Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the HTA programme as project number 97/10/03. The contractual start date was in June 2000. The draft report began editorial review in November 2006 and was accepted for publication in April 2008. As the funder, by devising a commissioning brief, the HTA Programme specified the research question and study design. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the referees for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
None known
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2008. This monograph may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NCCHTA, Alpha House, Enterprise Road, Southampton Science Park, Chilworth, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2008 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Introduction
The NIHR Health Technology Assessment Programme identified the need to evaluate and compare the advent of minimal access surgery for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) with medical management. This report describes the work commissioned to address this issue.
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
GORD causes some of the most frequently seen symptoms in both primary and secondary care; between 20% and 30% of a ‘Western’ adult population experience heartburn and/or reflux intermittently. 1–3 There is a clinical spectrum. The majority has only mild symptoms and requires little if any medication. A minority has severe reflux and develops overt complications, despite full medical therapy, and requires surgical intervention. Amongst the remainder, control of symptoms requires regular or continuous medical therapy, and it is from this intermediate group of patients with significant disease that most of the treatment costs for the health service arise.
Treatment of GORD includes a range of options, both medical and surgical. The simplest is self-administered antacids with advice to alter lifestyle factors such as dietary modification, smoking cessation and weight reduction. Many will require acid suppression therapy using either histamine receptor antagonists (H2RAs) or proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). Initial high-dose therapy may be followed by maintenance treatment using these drugs either intermittently or continuously at reduced doses sufficient to suppress symptoms. The role of surgery has traditionally been confined to the treatment of those with severe symptoms not responding to medication in appropriate dosage and medically fit for surgery. There has, however, been a paradigm shift since the introduction of laparoscopic techniques, with surgery suggested as an alternative treatment to long-term medication. The NHS costs of GORD are considerable. The yearly drug budget for H2RAs is in excess of £200 M and for PPIs it is £300 M. Of this budget, most of this prescribing occurs within the primary care setting. 4,5 Once started on PPIs, the majority of patients with significant GORD remain on long-term treatment,6 and an estimated 4–5 patients (age 18–60) per 10,000 are taking maintenance PPIs for oesophagitis and reflux.
Although PPIs are increasingly assumed to be safe there is a spectrum of short-term symptoms caused by PPIs7 and there are concerns regarding the impact of long-term use through profound acid suppression. PPIs cause hypergastrinaemia, the long-term significance of which is unknown but potentially important. Conditions associated with chronic hypergastrinaemia and low acid levels have been linked to a long-term increased risk of developing gastric cancer. There is some evidence of the formation of gastric carcinoid tumours in patients taking long-term PPIs8 and also of vitamin B12 deficiency. 9 Adenocarcinoma of the lower oesophagus is a complication of long-term GORD,10–13 and the incidence of this highly malignant disease has trebled in Western communities in the last 25 years. Whilst the overall incidence of gastric cancer is falling, adenocarcinoma of the gastro-oesophageal junction is now a common cause of death, especially in men. The reasons for this change are probably multifactorial, but there is a clear relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection with migration to the gastric fundus and acid suppression, whether naturally occurring or induced by drug therapy. 14,15
Laparoscopic fundoplication
Interest in surgery as an alternative to long-term medical therapy for GORD has been considerable since the introduction of the minimal access approach in the early 1990s. The operative method, whether using an open or a laparoscopic approach, involves performing a fundoplication by wrapping the fundus of the stomach around the lower oesophagus to create a high-pressure zone, thus reducing gastro-oesophageal reflux. The wrap created can be either complete (360°) or partial. Many operative variants have been described. The commonest operation is a 1-cm complete wrap fashioned over a large bougie, the so-called ‘short floppy Nissen’. 16,17 The use of a partial fundoplication has a number of potential advantages but several controlled studies have shown broad equivalence between the two approaches. 18,19 For the purpose of this study they are therefore regarded as equivalent. Although fundoplication will produce resolution of reflux symptoms in upwards of 90% of patients, there is continuing debate regarding the risks, side effects and durability of surgical therapy.
Medical management
There is no doubt that PPIs, sometimes combined with prokinetic agents, are the most effective treatment for moderate to severe GORD. For the purpose of this study, medical therapy has been taken to mean long-term therapy with PPIs (or H2RAs if intolerant to PPIs). Although fundoplication is highly effective for controlling GORD, there has been considerable uncertainty whether exchanging symptoms associated with the best medical management of GORD for those of the side effects of surgery is advantageous for the patient and cost-effective for the health-care provider.
The costs of laparoscopic fundoplication appear to be equivalent to those of 2–3 years of maintenance treatment with PPIs, although it is acknowledged that the costs of PPIs are falling. 20 The costs of surgery are related largely to two factors – the incidence of complications/length of hospital stay and the number of patients requiring long-term medical interventions after surgery.
Rationale for the study design
The study described in this report aimed to clarify the place of laparoscopic fundoplication in the belief that decisions about the management of GORD should be based on unbiased, statistically precise comparisons of alternative policies. All patients in this study fulfilled three criteria: they were on long-term acid suppression with PPIs; they had symptoms that were thought to be adequately controlled; and they were suitable in terms of fitness and co-morbidity for either surgical or continuing medical treatment for their GORD.
The most likely sources of bias were in the ways in which the groups being compared were selected, the ways in which their outcomes were assessed, and how the management was actually delivered. This is the basis for using a pragmatic randomised controlled trial design. Random allocation protects against selection bias. Confining the trial to those with no clear treatment preference limits biased patient-centred assessment of outcome, and pragmatic comparison of alternative policies (with intention to treat analysis) avoids bias introduced by non-compliance. This approach has limitations, however, and for this reason we chose to incorporate two parallel, non-randomised preference groups.
Excluding those with a clear preference for one policy or the other limits extrapolation and generalisation. Study of this group may give insights into the reasons for preference and hence give pointers to patient choices after the study. 21 Furthermore, preference may influence outcome and, if so, this may also help when making treatment decisions. 21,22 A third reason for including the parallel, non-randomised preference groups23 is that the addition of data from the preference groups may reduce imprecision around the estimates from the randomised comparison and this may be particularly useful for rare events, such as complications, that can be confidently ascribed to one or other treatment. (The limitation is that these groups are not derived by random allocation and hence the comparisons are prone to the biases of non-randomised studies.)
The decisions about, and comparisons between, randomised and preference groups require valid measurement of treatment outcome. Although there are a number of quality of life tools available, none was sufficiently specific to assess the spectrum of gastrointestinal symptoms associated with the treatment of GORD, particularly surgery. For this reason the development and validation of a new outcome measure (the REFLUX questionnaire; see Chapter 4) was an essential component of the study. 24
GORD and its management represent a very significant call on NHS resources. Although clinical effectiveness, acceptability and safety will be important determinants of future policy, the issues of cost and resource use may be over-riding. A prospective, multicentre study25 found that the total cost for chronic PPI (omeprazole) therapy over 5 years was less than the cost of an open fundoplication; however, two other studies26,27 found laparoscopic surgery to be less expensive in the long run than daily treatment with 20–40 mg of omeprazole. In one of these studies27 laparoscopic fundoplication became more cost-effective at 1.4 years post procedure. A Canadian Markov model comparing medical management with laparoscopic fundoplication concluded that laparoscopic fundoplication became cost-effective at 3.3 years post operation. 28
A recent UK trial-based economic analysis comparing laparoscopic fundoplication with PPIs using data on 100 GORD patients29 reported that the incremental cost per point improvement in combined gastrointestinal and psychological well-being scores at 12 months for laparoscopic fundoplication versus PPI was £293, and the incremental cost per additional patient returned to a physiologically normal acid score at 3 months was £5515. 29 There are, however, no existing studies in the UK that have compared laparoscopic fundoplication with PPIs using a generic measure of health, such as quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). Expressing health benefits in terms of QALYs would provide decision-makers with a basis for comparison with other uses of health-care resources in a range of disease areas and specialties.
There is little doubt that PPIs are the most effective pharmacotherapy30 for moderate to severe GORD and, for the purpose of this analysis, medical therapy will be taken to mean long-term therapy with PPIs. Although fundoplication is a highly effective therapy for controlling GORD, the question is whether surgery, which can alleviate GORD symptoms but may have unwanted side effects, is advantageous for the patient and cost-effective for the health-care provider.
This is the reason for the economic evaluation. Policy should be guided by both assessment of the relative cost-effectiveness of alternative policies and assessment of the impact that possible policy changes would have for the NHS and for patients with GORD.
Chapter 2 Methods
Study design
The study had two complementary components:
-
a multicentre, pragmatic randomised trial (with parallel non-randomised preference groups) comparing a laparoscopic surgery-based policy with a continued medical management policy to assess their relative clinical effectiveness
-
an economic evaluation of laparoscopic surgery for GORD comparing the cost-effectiveness of the two management policies to identify the most efficient provision of future care and describe the resource impact that various policies for fundoplication would have on the NHS.
Patients who consented to participate in the randomised trial were randomly allocated to either laparoscopic surgery or continued medical management. Those patients who had a strong preference for one or other of the two treatment options could be recruited to the preference study. Clinical history at trial entry was recorded on participants’ entry forms (see Appendix 1). Participants completed health status questionnaires at the time of recruitment to the study and then at specified times equivalent to 3 and 12 months after surgery (see Appendix 2).
Approval for this study was obtained from the Scottish Multicentre Research Ethics Committee and the appropriate local research ethics committees.
Clinical centres
Clinical centres were based on local partnerships between surgeons with experience of laparoscopic fundoplication and the gastroenterologists with whom they shared the secondary care of patients with GORD. Centres were eligible if they included:
-
a surgeon who had performed at least 50 laparoscopic fundoplication operations
-
one or more gastroenterologists who agreed to collaborate with the surgeon(s) in the trial.
Study population
Potential participants, who were identified both retrospectively and prospectively, were invited to attend an outpatient appointment (see Appendix 3). The participating clinician reviewed each patient’s symptoms and treatment regimen and assessed eligibility (see Appendix 4).
Eligible patients were those for whom care had been provided by a participating clinician who was uncertain which management policy (surgical or medical) was better. In addition, patients had to have documented evidence of GORD (based on endoscopy and/or manometry/24-hour pH monitoring) as well as symptoms for more than 12 months requiring maintenance PPI therapy for reasonable symptom control. Patients who were intolerant to PPIs and who therefore required H2RA therapy to control their symptoms were also included. Patients who were morbidly obese [body mass index (BMI) > 40 kg/m2], patients with Barrett’s oesophagus of more than 3 cm or who had evidence of dysplasia, patients who had a para-oesophageal hernia and patients with an oesophageal stricture were all excluded.
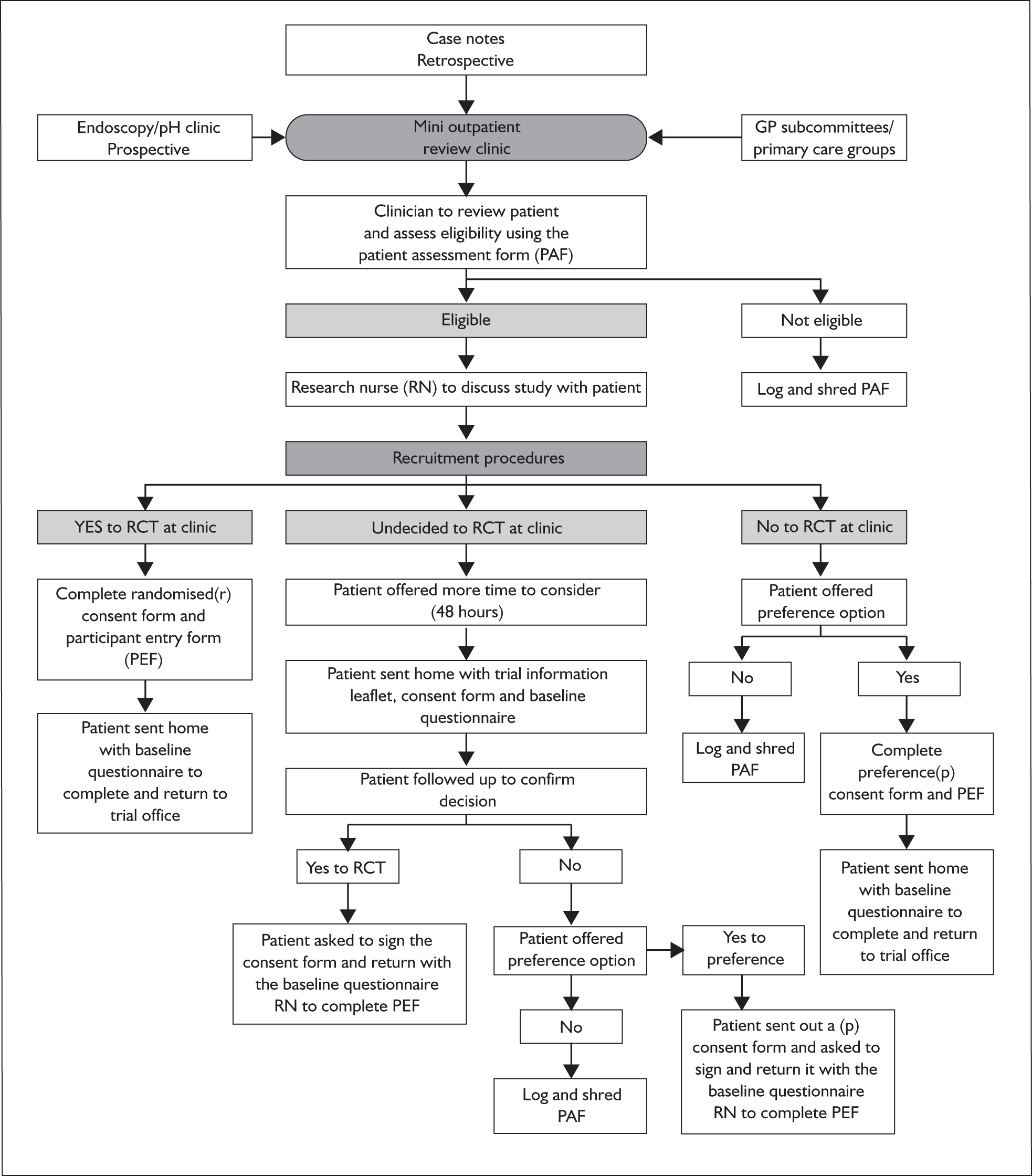
If eligibility was confirmed the patient was invited to see the local research nurse who described the trial, giving supplementary information describing the operation (see Appendix 5) and answering any questions or concerns. This process is summarised in Figure 1.
FIGURE 1.
Flow chart describing patient recruitment.
Consent to participate
The randomised trial
Some potential participants made a decision about participation at this appointment. Those who wished to participate in the randomised trial were asked to sign a consent form (see Appendix 6). On this, they confirmed that they had been given the information they required and that the study had been explained to them. They also confirmed that they understood that they would be sent questionnaires at participant-specific time intervals after joining the study (this would be at times equivalent to around 3 months and 12 months after surgery). They were also told that it was anticipated that further follow-up would be performed periodically thereafter for some years.
The preference study
A person who did not want to take part in the randomised trial because of a strong preference for one type of treatment management or the other was asked to take part in the preference arm of the study. Those who wished to participate in the preference study were given a preference information leaflet and asked to sign a consent form (see Appendix 7) confirming their preferred treatment allocation. For logistical reasons and to maintain a balance between the sizes of randomised and preference groups, the numbers of participants recruited to preference arms was limited to 20 per arm in each centre.
Anyone who was uncertain was given at least 48 hours to consider participation.
Health technology policies being compared
Laparoscopic surgery policy
For those participants allocated or recruited to the surgical arms of the trial, subsequent deferring or declining of surgery, by either the participant or the surgeon, was always an option (i.e. even after trial entry), particularly amongst those recruited by a gastroenterologist and referred to a surgeon for consideration of surgery within the trial. Participants who had not had manometry/pH studies performed underwent these tests before surgery to exclude achalasia.
The surgery was performed either by a surgeon who had undertaken more than 50 laparoscopic fundoplications or by a less experienced surgeon working under the supervision of an experienced surgeon. It was recommended that crural repair be routine and that non-absorbable, synthetic sutures (not silk) be used for the repair. The type of fundoplication used was left to the discretion of the experienced surgeon. For the purposes of the main comparisons, the different surgical techniques for laparoscopic fundoplication were considered as part of a single policy. The study design, however, allowed for indirect comparisons between techniques.
Medical therapy policy
Those allocated to the medical therapy policy had their therapy reviewed and adjusted as necessary by the local gastroenterologist to be ‘best medical management’. It was recommended that management conformed to the principles of the Genval Workshop Report. 31 These include stepping down anti-secretory medication in most patients to the lowest dose that maintains acceptable symptom control. However, patients with severe oesophagitis were not managed on the basis of symptoms alone. Although trial participants allocated to medical management were managed in this way, the protocol did include the option of surgery if a clear indication for it subsequently developed.
Study registration (and treatment allocation when randomised)
The entry procedure distinguished between those who agreed to randomisation and those who agreed to participate in the preference part of the study.
Once a participant had agreed to join the trial the research nurse recorded basic identifying and descriptive information on a standard form (see Appendix 1). A letter was sent to each participant, confirming their participation and whether they were taking part in the randomised or preference component of the trial. At this point the participant was also asked to complete a baseline questionnaire (see Appendix 2).
The treatment allocation for participants in the randomised component of the trial was computer generated in the trial office; it was stratified by centre, with balance in respect of other key prognostic variables – age (18–49 years or 50 + years), sex (male or female) and BMI (≤ 28 or > 29 kg/m2) – by a process of minimisation. Randomisation was organised centrally at the Health Services Research Unit, Aberdeen, and was independent of all clinical collaborators.
Clinical management
The first 146 randomised participants (70 allocated surgery and 76 allocated medical management) were sent details of their allocation at the same time as the baseline questionnaires. This was changed for subsequent participants at the request of the Data Monitoring Committee (DMC; see page 10) such that the allocation was only generated once completed baseline forms had been returned. This was to ensure that there was no possibility that knowledge of the allocation might influence responses to the baseline questionnaire (as well as ensuring that a completed baseline questionnaire would be received from all randomised participants). A summary of the trial procedure pathways is illustrated in Figure 2.
FIGURE 2.
Flow chart showing trial procedures post recruitment.
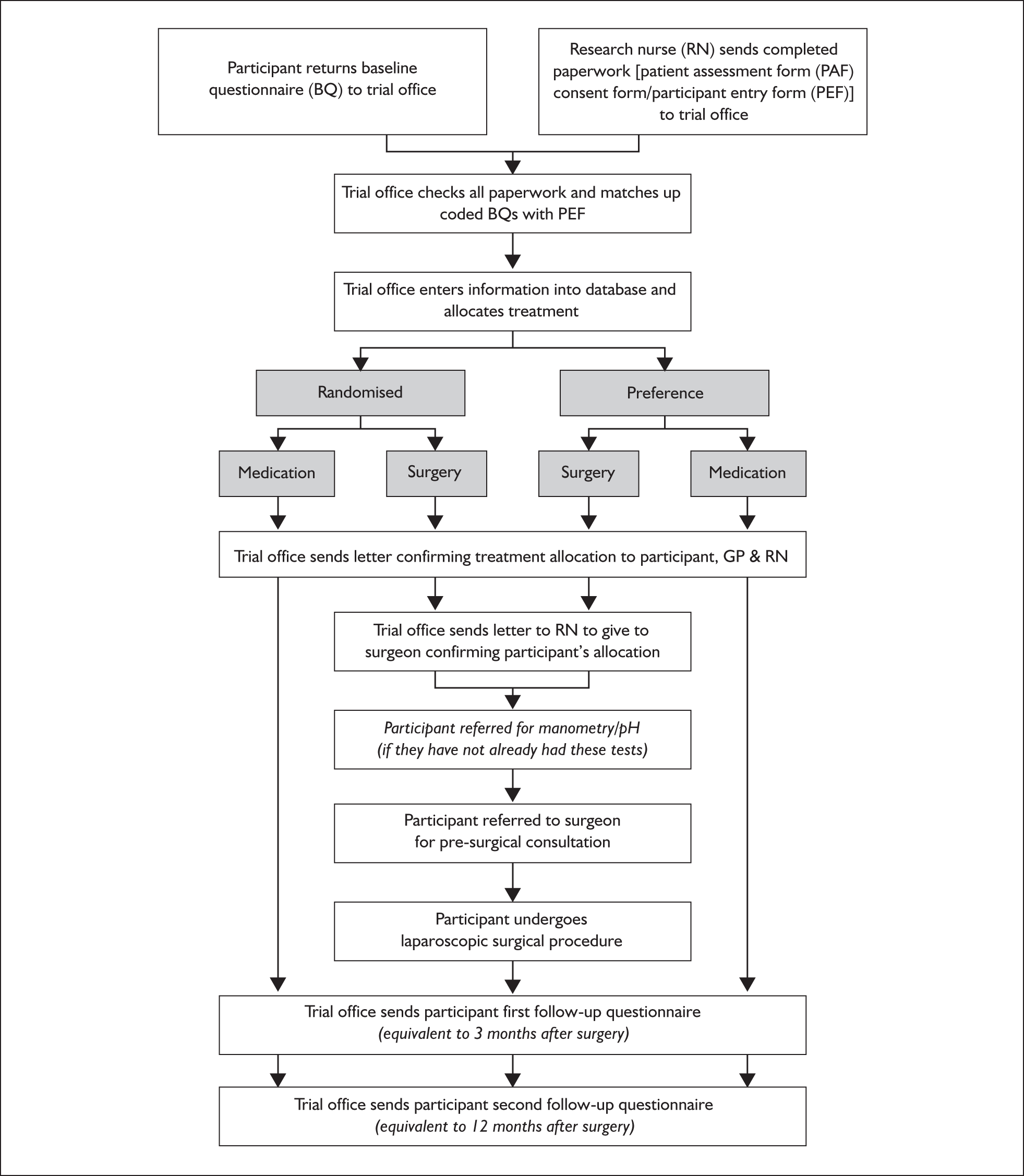
Participants who were allocated to the surgical arm were invited to a consultation with the collaborating surgeon. During this consultation the surgeon confirmed that there were no contraindications to surgery and discussed the operation in more detail, before arranging an operation date. The intraoperative details were recorded by the surgeon on specially designed study forms (see Appendix 8). All other in-hospital data collection was the responsibility of the local research nurse. In all respects, other than the trial interventions, clinical management was left to the discretion of the clinician responsible for care.
Data collection
Follow-up by postal questionnaire was performed at least twice at participant-specific time intervals after joining the study. This was around 3 and 12 months after surgery or at an equivalent time amongst those who did not have surgery. The latter times were chosen through a process of matching participants in the various groups. Participants received up to two reminder telephone calls or letters to encourage non-responders to return their postal questionnaires. On occasion, and at the convenience of participants, questionnaires were completed over the phone.
All data were sent to the trial office in Aberdeen for processing and staff in Aberdeen worked closely with participants’ local research nurses to secure as complete and accurate data as possible. A random 10% sample of all data was double entered to check accuracy. Extensive range and consistency checks further enhanced the quality of the data.
The principal study outcome measures
The primary outcomes for measuring the differences in effects between medical and surgical treatment were:
-
a ‘disease-specific’ measure incorporating assessment of reflux and other gastrointestinal symptoms and the side effects and complications of both therapies (the REFLUX questionnaire was developed specifically for this study as described in Chapter 4)
-
NHS costs including treatments, investigations, consultations and other contacts with the health service.
The secondary outcome measures were:
-
health-related quality of life (HRQoL) – EuroQol-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) and Short Form with 36 Items (SF-36)
-
patient costs including loss of earnings, reduction in activities, and the costs of prescriptions and travel for health care
-
other serious morbidity, such as operative complications
-
mortality.
The instruments for collecting this information are shown in Appendix 2.
Sample size
The original aim was to recruit 600 participants to the randomised trial to give 80% power to identify a difference between the two groups of 0.25 of a standard deviation in respect of the disease-specific instrument and other continuous variables such as EQ-5D or SF-36, using a significance level of 5%. Based on the same arguments it was planned that 300 people would be recruited to each arm of the preference study. The cost savings of a surgical policy largely depend on the number of patients managed surgically who no longer require PPI treatment, and a trial with 300 surgically managed patients would have estimated this proportion to within about 5% with 95% statistical confidence.
However, prompted by a lower rate of recruitment than expected, this target was revised in January 2003 in consultation with the DMC and representatives of the HTA programme. It was agreed that a larger benefit (0.3 of a standard deviation) was clinically plausible based on improvements seen after surgery amongst more severely affected people. This was calculated to require 196 in each group to give 80% power (p = 0.05). On this basis it was agreed that recruitment would be extended for an extra year, aiming for this revised sample size.
Statistical analysis
A single principal analysis of the randomised trial was planned when all participants had been followed up for 12 months after surgery (or an equivalent time if managed medically). The primary outcome measure [REFLUX quality of life (QoL) score at 12 months] and secondary outcome measures (REFLUX QoL score at 3 months; SF-36, EQ-5D, REFLUX symptom scores and use of reflux-related drugs at 3 months and 12 months) were analysed using general linear models that always adjusted for the minimisation covariates (age, BMI and sex) and where appropriate (defined by significant at the 5% significance level) also adjusted for baseline score and baseline score by treatment interaction. A secondary, pre-stated, subgroup analysis explored the differential effects of surgeons’ preferred operative procedures on the primary outcome measure. All analyses used 95% confidence intervals.
The primary analysis of the randomised trial was by intention to treat. The intention to treat approach gives the least biased estimate of effectiveness of the two interventions. As a secondary comparison we were also interested in estimating the efficacy of the treatment received. Given that a relatively large proportion of the randomised surgical participants did not receive surgery, we used two approaches to estimate the efficacy of the treatment – a per protocol analysis and an adjusted treatment received analysis. 32 In the per protocol analysis, participants who were randomised to surgery and actually received surgery were compared with participants who were randomised to medication and actually received medication (i.e. the compliers in the surgical group were compared with the compliers in the medical group). In an open trial design the per protocol estimate can have substantial selection bias. One way to estimate the effect when the allocation was complied with while adjusting for possible selection biases is to use a latent variable approach. 33 We used the method of adjusted treatment received as described by Nagelkerke et al. 32 The method used a two-stage least squares approach whereby treatment randomised was regressed onto treatment received and the residuals from that model were used as an independent variable in a second model together with the treatment received to estimate the effects on the various primary and secondary outcome measures.
For the preference group, only the primary outcome was analysed statistically. The analysis compared the preference surgical group with the preference medical group and adjusted for the minimisation factors. As described above, for logistical reasons and to maintain balance between the randomised and preference groups, we capped the number of preference participants at 20 per group per centre. The study design was not therefore a true comprehensive cohort. We did consider modelling differences between the randomised and preference groups; however, it is not universally accepted that formal modelling is appropriate in this context. In this case we knew from the randomised arms that there was a strong interaction with baseline reflux QoL, and in addition we also knew that there was a large difference in QoL between preference arms at baseline (and patient demographics). We therefore decided that formal modelling of the arms would not add much to the comparison given the large confounding between preference groups.
Missing items in the health-related outcome measures were treated as per the instructions for that particular measure. No further imputation for missing values was undertaken.
Data monitoring
In March 2003 an independent DMC met for the first time to review the overall conduct of the trial, patient accrual, data collection and an interim analysis of the data. They considered data available to them up to January 2003. At that time 146 participants had been recruited to the randomised trial, 76 allocated to the randomised medical group and 70 allocated to the randomised surgical group. Of the 177 preference participants, 77 chose the medical group and 100 chose the surgical group. On the basis of the data available to them they requested that the treatment allocation procedure be investigated. This led the DMC to instruct that the entry procedures be amended (as described on page 7) so that participants were only randomised once the trial office had received the baseline questionnaire and all of the other baseline paperwork (see Appendices 2, 4, and 6).
The DMC met on two further occasions (July 2003, January 2004) and were happy with the trial progress and interim analyses and saw no reason to recommend any further changes to the protocol.
Chapter 3 Preliminary economic modelling
A preliminary comparison of the cost-effectiveness of pharmacotherapy and surgery (laparoscopic fundoplication) in the treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
Background
Early in the study we chose to develop a preliminary economic model. Using the best evidence then available we developed a decision analytic model to provide preliminary estimates of costs and outcomes for medical and surgical management prior to the REFLUX trial reporting. 34,35 This chapter describes the preliminary economic model.
Methods
Description of the model
The model was probabilistic and took the perspective of the UK NHS. Health outcomes were expressed in terms of QALYs with a lifetime horizon. The model related to a 45-year-old patient as this is the peak age of presentation with GORD. 36 There proved to be very little difference between men and women; thus, only the results for males are presented here. Costs and QALYs have been discounted at a rate of 3.5% per annum. 37
The structure of the model can be seen in Figure 3. Two strategies were compared: long-term medical management and immediate laparoscopic surgery for GORD. Medical management was assumed to be prescribed for the remainder of a patient’s lifetime (30 years for a 45-year-old patient). Surgery was assumed to occur immediately following entry into the surgical arm of the model. The model was also split into short-term and long-term elements. The short-term model related to the period immediately following allocation to surgery or medical management. The longer-term element tracked the patient’s progression through a series of states over the remainder of their lifetime. Patients were assumed to stay in a ‘wait’ state before surgery, during which they would have received a maintenance dose of PPIs. The effects of alternative waiting times for surgery were also explored using alternative scenarios (1 month and 1 year) to represent the possible length of delay. In these cases it was still assumed that surgery following relapse would occur immediately, that is there would be no delay. Monthly cycles represented the monthly transition probabilities between states in the model.
FIGURE 3.
Structure of the preliminary economic model.
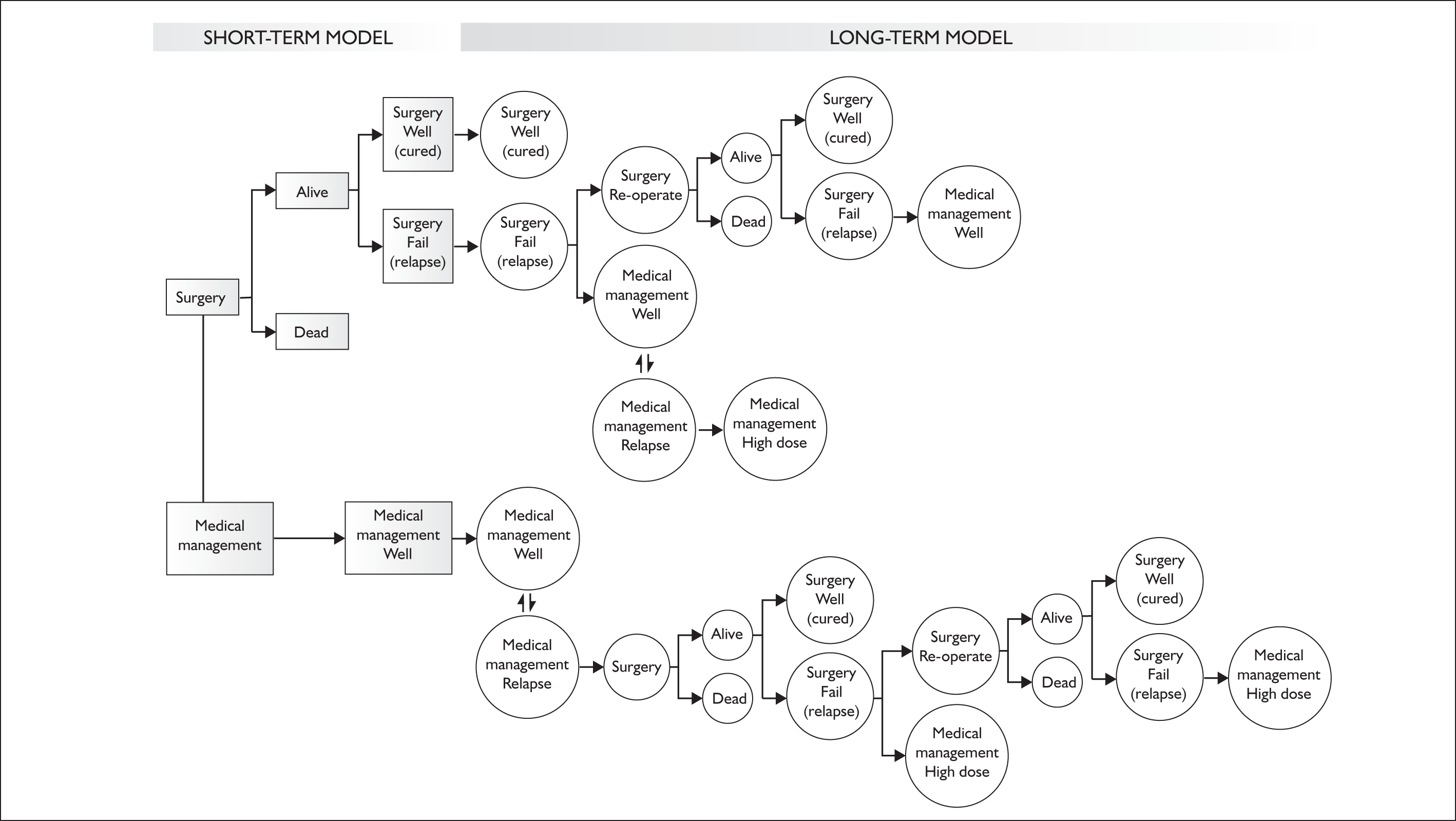
For patients receiving surgery a small mortality risk is associated with laparoscopic fundoplication (approximately 5 per 10,000 patients)38–47 and this was included in the model. If patients survived surgery the outcomes could be success (cured) or failure (relapse). In addition, patients could relapse from a successful surgery each month. This rate was constant and lasted for only one cycle, during which a patient received a double dose of PPI. A scenario is also presented in which the risk of failure from surgery (and the need for revision) ended at 5 years after initial surgery. Patients could be given a reoperation following surgery failure. If the reoperation failed, surgery was deemed a total failure and patients were considered to have been prescribed long-term medical management with PPIs. For patients offered medical management following initial surgical failure, medical management was deemed a total failure if there was subsequent relapse from medical management, and patients were placed on a double dose of PPIs for the remainder of their lives.
Medical management patients had a risk of relapsing each month. They could be offered surgery or could receive a double dose of PPIs for a cycle, followed by a return to a stable (well) medical management state at a normal dose of PPIs. Patients receiving surgery following relapse on medical management faced the same transition probabilities as surgical patients post surgery. They could also receive one reoperation following surgery failure. Medical management following two operations was deemed a total failure and patients were placed on a double dose of PPIs for the remainder of their lives.
For both surgical and medical management patients there was a monthly risk of all-cause mortality. The age-specific death rate for men aged from 45 to 54 years was obtained from the UK Office of National Statistics (ONS)48 and used to calculate the probability of death from natural causes from one cycle to the next.
Evidence to populate the model
Literature searches were undertaken to identify studies attempting to measure quality of life (measured by the EQ-5D) in relation to GORD or those providing information on the probability of movement between transition states during treatment. Searches were restricted to MEDLINE, EMBASE and internet sources, such as the Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effectiveness (DARE). Studies carried out before 1995 were not included as medical and surgical treatments for GORD were expected to have advanced significantly in the past 10 years, particularly in relation to relapse rates from surgery. The search strategies are shown in Appendix 9. This research was conducted in December 2005.
Fixed-effects meta-analysis techniques were used to synthesise data from multiple sources. Further details of the studies identified in the review are available from the author on request. Table 1 describes the probabilities and distributions of parameters used in the model.
| Parameter | Probability | Distribution | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Probability of death from surgery (instantaneous risk) | 0.0005 | Beta (4–3997) | Multiple studies: Contini et al., 2002;38 Gotley et al., 1996;39 Dallemagne et al., 1998;40 Kiviluoto et al., 1998;41 Booth et al., 2002;42 Landreneau et al., 1998;43 Finley and McKernan, 2001;44 Pessaux et al., 2002;45 van der Peet et al. 1998;46 Bais et al. 200047 |
| Probability of surviving surgery | (1–above) | ||
| Probability of surgery failure | 0.0044 | Beta (78–1429) | Multiple studies: Contini et al., 2002;38 Gotley et al., 1996;39 Dallemagne et al., 1998;40 Kiviluoto et al., 1998;41 Booth et al., 2002;42 Landreneau et al., 1998;43 Pessaux et al., 2002;45 Watson et al., 1995;49 Lundell et al., 2001;50 Lundell et al., 1996;18 Anvari and Allen, 2003;51 Ludemann et al., 2005;52 Hunter et al., 1999;53 Graziano et al., 2003;54 Soper and Dunnegan, 199955 |
| Probability of surgery success | (1–above) | ||
| Probability of reoperation after surgery failure (instantaneous risk) | 0.1034 | Beta (55–477) | Multiple studies: Contini et al., 2002;38 Finley and McKernan, 2001;44 Pessaux et al., 2002;45 Anvari and Allen, 2003;51 Soper and Dunnegan, 1999;55 Eshraghi et al., 1998;56 Bammer et al., 2001;57 Jamieson et al.,199458 |
| Probability of medical management after surgery failure | (1–above) | ||
| Probability of a relapse on medical management | 0.0256 | Beta (78.8–207) | Multiple studies: Lundell et al., 2001;50 Hatlebakk and Berstad, 1997;59 Festen et al.,1999;60 Bate et al., 199561 |
| Probability of stable maintenance on medical management | (1–above) | ||
| Probability of surgery to treat relapse on medical management (instantaneous risk) | 0.1133 | Beta (23–180) | Multiple studies: Lundell et al., 2001;50 Myrvold et al., 200162 |
| Probability of returning to medical management after relapse | (1–above) |
Resource use
Resource use associated with surgery consisted of: (1) procedures for screening for the presence of GORD (endoscopy, manometry pH monitoring, etc); (2) theatre staff; (3) surgical disposables; (4) length of surgery; (5) length of hospital stay; (6) postoperative procedures; and (7) surgical revision or conversion to open fundoplication when needed. The resources used were estimated through a survey of five of the hospitals involved in the REFLUX trial. The lengths of surgery and of hospital stay were taken from the laparoscopic fundoplication baseline data for the REFLUX trial. An additional 15 minutes was added to the duration of operation to derive a total length of surgery, as the time from anaesthesia to recovery recorded in the REFLUX trial did not allow for preparation time.
Typical daily dosages of PPIs and other medicines used in medical maintenance of GORD were also obtained from the REFLUX trial baseline questionnaire using data for the month before study entry. An average daily dose was calculated for each drug and used to derive an average daily cost of medical treatment.
Costs
Table 2 shows the estimated monthly cost of drugs or surgery per patient and their associated distributions, which reflect the heterogeneity between centres and differences in pack sizes for medications.
| Parameter | Cost (£) | Distribution | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monthly cost of medications | 18.25 | Gamma (1.77–0.33) | REFLUX study baseline data and British National Formulary63 |
| Cost of medications during months relapse (maintenance dose doubled) | 36.50 | ||
| Cost of surgery | 2787.39 | Gamma (113.60–16.50) | Survey of REFLUX centres (see Appendix 10) |
Costs of all medicines were taken from the British National Formulary (2005)63 and an assumption was made that lowest cost prescribing was used (e.g. generic formulations and tablets). The average daily cost of medical treatment was calculated and the model assumed that, in the event of a relapse on medical treatment, the dose would be doubled for a period of 1 month. Direct surgical treatment costs included the costs of preoperative screening for GORD, surgery and hospital stay. For theatre staff costs, salaries were taken as the mid-point on the relevant scale for each grade or professional. Costs of perioperative procedures were taken from provider-to-provider tariffs for various hospitals or from published sources,64,65 and the frequency of such procedures was calculated from the laparoscopic fundoplication baseline data in the REFLUX trial. Costs of surgical revision or conversion to open fundoplication were assumed to be the same as those of the original operation. In the case of open fundoplication, a hospital stay of 6 days was assumed and a cost loading (average cost was inflated to account for the expected number of high-cost rare events) applied based on a meta-analysis of published information. 45,51,58,66,67
The cost of oesophageal dilatation for dysphagia (swallowing difficulties), the most commonly occurring postoperative corrective surgery encountered, was taken from Leeds General Infirmary and a cost loading was added to the total cost of surgery. Along with death, this was the only complication of surgery considered in these analyses. Costs of endoscopic disposables were obtained from a manufacturer, Ethicon Endo-Surgery. Costs of disposable drapes and gowns came from Kimberly-Clark Health Care, UK. Capital costs associated with standard laparoscopic surgery installations were obtained from Karl Storz GmbH and Ethicon Endo-Surgery. An assumption was made that the service life of a laparoscopic installation was 5 years and the capital costs were amortised (3.5% per annum) over that period. Furthermore, a capital cost for laparoscopic fundoplication was calculated assuming 200 operations were undertaken in that period in each centre.
Appendix 10 summarises the costs associated with surgery. Variation between centres largely reflects differing staff mix and variation in the use of disposables.
Health outcomes
Outcomes were expressed as QALYs with patients’ HRQoL measured by the EQ-5D. This is a generic measure of health status in which health is characterised on five dimensions (mobility, self-care, ability to undertake usual activities, pain, anxiety/depression). 68 Each response to this instrument locates an individual into one of 245 mutually exclusive health states, each of which has previously been valued on the 0 (equivalent to dead) to 1 (equivalent to good health) ‘utility’ scale based on interviews with a sample of 3395 members of the UK public. 69
EQ-5D values for patients who were on medical treatment were obtained from the available (as of December 2004) baseline data (surgical and medical management patients) collected in the REFLUX trial. EQ-5D values obtained for the UK general population (population norms) aged from 45 to 54 years were taken from Kind et al. 70 and were considered to represent a ‘cured’ state (successful surgery). HRQoL in the month immediately following laparoscopic fundoplication was taken from EQ-5D values as measured in patients following laparoscopic cholecystectomy. 71 Patients with unresolved symptoms of GORD (relapse) were assigned a utility based on the decrement between stable medical management and reflux symptoms estimated in a published expert opinion (0.53). 72 The utility values used and their sources are summarised in Table 3.
| State | Utility | Distribution | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| QoL on stable medical maintenance | 0.72 | Gamma (0.02–8.38) | REFLUX study baseline data |
| QoL during relapse | 0.56 | Gamma (0.02–5.29) | REFLUX study baseline data; Heudebert et al., 199772 |
| QoL following surgery | 0.61 | Fixed | Ainslie et al., 200371 |
| QoL in cured post-surgical state | 0.84 | Gamma (0.25–11.29) | UK male (45–54 years) population norms (Kind et al., 199970) |
Analysis
The model was developed in Excel with the Crystal Ball ‘add-on’. Monte Carlo simulation was used to propagate the prior distributions assigned to model inputs and estimate the expected costs and outcomes associated with each alternative therapy; incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICER) were calculated. Distributions for parameters were selected on the basis of the nature of the parameter concerned. 73 To conduct the simulations, the distributions reported in Table 1 were assigned to the model inputs to characterise the current uncertainty surrounding their values. The simulation recalculated the results over 10,000 iterations. For each iteration, the value of each variable was sampled at random from the distributions specified. By repeating the calculations of expected costs and outcomes in this way, distributions of estimates are obtained, which allow estimation of the mean expected costs and QALYs and associated distributions.
The results of the model are presented in two ways. First, mean costs and QALYs for the various comparators are presented and their cost-effectiveness compared, using standard decision rules to estimate ICER as appropriate. Second, given that mean costs and QALYs gained are estimated with uncertainty, the output from the simulations have been used to generate cost-effectiveness acceptability curves. These curves illustrate the probability of surgery being more cost-effective than medical management given a range of values that an NHS decision-maker might attach to an additional QALY. Threshold values of cost-effectiveness ranging from £0 to £100,000 per additional QALY were used in the analysis. This is a Bayesian approach to the presentation of cost effectiveness, although this is not a full Bayesian analysis. 74,75
The output of these simulations was also used to estimate the expected value of perfect information (EVPI). 76,77 The cost in terms of health benefits and resources forgone if a wrong decision is made can be described using the probability of making an error based on current knowledge and the consequences of a wrong decision. Thus, the expected costs of uncertainty can be interpreted as the EVPI, as perfect information would obviate decision error. The EVPI is, therefore, the maximum that the health-care system should be willing to pay for additional evidence to inform this decision in the future, that is, the maximum expenditure in relevant future research. Per patient EVPI was calculated and, in addition, an analysis of the EVPI associated with particular items of evidence used in the model was also conducted. This can be used to focus research on those elements in the decision for which more precise estimates would be most valuable. 76–78
Results
Base-case cost-effectiveness
The base-case estimates of costs and QALYs associated with surgery are shown in Table 4. Over a lifetime, medical management (£4890) was estimated to cost less than surgery (£5014) but it was associated with fewer QALYs than surgery: 12.36 compared with 13.04.
| Total costs (£) | Total QALYs | ICER | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery | 5014.17 | 13.04 | £180.61 |
| Medical management | 4890.59 | 12.36 |
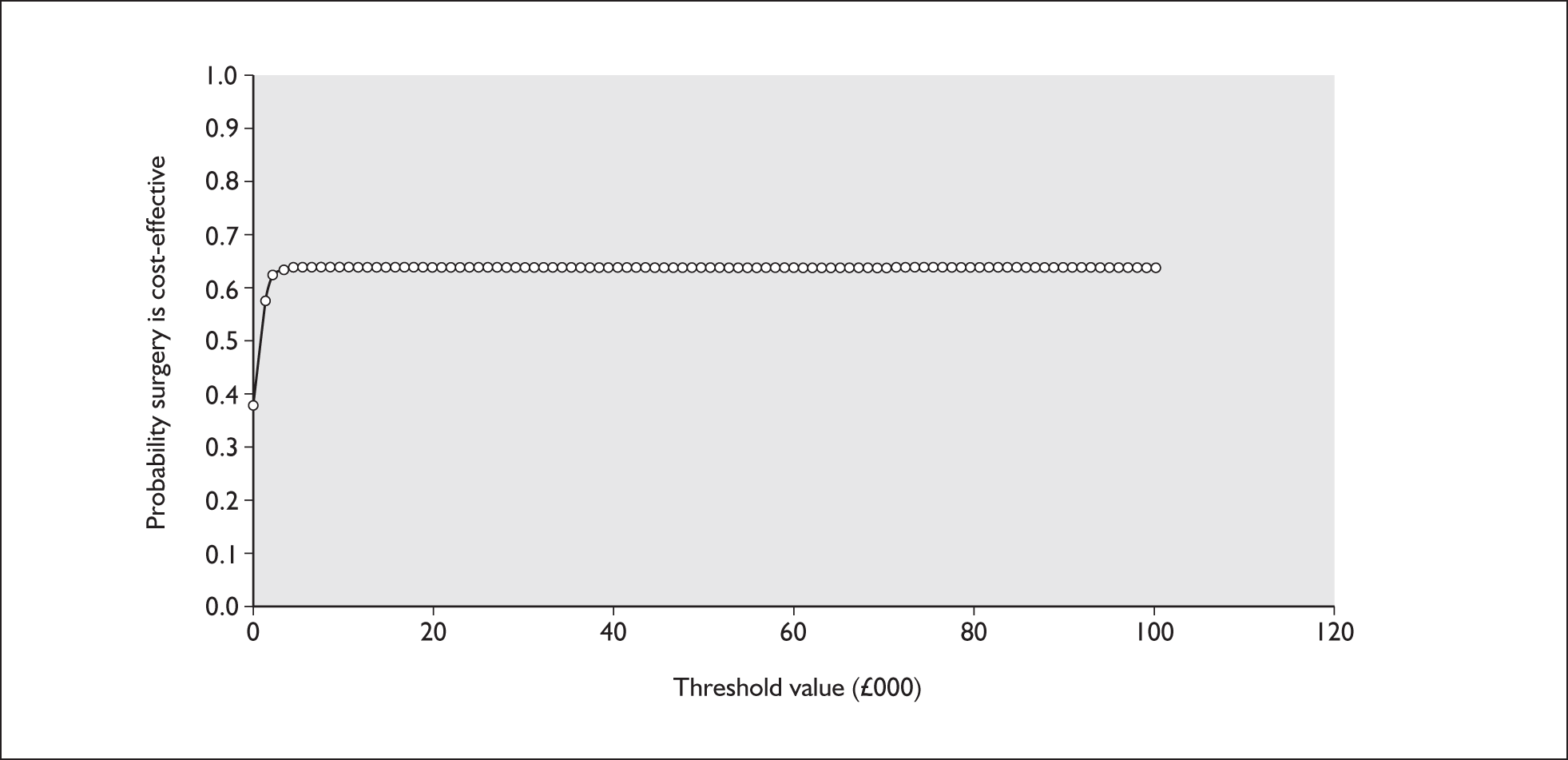
The lifetime ICER for surgery versus medical management is thus £180. Based on this, as long as decision-makers are willing to pay more than £180 for an additional QALY, surgery would be regarded as the more cost-effective treatment option. However, mean costs and QALYs were estimated with uncertainty. Figure 4 shows the potential impact of the uncertainty in mean differences (surgery minus medical management) in costs and QALYs gained between the two groups (i.e. it shows mean costs and QALY differences based on the 1000 simulations). Figure 5 represents this uncertainty in the form of a cost-effectiveness acceptability curve. The probability that surgery is cost-effective at a threshold of cost-effectiveness of £30,000 per QALY is 0.639.
FIGURE 4.
Representation of the uncertainty in differential mean costs and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs).
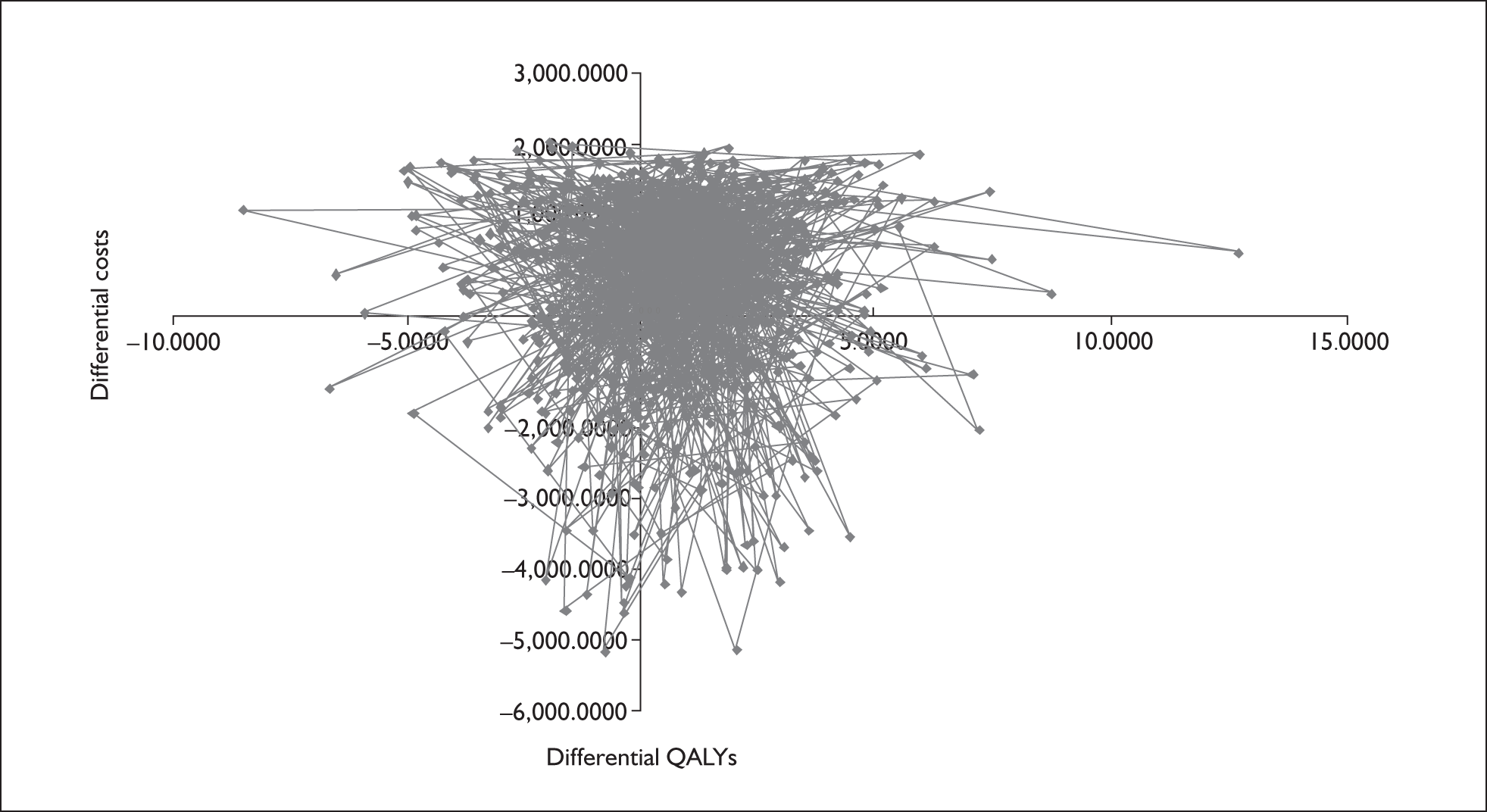
FIGURE 5.
Cost acceptability curve for surgery versus medical management.
Expected value of perfect information
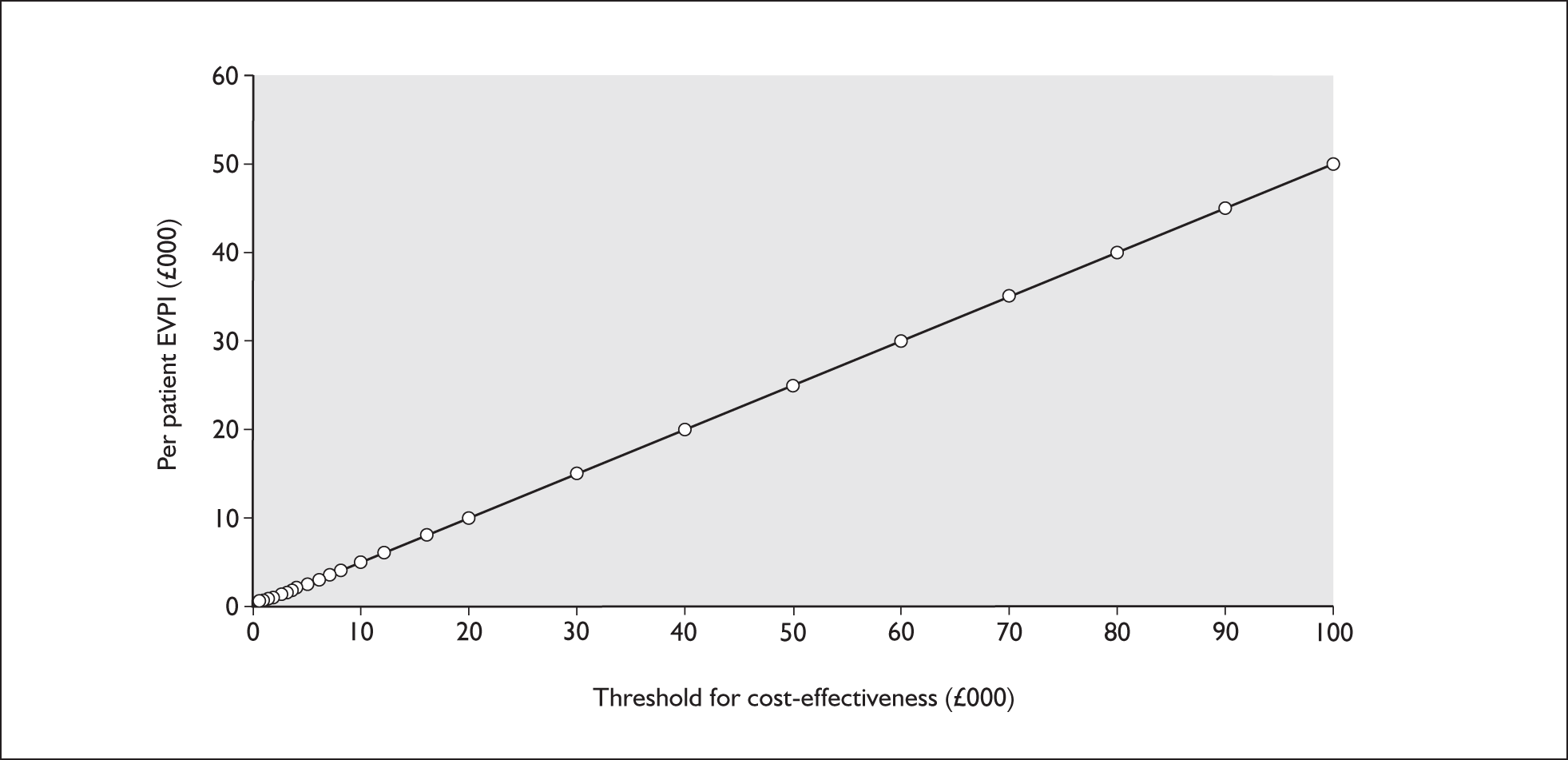
The per patient EVPI for adults with GORD is illustrated in Figure 6. At a cost-effectiveness threshold of £30,000, EVPI is substantial at £15,106. At a threshold of £20,000, the EVPI is £10,081. EVPI for groups of parameters showed that all of the value of further research (£11,346 at a threshold of £30,000 for cost-effectiveness) is associated with the quality of life implications of medical or surgical therapies, indicating that this is where future research should focus.
FIGURE 6.
Per patient expected value of perfect information (EVPI).
Alternative model assumptions
Alternative assumptions regarding the model structure were explored, specifically the effect of any delay to receiving surgery (1 month and 1 year) and the risk of relapse from surgery 5 years postoperatively.
Assuming that there is no risk of surgical failure 5 years post operation reduces the total cost of surgery (to £4121) and increases QALYs (to 13.48). Although total costs (£4887) and QALYs (12.38) change for medical management, because of the small number of people receiving surgery following medical management relapse, the effect of this is only minor. Surgery now dominates medical management as it has lower costs and higher QALYs. Decision uncertainty is, however, relatively insensitive to this structural change, with the probability that surgery is cost-effective increased from 0.639 in the base-case model to 0.642 at a threshold of £30,000. As we are somewhat more certain about the decision to recommend surgery as the most cost-effective treatment, per patient EVPI decreases by a small amount from £15,106 in the base-case model to £15,078.
Incorporating any delays to surgery had very little effect on both the costs and the QALYs. This is because time spent in the ‘wait’ state was assigned a relatively small cost of medical management and the utility of stable management. Decision uncertainty and EVPI was also largely unaffected by delays to surgery.
Discussion
This was the first investigation of the cost-effectiveness of lifelong medical treatment compared with immediate laparoscopic fundoplication for the treatment of GORD. The results of this model suggest that, even when the risk of spontaneous failure of surgery exists for a patient’s lifetime, surgery for GORD is more cost-effective than lifelong management with drugs. However, the true cost-effectiveness of surgery is uncertain and, at a threshold for cost-effectiveness of £30,000 per additional QALY, the value of information surrounding the decision problem is high. The number of people with GORD suitable for surgery is likely to be sizeable and therefore the EVPI of £15,106 at a threshold of £30,000 per QALY implies that the EVPI will exceed the cost of further investigation. This, in turn, suggests that further research will be potentially cost-effective. EVPI analysis on groups of parameters suggested that further research should focus on collecting evidence relating to the HRQoL of patients on medical management and following surgery.
It was necessary to make a number of assumptions in the model. First, in the absence of applicable data, it was necessary to simplify the dosing adjustment used to deal with relapse. In clinical practice a more complicated titration of dose and duration of step-up or step-down dosing would be used. The effect of this would probably be that patients in relapse spend more than 1 month on a higher dose (and at higher cost) and simultaneously experience lower HRQoL for longer than modelled here. At present, given that equal consequences of relapse have been applied to those patients relapsing on medical management or surgery, it is unlikely that applying a more complex relapse dosing structure would have a significant effect on the results of the model.
Second, the costs of surgery only partially capture true cost. Surgery may have unwanted side effects or may spontaneously fail at some point in the future. Treatment of side effects or surgical failure has costs both in monetary and quality of life terms. A common side effect, temporary difficulty with swallowing (dysphagia), has been considered in the model and a probabilised cost loading used to incorporate its treatment. However, no disutility of dysphagia, bloating, flatulence or other unwanted side effects following surgery has been included in the model because of a lack of data and consensus on the magnitude of effect. Related to this is the availability of data for other states in the model. In the absence of other suitable data, the utility values used to reflect the post-surgical state were based on patients measured following laparoscopic cholecystectomy,71 which has some surgical similarities to laparoscopic fundoplication but may not have the same spectrum of postoperative discomfort or complications. The utility value associated with a surgical cure has been taken from UK age-specific population norms. 70 Also, it is unclear to what extent the post-surgical state can be likened to the utility of an average member of the UK population, that is, whether surgery actually generates a cure in utility terms.
Finally, because of the focus on those patients currently maintained on medical management, the analysis reported here did not consider management strategies other than medical management or surgery. In many clinical settings lifestyle management advice is being favoured as a first-line option, with medical management or surgery considered only as second-line therapies in patients who do not respond to lifestyle changes. This may limit the applicability of this model in certain settings.
Despite these necessary assumptions, the model presented here represents the first attempt to generate estimates of cost per QALY for surgical and medical management strategies for the treatment of GORD patients in the UK. The results of the model suggest that, on the basis of current evidence, laparoscopic fundoplication may well represent a cost-effective means of treating GORD rather than lifelong medical management. Coupled with the apparent safety of the surgical procedure (in experienced hands), patients and the health service may benefit from increased substitution of surgery for medical management. What this preliminary analysis confirmed was the need for more robust data, especially in respect of HRQoL, and these data were being generated in the REFLUX trial.
Chapter 4 REFLUX outcome measure
The development of a new measure of quality of life in the management of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: the REFLUX questionnaire
Introduction
Although several GORD-specific or gastrointestinal-specific symptom scales and quality of life scales have been developed,79–87 we found that none captures the experience of patients receiving alternative treatments in sufficient detail for evaluating outcomes in the REFLUX trial. Of particular concern was that these measures do not reflect patients’ experiences of the side effects of surgery for GORD, which include general gastrointestinal symptoms as well as oesophageal reflux itself. 85 A new condition-specific outcome measure was therefore developed for use within the REFLUX trial. The aim of this measure was not only to assess the symptoms of GORD but also the side effects of both medical and surgical treatment for GORD and the effects that these have on HRQoL. There were two requirements for the new measure: it had to measure HRQoL and not merely symptom experience; and its content had to cover the effects of treatment for GORD as well as the symptoms of GORD. This chapter describes the development and assessment of the new measure.
Method
Questionnaire development
Between May and September 2000, a series of one-to-one interviews and focus groups were conducted with patients in two cities, Leeds and Aberdeen, to identify those themes and issues related to GORD and its treatment that were important to people affected by GORD. In total, 31 people were interviewed, 15 receiving medical treatment and 16 who had received surgery. In addition, two focus groups were conducted, each with six patients, one in Aberdeen and one in Leeds. Both focus groups included only patients who had received surgery for their GORD symptoms, identified via their gastroenterologist or surgeon.
Both the interviews and focus groups followed the same general format. Patients were asked questions about the types and severity of symptoms they experienced, how best to describe their symptoms, whether they felt that their symptoms were best described by their frequency, duration or level of distress, and about the impact that their symptoms had on their daily lives.
All interviews and focus groups were audiotaped and transcribed. These transcripts underwent thematic analysis by three members of the trial team. Emerging themes and issues suggested potential questionnaire items. Whenever possible the language used by patients was used when devising the questionnaire items. The transcripts showed that the frequency of symptoms and their effects on quality of life were the two most commonly reported themes by patients. This led to the development of 31 possible questions.
Piloting
The initial version of the questionnaire (with the 31 items) was piloted on a sample of 21 patients from Aberdeen, some of whom had taken part in the interview phase. The questionnaire was posted out to the patients asking them to complete it. At a later date they were interviewed about its readability and acceptability. Specifically, they were asked about whether they had any problems understanding the items, whether the response categories were appropriate for them and whether they thought that anything was missing from the questionnaire. The questionnaire was modified following the feedback from these interviews. At this stage a small number of items (three) were discarded as unsuitable or potentially ambiguous, others were reworded and three items that were not originally included in the initial version of the questionnaire, but were repeatedly mentioned by the patients and felt to be of importance, were added The new version therefore also had 31 items.
Final questionnaire
The 31 items that were included in the formally evaluated version of the questionnaire were grouped into seven categories (heartburn; acid reflux; wind; eating and swallowing; bowel movements; sleep; and work, physical and social activities) describing symptoms relating to GORD or side effects of treatment (Table 5). For each category respondents were asked to show how often they had experienced problems with specified symptoms over the past 2 weeks, followed by how much they felt that those symptoms had affected their quality of life over the past 2 weeks. The symptom items offered five responses, from ‘not at all’ to ‘every day’, and the quality of life items offered five responses – ‘not at all’, ‘a little’, ‘moderately’, ‘a lot’ and ‘extremely’. Items in the least clinical of the categories, work, physical and social activities, offered six responses including ‘not applicable’ (see the REFLUX questionnaire within Appendix 2).
| Category | Number of items |
|---|---|
| Heartburn | 3 |
| Acid reflux | 6 |
| Wind | 5 |
| Eating and swallowing | 3 |
| Bowel movements | 5 |
| Sleep | 4 |
| Work, physical and social activities | 5 |
Data
The new measure, along with two generic measures of HRQoL (EQ-5D88 and SF-3689) and information on background, demographics and use of medicine, was included in a postal questionnaire, which was sent to all REFLUX trial participants. Trial participants were sent a questionnaire at baseline after they had agreed to take part in the trial, at first follow-up (3 months after surgery or its equivalent for non-surgical participants) and at second follow-up (12 months after surgery or equivalent). This chapter reports on data received by December 2004. Most of the analysis presented here was performed on the baseline data, but analysis of sensitivity to change also used the first follow-up data.
Analysis
Developing a scoring system
We planned that the new measure would produce two different types of score:
-
a REFLUX quality of life score (RQLS) summarising the extent to which respondents’ symptoms affect their quality of life, where 0 is the worst quality of life and 100 is the best
-
a series of seven REFLUX symptom scores that profile respondents’ experiences of these groups of symptoms over the past 2 weeks.
Although it is possible to generate summary scores by merely summing the raw scores on each item, this assumes that all items in the measure are equally important. This disregards the possibility that some items are more important than others and should therefore have a larger emphasis in the final score. We chose to use two distinct methods of weighting the contribution of items to the total score.
The REFLUX questionnaire contains seven quality of life items, each relating to one of its seven categories, that require participants to indicate how much they feel their symptoms on a particular dimension in the past 2 weeks have affected their general quality of life. Weights for the RQLS were estimated by assessing the influence of these items on participants’ assessments of their general quality of life. We used the seven baseline quality of life items as independent variables in an ordinary least squares (OLS) regression model with participants’ assessments of their general HRQoL, as measured by the EQ-5D visual analogue scale (EQ-5D VAS), as the dependent variable. For modelling purposes we assumed that the data from these items were cardinal. EQ-5D VAS requires respondents to assess their current state of health on a 0–100 visual analogue scale, where 0 represents worst imaginable health and 100 best imaginable health. To remain in the model, regression coefficients did not have to be statistically significant but they did have to have the correct (negative) sign, i.e. a reported detrimental effect on quality of life should be associated with a decrease in EQ-5D VAS score. The resulting coefficients were used as weighting factors to calculate a general quality of life summary score.
In contrast, weights for the REFLUX symptom summary scores were generated by entering the 31 baseline symptom items into a principal components analysis (PCA) with a Varimax rotation. We judged how many components or factors to extract by using a combination of the Kaiser criterion (include all factors with an eigenvalue greater than 1) and a scree plot of those eigenvalues. The resulting factor loadings were used as the item weights to calculate a number of symptom scores.
Reliability, validity and sensitivity to change
We assessed the reliability of the REFLUX quality of life and symptom scores by internal consistency, as measured by Cronbach’s alpha. In contrast, our assessment of the validity and responsiveness or sensitivity to change concentrated on the quality of life score, as this was the main aim of the measure. The validity of the RQLS was assessed by comparing its performance against the SF-36. Sensitivity to change was assessed by the measure’s ability to reflect changes in the condition of participants, as assessed by self-reported change in prescribed medication between baseline and first follow-up. Participants were asked to give details of their prescribed medication use (PPIs, H2RAs and anti-emetics) at baseline and at first follow-up. This information was used to classify whether or not their medication use had changed between these times.
Results
Sample characteristics
Between March 2001 and June 2004 a total of 810 participants had been recruited into the REFLUX trial, of whom 799 had completed and returned their baseline questionnaires. By December 2004 602 participants out of 649 (93%) had returned a first follow-up questionnaire, and 418 out of 447 (94%) a second follow-up questionnaire. At baseline 64% of the sample was male, and the median age at trial entry was 46 years (range 18–74 years).
Scoring
Generating weights for the reflux quality of life score
All 727 participants with complete baseline data on the REFLUX quality of life items and EQ-5D VAS were included in the analysis. Although coefficients for three of the seven quality of life items were not statistically significant, we kept them in the regression model for completeness. In contrast, we excluded the wind item from the RQLS model as the coefficient consistently showed the wrong sign and was not statistically significant. In effect, the wind item will receive a weight of zero when calculating the final score. The work, physical and social activities item had the largest coefficient and thus had most effect on the EQ-5D VAS, and the sleep item had the smallest coefficient. The final model coefficients used to calculate the RQLS are given in Table 6.
| REFLUX quality of life item | B | SE | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heartburn | –1.346 | 0.81 | NS |
| Acid reflux | –1.700 | 0.70 | < 0.05 |
| Eating and swallowing | –1.103 | 0.68 | NS |
| Bowel movements | –1.954 | 0.61 | < 0.01 |
| Sleep | –0.351 | 0.66 | NS |
| Work, physical and social activities | –2.147 | 0.84 | < 0.05 |
| Constant | 89.995 | 1.51 | < 0.001 |
The coefficients from this model were used as weights for calculating the quality of life score by multiplying the response to each quality of life item (coded from 0 ‘not at all’ to 4 ‘extremely’) by the corresponding weight (i.e. the coefficient from Table 6) and subtracting these values from the constant term as follows:
The score was then standardised to a scale from 0 (worst quality of life) to 100 (best quality of life) as follows:
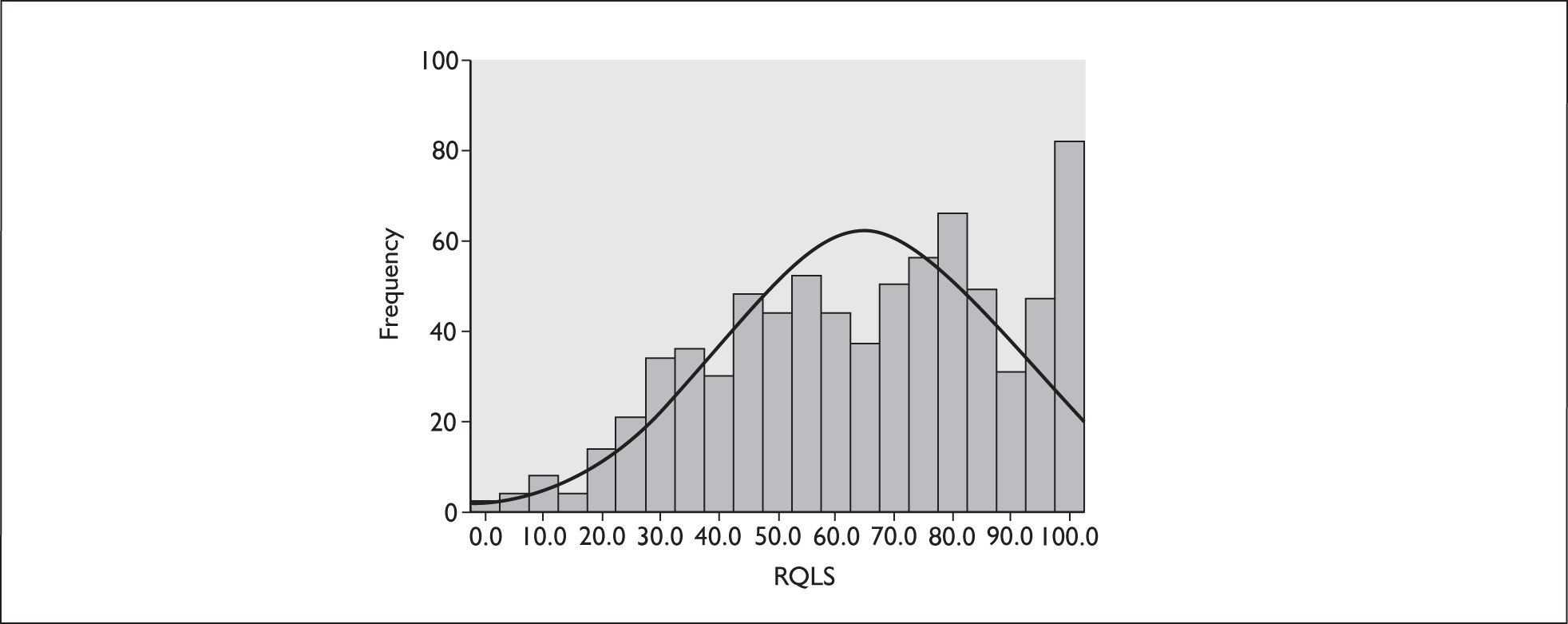
Figure 7 presents the frequency distribution of quality of life scores for patients at baseline. The mean score was 65.0 with a standard deviation of 24.3.
FIGURE 7.
Distribution of reflux quality of life scores (RQLS).
Generating weights for the reflux symptom scores
The PCA identified five components that accounted for 57% of the variance in the items (Table 7). In general, the component structure reflected the themes identified when the items were developed; however, component 1 grouped together heartburn-like symptoms and sleep disruption into general discomfort (Table 7). The first component after rotation explained 19% of the total variance and included seven items with loadings above 0.4. Component 2 explained 12% of the total variance and included six main items. The remaining three components accounted respectively for 10%, 9% and 8% of the total variance. Component loadings were used to construct a profile of five REFLUX symptom scores to summarise an individual’s symptom experience. In the first instance we suggested the following labels for these components: 1 = general discomfort; 2 = wind and frequency; 3 = nausea and vomiting; 4 = activity limitation; and 5 = constipation and swallowing.
| Item | Component 1 | Component 2 | Component 3 | Component 4 | Component 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1: Heartburn | 0.674 | ||||
| A2: Discomfort in chest | 0.643 | ||||
| B1: Acid reflux | 0.654 | ||||
| B2: Vomiting | 0.734 | ||||
| B3: Regurgitation | 0.556 | ||||
| B4: Nausea | 0.541 | ||||
| B5: Urge to be sick | 0.709 | ||||
| C1: Flatulence | 0.738 | ||||
| C2: Belching | 0.553 | ||||
| C3: Feeling bloated | 0.568 | ||||
| C4: Stomach gurgling | 0.515 | ||||
| D1: Difficulty swallowing | 0.338 | ||||
| D2: Eating restricted | 0.421 | ||||
| E1: Diarrhoea | 0.722 | ||||
| E2: Constipation | 0.839 | ||||
| E3: Urgent need to go | 0.696 | ||||
| E4: Feeling like bowels not emptied | 0.645 | ||||
| F1: Difficulty sleeping lying down | 0.777 | ||||
| F2: Difficulty getting to sleep | 0.814 | ||||
| F3: Disrupted sleep | 0.791 | ||||
| G1: Paid/unpaid work | 0.695 | ||||
| G2: Less strenuous activities | 0.571 | ||||
| G3: Strenuous activities | 0.755 | ||||
| G4: Social activities | 0.588 |
Each symptom score was calculated by multiplying the response to each of the symptom items in that score (coded from 0 ‘every day’ to 4 ‘not at all’) by the corresponding weight (i.e. the component loading for that item from Table 7) and then summing across the items. For the four items in activity limitation we grouped the response codes ‘not applicable’ and ‘no, my symptoms do not affect me’ as 4, and recoded the other categories from 0 ‘I no longer work/perform these activities because of my symptoms’ to 3 ‘my symptoms have affected me but I still work/perform these activities’. Symptom scores were then standardised to a scale from 0 (worst symptom score) to 100 (best symptom score) as follows:
Table 8 presents the mean symptom scores at baseline. There were pronounced ceiling effects for nausea and vomiting, constipation and swallowing, and activity limitations: 26%, 25% and 17% respectively of the sample had a maximum score of 100. In contrast, wind and frequency showed a more normal distribution.
| Reflux symptom dimension | Mean | SD | Median |
|---|---|---|---|
| General discomfort | 59.4 | 25.6 | 60.3 |
| Wind and frequency | 50.7 | 22.1 | 49.6 |
| Nausea and vomiting | 81.7 | 19.6 | 89.0 |
| Activity limitation | 79.2 | 16.5 | 81.5 |
| Constipation and swallowing | 77.7 | 20.6 | 79.6 |
Both the RQLS and REFLUX symptom scores were calculated only for individuals with complete data. However, there were few missing data. REFLUX scores could be calculated for over 95% of patients at baseline. Missing data rates for symptom items ranged from 1% to 2%, and for quality of life items from 3% to 5%.
Reliability
The reliability coefficient (Cronbach’s alpha) measuring the internal consistency of the RQLS was 0.90. For the REFLUX symptom scores, alphas were as follows: general discomfort 0.87; wind and frequency 0.78; nausea and vomiting 0.75; activity limitations 0.68; and constipation and swallowing 0.56. Apart from the last two items all alphas are greater than 0.70, which is generally considered satisfactory. 90
Validity
Table 9 presents the relationship (Pearson’s r) between the RQLS and the eight SF-36 dimension scores. Social functioning and bodily pain showed the best relationships with the RQLS, and mental health the worst.
| SF-36 dimension | RQLS |
|---|---|
| Physical functioning | 0.42 |
| Role limitations – physical | 0.49 |
| Bodily pain | 0.56 |
| General health perception | 0.46 |
| Energy/vitality | 0.34 |
| Social functioning | 0.59 |
| Role limitations – emotional | 0.41 |
| Mental health | 0.18 |
Table 10 presents the proportion of respondents who had a score of 100 (best health) on the SF-36 dimensions as a percentage of those who had a best score of 100 on the RQLS. Whereas 96% of those who had the maximum score on the SF-36 physical functioning dimension also had a score of 100 on the RQLS, only 31% of those who had a score of 100 on the SF-36 bodily pain dimension also had a score of 100 on the RQLS.
| SF-36 dimension | % (n) |
|---|---|
| Physical functioning | 96 (70) |
| Role limitations – physical | 66 (48) |
| Bodily pain | 31 (23) |
| General health perception | – |
| Energy/vitality | – |
| Social functioning | 74 (54) |
| Role limitations – emotional | 97 (71) |
| Mental health | – |
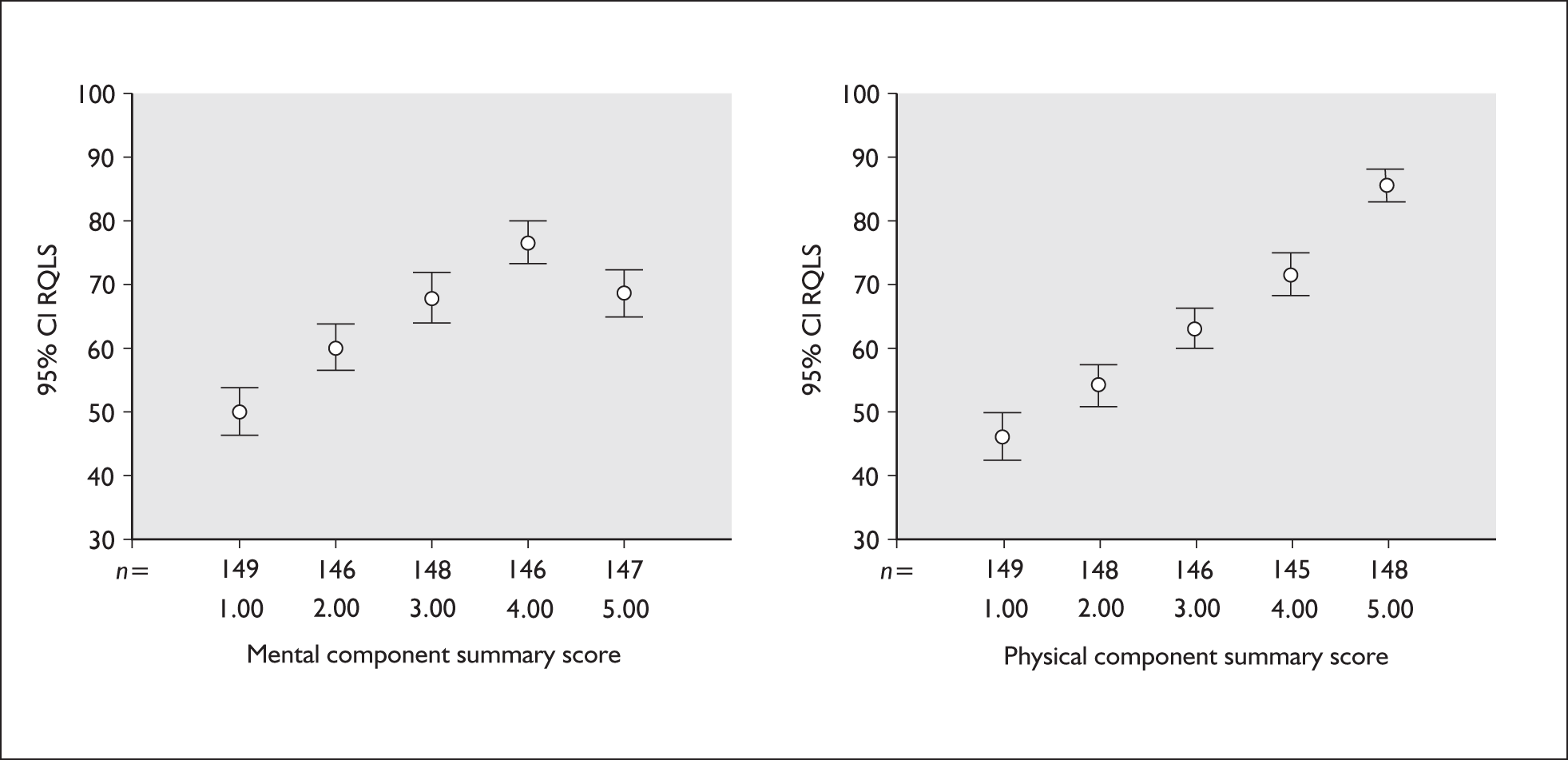
Figure 8 plots the mean RQLS against the SF-36 mental component score (MCS) and physical component score (PCS) grouped into fifths. The mean RQLS increases steadily and significantly between successive PCS groups. There is a similar pattern for MCS groups except that respondents in the highest fifth have a lower mean RQLS than those in the next lower fifth.
FIGURE 8.
Reflux quality of life score (RQLS) by SF-36 mental component summary score and physical component summary score (grouped into fifths).
Sensitivity to change
Participants reported whether they were being prescribed medication at baseline and first follow-up. This information was used to classify them into four groups: those prescribed medication at baseline and follow-up (n = 293); those prescribed medication at baseline but not follow-up (n = 186); those prescribed medication at follow-up but not baseline (n = 3); and those not prescribed medication at all (n = 7). As the last groups are reassuringly small, Figure 9 presents mean change in RQLS (baseline score – follow-up score) for the first two groups.
FIGURE 9.
Change in reflux quality of life score (RQLS) by change in prescribed medication (baseline to follow-up).
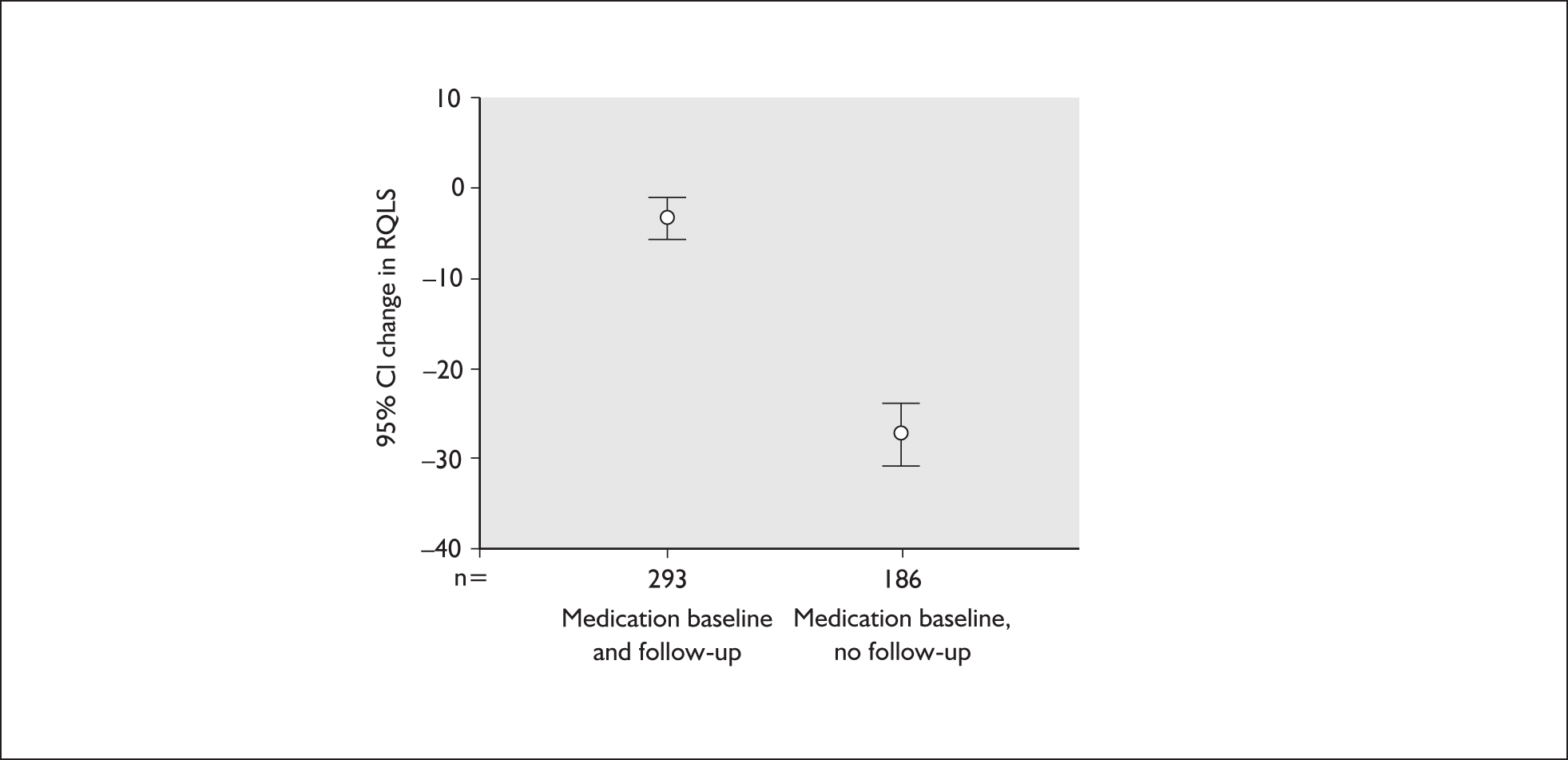
A negative score indicates an improvement in quality of life. Although the RQLS improved for both groups (paired t-tests showed significant change), patients whose medication status changed between baseline and follow-up (medication at baseline but not at follow-up) showed a greater improvement in their RQLS than patients whose medication status stayed the same (medication at baseline and follow-up).
Discussion
Principal findings
This chapter describes a new outcome measure for use with patients being treated for GORD. The REFLUX questionnaire comprises 31 items and generates a single score (RQLS) measuring the extent to which individual participants feel that their GORD symptoms, and any side effects of treatment, affect their quality of life. The 31 items also generate five reflux symptom scores measuring the extent to which participants experienced clusters of symptoms over the previous 2 weeks. Thus, the RQLS provides a single index that can be used to record change for evaluation, whereas the symptom scores provide a descriptive profile that describes whether respondents experience problems in specific clusters. The data presented provide evidence that the new measure is valid, reliable and sensitive to change.
Strengths of the study
The REFLUX questionnaire was designed as a patient-centred self-completed postal questionnaire. Items were generated by using GORD patients as key informants, rather than relying on the views of clinicians or other experts. Therefore the REFLUX questionnaire covers those elements of their illness that GORD patients indicated were important in determining their quality of life. A patient-centred approach also underlies the scoring system used to generate the RQLS. The weights used to create this score were based on the relationship between participants’ reports of their scores on seven quality of life items and of their general health status on a visual analogue scale. The score takes account of patients’ preferences through their self-reported effect on quality of life. In contrast, the REFLUX symptom scores, which were not intended as measures of HRQoL, used essentially statistical weights, generated from principal components analysis of symptom frequencies rather than patients’ views.
The performance of a measure may also be assessed by its acceptability to respondents. Although the REFLUX questionnaire has 31 items, it suffered very few reported difficulties or missing item responses within the REFLUX trial. During the pilot, modifications were based on patient feedback on the acceptability and readability of items.
Weaknesses of the study
The most common method of establishing the validity of a measure is to analyse its association with a criterion of known validity that is accepted as a gold standard. However, there is no gold standard for quality of life, or disease severity, in GORD by which to determine validity. Nevertheless, the REFLUX trial does use SF-36 and EQ-5D, two reputable measures of generic HRQoL, although not designed for use with GORD patients. As we had used the EQ-5D VAS to generate the RQLS, we used the SF-36 to establish construct validity. The RQLS showed good correlations with the SF-36 dimensions of bodily pain and social functioning, topics common to both measures, and weaker correlations with mental health and energy, topics not included in the REFLUX questionnaire. We used self-reported change in medication to assess the sensitivity of the RQLS to change, which assumes that changing from being prescribed medication to not being prescribed medication necessarily shows improved health status.
The second issue in establishing the validity of the REFLUX questionnaire is that the analysis was based on patients with controlled symptoms, as one of the trial inclusion criteria was reasonable symptom control with medication. Thus, 10% of patients achieved the best possible RQLS at baseline, showing that their GORD was affecting quality of life ‘not at all’, probably because medication provided complete symptom control. There is scope to ameliorate these ceiling effects in future.
The final issue relates to the interpretability of the five REFLUX symptom scores, derived through multivariate statistical analysis. To interpret the resulting weights we have suggested five labels: general discomfort; wind and frequency; nausea and vomiting; activity limitation; and constipation and swallowing. Although the first four are easy to interpret, the fifth contains only three items – difficulty in swallowing and two items relating to constipation. Although these appear to be heterogeneous, this is a common consequence of multivariate analysis, which takes full account of correlations between items. Furthermore, these items play little part in the other four dimensions and have been identified as potential side effects of surgical treatment. We have therefore retained this fifth dimension, more to assess changes after treatment than status at baseline.
Unanswered questions
The aim of this component of the study was to validate a new measure of the HRQoL of patients being treated for GORD. Further evidence about the performance of the measure will be available through detailed analysis of the REFLUX trial, some of which is described later in this report. Although our principal aim was to develop and validate an outcome measure for use in the REFLUX trial, we hope that the REFLUX questionnaire will prove more widely applicable.
Chapter 5 Beliefs about medicines and surgery
Background
This chapter describes a study that was conducted in addition to the research activities described in the trial protocol. It is the result of discussion among the trial team in which it was decided that it would be wise to check the validity of a questionnaire measure that was devised specifically for, and used for the first time in the context of, the REFLUX trial. We have called this measure the Beliefs about Surgery questionnaire (BSQ). It has the potential to be further developed as a tool for use by consultants and surgical teams. In the sections below we describe the initial analyses that were carried out to determine the validity of the measure. In the final section we suggest further work that could result in the development of a tool to support communication between consultants and patients with GORD as they discuss treatment preferences and decisions.
Introduction
Current health-care policy and practice acknowledge the importance of offering choice across the spectrum of health care to users of the health-care system. 91 It is plausible that people’s choices about treatment will be influenced by their beliefs about the risks and benefits of various treatments, which in turn will be shaped by their experiences or anticipated experiences of treatment processes. Indeed, this link between beliefs (cognitions) and action is represented in Leventhal’s common sense model of self-regulation in the face of a threat to health92 as follows. People appraise a health threat situation with reference to cognitions about the illness and then implement coping procedures to restore their physical or emotional equilibrium. The model specifies the cognitive components of this appraisal process in terms of factors that have become known as the illness representations framework. 93 The dimensions of this framework include beliefs about effective treatment or control of the illness (e.g. ‘taking medication will be effective’; ‘surgery may be more effective than medication’; ‘recovery from surgery could take a long time’). A questionnaire measure about illness representations has been developed and is frequently used to investigate people’s cognitions about illness in the context of Leventhal’s model. 92 This chapter reports the development and validation of a measure relating to beliefs about surgical treatments.
The treatment beliefs component of the Leventhal model has been investigated by Horne,94 who proposed that behaviour relating to treatment (e.g. adherence) is determined by perceptions about treatment rather than, or in addition to, perceptions about illness. There are two broad classes of treatments: those involving professional intervention (e.g. medicine, surgery, therapy) and those involving the adoption of different lifestyle behaviours (e.g. exercise, diet, stress management). The Beliefs about Medicines questionnaire (BMQ)93 developed by Horne and colleagues assesses perceptions about one form of treatment. The BMQ has been validated using a chronic illness sample (n = 524), including people diagnosed with asthma, diabetes, renal disease and psychiatric illness, and cardiac and general medicine inpatients. On the basis of principal components analysis and confirmatory factor analysis, four subscales were identified relating to beliefs about medications specific to the diagnosed condition (‘concerns’ about taking the medication and ‘necessity’ of taking the medication) and beliefs about medication in general (‘harmfulness’ of medication in general and ‘overuse’ of medication in general). The psychometric properties of these scales have been reported by Horne et al. 93 and demonstrate high levels of discriminant validity, criterion-related validity and stability of the factor structure across the different illness groups. This chapter investigates the measure of beliefs about medicine amongst people with GORD and also a parallel measure of beliefs about surgery, in the context of the REFLUX trial.
Because the REFLUX trial involved non-randomised preference groups, it was felt important from the start to include a measure that would investigate the process of patients’ decision-making about their treatment choices. Thus, this trial provided the opportunity to answer three questions relating to beliefs about treatment. First, would baseline measures provide support for the validity of the BMQ for individuals in a chronic illness group that was different from the groups investigated in the original validation study, namely people suffering GORD? Second, if participants were asked to answer questions relating to beliefs about surgery (in the form of a BSQ), would their answers suggest that these beliefs relate to professional interventions in general (i.e. would the dimensions of the BSQ converge with dimensions of the BMQ) or would distinguishable factors emerge? The answer to this question could be important when treatment options include both medical and surgical interventions. Third, would data from the BMQ and the BSQ, administered at baseline, provide evidence of criterion-related validity? Such evidence would be provided if the profile of scores on the BMQ and BSQ distinguished between the surgery group and the medication group in the preference groups (the ‘criterion’) but not in the randomised groups.
Methods
Item development
During the development of the new GORD-specific outcome measure (the REFLUX questionnaire)24 for use within the REFLUX trial as described in Chapter 4, a series of one-to-one interviews and focus groups were conducted involving a total of 43 people (15 of whom were receiving medical treatment and 28 who had had surgery). In addition to the relevance of these discussions for the outcome measure, the feedback also suggested that patients had a range of views about medical and surgical treatments and that they invoked these views when discussing the decision about whether to have surgery to treat their GORD. This suggested that it would be informative to ask trial participants to report their beliefs about taking medications and about having surgery. We decided to use the previously validated measure of beliefs about medication93 referred to above, but no measure has been developed to assess beliefs about surgery. We decided therefore that additional items to assess patients’ beliefs about surgery should be added.
Items for a BSQ were generated in two ways. First, some questions from the BMQ lent themselves to a directly parallel version referring to surgery (e.g. ‘Doctors place too much trust in medicines’: ‘Doctors place too much trust in surgery’). Second, additional items were included as a result of analysis of the interview data. Eight items were judged to be acceptable, answerable and relevant by this group. Similar to the BMQ, the response format for these items was from 1 (strongly agree) to 5 (strongly disagree).
Trial context
All 810 participants in the REFLUX trial were asked to complete the study baseline questionnaire. As described in detail in Chapter 6, 357 were recruited to the randomised component of the trial and 453 to the preference study (261 of these choosing surgery and 192 medical management).
In addition to the REFLUX questionnaire24 the baseline questionnaire contained the EQ-5D88 and the SF-36,89 and the BMQ and BSQ.
Analytic strategy
To achieve a clear replication of the original validation study by Horne et al. ,93 the same analytic procedures were used. That is, an exploratory PCA was conducted on the BMQ items and confirmatory factor analysis was performed by computing Pearson’s correlations for factor loadings against: (1) the theoretical model of predicted factor loadings; and (2) the empirical model of factor loadings reported by Horne et al. 93 As described by Horne et al. ,93 the theoretical model was defined by assigning a factor loading of 1 to all items expected to load on the factor, with all other items assigned a loading of 0. This strategy permitted a comparison of the expected pattern of factor loadings with the pattern derived from the REFLUX sample.
To assess the level of discrimination between beliefs about medication and beliefs about surgery, a further exploratory PCA was conducted on the combined items from the BMQ and BSQ using a non-orthogonal (direct oblimin) method of rotation. The factor scree plot and eigenvalues were used to select the number of factors.
Finally, discriminant function analysis was used to test the criterion-related validity of the combined BMQ/BSQ. This form of validity would be demonstrated if the profile of scores from the questionnaire enabled correct classification of cases to the surgery and medication groups in the preference groups but not in the randomised groups.
Results
Of the people recruited to the trial, 329 (92.12%) in the randomised groups and 419 (91.48%) in the preference groups completed the baseline questionnaire. Data from these 748 participants were analysed in this validation study.
Distributions of scores on the BMQ and BSQ items were generally acceptable. Skewness was greater than 1 for only two variables: ‘My health, at present, depends on my medicines’ (sk = 1.48); ‘I would be willing to have an uncomfortable test’ (sk = 1.09). Kurtosis was greater than 1 for six variables: ‘My health at present depends on my medicines’ (ku = 2.20, modal value = 1); ‘Natural remedies are safer than medicines’ (ku = 1.48, modal value = 3); ‘Medicines do more harm than good’ (ku = 1.81, modal value = 4); ‘I would be willing to have an uncomfortable test’ (ku = 1.74, modal value = 2); ‘Surgery does more harm than good’ (ku = 1.10, modal value = 4); ‘Doctors are too quick to suggest surgery’ (ku = 1.40, modal value = 4).
Exploratory principal components analysis on BMQ items
Based on the structure of the instrument, as reported by Horne et al. ,93 the BMQ was expected to comprise four factors (corresponding to the two subscales for each of the item pools relating to beliefs about general medicine and specific medicine). Using an eigenvalue cut-off of 1.1,95 the REFLUX data yielded three factors that together accounted for 48.99% of the variance in the scores. Using a cut-off of 0.4 for item inclusion, every item in the item pool loaded on to a factor and none of the 18 items had diffuse loading. Factor 1 corresponded to the combined ‘general harm’ and ‘general overuse’ scales of Horne et al. ,93 and factors 2 and 3 corresponded exactly to their ‘specific necessity’ and ‘specific concerns’ factors respectively. Table 11 presents the item loadings reported by Horne et al. 93 and the item loadings derived from the REFLUX BMQ data.
| Items | Loadings | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horne et al.94 (n = 524) | REFLUX baseline (n = 750) | |||||||
| F1: Specific concerns | F2: Specific necessity | F3: General harm | F4: General overuse | F1: General overuse/harm | F2: Specific necessity | F3: Specific concerns | Item meana (SD) | |
| Having to take medicines [this medicine]b worries me | 0.80 | 0.82 | 2.64 (1.14) | |||||
| I sometimes worry about becoming too dependent on my medicines | 0.78 | 0.72 | 2.47 (1.16) | |||||
| I sometimes worry about the long-term effects of my medicines | 0.76 | 0.84 | 2.06 (0.97) | |||||
| My medicines disrupt my life | 0.60 | 0.54 | 3.61 (1.06) | |||||
| My life would be impossible without my medicines | 0.81 | 0.81 | 2.21 (1.12) | |||||
| My health, at present, depends on my medicines | 0.76 | 0.82 | 1.68 (0.88) | |||||
| Without my medicines I would be very ill | 0.74 | 0.77 | 2.53 (1.12) | |||||
| My health, in the future, will depend on my medicines | 0.70 | 0.79 | 2.26 (0.93) | |||||
| My medicines protect me from becoming worse | 0.65 | 0.61 | 1.95 (0.86) | |||||
| If doctors had more time they would prescribe fewer medicines | 0.81 | 0.80 | 2.92 (0.98) | |||||
| Doctors place too much trust in medicines | 0.75 | 0.81 | 3.34 (0.88) | |||||
| Doctors use too many medicines | 0.71 | 0.72 | 3.11 (0.86) | |||||
| Natural remedies are safer than medicines | 0.47 | 0.45 | 0.42 | 3.07 (0.74) | ||||
| Most medicines are addictive | 0.71 | 3.37 (0.74) | ||||||
| Medicines do more harm than good | 0.67 | 0.52 | 3.79 (0.67) | |||||
| All medicines are poisons | 0.58 | 0.47 | 3.96 (0.84) | |||||
| My medicines are a mystery to me | 0.55 | 3.48 (1.00 | ||||||
| People who take medicines should stop their treatment every now and again | 0.51 | 0.31 | 3.11 (0.92) | |||||
| Eigenvalue | 3.38 | 2.92 | 1.60 | 1.44 | 4.13 | 3.08 | 1.61 | |
| Percentage variance explained | 18.8 | 16.2 | 8.9 | 8.0 | 22.96 | 17.10 | 8.94 | |
Confirmatory factor analysis on BMQ items
To test the consistency between the factor solution derived from the REFLUX sample and that of the chronic illness groups reported by Horne et al. ,93 a confirmatory factor analysis was conducted by computing the correlations between all of the factor loadings derived from the REFLUX data set and (1) a theoretical model, defined by assigning factor loadings of 1 to items expected to load on a factor, or else 0; and (2) the empirically derived factor loadings of Horne et al. 93 The confirmatory factor analysis was based on three factors (general overuse/harm, specific necessity, specific concerns). Results of the confirmatory factor analysis are presented in Table 12.
| Factor label | Pearson correlation of items with predicted factor loadings | |
|---|---|---|
| Theoretical model | Empirically derived model | |
| General overuse/harm | 0.90 | 0.92 |
| Specific necessity | 0.96 | 0.98 |
| Specific concerns | 0.90 | 0.92 |
Exploratory principal components analysis on BMQ/BSQ items
A PCA (with oblimin rotation) was conducted on all BMQ and BSQ items together. Based on the structure of the BMQ for this sample, the combined BMQ/BSQ was expected to comprise up to six discriminable factors (corresponding to the two subscales for each of general medicine, specific medicine and general surgery). The scree plot (Figure 10) suggested that it was appropriate to extract five factors, which together accounted for 50.95% of the variance in the scores. Using a cut-off of 0.4 for item inclusion, only one item in the item pool did not load on to a factor and none of the 26 items had diffuse loading. Table 13 presents the item loadings reported by Horne et al. 93 and the item loadings derived from the REFLUX data.
FIGURE 10.
Scree plot indicating that a five-factor solution would be appropriate.
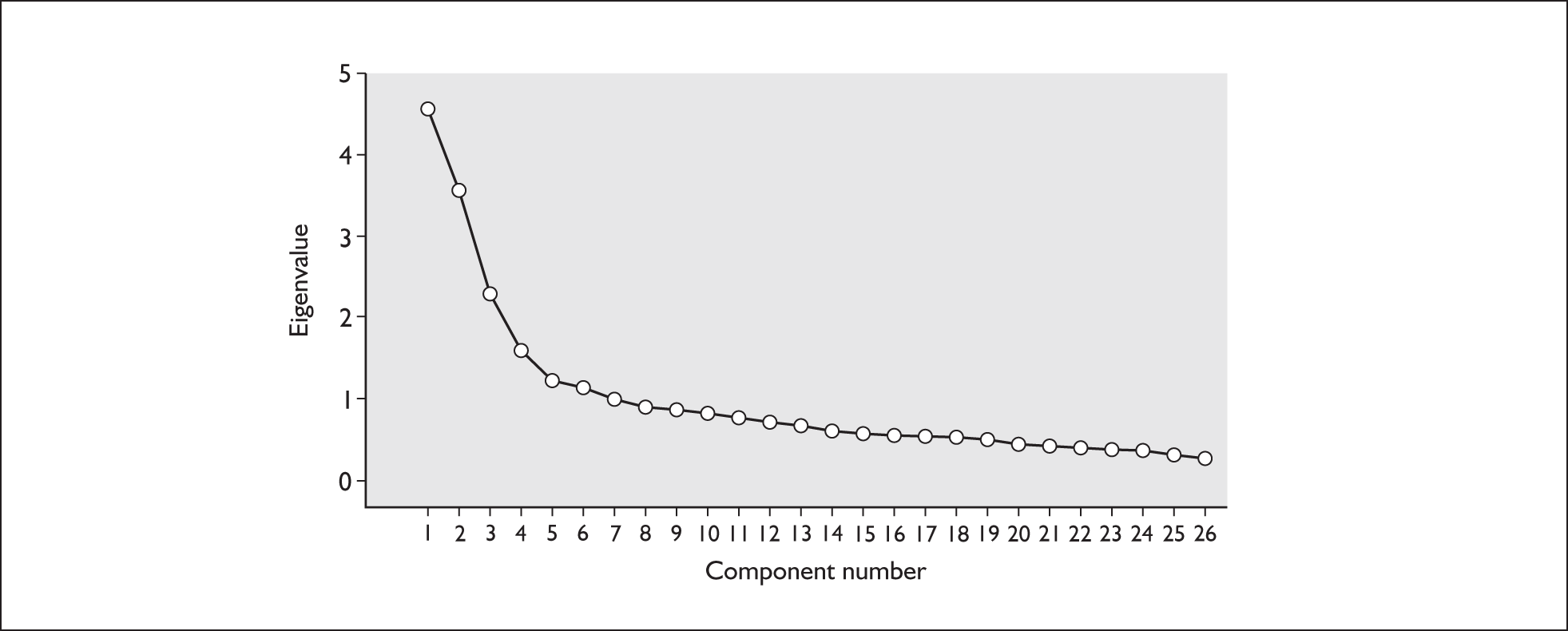
| Items | Loadings | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horne et al.94 (n = 524) | REFLUX baseline (n = 739) | ||||||||
| F1: Specific concerns | F2: Specific necessity | F3: General harm | F4: General overuse | F1: General medicine overuse | F2: Specific medicine necessity | F3: Surgery overuse/harm | F4: Specific medicine concerns | F5: Surgery concerns | |
| Having to take medicines [this medicine]a worries me | 0.80 | 0.81 | |||||||
| I sometimes worry about becoming too dependent on my medicines | 0.78 | 0.76 | |||||||
| I sometimes worry about the long-term effects of my medicines | 0.76 | 0.80 | |||||||
| My medicines disrupt my life | 0.60 | 0.60 | |||||||
| My life would be impossible without my medicines | 0.81 | 0.84 | |||||||
| My health, at present, depends on my medicines | 0.76 | 0.82 | |||||||
| Without my medicines I would be very ill | 0.74 | 0.79 | |||||||
| My health, in the future, will depend on my medicines | 0.70 | 0.79 | |||||||
| My medicines protect me from becoming worse | 0.65 | 0.59 | |||||||
| If doctors had more time they would prescribe fewer medicines | 0.81 | 0.74 | |||||||
| Doctors place too much trust in medicines | 0.75 | 0.80 | |||||||
| Doctors use too many medicines | 0.71 | 0.75 | |||||||
| Natural remedies are safer than medicines | 0.47 | 0.45 | 0.50 | ||||||
| Most medicines are addictive | 0.71 | 0.48 | |||||||
| Medicines do more harm than good | 0.67 | 0.61 | |||||||
| All medicines are poisons | 0.58 | 0.51 | |||||||
| My medicines are a mystery to me | 0.55 | (0.36) | |||||||
| People who take medicines should stop their treatment every now and again | 0.51 | 0.47 | |||||||
| Doctors rely on surgery too much | 0.75 | ||||||||
| Surgery does more harm than good | 0.74 | ||||||||
| Doctors place too much trust in surgery | 0.73 | ||||||||
| Doctors are too quick to suggest surgery | 0.71 | ||||||||
| I would be willing to have an uncomfortable test | –0.44 | ||||||||
| I worry about the risks of surgery | 0.40 | 0.64 | |||||||
| Surgery can result in new health problems | 0.51 | ||||||||
| Surgery should only be taken as a last resort | 0.40 | 0.51 | |||||||
| Eigenvalue | 3.38 | 2.92 | 1.60 | 1.44 | 4.56 | 3.57 | 2.31 | 1.59 | 1.22 |
| Percentage variance explained | 18.8 | 16.2 | 8.9 | 8.0 | 17.54 | 13.73 | 8.87 | 6.10 | 4.70 |
In the solution for the combined BMQ/BSQ, beliefs about medicines in general again formed one factor; the two factors relating to beliefs about medicines specific to the reflux condition mapped perfectly on to the solution reported by Horne et al. ,93 and beliefs about surgery also corresponded exactly to the pattern that was expected, based on the findings of Horne et al. 93 Beliefs about surgery appeared to be clearly discriminable from beliefs about medicines, as all between-factor correlations were less than 0.3 (Table 14).
| Factor | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1: Medication in general: overuse/harm | – | ||||
| F2: Specific medication: necessity | 0.014 | – | |||
| F3: Surgery in general: overuse/harm | 0.274 | –0.053 | – | ||
| F4: Specific medication: concerns | 0.296 | 0.160 | 0.035 | – | |
| F5: Surgery in general: concerns | –0.048 | –0.051 | 0.119 | –0.116 | – |
Discriminant function analysis
The next question concerned the capacity of the BMQ/BSQ scores to discriminate between participants who chose to undergo surgery and those who chose to remain on medical treatment. Five composite belief scores were computed for each participant, corresponding to the five factors in the combined BMQ/BSQ factor solution. The five variables were entered as independent variables in a discriminant function analysis of data from the preference groups. This profile of scores resulted in the correct classification of 76% of the cases into surgery or medication groups. This was significantly greater than chance (χ2(5) = 178.93, p < 0.001). In contrast, discriminant function analysis of data from the randomised groups resulted in correct classification of 58% of the cases into surgery or medication groups. This was not significantly greater than chance (χ2(5) = 6.68, p > 0.05). Table 15 presents classification results for (a) the preference groups and (b) the randomised groups.
| Predicted group membership | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical | Medical | Total | ||
| ( a ) Preference groups | ||||
| Actual group membership | Surgical | 184 (75.7) | 59 (24.3) | 243 (100) |
| Medical | 42 (23.9) | 134 (76.1) | 176 (100) | |
| 75.9% of original grouped cases correctly classified. | ||||
| ( b ) Randomised groups | ||||
| Actual group membership | Surgical | 99 (59.6) | 67 (40.4) | 166 (100) |
| Medical | 72 (44.2) | 91 (55.8) | 163 (100) | |
| 57.8% of original grouped cases correctly classified. | ||||
Discussion
Baseline measures in the REFLUX trial provided support for the validity of the BMQ for individuals suffering from GORD. However, the two general medicine scales (labelled harm and overuse) merged in this factor solution. It is possible that specific characteristics of the sample may explain this. For example, GORD is a condition for which medication is taken symptomatically whereas the original validation study was conducted with people experiencing chronic illnesses in which medications are taken continuously. This could have increased the tendency of the GORD sample to discriminate between items relating to medications specific to the illness and correspondingly decreased the tendency to discriminate between the items in the general medicine scales. Furthermore, all of the current sample were trial participants and their involvement in the recruitment and informed consent processes of the trial may have made the GORD-specific items more salient and therefore more discriminable than the items about medicines in general.
Importantly, when participants were asked to answer questions relating to beliefs about surgery, their answers yielded factors that were discriminable from those relating to beliefs about medications, suggesting that these participants held distinctive patterns of beliefs about these two kinds of treatment, rather than about professional interventions in general. Furthermore, data from the BMQ and the BSQ provided evidence of criterion-related validity of the BMQ and the BSQ in that the profile of scores on the BMQ and the BSQ distinguished between the surgery group and the medication group in the preference arm of the trial but not in the randomised arm. In other words, knowing nothing about the participants other than their BMQ/BSQ scores allowed a reasonably good prediction of their treatment choices.
Beliefs about treatment have previously been investigated in relation to adherence to medication regimens but little research in this area has explored the issue of patient choices about treatment. The addition of a measure of beliefs about surgery to the existing measure of beliefs about medication provided the opportunity to explore such decisions. In addition, it may be that a patient’s score on the BSQ can provide important clinically relevant information. It is possible that people with less negative beliefs about surgery experience less anxiety associated with the surgery and, as there is evidence that anxiety is associated with poorer clinical outcomes post surgery,96 this could be important information for surgeons to be aware of. Furthermore, it may be that knowing the scores on these two questionnaires could help clinicians to counsel patients who have higher levels of concern or to help patients make better decisions about their treatment. It could be helpful to explore these possibilities in future research.
In terms of the common sense self-regulation model more generally, there is ample evidence that people’s illness perceptions influence their emotional and behavioural responses to an illness threat. 92 Perceptions and beliefs about how an illness may be controlled – including the treatment options of medication and surgery – are potentially important factors that may link with other behaviours such as altered lifestyle. The development of additional measures that relate to other ways of controlling the symptoms of chronic illness could be useful in identifying people’s preferred ways of coping with illness.
In conclusion, the perceptions of people with chronic illness about potential treatments can be measured validly and reliably. Core elements of the factor structure of the BMQ (in particular the distinction between specific and general classes of beliefs) were replicated in this study. Furthermore, responses to the BSQ indicate that beliefs about surgery form a distinct pattern of treatment representations and there is no redundancy between these two scales. Used together, the two measures can significantly distinguish between groups of individuals who choose one form of treatment over the other.
Implications for future research
As proposed above, there is potentially important follow-up work to be carried out in this field. Some possibilities that could be followed up using the REFLUX data set are:
-
Can the correct classification rate be improved further by the addition of other patient characteristics, for example severity of symptoms at baseline, sociodemographic factors, co-morbidities?
-
Can the recruitment of participants into the randomised groups of the trial be predicted by using a discriminant function analysis as described above to classify those who chose (a) surgery, (b) continued medication, and (c) to be randomised?
-
Do underlying treatment beliefs modify treatment effects? If so, can subgroups be identified who are more likely or less likely to respond well to alternative approaches to treatment, such as surgery or medical management?
-
Can the length of the questionnaire be reduced without reducing its predictive power, for example by using item response theory97 to identify the discriminating items?
-
Are these treatment beliefs stable or do they change over time or as a function of changes in symptom severity?
-
Could the questionnaire be adapted for use as a communication tool by consultants and surgical teams?
In conclusion, this work has thus generated a number of possibilities for continued work in this field. It appears that the BSQ is a valid instrument that has a number of potential applications in surgical practice and research.
Chapter 6 Trial results
This chapter describes the partially randomised patient preference trial that was the cornerstone of this project. The chapter starts with an explanation of how the trial groups were derived. It then describes the study groups at trial entry and the management that they actually received. The results at the two follow-up points are then reported, followed by a formal statistical analysis of the data for the principal measures of outcome.
Recruitment to the trial
Participants were recruited in 21 clinical centres, all within the UK (Table 16). Recruitment to the trial was open from March 2001 until the end of June 2004, although not all centres enrolled over the total period because of the staggered introduction of centres and early closure for logistical reasons in a few places.
| Clinical centre | Randomised participants | Preference participants | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical, n (%) | Medical, n (%) | Surgical, n (%) | Medical, n (%) | |
| Aberdeen: Aberdeen Royal Infirmary | 38 (21.3) | 40 (22.3) | 20 (7.7) | 21 (10.9) |
| Belfast: Royal Victoria Hospital | 15 (18.4) | 14 (7.8) | 4 (1.5) | 20 (10.4) |
| Bournemouth: Royal Bournemouth Hospital | 4 (2.2) | 3 (1.7) | 20 (7.7) | 3 (1.6) |
| Bristol: Bristol Royal Infirmary | 12 (6.7) | 11 (6.1) | 18 (6.9) | 20 (10.4) |
| Bromley: Princess Royal Infirmary | 3 (1.7) | 3 (1.7) | 20 (7.7) | 17 (8.9) |
| Edinburgh: Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh | 11 (6.2) | 11 (6.1) | 1 (0.4) | 15 (7.8) |
| Guildford: Royal Surrey County Hospital | 10 (5.6) | 10 (5.6) | 17 (6.5) | 10 (5.2) |
| Hull: Hull Royal Infirmary | 7 (3.9) | 7 (3.9) | 1 (0.4) | 2 (1.0) |
| Inverness: Raigmore Hospital | 7 (3.9) | 8 (4.5) | 2 (0.8) | 8 (4.2) |
| Leeds: Leeds General Infirmary | 1 (0.6) | 2 (1.1) | 10 (3.8) | 3 (1.6) |
| Leicester: Leicester Royal Infirmary | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (1.1) | 1 (0.5) |
| London: St Mary’s Hospital | 8 (4.5) | 7 (3.9) | 4 (1.5) | 10 (5.2) |
| London: Whipps Cross Hospital | 4 (2.2) | 3 (1.7) | 16 (6.1) | 5 (2.6) |
| Poole: Poole Hospital | 10 (5.6) | 10 (5.6) | 25 (9.6) | 13 (6.8) |
| Portsmouth: Queen Alexandra Hospital | 10 (5.6) | 10 (5.6) | 15 (5.7) | 1 (0.5) |
| Salford: Hope Hospital | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.6) | 6 (2.3) | 3 (1.6) |
| Stoke-on-Trent: North Staffordshire Hospital | 5 (2.8) | 6 (3.4) | 20 (7.7) | 9 (4.7) |
| Swansea: Morriston Hospital | 8 (4.5) | 8 (4.5) | 14 (5.4) | 9 (4.7) |
| Telford: Princess Royal Hospital | 11 (6.2) | 12 (6.7) | 24 (9.2) | 8 (4.2) |
| Yeovil: Yeovil District Hospital | 9 (5.1) | 8 (4.5) | 18 (6.9) | 8 (4.2) |
| York: York District Hospital | 5 (2.8) | 5 (2.8) | 3 (1.1) | 6 (3.1) |
| Total | 178 (100) | 179 (100) | 261 (100) | 192 (100) |
Initial recruitment was limited to two centres (Aberdeen Royal Infirmary; St Mary’s Hospital, London) and these acted as pilot centres whilst systems for recruitment were developed. Roll-out of the trial to other centres started after 6 months with gradual extension to all remaining centres over the following 3 years. Figure 11 shows the total recruitment: the dotted line was the expected rate of recruitment over the last 16 months of the trial based on earlier recruitment. As can be seen, it proved difficult to sustain recruitment to the randomised component, although there was evidence for an increase in recruitment towards the time of recruitment closing.
FIGURE 11.
Actual versus expected recruitment rates: (a) randomised component; (b) preference component.
A total of 357 participants were recruited to the randomised component, with 178 allocated to surgery and 179 allocated to medical management. In total, 453 participants agreed to join the preference component, 261 choosing surgery and 192 choosing medical management. Table 16 shows recruitment by centre. Around 20% of the randomised participants were enrolled in Aberdeen; no centre contributed more than 11% of participants in the preference component.
Analysis populations
Throughout the analyses presented later in this chapter the participants in the randomised component are kept separate from those in the preference component (other than for rare surgical events). Primary analyses of the comparisons between surgical and medical management in both of these components are based on the allocated management at trial entry, that is, they are based on the intention to treat (ITT) principle. This sustains the integrity of the randomisation in particular. However, as described later in this chapter, a sizeable minority of participants did not actually receive their allocated management. To allow exploration of the impact (‘blunting effect’) that this might have on any observed differences, secondary analyses based on those who actually received their allocated management – per protocol (PP) analyses – were also undertaken and are presented alongside the ITT analyses.
The number of participants in each of the four main analysis populations is shown in Table 17. All 357 who joined the randomised component are in the randomised intention to treat (RITT) population whereas only the 280 within this group who actually received their allocated management are in the randomised per protocol (RPP) population. Similarly, all 453 participants who joined the preference component are in the preference intention to treat (PITT) population, and the 407 of these who were managed as originally chosen are in the preference per protocol (PPP) population.
| Surgical, n (%) | Medical, n (%) | Total, n | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Randomised intention to treat (RITT) | 178 (49.9) | 179 (50.1) | 357 |
| Randomised per protocol (RPP) | 111 (39.6) | 169 (60.4) | 280 |
| Preference intention to treat (PITT) | 261 (57.6) | 192 (42.4) | 453 |
| Preference per protocol (PPP) | 218 (53.6) | 189 (46.4) | 407 |
Trial conduct
The derivation of the main study groups and their progress through the trial is shown in Figure 12. This is in the form of a CONSORT (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) flow diagram. In total, 1078 patients were considered for trial entry. Of these, 200 were found not to meet one or more of the eligibility criteria. Of the 68 patients eligible for the study but not recruited, 51 declined to participate, 6 were subsequently deemed inappropriate for the study by the surgeon responsible for care, and the remaining 11 were missed.
FIGURE 12.
CONSORT diagram.
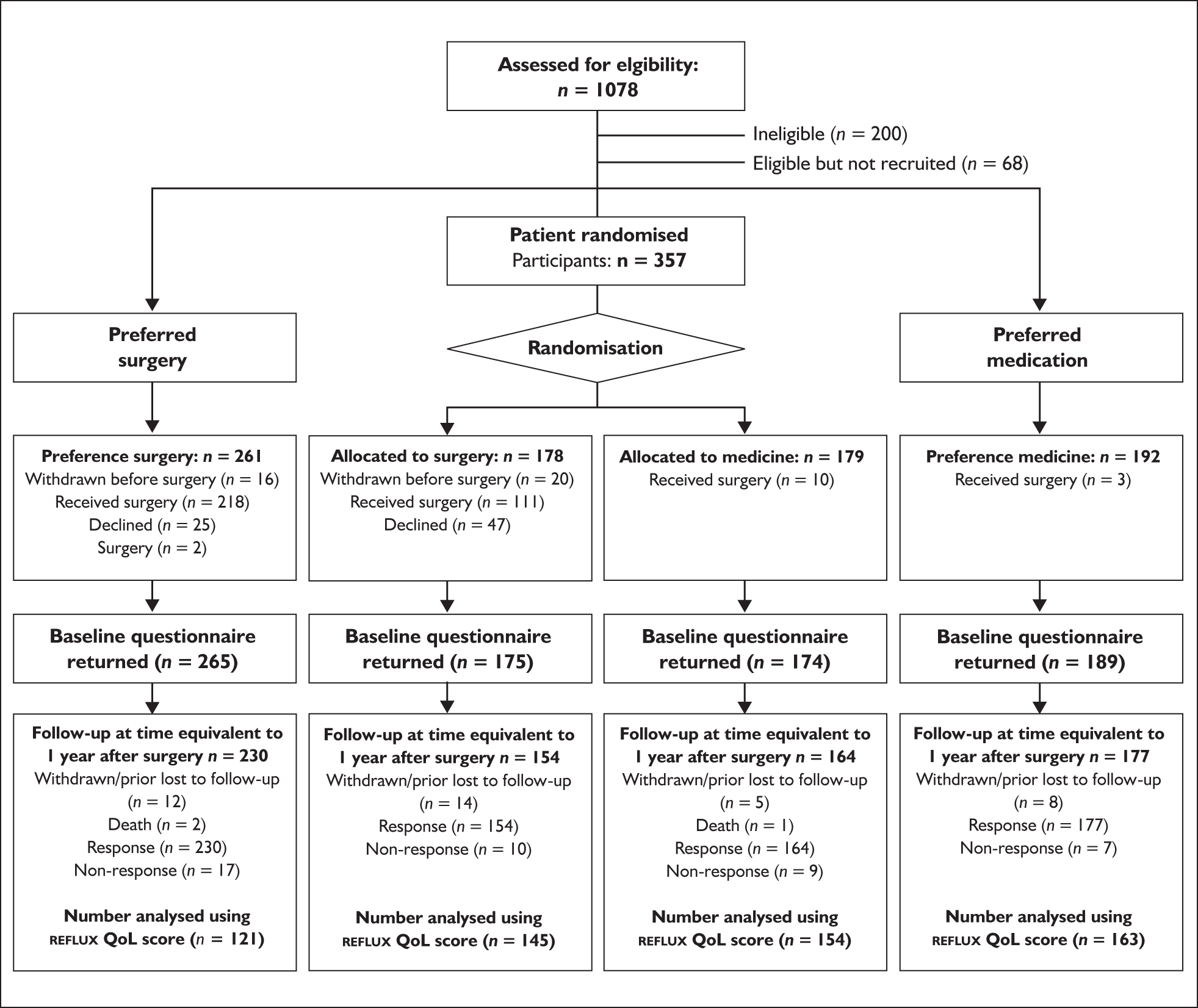
In total, 357 participants were recruited to the randomised component, with 178 randomly allocated to surgery and 179 to best medical management. A further 453 patients who wished to have one or other of the alternative approaches to management agreed to join the preference component – 261 to the surgical group and 192 to the medical management group.
In the early stages of the trial a few participants failed to return baseline questionnaires. After the first meeting of the Data Monitoring Committee, procedures were changed to prevent this, such that formal entry to the study (and random allocation if appropriate) occurred only after full baseline questionnaires had been received. The 1-year follow-up questionnaires were received from approximately 90% of the study participants. There were no substantive differences in response rates between the groups.
Three participants died before the 1-year follow-up was reached, two in the preference surgery group and one in the randomised medical group. None of these participants actually had surgery.
Description of the groups at trial entry
Sociodemographic and clinical factors
Randomised arms
Table 18 shows a description of the groups at trial entry. The table is first divided into whether participants were in the randomised or preference component, then divided according to their allocation, and finally subdivided according to intention to treat or per protocol. Within the randomised groups there were no apparent imbalances between the medical and surgical intervention arms. On average the patients were 46 years old, 66% were men and around two-thirds were in full employment; participants had been on GORD medication for a median of 32 months. The baseline characteristics in the randomised per protocol groups were similar.
| Randomised participants | Preference participants | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical | Medical | Surgical | Medical | |||||
| ITT (n = 178) | PP (n = 111) | ITT (n = 179) | PP (n = 169) | ITT (n = 261) | PP (n = 218) | ITT (n = 192) | PP (n = 189) | |
| Baseline questionnaire returned, n (%) | 175 (98.3) | 111 (100.0) | 174 (97.2) | 165 (97.6) | 256 (98.1) | 216 (99.1) | 189 (98.4) | 186 (98.4) |
| Mean age, years (SD) | 46.7 (10.3) | 46.3 (10.2) | 45.9 (11.9) | 45.9 (11.9) | 44.4 (12.0) | 44.5 (12.2) | 49.9 (11.8) | 50.0 (11.7) |
| Male, n (%) | 116 (65.2) | 68 (61.3) | 120 (67.0) | 115 (68.0) | 170 (65.1) | 139 (63.8) | 111 (57.8) | 110 (58.2) |
| Mean BMI (SD) | 28.5 (4.3) | 28.7 (4.1) | 28.4 (4.0) | 28.3 (4.0) | 27.7 (4.0) | 27.5 (3.7) | 27.4 (4.1) | 27.4 (4.1) |
| Duration in months (median) of prescribed medication for GORD – (IQR) | 33 (15–83) | 30 (16–76) | 31 (16–71) | 30 (15–71) | 35 (14–71) | 36 (14–65) | 27 (13–60) | 26.5 (13–60) |
| Employment status, n (%) | ||||||||
| Employed full-time | 116 (66.3) | 72 (65.5) | 110 (61.8) | 104 (61.9) | 168 (65.1) | 138 (64.2) | 100 (52.4) | 97 (51.6) |
| Employed part-time | 13 (7.4) | 12 (10.9) | 16 (9.0) | 15 (8.9) | 35 (13.6) | 29 (13.5) | 20 (10.5) | 20 (10.6) |
| Student | 5 (2.9) | 3 (2.7) | 3 (1.7) | 3 (1.8) | 2 (0.8) | 2 (0.9) | 3 (1.6) | 3 (1.6) |
| Retired | 12 (6.9) | 9 (8.2) | 22 (12.4) | 20 (11.9) | 18 (7.0) | 16 (7.4) | 35 (18.3) | 35 (18.6) |
| Housework | 11 (6.3) | 6 (5.5) | 10 (5.6) | 10 (6.0) | 17 (6.6) | 15 (7.0) | 15 (7.9) | 15 (8.0) |
| Seeking work | 6 (3.4) | 1 (0.9) | 3 (1.7) | 2 (1.2) | 5 (1.9) | 5 (2.3) | 2 (1.0) | 2 (1.1) |
| Other | 12 (6.9) | 7 (6.4) | 14 (7.9) | 14 (8.3) | 13 (5.0) | 10 (4.7) | 16 (8.4) | 16 (8.5) |
| Age left full-time education, n (%) | ||||||||
| 16 years or under | 110 (62.5) | 68 (62.4) | 108 (60.7) | 102 (60.7) | 151 (58.5) | 128 (59.3) | 105 (55.3) | 104 (55.6) |
| 17–19 years | 38 (21.6) | 24 (22.0) | 40 (22.5) | 40 (23.8) | 63 (24.4) | 51 (23.6) | 45 (23.7) | 43 (23.0) |
| 20 years or over | 28 (15.9) | 17 (15.6) | 30 (16.9) | 26 (15.5) | 44 (17.1) | 37 (17.1) | 40 (21.1) | 40 (21.4) |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 46 (25.8) | 29 (26.1) | 40 (22.3) | 36 (21.3) | 71 (27.2) | 61 (28.0) | 39 (20.3) | 39 (20.6) |
| Erosive oesophagitis, n (%) | 85 (54.8) | 48 (50.0) | 97 (62.2) | 91 (62.3) | 104 (46.4) | 80 (43.2) | 87 (50.9) | 86 (51.2) |
| Co-morbidity – H. pylori status, n (%) | ||||||||
| Positive (subsequently treated) | 12 (9.0) | 5 (6.1) | 14 (10.4) | 13 (10.3) | 18 (8.4) | 14 (7.9) | 15 (10.5) | 15 (10.7) |
| Positive (subsequently untreated) | 1 (0.8) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (2.2) | 3 (2.4) | 8 (3.7) | 8 (4.5) | 2 (1.4) | 2 (1.4) |
| Negative | 75 (56.4) | 48 (58.5) | 73 (54.1) | 67 (53.2) | 118 (54.9) | 101 (56.7) | 74 (51.7) | 72 (51.4) |
| Uncertain | 45 (33.8) | 29 (35.4) | 45 (33.3) | 43 (34.1) | 71 (33.0) | 55 (30.9) | 52 (36.4) | 51 (36.4) |
| Hiatus hernia present, n (%) | 94 (57.3) | 64 (61.0) | 102 (60.4) | 94 (59.1) | 168 (68.9) | 146 (71.2) | 101 (59.8) | 99 (59.6) |
| Asthma, n (%) | 21 (11.9) | 14 (12.7) | 21 (11.8) | 19 (11.3) | 30 (11.5) | 23 (10.6) | 36 (18.8) | 36 (19.0) |
Preference arms
The sociodemographic characteristics of the preference participants were broadly similar to those of the randomised groups. However, preference medical participants tended to be older (mean 50 years) and were more likely to be female, fewer were in full-time employment, and participants had been on GORD medication for a shorter period (approximately 6 months less than RCT participants).
Prescribed medications
The prescribed medications at the time of trial entry are shown in Table 19. There was a similar profile of prescribed medications across the randomised and preference groups. As would be expected, nearly all participants reported taking a reflux-related drug in the previous 2 weeks. Over 90% had taken a PPI, of which lansoprazole was the most common.
| Randomised participants | Preference participants | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical | Medical | Surgical | Medical | |||||
| ITT (n = 178) | PP (n = 111) | ITT (n = 179) | PP (n = 169) | ITT (n = 261) | PP (n = 218) | ITT (n = 192) | PP (n = 189) | |
| Any reflux-related drug, n (%) | 170 (97.1) | 108 (97.3) | 169 (97.1) | 160 (97.0) | 235 (91.8) | 198 (91.7) | 184 (97.4) | 181 (97.3) |
| Proton pump inhibitors, n (%) | ||||||||
| Any proton pump inhibitor | 161 (92.0) | 105 (94.6) | 162 (93.1) | 153 (92.7) | 225 (87.9) | 191 (88.4) | 173 (91.5) | 170 (91.4) |
| Omeprazole (Losec®b) | 46 (26.3) | 32 (28.8) | 46 (26.4) | 43 (26.1) | 49 (19.1) | 36 (16.7) | 61 (32.3) | 61 (32.8) |
| Lansoprazole (Zoton®b) | 77 (44.0) | 47 (42.3) | 72 (41.4) | 69 (41.8) | 100 (39.1) | 92 (42.6) | 69 (36.5) | 66 (35.5) |
| Pantoprazole (Protium®b) | 6 (3.4) | 6 (5.4) | 11 (6.3) | 11 (6.7) | 21 (8.2) | 17 (7.9) | 11 (5.8) | 11 (5.9) |
| Rabeprazole (Pariet®b) | 12 (6.9) | 6 (5.4) | 13 (7.5) | 13 (7.9) | 21 (8.2) | 16 (7.4) | 14 (7.4) | 14 (7.5) |
| Esomeprazole (Nexium®b) | 20 (11.4) | 14 (12.6) | 20 (11.5) | 17 (10.3) | 37 (14.5) | 33 (15.3) | 18 (9.5) | 18 (9.7) |
| Histamine receptor antagonists, n (%) | ||||||||
| Any histamine receptor antagonist | 14 (8.0) | 6 (5.4) | 12 (6.9) | 9 (5.5) | 22 (8.6) | 16 (7.4) | 13 (6.9) | 13 (7.0) |
| Ranitidine (Zantac®b) | 13 (7.4) | 6 (5.4) | 8 (4.6) | 6 (3.6) | 11 (4.3) | 7 (3.2) | 11 (5.8) | 11 (5.9) |
| Famotidine (Pepcid®b) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.4) | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.5) |
| Cimetidine (Tagamet®b) | 1 (0.6) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.6) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.4) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Nizatidine (Axid®b) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (1.2) | 3 (1.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Over-the-counter histamine receptor antagonist | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (2.3) | 3 (1.8) | 7 (2.7) | 4 (1.9) | 2 (1.1) | 2 (1.1) |
| Prokinetics, n (%) | ||||||||
| Any prokinetics | 12 (6.9) | 7 (6.3) | 8 (4.6) | 6 (3.6) | 11 (4.3) | 10 (4.6) | 5 (2.6) | 4 (2.2) |
| Domperidone (Motilium®b) | 8 (4.6) | 5 (4.5) | 4 (2.3) | 3 (1.8) | 7 (2.7) | 6 (2.8) | 4 (2.1) | 3 (1.6) |
| Metoclopramide (Maxolon®b) | 4 (2.3) | 2 (1.8) | 4 (2.3) | 3 (1.8) | 4 (1.6) | 4 (1.9) | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.5) |
| Other prescribed drugs, na | ||||||||
| Alginates (Gaviscon, etc., Topal®b) | 22 | 12 | 21 | 18 | 37 | 33 | 14 | 13 |
| Anti-spasmodics (e.g. dicycloverine ) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Chelates (sucralfate) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other ulcer healing drugs | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Antacids: Mucogel®b | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Antacids: Asilone®b | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Non-gastrointestinal | 7 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 6 |
| Anti-nausea | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Health status
Randomised arms
The HRQoL scores at study entry are displayed in Table 20. The scores were broadly similar in the randomised surgical and randomised medical groups, although they were slightly higher (better health) in the randomised medical group. As described in Chapter 2, after the Data Monitoring Committee first met after the first 143 participants had been recruited to the randomised component, we were asked to change the enrolment procedure to ensure that baseline questionnaires were completed before formal entry and randomisation. We understand that this is because the committee were concerned about an apparent imbalance between the randomised groups in baseline health status at that time. After satisfying themselves that this was not due to a breakdown in the randomisation procedure, the committee surmised that this might be due to prior knowledge of the treatment allocation affecting questionnaire responses (with those allocated surgery tending to project worse health status than those allocated medical management). Certainly, the groups based on the first 143 participants were well balanced in other respects, and there was subsequently good balance in health status as well. The apparent small imbalance between the total randomised groups in health status measures is therefore likely to be a reflection of the imbalance in the first 143 participants.
| Randomised participants | Preference participants | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical | Medical | Surgical | Medical | |||||
| ITT (n = 178) | PP (n = 111) | ITT (n = 179) | PP (n = 169) | ITT (n = 261) | PP (n = 218) | ITT (n = 192) | PP (n = 189) | |
| REFLUX QoL, mean (SD) | 63.6 (24.1) | 61.9 (24.5) | 66.8 (24.5) | 68.2 (24.2) | 55.8 (23.2) | 55.9 (23.2) | 77.5 (19.7) | 78.0 (19.1) |
| REFLUX symptom score, mean (SD) | ||||||||
| General discomfort symptom score | 58.5 (24.5) | 57.1 (25.1) | 61.3 (25.8) | 62.4 (25.7) | 49.1 (24.4) | 48.7 (25.2) | 73.1 (21.3) | 73.6 (20.9) |
| Wind and frequency symptom score | 48.1 (20.9) | 46.2 (20.9) | 49.3 (21.4) | 49.5 (21.7) | 47.1 (21.4) | 47.5 (21.2) | 59.6 (22.7) | 59.8 (22.7) |
| Nausea and vomiting symptom score | 81.5 (19.5) | 81.6 (18.8) | 80.7 (21.9) | 81.6 (21.7) | 76.9 (19.9) | 77.5 (19.5) | 89.7 (13.6) | 90.1 (12.9) |
| Activity limitation symptom score | 78.5 (16.9) | 77.6 (16.3) | 78.9 (17.3) | 79.5 (17.1) | 74.4 (16.1) | 73.9 (16.2) | 86.8 (13.0) | 87 (13.0) |
| Constipation and swallowing symptom score | 77.5 (19.9) | 77.3 (20.3) | 74.8 (21.0) | 75.6 (20.4) | 75.8 (22.0) | 74.8 (22.6) | 83 (17.7) | 83.3 (17.6) |
| SF-36 scores, mean (SD) | ||||||||
| Norm-based physical functioning | 46.8 (10.2) | 46.1 (10.3) | 47.5 (10.5) | 47.7 (10.5) | 46.3 (9.4) | 46.1 (9.3) | 47.1 (10.8) | 47.0 (10.9) |
| Norm-based role physical | 46.9 (10.7) | 46.6 (10.8) | 46.8 (10.6) | 47.0 (10.4) | 44.7 (10.9) | 44.6 (10.7) | 46.7 (10.9) | 46.6 (10.9) |
| Norm-based bodily pain | 44.4 (10.1) | 44.1 (9.9) | 44.6 (10.4) | 44.9 (10.3) | 41.8 (9.5) | 41.9 (9.6) | 47.1 (9.8) | 47.2 (9.8) |
| Norm-based general health | 40.9 (9.9) | 40.2 (9.6) | 41.1 (10.6) | 41.4 (10.6) | 40.6 (10.2) | 40.8 (10.0) | 42.4 (10.0) | 42.4 (9.9) |
| Norm-based vitality | 43.5 (10.5) | 43.9 (10.3) | 44.0 (11.7) | 44.4 (11.4) | 42.8 (11.1) | 42.8 (11.3) | 45.5 (10.7) | 45.6 (10.7) |
| Norm-based social functioning | 44.4 (11.1) | 44.1 (10.6) | 44.7 (11.7) | 45.2 (11.5) | 42.2 (11.6) | 42.1 (11.5) | 46.8 (10.2) | 46.7 (10.2) |
| Norm-based role emotional | 46.6 (11.5) | 47.2 (11.5) | 45.8 (12.9) | 46.3 (12.6) | 45.9 (12.2) | 46.1 (12.1) | 46.9 (11.8) | 46.8 (11.8) |
| Norm-based mental health | 46.0 (11.6) | 46.9 (11.0) | 46.7 (11.6) | 47.1 (11.3) | 44.6 (11.4) | 44.6 (11.6) | 46.4 (10.7) | 46.3 (10.8) |
| EQ-5D, mean (SD) | 0.71 (0.26) | 0.72 (0.24) | 0.72 (0.25) | 0.73 (0.25) | 0.68 (0.26) | 0.68 (0.26) | 0.75 (0.22) | 0.75 (0.22) |
| EQ-5D VAS, mean (SD) | 68.6 (17.1) | 69.2 (15.9) | 70.5 (18.1) | 71.2 (17.6) | 67.2 (18.5) | 67.0 (18.5) | 71.3 (16.7) | 71.5 (16.6) |
The most prevalent reflux symptoms (those with lowest scores) were general discomfort and wind and frequency. The participants had lower SF-36 and EQ-5D scores than a normal UK population with the same average age and sex characteristics (SF-36 population norm approximately 50 for all domains, and EQ-5D norm 0.88).
Preference arms
The preference for surgery participants reported worse REFLUX quality of life scores and worse health in general than the preference for medicine participants. It can be seen that the randomised participants reported quality of life measures in between these two extremes.
Surgical management
Table 21 gives details of the surgical management of those randomly allocated or in the preference for surgery group. For 47 allocated surgery there was subsequently a definite decision not to have surgery. For 25 of these, this was a clinical decision, most commonly the surgeon deciding that surgery was not appropriate. Most of the others changed their minds about having surgery for a variety of work- or home-related reasons, because of worries about the risks of surgery, because of a wish to avoid the preoperative tests, or because their symptoms had improved. A further 20 withdrew for uncertain reasons. There is no doubt, however, that a number of these participants suffered long delays before being formally offered surgery, and this was an important factor in their eventual decision to choose not to have surgery after all. The trial was conducted at a time when there was great pressure on surgical services in the NHS, with long delays for elective surgery for non-life-threatening benign conditions being common. Indeed, the average time between trial entry and surgery in the trial was 8–9 months (see Table 23).
| Surgical participants | ||
|---|---|---|
| Randomised (n = 178) | Preference (n = 261) | |
| Number declined surgery, n (%) | 47 (26.4) | 25 (9.6) |
| Number on waiting list, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.8) |
| Number withdrawn/lost to follow-up before surgery, n (%) | 20 (11.2) | 16 (6.1) |
| Number who received surgery, n (%) | 111 (62.4) | 218 (83.5) |
| Endoscopy before surgery, n (%) | 97 (87.4) | 196 (89.9) |
| pH monitoring before surgery, n (%) | 77 (69.4) | 158 (72.5) |
| Manometry before surgery, n (%) | 73 (65.8) | 164 (75.2) |
| Type of fundoplication, n (%) | ||
| Total wrap | 52 (46.8) | 158 (72.8) |
| Partial – anterior | 51 (45.9) | 35 (16.1) |
| Partial – posterior | 8 (7.2) | 24 (11.1) |
| Short gastric arteries divided, n (%) | 38 (34.2) | 98 (45.0) |
| Left hepatic from left gastric artery, n (%) | 13 (11.7) | 13 (6.0) |
| If present, left hepatic artery divided, n (%) | 4 (3.6) | 6 (2.8) |
| Hepatic branch vagus divided, n (%) | 30 (27.0) | 40 (18.3) |
| Hiatus hernia present, n (%) | 50 (45.0) | 101 (46.3) |
| Bougie used, n (%) | 25 (22.5) | 67 (30.7) |
| Crural repair, n (%) | 87 (78.4) | 167 (76.6) |
| Grade of operating surgeon, n (%) | ||
| Consultant | 100 (91.7) | 174 (80.6) |
| Staff grade, associate specialist | 5 (4.6) | 10 (4.6) |
| SPR | 3 (2.8) | 30 (13.9) |
| Other | 1 (0.9) | 2 (0.9) |
| Operation time in minutes (mean) (SD ) | 113 (38.0) | 123 (64.4) |
In total, 111 (62.4%) of those randomised to surgery and 218 (83.5%) of the preference participants actually received surgery. Amongst the randomised participants, about 50% had a total wrap and 50% a partial wrap fundoplication. A total wrap was, however, the predominant procedure in the preference group (72.8%). The difference between the randomised and preference group fundoplication procedures was a reflection of the surgeon’s preferred procedure and not any systematic surgeon bias between a surgeon’s randomised and preference participants. This is illustrated in Figure 13, which shows that, within a given centre, the surgeon(s) performed the same procedures on their randomised and preference patients. The majority of operations were performed by a consultant and took around 2 hours to complete.
FIGURE 13.
Type of fundoplication performed by centre.
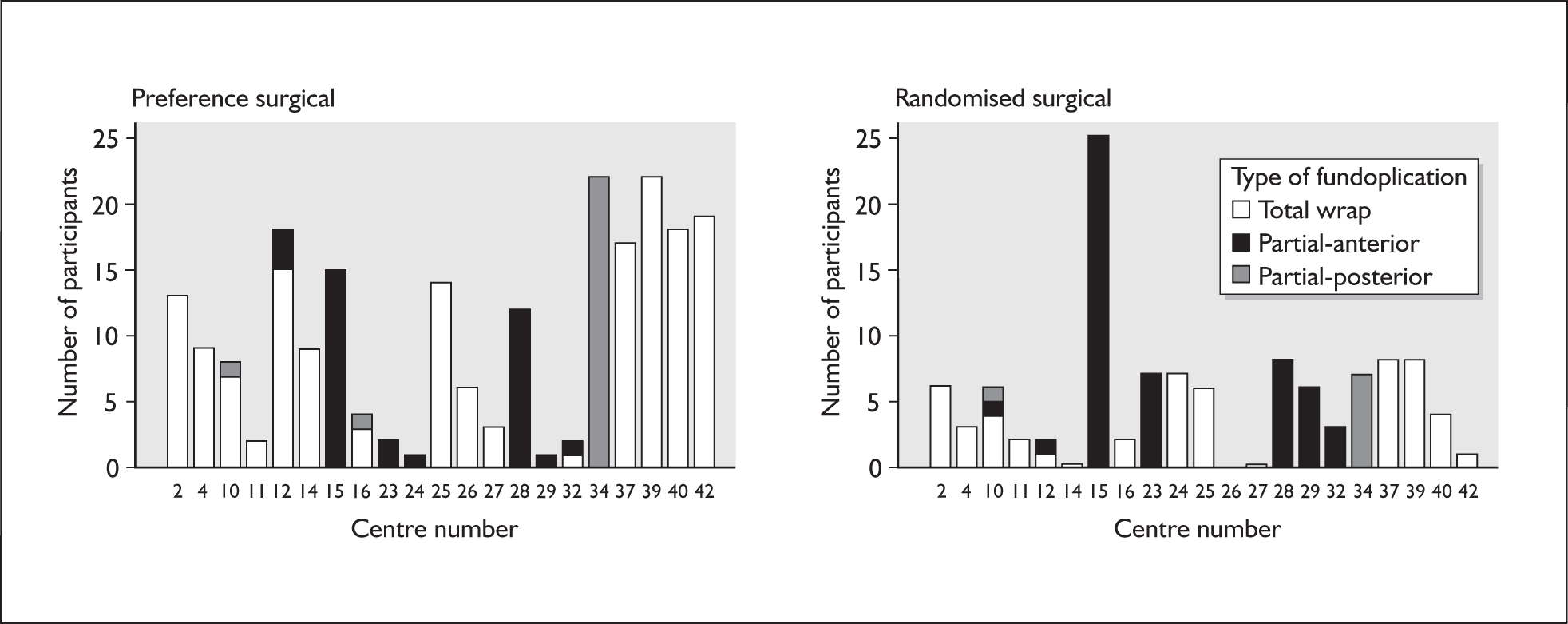
Intra- and postoperative surgical outcomes
Table 22 shows the intra- and postoperative surgical outcomes in the randomised and preference surgical participants who actually had a fundoplication. Two (0.6%) participants out of the total of 329 participants who had surgery required conversion to an open procedure (95% CI 0.2%–2.2%), and 8 (2.4%) had a visceral injury (95% CI 1.2%–4.7%). One participant had a blood transfusion. Three were admitted to a high dependency unit, but none to an intensive care unit. Nearly all were discharged to their homes after a median length of stay of 2 days. Three participants (0.9%) required a reoperation (95% CI 0.3%–2.6%) – all in the preference group – and three had dilatation of an oesophageal stricture or food disimpaction within 12 months of their initial surgery.
| Surgical participants | ||
|---|---|---|
| Randomised (n = 111) | Preference (n = 218) | |
| Conversion, n (%) | 2 (1.8) | 0 (0.0) |
| Liver injury, n (%) | 1 (0.9) | 1 (0.5) |
| Splenic injury, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.5) |
| Pleural injury, n (%) | 1 (0.9) | 2 (0.9) |
| Oesophageal injury, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Other visceral injury, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Haemorrhage, n (%) | 1 (0.9) | 1 (0.5) |
| Pneumothorax, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.9) |
| Blood transfusion, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.5) |
| Number of units transfused, mean (SD ) | – | 3 (–) |
| Other postoperative event, n (%) | 3 (2.7) | 5 (2.3) |
| ICU admission, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| HDU admission, n (%) | 1 (0.9) | 2 (0.9) |
| Reoperation within 12 months, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (1.4) |
| Stricture dilatation or food disimpaction required within 12 months, n (%) | 1 (0.9) | 2 (0.9) |
| Ward only, n (%) | 104 (93.7) | 206 (94.5) |
| Discharged status | ||
| Home, n (%) | 107 (96.4) | 213 (97.7) |
| Other, n (%) | 4 (3.6) | 5 (2.3) |
| Length of stay in days (median) (IQR) | 2 (2–3) | 2 (2–3) |
Follow-up at the time equivalent to 3 months after surgery
Patient flow
As mentioned earlier, around 90% of all participants returned completed questionnaires. As shown in Table 23, by the time of the first follow-up, some participants had formally withdrawn, and so were not sent questionnaires, and others had lost contact with the study office. Of the participants for whom it was appropriate to send a follow-up questionnaire, approximately 95% returned it (Table 23). For the surgical participants, the median and interquartile range (IQR) time from surgery to the first questionnaire was approximately 90 days. However, given that there were substantial waiting times for surgical participants, the median time from randomisation to sending the 3-month follow-up questionnaire was approximately 300 days (and this implied a waiting list time of 8–9 months). The median lag time from randomisation to follow-up was similar across all of the groups suggesting that our intention of pairing follow-up times between participants during the conduct of the trial (as described in Chapter 2) was successful.
| Randomised participants | Preference participants | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical | Medical | Surgical | Medical | |||||
| ITT (n = 178) | PP (n = 111) | ITT (n = 179) | PP (n = 169) | ITT (n = 261) | PP (n = 218) | ITT (n = 192) | PP (n = 189) | |
| Loss to follow-up, n | 10 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Formally withdrawn, n | 11 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 9 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Questionnaire sent, n | 157 | 111 | 169 | 159 | 247 | 213 | 190 | 187 |
| Questionnaire returned, n (%) | 150 (95.5) | 109 (98.2) | 158 (93.5) | 150 (94.3) | 230 (93.1) | 202 (94.8) | 182 (95.8) | 179 (95.7) |
| Lag in days (median) between surgery and 3-month follow-up (IQR) | 86 (85–90) | 86 (85–98) | ||||||
| Lag in days (median) between randomisation and 3-month follow-up (IQR) | 325 (266–435) | 278 (215–314) | 319 (210–455) | 287 (214–342) | ||||
Medications
The medications that participants were taking at the time of the 3-month follow-up are shown in Table 24. For the RITT surgery group, 33.3% were on a reflux-related drug compared with 92.4% of those randomised to medical management. When considering only randomised participants who received the intended management (the RPP groups), 9.2% of surgical participants and 92.7% of medical participants were on a reflux-related drug. The preference surgical and preference medical participants had a broadly similar proportion on medications as the randomised surgical and randomised medical groups respectively, although use of anti-reflux drugs was lower in the preference surgical ITT group than in the randomised surgical ITT group (as would be expected given that a higher proportion actually went on to have surgery).
| Randomised participants | Preference participants | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical | Medical | Surgical | Medical | |||||
| ITT (n = 178) | PP (n = 111) | ITT (n = 179) | PP (n = 169) | ITT (n = 261) | PP (n = 218) | ITT (n = 192) | PP (n = 189) | |
| Any reflux-related drug, n (%) | 50 (33.3) | 10 (9.2) | 146 (92.4) | 139 (92.7) | 45 (19.6) | 17 (8.4) | 176 (96.7) | 161 (89.9) |
| Proton pump inhibitors, n (%) | ||||||||
| Any proton pump inhibitor | 47 (31.3) | 8 (7.3) | 140 (88.6) | 133 (88.7) | 41 (17.8) | 13 (6.4) | 167 (91.8) | 152 (84.9) |
| Omeprazole (Losec) | 16 (10.7) | 5 (4.6) | 45 (28.5) | 45 (30.0) | 15 (6.5) | 3 (1.5) | 57 (31.3) | 57 (31.8) |
| Lansoprazole (Zoton) | 19 (12.7) | 3 (2.8) | 55 (34.8) | 54 (36.0) | 13 (5.7) | 7 (3.5) | 67 (36.8) | 64 (35.8) |
| Pantoprazole (Protium) | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (5.7) | 8 (5.3) | 3 (1.3) | 2 (1.0) | 14 (7.7) | 14 (7.8) |
| Rabeprazole (Pariet) | 4 (2.7) | 1 (0.9) | 9 (5.7) | 9 (6.0) | 3 (1.3) | 0 (0.0) | 13 (7.1) | 13 (7.3) |
| Esomeprazole (Nexium) | 7 (4.7) | 1 (0.9) | 22 (13.9) | 21 (14.0) | 7 (3.0) | 3 (1.5) | 21 (11.5) | 21 (11.7) |
| Histamine receptor antagonists, n (%) | ||||||||
| Any histamine receptor antagonist | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 12 (7.6) | 10 (6.7) | 4 (1.7) | 2 (1.0) | 14 (7.7) | 13 (7.3) |
| Ranitidine (Zantac) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (5.1) | 8 (5.3) | 2 (0.9) | 1 (0.5) | 10 (5.5) | 9 (5.0) |
| Famotidine (Pepcid) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.6) |
| Cimetidine (Tagamet) | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Nizatidine (Axid) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.6) |
| Over-the-counter histamine receptor antagonist | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (2.5) | 4 (2.7) | 2 (0.9) | 1 (0.5) | 3 (1.7) | 3 (1.7) |
| Prokinetics, n (%) | ||||||||
| Any prokinetics | 7 (4.7) | 3 (2.8) | 6 (3.8) | 5 (3.3) | 7 (3.0) | 6 (3.0) | 5 (2.7) | 4 (2.2) |
| Domperidone (Motilium) | 3 (2.0) | 1 (0.9) | 6 (3.8) | 5 (3.3) | 3 (1.3) | 2 (1.0) | 4 (2.2) | 3 (1.7) |
| Metoclopramide (Maxolon) | 4 (2.7) | 2 (1.8) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (1.7) | 4 (2.0) | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.6) |
| Other prescribed drugs, na | ||||||||
| Alginates (Gaviscon, etc., Topal) | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Anti-spasmodics (e.g. dicycloverine ) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Chelates (sucralfate) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other ulcer-healing drugs | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Antacids: Mucogel | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Antacids: Asilone | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Non-gastrointestinal | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Anti-motility | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Health status
The health status measures at the 3-month follow-up are shown in Table 25. Within the randomised component (RITT groups) there were clear differences across all measures, with the surgery group having better scores than the medical group. The differences were larger when only the per protocol participants were considered (RPP groups). Details of the formal statistical testing of these differences are described in the section on statistical analyses.
| Randomised participants | Preference participants | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical | Medical | Surgical | Medical | |||||
| ITT (n = 178) | PP (n = 111) | ITT (n = 179) | PP (n = 169) | ITT (n = 261) | PP (n = 218) | ITT (n = 192) | PP (n = 189) | |
| REFLUX QoL, mean (SD) | 83.9 (19.4) | 85.9 (19.0) | 70.6 (24.6) | 70.8 (24.4) | 80.4 (21.6) | 82.5 (20.3) | 80.2 (18.2) | 80.6 (17.7) |
| REFLUX symptom score, mean (SD) | ||||||||
| General discomfort symptom score | 84.8 (17.3) | 89.4 (14.0) | 66.9 (26.2) | 66.5 (26.0) | 84.1 (19.6) | 87.2 (16.6) | 75.7 (19.6) | 76.0 (19.5) |
| Wind and frequency symptom score | 58.1 (19.7) | 55.9 (19.7) | 53.7 (22.6) | 54.4 (22.5) | 52.2 (21.1) | 52.6 (20.7) | 60.7 (22.2) | 60.9 (22.3) |
| Nausea and vomiting symptom score | 91.5 (15.7) | 93.1 (15.7) | 82.1 (20.7) | 82.3 (20.2) | 90.2 (15.2) | 91.6 (13.7) | 89.5 (12.9) | 90.0(11.9) |
| Activity limitation symptom score | 88.2 (17.0) | 89.9 (16.7) | 81.6 (19.6) | 81.9 (19.0) | 88.4 (18.0) | 89.7 (17.5) | 87.9 (13.2) | 88.0 (13.3) |
| Constipation and swallowing symptom score | 79.2 (20.0) | 78.7 (20.7) | 75.8 (20.9) | 77.0 (19.8) | 77.1 (21.2) | 76.9 (21.3) | 84.2 (16.9) | 84.6 (16.5) |
| SF-36 scores, mean (SD) | ||||||||
| Norm-based physical functioning | 49.2 (10.0) | 49.3 (10.4) | 46.5 (11.5) | 46.6 (11.6) | 49.9 (9.7) | 50.4 (9.4) | 47.6 (10.3) | 47.5 (10.4) |
| Norm-based role physical | 47.7 (11.8) | 47.4 (12.1) | 44.8 (12.1) | 45.0 (12.1) | 48.1 (11.3) | 48.7 (10.7) | 47.1 (10.4) | 47.1 (10.4) |
| Norm-based bodily pain | 48.5 (10.3) | 48.8 (10.8) | 45.3 (11.4) | 45.3 (11.3) | 48.4(11.3) | 49.0 (11.2) | 46.5 (10.2) | 46.5 (10.3) |
| Norm-based general health | 46.3 (11.0) | 47.4 (11.0) | 40.7 (11.2) | 40.7 (11.2) | 47.2 (11.3) | 48.2 (11.1) | 42.5 (10.5) | 42.6 (10.4) |
| Norm-based vitality | 47.1 (11.9) | 48.0 (12.1) | 43.9 (12.4) | 44.3 (12.2) | 48.0 (11.9) | 48.4 (11.9) | 44.7 (11.4) | 44.8 (11.4) |
| Norm-based social functioning | 47.2 (11.5) | 47.5 (12.1) | 43.6 (12.7) | 43.8 (12.6) | 46.8 (12.3) | 47.6 (12.0) | 46.9 (10.5) | 46.9 (10.5) |
| Norm-based role emotional | 48.3 (12.3) | 48.4 (12.5) | 43.9 (14.2) | 44.1 (14.2) | 47.0 (12.6) | 48.9 (11.7) | 47.0 (11.4) | 46.9 (11.4) |
| Norm-based mental health | 48.7 (12.0) | 49.7 (11.9) | 44.5 (12.2) | 44.7 (11.9) | 48.3 (12.2) | 49.2 (11.8) | 47.1 (10.6) | 47.1 (10.7) |
| EQ-5D, mean (SD) | 0.79 (0.23) | 0.81 (0.24) | 0.69 (0.30) | 0.70 (0.30) | 0.81 (0.25) | 0.82 (0.24) | 0.76 (0.23) | 0.77 (0.23) |
| EQ-5D VAS, mean (SD) | 74.8 (19.7) | 77.0 (18.4) | 67.8 (20.8) | 68.1 (20.7) | 75.1 (18.6) | 76.3 (18.3) | 70.8 (17.6) | 70.9 (17.5) |
The health status scores of the two preference groups were more similar, although they tended to slightly favour the preference surgical group. Overall levels were equivalent to those of the randomised surgical group. (It is important to bear in mind, however, that the baseline levels were clearly lowest in the preference surgical group – see Table 20.)
Follow-up at the time equivalent to 12 months after surgery
Patient flow
As with the 3-month follow-up, of the participants for whom it was appropriate to send a follow-up questionnaire at 12 months, approximately 95% returned it (Table 26). The median lag time from randomisation to this second follow-up was similar across all of the groups. It was also approximately 270 days after the 3-month follow-up questionnaire, further demonstrating that the pairing of follow-up times between participants had been successful.
| Randomised participants | Preference participants | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical | Medical | Surgical | Medical | |||||
| ITT (n = 178) | PP (n = 111) | ITT (n = 179) | PP (n = 169) | ITT (n = 261) | PP (n = 218) | ITT (n = 192) | PP (n = 189) | |
| Formally withdrawn/loss to follow-up, n | 14 | 1 | 6 | 5 | 14 | 3 | 8 | 8 |
| Questionnaire sent, n | 164 | 110 | 173 | 164 | 247 | 215 | 184 | 181 |
| Questionnaire returned, n (%) | 154 (93.9) | 104 (94.5) | 164 (94.8) | 155 (94.5) | 230 (93.1) | 203 (94.4) | 177 (96.2) | 174 (96.1) |
| Lag in days (median) between surgery and 12-month follow-up (IQR) | 359 (358–361) | 360 (359–362) | ||||||
| Lag in days (median) between randomisation and 12-month follow-up (IQR) | 580 (540–683) | 541 (467–571) | 574 (460–708) | 546 (480–607) | ||||
Medications
The medications that participants had taken during the previous 2 weeks at the time of the 12-month follow-up are shown in Table 27. In the RITT groups, 38.3% of the randomised surgical participants had taken a reflux-related drug compared with 89.6% of the randomised medical participants (and nearly all of these were PPIs). When considering only randomised participants who received their intended management (the RPP groups), 14.4% of surgical participants and 92.9% of medical participants had been taking reflux-related drugs. As at 3 months, the preference medical groups reported similar patterns of drug use to the randomised medical groups; however, the rate of drug use in the preference surgical ITT group was about one-half of that in the randomised surgical ITT group. Omeprazole and lansoprazole were equally commonly reported and this contrasts with the findings at study entry when lansoprazole was the predominant PPI used.
| Randomised participants | Preference participants | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical | Medical | Surgical | Medical | |||||
| ITT (n = 178) | PP (n = 111) | ITT (n = 179) | PP (n = 169) | ITT (n = 261) | PP (n = 218) | ITT (n = 192) | PP (n = 189) | |
| Any reflux-related drug, n (%) | 59 (38.3) | 15 (14.4) | 147 (89.6) | 144 (92.9) | 46 (20.0) | 22 (10.8) | 165 (93.2) | 163 (93.7) |
| Proton pump inhibitors, n (%) | ||||||||
| Any proton pump inhibitor | 56 (36.4) | 13 (12.5) | 142 (86.6) | 139 (89.7) | 42 (18.3) | 19 (9.4) | 156 (88.1) | 154 (88.5) |
| Omeprazole (Losec) | 19 (12.3) | 6 (5.8) | 47 (28.7) | 45 (29.0) | 14 (6.1) | 4 (2.0) | 61 (34.5) | 60 (34.5) |
| Lansoprazole (Zoton) | 21 (13.6) | 2 (1.9) | 51 (31.1) | 50 (32.3) | 17 (7.4) | 12 (5.9) | 56 (31.6) | 5 (31.6) |
| Pantoprazole (Protium) | 2 (1.3) | 1 (1.0) | 9 (5.5) | 9 (5.8) | 3 (1.3) | 1 (0.5) | 16 (9.0) | 16 (9.2) |
| Rabeprazole (Pariet) | 3 (1.9) | 1 (1.0) | 12 (7.3) | 12 (7.7) | 2 (0.9) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (5.1) | 9 (5.2) |
| Esomeprazole (Nexium) | 11 (7.1) | 3 (2.9) | 25 (15.2) | 25 (16.1) | 8 (3.5) | 3 (1.5) | 15 (8.5) | 15 (8.6) |
| Histamine receptor antagonists, n (%) | ||||||||
| Any histamine receptor antagonist | 4 (2.6) | 3 (2.9) | 9 (5.5) | 9 (5.8) | 5 (2.2) | 2 (1.0) | 13 (7.3) | 13 (7.5) |
| Ranitidine (Zantac) | 3 (1.9) | 2 (1.9) | 7 (4.3) | 7 (4.5) | 2 (0.9) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (4.5) | 8 (4.6) |
| Famotidine (Pepcid) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.6) |
| Cimetidine (Tagamet) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Nizatidine (Axid) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Over-the-counter histamine receptor antagonist | 1 (0.6) | 1 (1.0) | 2 (1.2) | 2 (1.3) | 3 (1.3) | 2 (1.0) | 5 (2.8) | 5 (2.9) |
| Prokinetics, n (%) | ||||||||
| Any prokinetics | 6 (3.9) | 2 (1.9) | 4 (2.4) | 4 (2.6) | 5 (2.2) | 4 (2.0) | 6 (3.4) | 5 (2.9) |
| Domperidone (Motilium) | 4 (2.6) | 1 (1.0) | 4 (2.4) | 4 (2.6) | 1 (0.4) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (2.8) | 4 (2.3) |
| Metoclopramide (Maxolon) | 2 (1.3) | 1 (1.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (1.7) | 4 (2.0) | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.6) |
| Other prescribed drugs, na | ||||||||
| Alginates (Gaviscon, etc., Topal) | 3 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| Anti-spasmodics (e.g. dicycloverine ) | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Chelates (sucralfate) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other ulcer-healing drugs | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Antacids: Mucogel | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Antacids: Asilone | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Non-gastrointestinal | 2 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| Anti-motility | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Health status
The health status measures at the 12-month follow-up are shown in Table 28. Within the randomised trial (RITT groups) there were still substantial differences across all measures (of the order of magnitude of one-third or one-half of a standard deviation of the score), with the surgery group having better scores than the medical group. The differences were larger when only the per protocol participants were considered (RPP groups). Details of statistical testing of the health status scores can be found in the next section of this chapter. For the reflux symptoms, although there were improvements across all symptom groups for surgical participants, the largest improvement in symptom score was for the general discomfort dimension. A detailed description of the responses to each symptom question is given in the REFLUX questionnaire (see Appendix 2). These improvements were also reflected in the SF-36 scores where the biggest differences were observed in the general health and bodily pain dimensions.
| Randomised participants | Preference participants | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical | Medical | Surgical | Medical | |||||
| ITT (n = 178) | PP (n = 111) | ITT (n = 179) | PP (n = 169) | ITT (n = 261) | PP (n = 218) | ITT (n = 192) | PP (n = 189) | |
| REFLUX QoL, mean (SD) | 84.6 (17.9) | 88.3 (15.6) | 73.4 (23.3) | 73.1 (23.7) | 83.3 (20.7) | 86.0 (17.9) | 79.2 (19.2) | 79.4 (19.0) |
| Reflux symptom score, mean (SD) | ||||||||
| General discomfort symptom score | 84.7 (17.5) | 90.2 (14.0) | 67.4 (25.8) | 66.7 (25.8) | 85.0 (19.4) | 87.7 (16.5) | 73.9 (20.7) | 74.0 (20.8) |
| Wind and frequency symptom score | 56.7 (21.0) | 56.9 (21.7) | 52.6 (23.3) | 52.7 (23.5) | 56.9 (22.5) | 57.5 (22.1) | 61.4 (21.9) | 61.5 (22.0) |
| Nausea and vomiting symptom score | 91.9 (14.4) | 94.7 (11.8) | 84.0 (18.6) | 83.3 (18.8) | 91.1 (16.5) | 93.3(13.8) | 88.6 (15.4) | 88.9 (14.4) |
| Activity limitation symptom score | 90.7 (12.8) | 93.3 (11.5) | 82.2 (19.2) | 81.6 (19.4) | 90.8 (16.8) | 92.4 (14.8) | 87.3 (14.7) | 87.4 (14.8) |
| Constipation and swallowing symptom score | 79.3 (19.1) | 80.2 (19.6) | 74.5 (22.8) | 75.2 (22.3) | 78.5 (20.2) | 79.1 (19.7) | 83.6 (17.6) | 83.8 (17.4) |
| SF-36 scores, mean (SD) | ||||||||
| Norm-based physical functioning | 48.9 (10.3) | 49.6 (10.3) | 47.2 (11.0) | 47.2 (10.9) | 49.7 (10.8) | 50.3 (10.5) | 47.4 (10.5) | 47.4 (10.6) |
| Norm-based role physical | 46.7 (11.4) | 47.4 (11.3) | 45.8 (11.8) | 46.0 (11.7) | 49.0 (11.2) | 49.6 (10.5) | 46.8 (10.7) | 46.8 (10.7) |
| Norm-based bodily pain | 47.7 (10.4) | 48.5 (10.7) | 44.5 (10.9) | 44.5 (10.9) | 49.1 (11.3) | 49.9 (11.1) | 47.4 (9.9) | 47.4 (10.0) |
| Norm-based general health | 45.2 (11.1) | 46.2 (11.8) | 40.7 (11.2) | 40.5 (11.1) | 46.4 (10.8) | 47.2 (10.6) | 42.3 (10.1) | 42.3 (10.1) |
| Norm-based vitality | 46.9 (11.5) | 47.6 (11.6) | 44.2 (11.9) | 44.4 (11.7) | 47.3 (12.0) | 48.0 (11.7) | 45.1 (10.3) | 45.2 (10.3) |
| Norm-based social functioning | 46.9 (11.6) | 47.8 (11.7) | 45.2 (12.2) | 45.4 (12.1) | 46.9 (12.5) | 47.8 (12.1) | 46.6 (10.6) | 46.6 (10.6) |
| Norm-based role emotional | 46.4 (13.5) | 47.2 (12.9) | 44.2 (14.4) | 44.4 (14.2) | 47.3 (13.3) | 48.1 (12.7) | 46.2 (12.0) | 46.1 (12.0) |
| Norm-based mental health | 47.2 (11.7) | 48.5 (11.6) | 46.4 (12.1) | 46.5 (12.2) | 46.9 (12.0) | 47.4 (12.0) | 46.5 (10.9) | 46.6 (10.9) |
| EQ-5D, mean (SD) | 0.75 (0.25) | 0.78 (0.23) | 0.71 (0.27) | 0.71 (0.27) | 0.79 (0.26) | 0.80 (0.25) | 0.74 (0.24) | 0.74 (0.24) |
| EQ-5D VAS, mean (SD) | 74.3 (18.0) | 75.9 (17.8) | 69.3 (20.1) | 69.2 (20.0) | 75.6 (16.7) | 76.5 (16.1) | 71.5 (18.1) | 71.7 (17.8) |
For preference participants the health status measure scores tended to favour the surgical group. However, the differences between the preference groups were less marked than the differences between the randomised groups, mainly because the preference medical group had better scores than the randomised medical group.
Graphical displays of the changes in REFLUX QoL scores and EQ-5D scores for all study groups are displayed in Figures 14 and 15 respectively.
FIGURE 14.
Reflux quality of life (QoL) scores at baseline and follow-up. Scores ranged from 0 to 100; the higher the score the better the patient felt.
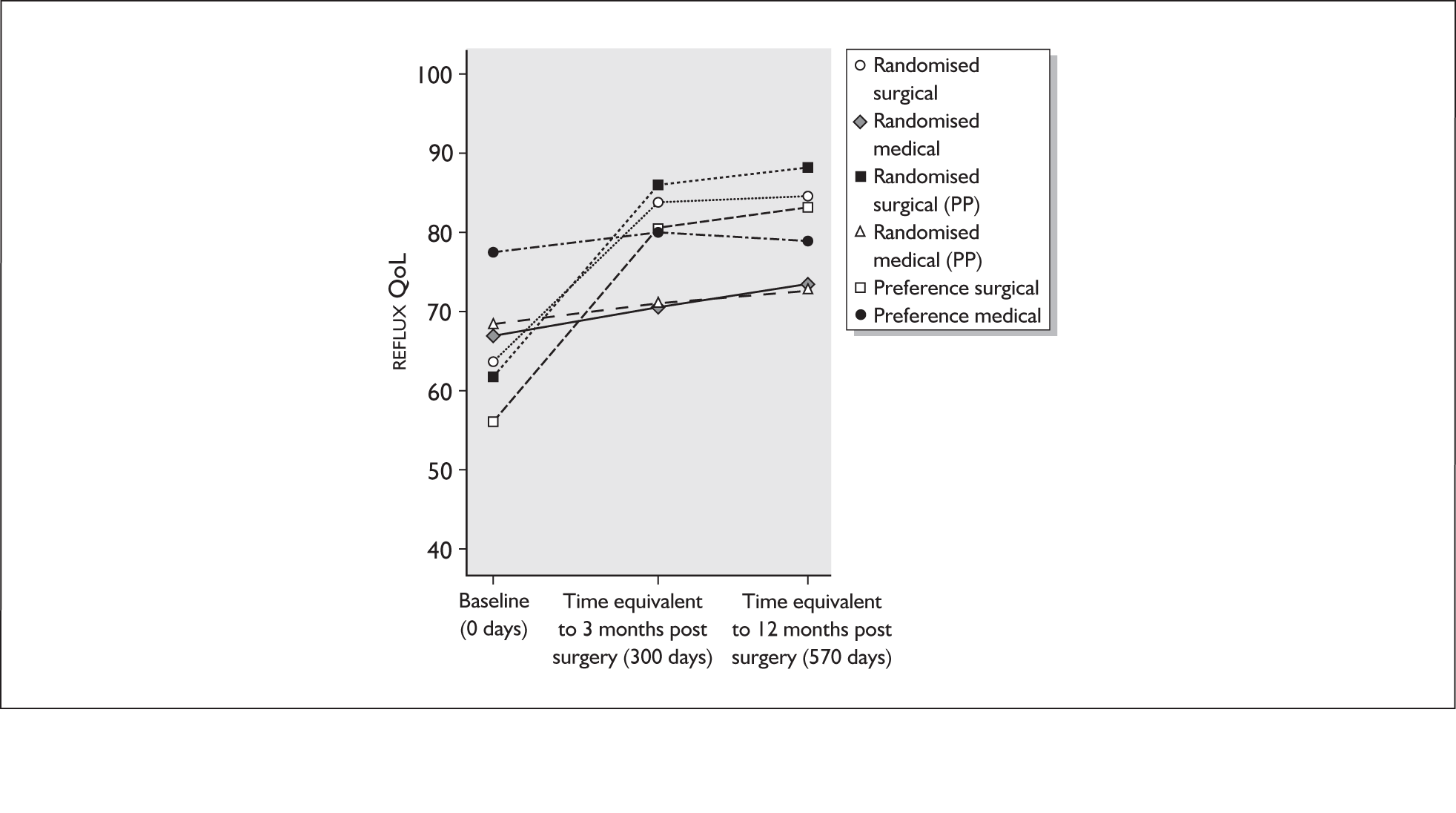
FIGURE 15.
EQ-5D scores at baseline and follow-up. Scores ranged from 100 (perfect health) to 0 (equivalent to death).
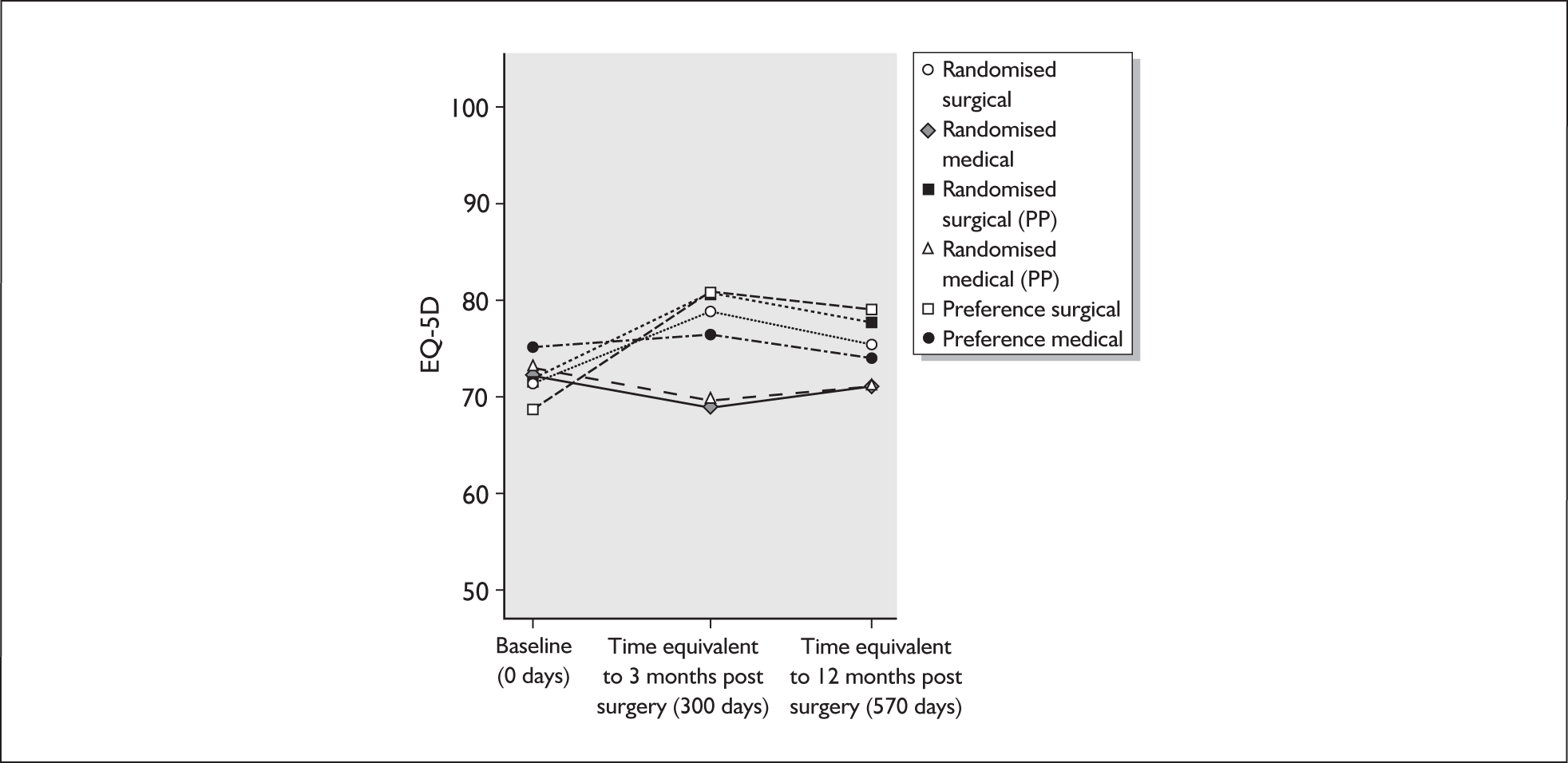
Three participants died, one in the randomised medical group (road traffic accident) and two in the preference surgical group, neither of whom had surgery (alcoholic liver disease and cause unknown).
Statistical analyses
Primary outcome
The pre-chosen primary outcome was the REFLUX QoL score at the time equivalent to 12 months after surgery. The mean and standard deviation of the score for each group at this follow-up are shown in Table 28. The differences between groups with corresponding 95% confidence intervals are shown in Table 29. Three types of analysis are presented for the randomised participants – intention to treat, per protocol and adjusted treatment received. Table 29 also displays the impact of including adjustment for baseline score and randomised group × baseline score interaction terms.
| Randomised participants | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intention to treat | Per protocol | Adjusted treatment received | |||||||
| Differencea | (95% CI) | p-value | Differencea | (95% CI) | p-value | Differencea | (95% CI) | p-value | |
| REFLUX QoL score, mean (SD) | |||||||||
| Adjusted for minimisation variables | 11.2 | (6.4–16.0) | < 0.001 | 15.4 | (10.0–20.9) | < 0.001 | 16.7 | (9.7–23.6) | < 0.001 |
| Adjusted for minimisation variables and baseline REFLUX QoL score | 14.1 | (9.6–18.6) | < 0.001 | 19.1 | (14.0–24.1) | < 0.001 | 20.3 | (13.8–26.8) | < 0.001 |
| Adjusted for minimisation variables, baseline score and treatment × baseline REFLUX QoL score interaction | 14.0 | (9.6–18.4) | < 0.001 | 18.4 | (13.6–23.2) | < 0.001 | 19.4 | (13.0–25.8) | < 0.001 |
Intention to treat
For the intention to treat analysis there was a mean difference in favour of surgery of 11.2 between the groups when only the minimisation variables were adjusted for (p < 0.001). This was not the most parsimonious model – there was strong evidence of an interaction effect between the randomised group and baseline REFLUX QoL score (interaction term was –0.35; 95% CI –0.53 to 0.17; p < 0.001). This implied that as baseline REFLUX QoL score increased the treatment effect decreased. Estimating the treatment difference at the trial baseline mean REFLUX QoL score of 65.4 resulted in a trial effect size of 14.0 (95% CI 9.6–18.4 ). If the average patient had a lower mean REFLUX QoL score at baseline of 56.0, the effect size increased to 17.2 (95% CI 12.6–21.9). If the patient had a higher baseline score of 78.0, the treatment effect decreased to 9.5 (95% CI 4.5–14.5). All results, however, showed strong evidence of increases in REFLUX QoL scores, favouring surgery.
Per protocol
The per protocol analysis in Table 29 estimated the difference between the randomised groups using only participants who received their allocated GORD management. This provided an estimate of the efficacy of the treatments. The per protocol analyses demonstrated larger effects in favour of surgery than the corresponding intention to treat analyses. Addition of the baseline score and interaction with the randomised group provided the best model fit resulting in a difference in favour of surgery of 18.4 (95% CI 13.6–23.2). Selection bias is to be expected in these estimates and indeed those who did not receive surgery in the randomised surgical group had higher (better) REFLUX QoL scores at baseline than those who did have surgery (69.0 versus 61.8).
Adjusted treatment received
The adjusted treatment received analyses attempted to reduce the selection bias effect inherent in the per protocol analyses. The effect sizes using the adjusted treatment received approach produced slightly larger estimates of differences than the per protocol estimates (see Table 29); however, the confidence interval widths increased. Nevertheless, the estimates and confidence intervals of the efficacy of the treatments suggested large benefits of surgery.
Preference groups
The preference for surgery participants reported considerably worse mean REFLUX QoL scores at baseline than the preference for medicine participants (55.8 versus 77.5; Table 20). Despite starting from a much lower baseline score, at follow-up at the time equivalent to 12 months after surgery, the REFLUX QoL score favoured the surgical group using an intention to treat analysis (difference = 3.9; 95% CI –0.2 to 8.0; p = 0.064) and using a per protocol analysis (difference = 6.3; 95% CI 2.4–10.2; p = 0.002).
Secondary outcomes
The secondary outcomes were the health status measures (EQ-5D, SF-36 and symptom scores) at the times equivalent to 3 and 12 months after surgery. The use of reflux medication at 12 months after surgery was also analysed.
At time equivalent to 12 months after surgery
Table 30 shows the health status measures at the time equivalent to 12 months after surgery described by the same three analyses as for the primary outcome (intention to treat, per protocol and adjusted treatment received).
| Randomised participants | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intention to treat | Per protocol | Adjusted treatment received | |||||||
| Differencea | (95% CI) | p-value | Differencea | (95% CI) | p-value | Differencea | (95% CI) | p-value | |
| REFLUX symptom score, mean (SD) | |||||||||
| General discomfort symptom score | 18.3 | (13.8–22.9) | < 0.001 | 25.0 | (20.2–29.8) | < 0.001 | 26.1 | (19.6–32.5) | < 0.001 |
| Wind and frequency symptom score | 4.9 | (0.8–9.1) | 0.019 | 6.1 | (1.5–10.8) | 0.01 | 6.7 | (0.6–12.8) | 0.033 |
| Nausea and vomiting symptom score | 7.8 | (4.6–10.9) | < 0.001 | 11.7 | (8.4–14.9) | < 0.001 | 11.5 | (7.0–16.0) | < 0.001 |
| Activity limitation symptom score | 8.4 | (5.2–11.7) | < 0.001 | 12.3 | (8.7–16.0) | < 0.001 | 12.0 | (7.3–16.7) | < 0.001 |
| Constipation and swallowing symptom score | 3.5 | (–0.5 to 7.5) | 0.085 | 4.8 | (0.1–9.4) | 0.045 | 5.0 | (–0.9 to 10.9) | 0.099 |
| SF-36 scores, mean (SD) | |||||||||
| Norm-based physical functioning | 2.3b | (0.6–4.0) | 0.007 | 3.4b | (1.5–5.4) | 0.001 | 3.4b | (0.9–5.9) | 0.008 |
| Norm-based role physical | 0.9 | (–1.1 to 3.0) | 0.383 | 1.7 | (–0.6 to 3.9) | 0.145 | 1.2 | (–1.8 to 4.3) | 0.434 |
| Norm-based bodily pain | 3.4b | (1.4–5.5) | 0.001 | 5.0b | (2.8–7.2) | < 0.001 | 5.1b | (2.1–8.0) | 0.001 |
| Norm-based general health | 4.8b | (2.7–6.8) | < 0.001 | 6.9b | (4.6–9.3) | < 0.001 | 7.0b | (4.0–10.0) | < 0.001 |
| Norm-based vitality | 2.5 | (0.4–4.6) | 0.018 | 3.6 | (1.2–6.0) | 0.003 | 3.7 | (0.6–6.8) | 0.019 |
| Norm-based social functioning | 2.3 | (0.1–4.5) | 0.040 | 3.5 | (1.0–6.0) | 0.006 | 3.3 | (0.04–6.6) | 0.047 |
| Norm-based role emotional | 1.8 | (–0.8 to 4.4) | 0.177 | 2.1 | (–0.7 to 5.0) | 0.142 | 2.7 | (–1.1 to 6.5) | 0.168 |
| Norm-based mental health | 1.0b | (–1.0 to 3.1) | 0.312 | 2.2b | (–0.1 to 4.5) | 0.055 | 1.5b | (–1.5 to 4.5) | 0.324 |
| EQ-5D index, mean (SD) | 0.047b | (–0.004 to 0.097) | 0.07 | 0.076b | (0.021–0.131) | 0.007 | 0.068b | (–0.006 to 0.142) | 0.072 |
Intention to treat
There were statistically significant improved REFLUX symptom category scores in favour of surgery across all domains (with the exception of the constipation and swallowing domain, which non-significantly favoured surgery). The bodily pain and general health scores had the largest SF-36 changes (p ≤ 0.001); there were relatively small, non-statistically significant changes in SF-36 role physical, role emotional and mental health scores, although the directions of difference all favoured surgery. The EQ-5Dindex score was also higher in the surgery group, although the difference did not reach conventional levels of statistical significance (p = 0.07).
Per protocol and adjusted treatment received
All the per protocol analyses had larger differences than the corresponding intention to treat analyses, but the differences in SF-36 role physical, role emotional and mental health scores were still not statistically significant. The adjusted treatment received estimates were broadly similar to those derived from the per protocol analyses.
Use of medication
There were large differences between the groups in the numbers of participants requiring any reflux medication at the 12-month follow-up (Table 27). For the intention to treat analysis, the odds ratio of requiring any reflux medication in the surgical group was 0.07 (95% CI 0.04–0.125; p < 0.001) compared with the medical group (absolute difference 38.3% versus 89.6%). The odds ratios for the per protocol analysis and adjusted treatment received were 0.012 (95% CI 0.005–0.029; p < 0.001) and 0.017 (95% CI 0.006–0.048; p < 0.001) respectively. This is related to an absolute difference of 14.4% versus 92.9%. Across the 312 participants (randomised and preference) who received surgery and completed follow-up, 37 (11.9%; 95% CI 8.7–15.9%) required any reflux medication and 21 (6.7%) required PPIs.
At time equivalent to 3 months after surgery
Table 31 shows the health status measures at the time equivalent to 3 months after surgery described by the three analyses (intention to treat, per protocol and adjusted treatment received). In general, the scores were higher at 3 months than at 12 months. The differences in EQ-5D, in particular, were about twice as big at 3 months and were clearly statistically significant at that time.
| Randomised participants | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intention to treat | Per protocol | Adjusted treatment received | |||||||
| Differencea | (95% CI) | p-value | Differencea | (95% CI) | p-value | Differencea | (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Reflux QoL, mean (SD) | 15.0 | (10.5–19.4) | < 0.001 | 17.7 | (12.9–22.5) | < 0.001 | 20.7 | (13.9–27.5) | < 0.001 |
| Reflux symptom score, mean (SD) | |||||||||
| General discomfort symptom score | 19.2 | (14.9–23.6) | < 0.001 | 24.5 | (20.1–28.9) | < 0.001 | 26.0 | (19.6–32.4) | < 0.001 |
| Wind and frequency symptom score | 4.6 | (0.5–8.6) | 0.027 | 2.9 | (–1.6 to 7.4) | 0.202 | 5.1 | (–1.0 to 11.3) | 0.101 |
| Nausea and vomiting symptom score | 8.8 | (5.8–11.9) | < 0.001 | 10.9 | (7.6–14.2) | < 0.001 | 12.4 | (7.7–17.1) | < 0.001 |
| Activity limitation symptom score | 7.1 | (3.2–11.0) | < 0.001 | 9.2 | (4.9–13.5) | < 0.001 | 9.1 | (3.2–15.1) | 0.003 |
| Constipation and swallowing symptom score | 2.0 | (–1.9 to 6.0) | 0.318 | 1.3 | (–2.9 to 5.6) | 0.536 | 2.1 | (–3.9 to 8.2) | 0.486 |
| SF-36 scores, mean (SD) | |||||||||
| Norm-based physical functioning | 3.1b | (1.3–4.9) | 0.001 | 3.7b | (1.6–5.8) | < 0.001 | 4.4b | (1.5–7.2) | 0.003 |
| Norm-based role physical | 2.7 | (0.5–4.9) | 0.018 | 2.6 | (0.1–5.0) | 0.043 | 3.4 | (–0.04 to 6.8) | 0.053 |
| Norm-based bodily pain | 3.2b | (1.1–5.3) | 0.003 | 4.3b | (2.0–6.7) | < 0.001 | 4.1b | (0.9–7.2) | 0.012 |
| Norm-based general health | 5.8b | (3.8–7.8) | < 0.001 | 7.9b | (5.6–10.1) | < 0.001 | 7.8b | (4.8–10.7) | < 0.001 |
| Norm-based vitality | 3.0 | (0.9–5.1) | 0.006 | 3.9 | (1.5–6.2) | 0.001 | 3.9 | (0.7–7.1) | 0.018 |
| Norm-based social functioning | 3.6 | (1.3–5.8) | 0.002 | 4.6 | (2.1–7.1) | < 0.001 | 4.6 | (1.1–8.1) | 0.010 |
| Norm-based role emotional | 3.3 | (0.7–5.8) | 0.012 | 3.7 | (0.9–6.6) | 0.010 | 4.1 | (0.2–8.0) | 0.042 |
| Norm-based mental health | 4.2b | (2.1–6.2) | < 0.001 | 5.5b | (3.3–7.7) | < 0.001 | 5.5b | (2.4–8.6) | 0.001 |
| EQ-5D index, mean (SD) | 0.099b | (0.048– 0.150) | < 0.001 | 0.130b | (0.074– 0.185) | < 0.001 | 0.129b | (0.051– 0.207) | 0.001 |
Subgroup analyses
Removal of data from the single largest clinical centre (Aberdeen)
No formal exploration of centre effects was undertaken because of the small numbers of participants recruited in many of the clinical centres. However, a sensitivity analysis removing the data from the Aberdeen centre, the centre where the largest number of participants were recruited, did not significantly change the conclusions (adjusted difference in REFLUX score +15.4; 95% CI 10.2–20.6).
Partial versus total wrap procedure
In an observational analysis there was no evidence of a difference between a total wrap procedure and a partial wrap procedure. The difference in the REFLUX QoL score between these procedures at the time equivalent to 12 months post surgery was –1.3 (95% CI –7.9 to 5.2; p = 0.687).
Discussion
The trial provides strong evidence of improvement in GORD symptoms following laparoscopic fundoplication as judged by the REFLUX quality of life score and its constituent domains. There were large differences between the randomised groups in these respects at 3 months post surgery, which were broadly sustained 9 months later. Also, scores in the preference surgical group were somewhat higher than those in the preference medical group despite starting from much lower baseline levels. The estimated sizes of differences varied depending on the assumptions being made. However, significant differences were observed even in the most conservative of the three main analyses – that based on intention to treat – where about one-third of those randomised to surgery did not actually receive it. Similar differences were also seen in most of the other measures of health status. There is, however, some evidence of a narrowing of the differences when the 3-month and 12-month follow-up results are compared. This was most marked for the EQ-5D, in which the surgical values had decreased and the medical values had increased somewhat (most easily seen in Figure 15).
We anticipated that this would be a difficult trial to deliver and so it proved. Trials comparing strikingly different interventions (such as surgery versus medical management) are often a challenge to recruit to. The explanation of such a trial needs to encompass a range of considerations and it is not unusual for some people, both clinicians and patients, to have strong views on the alternative procedures. As expected, many potential participants did have preferences for one approach or the other, and it was partly because we anticipated this that we included preference groups alongside the randomised core of the study. By enrolling surgeon/gastroenterologist pairs who were uncertain about the place of minimal access surgery in this context, we aimed to avoid clinician preferences. However, the differential recruitment to the preference groups in the clinical centres, in part reflecting which clinician actually first saw a potential participant, showed that there were differences in clinical perspective. This became a problem within the randomised comparison on the (relatively few) occasions in which a patient recruited by one clinician was deemed unsuitable for surgery by another clinician in the same centre.
To make the study more attractive to potential participants, those allocated medical management underwent a review of their medication to ‘optimise this’, rather than just carrying on with their existing regimen. This may be the reason why the types of PPI taken at follow-up differed from those at the time of trial entry (predominantly lansoprazole at entry, but omeprazole or lansoprazole equally at follow-up).
People suitable for the trial were not easy to identify. Most patients on long-term PPI treatment are managed in general practice, often through a repeat prescription system. We used a combination of three approaches: retrospective case note review to identify potentially eligible patients who had been seen in a participating hospital; prospectively, especially through endoscopy clinics; and (in selected centres) advertisements to the general public. All potentially eligible people had to be assessed clinically and they were only then formally approached about the trial. This was extra work over and above normal clinical duties, often through specially established monthly clinics. As described in Chapter 2, the numbers enrolled in individual centres tended to be small, reflecting all of these constraints. In the event, we found that those who agreed to join the randomised trial had characteristics mid-way between those of the two preference groups.
What we did not predict were the long waiting times for surgery in many centres. This was due to ambiguity about the responsibilities of participating hospitals in terms of the extra treatment costs of surgery. The intention had been that surgical slots would be pre-booked for the trial and that participants randomised to surgery would take the next available of these slots. In the event, emergencies such as cancer cases were given precedence, sometimes with repeated postponements of REFLUX trial patients. Anecdotally, long delays were an important factor in the decision of some of those participants allocated surgery ultimately not to have surgery. Delays became intractable in a few centres to the extent that special subvention funds were eventually found to allow the operations to be performed without any impact on normal clinical services. The availability of such funds to all centres from the start of the trial would almost certainly have overcome much of the waiting list problem.
In retrospect, given the long waits for surgery, it might have been better following enrolment to delay random allocation until there was a definite operation appointment. However, the likely impact would have been significant uncertainty amongst those enrolled about what they had agreed to, and greatly reduced numbers actually randomised (with some operations still postponed).
The standard rule in most trials is to time follow-up from randomisation. This was not appropriate in this trial because of the variable time between randomisation and surgery, exacerbated by the waiting list problem. The protocol specified follow-up at times equivalent to 3 and 12 months after surgery. It was important to have follow-up in the medical groups at equivalent times. We arranged this by pairing surgical and medical participants such that follow-up was linked and at (about) the same time after randomisation. The success of this manoeuvre can be assessed in Tables 23 and 26.
The large number of participants who did not get the management that they had been allocated to did have an impact on the results. For example, only 20% (10/50) of those allocated surgery who were taking reflux-related drugs at the 3-month follow-up had actually had surgery. As discussed earlier in this chapter, we have gone to some lengths to explore the likely impact of this non-adherence to the trial allocation. One way is through per protocol analyses limited to those randomised who received their allocated management. The second way is through an adjusted approach as a way of attempting to circumvent the likely selection bias of per protocol analyses. In this study the direction of effects was so clear, irrespective of the way that the analysis was performed, that the main issue became the size of effects. These did vary substantially (see, for example, Table 29) and this could be very important when policy decisions are being made, for example in the context of an economic evaluation. The approach that we took to address this in our economic analyses is described in the next two chapters.
One reason why we elected to have parallel non-randomised preference groups was to get more experience of the two forms of management. This particularly applied to surgery. Complications amongst the 319 participants who actually had fundoplication were rare (Table 22). Two operations were converted to open procedures, there were six visceral injuries and two pneumothoraces, and there were three admissions to a high dependency unit with no admissions to an intensive care unit. Patients stayed in hospital for a median of only 2 days. Three had reoperations and three had operations related to oesophageal stenosis.
As discussed in the following two chapters, an important measure of outcome is the proportion of patients continuing to take reflux-related drugs, especially after surgery. Rates did go up somewhat between the 3-month and 12-month assessment. Our rate of 11–14% at 12 months is higher than that in some other studies although estimates do vary both above and below this. Funding for this project was for follow-up to the time equivalent to 12 months after surgery. We have, however, instituted further annual follow-ups using similar questionnaires to those used at 3 and 12 months. Further follow-up will be important for assessing whether the benefits of surgery are sustained or whether differences in health status further narrow over time. We expect to report this after 5 years of follow-up are available for all participants.
The next two chapters on the economic evaluation reflect the position that we are in currently, having only 1 year of follow-up data, while recognising that long-term lifetime effects are likely to determine whether laparoscopic fundoplication is cost-effective. First, the within-trial cost-effectiveness analyses reported in Chapter 7 are developed within an economic framework. Then, an economic model is used to explore and extrapolate cost-effectiveness over a longer-term perspective.
Chapter 7 Within-trial cost-effectiveness results
Introduction
This chapter presents the within-trial cost-effectiveness analysis comparing laparoscopic fundoplication with medical management. Mean costs and health outcomes per patient are evaluated over 1 year using data from the REFLUX trial. The analysis is conducted from the perspective of the health and social care services. Costs are at 2006 prices and include the use of reflux-related health-care resources. Costs and outcomes are not discounted for this 1-year analysis.
Methods
Patients included
We compare the treatment strategies of immediate laparoscopic fundoplication with continued medical management on an intention to treat basis. The analysis includes data from 318 REFLUX patients (154 in the surgery group and 164 in the medical management group) who were randomised to a treatment strategy and who were followed up for a time equivalent to at least 1 year after surgery. We do not model the wait for surgery, that is, we model a best practice situation.
Because, as described in Chapter 6, the management of a high proportion of patients did not comply with their randomised treatment allocation, we also conducted a secondary analysis of the use of resources, costs and HRQoL for patients who received randomised per protocol treatment. However, it should be noted that these data are potentially biased, as described in Chapter 6.
Resource use
The use of the following health-care resources was collected retrospectively from clinical questionnaires for patients receiving randomised surgery: the use of endoscopy, pH monitoring and manometry prior to surgery; the length of time in surgery; and length of stay in wards, high dependency units and intensive therapy units post surgery. The trial also recorded whether patients had revision of surgery or non-randomised surgery, but did not collect detailed use of health-care resources or length of stay for these patients.
The use of anti-reflux medication taken in the previous 2 weeks was recorded at baseline and at each follow-up by questionnaires completed by the patients. There was a small amount of missing data for use of medication, which was handled as follows. If the patient confirmed that they were using an anti-reflux medication but did not report the dose, the median dose for other patients using that medication was imputed. All patients were assumed to be on medication at baseline as this was an inclusion criterion for entry into the REFLUX trial. If no medication was declared the missing data were imputed as the mean cost per day. We assume that all patients randomised to surgery undergo their procedure immediately and discontinue medication at that point unless they declare use of medication at a subsequent follow-up. The total cost per patient of anti-reflux medication was calculated using the trapezium rule using linear interpolation between follow-up points. 98,99
The REFLUX trial recorded use of the following health services for the previous 3 months at first follow-up (at a time equivalent to 3 months after surgery) and second follow-up (at a time equivalent to 12 months after surgery): visits to and from general practitioners; visits to outpatient clinics; and admissions to hospital during follow-up. These questionnaires did not record use of health services between the third month and the ninth month. To capture these data a postal survey of patients was undertaken in May 2006 asking patients about the use of health services at any time during the first year. The cost of use of hospital and community health services for each patient during the first year was estimated as the greater of the sum of the first and second follow-ups compared with the use of resources reported in the postal survey.
Unit costs
Costs per patient were calculated by multiplying use of health-care resources as collected in the trial by unit costs taken from surveys and published data sources (Table 32).
| Medical (n = 164) | Surgical (n = 154) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit cost (£) | Sourcea | Unit of measure | Any use (%) | Mean use | Mean cost (£) | SE (£) | Any use (%) | Mean use | Mean cost (£) | SE (£) | |
| Randomised surgery | |||||||||||
| Endoscopy | 172 | 1 | Tests | 59 | 0.59 | 102 | 7 | ||||
| pH tests | 64 | 1 | Tests | 47 | 0.47 | 30 | 3 | ||||
| Manometry | 61 | 1 | Tests | 45 | 0.45 | 27 | 2 | ||||
| Operation time | 4 | 1 | Minutes | 68 | 77.34 | 284 | 18 | ||||
| Consumables | 825 | 1 | 558 | 31 | |||||||
| Ward | 213 | 2 | Days | 68 | 1.91 | 407 | 22 | ||||
| ICU | 1470 | 2 | Days | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| HDU | 628 | 2 | Days | 2 | 0.03 | 20 | 20 | ||||
| Total surgery | 1428 | 74 | |||||||||
| Visit to GP | 24 | 3 | Visits | 45 | 1.21 | 29 | 4 | 44 | 1.18 | 28 | 4 |
| Visit from GP | 69 | 3 | Visits | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 |
| Outpatient | 142 | 2 | Visits | 15 | 0.30 | 43 | 9 | 35 | 0.46 | 65 | 9 |
| Day case | 460 | 2 | Admit | 12 | 0.17 | 79 | 19 | 32 | 0.38 | 173 | 24 |
| Inpatient | 1378 | 2 | Admit | 2 | 0.02 | 34 | 17 | 3 | 0.03 | 36 | 18 |
| Non-randomised surgery | 2596 | 2 | Admit | 5 | 0.05 | 142 | 46 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| Visit costs | 328 | 63 | 304 | 38 | |||||||
| Medication costs | 4 | 179 | 10 | 55 | 7 | ||||||
| Total costs | 506 | 63 | 1786 | 88 | |||||||
The use and costs of consumable items and laparoscopic surgical equipment was collected by a survey in 2003 of five centres participating in the trial, described in detail in Chapter 3 of this report. 100 This survey also estimated the mean cost per hour in surgical theatre in each centre, based on the use of staff in each centre and national salary scales. 64 The mean unit costs estimated by this survey were then applied to all centres in the within-trial cost analysis, updated for inflation. 64
Quality-adjusted life-years
The outcome used in the cost-effectiveness analysis was the difference in mean QALYs between the treatment groups. HRQoL was assessed at baseline and at each follow-up using the EQ-5D instrument. QALYs for each patient over the year of follow-up were calculated as the area under the curve using the trapezium rule, that is, assuming linear interpolation between follow-up points. The difference in mean QALYs per patient between the treatment groups was estimated using ordinary least squares regression, adjusting for baseline differences in EQ-5D between individuals. Bootstrap methods (resampling with replacement)101 were used to estimate confidence intervals for the differences in mean costs and QALYs and the correlation between them. Uncertainty regarding the treatment decision was represented using cost-effectiveness acceptability curves. 74 These show the proportion of samples from the data in which each therapy is the more cost-effective across a range of alternative threshold values that the health-care system may be willing to pay for a QALY. 102
Results
Use of health-care resources
Table 32 shows the average use of reflux-related health-care resources in the two groups at 1 year according to intention to treat. Nine patients randomised to medical management underwent laparoscopic surgery and 50 patients randomised to the surgical group did not receive surgery. Although the intention to treat analysis is unbiased, it is not very informative for describing the use of health-care resources, which depend on the treatment actually received.
Table 33 shows the average use of health-care resources according to the randomised per protocol analysis. Patients randomised to and who received laparoscopic fundoplication spent an average of 115 minutes in theatre and 2.4 days in wards postoperatively. Only one patient out of 104 required the use of a high dependency unit. During the year of follow-up similar numbers of patients in each group required use of general practitioner services but patients who had surgery tended to require more outpatient visits and day-case admissions. At the 12-month follow-up, 14 out of 104 (13%) in the surgical arm (who had surgery) had used anti-reflux medications in the past 2 weeks compared with 144 out of 155 (93%) in the medical arm who did not have surgery. A proportion of those not reporting use of prescription medications, however, were missing data, were using over-the-counter pharmaceuticals, had stopped temporarily or had stopped for non-reflux-related reasons such as pregnancy. No patients randomised to surgery required revision of the fundoplication procedure during the year.
| Medical (n = 155) | Surgery (n = 104) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit cost (£) | Sourcea | Unit of measure | Any use (%) | Mean use | Mean cost (£) | SE (£) | Any use (%) | Mean use | Mean cost (£) | SE (£) | |
| Endoscopy | 172 | 1 | Tests | 88 | 0.88 | 151 | 6 | ||||
| pH tests | 64 | 1 | Tests | 70 | 0.70 | 45 | 3 | ||||
| Manometry | 61 | 1 | Tests | 66 | 0.66 | 40 | 3 | ||||
| Operation time | 4 | 1 | Minutes | 100 | 114.50 | 420 | 14 | ||||
| Consumables | 825 | 1 | 825 | 0 | |||||||
| Ward | 213 | 2 | Days | 100 | 2.34 | 500 | 28 | ||||
| ICU | 1470 | 2 | Days | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| HDU | 628 | 2 | Days | 1 | 0.05 | 30 | 29 | ||||
| Total surgery | 2012 | 41 | |||||||||
| Visit to GP | 24 | 3 | Visits | 44 | 1.16 | 28 | 5 | 44 | 1.14 | 27 | 5 |
| Visit from GP | 69 | 3 | Visits | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 |
| Outpatient | 142 | 2 | Visits | 14 | 0.30 | 43 | 7 | 43 | 0.54 | 76 | 9 |
| Day case | 460 | 2 | Admit | 10 | 0.14 | 65 | 8 | 42 | 0.47 | 217 | 15 |
| Inpatient | 1378 | 2 | Admit | 3 | 0.03 | 36 | 6 | 4 | 0.04 | 53 | 7 |
| Visit costs | 173 | 38 | 375 | 49 | |||||||
| Medication costs | 4 | 183 | 10 | 18 | 5 | ||||||
| Total costs | 356 | 40 | 2405 | 69 | |||||||
Costs
Total mean costs per patient over the year on an intention to treat basis were £1786 for patients randomised to surgery and £506 for patients randomised to medical management (Table 32), a difference of £1280 (95% CI £1054–£1468) (Table 34). The mean cost per patient of the surgical procedure and hospital admission for those randomised to and who underwent surgery was £2012 (SE £41) (Table 33).
| Mean (95% CI) | |
|---|---|
| Difference in mean costs (£) | 1280 (1054–1468) |
| Difference in mean QALYs | 0.066 (0.026–0.107) |
| ICER (£/QALY) | 19,288 |
| Probability surgery is cost-effective when threshold = £20,000 | 46% |
| Probability surgery is cost-effective when threshold = £30,000 | 86% |
Quality-adjusted life-years
The HRQoL of patients, measured using the EQ-5D, tended to improve on average in the surgical group over the year of the analysis but not in the medical management group (Tables 35 and 36). After adjusting for baseline differences in HRQoL, patients gained 0.066 more QALYs (95% CI 0.026–0.107) during the trial period compared with medical management using an intention to treat analysis.
| Medical (n = 164) | Surgical (n = 154) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SE | Mean | SE | |
| Baseline EQ-5D index | 0.723 | 0.020 | 0.721 | 0.020 |
| First follow-up EQ-5D | 0.693 | 0.024 | 0.781 | 0.020 |
| Second follow-up EQ-5D | 0.709 | 0.021 | 0.754 | 0.020 |
| Unadjusted QALY | 0.704 | 0.020 | 0.773 | 0.017 |
| QALY adjusted for baseline differences in EQ-5D | 0.703 | 0.014 | 0.770 | 0.015 |
| Medical (n = 155) | Surgical (n = 104) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SE | Mean | SE | |
| Baseline EQ-5D index | 0.736 | 0.020 | 0.722 | 0.023 |
| First follow-up EQ-5D | 0.700 | 0.024 | 0.800 | 0.024 |
| Second follow-up EQ-5D | 0.710 | 0.022 | 0.777 | 0.023 |
| Unadjusted QALY | 0.710 | 0.019 | 0.786 | 0.020 |
| QALY adjusted for baseline differences in EQ-5D | 0.706 | 0.014 | 0.793 | 0.017 |
Cost-effectiveness
The estimated mean ICER is around £19,000 per QALY using intention to treat (Table 34). Bootstrap simulations were undertaken to estimate the uncertainty around the treatment decision. At a cost-effectiveness threshold ICER of £20,000 per QALY, surgery has a probability of 46% of being cost-effective, and at a threshold of £30,000 per QALY surgery is 86% likely to be cost-effective (Figure 16). This indicates that there is considerable uncertainty about whether surgery is cost-effective using the REFLUX trial data.
FIGURE 16.
Cost-effectiveness plane for laparoscopic surgery versus medical management using an intention to treat analysis. This figure shows the difference in mean cost and difference in mean quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) per patient in 1000 bootstrap simulations of the data.
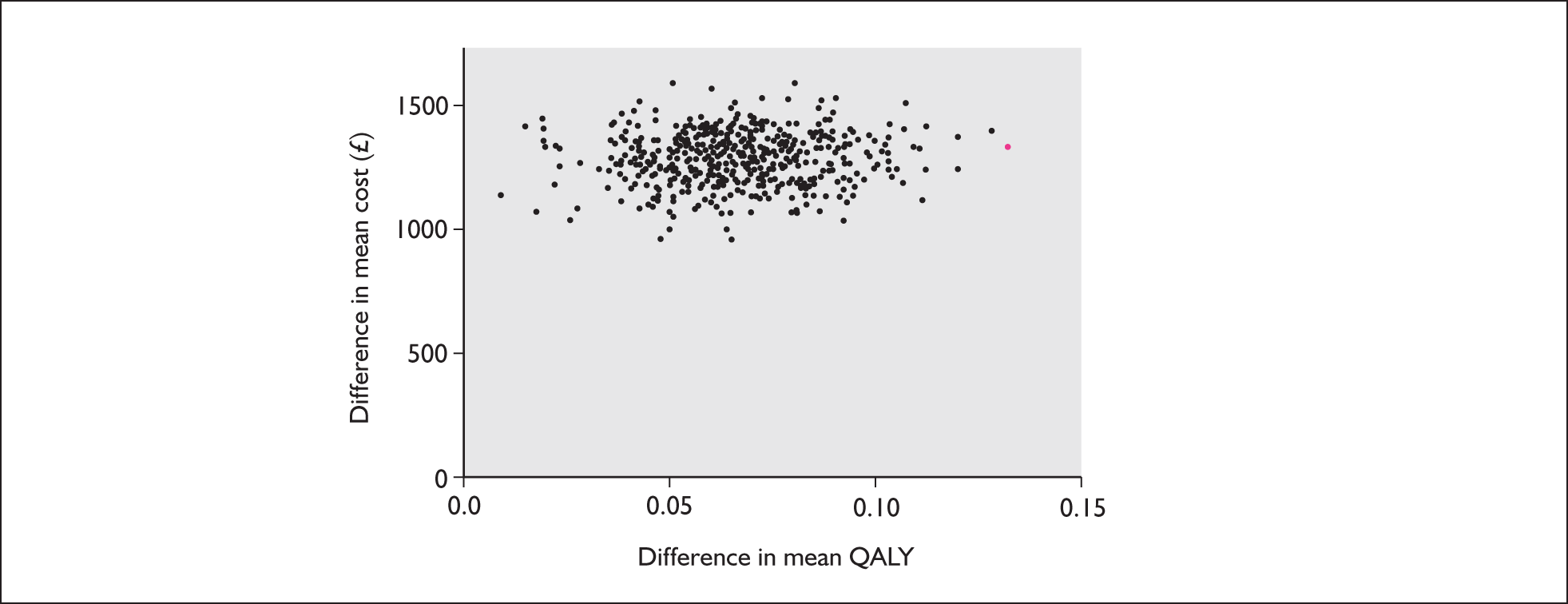
Sensitivity analyses
Whether a hospital visit was classified as a day-case admission or an outpatient visit could differ between providers even if similar procedures were undertaken. As a sensitivity analysis, if all of the visits classified as day-case admissions in the trial incurred the average cost of an outpatient visit, this would reduce the incremental mean cost by £90, from £1280 to £1190. If all visits incurred the average cost of a day-case admission, this would increase the incremental cost by £76 to £1356.
A cost-effectiveness analysis was also undertaken for patients who received randomised treatment per protocol and who were followed up for 1 year (Table 37). This estimated a greater mean difference in health benefit than the intention to treat analysis (0.088 QALYs) but a greater difference in mean cost per patient (£2049), and found surgery to be slightly less cost-effective with an ICER of £23,284.
| Mean (95% CI) | |
|---|---|
| Difference in mean costs (£) | 2049 (1907–2198) |
| Difference in mean QALYs | 0.088 (0.046–0.130) |
| ICER (£/QALY) | 23,284 |
| Probability surgery is cost-effective when threshold = £20,000 | 19% |
| Probability surgery is cost-effective when threshold = £30,000 | 80% |
| ICER, incremental cost-effectiveness ratio; QALY, quality-adjusted life-years. | |
Further sensitivity analyses were undertaken and are described in the cost-effectiveness modelling chapter (Chapter 8).
Discussion
Cost-effectiveness analysis is intended to inform two separate decisions. First, which strategy (medical management or laparoscopic fundoplication) is most cost-effective for the management of patients with reflux who are stable on medication from the perspective of the NHS and, second, what value there is in acquiring further information about these strategies.
This chapter presented the expected differences in costs and health outcomes between laparoscopic surgery and medical management over 1 year using the REFLUX trial data only. Surgery was on average more effective (in terms of QALYs gained over 1 year) but more costly. The ICER of £19,000 suggests that laparoscopic fundoplication might be cost-effective given that the threshold value in England and Wales is between £20,000 and £30,000. 102 However, there is still considerable uncertainty about this result (probability that surgery is cost-effective between 46% and 86%). The main limitation, however, is that the within-trial analysis ignores events, costs and health benefits that accrue after 1 year. The benefits of surgery are likely to be experienced by patients over the longer term,104 and the costs of medical management, even with widespread use of generics, are considerable when continued over a patient’s lifetime. Conversely, although no revisions of laparoscopic fundoplication were observed in the randomised surgical group over 1 year in this trial, the procedure may fail in the longer term. 105
More generally, new trials have to be placed in the context of existing evidence. Other randomised trials, and observational studies, have evaluated these strategies in the United Kingdom and elsewhere. A modelling framework can be used to extrapolate events, costs and health outcomes over a longer time horizon and to synthesise data from different sources to evaluate cost-effectiveness. 106 A modelling framework can also inform decisions about whether, and with what purpose, further research is needed. Value of information analysis can help to identify which variables contribute most to the overall uncertainty in the treatment decision and to quantify the benefits that would arise from having further information about these parameters. 107 To address these questions, a revised version of the decision model described in Chapter 3, updated with the evidence from the first year of the REFLUX trial, is described in the next chapter of this report.
Chapter 8 Cost-effectiveness analysis
Introduction
The REFLUX trial compared a strategy of laparoscopic surgery with one of continued medical management for patients with reasonable symptom control on anti-reflux medications. Data are now available from the clinical trial for at least 1 year after surgery for all patients. However, as discussed in the preceding chapter, as reflux is a chronic disease, an analysis that considers only events, costs and health benefits accruing over 1 year is too restricted. To accurately determine cost-effectiveness, and the value of conducting further research, a modelling approach is required that extrapolates costs and health benefits over an appropriate time horizon and allows the synthesis of evidence from different sources. This chapter describes a long-term decision-analytic model including evidence from the REFLUX trial and other sources.
The model presented here differs somewhat from the preliminary model described in Chapter 6. The preliminary model required evidence of the underlying disease process, that is, knowledge of whether treatment failure was temporary or permanent. Further treatment, such as dose adjustment, withdrawal of medication or revision of surgery, was then carried out conditional on the type of failure that occurred. However, in the reports from clinical trials, including the REFLUX trial, the follow-up points are infrequent and/or the underlying disease is rarely observed or described consistently. On the other hand, the treatments administered during follow-up are usually well recorded in these reports. Therefore, the model has been revised to define treatment failure in terms of change in treatment rather than return of symptoms.
Methods
Model structure
In the model patients follow a strategy of either immediate laparoscopic surgery or continuation of medical management (without an option of surgery following failure of medical management). In principle, immediate open surgery is feasible in this patient group but it is not considered here because it is widely considered to have been superseded by laparoscopic surgery, although conversion to open surgery is an option when laparoscopic surgery fails. Patients are assumed to be male and aged 45 when entering the model, which is the median age and commoner gender of patients in the REFLUX trial. Costs and health benefits are discounted at 3.5% per year and the price year is 2006.
The model structure is represented by Figure 17. As mentioned above, we define treatment failure following surgery as a change of treatment. Two options are considered for patients who fail surgery: patients may return to the use of anti-reflux medication or they may undergo a revision of surgery.
FIGURE 17.
Model structure diagram.
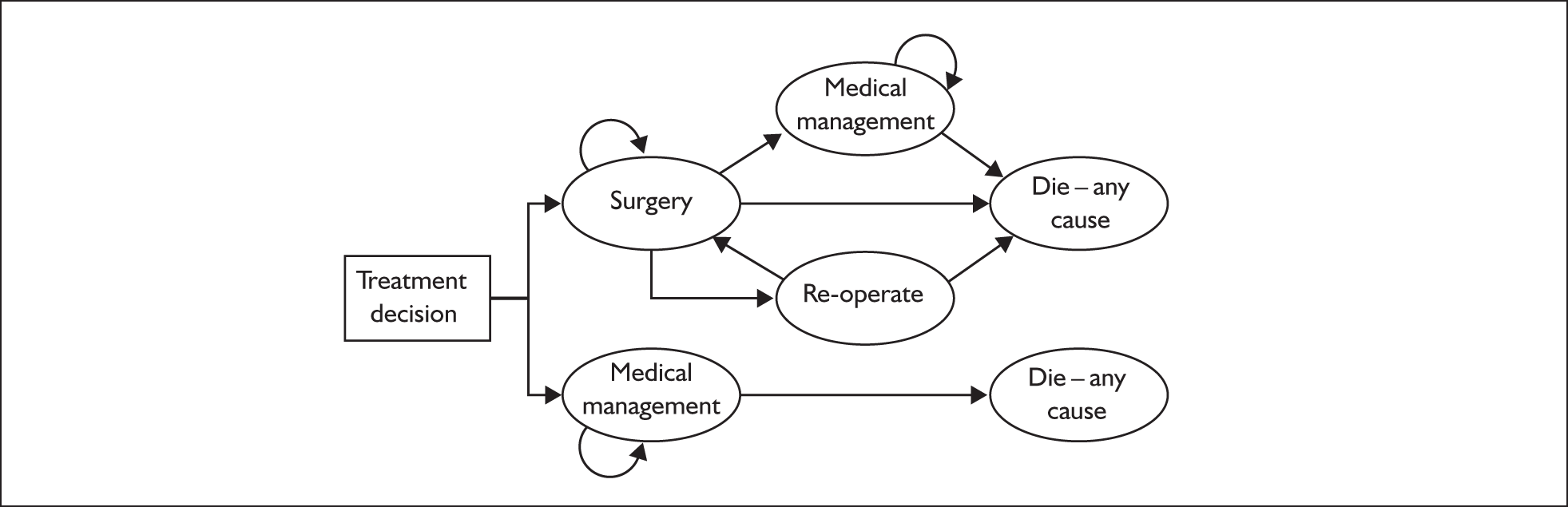
It is assumed that patients randomised to receive surgery who are found to be using medication at the end of a clinical trial are doing so to control reflux symptoms or symptoms related to surgery. It is further assumed that such patients will incur costs of medication indefinitely.
Although, in practice, patients who fail surgery may recommence anti-reflux drugs followed by revision of surgery, data on sequences of therapies were not available and so these events are treated as mutually exclusive competing risks in the model. Patients are assumed to have the same prognosis following revision as surgical patients who were not reoperated on.
To estimate the rates of return to medical management and revision of surgery, all of the available studies, whether randomised or not, are treated as observational data. The rates of failures could simply be estimated as the total number of events divided by the total patient years of exposure (Tables 38 and 39), which would estimate the rate of return to medical management as 4.8 per 100 patient-years. This estimate ignores any between-study heterogeneity, which might arise from patient selection, definition of outcomes, study design, surgical technique or other sources. To assess the assumption of homogeneity we also estimated the rate using a random effects Poisson regression using the statistical package WinBUGS® (see Appendix 11 for code). 113 We also explored whether any observed factors (length of follow-up, study design) might explain some of the heterogeneity, but these variables were not found to be statistically significant and were omitted from the final model.
| Study | Number of subjects | Years of follow-up | Exposure (person-years) | Number of failures | Rate of failure per person-year | Proportion of failures at end of study (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mahon et al., 2005108 | 109 | 1 | 109 | 2 | 0.018 | 1.8 |
| Booth et al., 200242 | 179 | 4 | 716 | 19 | 0.027 | 10.6 |
| Bammer et al., 200157 | 171 | 6.3 | 1094 | 24 | 0.022 | 14.0 |
| Contini et al., 200238 | 103 | 1 | 103 | 5 | 0.049 | 4.9 |
| Pessaux et al., 200245 | 1470 | 3 | 4410 | 60 | 0.014 | 4.1 |
| Papasaras et al., 2005109 | 289 | 2 | 578 | 150 | 0.260 | 51.9 |
| Granderath et al., 2002110 | 27 | 4 | 108 | 2 | 0.019 | 7.4 |
| Dassinger et al., 2004111 | 52 | 5 | 260 | 11 | 0.042 | 21.2 |
| Bloomston et al., 2003112 | 100 | 1 | 100 | 19 | 0.190 | 19.0 |
| Bloomston et al., 2003112 | 84 | 4 | 336 | 31 | 0.092 | 36.9 |
| Vidal et al., 2006105 | 124 | 4.3 | 533.2 | 10 | 0.019 | 8.1 |
| Madan and Minocha, 2006104 | 100 | 3 | 300 | 80 | 0.267 | 80.0 |
| Laine et al., 199767 | 18 | 1 | 18 | 0 | 0.000 | 0.0 |
| Reflux trial, 2006 | 104 | 1 | 104 | 14 | 0.135 | 13.5 |
| All studies | 8769 | 427 | 0.049 |
| Study | Number of subjects | Exposure (years) | Number of failures | Rate of failure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mahon et al., 2005108 | 50 | 50 | 2 | 0.040 |
| Booth et al., 200242 | 179 | 716 | 11 | 0.015 |
| Bammer et al., 200157 | 171 | 1094 | 5 | 0.005 |
| Contini et al., 200238 | 103 | 103 | 0 | 0.000 |
| Pessaux et al., 200245 | 1470 | 4410 | 35 | 0.008 |
| Laine et al., 199767 | 18 | 18 | 0 | 0.000 |
| Reflux trial, 2006 | 104 | 104 | 0 | 0.000 |
| All studies | 6495 | 53 | 0.008 |
A state of treatment failure for patients following medical management is not defined because there is no feasible alternative treatment, that is, in this model (unlike the preliminary model), surgery is not an option for patients following medical management. The estimates of mean HRQoL after successful surgery and after medical management, and the standard errors, are those observed in the randomised REFLUX trial at 1 year as there are no other randomised trials comparing surgery with medication that have used a preference-based utility instrument (see Chapter 6 for details of HRQoL data collected in the trial). HRQoL following treatment failure is estimated by the mean EQ-5D of all surgical patients (preference or randomised to surgery) who returned to medical management or required revision of surgery by 1 year. The base-case assumption in the model is that, although HRQoL decreases with age at the same rate as that in the age- and sex-matched general population, proportionate differences in HRQoL between health states are maintained over time.
To account for the decline in HRQoL with age, the HRQoL for each outcome observed at the end of the trial was compared with the average HRQoL of the general population aged from 45 to 55 years. 70 It was assumed that this proportionate decrement of HRQoL was constant as the cohort aged (Table 40). The age- and sex-stratified rate of death was taken from life tables,115 assuming that this patient group has a similar life expectancy to the UK general population after surgery. There is a small risk of operative mortality, estimated in a literature review as 4 deaths in 4000 procedures (see Chapter 3).
| Parameter | Mean | SE | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| HRQoL following medical management | 0.711 | 0.018 | Reflux trial EQ-5D in randomised medical arm at 1 year |
| Additional HRQoL following successful laparoscopic surgery compared with medical management | 0.071 | 0.028 | Reflux trial EQ-5D in randomised surgery arm at 1 year (off drugs) |
| HRQoL following unsuccessful laparoscopic surgery (on medication) | 0.686 | 0.048 | Reflux trial EQ-5D in all patients who failed surgery at 1 year |
| Average HRQoL during year if undergoing re-intervention | 0.686 | 0.048 | As for unsuccessful surgery |
| HRQoL for general population aged 45–55: men; women | 0.84; 0.85 | Kind et al., 199971 | |
| HRQoL for general population aged 55–65: men; women | 0.78; 0.81 | Kind et al.,199971 | |
| HRQoL for general population aged 65–75: men; women | 0.78; 0.78 | Kind et al., 199971 | |
| HRQoL for general population aged 75+: men; women | 0.75; 0.71 | Kind et al., 199971 | |
| Prevalence of GORD in population aged 18–60 | 0.0045 | McDougall et al., 1996;30 Trimble et al., 1995114 |
During the first year of follow-up, 35% of patients require an outpatient visit and 35% a day-case or hospital admission following surgery compared with 15% who require an outpatient visit and 14% a day-case or hospital admission following medical management (see Table 32; Chapter 7). The Nordic GORD study62 found that only a small proportion of patients required endoscopy after 12 months in either group, and here it is assumed that no further hospital admissions or outpatient visits are needed after 1 year other than revisions of surgery.
The model time horizon is a patient’s lifetime. However, there are significant sources of uncertainty surrounding several model parameters given that the main source of data in the model, the REFLUX trial, has reported only 1 year of follow-up. To provide a point of reference, the model analysis starts from a set of assumptions that are similar to those used in the within-trial cost-effectiveness analysis presented in Chapter 7, which assumed that there were no differences in cost or health benefits beyond 1 year. This is unlikely to be the case and so a series of scenarios that relax these assumptions is explored, described in Box 1.
| Scenario number | Assumption | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of cost of medication | Duration of relative health benefit of surgery | Annual rate of conversion from surgery to medical | Annual rate of reoperation | |
| 11 (within-trial analysis) | 1 year | 1 year | 13% convert year 1, 0.0% thereafter | 0.0% |
| 15 (temporary QoL advantage) | Lifetime | 5 years | 13% per year up to year 2, 4.9% thereafter | 0.0% year 1, 0.8% thereafter |
| 16 (low rate of surgical failure) | Lifetime | Lifetime | 4.9% | 0.8% |
| 17 (base-case) | Lifetime | Lifetime | 13% per year up to year 2, 4.9% thereafter | 0.0% year 1, 0.8% thereafter |
| 18 (very high rate of surgical failure) | Lifetime | Lifetime | 13% per year | 0.8% |
| 19 (high rate of surgical failure) | Lifetime | Lifetime | 8% per year | 0.8% |
One way of proceeding with this analysis might be to vary the time horizon over which the model is run, from 1 year up to a lifetime, in a series of scenarios; however, this would be naïve. Reflux is a chronic disease and, therefore, the only reasonable analysis is over a lifetime. The role of scenario analysis is to explore different assumptions about HRQoL, costs and clinical events over this time horizon. The sources for the alternative assumptions are presented in Chapter 3.
Analysis
The model was implemented in R, a programming language,116 as a discrete-time Markov model with a cycle length of 1 year. The model outputs were mean costs and QALYs in each treatment cohort. A probabilistic sensitivity analysis was used to represent the uncertainties in the model inputs. 117 Gamma distributions were assigned to the decrements in utility compared with perfect health and the costs used in the model. Log-normal distributions were assigned to the rates of surgical failure. Values were randomly sampled from these distributions in 1000 Monte Carlo simulations and these were used as inputs to the model to give 1000 calculations of costs and QALYs for the cohort. The ICER was calculated as the ratio of the difference in expected costs to the difference in expected QALYs. The overall uncertainty in the treatment decision arising from uncertainty in the model inputs is represented by the proportion of iterations in which laparoscopic surgery is cost-effective, given a threshold value for the ICER.
Results
Base-case analysis
The base-case analysis assumed that the relative treatment benefit from surgery endured for a lifetime, provided patients did not experience treatment failure. A summary of the assumptions used in the base-case analysis, and in alternative scenarios, is shown in Box 1.
Under base-case assumptions, surgery had an additional mean cost of £847 and additional mean QALYs of 0.37 over the lifetime of the patients (Table 41), which generates an incremental cost per additional QALY of about £3000. Uncertainty arising from imprecision of estimates of mean parameter values using base-case assumptions was characterised using a probabilistic sensitivity analysis. This showed that, at a threshold ICER of £20,000, surgery was about 74% likely to be cost-effective. However, this underestimates the uncertainty because the base-case model assumes the same imprecision about mean values of parameters for all years in the model, whereas the data on HRQoL is available only for the first year.
| Scenario | Cost M (£) | Cost S (£) | Cost difference (£) | QALY M | QALY S | QALY difference | ICER (£/QALY) | p (20k) | p (30k) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 (within-trial analysis) | 275 | 2302 | 2027 | 12.48 | 12.526 | 0.046 | 44,065 | 0.02 | 0.41 |
| 15 (temporary QoL advantage) | 3933 | 4780 | 847 | 12.48 | 12.51 | 0.03 | 28,233 | 0.53 | 0.56 |
| 16 (low rate of surgical failure) | 3933 | 4433 | 500 | 12.48 | 13.039 | 0.559 | 894 | 0.87 | 0.87 |
| 17 (base-case) | 3933 | 4780 | 847 | 12.48 | 12.848 | 0.369 | 2295 | 0.74 | 0.77 |
| 18 (very high rate of surgical failure) | 3933 | 5245 | 1312 | 12.48 | 12.596 | 0.116 | 11,310 | 0.56 | 0.57 |
| 19 (high rate of surgical failure) | 3933 | 4870 | 938 | 12.48 | 12.805 | 0.325 | 2886 | 0.73 | 0.74 |
Alternative scenarios
Under the base-case assumptions, laparoscopic fundoplication is cost-effective compared with medical management at a relatively low threshold ICER. This is because we assume that, although the annual costs of treatment on medical management are relatively modest, these costs accrue over a lifetime and offset much of the upfront cost of surgery. Furthermore, there is an HRQoL advantage of surgery over medical management that is assumed to persist in the long term. We explored how alternative assumptions would affect these conclusions using different scenarios (Table 41). Surgery is not likely to be cost-effective if HRQoL after successful surgery is similar to that on medical management after 5 years (scenario 15) or if the annual percentage of patients who restart anti-reflux medication after surgery is similar to that observed in the first year of the REFLUX trial (13%) (scenario 18).
Value of information analysis
The value of conducting additional research that, in principle, would reduce parameter uncertainty can be estimated using value of information analysis. The expected value of perfect information (EVPI) is the amount that a decision-maker should be willing to pay to eliminate all uncertainty that arises because of imprecision in the parameters of the model. The partial EVPI represents the amount a decision-maker should be willing to pay to eliminate all uncertainty in individual parameters or a subset of parameters, given the uncertainties elsewhere in the model.
To illustrate this we estimated the EVPI and partial EVPI for five sets of parameters: (1) the HRQoL of patients who fail surgery; (2) the estimates of HRQoL for all other model states; (3) the estimates of the annual rates of failure of surgery; (4) the estimates of unit costs used in the model; and (5) the rate of return to medical management post surgery together with the HRQoL of patients who fail. The analysis requires an estimate of the percentage of the population who would be eligible for surgery if it were cost-effective. A Spanish population survey (both sexes, ages 40–79 years) found that 287 out of 2500 (11%) interviewees used anti-reflux drugs, and 119 (4.8%) were stable (not having had reflux symptoms in the past year), although 43 (1.7%) acknowledged taking anti-reflux drugs to prevent symptoms. 118 This might be considered a conservative estimate of patients who could be considered for surgery. If we assume that about one-half of these might be excluded because of age, preference or co-morbidity, then prevalence is estimated at 1% of this population, equivalent to about 160,000 people in the UK. 115 Figure 18 shows an estimate of population EVPI at a range of values of the threshold ICER. EVPI in this case is increasing with the threshold ICER because at higher values of the ICER we are more willing to pay for the health benefits associated with surgery (and therefore more certain that surgery is the correct decision), but the consequences of a wrong decision are also greater (in terms of loss of health and wasted resources) and we are willing to pay more to avoid the possibility of these losses. Because the population is large, the model indicates that the EVPI is £300 million at a threshold ICER of £30,000, indicating that we would be willing to pay up to this to eliminate all of the uncertainty in the decision.
FIGURE 18.
Expected value of perfect information (EVPI) assuming a population of 160,000 patients in England and Wales, and partial EVPI for three sets of parameters: (1) all HRQoL parameters; (2) HRQoL after surgery failure; and (3) failure rates for surgery.
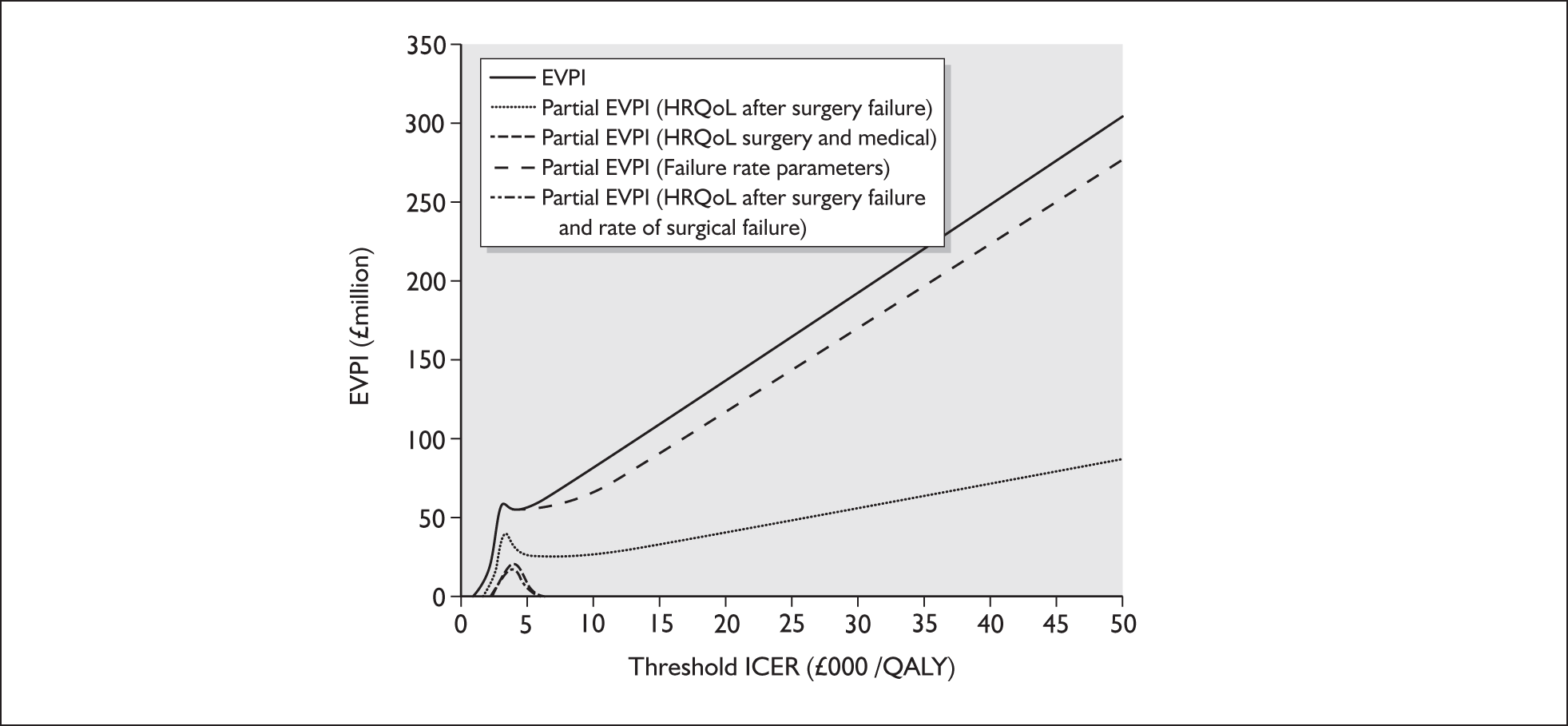
Figure 18 also shows the partial EVPI for selected sets of parameters. Partial EVPI is greatest for the rate of return to medical management post surgery together with the HRQoL of patients who fail. This indicates that almost all of the variation affecting the treatment decision is due to the interaction of these two parameters. Relatively little information is available on the HRQoL of patients who fail surgery; this could be captured in a longer follow-up but does not necessarily require a randomised trial. Figure 18 shows relatively little value of information in other parameters. However, this analysis does not on its own capture all of the uncertainty in the decision for two reasons. First, we have used mean estimates of HRQoL collected in a short-term trial to extrapolate over the longer term, without adjusting standard errors to take account of this additional uncertainty. There is, therefore, additional uncertainty over long-term differences in HRQoL, which is not captured in this value of information analysis. Second, we have assumed that the pooled rates of failure from observational studies of between 1 and 6 years are generalisable to our population, and that these rates will continue over the long term. We have attempted to represent this uncertainty as a series of scenario analyses. Taken together, this implies value in a continuing long-term follow-up to the randomised trial. The question remains, however, over how long this follow-up should optimally be.
Discussion
This chapter has presented a decision-analytic model comparing laparoscopic surgery with medical management, using data from the REFLUX trial and other sources to estimate cost-effectiveness over a lifetime. The results of this model are similar to those of the preliminary model presented in Chapter 6, which indicated that surgery was cost-effective but with a high degree of uncertainty. Other authors have examined the cost-effectiveness of laparoscopic surgery versus medical management. Cookson et al. 29 found that laparoscopic surgery broke even compared with medical management after 8 years and was cost saving thereafter. Romagnuolo et al. 28 evaluated cost-effectiveness over 5 years in a Canadian setting, in which both surgery and medical therapy is on average more expensive (generic formulations were not used in that model) than that found in the REFLUX trial and by Cookson in a UK setting. They concluded that there was little difference in HRQoL between the treatments and that surgery broke even relative to medical management after 3 years. Arguedas et al. 119 evaluated the strategies in a US setting with costs similar to Canada, assuming a relatively higher rate of symptom recurrence and failure of surgery, and relatively lower differences in HRQoL between the treatments, and concluded that medical therapy dominated surgery using a 10-year time horizon.
Although surgery seems likely to be cost-effective in terms of expected (mean) costs and health effects, there remains considerable uncertainty about this conclusion. Balances between risks and benefits and between costs and health gain will depend on patient characteristics such as age, the presence of serious co-morbidity and the severity of GORD symptoms. Furthermore, there are a number of practical issues to consider before the NHS could consider offering surgery to a wider range of patients who are currently stable on medical management. In particular, surgical capacity and availability of trained surgeons are potential barriers to implementation and should be addressed.
We have estimated the value of reducing some of the model uncertainty in the analysis of EVPI and partial EVPI, and through a series of scenario analyses. These have indicated that continued follow-up of the randomised trial would be valuable, particularly to obtain more information on HRQoL following surgery failure and the long-term difference in HRQoL between strategies. Further research to obtain more information on the long-term HRQoL and prognosis of patients would be valuable.
Chapter 9 Discrete choice experiment to measure preferences for treatment options
Introduction
This chapter reports an application of a discrete choice experiment (DCE) to measure patient preferences for treatment options for GORD. DCEs are increasingly recognised as an important method in health services research for measuring the strength of patients’ preferences (utility) for treatments and methods of delivery of care. 120
The aims of this work were to identify the strength of the trial participants’ preferences for the different treatments and outcomes of GORD; to investigate whether these preferences differ between the different arms of the trial; and finally to identify whether the mean benefits associated with each treatment vary. It should be noted that the utilities produced by the DCE reflect the preferences of people with GORD for the treatment and outcomes of GORD. As such, they are different from the utilities used to generate QALYs, which were based on the responses to the EQ-5D questionnaire and reflect the public preferences for the outcomes following treatment of GORD. It is these latter utilities that are arguably most useful for priority setting within the NHS. 102
In the following section a brief description of the DCE approach is provided. This is followed by the methods used to achieve the aims stated above and the subsequent results. Finally, a brief discussion is presented outlining the strengths and limitations of the approach and the implications of the findings.
The discrete choice experiment approach
DCEs are based on random utility theory,121 which defines a set of assumptions about desires and transforms them into a demand function describing the actions of a consumer under a defined set of circumstances. The following five stages are undertaken when a DCE is performed:
-
Identification of attributes (i.e. different dimensions of the process or outcome of care) that are potentially important to the people with the condition under study. This is performed by using literature reviews, group discussions, interviews and direct questioning of individual subjects. Sometimes there is a predefined policy question, in which case the dimensions may already be predefined,122 although that is not the case in this study.
-
Assigning plausible, actionable levels that are capable of being traded off. Again, these may be defined from the literature or by using any of the mechanisms mentioned above.
-
Identification of the profiles to present to potential respondents. These profiles describe all of the possible configurations of the dimensions and levels identified in the first two stages. As the number of dimensions and levels increases, the number of possible profiles increases. Because of the potentially very large number of profiles that might exist, it is not desirable to present each profile to potential respondents. Various methods, for example computer software, catalogues (e.g. Hahn and Shapiro), websites and expert advice, are used to reduce the number of profiles for inclusion in the questionnaire to a manageable number while still allowing utilities to be inferred for all possible profiles. Within the DCE the scenarios must then be placed in choice sets. A number of approaches have been used to do this that vary in the extent to which they meet specific statistical design criteria (orthogonality, balance, minimum overlap and balanced utilities).
-
Presentation of the choice sets to study participants. In the DCE, respondents are presented with the choice sets and asked to state which intervention they prefer. They make a series of choices and each choice indicates which scenario in a choice set would lead to the higher level of utility (or satisfaction or benefit).
-
Data input and analysis using regression techniques and interpretation. This stage of the DCE helps establish the overall importance of dimensions, their relative importance, willingness of respondents to trade between them, and benefits (or utility scores) for the different combinations of levels of dimensions.
In addition to these five standard stages for a DCE, a sixth stage, specific to this study, was also added. In this stage the results of the DCE are combined with data from the trial on the actual level observed for each dimension for each treatment group. This provides a summary score for each treatment group, the treatment group with the highest score being associated with the greatest benefit.
Methods
The study was performed in two stages: a methodological stage to develop the questionnaire and an applied stage to derive the utility estimates for the different treatments and outcomes for GORD.
Identification of dimensions and levels
As reported earlier, a qualitative study was performed to identify the potential issues related to GORD and its treatment that are important to patients (Chapter 4). The dimensions selected, therefore, represent those issues that are concerns to patients undergoing treatment for GORD. Some of the identified factors were combined into themes and, from these, four dimensions were eventually defined. These dimensions are frequency of troublesome symptoms, chance of serious complications, chance of undergoing surgery and chance of needing lifelong medication. Several considerations were taken into account when identifying the levels of the dimensions. They had to be realistic and they had to be set up in such a way that individuals could consider trade-off between improvements. The levels of the dimensions were derived from the trial data and discussions with gastroenterology experts. Table 42 provides a detailed description of the dimensions and levels that were used to develop the questionnaire.
| Dimension and description | Level of difficulty |
|---|---|
| Frequency of troublesome symptoms This aspect describes the frequency with which you may experience troublesome symptoms of GORD. These symptoms could include heartburn (a burning sensation that moves up the chest), acid reflux (an acid taste in mouth), excessive wind in lower bowel or trapped in stomach, difficulty eating and swallowing food, troublesome bowel movements (diarrhoea/constipation), and experiencing difficulty with lying down or getting to sleep | Not at all |
| Once a week | |
| Two or three times a week | |
| Most days or every day | |
| Chance of serious complications requiring hospitalisation This aspect refers to the possibility that you may experience complications/side effects as a result of your GORD treatment. These complications/side effects could lead to you spending a few days in hospital. They could include bleeding that could lead to anaemia, scarring of the oesophagus, or difficulty or pain when swallowing | 1 in 800 (0.1%) people |
| 1 in 500 (0.2%) people | |
| 1 in 300 (0.3%) people | |
| 1 in 100 (1%) people | |
| Chance of undergoing surgery This aspect describes the chance that you might have to undergo any surgery to treat your GORD symptoms | 1 in 20 (5%) people |
| 1 in 3 (33%) people | |
| 2 in 3 (66%) people | |
| 5 in 6 (83%) people | |
| Chance of needing lifelong medication This aspect describes the chance that you might have to take medication (e.g. PPIs) over a long period of time (months or years) for GORD | 1 in 20 (5%) people |
| 1 in 3 (33%) people | |
| 2 in 3 (66%) people | |
| 5 in 6 (83%) people |
Which scenarios to present
Once the dimensions and levels have been identified they are combined to generate combinations of dimension levels referred to as profiles. The four dimensions and four levels yield 246 possible profiles, too many to present to individuals. Therefore, a fractional factorial design was used to reduce the profiles to a manageable level while still being able to infer utilities for all possible profiles. Existing literature suggests that individuals can manage between 9 and 16 pairwise comparisons before they become bored or tired. 123 The identified design had 16 profiles and they were randomly split into two different questionnaires containing 8 questions (see Appendix 12). The design was derived from a web-based catalogue. 124–126
Although profiles from fractional factorial designs have statistical properties for the estimation of parameters of general linear models, we needed to ensure that the choice sets generated from these profiles were statistically efficient. Therefore, tests for the properties of an efficient design were performed. The properties of an efficient design include:
-
Level balance – this occurs when the levels of a dimension occur with equal frequency.
-
Orthogonality – this is satisfied when dimension levels are not correlated, that is, the joint occurrence of any two levels of different dimensions appears in profiles with a frequency that is equal to the product of their marginal frequencies (Addelman 1962, cited in Zwerina et al. , 1996126). Therefore, the levels of dimensions appear in choice sets with equal frequency to each level of each other dimension.
-
Minimum overlap – this means that the probability that a dimension level repeats itself in each choice set should be as small as possible, especially in instances when there is more than one choice, e.g. choice A and choice B. This is an important issue as the differences in dimension levels are only useful within a choice set if the respondents trade these levels. When this property is violated the choice sets provide no information on the dimension’s value.
The set of alternatives is typically the same for all subjects and the explanatory variables are all choice specific. Individuals were asked to make a number of such choices, and using the responses from these the preferences for alternative profiles could be elicited.
Eliciting preferences
Once the scenarios to be presented to patients were identified, preferences for these scenarios were obtained by using a forced choice approach. An example of the choices presented to participants is shown in Figure 19; respondents were asked which option they would choose, ‘A’ or ‘B’.
FIGURE 19.
Example of discrete choice experiment question presented to trial participants.
One important issue in preference elicitation is whose preferences should be elicited. Patients with the experience of both disease and treatment were considered appropriate for this study and therefore the completed questionnaire was sent to all active participants in the REFLUX trial during August 2006.
Piloting the questionnaire
The sample for piloting the questionnaire was obtained from individuals attending a gastroenterology clinic in Aberdeen. Patients were screened by a clinician and those assessed as having GORD were asked to complete the DCE questionnaire with a researcher (LV). The aim of the pilot work was to ensure that the guidance notes provided with the questionnaire were clear and that patients could understand them and that they were able to perform the task of making choices. The respondents were asked to complete the questionnaire using the guidance information provided and they were then asked about its readability and acceptability. They indicated that the guidance notes were clear and easy to understand and that they were able to answer the questions without much difficulty.
Consistency of responses
An important aspect of a DCE is that respondents should behave in a rational manner when making choices. Rationality within DCEs is mainly tested using non-satiation (dominance) tests. These tests are, however, perceived as easy to satisfy. 120 For this reason more sophisticated expansion property tests were conducted. 127 This involved adding two consistency questions to the questionnaire.
Respondents were first asked to choose the worse of two situations (A or B). In the consistency question, which was presented as a non-consecutive question, this choice was widened to a set of three situations (A, B or C). As with the simple two situation question, respondents were asked to choose one of the three situations (see example of both questionnaires in Appendix 12). A respondent was believed to behave rationally if the choice they made in the two situation question did not conflict with the choice they made when faced with the three situation question. For example, if the respondent choose situation B in the first choice set, then they should not choose situation A in the expanded choice set. Similarly, if the respondent chose situation A in the first choice set, then they should not choose situation B in the expanded choice set.
A sensitivity analysis was performed that excluded those respondents who failed the consistency test (i.e. they gave an inconsistent response in both consistency questions).
Estimating utilities
To establish the importance of the various dimensions, the relationship between the dimensions and utility must be specified. The linear additive model assumes that the overall valuation or utility derived from any combination of dimensions is given by the sum of the values of the separate dimensions. In this model the reference group for the modelling analysis was the best level of each dimension. This means that the results from the DCE will be able to illustrate how the different combinations of dimensions and levels compare with the best possible combination of dimensions and levels from the DCE.
The linear additive model for a simple model was specified as:
where ‘U’ is the utility or preference score for an outcome with a given level of each dimension; ‘frequency’ is the occurrence of troublesome symptoms and, as it was a categorical variable, dummy values were used for the analysis for each level; ‘serious complications’ is the chance of complications requiring hospitalisation; ‘surgery’ is the chance of undergoing surgery; and ‘lifelong medication’ is the chance of needing lifelong medication. The parameters β1–β6 are the coefficients of the model to be estimated.
The coefficients indicate the relative importance, or weight, of a unit change in that dimension in terms of overall benefit. The rate at which respondents are willing to trade between these dimensions (i.e. how much of the dimension they are willing to give up for improvements in other dimensions) is shown by the ratio of the coefficients (i.e. the marginal rate of substitution). For example, β5/β6 indicates how much of a change in the chance of having lifelong medication would be required if there was a 10% change in the chance of having surgery so that overall utility remains constant.
The internal validity (the extent to which the results are consistent with economic theory or a priori expectations) of the DCE can be determined by the results from the regression analysis. Given that the higher the chance an episode will be experienced, the less it will be preferred, we anticipated that the dimensions would have a negative sign in the regression equation.
Econometric techniques were used to analyse the DCE responses and to estimate a value such that the utility weights could be estimated for all of the outcomes in the instrument. As described above, the best level was used as the comparator for all dimensions. As participants provided multiple responses, a conditional fixed-effects logistic regression model was used to analyse the response data. Two models were estimated: a main model that measured preferences across the whole group and a further model that was used to establish whether the responses of individuals differed based upon the trial group to which they belonged. Although it would be possible to estimate a regression model for each arm of the study (i.e. to estimate four separate models), it would not be appropriate to make comparisons between the models. A more appropriate way of considering the effect that people’s initial preferences for a particular treatment have on the choices they make when responding to the DCE is to include interaction terms to explore the extent to which the preferences of those in the two preference arms differed. Interaction terms were included to explore whether the preferences of specific groups (e.g. preferred medicine, preferred surgery, randomised surgery, randomised medicine) for each dimension included in the model differed from the preferences of the whole model.
Sensitivity analyses
The analyses described above included all responses, even those for which there was evidence that the responses were not consistent. Therefore, in a first sensitivity analysis the effect of excluding the inconsistent responses from the main model was investigated.
The methods described above involve making the assumption that preferences for a unit change in risk are independent of the scale of that risk (i.e. a 10% change in risk from 4% to 14% would be valued the same as a 10% change in risk from 70% to 80%). To investigate whether it was appropriate to assume a linear relationship between the levels of each dimension, a quadratic variable (surgery 1, lifelong medicines 1, and serious complications 1) was included for each dimension.
Calculation of utilities for each treatment group
The results of the econometric analyses can be used to estimate a utility score. This can be accomplished by combining the information on the levels for each dimension, which was derived directly from the trial, with the coefficient for that dimension. Table 43 gives an example of how a utility might be calculated for hypothetical levels and coefficients.
| Dimension | Coefficient | Actual level (%) | Utility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Troublesome symptoms | |||
| None | 0.00 (baseline) | 60 | 0.00 |
| Once a week | –0.05 | 20 | –1.00 |
| Two/three times a week | –0.20 | 15 | –3.00 |
| Most days/every day | –0.40 | 5 | –2.00 |
| Serious complications | –1.00 per 0.1% change | 0.1 | –1.00 |
| Surgery | –5.00 per 10% change | 40 | –20.00 |
| Lifelong medication | –2.00 per 10% change | 40 | –8.00 |
| Total score | –35.00 |
Similar scores can be calculated for data taken from each arm of the trial. The scores from the different arms could be compared relative to each other (i.e. the ratio of the scores from two groups), but, to aid this comparison, a score has been estimated for both the worst possible and the best case situation (which is by definition 0). Using the coefficient values from Table 43, and assuming that people experienced the worst level of each dimension (i.e. symptoms most days/every day, 100% chance of surgery, lifelong medications and a hypothetical maximum of 10% for complications), the worst case scenario would be associated with a score of –210. Therefore, if the worst case scenario was rescaled to 0, then the best case scenario would equal +210 and the state described in Table 43 would have a score of 175 (i.e. 210–35). As a consequence it can be seen that the state described in Table 43 is equivalent to 0.833 (i.e. 175/210) of the utility of the hypothetical best case scenario.
Selection of respondents
The sample of respondents used in this DCE was made up of REFLUX trial participants. They were considered to be the appropriate group as they had already undergone treatment. As described in earlier chapters, the trial was composed of four arms: two arms involved the randomisation of individuals to either medical or surgical treatment and the other two arms included those who had expressed a preference for either medical management or surgical treatment.
Results
Of the 705 questionnaires sent out, 441 (63%) were returned; 17(3%) were returned uncompleted and 424 (60%) were fully or partially completed. Of these 424 questionnaires, 87 (21%) were from the randomised surgical group, 103 (24%) were from the randomised medical group, and 109 (26%) and 125 (29%) were from the preference medical and preference surgical groups respectively.
Consistency of responses
Ten (2%) people failed to answer the two consistency test questions consistently and so were excluded when the sensitivity analysis was performed.
Econometric analysis
The conditional logistic regression analysis was based on all of the respondents who returned completed questionnaires. Out of a possible 6784 (424 × 16) observations from the 424 completed and partially completed questionnaires, there were 6434 observations and 350 missing responses. Of these 6434 observations, 1392 (21%) were from the randomised surgical group, 1648 (24%) were from the randomised medical group, and 1744 (26%) and 2000 (29%) were from the preference medical and preference surgical groups respectively.
A sensitivity analysis performed after excluding the ten respondents who had failed both consistency tests was based on 6274 observations from 414 respondents.
Analysis based on the whole sample including inconsistent responses
The sign of the coefficient indicates the direction of the influence of preferences. All other things being equal, a higher negative coefficient indicates a higher negative influence on the overall preference (see Appendix 13). The regression coefficients all had the expected sign (negative) and decreased as expected (i.e. as more difficulty is experienced, the coefficient becomes larger). There was no statistically significant difference between the first two levels for the first dimension, frequency of troublesome symptoms. Therefore, in subsequent analyses these two levels were combined.
The results of the regression model in which the first two levels for frequency of troublesome symptoms were combined are presented in Table 44, and the results of the initial regression model in which the levels for frequency of troublesome symptoms were not combined are presented in Appendix 13.
| Dimension | Coefficient | Standard error | p-value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Troublesome symptoms | ||||
| Two or three times a week | –0.397 | 0.061 | 0.000 | –0.516 to –0.277 |
| Most days/every day | –1.130 | 0.065 | 0.000 | –1.258 to –1.001 |
| Serious complications | –5.454 | 0.661 | 0.000 | –6.750 to –4.158 |
| Surgery | –5.212 | 0.845 | 0.000 | –6.868 to –3.556 |
| Lifelong medication | –4.797 | 0.685 | 0.000 | –6.139 to –3.455 |
The absolute importance of the parameters included in the analysis can be established by comparing the sizes of the regression coefficients. As Table 44 illustrates, the most important factor was serious complications with a coefficient of –5.454, indicating that respondents experienced greater disutility for a unit increase (i.e. a 0.1% increase) in the probability of occurrence of serious complications than for a unit change in any other factor. The chance of undergoing surgery (–5.212 per 10% change), the chance of having lifelong medications (–4.797 per 10% change) and the chance of having troublesome symptoms most days/every day (–1.130 per 10% change) were the next largest dimensions.
The relative importance of the coefficients was estimated by investigating the marginal rates of substitution between coefficients. In absolute terms (i.e. ignoring the sign of the coefficient) the smallest coefficient was that for experiencing troublesome symptoms two or three time per week. Experiencing symptoms most days was over 2.8 times as important, whereas a 0.1% change in the risk of experiencing serious complications was 13.7 times more important. Similar rates were calculated for a 10% change in the risks of surgery and lifelong medication, which were 1.3 times and 1.2 times as important respectively (a full description of marginal rates of substitution between all coefficients is provided in Appendix 13).
Analysis to investigate whether preferences differ between the four groups of the REFLUX trial
Further analysis was performed to establish the effect of the treatment group that patients were assigned to, either through their own preferences or through randomisation. There was no evidence of any differences in preferences in the four treatment groups for either troublesome symptoms or serious complications. However, as would be anticipated, preferences did differ for surgery and lifelong medications. The exception to this was that there was no evidence of a statistically significant difference in the preferences for lifelong medication amongst those people that had expressed a preference for medication compared with the preferences from the whole sample.
The results of the analysis investigating whether preferences varied between treatment groups is reported in Table 45 (interaction terms for troublesome symptoms or serious complications have been omitted as they were not statistically significant).
| Dimension | Coefficient | Standard error | p-value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Troublesome symptoms | ||||
| Two or three times a week | –0.406 | 0.062 | 0.000 | –0.526 to –0.285 |
| Most days/every day | –1.146 | 0.066 | 0.000 | –1.275 to –1.016 |
| Serious complications | –5.525 | 0.664 | 0.000 | –6.826 to –4.224 |
| Surgery | –5.573 | 1.255 | 0.000 | –8.034 to –3.112 |
| Lifelong medication | –3.495 | 1.009 | 0.001 | –5.473 to –1.516 |
| Interactions | ||||
| Surgery for those that preferred medicine | –5.017 | 2.143 | 0.019 | –9.218 to –0.816 |
| Surgery for those that preferred surgery | 5.491 | 2.008 | 0.006 | 1.555–9.427 |
| Lifelong medication for those that preferred surgery | –5.258 | 1.632 | 0.001 | –8.457 to –2.059 |
| Lifelong medication for those that preferred medicine | 0.772 | 1.695 | 0.649 | –2.549 to 4.094 |
As would be expected, the results of this analysis indicate that people who expressed a preference for one treatment would experience a further loss of utility if they received the other treatment (indicated by the negative signs for ‘surgery for those that preferred medicine’ and ‘lifelong medication for those that preferred surgery’). Similarly, individuals who received the treatment that they preferred would experience less loss of utility (indicated by the positive signs for ‘lifelong medication for those that preferred medicine’ and ‘surgery for those that preferred surgery’).
Sensitivity analyses
Analysis based on the whole sample but excluding inconsistent responses
The econometric analysis was repeated for the whole sample, this time omitting those individuals who failed the consistency tests (Table 46). As reported above, this had the effect of reducing the sample size by ten respondents and 160 observations. The results of this analysis are reported in Table 46, although the values for all attributes are higher except for the chance of undergoing surgery.
| Dimension | Coefficient | Standard error | p-value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Troublesome symptoms | ||||
| Two or three times a week | –0.415 | 0.062 | 0.000 | –0.537 to –0.415 |
| Most days/every day | –1.166 | 0.067 | 0.000 | –1.297 to –1.166 |
| Serious complications | –5.649 | 0.673 | 0.000 | –6.967 to –5.648 |
| Surgery | –4.754 | 0.858 | 0.000 | –6.435 to –3.072 |
| Lifelong medication | –5.060 | 0.696 | 0.000 | –6.425 to –3.696 |
Analysis based on the whole sample but including quadratic functions
Quadratic functions were used in the model to establish the linear relationships in the continuous variables. All coefficients, except the chance of having lifelong medication and its associated quadratic function, were significant at the 5% level (Table 47). The quadratic functions for serious complications and chance of surgery are both positive and this indicates that, as these risks increase, the disutility still increases, but at a decreasing rate. However, these results should only be used to indicate that there may not be a linear relationship for serious complications and surgery. This is because the quadratic function is only a simple method and can provide estimates of utility that are counterintuitive for some levels of risk, for example utility increases as risk increases.
| Dimension | Coefficient | Standard error | p-value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Troublesome symptoms | ||||
| Two or three times a week | –0.398 | 0.061 | 0.000 | –0.518 to –0.278 |
| Most days/every day | –1.127 | 0.065 | 0.000 | –1.256 to –0.999 |
| Serious complications | –27.853 | 4.142 | 0.000 | –35.971 to –19.736 |
| Quadratic function | 1948.761 | 353.906 | 0.000 | 1255.118–2642.404 |
| Surgery | –12.868 | 3.921 | 0.001 | –20.554 to –5.182 |
| Quadratic function | 9.109 | 4.390 | 0.038 | 0.505–17.713 |
| Lifelong medication | –4.828 | 2.858 | 0.091 | –10.430 to 0.774 |
| Quadratic function | –0.046 | 0.3133 | 0.988 | –6.187 to 6.095 |
Estimation of utility scores for each treatment group
Table 48 reports the trial findings for the dimensions included in the DCE. Using these data and the results of the DCE regression model reported in Table 45 it is possible to calculate utility scores for each of the four groups (Table 49). Also included in Table 49 are the utility scores for the worst case scenario (by default the utility score for the best case scenario is 0). Using the approach outlined in the methods section, the relative weight of each of the four trial groups relative to the best case scenario was estimated from these data (Table 50).
| Dimension | Randomised surgical | Randomised medical | Preference surgical | Preference medical |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency of troublesome symptoms (heartburn only, %) | ||||
| Not at all | 63 | 29 | 73 | 32 |
| Once a week | 12 | 22 | 11 | 29 |
| Two or three times a week | 14 | 23 | 7 | 21 |
| Most days or every day | 10 | 26 | 9 | 19 |
| Chance of serious complications requiring hospitalisation (%) | ||||
| Reflux related (obtained from different source) | 1 | 0.12 | 1 | 0.12 |
| Chance of undergoing surgery (%) | 62.3 | 5.6 | 84.0 | 1.6 |
| Chance of needing lifelong medication at 12 months (%) | 33.8 | 84.8 | 19.6 | 85.9 |
| Dimension | Randomised surgical | Randomised medical | Preference surgical | Preference medical | Worst case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency of troublesome symptoms (heartburn only) | |||||
| Not at all | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Once a week | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Two or three times a week | –5.68 | –9.34 | –2.84 | –8.53 | 0.00 |
| Most days or every day | –11.46 | –29.80 | –10.31 | –21.77 | –114.60 |
| Chance of serious complications requiring hospitalisation | |||||
| Reflux related (obtained from different source) | –55.25 | –6.63 | –5.52 | –6.63 | –552.48 |
| Chance of undergoing surgery | –34.72 | –3.12 | –46.81 | –0.89 | –55.73 |
| Chance of needing lifelong medication at 12 months | –11.81 | –29.64 | –6.85 | –29.92 | –34.95 |
| Interactions | |||||
| Surgery for those who preferred medicine | –0.80 | ||||
| Surgery for those who preferred surgery | 46.12 | ||||
| Lifelong medication for those who preferred surgery | –17.77 | –52.58 | |||
| Lifelong medication for those who preferred medicine | |||||
| Total utility | –118.92 | –78.52 | –43.99 | –68.54 | –810.4 |
| Situation | Loss of utility from the best possible combination of attributes and levelsa | Gain in utility from the worst possible combination of attributes and levels | Relative weight compared with the best case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best case | 0 | 810 | 1.000 |
| Worst case | –810 | 0 | 0.000 |
| Randomised surgical | –119 | 691 | 0.853 |
| Randomised medical | –79 | 732 | 0.903 |
| Preference surgical | –44 | 766 | 0.946 |
| Preference medical | –69 | 742 | 0.915 |
As Table 49 illustrates, the largest component of total utility comes from serious complications. The data presented in this table also serve to illustrate the importance of patients’ preferences for utility. For example, the utility gained by a person who prefers surgery receiving the treatment they prefer (46.1) is just less than the disutility associated with surgery (46.8).
As indicated above, the comparisons between the four treatment groups are best informed by considering their relative weights. As there are several different relative weights that could be calculated, it was decided to compare the mean total utility for each arm with the total utility that is implied for the best possible combination of attributes and levels (the last column of Table 50). As the data in this table illustrate, relative to the best case, the preference surgical group has the highest weight and the randomised surgical group has the lowest weight. In this situation the preference arms are associated with higher mean utilities than the randomised arms.
Discussion
The aim of this chapter was to use a DCE to explore the strength of preference for the treatment and outcomes of GORD. This approach has been used to measure preferences of GORD patients previously128,129 but this earlier work sought to establish willingness to pay for complete symptom relief of GORD and for diagnostic uncertainty. The DCE reported in this chapter was different in that it attempted to explore preferences for the outcomes of treatment (e.g. troublesome symptoms and serious complications) and preferences for the process by which these outcomes were obtained.
The results of the DCE indicate that the most important single dimension is serious complications, followed by a 10% change in the chance of having surgery or receiving lifelong medication. Suffering troublesome symptoms most days was less important, although the unit of analysis was a 1% chance of this event occurring. There was no evidence that respondents placed any importance on suffering troublesome symptoms once a week in comparison with no symptoms.
The group that was associated with the highest utility relative to a best case situation was the preference surgical group, and the group that was associated with the lowest utility was the randomised surgical group. If the effect of serious complications is removed from the consideration of utility, then the preference groups are associated with higher levels of utility relative to the best case than the randomised groups. Furthermore, the surgical group is associated with higher utility than the medical group.
The exclusion of serious complications from the consideration of utility might be considered contentious. However, an analysis was conducted to explore whether the preferences for the continuous variables (risk of serious complications, risk of surgery and risk of receiving lifelong medication) in the econometric analysis were linear. The results of this analysis indicated that, although utility fell as risk increased, it fell at a decreasing rate for both the risk of serious complications and surgery (there was no evidence of this effect for lifelong medication). The implication of this is that it is possible that there is little or no difference in the loss of utility caused by serious complications between groups. Research is required to further investigate how this non-linearity in preferences might be most appropriately modelled, as the quadratic function would result in implausible utility estimates for higher risks of serious complications than were considered in the DCE questionnaire.
The results of the analysis presented in this chapter also provide some insight into the importance of people’s preferences for treatment with respect to utility. For example, people who have a preference for medicine but who actually undergo surgery experience almost twice the loss of utility (1.059 or –0.557 + –0.502) as those people in the randomised arm who receive surgery (–0.557) for a 1% increase in the risk of surgery. Similarly, people who preferred surgery and received surgery lost less utility (–0.008 or –0.557 + 0.549). This result indicates the importance of patient choice when decisions are made about which type of treatment to provide.
Some of the limitations of the analysis reported in this chapter have already been described but one further limitation relates to how the information derived by the DCE could have been used in the economic model reported earlier. It was not possible, nor was it planned, for these two ‘economic’ elements to be integrated. Indeed, methods to integrate DCEs into a trial remain relatively undeveloped. However, future work should consider how a DCE and an economic model conducted as part of a trial analysis can be developed in an integrated fashion. It is likely that this will involve the attributes and levels of the DCE being reflected in the model structure, with the values of attribute levels being produced by the model and fed into the estimation of utilities as part of the DCE analysis. Any attempt to integrate these approaches would be facilitated by the use of a common continuous measure, such as willingness to pay, so that all dimensions could be valued in terms of this numeraire.
The methods used to analyse and present the results of the DCE have limitations. One of the main limitations is the limited handling of uncertainty in the analysis. In economic studies it is expected that an extensive sensitivity analysis would be conducted to assess how robust the conclusions are. Increasingly, as exemplified by the economic evaluation presented in Chapter 7, it is becoming expected that a probabilistic sensitivity analysis will be used to develop credible intervals around mean estimates. Although sensitivity analysis has been performed as part of the work reported in this chapter, probabilistic sensitivity analysis has not been conducted. Probabilistic sensitivity analysis would also help overcome a further limitation of the DCE. When analysing the DCE, we followed the common econometric convention of combining levels of dimensions when there was no evidence of a statistically significant difference and of dropping parameters from an analysis when the coefficients were not statistically significant. There is some debate about how appropriate this approach is as it reduces the information available to decision-makers. However, with probabilistic sensitivity analysis a full model, including both statistically significant and insignificant coefficients, can be used to develop both mean utility scores and credible intervals. Therefore, further work might focus on conducting a probabilistic sensitivity analysis.
DCEs use hypothetical questions and, as such, they have been criticised. This is because it is unclear whether people would pick these scenarios if they were faced with these choices in real life. Nevertheless, the respondents to the DCE all had experience of GORD and its treatment (either medical, surgical or both); hence, it was hoped that the respondents would be able to consider the choices and trade-offs involved in each choice question.
A final concern relates to the number of choice questions to present to potential respondents. The greater the number of dimensions and levels that are considered relevant the greater the number of possible scenarios that individuals could potentially be presented with. Experimental design techniques were used to reduce the number of scenarios that were presented to individuals while still allowing for utilities to be inferred for all possible scenarios. However, even after the use of these techniques it was felt that the number of questions to be presented (n = 16) was too great. As a consequence, the questions were randomly split into two questionnaires, each containing eight questions. It was hoped that this would increase the completion rate of the questionnaire, although it did have the effect of reducing our ability to detect important differences in preferences. Overall, the completion rate achieved was quite high for a DCE questionnaire (which are thought to be cognitively demanding on respondents) and this may be attributed to the relatively short length of the questionnaire.
Conclusions
The results of the DCE presented in this chapter complement the evidence reported in earlier chapters. The results also aid the interpretation of the clinical evidence by indicating the importance placed on type of treatment and the ability of a treatment to resolve symptoms. The most important single dimension is serious complications, followed by changes in surgery, lifelong medication and troublesome symptoms most days. There was no statistically significant evidence that respondents placed any importance on suffering troublesome symptoms once a week in comparison with no symptoms. Relative to a best case situation the trial arm associated with the highest mean utility was the preference surgical group and that associated with the lowest mean utility was the randomised surgical group. The utility associated with surgery is dependent upon the risk of serious complications, which was assumed to be greater than that for lifelong medical treatment. If the effect of serious complications is removed from the consideration of utility, the preference arms are associated with higher levels of utility than the randomised groups. Furthermore, the surgical arms are associated with higher utility than the medical arms. Thus, the results of the analysis indicate the importance of quantifying the risk of serious complications and of considering patient choice when decisions are made about which types of treatment to provide and the type of treatment to recommend.
Additional further research is also indicated. Part of this research should focus on how approaches such as DCEs can be made more useful to trials-based research. A more specific research need is to consider how best to describe the imprecision surrounding the mean estimates of utilities that are generated.
Chapter 10 Conclusions
Implications for health care and recommendations for research
The advent of less invasive fundoplication performed laparoscopically opened up new possibilities for the management of people with chronic symptoms of GORD. Good results obtained amongst people whose symptoms were not satisfactorily controlled by medical management raised questions about the place of relatively early surgery in people with GORD whose symptom control from long-term medical management was reasonably acceptable. Would surgery be more effective than continuing medical management? Would surgery be sufficiently safe? And would widening the use of laparoscopic fundoplication to such patients be cost-effective? These are the principal questions addressed in this study.
The study had two main components: a pragmatic randomised controlled trial to assess clinical effectiveness and an economic evaluation to explore cost-effectiveness and the wider implications for efficient health-care provision.
The trial provided clear evidence of effectiveness in respect of reflux-related quality of life. Even though the number of participants in the trial was not as large as originally intended, the sizes of differences observed in the condition-specific reflux quality of life measure were so large that they were highly statistically significant. As with other disease-specific measures, the magnitude of these differences is hard to conceptualise. However, broadly similar differences were also observed in most components of the more accessible generic health status measures, SF-36 and EQ-5D.
As described in Chapter 6, clear differences were observed even though as many as one-third of those allocated surgery did not have fundoplication. Extra analyses explored how much of a blunting effect this might have had on the results and, arguably, these adjusted analyses provide better estimates of the true effects of surgery in this type of population as it might be used in normal clinical practice.
Current follow-up is to the equivalent of 12 months after surgery. In comparison with the results obtained at 3 months there were sustained better scores but with some evidence of attenuation of the differences. For example, the number taking reflux-related drugs after surgery went up from around 9% to 14%. Narrowing of differences was most marked for the EQ-5D health status measure. It is possible that some of the ‘improvement’ is due to a placebo effect of surgery and one explanation of any attenuation of difference is that the placebo effect has diminished over time. This could be clarified by further follow-up to find out if differences are sustained or whether there is more narrowing of the differences.
In addition to the randomised groups the trial also had two preference groups, which aid interpretation of the randomised trial results. As a group, the preference surgical participants had the lowest baseline REFLUX scores (worst symptoms) and the preference medical group the highest (with the randomised groups between them (see Figure 14). After surgery the preference surgical group had scores that rose to the level of the preference medical group and by 12 months they were the better of the two groups. The preference groups give an indication of likely behaviour if surgery were to become more freely available. In addition to having the least well-controlled symptoms at baseline, the preference surgical group had been on medication longer and were less concerned about possible adverse effects of surgery (described in Chapter 5).
The preference groups also add extra information about clinical events, in particular rare serious adverse events. Taken at face value, laparoscopic fundoplication appears to be a relatively safe procedure; however, even the experience of all of the 329 participants who had surgery is too little to provide sufficiently precise estimates of uncommon events. So, questions still remain about the extent of possible adverse effects of surgery and their frequency.
The within-trial (i.e. up to 12 months of follow-up) cost-effectiveness analysis related the extra mean costs associated with the surgical policy with the increase in mean QALYs that followed surgery to generate an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio. This was around £19,000 when the intention to treat approach to analysis was used. Taking into account uncertainties around the various estimates, it was calculated that the chances that the surgical policy would be cost-effective at a threshold of £20,000 per QALY was 46%. When a per protocol approach was used, the incremental cost per QALY increased to around £23,000, with a probability that this would be cost-effective at a threshold of £20,000 of only 19%. These results indicate considerable uncertainty at thresholds that are currently commonly applied to costs per QALY.
The within-trial analyses have significant limitations, however, as discussed in Chapters 7 and 8. The most important is that they ignore events, costs and benefits that accrue after 1 year. It is likely that surgery will continue to bestow benefits after 1 year, although there could also be relapse of symptoms, and medical management may require lifelong medication with significant costs. For this reason, the REFLUX trial data were synthesised with other data to develop an extended cost-effectiveness model. This explored a number of possible scenarios. Assuming that the benefits of surgery persist throughout a lifetime, that without surgery mediation use would continue for a lifetime, that there would be a 4.8% annual rate of additional uptake of medication in the surgery group, and that there would be an annual 0.8% reoperation rate led to an estimated incremental cost per QALY of around only £2000, with a 74% probability of surgery being considered cost-effective at a threshold of £20,000 per QALY. Applying other plausible assumptions, however, gave a range of incremental costs per QALY of between £1000 and £44,000, again indicative of wide uncertainty. The factors most contributing to the uncertainty were the projected HRQoL parameters and the long-term rate of uptake of medication following surgery.
The DCE was performed to provide an alternative way of assessing the weights that people with GORD place on their outcome and treatment. The results were broadly in line with the other economic evaluation in this project, based on the EQ-5D. The DCE did show, however, that respondents put considerable weight on avoiding rare but serious risks. The economic analysis found that these risks have little impact on QALYs on average and that the uncertainty in the clinical results about their incidence does not affect the treatment decision at the population level, all other things being equal. Nevertheless, the DCE highlights that these risks may be important when patients choose whether to accept surgery if it is offered.
Currently available evidence from the REFLUX trial indicates that surgery could be cost-effective at the thresholds (£20,000–£30,000) currently applied by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) but with considerable uncertainty. The extended model suggests that the true cost-effectiveness, when lifetime costs and benefits are taken into account, is likely to be more favourable. But this, too, is prone to major uncertainty.
Questions also remain about the generalisability of the study’s results. The economic model was based on a 45-year-old man, whereas many people receiving PPIs for GORD are older than this and can have significant co-morbidities.
The most urgent need for further research, therefore, is to acquire improved estimates of longer-term benefits and costs. This could be accomplished relatively easily by continuing annual follow-up in the REFLUX trial, and indeed arrangements for this have been put in place. Funds have recently been awarded by the HTA Programme to support follow-up to 5 years after surgery. Our analyses of cost-effectiveness will then be updated to take these results and other changes (such as in the costs of PPIs) into account. In the meantime it may be worth exploring whether there are other longer-standing non-randomised cohorts that could be useful in this respect. Perceptions of the risks of rare adverse events may play a major role in decision-making about surgery. Such cohorts could also be useful for getting more precise estimates of uncommon events associated with both surgical and medical management.
Acknowledgements
Contributions of authors
Adrian Grant (Director, HSR trialist) was the principal grant applicant and contributed to the development of the trial protocol and the preparation of the report and was responsible overall for the conduct of the trial.
Samantha Wileman (Trial Co-ordinator, HSR trialist) contributed to the development of the trial design, was responsible for the day-to-day management of the trial, monitored data collection and assisted in the preparation of the report.
Craig Ramsay (Senior Research Fellow, Health Statistics) contributed to the grant application and the trial design and conducted the statistical analysis.
Mark Sculpher (Senior Health Economist, Health Economics) was responsible for the economic evaluation section of the grant application and protocol, and Laura Bojke (Research Fellow, Health Economics) and David Epstein (Research Fellow, Health Economics) conducted the analysis of the economic models for the report.
Sue Macran (Research Fellow, Health Outcomes) led the development of the REFLUX outcome measure.
Luke Vale (Senior Research Fellow, Health Economics) and Mary Kilonzo (Research Fellow, Health Economics) conducted the discrete choice experiment (DCE) and assisted in the preparation of the DCE for the report.
Jill Francis (Senior Research Fellow, Health Psychology) conducted the analysis of the belief questionnaires and wrote the report for this part of the study.
Zygmunt Krukowski (Surgeon, Gastroenterology) and Ashley Mowat, Robert C Heading and Mark Thursz (Physicians, Gastroenterology) advised on clinical aspects of the trial design and the conduct of the trial and commented on the draft report.
Ian Russell (Director, HSR, Health Outcomes) contributed to the development of the trial design.
Marion Campbell (Programme Director, HSR statistician/trialist) contributed to the development of the trial design, commented on all aspects of the conduct of the trial and contributed to the preparation of the report.
Other members of the Trial Steering Group were as follows (those marked with an asterisk were independent of the trial): Wendy Atkin* (Chair), John Bancewicz, Garry Barton (1999–2002), Ara Darzi, Janusz Jankowski*, Richard Lilford*, Iain Martin (1997–2000).
Members of the independent Data Monitoring Committee were as follows: Jon Nicholl, Chris Hawkey, Iain MacIntyre.
The authors wish to thank the following researchers for their assistance in nurse co-ordination and patient recruitment and follow-up: Maureen GC Gillan, Marie Cameron, Christiane Pflanz-Sinclair; Sharon McCann who was involved in the piloting of the practical arrangements of this trial; Allan Walker for database and programming support; and Janice Cruden and Pauline Garden for their magnificent secretarial support and data management.
Members of the REFLUX trial group responsible for recruitment in the clinical centres are shown in the table below.
Finally, the authors are indebted to the referees for reading the report and for the quality of their comments.
The Health Services Research Unit is funded by the Chief Scientist Office of the Scottish Government Health Directorates.
| Aberdeen: Aberdeen Royal Infirmary | A Mowat, Z Krukowski, E El-Omar, P Phull, T Sinclair, L Swan |
| Belfast: Royal Victoria Hospital | B Clements, J Collins, A Kennedy, H Lawther |
| Bournemouth: Royal Bournemouth Hospital | D Bennett, N Davies, S Toop, P Winwood |
| Bristol: Bristol Royal Infirmary | D Alderson, P Barham, K Green, R Mittal |
| Bromley: Princess Royal Infirmary | M Asante, S El Hasani |
| Edinburgh: Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh | A De Beaux, RC Heading, L Meekison, S Paterson-Brown, H Barkell |
| Guildford: Royal Surrey County Hospital | G Ferns, M Bailey, N Karanjia, TA Rockall, L Skelly |
| Hull: Hull Royal Infirmary | M Dakkak, C Royston, P Sedman |
| Inverness: Raigmore Hospital | K Gordon, LF Potts, C Smith, PL Zentler-Munro, A Munro |
| Leeds: Leeds General Infirmary | S Dexter, P Moayeddi |
| Leicester: Leicester Royal Infirmary | DM Lloyd |
| London: St Mary’s Hospital | V Loh, M Thursz, A Darzi |
| London: Whipps Cross Hospital | A Ahmed, R Greaves, A Sawyerr, J Wellwood, T Taylor |
| Poole: Poole Hospital | S Hosking, S Lowrey, J Snook |
| Portsmouth: Queen Alexandra Hospital | P Goggin, T Johns, A Quine, S Somers, S Toh |
| Salford: Hope Hospital | J Bancewicz, M Greenhalgh, W Rees |
| Stoke-on-Trent: North Staffordshire Hospital | CVN Cheruvu, M Deakin, S Evans, J Green, F Leslie |
| Swansea: Morriston Hospital | JN Baxter, P Duane, MM Rahman, M Thomas, J Williams |
| Telford: Princess Royal Hospital | D Maxton, A Sigurdsson, MSH Smith, G Townson |
| Yeovil: Yeovil District Hospital | C Buckley, S Gore, RH Kennedy, ZH Khan, J Knight |
| York: York District Hospital | D Alexander, G Miller, D Parker, A Turnbull, J Turvill, |
Disclaimers
The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the HTA Programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Kay L, Jorgensen T, Hougaard Jensen K. Epidemiology of abdominal symptoms in a random population: prevalence, incidence, and natural history. Eur J Epidemiol 1994;10:559-66.
- Isolauri J, Laippala P. Prevalence of symptoms suggestive of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in adult population. Ann Med 1995;27:67-70.
- Locke GR, Talley NJ, Fett SL, Zinsmeister AR, Melton LJ. Prevalence and clinical spectrum of gastroesophageal reflux: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Gastroenterology 1997;112:1448-56.
- Roberts SJ, Bateman DN. Prescribing of antacids and ulcer-healing drugs in primary care in the north of England. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1995;9:137-43.
- Bashford JNR, Norwood J, Chapman SR. Why are patients prescribed proton pump inhibitors? Retrospective analysis of the link between morbidity and prescribing in the general practice research database. Br Med J 1998;317:452-6.
- Chiba N, De Gara CJ, Wilkinson JM, Hunt RH. Speed of healing and symptom relief in grade II to IV gastroesophageal reflux disease: a meta analysis. Gastroenterology 1997;112:1798-810.
- Leufkens H, Claessens A, Heerdink E, Van Eijk J, Lamers CBHW. A prospective follow-up study of 5669 users of lansoprazole in daily practice. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1997;11:887-97.
- Haga Y, Nakatsura T, Shibata Y, Sameshima H, Nakamura Y, Tanimura M, et al. Human gastric carcinoid detected during long-term antiulcer therapy of H2 receptor antagonist and proton pump inhibitor. Dig Dis Sci 1998;43:253-7.
- Termanini B, Gibril F, Sutliff VE, Yu F, Venzon DJ, Jensen RT. Effect of long-term gastric acid suppressive therapy on serum vitamin B12 levels in patients with Zollinger–Ellison syndrome. Am J Med 1998;104:422-30.
- Blot WJ, Devesa SS, Kneller RW, Fraumeni JF. Rising incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastric cardia. JAMA 1991;265:1287-9.
- Hansson LE, Sparen P, Nyren O. Increasing incidence of carcinoma of the gastric cardia in Sweden from 1970 to 1985. Br J Surg 1993;80:374-7.
- Locke GR, Talley NJ, Carpenter HA, Harmsen WS, Zinsmeister AR, Melton LJ. Changes in the site- and histology-specific incidence of gastric cancer during a 50-year period. Gastroenterology 1995;109:1750-6.
- Lagergren J, Bergstrom R, Lindgren A, Nyren O. Symptomatic gastoesophageal reflux as a risk factor for esophageal adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 1999;340:825-31.
- El Omar E, Carrington M, Chow W, McColl KE, Bream JH, Young HA, et al. Interleukin-1 polymorphisms associated with an increased risk of gastric cancer. Nature 2000;404:398-402.
- El Omar E, Oien K, Murray L, El-Nujumi A, Wirz A, Gillen D, et al. Increased prevalence of precancerous changes in relatives of gastric cancer patients: critical role of H. pylori. Gastroenterology 2000;118:22-30.
- Donahue PE, Larson GM, Stewardson RH, Bombeck CT. Floppy Nissen fundoplication. Rev Surg 1977;34:223-4.
- DeMeester TR, Bonavina L, Albertucci M. Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Evaluation of primary repair in 100 consecutive patients. Ann Surg 1986;204:9-20.
- Lundell L, Abrahamsson H, Ruth M, Rydberg L, Lonroth H, Olbe L. Long-term results of a prospective randomized comparison of total fundic wrap (Nissen-Rossetti) or semifundoplication (Toupet) for gastro-oesophageal reflux. Br J Surg 1996;83:830-5.
- Coster DD, Bower WH, Wilson VT, Brebrick RT, Richardson GL. Laparoscopic partial fundoplication vs laparoscopic Nissen-Rosetti fundoplication: short-term results of 231 cases. Surg Endosc 1997;11:625-31.
- British National Formulary 52. London: British Medical Association and the Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain; 2006.
- Henshaw RC, Naji SA, Russell IT, Templeton AA. Comparison of medical abortion with surgical vacuum aspiration: women’s preferences and acceptability of treatment. Br Med J 1993;307:714-17.
- Cooper KG, Grant AN, Garratt AM. The impact of using a partially randomised patient preference design when evaluating alternative managements for heavy menstrual bleeding. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1997;104:1367-73.
- Brewin CR, Bradley C. Patient preferences and randomised clinical trials. Br Med J 1989;299:313-15.
- Macran S, Wileman S, Barton G, Russell I. The development of a new measure of quality of life in the management of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: the REFLUX questionnaire. Qual Life Res 2007;16:331-43.
- Viljakka M, Nevalainen J, Isolauri J. Lifetime costs of surgical versus medical treatment of severe gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in Finland. Scand J Gastroenterol 1997;32:766-72.
- Coley CM, Barry MJ, Spechler SJ, Williford W, Mulley AG. Initial medical v surgical therapy for complicated or chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). A cost-effectiveness analysis. Gastroenterology 1993;104.
- van den Boom G, Go PMMYH, Hameeteman W, Dallemagne B, Ament AJHA. Cost-effectiveness of medical versus surgical treatment in patients with severe or refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease in the Netherlands. Scand J Gastroenterol 1996;31:1-9.
- Romagnuolo J, Meier MA, Sadowski DC. Medical or surgical therapy for erosive reflux esophagitis: cost-utility analysis using a Markov model. Ann Surg 2002;236:191-202.
- Cookson R, Flood C, Koo B, Mahon D, Rhodes M. Short-term cost-effectiveness and long-term cost analysis comparing laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with proton-pump inhibitor maintenance for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Br J Surg 2005;92:700-6.
- McDougall NI, Johnston BT, Kee F, Collins JS, McFarland RJ, Love AH. Natural history of reflux oesophagitis: a 10 year follow up of its effects on patient symptomatology and quality of life. Gut 1996;38:481-6.
- Dent J, Jones R, Kahrilas PJ, Talley NJ. Management of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in general practice. Br Med J 2001;322:344-7.
- Nagelkerke N, Fidler V, Bersen R, Borgdorff M. Estimating treatment effects in randomised clinical trials in the presence of non-compliance. Stat Med 2000;19:1849-64.
- White IR. Uses and limitations of randomization-based efficacy estimators. Stat Methods Med Res 2005;14:327-47.
- Weinstein MC, Stason WB. Foundations of cost-effectiveness analysis for health and medical practices. N Engl J Med 1977;296:716-21.
- Detsky AS, Naglie IG. A clinician’s guide to cost-effectiveness analysis. Ann Intern Med 1990;113:147-54.
- Dent J, Talley NJ. Overview: initial and long-term management of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003;17:53-7.
- HM Treasury . Green Book: Appraisal and Evaluation in Central Government 2003.
- Contini S, Zinicola R, Bertele A, Nervi G, Rubini P, Scarpignato C. Dysphagia and clinical outcome after laparoscopic Nissen or Rossetti fundoplication: sequential prospective study. World J Surg 2002;26:1106-11.
- Gotley DC, Smithers BM, Rhodes M, Menzies B, Branicki FJ, Nathanson L. Laparoscopic nissen fundoplication – 200 consecutive cases. Gut 1996;38:487-91.
- Dallemagne B, Weerts JM, Jeahes C, Markiewicz S. Results of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Hepatogastroenterology 1998;45:1338-43.
- Kiviluoto T, Siren J, Farkkila M, Luukkonen P, Salo J, Kivilaakso E. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: a prospective analysis of 200 consecutive patients. Surg Laparosc Endosc 1998;8:429-34.
- Booth MI, Jones L, Stratford J, Dehn TCB. Results of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication at 2–8 years after surgery. Br J Surg 2002;89:476-81.
- Landreneau RJ, Wiechmann RJ, Hazelrigg SR, Santucci TS, Boley TM, Magee MJ, et al. Success of laparoscopic fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Thorac Surg 1998;66:1886-92.
- Finley CR, McKernan JB. Laparoscopic antireflux surgery at an outpatient surgery center. Surg Endosc 2001;15:823-6.
- Pessaux P, Arnaud JP, Ghavami B, Flament JB, Trebuchet G, Meyer C, et al. Morbidity of laparoscopic fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux: a retrospective study about 1470 patients. Hepatogastroenterology 2002;49:447-50.
- van der Peet DL, Klinkenberg-Knol EC, Eijsbouts QAJ, van der Berg M, de Brauw LM, Cuesta MA. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Surg Endosc 1998;12:1159-63.
- Bais JE, Bartelsman JFWM, Bonjer HJ, Cuesta MA, Go PMNYH, Klinkenberg-Knol EC, et al. Laparoscopic or conventional Nissen fundoplication for gastro-oesphageal reflux disease: randomised clinical trial. Lancet 2000;355:170-74.
- Office for National Statistics . Key Population and Vital Statistics 2003.
- Watson DI, Jamieson GG, Devitt PG, Matthew G, Britten-Jones RE, Game PA, et al. Changing strategies in the performance of laparoscopic nissen fundoplication as a result of experience with 230 operations. Surg Endosc 1995;9:961-6.
- Lundell L, Miettinen P, Myrvold HE, Pedersen SA, Liedman B, Hatlebakk JG, et al. Continued (5-year) follow-up of a randomized clinical study comparing antireflux surgery and omeprazole in gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Am Coll Surg 2001;192:172-81.
- Anvari M, Allen C. Five-year comprehensive outcomes evaluation in 181 patients after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. J Am Coll Surg 2003;196:51-9.
- Ludemann R, Watson DI, Jamieson GG, Game PA, Devitt PG. Five-year follow-up of a randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic total versus anterior 180° fundoplication. Br J Surg 2005;92:240-3.
- Hunter JG, Smith DC, Branum GD, Waring JP, Trus TL, Cornwell M, et al. Laparoscopic fundoplication failures: patterns of failure and response to fundoplication revision. Ann Surg 1999;230:595-606.
- Graziano K, Teitelbaum DH, McLean K, Hirschl RB, Coran AG, Geiger JD. Recurrence after laparoscopic and open Nissen fundoplication: a comparison of the mechanisms of failure. Surg Endosc 2003;17:704-7.
- Soper NJ, Dunnegan D. Anatomic fundoplication failure after laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Ann Surg 1999;229:669-76.
- Eshraghi N, Farahmand M, Soot SJ, Rand-Luby L, Deveney CW, Sheppard BC. Comparison of outcomes of open versus laparoscopic nissen fundoplication performed in a single practice. Am J Surg 1998;175:371-4.
- Bammer T, Hinder RA, Klaus A, Klingler PJ. Five- to eight-year outcome of the first laparoscopic Nissen fundoplications. J Gastrointest Surg 2001;5:42-8.
- Jamieson GG, Watson DI, Britten-Jones RE, Mitchell PC, Anvari M. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Ann Surg 1994;220:137-45.
- Hatlebakk J, Berstad A. Lansoprazole 15 and 30 mg daily in maintaining healing and symptom relief in patients with reflux oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1997;11:365-72.
- Festen HP, Schenk E, Tan G, Snel P, Nelis F. Omeprazole versus high-dose ranitidine in mild gastroesophageal reflux disease: short and long-term management. Am J Gastroenterol 1999;94:931-6.
- Bate CM, Booth SN, Crowe JP, Mountford RA, Keeling PW, Hepworth-Jones B, et al. Omeprazole 10 mg or 20 mg once daily in the prevention of recurrence of reflux oesophagitis. Gut 1995;36:492-8.
- Myrvold HE, Lundell L, Miettinen P, Pedersen SA, Liedman B, Hatlebakk J, et al. The cost of long term therapy for GORD: a randomised trial comparing omeprazole and open antireflux surgery. Gut 2001;49:488-94.
- British National Formulary 50. London: British Medical Association and the Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain; 2005.
- Curtis L, Netten A. Unit costs of health and social care 2005. Canterbury: University of Kent; 2005.
- Johnston PW, Johnston BT, Collins BJ, Collins JSA, Love AH. Audit of the role of oesophageal manometry in clinical practice. Gut 1993;34:1158-61.
- Swanstrom L, Wayne R. Spectrum of gastrointestinal symptoms after laparoscopic fundoplication. Am J Surg 1994;167:538-41.
- Laine S, Rantala A, Gullichsen R, Ovaska J. Laparoscopic vs conventional Nissen fundoplication. A prospective randomized study. Surg Endosc 1997;11:441-4.
- Kind P, Spilker B. Quality of life and pharmacoeconomics in clinical trials. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; 1996.
- Dolan P, Gudex C, Kind P, Williams A. A social tariff for EuroQol: results from a UK general population survey. York: University of York Centre for Health Economics; 1995.
- Kind P, Hardman G, Macran S. UK population norms for EQ-5D. York: University of York Centre for Health Economics; 1999.
- Ainslie WG, Catton JA, Davides D, Dexter S, Gibson J, Larvin M, et al. Micropuncture cholecystectomy vs conventional laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomised controlled trial. Surg Endosc 2003;17:766-72.
- Heudebert GR, Marks R, Wilcox CM, Centor RM. Choice of long-term strategy for the management of patients with severe esophagitis: a cost-utility analysis. Gastroenterology 1997;112:1078-86.
- Briggs AH. Handling uncertainty in cost-effectiveness models. Pharmacoeconomics 2000;17:479-500.
- Van Hout BA, Al MJ, Gordon GS, Rutten FF. Costs, effects and c/e-ratios alongside a clinical trial. Health Economics 1994;3:309-19.
- Fenwick E, Claxton K, Sculpher M. Representing uncertainty: the role of cost-effectiveness acceptability curves. Health Economics 2001;10:779-89.
- Fenwick E, Claxton K, Sculpher M, Briggs A. Improving the efficiency and relevance of health technology assessment: the role of decision analytic modelling. York: University of York Centre for Health Economics; 2000.
- Claxton K. The irrelevance of inference: a decision making approach to the stochastic evaluation of health care technologies. J Health Econ 1999;18:341-64.
- Claxton K, Sculpher M, Drummond M. A rational framework for decision making by the National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE). Lancet 2002;360:711-15.
- DeMeester TR, Wang CI, Wernly JA, Pellegrini CA, Little AG, Klementschitsch P, et al. Technique, indications, and clinical use of 24 hour esophogeal pH monitoring. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1980;79:656-70.
- Eypasch E, Williams JI, Wood-Dauphinee S, Ure BM, Schmulling C, Neugebauer E, et al. Gastrointestinal quality of life index: development, validation and application of a new instrument. Br J Surg 1995;82:216-22.
- Locke GR, Talley NJ, Weaver AL, Zinsmeister AR. A new questionnaire for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Mayo Clin Proc 1994;69:539-47.
- Revicki DA, Wood M, Wilkund I, Crawley J. Reliability and validity of the gastrointestinal symptom rating scale in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Qual Life Res 1998;7:75-83.
- Svedlund J, Sjodin I, Dotevall G. GSRS – a clinical rating scale for gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and peptic ulcer disease. Dig Dis Sci 1988;33:129-34.
- Wiklund I, Bigard MA, Grace E, Talley NJ, Kamm M, Veldhuyzen van Zanten S, et al. Quality of life in reflux and dyspepsia patients. Psychometric documentation of a new disease-specific questionnaire (QOLRAD). Eur J Surg 1998;164:41-9.
- Stanghellini V, Armstrong D, Monnikes H, Bardhan KD. Systematic review: do we need a new gastro-oesophageal reflux disease questionnaire?. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004;19:463-79.
- Bardhan KD, Stanghellini V, Armstrong D, Berghofer P, Gatz G, Monnikes H. Evaluation of GERD symptoms during therapy: Part I. Development of the new GERD questionnaire ReQuest™. Digestion 2004;69:229-37.
- Monnikes H, Bardhan KD, Stanghellini V, Berghofer P, Bethke TD, Armstrong D. Evaluation of GERD symptoms during therapy: Part II. Psychometric evaluation and validation of the new questionnaire ReQuest™ in erosive GERD. Digestion 2004;69:238-44.
- Brooks R. with the EuroQol Group . EuroQol – a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy 1990;16:199-208.
- Jenkinson C, Layte R, Wright L, Coulter A. The UK SF-36: an analysis and interpretation manual. Oxford: Health Services Research Unit; 1996.
- Nunnally JC. Psychometric theory. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1978.
- Department of Health . Building on the Best: Choice, Responsiveness and Equity in the NHS 2003.
- Leventhal H, Leventhal EA, Contrada RJ. Self-regulation, health and behaviour: a perceptual-cognitive approach. Psychol Health 1998;13:717-33.
- Horne R, Weinman J, Hankins M. The beliefs about medicines questionnaire: the development and evaluation of a new method for assessing the cognitive representation of medication. Psychol Health 1999;14:1-24.
- Horne R, Cameron LD, Leventhal H. Self-regulation of health and illness behaviour. New York: Routledge; 2003.
- Jolliffe IT. Principal component analysis. New York: Springer; 1996.
- Johnston M, Vögele C. Benefits of psychological preparation for surgery: a meta-analysis. Ann Behav Med 1993;15:245-56.
- Lord FM. Applications of item response theory to practical testing problems. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 1980.
- Burden R, Faires D. Numerical analysis. Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks Cole; 2000.
- Manca A, Hawkins N. Estimating mean QALYs in trial-based cost-effectiveness analysis: the importance of controlling for baseline utility. Health Econ 2005;14:487-96.
- Bojke L, Hornby E, Sculpher M. A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of pharmacotherapy or surgery (laparoscopic fundoplication) in the treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Pharmacoeconomics 2007;25:829-41.
- Efron B, Tibshirani R. An introduction to the bootstrap. New York: Chapman and Hall; 1993.
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence . Guide to the Methods of Technology Apprasial 2004.
- Department of Health . NHS Reference Costs 2005 06 and National Tariff 2006.
- Madan A, Minocha A. Despite high satisfaction, majority of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease patients continue to use proton pump inhibitors after antireflux surgery. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2006;23:601-5.
- Vidal O, Lacy AM, Pera M, Valentini M, Bollo J, Lacima G, et al. Long-term control of gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms after laparoscopic Nissen-Rosetti fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 2006;10:863-9.
- Ades AE, Sculpher M, Sutton A, Abrams K, Cooper N, Welton N, et al. Bayesian methods for evidence synthesis in cost-effectiveness analysis. Pharmacoeconomics 2006;24:1-19.
- Ades AE, Lu G, Claxton K. Expected value of sample information calculations in medical decision modeling. Med Decis Making 2004;24:207-27.
- Mahon D, Rhodes M, Decadt B, Hindmarsh A, Lowndes R, Beckingham I, et al. Randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication compared with proton-pump inhibitors for treatment of chronic gastro-oesophageal reflux. Br J Surg 2005;92:695-9.
- Papasavas PK, Keenan RJ, Yeaney WW, Caushaj PF, Gagne DJ, Landreneau RJ. Effectiveness of laparoscopic fundoplication in relieving the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and eliminating antireflux medical therapy. Surg Endosc 2003;17:1200-5.
- Granderath FA, Kamolz T, Schweiger UM, Pointner R. Quality of life, surgical outcome, and patient satisfaction three years after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. World J Surg 2002;26:1234-8.
- Dassinger MS, Torquati A, Houston HL, Holzman MD, Sharp KW, Richards WO. Laparoscopic fundoplication: 5-year follow-up. Am Surg 2004;70:691-5.
- Bloomston M, Nields W, Rosemurgy AS. Symptoms and antireflux medication use following laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: outcome at 1 and 4 years. J Soc Laparoendosc Surg 2003;7:211-18.
- Spiegelhalter DJ, Thomas A, Best N. WinBUGS Manual 2001.
- Trimble KC, Douglas S, Pryde A, Heading RC. Clinical characteristics and natural history of symptomatic but not excess gastroesophageal reflux. Dig Dis Sci 1995;40:1098-104.
- National Statistics . KS02 Age Structure: Census 2001, Key Statistics for Local Authorities 2005.
- Venables W, Smith D. An Introduction to R: A Programming Environment for Data Analysis and Graphics 2005. http://cran.r-project.org.
- Briggs A, Sculpher M, Claxton K. Decision modelling for health economic evaluation. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2006.
- Diaz-Rubio M, Moreno-Elola-Olaso C, Rey E, Locke GR. Symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux: prevalence, severity, duration and associated factors in a Spanish population. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004;19:95-105.
- Arguedas MR, Heudebert GR, Klapow JC, Centor RM, Eloubeidi M, Wilcox CM, et al. Re-examination of the cost-effectiveness of surgical versus medical therapy in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: the value of long-term data collection. Am J Gastroenterol 2004;99:1023-8.
- Ryan M, Gerard K. Using discrete choice experiments to value health care: current practice and future prospects. Appl Health Econ Policy Analysis 2003;2:55-64.
- McFadden D, Zarembka P. Frontiers of econometrics. New York: Academic Press; 1973.
- Ryan M. A role for conjoint analysis in health technology assessment in health care?. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 1999;15:443-57.
- Permain D, Swanson J, Kroes E, Bradley M. Stated preference techniques: a guide to practice. Hague: Steer Davis Gleave and Hague Consulting Group; 1991.
- Hahn GH, Shapiro SS. A Catalogue and Computer Programme for the Design and Analysis of Orthogonal Symmetric and Asymmetric Fractional Factorial Experiments 1966.
- Sloane NJA. A Library of Orthogonal Arrays n.d. www.research.att.com/∼njas/oadir/ (accessed July 2006).
- Zwerina K, Huber J, Kuhfeld WF. A general method for constructing efficient choice designs. Durham, NC: Duke University Fuqua School of Business; 1996.
- San Miguel F, Ryan M, Amaya-Amaya M. Irrational stated preferences: a quantitative and qualitative investigation. Health Econ 2005;14:307-22.
- Kleinman L, McIntosh E, Ryan M, Schmeir J, Crawley MS, Locke GR, et al. Willingness to pay for complete symptom relief of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Arch Intern Med 2002;162:1361-6.
- Hirth RA, Bloom BS, Chernew ME, Fendrick AM. Patient, physician and payer perceptions and misperceptions of willingness to pay for diagnostic uncertainty. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 2000;16:35-49.
Appendix 1 Patient entry form
Appendix 2 Baseline questionnaire
Appendix 3 Patient letter of invitation and patient information leaflets 1 and 2
Appendix 4 Patient assessment form
Appendix 5 Surgical patient information leaflet
Appendix 6 Trial consent form
Appendix 7 Preference study: patient information leaflet and consent form
Appendix 8 Laparoscopic fundoplication operative data form
Appendix 9 Search strategies for literature searches
Search strategies
-
fundoplication or fundiplication or fundoplast$or stretta).mp.
-
(euroqol or EQ-5D or eq-5d or (eq adj 5d) or hui or qwb or utility or utilities).mp.
-
quality of life/
-
1 and (2 or 3)
Reference manager/MEDLINE
(SF-36) OR (sf 36)
(EQ-5D) OR (eq 5d) OR (euroqol) OR (euro qol)
(short form 36) OR (shortform 36) OR (sf thirtysix) OR (sf thirty six) OR (short form thirty six)
(hrql) OR (hrqol) OR (h qol) OR (hql) OR (hqol)
or (hye) OR (hyes) OR (health$year$equivalent$) OR (health util$)
or rosser
or (quality of life) OR (quality adjusted life year) OR (health status indicator) OR (qaly) OR (quality adjusted life) OR (life quality)
(ppi) OR (omeprazole) OR (pantoprazole) OR (lansoprazole) OR (esomeprazole) OR (rabeprazole)
(SF-36) OR (sf 36)
(EQ-5D) OR (eq 5d) OR (euroqol) OR (euro qol)
(short form 36) OR (shortform 36) OR (sf thirtysix) OR (sf thirty six) OR (short form thirty six)
or (64) OR (hrqol) OR (h qol) OR (hql) OR (hqol)
or (hye) OR (hyes) OR (health$year$equivalent$) OR (health util$)
or rosser
or (quality of life) OR (quality adjusted life year) OR (health status indicator) OR (qaly) OR (quality adjusted life) OR (life quality)
and (H2-blocker) OR (ranitidine) OR (famotidine) OR (cimetidine) OR (nizatidine)
Appendix 10 Costs of surgery and cost loadings
| Total surgical costs (£) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centre 1 | Centre 2 | Centre 3 | Centre 4 | Centre 5 | |
| Preoperative procedures | £314.66 | £299.42 | £314.66 | £321.66 | £364.66 |
| Theatre staff | £545.20 | £289.92 | £455.06 | £441.46 | £520.39 |
| Disposables | £725.30 | £853.52 | £1051.08 | £635.93 | £816.46 |
| Capital equipment | £9.22 | £9.22 | £9.22 | £9.22 | £9.22 |
| Bed costs | £1140.72 | £1140.72 | £1140.72 | £1140.72 | £1140.72 |
| Consumables | £47.57 | £47.57 | £47.57 | £47.57 | £47.57 |
| Total/centre | £2782.67 | £2640.37 | £3018.31 | £2596.56 | £2899.02 |
| Mean cost of LNF | £2787.39 | ||||
| SD | £175.95 | ||||
| Cost loadings (for complications) | |
|---|---|
| Cost of open fundoplication (conversion) allowing for longer LOS | £4490.67 |
| Probability of conversion being required | 0.05 |
| Cost of dilatation | £165 |
| Probability of dilatation being performed | 0.021 |
| Total cost of surgery | £3015.39 |
Appendix 11
Programming code using the WinBUGS® statistical package to estimate the pooled rate of surgery patients requiring medical management, using a random study effect
Model
#filename “poisson6.odc”
{
for (i in 1:N) {
#likelihood poisson family
n_cases[i] ∼ dpois(mu[i])
#beta0 = intercept
#no covariates
#total is the offset term (coefficient forced to = 1)
#estimate random effects b[i]
#log (multiplicative) link function
log(mu[i]) < –log(total[i]) + b[i]
#prior for random study effect
b[i] ∼ dnorm(beta0,tau)
}
#prior for log(pooled rate)
beta0 ∼ dnorm(0,1.0E-6)
#various priors are possible for precision
#eg (gamma(0.001,0.001) on tau,uniform(0,10) on sigma)
sigma ∼ dunif(0,10)
#recalculate intercept on natural scale
rate < –exp(beta0)
tau < –1/(sigma × sigma)
}
inits
#list(beta0 = 0, tau = 1,
b = c(0,0,0,0,0
0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0
))
list(beta0 = 0, sigma = 0.5,
b = c(0,0,0,0,0, 0,0,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0
))
data
list(N = 15,
n_cases = c(2,14,19,24,5,
10,60,150,2,11,
19,31,10,80,0
),
total = c(109,104,716,1094,103,
411,4410,578,108,260,
100,336,533,300,18
))
END
Results of WinBUGS regression model
| Node | Mean | SD | MC error | 2.5% | Median | 97.5% | Start | Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b[1] | –3.890 | 0.5914 | 0.005063 | –5.184 | –3.836 | –2.87 | 10001 | 20000 |
| b[2] | –2.096 | 0.2738 | 0.001975 | –2.666 | –2.083 | –1.593 | 10001 | 20000 |
| b[3] | –3.631 | 0.2259 | 0.001579 | –4.094 | –3.624 | –3.21 | 10001 | 20000 |
| b[4] | –3.815 | 0.2013 | 0.001423 | –4.224 | –3.808 | –3.439 | 10001 | 20000 |
| b[5] | –3.113 | 0.4303 | 0.003166 | –4.032 | –3.085 | –2.343 | 10001 | 20000 |
| b[6] | –3.709 | 0.3049 | 0.001992 | –4.342 | –3.695 | –3.154 | 10001 | 20000 |
| b[7] | –4.291 | 0.1289 | 8.542E-4 | –4.551 | –4.287 | –4.044 | 10001 | 20000 |
| b[8] | –1.361 | 0.08253 | 6.599E-4 | –1.525 | –1.360 | –1.203 | 10001 | 20000 |
| b[9] | –3.890 | 0.5920 | 0.004299 | –5.199 | –3.844 | –2.871 | 10001 | 20000 |
| b[10] | –3.197 | 0.2945 | 0.002113 | –3.817 | –3.181 | –2.663 | 10001 | 20000 |
| b[11] | –1.747 | 0.2347 | 0.001692 | –2.224 | –1.738 | –1.309 | 10001 | 20000 |
| b[12] | –2.417 | 0.1799 | 0.001345 | –2.781 | –2.412 | –2.078 | 10001 | 20000 |
| b[13] | –3.955 | 0.3002 | 0.002147 | –4.579 | –3.944 | –3.407 | 10001 | 20000 |
| b[14] | –1.345 | 0.1133 | 8.246E-4 | –1.574 | –1.343 | –1.129 | 10001 | 20000 |
| b[15] | –3.890 | 1.0070 | 0.008261 | –6.141 | –3.798 | –2.213 | 10001 | 20000 |
| beta0 | –3.086 | 0.3382 | 0.002570 | –3.774 | –3.077 | –2.433 | 10001 | 20000 |
| rate | 0.04833 | 0.01689 | 1.232E-4 | 0.02297 | 0.04608 | 0.08779 | 10001 | 20000 |
| sigma | 1.208 | 0.2936 | 0.003329 | 0.7787 | 1.159 | 1.919 | 10001 | 20000 |
| tau | 0.7991 | 0.3561 | 0.003369 | 0.2717 | 0.744 | 1.65 | 10001 | 20000 |
Appendix 12 Discrete choice experiment questionnaires
Appendix 13 Further results of the discrete choice experiment (DCE)
The regression model for the whole sample
| Dimension | Coefficient | Standard error | p-value | 95% confidence interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Troublesome symptoms | ||||
| Once a week | –0.068 | 0.066 | 0.299 | –0.197 to 0.061 |
| Two or three times a week | –0.445 | 0.077 | 0.000 | –0.596 to –0.295 |
| Most days/every day | –1.156 | 0.071 | 0.000 | –1.295 to –1.018 |
| Serious complications | –5.471 | 0.661 | 0.000 | –6.767 to –4.174 |
| Surgery | –5.176 | 0.844 | 0.000 | –6.830 to –3.521 |
| Lifelong medication | –4.815 | 0.685 | 0.000 | –6.159 to –3.472 |
Relative importance of dimensions
| Troublesome symptoms | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two or three times | Most days | Serious complications | Surgery | Lifelong medication | |
| Troublesome symptoms | |||||
| Two or three times | 1.00 | 2.85 | 13.74 | 13.13 | –12.08 |
| Most days | 0.35 | 1.00 | 4.83 | 4.61 | –4.25 |
| Serious complications | 0.07 | 0.21 | 1.00 | 0.96 | –0.88 |
| Surgery | 0.08 | 0.22 | 1.05 | 1.00 | –0.92 |
| Lifelong medication | –0.08 | –0.24 | –1.14 | –1.09 | 1.00 |
List of abbreviations
- BMQ
- Beliefs about Medicines Questionnaire
- BSQ
- Beliefs about Surgery Questionnaire
- CI
- confidence interval
- DCE
- discrete choice experiment
- DMC
- Data Monitoring Committee
- EQ-5D
- EuroQol-5 Dimensions
- EVPI
- expected value of perfect information
- GORD
- gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
- H2RA
- histamine receptor antagonist
- HRQoL
- health-related quality of life
- HSR
- Health Services Research
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- ITT
- intention to treat
- IQR
- interquartile range
- MCS
- mental component score
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
- ONS
- Office for National Statistics
- PCA
- principal components analysis
- PCS
- physical component score
- PP
- per protocol
- PPI
- proton pump inhibitor
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- QoL
- quality of life
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- RQLS
- REFLUX quality of life score
- SD
- standard deviation
- SE
- standard error
- SF-36
- Short Form with 36 Items
- VAS
- visual analogue scale
All abbreviations that have been used in this report are listed here unless the abbreviation is well known (e.g. NHS) or it has been used only once or it is a non-standard abbreviation used only in figures/tables/appendices, in which case the abbreviation is defined in the figure legend or in the notes at the end of the table.
Notes
Health Technology Assessment reports published to date
-
Home parenteral nutrition: a systematic review.
By Richards DM, Deeks JJ, Sheldon TA, Shaffer JL.
-
Diagnosis, management and screening of early localised prostate cancer.
A review by Selley S, Donovan J, Faulkner A, Coast J, Gillatt D.
-
The diagnosis, management, treatment and costs of prostate cancer in England and Wales.
A review by Chamberlain J, Melia J, Moss S, Brown J.
-
Screening for fragile X syndrome.
A review by Murray J, Cuckle H, Taylor G, Hewison J.
-
A review of near patient testing in primary care.
By Hobbs FDR, Delaney BC, Fitzmaurice DA, Wilson S, Hyde CJ, Thorpe GH, et al.
-
Systematic review of outpatient services for chronic pain control.
By McQuay HJ, Moore RA, Eccleston C, Morley S, de C Williams AC.
-
Neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism: cost, yield and outcome.
A review by Pollitt RJ, Green A, McCabe CJ, Booth A, Cooper NJ, Leonard JV, et al.
-
Preschool vision screening.
A review by Snowdon SK, Stewart-Brown SL.
-
Implications of socio-cultural contexts for the ethics of clinical trials.
A review by Ashcroft RE, Chadwick DW, Clark SRL, Edwards RHT, Frith L, Hutton JL.
-
A critical review of the role of neonatal hearing screening in the detection of congenital hearing impairment.
By Davis A, Bamford J, Wilson I, Ramkalawan T, Forshaw M, Wright S.
-
Newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism: a systematic review.
By Seymour CA, Thomason MJ, Chalmers RA, Addison GM, Bain MD, Cockburn F, et al.
-
Routine preoperative testing: a systematic review of the evidence.
By Munro J, Booth A, Nicholl J.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness of laxatives in the elderly.
By Petticrew M, Watt I, Sheldon T.
-
When and how to assess fast-changing technologies: a comparative study of medical applications of four generic technologies.
A review by Mowatt G, Bower DJ, Brebner JA, Cairns JA, Grant AM, McKee L.
-
Antenatal screening for Down’s syndrome.
A review by Wald NJ, Kennard A, Hackshaw A, McGuire A.
-
Screening for ovarian cancer: a systematic review.
By Bell R, Petticrew M, Luengo S, Sheldon TA.
-
Consensus development methods, and their use in clinical guideline development.
A review by Murphy MK, Black NA, Lamping DL, McKee CM, Sanderson CFB, Askham J, et al.
-
A cost–utility analysis of interferon beta for multiple sclerosis.
By Parkin D, McNamee P, Jacoby A, Miller P, Thomas S, Bates D.
-
Effectiveness and efficiency of methods of dialysis therapy for end-stage renal disease: systematic reviews.
By MacLeod A, Grant A, Donaldson C, Khan I, Campbell M, Daly C, et al.
-
Effectiveness of hip prostheses in primary total hip replacement: a critical review of evidence and an economic model.
By Faulkner A, Kennedy LG, Baxter K, Donovan J, Wilkinson M, Bevan G.
-
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in colorectal surgery: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials.
By Song F, Glenny AM.
-
Bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for malignancy.
A review by Johnson PWM, Simnett SJ, Sweetenham JW, Morgan GJ, Stewart LA.
-
Screening for speech and language delay: a systematic review of the literature.
By Law J, Boyle J, Harris F, Harkness A, Nye C.
-
Resource allocation for chronic stable angina: a systematic review of effectiveness, costs and cost-effectiveness of alternative interventions.
By Sculpher MJ, Petticrew M, Kelland JL, Elliott RA, Holdright DR, Buxton MJ.
-
Detection, adherence and control of hypertension for the prevention of stroke: a systematic review.
By Ebrahim S.
-
Postoperative analgesia and vomiting, with special reference to day-case surgery: a systematic review.
By McQuay HJ, Moore RA.
-
Choosing between randomised and nonrandomised studies: a systematic review.
By Britton A, McKee M, Black N, McPherson K, Sanderson C, Bain C.
-
Evaluating patient-based outcome measures for use in clinical trials.
A review by Fitzpatrick R, Davey C, Buxton MJ, Jones DR.
-
Ethical issues in the design and conduct of randomised controlled trials.
A review by Edwards SJL, Lilford RJ, Braunholtz DA, Jackson JC, Hewison J, Thornton J.
-
Qualitative research methods in health technology assessment: a review of the literature.
By Murphy E, Dingwall R, Greatbatch D, Parker S, Watson P.
-
The costs and benefits of paramedic skills in pre-hospital trauma care.
By Nicholl J, Hughes S, Dixon S, Turner J, Yates D.
-
Systematic review of endoscopic ultrasound in gastro-oesophageal cancer.
By Harris KM, Kelly S, Berry E, Hutton J, Roderick P, Cullingworth J, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of trials and other studies.
By Sutton AJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR, Sheldon TA, Song F.
-
Primary total hip replacement surgery: a systematic review of outcomes and modelling of cost-effectiveness associated with different prostheses.
A review by Fitzpatrick R, Shortall E, Sculpher M, Murray D, Morris R, Lodge M, et al.
-
Informed decision making: an annotated bibliography and systematic review.
By Bekker H, Thornton JG, Airey CM, Connelly JB, Hewison J, Robinson MB, et al.
-
Handling uncertainty when performing economic evaluation of healthcare interventions.
A review by Briggs AH, Gray AM.
-
The role of expectancies in the placebo effect and their use in the delivery of health care: a systematic review.
By Crow R, Gage H, Hampson S, Hart J, Kimber A, Thomas H.
-
A randomised controlled trial of different approaches to universal antenatal HIV testing: uptake and acceptability. Annex: Antenatal HIV testing – assessment of a routine voluntary approach.
By Simpson WM, Johnstone FD, Boyd FM, Goldberg DJ, Hart GJ, Gormley SM, et al.
-
Methods for evaluating area-wide and organisation-based interventions in health and health care: a systematic review.
By Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ.
-
Assessing the costs of healthcare technologies in clinical trials.
A review by Johnston K, Buxton MJ, Jones DR, Fitzpatrick R.
-
Cooperatives and their primary care emergency centres: organisation and impact.
By Hallam L, Henthorne K.
-
Screening for cystic fibrosis.
A review by Murray J, Cuckle H, Taylor G, Littlewood J, Hewison J.
-
A review of the use of health status measures in economic evaluation.
By Brazier J, Deverill M, Green C, Harper R, Booth A.
-
Methods for the analysis of quality-of-life and survival data in health technology assessment.
A review by Billingham LJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR.
-
Antenatal and neonatal haemoglobinopathy screening in the UK: review and economic analysis.
By Zeuner D, Ades AE, Karnon J, Brown J, Dezateux C, Anionwu EN.
-
Assessing the quality of reports of randomised trials: implications for the conduct of meta-analyses.
A review by Moher D, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Tugwell P, Moher M, Jones A, et al.
-
‘Early warning systems’ for identifying new healthcare technologies.
By Robert G, Stevens A, Gabbay J.
-
A systematic review of the role of human papillomavirus testing within a cervical screening programme.
By Cuzick J, Sasieni P, Davies P, Adams J, Normand C, Frater A, et al.
-
Near patient testing in diabetes clinics: appraising the costs and outcomes.
By Grieve R, Beech R, Vincent J, Mazurkiewicz J.
-
Positron emission tomography: establishing priorities for health technology assessment.
A review by Robert G, Milne R.
-
The debridement of chronic wounds: a systematic review.
By Bradley M, Cullum N, Sheldon T.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (2) Dressings and topical agents used in the healing of chronic wounds.
By Bradley M, Cullum N, Nelson EA, Petticrew M, Sheldon T, Torgerson D.
-
A systematic literature review of spiral and electron beam computed tomography: with particular reference to clinical applications in hepatic lesions, pulmonary embolus and coronary artery disease.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Hutton J, Harris KM, Roderick P, Boyce JC, et al.
-
What role for statins? A review and economic model.
By Ebrahim S, Davey Smith G, McCabe C, Payne N, Pickin M, Sheldon TA, et al.
-
Factors that limit the quality, number and progress of randomised controlled trials.
A review by Prescott RJ, Counsell CE, Gillespie WJ, Grant AM, Russell IT, Kiauka S, et al.
-
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in total hip replacement: a systematic review.
By Glenny AM, Song F.
-
Health promoting schools and health promotion in schools: two systematic reviews.
By Lister-Sharp D, Chapman S, Stewart-Brown S, Sowden A.
-
Economic evaluation of a primary care-based education programme for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee.
A review by Lord J, Victor C, Littlejohns P, Ross FM, Axford JS.
-
The estimation of marginal time preference in a UK-wide sample (TEMPUS) project.
A review by Cairns JA, van der Pol MM.
-
Geriatric rehabilitation following fractures in older people: a systematic review.
By Cameron I, Crotty M, Currie C, Finnegan T, Gillespie L, Gillespie W, et al.
-
Screening for sickle cell disease and thalassaemia: a systematic review with supplementary research.
By Davies SC, Cronin E, Gill M, Greengross P, Hickman M, Normand C.
-
Community provision of hearing aids and related audiology services.
A review by Reeves DJ, Alborz A, Hickson FS, Bamford JM.
-
False-negative results in screening programmes: systematic review of impact and implications.
By Petticrew MP, Sowden AJ, Lister-Sharp D, Wright K.
-
Costs and benefits of community postnatal support workers: a randomised controlled trial.
By Morrell CJ, Spiby H, Stewart P, Walters S, Morgan A.
-
Implantable contraceptives (subdermal implants and hormonally impregnated intrauterine systems) versus other forms of reversible contraceptives: two systematic reviews to assess relative effectiveness, acceptability, tolerability and cost-effectiveness.
By French RS, Cowan FM, Mansour DJA, Morris S, Procter T, Hughes D, et al.
-
An introduction to statistical methods for health technology assessment.
A review by White SJ, Ashby D, Brown PJ.
-
Disease-modifying drugs for multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By Clegg A, Bryant J, Milne R.
-
Publication and related biases.
A review by Song F, Eastwood AJ, Gilbody S, Duley L, Sutton AJ.
-
Cost and outcome implications of the organisation of vascular services.
By Michaels J, Brazier J, Palfreyman S, Shackley P, Slack R.
-
Monitoring blood glucose control in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review.
By Coster S, Gulliford MC, Seed PT, Powrie JK, Swaminathan R.
-
The effectiveness of domiciliary health visiting: a systematic review of international studies and a selective review of the British literature.
By Elkan R, Kendrick D, Hewitt M, Robinson JJA, Tolley K, Blair M, et al.
-
The determinants of screening uptake and interventions for increasing uptake: a systematic review.
By Jepson R, Clegg A, Forbes C, Lewis R, Sowden A, Kleijnen J.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of prophylactic removal of wisdom teeth.
A rapid review by Song F, O’Meara S, Wilson P, Golder S, Kleijnen J.
-
Ultrasound screening in pregnancy: a systematic review of the clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and women’s views.
By Bricker L, Garcia J, Henderson J, Mugford M, Neilson J, Roberts T, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the taxanes used in the treatment of advanced breast and ovarian cancer.
By Lister-Sharp D, McDonagh MS, Khan KS, Kleijnen J.
-
Liquid-based cytology in cervical screening: a rapid and systematic review.
By Payne N, Chilcott J, McGoogan E.
-
Randomised controlled trial of non-directive counselling, cognitive–behaviour therapy and usual general practitioner care in the management of depression as well as mixed anxiety and depression in primary care.
By King M, Sibbald B, Ward E, Bower P, Lloyd M, Gabbay M, et al.
-
Routine referral for radiography of patients presenting with low back pain: is patients’ outcome influenced by GPs’ referral for plain radiography?
By Kerry S, Hilton S, Patel S, Dundas D, Rink E, Lord J.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (3) antimicrobial agents for chronic wounds; (4) diabetic foot ulceration.
By O’Meara S, Cullum N, Majid M, Sheldon T.
-
Using routine data to complement and enhance the results of randomised controlled trials.
By Lewsey JD, Leyland AH, Murray GD, Boddy FA.
-
Coronary artery stents in the treatment of ischaemic heart disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Meads C, Cummins C, Jolly K, Stevens A, Burls A, Hyde C.
-
Outcome measures for adult critical care: a systematic review.
By Hayes JA, Black NA, Jenkinson C, Young JD, Rowan KM, Daly K, et al.
-
A systematic review to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions to promote the initiation of breastfeeding.
By Fairbank L, O’Meara S, Renfrew MJ, Woolridge M, Sowden AJ, Lister-Sharp D.
-
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators: arrhythmias. A rapid and systematic review.
By Parkes J, Bryant J, Milne R.
-
Treatments for fatigue in multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By Brañas P, Jordan R, Fry-Smith A, Burls A, Hyde C.
-
Early asthma prophylaxis, natural history, skeletal development and economy (EASE): a pilot randomised controlled trial.
By Baxter-Jones ADG, Helms PJ, Russell G, Grant A, Ross S, Cairns JA, et al.
-
Screening for hypercholesterolaemia versus case finding for familial hypercholesterolaemia: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Marks D, Wonderling D, Thorogood M, Lambert H, Humphries SE, Neil HAW.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists in the medical management of unstable angina.
By McDonagh MS, Bachmann LM, Golder S, Kleijnen J, ter Riet G.
-
A randomised controlled trial of prehospital intravenous fluid replacement therapy in serious trauma.
By Turner J, Nicholl J, Webber L, Cox H, Dixon S, Yates D.
-
Intrathecal pumps for giving opioids in chronic pain: a systematic review.
By Williams JE, Louw G, Towlerton G.
-
Combination therapy (interferon alfa and ribavirin) in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a rapid and systematic review.
By Shepherd J, Waugh N, Hewitson P.
-
A systematic review of comparisons of effect sizes derived from randomised and non-randomised studies.
By MacLehose RR, Reeves BC, Harvey IM, Sheldon TA, Russell IT, Black AMS.
-
Intravascular ultrasound-guided interventions in coronary artery disease: a systematic literature review, with decision-analytic modelling, of outcomes and cost-effectiveness.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Hutton J, Lindsay HSJ, Blaxill JM, Evans JA, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to evaluate the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of counselling patients with chronic depression.
By Simpson S, Corney R, Fitzgerald P, Beecham J.
-
Systematic review of treatments for atopic eczema.
By Hoare C, Li Wan Po A, Williams H.
-
Bayesian methods in health technology assessment: a review.
By Spiegelhalter DJ, Myles JP, Jones DR, Abrams KR.
-
The management of dyspepsia: a systematic review.
By Delaney B, Moayyedi P, Deeks J, Innes M, Soo S, Barton P, et al.
-
A systematic review of treatments for severe psoriasis.
By Griffiths CEM, Clark CM, Chalmers RJG, Li Wan Po A, Williams HC.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine for Alzheimer’s disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Clegg A, Bryant J, Nicholson T, McIntyre L, De Broe S, Gerard K, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of riluzole for motor neurone disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Stewart A, Sandercock J, Bryan S, Hyde C, Barton PM, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Equity and the economic evaluation of healthcare.
By Sassi F, Archard L, Le Grand J.
-
Quality-of-life measures in chronic diseases of childhood.
By Eiser C, Morse R.
-
Eliciting public preferences for healthcare: a systematic review of techniques.
By Ryan M, Scott DA, Reeves C, Bate A, van Teijlingen ER, Russell EM, et al.
-
General health status measures for people with cognitive impairment: learning disability and acquired brain injury.
By Riemsma RP, Forbes CA, Glanville JM, Eastwood AJ, Kleijnen J.
-
An assessment of screening strategies for fragile X syndrome in the UK.
By Pembrey ME, Barnicoat AJ, Carmichael B, Bobrow M, Turner G.
-
Issues in methodological research: perspectives from researchers and commissioners.
By Lilford RJ, Richardson A, Stevens A, Fitzpatrick R, Edwards S, Rock F, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (5) beds; (6) compression; (7) laser therapy, therapeutic ultrasound, electrotherapy and electromagnetic therapy.
By Cullum N, Nelson EA, Flemming K, Sheldon T.
-
Effects of educational and psychosocial interventions for adolescents with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review.
By Hampson SE, Skinner TC, Hart J, Storey L, Gage H, Foxcroft D, et al.
-
Effectiveness of autologous chondrocyte transplantation for hyaline cartilage defects in knees: a rapid and systematic review.
By Jobanputra P, Parry D, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
Statistical assessment of the learning curves of health technologies.
By Ramsay CR, Grant AM, Wallace SA, Garthwaite PH, Monk AF, Russell IT.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of temozolomide for the treatment of recurrent malignant glioma: a rapid and systematic review.
By Dinnes J, Cave C, Huang S, Major K, Milne R.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of debriding agents in treating surgical wounds healing by secondary intention.
By Lewis R, Whiting P, ter Riet G, O’Meara S, Glanville J.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.
By Burns T, Knapp M, Catty J, Healey A, Henderson J, Watt H, et al.
-
How to develop cost-conscious guidelines.
By Eccles M, Mason J.
-
The role of specialist nurses in multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By De Broe S, Christopher F, Waugh N.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of orlistat in the management of obesity.
By O’Meara S, Riemsma R, Shirran L, Mather L, ter Riet G.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pioglitazone for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a rapid and systematic review.
By Chilcott J, Wight J, Lloyd Jones M, Tappenden P.
-
Extended scope of nursing practice: a multicentre randomised controlled trial of appropriately trained nurses and preregistration house officers in preoperative assessment in elective general surgery.
By Kinley H, Czoski-Murray C, George S, McCabe C, Primrose J, Reilly C, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of the effectiveness of day care for people with severe mental disorders: (1) Acute day hospital versus admission; (2) Vocational rehabilitation; (3) Day hospital versus outpatient care.
By Marshall M, Crowther R, Almaraz- Serrano A, Creed F, Sledge W, Kluiter H, et al.
-
The measurement and monitoring of surgical adverse events.
By Bruce J, Russell EM, Mollison J, Krukowski ZH.
-
Action research: a systematic review and guidance for assessment.
By Waterman H, Tillen D, Dickson R, de Koning K.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of gemcitabine for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
By Ward S, Morris E, Bansback N, Calvert N, Crellin A, Forman D, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the evidence for the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer.
By Lloyd Jones M, Hummel S, Bansback N, Orr B, Seymour M.
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.
By Brocklebank D, Ram F, Wright J, Barry P, Cates C, Davies L, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging for investigation of the knee joint.
By Bryan S, Weatherburn G, Bungay H, Hatrick C, Salas C, Parry D, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.
By Forbes C, Shirran L, Bagnall A-M, Duffy S, ter Riet G.
-
Superseded by a report published in a later volume.
-
The role of radiography in primary care patients with low back pain of at least 6 weeks duration: a randomised (unblinded) controlled trial.
By Kendrick D, Fielding K, Bentley E, Miller P, Kerslake R, Pringle M.
-
Design and use of questionnaires: a review of best practice applicable to surveys of health service staff and patients.
By McColl E, Jacoby A, Thomas L, Soutter J, Bamford C, Steen N, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.
By Clegg A, Scott DA, Sidhu M, Hewitson P, Waugh N.
-
Subgroup analyses in randomised controlled trials: quantifying the risks of false-positives and false-negatives.
By Brookes ST, Whitley E, Peters TJ, Mulheran PA, Egger M, Davey Smith G.
-
Depot antipsychotic medication in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia: (1) Meta-review; (2) Patient and nurse attitudes.
By David AS, Adams C.
-
A systematic review of controlled trials of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of brief psychological treatments for depression.
By Churchill R, Hunot V, Corney R, Knapp M, McGuire H, Tylee A, et al.
-
Cost analysis of child health surveillance.
By Sanderson D, Wright D, Acton C, Duree D.
-
A study of the methods used to select review criteria for clinical audit.
By Hearnshaw H, Harker R, Cheater F, Baker R, Grimshaw G.
-
Fludarabine as second-line therapy for B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a technology assessment.
By Hyde C, Wake B, Bryan S, Barton P, Fry-Smith A, Davenport C, et al.
-
Rituximab as third-line treatment for refractory or recurrent Stage III or IV follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wake B, Hyde C, Bryan S, Barton P, Song F, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
A systematic review of discharge arrangements for older people.
By Parker SG, Peet SM, McPherson A, Cannaby AM, Baker R, Wilson A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of inhaler devices used in the routine management of chronic asthma in older children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Peters J, Stevenson M, Beverley C, Lim J, Smith S.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of sibutramine in the management of obesity: a technology assessment.
By O’Meara S, Riemsma R, Shirran L, Mather L, ter Riet G.
-
The cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance angiography for carotid artery stenosis and peripheral vascular disease: a systematic review.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Westwood ME, Davies LM, Gough MJ, Bamford JM, et al.
-
Promoting physical activity in South Asian Muslim women through ‘exercise on prescription’.
By Carroll B, Ali N, Azam N.
-
Zanamivir for the treatment of influenza in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burls A, Clark W, Stewart T, Preston C, Bryan S, Jefferson T, et al.
-
A review of the natural history and epidemiology of multiple sclerosis: implications for resource allocation and health economic models.
By Richards RG, Sampson FC, Beard SM, Tappenden P.
-
Screening for gestational diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Scott DA, Loveman E, McIntyre L, Waugh N.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of surgery for people with morbid obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clegg AJ, Colquitt J, Sidhu MK, Royle P, Loveman E, Walker A.
-
The clinical effectiveness of trastuzumab for breast cancer: a systematic review.
By Lewis R, Bagnall A-M, Forbes C, Shirran E, Duffy S, Kleijnen J, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of vinorelbine for breast cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Lewis R, Bagnall A-M, King S, Woolacott N, Forbes C, Shirran L, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty for treatment of hip disease.
By Vale L, Wyness L, McCormack K, McKenzie L, Brazzelli M, Stearns SC.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bupropion and nicotine replacement therapy for smoking cessation: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Woolacott NF, Jones L, Forbes CA, Mather LC, Sowden AJ, Song FJ, et al.
-
A systematic review of effectiveness and economic evaluation of new drug treatments for juvenile idiopathic arthritis: etanercept.
By Cummins C, Connock M, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of growth hormone in children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Cave C, Mihaylova B, Chase D, McIntyre L, Gerard K, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of growth hormone in adults in relation to impact on quality of life: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Loveman E, Chase D, Mihaylova B, Cave C, Gerard K, et al.
-
Clinical medication review by a pharmacist of patients on repeat prescriptions in general practice: a randomised controlled trial.
By Zermansky AG, Petty DR, Raynor DK, Lowe CJ, Freementle N, Vail A.
-
The effectiveness of infliximab and etanercept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Burls A.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of computerised cognitive behaviour therapy for depression and anxiety.
By Kaltenthaler E, Shackley P, Stevens K, Beverley C, Parry G, Chilcott J.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride for ovarian cancer.
By Forbes C, Wilby J, Richardson G, Sculpher M, Mather L, Reimsma R.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of interventions based on a stages-of-change approach to promote individual behaviour change.
By Riemsma RP, Pattenden J, Bridle C, Sowden AJ, Mather L, Watt IS, et al.
-
A systematic review update of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists.
By Robinson M, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Jones L, Riemsma R, Palmer S, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and barriers to implementation of thrombolytic and neuroprotective therapy for acute ischaemic stroke in the NHS.
By Sandercock P, Berge E, Dennis M, Forbes J, Hand P, Kwan J, et al.
-
A randomised controlled crossover trial of nurse practitioner versus doctor-led outpatient care in a bronchiectasis clinic.
By Caine N, Sharples LD, Hollingworth W, French J, Keogan M, Exley A, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost – consequences of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of sex offenders.
By Adi Y, Ashcroft D, Browne K, Beech A, Fry-Smith A, Hyde C.
-
Treatment of established osteoporosis: a systematic review and cost–utility analysis.
By Kanis JA, Brazier JE, Stevenson M, Calvert NW, Lloyd Jones M.
-
Which anaesthetic agents are cost-effective in day surgery? Literature review, national survey of practice and randomised controlled trial.
By Elliott RA Payne K, Moore JK, Davies LM, Harper NJN, St Leger AS, et al.
-
Screening for hepatitis C among injecting drug users and in genitourinary medicine clinics: systematic reviews of effectiveness, modelling study and national survey of current practice.
By Stein K, Dalziel K, Walker A, McIntyre L, Jenkins B, Horne J, et al.
-
The measurement of satisfaction with healthcare: implications for practice from a systematic review of the literature.
By Crow R, Gage H, Hampson S, Hart J, Kimber A, Storey L, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of imatinib in chronic myeloid leukaemia: a systematic review.
By Garside R, Round A, Dalziel K, Stein K, Royle R.
-
A comparative study of hypertonic saline, daily and alternate-day rhDNase in children with cystic fibrosis.
By Suri R, Wallis C, Bush A, Thompson S, Normand C, Flather M, et al.
-
A systematic review of the costs and effectiveness of different models of paediatric home care.
By Parker G, Bhakta P, Lovett CA, Paisley S, Olsen R, Turner D, et al.
-
How important are comprehensive literature searches and the assessment of trial quality in systematic reviews? Empirical study.
By Egger M, Jüni P, Bartlett C, Holenstein F, Sterne J.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and economic evaluation, of home versus hospital or satellite unit haemodialysis for people with end-stage renal failure.
By Mowatt G, Vale L, Perez J, Wyness L, Fraser C, MacLeod A, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of the effectiveness of infliximab for the treatment of Crohn’s disease.
By Clark W, Raftery J, Barton P, Song F, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
A review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine anti-D prophylaxis for pregnant women who are rhesus negative.
By Chilcott J, Lloyd Jones M, Wight J, Forman K, Wray J, Beverley C, et al.
-
Systematic review and evaluation of the use of tumour markers in paediatric oncology: Ewing’s sarcoma and neuroblastoma.
By Riley RD, Burchill SA, Abrams KR, Heney D, Lambert PC, Jones DR, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of screening for Helicobacter pylori to reduce mortality and morbidity from gastric cancer and peptic ulcer disease: a discrete-event simulation model.
By Roderick P, Davies R, Raftery J, Crabbe D, Pearce R, Bhandari P, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine dental checks: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Davenport C, Elley K, Salas C, Taylor-Weetman CL, Fry-Smith A, Bryan S, et al.
-
A multicentre randomised controlled trial assessing the costs and benefits of using structured information and analysis of women’s preferences in the management of menorrhagia.
By Kennedy ADM, Sculpher MJ, Coulter A, Dwyer N, Rees M, Horsley S, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost–utility of photodynamic therapy for wet age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Meads C, Salas C, Roberts T, Moore D, Fry-Smith A, Hyde C.
-
Evaluation of molecular tests for prenatal diagnosis of chromosome abnormalities.
By Grimshaw GM, Szczepura A, Hultén M, MacDonald F, Nevin NC, Sutton F, et al.
-
First and second trimester antenatal screening for Down’s syndrome: the results of the Serum, Urine and Ultrasound Screening Study (SURUSS).
By Wald NJ, Rodeck C, Hackshaw AK, Walters J, Chitty L, Mackinson AM.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of ultrasound locating devices for central venous access: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Calvert N, Hind D, McWilliams RG, Thomas SM, Beverley C, Davidson A.
-
A systematic review of atypical antipsychotics in schizophrenia.
By Bagnall A-M, Jones L, Lewis R, Ginnelly L, Glanville J, Torgerson D, et al.
-
Prostate Testing for Cancer and Treatment (ProtecT) feasibility study.
By Donovan J, Hamdy F, Neal D, Peters T, Oliver S, Brindle L, et al.
-
Early thrombolysis for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Boland A, Dundar Y, Bagust A, Haycox A, Hill R, Mujica Mota R, et al.
-
Screening for fragile X syndrome: a literature review and modelling.
By Song FJ, Barton P, Sleightholme V, Yao GL, Fry-Smith A.
-
Systematic review of endoscopic sinus surgery for nasal polyps.
By Dalziel K, Stein K, Round A, Garside R, Royle P.
-
Towards efficient guidelines: how to monitor guideline use in primary care.
By Hutchinson A, McIntosh A, Cox S, Gilbert C.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of acute hospital-based spinal cord injuries services: systematic review.
By Bagnall A-M, Jones L, Richardson G, Duffy S, Riemsma R.
-
Prioritisation of health technology assessment. The PATHS model: methods and case studies.
By Townsend J, Buxton M, Harper G.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of tension-free vaginal tape for treatment of urinary stress incontinence.
By Cody J, Wyness L, Wallace S, Glazener C, Kilonzo M, Stearns S, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of patient education models for diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Loveman E, Cave C, Green C, Royle P, Dunn N, Waugh N.
-
The role of modelling in prioritising and planning clinical trials.
By Chilcott J, Brennan A, Booth A, Karnon J, Tappenden P.
-
Cost–benefit evaluation of routine influenza immunisation in people 65–74 years of age.
By Allsup S, Gosney M, Haycox A, Regan M.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of pulsatile machine perfusion versus cold storage of kidneys for transplantation retrieved from heart-beating and non-heart-beating donors.
By Wight J, Chilcott J, Holmes M, Brewer N.
-
Can randomised trials rely on existing electronic data? A feasibility study to explore the value of routine data in health technology assessment.
By Williams JG, Cheung WY, Cohen DR, Hutchings HA, Longo MF, Russell IT.
-
Evaluating non-randomised intervention studies.
By Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, D’Amico R, Sowden AJ, Sakarovitch C, Song F, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to assess the impact of a package comprising a patient-orientated, evidence-based self- help guidebook and patient-centred consultations on disease management and satisfaction in inflammatory bowel disease.
By Kennedy A, Nelson E, Reeves D, Richardson G, Roberts C, Robinson A, et al.
-
The effectiveness of diagnostic tests for the assessment of shoulder pain due to soft tissue disorders: a systematic review.
By Dinnes J, Loveman E, McIntyre L, Waugh N.
-
The value of digital imaging in diabetic retinopathy.
By Sharp PF, Olson J, Strachan F, Hipwell J, Ludbrook A, O’Donnell M, et al.
-
Lowering blood pressure to prevent myocardial infarction and stroke: a new preventive strategy.
By Law M, Wald N, Morris J.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of capecitabine and tegafur with uracil for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ward S, Kaltenthaler E, Cowan J, Brewer N.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of new and emerging technologies for early localised prostate cancer: a systematic review.
By Hummel S, Paisley S, Morgan A, Currie E, Brewer N.
-
Literature searching for clinical and cost-effectiveness studies used in health technology assessment reports carried out for the National Institute for Clinical Excellence appraisal system.
By Royle P, Waugh N.
-
Systematic review and economic decision modelling for the prevention and treatment of influenza A and B.
By Turner D, Wailoo A, Nicholson K, Cooper N, Sutton A, Abrams K.
-
A randomised controlled trial to evaluate the clinical and cost-effectiveness of Hickman line insertions in adult cancer patients by nurses.
By Boland A, Haycox A, Bagust A, Fitzsimmons L.
-
Redesigning postnatal care: a randomised controlled trial of protocol-based midwifery-led care focused on individual women’s physical and psychological health needs.
By MacArthur C, Winter HR, Bick DE, Lilford RJ, Lancashire RJ, Knowles H, et al.
-
Estimating implied rates of discount in healthcare decision-making.
By West RR, McNabb R, Thompson AGH, Sheldon TA, Grimley Evans J.
-
Systematic review of isolation policies in the hospital management of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a review of the literature with epidemiological and economic modelling.
By Cooper BS, Stone SP, Kibbler CC, Cookson BD, Roberts JA, Medley GF, et al.
-
Treatments for spasticity and pain in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review.
By Beard S, Hunn A, Wight J.
-
The inclusion of reports of randomised trials published in languages other than English in systematic reviews.
By Moher D, Pham B, Lawson ML, Klassen TP.
-
The impact of screening on future health-promoting behaviours and health beliefs: a systematic review.
By Bankhead CR, Brett J, Bukach C, Webster P, Stewart-Brown S, Munafo M, et al.
-
What is the best imaging strategy for acute stroke?
By Wardlaw JM, Keir SL, Seymour J, Lewis S, Sandercock PAG, Dennis MS, et al.
-
Systematic review and modelling of the investigation of acute and chronic chest pain presenting in primary care.
By Mant J, McManus RJ, Oakes RAL, Delaney BC, Barton PM, Deeks JJ, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of microwave and thermal balloon endometrial ablation for heavy menstrual bleeding: a systematic review and economic modelling.
By Garside R, Stein K, Wyatt K, Round A, Price A.
-
A systematic review of the role of bisphosphonates in metastatic disease.
By Ross JR, Saunders Y, Edmonds PM, Patel S, Wonderling D, Normand C, et al.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of capecitabine (Xeloda®) for locally advanced and/or metastatic breast cancer.
By Jones L, Hawkins N, Westwood M, Wright K, Richardson G, Riemsma R.
-
Effectiveness and efficiency of guideline dissemination and implementation strategies.
By Grimshaw JM, Thomas RE, MacLennan G, Fraser C, Ramsay CR, Vale L, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and costs of the Sugarbaker procedure for the treatment of pseudomyxoma peritonei.
By Bryant J, Clegg AJ, Sidhu MK, Brodin H, Royle P, Davidson P.
-
Psychological treatment for insomnia in the regulation of long-term hypnotic drug use.
By Morgan K, Dixon S, Mathers N, Thompson J, Tomeny M.
-
Improving the evaluation of therapeutic interventions in multiple sclerosis: development of a patient-based measure of outcome.
By Hobart JC, Riazi A, Lamping DL, Fitzpatrick R, Thompson AJ.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography compared with diagnostic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
By Kaltenthaler E, Bravo Vergel Y, Chilcott J, Thomas S, Blakeborough T, Walters SJ, et al.
-
The use of modelling to evaluate new drugs for patients with a chronic condition: the case of antibodies against tumour necrosis factor in rheumatoid arthritis.
By Barton P, Jobanputra P, Wilson J, Bryan S, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism using tandem mass spectrometry: a systematic review.
By Pandor A, Eastham J, Beverley C, Chilcott J, Paisley S.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pioglitazone and rosiglitazone in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Czoski-Murray C, Warren E, Chilcott J, Beverley C, Psyllaki MA, Cowan J.
-
Routine examination of the newborn: the EMREN study. Evaluation of an extension of the midwife role including a randomised controlled trial of appropriately trained midwives and paediatric senior house officers.
By Townsend J, Wolke D, Hayes J, Davé S, Rogers C, Bloomfield L, et al.
-
Involving consumers in research and development agenda setting for the NHS: developing an evidence-based approach.
By Oliver S, Clarke-Jones L, Rees R, Milne R, Buchanan P, Gabbay J, et al.
-
A multi-centre randomised controlled trial of minimally invasive direct coronary bypass grafting versus percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty with stenting for proximal stenosis of the left anterior descending coronary artery.
By Reeves BC, Angelini GD, Bryan AJ, Taylor FC, Cripps T, Spyt TJ, et al.
-
Does early magnetic resonance imaging influence management or improve outcome in patients referred to secondary care with low back pain? A pragmatic randomised controlled trial.
By Gilbert FJ, Grant AM, Gillan MGC, Vale L, Scott NW, Campbell MK, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of anakinra for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Clark W, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Burls A.
-
A rapid and systematic review and economic evaluation of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for treatment of mania associated with bipolar affective disorder.
By Bridle C, Palmer S, Bagnall A-M, Darba J, Duffy S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Liquid-based cytology in cervical screening: an updated rapid and systematic review and economic analysis.
By Karnon J, Peters J, Platt J, Chilcott J, McGoogan E, Brewer N.
-
Systematic review of the long-term effects and economic consequences of treatments for obesity and implications for health improvement.
By Avenell A, Broom J, Brown TJ, Poobalan A, Aucott L, Stearns SC, et al.
-
Autoantibody testing in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus.
By Dretzke J, Cummins C, Sandercock J, Fry-Smith A, Barrett T, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of prehospital intravenous fluids in trauma patients.
By Dretzke J, Sandercock J, Bayliss S, Burls A.
-
Newer hypnotic drugs for the short-term management of insomnia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Dündar Y, Boland A, Strobl J, Dodd S, Haycox A, Bagust A, et al.
-
Development and validation of methods for assessing the quality of diagnostic accuracy studies.
By Whiting P, Rutjes AWS, Dinnes J, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PMM, Kleijnen J.
-
EVALUATE hysterectomy trial: a multicentre randomised trial comparing abdominal, vaginal and laparoscopic methods of hysterectomy.
By Garry R, Fountain J, Brown J, Manca A, Mason S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Methods for expected value of information analysis in complex health economic models: developments on the health economics of interferon-β and glatiramer acetate for multiple sclerosis.
By Tappenden P, Chilcott JB, Eggington S, Oakley J, McCabe C.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of imatinib for first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia in chronic phase: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Dalziel K, Round A, Stein K, Garside R, Price A.
-
VenUS I: a randomised controlled trial of two types of bandage for treating venous leg ulcers.
By Iglesias C, Nelson EA, Cullum NA, Torgerson DJ, on behalf of the VenUS Team.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and economic evaluation, of myocardial perfusion scintigraphy for the diagnosis and management of angina and myocardial infarction.
By Mowatt G, Vale L, Brazzelli M, Hernandez R, Murray A, Scott N, et al.
-
A pilot study on the use of decision theory and value of information analysis as part of the NHS Health Technology Assessment programme.
By Claxton K, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Philips Z, Palmer S.
-
The Social Support and Family Health Study: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of two alternative forms of postnatal support for mothers living in disadvantaged inner-city areas.
By Wiggins M, Oakley A, Roberts I, Turner H, Rajan L, Austerberry H, et al.
-
Psychosocial aspects of genetic screening of pregnant women and newborns: a systematic review.
By Green JM, Hewison J, Bekker HL, Bryant, Cuckle HS.
-
Evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding: comparison of three outpatient procedures within cohorts defined by age and menopausal status.
By Critchley HOD, Warner P, Lee AJ, Brechin S, Guise J, Graham B.
-
Coronary artery stents: a rapid systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hill R, Bagust A, Bakhai A, Dickson R, Dündar Y, Haycox A, et al.
-
Review of guidelines for good practice in decision-analytic modelling in health technology assessment.
By Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Claxton K, Golder S, Riemsma R, et al.
-
Rituximab (MabThera®) for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Knight C, Hind D, Brewer N, Abbott V.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of clopidogrel and modified-release dipyridamole in the secondary prevention of occlusive vascular events: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jones L, Griffin S, Palmer S, Main C, Orton V, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Pegylated interferon α-2a and -2b in combination with ribavirin in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Brodin H, Cave C, Waugh N, Price A, Gabbay J.
-
Clopidogrel used in combination with aspirin compared with aspirin alone in the treatment of non-ST-segment- elevation acute coronary syndromes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Main C, Palmer S, Griffin S, Jones L, Orton V, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Provision, uptake and cost of cardiac rehabilitation programmes: improving services to under-represented groups.
By Beswick AD, Rees K, Griebsch I, Taylor FC, Burke M, West RR, et al.
-
Involving South Asian patients in clinical trials.
By Hussain-Gambles M, Leese B, Atkin K, Brown J, Mason S, Tovey P.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for diabetes.
By Colquitt JL, Green C, Sidhu MK, Hartwell D, Waugh N.
-
Identification and assessment of ongoing trials in health technology assessment reviews.
By Song FJ, Fry-Smith A, Davenport C, Bayliss S, Adi Y, Wilson JS, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of a long-acting insulin analogue, insulin glargine
By Warren E, Weatherley-Jones E, Chilcott J, Beverley C.
-
Supplementation of a home-based exercise programme with a class-based programme for people with osteoarthritis of the knees: a randomised controlled trial and health economic analysis.
By McCarthy CJ, Mills PM, Pullen R, Richardson G, Hawkins N, Roberts CR, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of once-daily versus more frequent use of same potency topical corticosteroids for atopic eczema: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Green C, Colquitt JL, Kirby J, Davidson P, Payne E.
-
Acupuncture of chronic headache disorders in primary care: randomised controlled trial and economic analysis.
By Vickers AJ, Rees RW, Zollman CE, McCarney R, Smith CM, Ellis N, et al.
-
Generalisability in economic evaluation studies in healthcare: a review and case studies.
By Sculpher MJ, Pang FS, Manca A, Drummond MF, Golder S, Urdahl H, et al.
-
Virtual outreach: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of joint teleconferenced medical consultations.
By Wallace P, Barber J, Clayton W, Currell R, Fleming K, Garner P, et al.
-
Randomised controlled multiple treatment comparison to provide a cost-effectiveness rationale for the selection of antimicrobial therapy in acne.
By Ozolins M, Eady EA, Avery A, Cunliffe WJ, O’Neill C, Simpson NB, et al.
-
Do the findings of case series studies vary significantly according to methodological characteristics?
By Dalziel K, Round A, Stein K, Garside R, Castelnuovo E, Payne L.
-
Improving the referral process for familial breast cancer genetic counselling: findings of three randomised controlled trials of two interventions.
By Wilson BJ, Torrance N, Mollison J, Wordsworth S, Gray JR, Haites NE, et al.
-
Randomised evaluation of alternative electrosurgical modalities to treat bladder outflow obstruction in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
By Fowler C, McAllister W, Plail R, Karim O, Yang Q.
-
A pragmatic randomised controlled trial of the cost-effectiveness of palliative therapies for patients with inoperable oesophageal cancer.
By Shenfine J, McNamee P, Steen N, Bond J, Griffin SM.
-
Impact of computer-aided detection prompts on the sensitivity and specificity of screening mammography.
By Taylor P, Champness J, Given- Wilson R, Johnston K, Potts H.
-
Issues in data monitoring and interim analysis of trials.
By Grant AM, Altman DG, Babiker AB, Campbell MK, Clemens FJ, Darbyshire JH, et al.
-
Lay public’s understanding of equipoise and randomisation in randomised controlled trials.
By Robinson EJ, Kerr CEP, Stevens AJ, Lilford RJ, Braunholtz DA, Edwards SJ, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of electroconvulsive therapy for depressive illness, schizophrenia, catatonia and mania: systematic reviews and economic modelling studies.
By Greenhalgh J, Knight C, Hind D, Beverley C, Walters S.
-
Measurement of health-related quality of life for people with dementia: development of a new instrument (DEMQOL) and an evaluation of current methodology.
By Smith SC, Lamping DL, Banerjee S, Harwood R, Foley B, Smith P, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of drotrecogin alfa (activated) (Xigris®) for the treatment of severe sepsis in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Green C, Dinnes J, Takeda A, Shepherd J, Hartwell D, Cave C, et al.
-
A methodological review of how heterogeneity has been examined in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy.
By Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kirby J, Roderick P.
-
Cervical screening programmes: can automation help? Evidence from systematic reviews, an economic analysis and a simulation modelling exercise applied to the UK.
By Willis BH, Barton P, Pearmain P, Bryan S, Hyde C.
-
Laparoscopic surgery for inguinal hernia repair: systematic review of effectiveness and economic evaluation.
By McCormack K, Wake B, Perez J, Fraser C, Cook J, McIntosh E, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness, tolerability and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for epilepsy in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wilby J, Kainth A, Hawkins N, Epstein D, McIntosh H, McDaid C, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to compare the cost-effectiveness of tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and lofepramine.
By Peveler R, Kendrick T, Buxton M, Longworth L, Baldwin D, Moore M, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of immediate angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hartwell D, Colquitt J, Loveman E, Clegg AJ, Brodin H, Waugh N, et al.
-
A randomised controlled comparison of alternative strategies in stroke care.
By Kalra L, Evans A, Perez I, Knapp M, Swift C, Donaldson N.
-
The investigation and analysis of critical incidents and adverse events in healthcare.
By Woloshynowych M, Rogers S, Taylor-Adams S, Vincent C.
-
Potential use of routine databases in health technology assessment.
By Raftery J, Roderick P, Stevens A.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of newer immunosuppressive regimens in renal transplantation: a systematic review and modelling study.
By Woodroffe R, Yao GL, Meads C, Bayliss S, Ready A, Raftery J, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene and teriparatide for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
By Stevenson M, Lloyd Jones M, De Nigris E, Brewer N, Davis S, Oakley J.
-
A systematic review to examine the impact of psycho-educational interventions on health outcomes and costs in adults and children with difficult asthma.
By Smith JR, Mugford M, Holland R, Candy B, Noble MJ, Harrison BDW, et al.
-
An evaluation of the costs, effectiveness and quality of renal replacement therapy provision in renal satellite units in England and Wales.
By Roderick P, Nicholson T, Armitage A, Mehta R, Mullee M, Gerard K, et al.
-
Imatinib for the treatment of patients with unresectable and/or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumours: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wilson J, Connock M, Song F, Yao G, Fry-Smith A, Raftery J, et al.
-
Indirect comparisons of competing interventions.
By Glenny AM, Altman DG, Song F, Sakarovitch C, Deeks JJ, D’Amico R, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of alternative strategies for the initial medical management of non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome: systematic review and decision-analytical modelling.
By Robinson M, Palmer S, Sculpher M, Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Bowens A, et al.
-
Outcomes of electrically stimulated gracilis neosphincter surgery.
By Tillin T, Chambers M, Feldman R.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pimecrolimus and tacrolimus for atopic eczema: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Stein K, Castelnuovo E, Pitt M, Ashcroft D, Dimmock P, et al.
-
Systematic review on urine albumin testing for early detection of diabetic complications.
By Newman DJ, Mattock MB, Dawnay ABS, Kerry S, McGuire A, Yaqoob M, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trial of the cost-effectiveness of water-based therapy for lower limb osteoarthritis.
By Cochrane T, Davey RC, Matthes Edwards SM.
-
Longer term clinical and economic benefits of offering acupuncture care to patients with chronic low back pain.
By Thomas KJ, MacPherson H, Ratcliffe J, Thorpe L, Brazier J, Campbell M, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness and safety of epidural steroids in the management of sciatica.
By Price C, Arden N, Coglan L, Rogers P.
-
The British Rheumatoid Outcome Study Group (BROSG) randomised controlled trial to compare the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of aggressive versus symptomatic therapy in established rheumatoid arthritis.
By Symmons D, Tricker K, Roberts C, Davies L, Dawes P, Scott DL.
-
Conceptual framework and systematic review of the effects of participants’ and professionals’ preferences in randomised controlled trials.
By King M, Nazareth I, Lampe F, Bower P, Chandler M, Morou M, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of implantable cardioverter defibrillators: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Brodin H, Loveman E, Payne E, Clegg A.
-
A trial of problem-solving by community mental health nurses for anxiety, depression and life difficulties among general practice patients. The CPN-GP study.
By Kendrick T, Simons L, Mynors-Wallis L, Gray A, Lathlean J, Pickering R, et al.
-
The causes and effects of socio-demographic exclusions from clinical trials.
By Bartlett C, Doyal L, Ebrahim S, Davey P, Bachmann M, Egger M, et al.
-
Is hydrotherapy cost-effective? A randomised controlled trial of combined hydrotherapy programmes compared with physiotherapy land techniques in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
By Epps H, Ginnelly L, Utley M, Southwood T, Gallivan S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial and cost-effectiveness study of systematic screening (targeted and total population screening) versus routine practice for the detection of atrial fibrillation in people aged 65 and over. The SAFE study.
By Hobbs FDR, Fitzmaurice DA, Mant J, Murray E, Jowett S, Bryan S, et al.
-
Displaced intracapsular hip fractures in fit, older people: a randomised comparison of reduction and fixation, bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty.
By Keating JF, Grant A, Masson M, Scott NW, Forbes JF.
-
Long-term outcome of cognitive behaviour therapy clinical trials in central Scotland.
By Durham RC, Chambers JA, Power KG, Sharp DM, Macdonald RR, Major KA, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of dual-chamber pacemakers compared with single-chamber pacemakers for bradycardia due to atrioventricular block or sick sinus syndrome: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Castelnuovo E, Stein K, Pitt M, Garside R, Payne E.
-
Newborn screening for congenital heart defects: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Knowles R, Griebsch I, Dezateux C, Brown J, Bull C, Wren C.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of left ventricular assist devices for end-stage heart failure: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clegg AJ, Scott DA, Loveman E, Colquitt J, Hutchinson J, Royle P, et al.
-
The effectiveness of the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph and laser diagnostic glaucoma scanning system (GDx) in detecting and monitoring glaucoma.
By Kwartz AJ, Henson DB, Harper RA, Spencer AF, McLeod D.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of autologous chondrocyte implantation for cartilage defects in knee joints: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clar C, Cummins E, McIntyre L, Thomas S, Lamb J, Bain L, et al.
-
Systematic review of effectiveness of different treatments for childhood retinoblastoma.
By McDaid C, Hartley S, Bagnall A-M, Ritchie G, Light K, Riemsma R.
-
Towards evidence-based guidelines for the prevention of venous thromboembolism: systematic reviews of mechanical methods, oral anticoagulation, dextran and regional anaesthesia as thromboprophylaxis.
By Roderick P, Ferris G, Wilson K, Halls H, Jackson D, Collins R, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of parent training/education programmes for the treatment of conduct disorder, including oppositional defiant disorder, in children.
By Dretzke J, Frew E, Davenport C, Barlow J, Stewart-Brown S, Sandercock J, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine and memantine for Alzheimer’s disease.
By Loveman E, Green C, Kirby J, Takeda A, Picot J, Payne E, et al.
-
FOOD: a multicentre randomised trial evaluating feeding policies in patients admitted to hospital with a recent stroke.
By Dennis M, Lewis S, Cranswick G, Forbes J.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computed tomography screening for lung cancer: systematic reviews.
By Black C, Bagust A, Boland A, Walker S, McLeod C, De Verteuil R, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of neuroimaging assessments used to visualise the seizure focus in people with refractory epilepsy being considered for surgery.
By Whiting P, Gupta R, Burch J, Mujica Mota RE, Wright K, Marson A, et al.
-
Comparison of conference abstracts and presentations with full-text articles in the health technology assessments of rapidly evolving technologies.
By Dundar Y, Dodd S, Dickson R, Walley T, Haycox A, Williamson PR.
-
Systematic review and evaluation of methods of assessing urinary incontinence.
By Martin JL, Williams KS, Abrams KR, Turner DA, Sutton AJ, Chapple C, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for children with epilepsy. A systematic review.
By Connock M, Frew E, Evans B-W, Bryan S, Cummins C, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Surveillance of Barrett’s oesophagus: exploring the uncertainty through systematic review, expert workshop and economic modelling.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Somerville M, Stein K, Price A, Gilbert N.
-
Topotecan, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride and paclitaxel for second-line or subsequent treatment of advanced ovarian cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Main C, Bojke L, Griffin S, Norman G, Barbieri M, Mather L, et al.
-
Evaluation of molecular techniques in prediction and diagnosis of cytomegalovirus disease in immunocompromised patients.
By Szczepura A, Westmoreland D, Vinogradova Y, Fox J, Clark M.
-
Screening for thrombophilia in high-risk situations: systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. The Thrombosis: Risk and Economic Assessment of Thrombophilia Screening (TREATS) study.
By Wu O, Robertson L, Twaddle S, Lowe GDO, Clark P, Greaves M, et al.
-
A series of systematic reviews to inform a decision analysis for sampling and treating infected diabetic foot ulcers.
By Nelson EA, O’Meara S, Craig D, Iglesias C, Golder S, Dalton J, et al.
-
Randomised clinical trial, observational study and assessment of cost-effectiveness of the treatment of varicose veins (REACTIV trial).
By Michaels JA, Campbell WB, Brazier JE, MacIntyre JB, Palfreyman SJ, Ratcliffe J, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of screening for oral cancer in primary care.
By Speight PM, Palmer S, Moles DR, Downer MC, Smith DH, Henriksson M, et al.
-
Measurement of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of non-invasive diagnostic testing strategies for deep vein thrombosis.
By Goodacre S, Sampson F, Stevenson M, Wailoo A, Sutton A, Thomas S, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of HealOzone® for the treatment of occlusal pit/fissure caries and root caries.
By Brazzelli M, McKenzie L, Fielding S, Fraser C, Clarkson J, Kilonzo M, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trials of conventional antipsychotic versus new atypical drugs, and new atypical drugs versus clozapine, in people with schizophrenia responding poorly to, or intolerant of, current drug treatment.
By Lewis SW, Davies L, Jones PB, Barnes TRE, Murray RM, Kerwin R, et al.
-
Diagnostic tests and algorithms used in the investigation of haematuria: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.
By Rodgers M, Nixon J, Hempel S, Aho T, Kelly J, Neal D, et al.
-
Cognitive behavioural therapy in addition to antispasmodic therapy for irritable bowel syndrome in primary care: randomised controlled trial.
By Kennedy TM, Chalder T, McCrone P, Darnley S, Knapp M, Jones RH, et al.
-
A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapies for Fabry’s disease and mucopolysaccharidosis type 1.
By Connock M, Juarez-Garcia A, Frew E, Mans A, Dretzke J, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Health benefits of antiviral therapy for mild chronic hepatitis C: randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation.
By Wright M, Grieve R, Roberts J, Main J, Thomas HC, on behalf of the UK Mild Hepatitis C Trial Investigators.
-
Pressure relieving support surfaces: a randomised evaluation.
By Nixon J, Nelson EA, Cranny G, Iglesias CP, Hawkins K, Cullum NA, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of methylphenidate, dexamfetamine and atomoxetine for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents.
By King S, Griffin S, Hodges Z, Weatherly H, Asseburg C, Richardson G, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy for Gaucher’s disease: a systematic review.
By Connock M, Burls A, Frew E, Fry-Smith A, Juarez-Garcia A, McCabe C, et al.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of salicylic acid and cryotherapy for cutaneous warts. An economic decision model.
By Thomas KS, Keogh-Brown MR, Chalmers JR, Fordham RJ, Holland RC, Armstrong SJ, et al.
-
A systematic literature review of the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions to prevent wandering in dementia and evaluation of the ethical implications and acceptability of their use.
By Robinson L, Hutchings D, Corner L, Beyer F, Dickinson H, Vanoli A, et al.
-
A review of the evidence on the effects and costs of implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in different patient groups, and modelling of cost-effectiveness and cost–utility for these groups in a UK context.
By Buxton M, Caine N, Chase D, Connelly D, Grace A, Jackson C, et al.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Takeda A, Davidson P, Price A.
-
An evaluation of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of pulmonary artery catheters in patient management in intensive care: a systematic review and a randomised controlled trial.
By Harvey S, Stevens K, Harrison D, Young D, Brampton W, McCabe C, et al.
-
Accurate, practical and cost-effective assessment of carotid stenosis in the UK.
By Wardlaw JM, Chappell FM, Stevenson M, De Nigris E, Thomas S, Gillard J, et al.
-
Etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Woolacott N, Bravo Vergel Y, Hawkins N, Kainth A, Khadjesari Z, Misso K, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of testing for hepatitis C in former injecting drug users.
By Castelnuovo E, Thompson-Coon J, Pitt M, Cramp M, Siebert U, Price A, et al.
-
Computerised cognitive behaviour therapy for depression and anxiety update: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Kaltenthaler E, Brazier J, De Nigris E, Tumur I, Ferriter M, Beverley C, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.
By Williams C, Brunskill S, Altman D, Briggs A, Campbell H, Clarke M, et al.
-
Psychological therapies including dialectical behaviour therapy for borderline personality disorder: a systematic review and preliminary economic evaluation.
By Brazier J, Tumur I, Holmes M, Ferriter M, Parry G, Dent-Brown K, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of tests for the diagnosis and investigation of urinary tract infection in children: a systematic review and economic model.
By Whiting P, Westwood M, Bojke L, Palmer S, Richardson G, Cooper J, et al.
-
Cognitive behavioural therapy in chronic fatigue syndrome: a randomised controlled trial of an outpatient group programme.
By O’Dowd H, Gladwell P, Rogers CA, Hollinghurst S, Gregory A.
-
A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling.
By Brown TJ, Hooper L, Elliott RA, Payne K, Webb R, Roberts C, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computed tomography screening for coronary artery disease: systematic review.
By Waugh N, Black C, Walker S, McIntyre L, Cummins E, Hillis G.
-
What are the clinical outcome and cost-effectiveness of endoscopy undertaken by nurses when compared with doctors? A Multi-Institution Nurse Endoscopy Trial (MINuET).
By Williams J, Russell I, Durai D, Cheung W-Y, Farrin A, Bloor K, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of oxaliplatin and capecitabine for the adjuvant treatment of colon cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Pandor A, Eggington S, Paisley S, Tappenden P, Sutcliffe P.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness.
By Chen Y-F, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Jowett S, Bryan S, Clark W, et al.
-
Telemedicine in dermatology: a randomised controlled trial.
By Bowns IR, Collins K, Walters SJ, McDonagh AJG.
-
Cost-effectiveness of cell salvage and alternative methods of minimising perioperative allogeneic blood transfusion: a systematic review and economic model.
By Davies L, Brown TJ, Haynes S, Payne K, Elliott RA, McCollum C.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancer: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.
By Murray A, Lourenco T, de Verteuil R, Hernandez R, Fraser C, McKinley A, et al.
-
Etanercept and efalizumab for the treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review.
By Woolacott N, Hawkins N, Mason A, Kainth A, Khadjesari Z, Bravo Vergel Y, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of clinical decision tools for acute abdominal pain.
By Liu JLY, Wyatt JC, Deeks JJ, Clamp S, Keen J, Verde P, et al.
-
Evaluation of the ventricular assist device programme in the UK.
By Sharples L, Buxton M, Caine N, Cafferty F, Demiris N, Dyer M, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of immunosuppressive therapy for renal transplantation in children.
By Yao G, Albon E, Adi Y, Milford D, Bayliss S, Ready A, et al.
-
Amniocentesis results: investigation of anxiety. The ARIA trial.
By Hewison J, Nixon J, Fountain J, Cocks K, Jones C, Mason G, et al.
-
Pemetrexed disodium for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Dundar Y, Bagust A, Dickson R, Dodd S, Green J, Haycox A, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of docetaxel in combination with prednisone or prednisolone for the treatment of hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer.
By Collins R, Fenwick E, Trowman R, Perard R, Norman G, Light K, et al.
-
A systematic review of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of tuberculosis infection.
By Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kunst H, Gibson A, Cummins E, Waugh N, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women.
By Stevenson M, Davis S, Lloyd-Jones M, Beverley C.
-
A systematic review of quantitative and qualitative research on the role and effectiveness of written information available to patients about individual medicines.
By Raynor DK, Blenkinsopp A, Knapp P, Grime J, Nicolson DJ, Pollock K, et al.
-
Oral naltrexone as a treatment for relapse prevention in formerly opioid-dependent drug users: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Adi Y, Juarez-Garcia A, Wang D, Jowett S, Frew E, Day E, et al.
-
Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: a systematic review and cost–utility analysis.
By Kanis JA, Stevenson M, McCloskey EV, Davis S, Lloyd-Jones M.
-
Epidemiological, social, diagnostic and economic evaluation of population screening for genital chlamydial infection.
By Low N, McCarthy A, Macleod J, Salisbury C, Campbell R, Roberts TE, et al.
-
Methadone and buprenorphine for the management of opioid dependence: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Connock M, Juarez-Garcia A, Jowett S, Frew E, Liu Z, Taylor RJ, et al.
-
Exercise Evaluation Randomised Trial (EXERT): a randomised trial comparing GP referral for leisure centre-based exercise, community-based walking and advice only.
By Isaacs AJ, Critchley JA, See Tai S, Buckingham K, Westley D, Harridge SDR, et al.
-
Interferon alfa (pegylated and non-pegylated) and ribavirin for the treatment of mild chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Hartwell D, Davidson P, Price A, Waugh N.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of bevacizumab and cetuximab for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.
By Tappenden P, Jones R, Paisley S, Carroll C.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of epoetin alfa, epoetin beta and darbepoetin alfa in anaemia associated with cancer, especially that attributable to cancer treatment.
By Wilson J, Yao GL, Raftery J, Bohlius J, Brunskill S, Sandercock J, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of statins for the prevention of coronary events.
By Ward S, Lloyd Jones M, Pandor A, Holmes M, Ara R, Ryan A, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of different models of community-based respite care for frail older people and their carers.
By Mason A, Weatherly H, Spilsbury K, Arksey H, Golder S, Adamson J, et al.
-
Additional therapy for young children with spastic cerebral palsy: a randomised controlled trial.
By Weindling AM, Cunningham CC, Glenn SM, Edwards RT, Reeves DJ.
-
Screening for type 2 diabetes: literature review and economic modelling.
By Waugh N, Scotland G, McNamee P, Gillett M, Brennan A, Goyder E, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cinacalcet for secondary hyperparathyroidism in end-stage renal disease patients on dialysis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Anderson R, Mealing S, Roome C, Snaith A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of gemcitabine for metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Takeda AL, Jones J, Loveman E, Tan SC, Clegg AJ.
-
A systematic review of duplex ultrasound, magnetic resonance angiography and computed tomography angiography for the diagnosis and assessment of symptomatic, lower limb peripheral arterial disease.
By Collins R, Cranny G, Burch J, Aguiar-Ibáñez R, Craig D, Wright K, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of treatments for children with idiopathic steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome: a systematic review.
By Colquitt JL, Kirby J, Green C, Cooper K, Trompeter RS.
-
A systematic review of the routine monitoring of growth in children of primary school age to identify growth-related conditions.
By Fayter D, Nixon J, Hartley S, Rithalia A, Butler G, Rudolf M, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness of preventing and treating Staphylococcus aureus carriage in reducing peritoneal catheter-related infections.
By McCormack K, Rabindranath K, Kilonzo M, Vale L, Fraser C, McIntyre L, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation versus electroconvulsive therapy in severe depression: a multicentre pragmatic randomised controlled trial and economic analysis.
By McLoughlin DM, Mogg A, Eranti S, Pluck G, Purvis R, Edwards D, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of direct versus indirect and individual versus group modes of speech and language therapy for children with primary language impairment.
By Boyle J, McCartney E, Forbes J, O’Hare A.
-
Hormonal therapies for early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hind D, Ward S, De Nigris E, Simpson E, Carroll C, Wyld L.
-
Cardioprotection against the toxic effects of anthracyclines given to children with cancer: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Picot J, Levitt G, Sullivan I, Baxter L, Clegg A.
-
Adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By McLeod C, Bagust A, Boland A, Dagenais P, Dickson R, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Prenatal screening and treatment strategies to prevent group B streptococcal and other bacterial infections in early infancy: cost-effectiveness and expected value of information analyses.
By Colbourn T, Asseburg C, Bojke L, Philips Z, Claxton K, Ades AE, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bone morphogenetic proteins in the non-healing of fractures and spinal fusion: a systematic review.
By Garrison KR, Donell S, Ryder J, Shemilt I, Mugford M, Harvey I, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial of postoperative radiotherapy following breast-conserving surgery in a minimum-risk older population. The PRIME trial.
By Prescott RJ, Kunkler IH, Williams LJ, King CC, Jack W, van der Pol M, et al.
-
Current practice, accuracy, effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the school entry hearing screen.
By Bamford J, Fortnum H, Bristow K, Smith J, Vamvakas G, Davies L, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of inhaled insulin in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Black C, Cummins E, Royle P, Philip S, Waugh N.
-
Surveillance of cirrhosis for hepatocellular carcinoma: systematic review and economic analysis.
By Thompson Coon J, Rogers G, Hewson P, Wright D, Anderson R, Cramp M, et al.
-
The Birmingham Rehabilitation Uptake Maximisation Study (BRUM). Homebased compared with hospital-based cardiac rehabilitation in a multi-ethnic population: cost-effectiveness and patient adherence.
By Jolly K, Taylor R, Lip GYH, Greenfield S, Raftery J, Mant J, et al.
-
A systematic review of the clinical, public health and cost-effectiveness of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection and identification of bacterial intestinal pathogens in faeces and food.
By Abubakar I, Irvine L, Aldus CF, Wyatt GM, Fordham R, Schelenz S, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial examining the longer-term outcomes of standard versus new antiepileptic drugs. The SANAD trial.
By Marson AG, Appleton R, Baker GA, Chadwick DW, Doughty J, Eaton B, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of different models of managing long-term oral anti-coagulation therapy: a systematic review and economic modelling.
By Connock M, Stevens C, Fry-Smith A, Jowett S, Fitzmaurice D, Moore D, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of interventions for preventing relapse in people with bipolar disorder.
By Soares-Weiser K, Bravo Vergel Y, Beynon S, Dunn G, Barbieri M, Duffy S, et al.
-
Taxanes for the adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ward S, Simpson E, Davis S, Hind D, Rees A, Wilkinson A.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening for open angle glaucoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burr JM, Mowatt G, Hernández R, Siddiqui MAR, Cook J, Lourenco T, et al.
-
Acceptability, benefit and costs of early screening for hearing disability: a study of potential screening tests and models.
By Davis A, Smith P, Ferguson M, Stephens D, Gianopoulos I.
-
Contamination in trials of educational interventions.
By Keogh-Brown MR, Bachmann MO, Shepstone L, Hewitt C, Howe A, Ramsay CR, et al.
-
Overview of the clinical effectiveness of positron emission tomography imaging in selected cancers.
By Facey K, Bradbury I, Laking G, Payne E.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Anderson R, Rogers G, Dyer M, Mealing S, et al.
-
Drug-eluting stents: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hill RA, Boland A, Dickson R, Dündar Y, Haycox A, McLeod C, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cardiac resynchronisation (biventricular pacing) for heart failure: systematic review and economic model.
By Fox M, Mealing S, Anderson R, Dean J, Stein K, Price A, et al.
-
Recruitment to randomised trials: strategies for trial enrolment and participation study. The STEPS study.
By Campbell MK, Snowdon C, Francis D, Elbourne D, McDonald AM, Knight R, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of functional cardiac testing in the diagnosis and management of coronary artery disease: a randomised controlled trial. The CECaT trial.
By Sharples L, Hughes V, Crean A, Dyer M, Buxton M, Goldsmith K, et al.
-
Evaluation of diagnostic tests when there is no gold standard. A review of methods.
By Rutjes AWS, Reitsma JB, Coomarasamy A, Khan KS, Bossuyt PMM.
-
Systematic reviews of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors in acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
By Leontiadis GI, Sreedharan A, Dorward S, Barton P, Delaney B, Howden CW, et al.
-
A review and critique of modelling in prioritising and designing screening programmes.
By Karnon J, Goyder E, Tappenden P, McPhie S, Towers I, Brazier J, et al.
-
An assessment of the impact of the NHS Health Technology Assessment Programme.
By Hanney S, Buxton M, Green C, Coulson D, Raftery J.
-
A systematic review and economic model of switching from nonglycopeptide to glycopeptide antibiotic prophylaxis for surgery.
By Cranny G, Elliott R, Weatherly H, Chambers D, Hawkins N, Myers L, et al.
-
‘Cut down to quit’ with nicotine replacement therapies in smoking cessation: a systematic review of effectiveness and economic analysis.
By Wang D, Connock M, Barton P, Fry-Smith A, Aveyard P, Moore D.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of strategies for reducing fracture risk in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis with additional data on long-term risk of fracture and cost of disease management.
By Thornton J, Ashcroft D, O’Neill T, Elliott R, Adams J, Roberts C, et al.
-
Does befriending by trained lay workers improve psychological well-being and quality of life for carers of people with dementia, and at what cost? A randomised controlled trial.
By Charlesworth G, Shepstone L, Wilson E, Thalanany M, Mugford M, Poland F.
-
A multi-centre retrospective cohort study comparing the efficacy, safety and cost-effectiveness of hysterectomy and uterine artery embolisation for the treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroids. The HOPEFUL study.
By Hirst A, Dutton S, Wu O, Briggs A, Edwards C, Waldenmaier L, et al.
-
Methods of prediction and prevention of pre-eclampsia: systematic reviews of accuracy and effectiveness literature with economic modelling.
By Meads CA, Cnossen JS, Meher S, Juarez-Garcia A, ter Riet G, Duley L, et al.
-
The use of economic evaluations in NHS decision-making: a review and empirical investigation.
By Williams I, McIver S, Moore D, Bryan S.
-
Stapled haemorrhoidectomy (haemorrhoidopexy) for the treatment of haemorrhoids: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burch J, Epstein D, Baba-Akbari A, Weatherly H, Fox D, Golder S, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness of diabetes education models for Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.
By Loveman E, Frampton GK, Clegg AJ.
-
Payment to healthcare professionals for patient recruitment to trials: systematic review and qualitative study.
By Raftery J, Bryant J, Powell J, Kerr C, Hawker S.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (etodolac, meloxicam, celecoxib, rofecoxib, etoricoxib, valdecoxib and lumiracoxib) for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Chen Y-F, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Fry-Smith A, Harris G, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of central venous catheters treated with anti-infective agents in preventing bloodstream infections: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hockenhull JC, Dwan K, Boland A, Smith G, Bagust A, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Stepped treatment of older adults on laxatives. The STOOL trial.
By Mihaylov S, Stark C, McColl E, Steen N, Vanoli A, Rubin G, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial of cognitive behaviour therapy in adolescents with major depression treated by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. The ADAPT trial.
By Goodyer IM, Dubicka B, Wilkinson P, Kelvin R, Roberts C, Byford S, et al.
-
The use of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hind D, Tappenden P, Tumur I, Eggington E, Sutcliffe P, Ryan A.
-
Ranibizumab and pegaptanib for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Colquitt JL, Jones J, Tan SC, Takeda A, Clegg AJ, Price A.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of 64-slice or higher computed tomography angiography as an alternative to invasive coronary angiography in the investigation of coronary artery disease.
By Mowatt G, Cummins E, Waugh N, Walker S, Cook J, Jia X, et al.
-
Structural neuroimaging in psychosis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Albon E, Tsourapas A, Frew E, Davenport C, Oyebode F, Bayliss S, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children aged 12 years and over.
By Shepherd J, Rogers G, Anderson R, Main C, Thompson-Coon J, Hartwell D, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years.
By Main C, Shepherd J, Anderson R, Rogers G, Thompson-Coon J, Liu Z, et al.
-
Ezetimibe for the treatment of hypercholesterolaemia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ara R, Tumur I, Pandor A, Duenas A, Williams R, Wilkinson A, et al.
-
Topical or oral ibuprofen for chronic knee pain in older people. The TOIB study.
By Underwood M, Ashby D, Carnes D, Castelnuovo E, Cross P, Harding G, et al.
-
A prospective randomised comparison of minor surgery in primary and secondary care. The MiSTIC trial.
By George S, Pockney P, Primrose J, Smith H, Little P, Kinley H, et al.
-
A review and critical appraisal of measures of therapist–patient interactions in mental health settings.
By Cahill J, Barkham M, Hardy G, Gilbody S, Richards D, Bower P, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening programmes for amblyopia and strabismus in children up to the age of 4–5 years: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Carlton J, Karnon J, Czoski-Murray C, Smith KJ, Marr J.
-
A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness and economic modelling of minimal incision total hip replacement approaches in the management of arthritic disease of the hip.
By de Verteuil R, Imamura M, Zhu S, Glazener C, Fraser C, Munro N, et al.
-
A preliminary model-based assessment of the cost–utility of a screening programme for early age-related macular degeneration.
By Karnon J, Czoski-Murray C, Smith K, Brand C, Chakravarthy U, Davis S, et al.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Frampton GK, Tanajewski L, Turner D, Price A.
-
Absorbent products for urinary/faecal incontinence: a comparative evaluation of key product categories.
By Fader M, Cottenden A, Getliffe K, Gage H, Clarke-O’Neill S, Jamieson K, et al.
-
A systematic review of repetitive functional task practice with modelling of resource use, costs and effectiveness.
By French B, Leathley M, Sutton C, McAdam J, Thomas L, Forster A, et al.
Health Technology Assessment Programme
-
Director, NIHR HTA Programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield.
Prioritisation Strategy Group
-
Director, NIHR HTA Programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
-
Dr Bob Coates, Consultant Advisor, NCCHTA
-
Dr Andrew Cook, Consultant Advisor, NCCHTA
-
Dr Peter Davidson, Director of Science Support, NCCHTA
-
Professor Robin E Ferner, Consultant Physician and Director, West Midlands Centre for Adverse Drug Reactions, City Hospital NHS Trust, Birmingham
-
Professor Paul Glasziou, Professor of Evidence-Based Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Dr Nick Hicks, Director of NHS Support, NCCHTA
-
Dr Edmund Jessop, Medical Adviser, National Specialist, National Commissioning Group (NCG), Department of Health, London
-
Ms Lynn Kerridge, Chief Executive Officer, NETSCC and NCCHTA
-
Dr Ruairidh Milne, Director of Strategy and Development, NETSCC
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Ms Pamela Young, Specialist Programme Manager, NCCHTA
HTA Commissioning Board
-
Director, NIHR HTA Programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
-
Senior Lecturer in General Practice, Department of Primary Health Care, University of Oxford
-
Professor Ann Ashburn, Professor of Rehabilitation and Head of Research, Southampton General Hospital
-
Professor Deborah Ashby, Professor of Medical Statistics, Queen Mary, University of London
-
Professor John Cairns, Professor of Health Economics, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Peter Croft, Director of Primary Care Sciences Research Centre, Keele University
-
Professor Nicky Cullum, Director of Centre for Evidence-Based Nursing, University of York
-
Professor Jenny Donovan, Professor of Social Medicine, University of Bristol
-
Professor Steve Halligan, Professor of Gastrointestinal Radiology, University College Hospital, London
-
Professor Freddie Hamdy, Professor of Urology, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Allan House, Professor of Liaison Psychiatry, University of Leeds
-
Dr Martin J Landray, Reader in Epidemiology, Honorary Consultant Physician, Clinical Trial Service Unit, University of Oxford
-
Professor Stuart Logan, Director of Health & Social Care Research, The Peninsula Medical School, Universities of Exeter and Plymouth
-
Dr Rafael Perera, Lecturer in Medical Statisitics, Department of Primary Health Care, Univeristy of Oxford
-
Professor Ian Roberts, Professor of Epidemiology & Public Health, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Mark Sculpher, Professor of Health Economics, University of York
-
Professor Helen Smith, Professor of Primary Care, University of Brighton
-
Professor Kate Thomas, Professor of Complementary & Alternative Medicine Research, University of Leeds
-
Professor David John Torgerson, Director of York Trials Unit, University of York
-
Professor Hywel Williams, Professor of Dermato-Epidemiology, University of Nottingham
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programmes, Research and Development Directorate, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Medical Research Council
Diagnostic Technologies & Screening Panel
-
Professor of Evidence-Based Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Consultant Paediatrician and Honorary Senior Lecturer, Great Ormond Street Hospital, London
-
Professor Judith E Adams, Consultant Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Central Manchester & Manchester Children’s University Hospitals NHS Trust, and Professor of Diagnostic Radiology, Imaging Science and Biomedical Engineering, Cancer & Imaging Sciences, University of Manchester
-
Ms Jane Bates, Consultant Ultrasound Practitioner, Ultrasound Department, Leeds Teaching Hospital NHS Trust
-
Dr Stephanie Dancer, Consultant Microbiologist, Hairmyres Hospital, East Kilbride
-
Dr David Elliman, Consultant Paediatrician and Honorary Senior Lecturer, Great Ormond Street Hospital, London
-
Professor Glyn Elwyn, Primary Medical Care Research Group, Swansea Clinical School, University of Wales
-
Dr Ron Gray, Consultant Clinical Epidemiologist, Department of Public Health, University of Oxford
-
Professor Paul D Griffiths, Professor of Radiology, University of Sheffield
-
Dr Jennifer J Kurinczuk, Consultant Clinical Epidemiologist, National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, Oxford
-
Dr Susanne M Ludgate, Medical Director, Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency, London
-
Dr Anne Mackie, Director of Programmes, UK National Screening Committee
-
Dr Michael Millar, Consultant Senior Lecturer in Microbiology, Barts and The London NHS Trust, Royal London Hospital
-
Mr Stephen Pilling, Director, Centre for Outcomes, Research & Effectiveness, Joint Director, National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health, University College London
-
Mrs Una Rennard, Service User Representative
-
Dr Phil Shackley, Senior Lecturer in Health Economics, School of Population and Health Sciences, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Dr W Stuart A Smellie, Consultant in Chemical Pathology, Bishop Auckland General Hospital
-
Dr Nicholas Summerton, Consultant Clinical and Public Health Advisor, NICE
-
Ms Dawn Talbot, Service User Representative
-
Dr Graham Taylor, Scientific Advisor, Regional DNA Laboratory, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Professor Lindsay Wilson Turnbull, Scientific Director of the Centre for Magnetic Resonance Investigations and YCR Professor of Radiology, Hull Royal Infirmary
-
Mr James Whittell, Service User Representative
-
Dr Alan J Williams, Consultant in General Medicine, Department of Thoracic Medicine, The Royal Bournemouth Hospital
-
Dr Tim Elliott, Team Leader, Cancer Screening, Department of Health
-
Dr Catherine Moody, Programme Manager, Neuroscience and Mental Health Board
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Pharmaceuticals Panel
-
Consultant Physician and Director, West Midlands Centre for Adverse Drug Reactions, City Hospital NHS Trust, Birmingham
-
Professor in Child Health, University of Nottingham
-
Professor Stirling Bryan, Professor of Health Economics, Health Services Management Centre, University of Birmingham
-
Mr John Chapman, Service User Representative
-
Dr Peter Elton, Director of Public Health, Bury Primary Care Trust
-
Mrs Barbara Greggains, Service User Representative
-
Dr Bill Gutteridge, Medical Adviser, London Strategic Health Authority
-
Professor Jonathan Ledermann, Professor of Medical Oncology and Director of the Cancer Research UK and University College London Cancer Trials Centre
-
Dr Yoon K Loke, Senior Lecturer in Clinical Pharmacology, University of East Anglia
-
Professor Femi Oyebode, Consultant Psychiatrist and Head of Department, University of Birmingham
-
Dr Andrew Prentice, Senior Lecturer and Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, The Rosie Hospital, University of Cambridge
-
Dr Martin Shelly, General Practitioner, Leeds, and Associate Director, NHS Clinical Governance Support Team, Leicester
-
Dr Gillian Shepherd, Director, Health and Clinical Excellence, Merck Serono Ltd
-
Mrs Katrina Simister, Assistant Director New Medicines, National Prescribing Centre, Liverpool
-
Mr David Symes, Service User Representative
-
Dr Vaughan Thomas, Consultant Anaesthetist, Southampton University Hospitals Trust
-
Dr Lesley Wise, Unit Manager, Pharmacoepidemiology Research Unit, VRMM, Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Mr Simon Reeve, Head of Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness, Medicines, Pharmacy and Industry Group, Department of Health
-
Dr Heike Weber, Programme Manager, Medical Research Council
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Therapeutic Procedures Panel
-
Consultant Physician, North Bristol NHS Trust
-
Ms Maree Barnett, Acting Branch Head of Vascular Programme, Department of Health
-
Mrs Val Carlill, Service User Representative
-
Mrs Anthea De Barton-Watson Service User Representative
-
Mr Mark Emberton, Senior Lecturer in Oncological Urology, Institute of Urology, University College Hospital, London
-
Professor Steve Goodacre, Professor of Emergency Medicine, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Christopher Griffiths, Professor of Primary Care, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Mr Paul Hilton, Consultant Gynaecologist and Urogynaecologist, Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Nicholas James, Professor of Clinical Oncology, University of Birmingham, and Consultant in Clinical Oncology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital
-
Dr Peter Martin, Consultant Neurologist, Addenbrooke’s Hospital, Cambridge
-
Dr Kate Radford Occupational Therapist, Division of Rehabilitation and Ageing, University of Nottingham, Nottingham
-
Mr Jim Reece Service User Representative
-
Dr Karen Roberts, Nurse Consultant, Dunston Hill Hospital Cottages
-
Professor Scott Weich, Professor of Psychiatry, Division of Health in the Community, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Dr Phillip Leech, Principal Medical Officer for Primary Care, Department of Health
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Medical Research Council
-
Professor Tom Walley, Director, NIHR HTA Programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Disease Prevention Panel
-
Medical Adviser, National Specialist, National Commissioning Group (NCG), London
-
Director, NHS Sustainable Development Unit, Cambridge
-
Dr Elizabeth Fellow-Smith, Medical Director, West London Mental Health Trust, Middlesex
-
Dr John Jackson, General Practitioner, Parkway Medical Centre, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Mike Kelly, Director, Centre for Public Health Excellence, NICE, London
-
Dr Chris McCall, General Practitioner, The Hadleigh Practice, Corfe Mullen, Dorset
-
Ms Jeanett Martin, Director of Nursing, BarnDoc Limited, Lewisham Primary Care Trust
-
Miss Nicky Mullany, Service User Representative
-
Professor Ken Stein, Senior Clinical Lecturer in Public Health, University of Exeter
-
Professor Carol Tannahill, Glasgow Centre for Population Health
-
Professor Margaret Thorogood, Professor of Epidemiology, University of Warwick Medical School, Coventry
-
Ms Christine McGuire, Research & Development, Department of Health
-
Dr Caroline Stone, Programme Manager, Medical Research Council
Expert Advisory Network
-
Professor Douglas Altman, Professor of Statistics in Medicine, Centre for Statistics in Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Professor John Bond, Professor of Social Gerontology & Health Services Research, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Andrew Bradbury, Professor of Vascular Surgery, Solihull Hospital, Birmingham
-
Mr Shaun Brogan, Chief Executive, Ridgeway Primary Care Group, Aylesbury
-
Mrs Stella Burnside OBE, Chief Executive, Regulation and Improvement Authority, Belfast
-
Ms Tracy Bury, Project Manager, World Confederation for Physical Therapy, London
-
Professor Iain T Cameron, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology and Head of the School of Medicine, University of Southampton
-
Dr Christine Clark, Medical Writer and Consultant Pharmacist, Rossendale
-
Professor Collette Clifford, Professor of Nursing and Head of Research, The Medical School, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Barry Cookson, Director, Laboratory of Hospital Infection, Public Health Laboratory Service, London
-
Dr Carl Counsell, Clinical Senior Lecturer in Neurology, University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Howard Cuckle, Professor of Reproductive Epidemiology, Department of Paediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynaecology, University of Leeds
-
Dr Katherine Darton, Information Unit, MIND – The Mental Health Charity, London
-
Professor Carol Dezateux, Professor of Paediatric Epidemiology, Institute of Child Health, London
-
Mr John Dunning, Consultant Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Papworth Hospital NHS Trust, Cambridge
-
Mr Jonothan Earnshaw, Consultant Vascular Surgeon, Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Gloucester
-
Professor Martin Eccles, Professor of Clinical Effectiveness, Centre for Health Services Research, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Pam Enderby, Dean of Faculty of Medicine, Institute of General Practice and Primary Care, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Gene Feder, Professor of Primary Care Research & Development, Centre for Health Sciences, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Mr Leonard R Fenwick, Chief Executive, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Mrs Gillian Fletcher, Antenatal Teacher and Tutor and President, National Childbirth Trust, Henfield
-
Professor Jayne Franklyn, Professor of Medicine, University of Birmingham
-
Mr Tam Fry, Honorary Chairman, Child Growth Foundation, London
-
ProfessorFiona Gilbert, Consultant Radiologist and NCRN Member, University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Paul Gregg, Professor of Orthopaedic Surgical Science, South Tees Hospital NHS Trust
-
Bec Hanley, Co-director, TwoCan Associates, West Sussex
-
Dr Maryann L Hardy, Senior Lecturer, University of Bradford
-
Mrs Sharon Hart, Healthcare Management Consultant, Reading
-
Professor Robert E Hawkins, CRC Professor and Director of Medical Oncology, Christie CRC Research Centre, Christie Hospital NHS Trust, Manchester
-
Professor Richard Hobbs, Head of Department of Primary Care & General Practice, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Alan Horwich, Dean and Section Chairman, The Institute of Cancer Research, London
-
Professor Allen Hutchinson, Director of Public Health and Deputy Dean of ScHARR, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Peter Jones, Professor of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge
-
Professor Stan Kaye, Cancer Research UK Professor of Medical Oncology, Royal Marsden Hospital and Institute of Cancer Research, Surrey
-
Dr Duncan Keeley, General Practitioner (Dr Burch & Ptnrs), The Health Centre, Thame
-
Dr Donna Lamping, Research Degrees Programme Director and Reader in Psychology, Health Services Research Unit, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London
-
Mr George Levvy, Chief Executive, Motor Neurone Disease Association, Northampton
-
Professor James Lindesay, Professor of Psychiatry for the Elderly, University of Leicester
-
Professor Julian Little, Professor of Human Genome Epidemiology, University of Ottawa
-
Professor Alistaire McGuire, Professor of Health Economics, London School of Economics
-
Professor Rajan Madhok, Medical Director and Director of Public Health, Directorate of Clinical Strategy & Public Health, North & East Yorkshire & Northern Lincolnshire Health Authority, York
-
Professor Alexander Markham, Director, Molecular Medicine Unit, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Dr Peter Moore, Freelance Science Writer, Ashtead
-
Dr Andrew Mortimore, Public Health Director, Southampton City Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Sue Moss, Associate Director, Cancer Screening Evaluation Unit, Institute of Cancer Research, Sutton
-
Professor Miranda Mugford, Professor of Health Economics and Group Co-ordinator, University of East Anglia
-
Professor Jim Neilson, Head of School of Reproductive & Developmental Medicine and Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, University of Liverpool
-
Mrs Julietta Patnick, National Co-ordinator, NHS Cancer Screening Programmes, Sheffield
-
Professor Robert Peveler, Professor of Liaison Psychiatry, Royal South Hants Hospital, Southampton
-
Professor Chris Price, Director of Clinical Research, Bayer Diagnostics Europe, Stoke Poges
-
Professor William Rosenberg, Professor of Hepatology and Consultant Physician, University of Southampton
-
Professor Peter Sandercock, Professor of Medical Neurology, Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Edinburgh
-
Dr Susan Schonfield, Consultant in Public Health, Hillingdon Primary Care Trust, Middlesex
-
Dr Eamonn Sheridan, Consultant in Clinical Genetics, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Dr Margaret Somerville, Director of Public Health Learning, Peninsula Medical School, University of Plymouth
-
Professor Sarah Stewart-Brown, Professor of Public Health, Division of Health in the Community, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Professor Ala Szczepura, Professor of Health Service Research, Centre for Health Services Studies, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Mrs Joan Webster, Consumer Member, Southern Derbyshire Community Health Council
-
Professor Martin Whittle, Clinical Co-director, National Co-ordinating Centre for Women’s and Children’s Health, Lymington