Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the PHR programme as project number 14/183/08. The contractual start date was in March 2016. The final report began editorial review in May 2019 and was accepted for publication in October 2019. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The PHR editors and production house have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the final report document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Eileen Kaner sat on the Public Health Research Research Funding Board (2010–16) and reports National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Public Health Research grants during the conduct of this study. Denise Howel was a member of NIHR Health Services and Delivery Research Commissioning Board (2012–15) and is a member of NIHR Programme Grants for Applied Research Subpanel (2017–20). Elaine McColl was a member of the NIHR Journals Library Editorial Group; she was an editor for the NIHR Programme Grants for Applied Research programme (2013–16) and was a member of the NIHR Clinical Trials Unit Standing Advisory Committee until 2016. She reports grants from NIHR Public Health Research programme during the conduct of this study and other NIHR Journals Library-funded grants outside the submitted work.
Disclaimer
This report contains transcripts of interviews conducted in the course of the research and contains language that may offend some readers.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2020. This work was produced by Alderson et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2020 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Introduction
Structure of the report
The report is structured as a series of eight chapters, detailing the design, management and outcomes of both the formative research and the pilot feasibility study. The report begins by providing the background to the research, outlining the rationale informing the design and conduct of the study.
Chapter 1 ends with an overview of the project aims and objectives. Following this, a chapter is dedicated to each of the core components of the study.
Chapter 2 details the patient and public involvement (PPI) work that has taken place throughout the study.
Chapter 3 explores the formative phase of the study and the development of the intervention materials, as well as the training and supervision provided to drug and alcohol staff during the delivery of the interventions.
Chapter 4 reports the design, methods and results of the drug and alcohol treatment provider survey.
Chapter 5 provides the design, methods and results of the pilot feasibility trial.
Chapter 6 provides the design, methods and results of the parallel qualitative process evaluation.
Chapter 7 details the design, methods and results of the health economic evaluation of the study.
Finally, Chapter 8 draws together the main findings from the pilot feasibility study, alongside an assessment of whether or not the study met its aims and objectives, before detailing lessons learnt and recommendations for a future definitive trial.
Ethics approval
This study was granted a favourable ethics opinion by Newcastle and North Tyneside 1 National Research Ethics Service Committee (16/NE/0123). Newcastle University acted as trial sponsor.
Research management
The Supporting Looked After Children and Care Leavers In Decreasing Drugs, and alcohol (SOLID) Trial Management Group (TMG) was responsible for ensuring the appropriate and timely implementation of the trial. The TMG met bi-monthly and comprised the chief investigator, project co-ordinator, co-applicants and researchers working on the project. Professor Raghu Lingam, succeeded by Professor Eileen Kaner, chaired this group.
A Trial Oversight Committee (TOC) was appointed to provide an independent assessment of the progress the trial was making and to help determine if a future definitive trial was merited. This group met annually to oversee trial progress, with particular attention paid to recruitment, retention, adherence to trial protocol, participant safety and any new information deemed relevant to the research question. Professor Monica Lakhanpaul chaired this group. The agreed terms of reference can be seen in the Report Supplementary Material 1.
Research governance
This trial was conducted in compliance with the approved protocol and adhered to the UK policy framework for health and social care, good clinical practice guidelines, the relevant standard operating procedures and other regulatory requirements as applicable.
All researchers complied with the requirements of the General Data Protection Regulation, 2018,1 with regard to the collection, storage, processing and disclosure of personal information, and have upheld the Act’s core principles.
Researcher-administered questionnaires completed by participants online were identified by a unique study identification code. Only members of the research team are able to associate this unique study identification code with participant identifiable data needed for record linkage and participant contact.
All study records and investigator site files were stored in the Institute of Health and Society at Newcastle University in a locked filing cabinet with restricted access.
Amendments to study protocol
It was the responsibility of the research sponsor to determine if an amendment was substantial or not. A number of amendments have been made with the mutual agreement of the chief investigator, sponsor and the TOC.
Substantial amendments were submitted to the Research Ethics Committee by the chief investigator, on behalf of the sponsor, and changes to protocol were not implemented until approval was in place. The details of the substantial amendments made throughout the trial are shown in Report Supplementary Material 2.
Background to the research
Introduction
Drug and alcohol use is a major public health problem that places a significant economic strain on the NHS and society. 2 Substance use accounts for 11% of the total burden of disease, calculated as disability-adjusted life-years lost, in high-income countries. 3 It was estimated in 2013 that alcohol-related harm costs the UK £21B annually,4 with an additional £15.4B estimated to result from drug addiction. 5 The Modern Crime Prevention Strategy 2016 states that alcohol is a key driver of crime. 6 The north-east has the record highest rate of alcohol-related deaths in England. 7
Risky substance use in adolescence predicts adult alcohol and drug use and significantly increases the risk of adult mental health disorders, crime and poverty. 8–10 There have been some positive trends over recent years with regard to young people’s substance use and related risky behaviours. For example, fewer young people (aged 16–24 years) in England report drinking alcohol regularly,11,12 and more abstain from using alcohol than in previous years. 4,13 Although there has been an overall fall in drug use in teenagers over the last decade, the UK is still in the top five for lifetime use of cannabis and other illicit drugs in 15- to 16-year-olds and the top 10 for binge drinking (heavy sessional or risky single-occasion drinking) in the last 30 days across 36 European countries. 14 In a 2016 longitudinal survey of English secondary school pupils aged 11–15 years, 19% had tried smoking and 44% had tried alcohol. 15 In addition, 24% had tried drugs, compared with 15% in 2014, which the authors believe is accounted for by new questions on novel psychoactive substances (NPSs) and nitrous oxide. 15 The most recent figures from the National Drug Treatment Monitoring System (NDTMS) on young people accessing specialist services show that the number of adolescents accessing such services continues to decline year on year. 16 However, the number of younger people (those aged < 14 years) accessing services has increased by 10% since 2014–15. The most common drug used problematically by those in treatment was cannabis (88% of services users reported a problem with this drug), followed by alcohol at 49%. Eleven per cent of those in treatment reported problematic ecstasy use, 9% used cocaine, 3% used amphetamines and 4% displayed NPS use. 16 Encouragingly, the most recent NDTMS statistics on young people’s substance use suggest a decrease of 45% in problematic NPS use since 2016,16 perhaps because these ‘legal highs’ became illegal in May 2016.
The following sections highlight the specific health, substance use, education, employment and offending status of children in care, henceforth used to make reference to looked-after children and care leavers.
Children in care and health
In the UK context, looked-after children are children up to the age of 18 years who are under the legal guardianship of local authorities. 17 Such young people are described as being in ‘out-of-home’ care in both the USA and Australia. 18,19 Care leavers are young adults who were previously under the legal care of local authorities and are still entitled to support, depending on their circumstances. Care leavers are typically aged 18 to 21 years, but can range in age from 16 to 25 years depending on their circumstances, such as being in education. 17
On 31 March 2018 there were 75,420 children in care in England, which represents 64 children per 10,000 of those aged < 18 years. 20 The number of children ‘looked after’ in England has risen steadily over the past 9 years. The main reasons for children and young people entering the care system are abuse or neglect (61%), family dysfunction (15%), family acute stress (8%) and absent parenting (7%). 20
Children in care may live in a range of placement types, such as children’s residential homes or secure units with foster carers or relatives, or be adopted or unaccompanied asylum seekers, or can remain with birth parents while under supervision from social workers. 21 Recent evidence suggests that levels of placement stability for children in care are low. In 2016–17, the mean placement duration was 314 days (10.5 months) and the median was 140 days (just under 5 months). 20 Twenty-four per cent of placements lasted < 1 month and only 22% of placements lasted > 1 year. 20 The impact of this, as Unrau and Seita explore with care-experienced adults, can have a lasting emotional impact and affect an individual’s ability to trust and build relationships. 22
Children in care have multiple risk factors for substance use, poor mental health, school failure and early parenthood. 23 These factors include parental poverty, absence of support networks, parental substance misuse, poor maternal mental health, early family disruption and, in the majority of cases, abuse and/or neglect. 24,25
Young people who have experience of the care system are more likely than their peers to have experienced adverse childhood experiences. 26,27 A Social Care Institute for Excellence report, Improving Mental Health Support for our Children and Young People, highlights the combined effects of young people’s experiences prior to care and those during care as having an impact on their mental health. 28 Such experiences are associated with a number of poor long- and short-term health outcomes,29 including problematic substance use, mental health problems,30 obesity and cancer. 31 For example, more than 50% of children in care rate their well-being as low, compared with only 10% of their same-age peers. 32 Similarly, 50% of those in care meet the diagnostic criteria for a psychiatric disorder, compared with 10% of non-care children who have mental health issues. 32 All children in care in England aged 4–16 years are required to complete an annual Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) with their foster carer or main residential care worker. In 2017, 49% had a score within the normal range (score of 0–13), 12% had a borderline score (score of 14–16) and 38% had a score giving cause for concern (score of 17–40). 20 Those in foster care placements had the lowest scores, 51% scored within the normal range, 13% were borderline and 36% gave cause for concern. 33 By contrast, within the rest of the population of children in care, 39% were in the normal range, 13% were borderline and 47% gave cause for concern. 34 The mental health needs of children in care are evident in the Children’s Commissioner 2015 report. 35 Children in care significantly over-represented peers in relation to accessing specialist Community Adolescent Mental Health Services (CAMHS). Although < 0.1% of children in England are in care, they represented 4% of children referred to CAMHS. 35
Longitudinal data suggest that young people who have been in care have higher levels of depression in adulthood. In the British Cohort Study (BSC70), at age 30 years, 24.2% of care leavers reported depression, compared with 12.4% of those who had not been in care. 36,37 In addition, care leavers were four times more likely than their peers to self-harm in later life. 38 Children in care had a nearly fivefold increased odds of at least one mental health diagnosis, including anxiety, depression or behavioural disorders [odds ratio 4.92, 95% confidence interval (CI) 4.13 to 5.85], than their non-looked-after peers, further increasing their risk of substance misuse and poor life chances. 39
Evidence suggests that children in care have a higher rate of teenage pregnancy than their peers. 40 Over a 14-month period in 2012–13 in Wales, children in care aged 14–17 years had a conception rate of 5.8% compared with 0.8% among peers not in the care system.
Substance use
As outlined in Introduction, risky substance use in adolescence is a predictor of adult-related alcohol and drug use, mental health disorders, crime and poverty. 8–10 Children in care aged 11–19 years have a fourfold increased risk of drug and alcohol use compared with children not in care. 41 Twenty-five per cent of children in care aged 11–19 years drink alcohol at least once a month, compared with 9% of young people not looked after. A national survey of care leavers showed that 32% smoked cannabis41 daily and data from 2012 showed that 11.3% of children in care aged 16–19 years had a diagnosed substance use problem. 42,43
In the year to end of March 2017, 4.1% of children in care were identified as having a substance misuse problem (not including tobacco), with older teenagers being more likely to be identified as such (11% of 16- to 17-year-olds vs. 5% of 13- to 15-year-olds). 20 Those in foster care appear to be the least at risk: 2.1% were identified as having a substance misuse issue, of whom 46% received an intervention and 42% refused an intervention. However, within the rest of the population of children in care (non-foster care placements), 10% were identified as having a substance misuse problem, 62% of whom received an intervention and 39% refused an intervention. 33 In March 2018, there were 15,583 young people accessing specialist substance misuse services, of whom 7% (1093 young people) stated that they were living ‘in care’. In addition, of the 11,052 new presentations in 2017–18, in self-reports via the NDTMS, 1204 (11%) young people identified themselves as a looked-after child, 957 (9%) identified themselves as a child in need and 829 (8%) reported that they had a child protection plan in place. 44 International evidence suggests that those living in institutional or residential care homes are at particular risk of legal and illegal substance misuse, compared with non-care peers and those living in other placement types. 19,45–47
Children in care are over-represented among drug users in later life and tend to start using substances earlier, more regularly and at higher levels than their peers. 48 Relatedly, 12% of young people accessing substance misuse services are children in care,49 and this group are disproportionately represented in the criminal justice system.
Recent policies stress that children in care are a high-risk group who are vulnerable to substance misuse and linked mental health problems, as identified in Ethics approval. The 2017 Drug Strategy,49 the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) (2017) guidelines Drug Misuse Prevention: Target Interventions50 and the NICE (2010) guidelines Alcohol Use Disorders: Prevention51 identify children in care as a ‘high-priority group’ who are at increased risk from substance-related harm. Despite this, there is limited research and an absence of cost-effectiveness data, and, at the time of writing (2019), no national guidelines on the most effective interventions to decrease risky drug and alcohol use in this group. This lack of data was highlighted by the Chief Medical Officer’s annual report for 2012,23 which stated that one of the key research areas was to assess the most effective interventions to reduce multiple risk-taking behaviour, including drug and alcohol use, in this group. 23
Literature shows that risk-taking behaviour clusters in adolescence and behaviours, such as smoking, alcohol consumption and unprotected sexual intercourse, co-occur. 52,53 In addition, young people who engage in any one risk-taking behaviour are likely to engage in others. 54,55 The involvement in multiple risk-taking behaviours can be linked to contextual factors. The majority of young people presenting to specialist drug services have multiple and overlapping vulnerabilities in addition to substance use, such as being looked after, mental health problems, not in education, employment or training (NEET), experience of child sexual abuse, offending or domestic abuse. 16 Forty per cent of 19- to 21-year-old care leavers in England are NEET compared with 13% of all 19- to 21-year-olds more broadly. 34
Education
Fifty-seven per cent of children in care aged 11 years have a special educational need, a rate 40% higher than among their peers who are not in care. 20 A child will be defined as having special educational needs if they have a learning problems or disability that mean that they need special education support. 56 The disparity in educational achievement between young people in care and those who are not continues as they progress through the education system. At age 16 years, the average attainment score for children in care is 19.3, compared with a score of 44.5 for children not in care. 20 Children in care have lower educational attainment and participation post secondary level,57 and those who enter care later (i.e. between age 10 and 15 years) do less well in secondary education than those who enter care at a younger age. 58
A study of 181 children in care aged 7–15 years in an English local authority found that they performed less well than the general child population in regard to assessed mental health, emotional literacy, cognitive ability and literacy attainment. 59 However, there were some positive exceptions of children performing well (16%, n = 30) and this was positively correlated with having face-to-face parental contact at least once per month and being in mainstream education. However, there was no significant relationship with the age on entering care, the primary reason for entering care, the length of time in care, or placement type.
A study of longitudinal data of Danish children born in 1995 shows that those in ‘out of home’ care settings change school more often than other young people, and that such change is associated with adverse educational outcomes. 60 Longitudinal data from the UK, Finland and Germany show that, in all three countries, care leavers are more likely to have no qualifications and less likely to have a higher-level qualification than their same-age peers who have never been in care. Males, in particular, are more likely to have no qualifications. 36
Literature shows that young people who truant or are excluded from school have an increased risk of alcohol and/or drug use. 61 It is also reported that young people who have truanted from school are 1.85 times as likely to have consumed drugs within the past 12 months and are over twice as likely to have consumed alcohol within the past week. 62
Employment
Care leavers have a higher risk of unemployment than those who have not been in care. 63 Forty per cent of 19- to 21-year-olds are NEET, compared with 13% of all 19- to 21-year-olds. 20 Such disadvantage and poorer outcomes last into adulthood, showing ‘a continuing legacy of adversity’ for those who have been in care, particularly in relation to education and employment. 36 Across the UK, Finland and Germany, care leavers are over-represented in economically inactive categories. In the 1970 British Cohort Study, of those born in 1970, at age 30 years, 65.8% of those who had been in care had attended full- or part-time education compared with 82.1% of those who had never been in care. By age 30 years, 7.1% of care leavers were unemployed, compared with 3.1% of those who had never been in care. A total of 16.3% of care leavers were not working to take care of family/home, compared with 9.9% of those who had not been in care. In the UK, at age 30 years, care leavers were more likely to have claimed Jobseekers Allowance (4.3% vs. 1.6%), claimed income support (7.7% vs. 1.7%) and were much more likely to have been homeless or of no fixed address before the age of 25 (22.5% vs. 6.5%). 36 Care leavers have three times the risk of being homeless than those who have never been in care. According to the more recent Longitudinal Study of Young People in England (now referred to as Next Steps), a birth cohort study of those born in 1989–90, care leavers at age 20 years are showing similar trends to those in the 1970 cohort at age 30 years. Those who have been in care are over-represented among the unemployed (17.9% vs. 6.2% of 20-year-olds who have not been in care). 64
In line with the disrupted school attendance reported above, young people with poor attendance are more likely to leave school at 16 years of age, with few or no qualifications, and therefore are seven times more likely to be recorded as NEET. 62
Offending
In the year up to 31 March 2017, 4% of children in care aged between 14 and 17 years had received a conviction, final warning or reprimand. Children in care are five times more likely to offend than all children. 20 Of those in foster care and aged between 10 and 17 years, 1.2% received a conviction, final warning or reprimand, compared with 15% of children in all other placements. 33 Research from the criminal justice system in Scotland showed that 34% of youth offenders had been in care. Of these offenders, 75% reported drug use (vs. 57% of those not previously in care). 65
Summary of the needs of children in care and potential solutions
As highlighted in sections Children in care and health to Offending, children in care are at risk of experiencing a myriad of negative outcomes, which will affect their emotional, physical and economic prospects into adult life, resulting in a significant cost to society and increased risk of intergenerational poverty. Effective interventions for children in care could have a beneficial effect on the long-term mental and physical health of these vulnerable young people, importantly reduce health inequality and, due to their increased risk of early parenthood, potentially impact intergenerational health. In response to the needs of children in care, the SOLID trial was developed to test the feasibility and acceptability of two behaviour change interventions in an attempt to address the substantial gap in evidence relating to effective interventions for children in care residing in varying forms of placement.
Overview of the study
The study had two linked phases:
-
A formative phase consisting of adaptation and manualisation of two behaviour change interventions for children in care to help reduce risky substance use: (1) motivational enhancement therapy (MET); and (2) social behaviour and network therapy (SBNT). Phase 1 also incorporated a national survey of drug and alcohol treatment service leads to help characterise usual care across England and identify potential collaborative centres for a definitive trial.
-
A pilot feasibility randomised controlled trial (RCT). This second phase of the project also had a detailed process evaluation (see Chapter 5) and economic component outlined in Chapter 6.
Research aim
The SOLID pilot feasibility trial aimed to assess the feasibility and acceptability of a definitive three-arm multicentre RCT (two behaviour change interventions and care as usual) to reduce risky substance use (illicit drugs and alcohol), and improve mental health in looked-after children and care leavers (children in care aged 12–20 years).
Research objectives
The primary objectives within the SOLID pilot RCT were as follows.
Phase 1: formative study –
-
To adapt two behaviour change interventions for children in care to help reduce risky substance use (MET and SBNT). This phase was carried out with children in care, their carers (residential key workers and foster carers), drug and alcohol workers, and social workers with responsibility for children in care, to ensure acceptability and feasibility of the intervention packages.
Phase 2: pilot feasibility randomised controlled trial –
-
To conduct a three-arm pilot RCT [comparing MET, SBNT and a control (usual care)] to determine if rates of eligibility, recruitment and retention of children in care, and acceptability of the interventions, are sufficient to recommend a definitive multicentre RCT.
The secondary research objectives were as follows.
Phase 1: formative study –
-
To refine the intervention packages for integration into care pathways for children in care.
-
To conduct a survey of the leads for young people’s drug and alcohol treatment services across England to identify ‘standard practice’ within and across agencies.
Phase 2: pilot feasibility randomised controlled trial –
-
To establish response rates, variability of scores, data quality and acceptability of the proposed outcome measures for the future definitive trial (i.e. self-reported alcohol and drug use, health-related quality of life, mental health and well-being, sexual behaviour and placement stability 12 months post recruitment), to inform a sample size calculation for a definitive multicentre RCT.
-
To assess acceptability, engagement and participation with the MET- and SBNT-based interventions by children in care, their carers and front-line drug and alcohol workers.
-
To carry out a process evaluation to include fidelity of intervention delivery and qualitative assessment of the barriers to successful implementation, and to assess if key components from the MET and SBNT interventions can be combined to develop a new optimised intervention.
-
To develop cost assessment tools, assess intervention delivery costs and carry out a value of information analysis to inform a definitive study.
-
To apply prespecified STOP/GO criteria and determine if a definitive multicentre RCT is feasible, and, if so, to develop a full trial protocol.
-
To consider findings from the study as a whole in order to develop a core intervention delivery package, potentially of a single optimised intervention, linked to a theory of change model to use in the definitive trial.
The study setting
The research took place in six local authorities in the north-east of England (Newcastle, Gateshead, County Durham, Middlesbrough, Stockton and Redcar). The north-east of England is an area of increased health and social care need and has the highest rates of poverty in the country, with 24% of households living below the poverty line. The region is, however, not uniform and encompasses a mixture of urban, periurban and semi-rural areas. The percentage of black and ethnic minority groups across the region varies from 10% in Newcastle to 2% in Durham. 66 The North East region had 95 children in care per 10,000 as of March 2018, far higher than the average rate for England as a whole (64 children per 10,000) (Table 1). Each local authority area provides a range of placement types, such as residential care homes, foster care placement and kinship foster care. 67
| Region/local authority | Total number of children in care to end of March 2018 | Number of children in care per 10,000 children aged < 18 years |
|---|---|---|
| England | 75,420 | 64 |
| North East England | 5020 | 95 |
| Gateshead | 393 | 99 |
| Newcastle | 566 | 98 |
| County Durham | 800 | 80 |
| Stockton | 468 | 108 |
| Middlesbrough | 445 | 137 |
| Cleveland and Redcar | 284 | 103 |
Chapter 2 Participant and public involvement
Introduction
Patient and public involvement was sought at multiple time points and at various levels throughout the SOLID project.
Patient and public involvement representatives included children in care, local authority employees, drug and alcohol practitioners and non-looked-after young people. Their contributions have informed the development and delivery of this research. Input has included influencing the study design (see Patient and public involvement in study design and Patient and public involvement throughout the pilot randomised controlled trial) and the co-design of study documents and the adapted manuals to ensure acceptability and readability to both children in care and practitioners. Participating local authorities and drug and alcohol services were heavily involved in the conduct of the feasibility study through screening, recruitment and delivery of interventions.
Examples of PPI throughout the project are documented below.
Patient and public involvement in study design
Three groups of children in care (n = 11, aged 12–20 years) were consulted at the point of designing the study to develop the study proposal. As a result of our PPI, the target age range of the study changed from 13–17 years to 12–20 years, so that we did not exclude early substance users (at the lower end) or young people as they transition out of care and into adult services (at the upper end). The children in care judged it essential to involve young people in the development of the interventions and felt that this research was important, especially with the rise in use of ‘legal highs’. We also consulted widely with service providers, including drug and alcohol workers, social workers and managers. In response to this work, we amended our strategy for recruiting children in care into the study. Children in care and professionals felt that social workers, rather than ‘looked-after children’s’ nurses, were best placed to screen for substance use.
Patient and public involvement throughout the pilot randomised controlled trial
Patient and public involvement was carried out regularly during the study and fed into the management meetings and TOC. The following forums were used within the study.
The research team attended several young persons’ advisory group meetings. The north-east young persons’ advisory group is one of six groups across England and is made up of young people aged 11–18 years who live in the north of England. The groups meets on a monthly basis to help researchers with their projects and raise research awareness among young people. The research team attended a meeting in March 2016 to discuss study documentation to be used within the formative research phase of the study; this included looking at the initial consent leaflets, the participant information leaflets and consent forms. There were 29 participants at the meeting (13 male/16 female, aged 12–18 years). Following discussion at the meetings, a number of changes were recommended and actioned regarding the participant information leaflets. The changes included a complete reformat of the leaflets that we proposed to use, with a change of graphics, simplified language and it was agreed to devise two slightly different versions of the leaflets for those aged 12–15 years and those aged 16–20 years, to accommodate different literacy levels.
The research team attended a North East Children in Care Council Conference in May 2016. Six participants were present (three male/three female) to discuss the topic guides to be used with young people within the formative research and we explored how to introduce the theory of change models. The outcome of the discussions was that participants liked the idea of using graphics to explore the complex ideas of the models. The young people preferred graphics that included ‘people’ in them, as opposed to just words or pictures. Young people identified some graphics that could be used when conducting interviews with children in care.
We also attended a Regional Looked After Networking Group meeting in July 2016 to discuss the survey to be completed with looked-after children’s leads. There was eight participants present, all were female managers or senior members of local authority public health and social work teams. A number of recommendations were made regarding terminology used within the survey and the flow of questions.
Thirty-six participants across three of the local authority sites took part in developing and revising the initial contact form and the car, relax, alone, forget, friends, trouble(s) (CRAFFT) screening tool to be used within the RCT phase of the trial. A number of recommendations were made and implemented, inclusive of the graphics needing to be enlarged and the text to be presented in different colours. Participants also recommended that the research team developed a ‘crib sheet’ for social workers to guide them when introducing the study to young people and that training sessions be offered prior to screening beginning. All of the recommendations were implemented, ‘crib sheets’ were designed and distributed with the CRAFFT forms and training was delivered by researchers (HA and RB) in each local authority site.
The research team attended a further North East Children in Care Council meeting in July 2017. Eight participants were present, including the personal advisor (PA) facilitating the session (seven female/one male), to discuss the topic guides to be used with children in care as part of the process evaluation phase of the research project. Recommendations included minimising the number of questions asked and making the interviews as informal and ‘conversational’ as possible. The recommendations were taken on board and researchers had hints and probes to use, rather than lots of individual questions.
Research patient and public involvement group
While carrying out the PPI with young people, members of the Children in Care Council suggested that they would like to be involved more extensively in PPI work regarding research. This led to a successful application being written to enable a PPI-specific piece of work to be completed. A research PPI group was established at the request of children in care attending one of the North East Children in Care Councils. Additional funding from the Catherine Cookson Foundation covered expenses, such as vouchers, transcription costs and dissemination of the final product (which was a short, 5-minute video). When children in care participated in this particular piece of PPI work, the research team adhered to the same process of obtaining informed consent from children in care and their corporate parent, as explained fully in Chapter 3, Recruitment and sampling strategy. In addition, participants in the research PPI group also signed an additional release form to allow the video that they developed as part of the PPI work to be shown.
Eighteen qualitative semistructured interviews were conducted with seven children in care, the participation officer within a North East Children in Care Council and the four researchers involved in developing and facilitating the PPI group. PPI sessions (nine sessions), each approximately 1 hour in length, were conducted over an 18-month period. Data gathered within the qualitative methods were used to produce a video of the children in care, describing why it was important to have their voice heard and how they could influence research and ‘10 top tips’ of working with vulnerable young people, such as children in care. The overall findings of this piece of work suggested that it was feasible to develop a PPI group with children in care to be involved in academic research projects. The development process and findings from this PPI project have been published elsewhere. 68
Conclusion
Patient and public involvement has played a central role within this research project. It has ensured that the study design is as inclusive as possible and that the study documentation is acceptable to study participants. The relationships and links made with local Children in Care Council groups have been successful and have opened up dialogues regarding children in care’s involvement in future pieces of academic research.
Chapter 3 Development of intervention materials and training (formative research study)
Introduction
As outlined in Chapter 1, Overview of study, the formative phase of the study aimed to adapt the two intervention approaches (MET and SBNT), to ensure that they were feasible to deliver within the existing health and social care system, and acceptable to children in care and other key stakeholders inclusive of social workers, drug and alcohol workers and ‘carers’. The intervention adaptation process occurred through a series of stages, involving interviews, focus groups and workshops, which were all based on qualitative methodology. The steps taken are documented below (see Methods); qualitative research findings are included to illustrate how participants influenced the adaptation and manual development of our two evidence-based interventions so that they could be delivered through existing alcohol and drug treatment services.
Methods
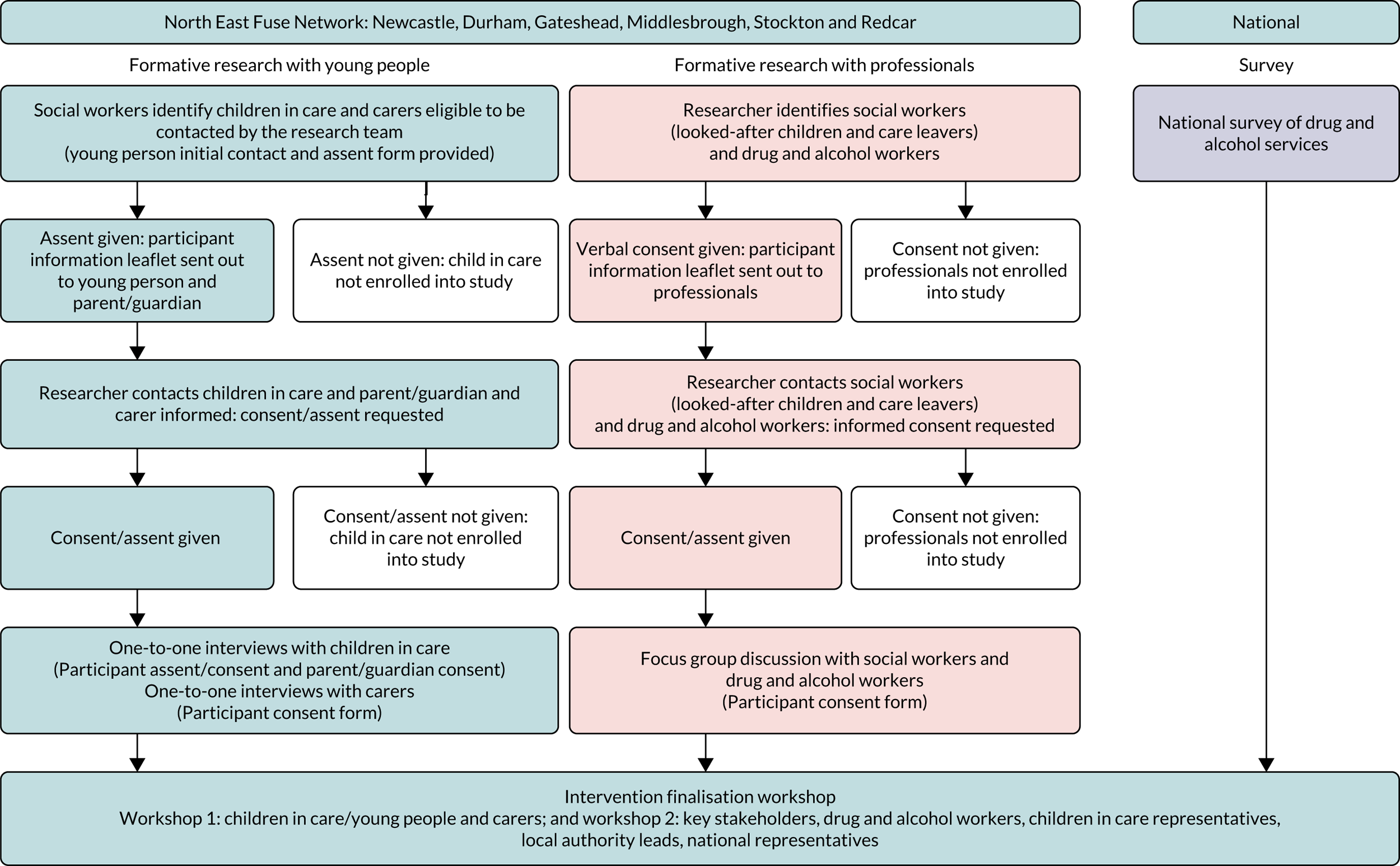
The formative research work consisted of five separate, but interconnected, stages. The first was to select two evidence-based interventions suitable for adaptation to be used with the population of children in care. This was followed by developing a theory of change model, conducting qualitative interviews and focus group discussions with key stakeholders and the analysis of the qualitative data, before co-producing the final interventional manuals within a finalisation workshop. Each stage is discussed in detail in sections Rationale for choosing SBNT and MET interventions to Consent. Figure 1 also visually shows the component parts of the formative phase of the study.
FIGURE 1.
Component parts of phase 1: formative study.
Rationale for choosing SBNT and MET interventions
Two evidence-based interventions, MET69 and SBNT,70 were chosen to be adapted as they have been shown to be effective in decreasing substance use in a range of participants including adolescents. 71
Motivational enhancement therapy is a concentrated version of motivational interviewing. This client-centred, counselling approach adds a problem feedback component to standard treatment. 72 The problem feedback component enables the practitioner to reflect on the material elicited about the impact of drug and alcohol use on the young person’s mental health, physical health, relationships, behaviour and offending, and encourages the young person to discuss this further, for example:
We discussed the fact that your foster carer was worried about your drinking. You told me that you found that you were more irritable the day after you had drunk alcohol. Can you tell me more about this?
Within the MET approach, there is a basic assumption that the motivation and responsibility for change lie within the client, and it is the therapist’s role to create an environment to enable the client to change. A systematic review by Carney and Myers73 concluded that motivational interviewing and MET have shown therapeutic promise for adolescents with problem substance use. 73–75
Social behaviour and network therapy is a counselling approach which utilises a combination of behavioural and cognitive strategies to help clients build social networks that are supportive of positive behaviour change in relation to problem substance use and goal attainment. 76 NICE recommends family interventions when working with young people presenting with complex needs, such as substance misuse and mental ill health. 77 SBNT offers an intervention with the potential to galvanise a support network for children in care that can draw support beyond the immediate family. This is important, as most forms of help focus mainly on the individual with the drug and/or alcohol problem and pay little or no attention to the social context. In addition, given the potential for family fragmentation and broken relationships, it is unlikely that the more traditional family interventions would be feasible for the population of children in care. Therefore, the challenge that Copello76 tried to address when developing the SBNT approach was to find a way of working and helping people that takes the social context into account and uses a whole social or family system to help and support change and reduce problems, while also developing an approach that is simple enough to be used in routine practice. The principle of incorporating a support network into the intervention was believed to be suitable to use within this study, as it was hoped that the six sessions could be used as a platform to create a support network, or at least start a dialogue that could consider potentially supportive individuals, and promote cohesion that could ideally continue to be developed beyond the period when the young person is in contact with services.
Although both MET and SBNT have been shown to be effective at reducing substance use in the general population of children and young people, less is known about their effect with those who are likely to have more fragmented family relationships and are currently looked after by the local authority. For the SBNT approach, the nature of social networks and how they differ for children within the care system was paramount to understanding how to effectively engage and work with this group of young people.
Developing a theory of change model
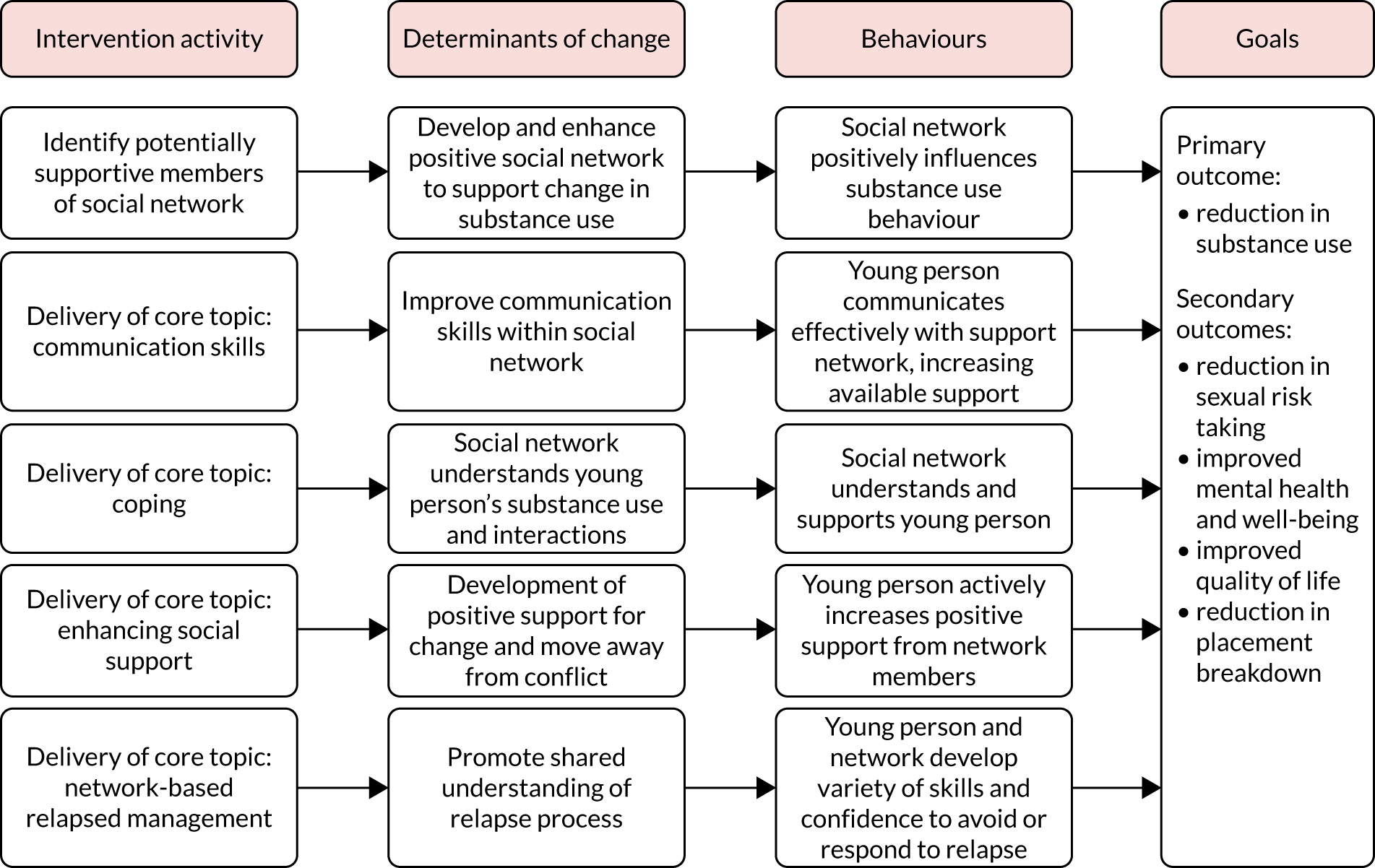
In accordance with guidance from the Medical Research Council (MRC) on developing and evaluating complex interventions,78 we commenced the adaptation of the interventions by building a theory of change model relating to our target population. We developed a behaviour determinants intervention (BDI) model for each intervention (RL, RM, EK and AC). 79 These models highlighted the key behaviours targeted by the interventions, the determinants for change and how the team visualised the proposed change pathways for the interventions. The models are illustrated in Figures 2 and 3. We also considered the absence of appropriate family support and supervisions, and the life experiences which led to an individual’s placement into care, as the central vulnerabilities of children in care. We predicted that an intervention seeking to decrease substance misuse by this group would need to address the behaviour determinants identified in the BDI models (see Figures 2 and 3).
FIGURE 2.
Behaviour determinants intervention theory of change model: MET.
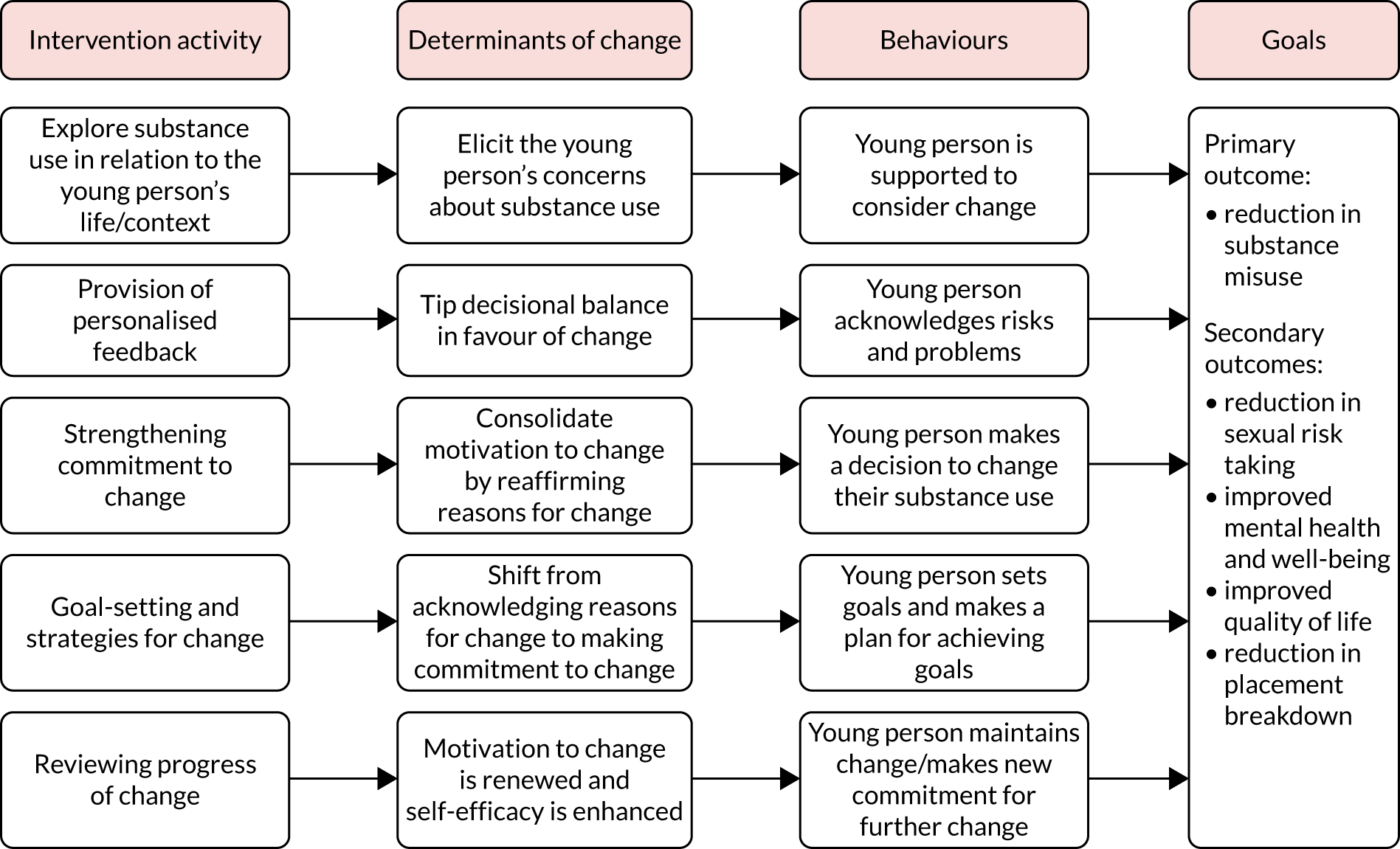
FIGURE 3.
Behaviour determinants intervention theory of change model: SBNT.
When delivering the MET intervention, the therapist can elicit self-motivational statements from children in care by employing strategies to build and strengthen their motivation. By using this technique it was hoped that children in care could resolve the inherent ambivalence about their substance-misusing behaviour. 69 When developing the MET BDI model (see Figure 2), alongside the goal of strengthening motivation, we thought that it would also be helpful to provide personalised feedback to assist the young person to consider risks and tip the decisional balance.
When developing the SBNT BDI model (see Figure 3), we thought that the approach should promote the recognition of an informal network of supports that extended beyond traditional caregivers. We were aware that networks of support available to children in care would differ from those available to children and young people residing within more traditional biological families. However, evidence exists that social network support is key to helping people deal with problem behaviours, including substance misuse. Therefore, within SBNT, the therapist could usefully employ cognitive and behavioural strategies to help children in care to build social networks of positive behaviour change in relation to their goal attainment. 76
Formative qualitative research methods
In-depth one-to-one interviews, dyad interviews and focus groups were used to explore the assumptions inherent within our logic models (see Figures 2 and 3), the principles behind the MET and SBNT approaches and their relevance to children in care, and the broader therapeutic approaches, including the key behavioural and motivational domains that the interventions should address when working with the population of children in care.
All data were collected using semistructured topic guides. Guides were developed and adapted throughout the study in response to early research findings to ensure deeper understanding of emerging themes. Interviews and focus groups were audio-recorded and transcribed verbatim. Data were collected until data saturation was reached within each participant group and no new themes were emerging. Transcripts were anonymised and identifiable participant details removed. A participant key was developed and stored separately. Pseudonyms were allocated to each transcript and have been used within all reports and publications to maintain participants’ anonymity.
Interviews with children in care and carers (foster and residential) were chosen as the method of data collection. Interviews were chosen, as the semistructured nature of the topic guides meant that sensitive issues could be explored and personal experiences shared. Interviews also recognised individuals as experts in their own experiences, in respect of the topics of drug and alcohol use, any barriers and facilitators experienced when engaging with services (e.g. substance misuse services, mental health and services, such as Barnardo’s) and any potential recommendations for service improvements. The topic guides used for the interviews with children in care were developed with the SOLID PPI group, as discussed previously in Chapter 2. All study documentation relating to the formative research is shown in Report Supplementary Material 3.
Focus groups and dyad interviews were chosen as the primary method of data collection with social workers and drug and alcohol practitioners and participants were interviewed with colleagues within the same profession (i.e. social workers were interviewed together and drug and alcohol practitioners were interviewed together). The group interaction encouraged the exploration of a range of responses in a relatively short space of time. Furthermore, they proved to be an effective way to explore issues and quickly establish a range of experiences, views and knowledge. The professional focus groups and interviews enabled us to discuss the original components and principles behind the MET and SBNT interventions, alongside the proposed adaptations and whether or not they were perceived to be relevant to the context of children in care. They also enabled us to explore the broader therapeutic approaches required to work with children in care, the feasibility of delivering the interventions to this population and to consider potential barriers to delivering the interventions at scale.
Recruitment and sampling strategy
Social workers within the looked-after children and 16+ teams (teams working with children in care aged ≥ 16 years and supporting young people who are transitioning out of the care system) approached eligible children in care from their caseload. Eligible participants were defined as children in care aged 12–20 years, known by a social worker to have experience of substance use (previous or current personal use or exposure to substance use), who were able to provide informed consent and who resided in the study area. Social workers acted as gatekeepers, and shared a brief participant information leaflet with the young person. If the young person in care was willing to take part, the social worker completed a written assent or consent form with the young person and returned it to the study team. Children in care (n = 19) expressed an interest in taking part in the study. Once the form was received the study team was able to formally approach the young person in care. All 19 interested children in care were contacted by the research team to discuss the research and to arrange an appropriate time to visit and conduct an interview. Written informed assent or consent (depending on age of the child in care) was taken by the researcher before starting the interview, as described in Consent.
A purposive sample was recruited to ensure diversity with regard to age, exposure to drug and alcohol use, and placement type. The final sample was representative of the population of children in care, in so far as there was an equal mix of male and female participants and a range of placement types across the different local authority areas, as identified in Table 2.
| Qualitative method | Participant group | Number of participants | Sex | Placement type/job role | Substance use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual interviews | Children in care | 19: aged between 12 and 20 years | 9 female and 10 male |
Foster care, n = 5 Residential care, n = 8 Independent/supported living, n = 5 Living with biological parent, n = 1 |
Current/previous substance use, n = 16 Never used substances, n = 3 |
| Carers | 13 | 8 female and 5 male |
Foster carers, n = 6 Residential workers, n = 4 Supported living workers, n = 2 Biological parent, n = 1 |
||
| Drug and alcohol workers | 3 | 1 female and 2 male |
Service manager, n = 1 Drug and alcohol workers, n = 2 |
||
| Dyad interviews | Social workers | 4 | 4 female |
Local authority managers, n = 2 Social workers, n = 2 |
|
| Focus groups | Drug and alcohol workers | 5 | 3 female and 2 male |
Service manager, n = 1 Drug and alcohol workers, n = 4 |
|
| Social workers | 4 | 3 female and 1 male |
Senior social workers, n = 3 Social worker, n = 1 |
||
| Carers | 4 | 3 female and 1 male | Foster carers, n = 4 | ||
| Total | 52 |
Separate one-to-one interviews (n = 13) were carried out with carers across the research sites to ensure diversity of sample in terms of age, ethnicity and carer type (i.e. foster carer/family member/residential worker). An additional focus group with four carers was also conducted as part of an already established carer support group.
Social workers (n = 8) were purposively approached to take part in a focus group and four took part. This was complemented with two further dyad interviews with four social work staff. Sampling took place to ensure diversity in terms of the local authority site in which they worked, level of experience (i.e. social worker, team manager) and sex. The social workers within the looked-after children and care leavers teams were interviewed because of their key knowledge of the context of children in care, as well as of many of the ethical issues that informed the intervention development.
A focus group also took place with specialist young people’s drug and alcohol practitioners (n = 5). Practitioners were purposively approached to ensure diversity in terms of local authority site they worked in, job title (substance misuse practitioner, service manager) and sex. The drug and alcohol practitioners had key knowledge of interventions that currently work well with young people and they used their professional knowledge and expertise to inform the adaptation of the MET and SBNT interventions.
In addition to the focus group with drug and alcohol practitioners described above, one-to-one interviews were also carried out with three drug and alcohol workers who had delivered youth social behaviour and network therapy as part of a previous trial. 70 These interviews aimed to build on previous knowledge and experience of delivering youth social behaviour and network therapy to young people within a substance misuse setting and contributed towards adapting the treatment manual for the population of children in care.
We initially proposed to carry out individual one-to-one interviews with children in care and carers, and focus groups with professional participants. For pragmatic reasons we conducted a combination of individual interviews, dyad interviews and focus groups, depending on participants’ availability and preferred method of involvement. On reflection, the research team felt that the combination of interview and focus group data collection had a positive impact on the quality of the data generated. As planned, the interviews enabled us to collect an individual’s thoughts, attitudes and personal beliefs about being involved in and interacting with the child welfare system, and the focus groups provided an opportunity to consider how the interactional data between participants resulted in similarities and differences in experiences being highlighted.
Table 2 shows the qualitative methods that participants engaged in and the demographics of the participants recruited in the first round of qualitative work.
Consent
The children in care aged < 16 years were seen with an accompanying adult (parent, carer, social worker, children’s home lead) prior to the interview taking place and they were asked to provide informed assent. If the accompanying adult did not have parental responsibility (PR), the research team contacted the adult with PR to obtain informed consent. If the parent was not contactable or, in the view of the designated social worker, it was a risk to the young person for the parent to be contacted, the social worker or local authority guardian with PR was contacted to sign the consent form. Informed young person assent and consent, dependent on age and carer consent, were obtained prior to the young person taking part in any element of the study. Information on the study was shared with parents and carers as appropriate.
For those children in care aged ≥ 16 years and for all other participants within the formative phase of the research, informed consent was taken directly from the individual concerned by the researcher. Prior to informed consent being taken, a participant information leaflet was shared with each participant, and the research team talked through the leaflet and provided an opportunity for any questions to be asked. The research team also explained that participants could withdraw at any point.
After informed consent had been given to the research team, interviews and focus groups were carried out by qualitative researchers with experience of working with young people. The data collection took place at a location convenient for the participant. For young people this was in their home or at an alternative convenient private location, which ensured the safety of both the young person and researcher. For professionals, data collection took place in a private location within their usual working environment. When interviewed the young person was given a choice of whether or not they wanted to be accompanied by a trusted adult who would act as an observer; however, only two young people requested this.
Children in care participants were remunerated for their time with a £10 ‘love2shop’ voucher.
Qualitative analysis
Transcripts were analysed thematically;80 it was an iterative process, using the constant comparative method,81 in order to identify key themes and concepts. In practice, this entailed a line-by-line coding process and then analysis within a given transcript and across the data set as a whole. Analysis with qualitative software (NVivo) aided the organisation of thematic codes. The data were compared across the participant groups (i.e. children in care, professionals and carers), with similarities and differences being highlighted. In the first instance, data were analysed by two researchers in order to ensure intercoder consistency and agreement. The main themes and findings were presented to the wider multidisciplinary team that included expertise in a variety of backgrounds, including community child health, public health, social care, social science, drug and alcohol use, and clinical psychology. These qualitative data were used to refine the SBNT and MET approaches to ensure that they were responsive to the needs and views of substance-using children in care.
Data analysis focused on understanding internal and external drivers of behaviour and also on views about interventions promoting well-being and self-care in early life. Components of the logic models (behaviours, determinants and intervention components) were explored with participants to further refine the theory of change pathway and clarify intervention delivery issues.
Finalisation workshops: modification of interventions
A series of intervention finalisation workshops took place, during which findings from the preliminary thematic analysis of the qualitative interviews and focus groups were presented. The purpose of the workshops was to co-produce the final intervention manuals. Within the initial phase of the workshop, the research team presented the main themes that had emerged from the interview and focus group data, and participants were asked to consider the MET and SBNT interventions and discuss what the final manual should ‘look like’.
Five workshops were conducted: one with professionals (n = 14), all of whom had been interviewed earlier; and four with young people (n = 13), none of whom had been previously interviewed. All participants involved in the young people’s workshops either were currently in or historically had experience of receiving specialist drug and alcohol treatment. The workshops were inclusive of both children in care (n = 5) and non-looked-after children (n = 8). We took the decision to include young people not involved with the care system, as this element of the study needed to understand current treatment provision. Owing to social workers not systematically recording this information and gatekeeping to ‘protect’ young people, we found it difficult to identify young people in care currently on their case load with experience (current or previous) of accessing treatment. We decided to approach the drug and alcohol services involved in the study to recruit young people into the workshops. We wanted to ensure that we had maximum variation of young people, regarding age, sex and location of participants, who had experience of accessing drug treatment agencies, to discuss the developed interventions. We held a workshop in each active study site to enable participants to be involved in the study without having to travel long distances to take part. The workshops were all held within the well-established young people’s drug and alcohol services involved in the study, so participants were in a familiar environment.
The workshops provided an opportunity for the research team to present the preliminary findings to key participants. Verbatim anonymised quotes were used to identify areas of potential importance and to facilitate discussion between researchers and participants. Four researchers and participants then worked collaboratively to co-produce the final manuals. Co-production occurred through group discussions and using flip charts and paper to design worksheets and complimentary materials to be used within sessions.
The themes discussed within the workshops are shown in Table 3.
| Theme | Subtheme |
|---|---|
| Therapeutic relationships |
Time and reciprocal self-disclosure Genuine care Non-judgemental approach |
| Engagement and challenges |
The need to use creative methods to enhance engagement Young person’s inability to recognise support Treatment goals wider than substance use |
Areas of potential intervention adaptation were discussed within and across interviews, focus groups and workshops, and the findings from the qualitative data collection have resulted in a number of adaptations being made to the manualised interventions.
Following the workshops, the final adaptation of both manuals took place. Ongoing communication took place between the on-the-ground researchers involved in developing the manuals and the original intervention authors [Professor Alex Copello (SBNT) and Dr Gillian Tober (who has adapted both MET and SBNT for other clinical trials)], to ensure that the core components of each approach were retained throughout the adaptation process.
Formative qualitative research findings
The formative phase highlighted generic principles of working with children in care, rather than changes to the core components of the interventions. These are outlined in Theme 1: therapeutic relationships and Theme 2: engagement and challenges of working with children in care. The main themes that arose were relevant regardless of which intervention (SBNT/MET) was being discussed and adapted. The influential themes and subthemes are discussed as follows.
Theme 1: therapeutic relationships
A successful therapeutic relationship was highlighted as important by both professionals and children in care when working towards reducing substance use. The qualities of trust and genuine care were identified as the two main constructs that underpin a successful therapeutic relationship. The ability of children in care (and often inability) to trust and confide in professionals was a recurrent theme. Professionals acknowledged that children in care often experience disorganised and difficult attachment and recognised that their experiences leading up to their placement in care may have had an impact on their ability to trust other people. Therefore, although trust is one of the necessary conditions for any therapeutic relationship to be successful, it is particularly important for children in care, who may have experienced relationship breakdown and abandonment, being let down and having their essential needs unmet.
Professionals displayed a clear understanding of these complex attachment issues and discussed the need to ‘earn’ trust when engaging with children in care:
You need to put in the groundwork initially. I think with teenagers you need to gain their trust, you need to work for it. Because if they have been hurt, which they will have been, they will try to push you away. They won’t want to trust you.
Carly, social worker, focus group
Owing to the often inherent ‘lack of trust’ in professionals, practitioners recognised that they were expected to demonstrate their trustworthiness when engaging with children in care. Typically this involved practitioners being consistent and reliable. Equally, children in care described seeking qualities such as empathy, reliability and partiality, all of which are qualities that may have been missing in their early attachments. One foster carer described displaying his reliability in terms of being available ‘24/7’, stating that he is permanently ‘on call’ if a young person needs him:
. . . it is not a job because there is no job that makes you work 24 hours a day, 7 days a week and 365 days of the year, but this one does.
James, foster carer, focus group
From the perspective of children in care, the relationship between themselves and their allocated key worker within an organisation was a pivotal factor that determined whether or not they engaged with services. When establishing and facilitating a trustworthy relationship, young people explained the importance that they placed on professionals allowing them to ‘work gradually’, only sharing ‘personal information’ and making disclosures when they felt ready. Furthermore, the idea of professionals making self-disclosures was repeatedly reported: children in care felt it was important for professionals to ‘trade’ personal information, such as a hobby they enjoyed, details of a pet they owned, or an example of how they had resolved a problem successfully in their own lives. This process of sharing information was perceived to be beneficial to developing a trusting relationship, as sharing information was not completely one-sided. Children in care reported that such disclosure enhanced their sense of connection to the practitioner, as well as their own safety to disclose information:
When you work with someone you have to build a bond up first, before you can open up to them . . . It’s, well the way I’ve done [it] is just ask questions about them, and then if they tell you, then you know well if they’ve told me this then I can tell them that.
Sophie, 17, young person interview
Children in care described having multiple professionals involved in their ‘care package’ and a quality that young people desired was ‘genuine care’, inclusive of professionals going ‘above and beyond’ what is expected and providing unconditional care, although they did not always feel that they received this. Professionals, especially those within the social services teams, take on the corporate parenting role. This role dictates that safeguarding and risk management take precedence over the provision of emotional support. Therefore, much of the care a child usually receives from family members within a personal environment is provided by a professional who is employed to provide such care. To demonstrate that they care, many social workers describe being available outside their contracted working hours and going ‘above and beyond’ their role:
Myself and his YOT [youth offending team] worker had agreed between us that we would have our phones on 24/7. So that if he wanted to get in touch and check in we knew he was OK. So we did, we took turns and he did check in and he did arrange to meet up which was really good.
Steph, social worker, focus group
Children in care showed an acute awareness that social workers had a corporate parenting role to fulfil and that carers provided a role that they were ‘paid’ to do. This led to children in care emphasising the importance of practitioners who made them feel like they ‘genuinely cared about their welfare’. Interestingly, foster carers reinforced that they attempted to provide the same level of care and support to both their biological children and the children placed in their care, despite the paid position they were in:
Any child that comes to live with me, I know they are not mine, however I will work with them, I will play with them, I will live with them and I will do everything to my best ability in every area, in every arena because I want what is best for them.
Liz, foster carer, interview
Genuine care also involved professionals showing empathy to the young person and being available to provide ‘unconditional’ support. There was a belief, sometimes verbalised explicitly, at other times more implicitly, that genuine care stemmed from personal investment rather than a contractual obligation:
Like Josie talks to me, not like I’m just someone she has to work with, she talks to me like she cares.
Carla, 17, young person interview
Children in care felt that they were cared for if they were shown unconditional positive regard, regardless of their behaviour. This was a recurrent theme for professionals, who reported children in care regularly disclosing information to them regarding historical experiences that they had been witness to or subjected to. Foster carers described having to respond in a sensitive and non-judgemental way:
We had a young man who had been abused by a family member. He was feeling guilty himself about it and thought that we would feel disgusted that things like that had been done. It is letting him see that we are not disgusted. Straight away, ‘I have heard all of this before, you are not the only one. It is not your fault’.
Carol, foster carer, focus group
The ability of professionals to be non-judgemental was important to children in care, and some participants voiced concerns that practitioners would not be able to ‘cope’ if they chose to share some of the experiences that led to them being placed into care. One young person in care explained that he elected not to engage with services and open up for fear that professionals would then ‘leave him’:
. . . my family is **** up, really **** up. And if I sat there and told someone they’d probably run a mile, they probably would. So that’s why I’ve never really opened up to anyone, cause if I did they probably would run away, do you know what I mean?
Ewan, 17, young person interview
The above quotations identified the practical issues and challenges that needed to be addressed to facilitate a therapeutic relationship with children in care; therefore, it was important to acknowledge the importance of overcoming insecure attachments and incorporating methods of developing a trusting relationship.
Theme 2: engagement and challenges of working with children in care
Throughout the formative data collection, there was consensus that, if used in isolation, the more traditional one-to-one talking therapies were often unproductive for children in care. From a professional perspective, this approach was thought to be overly formal and could result in children in care disengaging with support services. Children in care also verbalised that they found it harder to engage with overly structured and formalised sessions:
It was like in a room . . . and like there’s a table there and it had like little seats round, and like, he was just on about things. Do you know, he didn’t make it very good, like, he didn’t make it very fun and enjoyable kind of thing. It was just like, boring. He was just writing things down that I was saying basically and it just upset me. He just kept on going over it and over it and over it, he was like ‘so how did that feel? Bla bla bla.’ I didn’t really feel comfortable.
Isabelle, 13, young person interview
There was a clear need for practitioners to be equipped with a number of skills and strategies to engage with young people. Practitioners needed to be responsive to the individual presenting to them and described using techniques such as ‘node-link mapping’, as used in the International Treatment Effectiveness Project,82 and mood cards, while staying true to the intervention they were trying to deliver:
There are not many young people who you’ll get to the point where you’re doing that one to one counselling really. It is few and far between. You’re being creative . . .
Adam, drug and alcohol worker, focus group
Many of the participants in care expressed their desire to attend sessions that enabled them to be actively involved in the work being completed, with practitioners implementing strategies that facilitated young people connecting with the work and the professional themselves, and maintaining concentration:
Writing it down or doing it like arts and crafts way because I don’t like just talking and having conversations cause I just get a bit bored and lose track, then I’ll start fiddling about.
Abbie, 18, young person interview
Alongside the necessity for an interactive approach, was the need for practitioners to be aware of the complexities of living in the care system for the young person. This awareness would help to facilitate a holistic approach to be taken to the work being conducted and could also help to identify goals that are not solely ‘substance use’ related. Children in care stated that they valued discussions that recognised the difficulties occurring in their lives. Professionals also identified the importance of taking a bespoke approach to treatment:
I think what’s coming out here is that with the kids we work with, the drug and alcohol issue is over there, if you like, and a whole raft of other issues are here. As workers we’re dealing with all of these here and that tends to sort the drug and alcohol issues out quite naturally.
Laura, drug and alcohol worker, focus group
Professionals highlighted challenges that arose owing to the transient nature of the population of children in care. It was identified that, when young people experience frequent placement changes, it can result in young people experiencing fragmented support in terms of changes to key workers, carers and professionals supporting them. It can also result in young people being eager to find friends even if these relationships are potentially destructive:
So they might, you know, have contact with their brothers or sisters, you know, it is just they get moved around, and when they are moved around they are vulnerable, they are desperate to have friends or they are desperate to have somebody to call their own . . . people get attracted to them who are, I would say, not the type of kids I would want my kids to knock around with.
Liz, foster carer, interview
Social support was identified as a potential challenge regarding the SBNT approach. Children in care and practitioners recognised that a positive support network was a central part of SBNT and accepted that social interaction is necessary in the resolution of most substance misuse problems; however, it was felt that support was not always available:
It is quite sad sometimes when they haven’t got anybody in the family, not even an uncle or a cousin or somebody who they can put down as a support really.
Steph, social worker, focus group
The challenges of finding appropriate network members was explored. In many interviews, the participant in care struggled to identify someone that they felt they could turn to, and feelings of not having support and the need to be self-sufficient were verbalised:
My boyfriend and his friends, and there’s a few of my friends. Actually they’ve got their own lives as well, they’ve got their own houses and their partners and they’re all settling down as well, so . . . there’s not really many people there. When you think about it though, how many of them can you turn to if you’ve got a problem? Cause there’s not a lot.
Abbie, 18, young person interview
As was expected within the children in care population, when individuals were able to identify individuals who provided positive support, it was often people outside the traditional family support network. This had potential for sources of support to be transient (e.g. teachers who would change with each school year). Professionals were often identified as sources of support, which could be challenging for the delivery of SBNT, as individuals may not be able to provide ongoing or out-of-hours support in the same way as more traditional family members would. Nonetheless, children in care recognised the support that was provided to them:
There’s two main people I’ve got in my life which provides me with support. One’s my boss, he’s a farm manager, I work with him most days. Another person is the manager of [name of school], he owns the company and he helps quite a lot by, when I moved out of here [residential children’s home] the first time, he’s the one that made me come back, and let me get my head back.
Philip, 17, young person interview
Key adaptations made
The MRC framework guided the development and adaptation of the MET and SBNT manuals. 78 In line with the data collected throughout the formative phase of the study, interventions were adapted to reflect the practicalities of working with the population of children in care, often presenting with complex needs. The themes of trust, genuine care, being flexible regarding network members, working creatively and having treatment goals wider than substance misuse were key to the revised training and manuals.
Workshop participants (inclusive of professionals and children in care) recommended that additional resources, such as worksheets and exercises, be developed to support the training of drug and alcohol workers and to complement the adapted manuals. Therefore, additional sources of information were developed to link in with each topic area covered in the manuals; it was not compulsory to use the resources were used, but they were available to support practitioners when delivering the interventions. SOLID trial-specific appointment cards were devised at the request of drug and alcohol practitioners, so that participants could identify that appointments were for the SOLID trial as opposed to the usual treatment services. In addition, a pre-treatment session was written into the manuals as requested, to provide practitioners with an opportunity to contact the young person and encourage a rapport to be established prior to commencing sessions.
Regarding the length of sessions, the MET intervention originally consisted of three sessions and this was increased to six to enable more time for a therapeutic relationship to be built. Conversely, the SBNT intervention originally consisted of eight sessions but was reduced to six sessions, in an attempt to keep the sessions focused and in turn keep children in care interested and engaged in the work being done. However, importantly, it was also agreed that, as the both MET and SBNT interventions are delivered to meet the young person’s requirements, they could be completed in less than six sessions if the young person’s needs had been met and it was deemed appropriate to terminate the intervention early. If the young person attended all six intervention sessions and professionals deemed it necessary for the individual to have more intensive support to address complex needs, participants in care would be referred into tier 3 structured services for further work to take place.
Drug and alcohol practitioners were encouraged to consider a range of approaches when delivering the developed SBNT and MET interventions. Inclusion of a mixture of the traditional therapeutic approach, creative techniques, such as writing, and arts and crafts, and/or the completion of more formal worksheets was encouraged. By promoting a flexible approach to be used in the interventions, it was hoped that children in care would engage with practitioners as the new interventions could incorporate methods that children in care feel comfortable with.
The key findings were used to create a change matrix shown in Table 4, which identifies the recommended adaptation, the reason why the adaptation is felt to be necessary, the proposed method of meeting the identified need and which intervention the change is relevant for.
| Recommended adaptation | Reason for adaptation | How the recommended adaptations were incorporated into existing interventions | Relevant to which intervention |
|---|---|---|---|
| The interventions need to focus on overcoming insecure attachments and mistrust that children in care have experienced by default of being involved in the care system | Children in care want to build relationships slowly, allowing time to get to know their workers before they feel comfortable sharing their personal thoughts and feelings. Children in care also wanted choice and control when identifying their support needs |
|
MET and SBNT |
| The interventions needs to be more flexible with social network members due to the fragmented nature of available support networks and repeated broken relationships | Children in care may struggle to adhere to one of the traditional criteria of a ‘network member’, that of a network member being ineligible if they ‘have an alcohol or drug misuse problem themselves’. This may be problematic as it is known, as described above, that 25% of children in foster care and 42% of children in residential care drank alcohol at least once a month,41 32% smoked cannabis daily42 and 11.3% of children in care aged 16–19 years had a diagnosed substance use problem.83 This, alongside placement instability and multiple broken relationships, makes maintaining positive support networks problematic84,85 |
|
SBNT |
| The interventions needed to use creative non-traditional methods to engage children in care | Due to children in care having lower levels of functional literacy, the use of creative/visual approaches enables children in care to express their thoughts and feelings more easily |
|
MET and SBNT |
| The interventions needed to be able to address treatment goals wider than substance misuse alone to accommodate the diverse needs of children in care | It was essential that a young person’s needs should be addressed holistically, as substance misuse rarely happens in isolation but it often interacts with wider problems.86,87 Children in care are known to have higher rates of comorbid mental health problems and higher levels of risk-taking behaviour, such as drug and alcohol misuse |
|
MET and SBNT |
| Alter the number of sessions offered | The current number of sessions was viewed as unproductive when working with children in care |
|
Following the implementation of the recommended adaptations it was crucial to emphasise that both of the interventions retained the essential component that underpin the approaches, as shown in Table 5.
| Session/topic number | Intervention | |
|---|---|---|
| MET | SBNT | |
| 1 | The initial session focuses on developing a trusting relationship between the child in care and the practitioner | The initial session focuses on conducting a review of the young person’s social network |
| 2 | Session 2 is concerned with the child in care discussing the nature of their substance use | Sessions 2–5 deliver a combination of core topics to build positive support for change. Topic 1 focuses on deciding goals, eliciting commitment, agreeing the plan and recruiting the network. Topic 2 focuses on communication and coping. Topic 3 focuses on lifestyle changes and increasing pleasant activities |
| 3 | Session 3 consists of an individual cost–benefit analysis of the child in care’s substance use | |
| 4 | Session 4 is an individual cost–benefit analysis of change | |
| 5 | Session 5 focuses on trying to elicit a commitment to change | |
| 6 | The final session reviews the child in care’s progress in respect of agreed change and commitment to sustain change | The final session consists of a review of progress made, planning for the future and ending the treatment intervention |
A paper has been published that documents the manual adaptation process. 88
SBNT and MET training
Drug and alcohol practitioners were allocated to receive training in, and deliver, either MET or SBNT. Practitioners allocated to MET or SBNT received 2 full days’ training in the adapted allocated intervention. Training for each intervention took place at a specialist addiction service and was facilitated by two experienced members of the research team (AC and GT). The training consisted of working through the intervention manuals (see Report Supplementary Material 4 and 5) and practising the necessary skills to deliver the interventions through role play and group work, and also familiarising the practitioners with the treatment protocol (see Appendix 1). Practitioners allocated to deliver usual care did not receive any additional training.
The training for both approaches was structured so that day 1 of the training was followed by a 7- to 10-day gap, within which the practitioners were encouraged to practise the skills with young people currently on their caseload, familiarise themselves with the audio-recording equipment and prepare an audio-recording of an introductory session to be listened to within day 2 of the training.
Day 2 of the training continued to practise skills and use the training as a form of peer supervision. The MET and SBNT manuals were used to guide the flow of the training sessions, ensuring that practitioners had a clear understanding of what the six sessions could ‘look like’.
Intervention supervision
All drug and alcohol practitioners were offered a monthly individual supervision session with Alex Copello for SBNT and Gillian Tober for MET. Audio-recordings of their sessions and case notes formed the content of their supervision. Initially, supervision took place face to face; however, practitioners reported that it was too great a time commitment, due to it taking up approximately 3 hours to attend, including travel. This feedback was taken into consideration and it was agreed that supervision sessions could take place via Skype™ (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA). In addition to the planned supervision sessions, practitioners allocated to MET and SBNT had the option of accessing the research team, who also provided support and guidance. No additional supervision was provided to practitioners allocated to the control/usual-care arm.
Following the completion of the training with drug and alcohol practitioners, sessions of MET and SBNT could commence once eligible participants were randomised into the trial. The trial process and results are discussed within Chapter 5.
Limitations
We did not formally assess the validity of the adapted interventions compared with the original versions available due to time constraints of the project.
Conclusion
The formative phase of the study successfully involved 65 participants. Overall, findings have highlighted the importance of engaging children in care and key stakeholder in the adaptation process. Findings suggested that original components of both the MET and SBNT approach were feasible to deliver and would be acceptable once adaptations had been made. Key areas included increased emphasis on therapeutic relationships, the benefits of using creative non-traditional methods of engagement and identification of treatment goals wider than those narrowly focused on substance misuse. The manual adaptation process and findings regarding the importance children in care place on feeling genuinely cared for are discussed further in publications by Alderson et al. 88 and Brown et al. 89
Chapter 4 Drug and alcohol treatment provider survey
Introduction
The project included a survey of leads of young people’s drug and alcohol treatment services across England to identify ‘standard practice’ within and across agencies.
The aim of the survey was to collect data from each local authority area in England that had a service offer for a young person’s drug and alcohol service, in order to define usual care and identify potential research sites for a definitive trial. Of the 153 local authority areas, we obtained contact details for 150 commissioned or ‘in-house’ young people’s drug and alcohol services.
Methods
All of the services were contracted to deliver a service in a single local authority area, except one service which was contracted to deliver a service across two (adjoining) local authority areas. Therefore, at the time of conducting this survey there was 149 contactable young people’s services commissioned to deliver services across England.
Data collection took place over a 3-month period (December 2017–February 2018). The survey was carried out as a parallel activity to the formative research phase of the study. Each service was contacted by a researcher (HA, RB or DS) and a service manager or senior practitioner was identified. After introducing the study, researchers aimed to complete the survey (see Appendix 2) instantly over the telephone, or if participants preferred to complete the survey independently a qualtrics link was sent, enabling the survey to be completed online.
The survey explored whether or not the service offer available to children in care altered in any way (if so, how did it differ) compared with young people accessing the service who were not involved in the care system. It also assessed which screening tools services are used when young people accessed treatment and what a typical service offer would look like in terms of number, duration and frequency of sessions. In addition, it considered how managers monitored the content and quality of sessions provided to young people, the supervision and support arrangements that are in place for practitioners and the qualifications of practitioners within the agency. The survey aimed to capture the levels of standardisation or variability in practices across services.
Drug and alcohol survey results
Of the 149 services, 122 (82%) completed the survey, four (3%) declined to take part and 23 (15%) did not respond to multiple contact attempts. In total, 100% of participants provided answers to all questions when they agreed to take part in the survey; therefore, there were no missing data.
Organisations were commissioned and contracted to deliver a service for an individual local authority area; however, six third-sector organisations were providing 50% of the substance misuse services to children in care. They are organisations which have their foundations in adult recovery services and have diversified to offer substance misuse services to meet the needs of children and young people.
The remaining contracts were a combination of voluntary or third-sector agencies and in-house local authority services.
When exploring funding streams, most respondents reported that the drug and alcohol services were commissioned from local authority funding streams (n = 118), with only four services receiving money from alternative sources, such as Big Lottery funding.
Eighty (66%) services reported that children in care received exactly the same service offer as all young people accessing the service, whereas 42 services (34%) said that their service offer to children in care was different. Differences in the service offer included increased engagement work to identify children in care with problematic substance use; increased partnership working with children’s services once a young person accessed services (n = 32); the age at which a child in care is transferred into adult services was increased from 18 years to 21 years due to their vulnerability (n = 11); and children in care being prioritised on the waiting list (n = 6) to ensure they were seen as quickly as possible following a referral.
Screening tools used
Drug and alcohol treatment services were asked to provide information regarding the screening tools they used to assess the level of alcohol and/or drugs a child in care was consuming. The services reported using between one and three different screening tools. However, although some services reported solely on the screening tools used, other services completed the screening within the context of completing a more holistic initial assessment of need.
Ninety-four (84%) services reported using only one screening tool and for the most part, these were ad hoc, locally developed tools rather than validated tools. Twenty-nine (26%) services reported using two different tools and five (4%) services reported using three screening tools. Services reported using the different tools simultaneously during an initial meeting and over a prolonged period of time to establish levels of use and need. There was no standardisation regarding which tools were used and consistency varied even within agencies, as professionals reported using a tool that they felt best met the needs of the individual. Fifty-two (46%) services reported developing a tool ‘to meet their local need’, which, as identified above, could include an amalgamation of validated tools, such as the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT), Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test for consumption (AUDIT-C) and Drug Use Screening Tool (DUST), and could also incorporate items from an assessment of need. The screening tools identified as being used can be seen in Figure 4.
FIGURE 4.
Screening tools used.
Interventions offered
Participants were asked to describe the delivery of the interventions offered to children in care, including the number of sessions, duration of sessions and frequency. When discussing the delivery of interventions, 67 (55%) services stated that they offered a completely ‘bespoke’ service, with each individual being offered a package of care tailored to their individual needs. This package of care was not restricted to a minimum or maximum number of sessions and could incorporate a mixture of tier 2 and 3 services to meet the child in care’s identified needs. Thirty-five (31%) services reported that they were commissioned specifically to conduct structured work delivered within 12 sessions. Twenty-one (19%) services identified that they offered a variety of structured work, such as harm minimisation and drug education. A maximum of 12 sessions was offered, although this could be flexible and could lead onto more bespoke work if necessary. Despite working in a structured way, services often reported having the flexibility to recommence work at a later time with a young person if a further referral was received or if the child in care’s circumstances had changed.
Delivery of services
A final area of interest was to explore the qualifications and/or professional training that drug and alcohol practitioners had achieved or participated in. The qualifications reported as present within services currently and/or regarding previous employees can be seen in Figure 5.
FIGURE 5.
What qualifications/training do practitioners have? D and A, drugs and alcohol; H and S, health and social.
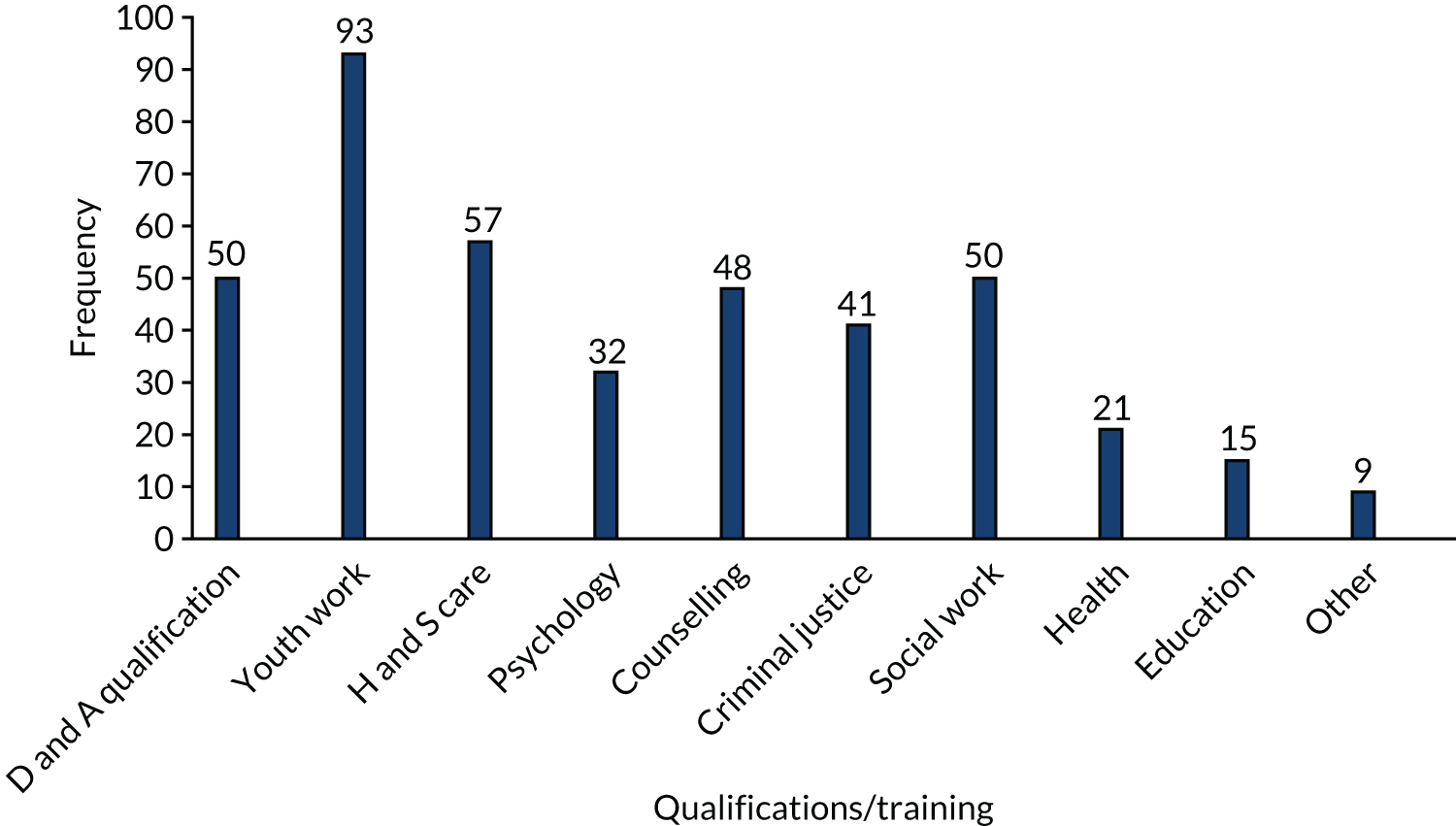
The qualifications held by drug and alcohol workers were varied. Often workers had multiple different skill sets and expertise. Multiple responses were possible to these questions and multiple responses were present from each of the responding services. Youth work was the qualification reported most frequently (n = 93), with health and social care (n = 57), counselling (n = 48) and social work (n = 50) being other qualifications often transferable to the drug and alcohol work. There was no standardisation of training of drug and alcohol practitioners, and individuals utilised different skill sets when moving into this line of work.
Quality monitoring
Owing to the variable and adaptable service offers available to children in care, services were asked to describe what mechanisms were put in place to oversee the quality and content of sessions being delivered. Figure 6 shows the procedures in place to monitor the work being completed.
FIGURE 6.
How is quality and content of sessions monitored? YPOR, young people’s outcome record.
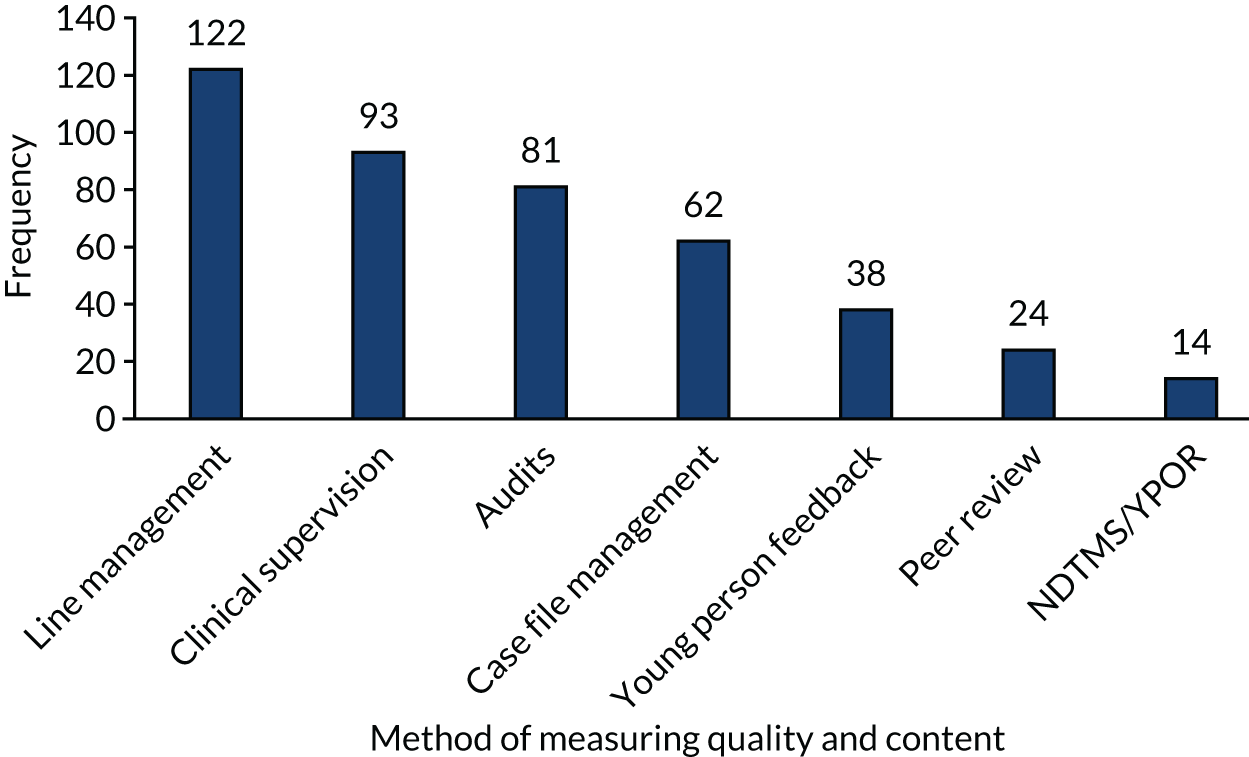
The quality of sessions was monitored using a number of different mechanisms, multiple responses were possible to these questions and multiple responses were present from the majority of the responding services. Line management was the most reported method and occurred at either monthly or 6-weekly intervals. Line management was used to incorporate both case management and professional development issues. Although 18 (15%) services reported that line management happens at ‘other’ frequencies and this spanned a range from managers having an open door policy within which practitioners accessed them as often as necessary, to formal line management only being scheduled every 8 weeks. Clinical supervision with an external supervisor or clinical psychologist was reported by 93 (76%) services, this provided an opportunity for practitioners to discuss individual ‘cases’, reflect on their practice and receive clinical guidance of how to work with children in care. Outcomes of care provision to young people were recorded within an individual’s case file.
Other mechanisms were audits completed by the local authority (n = 81, 66%); in-house case file management conducted by the service manager (n = 62, 51%); feedback received from the young people when they have completed a piece of work (n = 38, 31%); peer review, which often occurred in team meetings or within peer supervision (n = 24, 20%); and via the NDTMS or a young people’s outcome record (n = 14, 11%). Services referred to the young people’s outcome record more as a reporting process, rather than it reflecting the quality or contact of sessions.
When considering the number of methods used to measure quality and content of sessions, services reported using between one and six different mechanisms. Three services (2.5%) reported using one method, 17 (14%) reported using two methods, 32 (26%) reported using three methods, 49 (40%) reported using four methods, 20 (16%) reported using five methods and one service reported using six different methods to measure content and quality of the work delivered within their service.
Summary
The survey was designed to inform the definitive trial with regard to the specification of usual care. It was not designed to inform the pilot trial, it was conducted as a parallel activity to the formative phase of the study. The survey highlighted the high levels of variation in drug and alcohol service provision being delivered for children in care across the country. Although screening was carried out for drug and alcohol use by children in care, the tools used and the completeness in cover varied. The modalities of treatment differed across providers, the majority of services (n = 67, 55%) offered a bespoke service and 35 (29%) services reported only conducting structured work; however, even the latter could be delivered flexibly across sessions. The survey highlighted the lack of organisational readiness for protocol-driven research. None of the services reported delivering and adhering to a manualised evidence-based intervention. The survey also highlighted the range of qualifications that drug and alcohol practitioners have and a number of practitioners working within young people’s specialist agencies did not hold a formal drug and alcohol qualification. The levels of supervision and training were also variable. Owing to the high levels of variation regarding service provision, the lack of standardisation regarding screening tools used and the lack of adherence to manualised evidence-based interventions, future studies would be required to assess the organisational readiness of specific services to deliver interventions as part of a RCT or an evaluation study.
Chapter 5 Pilot randomised control trial
This chapter outlines the pilot RCT design, methods and data for screening, recruitment and follow-up. The methods of the pilot RCT are reported in the trial protocol paper. 90
Pilot trial design
The pilot feasibility RCT comprised three arms: MET, SBNT and usual care. The pilot RCT was conducted in six sites across the north-east of England (Newcastle, Gateshead, Durham, Middlesbrough, Stockton and Redcar), to assess the acceptability of the adapted interventions (SBNT and MET) and the feasibility of taking one or both of the interventions to a full-scale multicentre RCT. Details of the flow of participants through the study are presented in Figure 7.
FIGURE 7.
Randomised controlled trial flow diagram. ASAI, Adolescent Sexual Activity Index; ASSIST-Y, Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test–Youth; EQ-5D, EuroQol-5 Dimensions; EQ-5D-5L, EuroQol-5 Dimensions, five-level version; ESYT, Edinburgh study of youth transitions and crime; SDQ, Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire; TLFB, timeline follow-back; WEMWBS, Warwick–Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale.
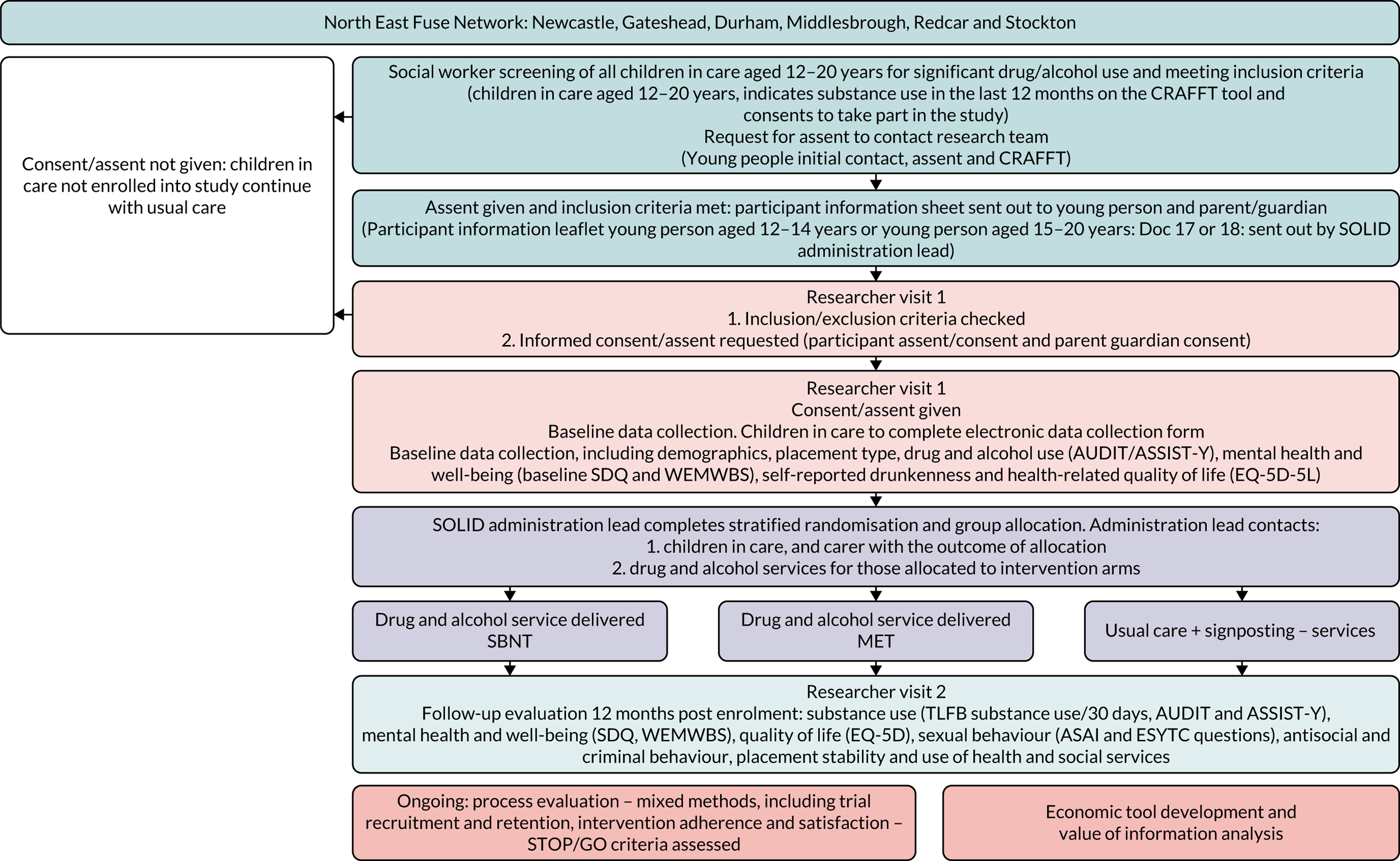
As previously highlighted in Chapter 1, Research objectives, the primary objective of the pilot RCT was to:
-
conduct a three-arm pilot RCT [comparing MET, SBNT and a control (usual care)], to determine if rates of eligibility, recruitment and retention of children in care, and acceptability of the interventions, are sufficient to recommend a definitive multicentre RCT.
The secondary research objectives were to:
-
establish response rates, variability of scores, data quality and acceptability of the proposed outcome measures for the future definitive trial (i.e. self-reported alcohol and drug use, health-related quality of life, mental health and well-being, sexual behaviour and placement stability 12 months post recruitment), to inform a sample size calculation for a definitive multicentre RCT
-
assess acceptability of, engagement with and participation in the MET- and SBNT-based interventions by children in care, their carers and front-line drug and alcohol workers
-
carry out a process evaluation to include fidelity of intervention delivery and qualitative assessment of the barriers to successful implementation, and to assess if key components from the MET and SBNT interventions can be combined to develop a new optimised intervention
-
develop cost assessment tools, assess intervention delivery costs and carry out a value of information analysis to inform a definitive study
-
apply prespecified ‘STOP/GO’ criteria and thereby determine if a definitive multicentre RCT would be feasible, and, if so, to develop a full trial protocol
-
consider findings from the study as a whole, in order to develop a core intervention delivery package, potentially of a single optimised intervention, linked to a theory of change model to use in the definitive trial.
Randomised controlled trial methods
Participant screening and identification
As part of the SOLID trial, social workers were asked to screen all young people on their caseloads aged 12–20 years, with a standardised instrument. Training sessions were conducted with social workers from each of the recruitment sites. These sessions introduced the CRAFFT screening tool, which is a nine-item tool that has been used extensively with young people and is sensitive and specific to identify problem substance use. 91 The researcher emphasised the importance of completing the CRAFFT screening tools with young people on their caseloads and explained how these data could be beneficial not only for recruitment into the study, but also for each local authority to develop a clearer understanding of the extent and nature of substance use within their local area. All young people aged 12–20 years, unless they were already in active treatment with drug and alcohol services, or were unable to access drug and alcohol services (e.g. due to currently residing out of the study area or an imminent move out of area), were eligible for screening.
Once training had been completed, each social worker carrying a caseload of children in care was provided with a screening log (see Appendix 1) and the appropriate number of CRAFFT forms, so that they could complete one form with each young person with whom they were currently working.
Prior to the social worker conducting the screening, a brief initial contact leaflet was provided to the child in care and discussed with them by their social worker, this provided details of the study. Following this discussion, the CRAFFT screening tool was completed. Page 1 of the form requested that the young person provide their contact details and asked if they consented to being contacted by a member of the research team to receive more information about the full study. Young people could elect not to provide their contact details and consent; in these cases, they could continue to complete the CRAFFT form anonymously.
Each screening tool had a pre-paid envelope attached for the completed forms to be returned to the research team. All of the screening data were entered and processed at Newcastle University, in accordance with the study ethics approval. Summary statistics on the data collected from the CRAFFT forms returned by the children in care within their locality were fed back to each local authority. These reports provided a breakdown of the number of children in care screened within that local authority area, along with the sex, age, placement type, self-reported drug and alcohol use, and self-reported risk taking behaviour of these young people.
If a child in care provided contact details, screened positive for substance use and agreed to be contacted, they were telephoned by a member of the research team, who introduced themselves, explained the purpose of the call, and checked that the young person could recall filling in the form and that they were happy to proceed. The researcher then arranged a date and time to meet the young person to take formal informed consent and complete the baseline questionnaire.
Trial inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria
-
Children in care aged ≥ 12 years and ≤ 20 years.
-
The young person must have screened positive for being at risk of substance misuse (i.e. indicate that they have used substances within the last 12 months).
-
Provided informed consent to take part in the study [for children aged < 16 years consent from parent/guardian (local authority) and assent from young person was required; for young people aged ≥ 16 years consent from the young person alone was required].
Exclusion criteria
-
Already in active treatment with drug and alcohol services.
-
Unable to access drug and alcohol services (e.g. owing to currently residing out of the study area or an imminent move out of area).
-
Unable to give informed consent (due to acute or severe mental health difficulties, mental capacity or language barriers).
The inclusion criterion regarding substance use was amended during the trial (June 2017), as outlined in Report Supplementary Material 2, after discussion with the TOC, the sponsor and ethics board. In summary, this saw the criterion change from having to score ≤ 2 on the CRAFFT to having used a substance within the last 12 months (CRAFFT = 1). This change was made because it was felt that children in care using any substance may be at risk of engaging in associated risky behaviours.
Consent to participate
Information on the study was shared with parents and carers and young people. Informed consent was taken directly from children in care aged ≥ 16 years. For participants aged < 16 years, assent was taken from the young person and consent was also obtained from an adult with PR. Those aged 12–15 years were seen by the researcher with an accompanying adult (such as a parent, carer, social worker or children’s home lead), who was asked to provide informed consent on behalf of the young person. If the accompanying adult did not have PR, the research team contacted the adult with PR (in most cases the allocated social worker) to obtain informed consent. If the parent was not contactable, or it was deemed by the designated social worker that it would pose a risk to the young person for their parent to be contacted, the social worker or local authority guardian with PR was contacted to sign the consent form. All of the RCT documents are shown in Report Supplementary Material 6.
Data collection methods
Data were collected on participants enrolled into the trial at two time points. Baseline information was collected on the first visit prior to randomisation and follow-up data collection were scheduled for 12 months post recruitment.
Baseline data collection
After informed written consent was obtained, the researcher collected baseline information from the child in care using a self-completed questionnaire, administered via a tablet computer to provide greater privacy for the respondent. The researcher was available to support young people in completing the questionnaire, if necessary, and to answer questions of clarification, if needed. The baseline questionnaire recorded demographics; placement type; drug and alcohol usage via the AUDIT92 and Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test – Youth (ASSIST-Y);92 mental health and well-being via the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ)93,94 and Warwick–Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale (WEMWBS);95 and health-related quality of life via the EuroQol-5 Dimensions, five-level version (EQ-5D-5L). 96
Alcohol use Disorders Identification Test
The AUDIT is a 10-question screening tool developed by the World Health Organization (WHO),97 used to identify signs of hazardous and harmful drinking and identify mild dependence. 98
When interpreting the AUDIT score, in adults a score of ≥ 8 is associated with harmful or hazardous drinking, and a score of ≥ 13 in women and ≥ 15 in men is likely to indicate alcohol dependency. An overall total score of ≥ 5 is deemed as AUDIT-C positive, and indicates increasing or higher-risk drinking. 97 NICE advises professionals that, given the more harmful effects of alcohol consumption for young people aged 10–16 years, the referral and intervention threshold on the AUDIT should be lower than the standard adult threshold. 99
Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test – Youth
The ASSIST-Y questionnaire is a ‘reduced’ version of the Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST) instrument. 100 The original ASSIST v3.1 questionnaire, developed by the WHO, is not validated for use by those aged < 18 years. ASSIST-Y, developed by Drug and Alcohol Services South Australia, under the guidance of the WHO, is suitable for use in this age group.
When interpreting the ASSIST-Y score, for young people aged 10–14 years, a score between 2 and 5 for tobacco, alcohol and inhalants indicates moderate risk, and a score of > 6 indicates high risk. Scores of > 2 for any other substance from the list indicate high risk.
For young people aged 15–17 years, for tobacco and cannabis, a score between 2 and 11 indicates moderate risk. For alcohol, a score between 5 and 17 indicates moderate risk. For amphetamines, inhalants and hallucinogens, a score between 2 and 8 indicates moderate risk. For cocaine, sedatives, opioids, NPSs and ‘other’ drugs, a score between 2 and 6 indicates moderate risk. Scores identifying moderate risk require brief intervention.
High-risk scores are a score of > 12 for tobacco and cannabis, a score of > 18 for alcohol, a score of > 7 for cocaine, sedatives, opioids, NPSs and ‘other’, and a score of > 9 for amphetamines, inhalants and hallucinogens. Scores identifying high risk require brief intervention and referral to specialist for assessment and treatment.
Strength and Difficulties Questionnaire
The SDQ is a standardised screening questionnaire to be used with young people aged 4–17 years. Although the SDQ is not validated for use with adults (aged ≥ 18 years), we used the same scoring systems for all participants to maintain consistency when reporting data. The SDQ comprises 25 questions that are arranged to assess four difficulty subscales (emotional, conduct, hyperactivity and peer problems) and to also measure pro-social behaviour. The four difficulty subscales are summed to give a ‘total difficulty score’ out of 40. The SDQ has been used extensively in mental health research with young people and used previously with children in care. 41
The SDQ total difficulties score is generated by summing all scales, except the pro-social scale. Scores range from 0 to 40. Once the SDQ has been completed, a set of final scores is generated, along with a categorisation for that score [close to average (score of 0–14), slightly raised (score of 15–17), high (score of 18–19) or very high (score of 20–40)]. Each 1-point increase in the total difficulties score corresponds with an increase in the risk of developing a mental health disorder.
Warwick–Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale
The WEMWBS is a 14-item scale covering subjective well-being and psychological functioning, with each item scored 1 (none of the time) to 5 (all of the time) on a Likert scale. Within the scale, all items are worded positively and address aspects of positive mental health. The tool has been used extensively with adults and has recently been validated for use in teenagers. 95
The WEMWBS produces scores of 0–70, with higher scores denoting positive mental health. When interpreting the well-being scores (using the NHS self-assessment tool), 0–32 denotes a very low score, 32–40 is below average score, 40–59 represents an average score and 59–70 is an above average score.
EuroQol-5 Dimensions, five-level version
The EQ-5D-5L is a questionnaire covering five dimensions of quality of life (mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort and anxiety/depression), each with five response options, ranging from no problem to extreme problems. Responses to the EQ-5D-5L can be used to calculate quality-adjusted life-years. 96 The EQ-5D-5L is discussed further in Data collection methods.
Full details of each screening tool and the scoring thereof are provided in Appendix 3 (see Tables 29–32).
Randomisation and group allocation methods
After consent was obtained and baseline characteristics were collected, the researcher contacted the trial administrator and provided the participant’s unique identification number, area in which the child in care resided, placement type and age. These details were entered, by the trial administrator, into Newcastle Clinical Trials Unit online randomisation service to ensure concealment of allocation. Individual randomisation to the three trial arms was stratified by placement type (residential/non-residential), site (local authority) and age band (12–14 years/> 14 years). Once randomisation was completed, five allocation letters, indicating the group to which the young person had been randomised, were generated automatically and distributed through the post by the trial administrator, one letter to the:
-
young person outlining study enrolment
-
parent outlining study enrolment (when appropriate)
-
carer (foster carer, residential key worker, etc.) outlining study enrolment
-
general practitioner (GP) outlining study enrolment (if consent for this level of contact had been provided)
-
drug and alcohol service outlining group allocation (only for those allocated to MET or SBNT) and requesting an initial appointment.
The time from baseline survey completion to letters being sent by the administrator was, on average, 2–4 days. The research team did not discuss with participants which intervention they would be allocated to; rather, they explained that the next stage of the process would be that the young person would receive a letter informing them of the intervention to which they had been allocated. The research team also clarified that, if the young person was allocated to an intervention arm, a drug and alcohol worker would give them a call to introduce themselves and to organise a convenient time and place to meet for their first appointment. The child in care was notified that letters would also be sent to their social worker and the individual with PR, to inform them of the trial arm to which the young person had been allocated. Children in care allocated to the control group were eligible to receive usual care, which involved their social worker making a referral along the usual drug and alcohol service pathway as required. 67
The allocation details were documented by the trial administrator on a password-protected drive to allow one member of the research team (HA) access so that they could liaise with drug and alcohol practitioners regarding trial participants. The trial administrator recorded the participant’s unique identification number, initials and date of birth, the arm the young person was allocated to and the date allocation took place. Blinding of group allocation was not possible for the children in care participants, or for those delivering the intervention; however, the trial statistician and health economist were blinded to group allocation until the statistical analysis plan had been agreed before the final analysis.
Delivery of interventions
Following randomisation, young people who had been allocated to an intervention arm were invited to attend face-to-face sessions of either SBNT or MET on a one-to-one basis. Six sessions of SBNT or MET were offered weekly to fortnightly over a maximum period of 12 weeks, with each session lasting approximately 50 minutes. The rationale for this number of sessions stems from learning derived from the United Kingdom Alcohol Treatment Trial (UKATT), pilot work using SBNT with young people referred to child and adolescent mental health services, and the formative research phase of this study (see Chapter 3). The treatment protocol stated that the drug and alcohol service should contact the child in care to offer treatment to the appropriate intervention group (MET or SBNT) to commence within a maximum of 6 weeks of randomisation in keeping with the service guidelines. For participants allocated to the control arm of usual care, responsibility was passed to the social worker to initiate a conversation with the young person and make a referral into drug and alcohol services, following their standard referral pathway, if the young person consented.
The drug and alcohol practitioners
In each of the participating local authority areas, the specialist young people’s drug and alcohol treatment was provided by voluntary sector organisations with charitable status. In each study area, a drug and alcohol service agreed to take part in the study by allocating a worker to deliver each of the three treatment arms. Separate experienced young people’s drug and alcohol practitioners were available to deliver the two active interventions (MET and SBNT) or usual care (control). The practitioners had varying professional backgrounds, including youth work, social work, counselling and unqualified workers; all were experienced in the delivery of drug and alcohol psychosocial interventions for young people. Drug and alcohol practitioners received training on the specific intervention they were to deliver throughout the trial as documented in Chapter 3, SBNT and MET training.
Practitioner intervention logs
When delivering sessions, each practitioner was provided with a practitioner intervention log; this provided a system of recording details for each study participant. Within each log, practitioners were requested to record their own name and the demographics of the participant, inclusive of the unique identifier for the young person, age, sex, placement type and geographic location. Details were also recorded regarding the interventions themselves, such as dates on which sessions took place; the type of casework that had been completed, inclusive of delivery of the intervention (service user contact and non-service user contact, which included any preparation work for sessions and/or completion of paperwork, such as referral to other services); the amount of time spent on each activity; the mileage and travel time attributed to each session; and the number of people present at the session. Finally, a summary of the interventions was requested, monitoring the number of sessions offered and attended, the reason for non-completion of sessions if known and any referrals into mainstream drug and alcohol services. Once a young person had completed a maximum of six sessions, depending on identified need, the practitioner returned the completed log to the research team.
The practitioner logs had two main purposes. First, they helped the research team to calculate the cost of delivering the interventions, as discussed in further detail in Chapter 7, Practitioner logs. Second, the logs contributed to the assessment of the acceptability and fidelity of delivering the interventions, in terms of the number of sessions delivered and number of people present within sessions.
The 12-month follow-up method
Participants were contacted again 12 months post recruitment to complete a follow-up questionnaire. A recruitment window of 8 weeks (i.e. 4 weeks either side of the 12-month anniversary) was put in place to maximise follow-up.
The method of follow-up contact the research team initially used was the preferred method of contact identified by the young person at baseline. However, if telephone contact numbers were no longer available, the research team contacted the child in care’s allocated social worker to request up-to-date contact details to enable a follow-up questionnaire to be completed.
Once contact had been made and the young person consented to take part in the follow-up, the research team arranged to visit the young person in their home or an alternative suitable location at a time and date convenient to them. If the researcher was not able to organise a convenient time to meet the young person for a face-to-face follow-up, a telephone follow-up was offered.
The questionnaire was administered by the researcher. At baseline, most data were self-completed on a tablet (unless completed over the telephone, in which case the researcher read out the questions and recorded the answers on the tablet on behalf of the young person); however, the researcher was also available to provide clarification on questions if necessary. The timeline follow-back (TLFB) substance use and self-reported occasions of ‘drunkenness’ in the last 30 days101 was completed at follow-up and this was researcher administered.
As at baseline data collection, children in care provided information on drug and alcohol usage via the AUDIT92 and ASSIST-Y,92 mental health and well-being via the SDQ93,94 and WEMWBS,95 and health-related quality of life via the EQ-5D-5L96 at follow-up. To minimise respondent fatigue, as recommended during peer review, questions relating to use of health and social services,96 placement stability and potentially sensitive questions on sexual behaviour [Adolescent Sexual Activity Index (ASAI)]14,102 and antisocial/criminal behaviour103 were asked only at follow-up. Details of the additional data collection tools are provided below.
Romantic and intimate behaviour/antisocial and criminal behaviour
The ASAI, as previously utilised in the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children, which was a UK longitudinal birth cohort study,102 was used in the SOLID trial to assess romantic and sexual activities. The ASAI is a standardised tool for measuring interpersonal heterosexual behaviours among youths. 104 Questions relating to enjoyment of sexual experience from the ASAI were replaced by two questions from the European School Survey Project on Alcohol and Other Drugs (ESPAD) multicountry survey of alcohol and drug use, assessing regret in engagement in sexual contacts and engagement in unprotected sexual intercourse, which are particularly relevant in relation to sexual encounters preceded by substance misuse. 14 The advantage of using the ASAI is that it is graded, with more intimate sexual contact not asked about if lesser contact, such as kissing and cuddling, has not yet been experienced. This instrument had been discussed with the study PPI group, who acknowledged the graded nature of administration and supported its use.
In addition, questions previously used in the Edinburgh Study of Youth Transitions and Crime105 were included to capture data on antisocial behaviour. This questionnaire contains 15 questions. For each of 15 questions, the tablet version used in the SOLID trial asks ‘How often in the last year have you done any of the following?’ The questionnaire seeks to evaluate co-occurrence of antisocial behaviour and alcohol use.
The romantic and intimate behaviour and antisocial and criminal behaviour questionnaires were completed only at the 12-month follow-up visit. Therefore, it is not possible to calculate and present the change from baseline for these questionnaires.
Four measures were derived from the questionnaire (see Appendix 3, Table 30, for details). Romantic and intimate behaviour was the standard questionnaire score calculated as per the skipping rules, but romantic and intimate behaviour (minor), romantic and intimate behaviour (advanced) and romantic and intimate behaviour (regret) were not standard scoring schemes from the questionnaire. The skip logic for the SOLID trial-specific outcomes derived from the questionnaire data is shown in Appendix 3 (see Table 31).
Alcohol timeline follow-back
The TLFB is a drinking assessment method that obtains estimates of daily drinking. A calendar was used to provide retrospective estimates of daily drinking over a 30-day period. The TLFB was used, as it provides a wide range of information about an individual’s drinking (e.g. pattern, variability and magnitude of drinking). The TLFB in the SOLID trial sought to identify the ‘number of occasions where five or more standard drink units are consumed on a single drinking day’.
Qualitative interview
At the point of completing the 12-month follow-up questionnaire, the young person was also asked if they would be willing to participate in a qualitative interview as part of the process evaluation (discussed in Chapter 6) for the SOLID trial. For those willing to be interviewed, the research team carried out the 12-month follow-up and process evaluation interview at the same time, to help reduce the burden placed on participants. If the young person was willing to take part in an interview, consent was obtained using the procedure outlined in Chapter 3, Consent.
Once the young person had completed the 12-month follow-up (and interview when appropriate), they were given a £10 ‘love2shop’ voucher to thank them for their time and for supporting the study. Following this, the researcher confirmed that their involvement in the study had now finished and that they would not be contacted by the research team again regarding this study.
Statistical analysis and sample size
As this study was a feasibility trial and had relatively small numbers of participants, the main outcomes are feasibility outcomes. Accordingly, we principally reported descriptive statistics in order to inform the design of a future definitive study. No formal comparisons are drawn, as the sample size was not powered to detect differences. 67 All statistical analyses were carried out on an intention-to-treat basis, retaining participants in their randomised treatment groups.
The majority of the outcome data are presented below in simple descriptive tables giving percentages, means and standard deviations (SDs), medians and interquartile ranges or a five-number summary [minimum, maximum, median and upper and lower quartiles (as appropriate)], separately for each arm of the study. This information could be used to inform the design, choice of primary outcome, necessary sample size and approach to the analysis, of the anticipated definitive trial.
The pilot feasibility trial aimed to obtain data from a minimum of 35 respondents in each trial arm at 12 months’ follow-up to estimate the critical parameters to the necessary degree of precision for a continuous primary outcome [number of occasions drinking, ≥ 5 standard drink units in a single occasion and frequency of use of the most problematic classified substance in preceding 30 days, both derived from the timeline follow-back – 30 days (TLFB-30)]. Assuming a pessimistic 30% loss to follow-up, the sample size to be recruited was inflated to 50 young people in each of the three arms. Therefore, we aimed to recruit and randomise 150 children in care.
Statistical software
Statistical analysis was carried out by the trial statistician, a member of Institute of Health and Society biostatistics team, downloading snapshots of the data from the trial database (administered by Vera Solutions, London, UK) into a comma-separated values (CSV) file. Randomisation details were exported by Newcastle Clinical Trials Unit from the Macro database into a CSV file. These two sources of data were merged and imported into the statistical software package Stata® 14 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA) for analysis.
Results
Screening data
Screening was conducted slightly differently across research sites in response to the capacity and standard procedures of each site team. The social workers across the Durham 16+ team (teams working with children in care aged ≥ 16 years and supporting young people who are transitioning out of the care system) and in the Middlesbrough sites screened children in care during their routine appointments. In Redcar, two PAs within the social work team led the screening. Across the Gateshead, Newcastle, Stockton and Durham ‘looked-after’ teams, a researcher spent time within the social work offices to support social workers in completing the screening. The research team kept in regular contact with a key point of contact within each service (in most cases this was the team leaders).
There were 1782 children in care registered with the local authorities, across the study sites, at the time of this study. A total of 332 (19%) were deemed ineligible by social work managers for the reasons shown in Table 6. Thus, the total number of children in care aged 12–20 years potentially eligible to complete the CRAFFT was 1450, 81% of all young people across the six study sites.
| Ineligibility reason | Number |
|---|---|
| No available contact details | 122 |
| Out of study area | 102 |
| YOI/prison/secure unit | 45 |
| Learning disability | 26 |
| Not engaging with social services | 10 |
| Cultural reasons | 7 |
| Mental health | 7 |
| Complex needs | 5 |
| Needs an interpreter | 5 |
| In hospital | 3 |
| Total | 332 |
Social workers were tasked by their team leads with screening as many of the 1450 children in care across the study sites as possible. The time period over which sites completed the CRAFFT was variable, ranging from 19 weeks and 1 day in Stockton to 47 weeks and 3 days in Newcastle, as shown in Table 7.
| Site | Screening duration |
|---|---|
| Newcastle | 47 weeks + 3 days |
| Durham | 32 weeks + 3 days |
| Middlesbrough | 30 weeks + 1 day |
| Redcar | 30 weeks + 1 day |
| Gateshead | 26 weeks + 1 day |
| Stockton | 19 weeks + 1 day |
| Total | 52 weeks |
The local authority sites experienced multiple competing demands while taking part in the SOLID trial, with other commitments influencing the progress made regarding screening. Two local authorities were preparing for and having an Office for Standards in Education, Children’s Services and Skills (Ofsted) inspection. Therefore, within that time frame, only essential work was completed and only a small number of participants were recruited. One site had commitments to another research project and three sites experienced significant periods of time without a senior manager in post.
Different techniques were introduced across the local authority sites in an attempt to support screening of children in care within the planned recruitment period. Bespoke support mechanisms were put in place by the research team following discussions with the TMG, social work team leaders, managers and on-the-ground social workers. Two teams introduced student social workers or PAs to support the recruitment process (Newcastle and Redcar). Members of the research team spent time embedded within four local authority sites to support the recruitment of participants (Gateshead, Newcastle, Stockton and Durham ‘looked-after’ teams). An alternative technique that proved to be efficient for one team (Durham 16+ team) was the use of ‘stop the clock’ sessions over a 3-month period (May–July 2017) for social workers to have a dedicated time allocated to contact every young person on their caseload.
Of the 1450 potentially eligible young people, 536 (37%) did not complete the screening, either due to them declining to complete the CRAFFT (n = 131, 9%), or the social workers not completing the screening tool with all the young people on their caseload (n = 405, 28%). Social workers did not consistently report the reason for non-completion, so it cannot be reported.
The flow of children from initial screening through to study completion is presented in Figure 8.
FIGURE 8.
The SOLID trial Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) flow diagram. Reproduced with permission from Alderson et al. 67 This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt and build upon this work, for commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The figure includes minor additions and formatting changes to the original figure.
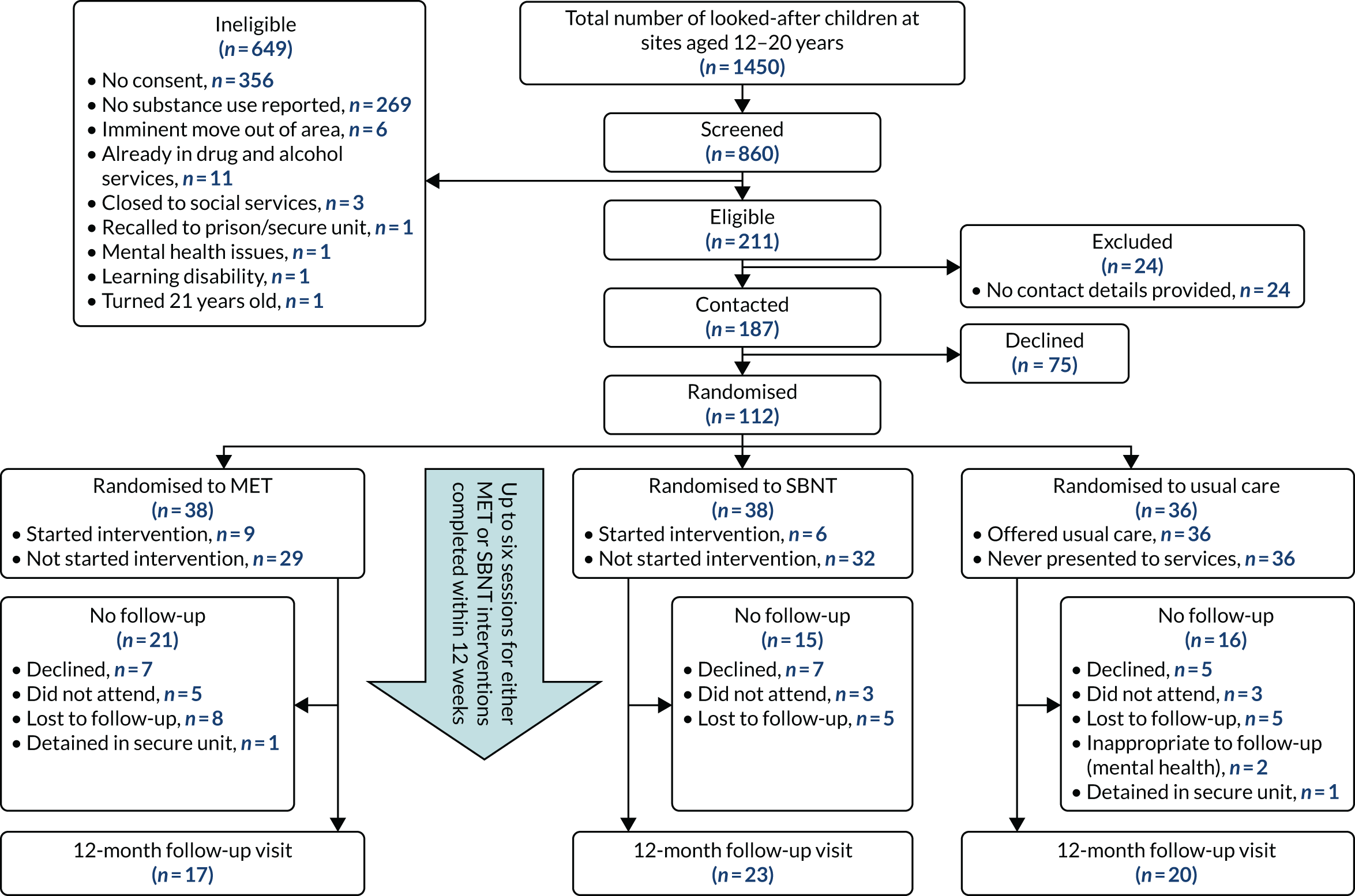
Social workers within the six study sites collectively screened 860 (59%) of children in care, aged 12–20 years, for drug and alcohol use, using the CRAFFT tool. 91,106,107 The numbers of children in care in each site, the number of potentially eligible young people (minus those identified in Table 6) and the number screened by each local authority site are shown in Table 8.
| Local authority | Number of children in care aged 12–20 years | Number of potentially eligible children in care | Number screened of potentially eligible children in care (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durham | 390 | 318 | 201 (63) |
| Gateshead | 278 | 177 | 125 (71) |
| Middlesbrough | 320 | 274 | 146 (53) |
| Newcastle | 427 | 358 | 189 (53) |
| Redcar | 170 | 145 | 95 (65) |
| Stockton | 197 | 178 | 104 (58) |
| Total | 1782 | 1450 | 860 |
Of the 860 children in care screened for drug and alcohol use, 369 reported drug and/or alcohol use in the last 12 months as shown in Figure 9.
FIGURE 9.
Self-reported drug and/or alcohol use.
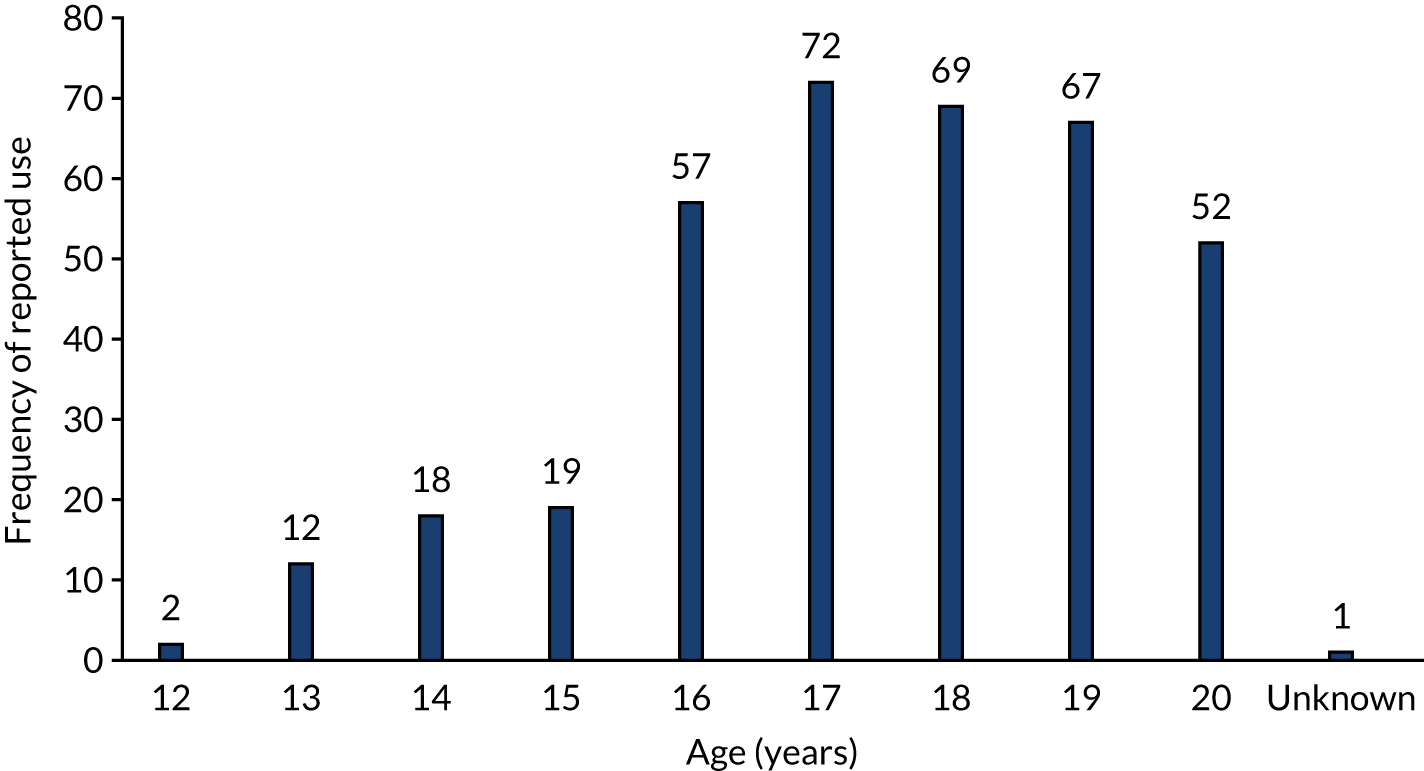
Out of the 860 young people screened, 2 (0.2%) 12-year-olds, 12 (1.4%) 13-year-olds, 18 (2.1%) 14-year-olds, 19 (2.2%) 15-year-olds, 57 (6.6%) 16-year-olds, 72 (8.4%) 17-year-olds, 69 (8.0%) 18-year-olds, 67 (7.8%) 19-year-olds and 52 (6.0%) 20-year-olds reported using one or more substances. Alongside reporting substance use, young people were asked to complete part b of the CRAFFT form to assess the number with ‘risky’ substance use. Just under one-third of young people screened (n = 278) reported one or more risk taking behaviour (Figure 10).
FIGURE 10.
Self-reported risk-taking behaviour.
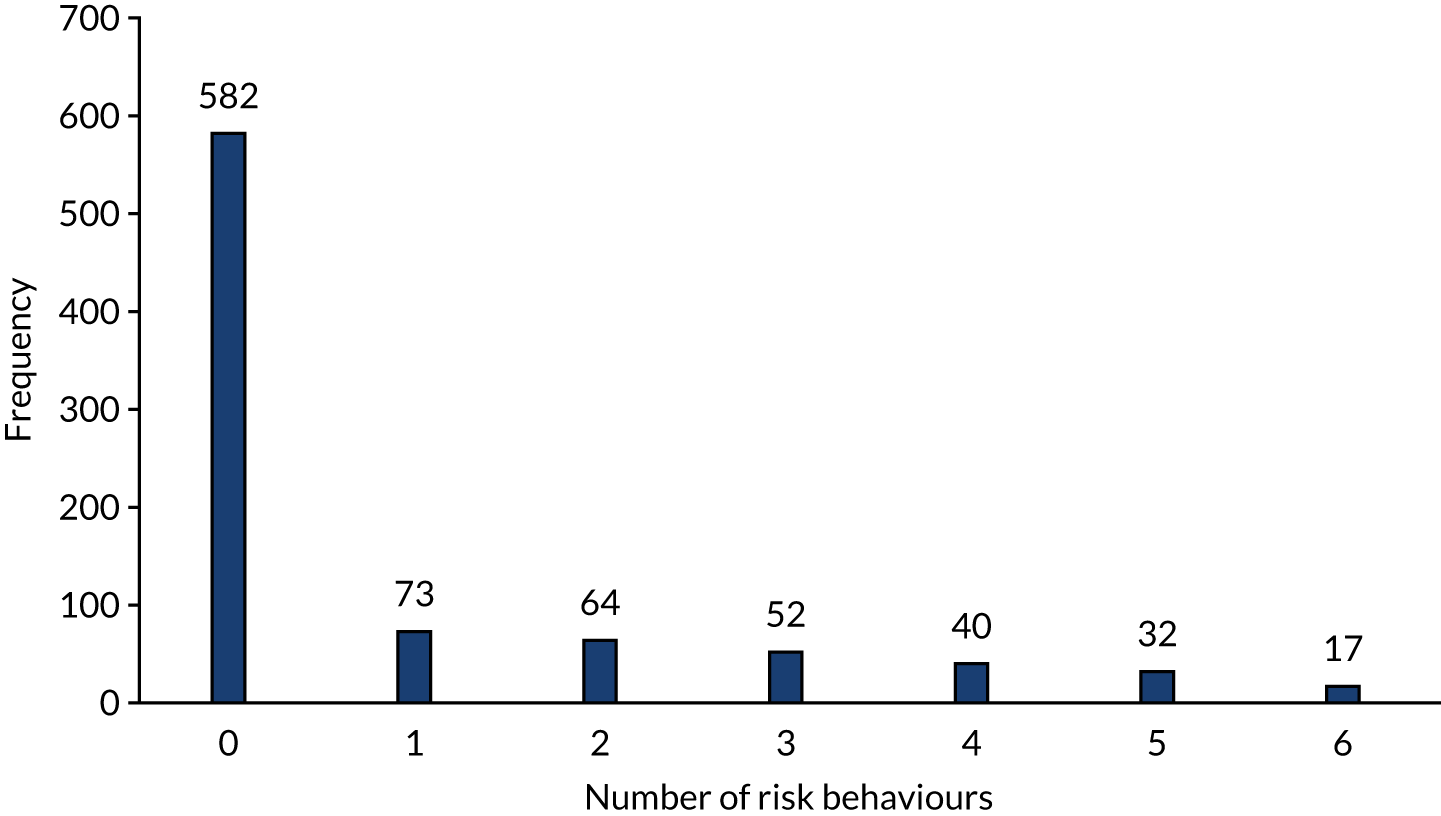
Recruitment data
A total of 860 children in care were screened. Contact attempts were not made with 356 (41%) children, as they did not provide consent to be contacted, and 269 (31%) children provided consent but reported no substance use in the last 12 months.
The research team initially used the contact details provided by the young person. Contact details included personal mobile/landline numbers (n = 185, 88%), e-mail (n = 22, 10%) and address only (n = 3, 1.5%), and one person provided a number for the supported accommodation they were in (n = 1, 0.5%).
Of the 235 children in care contacted, 24 young people (3%) were subsequently excluded; 11 were already in drug and alcohol services; six had an imminent move out of area; three had been closed to social services; and four for other reasons [recall to prison/secure unit (n = 1), mental health problems (n = 1), a learning disability (n = 1) and turning 21 years old (n = 1)]. 67
This left 211 young people who were potentially eligible to be recruited into the trial.
Once contacted, 75 (35.5%) children in care declined to take part for a number of reasons (Table 9), including not perceiving themselves to have a problem, not being interested in taking part and, for young people aged ≥ 18 years, the fact that drinking was legal.
| Reason declined | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| No reason given | 34 (45) |
| Substance use not a problem | 18 (24) |
| Not interested in the trial | 11 (15) |
| Too busy | 5 (7) |
| Drinking is legal | 3 (4) |
| Inappropriate due to criminal justice involvement/mental health issues | 3 (4) |
| Parent/guardian withdrew the young person | 1 (1) |
| Total declined | 75 (100) |
A total of 112 (7.7%) of the original 1450 children in care aged 12–20 years were recruited and randomised into the study. A minimum number of 35 children per study arm (n = 105 minimum) was required for us to proceed with the pilot RCT. Following extensive discussions with the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), the study TOC and the study management team, a decision was made to continue with the pilot RCT, despite recruiting only seven young people above our minimum target. To our knowledge, a RCT delivering drug and alcohol treatment interventions to children in care has not been conducted previously; therefore, after consultation, the pilot RCT was continued to specifically assess engagement with the adapted interventions and the retention of participants at 12 months’ follow-up.
A visual representation of the recruitment progress by site is in Table 10.
| Site | Year | Total | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | ||||||||||||||
| September | October | November | December | January | February | March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | ||
| Newcastle | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 20 | ||
| Durham | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 5 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 33 | ||
| Middlesbrough | 0 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 17 | ||
| Redcar | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 7 | ||
| Gateshead | 0 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 12 | ||||||||
| Stockton | 1 | 9 | 11 | 0 | 2 | 23 | |||||||||
| Total | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 7 | 12 | 9 | 13 | 23 | 19 | 5 | 5 | 112 |
The planned recruitment period was due to take place over a 3-month period from September to November 2016. The actual recruitment period was 1 year: 1 November 2016 to 31 October 2017.
Randomisation data
Children in care were distributed in a balanced manner across the trial arms and for each stratification variable (Table 11).
| Demographic | Randomised arm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET (N = 38) | SBNT (N = 38) | Usual care (N = 36) | Overall (N = 112) | |
| Sex, n (%) | ||||
| Male | 17 (45) | 21 (55) | 12 (33) | 50 (45) |
| Female | 21 (55) | 17 (45) | 24 (67) | 62 (55) |
| Age (years) | ||||
| Median (LQ, UQ) | 18 (16, 19) | 17 (16, 18) | 18 (16, 19) | 17 (16, 19) |
| Range (minimum, maximum) | 13–21a | 13–20 | 13–20 | 13–21a |
| Mean (SD) | 17.5 (2.1) | 17.0 (1.9) | 17.3 (2.0) | 17.3 (2.0) |
| What do you do during the day?, n (%) | ||||
| In school | 7 (18) | 10 (26) | 7 (19) | 24 (21) |
| Aged < 16 years and not in school | 2 (5) | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | 3 (3) |
| Sixth form/college/university | 8 (21) | 12 (32) | 8 (22) | 28 (25) |
| In training/apprenticeship | 4 (11) | 4 (11) | 1 (3) | 9 (8) |
| Aged ≥ 16 years not in training, employment or education | 15 (39) | 8 (21) | 17 (47) | 40 (36) |
| Aged ≥ 16 years and employed | 2 (5) | 3 (8) | 2 (6) | 7 (6) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (3) | 1 (< 1) |
| Placement type, n (%) | ||||
| Foster outside family | 7 (18) | 10 (26) | 11 (31) | 28 (25) |
| Foster within family | 2 (5) | 2 (5) | 2 (6) | 6 (5) |
| Residential home | 8 (21) | 6 (16) | 6 (17) | 20 (18) |
| Own accommodation | 21 (55) | 17 (45) | 11 (31) | 49 (44) |
| With parents | 0 (0) | 1 (3) | 5 (14) | 6 (5) |
| Other | 0 (0) | 2 (5) | 1 (3) | 3 (3) |
| Site, n (%) | ||||
| Newcastle | 6 (16) | 7 (18) | 7 (19) | 20 (18) |
| Durham | 12 (32) | 10 (26) | 11 (31) | 33 (29) |
| Gateshead | 4 (11) | 4 (11) | 4 (11) | 17 (15) |
| Middlesbrough | 6 (16) | 6 (16) | 5 (14) | 7 (6) |
| Redcar | 2 (5) | 3 (8) | 2 (6) | 12 (11) |
| Stockton | 8 (21) | 8 (21) | 7 (19) | 23 (21) |
| Ethnic group | ||||
| White British | 38 (100) | 34 (89) | 34 (94) | 106 (95) |
| Other ethnicity | 0 (0) | 4 (11) | 1 (3) | 5 (4) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (3) | 1 (< 1) |
Baseline data
Demographic characteristics
Baseline demographics, clinical characteristics and trial stratification factors are summarised across treatment groups descriptively in Table 11.
Note that participant 36 (female, aged 19 years) was randomised, but her baseline data did not transfer electronically to the trial database due to a technical fault. This participant’s data could not be included in the baseline analysis, leaving 111 participants providing baseline data. Follow-up data at 12 months post randomisation was collected for participant 36. (Some demographics for participant 36 were therefore not available, so these are coded as missing.)
Sex was fairly evenly distributed across the MET and SBNT groups, although females comprised 67% of those randomised to usual care. Ethnic group was well balanced, although there were very few non-white participants in each arm, reflecting the ethnic mix of the local authorities.
Recruitment errors
Baseline data are presented in Baseline questionnaire summaries. Further analyses looking at variables by sex, age and residential type are presented in Appendix 4 (see Tables 33–50).
Baseline questionnaire summaries
Table 12 shows the distribution of scores at baseline for the AUDIT, AUDIT-C, ASSIST-Y, SDQ and WEMWBS; the data for the EQ-5D-5L are discussed further in Chapter 6. Further analyses looking at variables by sex, age and residential type are presented in Appendix 4 (see Tables 33–50).
| Questionnaire | n a | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUDIT | ||||||
| AUDIT questionnaire score (range 0–40) | 111 | 0 | 4 | 8 | 15 | 30 |
| AUDIT-C (range 0–12) | 111 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 10 |
| ASSIST-Y | ||||||
| Tobaccob | 93 (84%) | 0 | 11 | 12 | 18 | 25 |
| Alcohol | 108 (97%) | 0 | 2.5 | 6.5 | 14.5 | 28 |
| Cannabis | 81 (73%) | 0 | 2 | 9 | 17 | 33 |
| Cocaine | 40 (36%) | 0 | 1 | 5 | 13.5 | 22 |
| Amphetamine | 27 (24%) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 21 |
| Inhalants | 9 (8%) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 9 |
| Sedative | 27 (24%) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 28 |
| Hallucinogen | 19 (17%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 21 |
| Opioid | 11 (10%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 21 |
| NPS | 19 (17%) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 14 |
| Otherc | 3 (3%) | |||||
| SDQ | ||||||
| Emotional problems (0–10) | 111 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 10 |
| Conduct problems (0–10) | 111 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 8 |
| Hyperactivity (0–10) | 111 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 10 |
| Peer problems (0–10) | 111 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 9 |
| Prosocial (0–10) | 111 | 0 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Total difficulties (0–40) | 111 | 3 | 11 | 15 | 20 | 31 |
| WEMWBS | 111 | 14 | 37 | 44 | 51 | 70 |
Owing to the questionnaires being completed on a tablet computer, there was no option to skip any questions. Participants could choose to exit the baseline data collection without completing all the questionnaires; however, this did not happen. All 112 children carefully completed the baseline data collection questionnaires; however, as discussed in Demographic characteristics, a data transfer error meant that data were missing for one child.
Intervention attendance
In total, 15 (20%) out of the 76 children in care randomised to an active intervention arm attended at least one session of the intervention across MET and SBNT arms combined. Sessions took place at their chosen location, for all participants this was at their placement address (foster placement, residential home or independent living). Closer inspection of participation data shows an impact of the change of inclusion criteria. Twelve out of the 15 (80%) young people who attended any sessions were recruited under the original threshold of reporting two or less risky behaviours, compared with only three (20%) young people recruited under the new criterion of reporting any substance use in the last 12 months and reporting more than two risky behaviours. This would suggest that individuals reporting higher levels of risky substance use behaviour are more likely to engage with interventions and that future trials should use the original criteria set for this trial. The summary statistics for time from randomisation to first intervention session are reported by way of summary statistics in Table 13.
| Intervention sessions attended by children in care | Intervention | |
|---|---|---|
| MET | SBNT | |
| Number of children in care randomised to arm | 38 | 38 |
| Number (%) of starting intervention sessions (attended at least one session) | 9 (24) | 6 (16) |
| Time from randomisation to first session (days) | 9 | 6 |
| Median (days) (LQ, UQ) | 16 (12, 28) | 24.5 (16, 53) |
| Range (days) | 3–52 | 13–78 |
| Number (%) of children in care who completed processa | 4 (11) | 2 (5) |
| Median number sessions to complete processa | 1 | 1.5 |
| Range: sessions required to complete processa | 1–6 | 1–2 |
| Time in days to complete processa (maximum 12 weeks = 84 days) | Three in 1 day; four in 35 days | One in 1 day; one in 6 days |
| Range: time taken to complete processa | 1–35 | 1–6 |
| Number (%) of children in care who did not complete processa | 34 (89) | 36 (95) |
| Median (LQ, UQ): sessions attended | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) |
| Range: sessions attended | 0–2 | 0–3 |
| Time in days attending sessions for non-completers, n (%) | 34 (89) | 36 (95) |
| Median (LQ, UQ): time attending sessions (incomplete processa) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) |
| Range: time attending sessions (incomplete process) | 0–35 | 0–53 |
| Discontinuation early (fewer than six sessions) for the 15 who started, n (%) | 8/9 (89) | 6/6 (100) |
| AE | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Young person’s choice (did not think they needed specialist support) | 6 (67) | 1 (17) |
| Other | 2 (22) | 5 (83) |
Of the 38 participants in the MET arm, five took up at least one session, three young people attended two sessions and one young person attended all six sessions. Similarly, of the 38 participants in the SBNT arm, four attended at least one session, one young person attended two sessions and one attended three sessions (Figure 11). 67 Regarding the SBNT sessions and the principle of young people recognising support available to them, all six young people who attended sessions could identify at least one person who could provide them support and the two participants whom attended more than one session could identify how their network could support them. However, due to them discontinuing sessions, we are unable to report how their support networks performed in practice.
FIGURE 11.
Attendance at MET and SBNT sessions.
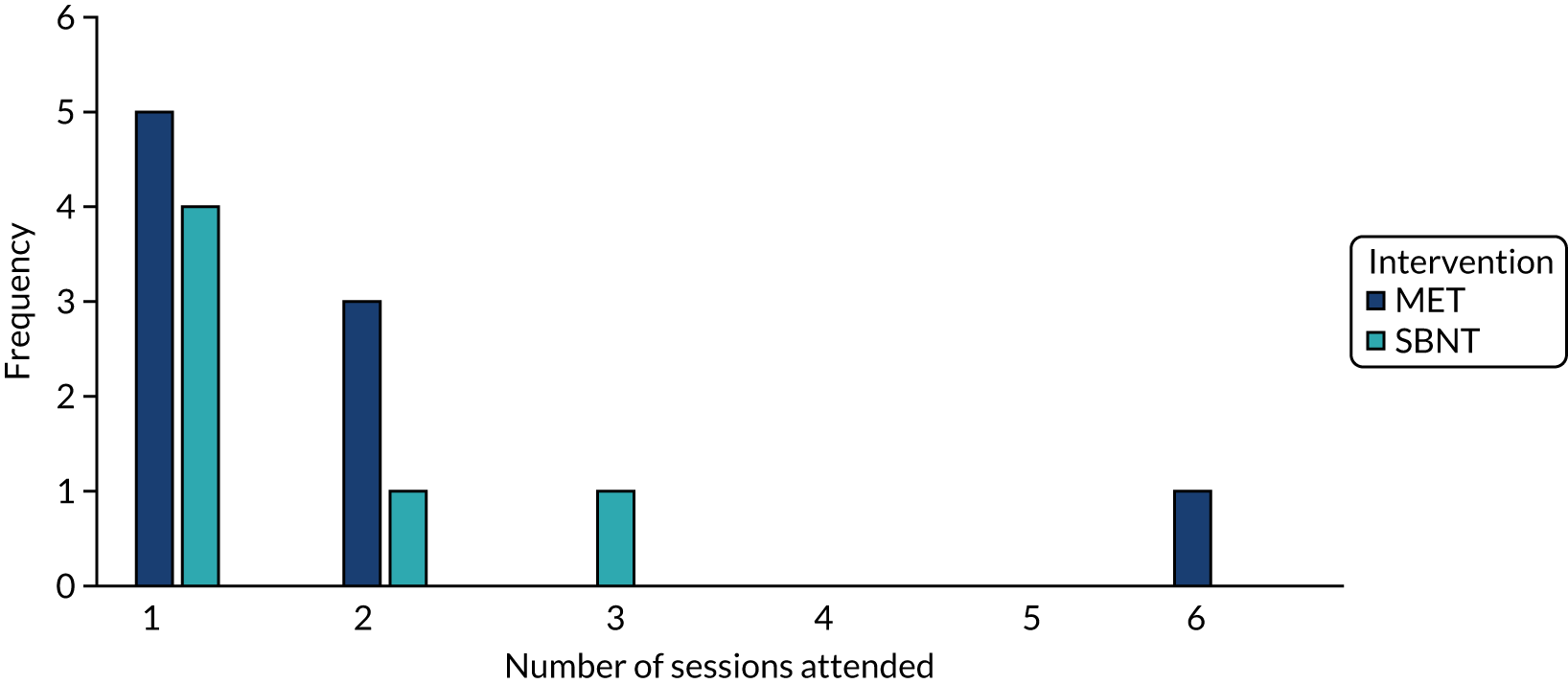
Seven young people provided reasons for early discontinuation of the intervention, as listed in Table 14 (note, pseudonyms are used within the descriptive analysis).
| ID | Reason not completed intervention session process | Intervention |
|---|---|---|
| Joanne, YP, 17 years | Too busy due to starting work | SBNT |
| Ellie, YP, 16 years | Too busy due to starting work | SBNT |
| Callum, YP, 17 years | Started sessions then contact was lost | SBNT |
| Gavin, YP, 20 years | Started sessions then contact was lost | SBNT |
| Claire, YP, 18 years | Referred to tier 3 | SBNT |
| Max, YP, 19 years | Started sessions then contact was lost | MET |
| Pippa, YP, 15 years | Moved out of area | MET |
The 12-month follow-up data
In total, 60 children in care out of a potential 112 (54%) attended the 12-month follow-up visit, 19 (17%) declined follow-up, 11 (10%) did not attend follow-up meetings that were arranged, 18 (16%) were lost to follow-up due to the research team being unable to contact them and four (4%) could not be followed up for other specific reasons (follow-up deemed to be inappropriate by the allocated social worker for two and two could not be contacted as they were detained in a secure unit). When attempting to contact young people at follow-up, for 58 (52%) young people, their contact number had changed and for 54 (48%) young people their address had changed. Details of follow-up status are given in Table 15.
| Follow-up status | Randomised arm, n | Combined arms, n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET | SBNT | Control | ||
| Follow-up completed | 17 | 23 | 20 | 60 (54) |
| Declined follow-up | 7 | 7 | 5 | 19 (17) |
| Appointment date set but did not attend | 5 | 3 | 3 | 11 (10) |
| Could not contact: lost to follow-up | 4 | 3 | 4 | 11 (10) |
| Closed to social services: lost to follow-up | 4 | 2 | 1 | 7 (6) |
| Follow-up inappropriate (mental health) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 (< 2) |
| Unable to contact due to circumstances (secure unit) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 (< 2) |
| Total | 38 | 38 | 36 | 112 |
Of the 60 children in care followed up, 5 out of the 15 young people who participated in the intervention completed the questionnaire, the other 10 were lost to follow-up for a range of reasons [declined (n = 2), an appointment was made but the young person did not attend (n = 4), unable to contact them (n = 1), inappropriate circumstance (n = 1) and closed to social services (n = 2)].
In many instances, young people were lost to follow-up due to the multiple competing demands that they had going on in their lives, the frequent changing of mobile numbers and the placement instability, which meant that the contact details originally given were no longer current. Forty-two children in care (38%) were followed up within an 8-week window of 12 months, as indicated in Table 16.
| Follow-up visit | Randomised arm, n (%) | Overall (N = 112), n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET (N = 38) | SBNT (N = 38) | Usual care (N = 36) | ||
| Completed | 13 (34) | 16 (42) | 13 (36) | 42 (38) |
| Early | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (< 1) |
| Late | 3 (8) | 7 (18) | 6 (17) | 16 (14) |
| Unknowna | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1a (3) | 1 (< 1) |
| No follow-up completed | 21 (55) | 15 (39) | 16 (44) | 52 (47) |
The distribution of data for the proposed primary outcomes – episodes of heavy episodic drinking (≥ 5 units in 1 day) in the preceding 30- and 7-day periods as shown in Tables 17 and 18 – outcomes for a definitive trial were obtained from the TLFB-30 administered during the 12-month follow-up interview.
| Episodes of heavy drinking (≥ 5 units in 1 day) in the preceding 30-day period | Randomised arm | Overall (n = 112) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET (n = 38) | SBNT (n = 38) | Usual care (n = 36) | ||
| Number at follow-up (% of randomised) | 17 (45) | 22a (58) | 20 (56) | 59 (53) |
| Median (LQ, UQ) | 1 (0, 4) | 0 (0, 2) | 1.5 (0, 5.5) | 1 (0, 4) |
| Range | 0–10 | 0–7 | 0–9 | 0–10 |
| Episodes of heavy drinking (≥ 5 units in 1 day) in the preceding 7 day period | Randomised arm | Overall (n = 112) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET (n = 38) | SBNT (n = 38) | Usual care (n = 36) | ||
| Number at follow up (% of randomised) | 17 (45) | 22a (58) | 20 (56) | 59 (53) |
| Median (LQ, UQ) | 0 (0, 1) | 0 (0, 1) | 0.5 (0, 1) | 0 (0, 1) |
| Range | 0–2 | 0–2 | 0–3 | 0–3 |
These questionnaires were assessed for completeness. For the questionnaire summaries, 60 young people had follow-up data, as shown in Table 19.
| Questionnaire | n a | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUDIT | ||||||
| AUDIT questionnaire score (range 0–40) | 60 | 0 | 4.5 | 7 | 11 | 26 |
| AUDIT-C (range 0–12) | 60 | 0 | 3 | 4.5 | 7 | 10 |
| ASSIST-Y | ||||||
| Tobaccob | 50 (83%) | 0 | 4 | 12 | 18 | 25 |
| Alcohol | 60 (100%) | 0 | 2 | 4 | 8.5 | 28 |
| Cannabis | 40 (67%) | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | 5.5 | 20 |
| Cocaine | 20 (33%) | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | 7.5 | 21 |
| Amphetamine | 17 (28%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 32 |
| Inhalants | 5 (8%) | |||||
| Sedative | 15 (25%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 17 |
| Hallucinogen | 11 (18%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 21 |
| Opioid | 4 (7%) | |||||
| NPS | 8 (13%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| Otherc | 0 (0%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SDQ | ||||||
| Emotional problems (0–10) | 60 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 10 |
| Conduct problems (0–10) | 60 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 7 |
| Hyperactivity (0–10) | 60 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 10 |
| Peer problems (0–10) | 60 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 8 |
| Prosocial (0–10) | 60 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Total difficulties (0–40) | 60 | 2 | 11 | 14.5 | 20 | 28 |
| WEMWBS | 60 | 23 | 38 | 46.5 | 53 | 65 |
An (adult) AUDIT score of ≥ 8 indicates hazardous alcohol consumption and a score of ≥ 13 for females and ≥ 15 for males indicates alcohol dependency. An AUDIT-C score of ≥ 4 in males and ≥ 3 in females indicates hazardous alcohol consumption.
Data on romantic relationships and antisocial behaviour are presented in Tables 20 and 21, respectively.
| Data | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Romantic and intimate behaviour | 60 | 0 | 15 | 36 | 52 | 70 |
| Romantic and intimate behaviour (minor) | 60 | 0 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Romantic and intimate behaviour (advanced) | 60 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 7 |
| Romantic and intimate behaviour (regret)a | 60 | 0 | 0 | 6.5 | 7 | 28 |
| Antisocial or criminal behaviour | Overall (N = 60), n (%) |
|---|---|
| Skipped or skived off school | |
| Yes | 28 (47) |
| Once | 3 (5) |
| Two to five times | 9 (15) |
| Six or more times | 16 (27) |
| Broken into a car or van with the intention of stealing something out of it | |
| Yes | 4 (7) |
| Once | 2 (3) |
| Two to five times | 0 (0) |
| Six or more times | 2 (3) |
| Hit, kicked or punched someone on purpose | |
| Yes | 21 (35) |
| Once | 10 (17) |
| Two to five times | 4 (7) |
| Six or more times | 7 (12) |
| Deliberately set fire or tried to set fire to somebody’s property or a building | |
| Yes | 4 (7) |
| Once | 1 (2) |
| Two to five times | 2 (3) |
| Six or more times | 1 (2) |
| Taken money or something else that did not belong to you from home without permission | |
| Yes | 6 (10) |
| Once | 3 (5) |
| Two to five times | 1 (2) |
| Six or more times | 2 (3) |
| Used force, threats or a weapon to get money or something else from somebody | |
| Yes | 1 (2) |
| Once | 0 (0) |
| Two to five times | 1 (2) |
| Six or more times | 0 (0) |
| Written things or sprayed paint on property that did not belong to you | |
| Yes | 5 (8) |
| Once | 2 (3) |
| Two to five times | 3 (5) |
| Six or more times | 0 (0) |
| Gone into or broken into a house or building with the intention of stealing something | |
| Yes | 4 (7) |
| Once | 3 (5) |
| Two to five times | 1 (2) |
| Six or more times | 0 (0) |
| Deliberately damaged or destroyed property that did not belong to you | |
| Yes | 8 (13) |
| Once | 3 (5) |
| Two to five times | 4 (7) |
| Six or more times | 1 (2) |
| Carried a knife or weapon with you for protection or in case it was needed in a fight | |
| Yes | 5 (8) |
| Once | 2 (3) |
| Two to five times | 0 (0) |
| Six or more times | 3 (5) |
| Taken money or something else that did not belong to you from school | |
| Yes | 2 (3) |
| Once | 1 (2) |
| Two to five times | 0 (0) |
| Six or more times | 1 (2) |
| Stolen or ridden in a stolen car or van or on a stolen motorbike | |
| Yes | 2 (3) |
| Once | 1 (2) |
| Two to five times | 0 (0) |
| Six or more times | 1 (2) |
| Been rowdy or rude in a public place so that people complained or you got into trouble | |
| Yes | 8 (13) |
| Once | 3 (5) |
| Two to five times | 4 (7) |
| Six or more times | 1 (2) |
| Taken something from a shop or a store without paying for it | |
| Yes | 8 (13) |
| Once | 3 (5) |
| Two to five times | 1 (2) |
| Six or more times | 4 (7) |
| Not paid the correct fare or not paid at all on a bus or train | |
| Yes | 11 (18) |
| Once | 3 (5) |
| Two to five times | 6 (10) |
| Six or more times | 2 (3) |
Missing data
As the RCT demographic and questionnaire data were collected using electronic tablet devices during baseline and follow-up visits, the only missing data are baseline data for one participant whose data were collected but not transferred owing to a technical fault and 12 months’ follow-up data for the 52 participants who did not attend.
There were no partially completed questionnaires because the electronic tablets necessitated that all questions be answered before moving on. Only one participant did not complete the TLFB at the 12-month follow-up visit, but did complete all other questionnaires at that visit. As there were so few missing data when they were collected using electronic tablet devices, there was no gain in using shorter tools, such as AUDIT, ASSIST-Y, TLFB – 7 days and CRAFFT.
Non-completion of 12 months’ follow-up
Participants had the right to withdraw from the trial at any time without having to give a reason. No children in care formally or explicitly withdrew from the trial, but 52 did not attend the 12-month follow-up.
End of trial
The end of the trial was defined as the 31 October 2018, which was the last date a participant could be contacted to complete the 12-month follow-up questionnaire.
Safety data
There were no reported adverse events or serious adverse events occurring from the time of randomisation in the pilot RCT until follow-up was completed (12 months post enrolment).
Conclusions
The pilot trial identified that a definitive trial using the same design as in this pilot is not feasible. We aimed to recruit 150 participants into the trial which allowed for 30% loss (45 participants) at follow-up, so aimed to retain 105 participants 12 months post recruitment. One hundred and twelve participants were recruited (75% of the target) and data were collected from 60 participants (53.5% of those recruited into the study) at 12 months post recruitment, which was a 46.5% loss at follow-up.
Seventy-six participants were randomised into the SBNT and MET arms. Delivery of the SBNT and MET intervention sessions was very low, with only 15 out of 76 participants (20%) allocated to the interventions receiving any session. With such low rates of delivery, it is not considered feasible to deliver the interventions using routine care pathways.
The inclusion criteria were amended during recruitment into the study, from children in care scoring more than two risky behaviours, which identified 74 participants, to reporting any substance use within the preceding 12 months, which led to the identification of a further 38 participants.
There were very few problems identified with the proposed data collection measures. The use of tablet computers was acceptable to young people and the programming to force a response meant that rates of completion of the baseline and follow-up questionnaires were consistently high once the young people had consented to take part. There were no missing data at baseline data and only one TLFB was missing at 12 months post recruitment.
Chapter 6 Process evaluation
Introduction
In keeping with the MRC guidelines,108 we used quantitative and qualitative methods to address the aims of the process evaluation. The qualitative work included semistructured interviews and focus groups conducted with five key groups of participants: (1) members of the local authority social work teams (social workers, PAs, social work team managers), (2) drug and alcohol practitioners, (3) children in care, (4) carers (foster and residential) and (5) the researchers conducting the study. The quantitative methods included collating data from drug and alcohol practitioner intervention logs and fidelity rating of audio-recordings of treatment sessions. This chapter provides a description of the methods used in the conduct and analysis of the interviews, followed by a discussion of the key findings and themes, and concludes with a critical discussion of the strengths and limitations of the work.
Aim
We aimed to understand and document the key lessons learned from implementing the SOLID trial in relation to the delivery of the adapted interventions the trial processes and to evaluate factors that would impact on delivering the intervention at scale. The process evaluation had three specific aims: (1) to examine the feasibility and acceptability of the interventions and the trial process; (2) to explore and aim to understand the mechanisms through which change occurred; and (3) to consider the role of context in shaping this change. 109
The components of the process evaluation are shown in Table 22.
| Process evaluation component | Key research question | Additional information | Data source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recruitment and reach | Were we able to recruit children in care (numbers screened, numbers screened positive, number consenting to participate in the study) as part of the SOLID trial? | Equity in terms of age, placement type and geography | Practitioner intervention logs, consent forms, records of who was retained at the 12-month follow-up, and records of when and if possible why participants dropped out of the study. Reported in Chapter 4 |
| Was recruitment equitable across demographic groups? | |||
| Dose delivered |
Were intervention sessions offered to children in care? What proportion of these sessions were completed? |
||
| Fidelity | Were the interventions delivered as planned? | Fidelity defined by Carroll et al.110 (i.e. content, frequency, duration and coverage) | Content: qualitative interview data from children in care, plus interview and focus group data from drug and alcohol practitioners |
| Frequency and duration: practitioner intervention logs | |||
| Coverage: practitioner intervention logs recorded number of sessions offered and received | |||
| Were the interventions delivered with sufficient quality? | UKATT PRS: seven items for MET and eight items for SBNT to measure quality (treatment fidelity) | Researcher analysis of audio-recordings available for the first session of each intervention using UKATT PRS for MET and SBNT | |
| To what extent have the new interventions been integrated into routine practices? | Interview topic guides developed based on NPT to probe: coherence, cognitive participation, collective action and reflexive monitoring (May and Finch111) | Qualitative focus group discussions, plus interviews with drug and alcohol practitioners | |
| Acceptability of intervention | Was the intervention acceptable to children in care? If not, why not? | Qualitative interviews with children in care | |
| Retention in the trial | What was the proportion of young people recruited into the trial who were retained for 12 months’ follow-up? | Trial records of recruitment and retention. Reported in Chapter 4 | |
| Contamination | To what extent was drug and alcohol practitioners’ trial delivery influenced by SBNT/MET being undertaken by colleagues in their services? | Qualitative interviews and focus group discussions with drug and alcohol practitioners and managers | |
| To what extent did children in care know about, and were influenced by, SBNT/MET interventions being offered to other children in care that they knew? | Qualitative interviews and focus group discussions with drug and alcohol practitioners and children in care | ||
| Mechanism of change (treatment system) | What were the facilitators of and barriers to integration of the interventions into the drug and alcohol service? | NPT components coherence, cognitive participation, collective action and reflexive monitoring (May and Finch111) | Qualitative interviews and focus group discussions with drug and alcohol practitioners and managers |
| Mechanism of change (children in care) | Did the interventions make a difference to the lives of children in care and did they alter their behaviour? Are the BDI models appropriate for the mechanism of change? | Qualitative interviews children in care and their carers |
Method
Qualitative interviews
In-depth one-to-one interviews and focus groups were selected as the primary method of qualitative data collection. The aim of all sets of interview was to explore the acceptability of using the adapted MET and SBNT interventions and to elicit participants’ views on the study processes employed throughout the delivery of the project.
Drug and alcohol practitioners
The interviews and focus groups with drug and alcohol practitioners allowed us to explore the extent to which staff understood the principles and core components of the adapted SBNT and MET interventions, whether or not they valued and believed in them, if modification to their usual work plan had to be made to enable integration of the interventions, and to capture reflections on ways which the study process could be modified in future trials. Interviews with drug and alcohol service managers allowed us to explore how they perceived practitioners had engaged with the delivery of the interventions and the potential barriers they felt would have to be considered if thinking of a future definitive trial.
Social workers
Interviews with members of the social work team explored the social workers’ understanding of the purpose of screening all children in care, their opinions of the CRAFFT form as a screening tool and how it could be improved for future trials, alongside perceived barriers to and facilitators of completing the CRAFFT form with children in care.
In addition, three focus groups were carried out in November 2018, to further explore some of the main themes that had arisen within the process evaluation interviews with children in care. The interviews with social workers covered the same topic areas as the carer interviews and discussed whether or not social workers felt that they would be able to deliver the interventions, the potential facilitators of and barriers to them delivering the interventions and the learning for future trials to increase the number of young people participating in the interventions.
Interviews with all practitioners (social workers and drug and alcohol practitioners) took place at a time, date and location convenient to them. Informed consent was obtained, as previously outlined in Chapter 3, Consent, and interviews were audio-recorded.
The topic guide can be seen in the Report Supplementary Material 7.
Children in care
Interviews with children in care aimed to understand if participants had found the process of involvement in the study acceptable, including being contacted by the research team and completing the baseline and follow-up data collection questionnaires, as well as receipt of their allocated interventions. Interviews also explored how the research process and the interventions may be improved to make them more user-friendly and acceptable.
Carers (foster carers and residential workers)
The original focus of interviews and focus groups with carers aimed to explore their understanding of the study process and whether or not they perceived an intervention effect on the drug and alcohol use of young people in their care. However, placement instability was common in the participating children in care. As a result, many participants were not in the same placements as they had been when baseline data were collected. Others were living independently or were in residential placements. When a placement had sustained, some foster carers were not available for interview. The topic guide was therefore altered to explore what skills foster carers thought were necessary to engage and care for children with care experiences, the role they perceived social workers played in children in care’s support package and who they thought was best placed to provide support to children in care.
Interview topic guides were developed iteratively throughout the research process. Within the focus groups conducted at the final stage of the study, researchers discussed emergent findings from the interviews and explored whether or not carers felt that they would be an appropriate group to deliver the interventions, and any potential facilitators of and barriers to them delivering the interventions were discussed.
Researchers
Interviews were conducted with research associates who had conducted the study. Interviews explored the researcher role within the study, the barriers to and facilitators of working with each participant group (social workers, drug and alcohol practitioners, foster and residential carers and children in care) at both an individual level and an organisational level. Interviews also considered how research involving the different participant groups could be improved in future trials and the overall lessons learnt.
Sample strategy
One hundred and sixteen sets of data were collected from across five participant groups, including children in care (n = 37), carers (foster and residential) (n = 30), social workers (n = 27), drug and alcohol practitioners (n = 19) and researchers working on the project (n = 3). Social worker participants were sampled purposively to ensure maximum variation in terms of participants recruited from each local authority site, sex and level of experience. A snowball sampling method was used with foster carers and residential workers. Carers were recruited at the same time as children in care or through carers identifying further participants who could take part. All of the drug and alcohol practitioners involved with the study were approached to take part in an interview and all children in care approached to complete the 12-month follow-up were provided with an opportunity to take part in an interview. In addition, all the researchers working on the study took part in an interview. All participants were approached directly by the researchers. At each stage it was stressed that participation was entirely voluntary. Informed consent was taken at the beginning of every interview, ensuring that the participants had read and understood the participant information sheets and had been given an opportunity to ask any questions or raise concerns with the interviewer. Interviews lasted between 20 and 40 minutes and focus groups lasted between 60 and 90 minutes. They were all digitally audio-recorded and transcribed verbatim by professional transcribers.
Drug and alcohol practitioners
Each drug and alcohol practitioner who had been involved in the study (n = 14) was asked to participate in an interview for the process evaluation. Only one practitioner declined, citing previous involvement in a focus group in the development phase as the reason (see Chapter 2). Service managers were also approached to undertake an interview and interviews were completed with three out of six service managers. One service had recently been retendered and the manager felt unable to comment on the study. In a second study area, the practitioner who had been delivering the MET intervention was ‘acting up’ into the manager’s role. Last, in the third service, interviews were scheduled to take place on two occasions, but unfortunately were later cancelled owing to unforeseen circumstances.
Children in care
The interviews with children in care (n = 37) were completed at the same time as the 12-month follow-up data collection (as described above in Chapter 5, The 12-month follow-up data).
Carers
Interviews and focus groups with carers (n = 30) included a mixture of residential workers (n = 23) and foster carers (n = 7). To reach our target audience, the research team organised interviews and focus groups with workers employed within residential homes in three local authority sites where the participating children in care resided at, as well as with foster carers who had experience of caring for children in care within the 12–20 years age range of the study and experience of managing substance misuse issues.
Social workers
Interviews with members of the social work teams (n = 27) took place at two separate time points. In both instances, participants within the study sites who had been involved with the initial CRAFFT screening were approached by a member of the research team and asked to take part in an interview. Interviews took place at the social worker’s place of work at a time and date convenient to them.
The first interviews and focus groups took place from July to October 2017, with 14 participants of varied experience and knowledge. Participants included front-line social workers, senior social workers and team leaders, a strategic manager, a social work student and PAs. PAs work closely with social workers to advise, assist and support young people in local authority care.
Researchers
Research associates (n = 3) carrying out the day-to-day work of the project were also interviewed by a researcher who had no prior involvement in this study.
Table 23 shows the qualitative methods that participants engaged in and the sex of participants recruited into the process evaluation.
| Qualitative method | Date | Participant group | Number of participants | Sex |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 : 1 interviews | During the 12-month follow-up appointment | Children in care | 37 | Female, n = 23; male, n = 14 |
| 1 : 1 interviews | August–October 2018 | Thirteen drug and alcohol practitioners | 16 | Female, n = 10; male, n = 3 |
| Three drug and alcohol service managers | Female, n = 2; male, n = 1 | |||
| 1 : 1 interviews | July–August 2018 | Six residential carers | 7 | Female, n = 6 |
| One foster carer | Male, n = 1 | |||
| 1 : 1 interviews | August–October 2017 | One social worker strategic manager | 11 | Female, n = 6;male, n = 5 |
| Six senior social workers/team leaders | ||||
| Three PAs within the social work teams | ||||
| One social work student | ||||
| 1 : 1 interviews | November 2018 | Three researchers | 3 | Female, n = 3 |
| Focus group (n = 1) | July 2017 (practitioners were still delivering interventions at this time) | Three drug and alcohol practitioners (two interviewed again from 1 : 1 PE interview) | 3 | Female, n = 2; male, n = 1 |
| Focus groups (n = 4) | November 2018 | Seventeen residential workers | 23 | Female, n = 11; male, n = 12 |
| Six foster carers | ||||
| Focus group (n = 1) | July 2017 | One social worker | 3 | Female, n = 2; male, n = 1 |
| Two senior social workers/team leaders | ||||
| Focus group (n = 3) | November 2018 |
Two team leaders (one interviewed again from PE FG in 2017) Eight social workers (one interviewed again from 1 : 1 PE interviews in 2017) Three PAs within the social work teams (all three interviewed again from 1 : 1 PE interviews in 2017) |
13 | Female, n = 11; male, n = 2 |
| Total | 116 sets of data from 109 participants |
Qualitative analysis
Interview schedules for the drug and alcohol practitioners delivering the interventions were designed to highlight the four core concepts of normalisation process theory:112
-
coherence – a shared understanding of the work (do the workers understand the aims and the logic behind the intervention?)
-
cognitive participation – a shared agreement and engagement with the techniques of the work (do the workers ‘buy into’ and ‘own’ the aims and logic behind the intervention and the ways in which it is being implemented?)
-
collective action – agreement with the organisation of the work (what do the workers and managers do in practice to make the intervention work in their setting for themselves and the client group?)
-
reflexive monitoring – assessment and monitoring of the work (are the workers engaged enough to be able to suggest improvements to the logic or practice of the intervention?).
Normalisation process theory was chosen as it provided an evidence-based framework to consider factors that either promoted or inhibited the successful implementation of the adapted MET and SBNT interventions into routine practice. 113 We analysed the data using the core constructs to examine the key barriers to successful delivery and integration of the interventions at the level of the system. Possible residual contamination of co-workers residing in the same premises but delivering different interventions was also explored within the process evaluation. The thematic analysis80 of all other data sources within the process evaluation was conducted as described in Chapter 3 of the report.
Qualitative findings
The qualitative findings from the thematic analysis are broadly categorised under four headings, namely exploring the acceptability of the screening tool, feasibility of the recruitment process, acceptability of the interventions and feasibility of retaining young people in the trial.
Was the screening process acceptable?
The CRAFFT screening tool was not wholly appropriate in its current format, areas of discussion arose regarding concerns about the screening tool. The CRAFFT form asked young people to identify their substance use within the last 12 months. Professionals, both social workers and drug and alcohol practitioners, thought that this time frame was too long and that a shorter time frame would produce more accurate results, and suggested modifying the CRAFFT form to capture data within a shorter time frame. Suggestions varied between the 28-day time frame used for the NDTMS up to a maximum of 3 months:
I would say 28 days because that way staff members can actually quantify it alongside the work that they’re doing anyway because that’s what we deal with on a day to day basis, that’s what we use as a guide . . . So I think the drug use needs to be more prevalent and more relevant within a shorter time frame upon referral.
Christopher, drug and alcohol practitioner
In addition, the current method of scoring was not felt to be appropriate for distinguishing between use of a substance on a single occasion and problematic use:
The scoring of it, it fails to recognise when someone, by just saying, ‘Do you drink? Have you had a drink?’ It doesn’t distinguish different and potential levels of potential problems. So, it basically pulls in everybody so it produces a lot of negatives or potentially ends up producing a lot of work for no result. Many people then don’t need further information.
Sam, drug and alcohol manager
Lessons learnt regarding the screening process
The logistics of the screening process were also explored. A number of practical measures that could be taken to make the process more acceptable were discussed, such as having an embedded researcher. Areas for consideration in a future trial included who should screen and the age of participants to include in the study.
Methods of completing the screening tool
There was full agreement that screening should not be completed by posting CRAFFT forms out to children in care. None of the sites reported any forms being returned if they had been sent out for young people to complete independently:
I think we had a couple where we posted them out, and they didn’t do them. Whenever we send a letter out to a young person – I know this sounds really stupid, whenever we send the letter out to a young person, we put it in a white envelope. Whenever they see a brown envelope they think it’s a bill. It just adds to the pile.
Tony, local authority administrative worker
Completing the CRAFFT forms face to face was the preferred method. In this study screening took place using paper forms, and it was suggested by social workers and children in care that completing the forms electronically would be preferable:
I mean there’s something you could send them by link to fill in, or as an app [application] or a link they could do. Sometimes they’ve got access to online. Then yes, I think they’d probably get more engaged if they’re being able to sit down without somebody asking them the direct questions, you fill in this link.
Carol, social work manager
Electronically completing the form would allow the completed data to be uploaded/transferred to the research team immediately and would minimise risk of data being lost.
Reconsider the inclusion age range
Based on discussion with the children in care PPI group at the time of study design, the study aimed to screen and recruit young people between the ages of 12 and 20 years. Social workers raised concerns that 12 years was ‘too young’ to screen for drug use:
I thought 12 was a little bit young. I think from the responses that I got in terms of talking to workers, they were a little bit edgy around the 12 remit.
Carol, social work manager
This was also voiced by one of the PAs, who felt that screening younger children in care may have caused participants to ‘panic’:
I think, personally, the age limit was a little bit low, just because some of the younger ones were like, ‘I’ve never done drugs, I’ve never done drugs, so what are you asking me this for?’ They were panicking, . . .
Kat, PA
It was also much harder to follow up children in care within the 18–20 years age range, as in a number of cases they had transitioned to independent living and had elected to end contact with children’s services. Once an individual was closed to social service input, research staff could not obtain up-to-date contact details:
Eighteen for me would have been a time where, you know, young people are leaving care effectively, the care orders are lapsing and that might have been a natural point to have actually have ended.
Alfie, social work manager
Social workers could be a barrier to screening
It was also questioned whether or not children in care would be honest with their social worker when completing the CRAFFT form. Social workers had concerns that children in care may not be truthful:
There was a potential for some of the children to not want to share that information with the social worker. The social worker’s going out to complete a document or to ask those questions. I don’t know, in some cases, it’s not going to have a significant impact on the responses but there would be some children who may not feel that they can be entirely honest with the social worker.
Alfie, social work manager
This concern appeared to be unfounded. Although a small number of children in care reported that they would usually not choose to speak to their social worker about their drug and alcohol use, the majority stated that they did not have any concerns regarding completing the CRAFFT form in the presence of their social worker. The relationship that the a child in care had with their social worker was highlighted to be an important factor:
So, because I had a relationship with her, I was like, ‘Yes, that’s fine.’ There have been a few social workers in the past, where they have recommended things and because I haven’t got on with them, I’m like, ‘No, don’t worry. I don’t want anything off you’, sort of thing. Again, it just depends if you’ve got a relationship with that professional, in order for you wanting to do something.
Mia, young person, 17 years
Participants questioned whether social workers were the correct person to screen, due to other elements of their work taking priority over screening:
I mean I think the problem is, whenever we’ve got something extra to do on top of our day-to-day work, it adds an extra stress, which I think people find difficult and I think the problem is, like when you’ve got a kid whose running away or there’s something around child protection, filling in a questionnaire, isn’t top of your priority.
Hazel, social worker
When social workers attempted to screen children in care as part of their standard visits, it was largely unsuccessful. It often took a single named point of contact (social work students, PAs, a visible researcher within the local authority site) to co-ordinate the site for screening to be successful.
All of the social work managers agreed that, in retrospect, having a researcher embedded in the local authority site would facilitate CRAFFT screening completion:
At least they’d have somebody who they can have that conversation with if they weren’t quite sure or if there was somebody on the phone that wanted a bit more information that maybe they didn’t have, you’ve obviously got a direct link.
Carol, social work manager
Realistic time frames need to be agreed with study sites
A number of barriers were discussed within the process evaluation interviews regarding the study process. One of the main areas of concern was having a realistic time frame to complete the screening. The first issue raised was regarding the social workers’ ability to physically see the young people on their caseload and complete any necessary screening forms for the research study:
The visiting frequency has now changed for some young people. It was always a minimum of 4-weekly for children in care. That’s now been changed to 6-weekly. We, in this team, have young people, we’ve now got one young person who is only visited twice a year.
Tina, social work manager
Despite the research team extending time frames due to poor response rates, and the extended time frames ultimately resulting in more forms being completed and returned, the social work managers deemed the ‘moving goalposts’ as ineffectual:
Initially we were going for one set time frame and it was all right then. I think we got an extra 28 days or something initially. Everyone was all right about that but then when you extended it again, I think the staff lost a bit of interest.
Jonathan, social work manager
The local authority teams reported becoming apathetic to completing the screening:
There was lots of momentum. I remember feeling under loads of pressure. I’ve got to get this done. It should have started already. It hasn’t started. Then we moved, and we needed it done by the New Year . . . As soon as that message come through, certainly in my mind – probably to anyone else who heard it – it felt there wasn’t the urgency that we thought there was initially.
Alfie, social work manager
The complexities of conducting research in the real world need to be factored in to study design
The process evaluation interviews identified the real-world organisational barriers that created challenges when trying to conduct the SOLID trial. In many cases, this was the only research study being carried out in the social work departments and therefore there was a limited research culture. The following quote makes reference to the fact that in this study, social workers were expected to recruit children in care into the trial:
They are very important learning points about your study group, about the difficulties of multicentre trials and recruiting people from different occupations, recruiting people into research studies who have no research orientation, no research knowledge and no research motivation, quite frankly.
Paula, clinical trainer/supervisor
From the perspective of one local authority, significant transformation took place regarding the structure and physical location of the social work teams, with negative impact on engagement with the SOLID trial:
Transformation took place, the social workers came together from across the city and there were a broad range of priorities and cases moving across different teams, complicated matters. So, the timing of that certainly had an impact.
Alfie, social work manager
Teams were functioning, with strategic manager ‘off sick’ or open vacancies, this was reported in three out of the six local authority sites within the lifetime of the study:
I’m not making excuses for the service, but we have had different managers off sick. So, somebody who would have been key and pivotal to doing that, wasn’t here for a number of months, there’s another assistant manager been off, nearly 6 months would have carried that vacancy. So, for them, this has just been, I guess not as high priority as it should have been.
Pat, social work manager
The pressure of preparing for, and enduring, Ofsted inspections was also experienced within two of the sites, this resulted in ‘core business’ being prioritised and all other commitments being suspended. There was an acknowledgement that the research is just another task to be undertaken ‘on top’ of and alongside the other commitments that teams have:
It was another ask on top of all the other asks . . . we will do our best to comply with it and as I said, it did come in at a difficult time for the service, both in terms of Ofsted and numbers of staff we have in post.
Ken, social work manager
The pressures were also present for staff within the drug and alcohol services who experienced their services going through the retendering process. Four out of the six services were retendered or were preparing for the retendering process within the lifetime of this study. The potential disruption of these service tendering processes to the conduct and completion of research is an important consideration. Retendering brought additional pressures to realign with the expectations of a new service:
I came back to the workplace and, specifically for me, with the change of two buildings, that’s come in due to being TUPED [Transfer of Undertakings (Protection of Employment) Regulations] over to a new service, it was kind of just forgotten about, if I’m completely honest.
Georgia, drug and alcohol practitioner
The pressure to complete all of their core business while being understaffed (two services had staff vacancies while taking part in this study) made it harder for practitioners to fully buy into and support the SOLID trial than they had first envisaged:
As I said before, time constraints, travel issues and our standard case load was impacting upon all of this so to us from a practitioner’s point of view, it became more of an onerous task.
Christopher, drug and alcohol practitioner
In addition to the professional social workers’ and drug and alcohol workers’ views reported above, the two clinical trainers/supervisors acknowledged the pressures that had an impact on the study:
Services being changed dramatically and then being on a trial and people’s workloads being changed . . . the whole thing is just a bit precarious, I suppose, and you’re trying to get something going and doing everything you can. But there’s a fragility in the system . . .
Dale, clinical trainer/supervisor
Young people will over- and under-report their substance use
Respondents reported the potential for young people to either under- or over-report their substance use:
We know we’ve got some young people that will embellish potential use. We’ve got others that will under report.
Tina, social work manager
I think what we tend to find with a lot of our young people . . . sometimes they overexaggerate, and I think where adults will reduce the amount that they’re taking and try and make it look a bit better. I think some of the young people might say that they’re using more than what they actually have been.
Pat, social work manager
In reality, the question of whether a young person over- or under-reports within the initial screening is in many cases unimportant. What is important is whether or not the young people identify themselves as a ‘substance user’ at any level. The screening data still provide an opportunity to start a conversation with the young person, which could potentially lead on to the provision of further advice, information or therapeutic support.
Was it feasible to retain children in care within the intervention?
Children in care require a faster response time
Professional participants (drug and alcohol practitioners and residential workers) clearly articulated that they felt a barrier to retaining children in care within the interventions was the number of steps in the study process and the potential for a time lapse to occur between the social worker completing the screening with a young person to the researcher visiting to complete baseline, and the eventual step of a referral onto an external drug and alcohol service:
Particularly with young people and again the looked-after children that momentum has to be jumped on quite quickly. I think there has been a bit of a time lapse from where the referral has been completed and the researchers have been able to visit the young person to when it comes to us. Sometimes that has been 3 or 4 weeks. I know that has improved slightly but you have to be shit hot with any young person because a day can be a lifetime. Four weeks could be like a previous life.
Olivia, drug and alcohol worker
There was consensus between the professionals that the whole process of screening, recruitment into the trial and first session of an intervention needs to happen within a week if it is to be successful:
I think it would have to be really trying to at least be within that same week, if at all possible. I know that is quite a high and very quick turnover but I do think it is important to get in there very quick.
Laura, residential carer
A multitude of factors influenced how quickly a young person transitioned from completing the CRAFFT screening form to completing the baseline data collection with a researcher. The completed CRAFFT form had to be returned to the research office and then the researcher had to successfully establish contact with the young person. Following this, the randomisation process had to be undertaken, and the letters had to be generated and sent to the drug and alcohol service before the drug and alcohol practitioner could contact the young person to offer them an initial appointment.
The young person’s perception of need and readiness to change
The participants’ perception of need and their readiness to change were highlighted as significant factors affecting retention in the interventions offered. From the child in care’s perspective, despite consenting to involvement in the trial and agreeing to attend sessions with a drug and alcohol worker in discussions about the research at two separate time points with researchers, when the young people were actually contacted by the drug and alcohol worker they declined appointments. When discussing this with the research team within the process evaluation interviews, young people stated:
. . . there was a lady who called, but I didn’t take her up on it. Just wasn’t necessary.
Lisa, young person, 17 years
I didn’t feel as though there was anything wrong with me drinking or anything, because I only had a couple if I was with friends or something.
Martha, young person, 16 years
Many children in care did not identify themselves as requiring any support, feeling that their substance use was not problematic and, therefore, they did not feel they wanted to attend intervention appointments:
I got offered [sessions], if I wanted the drug support or anything. I don’t need any support because I don’t have a problem. I smoke marijuana [cannabis] for pain, I don’t really see how people get addicted to it, to be honest. Maybe I have it, like, just when the pain’s unbearable I have a joint or something like that, but ye’.
Tom, young person, 16 years
Alongside young people reporting that they thought that interventions were not ‘necessary’, a multitude of other factors played a part in young people not attending sessions. Poor mental health was cited as a reason for failing to attend:
Well, as it happened I think I had went into hospital. I went into a mental health hospital just after you had thingy’d because I went a bit **** up. So, I couldn’t go.
Angelina, young person, 20 years
Individuals remembered being offered sessions but did not manage to attend:
When you got that phone call, did you actually then take them up on any sessions?
Researcher
I did, but then I had a bad period of my mental health, and I didn’t end up turning up.
Dylan, young person, 19 years
Both drug and alcohol practitioners and children in care highlighted the importance of the individual identifying a need to change prior to attending interventions sessions:
We as a service require consent on the referral, for our generic referrals. That means the young person is consenting to want to have some kind of drug and alcohol intervention. That’s the top and bottom of it. They must identify themselves that there is a problem. What we were getting the [SOLID] referrals is that they didn’t identify that there was a problem. So, that was why the engagement wasn’t very good.
Diane, drug and alcohol worker
Young people had a good insight into the fact that they had to have a desire to engage with support, rather than attending due to feeling pressurised by someone else:
I know me especially and I know through my friends and that, if people make you do something that you don’t want to do, it’s not going to help.
Angelina, young person, 20 years
Tom (young person, 16 years) articulated his thoughts about choice and control regarding decisions being made:
My social worker kept saying, ‘Do you want to be recommended for this service’ and I said, ‘No, I need to start living my life and the only way I’m going to do that is if you leave me alone’.
A number of young people acknowledge that making changes is hard and individuals need to be motivated. One individual captures this succinctly:
I think anyone who goes to therapy is quite a strong person. Just for the simple fact that’s what I’m going through now. It’s quite difficult. It’s a difficult thing to do. So, if you’re willing to go through therapy then you’re willing to change yourself.
Emily, young person, 19 years
From the research team perspective, this created an anomaly, as in reality young people had consented twice to attend intervention sessions prior to a referral being made to drug and alcohol services.
The process evaluation interviews explored whether or not opportunistic interventions would have been more effective. This may have helped to be more responsive to the young person’s needs.
The importance of contextual information: why children in care use substances
The majority of professionals displayed a pragmatic rationale as to why young people used substances:
They use them [substances], for lots of different reasons. It could be to block out what’s happened to them so actually they don’t really want to stop it, thank you very much, because it’s the only thing that they can manage with right now. To them it isn’t a problem. It is a strategy I guess to manage their day. Yes, there might be all those risky behaviours, all that stuff going on but it’s the only crutch they’ve got right now. You take that away, they’ve got nothing.
Laura, residential carer
It was identified that if the young person had been exposed to substance use and it is recognised as ‘normalised’ behaviour, then they do not identify that their own use is problematic:
If they’ve certainly come from families where using substances isn’t necessarily an automatic negative. It’s part of their self-identity and that’s what they do with their friends. That’s how they enjoy their free time. It’s not always something that they consider anything that needs to be worked on.
Cassie, residential carer
Up until now, they don’t see alcohol and drugs problematic. They think it’s a part of life. They’ve seen it with their own families, and that’s part of their living.
Sophie, foster carer
There was the recognition from the professionals working in supported accommodation that until young people perceived their substance use as problematic, then it was unlikely they would do anything to change their behaviour:
At work you see a lot of people that, they think they don’t have a problem, and until they admit that they have there’s not really any helping them is there? You can’t do a lot until they admit it, in my eyes, my opinion.
Gill, supported accommodation worker
Are the interventions acceptable to drug and alcohol practitioners?
One of the main aims of the process evaluation was to assess whether or not the principles and concepts of the interventions were acceptable to practitioners. The feasibility of intervention delivery also took into consideration the responses to the MET and SBNT training and supervision of the practitioners. One of the trainers stated:
By and large, these people came along with positive attitudes to training . . . as a trainer I want to motivate these people to practice in a particular way, because it’s good for them. It’s good for their practice and it’s good for their CVs [curricula vitae], and it’s good professional experience for them. I think, in the main, they were very open to it.
Paula, clinical trainer/supervisor
However, the consistency with which practitioners engaged with the clinical supervision was variable:
It was very mixed. There were a few highlights of people really doing hands-on work, and that was good. Then that went to another level where people aren’t doing it. But there were a handful of therapists that really ran with the idea and did really decent work.
Dale, clinical trainer/supervisor
Commitment to clinical supervision was difficult to gauge, as some drug and alcohol practitioners elected not to attend due to not delivering interventions to children in care as part of the study trial. They therefore deemed the clinical supervision sessions to be unnecessary.
How could future interventions be delivered differently?
Children in care emphasised the importance of flexibility when providing interventions, with traditional ‘talking therapy’ considered overly rigid and therefore hard to engage with. Multiple young people reinforced this belief:
I don’t like talking, it’s very easy to write it down on a piece of paper, than it is to say it, do you know what I mean?
Annabelle, young person, 15 years
I don’t know, it’s just hard to talk to people about saying, ‘Look, this is the problem now’, it’s hard to say isn’t it?
Angelina, young person, 20 years
Instead, children in care and practitioners reported that methods which sought to engage participants in creative methods of working may be useful. It was equally acknowledged that writing and other creative methods of engagement might not suit everyone:
I think it’s each to their own, isn’t it? Some people would rather just sit down, talk one-to-one, get it done and that, and some people would rather show themselves in a different way.
Dylan, young person, 19 years
In addition, alongside considering the content of the sessions, professionals thought that the low uptake of young people attending interventions could be attributed to the fact that it meant ‘another’ professional being involved in the care package for children in care. Discussion took place regarding amendments to the intervention delivery if the study was replicated. The main suggestion was that interventions should be delivered by a professional already involved in the young person’s care. However, the implication for this is that social workers, foster carers or residential care home workers may be expected to be involved in the delivery of interventions as key professionals involved in supporting children in care:
These children who have been taken into care have seen so many different people. They’ve had social workers and they’ve had foster carers, so they’ve been in court and they’ve been in trouble and all those kinds of things. You’re adding another person into the mix. What you probably want to think about is, ‘Who are all the people who are already in the mix by virtue of the legal requirements, which of those can we train to do this work?’
Paula, clinical trainer/supervisor
This prompted the research team to speak to professionals involved in children’s care and to explore whether or not they felt that delivering MET and SBNT sessions with a drug and alcohol focus was part of their remit, and whether or not they felt in a position to deliver the interventions.
Who is the most appropriate person to deliver the interventions?
None of the residential children’s home staff involved in the focus groups (n = 17) felt that the intervention delivery should become part of their role. They perceived that doing so could damage the relationships they had with children in care:
I think it would be more damaging for the young people, yes, definitely.
Kathryn, residential carer
. . . because, ‘Oh God, they’re going to put a block on his finances. His risk assessment is going to go up dead high. They’re not going to let him stay at his friend’s house’.
Jane, residential carer
Workers, within and across the focus groups with residential workers, identified that there is an inherent care–control dichotomy within their role with children in care. This creates a conflict wherein knowledge of the child in care’s substance use might mean that they would have to implement sanctions and this could, in turn, result in previous supportive relationships being dissolved:
I think you could alienate and might potentially damage our relationships if we went at it in the wrong way. It’s got to be an offer, not a requirement. It can’t be sanction-able.
Jane, residential carer
It’s opt in rather than opt out.
Kathryn, residential carer
They’re not going to be in any trouble. As a carer, I think if we could do that because otherwise it’s going to damage your relationship.
Jane, residential carer
The desire to uphold supportive relationships meant that residential workers did not feel that they should be the professional to deliver specialist drug and alcohol sessions:
You’re also risking jeopardising your relationship if you’re coming in at a naggy level. They might pull away from you and then you’ve lost that link.
Sue, residential carer
Furthermore, from the residential workers’ perspective, social workers did not have capacity to deliver specialist interventions, making it unrealistic to incorporate them into their current workload:
We get a statutory visit once a month and it’s about making that as much quality time as they can. They’ve got a number of placement issues to talk about and family issues. I think, actually, the expectation that they would be able to do that bit of work is, firstly, unrealistic and slightly unhelpful, if we’re talking about the need, the quality time, because their caseloads are ridiculous. They’re too diluted.
Cassie, residential carer
Social workers themselves agreed that they did not have the time, capacity or specialist knowledge to deliver the interventions. Rather, they believed that intervention delivery should be by a specialist drug and alcohol worker (as it was in this study) to give the work the credibility it deserved:
You need to be more specialised.
Chloe, social worker
I think there’s that much more on the street now, and it’s changing.
Donna, social worker
You’d have to do training all the time . . . would you ask your social workers to do the mental health input? Not in a million years.
Chloe, social worker
Exactly, its very specialist, isn’t it?
Simon, social worker
It’s very specialist.
Chloe, social worker
It’s more intense than what we can do.
Simon, social worker
You’re not giving it the importance it has if you just make it up.
Chloe, social worker
Carers (residential and foster) and social workers unanimously agreed that they lacked the level of specialist knowledge required to deliver an intervention regarding substance use. There was consensus within and across the focus groups conducted with social workers, foster carers and residential children’s home staff that it was not within their remit to deliver interventions regarding alcohol and drug use. A potential solution that was suggested by carers was for drug and alcohol practitioners to have regular sessions within care homes and/or within the social work teams, so that they become familiar to the young people. This, it was felt, would then enable the drug and alcohol worker to screen children in care and deliver interventions when necessary. One local authority area stated that this had happened previously and had been successful:
There have been services in the past which came here. They didn’t come here because any young person had a particular issue, they came here to be another friendly face, someone that isn’t on the staff team, so isn’t sanctioning. They’re not taking part of your money off you, they’re not challenging your behaviours. They’re just someone that comes from outside once a week, has tea, has a laugh, and then gradually gets into the C-Card, the sexual health, the drug and alcohol. Obviously that service isn’t available now, but when it was available we found it absolutely brilliant because the kids could go off one-to-one and they could open up about why they’re doing what they do.
Robert, residential carer
It was believed that the current system was not as effective as it should be. The benefit of having specialist drug and alcohol workers was acknowledged; however, it was felt that the worker needed to be more of a familiar face to children in care:
Personally, I think it should be a more familiar, I even think as far as a specific person within the home setting more trained up. Or, for example, we’ve got three homes, even that one person between the three maybe. I mean, I don’t know what the answers are, but I do think that it definitely doesn’t work as it is now, as it proved.
Linda, residential carer
Normalisation process theory analysis
Alongside the thematic analysis undertaken to identify the overarching themes (identified above) within the data across all participant groups, we applied normalisation process theory113 analysis to the data collected from drug and alcohol practitioners regarding the interventions. The findings identify how practitioners responded to the four core components of coherence, cognitive participation, collective action and reflexive monitoring.
Coherence
The drug and alcohol practitioners displayed coherence regarding the main aims and logic behind the interventions. Practitioners could clearly articulate the approaches that they were using when referring to SBNT. Examples practitioners provided were as follows:
The SBNT approach is about that young person finding a wider network of support for them. So, it doesn’t necessarily need to be one person, it could be various different people but it’s about using them to their advantage, to support their recovery.
Heather, drug and alcohol worker
My understanding was that it was getting the young person to identify a network of support that they could draw upon when they were feeling times of temptation or when they were feeling pressured into potentially making decisions and to hopefully get positive feedback and allowing them to make a rational decision based on the information that they were getting off that person or that group of people to change what they were potentially going to get drawn into.
Christopher, drug and alcohol worker
Similarly, for MET, practitioners could identify the aim of the intervention:
In a nutshell, you are, obviously, trying to motivate the young people to change, but you are trying to bring out what they already want to change. So, it is about them . . . you know, they want the best for themselves, and it’s about bringing that out, I suppose, through motivational interviewing.
Frank, drug and alcohol worker
Cognitive participation
The practitioners expressed a shared agreement of what the interventions were trying to achieve and ‘bought into’ the aims. Drug and alcohol practitioners reported using the interventions with other young people already on their caseloads who were not participating in the study. The SBNT approach especially created positive feedback:
The concept of it all, again, is really good. You can’t deny, on paper, it’s good, it really is . . . Because everything’s in place for it to be really good, a successful thing.
Karl, drug and alcohol worker
The element of using the SBNT approach to help to explore support networks was welcomed. The approach provided a tool to instigate discussions about other people surrounding young people who could provide support when attempting behaviour changes:
I think it’s so important and I still use it now but I think that it’s so important that it is very time-limited, the capacity that professionals are able to work with somebody for and especially those within the ‘looked-after’ remit is that sometimes they aren’t able to identify anybody really, that they’re able to go towards. So, I think that by going in the early days and getting them to start thinking about who else they’ve got around them, who’s a positive influence, who they’re able to really communicate and talk to, more than anything really, is such a powerful and positive factor for someone.
Heather, drug and alcohol practitioner
In addition, creating the support network map prompted practitioners to have conversations regarding support networks and to explore the rationale for young people identifying sources of support, including those, who, on the face of it, would not be perceived as ‘positive’:
It’s a useful tool to be able to open up that dialogue and exploration.
Olivia, drug and alcohol practitioner
Finally, the network map provided an opportunity for practitioners to challenge young people regarding their sources of support and to try to determine whether or not identified support networks could indeed help them to reach the end goals:
I thought there was some really good parts of it, in terms of picking out that supportive person. That is, as part of my assessment, I would ask the person to map out who was a good in their live. Bad influences, good influences, things like that. That part was really good. The practicalities, I think, of doing it on the ground, I didn’t think were going to be good. I didn’t think it was going to be practical, basically. Getting the supportive person in. I think we had discussions around the start, that supportive person could well be the dealer. It could well be the . . . they could identify anyway, that could be their dealer, or friends that they use with. That could be their only support network that they can identify. That was my first concerns around it. That, kind of went on, and in the end, I did think, actually, what’s good about this is, we can draw upon, what they are saying about their supportive person. Challenge that as well. Are they supportive, in what your goals are and where you are wanting to be?
Dianne, drug and alcohol practitioner
Alongside the above positive views and experiences of SBNT, practitioners did also raise concerns regarding using the approach with children in care, who may struggle to identify sources of support:
I mean looking at SBNT with young people in care, personally, I don’t think it’s particularly effective in so far as those young people who are in care, in my experience and looking at the ones who we’ve got through, didn’t necessarily have that network to be able to draw upon. So that network of support was very, very minimal. One of the girls, she used to speak a lot to her 8-year-old nephew and it was 8-year-old nephew or mum, that was literally it. Others, it was key worker in the home. So from my point of view, we had our basic premise of what the programme should look like and the amount of sessions and stuff like that and really, you wouldn’t need all of those sessions for them to establish a network because their network didn’t necessarily exist, other than within that unit.
Christopher, drug and alcohol practitioner
In addition, concerns were raised regarding the longevity of any support networks that were identified:
How do you identify the most positive support network? Original SBNT is very clearly about equality of relationships. When you’re with young people and then they start saying, ‘Oh, my school teacher, my YOT [youth offending team] worker’. You’re talking about . . . relationships of lasting length because your school teacher is your school teacher for this year.
Sam, drug and alcohol, service manager
Collective action
Practitioners reported feeling supported by their managers when trying to integrate the interventions into standard practice, they could access supervision regarding young people referred in through the study:
He [drug and alcohol manager] was really supportive and sometimes when I came back and I’d say, oh I’ve got a referral here I’m going to go to see this young person and when I came back I could discuss it with him definitely and he was very supportive of it.
Emma, drug and alcohol worker
Equally, practitioners felt that managers supported them to use the interventions with young people accessing the services outside of the SOLID trial, due to the intervention’s perceived effectiveness:
I mean now when I’m using it now, my manager is very, very supportive of it and is very interested in it as well and so we discussed that and she says to continue using it because it is very, very effective.
Heather, drug and alcohol worker
Managers also expressed being supportive of their staff and encouraging them to use the interventions within their standard work to benefit the young people accessing specialist services:
As a group, I suppose Adam [drug and alcohol worker] has experience of SBNT so I don’t think that there is any argument from us that, actually, as an approach, it’s really, really helpful.
Sam, drug and alcohol manager
Reflexive monitoring
The majority of the drug and alcohol practitioners who delivered the intervention to young people outside the study, reported that they did not think that six sessions of MET or SBNT would be enough to meet the needs of children in care, if a young person actually chose to engage with the intervention. The main belief behind this was the experience that practitioners had of initially engaging a young person in treatment services:
I know, myself, that I’ve sometimes had two or three sessions, before I’ve even been able to do an assessment. Because of that fire fighting, because of that building the relationship with kids who are just not interested. Trying to motivate them to get involved. By that point with SBNT, you’d have done half your intervention.
Dianne, drug and alcohol practitioner
This was confirmed by another practitioner, who stated that the principles of the intervention and the resources available were helpful to motivate a young person, but that they did not think six sessions of MET as a standalone treatment option were sufficient:
All the techniques and the workbook, the worksheets . . . it could help move people on towards their treatment goals. I just think in all the children’s and young people’s services, to just do this or to have a certain client group that only receive this, it’s too restrictive for what young people need. Because a lot of them could end up coming out of it and going into more of the usual care. The techniques and the aim of it and the feel of it, is really positive. It is a good refresher. But it couldn’t be just exclusively MET.
Amy, drug and alcohol practitioner
The qualitative data identified that a number of elements in the study process were not deemed acceptable; however, potential solutions were also offered to make the work possible in a future study.
Quantitative data collection
Audio-recording methods
The drug and alcohol practitioners delivering the SBNT and MET intervention were requested to audio-record every session that they delivered, with consent from the participant. Following each audio-recorded session, the practitioners were requested to clearly label the session as outlined in the treatment protocol (session X, date 01.01.2019, young person’s initials) and upload it on to a secure server so that it was accessible to the research team and the clinical supervisors. The purpose of the audio-recordings was to assess the quality of the intervention delivery (treatment fidelity).
The research team (HA and RB) applied the validated UKATT Process Rating Scale (PRS), which was developed in the UKATT. 114 The UKATT PRS is applicable to MET and SBNT and consists of 26 items, rated as follows:
-
maintaining structure
-
agenda setting
-
explanation of philosophy of treatment/treatment session
-
review intersession change
-
consistency of problem focus
-
end of session summary
-
homework
-
drinking feedback/negative consequences
-
alternative activities to drinking
-
eliciting client concern about drinking
-
social support for change
-
eliciting self-efficacy for change
-
involvement of others in behaviour change
-
commitment to drinking goal
-
identifying sources of support for change
-
ambivalence
-
creating conflict
-
eliciting commitment to change drinking
-
eliciting optimism for change
-
therapist as task orientated
-
therapist as active agent for change
-
reflective listening
-
collaboration
-
interpersonal focus
-
exploration of feeling
-
empathy.
Each item was rated on the extent to which the practitioners carried out each specific item and the quality of the therapist’s behaviour, using the following scales:
To what extent did the therapist perform the behaviour within each item?
| Not at all | A little | Somewhat | Considerably | Extensively |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
How well did the therapist perform the behaviour within each item?
| Not at all well | A little | Somewhat | Considerably | Very well |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
The research team assessed the extent to which the intervention delivery was true to the therapeutic principles on which it was based.
Audio-recording findings
In total, 26 sessions were delivered (MET n = 17, SBNT n = 9) and of these, practitioners only completed nine recordings in total (MET n = 3, SBNT n = 6). The small number of recorded interventions significantly limited our ability to assess the internal validity. Out of the 14 practitioners involved in the trial, only two practitioners submitted more than one recording for the same young person, two did not submit more than one recording for the same young person and 10 practitioners did not submit any recordings at all. (One practitioner did successfully manage to deliver all six sessions of MET; however, the young person declined to be audio-recorded.) Owing to the small number of findings, no conclusions can be drawn from these data. Further details are provided in Appendix 5 following the UKATT PRS.
Conclusion
Many participants in the study did not identify themselves as having a problem with drugs and alcohol, despite reporting using multiple substances. This could be due to their previous exposure to substance use and its normalisation within this population group. The qualitative process evaluation clearly showed that in a future trial the screening tool used needs to capture a young person’s substance use within the last month, to more accurately reflect their current use of alcohol and/or drugs, and the tool needs to be able to differentiate between recreational and problematic/excessive substance use. If the screening tool can establish that use is current and problematic, it would provide a seamless intervention window, linked with feeding back the screening results, even if the content of discussions is based on harm reduction rather than striving for an abstinence-based goal. An intervention accurately offered to young people who are current users may help to alleviate the problem experienced within this study of individuals having a diminished perception of need or readiness to change.
The trial implementation process, using existing referral systems, did not facilitate or encourage engagement of children in care throughout the study process. The difficulties of screening children in care, combined with the multiple steps and time lapses within the study process, resulted in few young people reaching services. However, multiple problems that were identified, such as how problematic the screening was perceived to be by social workers, the common problem of balancing real-world barriers (such as Ofsted) and competing demands of the social work role and the consistently reported need for faster response times throughout the study process, could all be addressed by having an embedded researcher or named practitioner to oversee the entire study process. A single point of contact to act as the ‘face’ of the research project, to screen, recruit, complete data collection and support each individual to attend the first intervention session would create an integrated service model and the necessary consistency to make the process feasible within a stretched system.
In conclusion, although the different professional groups understood the principles of the SBNT and MET approaches, were enthusiastic about the approaches within the formative work and had a shared agreement of what the interventions were trying to achieve, the study has also shown that, unless the interventions can be delivered in such a way that they dovetail into the often complex lives of children in care and the drug and alcohol practitioners’ workload, they are unlikely to become part of standard practice.
Chapter 7 Health economics
Introduction
The economic analysis aimed to assess the feasibility of a within-trial economic analysis in the context of a definitive trial. The secondary aim was to conduct a value of information analysis to determine the optimal sample size for a definitive trial based on the marginal gain from enrolling an additional individual in a trial compared with the additional cost.
Methods
Data
The target population and characteristics of the sample are described in Chapter 5. All cost data for the delivery of the intervention were obtained from the practitioner logs. An example of a log sheet is presented in Appendix 1. All cost data presented are in 2017 Great British pounds.
The participant questionnaire collected data on service usage, and health was measured by the EQ-5D-5L. 115 The EQ-5D-5L was chosen for this study as the sample is aged between 12 and 20 years. Thus, given this age range and recommendations from the EuroQol-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) user guide,116 the EQ-5D-5L adult version is more appropriate for this sample. For ages 12–15 years, both the youth and adult versions can be used, and for age ≥ 16 years the adult version is recommended. The EQ-5D-5L questionnaire was administered online and respondents had to provide an answer to a question before being allowed to move on to the next question. Thus, there are no missing responses for individuals who agreed to fill in the questionnaire.
Practitioner logs
Practitioners were asked to record every session for every client to enable us to calculate how cost-effective the interventions are to deliver. We asked practitioners to record (for each session) the date the session took place, the session number (1–6), if any travelling was required to deliver the intervention (practitioners were requested to record mileage and travel time in minutes) and the number of people present at the session (not including themselves).
Practitioners were asked to record the type of casework being undertaken. Activities would include any form of patient contact (e.g. telephone calls) and non-patient contact (including preparation work and completion of forms for referrals, etc.). We also requested that, for each session, practitioners recorded all activities associated with the preparation and delivery of the session, and the duration of each activity.
Once sessions had been completed, the practitioner log captured how many sessions had been offered, how many had been attended, the reason provided for non-completion of treatment, if known, and whether or not a referral into mainstream services was made.
There were 15 practitioners, and 76 young people were randomised to the intervention. Sixty of the young people contacted by practitioners declined to engage or participate with the intervention (the number of contact attempts and the reason for the young person deciding not to participate was recorded and is reported in Chapter 5). With the exception of one participant, practitioners did not fill out the second page of the log sheet, which captured the time spent contacting the young person and establishing that they did not want to attend the additional service offer of the SBNT/MET interventions.
Service usage
A total of 60 young people out of 112 who were eligible to participate in the follow-up agreed to take part in the health service usage survey. To better understand service usage of young people, all young people who agreed to participate in the follow-up were asked to complete a questionnaire on service usage on the tablet computer during the 12-month follow-up period. The method by which the electronic questionnaire was delivered meant that, in order to go on to the next question, each young person needed to provide a response to the previous question, thus ensuring completeness of data. The response rate was 54% (n = 60 young people). Five of the young people who participated in the intervention completed the follow-up questionnaire.
Primary outcome measure
The primary outcome measure for the health economic analysis was health-related quality of life, measured using EQ-5D-5L. 115 The EQ-5D-5L questionnaire was administered at baseline and at the 12-month follow-up to the control and intervention groups. The EQ-5D-5L contains five descriptive questions, tapping five dimensions of health-related quality of life: (1) mobility, (2) self-care, (3) usual activities, (4) pain/discomfort and (5) anxiety/depression. Each question can be answered on a five-point response scale: (1) no problems, (2) slight problems, (3) moderate problems, (4) severe problems and (5) unable. The ranking of states is ordinal and this means that, for example, a move from 1 to 2 and from 2 to 3 does not represent an equal change in health.
Analytic framework
A health and social care perspective was chosen to focus on the cost and benefits of the intervention to the health sector.
Feasibility of a definitive within trial economic evaluation
The within-trial feasibility study looked at the response rates and data provided in the practitioner logs and participant questionnaires to inform the development of survey material for a definitive trial.
Costs
We present the time spent on each activity, the hourly wage of the practitioner undertaking the activity and the cost per element of each activity. Mean, SD and range of travel time of practitioners to deliver the intervention, intervention delivery time and number of participants are presented. Costs for the first two sessions are presented, as only one young person participated in more than two sessions.
Benefits
Owing to a lack of engagement with the intervention, to avoid identification of the small number of participants who engaged with the intervention, the control and intervention groups are combined. Means and medians are presented for health service usage at 12 months’ follow-up (health service usage information was not collected at baseline). Proportions are presented for the five dimensions of the EQ-5D-5L across baseline and follow-up, with means, SDs and ranges presented for mean EQ-5D score at baseline and at follow-up.
Value of information analysis
It was originally proposed that the economic evaluation component for the feasibility study should involve a value of information analysis. 117 This analysis would have incorporated the data from the literature and data from the feasibility study. The data needed for the value of information analysis include cost data for the intervention and outcome data measured by quality-adjusted life-years. These data could come from the study and be supplemented with data from the literature. The purpose of this analysis would have been to help clarify the economic case for a definitive study and, by using a variant of value of information analysis, utilise expected value of sampling of information to inform decisions on the optimal sample size for a definitive trial. 67 Unfortunately, no useable data were available from the feasibility study and insufficient data were available from the literature to conduct the economic evaluation modelling exercise that underpins a value of information analysis.
Exploratory return on investment analysis was conducted to identify the range of values for benefits and total costs consistent with a return of investment of a minimum level; this is available on request to the authors.
Results
Costs
Summary statistics from the log files of the practitioners for the 16 young people who did engage with the intervention are reported in Table 24. Practitioners successfully returned a complete practitioner log for children in care who attended any sessions.
| Staff costs | Practitioner | Cost (£) per element | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time spent (minutes), (SD) [range] | Cost (£) of practitioner time (per hour) | ||
| Monthly clinical supervisiona | 60 | 12.85 | 12.85 |
| 2-day training to deliver the intervention | 960 | 12.85 | 205.60 |
| Mean travel time to deliver first session of interventionb | 28 (23) [0–80] | 12.85 | 6.45 |
| Mean session time for first sessionb | 47 (29) [0–90] | 12.85 | 9.64 |
| Mean number of participants in first session | 1.4 (1.1) [0–3] | 12.85 | |
| Mean travel time to deliver second session of interventionb | 23 (18) [0–52] | 12.85 | 4.24 |
| Mean session time for second sessionb | 35 (30) [0–90] | 12.85 | 7.07 |
| Mean number of participants in second session | 1.4 (1.5) [0–4] | 12.85 | |
| Total cost of intervention delivery | 4256 | ||
Health service usage
The mean and median for health service usage over a 12-month period are presented in Table 25.
| Type of service | Number of visits (n = 60) | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | Median | |
| A&E admissions | 2.38 | 1 |
| Nights in hospital | 1.27 | 0 |
| Number of hospital admissions | 0.83 | 0 |
| Number of outpatient appointments | 1.77 | 0 |
| GP appointments | 5.33 | 3 |
| GP home appointments | 0.03 | 0 |
| Nurse appointments | 2.57 | 2 |
| Nurse home appointments | 0.48 | 0 |
| Number of prescriptions | 5.18 | 2 |
| Social worker home visits | 7.58 | 6 |
| Social worker office appointments | 2.88 | 0 |
| Case worker home visits | 4.68 | 0 |
| Case worker office visits | 1.63 | 0 |
In free-text boxes, other health service usage reported by respondents was with midwives (n = 2) and CAMHS (n = 6). In this free-text box we do not know how many appointments they had with these health professionals.
EuroQol-5 Dimensions, five-level version (health-related quality of life)
Table 26 reports the proportions reporting each category in the baseline and follow-up questionnaire. These results are purely descriptive.
| EQ-5D category | Response | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No problems | Slight problems | Moderate problems | Severe problems | Unable | |
| Baseline (N = 111), n/N (%) | |||||
| Mobility | 99/111 (89) | 8/111 (7) | 3/111 (2.7) | 1/111 (0.01) | 0/111 (0) |
| Self-care | 108/111 (97) | 3/111 (2.7) | 0/111 (0) | 0/111 (0) | 0/111 (0) |
| Usual activities | 91/111 (82) | 11/111 (10) | 6/111 (5.4) | 3/111 (2.7) | 0/111 (0) |
| Pain/discomfort | 80/111 (72) | 19/111 (17.1) | 7/111 (6.3) | 4/111 (3.6) | 1/111 (0.01) |
| Anxiety/depression | 48/111 (43.2) | 27/111 (24.3) | 17/111 (15.3) | 12/111 (10.8) | 7/111 (6.3) |
| Follow-up (N = 60), n/N (%) | |||||
| Mobility | 52/60 (86.7) | 3/60 (5) | 3/60 (5) | 2/60 (3.3) | 0/60 (0) |
| Self-care | 57/60 (95) | 1/60 (1.6) | 2/60 (3.3) | 0/60 (0) | 0/60 (0) |
| Usual activities | 49/60 (81.6) | 9/60 (15) | 2/60 (3.3) | 0/60 (0) | 0/60 (0) |
| Pain/discomfort | 47/60 (78.3) | 8/60 (13.3) | 4/60 (6.6) | 0/60 (0) | 1/60 (1.6) |
| Anxiety/depression | 20/60 (33.3) | 16/60 (26.6) | 15/60 (25) | 6/60 (10) | 3/60 (5) |
At the 12-month follow-up, 60 (54%) of the young people who completed the baseline questionnaire completed the follow-up questionnaire. Five of the young people who participated in the intervention completed the questionnaire. As with the service usage questionnaire, the mode of data collection ensured that the young person could not move on to the next question without completing the previous question. Thus, there are no missing responses in the EQ-5D-5L questionnaires competed.
In Table 27, we use the EQ-5D-5L values to calculate the mean EQ-5D utility scores at baseline and follow-up.
| Time point | Mean utility score (SD), minimum/maximum |
|---|---|
| Baseline | 0.92 (0.14), 0.39/1 |
| Follow-up | 0.93 (0.13), 0.31/1 |
Discussion
Within-trial economic evaluation
This pilot study showed that overall the tools used to collect the cost information and participant data on service usage and health-related quality of life seemed feasible. Practitioners and participants engaged with these materials. However, we have some suggestions to make to further refine these tools to inform future research in the area.
Cost data
If the intervention was to be used in a definitive trial, an additional log sheet should be provided to practitioners to get a better understanding of non-engagement with the intervention. This log sheet should contain information outlining the means of contacting the young person, how many times they were contacted and the length of time they spoke with the young person, as this would be useful to get a better idea of the true cost of the intervention. Data also need to be collected on administrative support, room costs and building maintenance for when the interventions were delivered, if this is relevant.
Health service use
The information from the free-text boxes in the questionnaires suggests that, in a definitive trial, CAMHS should potentially be included in a health service usage questionnaire. As a very small percentage of respondents had GP home appointments, this could potentially be removed from a questionnaire that would be part of a definitive trial.
EuroQol-5 Dimensions
From looking at the proportion of responses to each of the dimensions of the EQ-5D, a large proportion of respondents reported suffering from anxiety and depression. However, it is possible that the health attributes in the EQ-5D may be too narrow for this client group. In a definitive trial, it may be worthwhile including a condition-specific tool that measures quality of life related to mental health. 118 In addition, the EQ-5D has ceiling effects that another utility tool, such as the Short Form questionnaire-6 Dimensions, does not (although that tool has floor effects), which may make it a more appropriate outcome measure for a definitive trial. 67
Summary
The limited engagement of young people with the intervention means that we cannot be certain if the practitioner logs would be feasible in a definitive trial. The health service usage questionnaire with some minor modifications related to including CAMHS and removing GP home appointments would be appropriate for a definitive trial. In a definitive trial it may also be appropriate to use a condition-specific tool that measures quality of life related to mental health.
Chapter 8 Summary and conclusion
Introduction
This final chapter provides a brief summary of the key findings in the SOLID trial in relation to the aims and objectives of the study as outlined in Chapter 1, Research objectives. Each element of the study process has been discussed in detail previously. This chapter presents the overall conclusion to the study and suggests recommendations regarding a future trial. A key aim of the SOLID trial has been achieved in terms of adapting and testing the feasibility of conducting a trial of two behaviour change interventions (MET and SBNT) delivered to children in care, aged 12–20 years, within standard care pathways. However, the findings from our pilot trial are less optimistic regarding future evaluative work. Nevertheless, as this is the first UK-based RCT that has attempted to assess the feasibility of delivering behaviour change interventions to reduce current substance use in children in care, the findings from this study should be used to inform future work with children in care in the UK context.
Formative study and key stakeholder survey
As part of this research phase we succeeded in recruiting 65 key stakeholders, including children in care, non-care young people, drug and alcohol practitioners (front-line staff and service managers), local authority staff (social workers, managers and PAs), and carers (foster and residential), and completing a process of intervention adaptation. Key thematic findings informed the adaptation, manual development and integration of the interventions into children in care health and social work pathways to enhance acceptability. Children participating in risky substance use were seen by a specialist drug and alcohol practitioner. In standard practice, the first one or two sessions would have been used to conduct an initial assessment and establish the young person’s level of need. The study enhanced the offer of usual care once an individual engaged with services, as the intervention started within the first session. In addition, the adapted intervention allowed a maximum of six sessions to be delivered (compared with usual care, which was unstructured and young people could attend as many or few sessions deemed necessary to meet their identified needs). Participants engaged in the formative research phase fully and showed enthusiasm when contributing to the adaptation of the two interventions.
An electronically administered survey was completed with the service managers of young people’s drug and alcohol services. Eighty-two per cent of services in England completed the survey which illustrated high levels of variation with regard to screening and treatment pathways for children in care with risky substance use. There was no standardisation regarding which screening tools were used: 52 services (46%) reported developing a tool ‘to meet their local need’. The modalities of treatment differed across providers, the majority (n = 67, 55%) offered a bespoke service and 35 (29%) services reported only conducting structured work; however, even the latter could be delivered flexibly across sessions. None of the services reported delivering and adhering to a manualised evidence-based intervention.
Pilot randomised controlled trial
The pilot RCT was conducted to assess if rates of eligibility, recruitment and retention of children in care and acceptability of the interventions were sufficient to recommend a definitive multicentre RCT.
Predetermined STOP/GO criteria (green/red) were developed for progression to a definitive trial (see Table 28 for green for progress and red for stop).
| STOP/GO criteria | Criteria | Achieved | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green | Amber | Red | ||
| Eligible participants consenting to trial, % | ≥ 60 | 40–60 | < 40 | 53 |
| Children attending 60% of offered sessions, % | ≥ 80 | 20–80 | < 20 | 9 |
| Participants retained to 12 months’ follow-up, % | ≥ 70 | 50–70 | < 50 | 54 |
| Were interventions delivered with fidelity? | Yes | Unclear | No | Unclear |
| Were interventions perceived acceptable by children in care and workers? | Yes | Unclear | No | Low uptake of intervention by children, but acceptable to workers |
| Does the value of information analysis show future research is worthwhile? | Worthwhile | Unclear | Not worthwhile | No available data |
Regarding the column reporting achievement (see Table 28, column 5), we assessed the key outcomes from the SOLID pilot trial and recommendations for a definitive trial are as follows.
Proportion of eligible participants consenting to pilot feasibility trial
The number of children in care screened was 860, of whom 211 were eligible.
Percentage of eligible participants consenting to feasibility trial: 112/211 × 100 = 53%.
Proportion recruited: 112/211 = 0.53 (amber).
Although the study did not recruit the target figure, lessons from this study could be used to maximise recruitment in a future study. The CRAFFT screening was completed by 860 (59%) of the 1450 children in care (aged 12–20 years) across the region, and 112 (53%) of the 211 eligible children in care were recruited and randomised into the study.
Proportion of children in care attending at least 60% of sessions as planned in combined intervention arms
MET
Four attended 100% of sessions offered, one attended 66% of sessions offered, one attended 50% of sessions offered, one attended 29% of sessions offered and 31 attended 0% of sessions offered. Therefore, 5 out of 38 (13%) attended > 60% of sessions offered.
SBNT
Two attended 100% of sessions offered and four attended 50% sessions offered. Therefore, 2 out of 38 (5%) attended > 60% of sessions offered.
Overall, 7 out of 76 (9%) attended > 60% of sessions offered (red).
Proportion of consented participants retained for measurement of key outcome data at 12 months
Sixty out of the 112 (54%) randomised provided follow-up data at 12 months (amber).
In total, 54% of recruited children were followed up to 12 months. Follow-up was particularly difficult due to frequent moves in this population and their changing contact details. However, the SOLID trial has shown that once participants were located and seen by the researcher, they were prepared to complete questionnaire data at both baseline and at follow-up. None of the participants asked to end the data collection process early and only one individual elected to not complete the TLFB at the 12-month follow-up.
Were interventions delivered with fidelity?
In total, only 26 intervention sessions were delivered to 15 young people out of the 76 children in care randomised to the two intervention arms. It was not possible to evaluate the fidelity of intervention delivery due to the low number of audio-recordings available, only nine audio-recordings were received.
Were interventions perceived acceptable by children in care and workers?
It was not possible to assess the acceptability of the MET and SBNT interventions due to the low number of participants who received the intervention sessions. Owing to the involvement of 24 children in care participants in the formative phase of the study, we believe the content should be acceptable. However, we can conclude that significant changes would need to be made to the location of these interventions within current service pathways, in order to increase participant engagement.
Does the value of information analysis show future research is worthwhile?
It was originally proposed that a value of information analysis would be conducted. Unfortunately, no useable data were available from the feasibility study and insufficient data were available from the literature to conduct the economic evaluation modelling exercise that underpins a value of information analysis. Therefore, an exploratory return on investment was conducted in order to identify the range of values for benefit and total cost consistent with a return on investment. The preliminary return on investment analysis suggests that a medium to large health effect would need to be demonstrated before the intervention would be considered cost-effective.
It is our judgement that criteria for progression to a definitive trial have not been met in this study.
As discussed in Chapter 5, major challenges were found in both screening and recruitment of children in care into the study. Screening of children by the six local authority social work teams took over a year to complete, with significant time and resource investment by the researcher and social work teams. The increased amount of time needed resulted from the impact of staff turnover, long-term sickness, restructuring of local authority sites and Ofsted inspections. Social workers acted as gatekeepers when deciding which children in care to screen, influenced, for example, by their preconceived beliefs of whether or not the young person used substances or were potentially too young to participate. Contact details for children within the care system were not always updated on the centralised systems, therefore obtaining the relevant contact details to make contact for the study follow-up was often problematic. These difficulties were fed back to team managers, leading to escalation to senior management level. It is hoped that future studies will benefit from this initial work to ensure that system data are accurate and up to date.
An embedded researcher or senior local authority member of staff seconded in a research role could provide an increasingly stable point of contact within the complex local authority setting, to facilitate more successful screening and recruitment. 67 The availability of a visible individual to be present throughout the research period would act as a facilitator within what is, primarily, a less research-mature environment.
The process evaluation highlighted that, no matter how effective an intervention is perceived to be by practitioners during development, if participants do not engage with it, the potential benefits cannot be achieved. It is essential that the service considers different methods to increase engagement. The participant interviews identified valuable insights into the facilitators of and barriers to engaging with interventions, and highlighted the role of self-perception regarding ‘problematic’ substance use. The children in care recruited in to this study did not feel that they have a problem, often due to the normative view of their drug and alcohol use. Participants did not feel that their use warranted an intervention from a specialist drug and alcohol practitioner, therefore a referral to a specialist service does not feel salient. This suggests that a different delivery agent is required if intervention delivery is to be successful.
Recommendations for a future evaluation
We have learnt several lessons that could inform a future trial or other form of evaluative work with children in care.
The delivery of future interventions
The typical screen, refer and treat model used in the SOLID trial was problematic. Children in care were recruited into this study based on a screening outcome, suggesting risk due to substance use behaviour. The study was designed in this way to mirror the current system and was based on public health principles related to prevention to address avoidable future problems. However, it could be argued that being in the care system was itself a risk factor for increased drug and alcohol use. Moreover, the interventions were delivered by specialist drug and alcohol workers in a referral context. Any future trial needs to think about how we deliver harm reduction and preventative care for children in the social care system. This may well require additional resource. Accepting the view that being in care can generate increased risk for children and young people, a broader ‘care pathway’ approach may be needed in keeping with the principles of the thrive model currently used by the CAMHS for children and young people. 119 The thrive model promotes five categories: thriving, getting advice and signposting, getting help, getting more help and getting risk support. Thus, substance use counselling would fit with ‘getting risk support’, but would be part of a process that understands wider determinants of risk and risk behaviour. By delivering the adapted intervention according to the thrive categories, it would allow a person-centred and needs-led approach to be delivered to children in care regarding their substance use. 67 In the SOLID trial, we tried to use the existing drug and alcohol referral system to deliver novel interventions. This working between different sectors of the care system did not work. A new way of working, in which drug and alcohol workers become embedded to social care services and residential units, could be a better way of delivering these interventions. This fits with principles of place-based approaches,120 which argue that providers of services (in this case social workers and drug and alcohol practitioners) work together to improve health and care for the population they serve. Within the process evaluation, social workers stated that they would not be able to deliver these interventions unless they were given specific training and ring fenced time.
Evaluation design and support
Prior to beginning the SOLID pilot trial, we had secured senior ‘buy-in’ across six local authorities. We had a team of experienced researchers, including an academic social worker as a co-applicant, and we saw real excitement and enthusiasm from social work staff about research work being conducted in social care. However, social services departments are often less research mature than clinical contexts that have benefited from specific resources through the Clinical Research Networks (CRNs) to support research delivery over many years. Local authorities have experienced reduced funding due to economic austerity and many social work settings are understaffed and overstretched in terms of workload. Consequently, without additional, dedicated research support, potentially from an embedded researcher/social worker, then applied research in social care and, particularly, with children in care will prove difficult. This researcher would add much needed academic leadership within departments. They could be jointly funded and managed across academia and the local authority, which would give them clearance to engage clients and could significantly change the research culture within the units. Within the lifetime of the SOLID trial, the NIHR CRN has implemented changes to the eligibility criteria for studies. The NIHR CRN has now extended support into research taking place in non-NHS settings, such as health and social care and public health, these changes could facilitate the necessary change as it has within NHS research trials. 121 In addition, future studies within the social care context would benefit from performing an organisational readiness study with social work teams and drug and alcohol services, to be involved in research and deliver interventions prior to implementation of a RCT or evaluation study. Pragmatic evaluation design coupled with additional research resource for children’s services are needed to evaluate these novel models of care at scale.
Screening and risk perception
Mass screening of children in care as part of ‘standard practice’ within the social work teams was not feasible. The findings of the SOLID trial have shown that attention needs to be paid to the identification, screening and intervention delivery for this high-risk group of young people. The screening results highlight that for this population, older teenagers are more likely to be reporting alcohol and/or drug use. Within this study, drug and/or alcohol use was most prevalent in young people aged between 16 and 19 years, with reported use peaking at 17 years of age [72 (8.4%) of respondents reporting use within the last 12 months]. However, the existing current models and pathways of care have been shown to be ineffective, resulting in a significant amount of need being unmet by services. Screening would need to be completed using an alternative method in a future study. The current screen and refer model used in the SOLID trial has been shown to be problematic. The completed screening tools could have detected problematic drug and/or alcohol use and provided an opportunity to offer an immediate therapeutic intervention. Having an embedded researcher with capacity to promptly engage a young person may have provided scope to tentatively explore the impact of their drug and/or alcohol use on their mental health, physical health, relationships and behaviour. This opportunistic interventions could be used to sensitively introduce a problem feedback component regarding their substance use and may have initiated a stronger recognition of risk by the young person. An embedded researcher within social care departments would have the potential to increase the uptake of screening with children in care, improve the engagement of social workers in very stretched services and provide an increasingly tailored response depending on the information provided at the screening stage. An embedded researcher could be an individual who is ‘either university based or employed with the purpose of implementing a collaborative, jointly owned research agenda in a host organisation’. 122 This model is often found within a health-care setting, such as medicine and nursing; however, is less established within social care settings. Cheetham et al. 122 provide an example of how having a researcher embedded within the local authority environment can increase the situated understanding of the cultures and norms of an organisation, and also recognise the realities of conducting public health interventions. 122 An embedded researcher would have the capacity to take into consideration the context of the environment and stakeholders’ interests. 123 In addition, the perceptions of ‘problem substance use’ differed between the children in care and practitioners working within the service systems currently in place. If the requirement is for children in care to be engaged with a substance misuse intervention and that intervention can be delivered opportunistically and quickly around the needs of children in care, then a place-based approach to intervention delivery needs to be taken. 120 In addition, the child in care needs to perceive their substance use as an area they want to address. In our sample, many young people were more concerned about other problems in their lives and that substance use was a symptom not a cause of problems. Consequently, work on any substance use needs to be set into a wider context of adverse childhood experiences30 and difficulties experienced in care. 89
Interventions
The MET and SBNT interventions modalities were chosen as they have both shown to be effective in decreasing substance use in participants, including adolescents. 69–71 There is strong evidence for the use of brief interventions. A Cochrane review by Kaner et al. 124 reported that at 1 year follow-up the amount of alcohol people drank each week had reduced and that longer counselling provided little additional benefit over brief interventions. However, we were unable to test the effectiveness of delivering brief interventions to this population of young people due to low attendance at the available sessions. Future studies would need to consider the best way to engage children in care in interventions that promote a harm reduction and prevention component, alongside offering a therapeutic approach.
Screening tool
The CRAFFT screening tool should be adapted to enable young people reporting substance use within the last 30 days, as opposed to 12 months as it is currently, to ensure that the information provided is current and relevant. The age range of young people being recruited into the study should be modified to 12–17 years. The rationale for suggesting this age range, is that data demonstrates that substance use is starting to emerge in children as young as 12 years. Among the young people screened, 66 forms (8%) were completed by children in care aged 12 years, with two (0.2%) children in care reporting substance use (alcohol, cannabis and NPS). By comparison, 93 forms (11%) were completed by children in care aged 13 years, with 12 (1.4%) positive for substance use, and 90 forms (10.5) completed by children in care aged 14 years, with 18 (2%) children in care reporting substance use. This suggests that if early intervention and preventative work is the aim of the study, 12 years is the correct age to commence screening, as it correlates with initiating substance use. This of course requires individuals to be approached sensitively due to their vulnerability, and issues of capacity and competency to engage with interventions would command further exploration.
Screening children in care aged ≥ 18 years also posed a dilemma. Young people within this age category are legally old enough to drink and by default did not identify their reported alcohol use as a problem as ‘alcohol is legal’. In addition, children in care were increasingly starting to transition into independent living accommodation, to enter the college environment in which exposure to alcohol in a social context was increasingly likely. Altering the inclusion age to children in care aged < 18 years would ensure that individuals were still ‘open’ to social services and would provide the necessary mechanism to follow up children in care. In addition, such young people are under the legal age to drink; therefore, any alcohol use could be deemed as risky and could warrant an intervention being delivered.
Conclusion
Current evidence shows that children in care are significantly more likely than their peers to use substances and have severe mental health morbidity. This study has shown that this population is amenable to be involved in research, with 65 participants engaging in the formative phase of the study and 109 participants engaging in the process evaluation. The enthusiastic ‘buy-in’ from children in care and professional participants within the more qualitative elements of the study, demonstrate that it may not be research, per se, that is the barrier to successful engagement, but it may be the rigid structure of the RCT protocol that is challenging for the children in care to participate in. Although the RCT is classed as the gold standard regarding making clinical decision, the social care context would benefit from alternative evaluations that can accommodate the increasingly complex causal pathways that occur between intervention delivery and behaviour change outcomes. 125,126 Data have suggested that the intervention components of the adapted MET and SBNT approaches seem broadly acceptable to them, and that drug and alcohol practitioners perceived these approaches as helpful. However, the way that our behaviour change interventions were delivered and integrated into existing services and pathways was problematic. The interventions were being introduced into an already complex system that identified the difficulty of delivering standardised interventions, this can be seen by the lack of manualised interventions used within drug and alcohol services. Pettigrew et al. 127 identify that interventions within public health need to be able to have sensitivity to features of the local context and our current design did not allow for this.
Moreover, our work showed that many children in care do not identify themselves as needing a drug and alcohol intervention, despite reporting use of licit and illicit substances and linked risky behaviours. This mismatch between professional’s and children in care’s views justifies further attention. The lessons learnt from the SOLID trial have implications for future evaluative work and we have suggested that a new model of embedded research in social care may be needed in the future. This additional capacity would enable research studies to be delivered in resource-constrained local authorities and also act as catalyst role models to help build a more research-conscious workforce in social care. In addition, future studies within the social care context would benefit from performing an organisational readiness study with social work teams and drug and alcohol services, to be involved in research and deliver interventions prior to implementation of a RCT or evaluation study. Finally, we do need to develop and evaluate models of prevention to help reduce the adverse outcomes of being a child in care. However, given the wider risks inherent in being placed in the care system, we need to embed substance use work within in a context of understanding wider determinants of risk behaviour. We also need to ensure that we address the specific concerns felt by the children whose outcomes we are trying to improve.
Acknowledgements
The research team would like to thank all the local authority staff and social work team members who helped to screen and maintain contact with the young people, the drug and alcohol practitioners whom delivered the interventions, and the young people and carers who took part in the research.
The research team give thanks to the members of the study management group and the Trial Steering Group for their involvement throughout the research.
The research team would also like to thank Dr Gillian Tober, who was involved in the intervention development phase of the study, the training of the drug and alcohol practitioners and the provision of clinical supervision to practitioners; Professor Janet Shucksmith for her involvement in the development of the formative phase of the study prior to her retirement; Louise Carr for her involvement in the recruitment of children in care within the formative phase of the study; Dr Frauke Becker for her involvement in the design of the economic components of the study; and Professor Luke Vale for his contribution to the design of the study, conduct of the trial and Project Management Group.
Contributions of authors
Hayley Alderson (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4674-561X) (Research Associate and SOLID Project Manager) project managed the study and led the report writing.
Eileen Kaner (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7169-9344) (Professor of Public Health Research) the current chief investigator, took overall responsibility for the study and co-writing the report.
Rebecca Brown (https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3424-3679) (Research Associate, Qualitative Research) contributed to the design of the study, conduct of the trial and Project Management Group, carried out data collection, co-analysed data and co-drafted Chapter 1 of the final report.
Denise Howel (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0033-548X) (Senior Lecturer, Statistics) contributed to the design of the study, conduct of the trial and Project Management Group, supervised the statistical component of the research, carried out statistical analysis and co-drafted the trial chapters.
Elaine McColl (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8300-3204) (Professor of Health Services Research and previously Director of the Newcastle Clinical Trials Unit, Methodology) contributed to the design of the study, conduct of the trial and Project Management Group.
Deborah Smart (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6354-2382) (Research Assistant) contributed to the design of the study, conduct of the trial and Project Management Group, and carried out data collection.
Alex Copello (https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3788-7197) (Honorary Professor of Addiction Research/Consultant Clinical Psychologist) contributed to the design of the study, conduct of the trial and Project Management Group, and co-developed the interventions.
Tony Fouweather (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2292-0495) (Statistics) contributed to the design of the study, conduct of the trial and Project Management Group, contributed to the statistical component of the research, carried out statistical analysis, and co-drafted Chapters 4 and 5.
Ruth McGovern (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4119-4353) (Senior Research Interventionist, Interventionist and Qualitative Researcher) contributed to the design of the study, conduct of the trial and Project Management Group, and co-developed the interventions.
Heather Brown (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0067-991X) (Senior Lecturer) drafted Chapter 7 and contributed to the conduct of the trial and Project Management Group.
Paul McArdle (https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0600-9914) (Consultant Child and Adolescent Psychiatrist) contributed to the design of the study, and conduct of the trial and Project Management Group.
Raghu Lingam (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0161-793X) (Professor of Population Child Health) was the original chief investigator on the study, and took overall responsibility for the study and co-writing of the report.
All authors read and agreed the final draft report.
Publications
Alderson H, McGovern R, Brown R, Howel D, Becker F, Carr L, et al. Supporting Looked After Children and Care Leavers In Decreasing Drugs, and alcohol (SOLID): a pilot feasibility randomised controlled trial of interventions to decrease risky substance use (drugs and alcohol) and improve mental health of looked after children and care leavers aged 12–20 years (protocol). Pilot Feasibility Stud 2017;3(25).
Alderson H, Brown R, Copello A, Kaner E, Tober G, Lingam R, McGovern R. Supporting Looked After Children and Care Leavers In Decreasing Drugs, and Alcohol (SOLID): the key therapeutic factors needed to deliver behavioural change interventions to decrease risky substance use (drug and alcohol) for looked after children and care leavers: a qualitative exploration with young people, carers and front line workers. BMC Med Res Methodol 2019;19:38.
Brown R, Alderson H, Kaner E, McGovern, Lingam R. ‘There are carers and carers who actually care’; conceptualisations of care among looked after children and care leavers, professionals and carers. Child Abuse Negl 2019;9:219–29.
lderson H, Brown R, Smart D, Lingam R, Dovey-Pearce G. ‘You’ve come to children that are in care and given us the opportunity to get our voices heard’. The journey of looked after children and researchers in developing a Patient and public involvement group. Health Expectat 2019;22:657–65.
Alderson H, Kaner E, McColl E, Howel D, Fouweather T, McGovern R, et al. A pilot feasibility randomised controlled trial of two behaviour change interventions compared to usual care to reduce substance misuse in looked after children and care leavers aged 12–20 years: The SOLID study. PLoS ONE 2020;15:e0238286.
Data-sharing statement
The data sets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the PHR programme or the Department of Health and Social Care. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the PHR programme or the Department of Health and Social Care.
References
- Information Commissioner’s Office . Guide to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) 2018. www.gov.uk/government/publications/guide-to-the-general-data-protection-regulation (accessed 26 November 2019).
- Hale DR, Viner RM. Policy responses to multiple risk behaviours in adolescents. J Public Health 2012;34:i11-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/pubmed/fdr112.
- Rehm J, Taylor B, Room R. Global burden of disease from alcohol, illicit drugs and tobacco. Drug Alcohol Rev 2006;25:503-13. https://doi.org/10.1080/09595230600944453.
- Alcohol Change UK . The Alcohol Change Report 2018.
- Department of Health and Social Care (DHSC) . Alcohol and Drugs Prevention, Treatment and Recovery: Why Invest? 2013.
- Home Office . Modern Crime Prevention Strategy 2016.
- Balance . Facts and Figures n.d. www.balancenortheast.co.uk/the-evidence/facts-and-figures (accessed 25 November 2019).
- Hodgins S, Larm P, Molero-Samuleson Y, Tengström A, Larsson A. Multiple adverse outcomes over 30 years following adolescent substance misuse treatment. Acta Psychiatr Scand 2009;119:484-93. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0447.2008.01327.x.
- Chen CY, Storr CL, Anthony JC. Early-onset drug use and risk for drug dependence problems. Addict Behav 2009;34:319-22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2008.10.021.
- Gilvarry E. Substance abuse in young people. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 2000;41:55-80. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021963099004965.
- Public Health England . Local Tobacco Control Profile 2018. https://fingertips.phe.org.uk/profile/tobacco-control (accessed 17 November 2019).
- Public Health England . Local Alcohol Profile 2018. https://fingertips.phe.org.uk/profile/local-alcohol-profiles (accessed 3 March 2019).
- Ng Fat L, Shelton N, Cable N. Investigating the growing trend of non-drinking among young people; analysis of repeated cross-sectional surveys in England 2005-2015. BMC Public Health 2018;18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5995-3.
- Hibell B. The 2011 ESPAD Report: Substance Use Among Students in 36 European Countries 2012.
- NHS Digital . Smoking, Drinking and Drug Use Among Young People in England – 2016 2017. https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/smoking-drinking-and-drug-use-among-young-people-in-england/2016 (accessed 17 December 2018).
- Public Health England . Young People’s Statistics from the National Drug Treatment Monitoring System (NDTMS): 1 April 2016 to 31 March 2017 2017. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/664945/Young-people-statistics-report-from-the-national-drug-treatment-monitoring-system-2016-2017.pdf (accessed 17 December 2018).
- Department for Education . Children Looked After in England (Including Adoption), Year Ending 31 March 2017 2017.
- Courtney M, Dworsky A. Early outcomes for young adults transitioning from out of home care in the USA. Child Fam Soc Work 2006;11:209-19. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2206.2006.00433.x.
- MacLean S. Out-of-home care as an institutional risk environment for volatile substance use. Children (Austr) 2012;37:23-30. https://doi.org/10.1017/cha.2012.4.
- Department for Education . Outcomes for Children Looked After by Local Authorities in England, 31 March 2017 2017.
- National Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Children (NSPCC) . Child Protection in England: Statistics 2017.
- Unrau Y, Seita J, Putney K. Former foster youth remember multiple placement moves: a journey of loss and hope. Child Fam Soc Work 2008;30:256-66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2008.03.010.
- Simkiss D, Lemer C. Annual Report of the Chief Medical Officer 2012. Our Children Deserve Better: Prevention Pays 2013:1-11.
- Simkiss DE, Spencer NJ, Stallard N, Thorogood M. Health service use in families where children enter public care: a nested case control study using the General Practice Research Database. BMC Health Serv Res 2012;12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-12-65.
- Simkiss DE, Stallard N, Thorogood M. A systematic literature review of the risk factors associated with children entering public care. Child Care Health Dev 2013;39:628-42. https://doi.org/10.1111/cch.12010.
- Apos HA, Sebba J, Gardner F. What are the factors associated with educational achievement for children in kinship or foster care: a systematic review. Child Youth Serv Rev 2017;79:198-220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2017.06.004.
- Evans R, Brown R, Rees G, Smith P. Systematic review of educational interventions for looked-after children and young people: recommendations for intervention development and evaluation. Br Educ Res J 2017;43:68-94. https://doi.org/10.1002/berj.3252.
- Social Care Institute for Excellence (SCIE) . Improving Mental Health Support for Our Children and Young People 2017.
- Hughes K, Bellis M, Hardcastle K, Sethi D, Butchart A, Mikton C, et al. The effect of multiple adverse childhood experiences on health: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Public Health 2017;2:e356-66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-2667(17)30118-4.
- Bellis MA, Hardcastle K, Ford K, Hughes K, Ashton K, Quigg Z, et al. Does continuous trusted adult support in childhood impart life-course resilience against adverse childhood experiences – a retrospective study on adult health-harming behaviours and mental well-being. BMC Psychiatry 2017;17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-017-1260-z.
- Bellis MA, Hughes K, Leckenby N, Jones L, Baban A, Kachaeva M, et al. Adverse childhood experiences and associations with health-harming behaviours in young adults: surveys in eight eastern European countries. Bull World Health Organ 2014;92:641-55. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.13.129247.
- Luke N, Sinclair I, Woolgar M, Sebba J. What Works In Preventing and Treating Poor Mental Health in Looked After Young People. London: National Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Children; 2014.
- Department for Education . LAC in Foster Care: Analysis (to End of March 2017) 2018.
- Department for Education . National Tables: Children Looked After in England Including Adoption 2017–2018 2018. www.gov.uk/government/statistics/children-looked-after-in-england-including-adoption-2017-to-2018 (accessed 21 February 2019).
- Children’s Commissioner . Lightning Review: Access to Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services 2016.
- Cameron C, Hollingworth K, Schoon I, van Santen E, Schröer W, Ristikari T, et al. Care leavers in early adulthood: how do they fare in Britain, Finland and Germany?. Child Youth Serv Rev 2018;87:163-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2018.02.031.
- Elliott J, Shepherd P. Cohort profile: 1970 British Birth Cohort (BCS70). Int J Epidemiol 2006;35:836-43. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyl174.
- Local Government Association . Healthy Futures: Supporting the Health Needs of Looked After Children 2016.
- Ford T, Vostanis P, Meltzer H, Goodman R. Psychiatric disorder among British children looked after by local authorities: comparison with children living in private households. Br J Psychiatry 2007;190:319-25. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.106.025023.
- Craine M, Midgley C, Zou I, Evans H. Elevated teenage conception rates amongst looked after children: a national audit. Public Health 2014;128:668-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2014.05.008.
- Meltzer H. The mental health of young people looked after by local authorities in England. London: The Stationery Office; 2003.
- Ward J, Henderson Z, Pearson G. One Problem Among Many: Drug Use Among Care Leavers in Transition to Independent Living. London: Home Office, Research, Development and Statistics Directorate; 2003.
- Blyth L. Outcomes for Children Looked After by Local Authorities in England, as of 31 March 2012. London: Office for National Statistics; 2012.
- Public Health England . Young People’s Statistics From the NDTMS 1st April 2017 to 31st March 2018 2018.
- Ward J. Substance use among young people ‘looked after’ by social services. Drugs Educ Prev Policy 1998;5:257-67. https://doi.org/10.3109/09687639809034087.
- McCrystal P, Percy A, Higgins K. Substance use among young people living in residential state care. Child Care Pract 2008;14:181-92. https://doi.org/10.1080/13575270701868819.
- Monshouwer K, Kepper A, Eijnden R, Koning I, Vollebergh W. Initiation of substance use by adolescents after one year in residential youth care. Child Youth Care Forum 2014;44:597-611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-014-9294-6.
- Department for Education and Skills . Care Matters: Transforming the Lives of Children and Young People in Care 2006.
- GOV.UK . Drug Strategy 2017 n.d. www.gov.uk/government/publications/drug-strategy-2017 (accessed 20 November 2019).
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) . Drug Misuse Prevention: Target Interventions (NICE Guidance NG64) 2017.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) . Alcohol Use Disorders: Prevention (Public Health Guidance PH24) 2010.
- Buck D, Frosini F. Clustering of Unhealthy Behaviours Over Time: Implications for Policy and Practice. London: The King’s Fund; 2012.
- Kipping RR, Smith M, Heron J, Hickman M, Campbell R. Multiple risk behaviour in adolescence and socio-economic status: findings from a UK birth cohort. Eur J Public Health 2015;25:44-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurpub/cku078.
- Brooks FM, Magnusson J, Spencer N, Morgan A. Adolescent multiple risk behaviour: an asset approach to the role of family, school and community. J Public Health 2012;34:i48-56. https://doi.org/10.1093/pubmed/fds001.
- Evans H, Buck D. Tackling Multiple Unhealthy Risk Factors: Emerging Lessons From Practice. London: The King’s Fund; 2018.
- Department for Education . Special Educational Needs and Disability Code of Practice: 0 to 25 Years 2015.
- Courtney M, Hook J. The potential educational benefits of extending foster care to young adults: Findings from a natural experiment. Child Youth Serv Rev 2017;72:124-32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2016.09.030.
- Sebba J, Berridge D, Luke N, Fletcher J, Bell K, Strand S, et al. The Educational Progress of Looked After Children in England: Linking Care and Educational Data. Oxford: Rees Centre: Research in Fostering and Education; 2015.
- Rees P. The mental health, emotional literacy, cognitive ability, literacy attainment and ‘resilience’ of ‘looked after children’: a multidimensional, multiple-rater population based study. Br J Clin Psychol 2013;52:183-98. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjc.12008.
- Olsen R, Montgomery C. Revisiting out-of-home place children’s poor educational outcomes: is school change part of the explanation. Child Youth Serv Rev 2018;88:103-13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2018.03.005.
- Addaction . Young People and Substance Misuse 2015.
- Mentor . Disengaged From School, Engaged With Drugs and Alcohol? Young People at Risk 2013.
- Rome S, Raskin M. Transitioning out of foster care: the first 12 months. Youth Soc 2017;51:529-47. https://doi.org/10.1177/0044118X17694968.
- Department for Education . A Review of the Longitudinal Study of Young People in England 2010.
- Broderick R, McCoard S, Carnie J. Prisoners Who Have Been in Care as ‘Looked After Children’. Edinburgh: Scottish Prison Service; 2014.
- Race for Opportunity . Ethnic Minorities in the North East: A Business Case for Inclusion 2013.
- Alderson H, Kaner E, McColl E, Howel D, Fouweather T, McGovern R, et al. A pilot feasibility randomised controlled trial of two behaviour change interventions compared to usual care to reduce substance misuse in looked after children and care leavers aged 12-20 years: The SOLID study. PLoS ONE 2020;15. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0238286.
- Alderson H, Brown R, Smart D, Lingam R, Dovey-Pearce G. ‘You’ve come to children that are in care and given us the opportunity to get our voices heard’. The journey of looked after children and researchers in developing a patient and public involvement group. Health Expect 2019;22:657-65. https://doi.org/10.1111/hex.12904.
- Lundahl B W, Kunz C, Brownell C, Tollefson D, Burke B. A meta-analysis of motivational interviewing: twenty-five years of empirical studies. Res Soc Work Pract 2010;20:137-60. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049731509347850.
- Watson J, Toner P, Day E, Back D, Brady LM, Fairhurst C, et al. Youth social behaviour and network therapy (Y-SBNT): adaptation of a family and social network intervention for young people who misuse alcohol and drugs – a randomised controlled feasibility trial. Health Technol Assess 2017;21. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta21150.
- Tevyaw TO, Monti PM. Motivational enhancement and other brief interventions for adolescent substance abuse: foundations, applications and evaluations. Addiction 2004;99:63-75. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2004.00855.x.
- Miller WR, Zweben A, DiClemente CC, Rychtarik RG. Motivational Enhancement Therapy Manual: A Clinical Research Guide for Therapists Treating Individuals With Alcohol Abuse and Dependence. Mattson 1999. https://motivationalinterviewing.org/sites/default/files/MATCH.pdf (accessed 20 November 2019).
- Dennis ML, Funk R, Godley SH, Godley MD, Waldron H. Cross-validation of the alcohol and cannabis use measures in the Global Appraisal of Individual Needs (GAIN) and Timeline Followback (TLFB; Form 90) among adolescents in substance abuse treatment. Addiction 2004;99:120-8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2004.00859.x.
- Carney T, Myers B. Effectiveness of early interventions for substance-using adolescents: findings from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy 2012;7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1747-597X-7-25.
- McCambridge J, Strang J. The efficacy of single-session motivational interviewing in reducing drug consumption and perceptions of drug-related risk and harm among young people: results from a multi-site cluster randomized trial. Addiction 2004;99:39-52. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2004.00564.x.
- Copello A. Social Behaviour and Network Therapy for Alcohol Problems. London: Routledge; 2009.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) . Interventions to Reduce Substance Misuse Among Vulnerable Young People: Evidence Update April 2014 2014.
- Medical Research Council (MRC) . Developing and Evaluating Complex Interventions: New Guidance 2006.
- Kirby D. BDI Logic Models: A Useful Tool for Designing, Strengthening and Evaluating Programmes to Reduce Adolescent Sexual Risk-Taking, Pregnancy, HIV and Other STDs 2004. www.etr.org/recapp/BDILOGICMODEL20030924.pdf (accessed 26 November 2019).
- Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol 2006;3:77-101. https://doi.org/10.1191/1478088706qp063oa.
- Donovan J, Sanders C, Bowling A, Ebrahim S. Handbook of Health Research Methods: Investigation, Measurement and Analysis. Maidenhead: Open University Press; 2005.
- Campbell A, Finch E, Brotchie J, Davie P. The International Treatment Effectiveness Project: Implementing Psychosocial Interventions for Adult Drug Misusers. London: National Treatment Agency for Substance Misuse; 2007.
- Blyth L. Outcomes for Children Looked After by Local Authorities in England, as of 31 March 2013. London: Office for National Statistics; 2013.
- Holland S, Floris C, Crowley A, Renold E. How Was Your Day? Learning From Experience: Informing Preventative Policies and Practice by Analysing Critical Moments in Care Leavers Life Histories. Cardiff: Cardiff University; 2010.
- Selwyn J, Saunders H, Farmer E. The views of children and young people on being cared for by an independent foster-care provider. Br J Soc Work 2010;40:696-713. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjsw/bcn117.
- Public Health England (PHE) . Specialist Substance Misuse Services for Young People: A Rapid Mixed Methods Evidence Review of Current Provision and Main Principles for Commissioning 2017.
- Kipping RR, Campbell RM, MacArthur GJ, Gunnell DJ, Hickman M. Multiple risk behaviour in adolescence. J Public Health 2012;34:i1-2. https://doi.org/10.1093/pubmed/fdr122.
- Alderson H, Brown R, Copello A, Kaner E, Tober G, Lingam R, et al. The key therapeutic factors needed to deliver behavioural change interventions to decrease risky substance use (drug and alcohol) for looked after children and care leavers: a qualitative exploration with young people, carers and front line workers. BMC Med Res Methodol 2019;19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-019-0674-3.
- Brown R, Alderson H, Kaner E, McGovern R, Lingam R. ‘There are carers, and then there are carers who actually care’; conceptualisation of care among looked after children and care leavers, professionals and carers. Child Abuse Negl 2019;92:219-29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2019.03.018.
- Alderson H, McGovern R, Brown R, Howel D, Becker F, Carr L, et al. Supporting Looked After Children and Care Leavers In Decreasing Drugs, and alcohol (SOLID): protocol for a pilot feasibility randomised controlled trial of interventions to decrease risky substance use (drugs and alcohol) and improve mental health of looked after children and care leavers aged 12-20 years. Pilot Feasibility Stud 2017;3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40814-017-0138-7.
- Knight JR, Sherritt L, Harris SK, Gates EC, Chang G. Validity of brief alcohol screening tests among adolescents: a comparison of the AUDIT, POSIT, CAGE, and CRAFFT. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2003;27:67-73. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ALC.0000046598.59317.3A.
- Gryczynski J, Kelly SM, Mitchell SG, Kirk A, O’Grady KE, Schwartz RP. Validation and performance of the Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST) among adolescent primary care patients. Addiction 2015;110:240-7. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.12767.
- Goodman R. Psychometric properties of the strengths and difficulties questionnaire. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2001;40:1337-45. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-200111000-00015.
- Goodman R, Ford T, Corbin T, Meltzer H. Using the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) multi-informant algorithm to screen looked-after children for psychiatric disorders. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2004;13:II25-31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-004-2005-3.
- Clarke A, Friede T, Putz R, Ashdown J, Martin S, Blake A, et al. Warwick–Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (WEMWBS): validated for teenage school students in England and Scotland. A mixed methods assessment. BMC Public Health 2011;11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-11-487.
- Janssen MF, Pickard AS, Golicki D, Gudex C, Niewada M, Scalone L, et al. Measurement properties of the EQ-5D-5L compared to the EQ-5D-3L across eight patient groups: a multi-country study. Qual Life Res 2013;22:1717-27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-012-0322-4.
- Babor T, Higgins-Biddle J, Saunders J, Monteiro M. The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test, Guidelines for Use in Primary Care. London: Department of Mental Health and Substance Abuse; 2001.
- Saunders JB, Aasland OG, Babor TF, de la Fuente JR, Grant M. Development of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): WHO collaborative project on early detection of persons with harmful alcohol consumption – II. Addiction 1993;88:791-804. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.1993.tb02093.x.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) . Alcohol-Use Disorders: Diagnosis, Assessment and Management of Harmful Drinking and Alcohol Dependence 2011.
- Humeniuk R, Ali R, Babor TF, Farrell M, Formigoni ML, Jittiwutikarn J, et al. Validation of the Alcohol, Smoking And Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST). Addiction 2008;103:1039-47. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2007.02114.x.
- Hjorthøj CR, Hjorthøj AR, Nordentoft M. Validity of timeline follow-back for self-reported use of cannabis and other illicit substances – systematic review and meta-analysis. Addict Behav 2012;37:225-33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2011.11.025.
- Waylen A, McGovern P, Dieter Wolke D, Low N. Romantic and sexual behavior in young adolescents: repeated surveys in a population-based cohort. J Early Adolesc 2010;30:432-43. https://doi.org/10.1177/0272431609338179.
- Cho SB, Heron J, Aliev F, Salvatore JE, Lewis G, Macleod J, et al. Directional relationships between alcohol use and antisocial behavior across adolescence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2014;38:2024-33. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12446.
- Hansen WB, Paskett ED, Carter LJ. The Adolescent Sexual Activity Index (ASAI): a standardized strategy for measuring interpersonal heterosexual behaviors among youth. Health Educ Res 1999;14:485-90. https://doi.org/10.1093/her/14.4.485.
- Smith DJ, McVie S. Edinburgh study of youth transitions and crime. Br J Criminol 2003;43:169-95. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjc/43.1.169.
- Knight JR, Sherritt L, Shrier LA, Harris SK, Chang G. Validity of the CRAFFT substance abuse screening test among adolescent clinic patients. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2002;156:607-14. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.156.6.607.
- Knight JR, Shrier LA, Bravender TD, Farrell M, Vander Bilt J, Shaffer HJ. A new brief screen for adolescent substance abuse. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1999;153:591-6. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.153.6.591.
- Medical Research Council (MRC) . Developing and Evaluating Complex Interventions: New Guidance 2006.
- Moore G, Audrey S, Barker M, Bond L, Bonnell C, Hardeman W, et al. Process Evaluation of Complex Interventions: Medical Research Council Guidance. London: MRC Population Health Science Research Network; 2014.
- Carroll C, Patterson M, Wood S, Rick J, Balain S. A conceptual framework for implementation fidelity. Implementation Sci 2007;2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-2-40.
- May C, Finch T. Implementing, embedding, and integrating practices: an outline of normalization process theory. Sociology 2009;43:535-54. https://doi.org/10.1177/0038038509103208.
- May CR, Mair F, Finch T, MacFarlane A, Dowrick C, Treweek S, et al. Development of a theory of implementation and integration: normalization process theory. Implement Sci 2009;4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-4-29.
- Murray E, Treweek S, Pope C, MacFarlane A, Ballini L, Dowrick C, et al. Normalisation process theory: a framework for developing, evaluating and implementing complex interventions. BMC Med 2010;8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-8-63.
- Tober G, Clyne W, Finnegan O, Farrin A, Russell I. UKATT Research Team . Validation of a scale for rating the delivery of psycho-social treatments for alcohol dependence and misuse: the UKATT Process Rating Scale (PRS). Alcohol Alcohol 2008;43:675-82. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/agn064.
- Noyes J, Edwards RT. EQ-5D for the assessment of health-related quality of life and resource allocation in children: a systematic methodological review. Value Health 2011;14:1117-29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2011.07.011.
- Van Reenen M, Janssen B, Oppe M, Kreimeier S, Greiner W. EQ-5D-Y User Guide: Basic Information on How to Use the EQ-5D-Y Instrument. Rotterdam: EuroQol; 2014.
- Wilson EC. A practical guide to value of information analysis. PharmacoEconomics 2015;33:105-21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-014-0219-x.
- Kwan B, Rickwood DJ. A systematic review of mental health outcome measures for young people aged 12 to 25 years. BMC Psychiatry 2015;15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-015-0664-x.
- Wolpert M, Harris R, Jones M, Hodges S, Fuggle P, James R, et al. THRIVE: The AFC-Tavistock Model for CAMHS. London: Anna Freud Centre; 2014.
- Local Government Association . Shifting the Centre of Gravity: Making Place-Based, Person Centred Health and Care a Reality 2018.
- Department of Health and Social Care (DHSC) . Eligibility Criteria for NIHR Clinical Research Network Support 2017.
- Cheetham M, Wiseman A, Khazaeli B, Gibson E, Gray P, Van der Graaf P, et al. Embedded research: a promising way to create evidence-informed impact in public health?. J Public Health 2018;40:i64-i70. https://doi.org/10.1093/pubmed/fdx125.
- Marshall M, Eyre L, Lalani M, Khan S, Mann S, de Silva D, et al. Increasing the impact of health services research on service improvement: the researcher-in-residence model. J R Soc Med 2016;109:220-5. https://doi.org/10.1177/0141076816634318.
- Kaner EF, Beyer FR, Muirhead C, Campbell F, Pienaar ED, Bertholet N, et al. Effectiveness of brief alcohol interventions in primary care populations. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2018;2. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004148.pub4.
- Eriksson C. Learning and knowledge-production for public health: a review of approaches to evidence-based public health. Scand J Public Health 2000;28:298-30. https://doi.org/10.1177/14034948000280040101.
- Victora C, Habicht J, Bryce J. Evidence-based public health: moving beyond randomised trials. Am J Public Health 2004;94:400-5. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.94.3.400.
- Petticrew M, Cummins S, Ferrell C, Findlay A, Higgins C, Hoy C, et al. Natural experiments: an under-used tool for public health. Public Health 2005;119:751-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2004.11.008.
Appendix 1 Treatment intervention protocol
Appendix 2 Drug and alcohol treatment provider survey
Appendix 3 Screening tools and scoring
Description and scoring schemes for study questionnaires
The questionnaires used in the SOLID trial to gather information from the children in care are listed. Were collected at baseline then again at the 12-month follow-up:
-
CRAFFT screening tool
-
AUDIT questionnaire (screen for alcohol misuse)
-
ASSIST-Y questionnaire
-
SDQ
-
WEMWBS.
In addition, the following questionnaires were administered at the 12-month follow-up meeting only:
-
computer-assisted self-interview (CASI): romantic and intimate behaviours
-
antisocial/criminal behaviour
-
use of health and social service questionnaire
-
Alcohol TLFB-30.
The following guide was used in conjunction with the actual questionnaires stored in the trial documentation.
CRAFFT screening questionnaire (screen for inclusion into the trial)
The CRAFFT questionnaire can be accessed at https://crafft.org/get-the-crafft (accessed 14 February 2020).
Individuals received a score for each yes response they provided, each individual was given a score out of 4 for part A and a score out of 6 for part B. The higher the score the more substances were being used and the more risky behaviours were taking place.
AUDIT questionnaire (screen for alcohol misuse)
The AUDIT screening tool (self-report version) can be accessed at www.drugabuse.gov/sites/default/files/files/AUDIT.pdf (accessed 14 February 2020). The AUDIT questionnaire consists of 10 questions. Questions 1–8 have five options to be chosen by the children in care to reflect their own personal drinking activities. Questions 9 and 10 have three options.
Scoring AUDIT
For all 10 questions, scores range from 0 to 4. For questions 1–8, the first option in the question scores 0 and the last option scores 4. For questions 9 and 10, which have only three options, the scores are allocated as 0 for the first option, 2 for the second option and 4 for the last option.
Interpretation of AUDIT score
A score of ≥ 8 is associated with harmful or hazardous drinking.
A score of ≥ 13 in women and ≥ 15 in men is likely to indicate alcohol dependency.
Missing items
Complete questionnaires will be analysed. Complete questionnaires should contain responses to all 10 questions, but there are two options to skip questions (when the questionnaires will be still considered to be complete): if participant answers ‘never’ to question 1 then skip to questions 9 and 10; and if questions 2 and 3 both score 0, again can skip to questions 9 and 10.
Note, that the AUDIT can be split into three domains. The questions measure different domains of alcohol consumption problems. The breakdown is as follows:
-
questions 1–3: measure frequency in alcohol consumption
-
questions 4–6: measure alcohol dependence
-
questions 7–10: measure alcohol-related problems.
The frequency in alcohol consumption is also known as the AUDIT-C and scores between 0 and 12. An AUDIT-C score of ≥ 4 for men and ≥ 3 for women indicates hazardous drinking or active alcohol use disorders.
ASSIST questionnaire
In the SOLID trial a ‘reduced’ version of the ASSIST instrument was used. The original ASSIST v3.1 questionnaire developed by the WHO is not validated for use by children and young people aged < 18 years.
The ASSIST-Y developed by Drug and Alcohol Services South Australia, under the guidance of the WHO, is suitable for use by children and young people aged < 18 years. The ASSIST-Y questionnaire and ASSIST feedback report card were used in the SOLID trial and can be accessed on the sa.gov website (URL: www.sahealth.sa.gov.au/wps/wcm/connect/public+content/sa+health+internet/clinical+resources/professional+development/drug+and+alcohol+training+and+development/assist+alcohol+smoking+and+substance+involvement+screening+test; accessed 14 February 2020).
The ASSIST-Y consists of six questions.
Question 1 asks if the looked after child has ever tried each of a list of substances (tobacco, alcohol, cannabis, cocaine, amphetamine, inhalants, sedatives, hallucinogens, opioids, NPSs and ‘other’). If the looked after child responds ‘no’ to all, then the interview stops. If the looked after child responds ‘yes’ to any substances in the list then move on to the second question. Question 2 asks how many times used in previous 3 months for each substance in the list in question 1. The options for question 2 are never (score 0), once or twice (score 2), monthly (score 3), weekly (score 4), daily or almost daily (score 6). If the looked after child answers ‘never’ to all items, skip to question 6. If any substance in the list were used in the previous 3 months, continue asking questions 3–5 for each substance used. Question 3 asks for details of substances used when the looked after child is away from their usual social situation or friends in the last 3 months. The options are never (score 0), once or twice (score 2), monthly (score 3), weekly (score 4), daily or almost daily (score 6). Question 4 asks if the use of each substance has led to problems with health, relationships, finances, school or with police. The options are never (score 0), once or twice (score 4), monthly (score 5), weekly (score 6), daily or almost daily (score 7). Question 5 asks if the use of each substance has had an impact on the looked after child’s usual activities. The options are never (score 0), once or twice (score 5), monthly (score 6), weekly (score 7), daily or almost daily (score 8). Question 6 asks if the use of each substance used from question 1 has resulted in expressed concern or worry from a friend or relative. The options are no, never (score 0); yes, in the past 3 months (score 6); and yes, but not in the past 3 months (score 3).
Scoring ASSIST-Y
For each substance listed, sum the scores for questions 2–6.
Note that tobacco is not coded for question 5 so should be sum of questions 2–4 and 6 for tobacco.
Interpretation of ASSIST-Y score
Aged 10–14 years
For tobacco, alcohol and inhalants, a score between 2 and 5 indicates moderate risk, requiring brief intervention (using the ASSIST feedback report card for part of the intervention).
For tobacco, alcohol and inhalants, a score of ≥ 6 indicates high risk. In addition, scores of ≥ 2 in any other substance from the list indicate high risk.
Aged 15–17 years
For tobacco and cannabis, a score between 2 and 11 indicates moderate risk. For alcohol, a score between 5 and 17 indicates moderate risk. For cocaine, sedatives, opioids, NPSs and ‘other’ drugs, a score between 2 and 6 indicates moderate risk. For amphetamines, inhalants and hallucinogens, a score between 2 and 8 indicates moderate risk.
Moderate risk requires brief intervention (using the ASSIST feedback report card for part of the intervention).
High risk scores are tobacco and cannabis (≥ 12), alcohol (≥ 18), cocaine, sedatives, opioids, NPS and ‘other’ (≥ 7), and amphetamines, inhalants and hallucinogens (≥ 9).
High risk requires brief intervention (using the ASSIST feedback report card for part of the intervention) and referral to specialist for assessment and treatment.
Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire
The SDQ can be accessed at www.sdq.info (accessed 14 February 2020). The SDQ has 25 items (questions). Note that the wording of some items vary slightly for use with young people aged < 18 years, but the scoring scheme is the same for all ages.
The 25 SDQ items can be subdivided into five subscales, each comprising five items each with a score range of 0 to 10. See Table 29 for the breakdown.
| Symptom scale | Response | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Not true | Somewhat true | Certainly true | |
| Emotional problems scale | |||
| Questions 3, 8, 13, 16 and 24 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Conduct problems scale | |||
| Questions 5, 12, 18 and 22 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Question 7 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Hyperactivity scale | |||
| Questions 2, 10 and 15 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Questions 21 and 25 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Peer problems scale | |||
| Questions 6, 19 and 23 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Questions 11 and 14 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Prosocial scale | |||
| Questions 1, 4, 9, 17 and 20 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
For all questions a response of ‘somewhat true’ scores 1, but ‘not true’ and ‘certainly true’ score either 0 or 2, depending on the question. Table 29 shows how the items are grouped to define certain problems/scales along with an indication of response scores.
Missing items
For any of the five subscales in Table 29, if at least three of the five items are completed then the scores can be scaled up pro rata (e.g. a score of 4 based on three items is scaled up to 6.67, rounded to 7 for all five items).
A total difficulties score is generated by summing all scales, except the prosocial scale. Scores range from 0 to 40.
Considered ‘missing’ if one of the four subscores is missing.
In addition, externalising score ranges from 0 to 20 and is sum of conduct problem and hyperactivity scales. Internalising score ranges from 0 to 20 and is sum of emotional problem and peer problem scales.
Note that the four separate scales add more value in high-risk samples, so are more appropriate for the looked after child.
The SDQ scores can be used as continuous scales, sometimes categories can be used for particular score ranges.
The full breakdown is 80% of population are ‘close to average’, 10% slightly lowered, 5% low and 5% very low.
Warwick–Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale
The WEMWBS consists of 14 items and can be accessed at https://warwick.ac.uk/fac/sci/med/research/platform/wemwbs (accessed 14 February 2020).
The items deal with feelings and thoughts that can be used to assess mental well-being, each scored 1 (none of the time) to 5 (all of the time) on a Likert scale.
The total score therefore ranges from 14 to 70.
The score should be presented as a mean with SD or 95% CI for the population of interest (looked after children in our trial). Subgroups, such as by site or age group should be presented in the same way.
Differences between two time points (baseline and follow-up in the SOLID trial) are assessed using the two-sample t-test.
It is recommended that samples include at least 50 in each group, if groups are to be compared. This may not be fully achieved in the SOLID trial, as the initial target was 50 per group allowing for 15 lost to follow-up.
Interpretation of well-being scores (for self-assessment, from the NHS)
-
0–32: very low score.
-
32–40: below average score.
-
40–59: average score.
-
59-70: above average score.
Missing items
A harsh approach to missing items is to drop any score that does not have all 14 items completed. This is acceptable when just a few of the responders have missing items, but often that is not the case. A softer approach can be appropriate, but none of the possible methods to deal with missing items have been assessed for the WEMWBS.
Suggested methods of dealing with missing data are (bold is approach expected in the SOLID trial):
-
calculate mean of answered items and use that as the value for missing responses.
The suggested limit for missing items is three, so responders missing more than three items should be omitted.
For the SOLID trial we assessed the missing items. We will consider the randomness of missing items (to ensure that certain items are not been systematically omitted).
Romantic and intimate behaviours
This questionnaire is filled out for looked-after children aged ≥ 12 years, which covers all of those recruited into the study, as the population is looked-after children aged 12–20 years.
Questions relating to enjoyment of sexual experience will be replaced by two questions from the ESPAD multicountry survey of alcohol and drug use, assessing regret in engagement in sexual contacts and engagement in unprotected sexual intercourse, particularly relevant in relation to sexual encounters preceded by substance misuse. The advantage of the CASI is that it is graded, with more intimate sexual contact not asked about if lesser contact, such as kissing and cuddling, has not yet been experienced. This instrument has been discussed with the study PPI group, which acknowledged the graded nature of administration and supported its use. A computerised version will be administered.
The questionnaire has 10 items, but some have subquestions so a total of 14 questions are asked. Table 30 shows the questions asked regarding romantic and intimate behaviours.
| Question number: original | Question number: the SOLID trial | Question text |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Not asked | Have you hugged anybody? |
| 2 | 1 | Have you held hands? |
| 3 | 2 | Have you spent time alone? |
| 4 | 3 | Have you kissed? |
| 4a | 4 | Have you been kissed by anybody? |
| 5 | 5 | Have you cuddled? |
| 6 | 6 | Have you lain down together? |
| 7 | 7 | Has someone put their hands under your clothing? |
| 8 | 8 | Have you put your hands under someone else’s clothing? |
| 9 | 9 | Have you been undressed with your [private parts] showing? |
| 9a | 9a | Have you touched or fondled someone’s private parts? |
| 9b | 9b | Has someone touched or fondled your private parts? |
| 9c | 9c | Have you had oral sex? |
| 10 | 10 | Have you had sexual intercourse? |
The responder is also asked how much they enjoyed each action after the initial question. Then after each item, the looked-after child is asked whether or not they had a condom with them. This is followed for question 14, by asking if they used the condom. Note that from question 7 onwards the looked-after child is asked if they regretted the action.
Interview can end early with certain responses:
-
If questions 4 and 4a are both answered ‘no’.
-
If the answer to question 6 is ‘no’.
-
If the answer to questions 7 and 8 is ‘no’.
From this point onwards only continues if responder answers ‘yes’ to a question. As soon as a response is ‘no’, interview ends.
Each question is scored as ‘no’ (0) or ‘yes’ (1).
For all questions also ask
If ‘yes’, ask how much did you enjoy it? Not at all (1), a bit (2), quite a lot (3) or very much (4).
Then ask did they have a condom? No (0), yes (1).
For question 7 onwards also ask
Did they regret? Not at all (1), a bit (2), quite a lot (3) or very much (4).
Descriptive statistics can be presented separately for males and females.
As there is not a scoring manual for this questionnaire, the chief investigator suggested that we split the activities in the questions into minor and advanced. Note that question 1 is not asked in the SOLID trial. The first five questions (questions 2–6) fall into the minor category, and the remaining four questions are the more advanced (questions 7–10). Note that question 1 was not asked in the SOLID trial, so minor category will be the sum of questions 2–6.
The stopping rules will also need to be considered in the analysis of this questionnaire.
Scored 1 for having done the activity, and 0 for not.
Summary statistics for both categories will be presented. The chief investigator also wanted to summarise the ‘regret’ subquestion asked after each item. (So the study will not be looking at the ‘enjoyed’ and ‘had a condom’ subquestions for this feasibility study.) The regret question is scored as 1 (not at all), 2 (a bit), 3 (quite a lot) or 4 (very much).
For the self-reported romantic and intimate behaviour, measured using items taken from the CASI questionnaire used in the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children and supplemented with questions relating to regret in sexual encounters and unprotected sex used in the ESPAD, four measures were derived from the questionnaire (number 1 was the score calculated as per the skipping rules, but numbers 2–4 were not standard scoring schemes from the questionnaire – the SOLID trial-specific outcomes derived from the questionnaire data).
-
Romantic and intimate behaviour. This summarises the whole questionnaire with a score for each participant. This includes the subquestions relating to ‘enjoy’, ‘regret’ and whether or not they had a condom with them during the particular specified activities.
-
Romantic and intimate behaviour (minor). This is simply a score derived from adding up the scores to questions 2, 3, 4, 4a, 5 and 6 of questionnaire (1 for yes, 0 for no, so scores range from 0 to 6).
-
Romantic and intimate behaviour (advanced). This is simply a score derived from adding up the scores to questions 7, 8, 9, 9a, 9b, 9c and 10 of the questionnaire (1 for yes, 0 for no, so scores range from 0 to 7).
-
Romantic and intimate behaviour (regret). For each of questions from question 7 onwards the participants were asked if they regretted the action. They can score the regret as 1 (not at all), 2 (a bit), 3 (quite a lot) or 4 (very much). The regret score is calculated as the sum of these regret parts of questions. Note that due to stopping rules the minimum regret score can be 0 if the participant did not take part in any of the activities for which the regret question was asked. Scores of 1–6 imply that the participant answered one to six questions, but had no regrets about any of them (score range is 0–28).
The skip logic for the questionnaire is shown in Table 31.
| Study ID | Question 1 | Question 2 | Question 3 | Question 4 | Question 5 | Skip logic 1 | Question 6 | Skip logic 2 | Question 7 | Question 8 | Skip logic 3 | Question 9 | Skip logic 4 | Question 9a | Skip logic 5 | Question 9b | Skip logic 6 | Question 9c | Skip logic 7 | Question 10 | Skip logic 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4002 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 5 | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 5 | End |
| 4005 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 2 | Continue | 3 | 3 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | End |
| 4006 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 2 | Continue | 3 | 3 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | End |
| 4007 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 5 | 4 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | End |
| 4008 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 4 | 4 | Continue | 0 | Stop | ||||||||
| 4009 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 0 | 0 | Stop | ||||||||||
| 4010 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | Continue | 2 | Continue | 3 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 0 | Stop | ||
| 4011 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Stop | |||||||||||||||
| 4012 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | 4 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | End |
| 4014 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | End |
| 4017 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | 4 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 6 | End |
| 4018 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 4 | 4 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | End |
| 4019 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Stop | |||||||||||||||
| 4020 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | Continue | 0 | Stop | |||||||||||||
| 4021 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Continue | 2 | Continue | 3 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 3 | End |
| 4022 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | End |
| 4023 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 4 | End |
| 5001 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 0 | Stop | |||||||||||||
| 5002 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | 5 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 6 | End |
| 5004 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 4 | Continue | 0 | Stop | |||||||||||||
| 5008 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Stop | |||||||||||||||
| 6003 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 0 | Stop | |||||||||||||
| 6004 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 2 | Continue | 6 | 5 | Continue | 7 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 7 | End |
| 6007 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 0 | Stop | ||
| 6008 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 | Continue | 0 | Stop | |||||||||||||
| 6009 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | End |
| 6012 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 2 | Continue | 6 | 6 | Continue | 7 | Continue | 7 | Continue | 7 | Continue | 7 | Continue | 7 | End |
| 6014 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 0 | 0 | Stop | ||||||||||
| 6017 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 2 | Continue | 3 | 3 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 4 | End |
| 6020 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 4 | 4 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | End |
| 7002 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 2 | Continue | 3 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 0 | Stop | ||||
| 7003 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 7 | 7 | Continue | 7 | Continue | 7 | Continue | 7 | Continue | 7 | Continue | 7 | End |
| 7005 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Stop | |||||||||||||||
| 7007 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | End |
| 7009 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | Continue | 2 | Continue | 0 | 0 | Stop | ||||||||||
| 7012 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 5 | 5 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 0 | Stop | ||
| 7013 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | End |
| 7015 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | End |
| 7016 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | 5 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 0 | Stop | ||
| 7017 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 2 | Continue | 5 | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | End |
| 7018 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 4 | 4 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | End |
| 7020 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | 4 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 7 | Continue | 5 | End |
| 7023 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | 5 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | End |
| 7024 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Continue | 0 | Stop | |||||||||||||
| 7025 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 5 | 4 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | End |
| 7026 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 0 | 3 | Continue | 0 | Stop | ||||||||
| 7027 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Continue | 2 | Continue | 0 | 0 | Stop | ||||||||||
| 7028 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | Continue | 0 | Stop | |||||||||||||
| 7029 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 5 | 4 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 5 | Continue | 6 | Continue | 6 | End |
| 7031 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Stop | |||||||||||||||
| 7033 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | 5 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 0 | Stop | ||
| 8005 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 2 | Continue | 3 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 3 | End |
| 8009 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 2 | Continue | 3 | 3 | Continue | 0 | Stop | ||||||||
| 8014 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 2 | Continue | 4 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 0 | Stop | ||
| 8015 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Continue | 0 | Stop | |||||||||||||
| 8016 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 0 | 0 | Stop | ||||||||||
| 8017 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Continue | 0 | Stop | |||||||||||||
| 9003 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 0 | 0 | Stop | ||||||||||
| 9005 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | 4 | Continue | 0 | Stop | ||||||||
| 9007 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Continue | 3 | Continue | 4 | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | Continue | 4 | End |
-
Skip logic 1: if participant answers ‘no’ to questions 3, 4 and 5 then stop, otherwise continue.
-
Skip logic 2: if participant answers ‘no’ to question 6 then stop, otherwise continue.
-
Skip logic 3: if participant answers ‘no’ to question 8, and also question 7 then stop, if question 8 is ‘no’ but question 7 was ‘yes’ then move to question 9 (continue).
-
Skip logic 4 to skip logic 7: from question 9 onwards, if answer is ‘no’ then stop, otherwise continue.
-
Skip logic 8: if answer to question 10 is ‘yes’ then end.
The score for each question are calculated as:
-
Questions 1–6: score is 0 if answer ‘no’ or if ‘yes’ enjoy (1 = not at all, 2 = a bit, 3 = quite a lot, 4 = very much). Score ranges from 0 to 4.
-
Questions 7 and 8: score as for questions 1–6 + regret (1 = not at all, 2 = a bit, 3 = quite a lot, 4 = very much). Score ranges from 0 to 8.
-
Questions 9 and 10: as for questions 7 and 8 + condom (no = 0, yes = 1). Score ranges from 0 to 9.
Antisocial/criminal behaviour
The questionnaire contains 15 questions. For each of the 15 questions the tablet version used in the SOLID trial asks how often in the last year have you done any of the following:
-
Skipped or skived off school.
-
Broken into a car or van with the intention of stealing something out of it.
-
Hit, kicked or punched someone on purpose.
-
Deliberately set fire or tried to set fire to somebody’s property or a building.
-
Taken money or something else that did not belong to you from home without permission.
-
Used force, threats or a weapon to get money or something else from somebody.
-
Written things or sprayed paint on property that did not belong to you.
-
Gone into or broken into a house or building with the intentions of stealing something.
-
Deliberately damaged or destroyed property that did not belong to you.
-
Carried a knife or weapon with you for protection or in case it was needed in a fight.
-
Taken money or something else that did not belong to you from school.
-
Stolen or ridden in a stolen car or van or on a stolen motorbike.
-
Been rowdy or rude in a public place so that people complained or you got into trouble.
-
Taken something from a shop or a store without paying for it.
-
Not paid the correct fare or not paid at all on a bus or train.
The options for each of the 15 questions are not at all (1), just once (2), two to five times (3) or six or more times (4).
The questionnaire seeks to evaluate co-occurrence of antisocial behaviour and alcohol use. Descriptive statistics will be presented separately for male and female.
As there is not a scoring manual for this questionnaire the chief investigator suggested that as all are quite serious, except for question 1 (skipping off school), we do not split into minor and advanced.
Scored 1 for having done the activity, and 0 for not.
Summary statistics will be presented.
The chief investigator also wanted to summarise the ‘How often in the last year have you done any of the following’ subquestion asked after each item. The subquestion is scored as 1 (not at all), 2 (just once), 3 (two to five times) and 4 (six or more times).
Use of Health and Social Services Questionnaire
This questionnaire asked about participants’ use of health and social resources within the last 12-month period. If the answer was none, participants were requested to enter a zero (0) into the survey.
The questions were as follows.
Hospital services
-
In the past 12 months how many times have you visited an accident and emergency department as a patient?
-
In the past 12 months how many nights have you spent in hospital as a patient?
-
In the past 12 months how many times have you been admitted to hospital but not been kept in overnight?
-
In the past 12 months how many appointments have you had as an outpatient at the hospital?
General practice services
-
In the past 12 months how many times have you visited a doctor at your general practice?
-
In the past 12 months how many times has a doctor visited you at home?
-
In the past 12 months how many times have you visited the nurse at your general practice?
-
In the past 12 months how many times has a nurse visited you at home?
-
In the past 12 months how many times have you received a prescription?
Social and care services
-
In the past 12 months how many times have you been visited by a social worker at home?
-
In the past 12 months how many times have you visited a social worker at their office?
-
In the past 12 months how many times have you been visited at home by a care worker or advisor?
-
In the past 12 months how many times have you visited a care worker or advisor at their office?
Criminal justice resources
-
In the past 12 months how many times have you been arrested, cautioned or received an on-the-spot fine?
-
In the past 12 months how many days have you appeared at a magistrate’s court?
-
In the past 12 months how many times have you appeared at a crown court?
-
In the past 12 months how many days have you spent in prison?
Descriptive statistics only were provided for this questionnaire.
Alcohol timeline follow-back
This is a drinking assessment method that obtains estimates of daily drinking. Use of calendar to provide retrospective estimates of daily drinking over a specified period (30 days in the SOLID trial). This method is recommended to gain fairly precise estimates.
The TLFB can generate variables that provide a wide range of information about an individual’s drinking (e.g. pattern, variability and magnitude of drinking). The method is recommended for use when relatively precise estimates of drinking are necessary, especially when a complete picture of drinking days (i.e. high- and low-risk days) is needed (evaluating drinking pre–post treatment).
The TLFB in the SOLID trial will seek to identify the ‘number of occasions when ≥ 5 standard drink units are consumed on a single drinking day’.
The TLFB-30 will be compared with first 7 days of TLFB and the shorter AUDIT, ASSIST-Y and CRAFFT tools. A summary of the questionnaires is in Table 32.
| Outcome measure | Definition | Scoring | Subscales | Missing value rules | Thresholds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUDIT questionnaire | Screen for alcohol misuse |
Ten questions Questions 1–8 have five options and questions 9 and 10 have three options Scoring: for all 10 questions scores range from 0 to 4 For questions 1–8: the first option in the question scores 0 and the last option scores 4 For questions 9 and 10: the scores are allocated as 0 for the first option, 2 for the second option and 4 for the last option Range of scores is 0 to 40 AUDIT-C range of scores is 0–12 |
Three subscales of the AUDIT-C screen is: Three questions on the amount and frequency of drinking (questions 1–3) Three questions on alcohol dependence (questions 4–6) Four questions on problems caused by alcohol (questions 7–10) |
None |
Total AUDIT score: A score of ≥ 8 is associated with harmful or hazardous drinking A score of ≥ 13 in women and ≥ 15 in men is likely to indicate alcohol dependency AUDT-C score: A score of ≥ 3 in women and ≥ 4 in men is likely to indicate hazardous drinking or active alcohol use disorders |
| ASSIST-Y | Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test (adapted) |
For each substance listed, sum the scores for questions 2–6 Note that tobacco is not coded for question 5, so should be sum of questions 2–4 and 6 for tobacco |
No subscales, but slightly different versions of questionnaire and different thresholds for those aged 10–14 years and ≥ 15 years | None |
Aged 10–14 years: For tobacco, alcohol and inhalants a score of 2–5 is moderate risk, a score of > 6 is high risk. Scores > 2 in any other substance indicates high risk Aged 15–17 years: Any injection of drugs is high risk. For tobacco and cannabis a score of 2–11 is moderate risk. For alcohol a score of 5–17 is moderate risk. For cocaine, sedatives, opioids, NPS and ‘other’ drugs a score of 2–6 is moderate risk. For amphetamines, inhalants and hallucinogens a score of 2–8 is moderate risk. High risk scores: tobacco and cannabis > 12; alcohol > 18; cocaine, sedatives, opioids, NPS and ‘other’ > 7; and amphetamines, inhalants and hallucinogens > 9 |
| SDQ | Behavioural screening questionnaire for young people aged 3–16 years |
SDQ scores can be used as continuous scales, sometimes categories can be used for particular score ranges Each of the five subscales is scored 0–10 Total difficulties score by summing all scales, except the prosocial scale. Scores range from 0 to 40 Check with TMG which category version 3 or 4 categories |
Total score (all 25) and five subscales each with five questions (emotional problems, conduct problems, hyperactivity, peer problems, prosocial) and two further subscales (externalising score which is sum of emotional and conduct subscales and internalising score which is sum of hyperactivity and peer scales) |
For any of five subscales, if at least three of five items is completed. Scores scaled up pro rata (e.g. a score of 4 based on three items is scaled up to 6.67, rounded to 7 for all five items) Total score missing if one of four subscores missing |
Total difficulties: close to average 0–14, slightly raised 15–17, high 18–19, very high 20–40 Emotional problems: close to average 0–4, slightly raised 5, high 6, very high 7–10 Conduct problems: close to average 0–3, slightly raised 4, high 5, very high 6–10 Hyperactivity: close to average 0–5, slightly raised 6, high 7, very high 8–10 Peer problems: close to average 0–2, slightly raised 3, high 4, very high 5–10 Prosocial: close to average 7–10, slightly lowered 6, low 5, very low 0–4 |
| WEMWBS | Deals with feelings and thoughts that can be used to assess mental well-being |
Fourteen items each scoring 1–5. Total score ranges from 14 to 70 The score should be presented as a mean with SD or 95% CI for the population of interest |
No subscales |
Missing more than three items are omitted The SOLID trial: calculate missing items as average of answered |
Well-being scores: 0–32, very low; 32–40, below average; 40–59, average; 59–70, above average |
| CASI: romantic and intimate behaviours | To assess relationships between alcohol consumption and sexual behaviours | Ten items, but some have subquestions, so a total of 14 questions asked | Looked after children aged ≥ 12 years analysed separately for boys and girls | Interview can end early with certain responses:
|
|
| Antisocial/criminal behaviour | To evaluate co-occurrence of antisocial behaviour and alcohol use |
Contains 15 questions For the SOLID trial (follow-up only) we will give the numbers choosing the ‘yes’ option to each question, as well as the numbers specifying that they have done the action once, two to five times or six or more times |
No subscales | None | None |
| Alcohol TLFB | Obtains estimates of daily drinking | No scoring, but use of calendar to provide retrospective estimates of daily drinking over a specified period, 30 days in the SOLID trial | 7-day period also of interest for comparisons in the SOLID trial | None | The TLFB in the SOLID trial will seek to identify the ‘number of occasions when ≥ 5 standard drink units are consumed on a single drinking day’ |
Appendix 4 Statistical data
Parts of this appendix have been adapted from Alderson et al. 67 This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt and build upon this work, for commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The text includes minor additions and formatting changes to the original text.
Baseline data
Tables 33–36 show the baseline data summary statistics by sex, age, residential status and placement type for the children in care.
| AUDIT and AUDIT-C (questionnaire scoring range) | Sex | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male (N = 50) | Female (N = 61) | |||||||||||||||
| n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | |
| AUDIT (0–40) | 50 | 0 | 2 | 7.5 | 14 | 23 | 8.1 | 6.6 | 61 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 16 | 30 | 11.3 | 7.7 |
| AUDIT-C (0–12) | 50 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 9 | 4.0 | 2.9 | 61 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 5.2 | 2.5 |
| AUDIT and AUDIT-C (questionnaire scoring range) | Age | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 18 years (N = 57) | ≥ 18 years (N = 54) | |||||||||||||||
| n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | |
| AUDIT (0–40) | 57 | 0 | 4 | 8 | 14 | 29 | 9.0 | 7.0 | 54 | 0 | 5 | 9.5 | 16 | 30 | 10.8 | 7.7 |
| AUDIT-C (0–12) | 57 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 4.1 | 2.6 | 54 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 10 | 5.2 | 2.8 |
| AUDIT and AUDIT-C (questionnaire scoring range) | Placement type | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residential (N = 19) | Non-residential (N = 92) | |||||||||||||||
| n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | |
| AUDIT (0–40) | 19 | 0 | 4 | 13 | 15 | 29 | 11.4 | 8.6 | 92 | 0 | 4 | 8 | 15 | 30 | 9.6 | 7.1 |
| AUDIT-C (0–12) | 19 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 4.5 | 2.6 | 92 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 4.7 | 2.8 |
| AUDIT and AUDIT-C (questionnaire scoring range) | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUDIT (0–40) | ||||||||
| Foster outside family | 28 | 0 | 2.5 | 6 | 13 | 20 | 7.3 | 5.8 |
| Foster within family | 6 | 0 | 5 | 9.5 | 13 | 17 | 9.0 | 6.4 |
| Residential home | 19 | 0 | 4 | 13 | 15 | 29 | 11.4 | 8.6 |
| Own accommodation | 49 | 0 | 4 | 10 | 17 | 30 | 10.8 | 7.9 |
| With parents | 6 | 4 | 5 | 9 | 17 | 21 | 10.8 | 6.8 |
| Other | 3a | |||||||
| AUDIT-C (0–12) | ||||||||
| Foster outside family | 28 | 0 | 2 | 4.5 | 6 | 9 | 4.1 | 2.7 |
| Foster within family | 6 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 4.0 | 2.8 |
| Residential home | 19 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 4.5 | 2.6 |
| Own accommodation | 49 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 10 | 5.2 | 2.9 |
| With parents | 6 | 3 | 4 | 4.5 | 8 | 9 | 5.5 | 2.4 |
| Other | 3a | |||||||
Tables 37–42 show the ASSIST-Y baseline data summary statistics by sex, age, residential status and placement type for the children in care.
| Type of substance used | Sex | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male (N = 50) | Female (N = 61) | |||||||||||||||||
| Tried (% n of N) | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n > 3ma | Tried (% n of N) | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n > 3ma | |
| Tobaccob | 43 (86) | 0 | 6 | 12 | 18 | 25 | 12.0 | 7.3 | 6 | 50 (82) | 0 | 12 | 12 | 18 | 25 | 13.8 | 6.3 | 2 |
| Alcohol | 47 (94) | 0 | 3 | 6 | 12 | 25 | 7.7 | 6.3 | 6 | 61 (100) | 0 | 2 | 7 | 15 | 28 | 9.6 | 8.1 | 4 |
| Cannabis | 39 (78) | 0 | 2 | 9 | 17 | 33 | 10.2 | 9.2 | 9 | 42 (69) | 0 | 2 | 9 | 18 | 30 | 10.3 | 8.7 | 10 |
| Cocaine | 20 (40) | 0 | 1 | 4 | 9 | 15 | 5.4 | 5.1 | 6 | 20 (33) | 0 | 1 | 5 | 17.5 | 22 | 8.8 | 8.4 | 7 |
| Amphetamine | 15 (30) | 0 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 3.6 | 3.2 | 7 | 12 (20) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.5 | 21 | 3.7 | 6.3 | 8 |
| Inhalants | 3c (6) | 1 | 6 (10) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 3 | |||||||
| Sedative | 10 (20) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 10 | 3.1 | 3.8 | 5 | 17 (28) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 28 | 6.1 | 8.3 | 5 |
| Hallucinogens | 9 (18) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 9 | 3.3 | 3.7 | 4 | 10 (16) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 21 | 3.6 | 7.3 | 7 |
| Opioids | 3c (6) | 1 | 8 (13) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.5 | 21 | 4.8 | 8.9 | 6 | |||||||
| NPS | 10 (20) | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | 8 | 14 | 4.3 | 4.7 | 4 | 9 (15) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 11 | 3.8 | 4.3 | 4 |
| Otherd | 0c (0) | 0 | 3c (5) | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Type of substance used | Age | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 18 years (N = 57) | ≥ 18 years (N = 54) | |||||||||||||||||
| Tried (% n of N) | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n > 3ma | Tried (% n of N) | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n > 3ma | |
| Tobaccob | 49 (86) | 0 | 7 | 12 | 16 | 25 | 12.0 | 7.2 | 7 | 44 (81) | 0 | 12 | 12 | 18 | 25 | 14.1 | 6.2 | 1 |
| Alcohol | 55 (96) | 0 | 2 | 6 | 13 | 24 | 7.6 | 6.6 | 5 | 53 (98) | 0 | 3 | 7 | 15 | 28 | 10.0 | 8.0 | 5 |
| Cannabis | 38 (67) | 0 | 0 | 9.5 | 17 | 33 | 9.6 | 8.7 | 11 | 43 (80) | 0 | 3 | 8 | 19 | 30 | 10.8 | 9.1 | 8 |
| Cocaine | 14 (25) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 19 | 4.4 | 5.5 | 5 | 26 (48) | 0 | 2 | 6.5 | 15 | 22 | 8.5 | 7.5 | 8 |
| Amphetamine | 11 (19) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 21 | 4.3 | 6.4 | 6 | 16 (30) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 9 |
| Inhalants | 4c (7) | 1 | 5c (9) | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Sedative | 12 (21) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5.5 | 22 | 5.1 | 7.1 | 4 | 15 (28) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 28 | 4.9 | 7.2 | 6 |
| Hallucinogens | 5c (9) | 2 | 14 (26) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 21 | 3.0 | 5.8 | 9 | |||||||
| Opioids | 3c (5) | 2 | 8 (15) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11.5 | 21 | 5.5 | 8.7 | 5 | |||||||
| NPS | 5c (9) | 2 | 14 (26) | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | 6 | 10 | 3.6 | 3.5 | 6 | |||||||
| Otherd | 2c (4) | 1 | 1c (2) | 0 | ||||||||||||||
| Type of substance used | Placement type | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residential home (N = 19) | Non-residential type (N = 92) | |||||||||||||||||
| Tried (% n of N) | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n > 3ma | Tried (% n of N) | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n > 3ma | |
| Tobaccob | 18 (95) | 2 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 25 | 14.8 | 6.0 | 0 | 75 (82) | 0 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 25 | 12.5 | 6.9 | 8 |
| Alcohol | 18 (95) | 0 | 2 | 6.5 | 15 | 21 | 8.6 | 7.3 | 2 | 90 (98) | 0 | 3 | 6.5 | 14 | 28 | 8.8 | 7.5 | 8 |
| Cannabis | 15 (79) | 0 | 5 | 12 | 20 | 33 | 13.8 | 8.9 | 1 | 66 (72) | 0 | 2 | 7 | 17 | 30 | 9.4 | 8.8 | 18 |
| Cocaine | 7 (37) | 0 | 2 | 5 | 12 | 19 | 7.0 | 6.8 | 1 | 33 (36) | 0 | 0 | 5 | 14 | 22 | 7.1 | 7.2 | 12 |
| Amphetamine | 4c (21) | 2 | 23 (25) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 3.0 | 3.2 | 13 | |||||||
| Inhalants | 2c (11) | 0 | 7 (8) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 4 | |||||||
| Sedative | 4c (21) | 2 | 23 (25) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 28 | 5.0 | 7.0 | 8 | |||||||
| Hallucinogens | 2c (11) | 0 | 17 (18) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 21 | 2.6 | 5.4 | 11 | |||||||
| Opioids | 1c (5) | 1 | 10 (11) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 21 | 4.6 | 7.9 | 6 | |||||||
| NPS | 4c (21) | 1 | 15 (16) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 10 | 3.3 | 3.5 | 7 | |||||||
| Otherd | 1c (5) | 0 | 2c (2) | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Type of substance used | Foster outside family (N = 28) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tried (% n of N) | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | Not taken substance in last 3 months but has previously | |
| Tobaccoa | 20 (71) | 0 | 3 | 12 | 18 | 25 | 11.6 | 7.9 | 4 |
| Alcohol | 27 (96) | 0 | 2 | 3 | 10 | 25 | 6.4 | 6.2 | 2 |
| Cannabis | 17 (61) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 22 | 5.2 | 6.4 | 7 |
| Cocaine | 6 (21) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 5 |
| Amphetamine | 2b (7) | 2 | |||||||
| Inhalants | 1b (4) | 0 | |||||||
| Sedative | 3b (11) | 1 | |||||||
| Hallucinogens | 2b (7) | 1 | |||||||
| Opioids | 1b (4) | 1 | |||||||
| NPS | 0b (0) | 0 | |||||||
| Other | 0b (0) | 0 | |||||||
| Type of substance used | Own accommodation (N = 49) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tried (% n of N) | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | Not taken substance in last 3 months but has previously | |
| Tobaccoa | 42 (86) | 0 | 12 | 12 | 18 | 25 | 13.0 | 7.0 | 4 |
| Alcohol | 48 (98) | 0 | 5 | 8 | 16.5 | 28 | 10.6 | 7.8 | 4 |
| Cannabis | 40 (82) | 0 | 4 | 10.5 | 19.5 | 30 | 11.9 | 9.2 | 8 |
| Cocaine | 25 (51) | 0 | 2 | 7 | 15 | 22 | 8.9 | 7.3 | 6 |
| Amphetamine | 20 (41) | 0 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 3.5 | 3.2 | 10 |
| Inhalants | 5b (10) | 3 | |||||||
| Sedative | 19 (39) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 28 | 5.5 | 7.7 | 7 |
| Hallucinogens | 15 (31) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 21 | 2.8 | 5.7 | 10 |
| Opioids | 7 (14) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 17 | 21 | 6.6 | 8.8 | 3 |
| NPS | 15 (31) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 10 | 3.3 | 3.5 | 7 |
| Otherc | 2b (4) | 1 | |||||||
| Type of substance used | Non-residential type (N = 92) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tried (% n of N) | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | Not taken substance in last 3 months but have previously | |
| Tobaccoa | 75 (82) | 0 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 25 | 12.5 | 6.9 | 8 |
| Alcohol | 90 (98) | 0 | 3 | 6.5 | 14 | 28 | 8.8 | 7.5 | 8 |
| Cannabis | 66 (72) | 0 | 2 | 7 | 17 | 30 | 9.4 | 8.8 | 18 |
| Cocaine | 33 (36) | 0 | 0 | 5 | 14 | 22 | 7.1 | 7.2 | 12 |
| Amphetamine | 23 (25) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 3.0 | 3.2 | 13 |
| Inhalants | 7 (8) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 4 |
| Sedative | 23 (25) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 28 | 5.0 | 7.0 | 8 |
| Hallucinogens | 17 (18) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 21 | 2.6 | 5.4 | 11 |
| Opioids | 10 (11) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 21 | 4.6 | 7.9 | 6 |
| NPS | 15 (16) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 10 | 3.3 | 3.5 | 7 |
| Otherc | 2b (2) | 1 | |||||||
Placement split by category
Tables 43–46 show baseline SDQ summary statistics by sex, age and placement type.
| SDQ subscale | Sex | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male (N = 50) | Female (N = 61) | |||||||||||||
| Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | |
| Emotional problems (0–10) | 0 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 3.1 | 2.3 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 10 | 5.4 | 2.4 |
| Conduct problems (0–10) | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 8 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 2.8 | 2.0 |
| Hyperactivity (0–10) | 0 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 4.6 | 2.2 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 5.5 | 2.6 |
| Peer problems (0–10) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 8 | 3.1 | 1.4 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 9 | 3.3 | 2.2 |
| Prosocial (0–10) | 0 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 7.1 | 2.2 | 3 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 8.0 | 1.7 |
| Total difficulties (0–40)a | 3 | 10 | 14 | 17 | 31 | 13.9 | 5.5 | 5 | 13 | 18 | 22 | 29 | 17.0 | 6.6 |
| SDQ subscale | Age | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 18 years (N = 57) | ≥ 18 years (N = 54) | |||||||||||||
| Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | |
| Emotional problems (0–10) | 0 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 3.8 | 2.8 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 5.0 | 2.2 |
| Conduct problems (0–10) | 0 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 3.1 | 1.9 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 2.7 | 1.9 |
| Hyperactivity (0–10) | 0 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 5.3 | 2.7 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 4.9 | 2.1 |
| Peer problems (0–10) | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 9 | 3.1 | 2.1 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.3 | 1.7 |
| Prosocial (0–10) | 0 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 7.3 | 2.2 | 4 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 7.8 | 1.7 |
| Total difficulties (0–40)a | 4 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 31 | 15.3 | 6.7 | 3 | 12 | 15.5 | 20 | 27 | 15.9 | 5.9 |
| SDQ subscale | Placement type | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residential (N = 19) | Non-residential (N = 92) | |||||||||||||
| Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | |
| Emotional problems (0–10) | 0 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 3.8 | 2.7 | 0 | 2 | 4.5 | 6 | 10 | 4.5 | 2.6 |
| Conduct problems (0–10) | 0 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 3.7 | 2.0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 2.8 | 1.8 |
| Hyperactivity (0–10) | 1 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 5.8 | 2.4 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 5.0 | 2.4 |
| Peer problems (0–10) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 8 | 2.6 | 1.9 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 9 | 3.3 | 1.9 |
| Prosocial (0–10) | 0 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 6.4 | 2.7 | 4 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 7.8 | 1.7 |
| Total difficulties (0–40)a | 7 | 11 | 15 | 20 | 31 | 15.9 | 6.1 | 3 | 11.5 | 15 | 20 | 29 | 15.5 | 6.4 |
| SDQ subscale | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emotional problems (0–10) | ||||||||
| Foster outside family | 28 | 0 | 1.5 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 4.0 | 2.8 |
| Foster within family | 6 | 1 | 2 | 4.5 | 6 | 7 | 4.2 | 2.5 |
| Residential home | 19 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 3.8 | 2.7 |
| Own accommodation | 49 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 5.1 | 2.3 |
| With parents | 6 | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | 5 | 2.5 | 2.4 |
| Other | 3a | |||||||
| Conduct problems (0–10) | ||||||||
| Foster outside family | 28 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 2.4 | 1.7 |
| Foster within family | 6 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 7 | 2.5 | 2.7 |
| Residential home | 19 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 3.7 | 2.0 |
| Own accommodation | 49 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 2.9 | 1.7 |
| With parents | 6 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 3.2 | 2.1 |
| Other | 3a | |||||||
| Hyperactivity (0–10) | ||||||||
| Foster outside family | 28 | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 4.7 | 2.8 |
| Foster within family | 6 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 3.2 | 1.7 |
| Residential home | 19 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 5.8 | 2.4 |
| Own accommodation | 49 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 5.1 | 2.2 |
| With parents | 6 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 9 | 9 | 6.5 | 2.6 |
| Other | 3a | |||||||
| Peer problems (0–10) | ||||||||
| Foster outside family | 28 | 0 | 2 | 2.5 | 4 | 9 | 3.1 | 2.1 |
| Foster within family | 6 | 0 | 2 | 2.5 | 5 | 5 | 2.8 | 1.9 |
| Residential home | 19 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 8 | 2.6 | 1.9 |
| Own accommodation | 49 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 3.7 | 1.7 |
| With parents | 6 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 2.2 | 2.3 |
| Other | 3a | |||||||
| Prosocial (0–10) | ||||||||
| Foster outside family | 28 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9.5 | 10 | 8.2 | 1.5 |
| Foster within family | 6 | 4 | 7 | 8.5 | 9 | 9 | 7.7 | 2.0 |
| Residential home | 19 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 6.4 | 2.7 |
| Own accommodation | 49 | 4 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 7.8 | 1.8 |
| With parents | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 7.8 | 1.3 |
| Other | 3a | |||||||
| Total difficulties (0–40)b | ||||||||
| Foster outside family | 28 | 4 | 7.5 | 13.5 | 18 | 29 | 14.2 | 7.0 |
| Foster within family | 6 | 6 | 7 | 13 | 16 | 21 | 12.7 | 5.6 |
| Residential home | 19 | 7 | 11 | 15 | 20 | 31 | 15.9 | 6.1 |
| Own accommodation | 49 | 3 | 14 | 17 | 21 | 27 | 16.7 | 6.1 |
| With parents | 6 | 10 | 10 | 11.5 | 21 | 22 | 14.3 | 5.7 |
| Other | 3a | |||||||
Tables 47–50 show baseline WEMWBS questionnaire summary statistics by sex, age and placement type.
| WEMWBS questionnaire scoring (range 0–70) | Sex | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male (N = 50) | Female (N = 61) | |||||||||||||
| Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | |
| WEMWBS | 14 | 40 | 47.5 | 54 | 70 | 47.1 | 11.3 | 17 | 35 | 42 | 50 | 70 | 41.8 | 11.5 |
| WEMWBS questionnaire scoring (range 0–70) | Age | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 18 years (N = 57) | ≥ 18 years (N = 54) | |||||||||||||
| Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | |
| WEMWBS | 14 | 40 | 44 | 50 | 70 | 44.5 | 11.3 | 17 | 37 | 45 | 53 | 66 | 43.7 | 12.4 |
| WEMWBS questionnaire scoring (range 0–70) | Placement type | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residential (N = 19) | Non-residential (N = 92) | |||||||||||||
| Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | |
| WEMWBS | 14 | 40 | 44 | 50 | 64 | 43.8 | 10.4 | 17 | 37 | 44 | 51.5 | 70 | 44.2 | 11.9 |
| Placement | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foster outside family | 28 | 18 | 41.5 | 47.5 | 50.5 | 70 | 46.4 | 11.7 |
| Foster within family | 6 | 36 | 42 | 45 | 55 | 61 | 47.3 | 9.3 |
| Residential home | 19 | 14 | 40 | 44 | 50 | 64 | 43.8 | 10.4 |
| Own accommodation | 49 | 17 | 33 | 40 | 50 | 70 | 41.8 | 12.7 |
| With parents | 6 | 40 | 48 | 49.5 | 53 | 54 | 49.0 | 5.0 |
| Other | 3a |
12-month follow-up data
Tables 51–62 present summary statistics for the follow-up data collected at 12 months post recruitment. Table 51 shows the follow-up status for children in care within the SOLID trial.
| Follow-up status | Randomised arm, n | Combined arms, n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET | SBNT | Control | ||
| Follow-up completed | 17 | 23 | 20 | 60 (54) |
| Declined follow-up | 7 | 7 | 5 | 19 (17) |
| Appointment date set but did not attend | 5 | 3 | 3 | 11 (10) |
| Could not contact: lost to follow-up | 4 | 3 | 4 | 11 (10) |
| Closed to social services: lost to follow-up | 4 | 2 | 1 | 7 (6) |
| Follow-up inappropriate (mental health) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 (< 2) |
| Unable to contact due to circumstances (secure unit) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 (< 2) |
| Total | 38 | 38 | 36 | 112 |
Tables 52 and 53 show the episodes of heavy drinking in the preceding 30- and 7-day periods at 12 months’ follow-up.
| Episodes of heavy drinking (≥ 5 units in 1 day) in the preceding 30-day period | Randomised arm | Overall (n = 112) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET (n = 38) | SBNT (n = 38) | Usual care (n = 36) | ||
| Number at follow-up (% of randomised) | 17 (45) | 22a (58) | 20 (56) | 59 (53) |
| Median (LQ, UQ) | 1 (0, 4) | 0 (0, 2) | 1.5 (0, 5.5) | 1 (0, 4) |
| Range | 0–10 | 0–7 | 0–9 | 0–10 |
| Episodes of heavy drinking (≥ 5 units in 1 day) in the preceding 7-day period | Randomised arm | Overall (n = 112) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET (n = 38) | SBNT (n = 38) | Usual care (n = 36) | ||
| Number at follow-up (% of randomised) | 17 (45) | 22a (58) | 20 (56) | 59 (53) |
| Median (LQ, UQ) | 0 (0, 1) | 0 (0, 1) | 0.5 (0, 1) | 0 (0, 1) |
| Range | 0–2 | 0–2 | 0–3 | 0–3 |
Tables 54 and 55 show follow-up summary statistics for AUDIT and AUDIT-C and numbers reporting hazardous drinking and alcohol dependency.
| Summary statistic | Time point | Randomised arm | Overall (N = 112) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET (N = 38) | SBNT (N = 38) | Control (N = 36) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | ||
| AUDIT questionnaire score | Baseline | 38 | 0 | 4 | 12 | 16 | 26 | 10.9 | 7.3 | 38 | 0 | 4 | 7 | 15 | 30 | 8.7 | 7.5 | 35 | 0 | 5 | 8 | 14 | 29 | 10.1 | 111 | 0 | 4 | 8 | 15 | 30 | 9.9 | 7.4 | |
| 12 month | 17 | 2 | 6 | 9 | 15 | 19 | 9.9 | 5.3 | 23 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 22 | 6.1 | 5.8 | 20 | 0 | 5.5 | 7.5 | 16.5 | 26 | 10.4 | 60 | 0 | 4.5 | 7 | 11 | 26 | 8.6 | 6.6 | ||
| Change | 17 | –20 | –5 | –1 | 2 | 5 | –3.0 | 6.9 | 23 | –23 | –4 | –1 | 4 | 22 | –0.7 | 8.1 | 19 | –15 | –3 | 0 | 2 | 13 | –0.2 | 59 | –23 | –4 | –1 | 3 | 22 | –1.2 | 7.1 | ||
| AUDIT-C | Baseline | 38 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 4.9 | 2.7 | 38 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 4.0 | 2.7 | 35 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 5.1 | 2.8 | 111 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 4.7 | 2.8 |
| 12 month | 17 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 4.4 | 2.3 | 23 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 4.0 | 2.6 | 20 | 0 | 3.5 | 5.5 | 8 | 10 | 5.5 | 2.9 | 60 | 0 | 3 | 4.5 | 7 | 10 | 4.6 | 2.7 | |
| Change | 17 | –8 | –2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | –0.9 | 3.1 | 23 | –6 | –1 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 0.6 | 3.1 | 19 | –4 | –2 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 0.0 | 2.7 | 59 | –8 | –2 | 0 | 2 | 7 | –0.0 | 3.0 | |
| Hazardous drinking and alcohol dependency (in terms of AUDIT and AUDIT-C) | Time point | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline (N = 111), n (%) | 12 months’ follow-up (N = 60), n (%) | |||
| AUDIT | AUDIT-C | AUDIT | AUDIT-C | |
| Hazardous alcohol | 61 (55) | 80 (72) | 29 (48) | 46 (77) |
| Alcohol dependency | 36 (32) | N/A | 13 (22) | N/A |
An AUDIT score of ≥ 8 indicates hazardous alcohol consumption and a score of ≥ 13 for females and ≥ 15 for males indicates alcohol dependency. An AUDIT-C score of ≥ 4 in males and ≥ 3 in females indicates hazardous alcohol consumption
Table 56 shows the follow-up summary statistics for ASSIST-Y.
| Summary statistics (ASSIST-Y) | Time point | Randomised arm | Overall (n = 112) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET (n = 38) | SBNT (n = 38) | Control (n = 36) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number usinga | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | Number usinga | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | Number usinga | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | Number usinga | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | ||
| Tobaccob | Baseline | 30 | 0 | 12 | 12 | 15 | 25 | 12.2 | 6.9 | 30 | 0 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 25 | 12.7 | 7.5 | 33 | 0 | 12 | 12 | 18 | 25 | 13.9 | 6.1 | 93 | 0 | 11 | 12 | 18 | 25 | 13.0 | 6.8 |
| 12 months | 14 | 0 | 9 | 13 | 18 | 25 | 13.1 | 7.7 | 18 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 15 | 25 | 8.8 | 8.4 | 18 | 0 | 12 | 12 | 15 | 22 | 12.6 | 5.2 | 50 | 0 | 4 | 12 | 18 | 25 | 11.4 | 7.3 | |
| Change | 13 | –12 | –1 | 0 | 3 | 9 | 0.2 | 5.2 | 16 | –25 | –7.5 | 0 | 2 | 9 | –2.9 | 9.0 | 17 | –15 | –6 | 0 | 0 | 11 | –1.9 | 6.7 | 46 | –25 | –6 | 0 | 2 | 11 | –1.7 | 7.2 | |
| Alcohol | Baseline | 37 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 15 | 28 | 9.8 | 8.0 | 37 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 12 | 26 | 7.3 | 6.4 | 34 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 17 | 24 | 9.4 | 7.7 | 108 | 0 | 2.5 | 6.5 | 14.5 | 28 | 8.8 | 7.4 |
| 12 months | 17 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 11 | 20 | 7.3 | 5.9 | 23 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 28 | 5.6 | 6.6 | 20 | 0 | 2 | 4.5 | 9 | 21 | 6.4 | 6.3 | 60 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 8.5 | 28 | 6.3 | 6.2 | |
| Change | 17 | –22 | –7 | 0 | 0 | 9 | –4.0 | 8.6 | 22 | –23 | –4 | 0 | 2 | 28 | –1.0 | 9.1 | 18 | –15 | –5 | –1 | 1 | 5 | –2.4 | 5.5 | 57 | –23 | –5 | 0 | 1 | 28 | –2.3 | 7.9 | |
| Cannabis | Baseline | 30 | 0 | 2 | 6.5 | 17 | 33 | 9.4 | 9.3 | 21 | 0 | 5 | 12 | 18 | 30 | 12.2 | 9.6 | 30 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 17 | 24 | 9.7 | 8.1 | 81 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 17 | 33 | 10.2 | 8.9 |
| 12 months | 12 | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | 13 | 20 | 6.3 | 7.7 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 18 | 4.7 | 6.5 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 9 | 2.3 | 2.4 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | 5.5 | 20 | 5.4 | 6.0 | |
| Change | 11 | –9 | –4 | –1 | 1 | 3 | –1.7 | 3.8 | 8 | –23 | –11.5 | –4 | 0 | 3 | –6.4 | 9.0 | 14 | –20 | –11 | –6.5 | –2 | 7 | –6.4 | 6.9 | 33 | –23 | –8 | –3 | 0 | 7 | –4.8 | 6.9 | |
| Cocaine | Baseline | 14 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 13 | 18 | 6.9 | 6.2 | 12 | 0 | 1 | 6.5 | 12 | 22 | 7.3 | 7.1 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | 17 | 22 | 7.1 | 8.3 | 40 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 13.5 | 22 | 7.1 | 7.1 |
| 12 months | 8 | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | 7.5 | 13 | 4.1 | 4.8 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 13 | 4.6 | 4.7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 21 | 4.7 | 7.9 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | 7.5 | 21 | 4.5 | 5.8 | |
| Change | 6 | –16 | –5 | –3.5 | 1 | 3 | –4.0 | 6.6 | 4 | 6 | –10 | –2 | 0 | 0 | 4 | –1.3 | 4.7 | 16 | –19 | –6.5 | –2.5 | 0.5 | 6 | –3.6 | 6.9 | ||||||||
| Amphetamine | Baseline | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 2.2 | 2.8 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 4.0 | 3.3 | 5 | 27 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 21 | 3.6 | 4.7 | |||||||
| 12 months | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 1.4 | 2.0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 17 | 2.7 | 6.3 | 3 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 32 | 3.7 | 8.4 | ||||||||
| Change | 4 | 4 | 2 | 10 | –7 | –6 | –0.5 | 2 | 11 | –0.7 | 5.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inhalants | Baseline | 2 | 3 | 4 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 9 | 3.0 | 3.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 months | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sedative | Baseline | 10 | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | 28 | 6.7 | 9.9 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 10 | 3.7 | 4.2 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 3.5 | 5 | 17 | 4.2 | 5.3 | 27 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 28 | 5.0 | 7.1 |
| 12 months | 6 | 0 | 0 | 9.5 | 12 | 17 | 8.0 | 6.8 | 4 | 5 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 17 | 4.3 | 6.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Change | 3 | 2 | 2 | 7 | –16 | –13 | –5 | –3 | 0 | –7.4 | 5.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hallucinogens | Baseline | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 9 | 2.1 | 3.8 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 3.5 | 8 | 21 | 6.3 | 7.7 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 2.2 | 5.3 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 21 | 3.5 | 5.7 |
| 12 months | 4 | 3 | 4 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 21 | 2.9 | 6.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | –9 | –5 | 0 | 3 | 8 | –0.5 | 6.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opioids | Baseline | 5 | 3 | 3 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 21 | 4.2 | 7.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 months | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NPS | Baseline | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 14 | 2.9 | 5.1 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 14 | 4.1 | 4.4 | |||||||
| 12 months | 3 | 3 | 2 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0.9 | 1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change | 2 | 3 | 3 | 7 | –14 | –9 | –5 | 0 | 3 | –4.9 | 5.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Otherc | Baseline | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 months | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 57 shows the summary statistics for the SDQ completed at the 12 months’ follow-up.
| Summary statistics (SDQ) | Time point | Randomised arm | Overall (N = 112) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET (N = 38) | SBNT (N = 38) | Control (N = 36) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | ||
| SDQ: total score | Baseline | 38 | 5 | 12 | 16 | 19 | 31 | 15.7 | 6.6 | 38 | 3 | 11 | 14 | 18 | 29 | 14.7 | 6.2 | 35 | 5 | 12 | 17 | 21 | 28 | 16.4 | 6.1 | 111 | 3 | 11 | 15 | 20 | 31 | 15.6 | 6.3 |
| 12 months | 17 | 3 | 13 | 19 | 24 | 28 | 17.5 | 7.8 | 23 | 3 | 10 | 14 | 18 | 26 | 13.5 | 6.0 | 20 | 2 | 12 | 13.5 | 19 | 26 | 14.7 | 5.6 | 60 | 2 | 11 | 14.5 | 20 | 28 | 15.0 | 6.5 | |
| Change | 17 | –9 | –3 | –2 | 5 | 14 | –0.1 | 5.7 | 23 | –16 | –4 | –1 | 3 | 9 | –0.9 | 5.8 | 19 | –8 | –5 | –2 | 2 | 10 | –1.2 | 4.6 | 59 | –16 | –4 | –2 | 3 | 14 | –0.7 | 5.3 | |
| SDQ: emotional problems | Baseline | 38 | 0 | 2 | 4.5 | 6 | 10 | 4.5 | 2.7 | 38 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 4.1 | 2.6 | 35 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 4.5 | 2.5 | 111 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 4.4 | 2.6 |
| 12 months | 17 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 5.4 | 3.2 | 23 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 4.3 | 2.3 | 20 | 0 | 2.5 | 3 | 5 | 9 | 3.9 | 2.3 | 60 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 4.5 | 2.6 | |
| Change | 17 | –4 | –2 | –1 | 1 | 4 | –0.1 | 2.3 | 23 | –4 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0.1 | 1.9 | 19 | –4 | –2 | –1 | 1 | 4 | –0.4 | 2.0 | 59 | –4 | –2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | –0.1 | 2.0 | |
| SDQ: conduct problems | Baseline | 38 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 8 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 38 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 2.6 | 1.7 | 35 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.2 | 2.0 | 111 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 8 | 2.9 | 1.9 |
| 12 months | 17 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 2.8 | 1.9 | 23 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 2.1 | 1.3 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3.5 | 6 | 2.5 | 1.6 | 60 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 2.4 | 1.6 | |
| Change | 17 | –4 | –1 | 0 | 0 | 5 | –0.3 | 1.9 | 23 | –3 | –1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | –0.3 | 1.4 | 19 | –4 | –2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | –0.8 | 1.5 | 59 | –4 | –1 | 0 | 0 | 5 | –0.5 | 1.6 | |
| SDQ: hyperactivity | Baseline | 38 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 4.8 | 2.4 | 38 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 4.9 | 2.5 | 35 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 5.6 | 2.4 | 111 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 5.1 | 2.4 |
| 12 months | 17 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 5.2 | 3.0 | 23 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 4.3 | 2.8 | 20 | 1 | 2.5 | 5 | 6.5 | 9 | 4.8 | 2.4 | 60 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 4.7 | 2.7 | |
| Change | 17 | –4 | –1 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0.2 | 2.0 | 23 | –5 | –2 | –1 | 2 | 6 | –0.3 | 2.9 | 19 | –4 | –2 | –1 | 0 | 3 | –0.8 | 1.9 | 59 | –5 | –2 | 0 | 2 | 6 | –0.3 | 2.4 | |
| SDQ: peer problems | Baseline | 38 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 8 | 3.4 | 2.0 | 38 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 9 | 3.1 | 1.9 | 35 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 111 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 9 | 3.2 | 1.9 |
| 12 months | 17 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 4.1 | 2.0 | 23 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 2.8 | 1.5 | 20 | 0 | 2 | 3.5 | 5 | 8 | 3.6 | 2.0 | 60 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 3.4 | 1.9 | |
| Change | 17 | –3 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0.1 | 2.0 | 23 | –5 | –1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | –0.3 | 1.7 | 19 | –2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 0.8 | 2.0 | 59 | –5 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 0.2 | 1.9 | |
| SDQ: prosocial | Baseline | 38 | 0 | 7 | 8.5 | 10 | 10 | 7.7 | 2.4 | 38 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 7.2 | 1.7 | 35 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 7.8 | 1.8 | 111 | 0 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 7.6 | 2.0 |
| 12 months | 17 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 7.5 | 2.3 | 23 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 7.5 | 1.8 | 20 | 5 | 6.5 | 8.5 | 9.5 | 10 | 8.2 | 1.6 | 60 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 7.7 | 1.9 | |
| Change | 17 | –5 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 0.2 | 2.9 | 23 | –2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0.3 | 1.7 | 19 | –3 | –1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | –0.1 | 1.4 | 59 | –5 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 0.1 | 2.0 | |
| SDQ: externalising score | Baseline | 38 | 1 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 18 | 7.8 | 3.9 | 38 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 11 | 15 | 7.5 | 3.7 | 35 | 0 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 17 | 8.9 | 4.0 | 111 | 0 | 5 | 8 | 11 | 18 | 8.0 | 3.9 |
| 12 months | 17 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 12 | 15 | 8.0 | 4.6 | 23 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 14 | 6.4 | 3.7 | 20 | 2 | 4.5 | 6 | 9.5 | 15 | 7.2 | 3.5 | 60 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 15 | 7.1 | 3.9 | |
| Change | 17 | –7 | –1 | 0 | 2 | 9 | –0.1 | 3.5 | 23 | –7 | –3 | –1 | 2 | 7 | –0.7 | 3.6 | 19 | –6 | –4 | –2 | 0 | 4 | –1.6 | 2.8 | 59 | –7 | –3 | –1 | 1 | 9 | –0.8 | 3.3 | |
| SDQ: internalising score | Baseline | 38 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 10 | 18 | 7.9 | 4.1 | 38 | 0 | 5 | 6.5 | 9 | 19 | 7.2 | 3.9 | 35 | 1 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 15 | 7.5 | 3.3 | 111 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 19 | 7.6 | 3.8 |
| 12 months | 17 | 0 | 6 | 9 | 13 | 17 | 9.5 | 4.6 | 23 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 13 | 7.1 | 3.3 | 20 | 0 | 5 | 7.5 | 10.5 | 14 | 7.5 | 3.8 | 60 | 0 | 5 | 8 | 11 | 17 | 7.9 | 3.9 | |
| Change | 17 | –5 | –4 | –1 | 4 | 5 | 0.1 | 3.7 | 23 | –9 | –2 | 0 | 2 | 6 | –0.2 | 3.0 | 19 | –4 | –1 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 0.4 | 3.0 | 59 | –9 | –2 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 0.1 | 3.2 | |
Tables 58 and 59 show the summary statistics for the WEMWBS completed at 12 month’ follow-up, broken down by scores and categories.
| Time point | Randomised arm | Overall (N = 112) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET (N = 38) | SBNT (N = 38) | Control (N = 36) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | |
| Baseline | 38 | 14 | 34 | 42 | 53 | 70 | 43.3 | 14.1 | 38 | 20 | 38 | 48 | 51 | 66 | 45.5 | 10.8 | 35 | 18 | 39 | 45 | 50 | 66 | 43.7 | 9.6 | 111 | 14 | 37 | 50 | 51 | 70 | 44.2 | 11.7 |
| 12 months | 17 | 25 | 29 | 46 | 51 | 64 | 42.7 | 11.9 | 23 | 24 | 37 | 46 | 53 | 65 | 45.2 | 11.2 | 20 | 23 | 41 | 47 | 53.5 | 61 | 45.3 | 10.4 | 60 | 23 | 38 | 46.5 | 53 | 65 | 44.5 | 11.0 |
| Change | 17 | –18 | –3 | 1 | 9 | 44 | 3.9 | 14.2 | 23 | –18 | –5 | 2 | 6 | 24 | 1.6 | 10.6 | 19 | –24 | –8 | –2 | 8 | 28 | –0.5 | 11.7 | 59 | –24 | –5 | 0 | 8 | 44 | 1.6 | 12.0 |
| Time point | Randomised arm | Overall (N = 112), n (%) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET (N = 38), n (%) | SBNT (N = 38), n (%) | Control (N = 36), n (%) | ||||||||||||||||||
| n | Very low score (0–32) | Below average score (32–40) | Average Score (40–59) | Above average score (59–70) | n | Very low score (0–32) | Below average score (32–40) | Average Score (40–59) | Above average score (59–70) | n | Very low score (0–32) | Below average score (32–40) | Average Score (40–59) | Above average score (59–70) | n | Very low score (0–32) | Below average score (32–40) | Average Score (40–59) | Above average score (59–70) | |
| Baseline | 38 | 8 (21) | 9 (24) | 15 (39) | 6 (16) | 38 | 3 (8) | 10 (26) | 20 (53) | 5 (13) | 35 | 3 (9) | 9 (26) | 22 (63) | 1 (3) | 111 | 14 (13) | 28 (25) | 57 (51) | 12 (11) |
| 12 months | 17 | 5 (29) | 2 (12) | 9 (53) | 1 (6) | 23 | 4 (17) | 2 (9) | 15 (65) | 2 (9) | 20 | 3 (15) | 2 (10) | 14 (70) | 1 (5) | 60 | 12 (20) | 6 (10) | 38 (63) | 4 (7) |
There are different interpretation cut-off points for categorising the WEMWBS, depending on who fills out the questionnaire (e.g. parent or teacher). In the SOLID trial the looked-after children fill in their own questionnaires, so these are the cut-off points for categorising the scores.
Interpretation of well-being scores (for self-assessment, from NHS)
-
0–32: very low score.
-
32–40: below average score.
-
40–59: average score.
-
59–70: above average score.
Tables 60 and 61 show the summary statistics collected for the romantic and intimate behaviour questionnaire at 12 months’ follow-up. Table 61 is broken down by sex.
| Romantic and intimate behaviour | Time point | Randomised arm | Overall (N = 112) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET (N = 38) | SBNT (N = 38) | Control (N = 36) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | ||
| Romantic and intimate behaviour | 12 months | 17 | 0 | 12 | 39 | 52 | 60 | 33.2 | 21.8 | 23 | 0 | 14 | 24 | 44 | 64 | 27.7 | 20.2 | 20 | 7 | 31 | 45.5 | 54 | 70 | 41.3 | 17.8 | 60 | 0 | 15 | 36 | 52 | 70 | 33.8 | 20.4 |
| Romantic and intimate behaviour: minor | 12 months | 17 | 0 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 5.0 | 1.8 | 23 | 0 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4.9 | 2.0 | 20 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 5.6 | 1.1 | 60 | 0 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 5.2 | 1.7 |
| Romantic and intimate behaviour: advanced | 12 months | 17 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 23 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 2.9 | 3.2 | 20 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 5.5 | 2.5 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 4.1 | 3.2 |
| Romantic and intimate behaviour: regreta | 12 months | 17 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 7 | 25 | 5.3 | 6.2 | 23 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 21 | 4.0 | 5.5 | 20 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 28 | 7.2 | 6.0 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 6.5 | 7 | 28 | 5.4 | 5.9 |
| Romantic and intimate behaviour | Time point | Sex | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female (N = 38) | Male (N = 22) | ||||||||||||||||
| n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | Minimum | LQ | Median | UQ | Maximum | Mean | SD | ||
| Romantic and intimate behaviour | 12 months | 38 | 0 | 17 | 38 | 54 | 70 | 36.1 | 20.6 | 22 | 0 | 11 | 31 | 46 | 59 | 29.9 | 20.0 |
| Romantic and intimate behaviour (minor) | 12 months | 38 | 0 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 5.4 | 1.5 | 22 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4.8 | 1.9 |
| Romantic and intimate behaviour (advanced) | 12 months | 38 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 4.3 | 3.2 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 3.6 | 3.3 |
| Romantic and intimate behaviour (regret)a | 12 months | 38 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 7 | 28 | 6.0 | 6.4 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 21 | 4.4 | 5.0 |
Table 62 shows the summary data for the antisocial/criminal behaviour questionnaire collected at 12 months’ follow-up.
| Anti-social or criminal behaviour | Randomised arm, n (%) | Overall (N = 60), n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET (N = 17) | SBNT (N = 23) | Control (N = 20) | ||
| Skipped or skived off school | ||||
| Yes | 4 (24) | 13 (57) | 11 (55) | 28 (47) |
| Once | 1 (6) | 1 (4) | 1 (5) | 3 (5) |
| 2–5 times | 2 (12) | 5 (22) | 2 (10) | 9 (15) |
| ≥ 6 times | 1 (6) | 7 (30) | 8 (40) | 16 (27) |
| Broken into a car or van with the intention of stealing something out of it | ||||
| Yes | 1 (6) | 2 (9) | 1 (5) | 4 (7) |
| Once | 1 (6) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 2 (3) |
| 2–5 times | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| ≥ 6 times | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 1 (5) | 2 (3) |
| Hit, kicked or punched someone on purpose | ||||
| Yes | 5 (29) | 9 (39) | 7 (35) | 21 (35) |
| Once | 2 (12) | 6 (26) | 2 (10) | 10 (17) |
| 2–5 times | 1 (6) | 2 (9) | 1 (5) | 4 (7) |
| ≥ 6 times | 2 (12) | 1 (4) | 4 (20) | 7 (12) |
| Deliberately set fire or tried to set fire to somebody’s property or a building | ||||
| Yes | 1 (6) | 2 (9) | 1 (5) | 4 (7) |
| Once | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) |
| 2–5 times | 1 (6) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 2 (3) |
| ≥ 6 times | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) |
| Taken money or something else that did not belong to you from home without permission | ||||
| Yes | 1 (6) | 4 (17) | 1 (5) | 6 (10) |
| Once | 0 (0) | 3 (13) | 0 (0) | 3 (5) |
| 2–5 times | 1 (6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) |
| ≥ 6 times | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 1 (5) | 2 (3) |
| Used force, threats or a weapon to get money or something else from somebody | ||||
| Yes | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) |
| Once | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| 2–5 times | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) |
| ≥ 6 times | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Written things or sprayed paint on property that did not belong to you | ||||
| Yes | 1 (6) | 2 (9) | 2 (10) | 5 (8) |
| Once | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 1 (5) | 2 (3) |
| 2–5 times | 1 (6) | 1 (4) | 1 (5) | 3 (5) |
| ≥ 6 times | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Gone into or broken into a house or building with the intention of stealing something | ||||
| Yes | 1 (6) | 2 (9) | 1 (5) | 4 (7) |
| Once | 1 (6) | 2 (9) | 0 (0) | 3 (5) |
| 2–5 times | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 1 (2) |
| ≥ 6 times | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Deliberately damaged or destroyed property that did not belong to you | ||||
| Yes | 3 (18) | 2 (9) | 3 (15) | 8 (13) |
| Once | 2 (12) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 3 (5) |
| 2–5 times | 1 (6) | 1 (4) | 2 (10) | 4 (7) |
| ≥ 6 times | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) |
| Carried a knife or weapon with you for protection or in case it was needed in a fight | ||||
| Yes | 1 (6) | 3 (13) | 1 (5) | 5 (8) |
| Once | 1 (6) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 2 (3) |
| 2–5 times | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| ≥ 6 times | 0 (0) | 2 (9) | 1 (5) | 3 (5) |
| Taken money or something else that did not belong to you from school | ||||
| Yes | 1 (6) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 2 (3) |
| Once | 1 (6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) |
| 2–5 times | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| ≥ 6 times | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 1 (2) |
| Stolen or ridden in a stolen car or van or on a stolen motorbike | ||||
| Yes | 1 (6) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 2 (3) |
| Once | 1 (6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) |
| 2–5 times | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| ≥ 6 times | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 1 (2) |
| Been rowdy or rude in a public place so that people complained or you got into trouble | ||||
| Yes | 3 (18) | 4 (17) | 1 (5) | 8 (13) |
| Once | 1 (6) | 1 (4) | 1 (5) | 3 (5) |
| 2–5 times | 1 (6) | 3 (13) | 0 (0) | 4 (7) |
| ≥ 6 times | 1 (6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) |
| Taken something from a shop or a store without paying for it | ||||
| Yes | 1 (6) | 4 (17) | 3 (15) | 8 (13) |
| Once | 1 (6) | 1 (4) | 1 (5) | 3 (5) |
| 2–5 times | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) |
| ≥ 6 times | 0 (0) | 2 (9) | 2 (10) | 4 (7) |
| Not paid the correct fare or not paid at all on a bus or train? | ||||
| Yes | 2 (12) | 6 (26) | 3 (15) | 11 (18) |
| Once | 1 (6) | 2 (9) | 0 (0) | 3 (5) |
| 2–5 times | 1 (6) | 3 (13) | 2 (10) | 6 (10) |
| ≥ 6 times | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 1 (5) | 2 (3) |
Appendix 5 Process rating findings
Audio-recording findings
Reasons provided for not recording sessions included young person refusal (n = 8) and human error (n = 9), such as forgetting to turn the recorder on and professionals not feeling comfortable with their practice being audio-recorded.
In line with advice from the TOC, only the six audio-recordings of the first session were rated (MET, n = 2, and SBNT, n = 4) in the interest of the session content being considered consistently. The audio-recordings of the first sessions with young people lasted between 19 and 32 minutes. When assessing the six available audio-recordings, two research associates (HA and RB) independently rated the audio-recorded intervention sessions for MET and SBNT and then compared scores, before agreeing a final score for each component of the PRS.
The quality of the audio-recordings was variable. One practitioner delivering MET did not carry out 12 of the items at all, and the extent of performance for the remaining items was rated at best as ‘somewhat’. The quality of performance for this therapist was also poor, with the practitioner delivering the items ‘not well at all’ or ‘a little’.
For the remaining five recordings, the frequency and content was changeable within sessions; however, the majority of the scores were rated at ≥ 2, showing that the practitioners were delivering the items at a frequency of ‘somewhat’ to ‘extensively’ and that quality was assessed as being ‘somewhat (well)’ to ‘very well’. For all of the six available recordings, a number of items consistently scored 0, these items including discussion of homework; however, this is not surprising due to all recordings relating to first sessions. Five out of the six recordings did not capture the practitioner providing an explanation of the philosophy or the treatment and four of the recordings did not capture agenda setting at the beginning of the session. In addition, four out of the six sessions did not capture an end of session summary. All of these items are important to the structure of the session and highlighted a further training need regarding use of the audio-recording equipment.
Practitioners often only started recording ‘once work’ had begun, it was obvious from the recording that conversations had been occurring prior to the audio-recording beginning, equally the recordings often finished despite the practitioner actively being in the process of arranging the next session and closing the session down. It was hard to establish whether or not the practitioner was consistent across sessions because of the limited number of recordings.
List of abbreviations
- ASAI
- Adolescent Sexual Activity Index
- ASSIST
- Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test
- ASSIST-Y
- Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test – Youth
- AUDIT
- Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test
- AUDIT-C
- Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test for consumption
- BDI
- behaviour determinants intervention
- CAMHS
- Community Adolescent Mental Health Services
- CASI
- computer-assisted self-interview
- CI
- confidence interval
- CRAFFT
- car, relax, alone, forget, friends, trouble(s)
- CRN
- Clinical Research Network
- CSV
- comma-separated values
- DUST
- Drug Use Screening Tool
- EQ-5D
- EuroQol-5 Dimensions
- EQ-5D-5L
- EuroQol-5 Dimensions, five-level version
- ESPAD
- European School Survey Project on Alcohol and Other Drugs
- GP
- general practitioner
- MET
- motivational enhancement therapy
- MRC
- Medical Research Council
- NDTMS
- National Drug Treatment Monitoring System
- NEET
- not in education, employment or training
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NIHR
- National Institute for Health Research
- NPS
- novel psychoactive substance
- Ofsted
- Office for Standards in Education, Children’s Services and Skills
- PA
- personal advisor
- PPI
- patient and public involvement
- PR
- parental responsibility
- PRS
- Process Rating Scale
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- SBNT
- social behaviour and network therapy
- SD
- standard deviation
- SDQ
- Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire
- SOLID
- Supporting Looked After Children and Care Leavers In Decreasing Drugs, and alcohol
- TLFB
- timeline follow-back
- TLFB-30
- timeline follow-back – 30 days
- TMG
- Trial Management Group
- TOC
- Trial Oversight Committee
- UKATT
- United Kingdom Alcohol Treatment Trial
- WEMWBS
- Warwick–Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale
- WHO
- World Health Organization
Notes
Supplementary material can be found on the NIHR Journals Library report page (https://doi.org/10.3310/phr08130).
Supplementary material has been provided by the authors to support the report and any files provided at submission will have been seen by peer reviewers, but not extensively reviewed. Any supplementary material provided at a later stage in the process may not have been peer reviewed.
