithromycin (as dihydrate), 250 mg | 4-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.83 | 1.83 | BNF 201450 |
| Azithromycin (as dihydrate), 250 mg | 6-capsule pack | Recipient | 15.10 | 15.10 | BNF 201450 |
| Azithromycin, 500 mg | 3-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.77 | 1.77 | BNF 201450 |
| Aztreonam | 2-g vial | Recipient | 18.82 | 18.82 | BNF 201450 |
| Bisoprolol fumarate, 1.25 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.35 | 2.35 | BNF 201450 |
| Bisoprolol fumarate, 2.5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.35 | 2.35 | BNF 201450 |
| Bisoprolol fumarate, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 0.98 | 0.98 | BNF 201450 |
| Bupivacaine hydrochloride, 1 mg/ml | 100-ml infusion bag | Recipient | 8.41 | 8.41 | BNF 201450 |
| Calcium carbonate (Adcal), 1.5 g | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 8.70 | 8.70 | BNF 201450 |
| Calcium carbonate, 1.25 g; and colecalciferol, 400 units (Calcichew D3 Forte) | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 4.24 | 4.24 | BNF 201450 |
| Calcium chloride dihydrate, 10% | 10-ml pre-filed disposable injection | Recipient | 6.94 | 6.94 | BNF 201450 |
| Calogen® (Nutricia, Danone, Paris, France) emulsion | 500-ml bottle | Recipient | 10.72 | 10.72 | BNF 201450 |
| Carbocisteine, 375 mg | 120-capsule pack | Recipient | 17.11 | 17.11 | BNF 201450 |
| Caspofungin (as acetate) | 50-mg vial | Recipient | 327.67 | 327.67 | BNF 201450 |
| Ceftazidime (as pentahydrate) | 2-g vial | Recipient | 17.90 | 17.90 | BNF 201450 |
| Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride, 5 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 8.07 | 8.07 | BNF 201450 |
| Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride [Librium Meda AB, Solna, Sweden)], 10 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 14.06 | 14.06 | BNF 201450 |
| Chlorhexidine gluconate, 4% | 500-ml surgical scrub | Recipient | 3.59 | 3.59 | BNF 201450 |
| Chlorhexidine hydrochloride | 500-mg pump pack | Recipient | 6.04 | 6.04 | BNF 201450 |
| Chlorhexidine hydrochloride, 1mg/g; and neomycin sulfate, 5 mg/g [Naseptin® (Alliance Pharma, Clippenham, UK)] | 15-g nasal cream | Recipient | 1.90 | 1.90 | BNF 201450 |
| Chlorhexidine hydrochloride, 10 mg/g; and nystatin, 100,000 units/g [Nystaform® (Typharm Ltd, Norwich, UK)] | 30-g cream | Recipient | 2.62 | 2.62 | BNF 201450 |
| Chlorphenamine maleate, 10 mg/ml | 1 ml ampoule | Recipient | 4.47 | 4.47 | BNF 201450 |
| Chlorpromazine hydrochloride, 25 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.31 | 2.31 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 25 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 16.79 | 16.79 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin, 50 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 25.50 | 25.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciclosporin, 100 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 48.50 | 48.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciprofloxacin (as hydrochloride), 500 mg (Ciproxin) | 10-tablet pack | Recipient | 12.49 | 12.49 | BNF 201450 |
| Ciprofloxacin (as hydrochloride), 750 mg | 10-tablet pack | Recipient | 8.00 | 8.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Citalopram (as hydrobromide), 20 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.09 | 1.09 | BNF 201450 |
| Citalopram (as hydrobromide), 40 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.28 | 1.28 | BNF 201450 |
| Clonidine hydrochloride, 25 µg | 112-tablet pack | Recipient | 5.02 | 5.02 | BNF 201450 |
| Codeine phosphate, 8 mg; and paracetamol, 500 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.19 | 1.19 | BNF 201450 |
| Codeine phosphate, 30 mg; and paracetamol, 500 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 5.80 | 5.80 | BNF 201450 |
| Codeine phosphate, 30 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.52 | 1.52 | BNF 201450 |
| Codeine phosphate, 60 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.70 | 2.70 | BNF 201450 |
| Colecalciferol, 500 µg (20,000 units) | 15-capsule pack | Recipient | 17.40 | 17.40 | BNF 201450 |
| Colistimethate sodium | 1-million-unit vial | Recipient | 3.24 | 3.24 | BNF 201450 |
| Colistimethate sodium | 2-million-unit vial | Recipient | 3.24 | 3.24 | BNF 201450 |
| CREON® (AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL, USA), 25,000 units | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 28.25 | 28.25 | BNF 201450 |
| CREON Micro Pancreatine, 20 g | 60.12-mg granules | Recipient | 31.50 | 31.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Cryoprecipitate | 8 units | Recipient | 711.29 | 711.29 | Medical supplies |
| Cyclizine hydrochloride, 50 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 10.97 | 10.97 | BNF 201450 |
| Dapsone, 100 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 92.51 | 92.51 | BNF 201450 |
| Diazepam, 2 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.09 | 1.09 | BNF 201450 |
| Digoxin, 250 µg/ml | 2-ml ampoule | Recipient | 0.70 | 0.70 | BNF 201450 |
| Diltiazem hydrochloride, 120 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 6.27 | 6.27 | BNF 201450 |
| Diltiazem hydrochloride, 200 mg | 7-capsule pack | Recipient | 6.27 | 6.27 | BNF 201450 |
| Docusate sodium, 100 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 6.98 | 6.98 | BNF 201450 |
| Domperidone (as maleate), 10 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 4.83 | 4.83 | BNF 201450 |
| Dopamine hydrochloride, 40 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 3.88 | 3.88 | BNF 201450 |
| Dosulepin hydrochloride, 25 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.86 | 1.86 | BNF 201450 |
| Doxazosin (as mesilate), 4 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 5.00 | 5.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Doxycycline (as hyclate), 100 mg | 8-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.13 | 1.13 | BNF 201450 |
| Enoxaparin sodium, 100 mg/ml | 0.4-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 3.03 | 3.03 | BNF 201450 |
| Ensure® (Abbott Laboratories, Chicago, IL, USA) liquid | 250 ml | Recipient | 2.26 | 2.26 | BNF 201450 |
| Erythromycin (as lactobionate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 10.98 | 10.98 | BNF 201450 |
| Esomeprazole (as magnesium dihydrate), 40 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 3.96 | 3.96 | BNF 201450 |
| Ethambutol hydrochloride, 400 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 42.74 | 42.74 | BNF 201450 |
| Ezetimibe, 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 26.31 | 26.31 | BNF 201450 |
| Ethinylestradiol, 30 µg; and gestodene, 75 µg | 21-day preparation | Recipient | 6.73 | 6.73 | BNF 201450 |
| Ferrous sulfate dried, 200 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.11 | 1.11 | BNF 201450 |
| Flucloxacillin (as sodium), 500 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.60 | 2.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Flucloxacillin (as sodium) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 4.90 | 4.90 | BNF 201450 |
| Fluconazole, 50 mg | 7-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.02 | 1.02 | BNF 201450 |
| Fluconazole, 200 mg | 7-capsule pack | Recipient | 6.36 | 6.36 | BNF 201450 |
| Fluconazole, 2 mg/ml | 100-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 27.45 | 27.45 | BNF 201450 |
| Fluoxetine (as hydrochloride), 20 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.16 | 1.16 | BNF 201450 |
| Fluticasone propionate, 50 µg | 150-unit dose nasal spray | Recipient | 11.01 | 11.01 | BNF 201450 |
| Fluticasone propionate, 250 µg (Flixotide 250 Accuhale) | 60-dose inhaler | Recipient | 21.26 | 21.26 | BNF 201450 |
| Fluticasone propionate, 250 µg; and salmeterol xinafoate, 50 µg (Seretide 250 Accuhaler) | 60-dose inhaler | Recipient | 35.00 | 35.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Folic acid, 400 µg | 90-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.71 | 2.71 | BNF 201450 |
| Foscarnet sodium, 24 mg/ml | 250-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 119.85 | 119.85 | BNF 201450 |
| Fosfomycin (as sodium) | 2-g vial | Recipient | 15.00 | 15.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Fresh-frozen plasma | 271-ml bag | Recipient | 28.46 | 28.46 | NHSBT |
| Furosemide, 10 mg/ml | 2-ml ampoule | Recipient | 0.35 | 0.35 | BNF 201450 |
| Furosemide, 20 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 0.98 | 0.98 | BNF 201450 |
| Furosemide, 40 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 0.88 | 0.88 | BNF 201450 |
| Ganciclovir (as sodium) | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 29.77 | 29.77 | BNF 201450 |
| Gelatin (Gelofusine®) | 1-l infusion bag | Recipient | 9.04 | 9.04 | BNF 201450 |
| Gelatin, 140 mg/g; and glycerol, 700 mg/g | 4-g supplementary pack | Recipient | 1.94 | 1.94 | BNF 201450 |
| Gliclazide (glycoside), 30 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 4.10 | 4.10 | BNF 201450 |
| Gliclazide, 40 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.36 | 3.36 | BNF 201450 |
| Glucose anhydrous, 500 mg/ml | 50-ml vial | Recipient | 2.01 | 2.01 | BNF 201450 |
| Glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), 1 mg/ml | 50-ml ampoule | Recipient | 15.90 | 15.90 | BNF 201450 |
| Haloperidol, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.30 | 3.30 | BNF 201450 |
| Haloperidol, 5 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 0.87 | 0.87 | BNF 201450 |
| Heparin sodium, 5000 units/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 2.90 | 2.90 | BNF 201450 |
| Heparin sodium, 5000 units/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 7.58 | 7.58 | BNF 201450 |
| Hydroxocobalamin, 1 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.75 | 1.75 | BNF 201450 |
| Hyoscine butylbromide [Buscopan® (Boehringer Ingelheim, Ingelheim, Germany)], 10 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Ibandronic acid (as sodium monohydrate) 50 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 10.76 | 10.76 | BNF 201450 |
| Iloprost (as THAM), 10 µg/ml | 30 × 1-ml unit dose vials | Recipient | 400.19 | 400.19 | BNF 201450 |
| Insulin, 3 ml | 5 × 3-ml pre-filled disposable injection devices | Recipient | 44.85 | 44.85 | BNF 201450 |
| Insulin aspart, 100 units/ml | 5 × 3-ml pre-filled disposable injection devices | Recipient | 32.13 | 32.13 | BNF 201450 |
| Insulin human (as soluble human) (ACTRAPID®), 100 units/ml | 10-ml vial | Recipient | 7.48 | 7.48 | BNF 201450 |
| Insulin human (as detemir), 100 units/ml (LEMEVIR®, Novo Nordisk, Bagsværd, Denmark) | 5 × 3-ml pre-filled disposable injection device | Recipient | 43.00 | 43.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Ipratropium bromide, 250 µg/ml | 60 × 1-ml unit dose vial | Recipient | 12.44 | 12.44 | BNF 201450 |
| Ipratropium bromide | 500-µg nebuliser solution | Recipient | 23.75 | 23.75 | BNF 201450 |
| Ipratropium bromide, 2.5 mg/2.5 ml | 60-unit dose vial | Recipient | 24.10 | 24.10 | BNF 201450 |
| Ipratropium bromide, 200 µg/ml; and salbutamol (as sulfate), 1 mg/ml (Combivent) | 60-unit dose vials | Recipient | 24.10 | 24.10 | BNF 201450 |
| Itraconazole, 100 mg | 15-capsule pack | Recipient | 4.57 | 4.57 | BNF 201450 |
| Itraconazole, 10 mg/ml | 150-ml oral solution | Recipient | 58.34 | 58.34 | BNF 201450 |
| Labetalol hydrochloride, 100 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 6.99 | 6.99 | BNF 201450 |
| Labetalol hydrochloride, 200 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 9.89 | 9.89 | BNF 201450 |
| Lactulose | 300-ml solution | Recipient | 1.95 | 1.95 | BNF 201450 |
| Lansoprazole, 15 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.17 | 1.17 | BNF 201450 |
| Lansoprazole, 30 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.52 | 1.52 | BNF 201450 |
| Loratadine, 10 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.11 | 1.11 | BNF 201450 |
| Levomepromazine maleate, 25 mg | 84-tablet pack | Recipient | 20.26 | 20.26 | BNF 201450 |
| Linezolid, 600 mg | 10-tablet pack | Recipient | 445.00 | 445.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Loperamide hydrochloride, 2 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.15 | 2.15 | BNF 201450 |
| Lorazepam, 1 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.67 | 2.67 | BNF 201450 |
| Lymecycline, 408 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 9.18 | 9.18 | BNF 201450 |
| Magnesium oxide, 160 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 17.50 | 17.50 | Medical supplies |
| Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 500 mg/ml | 2-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.18 | 1.18 | BNF 201450 |
| Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 500 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 5.56 | 5.56 | BNF 201450 |
| Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 500 mg/ml | 4-ml ampoule | Recipient | 10.23 | 10.23 | BNF 201450 |
| Menadiol phosphate (as sodium phosphate), 10 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 128.60 | 128.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Meropenem (as trihydrate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 16.00 | 16.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 9.60 | 9.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 17.30 | 17.30 | BNF 201450 |
| Metformin hydrochloride, 500 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.66 | 2.66 | BNF 201450 |
| Metoclopramide hydrochloride, 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 0.97 | 0.97 | BNF 201450 |
| Metronidazole, 400 mg | 21-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.70 | 1.70 | BNF 201450 |
| Midazolam (as hydrochloride), 1 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 6.00 | 6.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Milrinone (as lactate), 1 mg/ml | 10-ml ampoule | Recipient | 19.91 | 19.91 | BNF 201450 |
| Minocycline (as hydrochloride), 100 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 6.20 | 6.20 | BNF 201450 |
| Mirtazapine, 30 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.60 | 1.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Montelukast (as sodium), 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 26.97 | 26.97 | BNF 201450 |
| Mometasone furoate, 50 µg | 140-unit dose nasal spray | Recipient | 7.68 | 7.68 | BNF 201450 |
| Morphine sulfate, 1 mg/ml | 10-mg disposable syringe | Recipient | 15.00 | 15.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Morphine sulfate (Oramorph®), 10 mg/5 ml | 300-ml oral solution | Recipient | 5.45 | 5.45 | BNF 201450 |
| Movicol® (Norgine Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Amsterdam, the Netherlands) | 30-sachet pack | Recipient | 6.68 | 6.68 | BNF 201450 |
| Moxifloxacin (as hydrochloride), 400 mg | 5-tablet pack | Recipient | 12.43 | 12.43 | BNF 201450 |
| Multivitamins | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.50 | 1.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Mupirocin, 20 mg/g | 15-g ointment | Recipient | 5.35 | 5.35 | BNF 201450 |
| Micafungin (as sodium) | 100-mg vial | Recipient | 341.00 | 341.00 | BNF 201450 |
| N-acetylcysteine, 600 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 23.45 | 23.45 | Medical supplies |
| Naproxen, 500 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.67 | 1.67 | BNF 201450 |
| Nebivolol (as hydrochloride), 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.81 | 1.81 | BNF 201450 |
| Nifedipine, 5 mg | 84-capsule pack | Recipient | 15.20 | 15.20 | BNF 201450 |
| Nifedipine, 10 mg | 84-capsule pack | Recipient | 6.53 | 6.53 | BNF 201450 |
| Noradrenaline base, 1 mg/ml (as noradrenaline acid tartrate, 2 mg/ml) | 4-ml ampoule | Recipient | 4.40 | 4.40 | BNF 201450 |
| Nutrison energy multifibre | 1000-ml solution | Recipient | 11.74 | 11.74 | BNF 201450 |
| Nystatin, 100,000 units/ml | 30-ml oral suspension | Recipient | 3.35 | 3.35 | BNF 201450 |
| Omeprazole (as magnesium), 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.25 | 1.25 | BNF 201450 |
| Omeprazole (as magnesium), 20 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 6.11 | 6.11 | BNF 201450 |
| Omeprazole (as magnesium), 40 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 4.98 | 4.98 | BNF 201450 |
| Omeprazole (as sodium) | 40-mg vial | Recipient | 4.16 | 4.16 | BNF 201450 |
| Ondansetrol (as hydrochloride), 2 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Ondansetron (as hydrochloride), 4 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 5.37 | 5.37 | BNF 201450 |
| Oxycodone hydrochloride, 5 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 11.43 | 11.43 | BNF 201450 |
| Oxycodone hydrochloride, 10 mg | 56-capsule pack | Recipient | 22.86 | 22.86 | BNF 201450 |
| Pabrinex® (Archimedes Pharma Ltd, Reading, UK) vitamin B substances with ascorbic acid, 250 mg/10 ml | 2 × 5 ml ampoule | Recipient | 2.25 | 2.25 | BNF 201450 |
| Packed red blood cells | 274-ml bag | Recipient | 120.00 | 120.00 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Yvonne Scott, NuTH, July 2015, personal communication |
| Paracetamol, 500 mg | 32-tablet pack | Recipient | 0.96 | 0.96 | BNF 201450 |
| Paracetamol, 1 g | 10 mg/ml 100-ml vial | Recipient | 1.20 | 1.20 | BNF 201450 |
| Peppermint water | 100-ml solution | Recipient | 10.81 | 10.81 | BNF 201450 |
| Perindopril erbumine, 4 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.56 | 1.56 | BNF 201450 |
| Phenoxymethylpenicillin (as potassium), 250 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.20 | 1.20 | BNF 201450 |
| Phosphate | 500-ml bottle | Recipient | 5.15 | 5.15 | BNF 201450 |
| Piperacillin,(as sodium) 4 g; and tazobactam (as sodium), 500 mg (Tazocin) | 4.5-g vial | Recipient | 15.17 | 15.17 | BNF 201450 |
| Platelets | 250-ml bag | Recipient | 196.96 | 196.96 | BNF 201450 |
| Posaconazole, 100 mg | 96-tablet pack | Recipient | 2387.85 | 2387.85 | BNF 201450 |
| Potassium bicarbonate, 400 mg; and potassium chloride, 600 mg [Sando-K® (HK Pharma Ltd, Bedford, UK)] | 20 tablets | Recipient | 1.53 | 1.53 | BNF 201450 |
| Potassium chloride, 150 mg/ml | 10-ml ampoule | Recipient | 0.48 | 0.48 | BNF 201450 |
| Pravastatin sodium, 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.31 | 1.31 | BNF 201450 |
| Pravastatin sodium, 20 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.57 | 1.57 | BNF 201450 |
| Pravastatin sodium, 40 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.93 | 1.93 | BNF 201450 |
| Prednisolone, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.29 | 1.29 | BNF 201450 |
| Pregabalin, 25 mg | 56-capsule pack | Recipient | 64.40 | 64.40 | BNF 201450 |
| Pregabalin, 50 mg | 84-capsule pack | Recipient | 96.60 | 96.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Pregabalin, 75 g | 56-capsule pack | Recipient | 64.40 | 64.40 | BNF 201450 |
| Pregabalin, 100 mg | 84-capsule pack | Recipient | 96.60 | 96.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Prochlorperazine maleate, 3 mg | 5 × 10-tablet pack | Recipient | 6.49 | 6.49 | BNF 201450 |
| Propofol, 5 mg/ml | 20-ml ampoule | Recipient | 3.46 | 3.46 | BNF 201450 |
| Propofol, 10 mg/ml | 20-ml ampoule | Recipient | 3.07 | 3.07 | BNF 201450 |
| Propofol, 10 mg/ml | 50-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 10.10 | 10.10 | BNF 201450 |
| Ramipril, 2.5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.12 | 1.12 | BNF 201450 |
| Ramipril, 5 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.24 | 1.24 | BNF 201450 |
| Ranitidine (as hydrochloride), 25 mg/ml | 2-ml ampoule | Recipient | 0.54 | 0.54 | BNF 201450 |
| Ranitidine (as hydrochloride), 150 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.57 | 1.57 | BNF 201450 |
| Ranitidine (as hydrochloride), 300 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.48 | 1.48 | BNF 201450 |
| Remifentanil (as hydrochloride) | 5-mg vial | Recipient | 25.40 | 25.40 | BNF 201450 |
| Risperidone, 500 µg | 20-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.07 | 1.07 | BNF 201450 |
| Risperidone, 2 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.68 | 1.68 | BNF 201450 |
| Salbutamol (as sulfate), 2.5 mg/2.5 ml | 20-unit dose nebuliser | Recipient | 1.91 | 1.91 | BNF 201450 |
| Salbutamol (as sulfate), 200 µg | 100-dose unit inhaler | Recipient | 4.85 | 4.85 | BNF 201450 |
| Sennoside B (as sennosides), 7.5 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.52 | 3.52 | BNF 201450 |
| Sildenafil (as citrate), 25 mg | 4-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.09 | 1.09 | BNF 201450 |
| Sodium chloride, 0.9% | 20 × 2.5 ml spray | Recipient | 20.60 | 20.60 | BNF 201450 |
| Sodium chloride, 600 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 6.05 | 6.05 | BNF 201450 |
| Sodium cromoglycate, 5 mg/dose | 112-unit dose inhaler | Recipient | 17.07 | 17.07 | BNF 201450 |
| Sodium dihydrogen phosphate anhydrous, 1.936 g | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.29 | 3.29 | BNF 201450 |
| Sodium valproate, 200 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 4.49 | 4.49 | BNF 201450 |
| Strepsils® (Reckitt Benckiser Group, Slough, UK) | 24-lozenge pack | Recipient | 2.99 | 2.99 | Medical supplies |
| Sulfamethoxazole, 400 mg; and trimethoprim, 80 mg (co-trimoxazole) | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.34 | 3.34 | BNF 201450 |
| Tadalafil, 20 mg | 8-tablet pack | Recipient | 53.98 | 53.98 | BNF 201450 |
| Tamsulosin hydrochloride, 400 µg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 4.62 | 4.62 | BNF 201450 |
| T.E.D™ compression socks/hose (Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA) (knee length) | Stocking | Recipient | 8.12 | 8.12 | Medical supplies |
| Teicoplanin | 400-mg vial | Recipient | 7.32 | 7.32 | BNF 201450 |
| Theophylline [Uniphyllin® (Napp Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Cambridge, UK)], 200 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.96 | 2.96 | BNF 201450 |
| Thiamine hydrochloride, 100 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 9.18 | 9.18 | BNF 201450 |
| Tiotropium (as bromide), 18 µg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 34.87 | 34.87 | BNF 201450 |
| Tobramycin, 60 mg/ml | 56 × 5 ml – 300-mg unit | Recipient | 1305.92 | 1305.92 | BNF 201450 |
| Tobramycin, 75 mg/ml | 56 × 4-ml nebuliser | Recipient | 1187.00 | 1187.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Tramadol hydrochloride, 50 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.20 | 1.20 | BNF 201450 |
| Tramadol hydrochloride, 50 mg | 60-capsule pack | Recipient | 6.56 | 6.56 | BNF 201450 |
| Tramadol hydrochloride, 100 mg | 60-capsule pack | Recipient | 14.72 | 14.72 | BNF 201450 |
| Ursodeoxycholic acid, 150 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 18.99 | 18.99 | BNF 201450 |
| Ursodeoxycholic acid, 300 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 38.86 | 38.86 | BNF 201450 |
| Valaciclovir (as hydrochloride), 500 mg | 42-tablet pack | Recipient | 8.50 | 8.50 | BNF 201450 |
| Valganciclovir (as hydrochloride), 450 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 1081.46 | 1081.46 | BNF 201450 |
| Vancomycin (as hydrochloride) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 12.99 | 12.99 | BNF 201450 |
| Vitamin B compound strong | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.95 | 1.95 | BNF 201450 |
| Vitamins A, D, E | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 5.93 | 5.93 | BNF 201450 |
| Multivitamins | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 9.21 | 9.21 | BNF 201450 |
| Voriconazole, 200 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1102.74 | 1102.74 | BNF 201450 |
| Warfarin sodium, 3 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.07 | 1.07 | BNF 201450 |
| Water for injections | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 0.24 | 0.24 | BNF 201450 |
| Zopiclone, 3.75 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.68 | 1.68 | BNF 201450 |
Appendix 7 NHS resource use
| Resource or intervention | Unit | Patient details | Mean usage in standard donor lung transplantation | Mean usage in EVLP transplantation | Resource source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donor’s hospital | |||||
| Fixed costs | |||||
| Initial assessment | |||||
| ABG | Test | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 23/Anne Davison, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Bronchoscopy | Procedure | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Katharine Thornalley, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Chest X-ray (radiography) | Test | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 23/Anne Davison, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| ECG | Test | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | Anne Davison, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| FBC | Test | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | Anne Davison, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Drugs | |||||
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 500-mg vial | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 25 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 25/Tanveer Butt, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 2-g vial | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 25 |
| Lung retrieval | |||||
| Fixed costs | |||||
| Equipment | |||||
| DCD donor | |||||
| Bronchoscope | Instrument | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Pink spray 0.5% chlorhexidine | Spray | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| 2 l of 0.9% sodium chloride solution | 1-l solution | Donor | 16.00 | 16.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Strapple tape | Roll | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| DBD donor | |||||
| Blue 23-gauge 25-mm (1-inch) needles | 1-inch needle | Donor | 5.00 | 5.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Bronchoscope | Instrument | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| 1-l cardioplegia bag (green PLEGIVEX) | 1-l bag | Donor | 3.00 | 3.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Green vacutainers | Vacutainer | Donor | 6.00 | 6.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| i-STAT portable clinical analyser (Abbott Laboratories, Chicago, IL, USA) | Device | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| i-STAT cartridges | Cartridge | Donor | 8.00 | 8.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Pink spray 0.5% chlorhexidine | Spray | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| 1-l pressure infusion bag | 1-l bag | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Red vacutainers | Vacutainer | Donor | 6.00 | 6.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Sodium bicarbonate 8.4% | 10-ml ampoule | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| 2 l of 0.9% sodium chloride solution | 1-l solution | Donor | 20.00 | 20.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Spleen pots | Pot | Donor | 6.00 | 6.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Strapple tape | Roll | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| 1-ml syringes | 1-ml syringe | Donor | 5.00 | 5.00 | Retrieval team/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Staff time | |||||
| Scout Team | |||||
| Retrieval surgeon (fellow) | Hour | Donor | 0.80 | 0.80 | Tanveer Butt, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Scrub nurse (band 5) | Hour | Donor | 0.80 | 0.80 | Tanveer Butt, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Retrieval team | |||||
| Perfusionist (band 7) | Hour | Donor | 9.00 | 9.00 | Tanveer Butt, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Retrieval surgeon (fellow) | Hour | Donor | 9.00 | 9.00 | Tanveer Butt, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Scrub nurse (band 5) | Hour | Donor | 9.00 | 9.00 | Tanveer Butt, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Tests | |||||
| Chest X-ray (radiography) | Test | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 23/Anne Davison, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Perfusion (dosage) | |||||
| 2.8 l of PERFADEX solution | 2.8-l solution | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 27/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| 1 l of PERFADEX solution | 1-l solution | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 27/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Calcium chloride 1 mmol/ml (1.7 ml/2.8 l PERFADEX and 0.6 ml/1 l PERFADEX) | 10-ml ampoule | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| FLOLAN 0.5-mg vial (7 ml/2.8 l PERFADEX) | 0.5-mg vial | Donor | 3.00 | 3.00 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| FLOLAN 0.5-mg vial (2.5 ml/1 l PERFADEX) | 0.5-mg vial | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Heparin sodium 5000 units/5 ml (15,000 units/2.8 l PERFADEX) | 5-ml ampoule | Donor | 3.00 | 3.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Heparin sodium 5000 units/5 ml (5000 units/1 l PERFADEX) | 5-ml ampoule | Donor | 1.00 | 1.00 | BNF 201450 |
| THAM 1-ml ampoule (7 ml/2.8 l PERFADEX) | 1-ml ampoule | Donor | 7.00 | 7.00 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| THAM 1-ml ampoule (2.5 ml/1 l PERFADEX) | 1-ml ampoule | Donor | 3.00 | 3.00 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Variable costs | |||||
| Travelling | |||||
| Scout team | |||||
| Road | Transport type/case | Donor | 0.20 | 0.20 | Brian Leadbitter, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Retrieval team | |||||
| Road | Transport type/case | Donor | 0.74 | 0.74 | Brian Leadbitter, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Road and air | Transport type/case | Donor | 0.26 | 0.26 | Brian Leadbitter, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Organ (lung) | |||||
| Road | Transport type/case | Donor | 0.50 | 0.50 | Brian Leadbitter, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Road and air | Transport type/case | Donor | 0.50 | 0.50 | Brian Leadbitter, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| Transplant preparation | |||||
| Fixed costs | |||||
| Contacting potential recipients | |||||
| Transplant co-ordinator | Hour | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | Katie Morley, NuTH, October 2014, personal communication |
| Meeting potential recipients | |||||
| Transplant co-ordinator | Hour | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | Katie Morley, NuTH, October 2014, personal communication |
| Tissue typing | |||||
| Tissue typing test | Test | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | Katie Morley, NuTH, October 2014, personal communication |
| Tests | |||||
| ABG | Test | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 20 |
| Chest X-ray (radiography) | Test | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 21 |
| ECG | Test | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | Katie Morley, NuTH, October 2014, personal communication/Anne Davison, NuTH, June 2015, personal communication |
| FBC | Test | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 20 |
| Ward time | |||||
| Transplant centre ward | Bed-day | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | Care Pathway/Katie Morley, NuTH, October 2014, personal communication |
| Drugs | |||||
| Azathioprine 50 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 0.02 | 0.02 | Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication |
| Variable costs | |||||
| Transfer to ward | |||||
| Air | Transport type | Recipient | Missing | Missing | Missing |
| Road | Transport type | Recipient | Missing | Missing | Missing |
| EVLP procedure | |||||
| Fixed costs | |||||
| Staff time | |||||
| Anaesthetic registrar | Hour | EVLP recipient | – | 2.00 | Katie Morley, NuTH, October 2014, personal communication/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Consultant surgeon | Hour | EVLP recipient | – | 0.33 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Perfusionist (band 7) | Hour | EVLP recipient | – | 6.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Scrub nurse/ODA (band 5) | Hour | EVLP recipient | – | 3.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Surgical fellow | Hour | EVLP recipient | – | 4.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Equipment | |||||
| Bronchoscope | Instrument | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| DeBakey tissue forceps | Forceps | EVLP recipient | – | 3.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| McIndoe scissors | Scissor | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| Nebuliser circuit | Item | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| 4–0 Prolene (no. 8935) suture pack | Pack | EVLP recipient | – | 2.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| 10FG suction catheter (SHODS) | Catheter | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| Suction connecting tubing | Tubing | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| Consumables | |||||
| Nylon surgical tape | Roll | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| Gas (2000 l of N2/CO2) | Cylinder | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| PERFADEX solution | 1-l solution | EVLP recipient | – | 2.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| Packed red blood cells | 274-ml bag | EVLP recipient | – | 2.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Syringes for blood gases | Syringe | EVLP recipient | – | 9.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| Syringes (other) | Syringe | EVLP recipient | – | 10.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| Vivoline disposable lung set | Set | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| Miscellaneous equipment | |||||
| Blood gases samples | Sample | EVLP recipient | – | 20.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication |
| Vivoline system | System | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | Anna Soderlund, Vivoline, July 2014, personal communication/protocol103 |
| Theatre usage | |||||
| Operating theatre | Hour | EVLP recipient | – | 6.00 | Protocol p. 35/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Drugs | |||||
| 2 l of Steen Solution | 500-ml solution | EVLP recipient | – | 4.00 | CRF p. 34/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Heparin sodium, 1000 units/ml | 1-ml ampoule | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | CRF p. 34/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Heparin sodium, 5000 units/ml | 1-ml ampoule | EVLP recipient | – | 2.00 | CRF p. 34/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Insulin human (ACTRAPID HM), 100 IU/ml | 10-ml vial | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | CRF p. 34/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 500-mg vial | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | CRF p. 34/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | CRF p. 34/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 2-g vial | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | CRF p. 34/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| THAM, 30 mg/ml (3.0 mmol/ml) | 1-ml ampoule | EVLP recipient | – | 20.00 | CRF p. 34/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Antibiotics | |||||
| Meropenem (as trihydrate) | 500-mg vial | EVLP recipient | – | 2.00 | CRF p. 34/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication |
| Moxifloxacin (as hydrochloride), 1.6 mg/ml | 250-ml solution for infusion bottle (400 mg) | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | CRF p. 34/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication |
| Antifungal | |||||
| Amphotericin B | 50-mg vial | EVLP recipient | – | 1.00 | CRF p. 34/Anders Andreasson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication/Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication |
| Lung transplant | |||||
| Fixed costs | |||||
| Anaesthetic preparation | |||||
| Anaesthetic room | Hour | Recipient | 0.75 | 0.75 | Transplant co-ordinators |
| Anaesthetic nurse (band 5) | Hour | Recipient | 0.75 | 0.75 | Transplant co-ordinators |
| Consultant anaesthetist | Hour | Recipient | 0.75 | 0.75 | Transplant co-ordinators |
| Staff time | |||||
| Single lung surgery | |||||
| Anaesthetic fellow | Hour | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Anaesthetic nurse (band 5) | Hour | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Consultant anaesthetist | Hour | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Consultant surgeon | Hour | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Perfusionist (band 7) | Hour | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Scrub nurse (band 7) | Hour | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Scrub nurse (band 5) | Hour | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Surgical fellow | Hour | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | Qualtrics survey/0Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Double lung surgery | |||||
| Anaesthetic fellow | Hour | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Anaesthetic nurse (band 5) | Hour | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Consultant anaesthetist | Hour | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Consultant surgeon | Hour | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Perfusionist (band 7) | Hour | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Scrub nurse (band 7) | Hour | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Scrub nurse (band 5) | Hour | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Surgical fellow | Hour | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | Qualtrics survey/Paul Henderson, NuTH, September 2014, personal communication |
| Theatre usage | |||||
| Single lung surgery | |||||
| Operating theatre | Hour | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF p. 43/Qualtrics survey |
| Double lung surgery | |||||
| Operating theatre | Hour | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | CRF p. 43/Qualtrics survey |
| Equipment/consumables | |||||
| Usual surgical set | Set | Recipient | Missing | Missing | Missing |
| Post-operative care | |||||
| Fixed costs | |||||
| Staff time in ITU/HDU | |||||
| Anaesthetic fellow | Hour | Recipient | 1.50 | 1.50 | Qualtrics survey/Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication |
| Consultant anaesthetist | Hour | Recipient | 0.50 | 0.50 | Qualtrics survey/Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication |
| Consultant physician | Hour | Recipient | 0.17 | 0.17 | Qualtrics survey/Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication |
| Consultant surgeon | Hour | Recipient | 0.25 | 0.25 | Qualtrics survey/Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication |
| Surgical fellow | Hour | Recipient | 0.25 | 0.25 | Qualtrics survey/Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication |
| Staff time in hospital | |||||
| Consultant physician | Hour | Recipient | 0.34 | 0.34 | Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication |
| Surgical fellow | Hour | Recipient | 0.25 | 0.25 | Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication |
| Transplant specialist registrar | Hour | Recipient | 0.67 | 0.67 | Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication |
| Tests | |||||
| ABG | Test | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 47 |
| Chest X-ray (radiography) | Test | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 56 |
| FBC | Test | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 56 |
| Pulmonary/lung function test | Test | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 56 |
| Variable costs | |||||
| Ward usage (if needed) | |||||
| HDU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 10.00 | 10.00 | CRF p. 51/52 |
| ITU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 11.00 | 11.00 | CRF p. 51/52 |
| ITU/HDU readmission | Bed-day | Recipient | 15.00 | 15.00 | CRF p. 52 |
| Level 1 ward care (hospital stay) | Bed-day | Recipient | 34.00 | 34.00 | Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication/CRF p. 51/52 |
| Procedures (if needed) | |||||
| Bronchoscopy | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 46 |
| Tracheostomy | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 51 |
| Equipment (if needed) | |||||
| ECMO | Machine | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 45 |
| iLA membrane ventilator | Device | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 45 |
| Consumables (if needed) | |||||
| 2 l of colloid (plasma and plasma substitutes) | 500 ml | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF p. 45 |
| 1 l of crystalloid (fluids containing electrolytes) | 500 ml | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 45 |
| Fresh-frozen plasma | 271-ml bag | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 45 |
| Packed red blood cells | 274-ml bag | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF p. 45 |
| Platelets | 250-ml bag | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 45 |
| Inotropes (if needed) | |||||
| Adrenaline (base), 1 mg/10 ml (1 in 10,000) | 10-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 45 |
| Dobutamine (as hydrochloride), 12.5 mg/ml | 20-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 45 |
| Glyceryl trinitrate, 1 mg/ml | 50-ml vial | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 45 |
| Milrinone, 1 mg/ml | 10-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 45 |
| Noradrenaline (as acid tartrate), 1 mg/ml | 4-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 45 |
| Pitressin (argipressin – synthetic vasopressin), 20 units/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 45 |
| Other | |||||
| Dopamine hydrochloride, 40 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 46 |
| Enoximone, 5 mg/ml | 20-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 46 |
| Isoprenaline | – | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 46 |
| Metaraminol | – | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 46 |
| Post implantation haemodynamic support (if needed) | |||||
| Adrenaline (base), 1 mg/10 ml (1 in 10,000) | 10-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 50 |
| Dobutamine (as hydrochloride), 12.5 mg/ml | 20-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 50 |
| Glyceryl trinitrate, 1 mg/ml | 50-ml vial | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 50 |
| Milrinone, 1 mg/ml | 10-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 50 |
| Noradrenaline (as acid tartrate), 1 mg/ml | 4-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 50 |
| Pitressin (argipressin – synthetic vasopressin), 20 units/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 50 |
| Complications (if reported) | |||||
| Cerebrovascular accident | Treatment | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 52 |
| Hemofiltration | Procedure | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF p. 52 |
| Haemodialysis | Procedure (days) | Recipient | 9.00 | 9.00 | CRF p. 52 |
| Re-exploration | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 52 |
| Airway complications (if reported) | |||||
| Balloon dilatation | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 53 |
| Cryotherapy | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 53 |
| Diathermy | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 53 |
| Stenting | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 53 |
| Surgical intervention | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 53 |
| ITU rejection episodes (if reported) | |||||
| Ward usage | |||||
| HDU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 18.00 | 18.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| ITU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 26.00 | 26.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Procedures | |||||
| Clinical diagnosis/biopsy | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 57 |
| Treatment | |||||
| Cefuroxime (as sodium), 750 mg | 750-mg vial | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 54 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 54 |
| Piperacillin (as sodium), 2 g; and tazobactam (as sodium), 250 mg (Tazocin) | 2.25-g vial | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 54 |
| Changes in maintenance therapy | |||||
| Methylprednisolone, 100 mg | 20-tablet pack | Recipient | 0.50 | 0.50 | CRF p. 54 |
| Tacrolimus, 5 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 54 |
| Ward rejection episodes (if reported) | |||||
| Procedures | |||||
| Clinical diagnosis/biopsy | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 57 |
| Treatment | |||||
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate), 500 mg | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 57 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 57 |
| Methylprednisolone, 100 mg | 20-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 57 |
| Prednisolone acetate, 25 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 57 |
| Prednisolone, 25 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 57 |
| Sulfamethoxazole, 400 mg; and trimethoprim, 80 mg (co-trimoxazole 480 mg) | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 57 |
| Tacrolimus, 5 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 57 |
| Infection episodes (if reported) | |||||
| Treatment | |||||
| Aciclovir (as sodium), 25 mg/ml | 20-ml vial (500 mg) | Recipient | 15.00 | 15.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Adefovir dipivoxil, 10 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Amikacin (as sulfate), 250 mg/ml | 2-ml vial | Recipient | 30.00 | 30.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Amoxicillin (as trihydrate), 500 mg | 21-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Amoxicillin (as trihydrate), 500 mg; and clavulanic acid (as potassium), 125 mg (co-amoxiclav) | 21-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Amphotericin B liposomal (AmBisome) | 50-mg vial | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Amphotericin B (as sodium deoxycholate complex) | 50-mg vial | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Anidulafungin | 100-mg vial | Recipient | 16.00 | 16.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Azithromycin (as dihydrate), 250 mg | 4-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Aztreonam | 1-g vial | Recipient | 42.00 | 42.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| BAL | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Budesonide, 100 µg; and formoterol fumarate, 6 µg (Symbicort Turbohaler) | 120-dose inhaler | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Caspofungin (as acetate) | 70-mg vial | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Ceftazidime (as pentahydrate) | 2-g vial | Recipient | 42.00 | 42.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Cefuroxime (as sodium) | 750-mg vial | Recipient | 21.00 | 21.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Chloramphenicol (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 84.00 | 84.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Ciprofloxacin (as lactate), 2 mg/ml | 200-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Ciprofloxacin (as hydrochloride), 500 mg | 20-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Ciprofloxacin (as hydrochloride), 3 mg/ml | 5-ml 0.3% eye drops | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Clarithromycin | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 10.00 | 10.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Clindamycin (as phosphate), 150 mg/ml | 4-ml ampoule | Recipient | 20.00 | 20.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Colistimethate sodium | 2-million-unit vial | Recipient | 28.00 | 28.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Domperidone (as maleate), 10 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Doxycycline (as hyclate), 100 mg | 8-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Eradication therapy for H. pylori | 7-day course | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Ertapenem (as sodium) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Ethambutol hydrochloride, 100 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Flucloxacillin (as sodium) | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Flucloxacillin (as sodium) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 12.00 | 12.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Fluconazole, 50 mg | 7-capsule pack | Recipient | 8.00 | 8.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Fluconazole, 2 mg/ml | 100-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 43.00 | 43.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Fluconazole, 50 mg | 7-capsule pack | Recipient | 8.00 | 8.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Foscarnet sodium, 24 mg/ml | 250-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 42.00 | 42.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Fosfomycin (as sodium) | 2-g vial | Recipient | 30.00 | 30.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Furosemide, 10 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 21.00 | 21.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Ganciclovir (as sodium) | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 42.00 | 42.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Gentamycin (as sulfate), 40 mg/ml | 2-ml vial | Recipient | 28.00 | 28.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Immunoglobulin | 10-g vial | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Itraconazole, 10 mg/ml | 25-ml ampoule | Recipient | 16.00 | 16.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Lamivudine, 150 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Lesion excision | Day case | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Linezolid, 2 mg/ml | 300-ml infusion bag | Recipient | 84.00 | 84.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Meropenem (as trihydrate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 12.25 | 12.25 | CRF p. 58 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Metochlopramide hydrochloride, 5 mg/ml | 2-ml ampoule | Recipient | 15.00 | 15.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Metronidazole, 200 mg | 21-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Micafungin (as sodium) | 100-mg vial | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Moxifloxacin (as hydrochloride), 1.6 mg/ml | 250-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Oseltamivir (as phosphate), 75 mg | 10-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Packed red blood cells | 274-ml bag | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Piperacillin (as sodium), 4 g; and tazobactam (as sodium), 500 mg (Tazocin) | 4.5-g vial | Recipient | 43.00 | 43.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Posaconazole, 100 mg | 96-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Prednisolone, 25 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Respiratory failure (inpatient) | Treatment | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Sirolimus, 2 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Streptokinase | 250,000-unit powder vial | Recipient | 12.00 | 12.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Sulfamethoxazole, 80 mg; and trimethoprim, 16 mg (Septrin) | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 24.00 | 24.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Surgical intervention or VATS | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Teicoplanin | 200-mg vial | Recipient | 10.00 | 10.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Trimethoprim, 100 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Tobramycin (as sulfate), 40 mg/ml | 1-ml vial | Recipient | 12.25 | 12.25 | CRF p. 58 |
| Tigecycline | 50-mg vial | Recipient | 30.00 | 30.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Valganciclovir (as hydrochloride), 450 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Vancomycin (as hydrochloride) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Voriconazole | 200-mg vial | Recipient | 34.00 | 34.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Ward usage | |||||
| HDU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 18.00 | 18.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| ITU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 26.00 | 26.00 | CRF p. 58 |
| Outpatient care | |||||
| Fixed costs | |||||
| Outpatient reviews | |||||
| Bronchoscopy | Procedure/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Chest X-ray (radiography) | Test/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| FBC | Test/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Liver function test | Test/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication |
| Pulmonary/lung function test | Test/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Urea and electrolytes test | Test/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | Andrew Fisher, NuTH, November 2015, personal communication |
| Staff time | |||||
| Consultant physician | Hour/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 0.50 | 0.50 | Care pathway/Katie Morley, NuTH, October 2014, personal communication |
| Scrub nurse (band 5) | Hour/visit (4 visits) | Recipient | 0.50 | 0.50 | Care pathway/Katie Morley, NuTH, October 2014, personal communication |
| Variable costs | |||||
| Rejection episodes (if reported) | |||||
| Procedures | |||||
| Clinical diagnosis/biopsy | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Ventilation–perfusion scan | Test | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Treatment | |||||
| Anti-thymocyte immunoglobulin (rabbit), 25 mg | 25-mg vial | Recipient | 40.00 | 40.00 | CRF |
| Azathioprine, 25 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Azathioprine, 50 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin, 25 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin, 50 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin, 100 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 10 mg | 60-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 25 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 50 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 100 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Immunoglobulin | 10-g vial | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Meropenem (as trihydrate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 30.00 | 30.00 | CRF |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 125-mg vial | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF |
| Mycophenolate mofetil, 500 mg | 50-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Mycophenolate mofetil, 250 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Prednisolone, 1 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Prednisolone, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF |
| Prednisolone, 25 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Rituximab, 100 mg/ml | 10-ml vial | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 500 µg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 1 mg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 1 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 5 mg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Valganciclovir (as hydrochloride), 450 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Ward usage | |||||
| HDU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 30.00 | 30.00 | CRF |
| ITU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | CRF |
| GP visits (if needed) | |||||
| Out-of-surgery visit | Visit | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Surgery visit | Visit | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Transplant centre advice | Call | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Unplanned hospital admission (if needed) | |||||
| Treatment | |||||
| Aciclovir (as sodium), 25 mg/ml | 20-ml vial | Recipient | 15.00 | 15.00 | CRF |
| Aciclovir, 400 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Adrenaline (base), 100 µg/ml (1 in 10,000) | 10-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Amiodarone hydrochloride, 30 mg/ml | 10-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | CRF |
| Amoxicillin (as sodium), 500 mg; and clavulanic acid (as potassium), 125 mg (co-amoxiclav) | 500/100-mg vial | Recipient | 15.00 | 15.00 | CRF |
| Amphotericin B | 50-mg vial | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF |
| Aspirin, 300 mg | 32-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Azathioprine, 25 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Azithromycin (as dihydrate), 250 mg | 4-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Aztreonam | 1-g vial | Recipient | 42.00 | 42.00 | CRF |
| Balloon dilatation | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Basiliximab | 20-mg vial | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF |
| Bisoprolol fumarate, 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Bortezomib | 3.5-mg vial | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Bronchoscopy | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Budesonide, 100 µg; and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, 6 µg (Symbicort 100/6 Turbohaler®) | 120-dose unit inhaler | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Calcium gluconate, 1 g | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Calcium polystyrene sulfonate (Calcium Resonium) | 300-g powder | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Candesartan cilexetil, 4 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF |
| Caspofungin (as acetate) | 70-mg vial | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin, 100 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin, 50 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 17.00 | 17.00 | CRF |
| Ciprofloxacin (as hydrochloride), 500 mg | 20-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF |
| Clarithromycin | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 10.00 | 10.00 | CRF |
| Clinical diagnosis/biopsy | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Colistimethate sodium | 1-million-unit vial | Recipient | 28.00 | 28.00 | CRF |
| Colistimethate sodium | 2-million-unit vial | Recipient | 28.00 | 28.00 | CRF |
| Computerised tomography | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| DeBakey tissue forceps | Forceps | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Docusate sodium, 100 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF |
| Doxazosin (as mesilate), 4 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF |
| Doxycycline (as hyclate), 100 mg | 8-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| ECG | 24-hour test | Recipient | 24.00 | 24.00 | CRF |
| Enoxaparin sodium (Clexane Forte), 150 mg | 1-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 5.00 | 5.00 | CRF |
| ECMO | Machine | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Filgrastim, 30 million units (300 µg/ml) | 1-ml vial | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF |
| Flucloxacillin (as sodium) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 12.00 | 12.00 | CRF |
| Fluticasone propionate, 250 µg; and salmeterol xinafoate, 50 µg (Seretide 250 Accuhaler) | 120-unit dose inhaler | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Foscarnet sodium, 24 mg/ml | 250-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Furosemide, 10 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 21.00 | 21.00 | CRF |
| Ganciclovir (as sodium) | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 42.00 | 42.00 | CRF |
| Gastrograffin | Solution | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Glucose anhydrous, 50 mg/ml | 1000-ml bag | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | CRF |
| iLA membrane ventilator | Device | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Immunoglobulin | 10-g vial | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Insulin, 3 ml | 5 × 3-ml pre-filled disposable injection devices | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Intubation | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Hydralazine hydrochloride, 50 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Hydrocortisone (as sodium succinate) | 100-mg vial | Recipient | 28.00 | 28.00 | CRF |
| Lansoprazole, 30 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Level 1 ward care (hospital stay) | Bed-day | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Macrogol compound oral powder | 50-sachet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Magnesium hydroxide with liquid paraffin | 150-ml bottle | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 100 mg | 10-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Magnetic resonance imaging scan | Test | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Meropenem (as trihydrate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 11.00 | 11.00 | CRF |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate), 500 mg | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF |
| Metoclopramide hydrochloride, 5 mg/ml | 2-ml ampoule | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF |
| Midazolam (as hydrochloride), 1 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Minocycline (as hydrochloride), 100 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Moxifloxacin (as hydrochloride), 1.6 mg/ml | 250-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF |
| Nefopam hydrochloride, 30 mg | 90-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Non-invasive ventilation | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Normal immunoglobulin, 10 g | 200-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Oxycodone hydrochloride, 10 mg/ml | 120-ml oral solution | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Packed red blood cells | 274-ml bag | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF |
| Phosphate enema | 133-ml enema pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Piperacillin (as sodium), 4 g; and tazobactam (as sodium), 500 mg (Tazocin) | 4.5-g vial | Recipient | 40.00 | 40.00 | CRF |
| Posaconazole, 100 mg | 96-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Prednisolone, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF |
| Pregabalin, 150 mg | 56-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Redo lung transplantation | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Renal support | Treatment | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Ribavirin, 200 mg | 42-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Ribavirin, 400 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Salbutamol (as sulfate), 5 mg/2.5 ml | 20-unit dose nebuliser liquid vial | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Sirolimus, 2 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF |
| Sodium bicarbonate, 42 mg/ml | 500-ml intravenous infusion bottle | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| 2 l of 0.9% sodium chloride solution | 1-l solution | Recipient | 20.00 | 20.00 | CRF |
| Stenting | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Sulfamethoxazole, 80 mg; and trimethoprim, 16 mg (Septrin) | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 18.00 | 18.00 | CRF |
| Sulfamethoxazole, 400 mg; and trimethoprim, 80 mg (co-trimoxazole) | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 12.00 | 12.00 | CRF |
| Surgical intervention | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 1 mg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 1 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 5 mg/ml | 10 × 1-ml ampoules | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | CRF |
| Tinzaparin sodium, 20,000 units/ml (Innohep) | 0.5-ml vial | Recipient | 630.00 | 630.00 | CRF |
| Tracheostomy | Procedure | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Tramadol hydrochloride, 150 mg | 60-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Ultrasound scan | Test | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Valganciclovir (as hydrochloride), 450 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Vancomycin (as hydrochloride), 125 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF |
| Voriconazole | 200-mg vial | Recipient | 78.00 | 78.00 | CRF |
| Warfarin sodium, 3 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Warfarin sodium, 1 mg/ml | 150-ml oral suspension | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF |
| Ward usage | |||||
| HDU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF |
| ITU care | Bed-day | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF |
| Immunosuppressive medications (if needed) | |||||
| Azathioprine, 25 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Azathioprine, 50 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF/Ruth Coxhead, NuTH, March 2015, personal communication |
| Ciclosporin, 25 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin, 50 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin, 100 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF/Ruth Coxhead, NuTH, March 2015, personal communication |
| Mycophenolate mofetil, 500 mg | 50-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF/Ruth Coxhead, NuTH, March 2015, personal communication |
| Prednisolone, 1 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Prednisolone, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF/Ruth Coxhead, NuTH, March 2015, personal communication |
| Prednisolone, 25 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Prednisolone acetate, 25 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 26.00 | 26.00 | CRF |
| Sirolimus, 500 µg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Sirolimus, 1 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Sirolimus, 2 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF/Ruth Coxhead, NuTH, March 2015, personal communication |
| Tacrolimus, 500 µg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Tacrolimus, 1 mg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF/Ruth Coxhead, NuTH, March 2015, personal communication |
| Tacrolimus, 1 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Tacrolimus, 5 mg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Other | |||||
| Aciclovir, 200 mg | 25-tablet pack | Recipient | 28.00 | 28.00 | CRF |
| Amoxicillin (as trihydrate), 500 mg | 21-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Azithromycin (as dihydrate), 250 mg | 4-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Beclomethasone dipropionate, 400 µg/dose | 100-dose unit | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Calcium carbonate (Adcal), 1.5 g | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Cetirizine hydrochloride, 10 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 10 mg | 60-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 25 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 50 mg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF |
| Ciclosporin, 100 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Citalopram (as hydrobromide), 20 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Dapsone, 100 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Dexamethasone, 2 mg | 50-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Doxycycline (as hyclate), 100 mg | 8-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Furosemide, 40 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Hydrocortisone, 10 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 5.00 | 5.00 | CRF |
| Hydrocortisone, 20 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Lisinopril dihydrate, 2.5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Lisinopril dihydrate, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF |
| Methylprednisolone, 2 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 40-mg vial | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Mycophenolic acid (as sodium), 180 mg | 120-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Mycophenolic acid (as sodium), 360 mg | 120-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| N-acetylcysteine, 200 mg/ml | 10-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Perindopril erbumine, 2 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Perindopril erbumine, 4 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Sulfamethoxazole, 400 mg; and trimethoprim, 80 mg (co-trimoxazole) | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 1 mg | 50-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Tacrolimus (Prograf), 1 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Tinzaparin sodium, 3500 units | 0.35-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF |
| Concomitant medications | |||||
| Variable costs | |||||
| Treatment | |||||
| Aciclovir, 200 mg | 25-tablet pack | Recipient | 9.00 | 9.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Adrenaline (base), 100 µg/ml (1 in 10,000) | 10-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 15.00 | 15.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Alendronic acid (as sodium), 70 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Alfentanil (as hydrochloride), 500 µg/ml | 2-ml ampoule | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Alfentanil (as hydrochloride), 5 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 9.00 | 9.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Allopurinol, 300 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Amiloride hydrochloride, 5 mg; and furosemide, 40 mg (co-amilofruse) | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Amiodarone hydrochloride, 30 mg/ml | 10-ml pre-filled disposable syringe | Recipient | 60.00 | 60.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Amiodarone hydrochloride, 100 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Amiodarone hydrochloride, 200 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 6.00 | 6.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Amitriptyline hydrochloride, 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Amlodipine, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Amlodipine, 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Amoxicillin (as trihydrate), 500 mg | 21-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Amoxicillin (as amoxicillin trihydrate), 500 mg; and clavulanic acid (as potassium), 125 mg | 21-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Amphotericin B, 5 mg/ml | 20-lozenge pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Amphotericin B (as phospholipid complex, 5 mg/ml | 20-ml vial | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Antiembolism socks | Socks pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Anti-thymocyte immunoglobulin (rabbit) | 25-mg vial | Recipient | 20.00 | 20.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Aspirin, 75 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Atracurium besilate, 10 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Azathioprine, 25 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Azathioprine, 50 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Azithromycin (as dihydrate), 250 mg | 4-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Azithromycin (as dihydrate), 250 mg | 6-capsule pack | Recipient | 9.00 | 9.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Azithromycin, 500 mg | 3-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Aztreonam | 2-g vial | Recipient | 12.00 | 12.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Bisoprolol fumarate, 1.25 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Bisoprolol fumarate, 2.5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 5.00 | 5.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Bisoprolol fumarate, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Bupivacaine hydrochloride, 1 mg/ml | 100-ml infusion bag | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Calcium carbonate (Adcal), 1.5 g | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Calcium carbonate, 1.25 g; and colecalciferol, 400 units (Calcichew D3 Forte) | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Calcium chloride dihydrate, 10% | 10-ml pre-filed disposable injection | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Calogen emulsion | 500-ml bottle | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Carbocisteine, 375 mg | 120-capsule pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Caspofungin (as acetate) | 50-mg vial | Recipient | 18.00 | 18.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ceftazidime (as pentahydrate) | 2-g vial | Recipient | 11.00 | 11.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride, 5 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride (Librium), 10 mg | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Chlorhexidine gluconate, 4% | 500-ml surgical scrub | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Chlorhexidine hydrochloride, 500 mg | 500-mg pump pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Chlorhexidine hydrochloride, 1 mg/g; and neomycin sulfate, 5 mg/g (Naseptin) | 15-g nasal cream | Recipient | 8.00 | 8.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Chlorhexidine hydrochloride, 10 mg/g; and nystatin, 100,000 units/g (Nystaform) | 30-g cream | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Chlorphenamine maleate, 10 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Chlorpromazine hydrochloride, 25 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ciclosporin (NEORAL), 25 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ciclosporin, 50 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ciclosporin, 100 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ciprofloxacin (as hydrochloride), 500 mg (Ciproxin) | 10-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ciprofloxacin (as hydrochloride), 750 mg | 10-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Citalopram (as hydrobromide), 20 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Citalopram (as hydrobromide), 40 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Clonidine hydrochloride, 25 µg | 112-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Codeine phosphate, 8 mg; and paracetamol, 500 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Codeine phosphate 30 mg and paracetamol, 500 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Codeine phosphate, 30 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Codeine phosphate, 60 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Colecalciferol, 500 µg (20,000 units) | 15-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Colistimethate sodium | 1-million-unit vial | Recipient | 56.00 | 56.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Colistimethate sodium | 2-million-unit vial | Recipient | 28.00 | 28.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| CREON, 25,000 units | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| CREON Micro Pancreatine, 20 g | 60.12-mg granules | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Cryoprecipitate | 8 units | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Cyclizine hydrochloride, 50 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Dapsone, 100 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Diazepam, 2 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Digoxin, 250 µg/ml | 2-ml ampoule | Recipient | 28.00 | 28.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Diltiazem hydrochloride, 120 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Diltiazem hydrochloride, 200 mg | 7-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Docusate sodium | 100-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Domperidone (as maleate), 10 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Dopamine hydrochloride, 40 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 8.00 | 8.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Dosulepin hydrochloride, 25 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Doxazosin (as mesilate), 4 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Doxycycline (as hyclate), 100 mg | 8-capsule pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Enoxaparin sodium, 100 mg/ml | 0.4-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 19.00 | 19.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ensure liquid | 250 ml | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Erythromycin (as lactobionate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 18.00 | 18.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Esomeprazole (as magnesium dihydrate), 40 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ethambutol hydrochloride, 400 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ezetimibe, 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ethinylestradiol, 30 µg; and gestodene, 75 µg | 21-day preparation | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ferrous sulfate dried, 200 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Flucloxacillin (as sodium), 500 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 8.00 | 8.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Flucloxacillin (as sodium) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 5.00 | 5.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Fluconazole, 50 mg | 7-capsule pack | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Fluconazole, 200 mg | 7-capsule pack | Recipient | 11.00 | 11.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Fluconazole, 2 mg/ml | 100-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 12.00 | 12.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Fluoxetine (as hydrochloride), 20 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Fluticasone propionate 50 µg | 150-unit dose nasal spray | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Fluticasone propionate, 250 µg (Flixotide 250 Accuhaler) | 60-dose inhaler | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Fluticasone propionate, 250 µg; and salmeterol xinafoate, 50 µg (Seretide 250 Accuhaler) | 60-dose inhaler | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Folic acid, 400 µg | 90-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Foscarnet sodium, 24 mg/ml | 250-ml solution for infusion bottle | Recipient | 42.00 | 42.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Fosfomycin (as sodium) | 2-g vial | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Fresh-frozen plasma | 271-ml bag | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Furosemide, 10 mg/ml | 2-ml ampoule | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Furosemide, 20 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Furosemide, 40 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ganciclovir (as sodium) | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 21.00 | 21.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Gelatin (Gelofusine) | 1-l infusion bag | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Gelatin, 140 mg/g; and glycerol, 700 mg/g | 4-g supplement pack | Recipient | 72.00 | 72.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Gliclazide (glycoside), 30 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Gliclazide, 40 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Glucose anhydrous, 500 mg/ml | 50-ml vial | Recipient | 168.00 | 168.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Glyceryl trinitrate, 1 mg/ml | 50-ml ampoule | Recipient | 10.00 | 10.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Haloperidol, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Haloperidol, 5 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 248.00 | 248.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Heparin sodium, 5000 units/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 49.00 | 49.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Heparin sodium, 5000 units/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 6.00 | 6.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Hydroxocobalamin, 1 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Hyoscine butylbromide (Buscopan), 10 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ibandronic acid (as sodium monohydrate), 50 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Iloprost (as THAM), 10 µg/ml | 30 × 1-ml unit-dose vials | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Insulin, 3 ml | 5 × 3-ml pre-filled disposable injection devices | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Insulin aspart, 100 units/ml | 5 × 3-ml pre-filled disposable injection devices | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Insulin human (as soluble human) (ACTRAPID), 100 units/ml | 10-ml vial | Recipient | 27.00 | 27.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Insulin human (as detemir), 100 units/ml (LEMEVIR) | 5 × 3-ml pre-filled disposable injection device | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ipratropium bromide, 250 µg/ml | 60 × 1 ml unit-dose vial | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ipratropium bromide, 500 µg | 500-µg nebuliser solution | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ipratropium bromide, 2.5 mg/2.5 ml | 60-unit-dose vial | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ipratropium bromide, 200 µg/ml; and salbutamol (as sulfate), 1 mg/ml (Combivent) | 60-unit dose vial | Recipient | 9.00 | 9.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Itraconazole, 100 mg | 15-capsule pack | Recipient | 10.00 | 10.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Itraconazole, 10 mg/ml | 150-ml oral solution | Recipient | 33.00 | 33.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Labetalol hydrochloride, 100 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Labetalol hydrochloride, 200 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Lactulose | 300-ml solution | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Lansoprazole, 15 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Lansoprazole, 30 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Loratadine, 10 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Levomepromazine maleate, 25 mg | 84-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Linezolid, 600 mg | 10-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Loperamide hydrochloride, 2 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Lorazepam, 1 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Lymecycline, 408 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Magnesium oxide, 160 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 500 mg/ml | 2-ml ampoule | Recipient | 98.00 | 98.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 500 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 29.00 | 29.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 500 mg/ml | 4-ml ampoule | Recipient | 56.00 | 56.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Menadiol phosphate (as sodium phosphate), 10 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Meropenem (as trihydrate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 24.50 | 24.50 | CRF p. 111 |
| MEROCAINE | 24-lozenge pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 500-mg vial | Recipient | 26.00 | 26.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Methylprednisolone (as sodium succinate) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Metformin hydrochloride, 500 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Metoclopramide hydrochloride, 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Metronidazole, 400 mg | 21-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Midazolam (as hydrochloride), 1 mg/ml | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Milrinone (as lactate), 1 mg/ml | 10-ml ampoule | Recipient | 228.00 | 228.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Minocycline (as hydrochloride), 100 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Mirtazapine, 30 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | BNF 201450 |
| Montelukast (as sodium), 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Mometasone furoate, 50 µg | 140-unit dose nasal spray | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Morphine sulfate, 1 mg/ml | 10-mg disposable syringe | Recipient | 16.00 | 16.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Morphine sulfate (Oramorph), 10 mg/5ml | 300-ml oral solution | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Movicol | 30-sachet pack | Recipient | 6.00 | 6.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Moxifloxacin (as hydrochloride), 400 mg | 5-tablet pack | Recipient | 18.00 | 18.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Multivitamins | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Mupirocin, 20 mg/g | 15-g ointment | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Micafungin (as sodium) | 100-mg vial | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| N-acetylcysteine, 600 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Naproxen, 500 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Nebivolol (as hydrochloride), 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Nifedipine, 5 mg | 84-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Nifedipine, 10 mg | 84-capsule pack | Recipient | 5.00 | 5.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Noradrenaline base, 1 mg/ml (as noradrenaline acid tartrate, 2 mg/ml) | 4-ml ampoule | Recipient | 32.00 | 32.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Nutrison energy multifibre | 1000-ml solution | Recipient | 28.00 | 28.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Nystatin, 100,000 units/ml | 30-ml oral suspension | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Omeprazole (as magnesium), 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Omeprazole (as magnesium), 20 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Omeprazole (as magnesium), 40 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Omeprazole (as sodium) | 40-mg vial | Recipient | 24.00 | 24.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ondansetrol (as hydrochloride), 2 mg/ml | 1-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ondansetron (as hydrochloride), 4 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Oxycodone hydrochloride, 5 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Oxycodone hydrochloride, 10 mg | 56-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Pabrinex vitamin B substances with ascorbic acid, 250 mg/10 ml | 2 × 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Packed red blood cells | 274-ml bag | Recipient | 61.00 | 61.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Paracetamol, 500 mg | 32-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Paracetamol, 1 g | 10 mg/ml 100-ml vial | Recipient | 28.00 | 28.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Peppermint water | 100-ml solution | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Perindopril erbumine, 4 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Phenoxymethylpenicillin (as potassium), 250 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Phosphate | 500-ml bottle | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Piperacillin (as sodium), 4 g; and tazobactam (as sodium), 500 mg (Tazocin) | 4.5-g vial | Recipient | 59.00 | 59.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Platelets | 250-ml bag | Recipient | 134.00 | 134.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Posaconazole, 100 mg | 96-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Potassium bicarbonate, 400 mg; and potassium chloride, 600 mg (Sando-K) | 20 tablets | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Potassium chloride, 150 mg/ml | 10-ml ampoule | Recipient | 14.00 | 14.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Pravastatin sodium, 10 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Pravastatin sodium, 20 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Pravastatin sodium, 40 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Prednisolone, 5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Pregabalin, 25 mg | 56-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Pregabalin, 50 mg | 84-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Pregabalin, 75 g | 56-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Pregabalin, 100 mg | 84-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Prochlorperazine maleate, 3 mg | 5 × 10-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Propofol, 5 mg/ml | 20-ml ampoule | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Propofol, 10 mg/ml | 20-ml ampoule | Recipient | 6.00 | 6.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Propofol, 10 mg/ml | 50-ml pre-filled disposable injection | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ramipril, 2.5 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ramipril, 5 mg | 28-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ranitidine (as hydrochloride), 25 mg/ml | 2-ml ampoule | Recipient | 6.00 | 6.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ranitidine (as hydrochloride), 150 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ranitidine (as hydrochloride), 300 mg | 30-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Remifentanil (as hydrochloride) | 5-mg vial | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Risperidone, 500 µg | 20-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Risperidone, 2 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Salbutamol (as sulfate), 2.5 mg/2.5 ml | 20-unit dose nebuliser | Recipient | 6.00 | 6.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Salbutamol (as sulfate), 200 µg | 100-dose unit inhaler | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Sennoside B (as sennosides), 7.5 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Sildenafil (as citrate), 25 mg | 4-tablet pack | Recipient | 7.00 | 7.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Sodium chloride, 0.9% | 20 × 2.5-ml spray | Recipient | 9.00 | 9.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Sodium chloride, 600 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Sodium cromoglycate, 5 mg/dose | 112-unit dose inhaler | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Sodium dihydrogen phosphate anhydrous, 1.936 g | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Sodium valproate, 200 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 13.00 | 13.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Strepsils | 24-lozenge pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Sulfamethoxazole, 400 mg; and trimethoprim, 80 mg (co-trimoxazole) | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Tadalafil, 20 mg | 8-tablet pack | Recipient | 4.00 | 4.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Tamsulosin hydrochloride, 400 µg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| T.E.D. compression socks/hose (knee length) | Stocking | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Teicoplanin | 400-mg vial | Recipient | 21.00 | 21.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Theophylline (Uniphyllin), 200 mg | 56-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Thiamine hydrochloride, 100 mg | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Tiotropium (as bromide), 18 µg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Tobramycin, 60 mg/ml | 56 × 5 ml–300 mg unit | Recipient | 11.00 | 11.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Tobramycin, 75 mg/ml | 56 × 4-ml nebuliser | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Tramadol hydrochloride, 50 mg | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Tramadol hydrochloride, 50 mg | 60-capsule pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Tramadol hydrochloride, 100 mg | 60-capsule pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ursodeoxycholic acid, 150 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Ursodeoxycholic acid, 300 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Valaciclovir (as hydrochloride), 500 mg | 42-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Valganciclovir (as hydrochloride), 450 mg | 60-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Vancomycin (as hydrochloride) | 1-g vial | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Vitamin B compound strong | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 2.00 | 2.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Vitamins A, D and E | 30-capsule pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Multivitamins | 100-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Voriconazole, 200 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 3.00 | 3.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Warfarin sodium, 3 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Water for injections | 5-ml ampoule | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
| Zopiclone, 3.75 mg | 28-tablet pack | Recipient | 1.00 | 1.00 | CRF p. 111 |
Appendix 8 Trial documentation
Appendix 9 Trial letters
Appendix 10 End of study information sheet version 1.0, 22 October 2015
Appendix 11 Forms: extracts from case report form booklet
Appendix 12 Patient and public involvement
Two lay member representatives were appointed to the Trial Steering Committee.
During the study, they attended:
-
Trial Steering Committee meeting on 14 February 2012
-
Trial Steering Committee teleconference on 8 October 2012
-
Trial Steering Committee meeting on 16 April 2013
-
Trial Steering Committee teleconference on 21 October 2013.
The lay member representatives contributed their personal patient experiences in advising the consent process and approaching patients, as well as designing patient-related study documents.
One lay member expressed concerns about running both the INSPIRE trial and DEVELOP-UK study at the same time, and asked what the Research Ethics Committee view might be. As a result, the Research Ethics Committee chairperson was contacted for further advice.
The lay representatives supported the restart of EVLP activity in the study and commented on the patient information sheet to provide additional information on how the lungs are handled. The proposed patient-related documents were subsequently approved by the Research Ethics Committee without any changes.
Appendix 13 Videos/podcasts
A video, entitled ‘Reconditioned Lungs’, with information about the study, has been posted on Transplant TV, an online channel for medical professionals, patients and carers to share scientific and medical information and stories about organ transplantation. Transplant TV is based at the Institute of Transplantation, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne (jointly between The NuTH NHS Foundation Trust and Newcastle University). The URL for the DEVELOP-UK video is: http://transplant.tv/portfolio/reconditioned-lungs/?id=272 (accessed 10 January 2016).
List of abbreviations
- ABG
- arterial blood gas
- AE
- adverse event
- BAL
- bronchoalveolar lavage
- BNF
- British National Formulary
- CF
- cystic fibrosis
- CI
- confidence interval
- CONSORT
- Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials
- CRF
- case report form
- CTIMP
- clinical trial of investigational medicinal product
- DBD
- donation after brain death
- DCD
- donation after circulatory death
- DEVELOP-UK
- Donor Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion in UK lung transplantation
- ECG
- electrocardiography
- ECMO
- extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- EOI
- expression of interest
- EVLP
- ex vivo lung perfusion
- FBC
- full blood count
- FEV1
- forced expiratory volume in 1 second
- FiO2
- fraction of inspired oxygen
- FVC
- forced vital capacity
- GP
- general practitioner
- HDU
- high-dependency unit
- HLA
- human leucocyte antigen
- HRQoL
- health-related quality of life
- HTA
- Health Technology Assessment
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- IL-10
- interleukin 10
- iLA
- interventional lung assist
- INSPIRE
- International Randomized Study of the TransMedics Organ Care System for Lung Preservation and Transplantation
- IQR
- interquartile range
- ISD
- Information Services Division
- ISHLT
- International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation
- ISPOR
- International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research
- ITU
- intensive therapy unit
- MCS
- mental component score
- NHSBT
- NHS Blood and Transplant
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NIHR
- National Institute for Health Research
- NOVEL
- NOrmothermic ex Vivo lung perfusion as an assessment of Extended/marginal donor Lungs
- NuTH
- Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals
- OCS
- Organ Care System
- PaO2
- partial pressure of oxygen
- PCS
- physical component score
- PGD
- primary graft dysfunction
- PI
- principal investigator
- PSSRU
- Personal Social Services Research Unit
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- R&D
- research and development
- SAE
- serious adverse event
- SD
- standard deviation
- SF-36
- Short Form questionnaire-36 items
- SF-6D
- Short Form questionnaire-6 Dimensions
- SNOD
- specialist nurse for organ donation
- SOP
- standard operating procedure
- THAM
- trometamol